Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
911results about "Optical recording heads" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
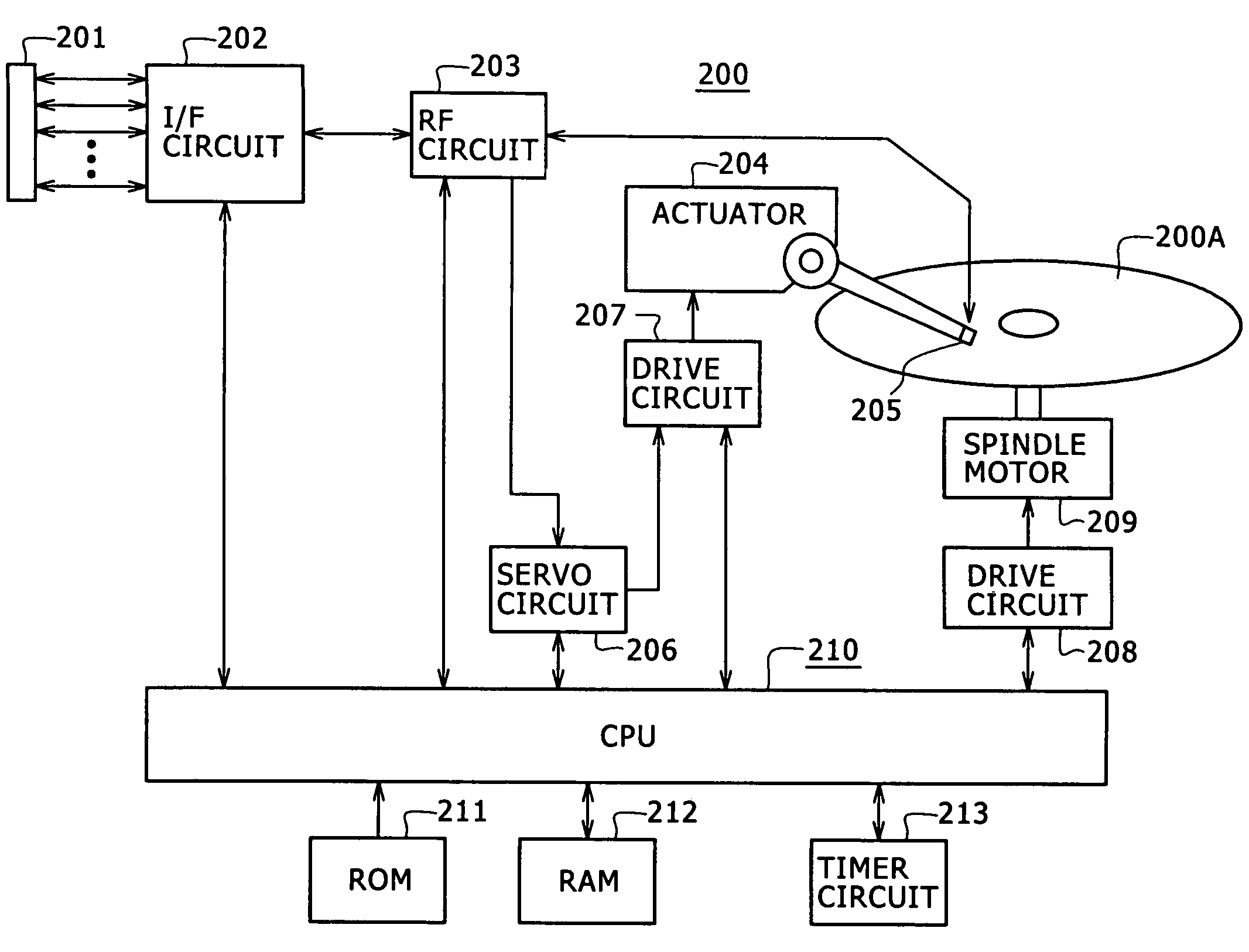
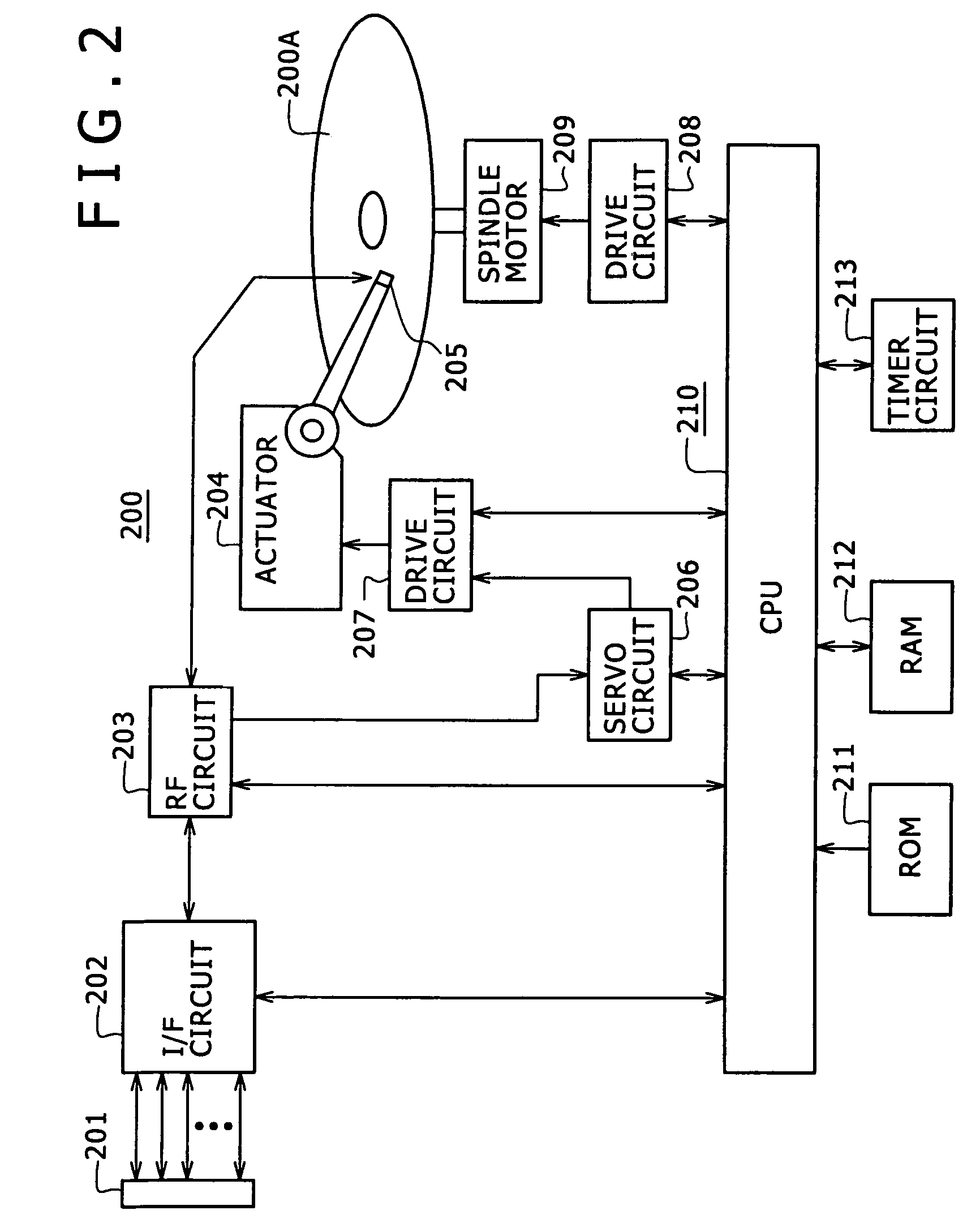
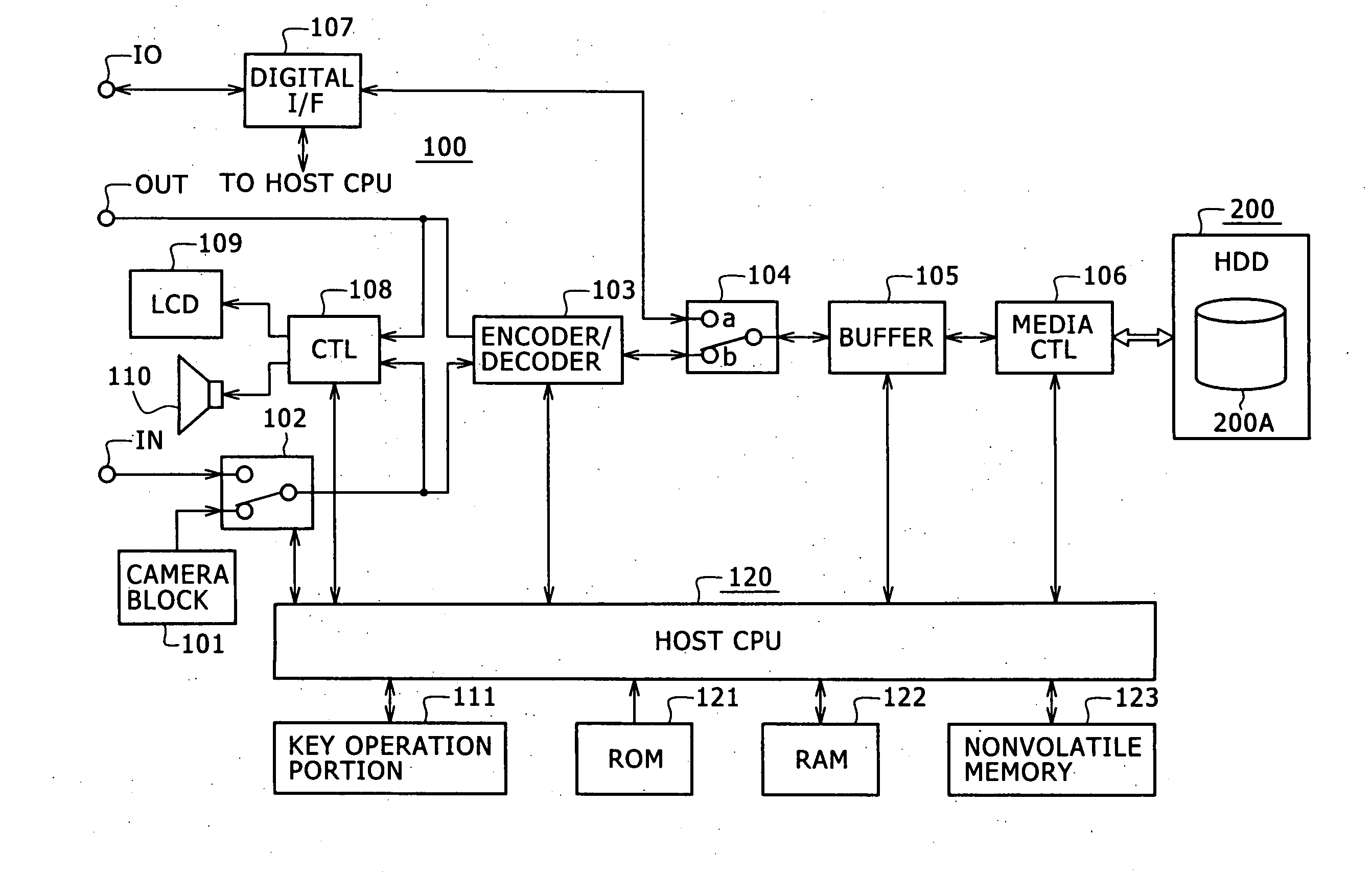
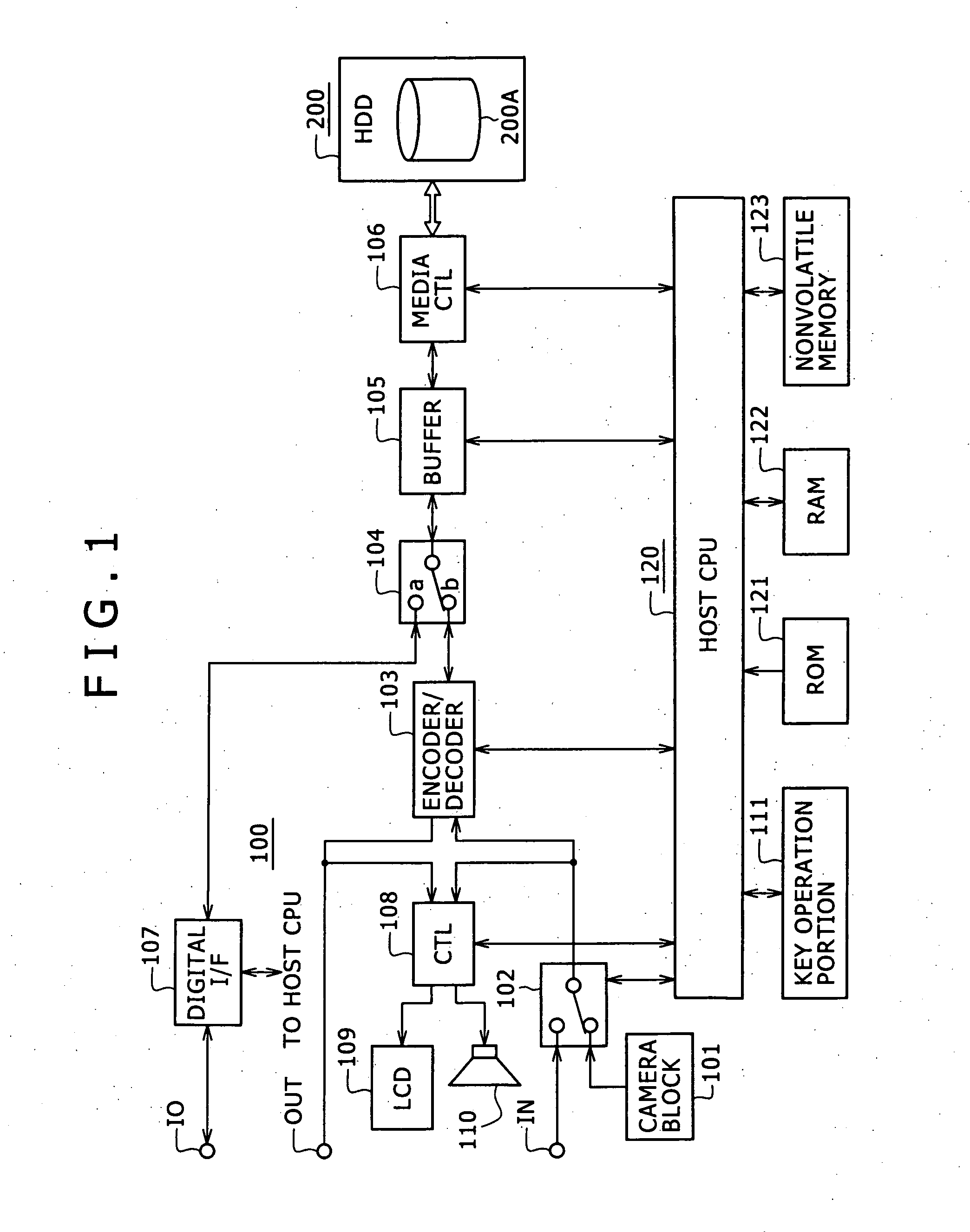
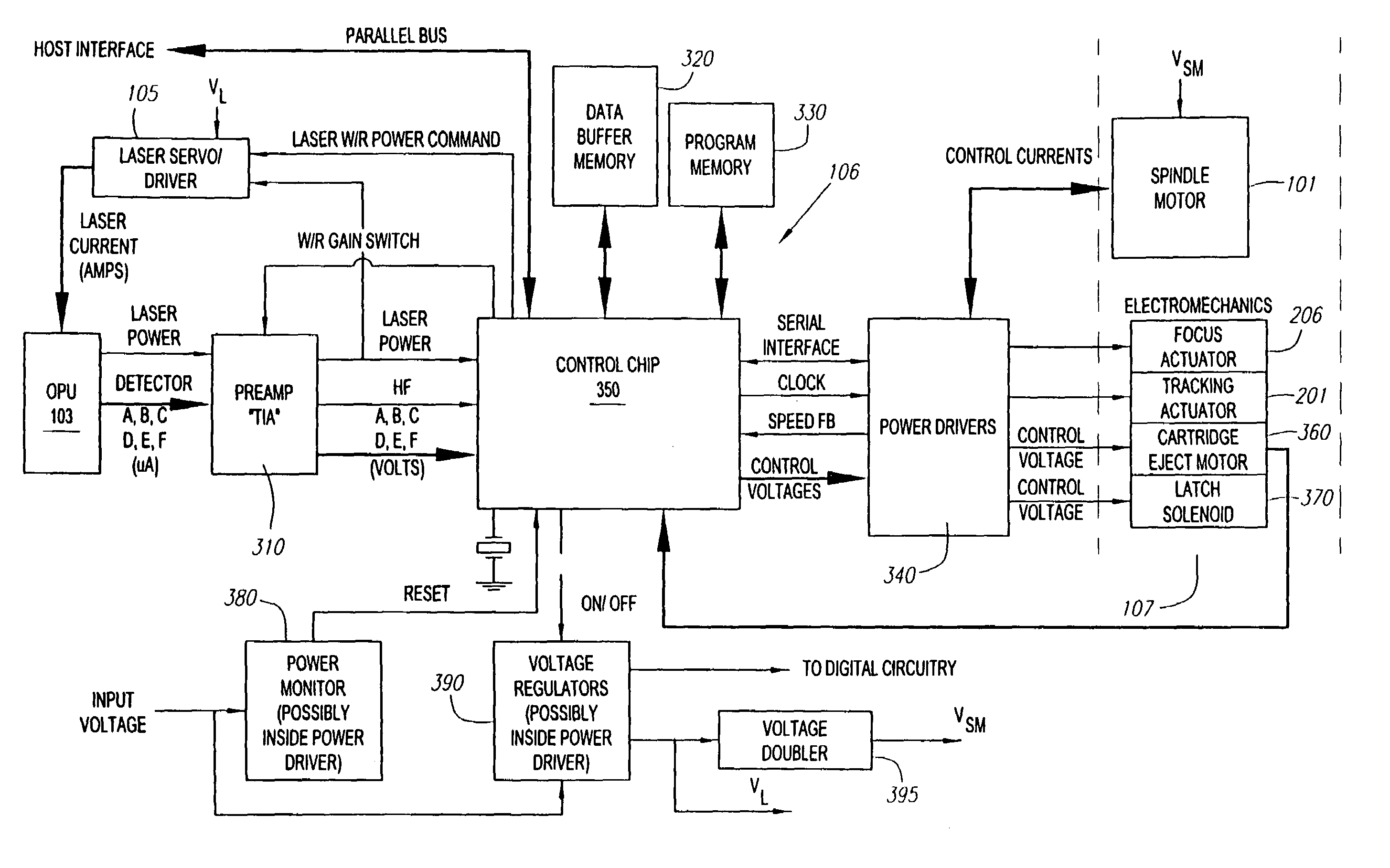
Information processing equipment and power consumption control method
InactiveUS7412615B2Average power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTTelevision system detailsComputer hardwareInformation processing
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for on-demand multimedia rental and sales services
InactiveUS20050240958A1Reduce user waiting timeCreate quicklyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningMass storageOptical storage
The present invention provides a system and method for dispensing multimedia content. The invention discloses a network kiosk configured to receive multimedia materials from a variety of sources that may be stored, combined and recorded on mass storage devices such as solid state memory, multimedia players and rewriteable optical storage devices including rewriteable Digital Versatile Discs (DVDs) and rewriteable Compact Discs (CDs). Users may select material for purchase or rent at the kiosk or through external wired and wireless computing devices such as computers, cellular telephones, personal data assistants (PDAs), multimedia players.
Owner:MOVIECRAZY
Optical disc having uniform structure
InactiveUS7065015B2Increase productionReduce manufacturing costFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
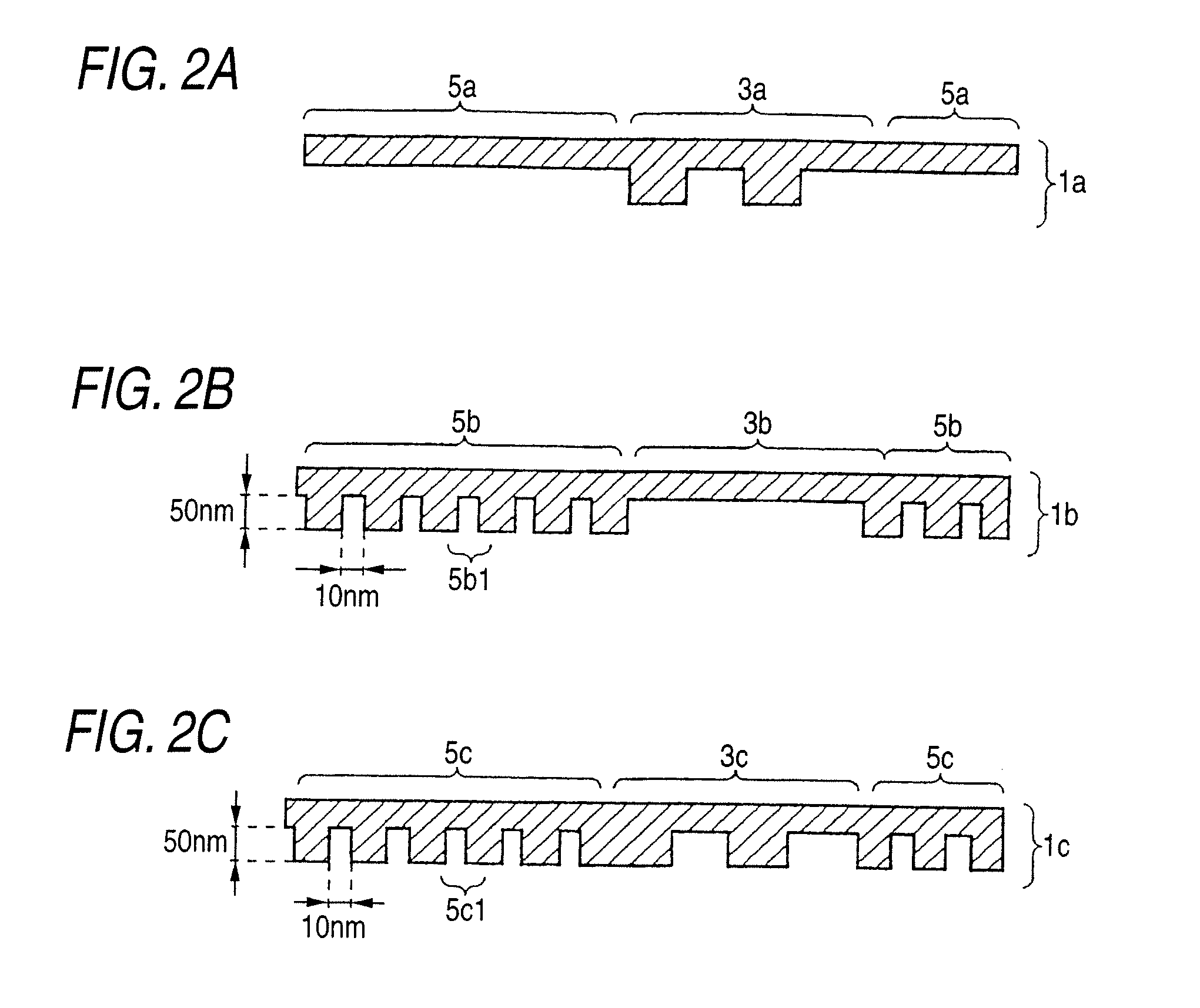
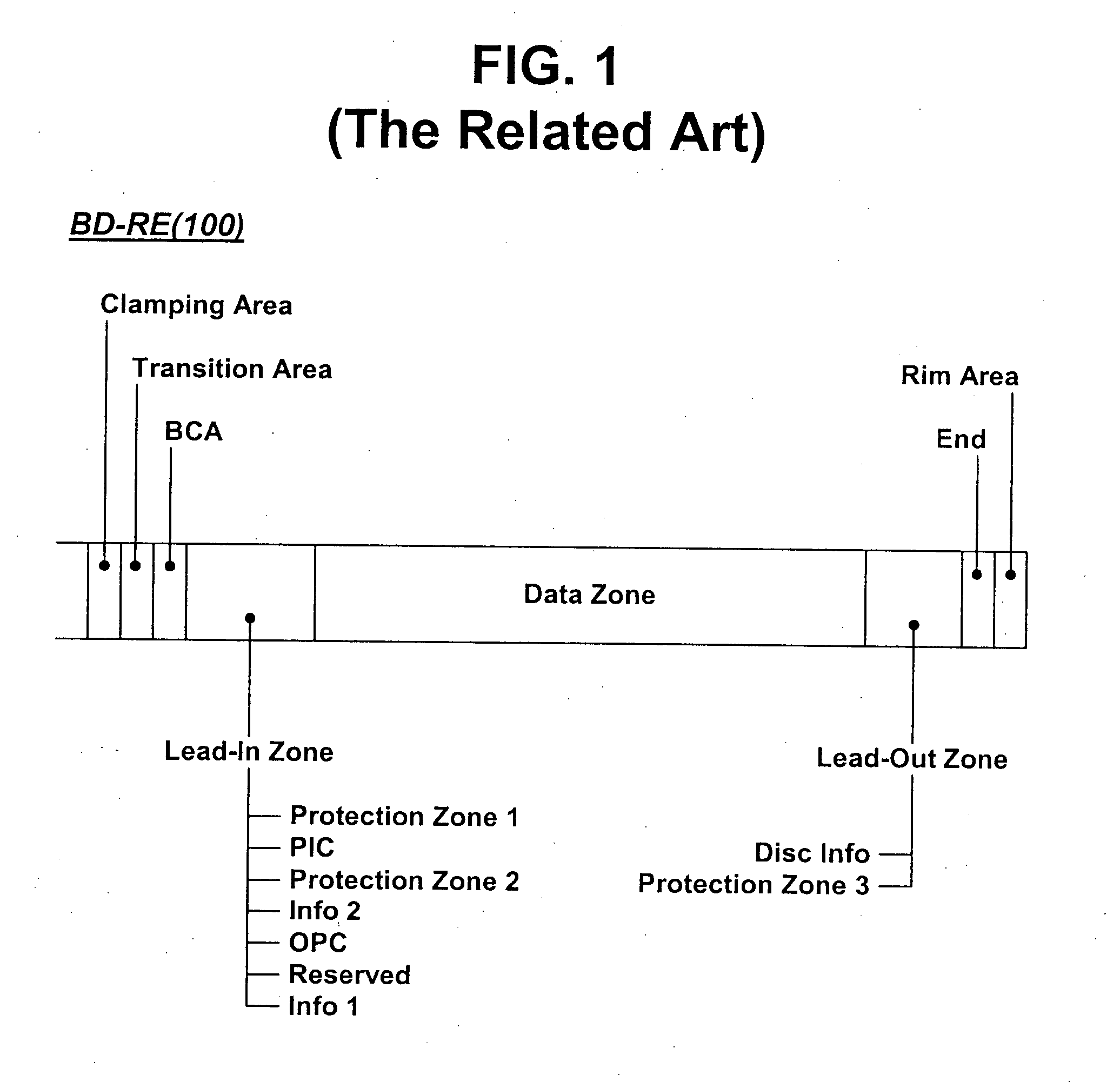
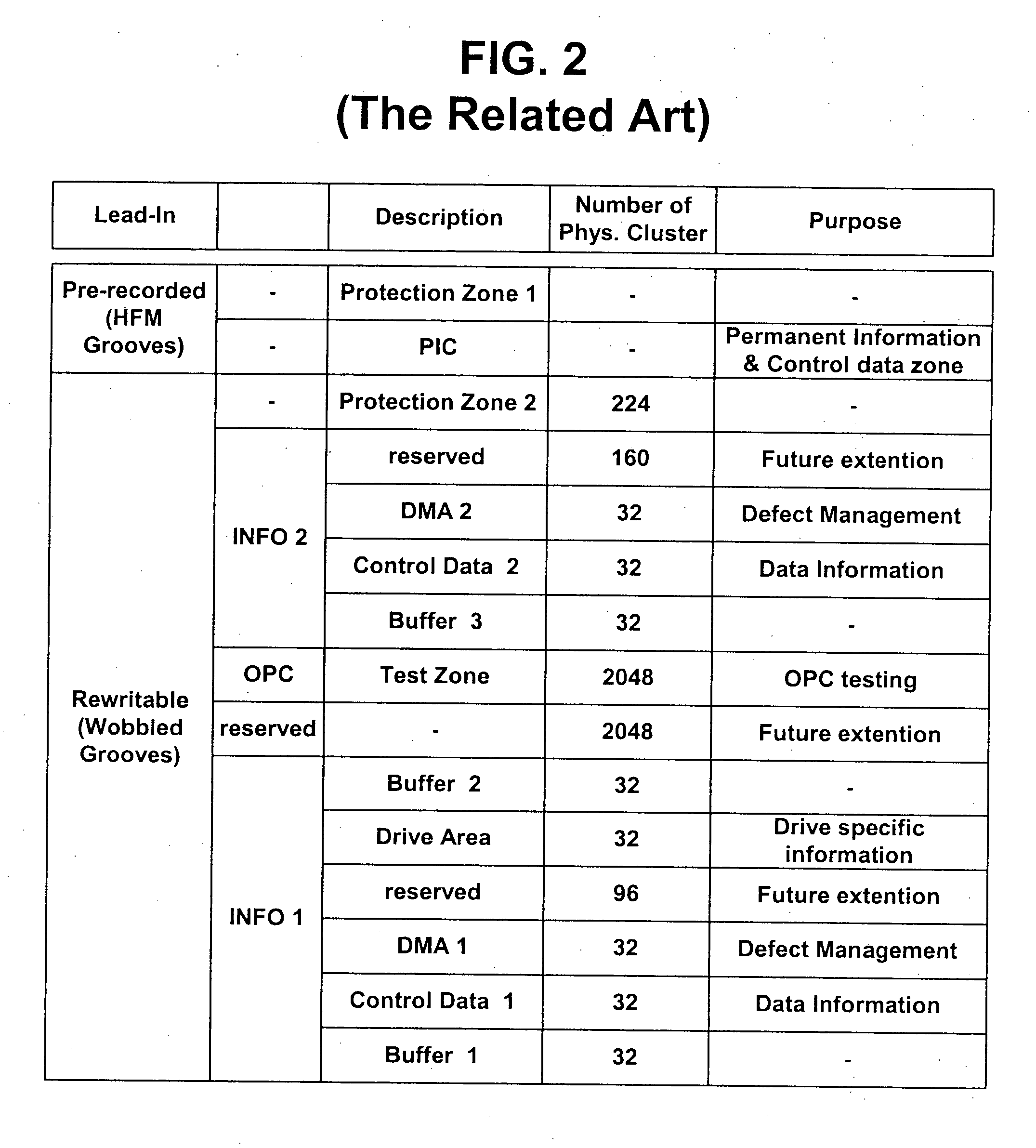
An optical disc is manufactured under a uniform condition by forming grooves and lands on the entire surface of the disc. The optical disc is configured to obtain a reliable reproduction signal, and the grooves and lands are formed on a lead-in area, a user data area and a lead-out area of the optical disc. Since the same manufacturing condition can be adopted in mastering discs, the yield can be enhanced and the manufacturing cost can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Disk drive input sequencing for staggered drive spin-up
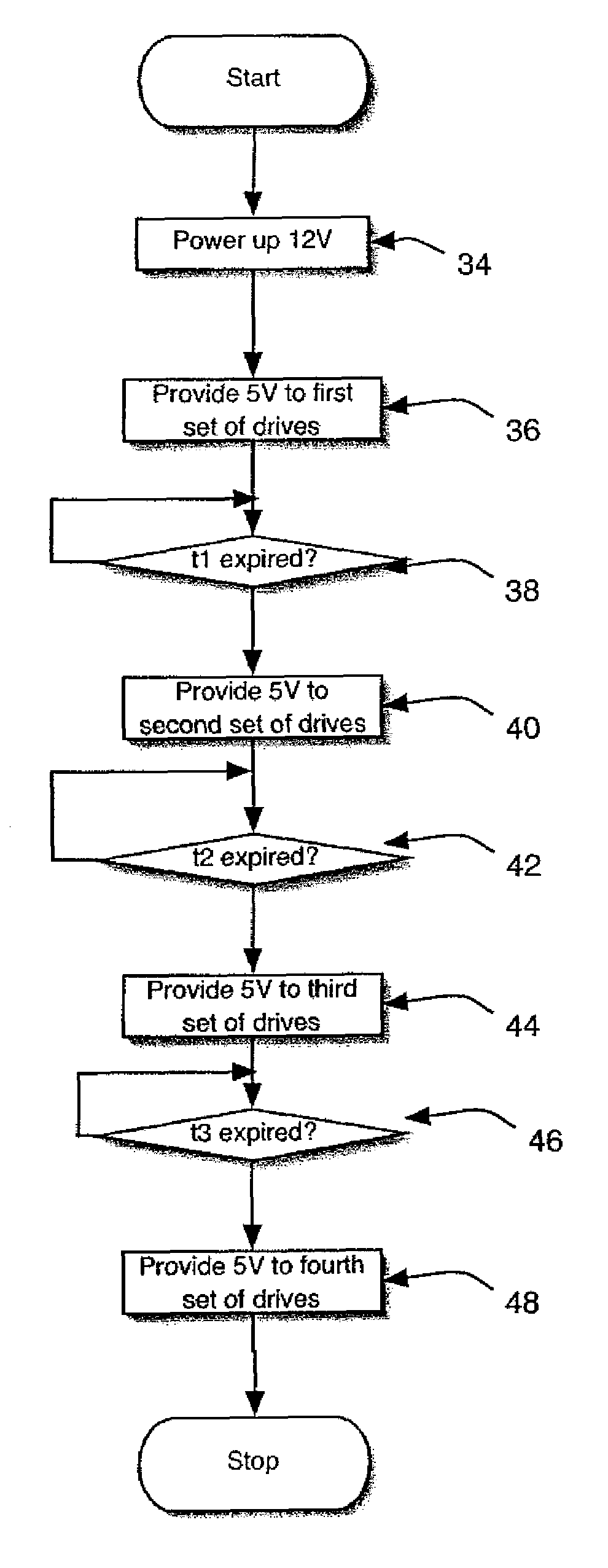
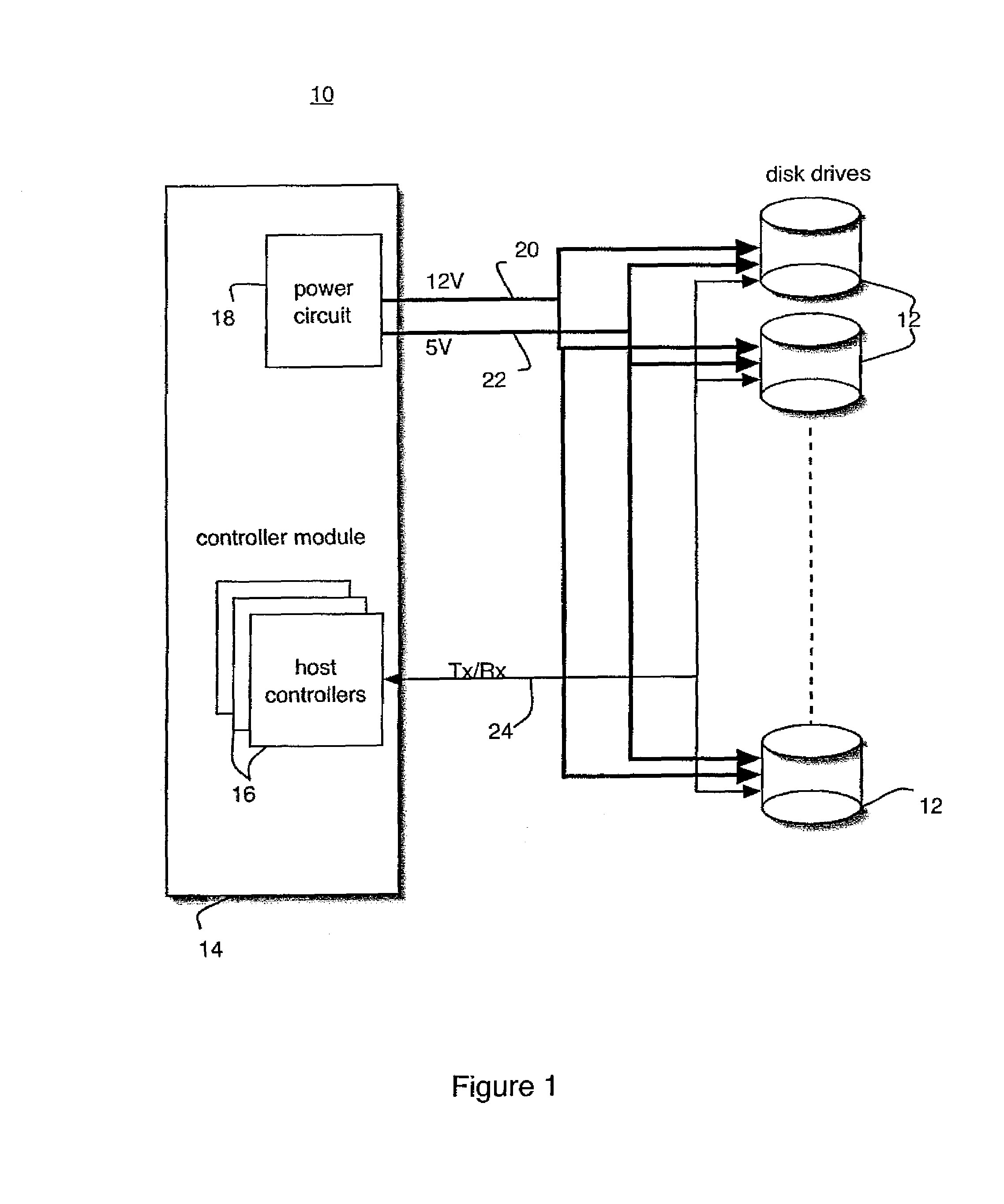
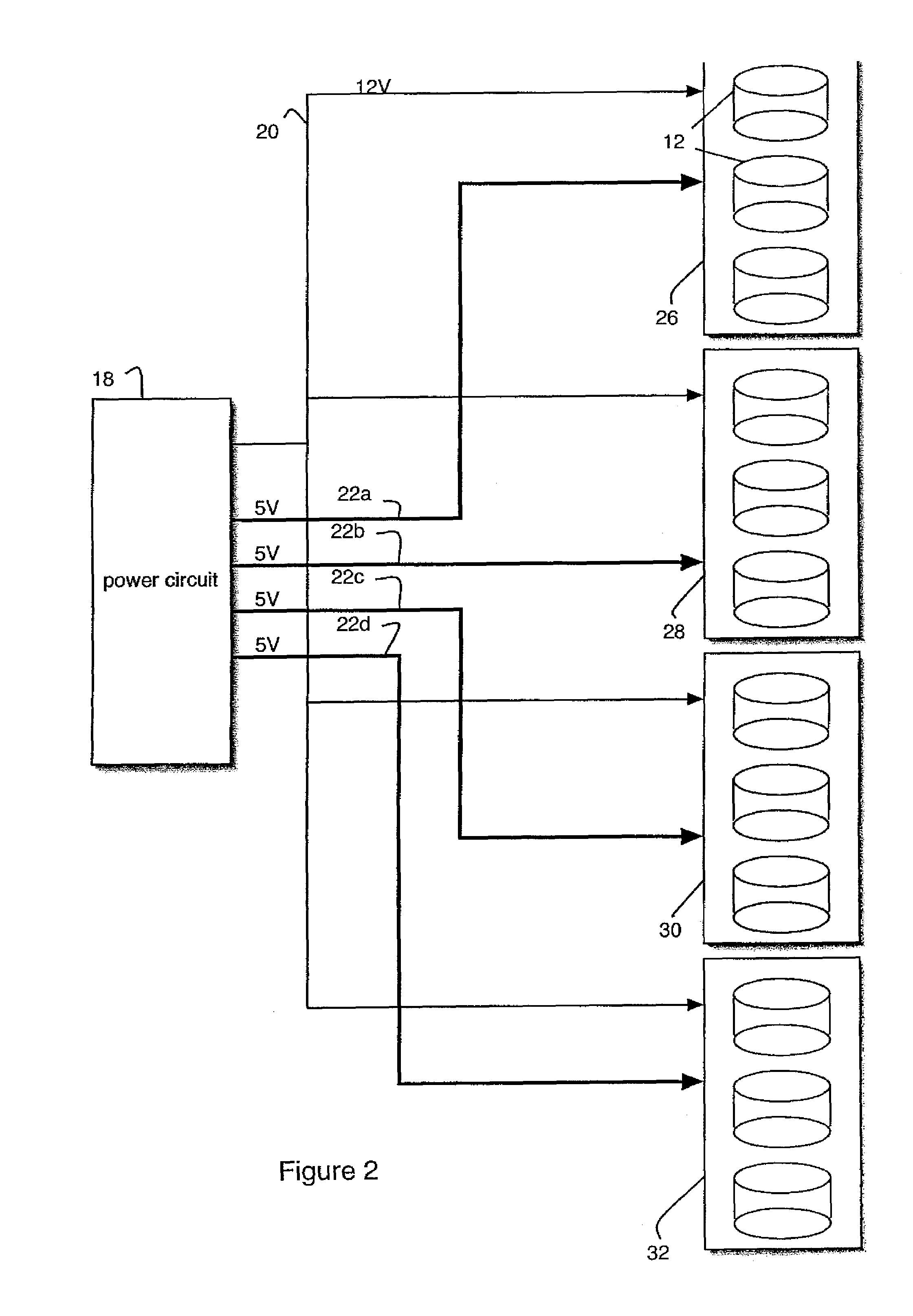
ActiveUS7305572B1Reduction in system peak power requirementSave budgetDisposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsControl theorySpin-up
Disk drive spin-up is staggered to reduce peak power requirements. Spin-up of the drives is controlled by selectively delaying voltage inputs to the disk drives. Alternately, spin-up of the drives is controlled by staggering the timing of communications to the disk drives.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
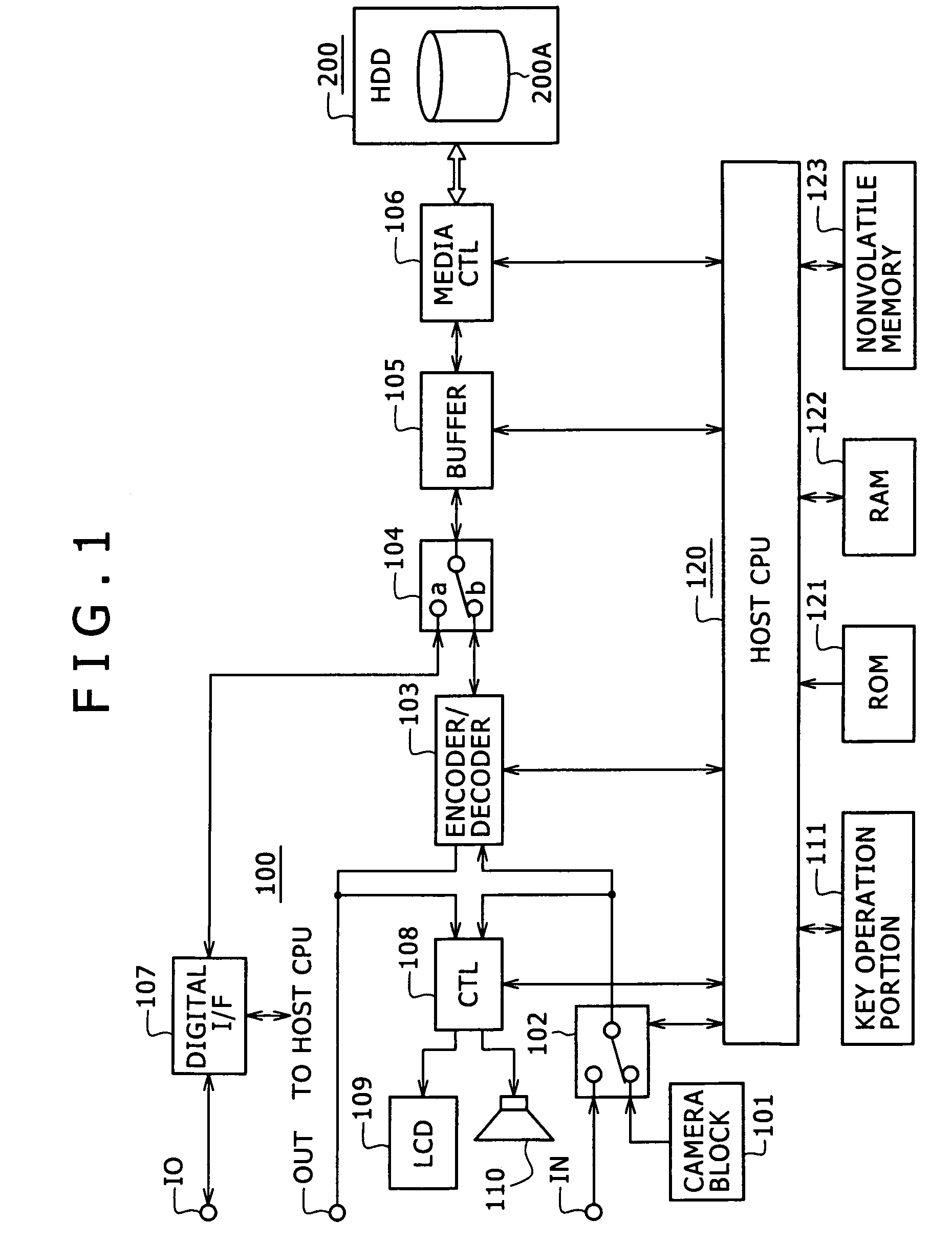
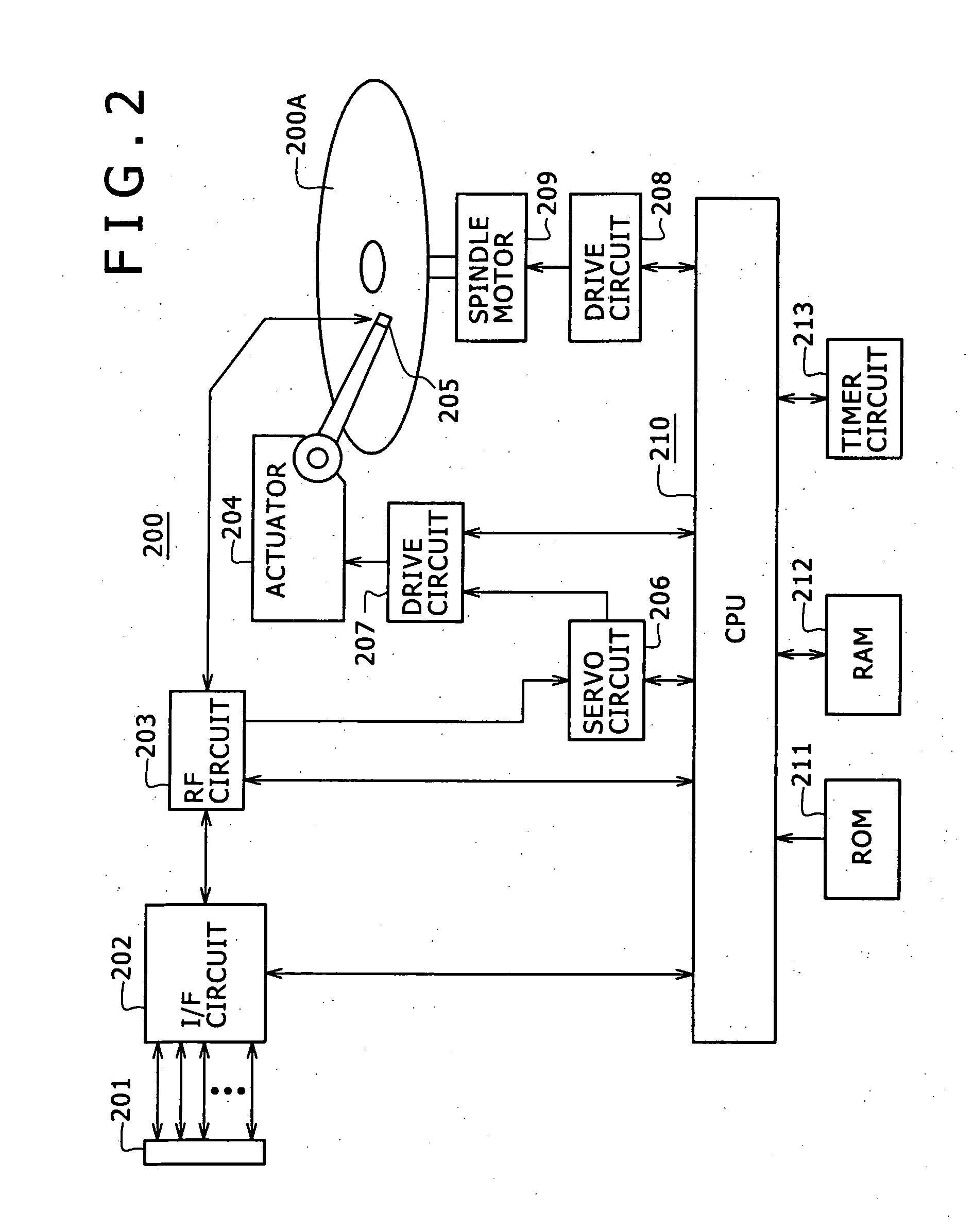
Information processing device and consumption power control method
InactiveUS20060123259A1Accurate graspAverage power consumptionTelevision system detailsEnergy efficient ICTComputer hardwareInformation processing
Information processing equipment is so constructed that the power consumption of a disk drive for hard disks, optical disks, or the like can be reliably and sufficiently reduced. The host CPU (120) of an information processing unit (100) forms a command for changing the power consumption mode of a HDD (200) based on the state of control on the HDD (200). The host CPU supplies the command to the HDD (200) through a media controller (106). When the HDD (200) accepts the command, it changes its power consumption mode according to the instruction from the information processing unit. Thus, the information processing unit can control the power consumption mode of the HDD (200) based on the state of control on the HDD (200).
Owner:SONY CORP
Disc having a segment code for prohibiting a play control function during a playing of a video segment
InactiveUS7054547B1Efficiently previewingView effectivelyTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersUser interfaceLine segment
Owner:NISSIM CORP
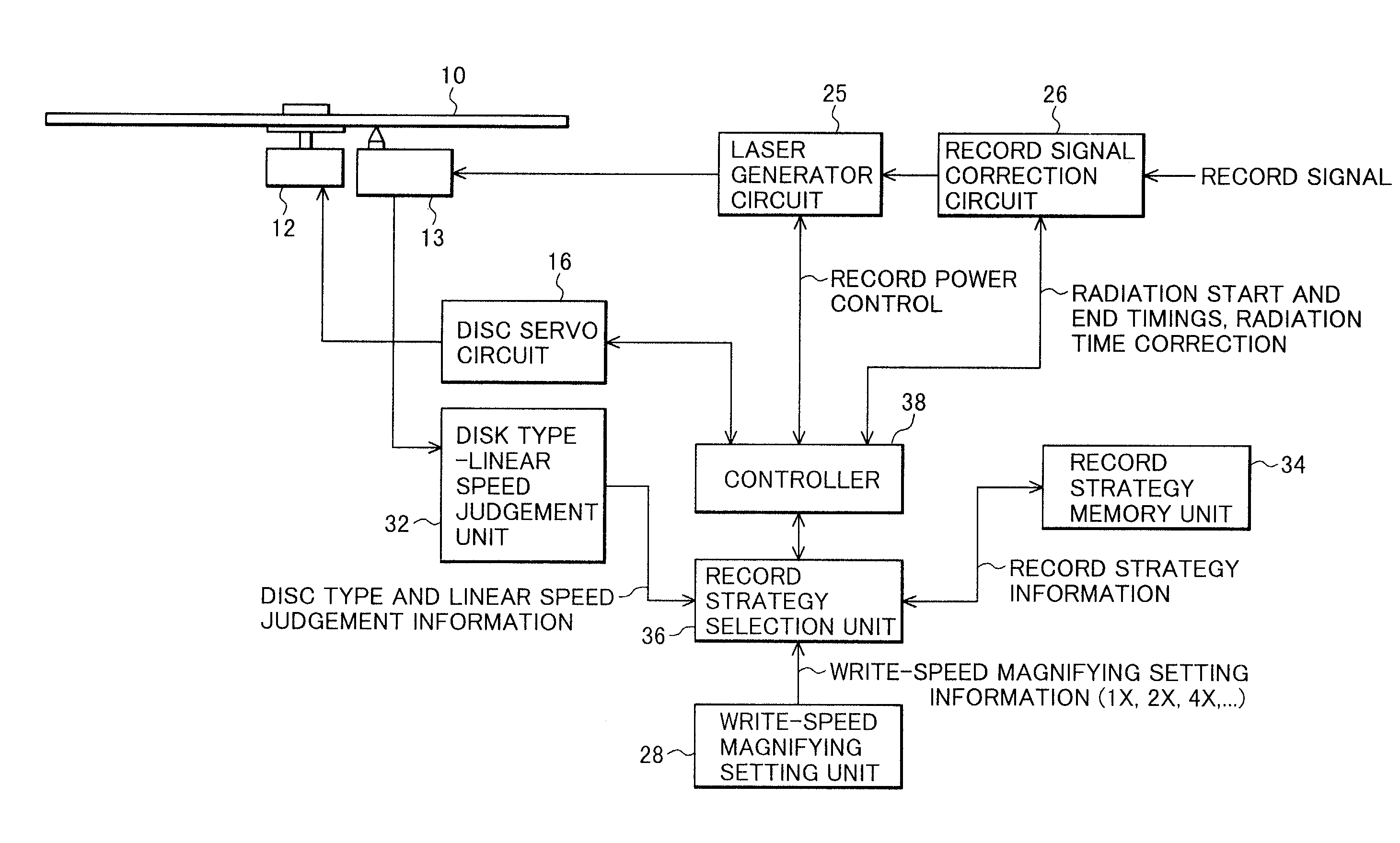
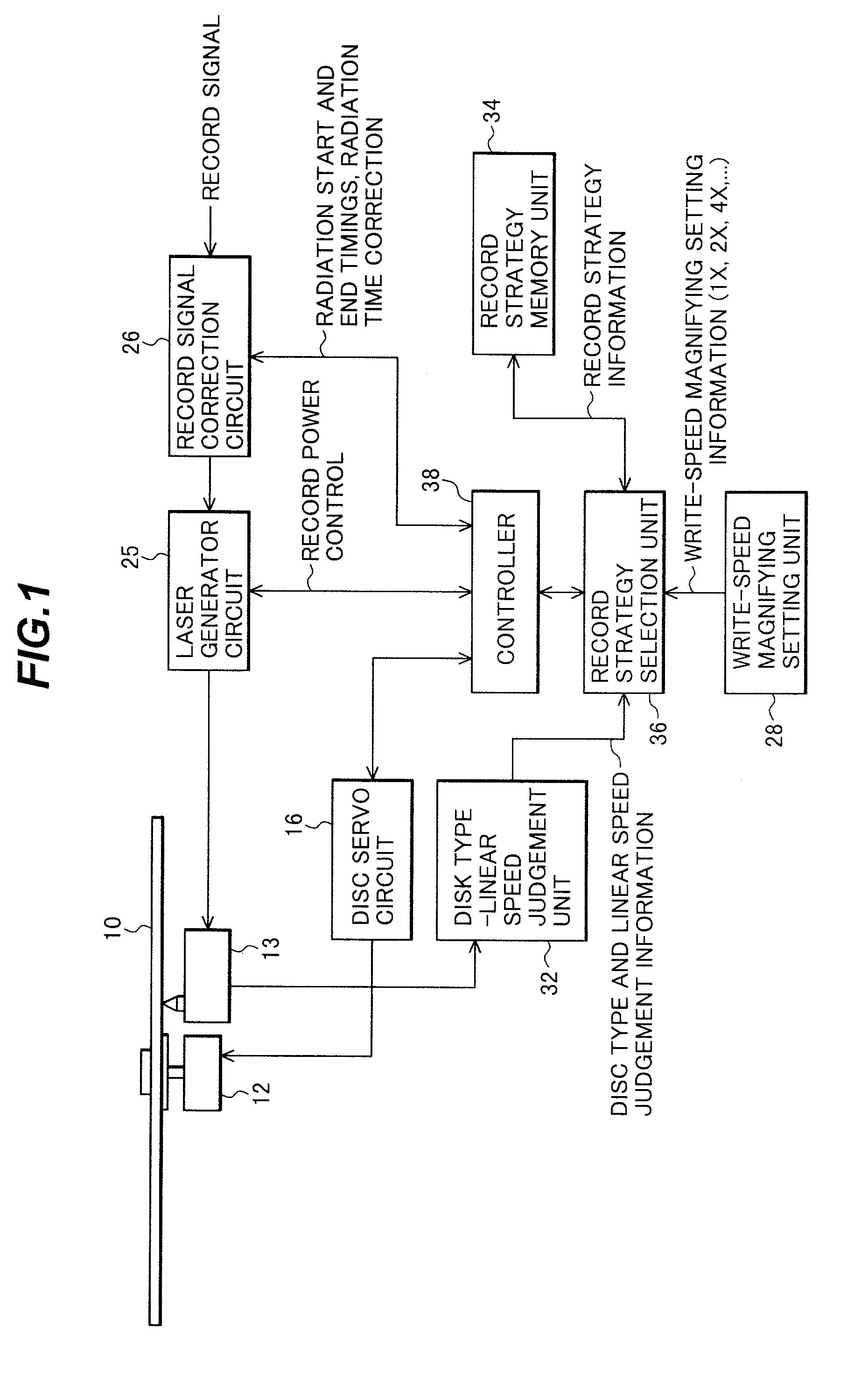
Optical disc recording method and apparatus
InactiveUS6996047B2Improve signal qualityRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLight beamOptoelectronics
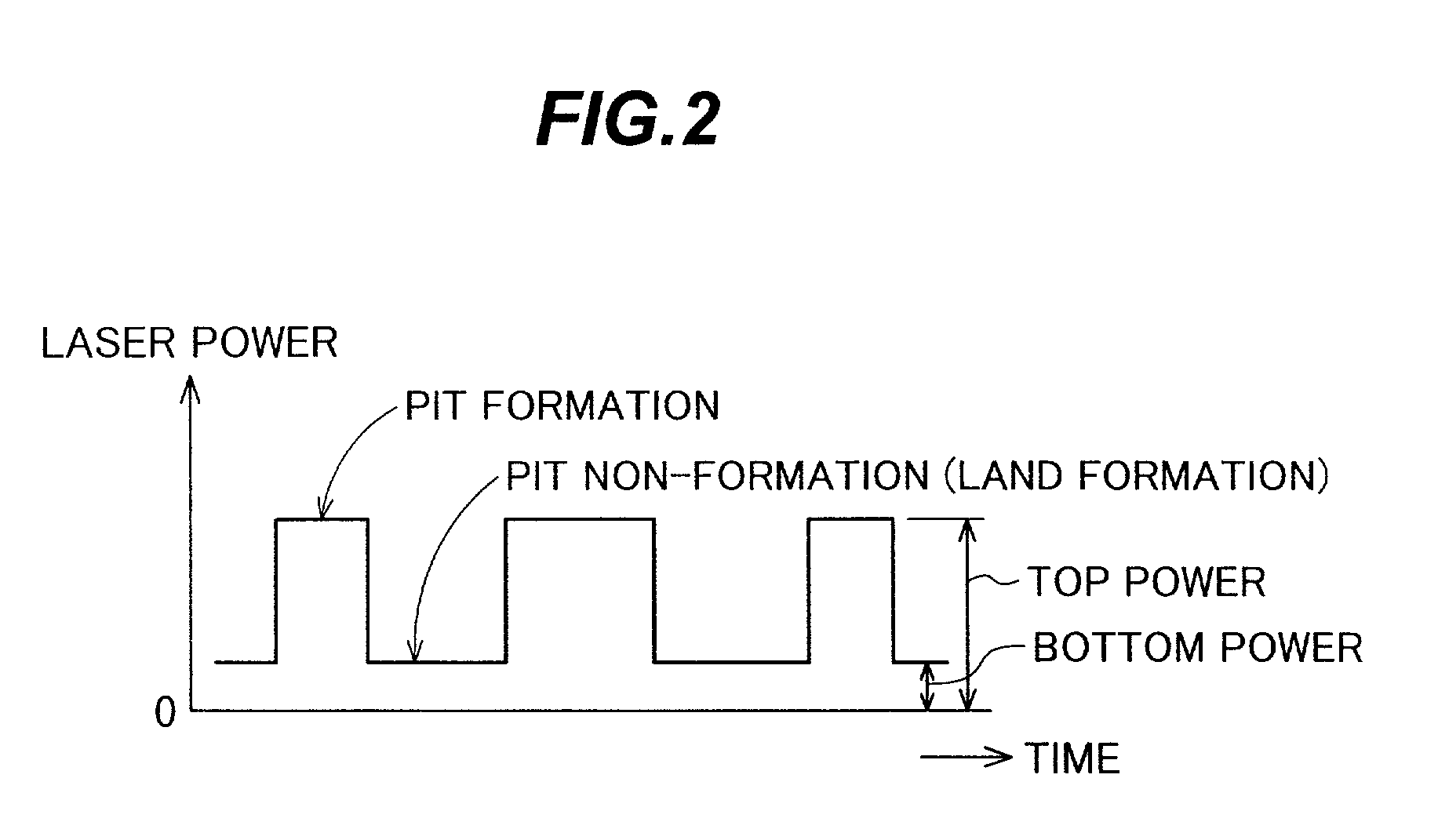
An opical disc recording method, comprises the steps of: a) forming a record signal in accordance with input information; b) generating a recording laser beam modulated with the record signal; c) controlling a laser radiation time at a record power for a 16× or higher write-speed to be (n+K)T for a pit length nT, where n=three to eleven, K is a constant (0≦K≦1.6), and T is a unit time corresponding to a pit length or a land length at a write-speed; and d) radiating the recording laser beam alternately at the recording power for the controlled radiating time to form pits and at a non-recording power to form lands toward a record surface of a recordable optical disc.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Writable optical drive with dynamically variable linear velocity to prevent buffer under-run
InactiveUS6901039B1Extended durationIncrease exposureRecording strategiesFilamentary/web record carriersMicrocontrollerEngineering
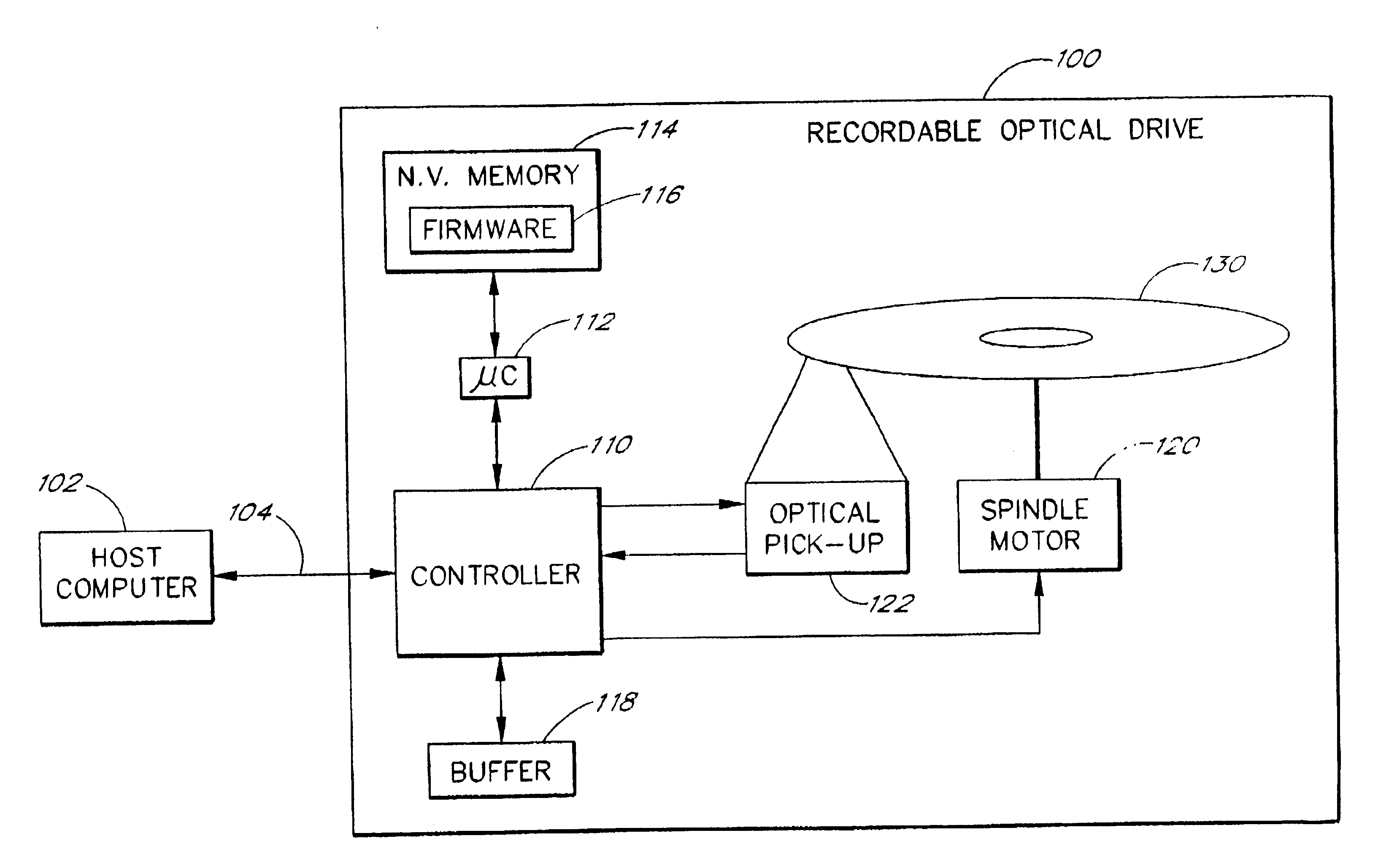
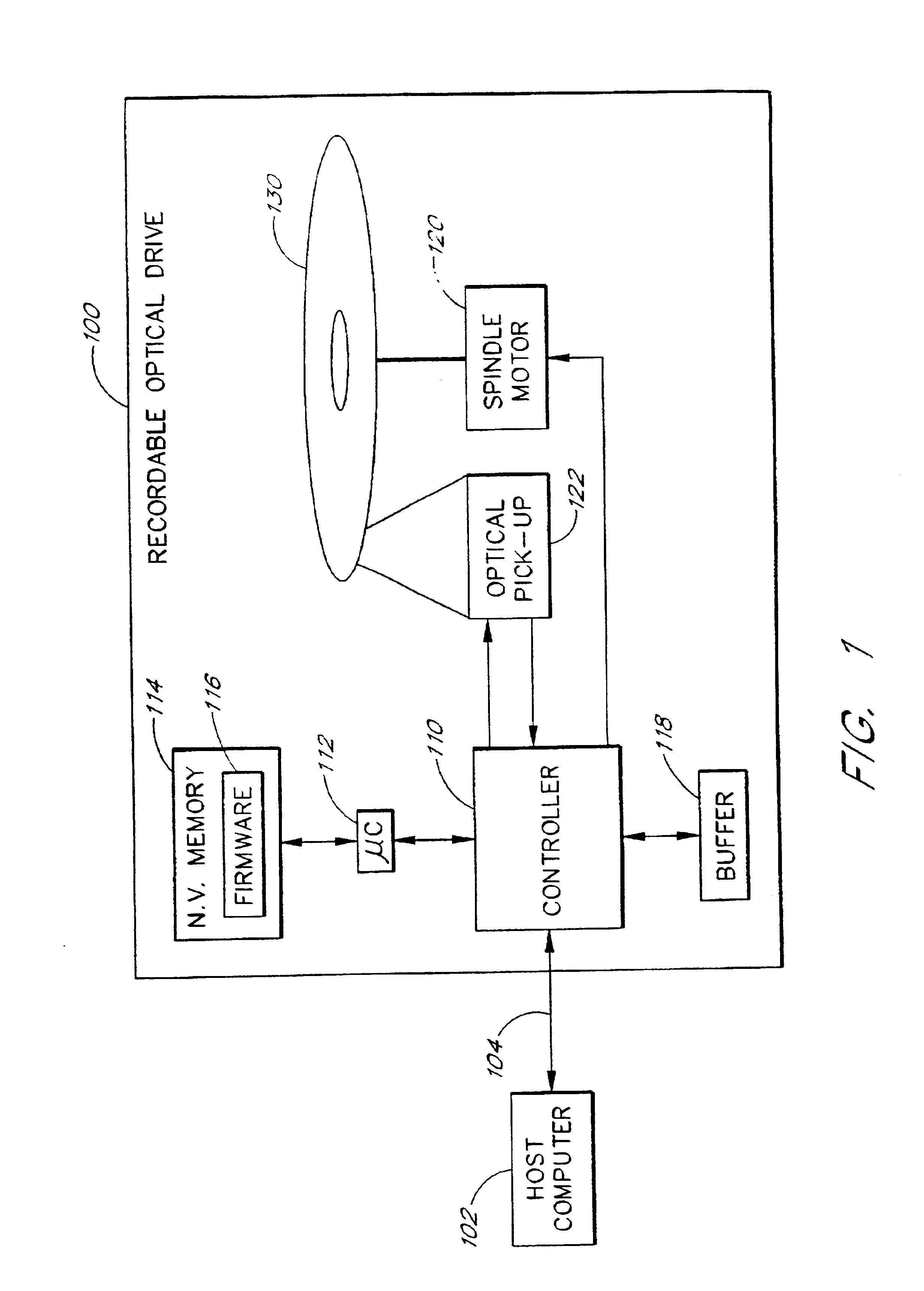
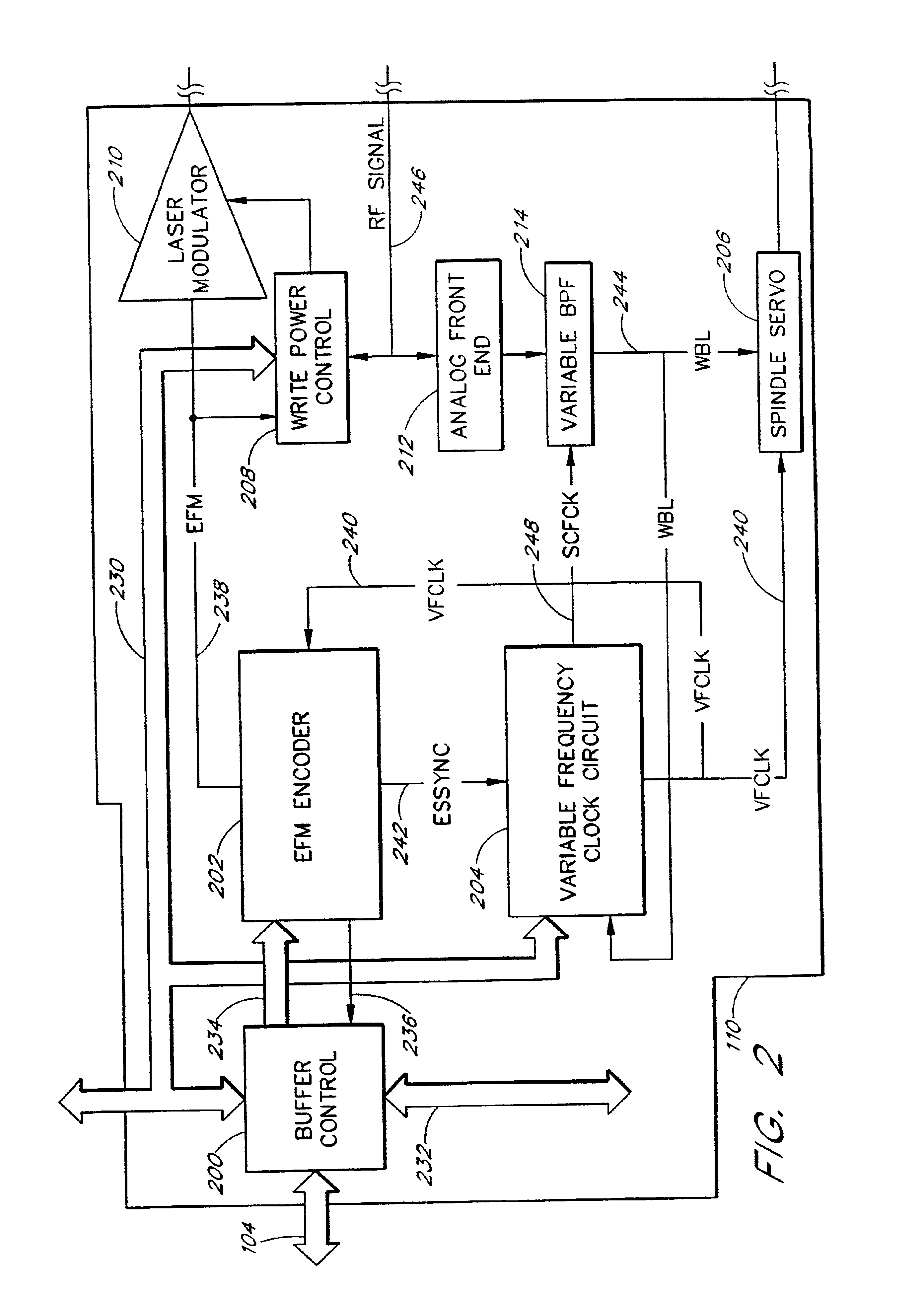
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for dynamically varying a linear velocity of an optical drive during a write operation to an optical disc to reduce the likelihood of a buffer under-run event. By reducing a linear velocity and writing speed while the optical drive writes on the disc, an embodiment of the invention preserves the buffer and reduces a minimum data transfer rate required to sustain writing to the disc for a sustained period of time. The basic components of one embodiment of a CD-RW drive (100) in which the present invention may be implemented include a controller (110), a microcontroller (112), a nonvolatile memory (114), which stores firmware (116) executed by the microcontroller (112), a buffer (118), a spindle motor (120) and an optical pick-up (122).
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and apparatus for buffering data in a multi-beam optical disk reader
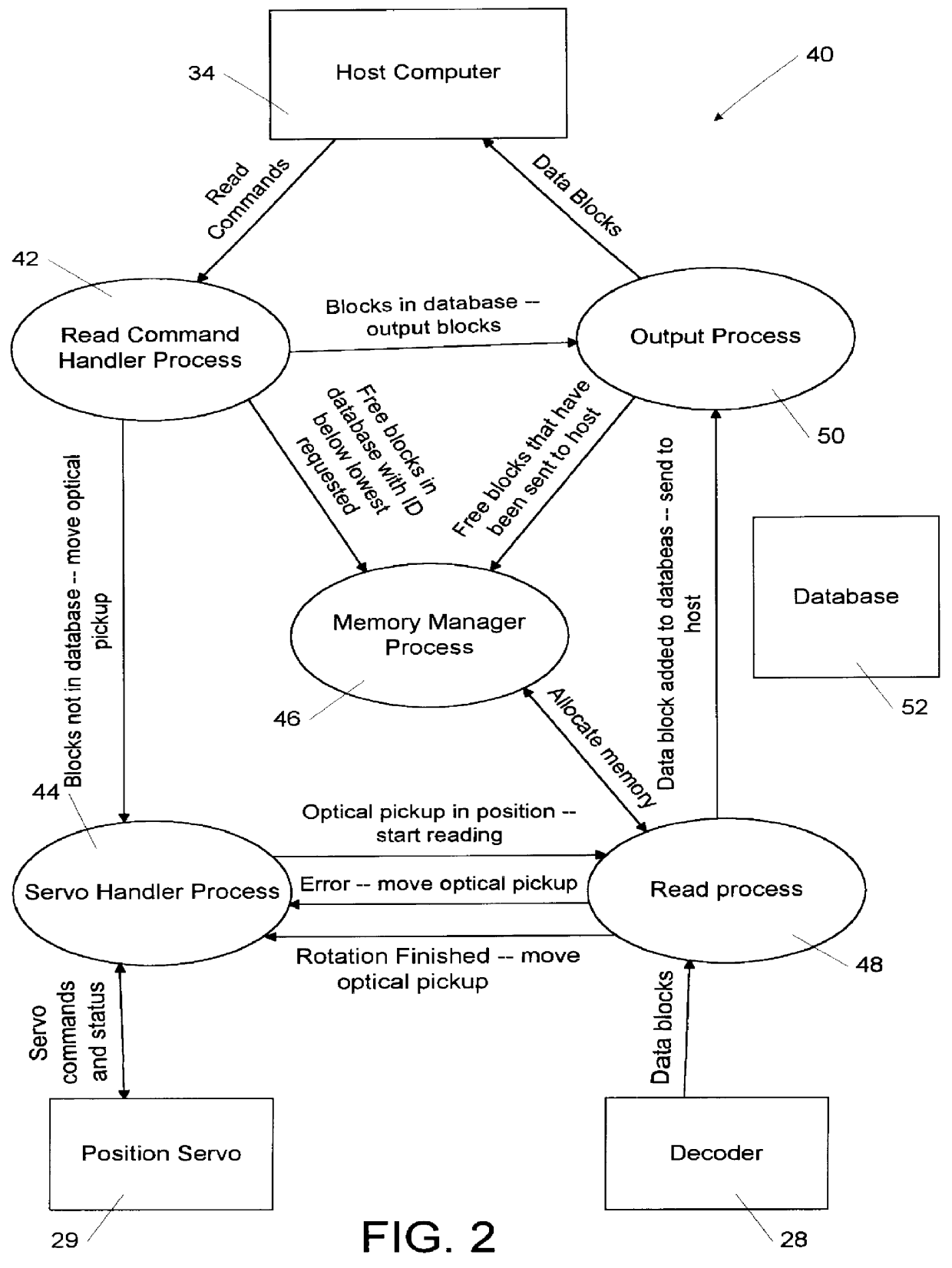
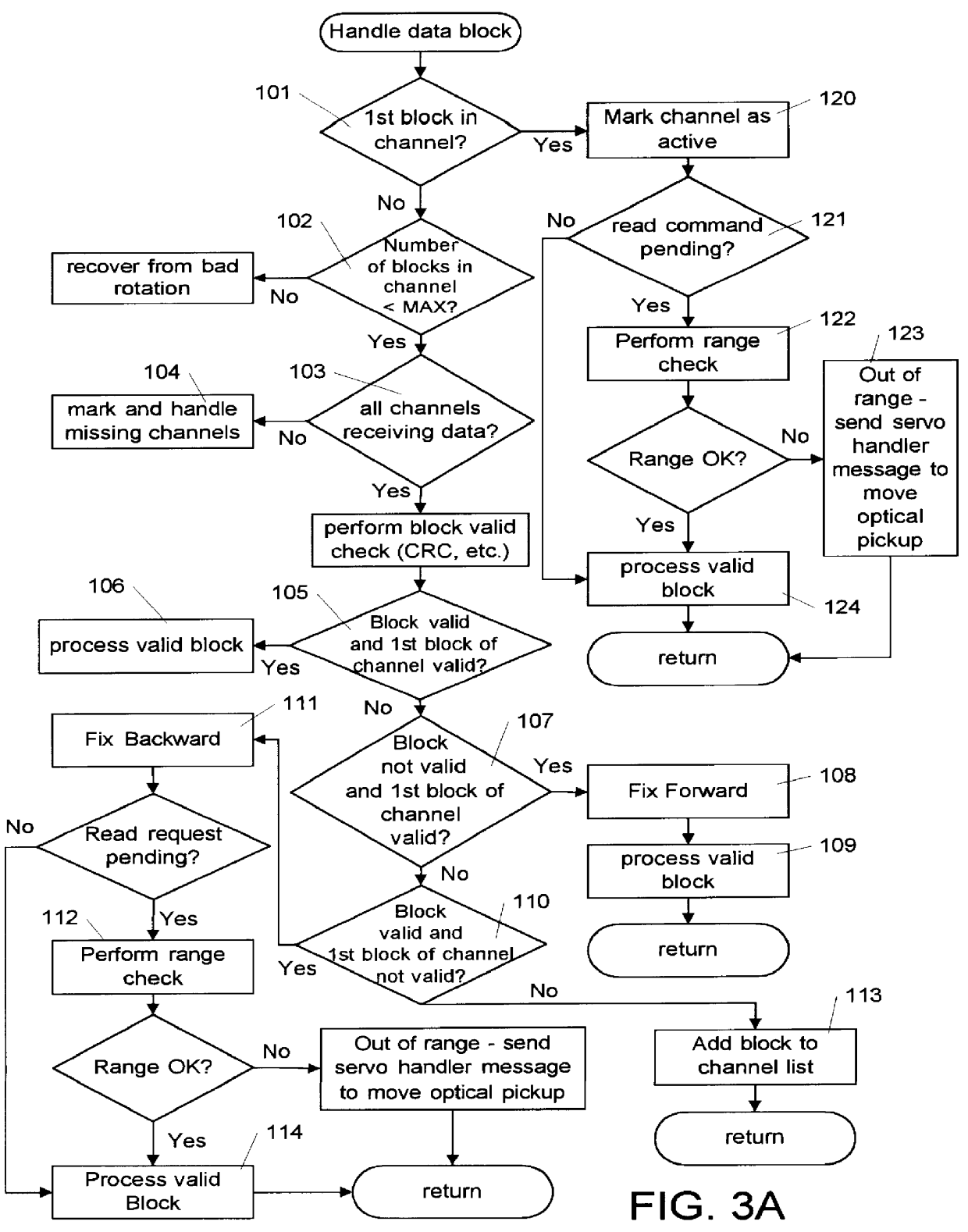
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for buffering and reordering data blocks read simultaneously from multiple tracks of an optical disk, so that they may be delivered in sequential order to a host computer. The methods involve the use of numerous processes to receive read commands, position an optical pickup, handle memory management tasks, process data blocks as they arrive, and send data blocks to the host computer in sequential order as they become available. The reordering of data blocks is achieved by checking each data block as it arrives in a "read process" to see if it may be linked in a sequential chain with a data block that arrived from the next track. Additionally, methods for determining if a requested data block is in the range of blocks that are currently being read, and methods for determining when the optical pickup may be moved to read the next set of tracks are described.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Method for writing of data in an optical memory, apparatus for performing the method and optical memory formed thereby
PCT No. PCT / NO96 / 00154 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 23, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 23, 1997 PCT Filed Jun. 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 01165 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 9, 1997In writing of optical data in an optical memory, the optical memory is linearly transported along a path past two or more physically separated write units. The two write units are provided at a distance from one another along the path and are mutually stepwise displaced in the path's transverse direction. The distance along the path separating write units is greater than a width of a preceding write unit. Each write unit is assigned to a section of the optical memory, with the result that the writing data is performed in the transport direction in separate and successive stages. Each stage contributes a fraction of the volume of information to be recorded during the writing.
Owner:OPTICON +1
Optical information recording medium containing a plurality of recording layers provided with characteristics to achieve optimum recording conditions
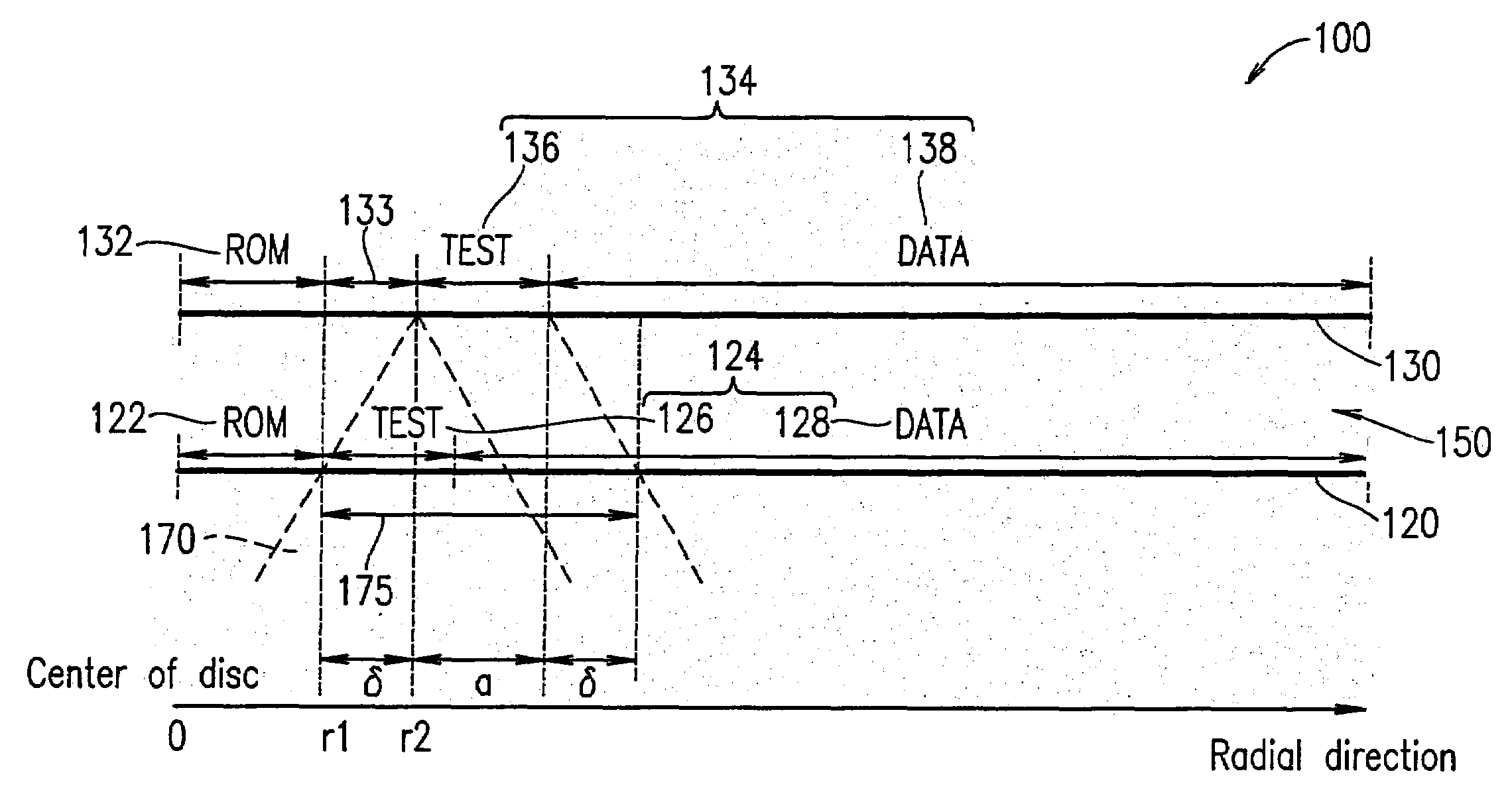
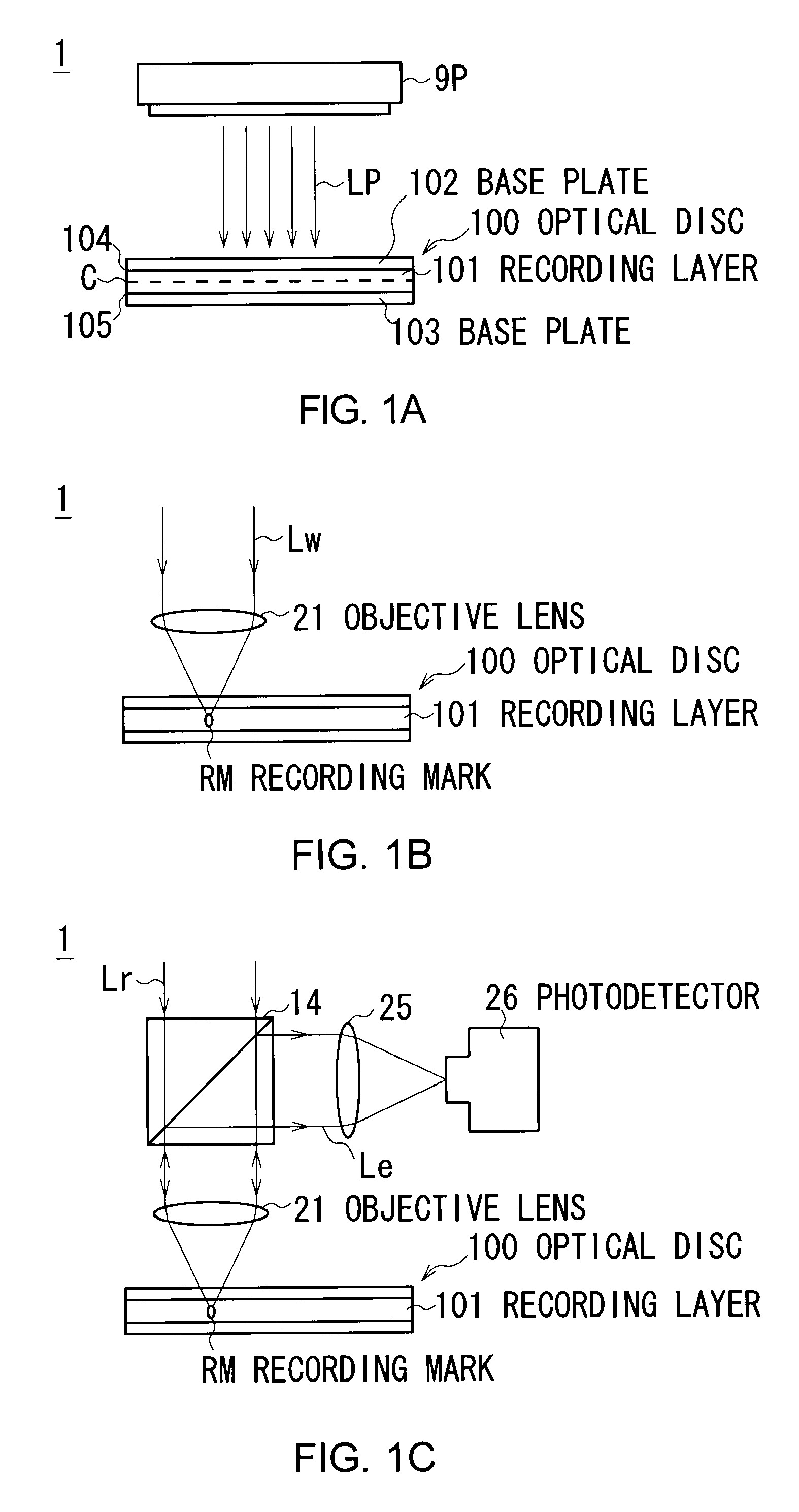
An optical information recording medium according to the present invention includes a first information recording layer on which information is to be recorded by laser light; and a second information recording layer on which information is to be recorded by the laser light which has passed through the first information recording layer. The first information recording layer includes at least one of a reproduction-only area and a recording and reproduction area. The second information recording layer includes a test recording area. At least one of the reproduction-only area and the recording and reproduction area, and the test recording area is located such that one of the reproduction-only area and the recording and reproduction area includes an area of the first information recording layer through which the laser light for recording information in the test recording area passes.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and apparatus for recording data on and deleting already recorded data from a recording medium
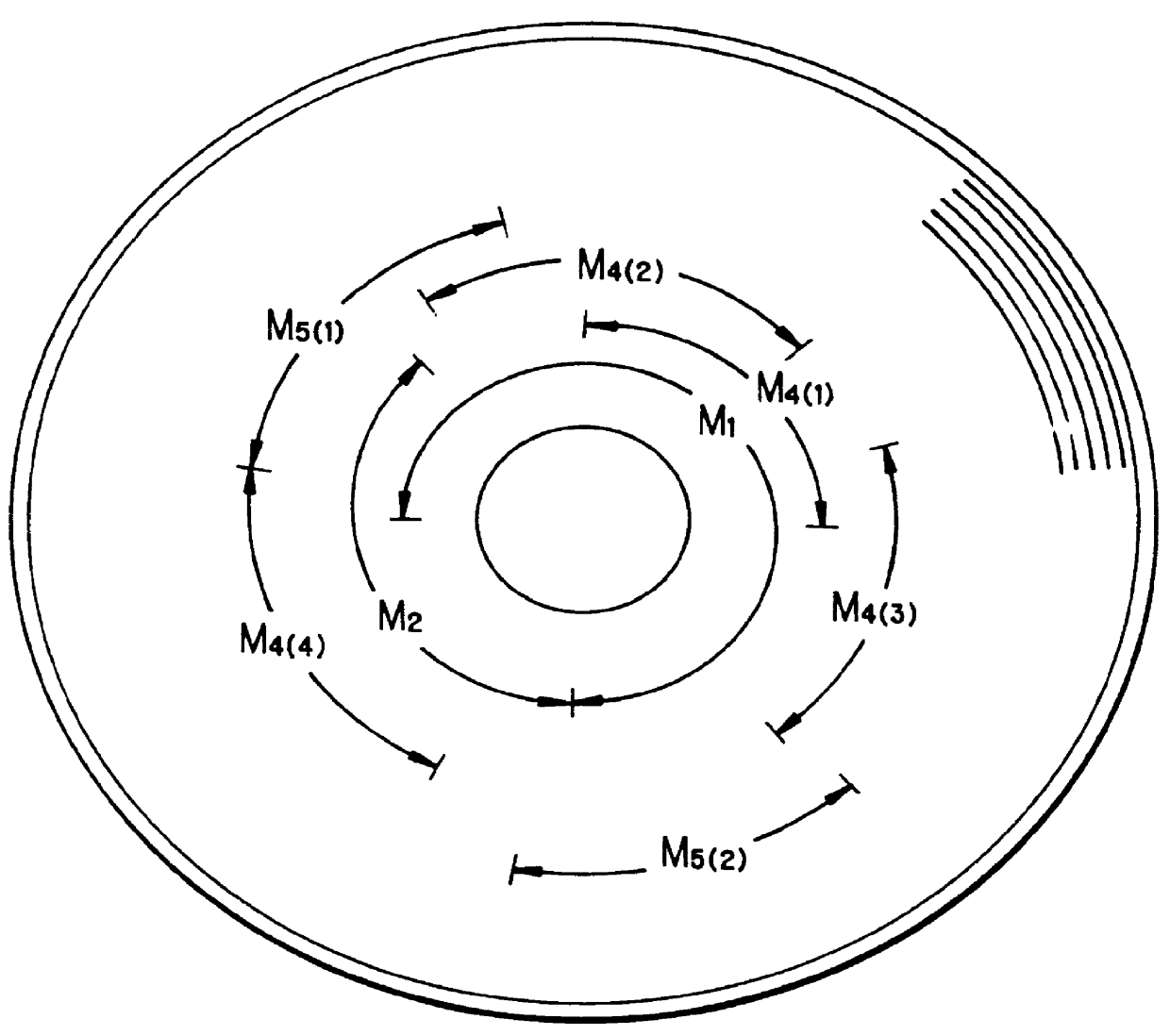
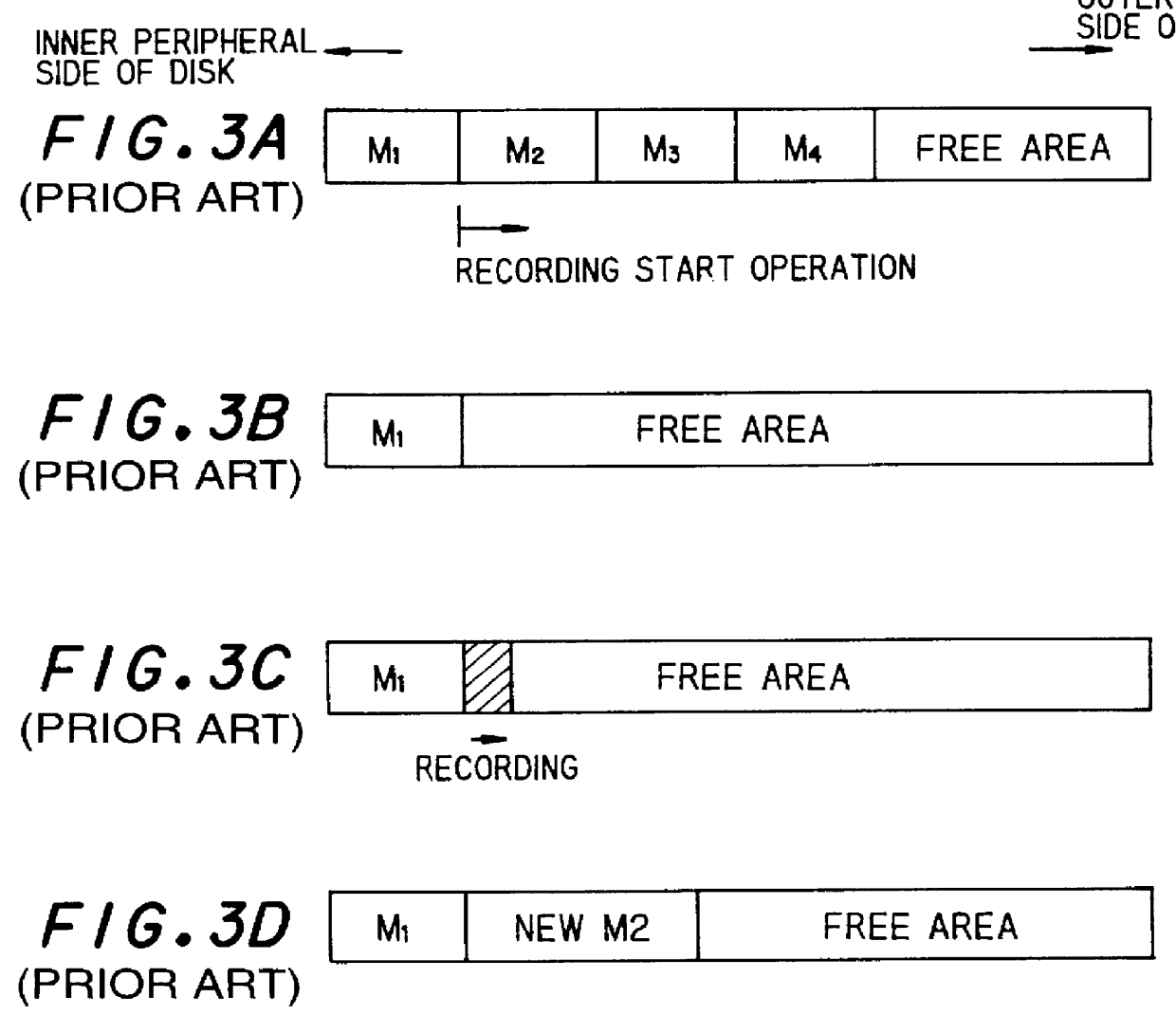
In a recording method for a recording medium having a data recording area on which a data recording and / or reproducing operation is carried out, and a management data area on which management data to manage a recording and / or reproducing operation for the recording medium are recorded, when new data are recorded on the recording medium in a state where data have been already recorded on the recording medium and a data-recordable area on which the new data can be recorded exists on the data recording area, the recording operation of the new data is started from the head position of the data-recordable area on the basis of the management data recorded on the management data area, and data which have been already recorded on the recording medium are deleted by the same data amount as the new data to be recorded on the data-recordable area from a position on the data recording area of the recording medium at which the recording operation is instructed to start.
Owner:SONY CORP
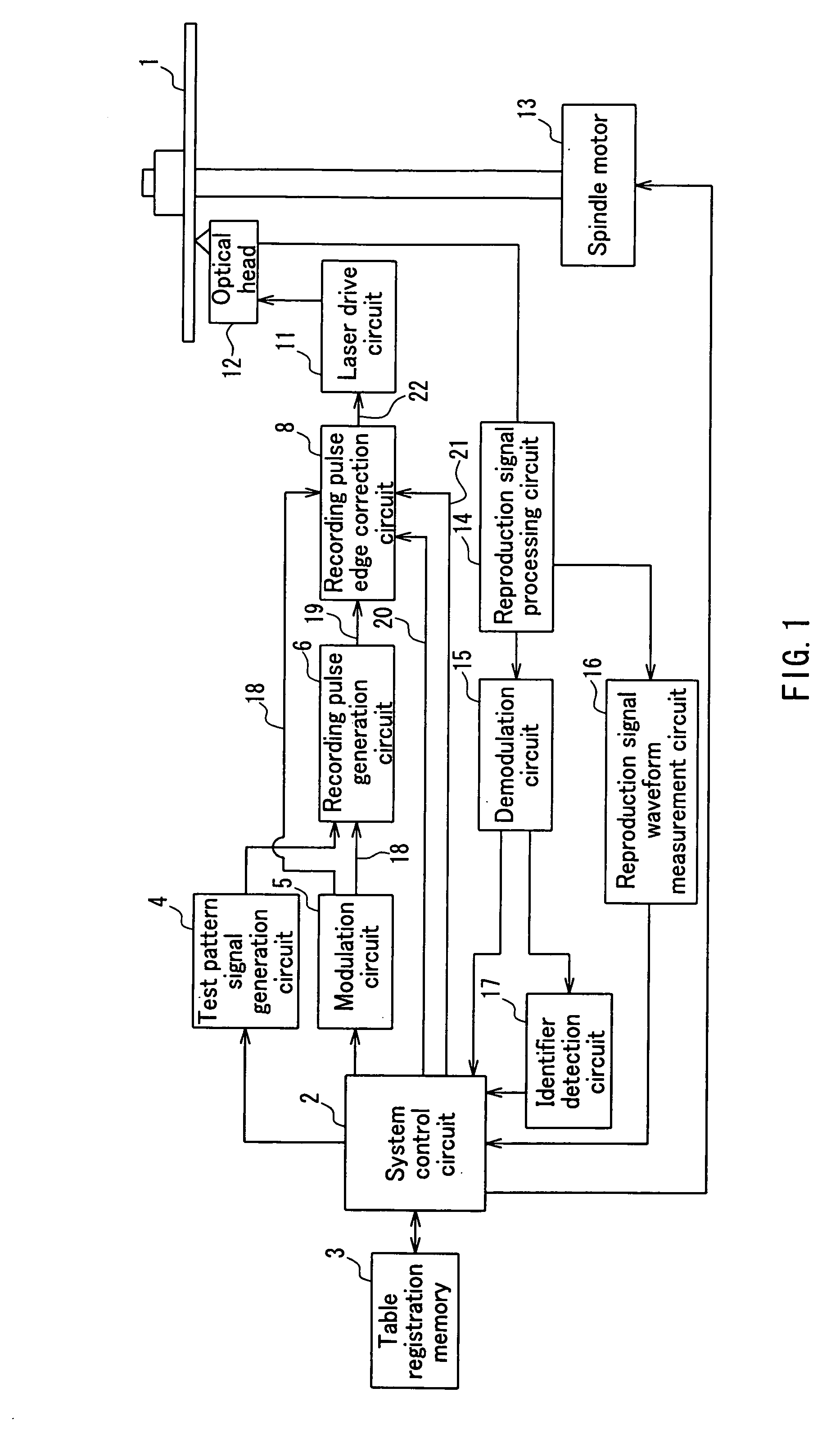
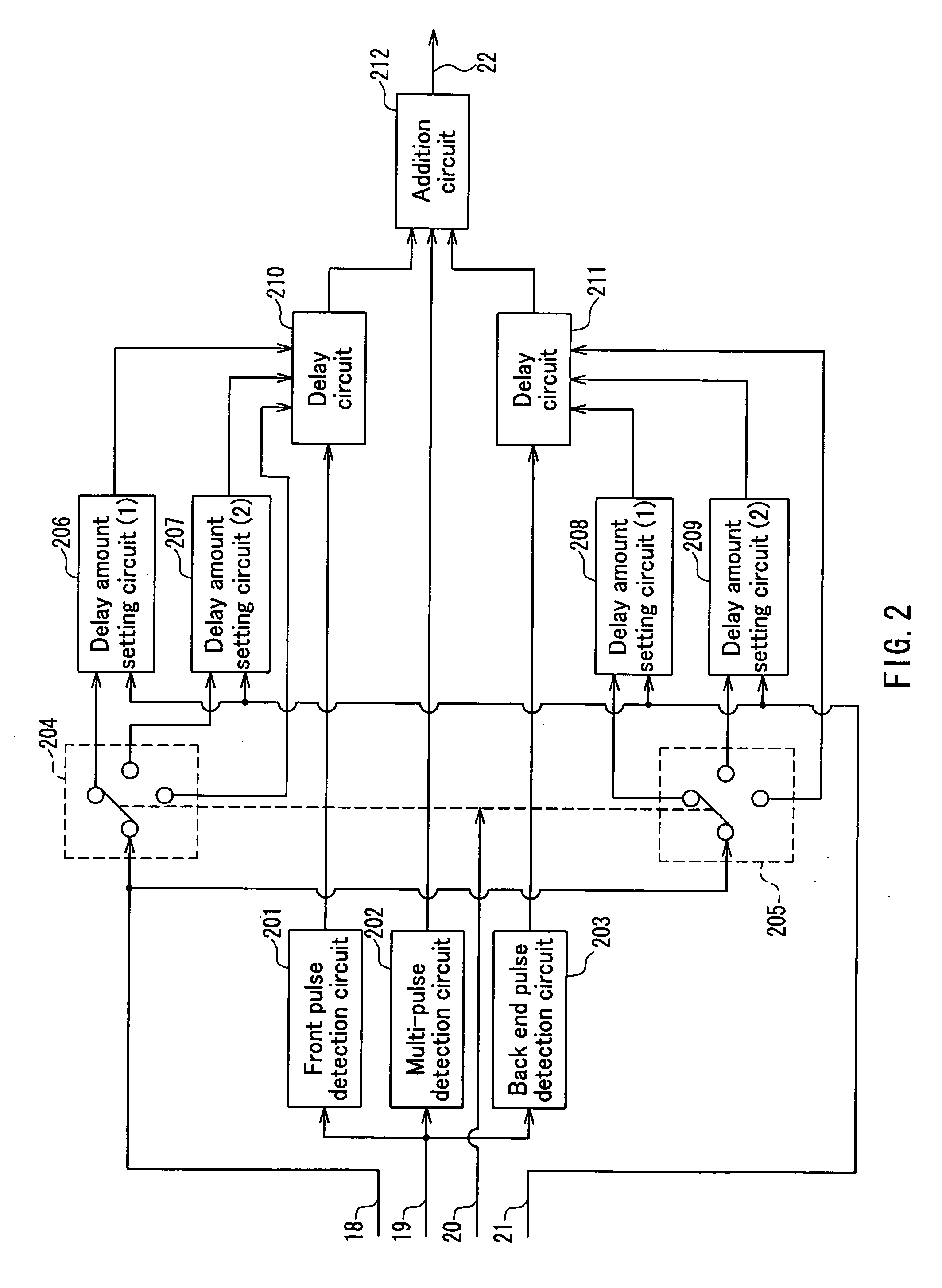
Recording method and optical disc apparatus
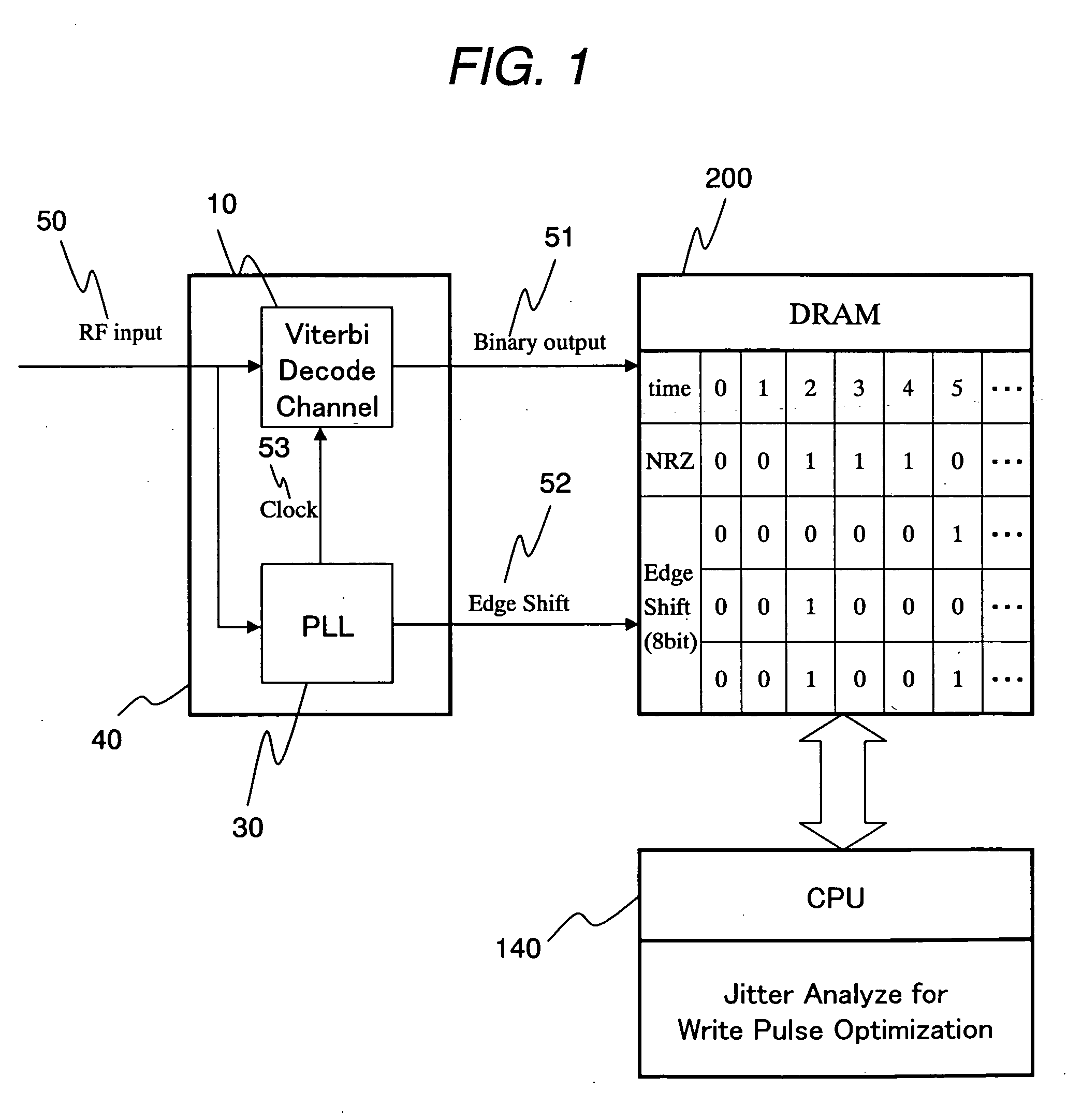
InactiveUS20060083135A1Short timeTelevision system detailsModification of read/write signalsDigital dataExternal storage
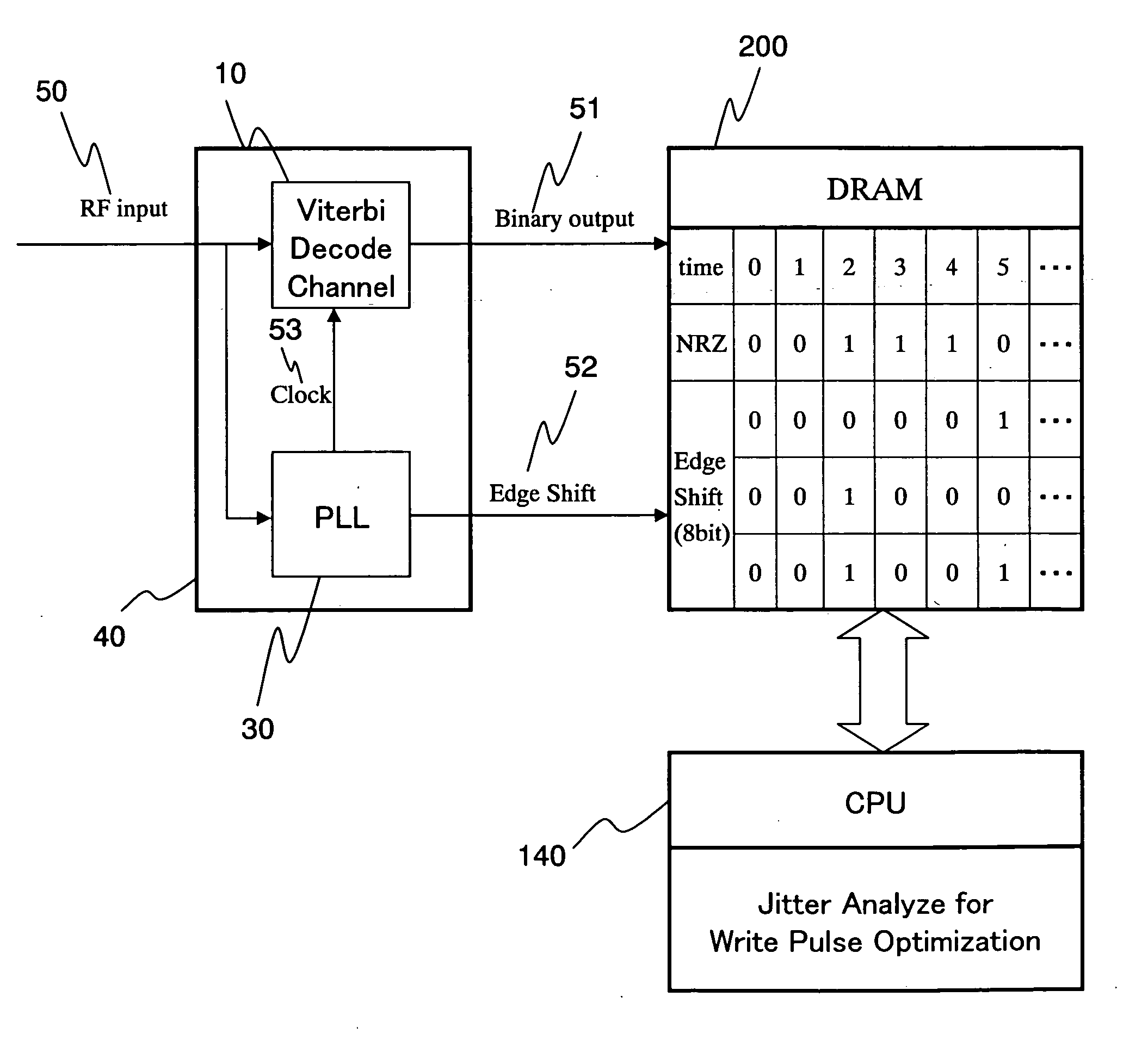
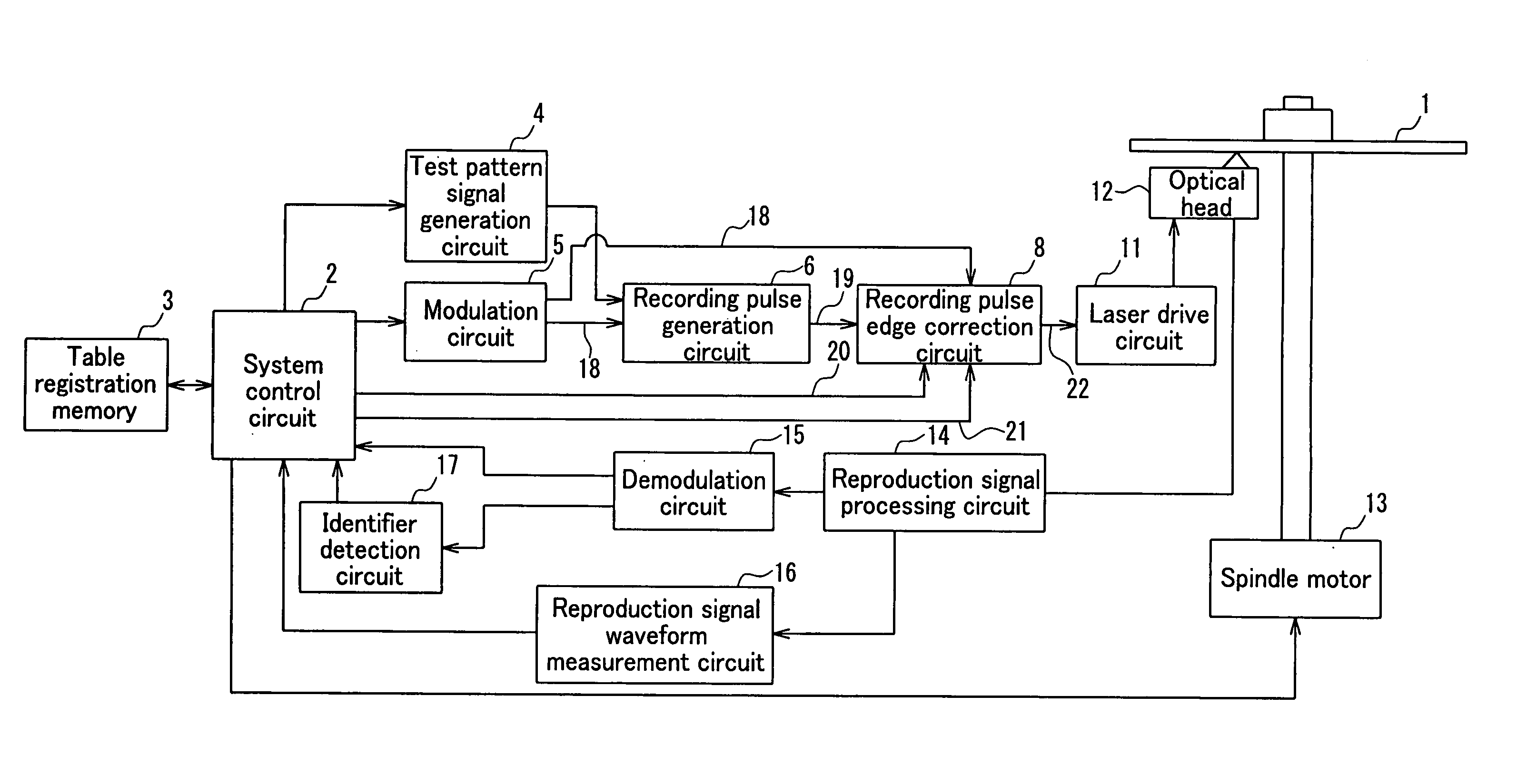
In a recordable optical disc apparatus, the efficiency of the work necessary for optimizing the write pulse condition (write strategy) is improved and the read compatibility among drive units is ensured by a minimum addition of circuitry. An edge shift amount or a read signal and a binarized result are stored in an external memory as digital data and are later processed by analysis software in a host PC. The write pulse shape and power conditions can be optimized to individual optical disc media in a short time by means of a simple circuit. Further, by optimizing the write pulse shape and power condition in view of the PRML class or the difference in NA of the head, any deterioration of read compatibility can be avoided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Light intensity modulated direct overwrite magneto-optical microhead array chip hard disk drive
InactiveUS20030007442A1Mechanical record carriersRecord information storageHard disc driveImage resolution
A magneto-optical data storage hard disk drive that uses stationary "Light Intensity Modulated Direct Over-Writey" (LIMDOW) or "Magnetically induced Super Resolution" (MSR) "Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chips' in place of conventional flying-heads, rotary voice-coil actuators, or other similar types of "servo-tracking' mechanisms to simultaneously record and / or reproduce data to and / or from a multitude of data-tracks located across the data-surfaces of a multitude of LIMDOW or MSR disc media that comprise two or more different coercive force regions at room temperature, using a multitude of microheads.
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
Recording medium having a substrate containing microscopic pattern of parallel groove and land sections and recording/reproducing equipment therefor
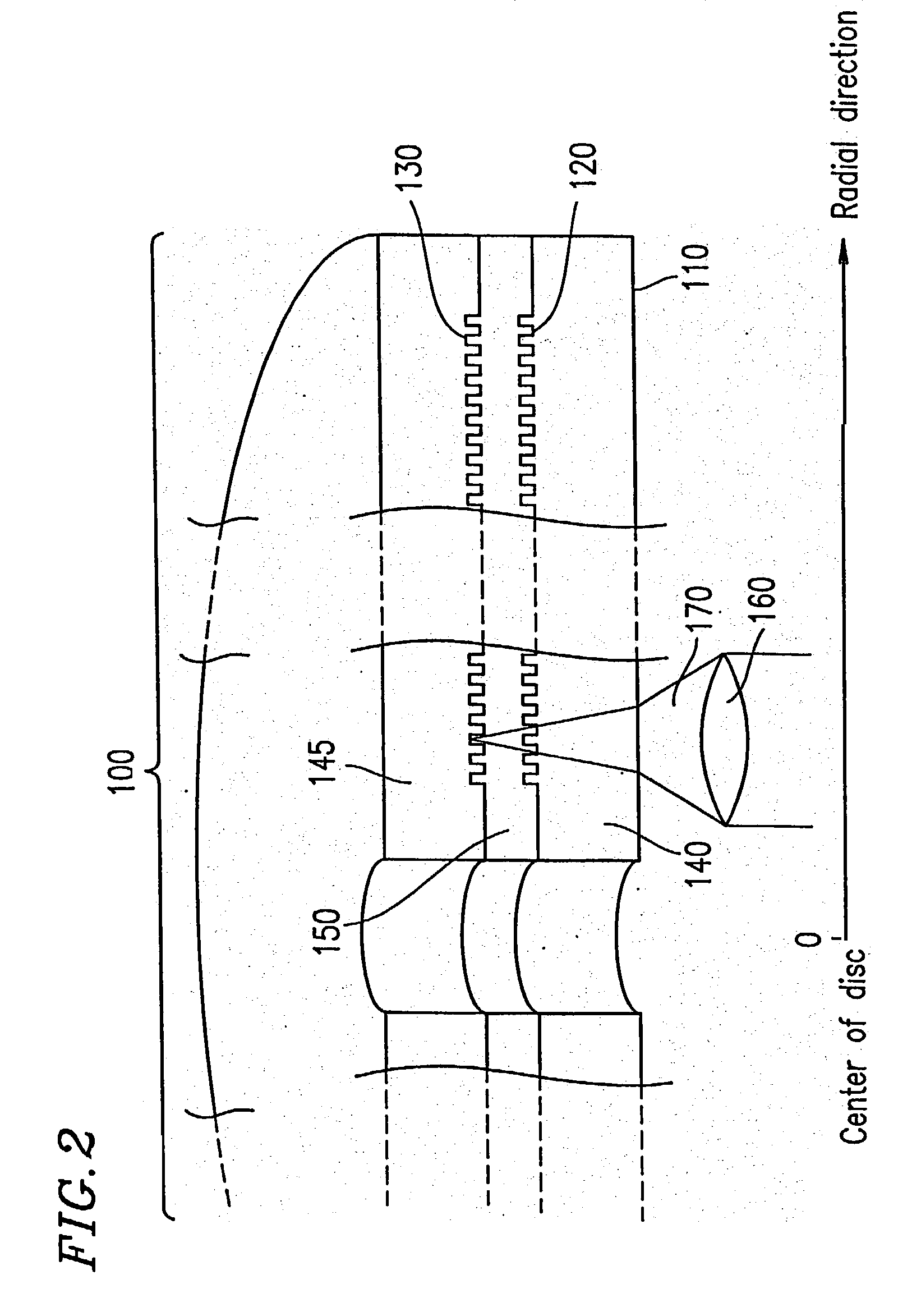
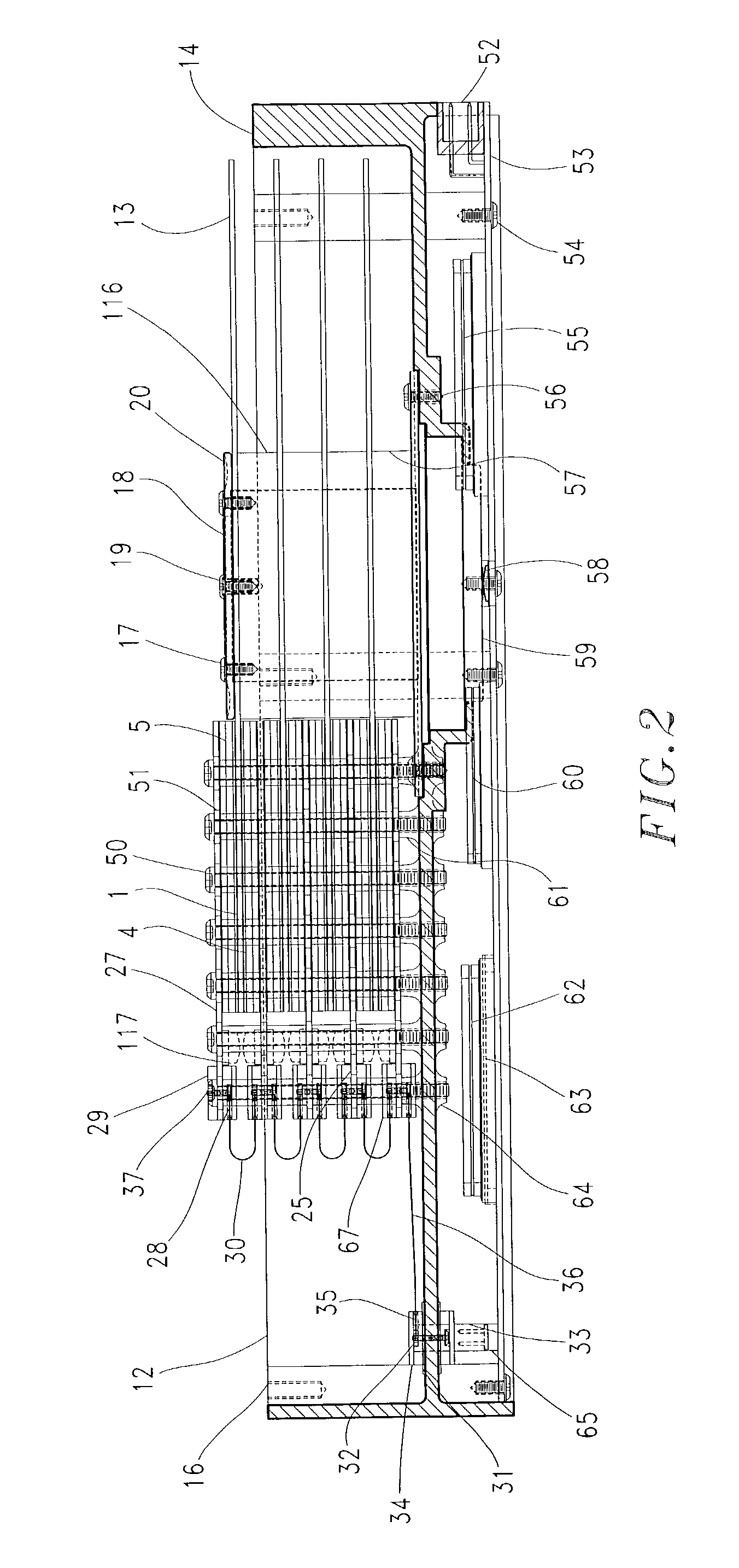
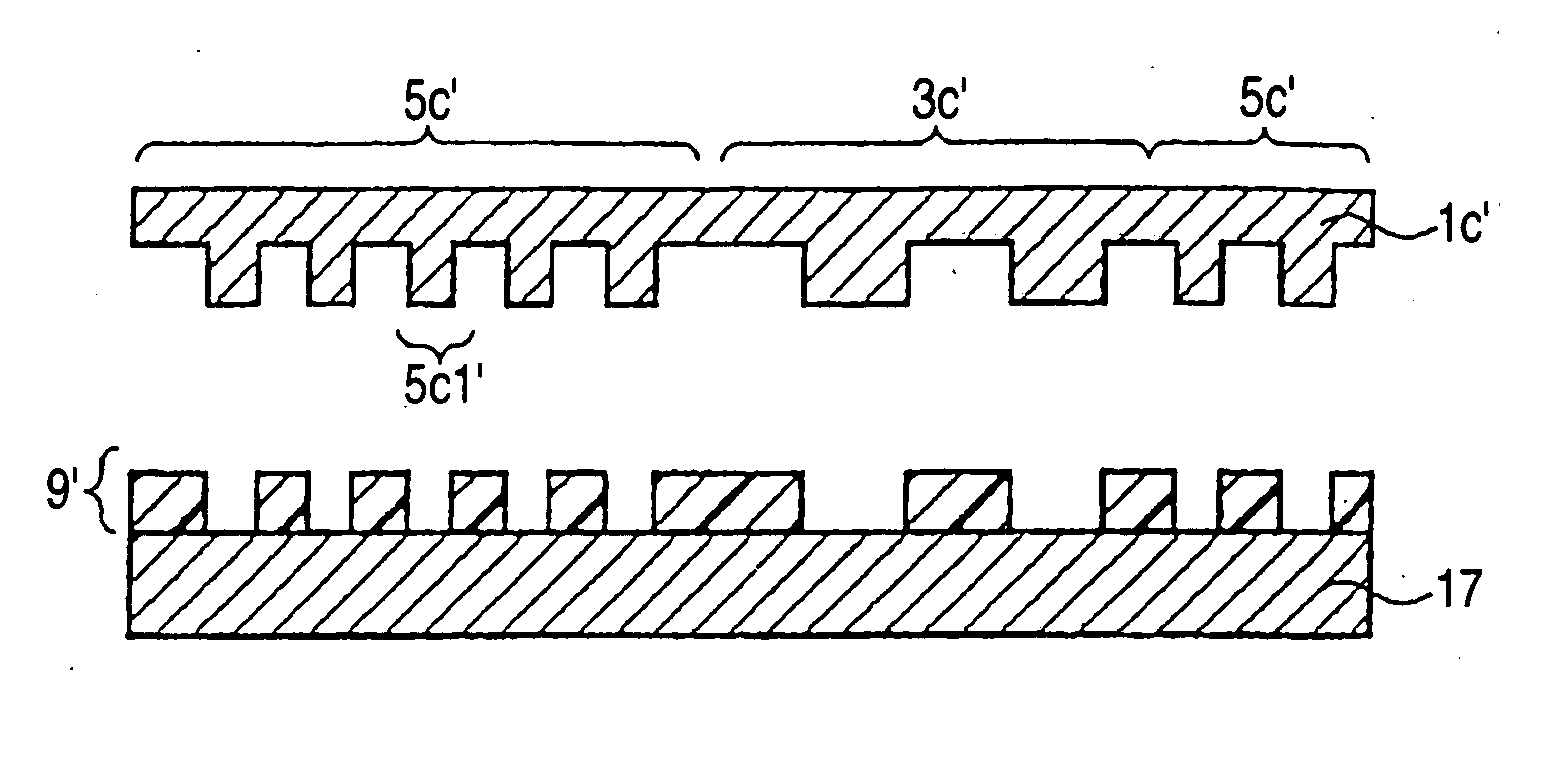
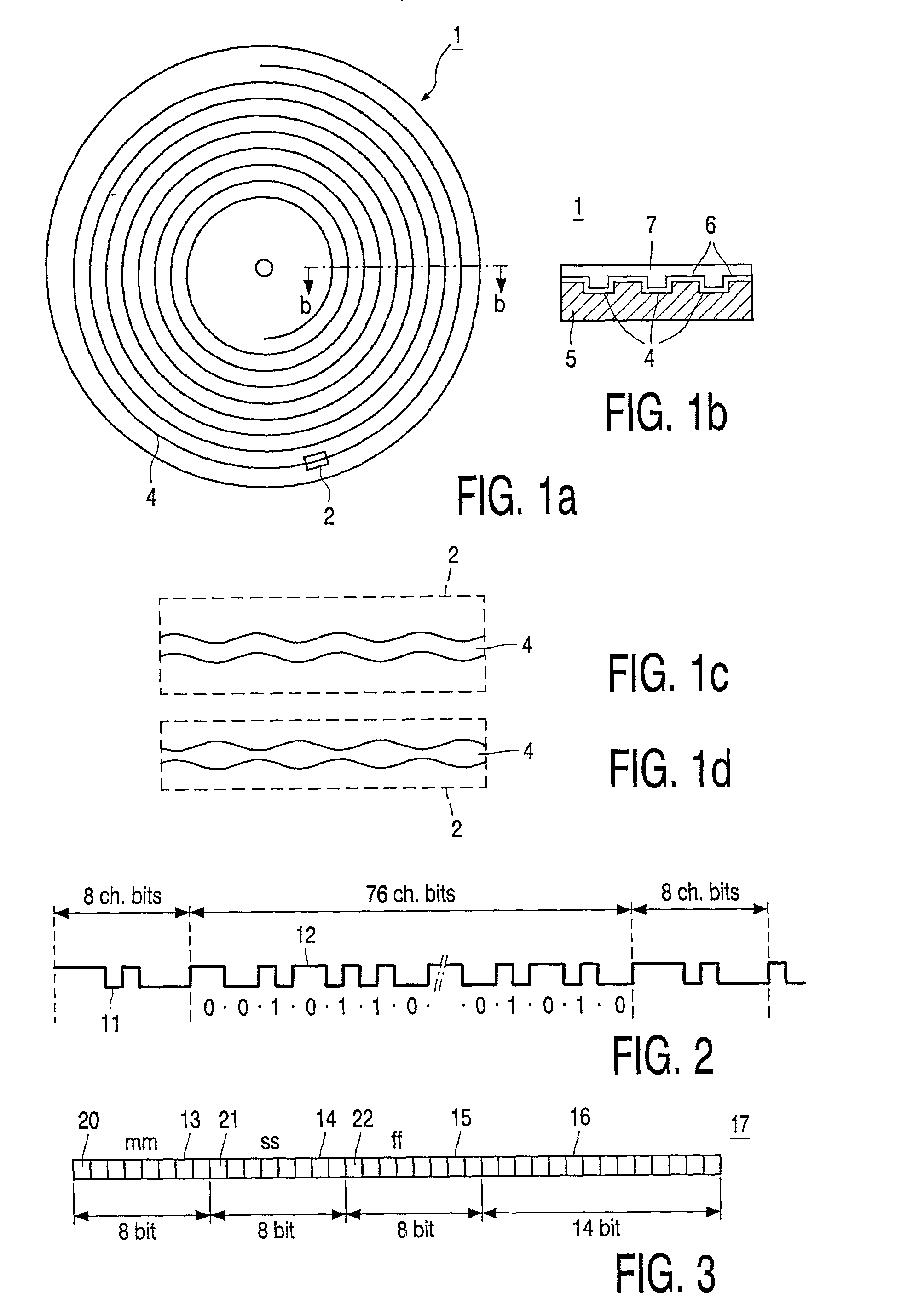
An information recording medium 1 at least comprises a substrate 13 having a microscopic pattern 20, which is constituted by a shape of continuous substance of approximately parallel grooves formed with a groove section G and a land section L alternately, a recording layer 12 formed on the microscopic pattern 20 and a light transmission layer 11 formed on the recording layer. The microscopic pattern 20 is formed so as to satisfy a relation of P<λ / NA and a thickness of the light transmission layer 11 is within a range of 0.07 to 0.12 mm, wherein P is a pitch of the groove section G or the land section L, λ is a wavelength of reproducing light beam and NA is a numerical aperture of an objective lens. Further, there provided an information recording medium, which is improved in cross erase and recorded in high density, and a reproducing apparatus and a recording apparatus for the information recording medium.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
Calibration storage methods for a digital focus and tracking servo system with calibration
Owner:RPX CORP
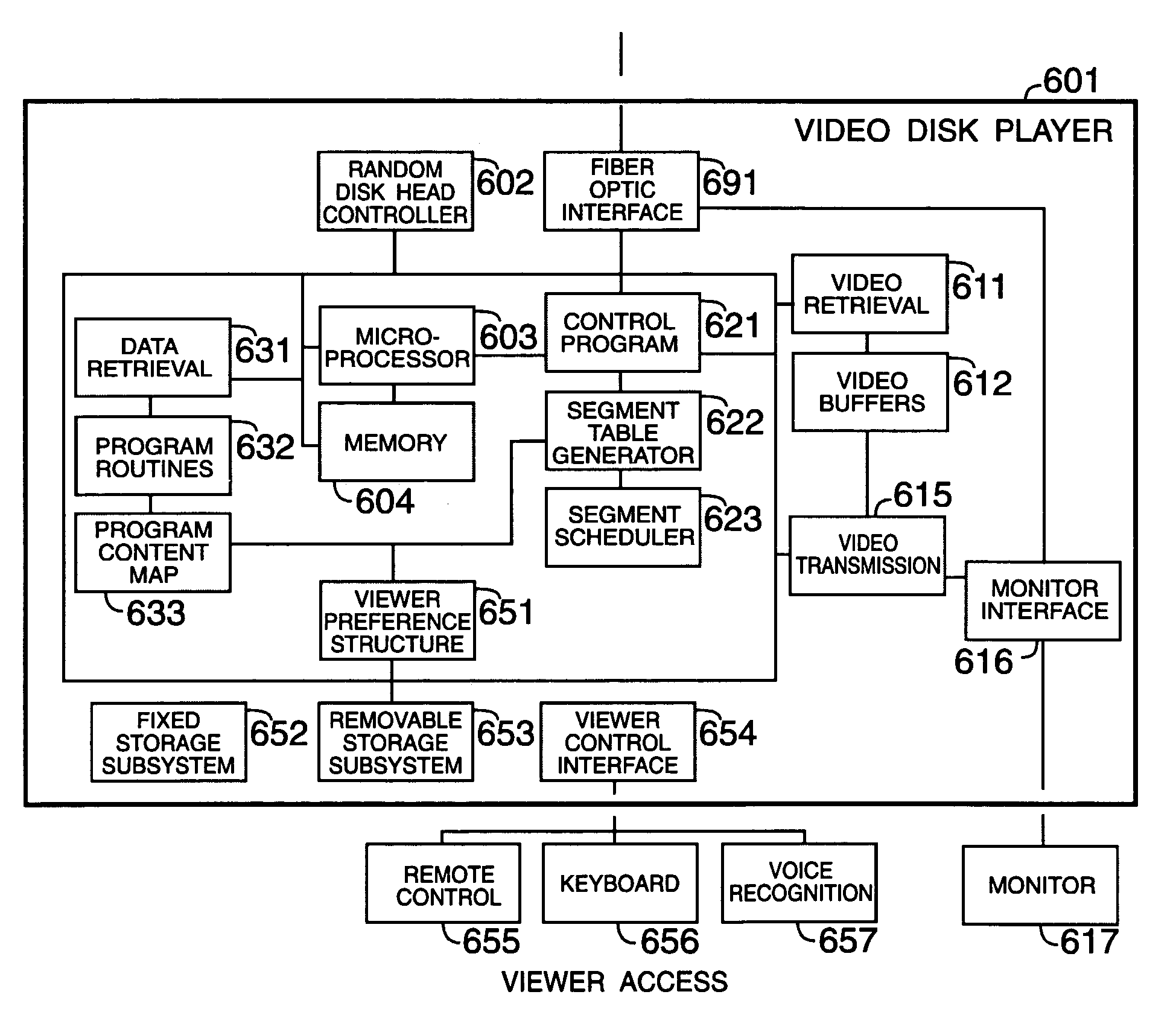
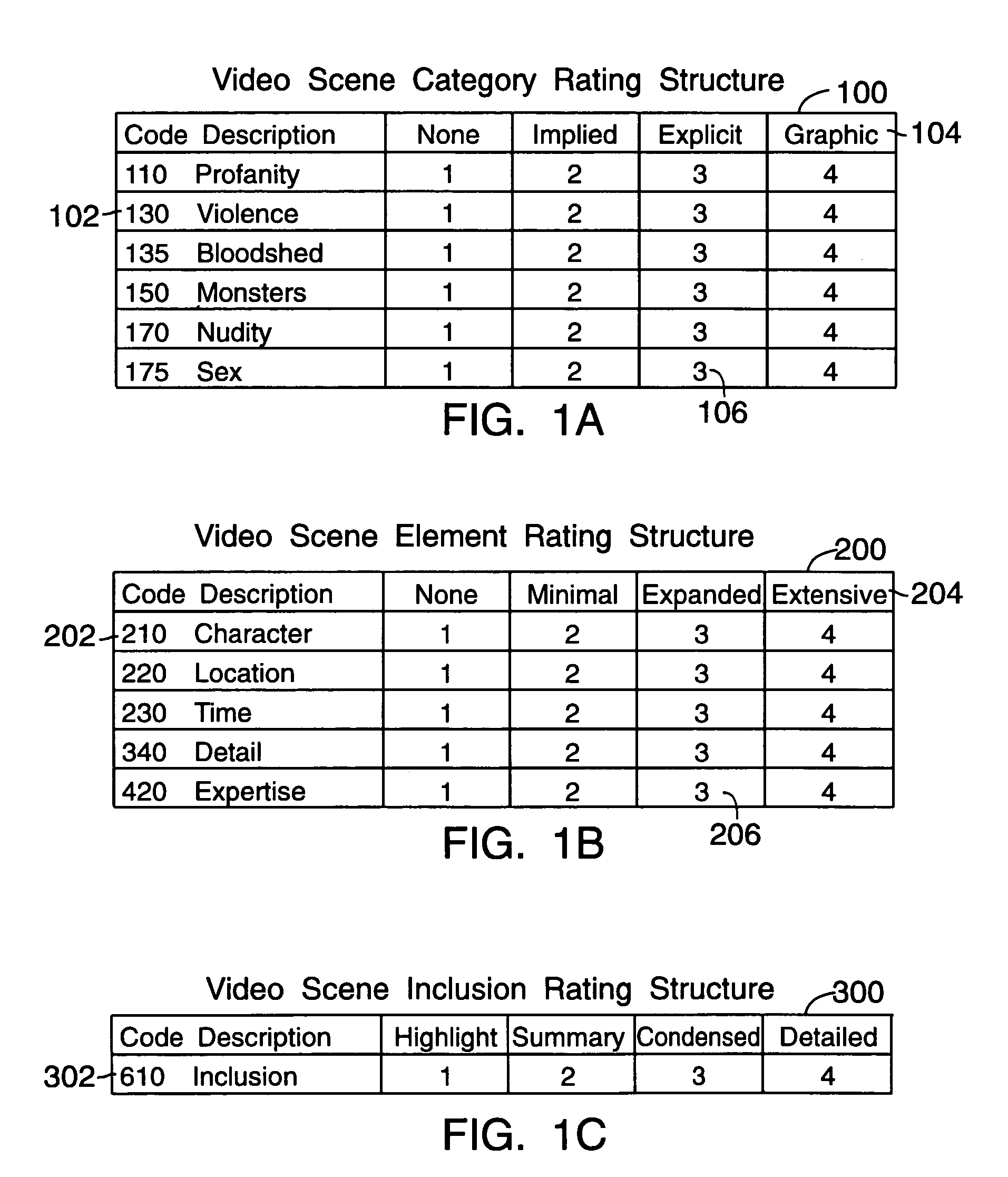
Video playing responsive to usage restriction
InactiveUS20060110136A1Efficiently previewingView effectivelyTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersPersonalizationControl system design
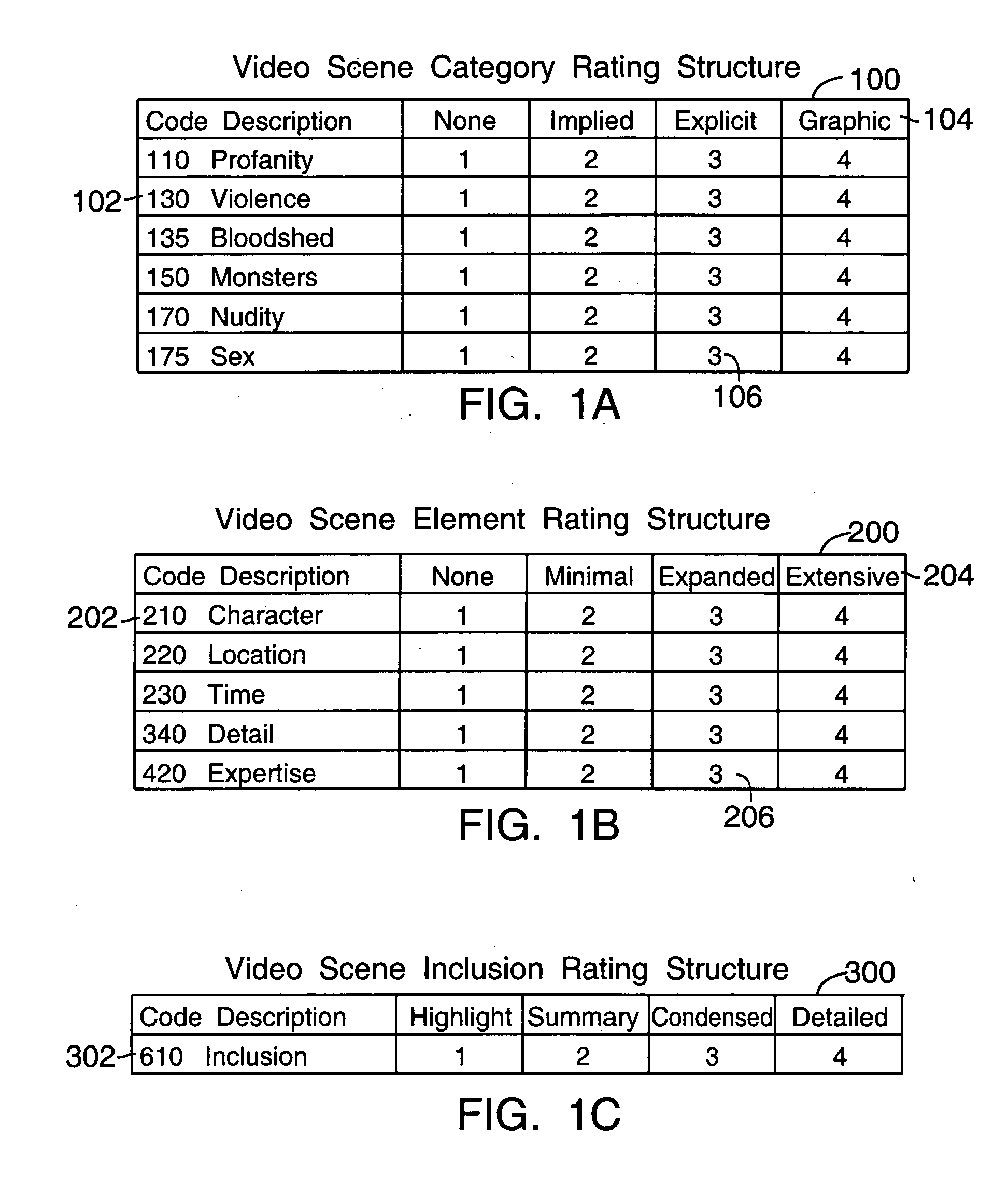
This invention relates to an automated control system and method that furnishes viewers with individualized automated editing and retrieval capabilities over the contents and length of a variable content video program in order to produce a transparently continuous and complete show. The system capabilities include an automated flexible control system design that enables an operator to selectively apply different editing criteria to the variety of subject matters that may be contained within the program. The system controls also include an automated capability for efficiently previewing program scenes of pre-identified categories and classes of subject matter and a capability for determining their inclusion in the program seen by the viewer. Finally, the control system provide a keyword / menu segment / program retrieval facility from an existing program and program database, and a requesting capability for programs to be produced according to viewer-specified requirements.
Owner:NISSIM CORP
Imprint stamper, method for manufacturing the same, recording medium, method for manufacturing the same, information recording/reproducing method, and information recording/reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20070211592A1Efficient preparationHigh densityMagnetic materials for record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High-density read-only optical disc, method for recording disc information (DI) on the high-density read-only optica disc, and method for reproducing data recorded on the high-density read-only optical disc
InactiveUS20040076101A1Television system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersComputer hardwareHigh density
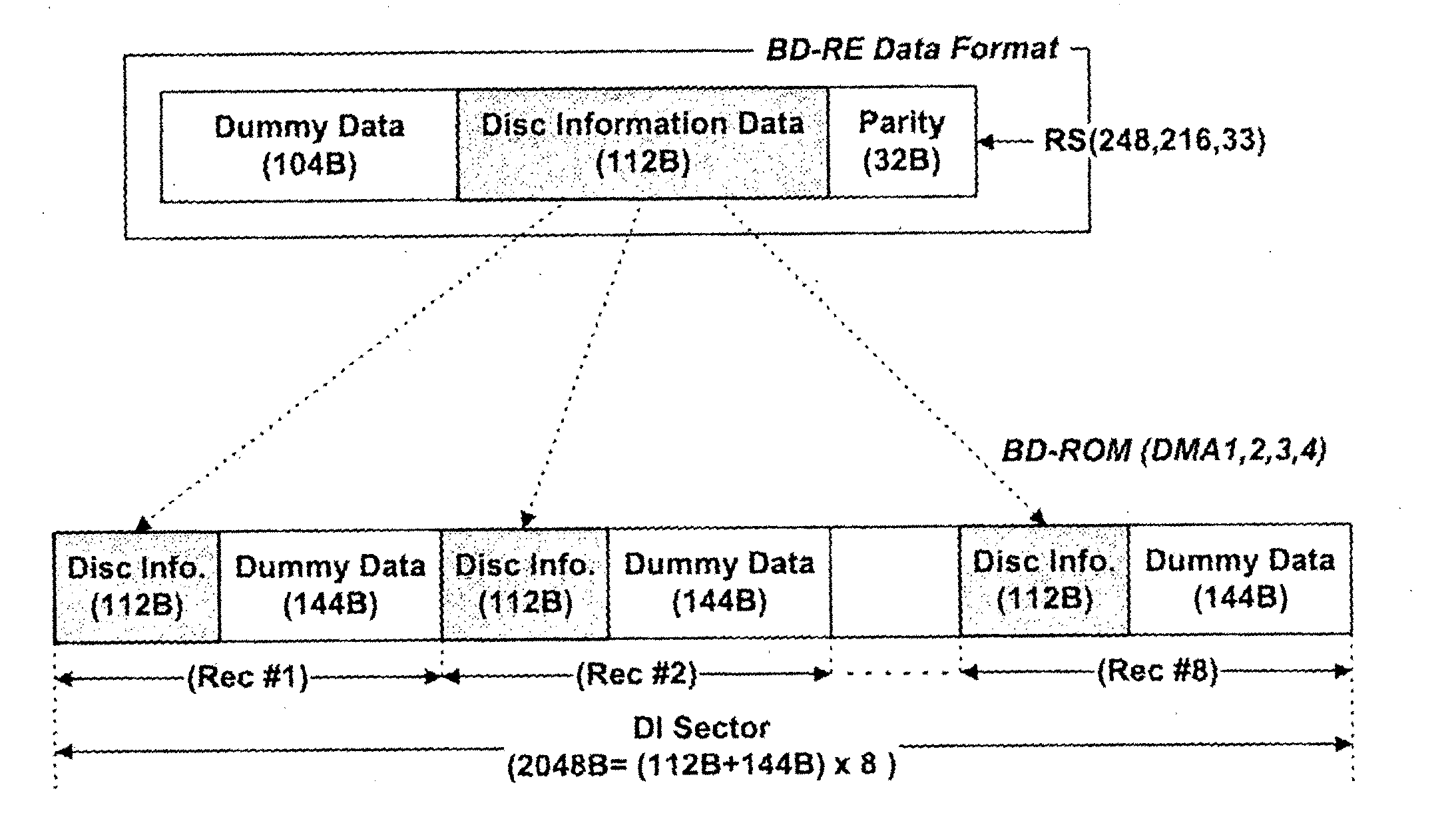
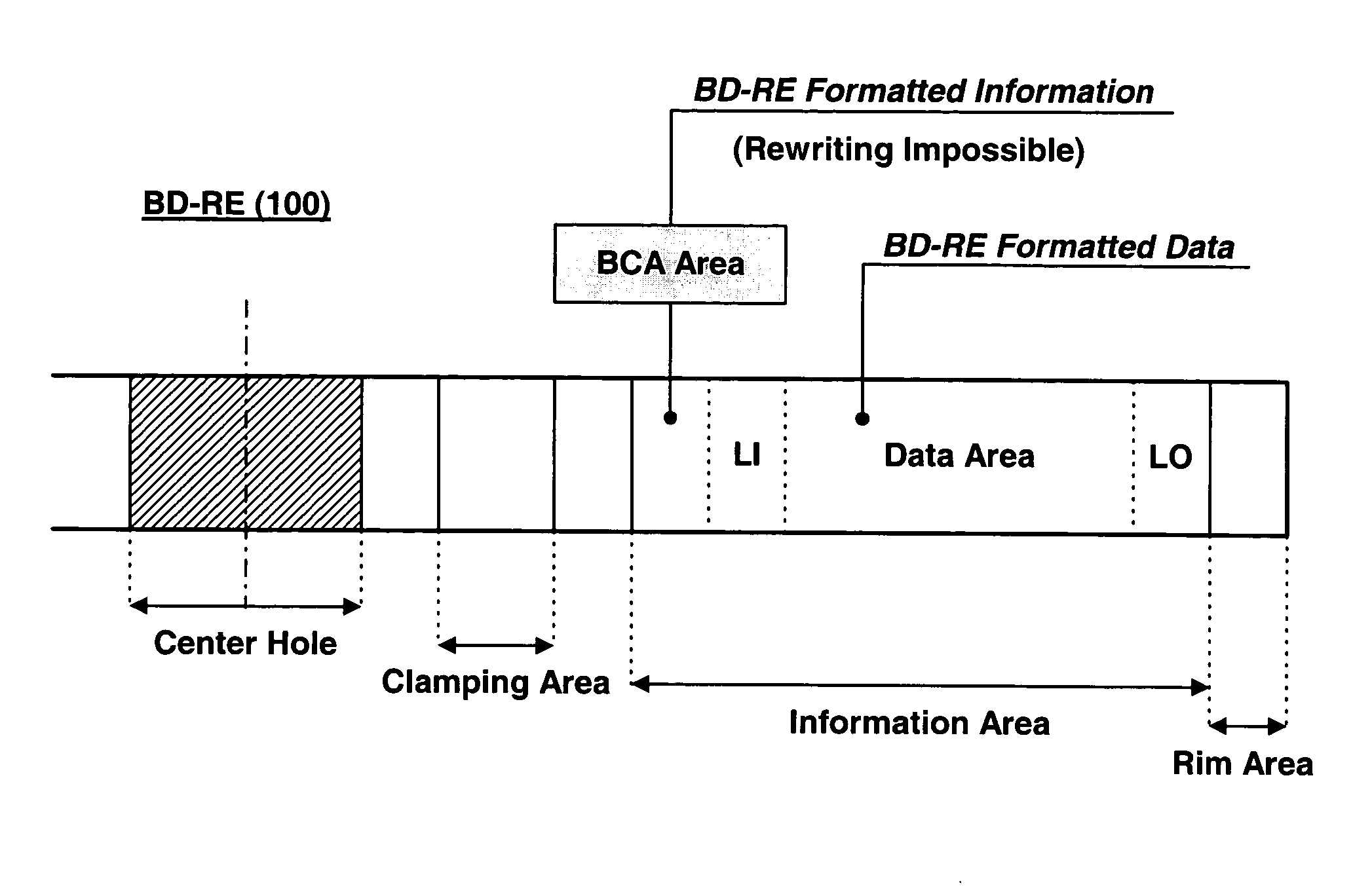
A high-density read-only optical disc, a method for recording DI (Disc Information) on the high-density read-only optical disc, and a method for reproducing data recorded on the high-density read-only optical disc. The DI recording method for repeatedly recording pit-shaped DI appropriate for the high-density read-only optical disc in a specific recording area contained in a Lead-In or Lead-Out zone more than a predetermined number of times. Therefore, it quickly reads DI recorded in a specific recording area, and normally reproduces data based upon the read DI.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Record carrier of the optical type and a device for recording and/or playback for use with such a record carrier
InactiveUS20020150014A1Improve speed performanceRecord information storageOptical record carriersControl data
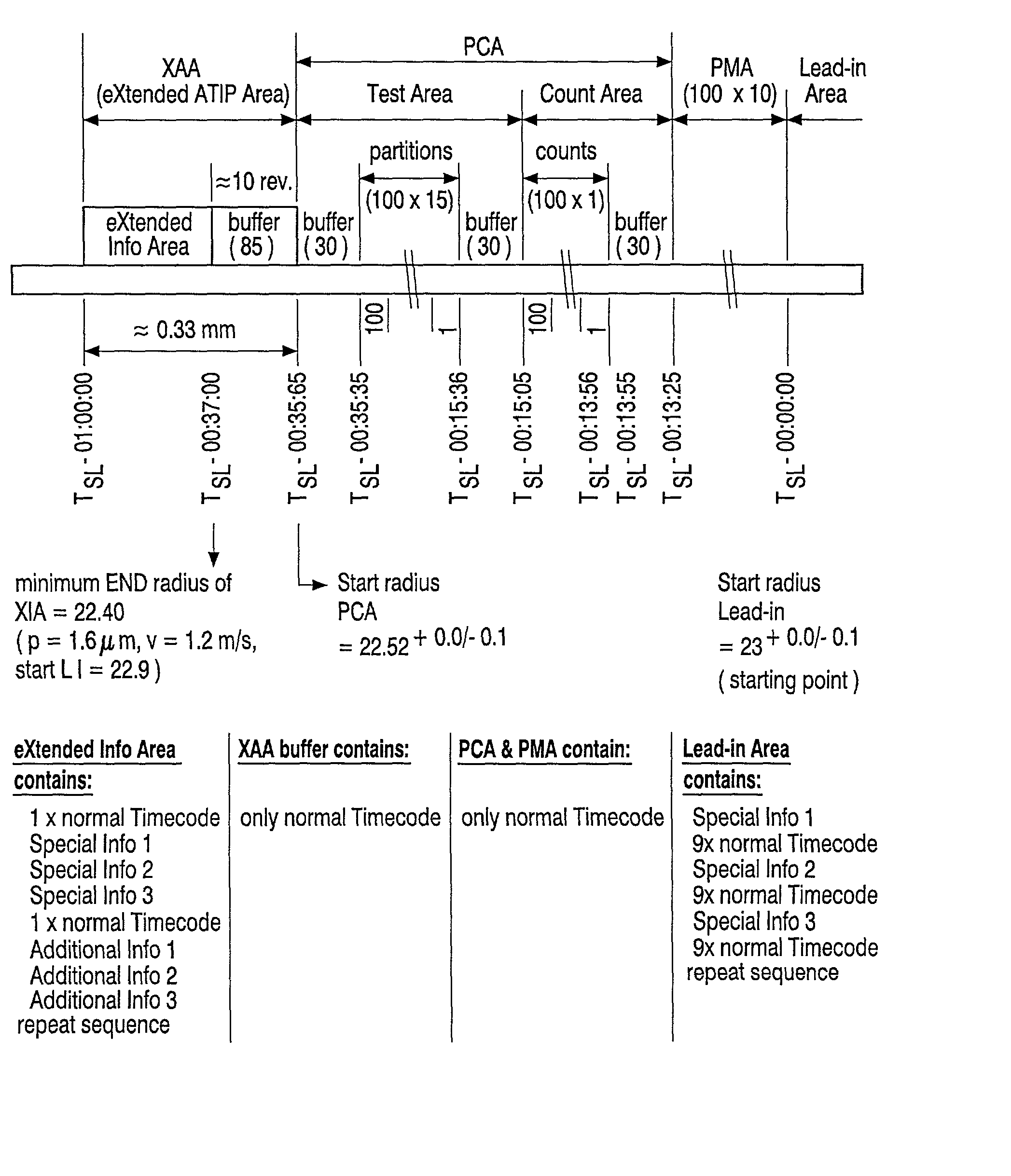
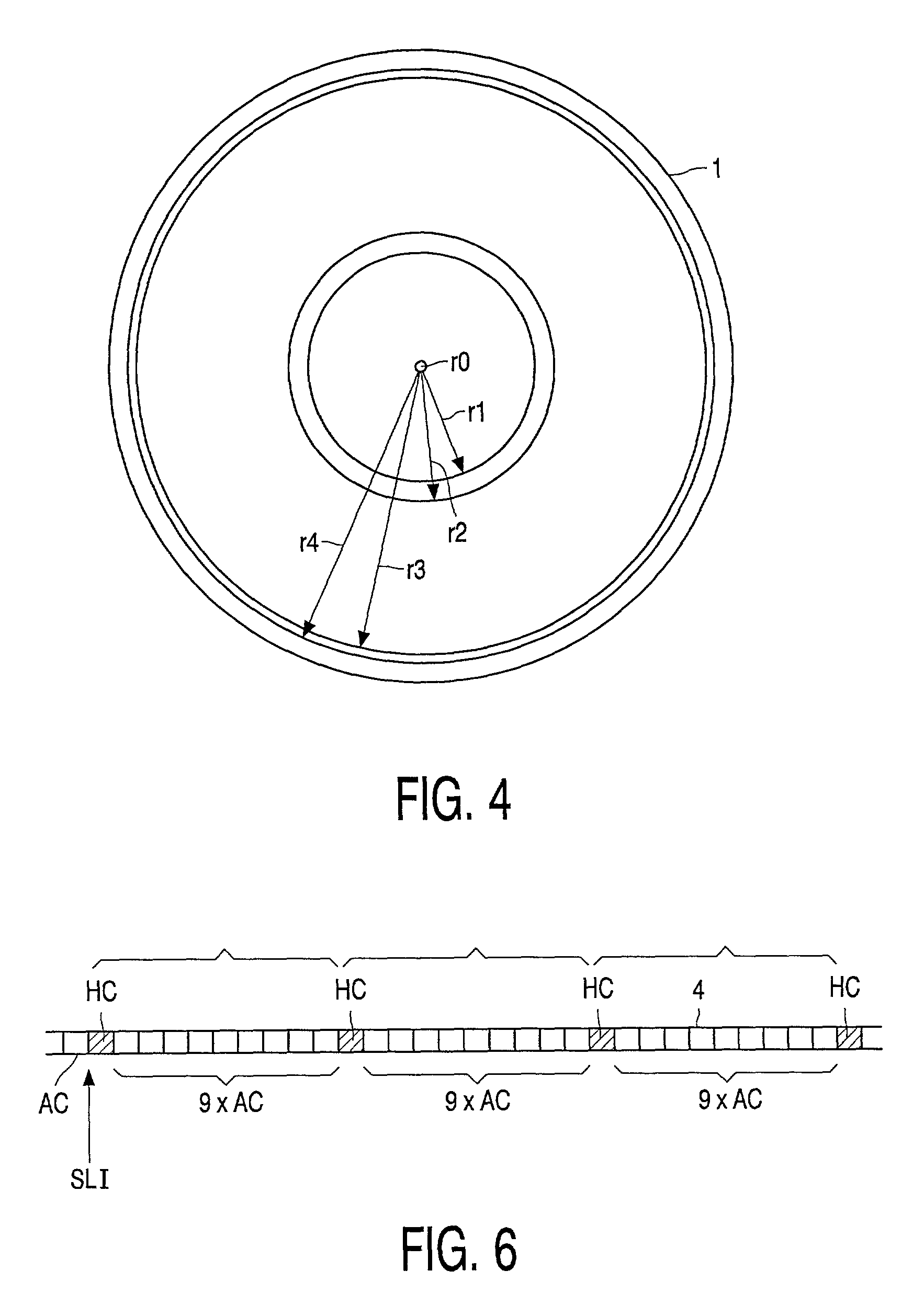
The invention relates to a record carrier of a disc-like optically inscribable type, having a preformed track in which an auxiliarily signal comprising a sequence of codes is recorded by means of a preformed track modulation. The codes comprise a sequence of address codes (AC) specifying the addresses of the track portions in which said address codes (AC) are recorded and special codes (SC). The special codes (SC) can be distinguished from said address codes (AC) and specify control data for controlling a recording by a recording device. The record carrier is provided with an extended area (XAA) proceeding a program calibration area (PCA), the extended area (XAA) comprising special codes (SC) representing additional control information for controlling a recording.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optical information recording method, optical information recording device, and optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20050174906A1Shorten the timeExact reproductionRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsComputer scienceRecording media
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
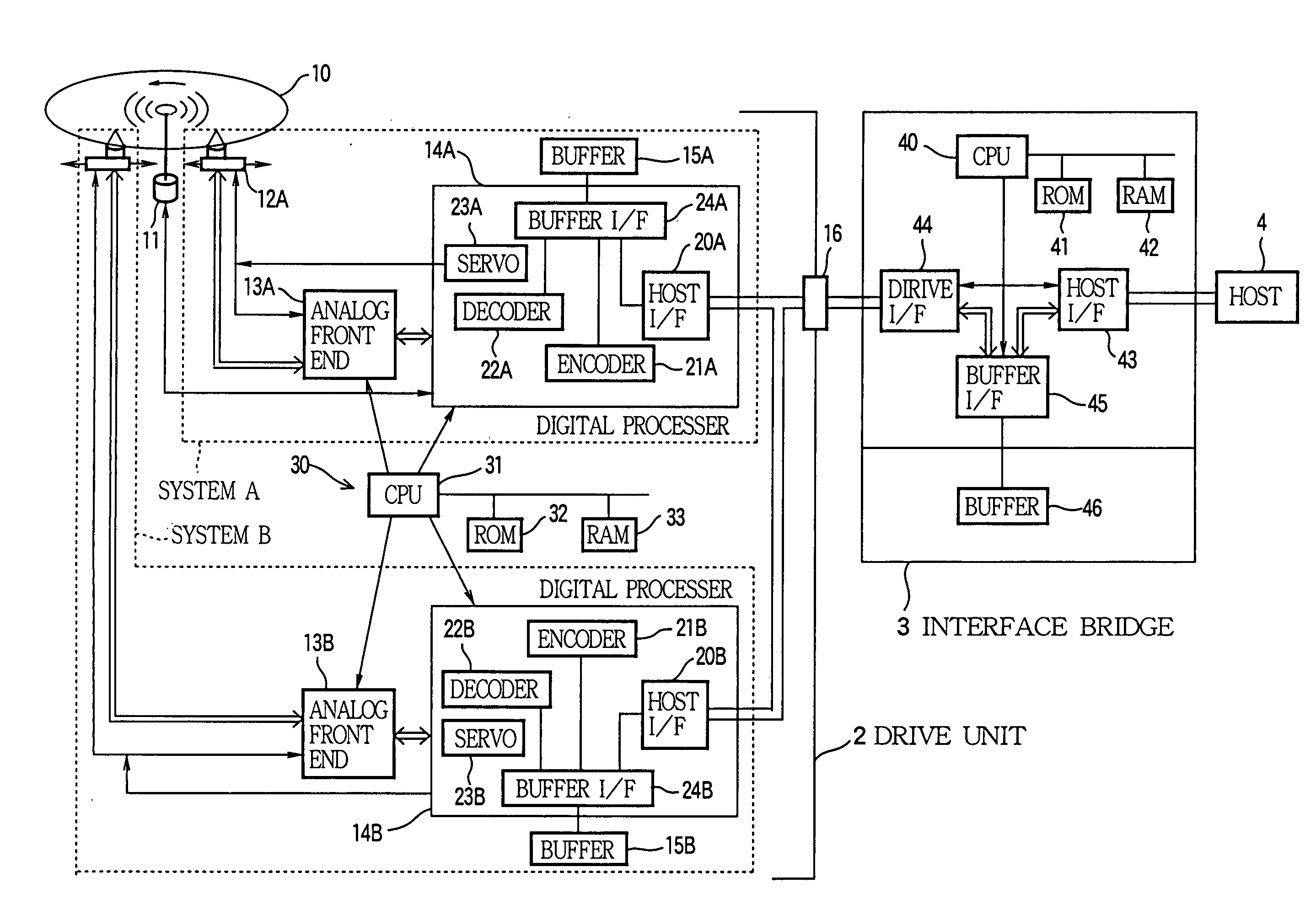
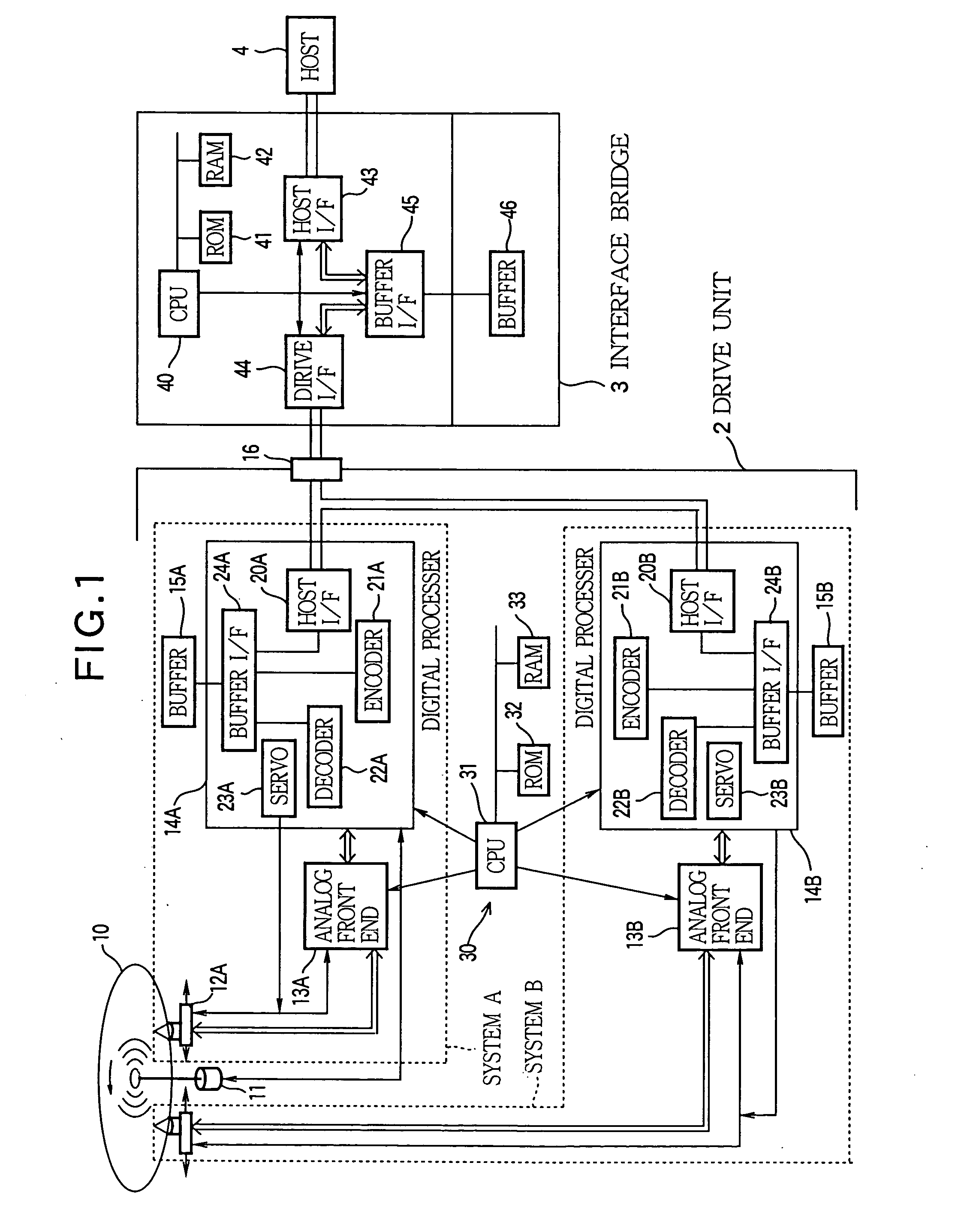
Optical disk apparatus with multiple reproduction/record units for parallel operation
InactiveUS20050162990A1Easy to controlReduce construction costsTelevision system detailsInput/output to record carriersInformation processingDigital data
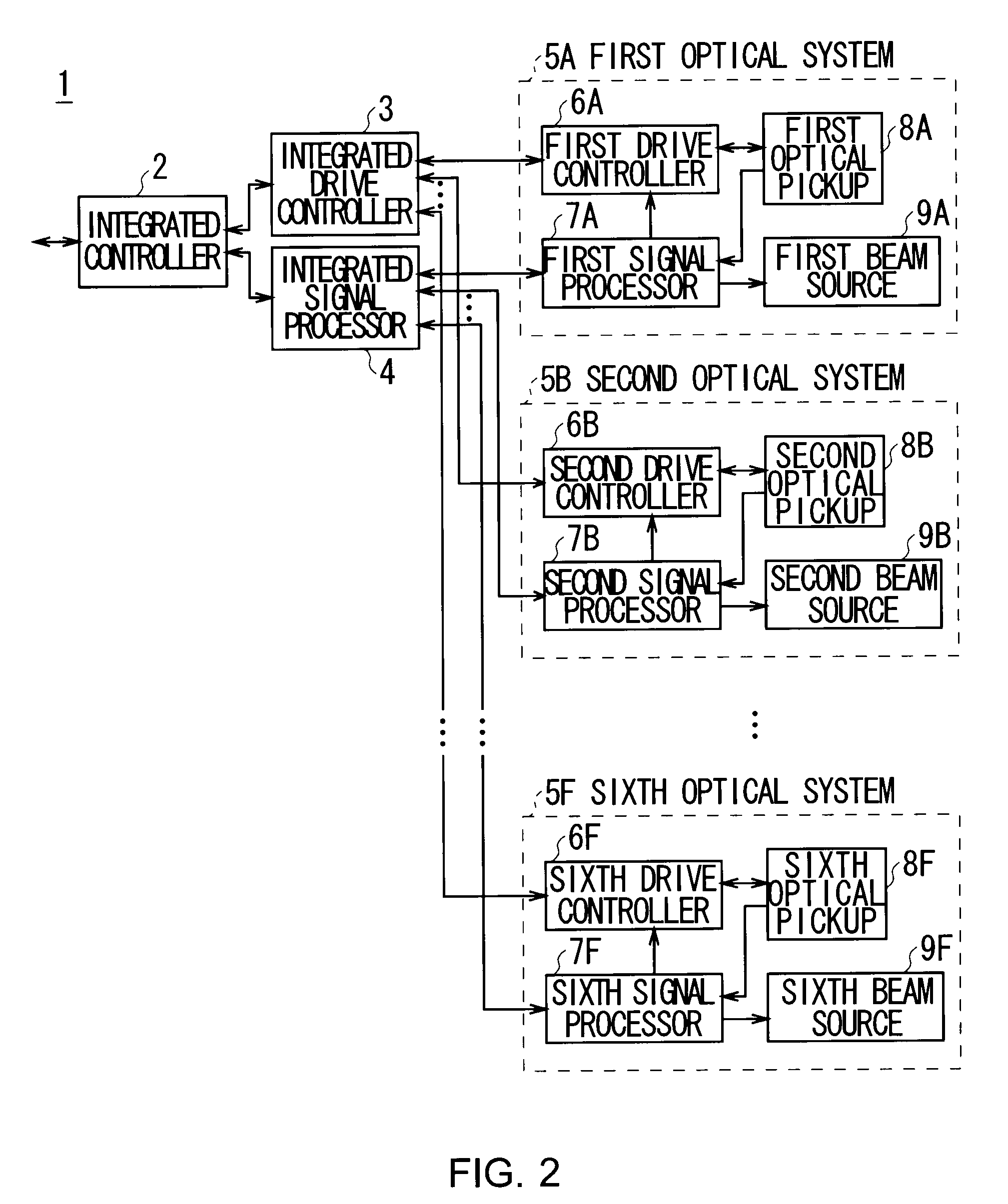
A disk drive device is constructed for driving an optical disk while communicating with a host apparatus. The device is assembled by a rotation drive section that rotatively driving one optical disk, a plurality of reproduction / record units that can write or read information on the optical disk in parallel with one another, a control section that controls the rotation drive section and controls the plurality of the reproduction / record units concurrently and independently with one another, and an input / output port that connects the plurality of the reproduction / record units to the host apparatus. Each reproduction / record unit has an optical pickup for irradiating an optical beam to write or read the information on the optical disk, an analog front-end circuit for treating the information as a form of an analog signal to be inputted to the optical pickup or outputted from the optical pickup, a digital processing section connected to the analog front-end circuit for processing the information as a form of digital data, and a host interface for controlling the communication between the digital processing section and the host apparatus through the input / output port.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Optical recording method, optical recording medium, optical recording medium recording device, optical recording device, optical disk, optica disk recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS20060140094A1Relatively low linear speedRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsEngineeringIrradiation laser
A mark having a length nT (n being an integer equal to or greater than 3 and T being a clock period) is formed by modulating irradiation laser power with three values of recording power Pw, erase power Pe, and bias power Pb (Pw>Pe>Pb). Constant strength periods (At) of the recording power Pw are set as AtT, A1T, . . . and AmT and constant strength periods (Bt) of the bias power Pb are set as BtT, B1T, . . . BmT, and CT (C=−1 to 3). The application of laser is divided into pulses in order of AtT, BtT, A1T, B1T, . . . , AmT, BmT, and CT (m=(n−k) / 2, k=3 (if n is an odd number), or k=4 (if n is an even number)). (Here, the constant strength period of the recording power Pw for n=3, n=4, n≧5 (odd number), and n≧6 (even number) is set as At3, At4, Atod, and Atev, the constant strength period of the bias power Pb for n=3, n=4, n≧5 (odd number), and n≧6 (even number) is set as Bt3, Bt4, Btod, and Btev, and then, At3+Bt3=Atod+Btod=Am+Bm=2T and At4+Bt4=Atev+Btev=3T).
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Method Of Controlling Power States In A Multimedia System
ActiveUS20080232209A1Efficiently informedTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersControl powerPower switching
This invention relates to controlling the power states in a multimedia system comprising a multimedia connector box including a multimedia source interconnected to a transmitter module, and a multimedia device including a receiver module interconnected to a multimedia sink, wherein the transmitter and the vice via multimedia interfacing means. A signal detector detects the signal activity between the power sources of the multimedia system for determining the current power state of the power sources, and a power switching mechanism adapts the power states of the transmitter and receiving modules to the power states of the power sources.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Patterned media having offset tracks
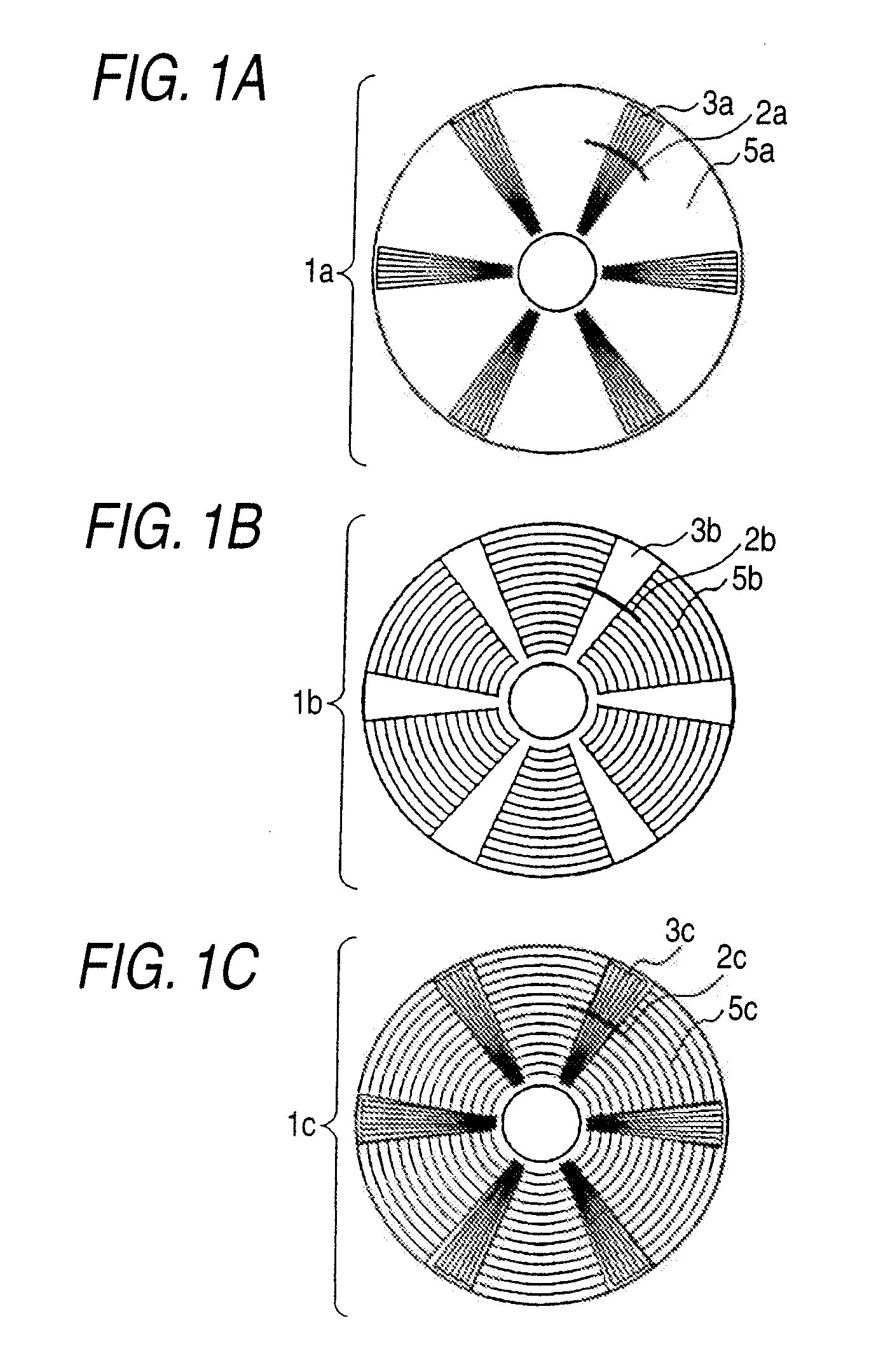
InactiveUS6937421B2Improve performanceNanoinformaticsRecord information storagePatterned mediaOptical medium
An information recording system includes a storage medium, such as a magnetic or an optical medium, that is formed to have a plurality of adjacent tracks. Each track includes a plurality of storage elements that are arranged substantially along the track in a regular manner. A head disposed in proximity to the storage medium and has a width that spans at least two adjacent tracks. The storage elements are further arranged substantially along first and second axes, such that the first and second axes are substantially perpendicular to each other and are each substantially oriented 45° from an along-track direction associated with a track. The head reads and / or writes information from at least two adjacent tracks spanned by the head.
Owner:IBM CORP
Recording medium, and method and apparatus for recording data in the recording medium
InactiveUS20060153055A1Eliminate the problemFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageComputer hardwareRecording layer
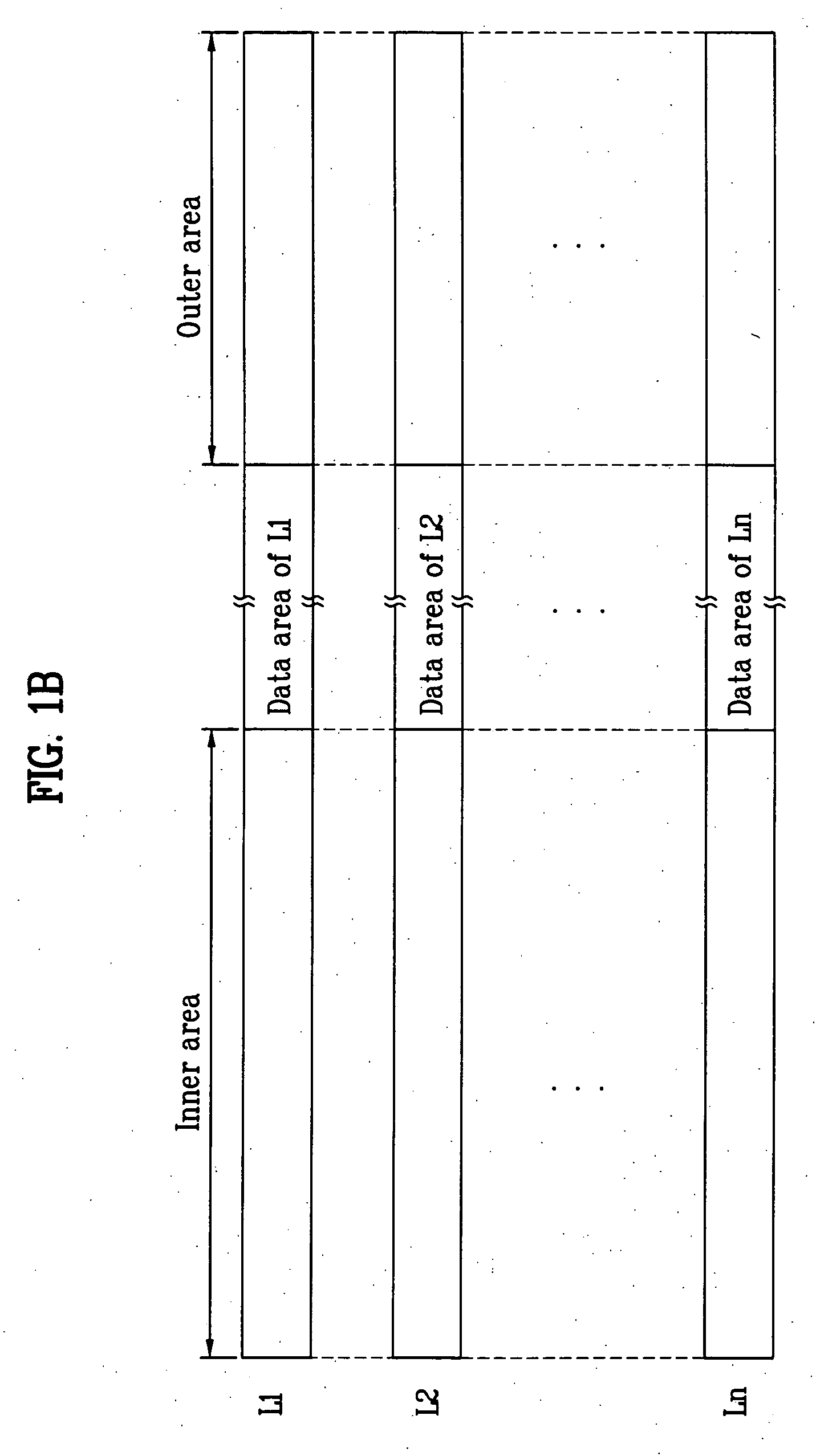
A recording medium, and a method and apparatus for recording data in the recording medium are disclosed. The recording medium including at least two record layers, each of which includes an inner area, a data area, and an outer area, includes; at least one Optimum Power Control (OPC) area contained in at least one of the inner and outer areas, wherein respective OPC areas contained in neighboring record layers are not arranged at the physically same positions with respect to optical beam. Therefore, data can be effectively recorded in the recording medium.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Optical information recording device, optical information recording method, optical information reproduction device and optical information reproduction method
InactiveUS20090003153A1Increase speedRecording involving bubble/bump formingRecord information storageLight beamComputer science
An optical information recording device includes: a section that acquires recording information that should be recorded on an optical information recording medium on which information are recorded by forming a recording mark at a position where an optical beam is focused on and from which the information are reproduced based on the reflectance of the recording mark; a section including at least one or more one-surface beam emission sections that emit a recording beam according to part of the recording information to one surface of the recording medium and focus the beam on a target position to form the recording mark; and an section including at least one or more other-surface beam emission sections that emit an recording beam according to the rest of the recording information to the other surface of the recording medium and focus the beam on a target position to form the recording mark.
Owner:SONY CORP
Recording medium with restricted playback feature and apparatus and methods for forming, recording, and reproducing the recording medium
InactiveUS20040233809A1Avoid repetitionFilamentary/web record carriersAccessories for indicating/preventing prior/unwanted useComputer hardwareData stream
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Information recording medium, information reproducing apparatus, information reproducing method and information recording method
InactiveUS20050213481A1Easy to recordPromote reproductionRecording verificationFilamentary/web record carriersRecording mediaUser information
An information recording medium includes a user information storage area which stores user information, a test write area which is extendable and for test write of information, a spare area which is extendable and capable of alternatively storing user information, and a recording position management information area including recordable range information expressing recordable ranges in the aforesaid test write area and the aforesaid spare area. The information recording medium, an information reproducing apparatus, an information reproducing method and an information recording method which make it easy to record and reproduce information properly are provided.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
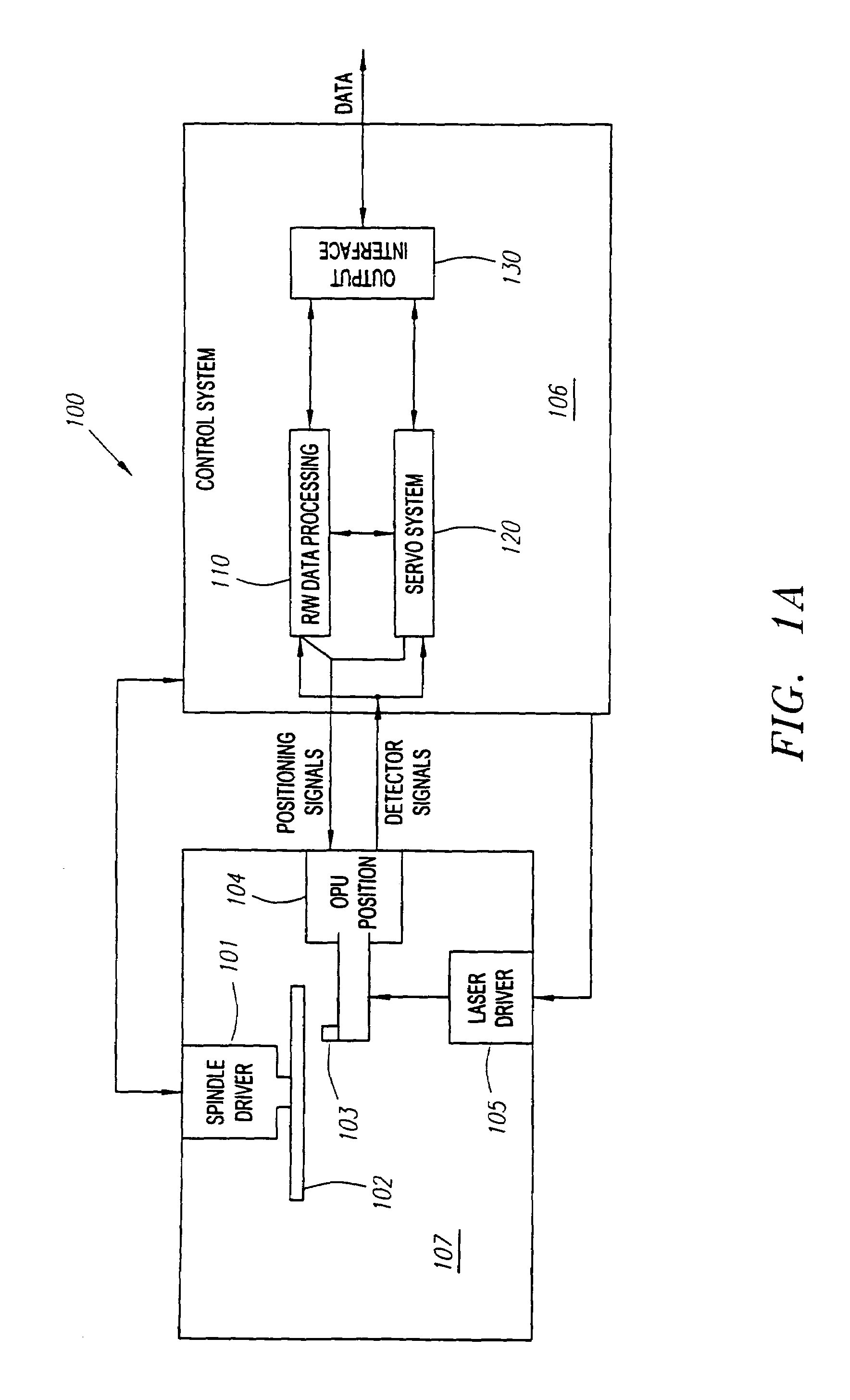
Image processing system and method for silhouette rendering and display of images during interventional procedures
InactiveUS20090046543A1Solve the slow scanning speedNarrow field of viewRecord information storageMicroscopesImaging processingA d converter
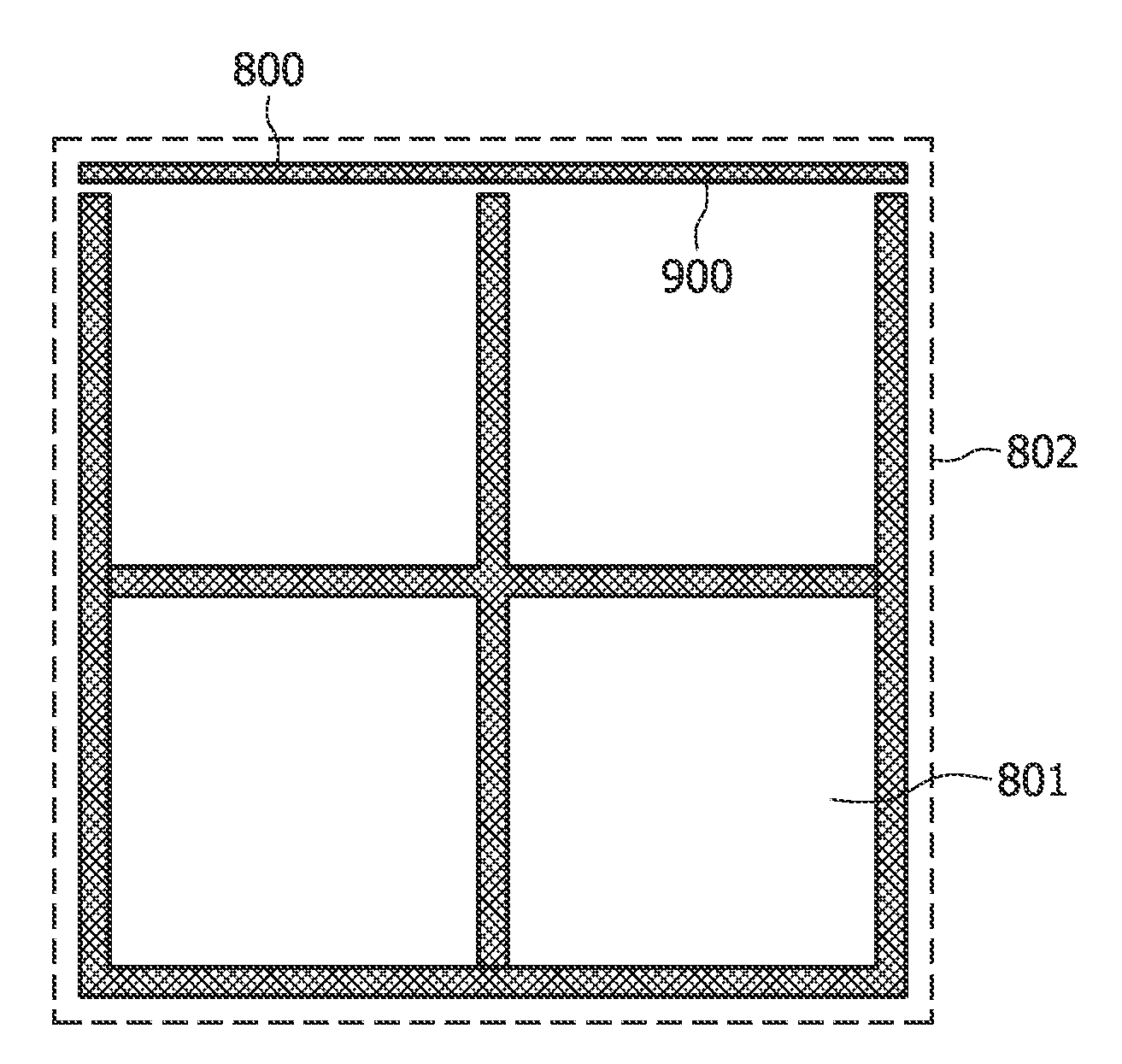
A positioning system in an optical card reading apparatus, for accurately positioning the optical card (801) relative to the probe array (102) used to read the data stored on the card. The card (801) is provided with a pattern of servo bands (800) and the sensor (103) used to read out data stored on the optical card (801) has a windowing function which is used to narrow its field of view (802) to define a region of interest (900) corresponding to one or the servo bands (800), and the output is fed to an analogue-to-digital converter. Thus, the “windowing” function of the sensor (103) is used to increase the readout speed and, therefore, the speed of detection of servo marks (800) to enable more rapid positioning of the probe array (102) relative to the optical card (801).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com