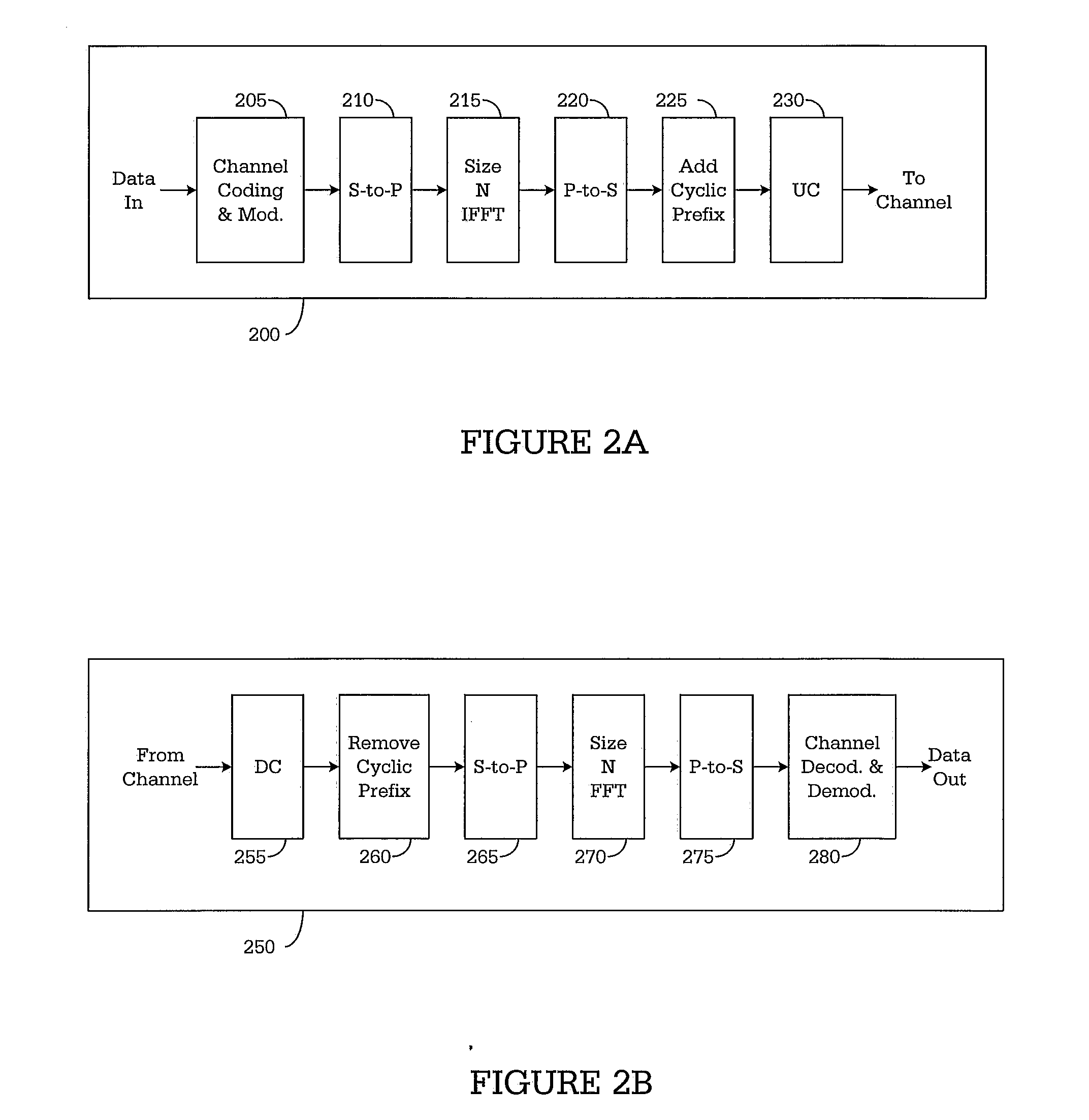
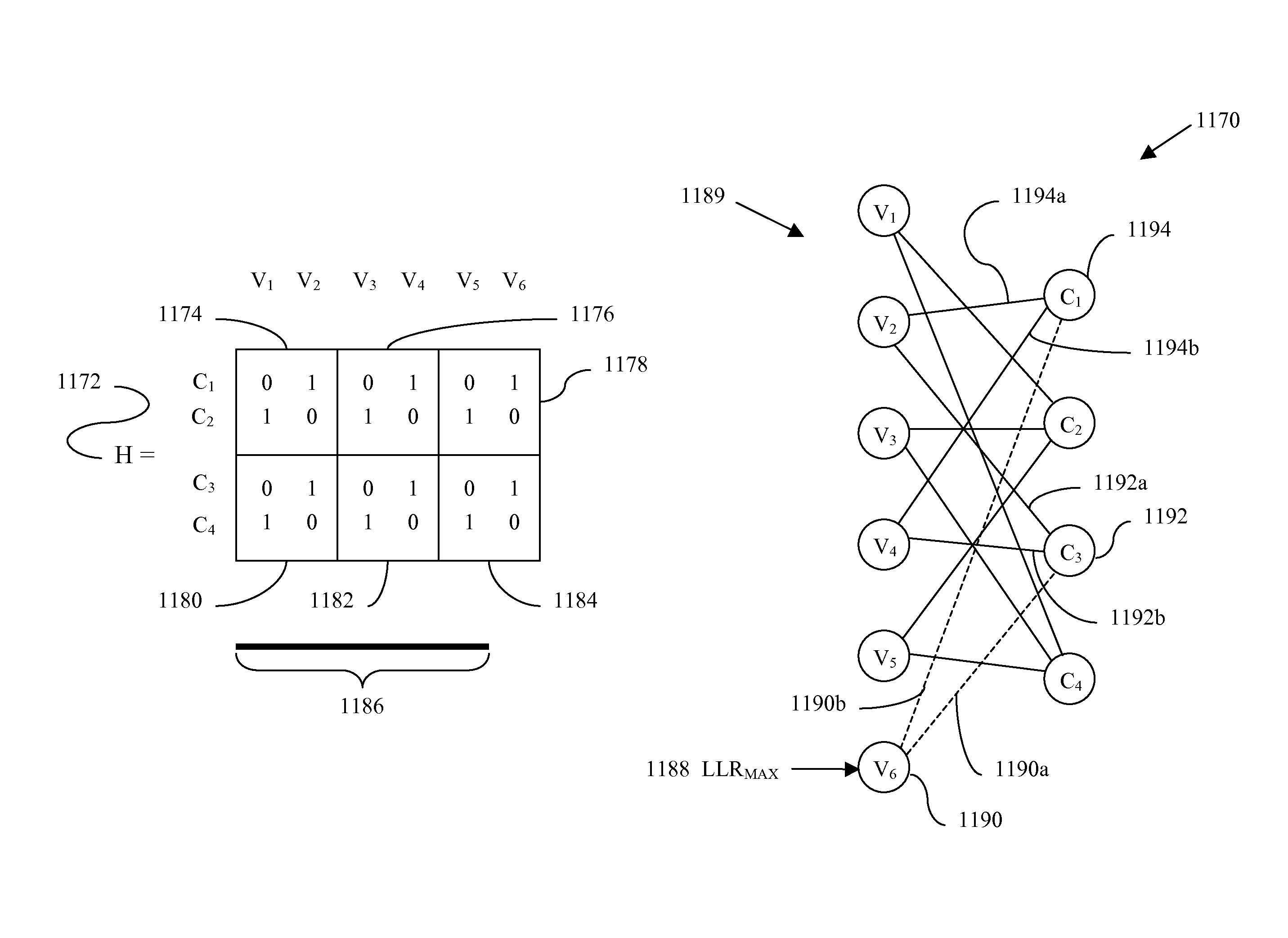
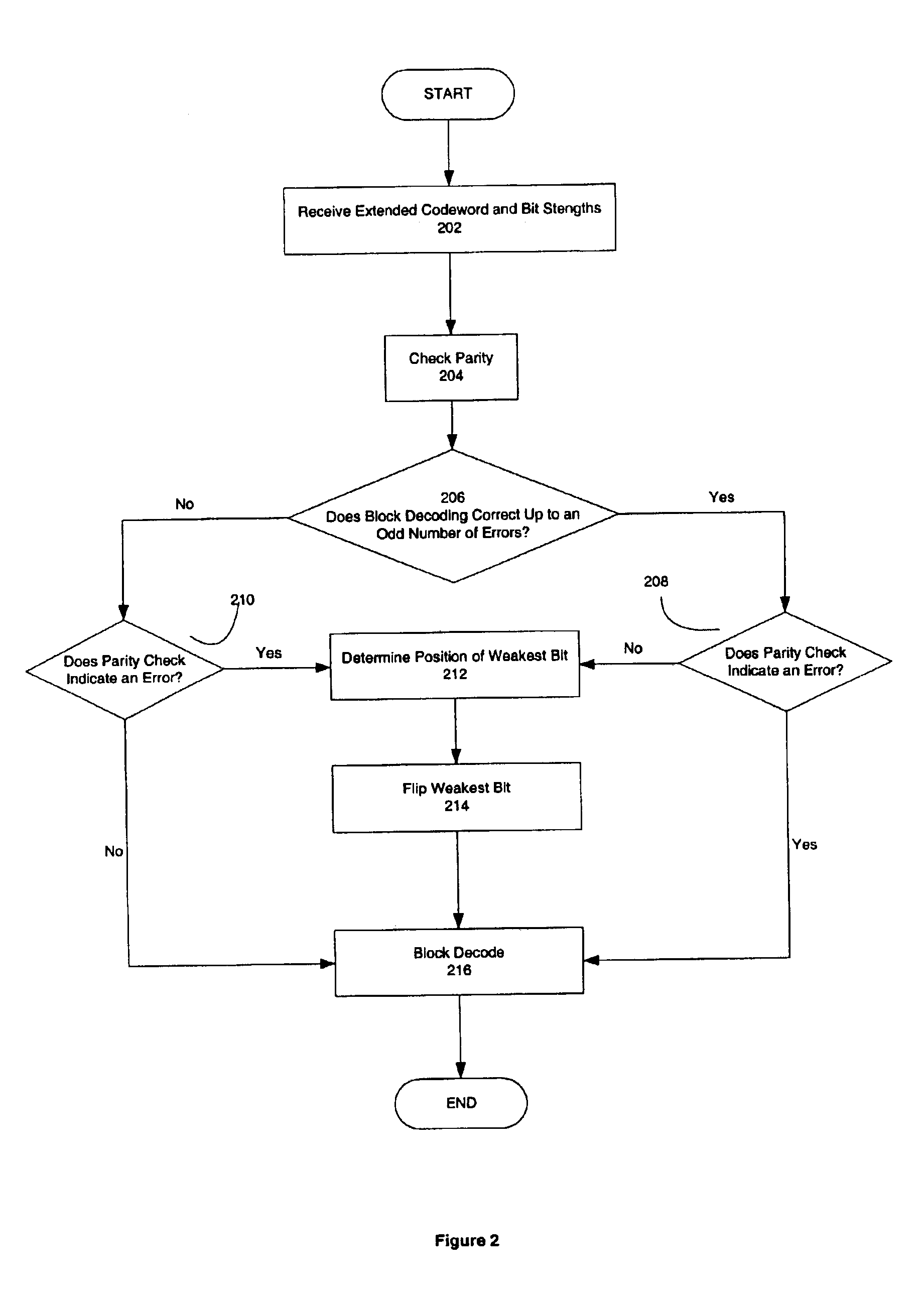
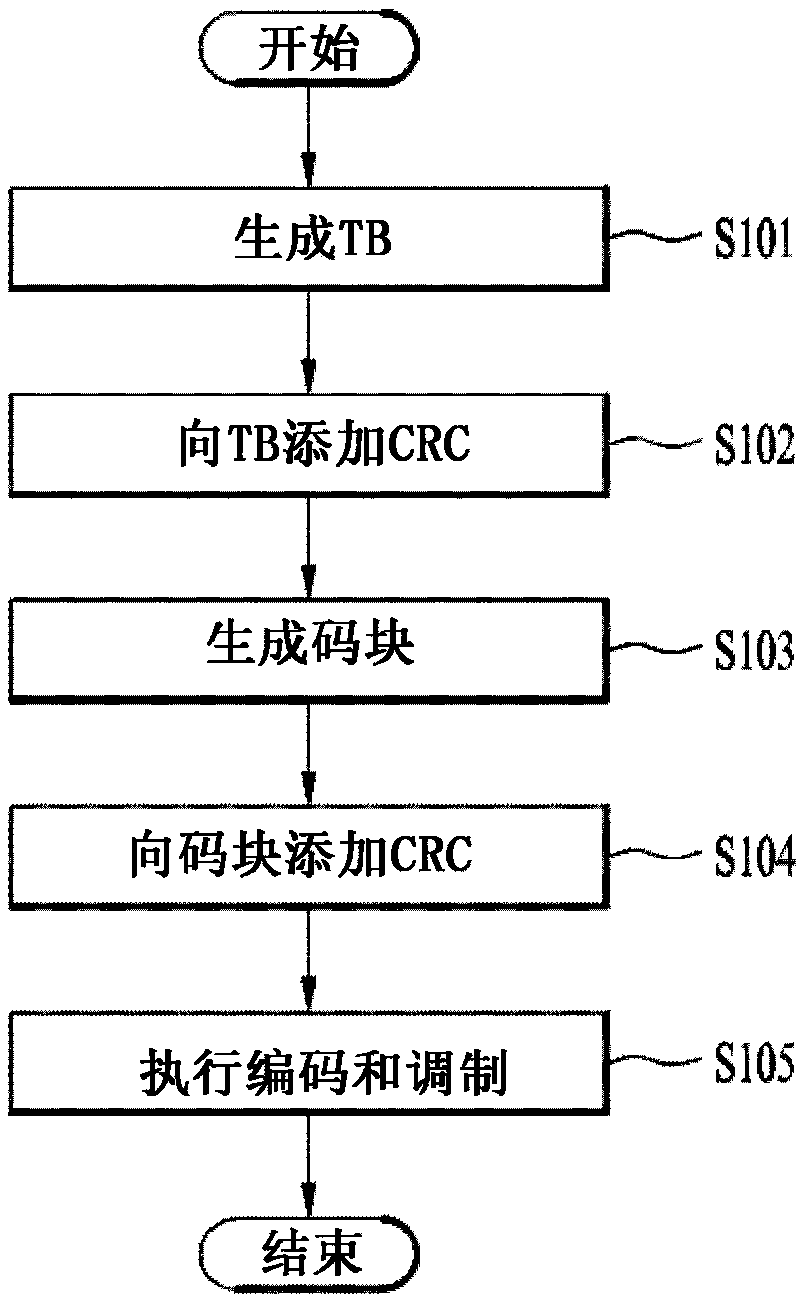
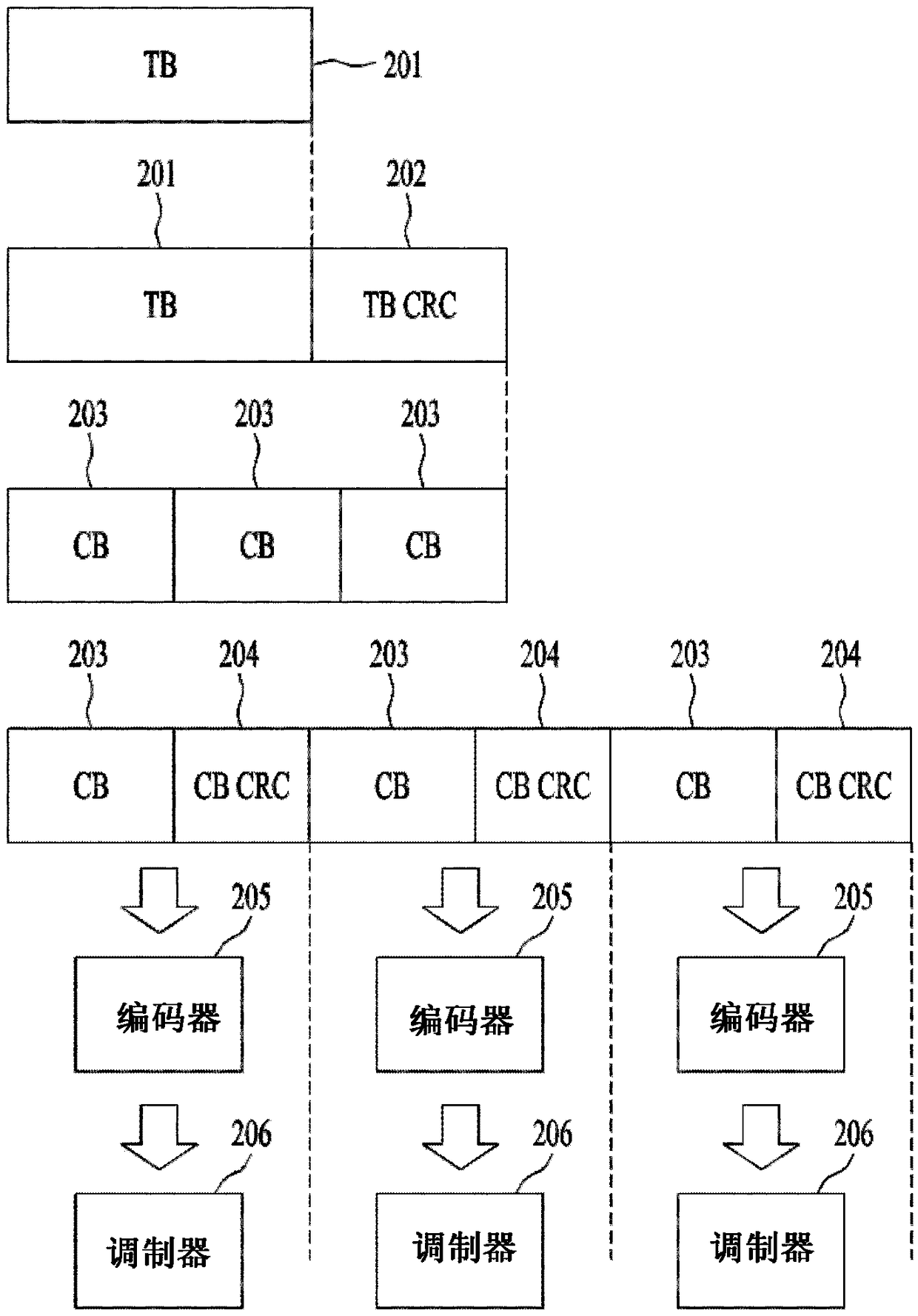
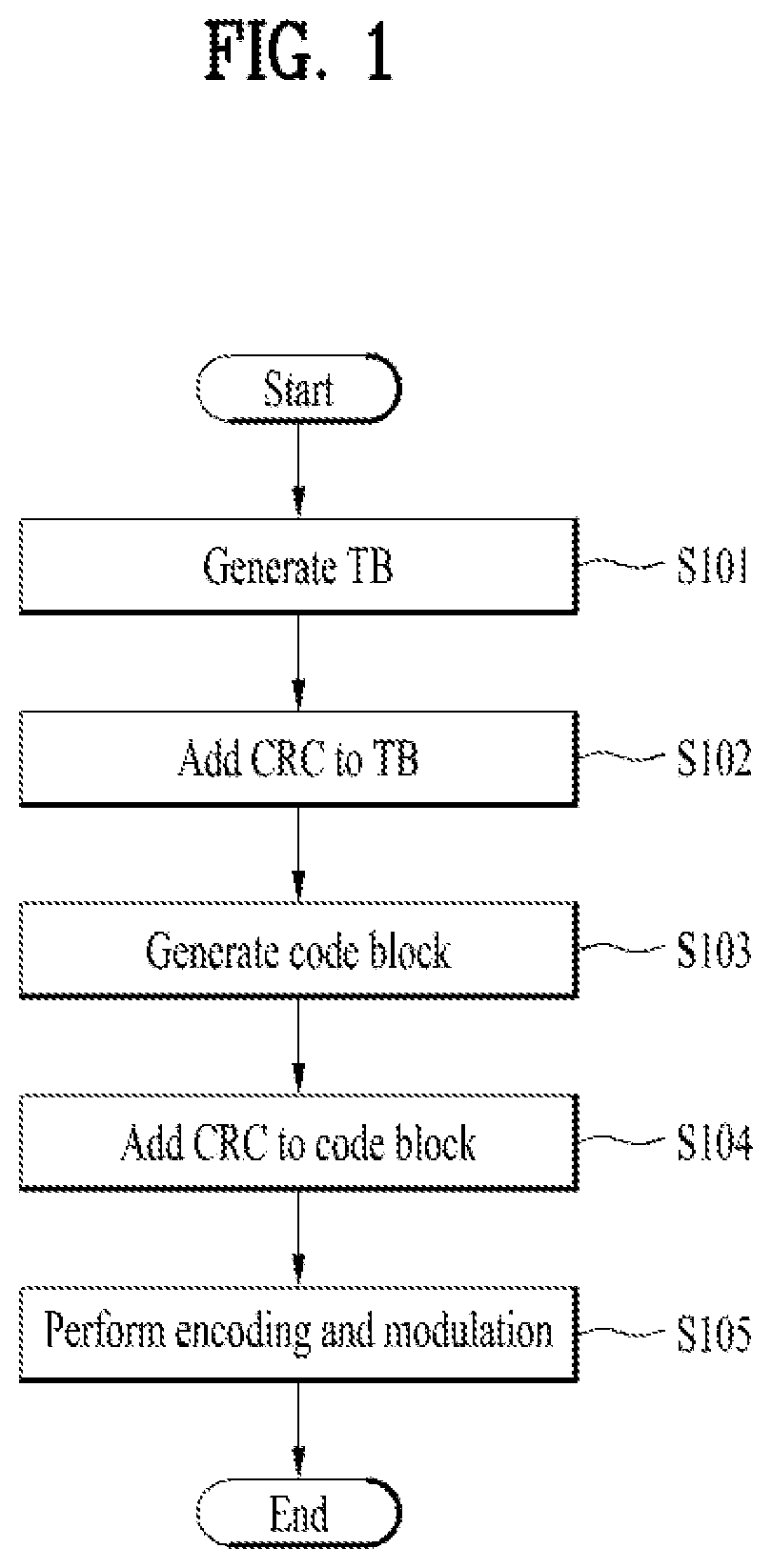
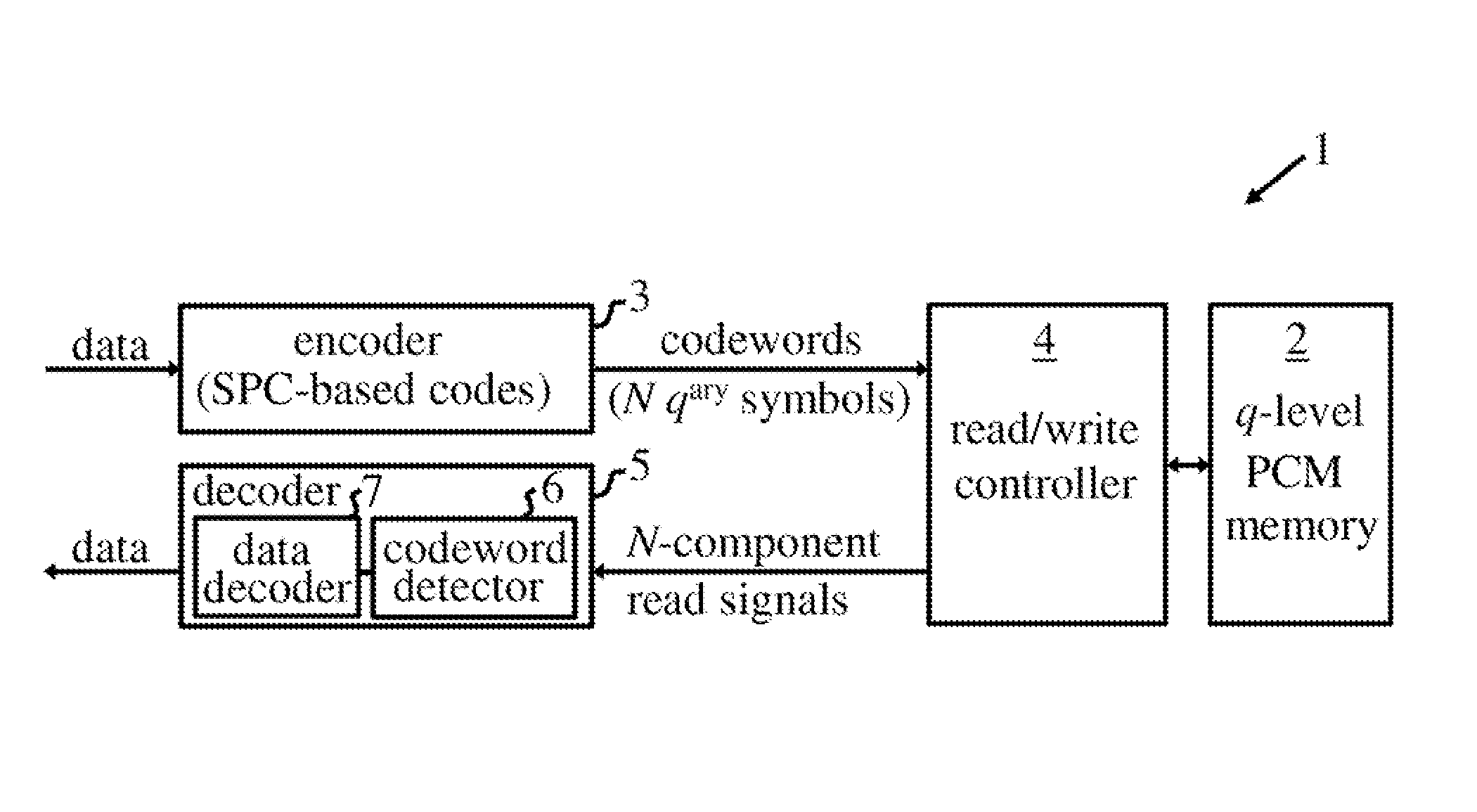
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Single parity check" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for communications using improved turbo like codes
ActiveUS20060031737A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionSingle parity checkConvolutional code
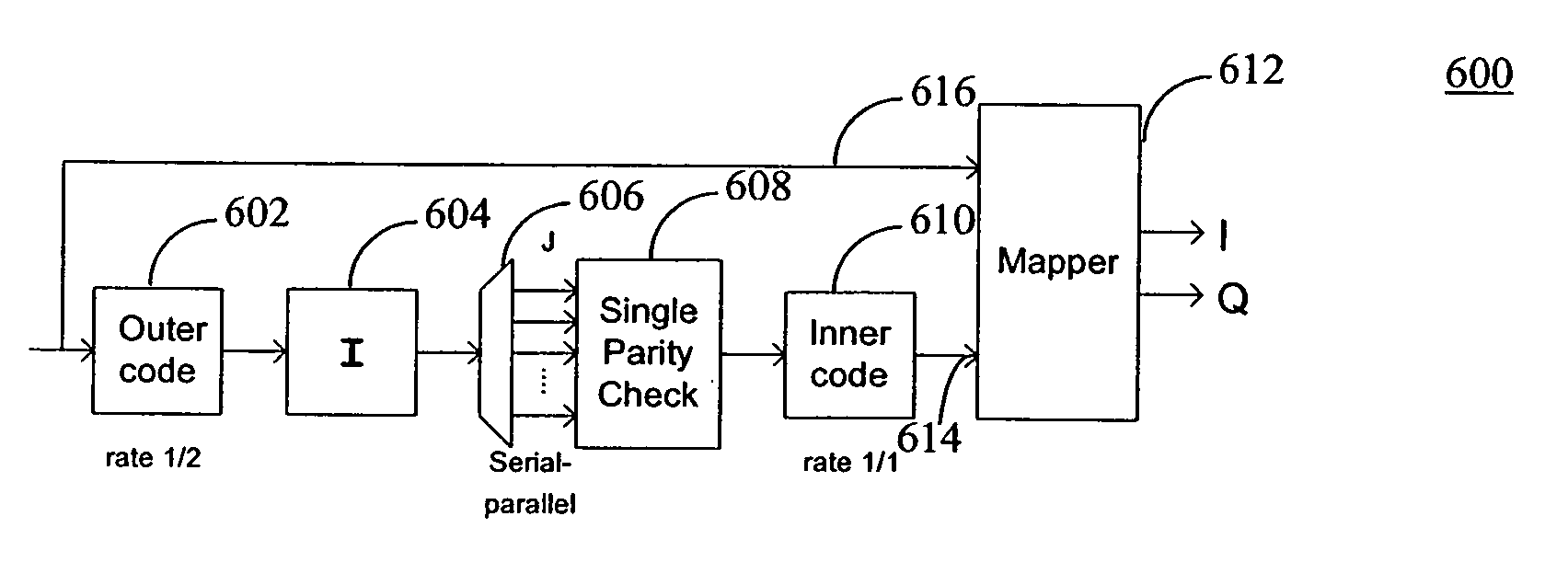
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for performing data encoding involving encoding data bits according to an outer convolutional code to produce outer encoded bits, processing the outer encoded bits using an interleaver and a single parity check (SPC) module to produce intermediate bits, encoding the intermediate bits according to an inner convolutional code to produce inner encoded bits, processing the inner encoded bits using a puncture module to produce punctured bits, and combining the data bits and the punctured bits to produce encoded outputs. Methods, apparatuses, and systems are also presented for performing data decoding based on soft channel metrics derived from a channel using various iterative techniques.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
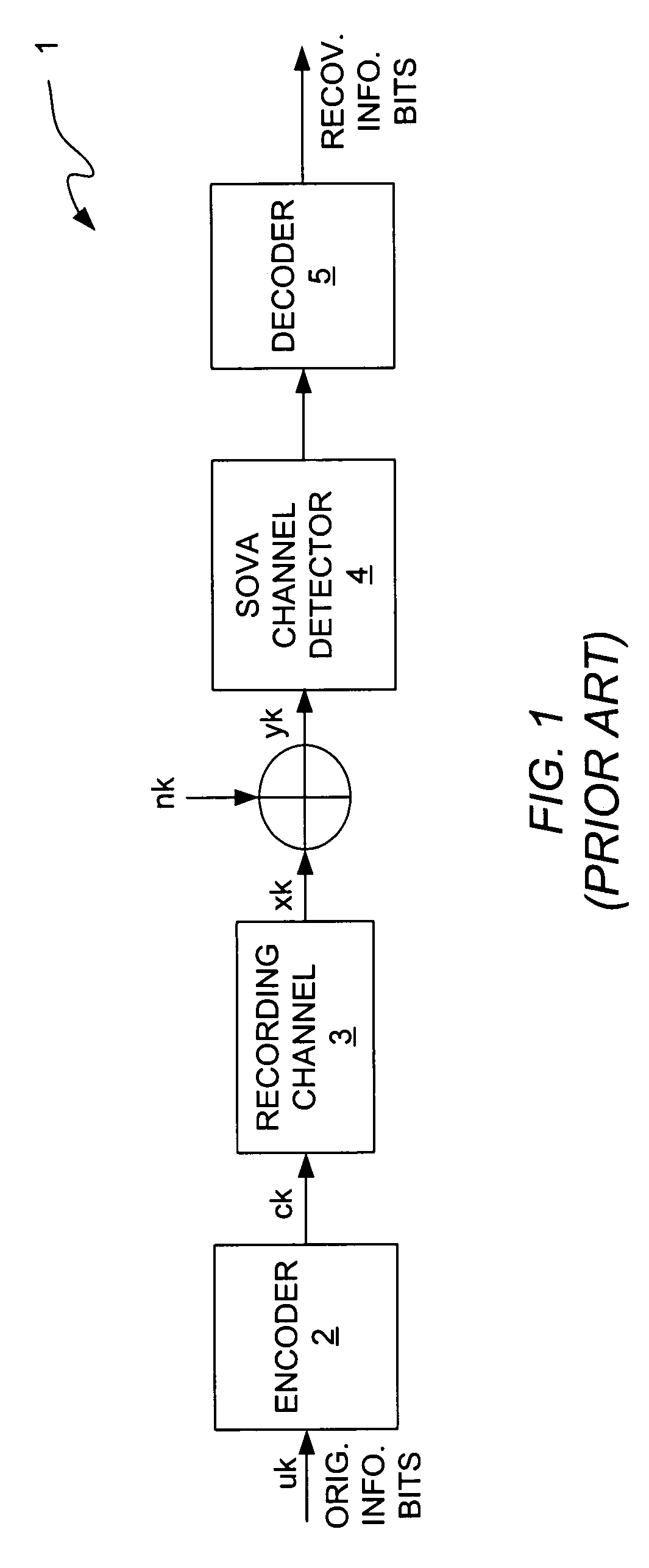
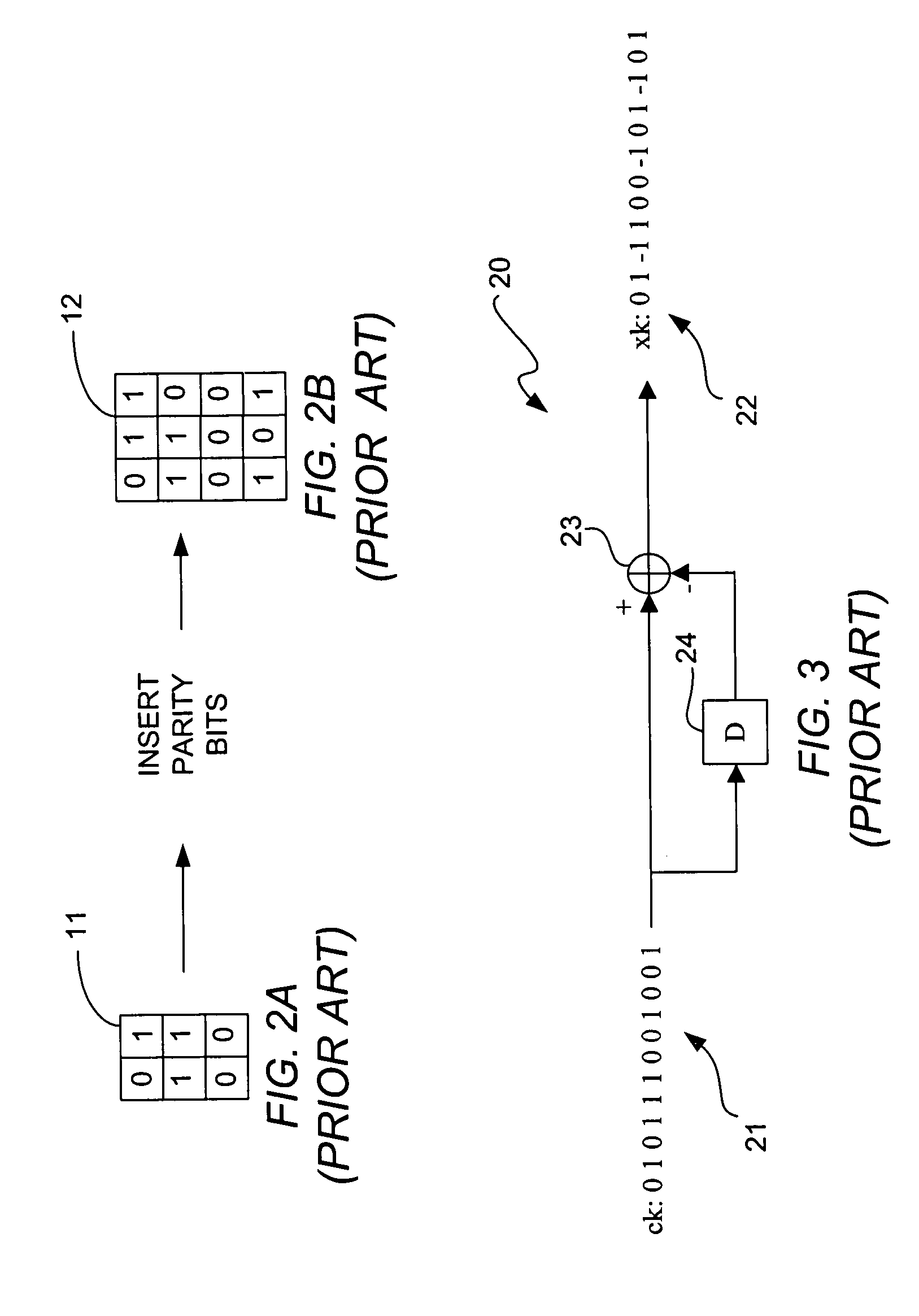
Data detection and decoding system and method
ActiveUS20060168493A1Data representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesSingle parity checkAlgorithm
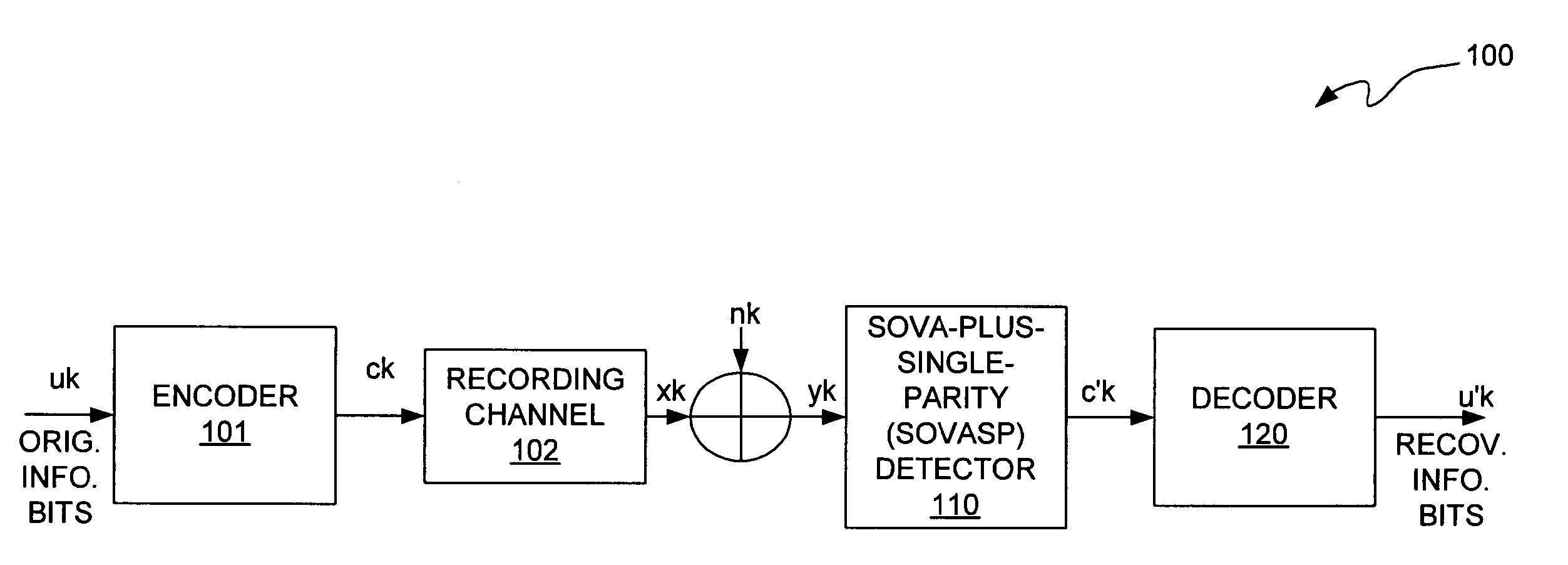
A data detection and decoding system includes a SOVA channel detector that uses single parity (SOVASP) to improve the accuracy with which the detector estimates bits. Each column or row read back from the read channel constitutes a code word and each code word is encoded to satisfy single parity. Because the SOVASP channel detector detects whether each code word satisfies single parity, it is unnecessary to use both a column decoder and a row decoder in the channel decoder. Either the row decoder or the column decoder can be eliminated depending on whether bits are read back on a column-by-column basis or on a row-by-row basis. This reduction in components reduces hardware complexity and improves system performance. The output of the row or column decoder is received by a second detector that processes the output received from the decoder to recover the original information bits.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
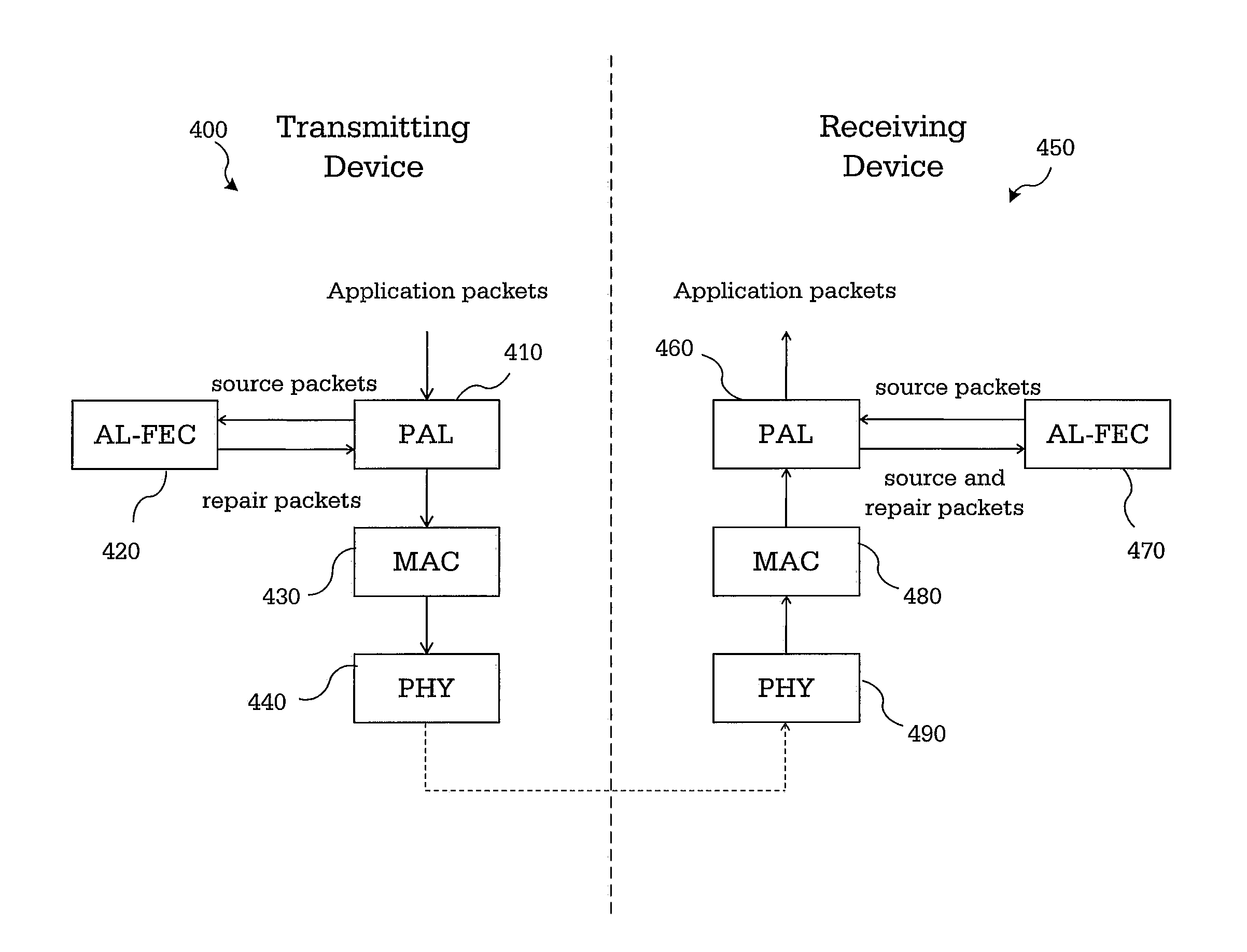
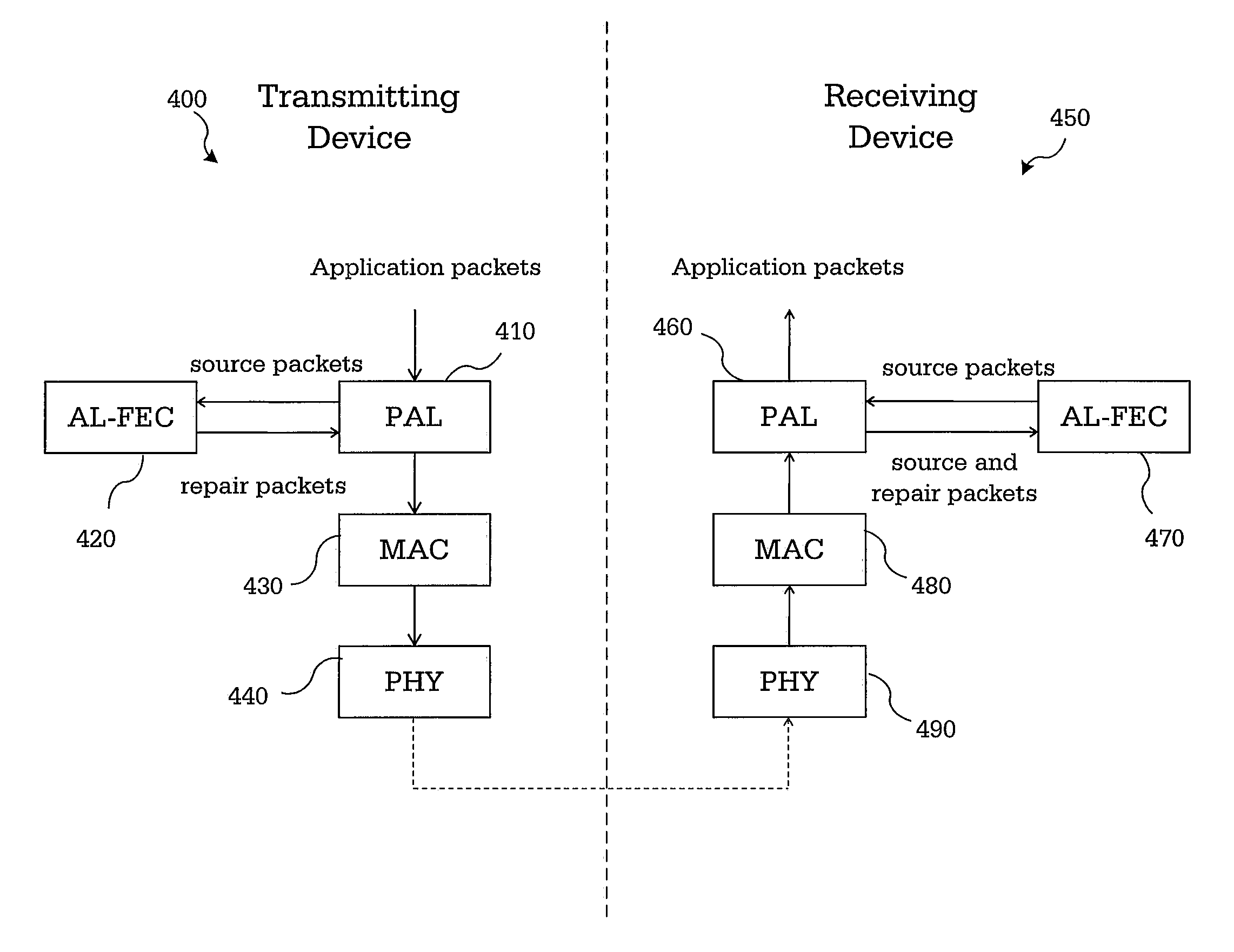
APPLICATION LAYER FEC FRAMEWORK FOR WiGig
InactiveUS20110219279A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer hardwareSingle parity check
A method and apparatus perform forward error correction in a wireless communication device in a wireless communication network. Application layer forward error correction (AL-FEC) capability information is transmitted during a capabilities exchange. A set of source packets are reshaped to k equal-sized source symbols. Systematic packets for the source symbols and at least one parity packet is encoded using a single parity check (SPC) AL-FEC code on the k source symbols. A header of each encoded packet includes a parity packet indicator. The encoded packets are processed in a media access control (MAC) layer and a physical (PHY) layer for transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for adjusting a correctable raw bit error rate limit in a memory system using strong log-likelihood (LLR) values
ActiveUS9128858B1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresSingle parity checkComputer hardware
Apparatuses and methods for correcting errors in data read from memory cells of an integrated circuit device includes an encoder. The encoder is configured from a single parity check matrix and the encoder is configured to be virtually adjustable by setting a number of bits in the encoder to zero. A decoder is configured from the single parity check matrix and the decoder is configured to be virtually adjustable by setting a log-likelihood ratio (LLR) for a number of bits in the decoder to a strong value. A code-rate that the encoder and decoder uses can be changed by adjusting the number of bits in the encoder that are set to zero and the number of bits in the decoder that are set to the strong LLR value.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS US INC
Communication channel with reed-solomon encoding and single parity check
InactiveUS20070288833A1Data representation error detection/correctionModification of read/write signalsSingle parity checkComputer hardware
A communication channel including Reed-Solomon (RS) and single-parity-check (SPC) encoding / decoding. Multiple RS codewords are combined and then SPC encoded into an RS / SPC array. A soft-input soft-output (SISO) channel detector detects the RS / SPC encoded bits and provides soft (reliability) information on these bits. A combined RS and SPC error correction block provides a recovered user output. An iterative soft input decoding algorithm combines RS and SPC error correction.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Decoding extended error correcting codes using soft information
InactiveUS6931583B2Correction errorOther decoding techniquesError detection/correctionSingle parity checkComputer hardware
In one embodiment, the present invention can be used to correct one more error in an extended codeword encoded with a block code and a single parity check code than the block code is able to correct. In one embodiment, a communications device includes a decoder that has a soft decoder to receive an extended codeword and a strength of each bit of the extended codeword, and to produce a codeword by soft decoding the extended codeword using the received strengths, and a block decoder coupled to the soft decoder to produce a corrected codeword by block decoding the codeword using an error correcting block code.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for communications using improved turbo like codes
ActiveUS7673213B2Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionSingle parity checkConvolutional code
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for performing data encoding involving encoding data bits according to an outer convolutional code to produce outer encoded bits, processing the outer encoded bits using an interleaver and a single parity check (SPC) module to produce intermediate bits, encoding the intermediate bits according to an inner convolutional code to produce inner encoded bits, processing the inner encoded bits using a puncture module to produce punctured bits, and combining the data bits and the punctured bits to produce encoded outputs. Methods, apparatuses, and systems are also presented for performing data decoding based on soft channel metrics derived from a channel using various iterative techniques.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
Communication channel with Reed-Solomon encoding and single parity check
InactiveUS7814398B2Modification of read/write signalsData representation error detection/correctionSingle parity checkComputer hardware
A communication channel including Reed-Solomon (RS) and single-parity-check (SPC) encoding / decoding. Multiple RS codewords are combined and then SPC encoded into an RS / SPC array. A soft-input soft-output (SISO) channel detector detects the RS / SPC encoded bits and provides soft (reliability) information on these bits. A combined RS and SPC error correction block provides a recovered user output. An iterative soft input decoding algorithm combines RS and SPC error correction.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Encoding/decoding method of multidimensional crossing parallel cascade single-parity check code
InactiveCN101345607AChange relationshipReduce bit error rateError preventionSingle parity checkComputer hardware
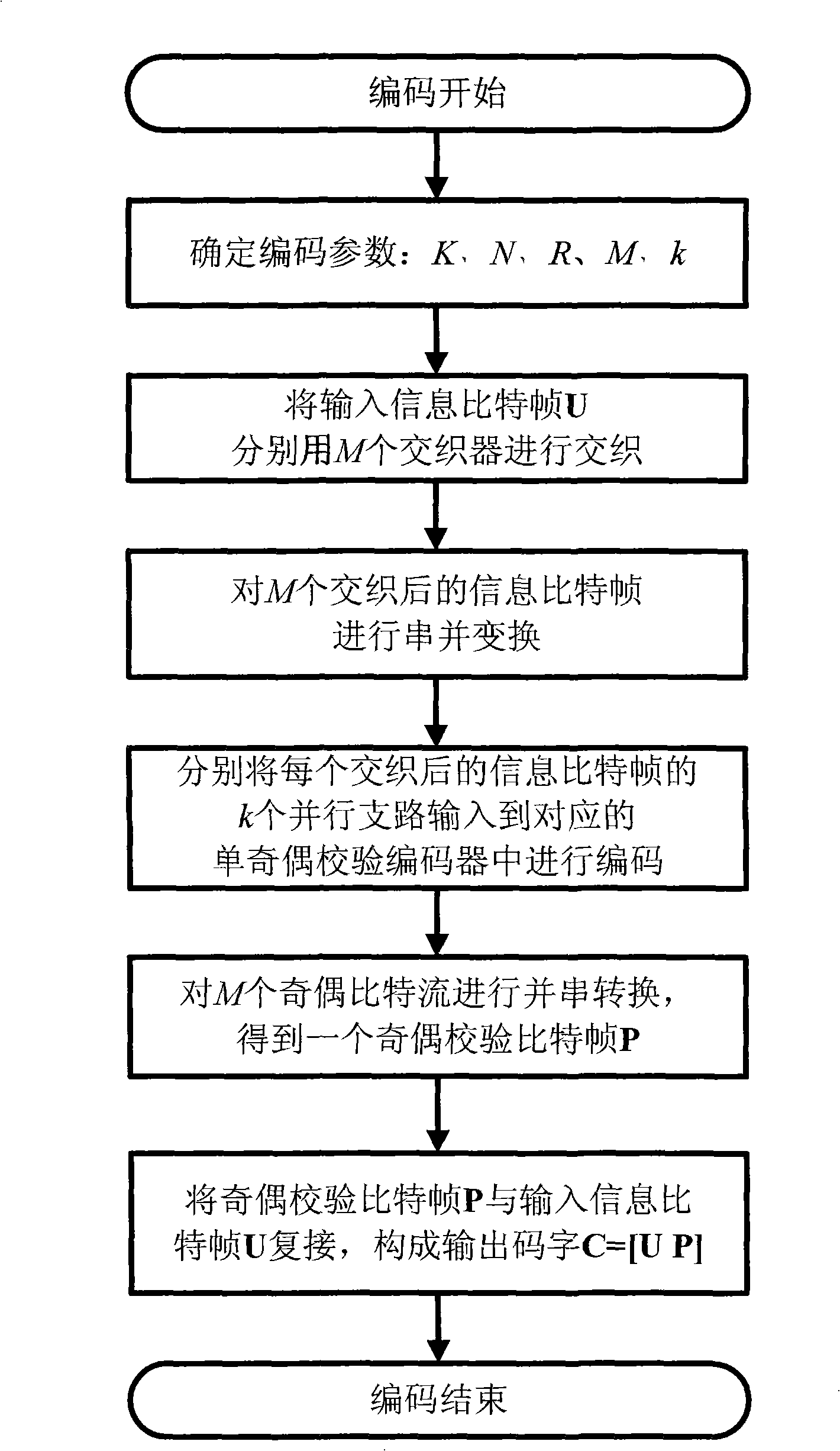
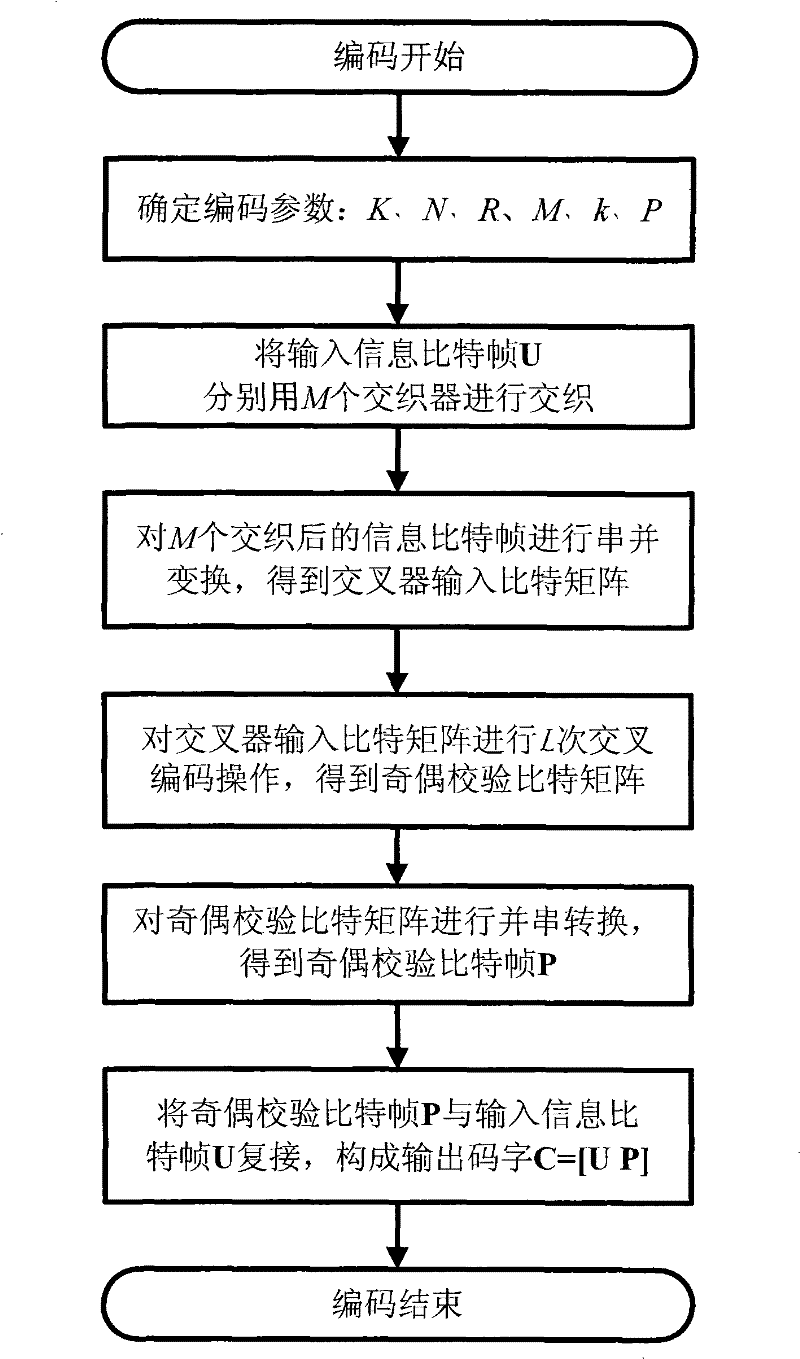
The invention discloses a coding method for multi-dimensional crossing parallel cascade single-parity check code comprising that input information bit frame is separately passed through M interweavers and serial to parallel conversion then enters into crossover; output of crossover generates parity check bit frame P by passing P single-parity check encoder; U and P constitutes code word C; encoder computes code word C channel prior information according to receiving signal; U channel prior information is separately interweaved by M interweavers to get M channel prior information of interweaved information bit frame and first generation iteration coding; encoder executes iteration coding and simultaneously executes local coding, then gets outer information of M interweaved information bit frame, and computing prior information of next iteration; judging logarithm likelihood ratio information for U, obtaining coding result. The invention has merits of simple encoding and coding, low error floor and is used for correcting error of receiving signal.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Application layer FEC framework for WiGig
InactiveUS8839078B2Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionSingle parity checkComputer hardware
A method and apparatus perform forward error correction in a wireless communication device in a wireless communication network. Application layer forward error correction (AL-FEC) capability information is transmitted during a capabilities exchange. A set of source packets are reshaped to k equal-sized source symbols. Systematic packets for the source symbols and at least one parity packet is encoded using a single parity check (SPC) AL-FEC code on the k source symbols. A header of each encoded packet includes a parity packet indicator. The encoded packets are processed in a media access control (MAC) layer and a physical (PHY) layer for transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-rate code encoding method for grouped Markov superposition coding based on time division
ActiveCN104410428AImprove error correction performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesError detection onlySingle parity checkSuperposition coding
The invention belongs to the fields of digital communication and digital storage and in particular relates to a multi-rate code encoding method for grouped Markov superposition coding based on time division. The method is used for encoding a binary information sequence u- with the length K being equal to (n-2)kBL into code words c- with the length N being equal to (n-2)nB(L+m<k>), wherein n is more than 2, k refers to a range of {1, 2,..., n-1}, namely a code rate set refers to {1 / n, 2 / n,..., (n-1) / n}, L is the number of (n-2)kB sequenced packets of equal length, m<k> is the memory length of subcodes with the code rate of k / n, and the memory length of an encoder is as shown in the specification. The method comprises the following steps: dividing the information sequence u- into L packets of equal length which are as shown in the specification, wherein t is equal to -1, -2,..., -(m<k>-1), -m<k>, and initializing a sequence v-(t) with the length of (n-2)nB; dividing a sequence which is as shown in the specification with the length of (n-2)kB into B packets at the moment t being equal to 0, 1,..., L-1 for performing time division encoding on [n, 1] repetition codes and [n, n-1] single parity check codes, thereby obtaining an encoding sequence which is as shown in the specification with the length of (n-2)nB; and calculating the t-th subsequence of the code words c- by combining the sequence as shown in the specification. The multi-rate codes based on time division provided by the invention are simple in design, wide in code rate range, low in decoding complexity and excellent in performance.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
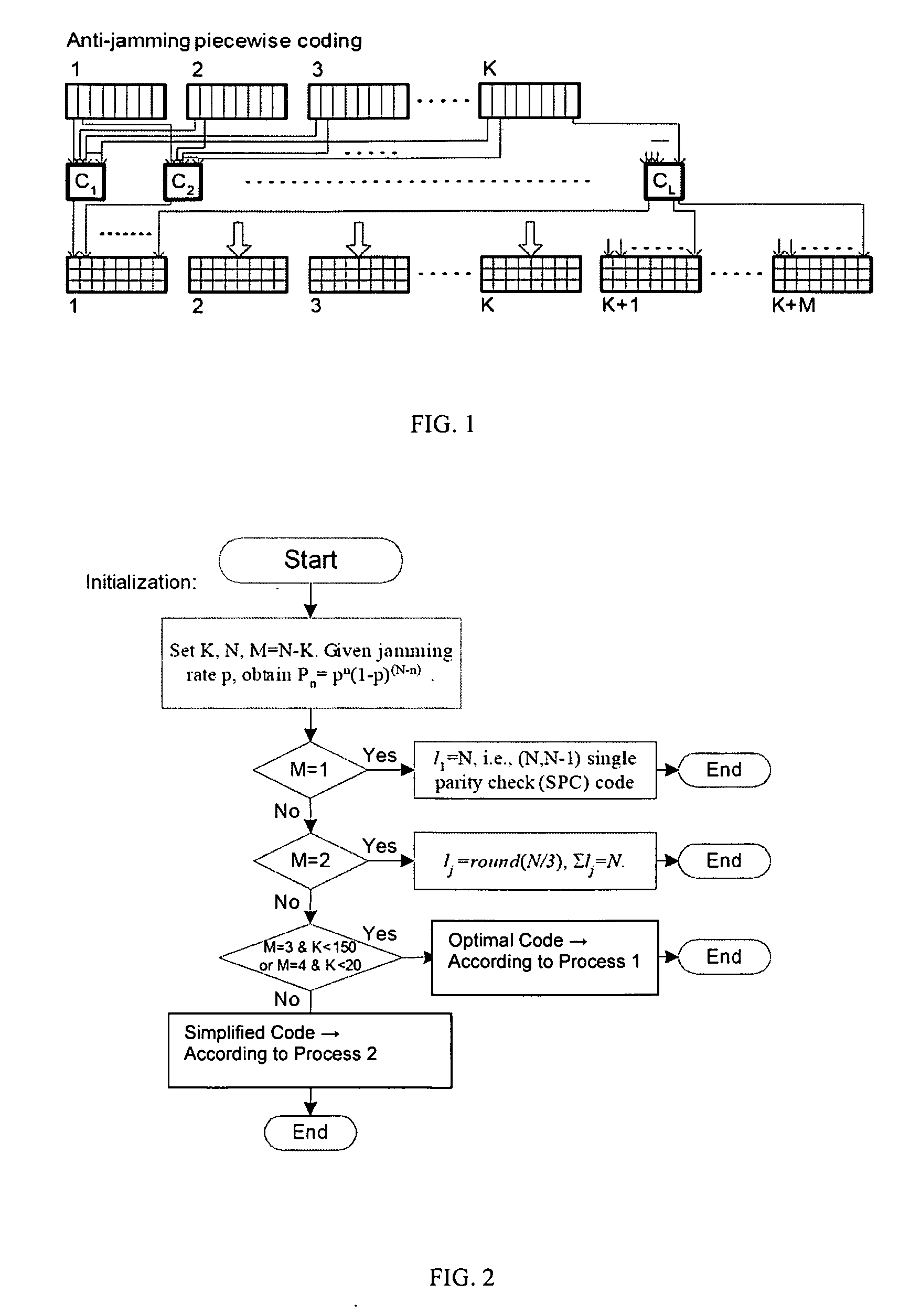
Anti-Jamming Piecewise Coding Method for Parallel Inference Channels
A method for encoding includes encoding K blocks of information for transmission on N subchannels responsive to a number of redundant blocks M according to one of i) employing a single parity check code when the number of redundant blocks M is about 1; ii) employing a code exhibited by a code graph having one third of variable nodes are connected to one of the check nodes, another one third of variable nodes is connected to the other check node and the remaining one third of variable nodes is connected to both check nodes, when the number of redundant blocks M is 2; iii) employing a first process for determining a code for the K blocks of information, when the number of redundant blocks M is about 3 together with K blocks of information less than about 150 or the number of redundant blocks M is about 4 together with K blocks of information less than about 20; and iv) employing a second process for determining a code for the K blocks of information with redundant block M values other than for steps i), ii) and iii).
Owner:NEC CORP
Low complexity decoding schemes for single-parity-check (SPC) based concatenated codes
ActiveUS7653858B2Improve performanceReduce complexityOther decoding techniquesCode conversionSingle parity checkTheoretical computer science
This invention provides an iterative PCZZ data decoder that includes circuitry for utilizing all extrinsic information during iterative decoding by updating likelihood information for parity bits LPi, i=1, . . . , M during iterations. The extrinsic information for the parity bits is included in iterations by re-calculating soft values for parity bits LPi(k) for each iteration k. In one embodiment the parity bit soft values are re-calculated in a plurality of circuit blocks following Max-Log-APP (MLA) decoder blocks, based on soft values for data bits LDi(k). In another embodiment the parity bit soft values are re-calculated recursively within the plurality of MLA decoders. The decoder operates to control the convergence of the decoder by monitoring a soft value of one parity check symbol, e.g., L(k−1)[p(IM)], where p(IM) represents the last parity check bit in an I×M parity check array. A decoder iteration stopping rule may be implemented by testing a likelihood measure associated with a last parity check symbol in a parity check column. In one case the likelihood measure may be given by L(k−1)[p(IM]>threshold, and in another case the likelihood measure may be given by L(k−1)[p(I)]>threshold. The likelihood measure is given in general by: L(k−1)[p(I)]>threshold, L(k−1)[p(2I)]>threshold, . . . , L(k−1)[p(IM)]>threshold, where the value of the threshold is a function of data block size.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
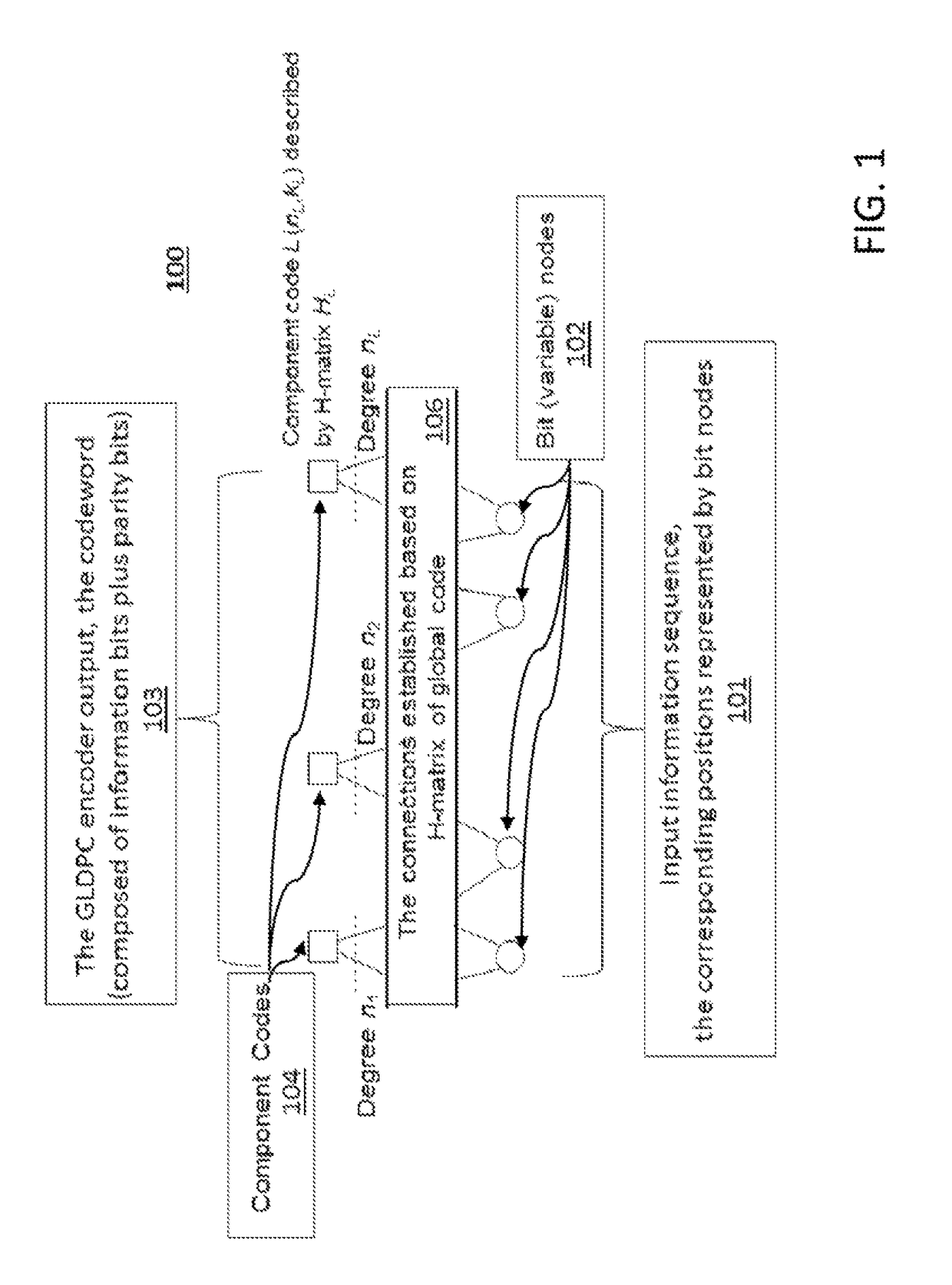
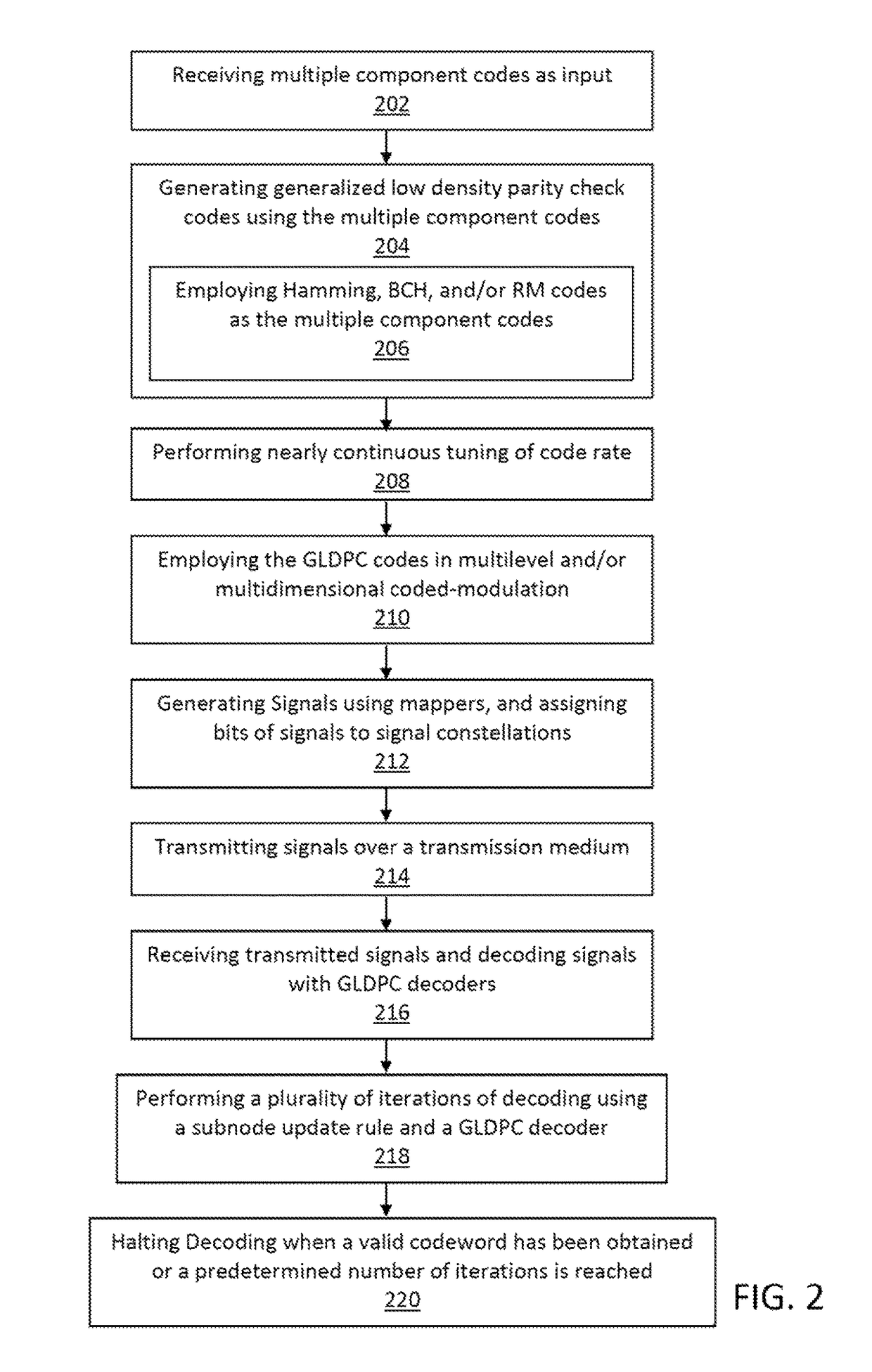
Multiple component codes based generalized low-density parity-check codes for high-speed optical transport
ActiveUS20150106680A1High strengthError preventionError correction/detection using LDPC codesSingle parity checkData stream
Systems and methods for data transport, including encoding streams of input data using generalized low-density parity check (GLDPC) encoders, the one or more GLDPC encoders being configured to generate GLDPC coded data streams using a plurality of component local codes to improve error correction strength, employ single-parity checks and two or more local block codes during generation of the GLDPC codes, and enable continuous tuning of code rate using the generated GLDPC codes. Signals may be generated using mappers, the mappers configured to assign bits of signals to signal constellations and to associate the bits of the signals with signal constellation points. The signal may be modulated using an I / Q or 4-D modulator composed of one polarization beam splitter, two I / Q modulators, and one polarization beam combiner. The modulated signals are multiplexed using a mode-multiplexer, transmitted over a transmission medium, and the signals are received and decoded using GLDPC decoders.
Owner:NEC CORP
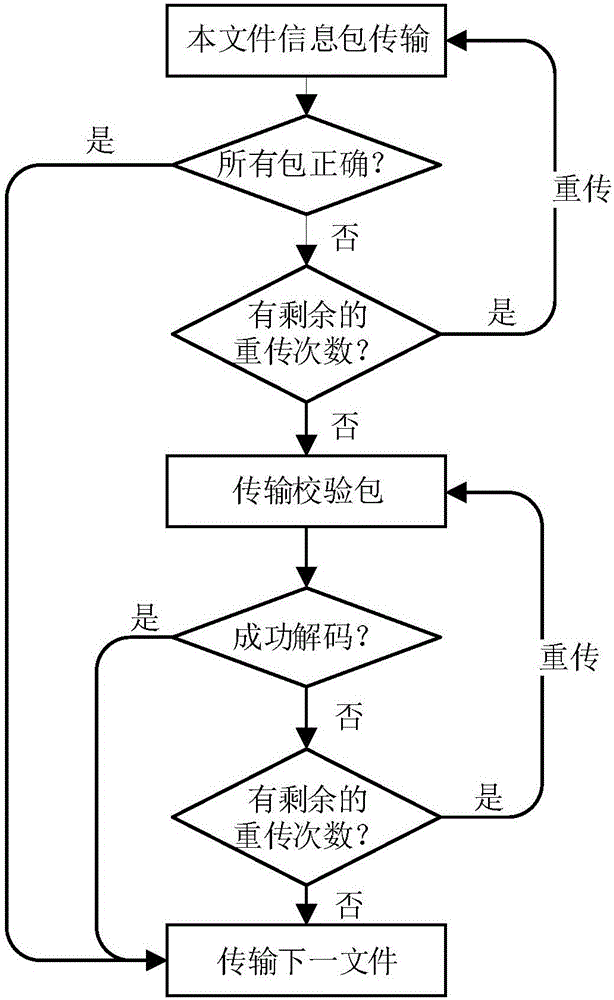
HARQ (Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request) method based on maximum distance separable codes
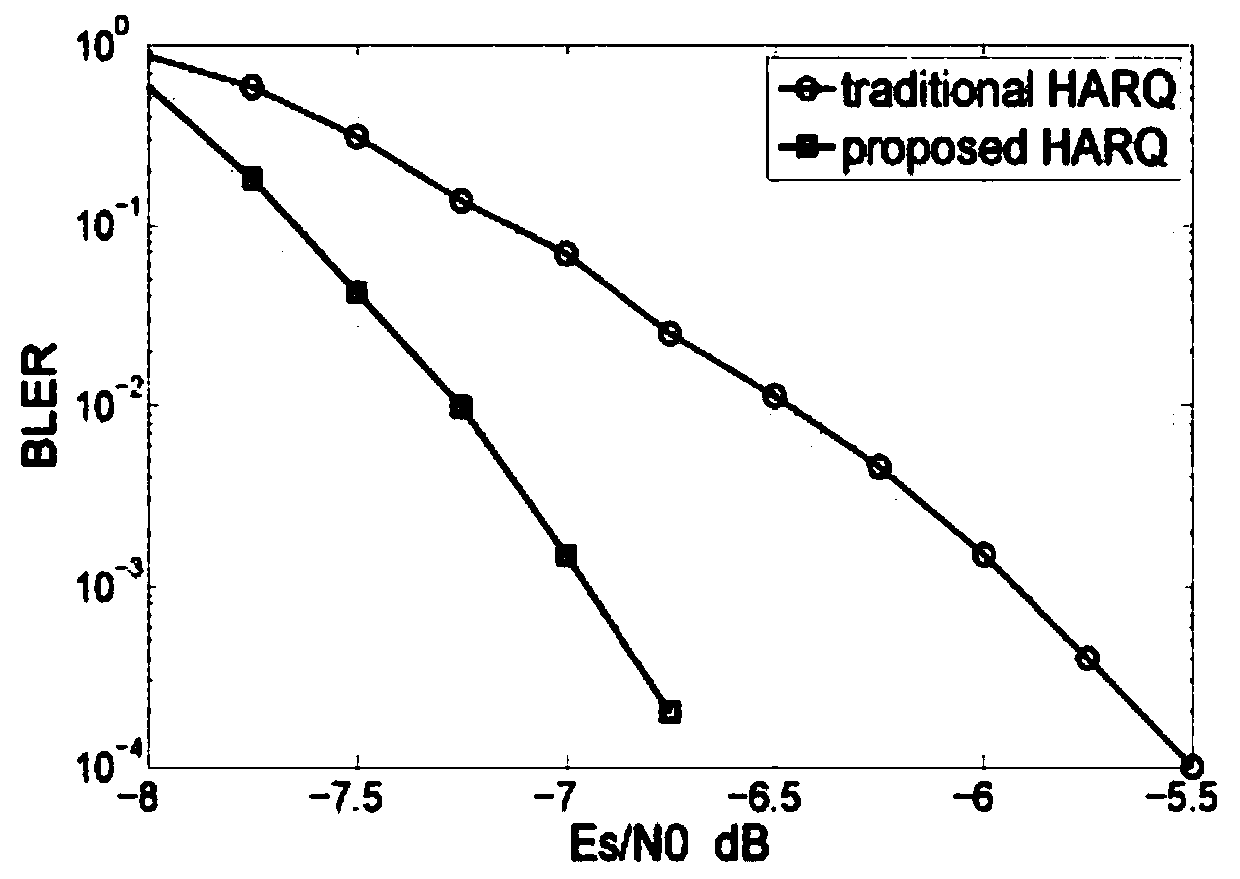
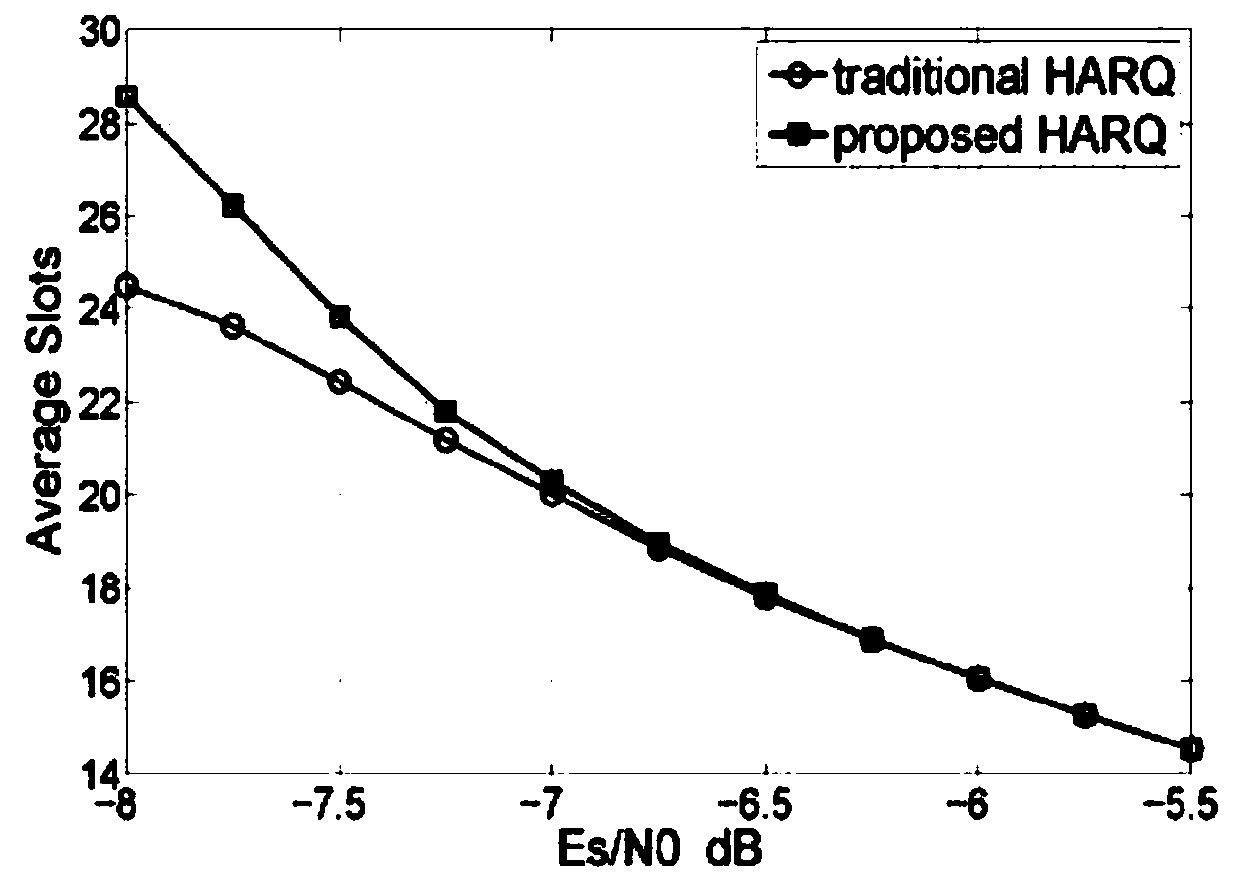
ActiveCN105162559AImprove error correction performanceImproved block error rate performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelForward error control useSingle parity checkNetwork packet
The invention relates to a HARQ (Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request) method based on maximum distance separable codes and belongs to the technical field of communication. The coding performing of the HARQ method is improved by adopting a coding mode with maximum distance separable code characteristics, such as SPC (Single Parity Check) codes, so that the coding performance is improved, the correction capability is further is increased, correct decoding and original information retrieval can be achieved when a channel state is poor, that is to say, a check packet is combined to correctly decode wrongly-transmitted data packets. Compared with the traditional HARQ method, the method performs normal transmission and has the same complexity as the prior art when the channel state is good, and transmits the check packet to assist decoding when the channel state is poor, so that the error correction capability is improved, and the block error rate performance is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
LDPC code transmission method using row-orthogonal structure, and device therefor
InactiveCN109478896AError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSingle parity checkAlgorithm
A method for encoding a quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (LDPC) code according to an embodiment of the present invention may comprise the steps of: generating a multi-edge LDPC code matrix including a high rate code matrix and a single parity check code matrix; and encoding a signal by using the multi-edge LDPC code matrix, wherein the single parity check code matrix includes a first matrix having a non-row-orthogonal structure matrix and a second matrix having a pure row-orthogonal structure, which are concatenated.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for transmitting LDPC code using row-orthogonal and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS20200395957A1Error preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSingle parity checkAlgorithm
A method for encoding a quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (LDPC) code according to an embodiment of the present invention may comprise the steps of: generating a multi-edge LDPC code matrix including a high rate code matrix and a single parity check code matrix; and encoding a signal by using the multi-edge LDPC code matrix, wherein the single parity check code matrix includes a first matrix having a non-row-orthogonal structure matrix and a second matrix having a pure row-orthogonal structure, which are concatenated.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Read/write operations in solid-state storage devices
InactiveUS8972837B2Improve performanceEfficiently mappedCode conversionCoding detailsSingle parity checkSolid-state storage
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Label inspection method in satellite MPLS network
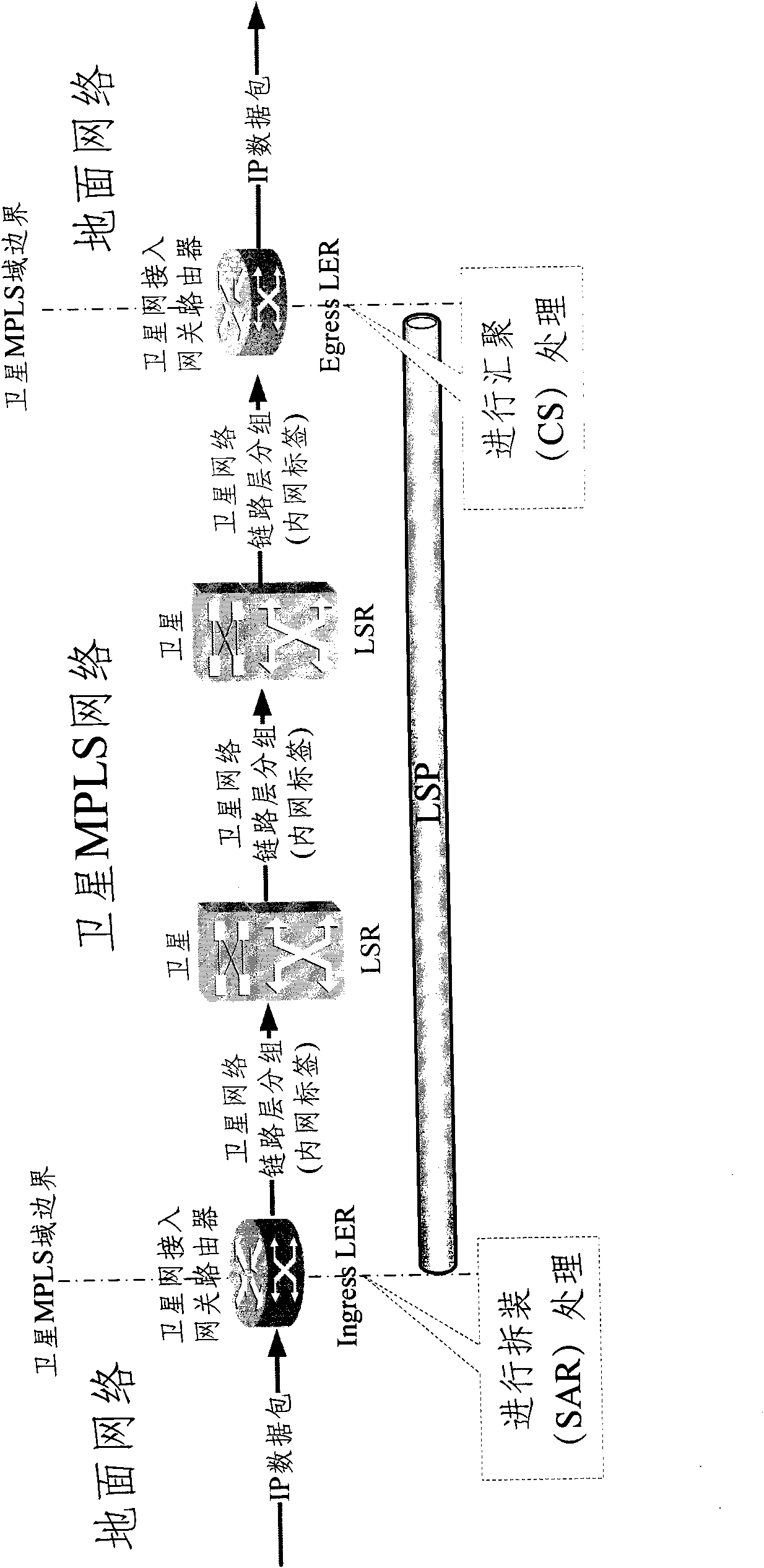
InactiveCN101552782AReduce the loss of bearing capacityReduce frequencyError preventionData switching networksSingle parity checkDesign methods
The present invention relates to label inspection method in satellite MPLS network, using single-parity check codes to encode each node using the labels in label switch path of satellite MPLS network; the label switching router and label edge router in the network proceed parity check to the labels and discard packet with false label. The invention can effectively check label error caused by error codes of satellite communication environment in the label switch path of the satellite MPLS network, so as to reduce frequency of packet 'error insertion' in LSP and finally reduce LSP business load carrying properties loss. The invention is provided with advantages of simple implementing, good impacts and suitable for different label design methods, possessing wide application foreground.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Application layer FEC framework for WIGIG
InactiveCN102783074AReduce the probability of packet lossError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionSingle parity checkComputer hardware
A method and apparatus perform forward error correction in a wireless communication device in a wireless communication network. Application layer forward error correction (AL-FEC) capability information is transmitted during a capabilities exchange. A single parity check (SPC) AL-FEC code is applied on a set of k source packets to encode systematic packets for the source packets and at least one parity packet. A header of each encoded packet includes a parity packet indicator. The encoded packets are processed in a media access control (MAC) layer and a physical (PHY) layer for transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiple component codes based generalized low-density parity-check codes for high-speed optical transport
ActiveUS9722634B2High strengthError preventionError correction/detection using LDPC codesSingle parity checkData stream
Owner:NEC CORP
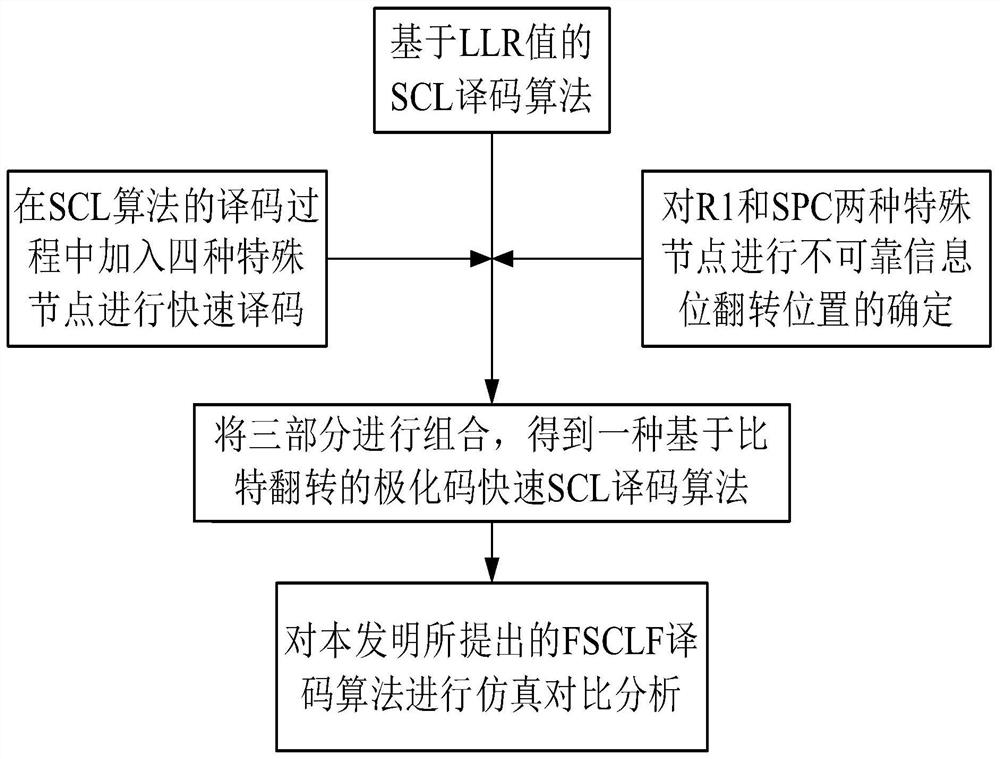
Polar code fast serial cancellation list decoding algorithm based on bit flipping
ActiveCN111654291AImprove performanceIncrease decoding rateError correction/detection using linear codesHigh level techniquesSingle parity checkRound complexity
The invention discloses a polar code fast serial cancellation list decoding algorithm based on bit flipping. According to the algorithm, the decoding rate is increased by adding identification of fourspecial nodes; meanwhile, a critical set is constructed, error propagation caused by previous decoding errors is avoided; a turnover position is judged and determined by respectively calculating loglikelihood ratio (LLR) values of two special nodes, namely an information bit R1 node and a single parity check (SPC) node; when the parity check bit does not meet the requirement, only the information bit corresponding to the most unreliable input LLR needs to be overturned, so that the overturning frequency is reduced, and the complexity is reduced. Simulation results show that when the block error rate is 10 <-5 >, the signal-to-noise ratio of the improved fast SCL decoding algorithm based on bit flipping is improved by 0.09 dB compared with that of an original SCL decoding algorithm basedon bit flipping, so that the improved decoding algorithm provides a reference algorithm under the condition of medium and short code lengths.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Lpdc code transmission method using row-orthogonal structure and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS20210111737A1Error preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSingle parity checkAlgorithm
A method for encoding a quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (LDPC) code according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: a step of generating a multi-edge LDPC code matrix which comprises a high rate code matrix and a single parity check code matrix; and a step of encoding a signal using the multi-edge LDPC code matrix, wherein the single parity check code matrix may be configured by connecting a first matrix which is configured as a quasi row-orthogonal structure matrix and a second matrix which is configured as a pure row-orthogonal structure.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Apparatus and method for LDPC encoding suitable for highly reliable and low latency communication
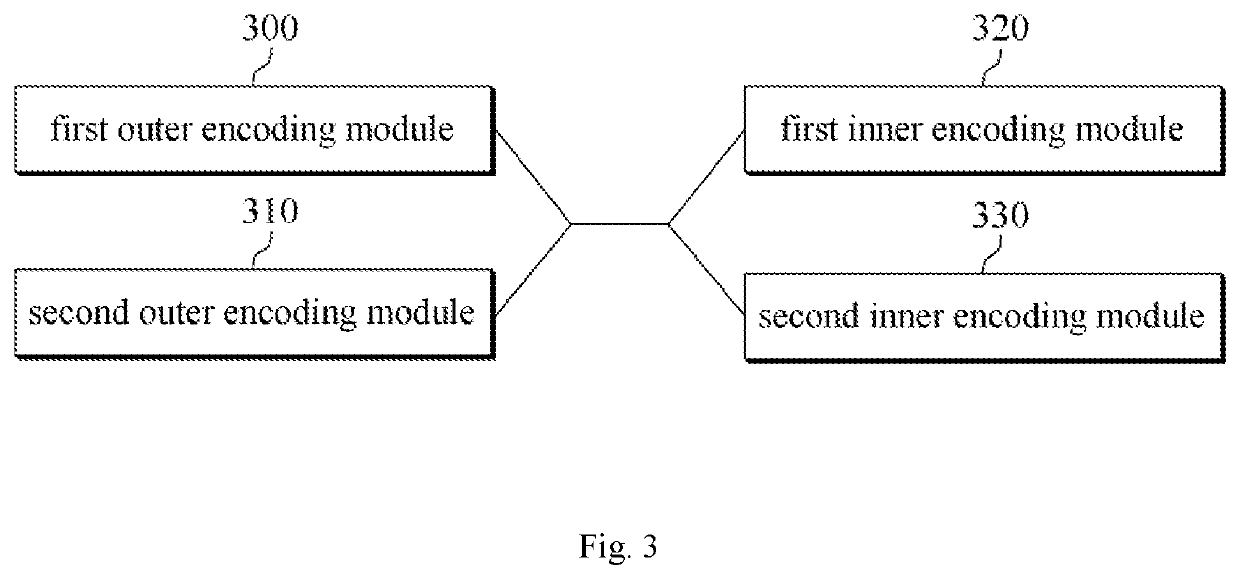
ActiveUS20190036547A1Reduce complexityImprove reliabilityError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionSingle parity checkLatency (engineering)
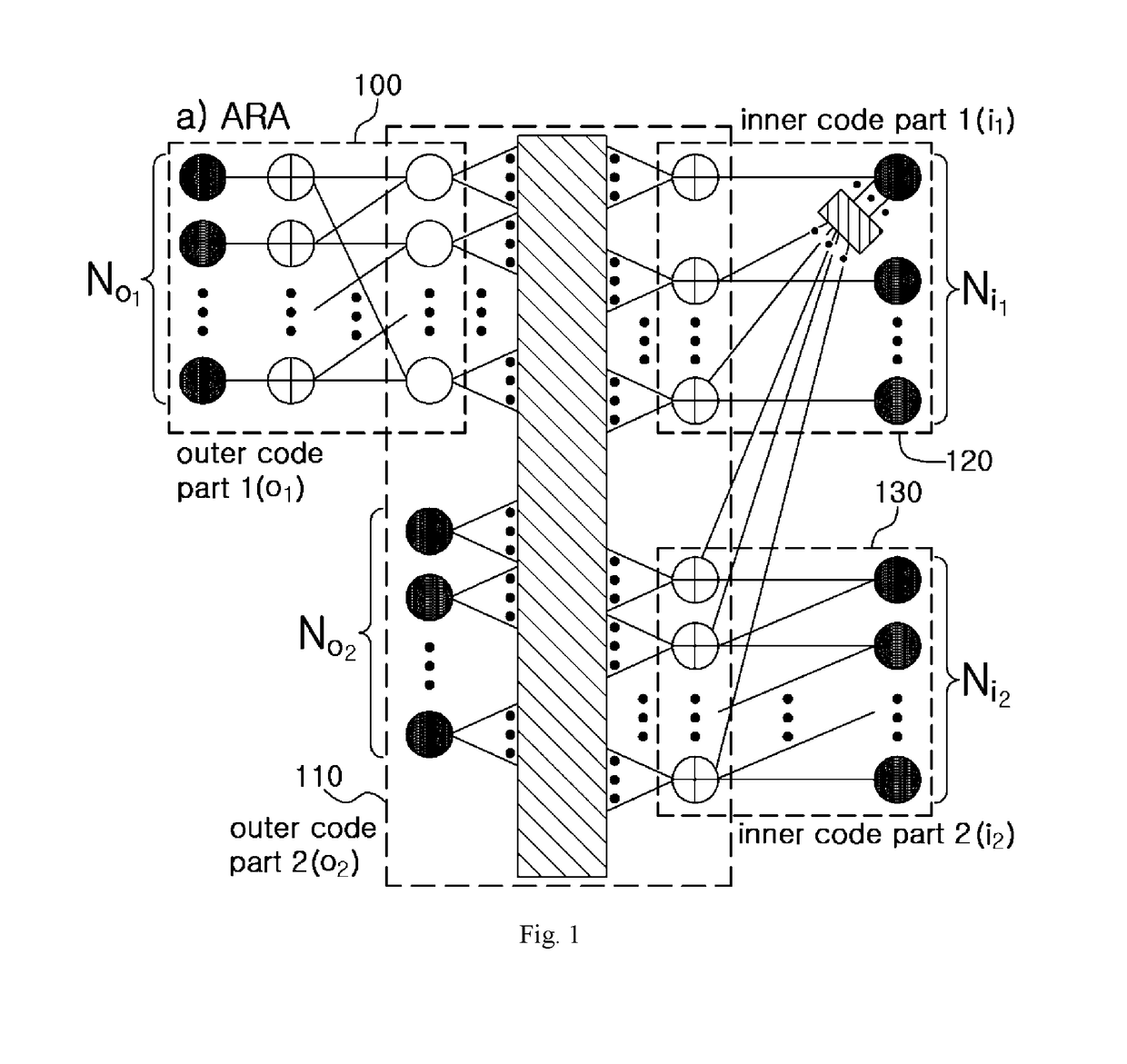
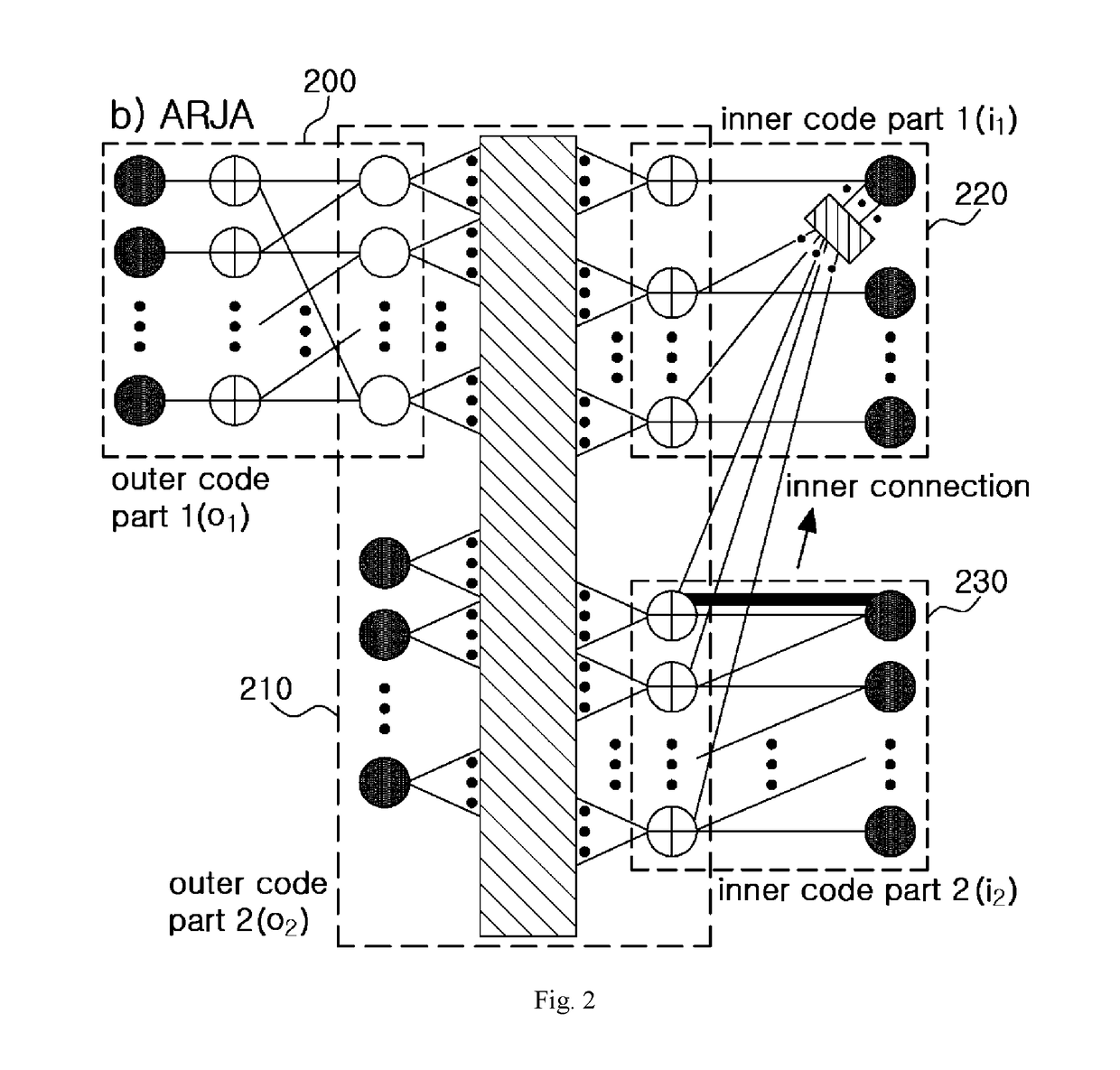
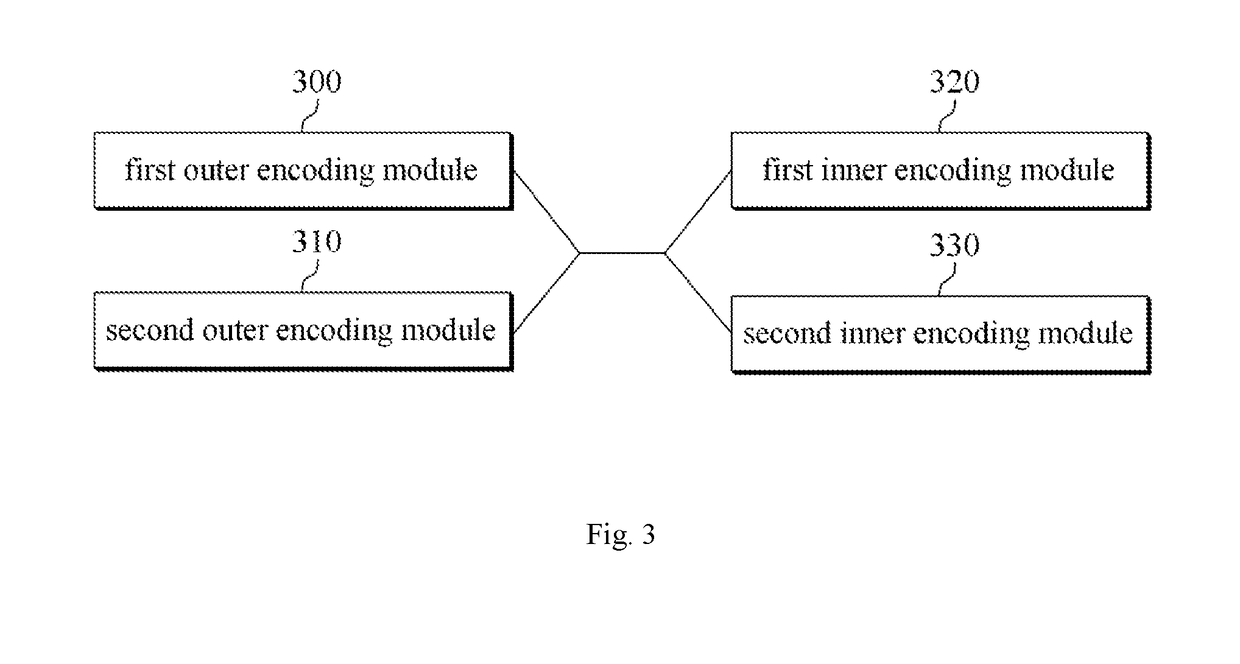
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for LDPC encoding suitable for highly reliable and low latency communication. The disclosed apparatus comprises: a second inner encoding module for outputting parity bits by means of single parity calculations and accumulation device calculations using bit strings outputted from a first inner encoding module; and the first inner encoding module for outputting a part of the parity bits by means of single parity check calculations for the bits output from a second outer module, and for outputting rest of the parity bit strings by means of single parity check calculations and accumulation device calculations, with a part of the parity bits output by the second inner encoding module as an additional input.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Label inspection method in satellite MPLS network
InactiveCN101552782BReduce the loss of bearing capacityReduce frequencyError preventionData switching networksSingle parity checkDesign methods
The present invention relates to label inspection method in satellite MPLS network, using single-parity check codes to encode each node using the labels in label switch path of satellite MPLS network;the label switching router and label edge router in the network proceed parity check to the labels and discard packet with false label. The invention can effectively check label error caused by errorcodes of satellite communication environment in the label switch path of the satellite MPLS network, so as to reduce frequency of packet 'error insertion' in LSP and finally reduce LSP business loadcarrying properties loss. The invention is provided with advantages of simple implementing, good impacts and suitable for different label design methods, possessing wide application foreground.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Encoding/decoding method of multidimensional crossing parallel cascade single-parity check code
InactiveCN101345607BChange relationshipReduce bit error rateError preventionSingle parity checkPrior information
The invention discloses a coding method for multi-dimensional crossing parallel cascade single-parity check code comprising that input information bit frame is separately passed through M interweavers and serial to parallel conversion then enters into crossover; output of crossover generates parity check bit frame P by passing P single-parity check encoder; U and P constitutes code word C; encoder computes code word C channel prior information according to receiving signal; U channel prior information is separately interweaved by M interweavers to get M channel prior information of interweaved information bit frame and first generation iteration coding; encoder executes iteration coding and simultaneously executes local coding, then gets outer information of M interweaved information bitframe, and computing prior information of next iteration; judging logarithm likelihood ratio information for U, obtaining coding result. The invention has merits of simple encoding and coding, low error floor and is used for correcting error of receiving signal.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for LDPC encoding suitable for highly reliable and low latency communication
ActiveUS10693499B2Improve reliabilityLow latency communicationError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionSingle parity checkComputer architecture
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for LDPC encoding suitable for highly reliable and low latency communication. The disclosed apparatus comprises: a second inner encoding module for outputting parity bits by means of single parity calculations and accumulation device calculations using bit strings outputted from a first inner encoding module; and the first inner encoding module for outputting a part of the parity bits by means of single parity check calculations for the bits output from a second outer module, and for outputting rest of the parity bit strings by means of single parity check calculations and accumulation device calculations, with a part of the parity bits output by the second inner encoding module as an additional input.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
A harq method based on maximum distance separable coding
ActiveCN105162559BImprove error correction performanceImproved block error rate performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelForward error control useSingle parity checkRound complexity
The invention relates to a HARQ (Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request) method based on maximum distance separable codes and belongs to the technical field of communication. The coding performing of the HARQ method is improved by adopting a coding mode with maximum distance separable code characteristics, such as SPC (Single Parity Check) codes, so that the coding performance is improved, the correction capability is further is increased, correct decoding and original information retrieval can be achieved when a channel state is poor, that is to say, a check packet is combined to correctly decode wrongly-transmitted data packets. Compared with the traditional HARQ method, the method performs normal transmission and has the same complexity as the prior art when the channel state is good, and transmits the check packet to assist decoding when the channel state is poor, so that the error correction capability is improved, and the block error rate performance is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for transmitting LDPC code using row-orthogonal and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS11043970B2Error preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSingle parity checkAlgorithm
A method for encoding a quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (LDPC) code according to an embodiment of the present invention may comprise the steps of: generating a multi-edge LDPC code matrix including a high rate code matrix and a single parity check code matrix; and encoding a signal by using the multi-edge LDPC code matrix, wherein the single parity check code matrix includes a first matrix having a non-row-orthogonal structure matrix and a second matrix having a pure row-orthogonal structure, which are concatenated.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
LPDC code transmission method using row-orthogonal structure and apparatus therefor
ActiveUS11082060B2Error preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSingle parity checkAlgorithm
A method for encoding a quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (LDPC) code according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: a step of generating a multi-edge LDPC code matrix which comprises a high rate code matrix and a single parity check code matrix; and a step of encoding a signal using the multi-edge LDPC code matrix, wherein the single parity check code matrix may be configured by connecting a first matrix which is configured as a quasi row-orthogonal structure matrix and a second matrix which is configured as a pure row-orthogonal structure.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com