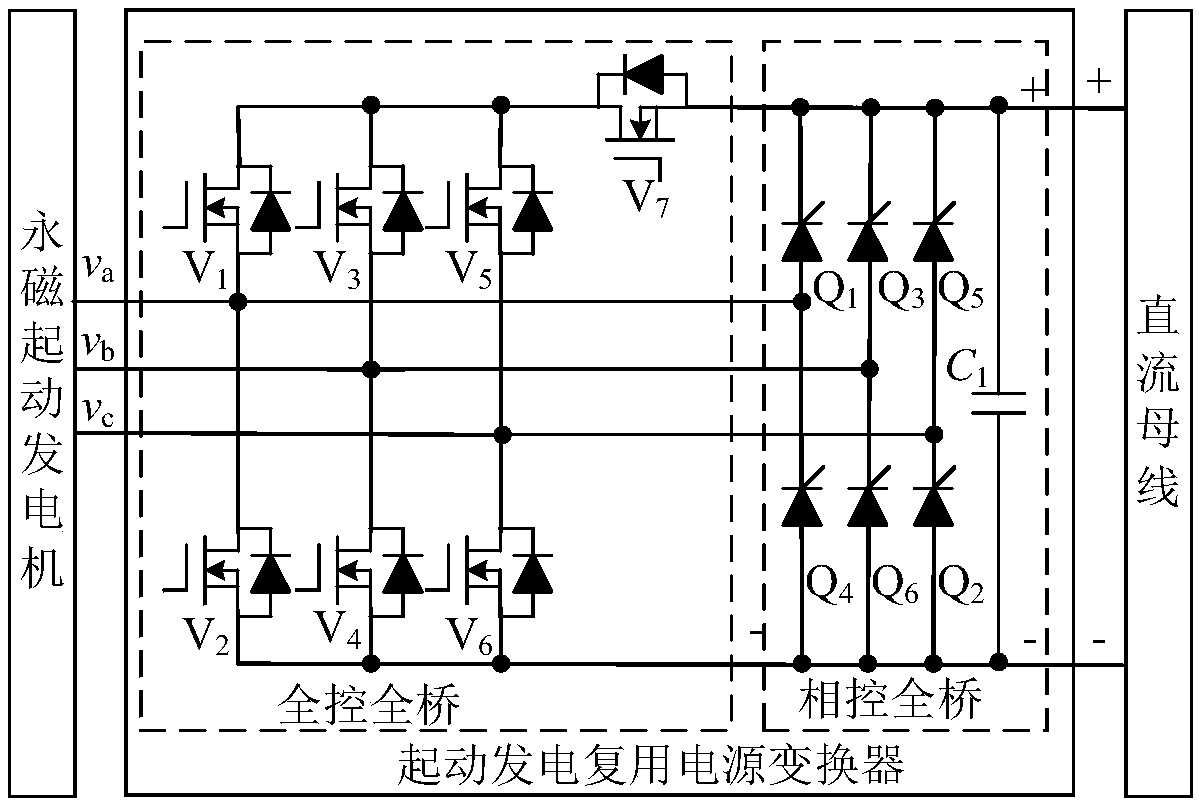
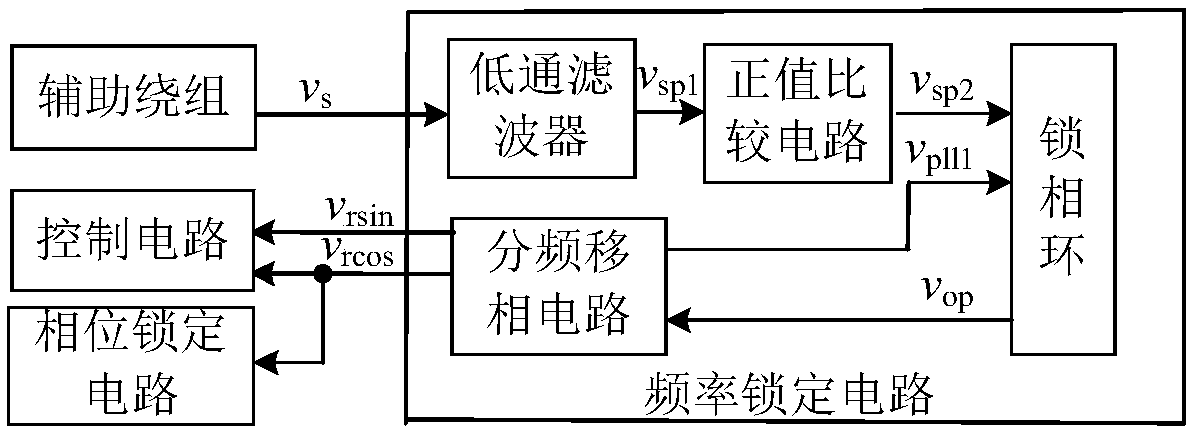
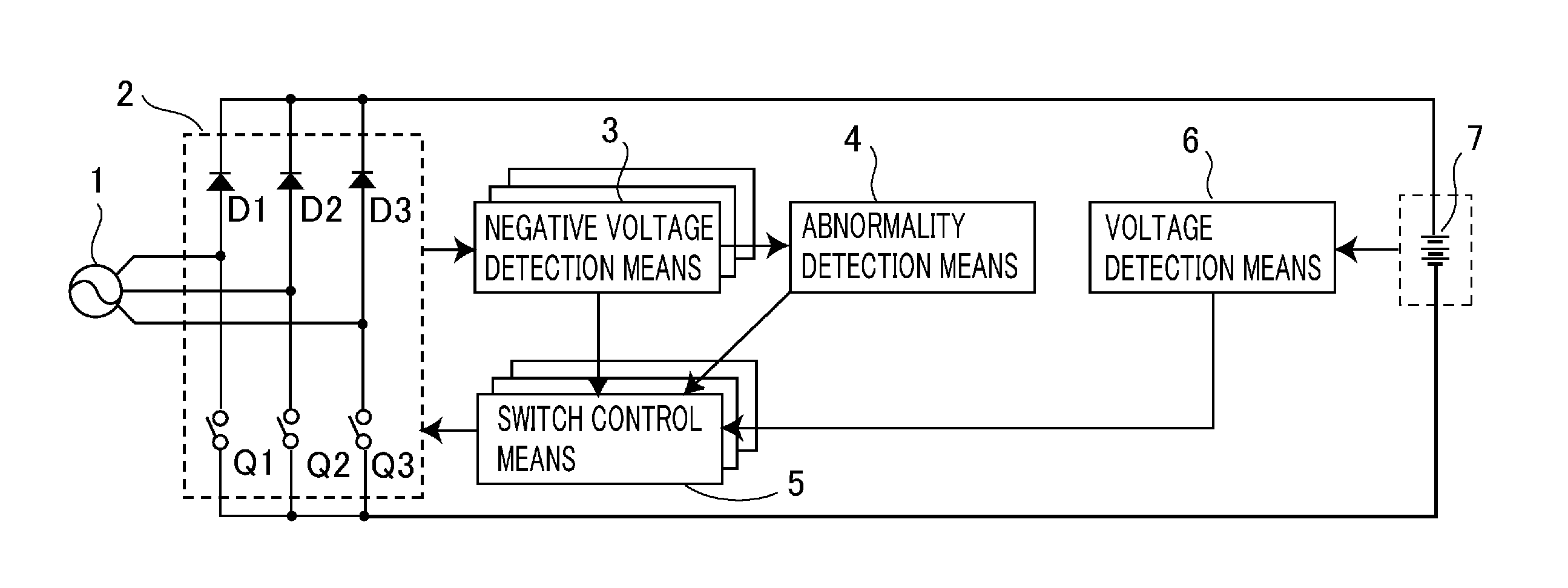
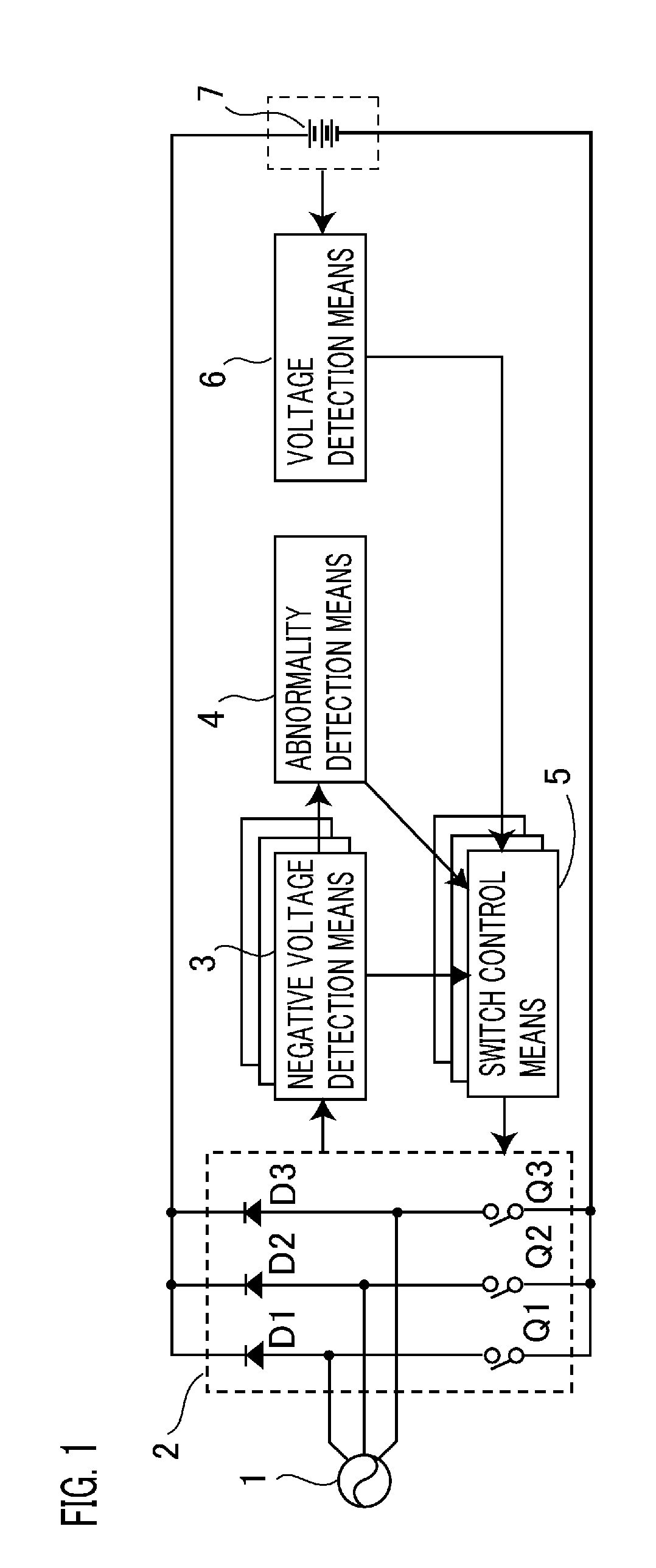
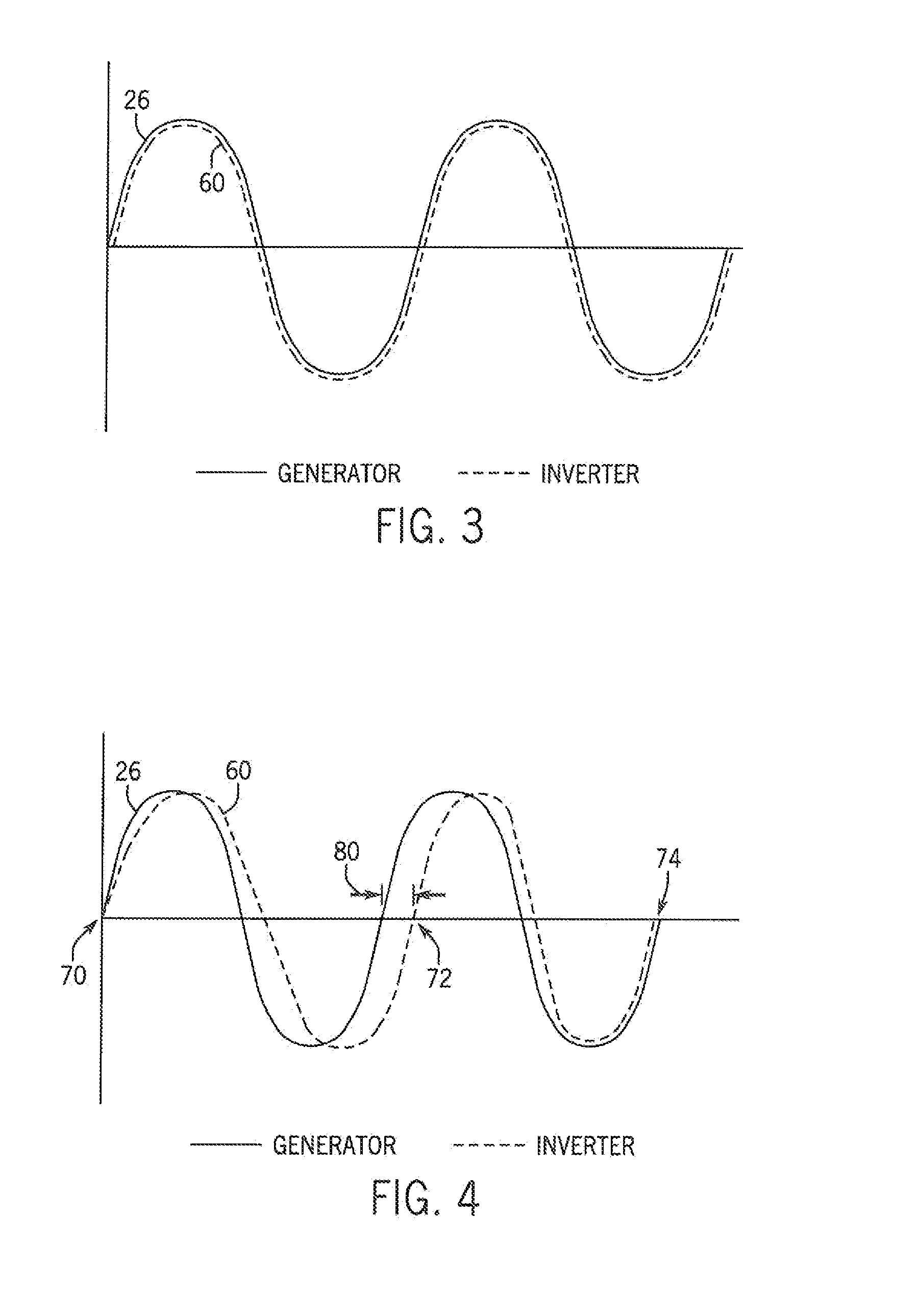Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107results about "Generator circuit arrangements control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
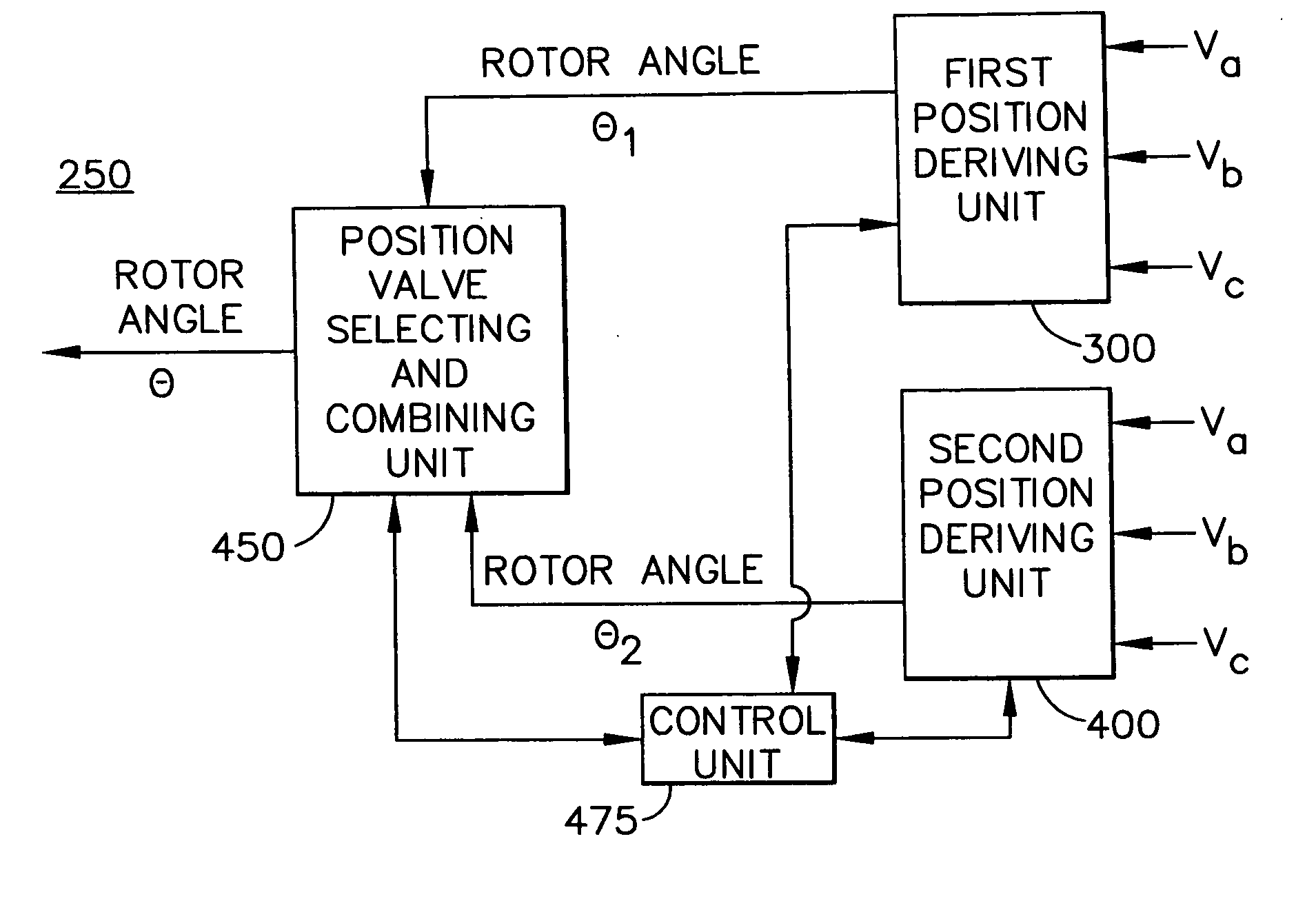
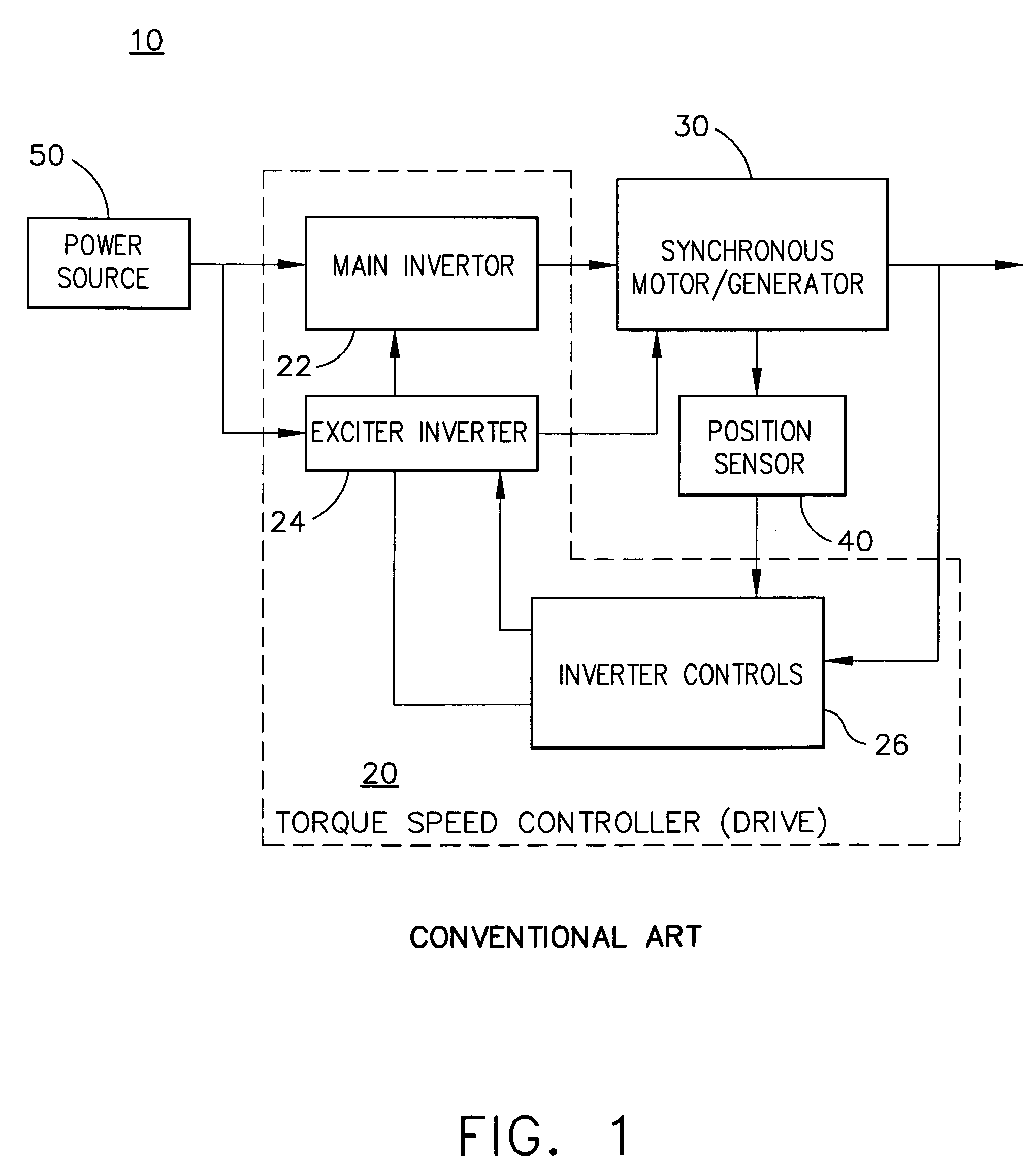
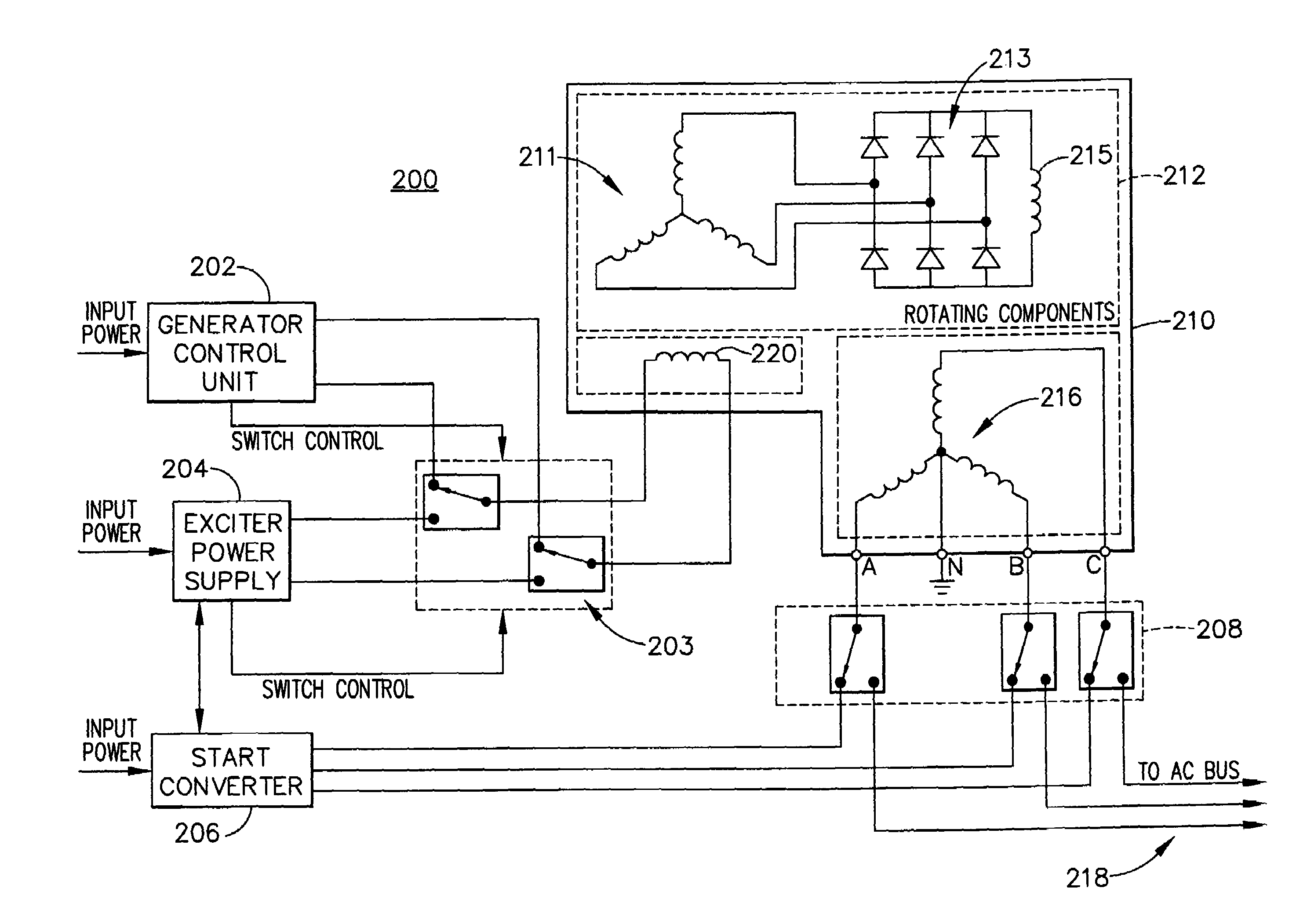
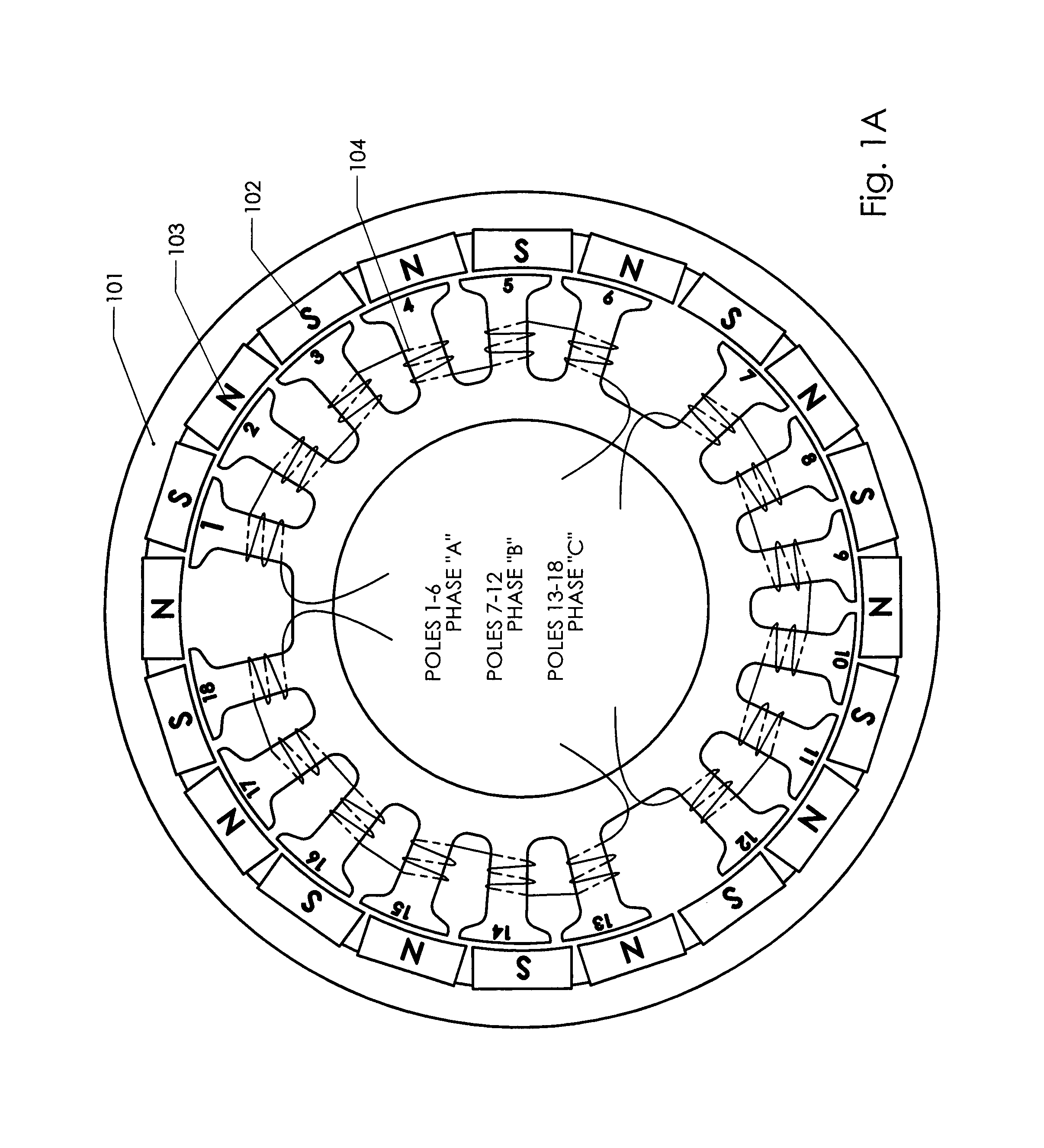
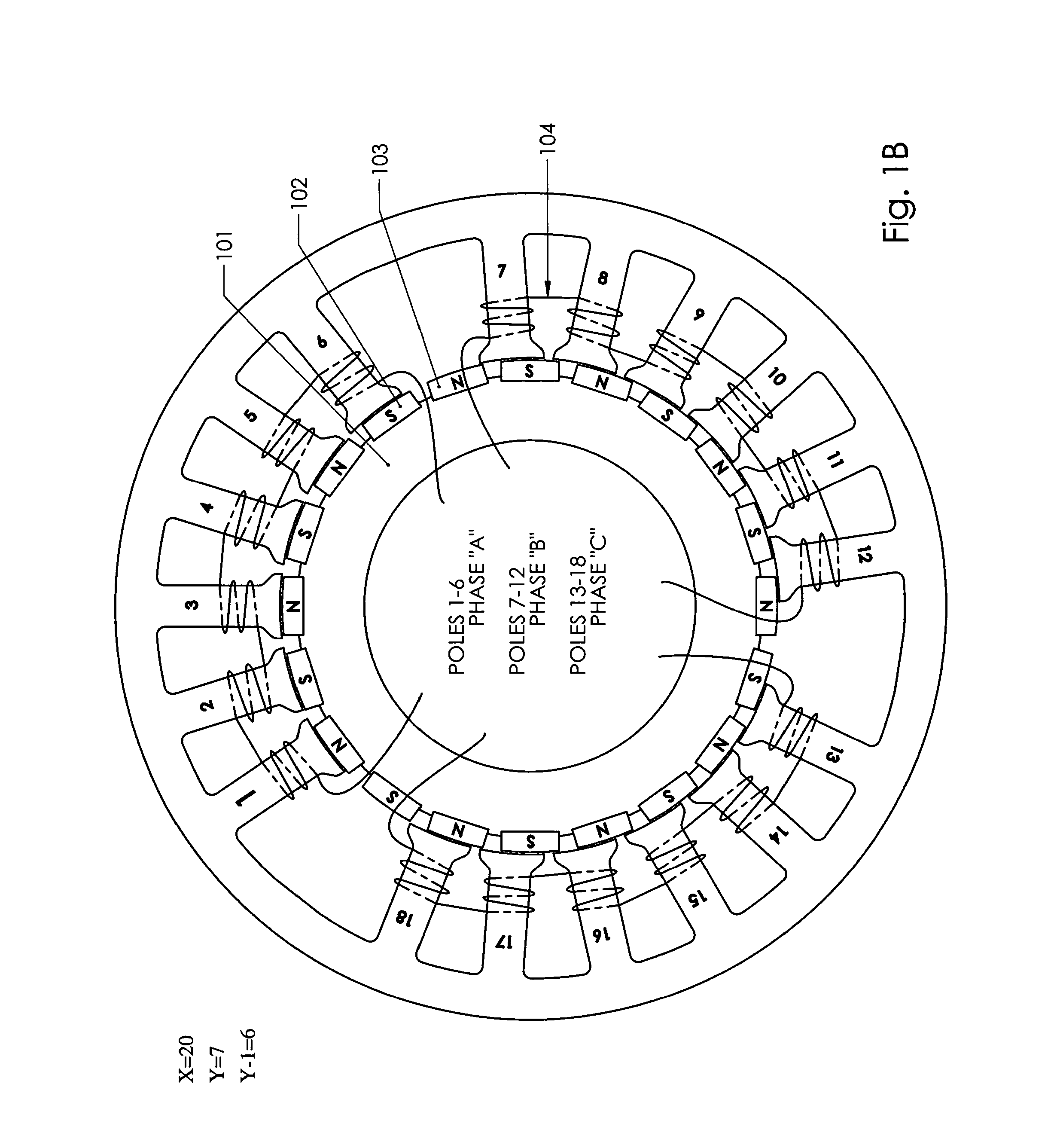
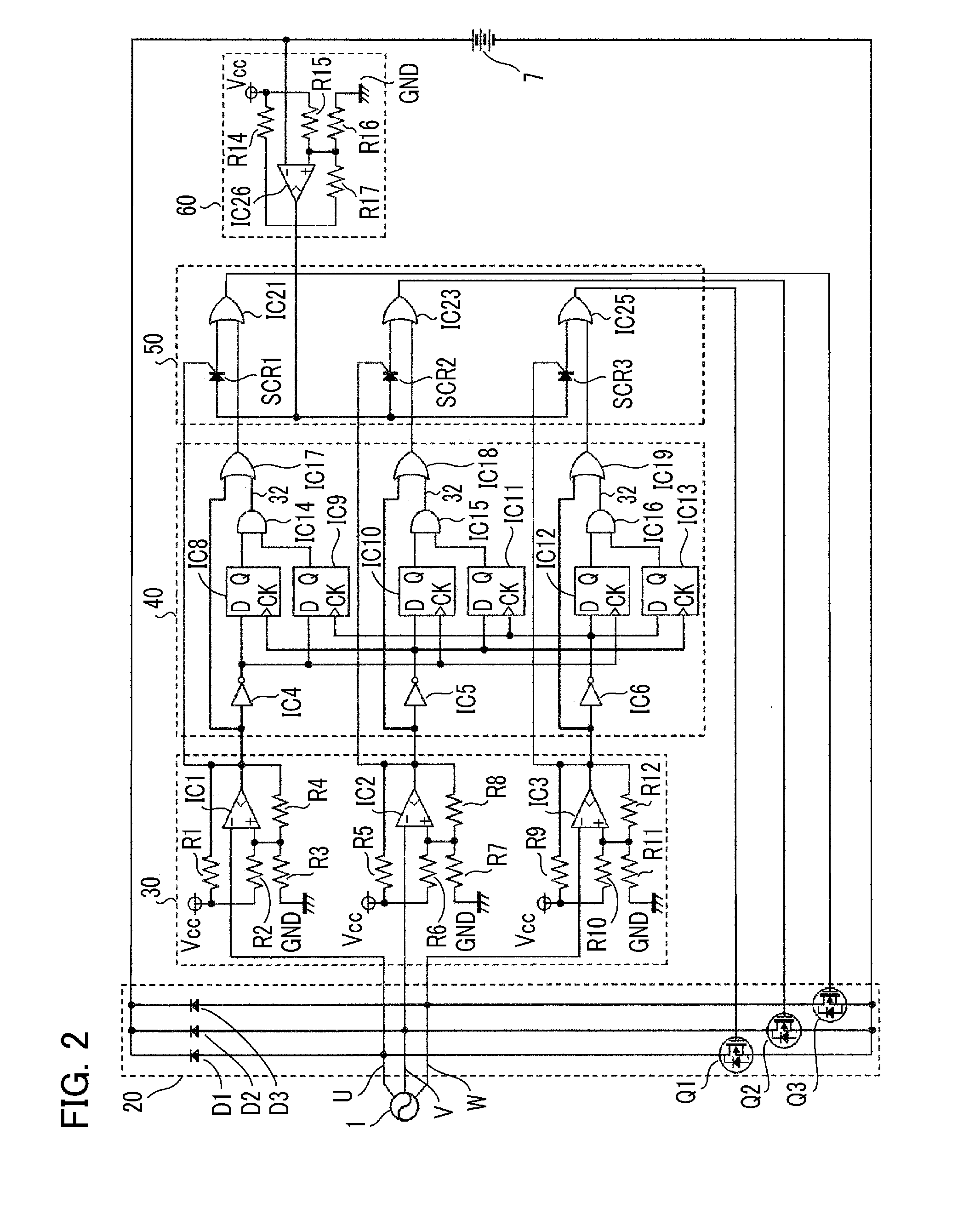
Adaptive position sensing method and apparatus for synchronous motor generator system
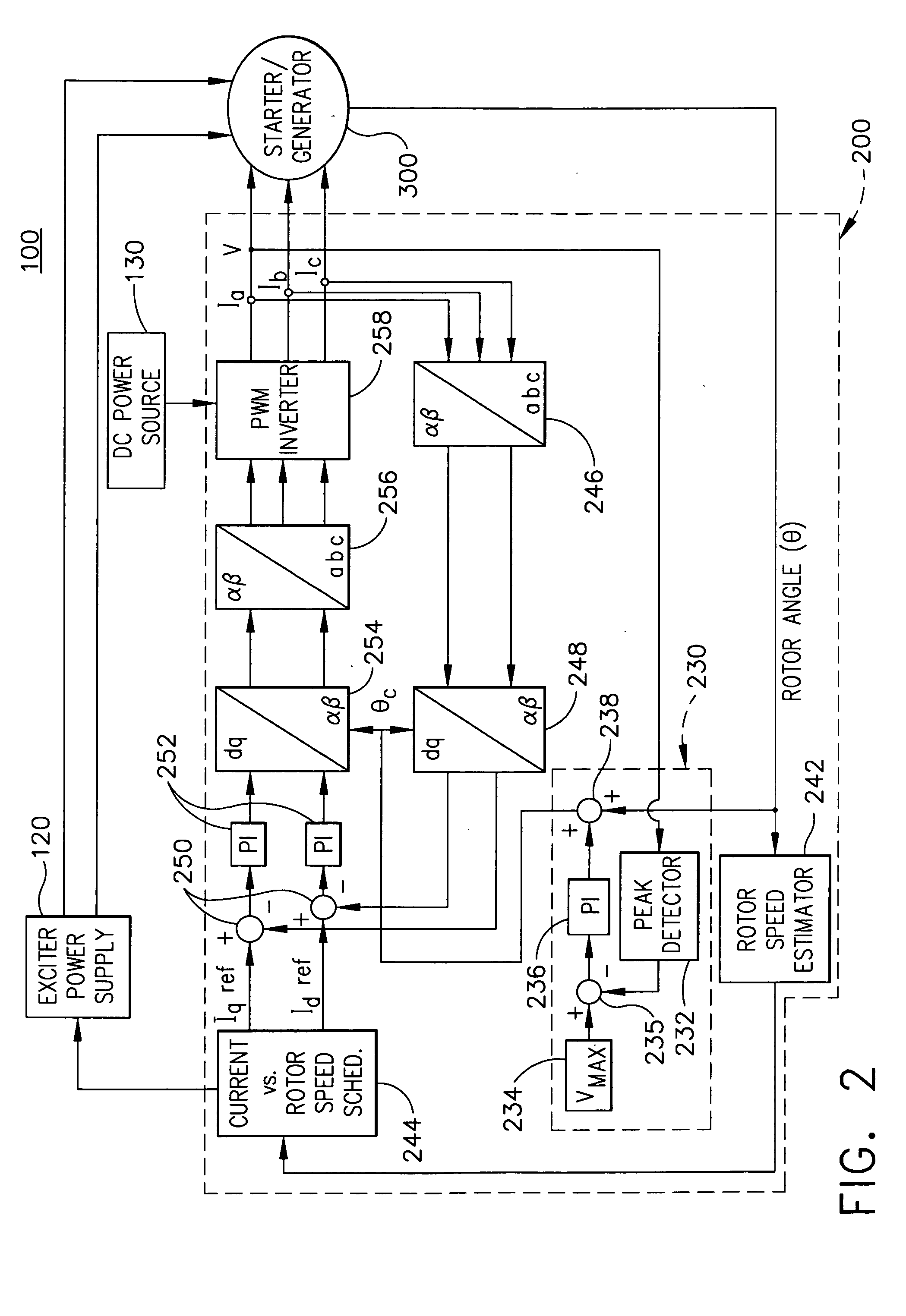
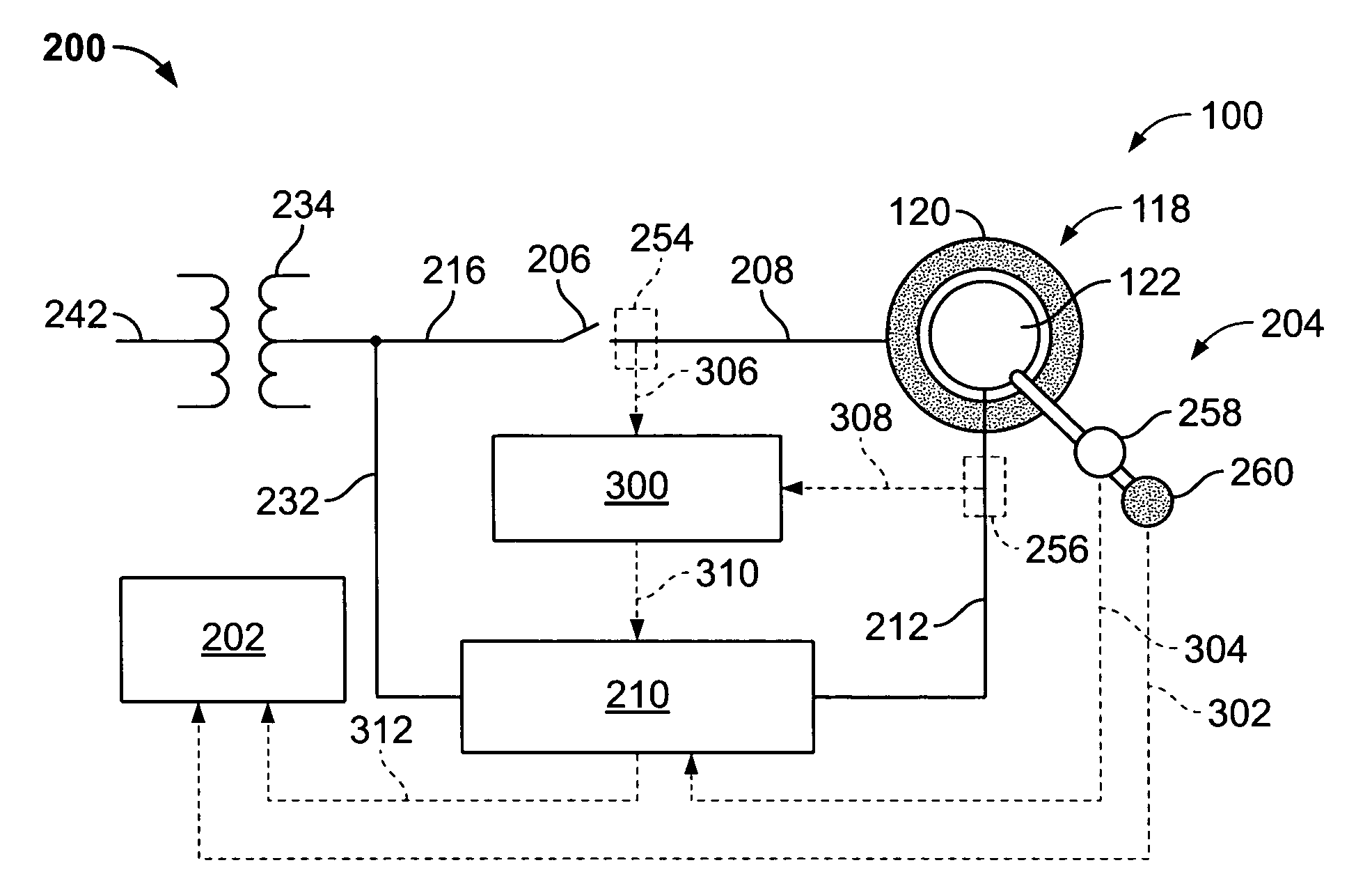
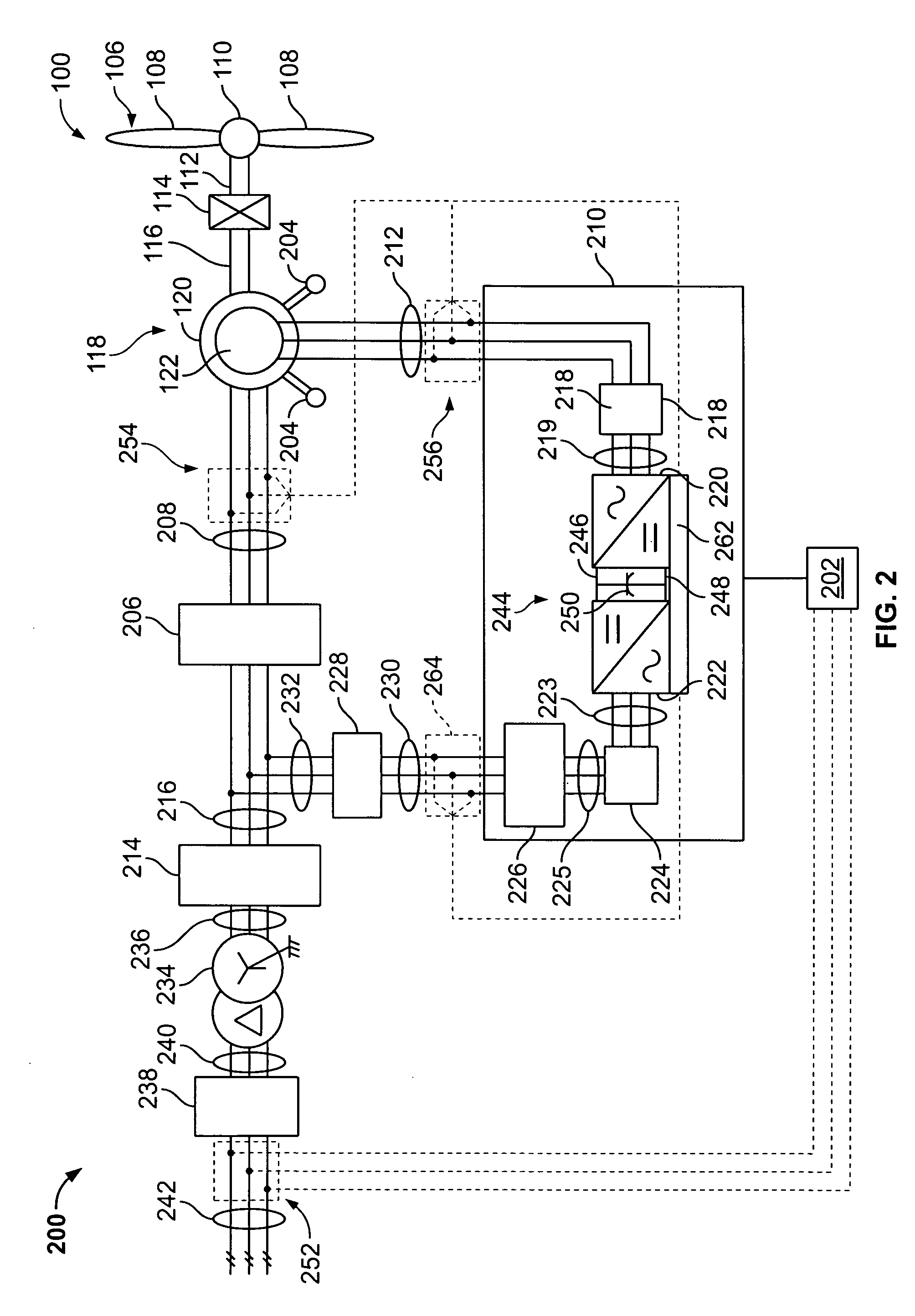
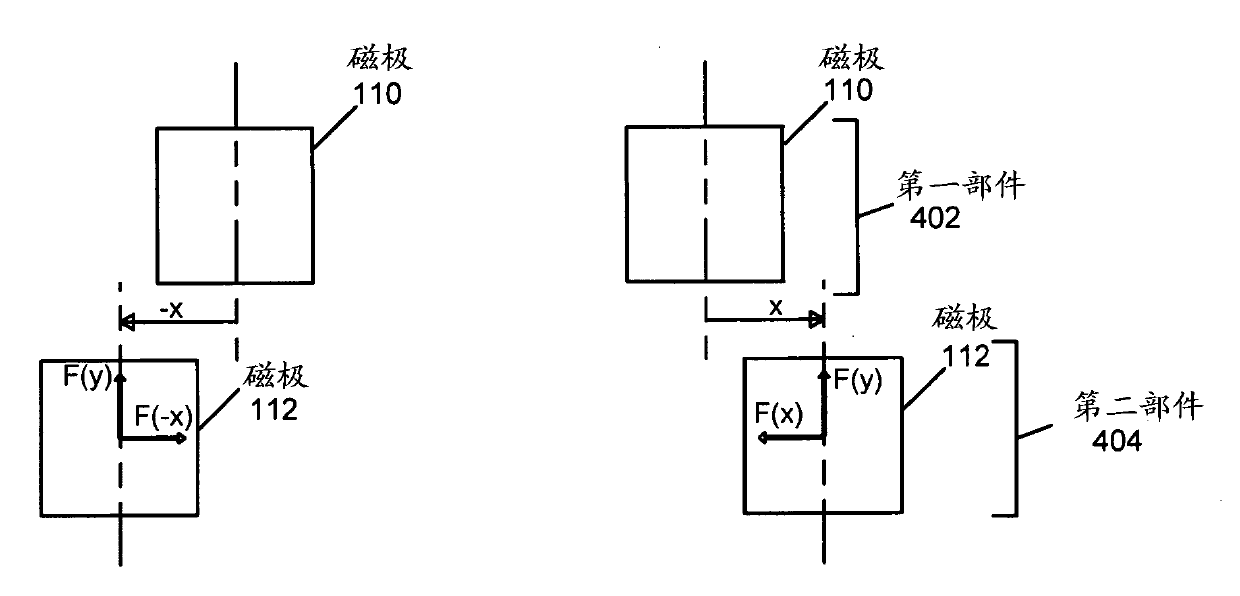
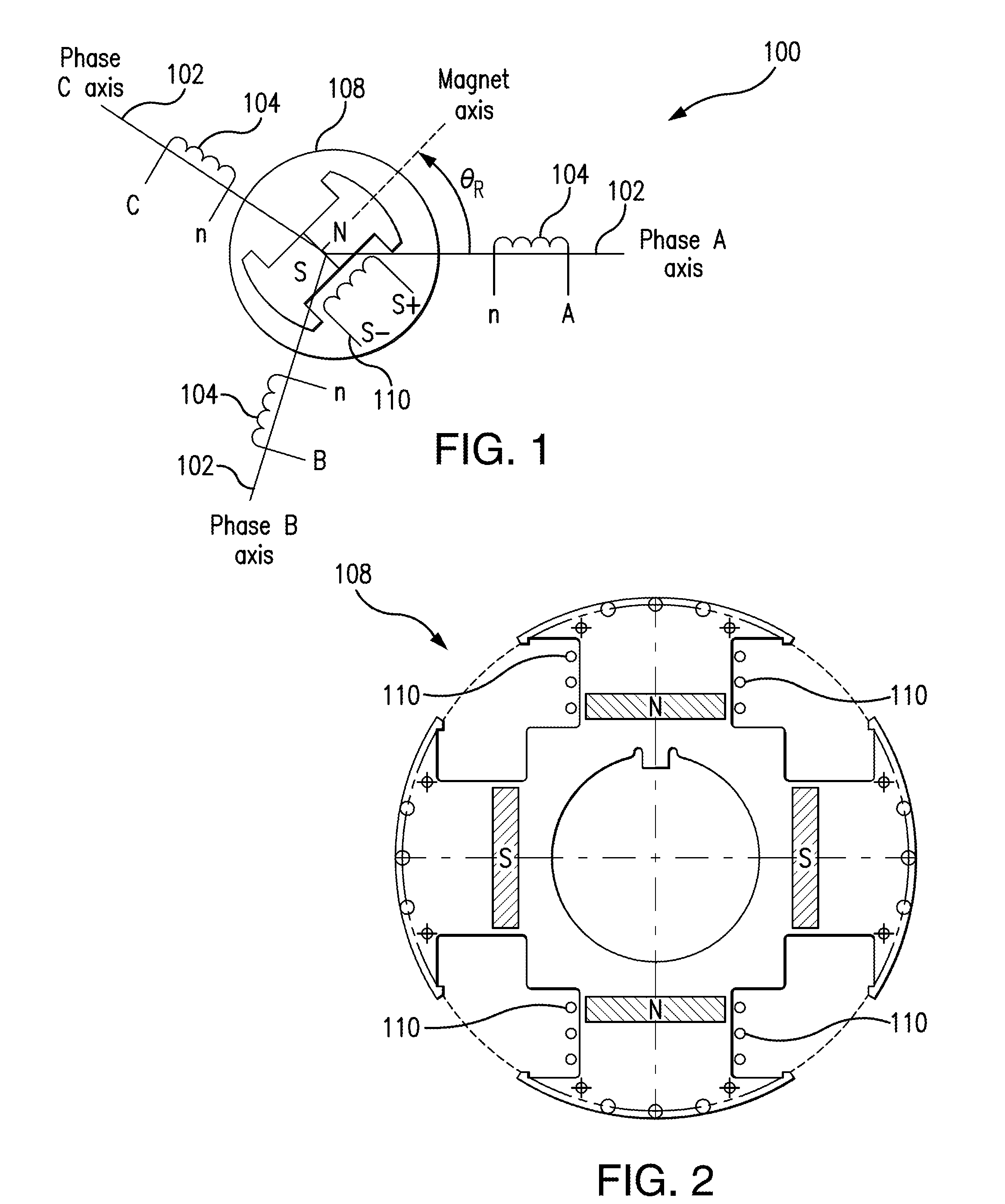
An adaptive, sensorless position sensing apparatus (250) derives rotor position of a synchronous machine (200). The apparatus (250) comprises a first rotor position deriving unit (300) for generating first rotor position values by applying a first sensorless rotor position calculation technique, which emulates a resolver; a second rotor position deriving unit (400) for generating second rotor position values by applying a second sensorless rotor position calculation technique; and a rotor position result output unit (450) for outputting rotor position results over a range of rotor speeds as a function of the first rotor position values, the second rotor position values, and rotor speed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
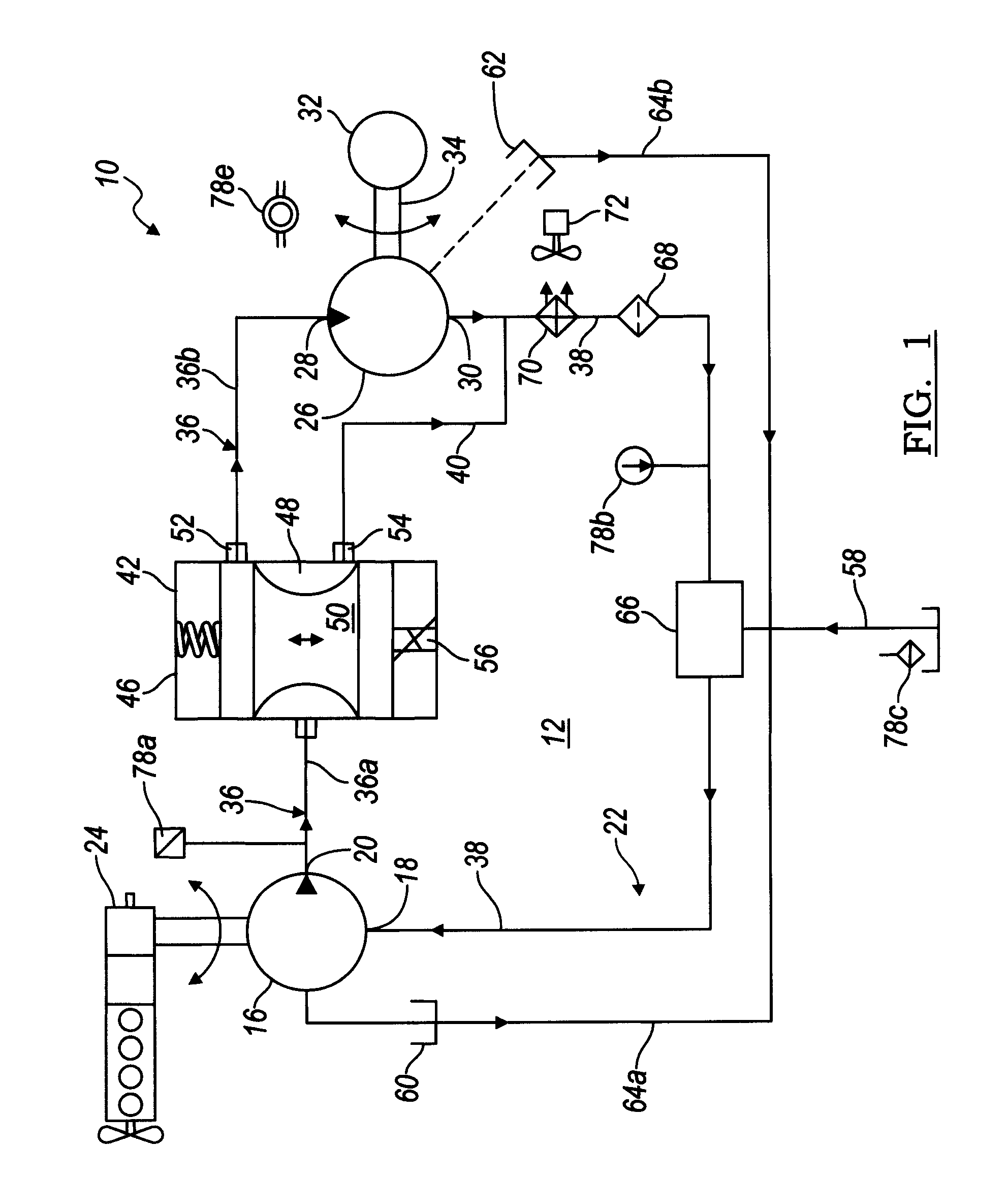
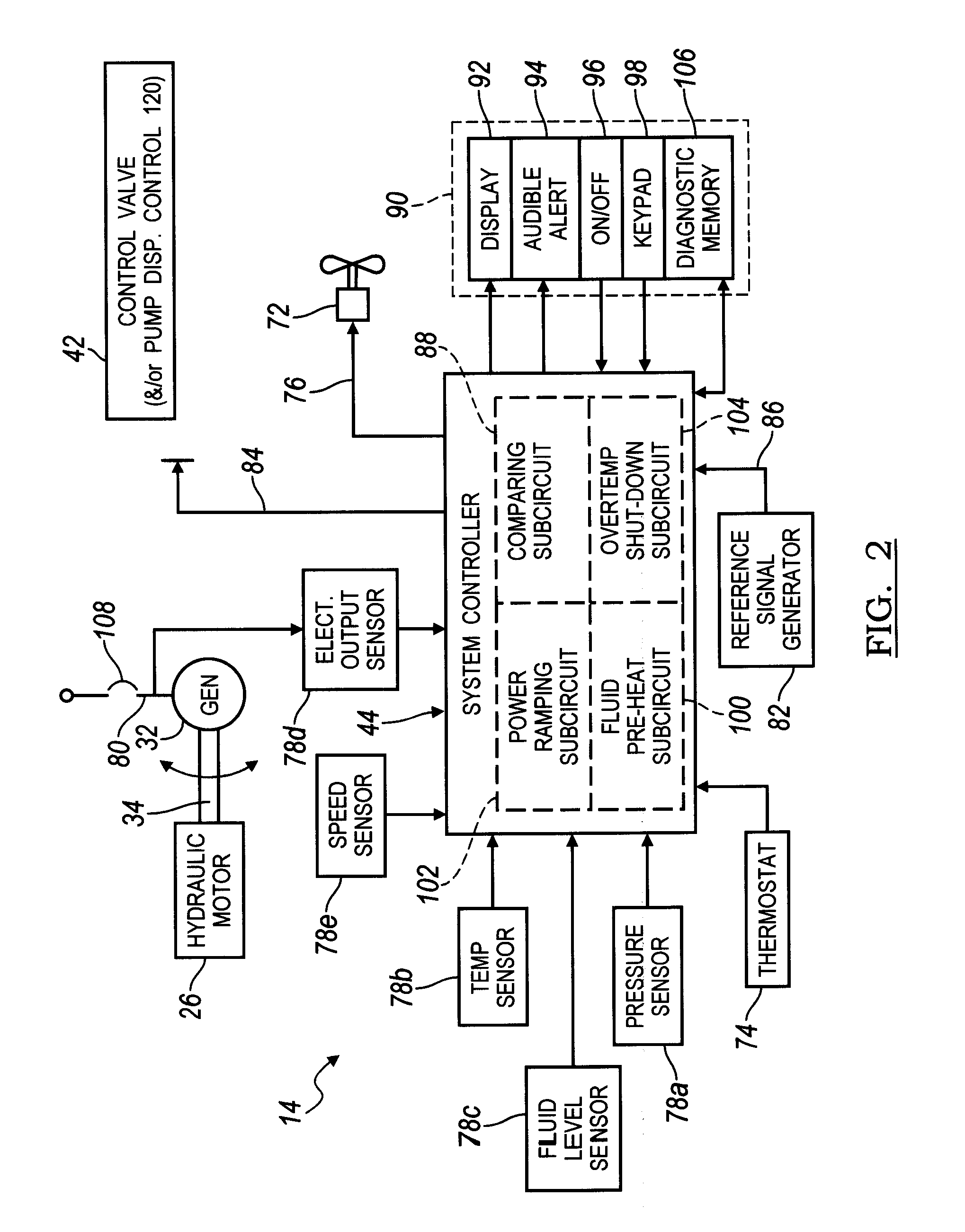
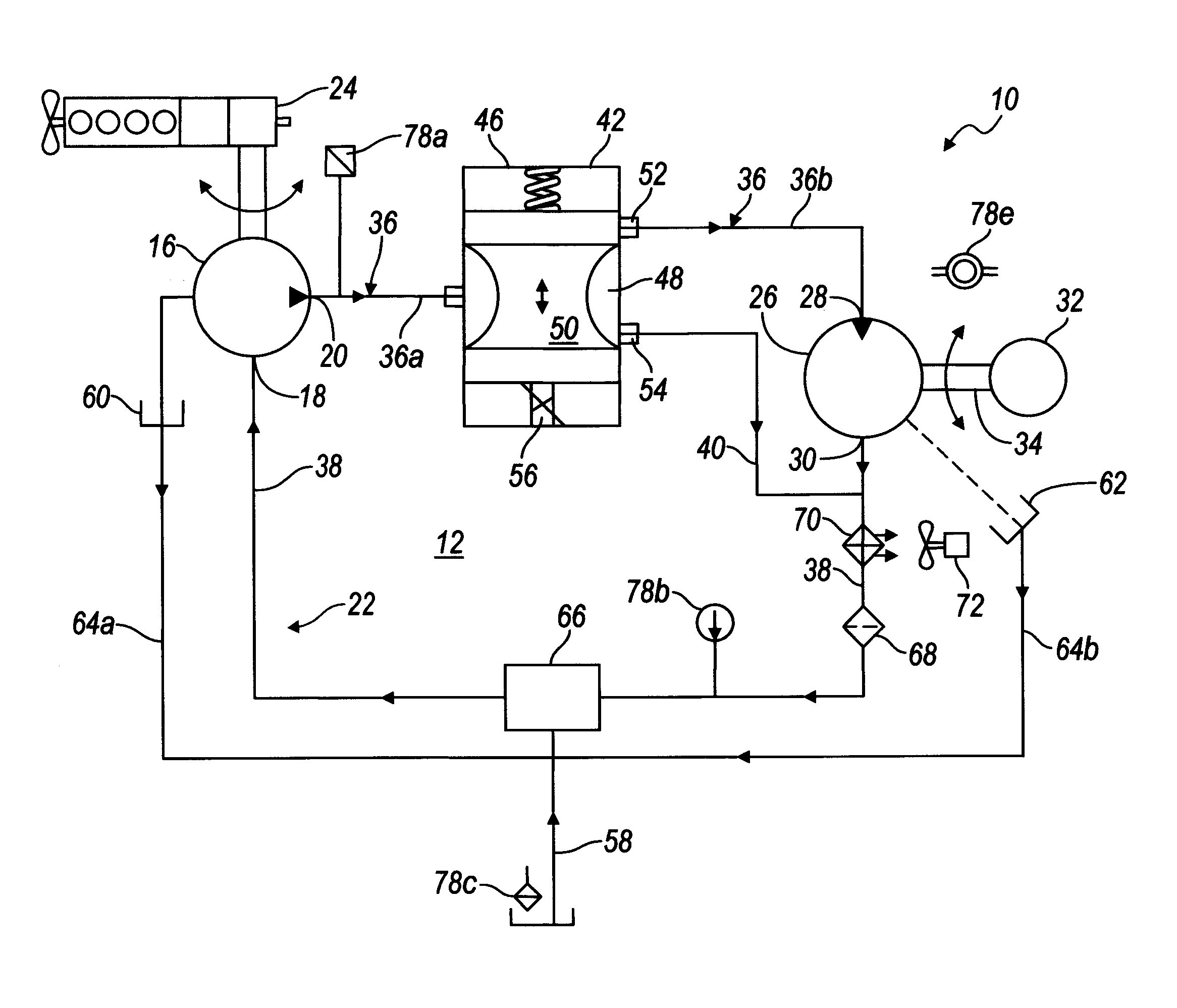
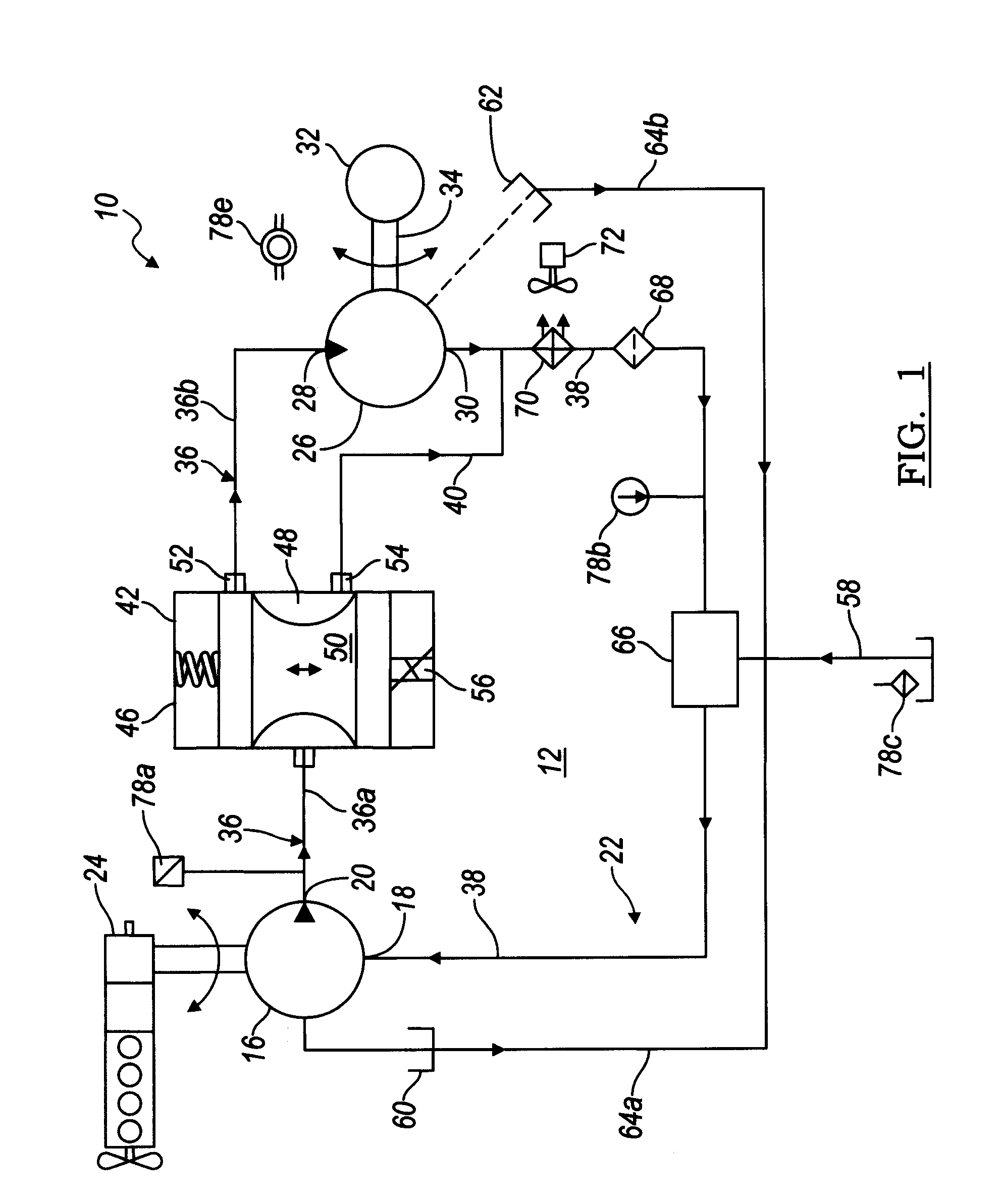
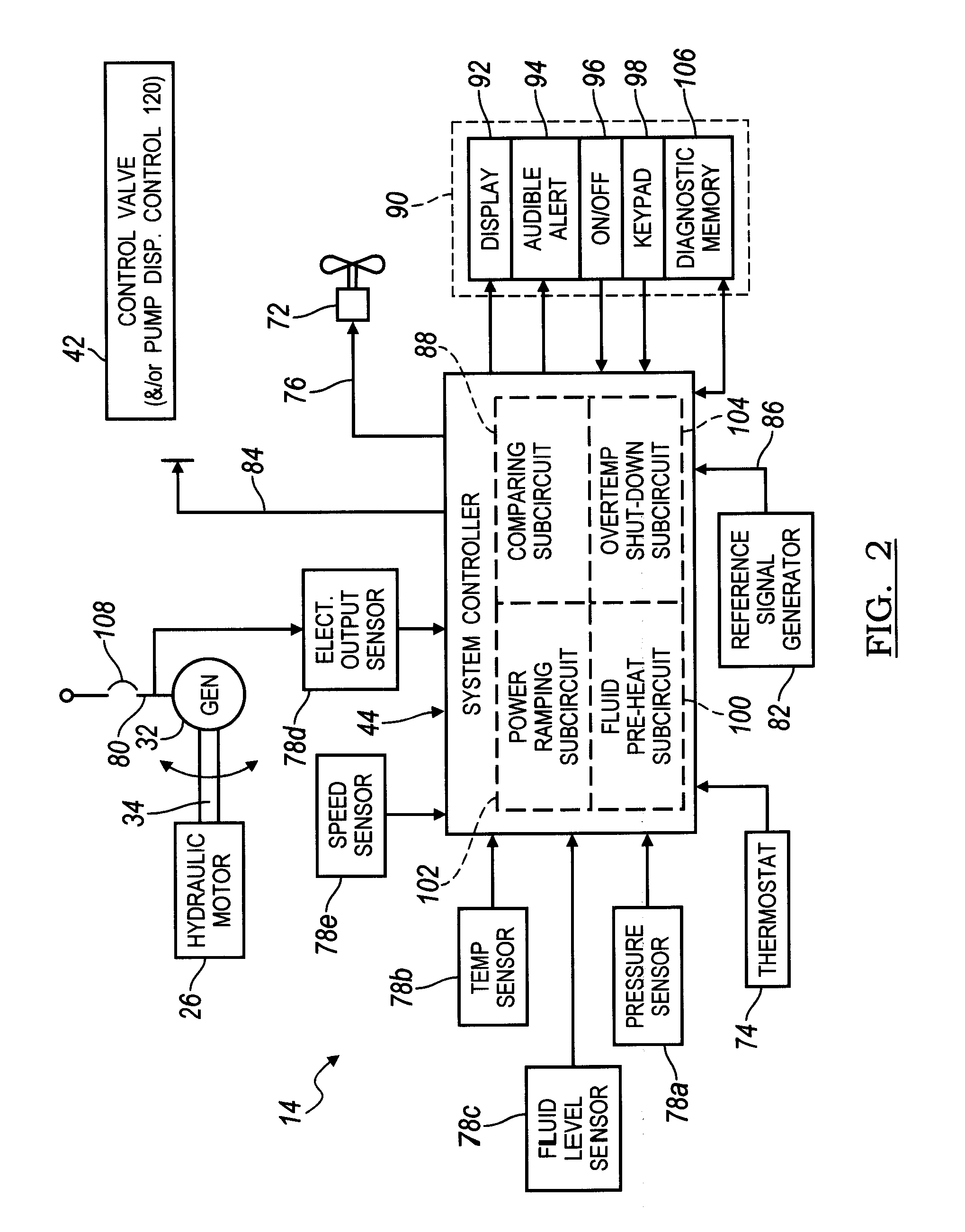
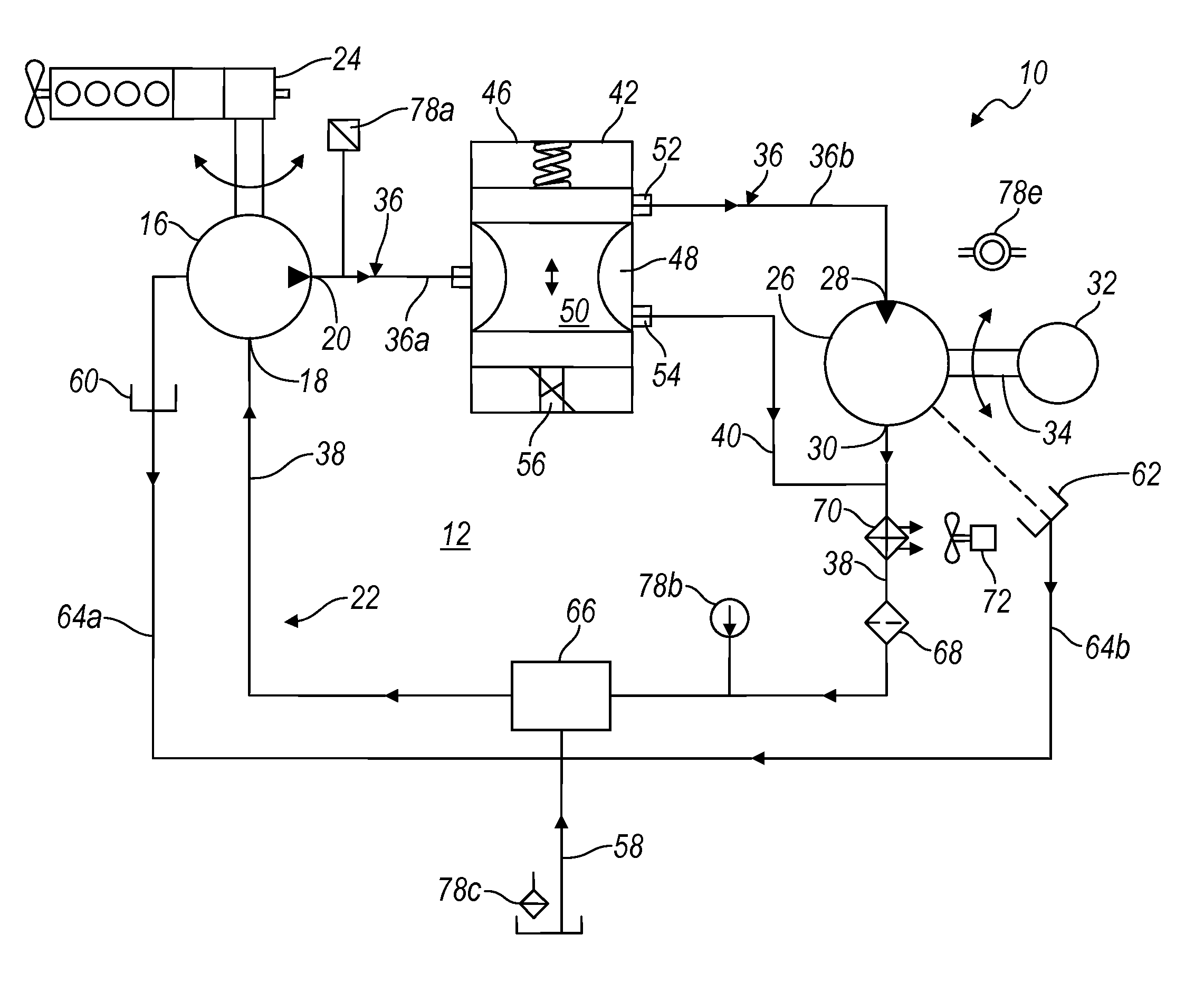
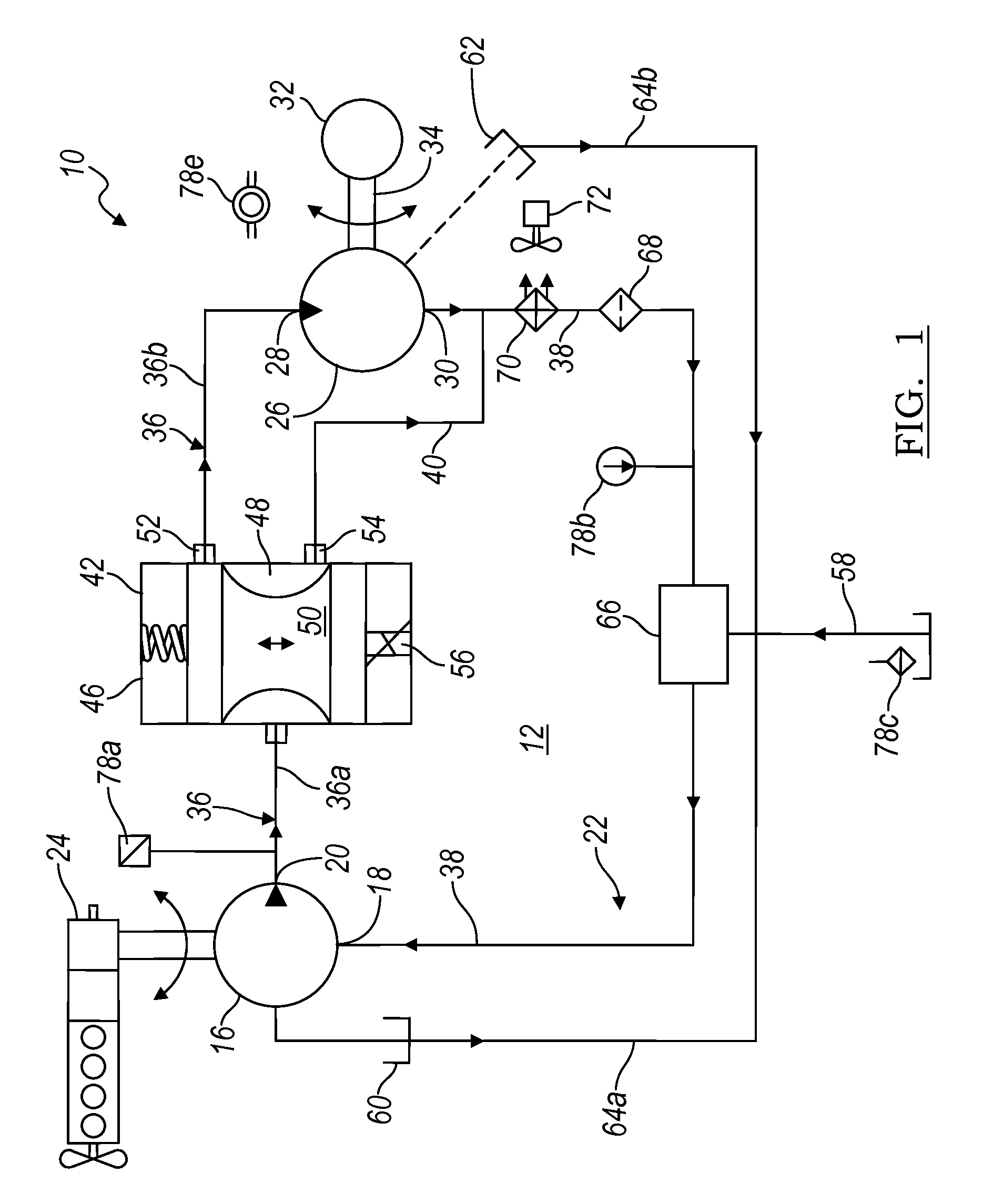
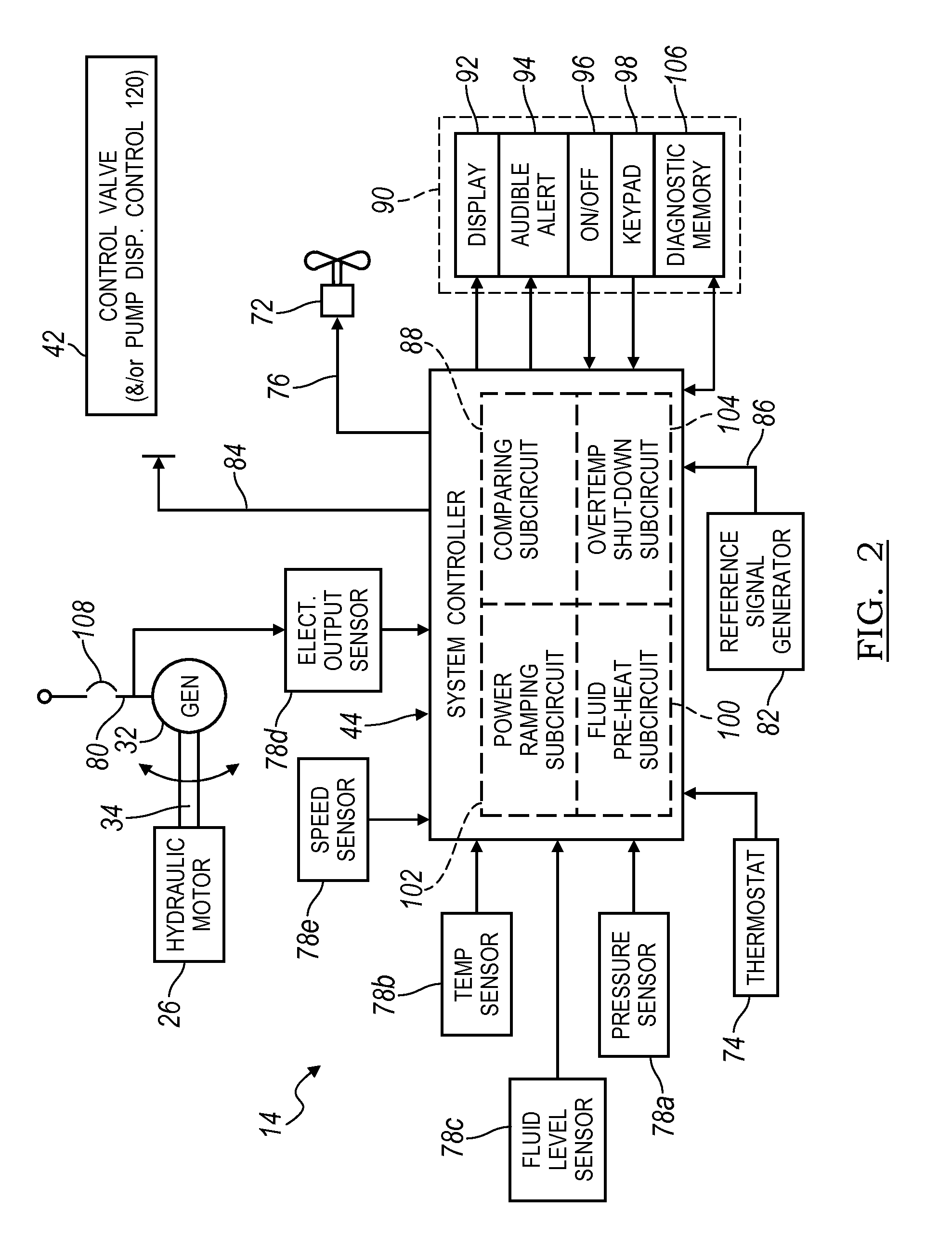
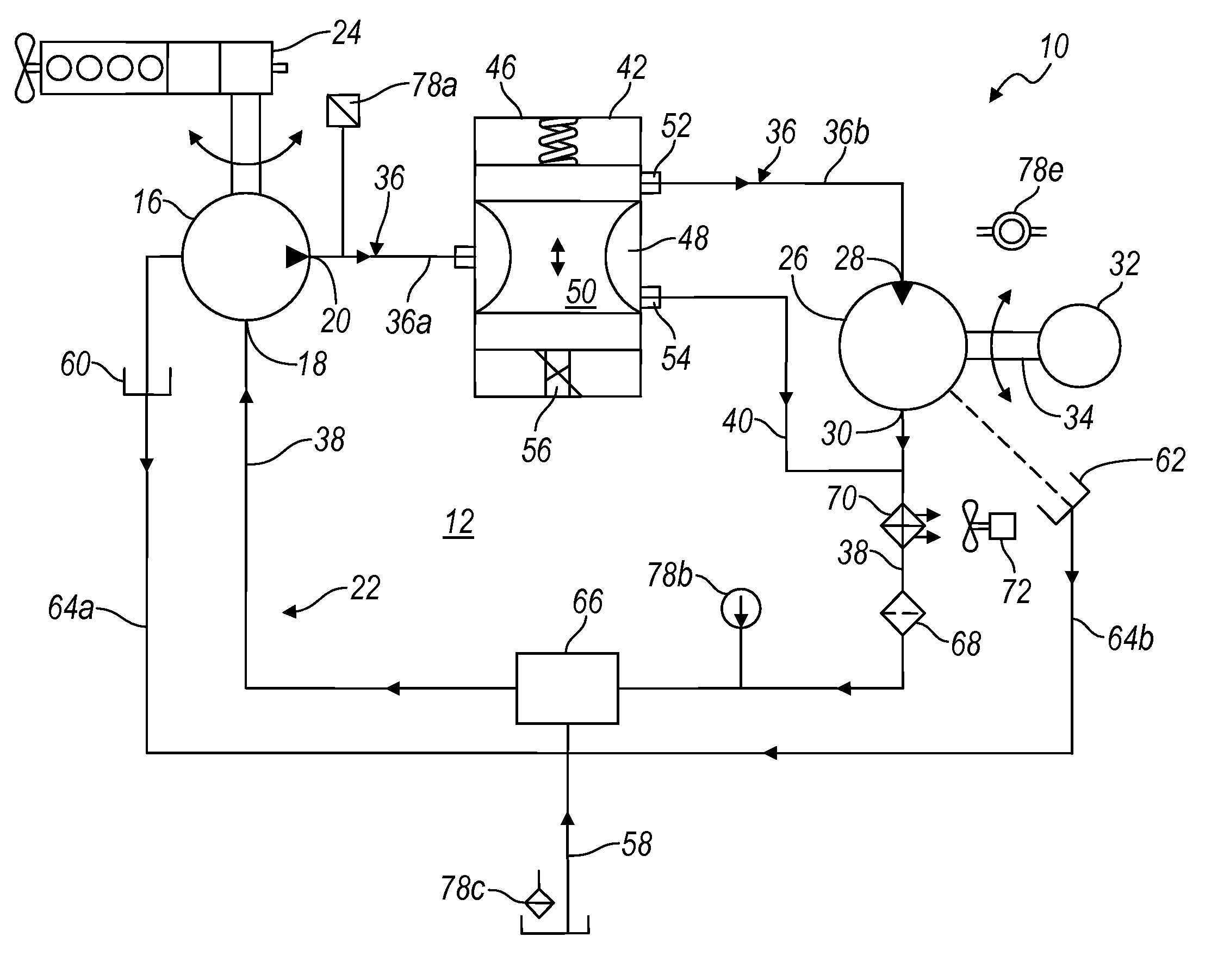
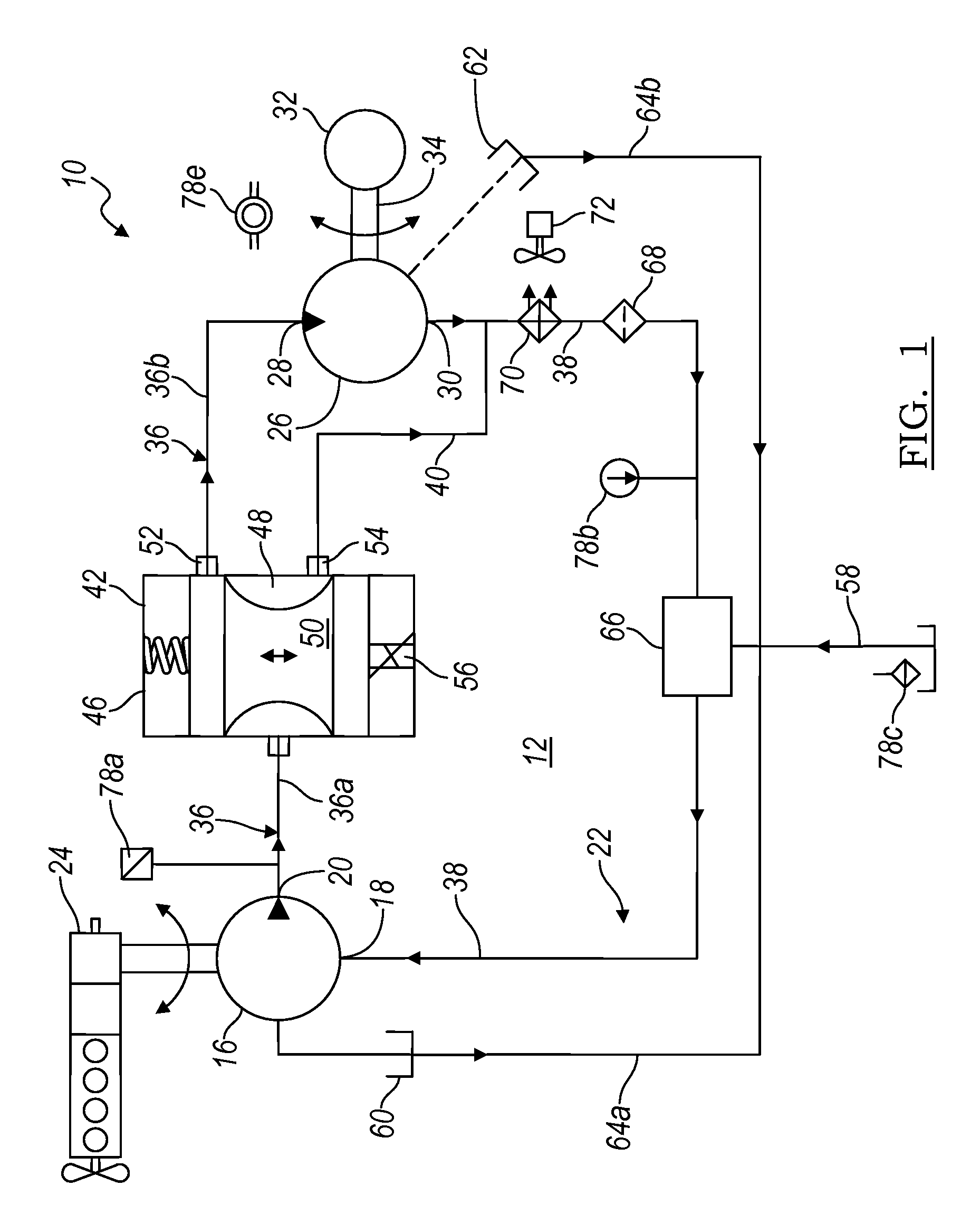
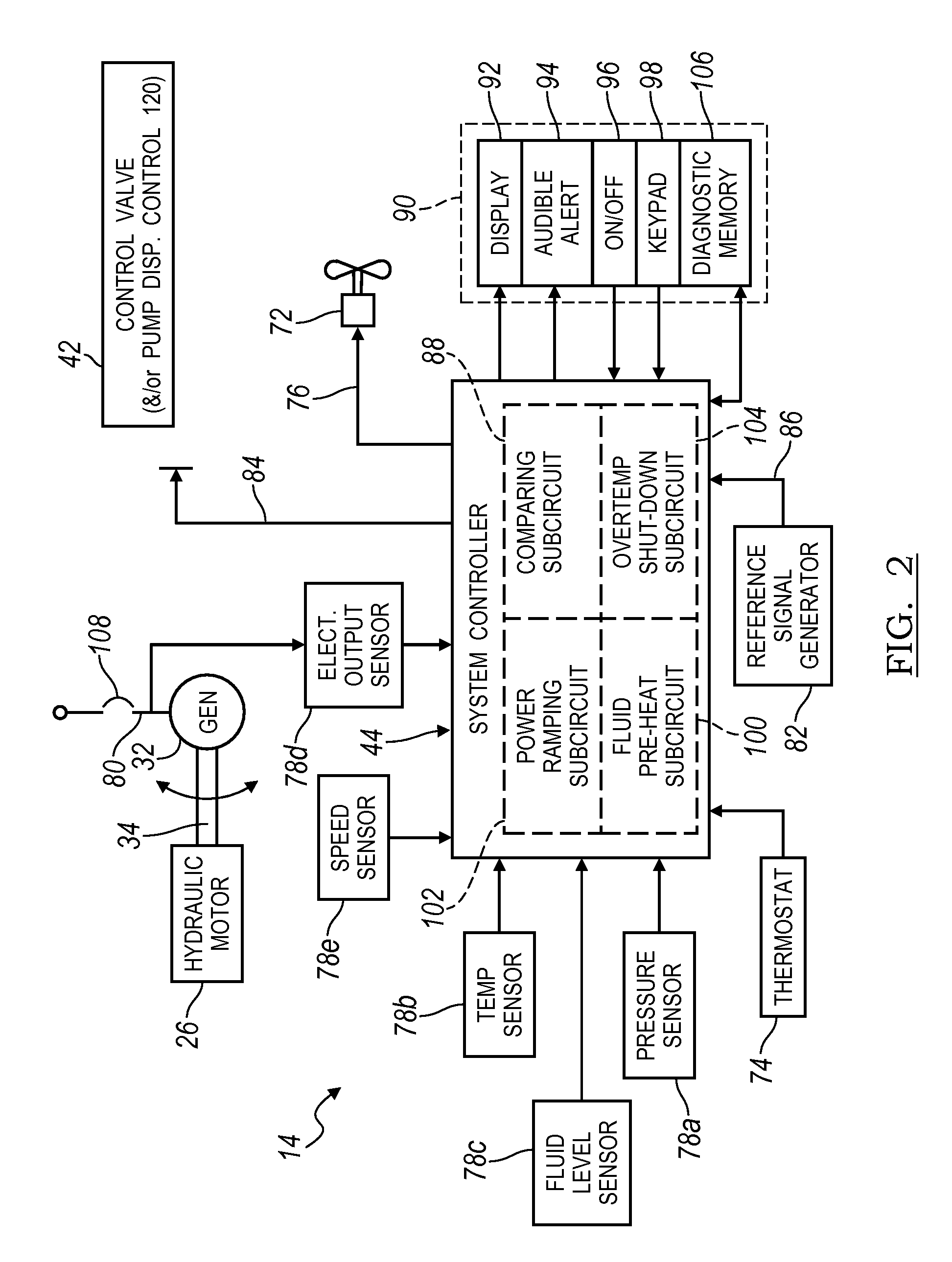
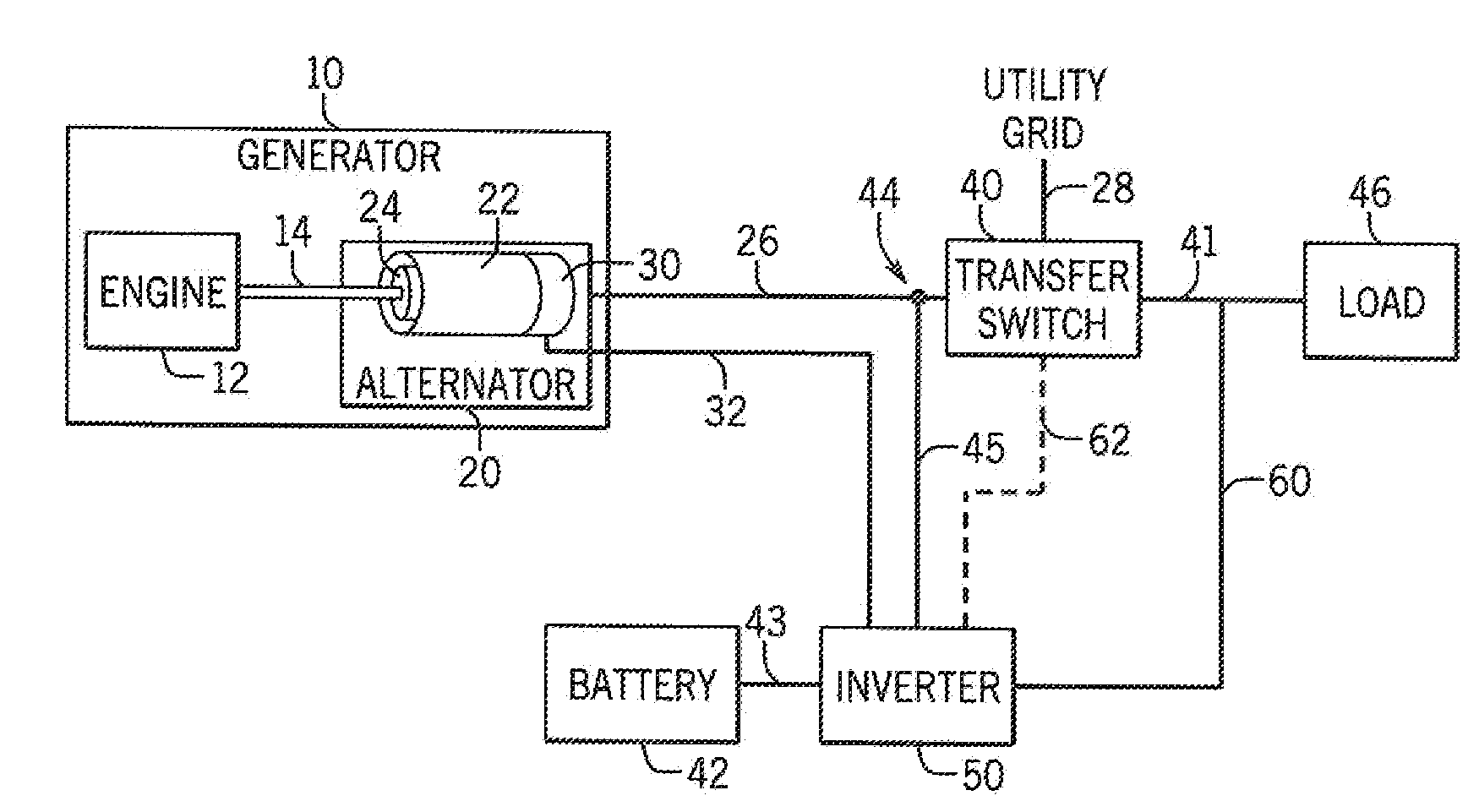
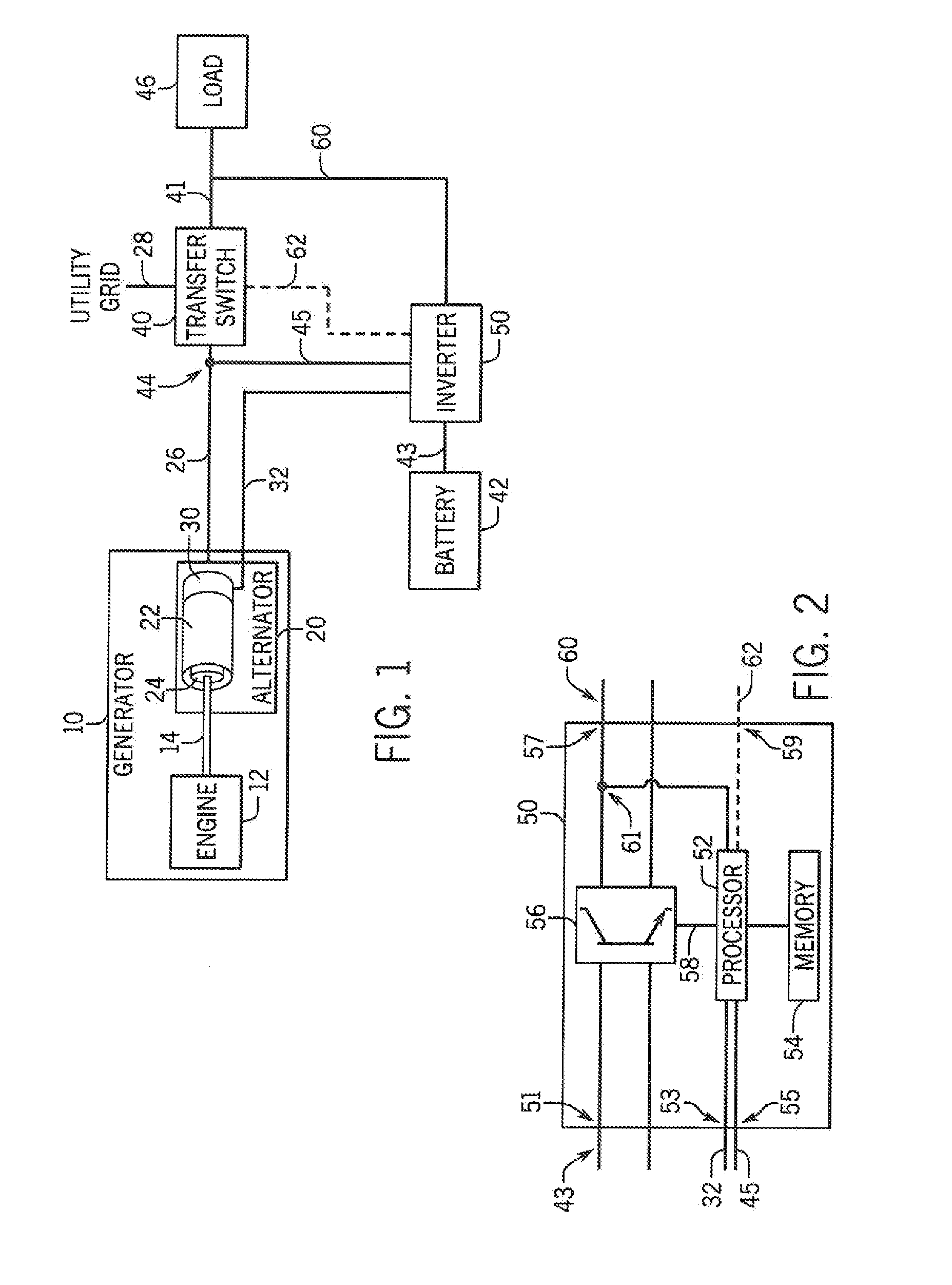
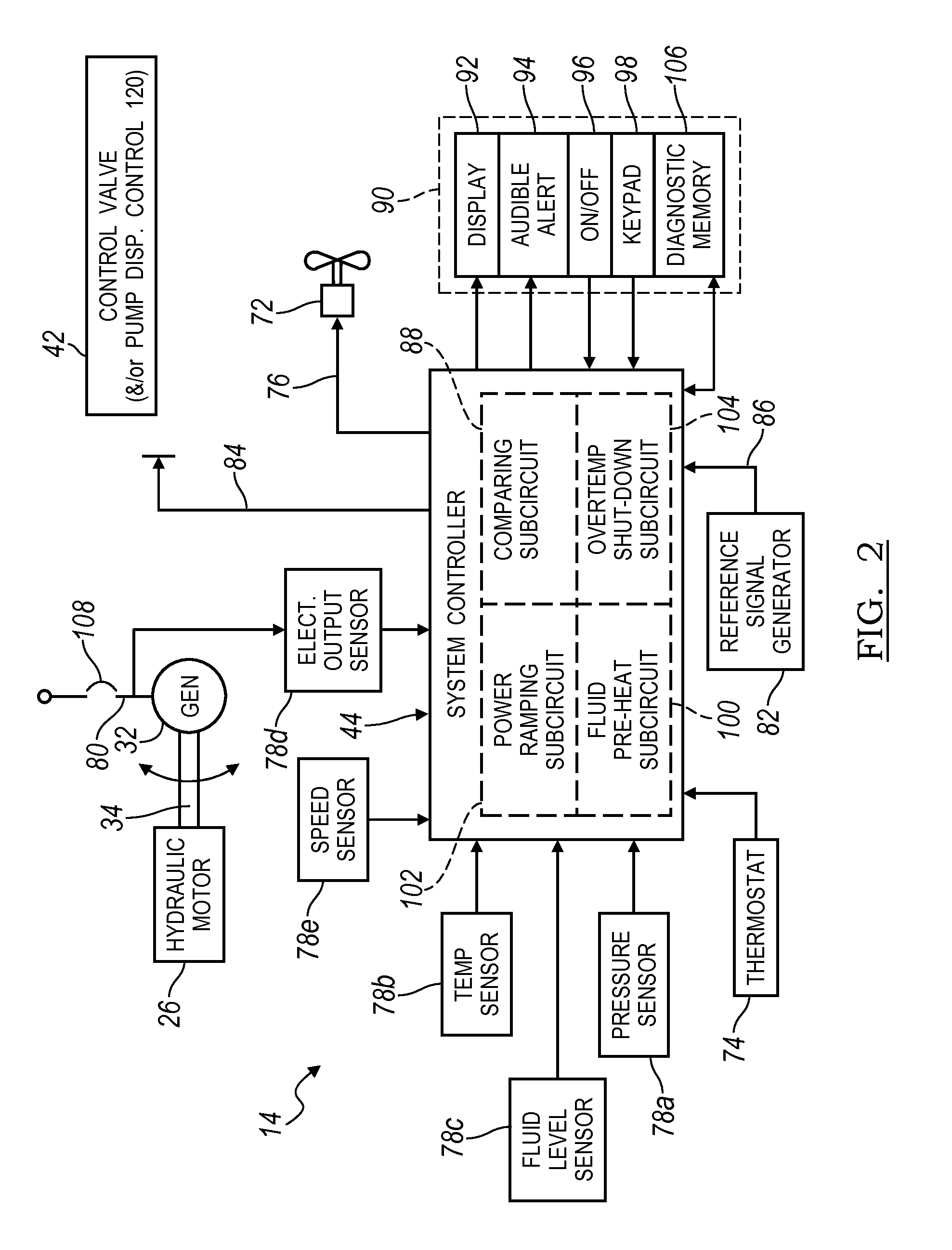
Electronic control for a hydraulically driven auxiliary power source
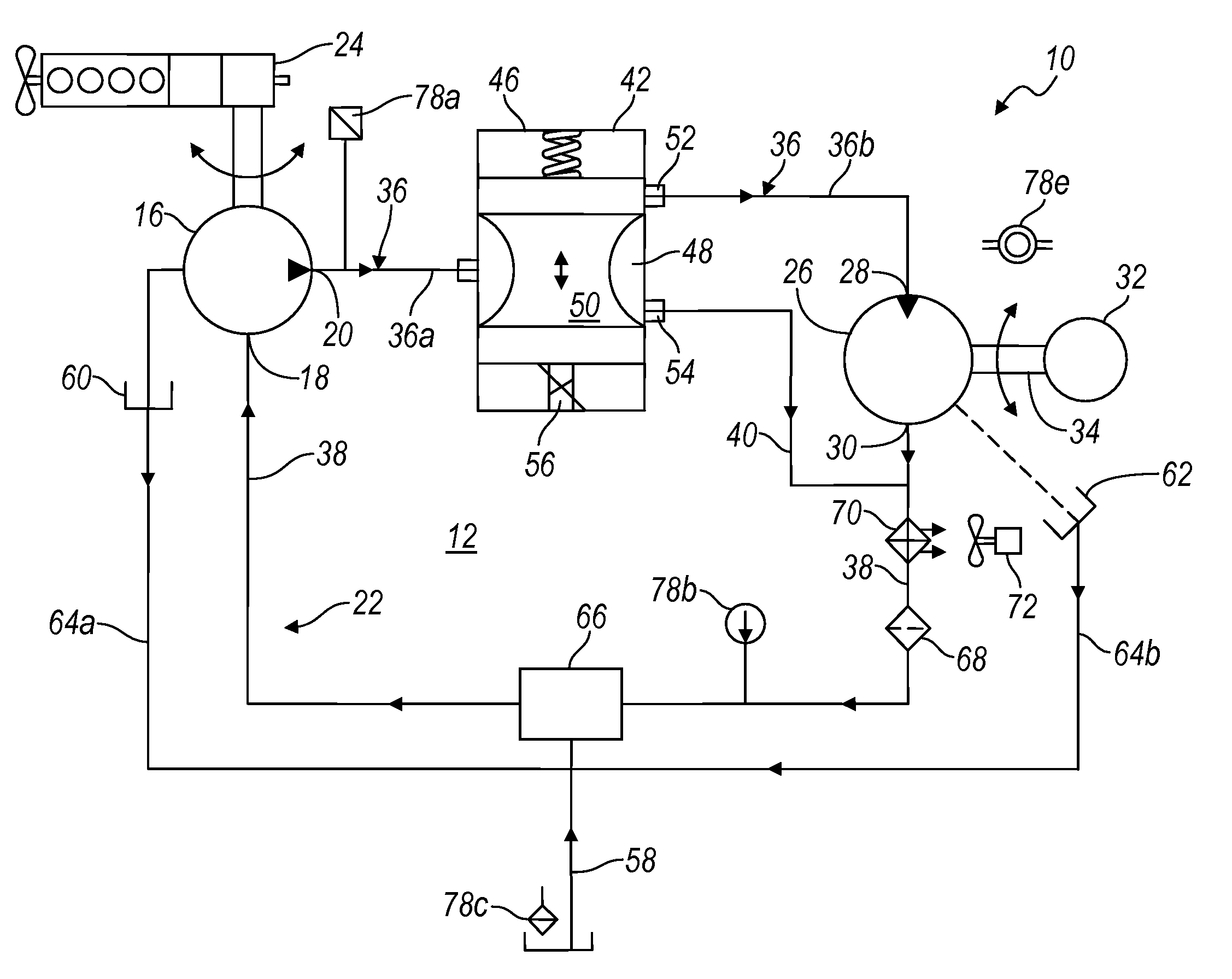
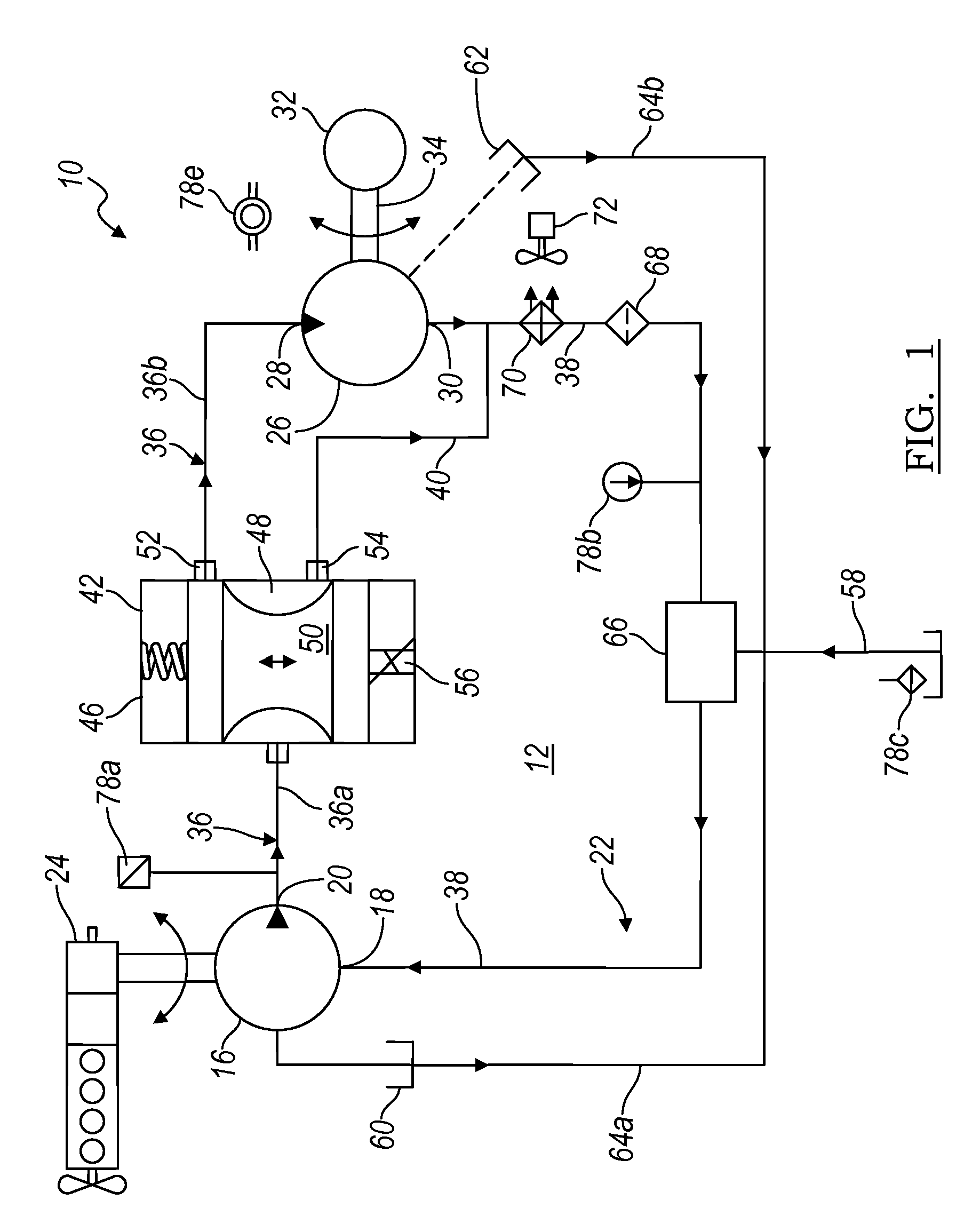
ActiveUS8269360B2Extend system lifeLow costGenerator circuit arrangements controlFluid couplingsHydraulic motorHydraulic pump
A hydraulic system includes a variable displacement hydraulic pump connectable to a power source, a hydraulic motor, a fluid circuit, a pump displacement control, and a controller. The pump has an inlet for receiving fluid, an outlet for discharging pressurized fluid, and a pump displacement input. The motor has an inlet for receiving pressurized fluid and an outlet for discharging spent fluid. The fluid circuit includes a supply conduit for conducting fluid discharged by the pump to the motor and a return conduit for returning fluid discharged by the motor to the pump. The pump displacement control cooperates with the pump displacement input to vary pump displacement. The controller communicates with the pump displacement control to control the pump output such that the motor is driven at a constant speed to thereby drive a generator connected to the motor at a constant speed despite speed fluctuations of the power source.
Owner:UUSI
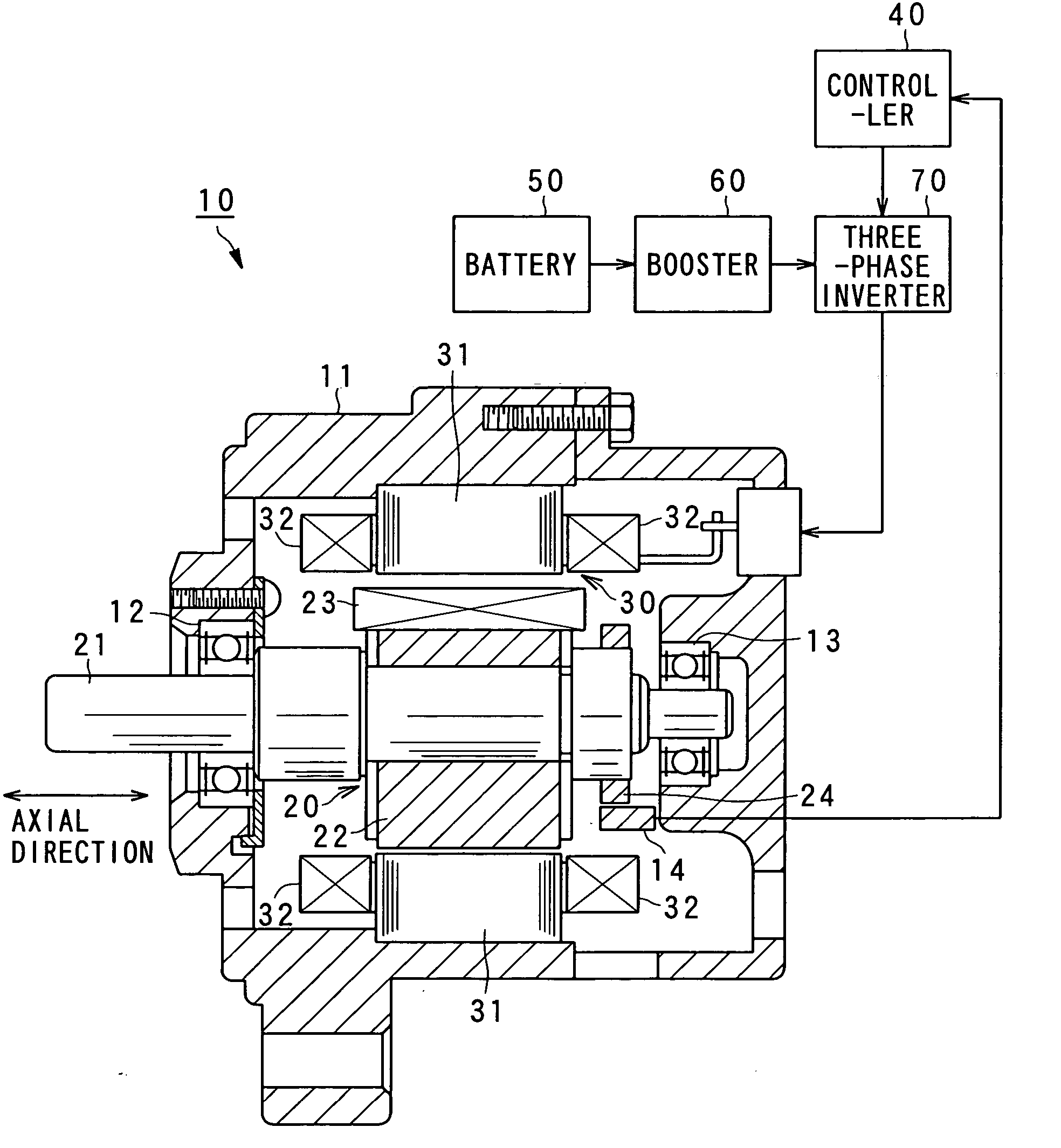
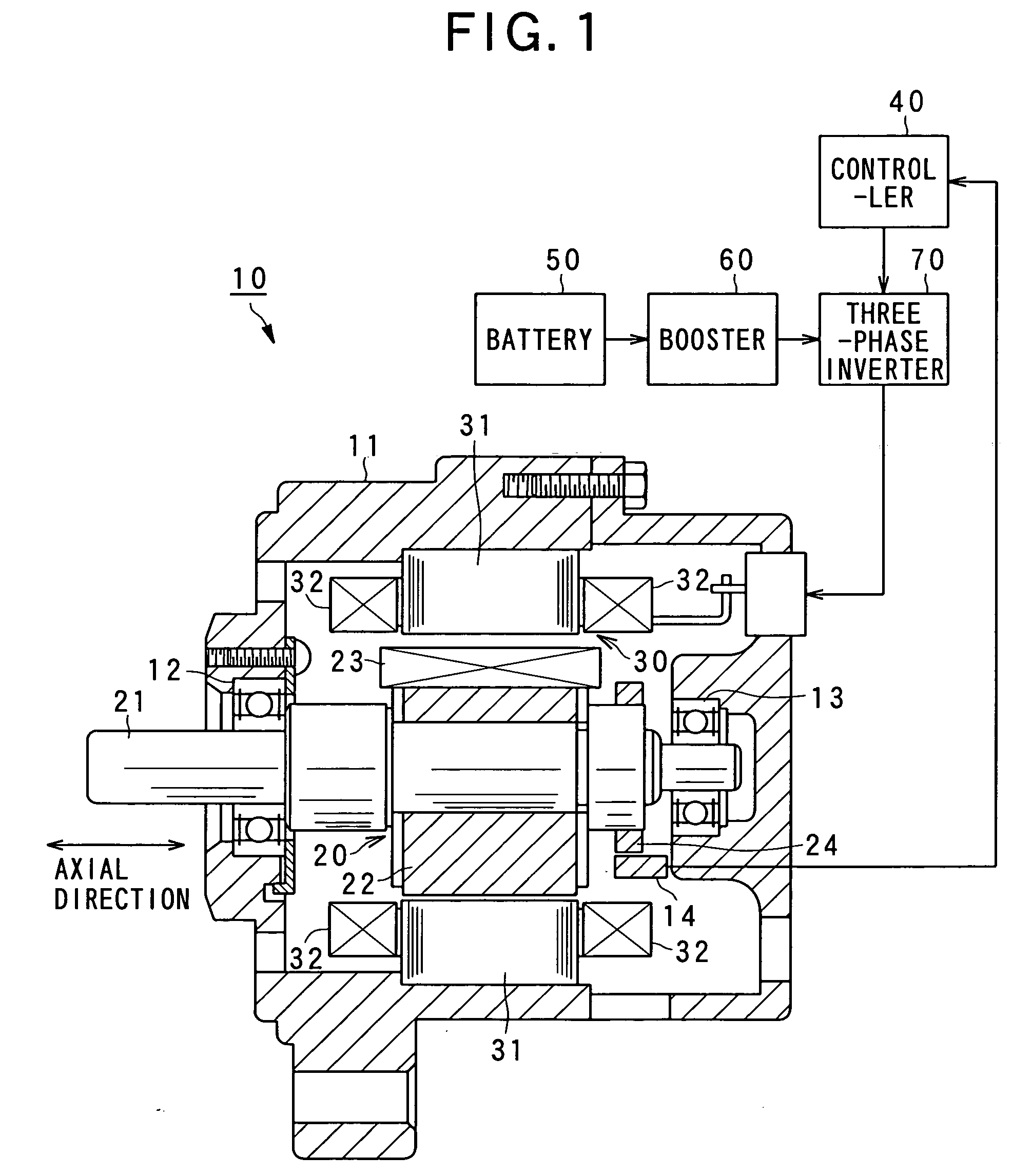
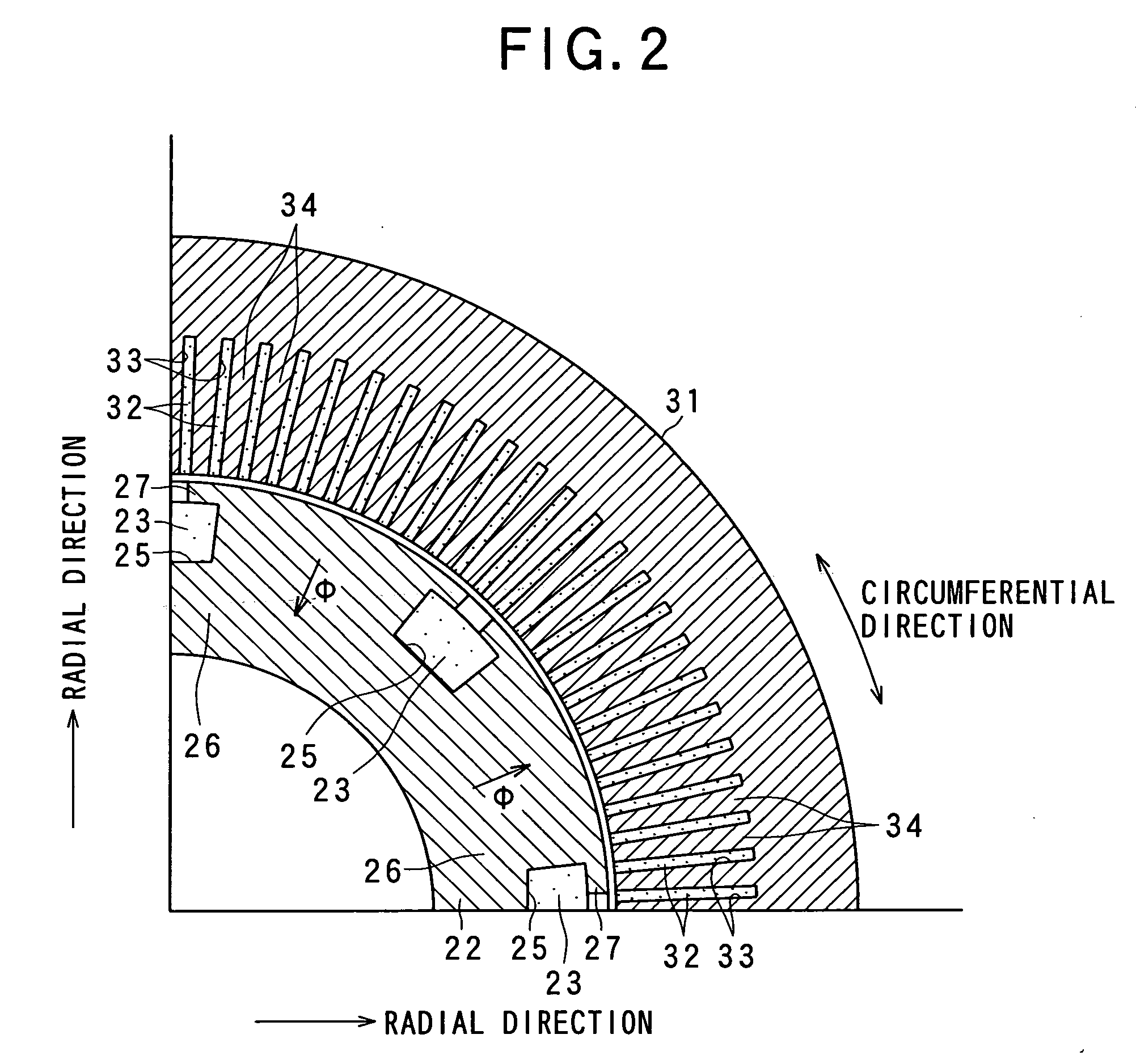
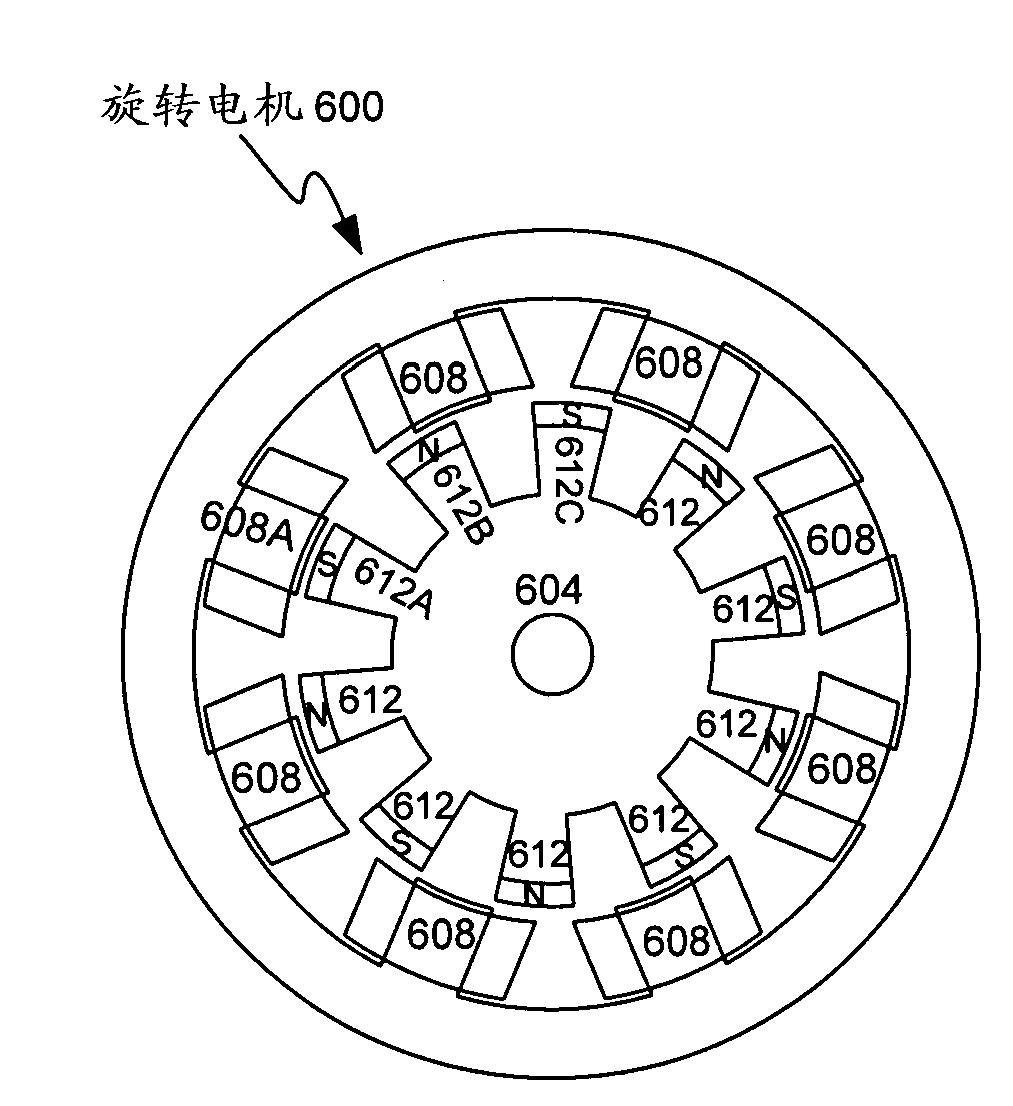
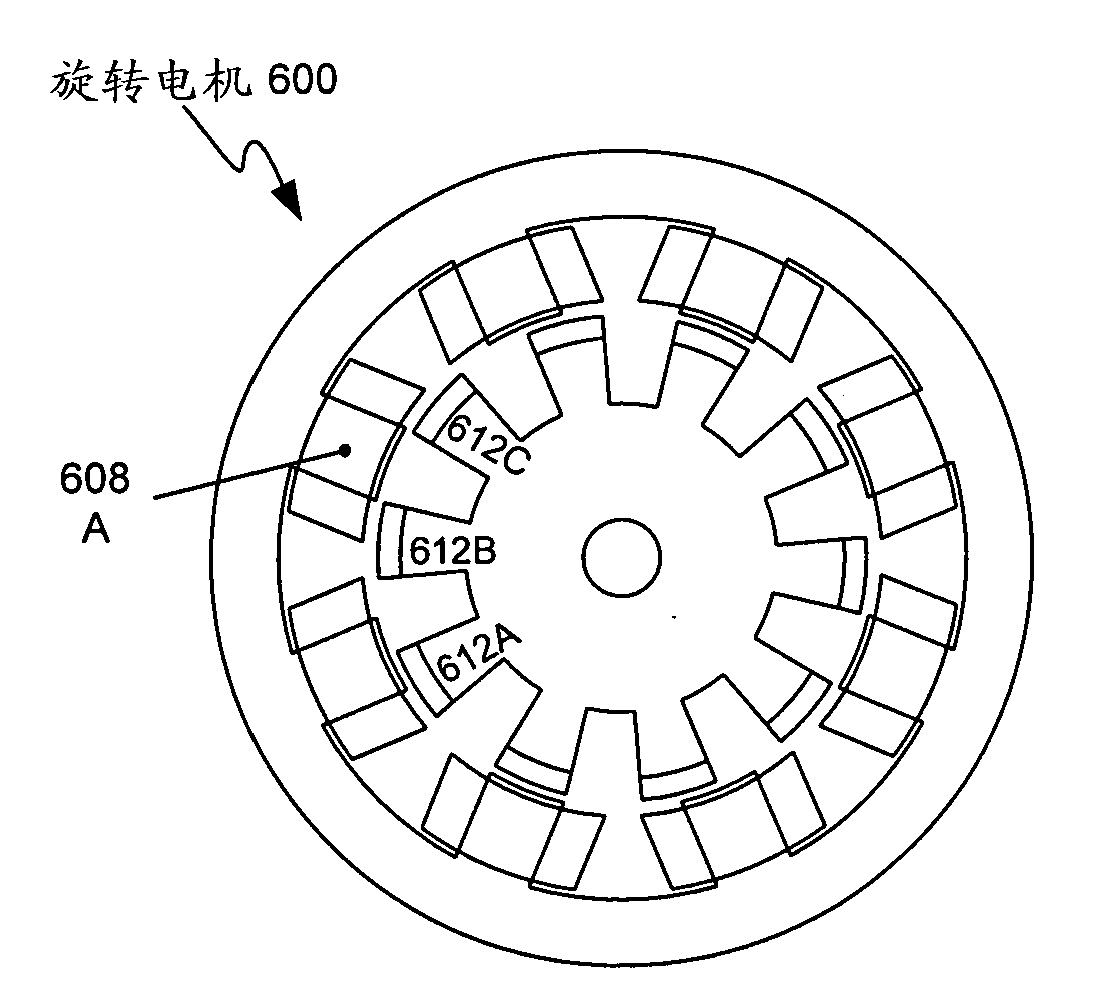
Rotary electric apparatus having rotor with field winding inducing current therethrough for generating magnetic field
ActiveUS20080079375A1Increase resistanceMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersElectricityElectric machine
A rotary electric apparatus comprise a synchronous machine of field winding type, an inverter, a DC power supply, a current flow regulator, and a controller. The DC power supply outputs first voltage of a first voltage value and second voltage of a second voltage value higher than the first voltage value. The current flow regulator regulates directions of currents flowing through a field winding by rotor exciting currents into one way, the current flow regulator being electrically connected to the field winding. The controller controls the inverter such that the inverter produces armature currents consisting of synchronized currents producing rotating fields depending on a rotating position of a rotor and rotor exciting currents different in waveforms from the synchronized currents and superposed on the synchronized currents. At least the rotor exciting currents are powered on a second voltage from the DC power supply.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electronic control for a hydraulically driven auxiliary power source
ActiveUS20100097040A1Extend system lifeLow costGenerator circuit arrangements controlServomotor componentsHydraulic motorHydraulic pump
A hydraulic system includes a variable displacement hydraulic pump connectable to a power source, a hydraulic motor, a fluid circuit, a pump displacement control, and a controller. The pump has an inlet for receiving fluid, an outlet for discharging pressurized fluid, and a pump displacement input. The motor has an inlet for receiving pressurized fluid and an outlet for discharging spent fluid. The fluid circuit includes a supply conduit for conducting fluid discharged by the pump to the motor and a return conduit for returning fluid discharged by the motor to the pump. The pump displacement control cooperates with the pump displacement input to vary pump displacement. The controller communicates with the pump displacement control to control the pump output such that the motor is driven at a constant speed to thereby drive a generator connected to the motor at a constant speed despite speed fluctuations of the power source.
Owner:UUSI
Electronic control for a hydraulically driven generator
ActiveUS8269359B2Extend system lifeLow costGenerator circuit arrangements controlFluid couplingsHydraulic motorOperator interface
Owner:UUSI
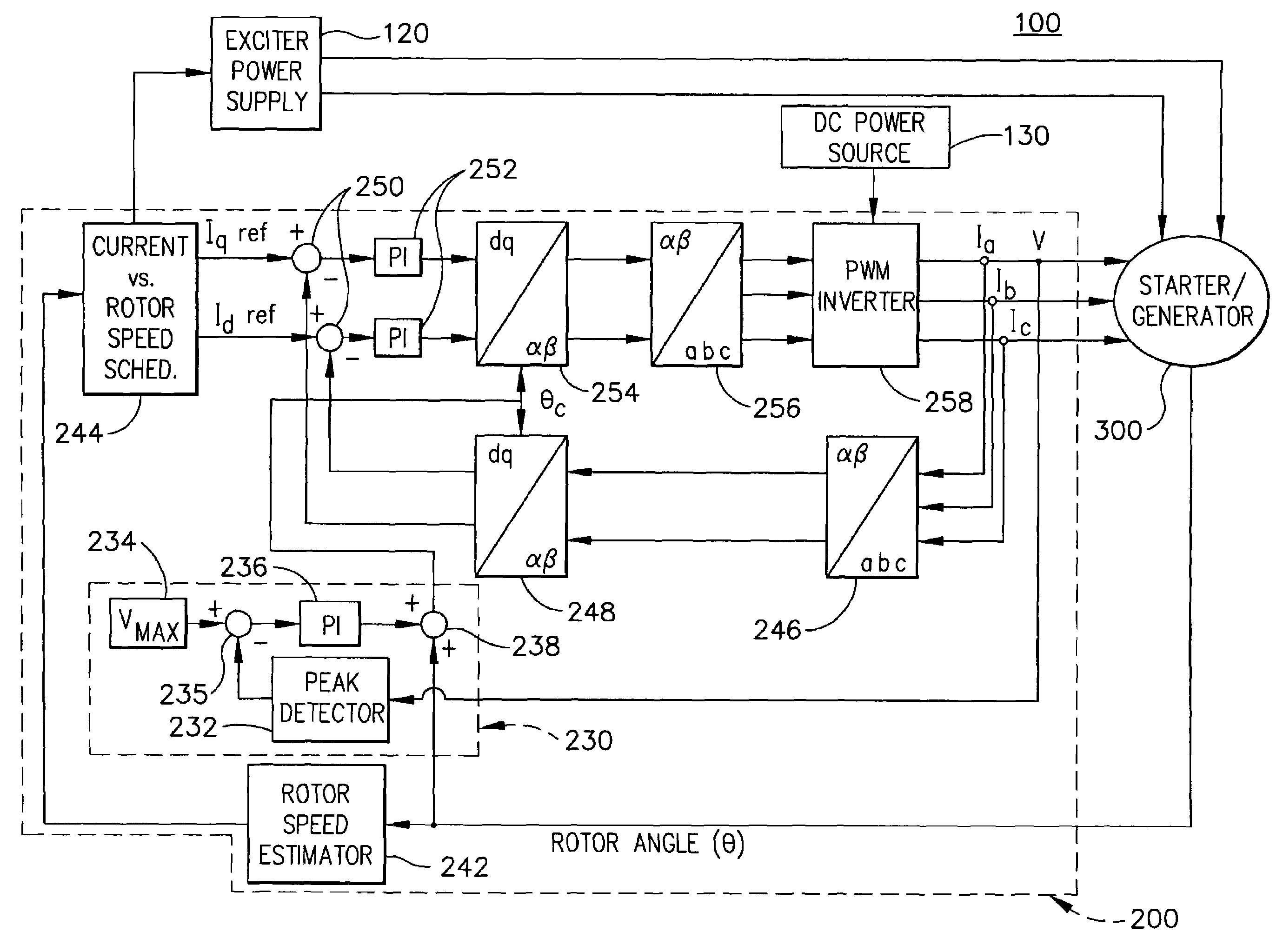
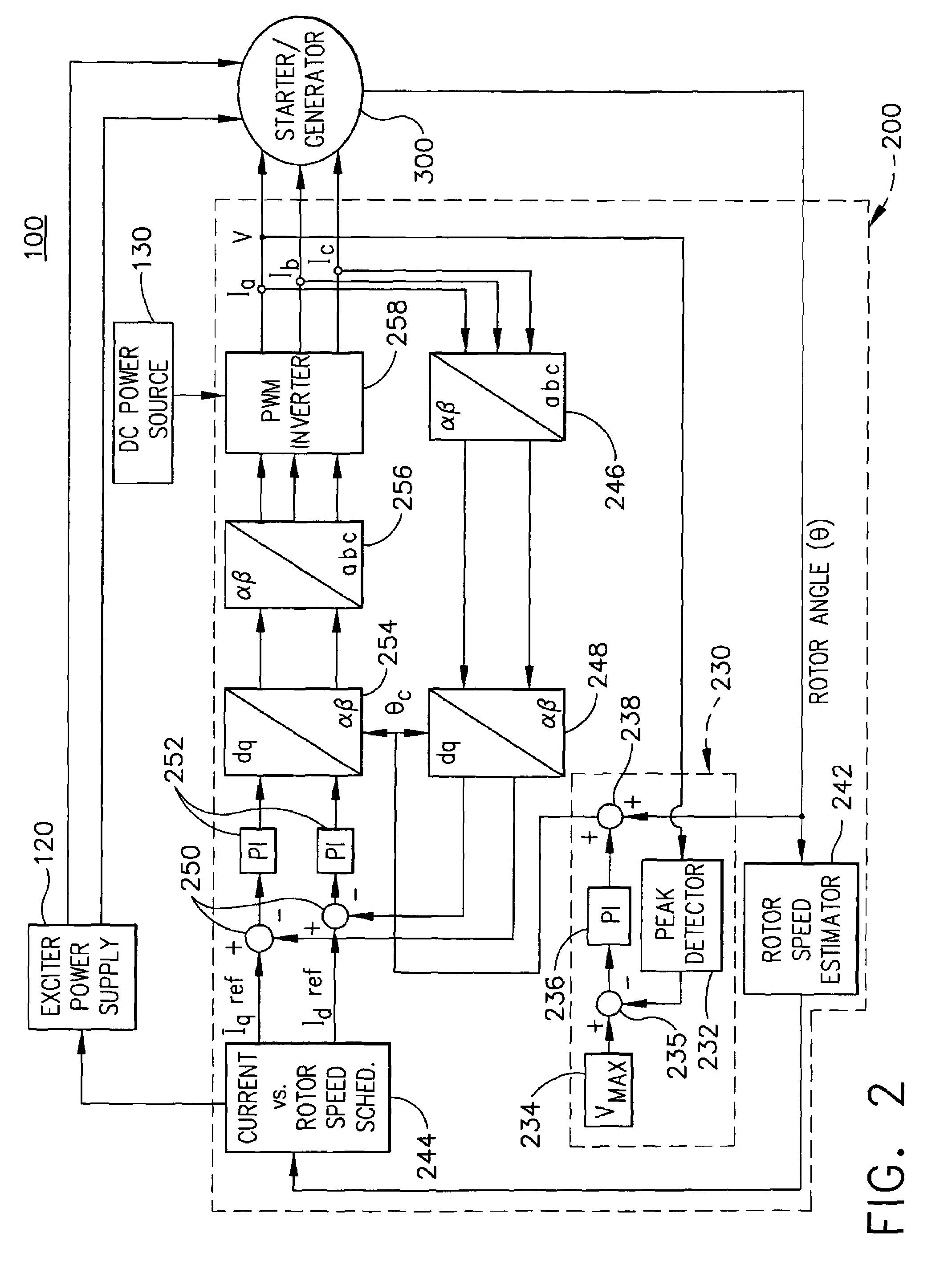
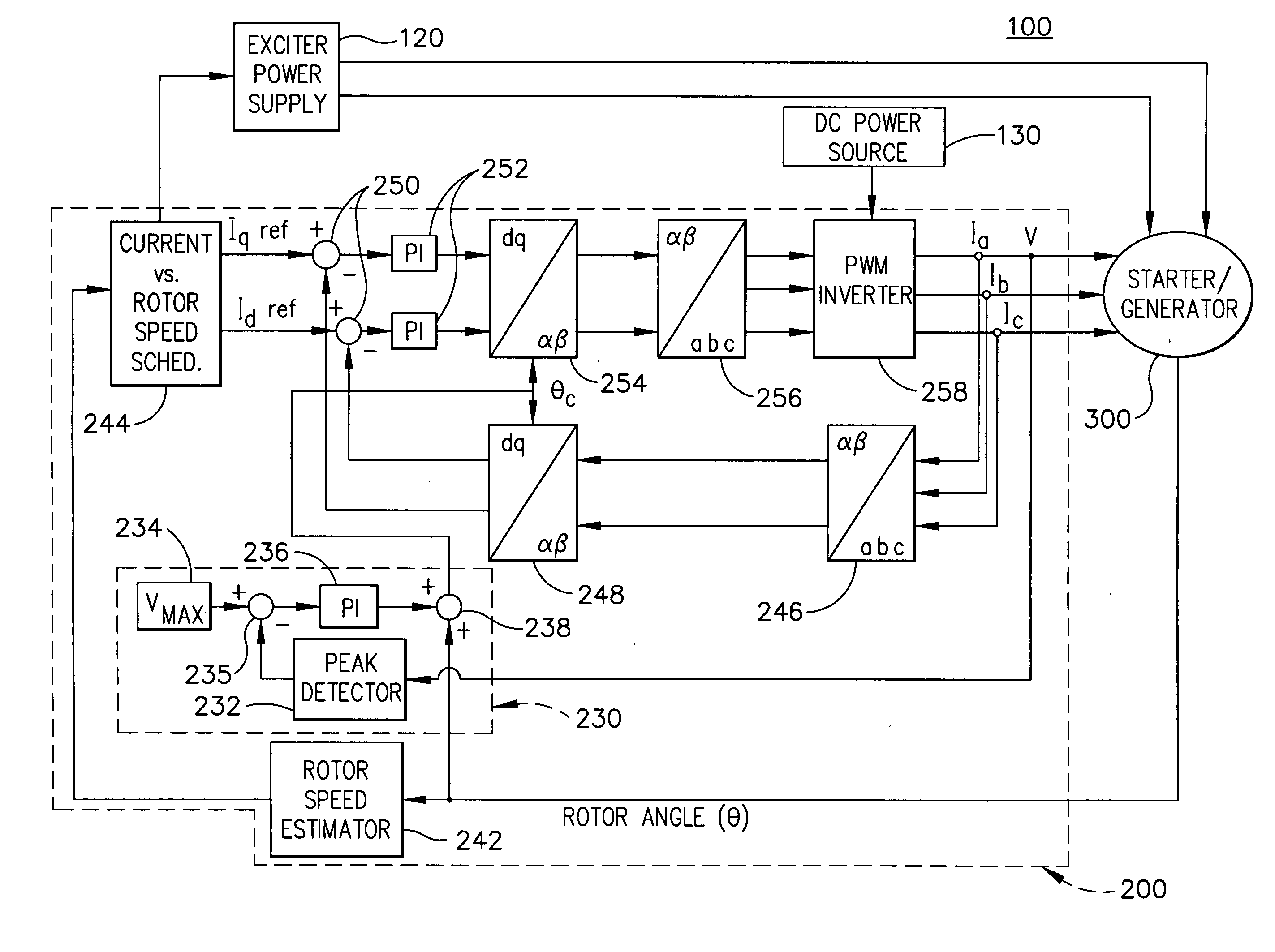
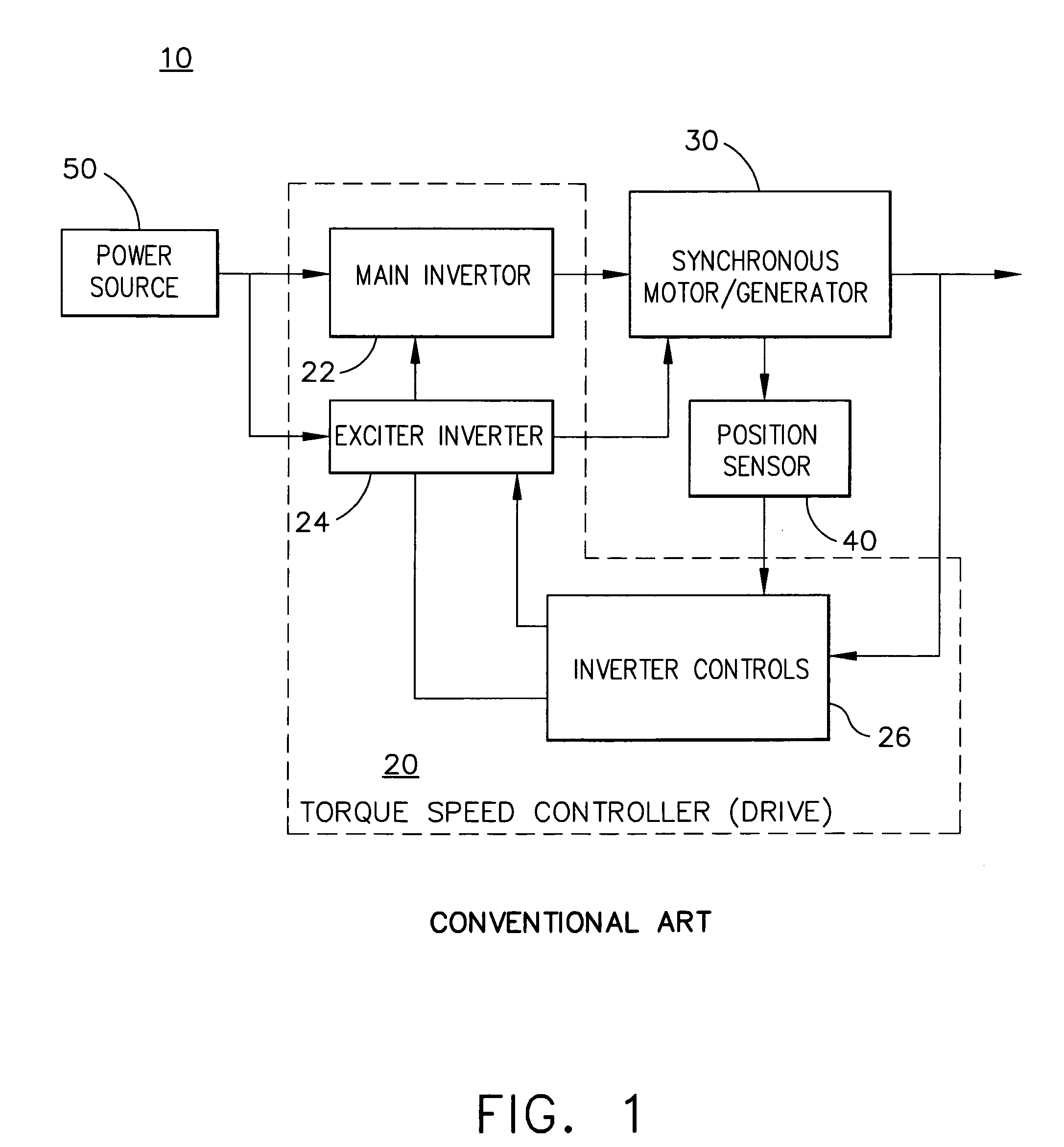
Apparatus and method to control torque and voltage of an AC machine
ActiveUS7208908B2Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersMaximum levelEngineering
A method of controlling a power converter (258) of a synchronous machine drive system (100) determines position and speed of a rotor (350) of the synchronous machine (300); regulates a current vector relative to a reference frame, having a direct-axis component and a quadrature-axis component, the regulating step selectively causing the current vector to lag a quadrature axis of the machine (300); and outputs a command signal to the power converter (258) as a function of the regulating step. According to one implementation, this process creates higher total torque and maintains supply voltage within a maximum level during a high speed range of the machine.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
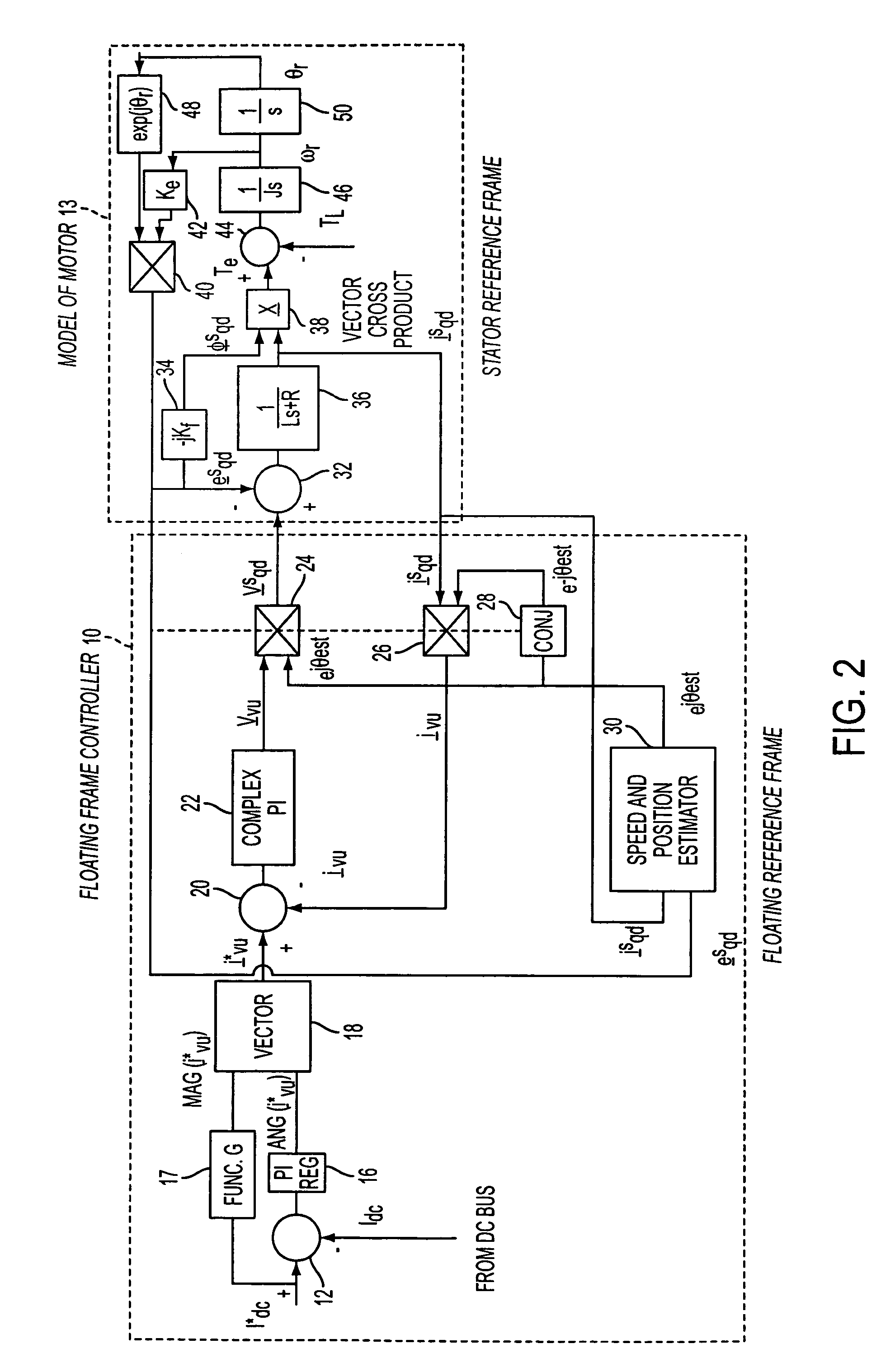
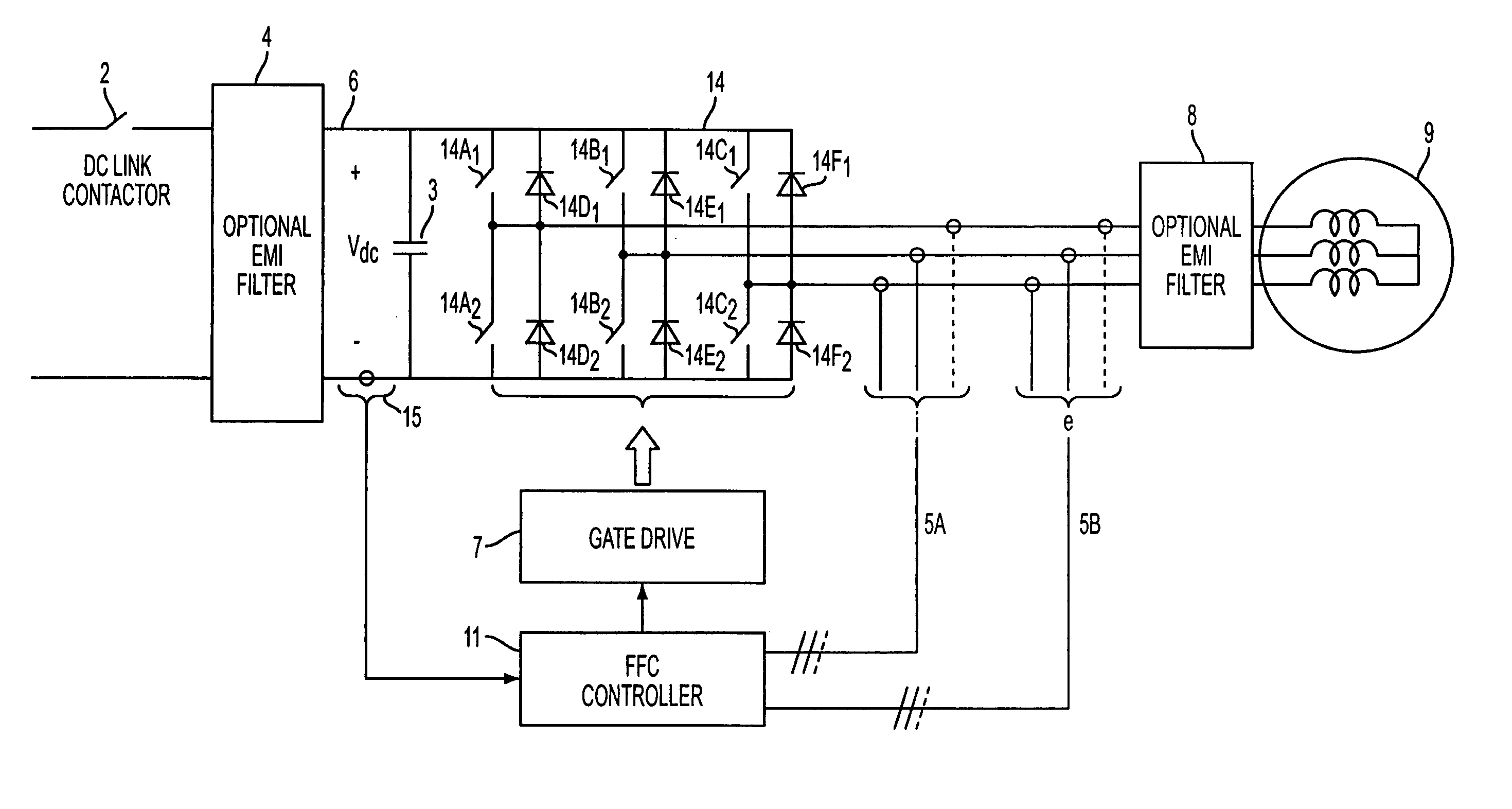
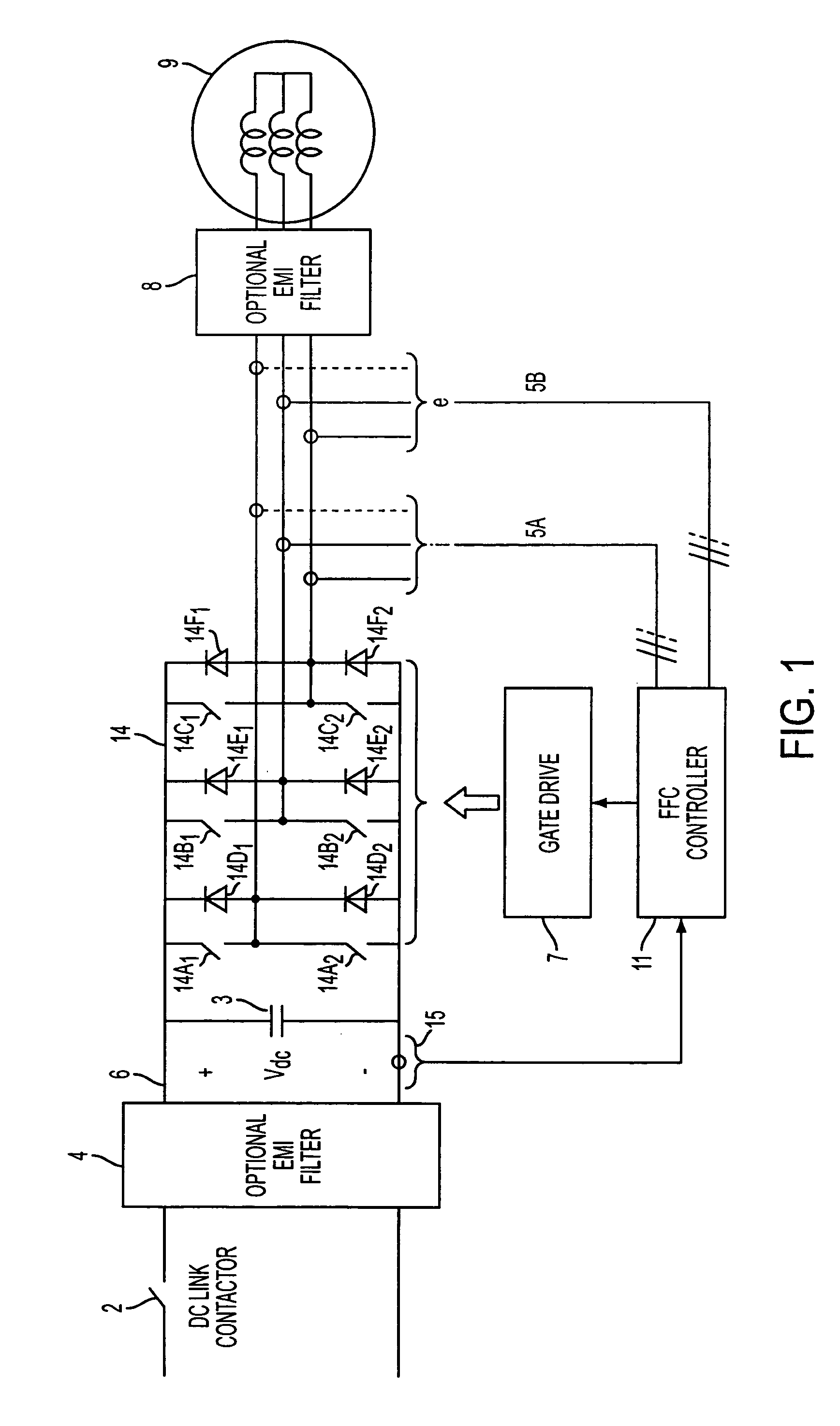
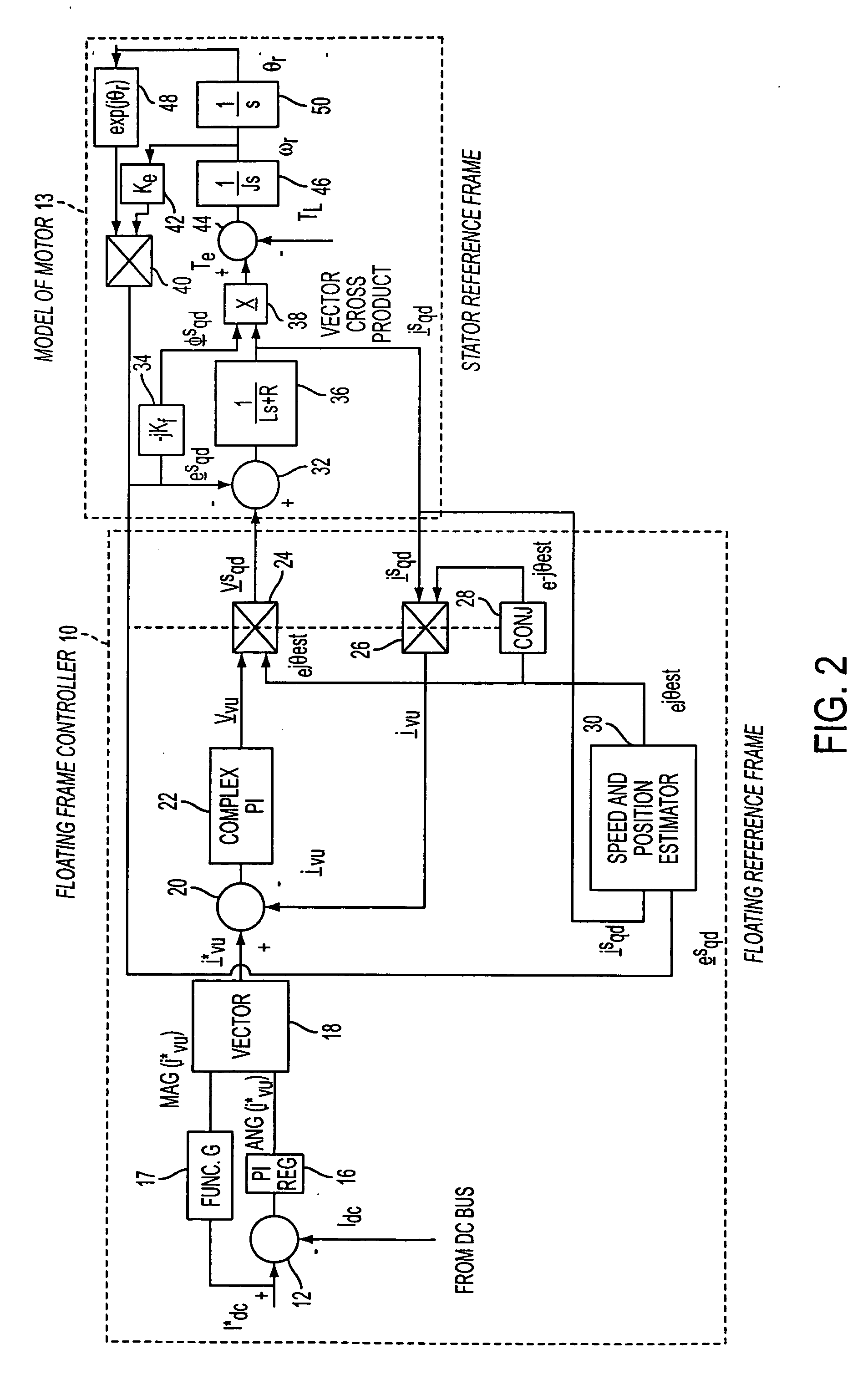
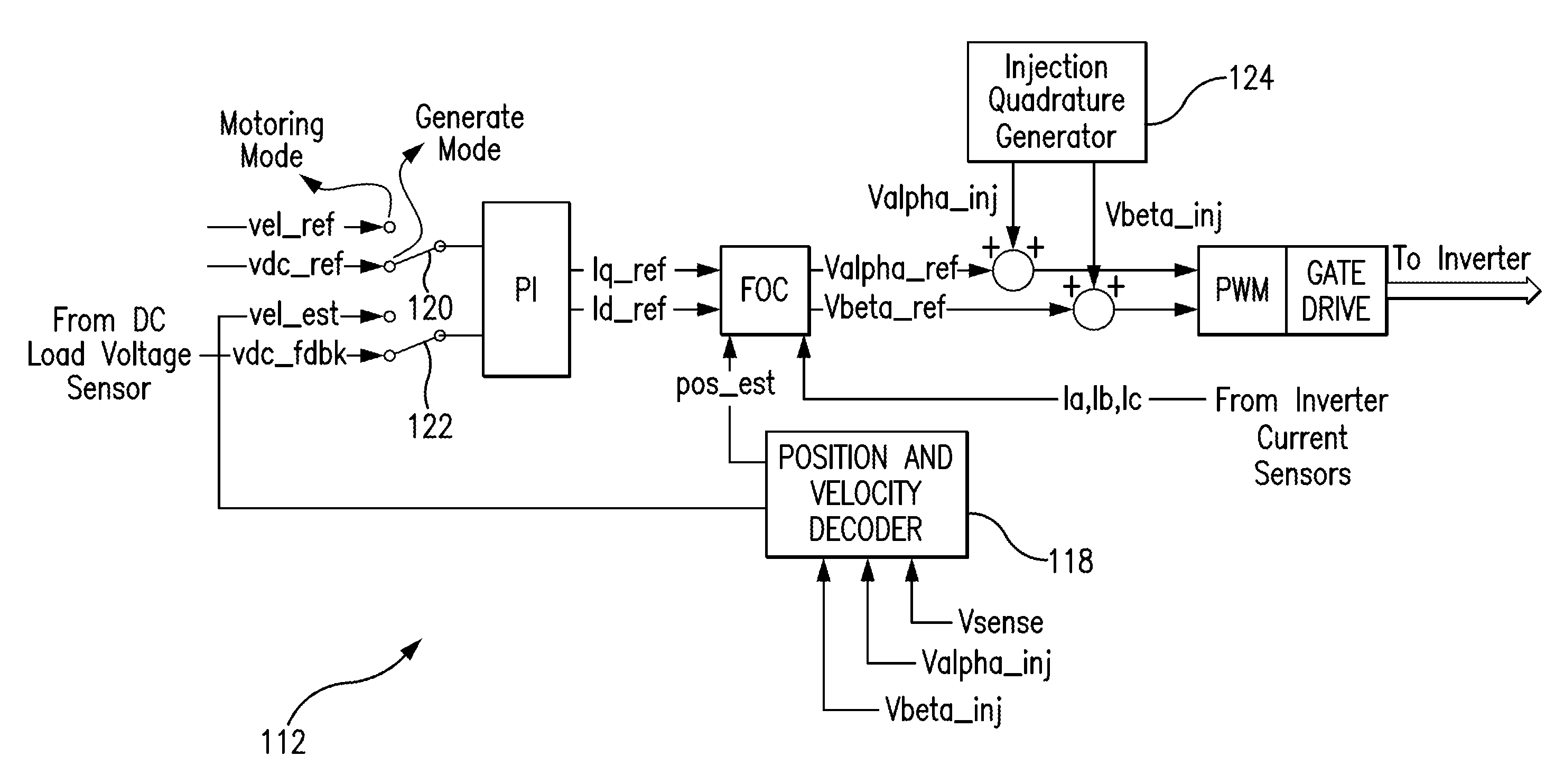
Enhanced floating reference frame controller for sensorless control of synchronous machines
ActiveUS7193383B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlPhase currentsControl theory
A method and system for controlling a power converter coupled to a polyphase power line. The method includes measuring at least two motor phase currents, obtaining a floating reference frame for the current Park vector, adjusting the reference frame based on an estimated rotor speed, and controlling the power converter via the floating reference frame to reinitiate power to a motor while a rotor is still moving.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Adaptive position sensing method and apparatus for synchronous motor generator system
An adaptive, sensorless position sensing apparatus (250) derives rotor position of a synchronous machine (200). The apparatus (250) comprises a first rotor position deriving unit (300) for generating first rotor position values by applying a first sensorless rotor position calculation technique, which emulates a resolver; a second rotor position deriving unit (400) for generating second rotor position values by applying a second sensorless rotor position calculation technique; and a rotor position result output unit (450) for outputting rotor position results over a range of rotor speeds as a function of the first rotor position values, the second rotor position values, and rotor speed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
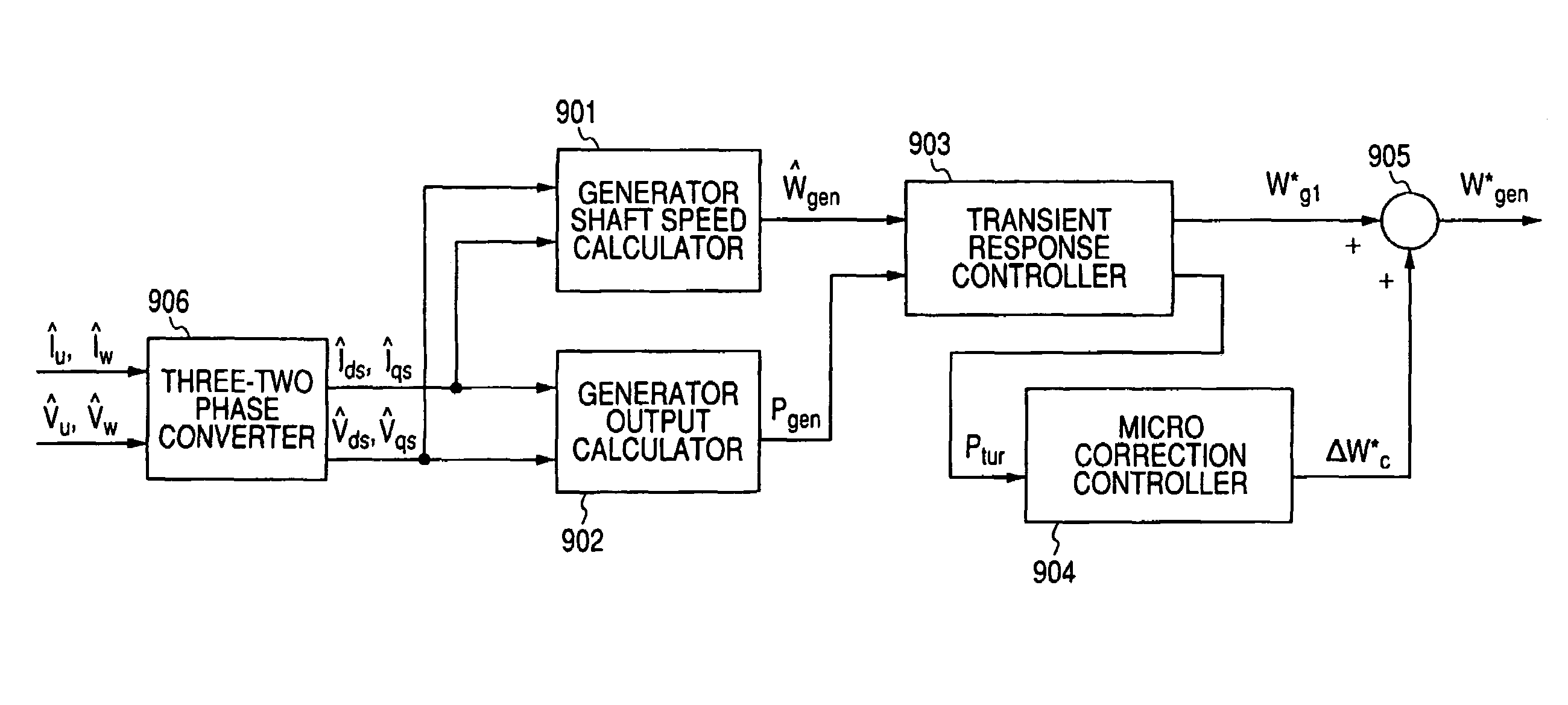
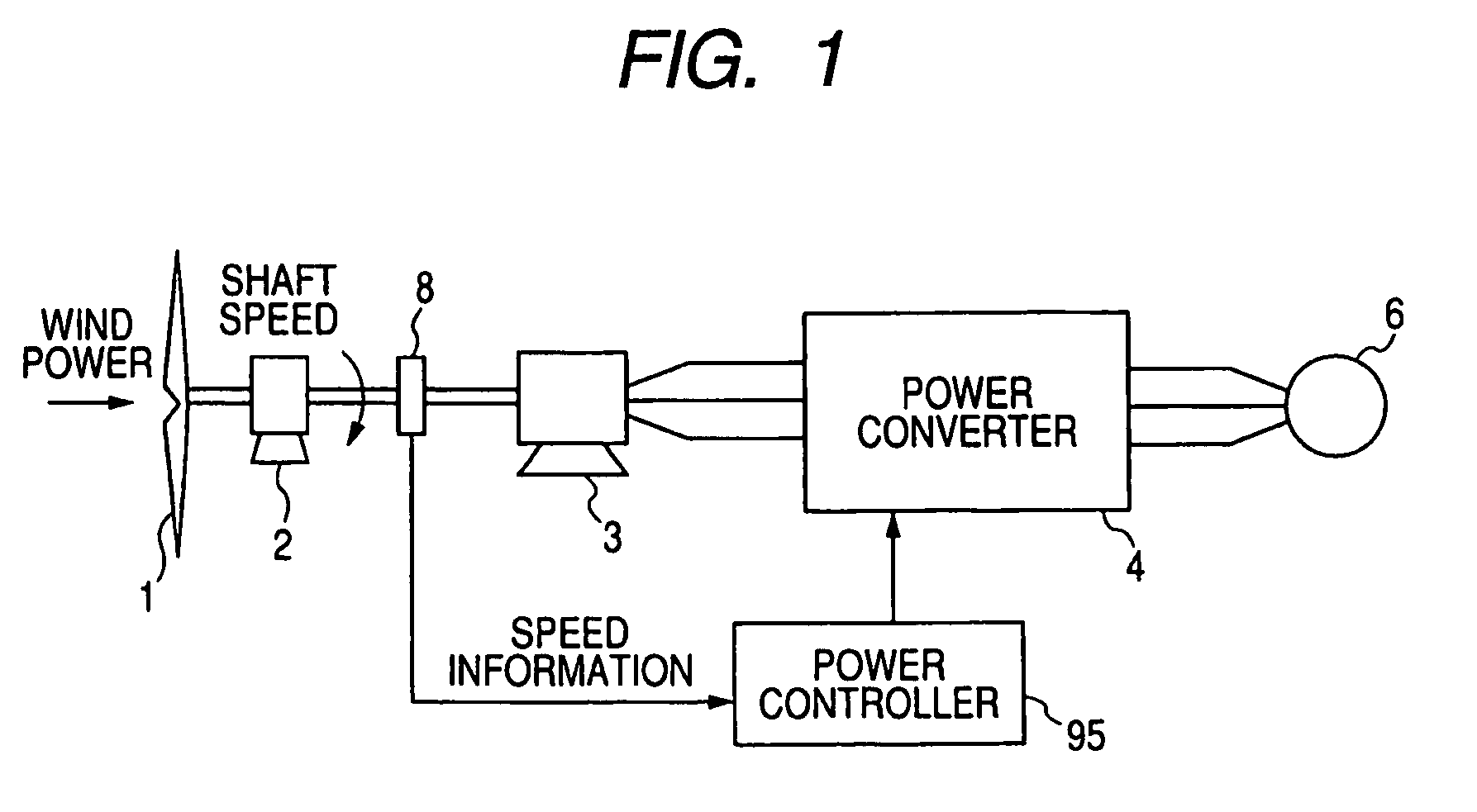
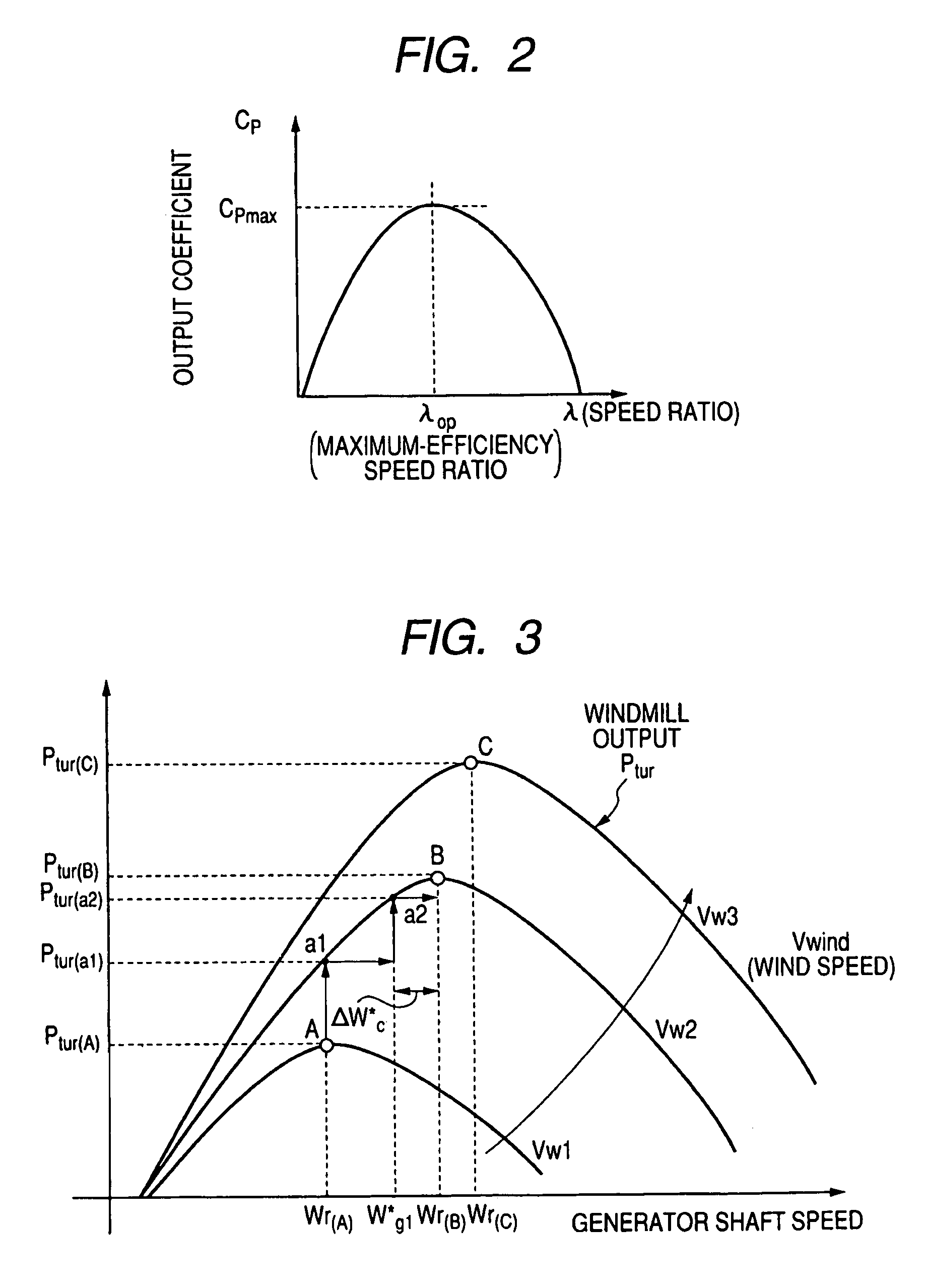
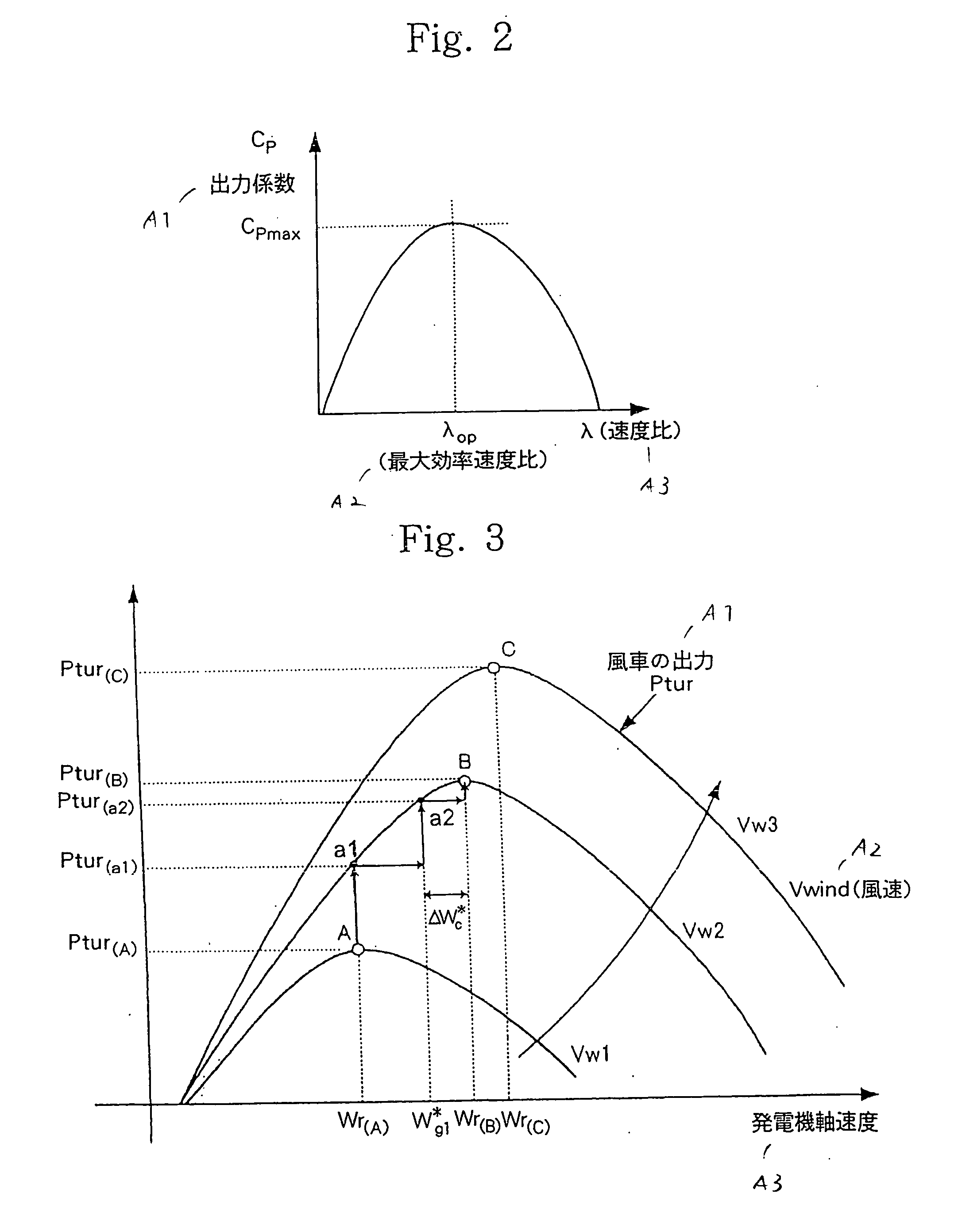
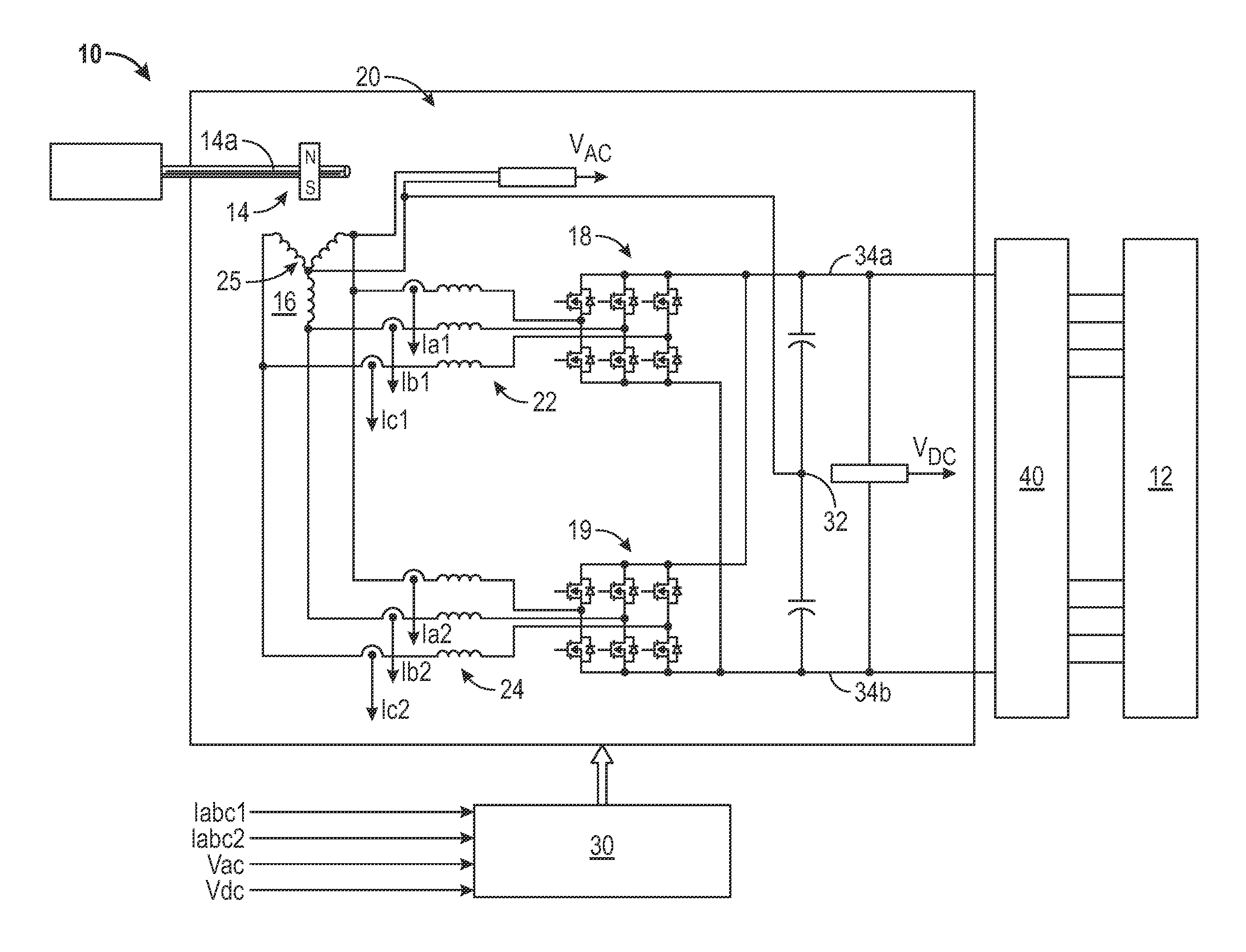
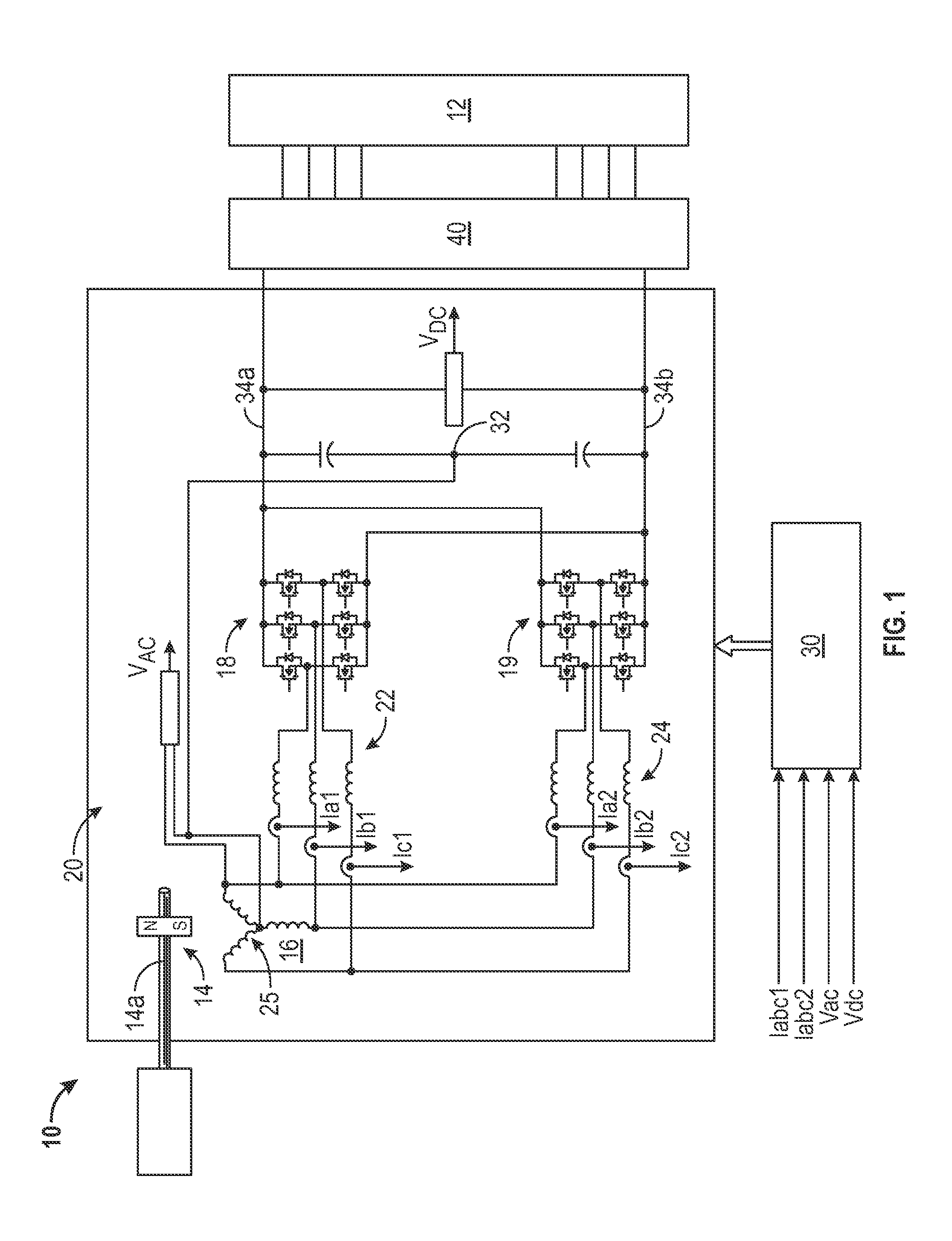
Power generating system and its control method
InactiveUS7304400B2Improve reliabilitySimple processGenerator circuit arrangements controlVector control systemsPower controllerControl theory
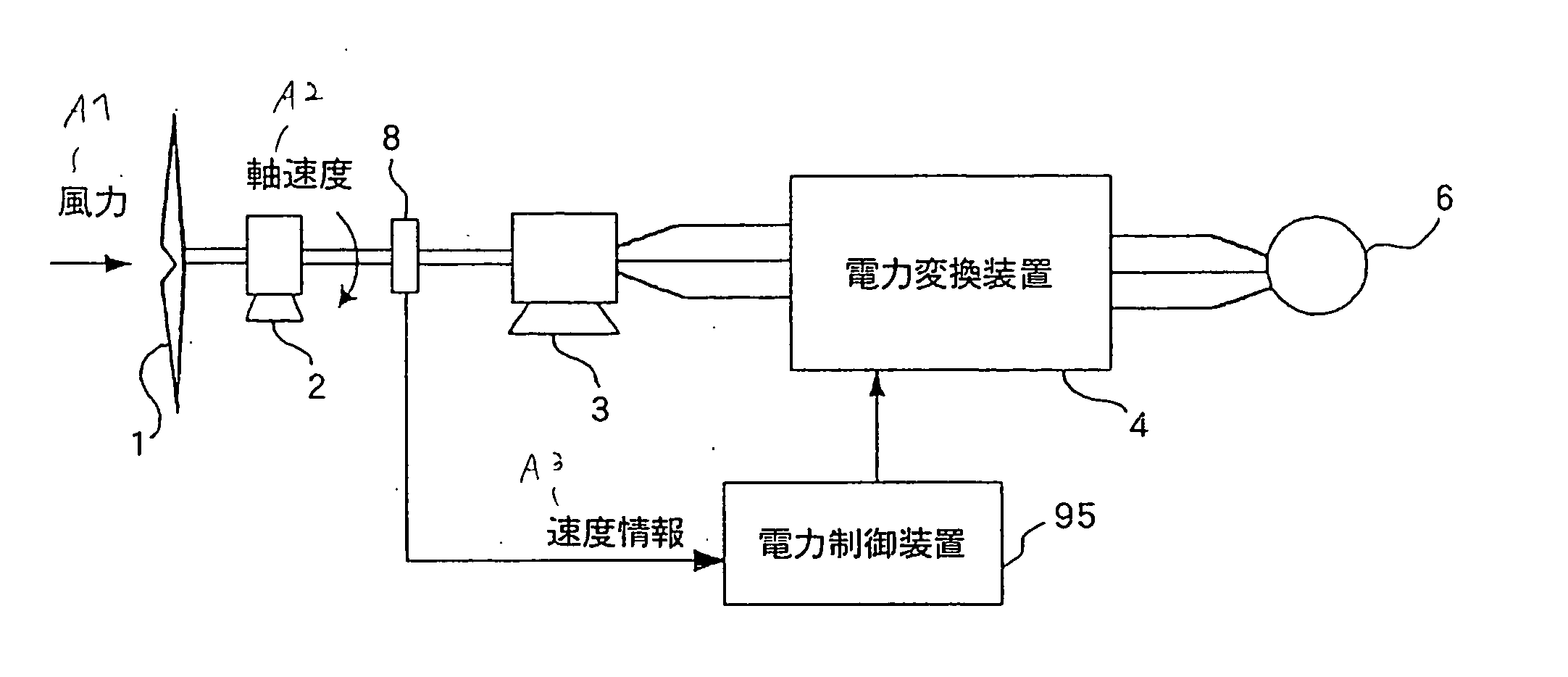
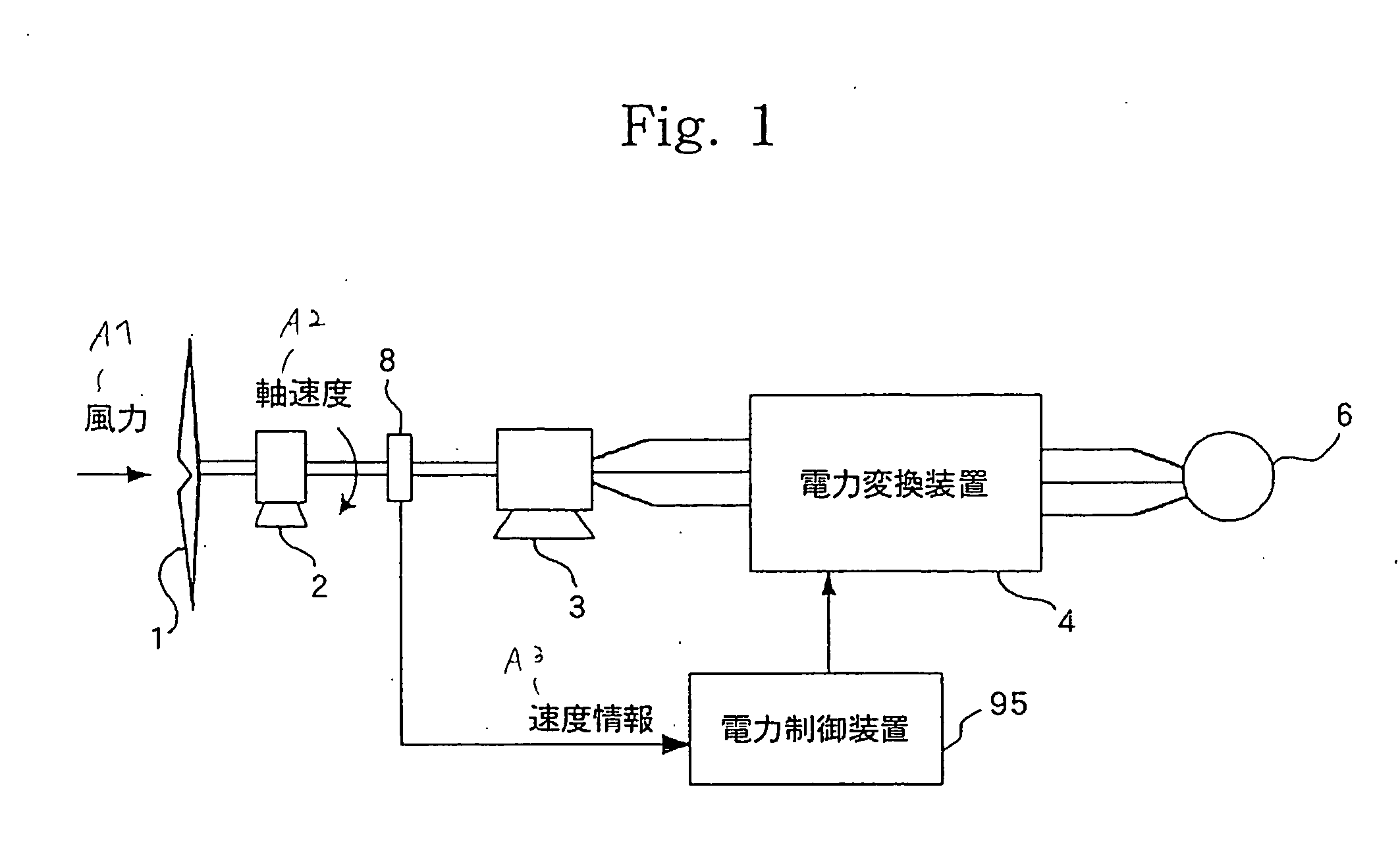
A power controller 5 calculates the induced voltage or rotor magnetic flux from the output voltage and the output current of a generator 3, estimates a shaft speed of the generator 3 from the phase of the induced voltage or the phase of the rotor magnetic flux, and calculate the output of a windmill 1 from the estimated value of the shaft speed and the output of the generator 3. As a result, since the output of the windmill 1 can be calculated without requiring a speed sensor for detecting the shaft speed of the generator 3, it is possible to accomplish simplification of circuits, reduction of cost, and high reliability.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Electronic control for a hydraulically driven generator
ActiveUS20090134848A1Extend system lifeReducing warranty returnGenerator circuit arrangements controlElectric propulsion mountingHydraulic motorHydraulic pump
Hydraulic system for driving an auxiliary power source is provided, which is specifically adapted for use with a system for controlling hydraulically driven AC generator. The system includes a hydraulic pump and hydraulic motor that are connected by a fluid circuit. The hydraulic motor drivably connected to an AC generator and is operated in a manner to generate a stable AC power output. The system may include a valve which bypasses fluid around the motor or a variable displacement pump so that the fluid flow rate through the hydraulic motor is controlled in a manner to maintain the desired AC generator output level. Sensors are further provided measuring operating parameters of the system so that the controller can maintain desired operating condition limits
Owner:UUSI
Apparatus and method to control torque and voltage of an AC machine
ActiveUS20060006829A1Increase torqueElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersMaximum levelAc machine
A method of controlling a power converter (258) of a synchronous machine drive system (100) determines position and speed of a rotor (350) of the synchronous machine (300); regulates a current vector relative to a reference frame, having a direct-axis component and a quadrature-axis component, the regulating step selectively causing the current vector to lag a quadrature axis of the machine (300); and outputs a command signal to the power converter (258) as a function of the regulating step. According to one implementation, this process creates higher total torque and maintains supply voltage within a maximum level during a high speed range of the machine.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
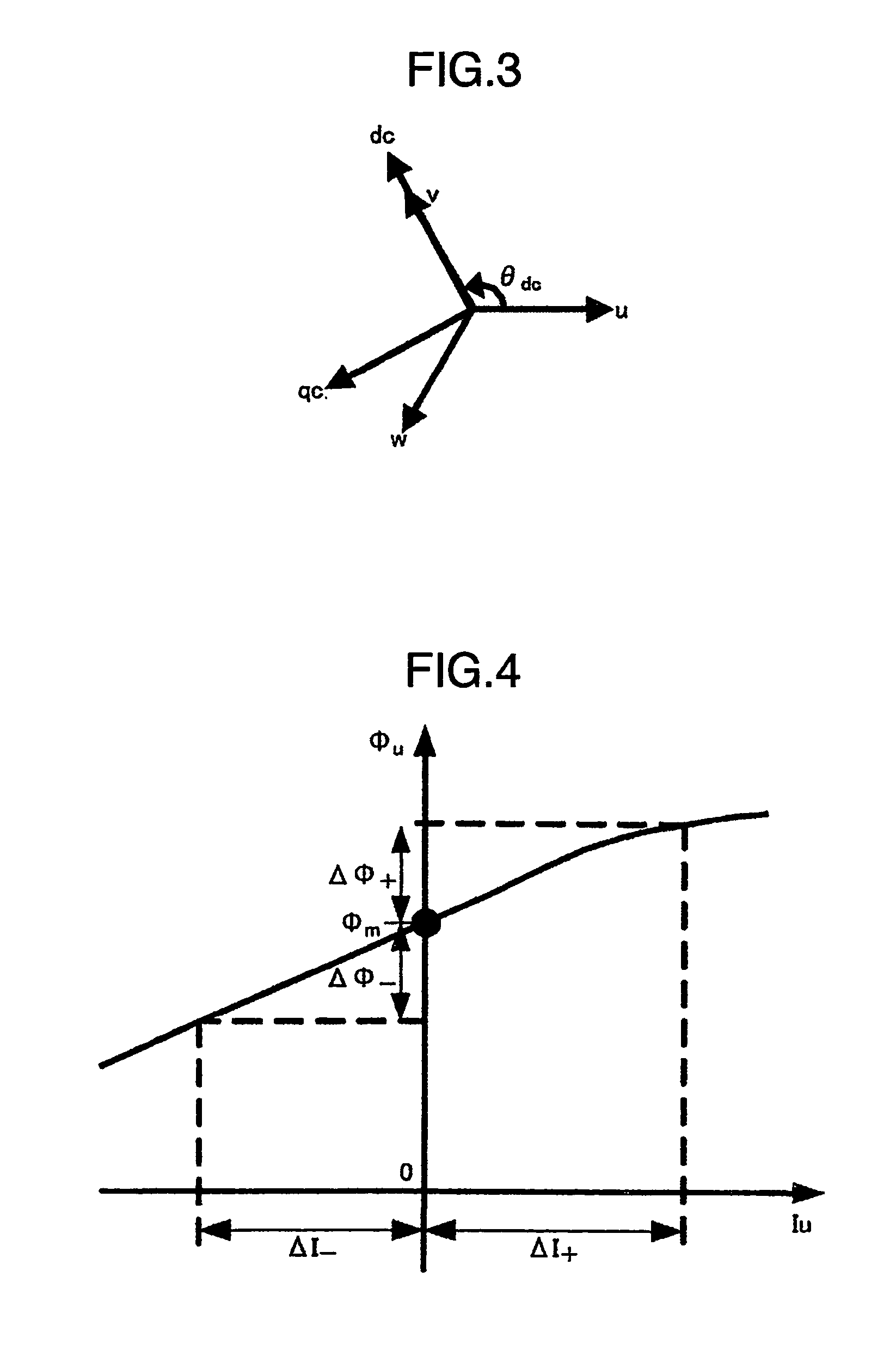
Method and apparatus for assembling electrical machines
ActiveUS20090212564A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersGenerator circuit arrangements controlElectric forceElectricity
A method of assembling an electrical machine includes programming at least one processor with a stator flux vector estimation scheme. The electrical machine has a stator at least partially extending around a rotor. The electrical machine is electrically coupled to an electric power system. The electric power system transmits at least one phase of electric power to and from the electrical machine with at least partial power conversion. The stator flux vector estimation scheme is programmed to generate at least one stator back-electromagnetic force (back-EMF) signal and to generate at least one stator flux vector signal using the at least one stator back-EMF signal. The at least one stator flux vector signal at least partially represents an estimated rotor position. The method also includes coupling at least one output device in data communication with the at least one processor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Enhanced floating reference frame controller for sensorless control of synchronous machines
A method and system for controlling a power converter coupled to a polyphase power line. The method includes measuring at least two motor phase currents, obtaining a floating reference frame for the current Park vector, adjusting the reference frame based on an estimated rotor speed, and controlling the power converter via the floating reference frame to reinitiate power to a motor while a rotor is still moving.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High efficiency low torque ripple multi-phase permanent magnet machine
InactiveUS8922087B1Improve efficiencyTorque ripple is all but eliminatedWindingsGenerator circuit arrangements controlDrive motorMulti phase
An electrically driven motor, an electrical generator, a rotating electrical machine and method of operating, that includes a rotating rotor having an even number of alternating polarity permanent magnet poles and a stator with an odd number of evenly spaced alternating magnetic polarity electromagnetic poles divided into an odd number of equal stator phase groups with a magnetically unbalanced orphan, pole from each stator phase group removed without re-spacing the remaining stator poles to produce a gap between stator phase groups that is greater than the spacing between adjacent poles in each stator phase group. The rotor can be a rotating external rotor or a stationary internal rotor and the stator can be a stationary interior stator or a rotating exterior stator.
Owner:RITTENHOUSE NORMAN P
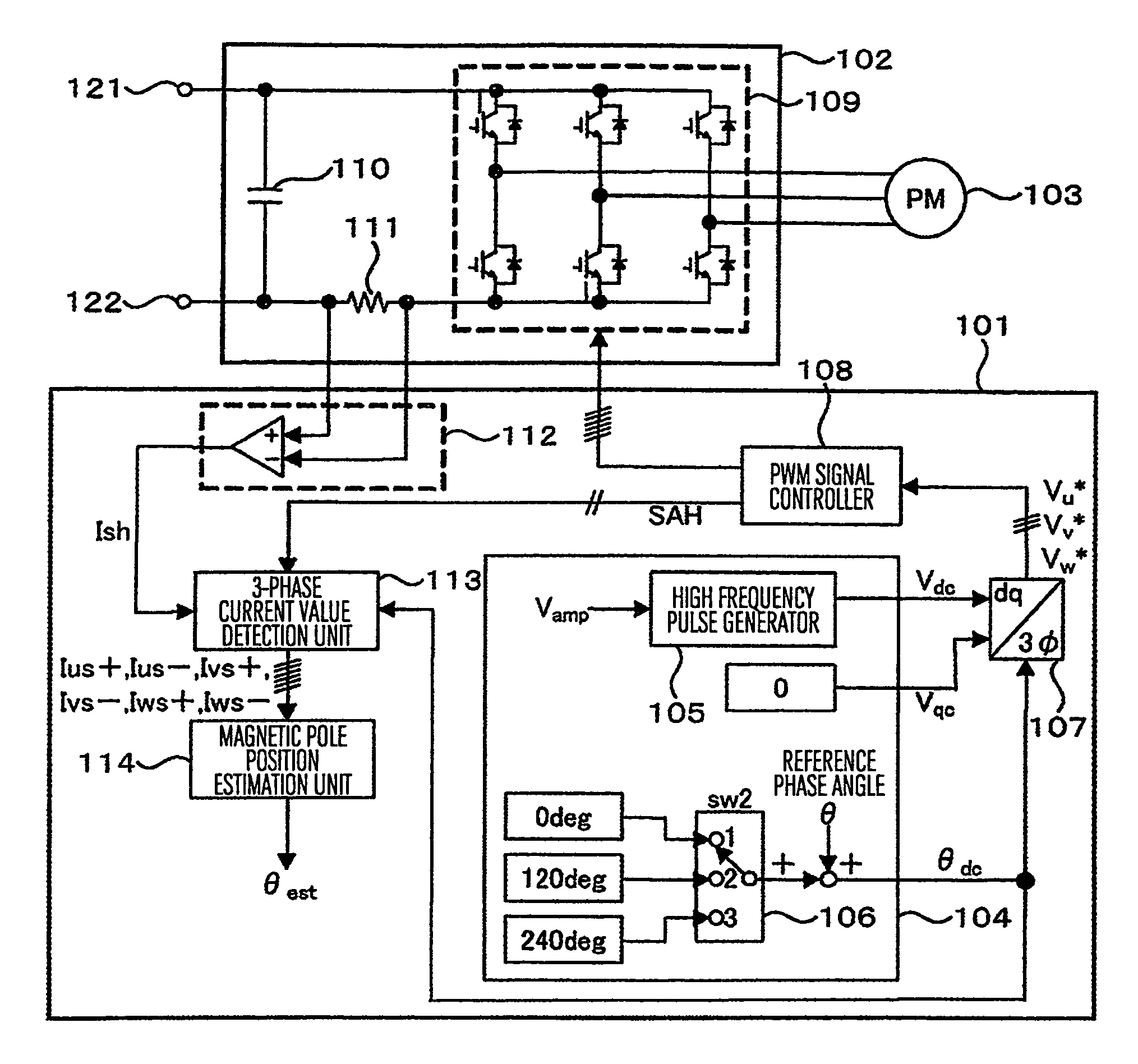
Method Of Operating A Single-Phase Generator In Parallel With An Inverter
ActiveUS20150180367A1AC motor controlGenerator circuit arrangements controlSingle-phase generatorPosition sensor
A system for connecting a single-phase generator in parallel with an inverter is disclosed. A signal corresponding to the angular position of the rotor in the generator is provided to the inverter, for example, from an angular position sensor connected to the rotor in the generator. Because variations in the load applied to the generator cause variations in the frequency of the power output by the generator, the inverter synchronizes the phase angle of the voltage output by the inverter to the angular position of the rotor.
Owner:GENERAC POWER SYSTEMS
Driving system of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveUS8541971B2Improve positionIncrease the number ofCommutation monitoringSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsMagnetic poles
Owner:HITACHI IND EQUIP SYST CO LTD
Method and apparatus for assembling electrical machines
ActiveUS7745949B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersGenerator circuit arrangements controlElectric power transmissionMagnetic tension force
A method of assembling an electrical machine includes programming at least one processor with a stator flux vector estimation scheme. The electrical machine has a stator at least partially extending around a rotor. The electrical machine is electrically coupled to an electric power system. The electric power system transmits at least one phase of electric power to and from the electrical machine with at least partial power conversion. The stator flux vector estimation scheme is programmed to generate at least one stator back-electromagnetic force (back-EMF) signal and to generate at least one stator flux vector signal using the at least one stator back-EMF signal. The at least one stator flux vector signal at least partially represents an estimated rotor position. The method also includes coupling at least one output device in data communication with the at least one processor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electronic control for a hydraulically driven generator
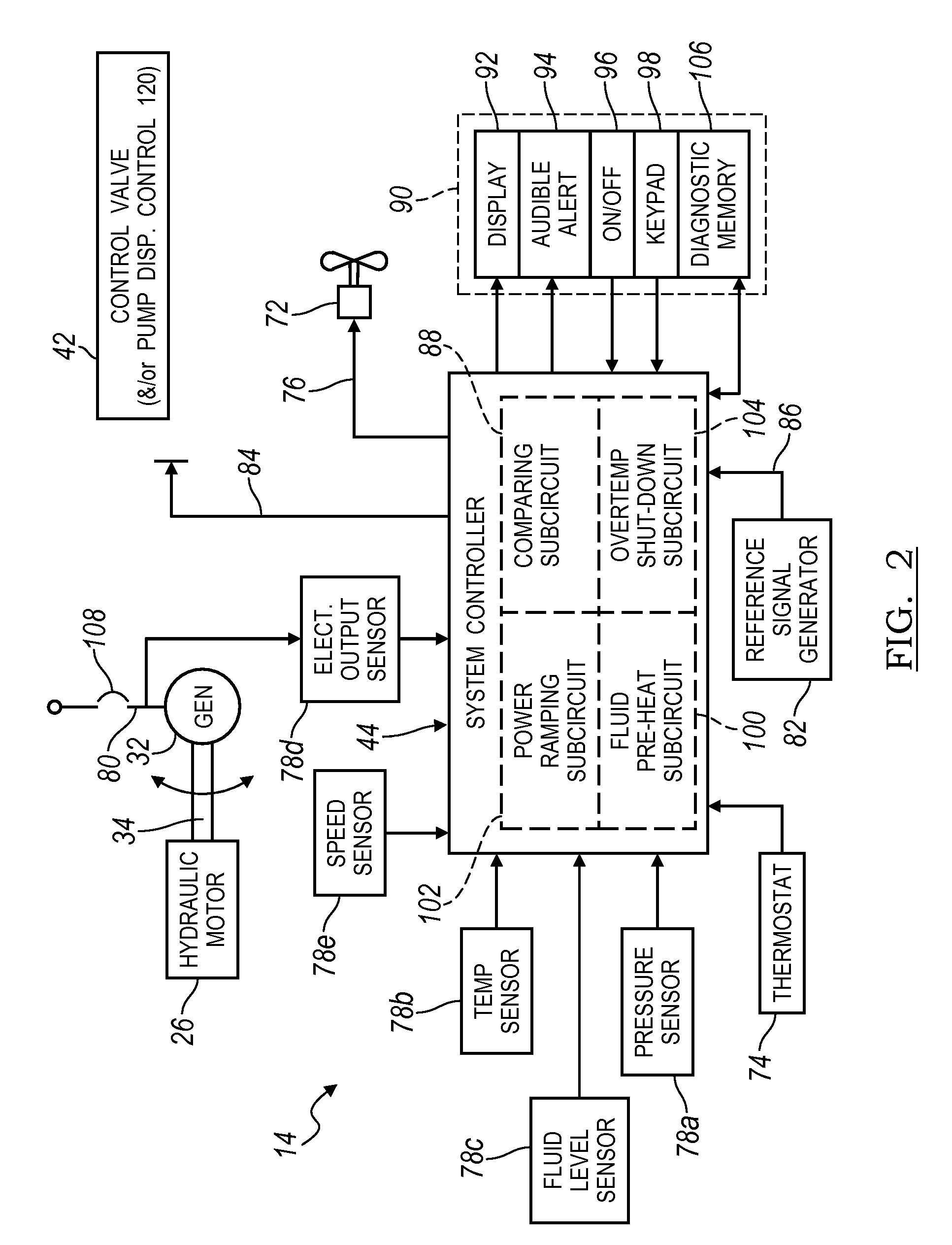
ActiveUS20100097038A1Extend system lifeLow costGenerator circuit arrangements controlServomotor componentsHydraulic motorOperator interface
Electronic control for a hydraulic system to drive an auxiliary power source is provided, with an application as a system for controlling the operation of a hydraulically driven AC generator. The system includes a hydraulic pump, a hydraulic motor drivably connected to the generator, and a fluid circuit for circulating fluid from the pump to the motor and back. The feedback circuit contains a feedback conduit to feedback the motor. The system also includes a proportional servo control valve assembly for controlling the fluid conduits and a control circuit for controlling the control valve assembly to thereby control the flow of fluid to the motor. Sensors for measuring the operating parameters of the system and an operator interface module are both able to influence the operation of the system.
Owner:UUSI
Rotary electric apparatus having rotor with field winding inducing current therethrough for generating magnetic field
ActiveUS7880424B2Increase resistanceTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPower inverterElectricity
A rotary electric apparatus comprise a synchronous machine of field winding type, an inverter, a DC power supply, a current flow regulator, and a controller. The DC power supply outputs first voltage of a first voltage value and second voltage of a second voltage value higher than the first voltage value. The current flow regulator regulates directions of currents flowing through a field winding by rotor exciting currents into one way, the current flow regulator being electrically connected to the field winding. The controller controls the inverter such that the inverter produces armature currents consisting of synchronized currents producing rotating fields depending on a rotating position of a rotor and rotor exciting currents different in waveforms from the synchronized currents and superposed on the synchronized currents. At least the rotor exciting currents are powered on a second voltage from the DC power supply.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electronic control for a hydraulically driven generator
ActiveUS7759811B2Extend system lifeLow costGenerator circuit arrangements controlElectric propulsion mountingHydraulic motorHydraulic pump
Hydraulic system for driving an auxiliary power source is provided, which is specifically adapted for use with a system for controlling hydraulically driven AC generator. The system includes a hydraulic pump and hydraulic motor that are connected by a fluid circuit. The hydraulic motor drivably connected to an AC generator and is operated in a manner to generate a stable AC power output. The system may include a valve which bypasses fluid around the motor or a variable displacement pump so that the fluid flow rate through the hydraulic motor is controlled in a manner to maintain the desired AC generator output level. Sensors are further provided measuring operating parameters of the system so that the controller can maintain desired operating condition limits.
Owner:UUSI
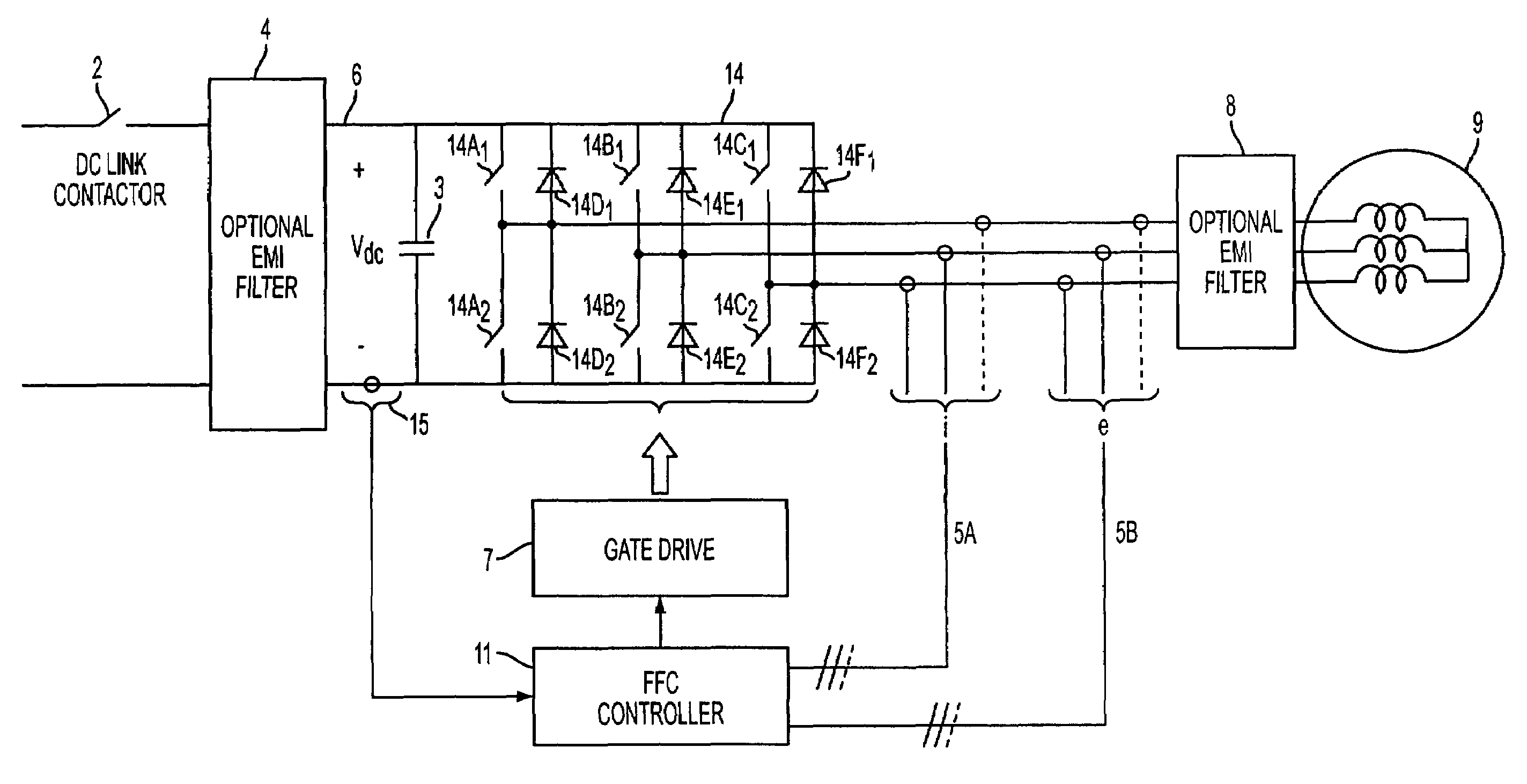
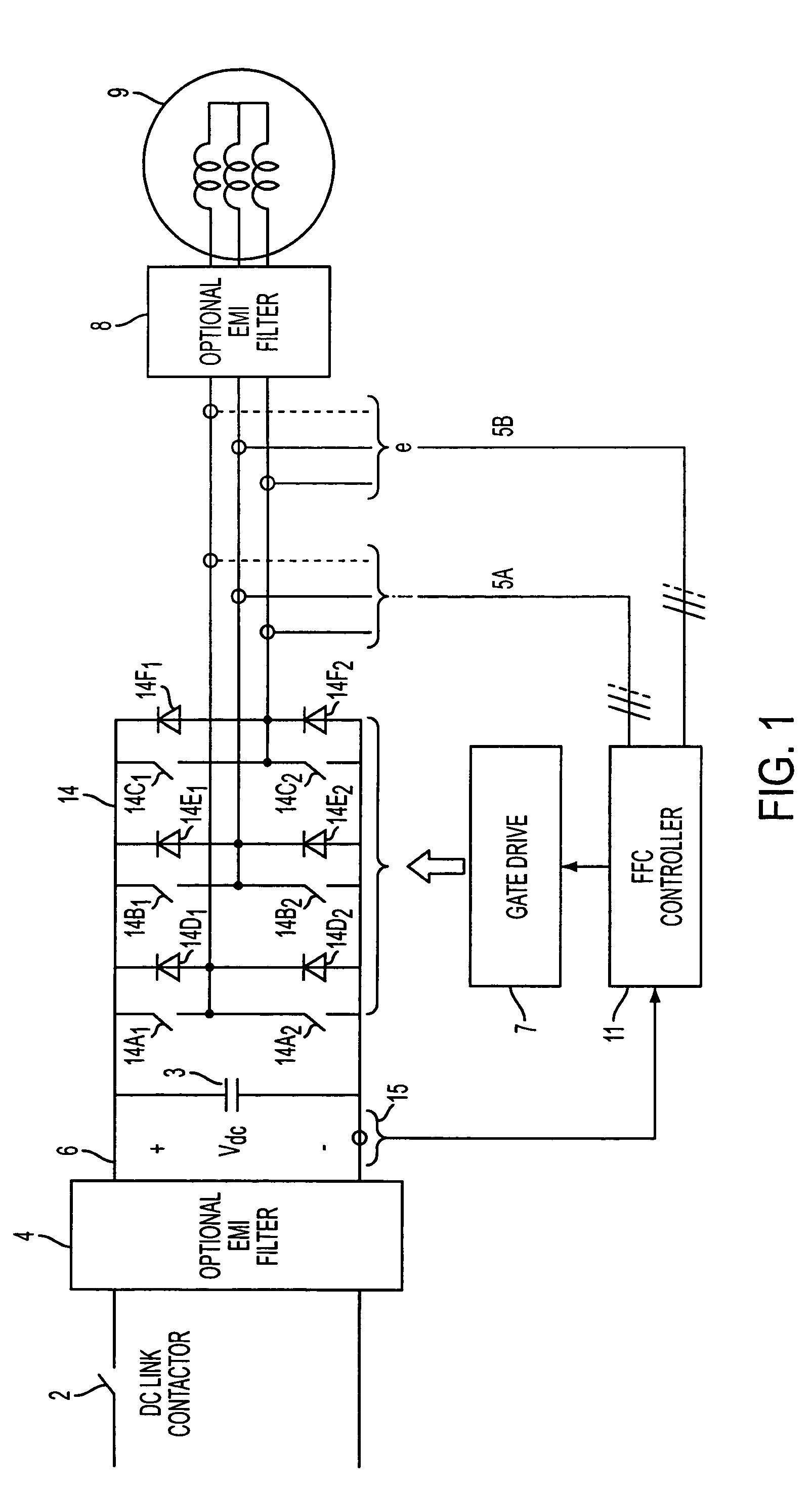
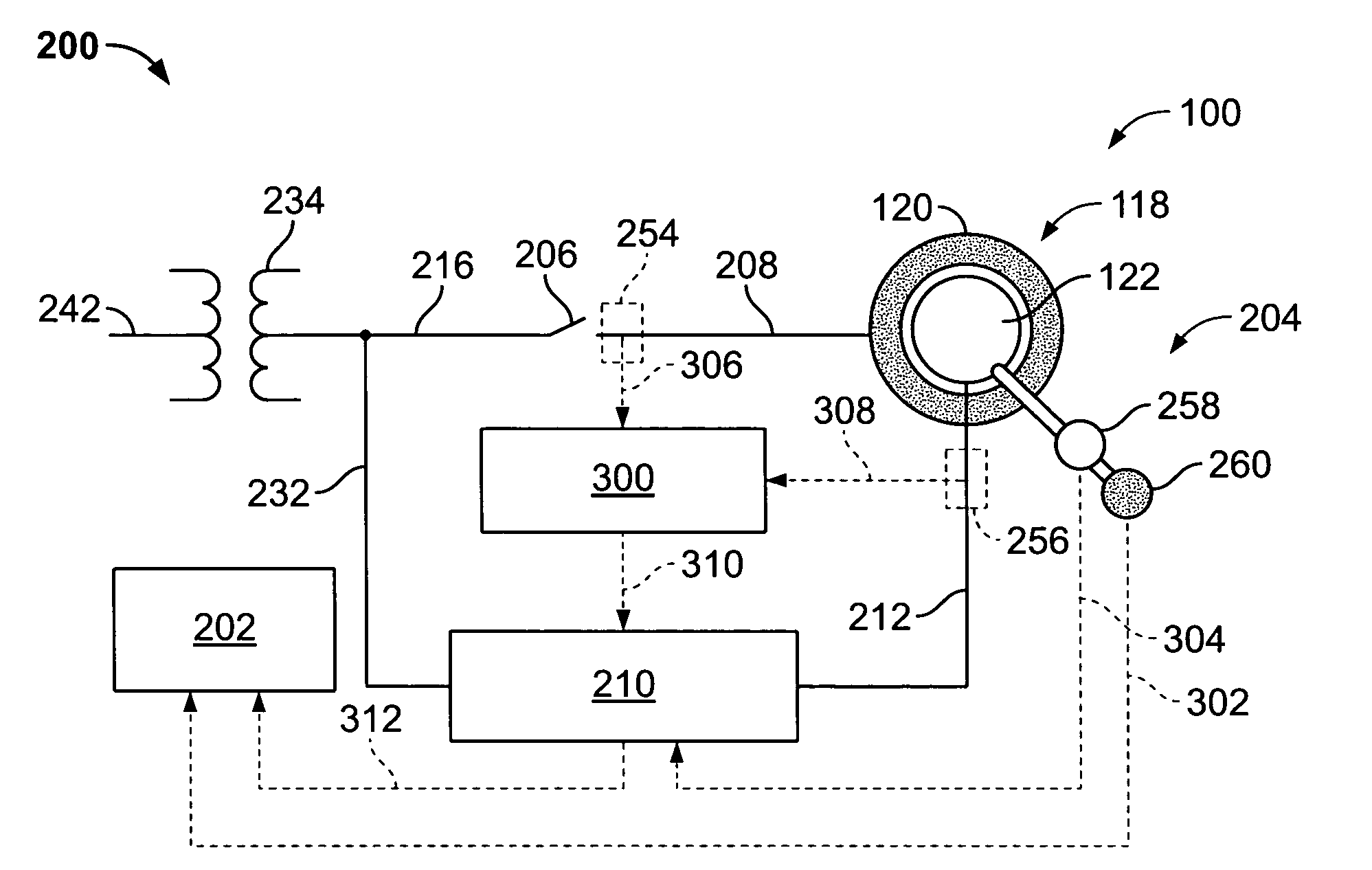
Pole-slip protection system and method for synchronous machines
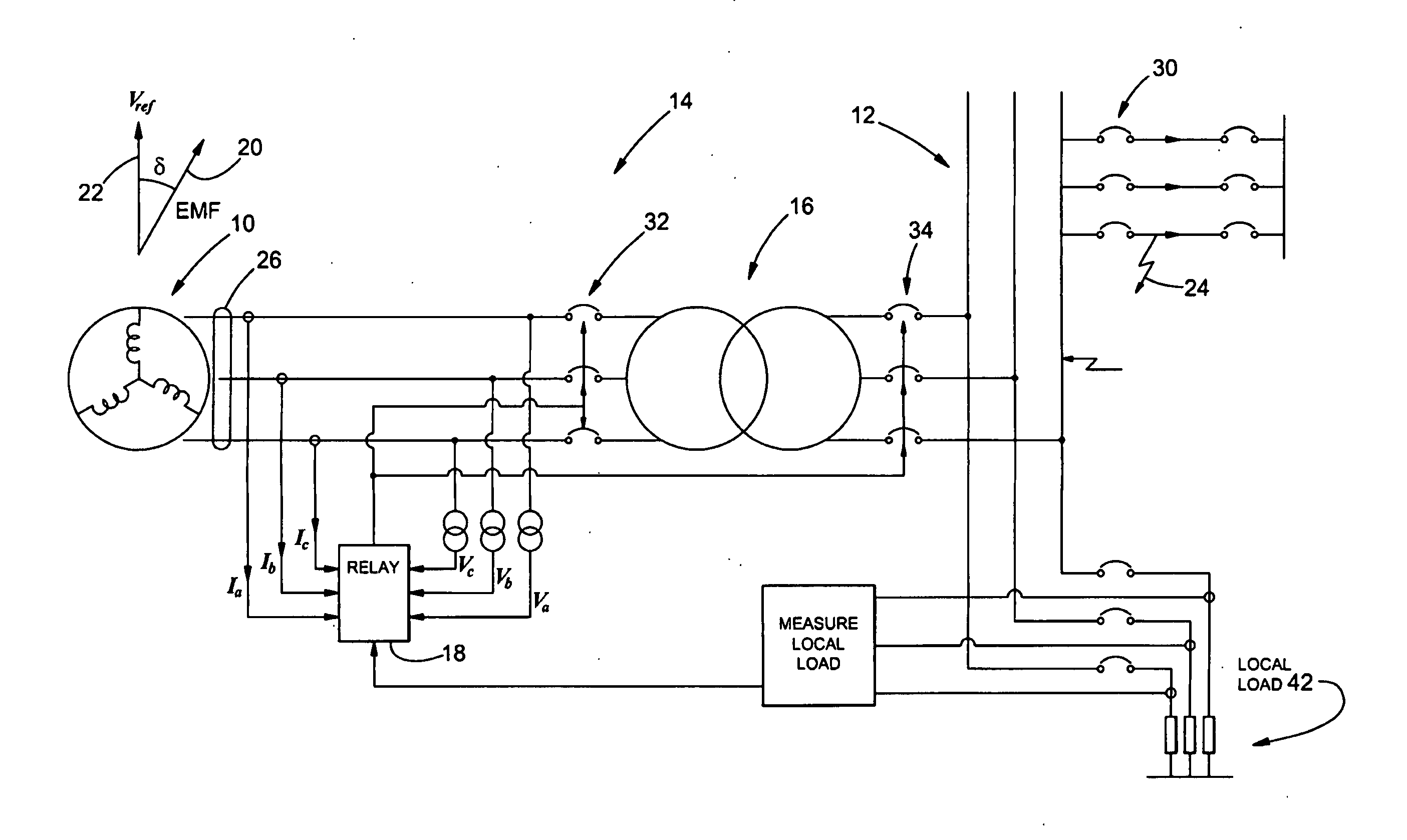
ActiveUS20130176648A1Reduce disadvantagesAC motor controlGenerator circuit arrangements controlElectricityPower grid
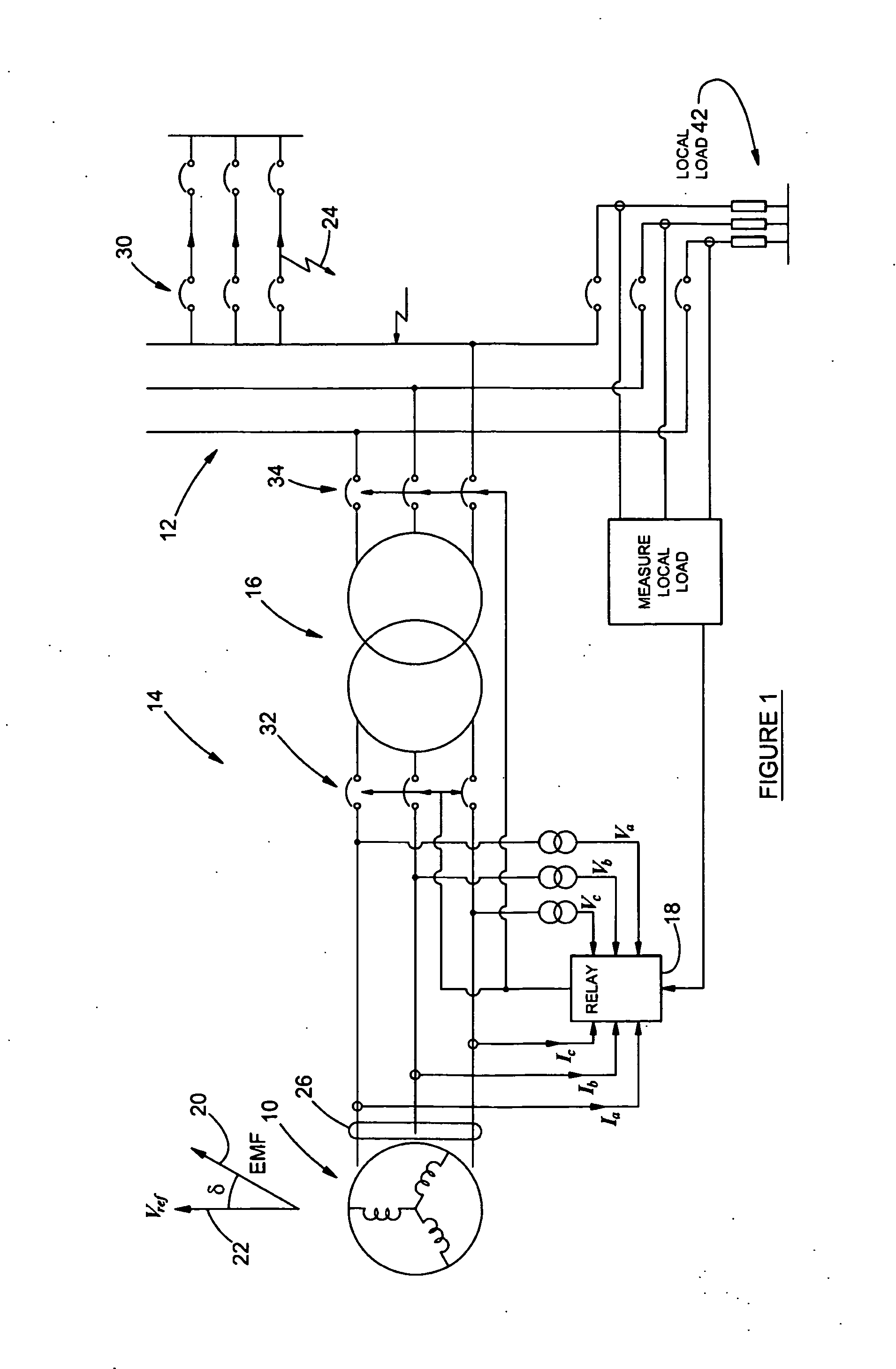
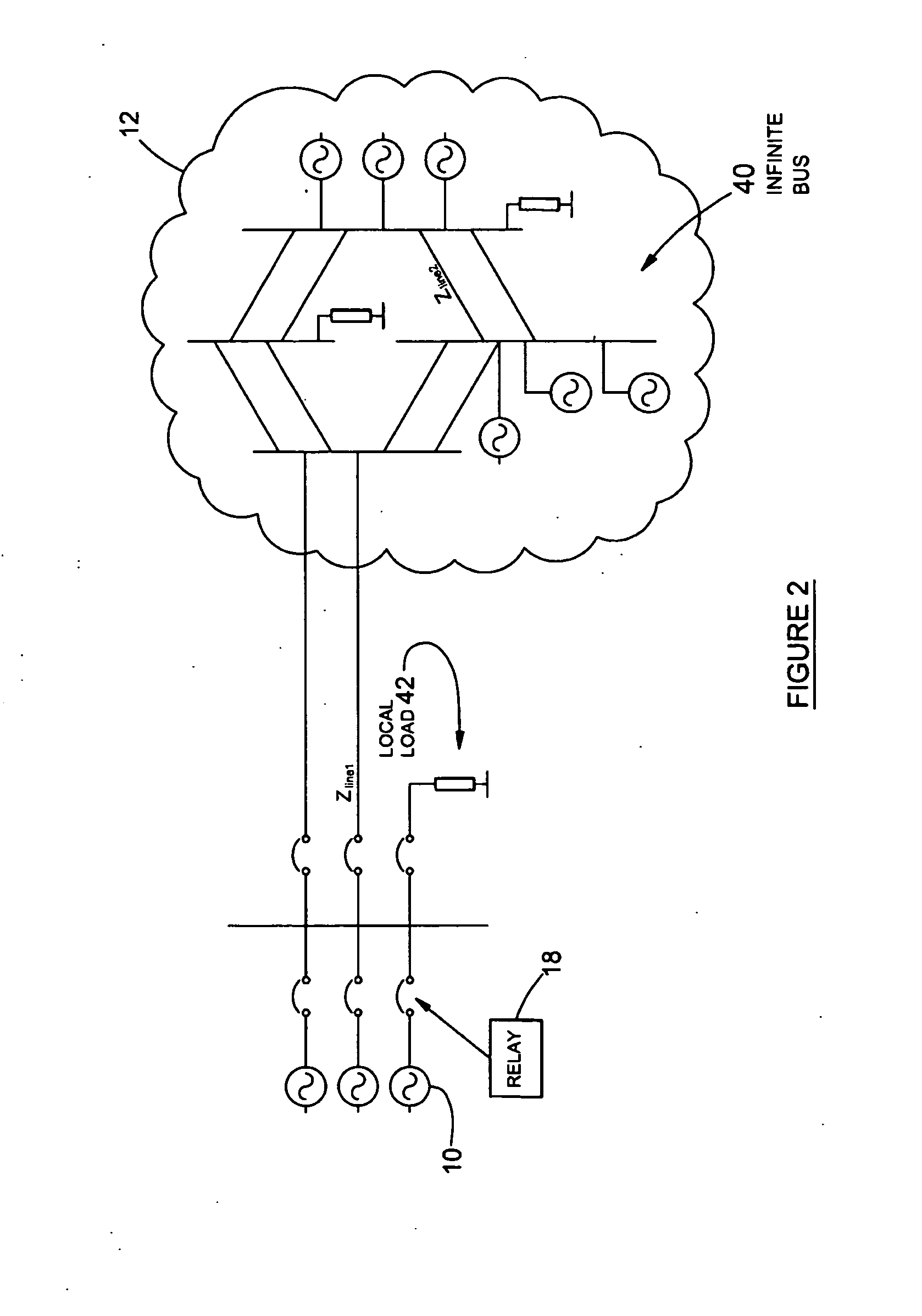
A method of protecting a synchronous machine (10) connected to an electricity network (12) against pole-slip comprises the steps of continuously monitoring a power transfer angle (δ) between an electromotive force (EMF) of the machine and a reference voltage Vref. In the event of a fault (24) on the electricity network which may result in pole-slip of the machine (10), deriving a representation of power transfer (P) relating to the machine against the power transfer angle (δ) utilizing data relating to a value of a current or a voltage measured on a terminal (26) of the machine before the fault has occurred and computed data relating to an expected future value of a current or voltage on the terminal (26), after the fault has occurred. The method then utilizes the representation and a stability criterion to predict whether the machine (10) may become unstable and if instability is predicted, causes the machine (10) to be disconnected at 32 or 34 from the electricity network (12).
Owner:NORTH WEST UNIV (ZA)
Power generating system and its control method
InactiveUS20060119105A1Fast transient response characteristicStable micro adjustmentGenerator circuit arrangements controlVector control systemsPower controllerEngineering
A power controller 5 calculates the induced voltage or rotor magnetic flux from the output voltage and the output current of a generator 3, estimates a shaft speed of the generator 3 from the phase of the induced voltage or the phase of the rotor magnetic flux, and calculate the output of a windmill 1 from the estimated value of the shaft speed and the output of the generator 3. As a result, since the output of the windmill 1 can be calculated without requiring a speed sensor for detecting the shaft speed of the generator 3, it is possible to accomplish simplification of circuits, reduction of cost, and high reliability.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
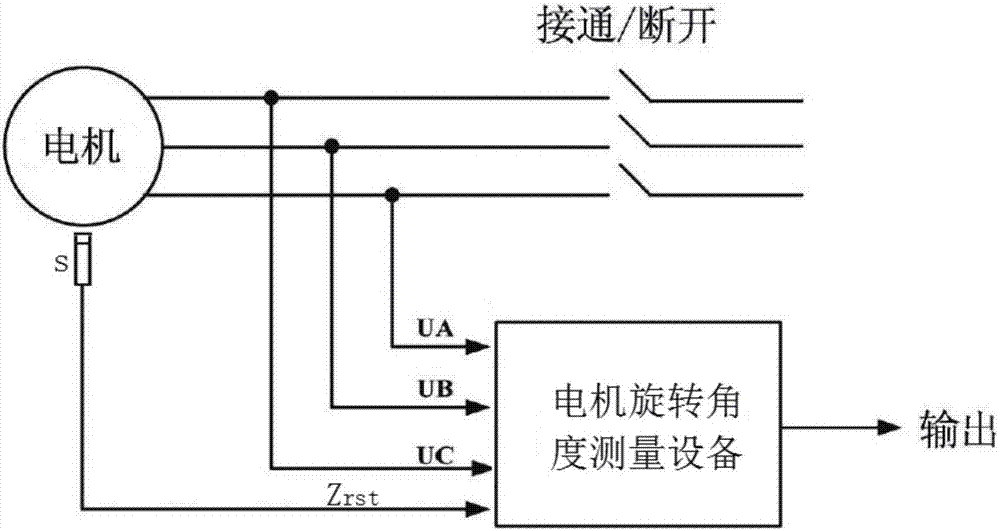
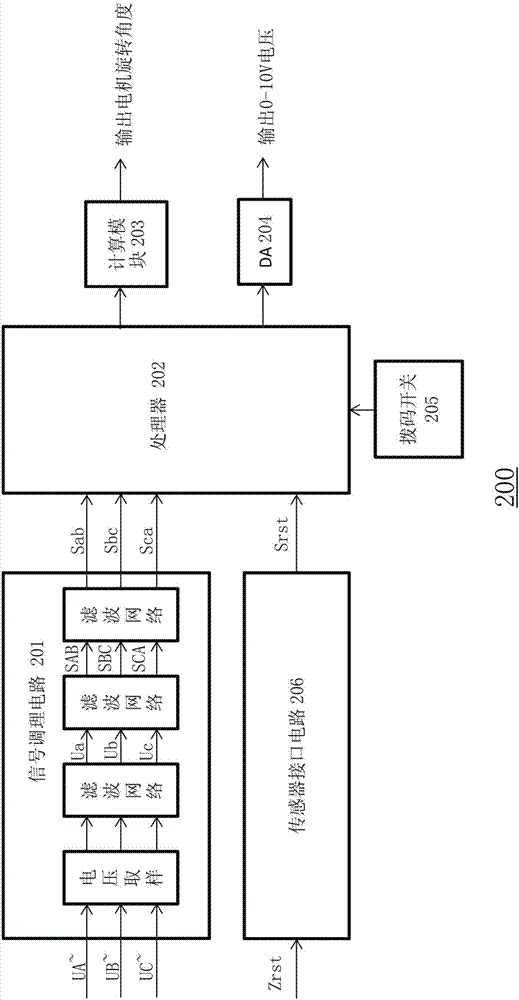
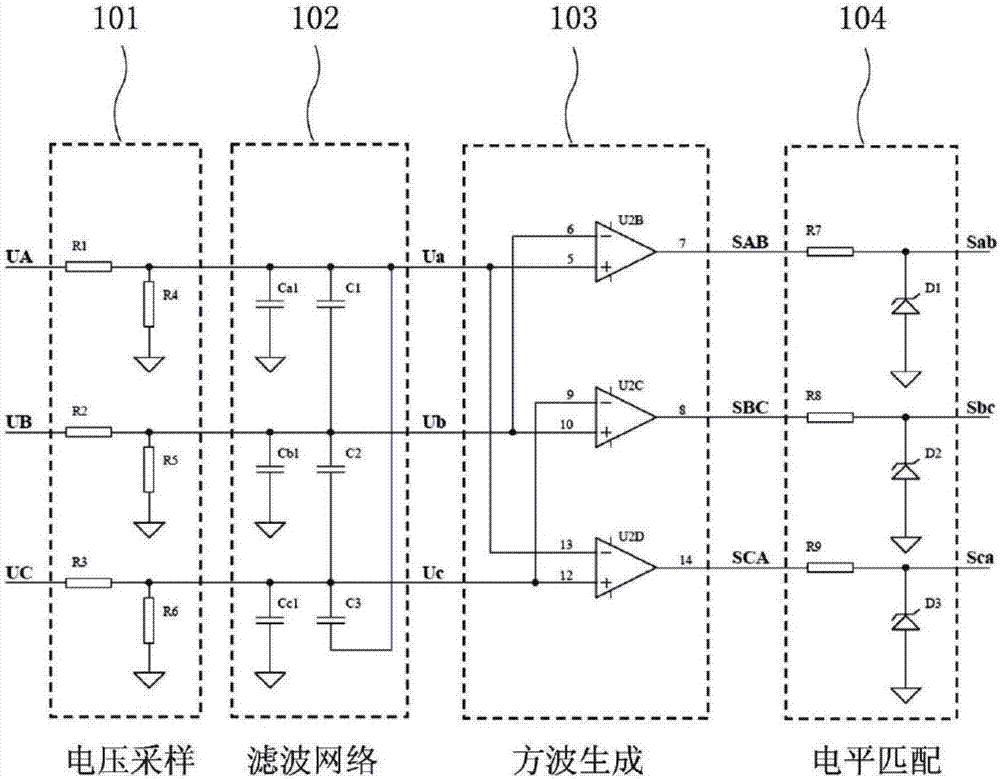
Motor rotation angle measurement device and method
ActiveCN107101607ACannot affect the measurementLifespan cannot be affectedElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlSignal conditioning circuitsMeasurement device
The present invention provides a motor rotation angle measurement device and method. The device comprises: a signal conditioning circuit configured to receive three-phase output voltage of a motor and generate first square wave signals, second square wave signals and third square wave signals; and a processor used in one rotation period of the motor and configured to generate one six-multiplying frequency pulse when jumping of any one square wave signal in the first square wave signals, the second square wave signals and the third square wave signals is detected, generate compensation pulse between the current six-multiplying frequency pulse and a next six-multiplying frequency pulse based on the time interval between the current six-multiplying frequency pulse and a previous six-multiplying frequency pulse and a preset compensation subdivision coefficient k, and accumulate the number of the compensation pulse, wherein the number of the compensation pulse is correlated to the rotation angle of the motor. The motor rotation angle measurement device can improve the precision, the reliability and the stability of the rotation angle measurement of the motor and reduce the cost.
Owner:XINJIANG GOLDWIND SCI & TECH
An electric machine
InactiveCN102210082AReduced magnetic interferenceLow powerGenerator circuit arrangements controlLinear motor controlStatorMagnet
Owner:钱蒂 森格钱
Permanent magnet starter-generator position detection system based on auxiliary winding, and a method
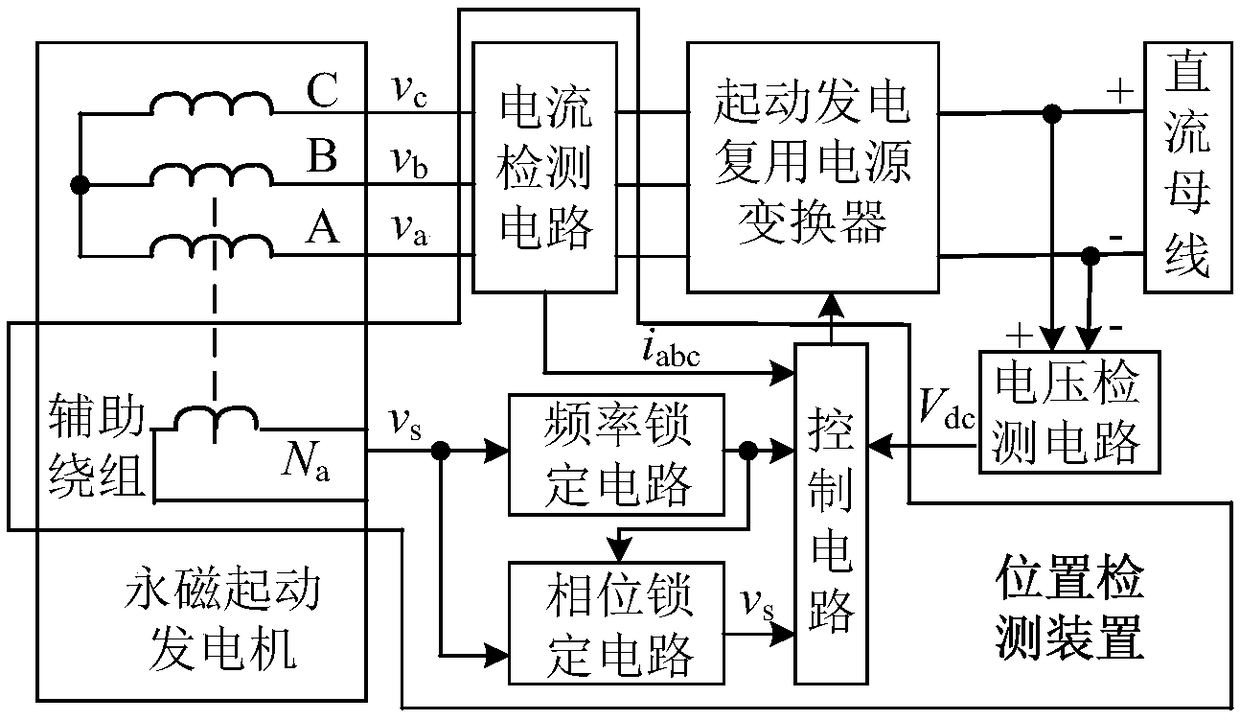
PendingCN108649842ASatisfy the requirement of fast response of controlAvoid software operationsGenerator circuit arrangements controlMotor parameters estimation/adaptationPhase lockingMagnet
The invention provides a permanent magnet starter-generator position detection system, and a method. The permanent magnet starter-generator position detection system comprises a current detection circuit, an auxiliary winding, a frequency locking circuit, a phase locking circuit and a control circuit. By adding an auxiliary position sensor and constructing a simulation circuit, the deviation between a phase lock signal of the auxiliary winding and a motor position reference signal under different working modes, rotational speeds and current amplitudes of a starter-generator multiplexed power converter is calibrated. During normal operation, the auxiliary position sensor is removed, and the control circuit compensates the phase locking signal by calibrating the obtained position deviation according to the working mode, the rotational speed and the magnitude of the current of the starter-generator multiplexed power converter, so as to obtain the position information of the permanent magnet starter-generator.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE LINQUAN MOTOR CO LTD
Power supply device
ActiveUS20120074897A1Circuit monitoring/indicationGenerator circuit arrangements controlBattery chargeEngineering
A power supply device capable of switching over semiconductor switches of a synchronous rectification means so as to efficiently charge up a battery in response to its charging status is provided. The device includes a switch control means for controlling the semiconductor switches in response to the battery charging status; a negative voltage detection means for detecting a negative voltage at each phase of three-phase AC voltages; and a voltage detection means for detecting the battery voltage being higher than a predetermined voltage, wherein when the negative voltage or the battery voltage higher than the predetermined voltage is detected, the switch control means controls the semiconductor switches. The device further includes an abnormality detection means for monitoring the negative voltage detected by the negative voltage detection means and thereby detecting an abnormality in at least one of the three phases, and when an abnormality is detected, the switch control means controls the semiconductor switch corresponding to the phase of the abnormality.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Integrated high-voltage direct current electric power generating system
InactiveUS20130193813A1Synchronous generatorsAc-dc conversion without reversalHigh-voltage direct currentInductor
An integrated high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power generating system (EPGS) comprises a permanent magnet generator (PMG) including a PMG stator and a PMG rotor, wherein the PMG is disposed within a PMG housing. Also included is an armature winding operably connected to the PMG and a first rectifier for converting high-voltage AC from the armature winding, wherein the armature winding is in communication with a first boost inductor, wherein the armature winding, the first rectifier and the first boost inductor are each disposed within the PMG housing. The armature winding is operably connected to a second rectifier for converting high-voltage AC from the armature winding, wherein the armature winding is in communication with a second boost inductor, wherein the armature winding, the second rectifier and the second boost inductor are each disposed within the PMG housing.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Sensing pm electrical machine position
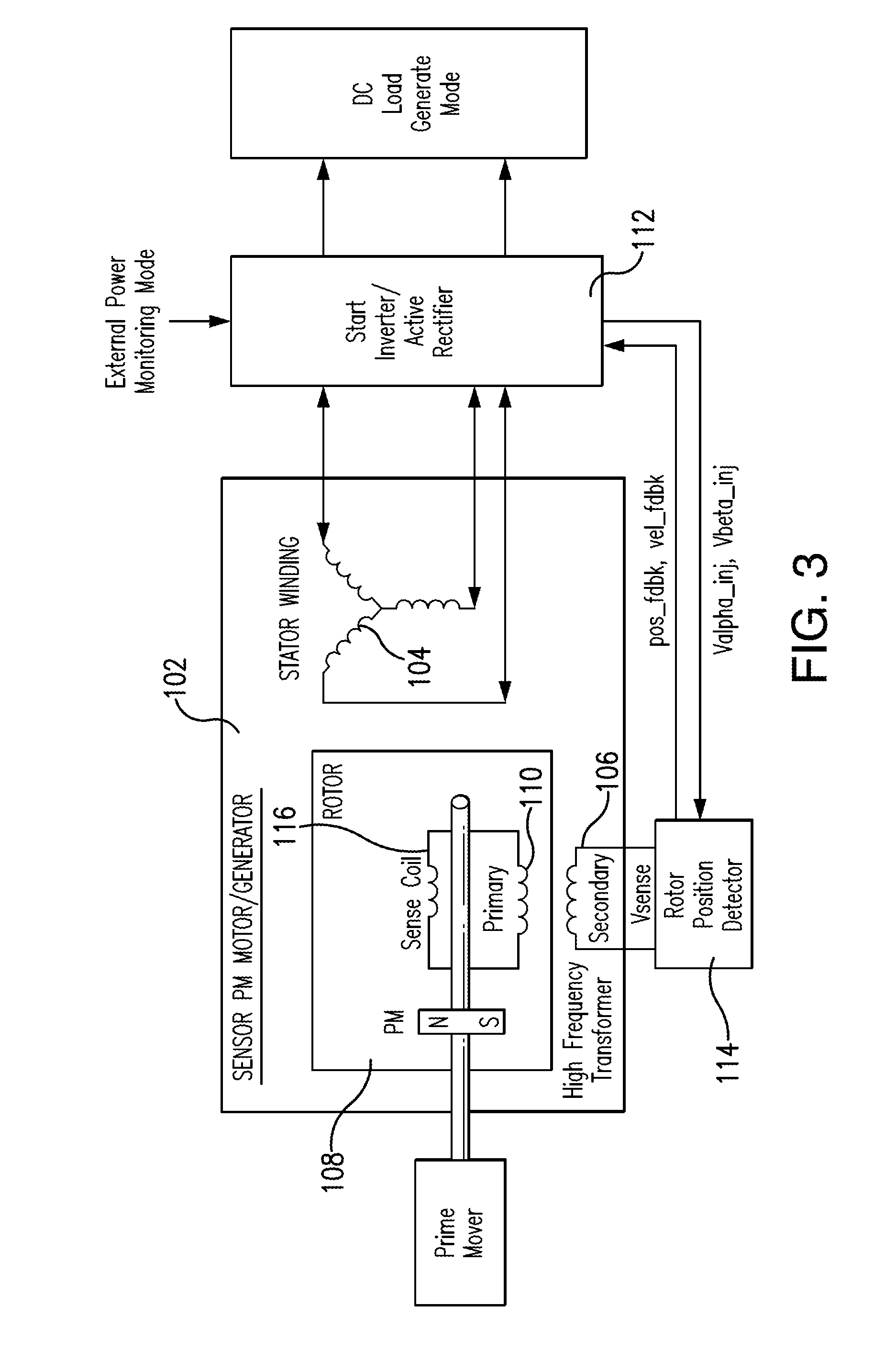
ActiveUS20150035469A1Generator circuit arrangements controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsConductor CoilRectifier
An electrical machine includes a stator having a stator winding and a secondary transformer coil. A rotor is operatively connected to rotate relative to the stator, wherein the rotor includes a plurality of embedded permanent magnets. A primary transformer coil is wound on the rotor and is operatively connected to form a rotating transformer with the secondary transformer coil. An inverter / active rectifier component is operatively connected to the stator winding and the secondary transformer coil to control the stator winding based on a sense in the secondary transformer coil received from the primary transformer coil.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Third-level type motor rotor position estimation method for salient pole characteristic change
ActiveCN105871276AEstimated realizationGenerator circuit arrangements controlSynchronous generator controlEstimation methodsElectric machine
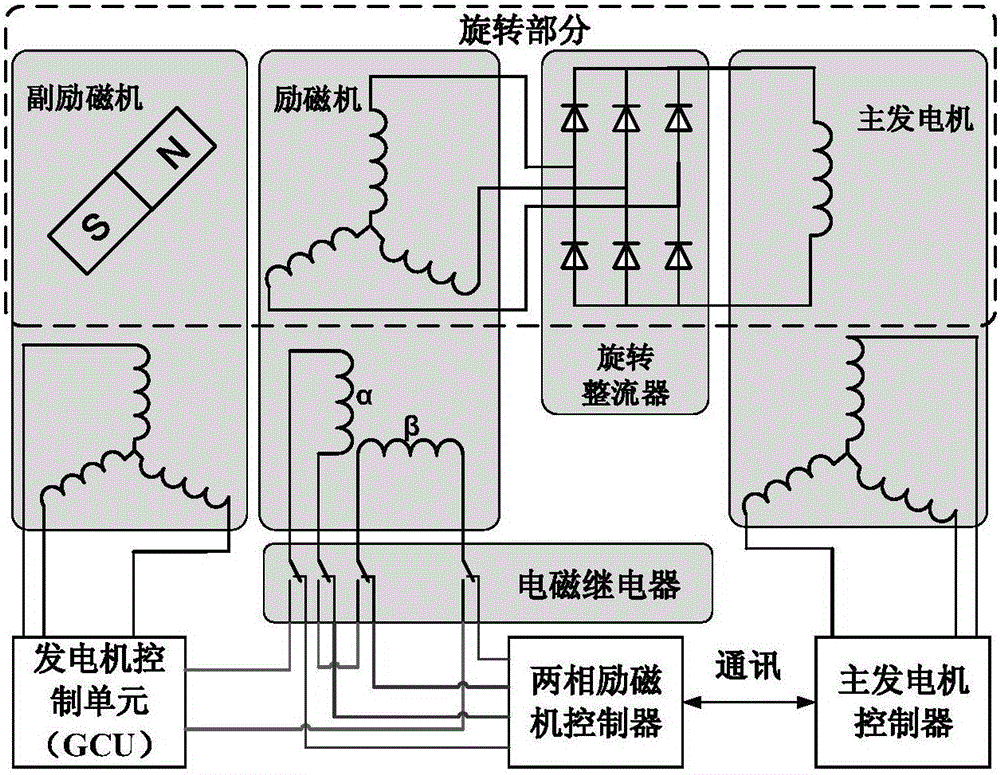
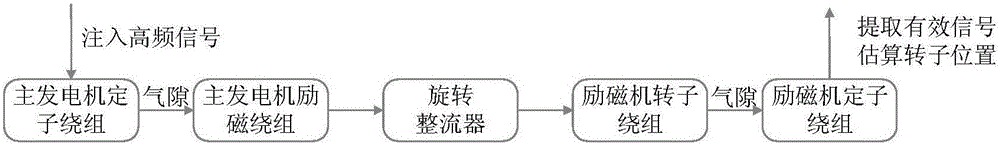
The invention relates to a third-level type motor rotor position estimation method for salient pole characteristic change. Targeted to characteristics of a third-level type motor multi-level combination structure, a new signal transfer and detection channel is established between a main generator and an exciter and is shown as the graph 2; high-frequency signals are injected on the stator side of the main generator through the signal transfer channel, the signals sequentially pass through a main generator air-gap magnetic field, a rotating rectifier and an exciter air-gap magnetic field, then high-frequency response signals are extracted out of an exciter stator winding, and estimation of the position of a motor rotor is achieved. According to the main generator injection-exciter detection signal transfer and detection thought, the characteristic that mutual inductance between the main generator stator winding and the exciter winding changes along with the position of the rotor is fully utilized, and the position of the main generator exciter winding, namely the position of the rotor magnetic pole is estimated. The estimation method does not depend on salient polarity of a motor, and the method is still applicable when the main generator salient polarity changes in the starting process.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Synchronous machine starting device
ActiveUS20110298406A1Smooth startMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlEngineeringElectric power
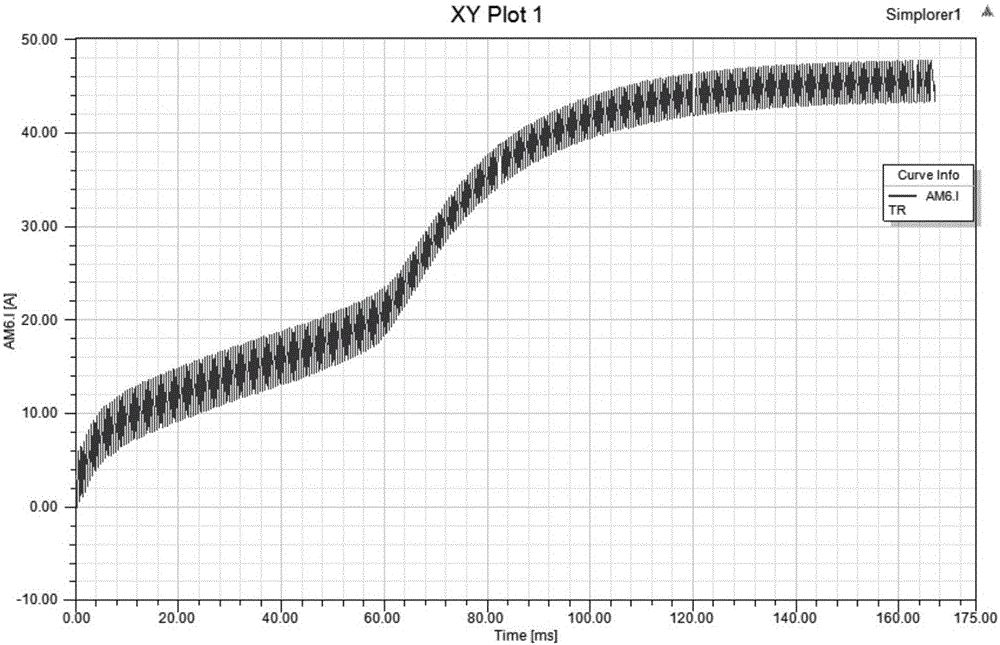
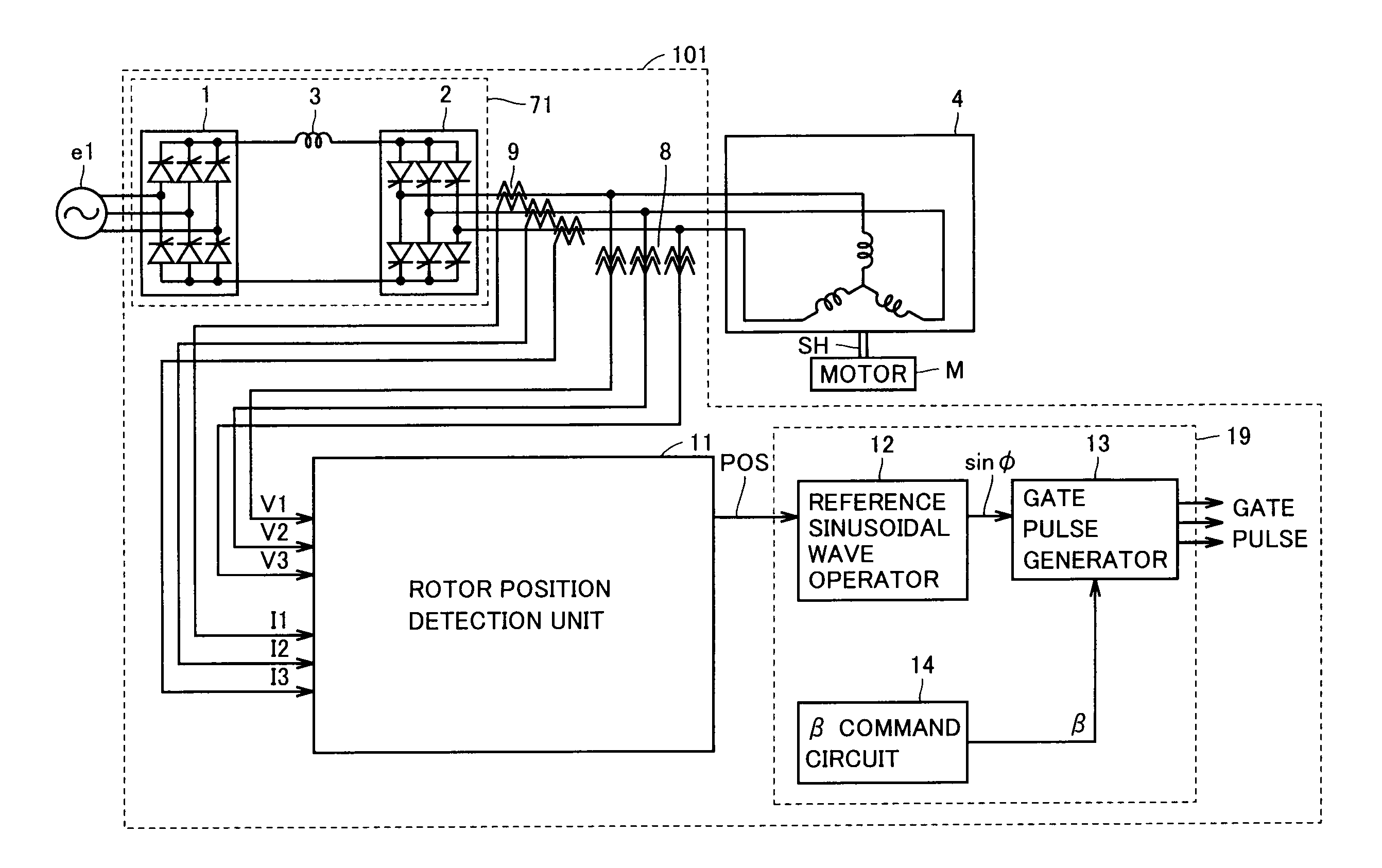
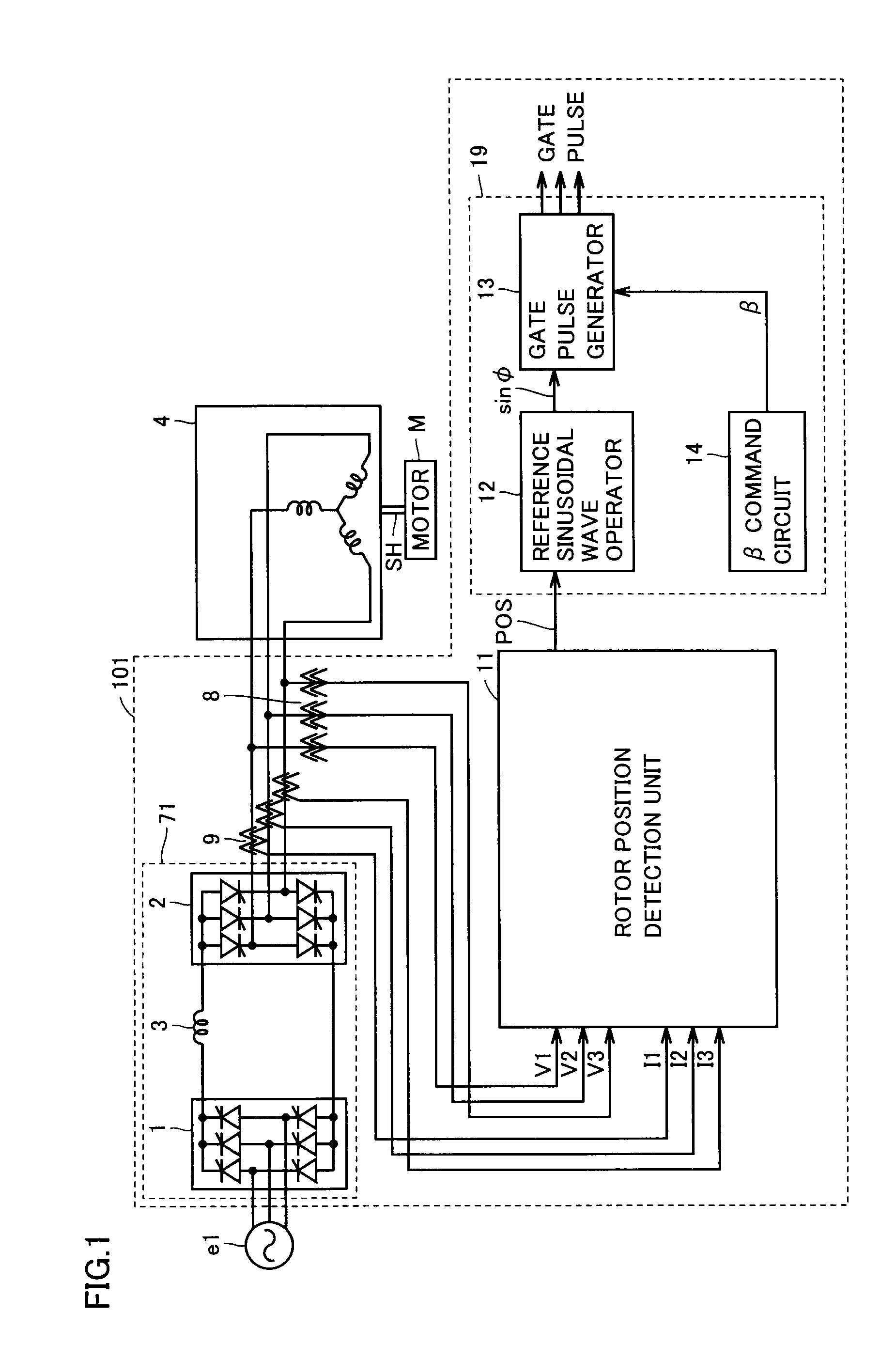
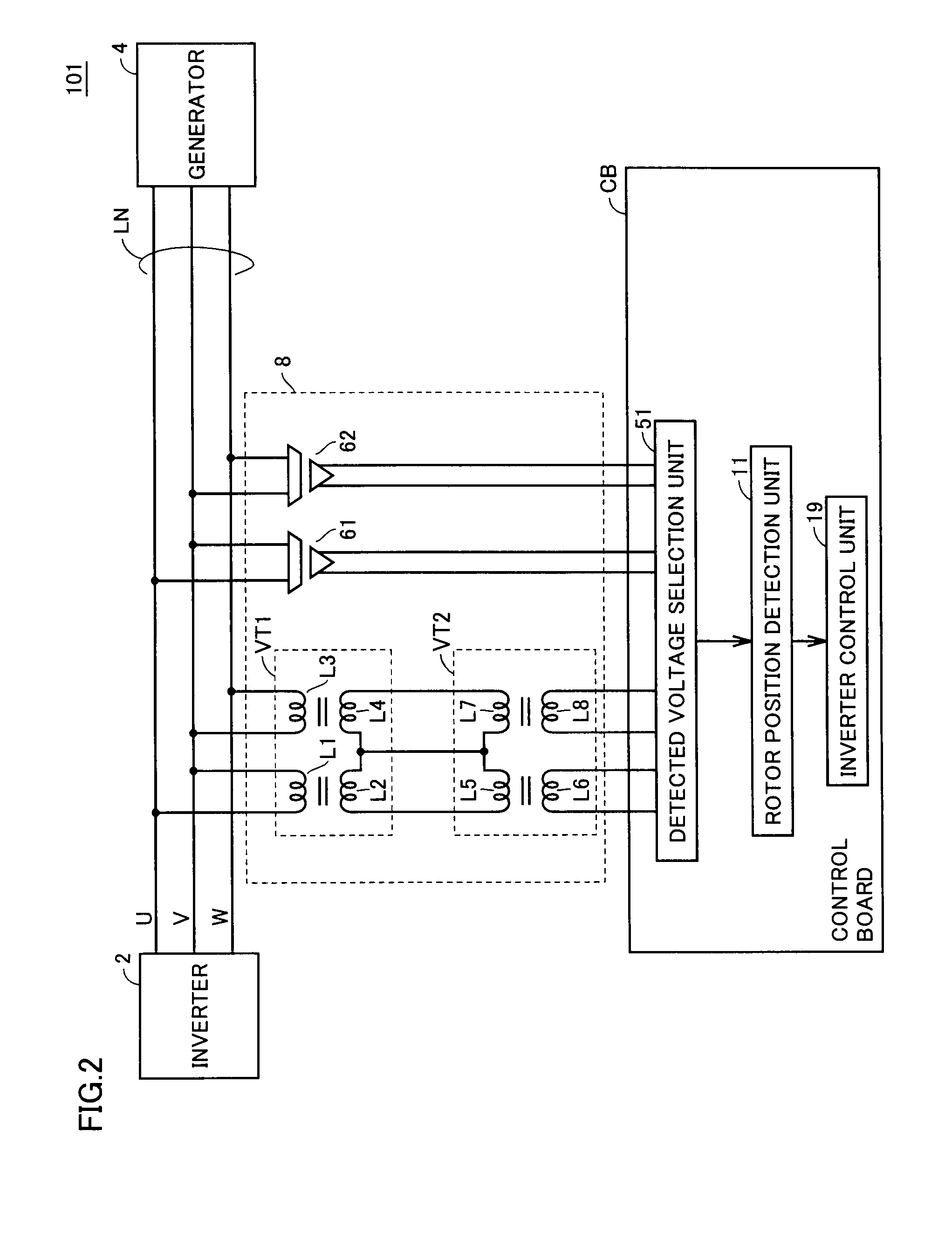
In a synchronous machine starting device, an AC voltage detection unit detects AC voltage supplied to an armature of a synchronous machine through an electric power line from a power conversion unit. The AC voltage detection unit has a first output end and a second output end isolated from the electric power line, transforms AC voltage supplied through the electric power line at a first ratio to output the transformed voltage from the first output end, and transforms AC voltage supplied through the electric power line at a second ratio and then limits the transformed voltage to a prescribed positive voltage value or lower and a prescribed negative voltage value or higher for output from the second output end. Then, a detected voltage selection unit selects one of the voltage received from the first output end and the voltage received from the second output end, and outputs the selected one to a rotor position detection unit. The rotor position detection unit detects a rotor position of the synchronous machine based on the voltage received from the detected voltage selection unit. A power conversion control unit controls the power conversion unit based on the detected rotor position.
Owner:TOSHIBA MITSUBISHI-ELECTRIC IND SYST CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com