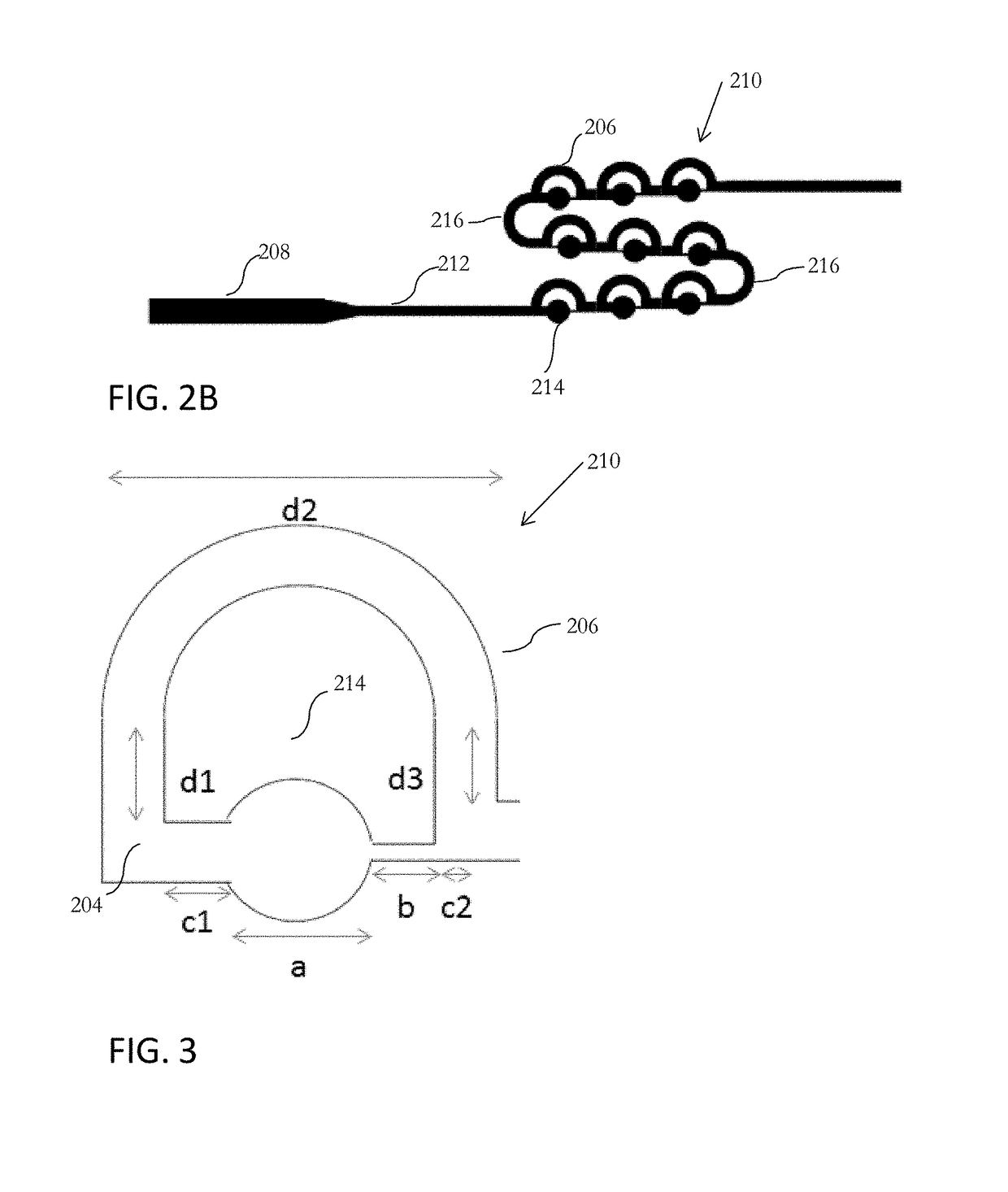
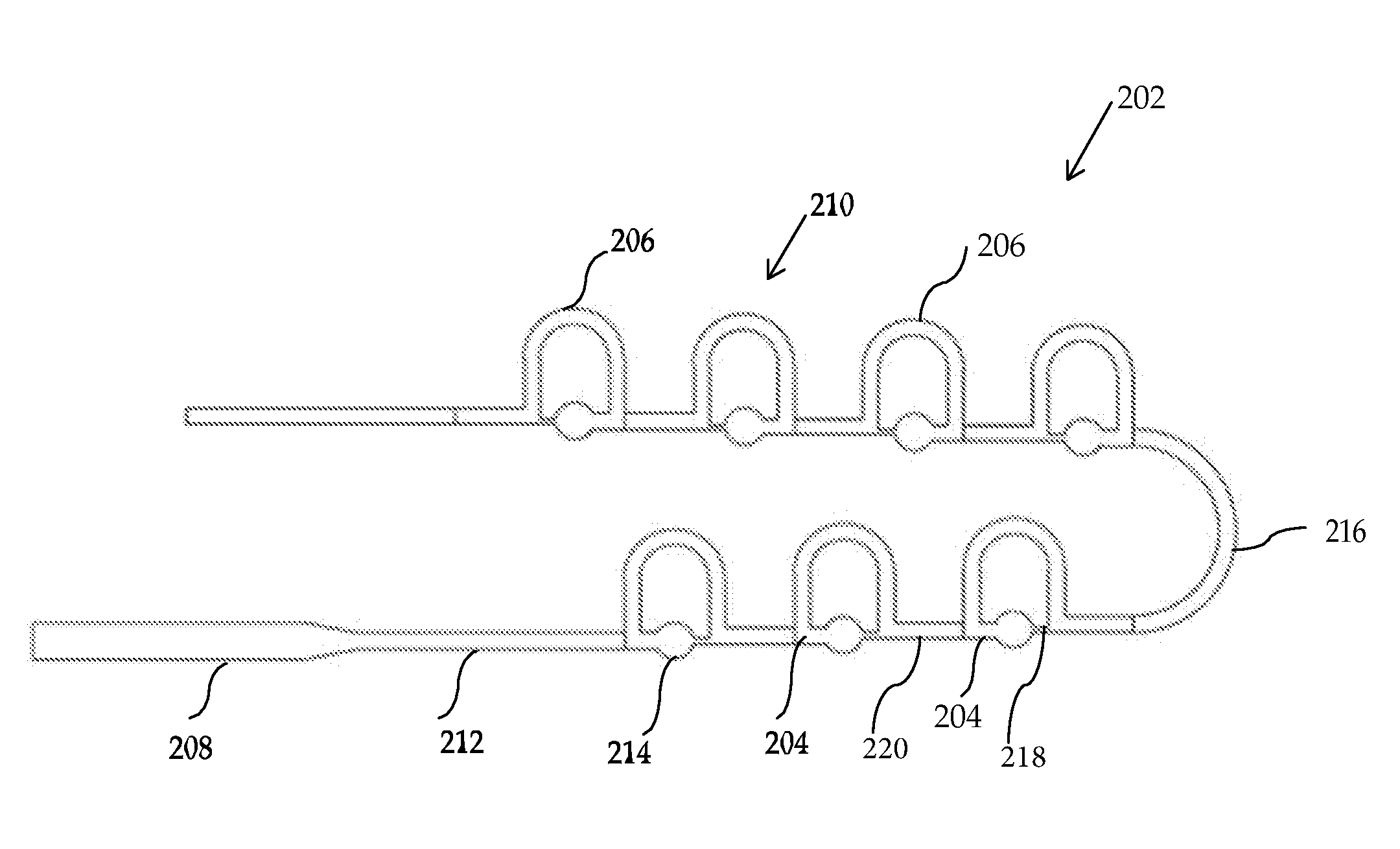
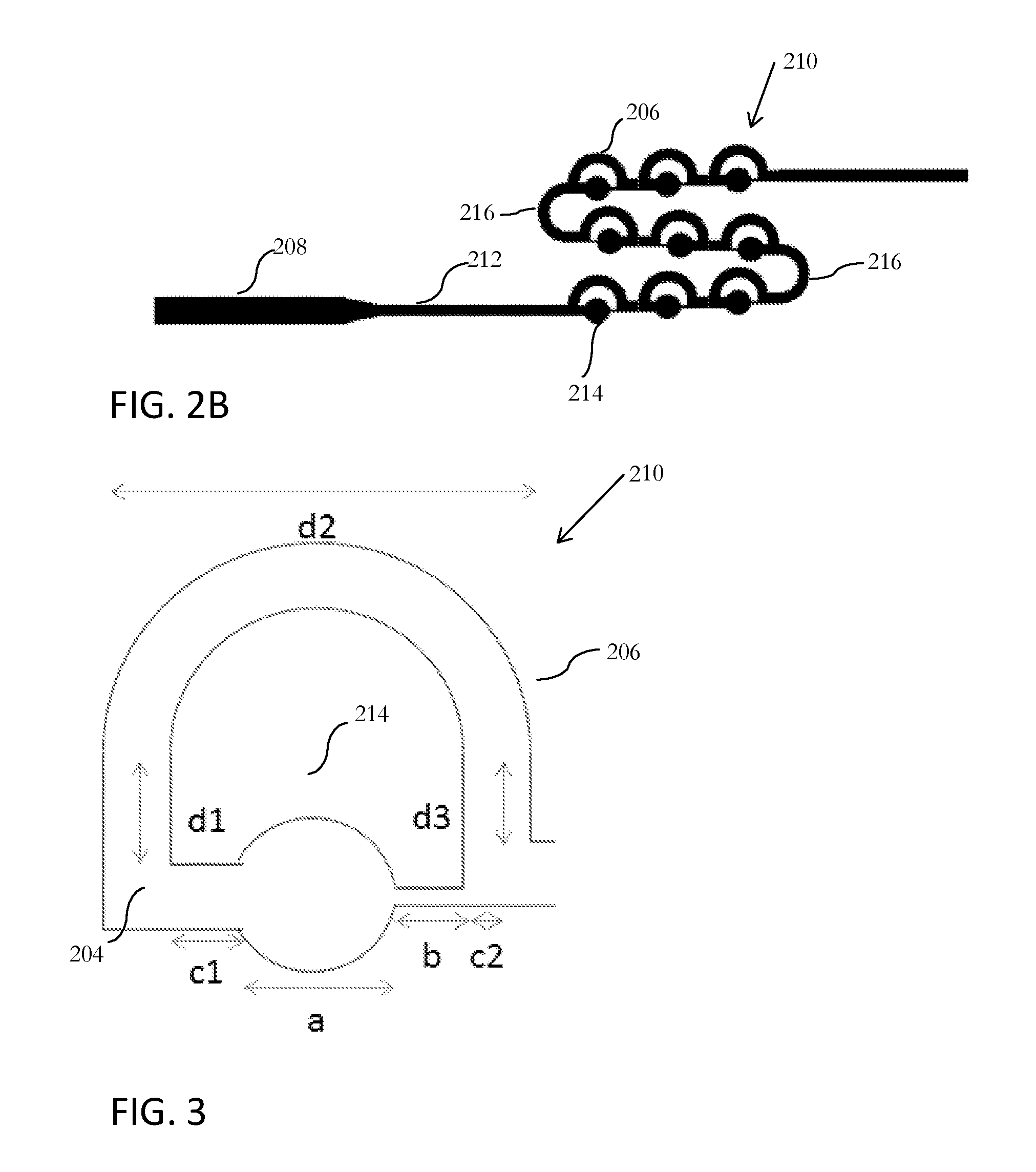
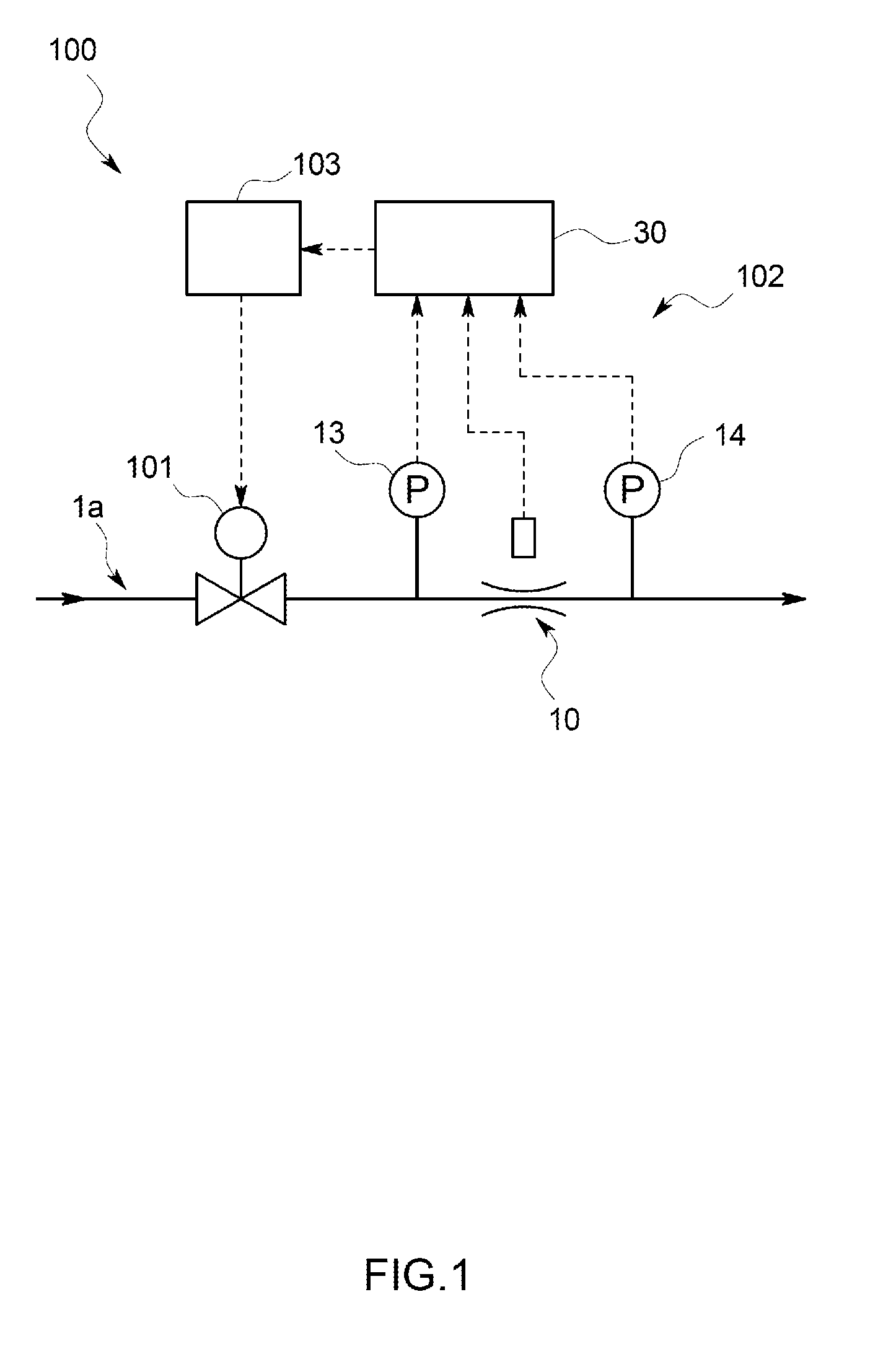
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Hydrodynamic resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
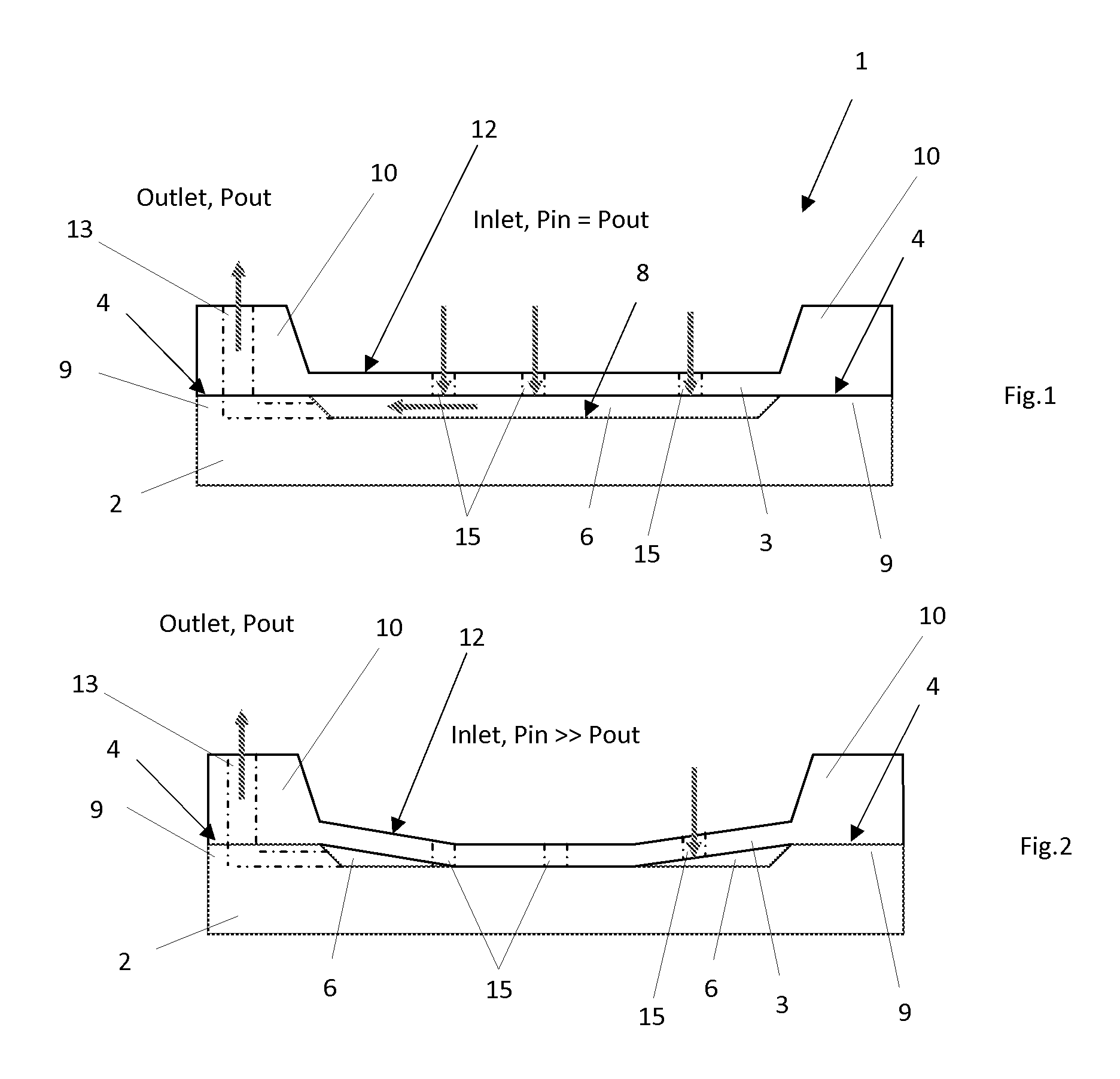
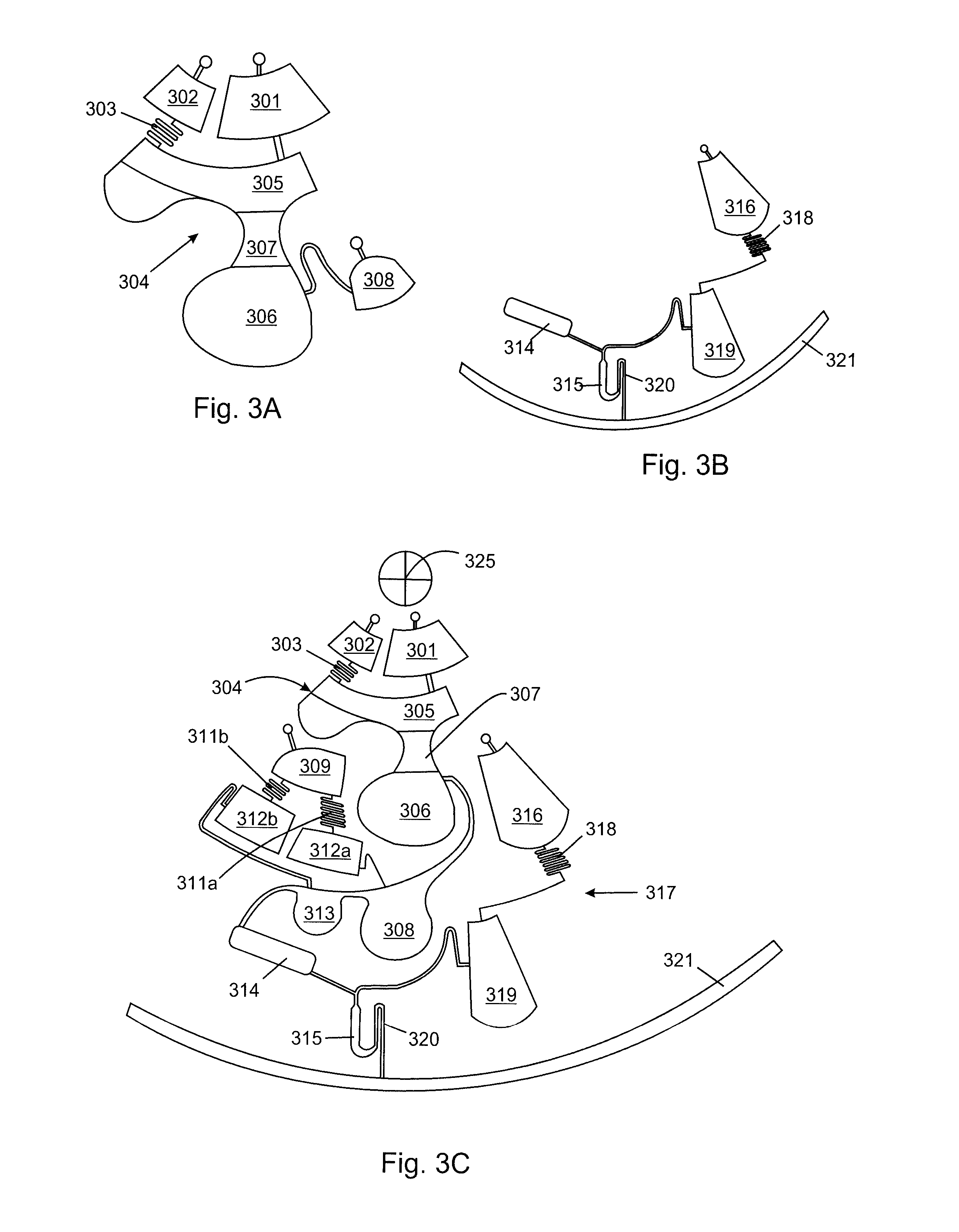
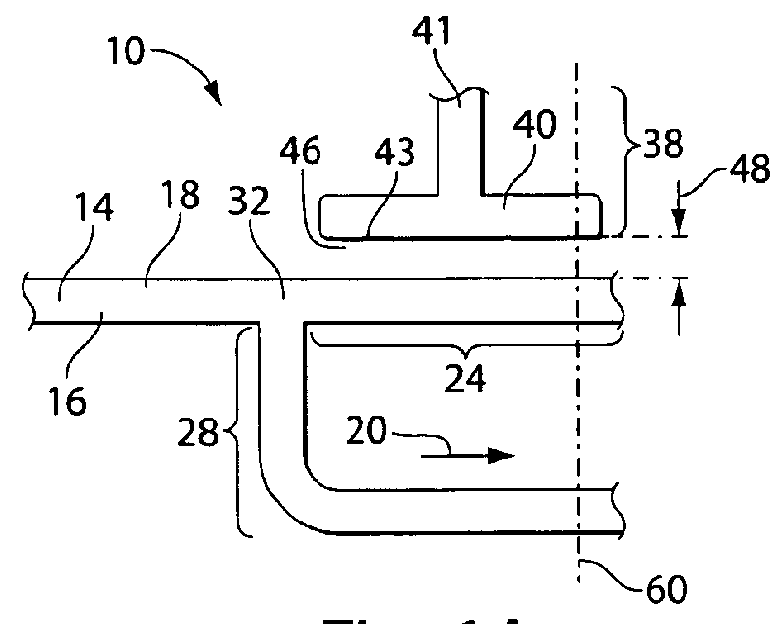
Valves and other flow control in fluidic systems including microfluidic systems
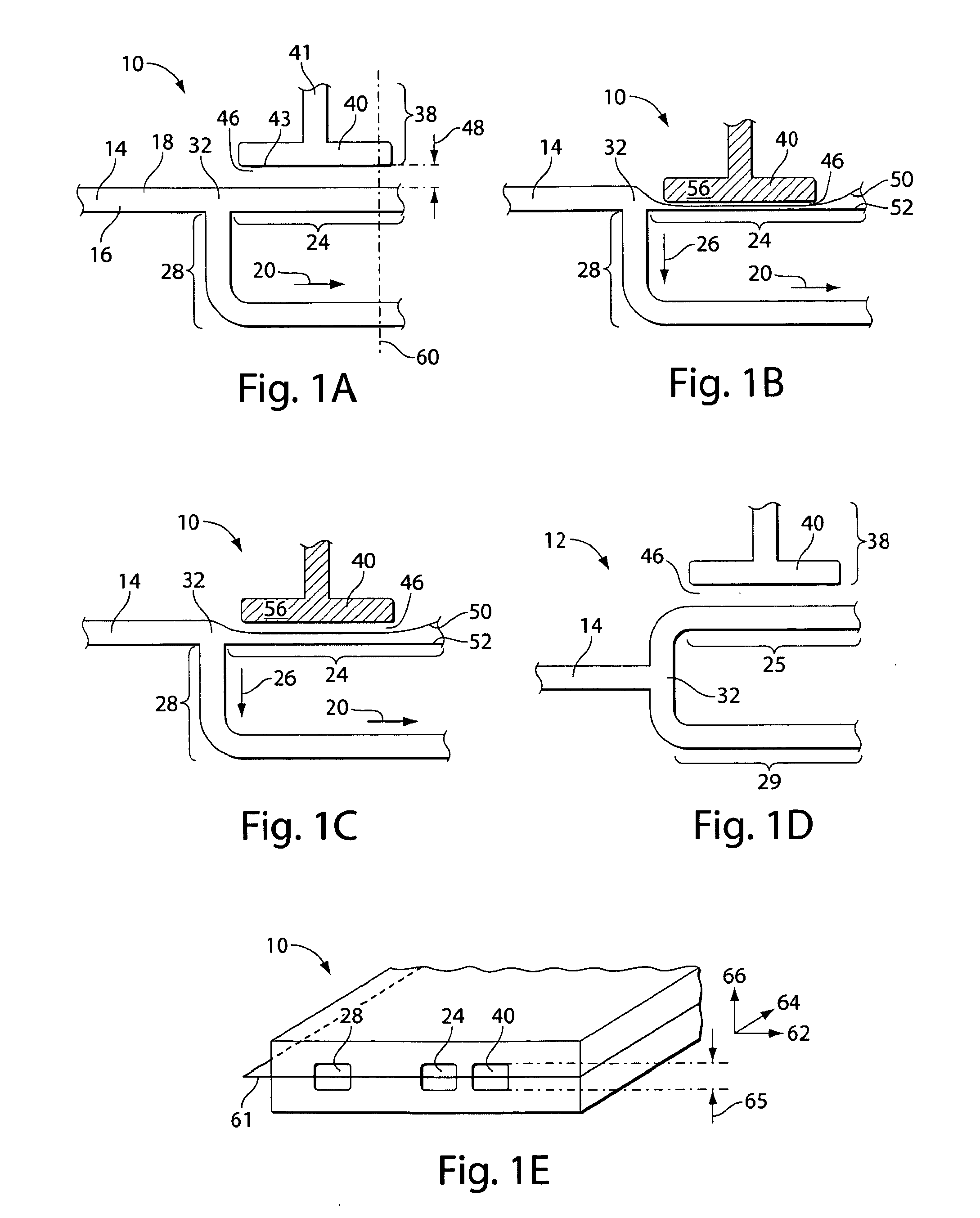
ActiveUS20110151578A1Variation in amountValve arrangementsWithdrawing sample devicesControl flowControl channel
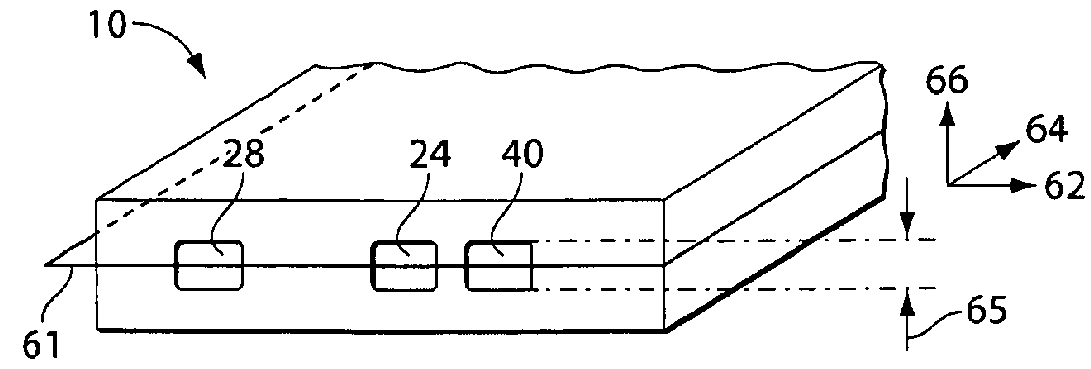
Articles and methods for controlling flow in fluidic Systems, especially in microfluidic Systems, are provided. A microfluidic System includes a configuration such that the actuation of a single valve can allow the switching of fluids from a first fluid path (e.g., a first channel section) to a second fluid path (e.g., a second channel section). This may be achieved by incorporating a valve (38) with a first channel section (24), which may have a lower hydrodynamic resistance than a second channel section (28) prior to actuation of the valve. Actuation of the valve (38) can cause only the hydrodynamic resistance of the first channel section (24) to increase, thereby redirecting fluid flow into the second channel section (28) (which now has a relatively lower hydrodynamic resistance). The valve comprises a control channel (40) for introducing a positive or reduced pressure, and is adapted to modulate fluid flow in an adjacent channel section by constricting or expanding the channel section (24).
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
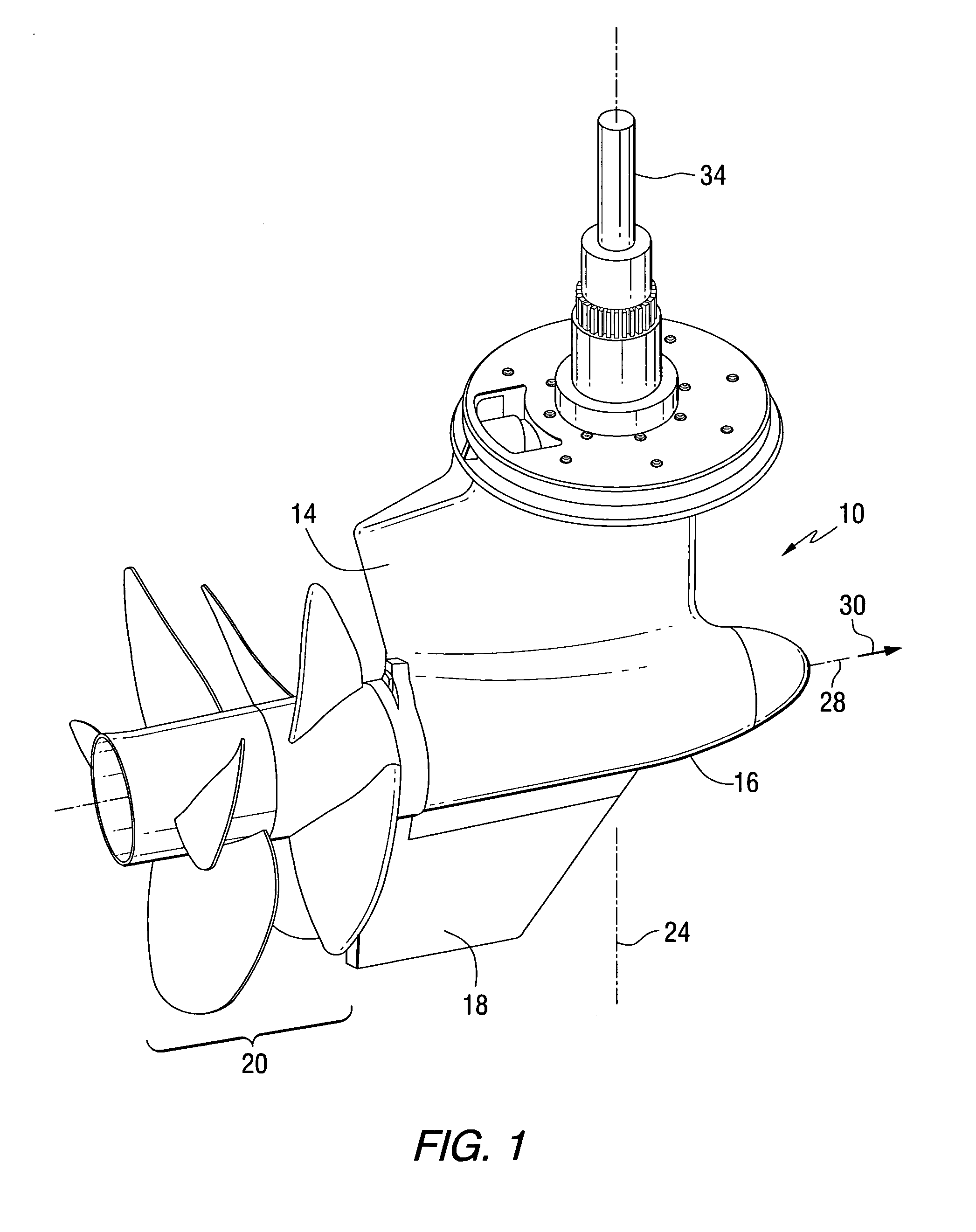
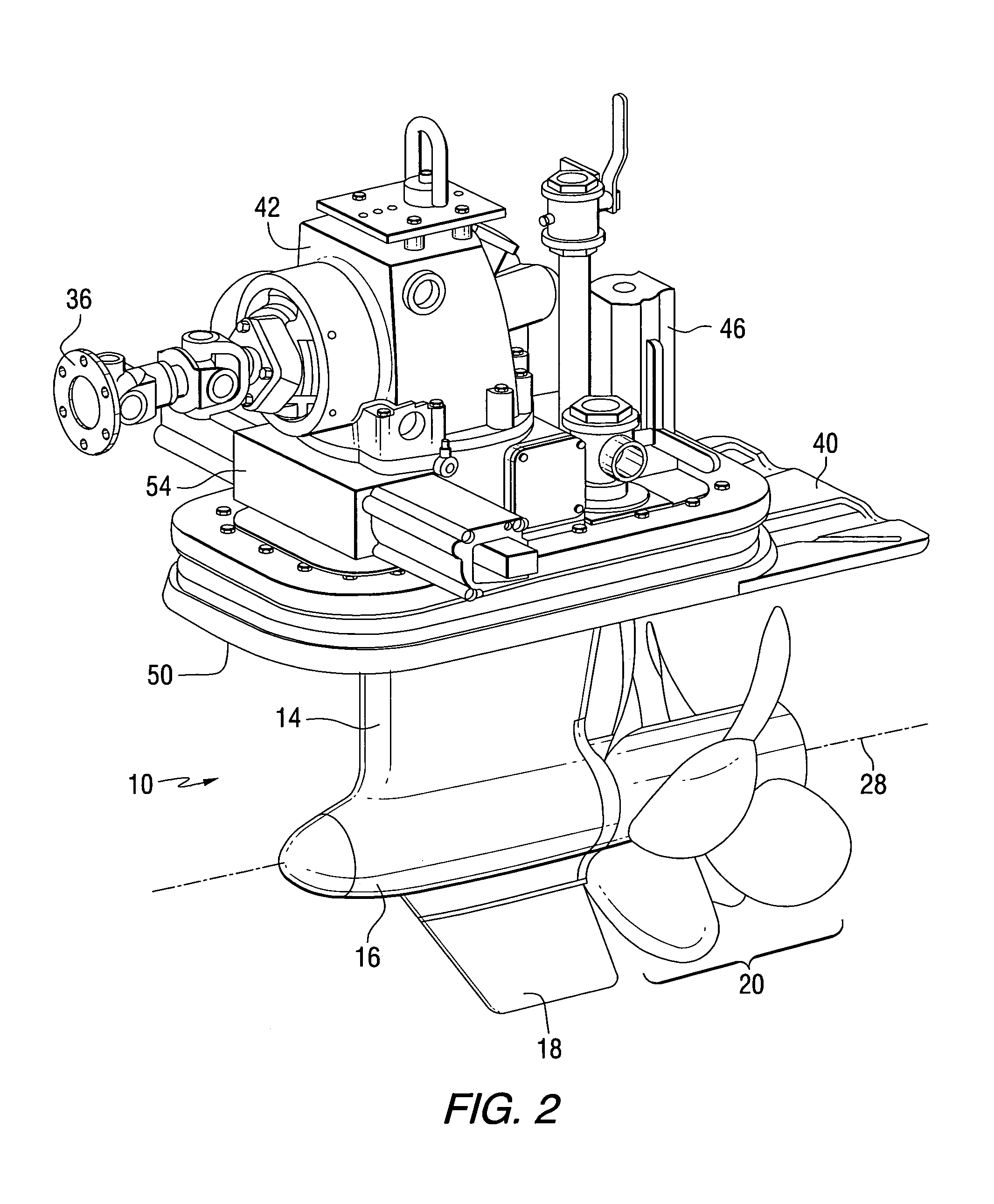
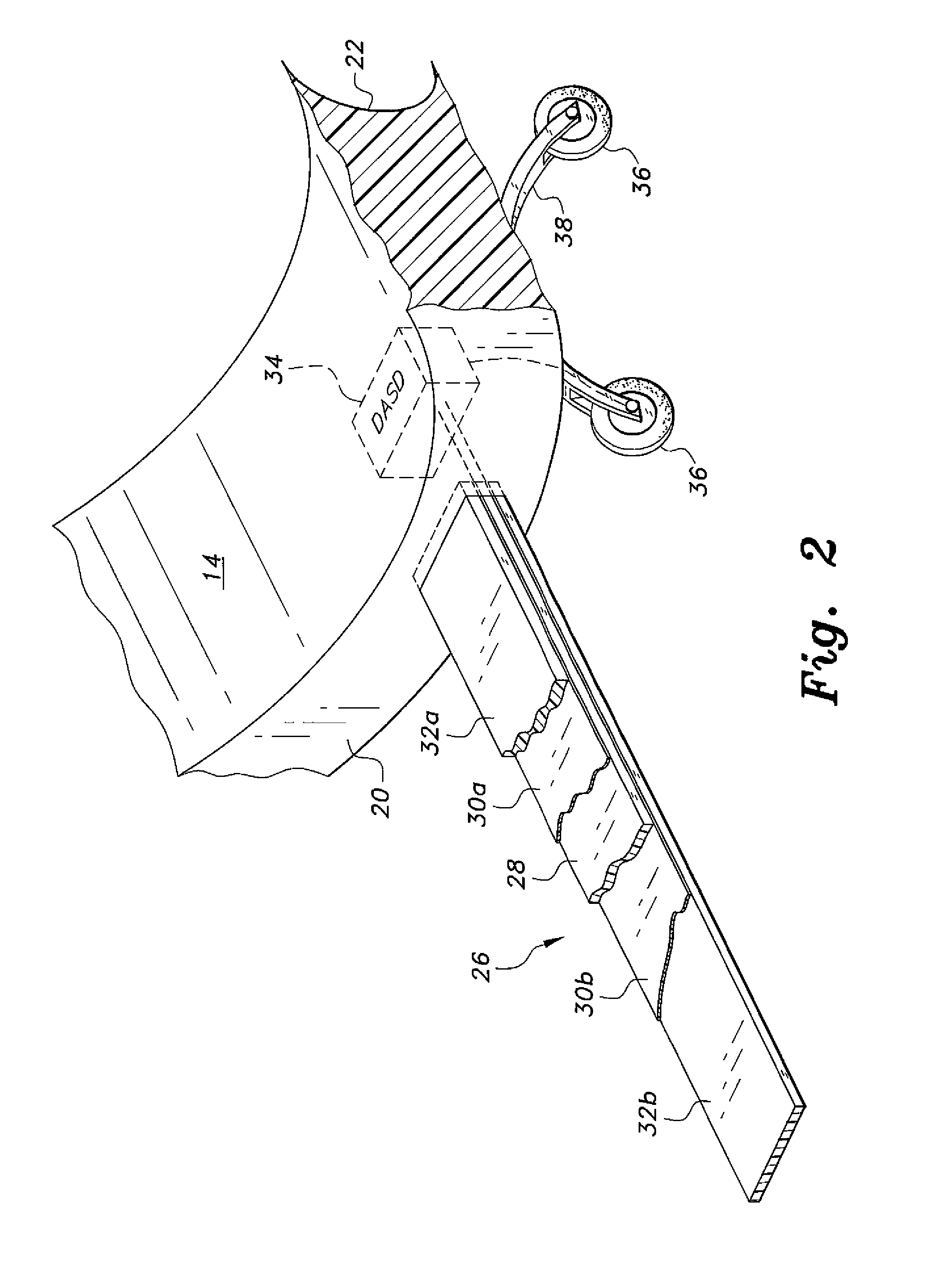
Method for braking a vessel with two marine propulsion devices
InactiveUS7131385B1Steering by extensible flapsSteering by propulsive elementsMarine propulsionMarine engineering
A method for controlling the movement of a marine vessel comprises steps that rotate two marine propulsion devices about their respective axes in order to increase the hydrodynamic resistance of the marine propulsion devices as they move through the water with the marine vessel. This increased resistance exerts a braking thrust on the marine vessel. Various techniques and procedures can be used to determine the absolute magnitudes of the angular magnitudes by which the marine propulsion devices are rotated.
Owner:BRUNSWICK CORPORATION
Filter material, method for the production thereof, a filter and filtering method
ActiveUS20080164214A1High propertyLow hydrodynamic resistanceOther chemical processesLayered productsFiberRetention efficiency
The invention concerns the production of filter materials for the purification and disinfection of water, water solutions and other liquids, as well as for sterilizing filtration of injections and other solutions, for concentration of biomolecules in physiological liquids, concentration and extraction of viruses, preparation of apyrogenic water, in biocatalytic diaphragm reactors. The invention solves the problems of a new filter material production, characterized by high sorption properties, high retention efficiency of submicron electronegative particles, microorganisms, submicron non-polar particles and chemical contaminations, and, at the same time, characterized by low hydrodynamic resistance. A base of filter material is the nonwoven organic synthetic polymeric fabric, modified by the aluminum hydroxide particles, fixed to the surface of base fibers for improvement of its sorption properties and for making it positively charged. A method of filter material production comprises: applying the modifying composition onto the fibrous base in the form of organic nonwoven synthetic polymeric fabric, wherein said modifying composition comprises the particles of the aluminum-based material, hydrolysis thereof results to formation and fixation of the aluminum hydroxide particles to the base fibers. A method of fluid filtration is carried out using the filter material as a non-woven organic synthetic polymeric fabric, to the fibers of which the aluminum hydroxide particles are fixed.
Owner:INST OF STRENGTH PHYSICS & MATERIALS SCIENC
Methods and Devices to Control Fluid Volumes, Reagent and Particle Concentration in Arrays of Microfluidic Drops
ActiveUS20140051062A1Small hydrodynamic resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringReagent
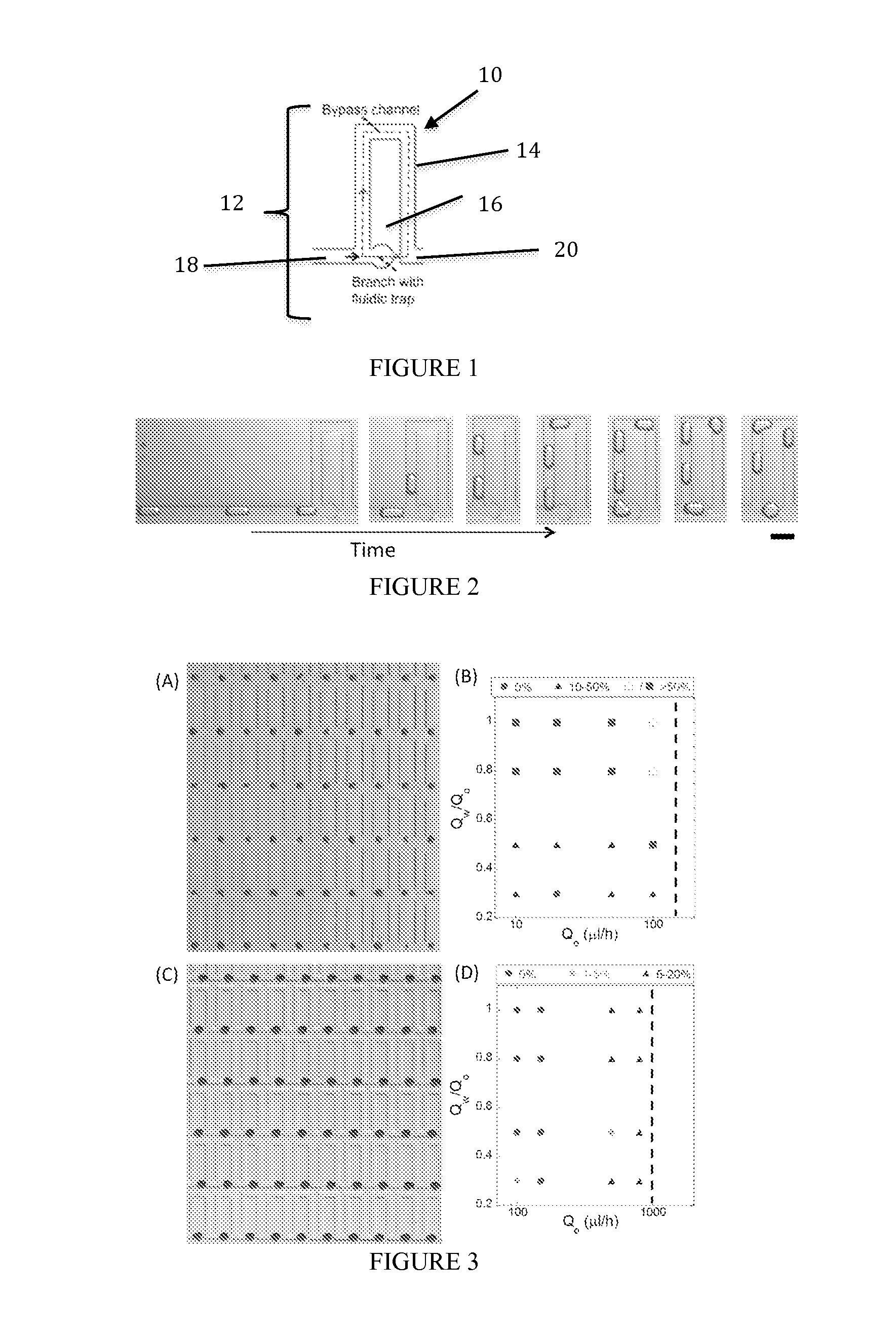
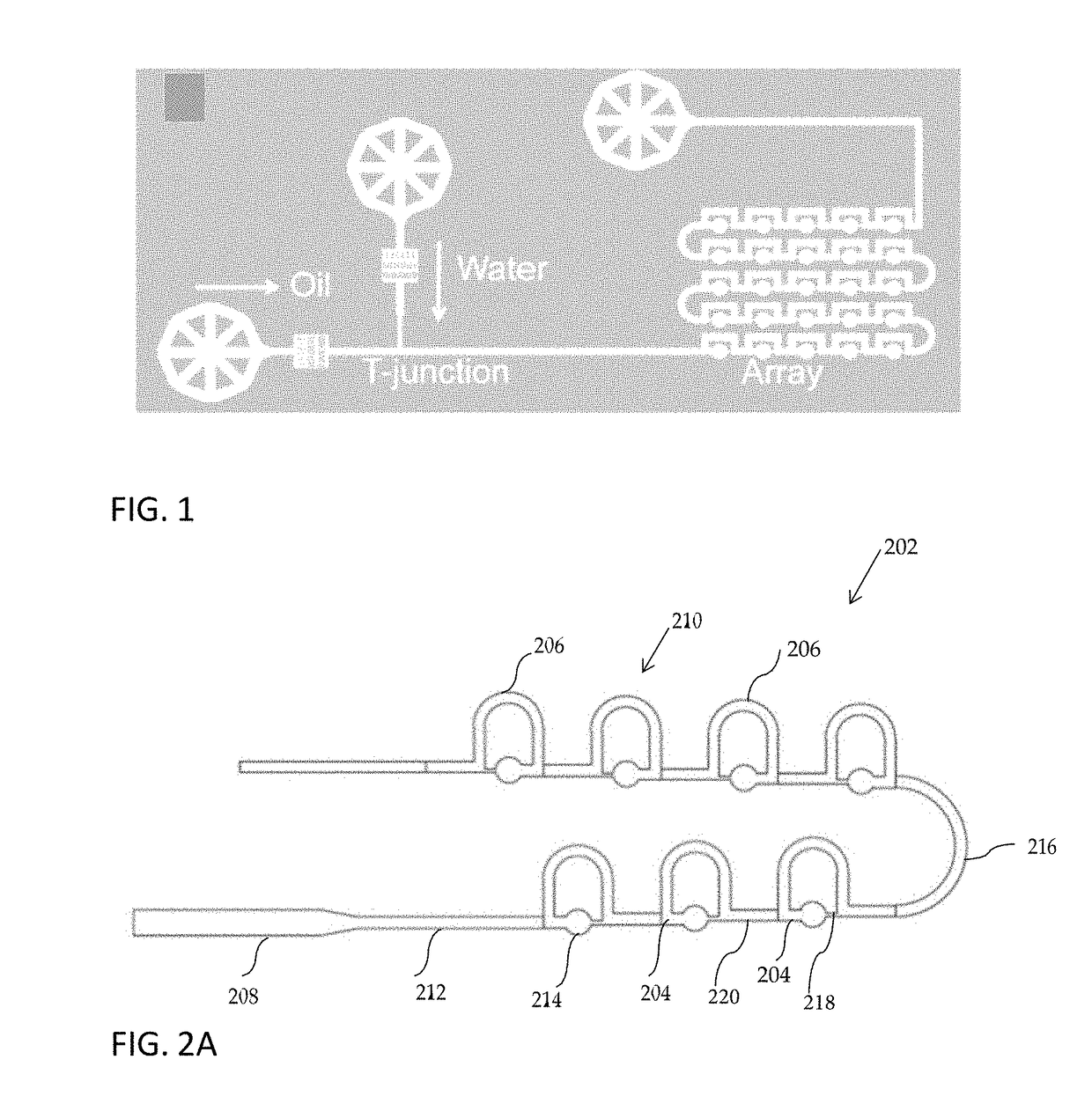
The present invention includes a microfluidic device comprising one or more parking loops 12, each parking loop 12 comprising a bypass channel 14 and a lower branch 16 capable of retaining one or more drops, wherein bypass channel 14 has a smaller hydrodynamic resistance than the lower branch 16.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
Vane type hydraulic actuator
InactiveUS6237466B1Improve productivityLow production costValve arrangementsOscillating piston enginesEngineeringActuator
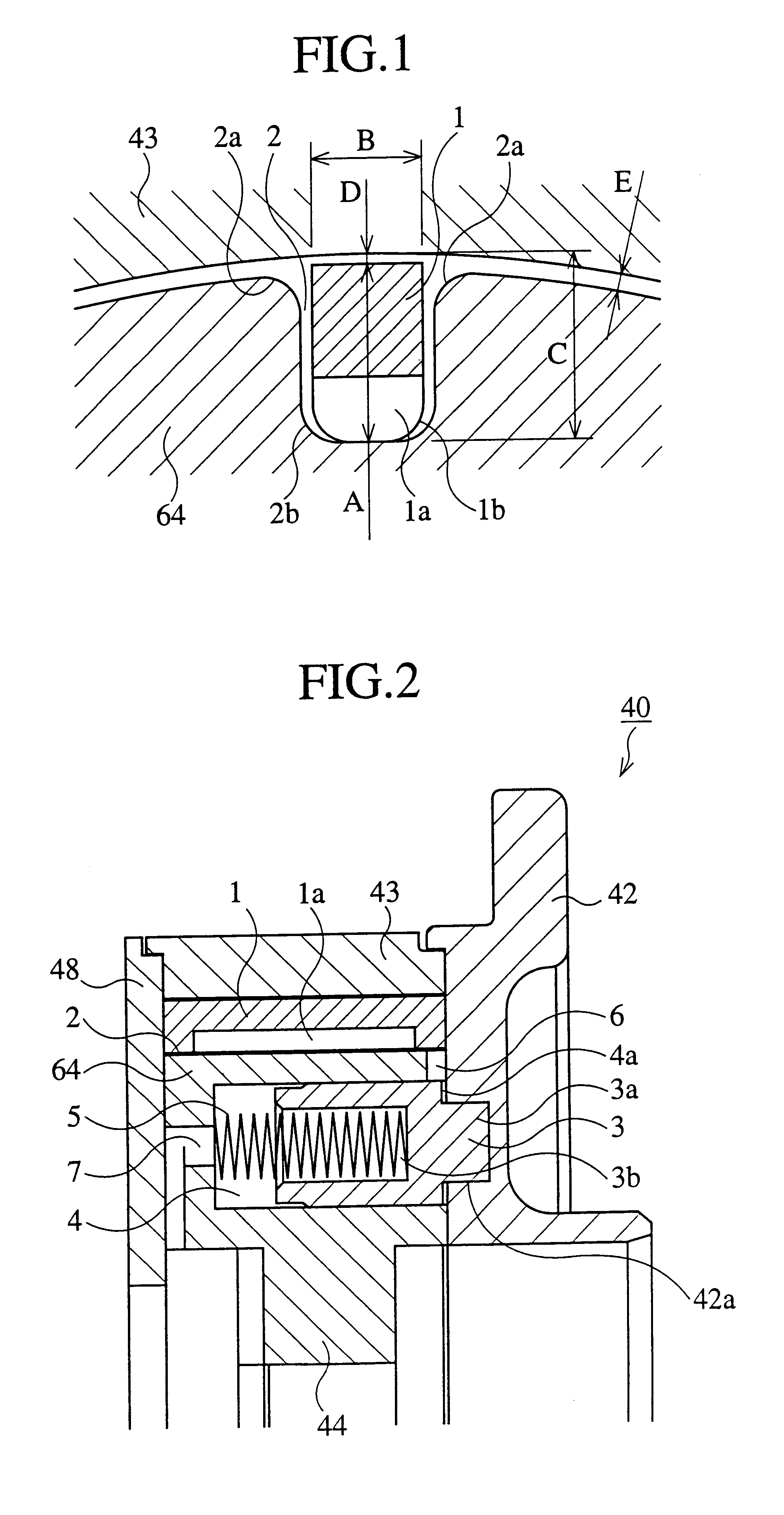
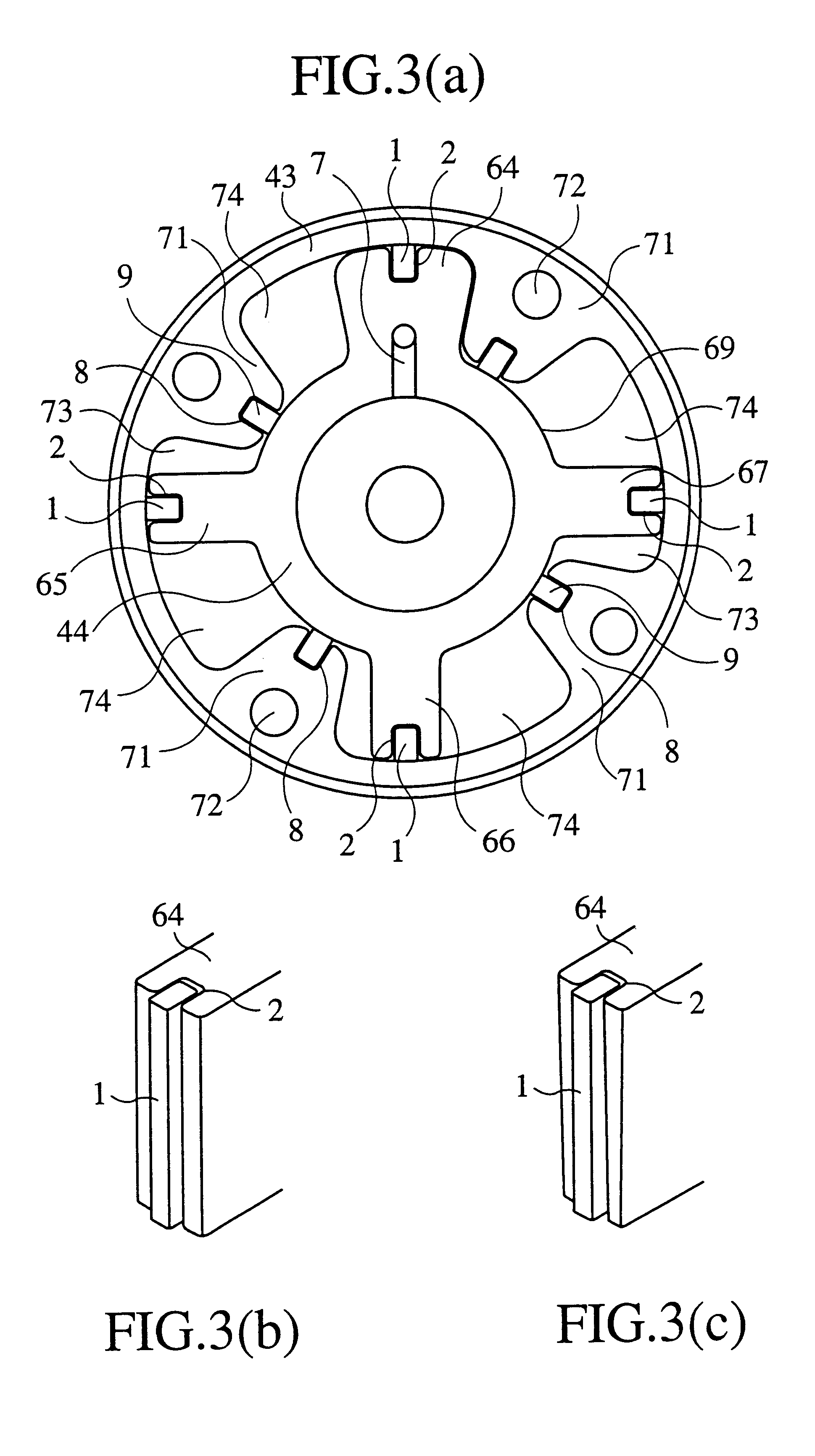
A vane type hydraulic actuator, wherein a chip seal 1, as a seal element between the case 43 and the rotor 44, can be pressed to contact tightly with the counter surface, without using a spring 47 as in the prior art, when a working oil is supplied either from the oil pressure chambers for timing retard or for timing advance. Simultaneously, the locking between the rotor 44 and the case 43 can be released. The hydrodynamic resistance at the gap between the tip of the seal element (chip seal) 1 and the counter surface of the seal element is made larger than that at the gap between the flank of the seal element 1 and the flank of the seal groove 2, which accomodates the seal element, so that the working oil of the hydraulic actuator flows between the flanks. The working oil at the bottom of the seal element urges the seal element to contact tightly with the counter surface. An oil channel 6 connects the bottom of the seal groove and a stopper pin holding hole 4, which holds a stopper pin 3 pressed by a spring 5. When a working oil is supplied from either of oil pressure chambers for timing retard or advance, the channel 6 opens to supply a working oil into the stopper pin holding hole 5 so as to displace the pin against the biasing force of the spring 5 to release the suppression of rotation.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Passive fluid flow regulator
ActiveUS20110132480A1Simple and cheap to manufactureAvoid less flexibilityDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBiomedical engineeringStreamflow
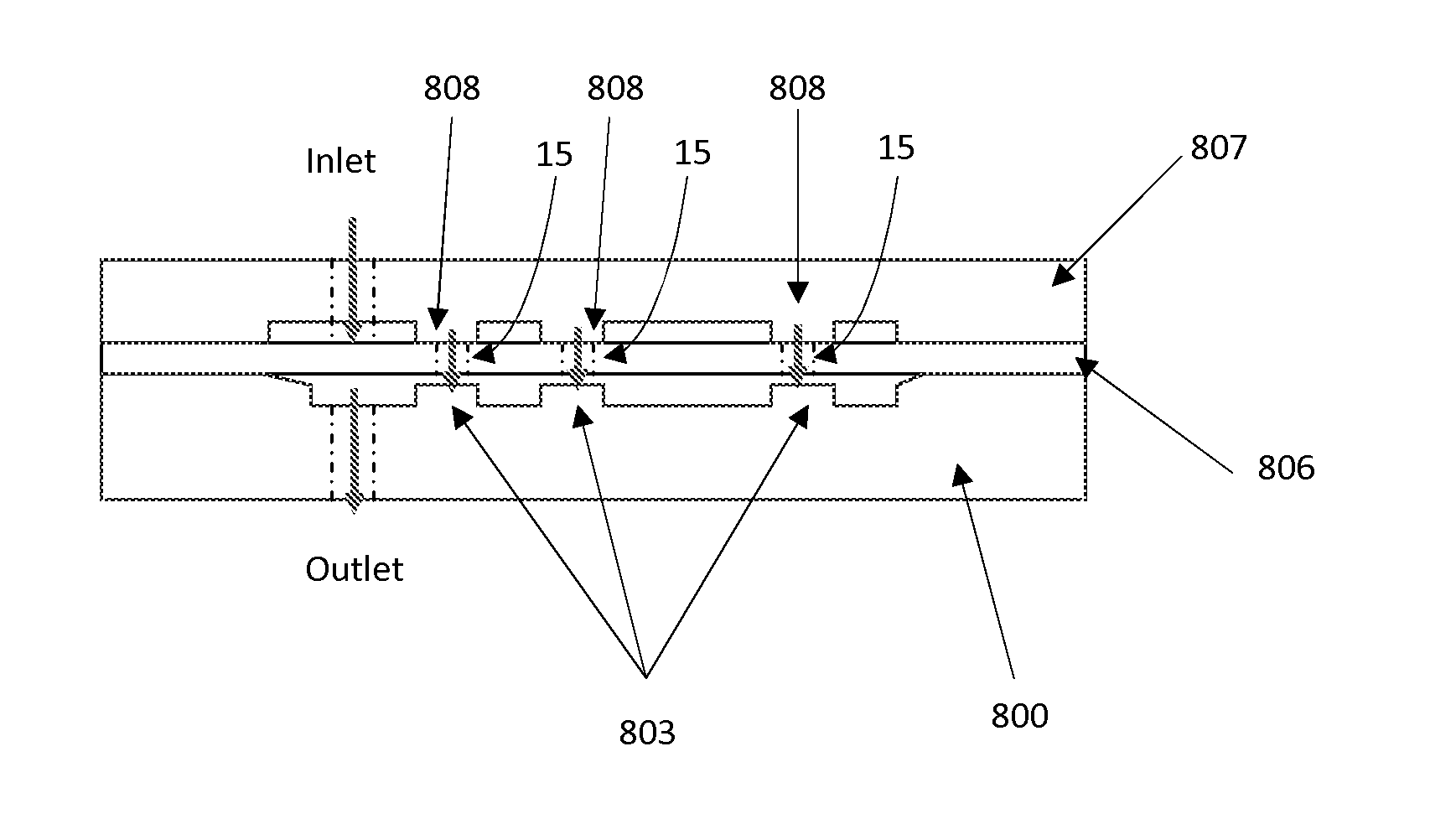
A fluid flow regulator (1) of the passive type is disclosed which has a fluid inlet adapted to be connected to a fluid reservoir and a fluid outlet (13) adapted to be connected to a patient's body. The regulator comprises a rigid substrate (2) and a resilient membrane (3) tightly linked together so as to define a cavity (6) there between which is disconnected to the fluid outlet while the membrane has a first surface (12) opposite the cavity which is connected to the fluid inlet. The membrane has a plurality of through holes (15) contiguous with the cavity, to define a pathway for a fluid from the fluid inlet to the fluid outlet, and is flexible so as to be able to come into contact with the substrate as a fluid applies a sufficient pressure on the first surface. The through holes are arranged such that, when the fluid pressure increases, they close one after the other to increase the regulator fluidic resistance so that a fluid flow rate would be substantially constant as a function of the pressure applied on the first surface within a predefined pressure range.
Owner:DEBIOTECH SA
Centrifugal microfluidic platform
InactiveUS20140134631A1Avoid flowEasy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringCentrifugal microfluidics
A centrifugal microfluidic device is provided having a microfluidic circuit, a fluid reservoir for providing fluid in the microfluidic circuit, a hydrodynamic resistance element in fluid communication with the reservoir for controlling rate of flow of a fluid out of the reservoir, and a siphoned chamber in fluid communication with the hydrodynamic resistance element and the microfluidic circuit for receiving fluid from the hydrodynamic resistance element and for delaying and metering of the fluid into the microfluidic circuit. The microfluidic device is useful for performing a biological assay. Operation of the device is completely independent on the liquid-solid contact angle and wetting properties of the liquids on the solid material of the platform, and the device does not need a carefully controlled rotation protocol.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Microfluidic Device for the Generation of Combinatorial Samples
InactiveUS20170282145A1Increase resistanceGood choiceSequential/parallel process reactionsFlow mixersInlet channelEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a microfluidic device and a method allowing the generating and screening of combinatorial samples. A microfluidic device for producing droplets of at least one sample into an immiscible phase is provided, the device comprising a droplet maker connecting an immiscible phase channel and a sample channel having at least one sample inlet connected to at least one sample inlet channel injecting the at least one sample into the sample channel, wherein the injection of the at least one sample is controlled by at least one sample valve, so that the at least one sample flows either towards a sample waste outlet or into the at least one sample inlet channel, wherein different sample inlet channel of the at least one sample inlet channel have the same hydrodynamic resistance resulting from the length, height and width of each sample inlet channel upstream of the droplet maker.
Owner:EURO LAB FUER MOLEKULARBIOLOGIE EMBL
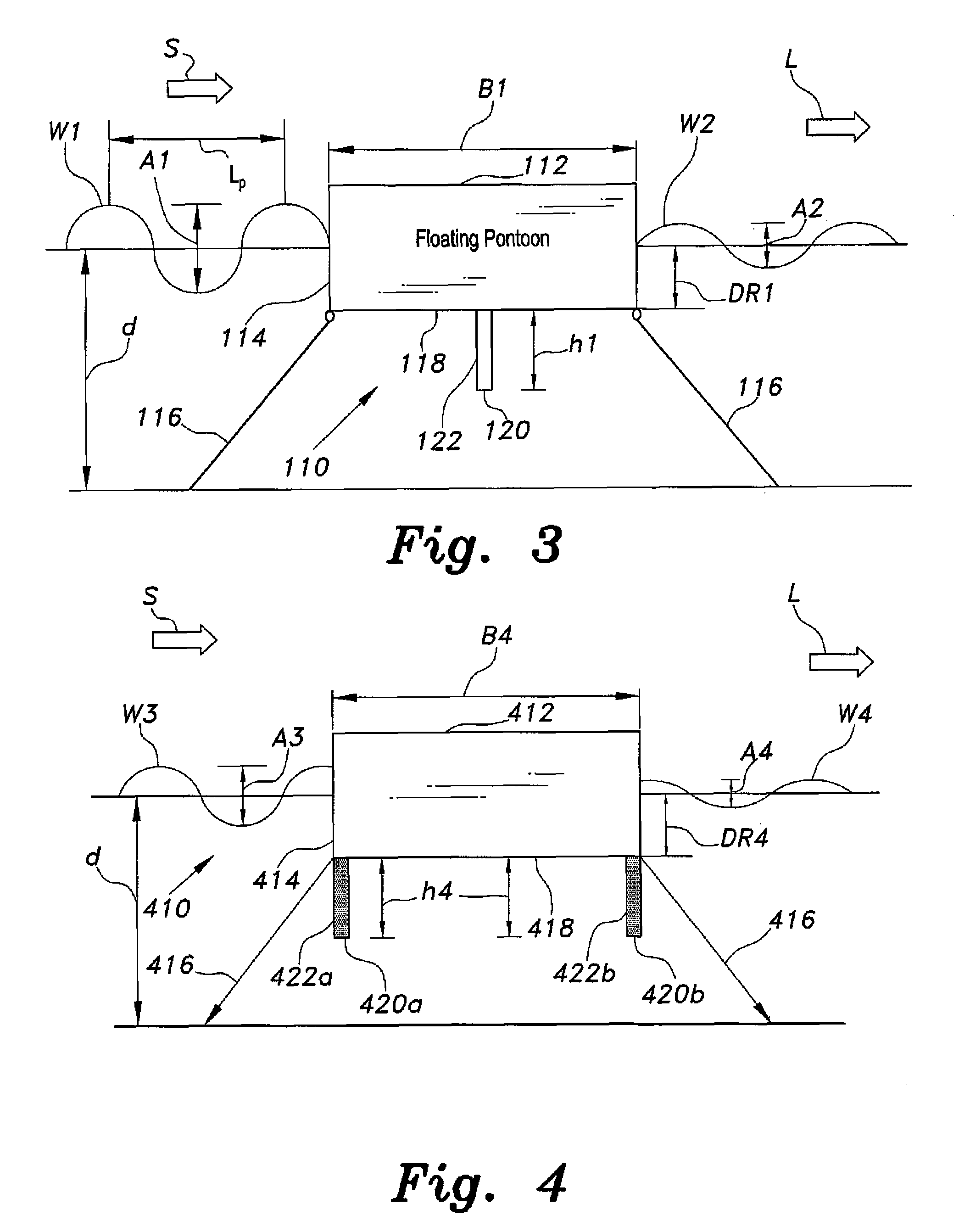
Floating breakwater
The floating breakwater includes various different embodiments, as can have an anchored or moored float. The float is desirably in the geometric form of a generally rectangular solid configuration, but can include other forms. One or more baffles or skirt walls extend from the bottom surface of the float, thereby attenuating subsurface wave action to a greater depth than the bottom of the float. Each of the baffles or skirt walls desirably includes a thin, flat, monolithic plate member for enhancing hydrodynamic resistance. The one or more baffles or skirt walls can be continuous and unbroken, or can have a plurality of apertures therethrough. When three or more baffles or skirt walls are provided they can be evenly spaced, or the spacing therebetween can vary. When two or more baffles or skirt walls are provided they can have equal depths, or their depths can differ from one another.
Owner:KUWAIT INST FOR SCI RES
Floating breakwater
The floating breakwater includes various different embodiments, as can have an anchored or moored float. The float is desirably in the geometric form of a generally rectangular solid configuration, but can include other forms. One or more baffles or skirt walls extend from the bottom surface of the float, thereby attenuating subsurface wave action to a greater depth than the bottom of the float. Each of the baffles or skirt walls desirably includes a thin, flat, monolithic plate member for enhancing hydrodynamic resistance. The one or more baffles or skirt walls can be continuous and unbroken, or can have a plurality of apertures therethrough. When three or more baffles or skirt walls are provided they can be evenly spaced, or the spacing therebetween can vary. When two or more baffles or skirt walls are provided they can have equal depths, or their depths can differ from one another.
Owner:KUWAIT INST FOR SCI RES
Valves and other flow control in fluidic systems including microfluidic systems
Articles and methods for controlling flow in fluidic Systems, especially in microfluidic Systems, are provided. A microfluidic System includes a configuration such that the actuation of a single valve can allow the switching of fluids from a first fluid path (e.g., a first channel section) to a second fluid path (e.g., a second channel section). This may be achieved by incorporating a valve (38) with a first channel section (24), which may have a lower hydrodynamic resistance than a second channel section (28) prior to actuation of the valve. Actuation of the valve (38) can cause only the hydrodynamic resistance of the first channel section (24) to increase, thereby redirecting fluid flow into the second channel section (28) (which now has a relatively lower hydrodynamic resistance). The valve comprises a control channel (40) for introducing a positive or reduced pressure, and is adapted to modulate fluid flow in an adjacent channel section by constricting or expanding the channel section (24).
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Solving method of takeoff performance of ground effect vehicle
ActiveCN105046048AAccurate acquisitionCalculation method is simpleSpecial data processing applicationsFlight vehicleModel test
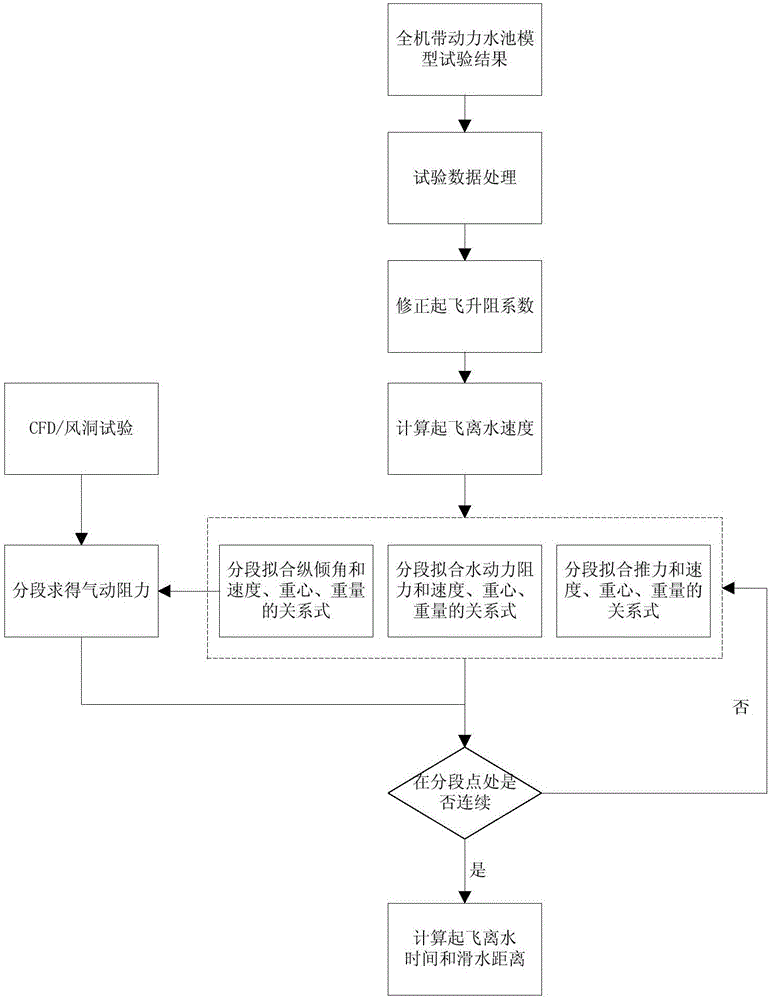
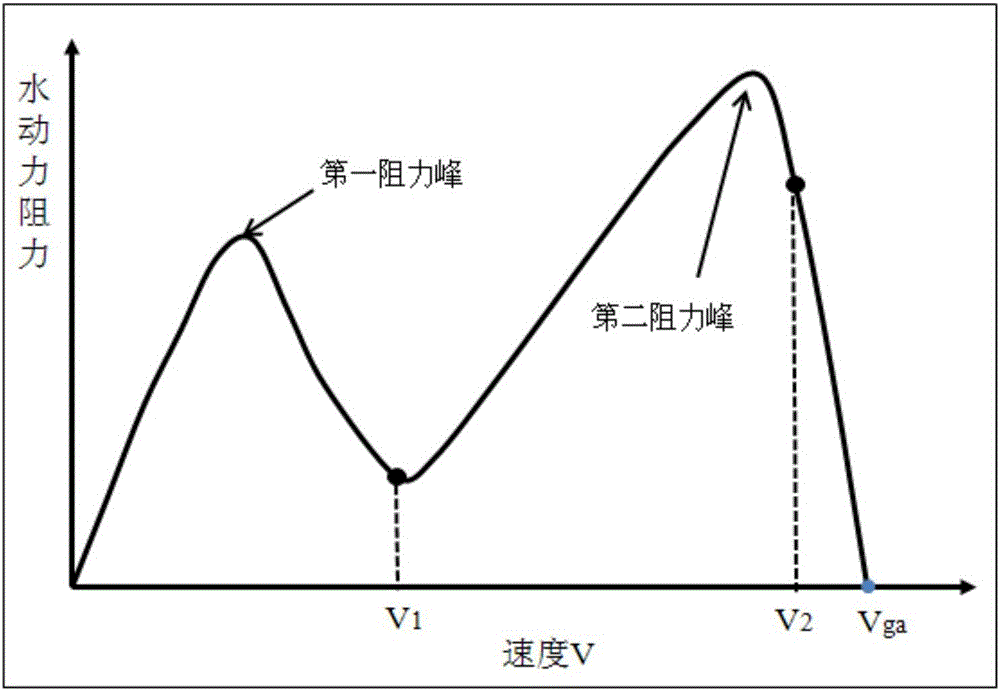
The invention discloses a solving method of the takeoff performance of a ground effect vehicle. The takeoff performance comprises takeoff water-leaving speed, water-leaving time and water skiing distance. The method comprises the steps of carefully analyzing a relationship between hydrodynamic resistance / thrust / angle of trimming in full-aircraft powered pool model test data and speed, a relationship between the hydrodynamic resistance / thrust / angle of trimming and the center of gravity, and the relationship between the hydrodynamic resistance / thrust / angle of trimming and weight; finding feature points; carrying put segmentation fitting on the hydrodynamic resistance, the thrust and the angle of trimming to obtain the relational expressions of the hydrodynamic resistance, the thrust and the angle of trimming; obtaining the relational expression of the hydrodynamic resistance and the speed by combining with a CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) computation result or a wind tunnel test result; and quickly and effectively calculating the takeoff performance of the ground effect vehicle in different states according to an equation of motion of the ground effect vehicle. The invention provides a computation method suitable for the takeoff performance of the ground effect vehicle and provides a good condition for the total performance computation of the ground effect vehicle.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Method and device for analysing molecular interactions, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130196347A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalysis methodMolecular interactions
The invention relates to a method for analysing an interaction between a first molecule and a second molecule bonded to a particle, including the following steps: contacting the first molecule with the second molecule bonded to the particle under conditions enabling the interaction thereof; applying a predetermined liquid flow to the particle bonded to the second molecule; observing a movement of the particle bonded to the second molecule caused by the applied flow; analysing the interaction according to the movement observed and the applied flow, the particle having a greater hydrodynamic resistance than the first and / or second molecule, and a mass Péclet number of greater than 1. The invention also relates to a device for analysing an interaction between a first molecule and at least one second molecule, as well as to the use of the method or of the device in screening a candidate molecule for developing a drug.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE
Generation and trapping of aqueous droplets in a microfluidic chip with an air continuous phase
ActiveUS9855555B2Withdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansTrappingAqueous droplet
The invention relates to a method and system for generating droplets of an aqueous solution on a microfluidic chip with an air continuous phase. Specifically, the droplet generator according to the present invention is integrated into a microfluidic chip to generate and introduce droplets of an aqueous solution into the microfluidic chip. The droplets travelling in a network of chip channels may be captured in on-chip traps in a manner defined by hydrodynamic resistances of chip channels. A biological reaction may be performed on a droplet trapped on the microfluidic chip.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Generation and trapping of aqueous droplets in a microfluidic chip with an air continuous phase
The invention relates to a method and system for generating droplets of an aqueous solution on a microfluidic chip with an air continuous phase. Specifically, the droplet generator according to the present invention is integrated into a microfluidic chip to generate and introduce droplets of an aqueous solution into the microfluidic chip. The droplets travelling in a network of chip channels may be captured in on-chip traps in a manner defined by hydrodynamic resistances of chip channels. A biological reaction may be performed on a droplet trapped on the microfluidic chip.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Fluid resistance device
InactiveUS20150013792A1Stable productionReduce errorsPipe elementsBranching pipesElectrical resistance and conductanceBiomedical engineering
Owner:HORIBA STEC CO LTD
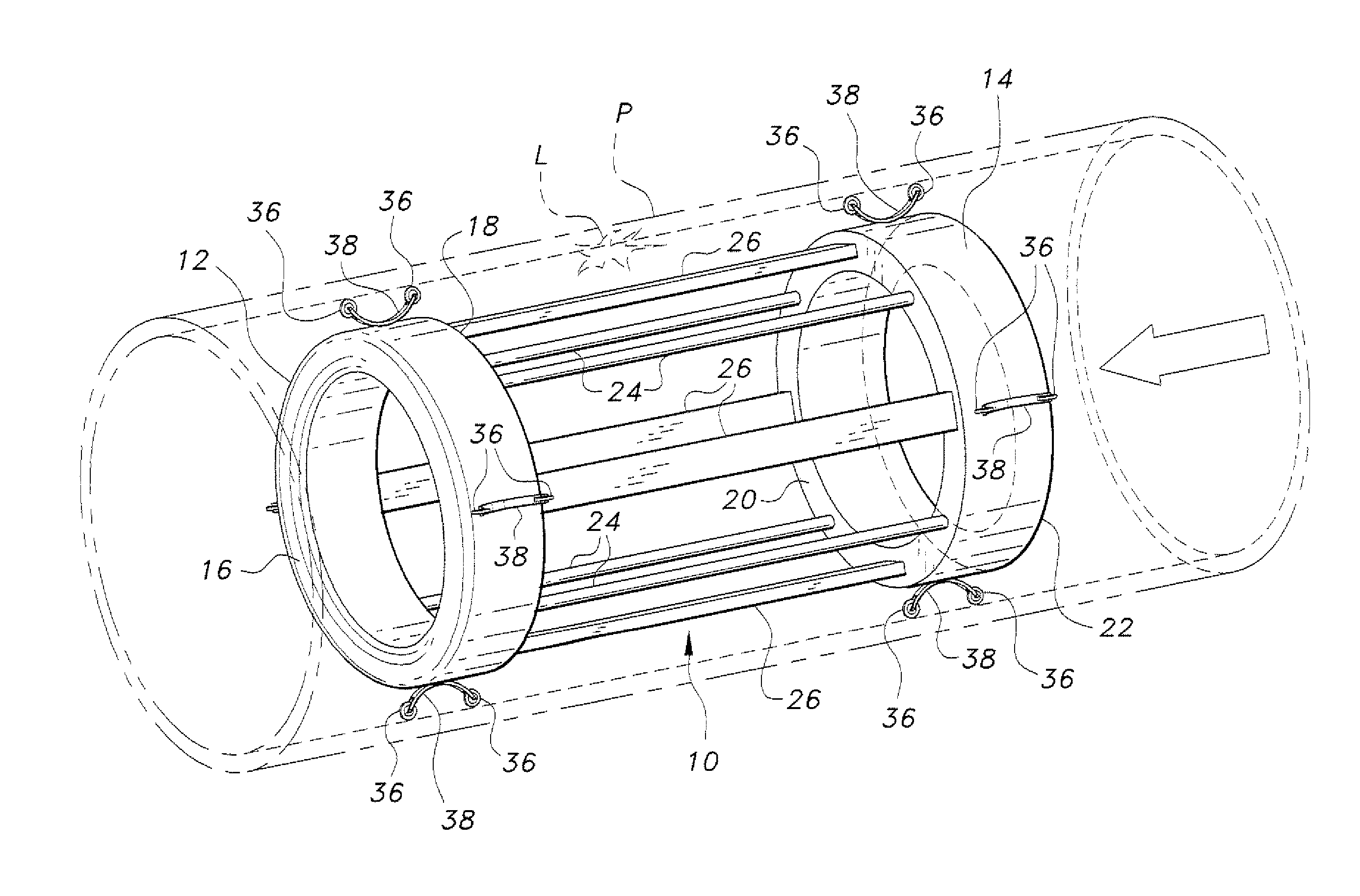
Pipeline leak detector
The pipeline leak detector travels through a pipeline passively due to the flow of liquid through the pipeline. The device includes leading and trailing rings shaped to produce hydrodynamic resistance in order for the device to be carried through the pipeline. Wheels are provided about each ring. At least one wheel has an odometer to measure distance traveled through the pipe. The rings are joined by a plurality of axially oriented connecting rods. A plurality of sensing elements extend between the rings. Each sensing element has a thin laminate of a piezoelectric film sandwiched between two electrically conductive layers, and an electrically insulating coating on the outside of each conductive layer. One of the rings, e.g., the trailing ring, includes microelectronic circuitry for data acquisition and storage, e.g., estimates of the magnitude of any leakage encountered, the location of the leakage based upon the odometer travel, etc.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Generation and trapping of aqueous droplets in a microfluidic chip with an air continuous phase
The invention relates to a method and system for generating droplets of an aqueous solution on a microfluidic chip with an air continuous phase. Specifically, the droplet generator according to the present invention is integrated into a microfluidic chip to generate and introduce droplets of an aqueous solution into the microfluidic chip. The droplets travelling in a network of chip channels may be captured in on-chip traps in a manner defined by hydrodynamic resistances of chip channels. A biological reaction may be performed on a droplet trapped on the microfluidic chip.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Hull configuration for submarines and vessel of the displacement type with multihull structure
ActiveUS20150217844A1Improve stabilityLarge breadthAmphibious vehiclesPropulsive elementsCargo vesselMulti body
This invention relates to a design of a ship hull, and more particularly, to cargo ship or submarine configurations featuring flow channels on the hull surfaces, and multihull structure, and improved diving and surfacing properties, and reduced hydrodynamic resistance, and improved hull damage resistance, and further comprising underwater hub cargo loading and unloading, and relates to manned or unmanned or semi-autonomous sea vessels. A hull design consists of a curvative hull form transversally and symmetrical about its center line CL and design water line, and consists of ballast and storage tanks and cargo compartment within the hull portions and operable to adjust the draft and the depth of the vessel according to the loaded weight, and provides detachable installation options. The invention relates to a ship hull design with reduced block coefficient (Cb) values.
Owner:FIRKAN SERDAR
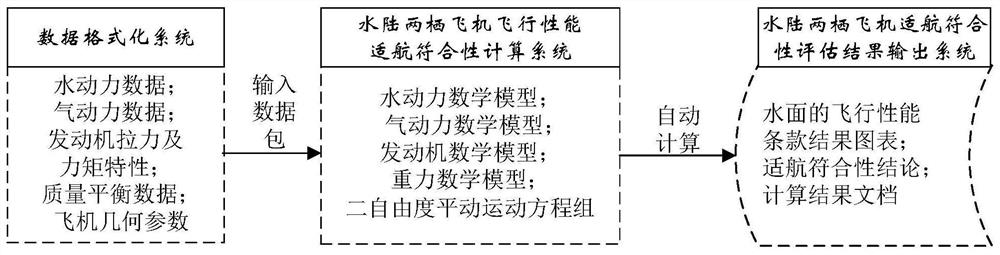
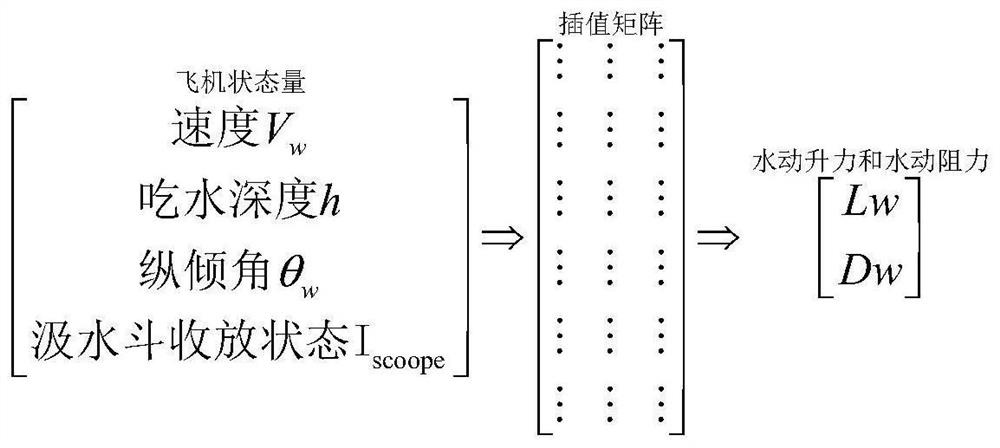
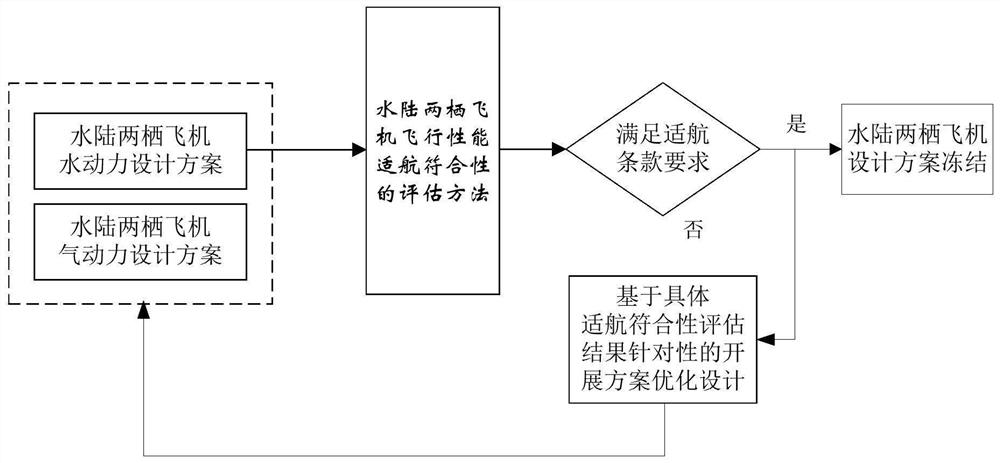
Method for evaluating airworthiness conformity of flight performance of amphibious aircraft
PendingCN112380792ASolve the unity problemImprove Design Iteration EfficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelClassical mechanics
The invention provides a method for evaluating airworthiness conformity of flight performance of an amphibious aircraft comprising the following steps: obtaining first data according to a design scheme of the amphibious aircraft; wherein the first data comprises aircraft hydrodynamic lift and hydrodynamic resistance data, aerodynamic lift and aerodynamic resistance data, engine tension characteristics under different accelerators, heights, speeds and temperatures, engine oil consumption characteristics and weight characteristic data; according to the first data, the amphibious aircraft external force mathematical model and the aircraft two-degree-of-freedom translational motion equation set, acquiring a calculation result, wherein the calculation result comprises operation parameters of the aircraft under operation state value combinations specified by different airworthiness terms; and comparing the operating parameters under the airworthiness terms with the requirements of the corresponding airworthiness terms for the operating parameters of the aircraft to obtain a flight performance airworthiness conformance conclusion.
Owner:中航通飞华南飞机工业有限公司
Non-woven polymeric fabric including agglomerates of aluminum hydroxide nano-fibers for filtering water
InactiveUS8033400B2High propertyLower resistanceLiquid surface applicatorsOther chemical processesFiberRetention efficiency
The invention concerns the production of filter materials for the purification and disinfection of water, water solutions and other liquids, as well as for sterilizing filtration of injections and other solutions, for concentration of biomolecules in physiological liquids, concentration and extraction of viruses, preparation of apyrogenic water, in biocatalytic diaphragm reactors. The invention solves the problems of a new filter material production, characterized by high sorption properties, high retention efficiency of submicron electronegative particles, microorganisms, submicron non-polar particles and chemical contaminations, and, at the same time, characterized by low hydrodynamic resistance. A base of filter material is the nonwoven organic synthetic polymeric fabric, modified by the aluminum hydroxide particles, fixed to the surface of base fibers for improvement of its sorption properties and for making it positively charged. A method of filter material production comprises: applying the modifying composition onto the fibrous base in the form of organic nonwoven synthetic polymeric fabric, wherein said modifying composition comprises the particles of the aluminum-based material, hydrolysis thereof results to formation and fixation of the aluminum hydroxide particles to the base fibers. A method of fluid filtration is carried out using the filter material as a non-woven organic synthetic polymeric fabric, to the fibers of which the aluminum hydroxide particles are fixed.
Owner:INSTITUTE OF STRENGTH PHYSICS AND MATERIALS SCIENCE OF SIBERIAN BRANCH OF RUSSIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES (ISPMS SB RAS)
Pipeline leak detector
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Method for producing a reagent to decrease hydrodynamic resistance of turbulent flow of liquid hydrocarbons in pipelines
InactiveCN110088143AReduce shipping costsLarge capacityLiquid carbonaceous fuelsPipeline systemsPetroleum productMass ratio
The invention relates to inorganic and polymer chemistry, and more specifically to the transport of oil and petroleum products via pipelines. A method for producing a reagent to decrease hydrodynamicflow resistance of liquid hydrocarbons in pipelines comprises polymerization of alpha-olefins C6-C14 in the presence of a catalyst and a catalyst activator. Furthermore, the polymerization of alpha-olefins C6-C14 is performed in a monomer medium with the addition of 0.1 to 5 mass percent of saturated alicyclic hydrocarbon composition C8-C32 and a saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon composition C6-C18with monomer conversion of 96.0 to 99.5 mass percent, wherein microspherical titanium trichloride is used as the catalyst, and a mixture of diethylaluminum chloride and triisobutylaluminum in a mass ratio of 1:10 to 10:1 is used as the catalyst activator. A polymer is then produced with a molecular mass of more than 107 amu with a narrow molecular mass distribution of no more than 1.5 with the specified component ratio. The polymer is then ground, thereby obtaining the commodity form of the reagent for decreasing hydrodynamic flow resistance of liquid hydrocarbons in pipelines. The technical result of the invention consists in producing a reagent that provides a decrease in the hydrodynamic resistance of the flow of liquid hydrocarbons in pipelines and, as a result, increases the throughput capacity of a pipeline and decreases the cost of transport.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTJU MIRRIKO
Microfluidic particle analysis device
ActiveUS20170370819A1Improve measurement qualityQuality improvementWithdrawing sample devicesIndividual particle analysisMain channelEngineering
The present invention relates to a microfluidic particle analysis device comprising an inlet in fluid communication via a main channel defining a main flow direction with an inlet manifold providing parallel fluid communication witha bypass channel of hydrodynamic resistance Rbypass, anda measuring channel of hydrodynamic resistance Rmeasuring, the measuring channel having a cross-sectional dimension in the range of from 1 μm to 50 μm and further having a sensor system for detecting a particle,wherein a flow distribution parameter Xmeasuring=Rmeasuring−1(Rmeasuring−1+Rbypass−1)−1 is in the range from 10−6 to 0.25, wherein the angle of the measuring channel relative to the main flow direction is in the range of 0° to 60°, and wherein the angle of the bypass channel relative to the main flow direction is in the range of 0° to 60°, andthe microfluidic particle analysis device further comprising an outlet in fluid communication with the bypass channel and the measuring channel. The present invention relates to a method of using the device microfluidic particle analysis.
Owner:SBT INSTR AS
Numerical simulation method of hydrodynamic resistance torque when in opening and closing of straight gate of navigation lock
ActiveCN105512432AEasy accessSolve time-consuming and labor-intensive problemsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelPhysical model
The invention relates to a numerical simulation method of hydrodynamic resistance torque when in opening and closing of a straight gate of a navigation lock, belonging to the technical field of navigation lock hydraulics. Based on an FLUENT fluid computation platform, the opening and closing dynamic process of the straight gate is controlled by virtue of a User-Defined Function (UDF), and numerical simulation of the hydrodynamic resistance torque in the opening and closing dynamic process of the straight gate is realized through establishing a three-dimensional mathematical model of the straight gate of the navigation lock, a gate chamber region and a lock chamber. The numerical simulation method proposed by the invention has the advantages that the accuracy is good, the possibility of fast and conveniently acquiring the hydrodynamic resistance torque when in opening and closing of the straight gate of the navigation lock can be provided, the numerical simulation method can be applied to determination of the hydrodynamic resistance torque of the straight gate of the navigation lock, determination of opening and closing force, design of capacity of a hoist, optimization of boundary conditions of a gate chamber, and the like, and the problems existing in test and study means of a physical model of time and energy waste, and the like can be solved.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
Hull configuration for submarines and vessel of the displacement type with multihull structure
ActiveUS9193423B2Reduce resistanceImprove stabilityAmphibious vehiclesPropulsive elementsCargo vesselMulti body
This invention relates to a design of a ship hull, and more particularly, to cargo ship or submarine configurations featuring flow channels on the hull surfaces, and multihull structure, and improved diving and surfacing properties, and reduced hydrodynamic resistance, and improved hull damage resistance, and further comprising underwater hub cargo loading and unloading, and relates to manned or unmanned or semi-autonomous sea vessels. A hull design consists of a curvative hull form transversally and symmetrical about its center line CL and design water line, and consists of ballast and storage tanks and cargo compartment within the hull portions and operable to adjust the draft and the depth of the vessel according to the loaded weight, and provides detachable installation options. The invention relates to a ship hull design with reduced block coefficient (Cb) values.
Owner:FIRKAN SERDAR
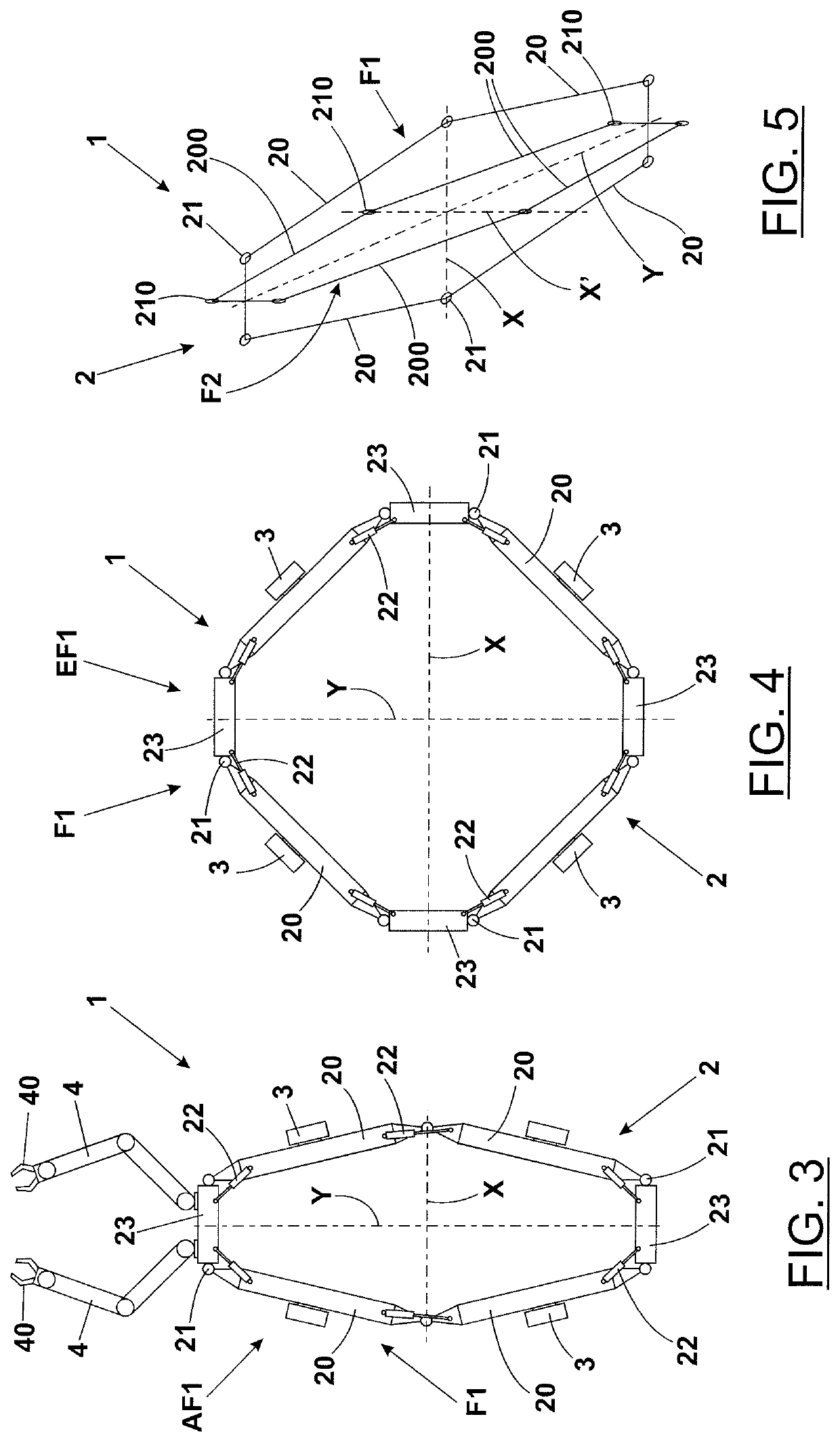
Underwater Vehicle with Variable Configuration
ActiveUS20210300513A1Easy to operateImprove mobilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorUnderwater vesselsRobotic armStructural engineering
The underwater vehicle with variable configuration (1) comprises: a hull (2) consisting of at least four elongated elements (20), mutually articulated by means of joints (21), to form a first closed polygonal structure (F1), arranged on a plane; thrusters (3), associated in parallel with said elements (20) of the hull (2); actuating means (22), associated with said joints (21), provided for automatically modifying said first closed polygonal structure (F1), from an elongated shape configuration (AF1) to an expanded shape (EF1), corresponding to an elongated conformation of said hull (2), to determine a low hydrodynamic resistance and a longitudinal thrust of the thrusters (3) in the cruising of said underwater vehicle (1), and to a substantially isotropic conformation, wherein the same elements (20) of the hull (2), as well as the thrusters (3) are mutually angled, intended for the hovering of the same underwater vehicle (1), respectively. The latter can be suitably equipped with robotic arms (4) intended for performing maintenance or similar interventions in underwater locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF FLORENCE
Pressure flow meter and fluid control device
PendingCN114166293AImprove sealingEffect of flow characteristicsEngine sealsFlow control using electric meansFluid controlStress sensors
Owner:HORIBA STEC CO LTD
A Numerical Simulation Method of Dynamic Water Resistance Moment when Opening and Closing a Lock Gate
ActiveCN105512432BEasy accessSolve time-consuming and labor-intensive problemsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelPhysical model
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
Method and device for analysing molecular interactions, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20180224376A1Laboratory glasswaresBiological testingMolecular interactionsMolecular physics
The invention relates to a method for analysing an interaction between a first molecule and a second molecule bonded to a particle, including the following steps: contacting the first molecule with the second molecule bonded to the particle under conditions enabling the interaction thereof; applying a predetermined liquid flow to the particle bonded to the second molecule; observing a movement of the particle bonded to the second molecule caused by the applied flow; analysing the interaction according to the movement observed and the applied flow, the particle having a greater hydrodynamic resistance than the first and / or second molecule, and a mass Péclet number of greater than 1. The invention also relates to a device for analysing an interaction between a first molecule and at least one second molecule, as well as to the use of the method or of the device in screening a candidate molecule for developing a drug.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com