Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1692results about "Shipping equipment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
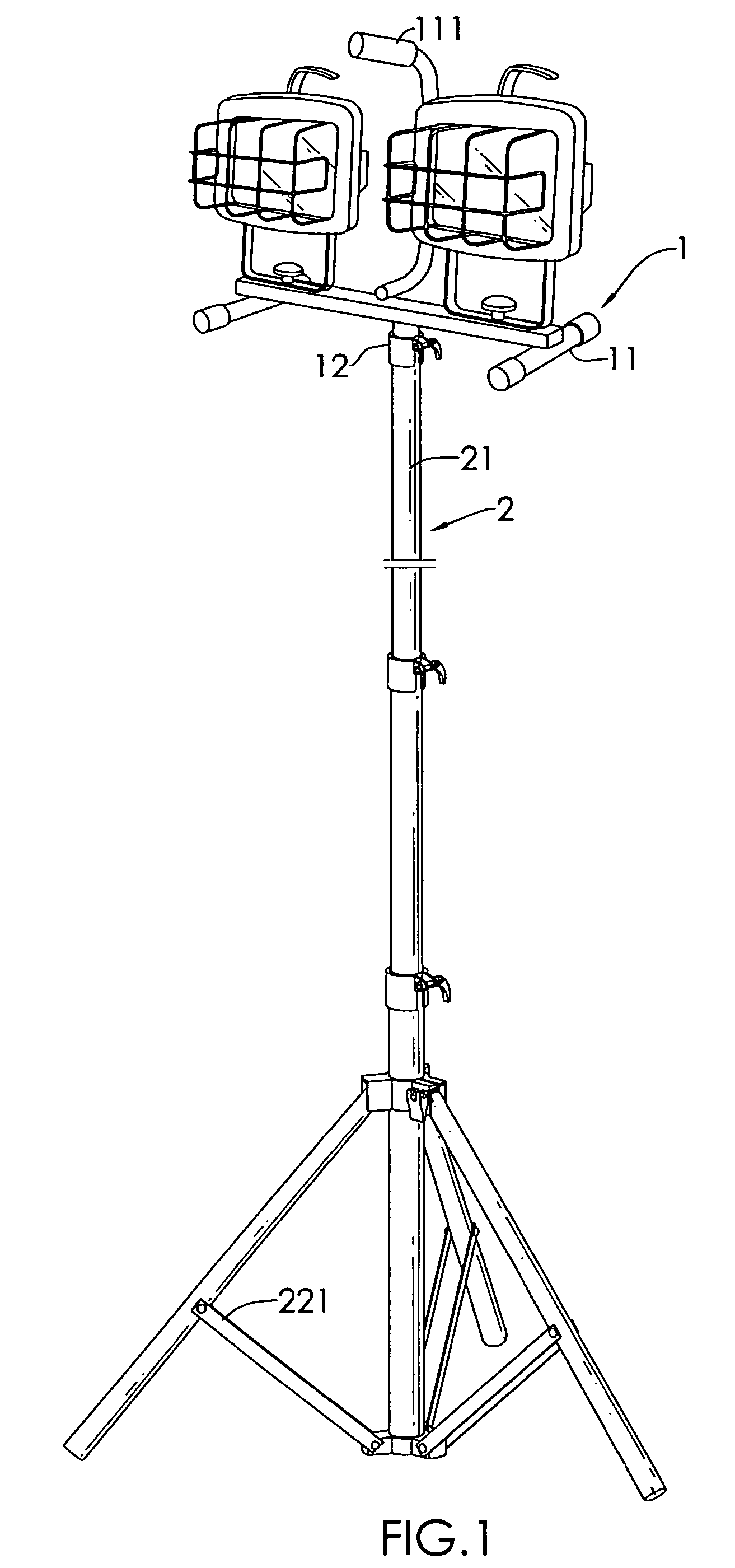
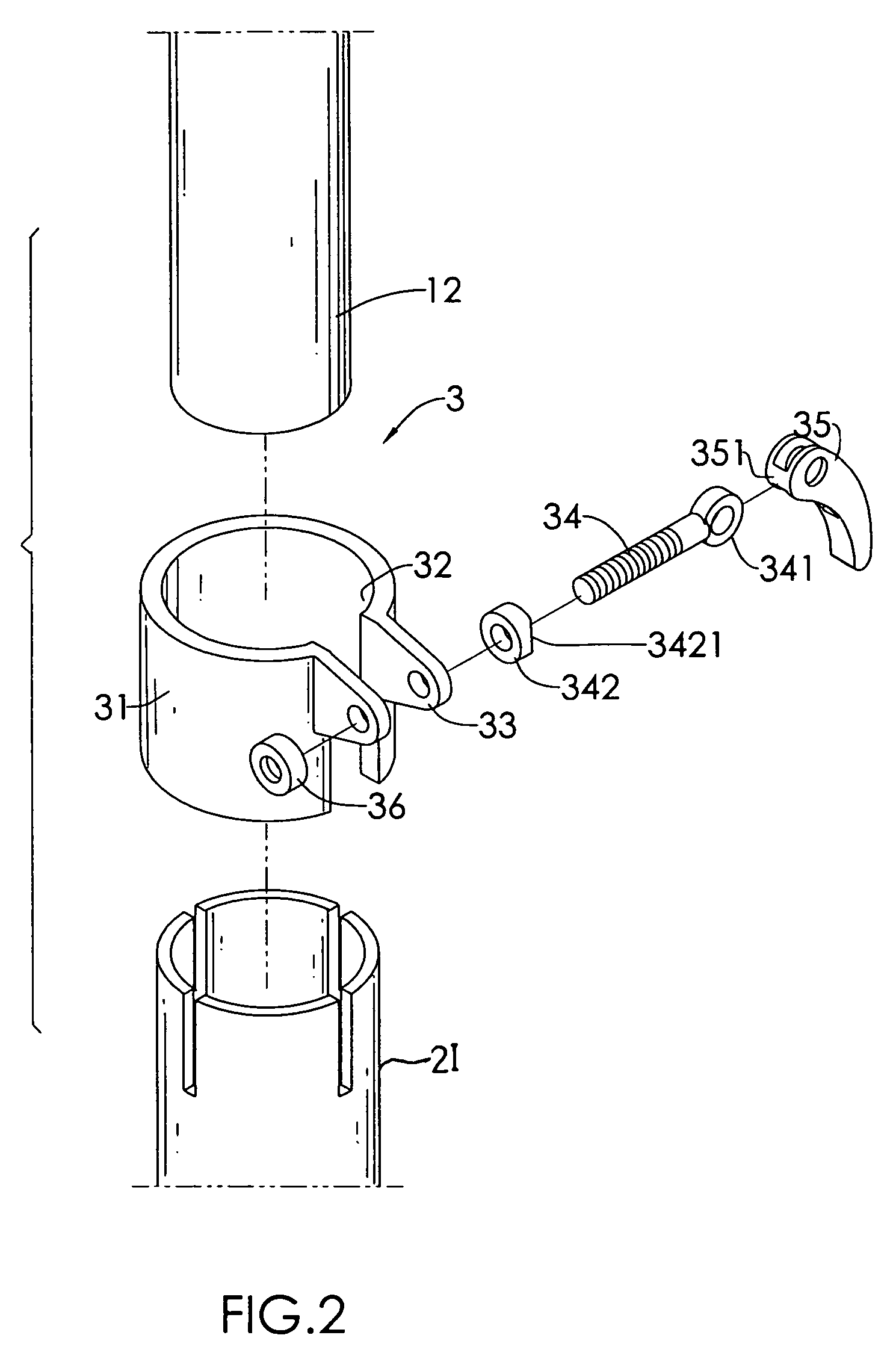
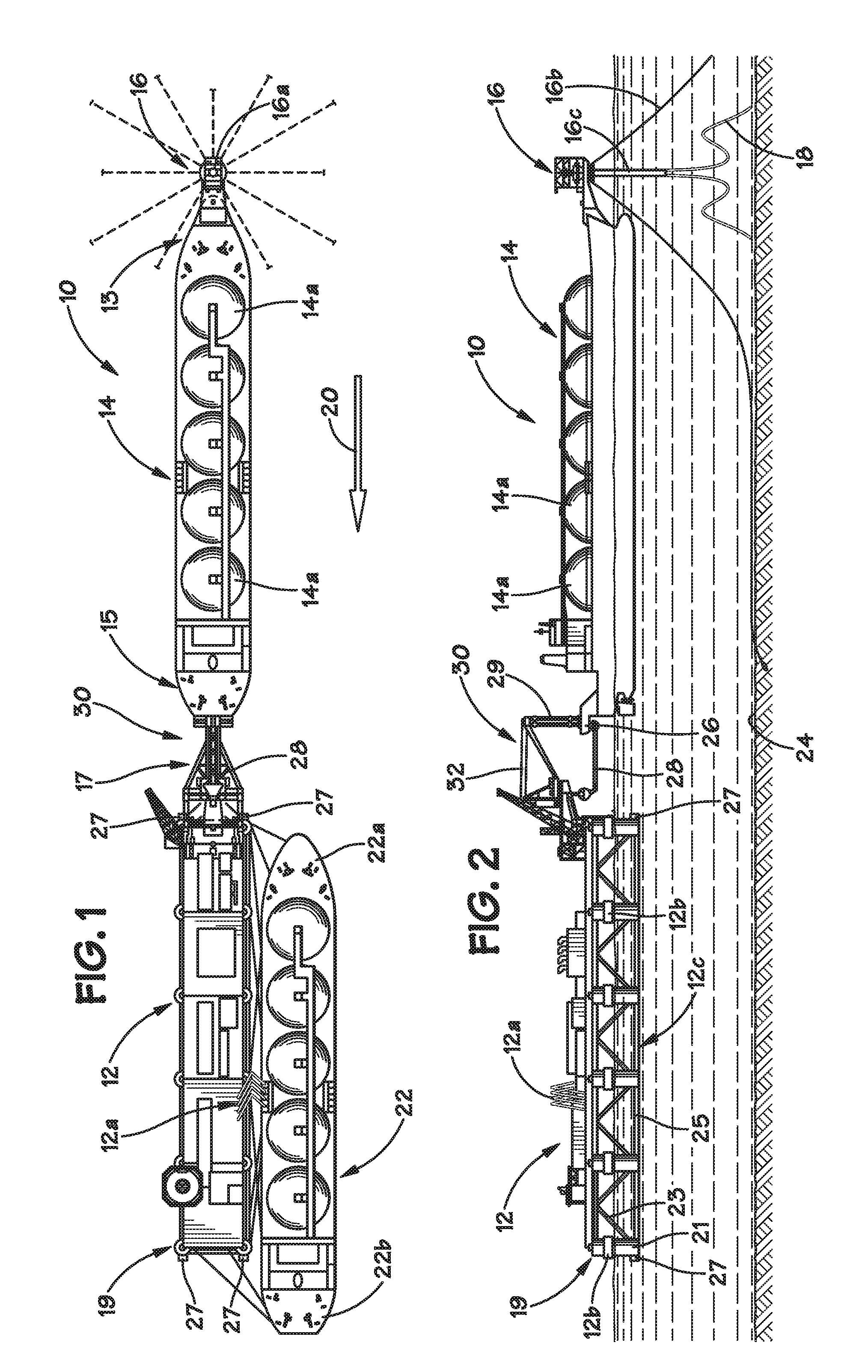
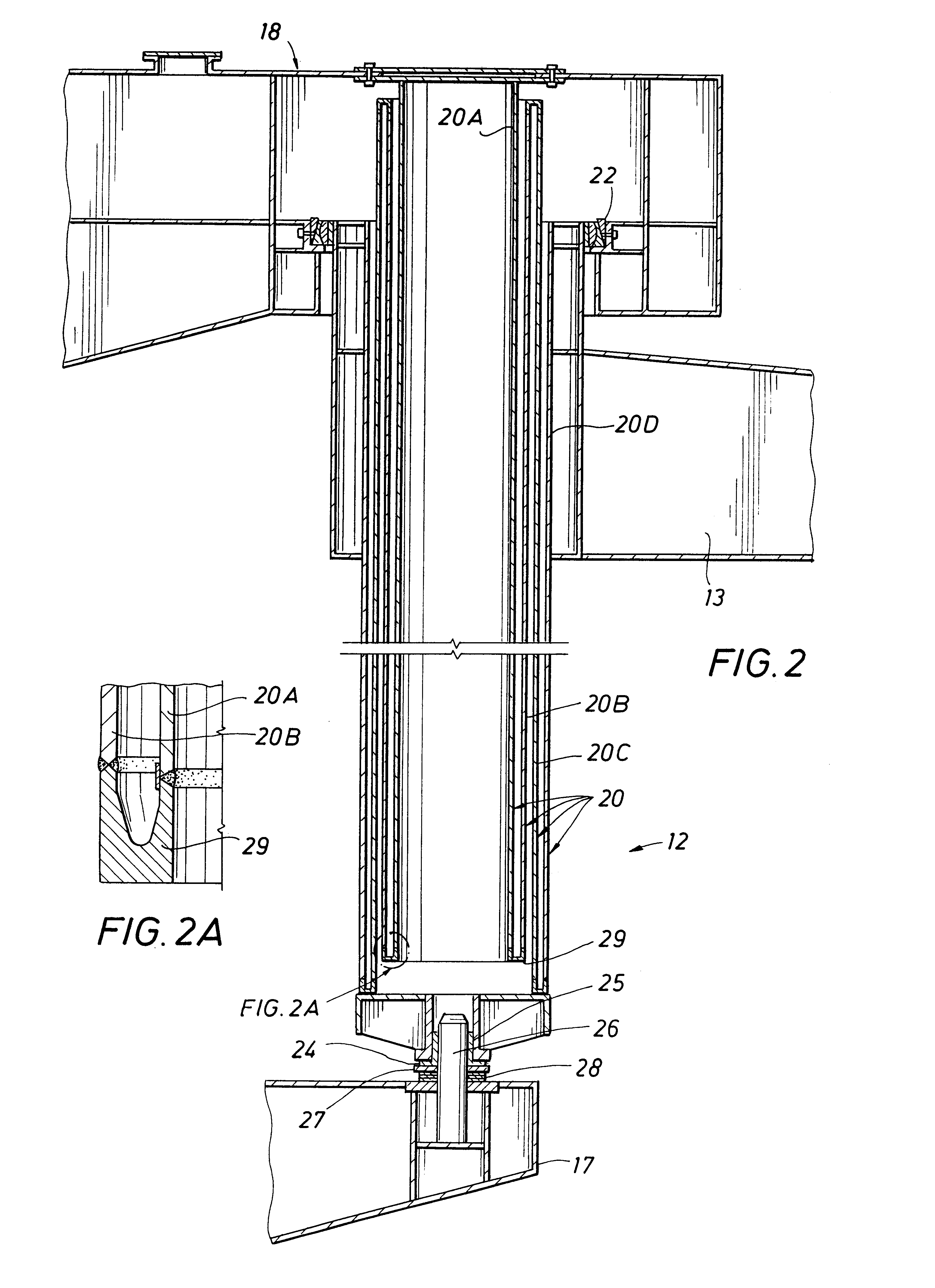
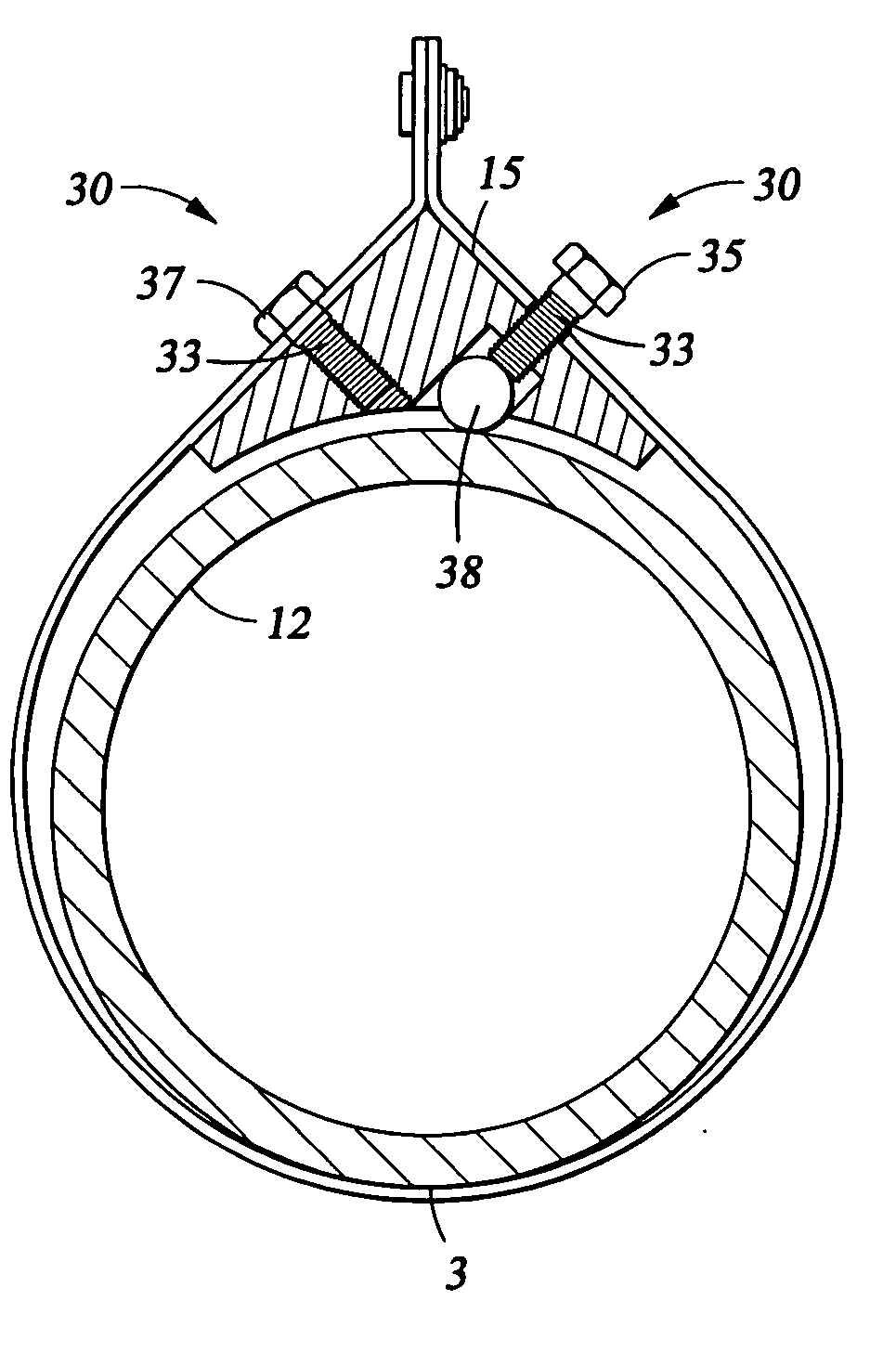
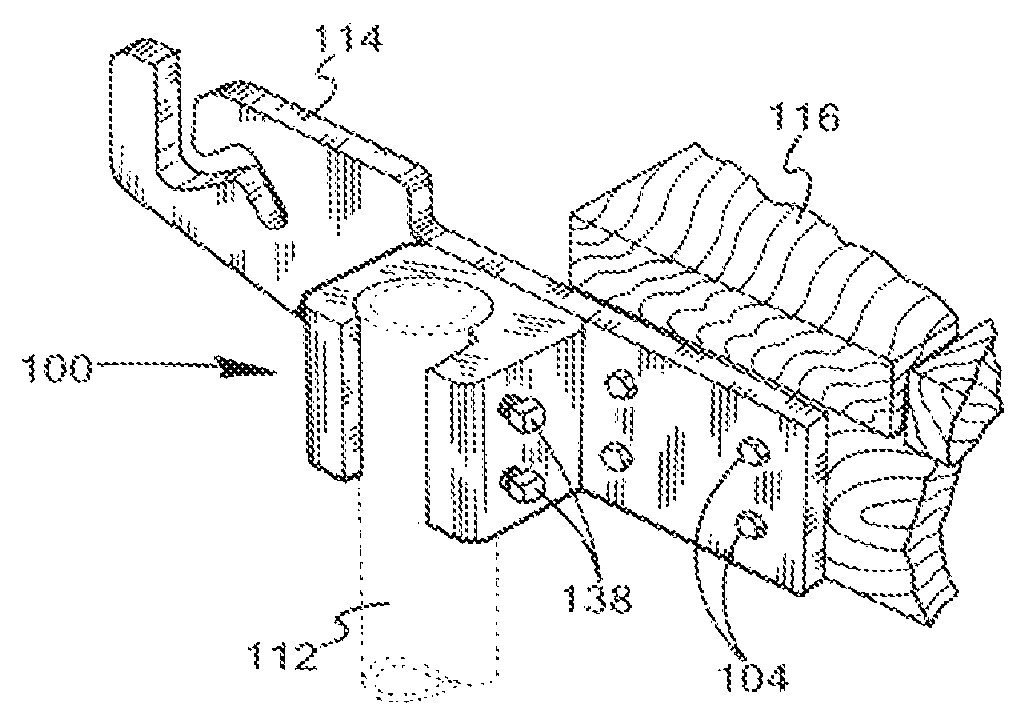
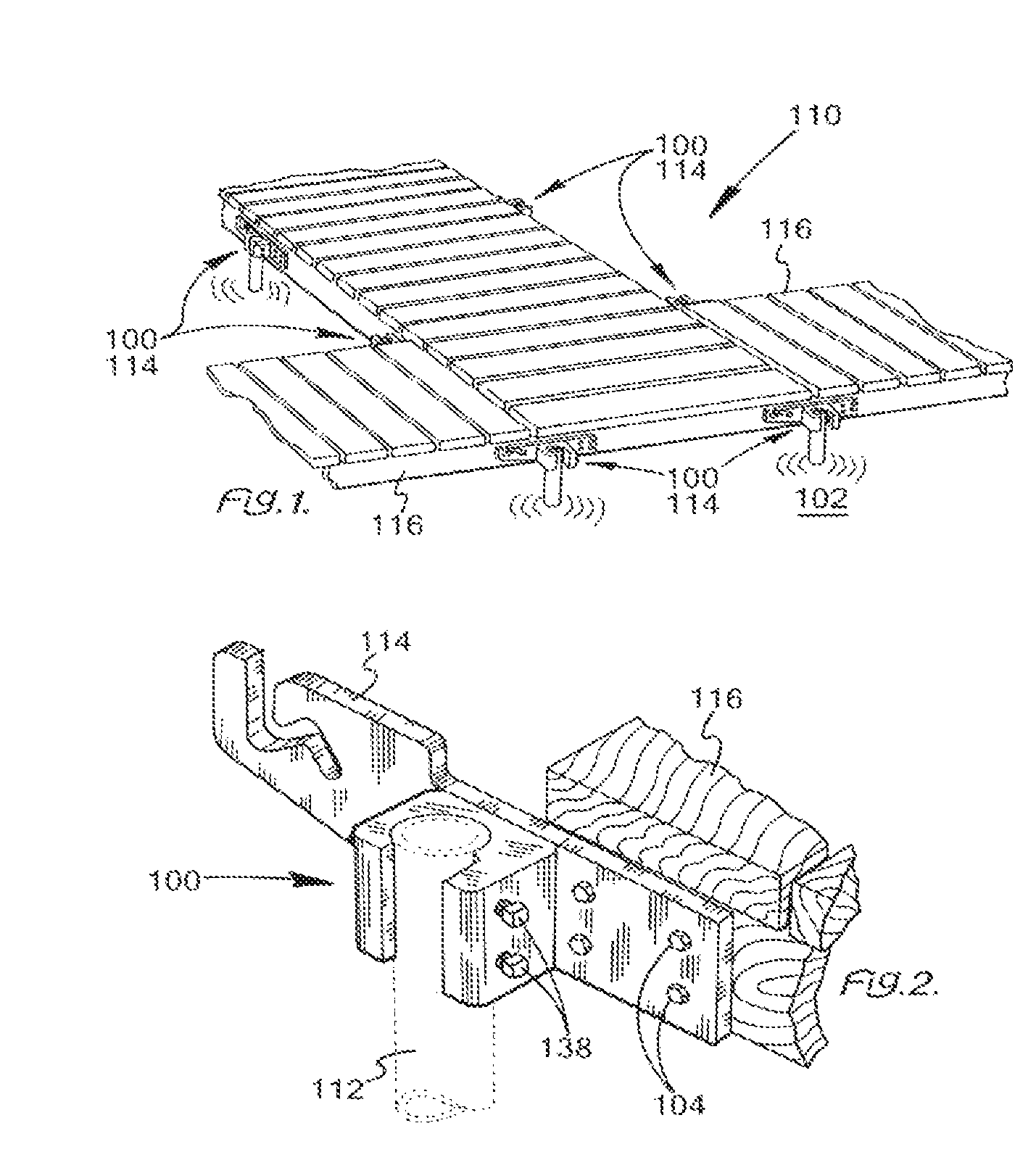
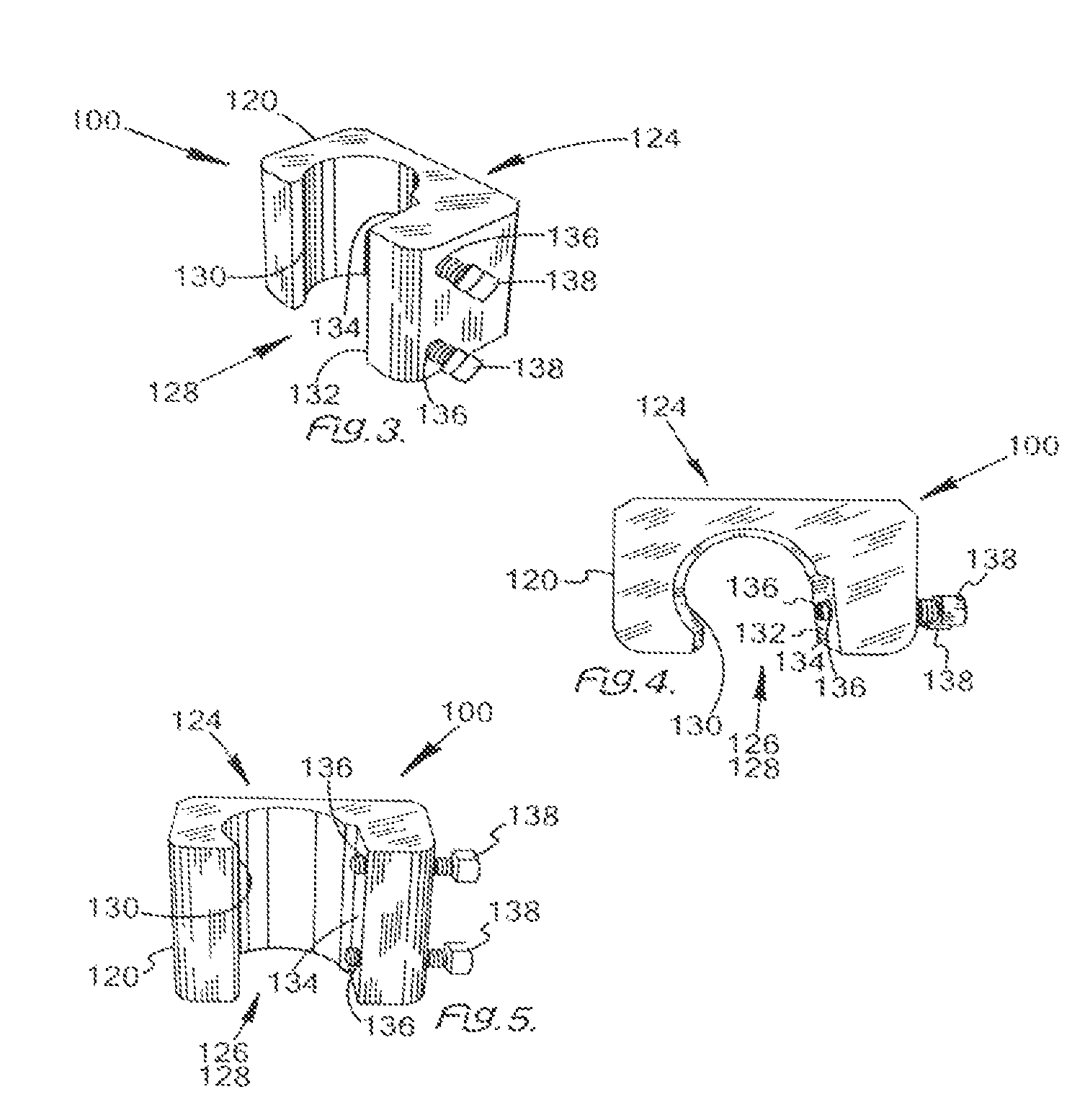
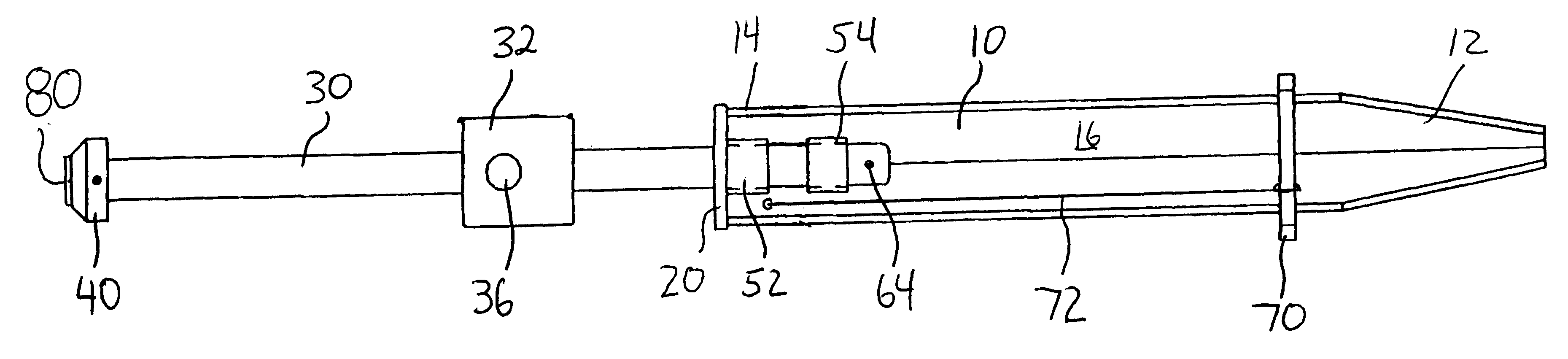
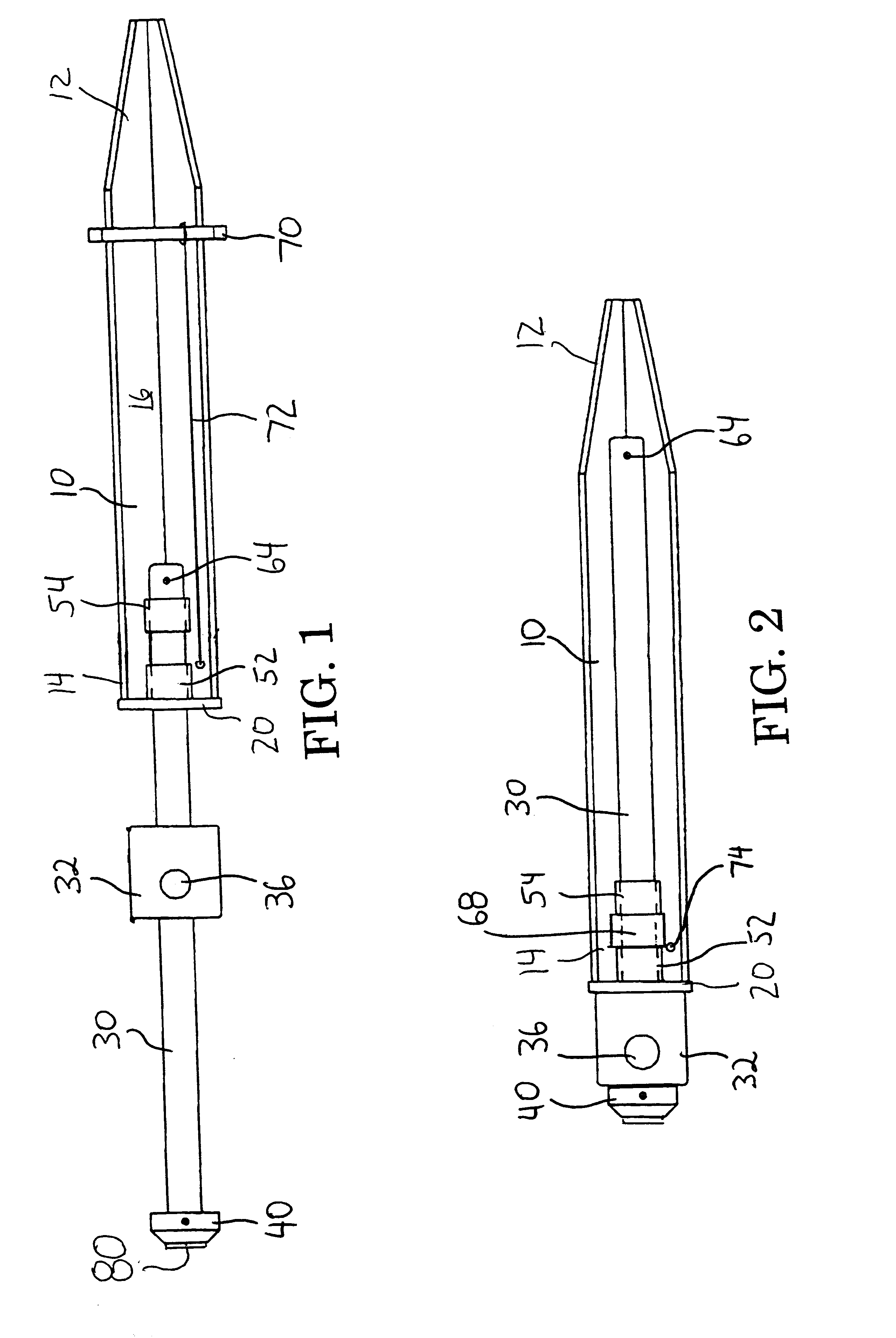
Worklight support with stand
A worklight support includes a platform for mounting thereon worklights and has an extension extending from on a bottom of the platform for extension into one of the stand sections. A stand includes couplers applied for combination of each of the stand sections. Each coupler includes an annular ring for receiving therein a portion of one of the stand sections and a portion of the extension of the worklight support and a pivotal handle pivotally connected to the annular ring via a threaded bolt to selectively reduce an internal diameter of the annular ring to abut an outer periphery of the extension so as to fix the extension relative to one of the stand sections.
Owner:TSAI PETER
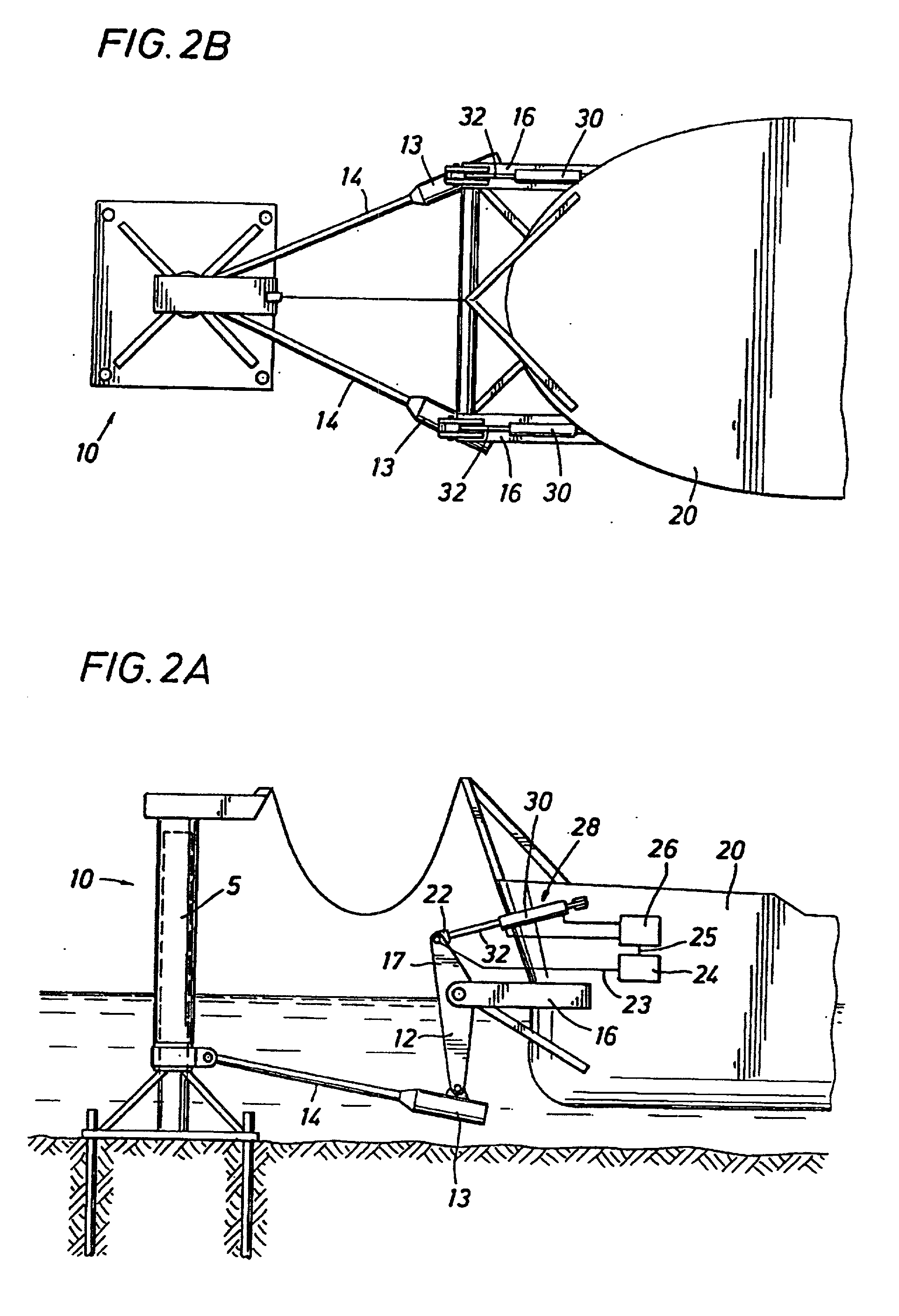
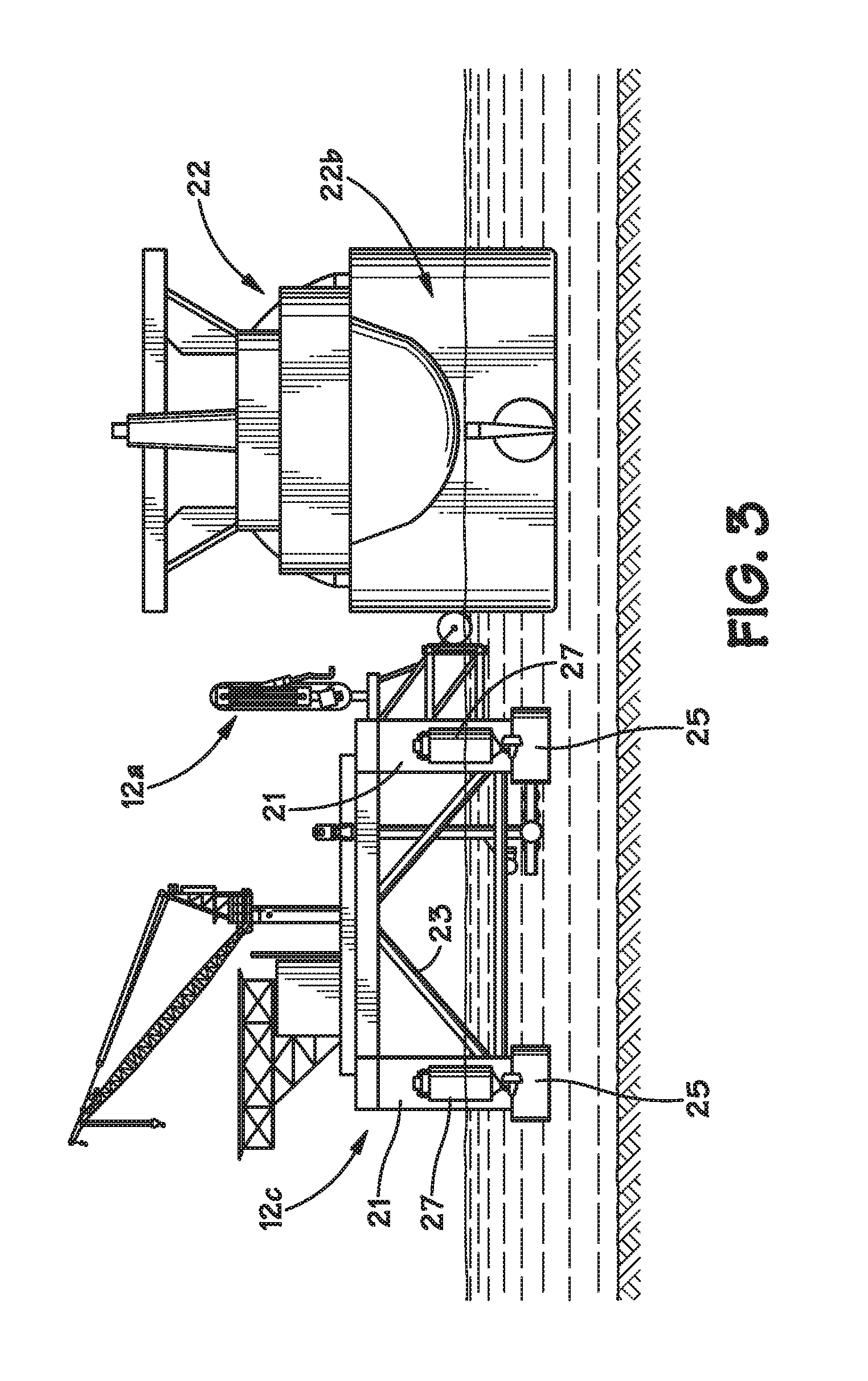
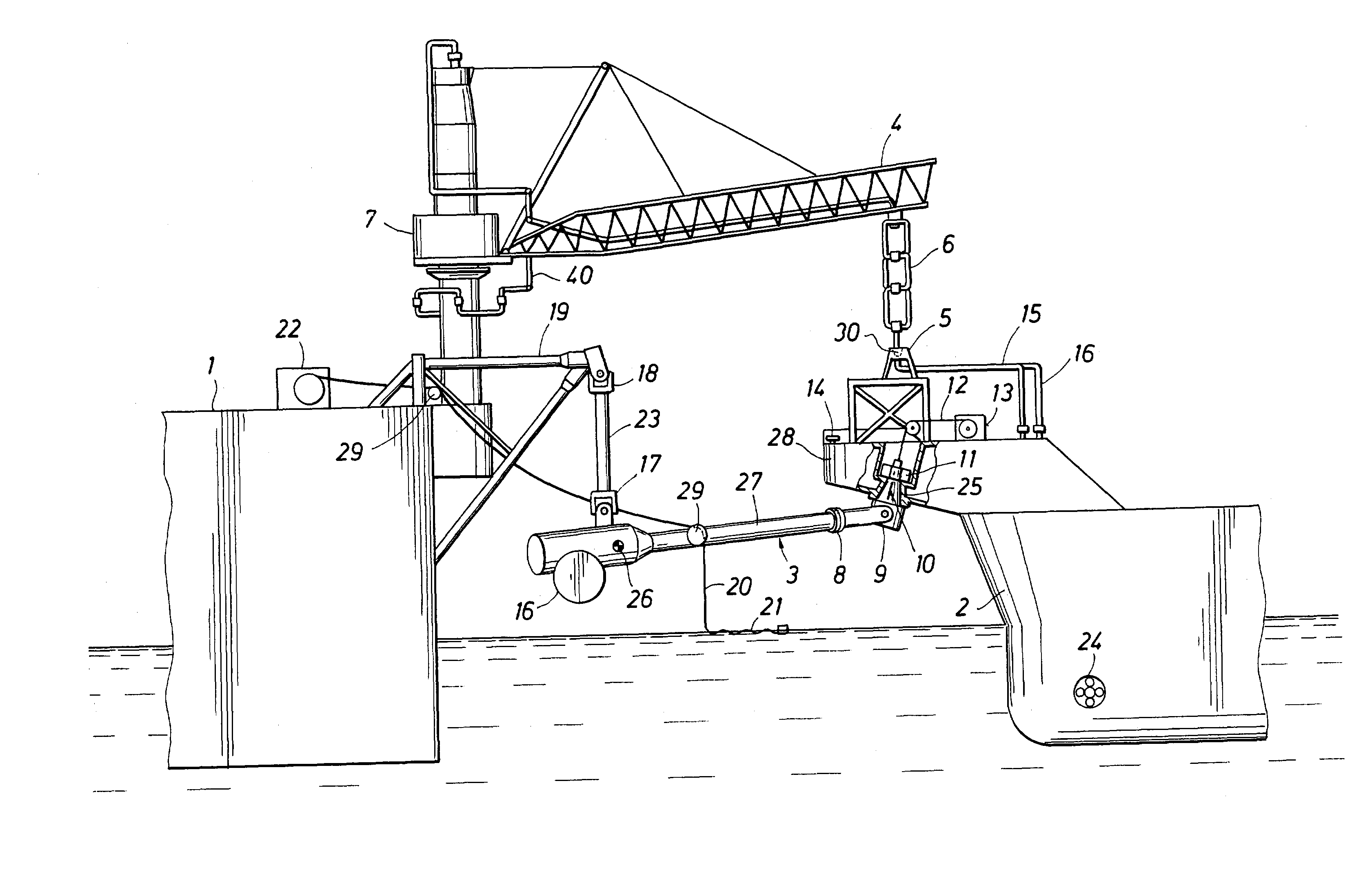
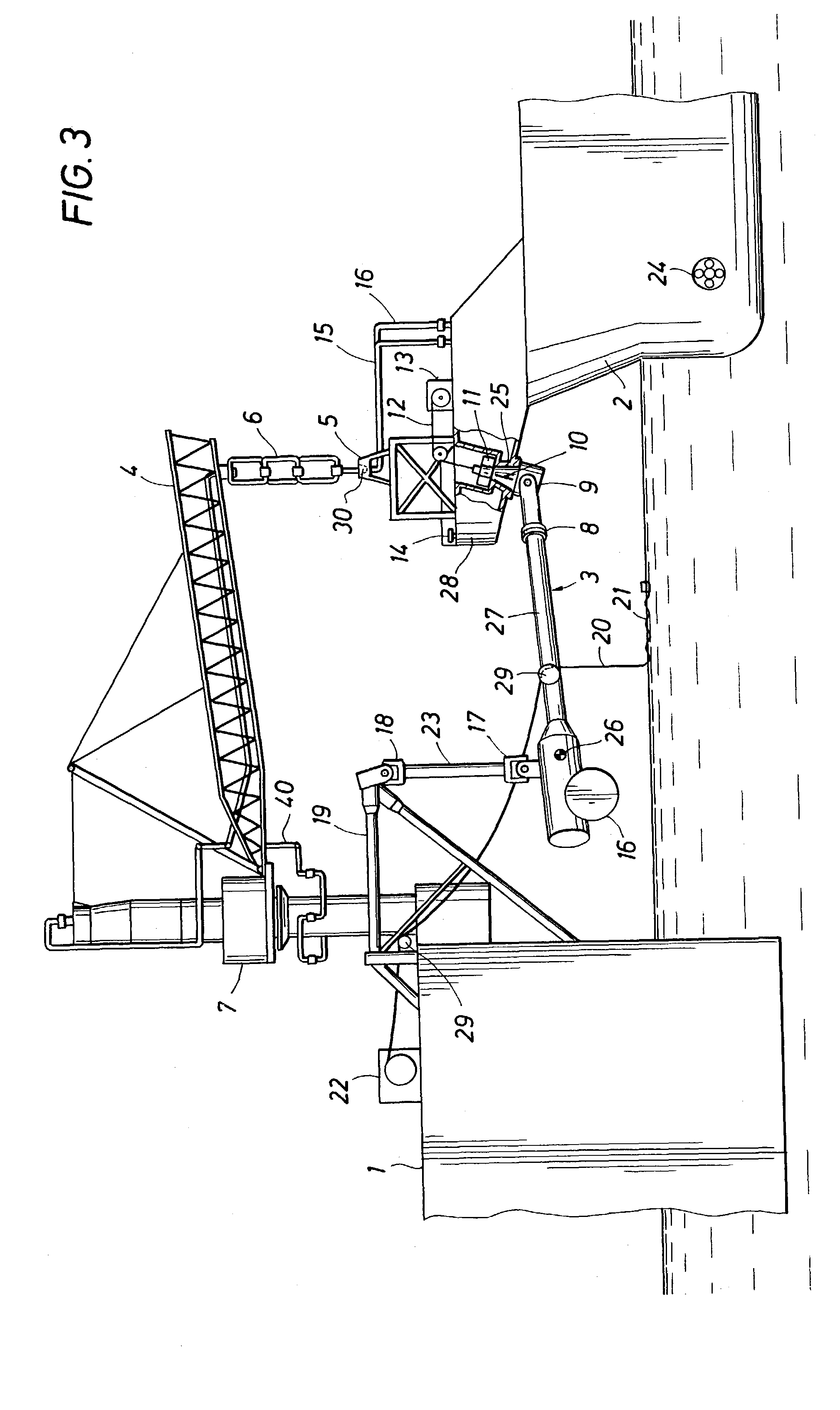
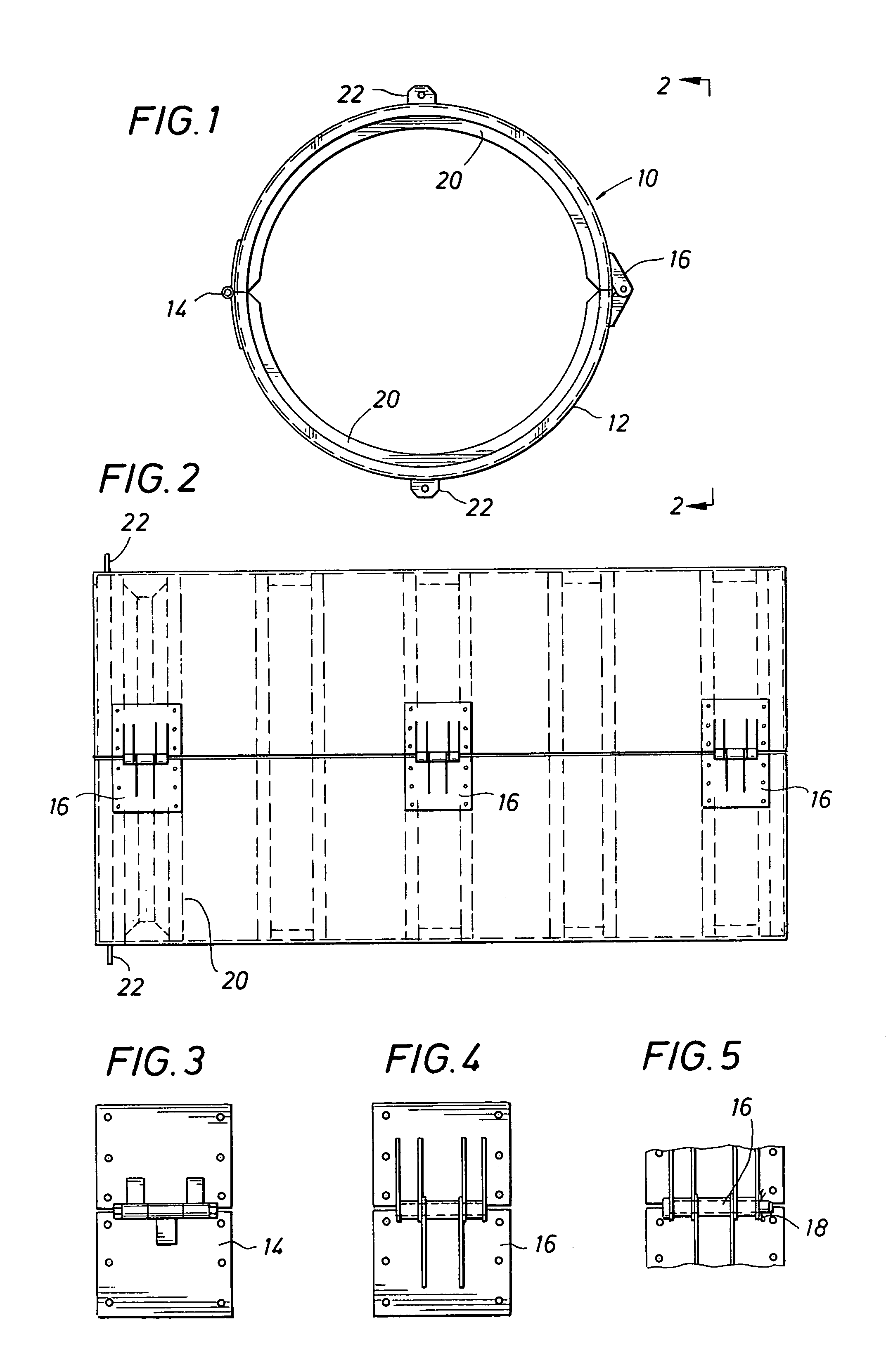
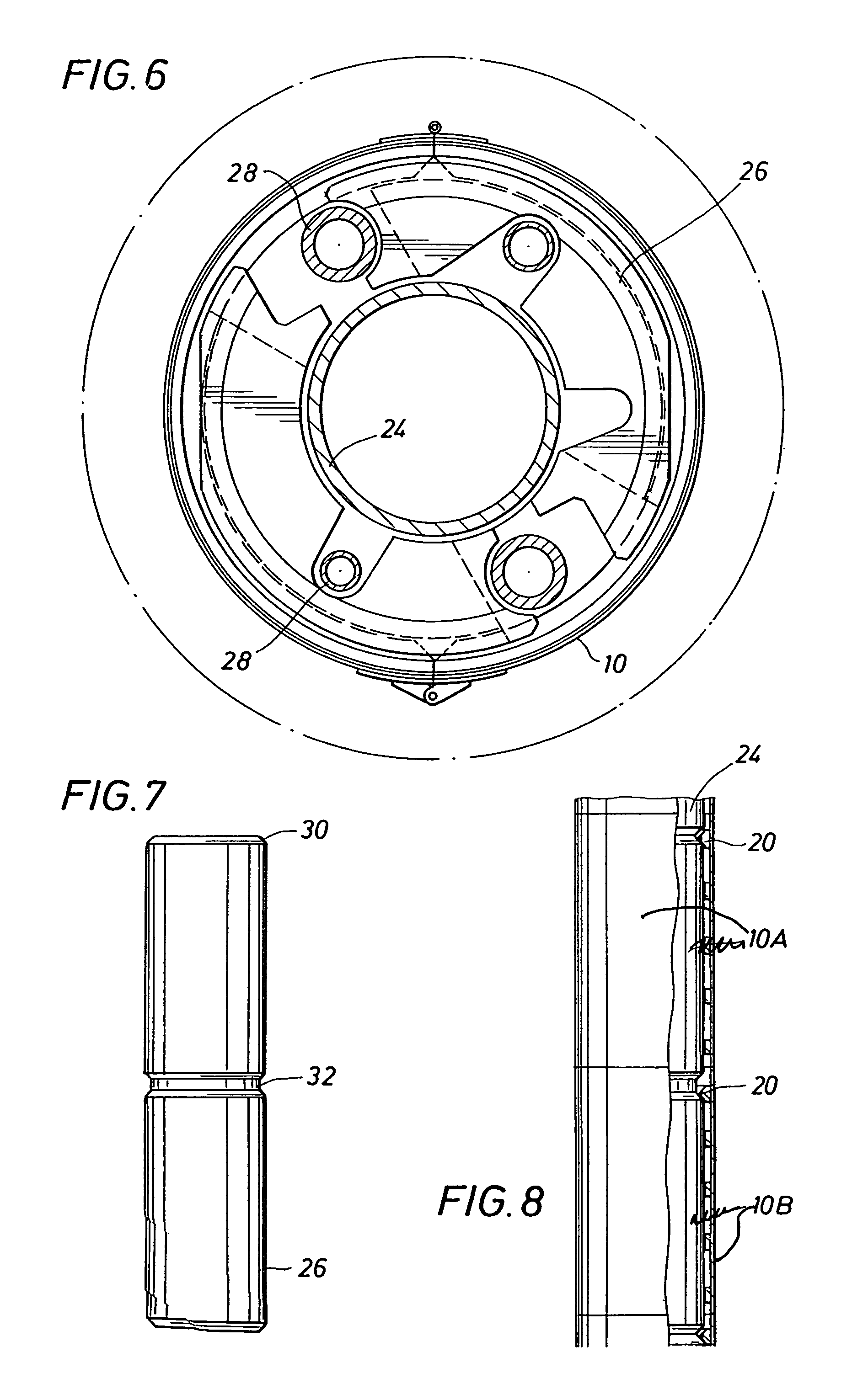
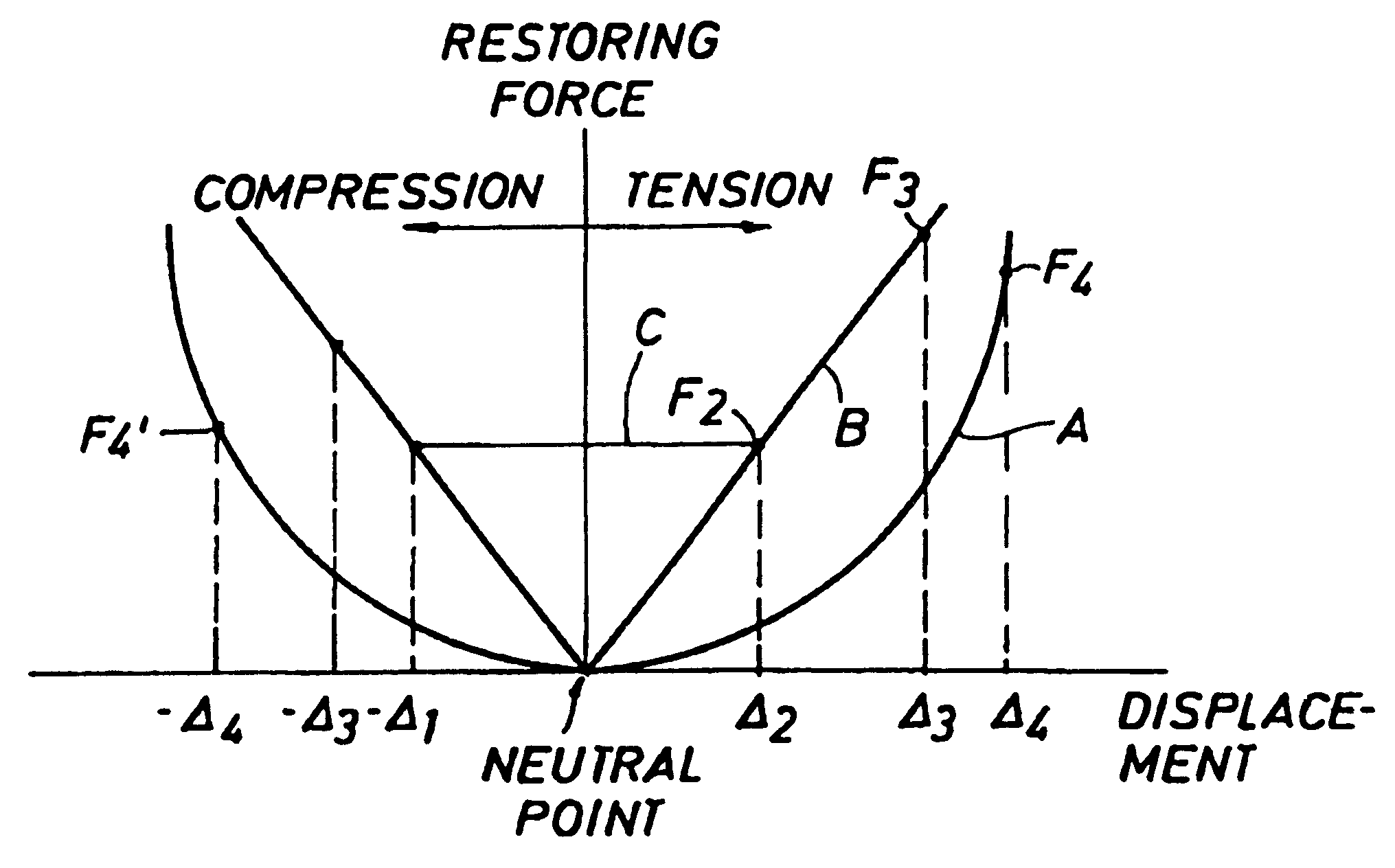
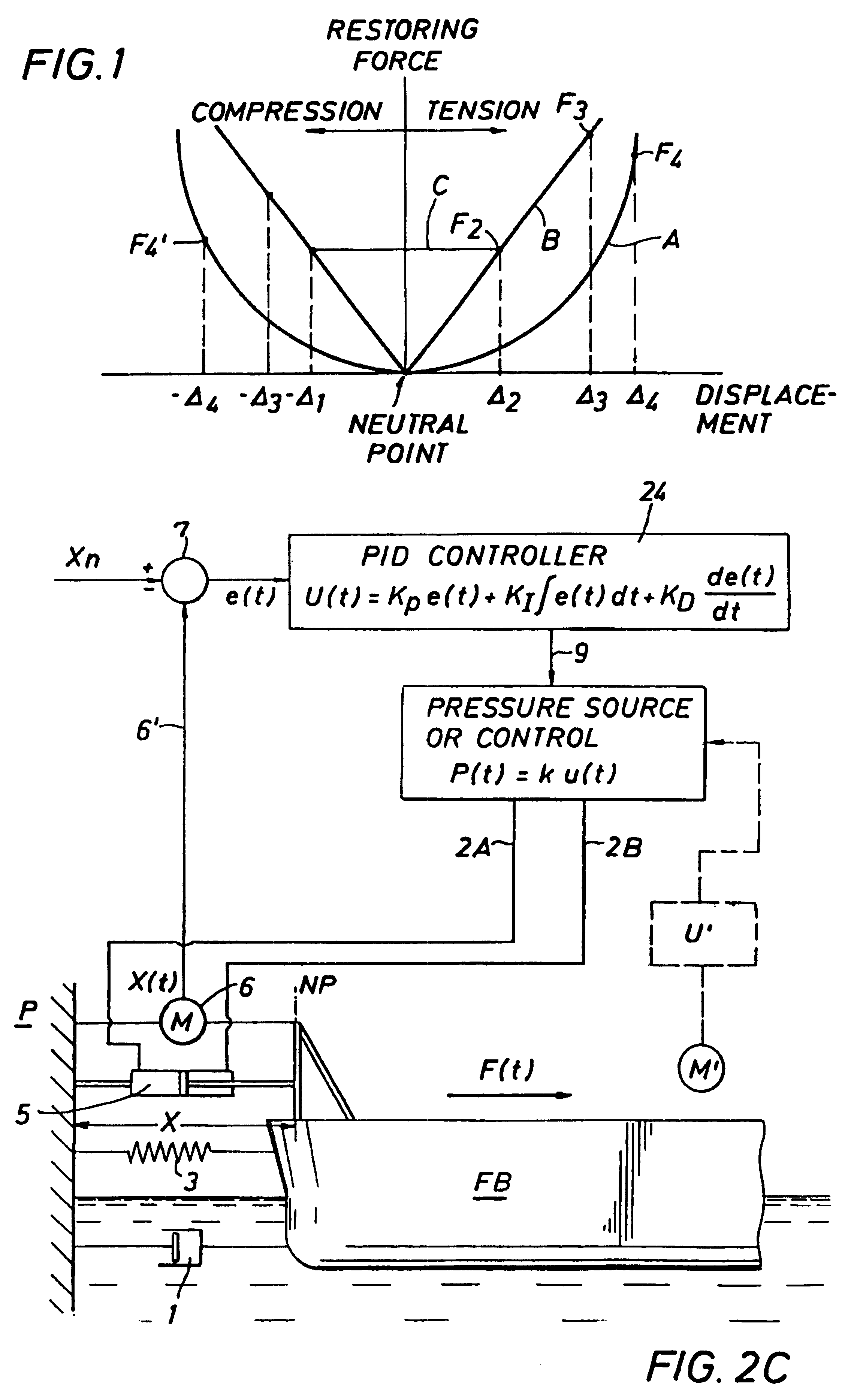
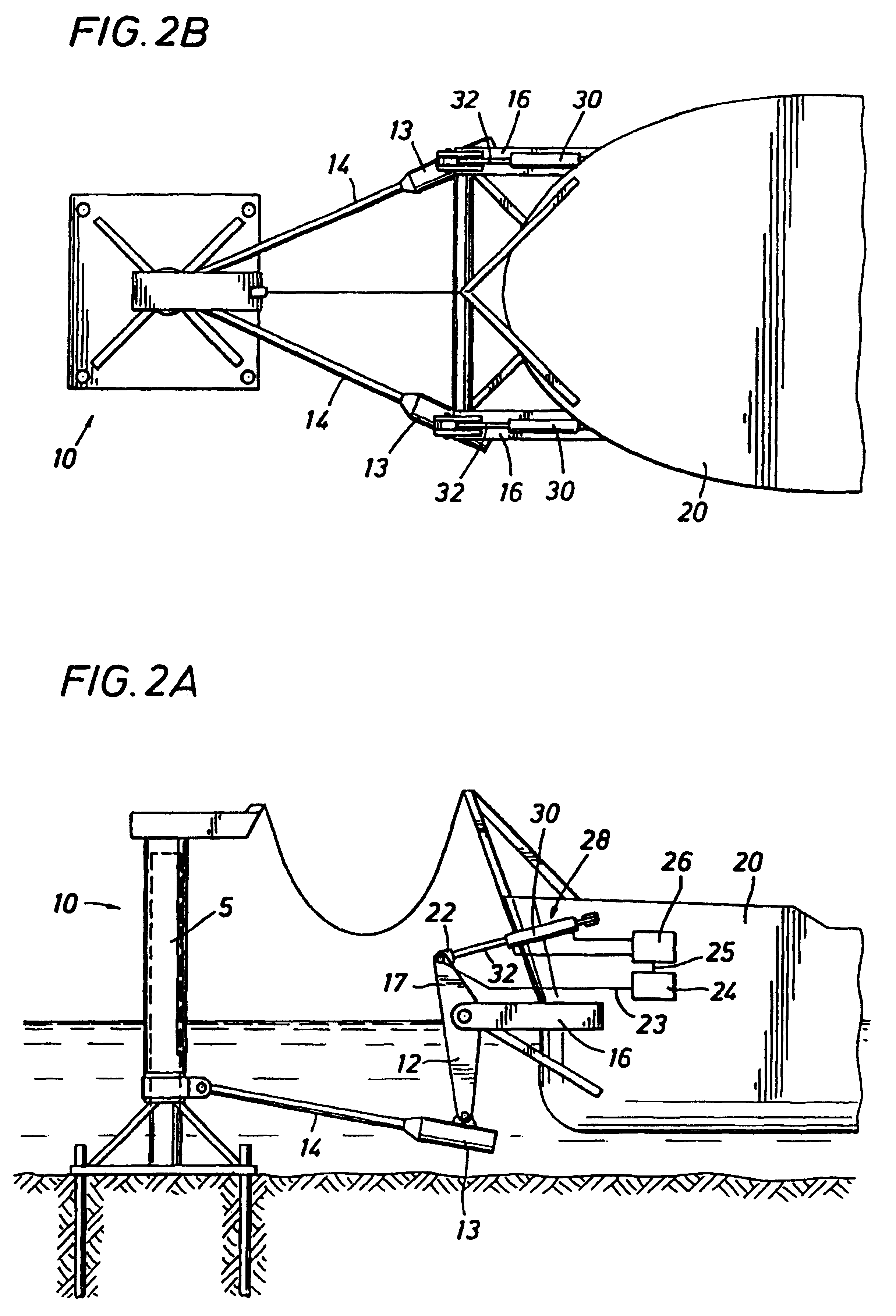
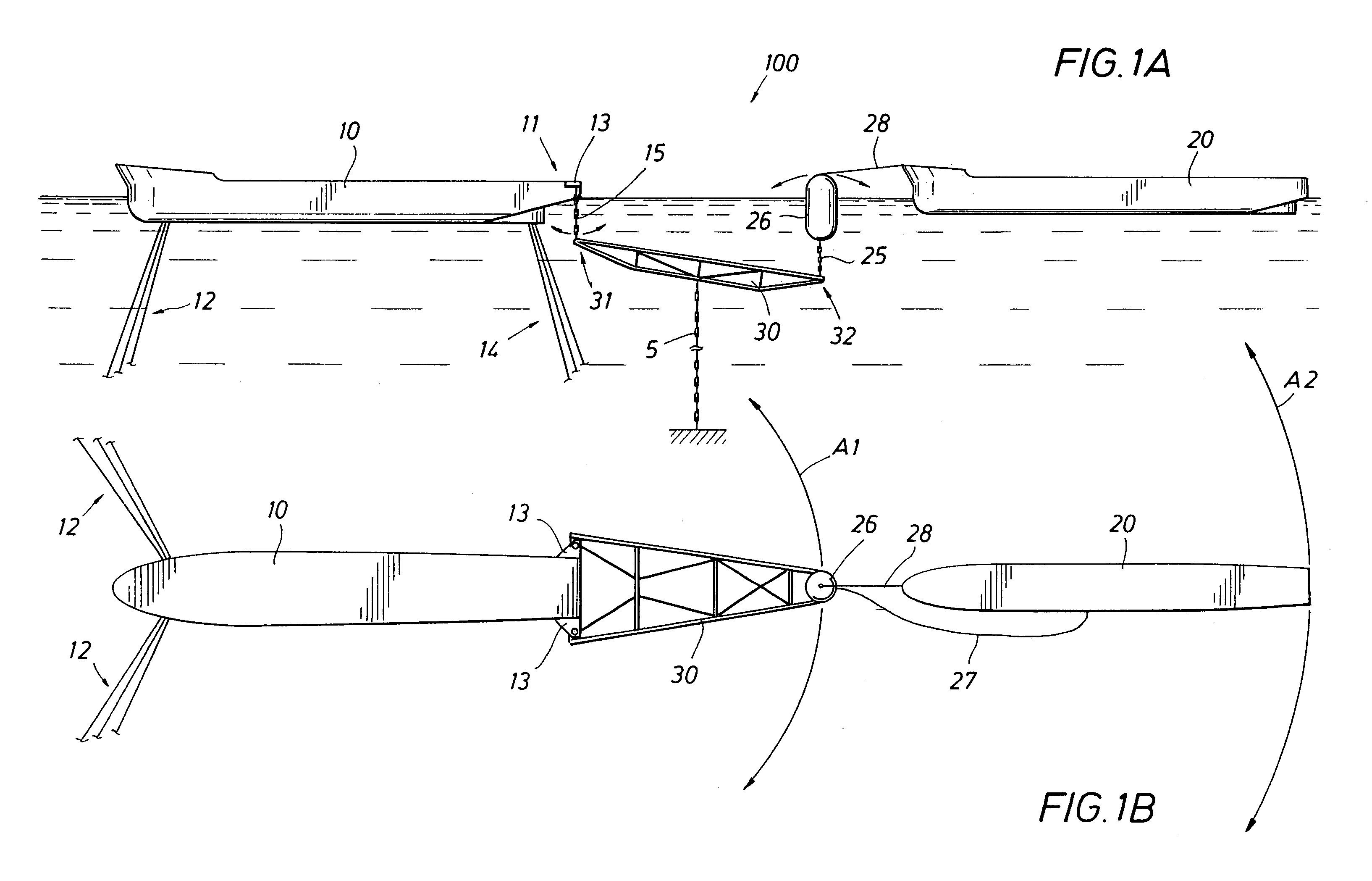
Mooring systems with active force reacting systems and passive damping
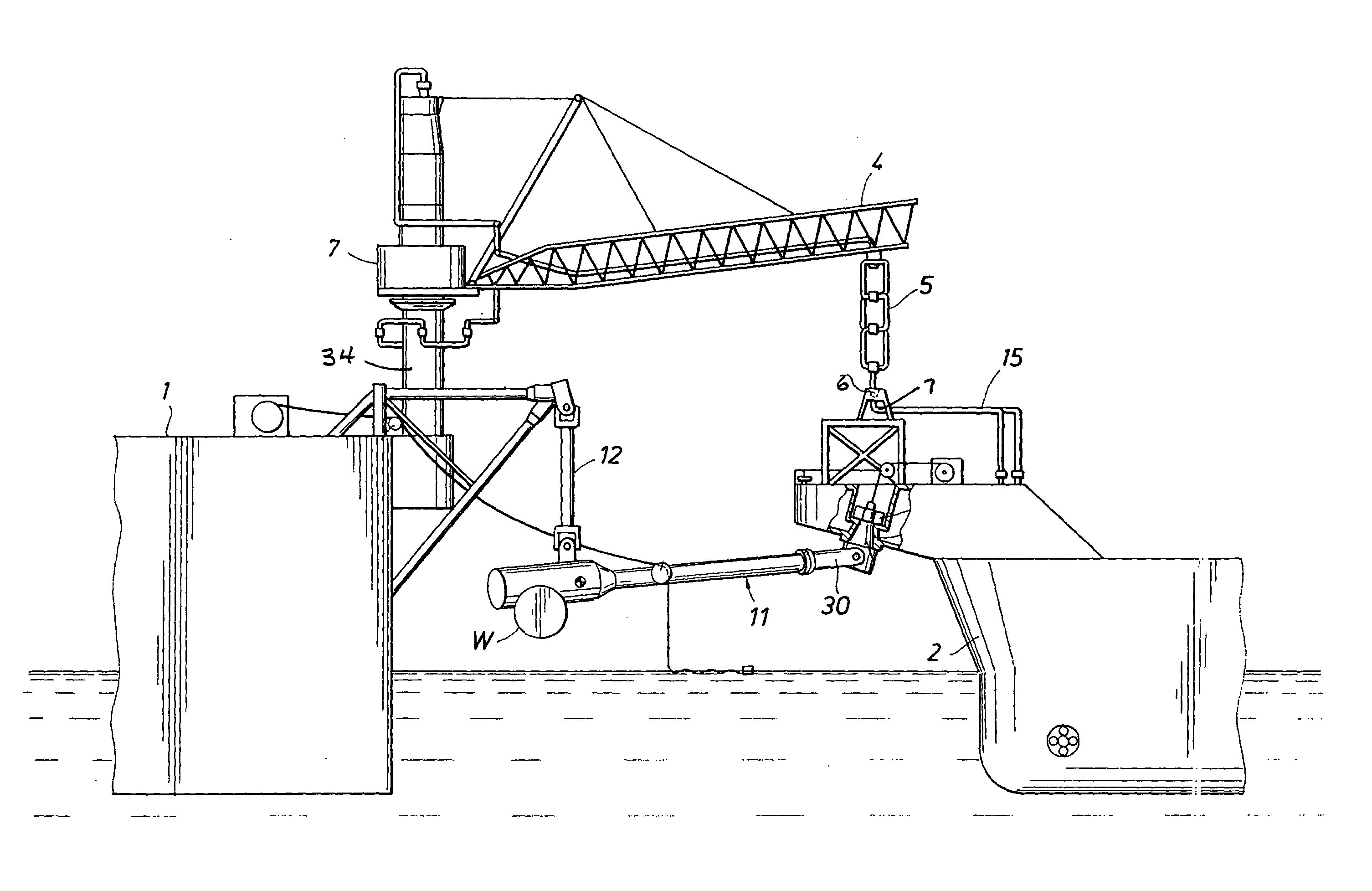
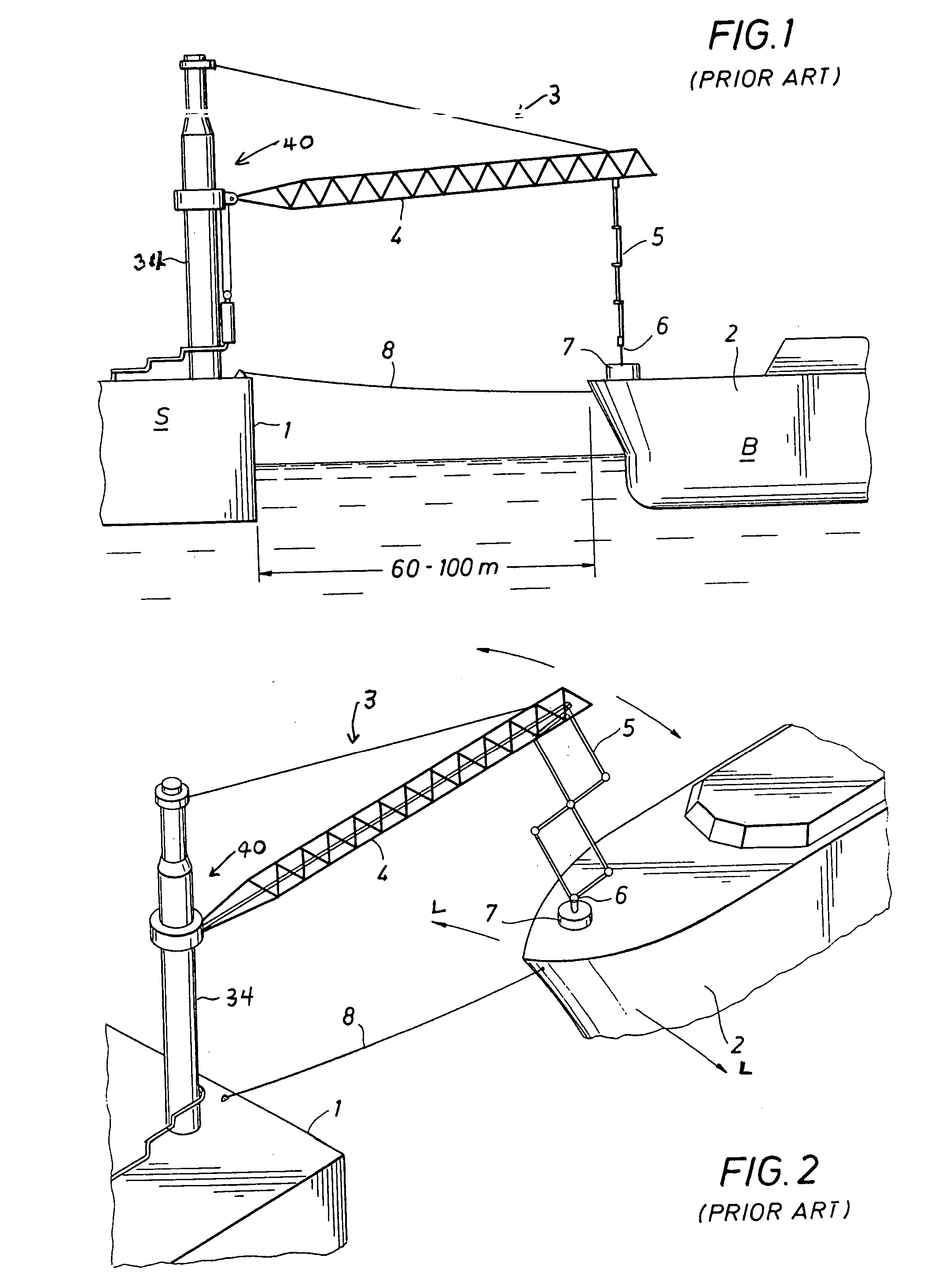
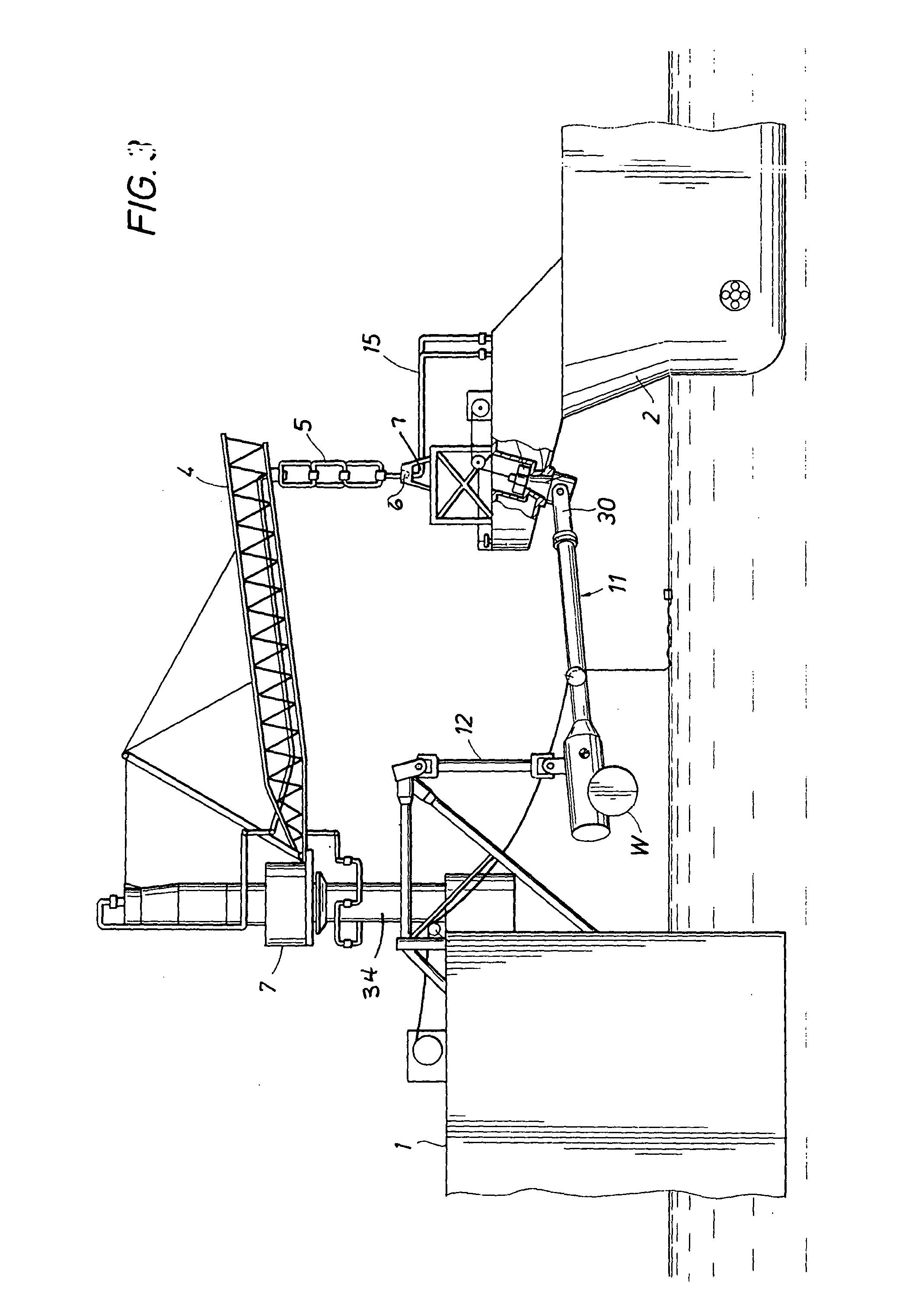
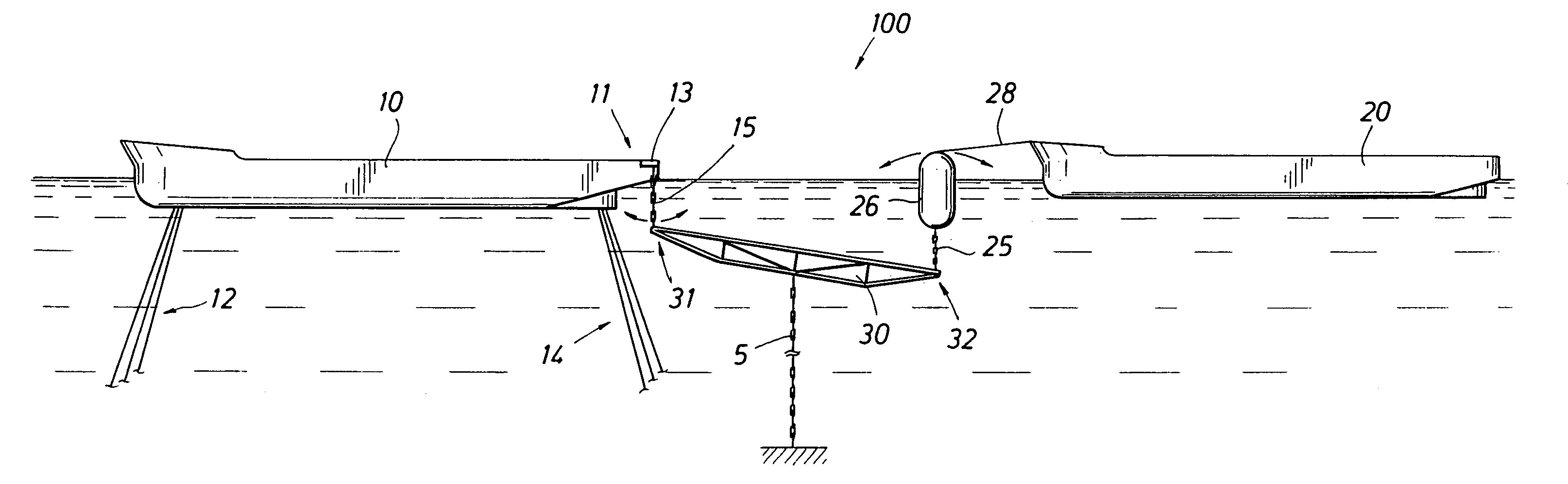
A mooring system including a body / arm / vessel arrangement with passive damping and / or an active force restoring system. The active force restoring system includes a sensor for generating a displacement signal representative of the displacement of the vessel from a quiescent position and an active forcing device which responds to the displacement signal to force the arm in a direction to move the vessel toward the quiescent position. The passive damping arrangement includes a device, independent of and in addition to the damping of the water on the vessel or the arm, that damps the oscillation of the vessel in response to environmental conditions which force the vessel from its quiescent position. Hydraulic cylinder arrangements are provided for active forcing and passive damping. Powered winch / cable arrangements are also provided for active force systems. Alternative devices for active and passive damping systems of torque actuators include hydraulic powered cans with internal fins, or cans with internal elastomeric elements or disk brake elements.
Owner:SOFEC
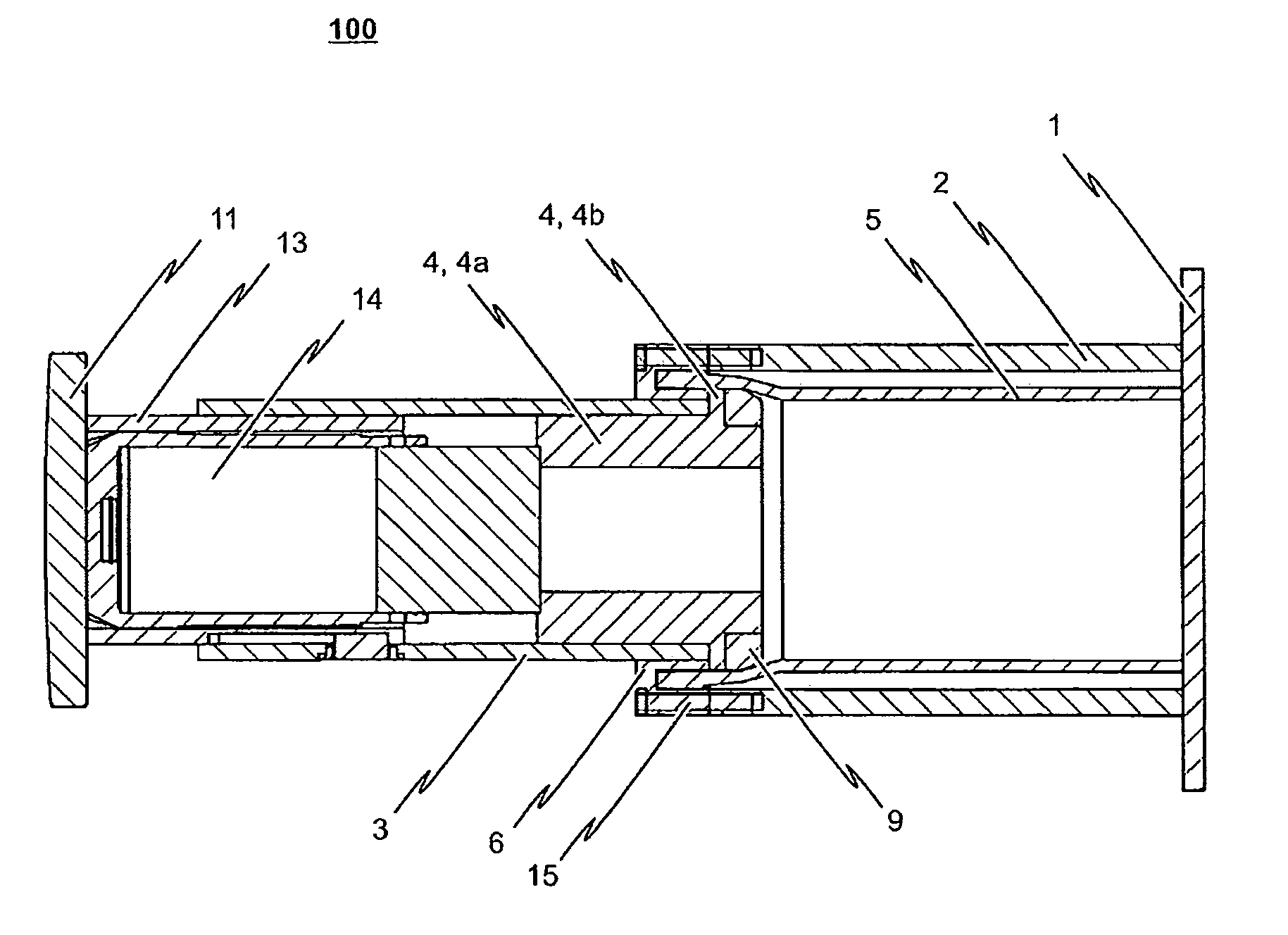
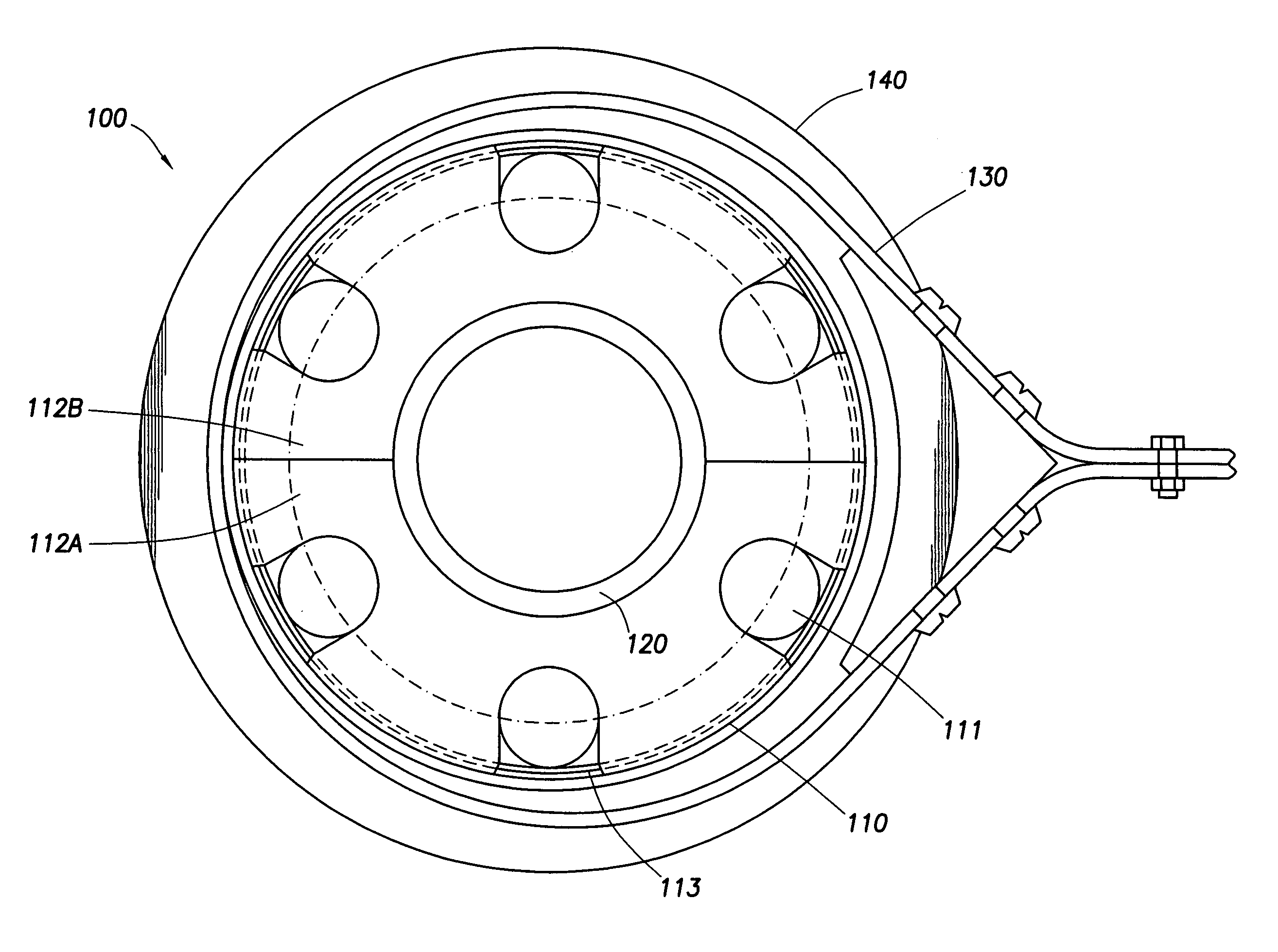
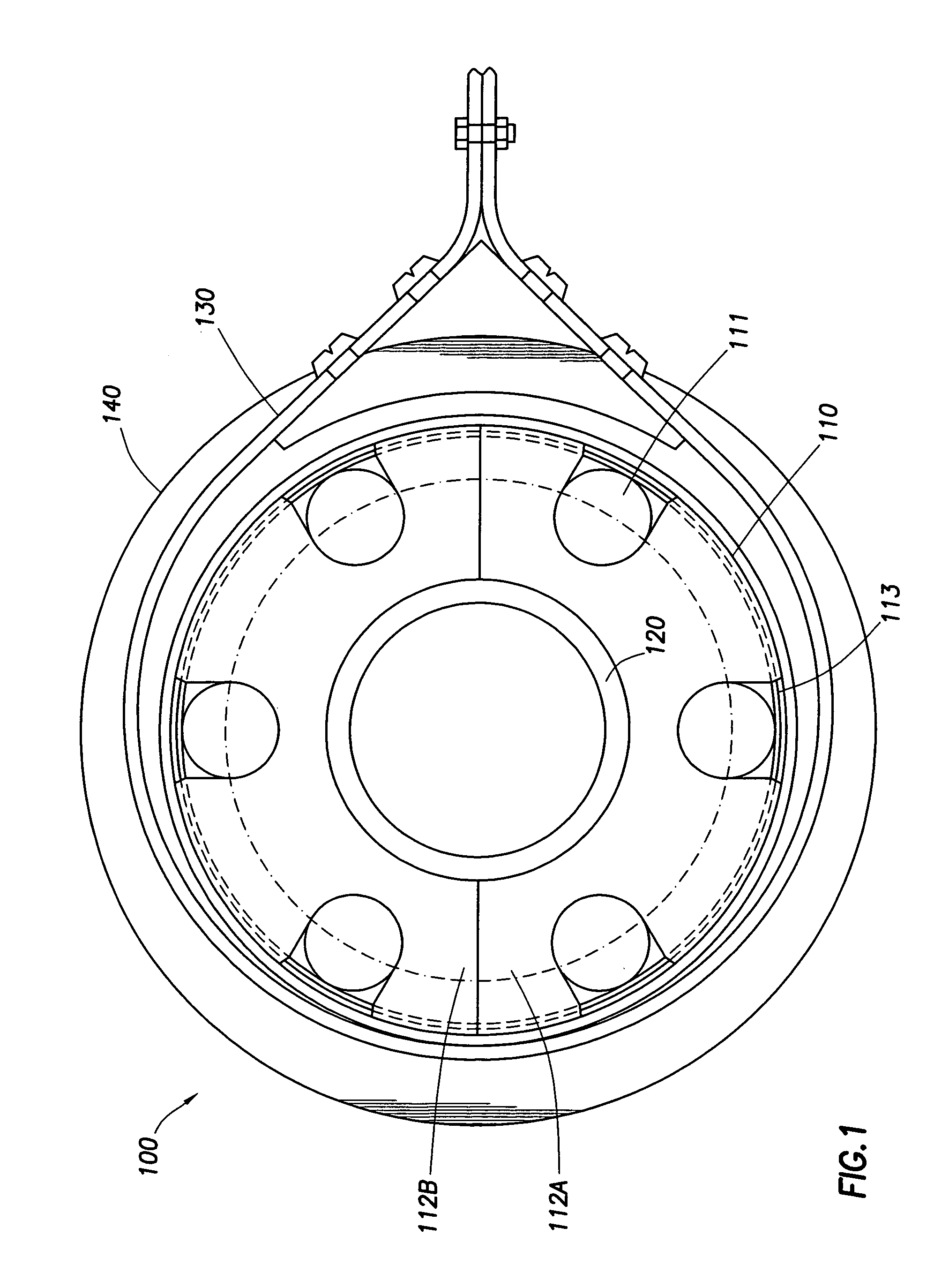
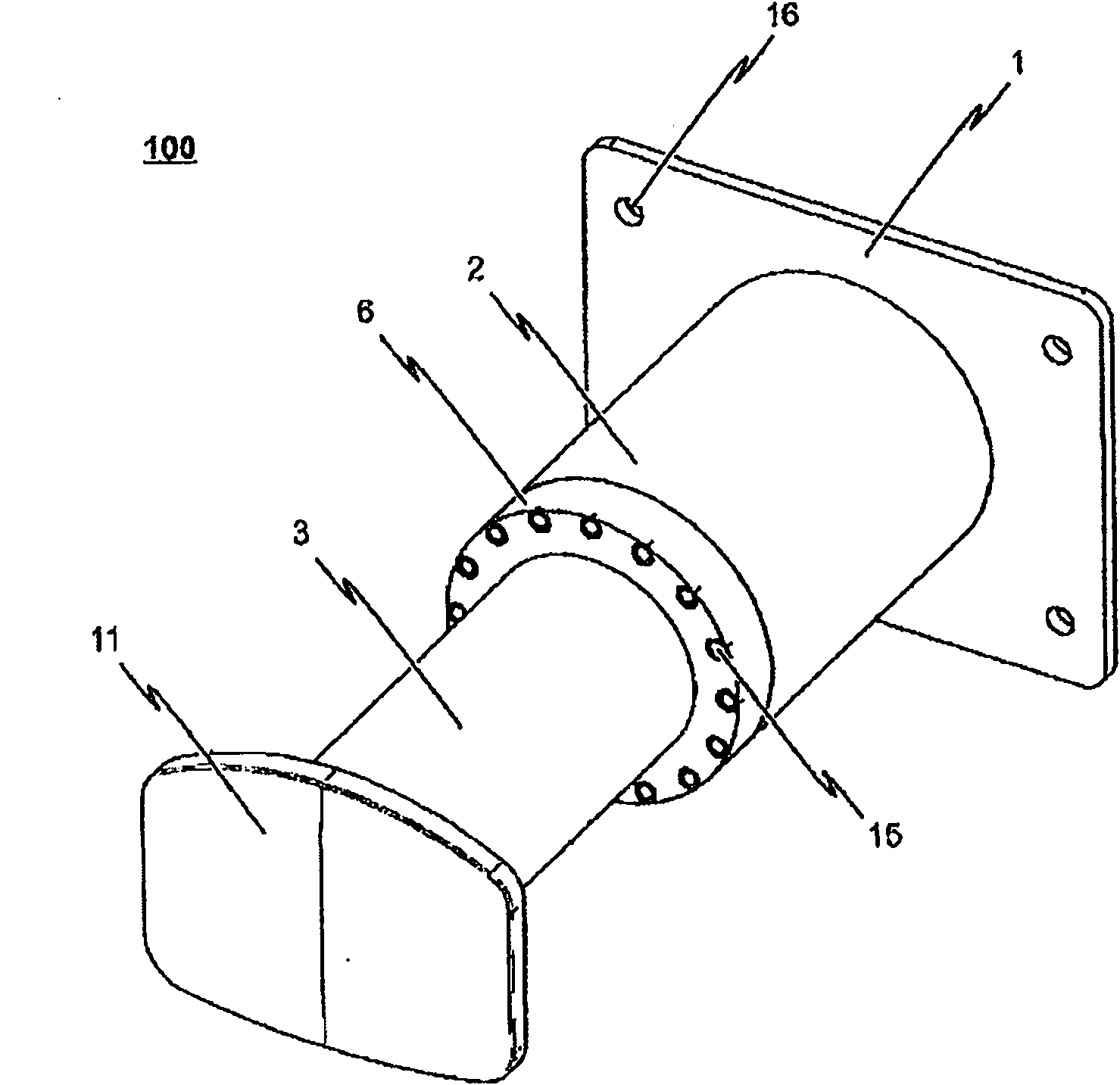
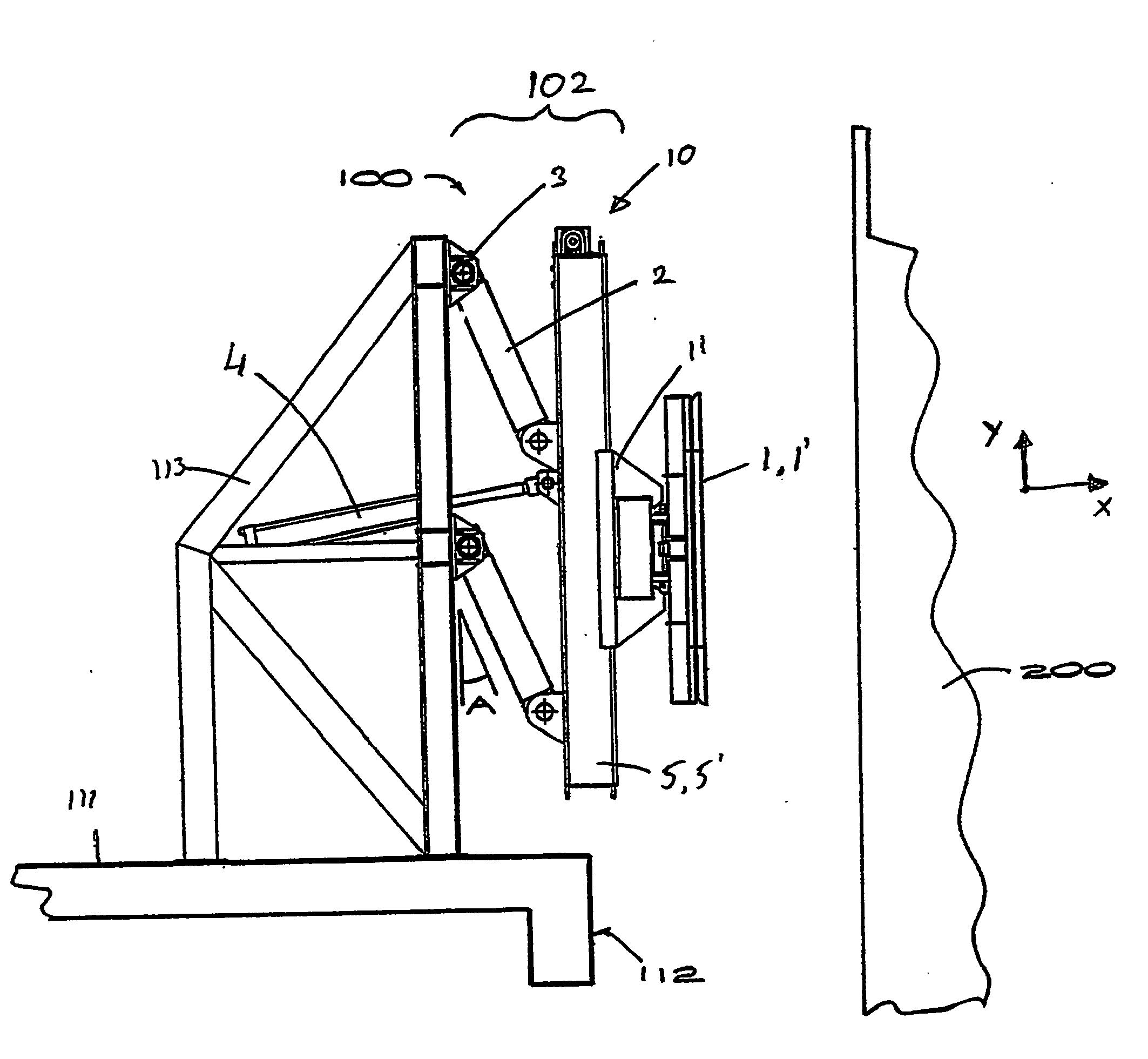
Shock absorber
InactiveUS20090065462A1Protection from damageBuffer carsClimate change adaptationEnergy absorptionEngineering
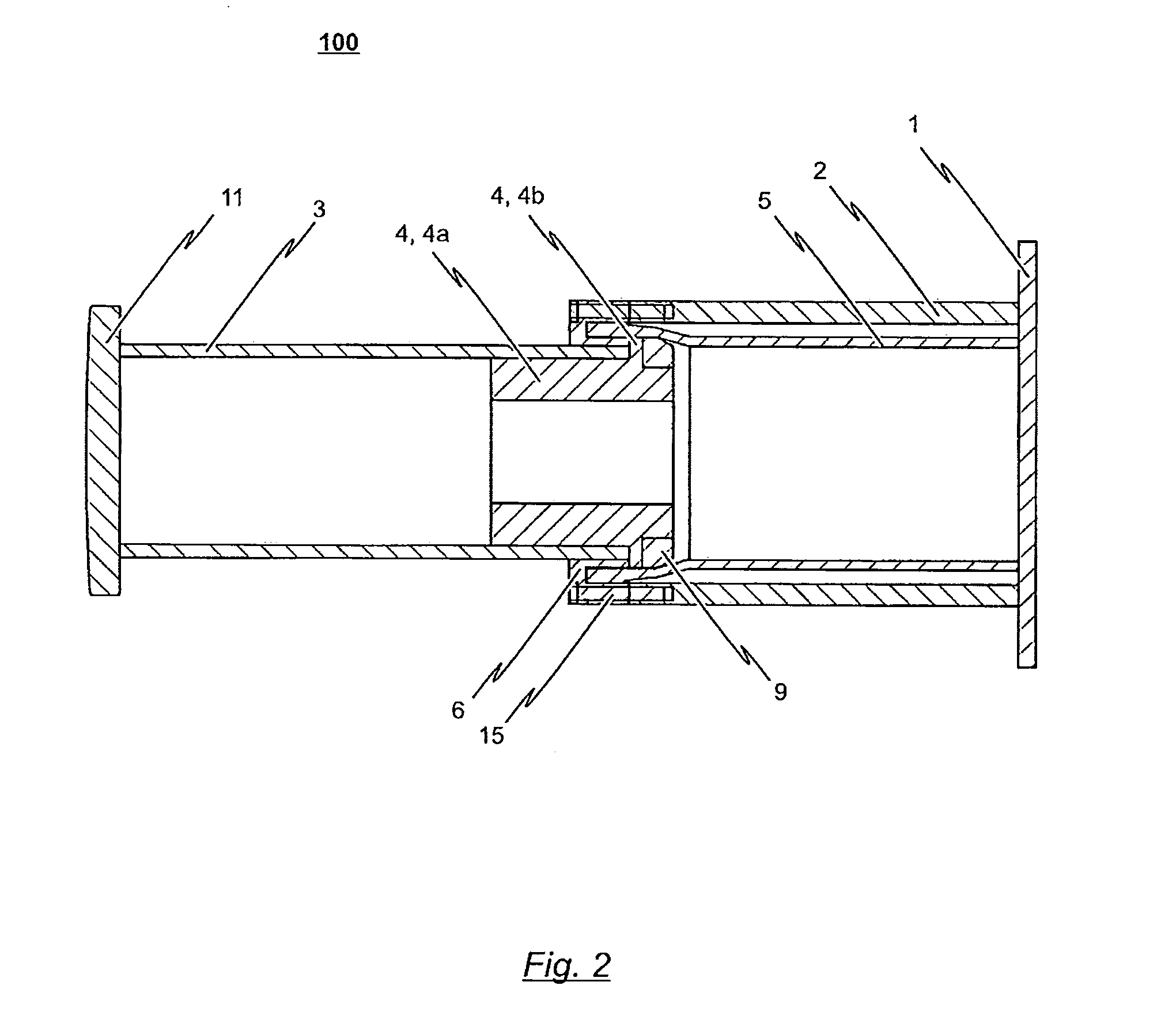
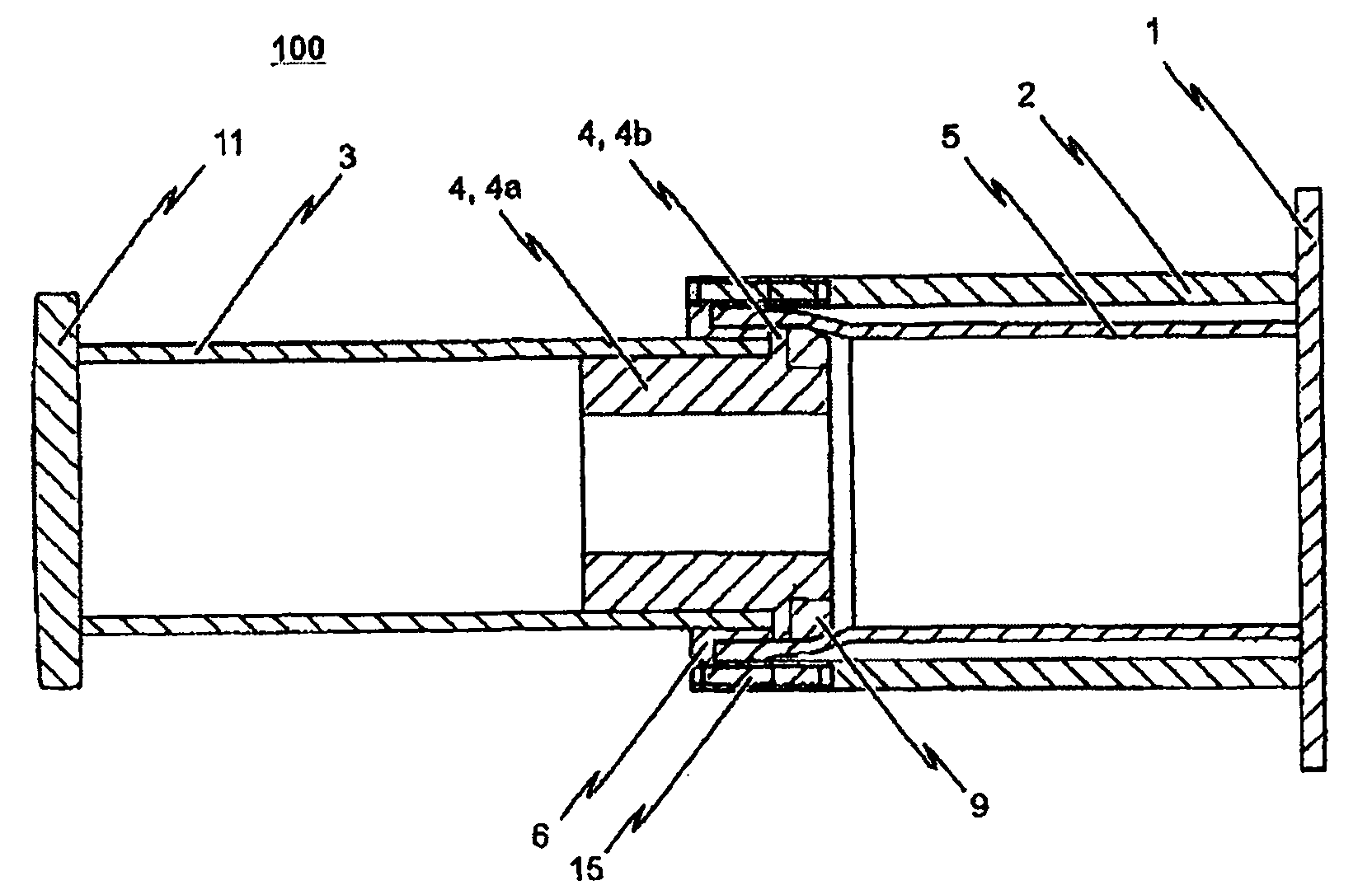
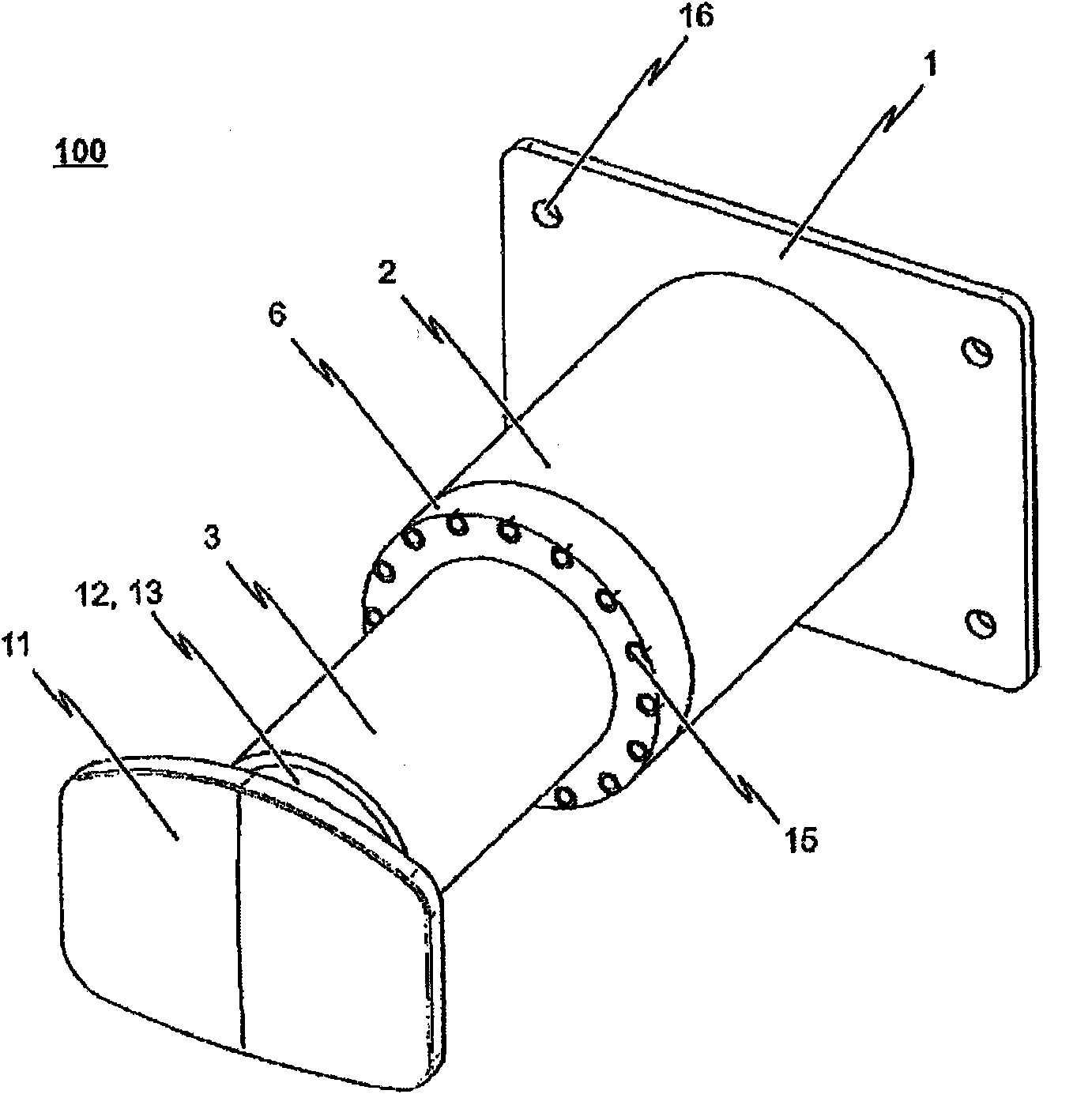
The invention relates to a shock absorber (100), in particular for use as an additional irreversible shock-absorbing stage together with a component for transferring force. In order to achieve the reliable dissipating of high impact energies, a shock absorber (100) comprising the following is indicated in accordance with the invention: a base plate (1); a force-transferring element (3) having a tensioning element (4); an energy-absorbing element in the form of a deformation tube (5) which is connected by a first end section to the base plate (1); and a connecting element (6) for the disengageable connecting of the force-transferring element (3) to a second end section of the deformation tube (5), wherein the connecting element (6) is pressed against the tensioning element (4) such that the deformation tube (5) is braced between the tensioning element (4) and the base plate (1) without play.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
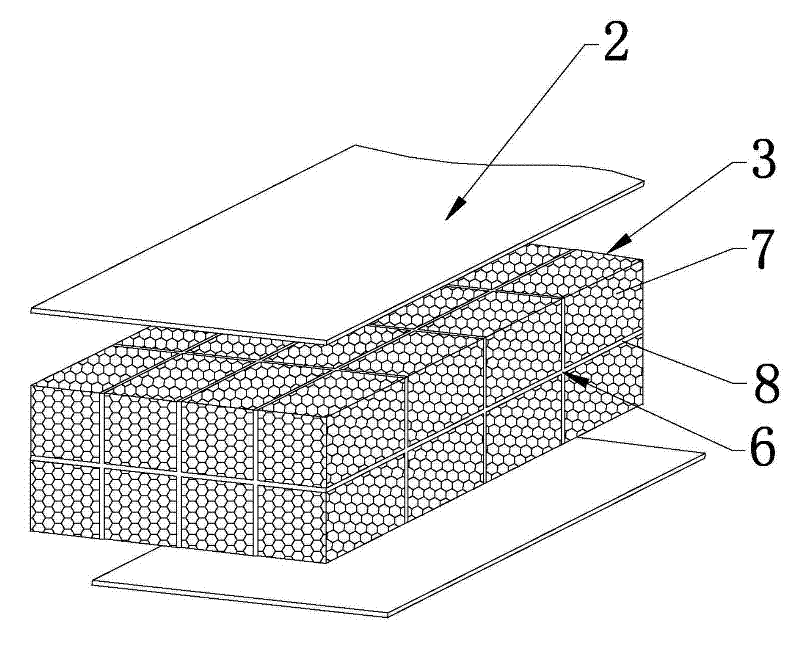
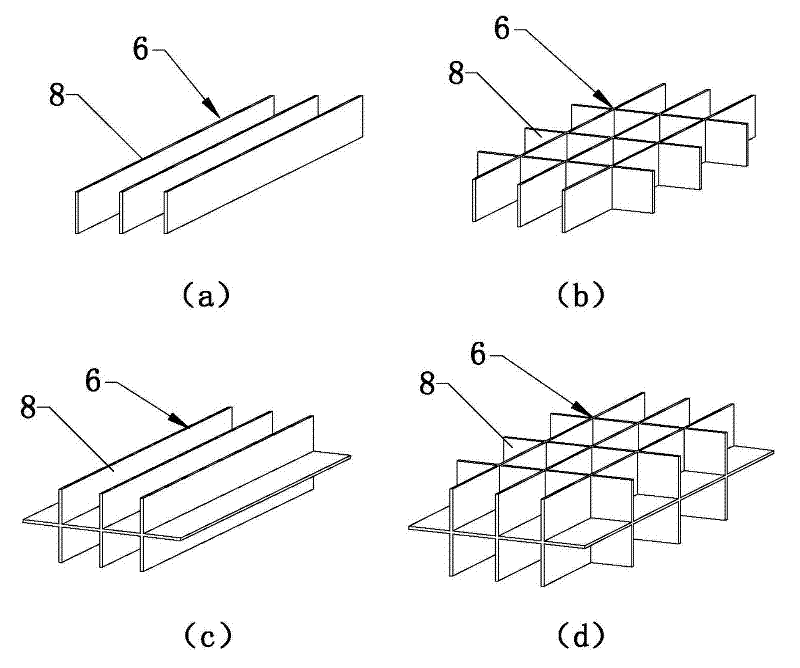
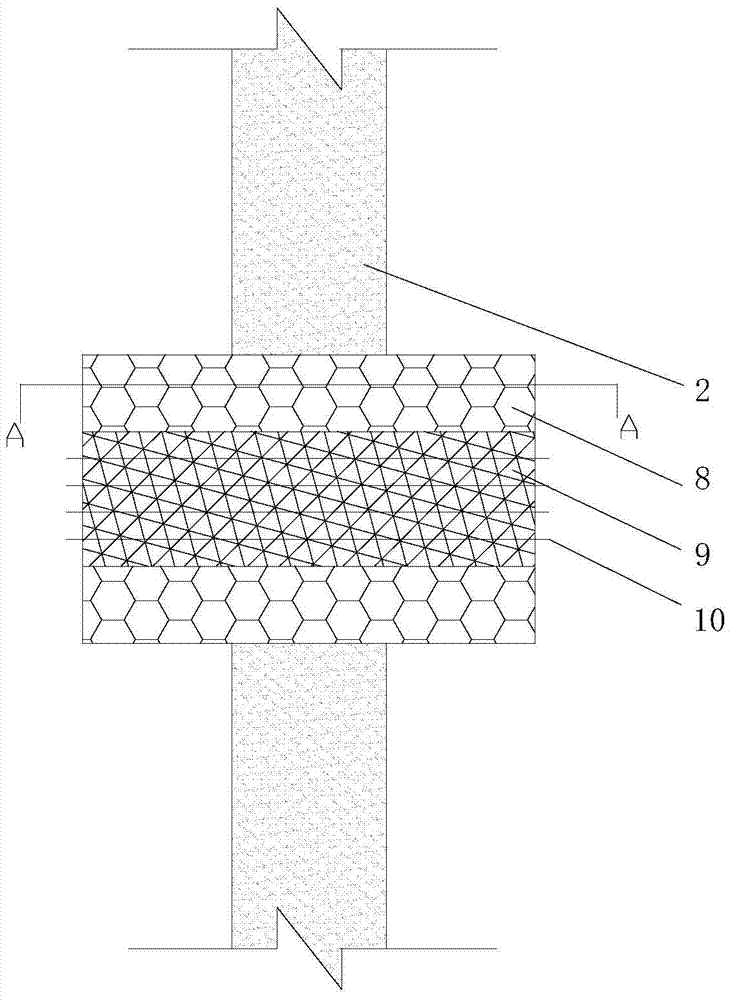
Honeycomb lattice enhanced type composite material double-cylinder structure and anti-collision system using same
InactiveCN103031817AEffectively distributes impact loadsWithstand multiple impactsClimate change adaptationShipping equipmentMortise and tenonFilling materials
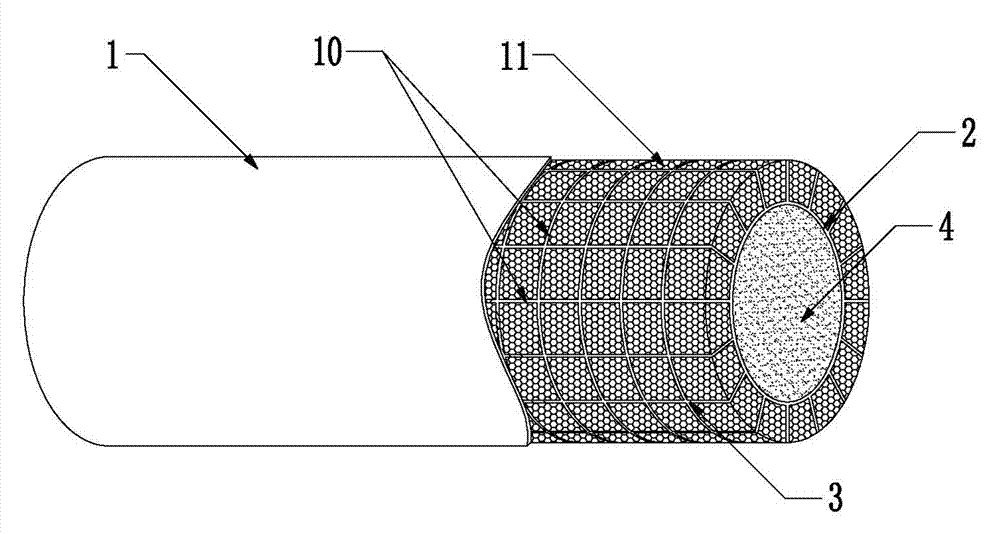
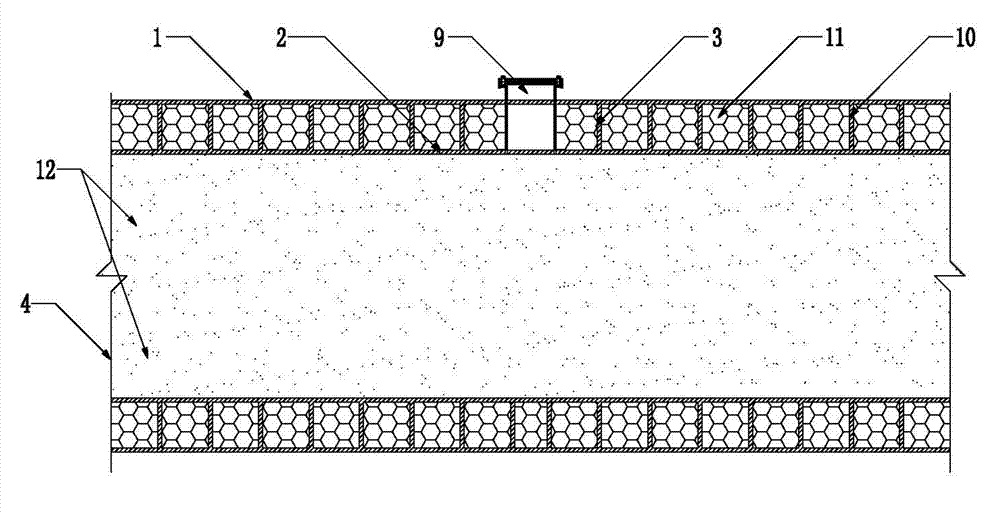
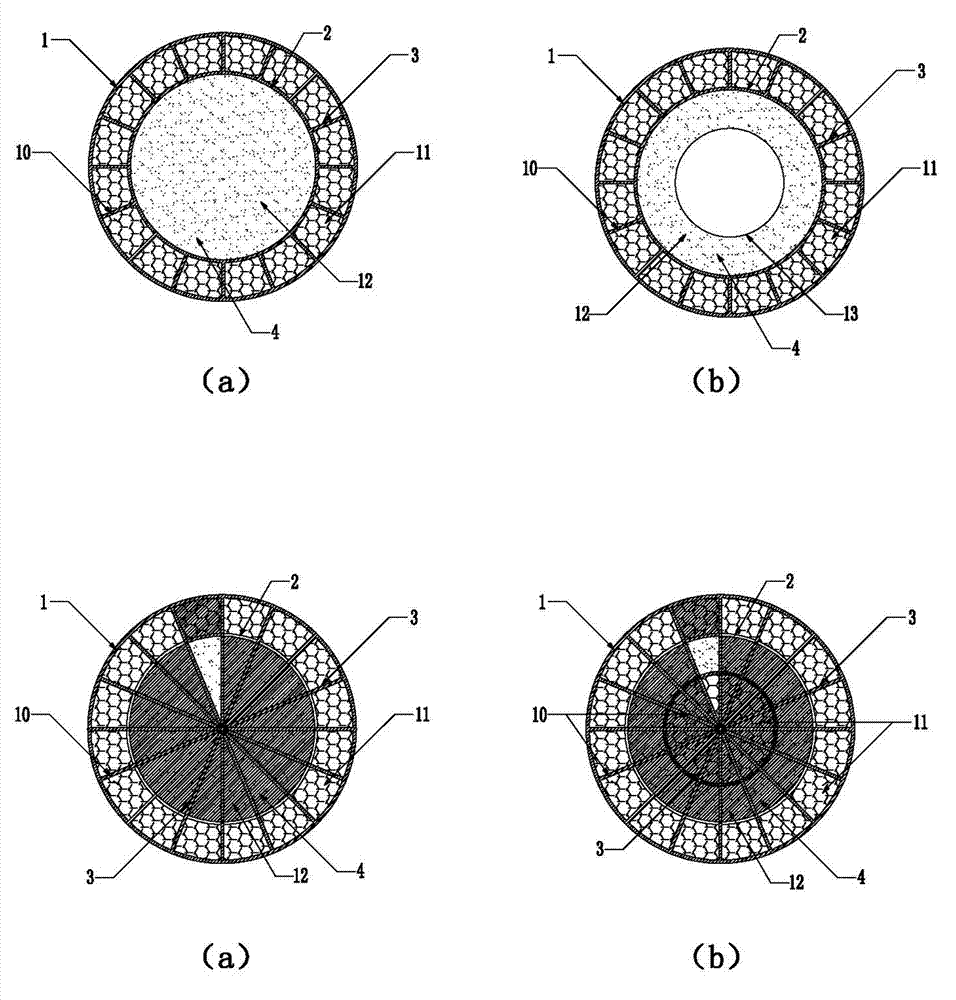
The invention discloses a honeycomb lattice enhanced type composite material double-cylinder structure and an anti-collision system using the same. The double-cylinder structure comprises an outer cylinder (1) and an inner cylinder (2), wherein a honeycomb lattice enhanced body (3) is arranged between the outer cylinder (1) and the inner cylinder (2); and a filling material body (4) is filled into the inner cylinder (2). The anti-collision system comprises the honeycomb lattice enhanced type composite material double-cylinder structure, wherein the double-cylinder structure comprises straight cylinder units (5) and bent cylinder units (6); adjacent and mutually connected straight cylinder units (5), the straight cylinder units (5) and the bent cylinder units (6), or the bent cylinder units (6) are connected together through mortise and tenon joints (7) and bolts bars (16) so as to form a strip-shaped or annual anti-collision system; and a moving device (8) is arranged on the inner side of the anti-collision system. The double-cylinder structure is integrally formed in a weaving mode, and the filling material body has higher rigidity, so that the deformation degree can be limited without crack, and the double-cylinder structure is long in service life, low in cost and easy to maintain.
Owner:JIANGSU BOHONG NEW MATERIAL TECH +1
Floating LNG regasification facility with LNG storage vessel
InactiveUS20080295526A1Well formedContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsMarine engineeringSubmarine pipeline
An LNG terminal is disclosed which includes an offshore mooring turret, an LNG storage vessel operatively coupled to the mooring turret, the LNG storage vessel including at least one LNG storage tank for the storage of liquid natural gas and a regasification vessel operatively coupled to the LNG storage vessel. A method of operating an offshore LNG terminal is also disclosed which includes obtaining liquefied natural gas from at least one LNG storage tank on an LNG storage vessel that is operatively coupled to a mooring turret, regasifying the liquefied natural gas from the LNG storage vessel using a regasification vessel operatively coupled to the LNG storage vessel, and supplying the regasified gas to at least one subsea pipeline via the mooring turret.
Owner:SOFEC
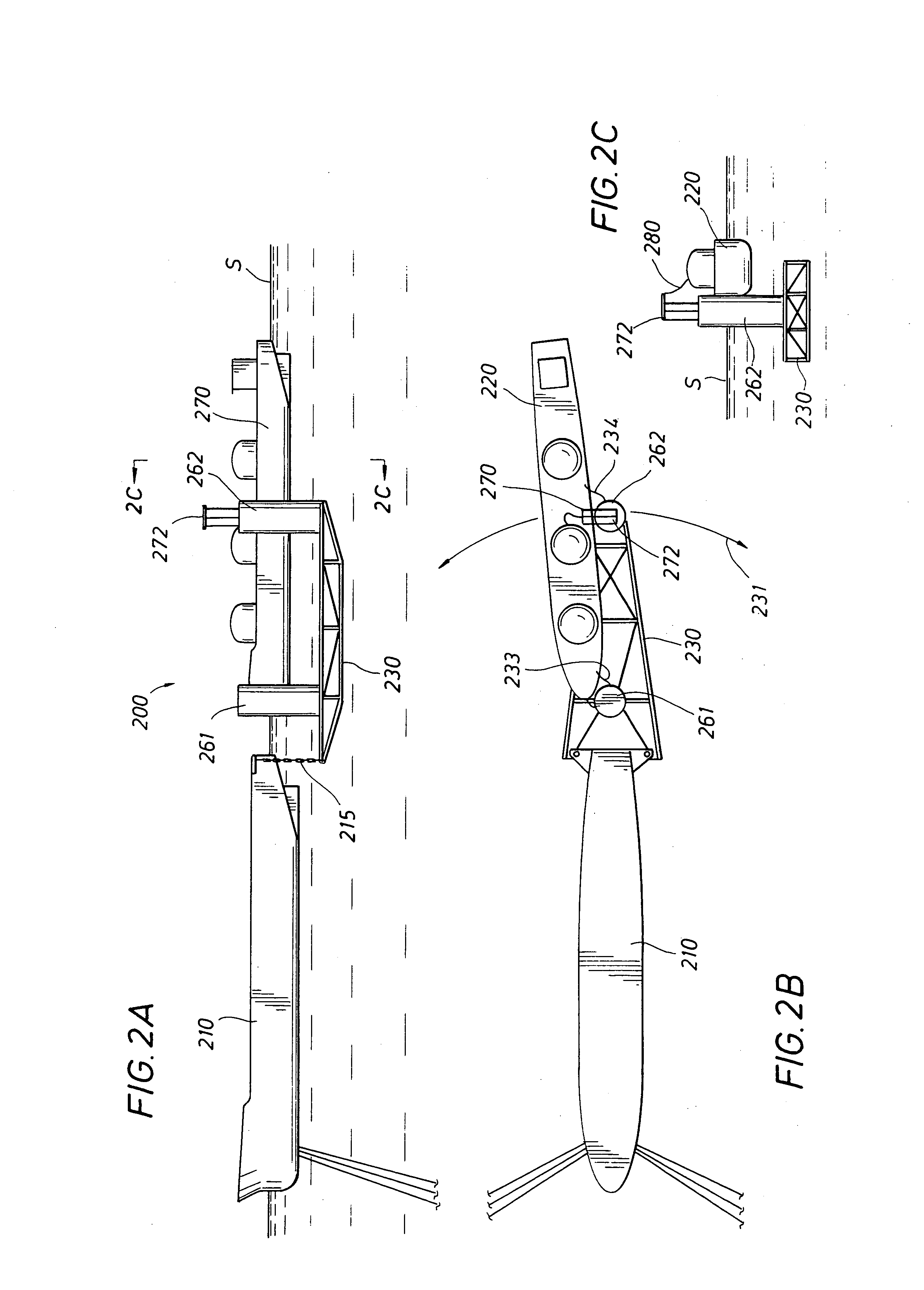
Apparatus and methods for providing VIV suppression to a riser system comprising umbilical elements
InactiveUS7070361B2Suppressing vortex-induced vibrationProvide protectionPipe laying and repairDrilling rodsMarine engineering
Apparatus for suppressing vortex induced vibrations on a marine element of a riser system wherein the riser system comprises at least one umbilical element. Systems comprising and methods of using said apparatus to suppress vortex induced vibrations. The apparatus, systems, and methods comprise module elements which provide: i) a surface around a marine element for installing VIV suppression devices; and ii) passages for housing the at least one umbilical element.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Disconnectable mooring system and LNG transfer system and method
InactiveUS20030226487A1Cargo handling apparatusPassenger handling apparatusMooring systemTransfer system
A disconnectable mooring system for connecting an LNG carrier vessel to a permanently moored LNG liquefaction process vessel in combination with an LNG offloading system. One end of a mooring yoke is suspended from a frame at the stern of the LNG process vessel. A male coupler is mounted to an opposite end of the mooring yoke via a universal joint. A female coupler is mounted on the LNG carrier vessel, with pull-in arrangements for pulling the LNG carrier vessel into position and the male coupler into selective coupling with the female coupler.
Owner:SOFEC
Cylindrical composite bridge anticollision device
InactiveCN102251470AExcellent mechanical propertiesLow maintenanceClimate change adaptationBridge structural detailsFilling materialsEngineering
The invention discloses a cylindrical composite bridge anticollision device which comprises an anticollision unit (1), wherein the anticollision unit (1) is composed of a shell (2) and a packing body (3) filled in the shell (2); the anticollision unit (1) comprises straight cylindrical anticollision members (4) and bent cylindrical anticollision members (5); the straight cylindrical anticollision members (4) which are not mutually adjacent are connected in series or in parallel so as to form a strip anticollision device; the straight cylindrical anticollision members (4) which are mutually adjacent and connected, or, one straight cylindrical anticollision member (4) and one bent cylindrical anticollision member (5), or, the bent cylindrical anticollision members (5) are connected by virtue of a socket flange (7) and bolts (8) so as to form a circular or C-shaped anticollision device; and the inside of each straight cylindrical anticollision member (4) is provided with a rolling device (9), and the inside of the socket flange (7) is provided with a slide device (10). The device disclosed by the invention is low in cost, large in elastic deformation and good in anticollision performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Smooth sleeves for drag and VIV reduction of cylindrical structures
A method for controlling drag and vortex induced vibration in a substantially cylindrical element by providing an ultra-smooth surface about the cylindrical element. The system for controlling drag and vortex induced vibration utilizes a substantially cylindrical marine element having an ultra-smooth effective surface.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Mooring systems with active force reacting systems and passive damping
InactiveUS6439147B2Displacement amplitude can be reduced and evenLow costBuoysShipping equipmentHydraulic cylinderMooring system
A mooring system including a body / arm / vessel arrangement with passive damping and / or an active force restoring system. The active force restoring system includes a sensor for generating a displacement signal representative of the displacement of the vessel from a quiescent position and an active forcing device which responds to the displacement signal to force the arm in a direction to move the vessel toward the quiescent position. The passive damping arrangement includes a device, independent of and in addition to the damping of the water on the vessel or the arm, that damps the oscillation of the vessel in response to environmental conditions which force the vessel from its quiescent position. Hydraulic cylinder arrangements are provided for active forcing and passive damping. Powered winch / cable arrangements are also provided for active force systems. Alternative devices for active and passive damping systems of torque actuators include hydraulic powered cans with internal fins, or cans with internal elastomeric elements or disk brake elements.
Owner:SOFEC
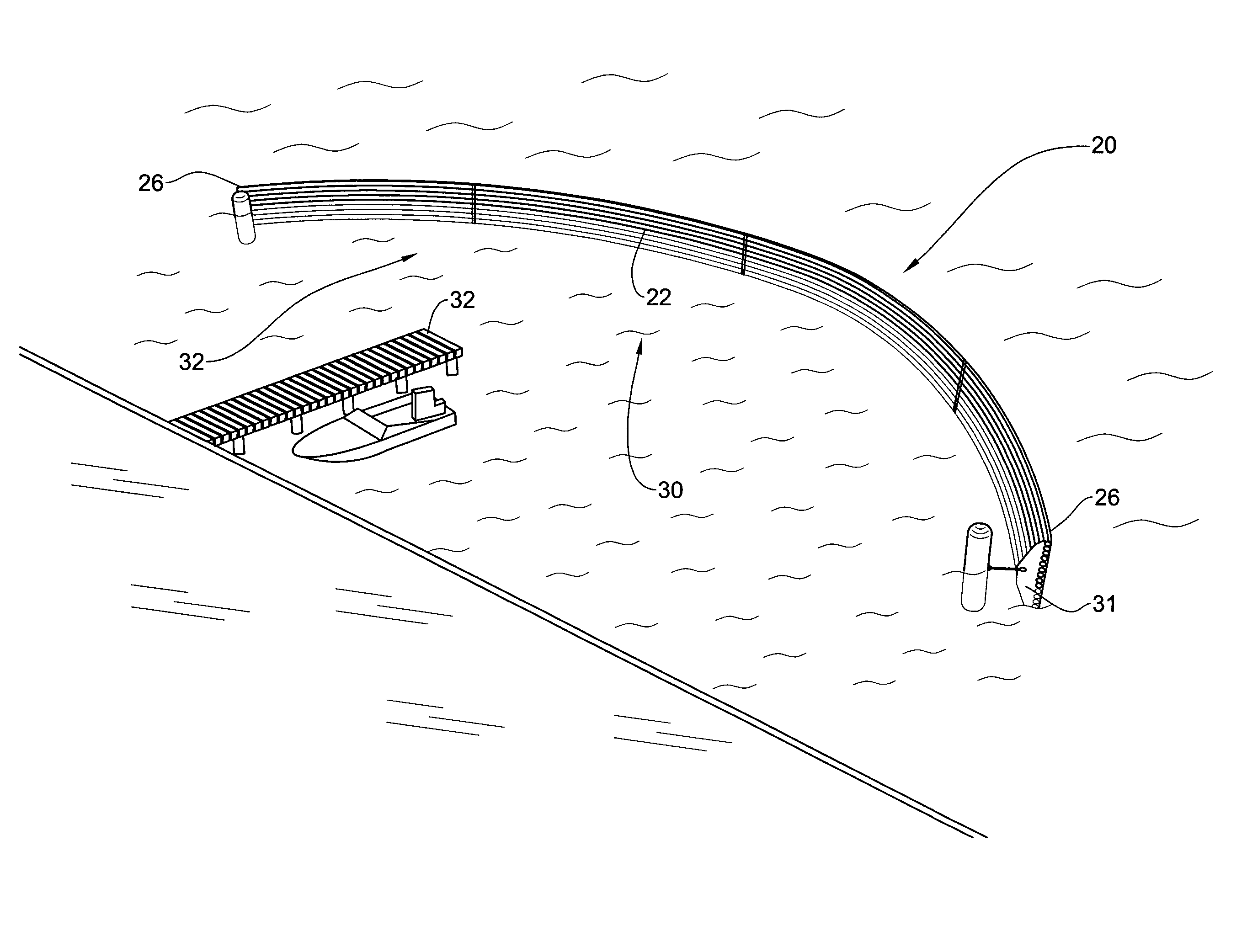
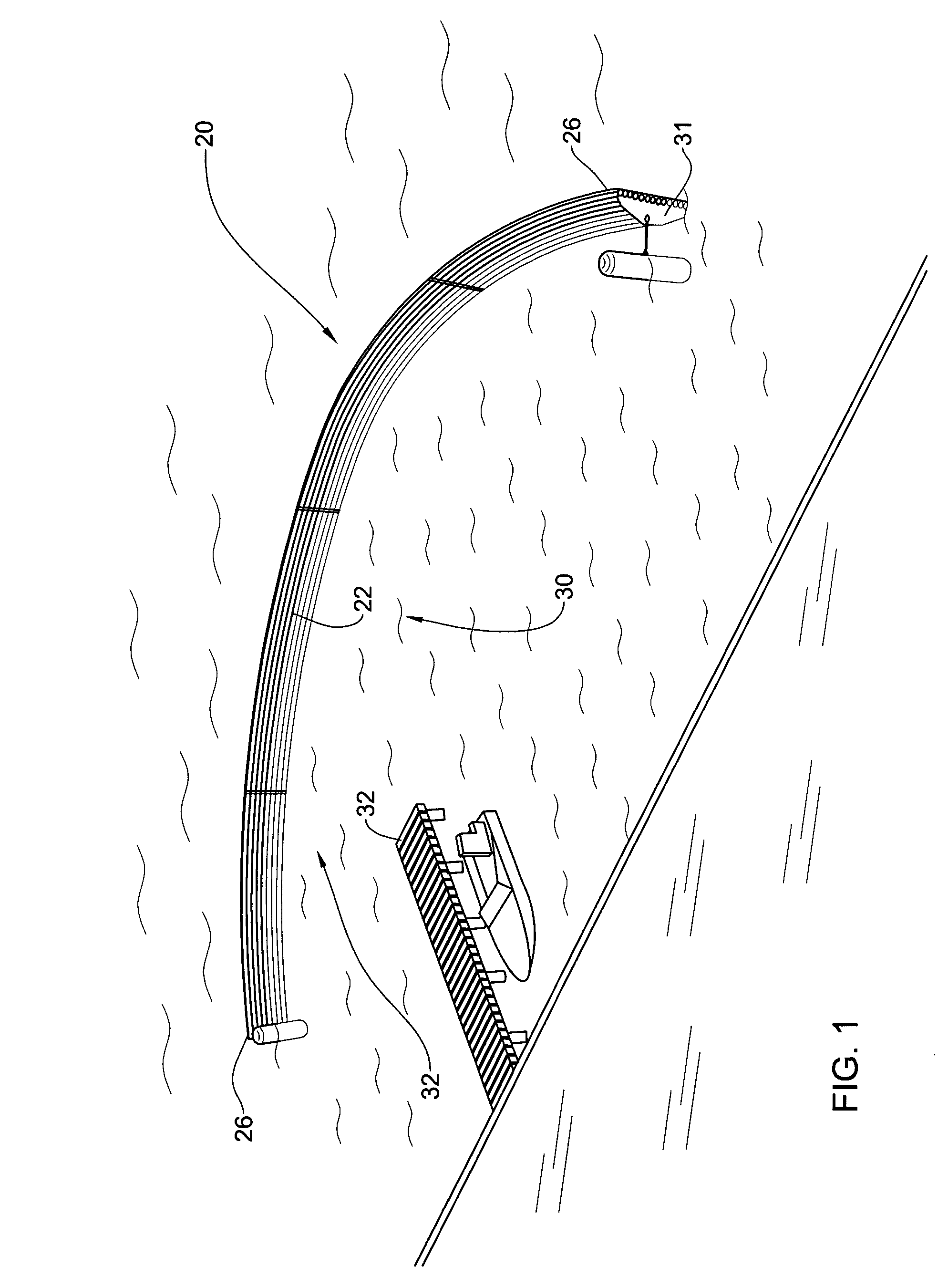
Floating modular breakwater
InactiveUS20050058509A1Easy accessReducing vertical vector of forceBreakwatersWater cleaningEngineeringArcuate shape
A floating breakwater assembly comprising an array of elongate rods articulated to one another for extending at a substantial vertical position at least partially submersed in water, wherein the rods are made of a flexible material and where the array is elastically deformable into an arcuate shape by bending the array.
Owner:STEINBERG DOV
Shock absorber
The invention relates to a shock absorber (100) especially for use as an additional irreversible shock absorbing element in combination with a component for transmitting force. In order to reliably absorb high impact energies, a shock absorber (100) comprises the following elements: a base plate (1); a force transmitting element (3) having a tensioning element (4); an energy absorption element in the form of a deformable tube (5) which is connected to the base plate (1) via a first end section; and a connecting element (6) for detachably connecting the force transmitting element (3) to a second end section of the deformable tube (5), the connecting element (6) pressing against the tensioning element (4) in such a manner that the deformable tube (5) is tensioned between the tensioning element (4) and the base plate (1) without play.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
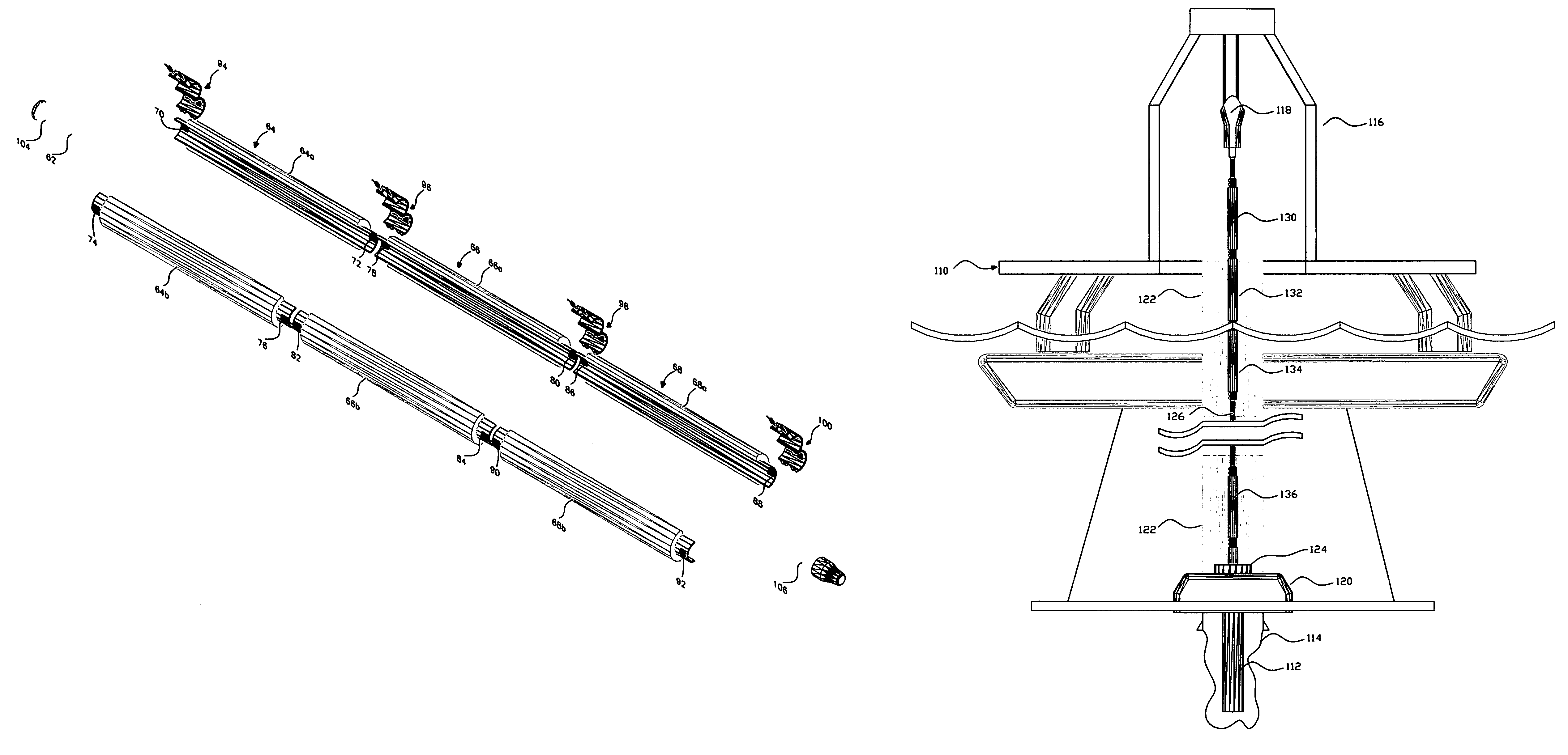
Torsion spring torque arm yoke mooring system
InactiveUS6227135B1Improve performanceCost effectiveWaterborne vesselsShipping equipmentMooring systemTorsion spring
A soft yoke mooring system, with torsional spring devices to provide restoring force to yoke arms coupled to a mooring body. Two torsional spring device types are preferred. A first torsional spring device type includes a plurality of nested tubular shafts, which are coupled end to end to each other in a coaxial array. Torque arms extend from a yoke arm end to one end of the tubular shafts, with the other end of the shafts coupled to a vessel. A second torsional spring device type includes stacks of elastomeric shear unit arrays or blocks of elastomeric material, which are coupled between a torque diaphragm device and a vessel and with the torque diaphragm device coupled by a torque arm to an end of a yoke arm.
Owner:FMC TECH INC
Methods and apparatus for installation of VIV suppression during installation of marine pipeline
InactiveUS20050254903A1Reduce resistanceReducing vortex-induced-vibrationsPipe laying and repairProtective foundationOcean bottomEngineering
Methods and apparatus for the installation of VIV suppression during the S-Lay installation of a subsea pipeline. A locking member will be interposed between a pipe and a fairing rotatably mounted on the pipe, sufficient to bias the fairing against rotating. Upon marine application, the locking member will degrade, thereby releasing the fairing.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Duplex yoke mooring system
ActiveUS20040025772A1Improve reliabilityImprove securityCargo handling apparatusPassenger handling apparatusElectricityTransverse force
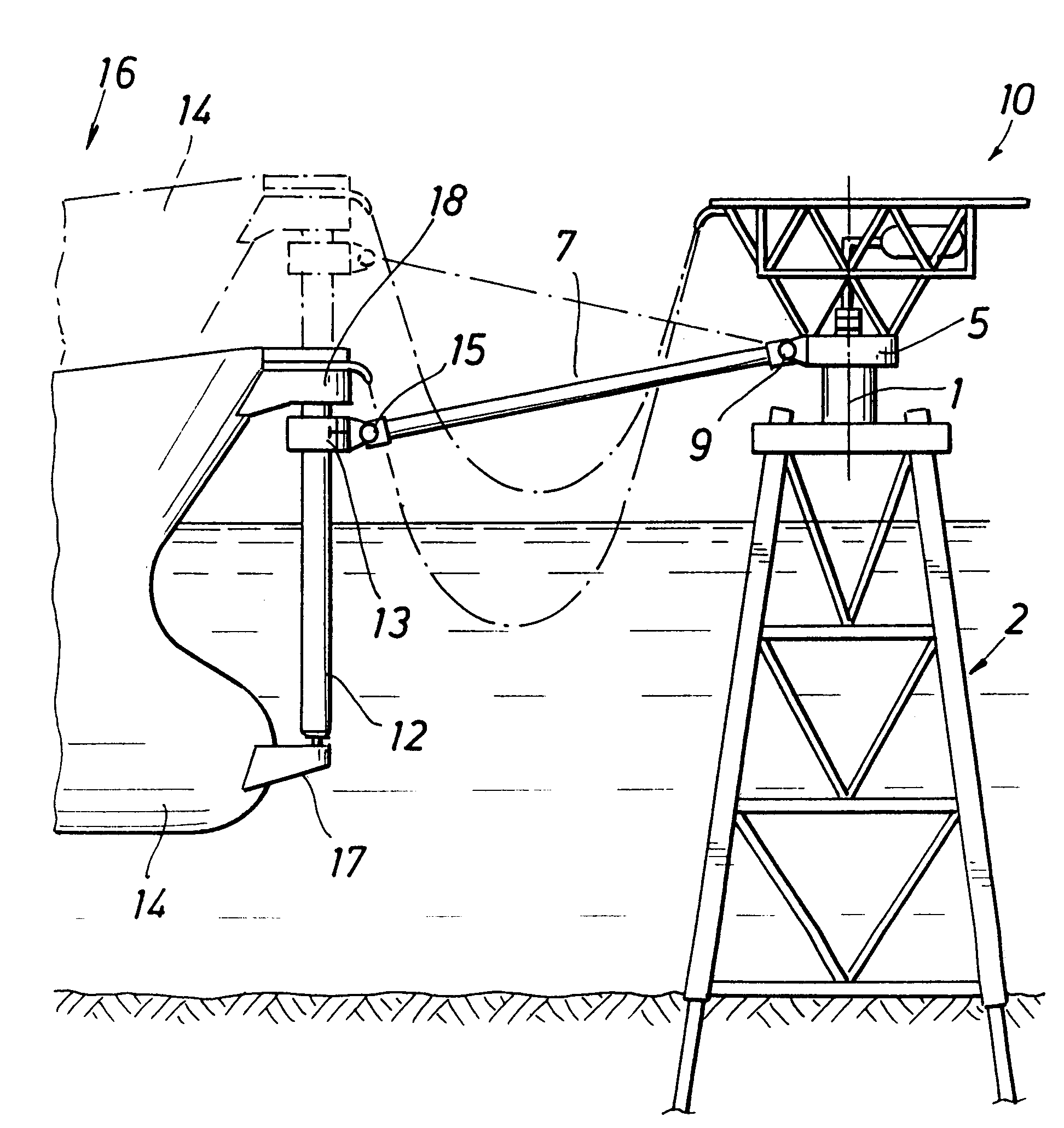
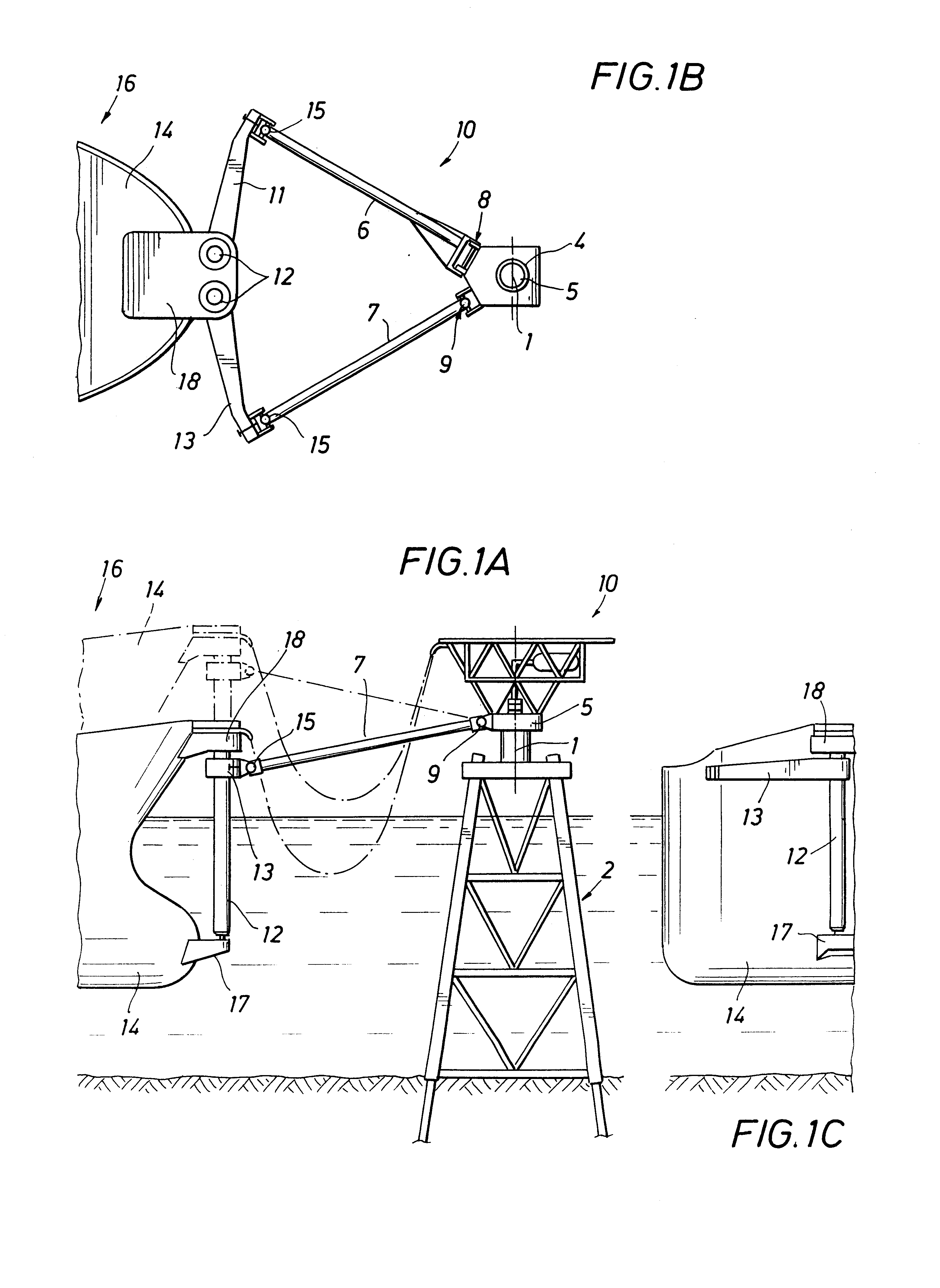
An offshore offloading system for hydrocarbon products from a storage station such as an LNG / FPSO to a shuttle vessel. The system includes a yoke mooring arrangement having a yoke and a connection assembly. One end of the yoke is selectively disconnectable to the shuttle vessel, while the other end of the yoke is rotatably connected to an end of the connection assembly which has its other end rotatably connected to a frame which extends from an end of the storage station. The yoke and connection assembly are arranged such that a transverse force in the lateral or y-direction moves the end of the yoke less than twice the movement of the yoke in response to an x-direction force. The system also includes arrangements for providing a hydrocarbon fluid flow path from the storage station to the shuttle vessel when the shuttle vessel is disconnectably moored to the storage station. A first fluid flow path arrangement includes a crane / boom arrangement mounted on a frame extension of the storage station so that a crane slewing arc radius of the transfer system is not larger than one half the separation distance between the storage station and a forward perpendicular of the shuttle vessel. A second arrangement includes a fixed frame with a piping pantograph mount at its end. A trolley and service platform suspended therefrom move between an operational position away from the pantograph and a service position beneath the pantograph when it is folded into a storage position.
Owner:SOFEC
Offloading arrangements and method for spread moored FPSOs
InactiveUS6983712B2Avoid contactRapid disconnectionCargo handling apparatusPassenger handling apparatusMooring systemDynamic positioning
A mooring arrangement between a floating storage body spread moored in deep water and a shuttle tanker, the arrangement including a single point buoyant member that is adapted for mooring a shuttle tanker in offloading position relative to a floating production, storage and offloading vessel (FPSO) with a link between the floating storage body and the single point buoyant member. One embodiment (100) of the invention employs a submerged yoke (30), having one end (31) rotatably coupled to a FPSO (10) and a second end (32), supported by a buoy. A mooring hawser (28) extends from the buoy to the shuttle tanker and product hoses connect the shuttle tanker with the FPSO and extend along the submerged yoke. In another embodiment, the mooring buoy is stationed by a hold-back mooring system (303–304) and the FPSO or the tanker or both is provide with traction device (308) to move the tanker into loading position with respect to the FPSO. Other embodiments of the invention establish mooring of a shuttle tanker so that it can weathervane 360 degrees during offloading activity. In another embodiment, the mooring buoy (600) is provided with a dynamic positioning system (614) for controlling shuttle tanker positioning with respect to conditions of the environment or for moving the tanker to a desired position during loading.
Owner:SOFEC
Floatation module and method
Owner:VON EBERSTEIN WILLIAM
Floating dock and dock unit for making such
The present document describes a dock unit attachable to another dock unit with a fastener for forming a floating dock. The dock unit comprises a floating body having a mating surface and an attachment adapted to receive the fastener. Thereby attaching the floating body is able to be attached to the other dock unit. The dock unit further comprises a cover for covering the mating surface, the cover having a contact surface adapted to contact the fastener. In use, the contact surface is positioned proximate the attachment so that, when the attachment receives the fastener, the contact surface is contacted by the fastener, thereby limiting the movement of the cover with respect to the floating body.
Owner:CANDOCK
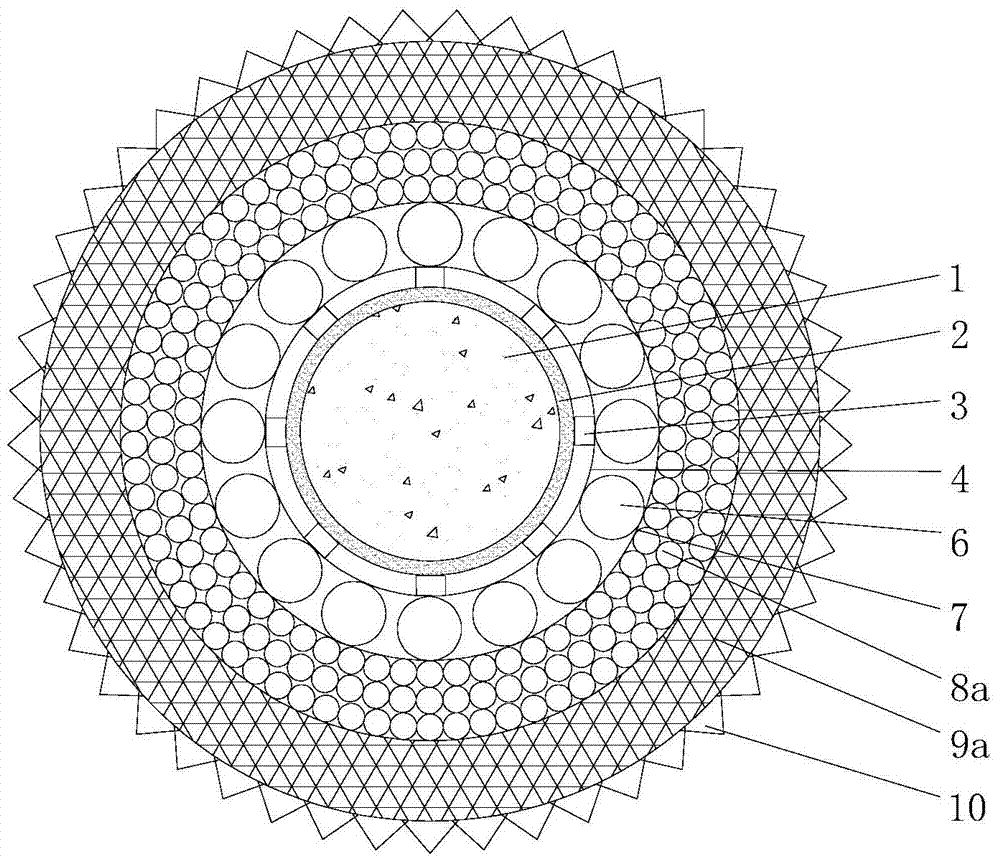
Buffering energy-absorbing web reinforced composite anti-collision device
InactiveCN102561230AEasy to replace if damagedIncreased shear strengthClimate change adaptationShipping equipmentFiberFilling materials
The invention discloses a buffering energy-absorbing web reinforced composite anti-collision device. The device comprises an anti-collision unit (1); the anti-collision unit (1) comprises a shell (2) and a filling material body (3) positioned in the shell (2); the shell (2) is a solid shell consisting of a composite surface layer (4) or a sandwiched shell consisting of a composite surface layer (4) in which a sandwich material (5) is filled and the sandwich material (5); and the filling material body (3) comprises a spatial lattice body (6) and a dissipative material (7), the spatial lattice body (6) is formed by arranging fiber webs (8) in the shell (2) in a single-layer unidirectional, single-layer bidirectional, multi-layer unidirectional or multi-layer multi-directional mode, and the dissipative material (7) is positioned between the fiber webs (8) and / or the fiber webs (8) and the inner wall of the shell (2). The anti-collision device has the characteristics of low cost, strong anti-collision property and long service life, and is easy to assemble and replace and suitable for popularization and use.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Modular floating dock with inflatable pontoons
InactiveUS20060153643A1Simple modular configurationEasy to installDry-dockingSlipwaysModularityPontoon bridge
A modular buoyant support apparatus is comprised of buoyant support modules of inflatable pontoons. The pontoons comprise inflatable tubular chambers, typically fabricated of polymer coated fabric sheet material. A buoyant support module comprises a rigid frame connected to an inflatable pontoon. A means is provided to interconnect buoyant support modules to form a modular buoyant support apparatus of varied support area and configuration. Means are provided to attach an appropriately configured dock surface to the modular buoyant support apparatus.
Owner:BASTA SAMUEL T
Pole bracket for a dock
InactiveUS7406924B1Good adhesionReduce distractionsDry-dockingSlipwaysEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:IMPEY BRIAN C
Mooring system with active control
InactiveUS20060081166A1Performance maximizationReduce energy consumptionShipping equipmentMooring equipmentMooring systemMarine engineering
A vessel mooring system which includes at least two mooring robots secured to a terminal, each robot includes an attractive force attachment element eg. a vacuum cup and a base structure fixed relative to the terminal. The attachment element is able to be engaged with a vertically extending side vessel surface and to exert an attractive force normal to the vessel surface at where it is to be attached. Each robot can measure the attractive force between the attachment element and the vessel to provide an “attractive force capacity reading”. Also provided is capability to measure the force between the attachment element and the fixed structure of the mooring robot to provide a “normal force reading”. From monitoring of the relationship between the attractive force capacity reading and the normal force a control of the mooring robot can be provided such that if there is a tending to separate the attachment elements from said vessel the attractive force may be increased and / or alarm is sounded.
Owner:CAVOTEC MOORMASTER
Protection barrier apparatus
InactiveUS6960047B2Provide protectionOffensive equipmentProtective foundationEngineeringWaterborne craft
Owner:ITA INDAL +1
Vessel, provided with a gang plank for coupling to an offshore pole structure
A vessel provided with a telescopingly extendable gang plank mounted thereon for movement about a vertical axis. A coupling device provided at the free end of the gang plank is adapted to enclose a vertically directed engagement rod on an offshore pole body and thus connect the ship to the pole body. With tile ship manoeuvred in a certain position the gang plank may be either directed and extended towards tile engagement rod or be manoeuvred while taking its extended position laterally into contact with the engagement rod and subsequently (partially) retracted again.
Owner:AMPELMANN OPERATIONS BV
Method for lifting and transporting a heavy load using a fly-jib
InactiveUS6932326B1Increase reachIncrease heightArtificial islandsDry-dockingMooring systemHeavy load
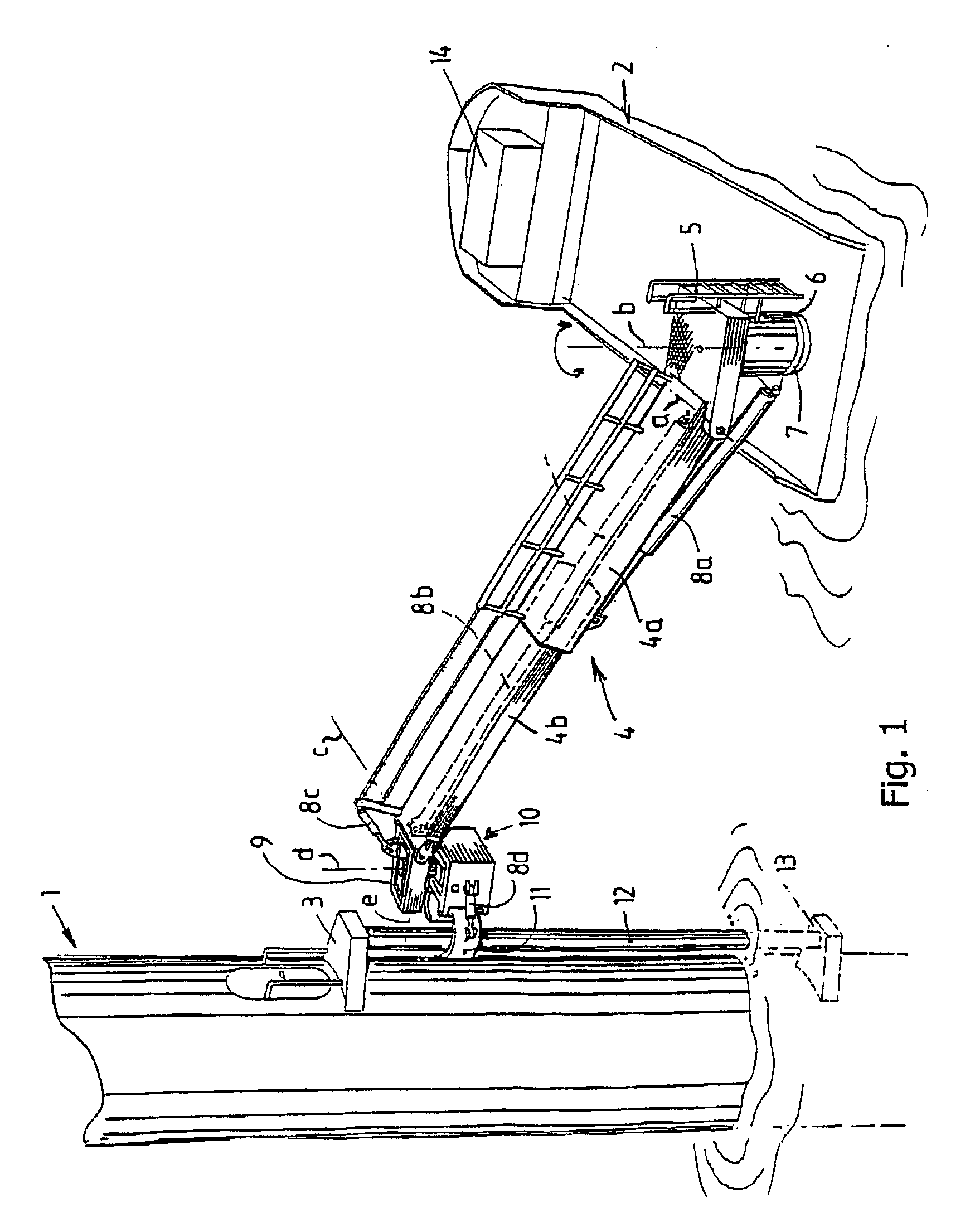
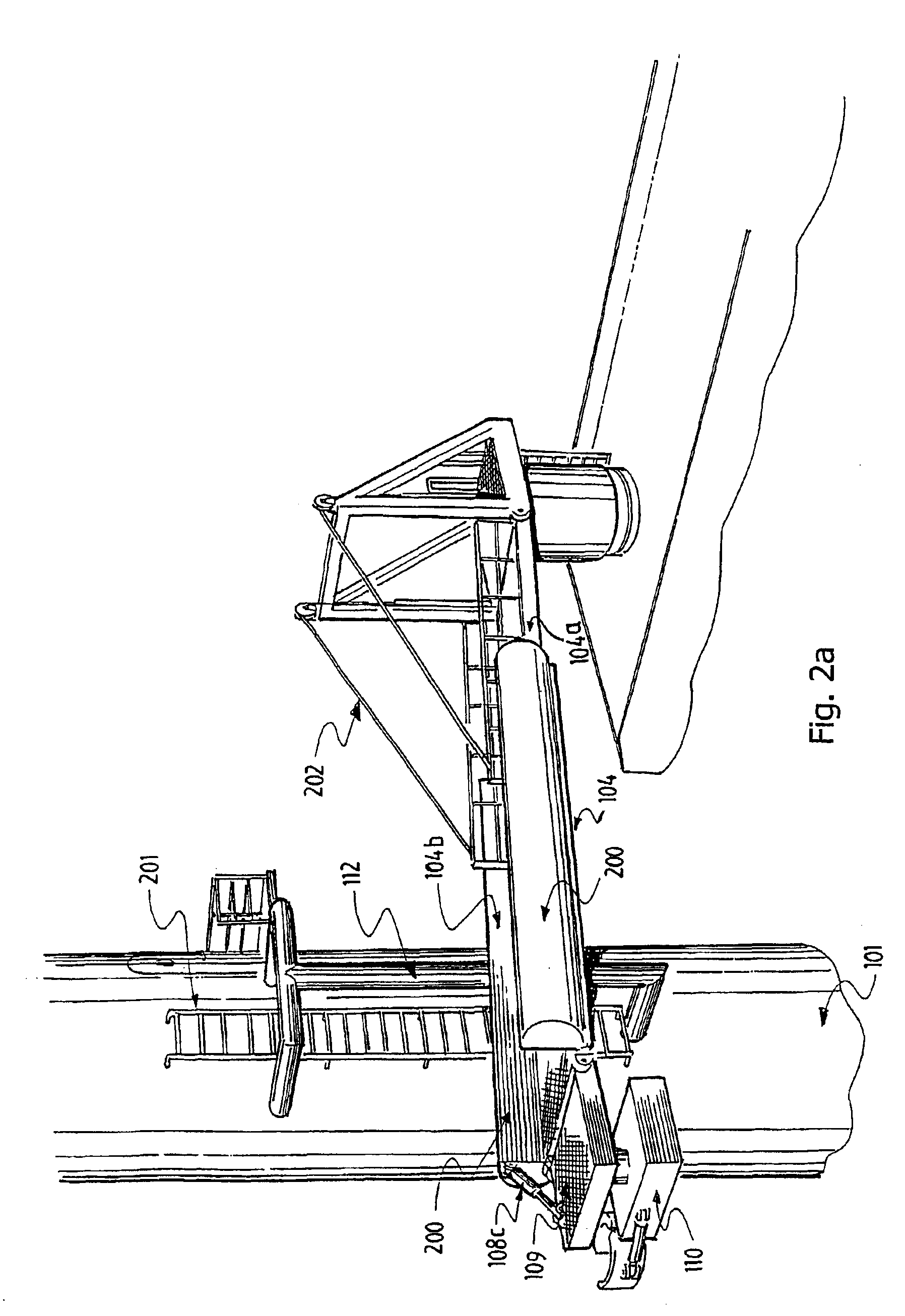
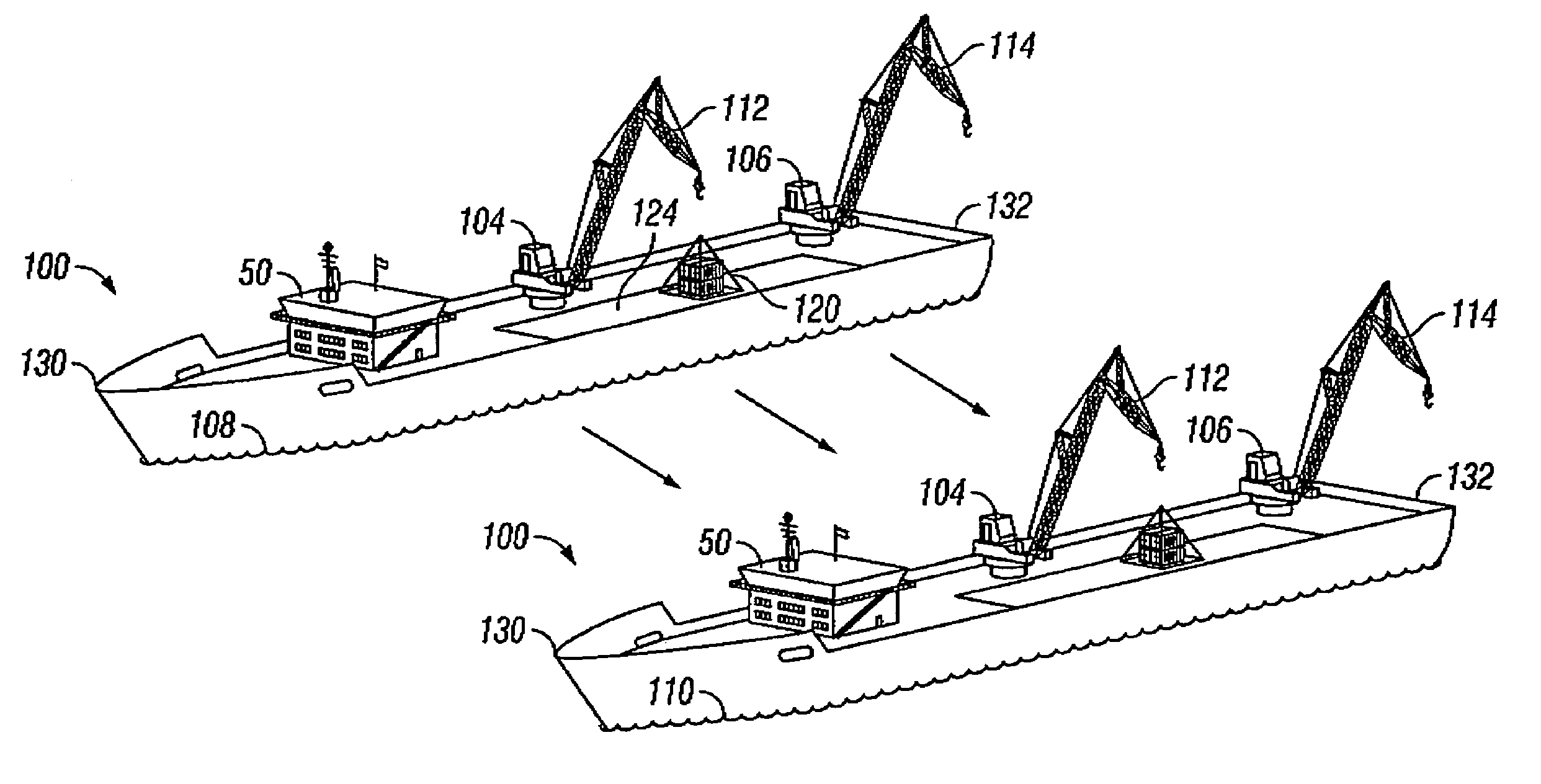
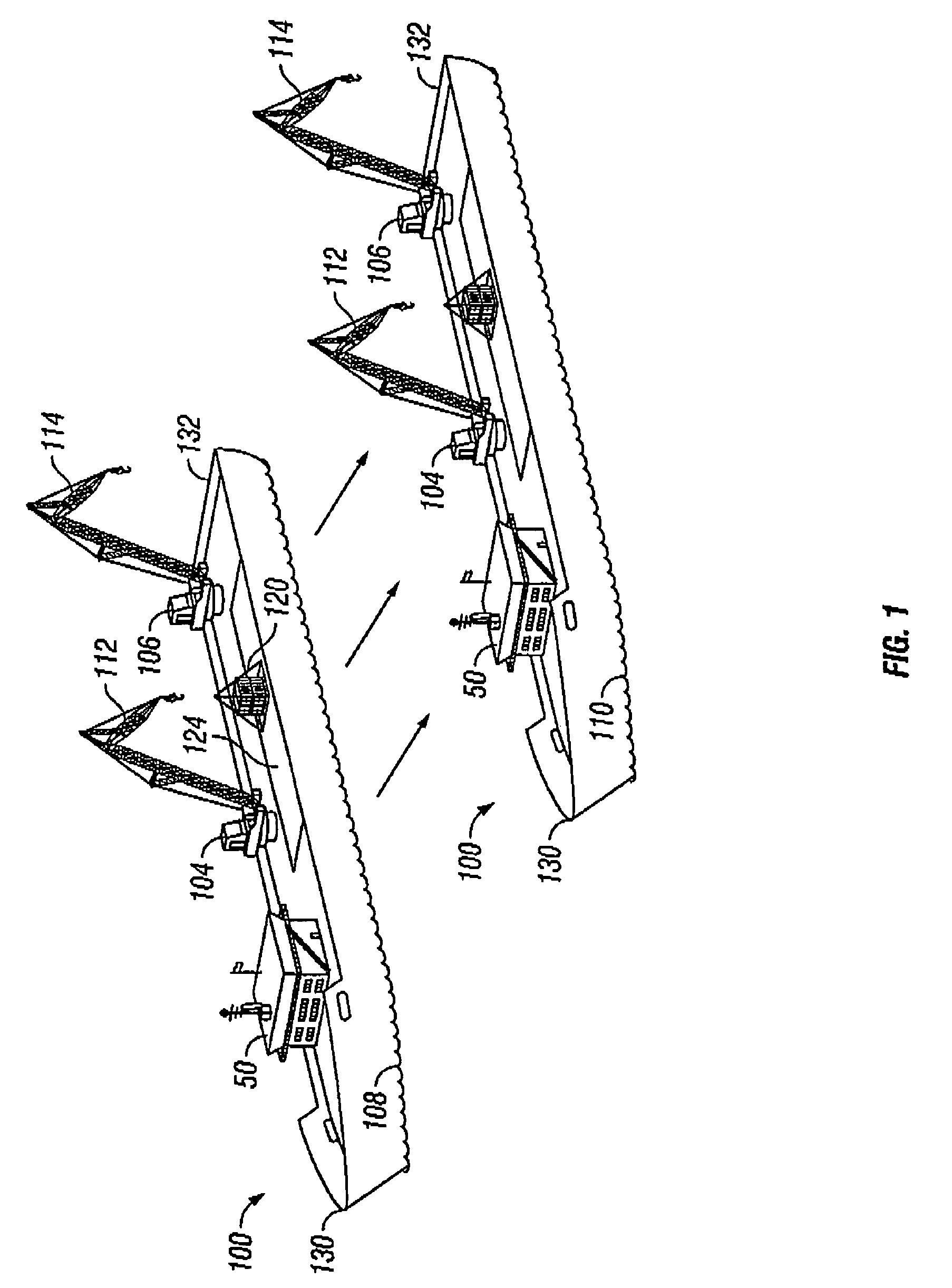
The invention is a method for lifting and transporting a heavy load by using a heavy lift vessel with at least two heavy lift cranes adapted to operate simultaneously; mounting fly-jibs on the heavy lift crane to increase reach and height of the heavy lift crane; picking up a load from a first location using the fly-jib modules simultaneously; shifting the load from the first location to over a second location on the heavy lift vessel; placing the load on the second location; moving the heavy lift vessel to a second position; using a mooring system to maintain the heavy lift vessel at the second position; picking up the load from the second location using the fly-jib modules simultaneously; shifting the load from a second location to over a third location; and placing the load on the third location.
Owner:KRABBENDAM RICHARD L
Mooring apparatus
ActiveUS20050145154A1Increase buoyancySuppress differential motionDry-dockingCargo handling apparatusMooring systemMarine engineering
Apparatus is described for mooring a floating vessel (10) particularly suited to a tanker transporting liquid natural gas which needs to be moored in an offshore environment. The apparatus comprises a semi-submersible floating dock (1) a single point mooring system (5) and at least one rigid arm (3). The arm (3) is pivotally attached to one of the dock (1) and the single point mooring system (5). The arm (3) is suspended from the other of the dock (1) and the single point mooring system (5) by at least one tension member (19).
Owner:BLUEWATER ENERGY SERVECES BV
Semi-submersible dry-docking lift apparatus
A portable marine lift capable of multi-directional off-loading of yachts, ships, and other marine vessels at ground level to dry-dock them. It is compact and barge-like, and can be shared by independent shipyards, or used to expand the work area within a single port facility or shipyard. It is also self-contained when fitted with generators and / or propulsion means via add-on pods, and comprises independent platform sections joined together to meet any hull design, length and water depth. Platform sections have the ability to submerge, and may also be employed to capture and temporarily contain environmentally hazardous materials commonly produced by shipyards. In addition, the platform sections are preferably open-framed for weight savings. Computerized lifting, via multiple lift modules secured to platform sections, assures lifting of vessels in substantially level orientation. Optionally, platform sections can be configured for shallow water operation, with locking devices, and / or guides usable for off-loading railway alignment.
Owner:TAFOYA CRAIG ALLEN
Underwater Docking System and Docking Method Using the Same
InactiveUS20150376851A1Reliable dockingMore reliabilityDry-dockingBreakwatersDocking stationMarine engineering
Disclosed herein are an underwater docking system and a docking method using the system. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention relates to a system for docking a target body on a docking station under water, the system comprising: a guide unit provided to the docking station to transmit at least one guide signal to the target body; an agent unit connected to the docking station by a smart cable and disposed at a position spaced apart from the docking station so that the agent unit is moored under the water in a direction corresponding to a tidal current; and the target body configured to be guided toward the agent unit by the guide signal and then connected to a portion of the agent unit.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Land anchor
InactiveUS6606829B2Easy to storeReciprocating drilling machinesTents/canopiesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:BENINCASA FR +1
Anti-collision device for bridge pier
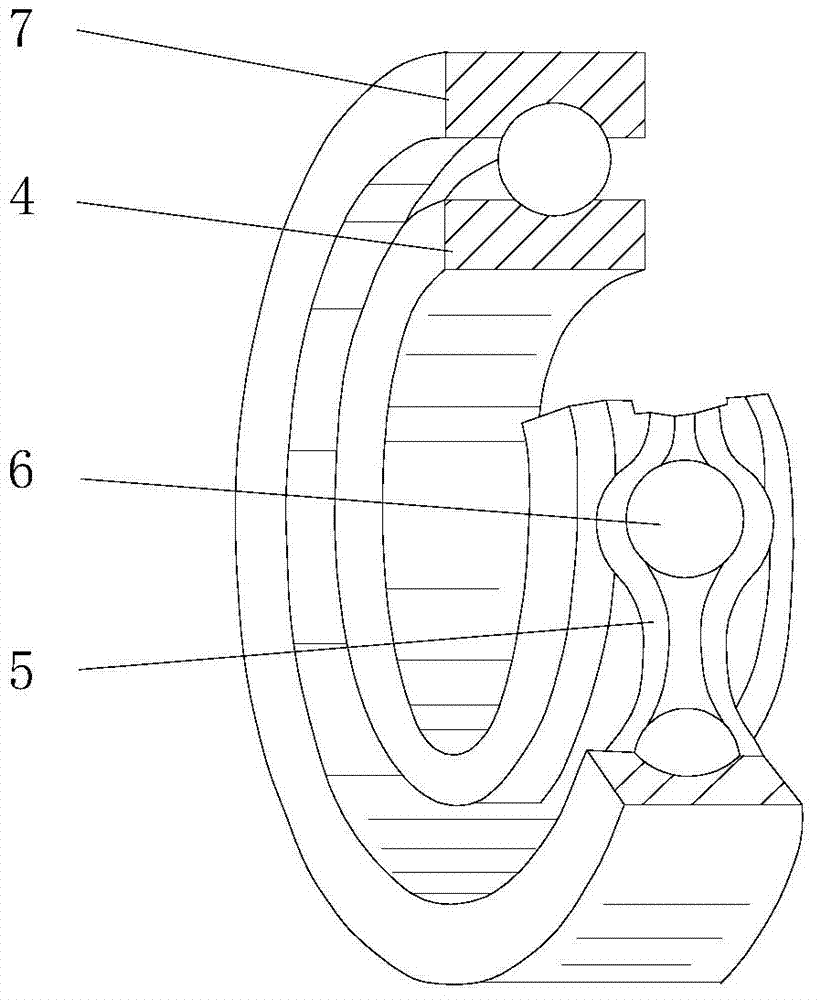
ActiveCN103774621AReduce impact forceImprove securityClimate change adaptationBridge structural detailsEngineeringStress time
The invention discloses an anti-collision device for a bridge pier. The anti-collision device comprises an inner buffering cushion, a rotating assembly and an outer anti-collision assembly which are coaxially arranged from inside to outside. The pier is tightly wrapped by the inner buffering cushion, the outer anti-collision assembly can rotate around the axial central line through the rotating assembly, the rotating assembly comprises an inner ring, an outer ring and spherical rolling bodies evenly distributed between the inner ring and the outer ring, the outer ring can rotate relative to the inner ring, and the inner ring can be matched with the inner buffering cushion in a relatively rotating mode. Not only can the aims of prolonging stress time and reducing impact force borne by the pier be achieved through the outer anti-collision assembly, but also the outer anti-collision assembly can rotate around the axial central line through the rotating assembly when the pier is impacted, so that the impact force caused by objects of ships and the like is guided to shift away from the pier, the remaining huge impact force after buffering of the outer anti-collision assembly is shifted away as much as possible, and safety of a bridge is greatly improved. In addition, the inner ring of the rotating assembly further can rotate relative to the lateral face of the outer circumference of the inner buffering cushion to generate a secondary rotating effect, and the effect of shifting the impact force away from the pier is further improved.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com