Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Hcv therapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Initial treatment of HCV infection includes patients with chronic hepatitis C who have not been previously treated with interferon, peginterferon, ribavirin, or any HCV direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agent, whether experimental, investigational, or US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved.
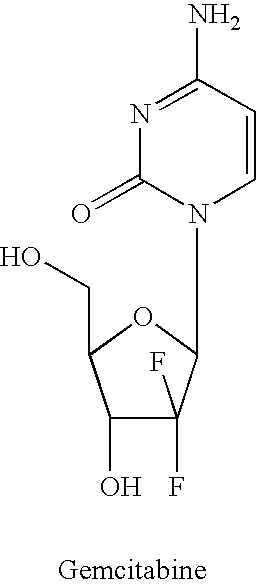
Dosing regimen for gemcitabine HCV therapy
InactiveUS20030225029A1Reduce viral loadRapid and large in viral loadBiocideSugar derivativesDosing regimenHepatitis c viral
A dosage regiment for the treatment of a Flaviviridae infection, including a hepatitis C viral infection, that includes administering gemcitabine (or its salt, prodrug or derivative, as described herein) in a dosage range of approximately 50 mg / m<2 >to about 1300 mg / m<2 >per day for between one and seven days (e.g. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7 days) followed by cessation of therapy. Viral load is optionally monitored over time, and after cessation, viral rebound is monitored. Therapy is not resumed unless a significant viral load is again observed, and then therapy for 1-7 days and more preferred, 1, 2 or 3 days, is repeated. This therapy can be continued indefinitely to monitor and maintain the health of the patient.
Owner:PHARMASSET
Immunotherapy for chronic hepatitis c virus infection
InactiveUS20110256098A1Increase the number ofReduce in quantitySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsChronic viral hepatitis CInterferon therapy
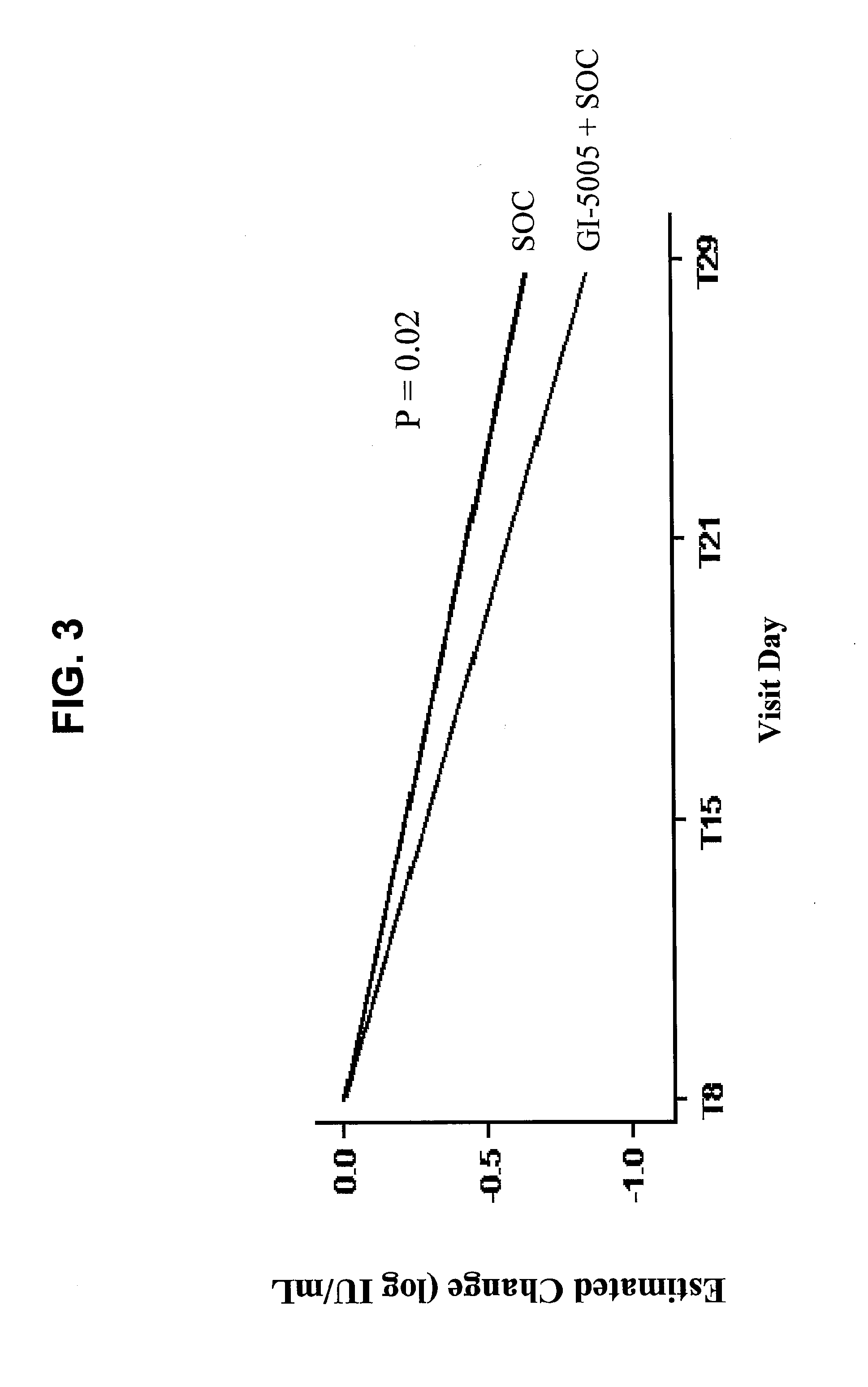
Disclosed are uses of immunotherapeutic compositions in combination with Standard of Care (SOC), or interferon therapy combined with anti-viral therapy, for the improved treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and related conditions, including liver function. The compositions, kits and uses of the invention, as compared to the use of SOC therapy alone: improves the rate of early response to therapy as measured by early virologic markers (e.g., RVR and EVR), enlarges the pool of patients who will have sustained responses to therapy over the long term, offers shortened courses of therapy for certain patients, enables “rescue” of patients who are non-responders or intolerant to SOC therapy, improves liver function and / or reduces liver damage in patients, and enables the personalization of HCV therapy for a patient, which can result in dose sparing, improved patient compliance, reduced side effects, and improved long term therapeutic outcomes.
Owner:GLOBE IMMUNE INC
Use of dronabinol for treatment of side effects of Hepatitis C therapy
InactiveUS20060258738A1Avoid gastrointestinal side effectsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSide effectDelta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol
The present invention provides methods for treating and preventing the gastrointestinal side effects associated with anti-HCV therapy comprising administering delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
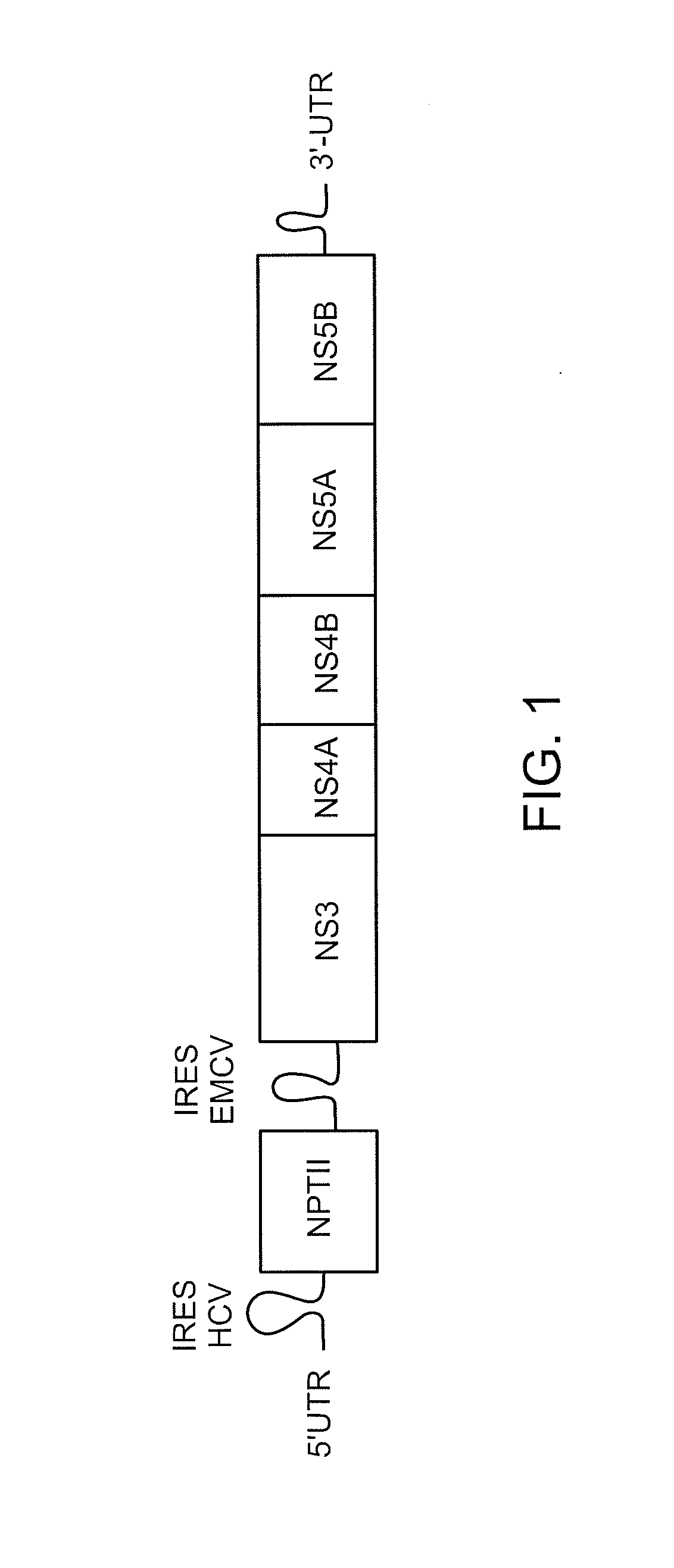
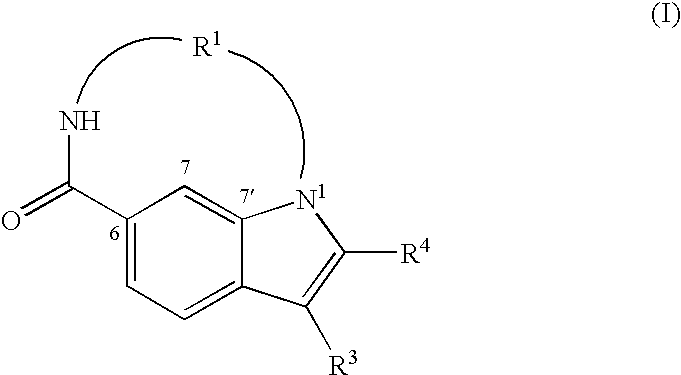
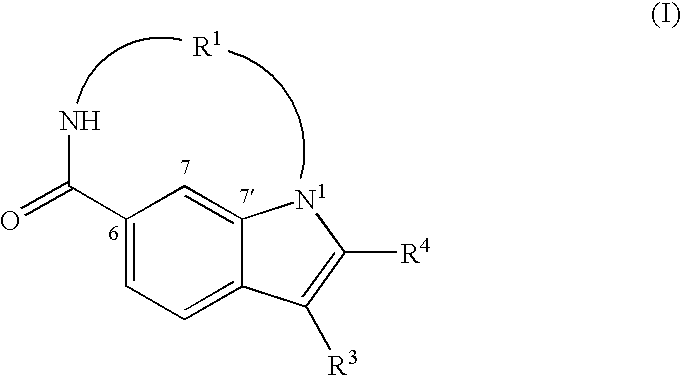
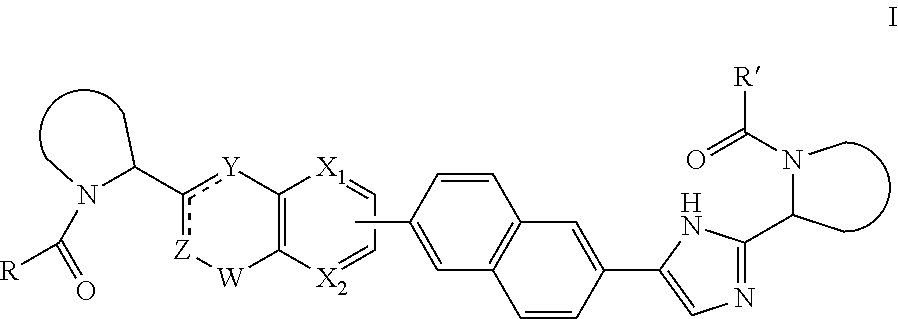
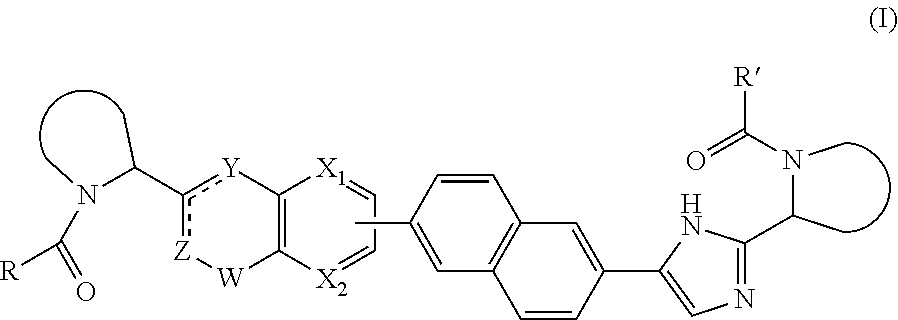
Macrocyclic indoles as hepatitis C virus inhibitors
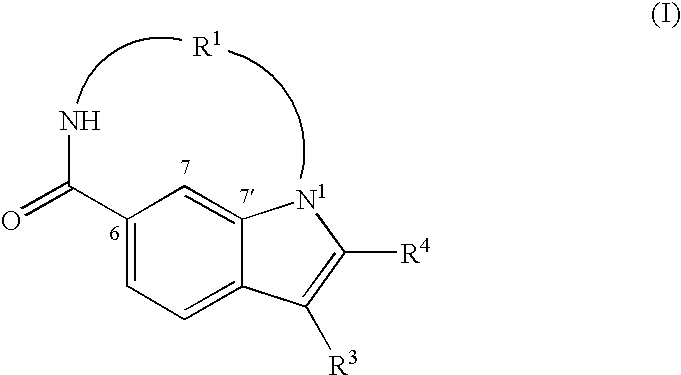
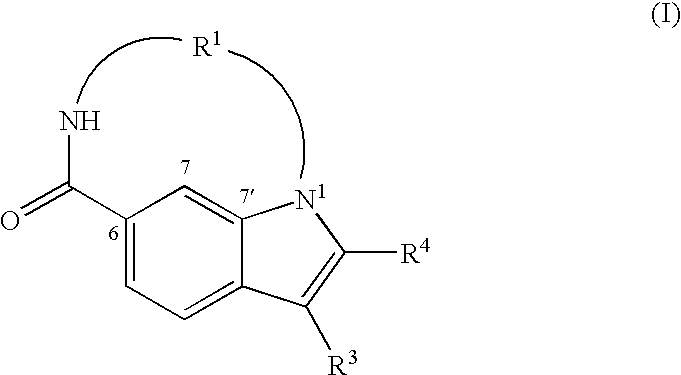
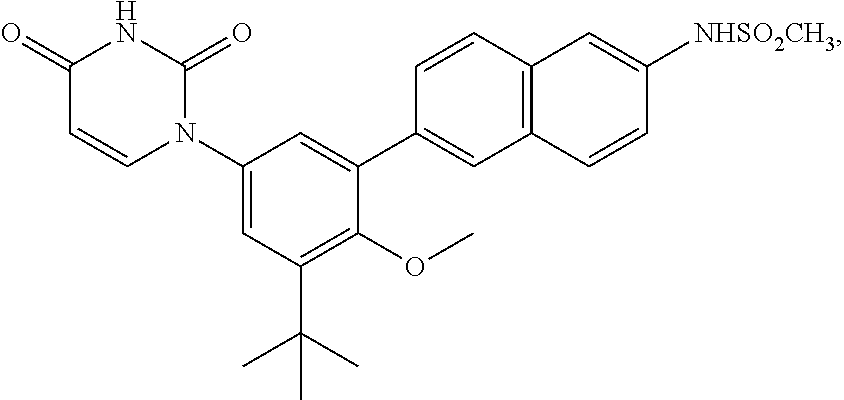
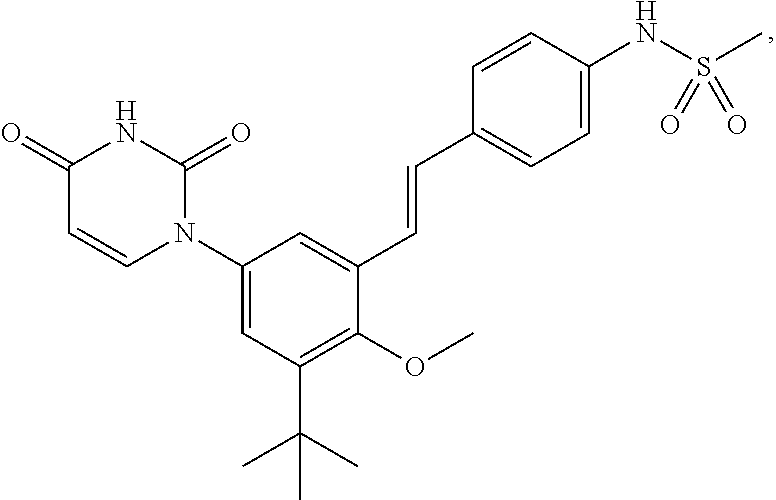
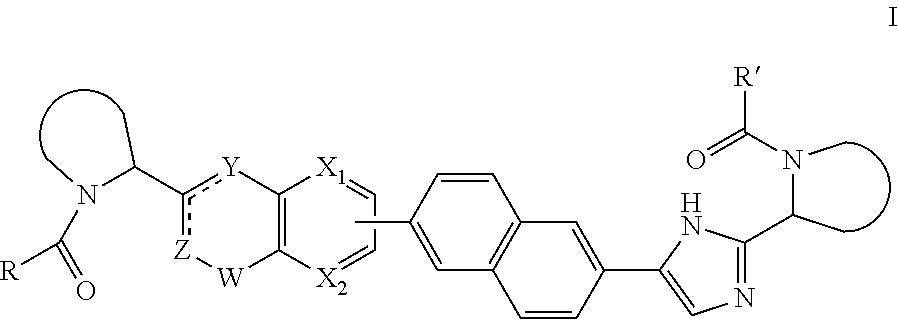
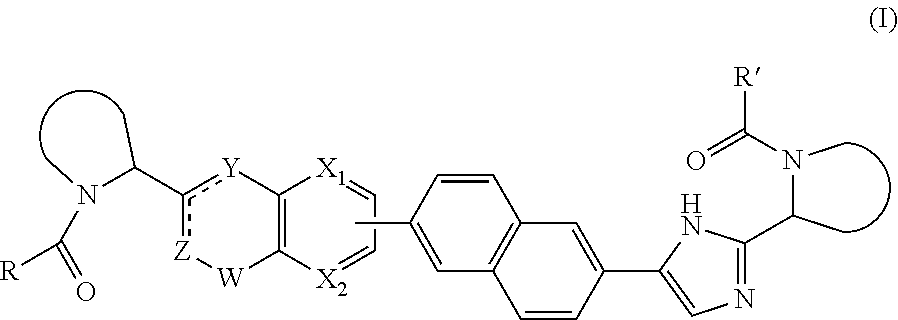
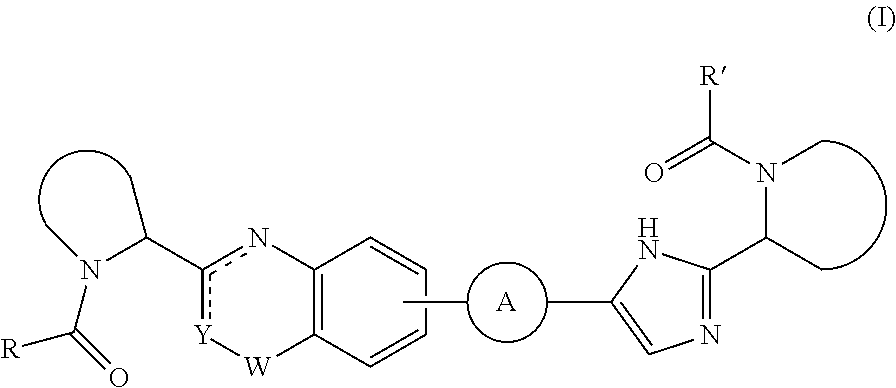
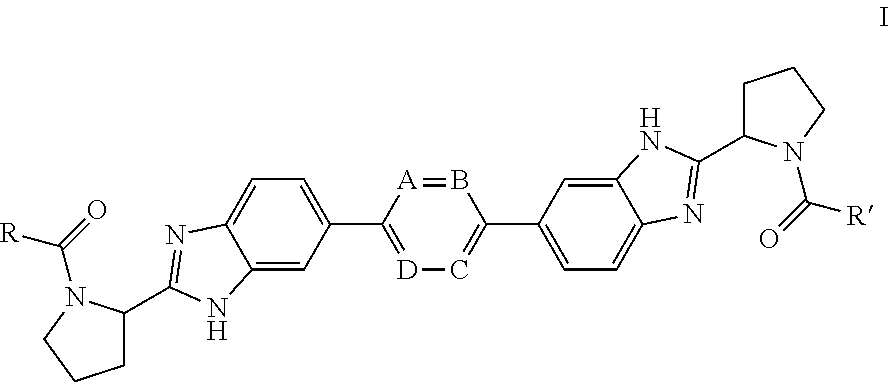
The present invention relates to inhibitors of HCV replication of formula (I), the N-oxide forms, the pharmaceutically acceptable addition salts, the quaternary amines and the stereochemically isomeric forms thereof,wherein R1; R3; and R4 have the meaning defined in the claims.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Methods for Treating HCV
InactiveUS20140024613A1Improve pharmacokineticsDose lessBiocideDipeptide ingredientsTotal cholesterolHcv therapy
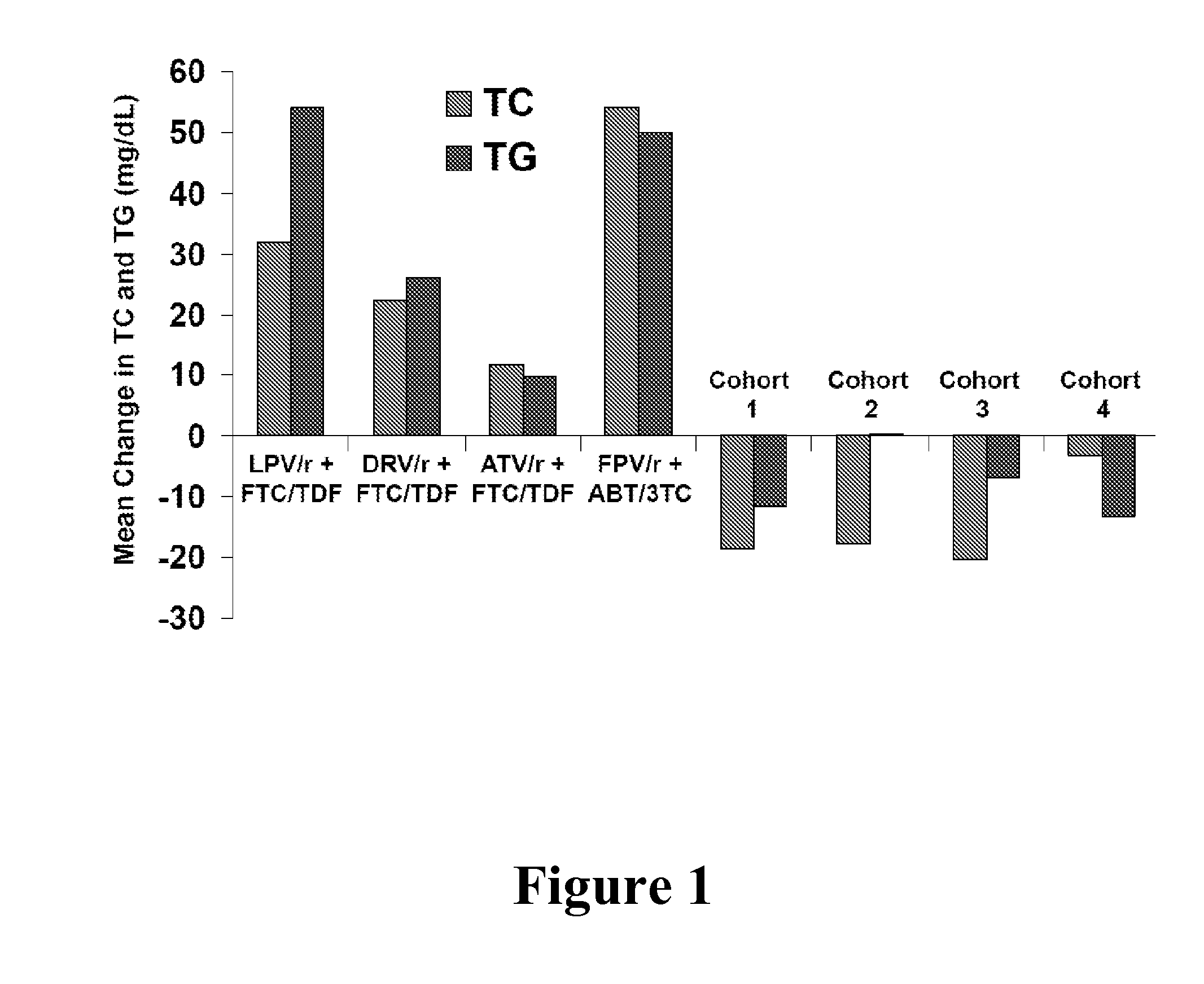
In one aspect, the present invention features HCV therapies comprising administering to a patient in need thereof an HCV protease inhibitor and ritonavir, wherein ritonavir is used as a pharmacokinetic booster to improve the pharmacokinetics of the HCV protease inhibitor. The HCV therapies do not require the testing of total cholesterol and triglyceride levels prior to and after the therapies.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
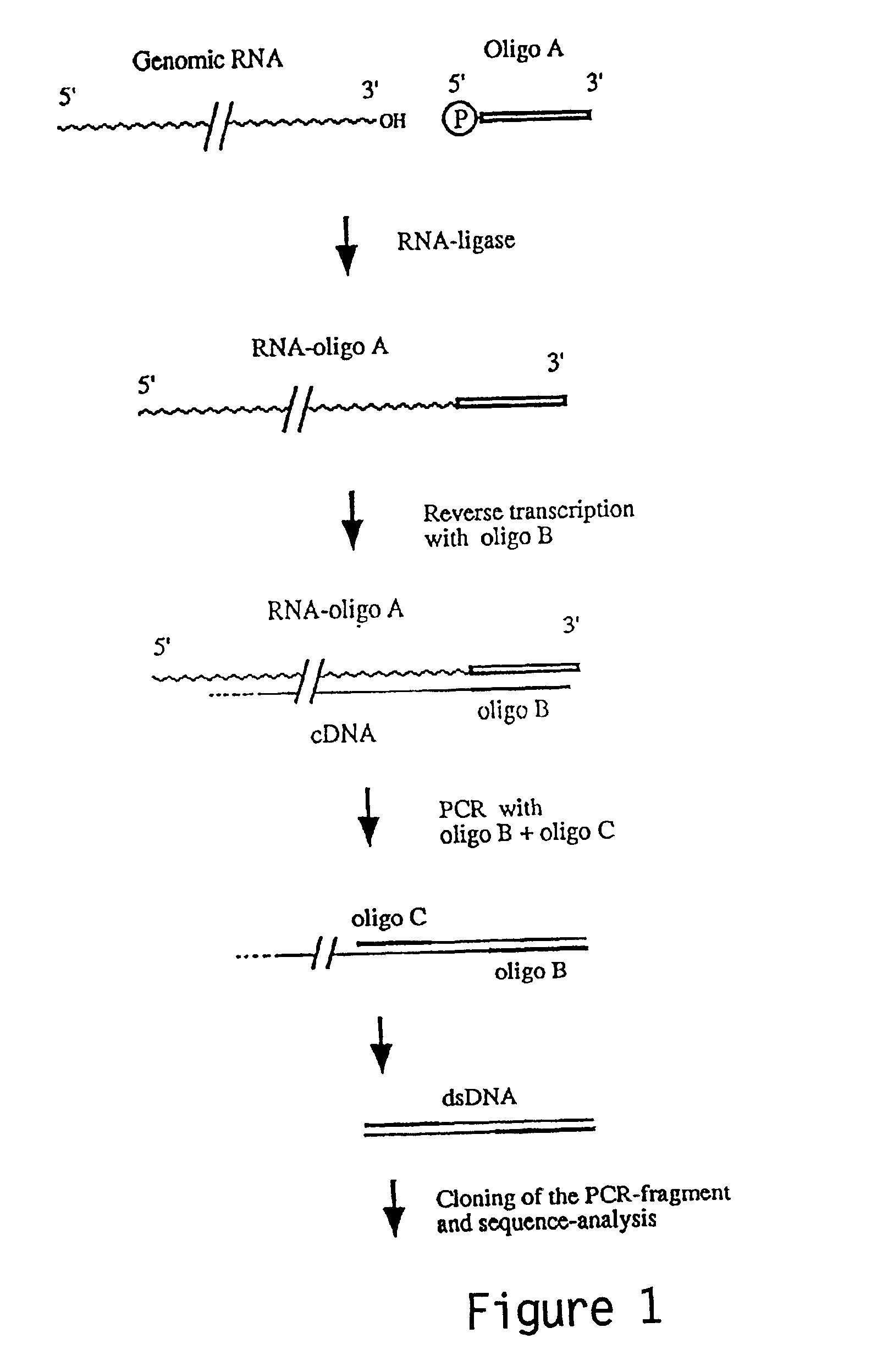
3′terminal sequence of hepatitis C virus genome and diagnostic and therapeutic uses thereof
InactiveUS6943246B2Effective strikeAlter adverse consequenceOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseHCV GenotypingVaccination
The invention relates to the discovery of a novel RNA sequence at the 3′ terminal sequence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome RNA. Included in the invention are the 3′ sequence, its complement, and their use for nucleic-acid based diagnostics and for developing and evaluating novel anti-HCV therapies. This sequence element, which is conserved among HCV genotypes, is likely to be essential for viral replication, and required for construction of full-length HCV cDNA clones capable of yielding infectious RNA, progeny virus or replication-competent HCV replicons. Such functional clones are useful tools for evaluation of therapeutic approaches and as substrates for developing candidate attenuated or inactivated HCV derivatives for vaccination against HCV.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
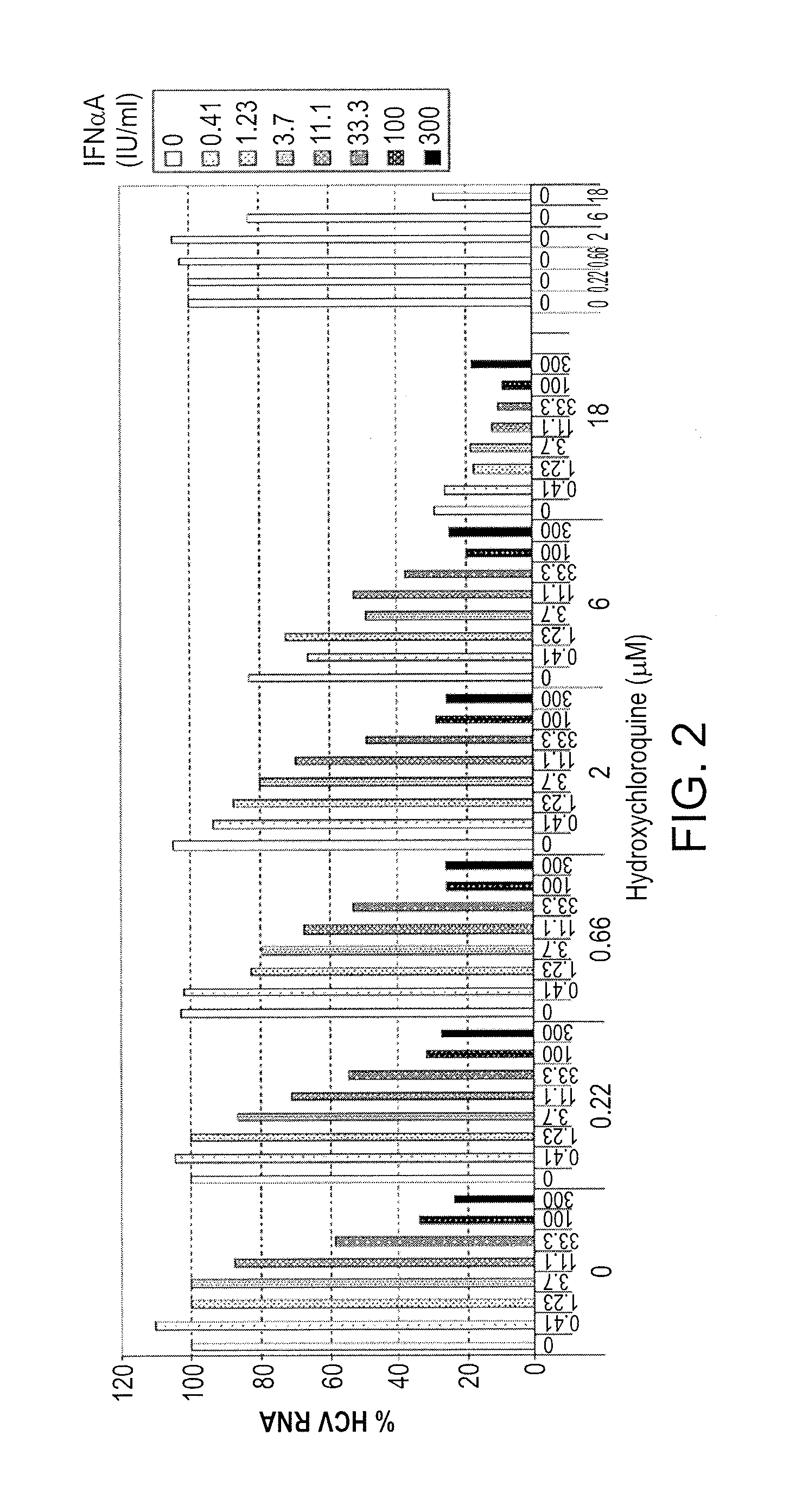
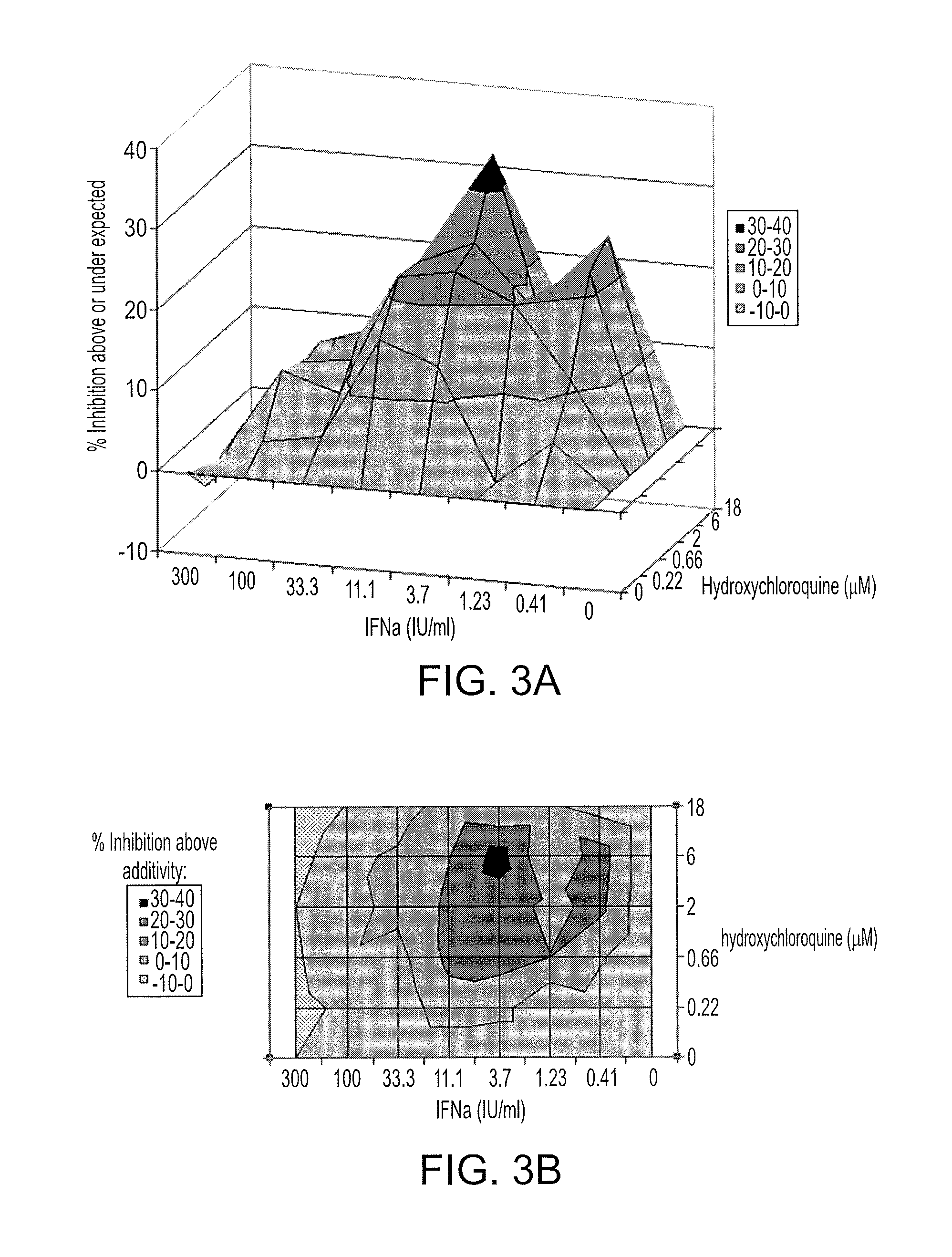
Treatment of hepatitis C virus related diseases using hydroxychloroquine or a combination of hydroxychloroquine and an anti-viral agent
Methods of treating a hepatitis C virus (HCV) related disease, such as HCV infections in subjects non-responsive to anti-HCV therapy, are described herein, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of hydroxychloroquine. An antiviral agent may be co-administered with the hydroxychloroquine. Methods utilizing synergistic combinations of hydroxychloroquine and an antiviral agent are disclosed. Further disclosed are compositions comprising hydroxychloroquine and an antiviral agent, as well as hydroxychloroquine and uses thereof for the treatment of a hepatitis C virus (HCV) related disease.
Owner:PANMED +1
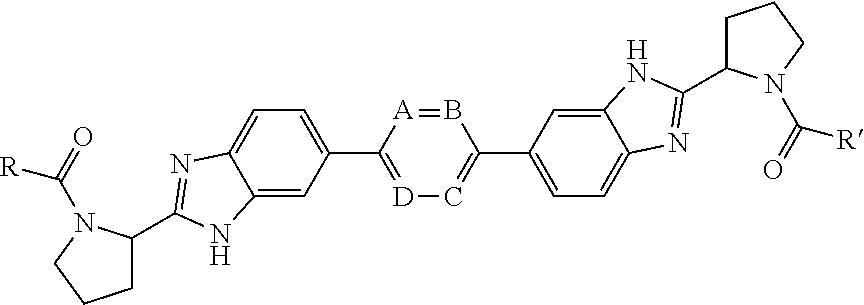
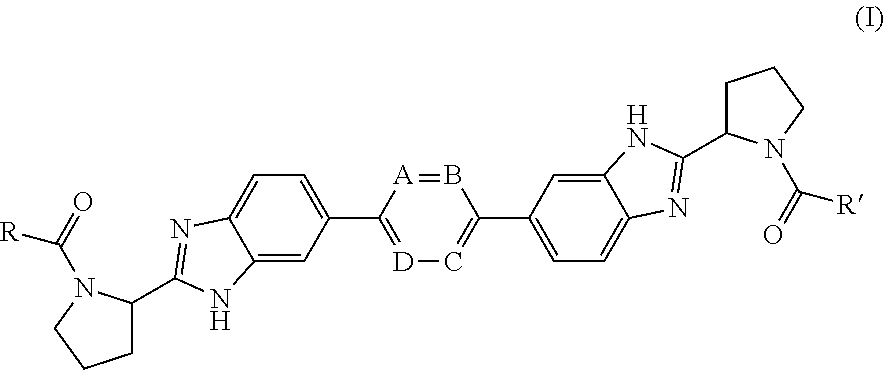
Bis-Benzimidazole Derivatives As Hepatitis C Virus Inhibitors
InactiveUS20120135953A1Improved profileToxic reductionBiocideOrganic chemistryBenzimidazole derivativeHcv hepatitis c virus
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula Iincluding stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R and R′ have the meaning as defined herein.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use, alone or in combination with other HCV inhibitors, in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
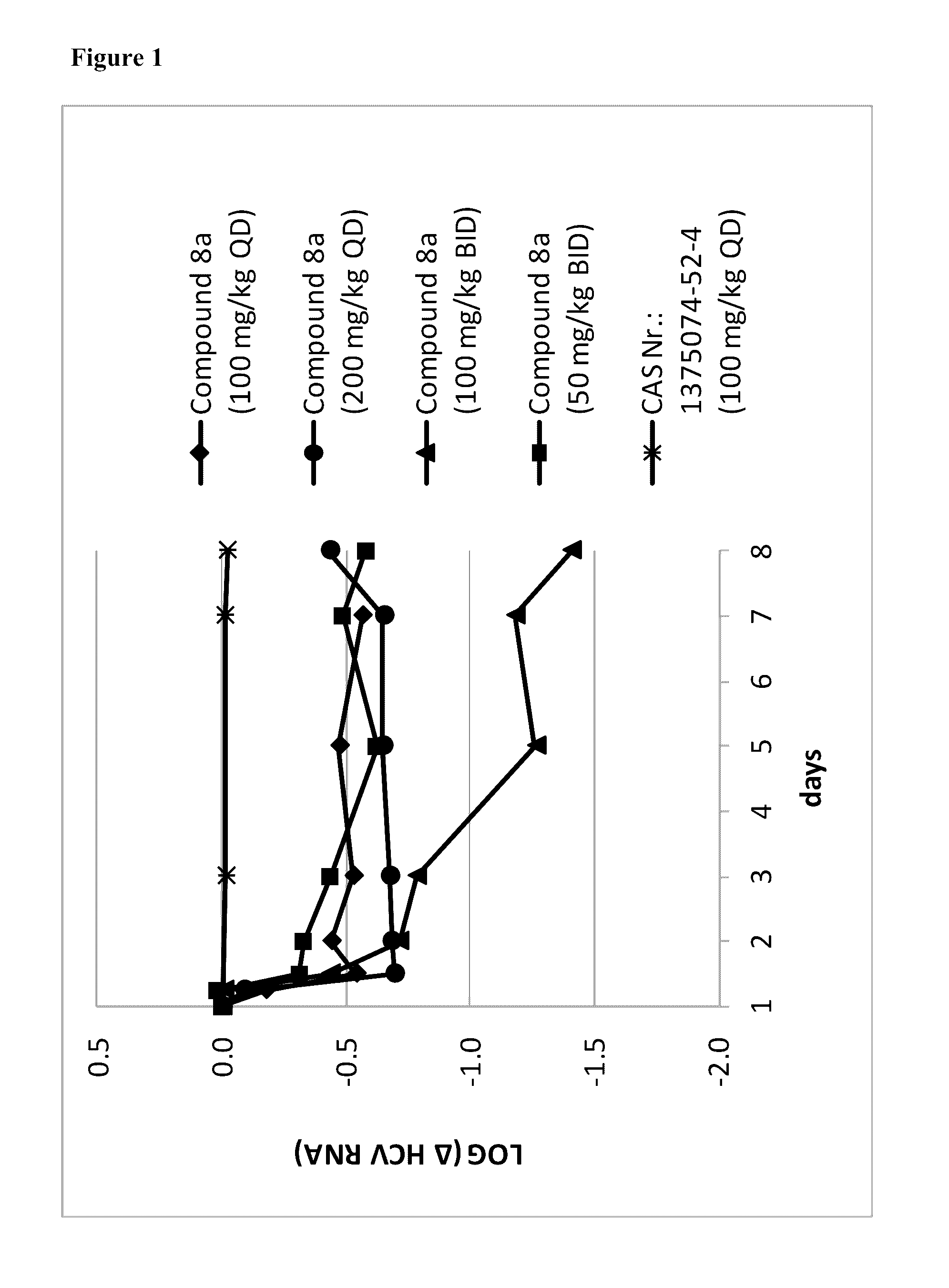
Methods for predicting the efficacy or outcome of hcv therapy
InactiveUS20070166702A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHcv hepatitis c virusEfficacy
The present invention relates to a novel method for predicting likeliness of the outcome or efficacy of an antiviral therapy against Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). This method is based on the detection of antibodies against the proteins NSta and or NS5a in a sample of a patient. This method can be further combined with the detection of viral titers of HCV in a sample of a patient. The method of the invention allows a more reliable identification of a subset of non-responders in an early stage of treatment.
Owner:UNIV GENT
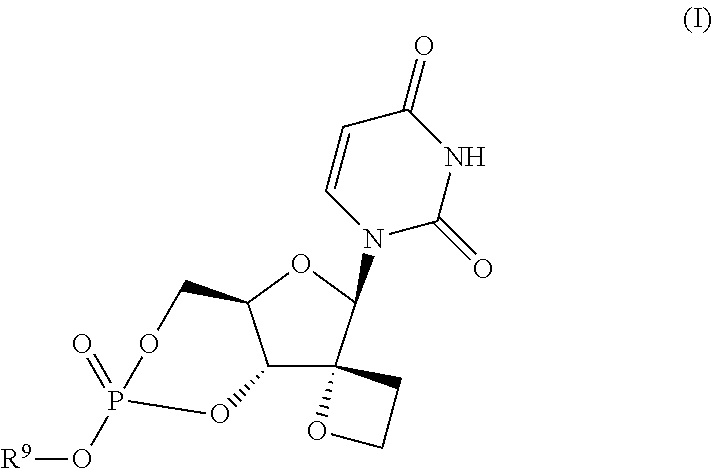
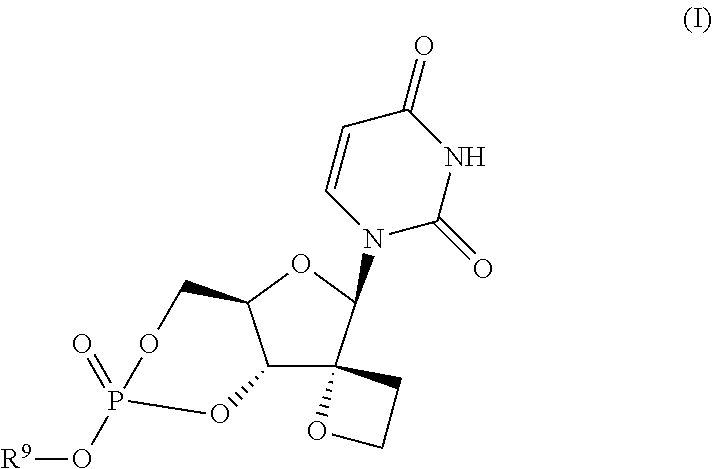
Uracyl spirooxetane nucleosides
The present invention relates to compounds of the formula I:including any possible stereoisomers thereof, wherein R9 has the meaning as defined herein,or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use, alone or in combination with other HCV inhibitors, in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Macrocyclic Indole Derivatives Useful as Hepatitis C Virus Inhibitors
ActiveUS20140107101A1Favorable mutant prophileNo toxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryMedicineHcv hepatitis c virus
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula (I)including stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R1, R2, R4, R5, R6 and R7 have the meaning defined in the claims.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Macrocyclic indoles as hepatitis c virus inhibitors
InactiveUS20100273792A1Inhibition of replicationBiocideOrganic chemistryHcv hepatitis c virusPharmaceutical medicine
The present invention relates to inhibitors of HCV replication of formula (I), the N-oxide forms, the pharmaceutically acceptable addition salts, the quaternary amines and the stereochemically isomeric forms thereof,wherein R1; R3; and R4 have the meaning defined in the claims.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Application of aryl naphthalene type lignan in hepatitis C virus (HCV) therapy
InactiveCN103127159AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesLignanPhotochemistry
The invention relates to application of an aryl naphthalene type lignan in hepatitis C virus (HCV) therapy and belongs to the technical field of medicine, and discloses an aryl naphthalene type lignan (red fish eye glycoside B) which has the activity of HCV resistance and is extracted and prepared from a Guangxi special Zhuang medicine, namely, red fish eye Phyllanthus reticulatus. The application of the aryl naphthalene type lignan in the HCV therapy is characterized in that obvious inhibitory effect (p < 0.01) is supplied to replicon ribonucleic acid (RNA) of HCV within a concentration range of 125 microgrammes per rnl to 15625 microgrammes per rnl, and a concentration range of non-cytotoxic drugs is from 0 to 3125 microgrammes per rnl (p < 0.01). According to the application of the aryl naphthalene type lignan in the HCV therapy, the market prospect of aryl naphthalene type lignan (red fish eye glycoside B) in HCV resistance new drug research and development is wide.
Owner:GUANGXI BOTANICAL GARDEN OF MEDICINAL PLANTS
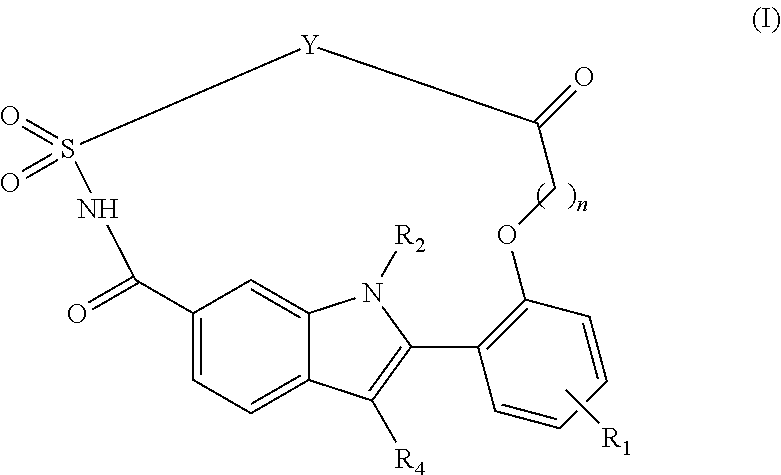
Macrocyclic indole derivatives useful as hepatitis C virus inhibitors
InactiveUS8357687B2Enhance the imageNo toxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryHcv treatmentHepatitis C Virus NS5A Inhibitor
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula (I) including stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein Y, R1, R2, R4 and n have the meaning defined in the claims. The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Hetero-bicyclic derivatives as HCV inhibitors
InactiveUS8815849B2Improved profileToxic reductionBiocideOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical drugPerylene derivatives
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula Iincluding stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R and R′ have the meaning as defined herein.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use, alone or in combination with other HCV inhibitors, in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Macrocyclic indole derivatives useful as hepatitis c virus inhibitors
ActiveUS20110105473A1No toxicityFavorable metabolic profileBiocideOrganic chemistryMedicineHcv hepatitis c virus
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula (I) including stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R1, R2, R4, R5, R6 and R7 have the meaning defined in the claims. The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Immunotherapy for chronic hepatitis C virus infection
InactiveUS8728489B2High frequencyReduce in quantityBiocideFungiChronic viral hepatitis CInterferon therapy
Disclosed are uses of immunotherapeutic compositions in combination with Standard of Care (SOC), or interferon therapy combined with anti-viral therapy, for the improved treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and related conditions, including liver function. The compositions, kits and uses of the invention, as compared to the use of SOC therapy alone: improves the rate of early response to therapy as measured by early virologic markers (e.g., RVR and EVR), enlarges the pool of patients who will have sustained responses to therapy over the long term, offers shortened courses of therapy for certain patients, enables “rescue” of patients who are non-responders or intolerant to SOC therapy, improves liver function and / or reduces liver damage in patients, and enables the personalization of HCV therapy for a patient, which can result in dose sparing, improved patient compliance, reduced side effects, and improved long term therapeutic outcomes.
Owner:GLOBE IMMUNE INC
Hetero-Bicyclic Derivatives as HCV Inhibitors
InactiveUS20130123244A1Improved profileToxic reductionBiocideOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical drugPerylene derivatives
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula Iincluding stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R and R′ have the meaning as defined herein.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use, alone or in combination with other HCV inhibitors, in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Treatment of hepatitis c virus related diseases using hydroxychloroquine or a combination of hydroxychloroquine and an Anti-viral agent
Methods of treating a hepatitis C virus (HCV) related disease, such as HCV infections in subjects non-responsive to anti-HCV therapy, are described herein, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of hydroxychloroquine. An antiviral agent may be co-administered with the hydroxychloroquine. Methods utilizing synergistic combinations of hydroxychloroquine and an antiviral agent are disclosed. Further disclosed are compositions comprising hydroxychloroquine and an antiviral agent, as well as hydroxychloroquine and uses thereof for the treatment of a hepatitis C virus (HCV) related disease.
Owner:PANMED +1
Hetero-bicyclic derivatives as HCV inhibitors
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula I, including stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R and R′ have the meaning as defined herein. The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use, alone or in combination with other HCV inhibitors, in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
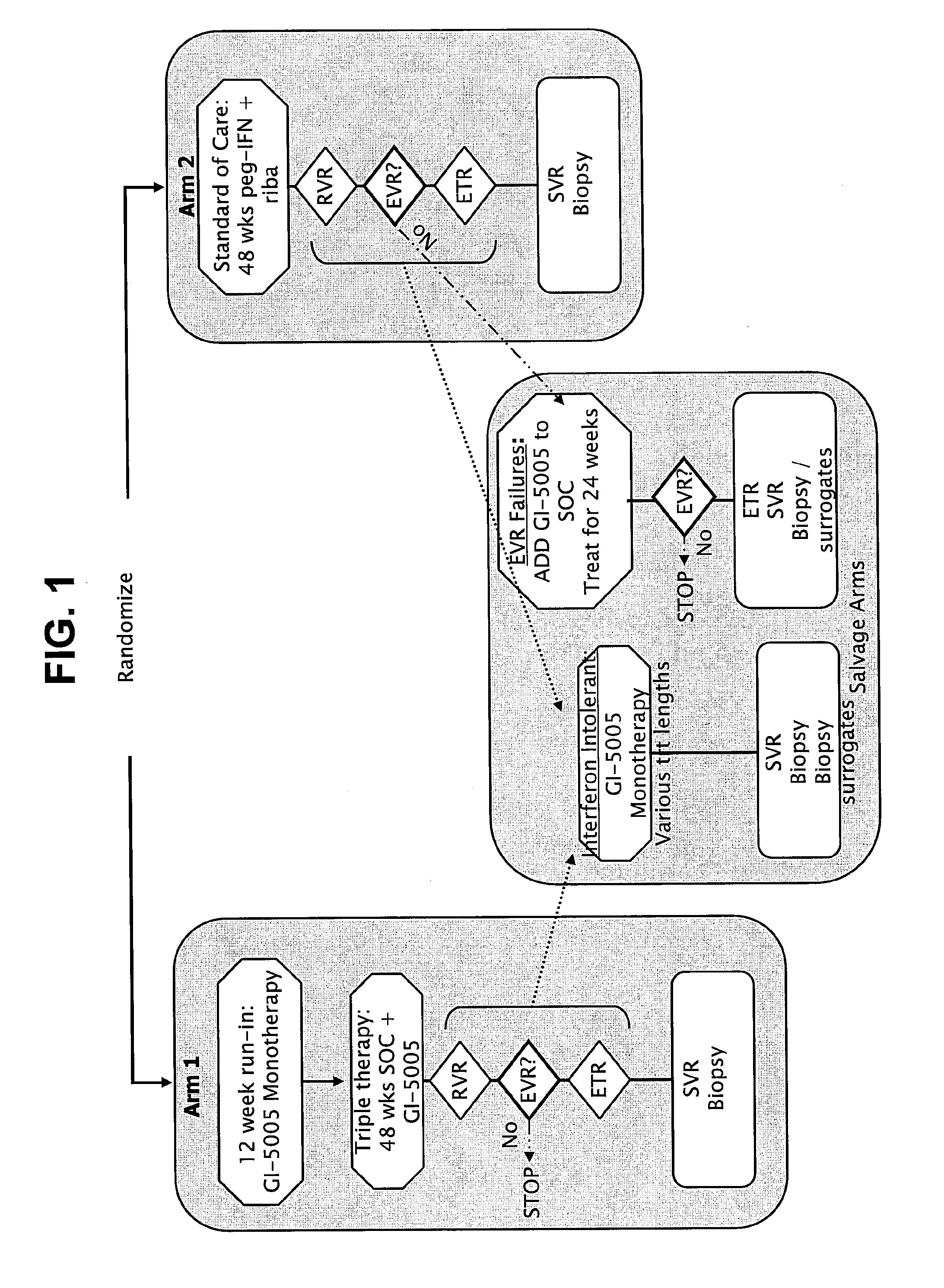
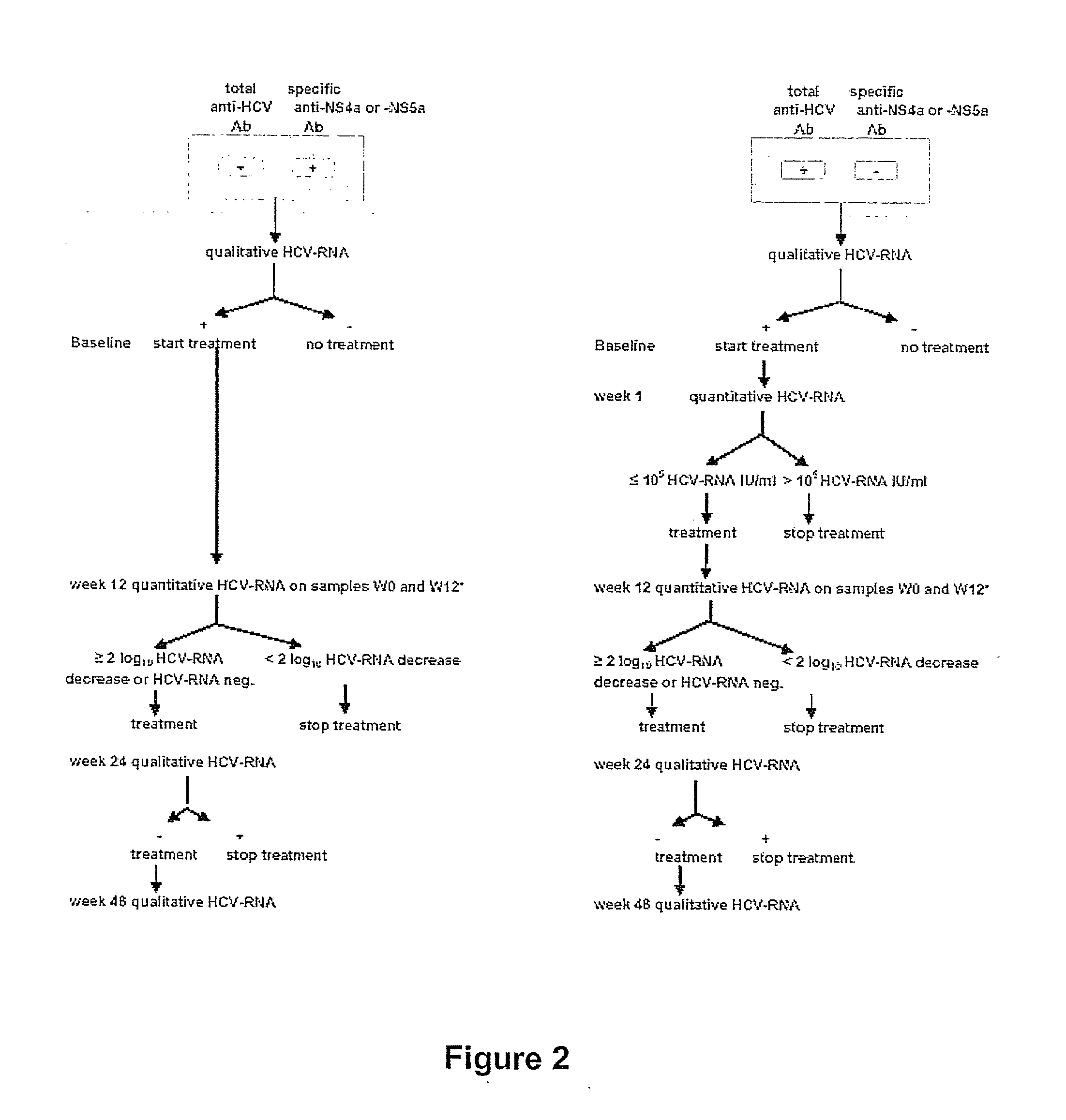
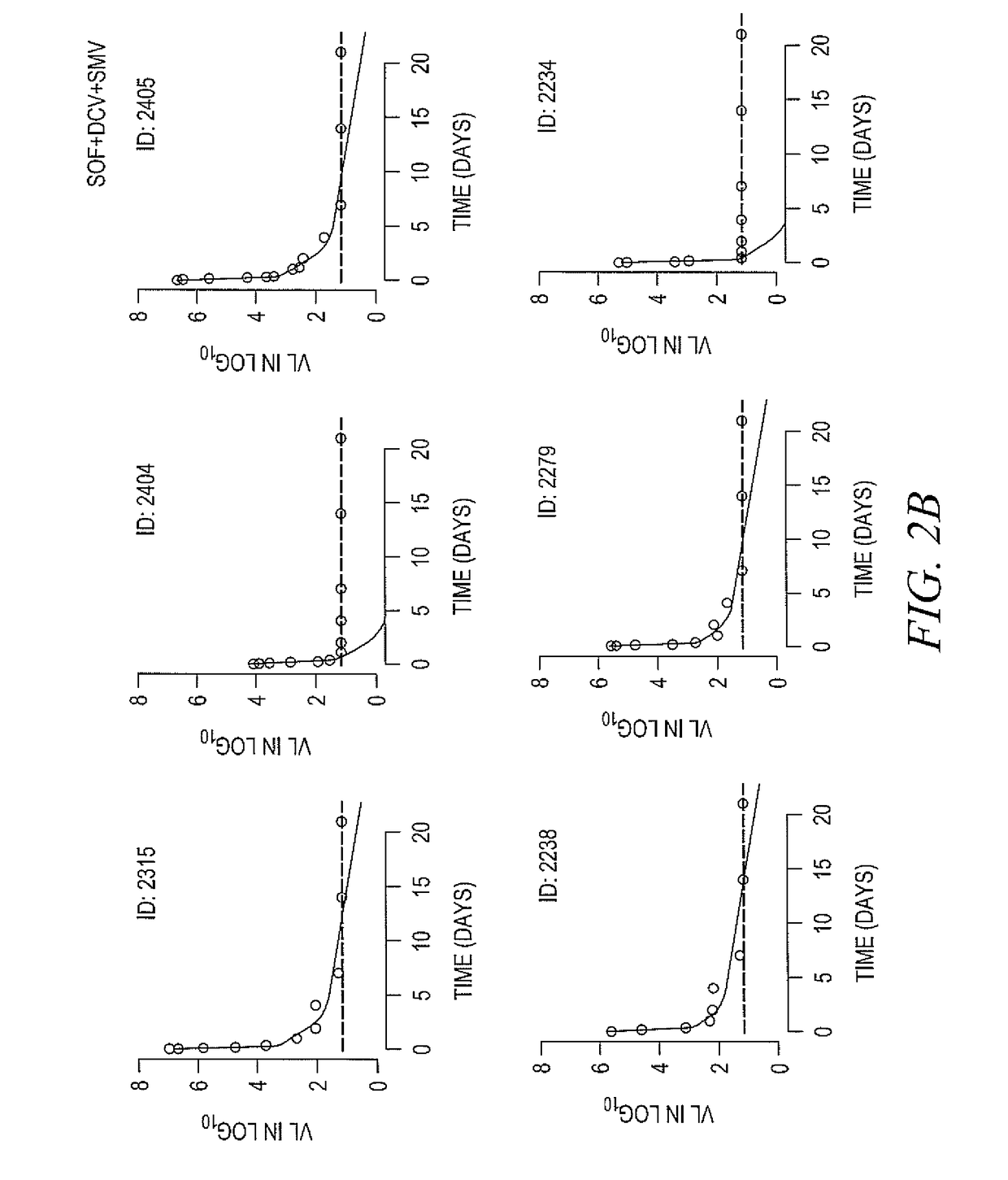
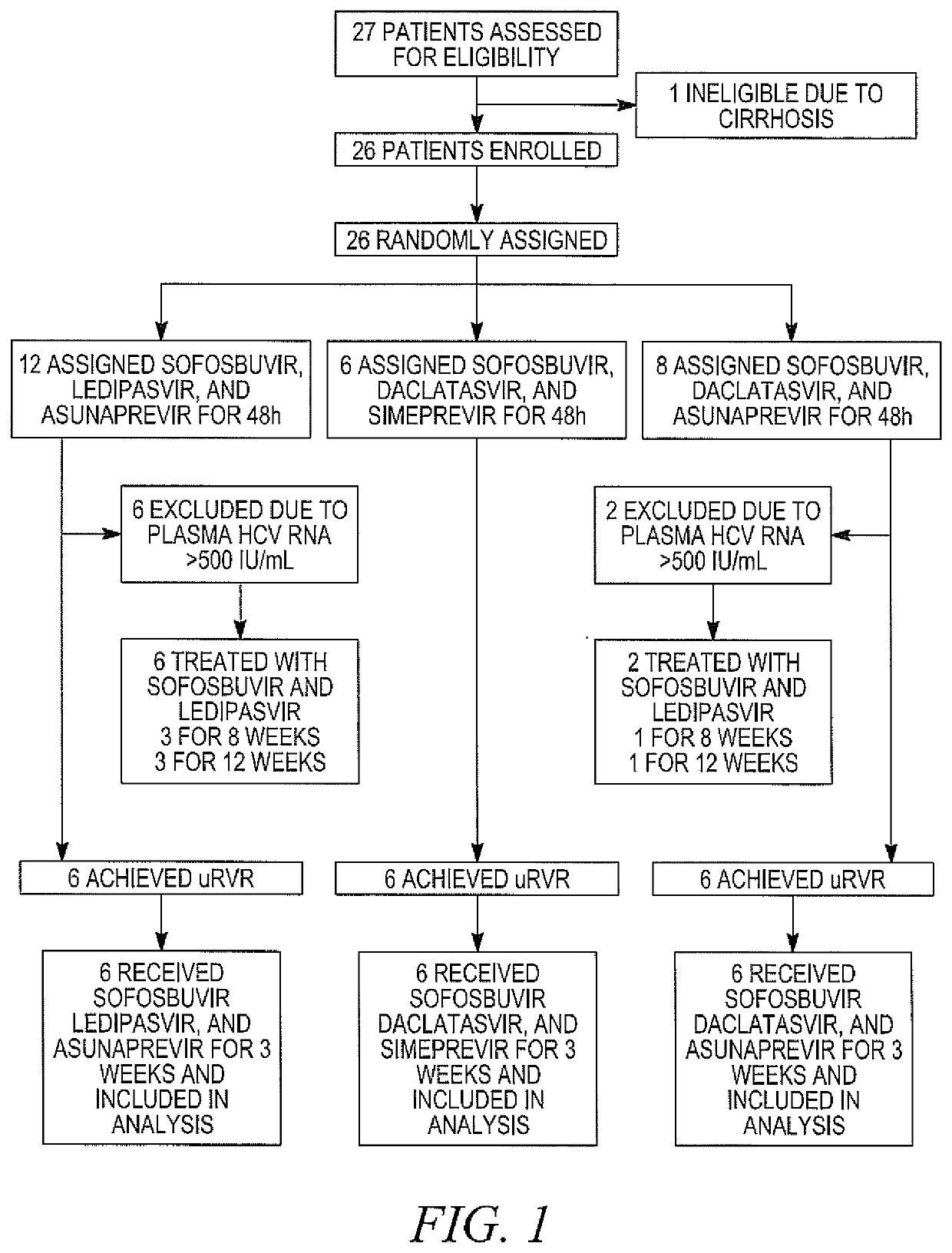
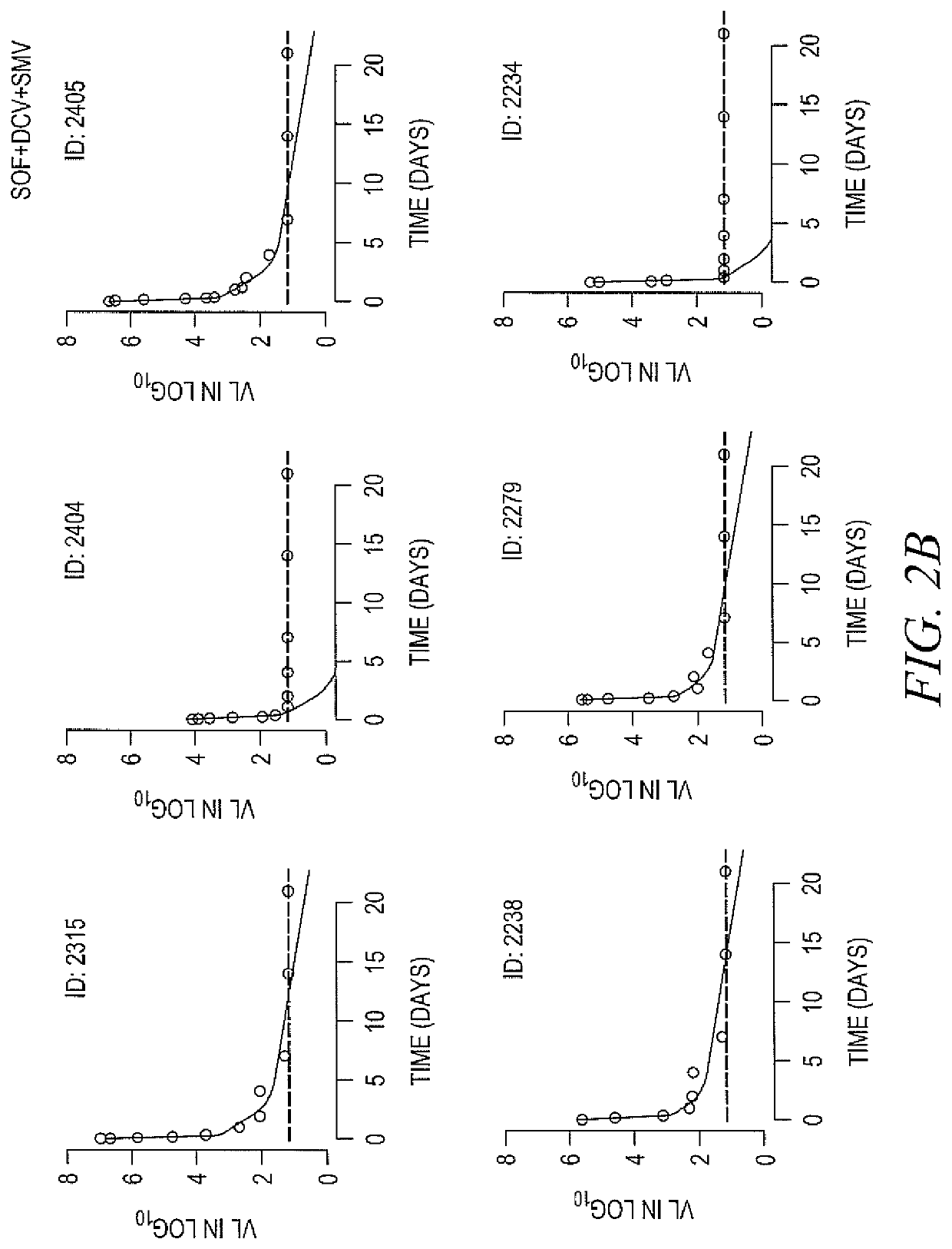
Response-guided hcv therapy
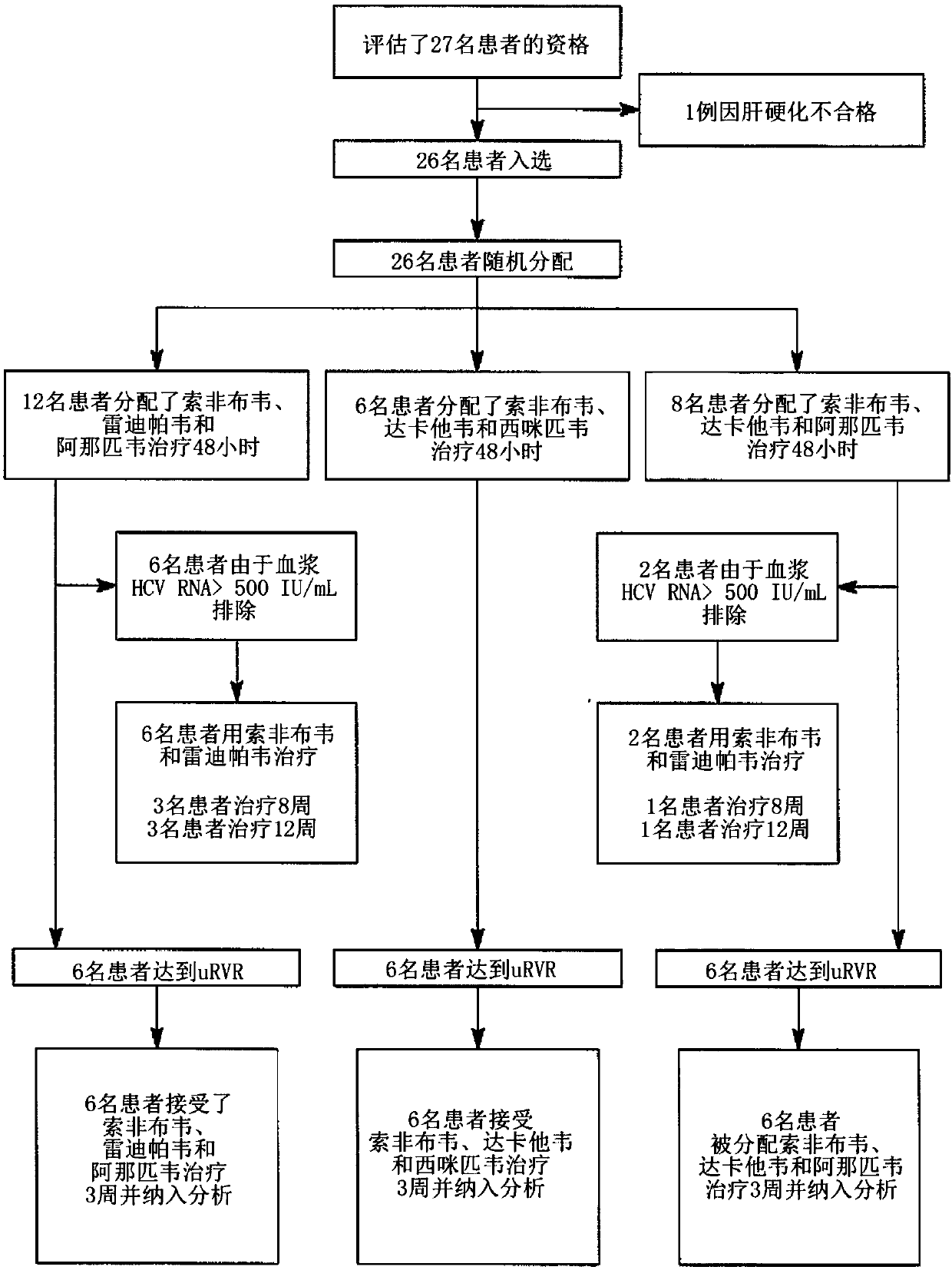
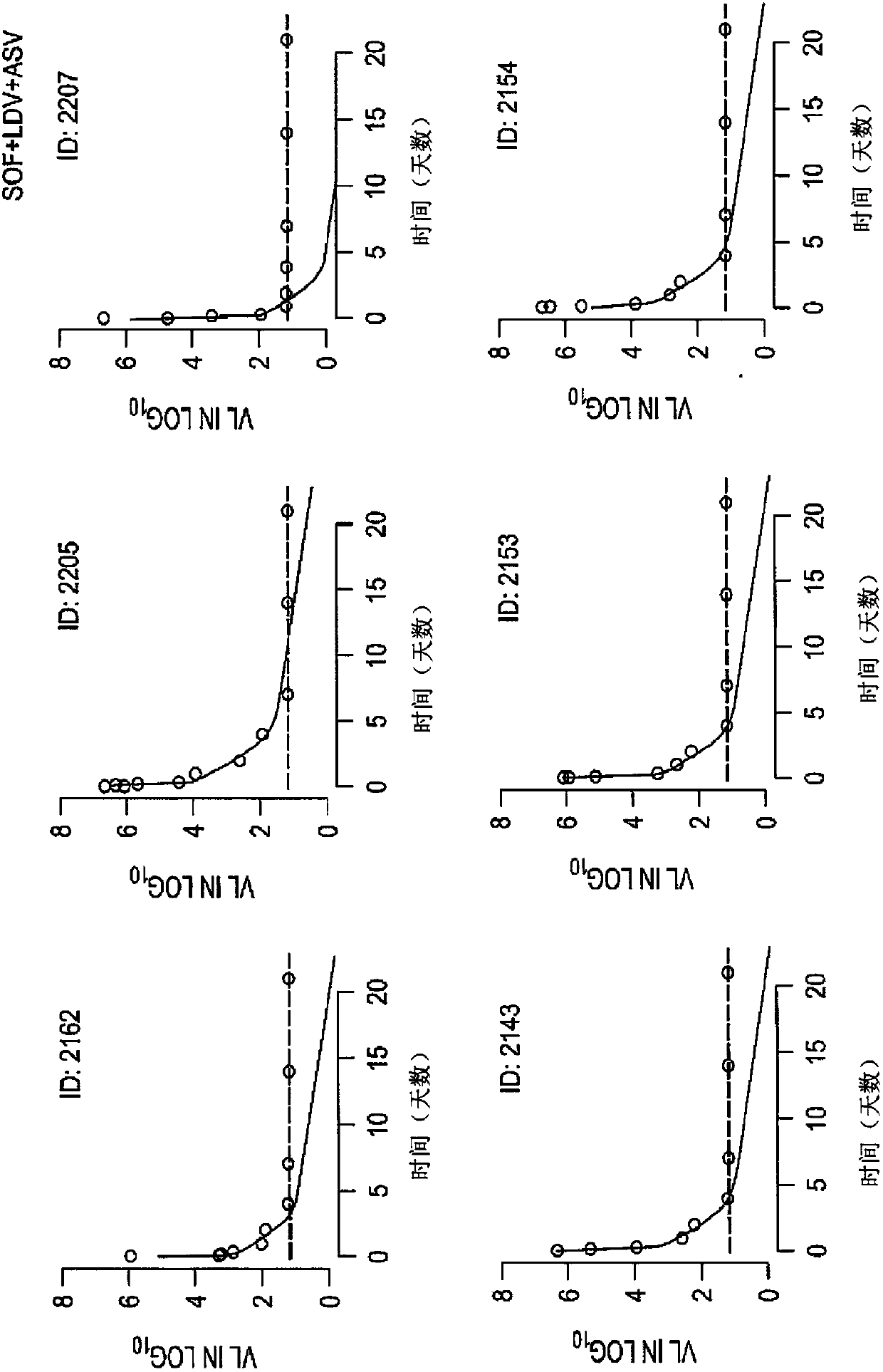
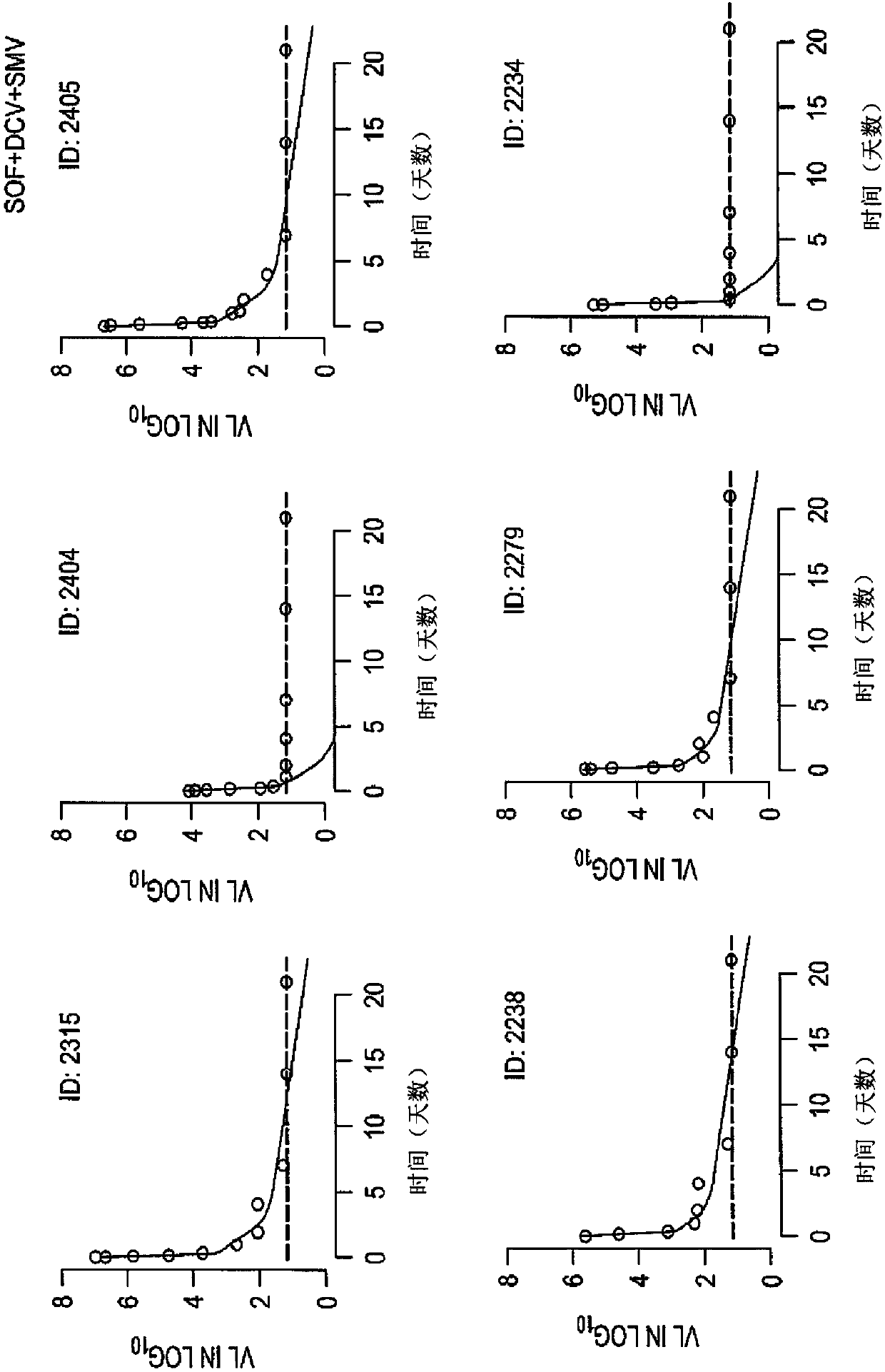
The present disclosure relates to solid dosage forms comprising anti-HCV compounds and methods of using such dosage forms to treat or prevent HCV infection. Direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) havea high cure rate, and favorable tolerability in persons infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). However, shorter courses of therapy can improve adherence, affordability, and increase DAAs accessibility. The addition of an NS3 protease inhibitor to dual NS5A-NS5B (nucleoside) inhibitors enhances antiviral efficacy, and reduces treatment duration to 3 weeks (wks) in individuals with a rapid virologicresponse (RVR), defined as plasma HCV RNA<500, or < 1,000, IU / mL by Day 2 of treatment.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
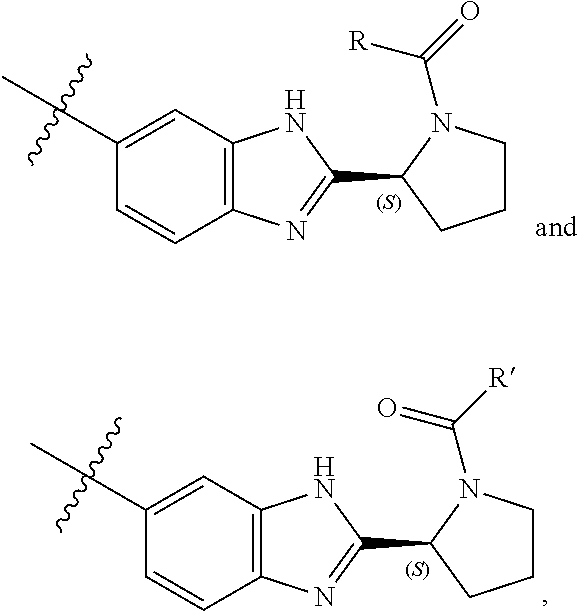
Bis-Benzimidazole Derivatives
InactiveUS20120172368A1Improved profileToxic reductionBiocideOrganic chemistryBenzimidazole derivativeHcv treatment
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula Iincluding stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R and R′ have the meaning as defined herein.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN R&D IRELAND UC
Macrocyclic indole derivatives useful as hepatitis c virus inhibitors
InactiveUS20110152279A1Enhance the imageNo toxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryHcv treatmentStereochemistry
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula (I) including stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein Y, R1, R2, R4 and n have the meaning defined in the claims. The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Response-guided hcv therapy
InactiveUS20180311268A1Clear the virus more effectivelyOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsTolerabilityRegimen
The present disclosure relates to solid dosage forms comprising anti-HCV compounds and methods of using such dosage forms to treat or prevent HCV infection. Direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) have a high cure rate, and favorable tolerability in persons infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). However, shorter courses of therapy can improve adherence, affordability, and increase DAAs accessibility. The addition of an NS3 protease inhibitor to dual NS5A-NS5B (nucleoside) inhibitors enhances antiviral efficacy, and reduces treatment duration to 3 weeks (wks) in individuals with a rapid virologic response (RVR), defined as plasma HCV RNA<500, or <1,000, IU / mL by Day 2 of treatment.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
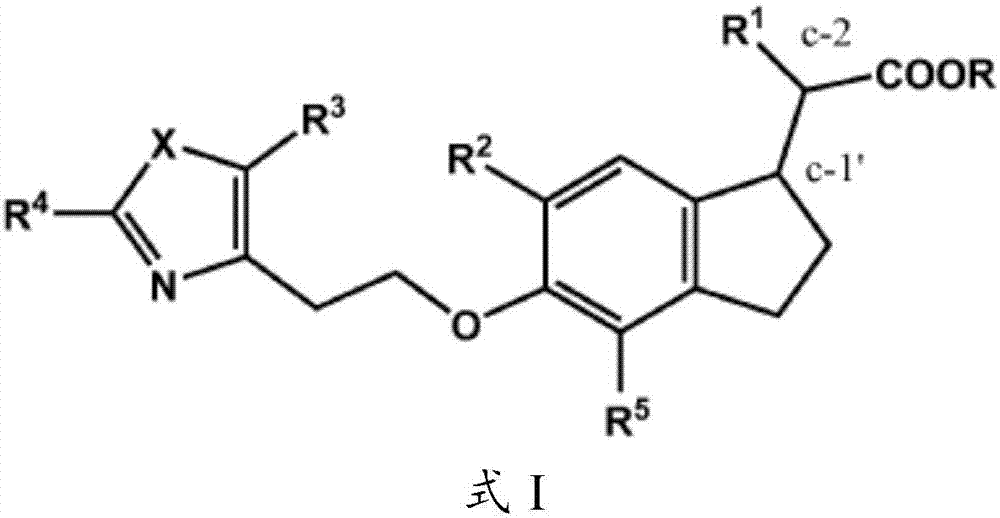
Methods of treating liver disease using indane acetic acid derivatives
InactiveCN107530352AOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemSevere hypertriglyceridemiaSustained viral response
This invention describes the use of indane acetic acid derivatives which are dual PPAR delta / gamma agonists for the treatment of liver diseases including one or more of the following: NAFLD (Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease), NASH (Non Alcoholic Steatohepatitis), Farber's Disease, ACLF (Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure), CLF (Chronic Liver Failure), POLT-HCV-SVR (Post-Orthotopic Liver Transplantdue to Hepatitis C Virus infection after Sustained Viral Response following anti-HCV therapy), Alagille syndrome, PFIC (Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis), PBC (Primary Biliary Cirrhosis),Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis, ADPCLD (Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Liver Disease), Treatment of liver transplant patients with reestablished fibrosis, CESD (Cholesteryl Ester Storage Disease), SHTG (Severe Hypertriglyceridemia), HoFH (Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia), HE (Hepatic Encephalopathy), or Alcoholic Liver Disease.
Owner:T3D THERAPEUTICS INC
Response-guided hcv therapy
InactiveUS20200352974A1Clear the virus more effectivelyOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsRapid Virologic ResponseEfficacy
The present disclosure relates to solid dosage forms comprising anti-HCV compounds and methods of using such dosage forms to treat or prevent HCV infection. Direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) have a high cure rate, and favorable tolerability in persons infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). However, shorter courses of therapy can improve adherence, affordability, and increase DAAs accessibility. The addition of an NS3 protease inhibitor to dual NS5A-NS5B (nucleoside) inhibitors enhances antiviral efficacy, and reduces treatment duration to 3 weeks (wks) in individuals with a rapid virologic response (RVR), defined as plasma HCV RNA<500, or <1,000, IU / mL by Day 2 of treatment.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
HCV therapy
InactiveUS20060067913A1Eliminate side effectsEnhance interferon efficacyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEzrinPeptide
A peptide which has at least 80% identity to a fragment of Domain A or B of the Hepreceptor of ezrin, is used in the treatment of viral hepatitis.
Owner:REGENT RES
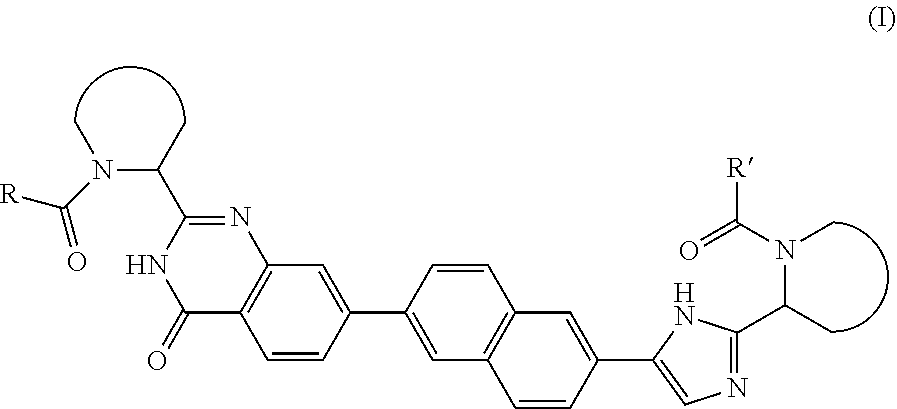
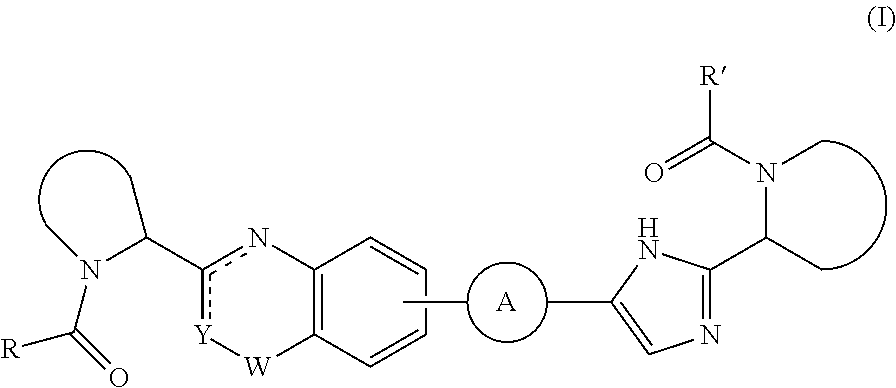
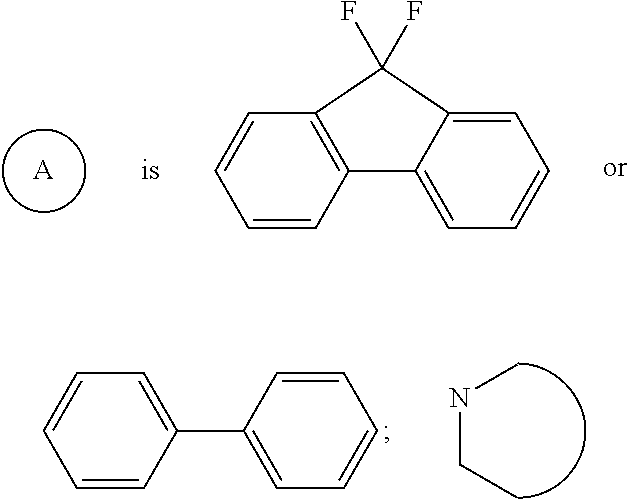
Quinazolinone derivatives as hcv inhibitors
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula (I) including stereochemically isomeric forms, salts, and solvates thereof, wherein R and R′ have the meaning as defined herein. The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use, alone or in combination with other HCV inhibitors, in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Hetero-Bicyclic Derivatives As HCV Inhibitors
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula I, including stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R and R′ have the meaning as defined herein. The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use, alone or in combination with other HCV inhibitors, in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Bis-benzimidazole derivatives as hepatitis C virus inhibitors
InactiveUS8623899B2Improved profileToxic reductionBiocideOrganic chemistryHcv treatmentBenzimidazole derivative
Inhibitors of HCV replication of formula Iincluding stereochemically isomeric forms, and salts, hydrates, solvates thereof, wherein R and R′ have the meaning as defined herein.The present invention also relates to processes for preparing said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them and their use, alone or in combination with other HCV inhibitors, in HCV therapy.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com