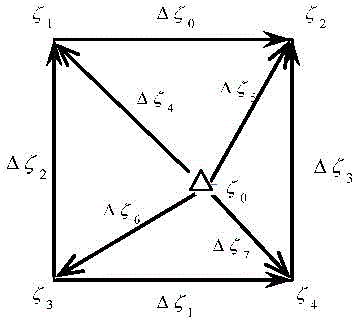
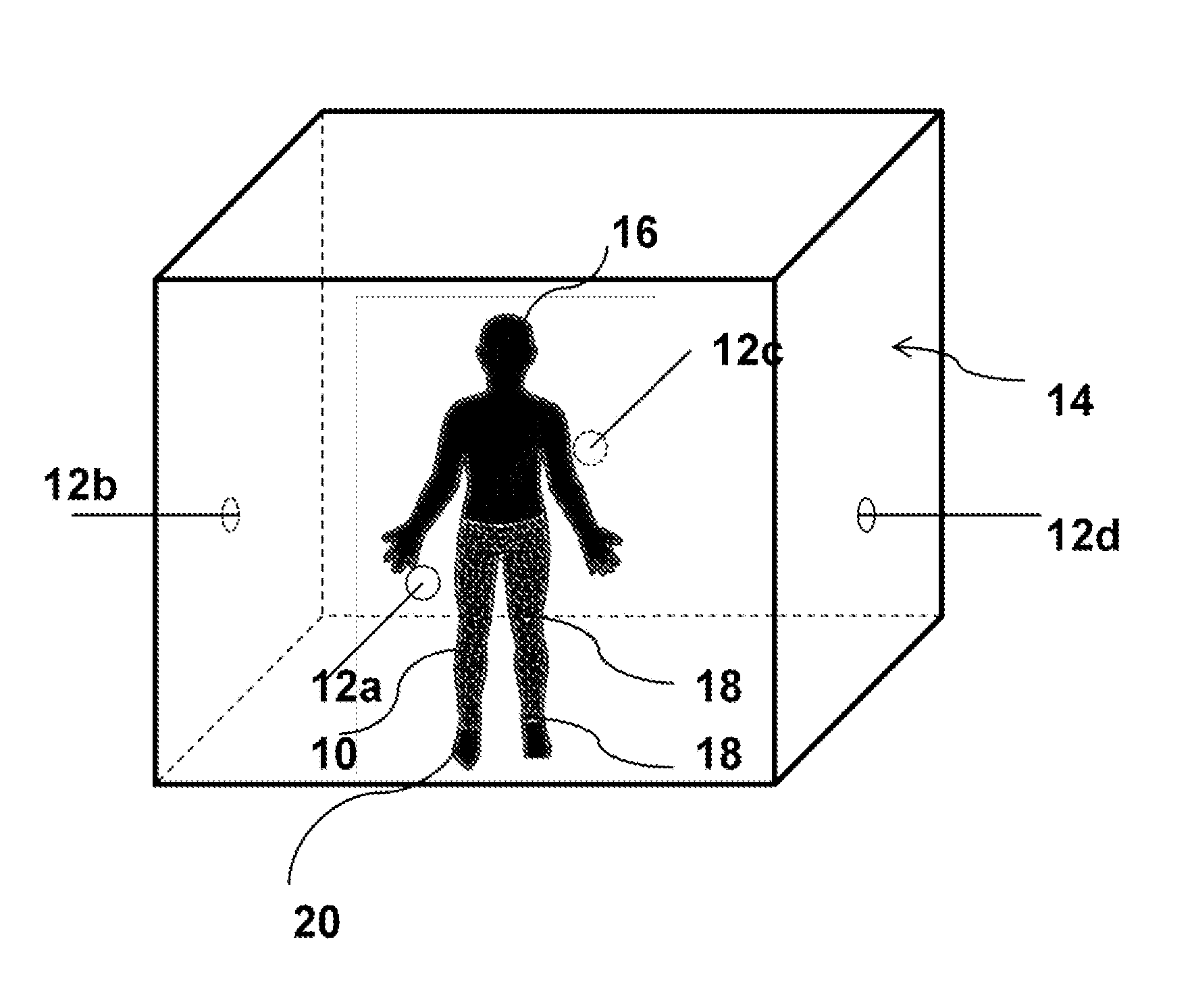
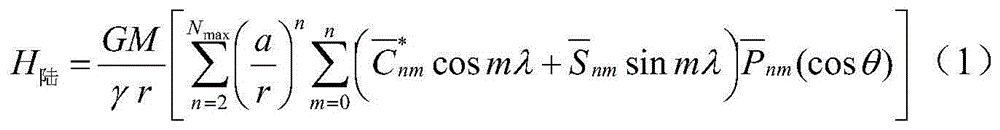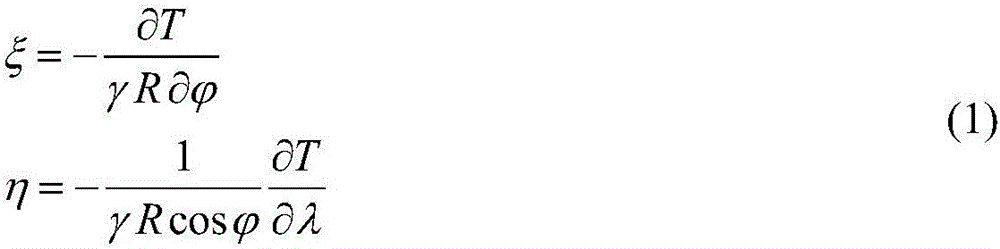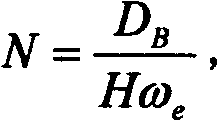Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
138 results about "Geodetic survey" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of generating a Geodetic Reference Database Product
ActiveUS20110282578A1Precise definitionSuperior hardwareInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTriangulationVehicle driving
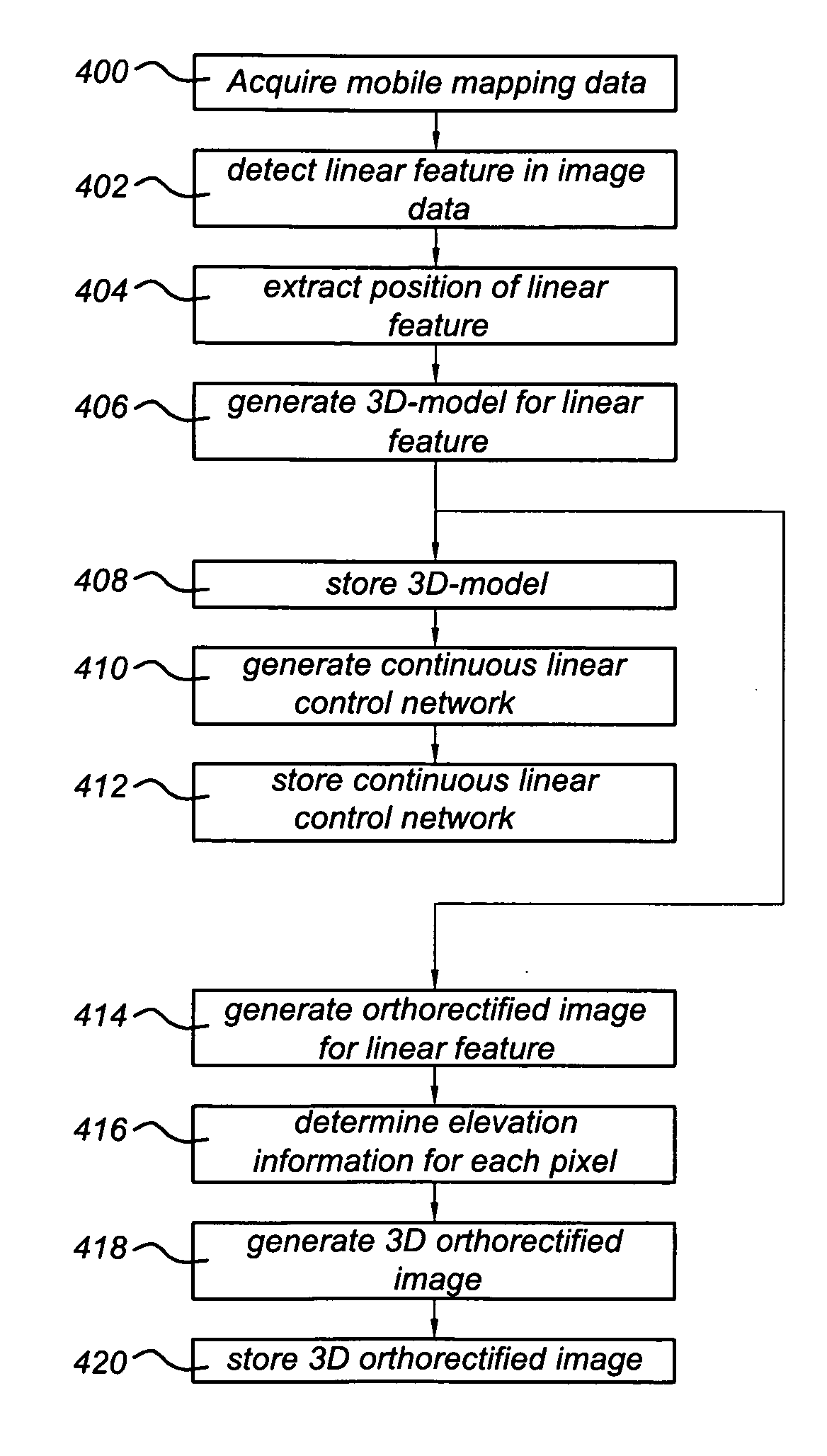
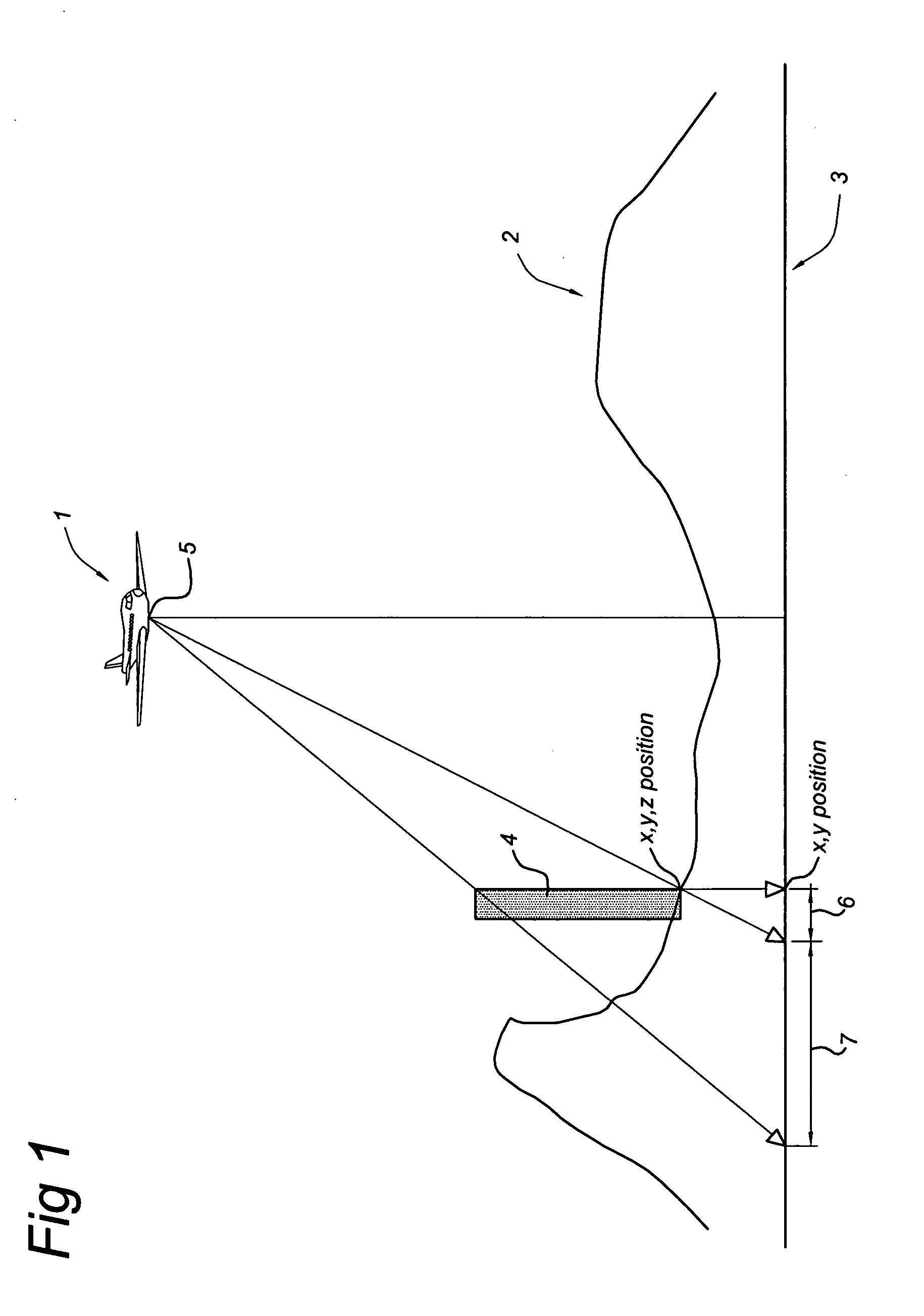
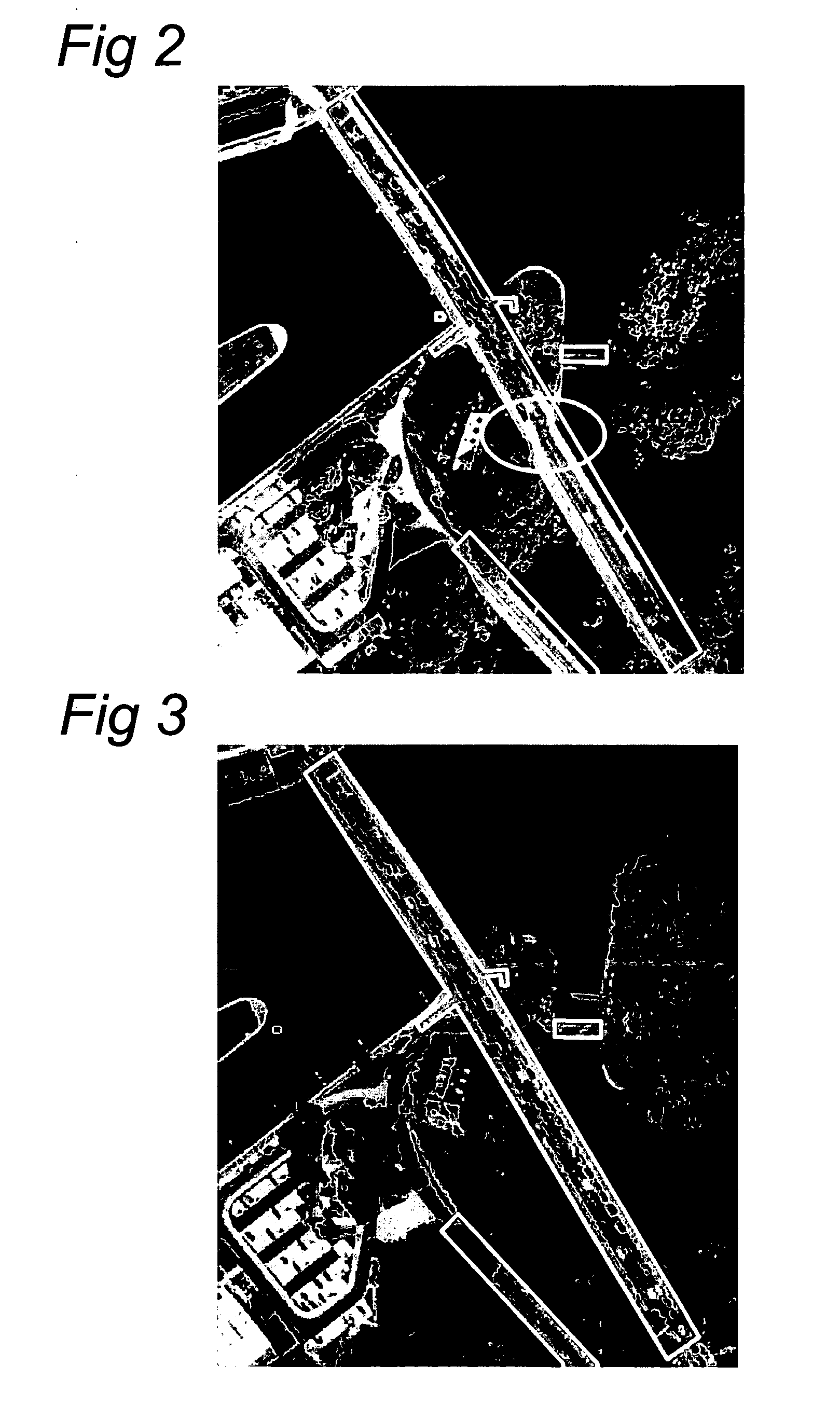
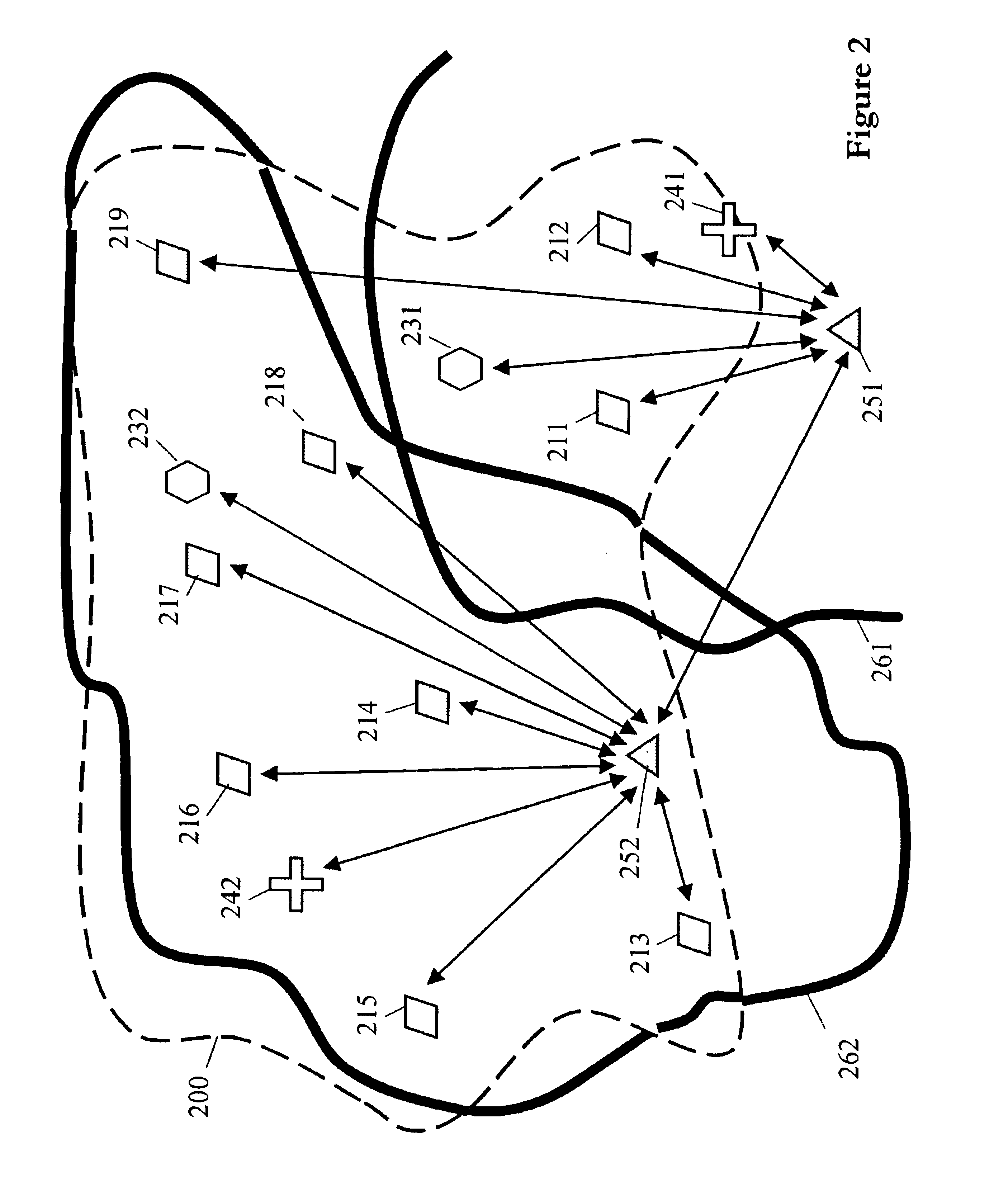
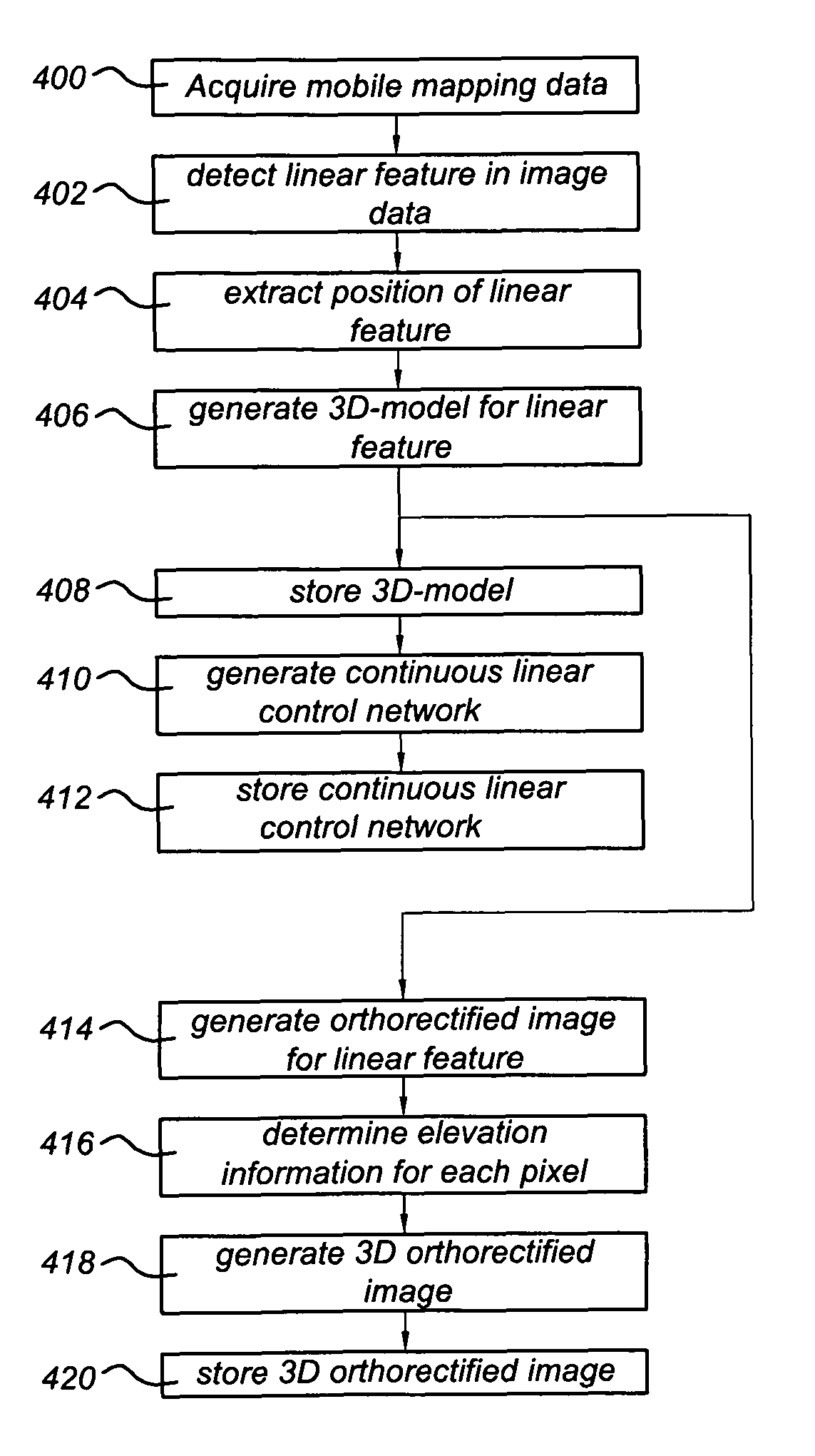
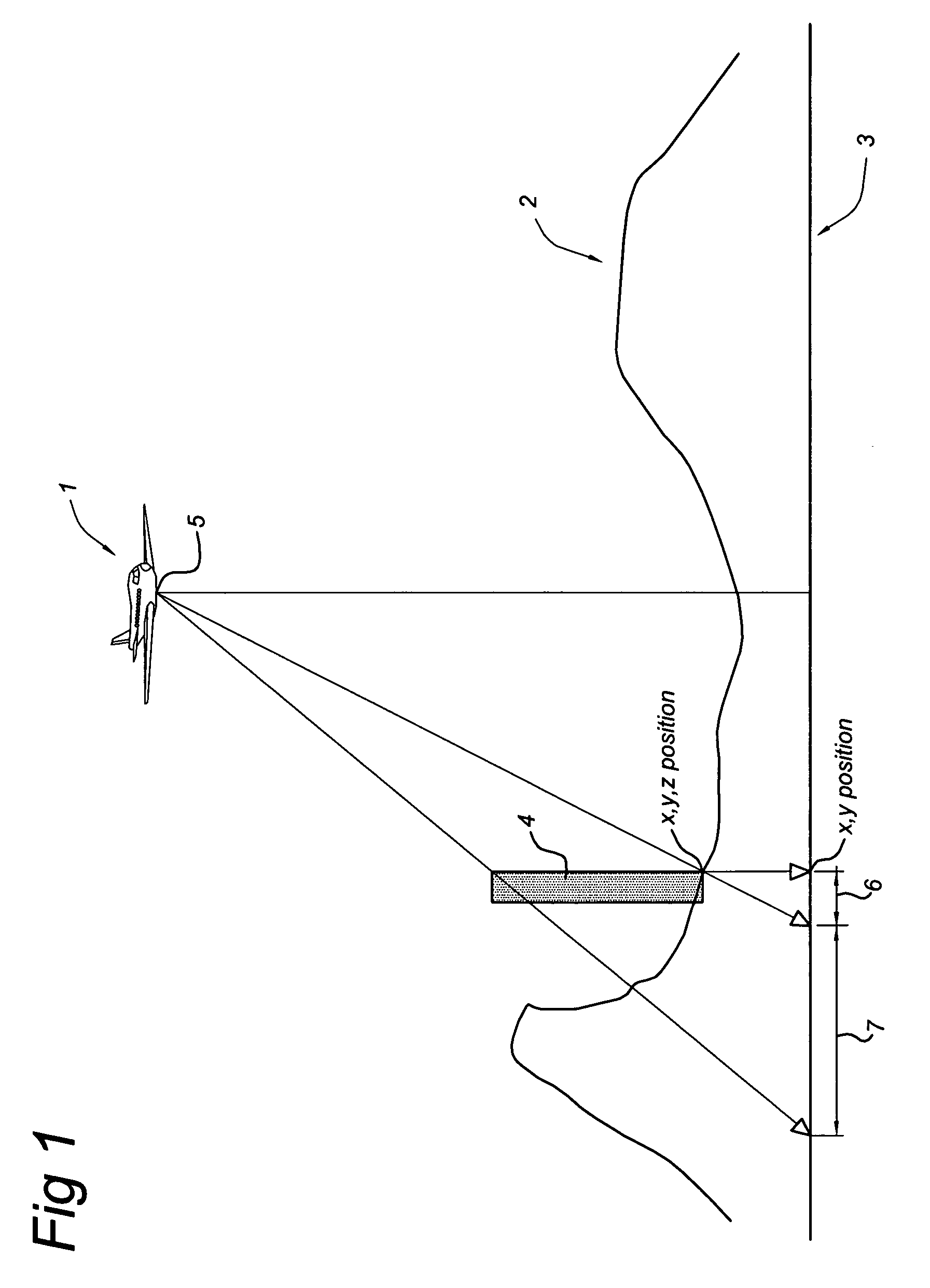
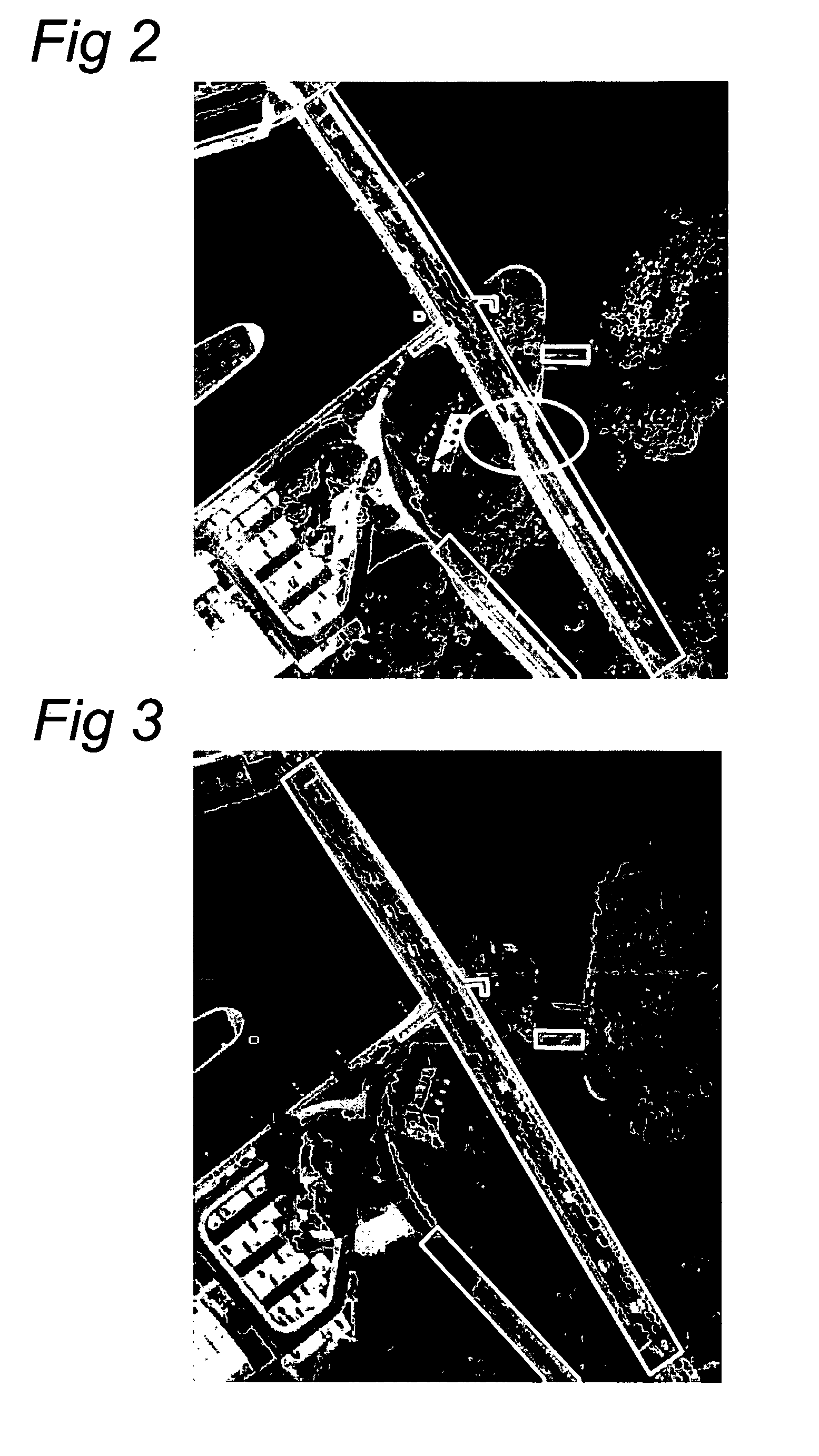
A method of generating a geodetic reference database product is disclosed The method comprises acquiring mobile mapping data captured by means of digital cameras, range sensors and position determination means including GPS and IMU mounted to a vehicle driving across the earth surface, the mobile mapping data comprising simultaneously captured image data, range data and associated position data in a geographic coordinate system. Linear stationary earth surface features are derived from the mobile mapping data by processing the image data, range data and associated position data. 3D-models are generated for the linear stationary earth surface features in the geographic coordinate system from the image data, range data and associated position data and stored in a database to obtain the geodetic reference database product. A 3D-model could include an image representing the colors of the surface of the 3D model or a set of smaller images representing photo-identifiable objects along the model. The 3D-models could be used to rectify aerial imagery, to correct digital elevation models and to improve the triangulation of digital elevation models.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
Automated calibration of a surveying instrument
ActiveUS20110023578A1Simple designLower requirementWave based measurement systemsSurveying instrumentsSurvey instrumentMeasuring instrument
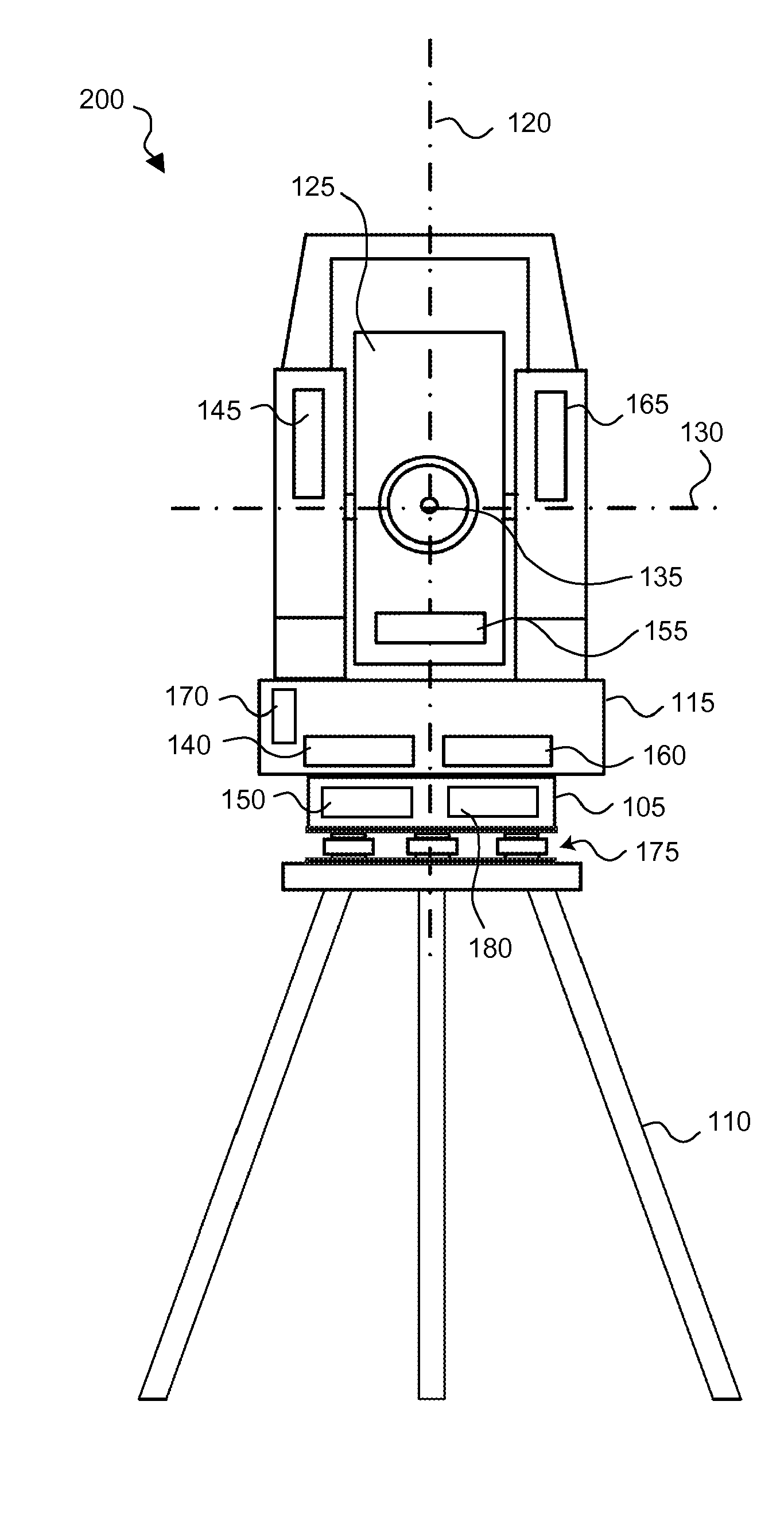
The present invention provides a method for calibrating a geodetic instrument, an instrument and a computer program product thereof. In the method and geodetic instrument of the present invention, a value of at least one parameter affecting the measurements made by the instrument is detected and compared with a predetermined threshold. On the basis of the comparison between the detected value and the predetermined threshold, the instrument aims at a reference target and a calibration is performed using the reference target. The present invention is advantageous in that the accuracy and reliability of the measurements performed by the instrument are increased. Further, the present invention is advantageous in that the requirements on mechanical stability are reduced.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
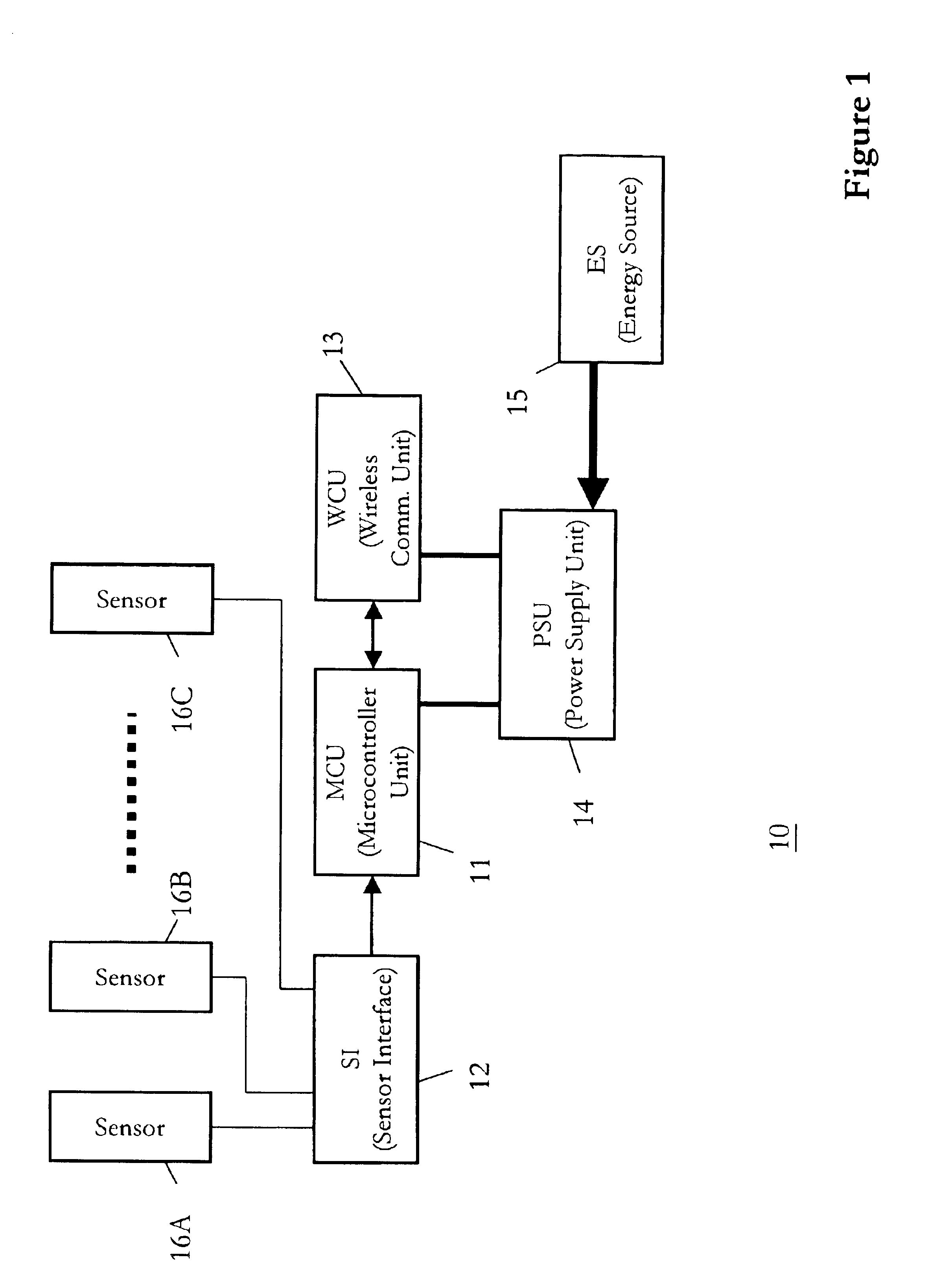
Alert system and method for geographic or natural disasters utilizing a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6914525B2Avoid lostLow costFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCommunication unitTelecommunications network
The invention advantageously provides an alert system and method for geographic or natural disasters that utilize a telecommunications network for monitoring geographic data in disaster-prone areas and accordingly issuing warnings against potential disasters to people inside the monitored area. An alert system according to a preferred embodiment of the invention comprises a telecommunications service network, one or more wireless sensor modules and a control center. The telecommunications network according to this particular embodiment includes service coverage over the monitored areas. The wireless sensor modules are installed to selected locations inside monitored areas. Each of the sensor modules further comprises at least one sensor for collecting geographic or geodetic data and a wireless communications unit for sending collected geographic data to the control center via the telecommunications network. The control center then receives and processes the monitored geographic or geodetic data sent by the wireless sensor modules for further algorithmic analysis. The control center accordingly issues alerts for imminent geographic or natural disasters if the processing of the geographic or geodetic data produces adverse results.
Owner:FAR EASTONE TELECOMM
Method of generating a geodetic reference database product
ActiveUS8958980B2Superior hardwareSpeed up the processInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlReference databaseMobile mapping
A method of generating a geodetic reference database product is disclosed The method comprises acquiring mobile mapping data captured by means of digital cameras, range sensors and position determination means including GPS and IMU mounted to a vehicle driving across the earth surface, the mobile mapping data comprising simultaneously captured image data, range data and associated position data in a geographic coordinate system. Linear stationary earth surface features are derived from the mobile mapping data by processing the image data, range data and associated position data. 3D-models are generated for the linear stationary earth surface features in the geographic coordinate system from the image data, range data and associated position data and stored in a database to obtain the geodetic reference database product. A 3D-model could include an image representing the colors of the surface of the 3D model or a set of smaller images representing photo-identifiable objects along the model. The 3D-models could be used to rectify aerial imagery, to correct digital elevation models and to improve the triangulation of digital elevation models.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
Method for monitoring roadbed subsidence of express way by InSAR
InactiveCN101706577AImprove monitoring accuracyHigh degree of automationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRoad surfaceLandform
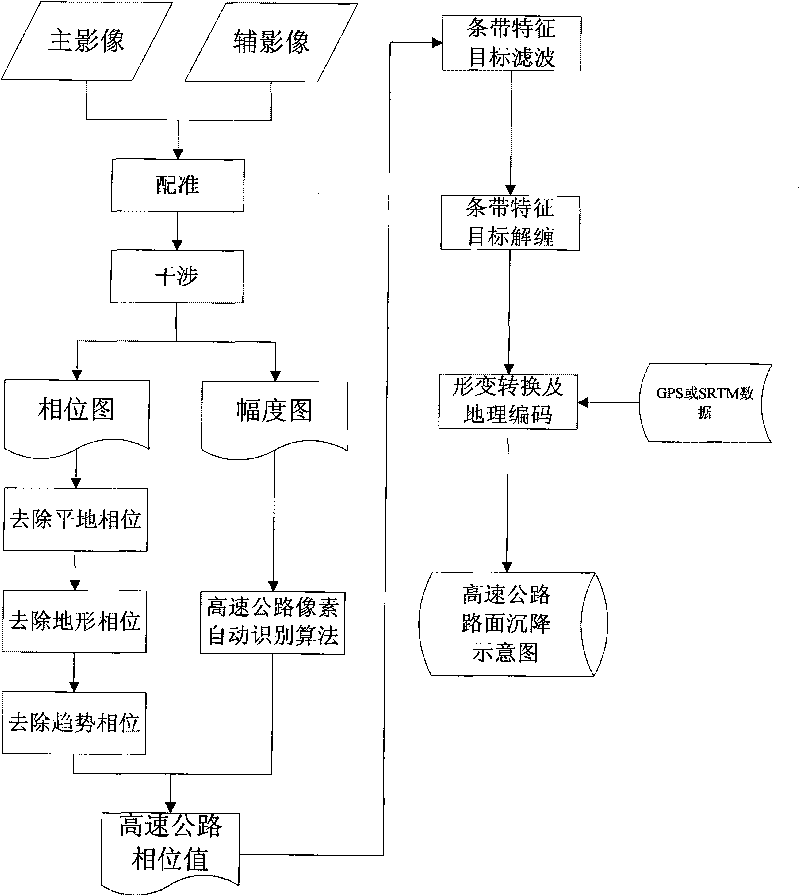
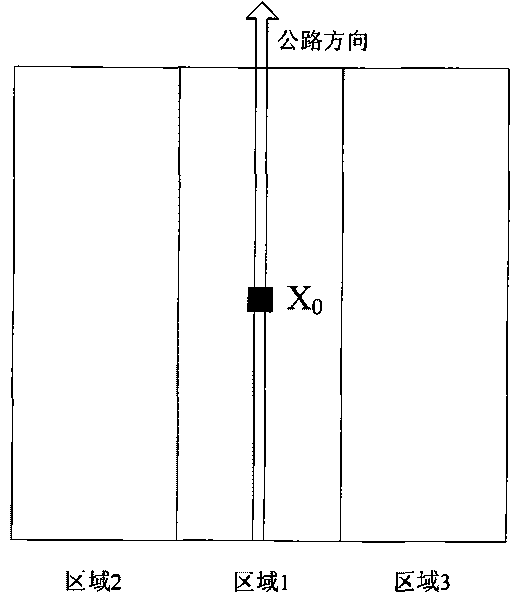
The invention relates to the field of geodetic survey based on remote sensing images, in particular to a method for monitoring roadbed subsidence of express way by an InSAR, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, preprocessing, rectifying and interfering SAR data to obtain an InSAR interfered phase and amplitude image; secondly, carrying out flat earth effect, orographic effect and track residual trend phase elimination on the InSAR interfered phase to obtain a phase value only including surface deformation information; thirdly, recognizing positions and coordinates of strips of the express way in the SAR image by strip characteristics of the express way in the InSAR amplitude image; fourthly, extracting the phase value of the corresponding position in the interfered phase image by using the coordinates, and restoring a real phase value by adopting a filtering and unwrapping algorithm of a strip characteristic target; and fifthly, carrying out geocoding and deformation value transformation on the real phase value to obtain a roadbed subsidence value of the express way. The method has the advantages of simple implementation, low expense, high monitoring precision, large monitoring range, high automation degree and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
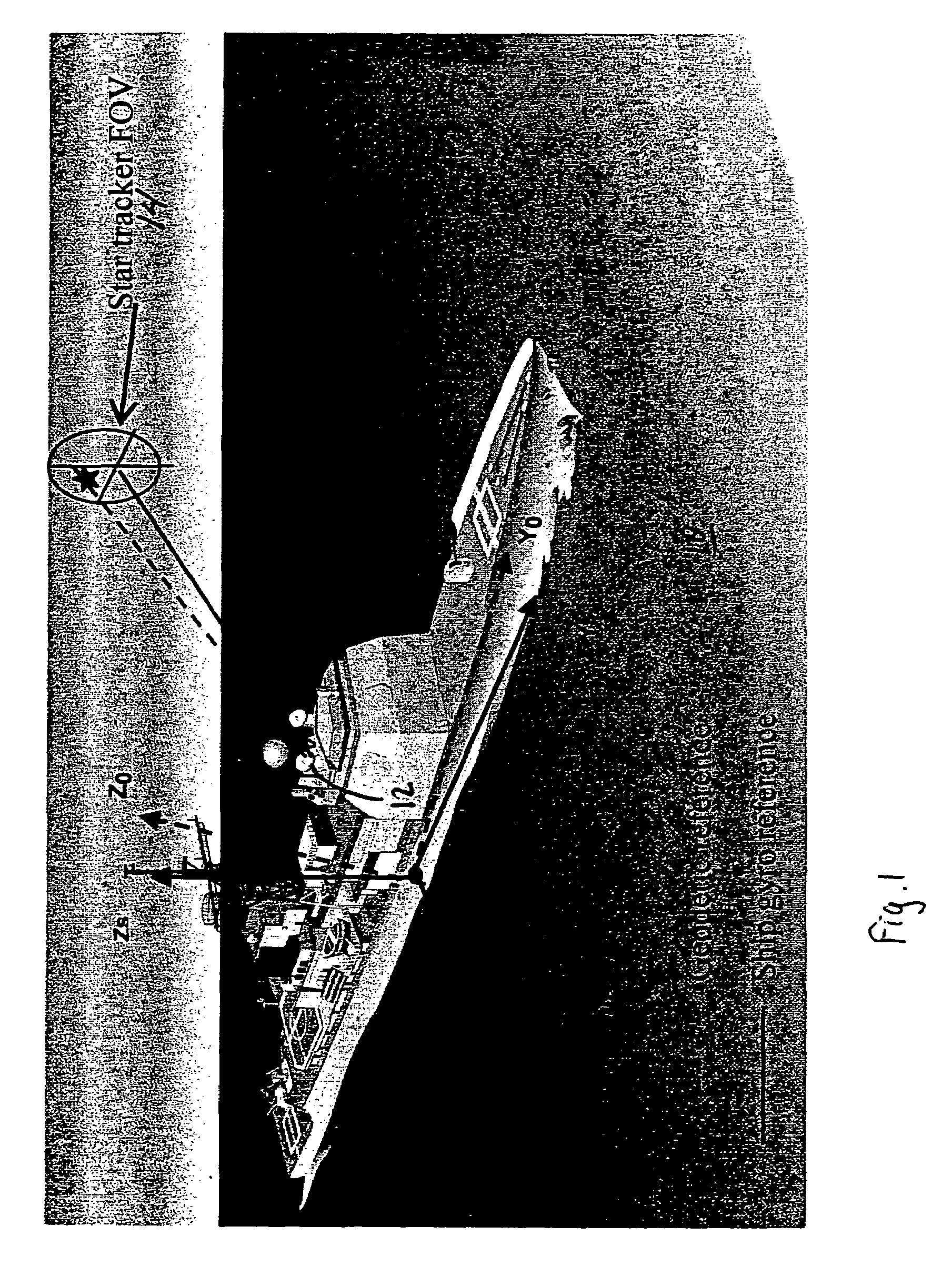
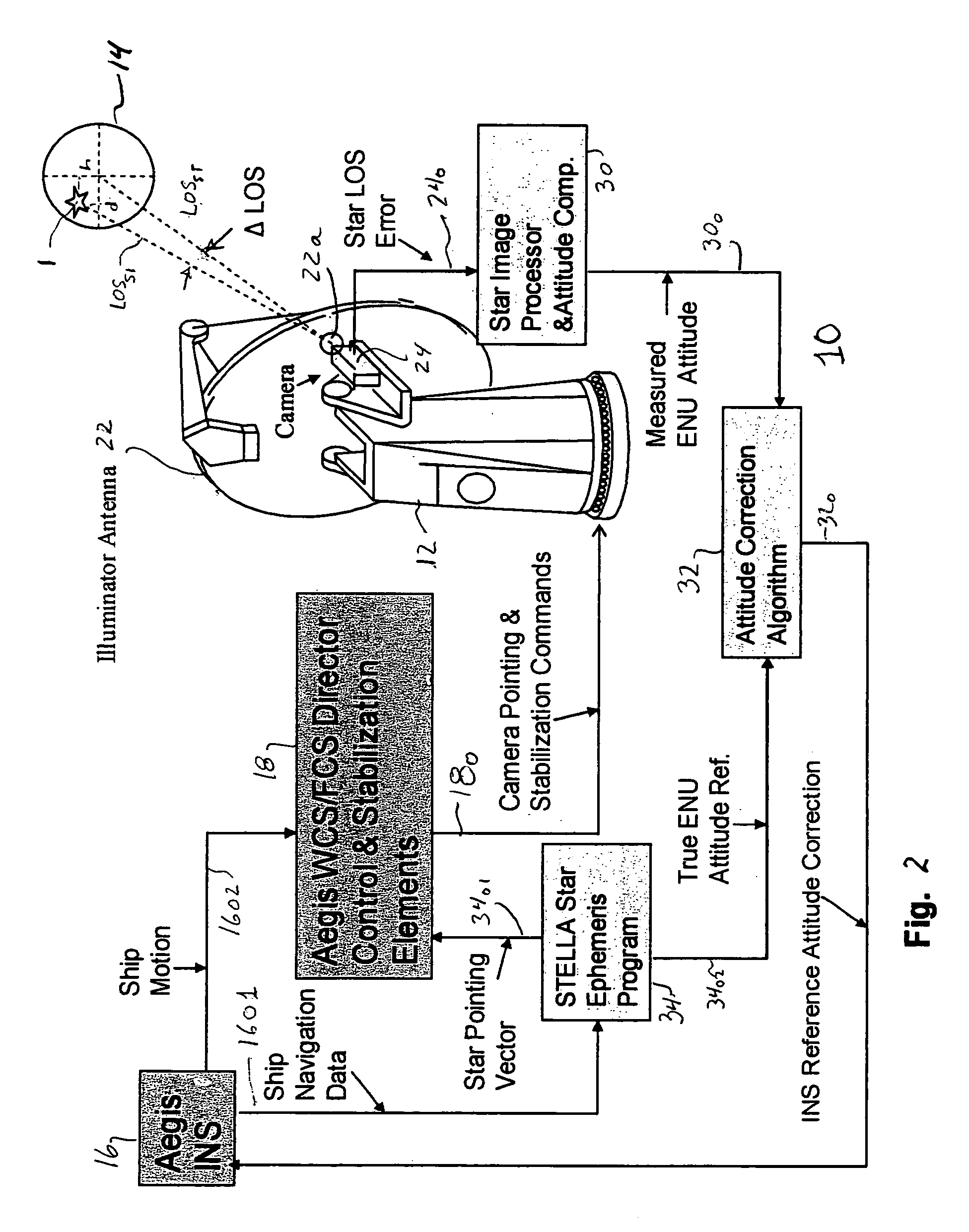
Calibration of ship attitude reference
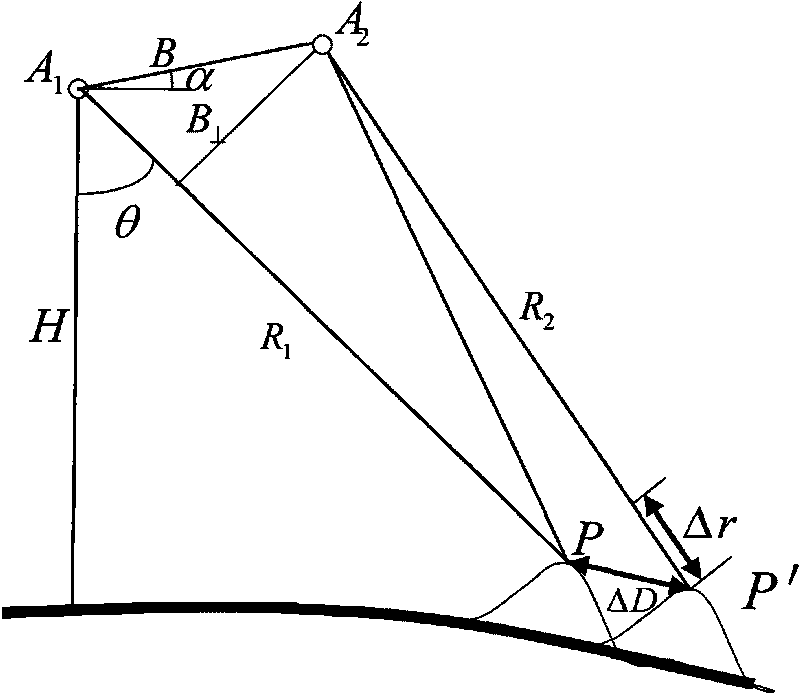
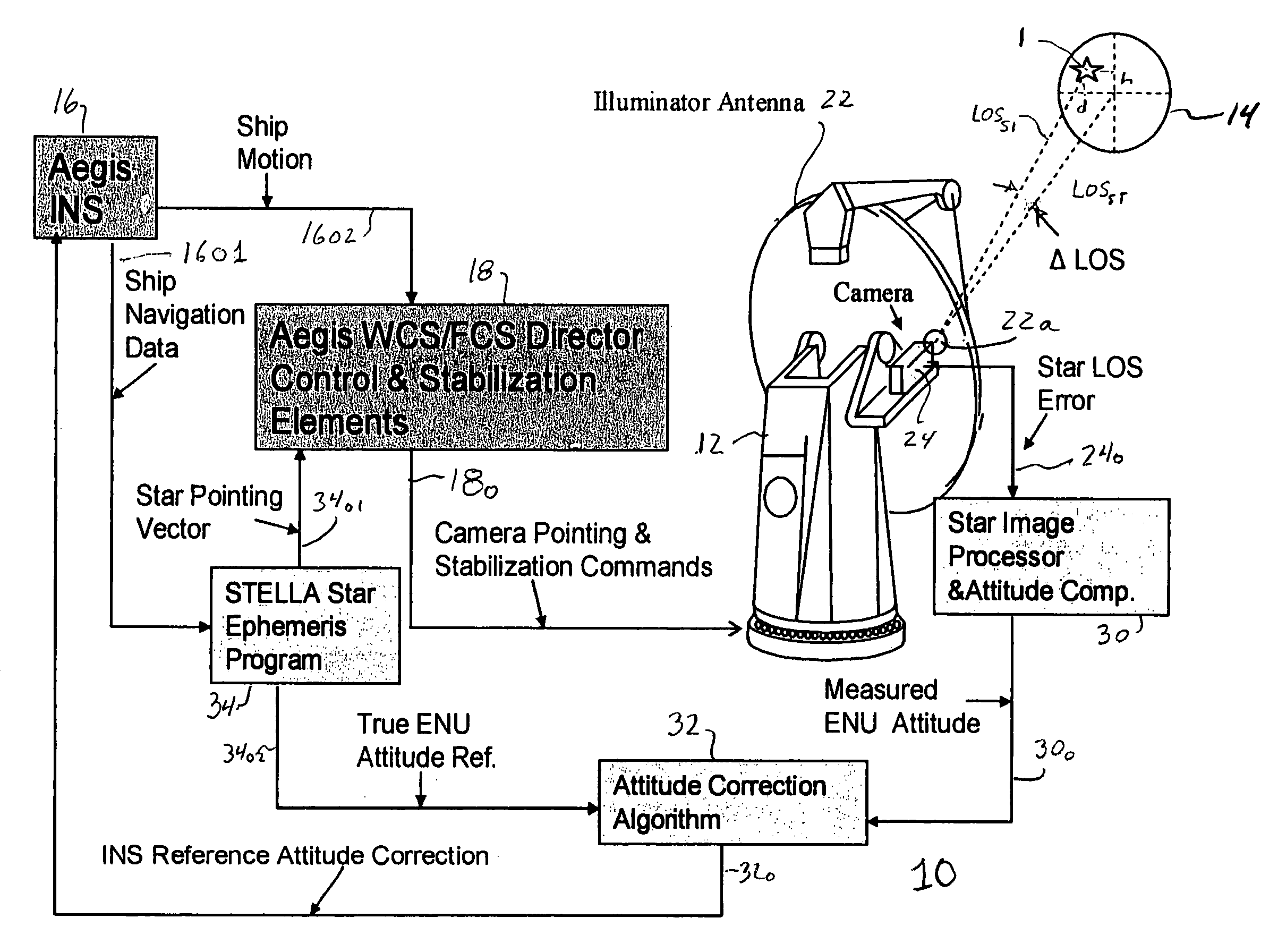
A ship includes a star tracker mounted on a platform stabilized in ENU by the inertial navigation system (INS). The line-of-sight (LOS) of the star tracker is directed toward two separated stars, and the LOS difference angles are noted. The angles are processed to generate vector triads representing geodetic (ephemeris) and navigation system attitude. The triads are processed to generate a coordinate transformation matrix. The transformation matrix is separated into systematic error and reference attitude error. The reference attitude error is summed with the inertial navigation system attitude to generate corrected ENU attitude. The corrected attitude is used as a reference for shipboard sensors, to reduce errors when the sensor data is linked to other platforms.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
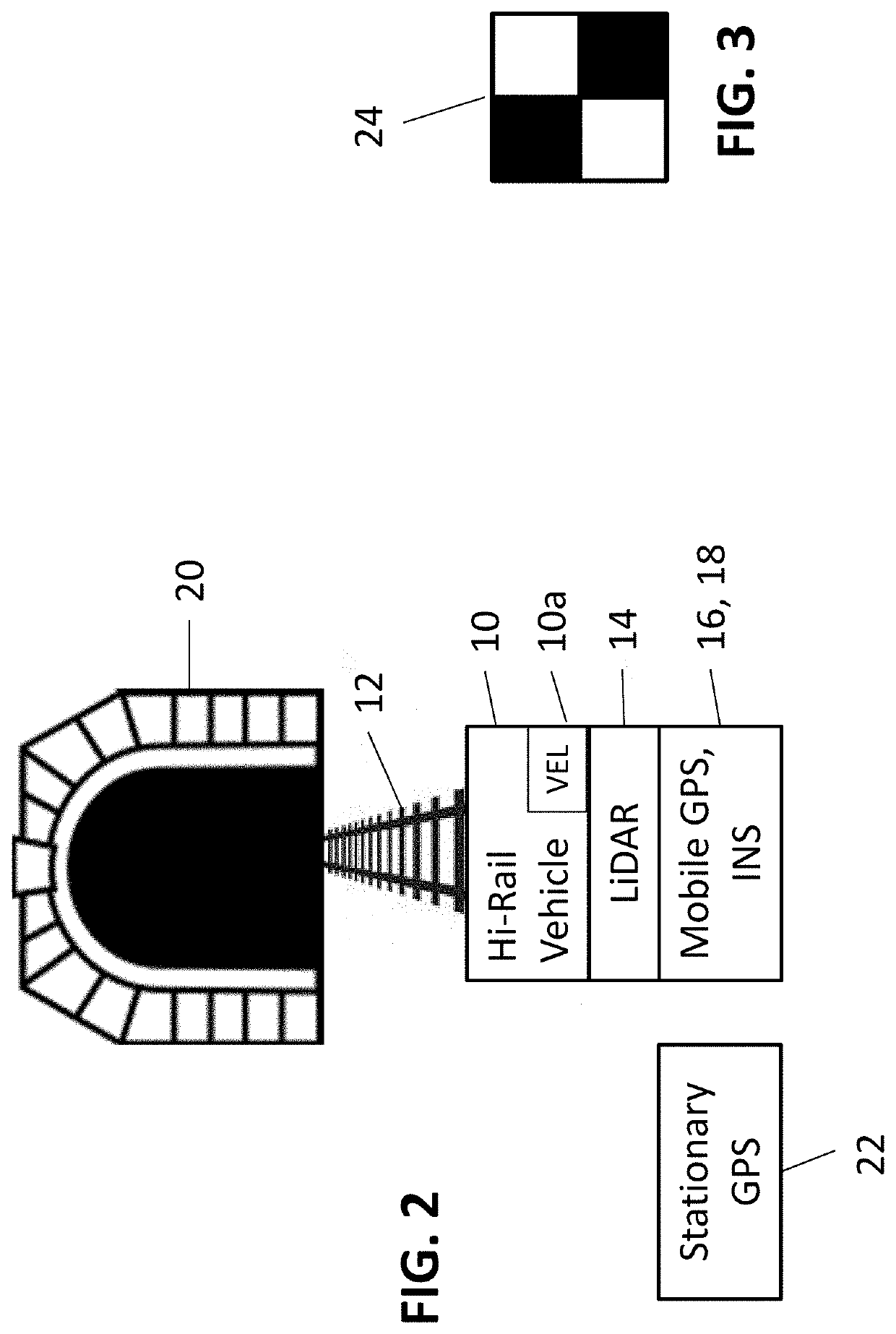
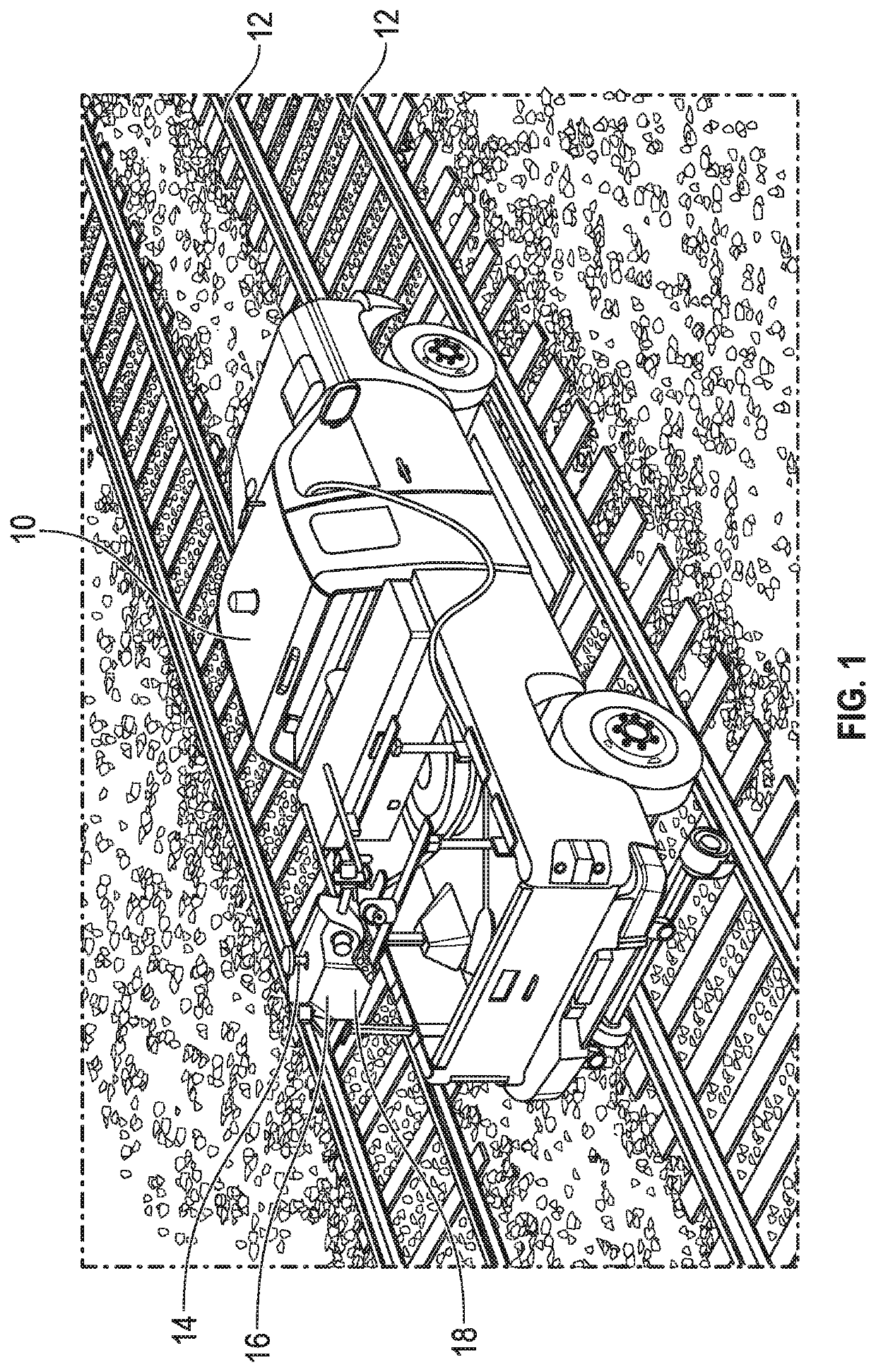
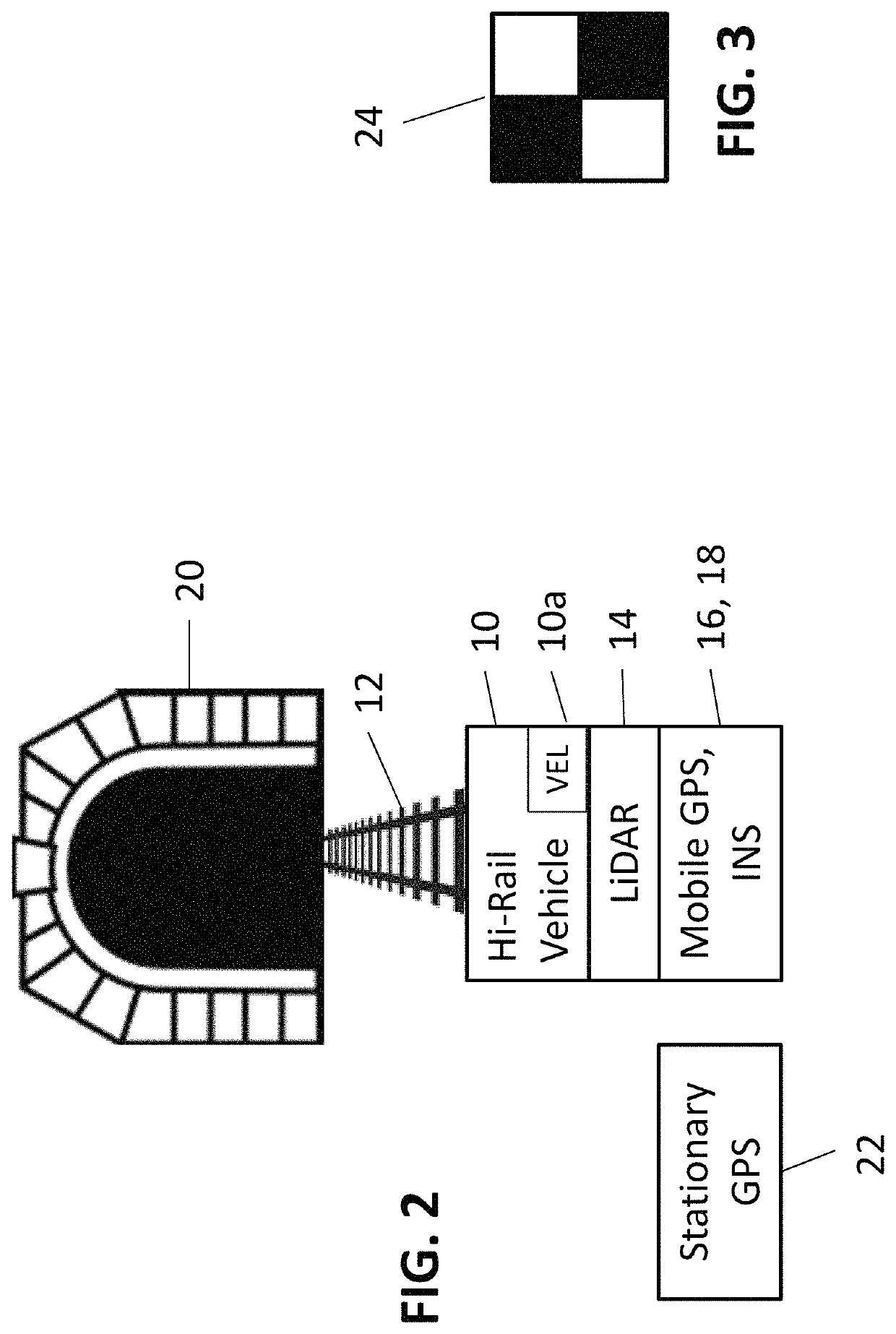
Tunnel mapping system and methods
ActiveUS20200025578A1Overcome difficultiesInstruments for road network navigationSatellite radio beaconingRailway tunnelData set
A process for constructing highly accurate three-dimensional mappings of objects along a rail tunnel in which GPS signal information is not available includes providing a vehicle for traversing the tunnel on the rails, locating on the vehicle a LiDAR unit, a mobile GPS unit, an inertial navigation system, and a speed sensor to determine the speed of said vehicle. A stationary GPS, whose geolocation is well-defined, is located near the entrance of the tunnel. Image-identifiable targets having a well-defined geodetic locations are located at preselected locations within the tunnel. The vehicle traverses the tunnel, producing mass point cloud datasets along said tunnel. Precise measurements of 3D rail coordinates are also obtained. The datasets are adjusted based on the mobile GPS unit, the inertial navigation system, the speed sensor, the location of the image-identifiable targets, and the precise measurements of 3D rail coordinates, to thereby produce highly accurate, and substantially geodetically correct, three-dimensional mappings of objects along the tunnel.
Owner:MASER CONSULTING INC
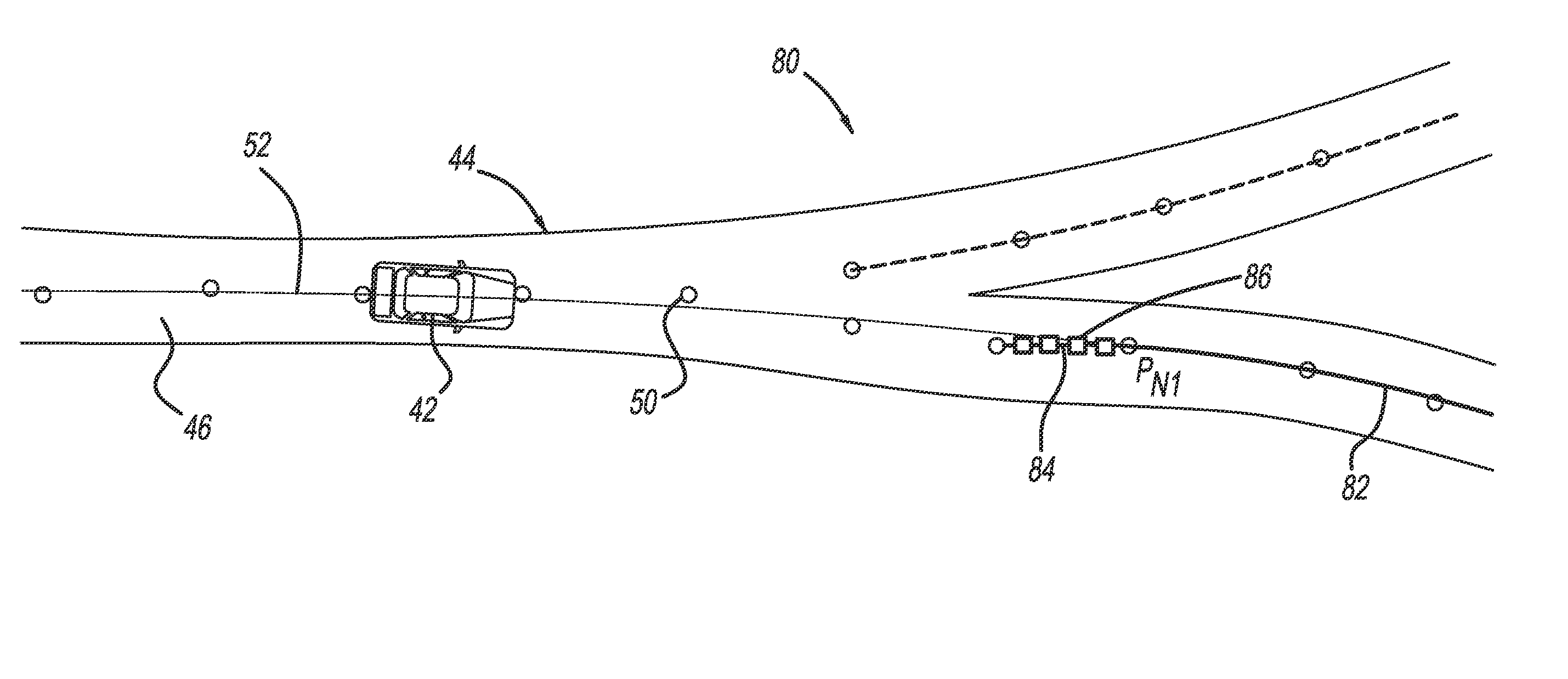
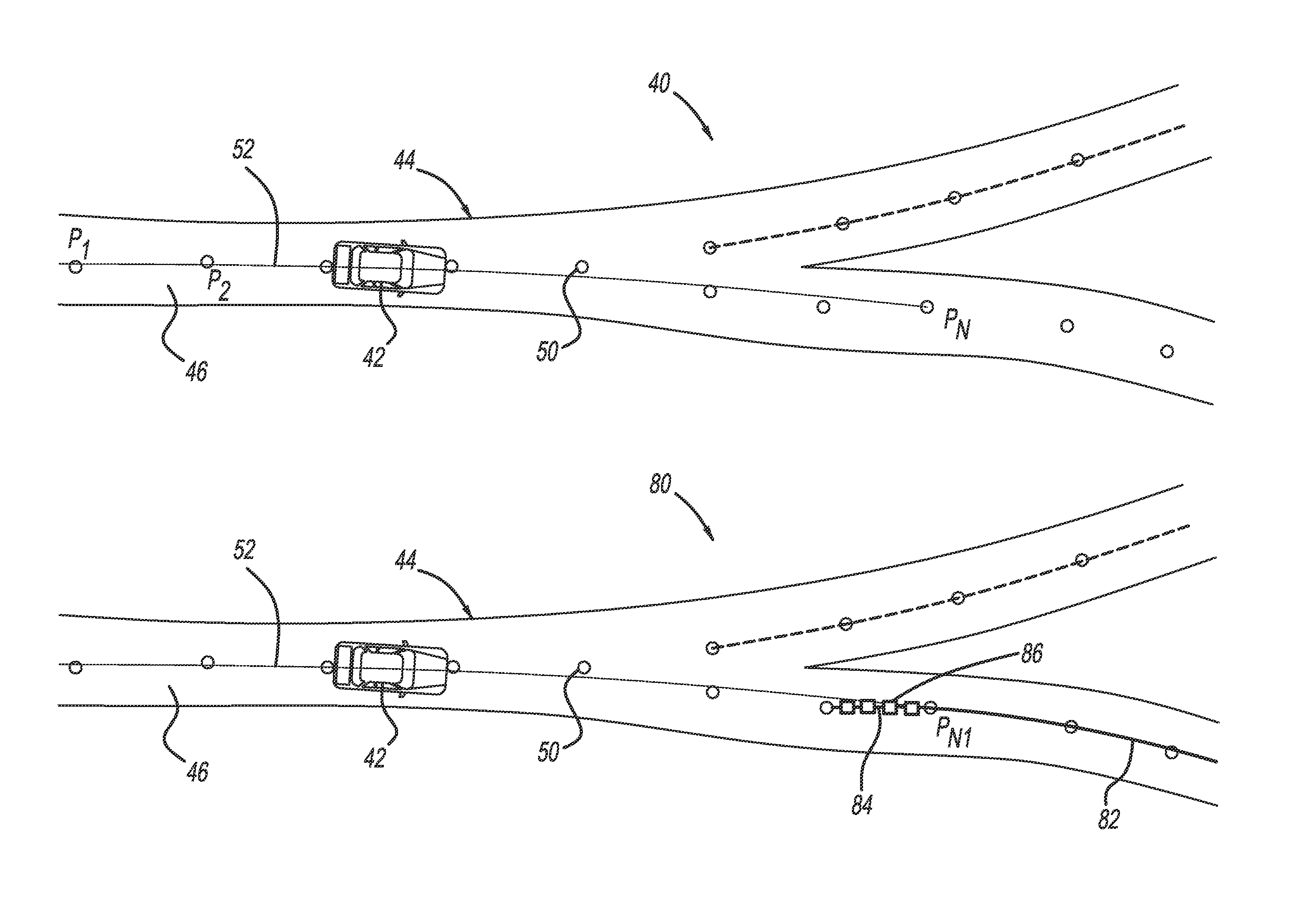
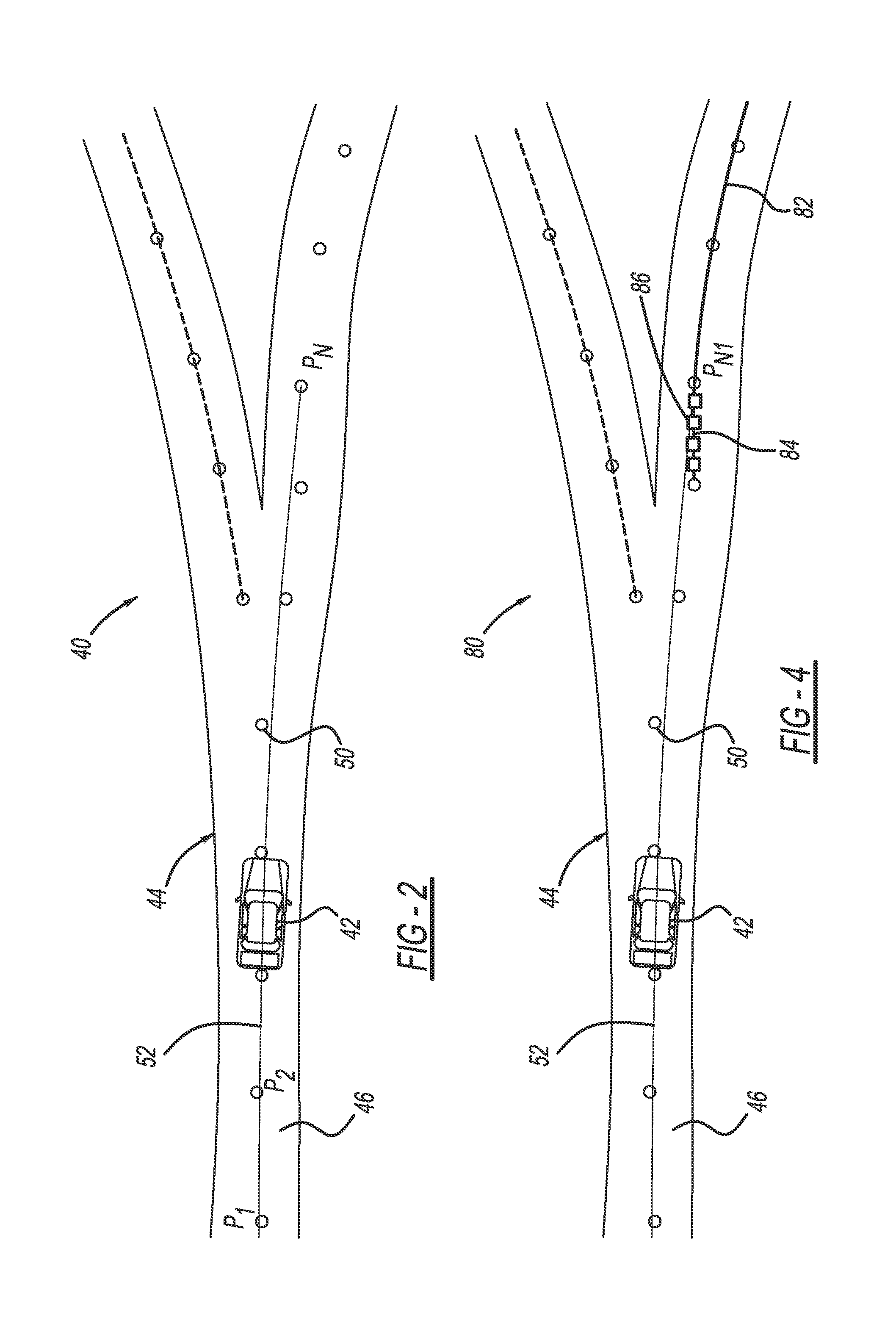
Accurate curvature estimation algorithm for path planning of autonomous driving vehicle
InactiveUS20160018229A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlAlgorithmSimulation
A method for identifying roadway curvature that includes determining a range of interest and collecting shape points from a map database from a current position of the vehicle to an end of the range of interest that define the location of the roadway. The method converts the shape points from World Geodetic System 84 (WGS84) coordinates to UTM coordinates, and then fits a single set of polynomial equations to define a curve using the converted shape points. The method determines whether the single set of polynomial equations exceeds a predetermined curvature accuracy threshold, and if so, fits multiple sets of polynomial equations to multiple roadway segments over the range of interest using the converted shape points. The method then determines the roadway curvature at any roadway location using solutions to the multiple sets of polynomial equations.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
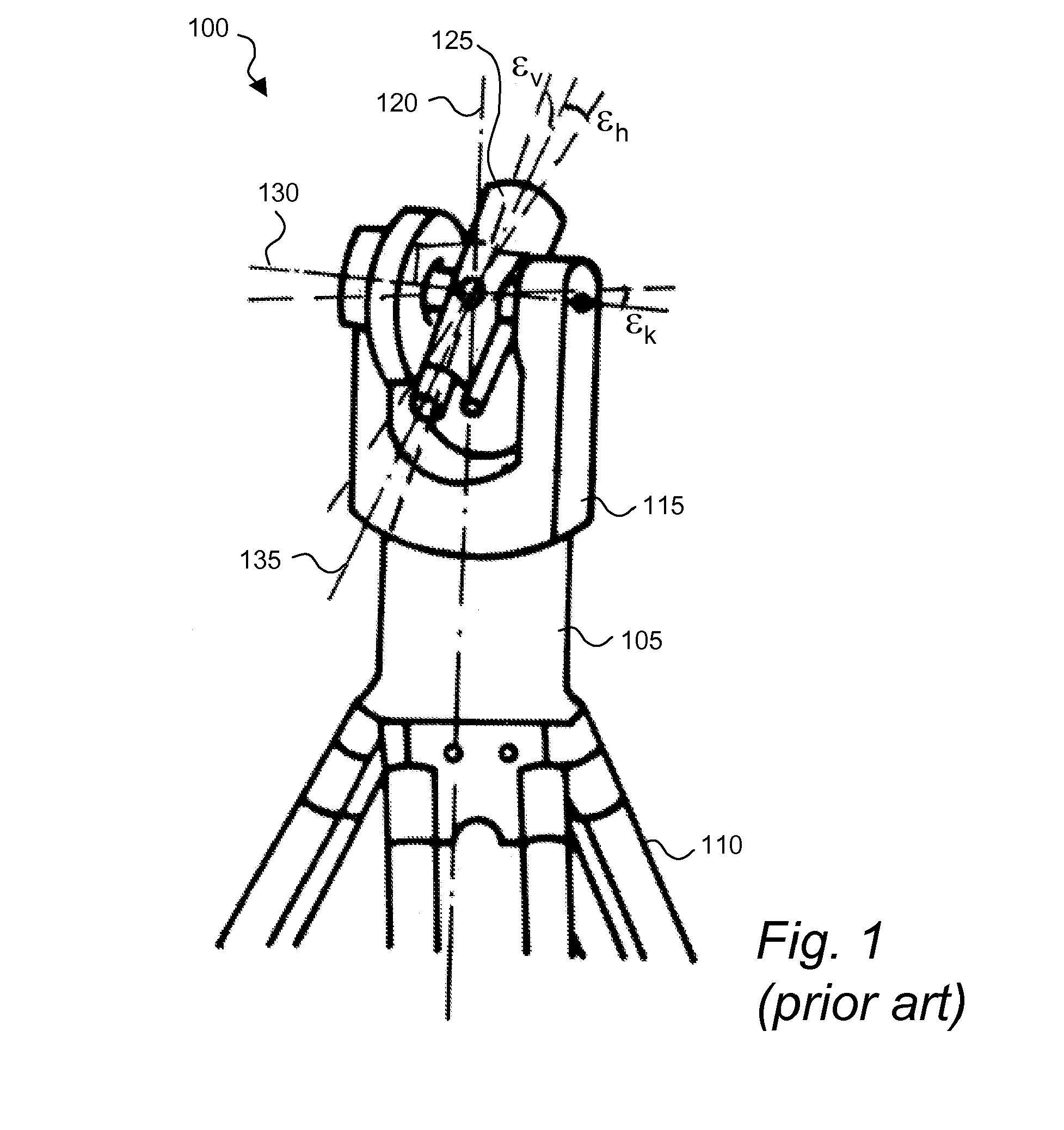
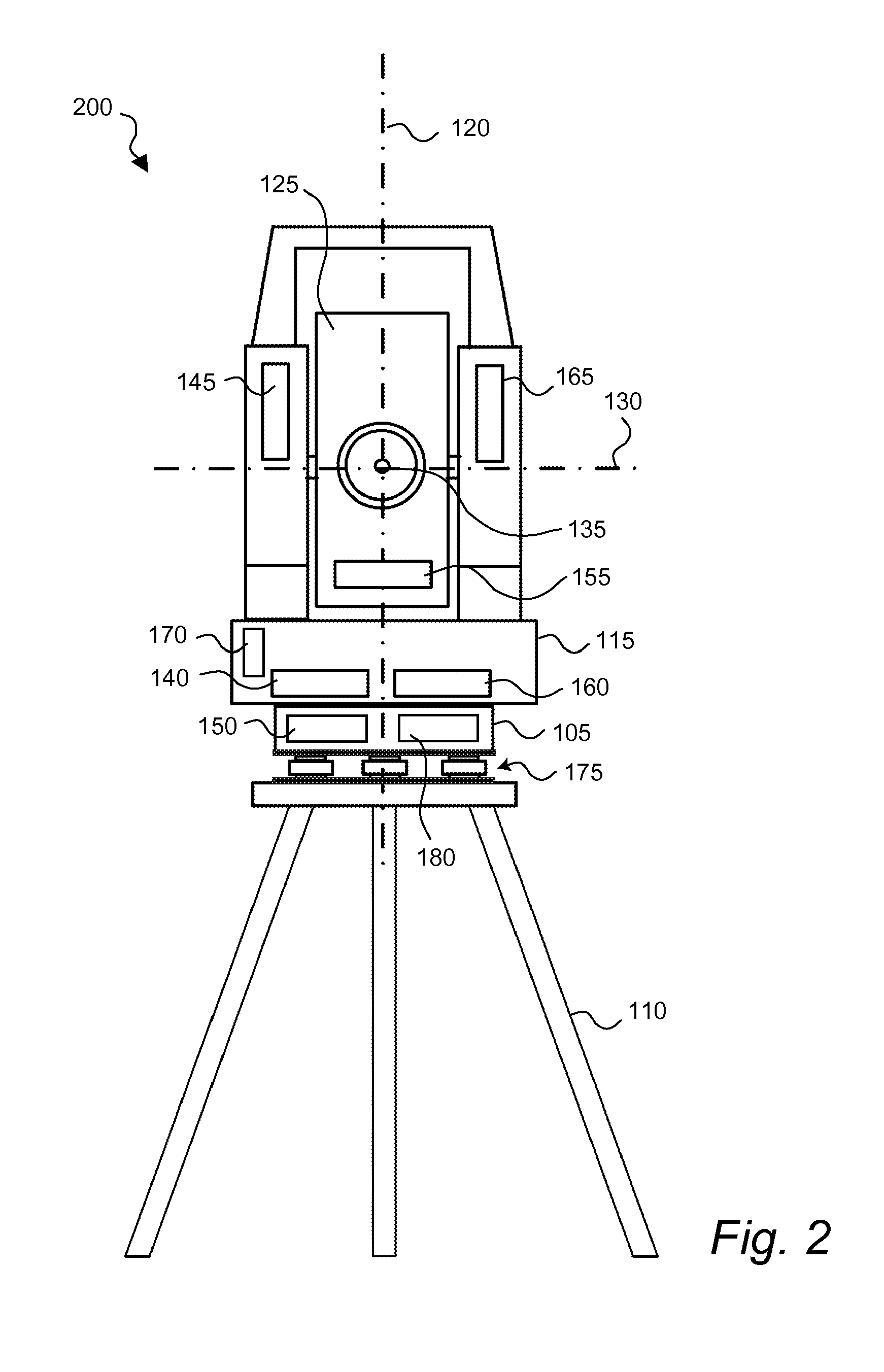
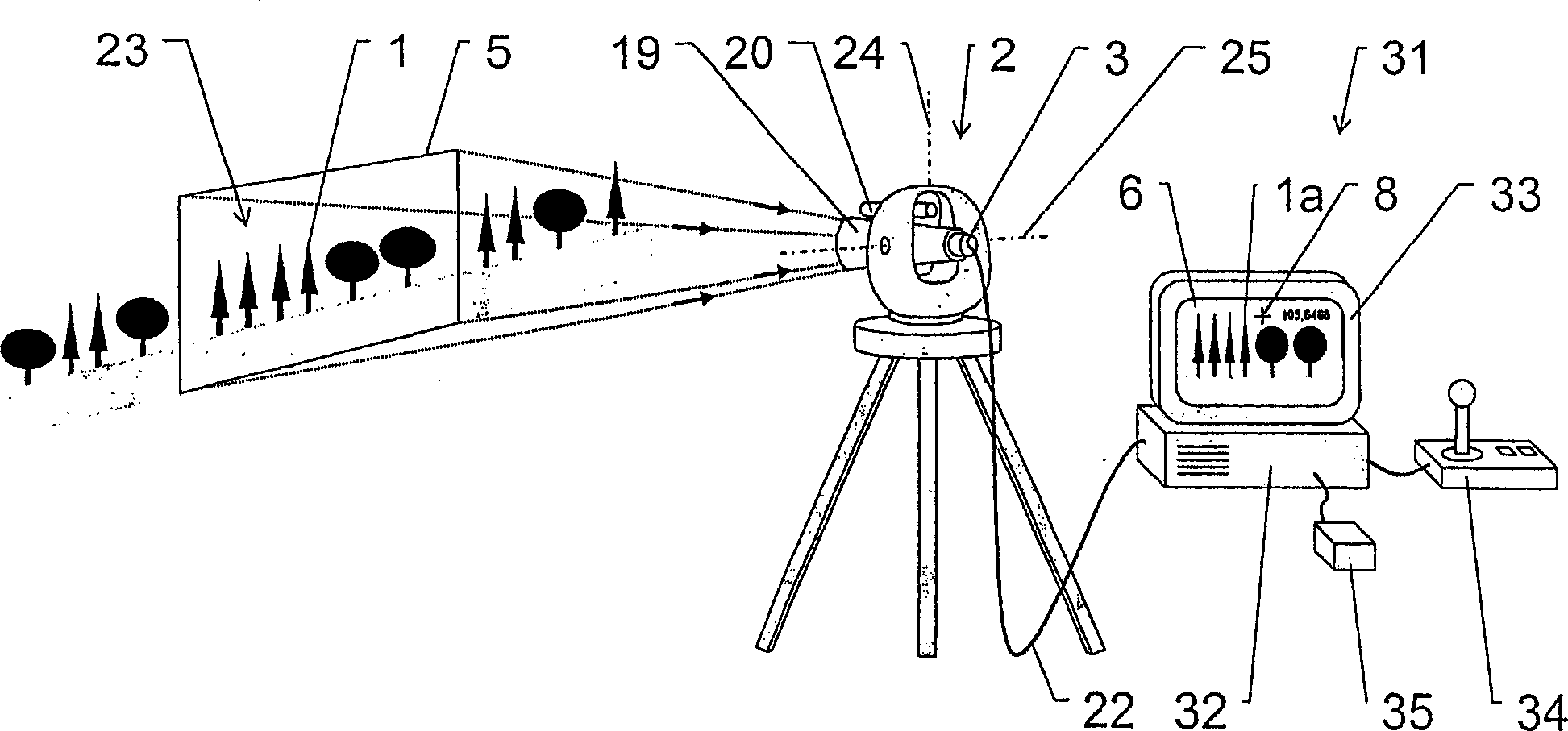
Method and device for image processing in a geodetic measuring device
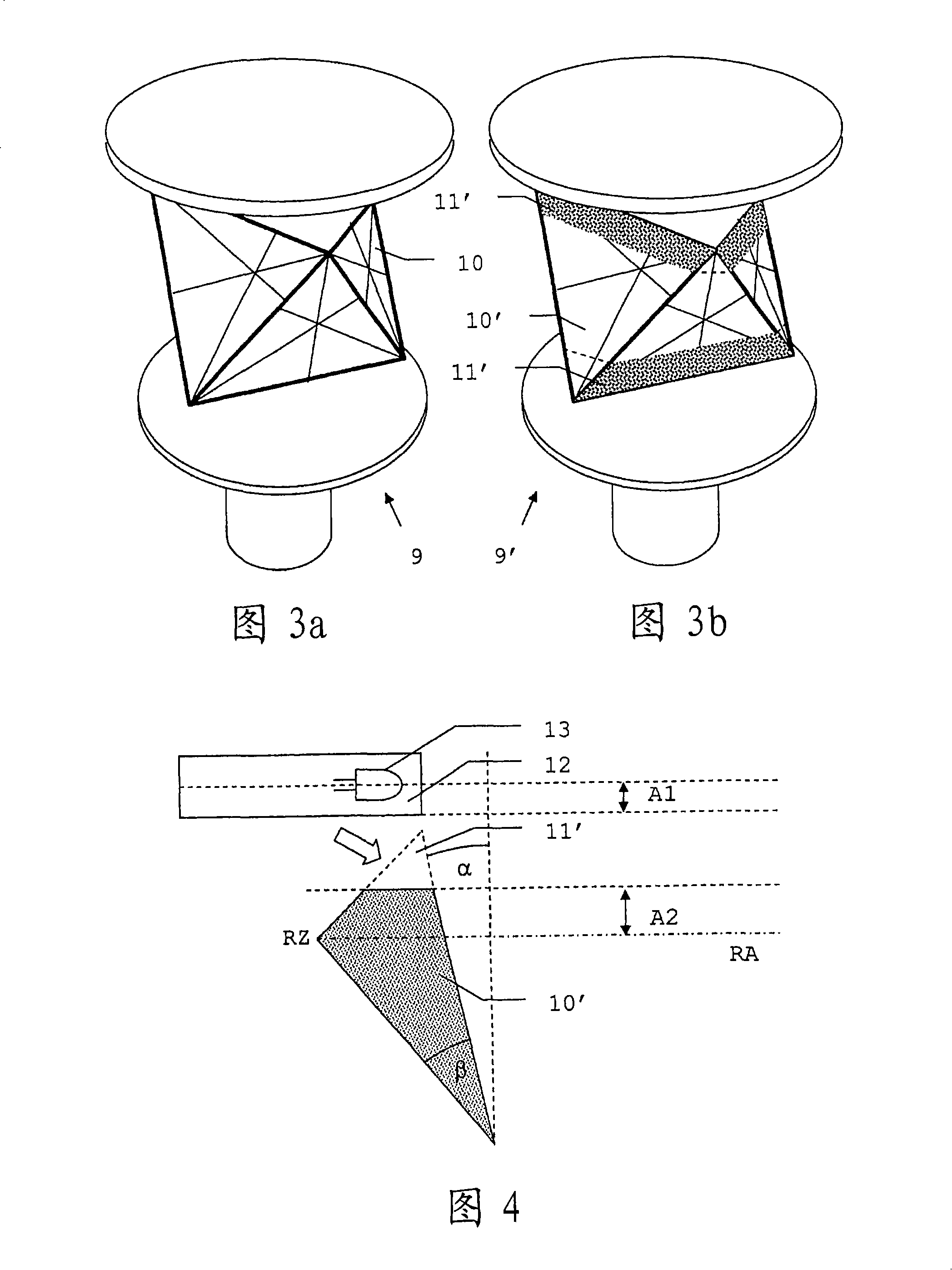
ActiveCN1761855AReduce dataMeasuring points markingPicture taking arrangementsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
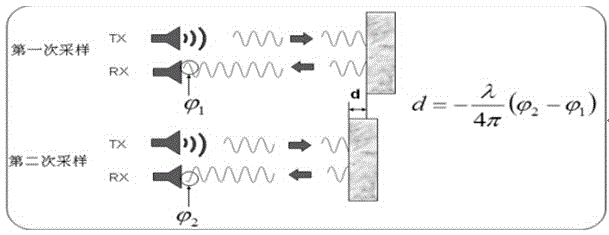
The invention relates to a method for the geodesical measurement of an object (1), using a geodesical measuring appliance (2) comprising recording means (3) for acquiring a recorded image (4) at least of the object (1) to be geodesically measured. Once the angular orientation of a coverage strip (5) of the recording means (3) has been determined, the image (4) is captured and represented at least partially in the form of a display image (6). A set of recorded image co-ordinates (7) are determined by establishing at least one set of associated display image co-ordinates (8), and the set of recorded image co-ordinates (7) is transformed into at least one geodesical measuring variable, especially a solid angle. Templates (10) which are in the form of models that can be placed on the display image and at least partially describe the object (1) are used to support the user during the fixing of the target point. Once the template (10) has been selected and positioned, it is adapted to the recorded object (la) and determines the set of recorded image co-ordinates (7) by means of a characteristic point (11) of the template (10). The invention also relates to an electronic display and control device (31), a geodesical measuring appliance (2), and a computer program product for carrying out the method.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
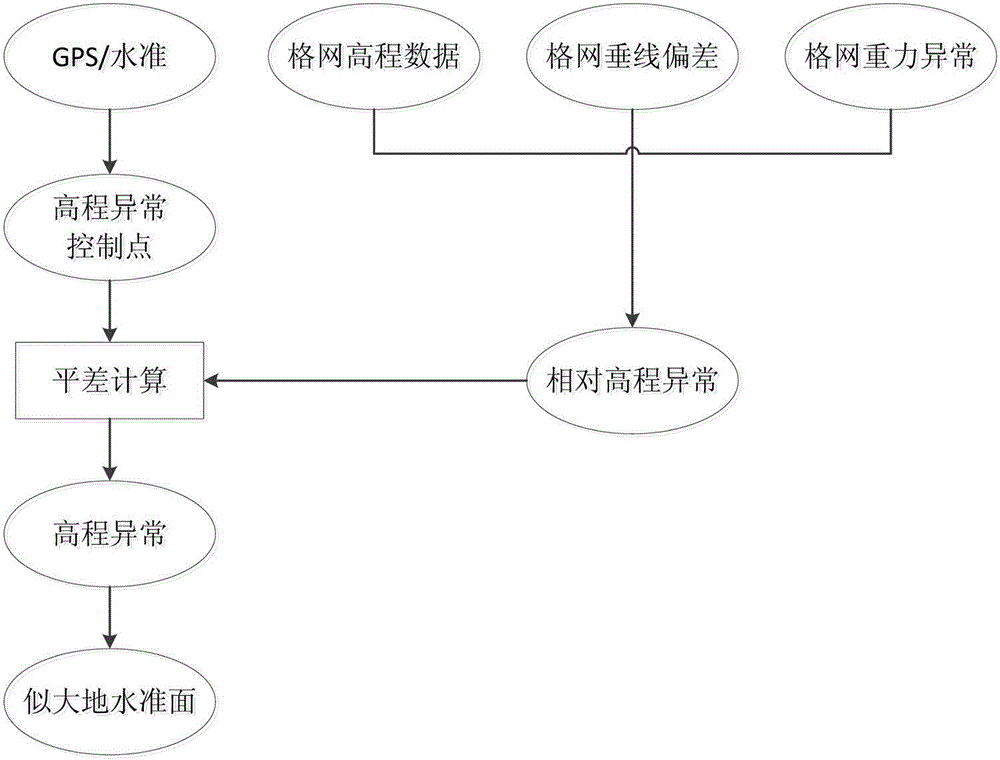
Method for determining quasigeoid models by utilizing deviation of plumb line and gravity anomaly
InactiveCN104613932ANovel methodImprove efficiencyHeight/levelling measurementBenchmark (surveying)Gravity anomaly
The invention relates to a method for determining quasigeoid models by utilizing deviation of plumb line and gravity anomaly, and aims at effectively improving the modeling precision of quasigeoid and solving the determination problem of height datum in geodetic surveying. The method comprises the following steps: by adopting the differential relation of height anomalies, computing the grid relative height anomaly difference via the deviations of plumb lines and gravity anomalies of the grids; imposing restriction through a GPS / benchmark to obtain height anomaly of grid nodes, and computing the relative height anomaly difference between adjacent nodes by utilizing the deviation of plumb line, gravity anomaly and digital height data of each node; computing the height anomaly difference of adjacent grids, carrying out adjustment computation by a parameter adjustment model and determining the quasigeoid models; selecting three million-sheet 4 DEG*6 DEG areas with deviations of plumb lines, gravity anomalies and terrain grid data to respectively computing and establishing the quasigeoid models of the three areas, and analyzing the precision. The method provided by the invention is novel, unique, high in efficiency and high in precision, and is an innovation in geodetic surveying.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Method, apparatus and system for mapping a course of a mobile device
ActiveUS20140088860A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTimestampContext data
Techniques and mechanisms for providing information to represent a course traversed by a mobile device. In an embodiment, navigation logic of the mobile device determines context data other than any geodetic data that specifies a position of the mobile device. With such context data, the navigation logic determines a sequence of estimates each for a respective position of the device on a course traversed by the mobile device. In another embodiment, determining the sequence of estimates includes determining a first estimate of a first position of the mobile device independent of any geodetic data that specifies the first position. Course information representing such a determined sequence includes timestamp information for the first estimate.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Accurate and rapid calculation method for global and local ocean disturbing gravity
The invention discloses an accurate and rapid calculation method for global and local ocean disturbing gravity, which belongs to the technical field of geodetic surveying. The method is used for global ocean disturbing gravity calculation, FFT calculation is carried out on each latitude circle by supplementing observation data in a global area, and then summation calculation is carried out in a longitude direction, and the processing method ensures the consistency of the result after the FFT calculation and the result of the original analysis algorithm. With respect to local ocean disturbing gravity calculation, a kernel function forms a cyclic matrix by supplementing a certain amount of data in the kernel function and the observation data, and then the consistency of the result and the result of the original analysis algorithm is ensured by virtue of FFT calculation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a calculation formula is provided for calculating disturbing gravity by virtue of ocean height measurement satellite data, and an accurate and rapid method is given simultaneously. The method disclosed by the invention can also be applied to resolution for most of integral problems in physical geodesy, for example, resolution for geoidal surface, the deviation of plumb line, terrain correction and the like.
Owner:西安测绘研究所
Optical fiber gyroscope theodolite and north-seeking method thereof
The invention relates to an optical fiber gyroscope theodolite and a north-seeking method thereof. The optical fiber gyroscope theodolite comprises an optical fiber gyroscope and a theodolite, wherein the theodolite covers a total station. The optical fiber gyroscope is arranged on a horizontal rotating part of the theodolite; the normal of the closed light path of the optical fiber gyroscope is perpendicular to a horizontal rotating shaft of the theodolite; a theodolite base gear is arranged on the outer side of a theodolite base fixing part; the theodolite base gear is connected with a driving motor which is arranged on the horizontal rotating part of the theodolite through a gear set. The north-seeking method for the optical fiber gyroscope theodolite comprises the steps of dynamic north-seeking and static north-seeking. The optical fiber gyroscope theodolite is compact in structure, small in size, light in weight and suitable for being carried by a single person to be used in a complex terrain district. The instrument and the north-seeking method have the advantages of simplicity in operation, high rapidness, one-key north-seeking function, convenience in use and the like. In addition, the optical fiber gyroscope theodolite is wide in application range, is dual-purpose for the army and people and can be used for determination of north benchmark, mine and geodetic measurement, military survey and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST +1
Method and apparatus to create 3-dimensional computer models of persons from specially created 2-dimensional images
InactiveUS8736606B2Character and pattern recognitionComputer aided designGrid patternMeasurement point
A method to create a computer retrievable three dimensional model of a person that can be used as a replacement for manual measurements in the garment industry. The method uses a garment which has geometrical patterns, such as a grid pattern. The garment also contains marks that would identify landmark locations for identifying geodetic points on the person wearing it and thus could be aligned to predetermined points when wearing. A calibrated set of images are captured by multiple cameras with the person wearing this garment. These images are analyzed by a computer program which will calculate the exact spatial location of points along the geometric pattern, thus recreating the measurements of the person. A model thus created can be used in multiple industries such as, but not limited to the garment industry.
Owner:RAMALINGAM SATHYAKUMAR ANDRE
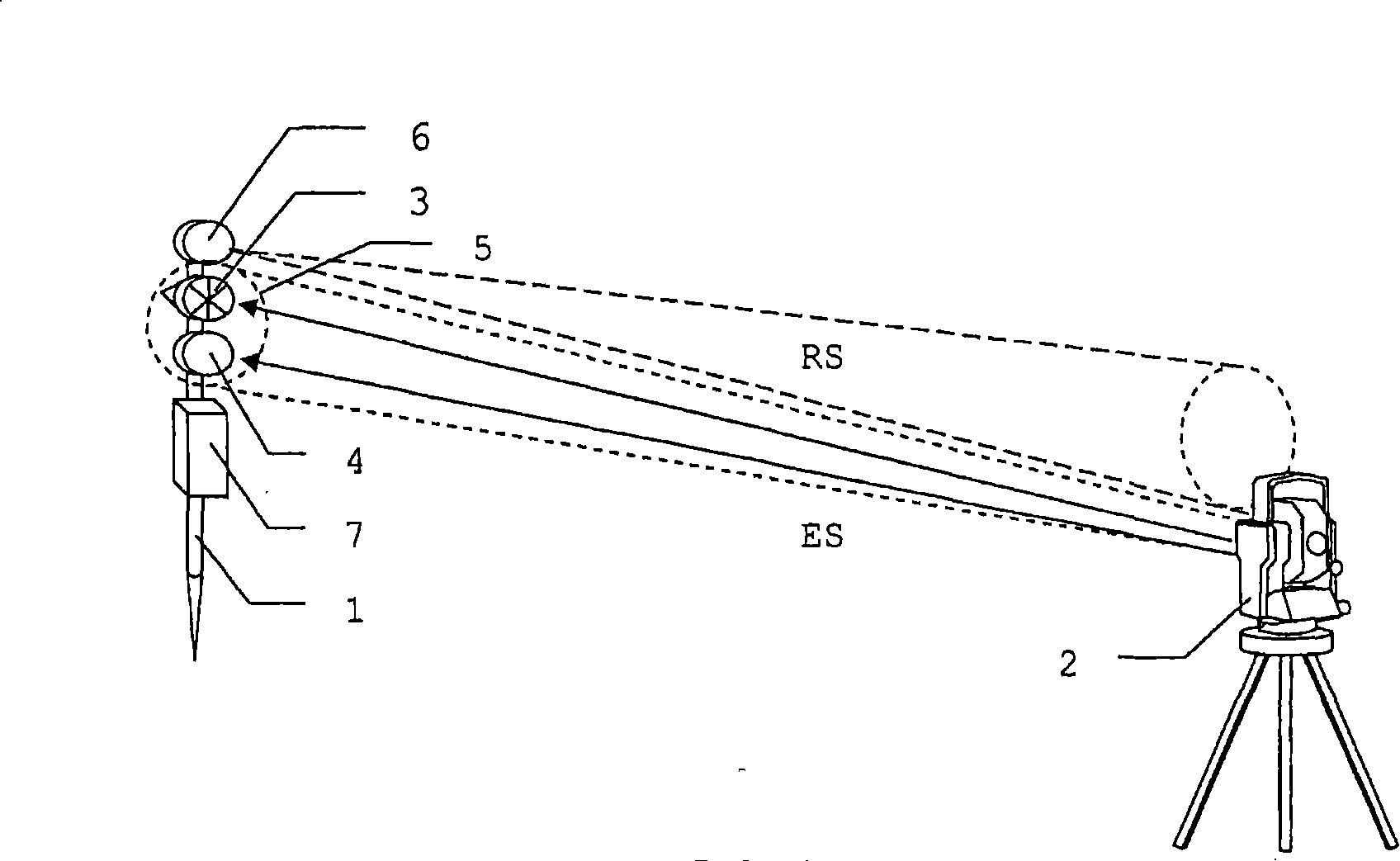
Geodetic target object and measuring system
ActiveCN101198839ASmall divergenceIncrease signal strengthSurveyor's staffsMovable markersElectromagnetic radiationRadiation
Disclosed is a geodetic target object comprising at least one reflector surface, a receive channel with a detector (18) for receiving electromagnetic radiation (ES) transmitted by a measuring unit (2''), and a transmit channel with a radiation source (13'). The associated transmission port and / or reception port is / are integrated into the reflector surface or is / are embodied so as to adjoin the reflector surface such that radiation (RS) that is modulated for transmitting data can be transmitted in the direction of the measuring unit (2'') within the cross section (5'') of the radiation (ES) generated by the measuring unit (2'').
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
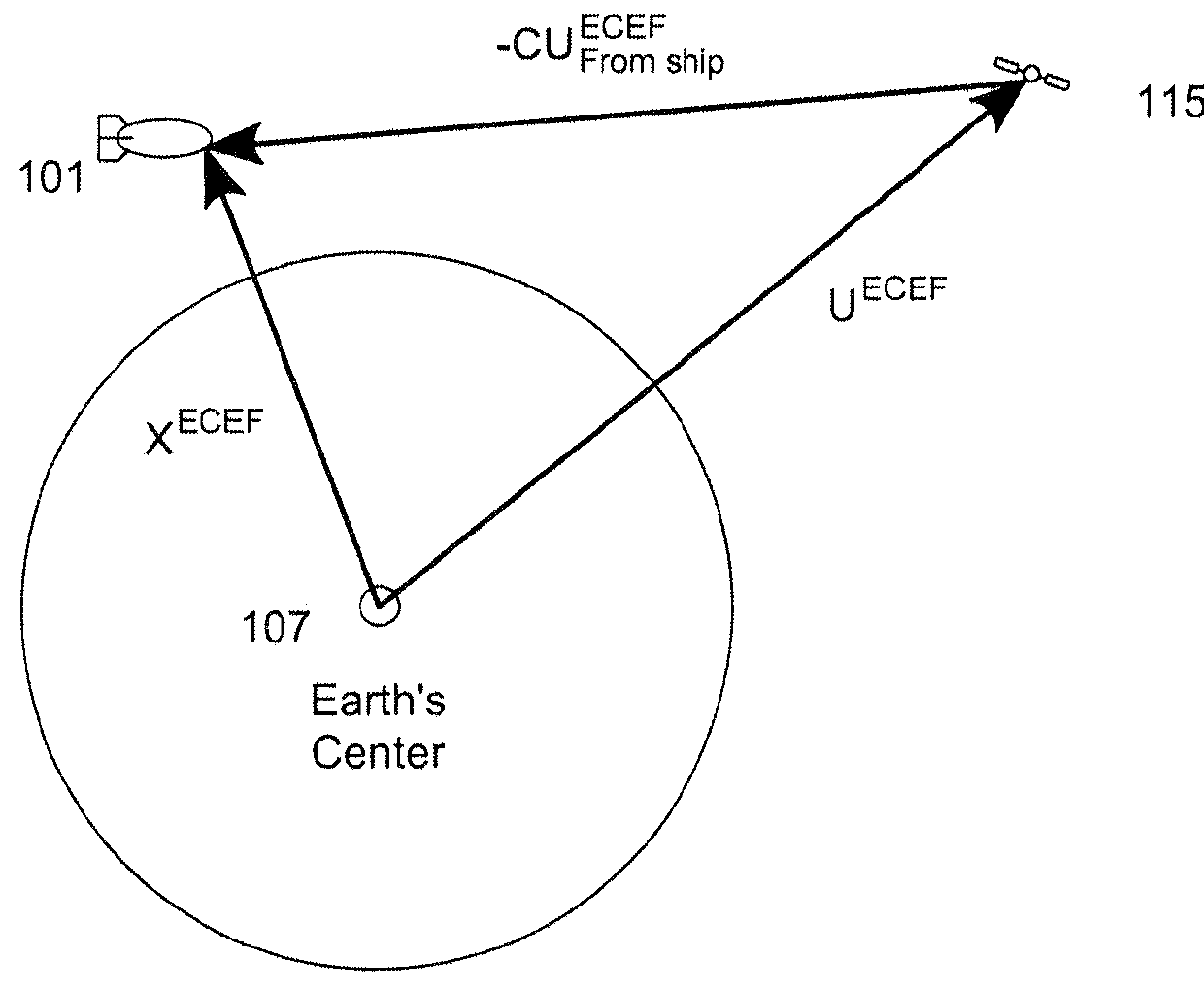
High altitude radio frequency positioning system
A method and system for determining the geolocation of a vehicle in the absence of a GPS signal includes determining the geodetic position of each of a plurality of airborne objects based on the relative position of at least one star and at least one satellite. The determined geodetic positions of each of the airborne objects is transmitted to the vehicle. A distance from the vehicle to each airborne vehicle is calculated. Based on the geodetic position determined for each airborne object and the distance from the vehicle to each of the airborne objects, the geodetic position of the vehicle is determined. A receiver receives the geodetic position of each airborne object, calculates a distance to each airborne object, and determines a current geodetic position based on the received geodetic positions of the airborne objects and the distance from the vehicle to each airborne object.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and system for real time navigation using satellite transmitted three-carrier radio signals and ionospheric corrections
ActiveUS7256730B2Improve performanceReduce in quantityPosition fixationBeacon systemsReal time navigationAmbiguity
The invention concerns a real-time navigation method for locating a rover using three-carrier radio signals of three different frequencies to determine the position of a user, transmitted by satellites. The method comprises a first step for determining “extra-wide lane” carrier phase ambiguity, a second step for estimating “wide-lane” phase ambiguity, and a third step for resolving the phase ambiguity of one of the frequencies. An additional step consists in the application of real-time ionospheric corrections during the third step, these ionospheric corrections being based on a continuously updated ionospheric model of said ionospheric layer calculated by a fixed ground reference station combined with geodetic data calculated by a so-called master fixed ground reference station. The invention also concerns a system for implementing the method.
Owner:EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY
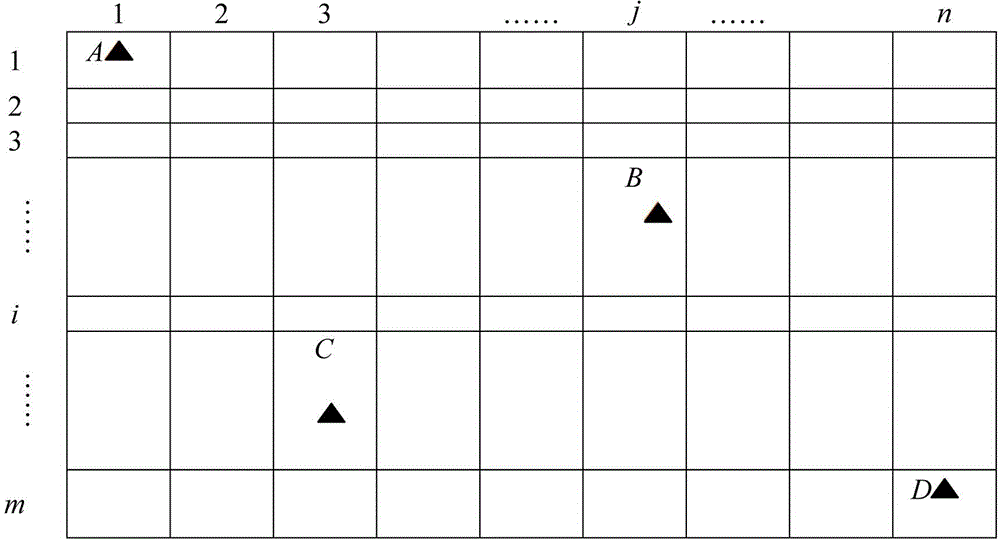
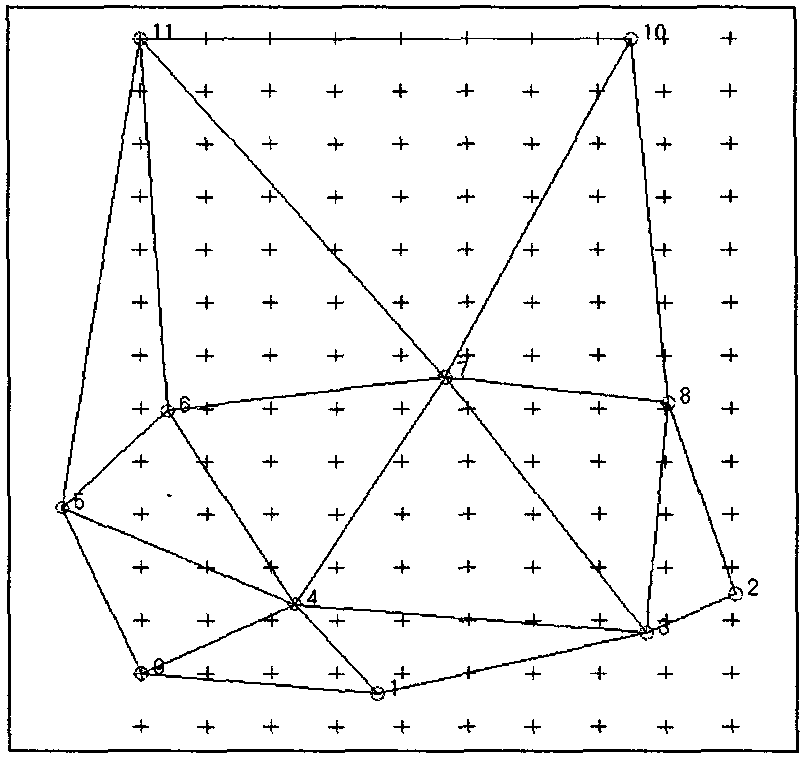
Coordinate conversion parameter calculating method based on adjacent control point sets
InactiveCN102779231AMaps/plans/chartsSpecial data processing applicationsTransformation parameterEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a coordinate conversion parameter calculating method based on adjacent control point sets and belongs to the technical field of earth measurement, digital maps and geographic information. The coordinate conversion parameter calculating method mainly aims at how control points on the periphery of a point to be solved performs automatic and reasonable selection and how to achieve reasonable and efficient automatic calculating of seamless coordinate conversion parameters in large-range seamless coordinate conversion parameter calculating. The coordinate conversion parameter calculating method includes: building a Delaunay triangular net on the basis of known control points, automatically extracting an adjacent control point set of each control point on the basis of the triangular net, calculating parameter back substitution and then calculating residual of each point, and accordingly filtering gross error and suspicious control points; and adding parameter points such as map border points or grids, automatically calculating the adjacent control point set corresponding to each point through the Delaunay triangular net built on the basis of control points, and solving coordinate conversion parameters needed by all points on the basis of corresponding adjacent control point sets. By adopting the coordinate conversion parameter calculating method, the coordinate conversion parameters in a wide range can be calculated massively, efficiently and seamlessly, the coordinate conversion parameter calculating method plays an important role in the fields of geodetic coordinate conversion, map data coordinate conversion and the geographic information system, and good economic benefit is obtained.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Endoscopic measurement system and method
The invention is a system and method for measuring 3D distances and dimensions of objects in endoscopic images by using a light plane to make Euclidean and geodesic measurements. The endoscopic measurement system of the invention comprises a flexible or rigid endoscopic device equipped with standard visualization means and a module containing components for generating a light plane. Based on triangulation, the intersection curve between the light lane and the object of interest is measureable in 3D in the coordinate system of the visualization means.
Owner:V T M VIRTUAL TAPE MEASURE TECH LTD
Accurate curvature estimation algorithm for path planning of autonomous driving vehicle
InactiveUS9283967B2Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsEquation of the centerAlgorithm
A method for identifying roadway curvature that includes determining a range of interest and collecting shape points from a map database from a current position of the vehicle to an end of the range of interest that define the location of the roadway. The method converts the shape points from World Geodetic System 84 (WGS84) coordinates to UTM coordinates, and then fits a single set of polynomial equations to define a curve using the converted shape points. The method determines whether the single set of polynomial equations exceeds a predetermined curvature accuracy threshold, and if so, fits multiple sets of polynomial equations to multiple roadway segments over the range of interest using the converted shape points. The method then determines the roadway curvature at any roadway location using solutions to the multiple sets of polynomial equations.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Tunnel mapping system and methods
ActiveUS10816347B2Instruments for road network navigationSatellite radio beaconingRailway tunnelData set
Owner:MASER CONSULTING INC
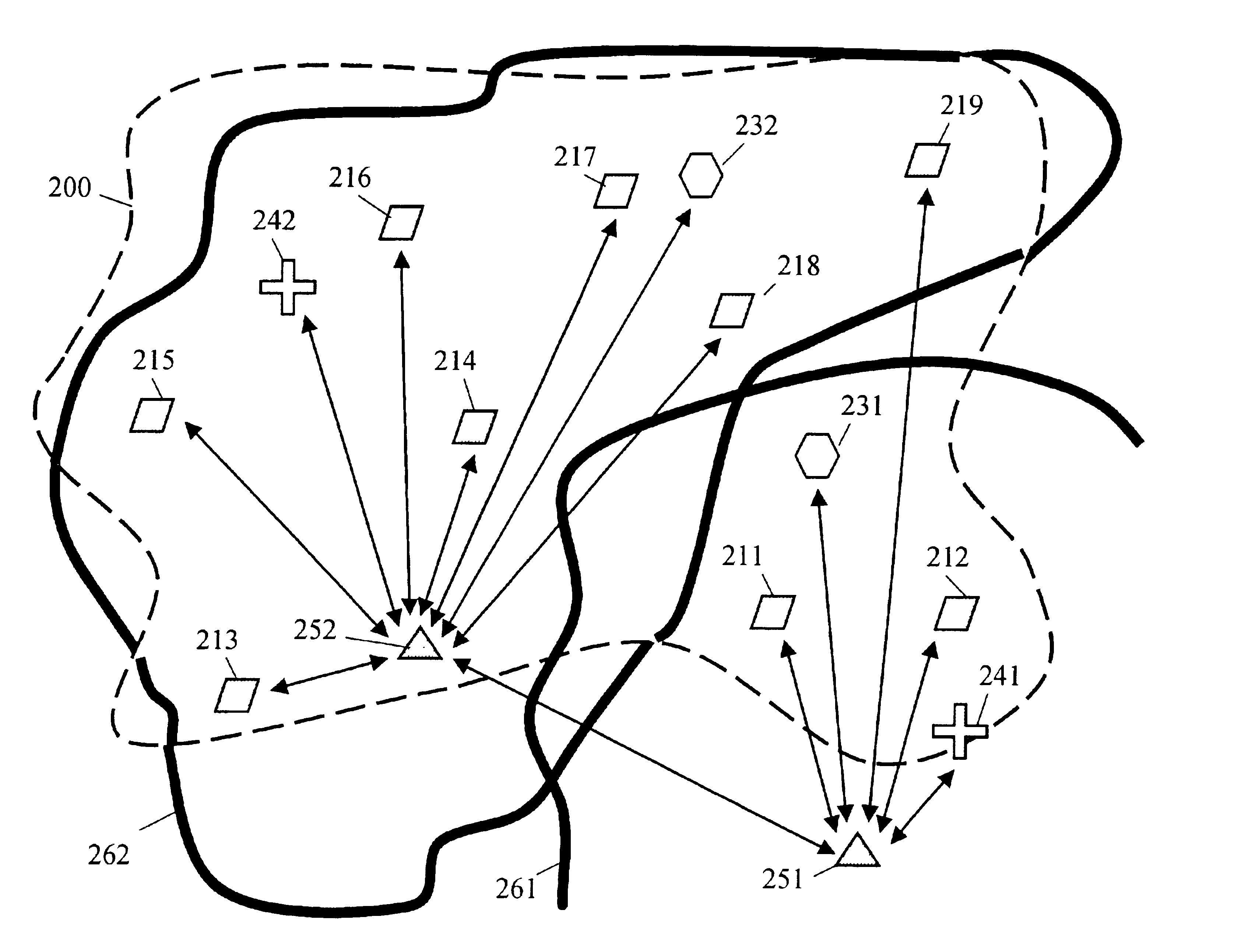
Digital map projection
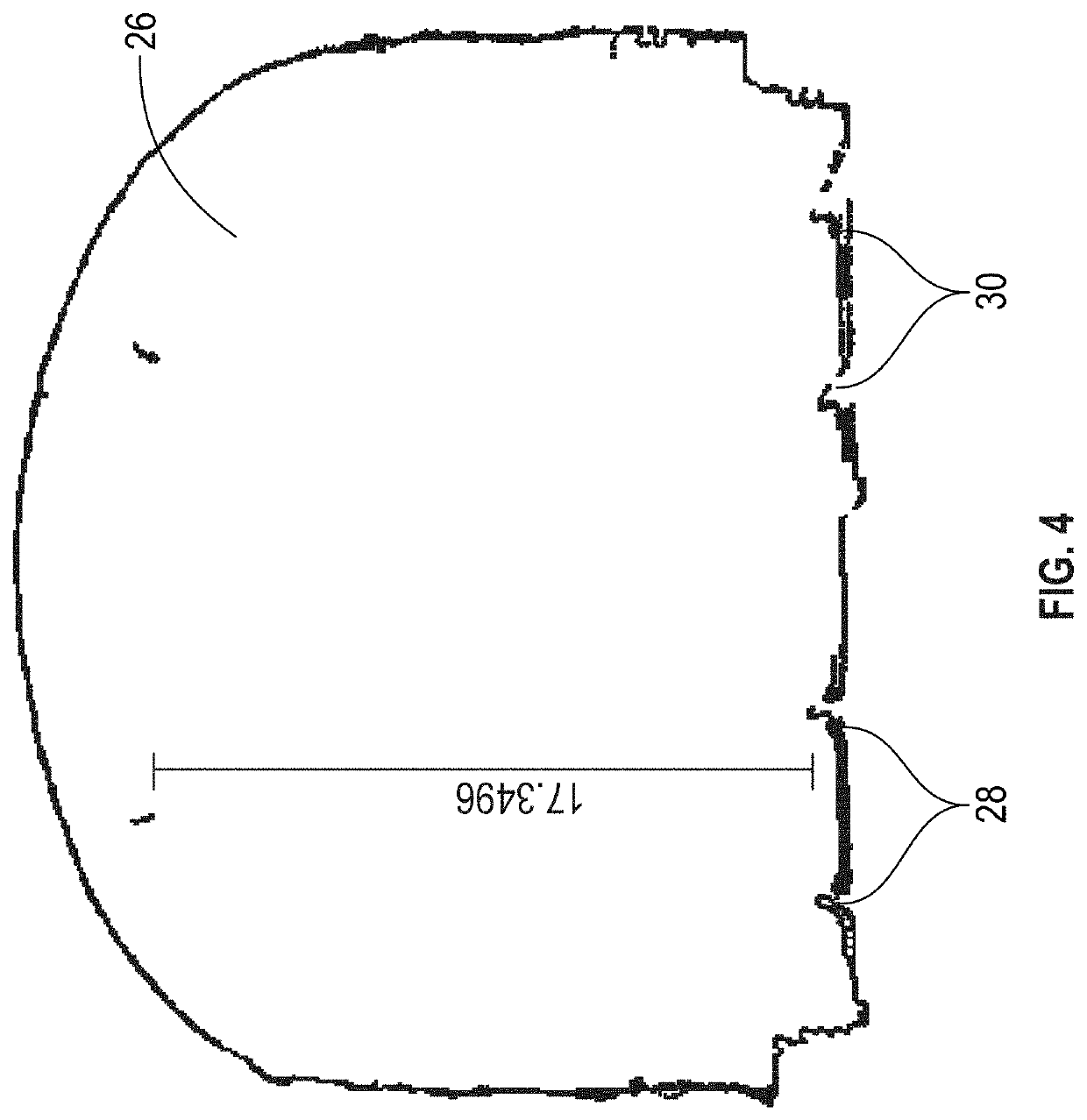
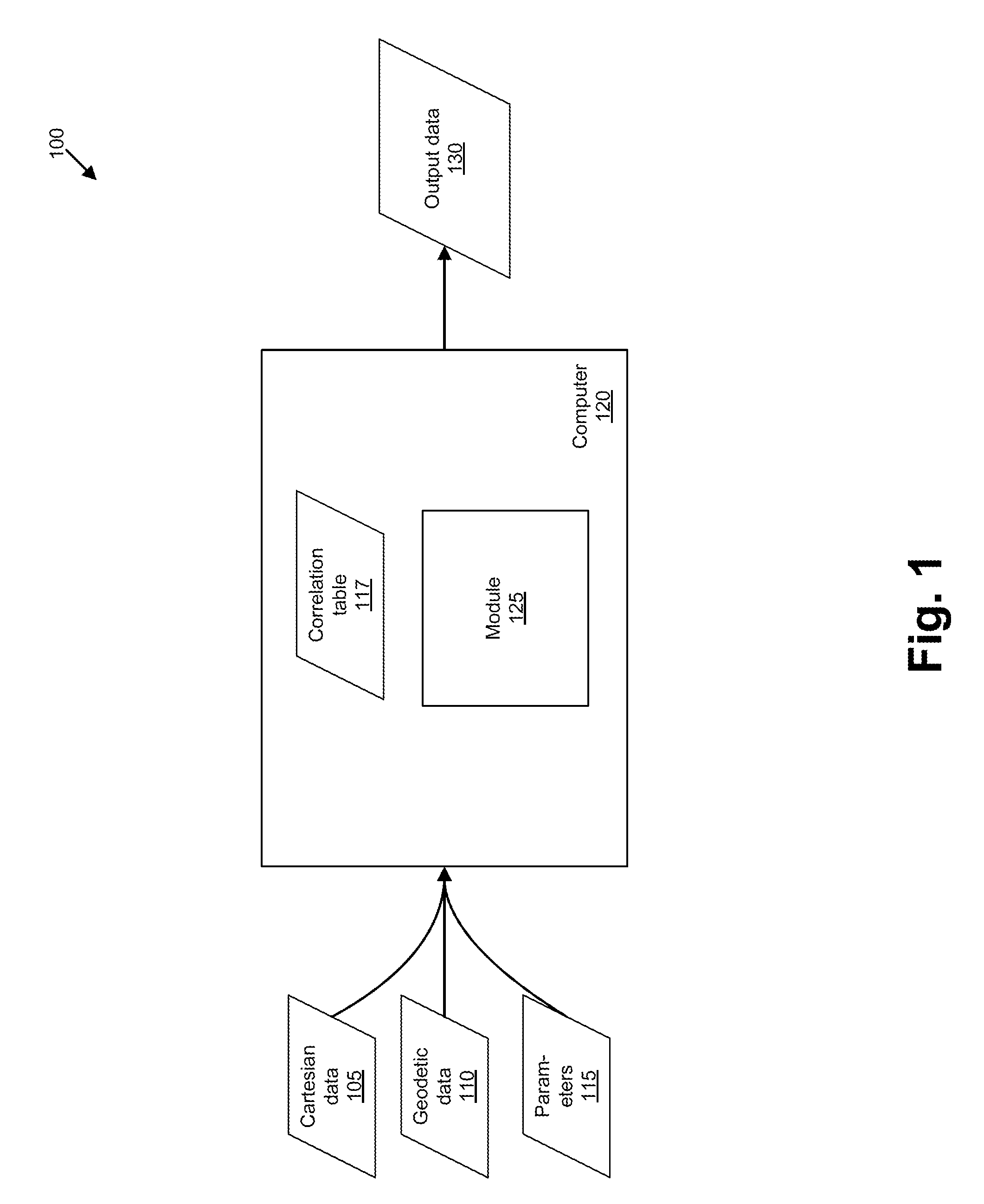
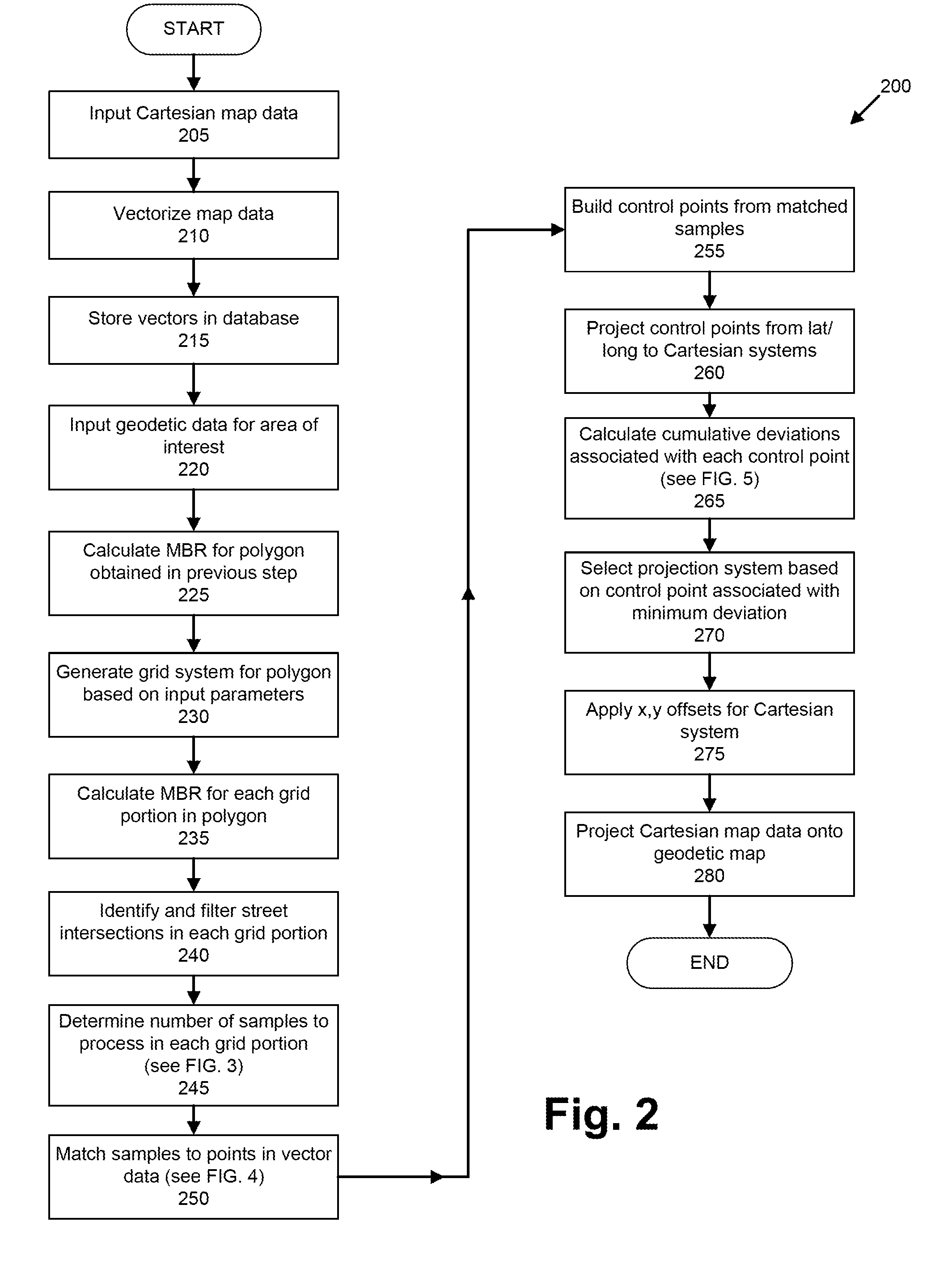
InactiveUS20120089333A1Navigational calculation instrumentsMaps/plans/chartsGeodetic surveyGeographic area
A computer receives a set of Cartesian data and a set of geodetic data relating to a geographic area. A set of control points is generated, each control point being associated with a coordinate expressed in terms of latitude and longitude, and with a corresponding point in the Cartesian data. A plurality of sets of Cartesian coordinates is determined for each of the control points, each of the sets of Cartesian coordinates for one of the control points corresponding to a Cartesian system. A deviation is determined for a combination that includes a control point and a Cartesian system, the deviation being a difference between coordinates for the point in the Cartesian data and the set of Cartesian coordinates for the control point. For each set of Cartesian coordinates associated with the Cartesian system that is included in the combination, but further associated with a control point not in the combination, the set of Cartesian coordinates is modified according to the deviation. A cumulative deviation is determined for the combination by determining a sum of distances of each set of modified Cartesian coordinates from the coordinates of the corresponding point in the Cartesian data. Cumulative deviations are thus determined for a plurality of combinations. A combination associated with a minimum cumulative deviation is identified.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Method and system for indirectly influencing tightness by spherical terrain niches in determination of plumb line deviation
ActiveCN106845035AEfficient removalSpecial data processing applications3D modellingTerrainVertical deflection
The invention relates to a method and system for indirectly influencing tightness by spherical terrain niches in determination of a plumb line deviation. The method comprises the steps: calculating a modeled value of plumb line deviation of any point of the ground; calculating Helmert residual gravity anomaly: presenting a universal curvature term of spherical integral of a terrain effect, replacing a plane approximation term with the obtained universal curvature term of spherical integral of the terrain effect, carrying out tightness integration so as to obtain a tightness equation for gravitational potentials of ground points by terrain gravitational potential and Helmert terrain agglomerated layers, calculating indirect influence on a basic terrain and second indirect influence on gravity anomaly caused by a geoid, and eliminating direct influence and indirect influence caused by a spherical terrain, so as to calculate the Helmert residual gravity anomaly; calculating a residual plumb line deviation of any point of the ground; restoring a removed model plumb line deviation, thereby determining the plumb line deviation. According to the method and the system, the indirect influence caused by the spherical terrain niches can be more effectively removed, and a high-precision geoid is determined, so that the method and the system are very suitable for being applied to the field of geodetic surveying and surveying / mapping engineering.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of pendulum gyro north seeker
The invention relates to an automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of a pendulum gyro north seeker. The method is characterized in that the geographic latitude is resolved by utilizing the pendulum period measured by an alidade of the pendulum gyro north seeker under a non-tracking state, and the directive coefficient is calculated, so that the precision compensation of deviation brought about by torsion zero deviating from true north is completed, and the method comprises the four steps of calibrating the relationship coefficient of the period and the latitude, starting a north seeking process, measuring the period under the non-tracking state, resolving the latitude by the non-tracking period, and correcting the torsion zero deviation automatically. Compared with the prior art, the automatic latitude measuring and calculating and automatic precision compensating method of the pendulum gyro north seeker has the advantages that in actual applications, the latitude is not required to be input before measurement, and the directive coefficient is also not required to be calibrated and calculated; through the constant coefficient relationship of the period and the latitude, which is calculated in advance in a calibrating site, the latitude at the site can be resolved only by measuring the non-tracking pendulum period of a measured site, and further a measurement result is corrected. The method can be widely applied to the fields of aviation, aerospace, geodetic measurement, guided missile aiming and the like.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
Arrangement for retroreflection of a ray using triple prisms
InactiveUS6123427AHigh measurement accuracyImprove accuracySurveyor's staffsPrismsShortest distanceConstruction surveying
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 03577 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 19, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 19, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 13, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 08572 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 6, 1997The invention relates to an arrangement for retroreflection of an optical ray using triple prisms. Six to ten triple prisms (1, 2, 3, 131, 132, 133) arm provided with triangular light entry surfaces, wherein the side faces of adjacent triple prisms are in contact. This results in continuous retroreflection at a high level of intensity for one angle area, of 360 DEG . When used in particular in geodesy or in construction surveying, this all-round reflector provides a high degree of measurement accuracy for angles and distances from any direction on which a bearing is taken. Alignment towards a surveying instrument is therefore not necessary. Measurement of short distances is also definite and reliable. The all-round reflector is particularly advantageous for automatic surveying, since, irrespective of its orientation, it can be automatically tracked by a motorised surveying instrument.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Method and device for the determination of the actual position of a geodesic instrument
InactiveCN1856692AOmit to determineReduce ambiguitySurveying instrumentsPicture taking arrangementsEngineeringInstrumentation
In order to determine the actual position (A) of a geodetic measuring instrument (1) inside a dead range (T) wherein signals originating from a positioning system are shadowed, two reference structures (5) are detected from at least two known positions and the distances associated with the reference structures (5) are measured. Image information linked to said distance measurements is captured. Said information contains data on the arrangement of the reference structures (5). The actual position (1) can be derived from subsequent capture of the reference structures (5) from a position inside the dead range (T). Image processing methods are used advantageously to identify and measure the reference structures (5).
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Meteorologic correction model in slope deformation monitoring
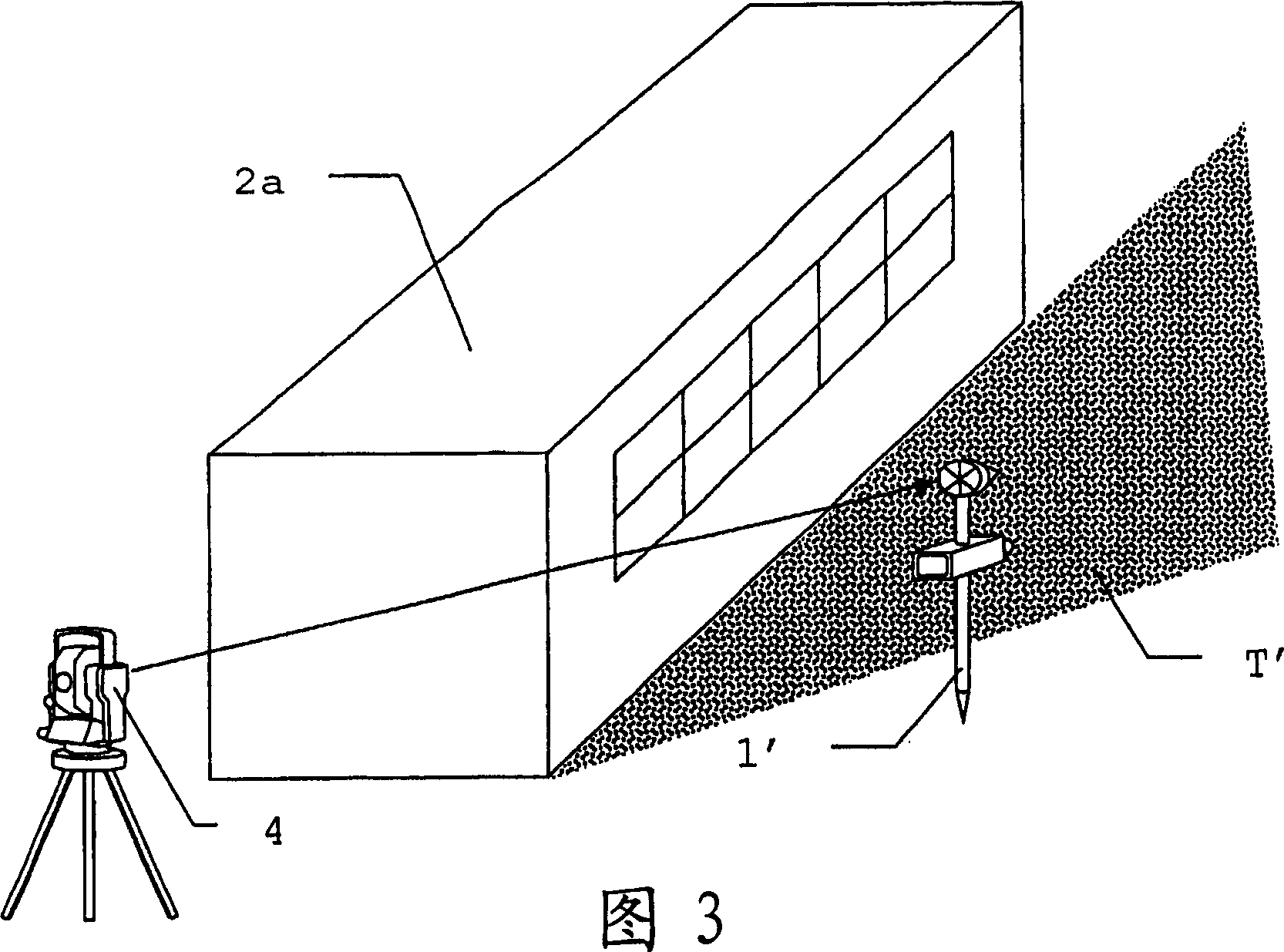
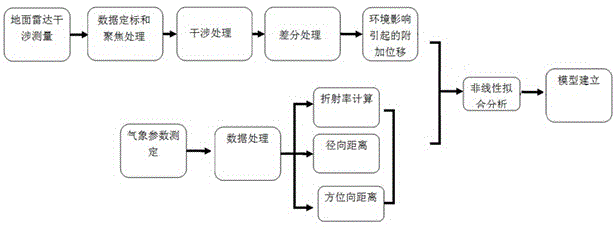
ActiveCN105136073AMonitor temperature in real timeReal-time monitoring of relative humidityUsing wave/particle radiation meansGround based radarDeformation monitoring
The invention relates to a meteorologic correction model in slope deformation monitoring, wherein the meteorologic correction model belongs to the technical field of ground radar monitoring. Firstly according to a temperature, a relative humidity and an air pressure which are monitored in real time, a refractive index change value is calculate through an Essen Froome empirical formula which is recommended by International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics. Scaling, focusing, interference and difference processing are performed on radar monitoring data. An additional displacement of an angle reflector caused by a meteorologic effect is obtained according to the geometric position, an estimated signal-to-noise ratio, a thermal signal-to-noise ratio and correlation information of the angle reflector. According to the calculated refractive index change value, the azimuth coordinate value and the range coordinate value of the angle reflector, the meteorologic correction model of the ground radar in slope deformation monitoring is established by means of a nonlinear fitting method, so that a difference between the calculated value of the model and the additional displacement which is caused by an environment effect is minimized. The meteorologic correction model can effectively correct the meteorologic effect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Feature based data structure for computer manikin
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Method for calibrating radio wave refraction correction effects by virtue of precision trajectory
ActiveCN106052717AGuaranteed smoothGuaranteed continuitySatellite radio beaconingLaser rangingClassical mechanics
The invention provides a method for calibrating radio wave refraction correction effects by virtue of a precision trajectory. A precision trajectory of a satellite is obtained by virtue of laser ranging or satellite-born GPS ranging or altimeter data, a calibrated coordinate of a geometric center of measurement and control equipment is acquired by geodetic measurement, a standard value of each measurement element for exterior measurement is obtained by precise ephemeris and measurement and control equipment coordinate conversion as well as spatial geometric vector calculation, a main error and post-fit residual caused by atmospheric refraction are solved according to an observed value of exterior measurement data and the standard value of each measurement element, a testing model for quantitatively evaluating atmospheric refraction correction effects is designed, and the refraction correction accuracy is calculated. According to the method, time and space limits are broken, and the refraction correction effects of each measurement element for exterior measurement can be tested and evaluated in real time.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
Tiltsensor
InactiveUS7055254B1Large tilt angle measuring rangeWithout costly adjustmentPlumb lines for surveyingIncline measurementGeodesics on an ellipsoidImage resolution
An adjustment-free tiltsensor for application in the fields of geodesy, geophysics and geotechnics, with a tilt angle measuring range greater than ±5° to ±10° and an essentially enhanced angular resolution better than 1 microradiant, in which an electrolytic liquid and a gas bubble are present in a closed spirit level, the spirit level is curved over an angle of up to 360°, a plurality of electrode configurations each having a plurality of electrodes are arranged along the spirit level for sensing the position of the gas bubble, the electrodes are in electric contact with the electrolytic liquid, and the electrodes are connected to a first electronic circuit, by means of which the electric quantities between selected electrodes can be measured.
Owner:UNIV OF BREMEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com