Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45results about How to "Avoid unnecessary processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
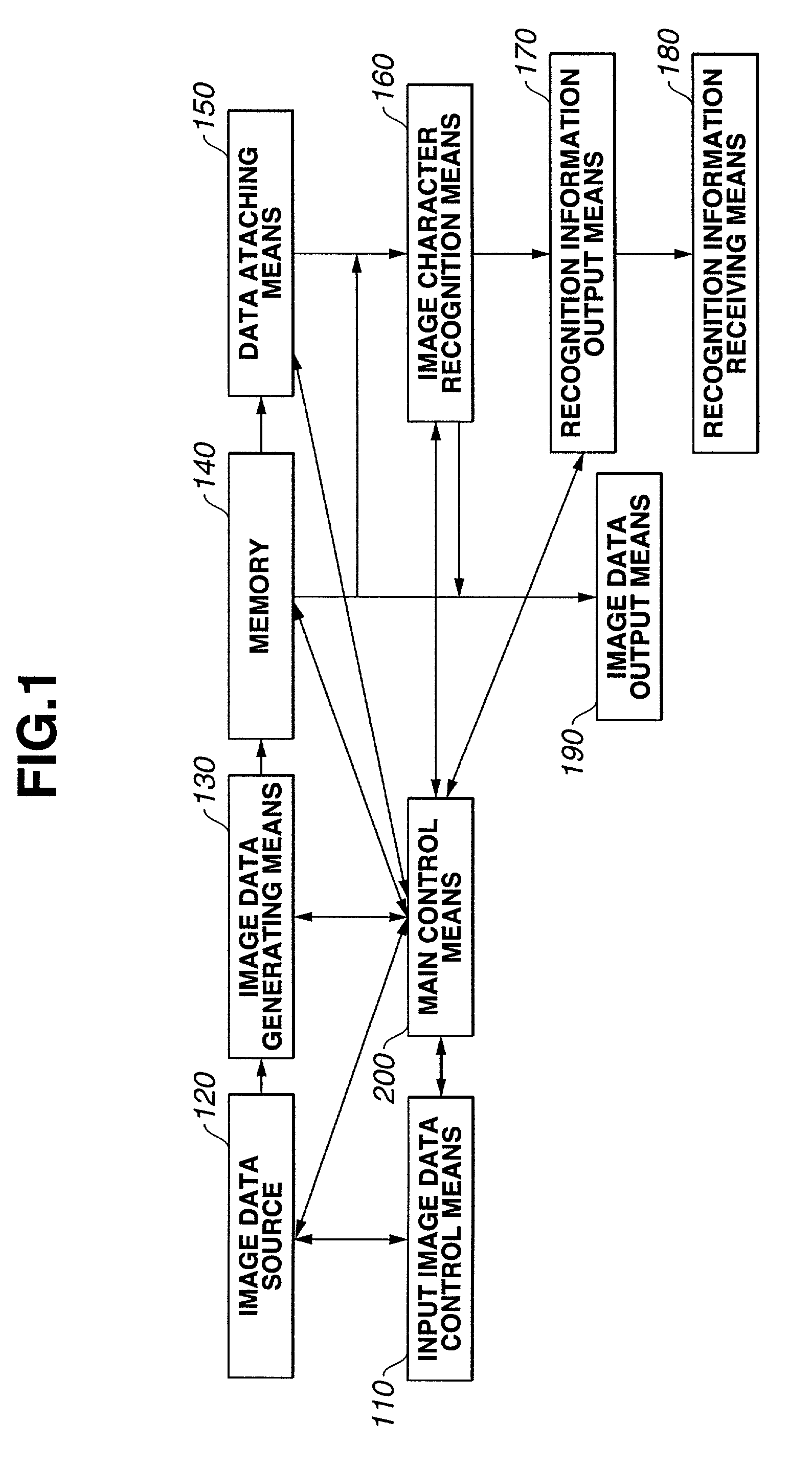
Recovery from failures within data processing systems
InactiveUS20070088970A1Improve availabilityConsistent stateSpecial data processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionSuccessful completionData processing system
Provided are methods, data processing systems, recovery components and computer programs for recovering from storage failures affecting data repositories. At least a part of the recovery processing is performed while the data repositories are able to receive new data and to allow retrieval of such new data. Although new data items may be received into the repository and retrieved therefrom during recovery processing, updates to the data repository which were performed before the failure and which are then restored to the repository by the recovery processing are restored within a recovery unit of work and are inaccessible to processes other than the recovery process until successful completion of the recovery unit of work. The recovery processing ensures that the recovered repository is consistent with the state of the repository at the time of the failure, but is available for addition and retrieval of new data items before completion of the recovery processing.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
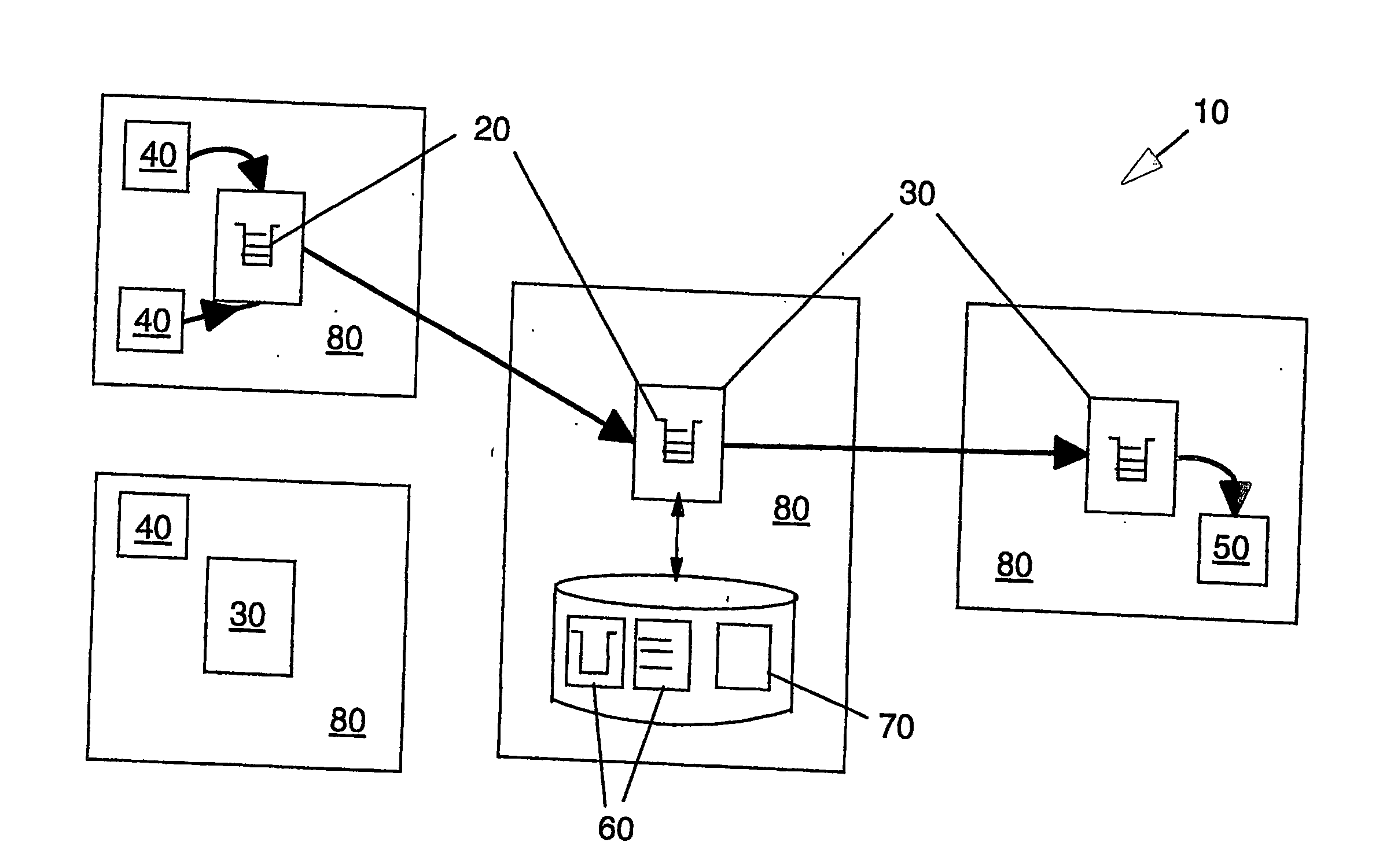
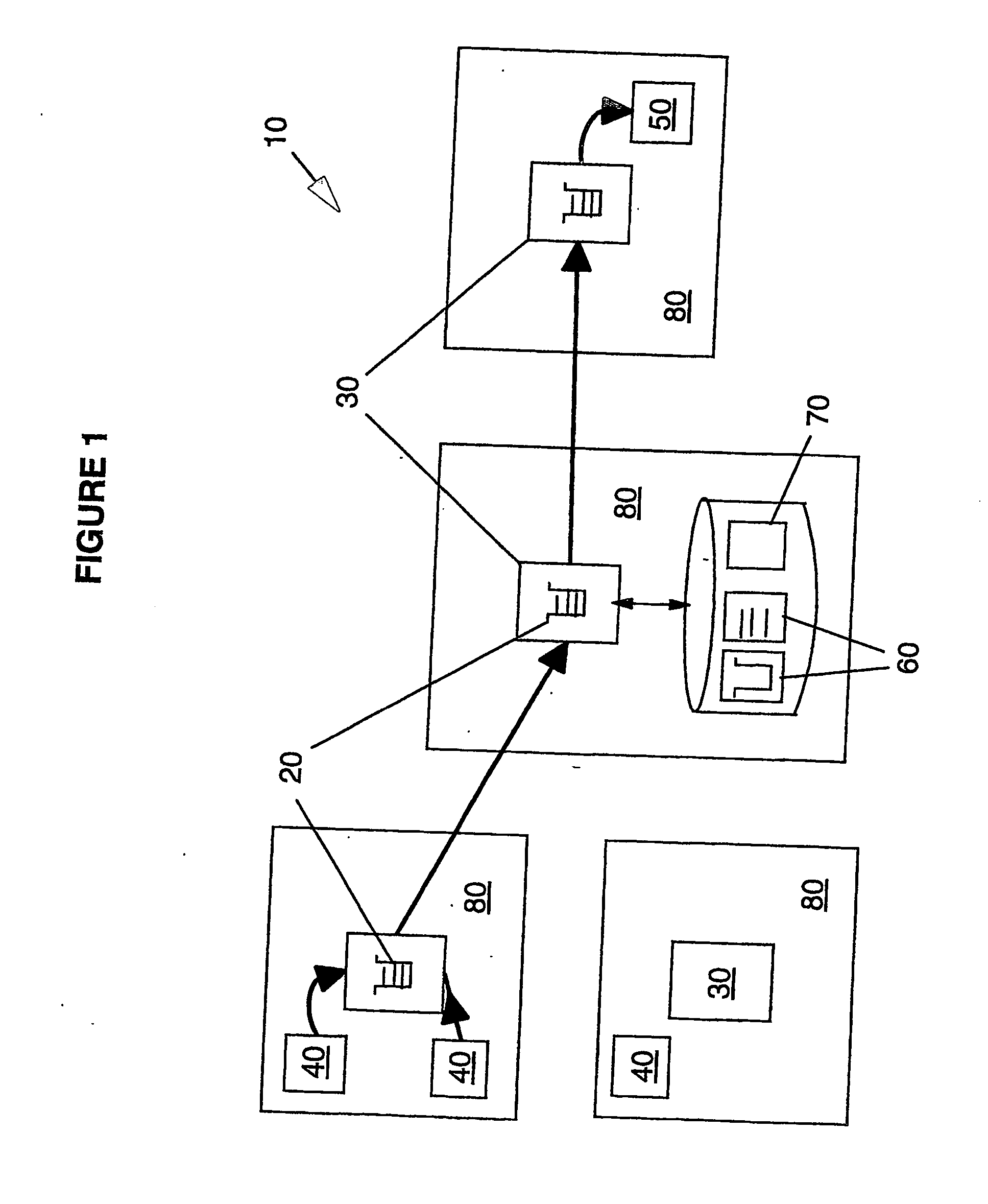
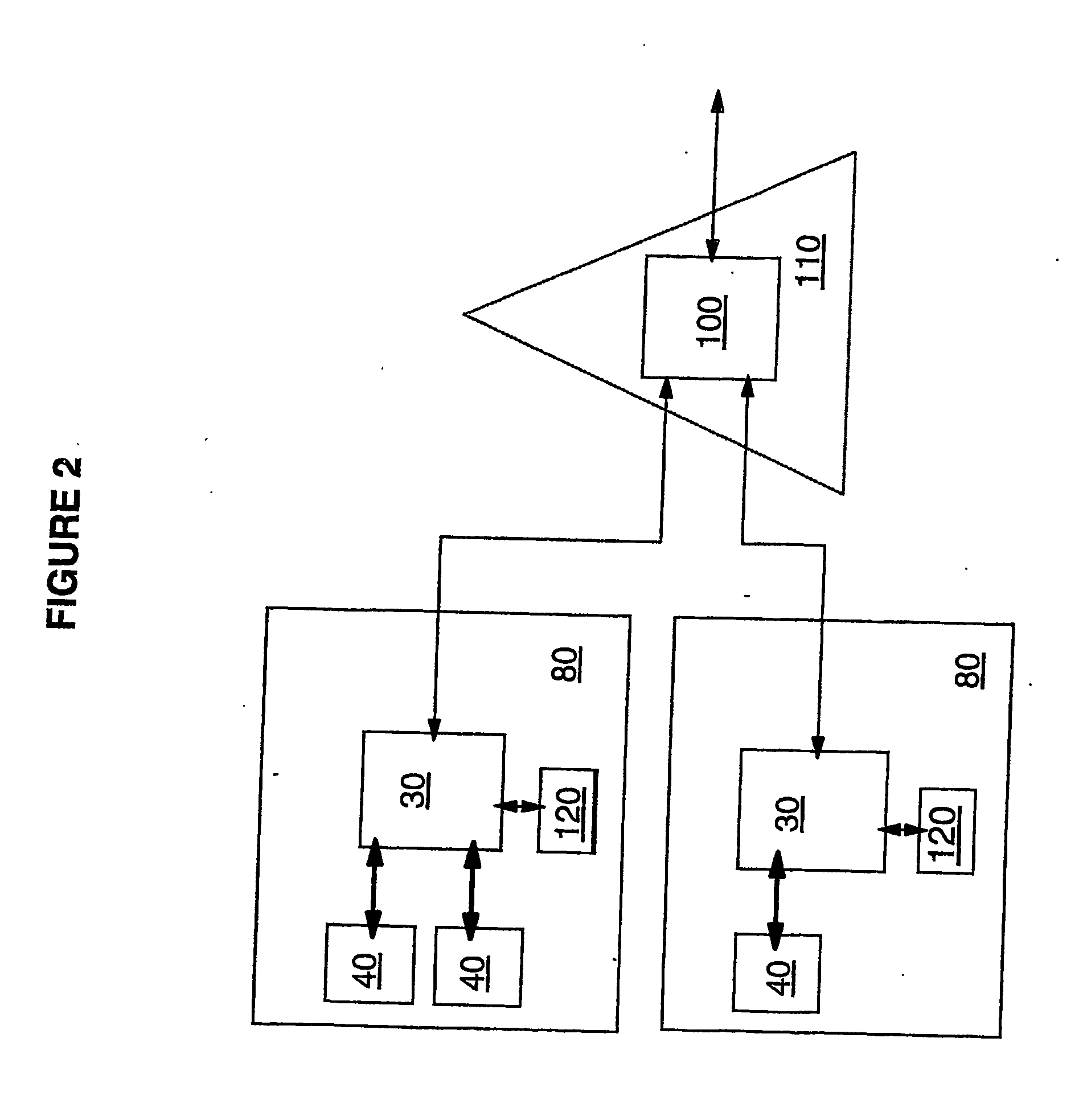
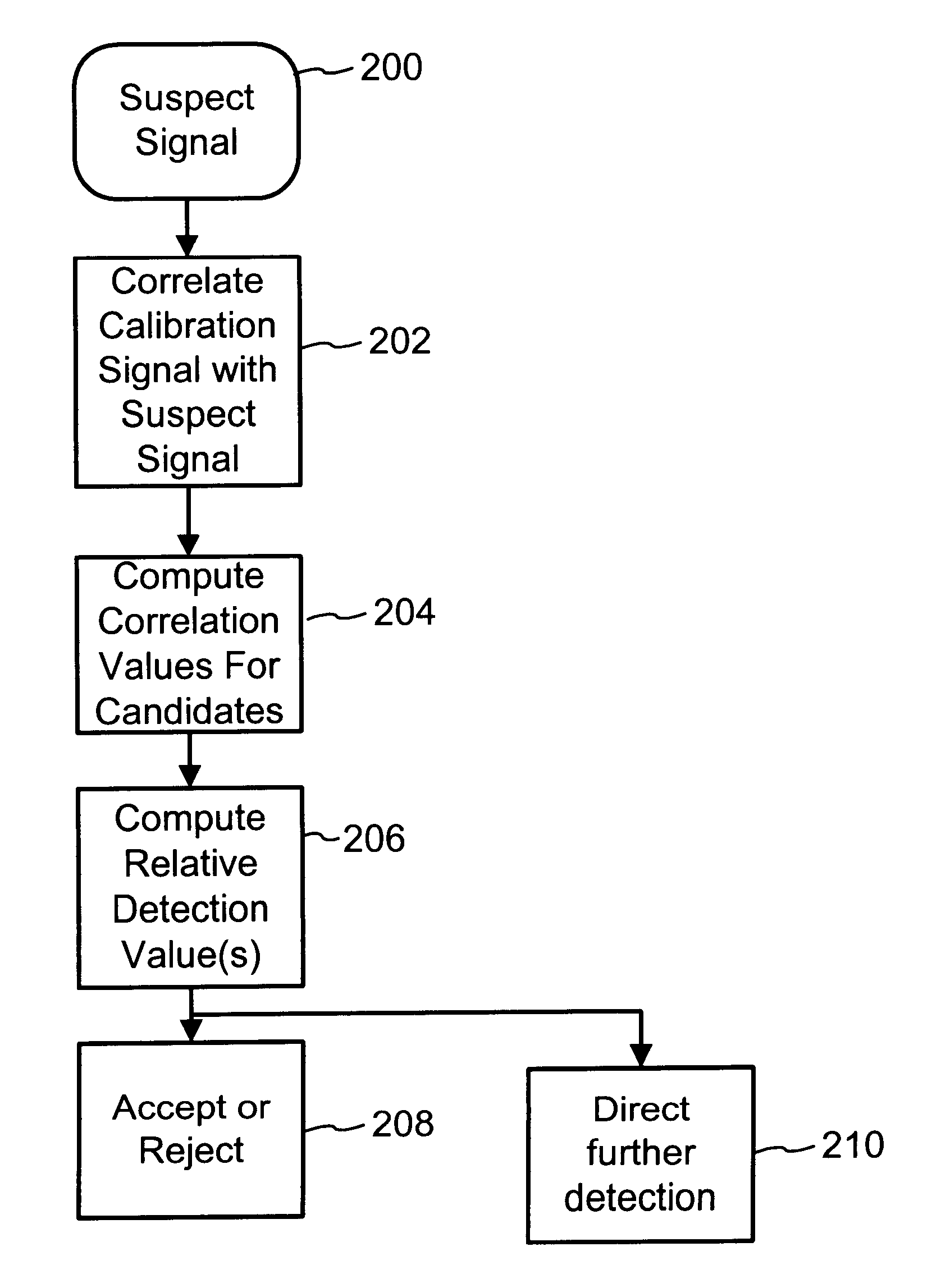
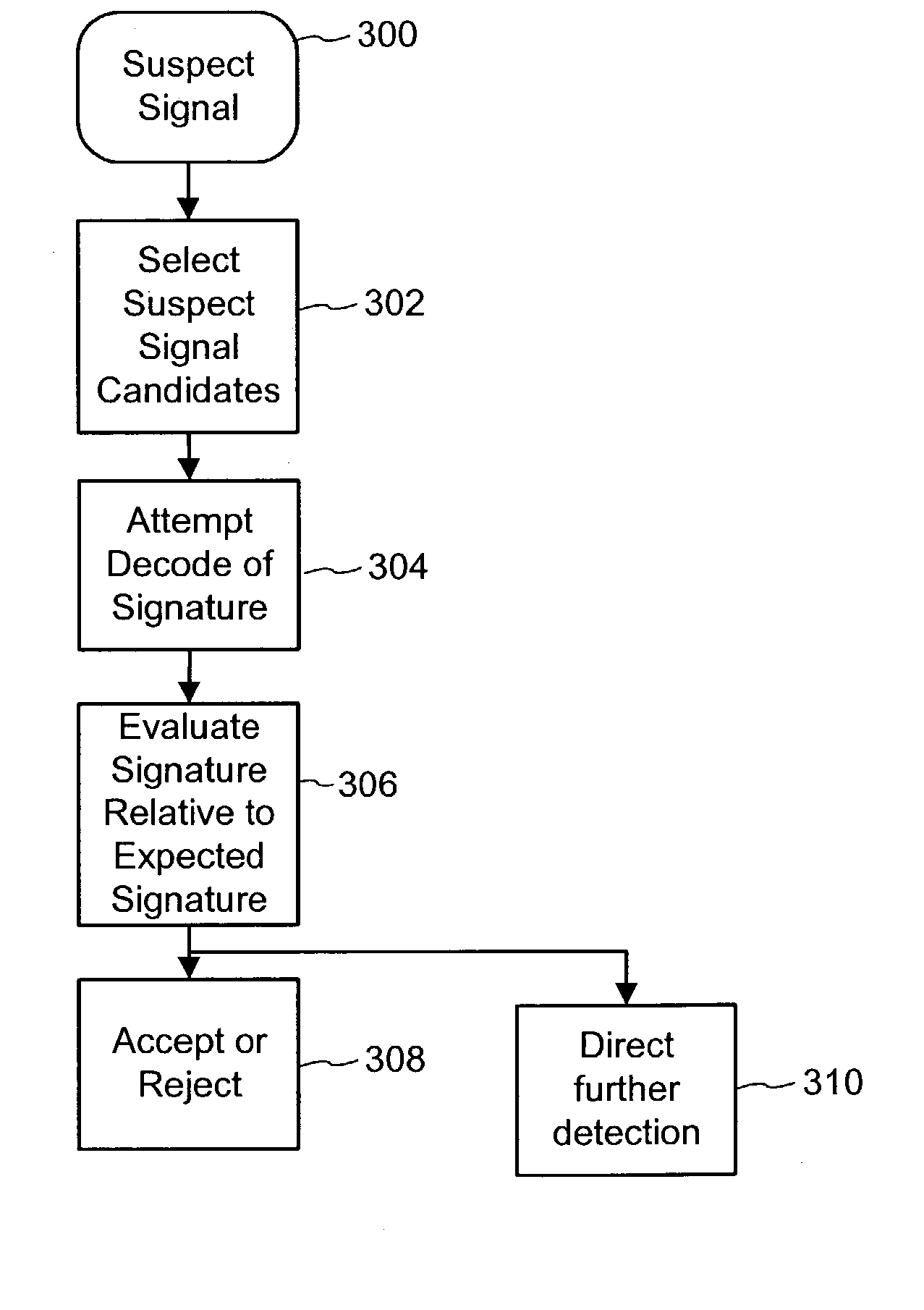
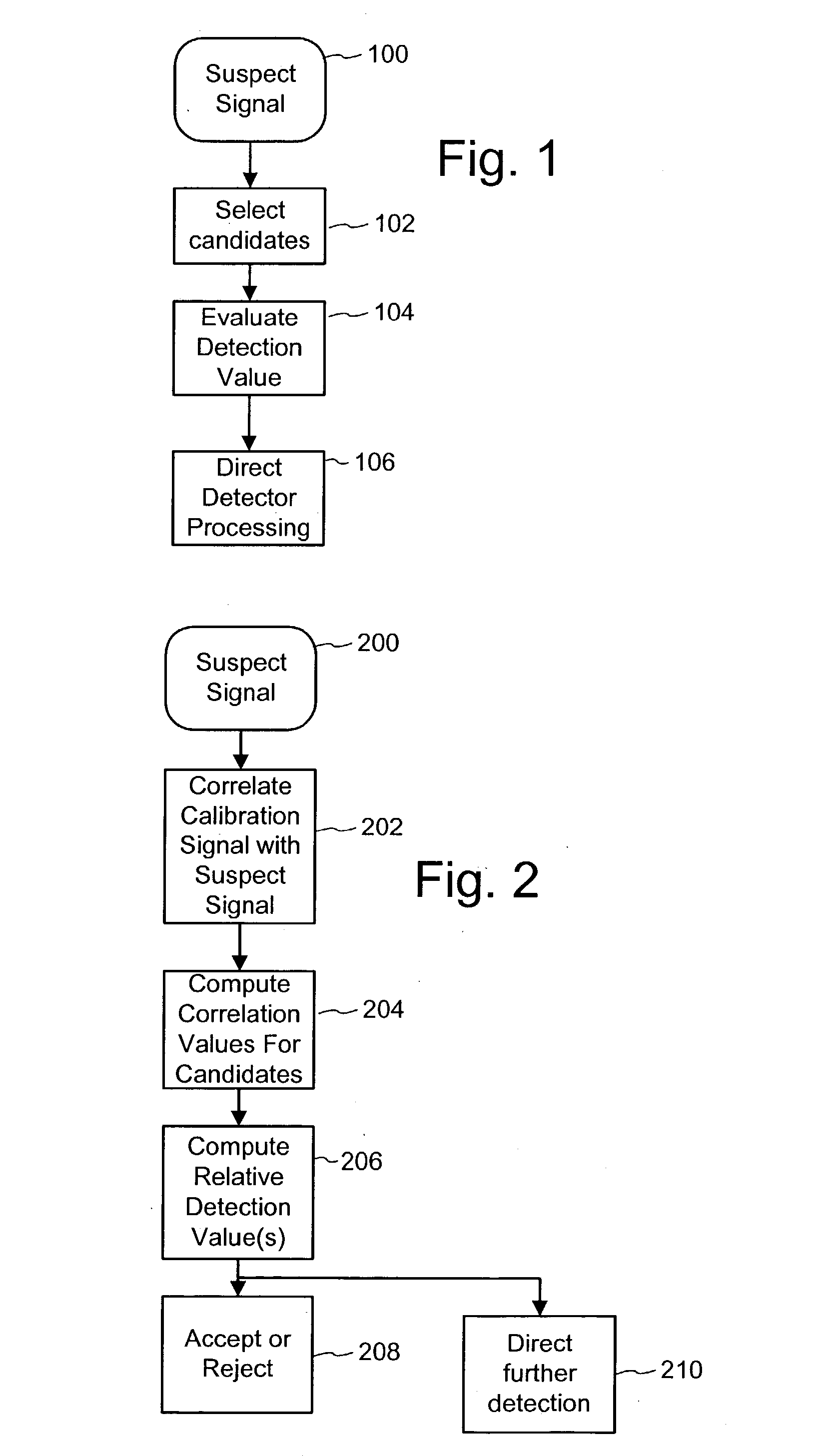
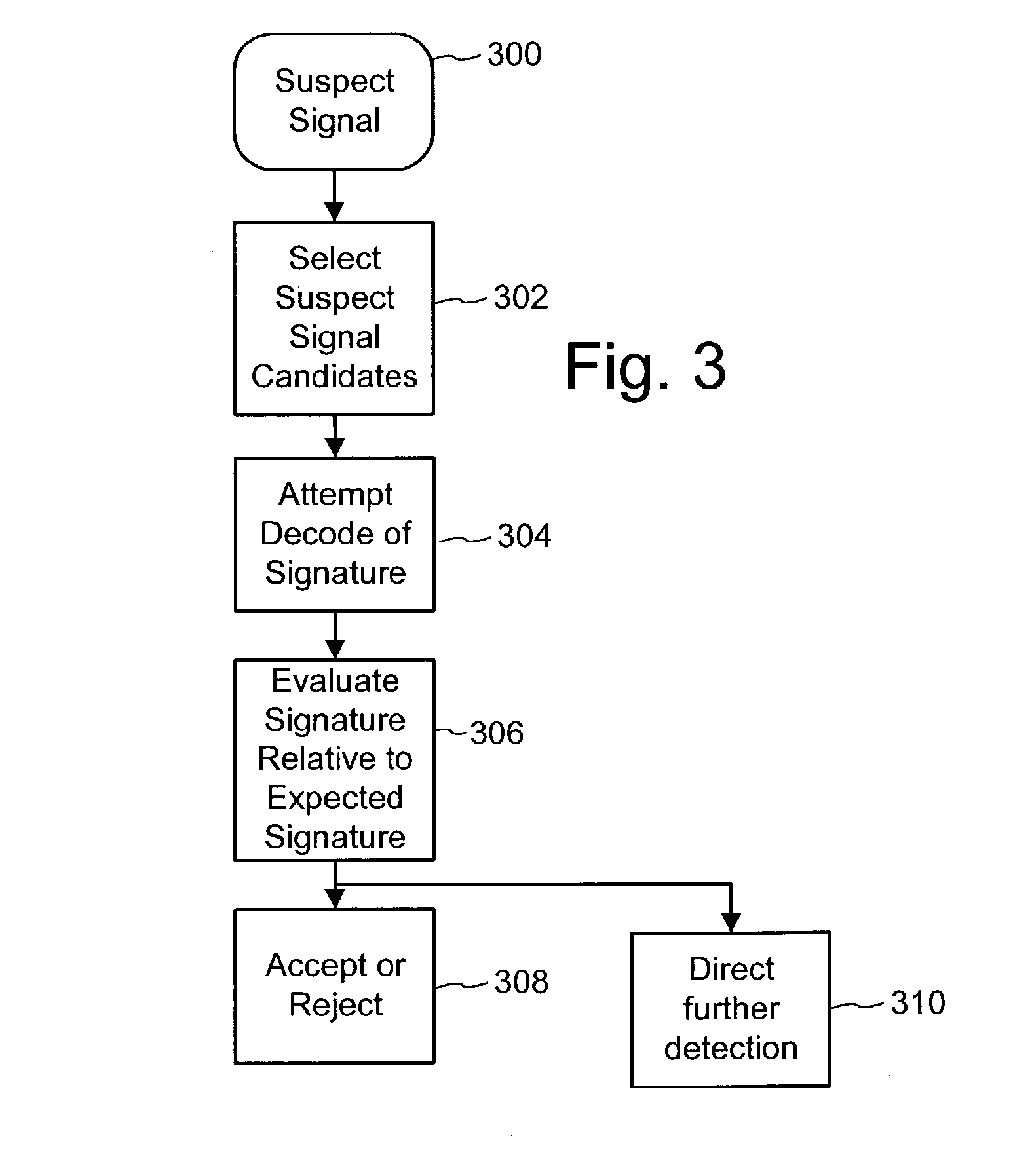
Digital watermark screening and detecting strategies
InactiveUS6516079B1Increase likelihoodPromote recoveryTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsDigital watermarkingPhysics
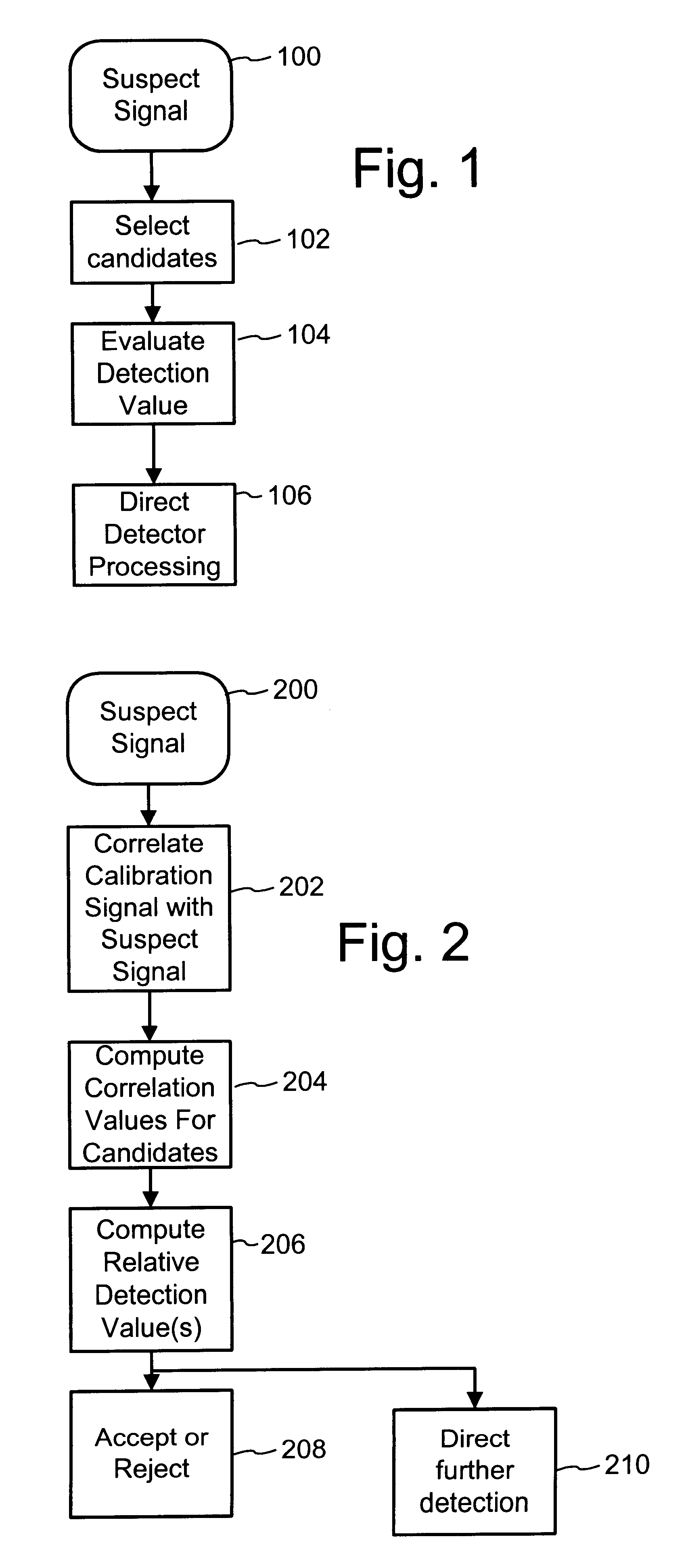
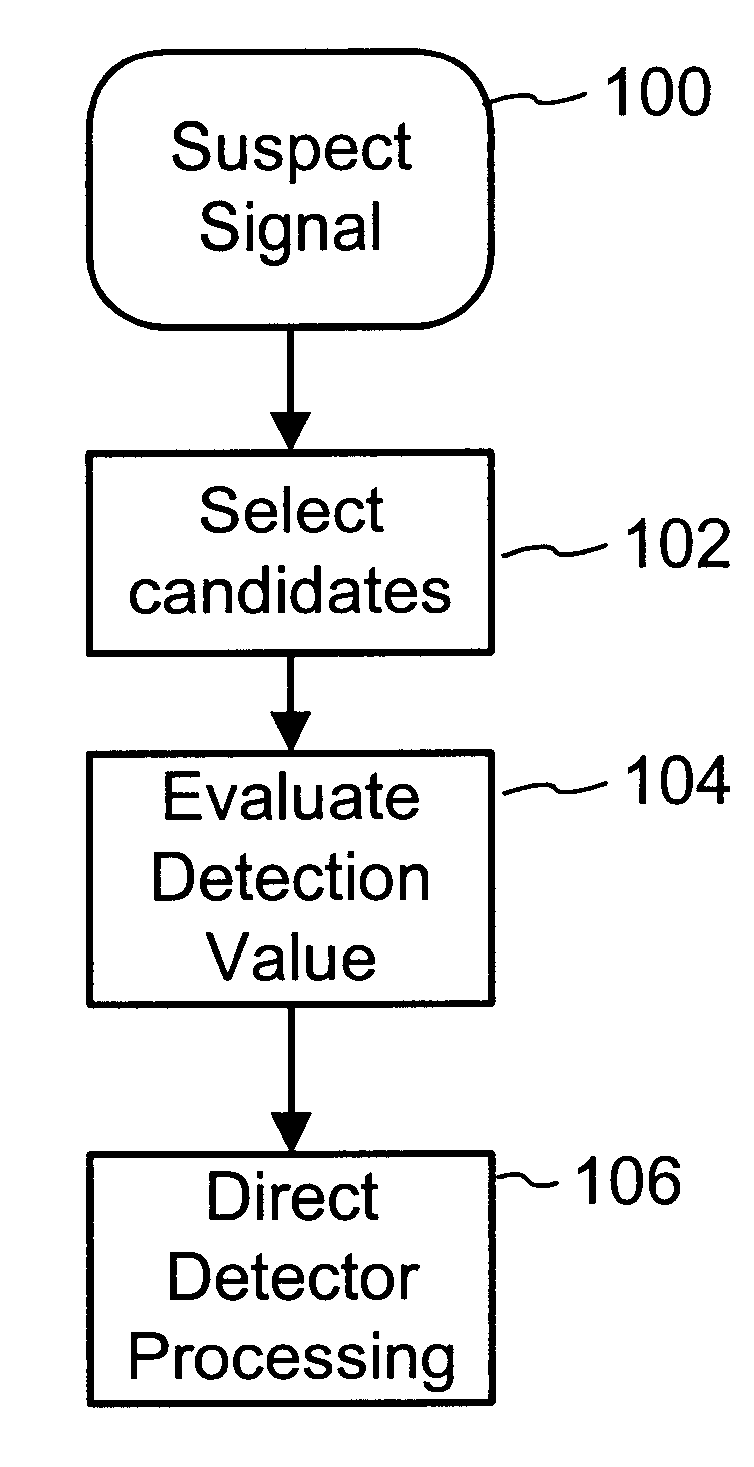
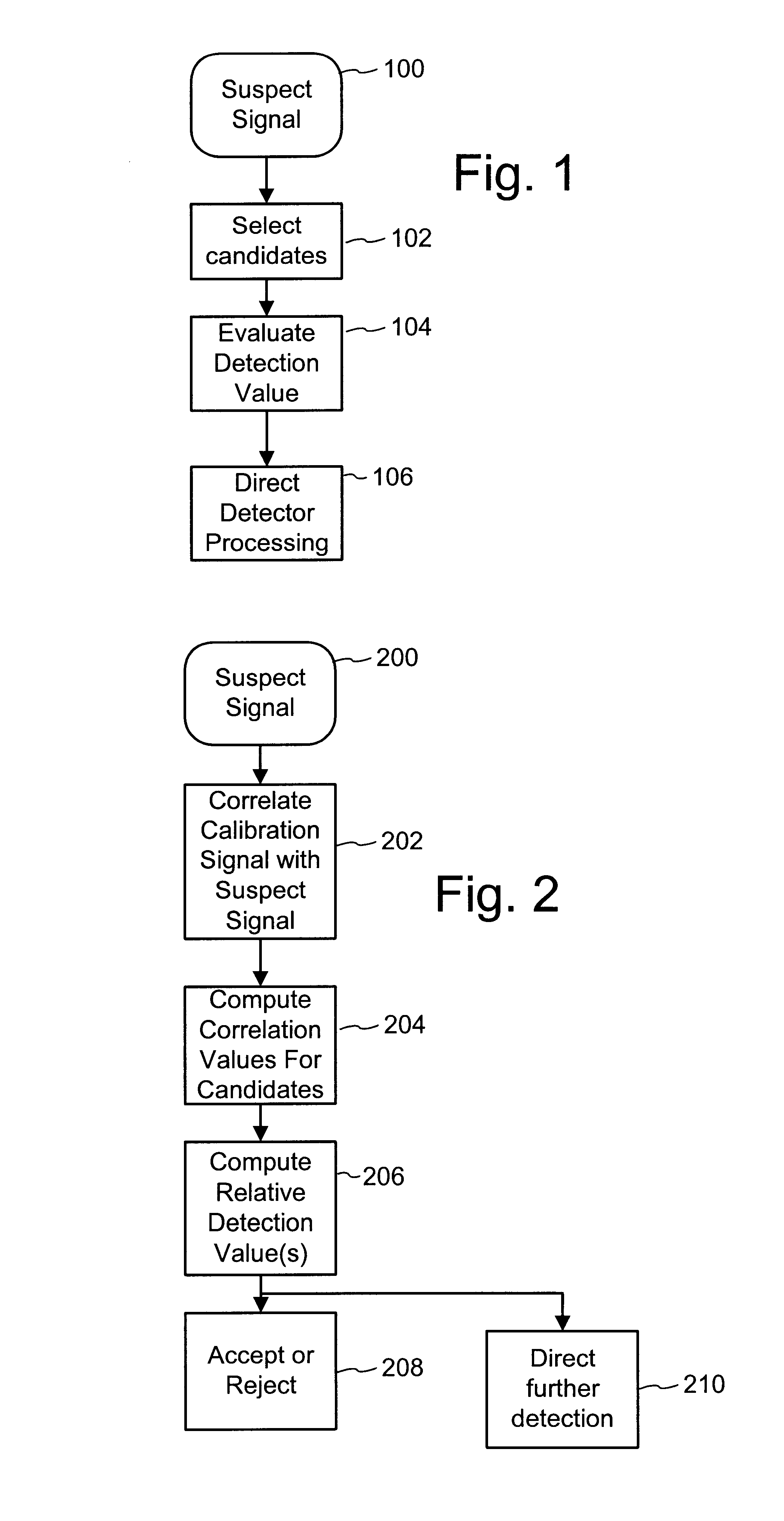
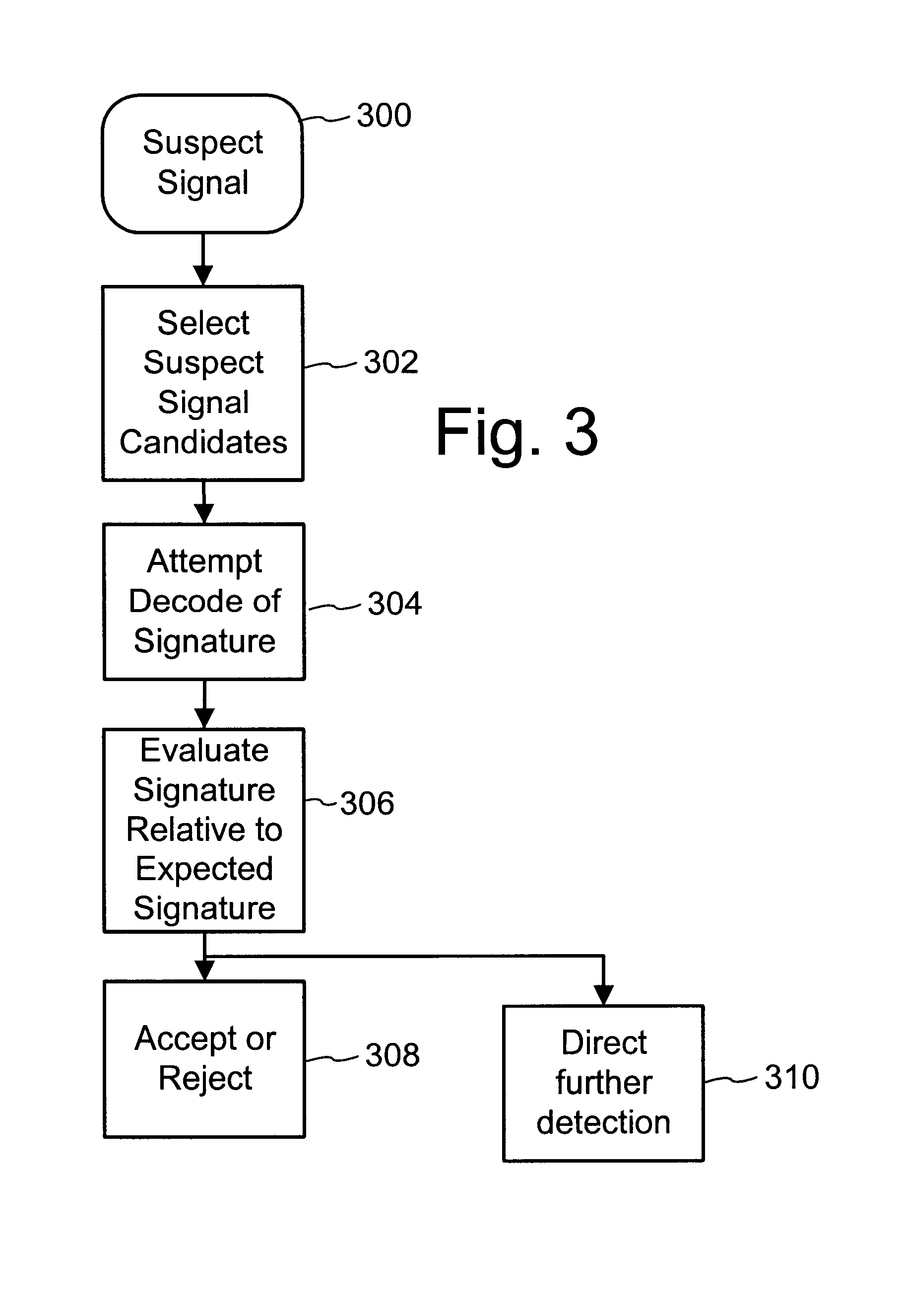
To enhance decoding of signals suspected of containing a watermark, a suspect signal is screened to compute detection values evincing presence and strength of a watermark. Screening strategies control detector actions, such as rejecting un-marked signals and improving synchronization of watermarks in suspect signals.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Digital watermark screening and detection strategies
InactiveUS6768809B2Avoid unnecessary processingPreventing copying, playing or recordingTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsComputer scienceDigital watermarking
To enhance decoding of signals suspected of containing an embedded auxiliary signal, a suspect signal is screened to compute detection values evincing presence and strength of the embedded signal. Screening strategies control detector actions, such as rejecting un-marked signals, improving synchronization of a reader used to extract hidden messages in suspect signals, determining authenticity of signals, and controlling use of the signals.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
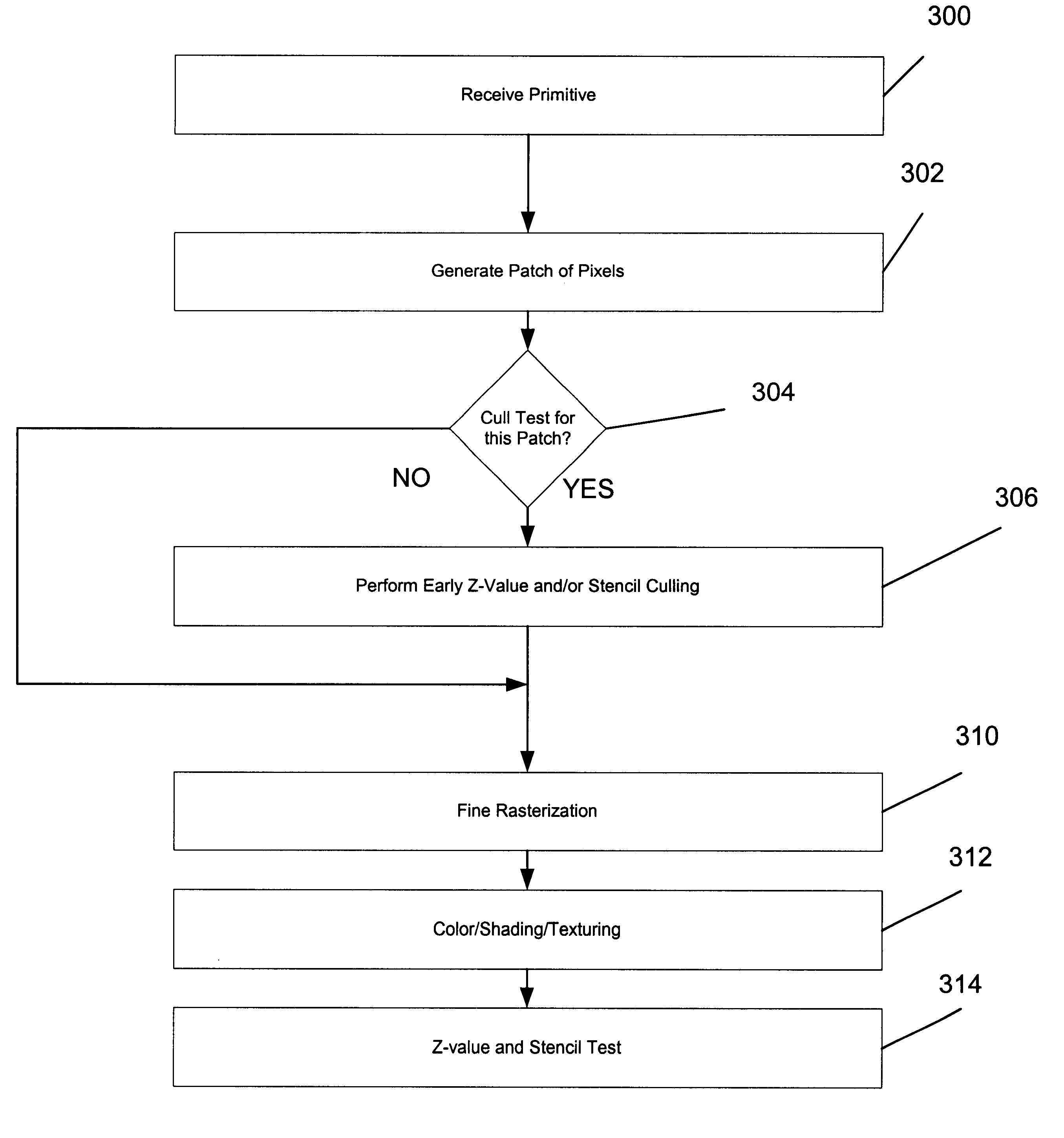
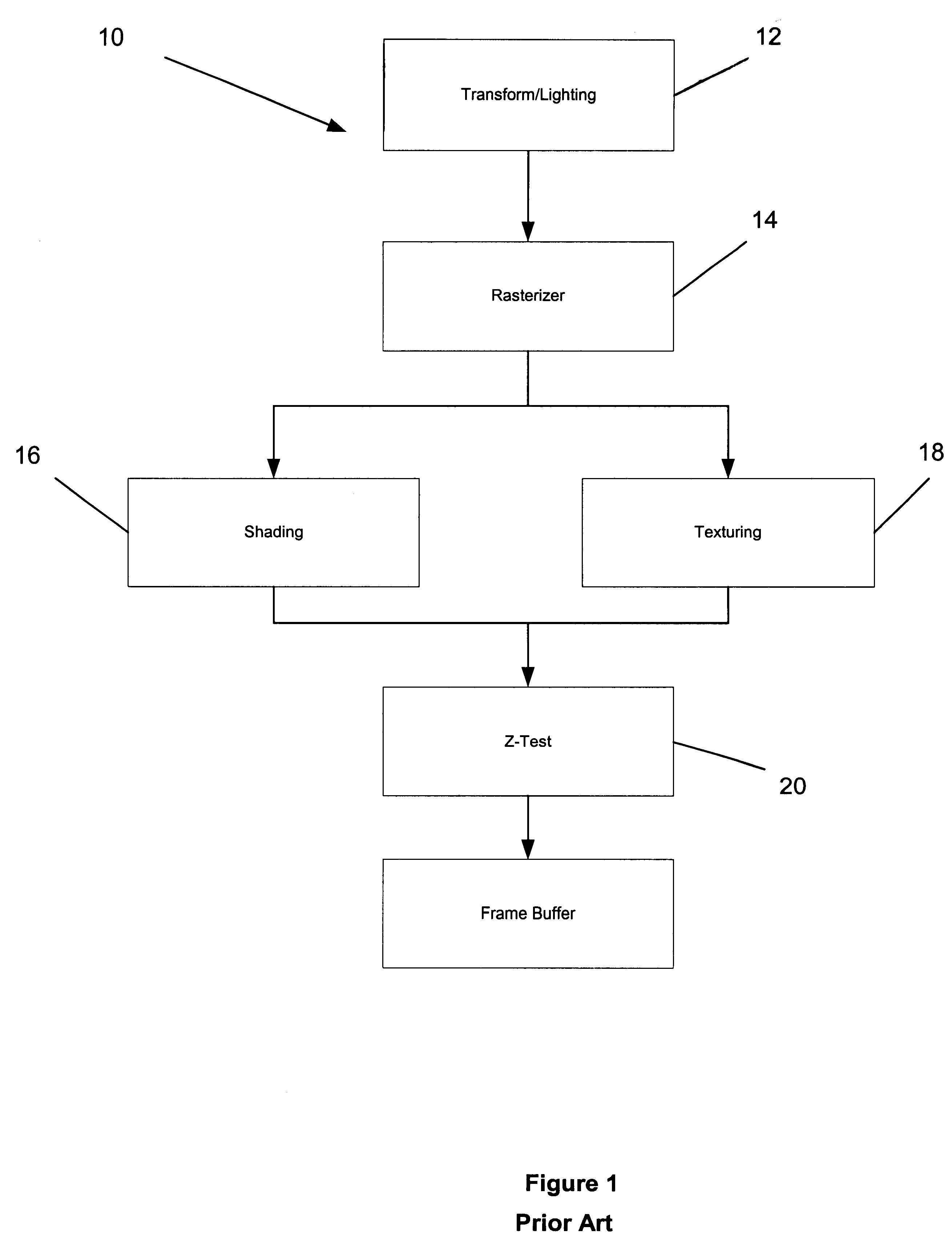
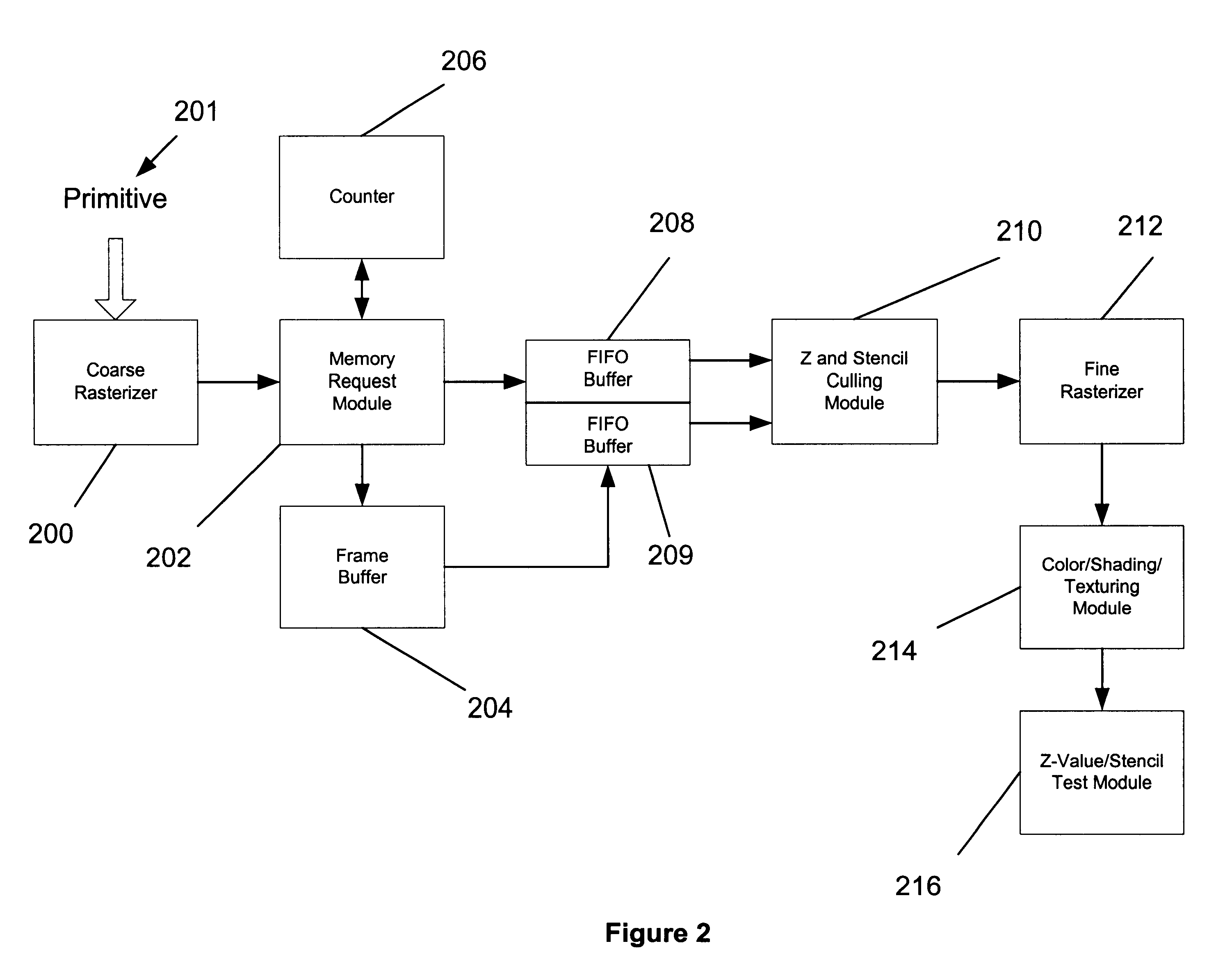
System, method and article of manufacture for Z-value and stencil culling prior to rendering in a computer graphics processing pipeline
ActiveUS7068272B1Solve many processesReduce processing steps3D-image rendering3D modellingGraphicsGraphics pipeline
A system, method and article of manufacture are provided for early Z-value based culling prior to pixel rendering in a graphics pipeline. In initial stages of processing, Z-value culling is performed on at least one pixel. Thereafter, the pixel is conditionally rendered. Whether the pixel is rendered or not is conditioned on results of the Z-value culling. By culling, or removing, the pixels that do not meet certain criteria prior to rendering, much processing is avoided in the rendering portion of the graphics pipeline.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
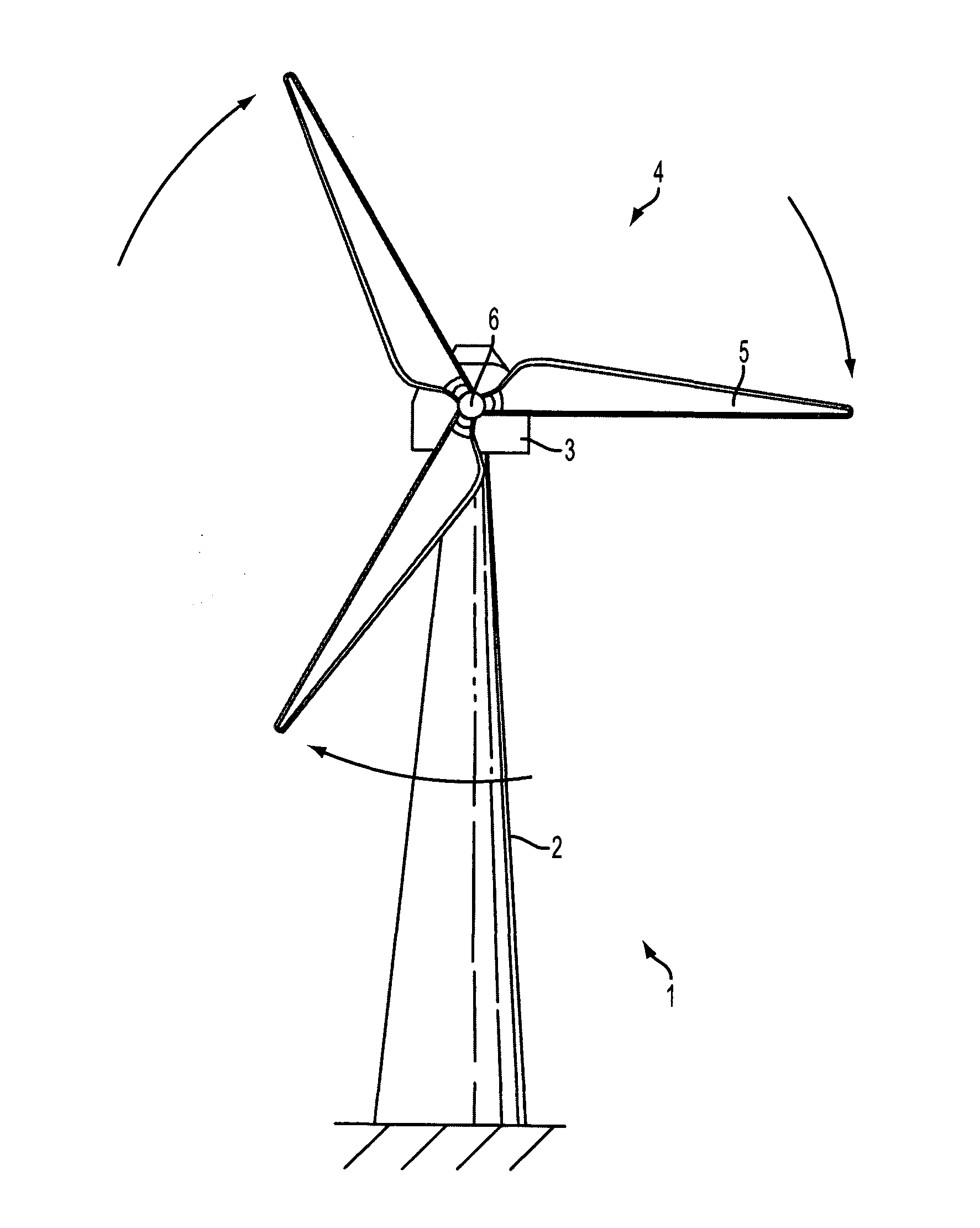
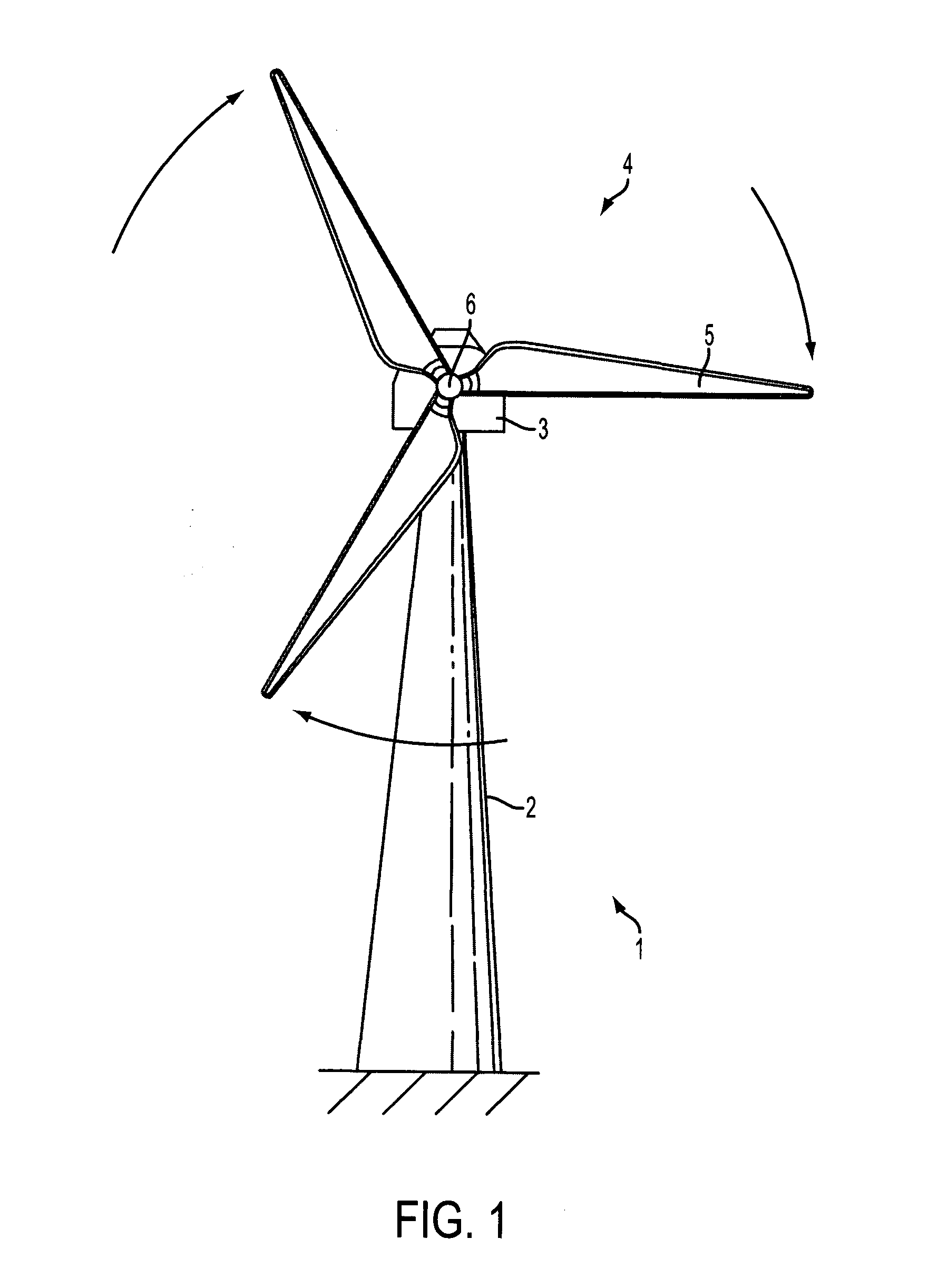
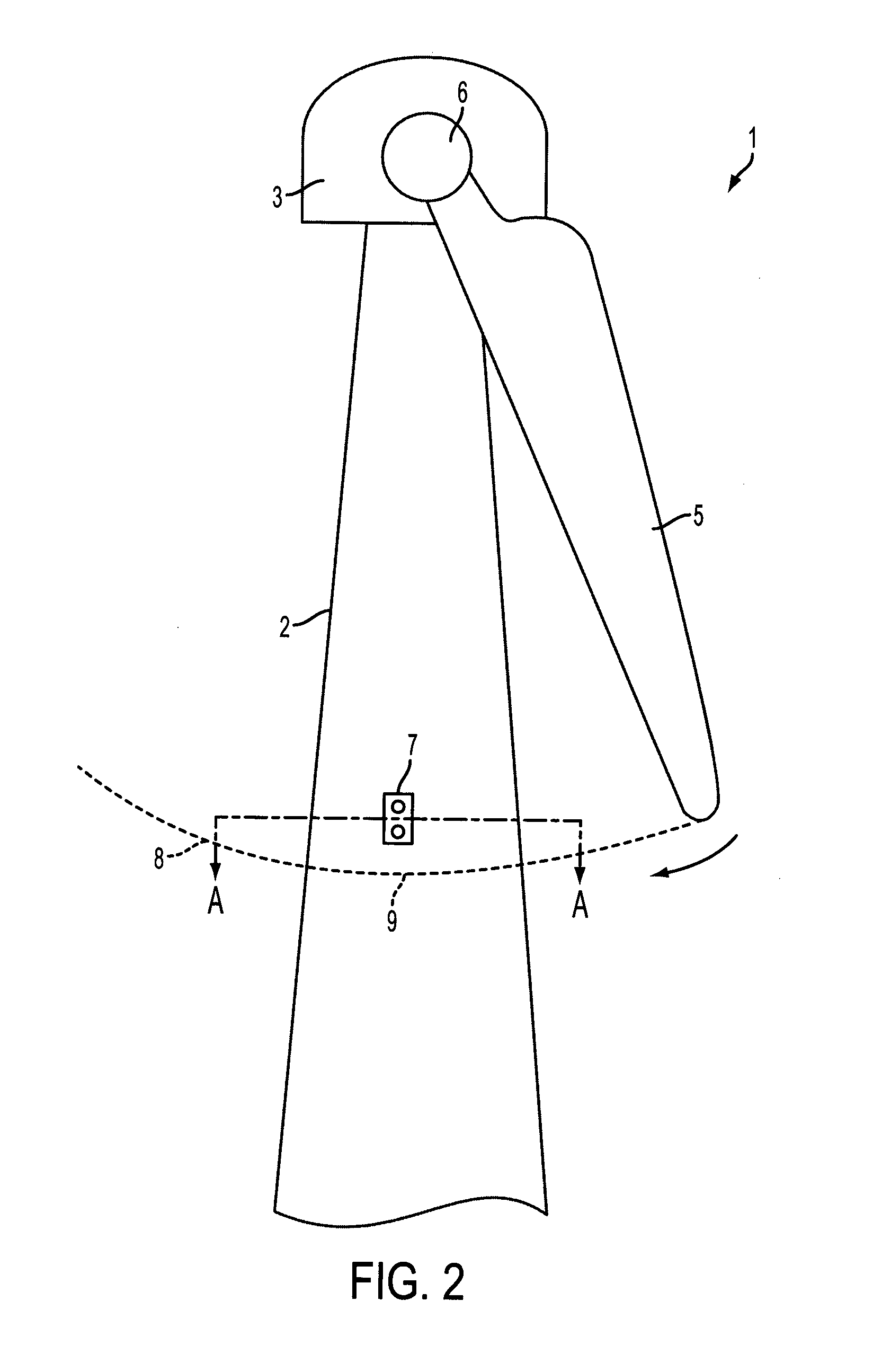
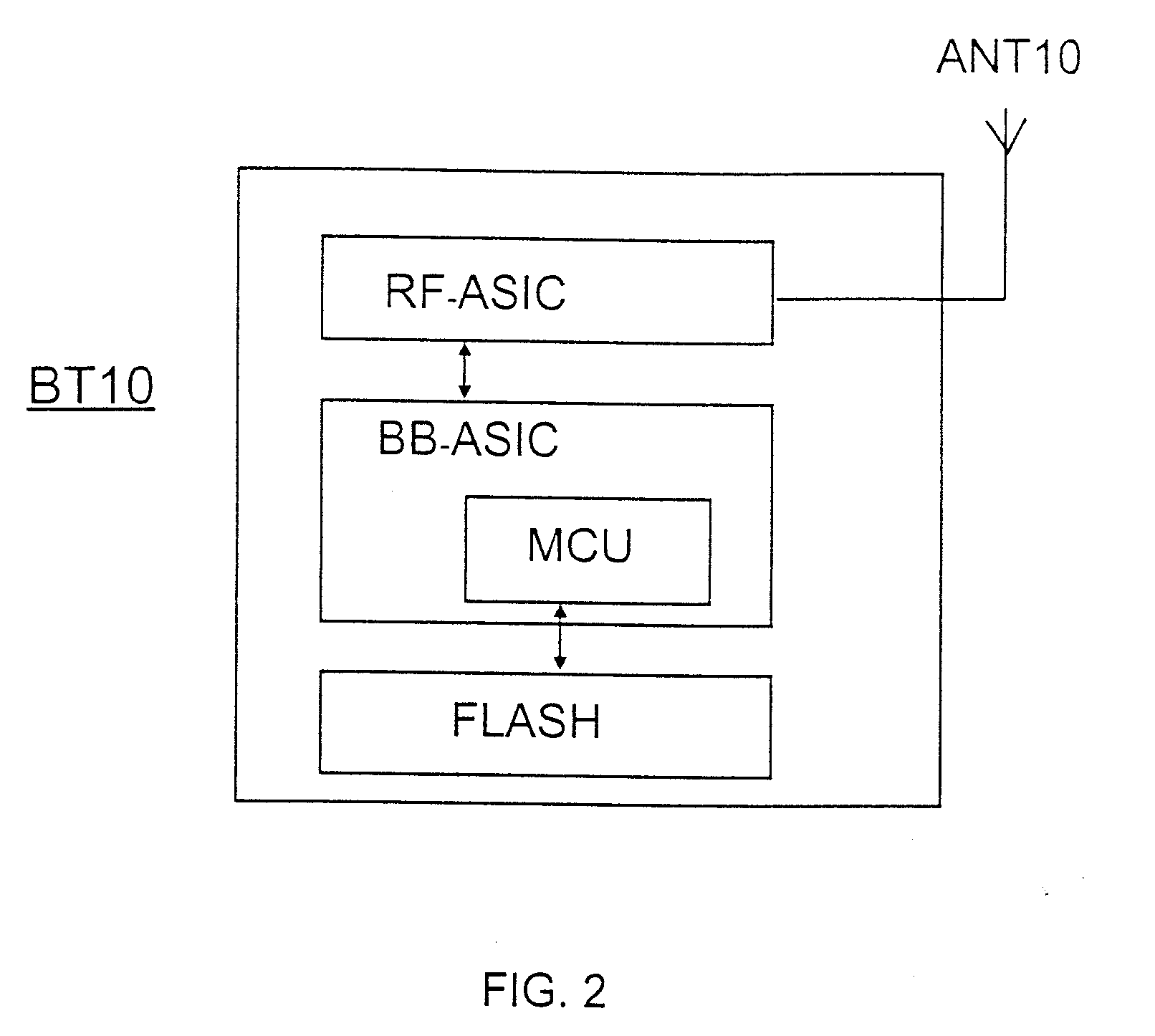
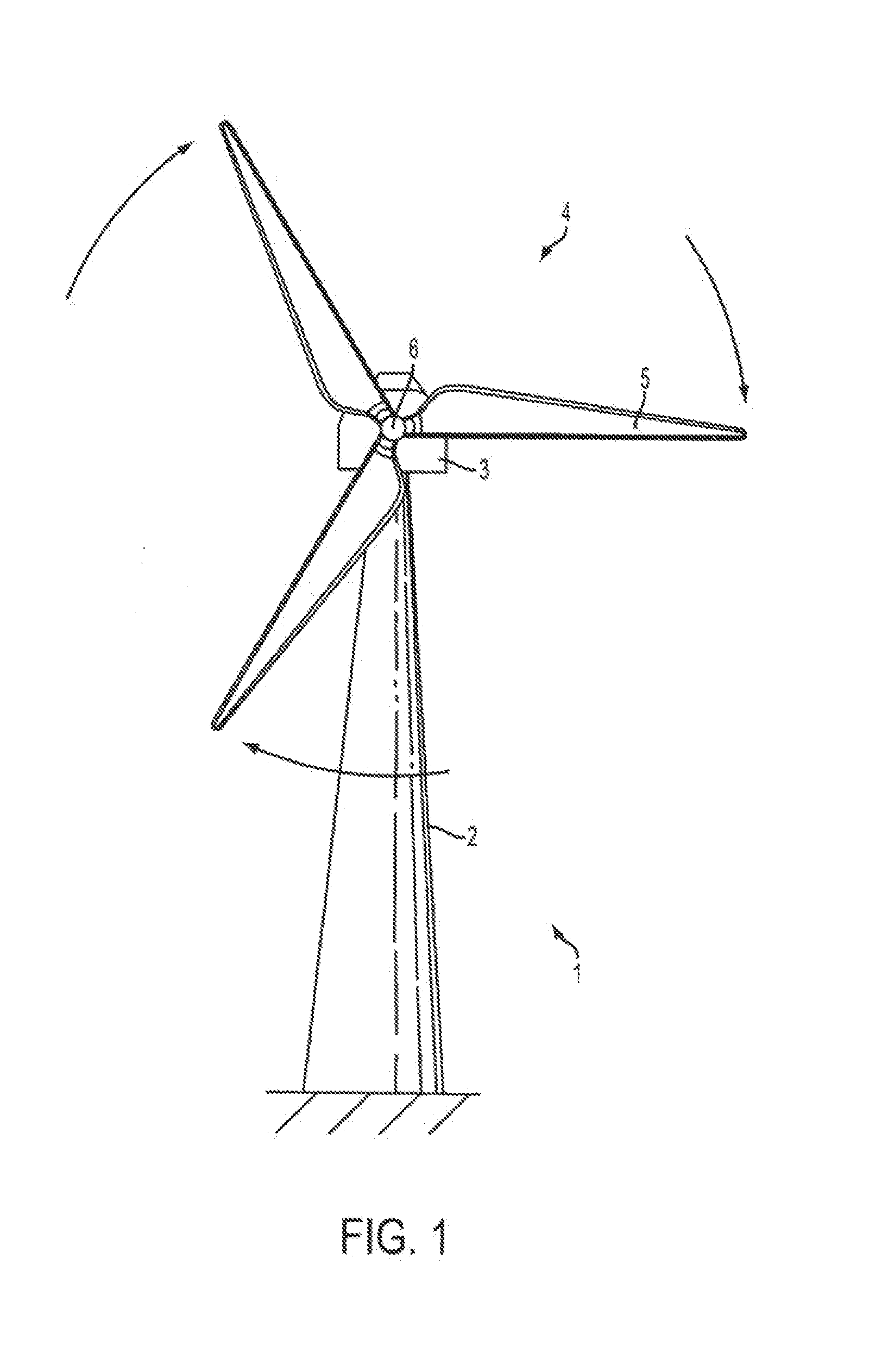
Wind turbine blade vibration detection and radar calibration
ActiveUS20150159632A1Reduces manufacturing and maintenance costEasy to replacePropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeTower
A wind turbine (1) is provided, having a wind turbine tower (2) and at least one rotatable blade (5), and further comprising a system for measuring rotor blade vibration of said wind turbine. The system comprises at least one Doppler radar unit (7) operatively configured to emit and receive radar signals, the radar unit being mounted on the wind turbine tower at a position above the lowest position of the at least one blade, the radar unit being positioned so as to measure reflections of an emitted radar signal from the turbine blade. A processing unit is configured to receive measurement data from the radar unit and to determine, by analysis of Doppler shift in received radar signals relative to transmitted signals due to movement of the blade towards or away from the turbine tower, the velocity of the blade in the direction towards or away from the turbine tower. Using a radar unit to measure blade velocity allows a determination to be made of the vibrations occurring in the blade without needing an internal sensor in the blade. This reduces manufacturing and maintenance costs of the blades since sensors in the blades will not need to be replaced, and sensors positioned on the tower are easier to replace in the field.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Digital watermark screening and detection strategies
InactiveUS20030174862A1Avoid unnecessary processingPreventing copying, playing or recordingTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsControl signalComputer science
To enhance decoding of signals suspected of containing an embedded auxiliary signal, a suspect signal is screened to compute detection values evincing presence and strength of the embedded signal. Screening strategies control detector actions, such as rejecting un-marked signals, improving synchronization of a reader used to extract hidden messages in suspect signals, determining authenticity of signals, and controlling use of the signals.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
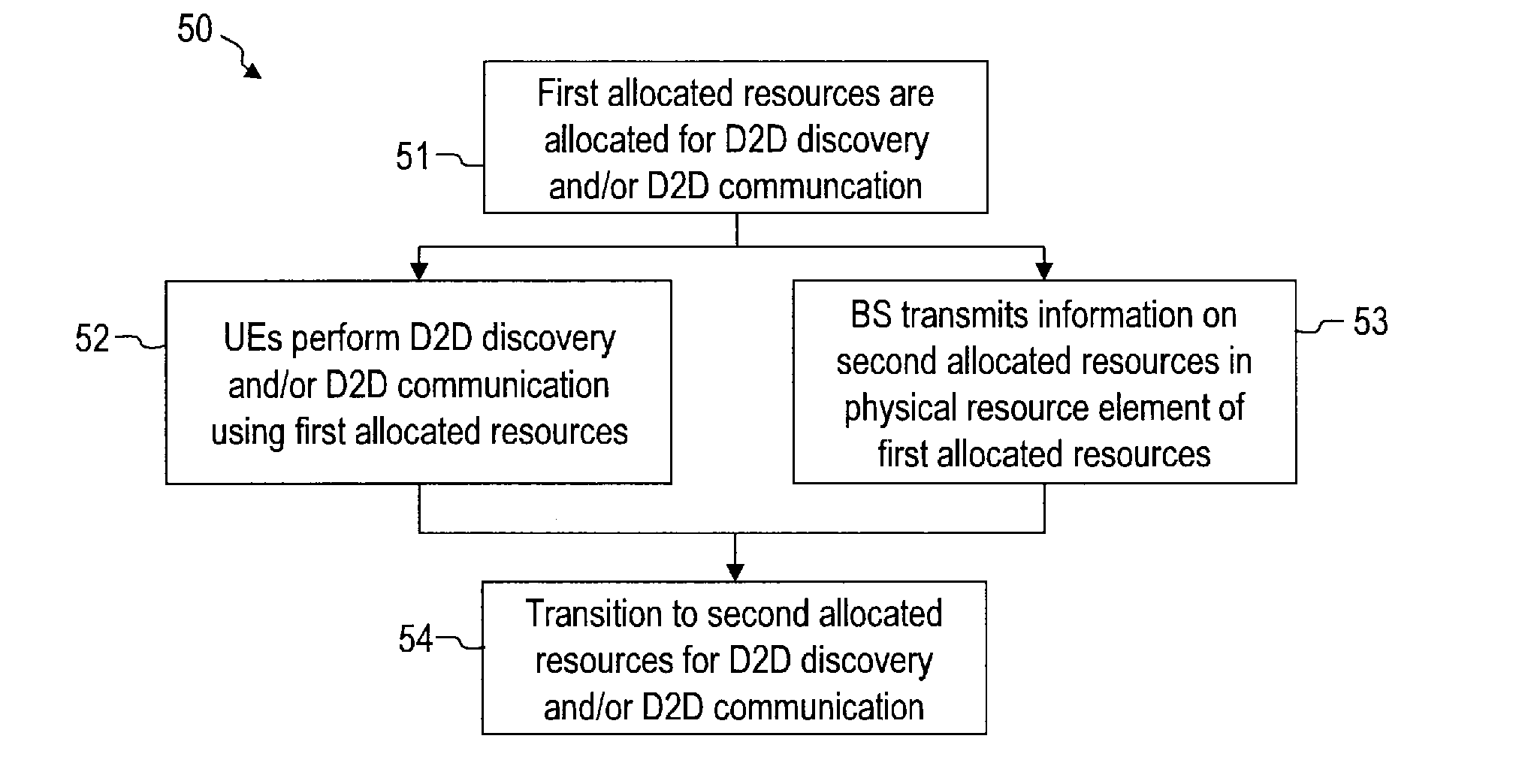
Method, base station and user equipment for adapting device-to-device resource allocation
ActiveUS20160323870A1Interference problemEasy to adaptAssess restrictionConnection managementResource elementResource allocation
To allocate resources for a device-to-device discovery and / or communication to at least one user equipment of a mobile communication network, the at least one user equipment is informed of a change of the resources allocated for the device-to-device discovery and / or communication from first allocated resources to second allocated resources. To inform the at least one user equipment of the change, a base station or a user equipment which act as central controller for a group of users of the mobile communication network transmits information on the second allocated resources in at least one physical resource element of the first allocated resources..
Owner:SONY CORP
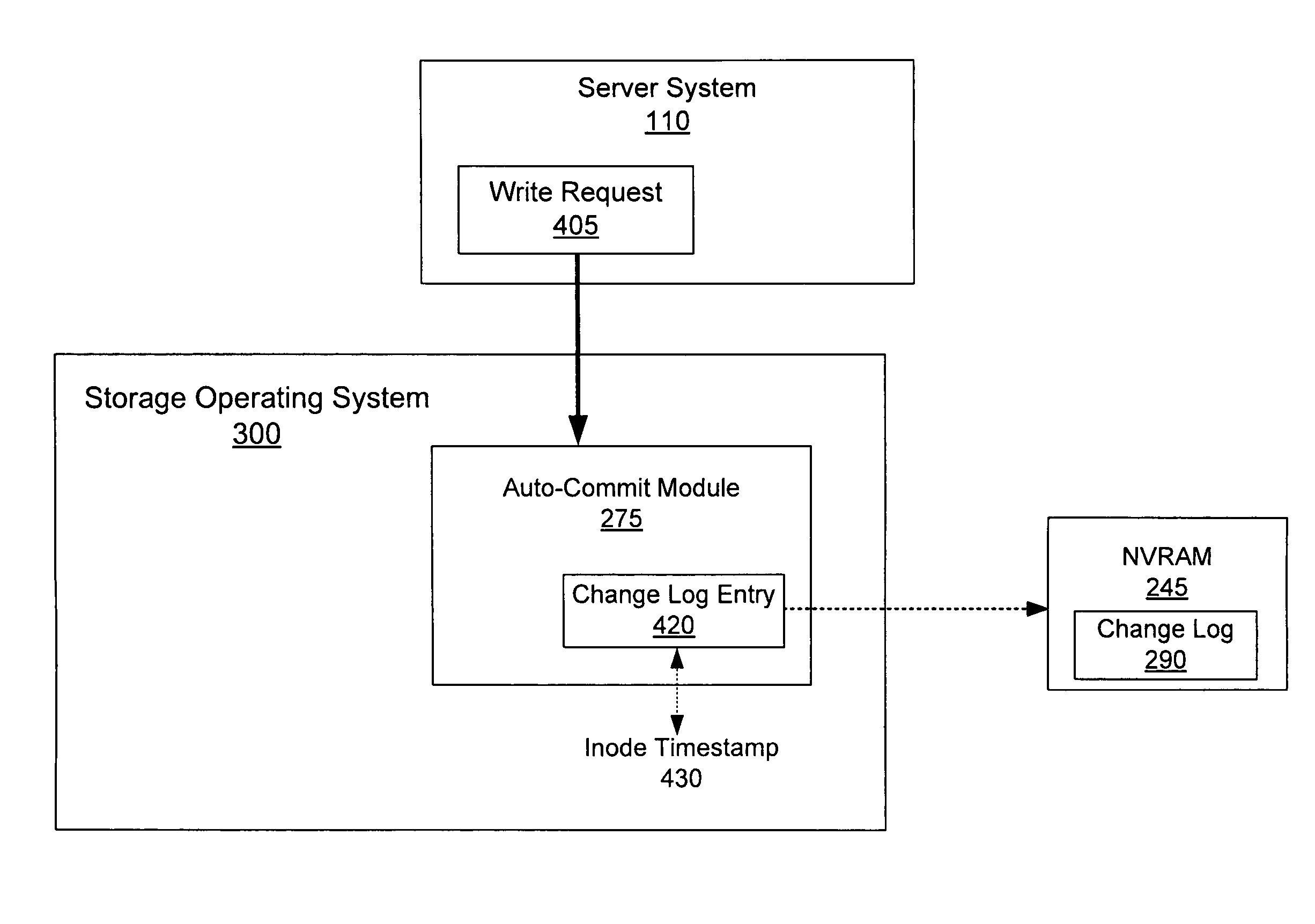
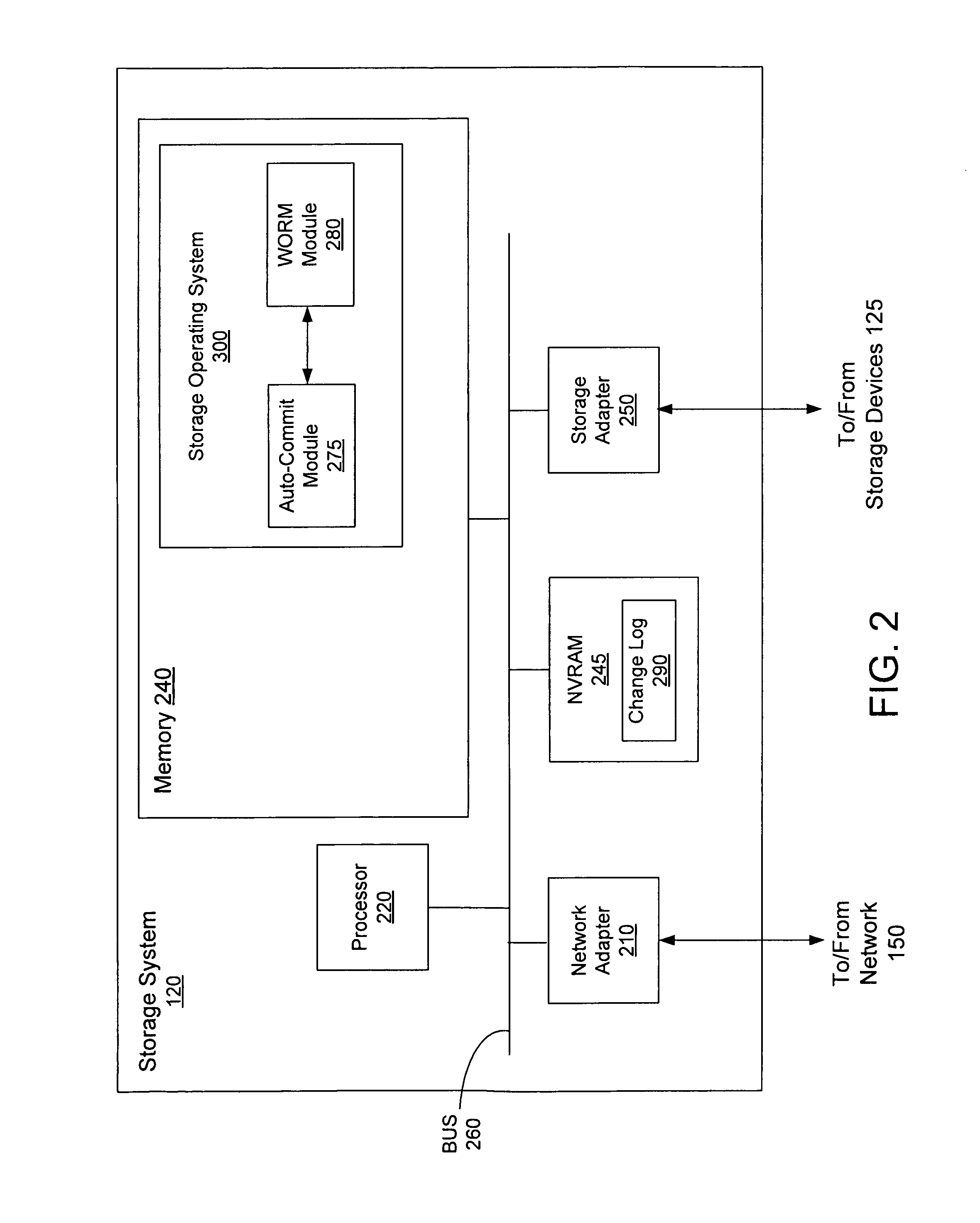
Auto-committing files to immutable status based on a change log of file system activity
ActiveUS8234317B1Guarantee the best timeAvoid unnecessary processingDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsResting timeFile system
A system and method are provided for auto-committing files of a storage system to immutable status based on a change log of file system activity. The system is configured for producing and analyzing the change log. Producing the change log involves generating change log entries associated with changes made to files of the storage system and organizing the change log entries from the oldest to newest entries. Analyzing the change log involves processing the change log beginning with the oldest entry to determine whether any entries have met the auto-commit time period, and if so, to set the files associated with such entries to immutable status. If a change log entry is found not to have met the auto-commit time period, a resting time period is determined based on the oldest change log entry, and processing of the change log proceeds after expiration of the resting time period.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
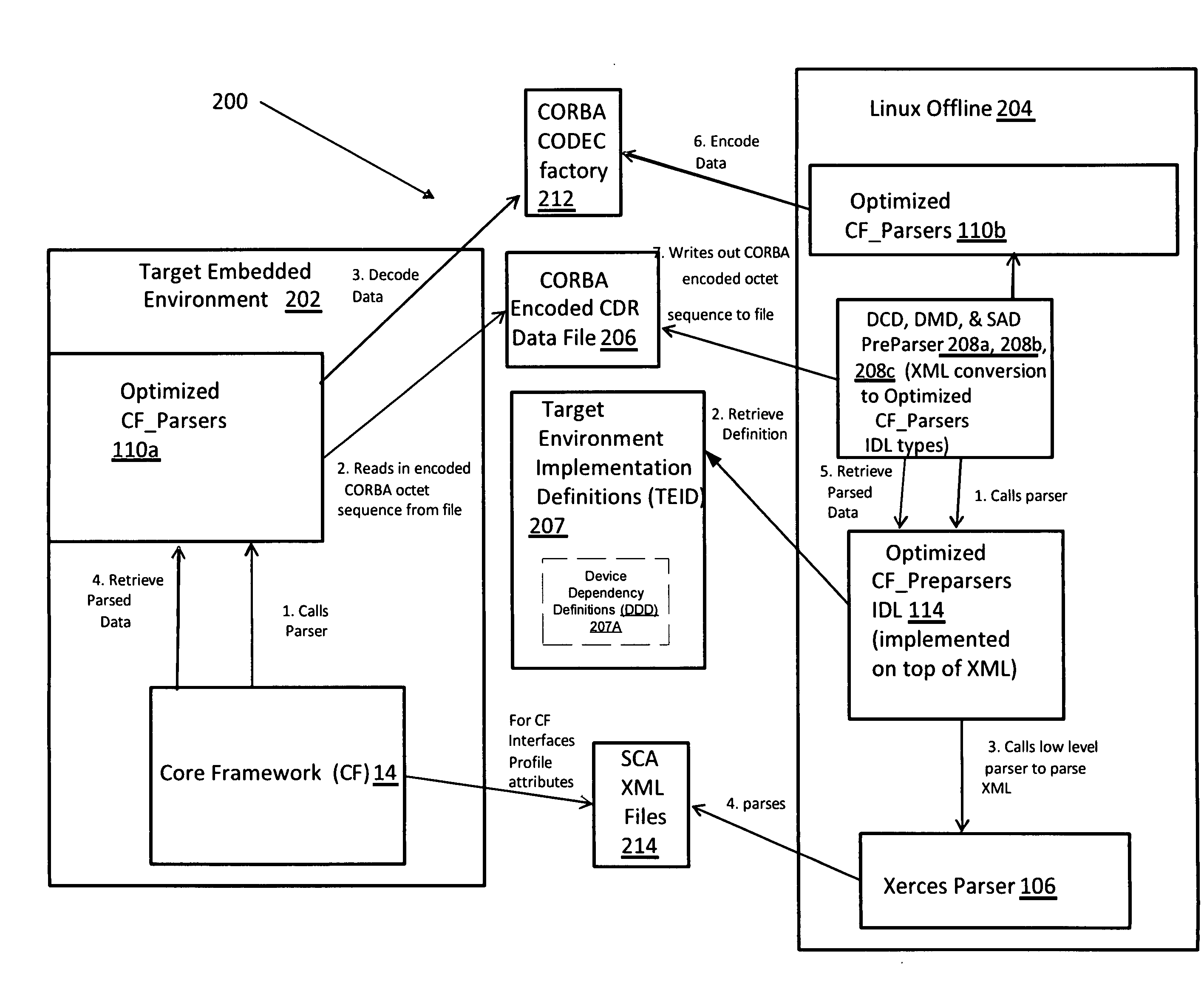
Optimized SCA CORBA descriptor for SCA CORBA descriptor files
ActiveUS20130139146A1Speed up parsing processEliminate effectiveSemi-structured data mapping/conversionProgram loading/initiatingXMLStructure type
A preparsers tool is provided for converting SCA XML files into CORBA structures usable by an SCA Core Framework (CF). The preparsers tool retrieves a set of target environment implementation definitions (TEID) that define at least one characteristic of a target environment to which a CORBA CDR file is provided. For each component in the target environment, at least one of the component instantiation implementation software device dependencies, usesdevice dependencies, and deployment dependencies, are merged together into an implementation device dependencies list having a first part comprising visible device dependencies and a second part comprising external device dependencies. The parsed set of XML files is converted into a CORBA structure type, the conversion based at least in part on the TEID, such that the conversion of the parsed set of XML files results in a CORBA structure having a type and precedence order that is correct for the target environment.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Video-based warning system for a vehicle
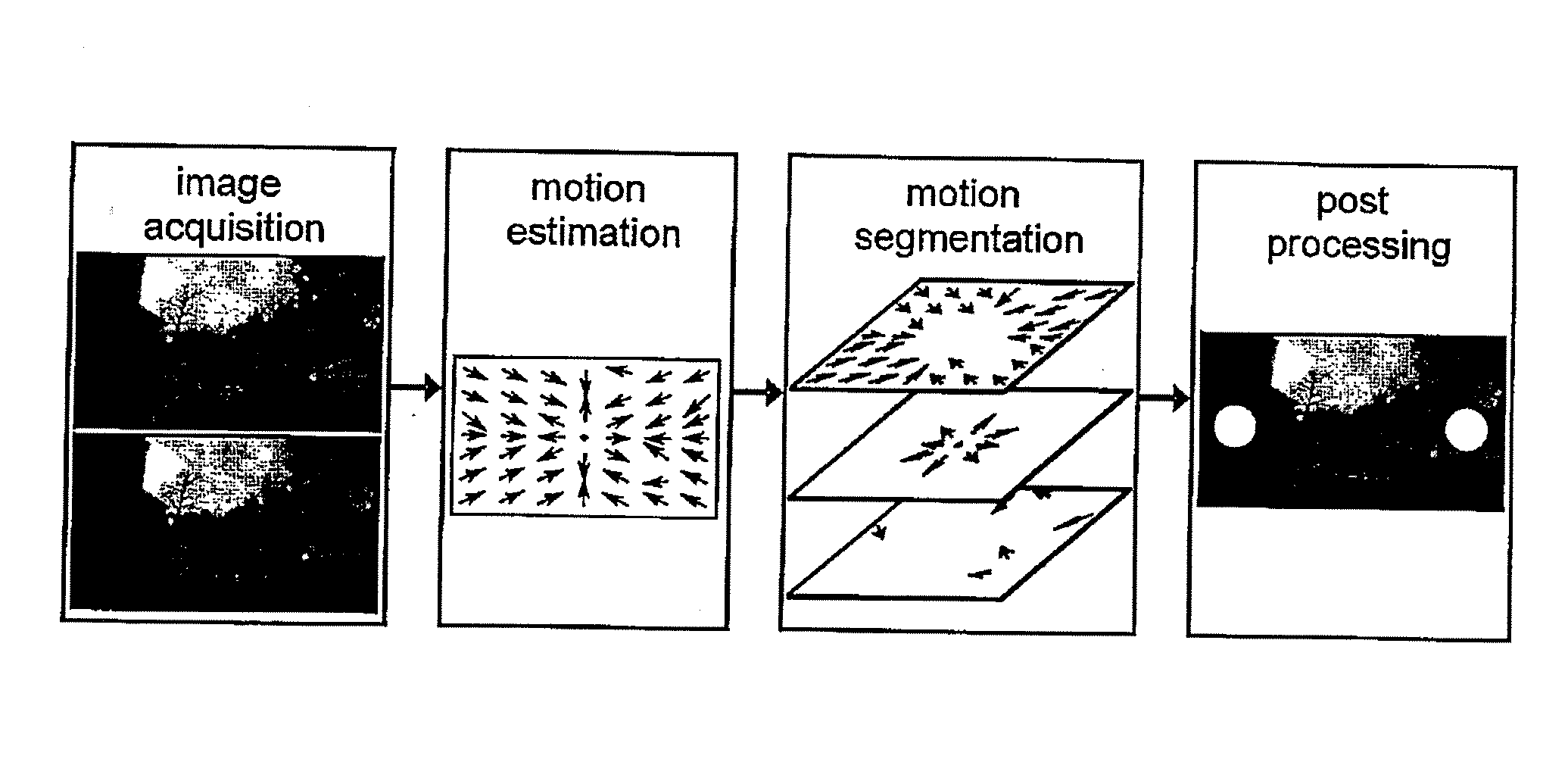
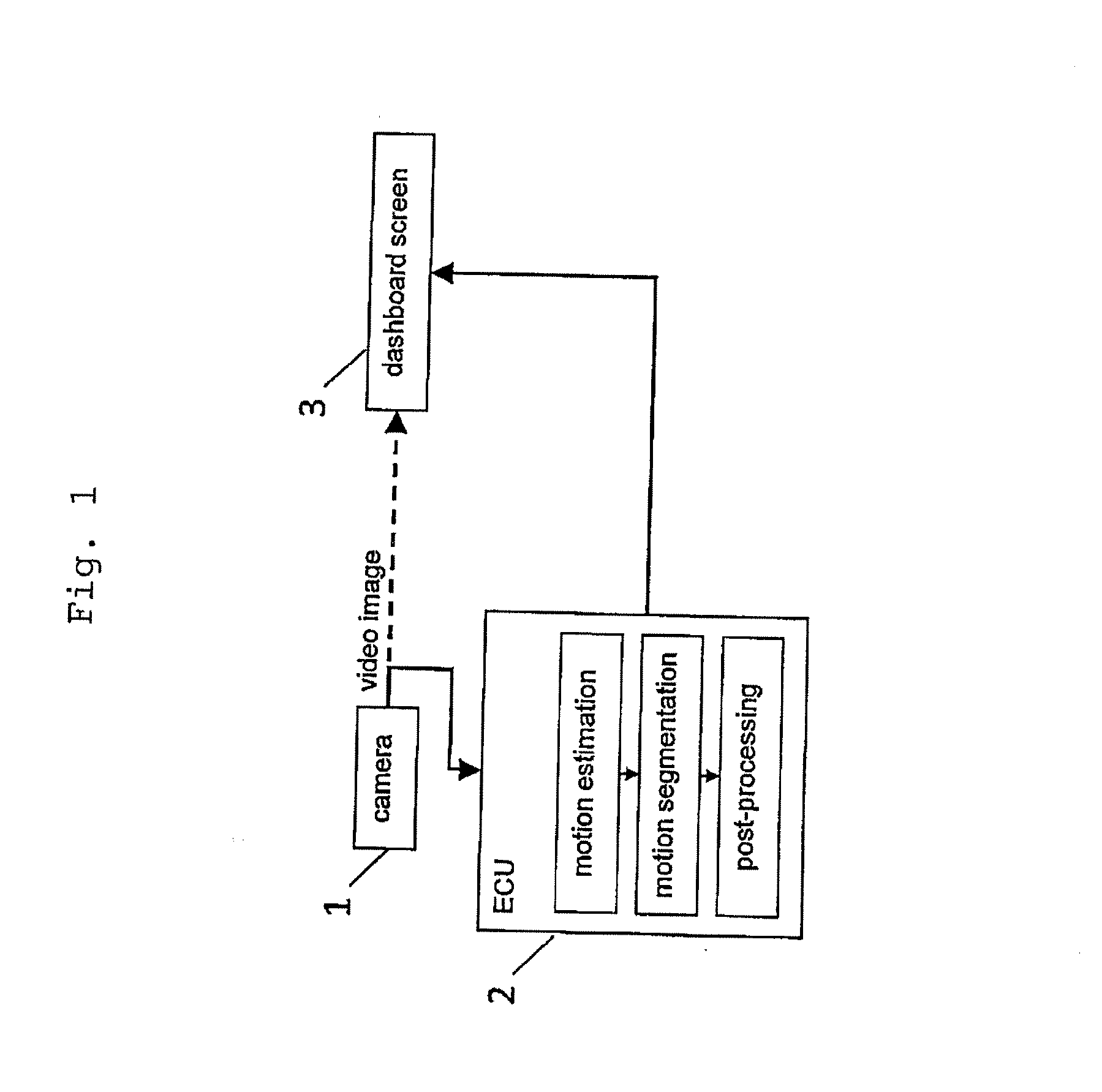
InactiveUS20130088343A1Possible to separateImprove system reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisCamera imageObject based
The present invention proposes a warning system that can be implemented in any kind of vehicle, in order to efficiently detect moving objects. The system utilizes at least one camera for a continuous imaging of the surroundings of the vehicle. Thereby, moving objects can be monitored. A computing unit is programmed to estimate a motion of any moving object based on a pixel motion in the camera image. If a dangerously moving object is detected, a warning unit can be used for issuing a warning signal. To take such a decision, the estimated motion of at least one of the moving objects can be correlated or compared to predetermined motion patterns.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
Recovery from failures within data processing systems
InactiveUS7543181B2Improve availabilityConsistent stateSpecial data processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionData processing systemSuccessful completion
Provided are methods, data processing systems, recovery components and computer programs for recovering from storage failures affecting data repositories. At least a part of the recovery processing is performed while the data repositories are able to receive new data and to allow retrieval of such new data. Although new data items may be received into the repository and retrieved therefrom during recovery processing, updates to the data repository which were performed before the failure and which are then restored to the repository by the recovery processing are restored within a recovery unit of work and are inaccessible to processes other than the recovery process until successful completion of the recovery unit of work. The recovery processing ensures that the recovered repository is consistent with the state of the repository at the time of the failure, but is available for addition and retrieval of new data items before completion of the recovery processing.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
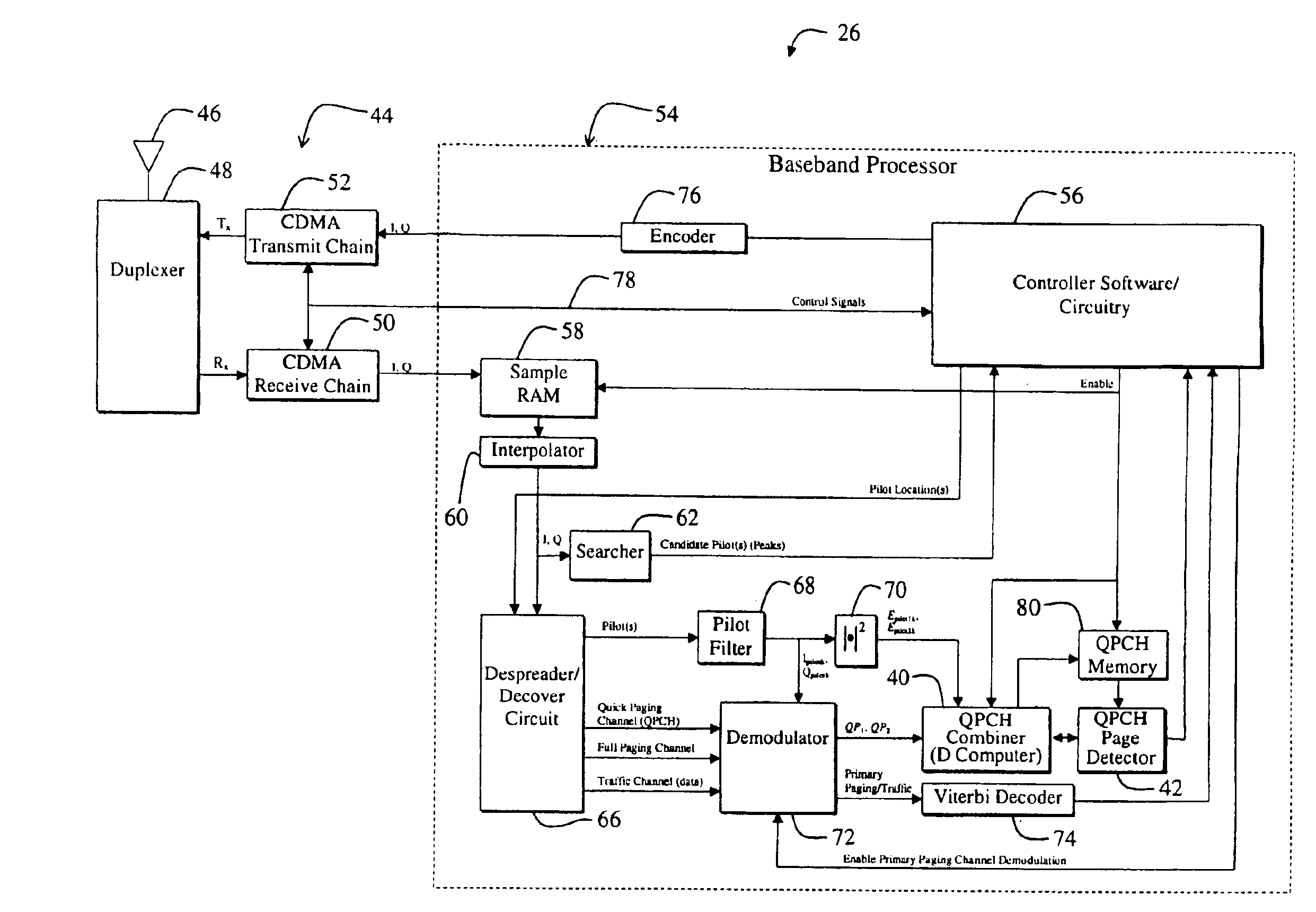
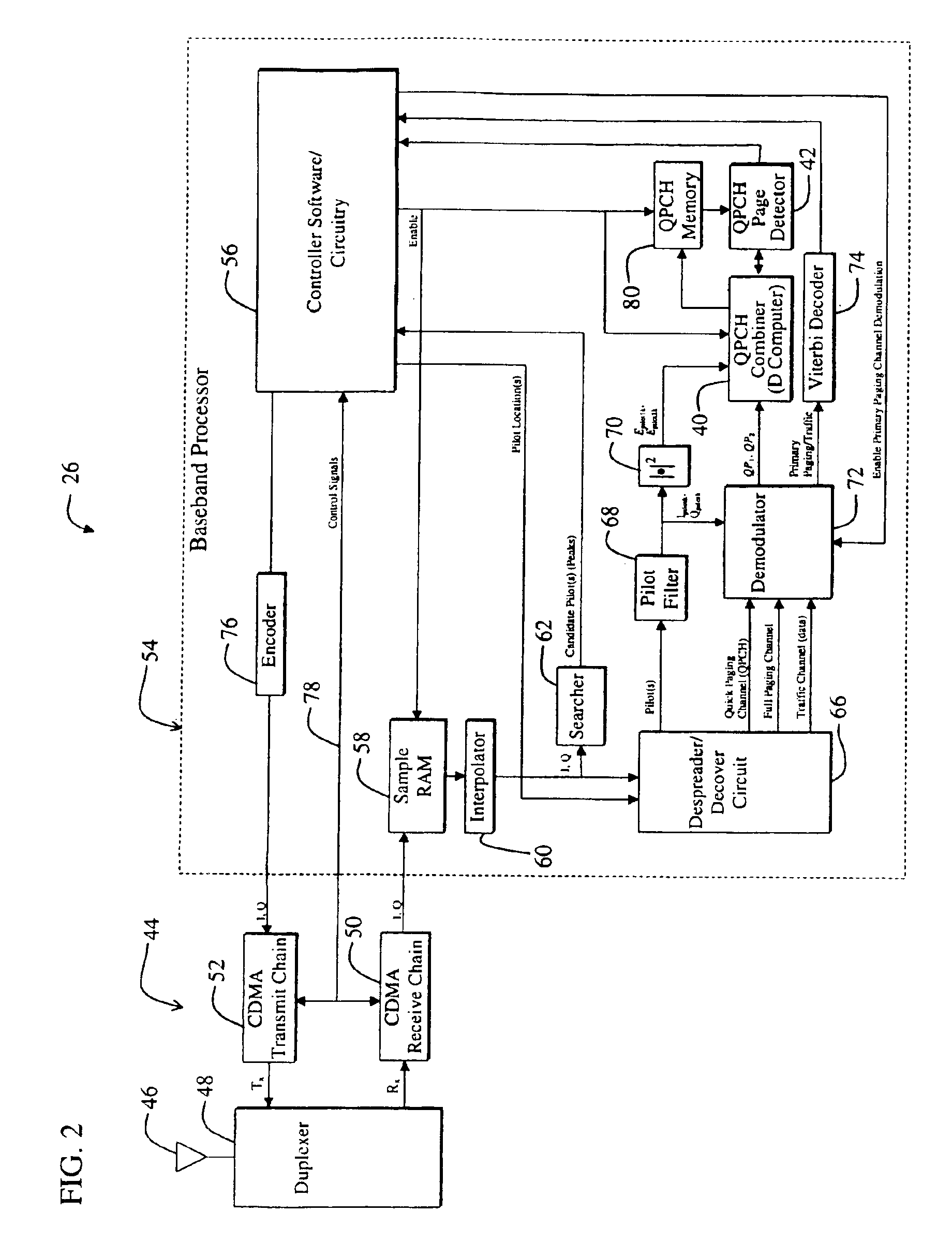
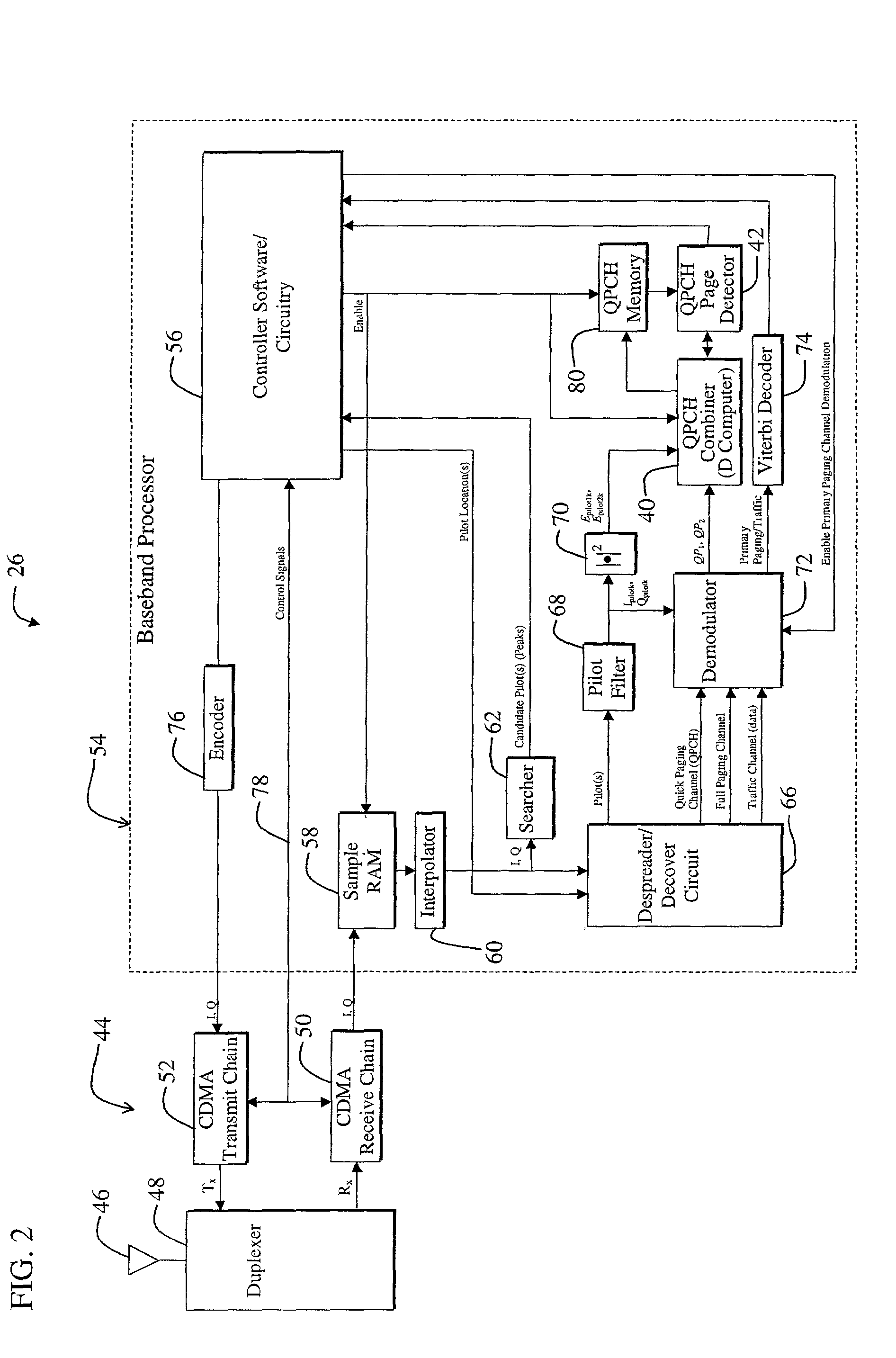
Dual paging channel receiver for a wireless communications system
InactiveUS6895058B2Easy to detectAccurate valueAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCommunications systemCommunication device
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Hiding a device
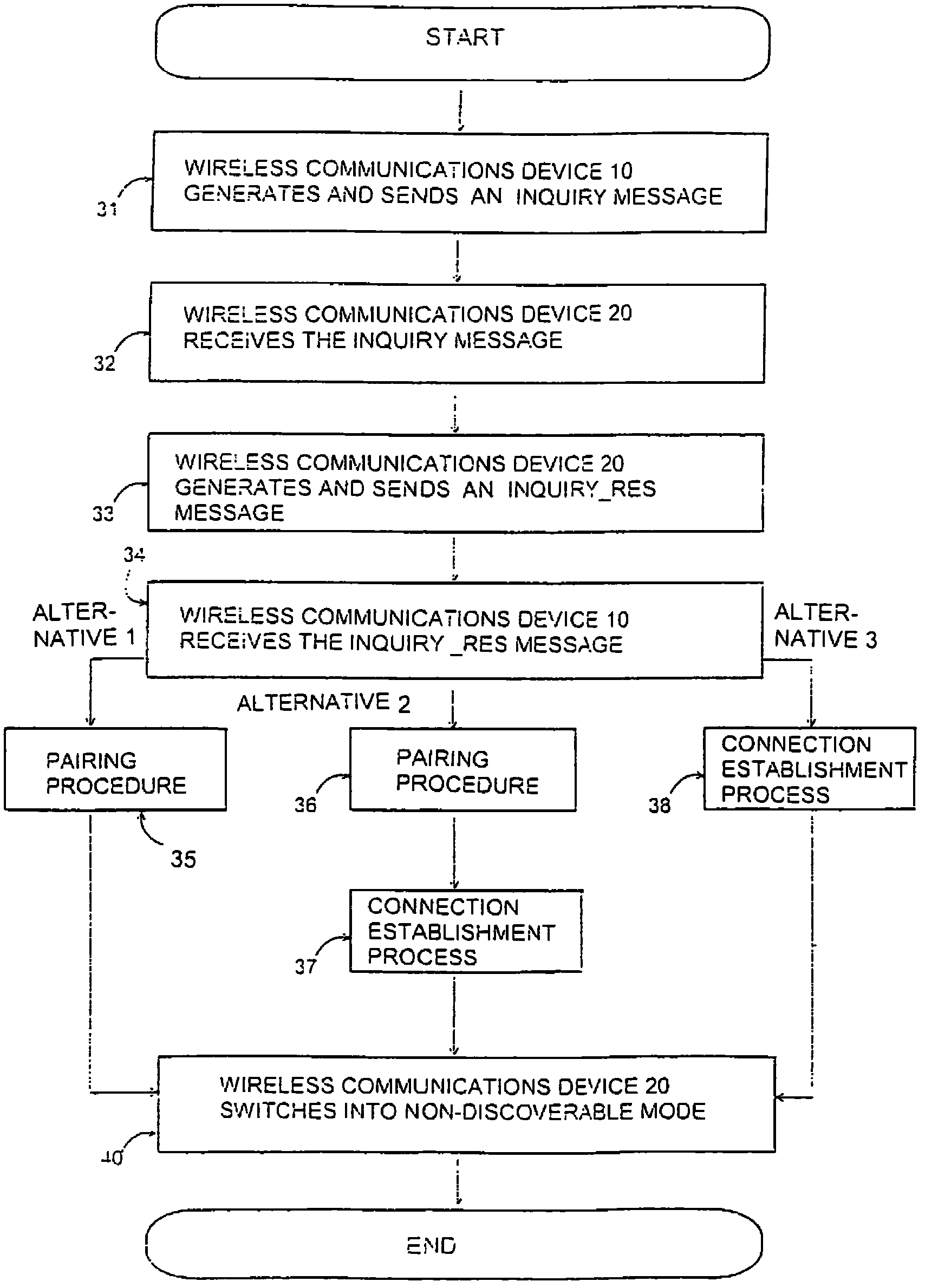
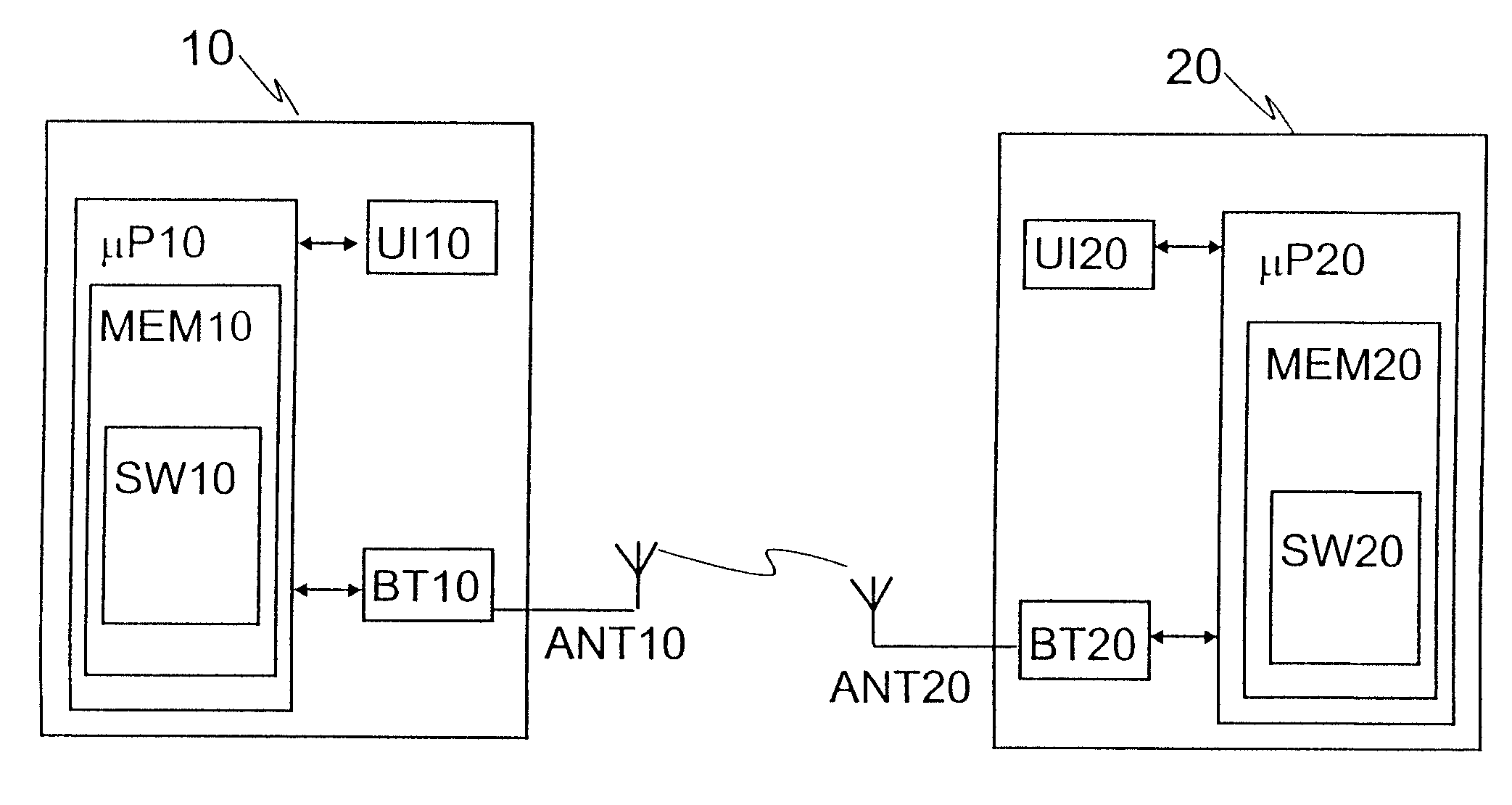
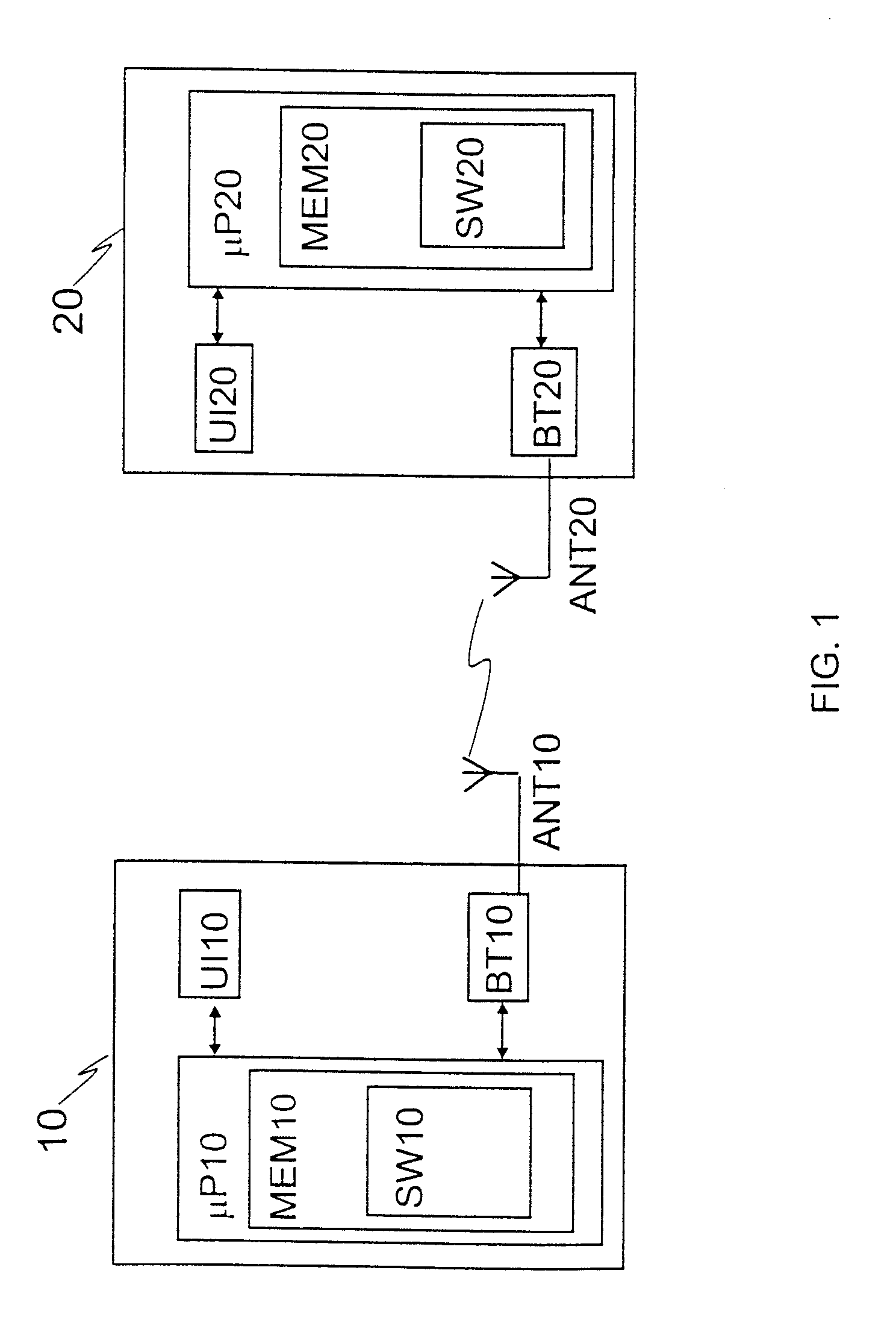
ActiveUS7792490B2Save processing resourcesAvoid unnecessary processingNear-field transmissionAssess restrictionSuccessful completionRadio frequency
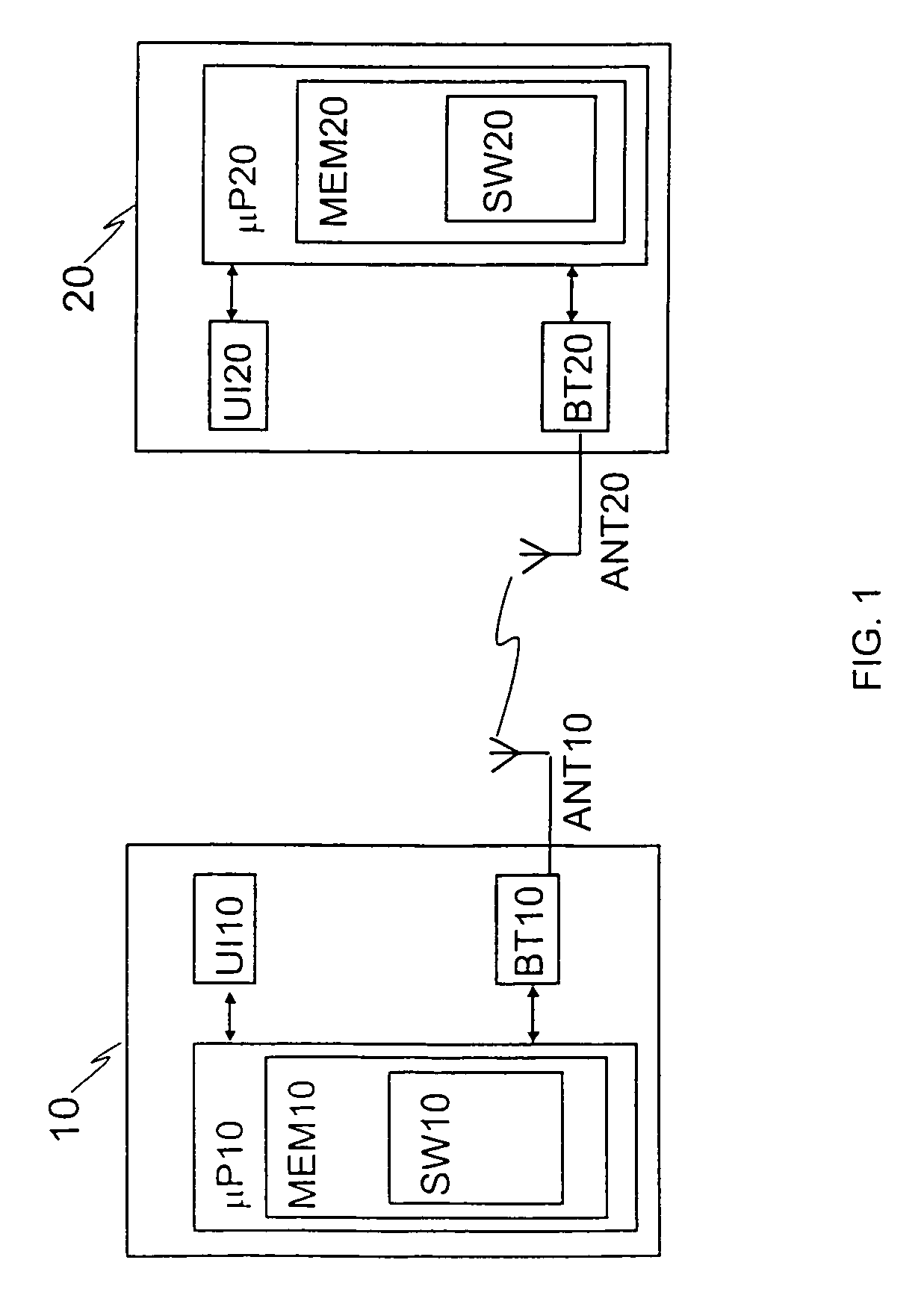
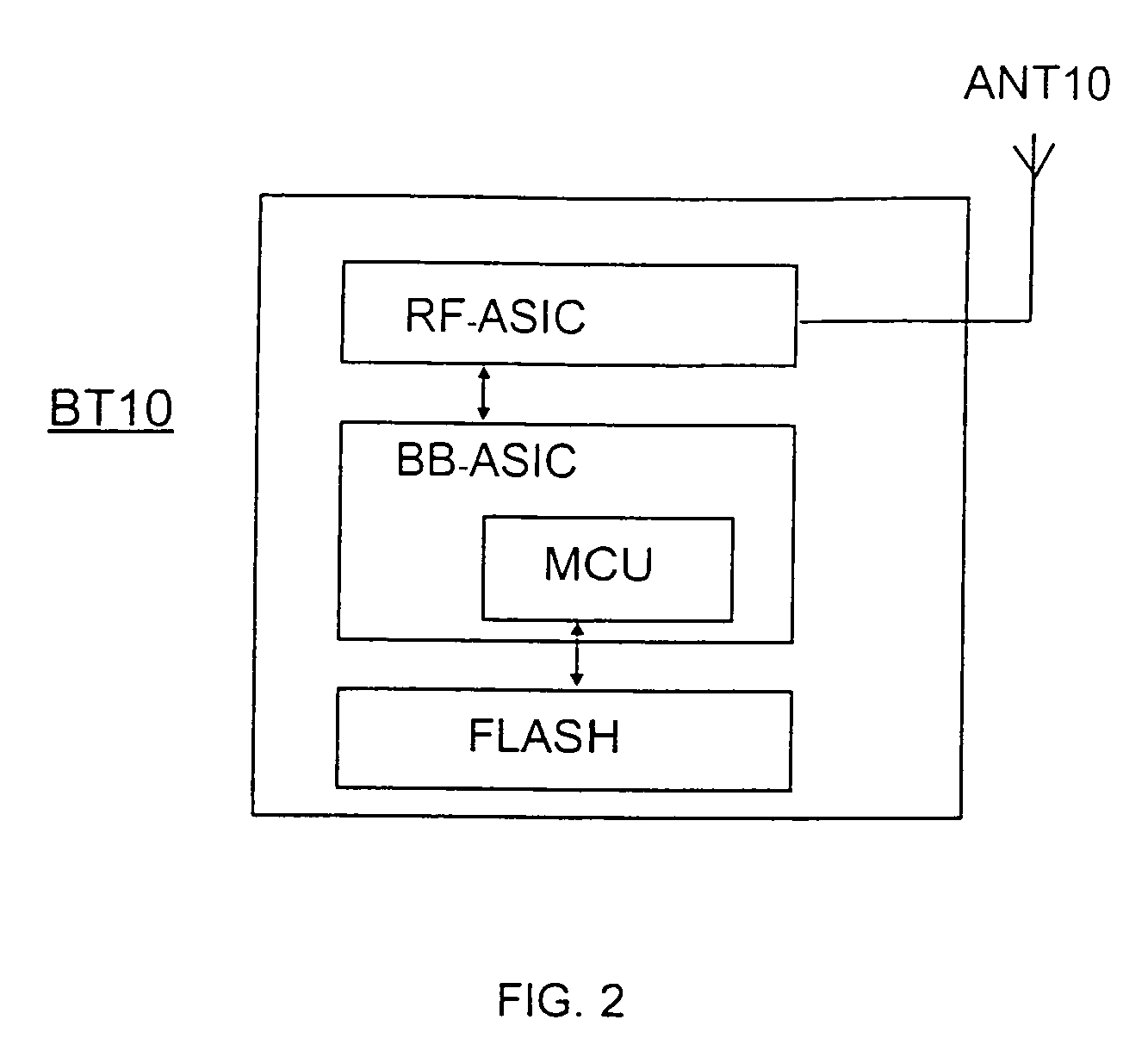
In accordance with the exemplary embodiments of the invention there is at least a method, apparatus, and an executable computer program enabling a first communications device and a second communications device, possibly previously unknown to each other, to communicate with each other wirelessly using short-range radio frequency technology. A connection establishment process is executed to establish a connection between the first communications device and said second communications device. Further, in accordance with the embodiments, during the connection establishment process, or in response to successful completion of the connection establishment process, at least one of said first and second communications devices switches from said first mode into a second mode, in which second mode, the communications device that has switched into said second mode does not respond to messages arriving at it which have been sent to discover the address of the communications device that has switched into said second mode.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
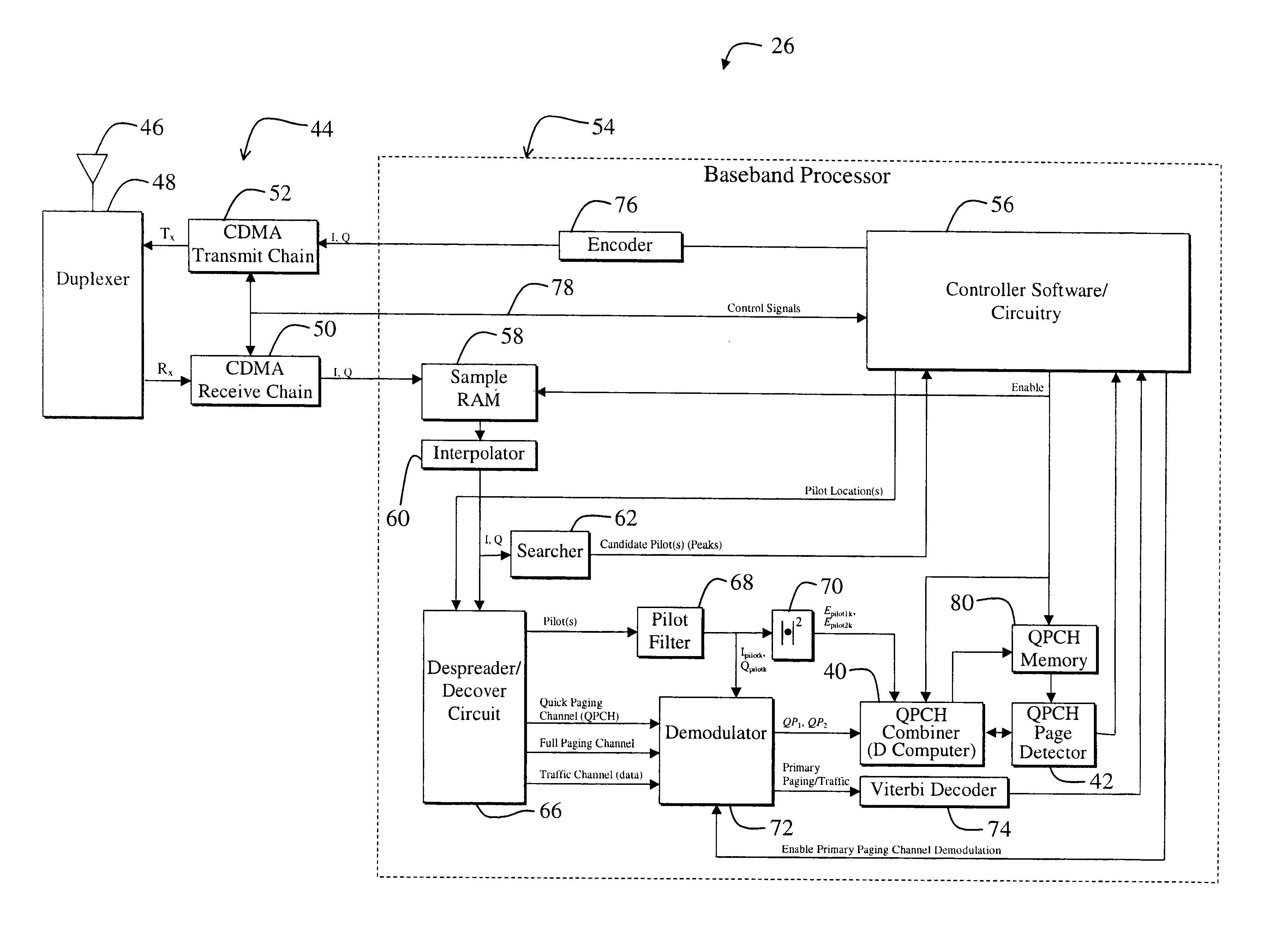
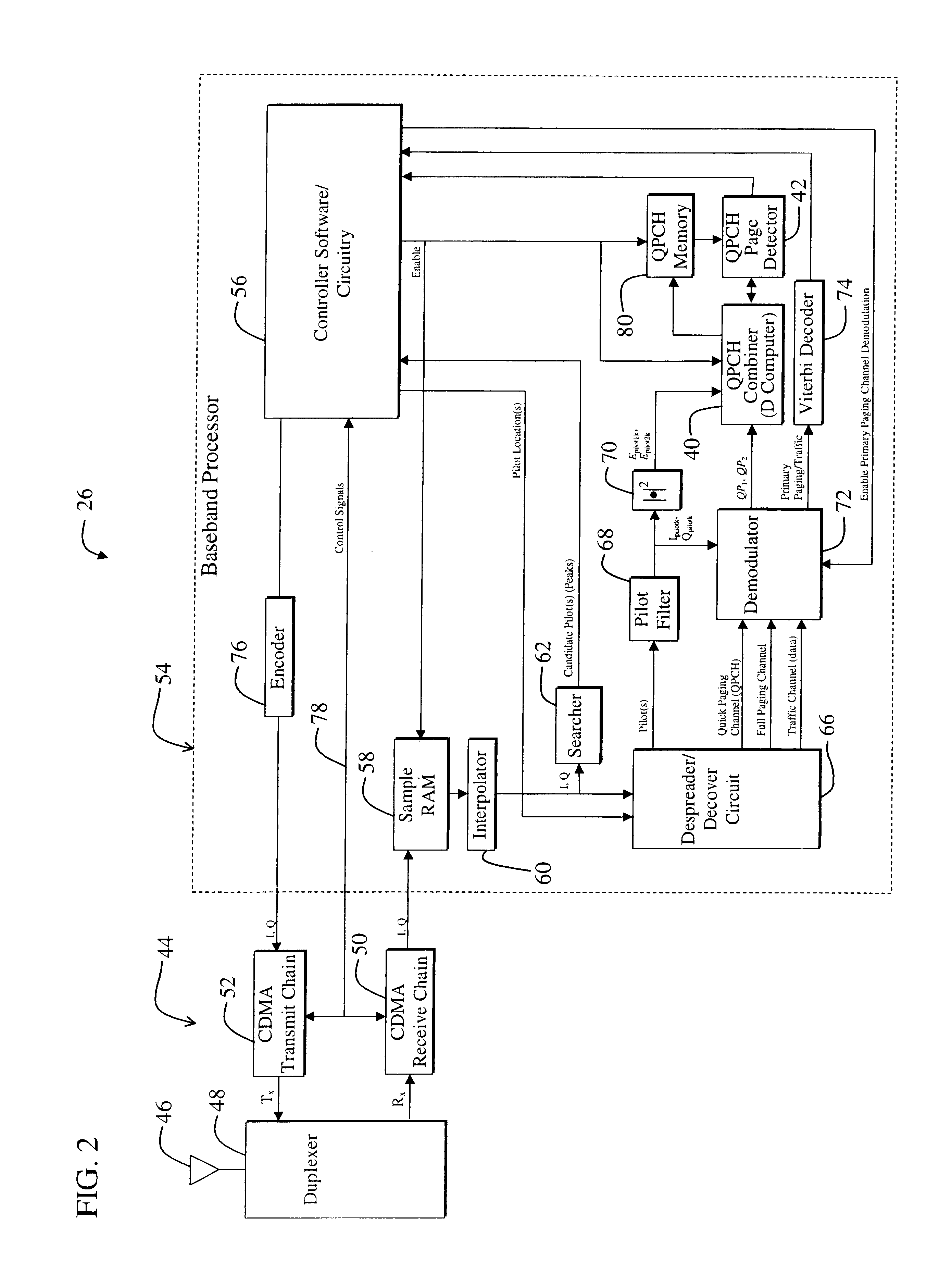
Sequential combined QPCH demodulation
InactiveUS20020142784A1Innovative designPresent inventionPower managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringDemodulation
A system determines if a primary paging channel should be received based on an examination of a quick paging channel. A first QPCH symbol is examined (102) and the normalized pilot energy is determined (104). If the normalized pilot energy is above a first threshold (106), the symbol is demodulated and the QPCH-symbol-to-pilot-energy ratio is determined (110) and compared against another threshold (114). If the normalized pilot energy is below the first threshold, the system proceeds to the second QPCH symbol immediately. Based on the two comparisons, a second QPCH signal is examined (108) or the system sleeps (116). If the second signal is examined, and if its normalized pilot energy is high enough, it also is demodulated and the ratio of the sum-of-the-combined-QPCH-symbols to the sum-of-the-combined-pilot-energies is determined (122). If this ratio exceeds a threshold (124), the primary paging channel is processed (120); otherwise the system sleeps (116).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
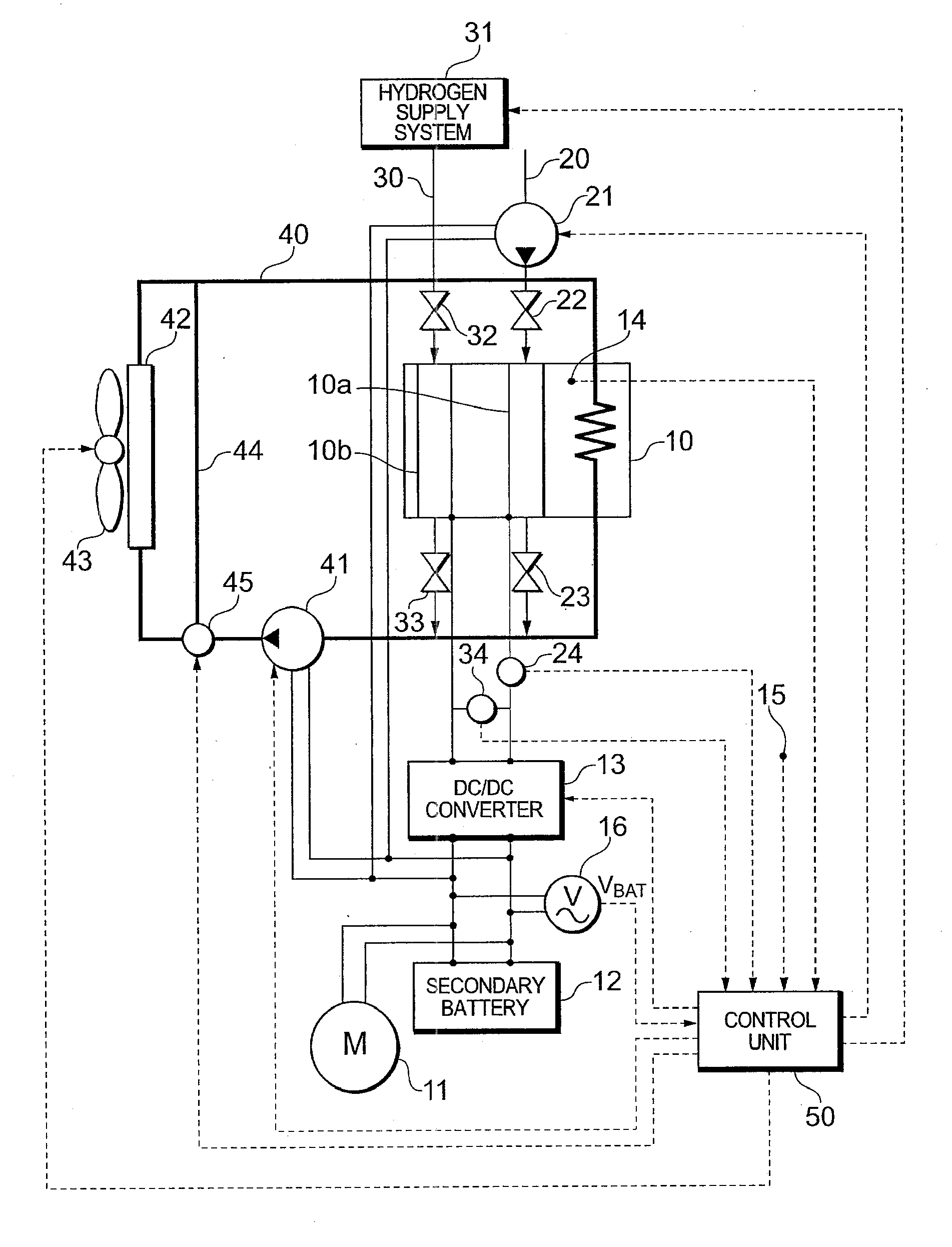
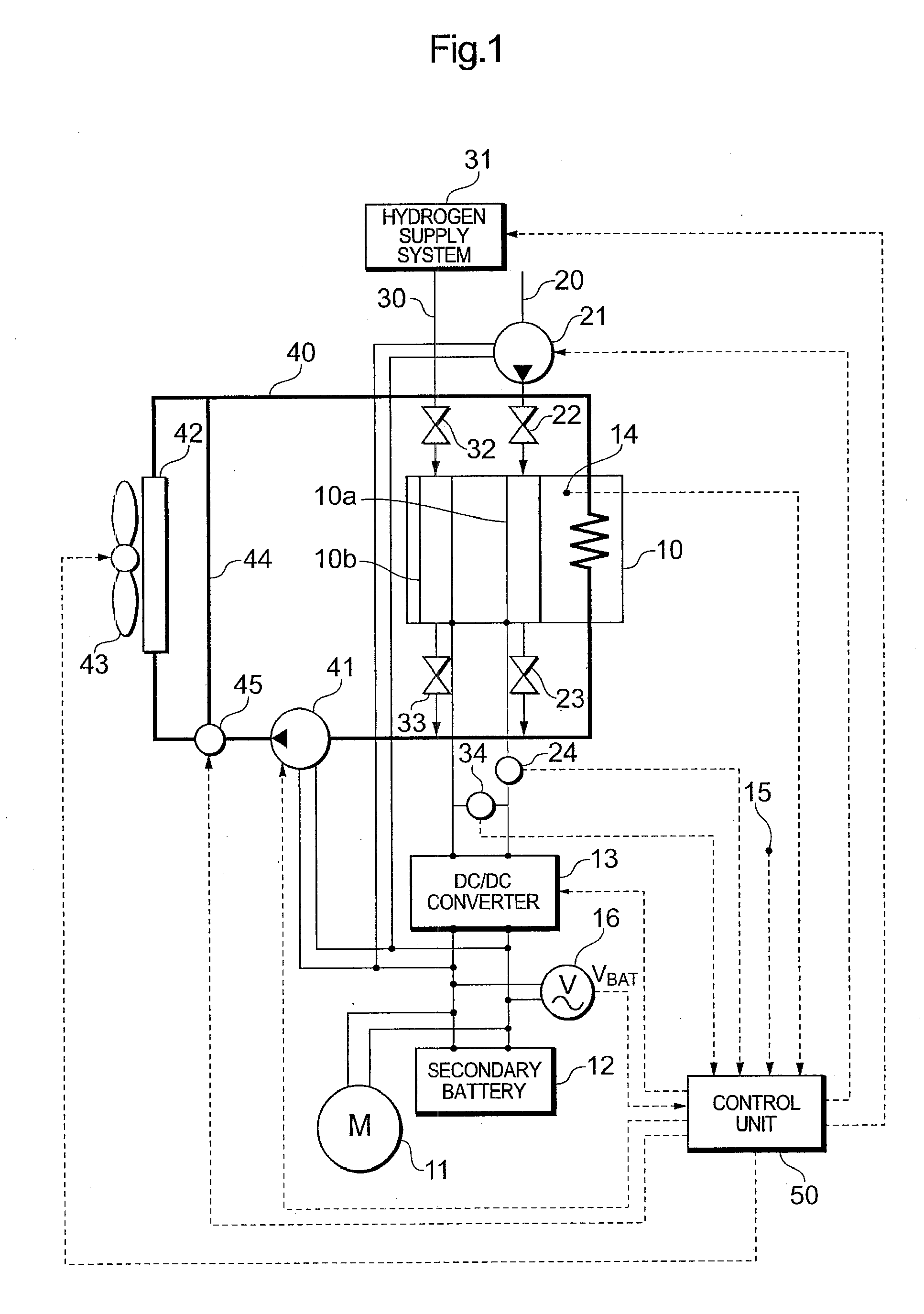
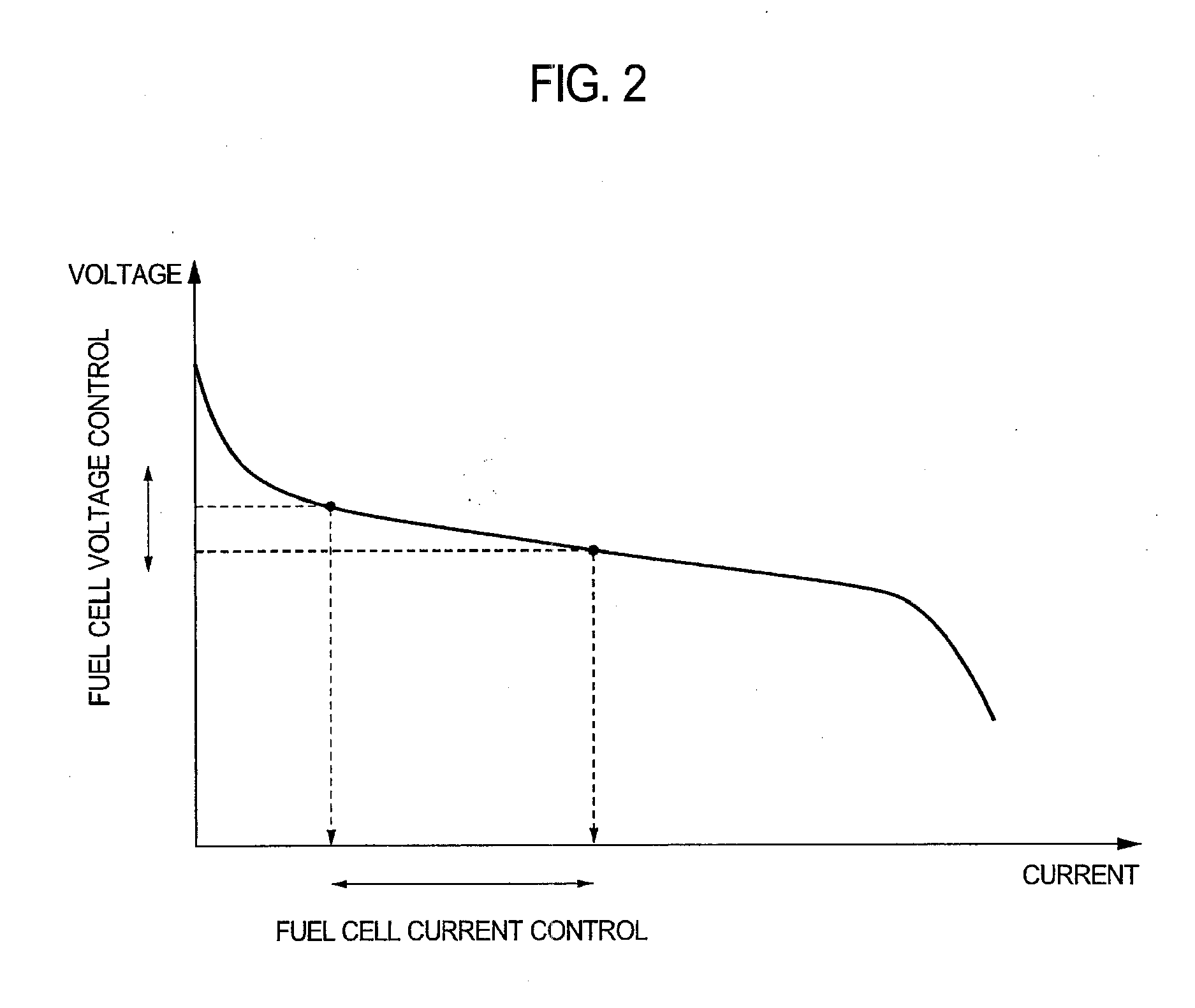
Fuel cell system
ActiveUS20100127710A1Avoid unnecessary processingReduce restrictionsBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFuel cellsSignal on
A fuel cell system is configured to have: a voltage superimposing unit that superimposes a predetermined AC signal on an output voltage of a fuel cell; a unit that detects an output voltage value of a battery device, the output voltage value varying as the fuel cell output voltage value on which the AC signal has been superimposed varies; a battery device voltage comparison unit that compares the detected battery device output voltage value with a predetermined threshold voltage; and a measurement permission determination unit that determines whether the AC impedance measurement is permitted or not based on whether or not the battery device output voltage value exceeds the threshold voltage. The fuel cell system can protect the battery device in the impedance measurement of the fuel cell based on an AC impedance method.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Sequential combined QPCH demodulation
InactiveUS6771616B2Avoid unnecessary processingFailure can not be detectedPower managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringDemodulation
A system determines if a primary paging channel should be received based on an examination of a quick paging channel. A first QPCH symbol is examined (102) and the normalized pilot energy is determined (104). If the normalized pilot energy is above a first threshold (106), the symbol is demodulated and the QPCH-symbol-to-pilot-energy ratio is determined (110) and compared against another threshold (114). If the normalized pilot energy is below the first threshold, the system proceeds to the second QPCH symbol immediately. Based on the two comparisons, a second QPCH signal is examined (108) or the system sleeps (116). If the second signal is examined, and if its normalized pilot energy is high enough, it also is demodulated and the ratio of the sum-of-the-combined-QPCH-symbols to the sum-of-the-combined-pilot-energies is determined (122). If this ratio exceeds a threshold (124), the primary paging channel is processed (120); otherwise the system sleeps (116).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
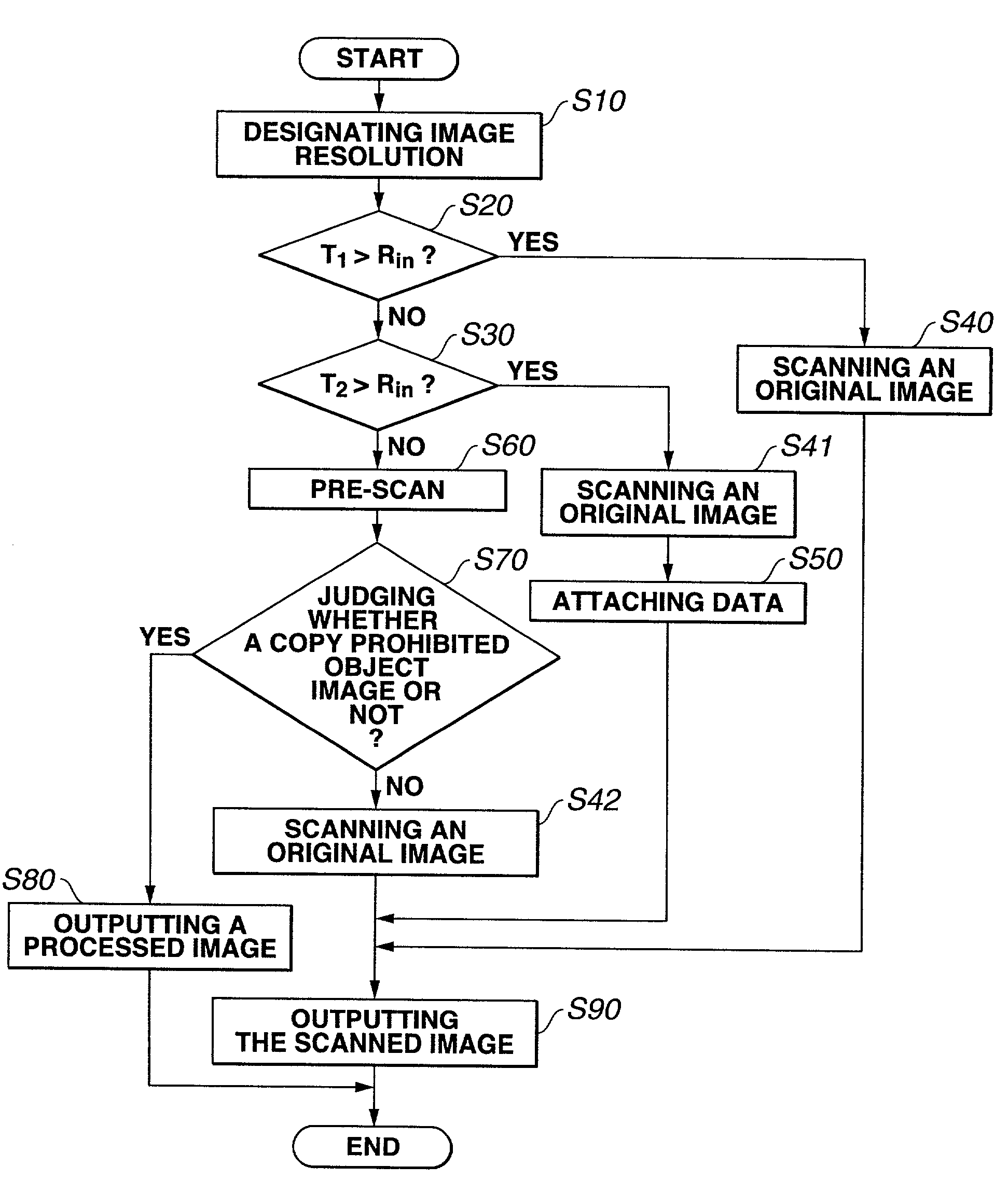
Image processing apparatus, image processing method and a computer program product for judging whether image data include specific information related to copy protection
InactiveUS7035426B2Efficient judging processingQuick judgmentPaper-money testing devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
The present invention relates to image processing in which an image resolution of input image data is compared to information of predetermined standard resolution, and the image data is judged to determine whether it includes specific information related to copy protection. Whether or not to perform judging is controlled based on the result of the comparison. Because the control technique of the present invention controls whether or not to perform the judgment based on the result of the c comparison, the control technique according to the invention provides an efficient judging processing, since no judgment is performed on low resolution image data which is not prone to counterfeiting.
Owner:CANON KK
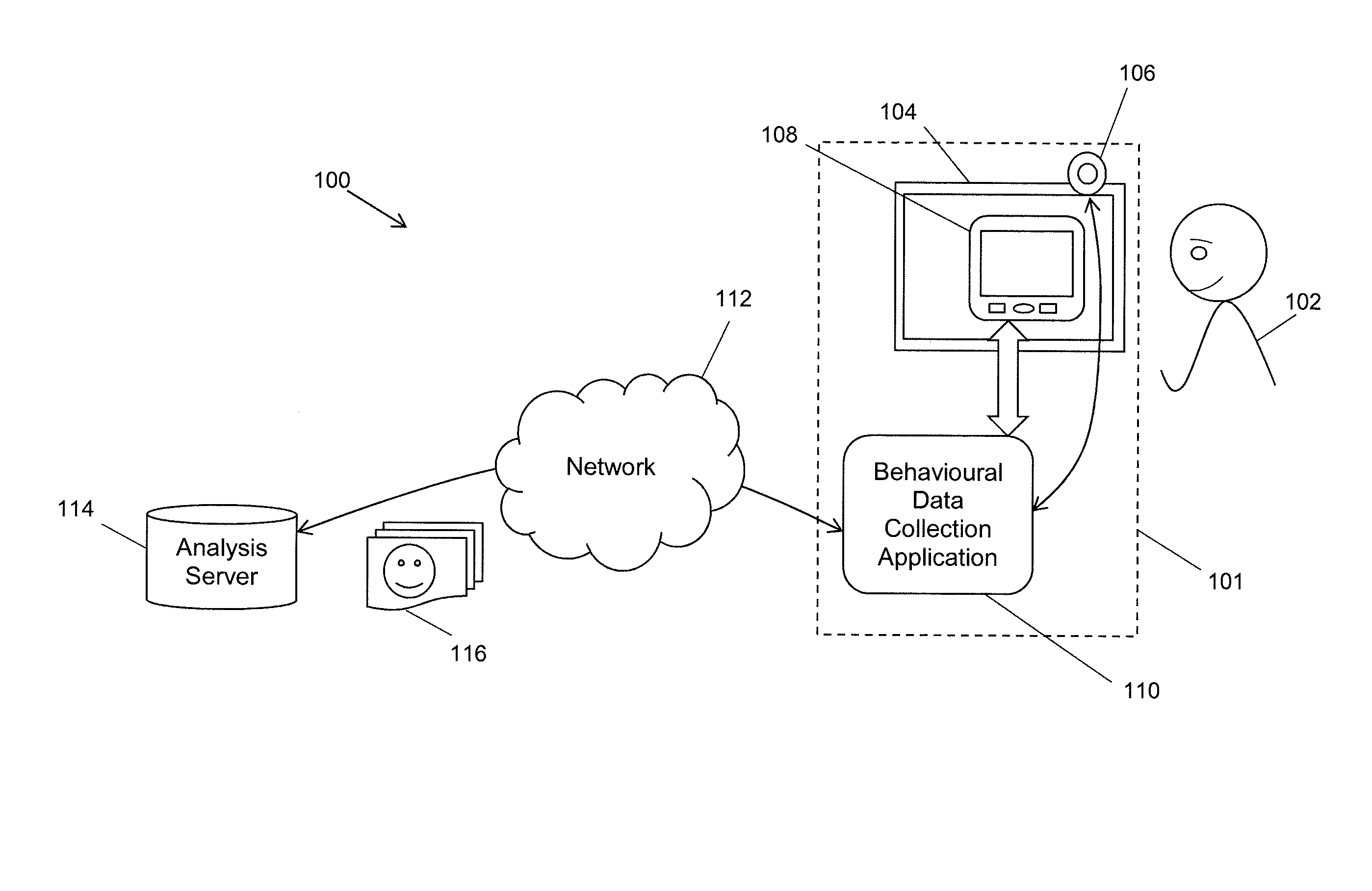
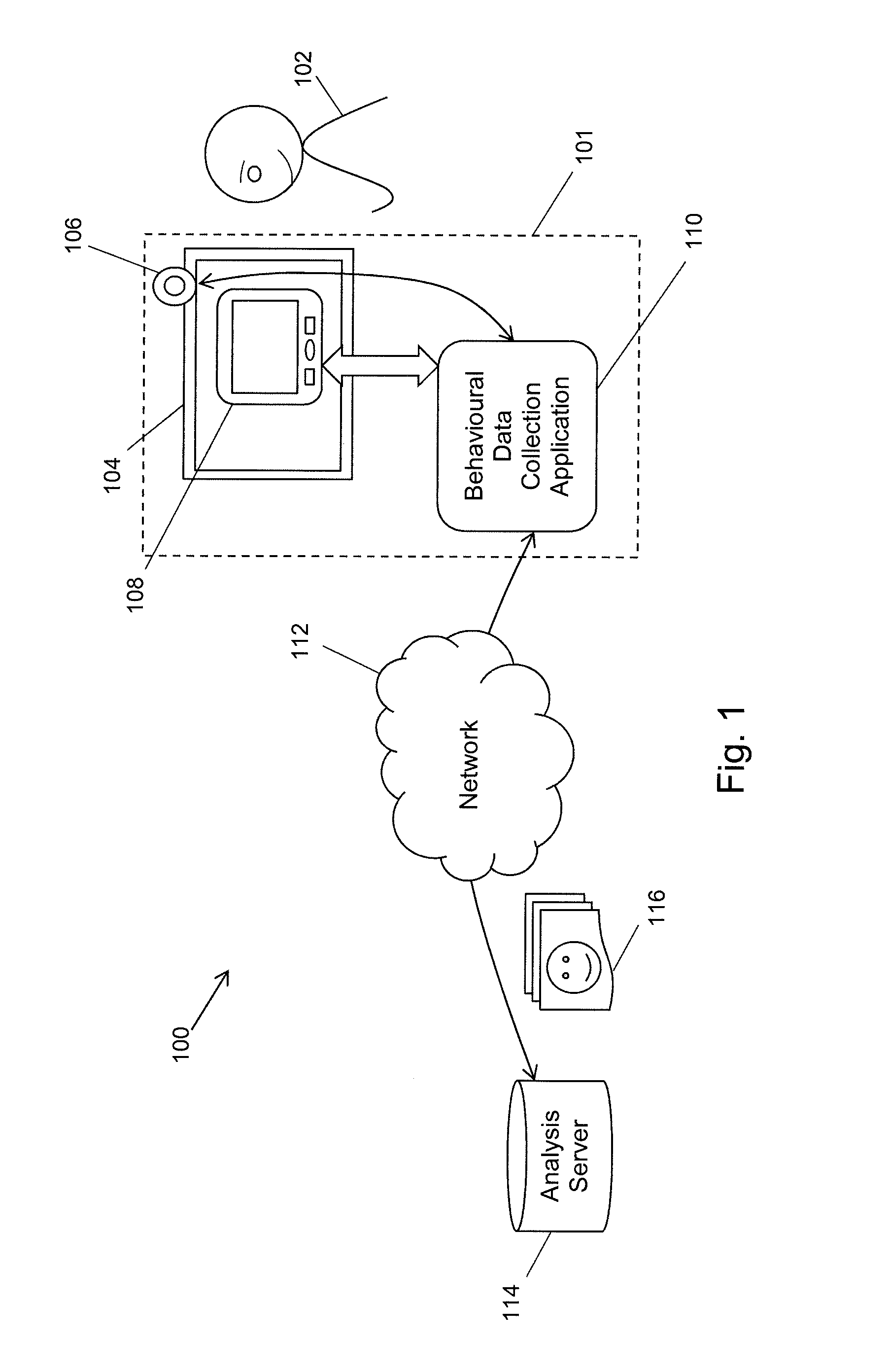
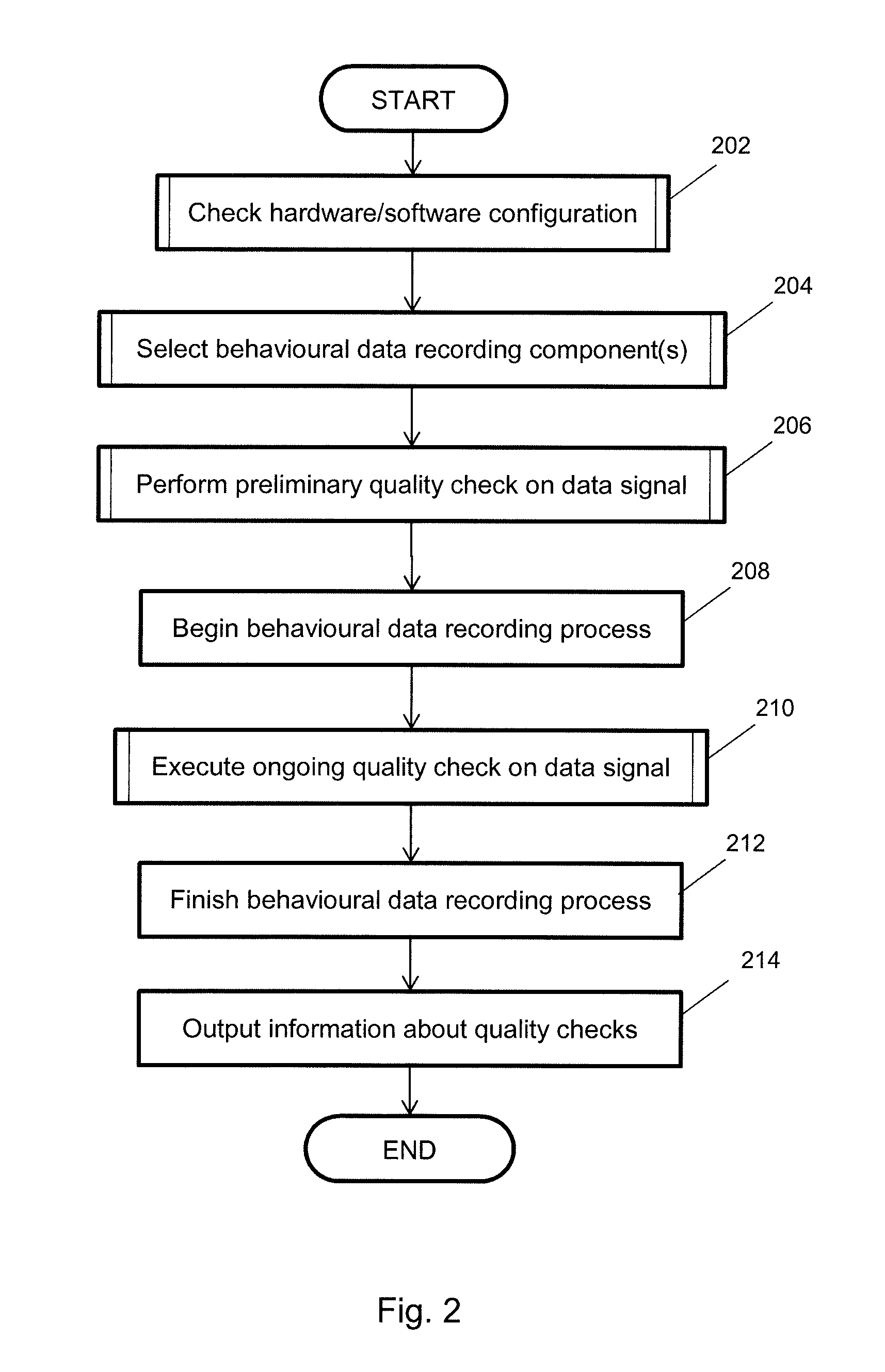
Method of quality analysis for computer user behavourial data collection processes
ActiveUS20160316271A1Good signalReduce generationBroadcast information monitoringSelective content distributionPresent methodComputer users
Embodiments of the present method comprise activating a data recording component on the computing device to receive information relating to the environment of the computer user and executing a quality check module in the computing device operative to analyse the environment of the computer user. The quality check module performs the steps of: assessing a received signal from the data recording component against a predetermined quality metric to ascertain if an informational content of the received signal meets a predetermined minimum quality to permit computer user behavioural data to be collected therefrom, determining and executing a responsive action where the received signal does not satisfy the quality metric, and initiating a computer user behavioural data collection process to computer user collect behavioural data during the interaction between the computer user and the computing device where the received signal satisfies the quality metric.
Owner:REALEYES OU
system for reading information transmitted from a transponder
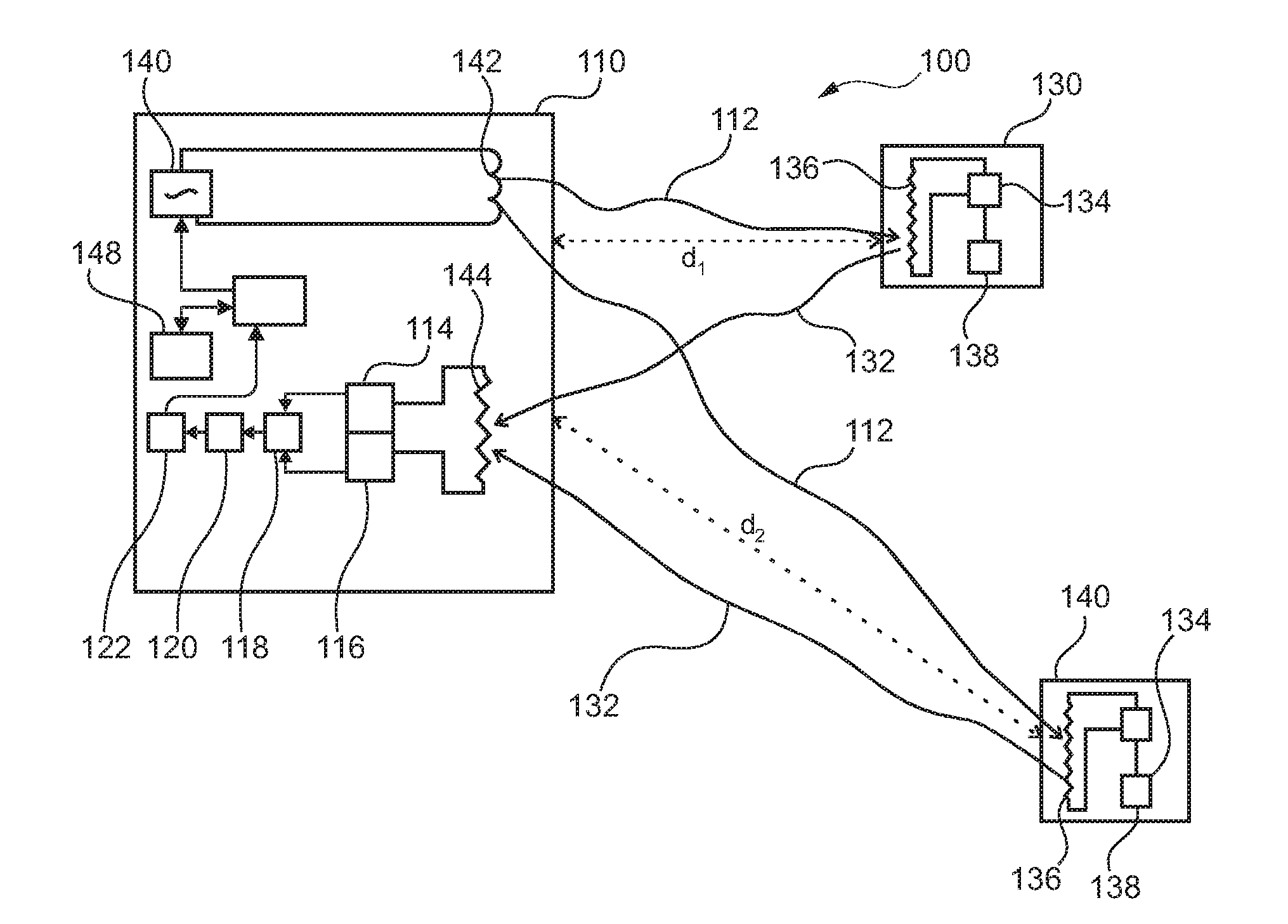
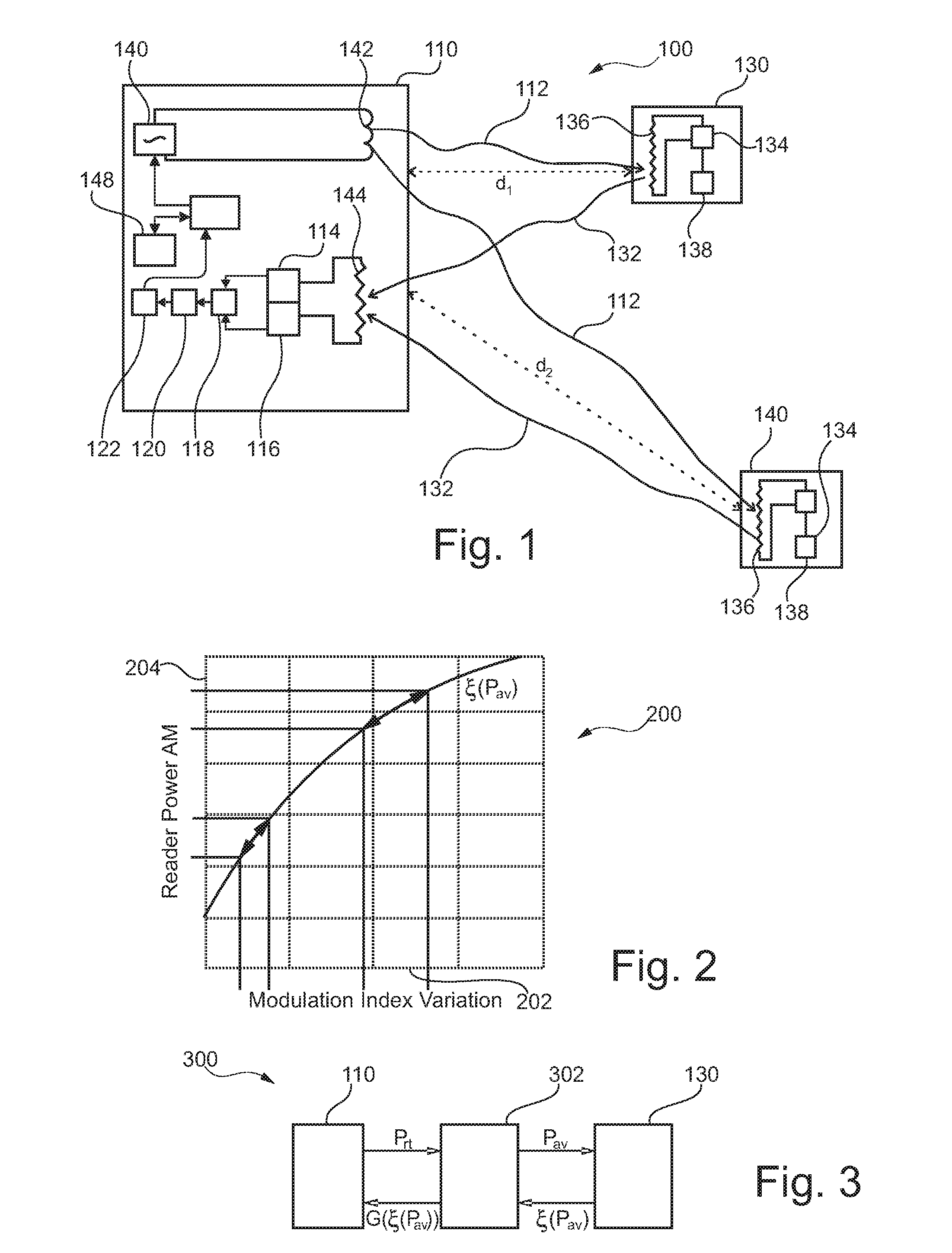
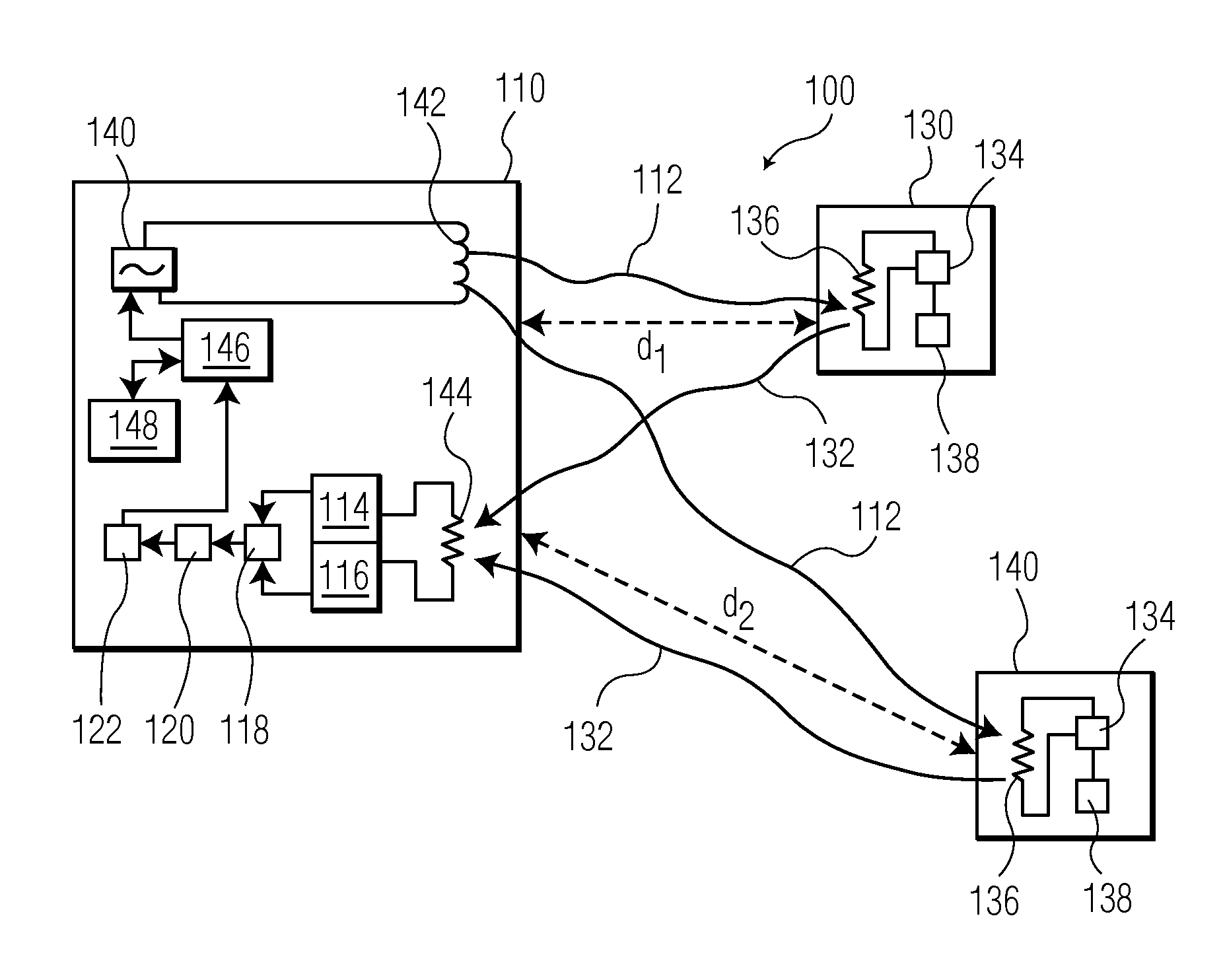
InactiveUS20110122015A1Save processing capabilityAvoid unnecessary processingPosition fixationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
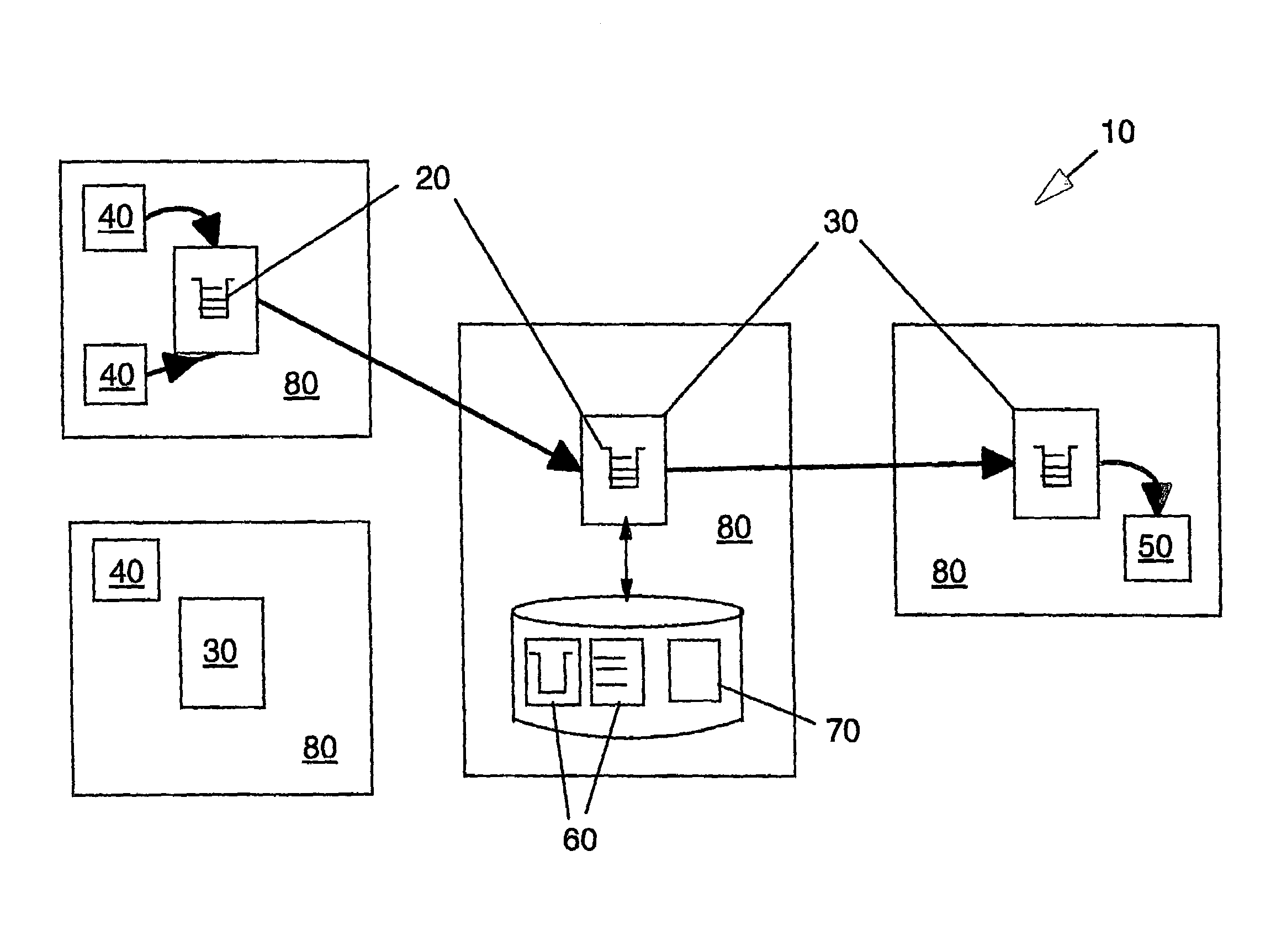
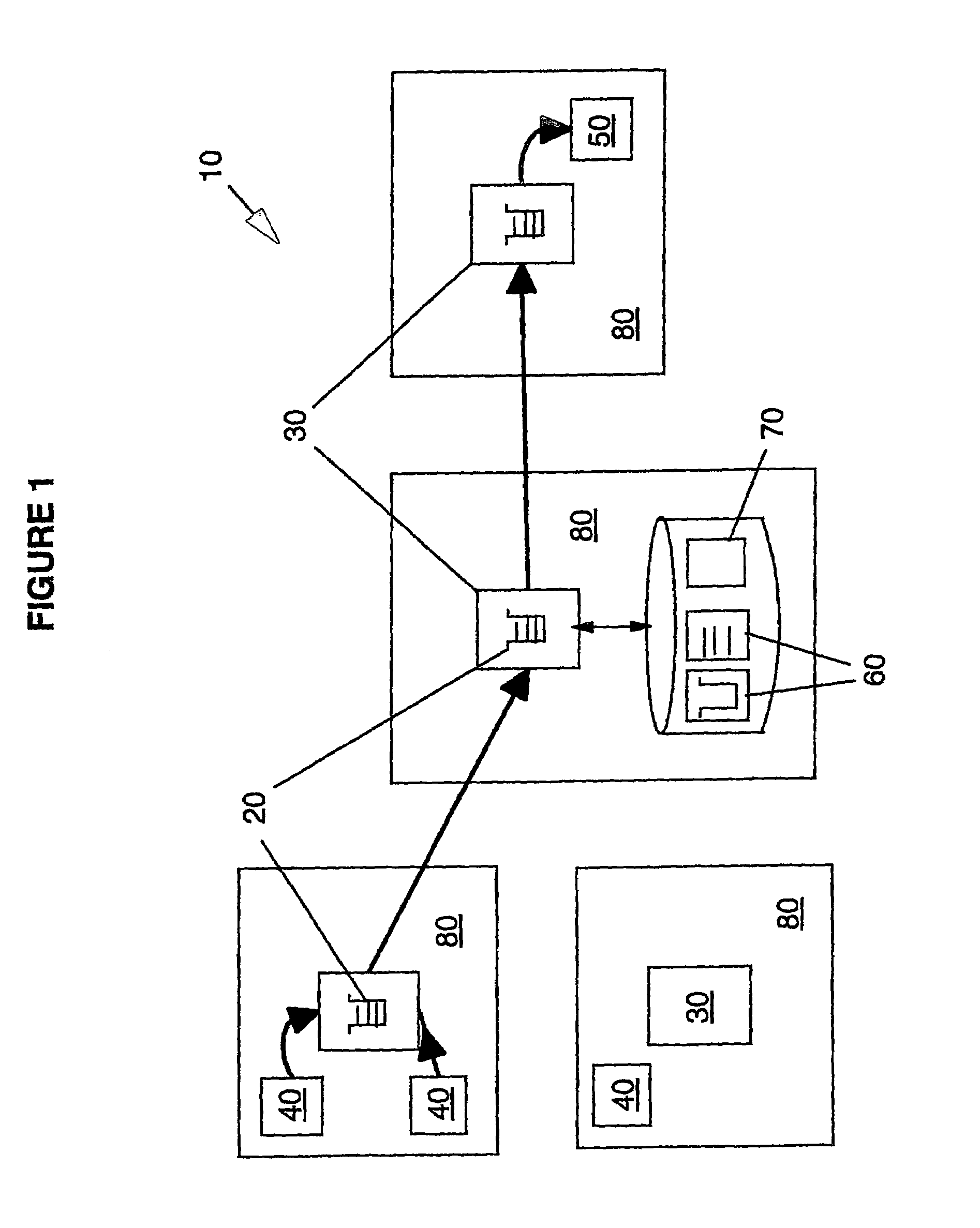
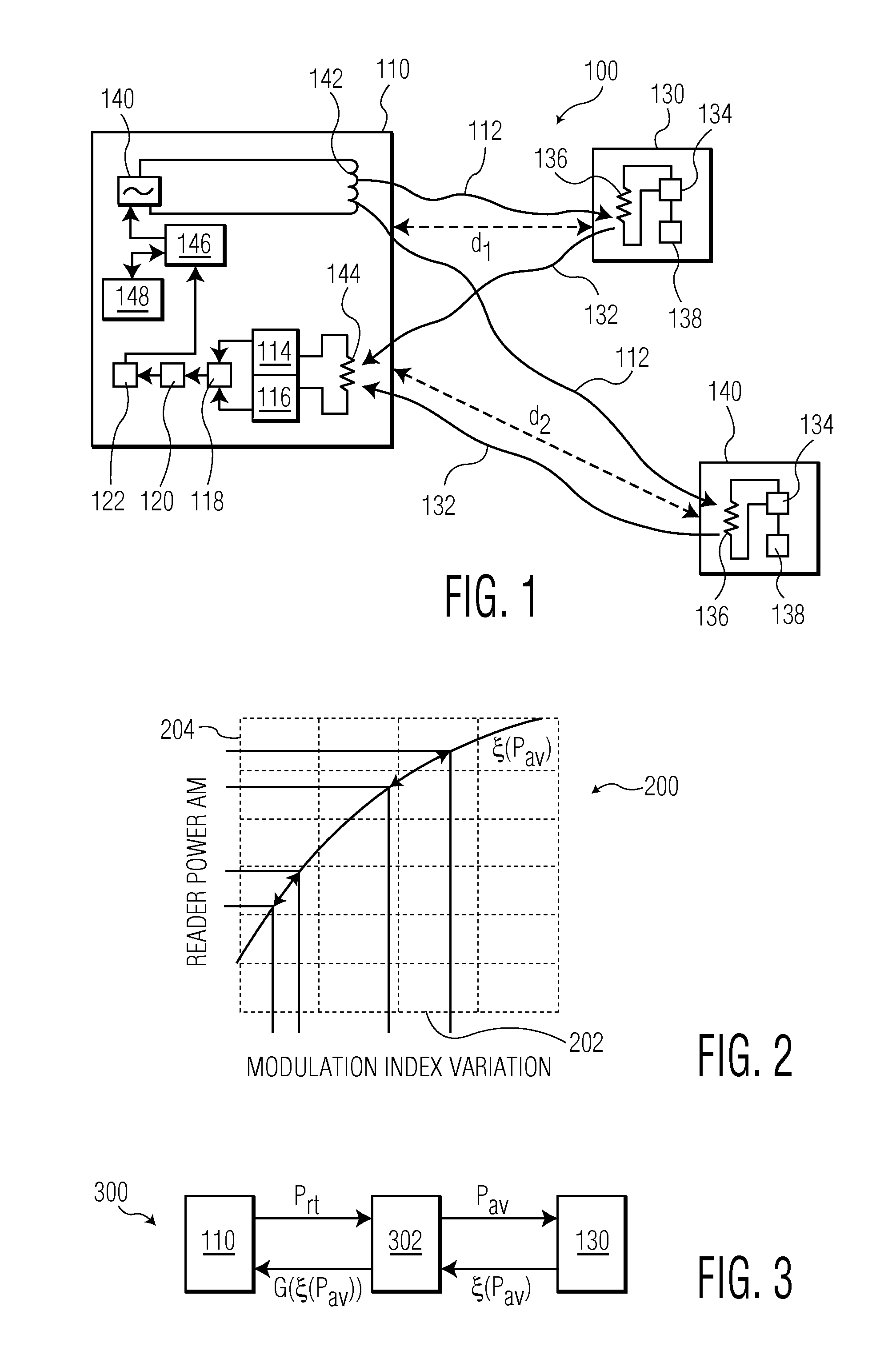
A reader device (110) for reading information transmitted from a transponder (130) via a backscatter signal (132) generated by the transponder (130) in response to a stimulus signal (112) generated by the reader device (110), the reader device (110) comprising a first power estimation unit (114) adapted for estimating a first power value indicative of the power of the stimulus signal (112) at a position of the transponder (130) by evaluating a power information included in the backscatter signal (132), a second power estimation unit (116) adapted for estimating a second power value indicative of the power of the backscatter signal (132) at a position of the reader device (110), and a distance estimation unit (118) adapted for estimating a distance (d1) between the reader device (110) and the transponder (130) based on the first power value and the second power value.
Owner:NXP BV
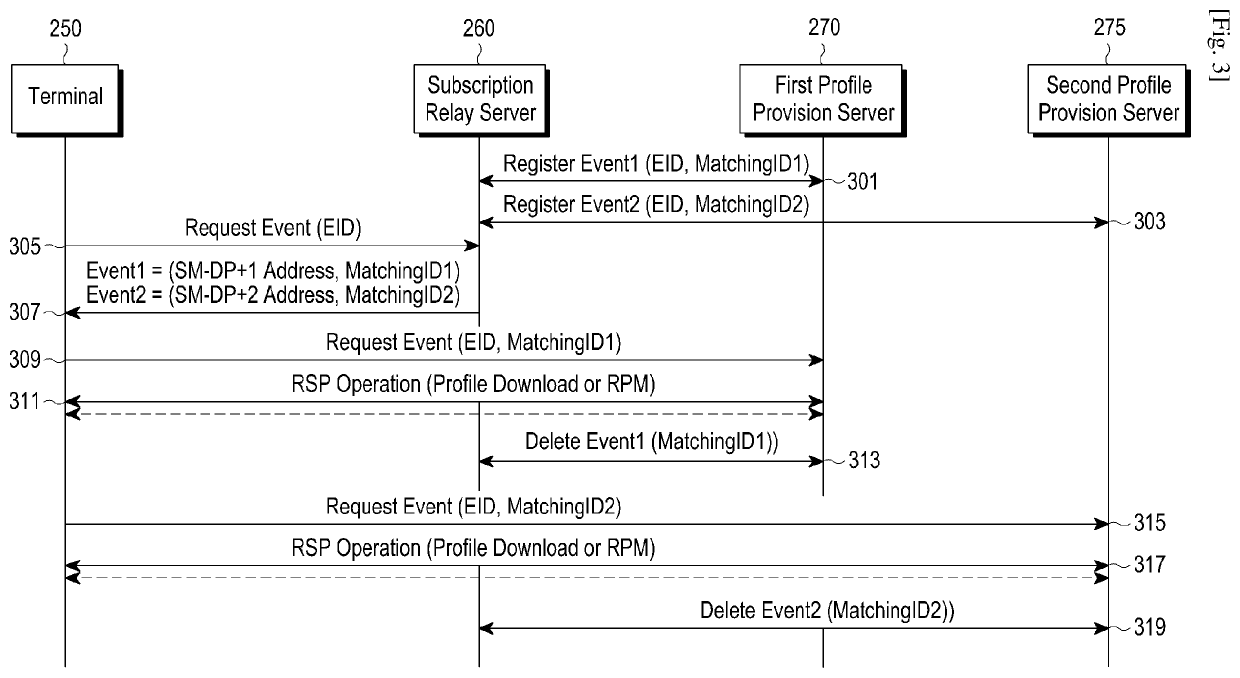
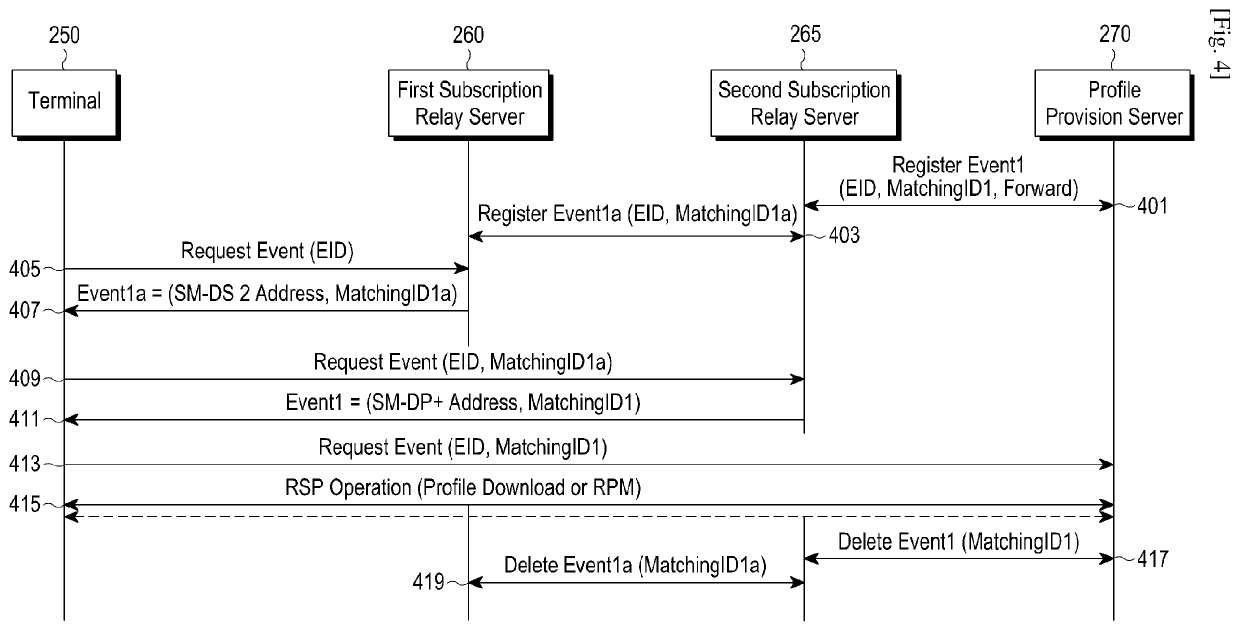
Method and apparatus for managing event in communication system
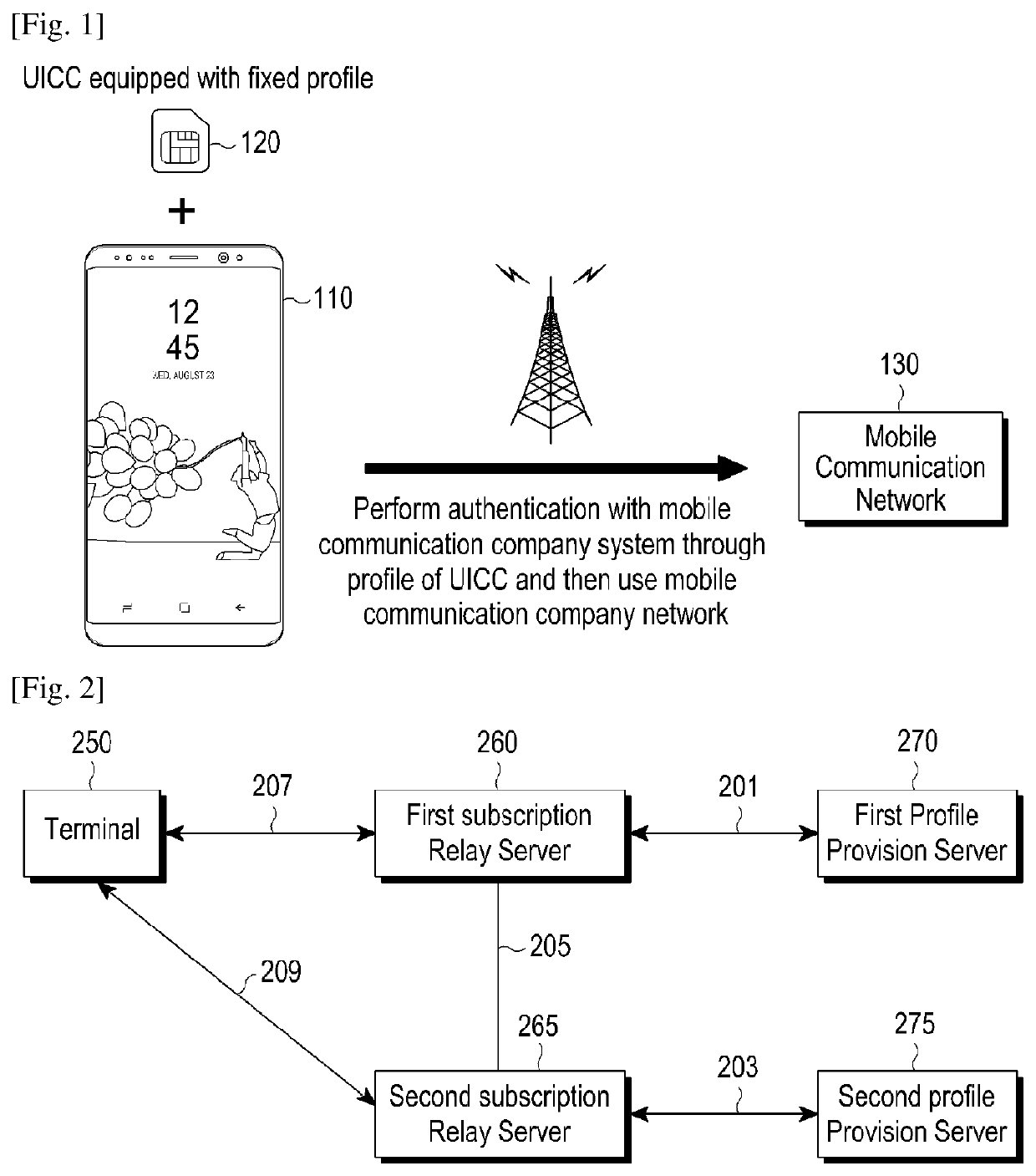
ActiveUS20200389785A1Reduce resource consumptionAvoid unnecessary processingTransmissionSecurity arrangementCommunications systemTransceiver
Disclosed is a terminal including a transceiver; and at least one processor, wherein the at least one processor transmits a first message which makes a request for an event to a subscription relay server, receives event-related information from the subscription relay server in response to the first message, transmits a second message which makes a request for an event to a profile provision server, based on the event-related information, and controls the transceiver to receive information related to event processing from the profile provision server in response to the second message.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hiding A Device
InactiveUS20100285749A1Save processing resourcesAvoid unnecessary processingAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesSuccessful completionTelecommunications
The object of the invention is a method where a first communications device (10) and a second communications device (20), previously unknown to each other, communicate with each other wirelessly using short-range RF technology, said second communications device being at a certain moment of time in a first mode where the address of said second communications device is determinable by means of an inquiry wirelessly sent to it. In the method, the first communications device (10) sends (31) a first message in order to determine the address of said second communications device, said second communications device (20) receives (32) the first message, and said second communications device (20) generates and sends (33) to the first communications device a second message in response to the first message, the second message containing the address of said second communications device. In the method, a connection establishment process (35-38) is executed to establish a connection between the first communications device and said second communications device. During the connection establishment process, or in response to successful completion of the connection establishment process, at least one of said first and second communications devices (10, 20) switches (40) from said first mode into a second mode, in which second mode, the communications device that has switched into said second mode does not respond to messages arriving at it which have been sent to discover the address of the communications device that has switched into said second mode.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
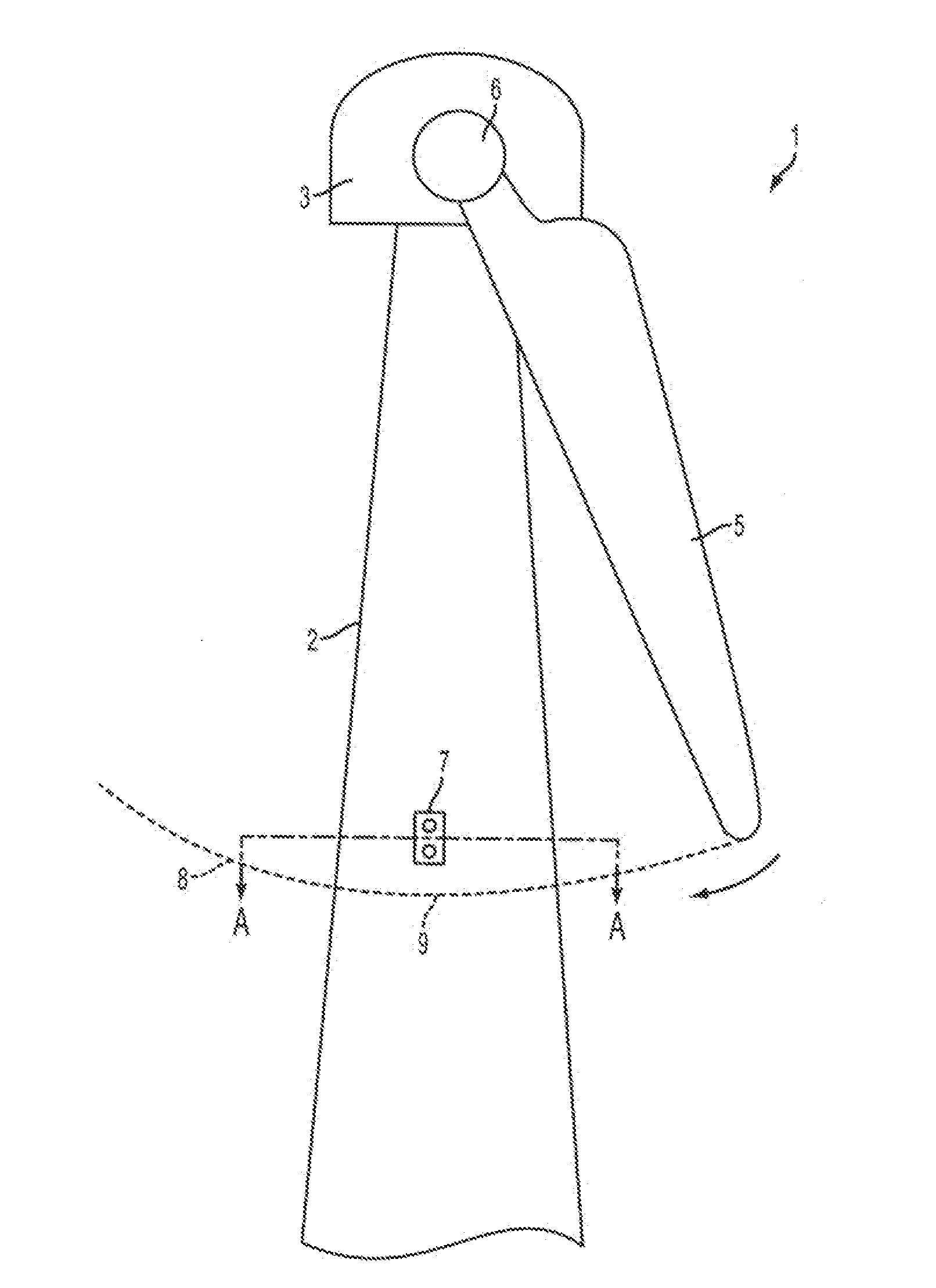
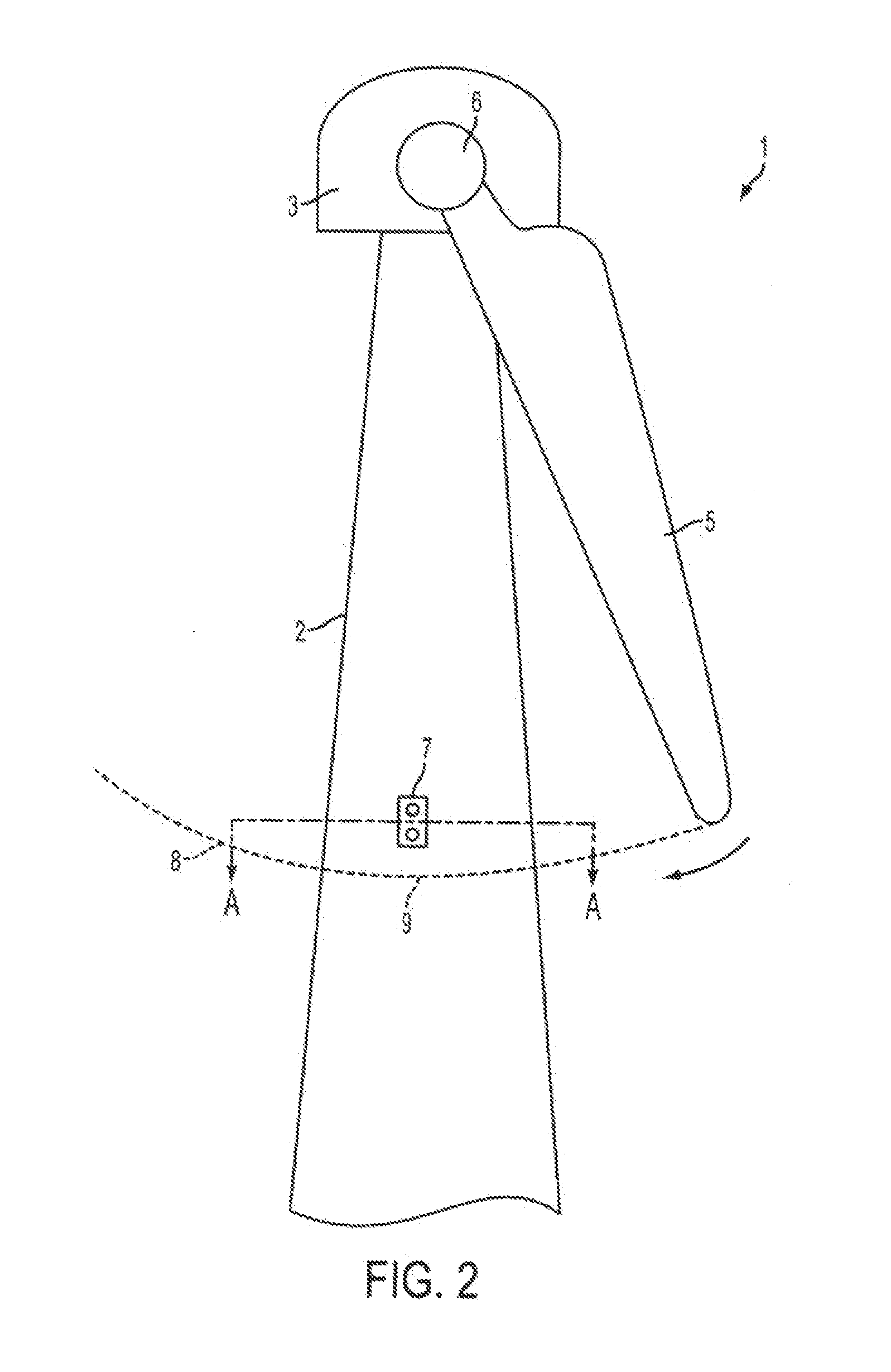
Wind turbine blade vibration detection and radar calibration
ActiveUS20160215763A1Reduces manufacturing and maintenance costEasy to replaceAvoid excessive blade deflectionWind motor controlTurbine bladeTower
A wind turbine is provided, having a wind turbine tower and at least one rotatable blade, and further comprising a system for measuring rotor blade vibration of said wind turbine. The system comprises at least one Doppler radar unit operatively configured to emit and receive radar signals, the radar unit being mounted on the wind turbine tower at a position above the lowest position of the at least one blade, the radar unit being positioned so as to measure reflections of an emitted radar signal from the turbine blade. A processing unit is configured to receive measurement data from the radar unit and to determine, by analysis of Doppler shift in received radar signals relative to transmitted signals due to movement of the blade towards or away from the turbine tower, the velocity of the blade in the direction towards or away from the turbine tower. Using a radar unit to measure blade velocity allows a determination to be made of the vibrations occurring in the blade without needing an internal sensor in the blade. This reduces manufacturing and maintenance costs of the blades since sensors in the blades will not need to be replaced, and sensors positioned on the tower are easier to replace in the field.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
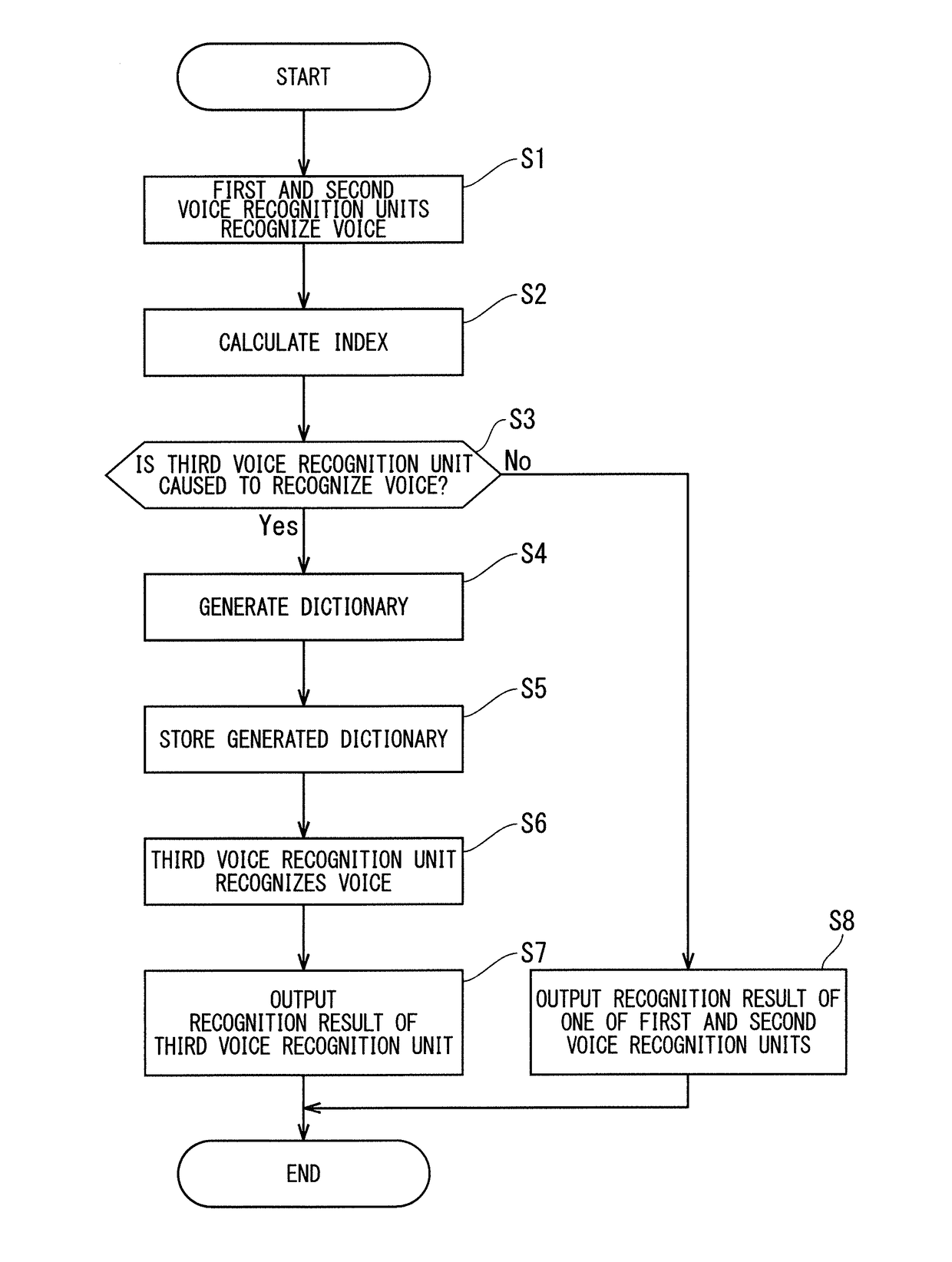
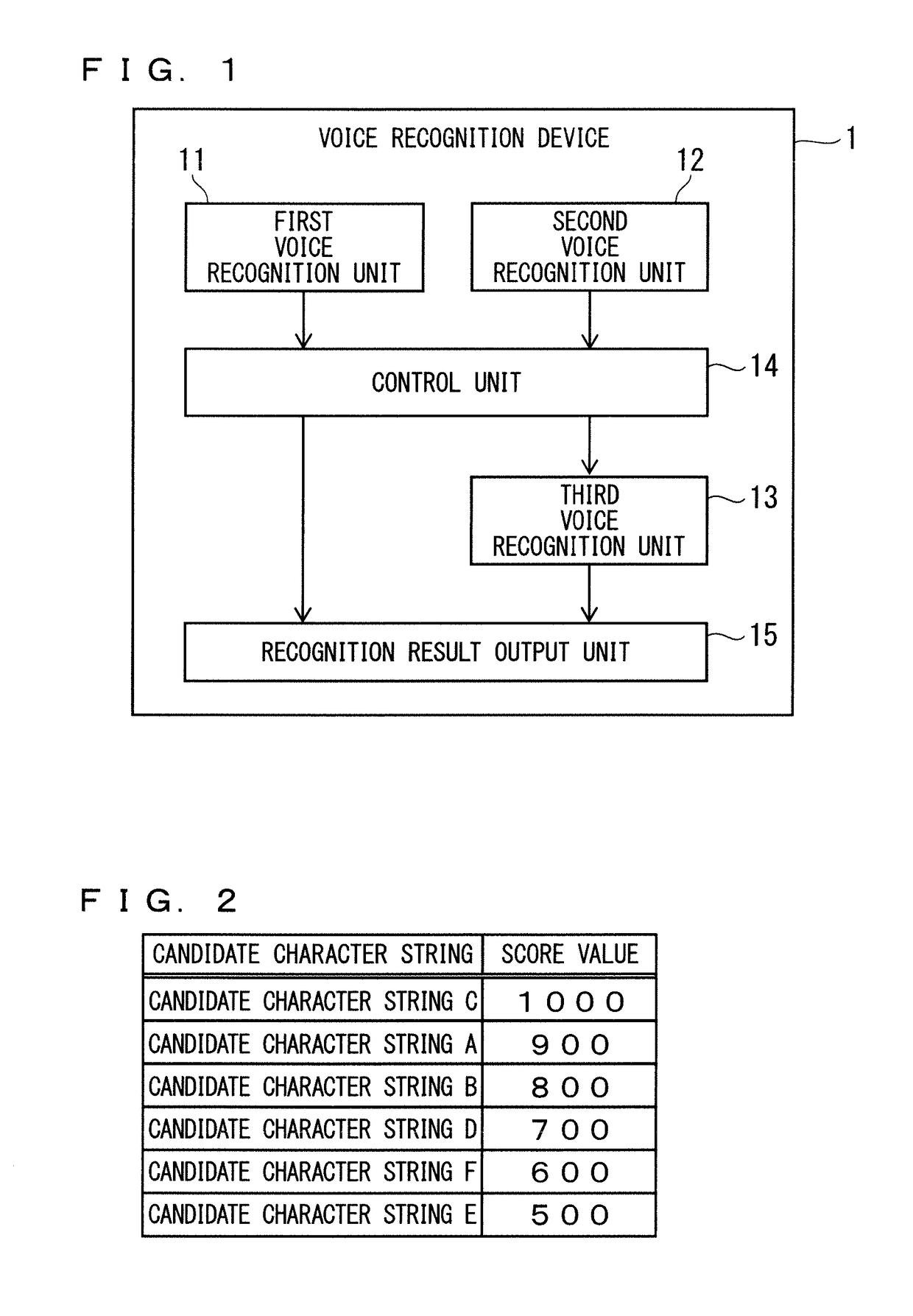
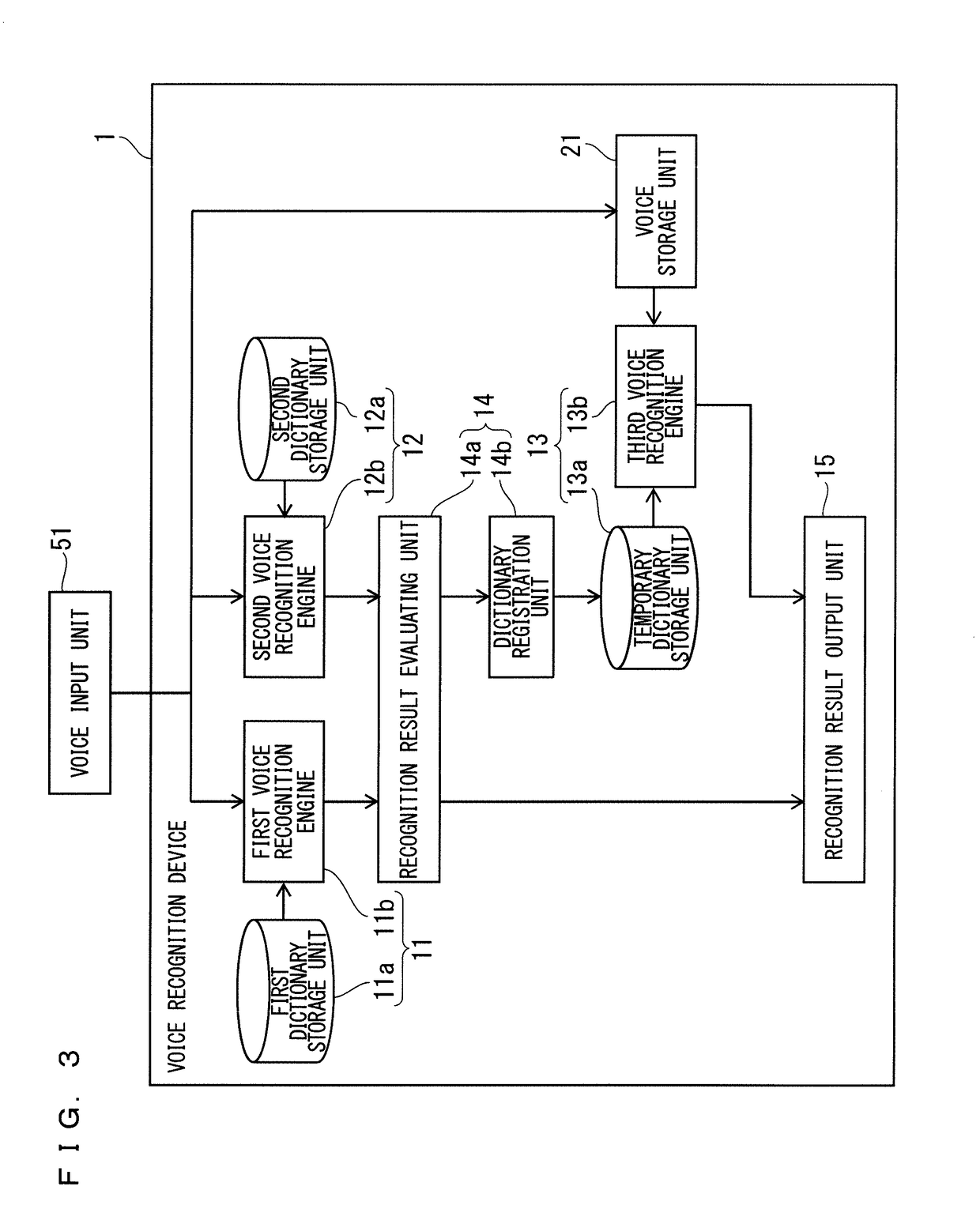
Voice recognition apparatus and voice recognition method
ActiveUS20170140752A1Prevent unnecessary processAvoid unnecessary processingSpeech recognitionSpeech soundSubvocal recognition
An object is to provide a technique which can provide a highly valid recognition result while preventing unnecessary processing. A voice recognition device includes first to third voice recognition units, and a control unit. When it is decided based on recognition results obtained by the first and second voice recognition units to cause the third voice recognition unit to recognize an input voice, the control unit causes the third voice recognition unit to recognize the input voice by using a dictionary including a candidate character string obtained by at least one of the first and second voice recognition units.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
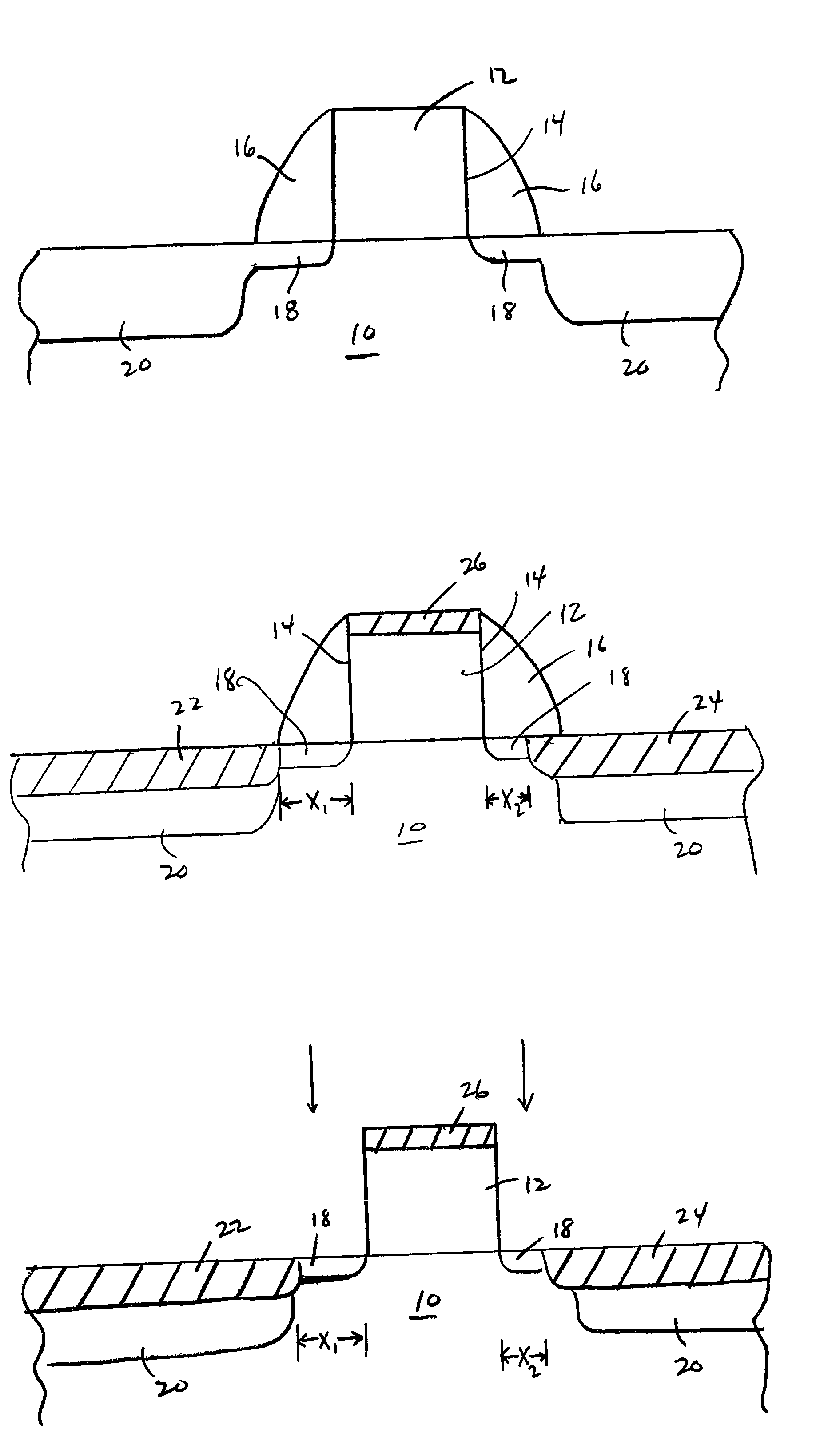
Method for detecting silicide encroachment of a gate electrode in a semiconductor arrangement
ActiveUS6955931B1Accurate detectionAvoid unnecessary processingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideSemiconductor
A method of detecting silicide encroachment to the sidewalls of a gate electrode includes forming silicide at a device, with sidewall spacers defining a desired separation of the silicide from the sidewalls of the gate electrode. After silicide formation, the sidewall spacers are removed and line-of-sight monitoring is performed of the region previously obscured by the sidewall spacers, thereby permitting detection of silicide encroachment.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
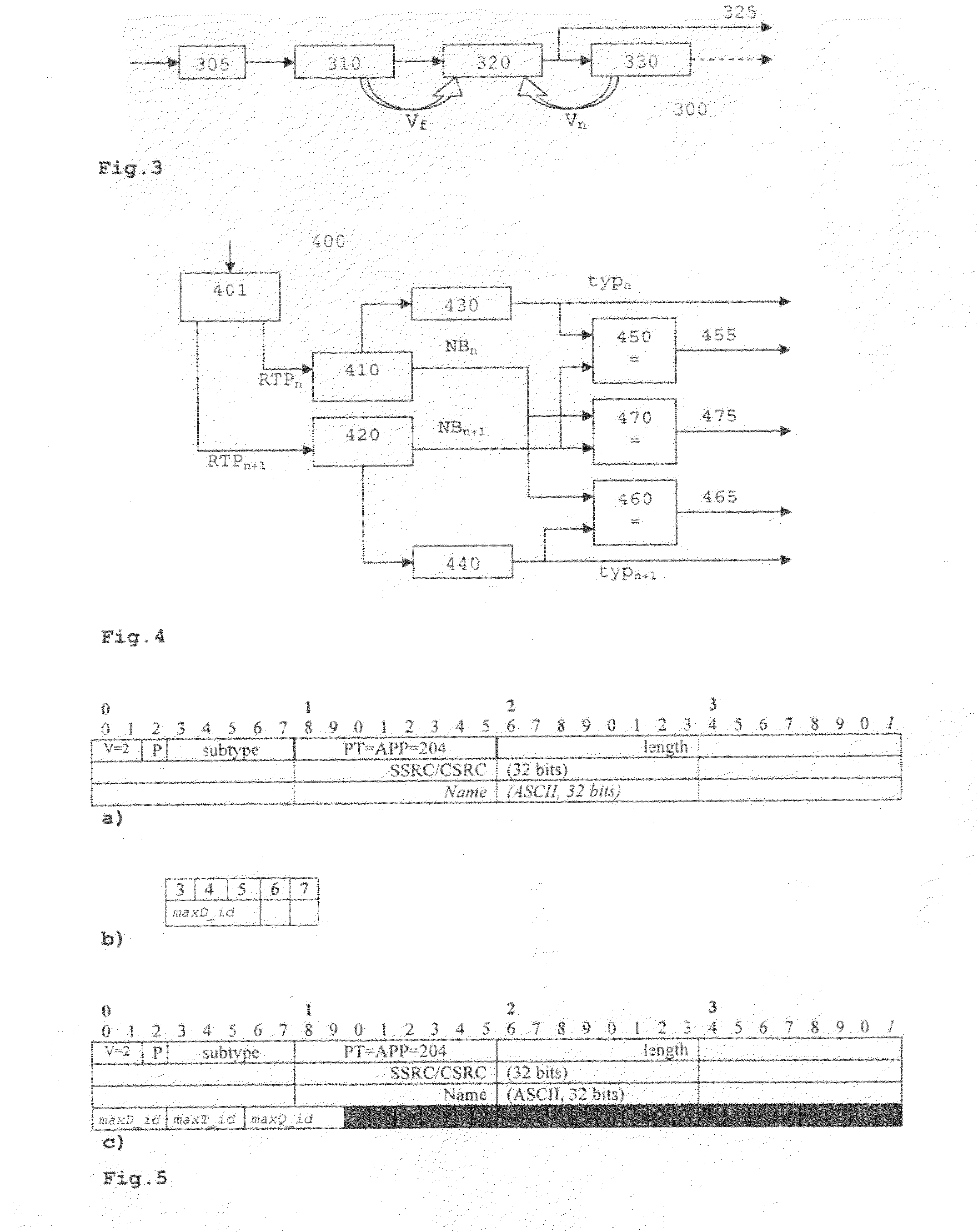
Data stream comprising RTP packets, and method and device for encoding/decoding such data stream
InactiveUS20100020865A1Avoiding unnecessary processingAvoid unnecessary processingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionError concealmentSyntax
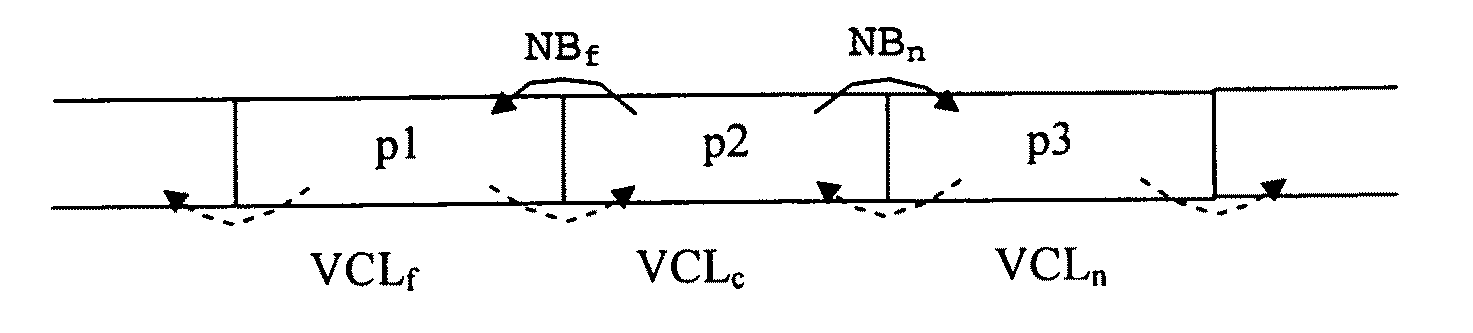
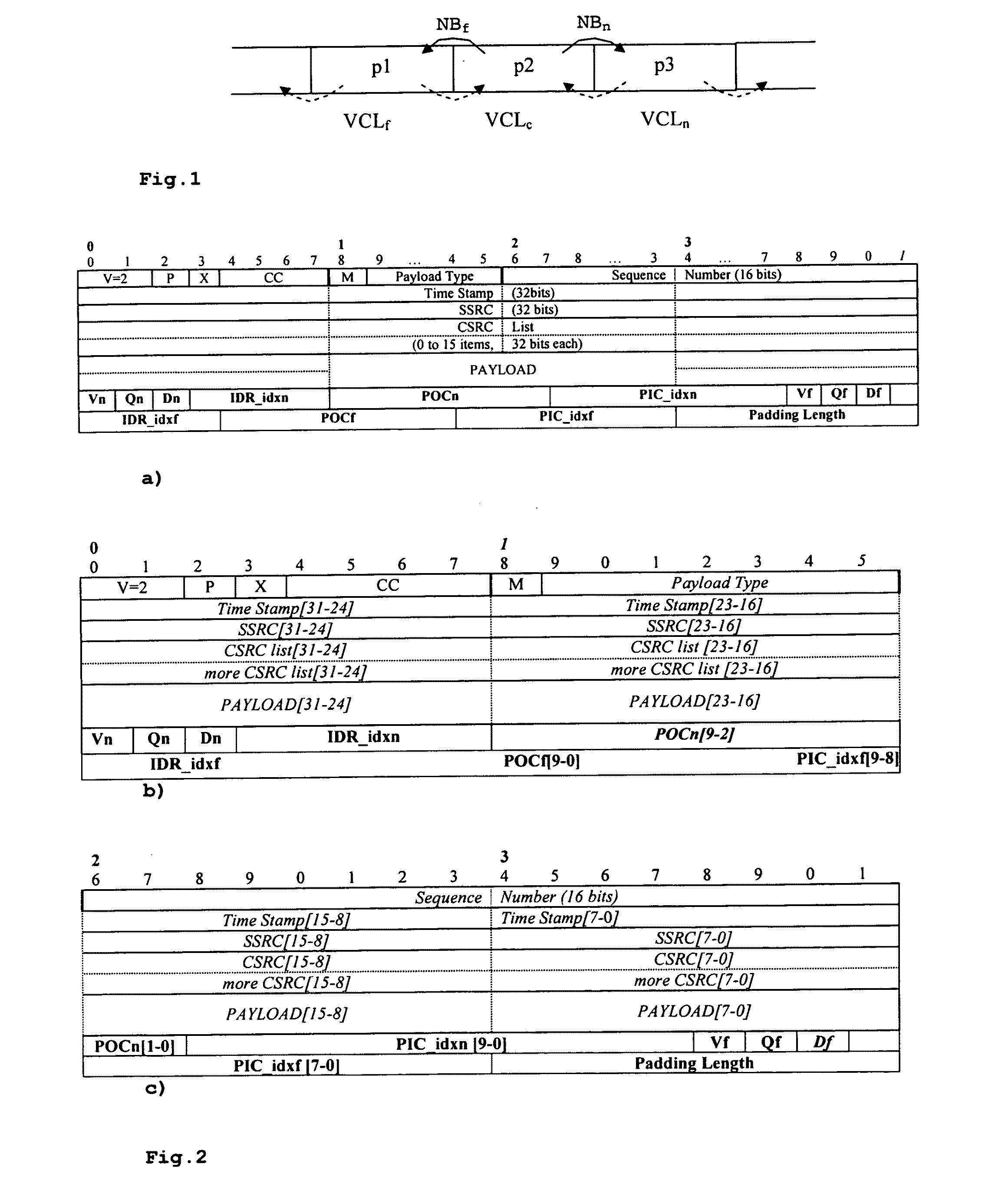
In the case of packet loss during transmission over an error-prone transmission channel, some decoders may perform error concealment. In real-time systems, application decoders must handle the data loss alone and find out which data are missing. A special syntax within a packet-based framework is provided which is based on identifying and indicating the relationship between RTP packets and the application layer data they carry, before the packets are fed to the multi-layer application decoder. This helps the decoder to employ proper error concealment techniques in time, and prevents unnecessary processing in the decoder. A data stream comprises RTP packets containing application data of a multi-layer application, wherein an RTP packet (p2) contains two kinds of application layer information (NBf, NBn): one relating to the next RTP packet (p3), and one relating to the previous RTP packet (p1). In case of packet loss, the decoder can immediately determine the amount and type (VCLx) of missing data.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Feedback cancellation in a sound system
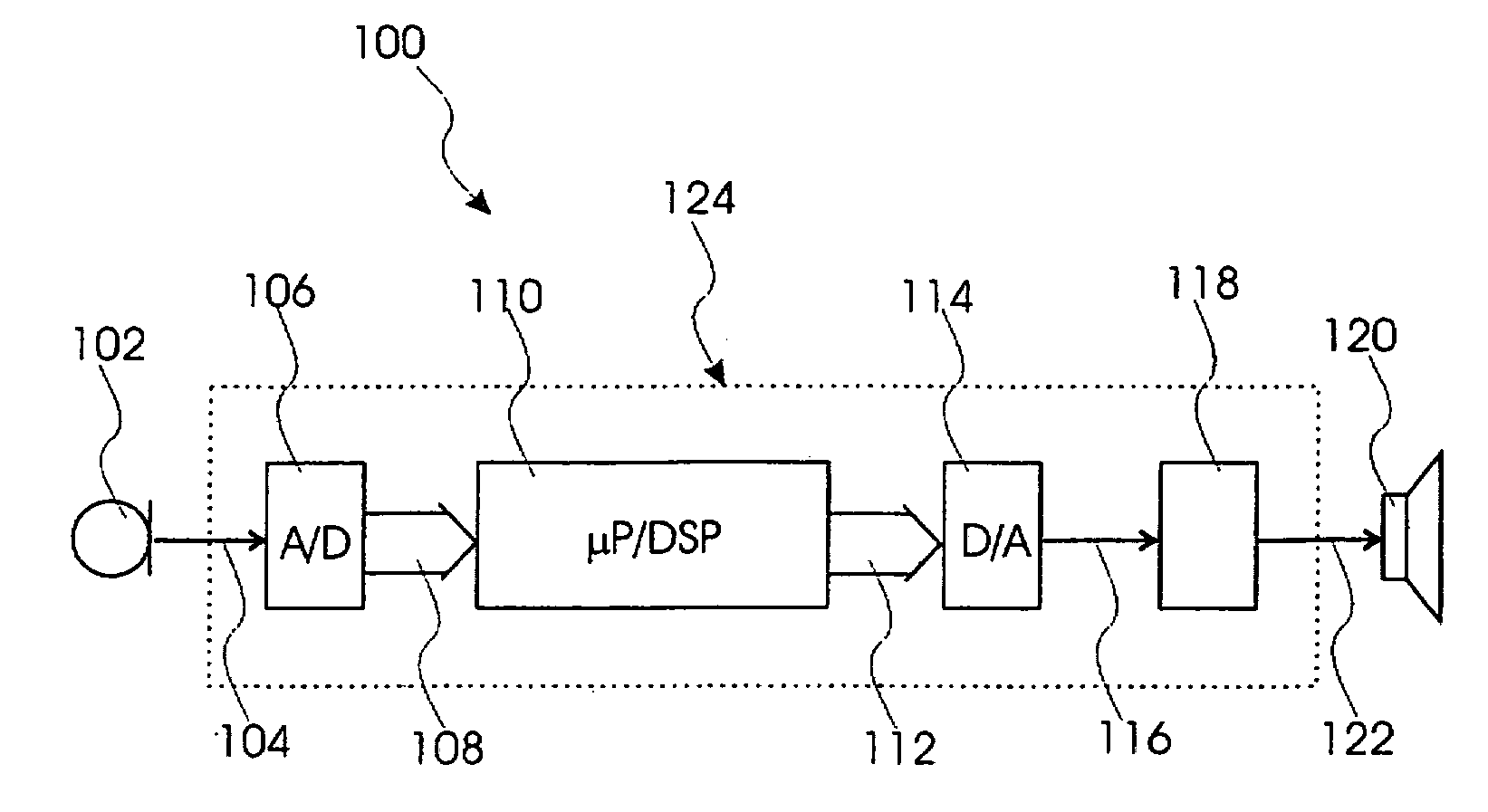
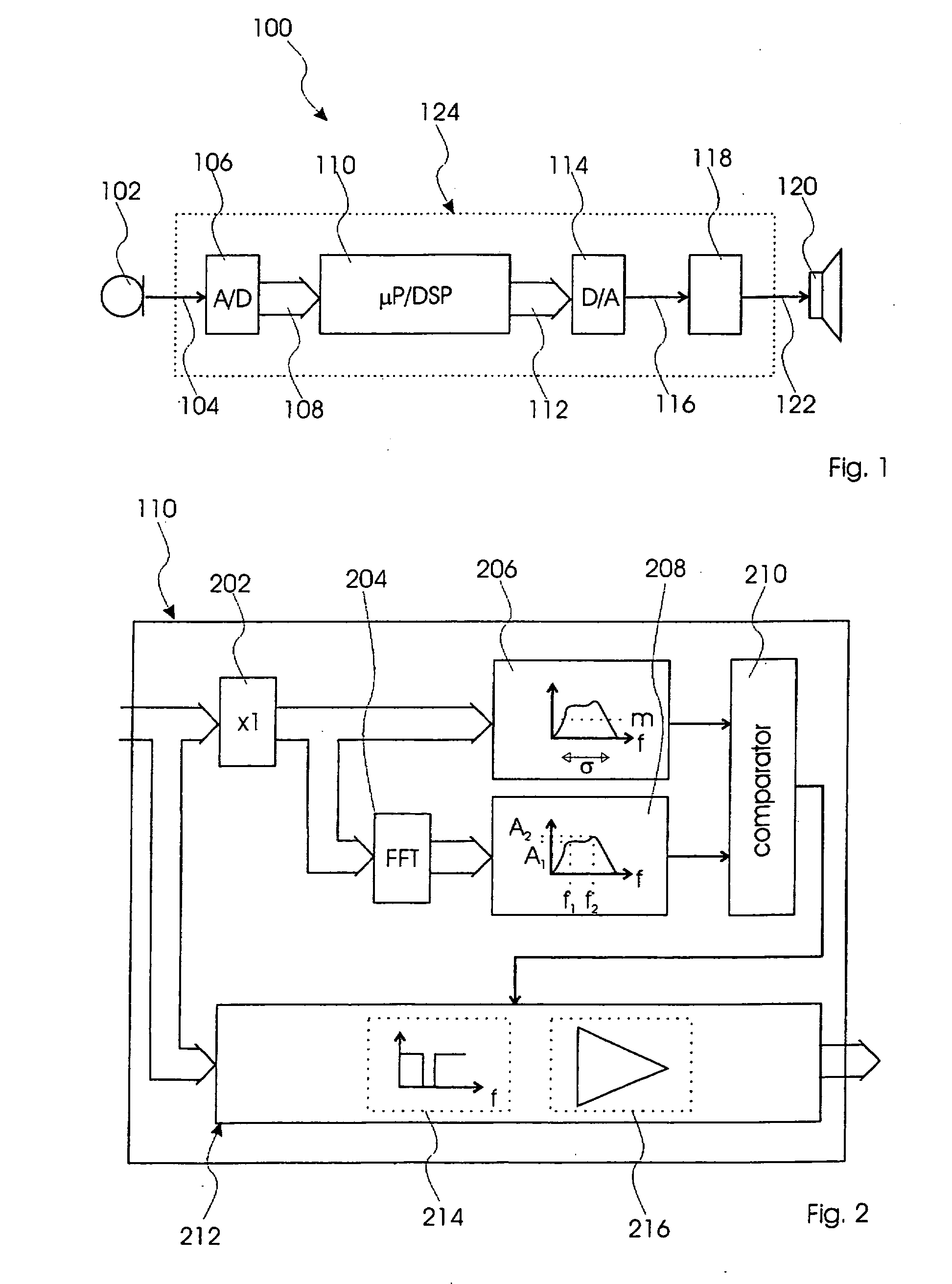
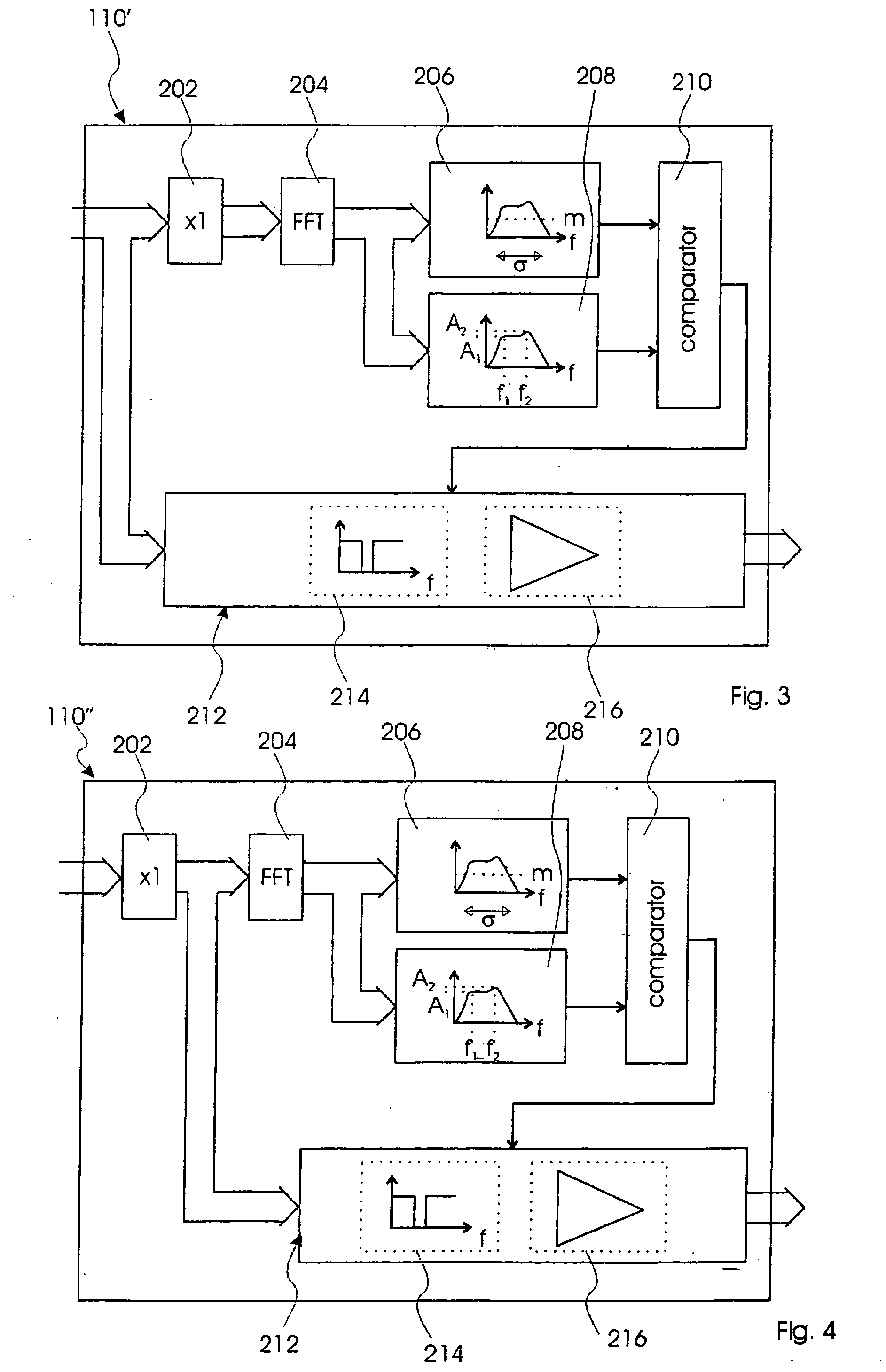
InactiveUS20080085013A1Avoid unnecessary processingTransducer acoustic reaction preventionDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlControl signalPeak value
This invention relates to a sound system and method for processing acoustical sound. The sound system comprises a microphone for converting an acoustical sound to an electrical sound signal, a processor for processing the sound signal and for generating a processed sound signal, and a speaker for converting the processed sound signal to a processed acoustical sound. The processor comprises a calculating unit for calculating a threshold value based on mean magnitude and standard deviation of the sound signal, a FFT unit for transforming the sound signal into frequency domain, a peak identification unit for identifying a peak in the sound signal in frequency domain and for generating a peak signal, a comparator for comparing the threshold value with the peak signal and for generating a control signal identifying frequency of said peak, and a programmable notch-filter unit receiving said control signal and filtering out a bandwidth of the sound signal in accordance with the control signal thereby generating the processed sound signal.
Owner:PHONIC EAR
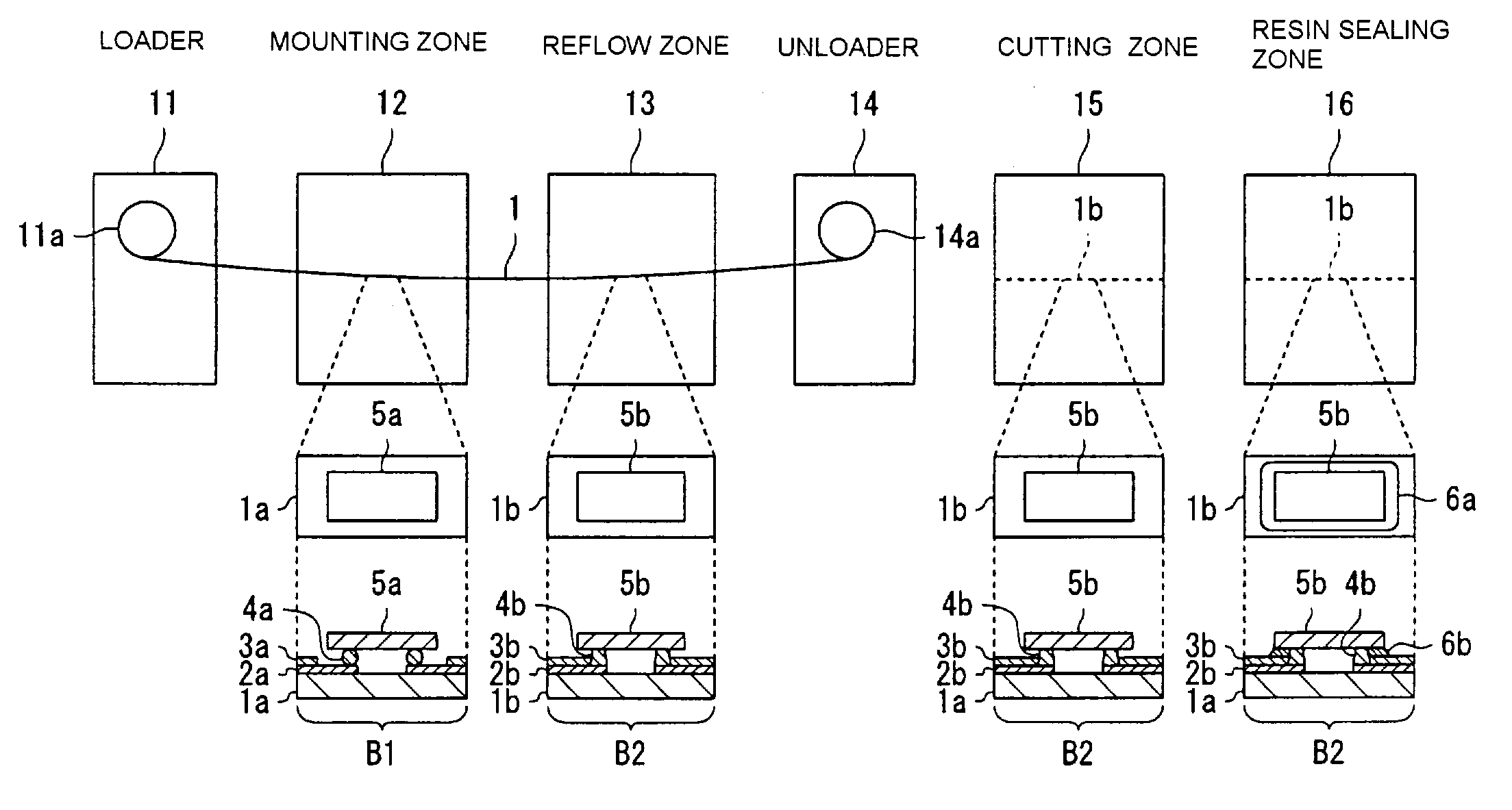
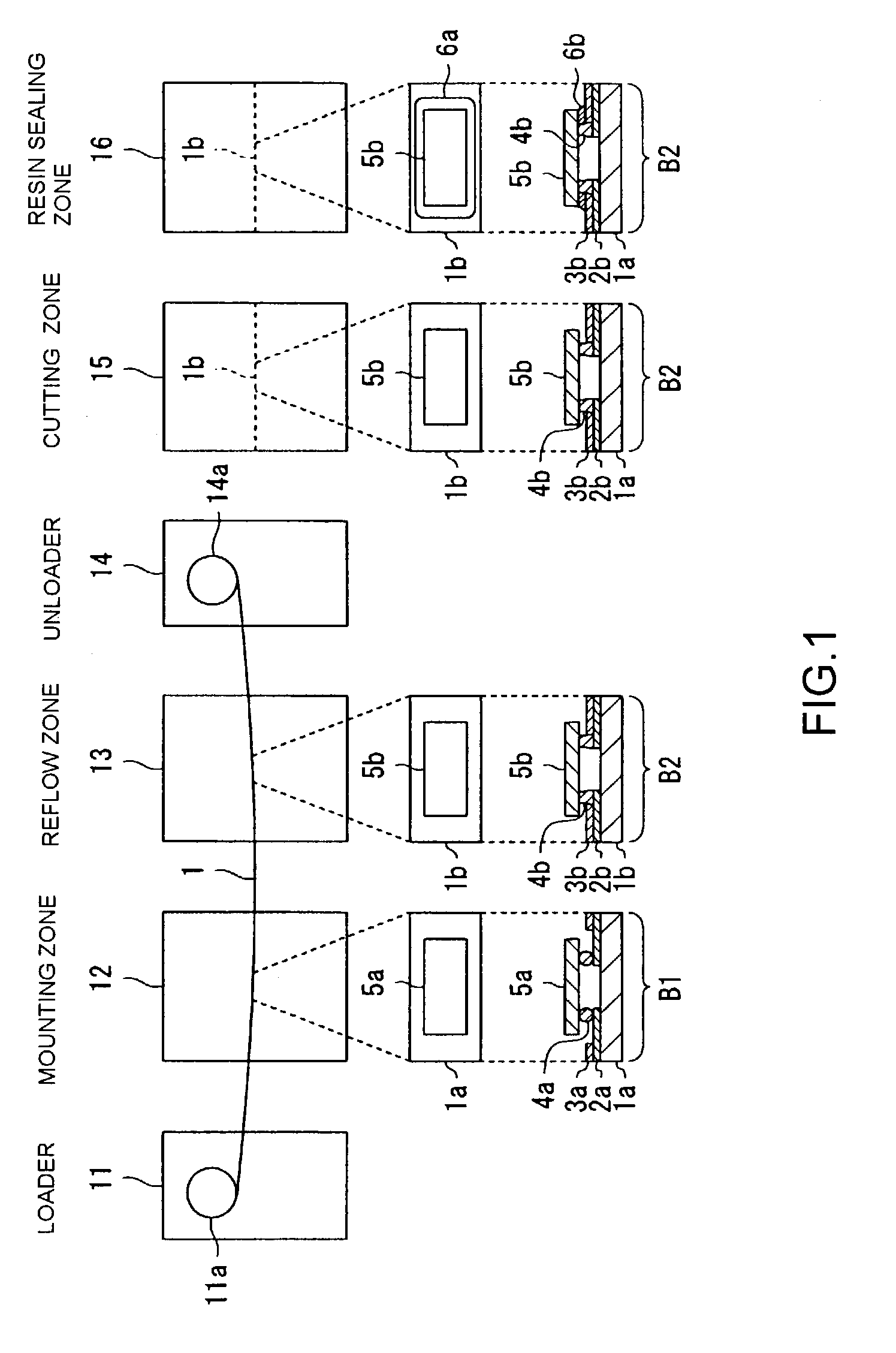
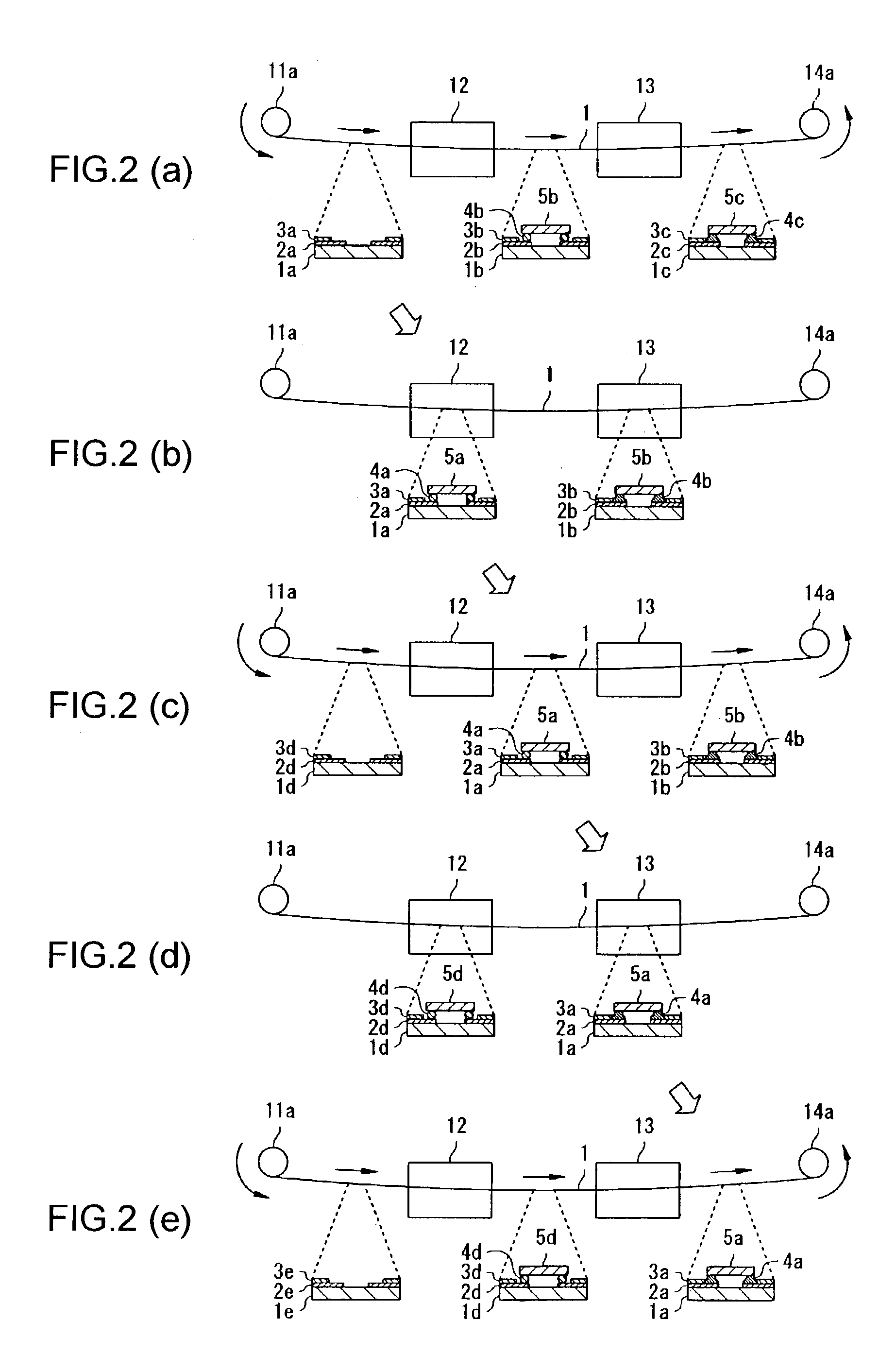
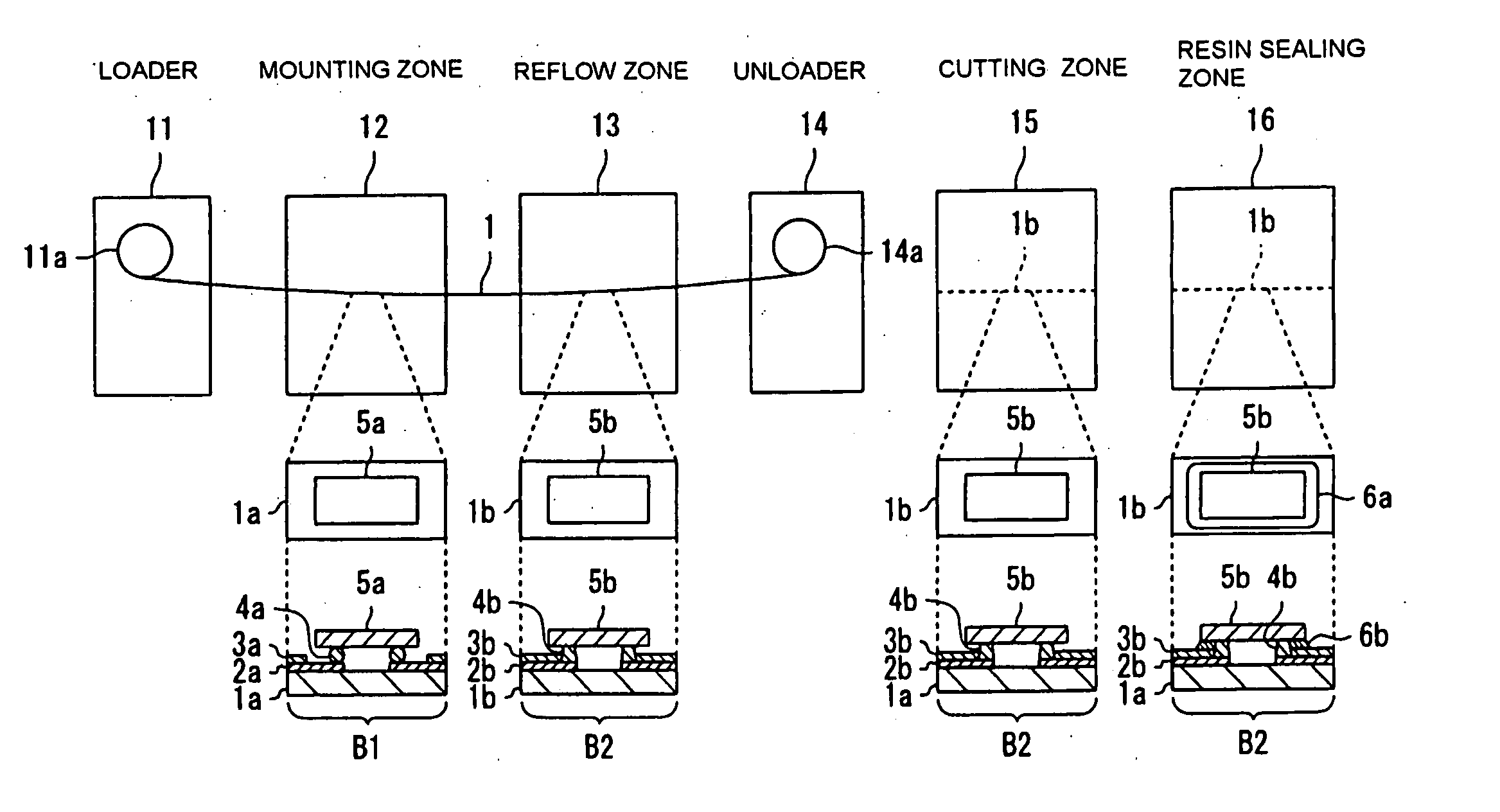
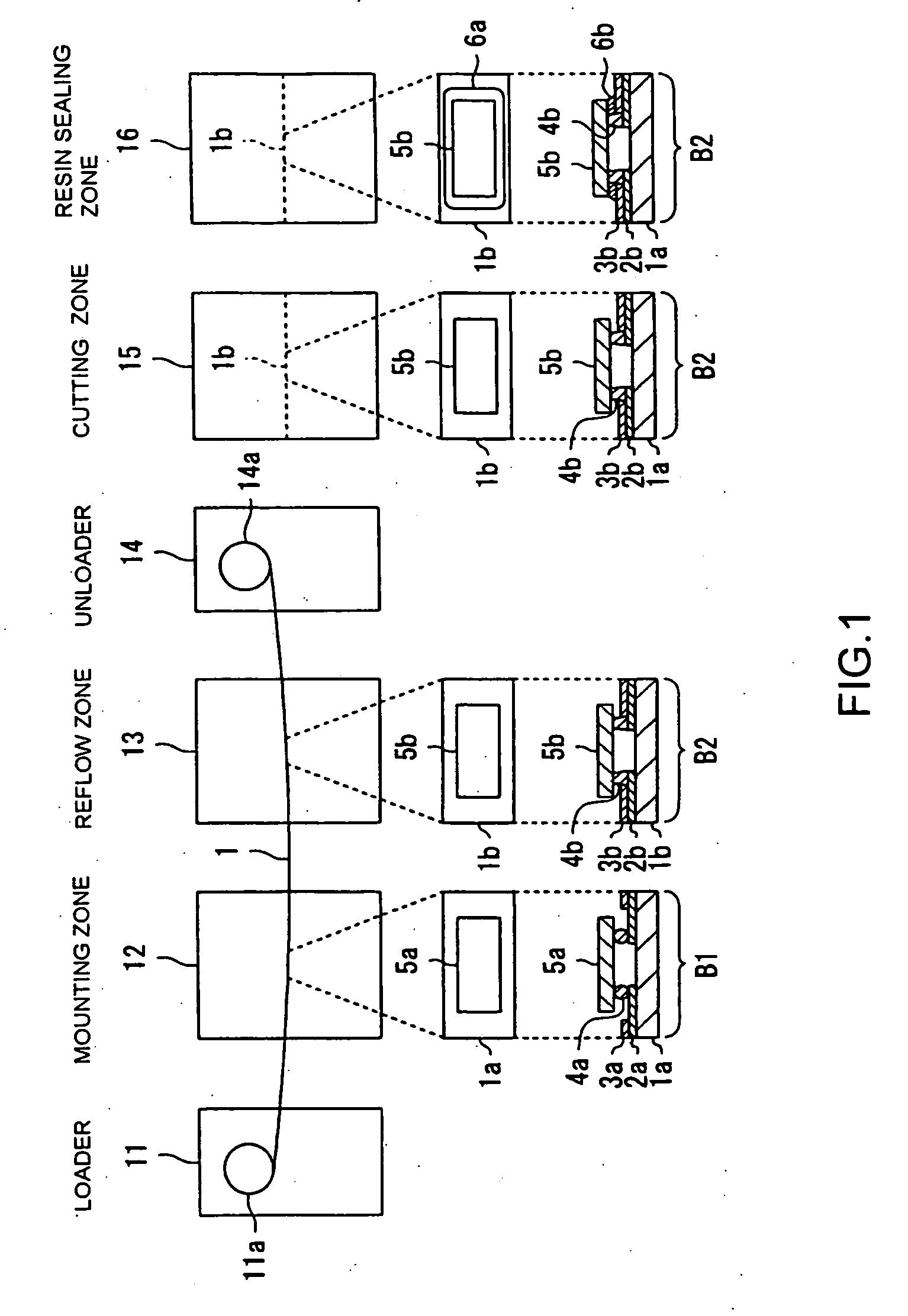
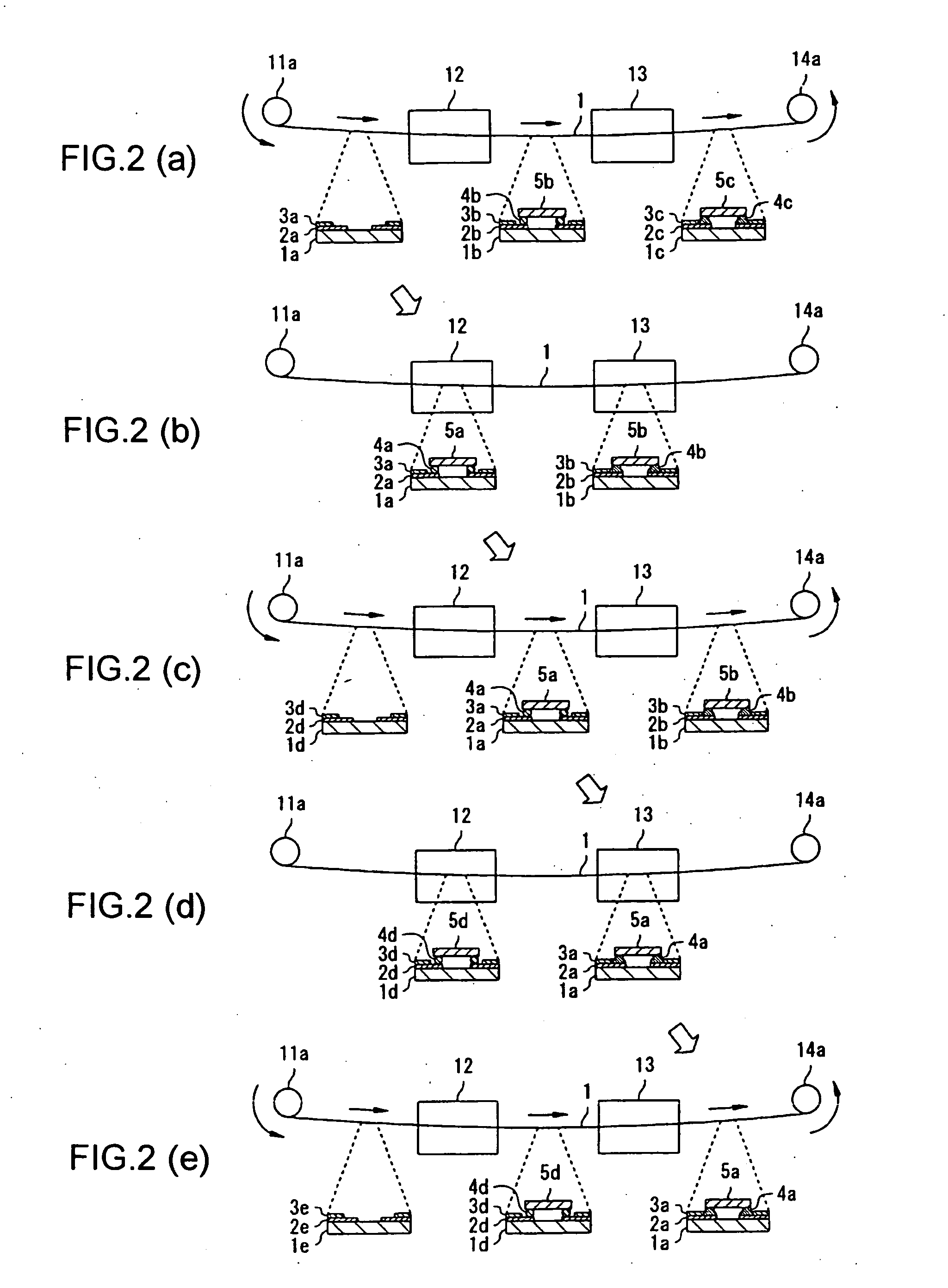
Apparatus for manufacturing an electronic device, method of manufacturing an electronic device, and program for manufacturing an electronic device
InactiveUS7017636B2Efficient preparationReduce the number of shipmentsAdhesive processesLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A mounting zone and a reflow zone are arranged in parallel between a loader and an unloader, and mounting and reflow processes are performed simultaneously.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System for reading information transmitted from a transponder
InactiveUS8638255B2Avoid unnecessary processingSave processing capabilityPosition fixationSubscribers indirect connectionEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A reader device (110) for reading information transmitted from a transponder (130) via a backscatter signal (132) generated by the transponder (130) in response to a stimulus signal (112) generated by the reader device (110), the reader device (110) comprising a first power estimation unit (114) adapted for estimating a first power value indicative of the power of the stimulus signal (112) at a position of the transponder (130) by evaluating a power information included in the backscatter signal (132), a second power estimation unit (116) adapted for estimating a second power value indicative of the power of the backscatter signal (132) at a position of the reader device (110), and a distance estimation unit (118) adapted for estimating a distance (d1) between the reader device (110) and the transponder (130) based on the first power value and the second power value.
Owner:NXP BV
Apparatus for manufacturing an electronic device, method of manufacturing an electronic device, and program for manufacturing an electronic device
InactiveUS20060096701A1Reduce the number of shipmentsEliminate processingSolid-state devicesSoldering apparatusMechanical engineeringEngineering
A mounting zone and a reflow zone are arranged in parallel between a loader and an unloader, and mounting and reflow processes are performed simultaneously.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Data transmission
InactiveUS7631037B2Simple formatAvoid unnecessary processingConnection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsData transmissionMessage passing
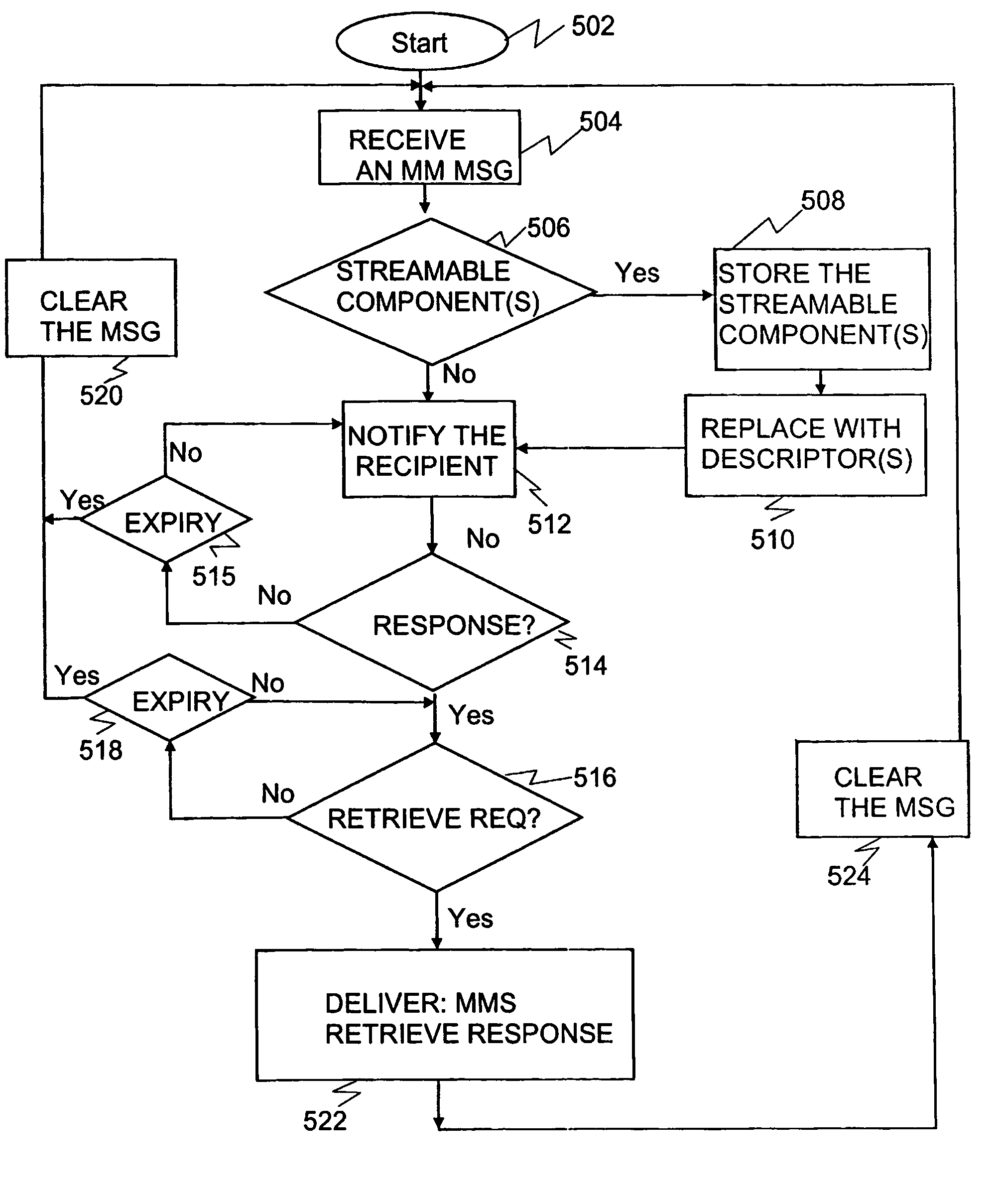
A multimedia messaging service (MMS), wherein a user agent is notified of availability of a multimedia message and subsequently, after the user agent has sent a retrieve request, a streamable media component of a multimedia message is streamed to the user agent in a streaming session. The streaming session is established according to Session Description Data (SDD). Responsive to the retrieve request, the multimedia message is delivered to the user agent so that the streamable media component is represented with a descriptor pointing to a location from which the SDD can be obtained. The SDD is generated before or after the user agent requests for retrieval of the multimedia message but not necessarily by the time the user agent is notified for the availability of the multimedia message.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com