Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
246results about How to "Improve cornering performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
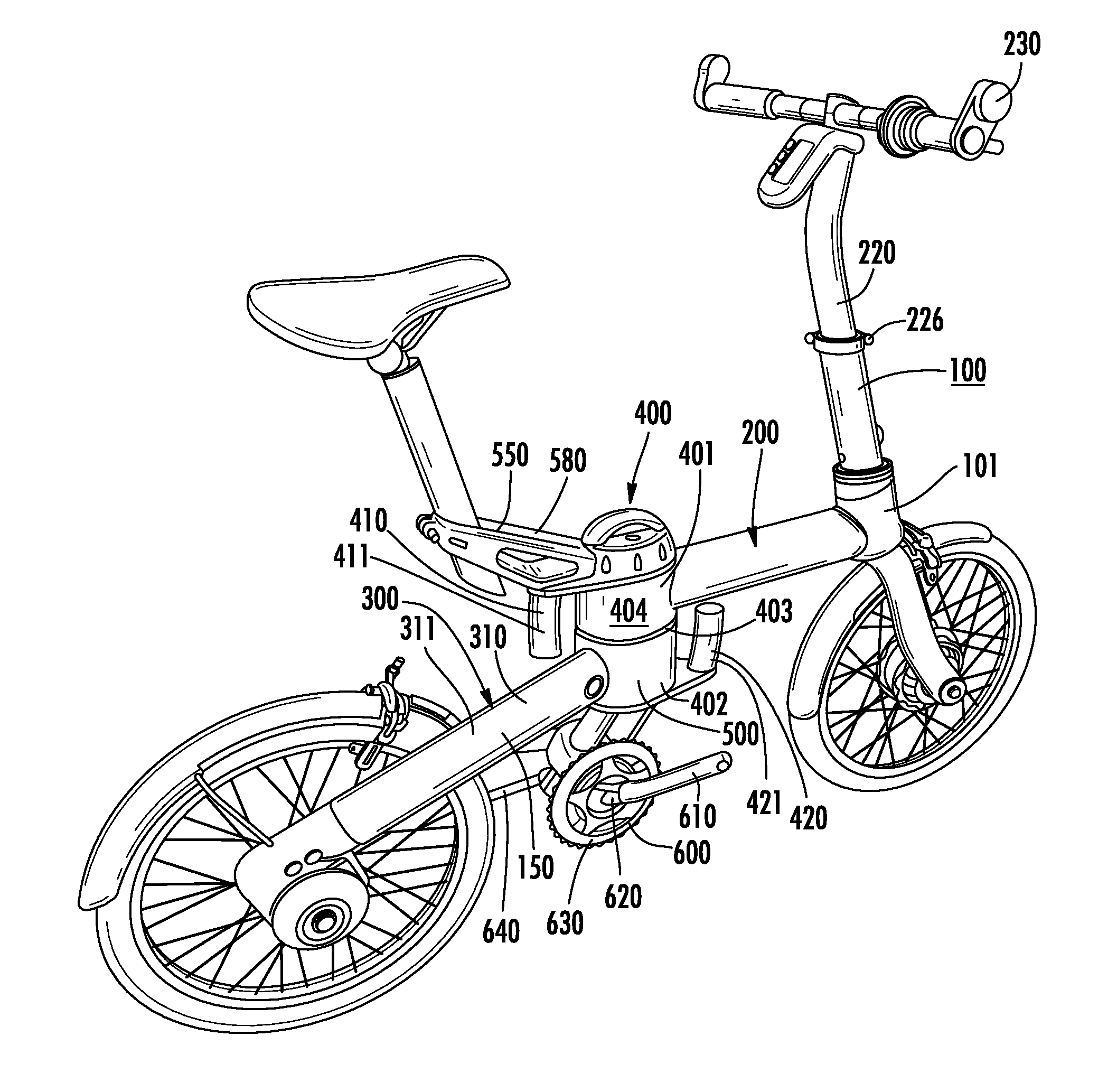
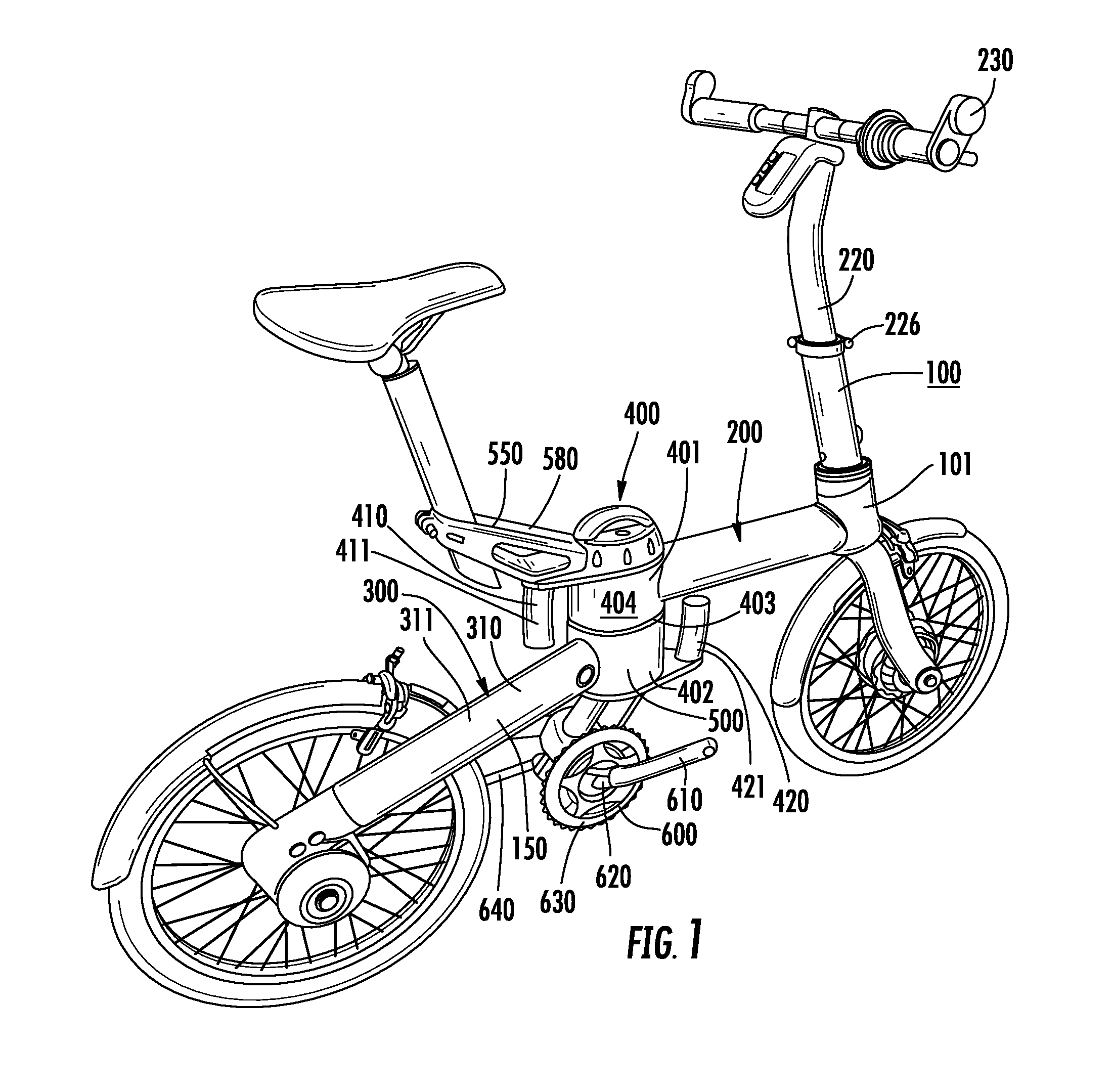
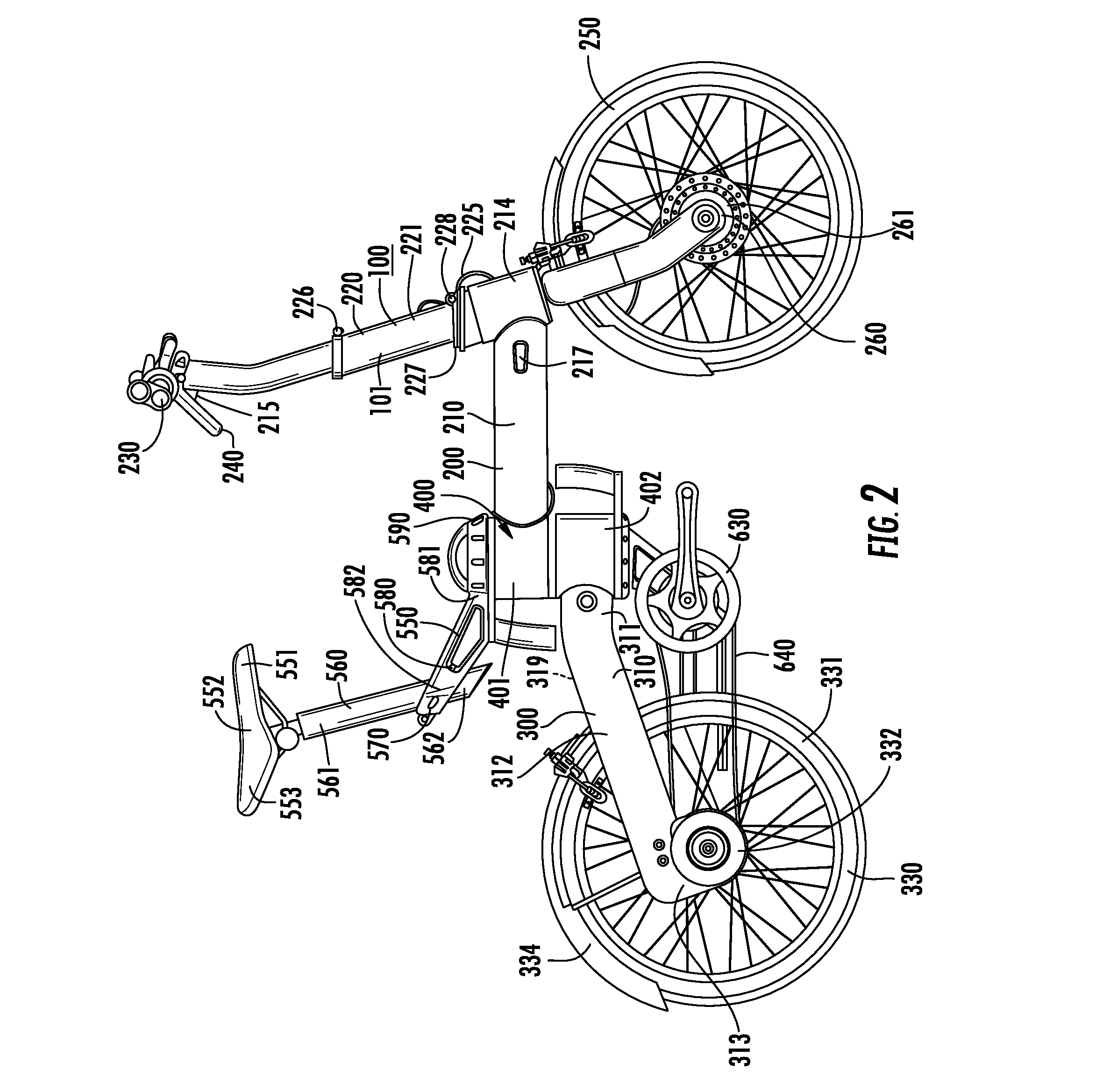
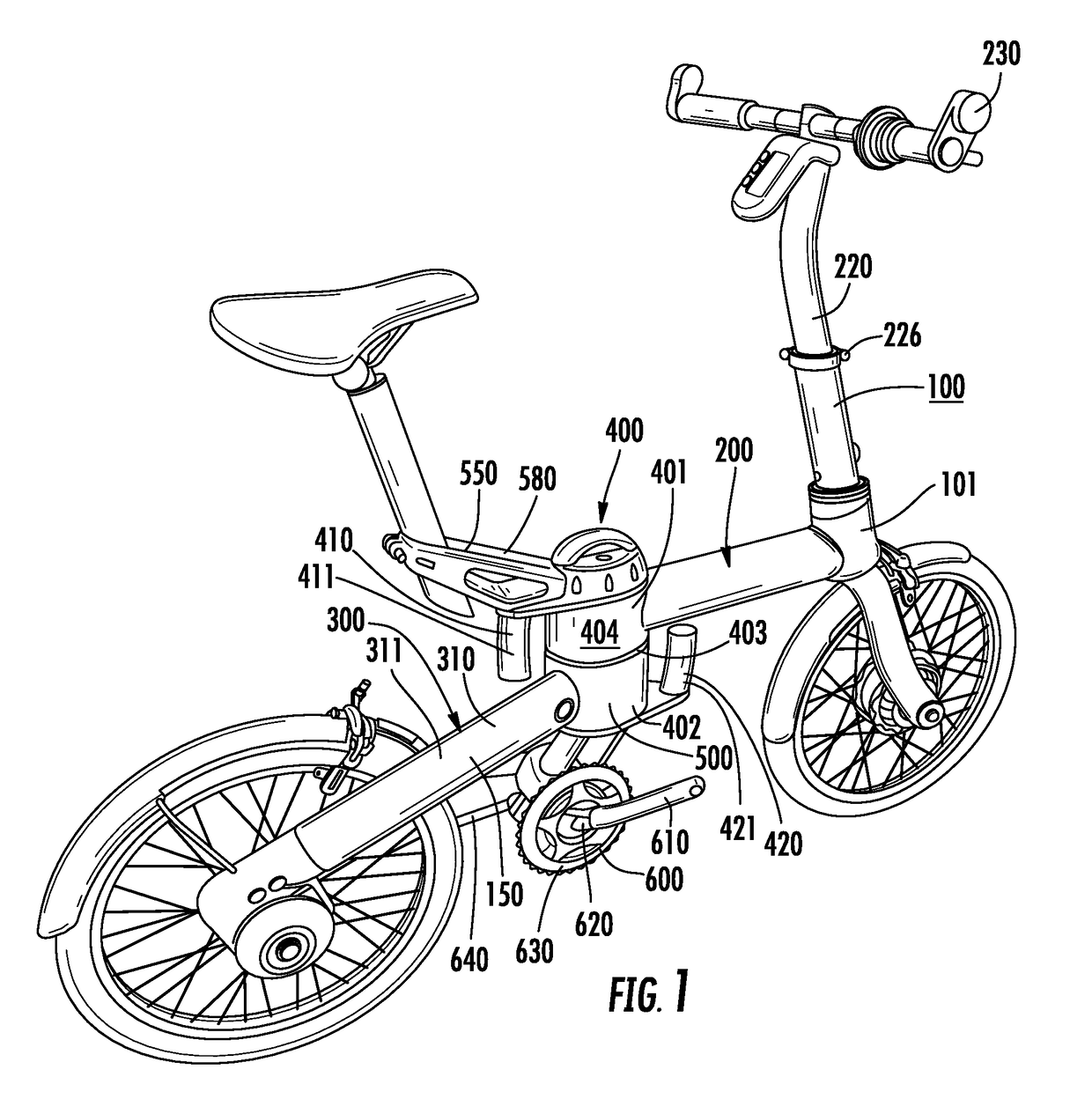
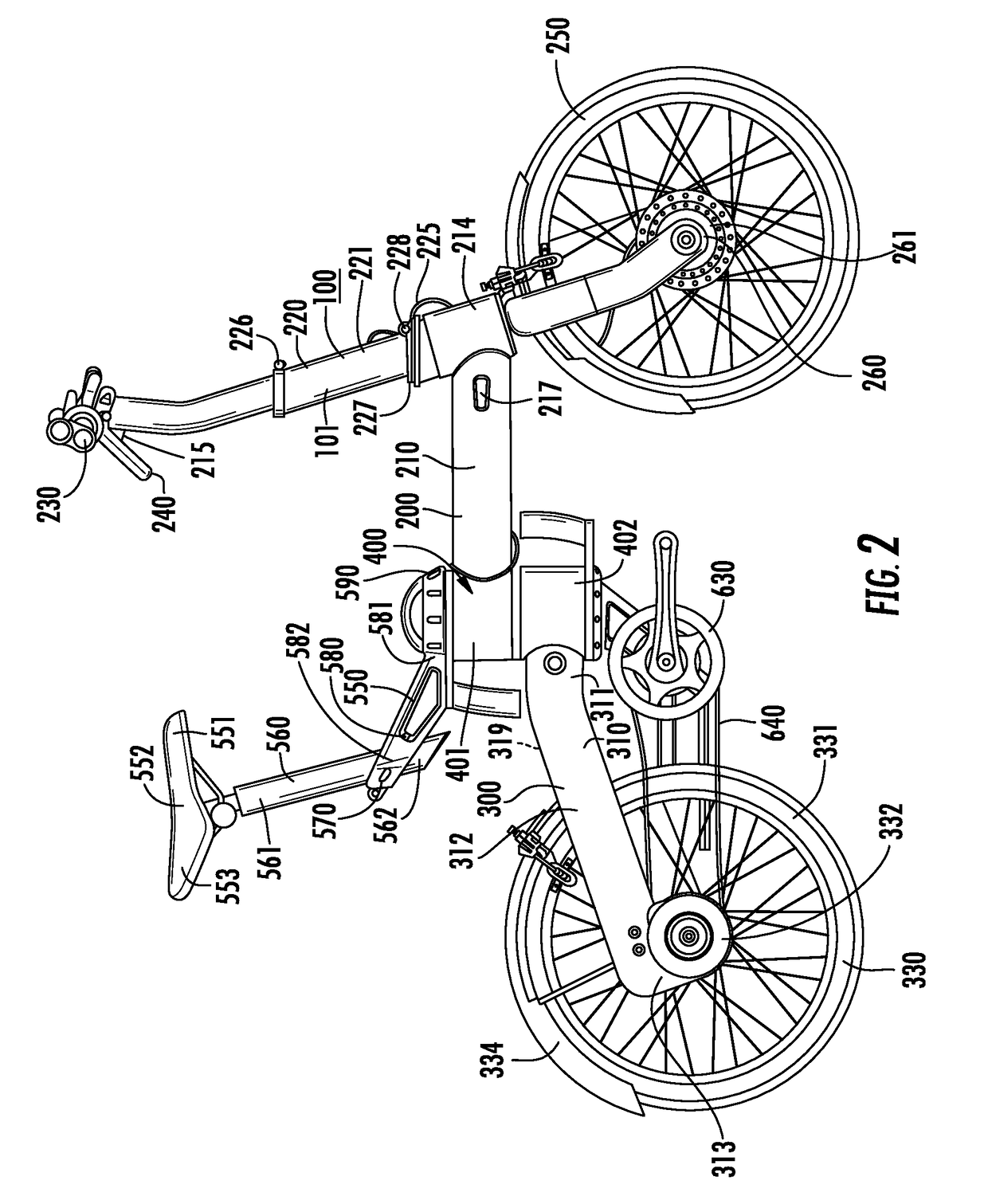
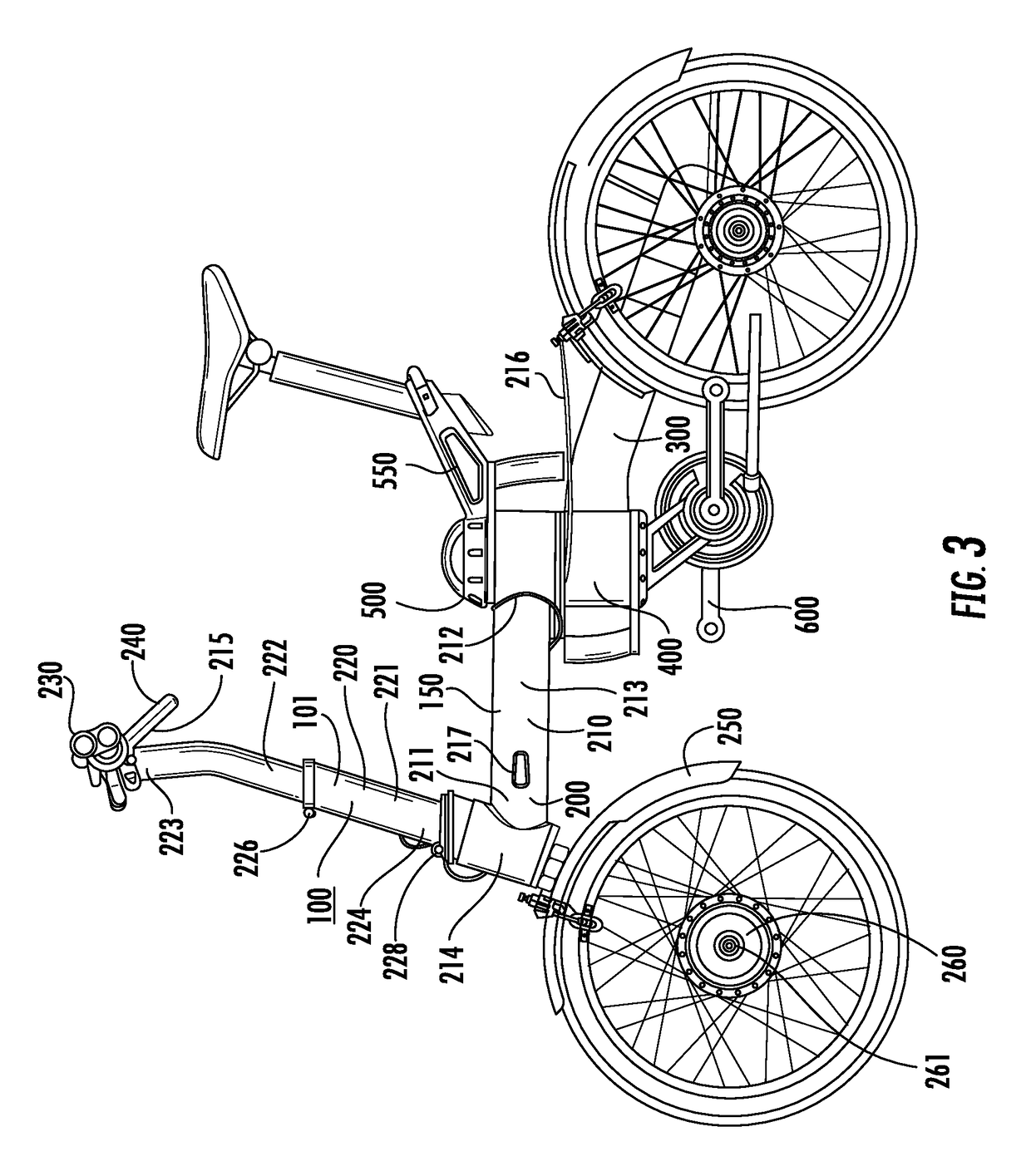
Folding bicycle with electric power train assist
InactiveUS20120043148A1Small sizeReduce bulkWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionElectricityElectric power transmission
The invention is directed to a foldable electric bicycle with power assist having a front portion attached to a rear portion via a central pivot post. The front portion maintains a steering column, handle bar system and a front wheel assembly having a front wheel and an electric power train. The rear portion includes a rear connecting arm to maintain the rear wheel. The central pivot post includes a first end that connects with the front portion and a second end which connects with the rear portion. A peddle assembly connects below the central pivot post and communicates with the rear wheel through a drive chain. A rechargeable battery capable of providing electricity to the electric power train is shaped to fit within a cavity and is located within the central pivot post. The rechargeable battery is positioned proximate the user so as to vertically align with the user's girth.
Owner:ROBRADY CAPITAL
Folding bicycle with electric power train assist
InactiveUS8473130B2Sufficient sizeSufficient dimensionWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionElectric power transmissionElectricity
The invention is directed to a foldable electric bicycle with power assist having a front portion attached to a rear portion via a central pivot post. The front portion maintains a steering column, handle bar system and a front wheel assembly having a front wheel and an electric power train. The rear portion includes a rear connecting arm to maintain the rear wheel. The central pivot post includes a first end that connects with the front portion and a second end which connects with the rear portion. A peddle assembly connects below the central pivot post and communicates with the rear wheel through a drive chain. A rechargeable battery capable of providing electricity to the electric power train is shaped to fit within a cavity and is located within the central pivot post. The rechargeable battery is positioned proximate the user so as to vertically align with the user's girth.
Owner:ROBRADY CAPITAL
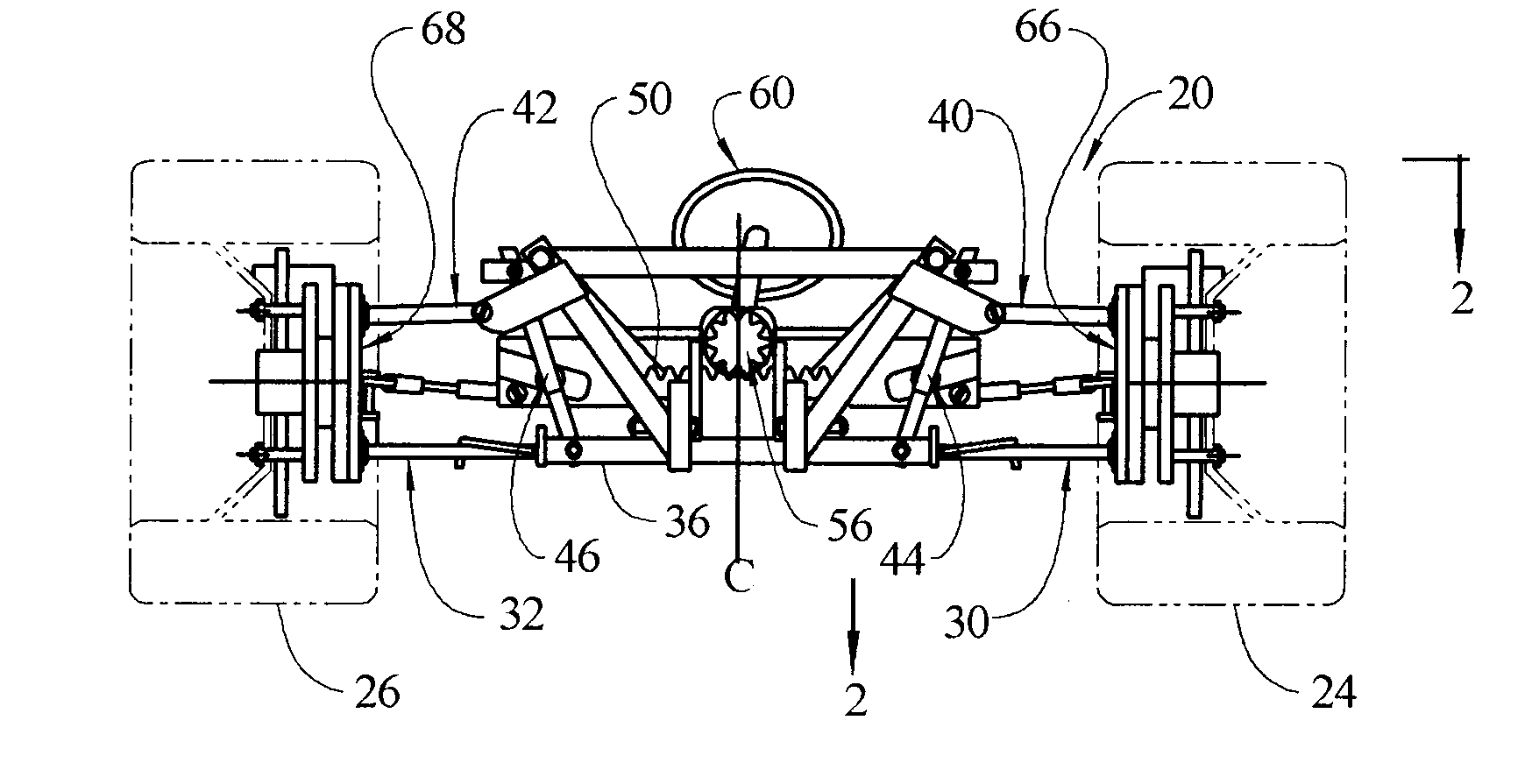
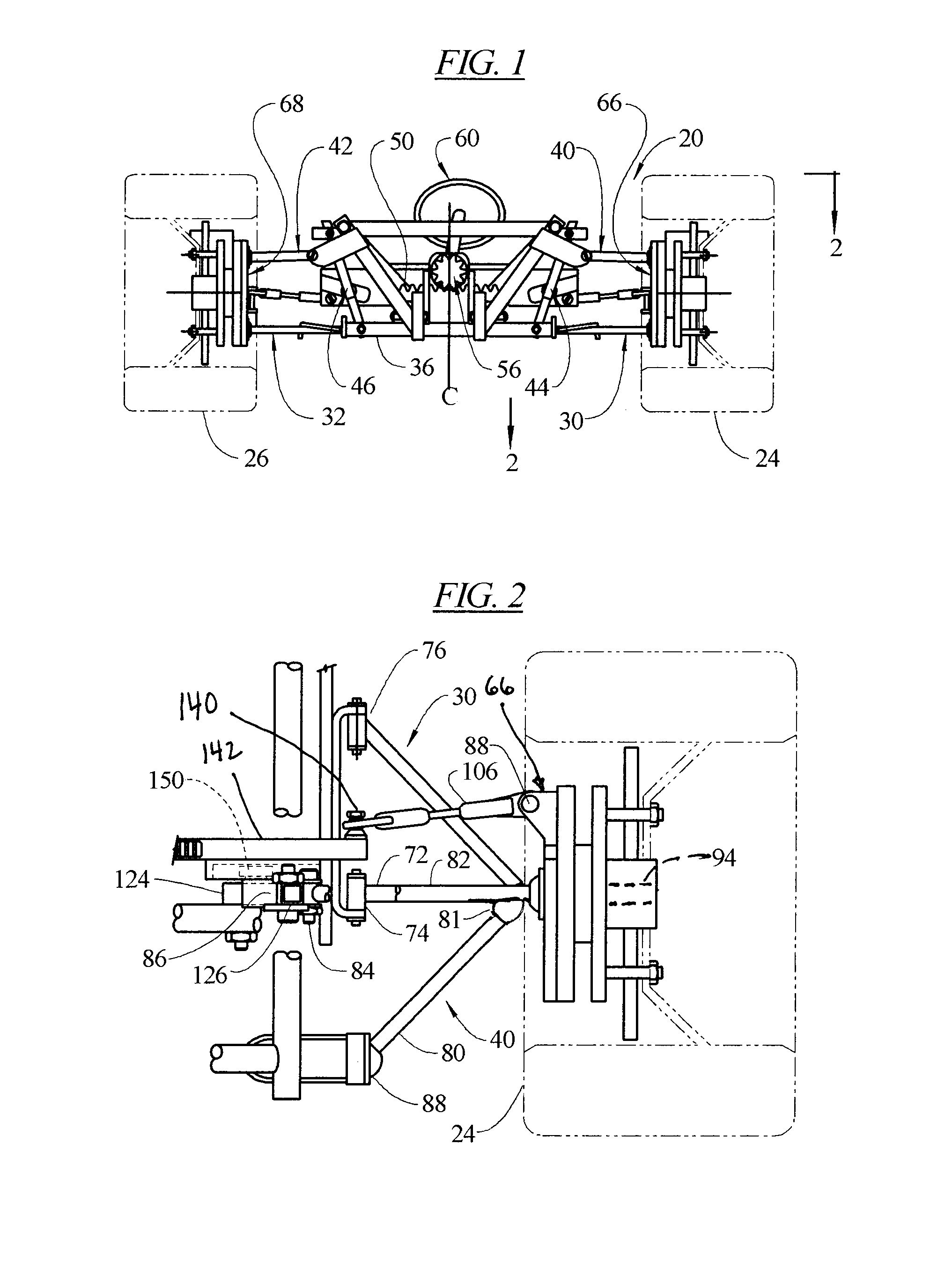
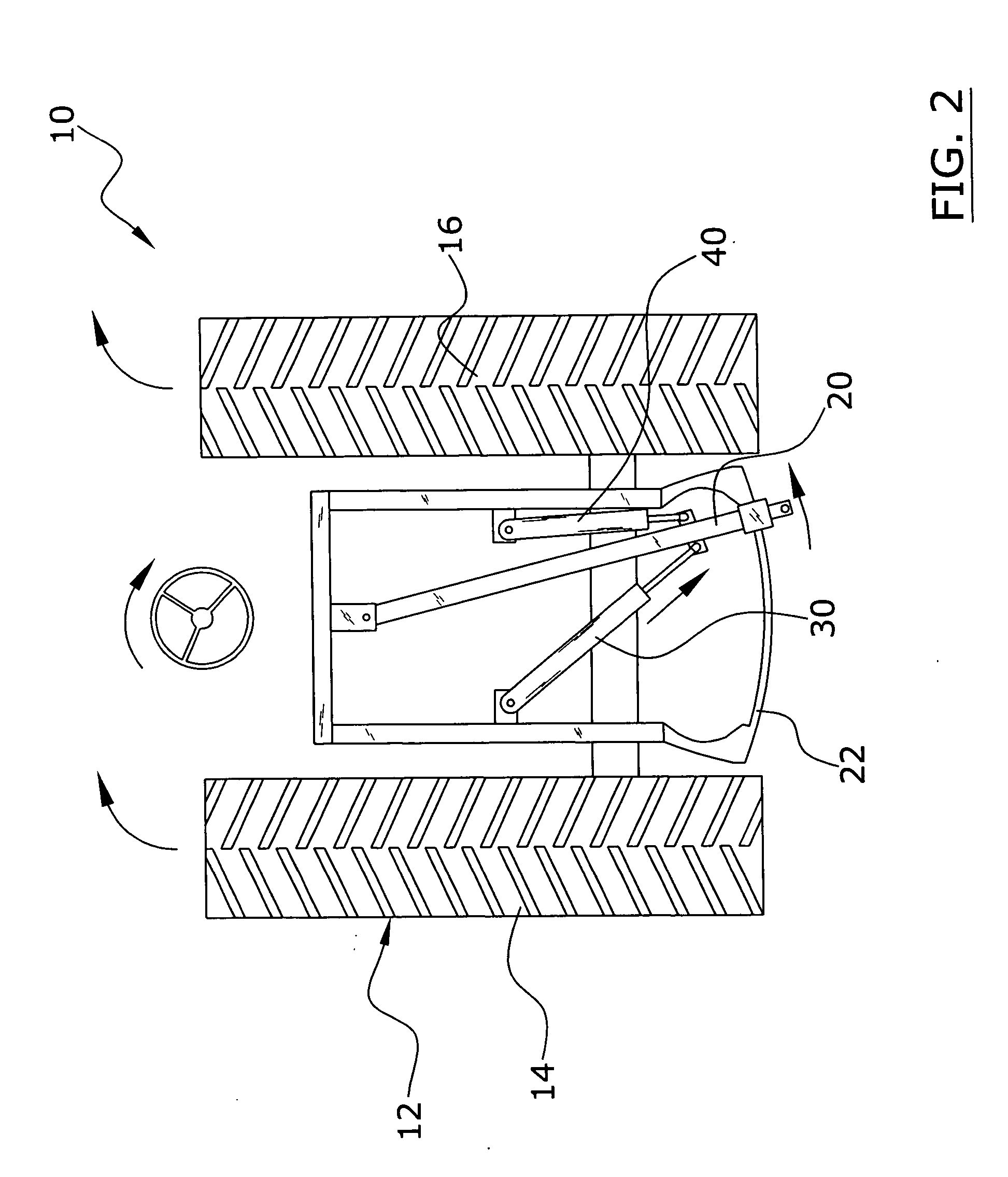
Vehicle Suspension System with a Variable Camber System
InactiveUS20090194965A1Negative changeOptimal tire contactDeflectable wheel steeringResilient suspensionsEngineeringVehicle suspension system
A suspension system for a vehicle provides a camber adjusting system that during a turn, lowers and draws inward the upper A-arm, or draws inward a strut head, which supports the outer front wheel, thereby providing more negative camber to that wheel in dynamic optimal proportion to the degree of the turn. The suspension system can be configured to remain at zero camber on the inner front wheel during the turn or can be configured to raise and move outward the upper A-arm, or move outward a strut head, which supports the inner front wheel, thereby providing more positive camber to that wheel in dynamic optimal proportion to the degree of turn.
Owner:BOSTON ROY
Inspection robot
ActiveCN103802086AAvoid repeated positioning difficultiesGuaranteed uptimeManipulatorCushioningEngineering
An inspection robot comprises a supporting frame body, a driving mechanism and a guiding wheel mechanism closely stuck to the orbital wall, wherein the driving mechanism comprises a driving device with adjustable actuating speed, a differential mechanism and at least two groups of marching wheels. The driving device is connected with the differential mechanism in a transmission mode, the differential mechanism is arranged between the marching wheels and is connected with the marching wheels in a transmission mode, and the driving device, the differential mechanism and the marching wheels are all arranged on the supporting frame body respectively. The guiding wheel mechanism closely stuck to the orbital wall comprises at least two groups of guiding wheel components which are arranged on the supporting frame body. According to the inspection robot, the driving device drives the differential mechanism and the differential mechanism drives the marching wheel so that multi-driving can be achieved, uphill slipping and difficulty in repeated positioning can be avoided, braking performance can be improved and turning capability can be improved, and the guiding wheel mechanism is closely stuck to the orbit so that waggle in the robot can be avoided, shock absorption and cushioning function which absorb goggling and shaking of the robot caused by unflatness of the orbital wall can be achieved, and stability and security in the operation of the inspection robot can be improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU POWER SUPPLY BUREAU GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Method for controlling direction of rotation axis and rotation direction of space universal superposition rotating magnetic field
ActiveCN102579048AImprove cornering performanceEasy to adjustSurgeryEndoradiosondesHelmholtz coilCurrent amplitude
The invention belongs to the technical field of automation engineering and discloses a method for controlling the direction of a rotation axis and the rotation direction of a space universal superposition rotating magnetic field. Three z-axis, y-axis and x-axis square Helmholtz coil groups are orthogonally nested, so that when the three groups of coils are driven by direct currents with the same current strength, the magnetic inductions generated at the center points of the three groups of coils have the same strength; the superposition rotating magnetic field is driven by an amplitude and phase compensation voltage signal through digitization so as to eliminate the influence of current lagging and inductive reactance on the current amplitude; and a same-frequency three-phase sinusoidal signal with the amplitude and the phase related to the axis azimuthal angle of a robot is used for driving to form the space universal uniform rotating magnetic field with the corresponding azimuthal rotating axis in a superimposed mode in a certain space surrounded by the three-axis orthogonal Helmholtz coil devices. According to the invention, by implementing the random regulation of the direction of the rotation axis and the rotation direction of the space universal rotating magnetic field, various operations of turning, moving forward, moving backward and the like of the micro robot in the bent or branch cavity environment are further implemented; and the method has wide application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Intelligent pipe inner wall walking robot
The invention discloses an intelligent pipe inner wall walking robot. The intelligent pipe inner wall walking robot comprises two machine bodies; the two machine bodies are connected through an universal joint; walking mechanisms and extension leg structures are respectively mounted at two unconnected ends of the machine bodies; in the working process, a WIFI module is remotely connected to control driving wheels; motors drive the driving wheels; the driving wheels drive the machine bodies to move in pipes; under the condition of meeting with curves, the rotating speeds of two driving wheel motors are adjusted, and the rotating speeds of the two wheels are asynchronous to realize curving; when the pipes suddenly change the diameters, the adaption to the pipe diameters is realized through extension mechanisms, specifically, the pressure is applied to the driving wheels and driven wheels by pipe walls, so that three machine legs are inwards gathered, and meanwhile, slide sleeves are driven to compress springs; and after normal pipe diameters are recovered, the springs push the slide sleeves to drive outward expansion of the machine legs so as to adapt to new pipe diameters. The intelligent pipe inner wall walking robot has the characteristics of simple structure, convenience and practicability.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Pneumatic tire
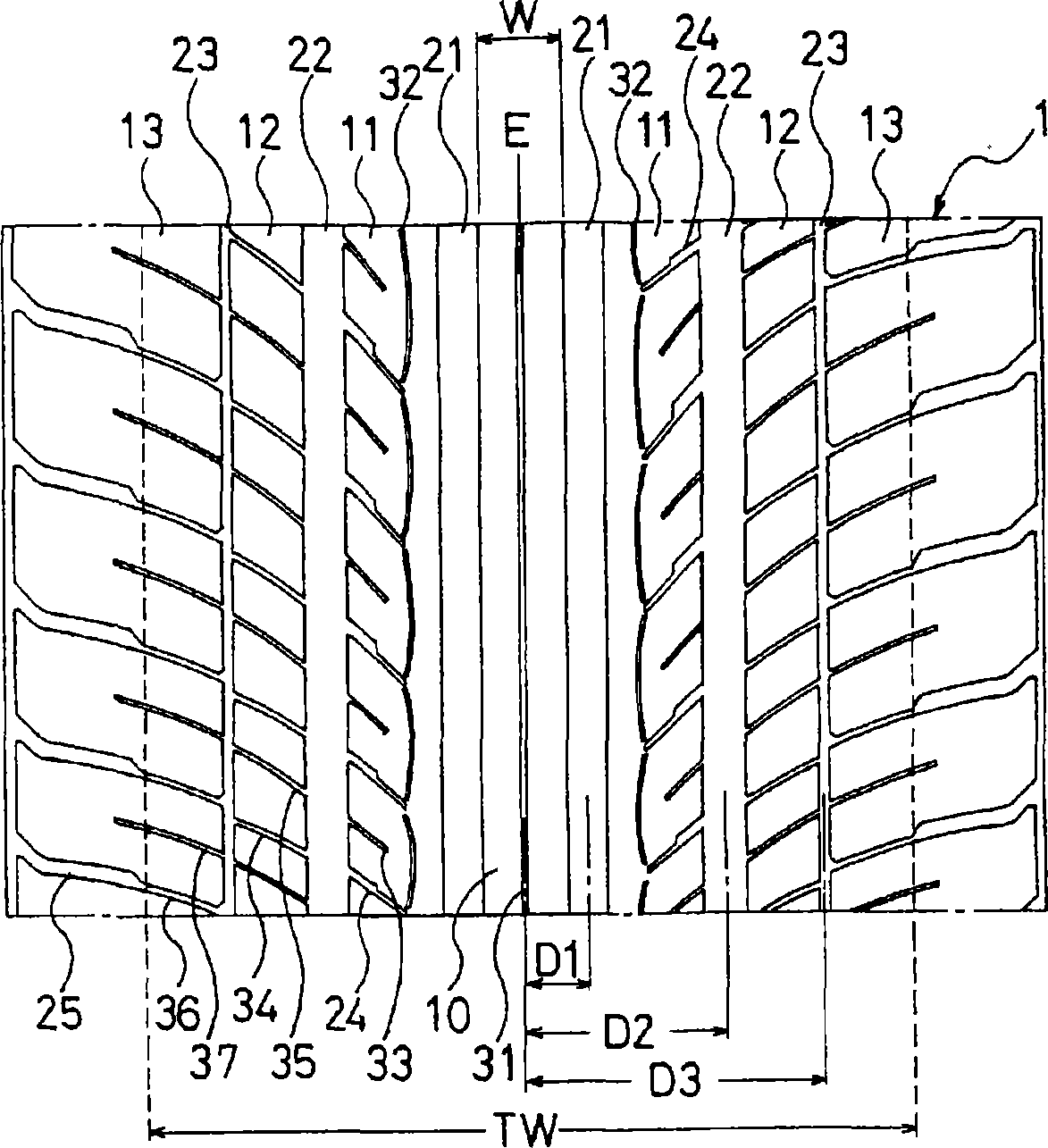
InactiveCN1867464AImprove wetting performanceImprove noiseTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringOperational stability
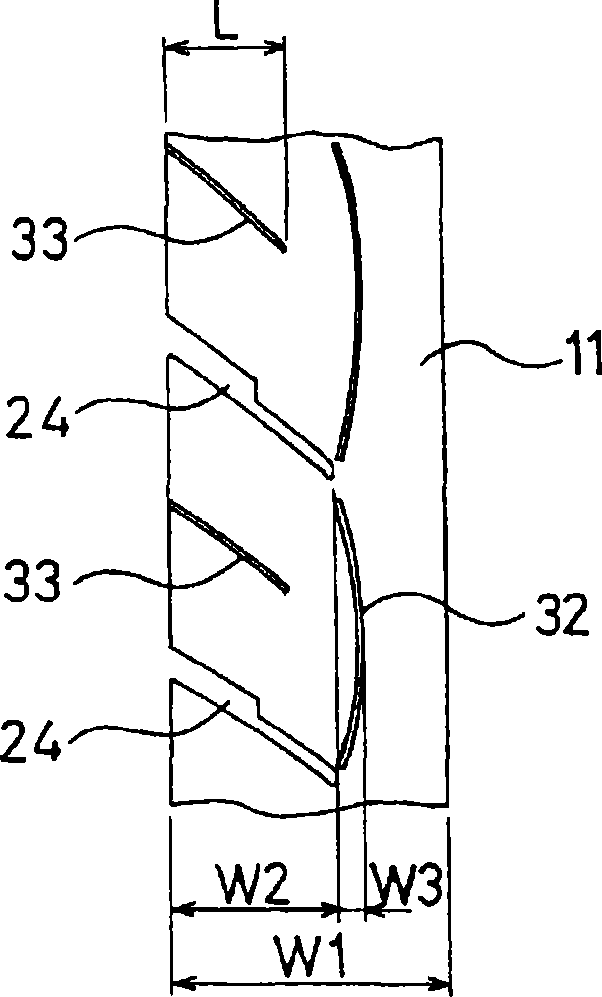
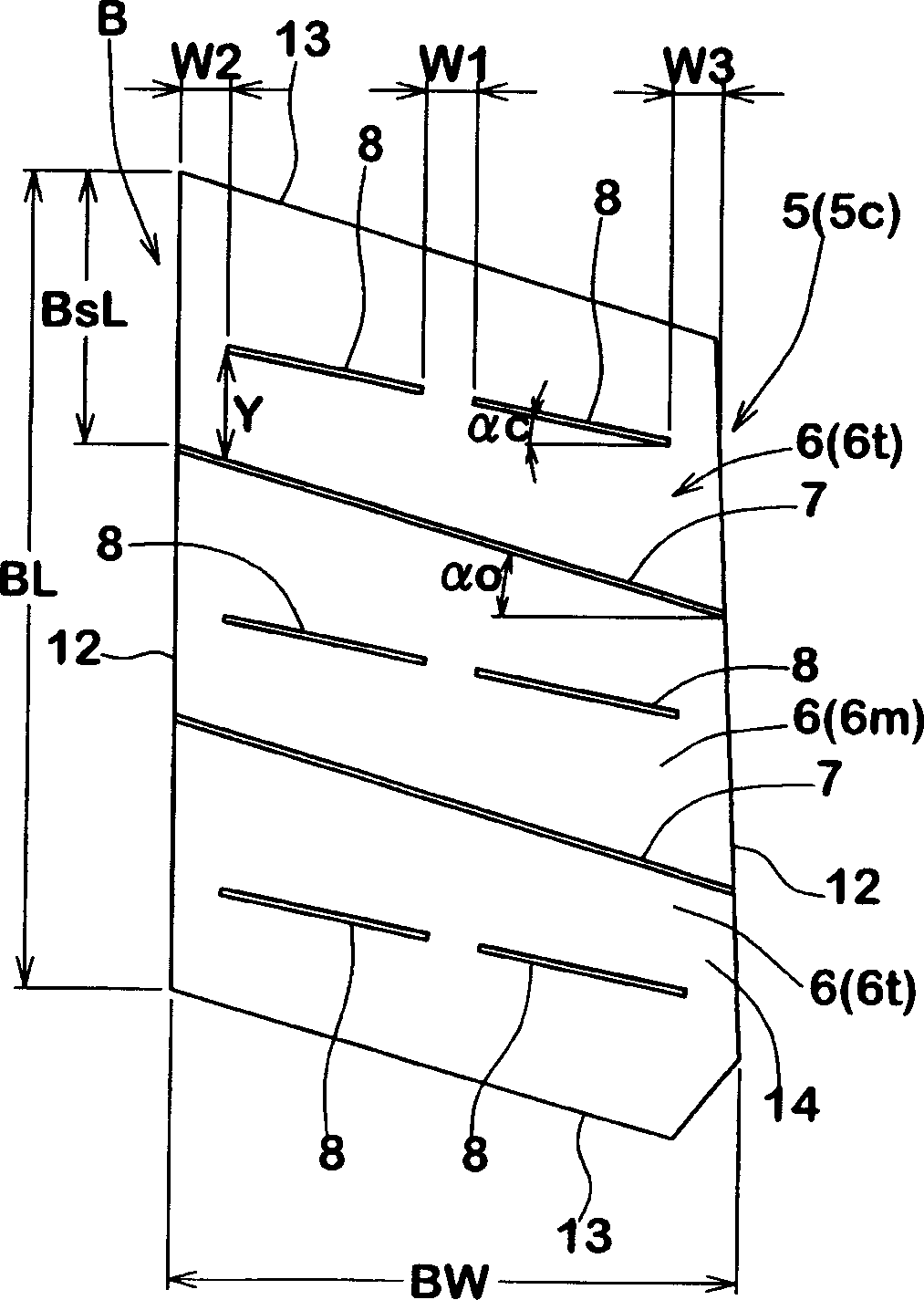
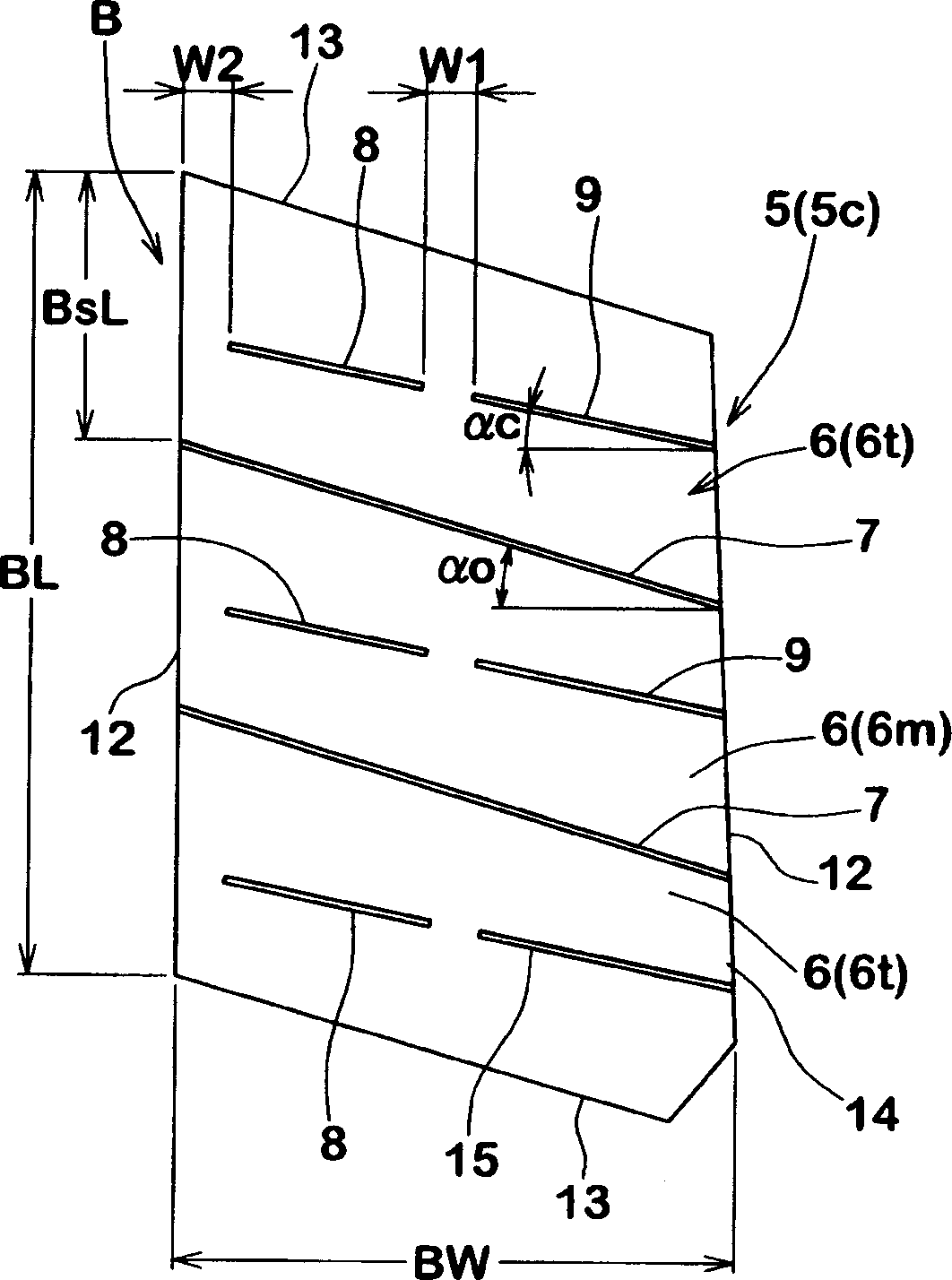
A pneumatic tire capable of simultaneously achieving wet performance and noise performance while enhancing driving stability. The pneumatic tire has a rib-like land portion extending in the circumferential direction of the tire, in the central portion of the tread; a left and right pair of first grooves extending in the circumferential direction of the tire while being next to both sides of the rib-like land portion; and a left and right pair of first land portions extending in the circumferential direction of the tire while being next to the outsides of the first grooves. Narrow grooves extending in the circumferential direction of the tire are provided in the rib-like land portion. Further, lug grooves and zigzag narrow grooves are provided in the first land portions, where the lug grooves do not communicate with the first grooves and incline relative to the tire equator, and the undulating or zigzag narrow grooves extend in the tire circumferential direction. The minimum distance (W2) between an undulating or zigzag narrow groove and the outer side wall of a first land portion is set 60-70% of the width (W1) of the first land portion, and the amplitude (W3) of the undulating or zigzag narrow groove is set 5-12% of the width (W1) of the first land portion.
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Pneumatic tire
ActiveCN103029526AImprove rigidityImprove cornering performanceTyre tread bands/patternsMechanical engineeringTread
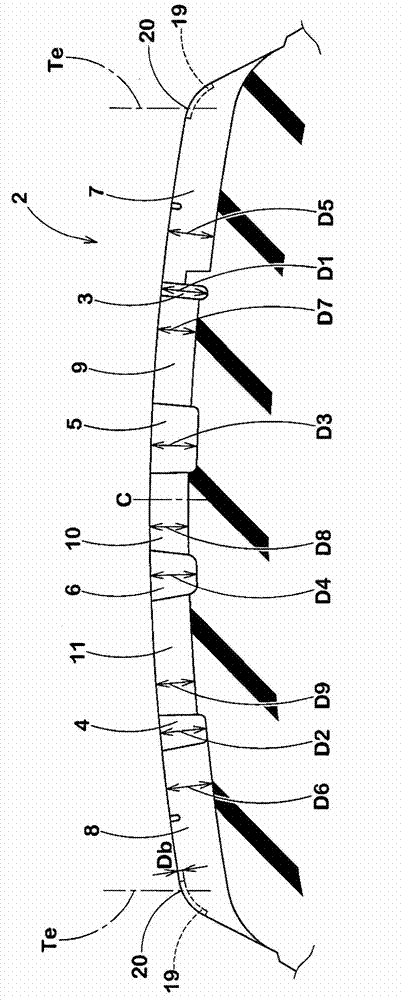
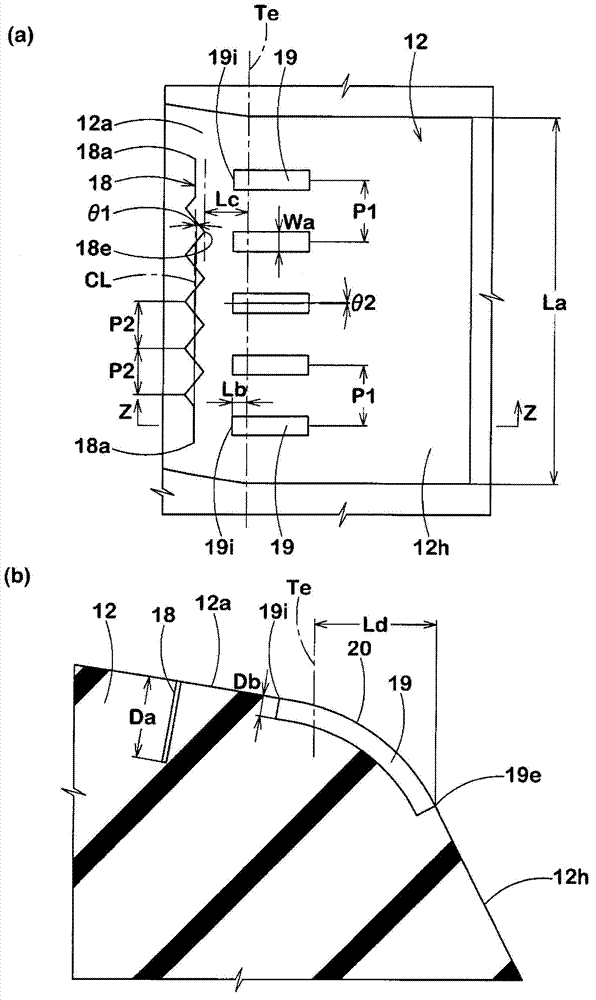
The present invention provides a pneumatic tire capable of evenly improving cornering performance and behavior in critical cornering on snowy / icy roads. The direction of the pneumatic tire to be arranged to a vehicle is specified. Outboard shoulder block (12) and inboard shoulder blocks (13) are formed at a tread portion (2). Both the outboard / inboard shoulder blocks (12, 13) are provided with sipes. The outboard shoulder blocks (12) have an axial width more than the axial width of the inboard shoulder blocks (13). The circumferential sipe (18) of the outboard shoulder blocks (12) extending at an angle of not more than 10 degrees with respect to the tire circumferential direction is arranged at the side of an outboard tread edge (Te) of the vehicle in sipes (17). The outboard shoulder block (12) has an axially outer sidewall (12h) of which surface is provided with a plurality of narrow buttress grooves (19) extending radially inwardly from the outboard tread edge (Te).
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Pneumatic tire
InactiveCN1733511AReduce distortionReduce tiltTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
FSAE racing car aerodynamic suite
InactiveCN104742987AIncrease downforceImprove ground adhesionVehicle body stabilisationVehicle body streamliningVehicle frameObstacle avoidance
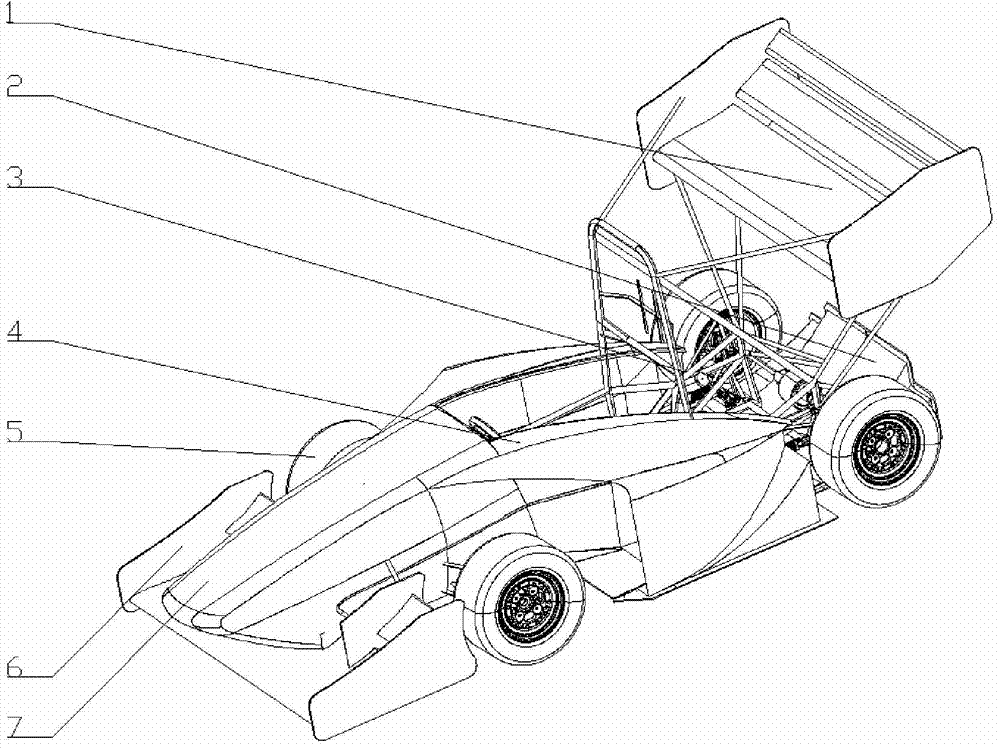
The invention discloses an FSAE racing car aerodynamic suite. The FSAE racing car aerodynamic suite comprises a rear wing (1), a tail-end diffuser (2) and a front nose wing (6) which are in rigidity connection with a car frame (3), wherein the front nose wing (6) is located at the lower portion of the racing car head, and the rear wing (1) and the tail-end diffuser (2) are upper-and-lower arranged and are installed at the tail of the racing car. The FSAE racing car aerodynamic suite can improve the down force of the FSAE racing car greatly, so that a good ground adhesive force is obtained by the racing car, and excellent dynamic property is acquired; the aerodynamic property and handling stability of the racing car can be improved, so that the speed and accelerated speed of the racing car when entering a curve and pulling out of the curve are greatly improved, and excellent turning driving property is obtained; thereby, the FASE racing car can acquire outstanding grades in the competition items of high-speed obstacle avoidance, eight-character circling and the like, and the FSAE racing car aerodynamic suite further has the advantages of being light in weight, simple in structure, convenient to assemble and disassemble, reliable in property, good in practicability and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Intelligent remote control self-adaption pipe robot
The invention provides an intelligent remote control self-adaption pipe robot. The intelligent remote control self-adaption pipe robot comprises a control guide module, an universal transmission module and six self-adaption adjusting bracket modules; the control guide module includes a traction pin shaft, a traction shell, a battery box, a battery set, a conical adaptershell, a circuit board, a speed reducing motor, a speed reducing motor mounting shell, a transmission step shaft, a rolling bearing, a bearing retainer ring and a nylon stopper; the universal transmission module includes a damping spring, an universal joint, a spring pretightening hand wheel, a hand wheel sleeve, a plane thrust bearing, a transmission shaft, a hexahedron sleeve and a conical flange; and each self-adaption adjusting bracket module includes a polyurethane wheel, a deep groove ball bearing, a polyurethane wheel rotating shaft, a double-lug bracket, a double-lug fixed base, two connecting rods, two spring dowel pins, two springs, a positioning pin shaft and a mounting base. The intelligent remote control self-adaption pipe robot can climb in pipes with different diameters, and is simple in structure, excellent in flexibility and high in stability.
Owner:福建巨联环境科技有限公司
Turning control apparatus for vehicle
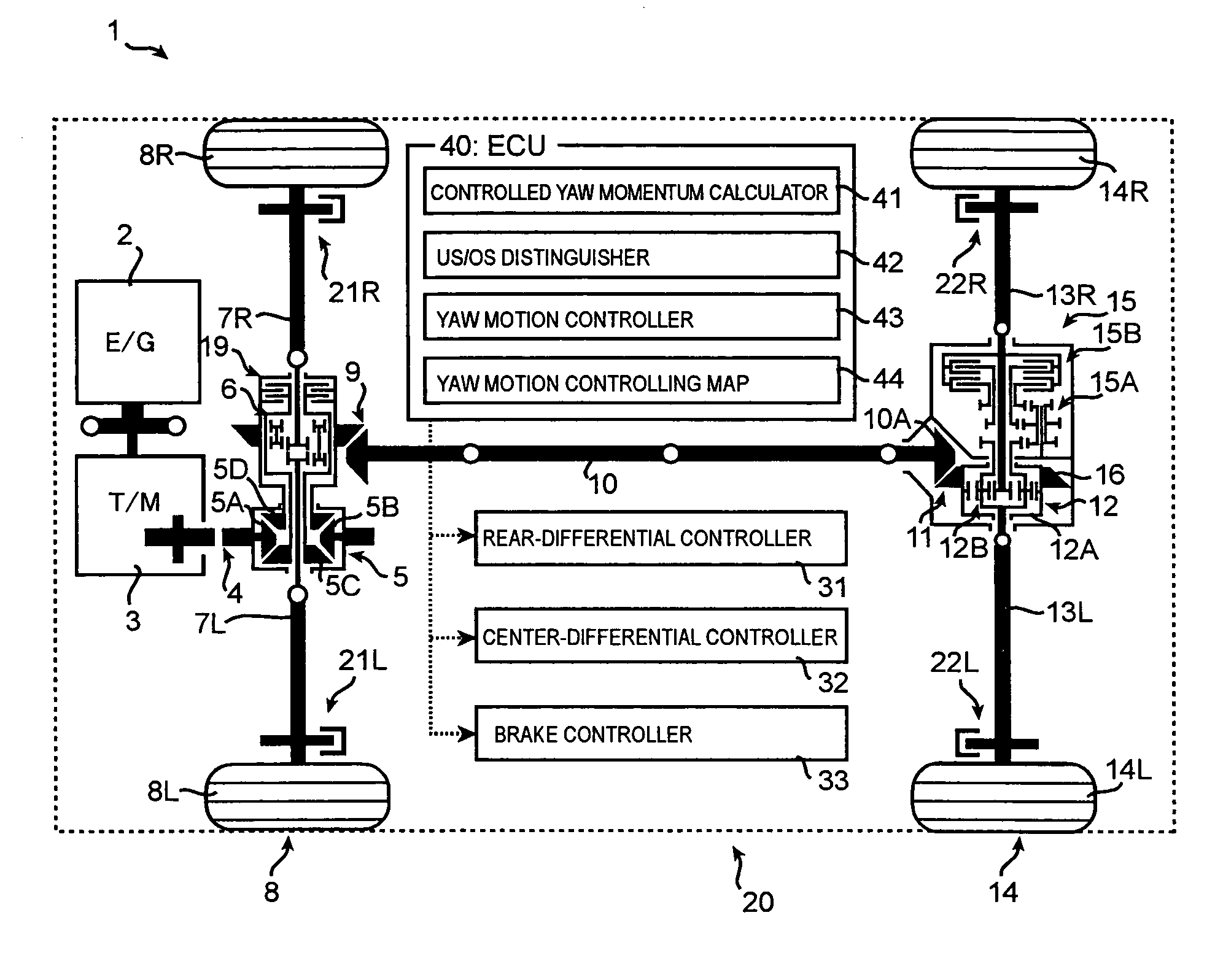
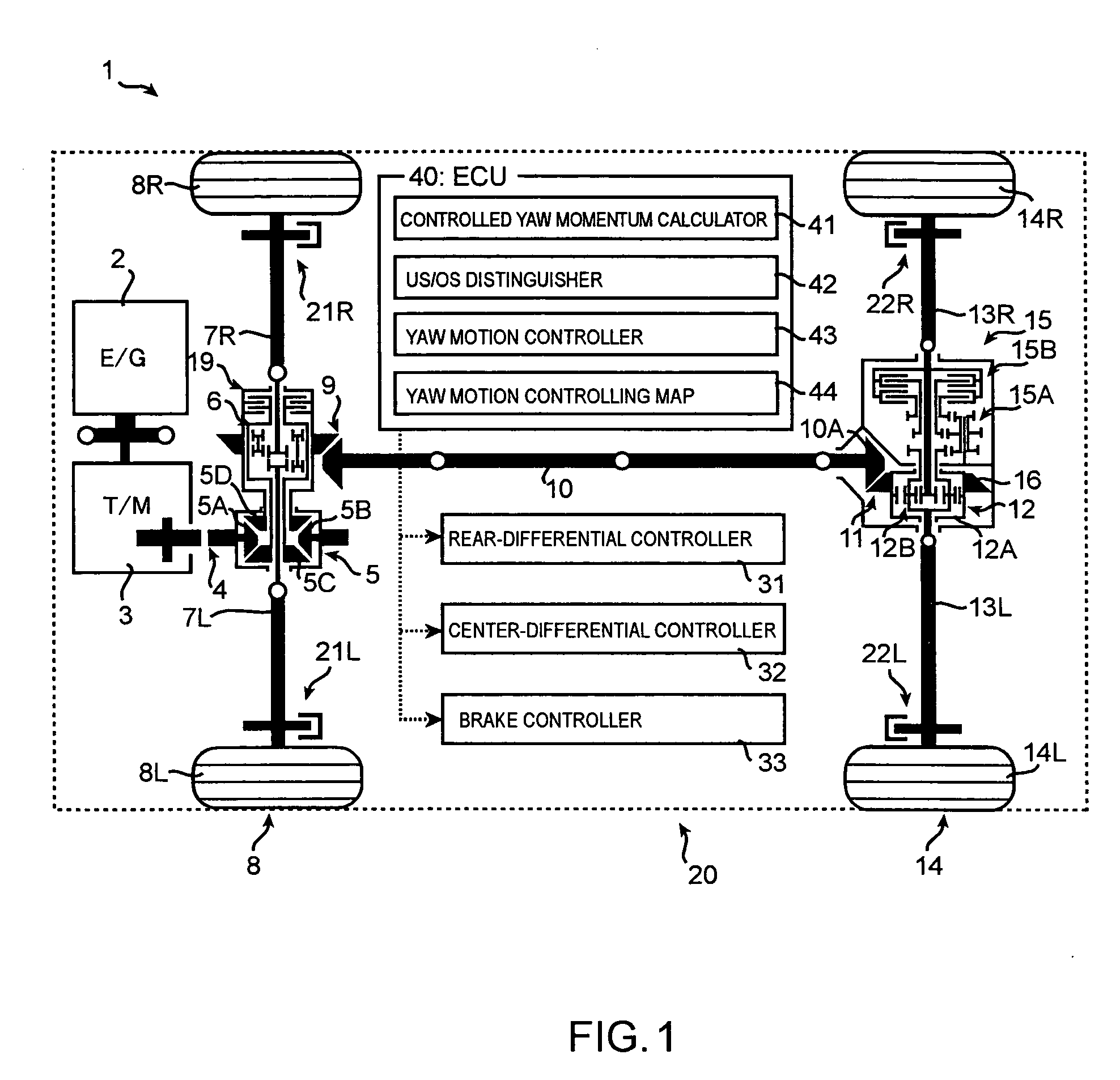
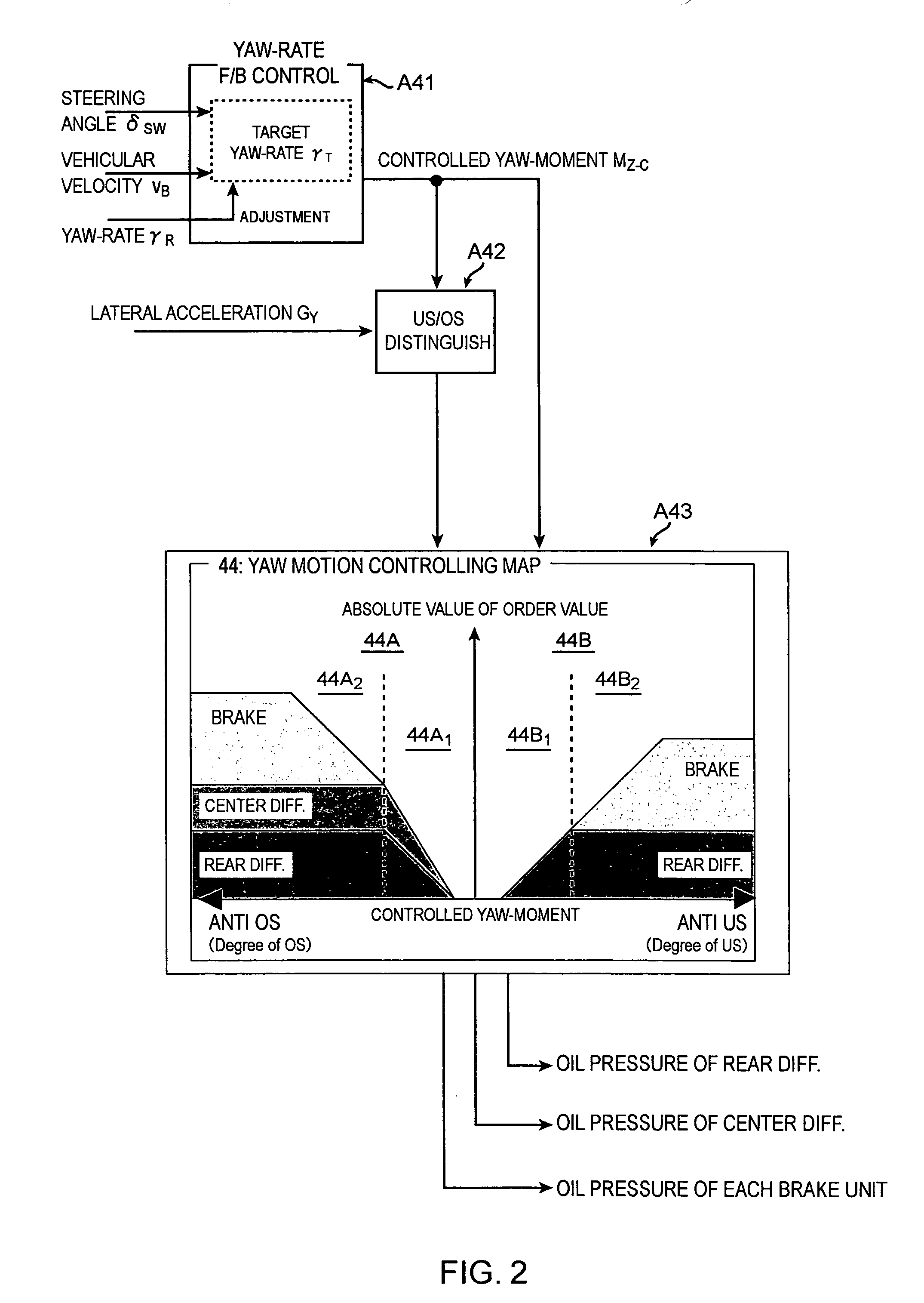
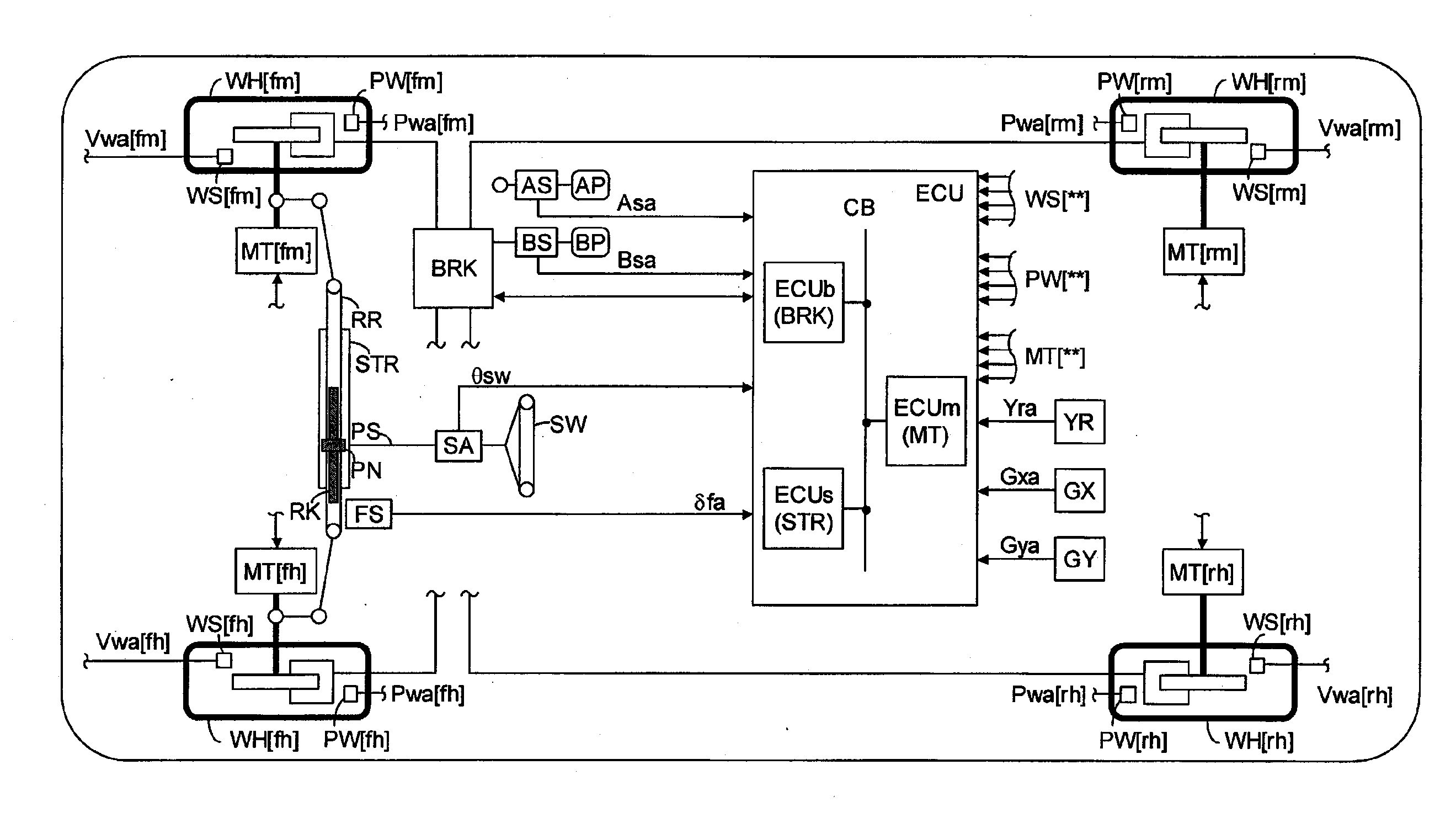
ActiveUS20070112497A1Improve cornering performanceAvoiding degradation accelerationDigital data processing detailsDifferential gearingsEngineeringYaw control
The present invention provides a turning control apparatus for a vehicle to improve turning ability and to avoid degradation of acceleration ability. The turning control apparatus comprises a first yaw controller for adjusting at least one of driving torque of a left wheel and a right wheel; a second yaw controller for adjusting a speeds difference between a front wheel and a rear wheel; and an integrated yaw controller for controlling yaw momentum of the vehicle by managing the first and second yaw controller, wherein when the yaw of the vehicle should be reduced, the integrated yaw controller controls the first yaw controller so as to decrease the driving torque of a inside wheel, which is one of the right and left wheel and is near to a center axis of turning, and the second yaw controller so as to decrease the speeds difference between the front and rear wheel.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Vehicle speed control device
ActiveUS20110160963A1Turning radius is reducedImprove cornering performanceSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorEngineering
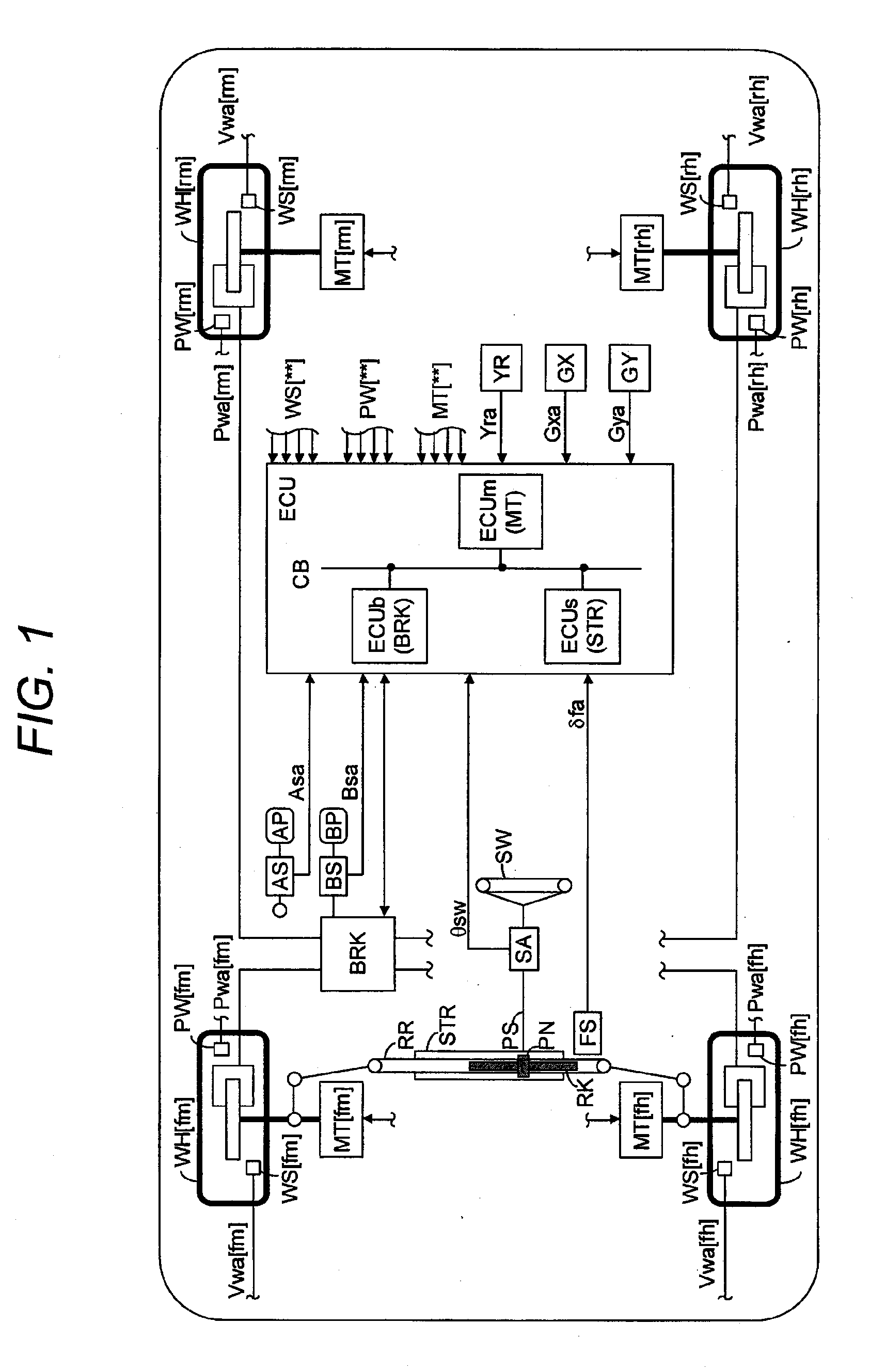
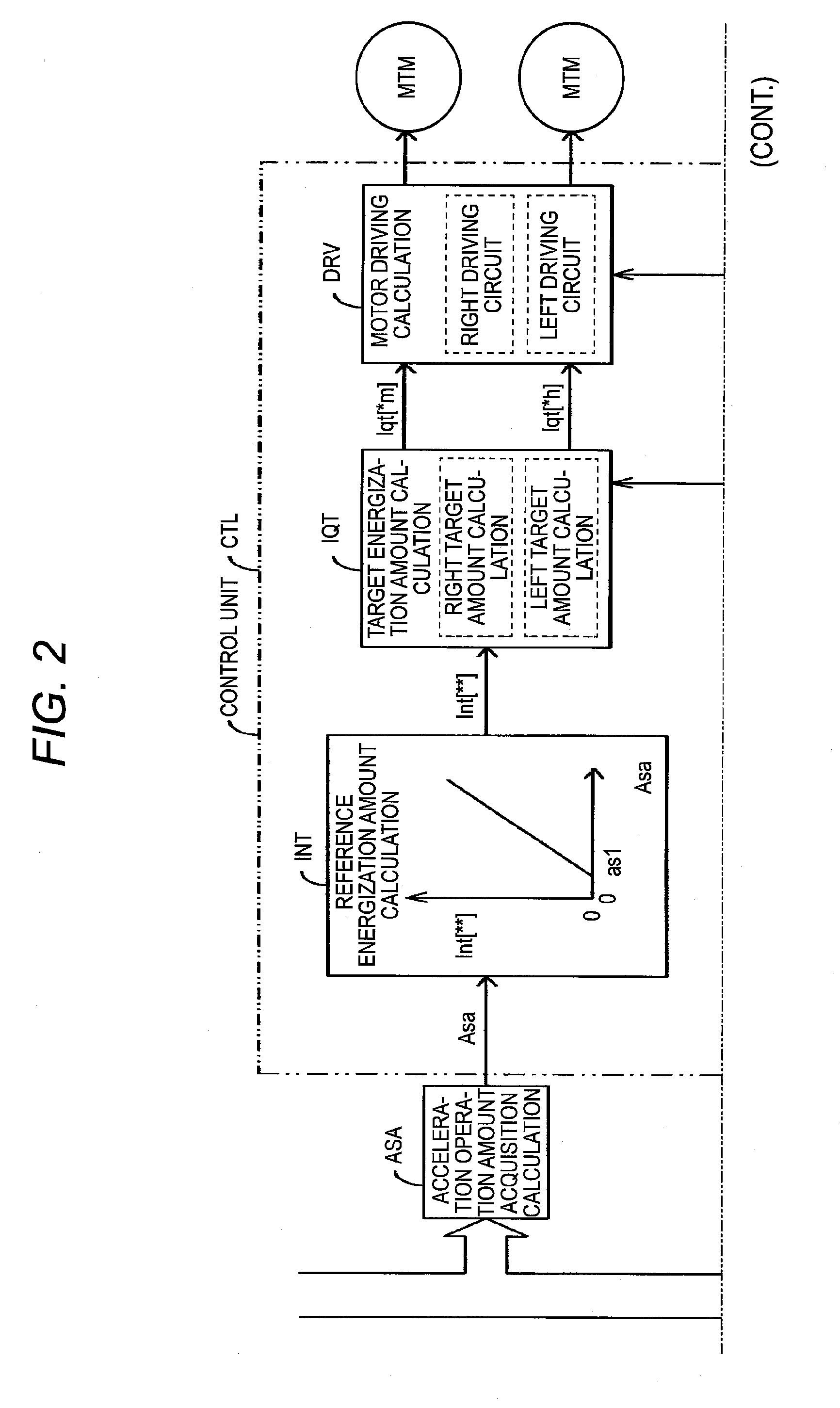
A vehicle speed control device is provided. The device includes a steering device which steers left and right wheels, first and second electric motors which separately apply power to the left and right wheels, an operation amount acquisition unit which acquires an acceleration operation amount by the driver of the vehicle, a steering angle acquisition unit which acquires a steering angle which is a value between an inner wheel steering angle and an outer wheel steering angle; a vehicle speed acquisition unit configured to acquire an actual speed of the vehicle; and a control unit configured to control the first electric motor and the second electric motor on the basis of the acceleration operation amount, the actual speed, the steering angle, and a steering geometry indicating a geometric relationship between the steering angle and a turning center of the vehicle.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Lean-to-turn wheeled device
InactiveUS7988159B2Improve cornering performancePotential for wheels significantly largerSkatesSkate-boardsCamber angleEngineering
A wheeled device having pairs of wheels positioned on opposite sides (e.g. skateboard or “quad” skate) that includes a base and at least one turnable wheel assembly. A turnable wheel assembly includes two wheels having negative camber angle, and is configured such that the axles of the wheels can pivot about an axis disposed substantially perpendicular to the direction of travel. This configuration is conducive to the use of large wheels.
Owner:CHEN SHANE
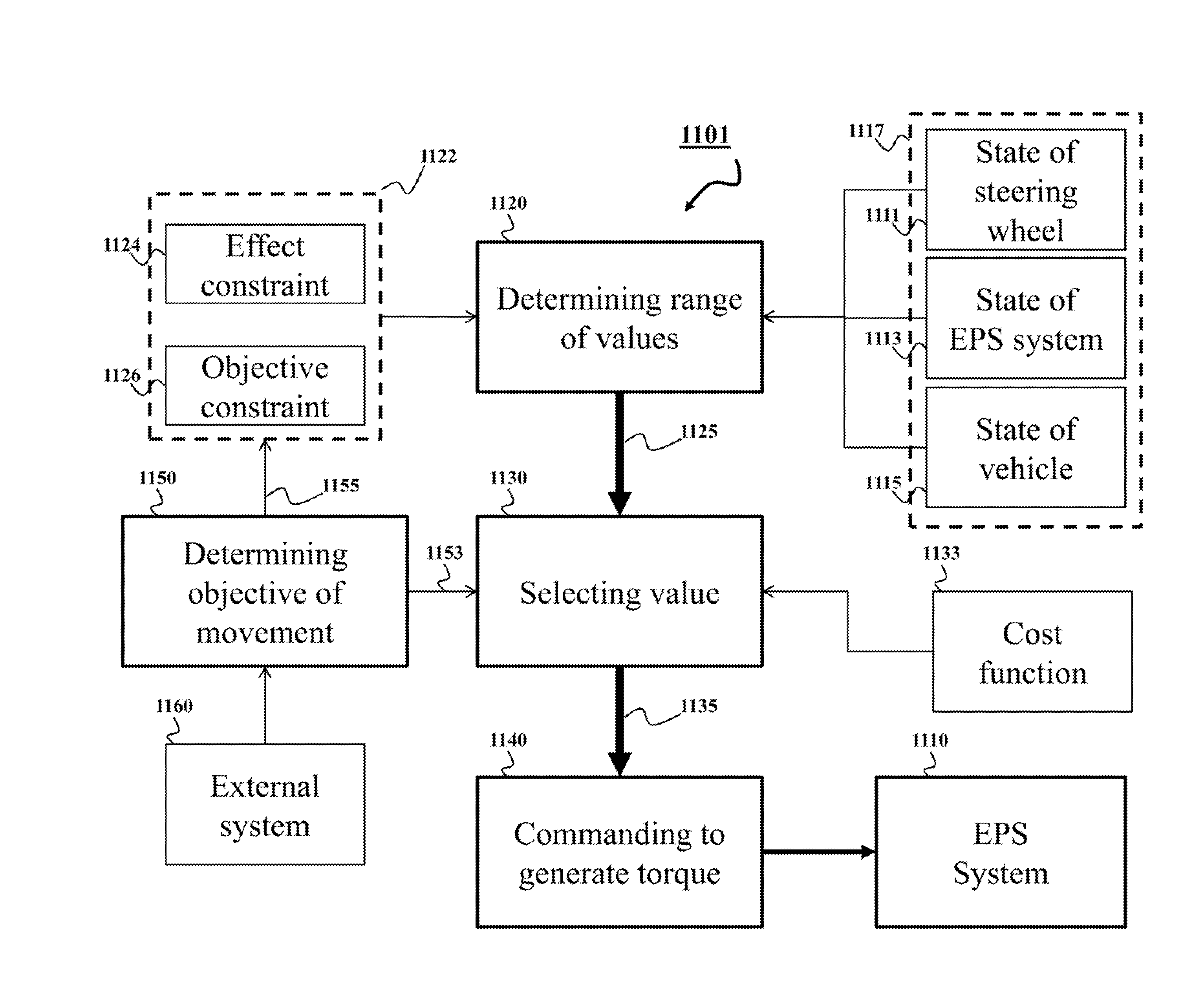
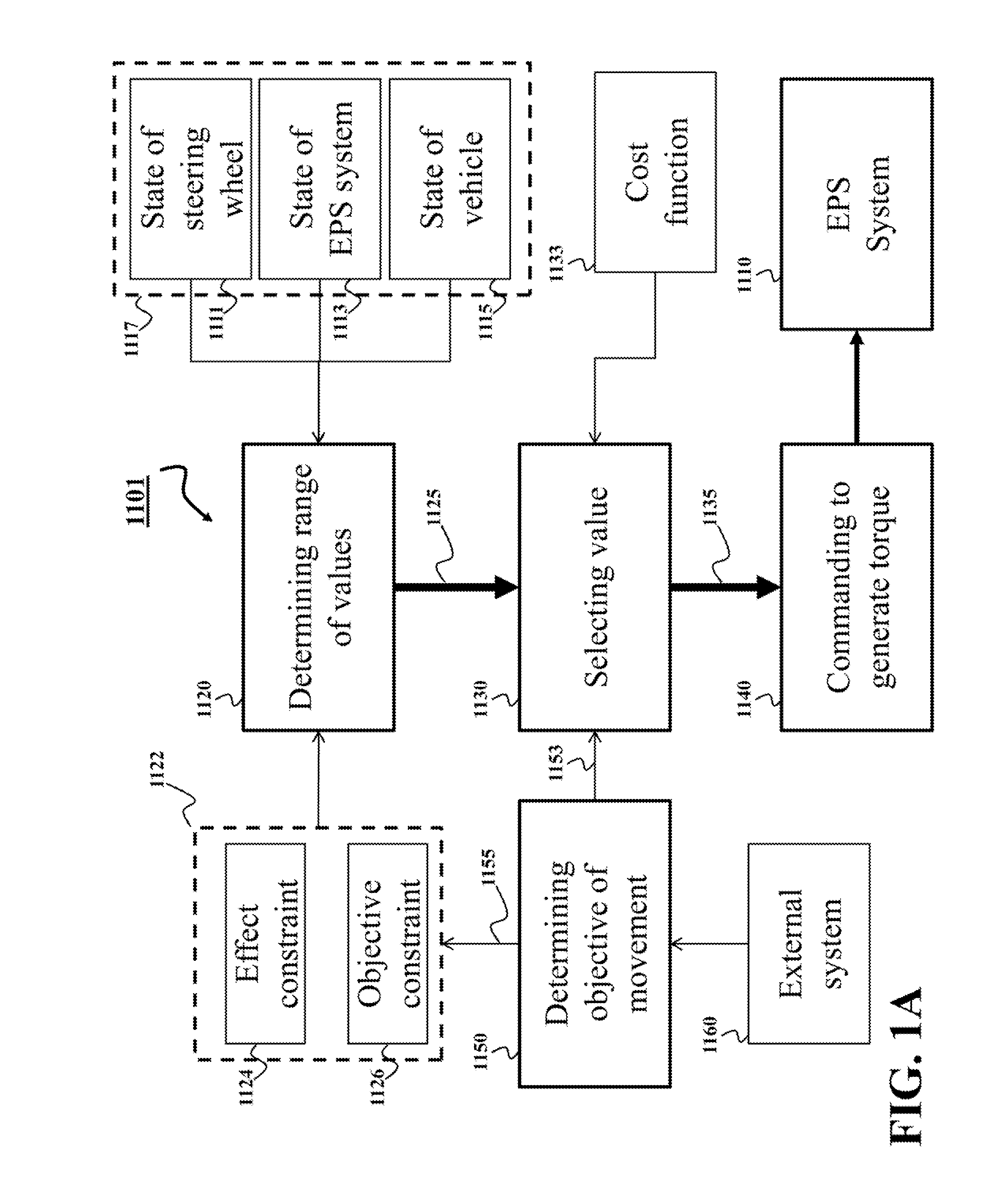
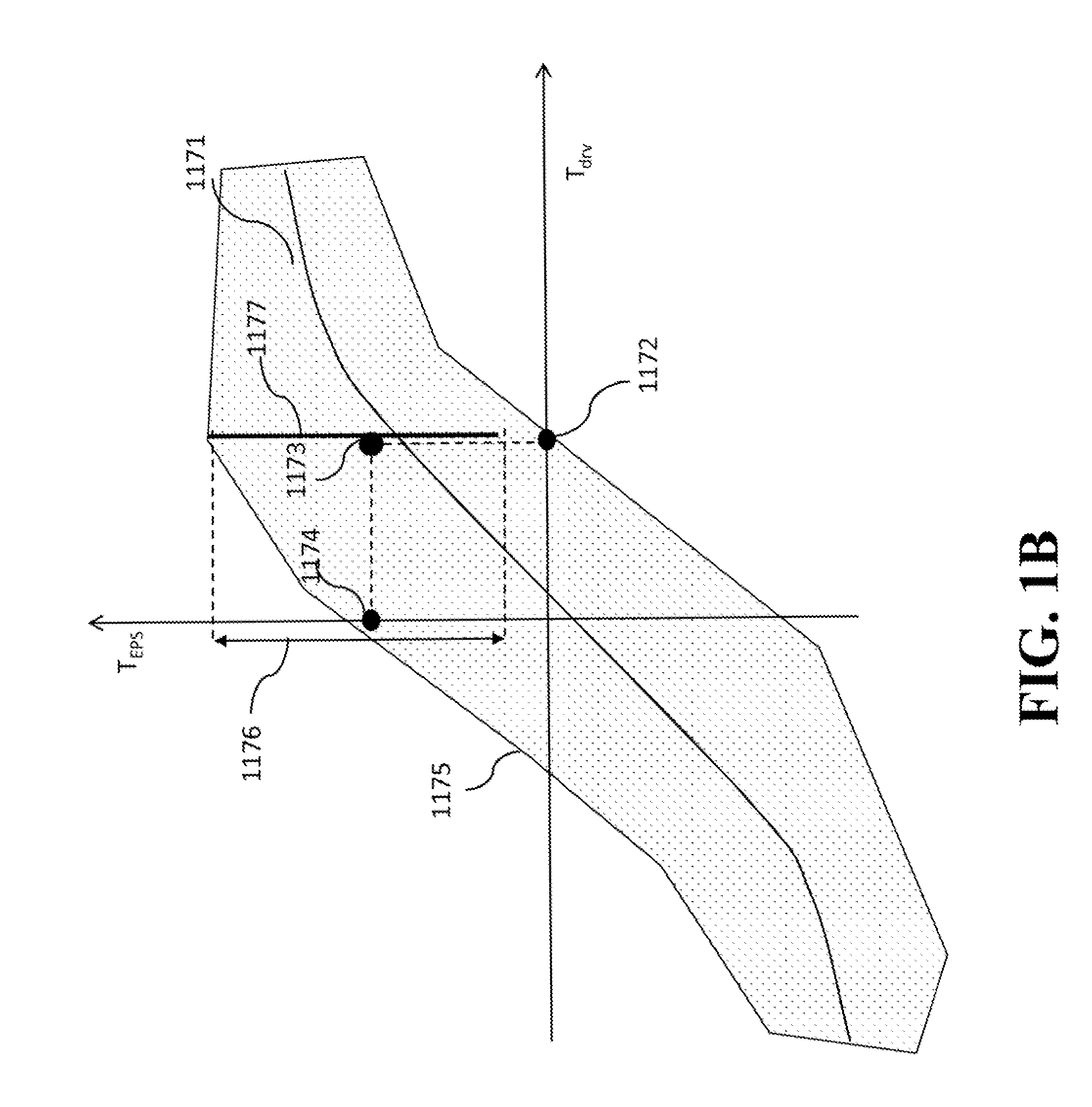
System and Method for Controlling Electric Power Steering System
ActiveUS20140371992A1Improving turning angleReduce effortSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringSteering wheel
A method controls a torque of an electric power steering (EPS) system of a vehicle. The method determines, based on a state of a movement of the vehicle, a range of values of the torque of the EPS system satisfying constraints. The constraints include at least one constraint on an effect of the torque of the EPS system on the steering wheel. The method selects a value of the torque within the range of values based on an objective of the movement of the vehicle and commands the EPS system to generate the torque according to the value of the torque.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Autonomous moving body and method for controlling movement thereof
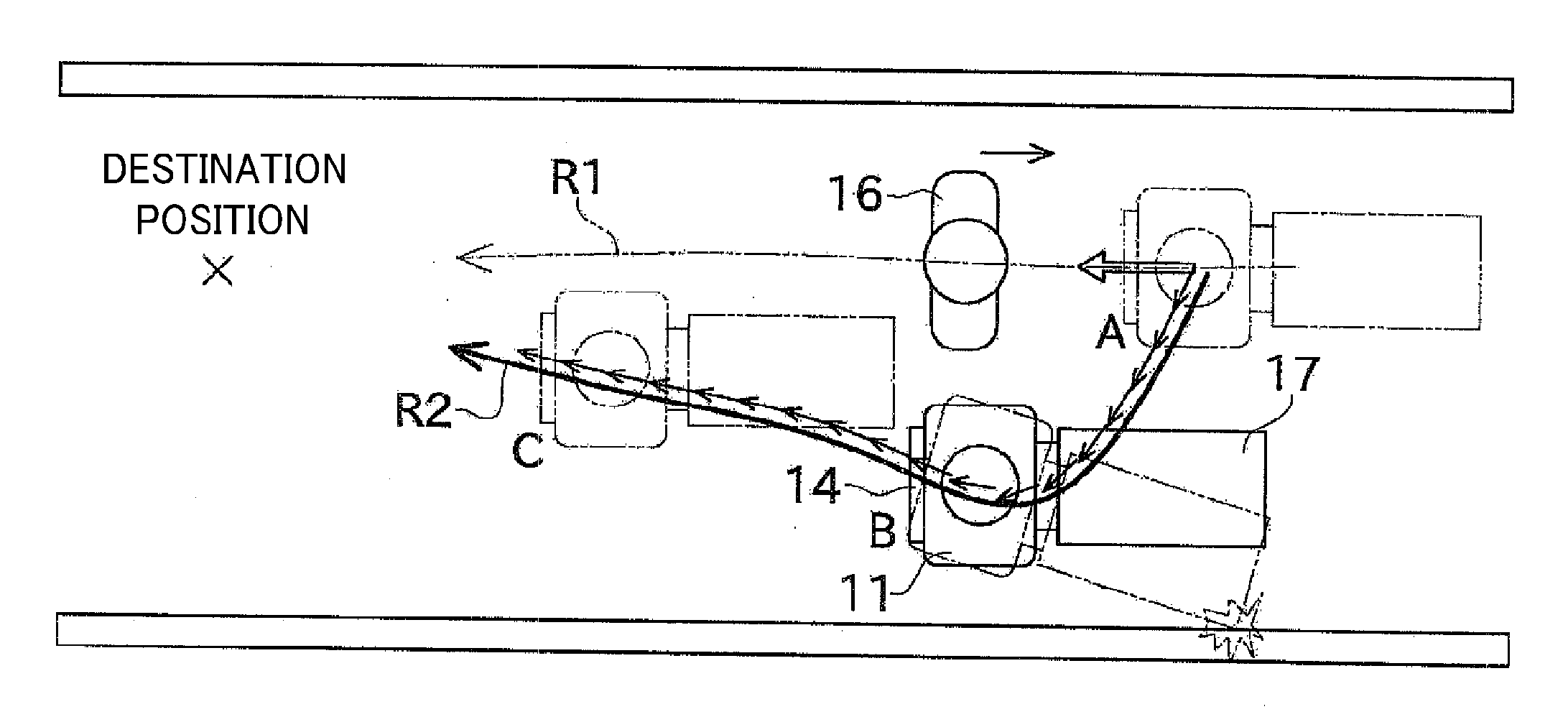
InactiveUS20090299525A1Simple structureImprove cornering performanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorMovement controlComputer science
An autonomous moving body includes: an omnidirectional moving mechanism for moving the moving body; a detecting unit for detecting an obstacle; and a movement control unit for generating a movement instruction signal for avoiding the obstacle detected by the detecting unit while maintaining a frontal direction of the moving body to be substantially constant and transmitting the generated signal to the omnidirectional moving mechanism.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD +1
Pneumatic tire for motorcycle
InactiveUS20090266462A1Improve driving stabilityReduce weightPneumatic tyre reinforcementsYarnGround contactFiber
A pneumatic tire for a motorcycle, wherein the tire is optimized in the ground contact shape and the ground contact pressure distribution during high-speed running to achieve excellent driving stability, is provided. Furthermore, a pneumatic tire for a motorcycle, wherein the tire is optimized in the ground contact shape and the ground contact pressure distribution during high-speed running to realize excellent gripping force to stabilize the behavior of the tire near its cornering limit and excellent cornering ability, is provided.Provided is a pneumatic tire for a motorcycle, which employs a multifilament-twist polyketone fiber cord, as a reinforcing material, having a total dtex value of 1000 to 20000 dtex per cord and satisfying the relationships represented by the following Expressions (I) and (II):σ≧−0.01E+1.2 (I)σ≧0.02 (II)(wherein, E is an elastic modulus (cN / dtex) at 25° C. under a load of 49 N, and σ is a heat shrinkage stress (cN / dtex) at 177° C.).
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
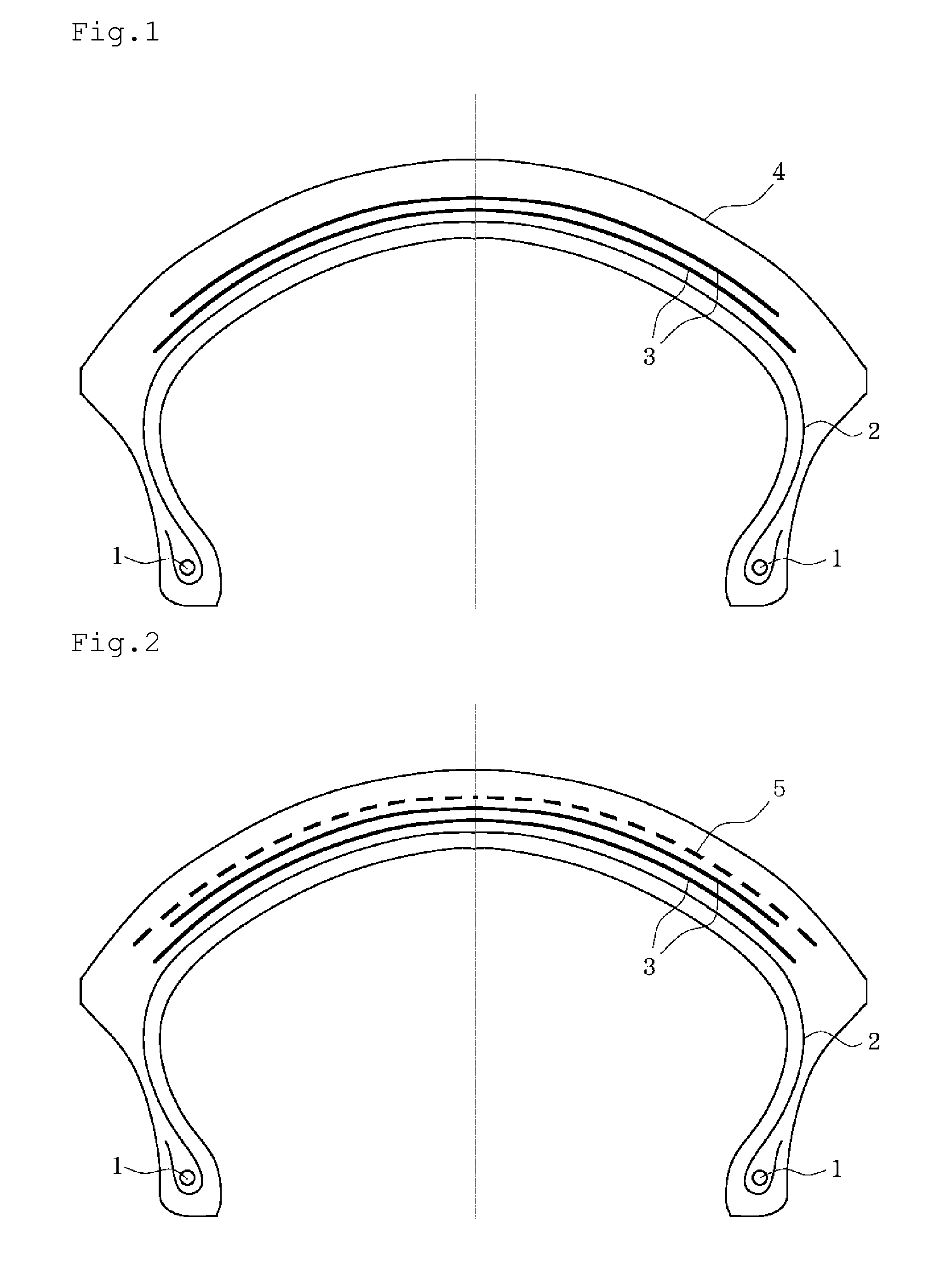
Snow Skis And Snowboards Having Split Tips And/Or Tails
InactiveUS20050269801A1Improving turning capabilityImproved characteristicSki bindingsSki-brakesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A snow ski or snowboard having enhanced turning capability compared to traditional skis or snowboards has a split tip and / or tail portion. The split tip / tail provides enhanced turning characteristics of the ski or snowboard. The split tips and / or tails may have additional active turning edges may have the same, or similar, curvature as the primary turning edge, thereby effectively increasing the length of the turning edge. A symmetrical or asymmetrical ski tail may be provided to further enhance turning on skis. Such a symmetrical or asymmetrical tail may have varying tail edge lengths, varying widths of split tails, interior edges, varying thickness of split tails, and / or varying core material of split tails that provides such enhanced turning ability.
Owner:SKI LOGIC SCOTTYBOB
Pneumatic tire
ActiveCN101190644AInhibition of snapping effectImprove braking effectTyre tread bands/patternsRoad surfaceTread
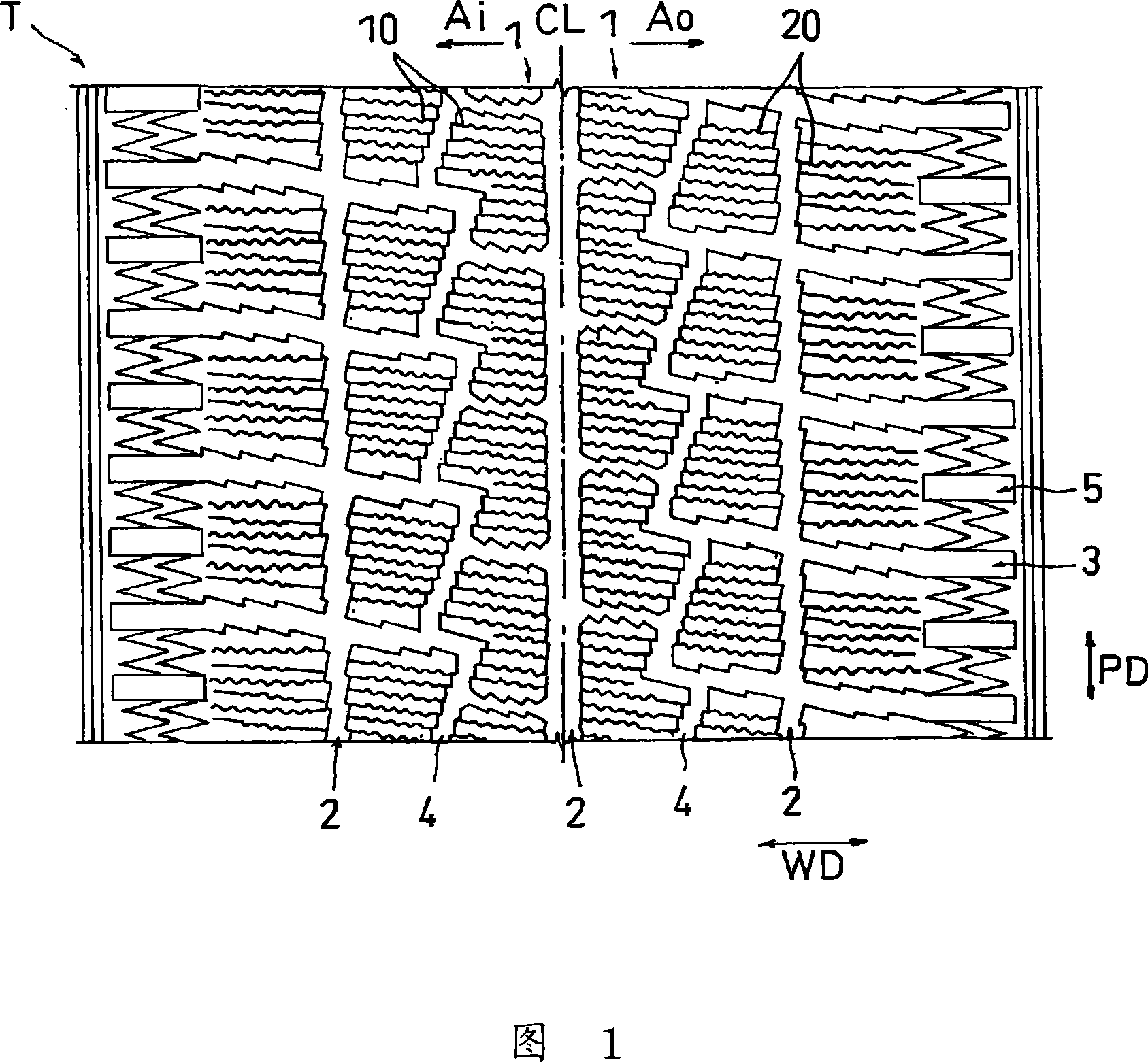
A pneumatic tire simultaneously satisfying both on-ice turning performance and ice braking performance and also simultaneously satisfying both dry turning performance and dry braking performance. The pneumatic tire has a tread pattern (T) having land sections such as blocks (1) in which sipes (10) are formed. First sipes (10) are provided in a region (Ai) on the inner side, in the direction of installation of the tire on the vehicle, of a tire equator line (CL), and second sipes (20) are provided in a region (Ao) on the outer side of the tire equator line (CL). The first sipes (10) each have a recessed or projected engagement section in a cross-section parallel to the tire equator line (CL). In each second sipe (20), an inner wall surface extending in a tire width direction (WD) or in a direction inclined from the tire width direction has rows of grooves and ridges, and each row has a portion inclined in the direction where the sipe are formed.
Owner:TOYO TIRE & RUBBER CO LTD
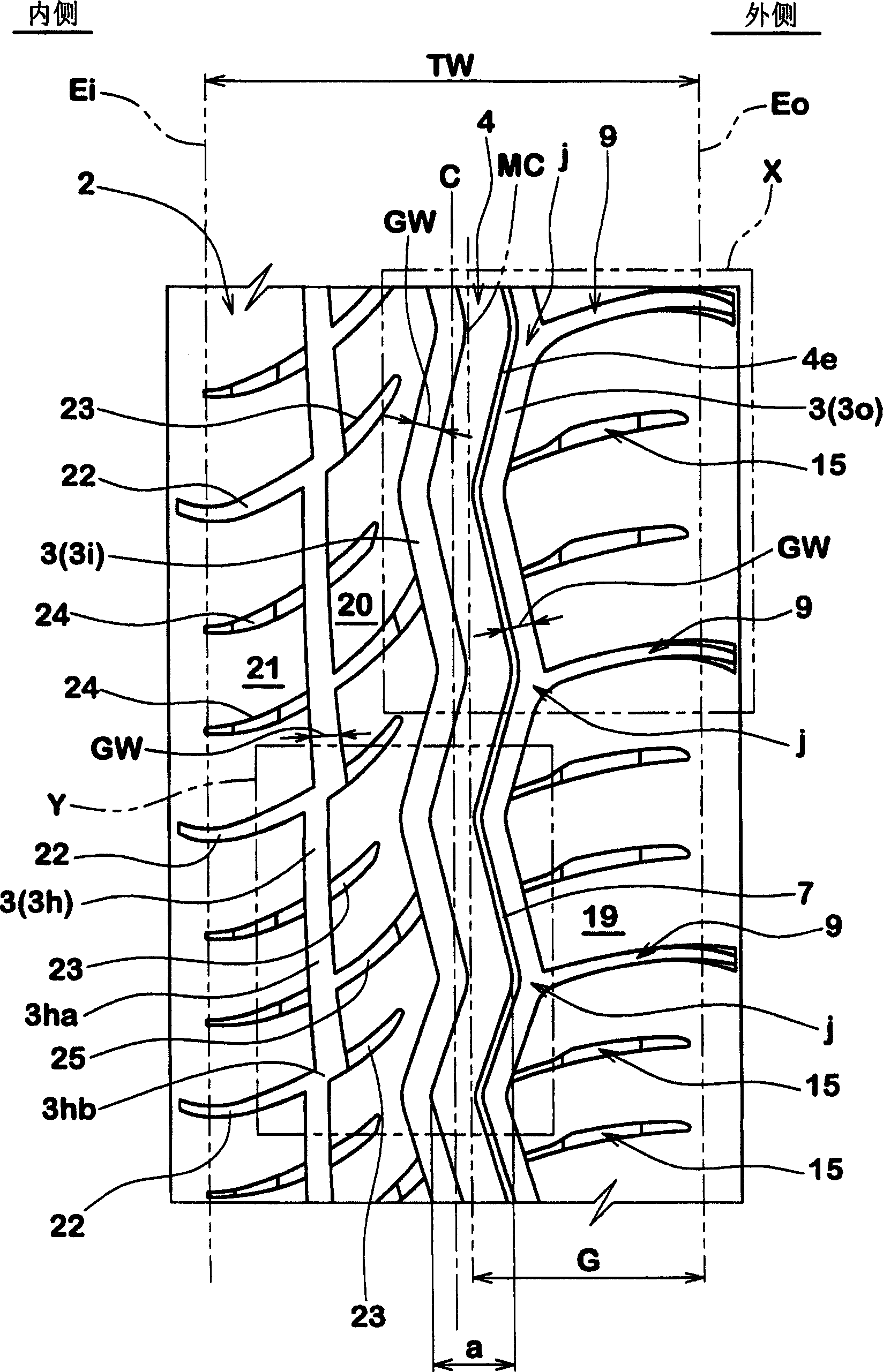
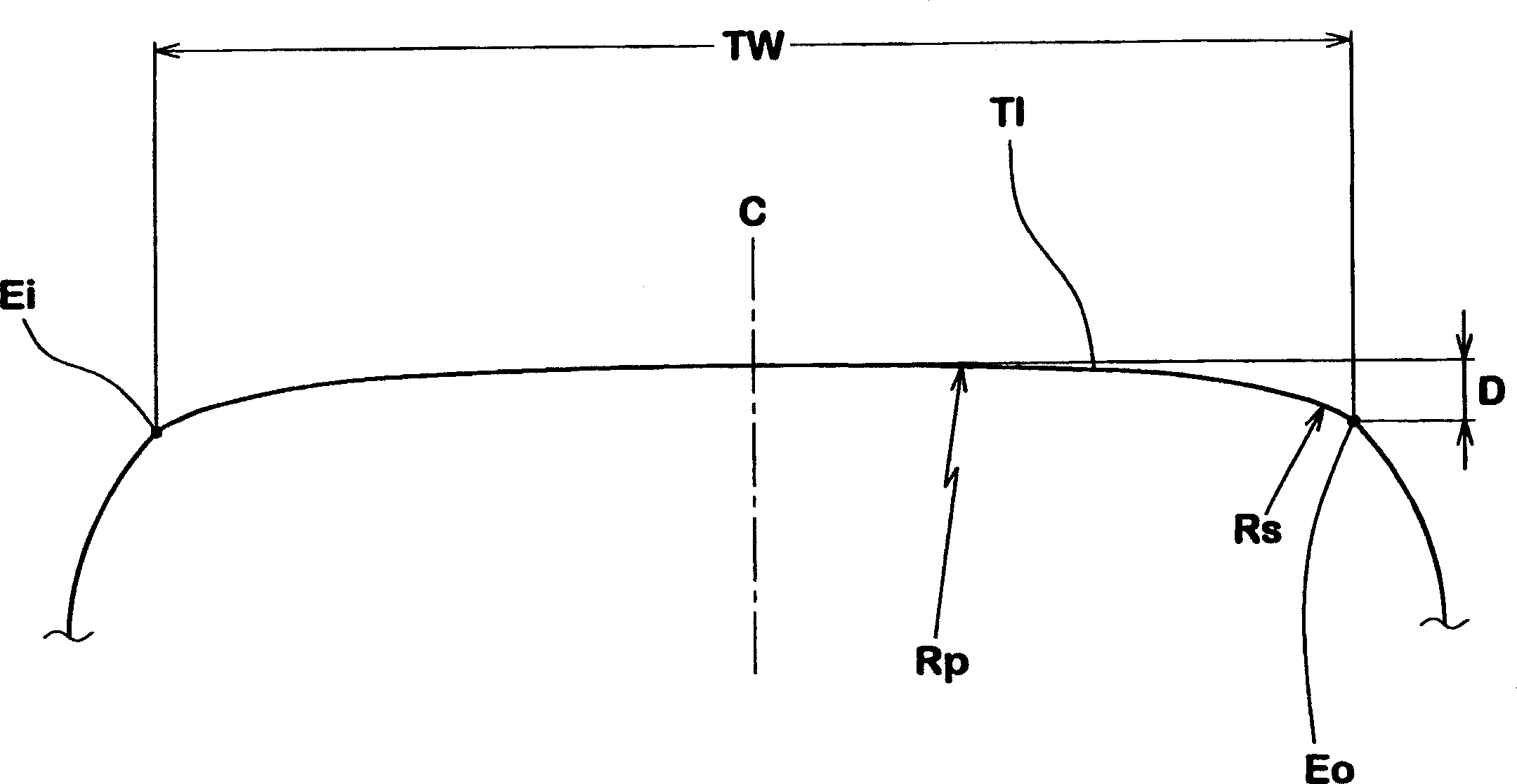
Pneumatic tyre
ActiveCN101505976AEnsure wear resistanceImprove handling stabilityTyre tread bands/patternsShoulder regionMechanical engineering
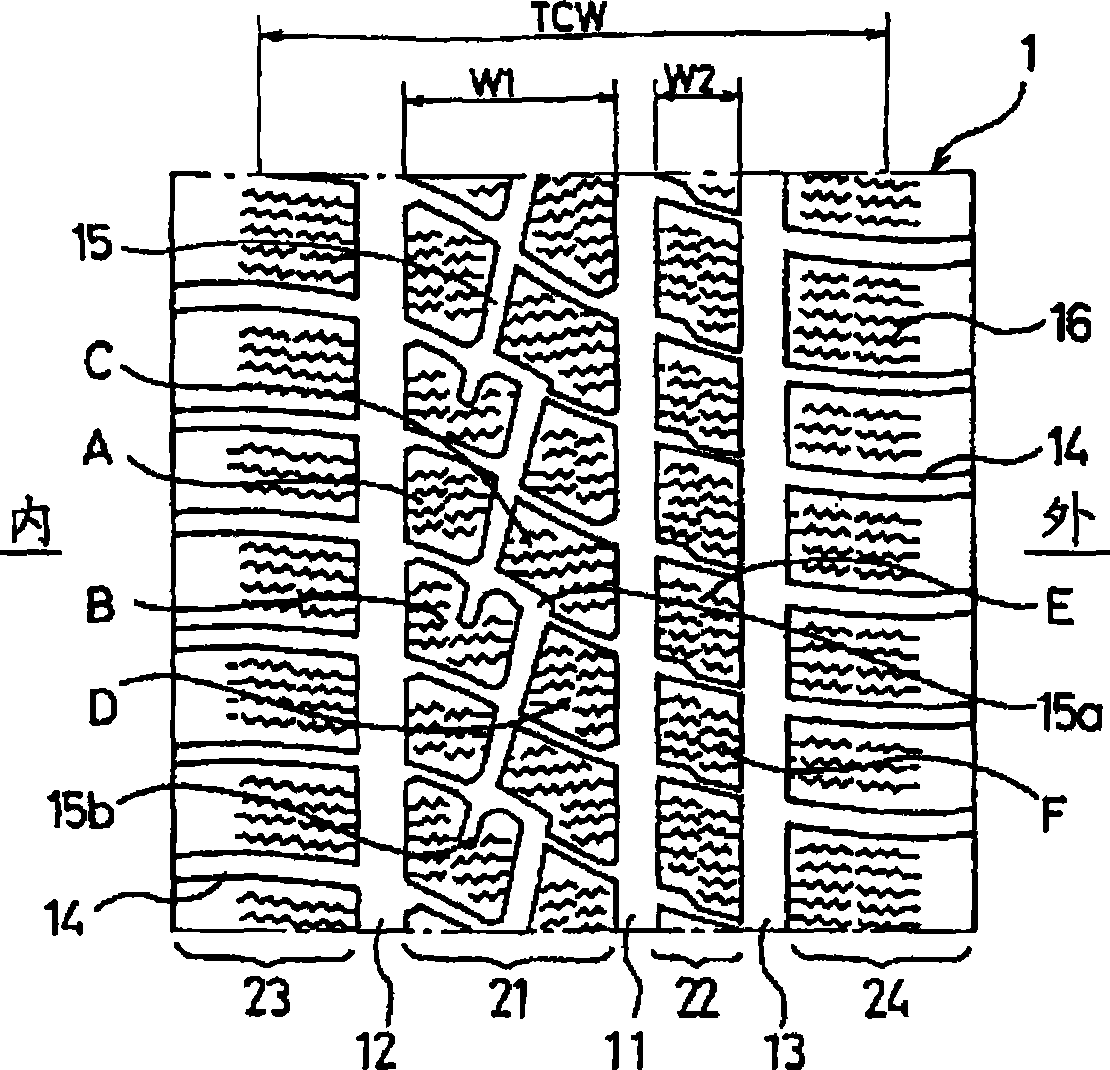
A pneumatic tire whose front and rear sides need to be oriented to specific directions when it is mounted on a vehicle. The tire has, on a tread section, a first groove extending in the circumferential direction of the tire, a second main groove extending in the circumferential direction of the tire, in a shoulder region that is closer to the inner side of a vehicle than the first groove, a third main groove extending in the circumferential direction of the tire, in a shoulder region that is closer to the outer side of the vehicle than the first main groove, and lug grooves extending from one shoulder side to the other shoulder side. The width of a first land section segmented between the first main groove and the second main groove is set greater than the width of a second land section segmented between the first main groove and the third main groove. Inclined grooves are formed in the first land section, and the grooves communicate with at least three lug grooves while inclining relative to the circumferential direction of the tire. One end of each inclined groove is opened in the lug grooves and the other end is ended in a block.
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Pneumatic tire
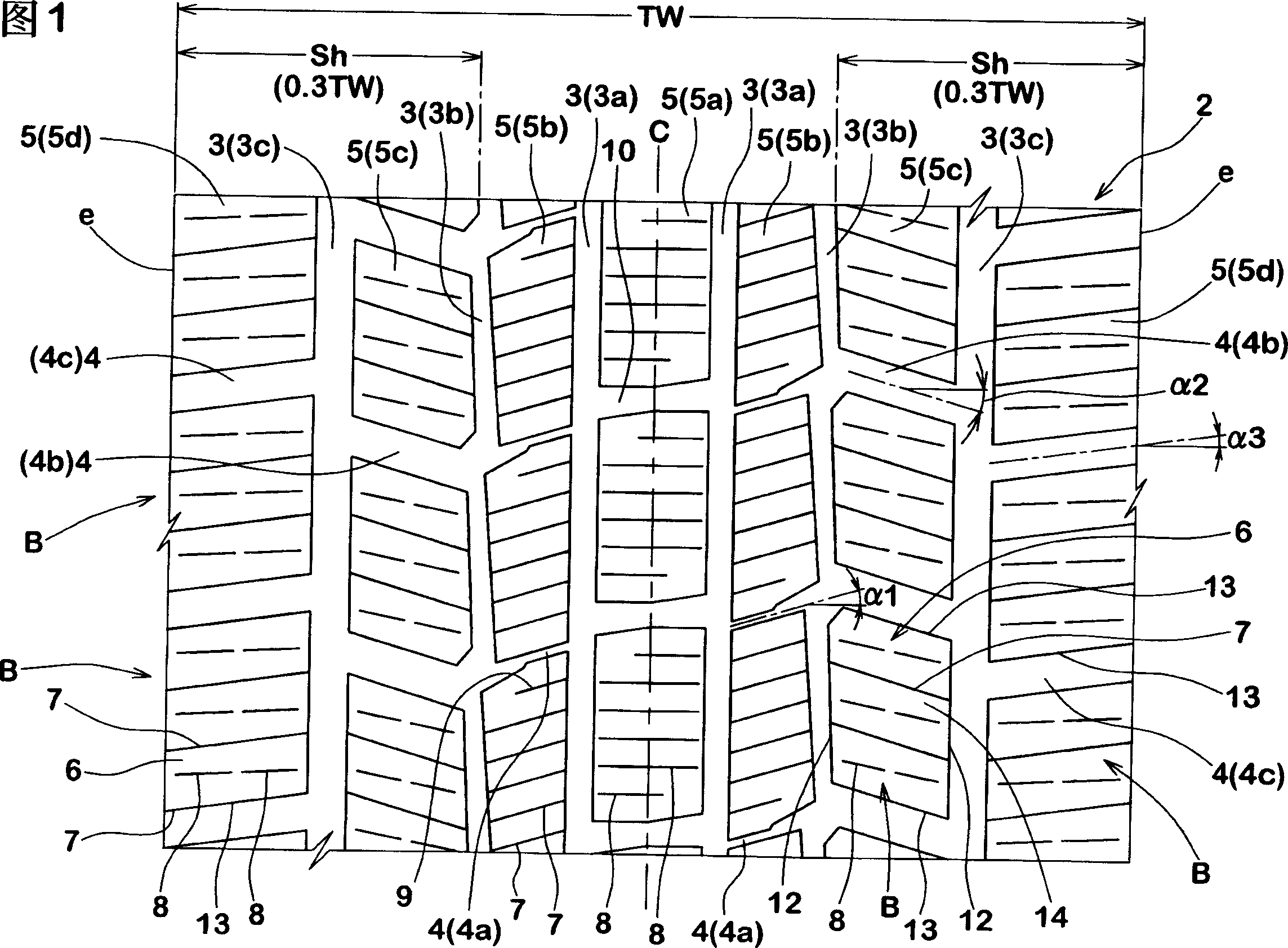
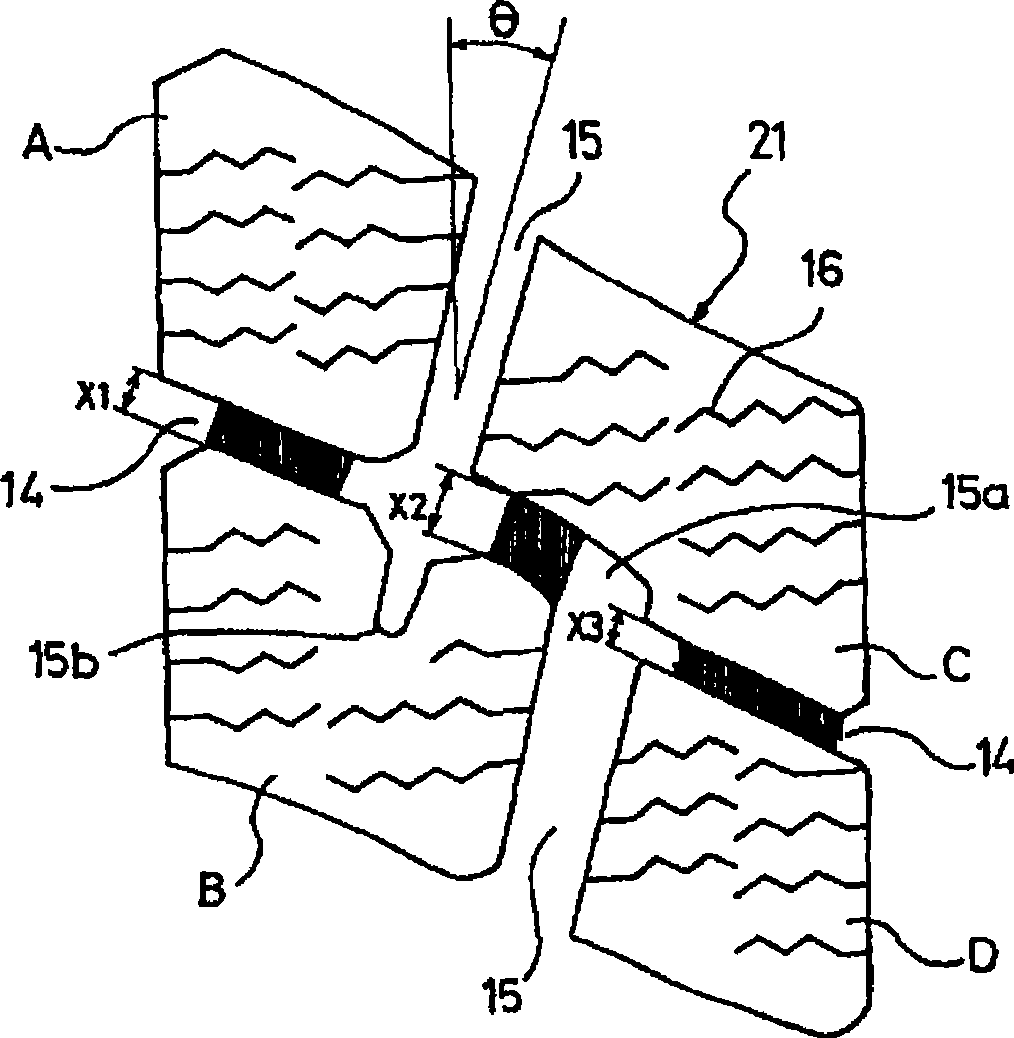
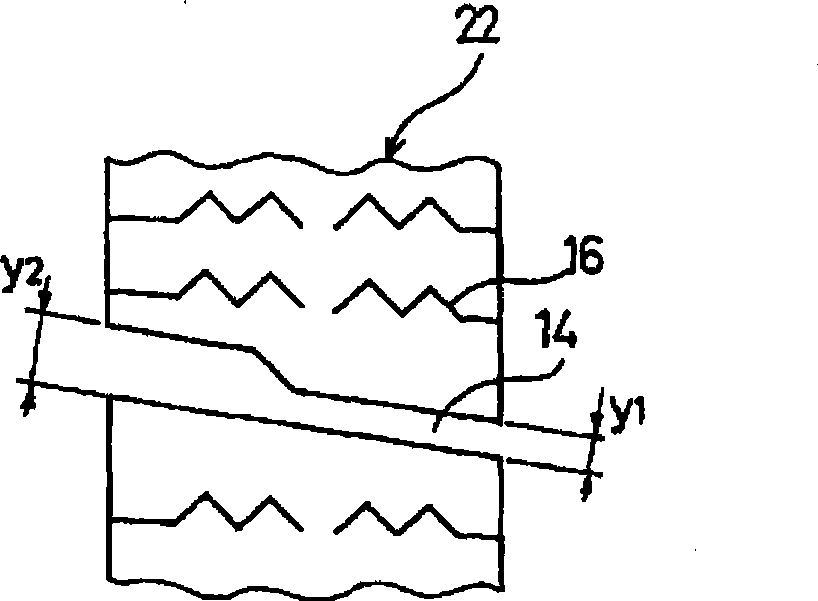
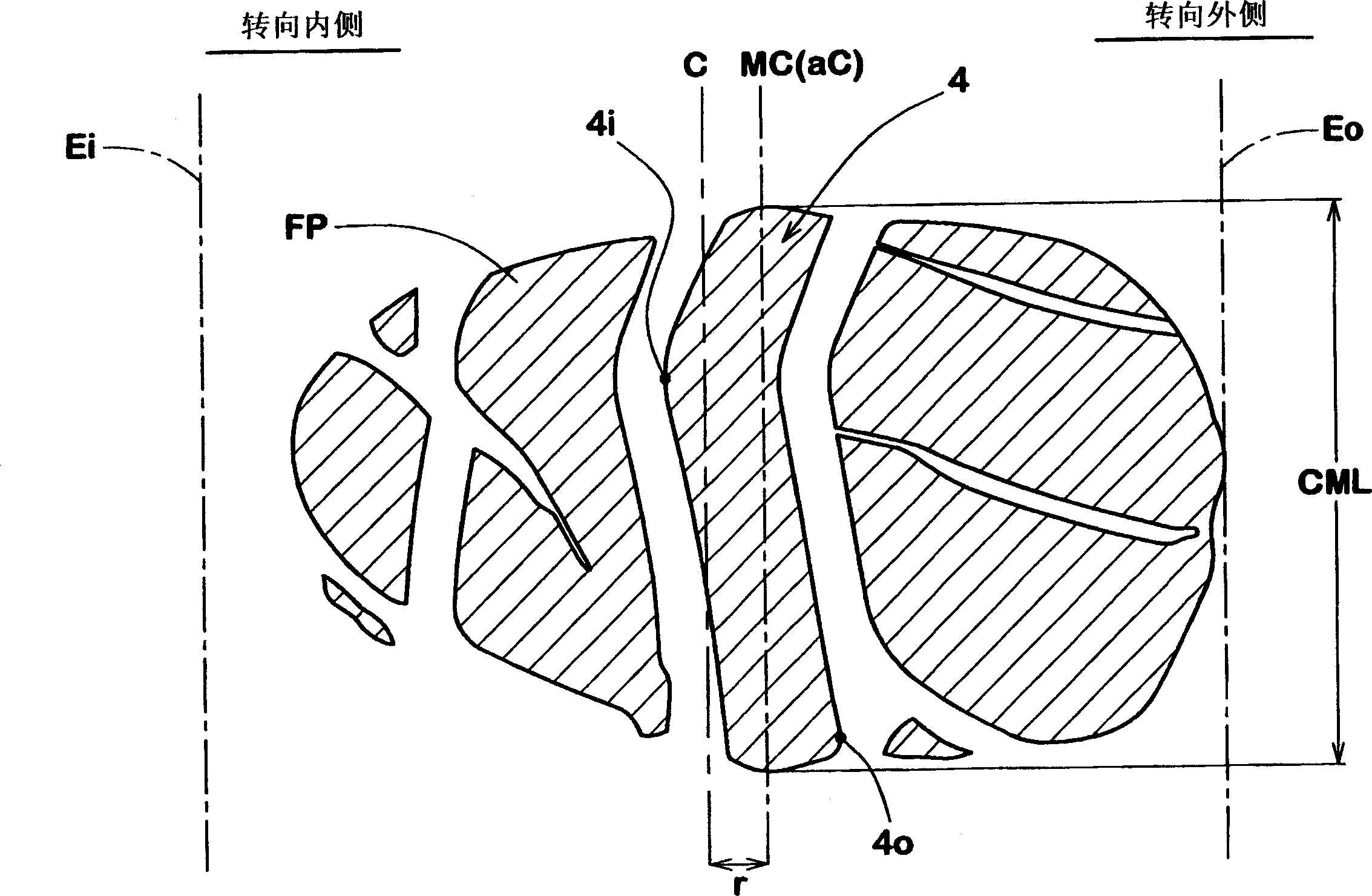
InactiveCN1891500ASufficient ground areaImprove cornering performanceTyre tread bands/patternsCamber angleTread
A pneumatic tire comprises a tread portion provided with a nonlinear rib having an amplitude having a center in the tire axial direction. In a normally loaded condition of the tire, the tread portion has an outside tread edge and an inside tread edge when the camber angle of the tire is 0 degrees. In the normally loaded condition, when the a camber angle of 4 degrees is given to the tire to inline towards the outside tread edge, a foot print shape of the tire has a maximum circumferential length at an axial position MC which is off the tire equator towards the outside tread edge. The nonlinear rib is positioned off the tire equator towards the outside tread edge such that the axial position MC lies within the amplitude of the nonlinear rib, and one of the edges of the nonlinear rib on the outside tread edge side is chamfered.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Active colon micro-robot structure and working method thereof
ActiveCN109303541ALarge expansion capacityEasy to controlEndoscopesEndoradiosondesElectricityElectric machinery
The invention discloses an active colon micro-robot structure and a working method thereof. The active colon micro-robot structure comprises an axial walking mechanism and two radial expansion mechanisms which are symmetrically and flexibly connected to the two ends of the axial walking mechanism; the axial walking mechanism comprises a walking casing, a walking battery, a walking motor, a motor driver, a screw nut mechanism A and a walking device, wherein the walking battery, the walking motor, the motor driver, the screw nut mechanism A and the walking device are arranged in the walking casing; each radial expansion mechanism comprises an expansion casing, an expansion battery, an expansion motor, a screw nut mechanism B and an expansion device, wherein the expansion battery, the expansion motor, the screw nut mechanism B and the expansion device are arranged in the expansion casing; the motor driver is electrically connected to the walking motor and the expansion motors. The axial walking mechanism achieves walking actions by adopting the walking motor for driving the walking device, and the radial expansion mechanisms achieve expansion actions by adopting the expansion motors for driving the expansion devices. The active colon micro-robot structure is simple, easy to control, low in cost, reliable in performance and capable of conveniently achieving actions such as moving forward, moving backward, stopping moving and making turns.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Medical connecting device
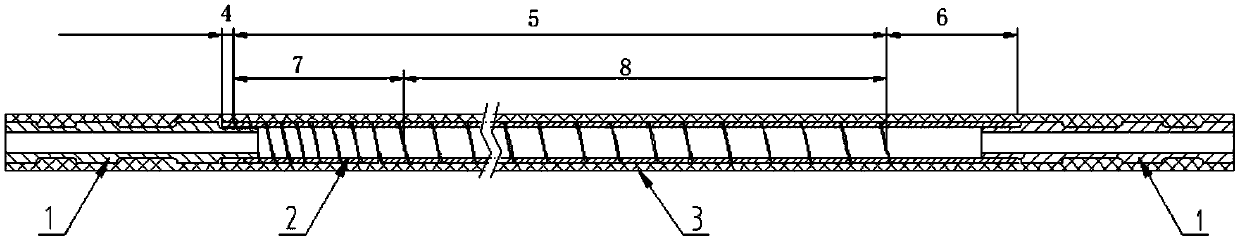
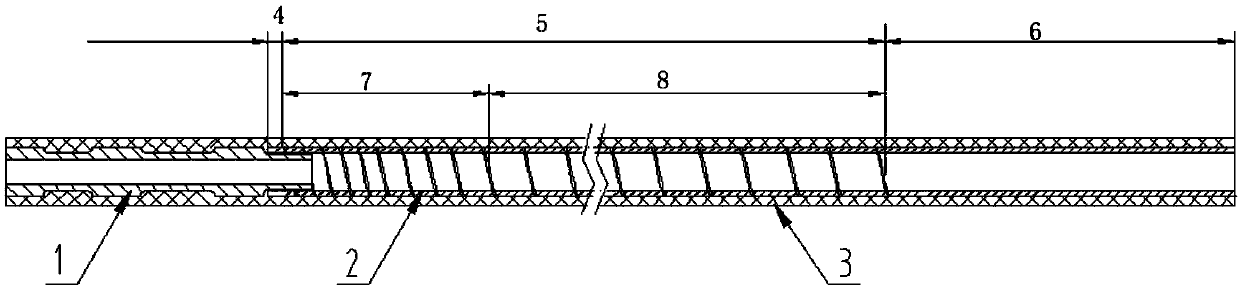
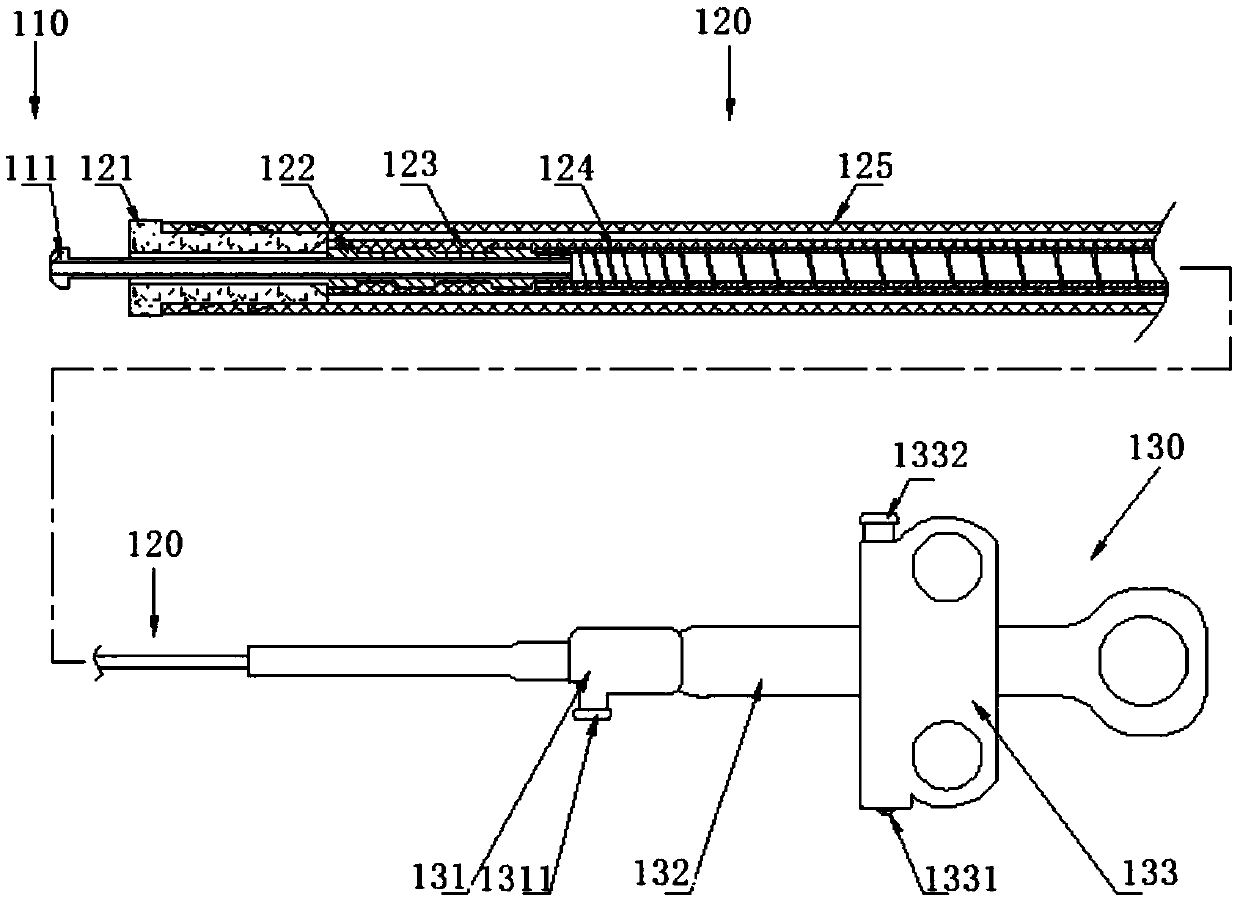
PendingCN111202485ASmall pitchLarge pitchSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsMechanical engineeringPowder Spray
The invention discloses a medical connecting device. The medical connecting device has a near end and a far end and comprises an insulating layer and a spiral tube, wherein the insulating layer coversthe outermost layer of the whole device; the spiral tube is of a conductive hollow tubular structure and has a spiral structure; and the spiral structure has a screw pitch gradually changing from thenear end to the far end. According to the medical connecting device, the functions of electric conduction, liquid passing, powder spraying, negative pressure suction, sealing, insulation, supportingand the like can be integrated.
Owner:MICRO TECH (NANJING) CO LTD
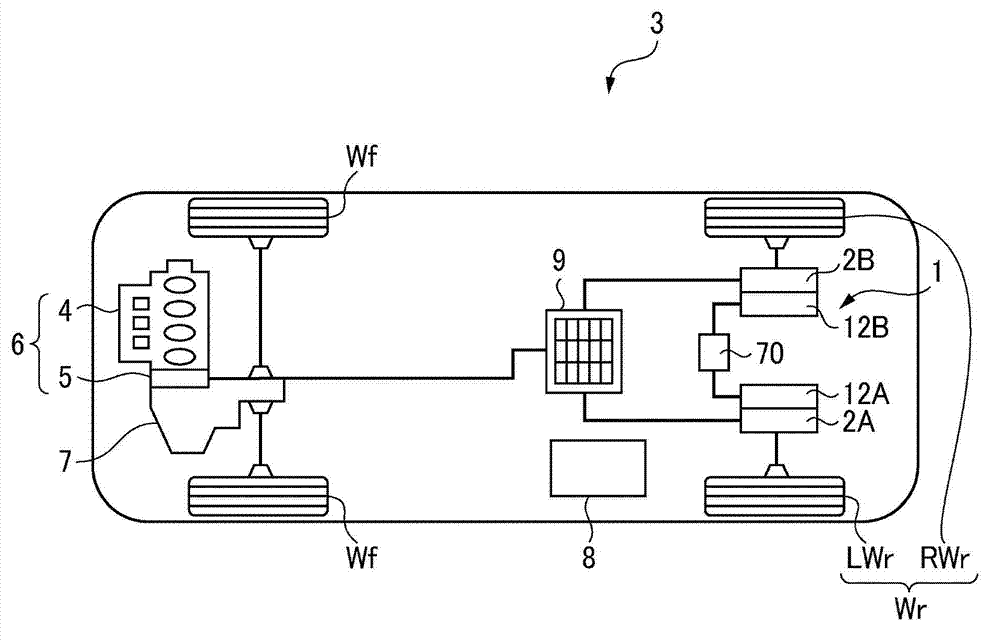
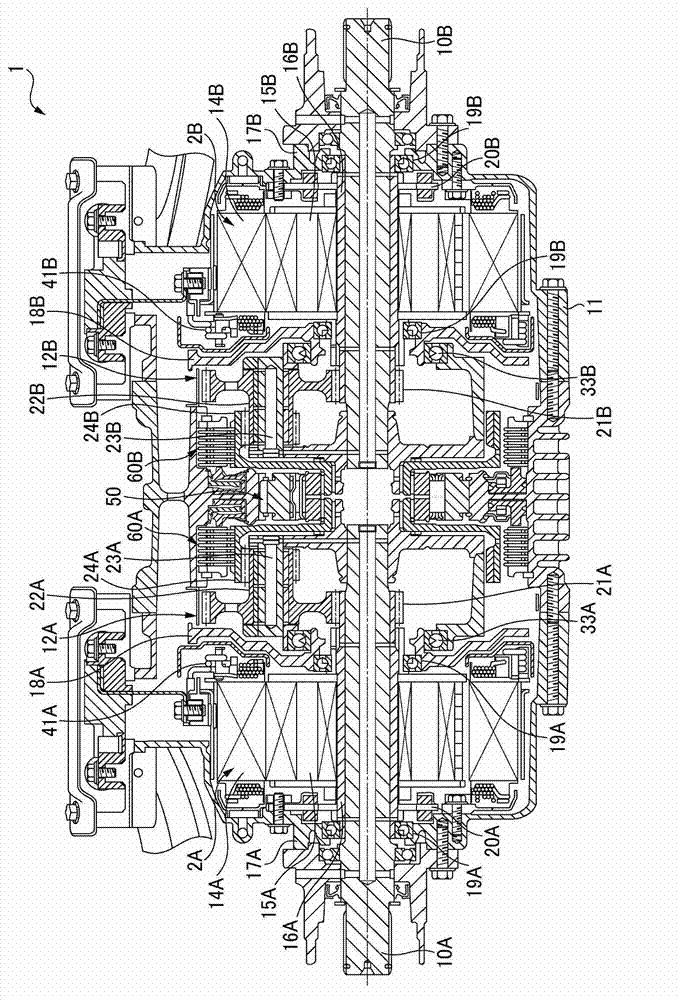
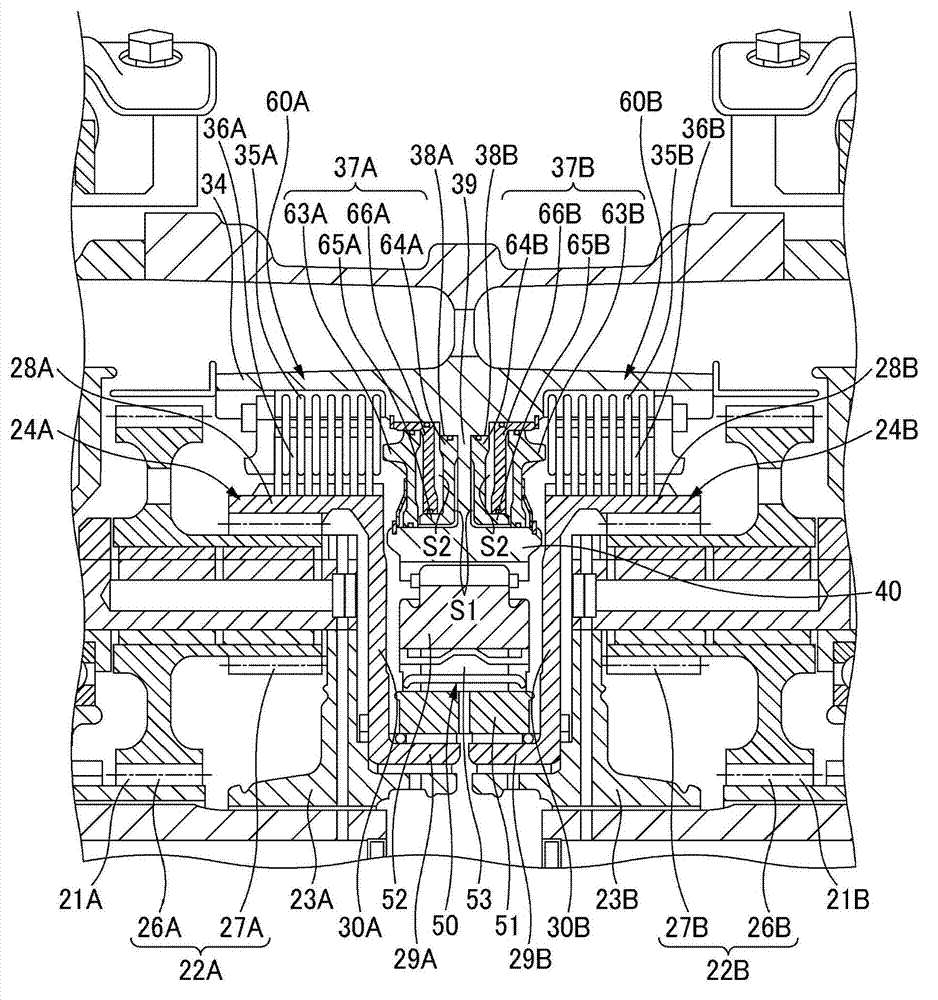
Vehicle drive device
ActiveCN103171430AIncrease profitReduce power consumptionHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresWheel driveSpur gear
The present invention provides a vehicle drive device which can generate a desired yawing moment when left and right reverse torque control is carried out and control first and second motors to be at any target rotating speed simultaneously. A back-wheel drive device is equipped with a left-wheel drive unit possessing a first motor and a first planetary gear reducer arranged on the transmission paths of the first motor and a left back-wheel; a right-wheel drive unit possessing a second motor and a second planetary gear reducer arranged on the transmission paths of the second motor and a right back-wheel; and a control unit. The first motor is connected with a sun gear of the first planetary gear reducer, and the second motor is connected with a sun gear of the second planetary gear reducer; the left back-wheel is connected on a planetary gear carrier of the first planetary gear reducer, the right back-wheel is connected on a planetary gear carrier of the second planetary gear reducer, and inner gears are connected with each other.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Universal wheeled robot
InactiveCN107139709AWheeled move quicklyMove quicklyElectric propulsion mountingVehiclesVehicle frameDrive wheel
The invention relates to a universal wheeled robot. The universal wheeled robot is mainly composed of a robot vehicle body, a comprehensive control system, travelling mechanisms and a sensor system. The wheeled robot is of a bilateral motor driving structure, the travelling mechanisms adopt wheeled travelling mechanisms, and a front driving gear, a rear driving gear and a chain wheel are installed on each side of the vehicle body; the chain wheel drives a driven chain to pass the torque output by a driving motor to the driving gears on the same side, the driving gears on the same side and the chain are installed in a damping box, the damping box is fixed to a vehicle frame through a suspension swinging arm and an independent suspender, and the wheel base between driving wheels is larger than 1.25 times of the wheel tread. According to the universal wheeled robot, the specific travelling mechanisms both enhance the obstacle surmounting capability of the robot and improve the travelling stability of the robot, so that not only does the robot have the characteristic of fast moving like a wheeled mobile robot, but the robot has the capability of surmounting an obstacle like a crawling mobile robot.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Motorcycle tire for running on rough terrain
ActiveCN103963571AImprove driving performanceInhibition of attachmentOff-road vehicle tyresMotorcycle tyresTerrainRoad surface
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Differential limiting control device of four-wheel drive vehicle
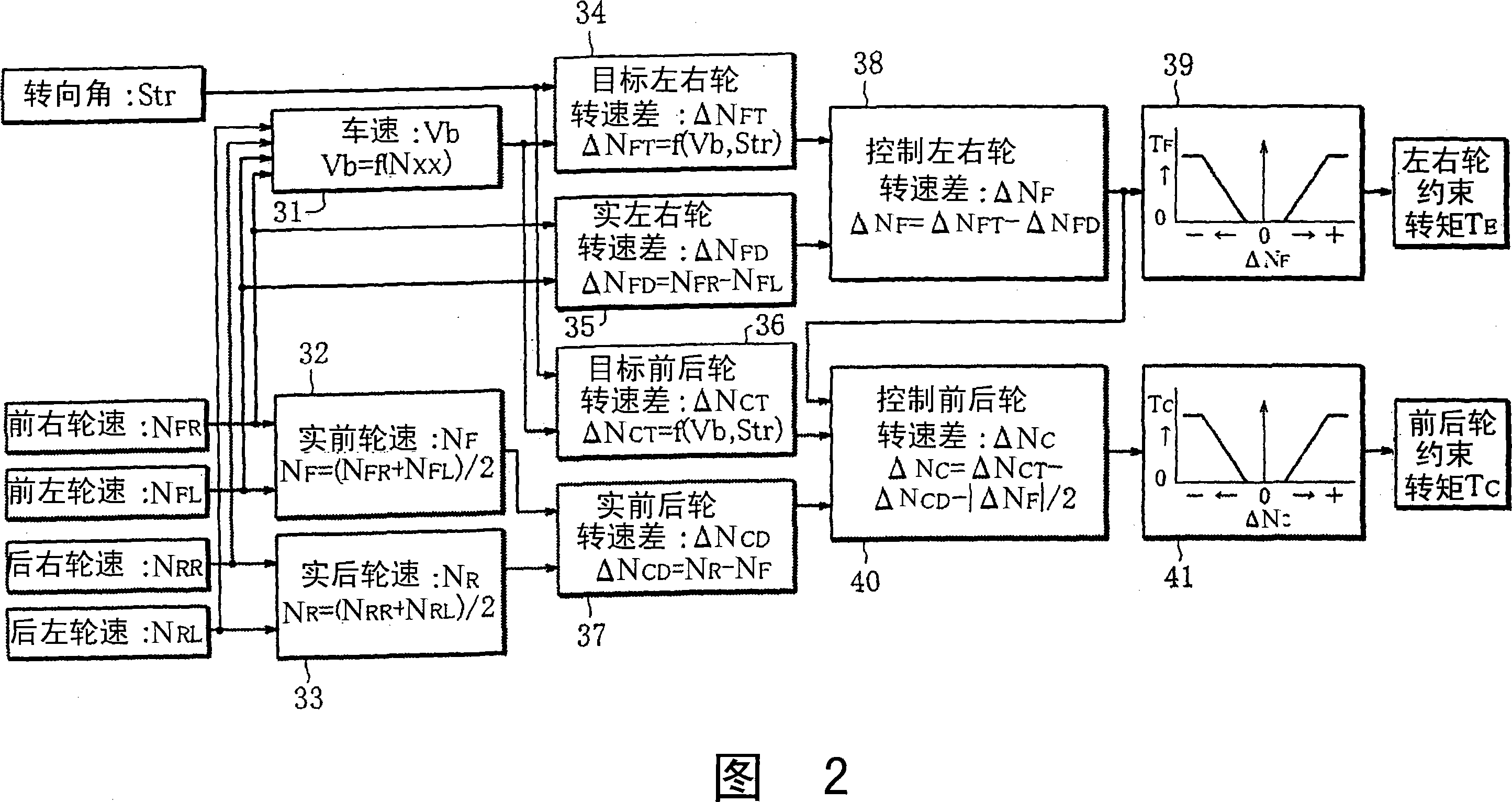
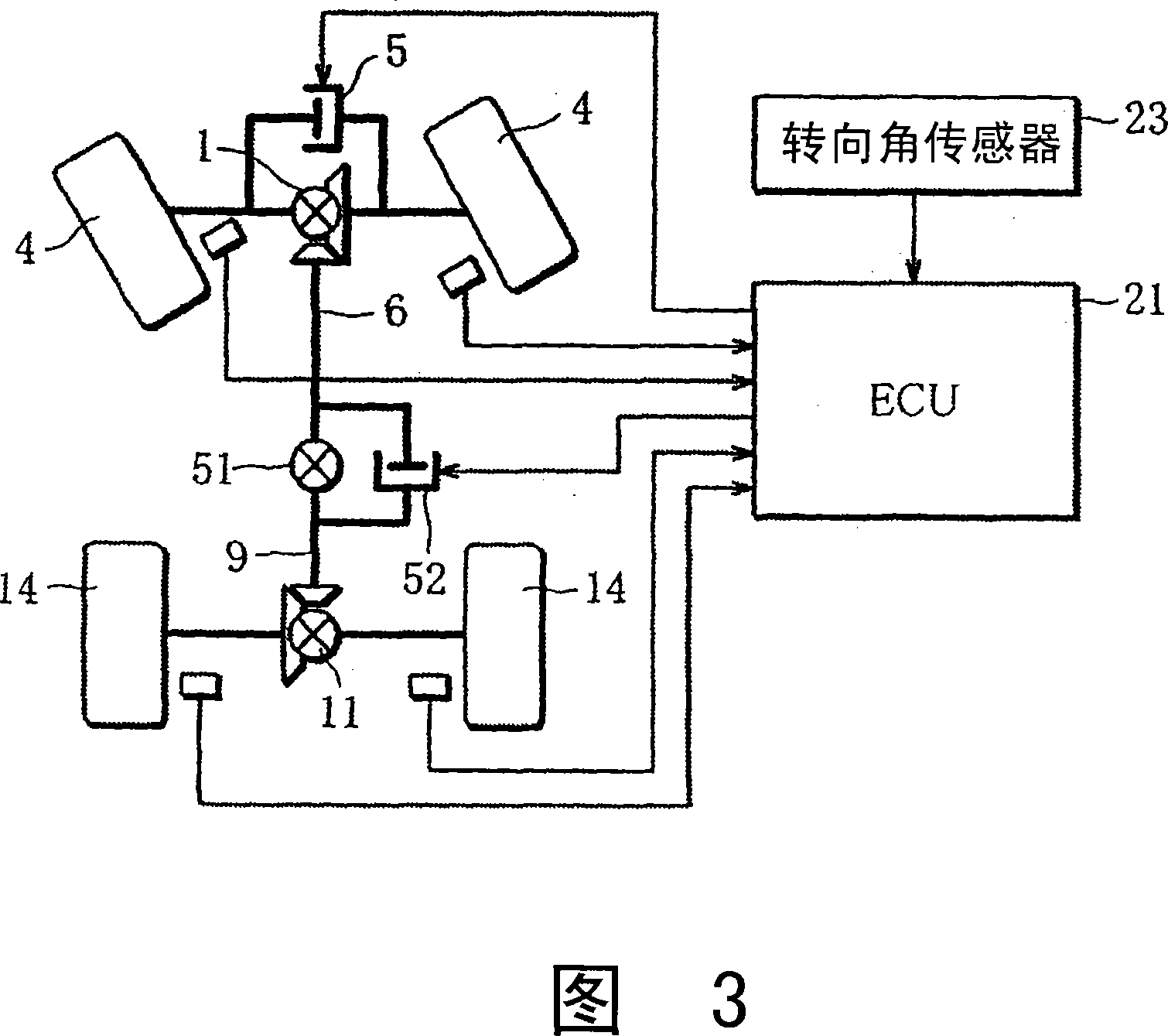
ActiveCN101223047ASuppression of increasing understeer tendencyPreventing the situation of differential limitationDriver input parametersPropulsion unit safety devicesLimited-slip differentialCoupling
A differential limiting control device of a four-wheel drive vehicle, wherein the restraint torque TF of an electronically controlled front limited slip differential (5) between front right and front left wheels is controlled based on a right and left wheel rotational speed difference Delta NF for control as a rotational speed difference between the front right and front left side wheels. Furthermore, the restraint torque TC of an electronically controlled coupling (8) between the front and rear wheels is controlled based on a front and rear wheel rotational speed difference Delta NC for control provided by deducting 1 / 2 (|Delta NF| / 2) of the rotational speed difference between the right and left wheels from a rotational speed difference (Delta NCT - Delta NCD) between the front and rear wheels.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Automatic swinging drawbar system
InactiveUS20050248123A1Improve steering performanceImprove cornering performanceTowing devicesTractorActuator
An automatic swinging drawbar system for efficiently and automatically controlling a tractor's swinging drawbar. The automatic swinging drawbar system includes a swinging drawbar, a first actuator connected to the swinging drawbar, a second actuator connected to the swinging drawbar, and a control unit for controlling the operation of the actuators to control the rotational position of the swinging drawbar. The control unit is in communication with the steering controller of the tractor for monitoring the rotational position and movement of the steering wheel. When the steering wheel is rotated clockwise to turn the tractor to the right, the actuators pivot the swinging drawbar proportionately to the right to increase the steering ability of the tractor pulling an implement. When the steering wheel is rotated counterclockwise to turn the tractor to the left, the actuators pivot the swinging drawbar proportionately to the left.
Owner:SYMINGTON OWEN D
Wheel-track combined self-adaption robot mobile platform based on planet wheels
ActiveCN106965864AEasy to adaptForward and reverse obstacle surmountingEndless track vehiclesEngineeringCentral symmetry
The invention relates to a wheel-track combined self-adaption robot mobile platform based on planet wheels. The wheel-track combined self-adaption robot mobile platform based on the planet wheels is characterized in that the platform comprises a car body module, two wheel-track combined modules and two tail wheel modules; the two wheel-track combined modules are distributed on the left side and the right side of the car body module in a central symmetry mode around the symmetry axis of the car body module, a power driving system used for driving the two wheel-track combined modules to act is mounted in the car body module, and the two rail wheel modules are symmetrically distributed at the front end and the rear end of the car body module; the mobile platform is of a central symmetry structure around the symmetry axis of the car body module on the whole; and taking the wheel-track combined module on the right side as an example, the wheel-track combined module comprises two part structures which are symmetrical in the front-back direction, a synchronous belt, synchronous belt wheels and a caterpillar track supported by the two part structures, the two part structures symmetrical in the front-back direction are arranged symmetrically on the front and rear positions of the car body module, and the synchronous belt and the synchronous belt wheels are mounted on the front part structure. The mobile platform has the capacity to passively adapt to obstacles, and is capable of crossing the obstacles forwards and backwards.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Scraping device of floating robot and floating robot
InactiveCN110528887AImprove smoothing effectAchieve destructionBuilding material handlingAutomationBuilding construction
The invention discloses a scraping device of a floating robot and the floating robot. The scraping device comprises a supporting part, a lifting board, a driving part and a scraper assembly, wherein the lifting board can go up and down relative to the supporting part; one end of the driving part is connected onto the supporting part, and the other end of the driving part is connected onto the lifting board; the scraper assembly is arranged on the lifting board, and the bottom part of the scraper assembly is provided with a scraping bar; and the driving part is capable of driving the lifting board to go down so as to make the scraping bar of the scraper assembly touch the to-be-constructed surface of concrete. According to the scraping device, by installing the scraper assembly, the surfaceof initially set concrete can be broken in the construction process of the floating robot, and the mud extracting and floating effect of the floating robot is promoted; moreover, the scraper assemblyis driven by the driving part to go up and down, so that the scraper assembly is more flexible to use, and simpler and more convenient to operate, so that the automation degree of the whole device isimproved.
Owner:GUANGDONG BOZHILIN ROBOT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com