Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Loss of function mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Loss-of-function mutation. A change in DNA that results in the decreased production of a protein or a protein with impaired function. Loss-of-function mutations are usually recessive. Synonym: inactivating mutation.
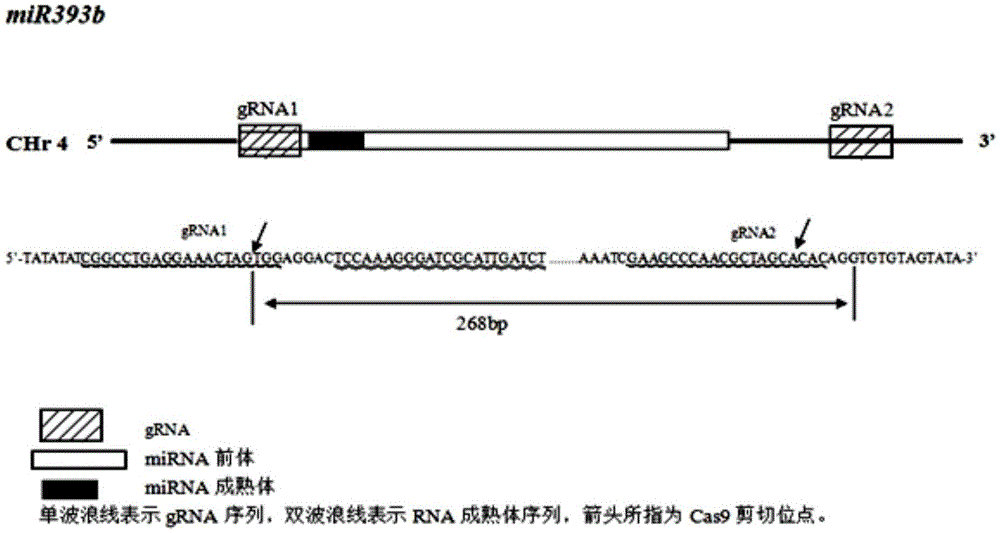
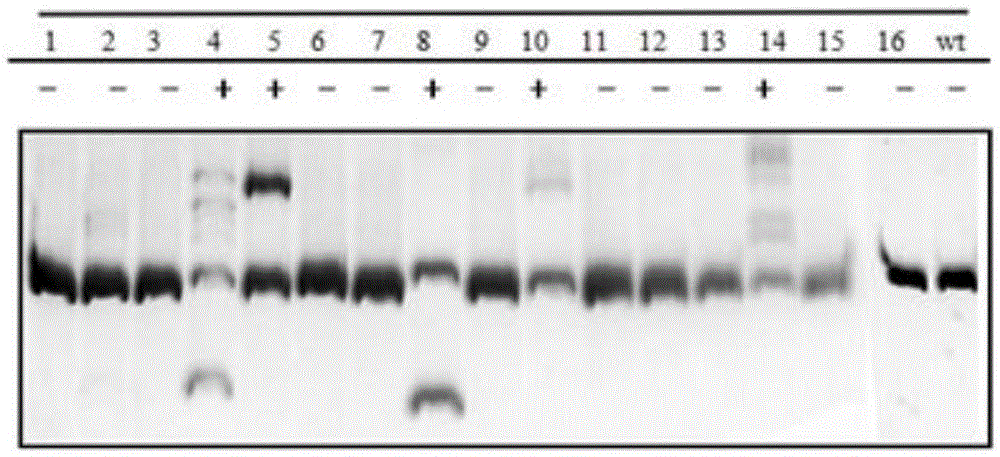
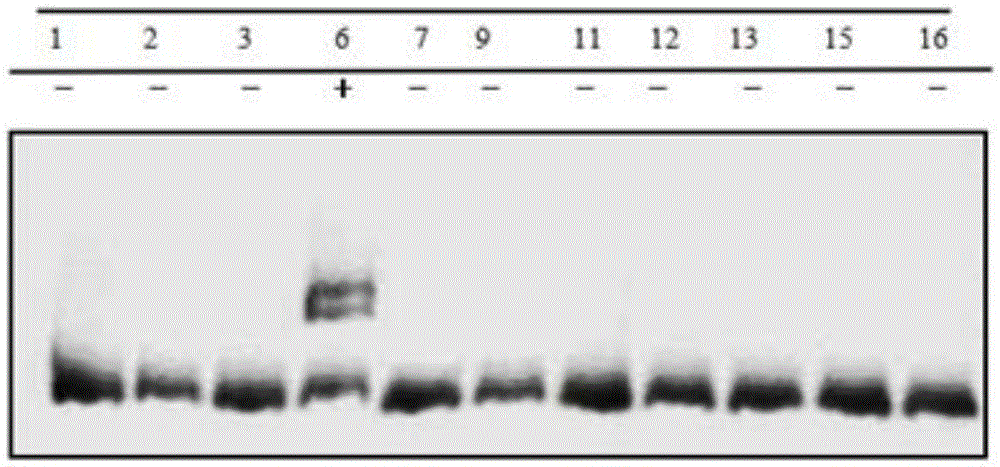
Gene editing method for knocking out rice MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences with application of CRISPR(clustered regulatory interspersed short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 system
InactiveCN105647962AKnockout worksNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to construction of rice transgenic materials and aims to provide a gene editing method for knocking out rice MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences with application of a CRISPR(clustered regulatory interspersed short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 system. The gene editing method comprises steps as follows: gRNA target sites are selected for cloning and GG linking, enzyme digestion is performed after amplification, and a product is linked with a pGREB 32 vector; escherichia coli competent cells are transformed; plasmids with a correct sequencing result are used for transforming agrobacteria, transgenic plants are obtained through mediated transformation of rice calli, and transgenic positive lines are obtained; the T0-generation mutant plant seeds are collected for seeding, and the T1-generation plants are subjected to homozygote screening; homozygous lines which are discovered to be negative through MIRNA393b expression are rice mutants completely losing the MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences and MIRNA393b stem-loop sequence expression. According to the gene editing method, MIRNA stem-loop sequences can be effectively knocked out, and loss-of-function mutants of different members in the same MIRNA family can be prepared; the mutant plant propagates to obtain a large number of seeds and is an ideal material for acquiring rice MIRNA393b gene functions successfully.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
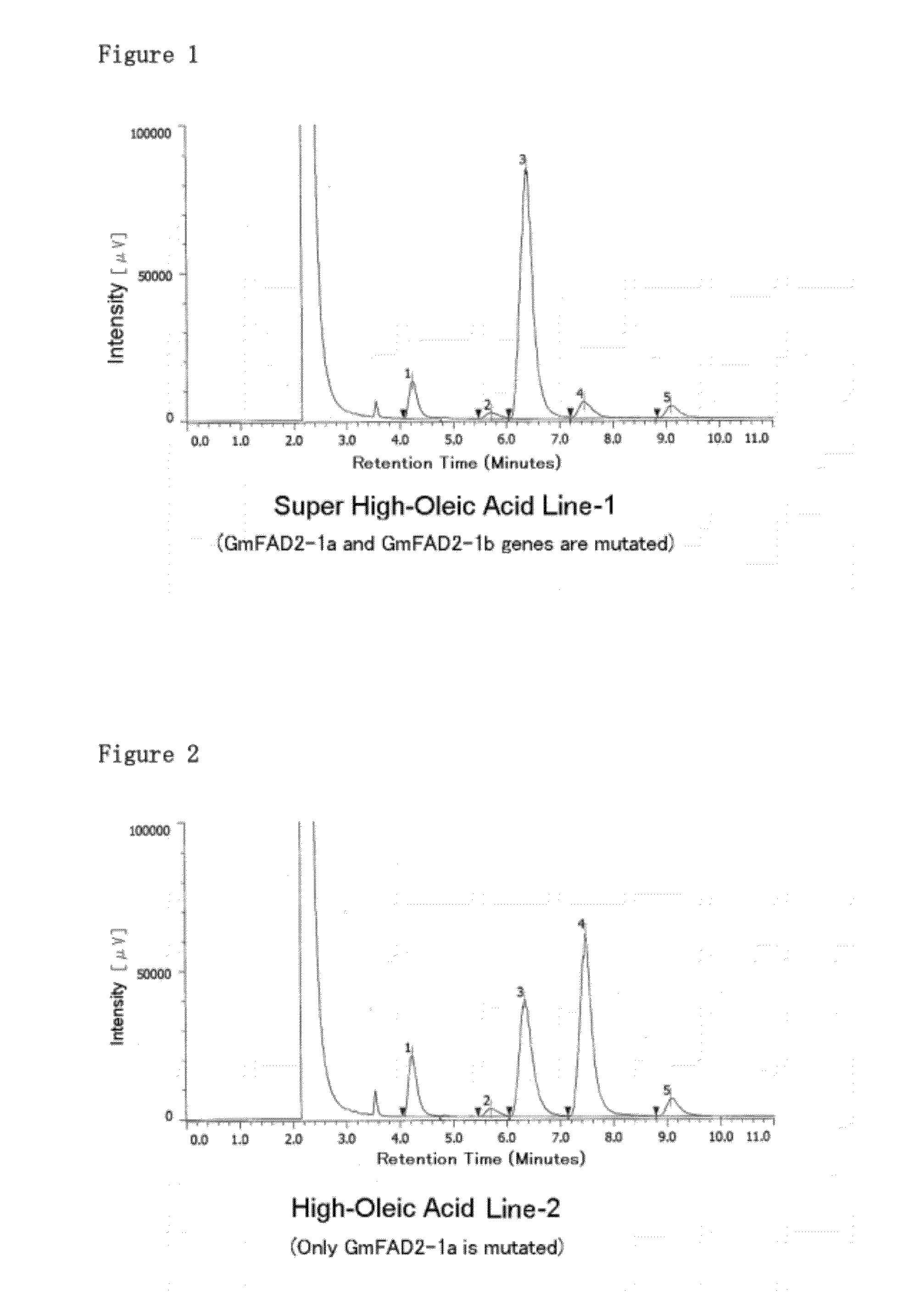
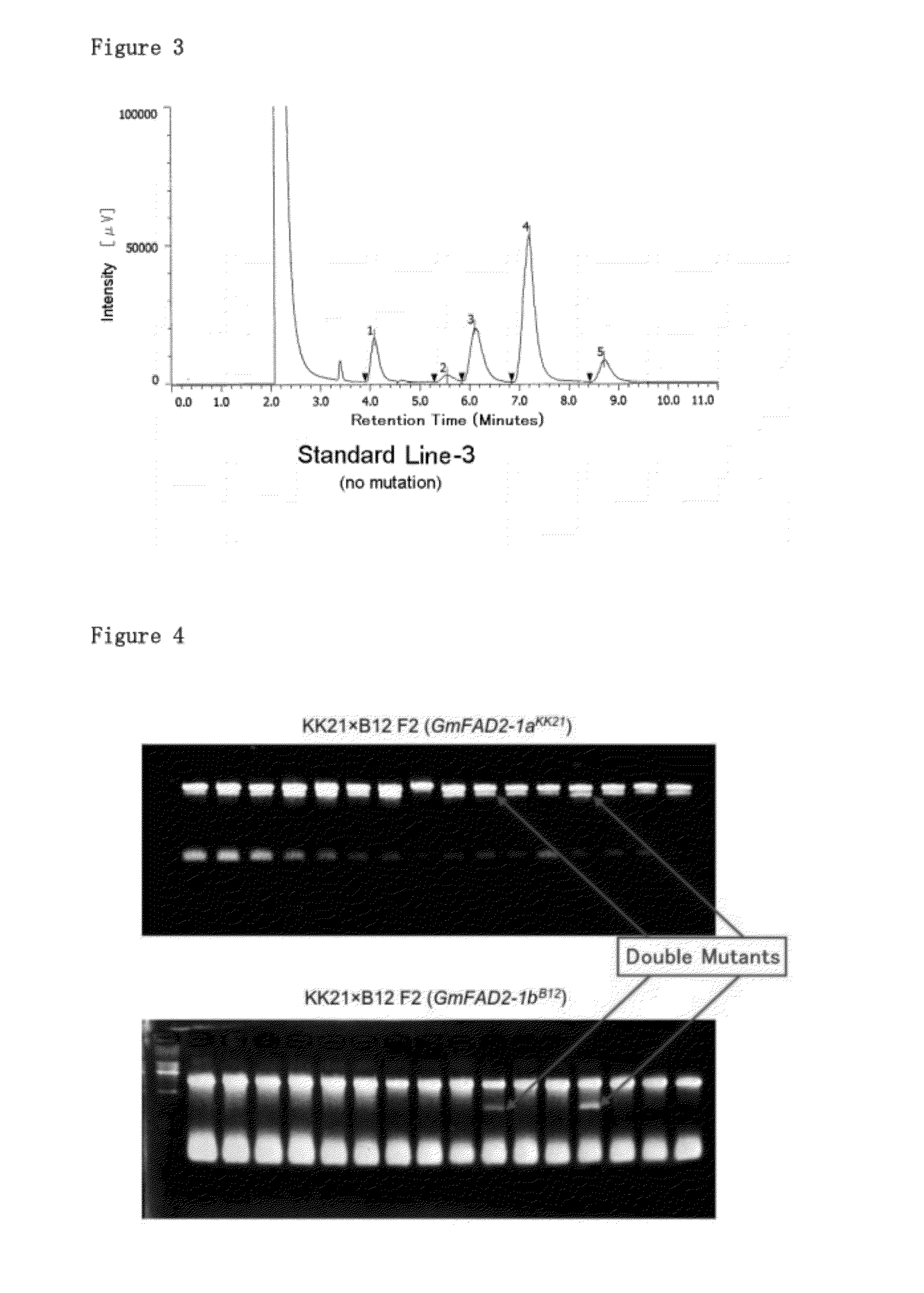
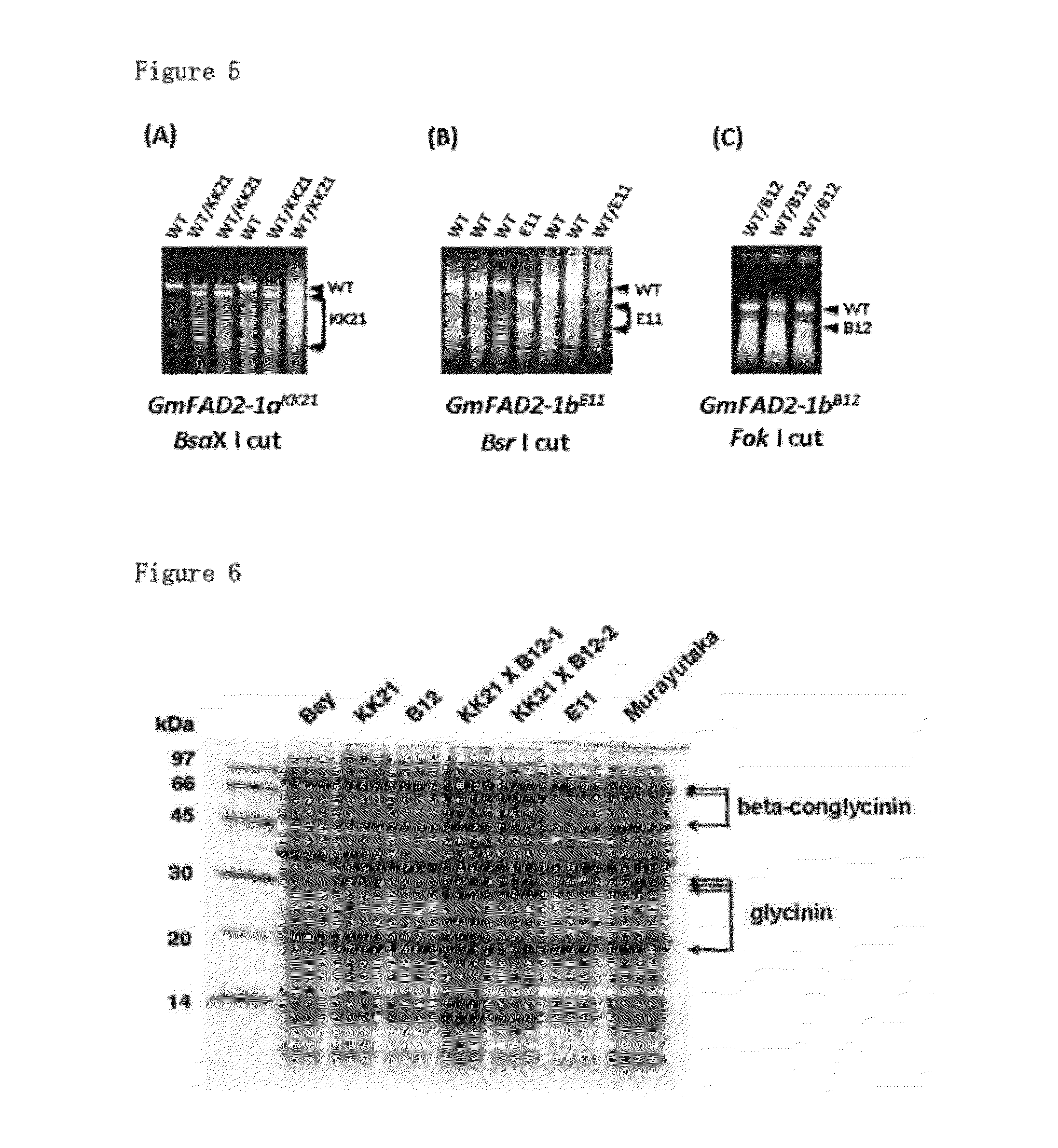
Mutation that increases the oleic acid content in soybean oil and responsible gene thereof
ActiveUS20120102587A1Increase contentHigh oleic acid contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFatty acid chemical modificationGene engineeringLoss of function mutation
[Problem]Providing soybean including oleic acid that will exceed the heretofore developed high-oleic soybean without using gene engineering technology.[Means to Solve the Problem]The present invention provides a GmFAD2-1b gene loss of function mutation and a type of soybean that includes a GmGAD2-1b gene loss of function mutation.
Owner:SAGA UNIVERSITY
Breeding method for yeast, yeast and a production method for glycoprotein or beta-glucan
InactiveUS7803605B2Avoiding high-temperature sensitivityExcellent thermotoleranceFungiEnzymesYeastBiotechnology
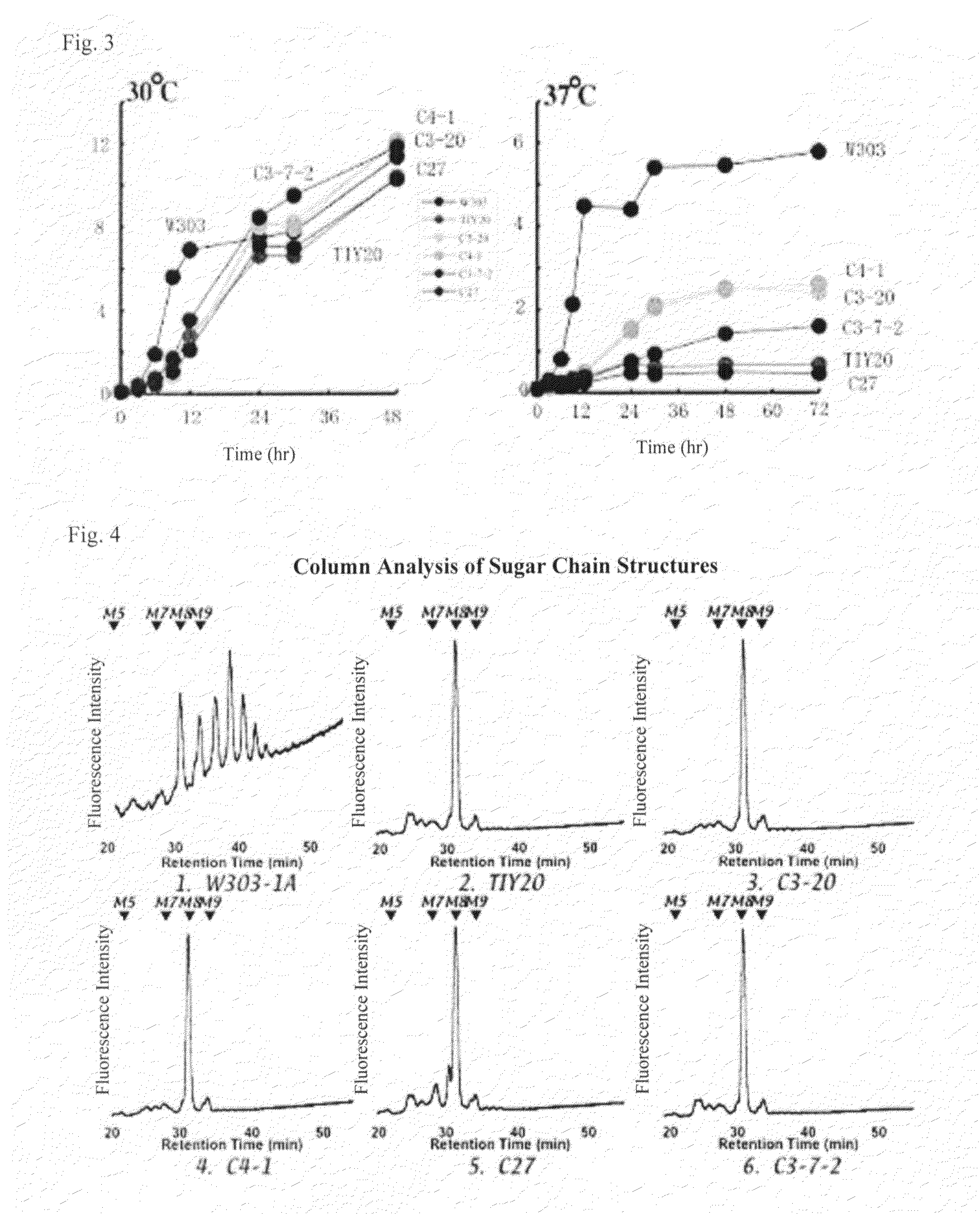
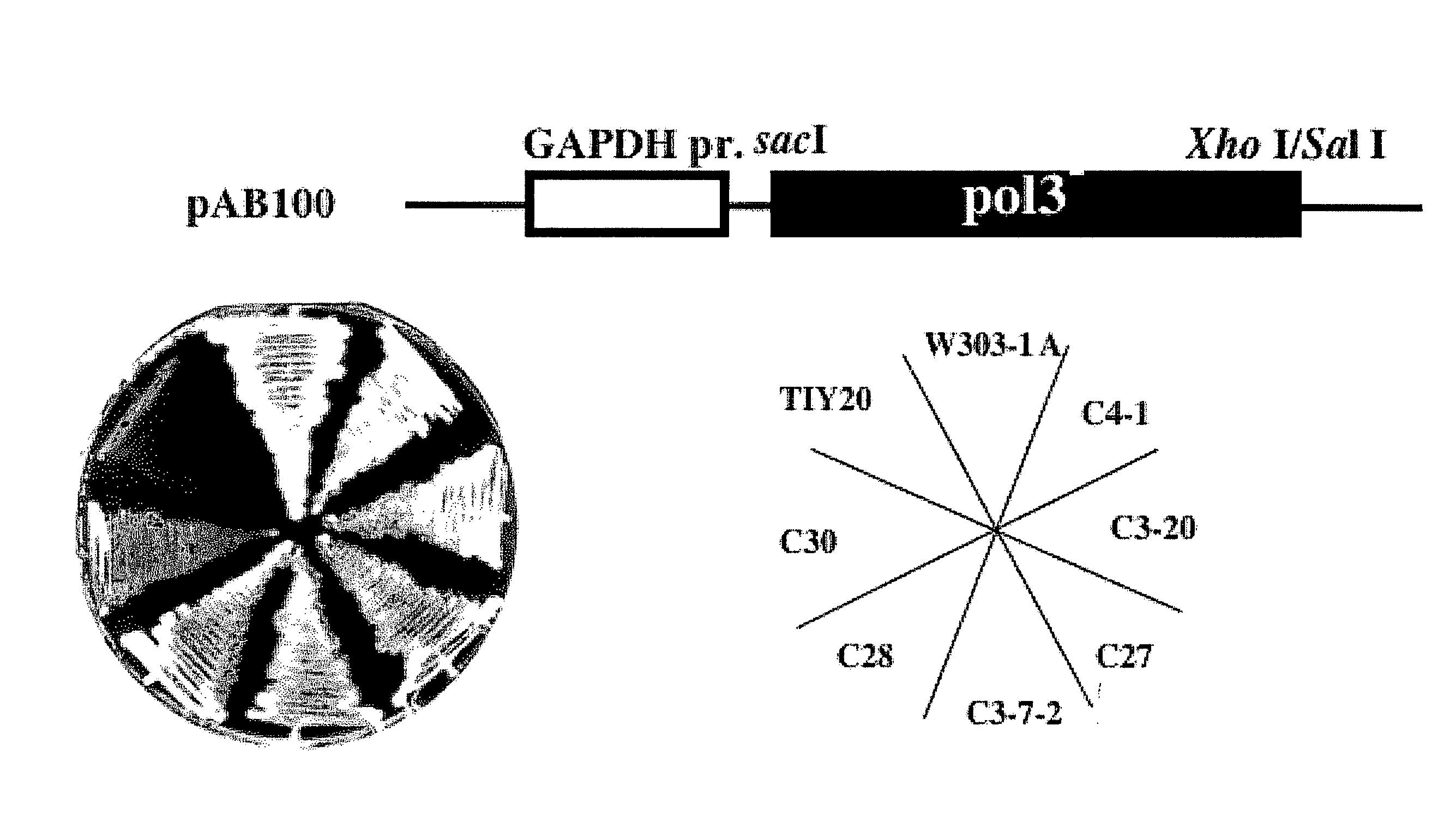
A method for breeding yeast having thermotolerance or recovering growth activity and a method for breeding yeast which produces beta-glucan efficiently as well as an yeast obtained by such methods for breeding are presented by a method for breeding yeast having thermotolerance or recovering growth activity including a step for controlling proofreading function of DNA polymerase in a loss-of-function mutant of yeast (for example, a step for including mutant pol3 gene or mutant cdc6− gene in a gene-disruptant.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
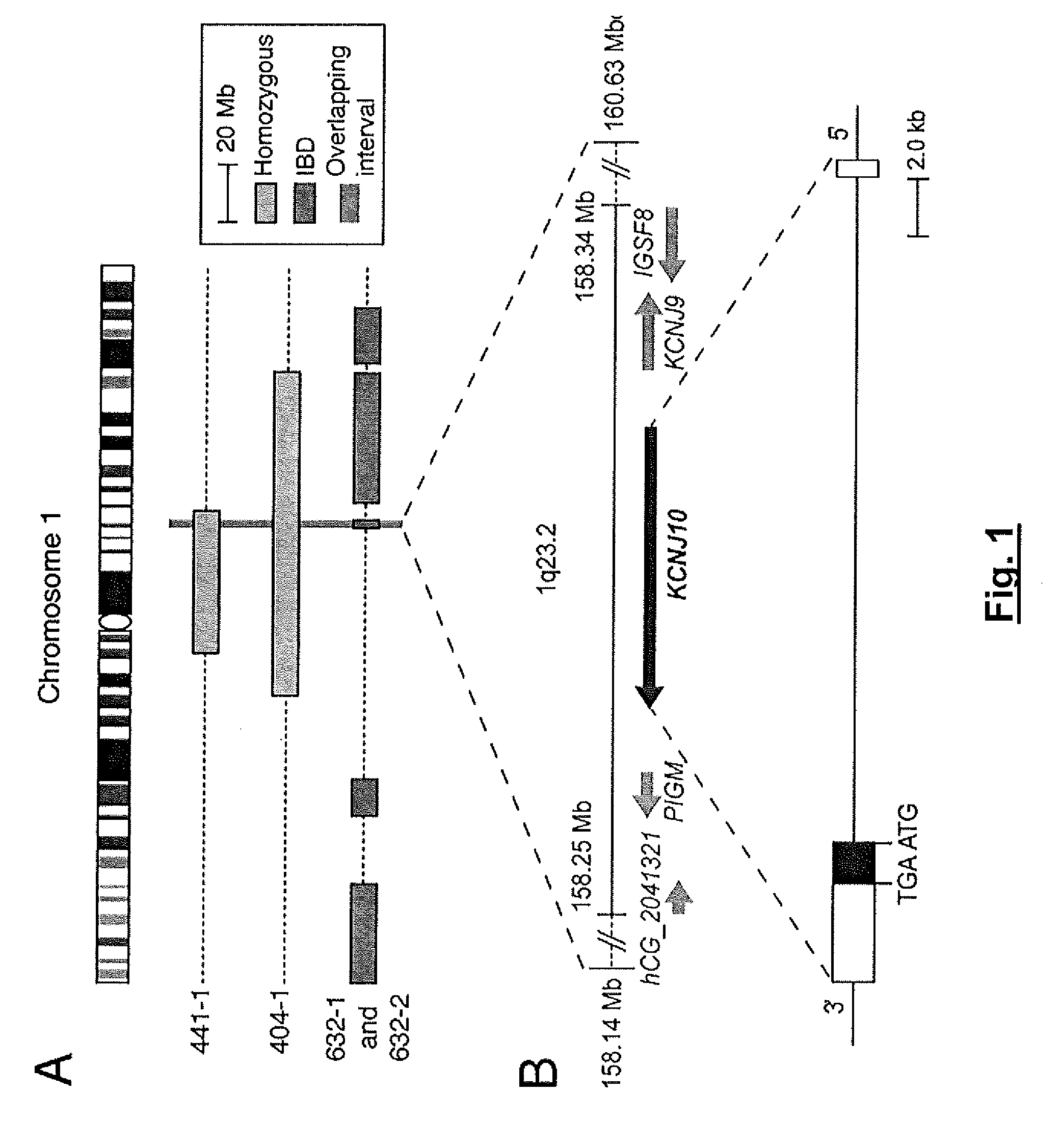
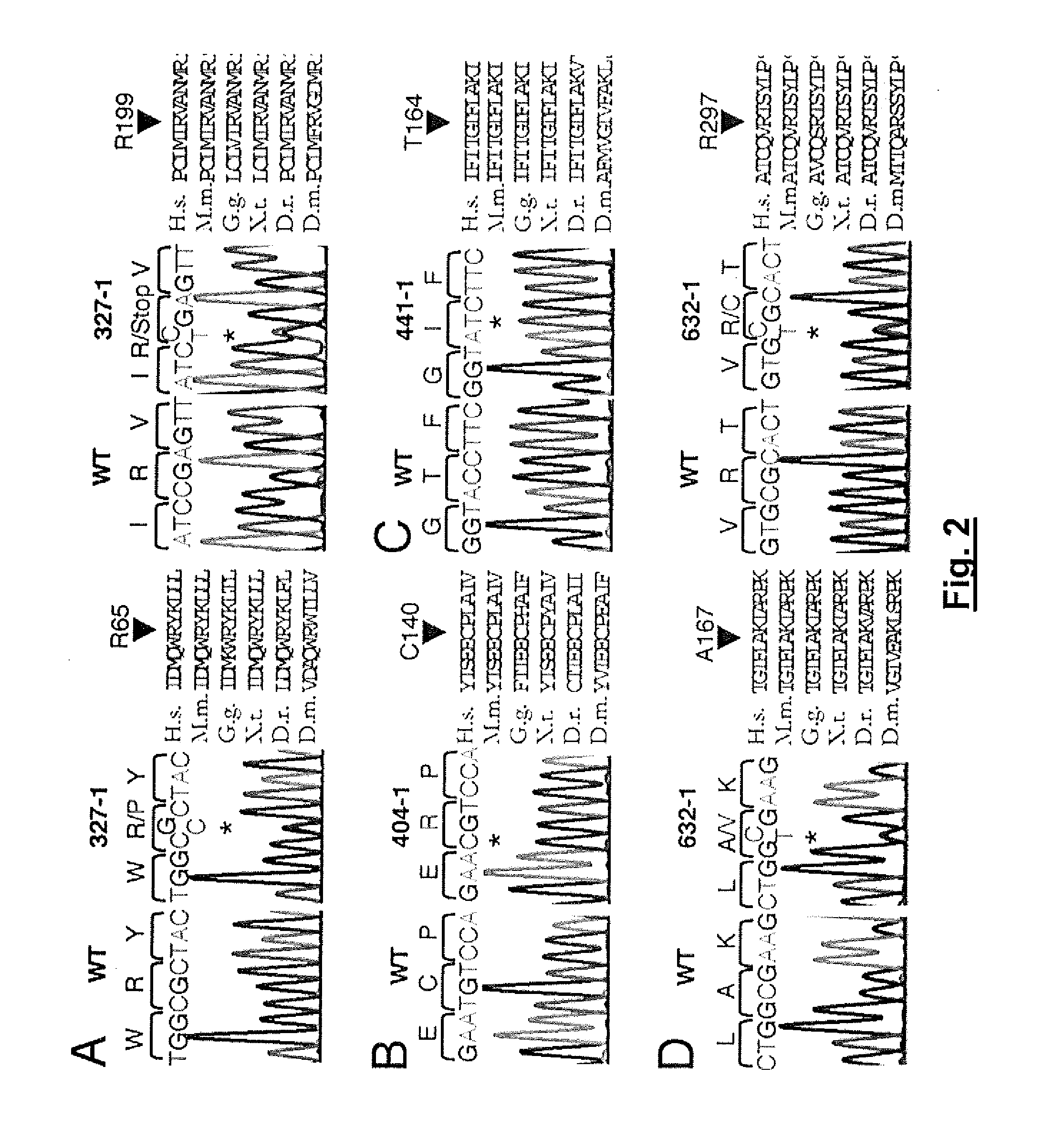
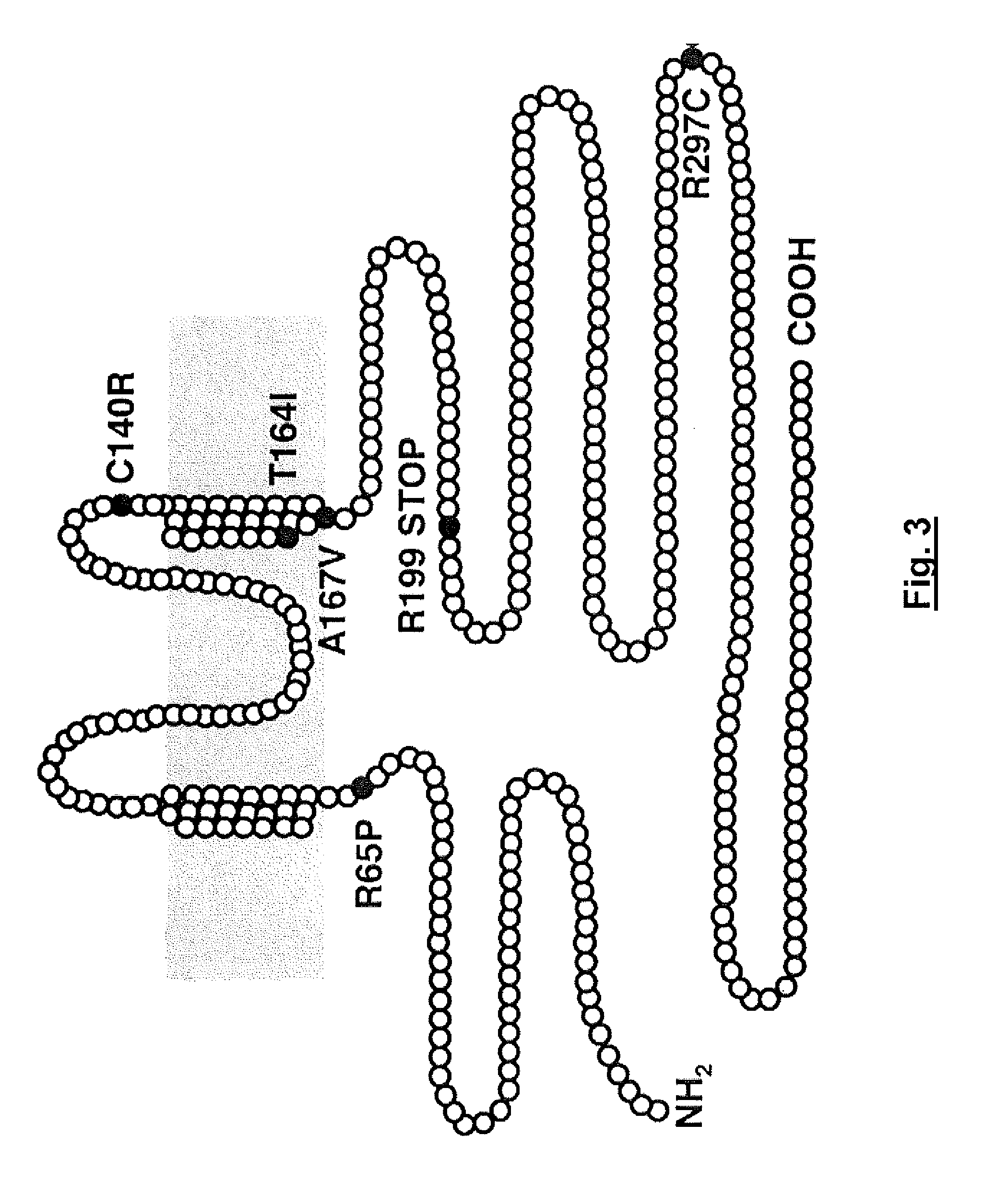
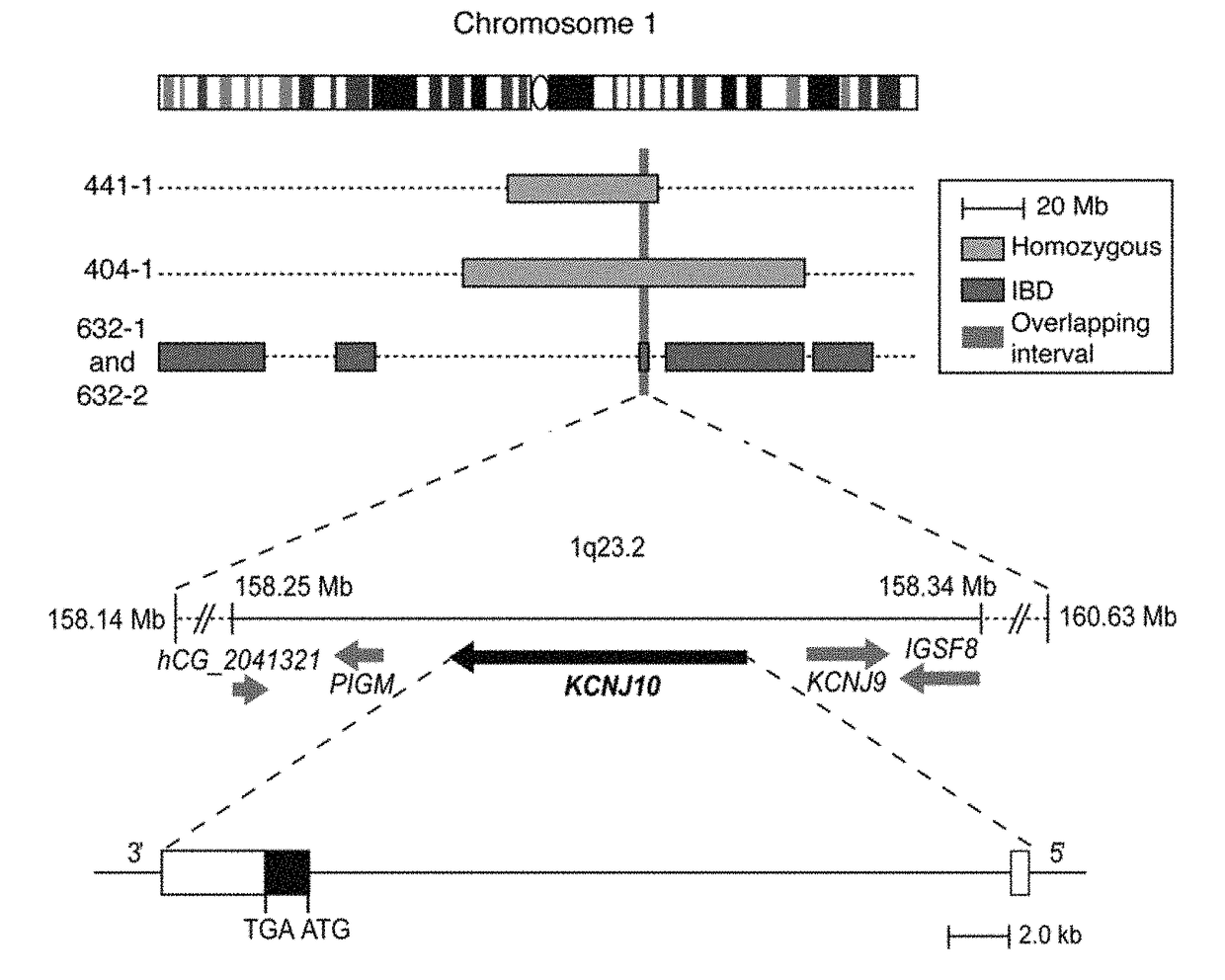
Loss of Function mutations in KCNJ10 cause SeSAME, a human syndrome with sensory, neurological, and renal deficits
The invention includes a method of identifying a human subject at-risk of developing SeSAME syndrome. The invention also includes a method of diagnosing a human subject afflicted with SeSAME syndrome. The invention further includes a method of identifying a therapeutic agent that modulates a given KCNJ10 mediated K+ current in a mammalian cell. The invention also includes a method of diagnosing a subject as a carrier of SeSAME syndrome.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method of treating autoimmune inflammatory disorders using il-23r loss-of-function mutants
InactiveUS20140037618A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingLoss of function mutationInflammatory disorder
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Breeding method for yeast, yeast and a production method for glycoprotein or beta-glucan
InactiveUS20080038778A1Avoiding high-temperature sensitivityExcellent thermotoleranceFungiEnzymesYeastBiotechnology
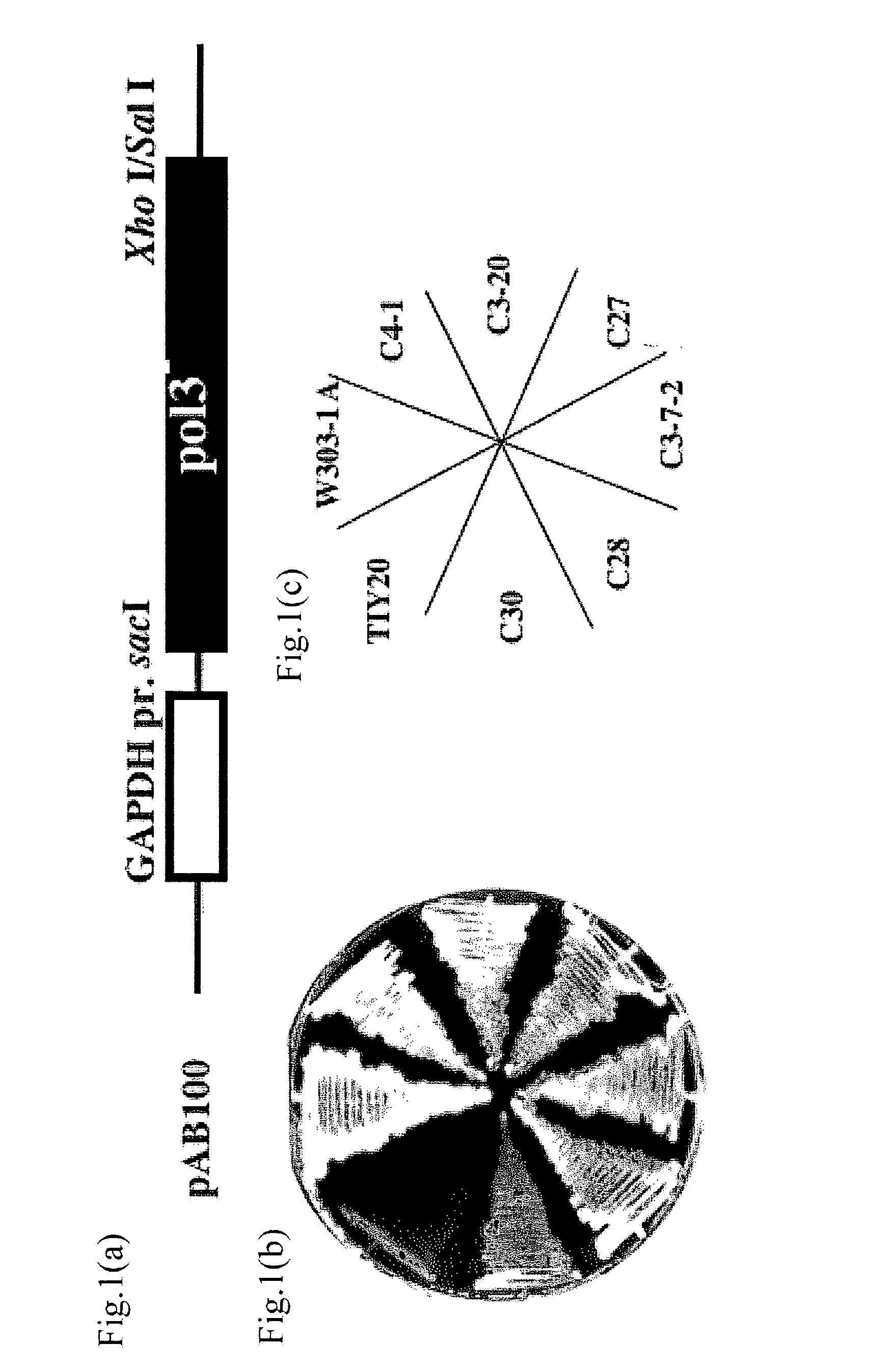
A method for breeding yeast having thermotolerance or recovering growth activity and a method for breeding yeast which produces beta-glucan efficiently as well as an yeast obtained by such methods for breeding are presented by a method for breeding yeast having thermotolerance or recovering growth activity including a step for controlling proofreading function of DNA polymerase in a loss-of-function mutant of yeast (for example, a step for including mutant pol3 gene or mutant cdc6−gene in a gene-disruptant.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Prevention/treatment of ichthyosis vulgaris, atopy and other disorders
The present invention relates to the prevention / treatment of ichthyosis vulgaris (IV), atopy and potentially other disorders associated with loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene sequence. The prevention / therapy is based on the use of agents which enable the host's translational machinery to read through a nonsense mutation found in a mutant allele of the filaggrin gene.
Owner:UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF DUNDEE
Cloning and application of flowering period BnFLC.A2 and Bnflc.a2 genes of brassica napus
The invention provides cloning and application of flowering period BnFLC.A2 and Bnflc.a2 genes of brassica napus, and particularly provides isolation cloning, functional verification and application of two DNA fragments of an early flowering Bnflc.a2 gene and a later flowering BnFLC.A2 allele of rape. The early flowering Bnflc.a2 allogene is a loss-of-function mutant of the BnFLC.A2 gene. A functional marker of the early flowering gene is developed; the Bnflc.a2 gene has remarkable influence on the flowering period in a natural population under seven environments through the natural population genotype and flowering period phenotypic analysis of 495 portions of brassica napus, which shows that the copy function loss caused by the insertion of long fragments in the Bnflc.a2 is an important factor influencing the natural variation of the flowering time of the brassica napus. A serial design functional marker of the Bnflc.a2 itself is used for carrying out assisted selection of molecular markers and breeding early-flowering materials, thereby breeding early-flowering and early-maturing rape. The invention has the characteristics of accuracy, high efficiency and economy.
Owner:武汉联农种业科技有限责任公司
Method for determination of a potential mutation
InactiveUS20100322860A1Method is fastDiagnostics using lightPreparing sample for investigationStratum corneumFilaggrin
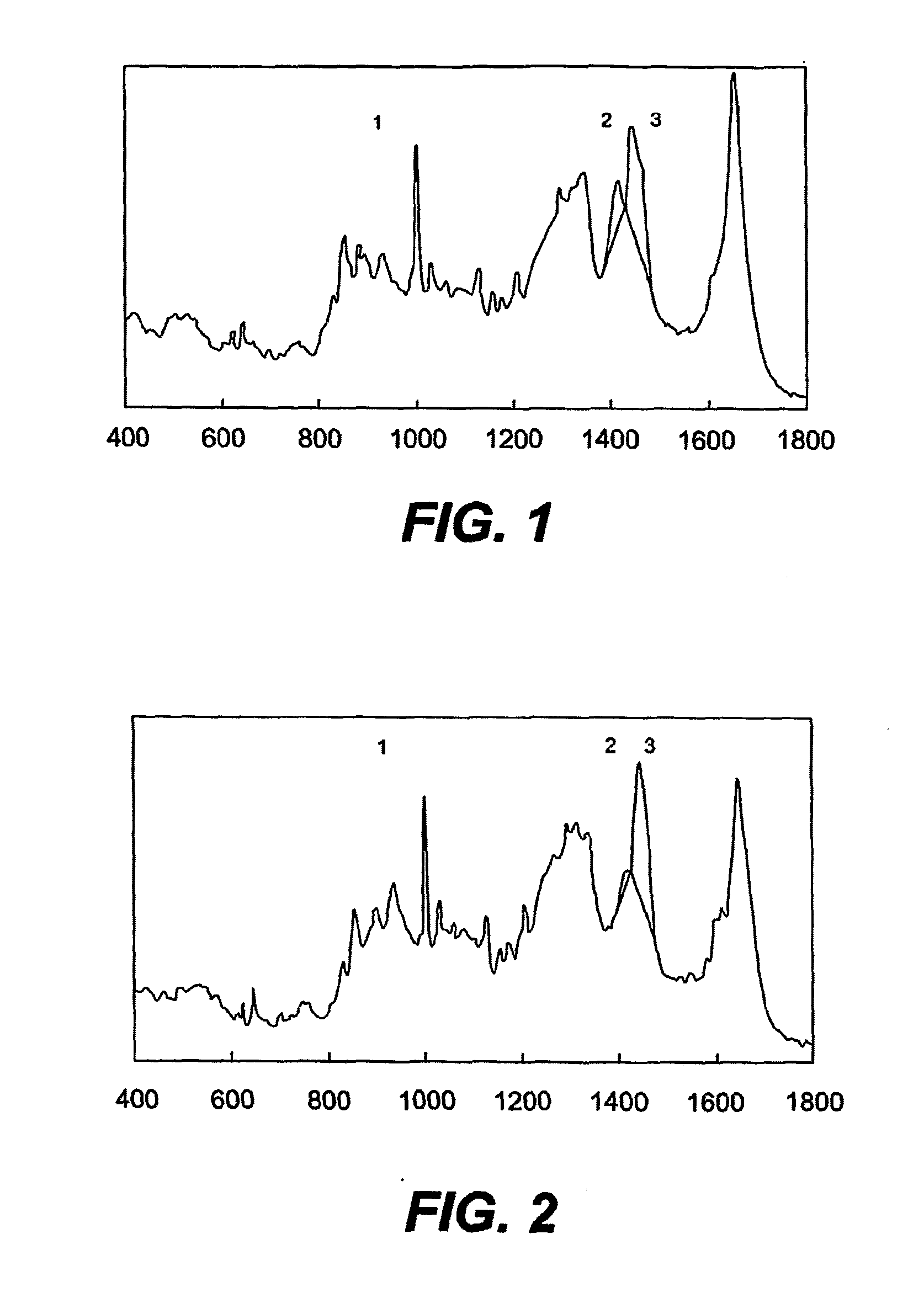
The invention is directed to a method for non-invasive determination of the potential presence of one or more loss-of-function mutation(s) in the gene encoding for filaggrin.The method of the invention comprises(i) obtaining a vibrational spectrum from the stratum corneum of the individual;(ii) determining the local natural moisturising factor content from the vibrational spectrum;(iii) optionally repeating steps (i) and (ii); and(iv) comparing the local natural moisturising factor content of the individual to a reference value,wherein said stratum corneum is stratum corneum of a location of the body of said individual at which said one or more loss-of-function mutation(s) in the gene encoding for filaggrin has a stronger influence on the natural moisturising factor concentration than other factors influencing the natural moisturising factor concentration.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
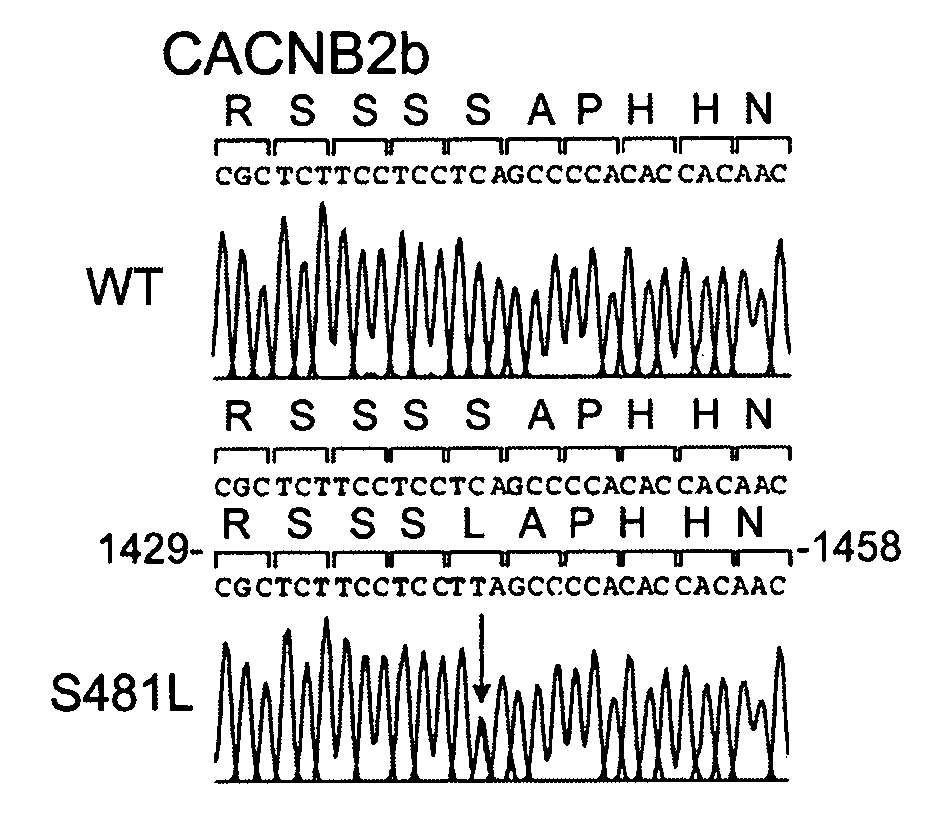
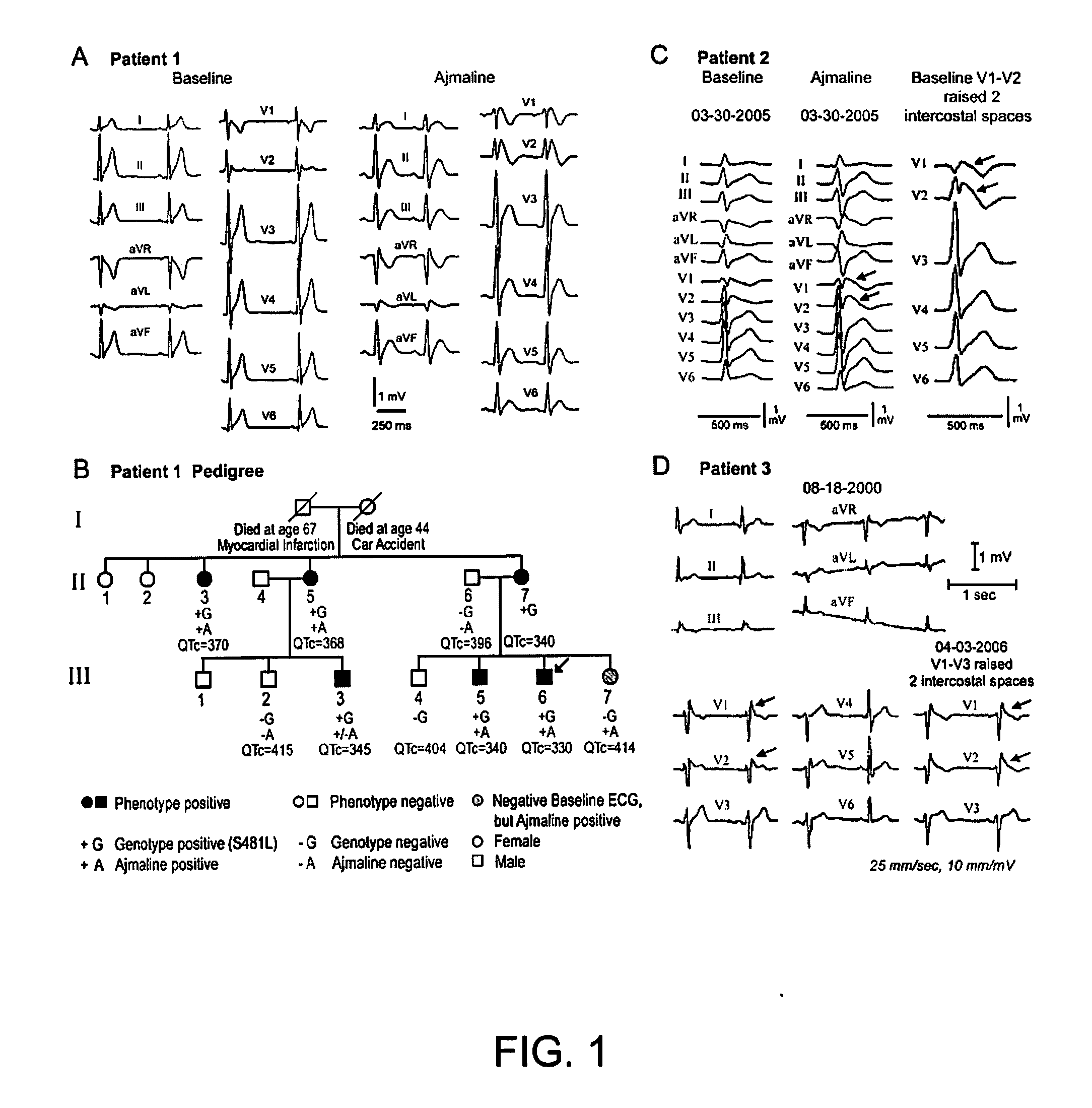
Loss of function mutations in calcium channel polypeptides associated with sudden cardiac death
InactiveUS20080118438A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionAntiendomysial antibodiesNucleic Acid Probes
Previously unknown mutations of the CACNA1C and CACNB2b genes are disclosed which are involved in ion channel disruptions associated with shorter than normal QT interval and ST segment elevation syndrome. These mutations are utilized to diagnose and screen for shorter than normal QT interval and ST segment elevation syndrome, thus providing modalities for diagnosing syncope and / or sudden cardiac death and / or predicting susceptibility to syncope and / or sudden cardiac death. Nucleic acid probes are provided which selectively hybridize to the mutant nucleic acids described herein. Antibodies are provided which selectively bind to the mutant polypeptides described herein. The mutations described herein are also utilized to screen for compounds useful in treating the symptoms manifest by such mutations.
Owner:MASONIC MEDICAL RES LAB A CORP OF NY
Loss of function mutations in KCNJ10 cause SeSAME, a human syndrome with sensory, neurological, and renal deficits
The invention includes a method of identifying a human subject at-risk of developing SeSAME syndrome. The invention also includes a method of diagnosing a human subject afflicted with SeSAME syndrome. The invention further includes a method of identifying a therapeutic agent that modulates a given KCNJ10 mediated K+ current in a mammalian cell. The invention also includes a method of diagnosing a subject as a carrier of SeSAME syndrome.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Genetically modified somatic cells for sustained secretion of lysosomal proenzymes deficient in lysosomal storage disorders
InactiveUS20060188975A1Avoids adverse immunological side effectAvoids renal clearance problemNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsProgenitorZymogen
The invention relates to various methods of treating lysosomal storage disorders using somatic cells and methods of delivering therapeutic enzymes. More particularly, gain-of-function or loss-of-function mutations in components of the intracellular Golgi to lysosome sorting pathway are used to enhance secretion of one or more lysosomal enzymes in somatic cells, thereby providing treatment for lysosomal storage disorders, particularly in neuronal cells. In addition, homologous recombination may be used to engineer therapeutically useful cells, for example, somatic cells, such as, glial progenitor cells, mesenchymal stem cells and astrocyte precursor cells, to enhance secretion of one or more lysosomal enzymes.
Owner:Q THERAPEUTICS
Gene editing of pcsk9
Provided herein are systems, compositions, and methods of introducing loss-of-function mutations in to protein factors involved in the LDL-R-mediated cholesterol clearance pathway, e.g., PCSK9, APOC3,LDL-R, or IDOL. Loss-of-function mutations may be introduced using a CRISPR / Cas9-based nucleobase editor described in. Further provided herein are compositions and methods of treating conditions related to high circulating cholesterol levels.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Marker for diagnosing forelimb-girdle muscular anomaly in mammal individual, and detection method using same
The present invention uses an isolated polynucleotide having a part or whole of GFRA1 gene, mutant GFRA1 protein, and mRNA encoding the mutant GFRA1 protein, each of which includes a loss-of-function mutation of GFRA1, as markers for diagnosing an animal as affected by forelimb-girdle muscular anomaly or as a carrier of forelimb-girdle muscular anomaly. In addition, an isolated polynucleotide comprising one or more selected from the group consisting of MOK2630, MOK2637, SNP B, and SNP D can be used as markers for diagnosing whether a bovine animal is affected by forelimb-girdle muscular anomaly or whether a bovine animal is a carrier of forelimb-girdle muscular anomaly.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA
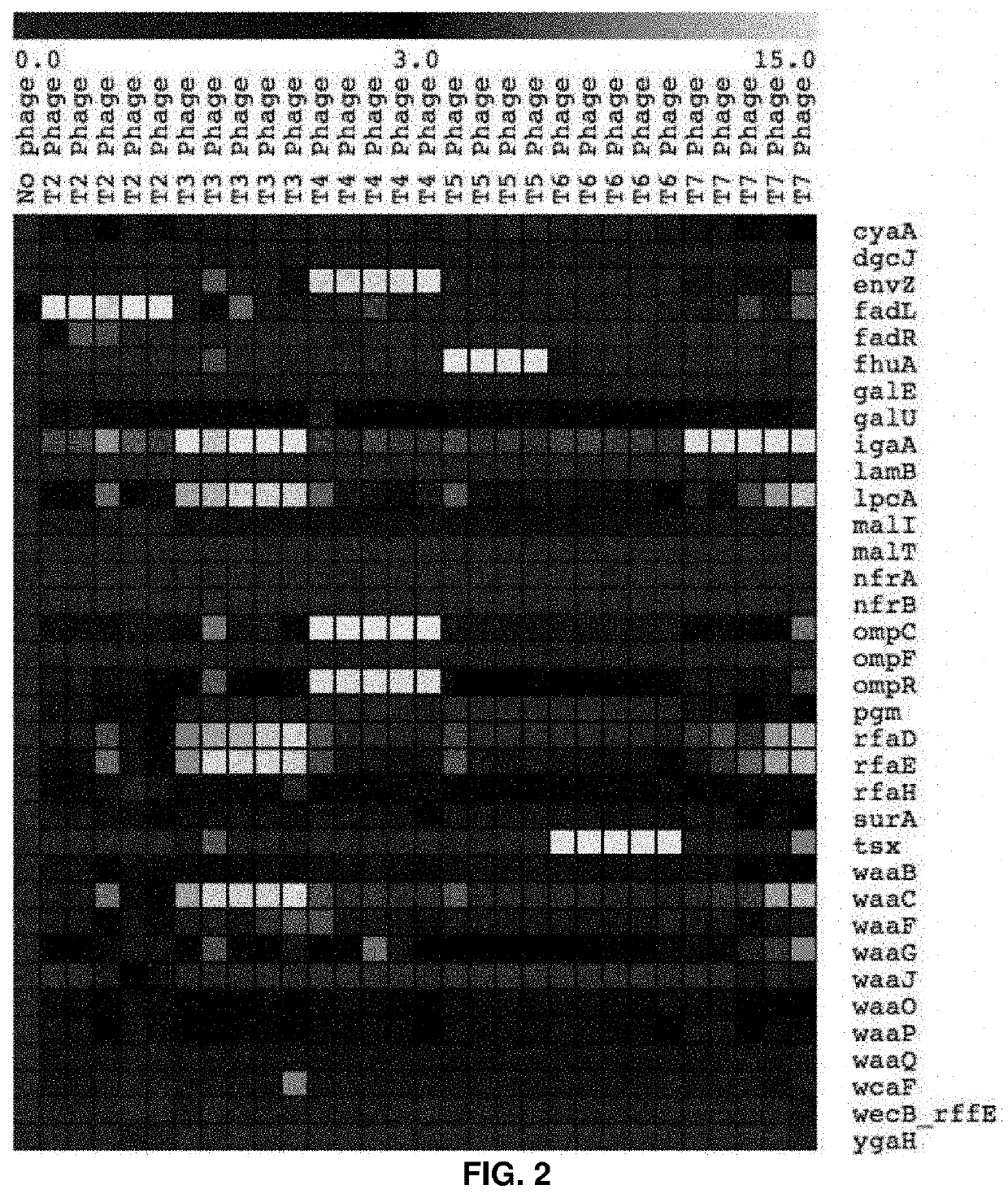
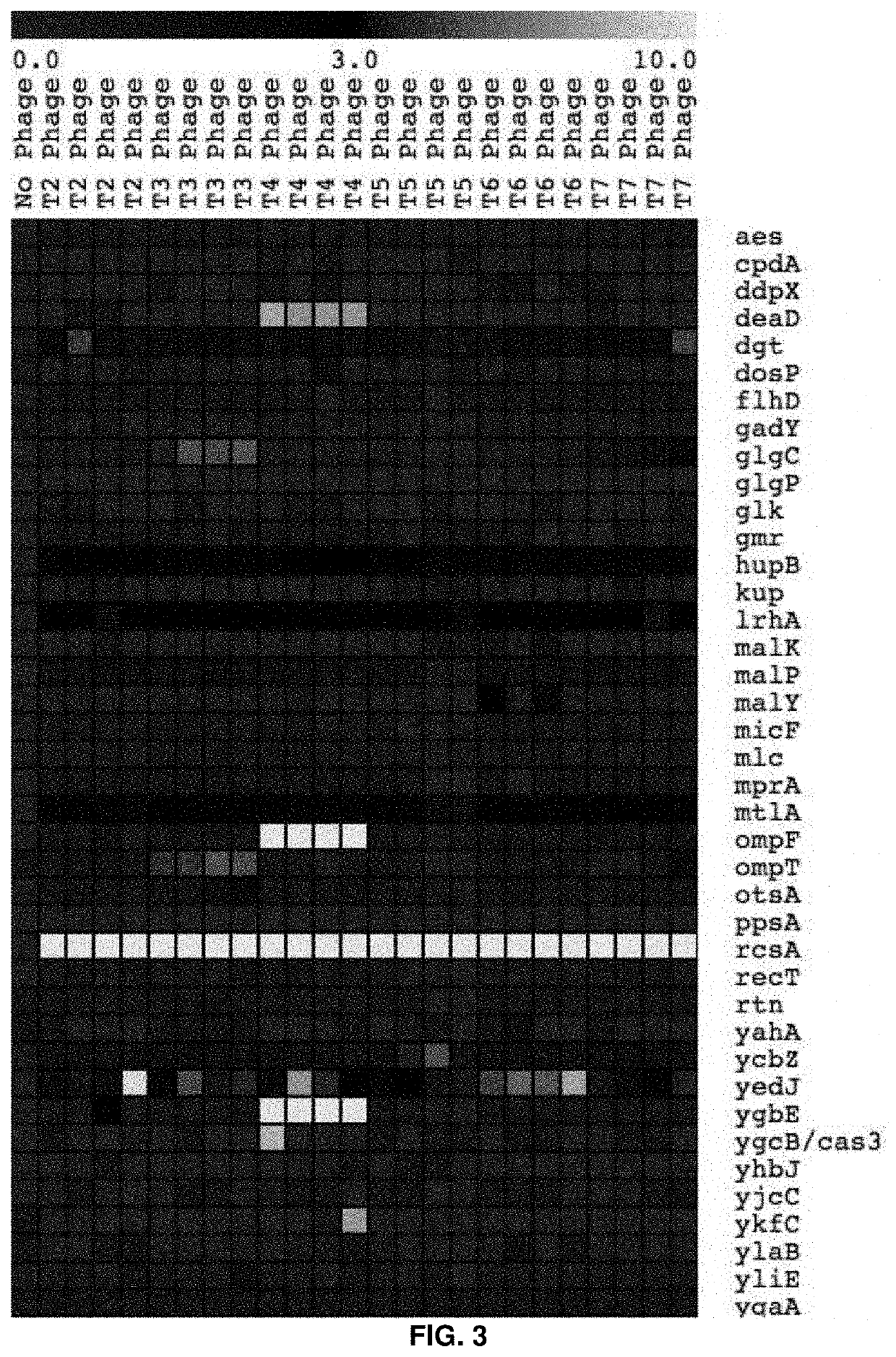
High-throughput methods to characterize phage receptors and rational formulation of phage cocktails
PendingUS20210403995A1Cost-effective and genome-wide assayMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism librariesPhage ReceptorsMutant phenotype
The present invention provides for a method for screening for gene function for a bacteriophage, the method comprising: (1) (a) providing one or more host organism, such as a species or strain, libraries, (b) providing randomly barcoded transposon sequencing (such as RB-TnSeq), and (c) screening for loss-of-function (LOF) mutant phenotypes; or (2) (a) providing one or more DNA barcoded overexpression strain libraries (such as Dub-seq) using DNA of the host organism and / or phage, and (b) screening for gain-of-function (GOF).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Construction method of activation tag carrier and apocynum venetum seed mutant library
ActiveCN109337922AGenetic stabilityOvercome the influence of seed setting rateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgricultural scienceMutant
The invention relate to the technical field of plant genetic breeding, in particular to a construction method of an activation tag carrier and apocynum venetum seed mutant library. Compared with the prior art, a large-scale apocynum venetum mutant seed group can be rapidly obtained through selection of explants, genetic transformation and construction of a regeneration system; an activation tag sequence in the mutant group comprises four series-connected 35s enhancers, activation tags are randomly distributed in the overall apocynum venetum genome, expression of adjacent genes is enhanced, mutants are formed by induction, the produced mutants are in dominant mutation, and lethal effect produced by loss-of-function mutation is avoided.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Biomarkers for response to rapamycin analogs
The present invention relates to the use of one or more biomarkers to evaluate the likelihood that a rapamycin analog would produce an anti-cancer effect in a subject. It is based, at least in part, on the results of experiments employing an integrated next-generation sequencing approach to interrogate spatially separated tumor specimens from the same individuals to decipher intra-tumor and intertumor heterogeneity and determine the oncogenomic basis of exceptional therapeutic benefit to rapalogs in kidney cancer patients. These experiments implicated loss of function mutations in TSC1 and / or TSC2 and / or gain-of-function of mTOR in therapeutic responsiveness to rapamycin analogs. Accordingly, in non-limiting embodiments, the present invention provides for assay methods and kits for determining the presence of loss of function mutations in TSC1 and / or TSC2 and / or gain-of-function of mTOR, and methods of using such determinations in selecting a therapeutic regimen for a cancer patient and in methods of treating cancer patients. In particular non-limiting embodiments, a plurality of tumor sites are evaluated and the composite effect of the genetic background on mTOR function is assessed.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
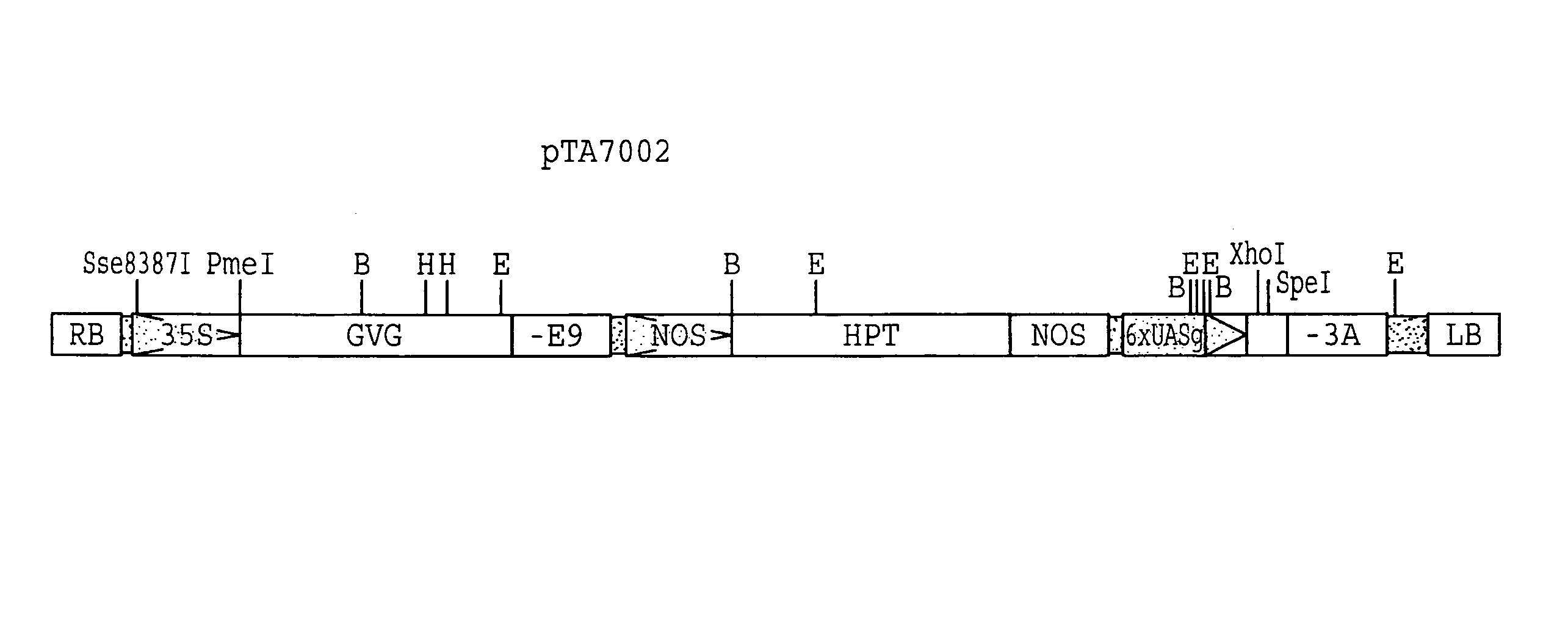
Chemical inducible promoter used to obtain transgenic plants with a silent marker and organisms and cells and methods of using same for screening for mutations
InactiveUS7230157B1Elevates endogenous levelImprove efficiencyBryophytesSugar derivativesGlucocorticoidPlant cell
Disclosed is a chemically inducible promoter for transforming plants or plant cells with genes which are regulatable by adding the plants or cells to a medium containing an inducer or by removing them from such medium. The promoter is inducible by a glucocorticoid, estrogen or inducer not endogenous to plants. Such promoters may be used with any plant genes that can promote shoot regeneration and development to induce shoot formation in the presence of a glucocorticoid, estrogen or inducer. The promoter may be used with antibiotic or herbicide resistance genes or other genes which are regulatable by the presence or absence of a given inducer. Also presented are organisms or cells comprising a gene wherein the natural promoter of the gene is disrupted and the gene is placed under the control of a transgenic inducible promoter. These organisms and cells and their progeny are useful for screening for conditional gain of function and loss of function mutations.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Methods for the diagnosis and the treatment of familial thoracic aortic aneurysms caused by tgfb2 loss of function mutations
InactiveUS20150133381A1Good curative effectLow toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProphylactic treatmentLoss of function mutation
The present invention relates to methods for the diagnosis and the treatment of familial thoracic aortic aneurysms caused by TGFB2 loss of function mutations. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for determining whether a subject is predisposed to thoracic aortic aneurysms comprising detecting a TGFB2 loss of function mutation wherein the presence of the mutation indicated that the subject is predisposed to thoracic aortic aneurysms. The present invention also relates to a transforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-β2) polypeptide for use in the prophylactic treatment of a subject who has been considered as predisposed to thoracic aortic aneurysms by the method of the invention (i.e. a subject having one TGB2 loss of function mutation according to the invention).
Owner:UNIV VERSAILLES SAINT QUENTIN EN YVELINES +5
Method for determination of a potential mutation
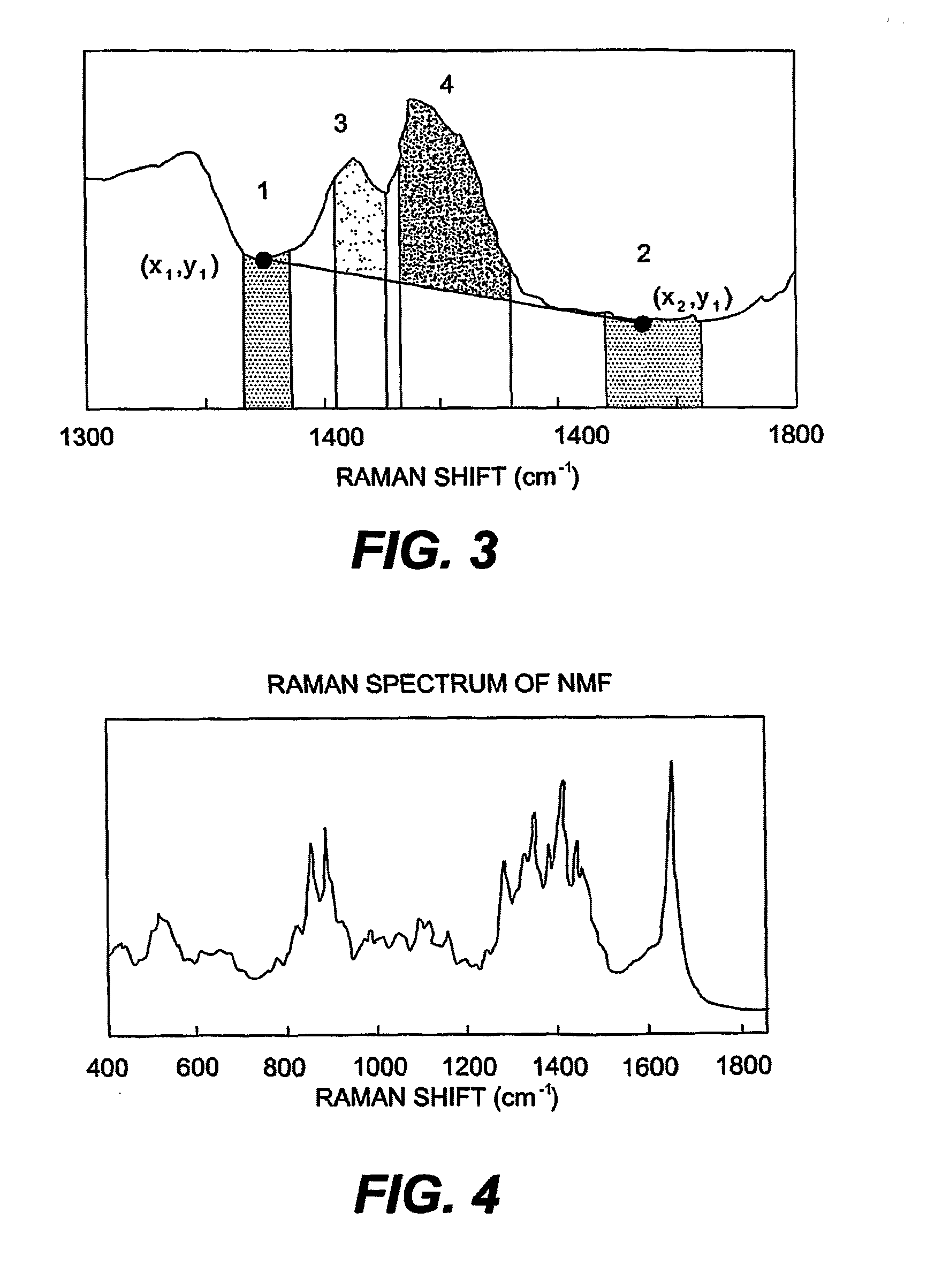
The invention is directed to a method for non-invasive determination of the potential presence of one or more loss-of-function mutation(s) in the gene encoding for filaggrin.The method of the invention comprises(i) obtaining a vibrational spectrum from the stratum corneum of the individual;(ii) determining the local natural moisturising factor content from the vibrational spectrum;(iii) optionally repeating steps (i) and (ii); and(iv) comparing the local natural moisturising factor content of the individual to a reference value,wherein said stratum corneum is stratum corneum of a location of the body of said individual at which said one or more loss-of-function mutation(s) in the gene encoding for filaggrin has a stronger influence on the natural moisturising factor concentration than other factors influencing the natural moisturising factor concentration.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Biomarkers for response to rapamycin analogs
The present invention relates to the use of one or more biomarkers to evaluate the likelihood that a rapamycin analog would produce an anti-cancer effect in a subject. It is based, at least in part, on the results of experiments employing an integrated next-generation sequencing approach to interrogate spatially separated tumor specimens from the same individuals to decipher intra-tumor and intertumor heterogeneity and determine the oncogenomic basis of exceptional therapeutic benefit to rapalogs in kidney cancer patients. These experiments implicated loss of function mutations in TSC1 and / or TSC2 and / or gain-of-function of mTOR in therapeutic responsiveness to rapamycin analogs. Accordingly, in non-limiting embodiments, the present invention provides for assay methods and kits for determining the presence of loss of function mutations in TSC1 and / or TSC2 and / or gain-of-function of mTOR, and methods of using such determinations in selecting a therapeutic regimen for a cancer patient and in methods of treating cancer patients. In particular non-limiting embodiments, a plurality of tumor sites are evaluated and the composite effect of the genetic background on mTOR function is assessed.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Compositions and methods for increasing shelf-life of banana
InactiveUS20200102570A1Reduced activityReduction of activity of proteinHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorBiotechnologyBanana Plant
A banana plant comprising a genome comprising a loss of function mutation in a nucleic acid sequence encoding a component in an ethylene biosynthesis pathway of the banana is provided. Also provides is a method of increasing shelf-life of banana.
Owner:TROPIC BIOSCI UK LTD
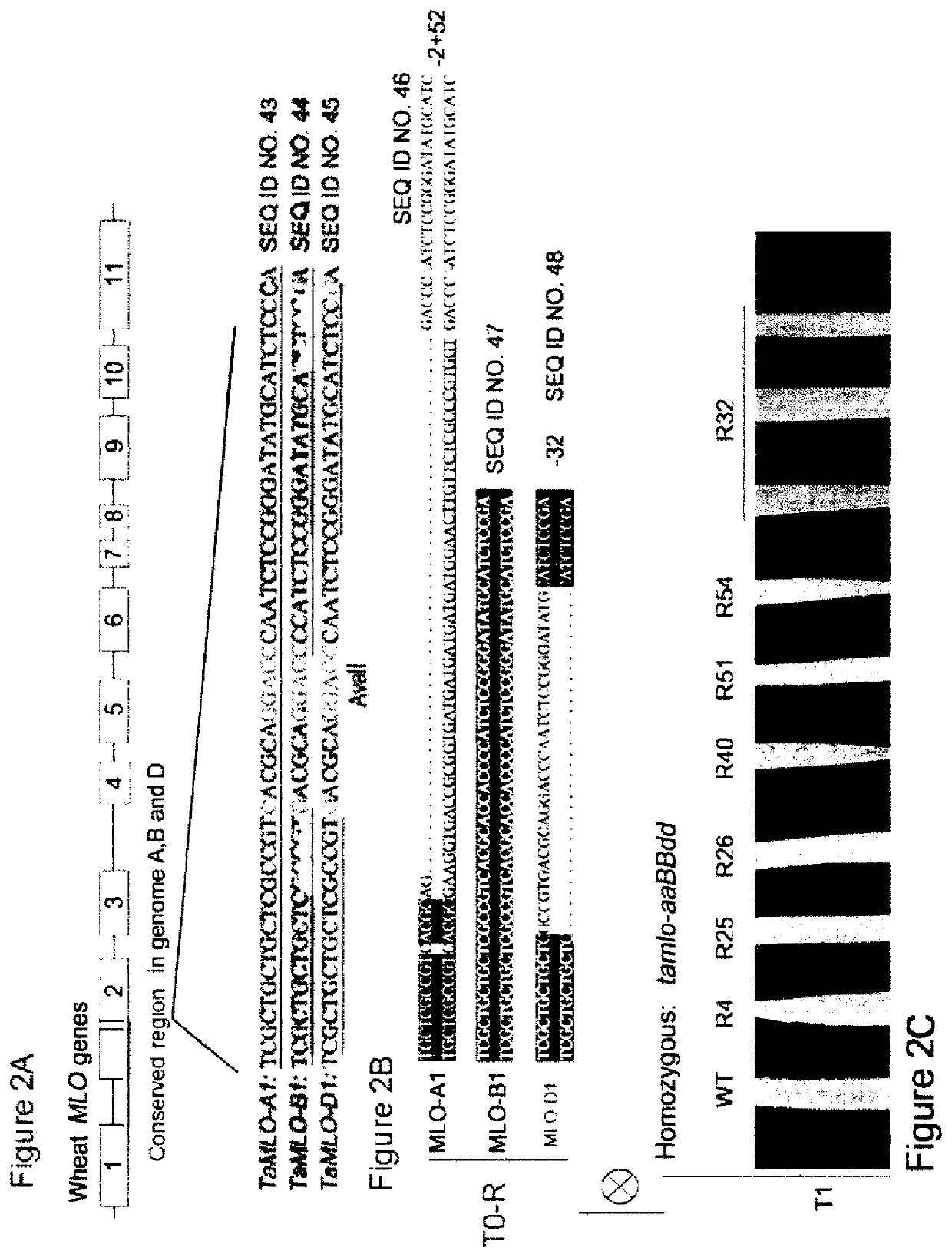
Wheat plants resistant to powdery mildew
ActiveUS10988775B2Vector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGenetics
In one aspect, this disclosure relates to a wheat plant, plant part or plant cell that has increased resistance to powdery mildew, wherein said plant comprises a loss of function mutation in the coding regions of two alleles selected from TaMLO-A1, TaMLO-B1 and TaMLO-D1 and reduced expression of the third TaMLO allele. In another aspect, this disclosure provides a method for producing a wheat plant, plant part or plant cell with increased resistance to powdery mildew, wherein the method comprises using targeted genome modification comprising introducing a loss of function mutation into the coding regions of two MLO alleles selected from TaMLO-A1, TaMLO-B1 and TaMLO-D1 and decreasing expression of the third TaMLO allele.
Owner:SUZHOU QI BIODESIGN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Methods of producing polypeptides using a cell line resistant to apoptosis
PendingCN113631714AGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsAntigenAntigen Binding Fragment
Provided herein are cell lines (e.g., HEK293 cell lines) that comprise a loss-of-function mutation in each of the human Bax and Bak genes, as well as cell cultures comprising the cell lines. The cell lines and / or cell cultures may find use, e.g., in methods for producing a recombinant polypeptide (such as an antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof) or a viral vector.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Dynamic clamps and methods of use thereof
PendingUS20210215665A1Good choiceNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDiseasePhysiology
The present invention provides methods for determining the phenotype (e.g., gain-of-function or loss-of-function) of a mutation in an ion channel or receptor by using a dynamic voltage clamp. The invention also features methods of determining whether a mutation is a gain-of-function or loss-of-function mutation and treating a disease or disorder associated with the particular gain-of-function or loss-of-function mutation.
Owner:THE FLOREY INST OF NEUROSCIENCE & MENTAL HEALTH
Method and kit for detecting risk of colorectal cancer
There is provided a method for determining the risk of colorectal cancer, including a step of detecting a loss-of-function mutation of a gene involved in interleukin (IL)-17 signaling in a colorectal epithelial tissue sample derived from a subject, in which a presence of the loss-of-function mutation indicates that the subject has a high risk of colorectal cancer.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Prevention/treatment of ichthyosis vulgaris, atopy and other disorders
InactiveCN101400697BOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant alleleRead through
The present invention relates to the prevention / treatment of ichthyosis vulgaris (IV), atopy and potentially other disorders associated with loss-of-function mutations in the filaggrin gene sequence. The prevention / therapy is based on the use of agents which enable the host's translational machinery to read through a nonsense mutation found in a mutant allele of the filaggrin gene.
Owner:UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF DUNDEE
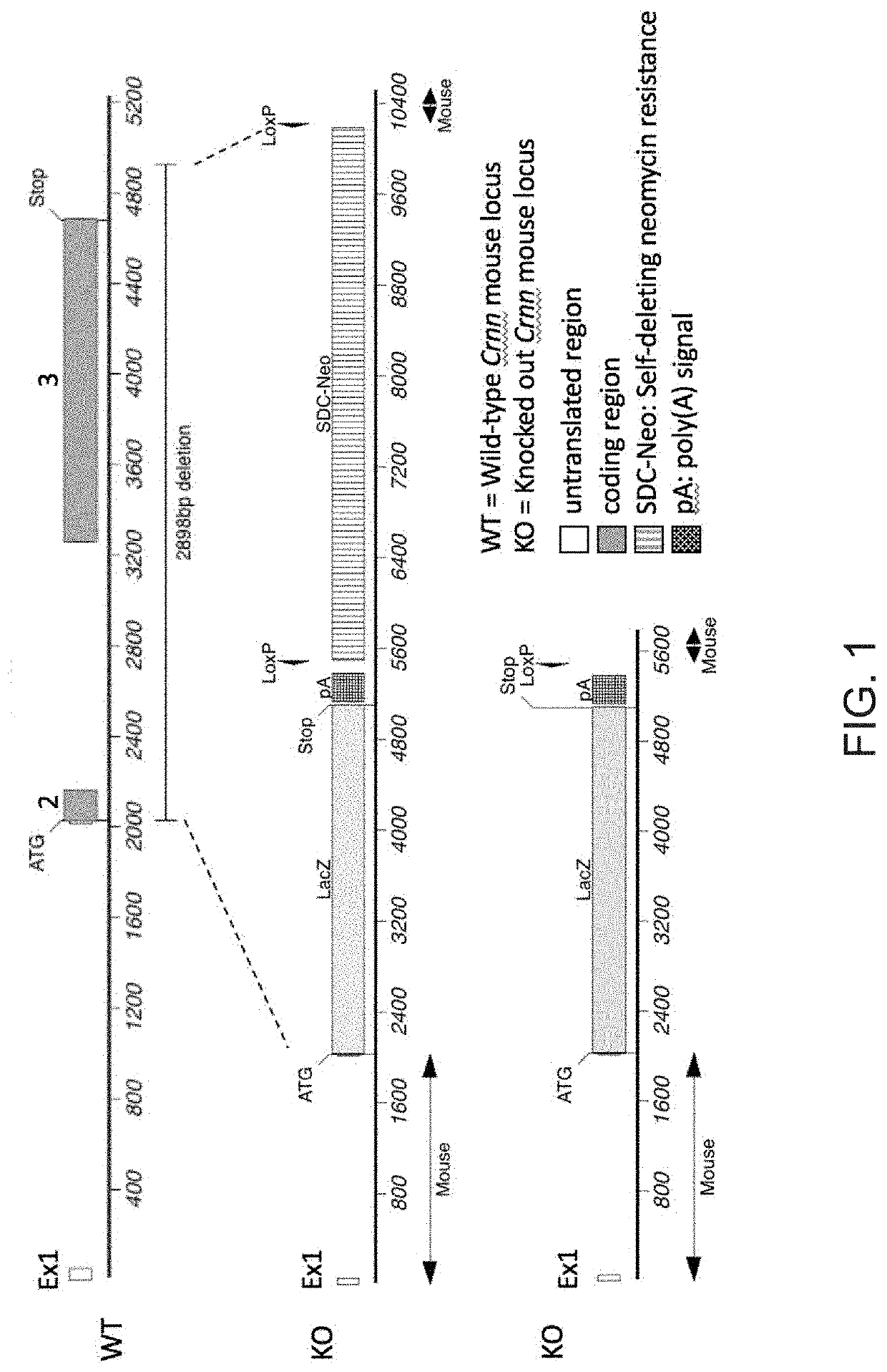
Crnn loss of function rodent model
PendingUS20210100227A1Improve inflammationCompounds screening/testingAnimals/human peptidesDiseaseAnimal science
This disclosure relates to a genetically modified rodent and use thereof as a rodent model. More specifically, this disclosure relates to rodent (e.g., mouse or rat) comprising a loss of function mutation in an endogenous Crnn (cornulin) gene, and to use of such a rodent animal as a rodent model of skin inflammation disorders (e.g., psoriasis),
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Parthenocarpic plants and methods of producing same
A Solanaceous plant exhibiting a facultative parthenocarpy is provided. The plant comprises a loss-of-function mutation in a SlAGL6 gene and alternatively or additionally characterized by an average fruit weight / plant at least about the same as that of a non-parthenocarpic tomato of the same genetic background under fertilization permissive conditions of the non-parthenocarpic tomato. Also provided are methods of producing such plants and processed products produced from same.
Owner:THE STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG ARO VOLCANI CENT
Ferroportin-1 mutant
A mutant, human ferroportin-1 protein and encoding nucleic acid are provided. The mutant ferroportin-1 protein has a deletion of valine 162 compared to wild-type ferroportin-1 protein. The mutant protein and nucleic acid may be useful in detection of a predisposition to iron overload disorders such as haemochromatosis. Furthermore, it is proposed that the valine 162 deletion is a loss-of-function mutation that may underlie iron overload disorders such as haemochromatosis. Therefore, methods of both diagnosis and treatment of haemochromatosis are provided.
Owner:COUNCIL OF THE QUEENSLAND INST OF MEDICAL RES
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com