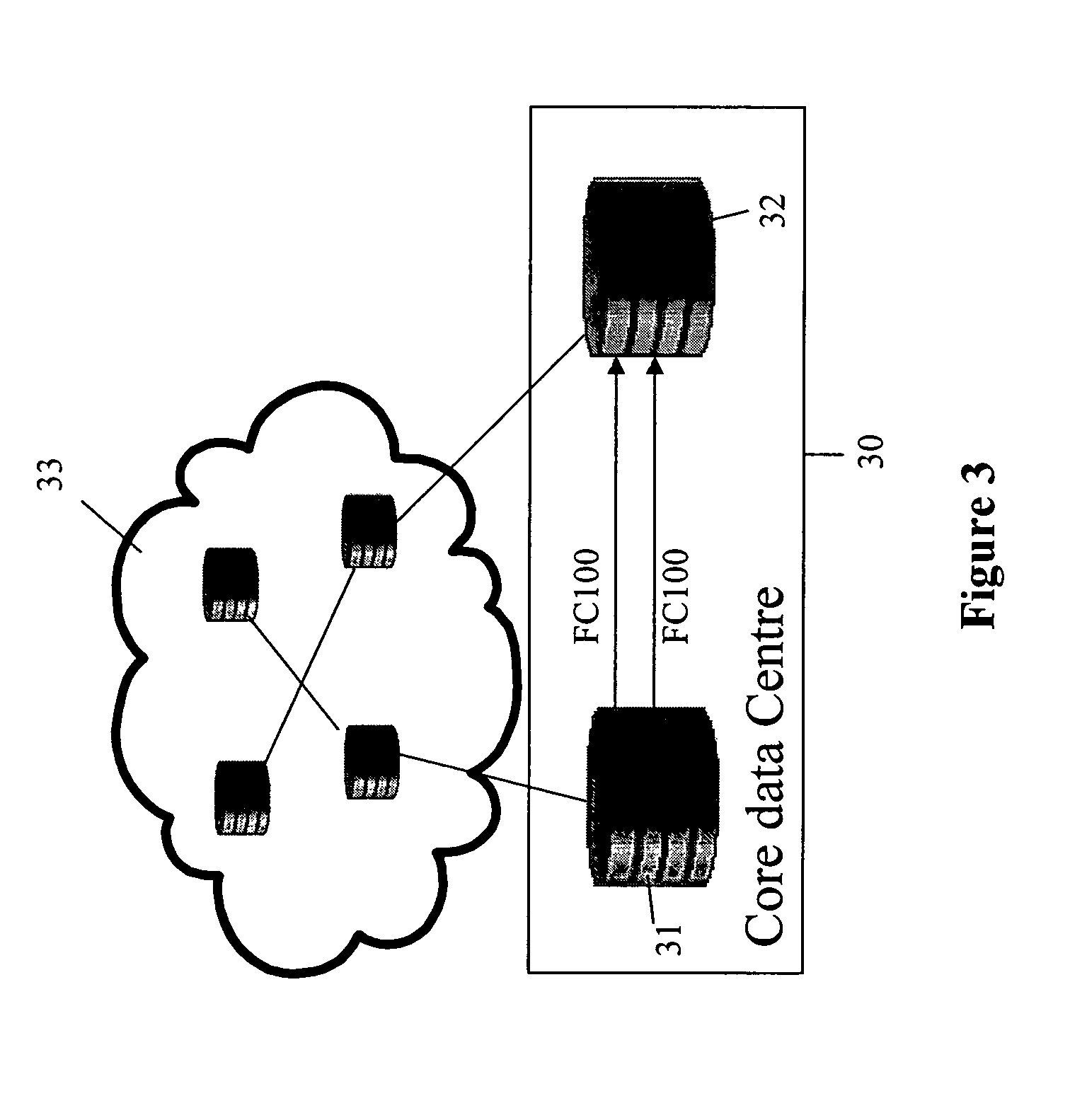
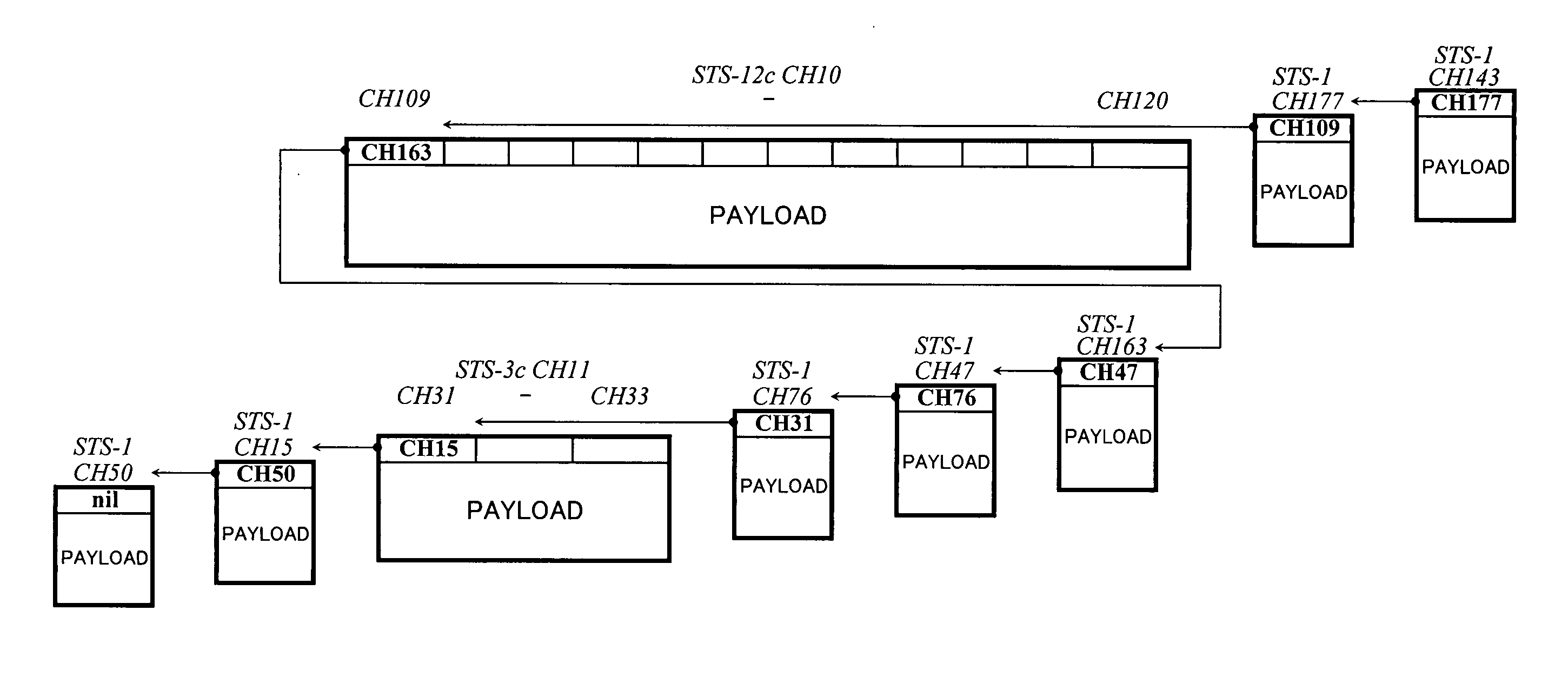
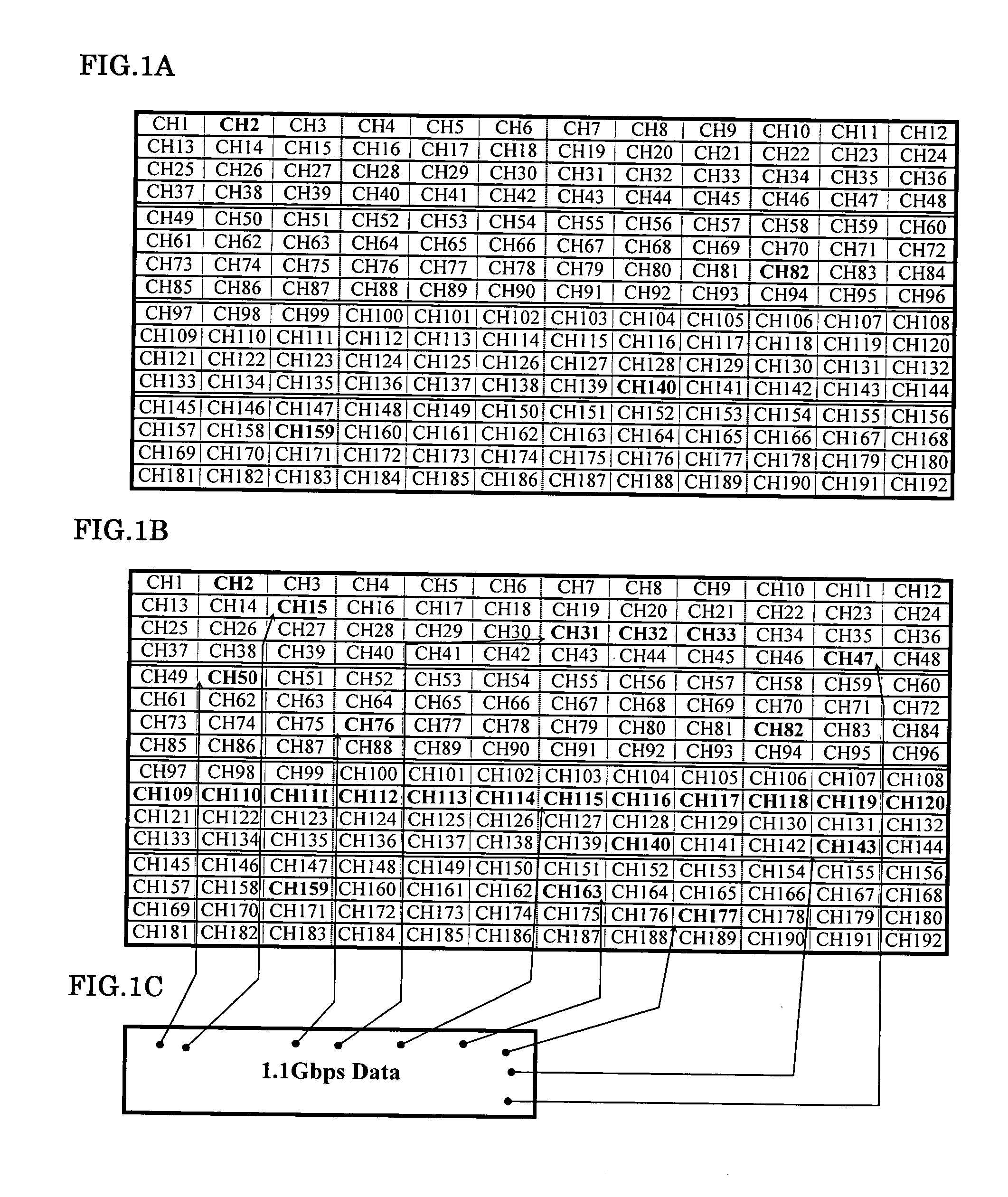
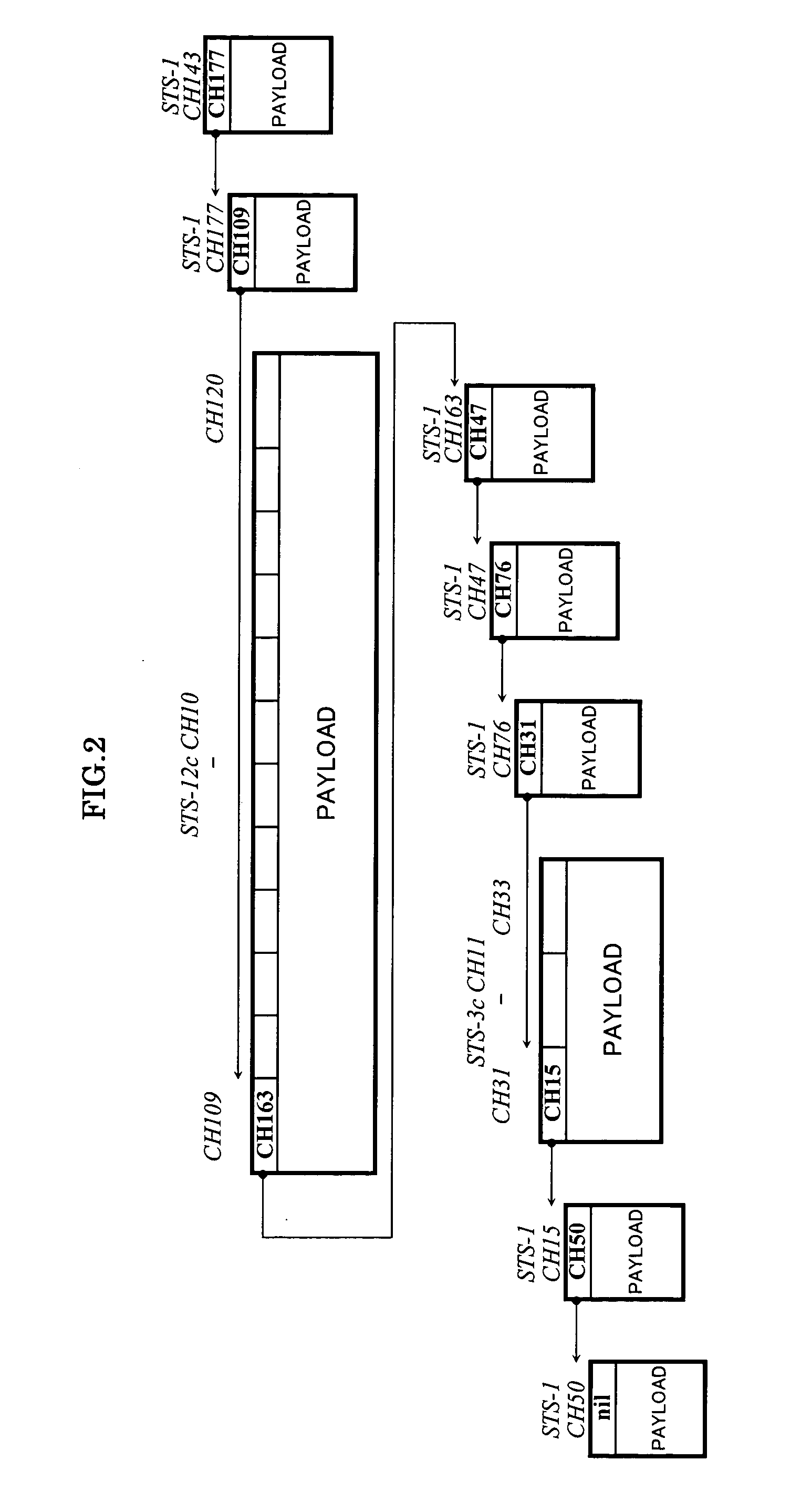
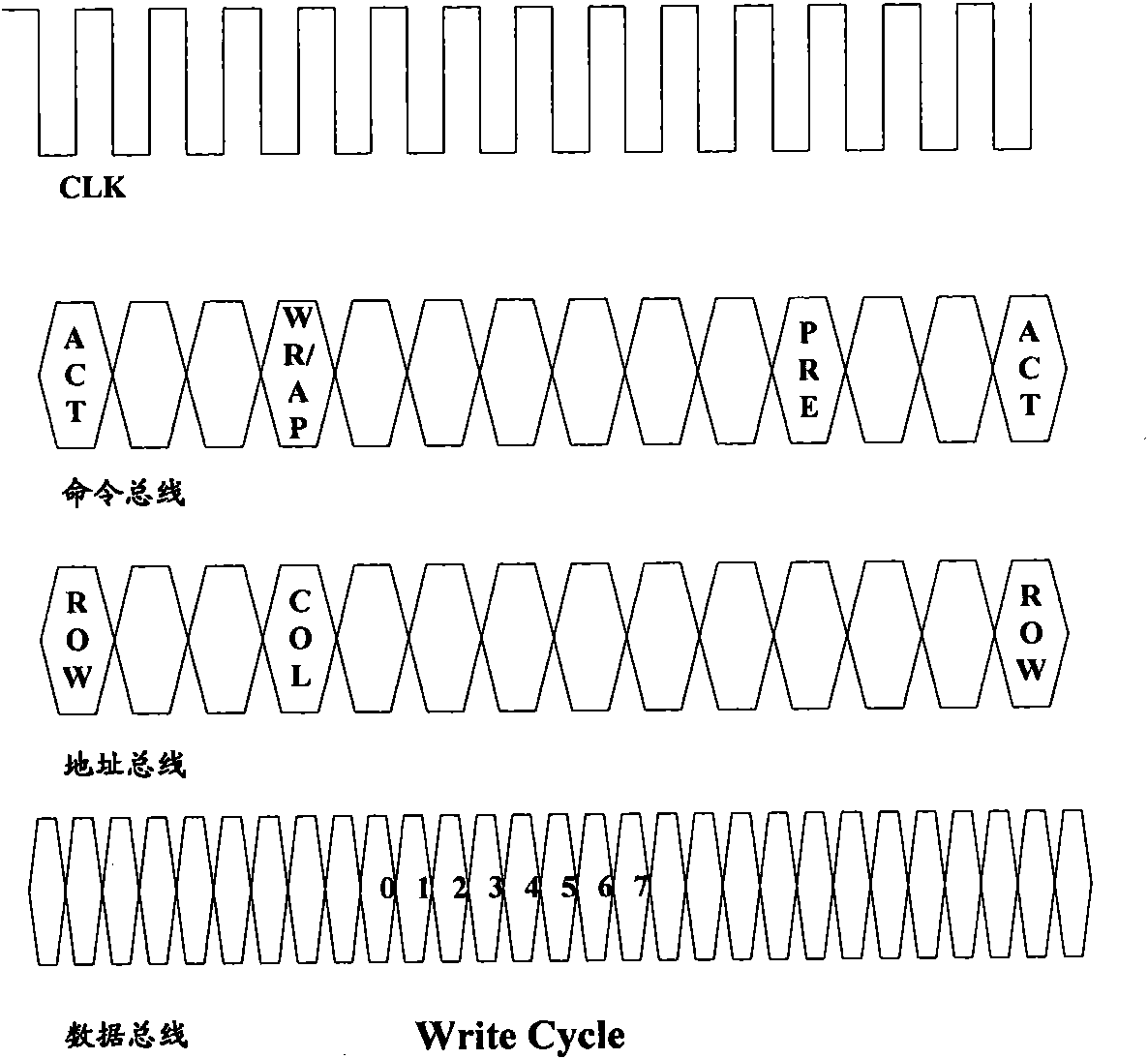
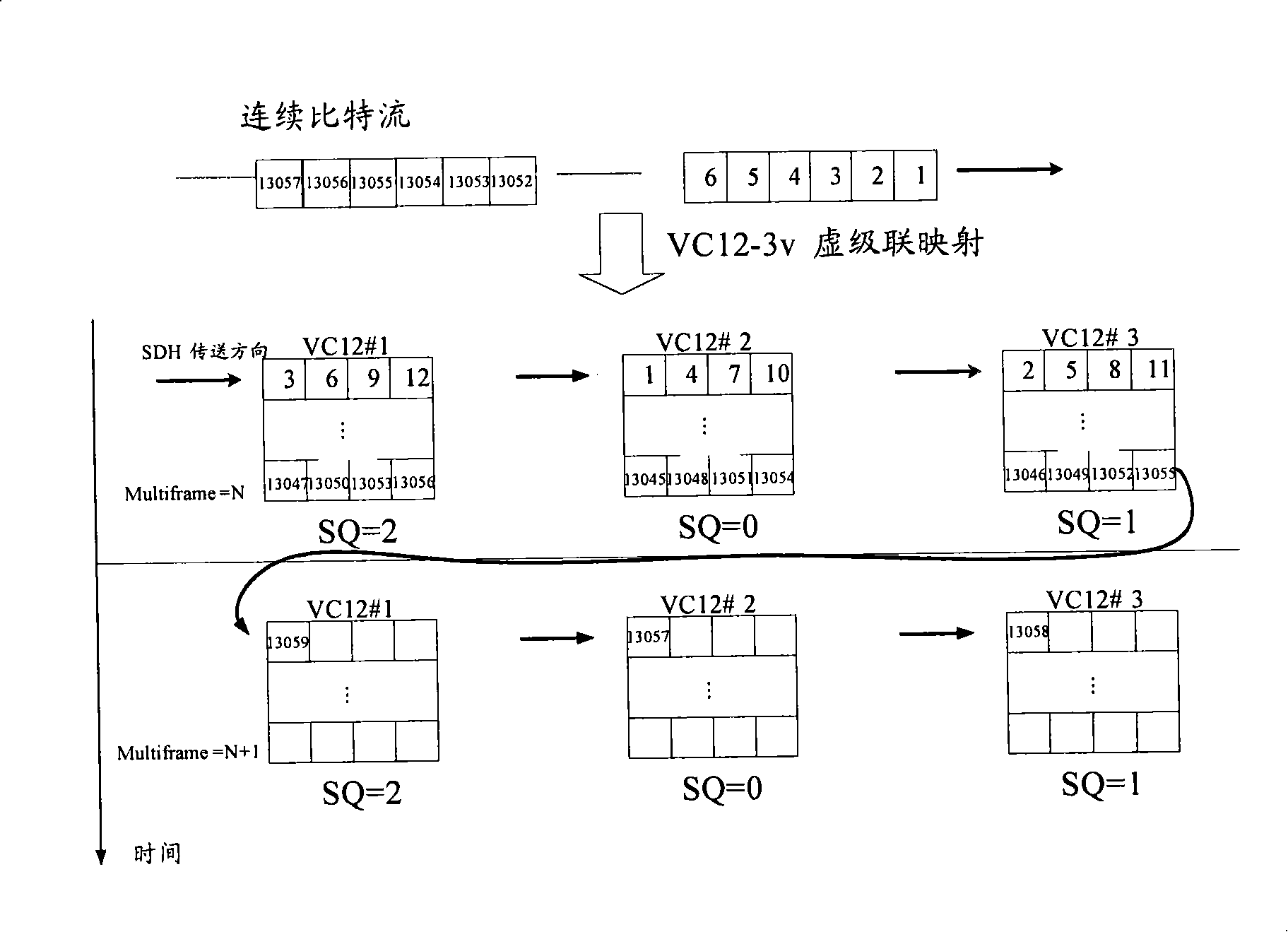
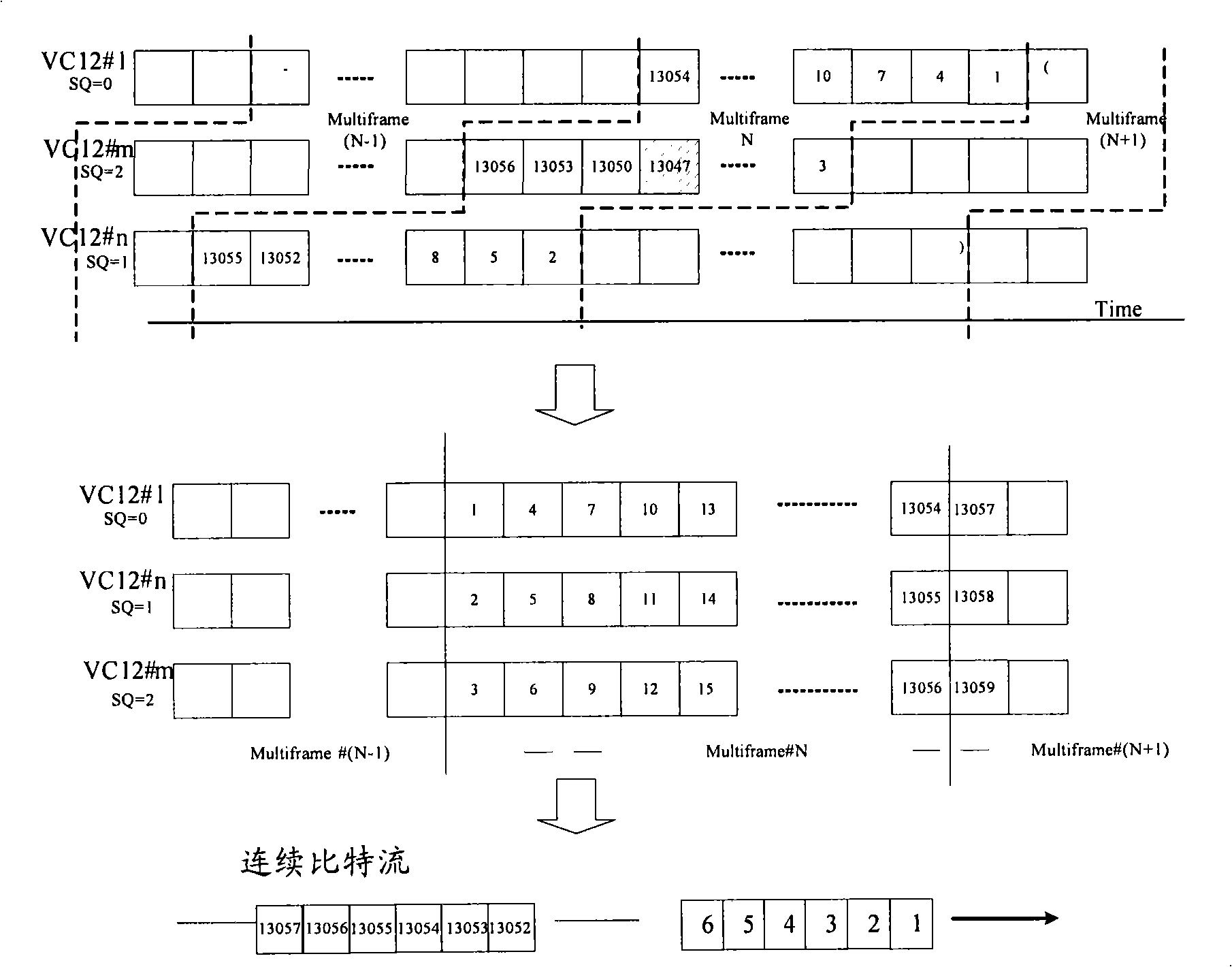
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
123 results about "Virtual concatenation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
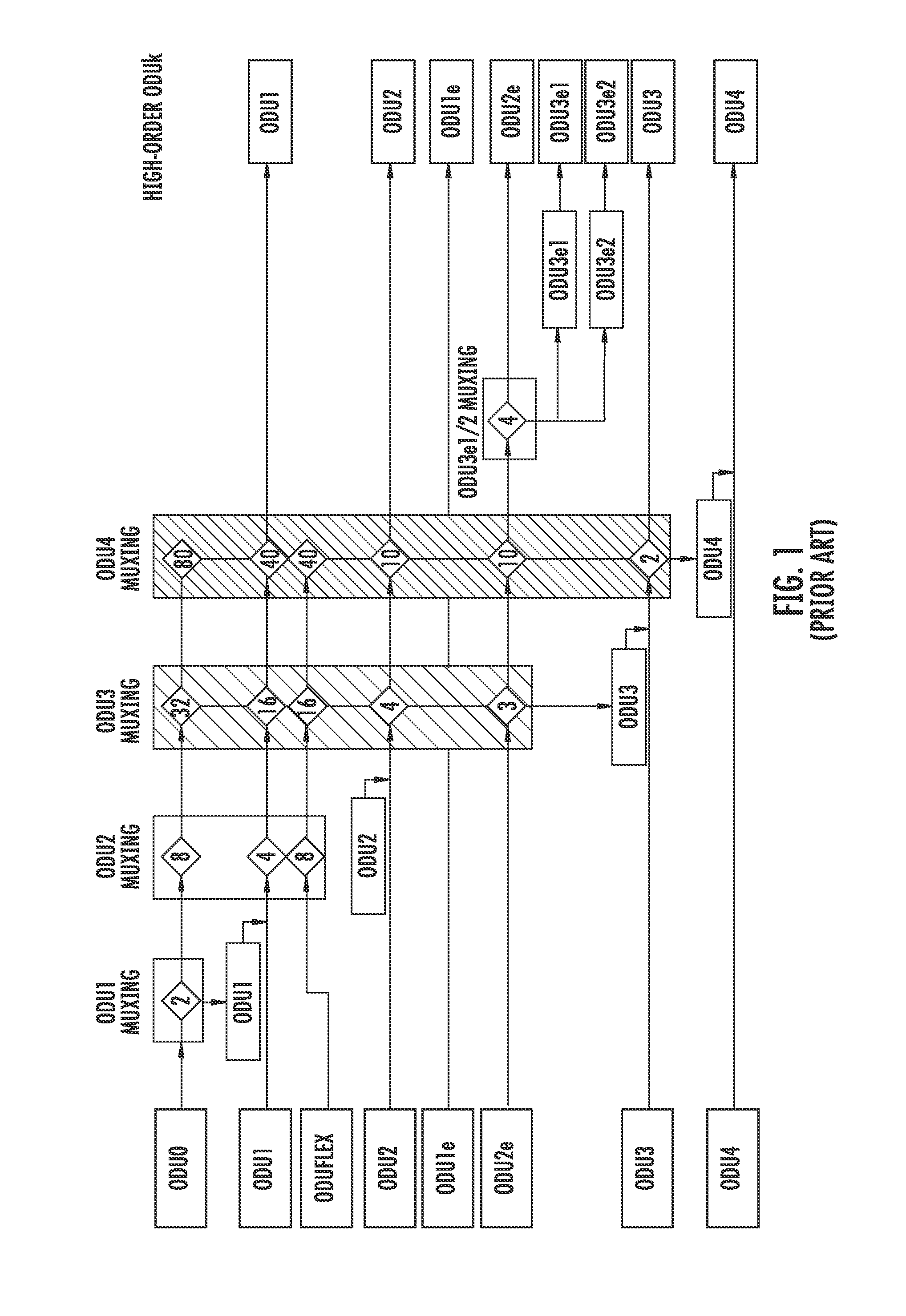
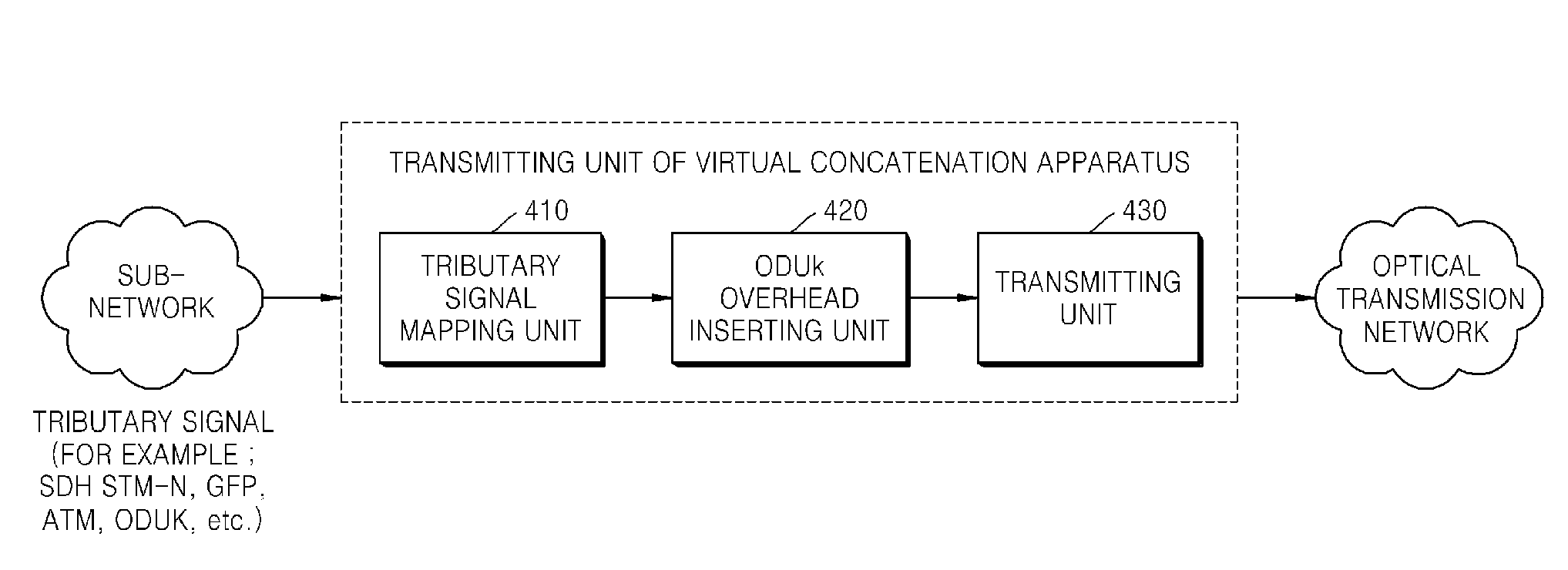
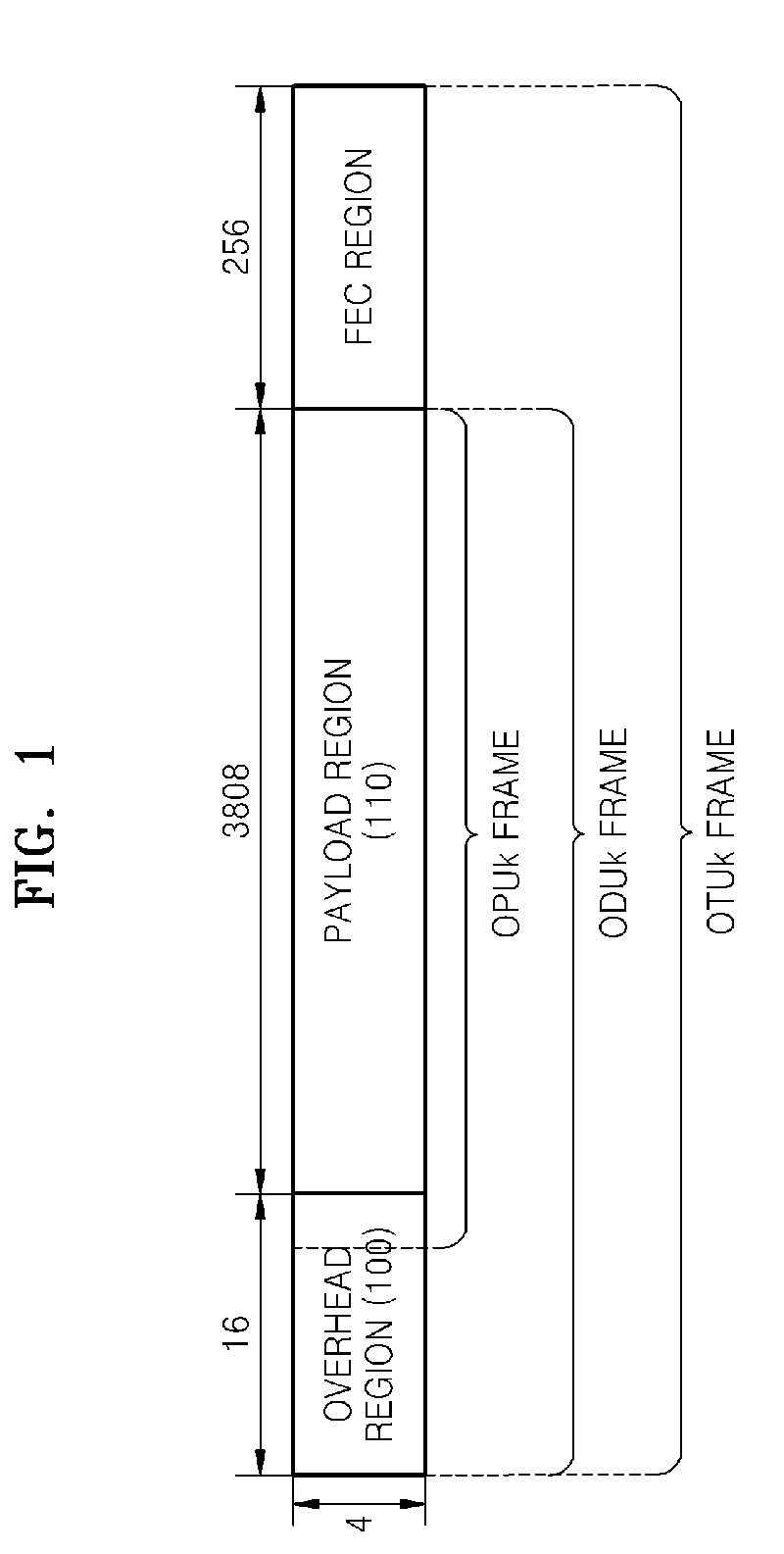
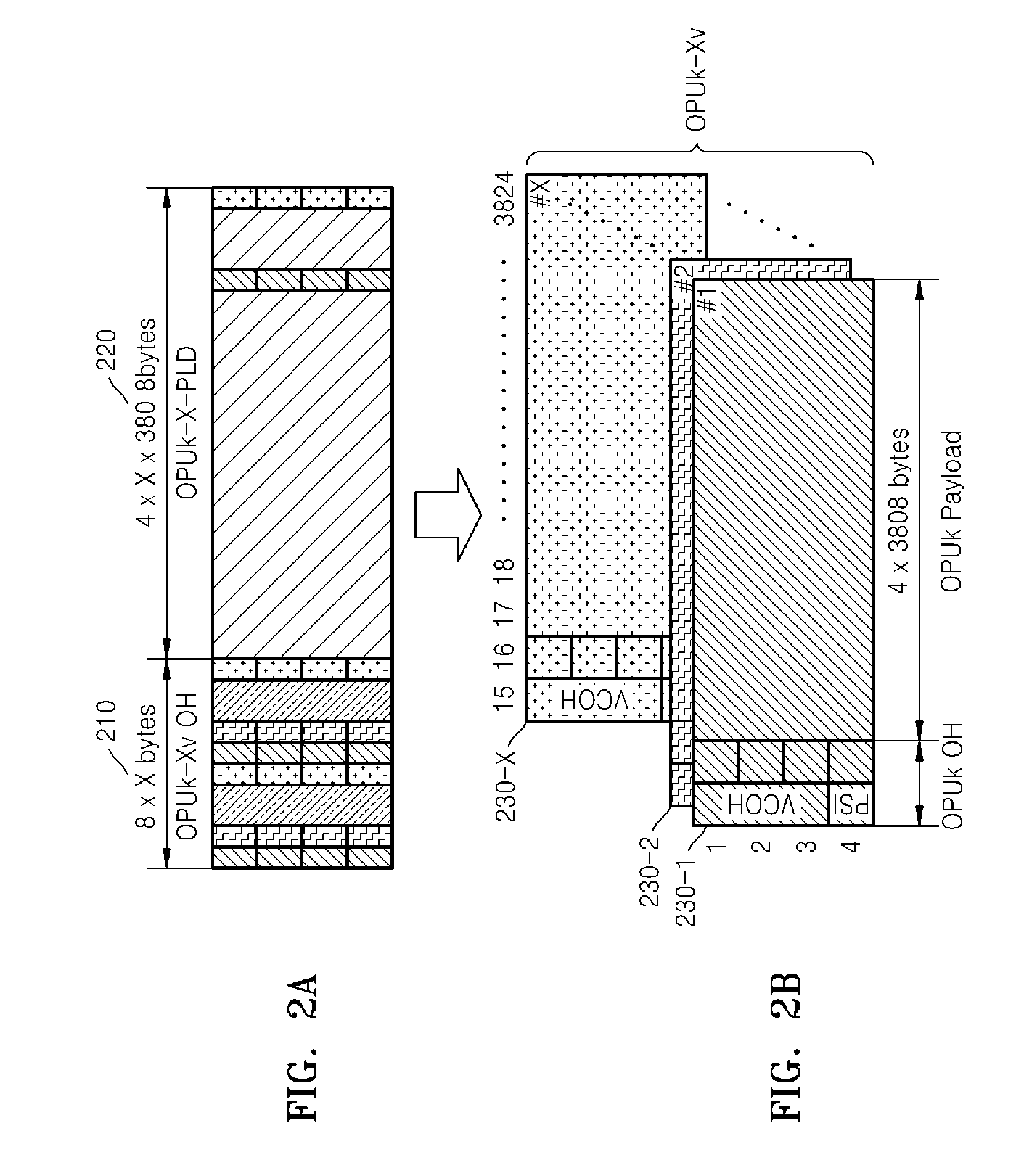
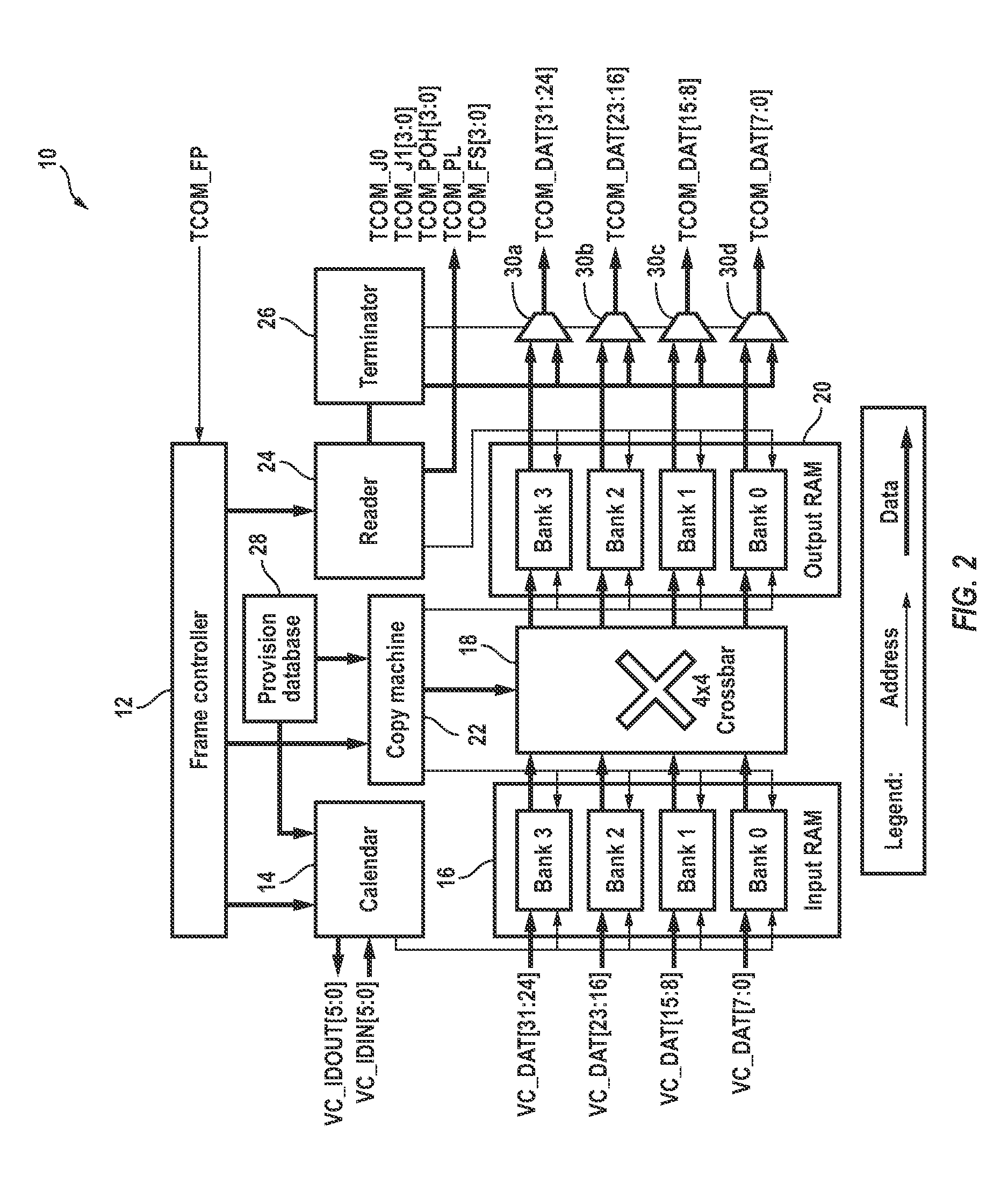
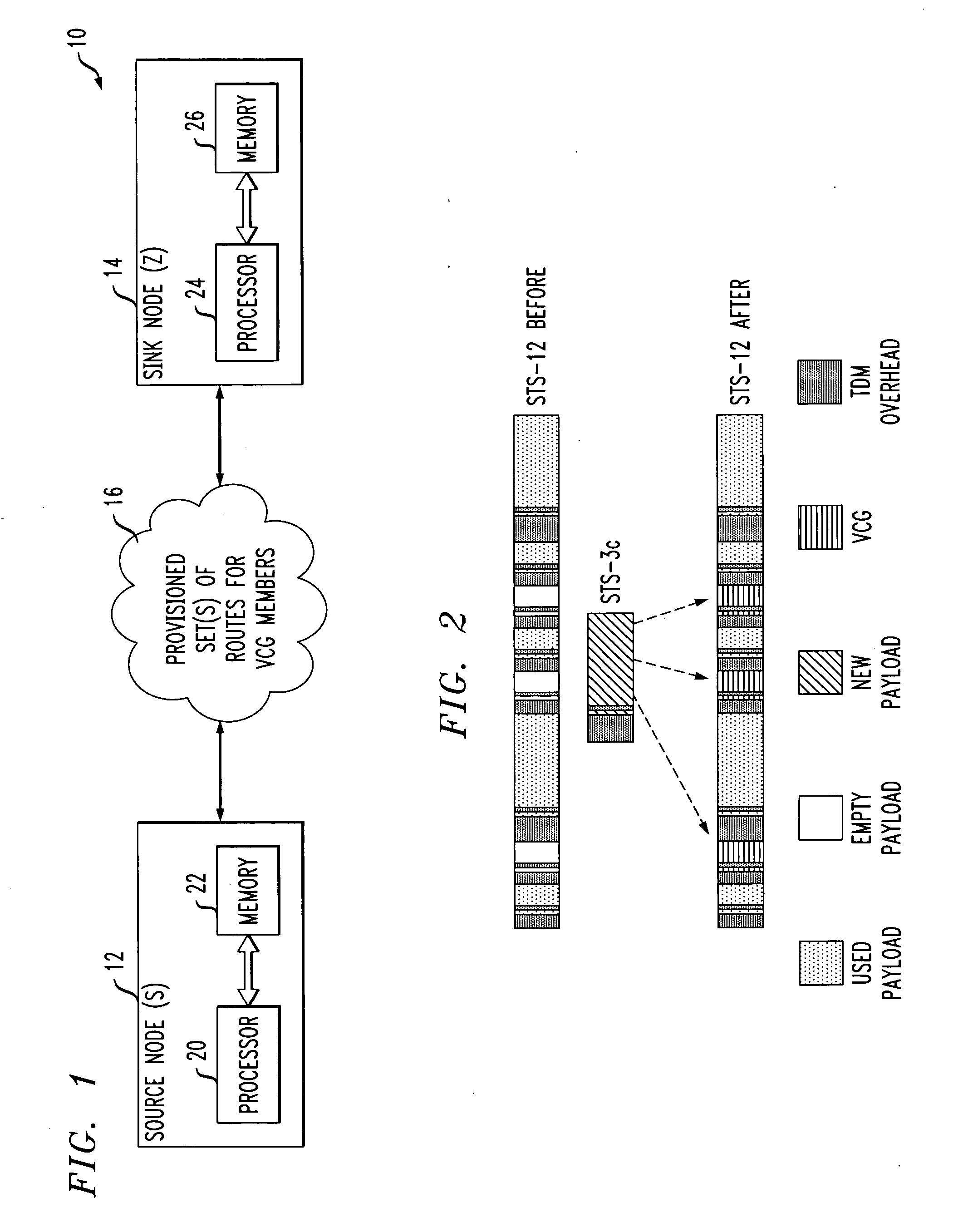
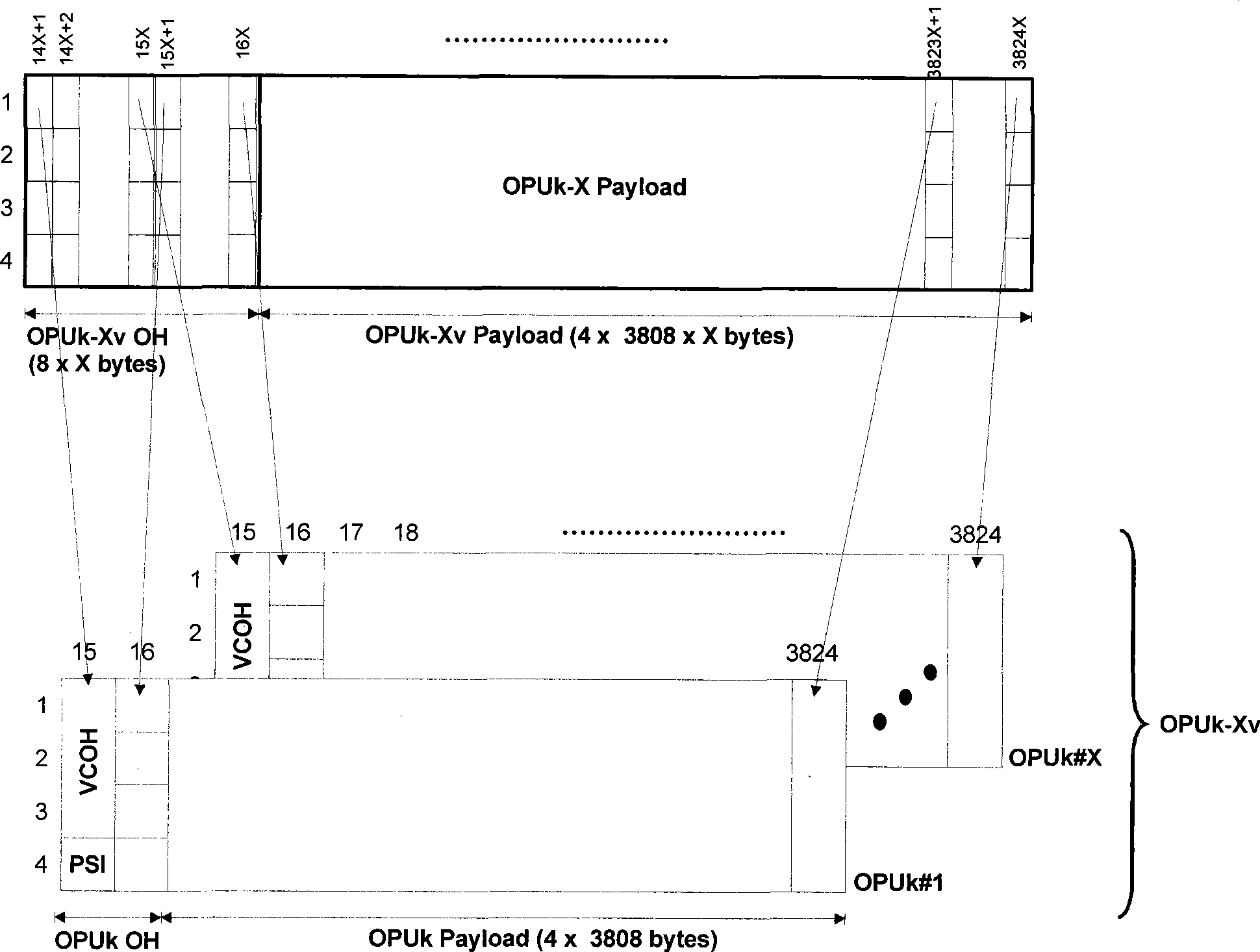
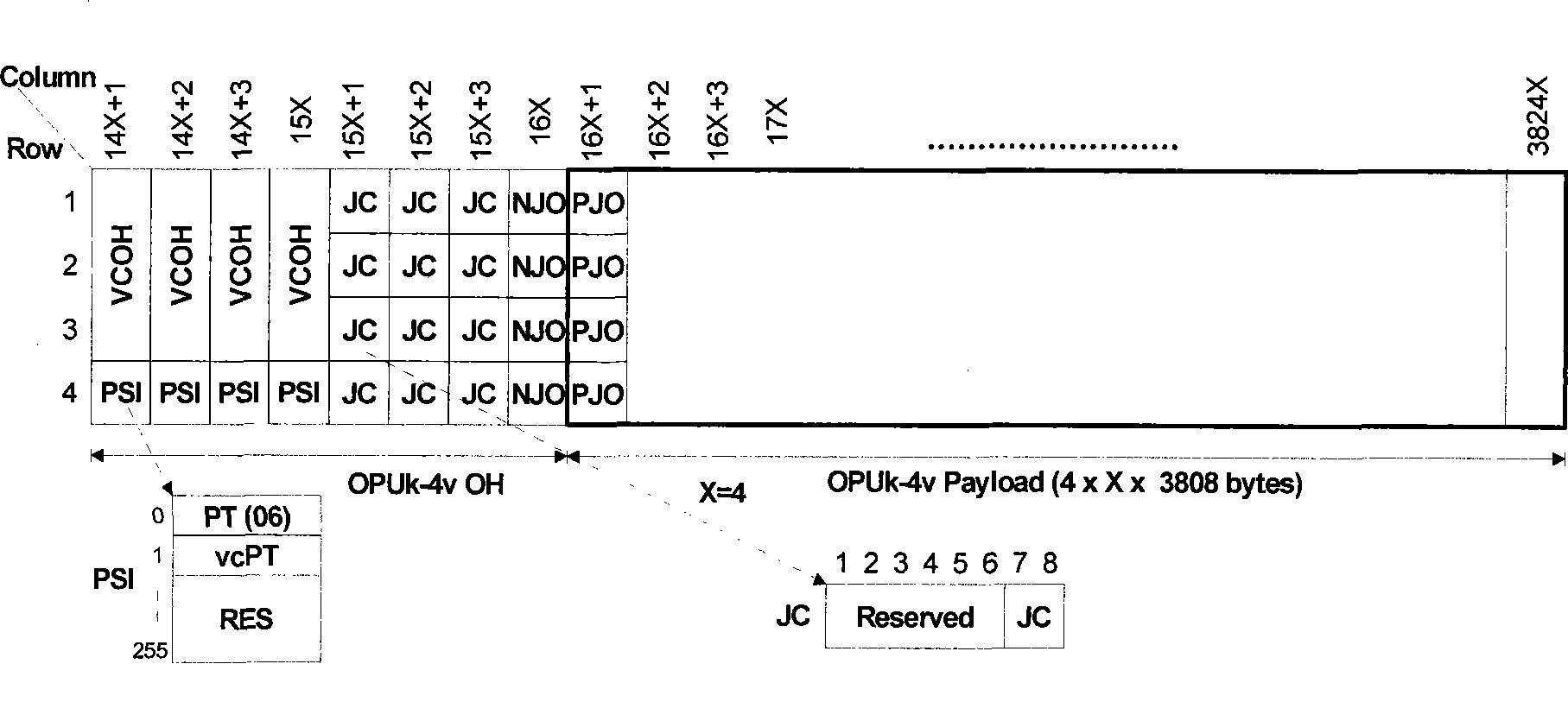
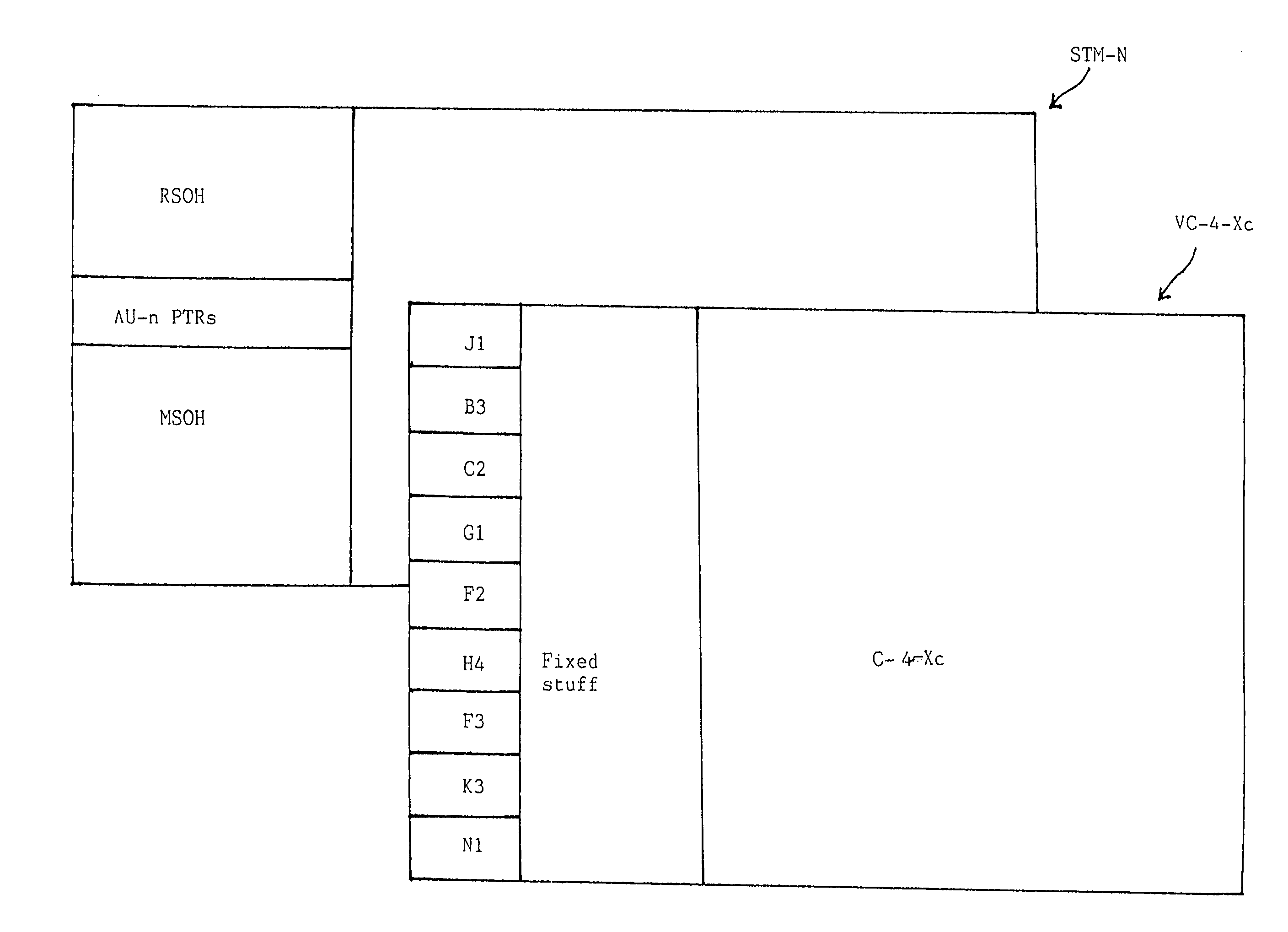
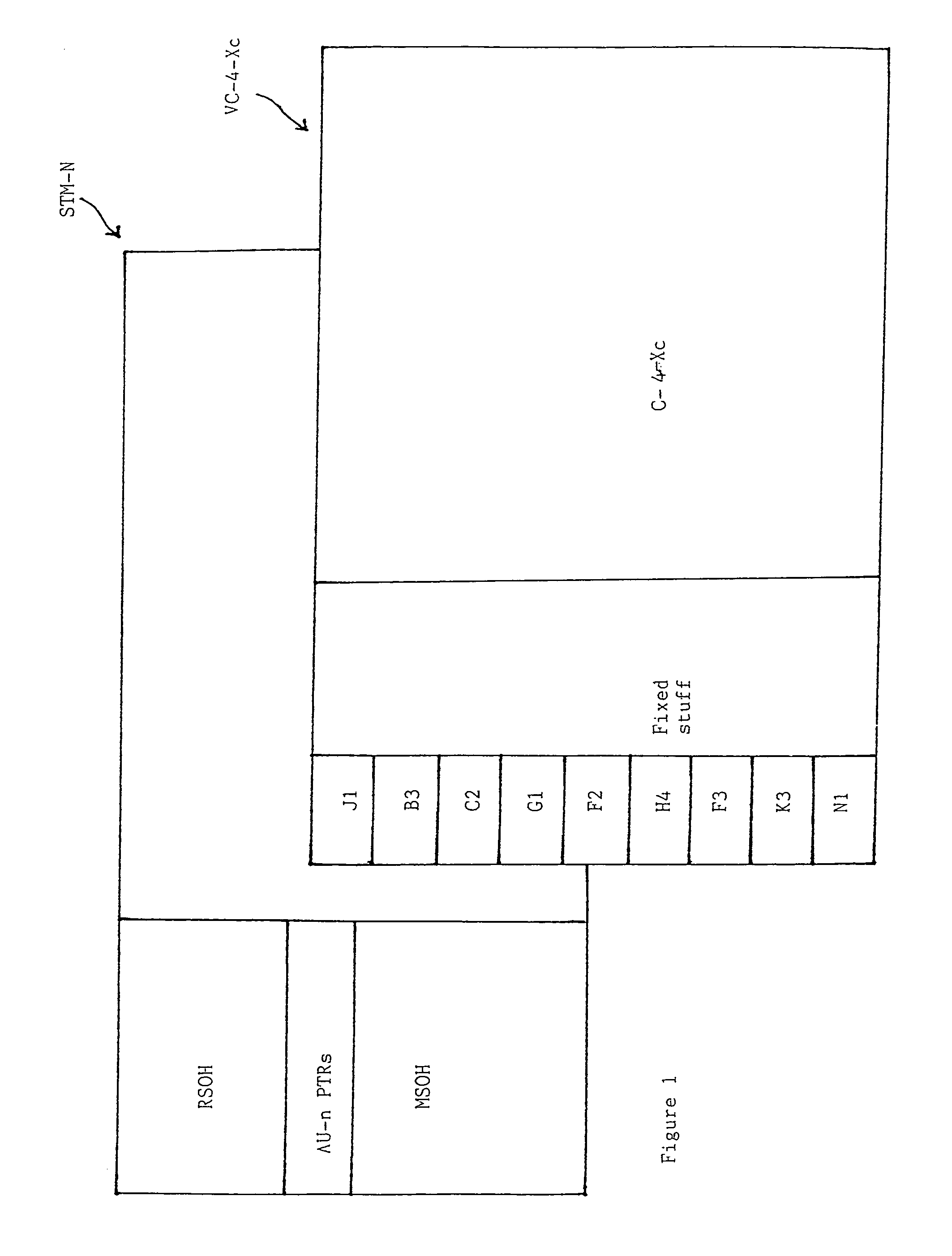
Virtual concatenation (VCAT) is an inverse multiplexing technique creating a large capacity payload container distributed over multiple smaller capacity TDM signals. These signals may be transported or routed independently. Virtual concatenation has been defined for SONET/SDH, OTN and PDH path signals.
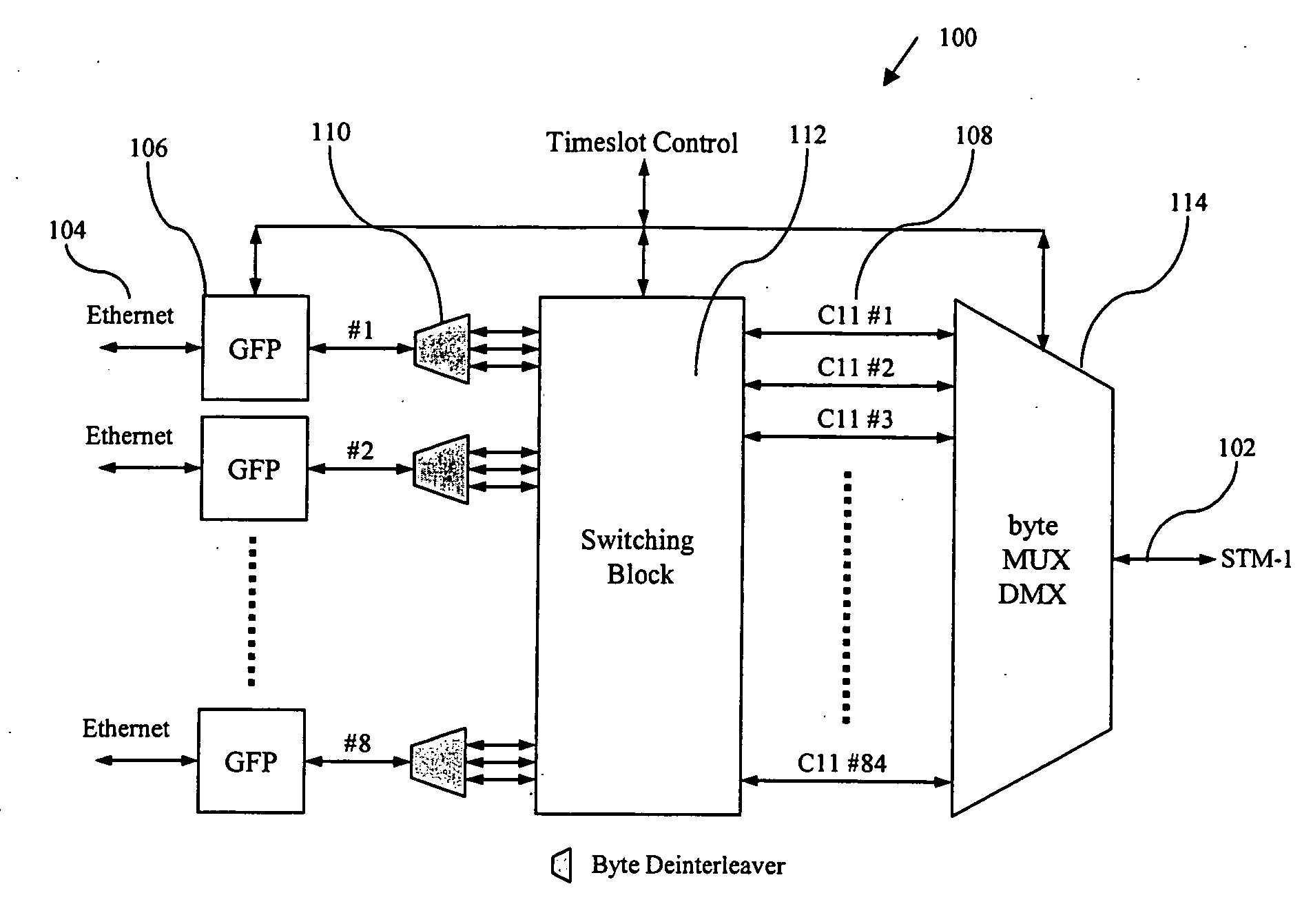
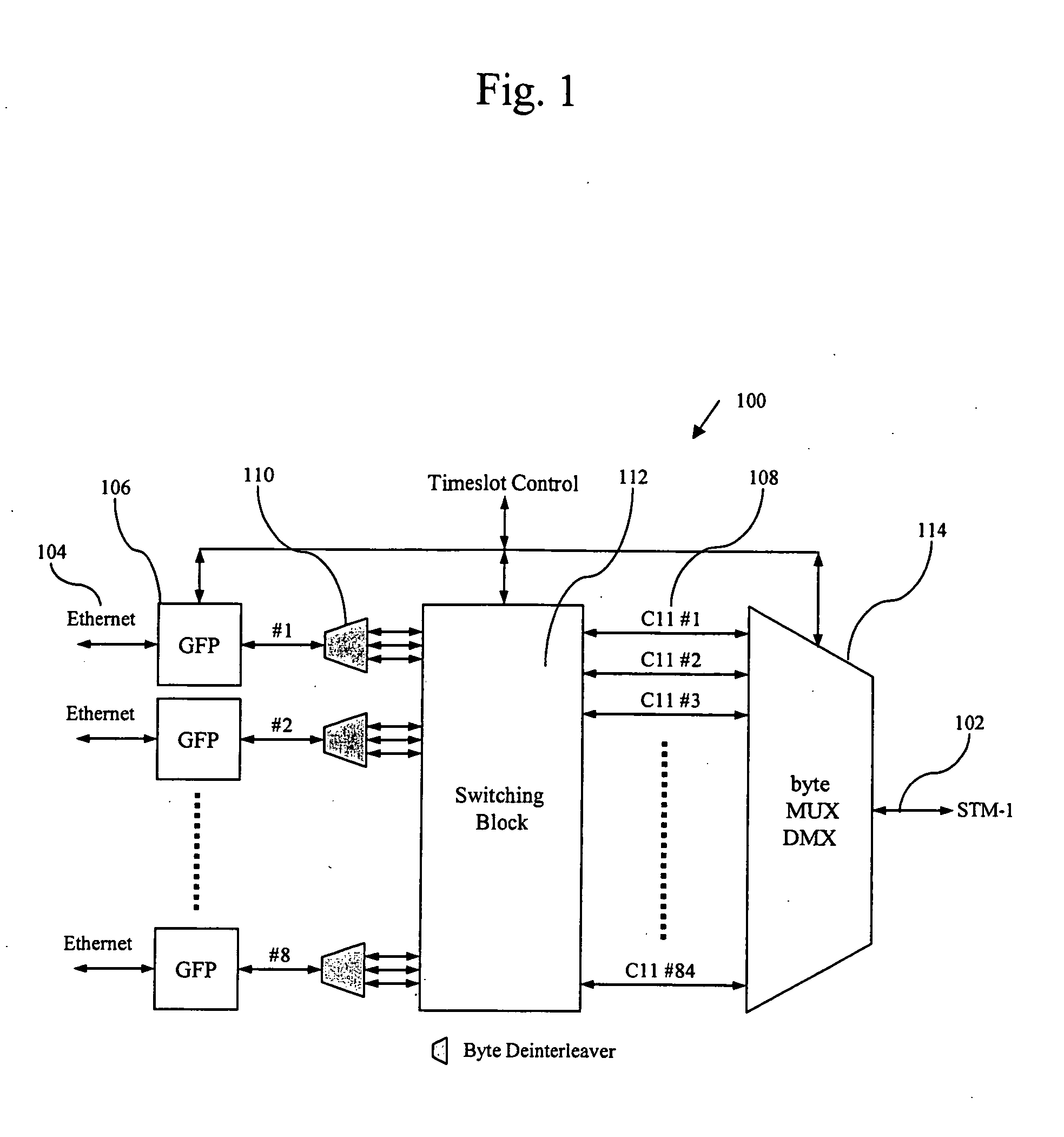
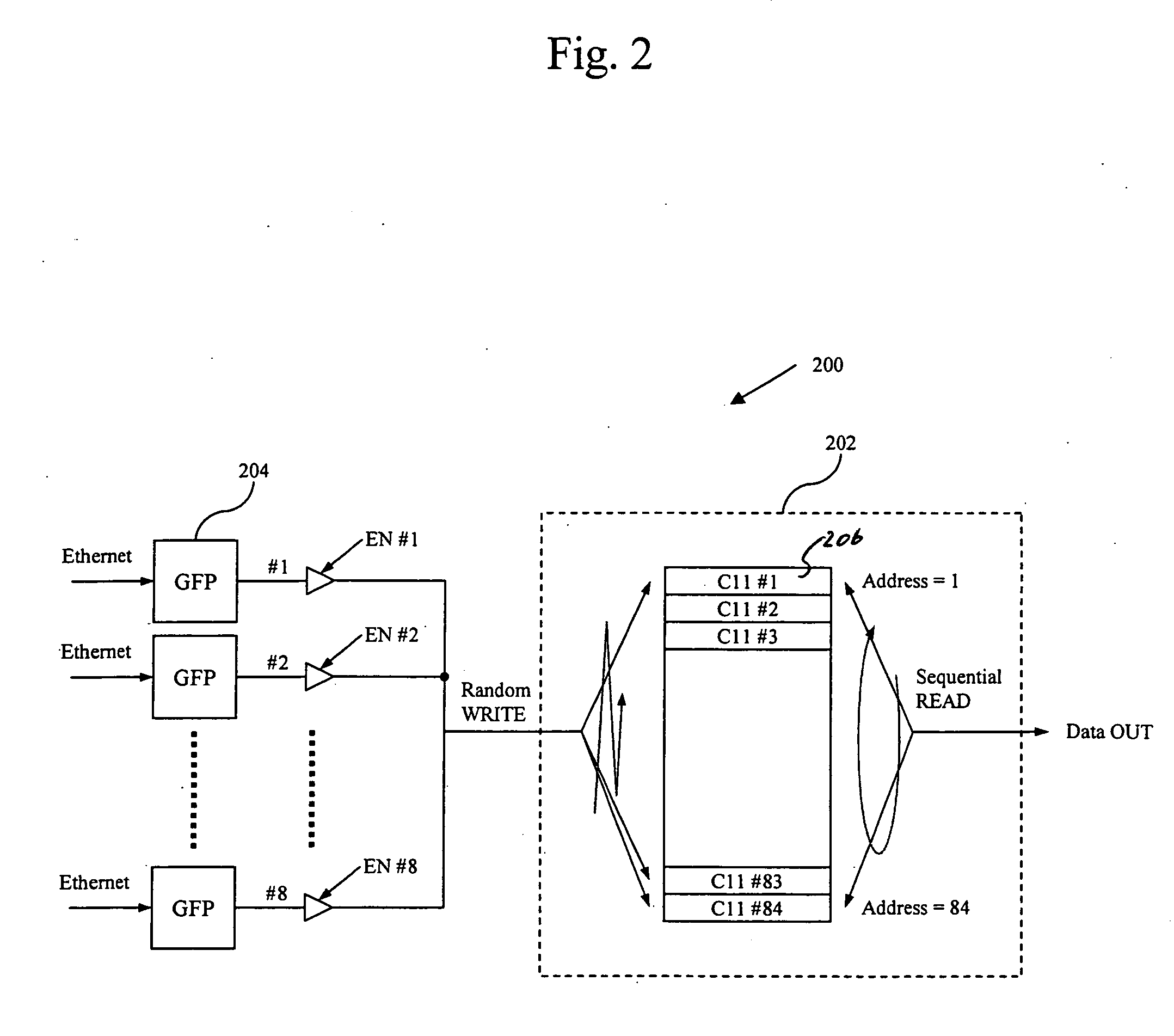
Method and apparatus for packet grooming and aggregation
InactiveUS7492714B1Improve bandwidth efficiencyEfficient forwardingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiplexingEdge node
A method and apparatus for building a packet grooming and aggregation engine is disclosed. The grooming and aggregation engine can be applied to the network for providing flexible aggregation and service multiplexing functions. A method and apparatus achieves the intended function that is easy to implement and easy for the network operator to manage, yet provides enough flexibility to mix and match various services at the edge node of the network. One specific embodiment of the patent is an Ethernet over SONET mapping system where user traffic is aggregated and groomed into SONET transport virtual concatenation channels.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
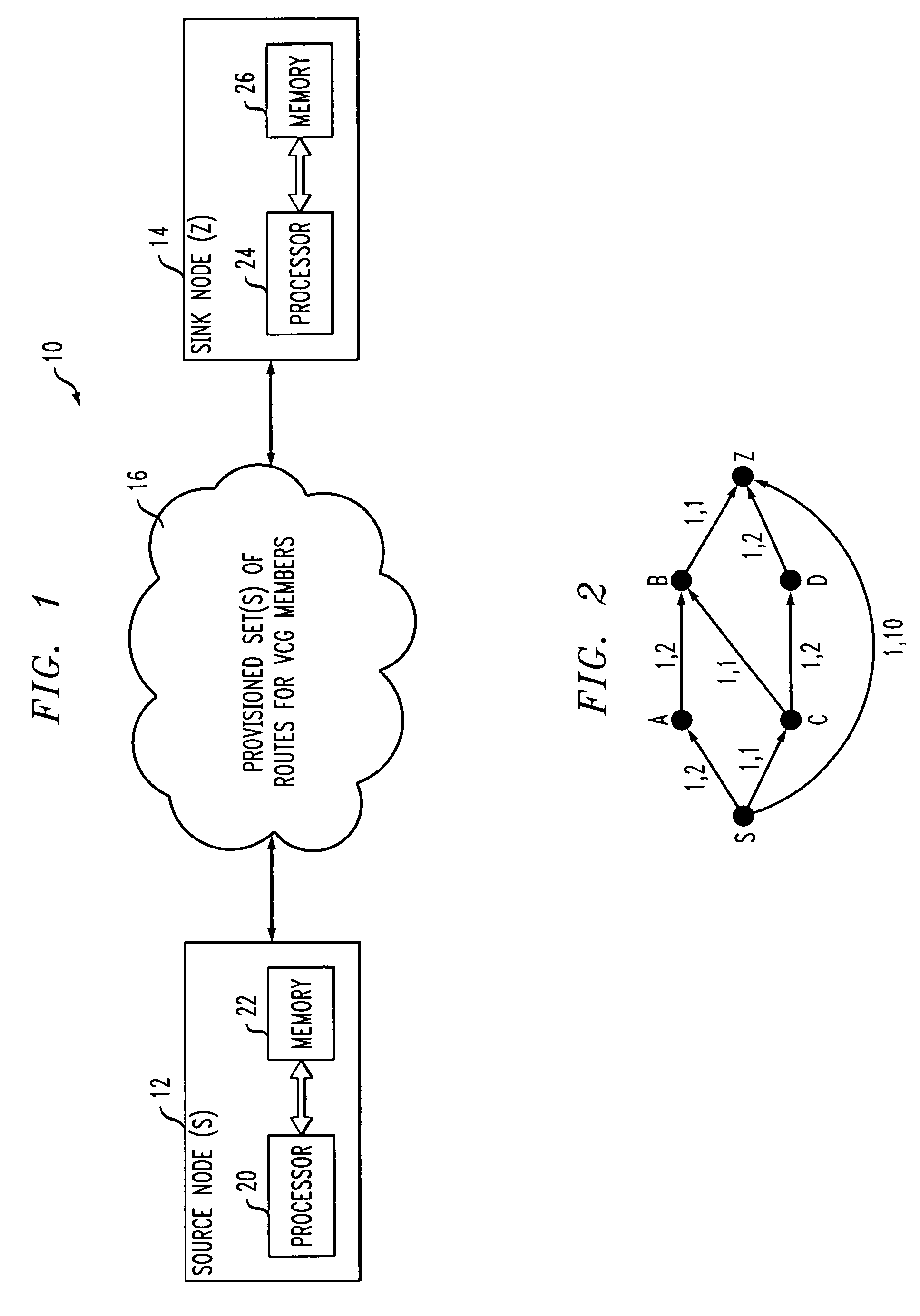
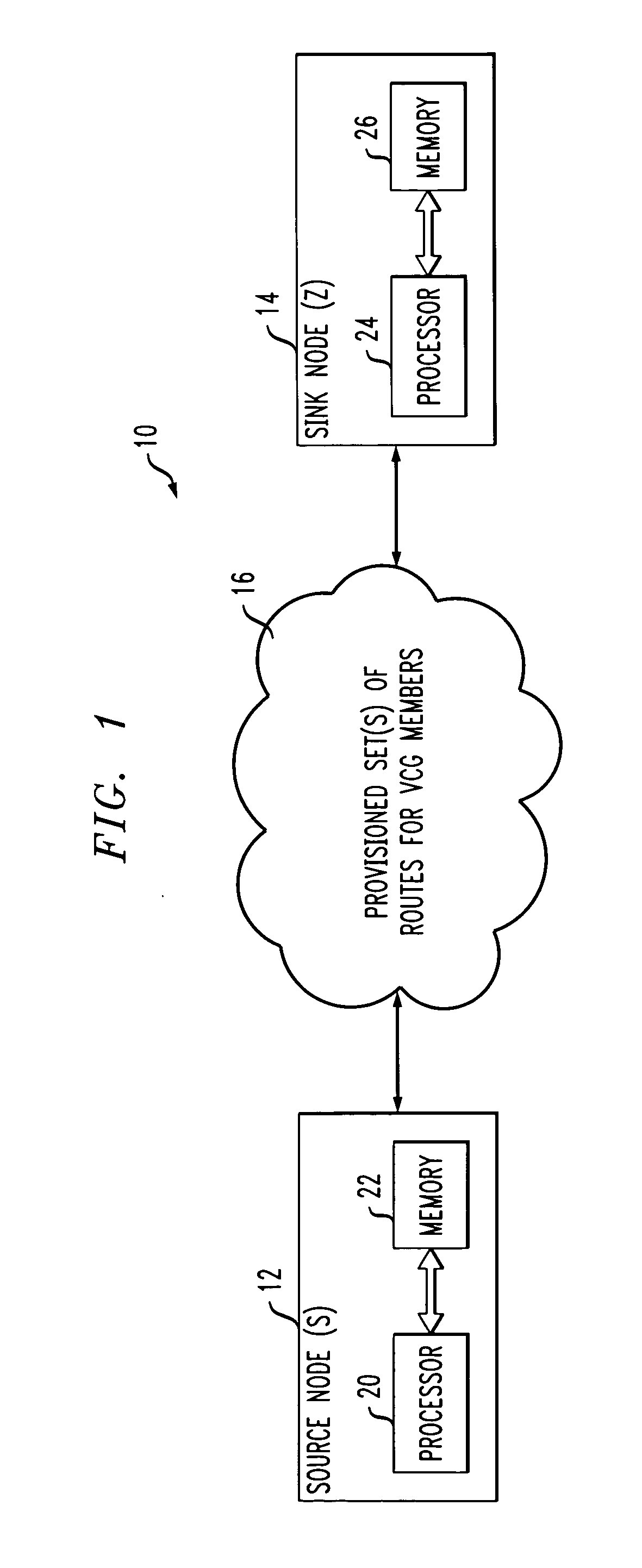
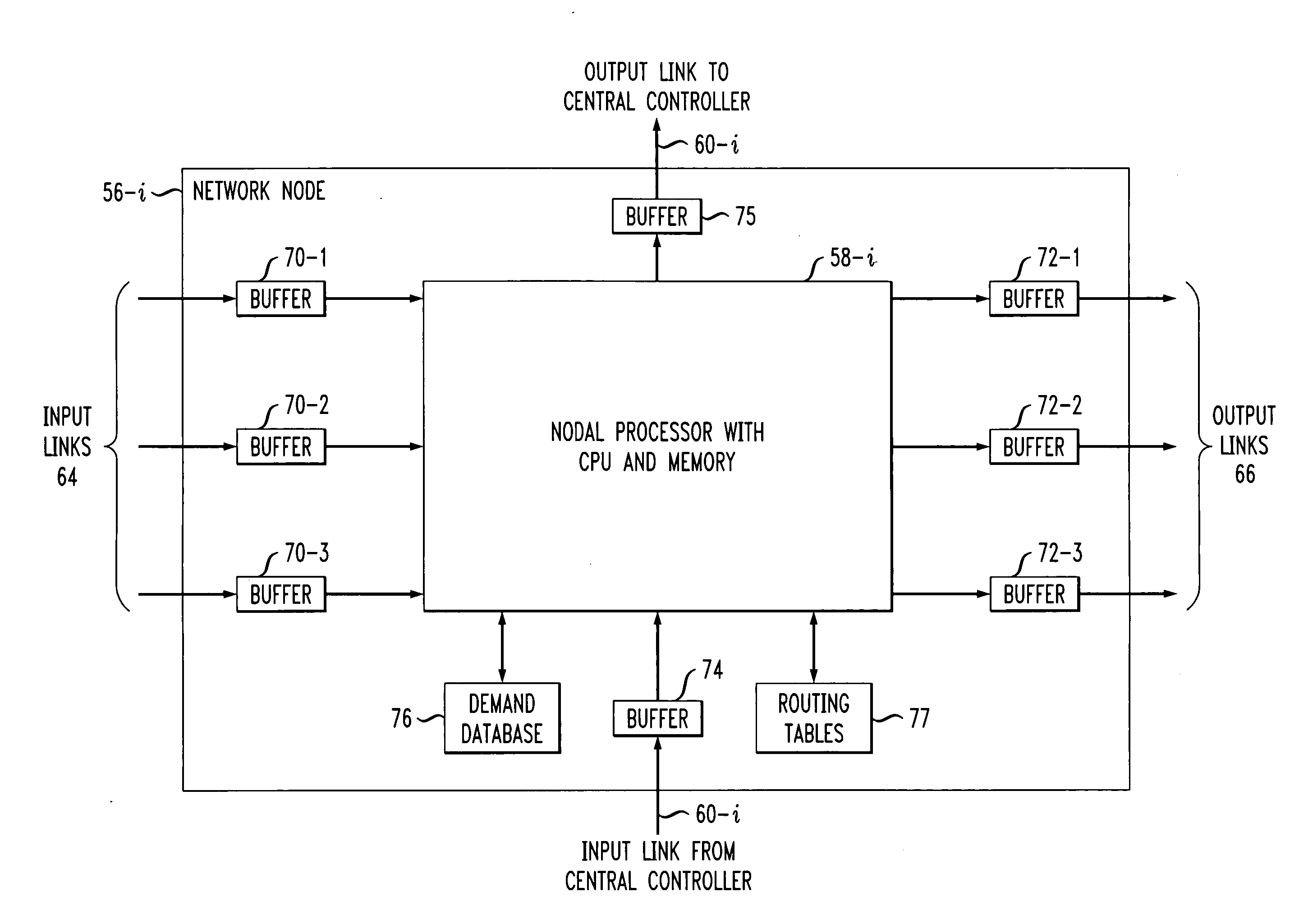
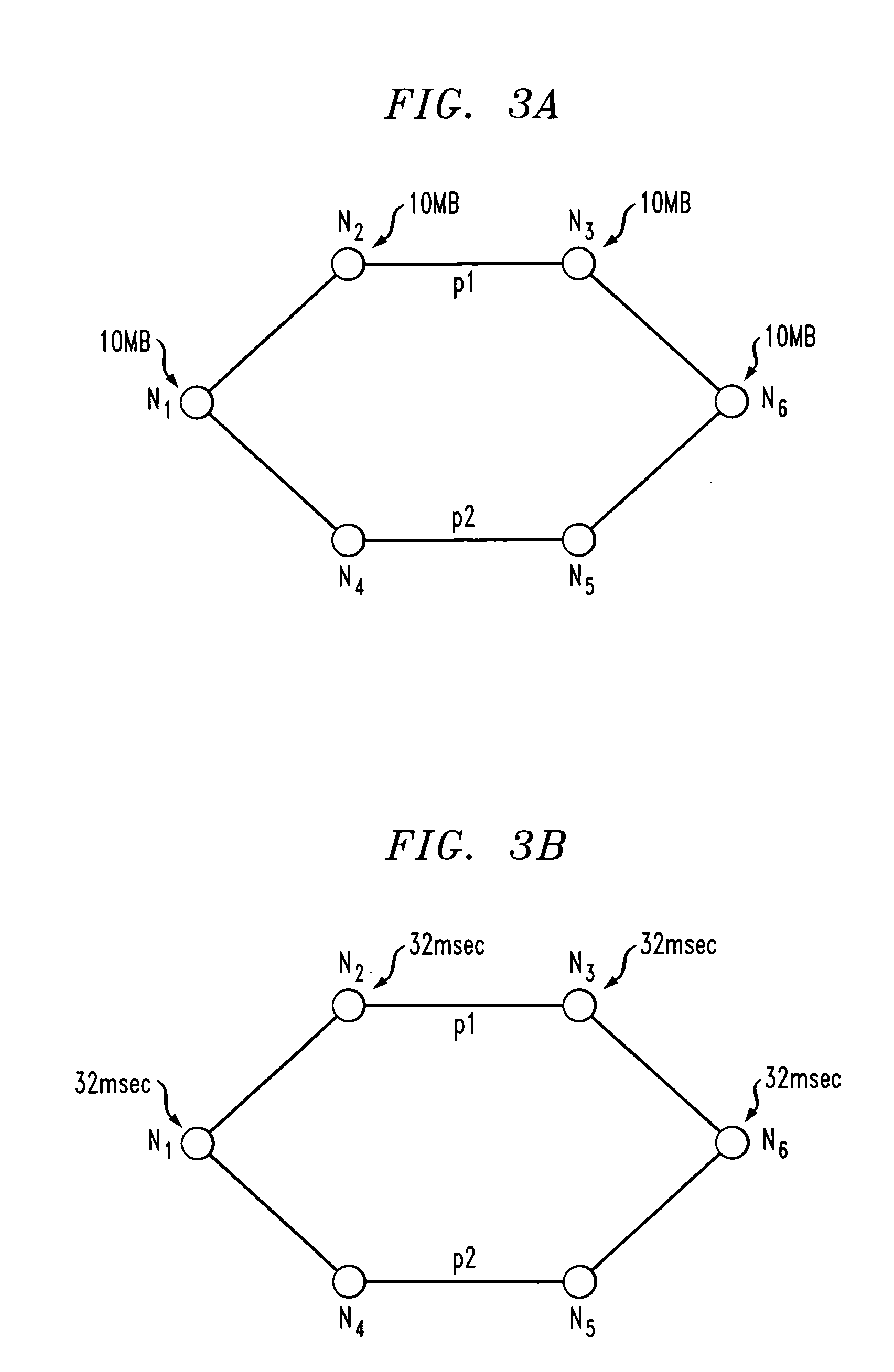
Differential delay constrained routing for virtually-concatenated data traffic
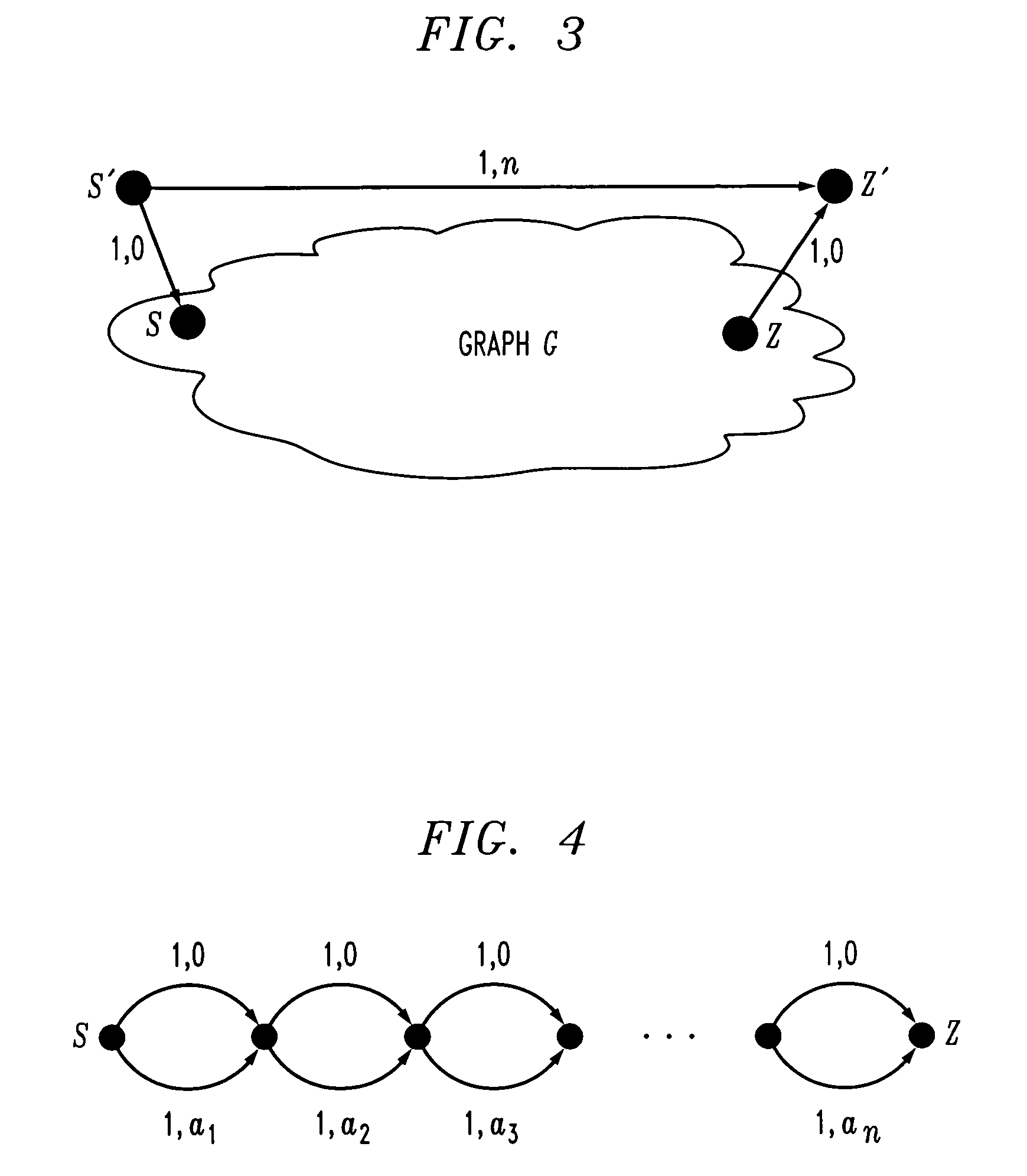
Virtually-concatenated data traffic is routed in a network comprising a plurality of nodes. For a given traffic demand to be routed from a source node to a destination node in the network, an initial candidate path set satisfying a differential delay constraint is determined by arranging a plurality of paths in order of increasing delay and selecting a particular subset of the plurality of paths as the initial candidate set. A determination is then made as to whether the initial candidate path set is able to support a bandwidth requirement of the traffic demand. If the initial candidate path set is able to support the bandwidth requirement of the traffic demand, the initial candidate path set is utilized to route the traffic demand. Otherwise, the process is repeated for one or more additional iterations, with a different candidate path set satisfying the differential delay constraint being selected for a given additional iteration by application of a sliding-window function to the plurality of paths arranged in order of increasing delay, until a different candidate path satisfying the differential delay constraint is determined to support the bandwidth requirement of the traffic demand.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
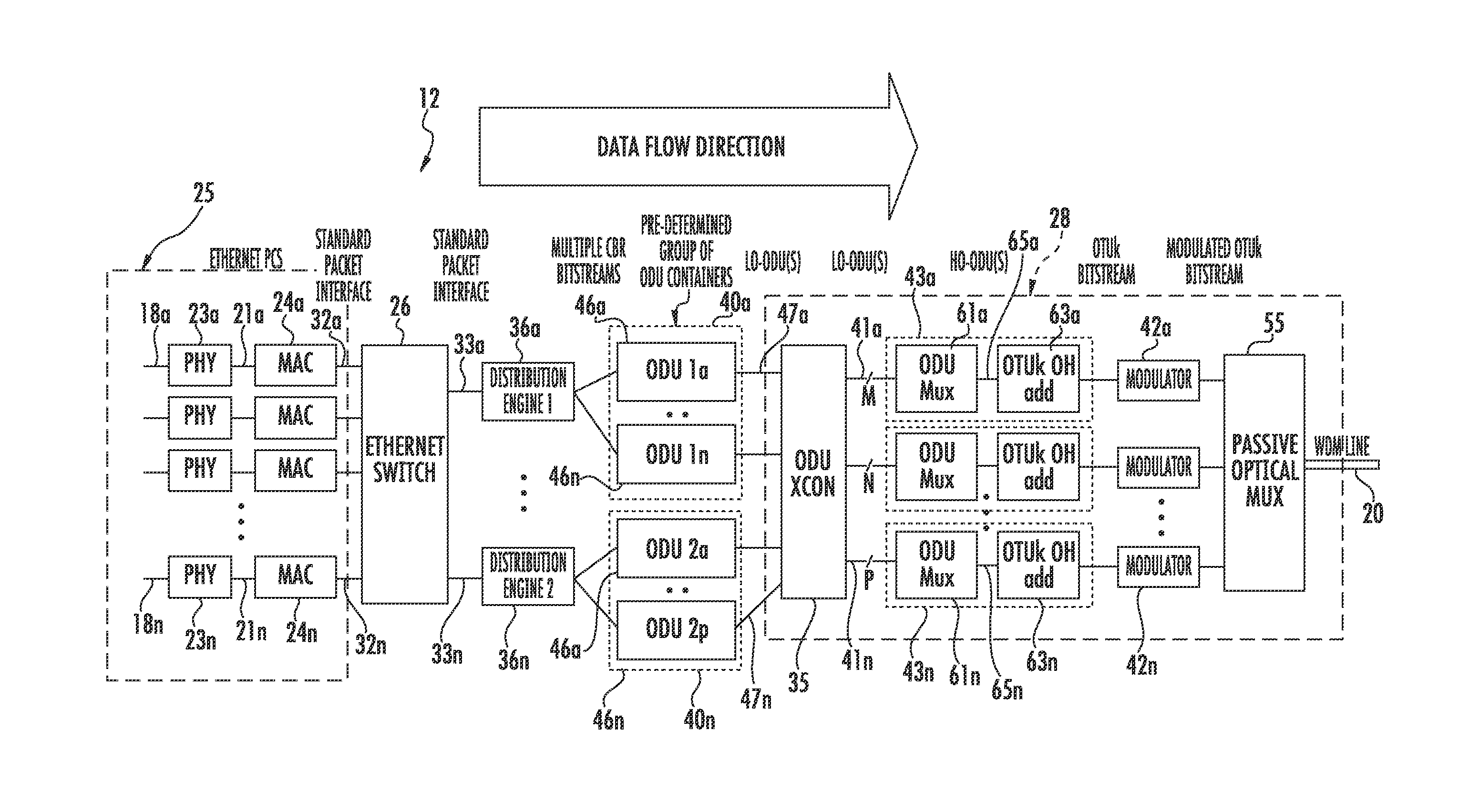
Method and apparatus for mapping traffic using virtual concatenation
A node comprising a packet network interface, an ethernet switch, an optical port, and a distribution engine. The packet network interface adapted to receive a packet having a destination address and a first bit and a second bit. The ethernet switch is adapted to receive and forward the packet into a virtual queue associated with a destination. The optical port has circuitry for transmitting to a plurality of circuits. The distribution engine has one or more processors configured to execute processor executable code to cause the distribution engine to (1) read a first bit and a second bit from the virtual queue, (2) provide the first bit and the second bit to the at least one optical port for transmission to a first predetermined group of the plurality of circuits.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
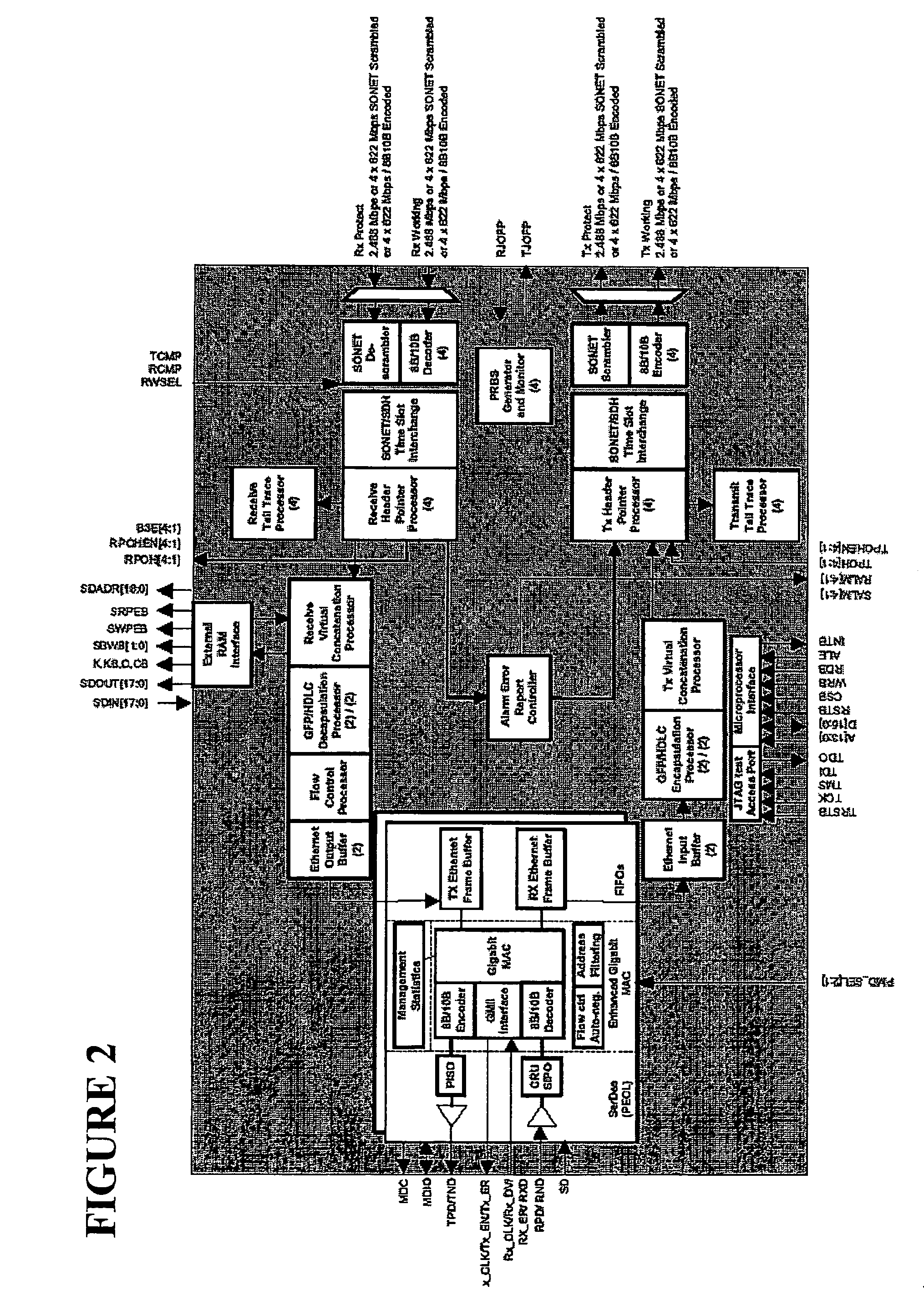
Method and apparatus for transmitting multiple signal, method and apparatus for receiving multiple signal, multiple signal transmission method and multiplexer/demultiplexer
InactiveUS7042904B2Efficient multiplexingTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMultiplexerComputer science
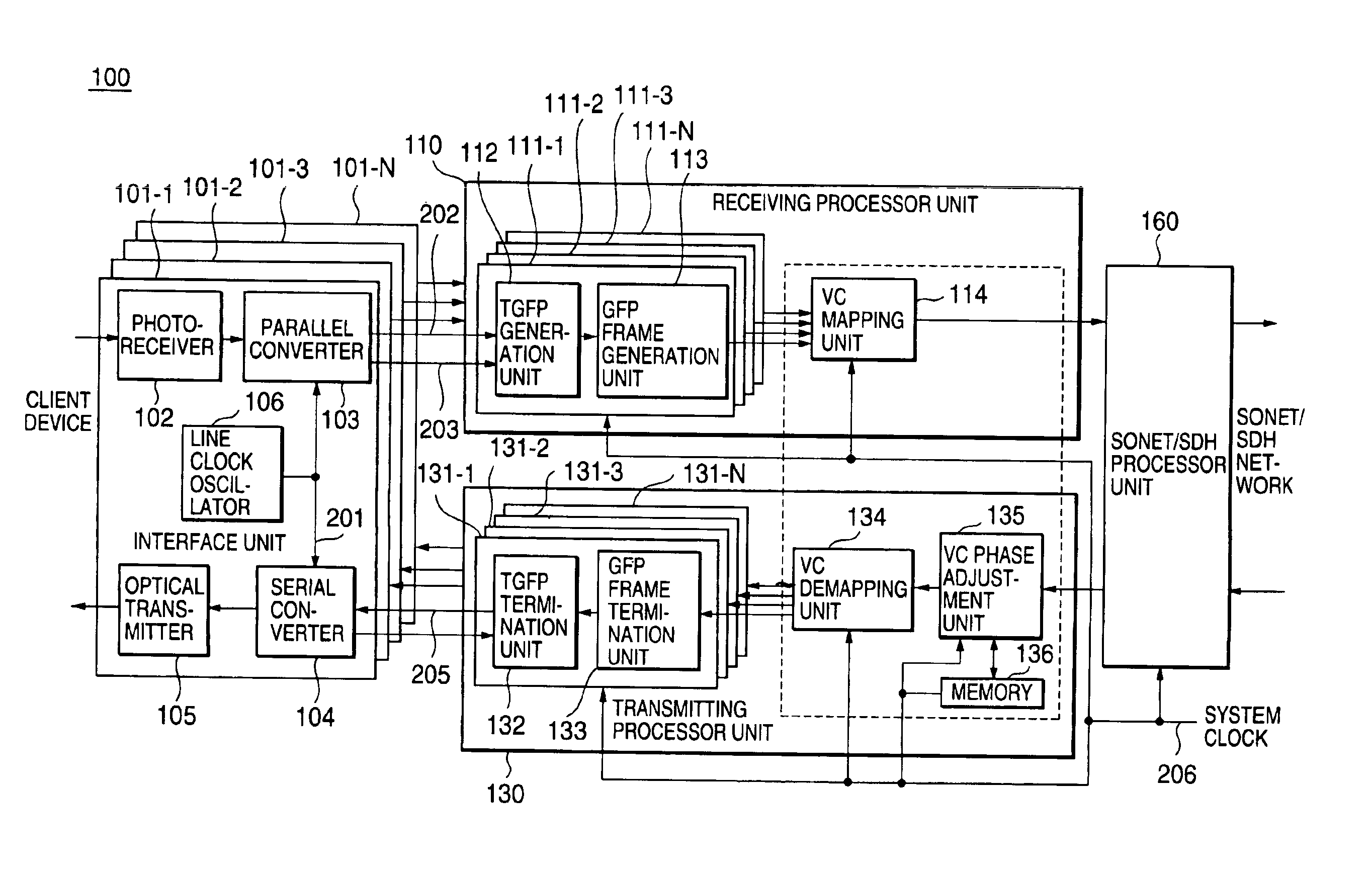
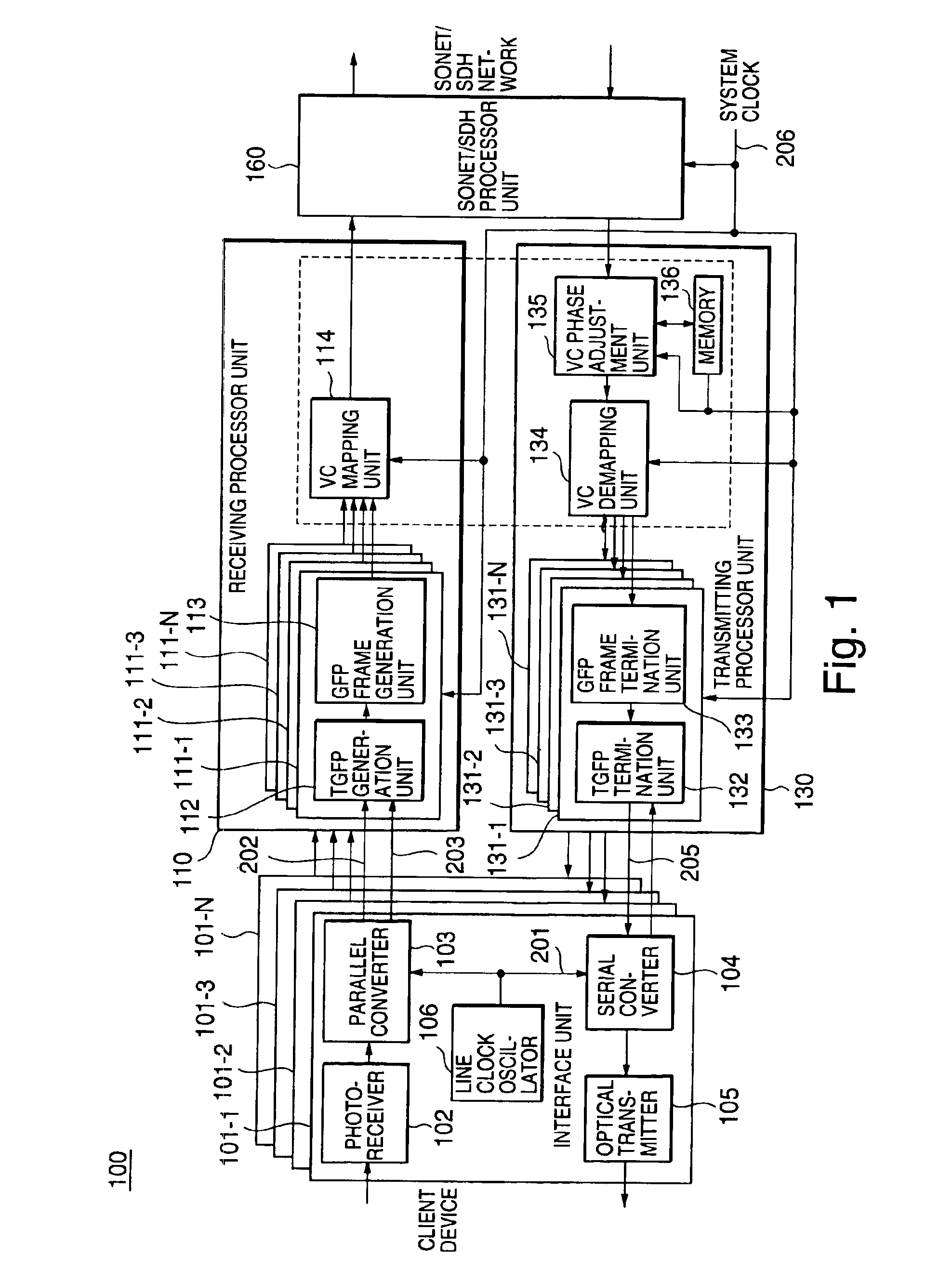
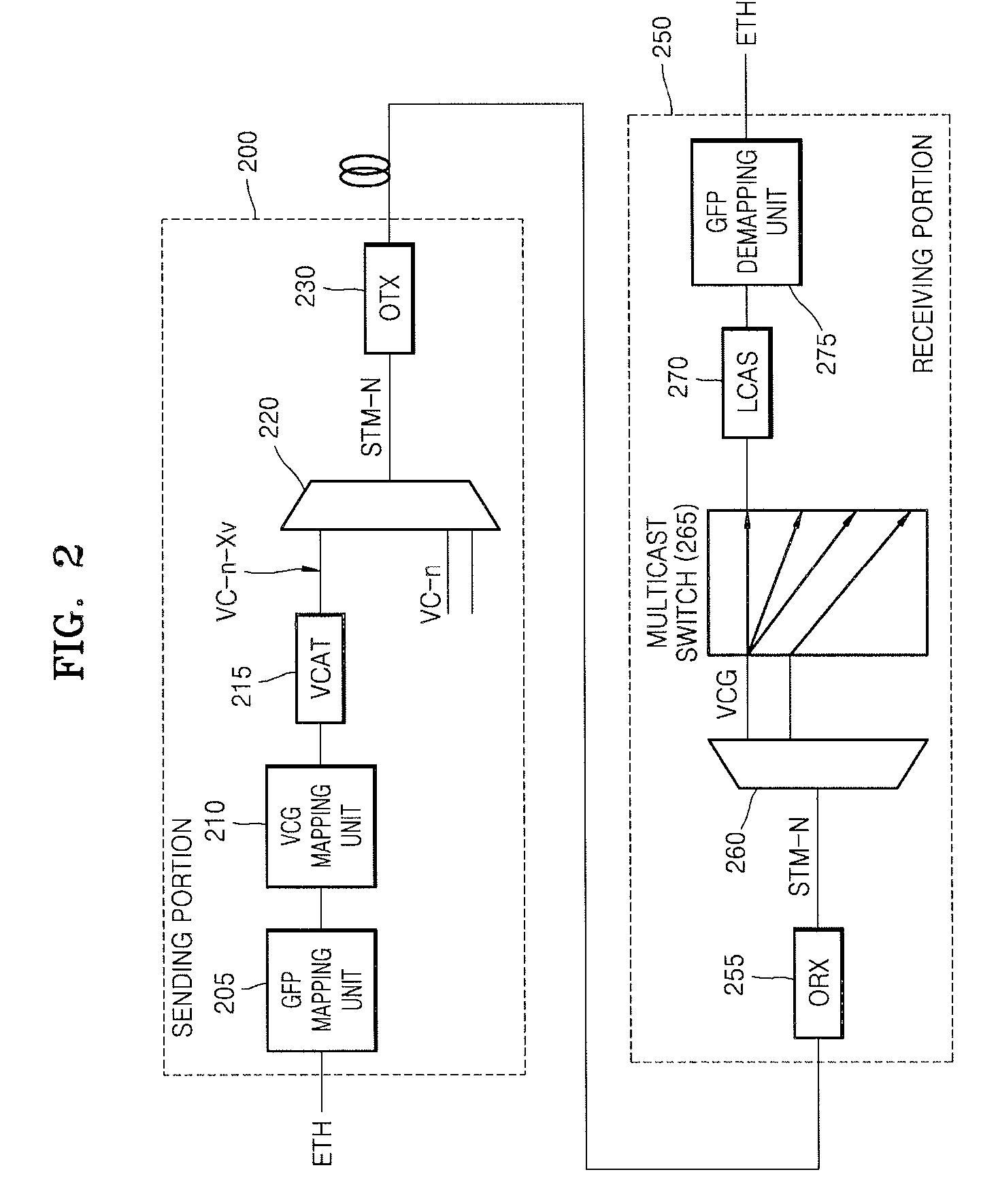
A client channel receiving processor unit converts each reception client signal of a 10B-character form into a GFP frame form. A mapping unit maps the client signal of the GFP frame form on a channel of virtual concatenation. A SONET / SDH processor unit transmits or receives a SONET / SDH frame, in which a GFP frame is mapped, to / from a network. A demapping unit separates each channel of the SONET / SDH frame received by the SONET / SDH processor unit. A client channel transmitting processor unit detects the client signal of the GFP frame from each separated channel to convert the signal into a 10B-character form.
Owner:NEC CORP
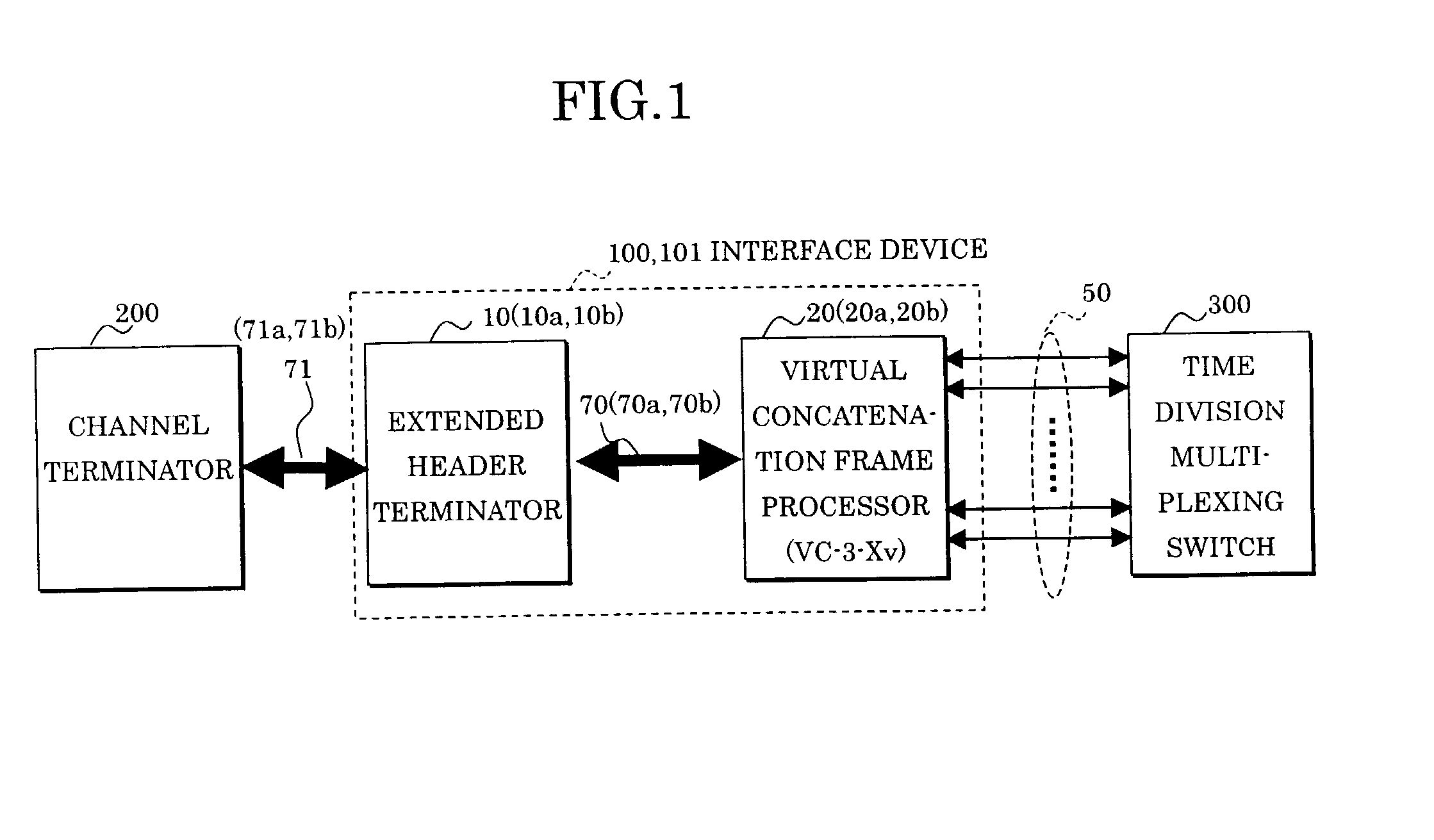
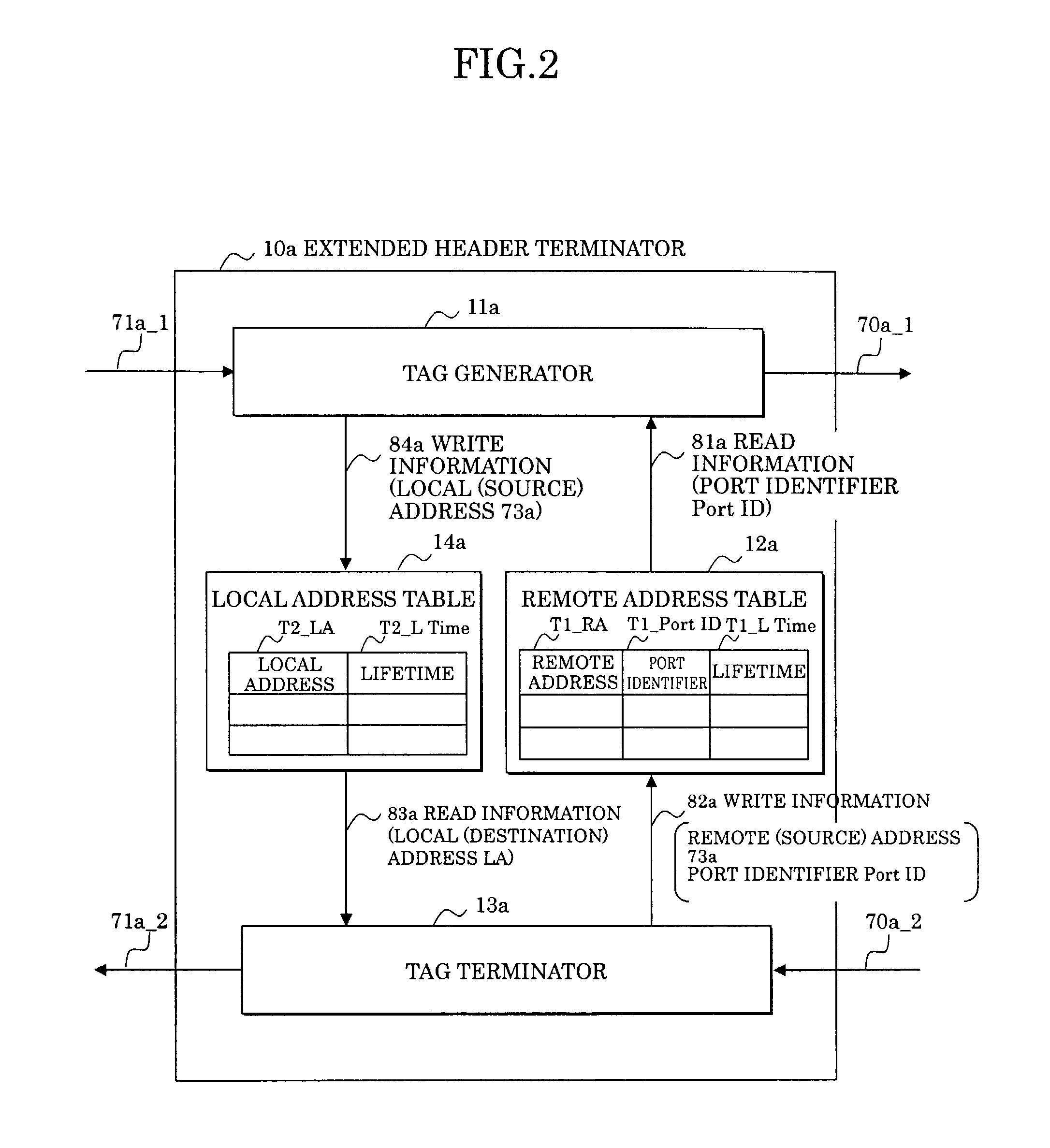
Interface device
InactiveUS20030108069A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexComputer networkMultiplexer
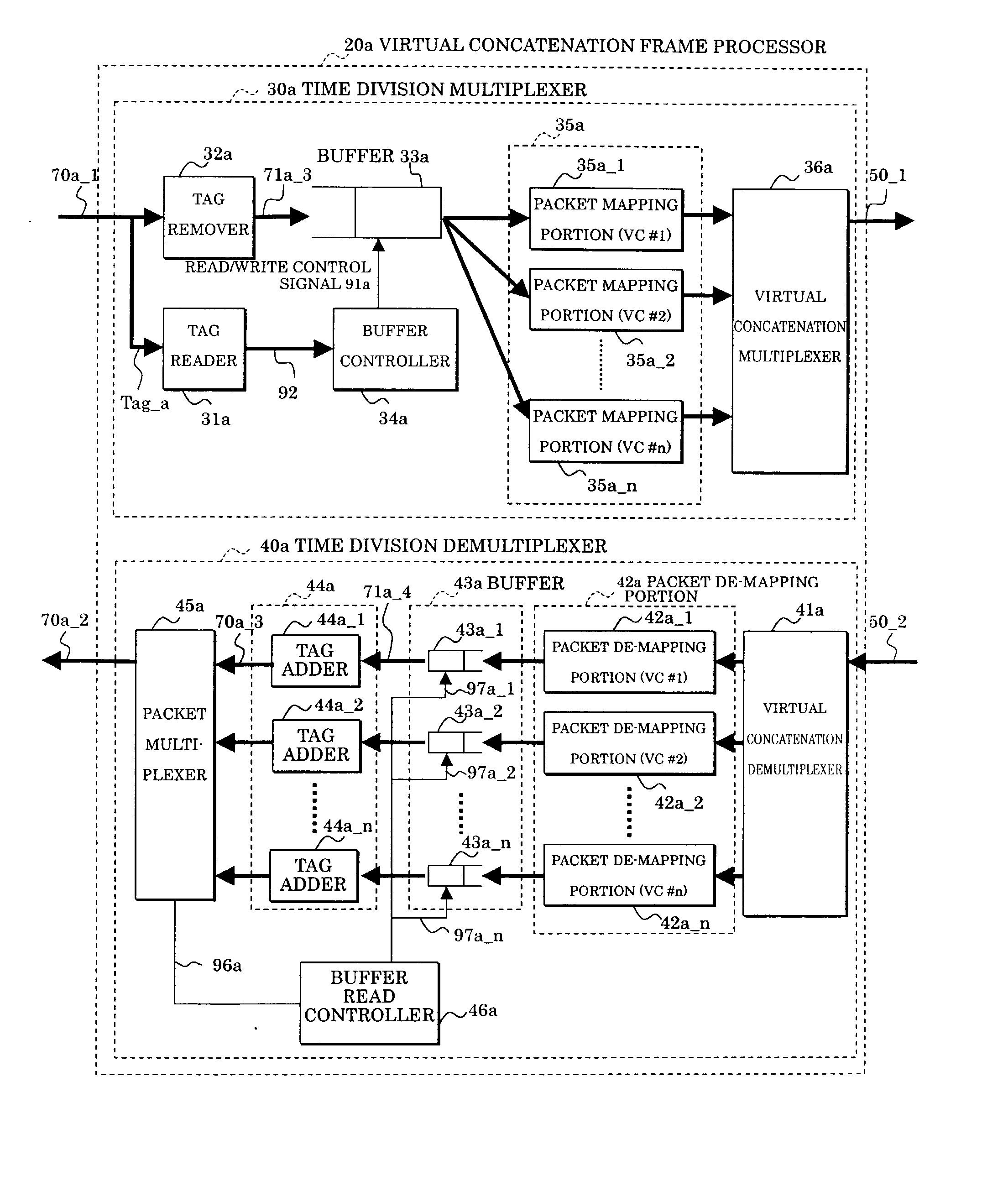
In an interface device connecting packet multiplexing networks and a time division multiplexing channel network having different multiplexing systems, and a network system, an address table associates a destination address with a broadcast identifier, a group identifier, and a port identifier uniquely indicative of a virtual concatenation channel for transmitting a packet to be stored, a tag generator of an extended header terminator, based on this address table, adds the broadcast identifier, the group identifier, and the port identifier to a received packet to be transmitted. A time division multiplexer of a frame processor having received this packet performs mapping on a virtual concatenation channel corresponding to the port identifier, and broadcasts or multicasts the packet according to the broadcast identifier and the group identifier.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
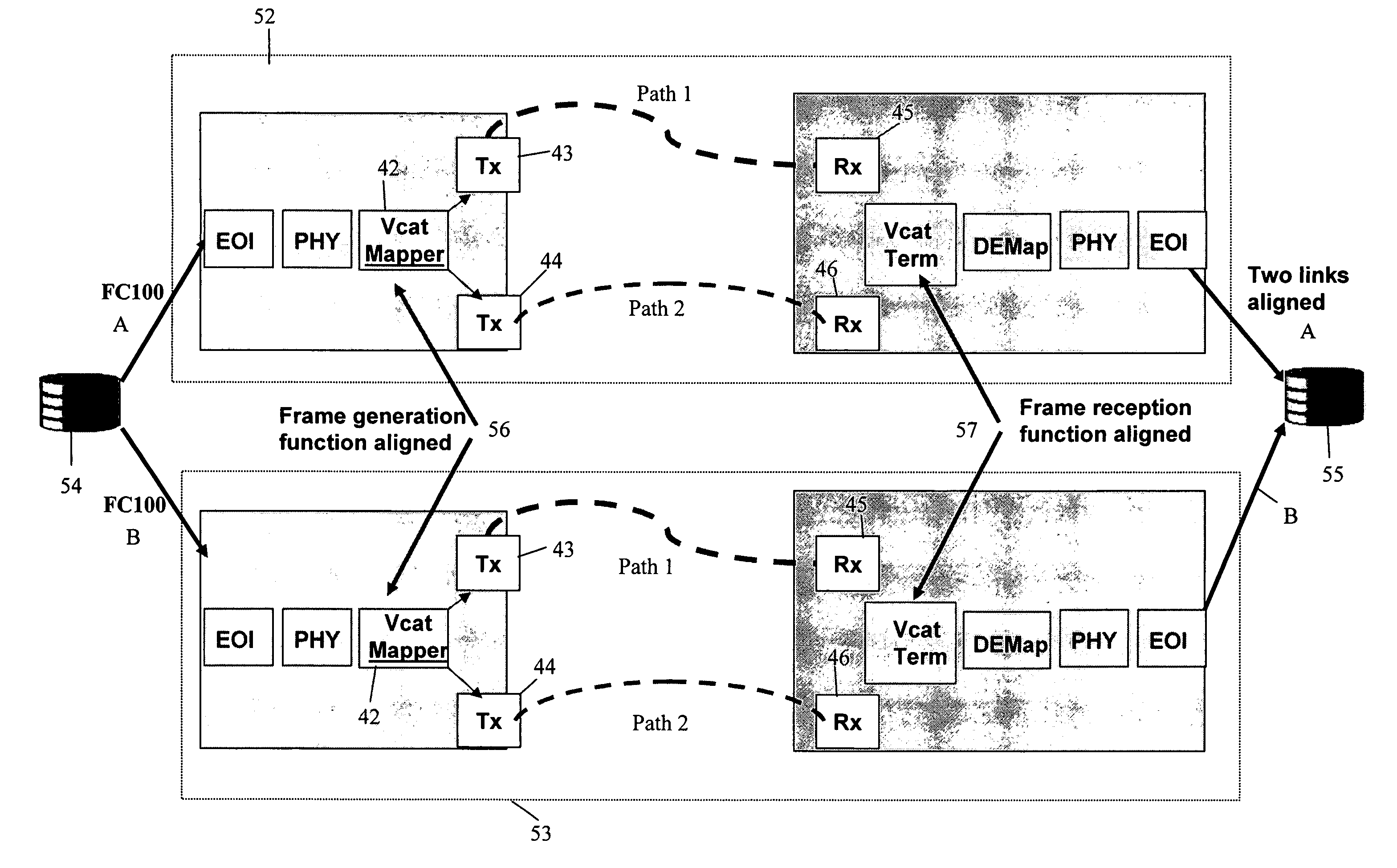
Virtual concatenation for parallel data streams
ActiveUS8204085B1The process is simple and effectiveTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData streamCo ordinate
It is often required to send a plurality of streams of data in parallel between two network nodes in a synchronous transmission network and also to maintain a particular alignment between those streams of data. This is particularly required when the streams of data are to be transmitted over a wide area network, for example, for data mirroring applications. Virtual concatenation is used for each of the individual data streams as known in the art and in addition, the individual virtual concatenation processes are synchronized or co-ordinated. At a destination node it is then possible to realign the individual data streams with respect to one another.
Owner:CIENA
Method and device for virtual concatenation transmission
InactiveUS20040196847A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMultiplexingLow speed
In a method and a device for virtual concatenation transmission which multiplex traffics of low-speed frames into a high-speed frame based on a virtual concatenation, a virtual concatenation with an excellent transmission efficiency is provided. Specifically, in order to provide the transmission method and the device which do not waste channels, require little labor of operators, do not cause an instantaneous interruption, and require no memory capacity, a plurality of low-speed frames are multiplexed into arbitrary positions within a high-speed frame to compose a virtual concatenation, and are transmitted together with virtual concatenation information indicating a concatenation state of positions of the low-speed frames, with a phase relationship being maintained.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
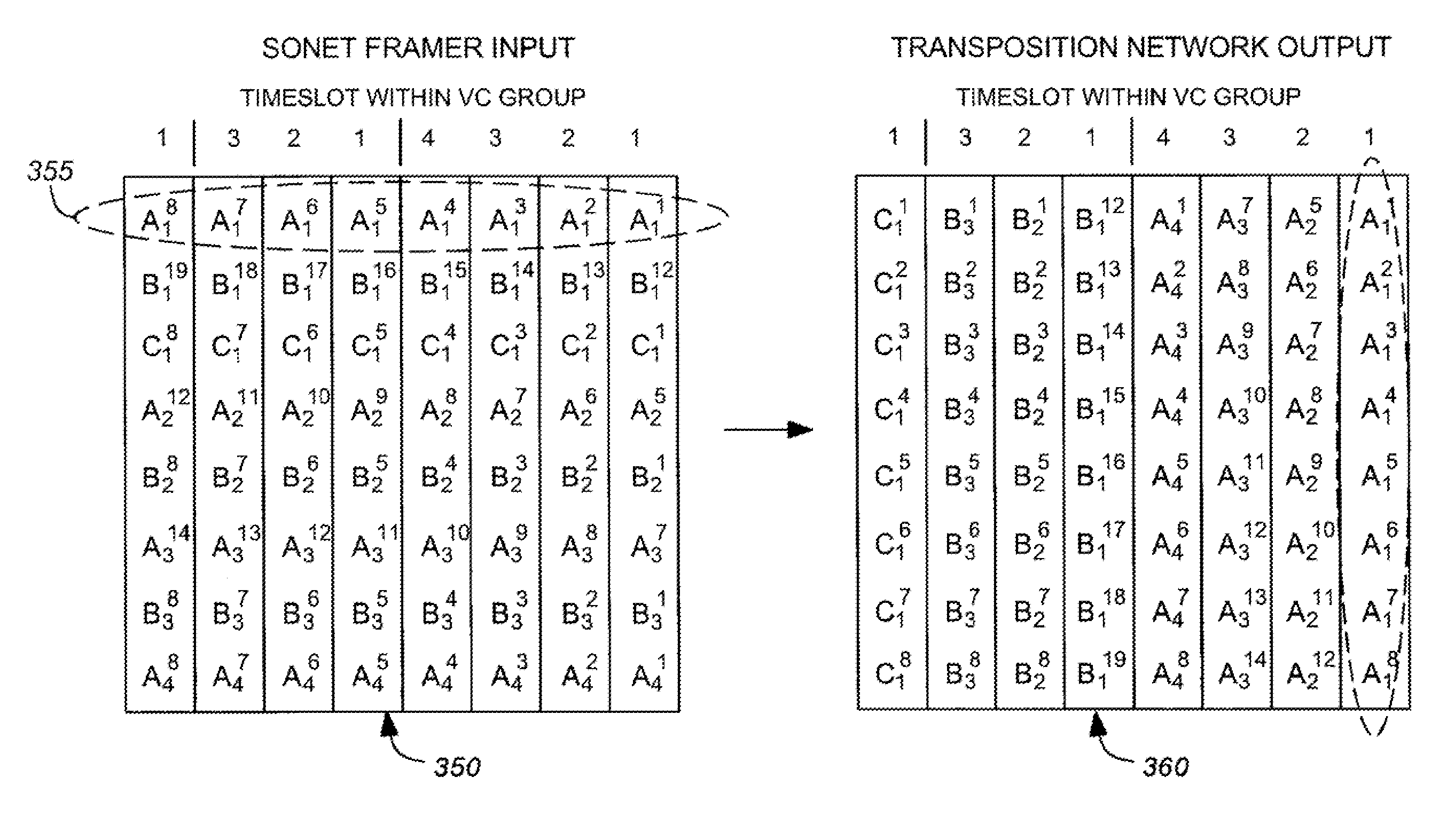
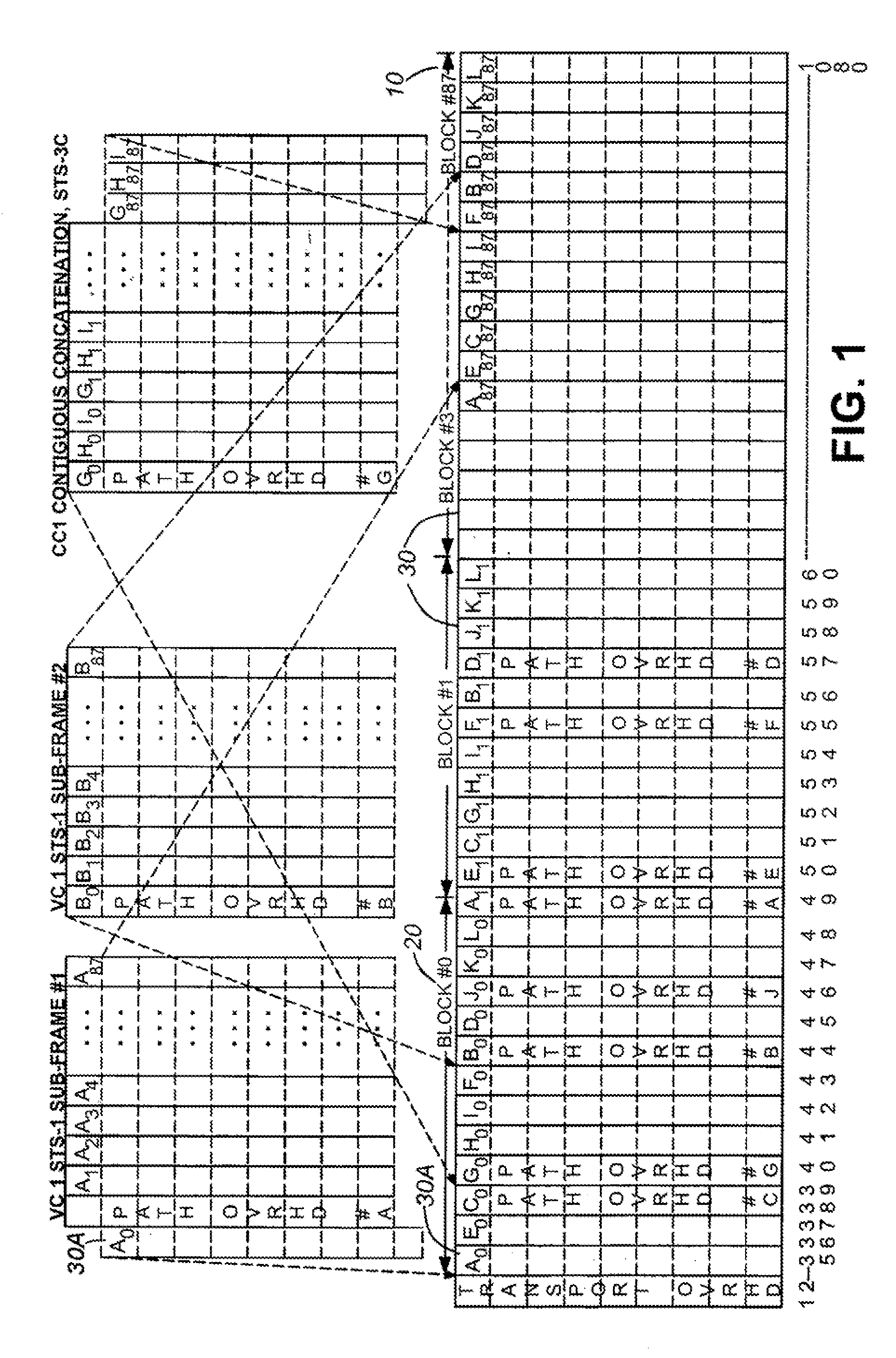
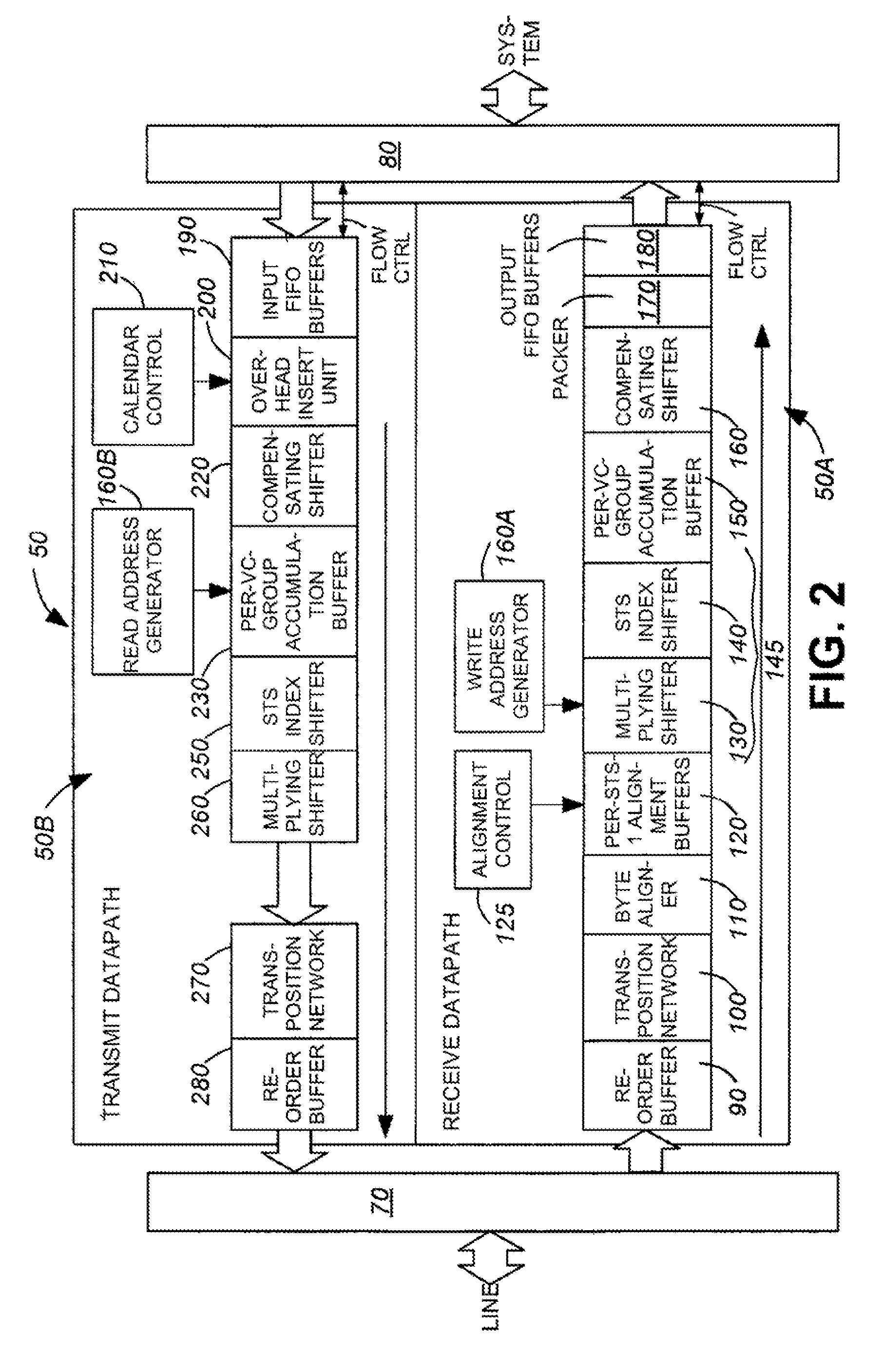
Efficient virtual concatenation datapath for SONET/SDH
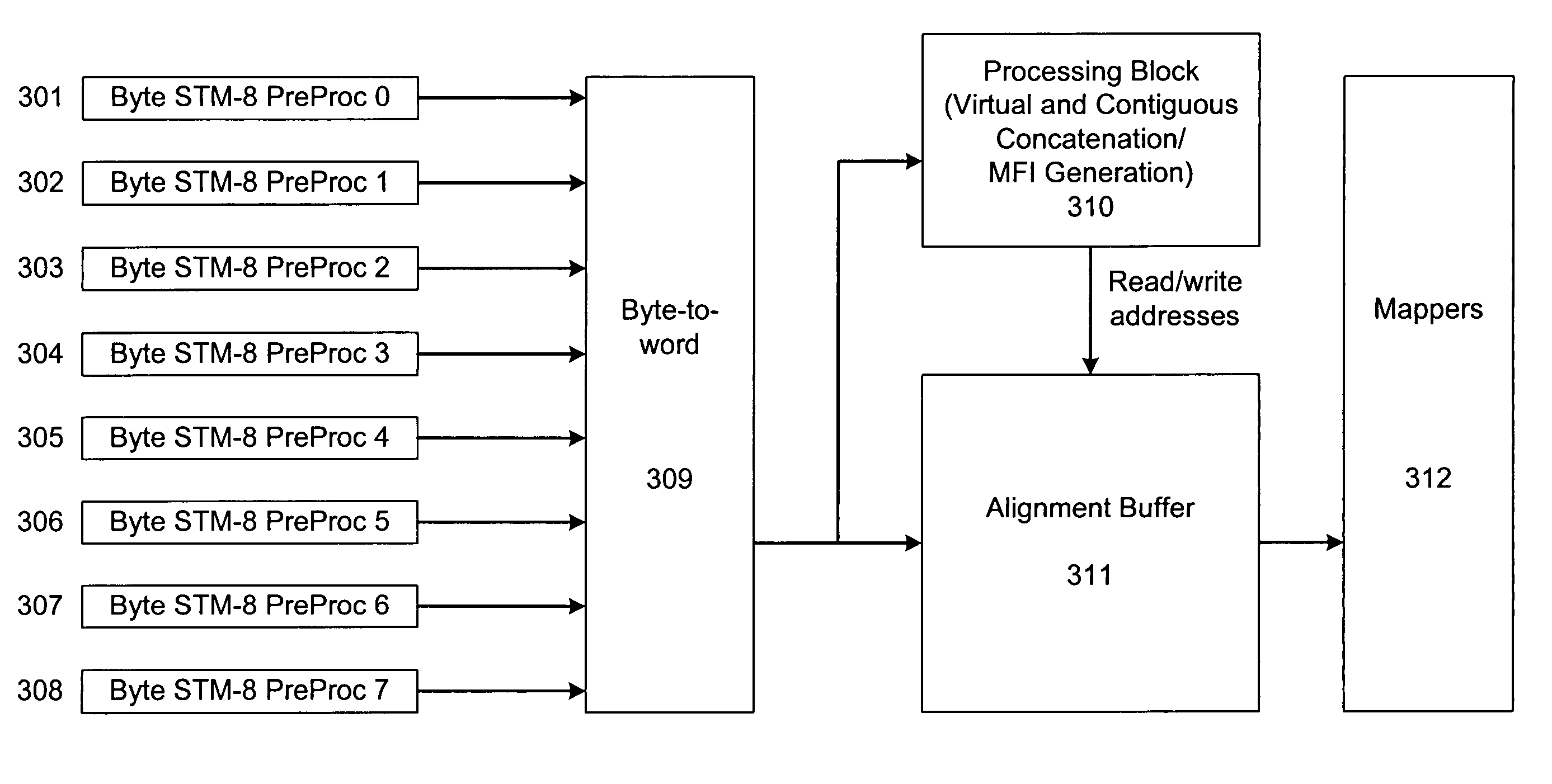
The present invention is a SONET payload processing system capable of handling virtual concatenation of SONET payloads. The payload processing system enables combinations of sub-frames, comprising an arbitrary number of virtual concatenation data streams, to be multiplexed into a single SONET frame stream. The present invention further provides a processing system that is not limited by the number of sub-frames or the grouping arrangement. The payload processing system accepts both virtual concatenation and contiguous concatenation within the same SONET frame stream and processes them into blocks of data that do not intermix information from different channels.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Link delay determination using virtual concatenation
ActiveUS20050265251A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsVirtual concatenationReal-time computing
Link delay is determined in a network comprising a plurality of nodes by identifying pairs of nodes associated with a given link, and, for each of the identified pairs, setting up a virtually-concatenated group (VCG) between the nodes of that pair. The VCGs are utilized to make delay measurements, and the delay measurements are processed to determine delay of the given link. In an illustrative embodiment, the VCGs comprise two-member VCGs with the members being routed on opposite sides of a logical ring. For a given one of these two-member VCGs, a differential delay measurement is made at a particular one of the associated nodes by comparing frame indicator fields for concurrently arriving frames. A system of equations is generated based on the differential delay measurements made utilizing the VCGs, and the system of equations is solved to obtain information utilizable to determine delay of the given link.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
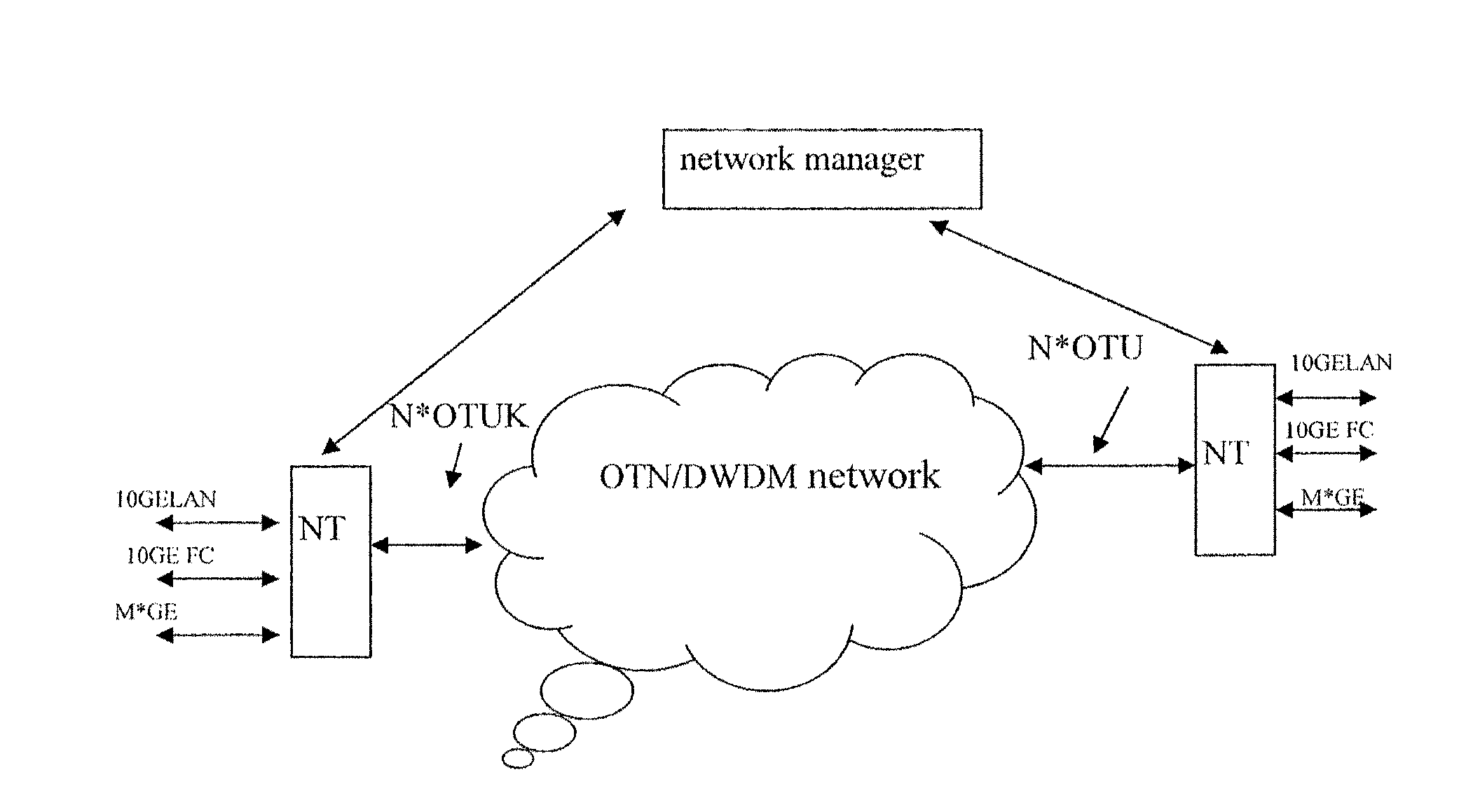
Method and apparatus for transporting local area network signals in optical transport network
InactiveUS20080124079A1Improve bandwidth utilizationTransparent transportationTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationChannel dataTransport network
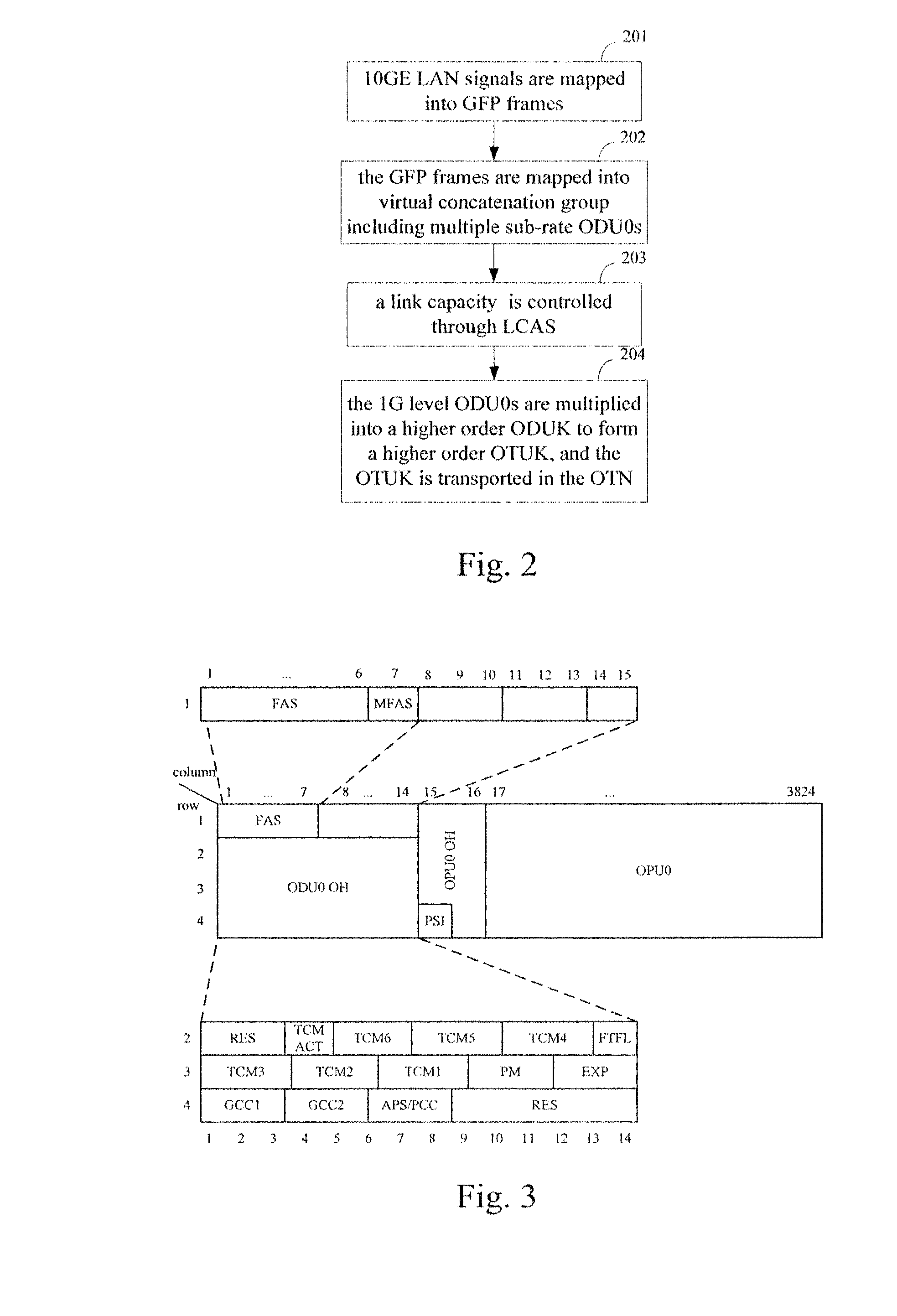
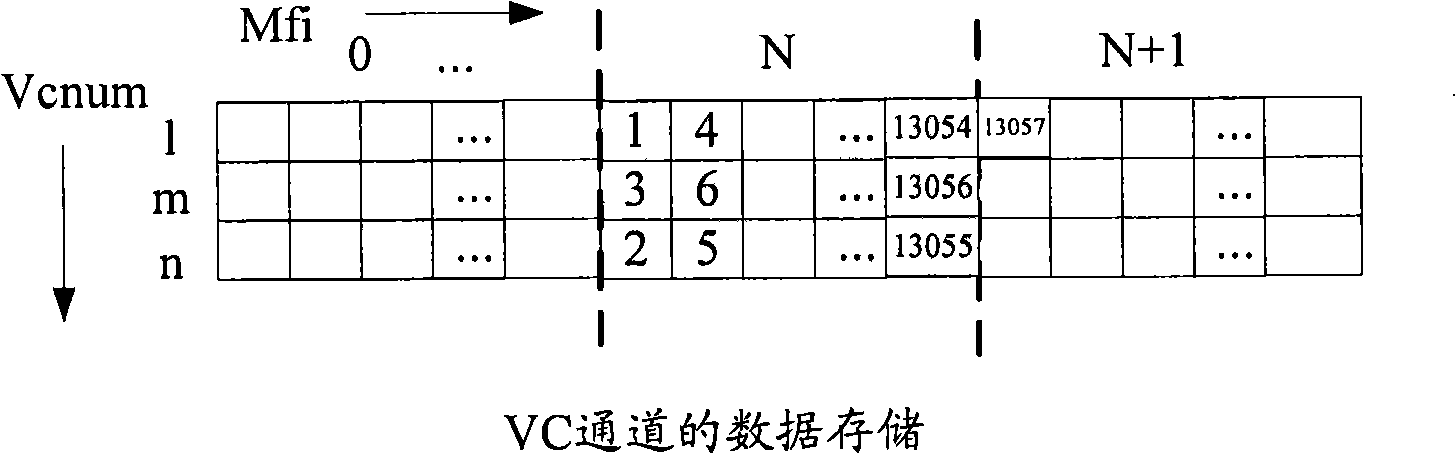
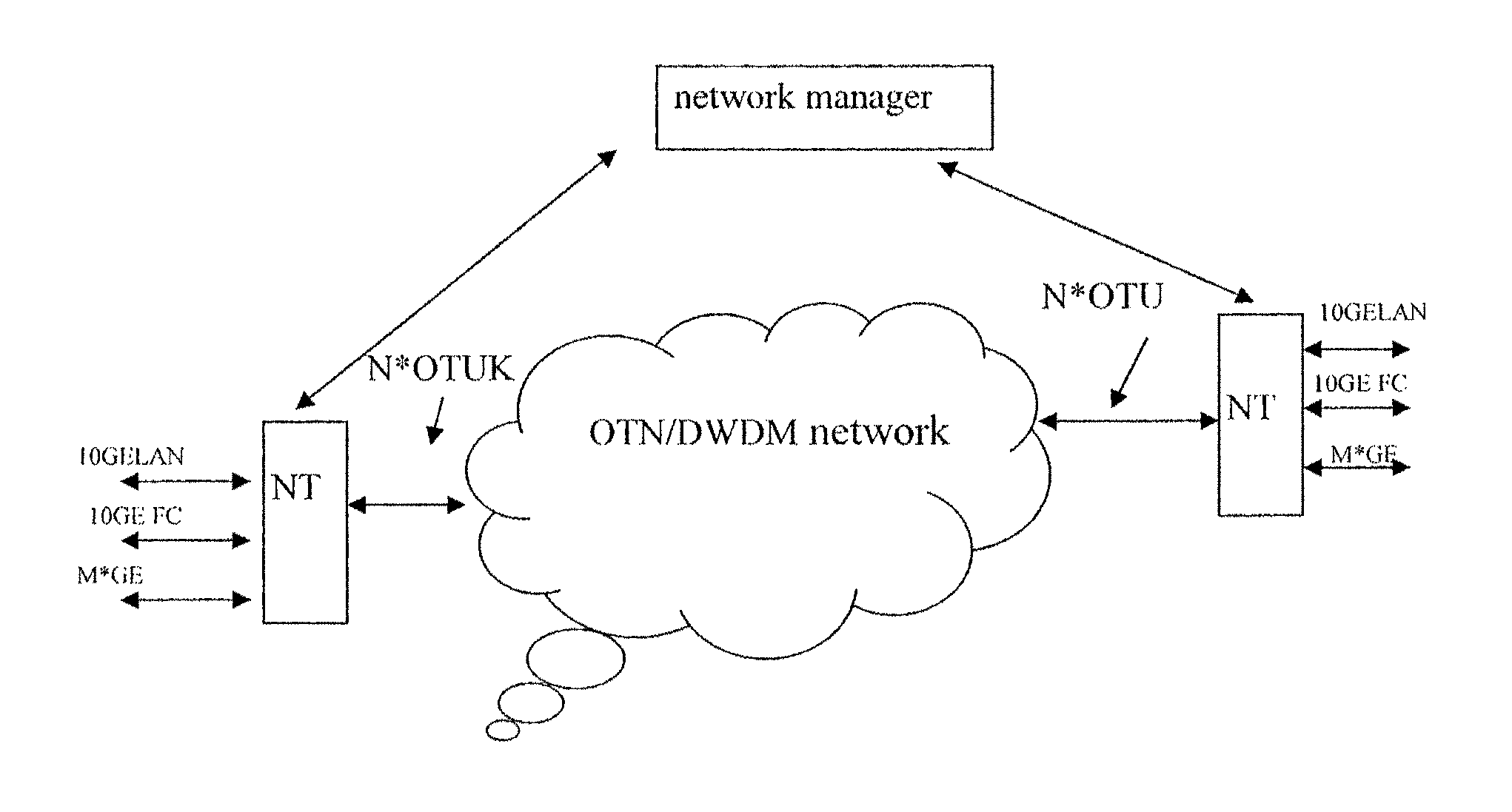
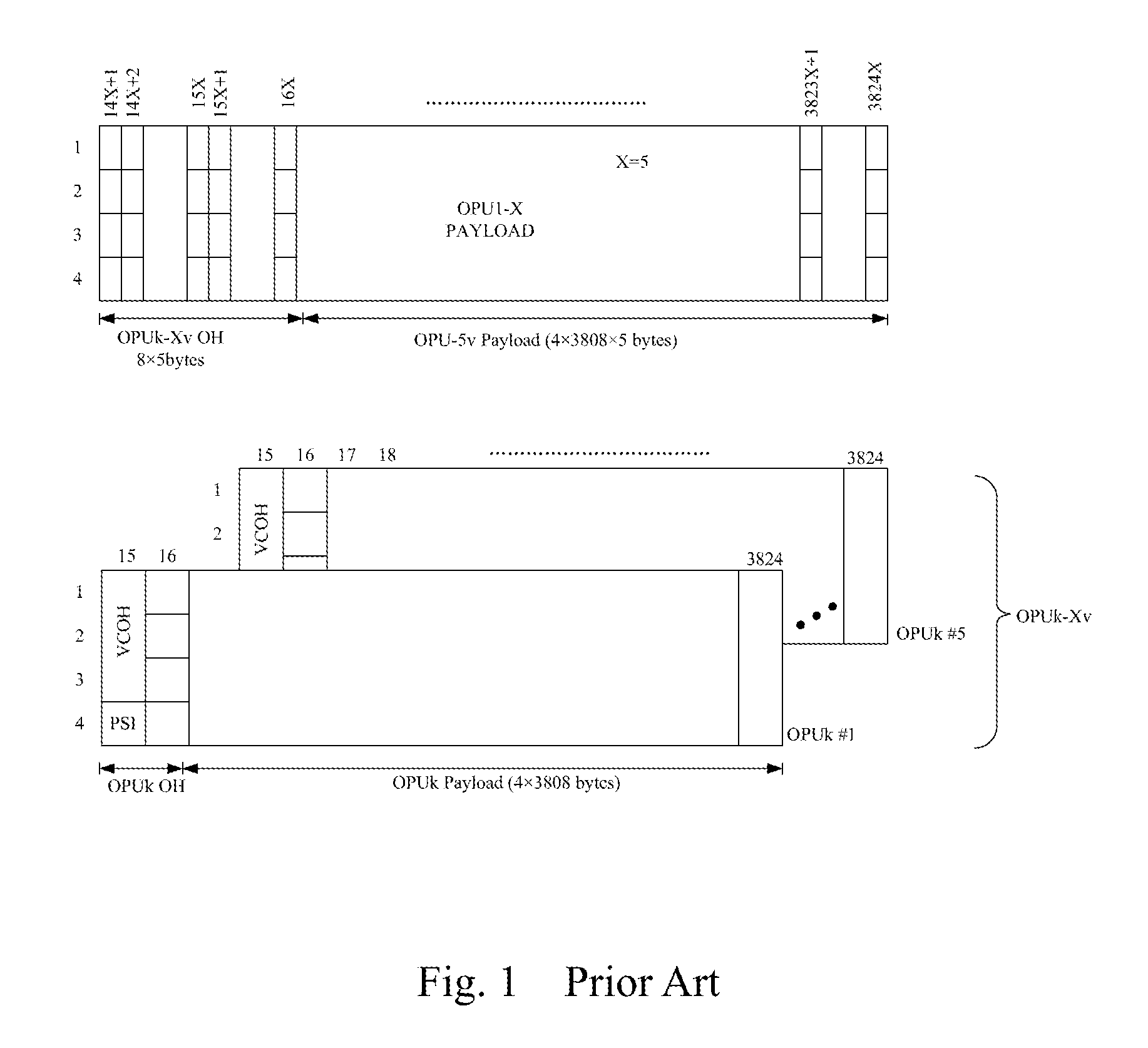
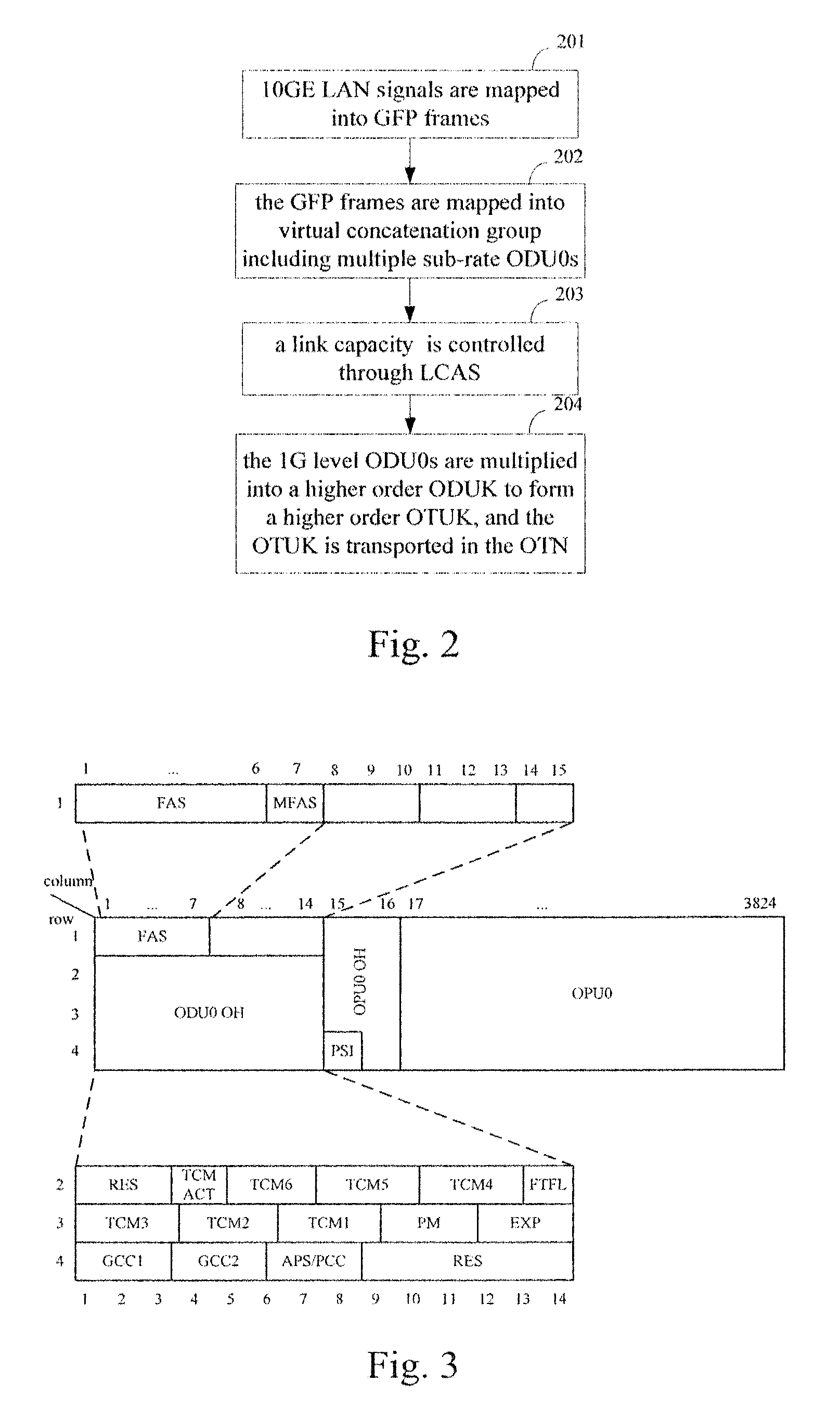
The method for transporting LAN signal in an OTN is provided by embodiments of the present invention includes mapping a LAN signal into an adaptation protocol frame; mapping the adaptation protocol frame into a virtual concatenation group comprising at least one 1 Gbps level Optical Channel Data Unit (ODU); multiplying the 1 Gbps level ODU in the virtual concatenation group into a higher order ODU; mapping the higher order ODU into a higher order Optical Channel Transport Unit (OTU); and outputting the higher order OTU to the OTN. Embodiments of the present invention improve the bandwidth utilization rate while implementing the transparent transporting of the LAN signal in the OTN.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for increasing transmission capacity in optical transport network
InactiveUS20080131117A1Improve transmission performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexSignaling networkEngineering
Provided are a method and apparatus for increasing transmission capacity for large-capacity high-speed signal transmission in an optical transport network (OTN). A method and apparatus for increasing transmission capacity are needed, which can transmit a large-capacity high-speed signal in order to transmit a signal through a united OTN by adapting signals from various tributary signal networks which have been independently operated for voice, image, or data transmission. Although various types of techniques such as Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), and an optical Printed Circuit Board (PCB) method have been performed, the techniques have various limitations. Therefore, a method and apparatus is provided for embodying a large-capacity optical transmission network, which overcome the limitations by using a Virtual Concatenation (VC) method.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Mapping system of virtual concatenation group signals
InactiveUS20060126641A1Efficient mappingSmall sizeTime-division multiplexWide area networksFiberStorage area network
An interface system is capable of transmitting packet data or non-continuous data through a network that is adapted to transmit continuous data. In particular, the interface system is directed to transmitting data from Ethernet, Storage Area Network (SAN), and / or Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) signals through a SONET fiber optics system. The interface system uses a Virtual Concatenation Group (VCG) signal to match the transmitting signal's bandwidth and effectively map it on to SONET / SDH frame. The interface system applies VCG mapping related to low order virtual container signals, VC-11 and VC-12 and higher order virtual container signals, VC-3 and VC-4. Likewise, the interface system may allow packet data to be transmitted through SDH configured network. The interface system may also use DPRAM (dual-port RAM) as the basic element of VCG mapping for the physical embodiment of VCG to reduce the size of the circuit. The interface system may also use two or more memories to prevent read / write collision that may occur when the input and output addresses are the same.
Owner:PONTUSYS
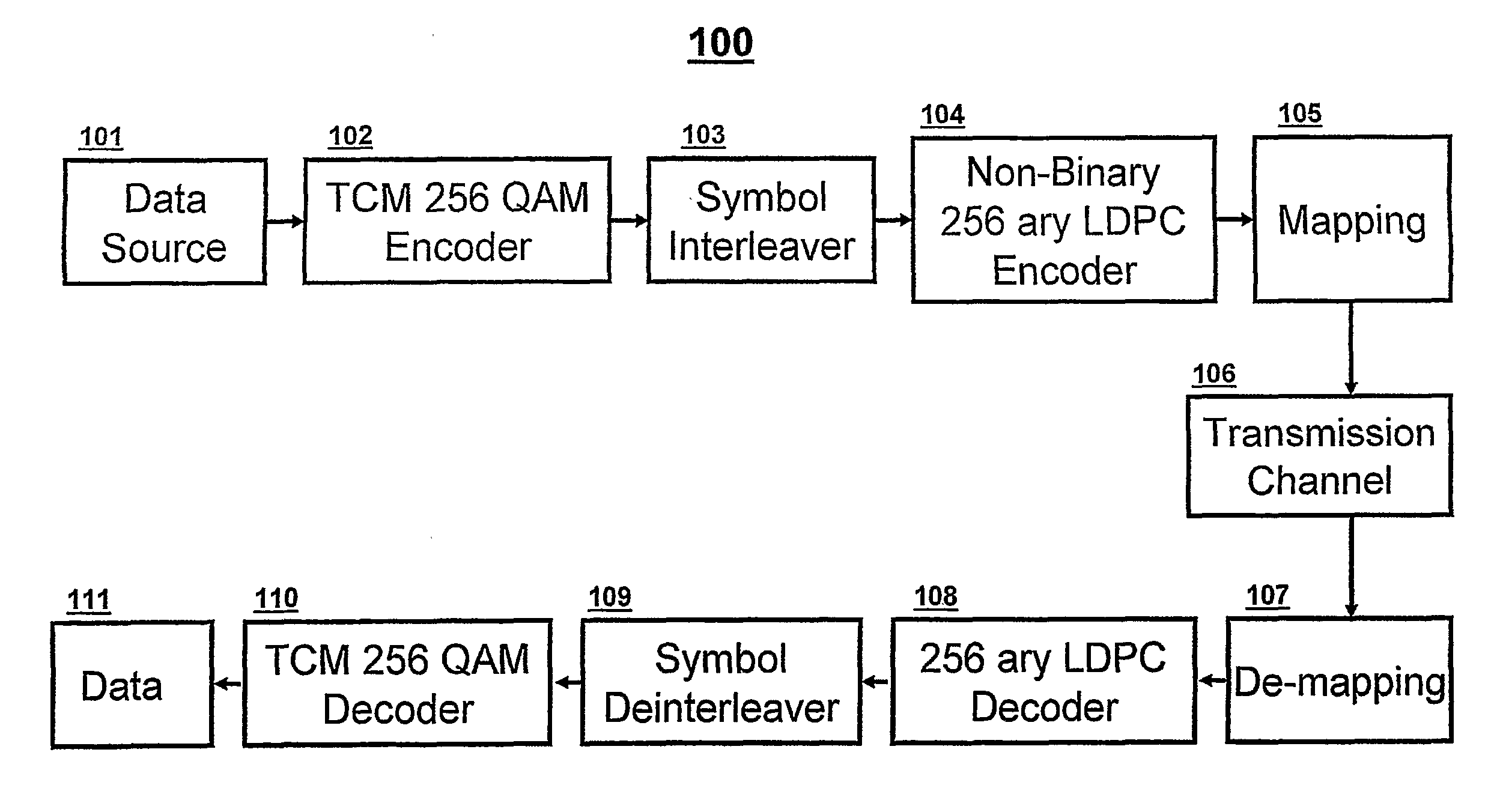
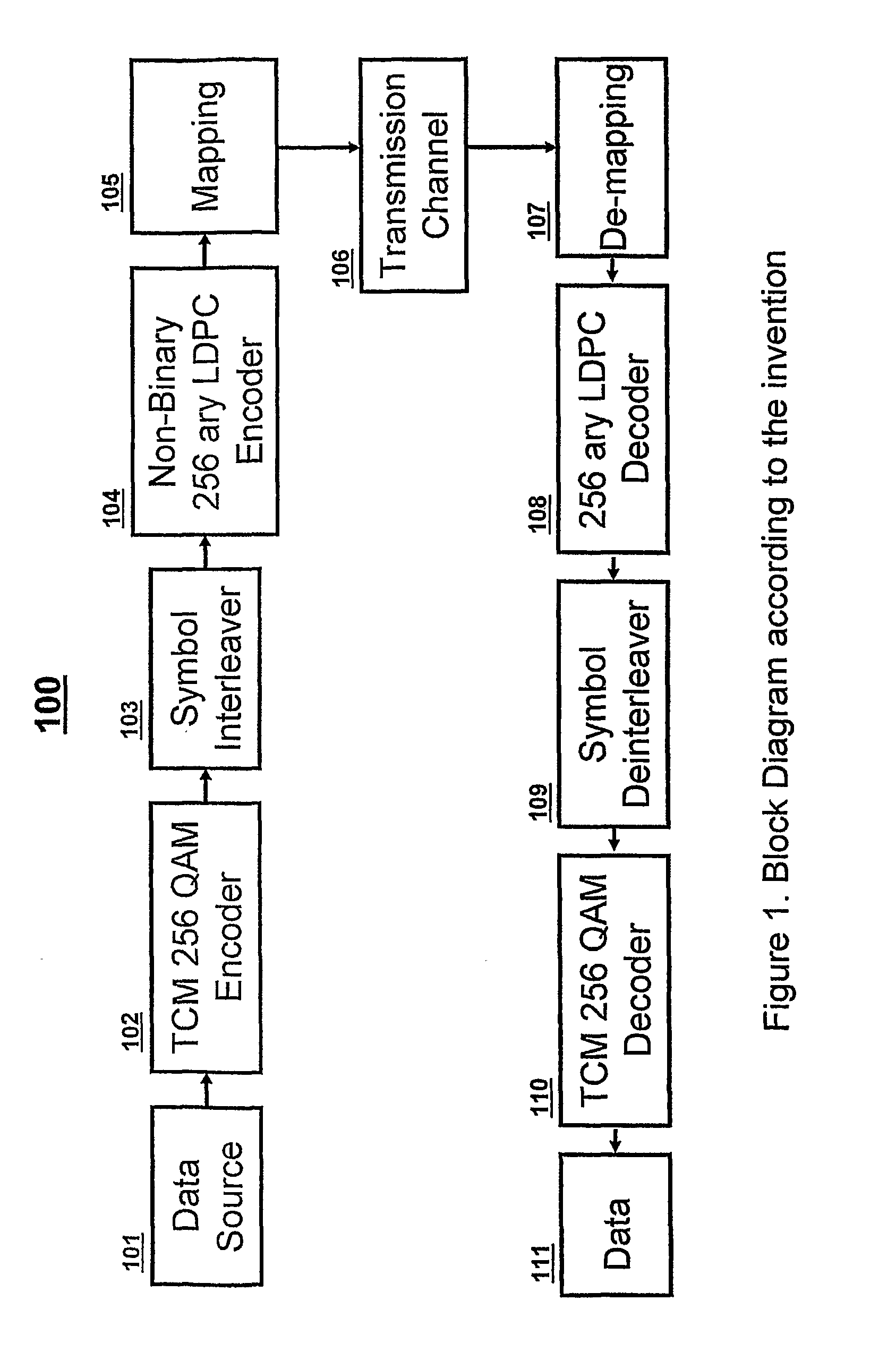
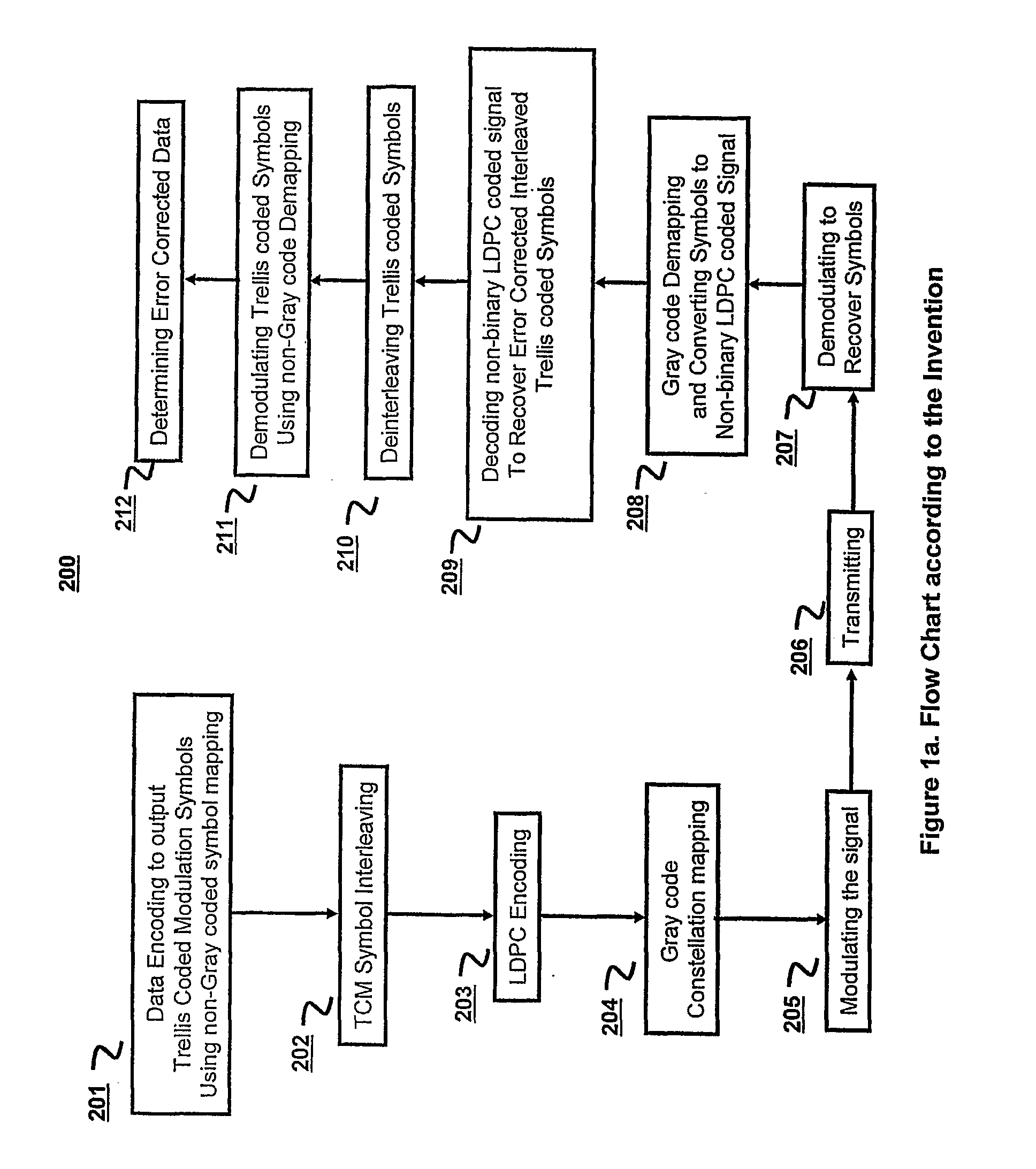
Serial concatenation of trelliscoded modulation and an inner non-binary LDPC code
InactiveUS20110078533A1Improve error performanceImproves burst error performanceError correction/detection using concatenated codesError correction/detection using trellis codingCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
A concatenated coded modulation communication system and method combines Trellis Coded Modulation with non-Gray code constellation mapping, interleaving, and non-binary Low Density Parity Check coded channel modulation with Gray code constellation mapping to improve error performance.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
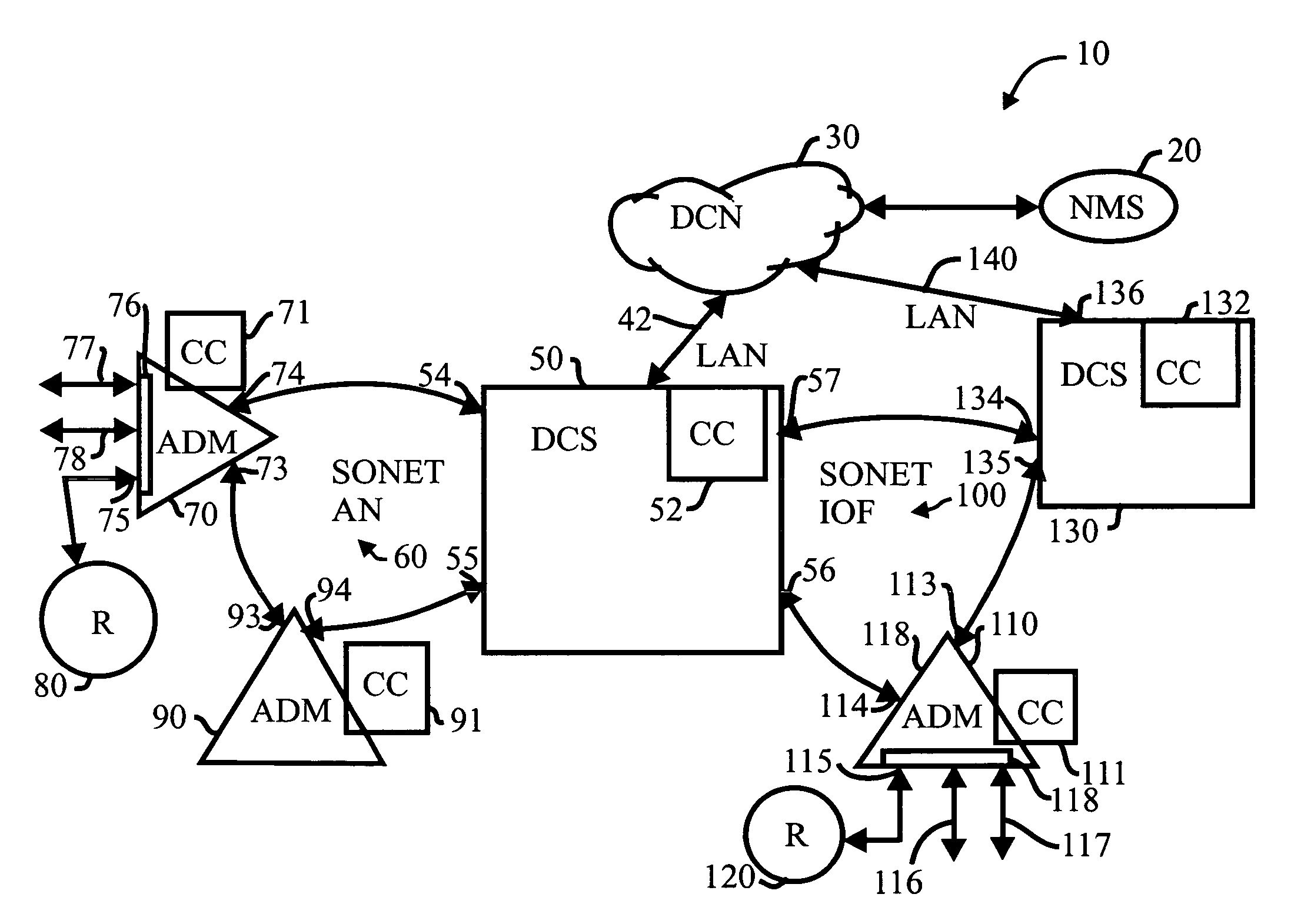
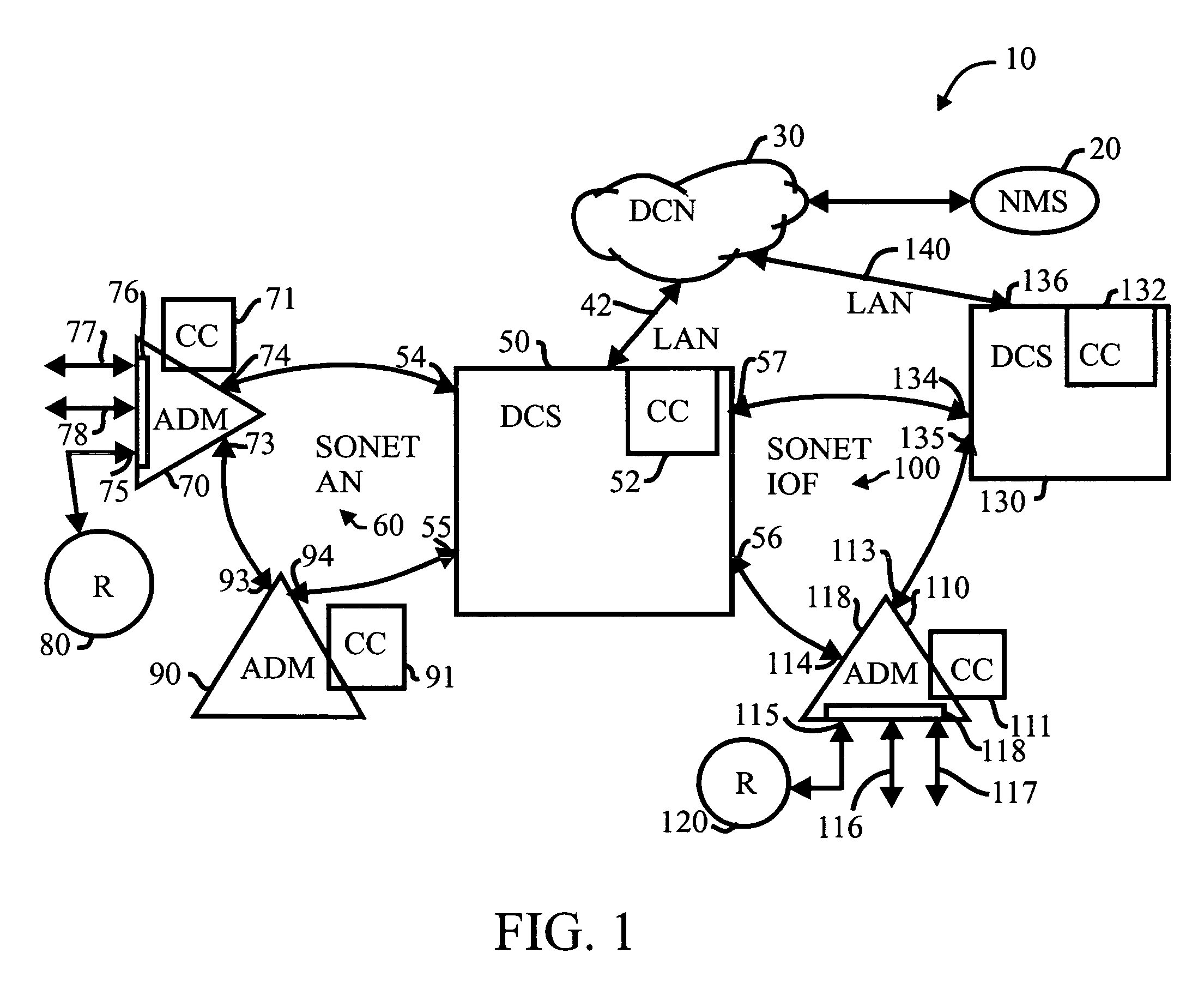
Dynamic bandwidth management using signaling protocol and virtual concatenation
InactiveUS7352758B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemMultiplexer
A communication system (10) employs switching circuits, such as an add / drop multiplexer (70) and another add / drop multiplexer (110). The bandwidth of a circuit switched connection between the switching circuits is altered without taking down the connection.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
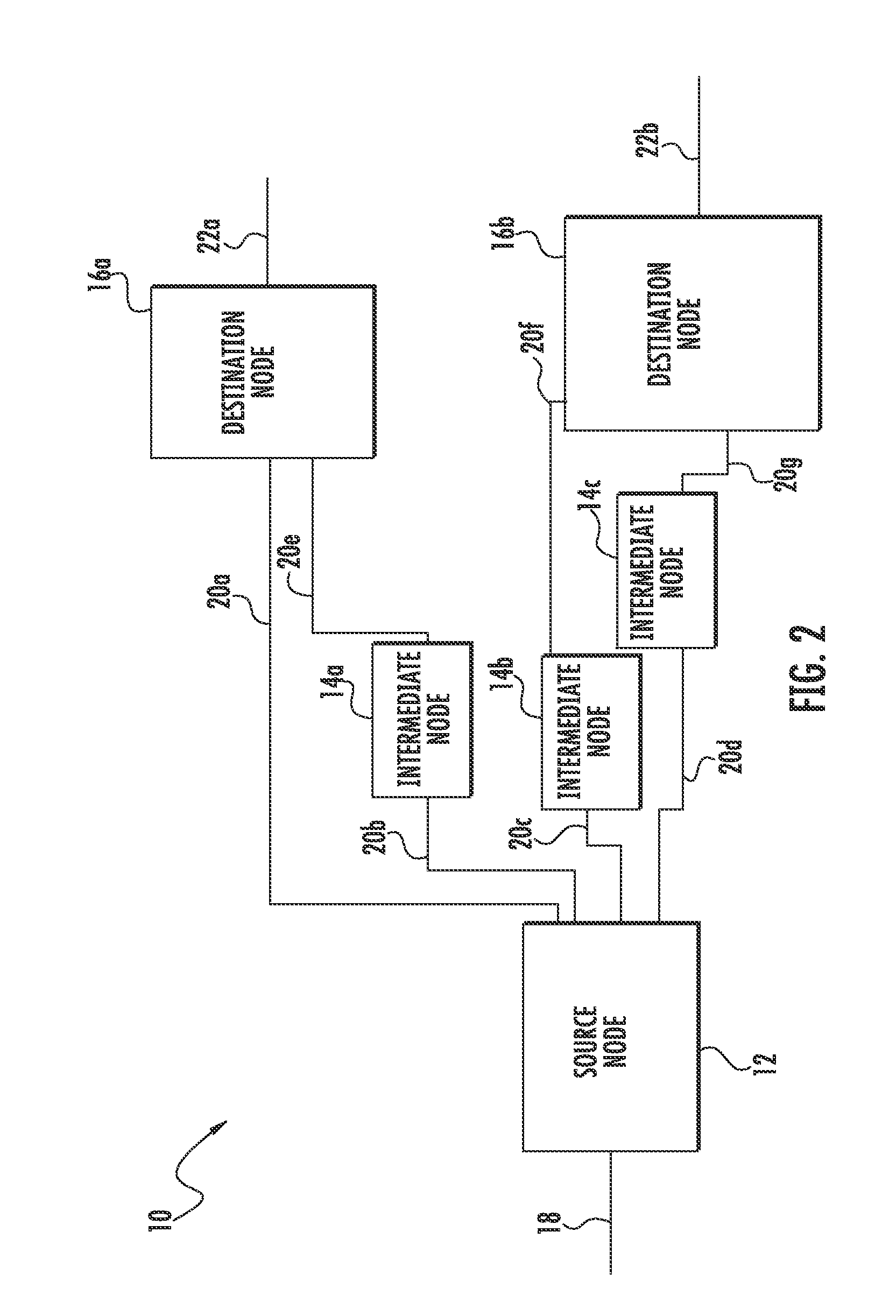
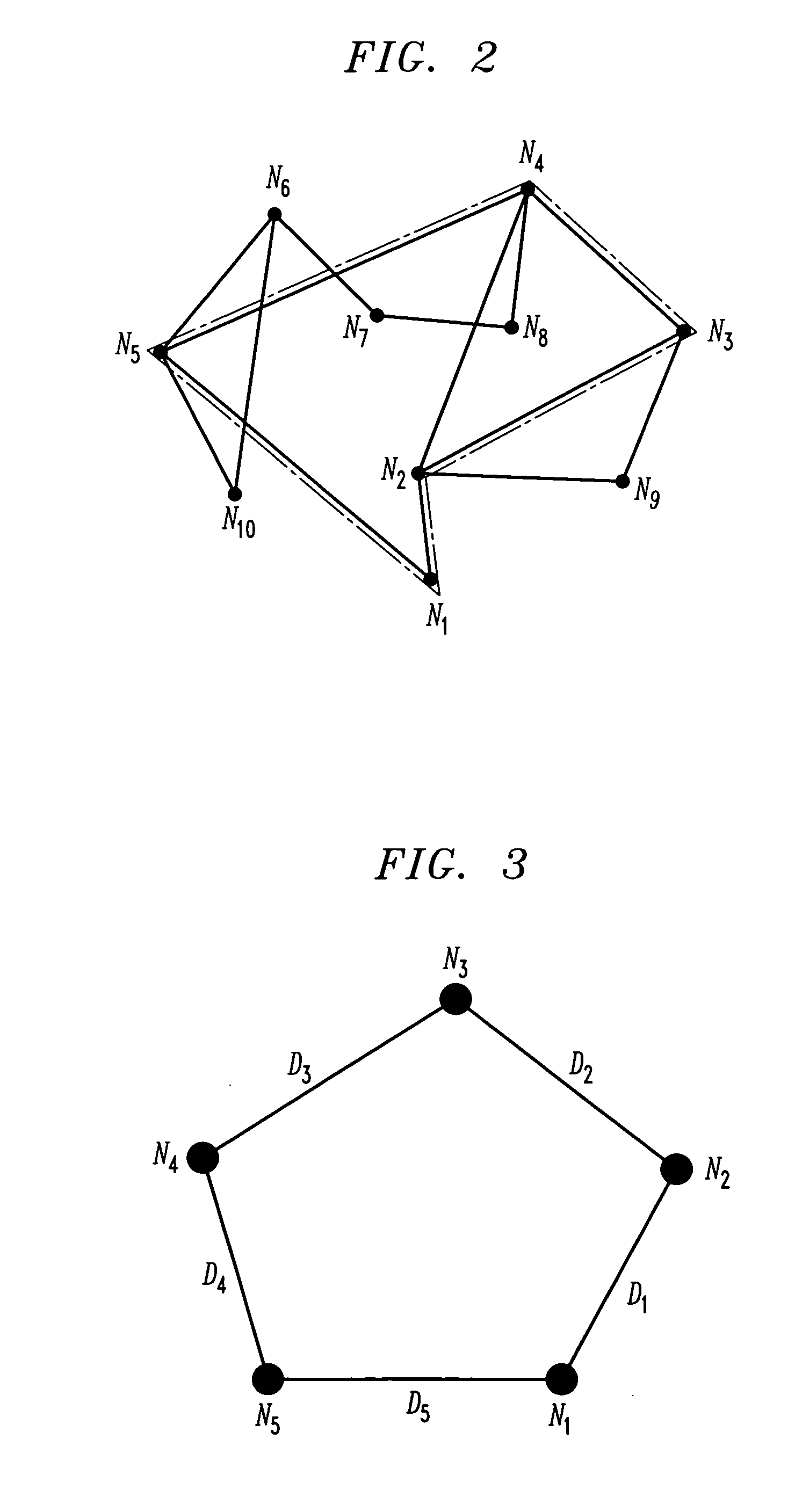
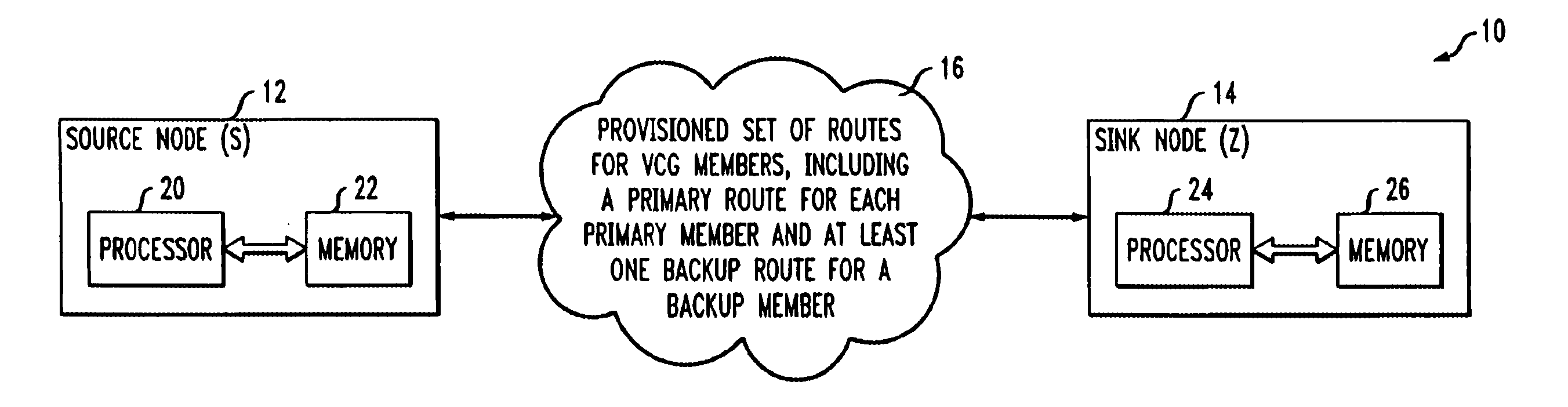
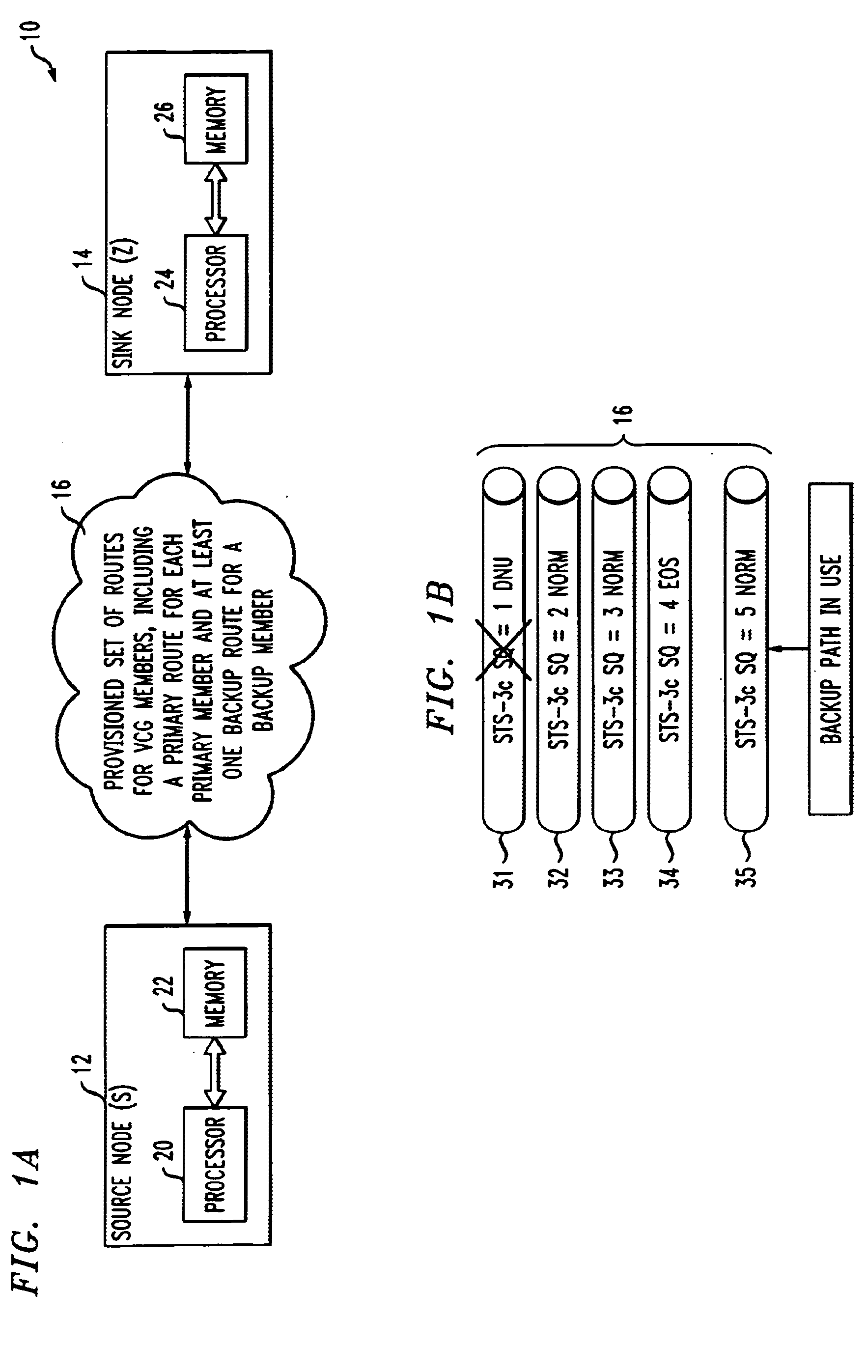
Route determination with differential delay compensation for virtually-concatenated data traffic
InactiveUS20050286425A1Easy to implementError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData trafficDistributed computing
Virtually-concatenated data traffic is routed in a network comprising a plurality of nodes, the plurality of nodes including one or more nodes that are differential delay enabled and one or more nodes that are not differential delay enabled. For a given traffic demand to be routed from a source node to a destination node in the network, at least one route is determined for routing the demand between an intermediate node that is differential delay enabled and one of the source node and the destination node that is not differential delay enabled. Also, a set of routes is determined for routing the demand between the intermediate node that is differential delay enabled and at least one other node of the network, that may or may not be differential delay enabled, with each of the routes in the set corresponding to a member of a virtually-concatenated group. The given traffic demand is routed from the source node to the destination node, utilizing the at least one route and the set of routes.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
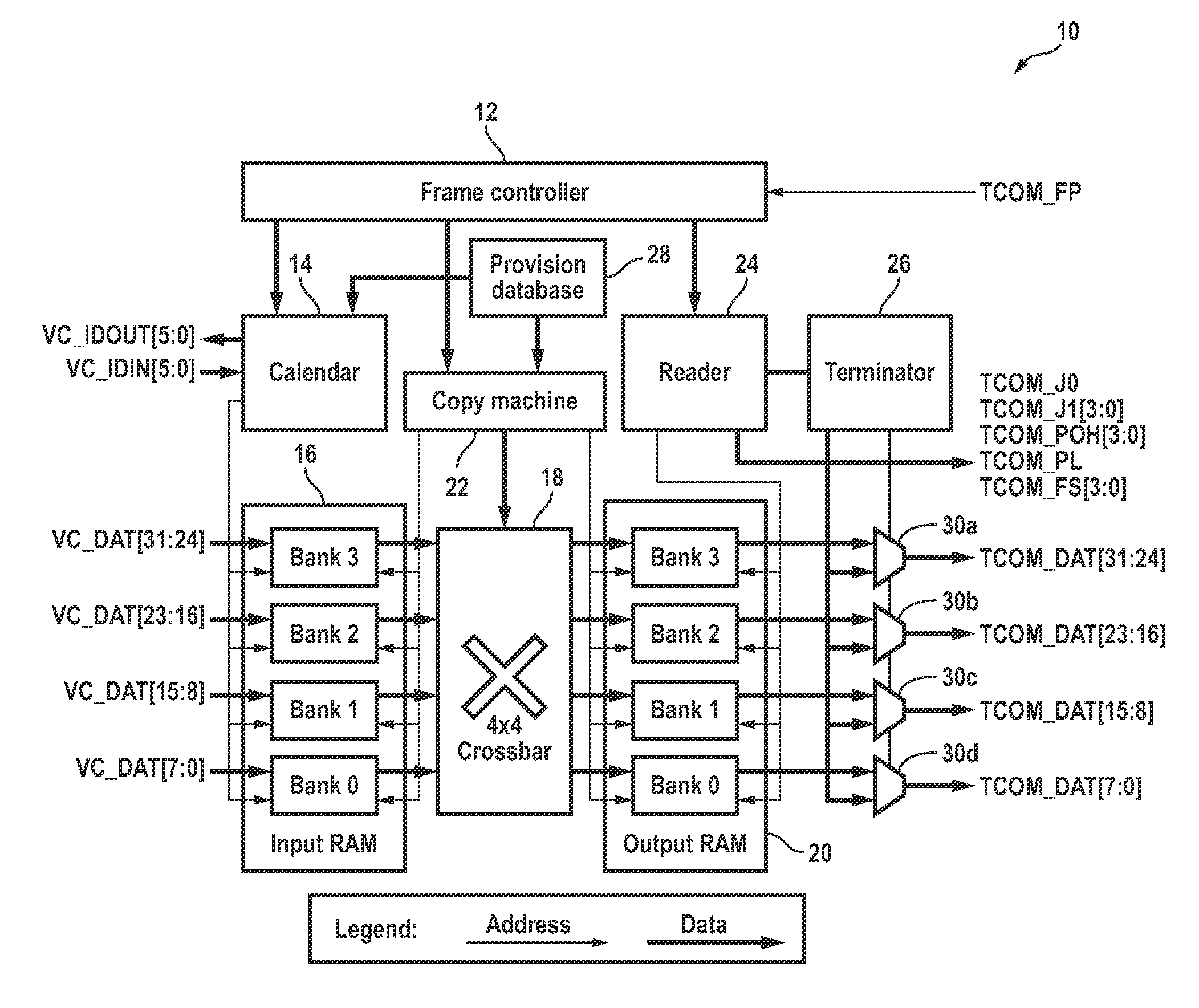
Transmit virtual concatenation processor
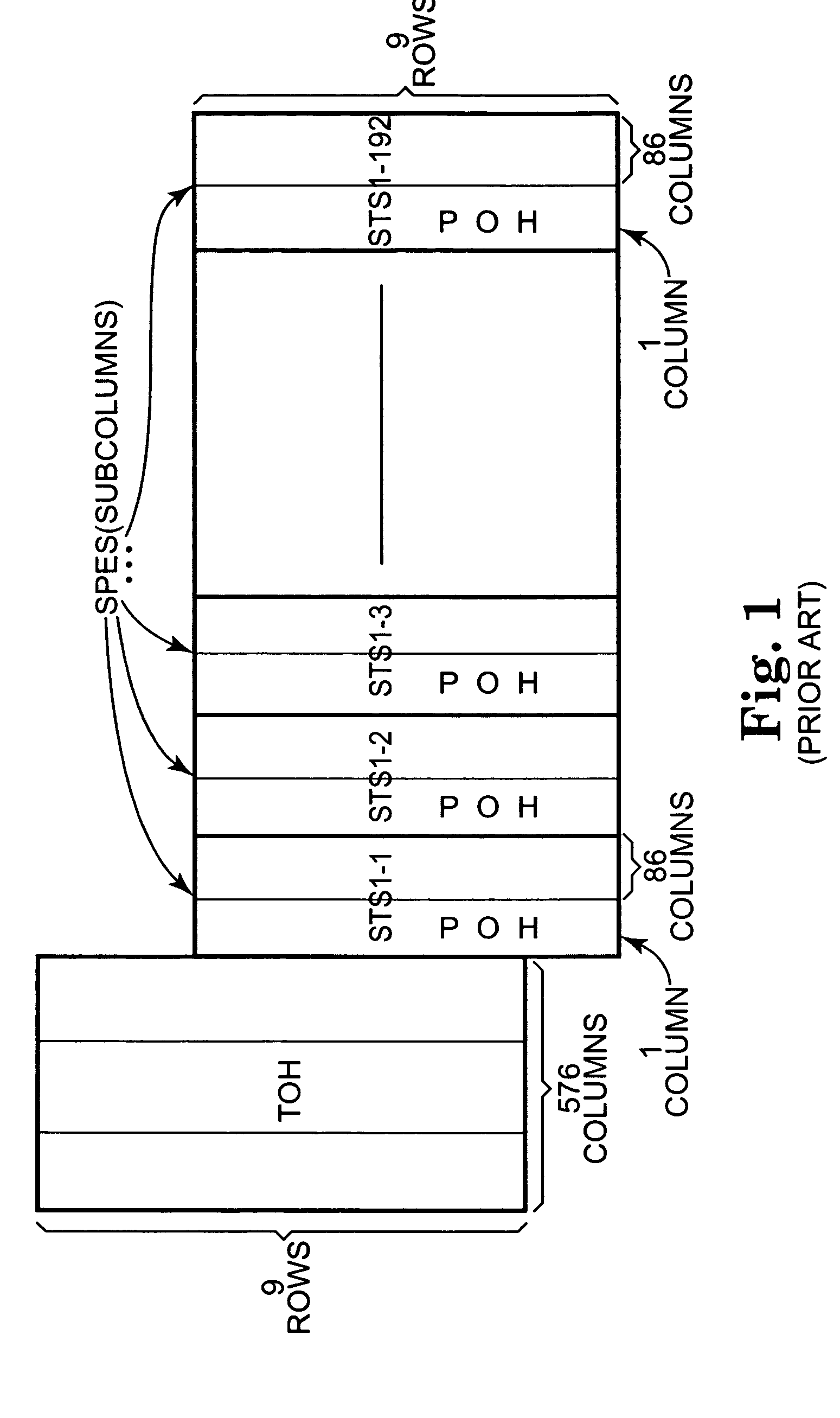
A transmit virtual concatenation processor for multiplexing channelized data onto a SONET / SDH frame is disclosed. The processor is scalable and is able to handle mapping a number of data channels to a number of different frame sizes including STS-12, STS-48, STS-192 and STS-768. The processor supports virtual concatenation with arbitrary channel mapping at both STS-1 and STS-3c granularities. The processor also supports contiguous concatenation with STS-12c, STS-24c, STS-48c, STS-192c, etc. capacities (i.e., STS-Nc where N is a multiple of 3). In addition, the processor supports mixed concatenation where some channels are using contiguous concatenation and some other channels are using STS-3c-Xv virtual concatenation. Alternatively, the processor is able to support any virtual concatenation, any contiguous concatenation and any mixed concatenation. The processor terminates the H1, H2 and H3 bytes in the line overhead of a SONET / SDH frame and inserts the multi-frame indicator and sequence number in the H4 byte of the path overhead.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
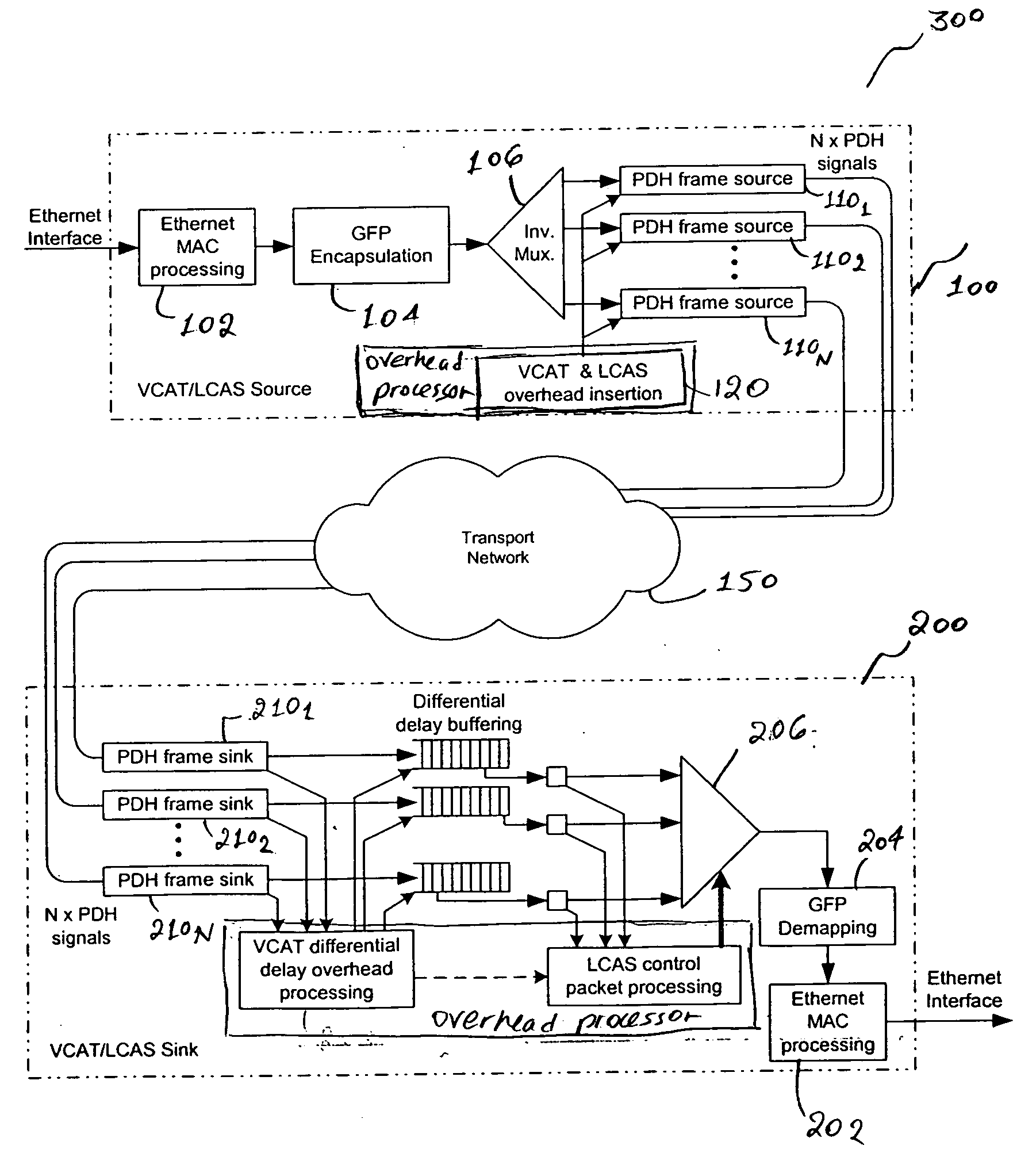
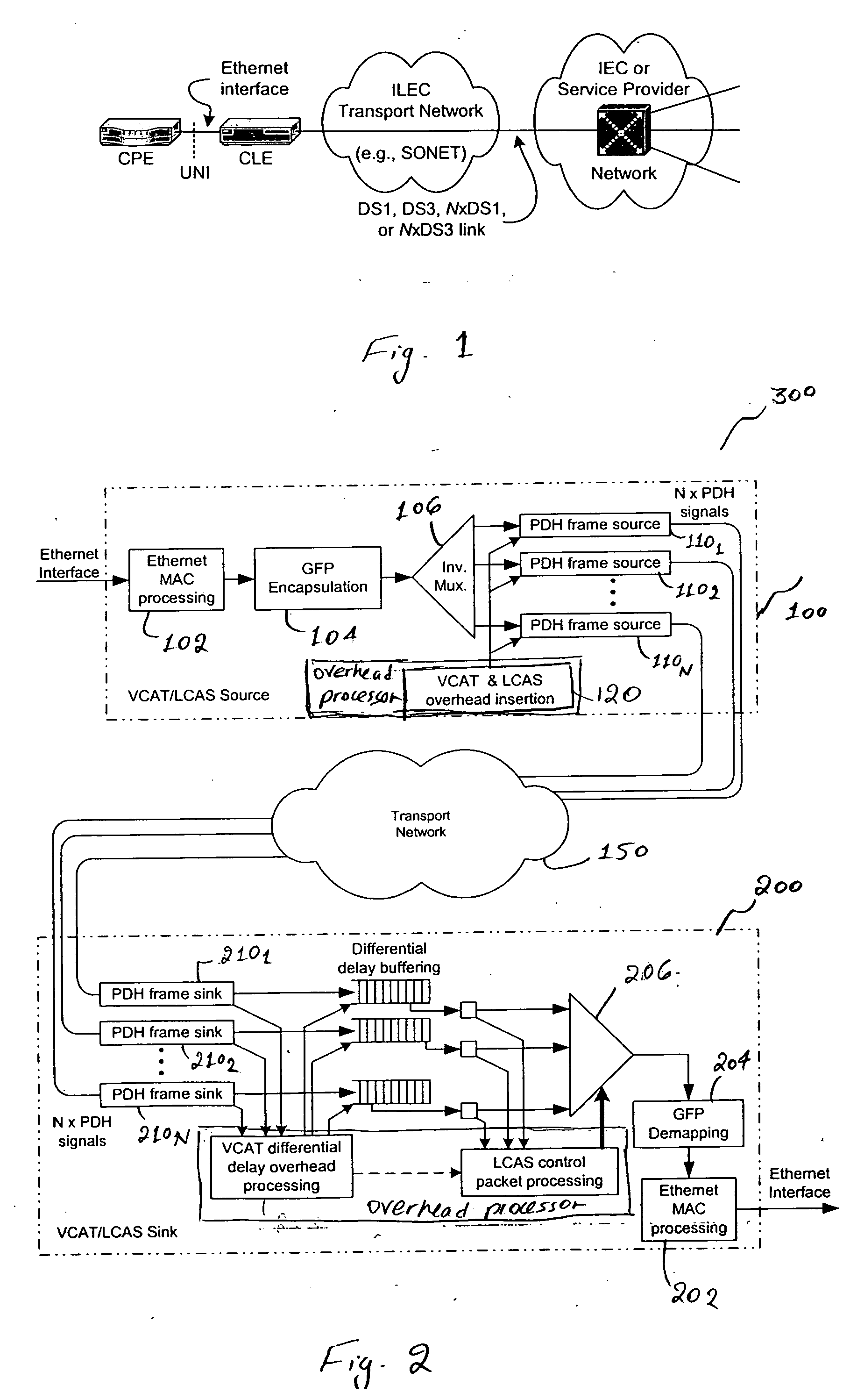
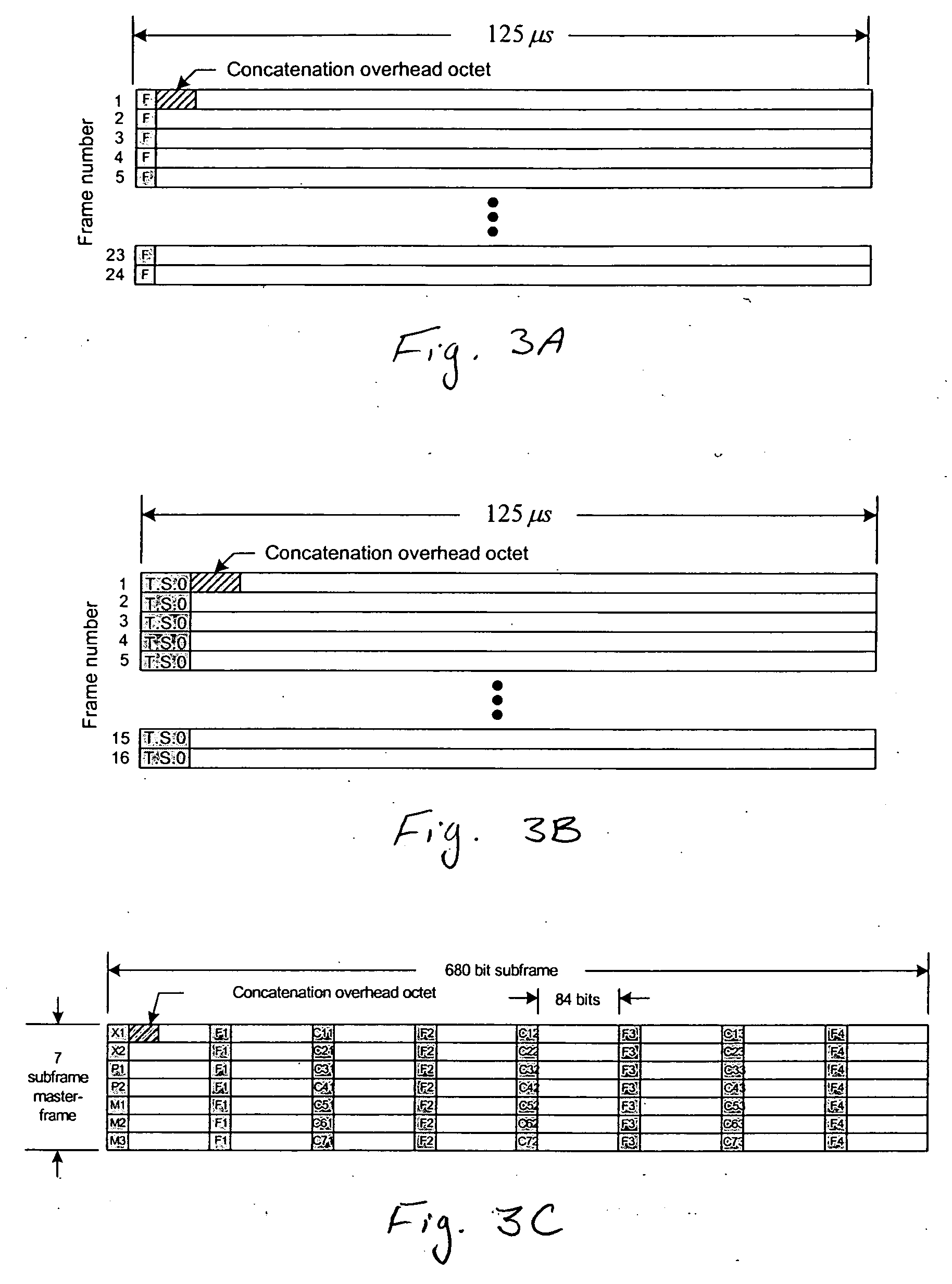
Virtual concatenation of PDH signals
Asynchronous / plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) signals, such as DS1 and E1, are transported using virtual concatenation. The packetized data signals are frame encapsulated and subsequently inverse multiplexed into a plurality of PDH frames. An overhead packet is inserted in the transmitted frames to enable the receiver to determine the status of the frames and extract the differential delay experienced by various frames as they are routed through virtually concatenated channels. The extracted delays enables the receiver to realign the various frames of the PDH signal to reconstitute the originally transmitted signals that travel through different paths of the transport network linking the source and sink of the virtually concatenated channel.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA +1
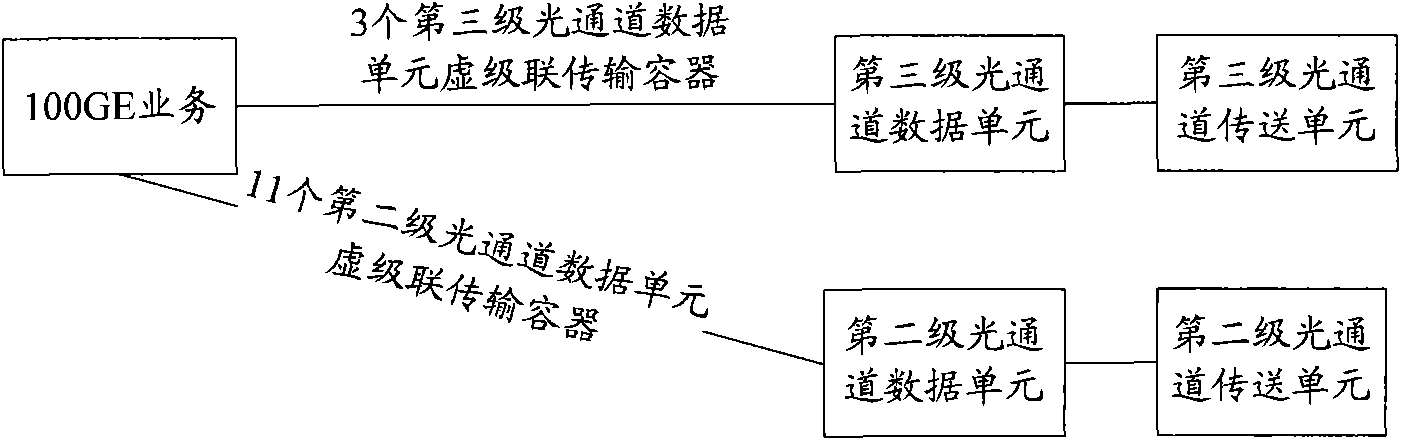
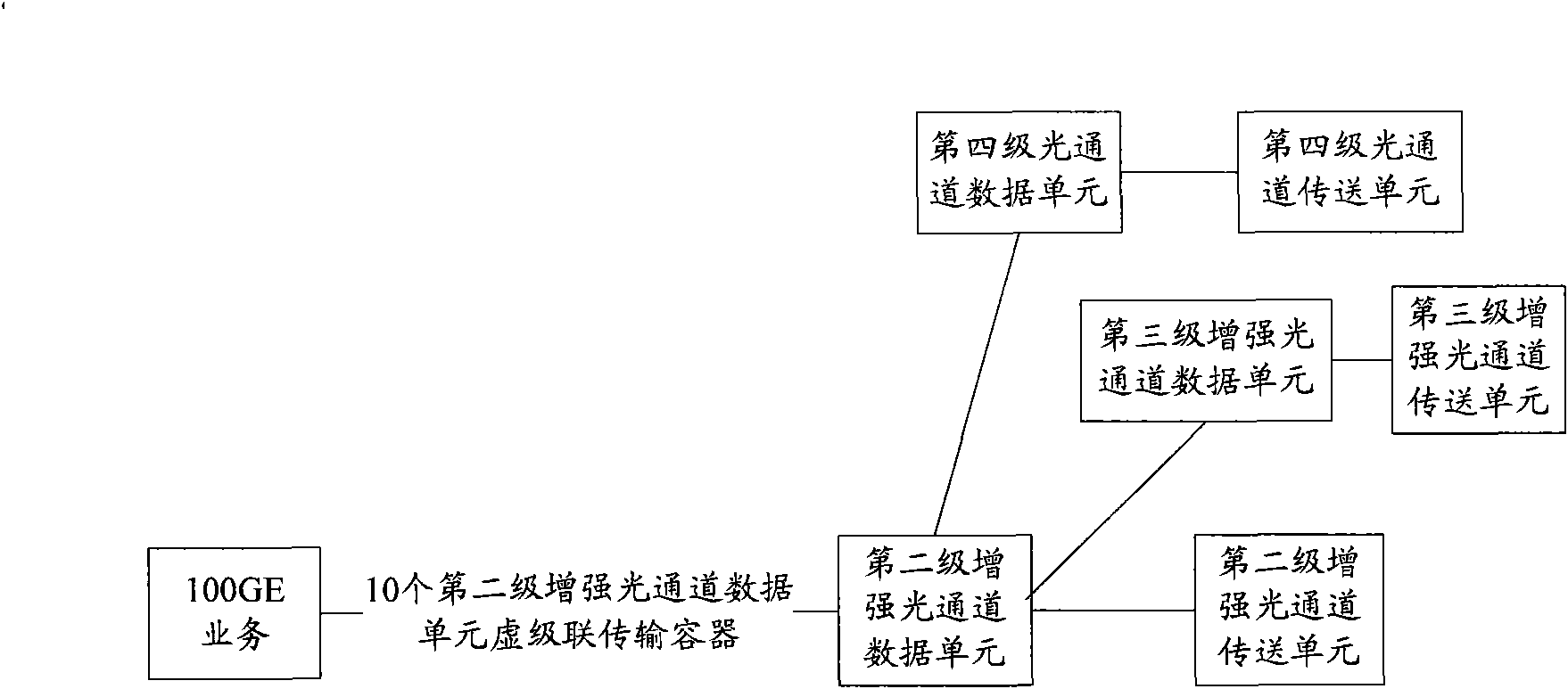
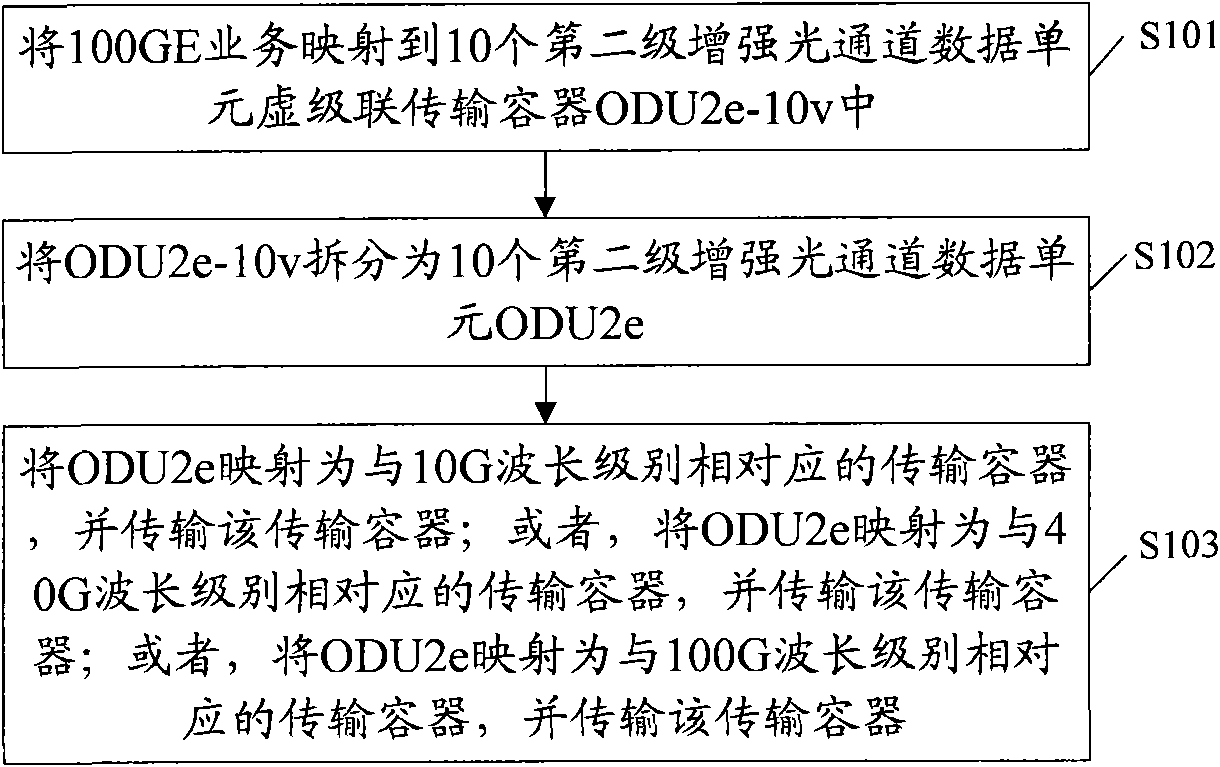
Method and device for transmitting business
InactiveCN101827285AImprove bandwidth utilizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsCode division multiplexTelecommunicationsLength wave
The invention relates to a method and a device for transmitting business. The method comprises the following steps of: mapping business to be transmitted to a preset virtual concatenation transmission container; splitting the virtual concatenation transmission container; selecting the wavelength grade for transmitting the business; mapping the split transmission container into a transmission container corresponding to the wavelength grade; and transmitting the business to the transmission container corresponding to the wavelength grade. The use ratio of bandwidth can be improved and the hardware cost is reduced by the embodiment of the invention.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Delay distributed virtually-concatenated data traffic
ActiveUS20060140116A1Buffer size requiredDestination be minimizedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityLatency distribution
Network design techniques and techniques for routing virtually-concatenated data traffic in a network in a manner which distributes delay to intermediate nodes of the network are disclosed. For example, in one aspect of the invention, a technique for routing virtually-concatenated data traffic in a network comprising a plurality of nodes comprises, for a given traffic demand to be routed from a source node to a destination node in the network, the following steps / operations. Two or more paths are determined to route the given traffic demand. Each of the two or more paths correspond to a member of a virtually-concatenated group. At least one path of the two or more paths comprises the source node, the destination node and at least one other node coupled between the source node and the destination node. Further, at least a subset of the source node, the destination node and the one other node buffer at least a portion of the given traffic demand such that a delay is distributed over the at least one path. The given traffic demand is routed over the two or more determined paths. The at least one path is preferably the shorter of the two or more determined paths.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
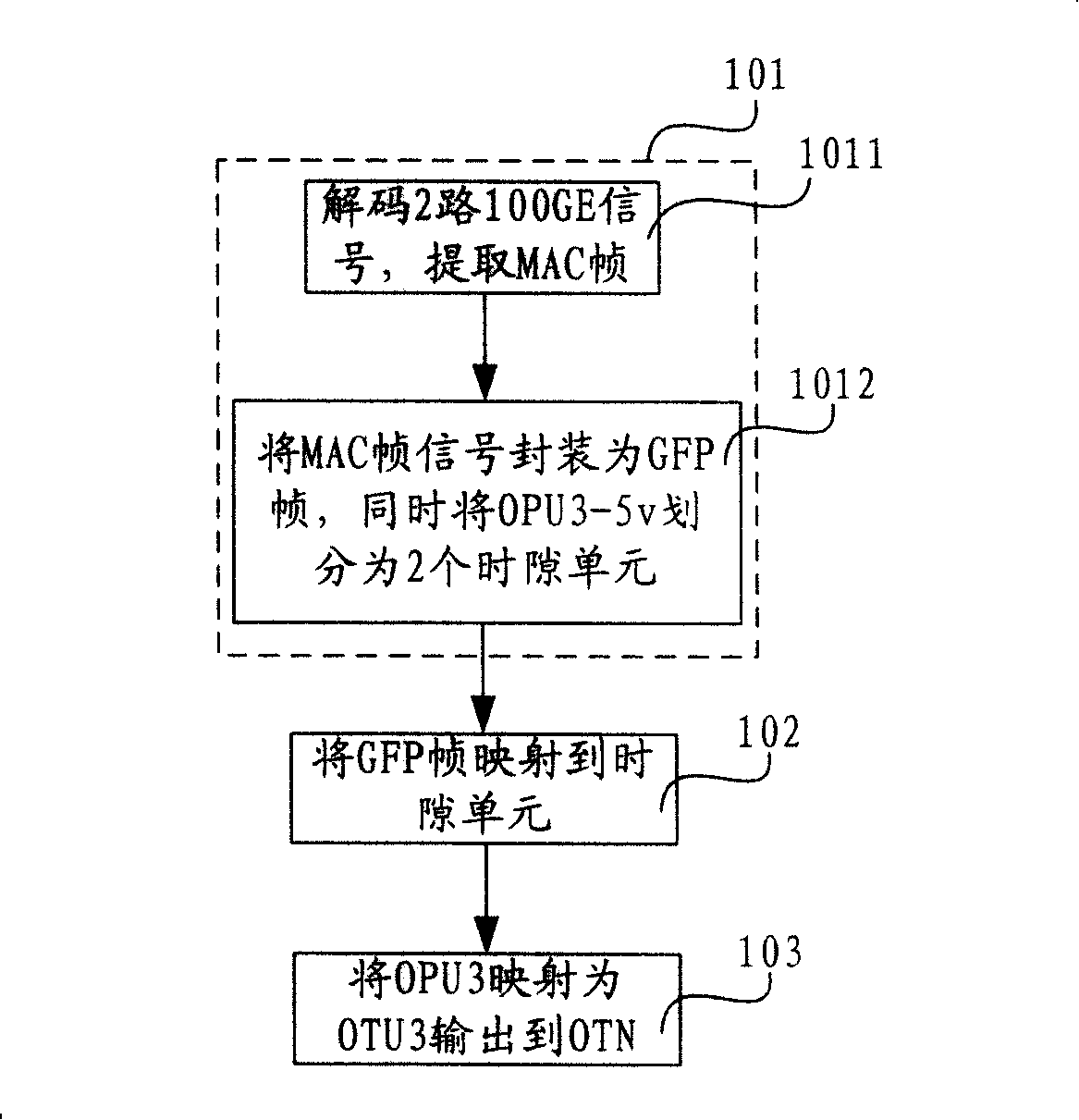
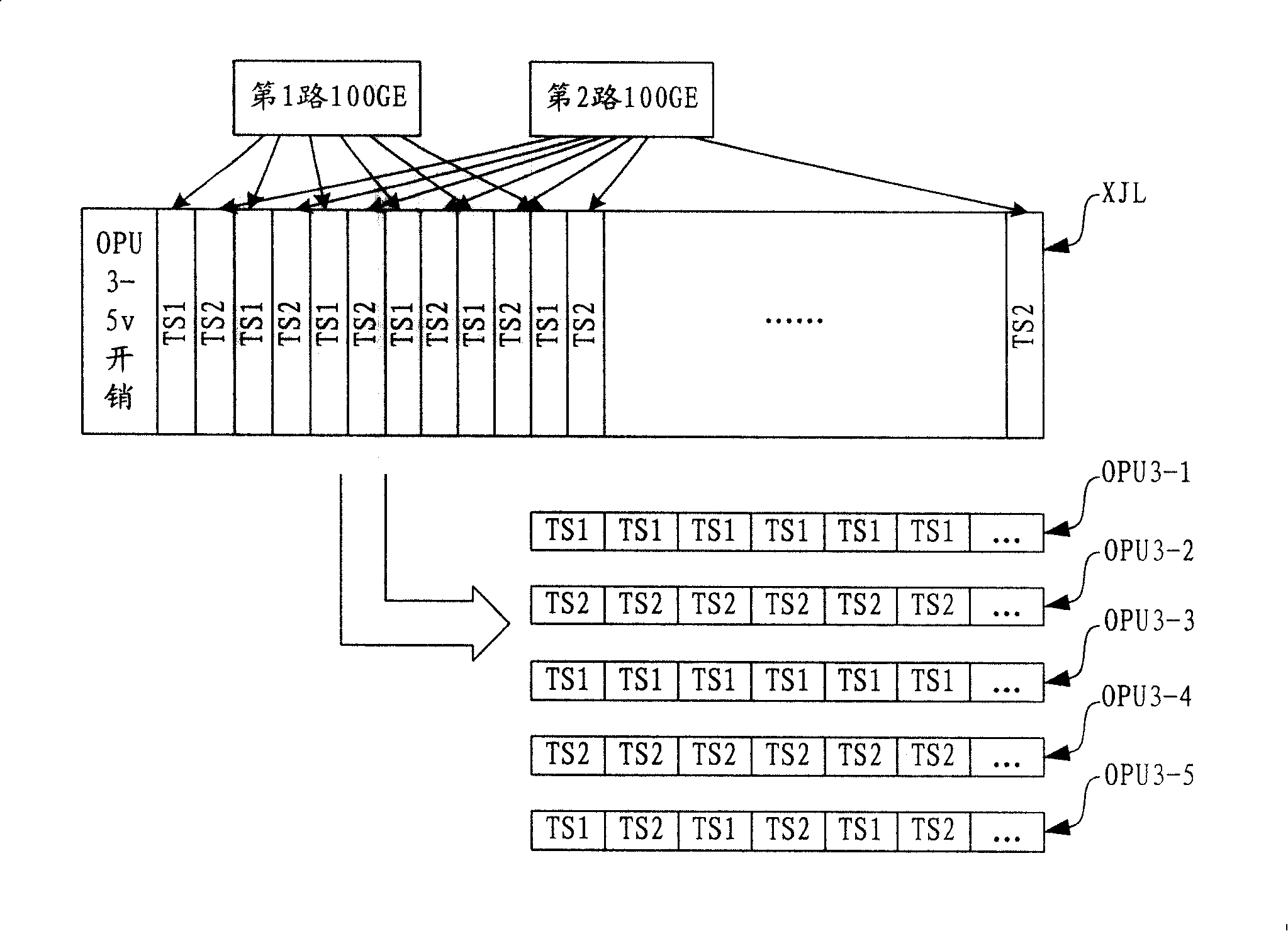
Method, device and system for transmitting Ethernet signals in optical transmission network
ActiveCN101242232ARealize transparent transmissionReduce delivery costsMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringOptical Transport Network
The invention relates to a method, device and system for transmitting Ethernet signals in an optical transport network. The method includes: mapping the Ethernet signals to a time slot unit divided by a virtual concatenation group which is made up of a plurality of optical channel pure-load unit; mapping the Ethernet signals to the optical channel pure-load unit and then being mapped to the optical channel transport unit and output to the optical transport network to transmit, thus realizing the transparent transmission of the Ethernet signals in the optical transport network. The device includes a first adaptation protocol frame mapping module, a first virtual concatenation module, and a first line terminal module, which convert the Ethernet signals to the optical channel transport unit. The device includes a second line terminal module, a second virtual concatenation module and a second adaptation protocol frame mapping module. The optical channel transport unit is reduced to the Ethernet signals. The system may include the first adaptation protocol frame mapping module, the second adaptation protocol frame mapping module, the first virtual concatenation module, the second virtual concatenation module, the first line terminal module, and the second line terminal module, which convert the Ethernet signals to the OTUs and vice versa.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Synchronizing system and method for virtual cascade of light transportation network
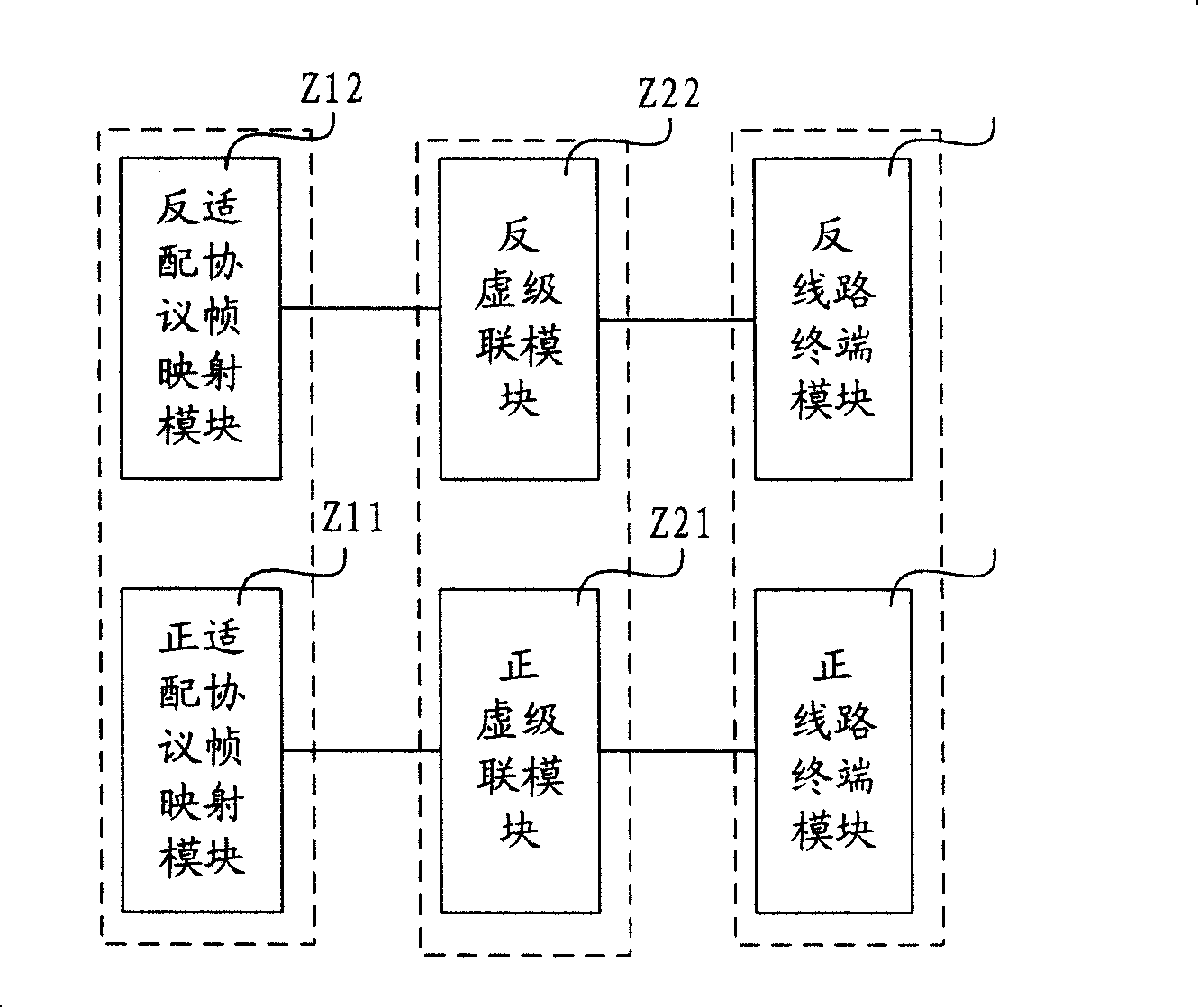
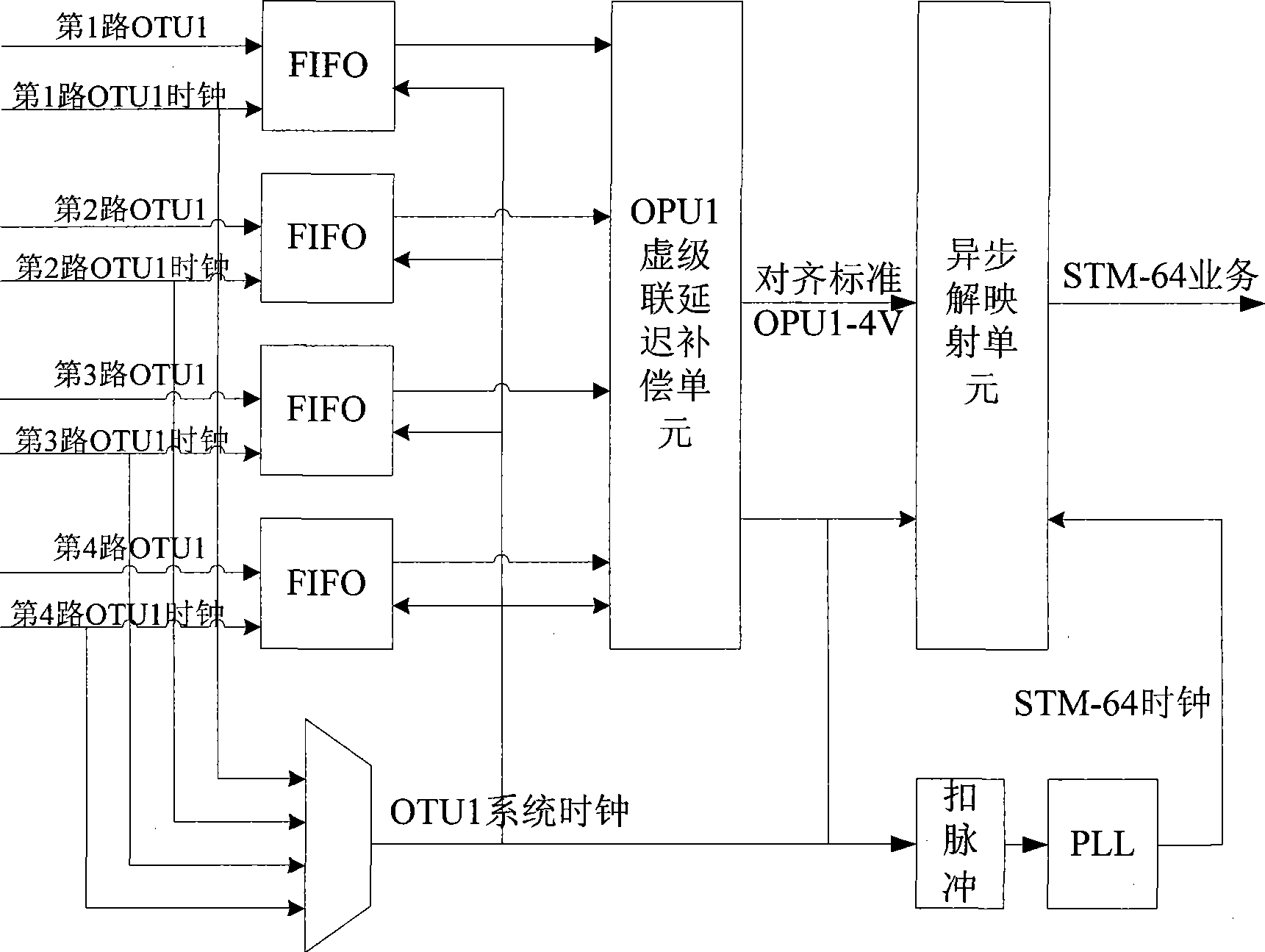
InactiveCN101374030ASuppress jitterSolve the problem of clock jitter index degradationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexSimulationOptical communication
The invention discloses a virtual concatenation synchronization system in an optical transport network (OTN) and a method thereof, belonging to the field of optical communications. The system comprises a synchronization unit, a virtual concatenation delay compensation unit, an asynchronous demapping unit, a smooth service acquisition unit, and a service data recovery unit. The method comprises the steps of carrying out virtual concatenation delay compensation by using fixed-point floatation of an optical channel payload unit (OPUk), and recovering service data by combining asynchronous demapping during synchronization process. The technical proposal provided in the invention can effectively inhibit jitter due to synchronization and virtual concatenation delay compensation, thereby solving the deterioration problem of clock jitter performance arising from transport of constant bit rate services via virtual concatenation in the OTN.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Data transmission in an SDH network
InactiveUS7277459B1High bandwidthTime-division multiplexTime-division multiplexing selectionHigh bandwidthData signal
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
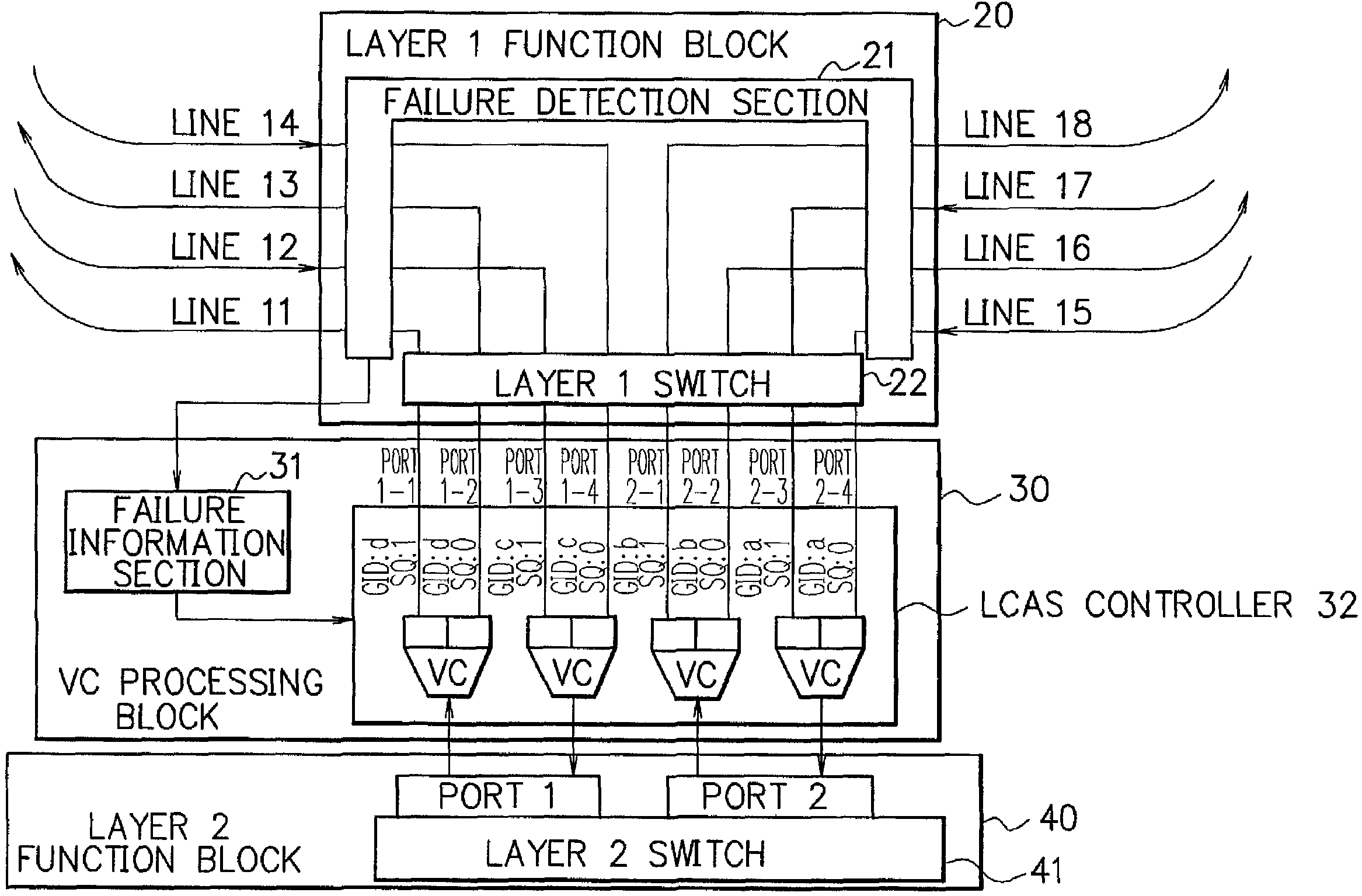
Protection system, virtual concatenation processing block, node and ring network
A protection system, a virtual concatenation processing block, a node and a ring network, in which bands of ring network system are effectively utilized when no failure occurs on the network, and all data can be transmitted to destinations using an LCAS function even when failure occurs. When no failure occurs on the network, a working channel and a protection channel are treated as a continuous band by the LCAS function and working traffic is transmitted using the band by a virtual concatenation function. When failure occurs on the network, the channels of paths prepared by cooperating a layer 1 protection function and the LCAS function to avoid a troubled part are used for data transmission, and the working traffic is transmitted through the band by the virtual concatenation function.
Owner:NEC CORP
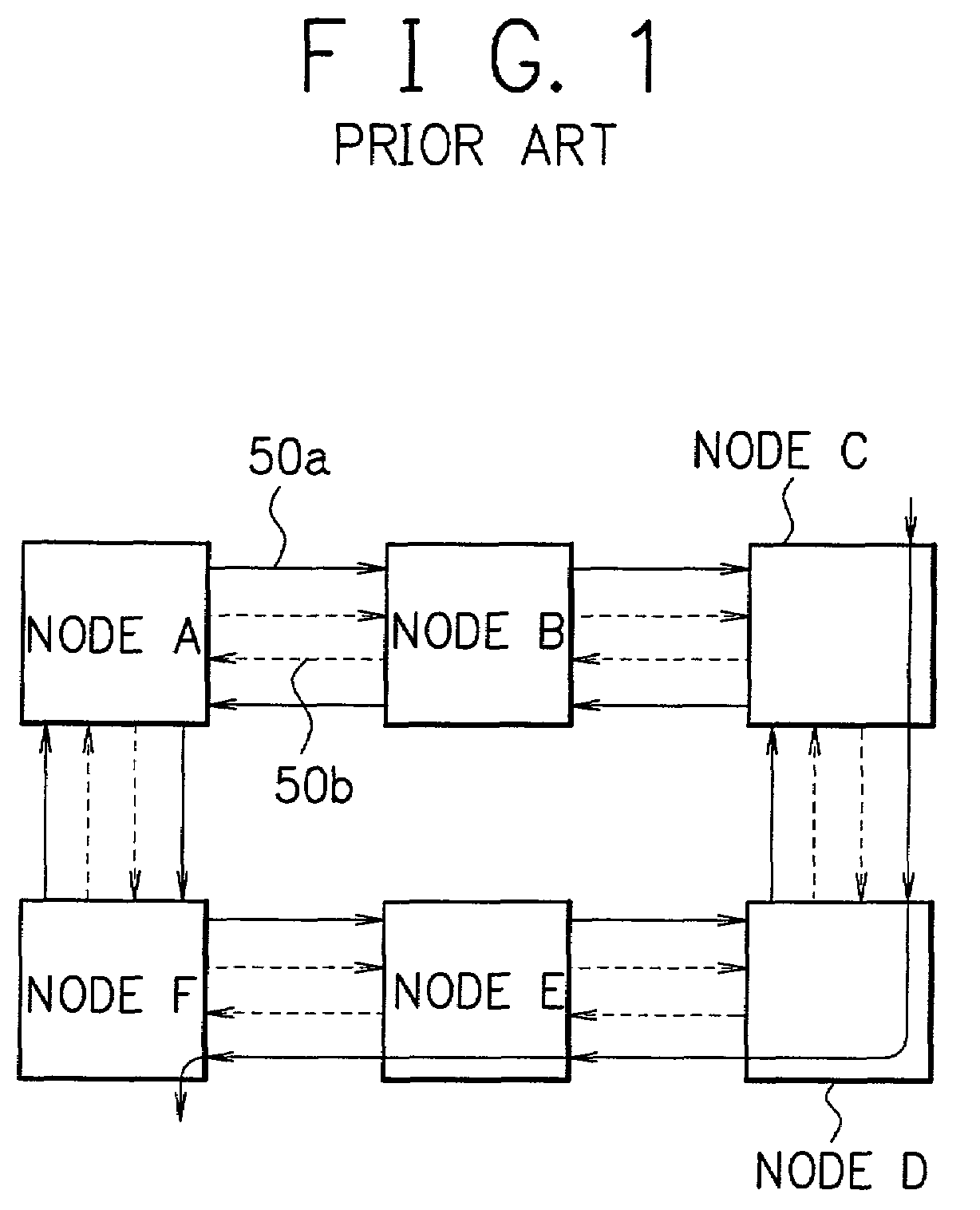
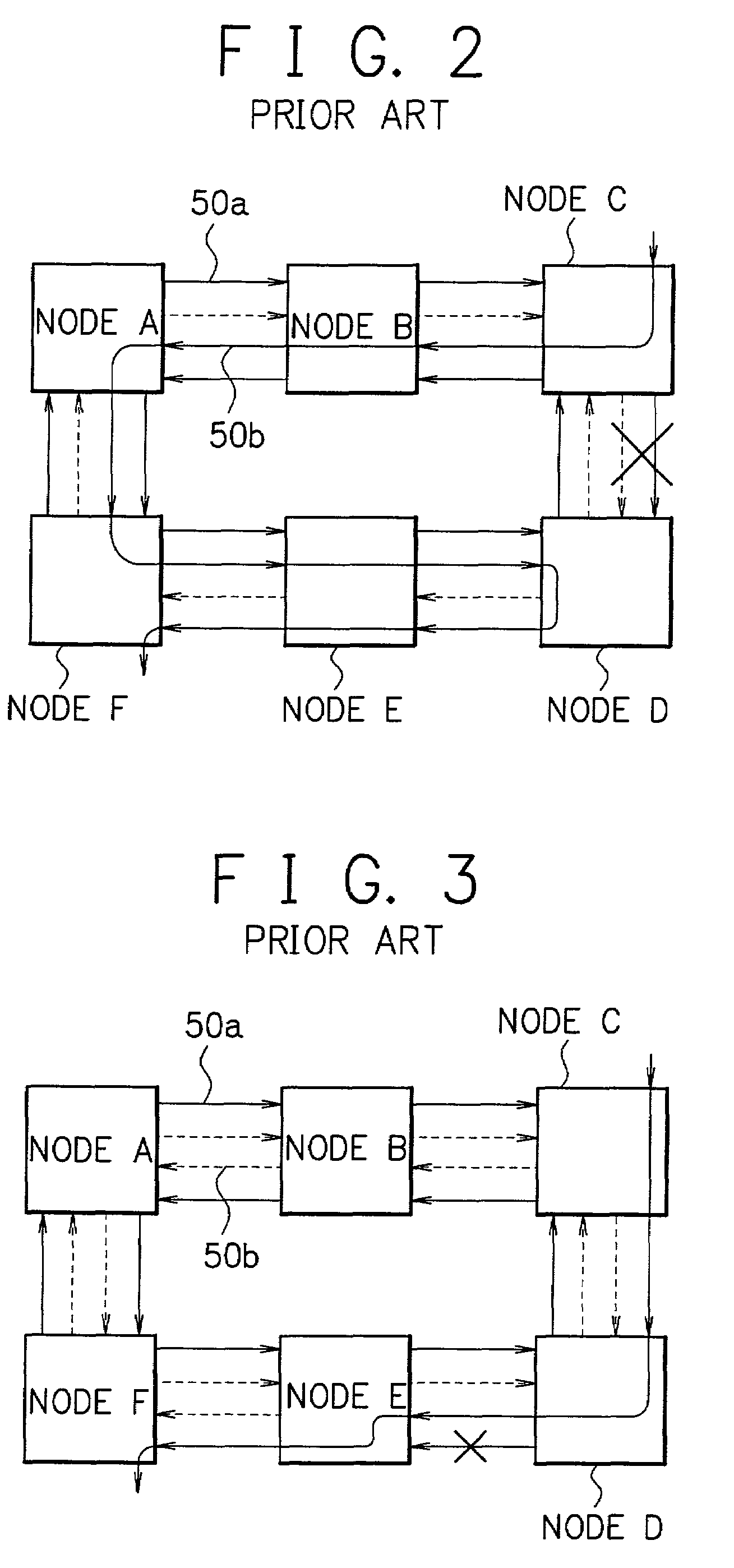
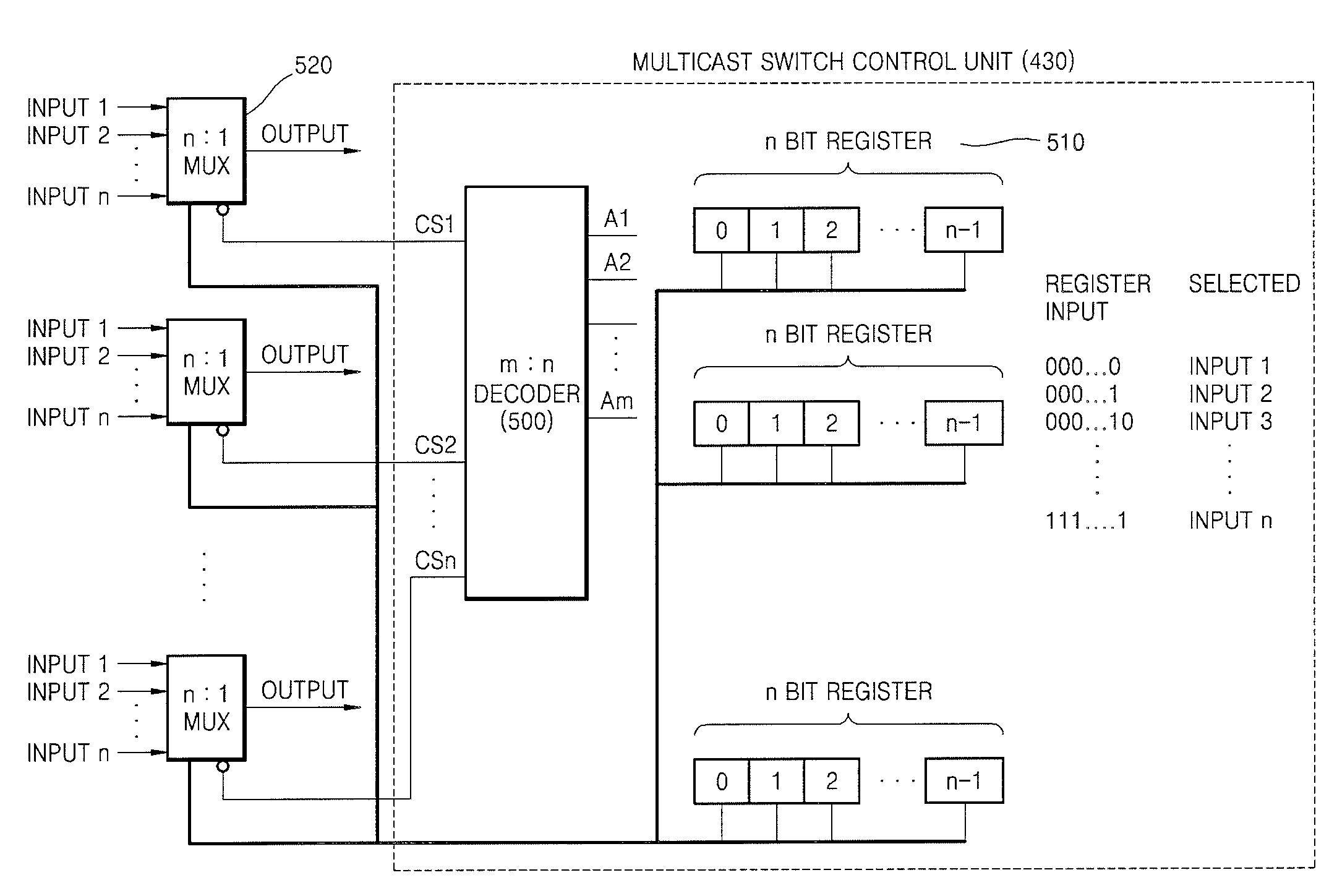
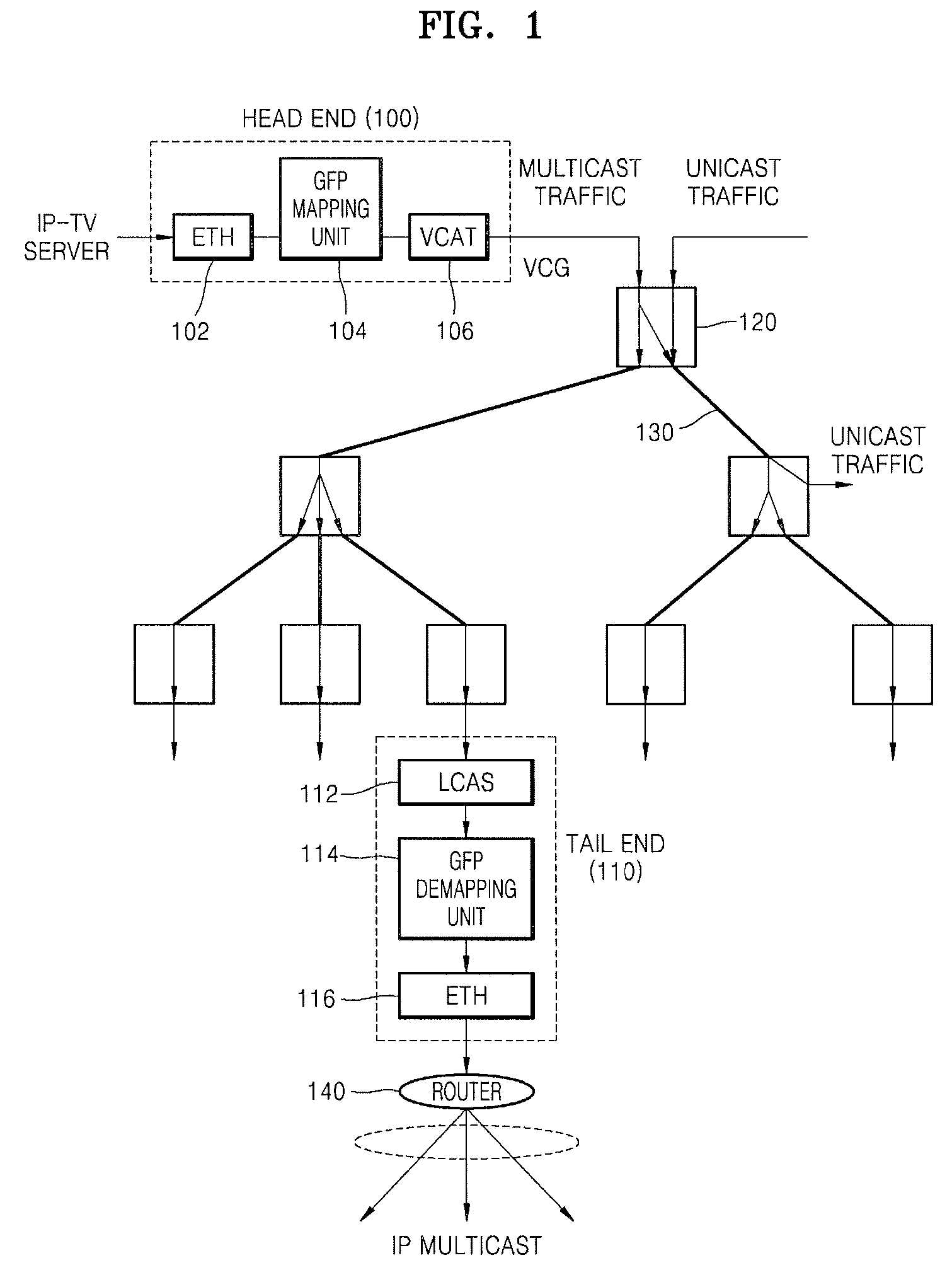
IP-TV broadcasting service system and method using physical layer's multicast switch
ActiveUS7675870B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexIP multicastPhysical layer
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
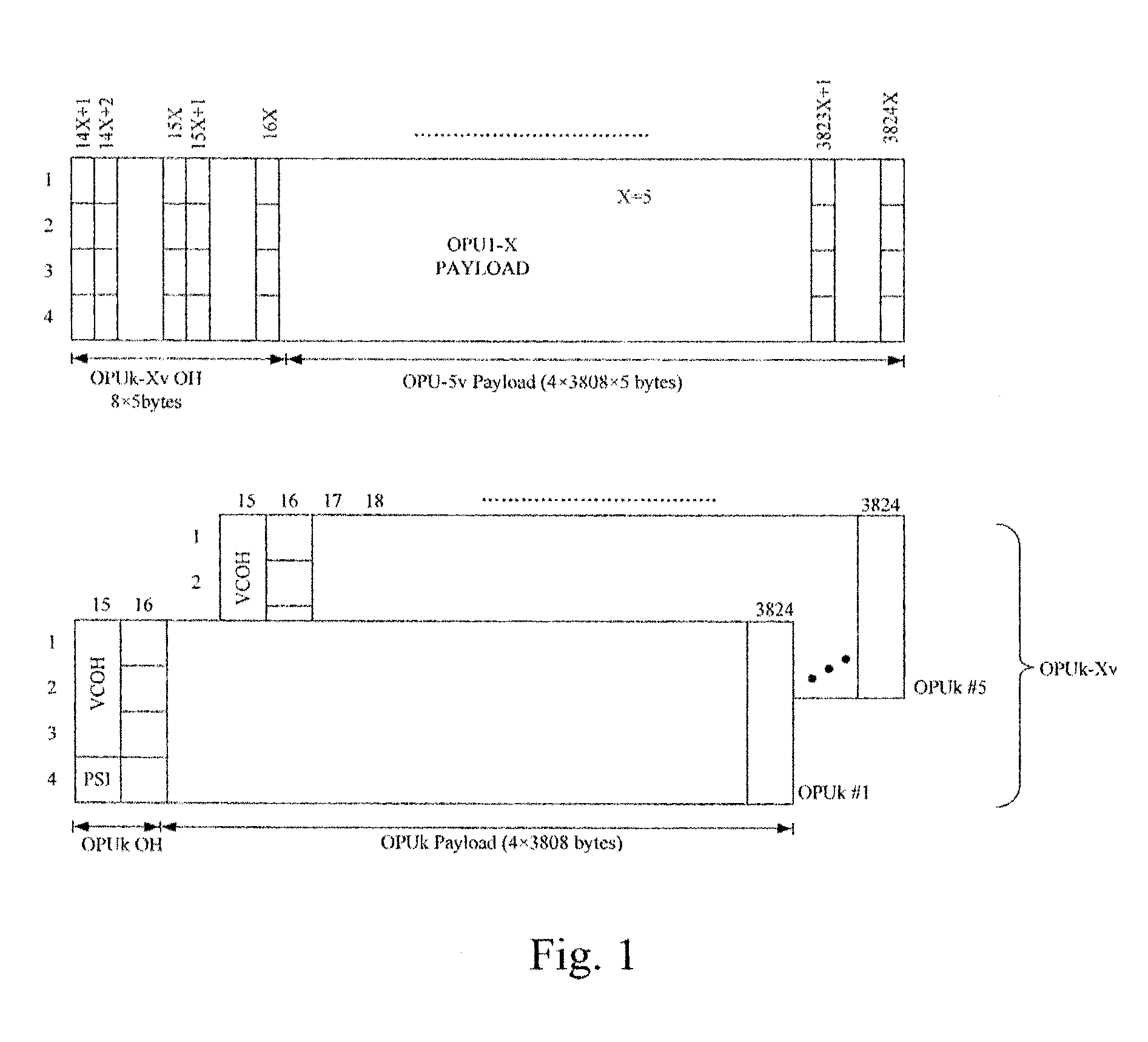
Method and apparatus for centralized processing of contiguously and virtually concatenated payloads
InactiveUS7298744B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsPayloadVirtual concatenation
A method and apparatus for processing at least two types of payloads received at varying intervals in a communications network using a single processing path is provided. The two types of payloads may include virtually and contiguously concatenated payloads according to SONET / SHD architecture. The method comprises assigning pseudo indices to payloads having no indices associated therewith and providing both sets of payloads, including indices and pseudo indices, to the single processing path.
Owner:INTEL CORP
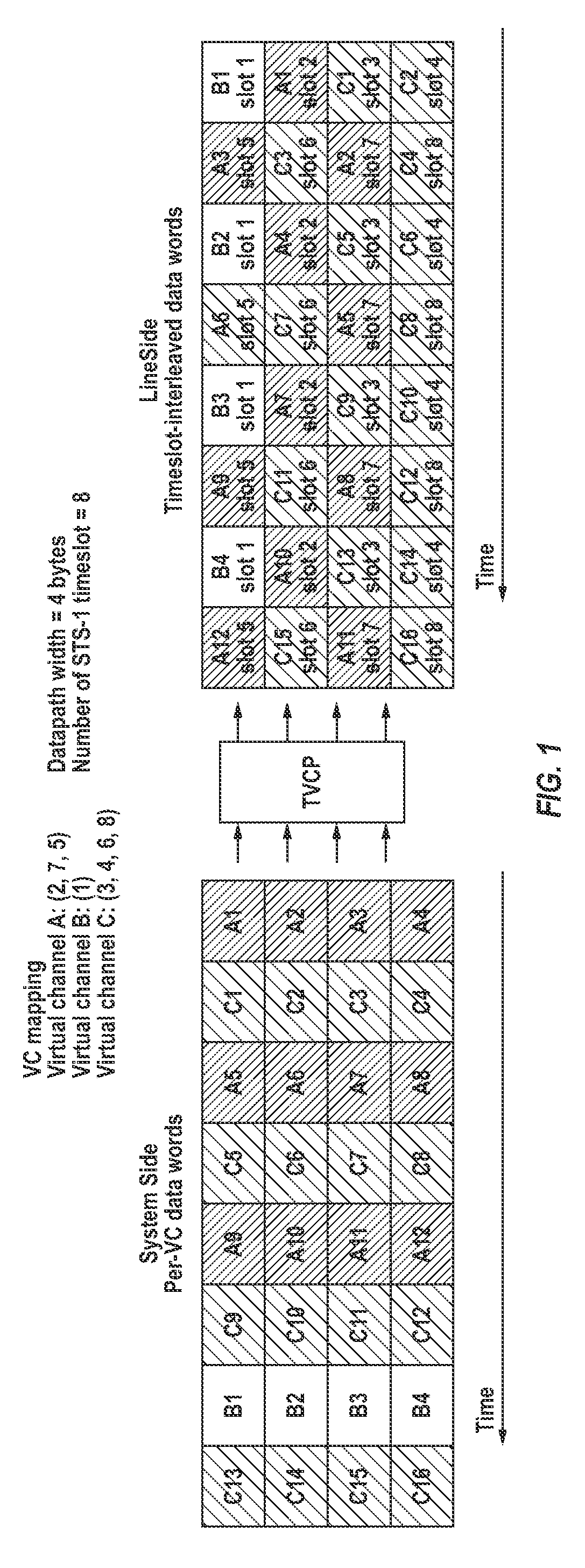
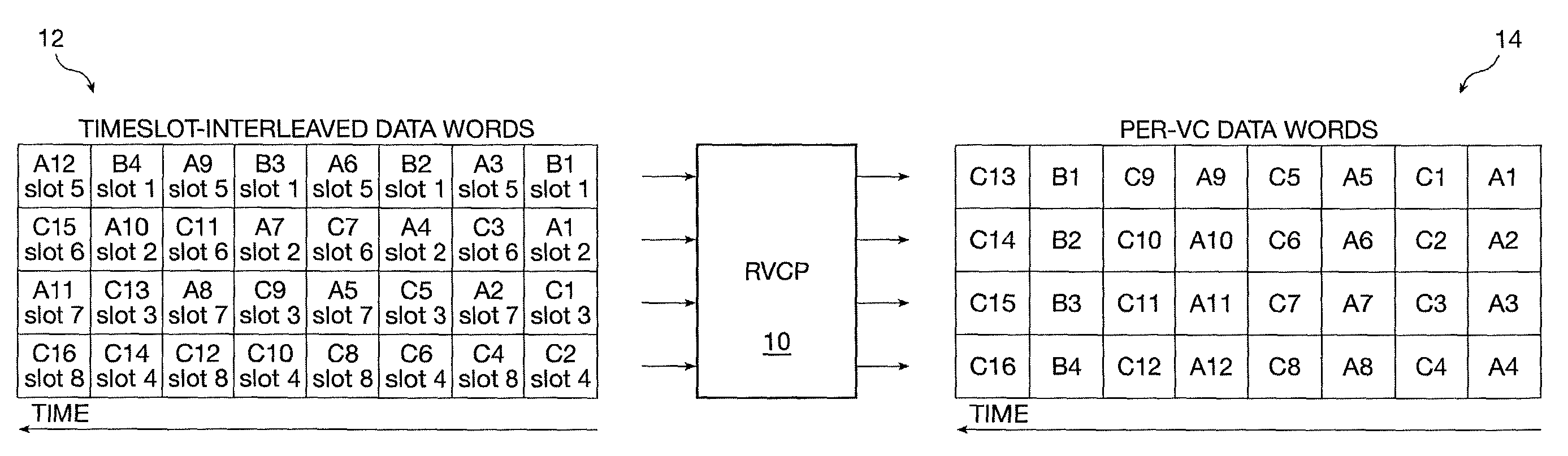
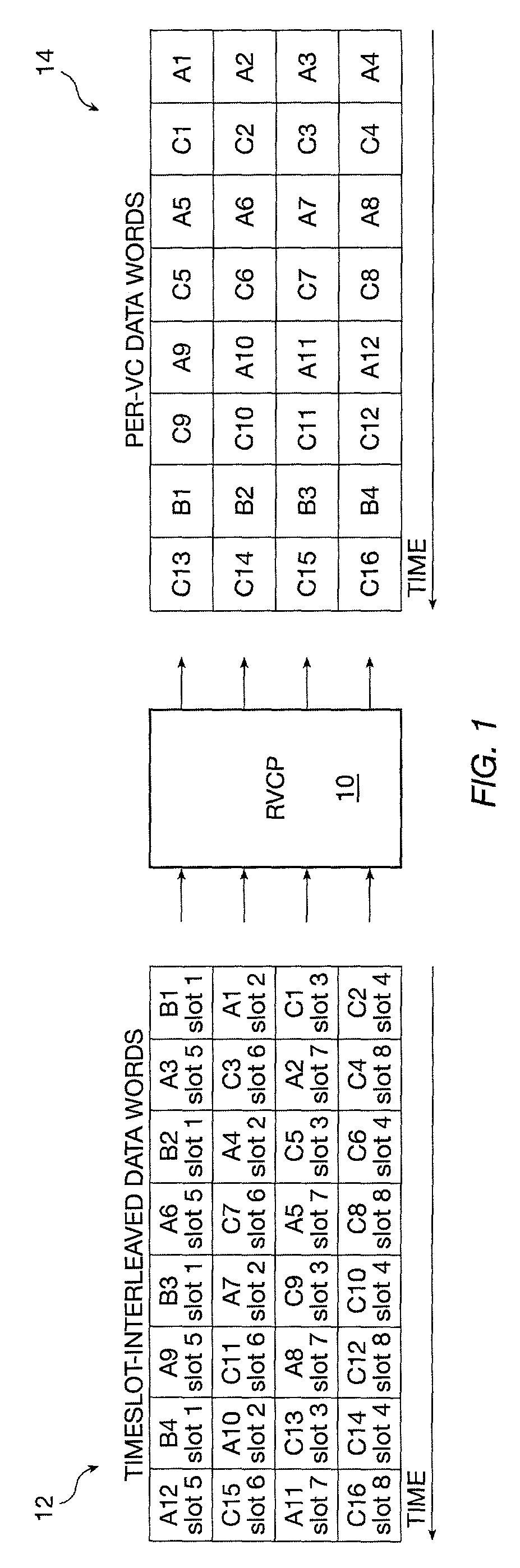
Data format conversion for virtual concatenation processing
A data format conversion method and apparatus are presented to convert time-slot interleaved SONET / SDH data to per time-slot data for virtual concatenation processing. The converter consists of an input buffer and a matrix transposer. The input buffer discards the overhead and fixed stuff bytes of each SPE that it receives, while the matrix transposer packs the N payload bytes into N-byte words with alignment to a start-of-frame indicator. Because each N-byte word is associated with a different time slot, the N-byte words form per time-slot data.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
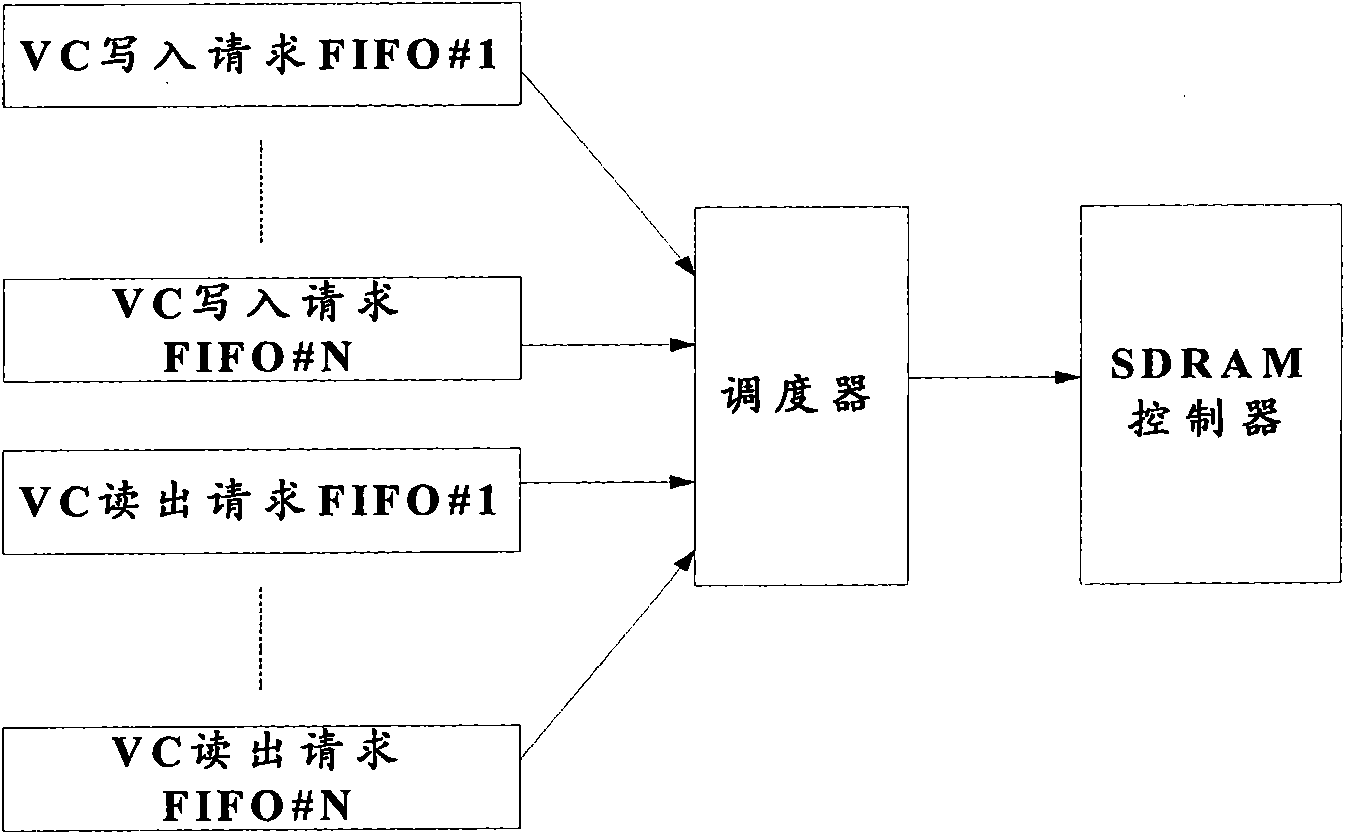
Method and device for improving virtual concatenation delay compensation caching efficiency in synchronous digital hierarchy
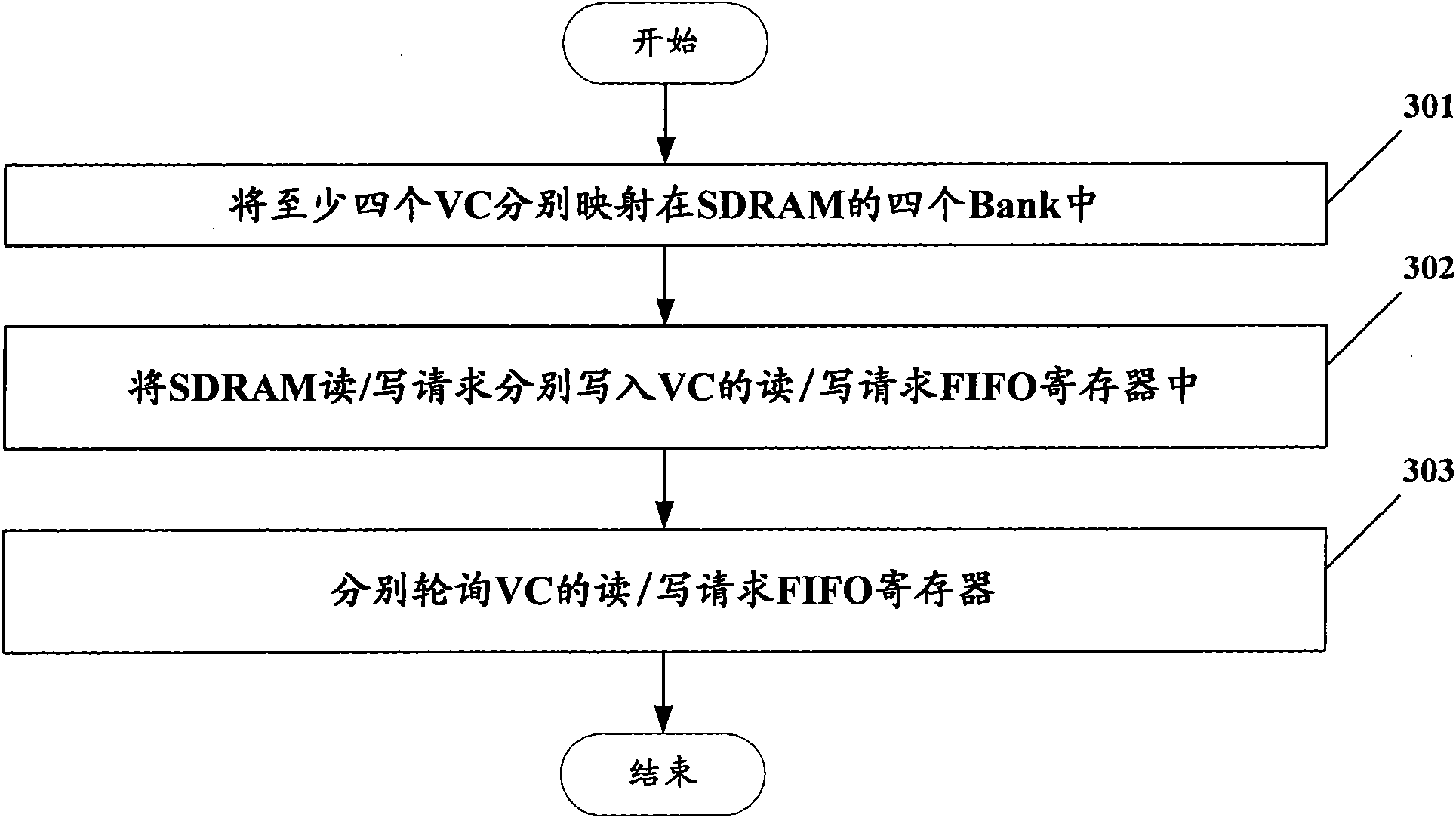
InactiveCN101656586AReduce useless overheadImprove the efficiency of latency compensation cacheTime-division multiplexMemory systemsComputer architectureSynchronous dynamic random-access memory
The invention discloses a method and a device for improving virtual concatenation delay compensation caching efficiency in a synchronous digital hierarchy, which belong to the technical field of communications. The method comprises the following steps: mapping at least four virtual containers VCs into four banks of a synchronous dynamic random access memory SDRAM respectively; writing a synchronous dynamic random access memory SDRAM write request into write request first in first out FIFO registers of the VCs respectively; writing a synchronous dynamic random access memory SDRAM read request into read request first in first out FIFO registers of the VCs respectively; and polling the write request FIFO registers and read request FIFO registers of the VCs; therefore, unnecessary overhead of SDII operation is reduced and the virtual concatenation delay compensation caching efficiency in the SDH is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Ranking method of virtual concatenation group member
InactiveCN101272212AAvoid dealing with issues that don't go smoothlyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexComputer scienceVirtual concatenation
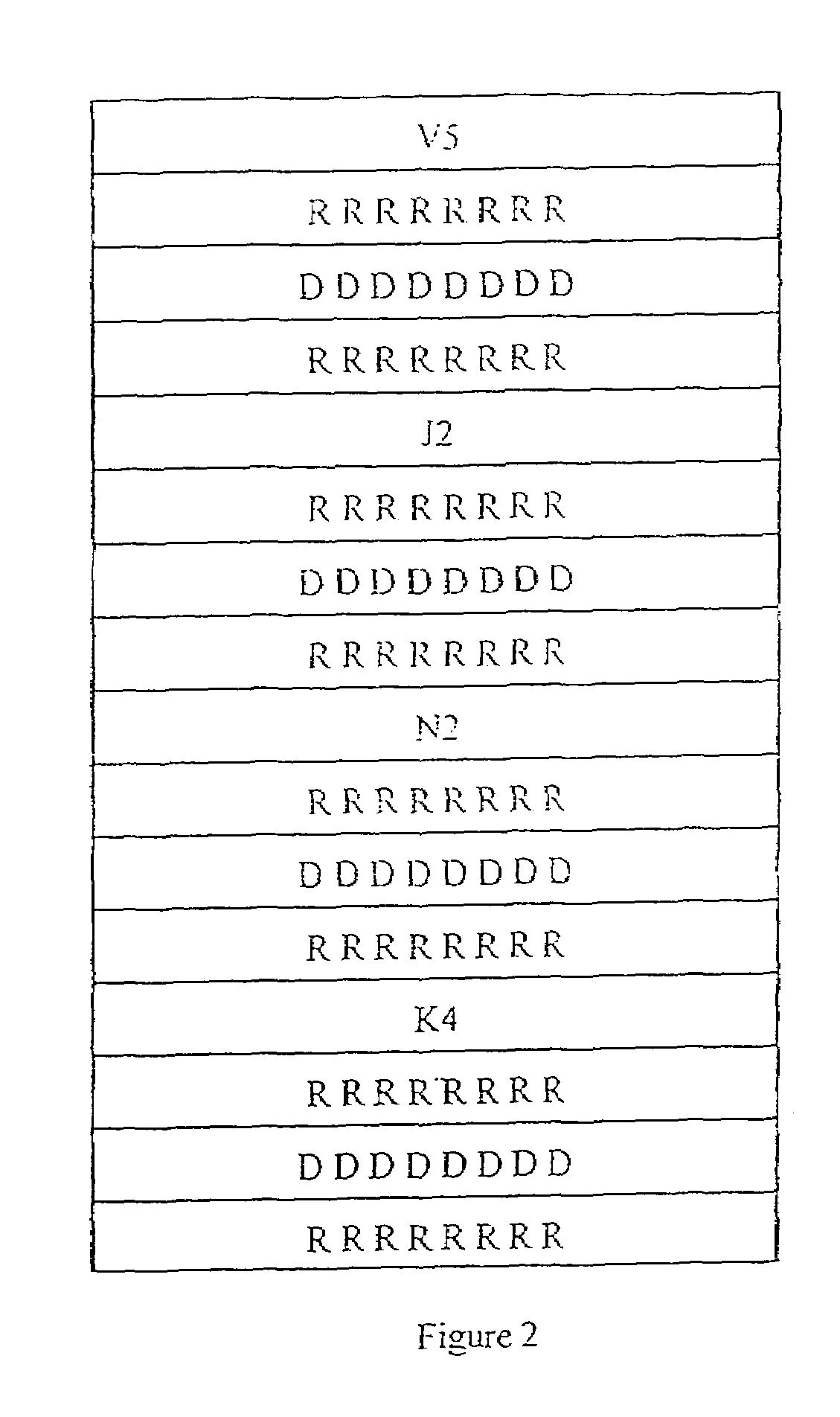
The invention discloses a sorting method for virtual concatenation group members which comprises: step S502 is that the state information and the sequence number SQ of a virtual container channel are stored by the channel number and the multiframe number of the virtual container channel and a sink end in a virtual concatenation group; step S504 is that the stored channel number of the virtual container channel is utilized to obtain the SQ of the virtual container channel and a corresponding channel state and the virtual container channel is carried out sequencing by the obtained SQ so as to obtain a first relation table consisting of the SQ from small to big and the corresponding channel number thereof; step S506 is that the channel number and the channel state in the first relation table is traversed from the smallest SQ to the largest SQ in an order of from small to large in the first relation table, the traversed channel the state information of which is loading effective data is accumulated from the smallest SQ and the new SQ obtained by accumulation is corresponding to the channel number and the state information of the currently traversed channels so as to obtain the new SQ and the channel number of the channel, the state information of which is loading the effective data in the first relation table, and a second relation table of the state information.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for transporting local area network signals in optical transport network
InactiveUS7944928B2Improve bandwidth utilizationTransparent transportationTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationChannel dataOTN Systems
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
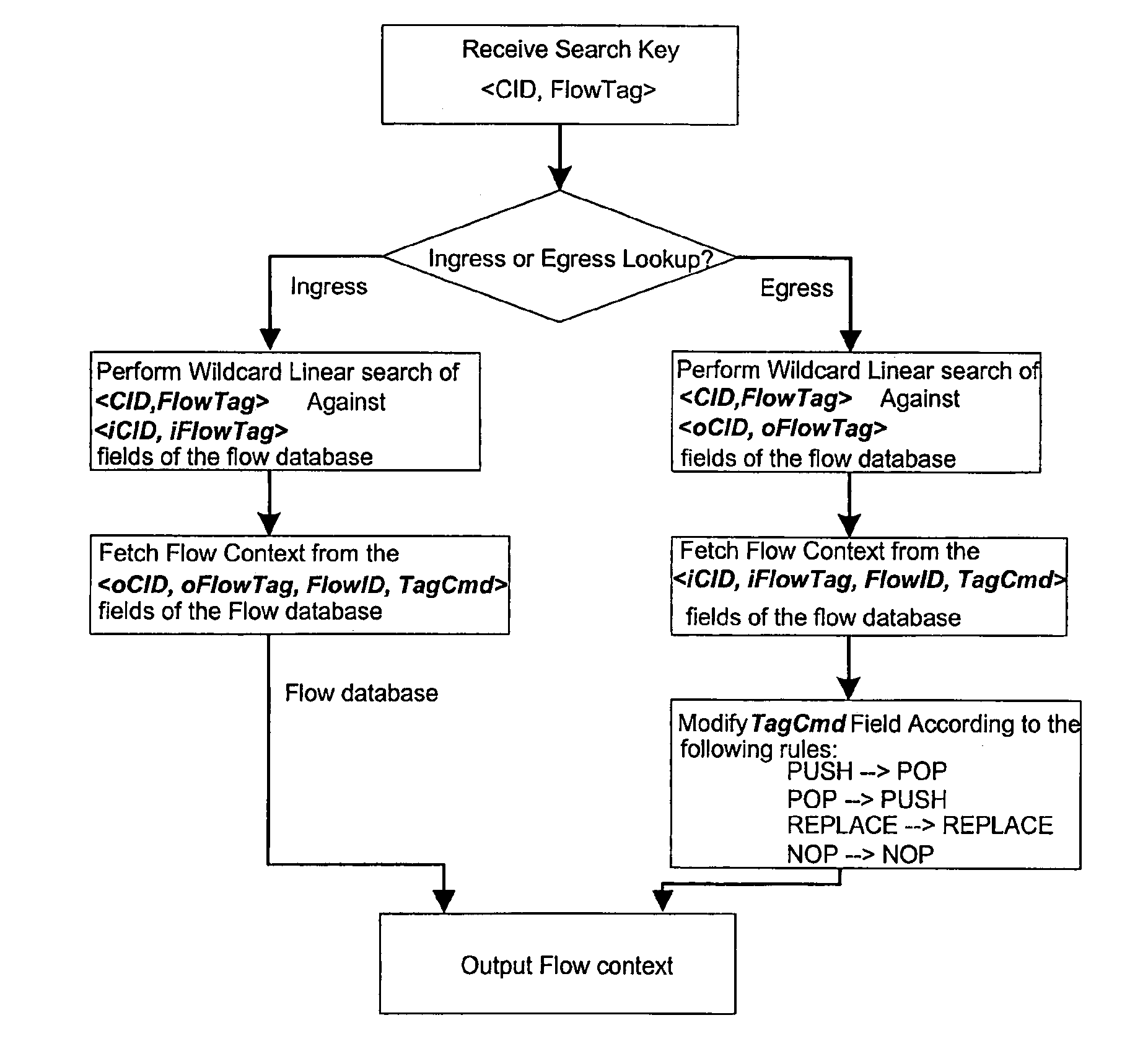
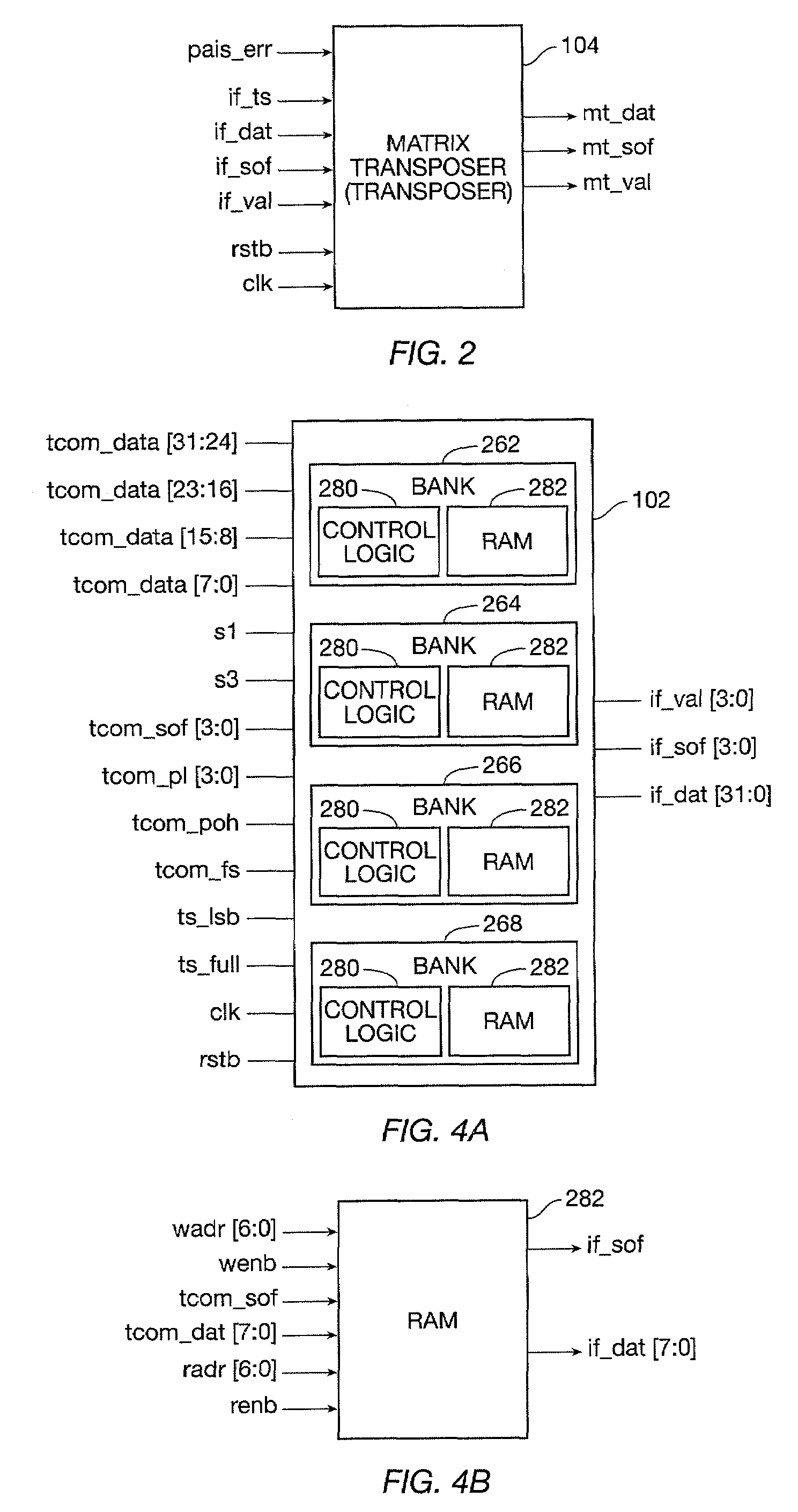
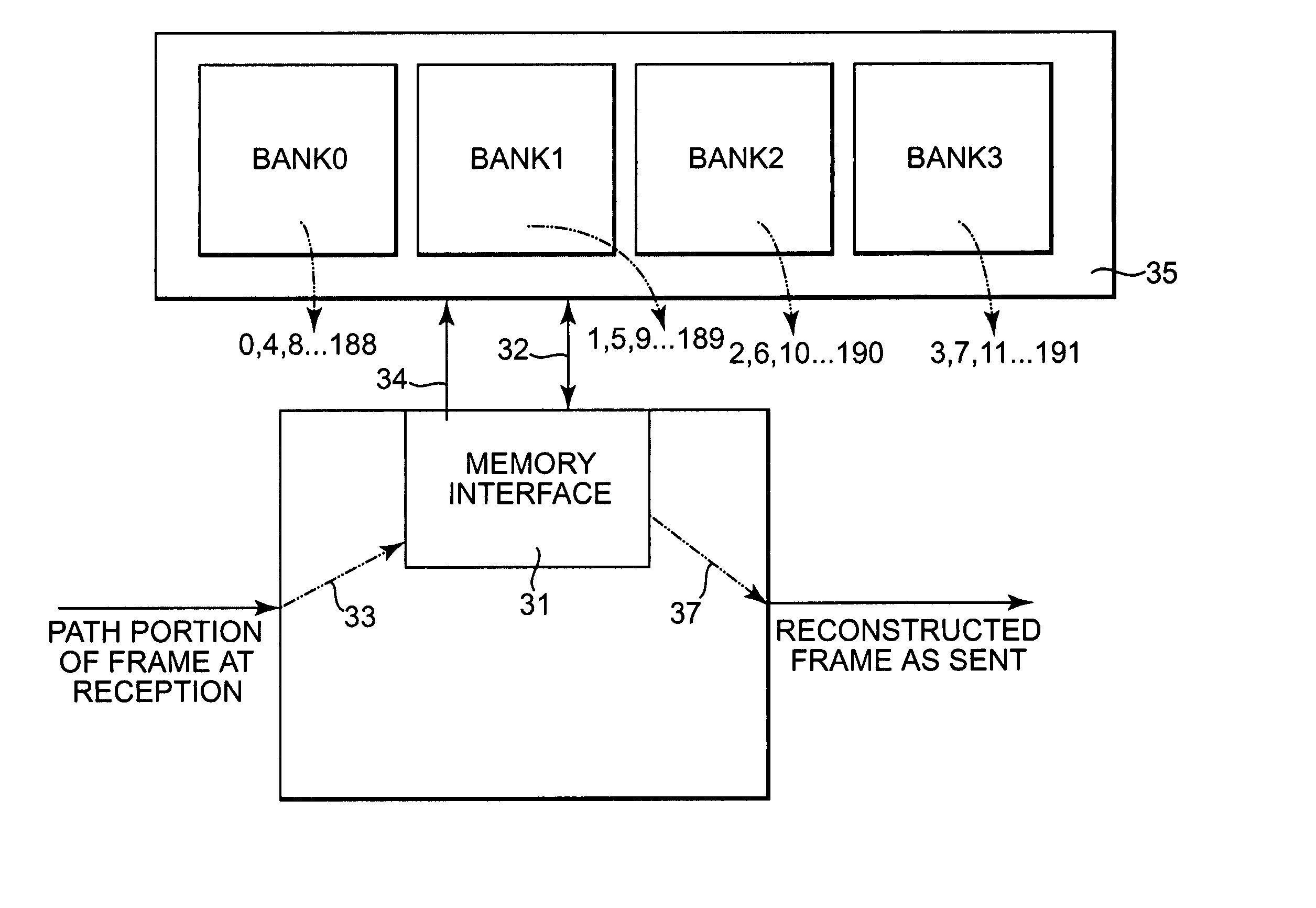
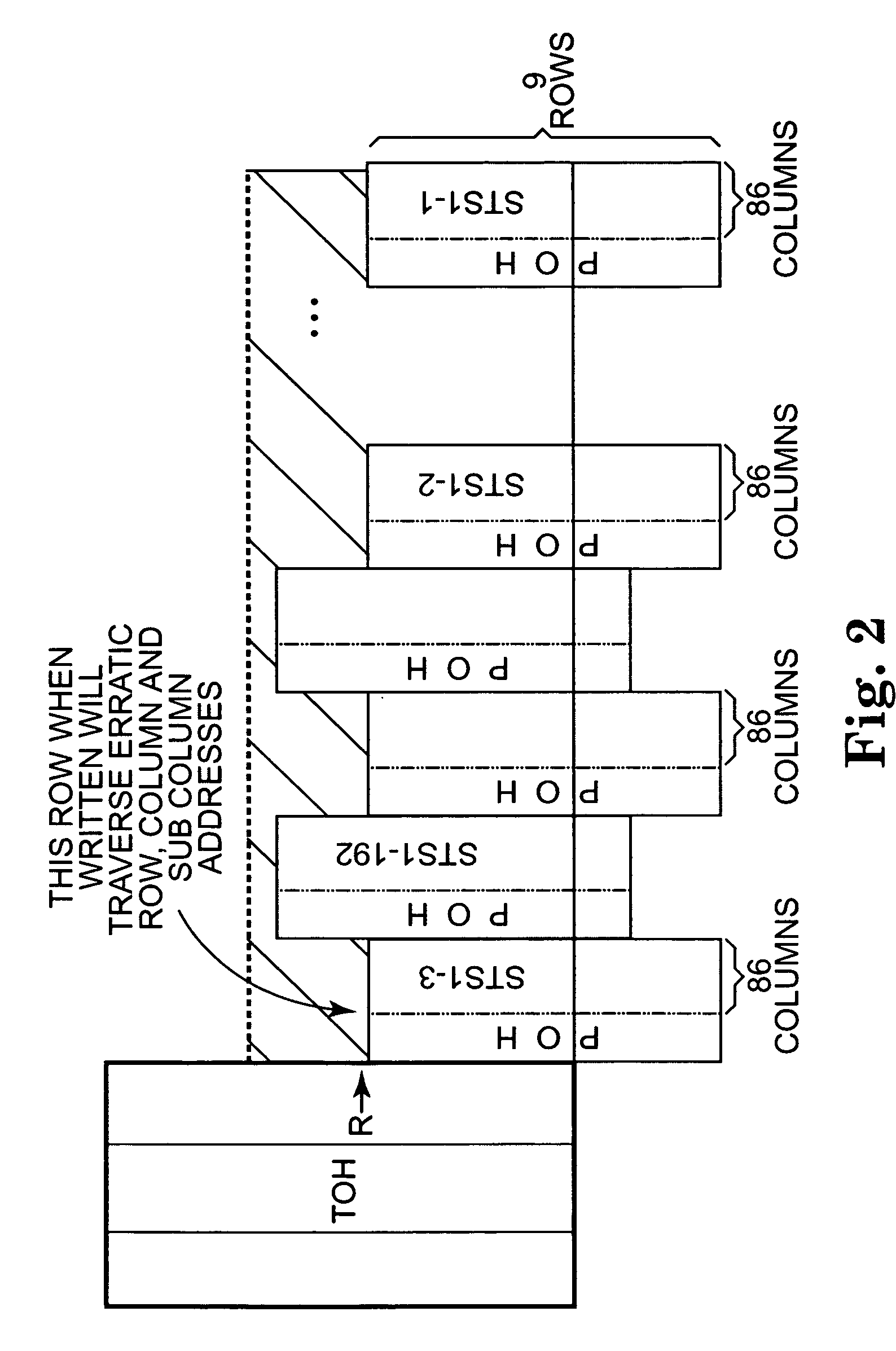
Virtual concatenation receiver processing with memory addressing scheme to avoid delays at address scatter points
In processing received virtual concatenation frames, the memory write address can be appropriately controlled to force bank switches where address scattering occurs. Arbitrary identifiers assigned to the arriving frames and the subcolumns thereof are used instead of H4 information to calculate the memory write addresses.
Owner:EXAR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com