Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Latency (audio)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
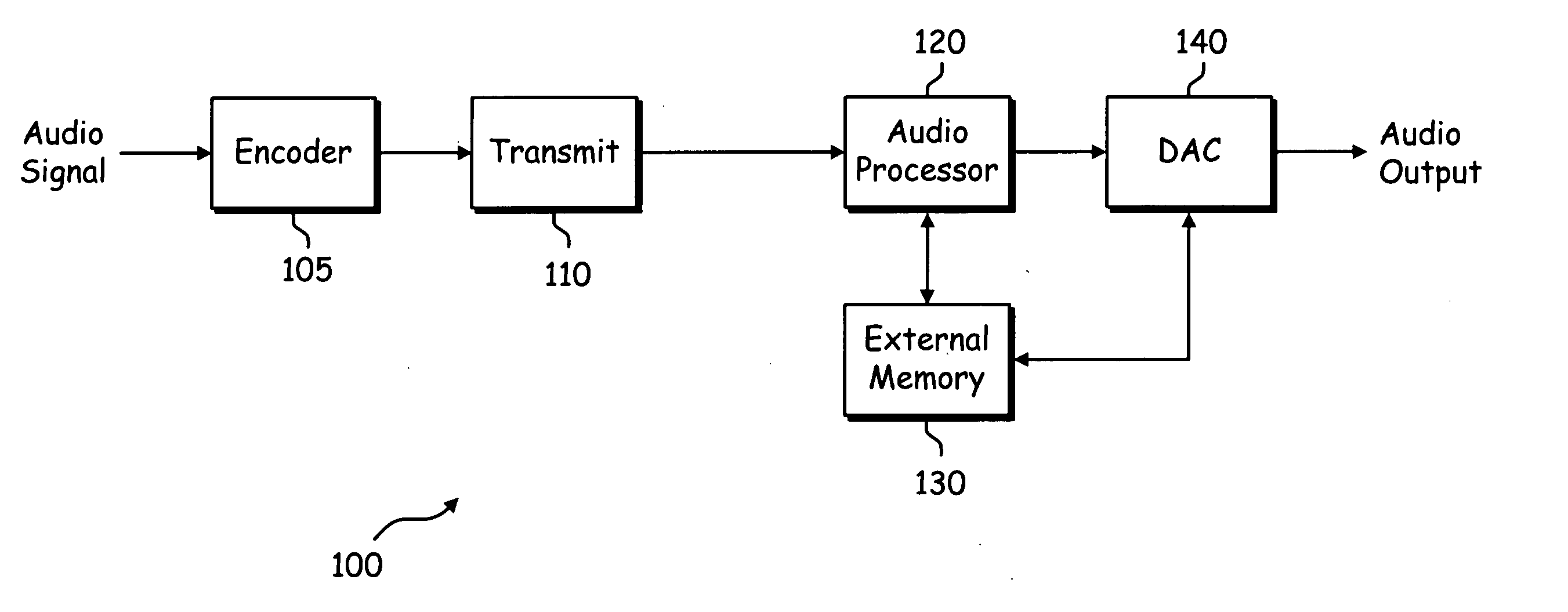
Latency refers to a short period of delay (usually measured in milliseconds) between when an audio signal enters a system and when it emerges. Potential contributors to latency in an audio system include analog-to-digital conversion, buffering, digital signal processing, transmission time, digital-to-analog conversion and the speed of sound in the transmission medium.
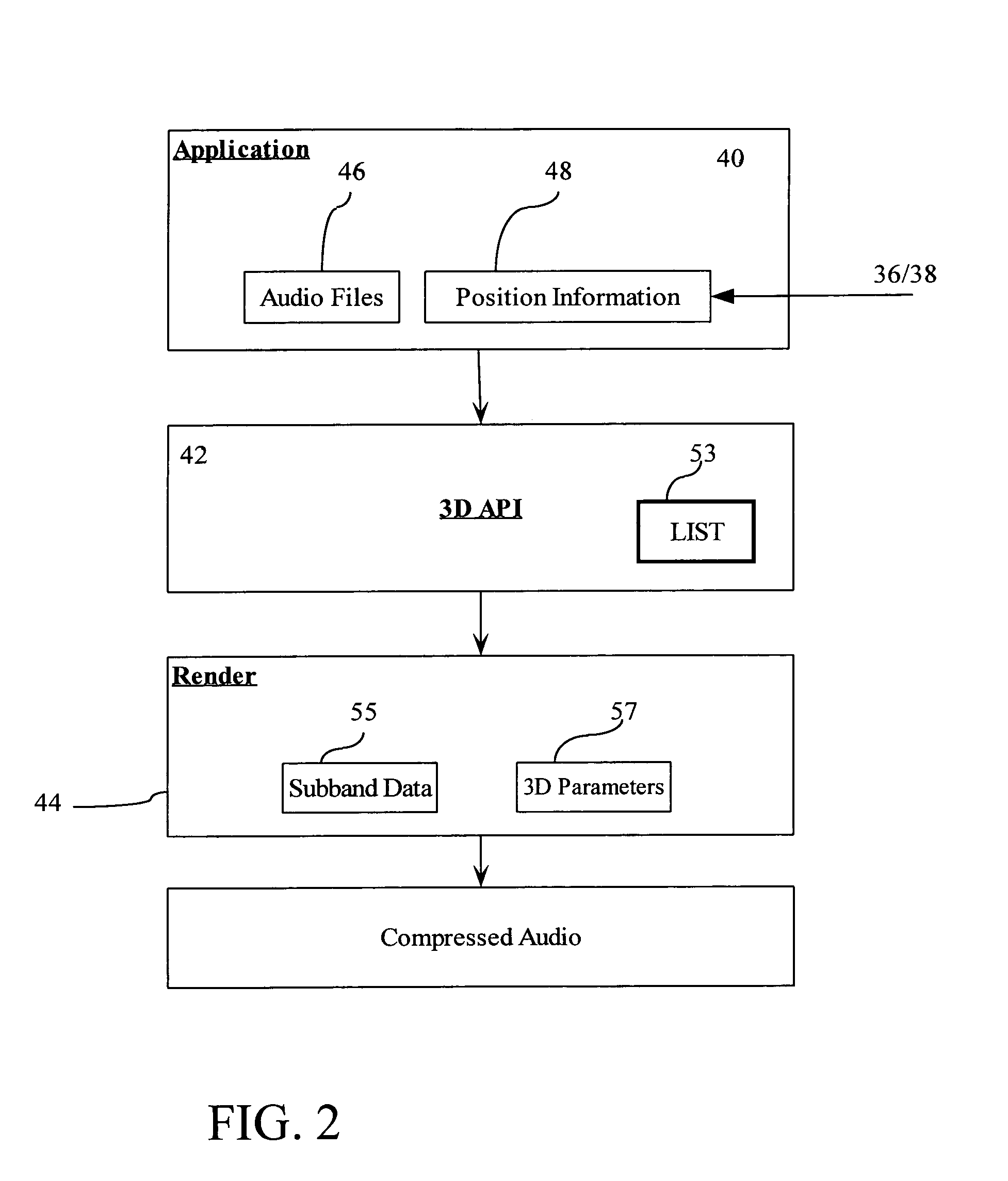
System and method for providing interactive audio in a multi-channel audio environment
InactiveUS6931370B1Low costImprove fidelityFluid pressure measurementPseudo-stereo systemsComputer hardwareVocal tract
DTS Interactive provides low cost fully interactive immersive digital surround sound environment suitable for 3D gaming and other high fidelity audio applications, which can be configured to maintain compatibility with the existing infrastructure of Digital Surround Sound decoders. The component audio is stored and mixed in a compressed and simplified format that reduces memory requirements and processor utilization and increases the number of components that can be mixed without degrading audio quality. Techniques are also provided for “looping” compressed audio, which is an important and standard feature in gaming applications that manipulate PCM audio. In addition, decoder sync is ensured by transmitting frames of “silence” whenever mixed audio is not present either due to processing latency or the gaming application.
Owner:DTS
Zero latency digital assistant
ActiveUS20200319850A1Reducing and eliminating latencyImprove efficiencyInput/output to record carriersDevices with voice recognitionComputer hardwareHuman–computer interaction
An electronic device can implement a zero-latency digital assistant by capturing audio input from a microphone and using a first processor to write audio data representing the captured audio input to a memory buffer. In response to detecting a user input while capturing the audio input, the device can determine whether the user input meets a predetermined criteria. If the user input meets the criteria, the device can use a second processor to identify and execute a task based on at least a portion of the contents of the memory buffer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems, methods and computer-readable media for configuring receiver latency
ActiveCN101731011AGuaranteed to receiveReliable receptionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsAudio frequency
Owner:敖联控股私人有限公司
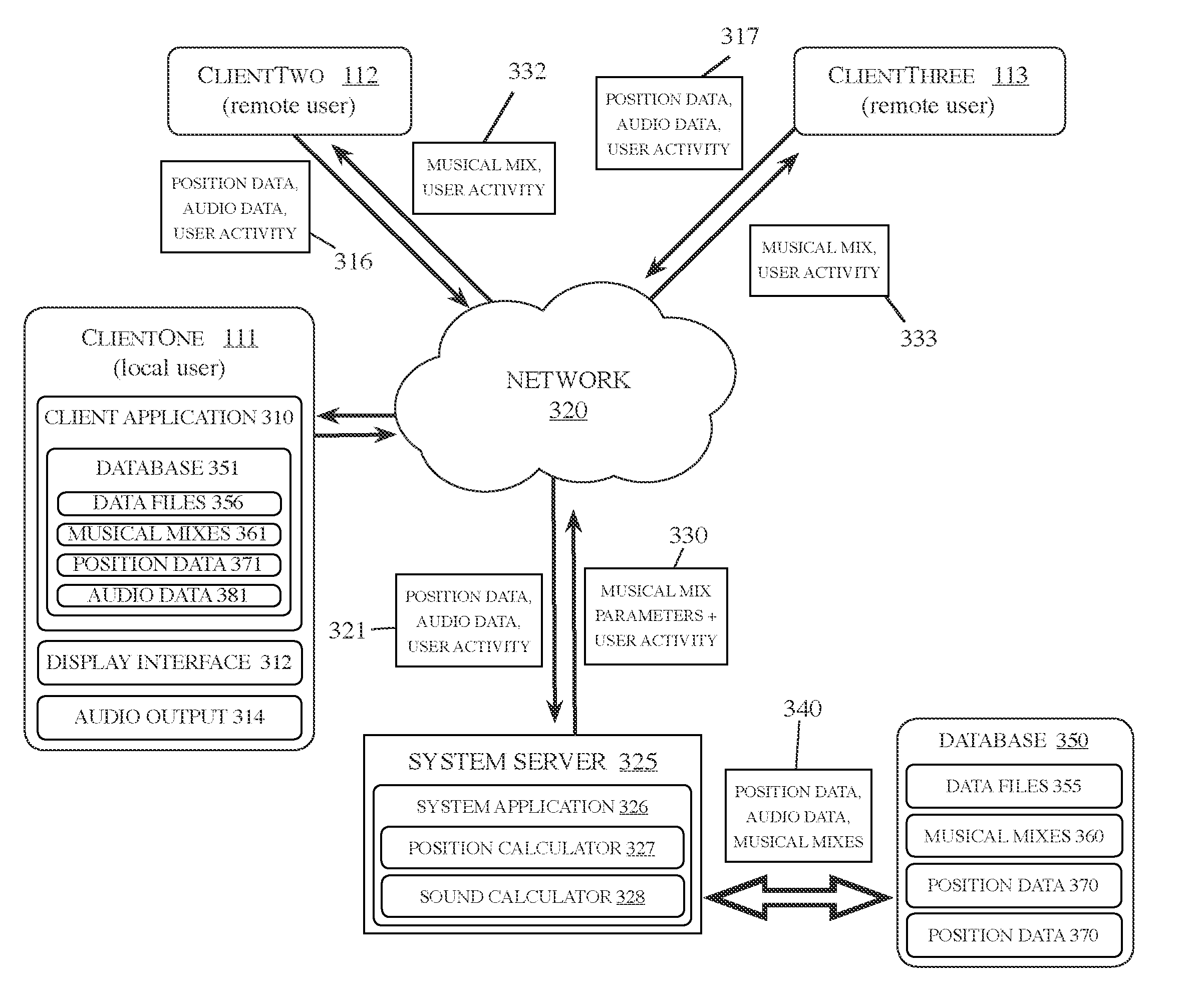
System and method for musical collaboration in virtual space
A system and method for musical collaboration in virtual space is described. This method is based on the exchange of data relating to position, direction and selection of musical sounds and effects, which are then combined by a software application for each user. The musical sampler overcomes latency of data over the network by ensuring that all loops and samples begin on predetermined temporal divisions of a composition. The data is temporarily stored as a data file and can be later retrieved for playback or conversion into a digital audio file.
Owner:PODSCAPE HLDG
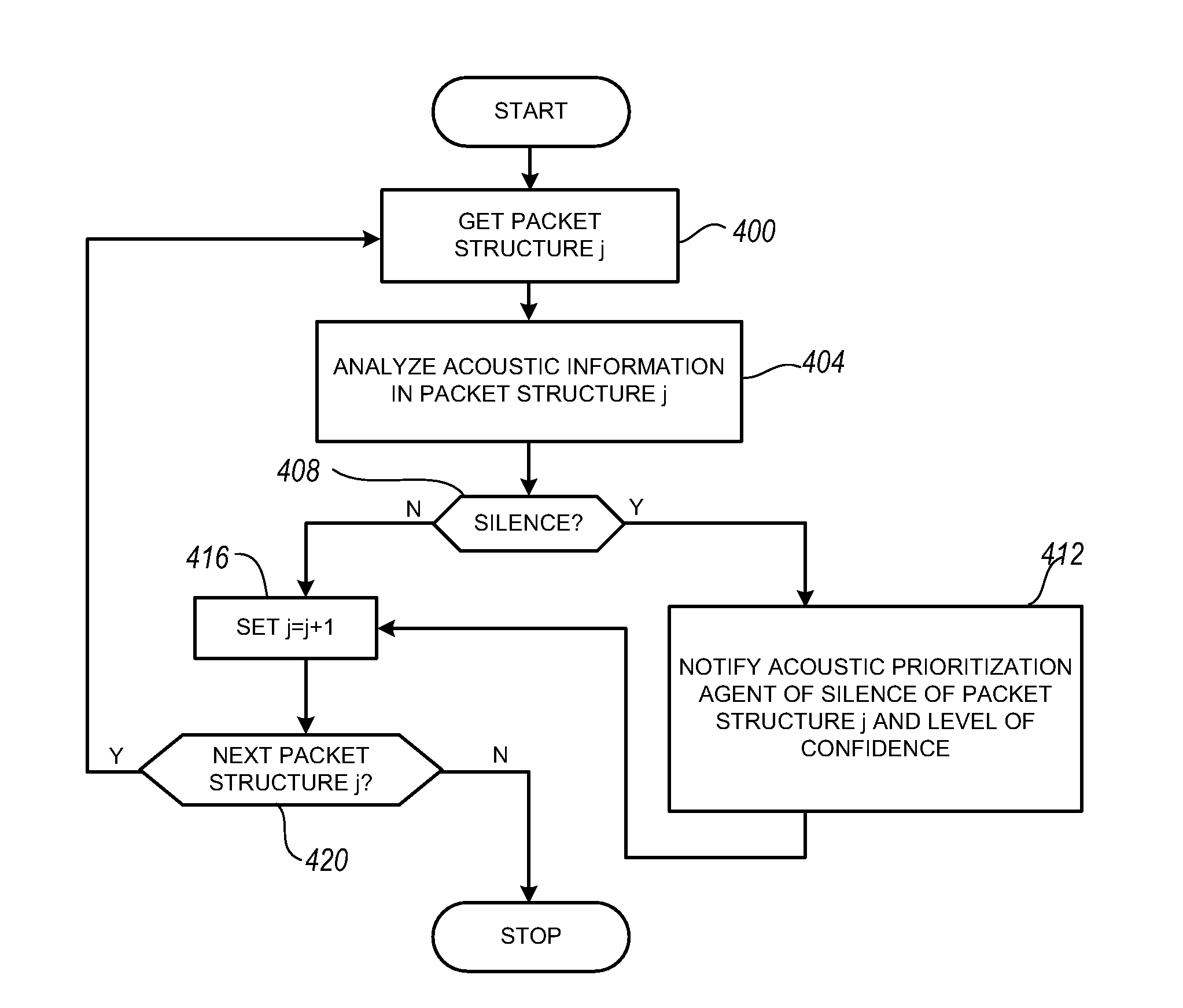
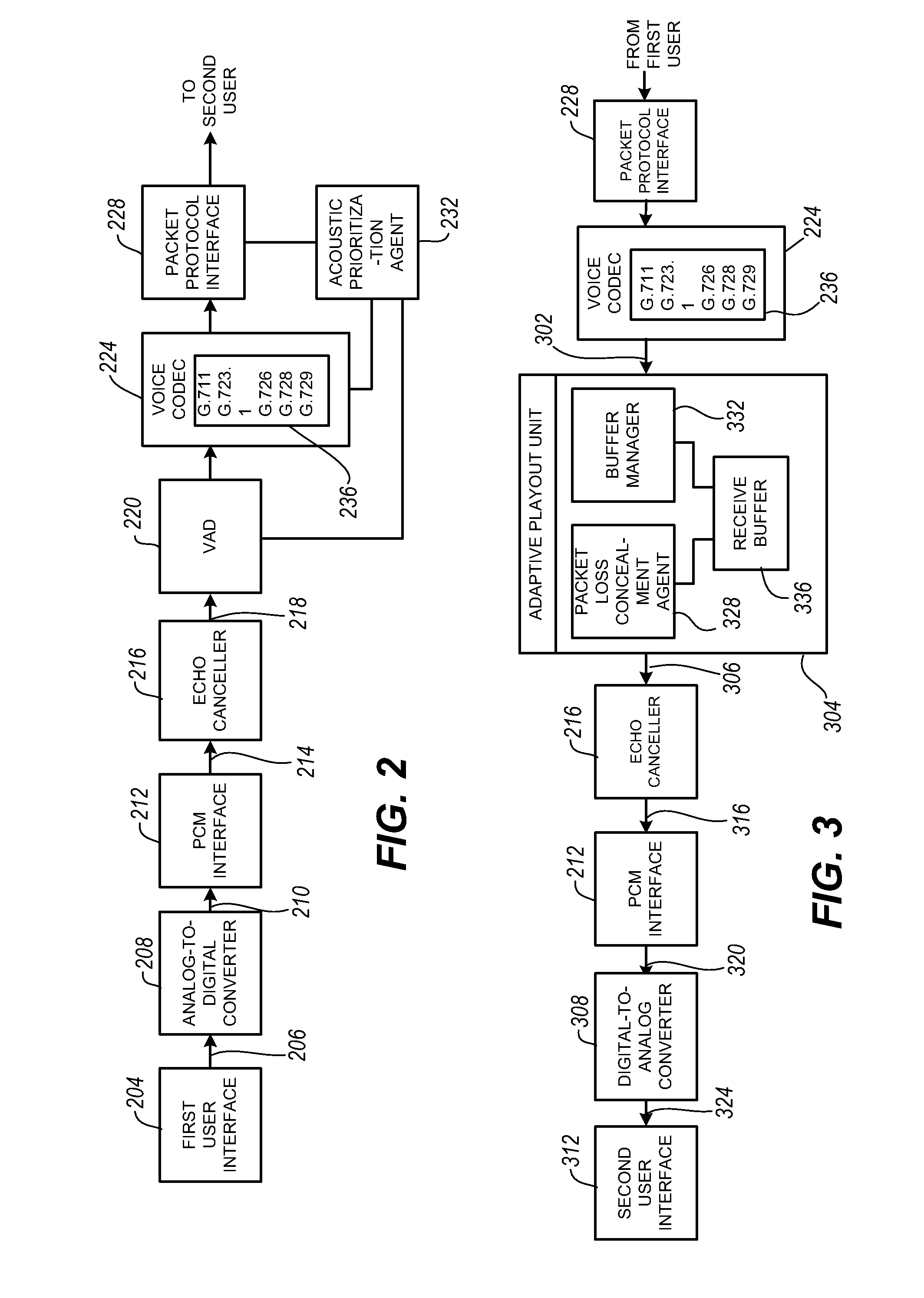
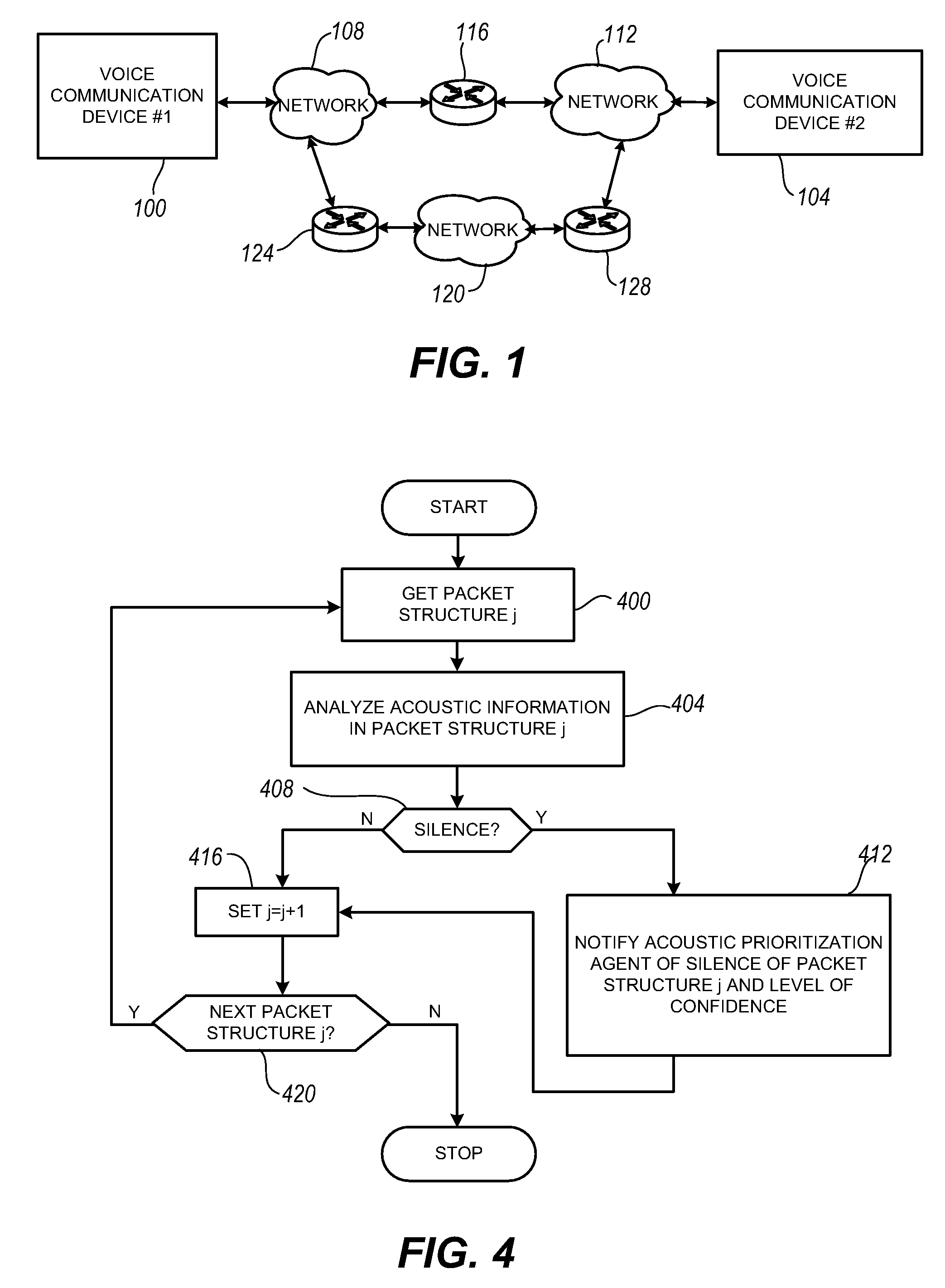
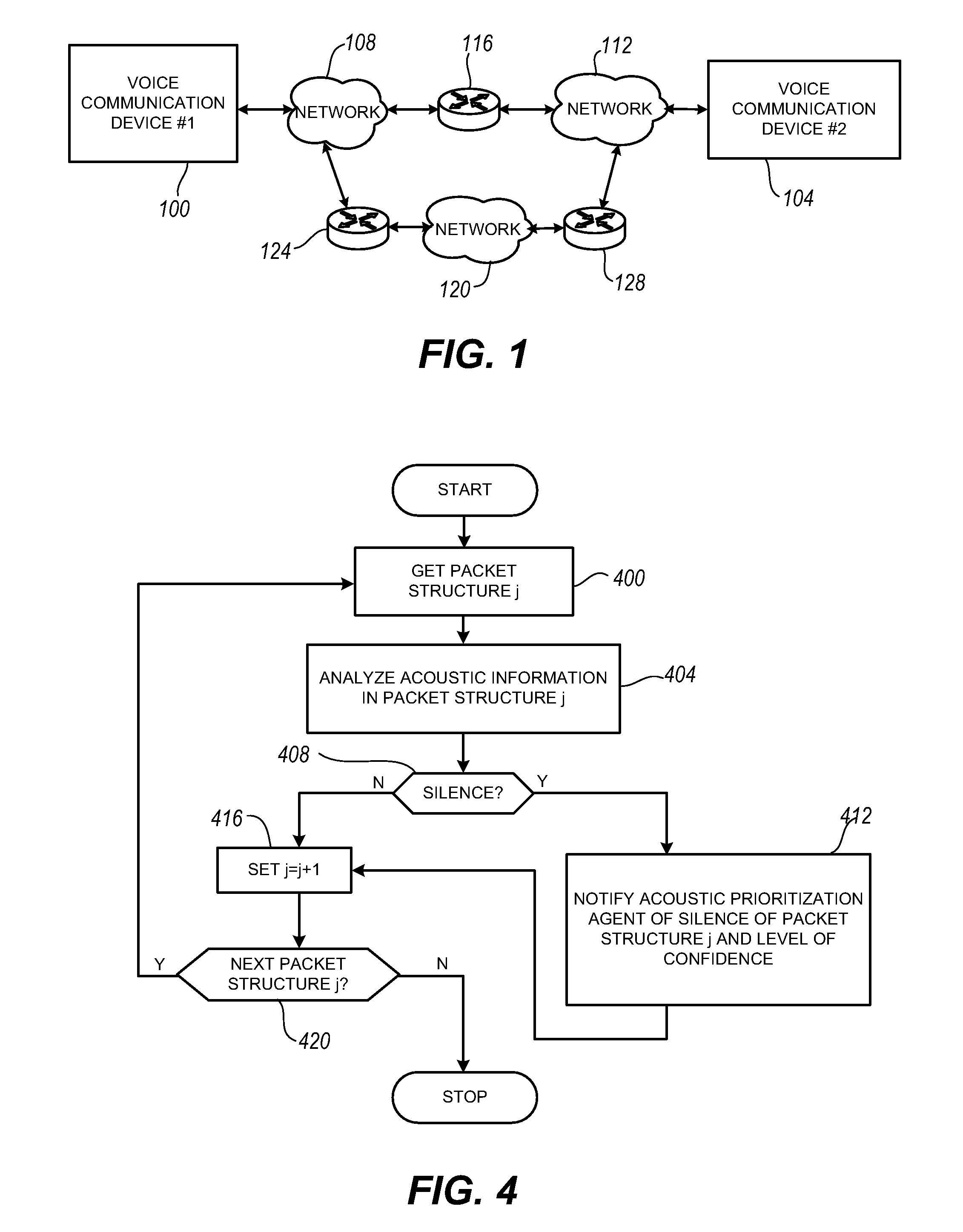
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
InactiveUS20080151921A1Raise priorityReduce the possibilityData switching by path configurationVoice communicationVoice activity
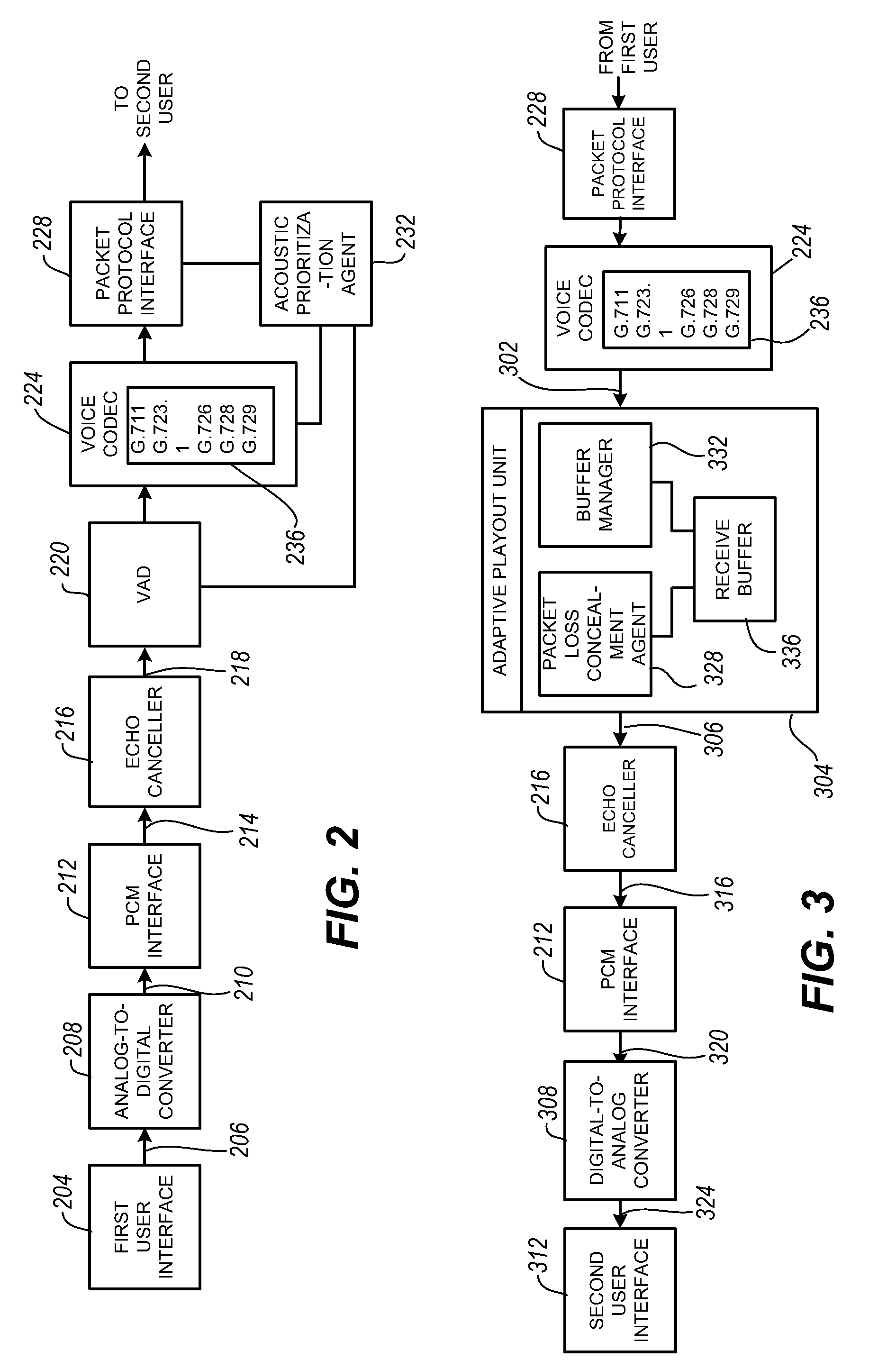
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
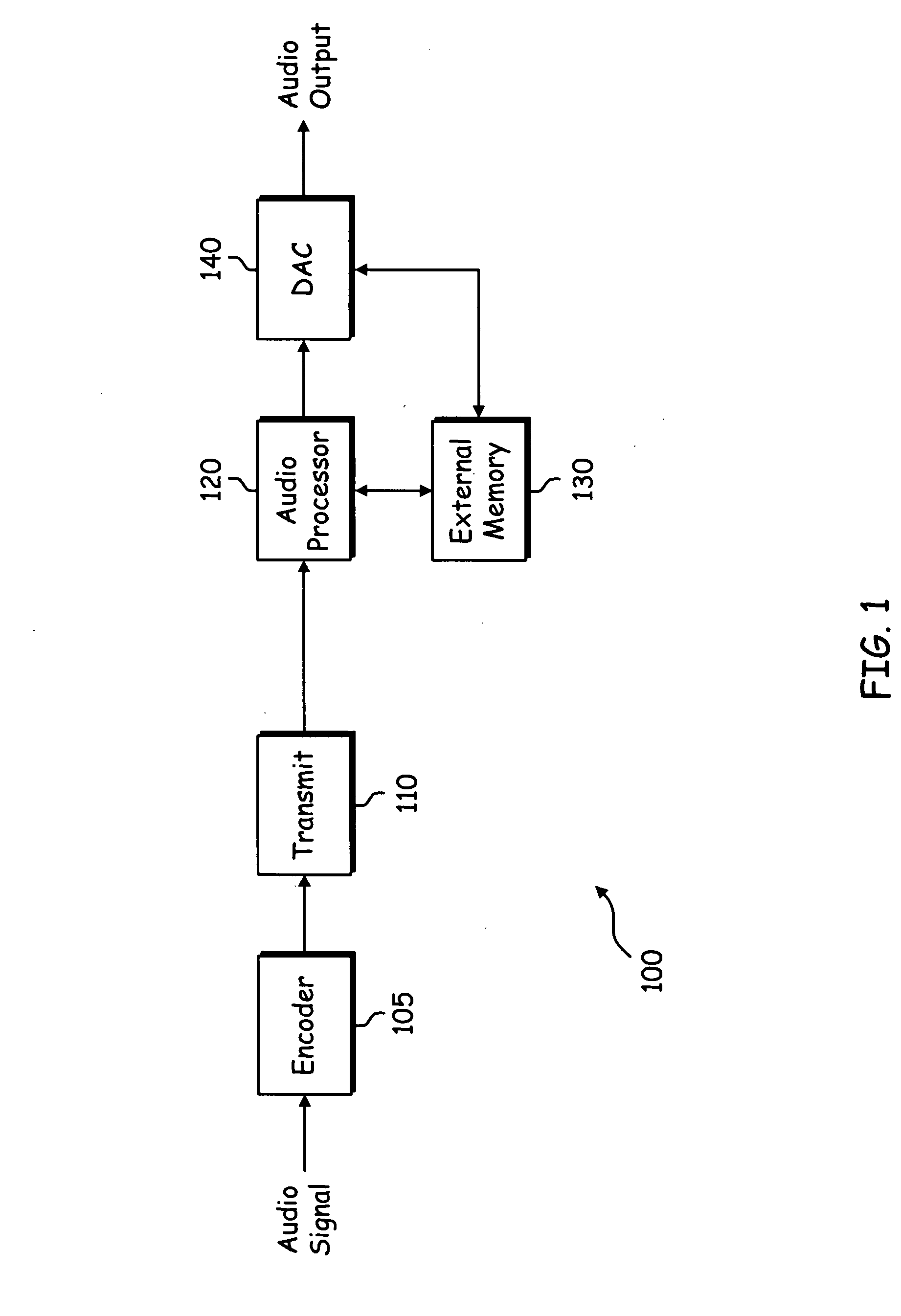
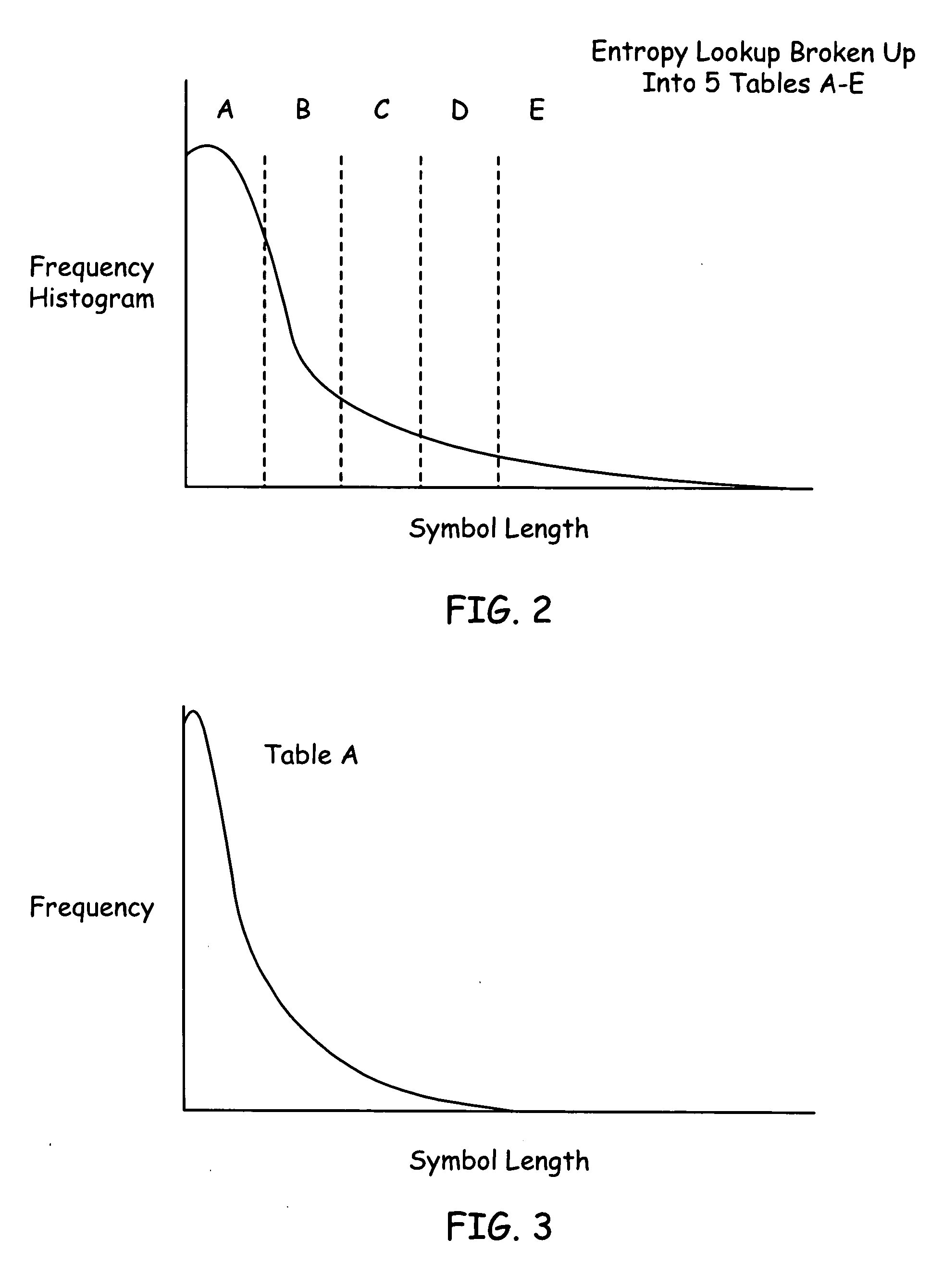
Method and system for memory usage in real-time audio systems
System and method for encoding, transmitting and decoding audio data. Audio bit steam syntax is re-organized to allow system optimizations that work well with memory latency and memory burst operations. Multiple small entropy coding tables are stored in RAM and loaded to on-chip memory as needed. Audio prediction is pipelined in the bitstream syntax. Intra frames, independent of other frames in the bitstream, are included in the bitstream for error recovery and channel change. New algorithms are implemented in legacy syntax by including the new information in the user data space of the audio frame. The new decoder can use projection to determine where the new information is and read ahead in the stream. Audio prediction from the immediately previous frame is restricted. Audio prediction is performed across channels within a single audio frame. A variable re-order function comprises storing channels of data to DRAM in the order they are decoded and reading them out in presentation order.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
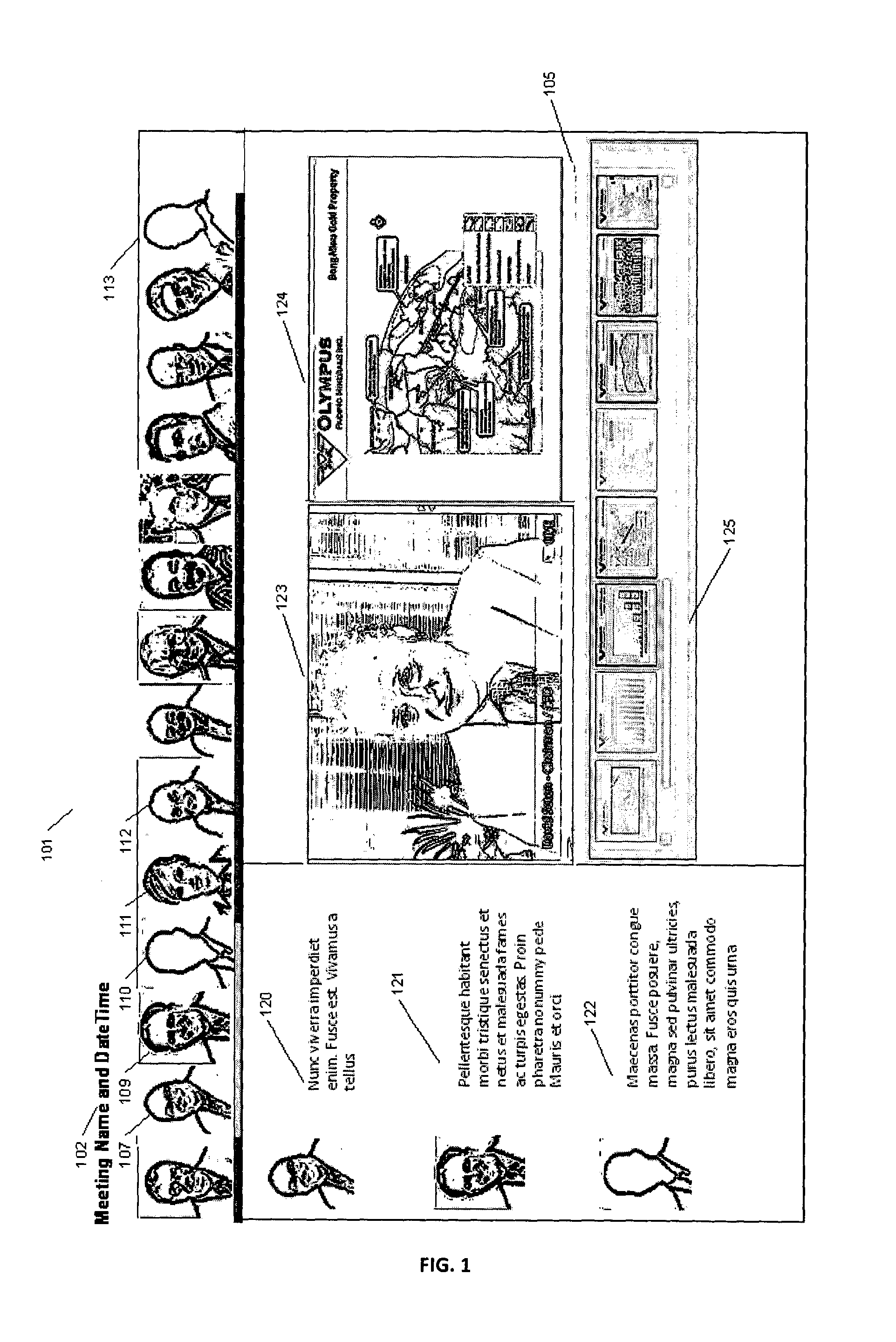
Collaboration extension system
ActiveUS20150002618A1Television conference systemsTwo-way working systemsConference managementManagement system
A meeting management system for managing the conduct of a large meeting online provides the ability to split the online attendees into two classes, those who will actively take part in the meeting or videoconference and who will both receive and provide a video and audio stream, and those who will only receive a video and audio stream. The latter attendees will receive the stream from servers remote from the actual meeting manage system, possibly after the stream has been forwarded through several remote servers and has gained considerable latency. The latency will not be an issue as these attendees have no comparison with the live stream.
Owner:LETS POWOW
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
InactiveUS20080151886A1Raise priorityReduce the possibilityData switching by path configurationVoice communicationVoice activity
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
InactiveUS20080151898A1Raise priorityReduce the possibilityData switching by path configurationPacket loss concealmentReal-time computing
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
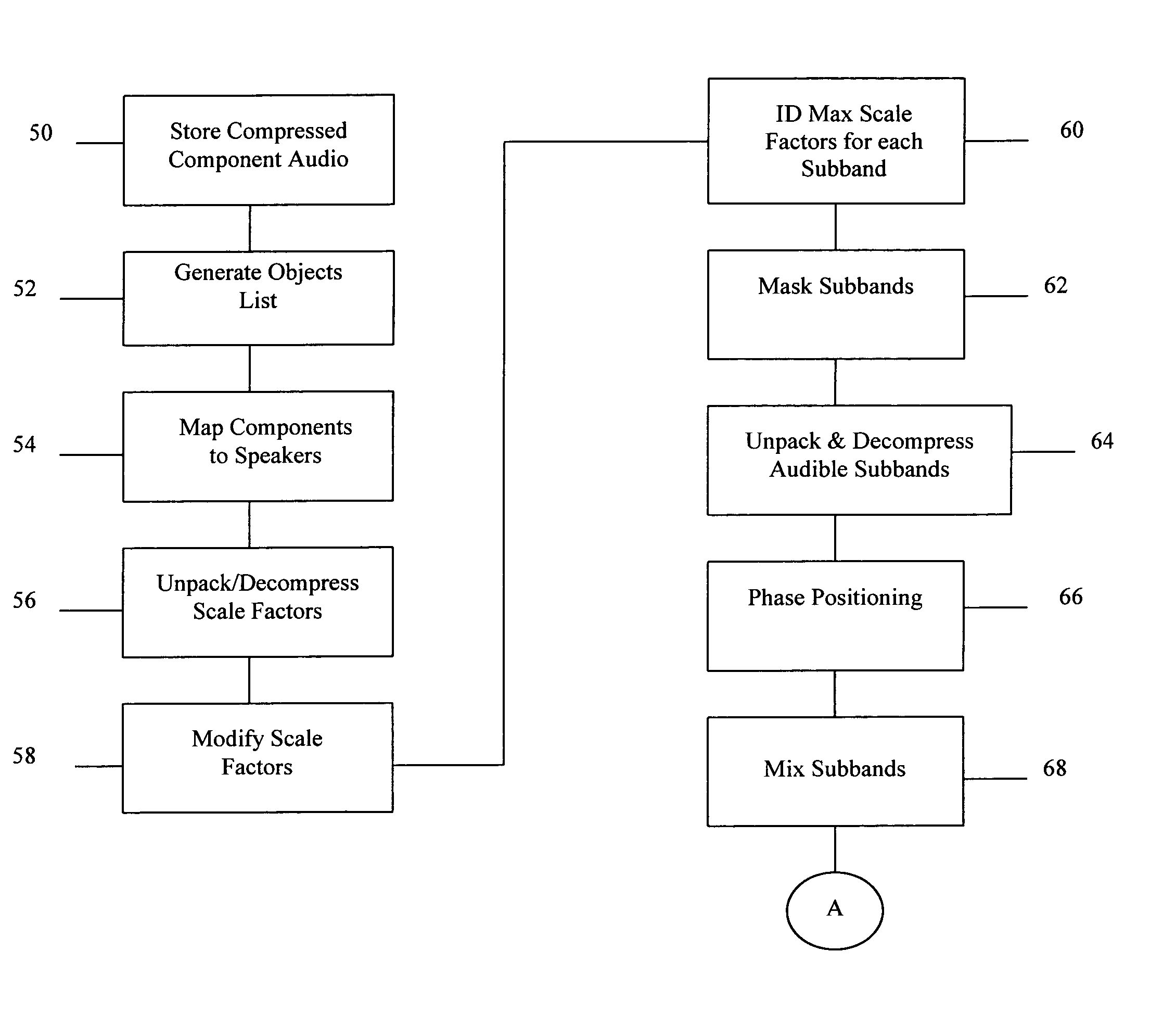
Forward error correction for burst and random packet loss for real-time multi-media communication
ActiveUS8230316B2Flexibility of deploymentEasy to implementError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionPacket lossMissing data
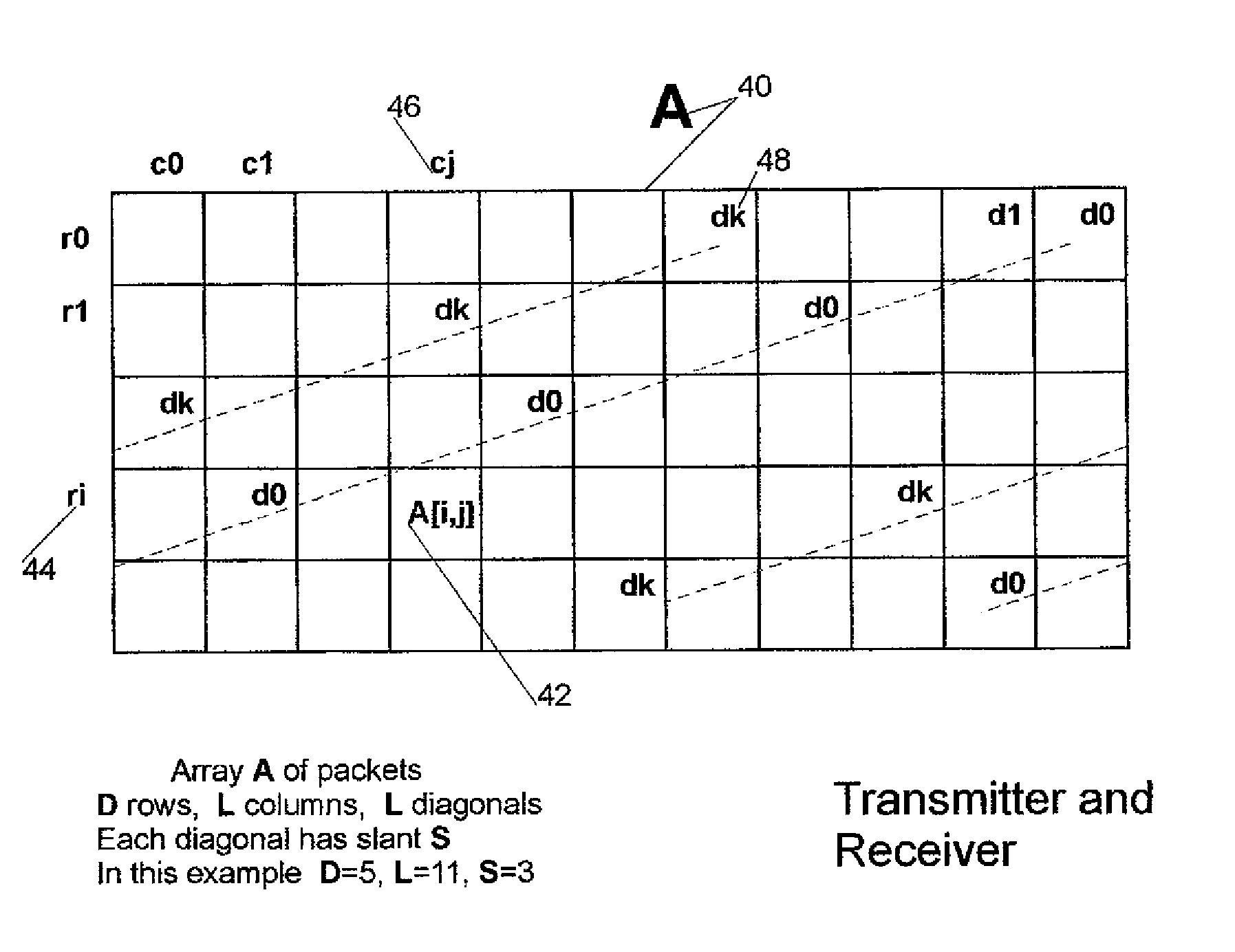
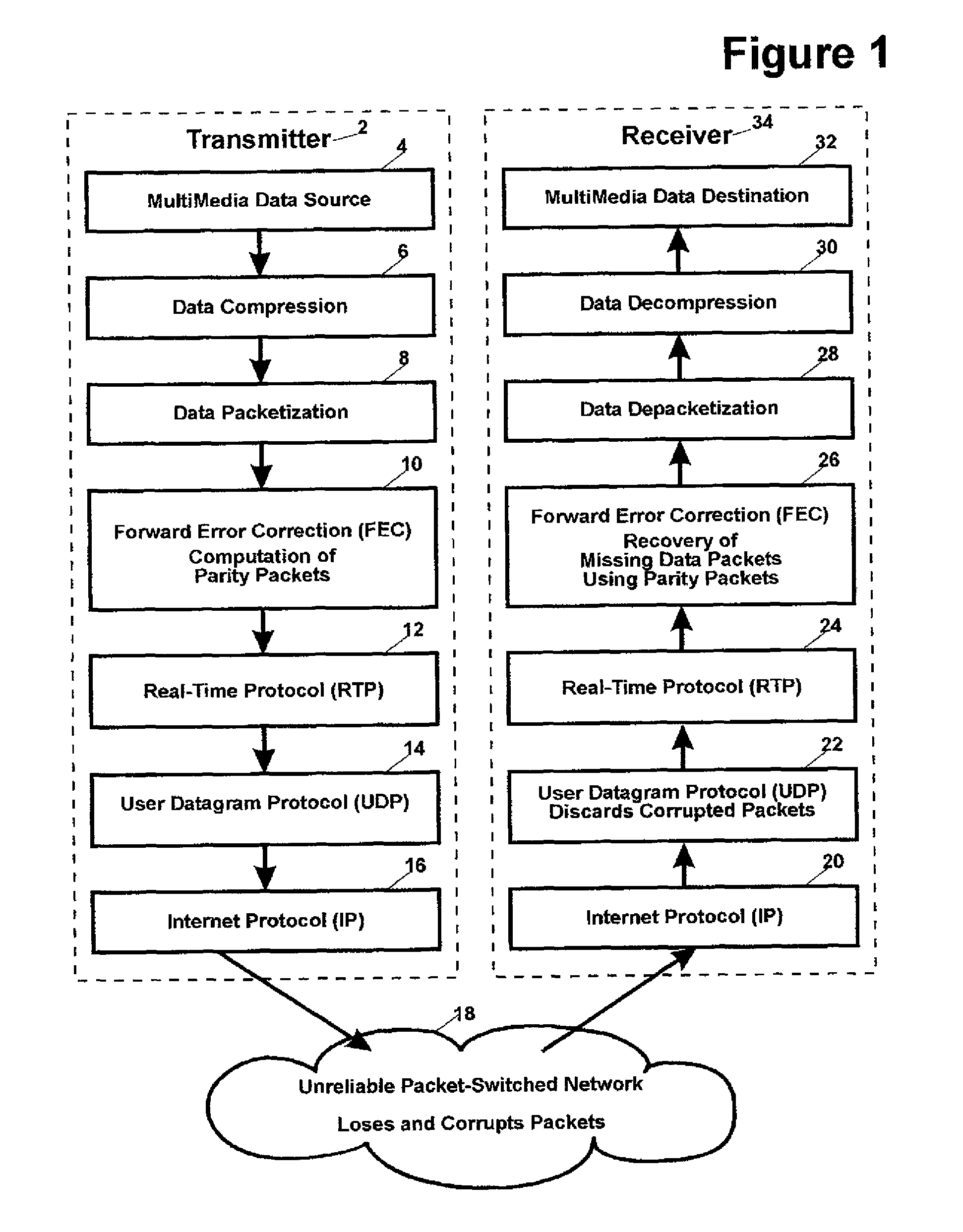
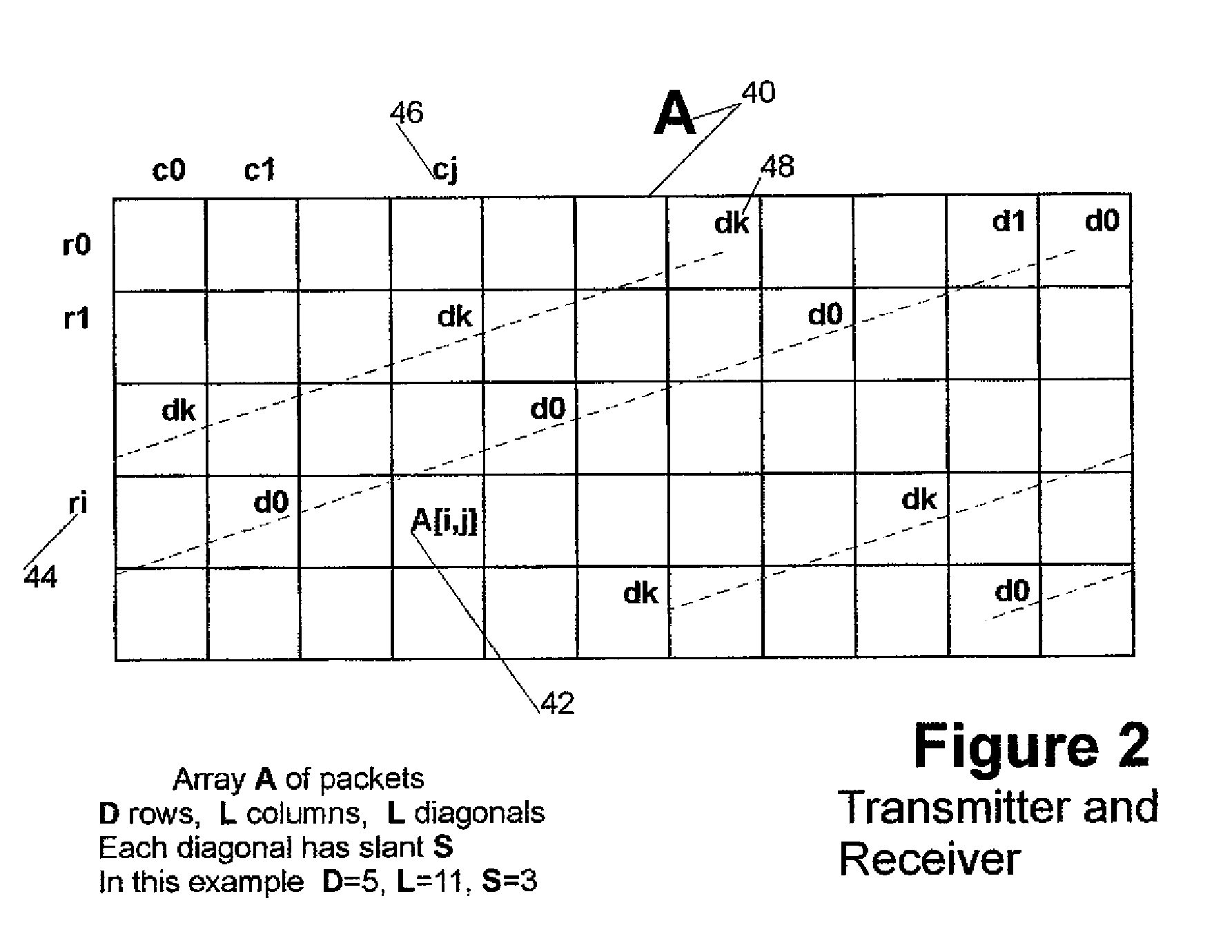
This invention relates generally to a packet recovery algorithm for real-time (live) multi-media communication over packet-switched networks, such as the Internet. Such multi-media communication includes video, audio, data or any combination thereof. More specifically, the invention comprises a forward error correction (FEC) algorithm that addresses both random and burst packet loss and errors, and that can be adjusted to tradeoff the recoverability of missing packets and the latency incurred. The transmitter calculates parity packets for the rows, columns and diagonals of a block of multi-media data packets using the exclusive or (XOR) operation and communicates the parity packets along with the multi-media data packets to the receiver. The receiver uses the parity packets to recover missing multi-media data packets in the block. The FEC algorithm is designed to be able to recover long bursts of consecutive missing data packets. If some parity packets are missing, they too can be recovered using an extra single parity packet, so that they can be used to recover other missing data packets. The invention applies to both one-way real-time streaming applications and two-way real-time interactive applications, and to both wired and wireless networks. The invention retains backwards compatibility with existing standards governing FEC for professional video over IP networks.
Owner:NEVION EURO
Low latency data encoder
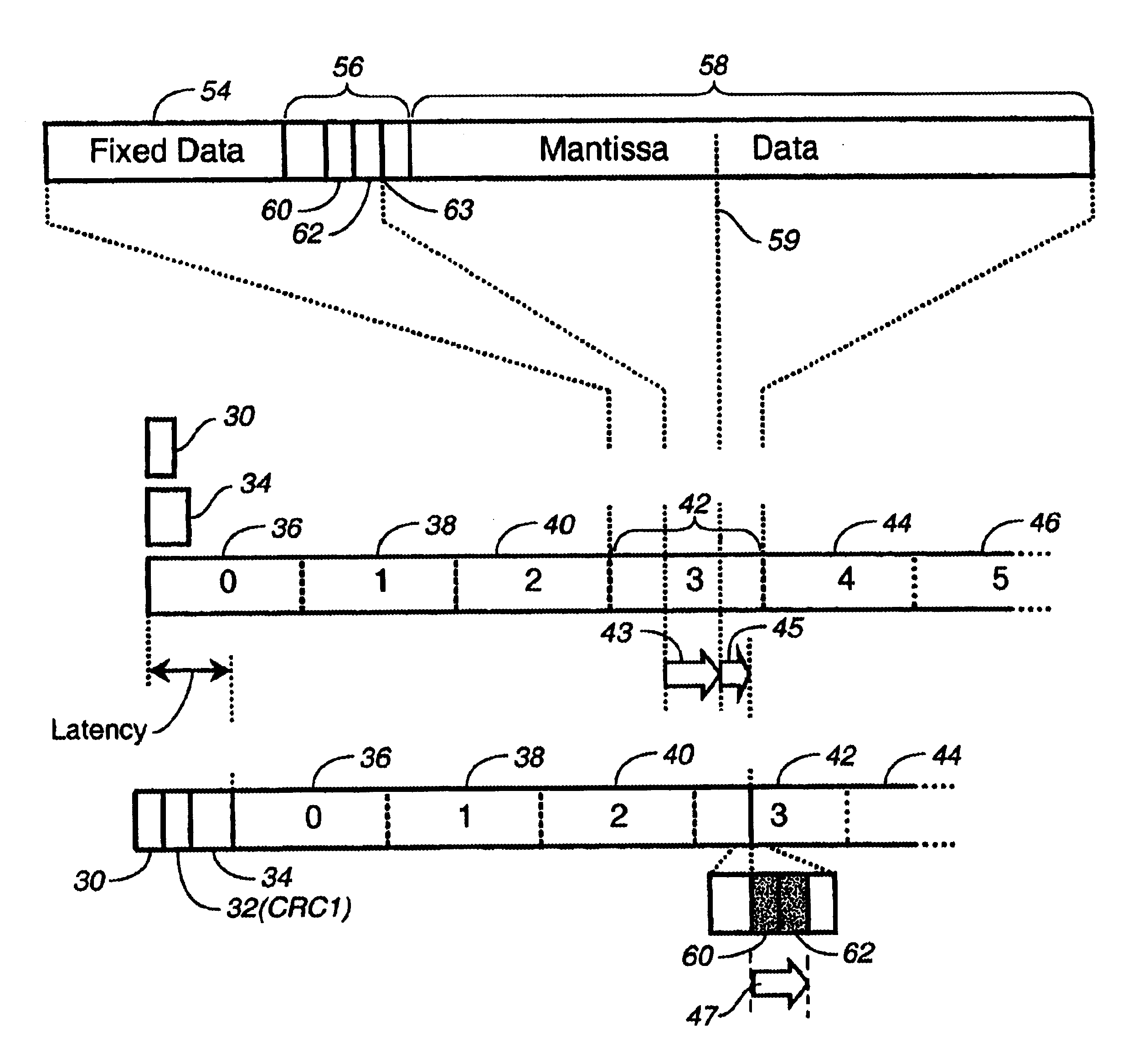
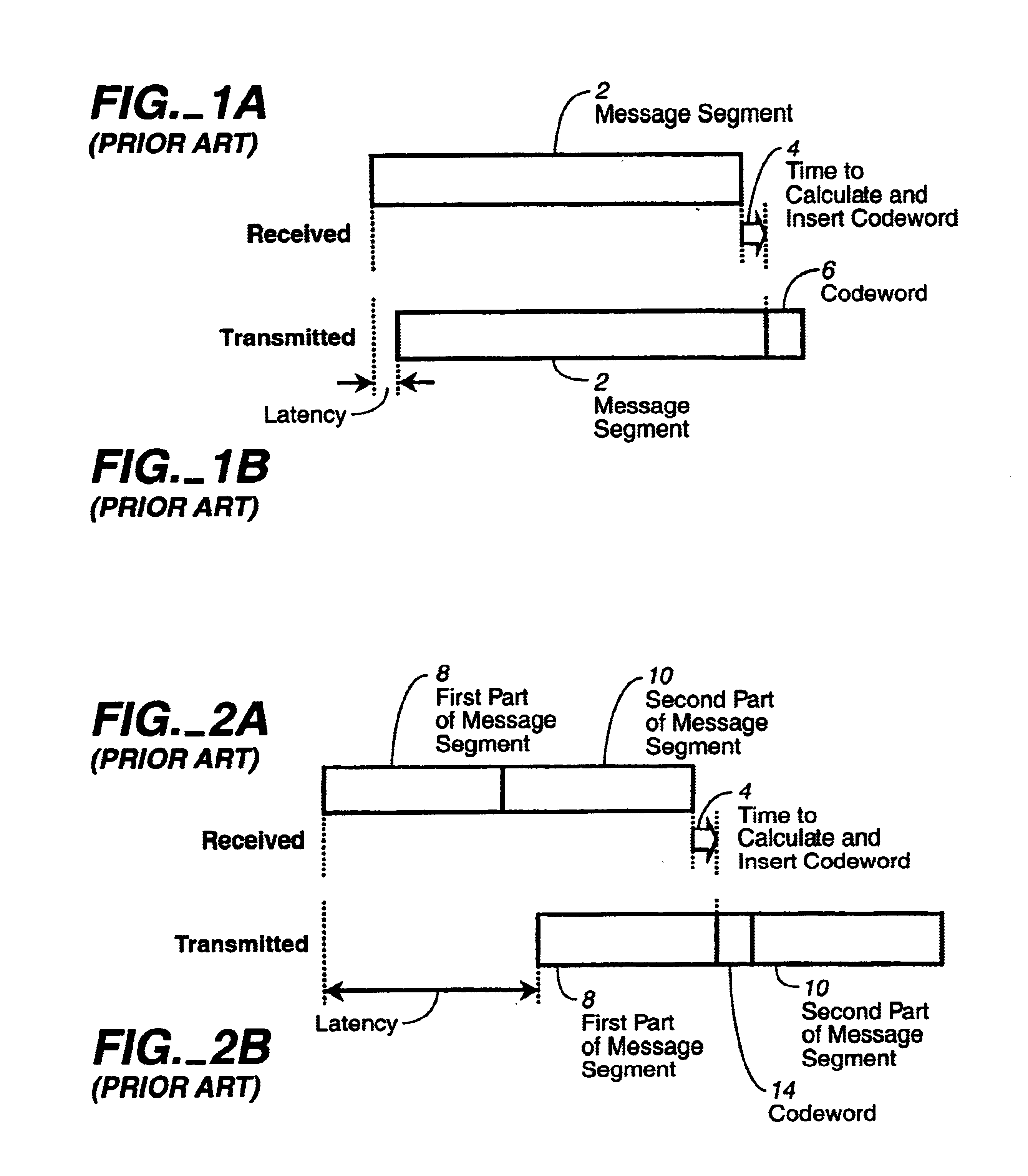
InactiveUS6725412B1Reduce codeword-position-caused latencyPromote lowerSpeech analysisCode conversionAlgorithmLow delay
Codeword-position-caused encoder latency is reduced by avoiding the requirement for knowledge of the message prior to generating an error detecting or concealing codeword associated with the message. A pseudo error detecting or concealing codeword is inserted in place of the normal error detecting or concealing codeword appropriate for the segment of information to which the error detecting or concealing codeword relates. In order to satisfy the requirement of conventional decoders, the pseudo error detecting or concealing information must match or be appropriate for the segment so that the decoder sees the codeword and message segment as valid or error free. This is accomplished by modifying or perturbing at least a portion of the segment to which the pseudo codeword relates. The invention is particularly useful for maintaining the backward compatibility of audio data encoding formats in which the minimum latency is too long (e.g., computer games, where the player performs some operation leading to a sound, and that sound must not be perceptibly delayed with respect to the operation).
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
System and method to assist synchronization of distributed play out of content
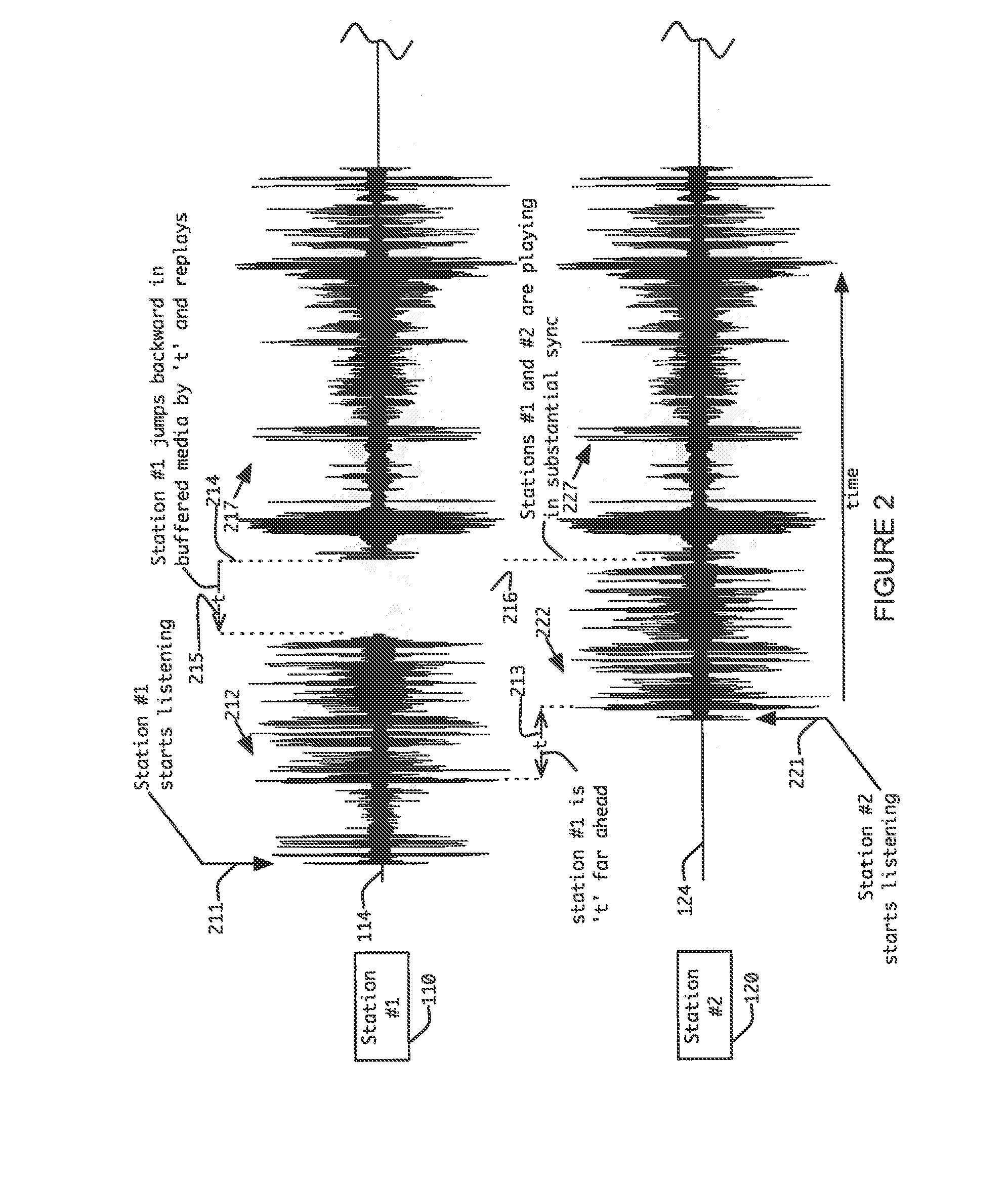
A method for synchronizing content undergoing play out at first and second stations commences by comparing audio within content undergoing play out on the first station to the audio within content undergoing play out on the second station to determine if a latency exists between the first and second stations. If such a latency exists, then at least one of a pause or jump operations is performed in connection with content playing out by at least one of the first and second stations for an interval corresponding to an interval by which one station leads the other station to bring the two stations into substantial synchronism
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Systems and methods for providing real-time audio and data
ActiveUS20180329671A1Enhance listening experienceLower latencyBroadcast service distributionSound input/outputElectronic communicationClient
Owner:MIXHALO CORP
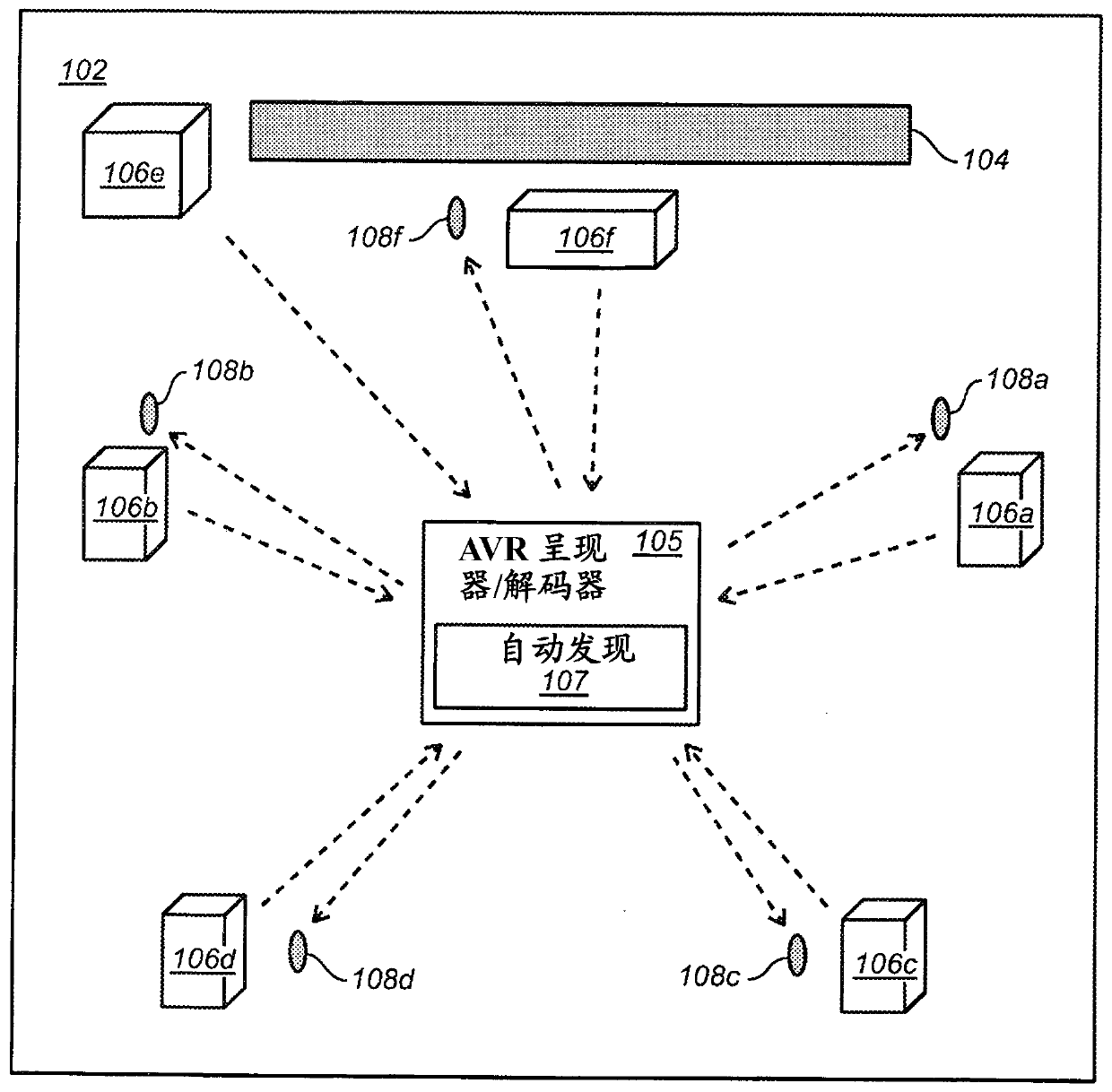
Automatic discovery and localization of speaker locations in surround sound systems
PendingCN109791193AStereophonic circuit arrangementsPosition fixationLoudspeakerAcquisition technique
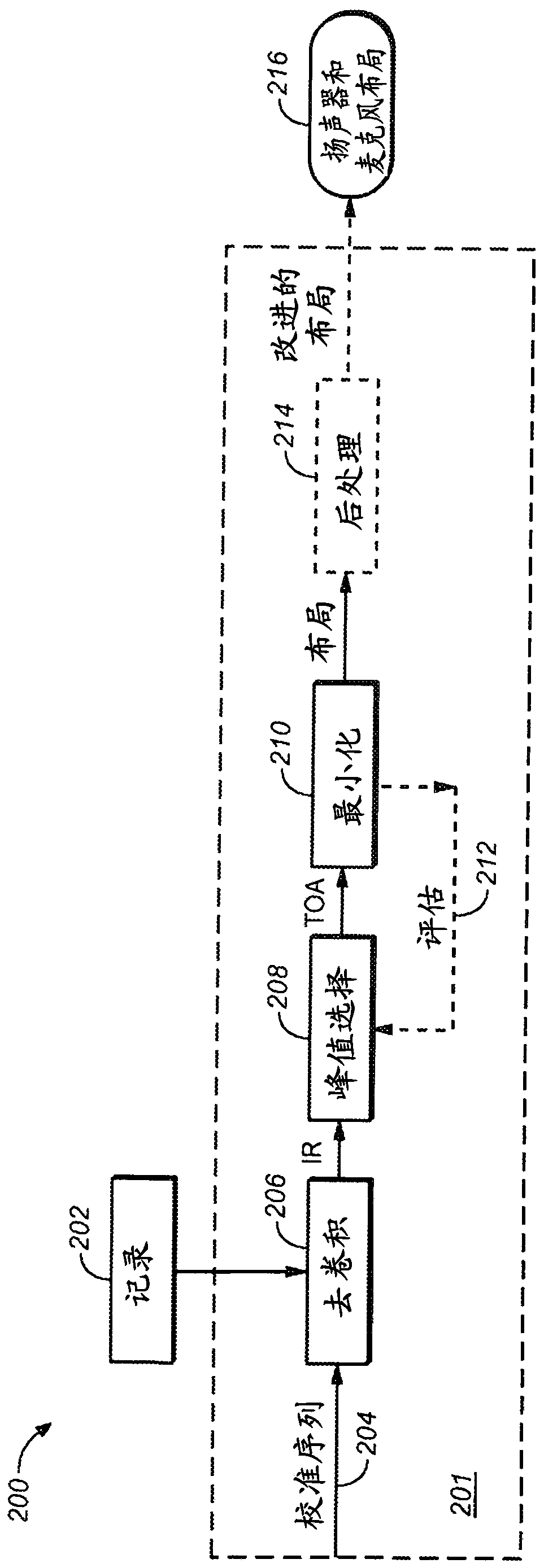
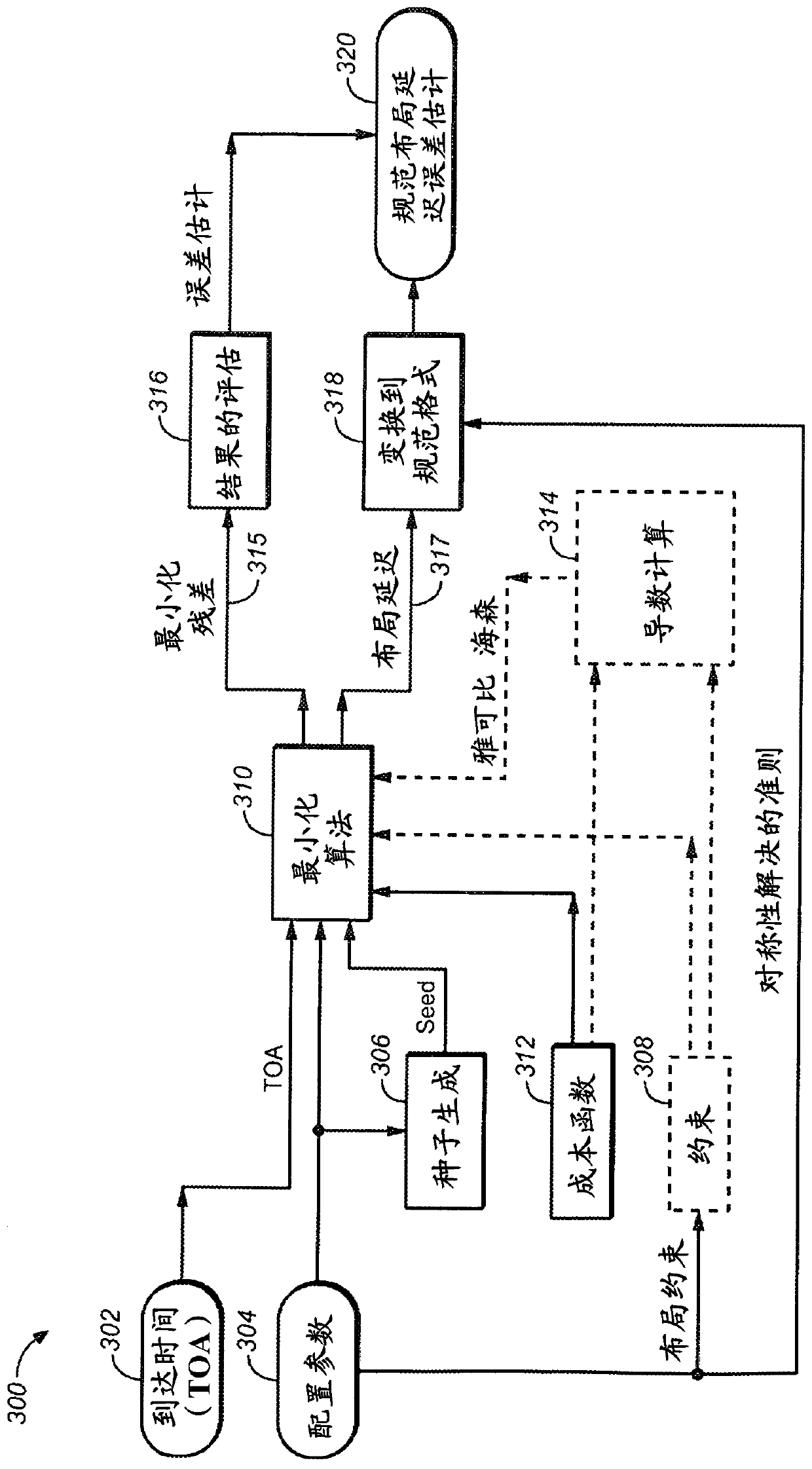
Embodiments are described for a method for localizing a set of speakers (106) and microphones (108), having only the times of arrival between each of the speakers and microphones. An autodiscovery process (107) uses an external input to set: a global translation (3 continuous parameters), a global rotation (3 continuous parameters), and discrete symmetries, i.e., an exchange of any axis pairs and / or reversal of any axis. Different time of arrival acquisition techniques may be used, such as ultrasonic sweeps or generic multitrack audio content. The autodiscovery algorithm is based in minimizinga certain cost function, and the process allows for latencies in the recordings, possibly linked to the latencies in the emission.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
System and method for combining synchronous and asynchronous communications on a communications network
InactiveUS20070274214A1Improve reliabilityLower latencyError preventionTransmission systemsData contentNetwork management
Management and control of the distribution of multiple, synchronous and asynchronous, simultaneously occurring audio and video data content in a communications network, as well as the bandwidth used for distributing the content on the network, is performed by all of the content source and content rendering devices operating in unison. The devices, by utilizing a method of establishing dedicated communication channels based on available bandwidth, data content, and network link reliability, can perform the distribution of content throughout the network in a manner that will reduce the latency and improve the reliability of the data distribution.
Owner:ARKADOS
Music network for collaborative sequential musical production
ActiveUS10929092B1Reduce usageElectrophonic musical instrumentsSound input/outputUser deviceExtended time
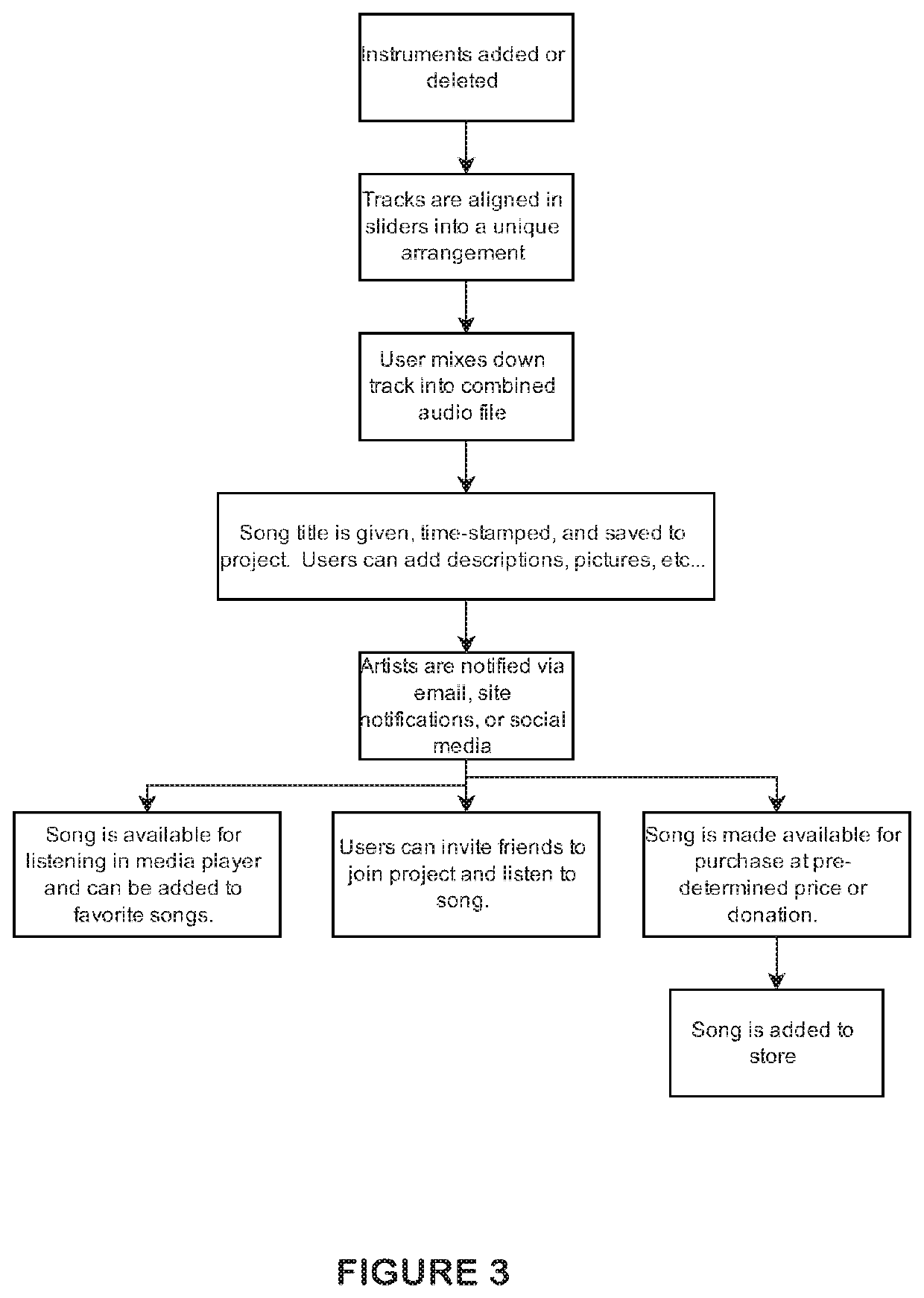
The present invention is a method and a computer program for allowing individual artists to produce a latency corrected collaborative audio work by providing a first artist the opportunity to create a base track which may then be accessed by additional artists who can add audio tracks which harmonize with the base track. Artists may add synchronized tracks to the base track at any time from a remote location thereby allowing artists in different geographical locations to produce a collaborative work of art simultaneously or over an extended time period. The present invention includes a novel method for latency correction, which corrects for delays caused by various types of user equipment, and ensures each track is properly synchronized with the others. The present invention also includes a novel interface where a slot machine or slider user interface allows for ease of use from a browser.
Owner:COLLABRA LLC
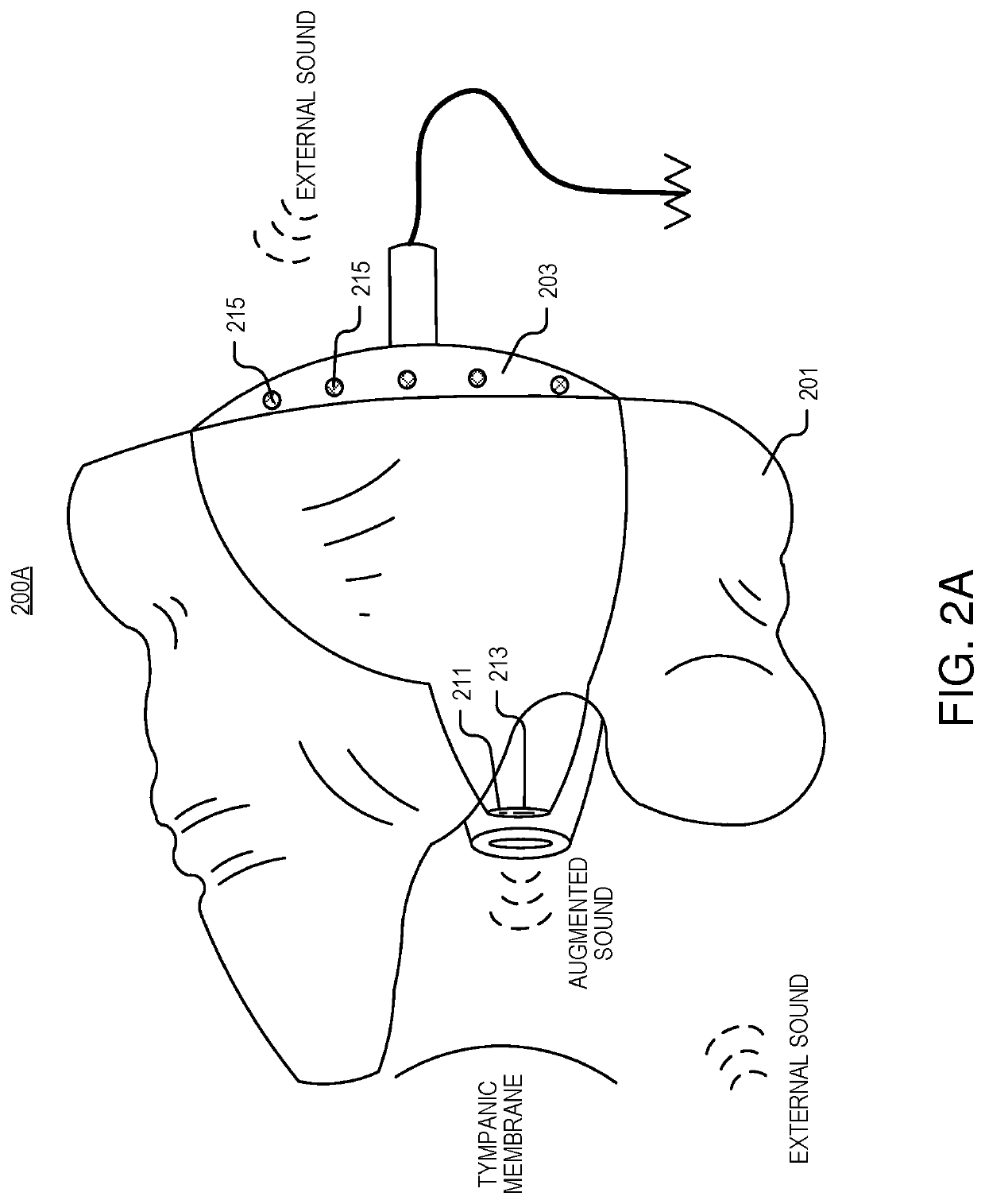
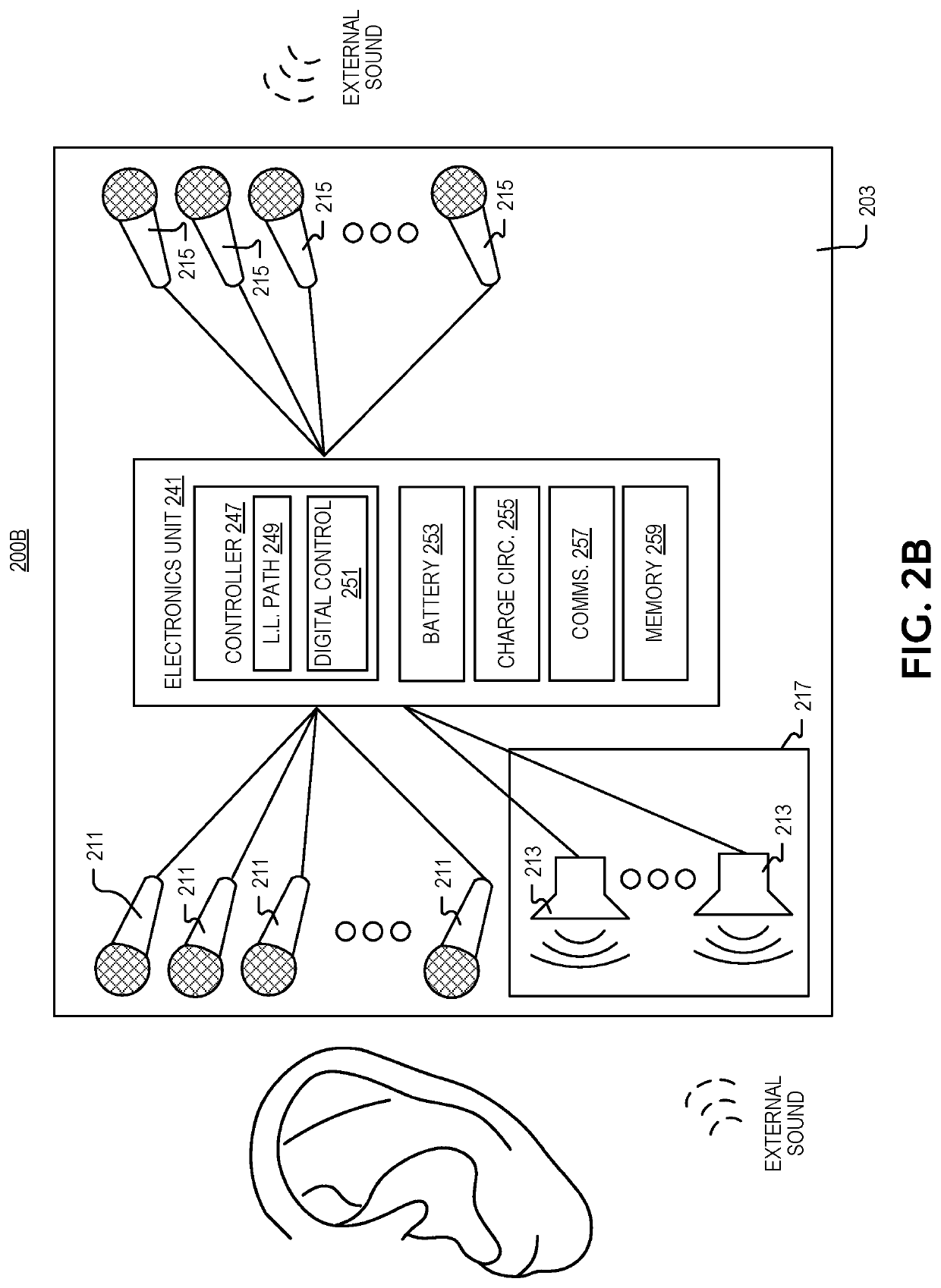
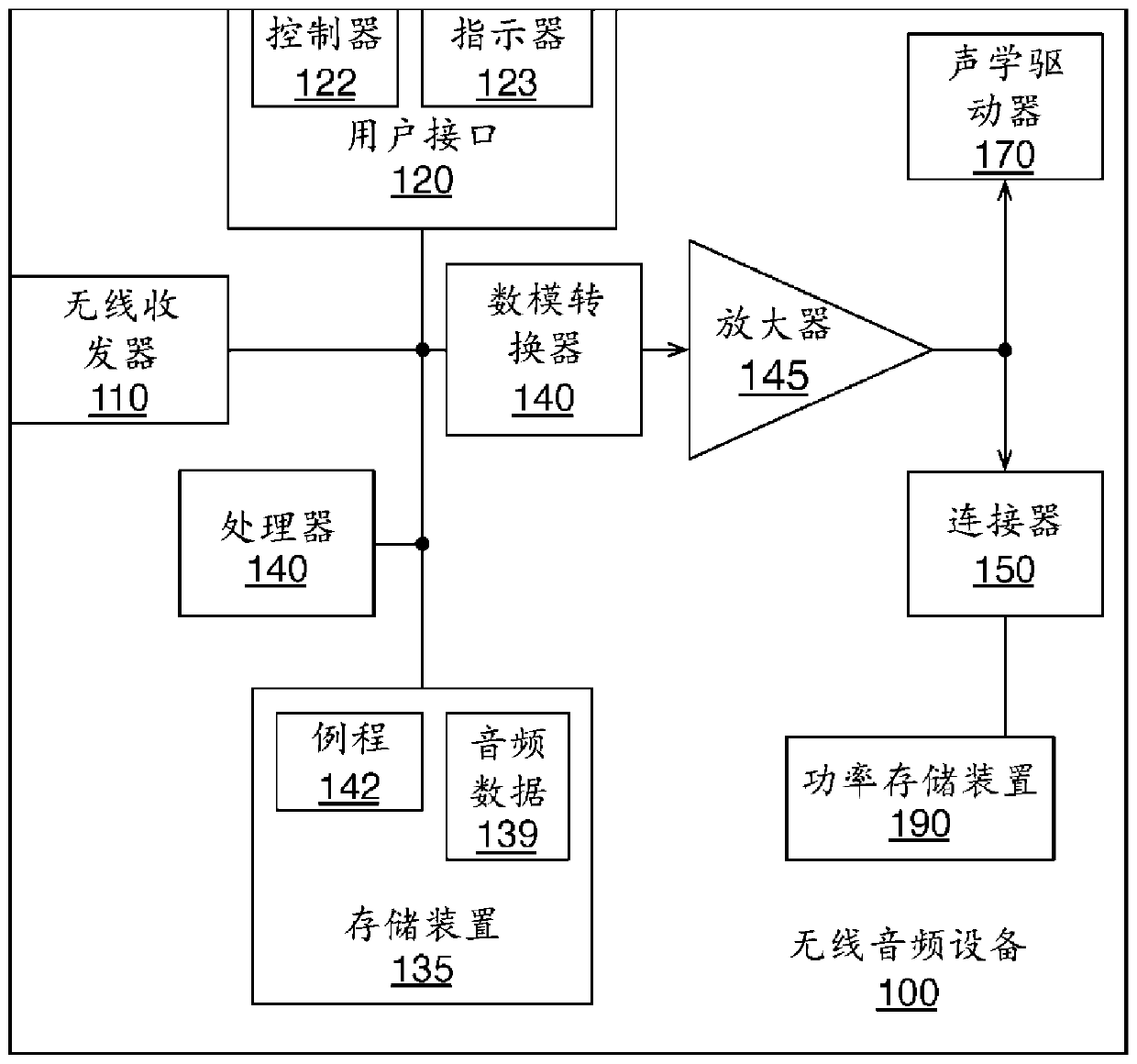
Transparent sound device
An in-ear device includes a housing shaped to hold the in-ear device in an ear of a user, and an audio package, disposed in the housing, to emit augmented sound. A first set of one or more microphones is positioned to receive external sound, and a controller is coupled to the audio package and the first set of one or more microphones. The controller includes a low-latency audio processing path, digital control parameters, and logic that when executed by the controller causes the in-ear device to perform operations. The operations may include receiving the external sound with the first set of one or more microphones to generate a low-latency sound signal; augmenting the low-latency sound signal by passing the low-latency sound signal through the low-latency audio processing path to produce an augmented sound signal; and outputting, with the audio package, the augmented sound based on the augmented sound signal.
Owner:IYO INC
Systems and methods for providing real-time audio and data
ActiveUS11461070B2Enhance listening experienceLower latencyMultiple digital computer combinationsBroadcast service distributionElectronic communicationLatency (audio)
Owner:MIXHALO CORP
Methods and systems for performing and recording live internet music near live with no latency
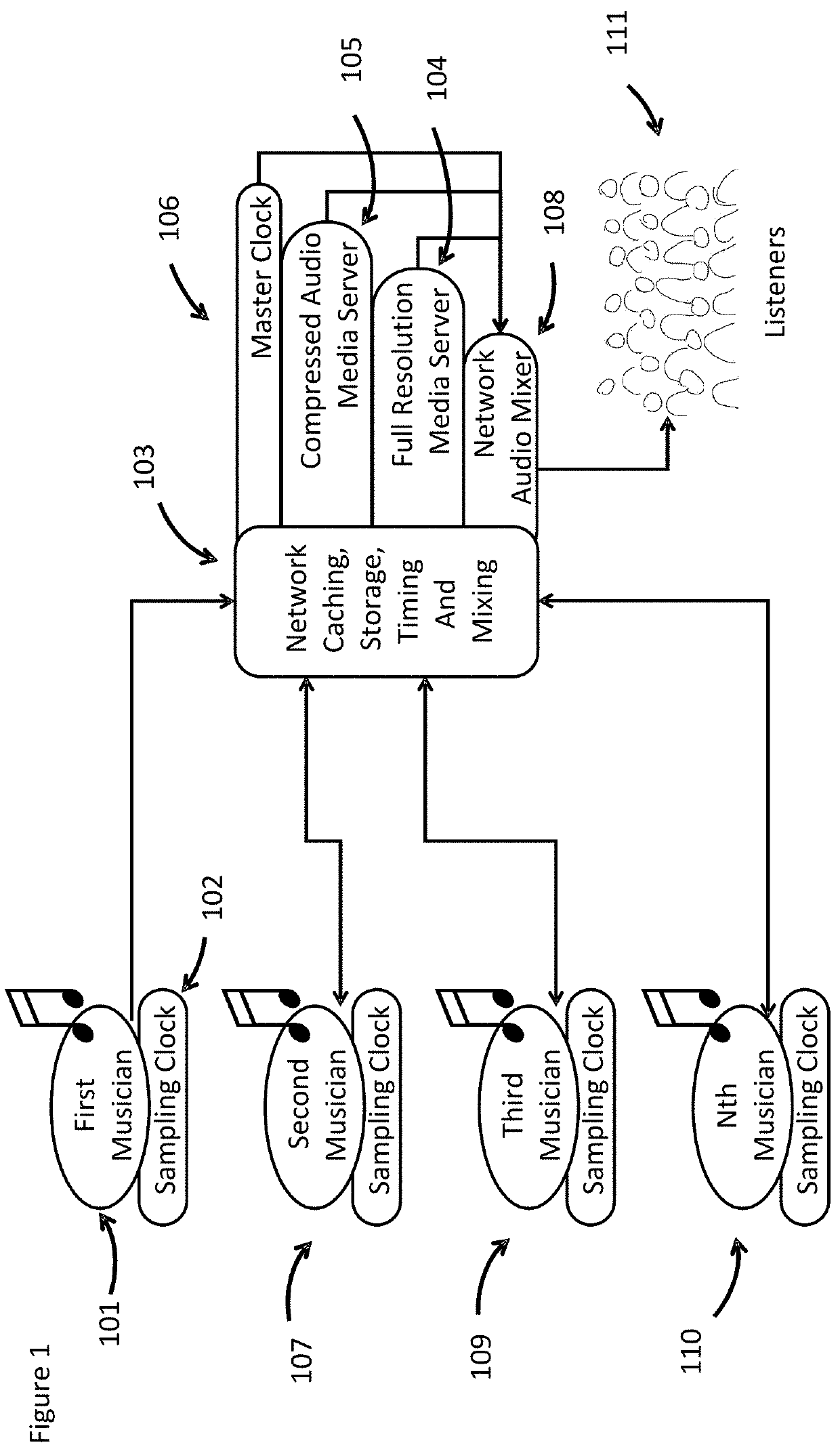
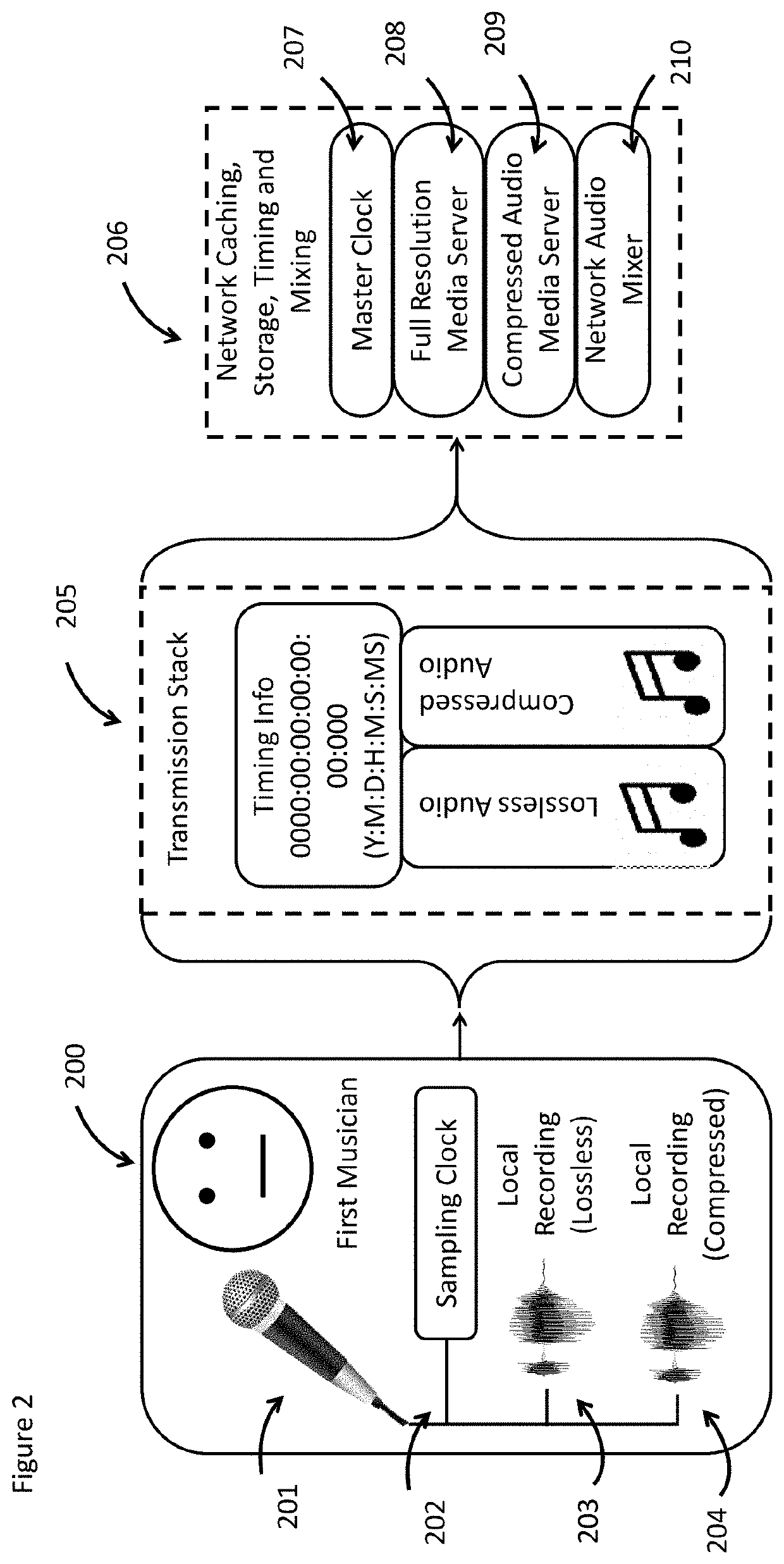
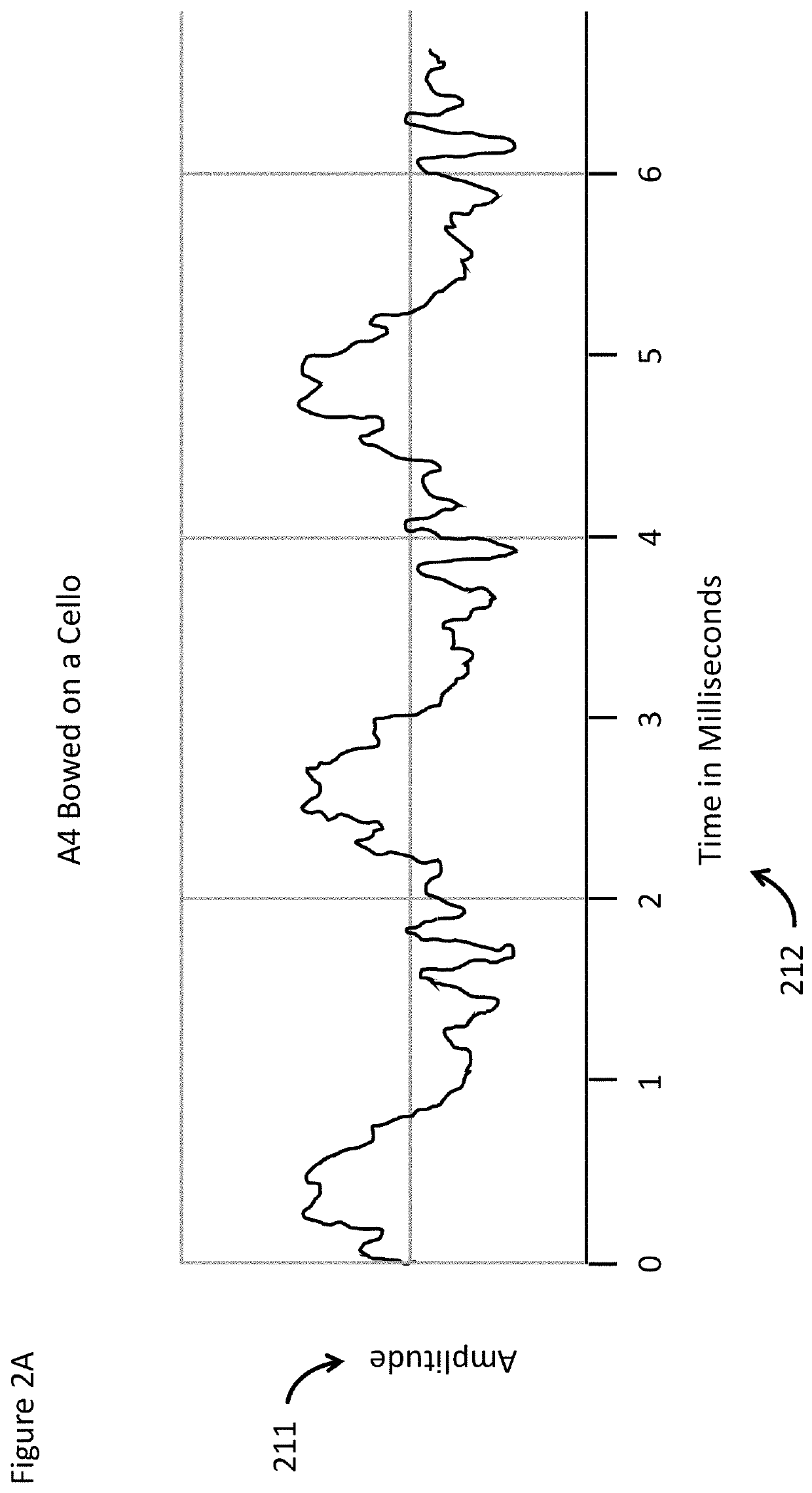
ActiveUS20210409138A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsTime-division multiplexLatency (audio)Master clock
Exemplary methods include a processor executing instructions stored in a memory for generating an electronic count-in, binding the electronic count-in to a first performance to generate a master clock and transmitting a first musician's first performance and first timing information to a network caching, storage, timing and mixing module. The first musician's first performance may be recorded locally at full resolution and transmitted to a full resolution media server and the first timing information may be transmitted to the master clock. The first musician's first performance is transmitted to a sound device of a second musician and the second musician creates a second performance, transmits it and second timing information to a network caching, storage, timing and mixing module. The first and second performances are mixed along with the first and the second timing information to generate a first mixed audio, which can be transmitted to a sound device of a third musician.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTRTAINMENT LLC
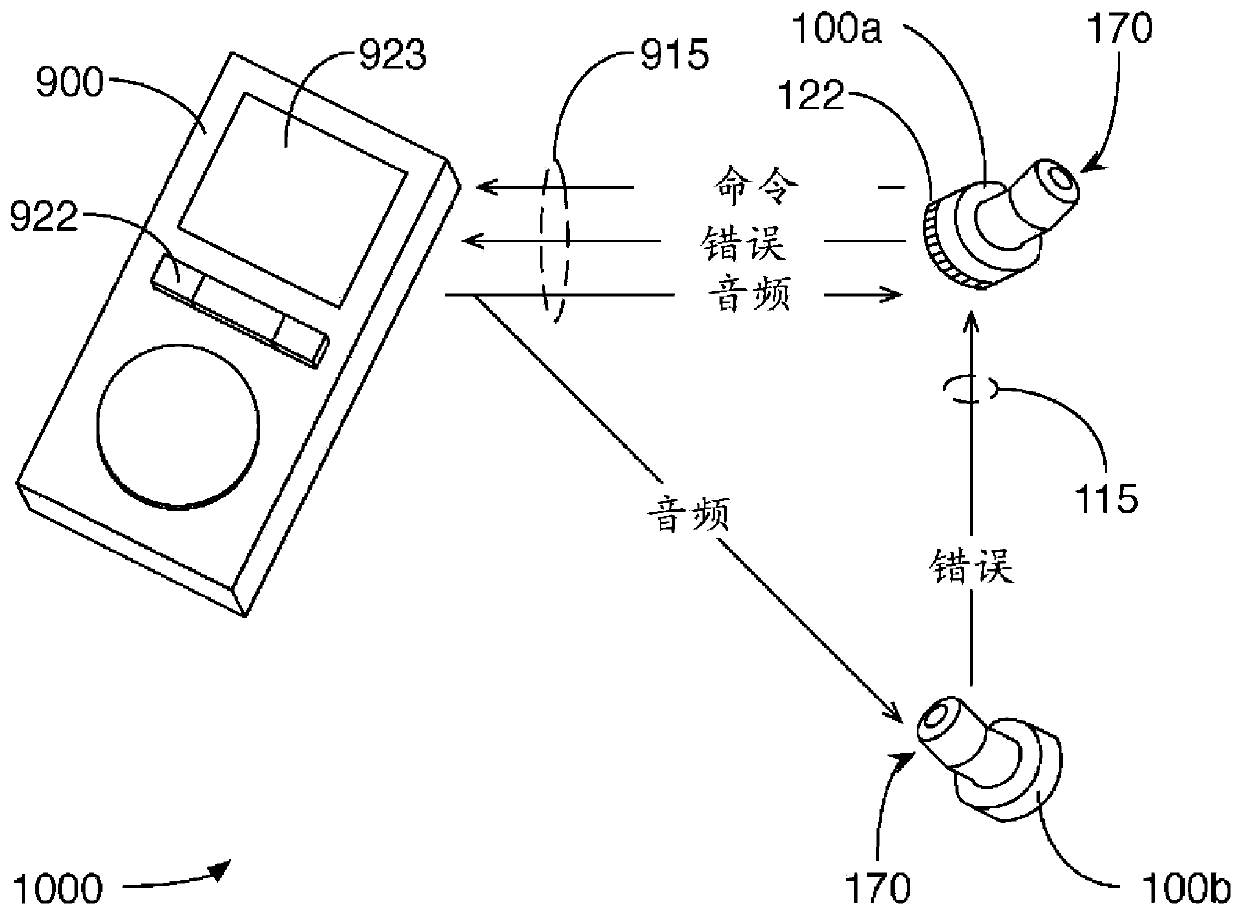
Wireless low-latency audio content sharing
PendingCN111386717APower managementHeadphones for stereophonic communicationComputer hardwareTelecommunications
A first audio device exchanges first control signals with a source device and thereby receives first audio signals from the source device. A second audio device exchanges second control signals with the first audio device including information the second audio device needs to receive the first audio signals from the source device. The first control signals include communications using Bluetooth BR / EDR protocols and establish a first Bluetooth link for audio streaming from the source device to the first audio device. The second control signals include communications using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) protocols and transfer to the second audio device parameters of the first Bluetooth link, such that the second audio device can receive and decode an audio stream transmitted from the source device to the first audio device over the first Bluetooth link.
Owner:BOSE CORP
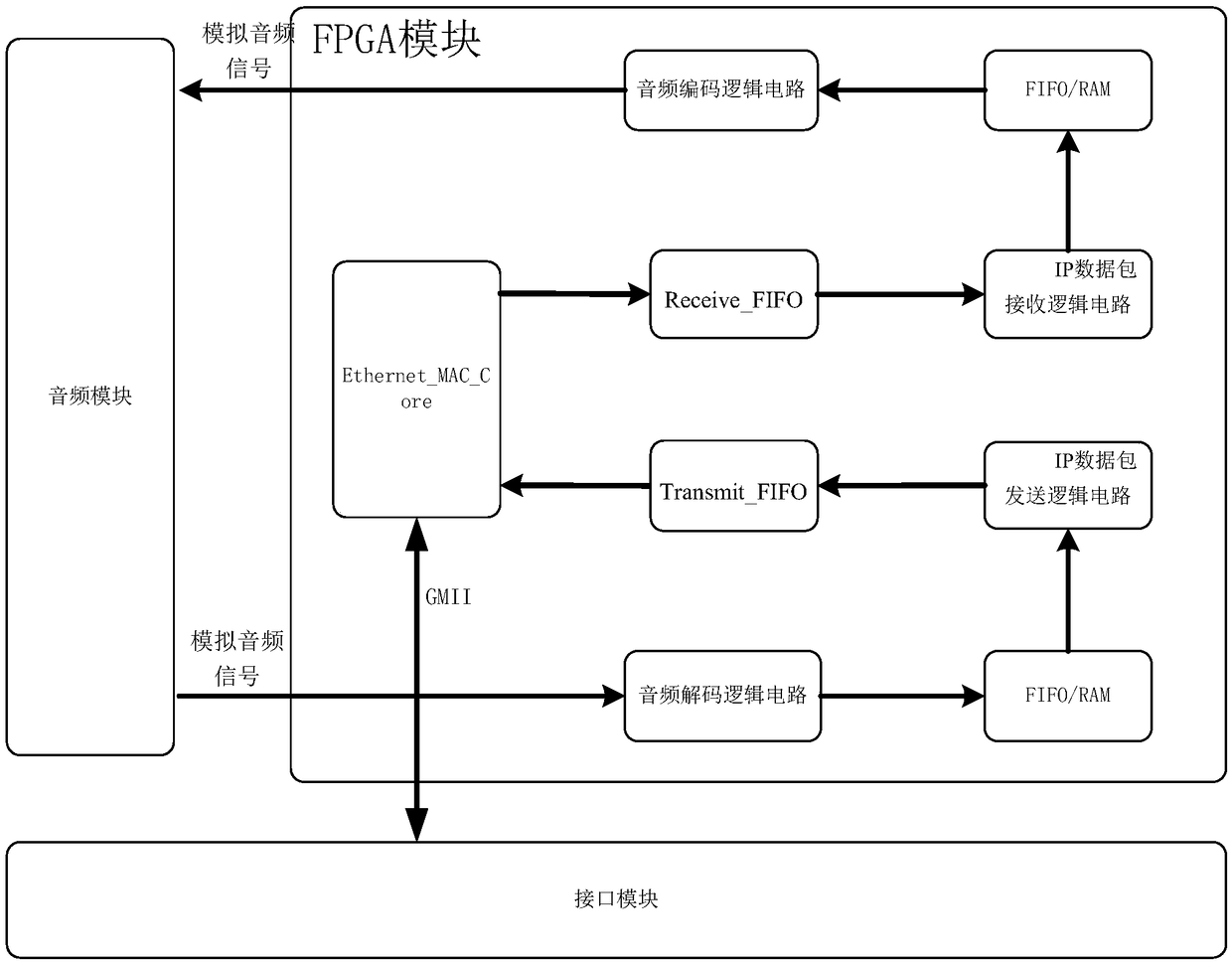
Low-latency on-board Ethernet audio stream processing system and method
The invention discloses a low-latency on-board Ethernet audio stream processing system. The system comprises an audio module, an FPGA module, and an interface module, wherein the audio module is connected with the interface module through the FPGA module, the audio module receives and plays an analog audio processed by the FPGA module, and collects and sends an analog audio to the FPGA module, theFPGA module receives and decodes the analog audio sent by the audio module so as to obtain a digital audio, packages the digital audio according to an ARINC628P3 protocol and then sends out through the interface module, receives an audio data packet sent by the interface module, unpacks according to an ARINC628P3 protocol and then processes to obtain an analog audio and sends the analog audio tothe audio module, and the interface module provides an interface between the external environment and the FPGA module, an interface circuit between the FPGA module and periphery, and provides power for devices. Through adoption of the low-latency on-board Ethernet audio stream processing system, the problem that audio broadcast freezes or has noise due to overlarge fluctuation of processing latency is solved.
Owner:CETC AVIONICS
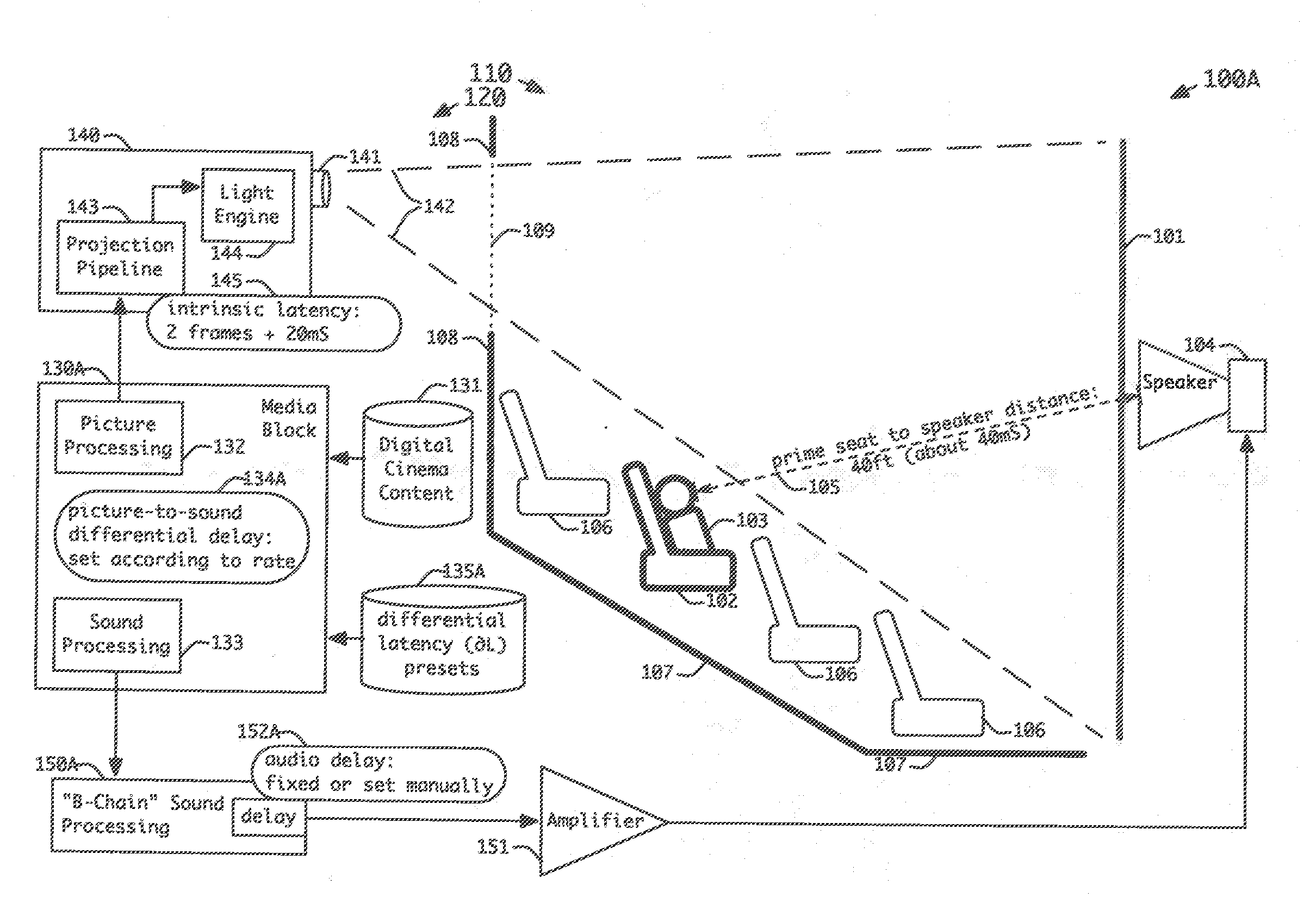
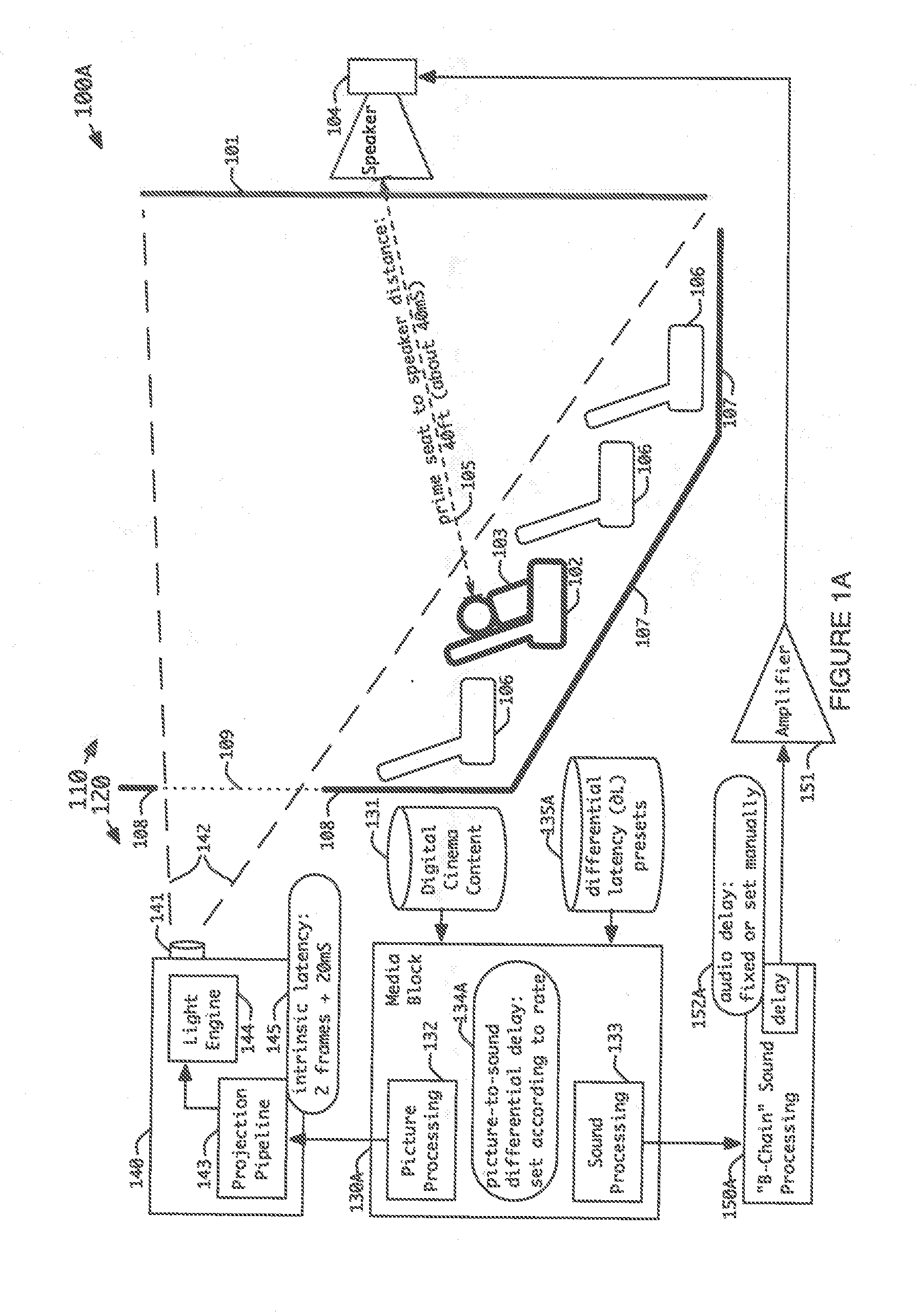
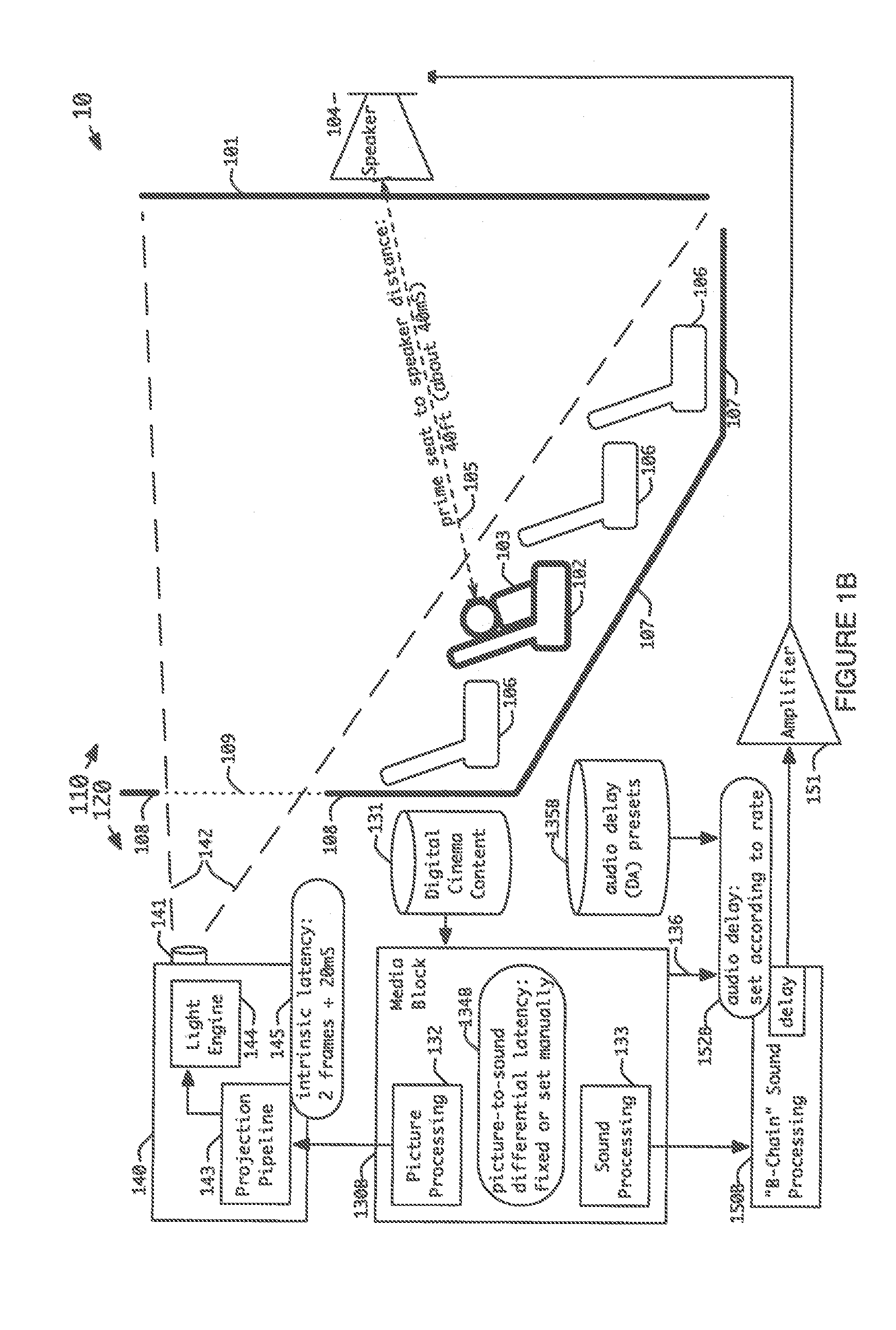
Method and apparatus for adapting audio delays to picture frame rates
To synchronize sound information with corresponding picture information for digital cinema compositions at different frame rates in a play list during play out of the digital cinema compositions, associated audio latency settings are first established for the corresponding picture information of the digital cinema compositions in the play list in accordance with the digital cinema composition frame rates. The timing between the sound information and the picture information is then adjusted during play out of the digital cinema compositions in accordance with the associated audio latency settings for the corresponding digital cinema composition frame rates.
Owner:DIATEK LICENSING LLC
Method and system for transmission and low-latency real-time output and/or processing of an audio data stream
ActiveUS10686897B2Lower latencyTime-division multiplexData switching networksComputer hardwareData stream
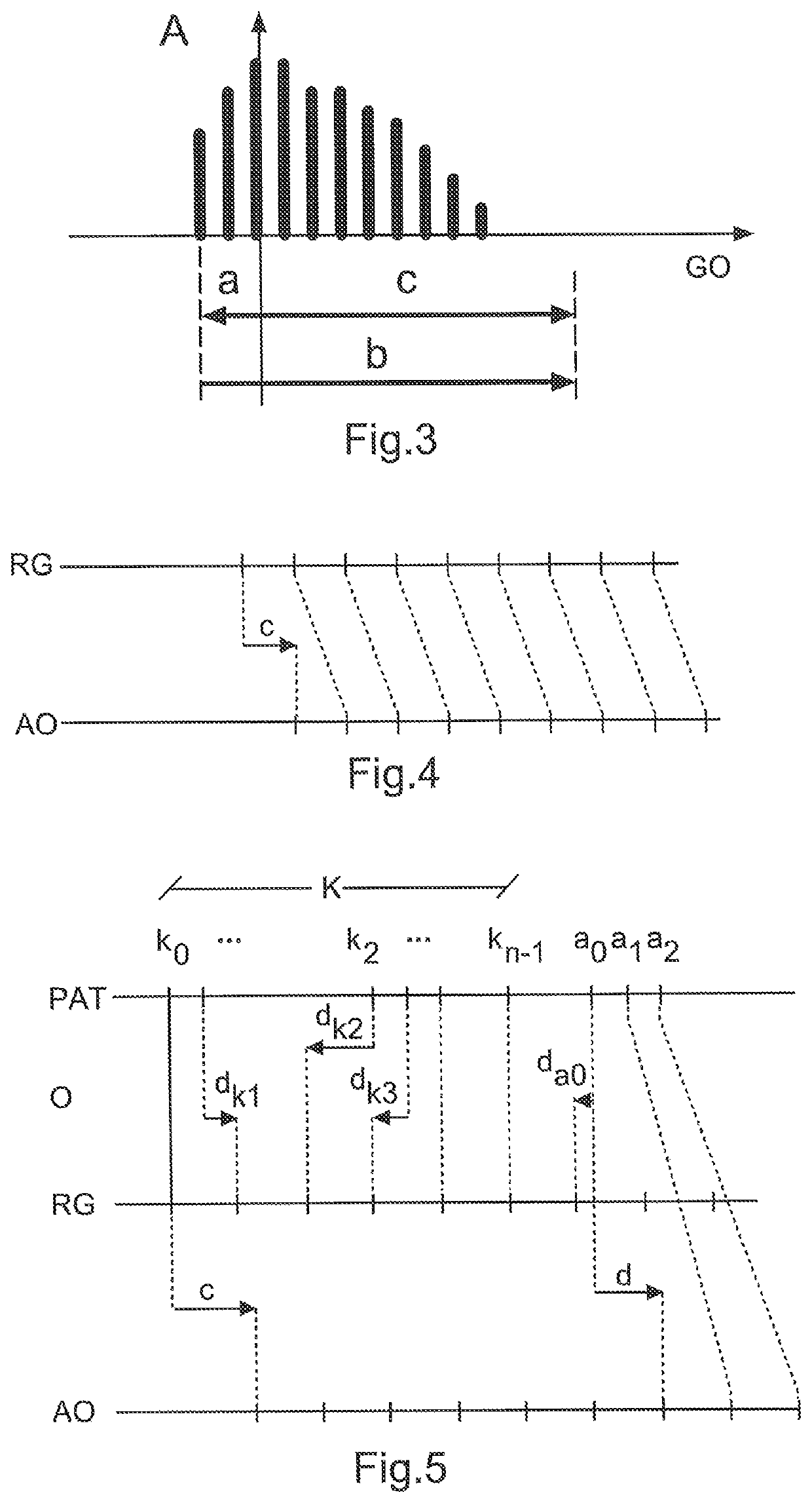
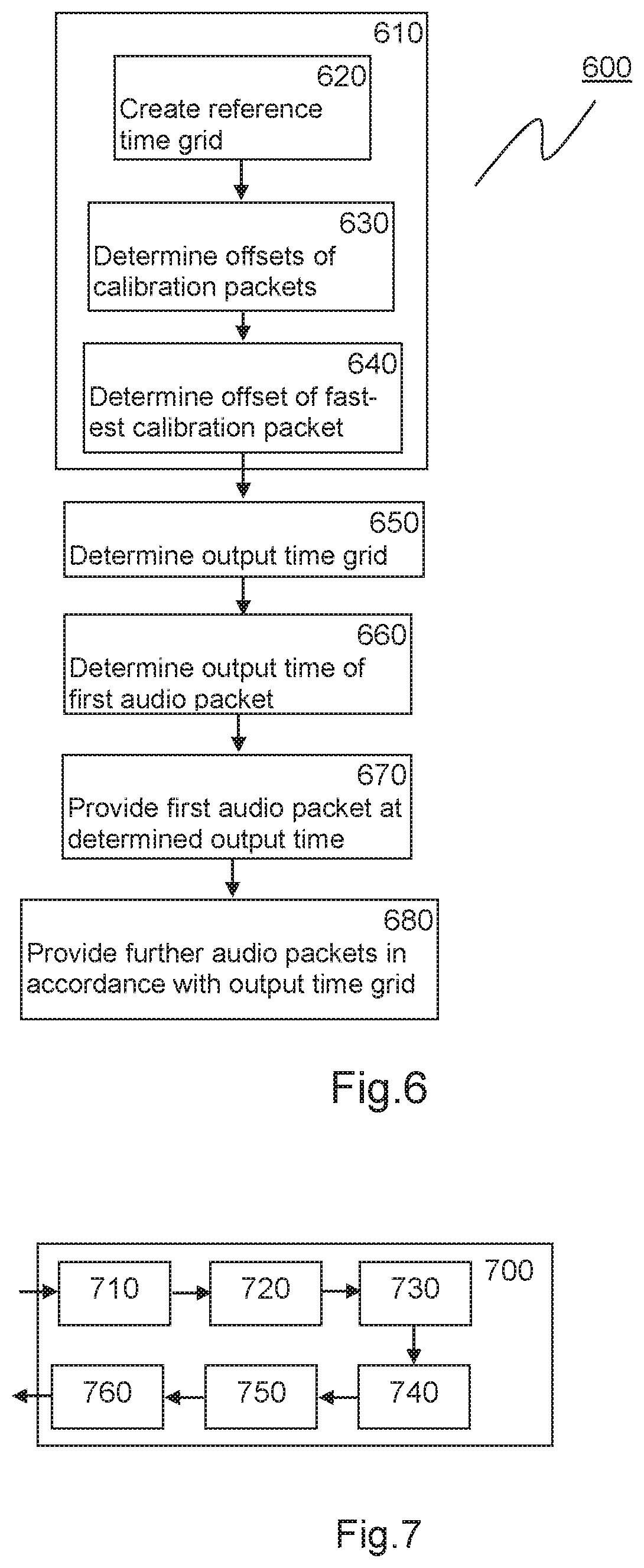
A method for transmission and low-latency real-time output and / or processing of an audio data stream that is transmitted from at least one transmitter to at least one receiver over a jittering transmission path. The method includes a calibration for determining a distribution of latencies in transmission of packets of the audio data stream, whereby a group of packets of the audio data stream is used as calibration packets and wherein a reference time grid and an offset of a fastest calibration packet are determined. Then, a shift of an output time grid for audio output and / or processing, based on the reference time grid and the determined offset of the fastest calibration packet, and the audio packets of the audio data stream are provided according to the output time grid for audio output and / or processing.
Owner:SENNHEISER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
Stream adaptation for latency
ActiveUS20190214034A1Lower latencyReduce capacityNetwork topologiesSpeech analysisTiming marginAudio frequency
A system and method for adapting an audios stream for reducing latency. The method may include the steps of, and the system may function to, receive an audio stream having a packet buffer and an audio buffer, measure the audio buffer depth of the audio buffer, measure the presentation time margin of at the input to the packet buffer, and determine an adaptation level for latency based on the measured values.
Owner:WISA TECH INC
Zero latency digital assistant
ActiveUS10747498B2Reducing and eliminating latencyImprove efficiencyInput/output to record carriersDevices with voice recognitionComputer hardwareHuman–computer interaction
An electronic device can implement a zero-latency digital assistant by capturing audio input from a microphone and using a first processor to write audio data representing the captured audio input to a memory buffer. In response to detecting a user input while capturing the audio input, the device can determine whether the user input meets a predetermined criteria. If the user input meets the criteria, the device can use a second processor to identify and execute a task based on at least a portion of the contents of the memory buffer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Multi-device audio streaming system with synchronization
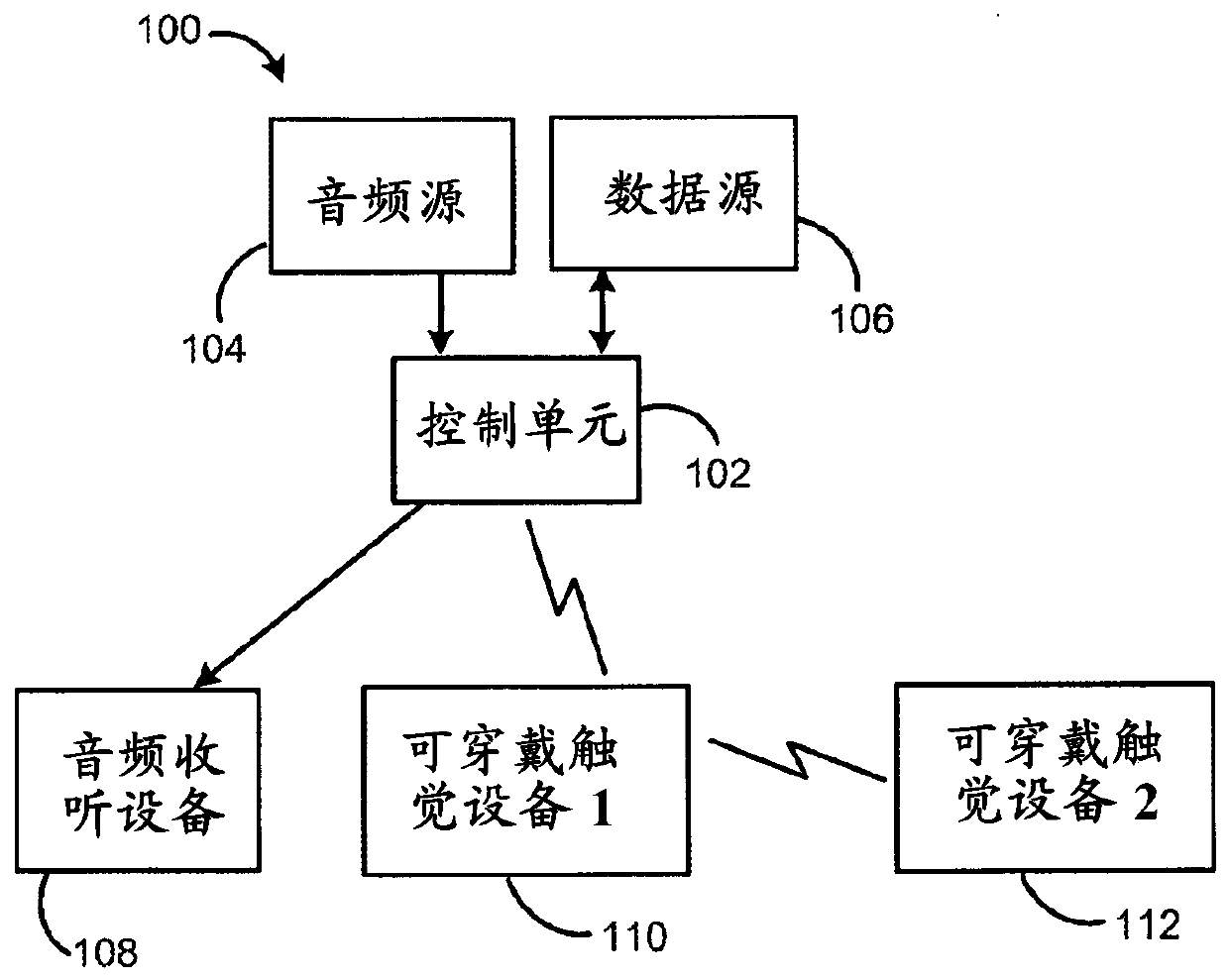
InactiveCN110035808ADelivery synchronizationInput/output for user-computer interactionSpeech analysisTransport systemWireless transceiver
Embodiments include an electronic control unit comprising an audio input device for receiving an audio stream from an external audio source, the audio stream being split between an audio path and a haptic path; a wireless transceiver in the haptic path for transmitting the audio stream to at least one wearable haptic device using short-range wireless communication; and a processor coupled to the transceiver and configured to calculate an amount of latency associated with transmission of the audio stream to the wearable haptic device(s), and partition the audio stream into a plurality of audiopackets including a time-to-play based on the calculated latency. The control unit further includes a buffer in the audio path for inserting a time delay into the audio stream based on the calculatedlatency, and an audio output device in the audio path for outputting the time-delayed audio stream to an external audio listening device.
Owner:SONICSENSORY INC
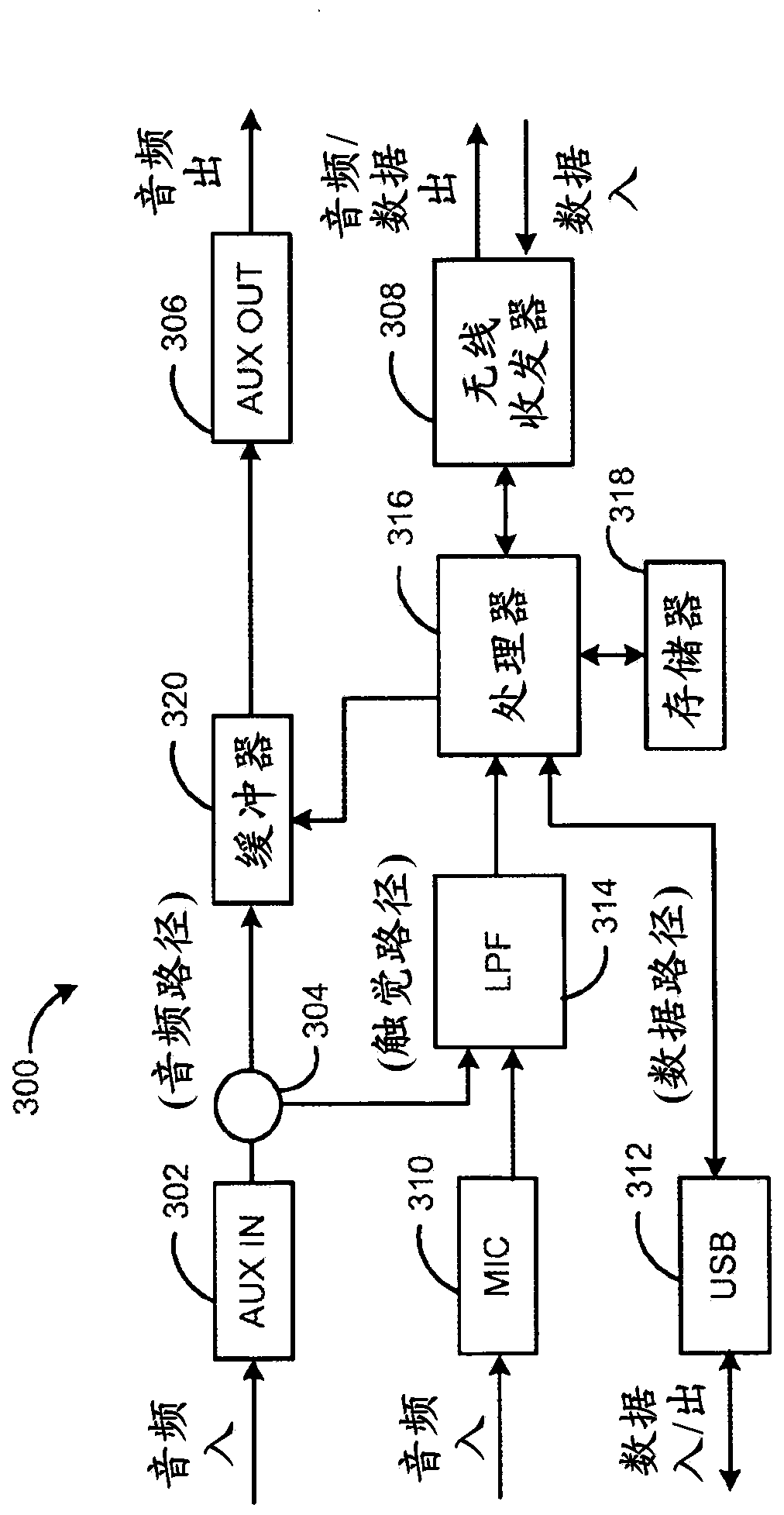
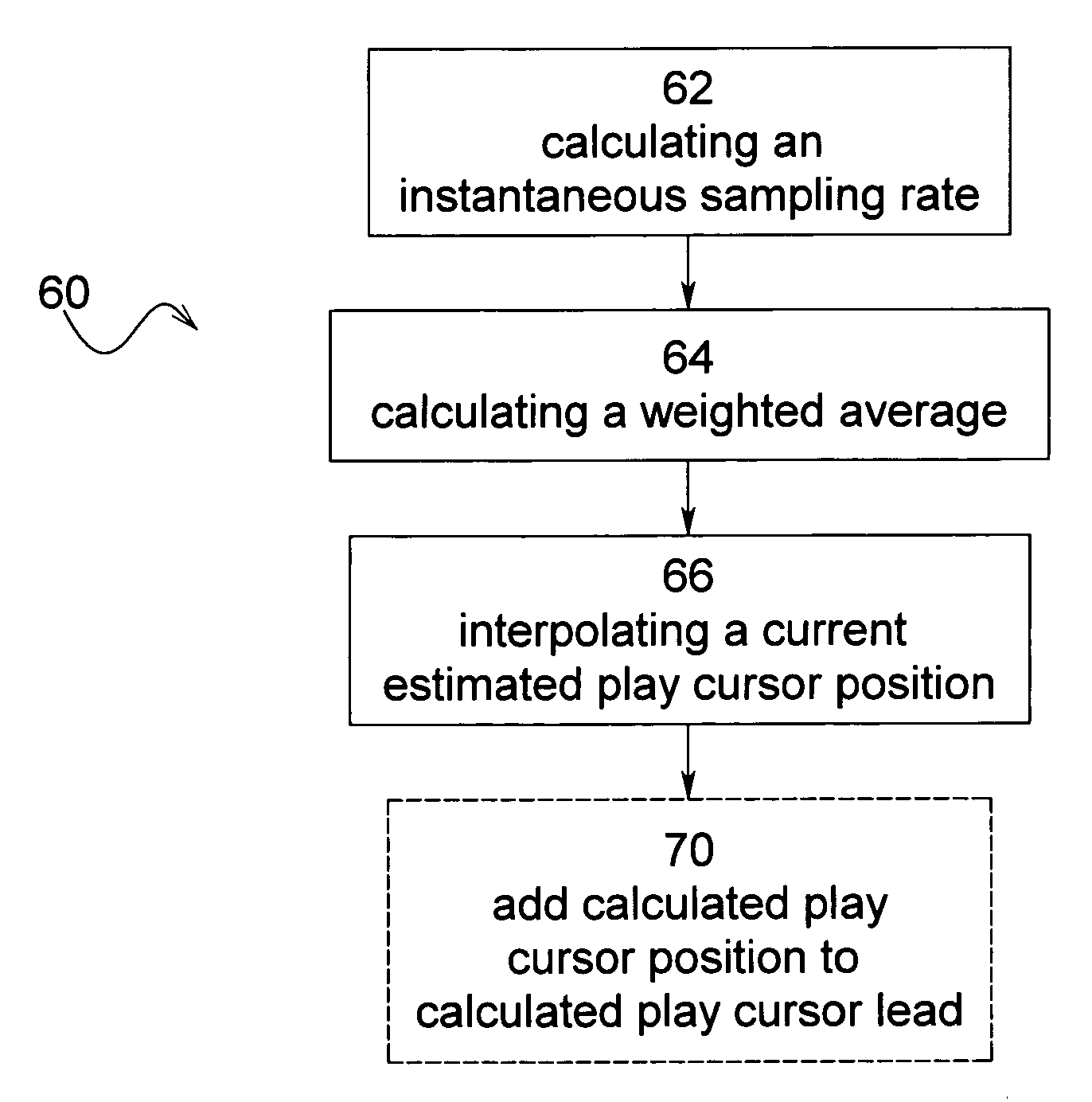
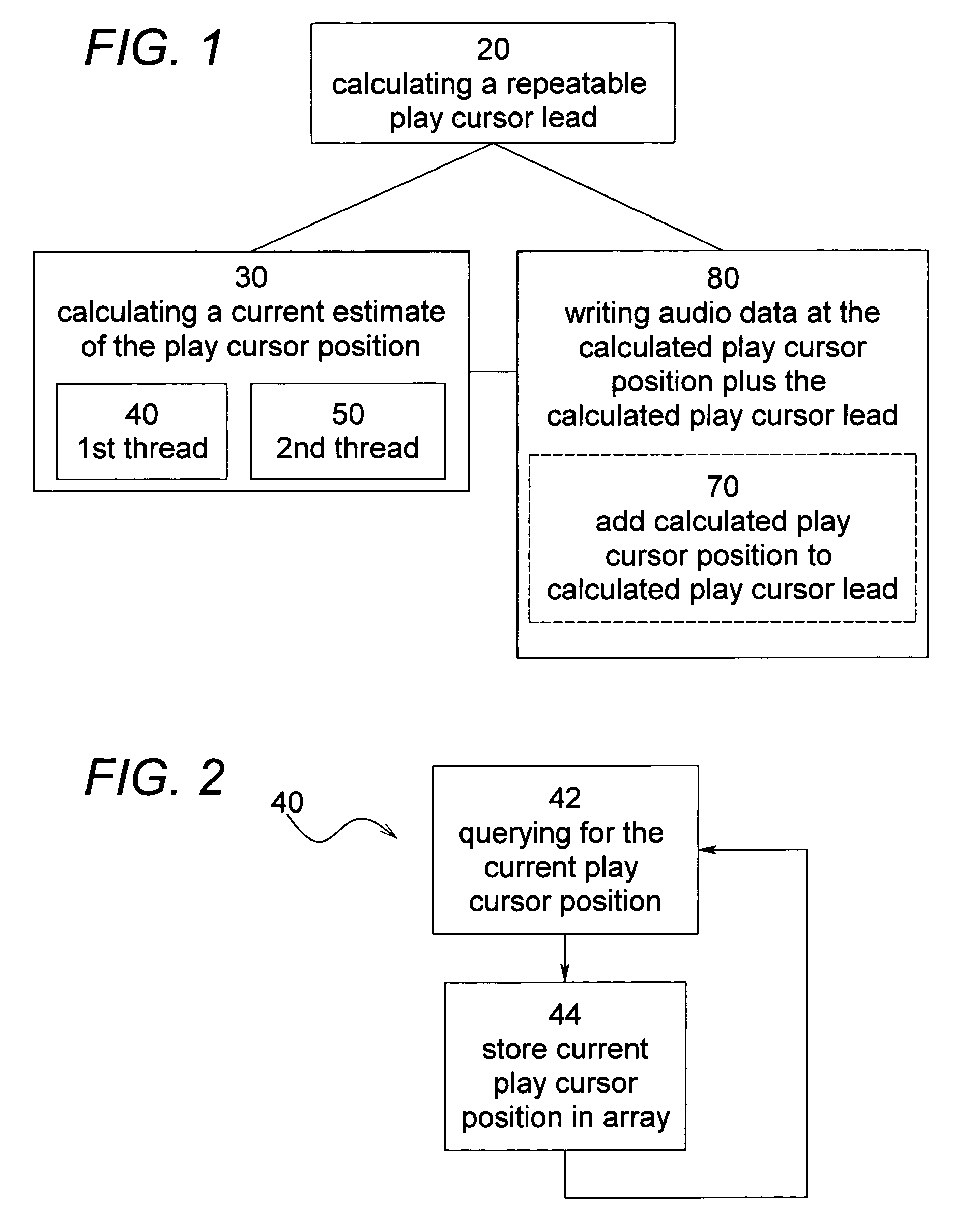
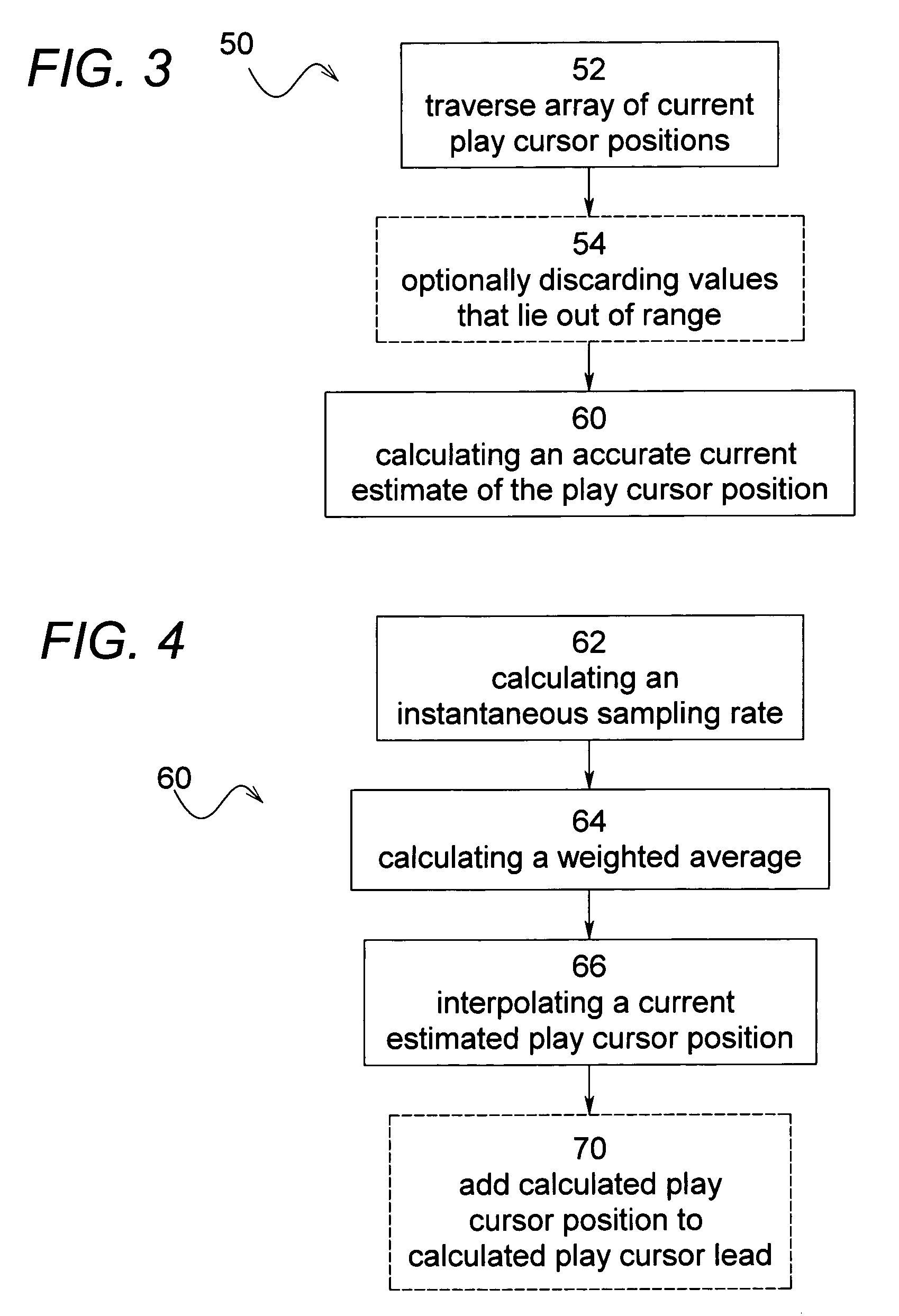
Software and process for play-cursor calculation
ActiveUS7218977B2Reduce and eliminate typeHighly accurate on-demand calculationBroadcast with distributionSound input/outputComputer engineeringSoftware
A process and software for achieving minimal latency in digital audio recording, which includes calculating a repeatable play cursor lead and a play cursor position and writing audio data at the play cursor position plus the play cursor lead.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Latency enhanced note recognition method in gaming
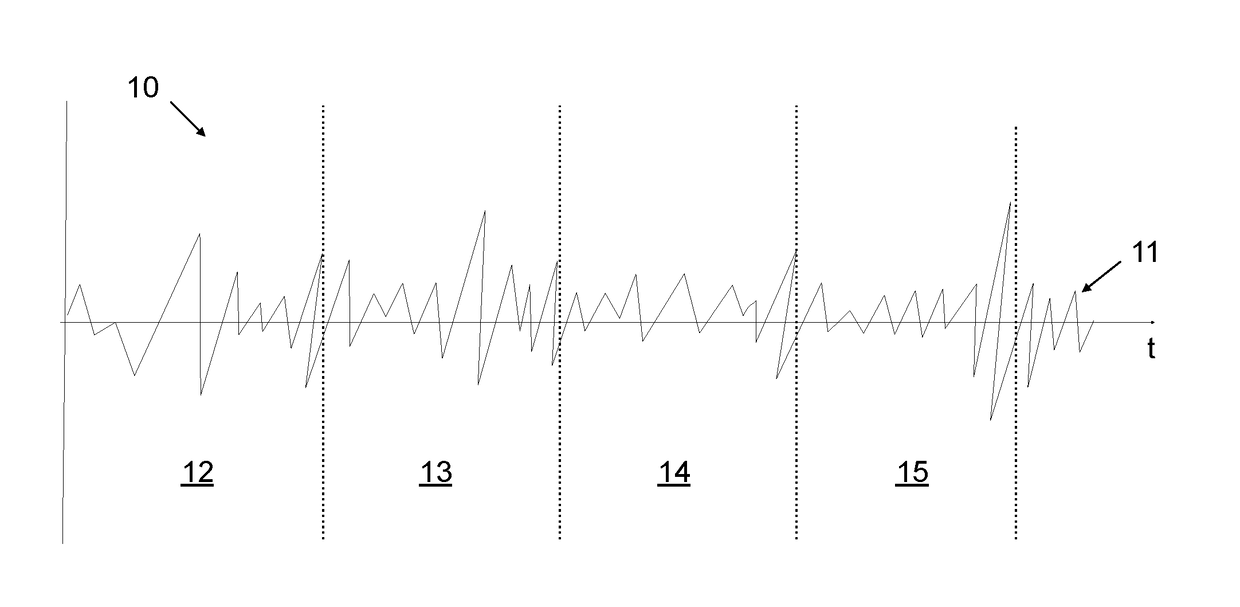
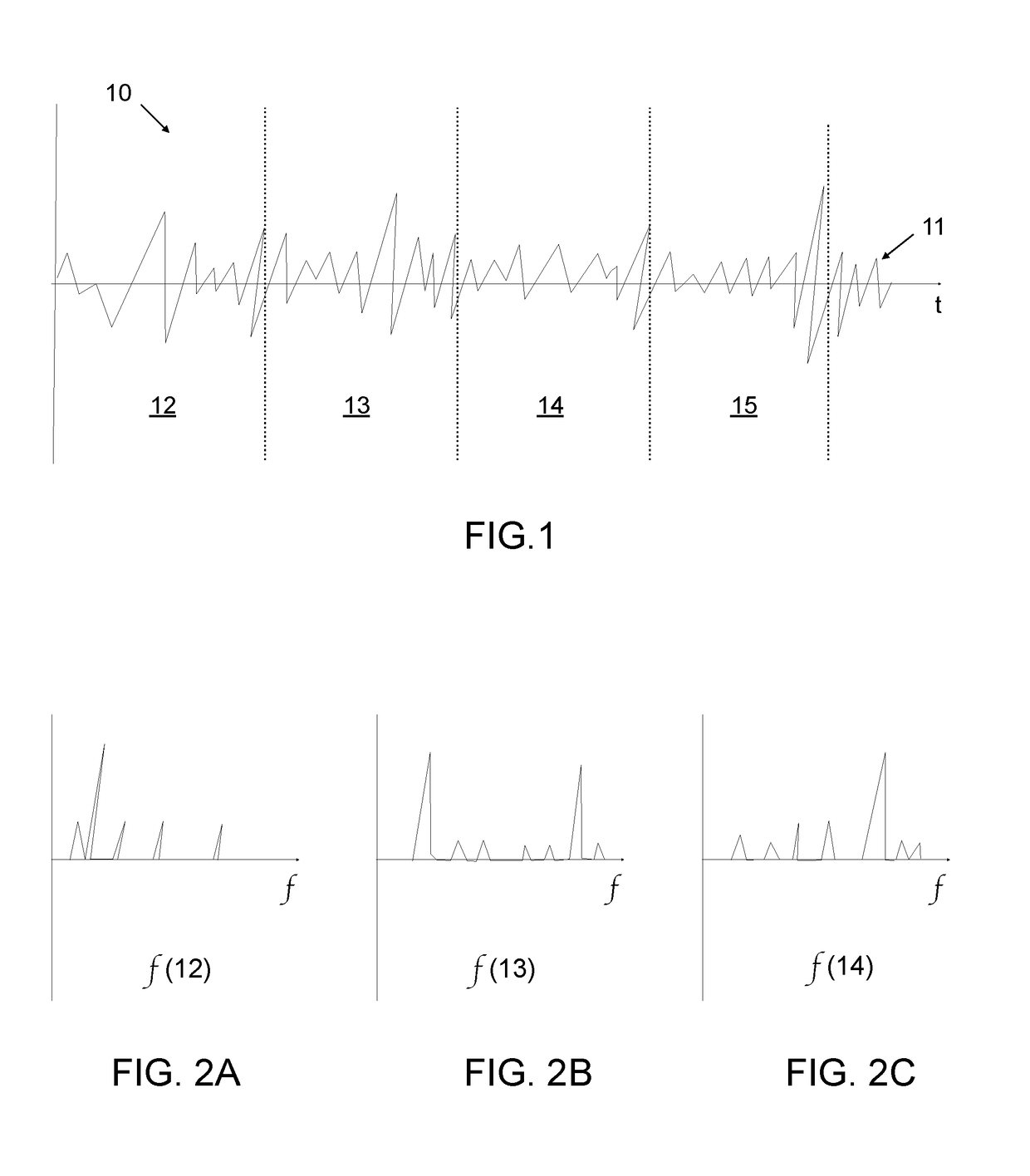
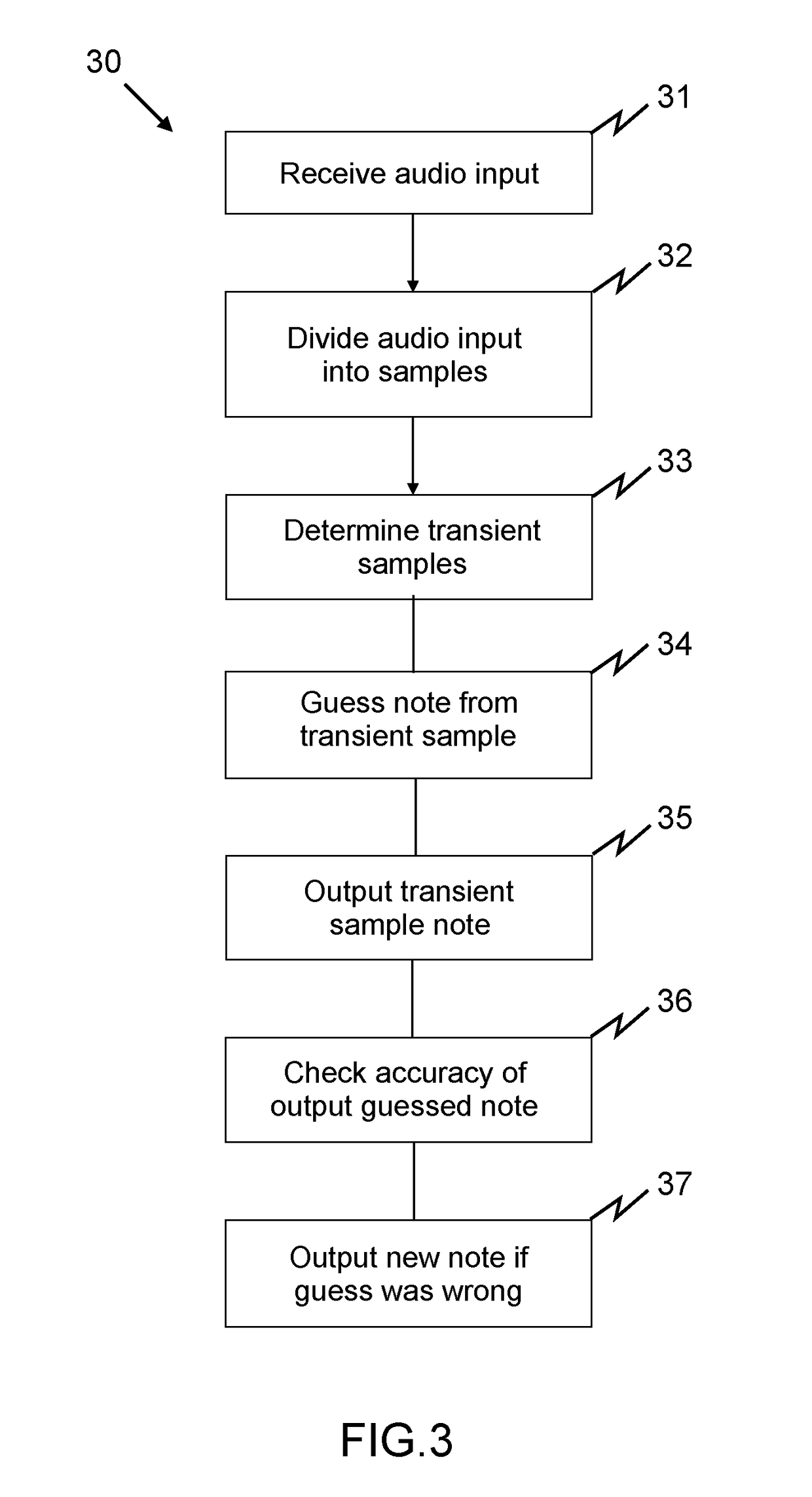
ActiveUS20170186413A1Reduce lagReduce latencyElectrophonic musical instrumentsVideo gamesEnhanced noteVoice pitch
The present invention relates to the field of audio recognition, in particular to computer implemented note recognition methods in a gaming application. Furthermore, the present invention relates to improving latency of such audio recognition methods. One of the embodiments of the invention described herein is a method for note recognition of an audio source. The method includes: dividing an audio input into a plurality of frames, each frame having a pre-determined length, conducting a frequency analysis of at least a set of the plurality of frames, based on the frequency analysis, determining if a frame is a transient frame with a frequency change between the beginning and end of the frame, comparing the frequency analysis of each said transient frame to the frequency analysis of an immediately preceding frame and, based on said comparison, determining at least one probable pitch present at the end of each transient frame, and for each transient frame, outputting pitch data indicative of the probable pitch present at the end of the transient frame.
Owner:ZOUNDIO AB
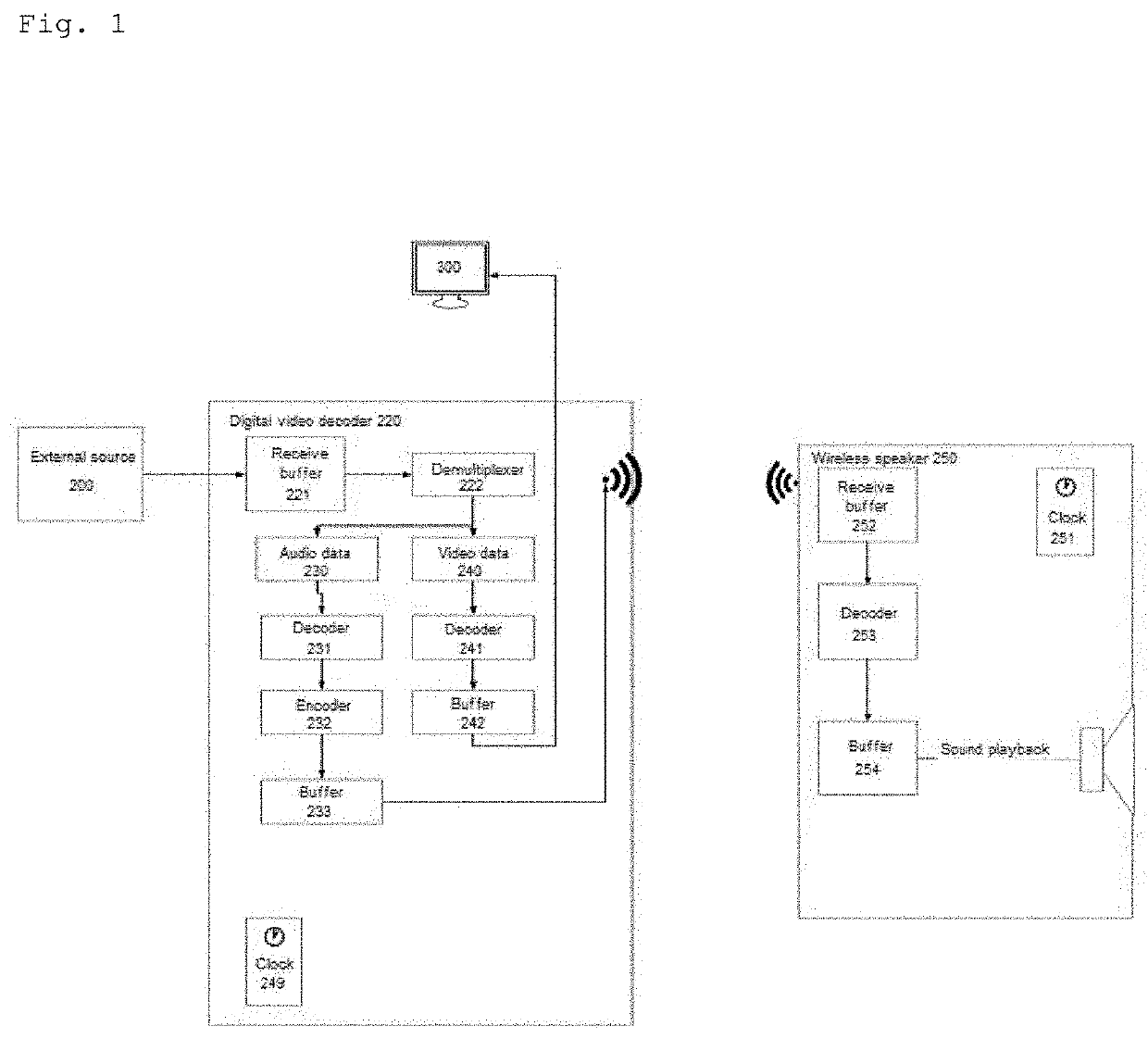
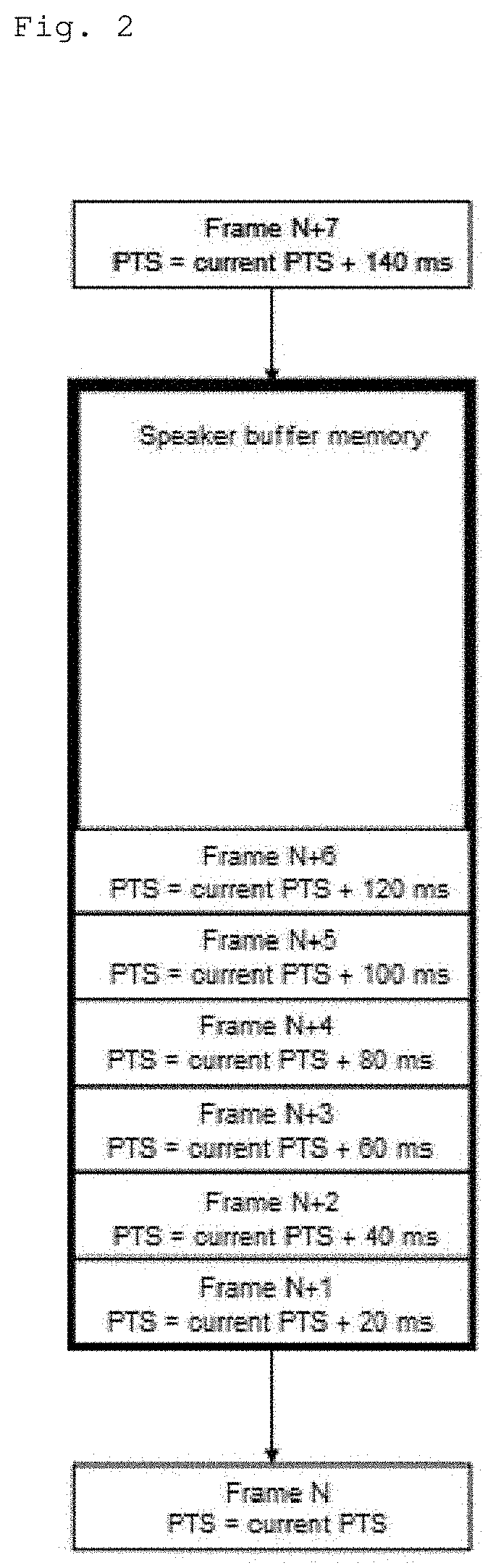
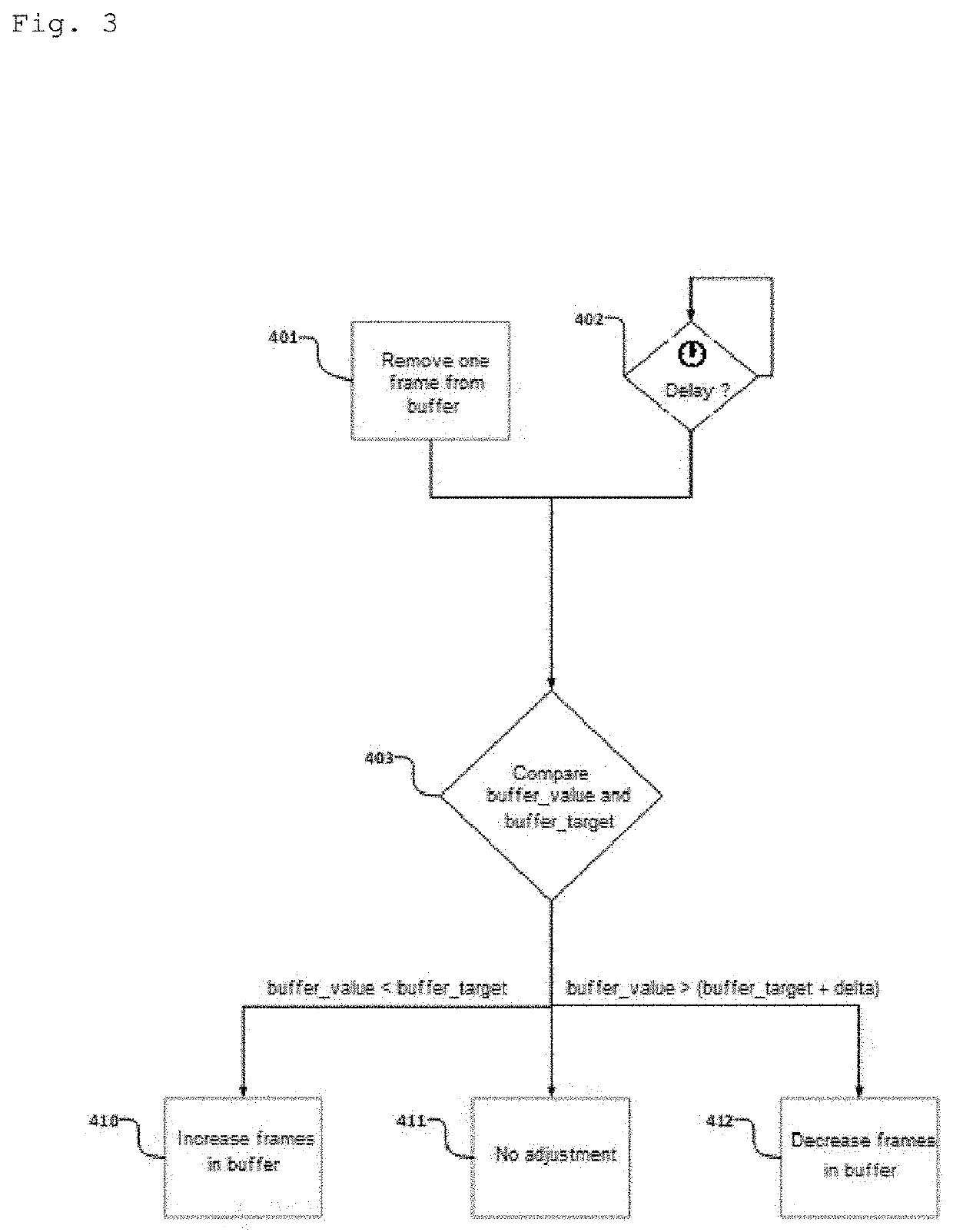
Method, a system, and a program for playing back audio/video signals with automatic adjustment of latency
PendingUS20220013131A1Keep in syncAdjust latencyStereophonic circuit arrangementsSpeech analysisComputer hardwareEngineering
A method of playing back audio / video signals by means of an audio / video system includes a decoder appliance connected to a display screen and to a wireless speaker including a buffer storing audio frames so as to allow latency between receiving encoded audio frames and supplying decoded audio frames. The method comprises the steps of: determining a filling level of the buffer; comparing the filling level of the buffer with a filling target for the buffer and deducing a filling difference therefrom; and increasing or decreasing the number of audio frames that are stored as a function of the filling difference so as to adjust latency.
Owner:SAGEMCOM BROADBAND
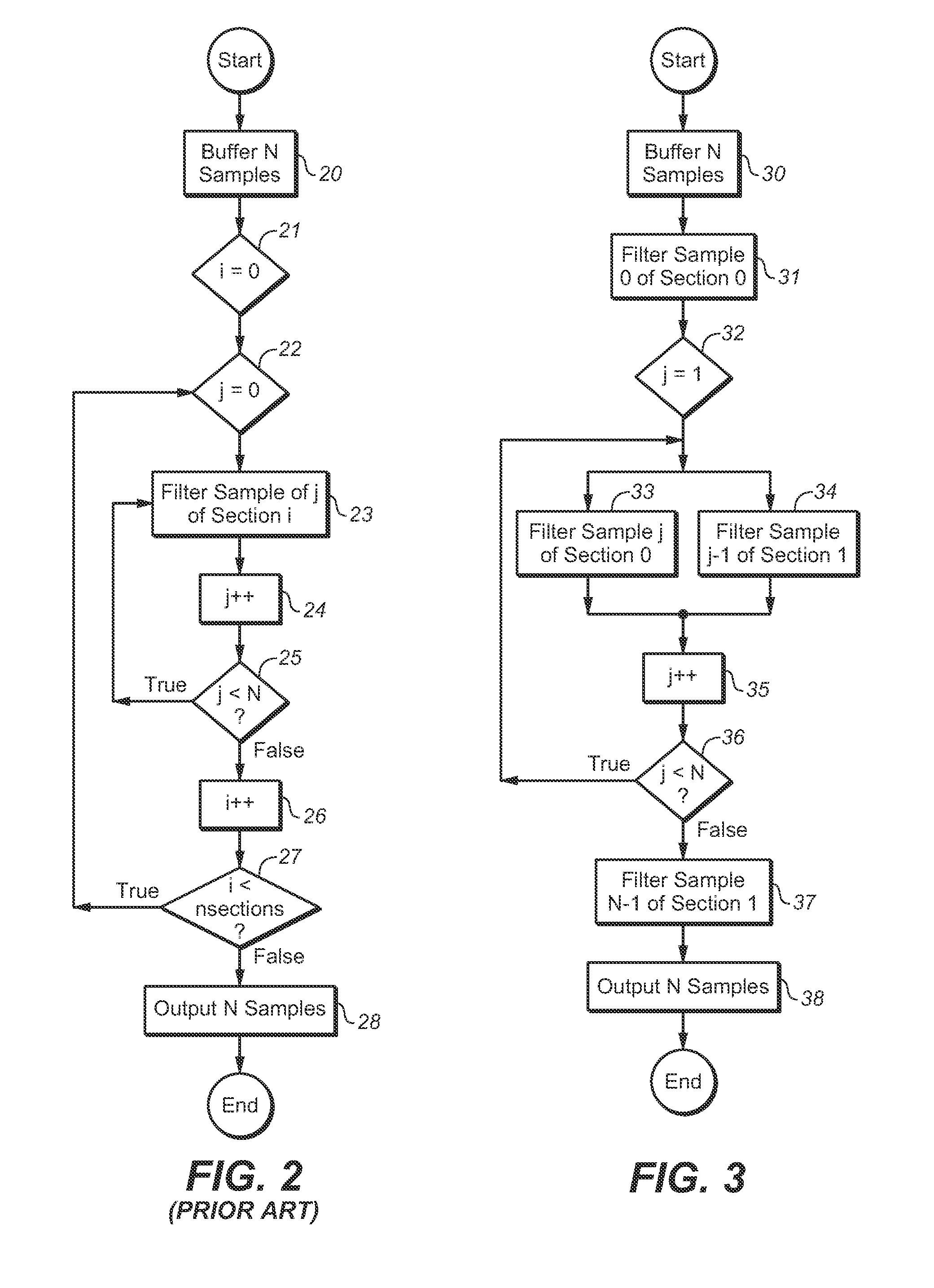
Multistage IIR Filter and Parallelized Filtering of Data with Same
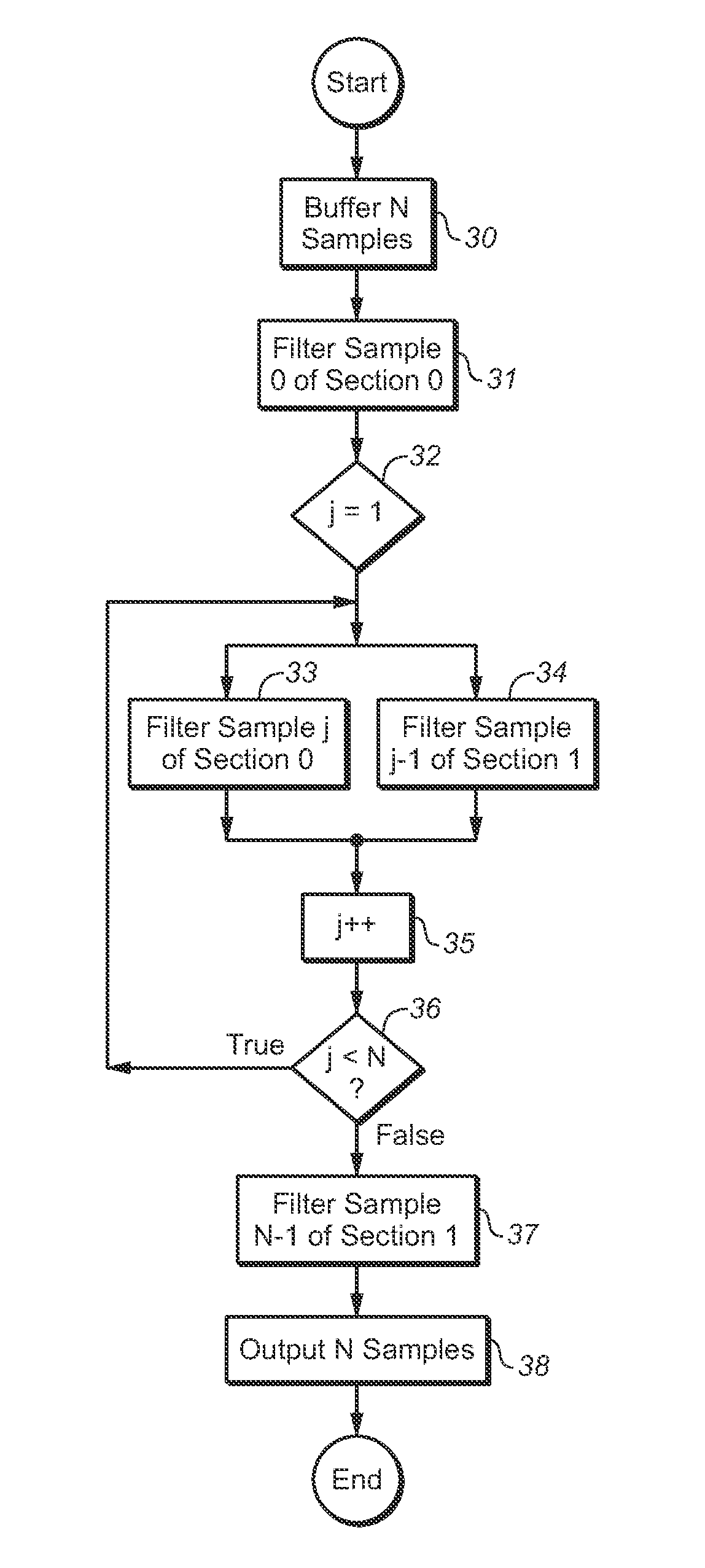
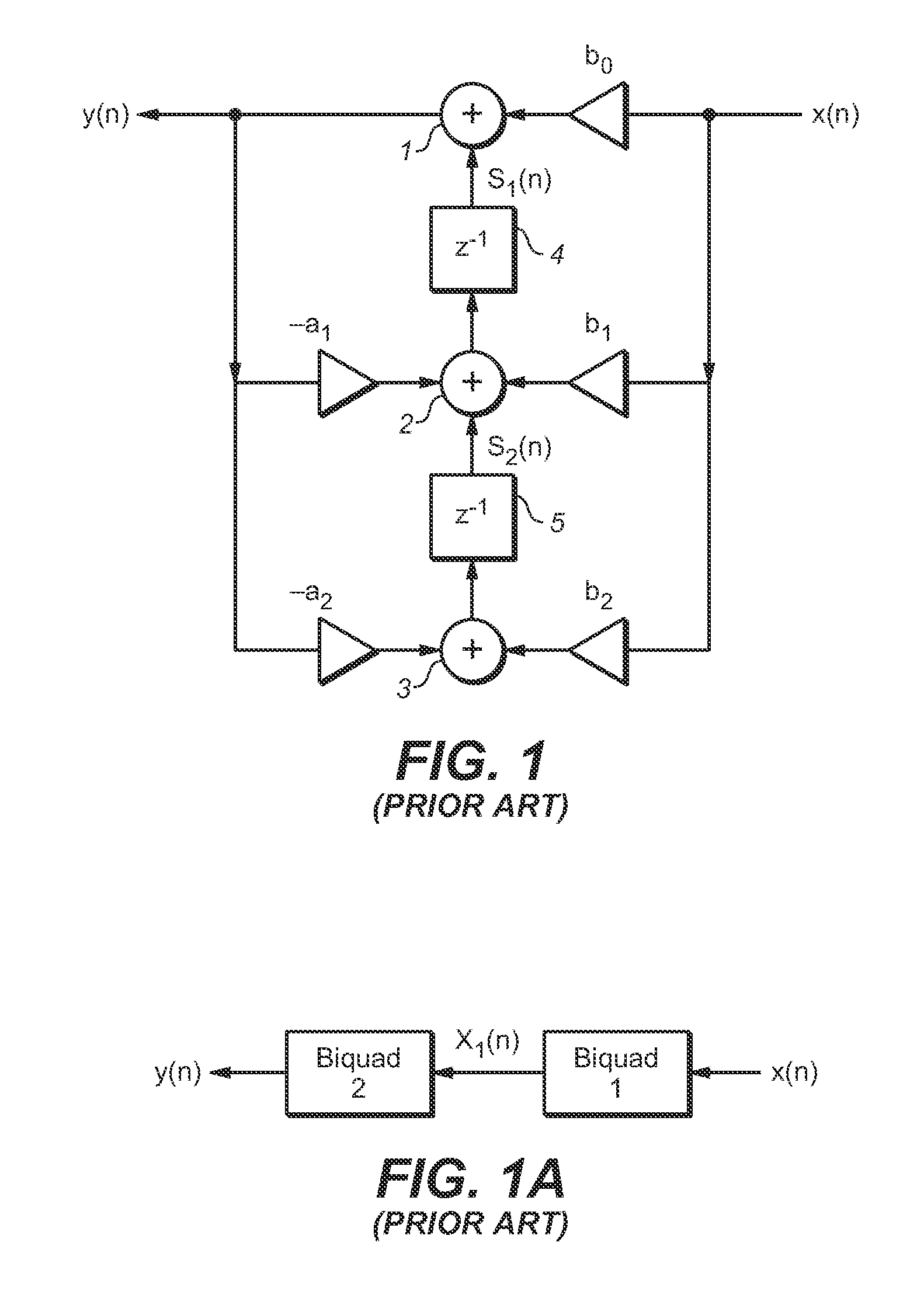
ActiveUS20140046673A1Digital technique networkSpeech analysisBiquadratic filterComputational science
In some embodiments, a multistage filter whose biquad filter stages are combined with latency between the stages, a system (e.g., an audio encoder or decoder) including such a filter, and methods for multistage biquad filtering. In typical embodiments, all biquad filter stages of the filter are operable independently to perform fully parallelized processing of data. In some embodiments, the inventive multistage filter includes a buffer memory, at least two biquad filter stages, and a controller coupled and configured to assert a single stream of instructions to the filter stages. Typically, the multistage filter is configured to perform multistage filtering of a block of input samples in a single processing loop with iteration over a sample index but without iteration over a biquadratic filter stage index.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com