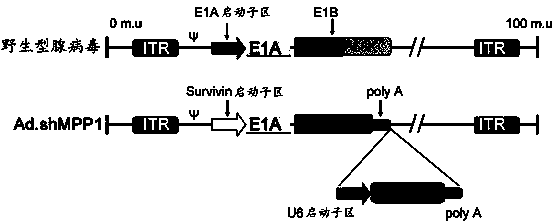
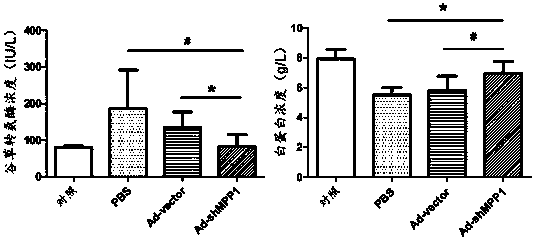
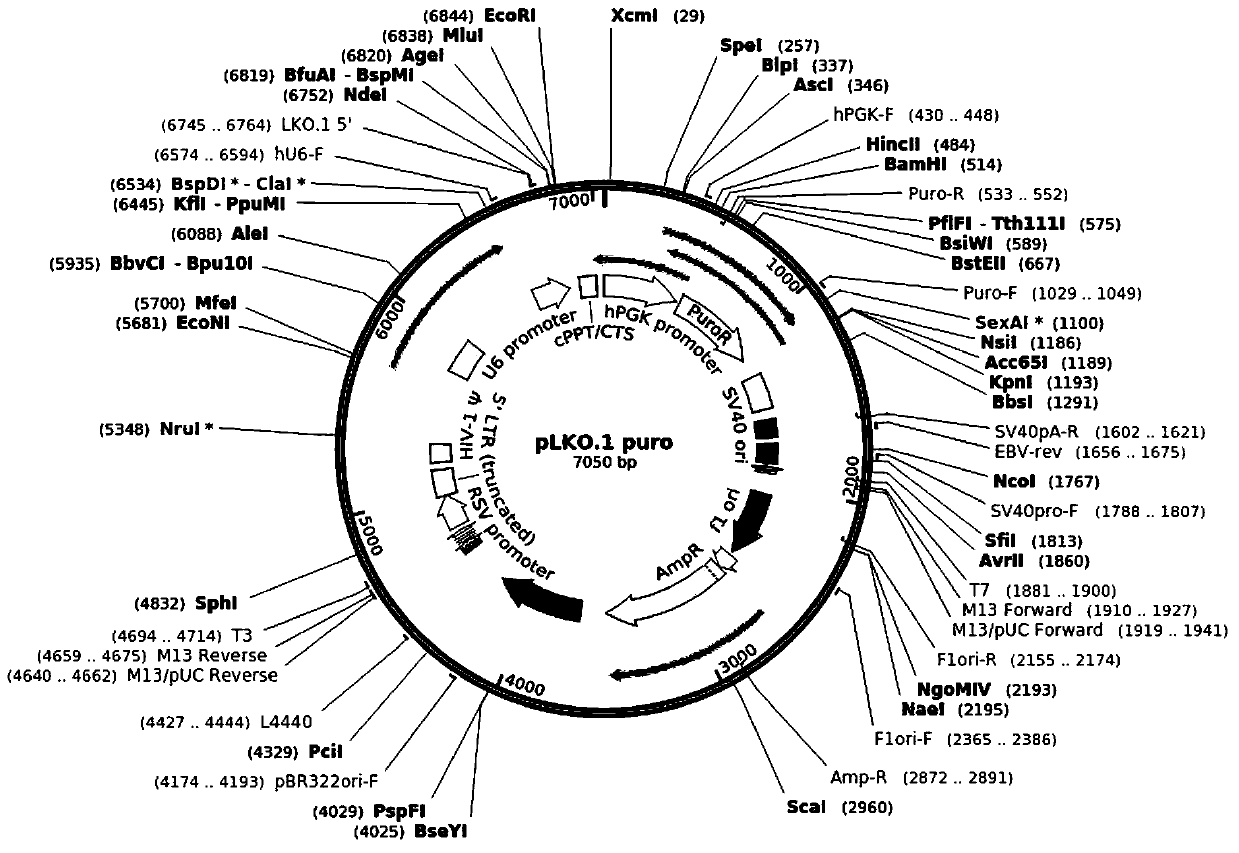
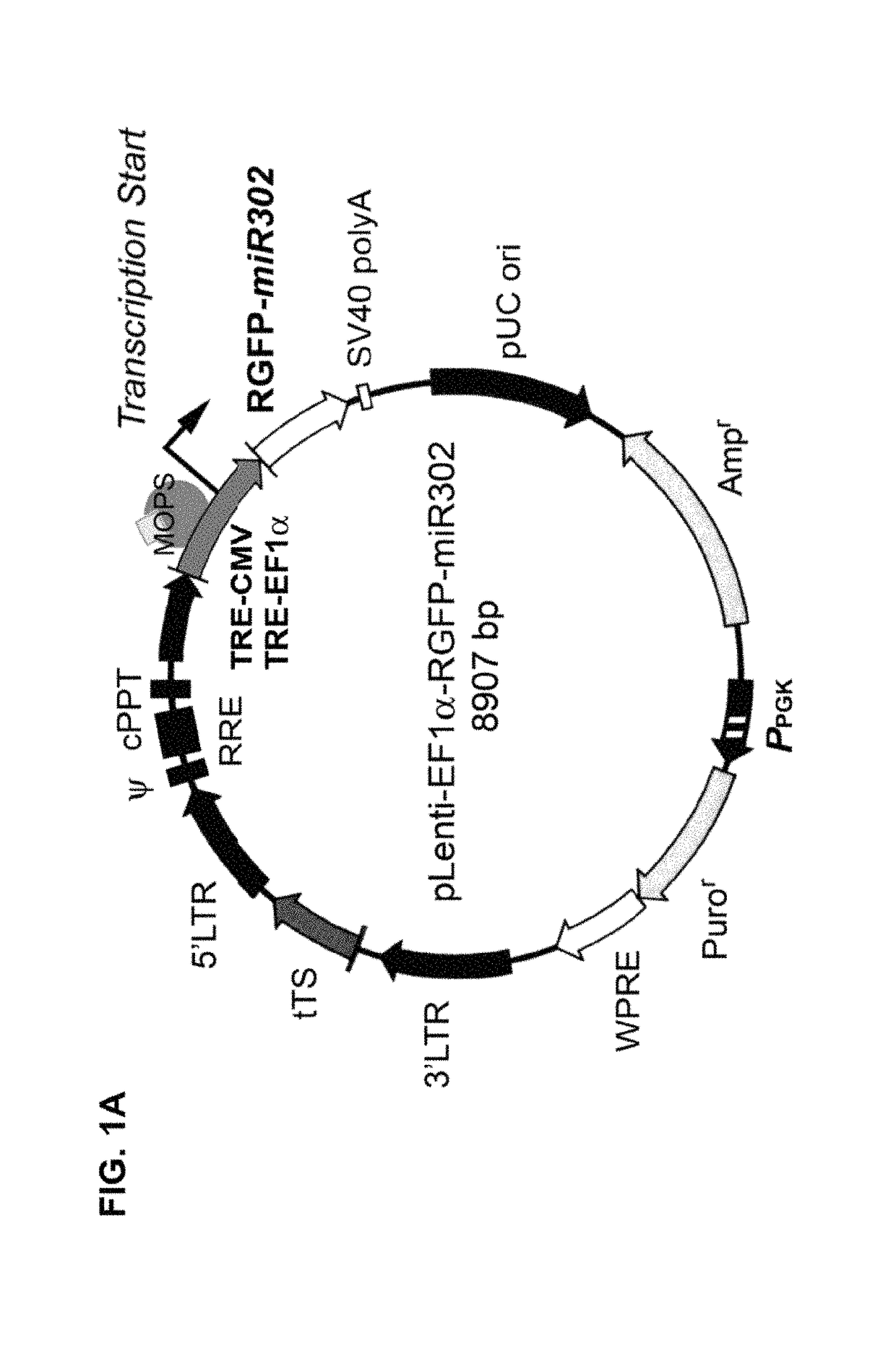
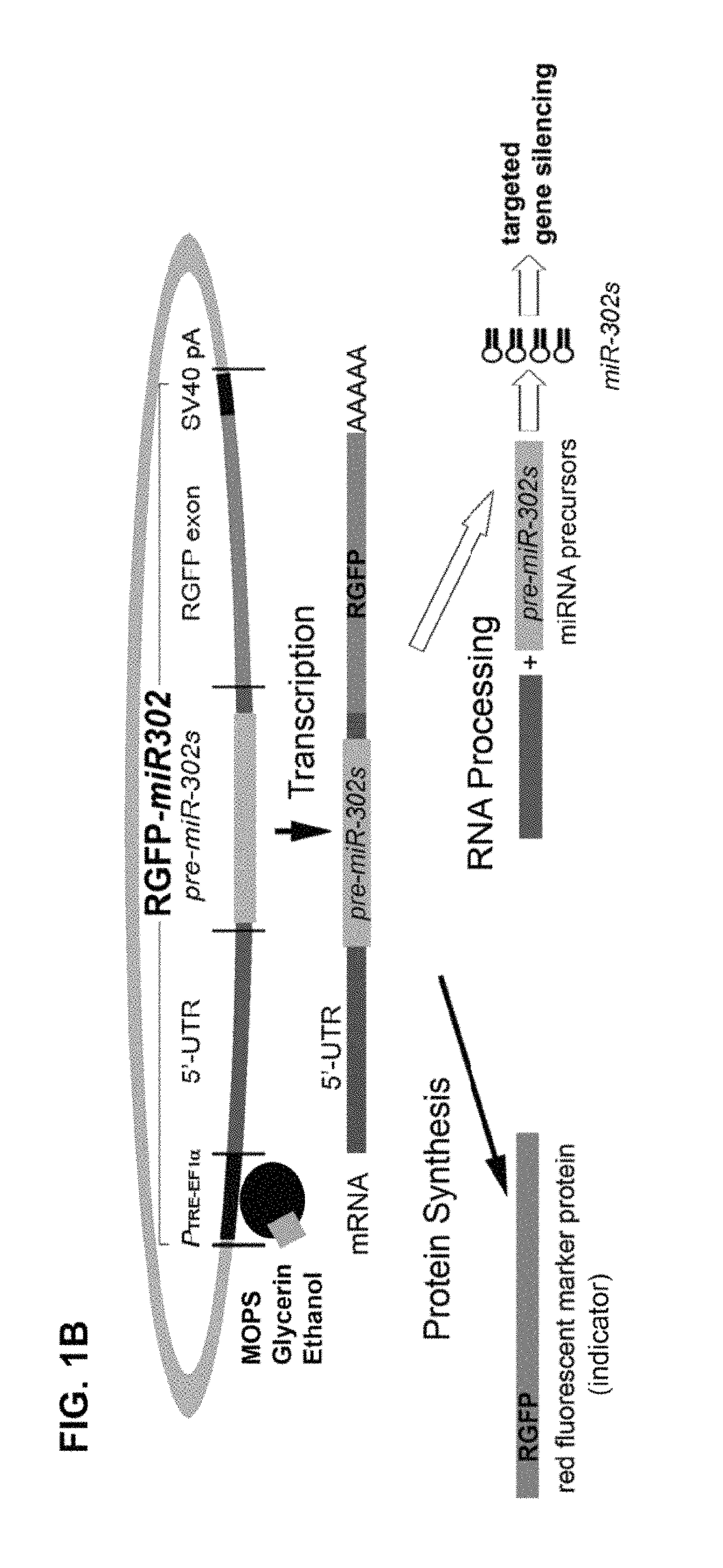
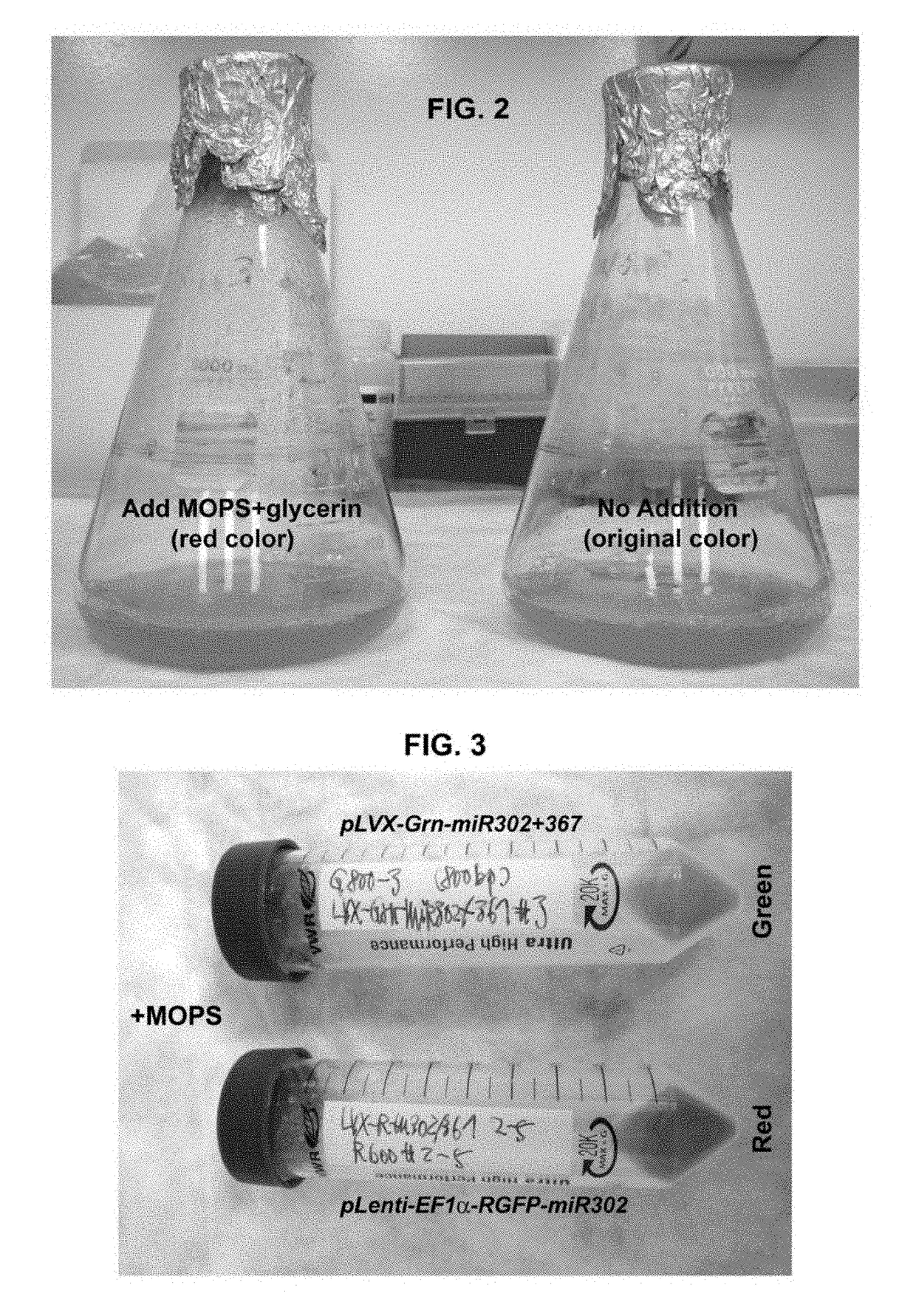
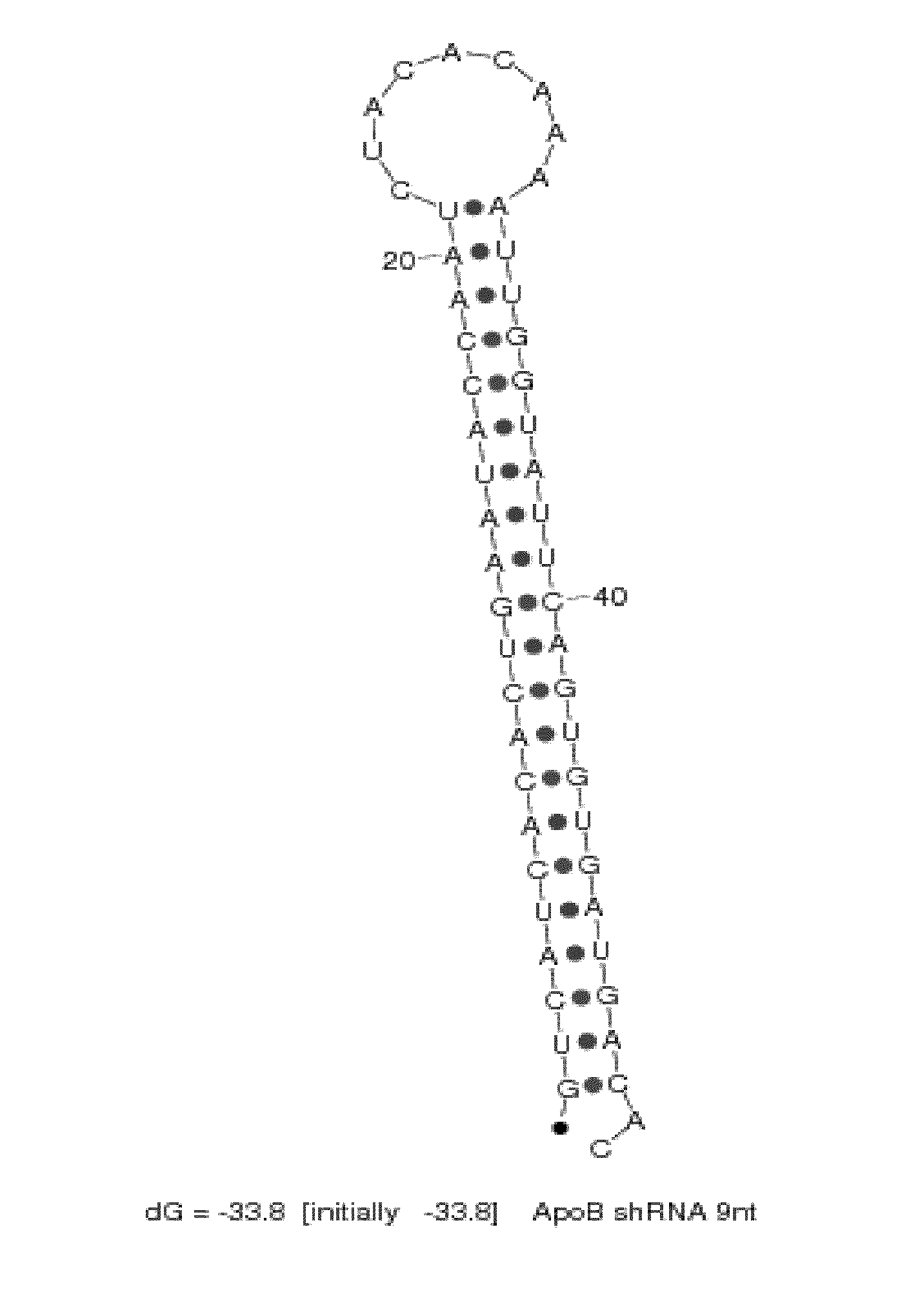Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Small hairpin RNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
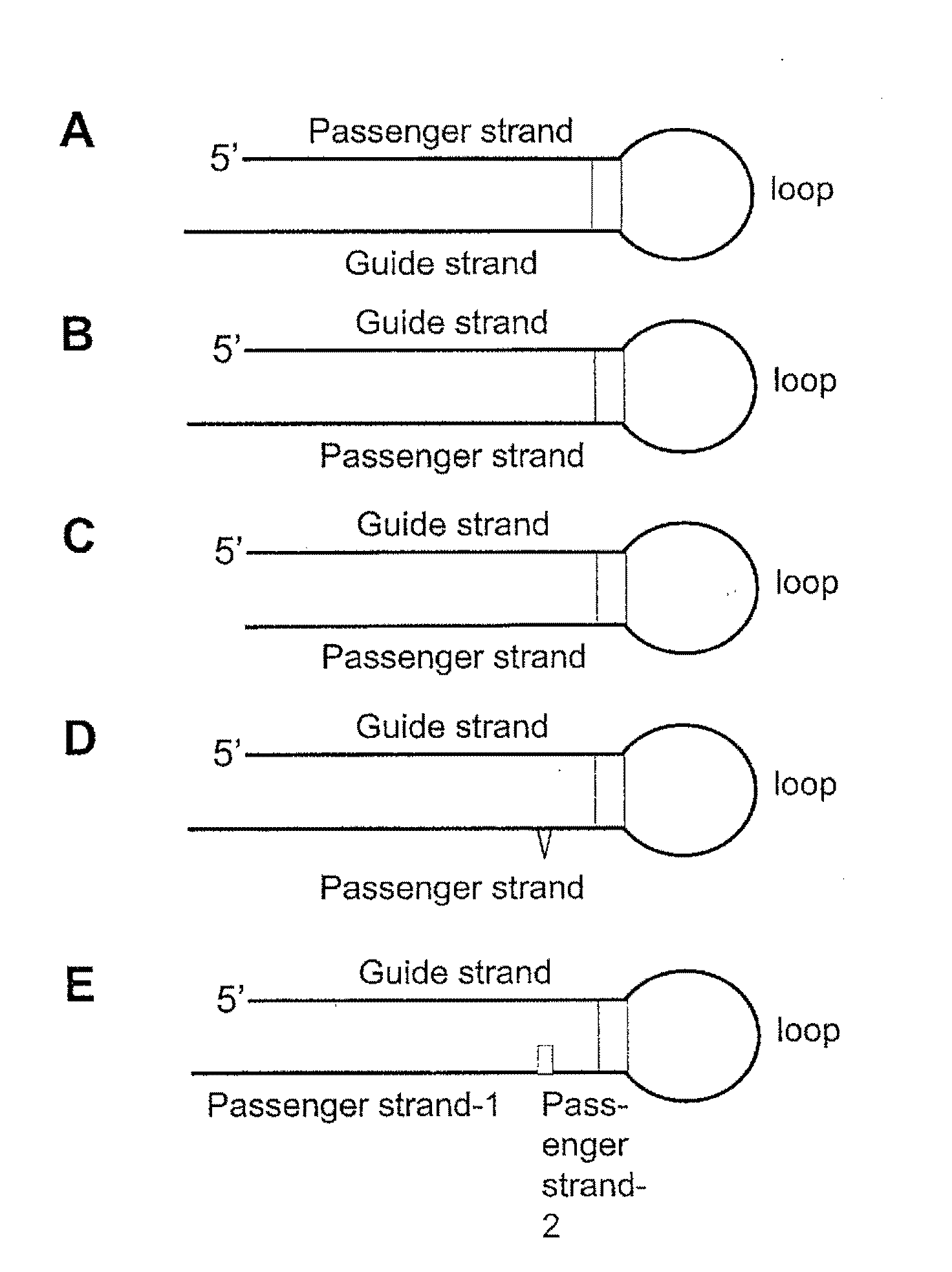
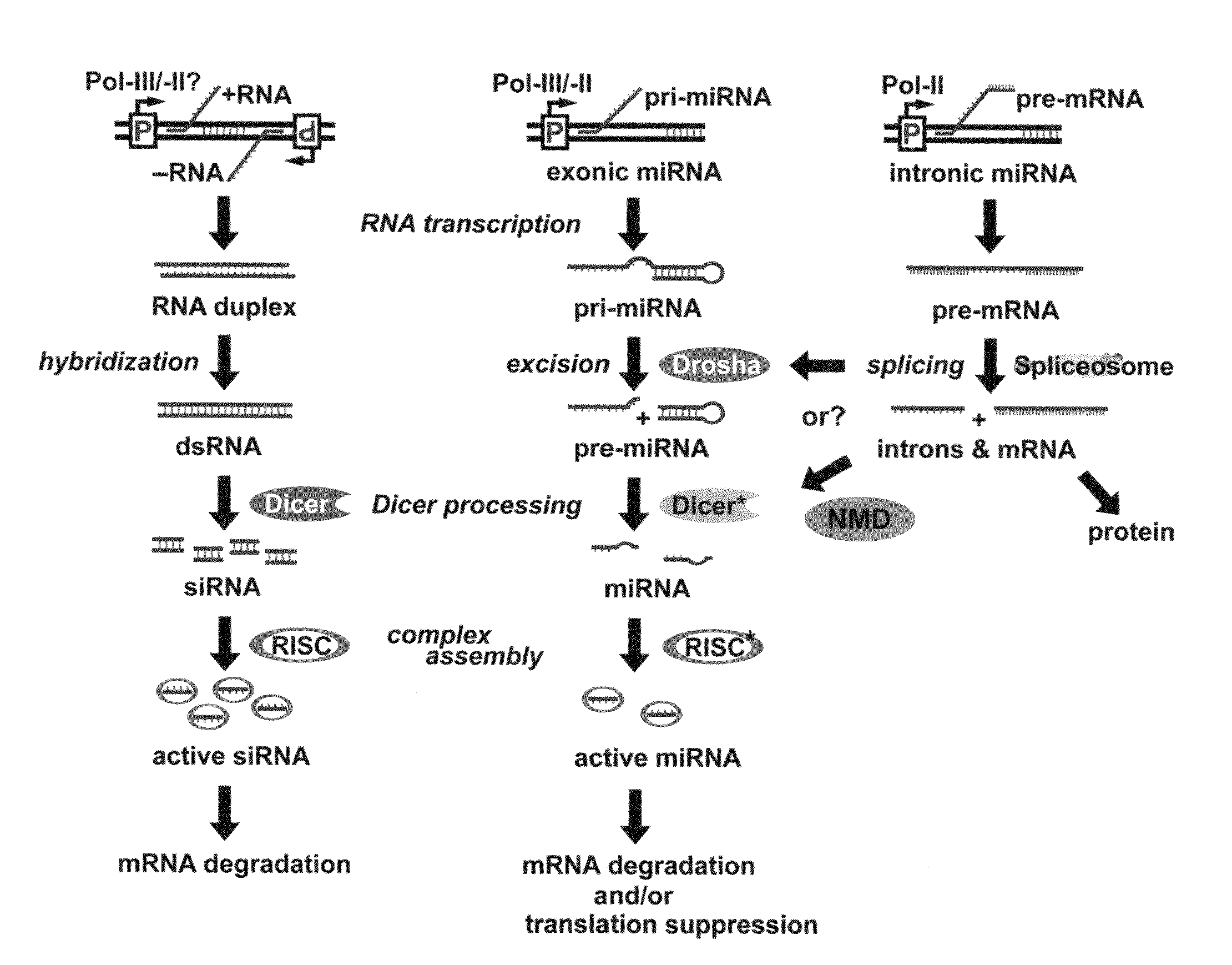
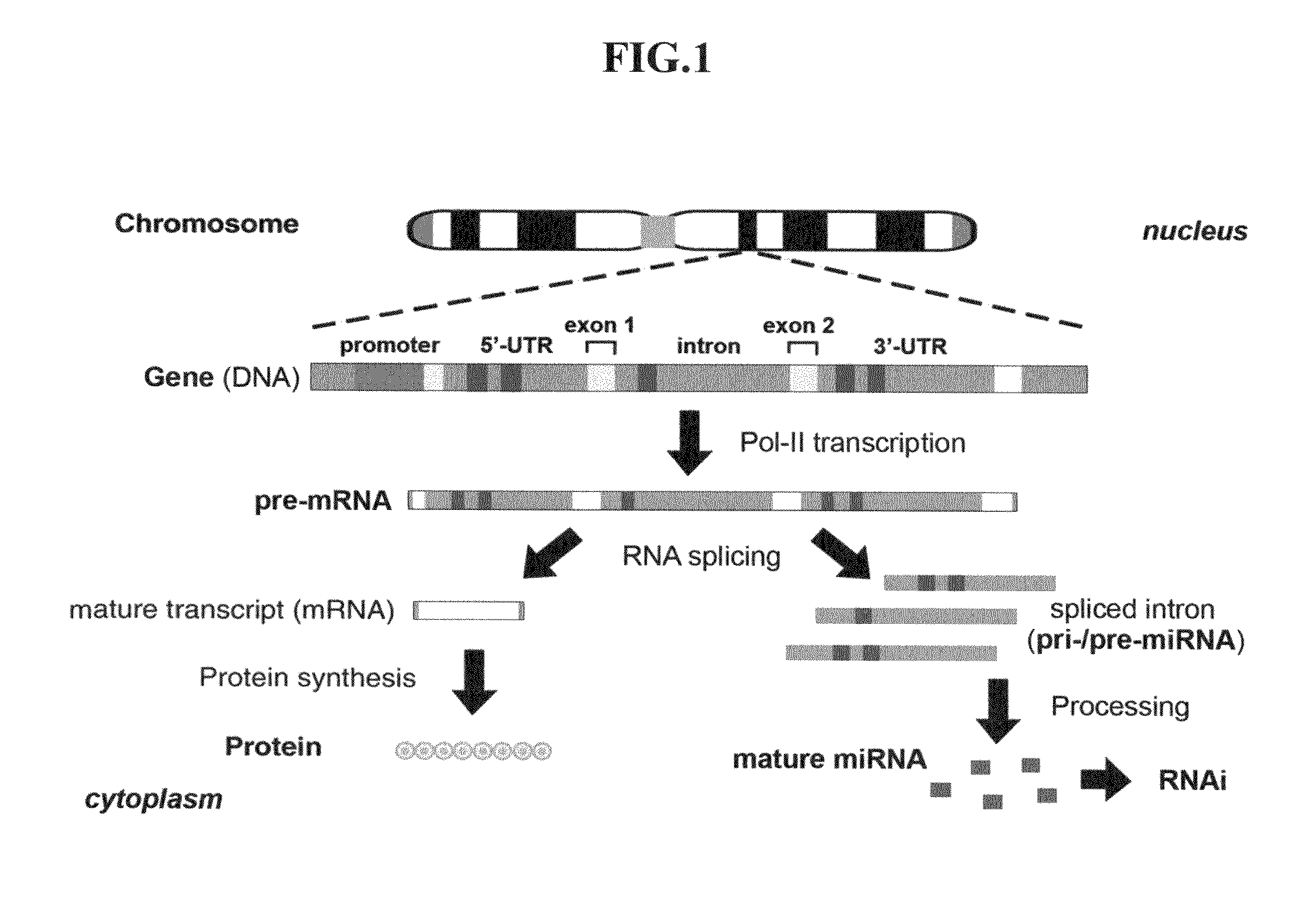
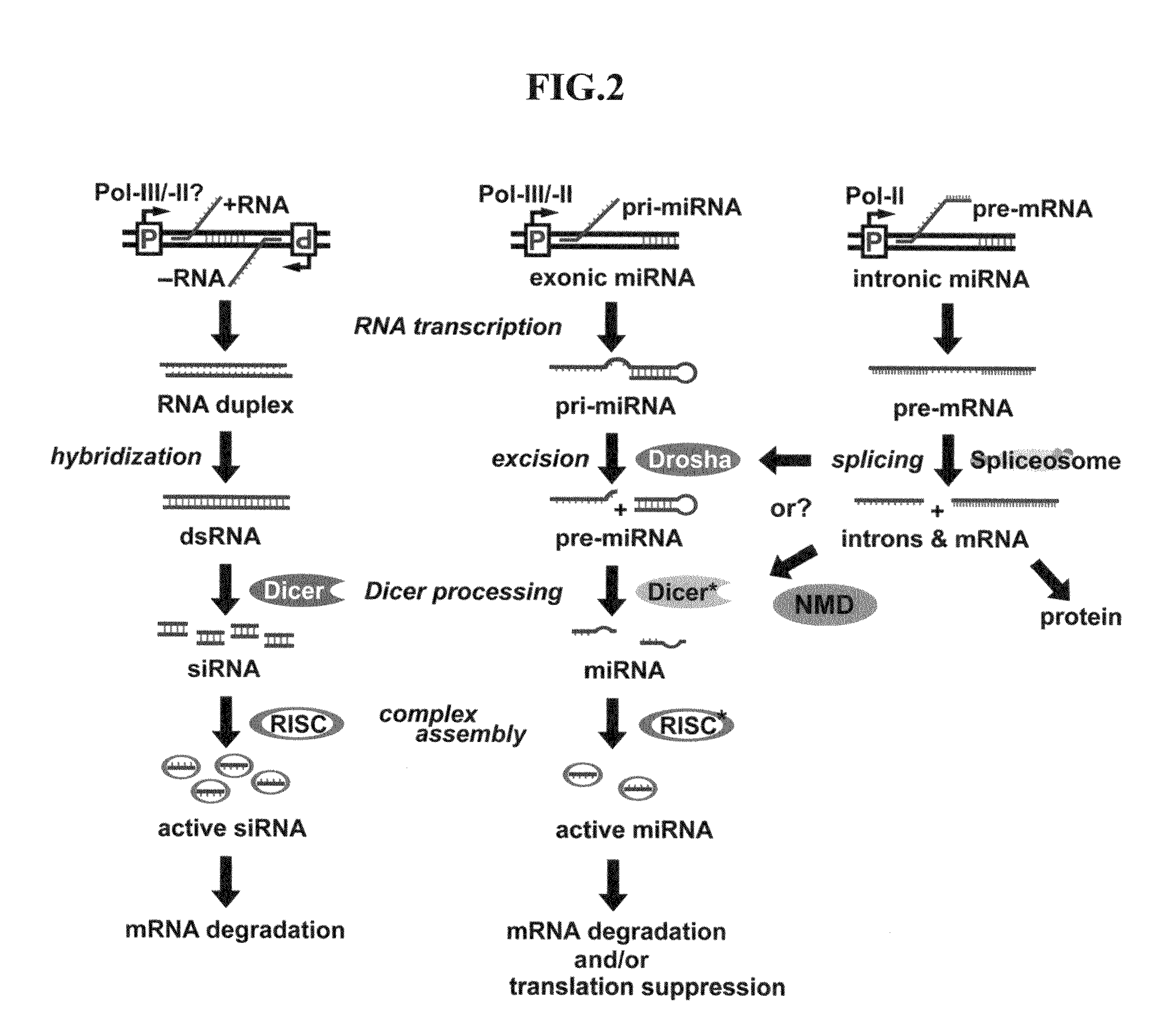
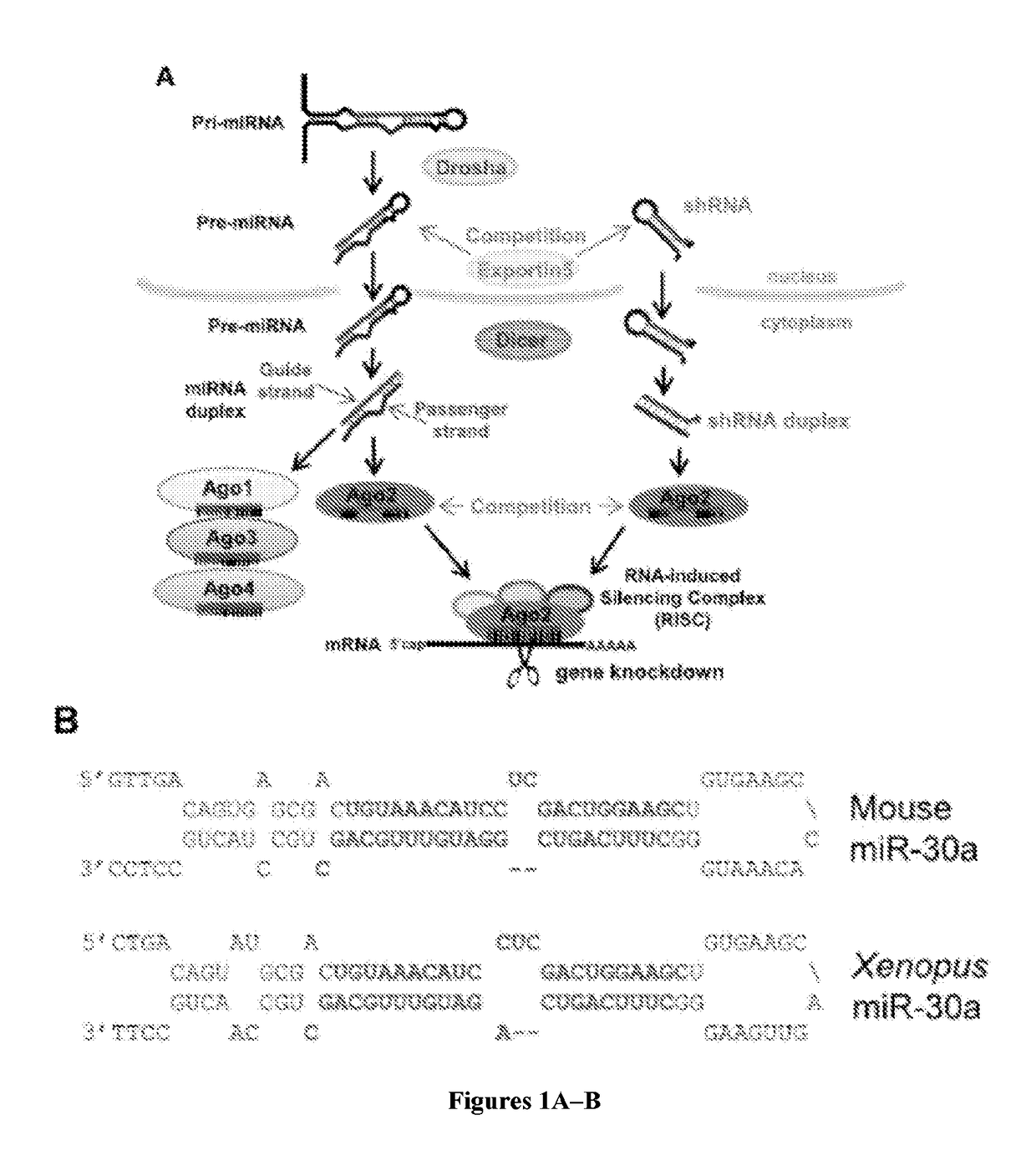
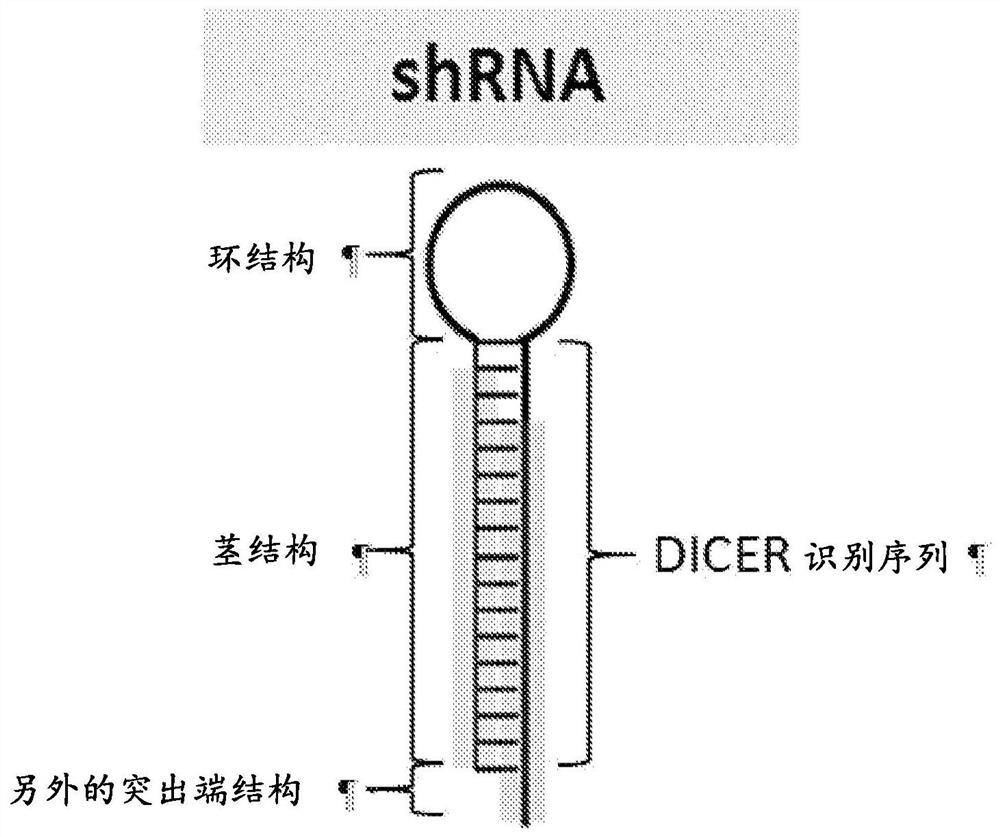
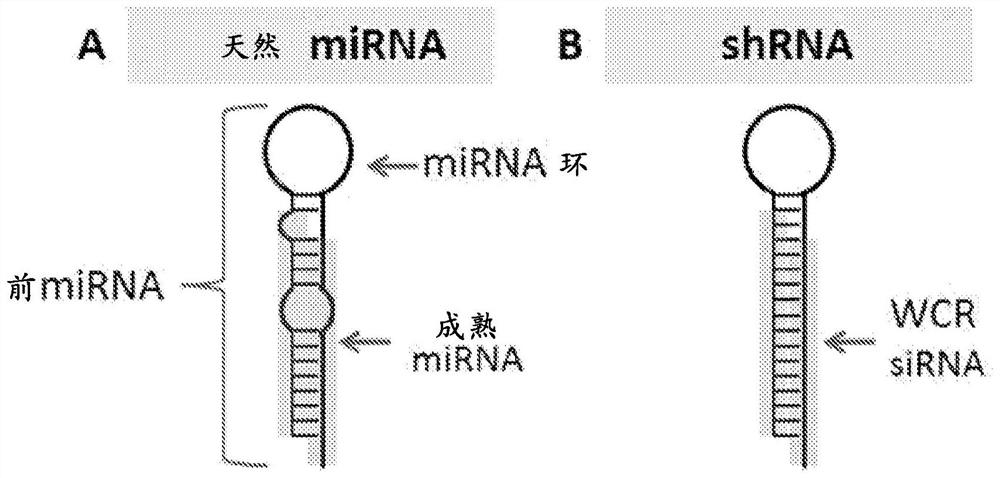
A short hairpin RNA or small hairpin RNA (shRNA/Hairpin Vector) is an artificial RNA molecule with a tight hairpin turn that can be used to silence target gene expression via RNA interference (RNAi). Expression of shRNA in cells is typically accomplished by delivery of plasmids or through viral or bacterial vectors. shRNA is an advantageous mediator of RNAi in that it has a relatively low rate of degradation and turnover. However, it requires use of an expression vector, which has the potential to cause side effects in medicinal applications.
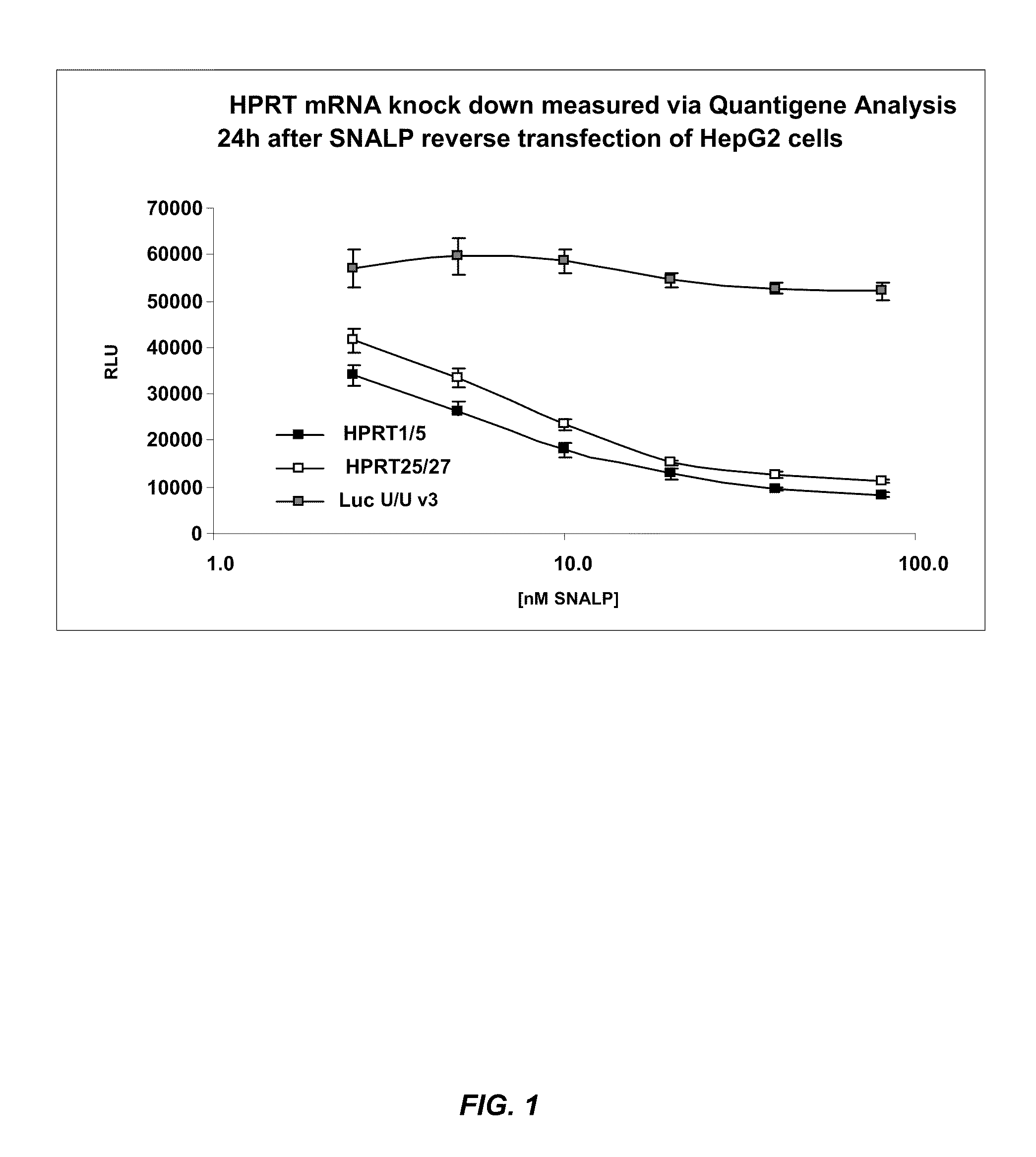
Lipid encapsulated dicer-substrate interfering RNA
The present invention provides novel, stable nucleic acid-lipid particles comprising one or more Dicer-substrate dsRNAs and / or small hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), methods of making the particles, and methods of delivering and / or administering the particles (e.g., for the treatment of a disease or disorder). In some embodiments, the nucleic acid-lipid particles of the invention comprise Dicer-substrate dsRNAs and / or shRNAs. In other embodiments, the nucleic acid-lipid particles of the invention comprise Dicer-substrate dsRNAs and / or shRNAs in combination with one or more additional interfering RNAs (e.g., siRNA, aiRNA, and / or miRNA). In further embodiments, the Dicer-substrate dsRNAs and / or shRNAs present in the nucleic acid-lipid particles of the invention are chemically synthesized.
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
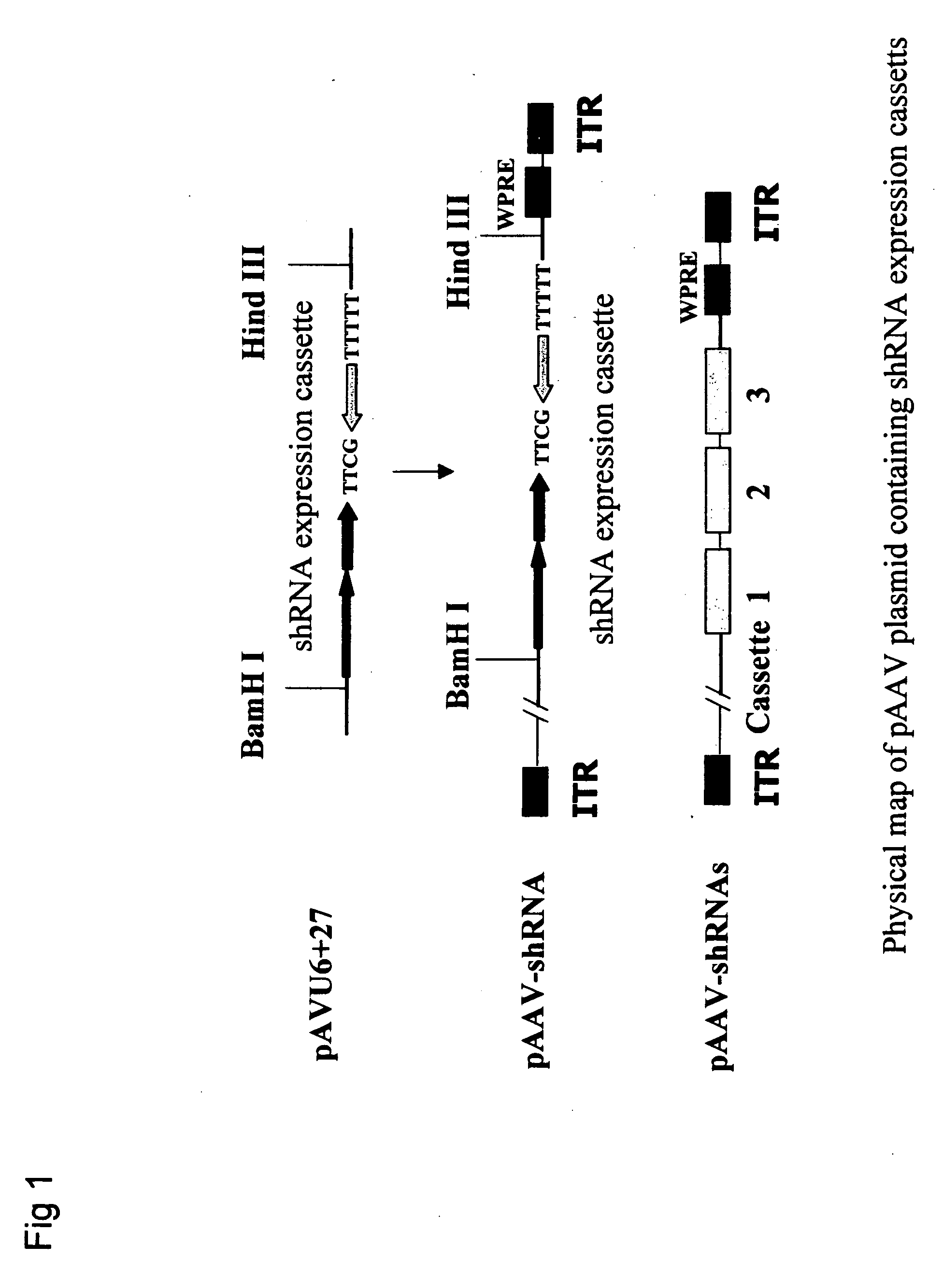
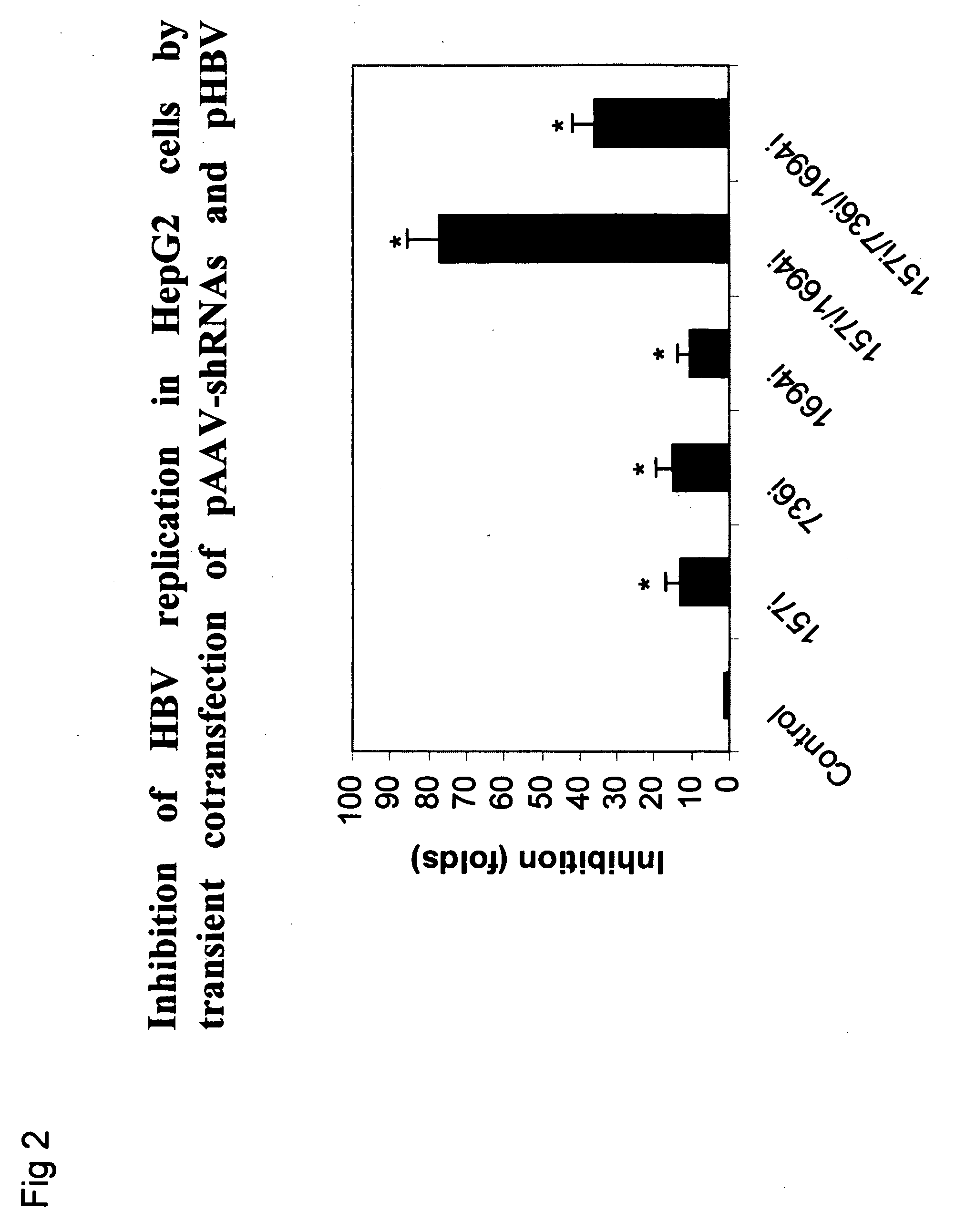
Gene therapy of HBV infection via adeno-associated viral vector mediated long term expression of small hairpin RNA (shRNA)
InactiveUS20070027099A1Reduces HBV viral loadInhibited HBV gene expressionGenetic material ingredientsFermentationHbv replicationViral vector
The invention provides a vector comprising an AAV-shRNA vector. The vector is preferably rAAV-151i / 1694i. The invention also provides a method of suppressing or inhibiting HBV replication in liver cells infected therewith, comprising administering an amount of an AAVB-shRNA vector effective to suppress, inhibit or reduce HBV replication.
Owner:HONG KONG THE UNIV OF
Short hairpin rnas for inhibition of gene expression
Methods, compositions, and kits that include small hairpin RNA (shRNA) useful for inhibition of gene expression, such as viral-mediated gene expression, are described.
Owner:SOMAGENICS INC
Methods for modulating KLHL1 levels, methods for modulating current activity in T-type calcium channels, molecules therefor, and methods for identifying molecules therefor
ActiveUS10047377B2Indirectly modulate current activity in T-type calcium channelsCertain adverse side effectSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsDirect effectsKLHL1 gene
Owner:LOYOLA UNIV OF CHICAGO
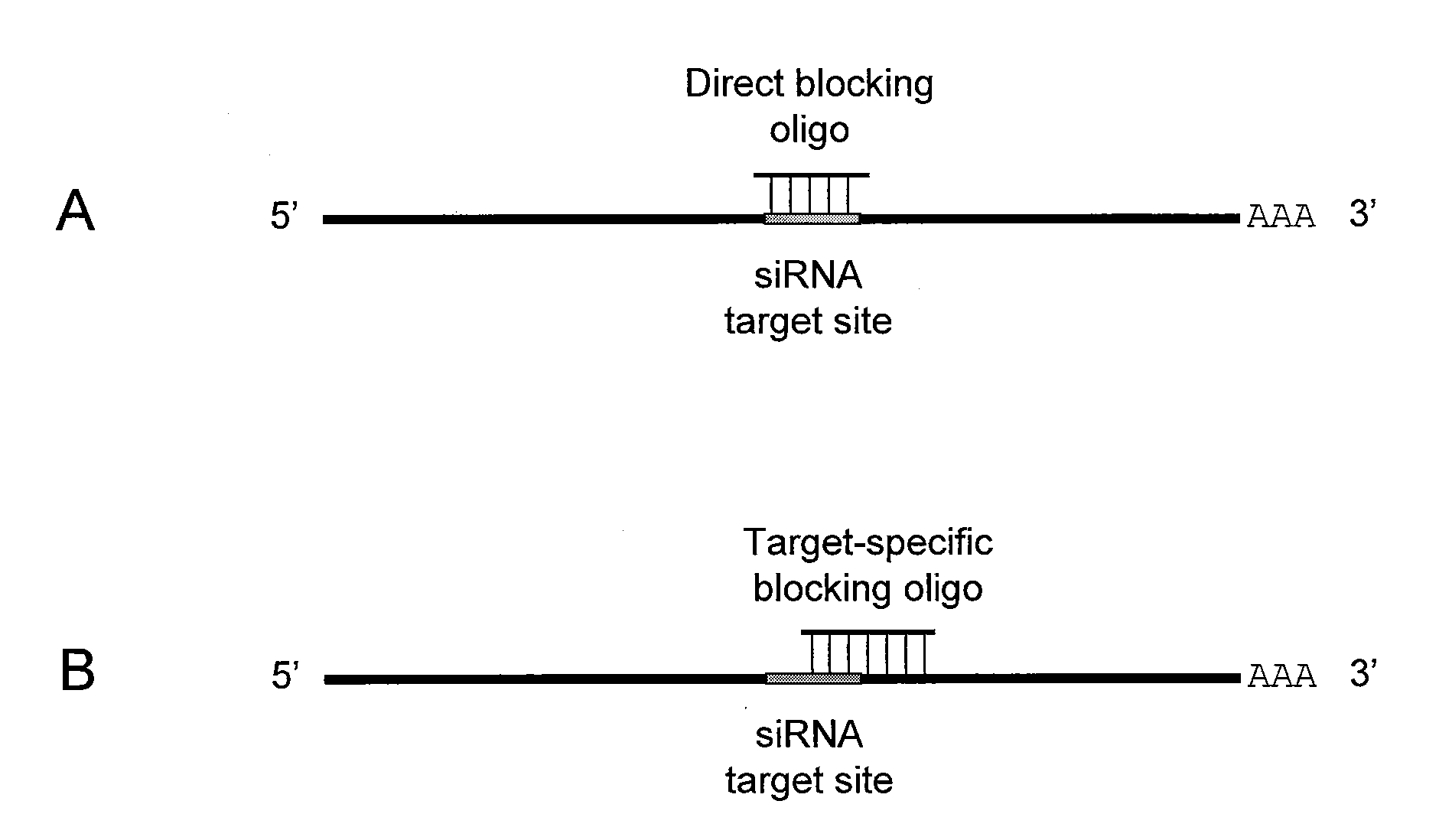
Small interfering RNA (SIRNA) target site blocking oligos and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100113284A1High sensitivityStrong specificitySugar derivativesActivity regulationSingle-Stranded RNASmall interfering RNA
The present invention relates to nucleic acids designed to prevent the binding of single strand RNA in protein complexes originatig from small interfering RNA (siRNA) or small hairpin RNA (shRNA) and uses thereof.
Owner:EXIQON AS
Short hairpin RNAs for inhibition of gene expression
Methods, compositions, and kits that include small hairpin RNA (shRNA) useful for inhibition of gene expression, such as viral-mediated gene expression, are described.
Owner:SOMAGENICS INC
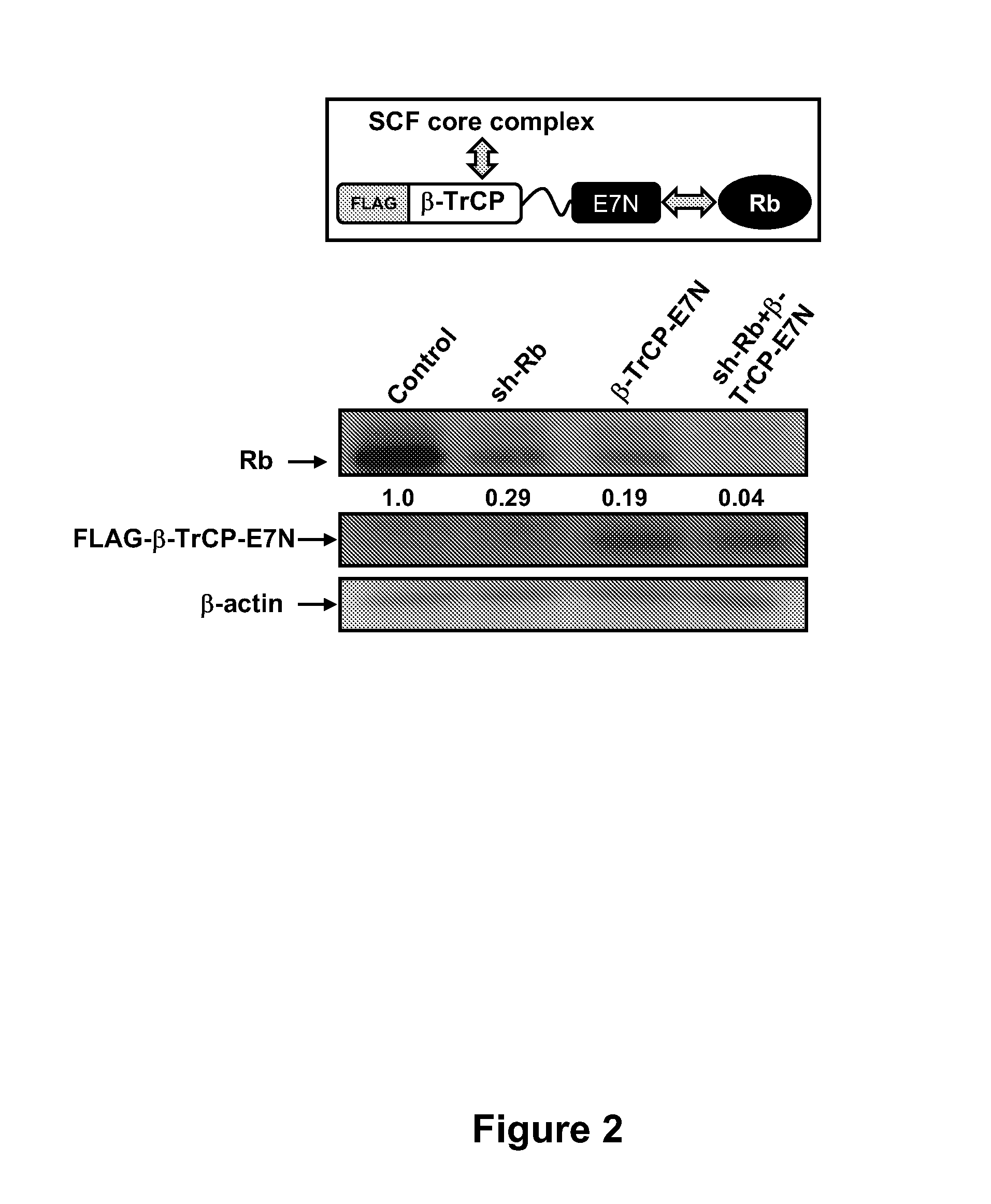
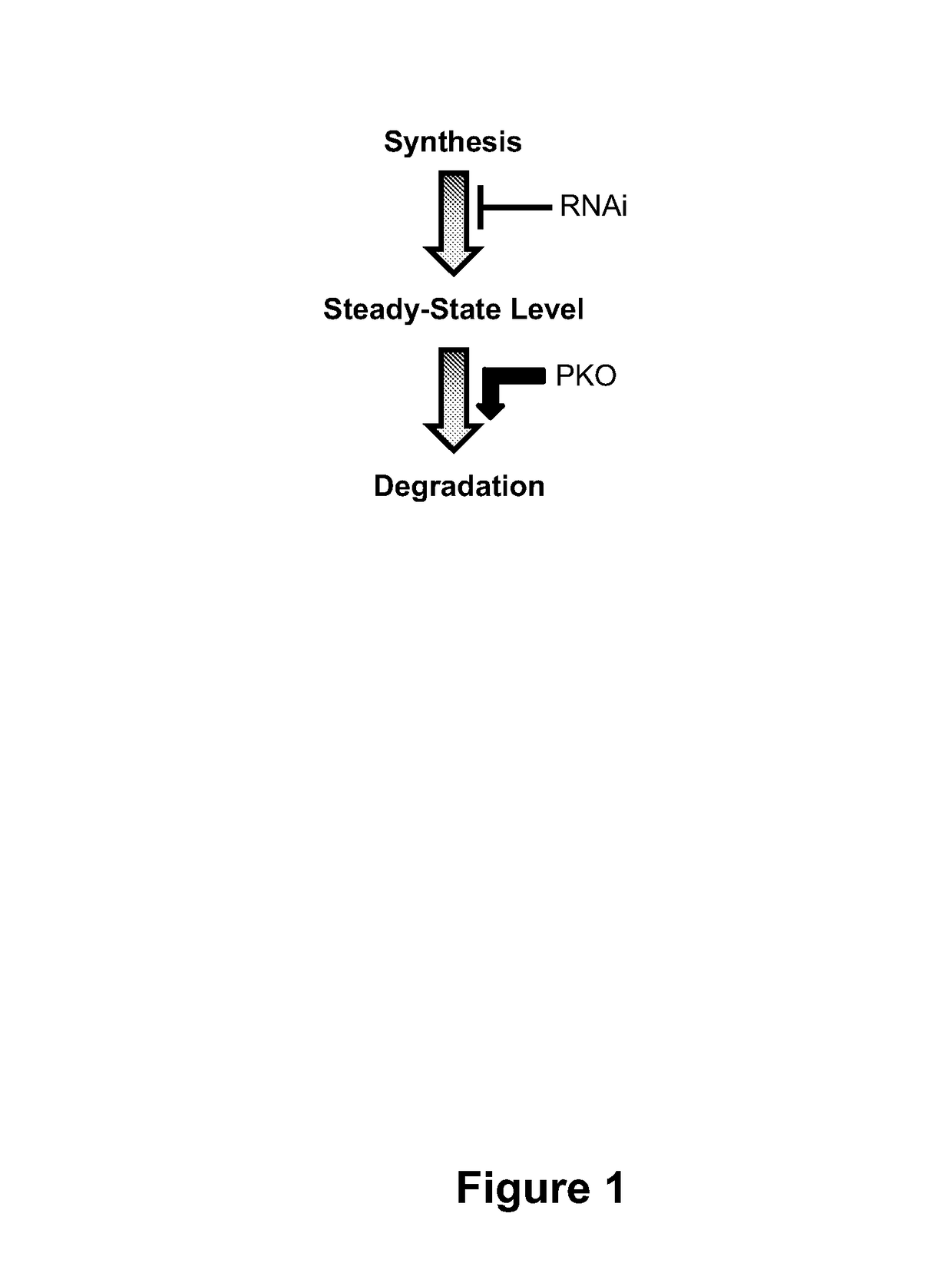
Methods for Reducing Protein Levels in a Cell
ActiveUS20130011920A1Reduce synthesisPromote degradationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein targetDelivery vehicle
The present invention provides a method of reducing levels of at least one target protein in a cell. The cell is contacted with a first agent and a second agent. The first agent reduces synthesis of the target protein, e.g., by reducing levels of the mRNA of the target protein or inhibits translation of the mRNA. The second agent accelerates degradation of the target protein. The first agent may contact the cell before, after or simultaneously with the second agent. The first agent and the second agent may be in separate delivery vehicles, or in a single delivery vehicle. The first agent may be an RNAi (RNA interference) molecule, such as a small interfering RNA (siRNA), a small hairpin RNA (shRNA) or a microRNA (miRNA). The second agent may be a chimeric polypeptide containing a ubiquitin ligase polypeptide and a target protein interacting domain. The ubiquitin ligase polypeptide can be an E3 ubiquitin ligase, including, but not limited to, an SCF polypeptide, a HECT polypeptide and a UBR1 polypeptide. In one embodiment, the SCF polypeptide is an F-box polypeptide.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Novel cosmetic designs and products using intronic rna
InactiveCN101569597ASuppress gene silencing effectPerformance increase or decreaseCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsInteinSkin color
The present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a non-naturally occurring intron and its components capable of being processed into small hairpin RNA (shRNA) and / or microRNA (miRNA) molecules by skin cells and thus inducing specific gene silencing effects on skin pigment-related genes and / or aging-causing genes in the cells. The gene silencing effects so obtained are not only useful for lightening and whitening skin colors but also useful for suppressing unwanted aging gene activities in skins.
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH
Detection, treatment and prognosis target of depression and applications
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, and relates to a detection, treatment and prognosis target of depression and applications. An accumbens nucleus HDAC7 in neurons can be inhibited by a small hairpin RNA in an HDAC7-shrna lentivirus, and the sequence of the small hairpin RNA is 5'-GAC AAG AGC AAG CGA AGT G-3'. Experiments in the invention confirm that the HDAC7 can regulate and control the expression of many genes closely related to depression-like behavior and can be used as the detection, treatment and prognosis target of the depression; and the target provides a novel idea for the treatment of the depression, and provides a novel idea for the research and development of drugs for preventing and treating the depression.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV
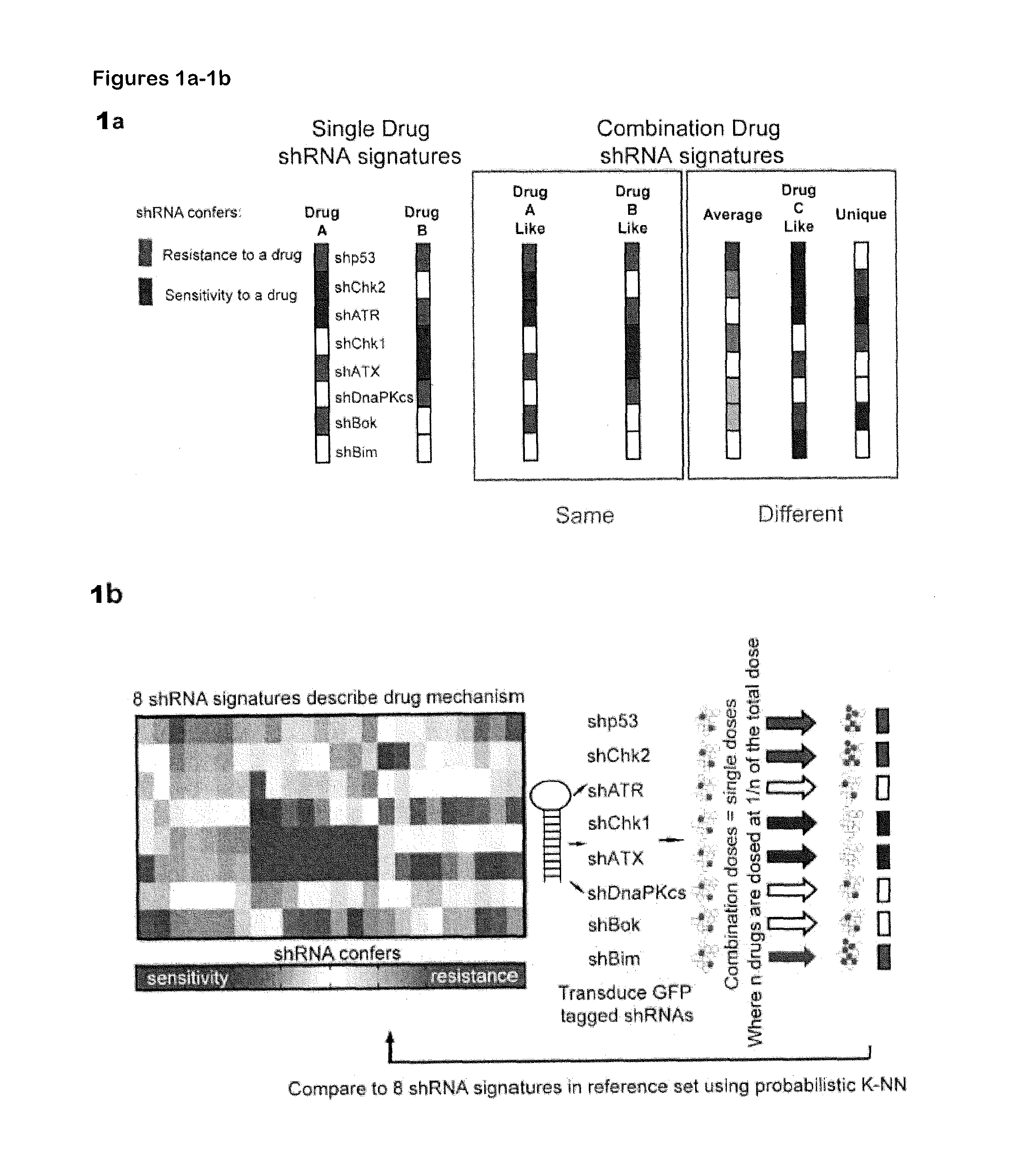
RNAi-Based Method of Drug Screening and Characterization
ActiveUS20140134635A1Simple powerMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMechanism of actionBiology
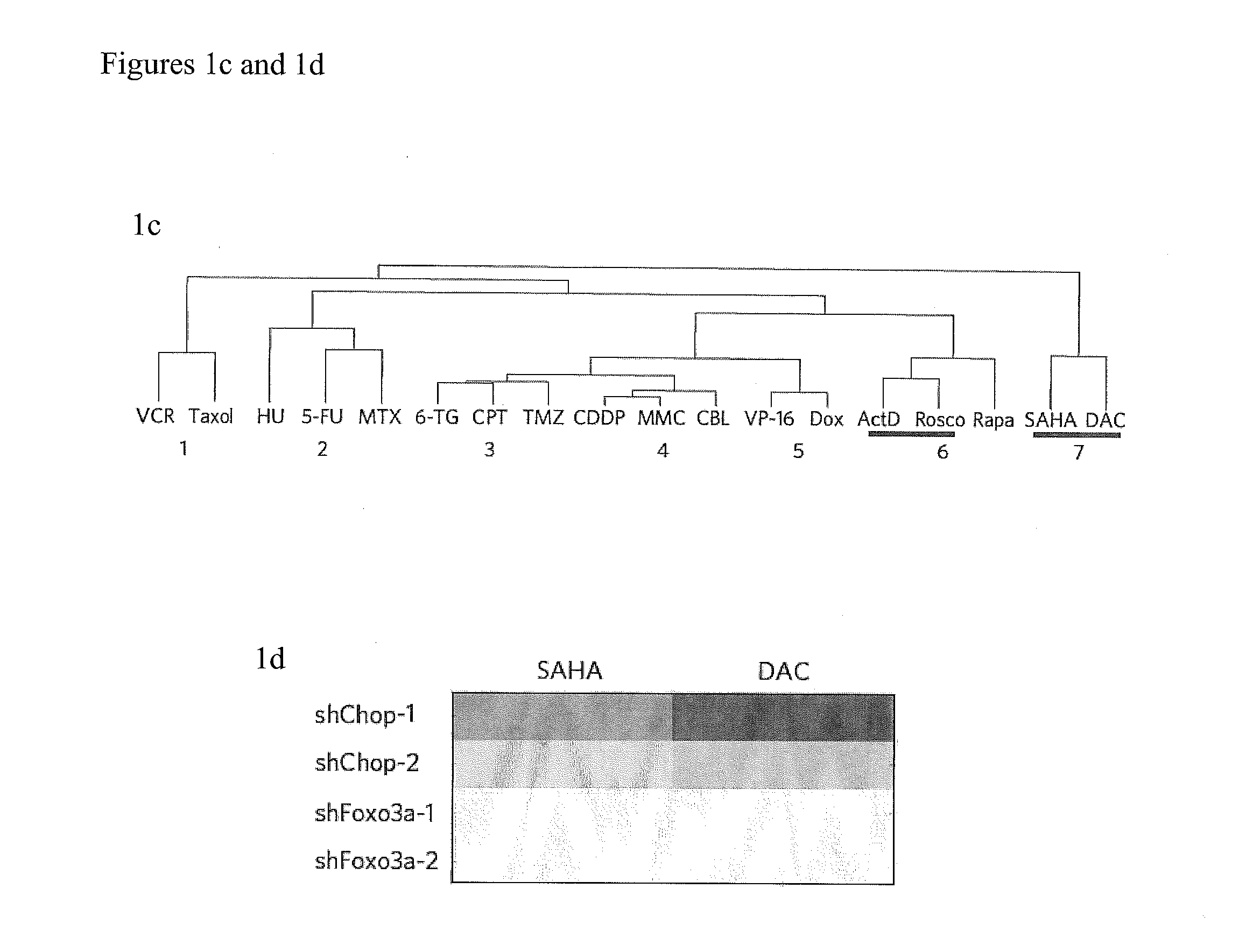
The invention is directed to a method of characterizing a mechanism of action of an agent (e.g., a chemotherapeutic agent, a genotoxic agent). The method comprises contacting a plurality of populations of cells with an agent to be assessed, wherein each population of cells have one gene of interest targeted by a small hairpin RNA (shRNA) and wherein said gene of interest regulates cell death and a plurality of genes that regulate cell death are targeted in the plurality of populations of cells. A responsiveness of each population of cells to the agent is determined, thereby obtaining an shRNA signature of the agent, so as to identify one or more genes that mediate a response to the agent, thereby characterizing the mechanism of action of the agent. The invention is also directed an article of manufacture for characterizing a mechanism of action of a chemotherapeutic or genotoxic agent.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Tri-cistron muscle specific two-way co-expression gene transferant and preparation method
InactiveCN105063079AImprove disease-related traitsVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseGene Knock-Down
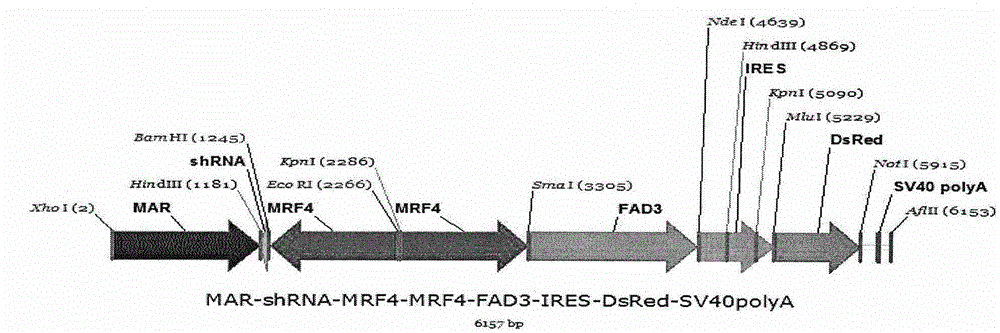
The invention discloses a tri-cistron muscle specific two-way co-expression gene transferant and a preparation method thereof. The gene transferant comprises an MARs cow matrix attachment region, short hairpin RNA (shRNA) taking the third exon (926-947 loca) of cow muscle colyone as a target spot, an optimally synthesized muscle specific promoter (MRF4), a humanization n-3 desaturase gene (FAD3), an internal ribosome entry site (IRES), a red fluorescent protein gene (DsRed) and a termination signal region (SV40polyA), and the independent gene transferant does not have a pronucleus main vector sequence. According to the tri-cistron muscle specific two-way co-expression gene transferant and the preparation method, an RNA interference technology is firstly combined with the muscle specific overexpression FAD3 and DsRed, therefore, gene knock-down and inverse overexpression of related genes can be performed simultaneously, and a novel thought and approach can be supplied for safely and efficiently improving characters, such as muscle and disease related characters, controlled by polygenes.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Bicistronic co-expression gene transfer bodyand preparation method
InactiveCN104195153AEnhanced knockdownVector-based foreign material introductionMyostatinFollistatin
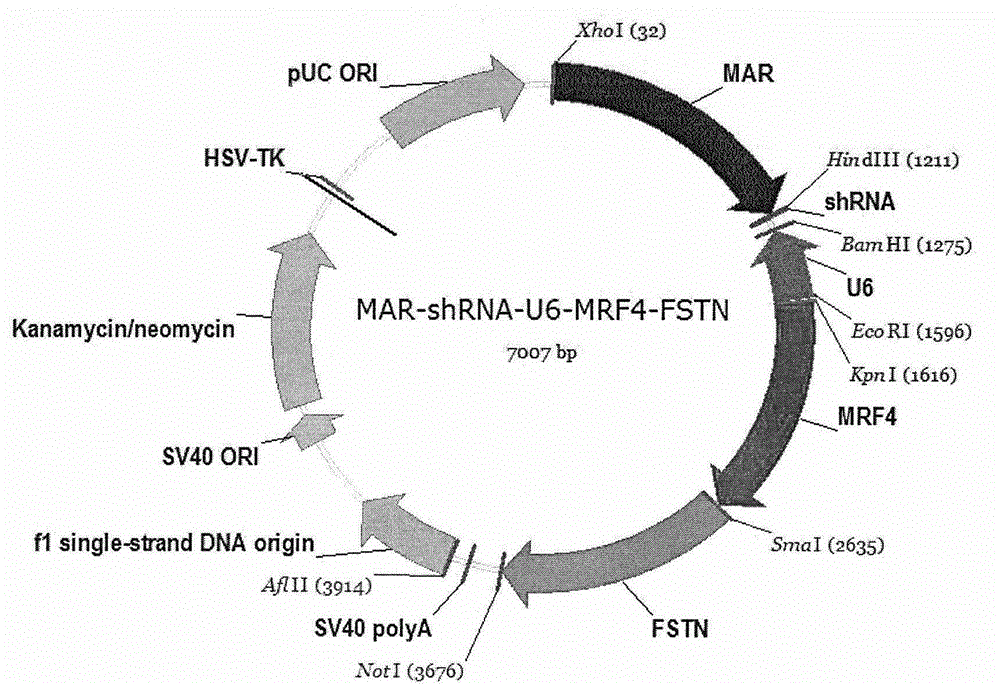
The invention discloses a bicistronic co-expression gene transfer body and a preparation method. The gene sequence of the gene transfer body is SEQ ID NO: 17. The gene transfer body comprises bovine matrix attachment regions (MARs), an RNA polymerase promoter III (U6), short hairpin RNA (shRAN) targeting the third exon of bovine myostatin (MSTN), a CMV promoter, a bovine follistatin (FSTN) and an SV40polyA signal region from the five prime end to the three prime end in order. The gene transfer body provided by the invention doesn't contain a vector backbone sequence and is a clean and safe gene transfer; and the gene transfer body combines the MAR with a knock-down vector for the first time and can effectively enhance the knock-down effect of the vector. Besides, the gene transfer body achieves the purpose of conducting knock-down and over-expression simultaneously by independently starting double promoters, and provides new ideas and paths for improving the characteristics (such as economic characteristics) of double-gene / multi-gene control.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
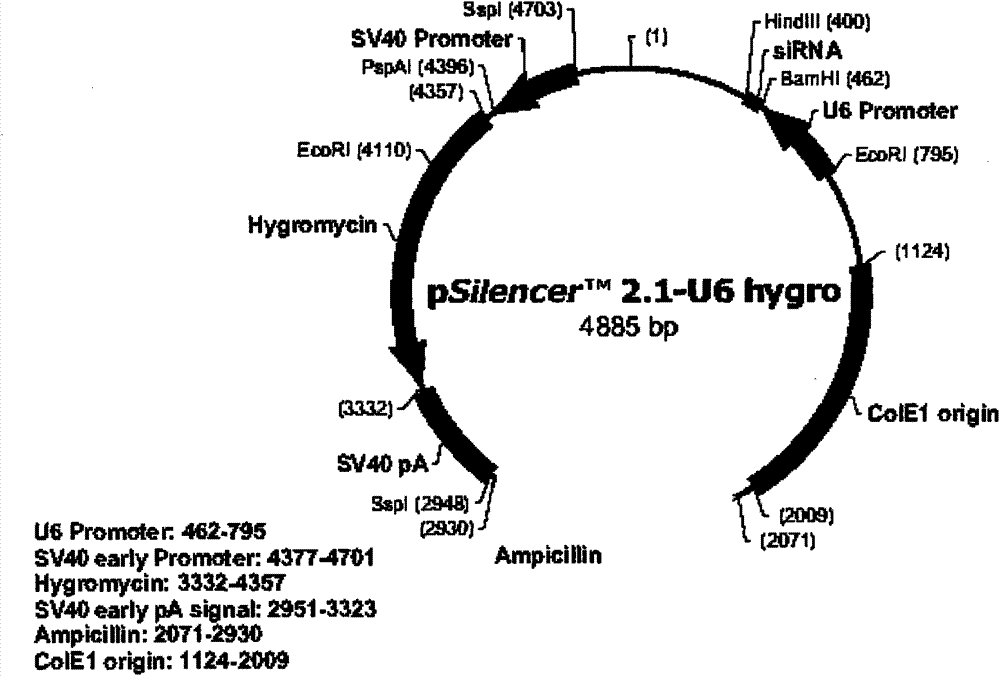
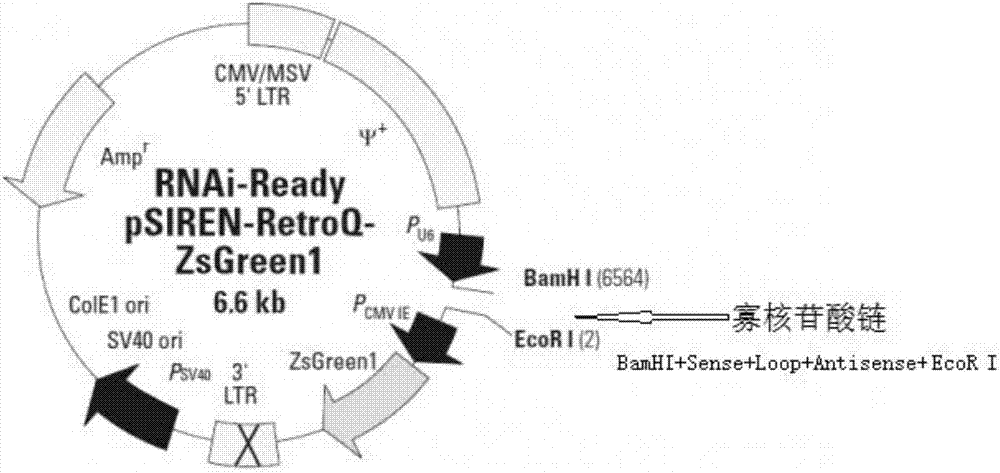
Small-hairpin RNA recombinant carrier expressed by targeted inhibition integrin beta 1 and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106947778AEfficient expressionEfficient and stable expressionVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme digestionResistant genes
The invention discloses a small-hairpin RNA recombinant carrier expressed by targeted inhibition integrin beta 1, which includes a basic sequence, a resistant gene sequence, a polyclonal locus sequence, a promoter sequence of an RNAi-Ready pSIREN-RetroQ-ZsGreen1 carrier, and an oligonucleotide chain of a targeted integrin beta 1 gene. The polyclonal locus includes a BamH I enzyme digestion locus and an EcoR I enzyme digestion locus. The oligonucleotide chain is composed of the BamH I enzyme digestion locus, a target sequence positive-sense strand, a stem-loop structure, a target sequence antisense strand, and the EcoR I enzyme digestion locus. The oligonucleotide chain is inserted into the polyclonal locus in the forward direction. The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The small-hairpin RNA recombinant carrier can targetedly inhibit expression of the integrin beta 1, has high specificity, high-effective and stable expression and high transfection efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Novel cosmetic designs and products using intronic RNA
InactiveUS20090170204A1Less attentionInhibits gene silencing effectSugar derivativesActivity regulationInteinSkin pigment
The present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a non-naturally occurring intron and its components capable of being processed into small hairpin RNA (shRNA) and / or microRNA (miRNA) molecules by skin cells and thus inducing specific gene silencing effects on skin pigment-related genes and / or aging-causing genes in the cells. The gene silencing effects so obtained are not only useful for lightening and whitening skin colors but also useful for suppressing unwanted aging gene activities in skins.
Owner:WU DAVID TS +1
RNAi-Based Method of Screening and Characterizing Drug Combinations
ActiveUS20140206544A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMechanism of actionTreatment use
In one aspect, the invention is directed to a method of characterizing a mechanism of action of a combination of agents. The method comprises contacting a plurality of populations of cells with a combination of agents to be assessed, wherein each population of cells have one gene of interest targeted by a small hairpin RNA (shRNA) and wherein the gene of interest regulates cell death and a plurality of genes that regulate cell death are targeted in the plurality of populations of cells. A responsiveness of each population of cells to the combination of agents is determined, thereby obtaining an shRNA signature of the combination of agents so as to identify one or more genes that mediate a response to the combination of agents, thereby characterizing the mechanism of action of the combination of agents. In another aspect, the invention is directed to a method of determining whether a patient population treated with a first agent would benefit from a treatment using the first agent in combination with one or more additional agents. In yet another aspect, the invention is directed to method of determining whether a formulation of one or more agents maintains a mechanism of action of the one or more agents when unformulated.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Flat wire having indication wire and its insertion method
RNA interference (RNAi) has become a powerful tool for blocking gene expression in mammals and mammalian cells. This approach requires the delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) either as RNA itself or as DNA, using an expression plasmid or virus and the coding sequence for small hairpin RNAs that are processed to siRNAs. Current expression systems for the production of siRNA in vivo rely on RNA polymerase III promoters. These are difficult to regulate and leave most of the RNA in the nucleus of the cell where it is inactive for RNA interference. The invention provides a DNA cassette for the cloning of small hairpin sequences which permit their expression and processing using RNA polymerase II. This system enables efficient transport of the pre-siRNAs to the cytoplasm where they are active and permits the use of regulated and tissue specific promoters for gene expression.
Owner:BENQ CORP
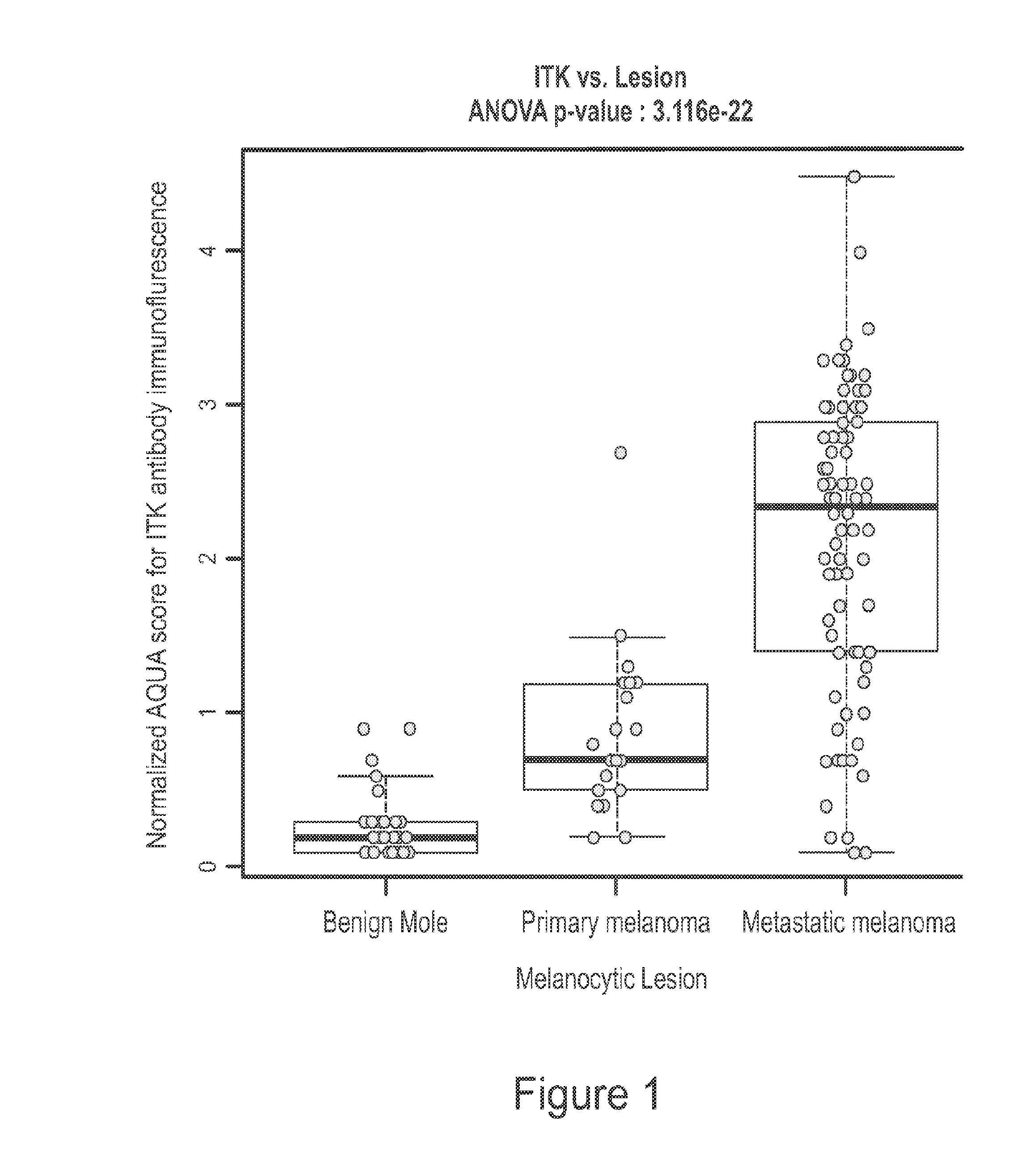
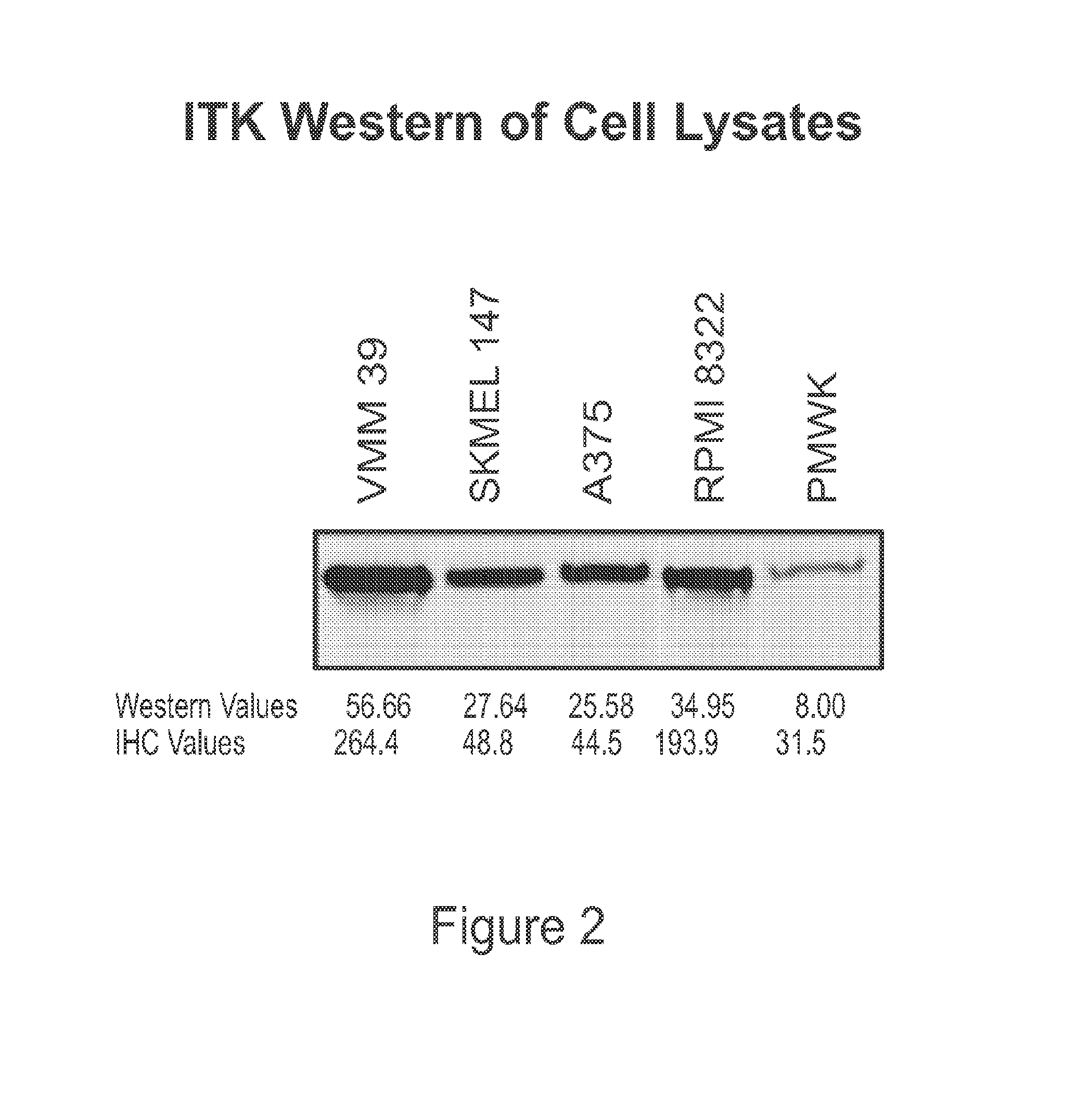
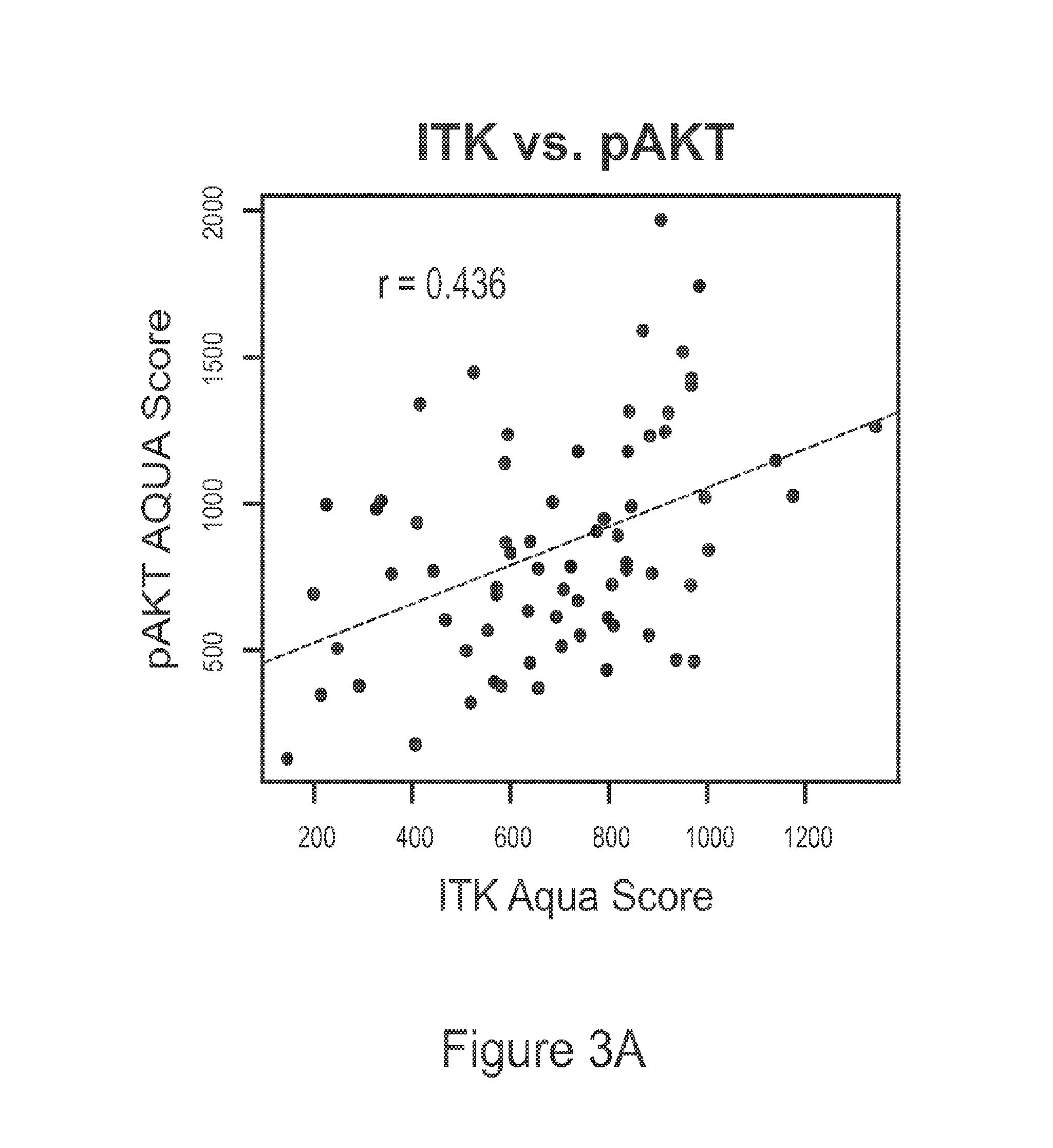
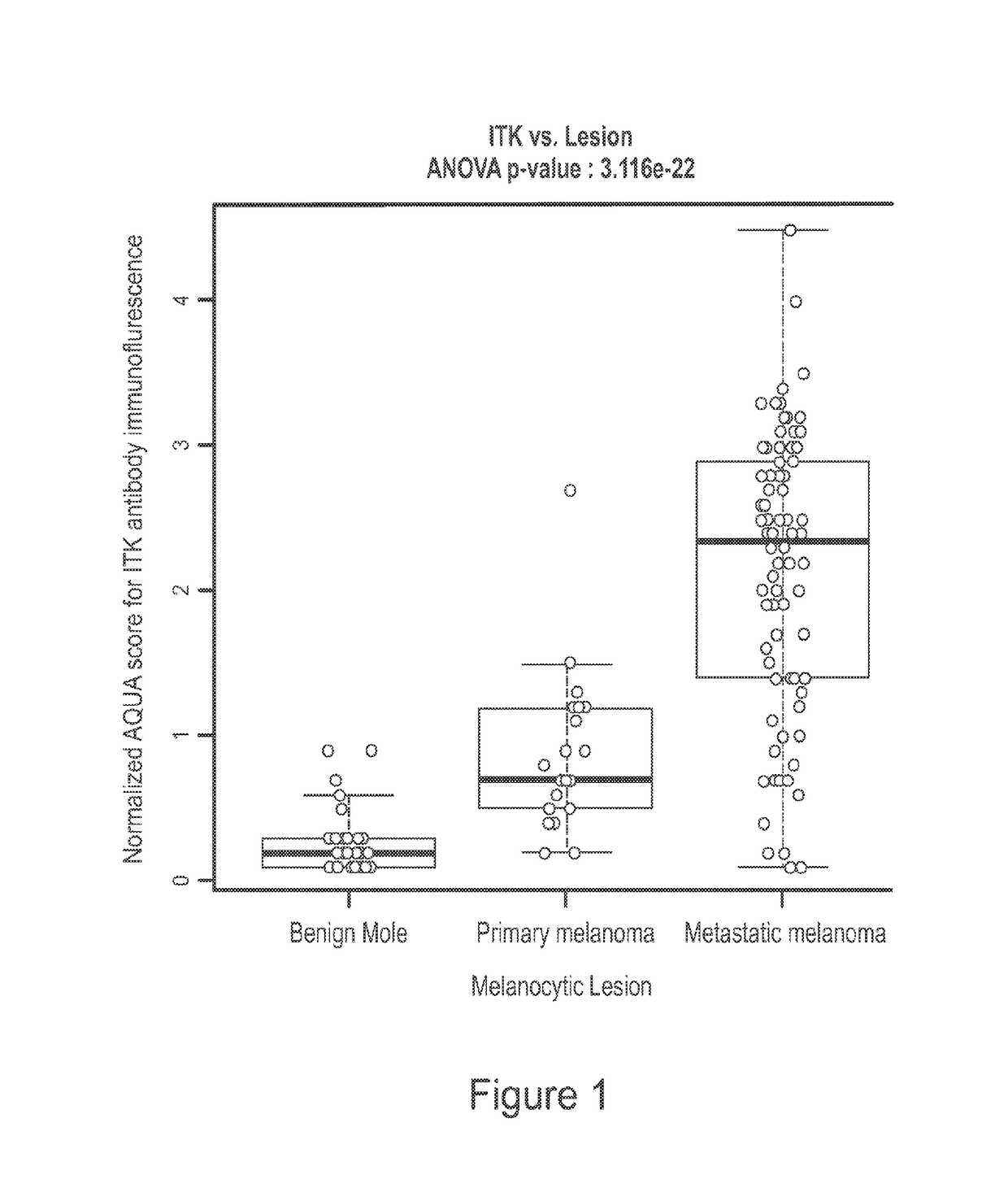
Use of itk inhibitors for the treatment of cancer
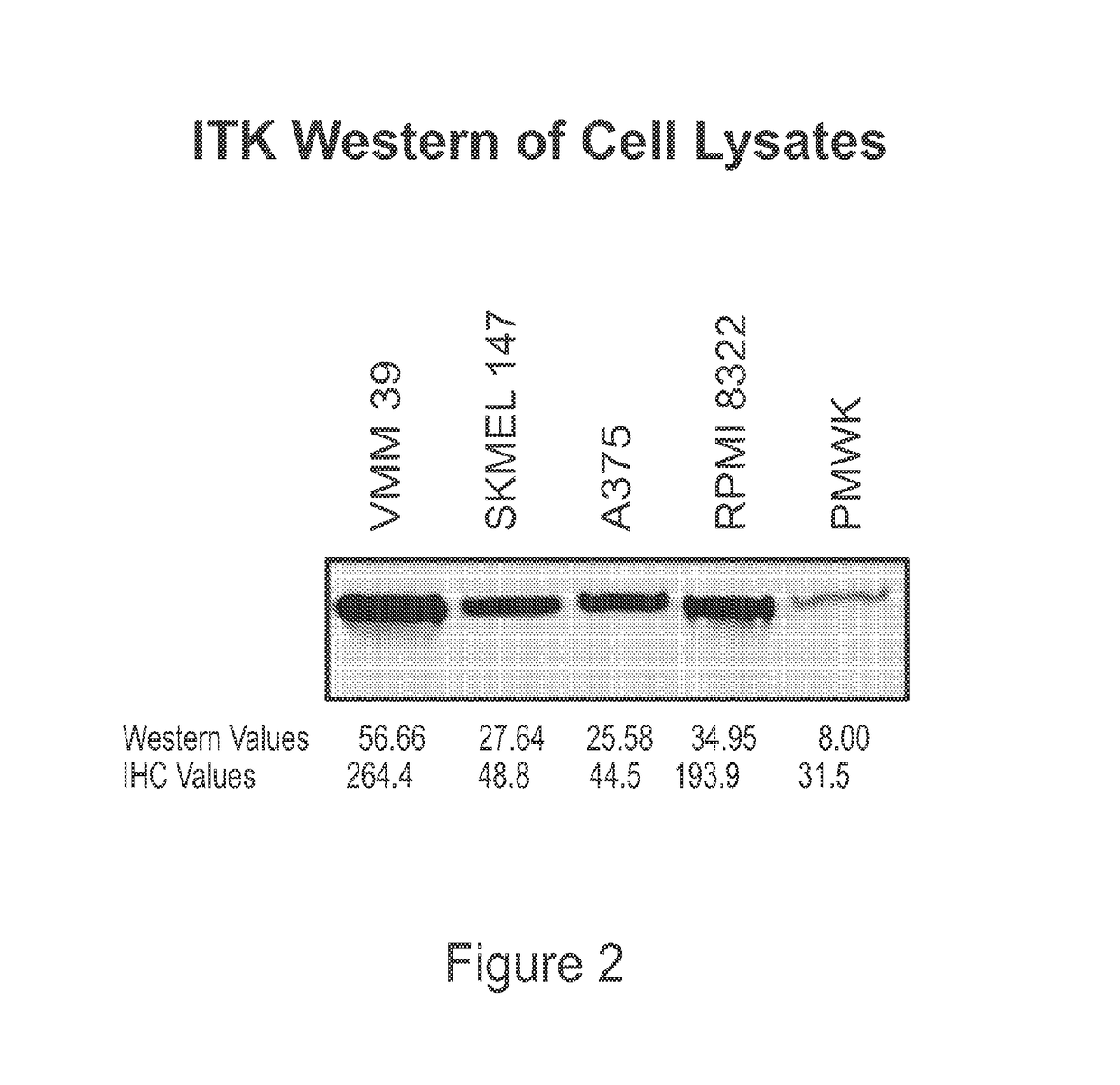
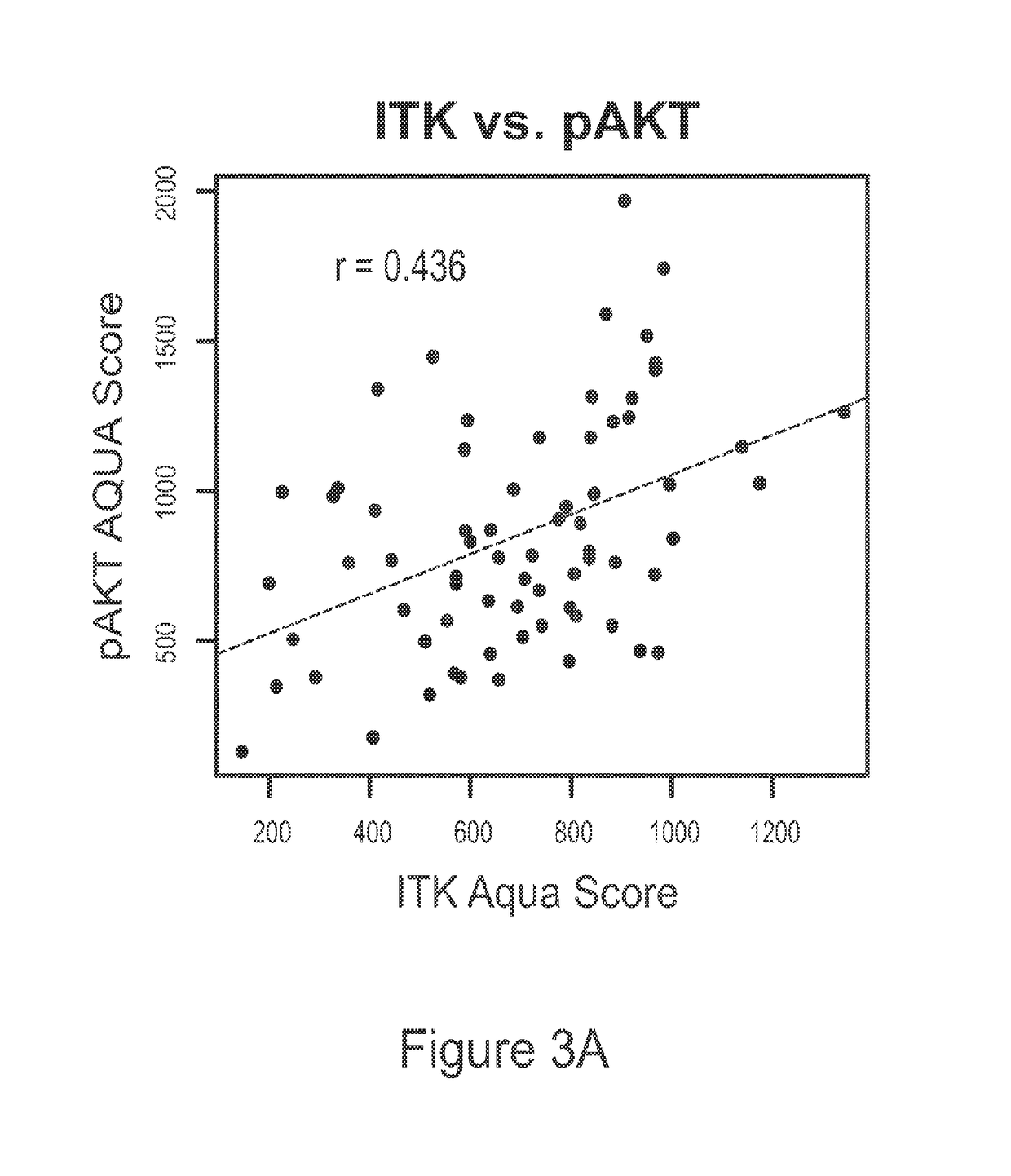
This invention relates generally to the use of ITK (IL-2 inducible T-cell kinase) inhibitors for the treatment of patients who have melanoma or other solid tumors. Applicants demonstrate that ITK lentiviral small hairpin RNA knockdowns and a small molecule inhibitor can each decrease the proliferation and migration of melanoma cell lines and a small molecule inhibitor can be used to inhibit the growth of melanomas in vivo.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Small hairpin RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) recombination oncolytic adenovirus carrying target mitotic phase phosphoprotein 1 gene
InactiveCN104195117AInhibitionInhibitory activityGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesOncolytic adenovirusKinesin
The invention belongs to the field of biopharmacy and relates to a small hairpin RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) recombination oncolytic adenovirus carrying a target human kinesin (mitotic phase phosphoprotein 1) gene and a preparation method of the recombination oncolytic adenovirus. The invention provides a brand-new liver cancer drug target, namely mitotic phase phosphoprotein 1 which has a broad spectrum that the traditional gene therapy target p53 gene does not have; the invention further provides the preparation method of the small hairpin RNA recombination oncolytic adenovirus for expressing the mitotic phase phosphoprotein 1; and at the same time, the invention provides an application of the recombination oncolytic adenovirus in preparing a cancer treatment drug.
Owner:WUHAN BAIAOJING BIOLOGICAL PHARMA CO LTD
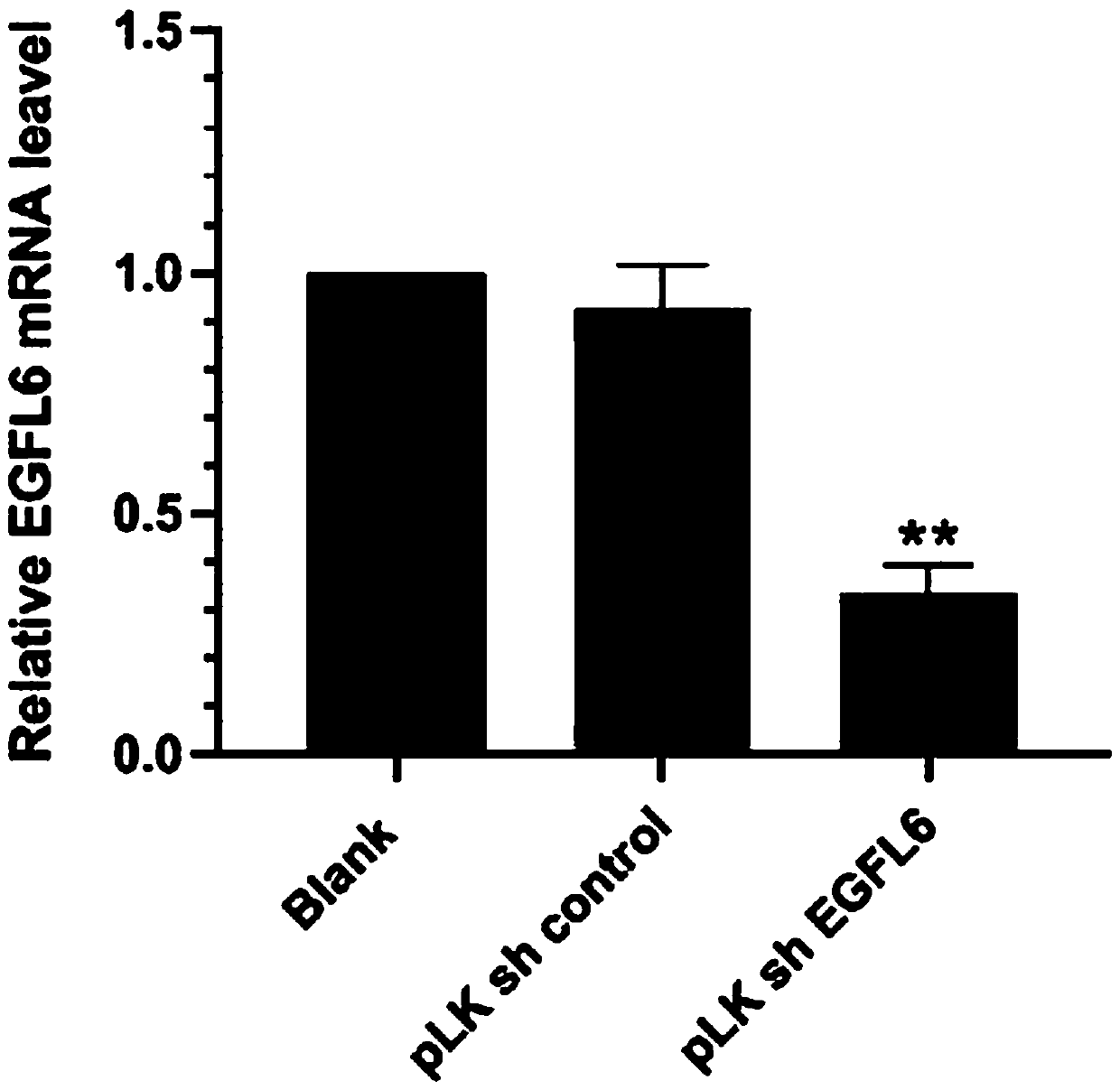
SiRNA (small interference Ribonucleic Acid) for targeted inhibition on expression of esophagus cancer EGFL6 gene, constructed expression vector and application
PendingCN110951733AHigh infection rateInhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsFermentationA-DNAIn vivo
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicines and molecular biology and relates to siRNA (small interference Ribonucleic Acid) for targeted inhibition on expression of an esophagus cancer EGFL6 gene, and an RNA interference recombinant lentiviral vector for the targeted inhibition on the expression of the esophagus cancer EGFL6 gene. The constructed RNA interference recombinant lentiviral vector is used to inhibit the expression of the esophagus cancer EGFL6 gene and effectively inhibit the expression of the esophagus cancer EGFL6 gene. The siRNA has double strands and is markedas si EGFL6; a deactivated lentiviral vector is used to carry a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) template of a UCP2 RNA interference segment, and is transcribed into shRNA (small hairpin RNA) in vivo, sothat the problems of targeting ability, safety and expression continuity of RNA interference are perfectly solved. A target gene is integrated to a target cell genome, is expressed for long time and has a small immune response, so that the siRNA is a relatively ideal interference vector which is introduced into tumor cells and is used for silencing the EGFL6 gene in the tumor cell.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
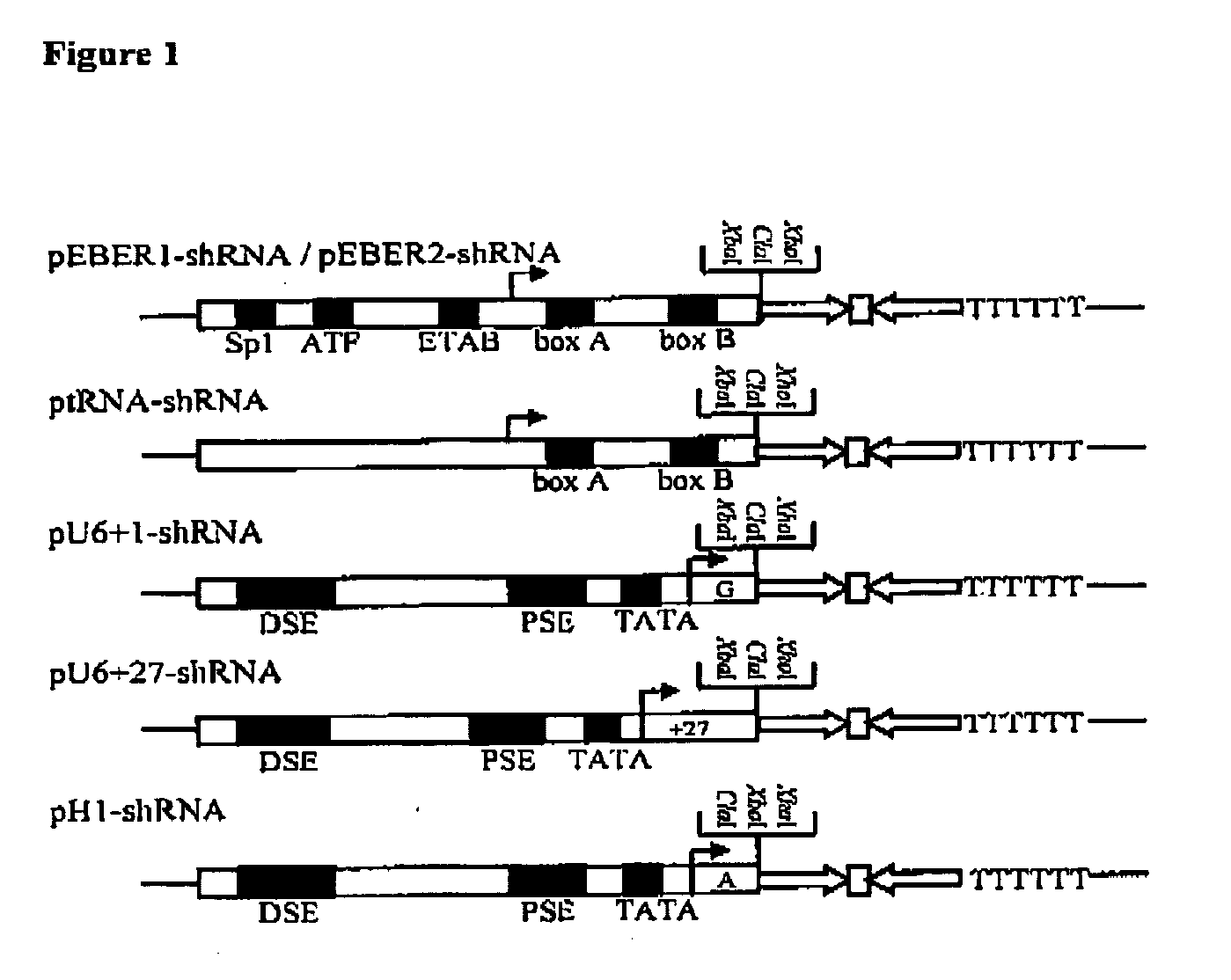
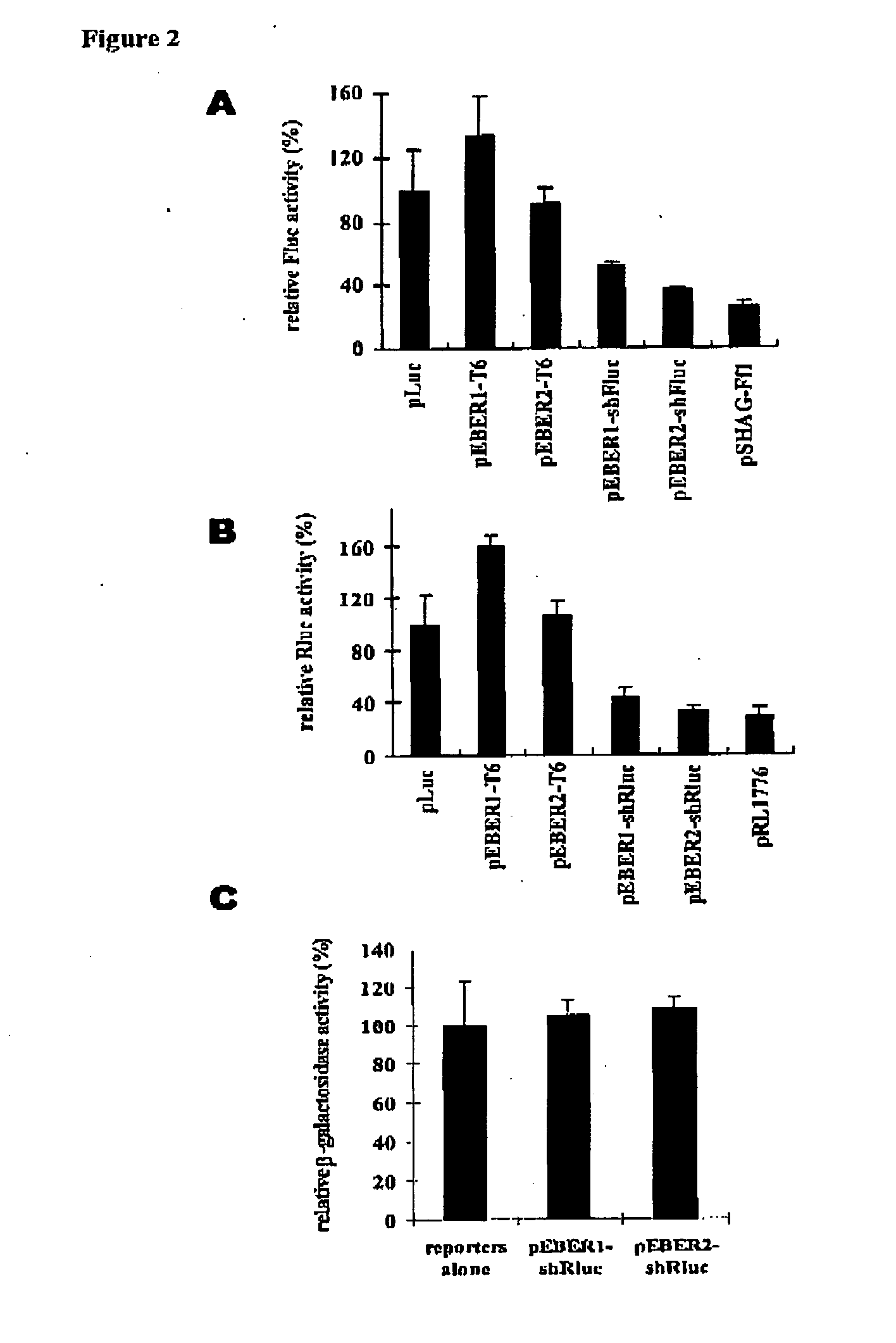
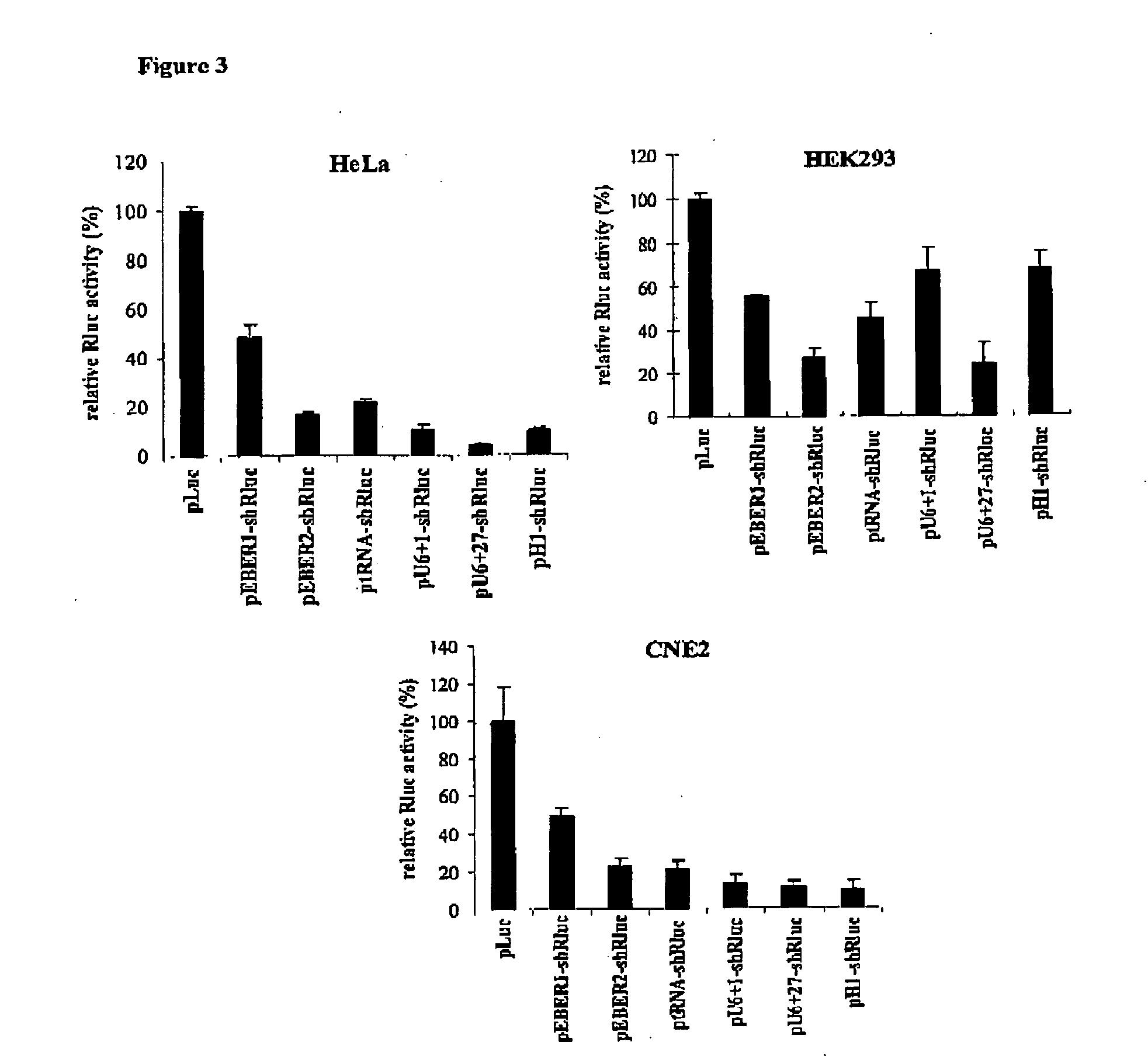
Promoters for RNA interference
This invention provides vector systems based on the promoters of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs that can be used to express and deliver desired RNA molecules such as small hairpin RNAs in mammalian cells. Such small hairpin RNAs are useful for RNA interference.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Composition for producing microRNA precursors as drugs for enhancing wound healing and production method of the microRNA precursors
ActiveUS10196662B2Reduce the number of copiesStrong specificityCarbohydrate active ingredientsFermentationWound healingBiotechnology
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH
Methods for modulating klhl1 levels, methods for modulating current activity in t-type calcium channels, molecules therefor, and methods for identifying molecules therefor
ActiveUS20180273951A1Indirectly modulate current activity in T-type calcium channelsCertain adverse side effectMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionDirect effectsKLHL1 gene
Methods for modulating T-type calcium channel activity without directly targeting the T-type calcium channels are provided that include modulating kelch-like protein 1 (KLHL1) levels in a subject by providing a small hairpin RNA (shRNA) that targets a KLHL1 gene, and then administering the shRNA to the subject in an amount sufficient to modulate KLHL1 gene expression. The KLHL1 level directly effects current activity in T-type calcium channels and therefore modulation of KLHL1 gene expression indirectly modulates current activity in T-type calcium channels. The methods may be implemented with, for example, an shRNA molecule suitable for modulating a KLHL1 level in the subject which may be provided as a plasmid encoding the shRNA molecule or an adeno-associated virus vector encoding the shRNA molecule. Methods of identifying compounds that modulate current activity in T-type calcium channels by determining an effect of the compound on KLHL1 gene expression are also provided.
Owner:LOYOLA UNIV OF CHICAGO
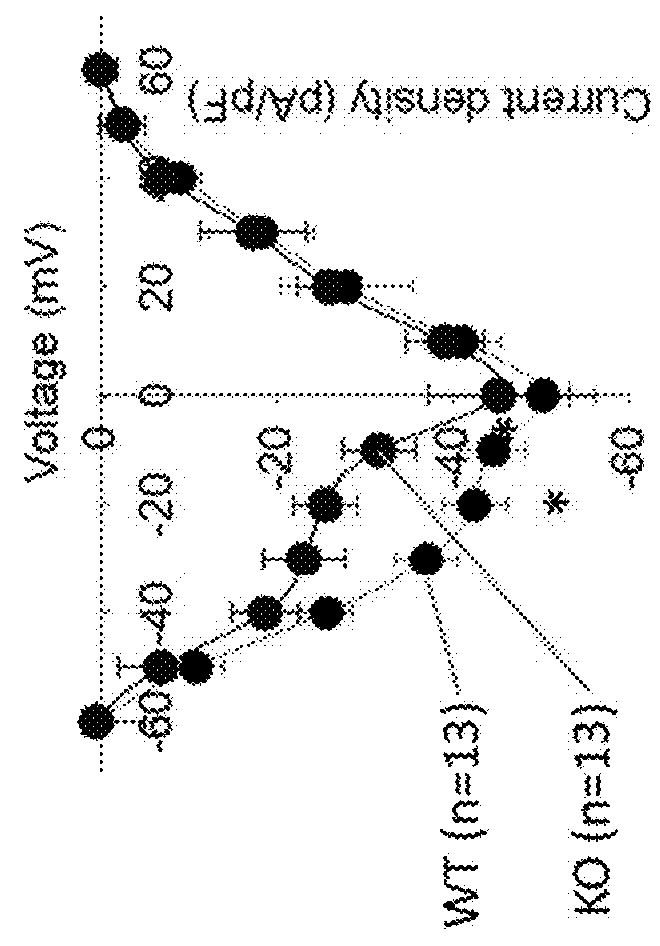
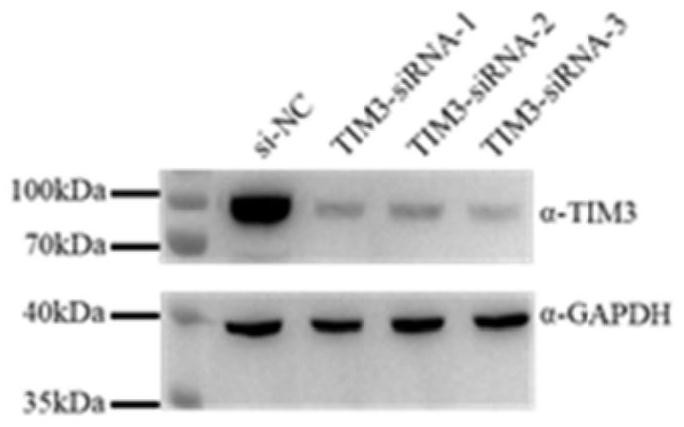
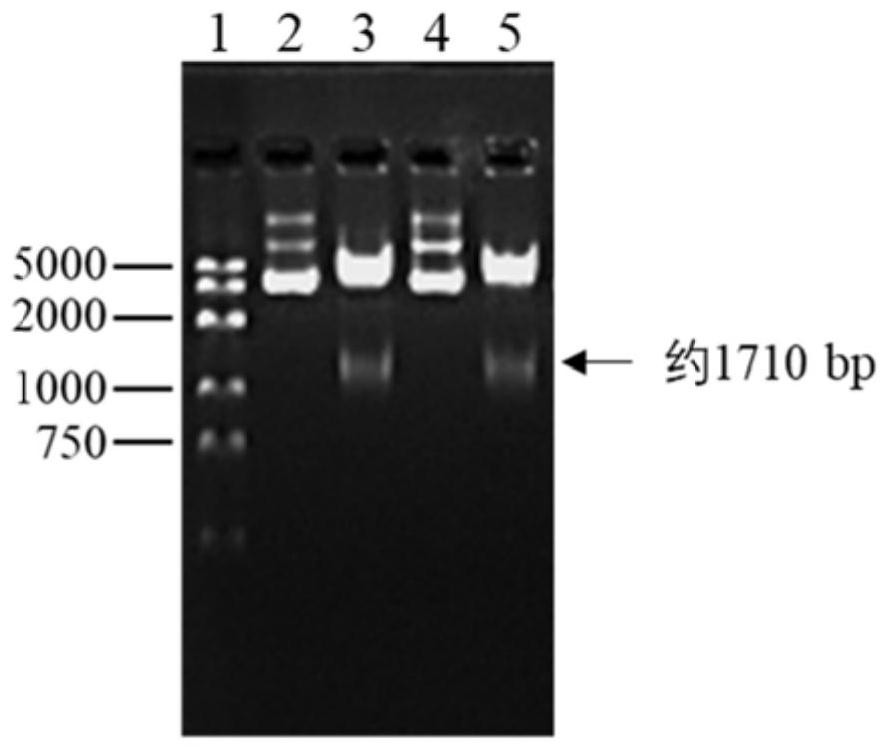
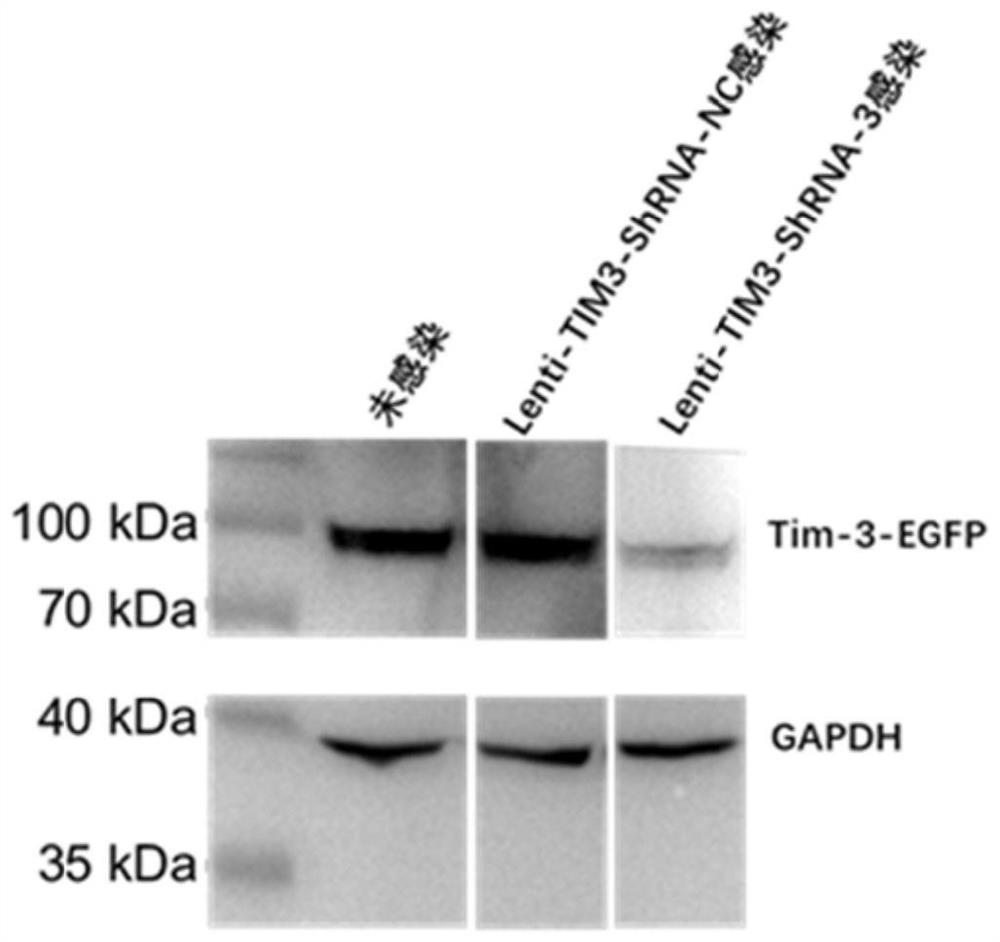
Method for constructing CAR-T cell by silencing human Tim-3 gene through shRNA and application of CAR-T cell
The invention provides a method for constructing a targeting ROR1 CAR-T cell by using shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) to silence a human Tim-3 gene and application of the targeting ROR1 CAR-T cell. The HKP55 CAR-T cell prepared by the method can be applied to cancer treatment. According to the invention, three different targeting Tim-3 genes with small hairpin RNA (shRNA) sequence specificity are designed, and the shRNA-3 sequence with the best silencing effect is obtained through screening. Therefore, the shRNA-3 sequence and the CAR sequence of the targeted ROR1 are co-transfected into the T cell, and the ROR1 CAR-T (HKP55 CAR-T) cell with the silent Tim-3 gene is prepared. The Tim-3 expression level of HKP55 CAR-T cells is greatly reduced, and compared with ROR1 CAR-T (HKP69 CAR-T) cells, the in-vitro killing of the ROR1 CAR-T cells on target cells with high expression of Galectin-9 and cell proliferation dependent on the target cells are remarkably enhanced through silencing of the Tim-3 gene. Therefore, the HKP55 CAR-T cell can overcome a complex immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, continuously proliferate and exert an anti-tumor effect function.
Owner:SUZHOUEVERHEALTH BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
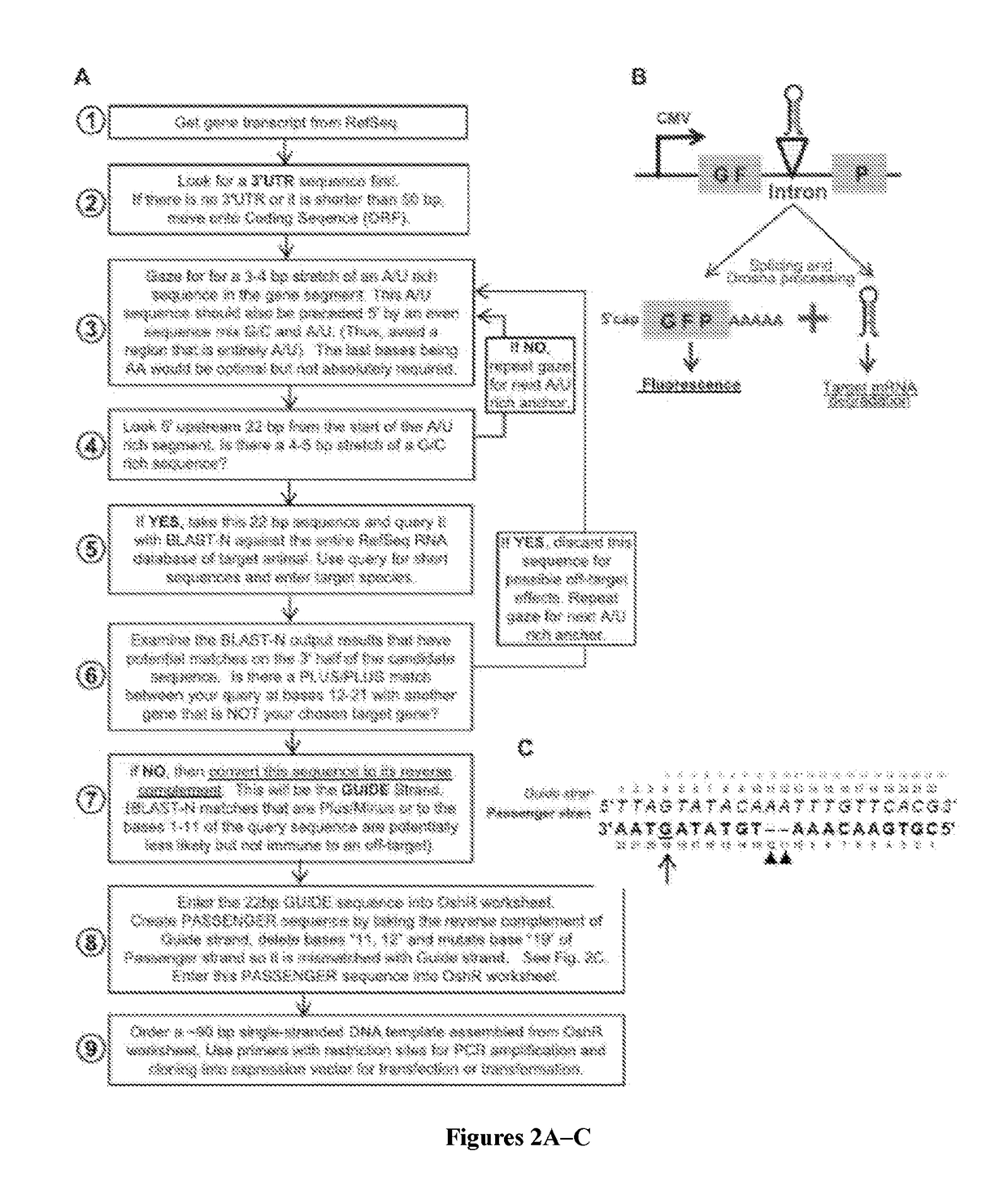
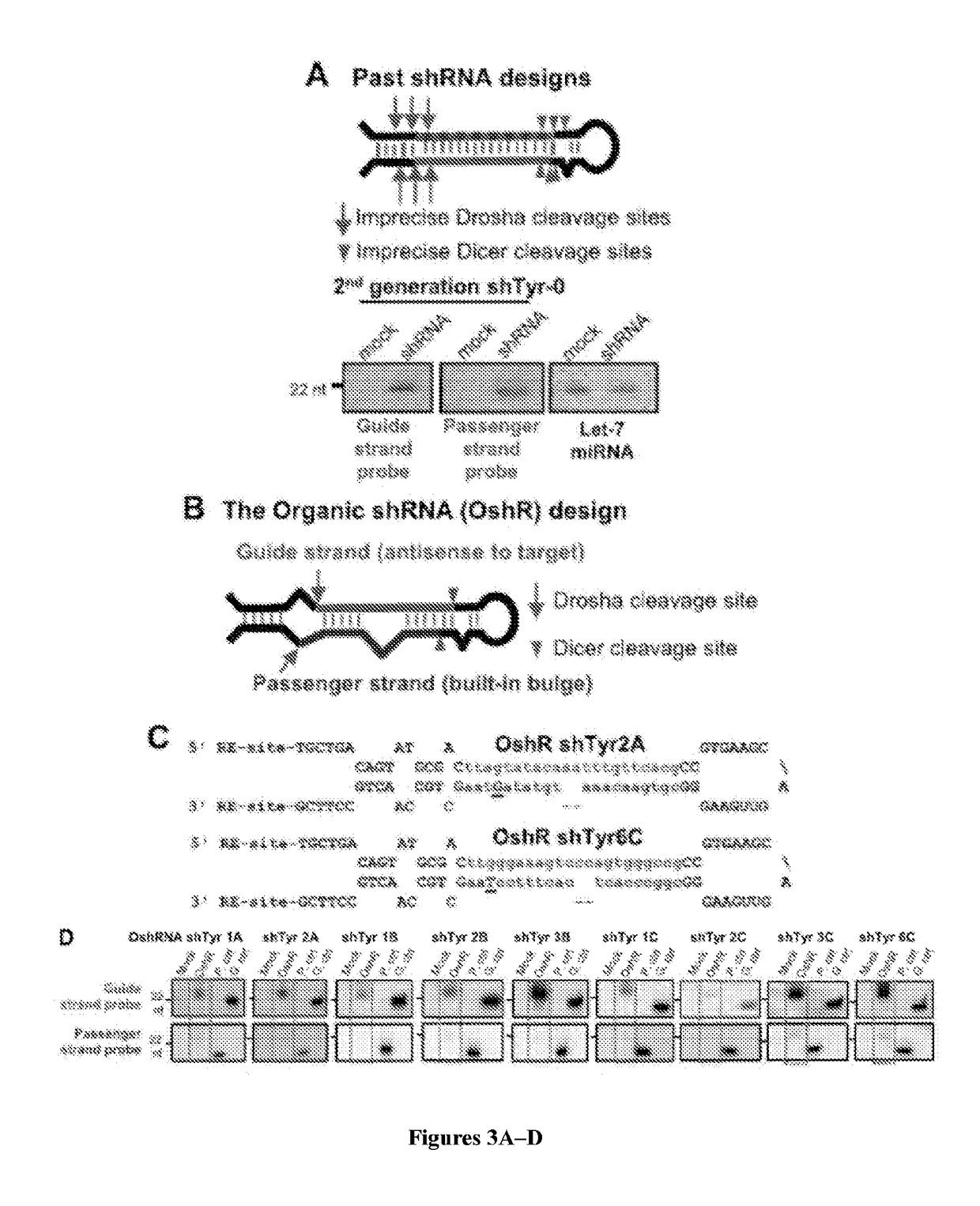
Organic small hairpin RNAs
ActiveUS9777277B2Raise the possibilityReduce accumulationSugar derivativesGene therapyOff targetsNucleic acid
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Plasma cell cytokine vehicle containing fusion proteins for targeted introduction of siRNA into cells and tissues
ActiveUS10485879B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsPlasma cellCCL11
A fusion molecule is provided that includes one or more inhibitory nucleic acids, a targeting polypeptide, and a nucleic acid binding moiety. The targeting polypeptide and the nucleic acid binding moiety include specific the amino acid sequences. A fusion molecule is also provided that includes one or more inhibitory nucleic acids, a targeting polypeptide, and a nucleic acid binding moiety adapted to bind a double-stranded RNA or to a small hairpin RNA. The targeting polypeptide being CCL27 or CCL11 or a fragment thereof.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH +1
Use of ITK inhibitors for the treatment of cancer
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Short/small hairpin RNA molecules
This disclosure concerns compositions and methods for novel RNA inhibition molecules (e.g., small / short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules), polynucleotides encoding such molecules, use of such novel RNA inhibition molecules to inhibit a target gene by suppressing the expression of the mRNA of the target gene, and for application such as the of control insect pests, and transgenic plants that produce,and are protected, by these novel RNA inhibition molecules are described.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC +1
Method for generating dumbbell-shaped DNA vector
PendingCN114616338AMicrobiological testing/measurementNon-active genetic ingredientsPlasmid VectorA-DNA
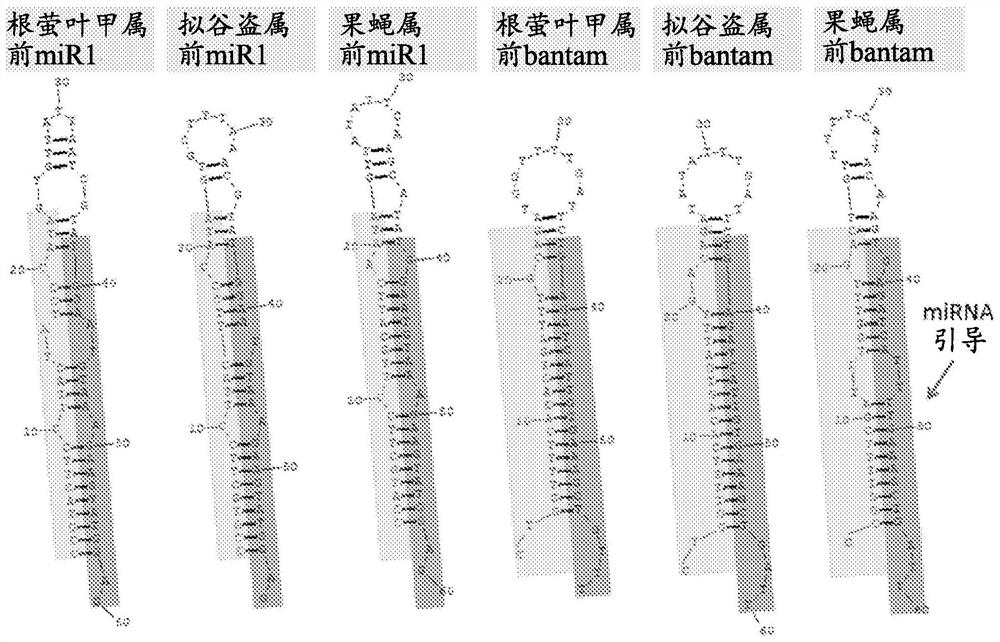
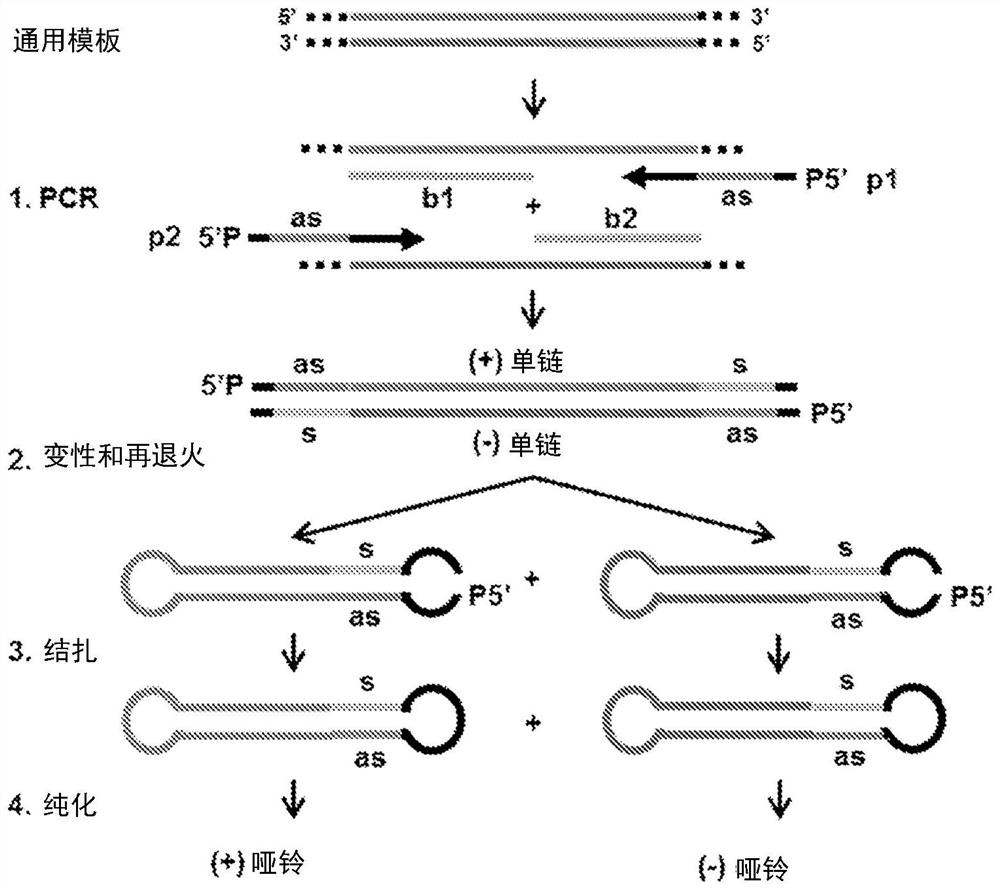
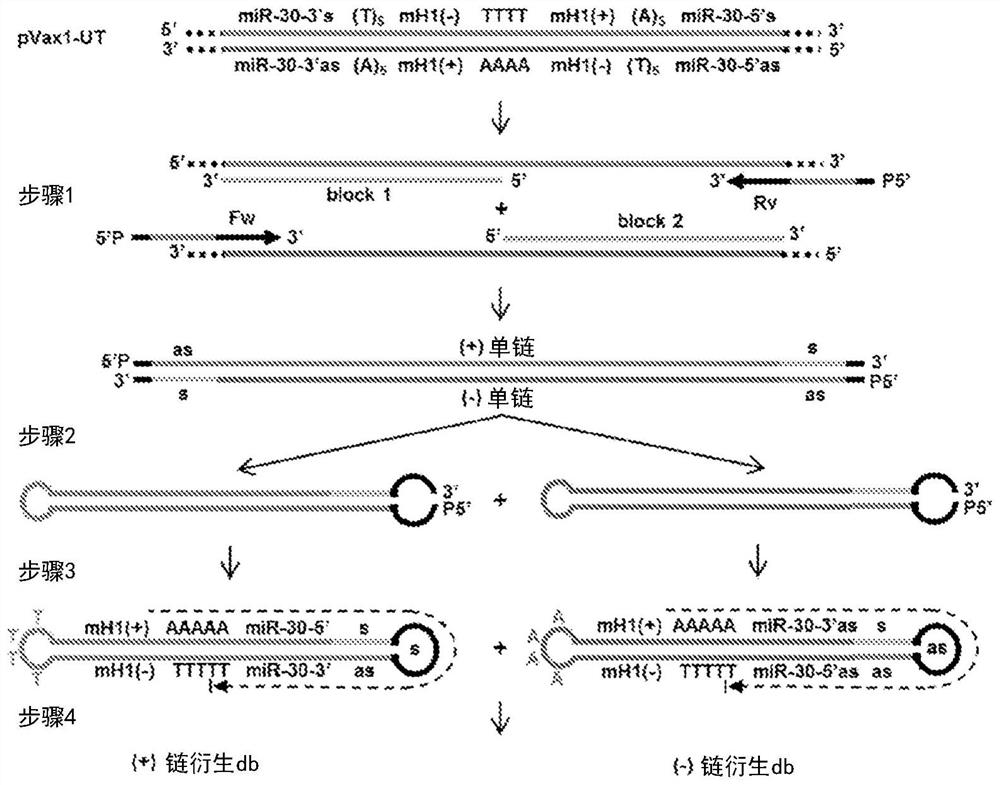
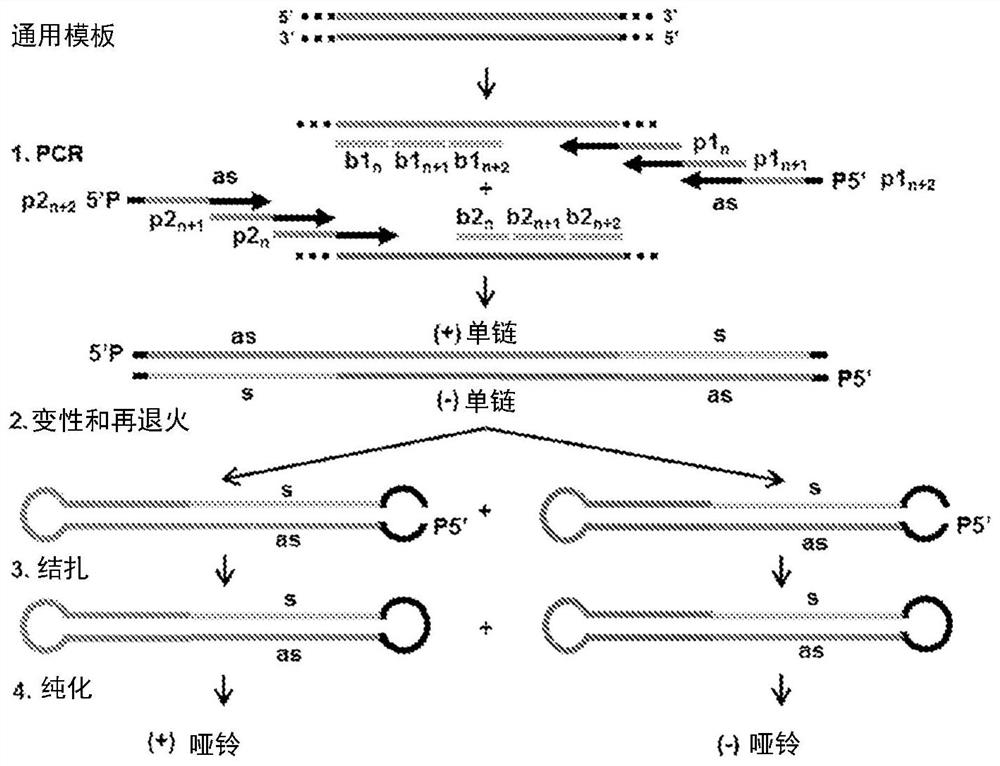
The dumbbell-shaped DNA minimum vector represents a genetic vector consisting only of a gene expression cassette of interest and a terminal closed loop structure. The dumbbell vector for small hairpin RNA or microRNA expression is very small in volume, which is advantageous for cell delivery and nuclear diffusion. Conventional strategies for generating dumbbell vectors expressing small RNA entail cloning of corresponding plasmid vectors, which are then used for dumbbell protection. Herein, we provide a novel cloning-free method for generating dumbbell vectors that express small RNA, which do not require any restriction endonuclease. The method comprises performing PCR amplification on a universal DNA template using a primer containing a sense or antisense strand of a sequence of interest, denaturing and refolding the amplification product to form a stem-loop structure, and covalently closing the structure using a DNA ligase to obtain a dumbbell structure.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Methods for reducing protein levels in a cell
ActiveUS9597346B2Reduce synthesisPromote degradationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDelivery vehicleUbiquitin ligase
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Plasma cell cytokine vehicle containing fusion proteins for targeted introduction of sirna into cells and tissues
InactiveUS20200022999A1Decreased gene expression levelLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsFusion with RNA-binding domainPlasma cellCytokine
A fusion molecule is provided that includes one or more inhibitory nucleic acids, a targeting polypeptide, and a nucleic acid binding moiety. The targeting polypeptide and the nucleic acid binding moiety include specific the amino acid sequences. A fusion molecule is also provided that includes one or more inhibitory nucleic acids, a targeting polypeptide, and a nucleic acid binding moiety adapted to bind a double-stranded RNA or to a small hairpin RNA. The targeting polypeptide being IL6 or IL21 or a fragment thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com