Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Endodontic files" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
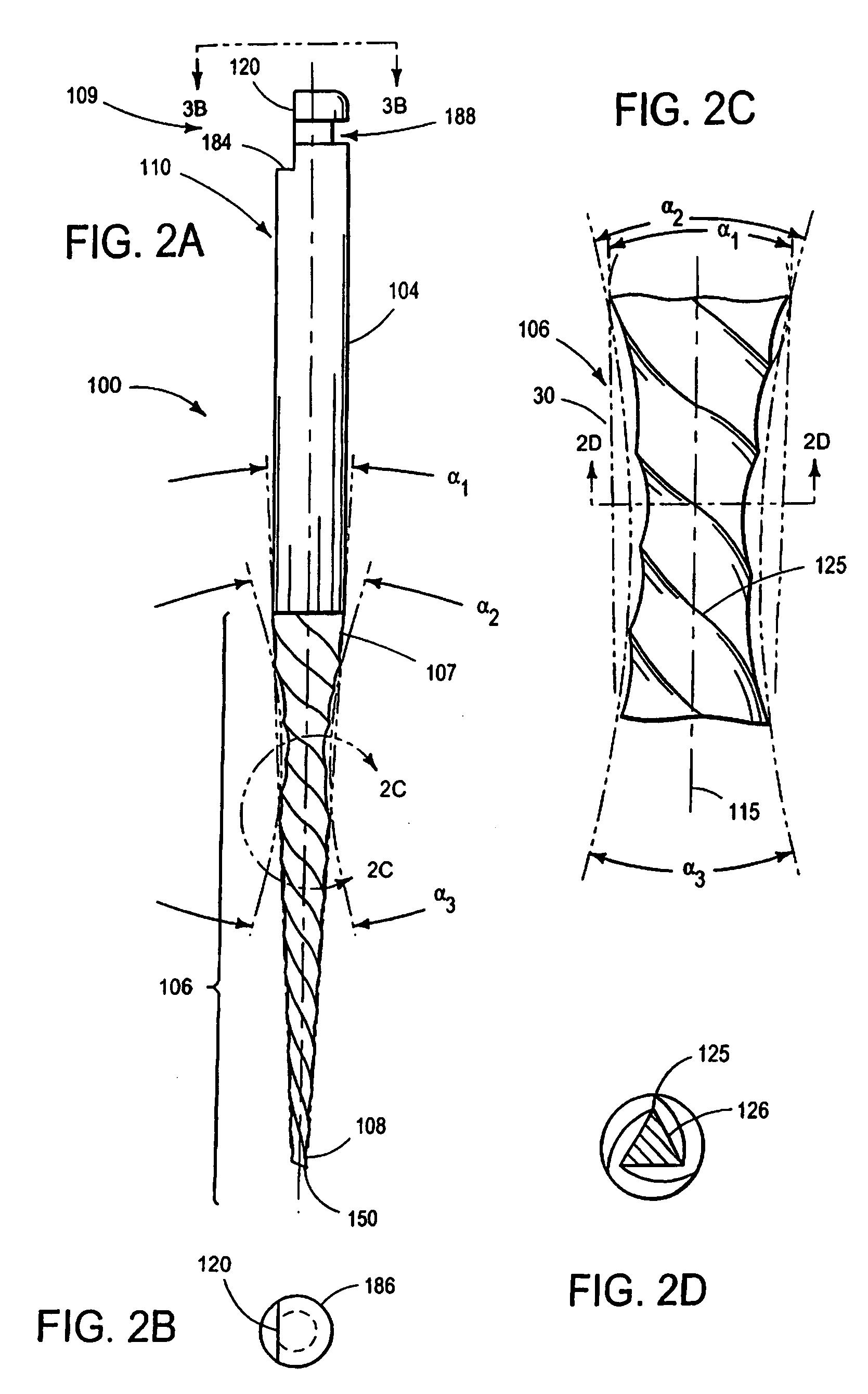
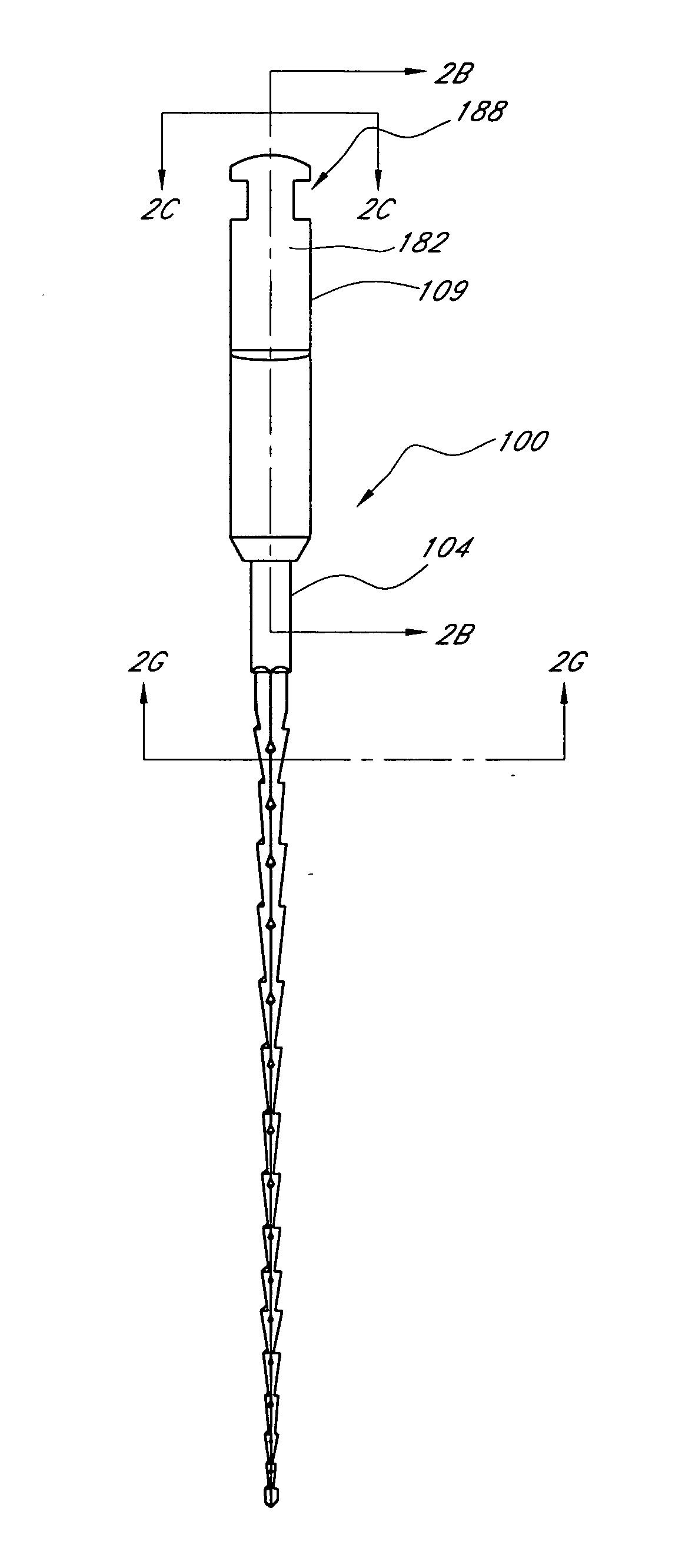
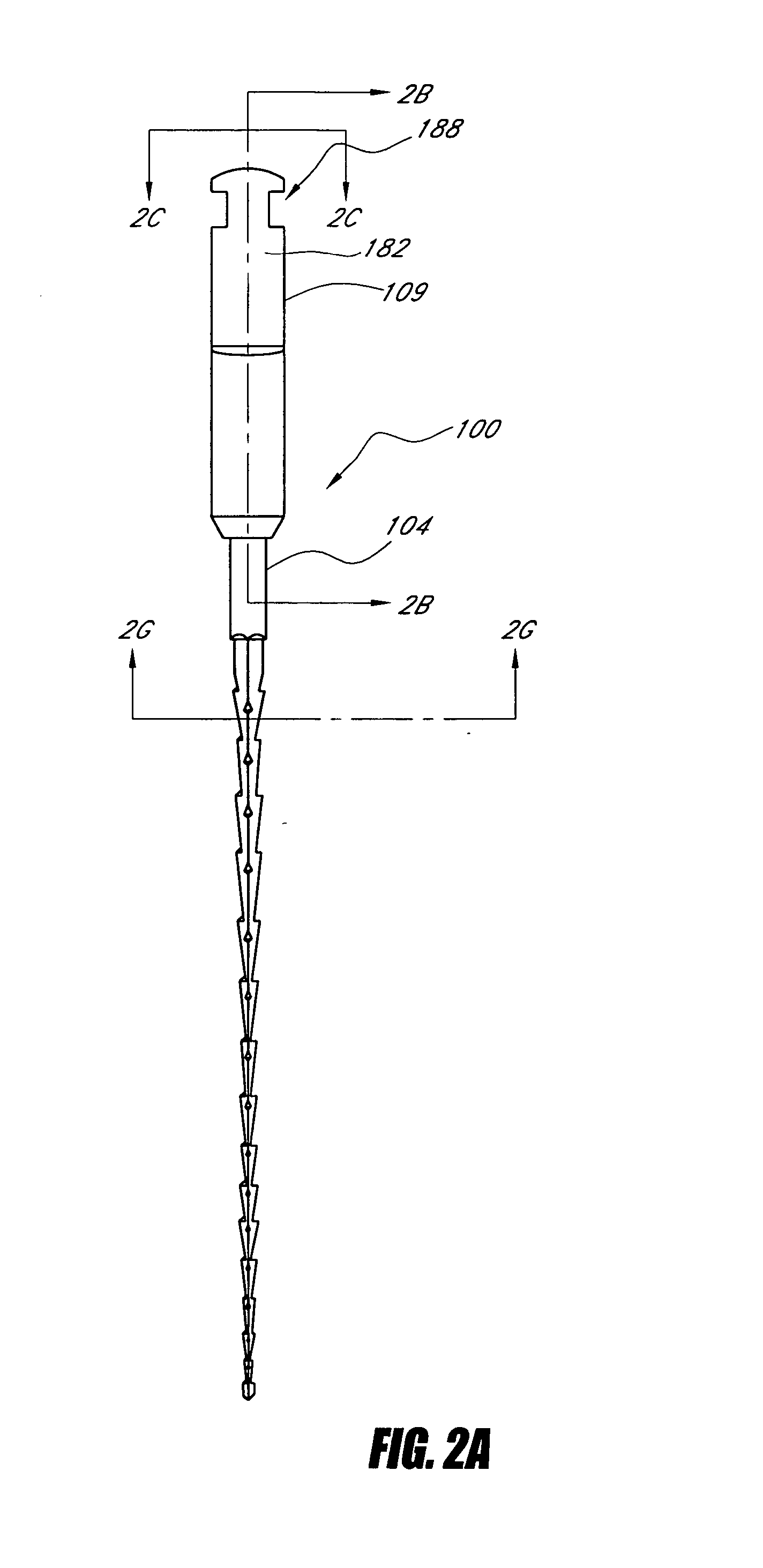
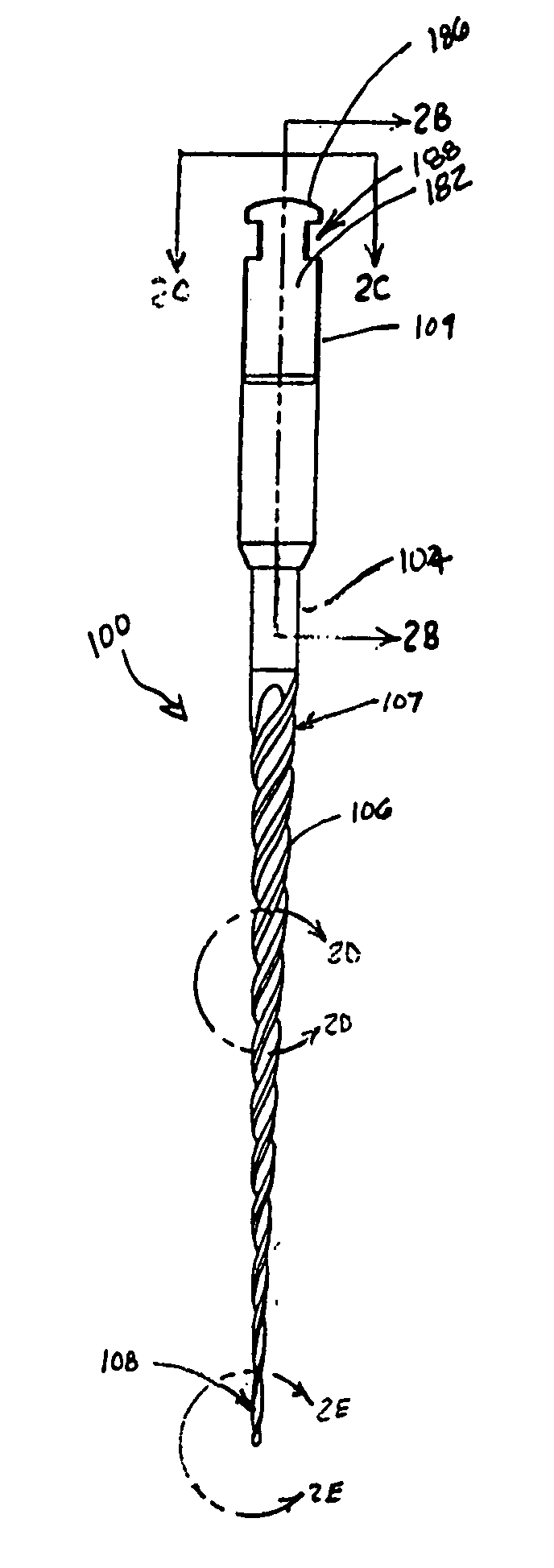
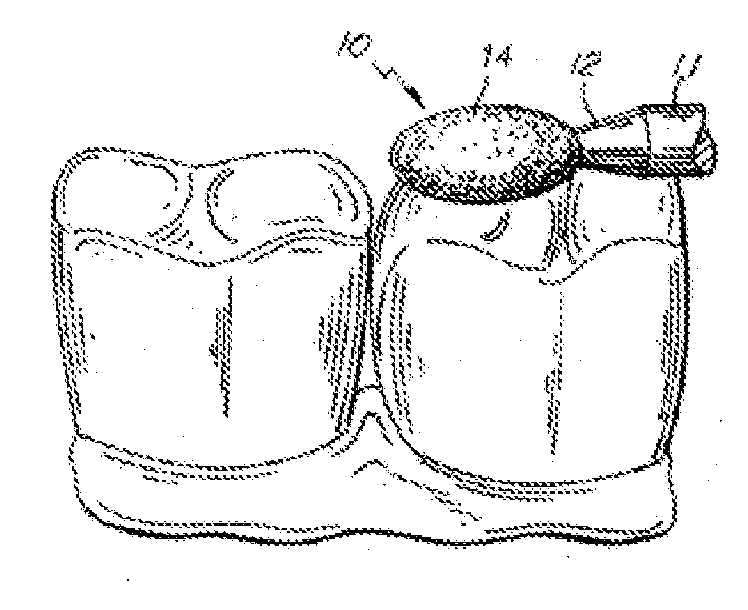
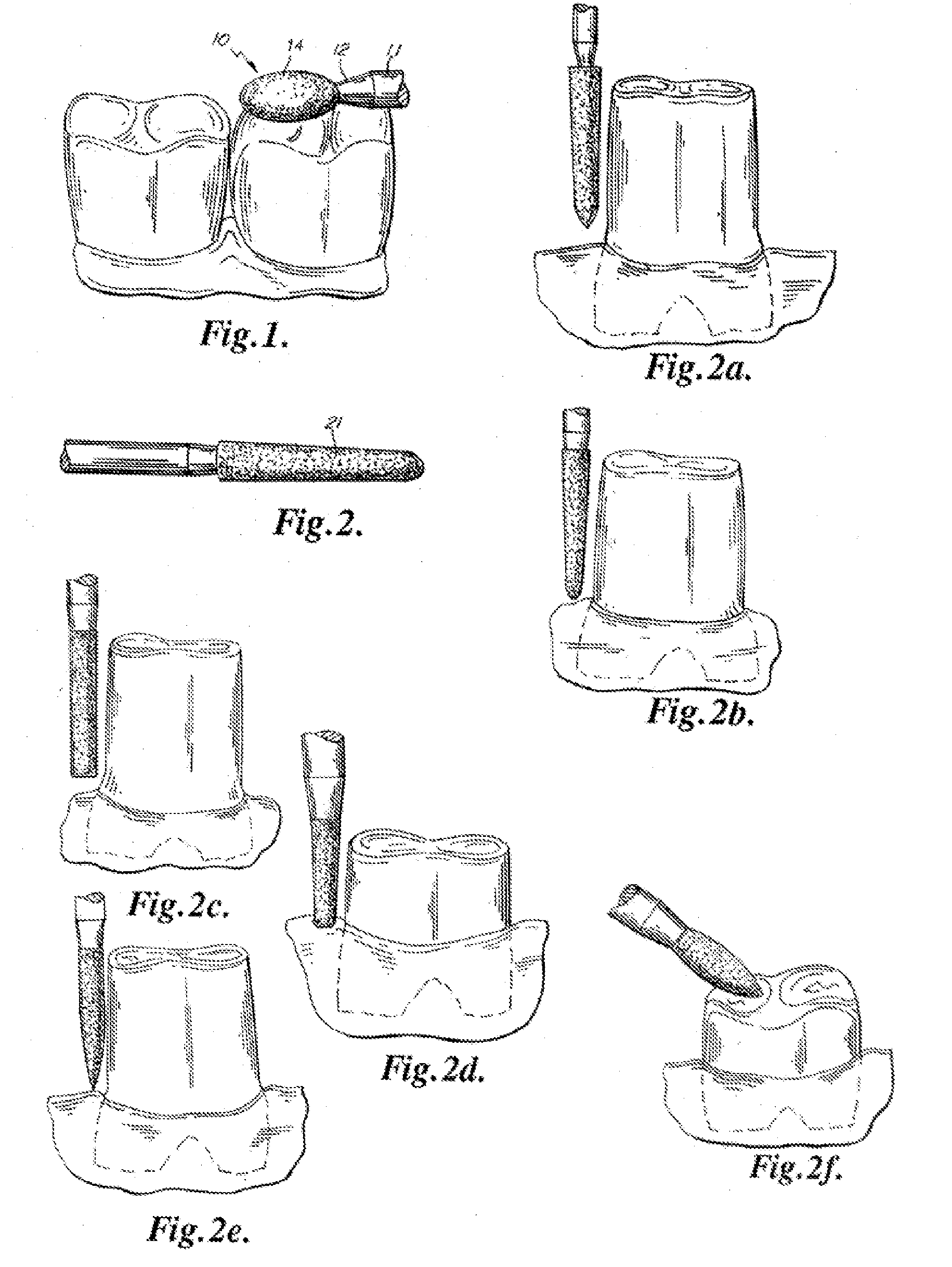
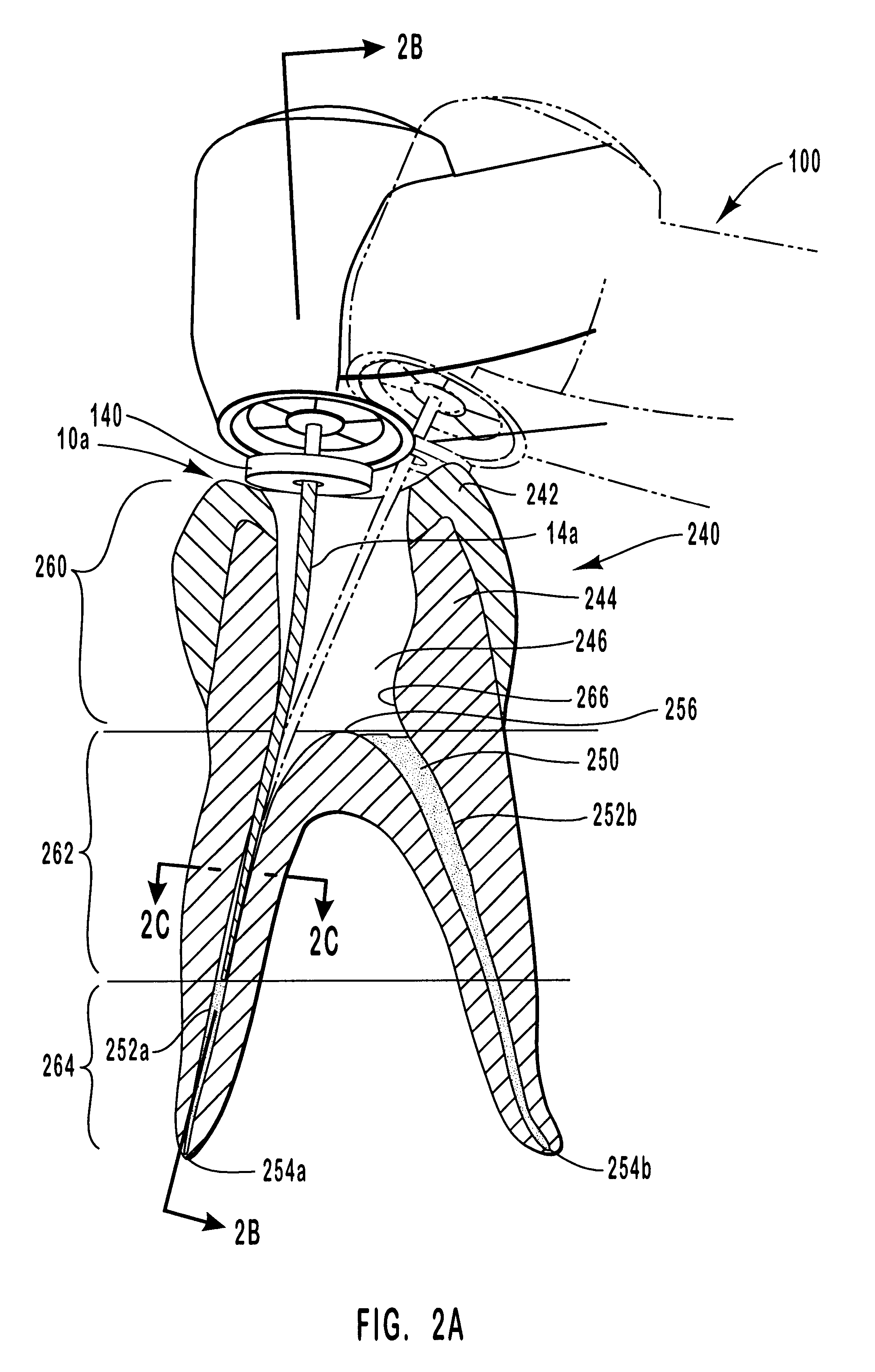
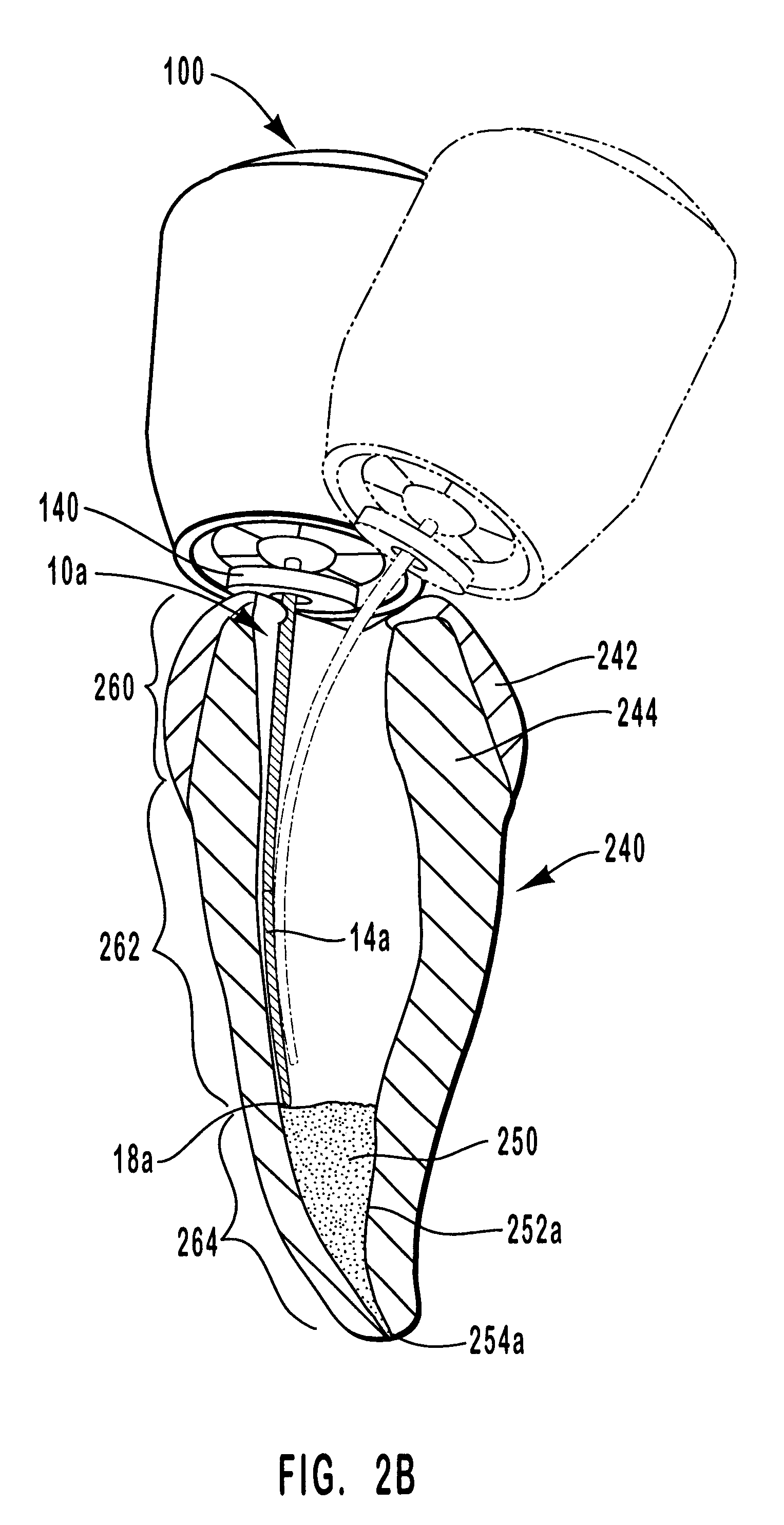
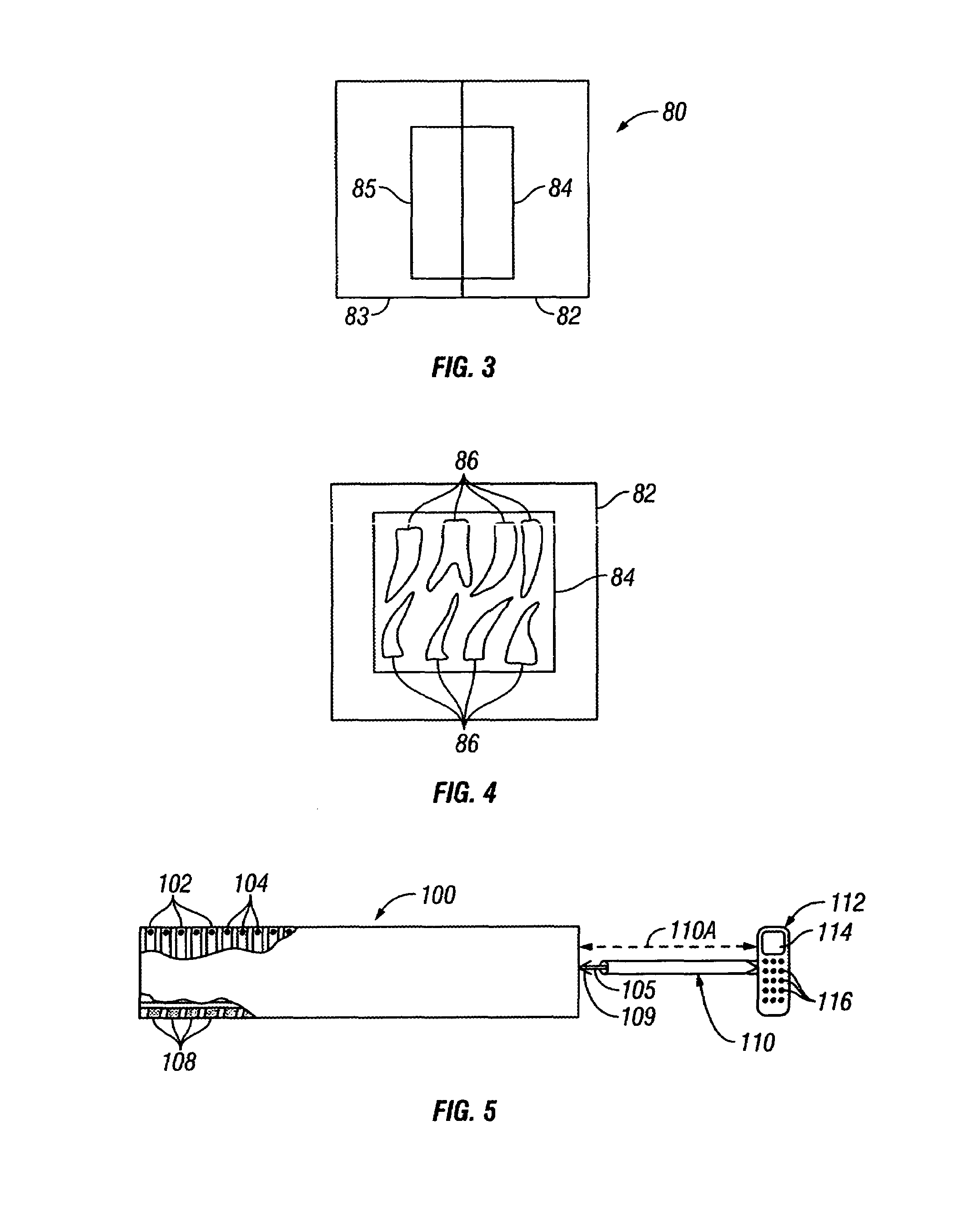
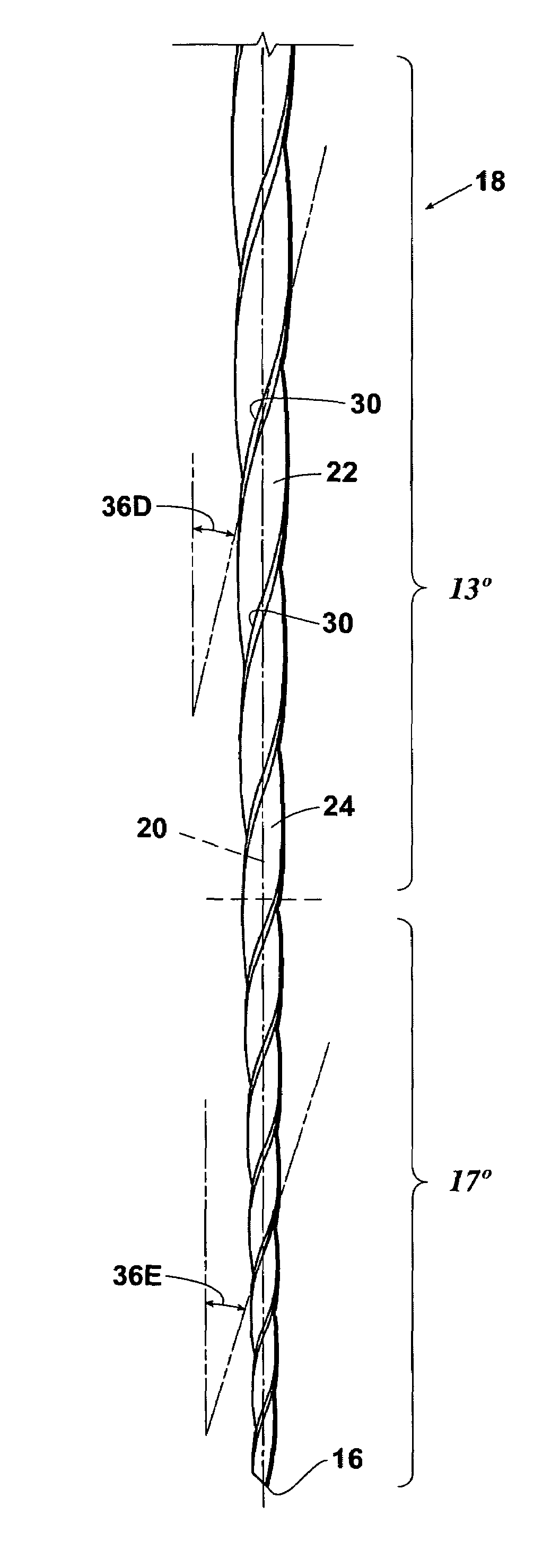
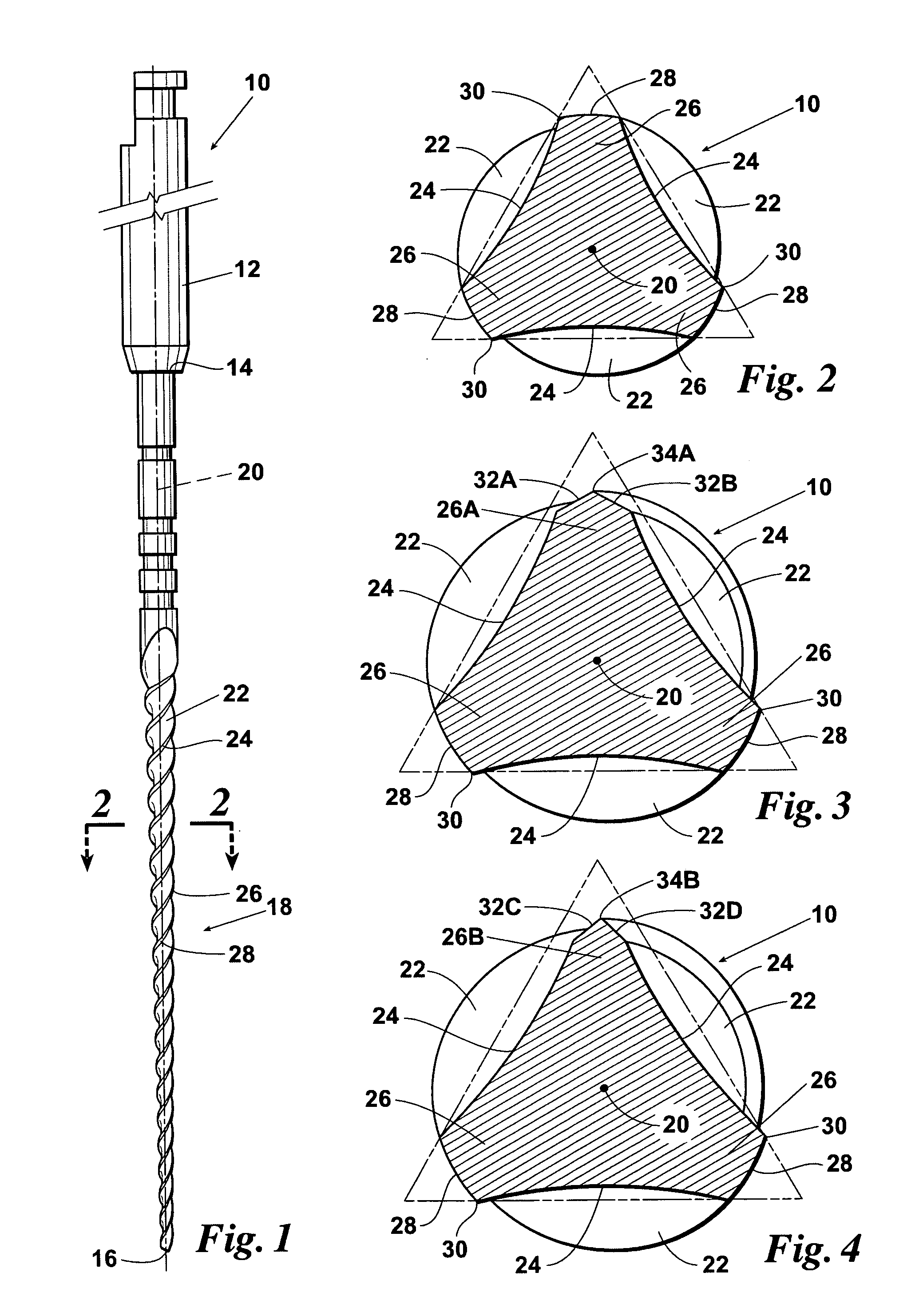
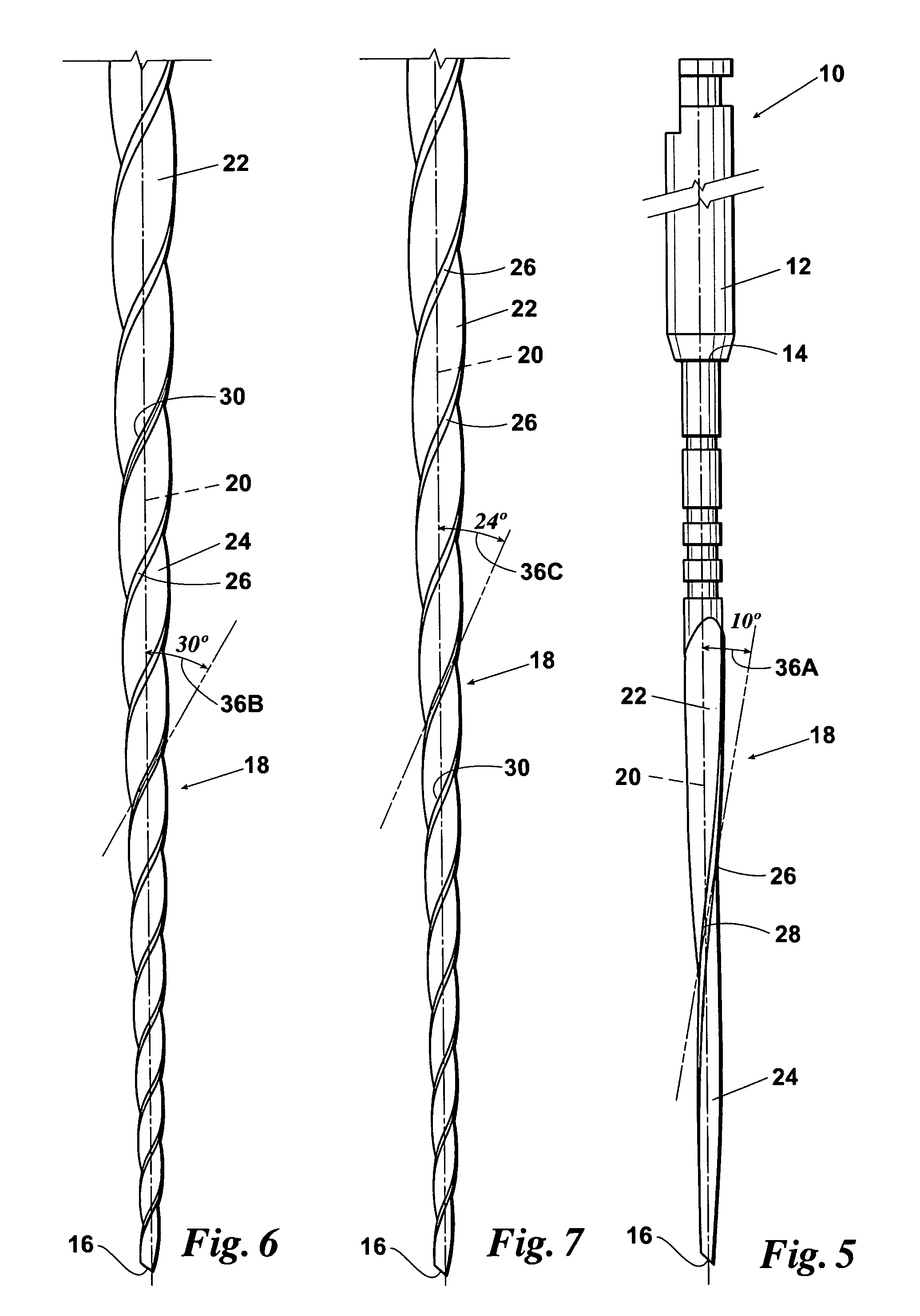
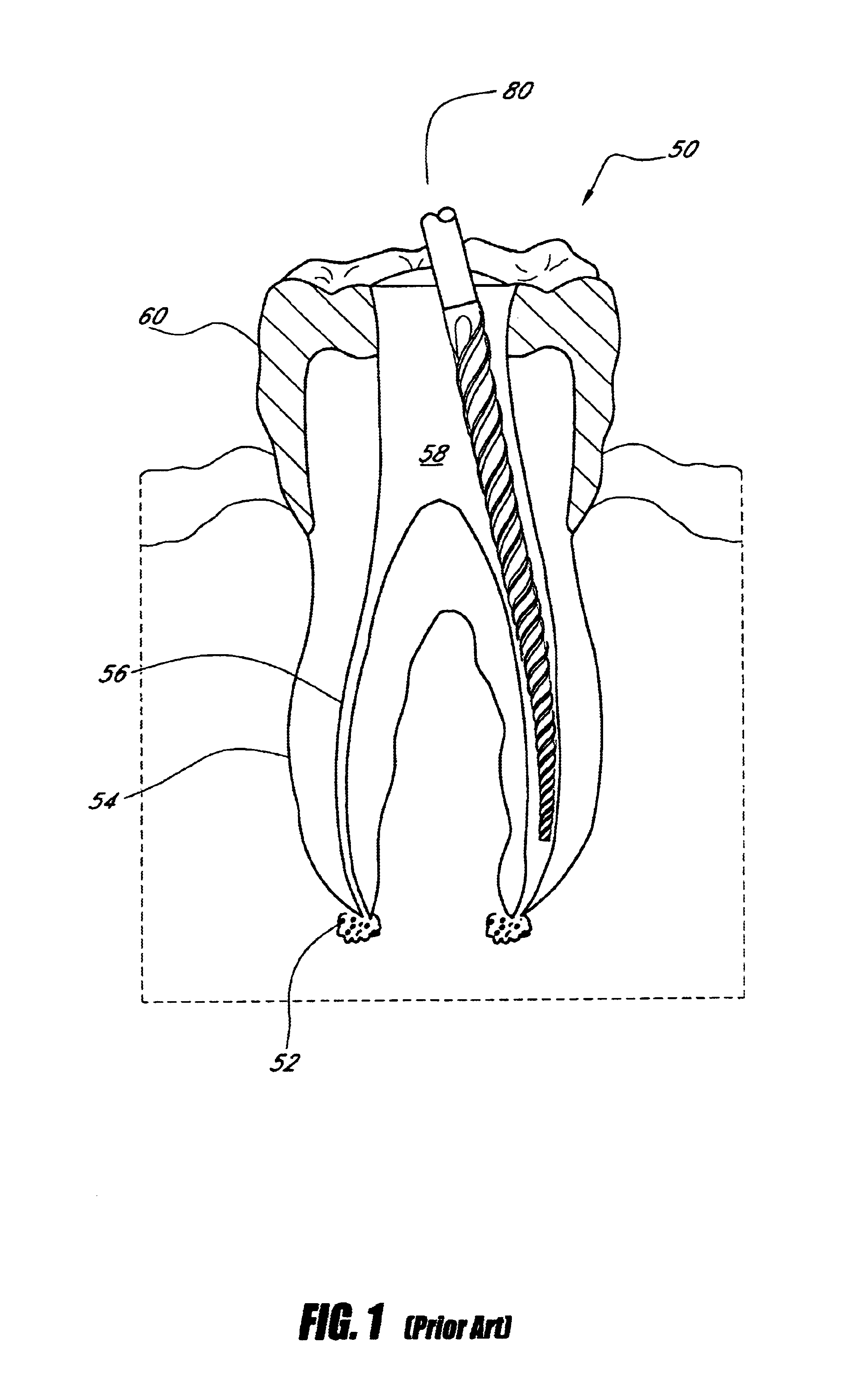
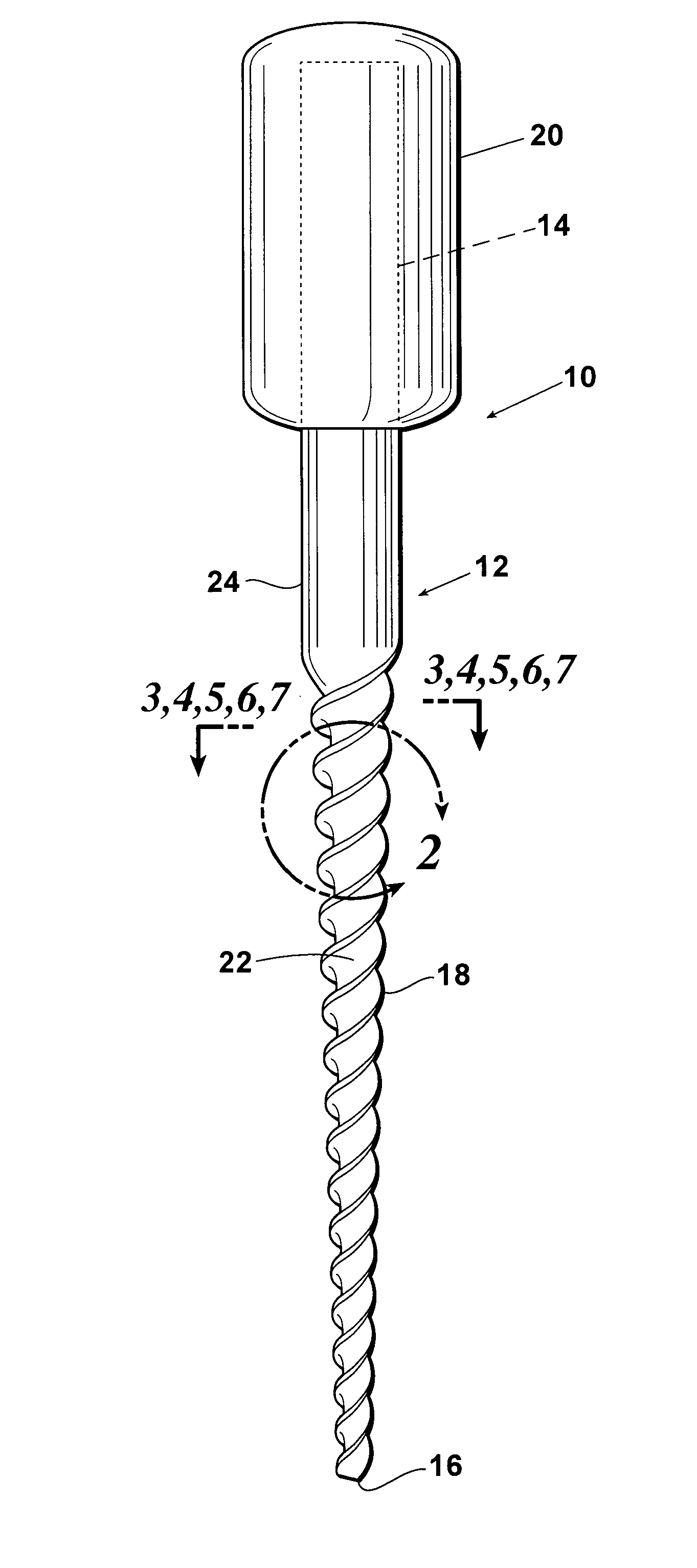
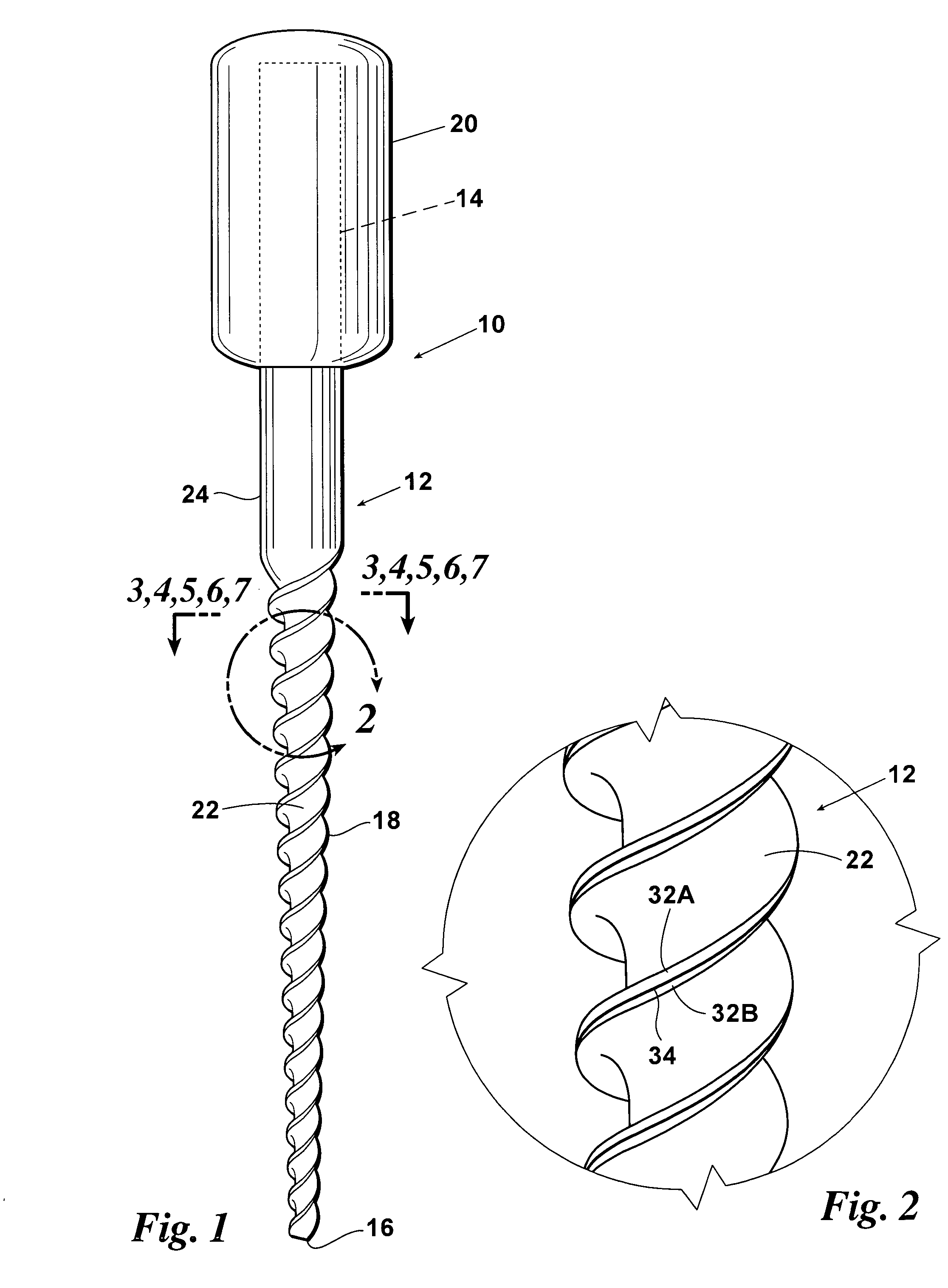
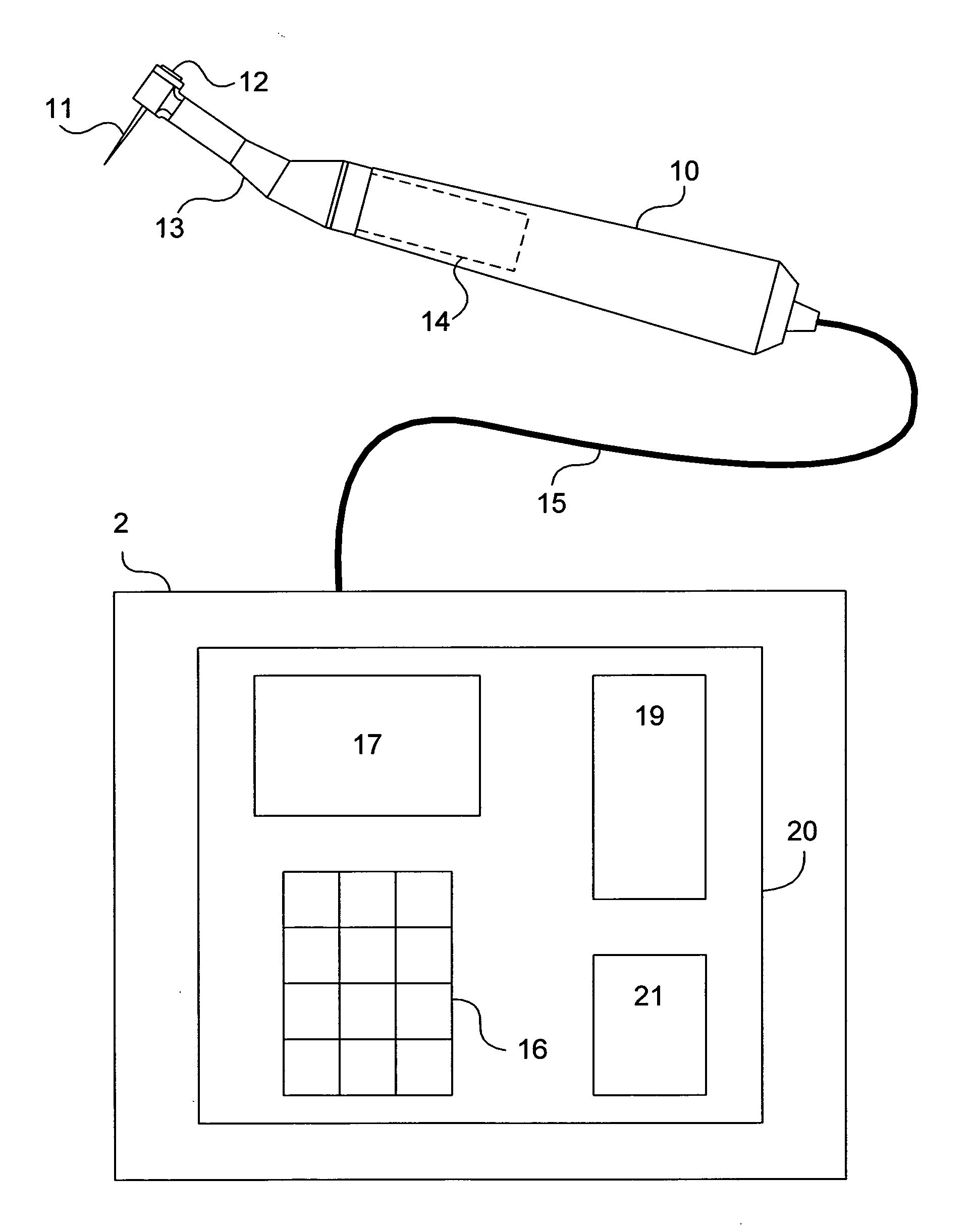
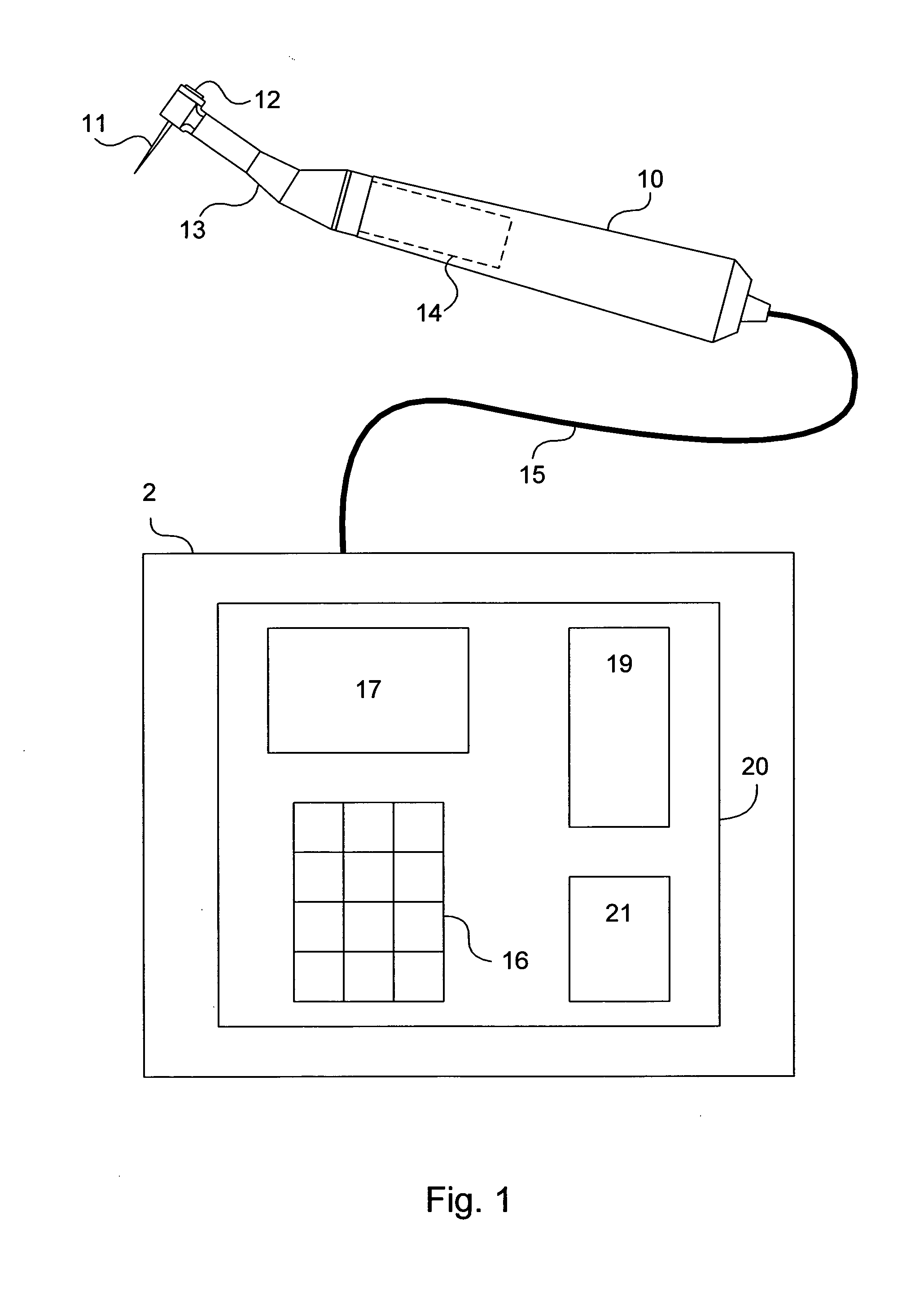
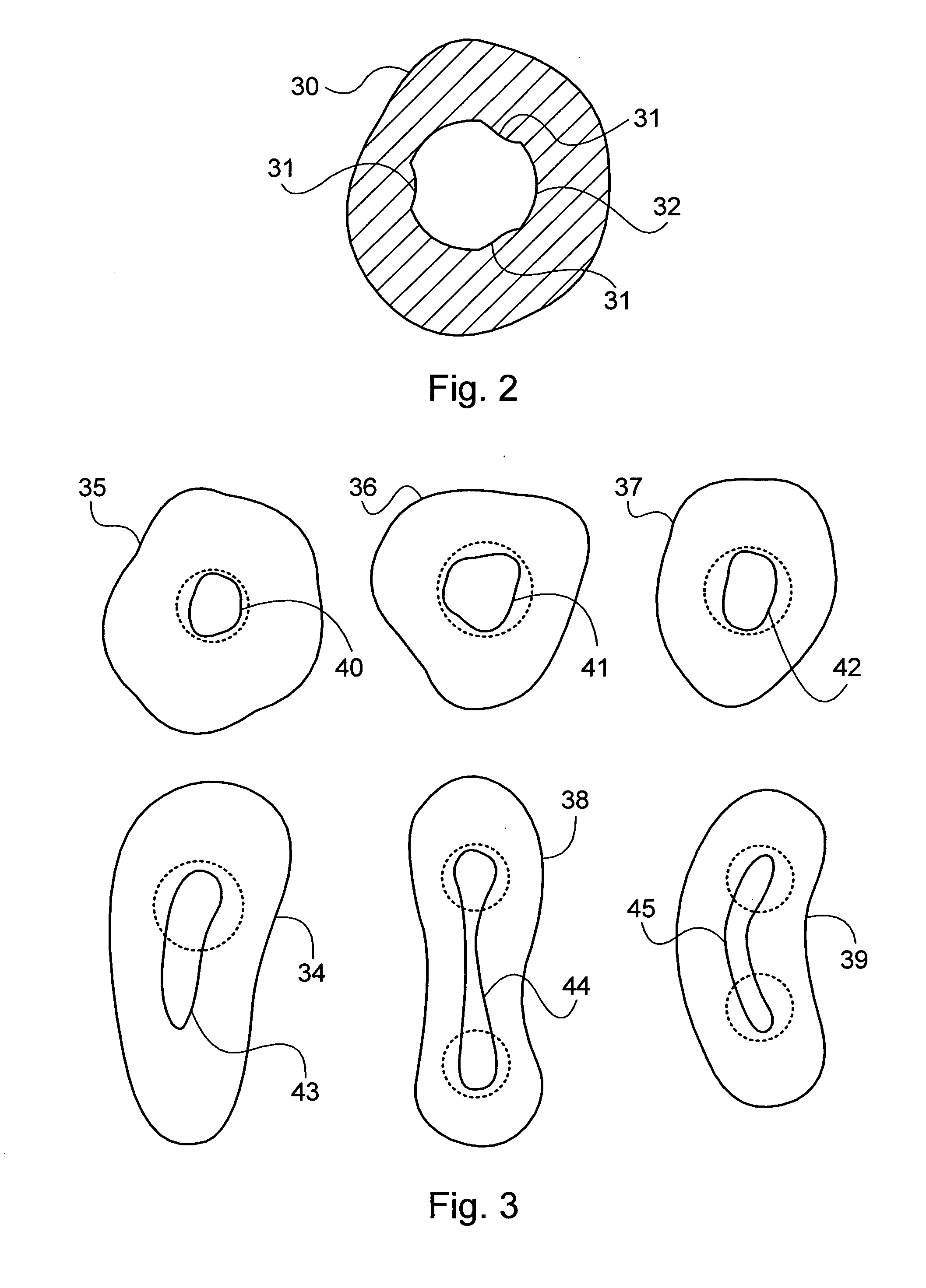
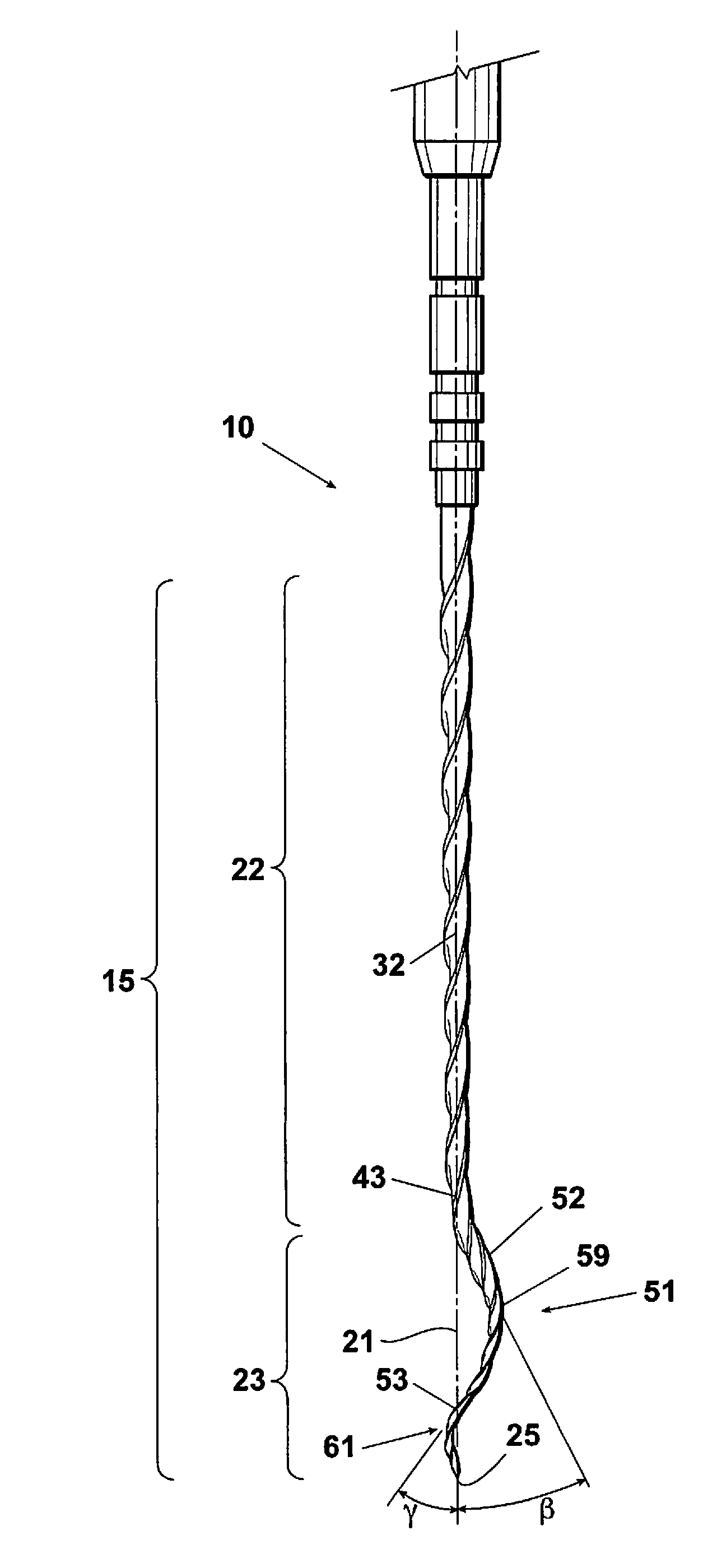
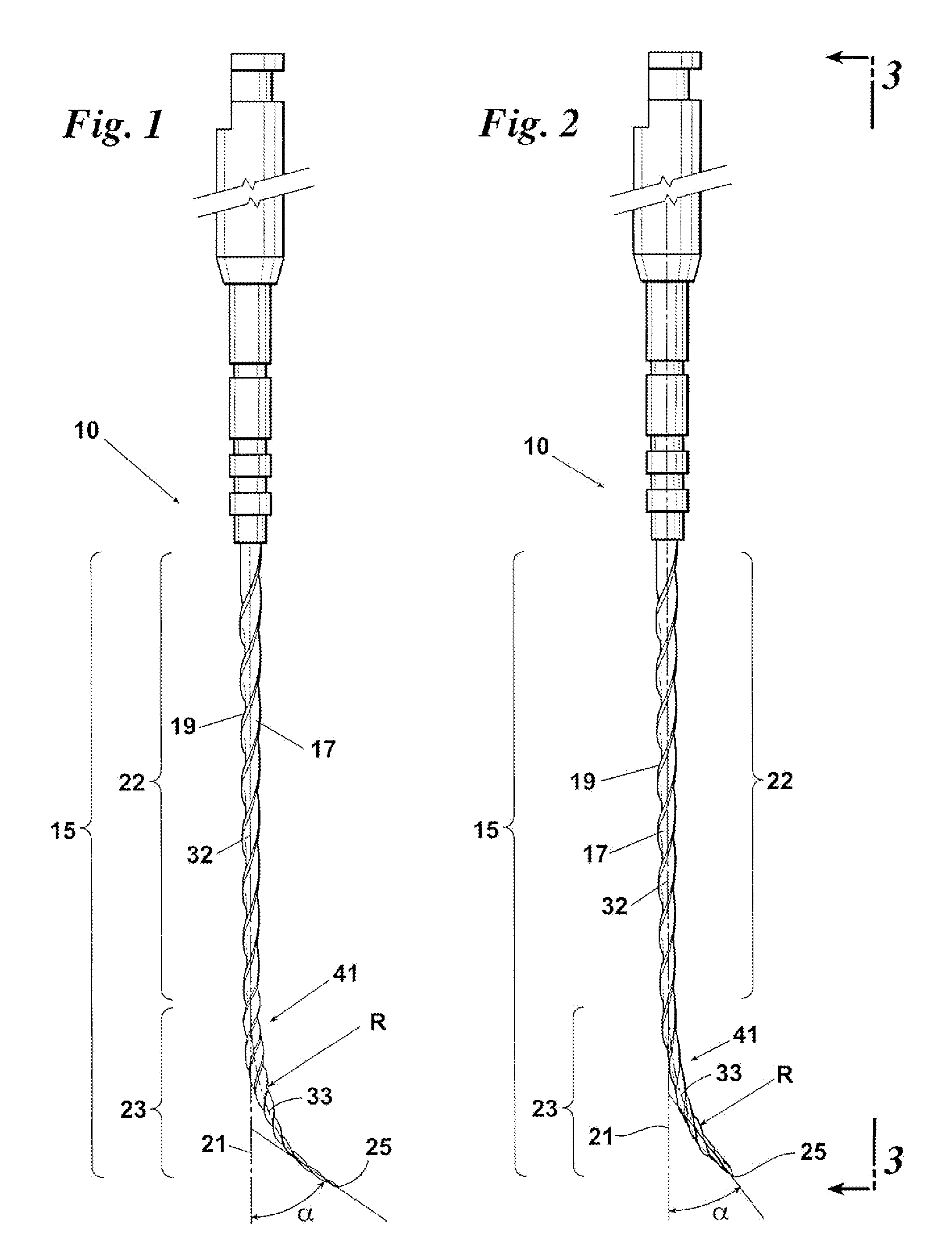
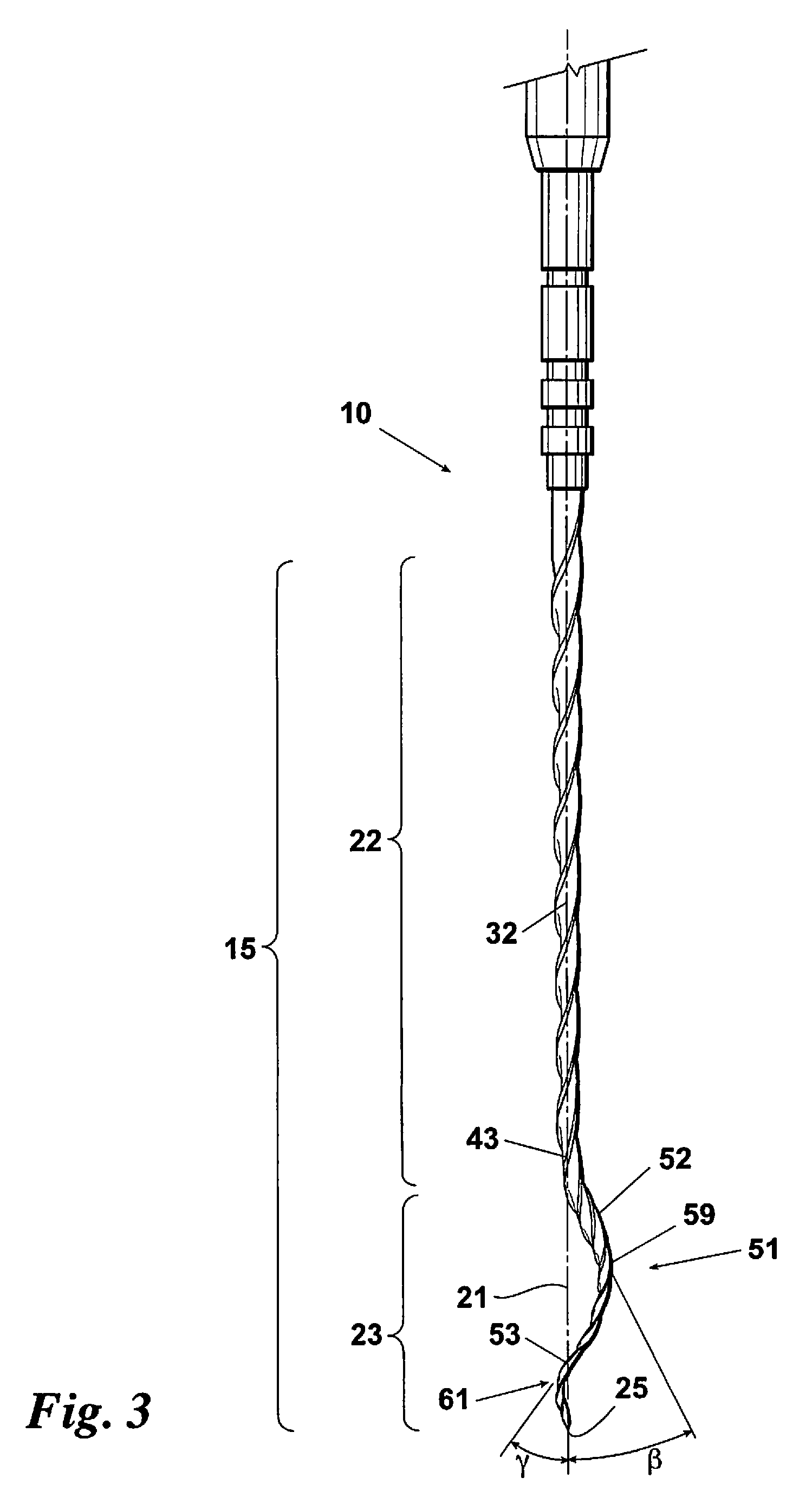
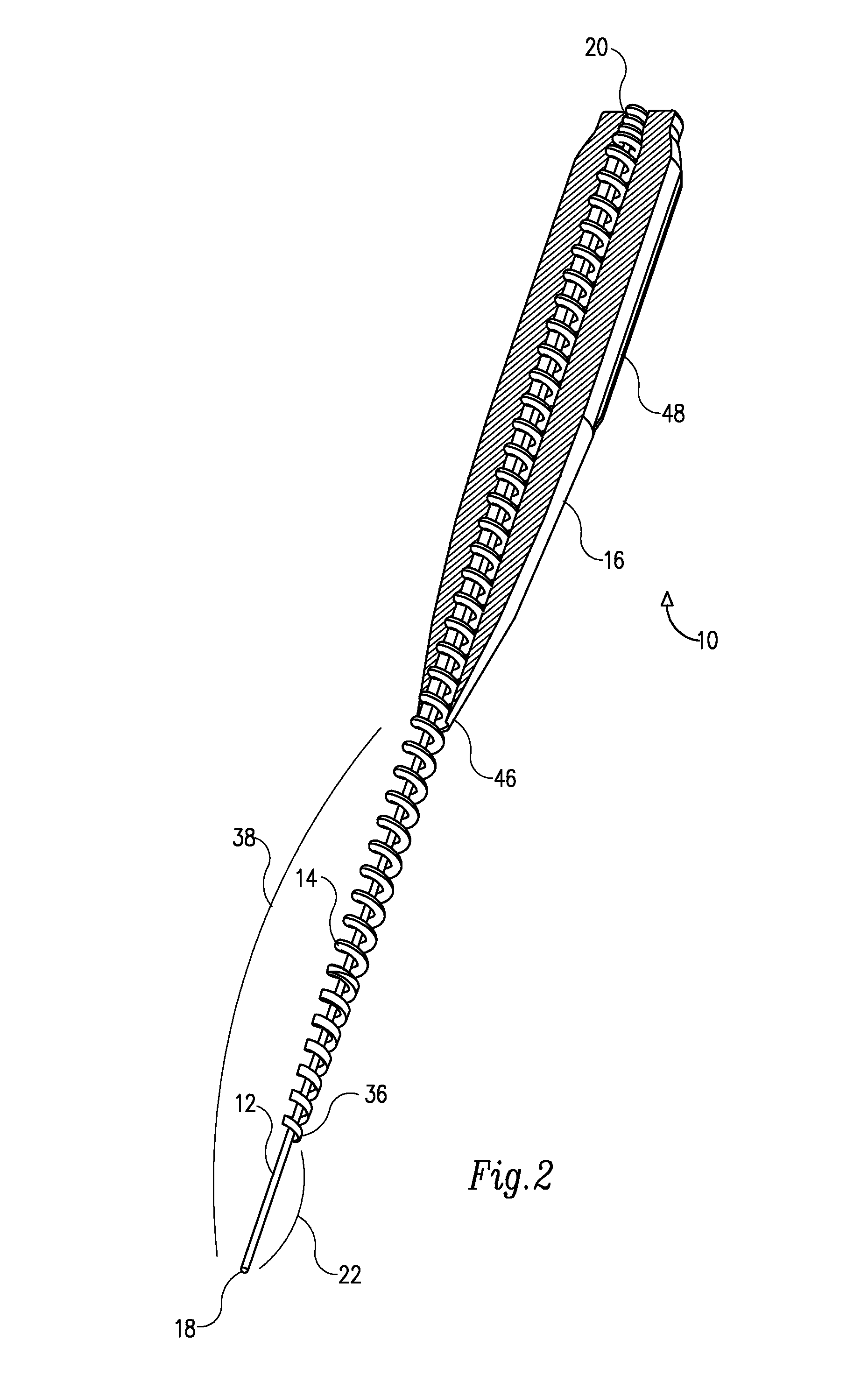
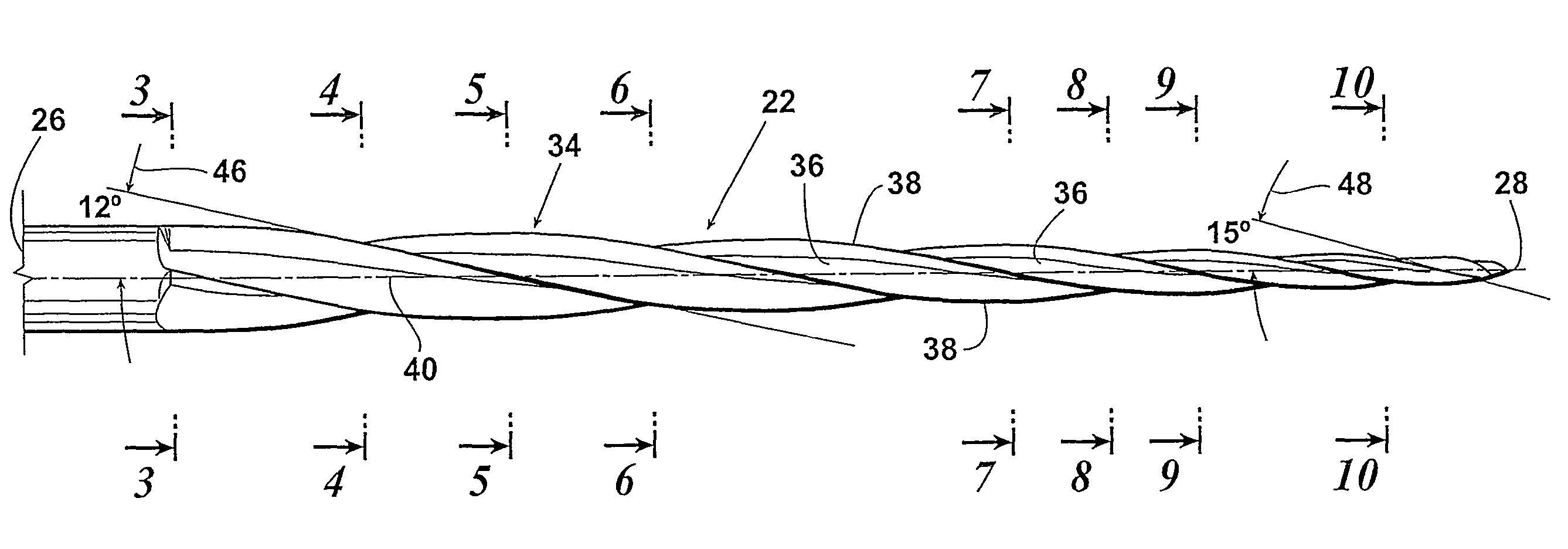
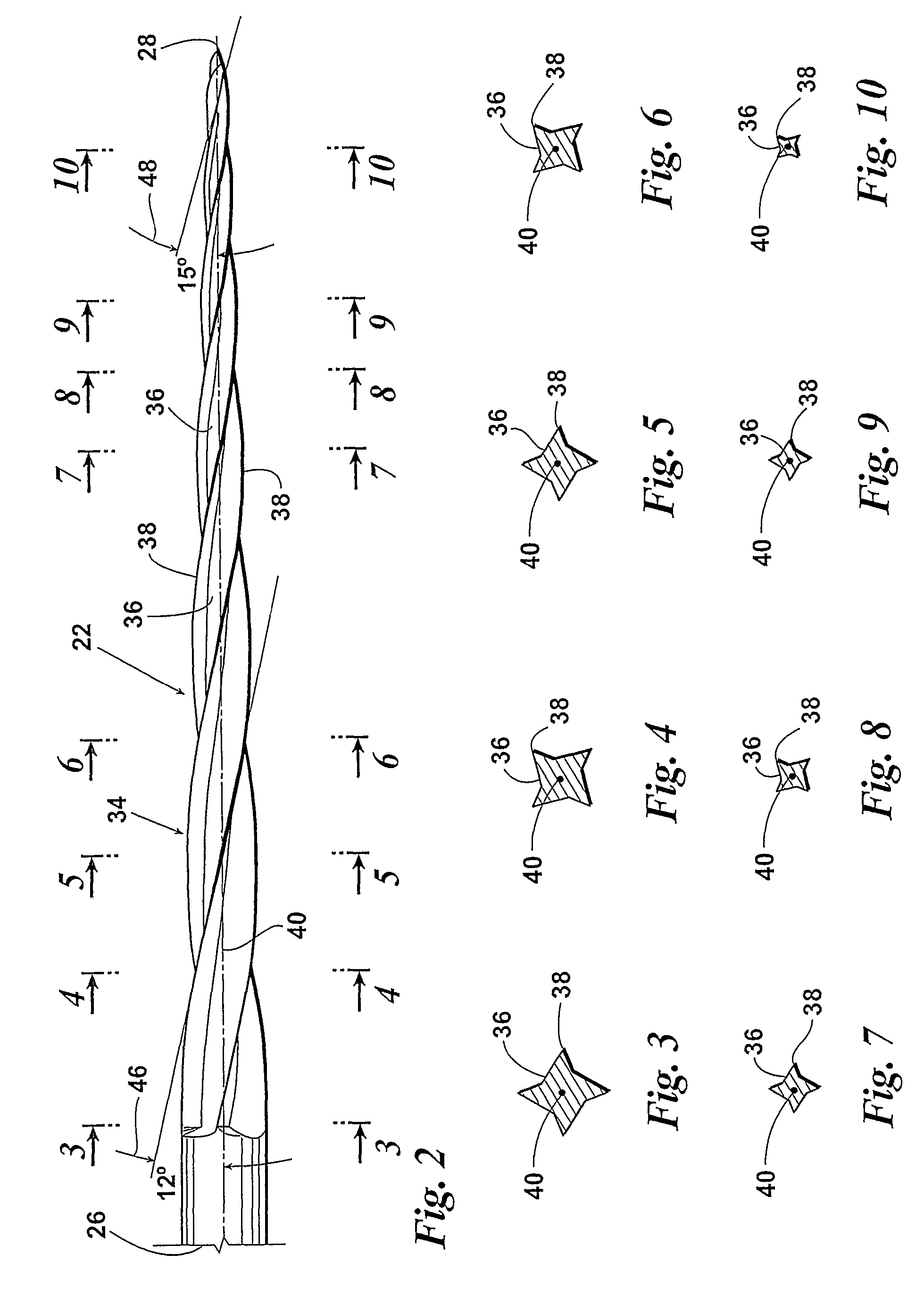
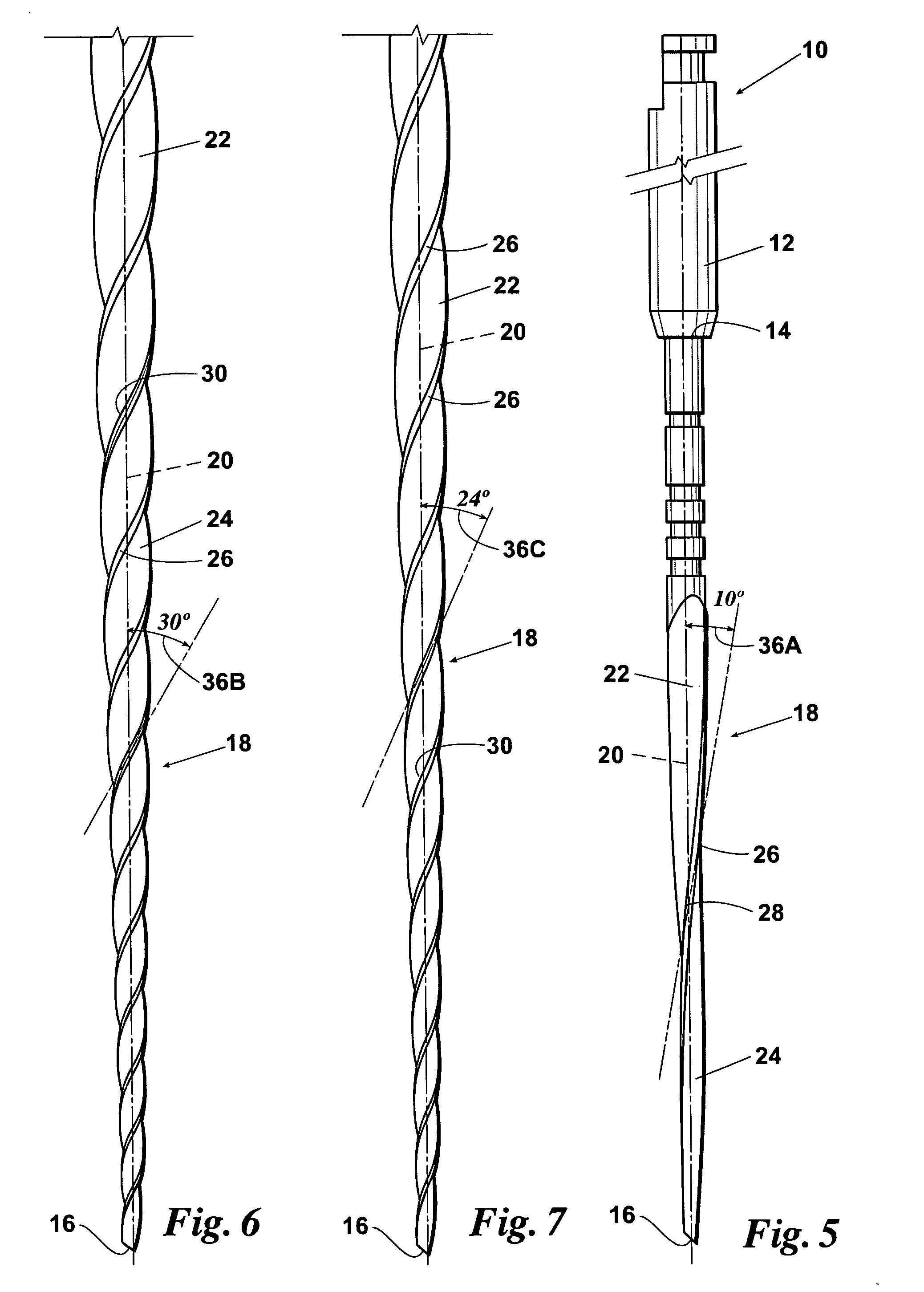
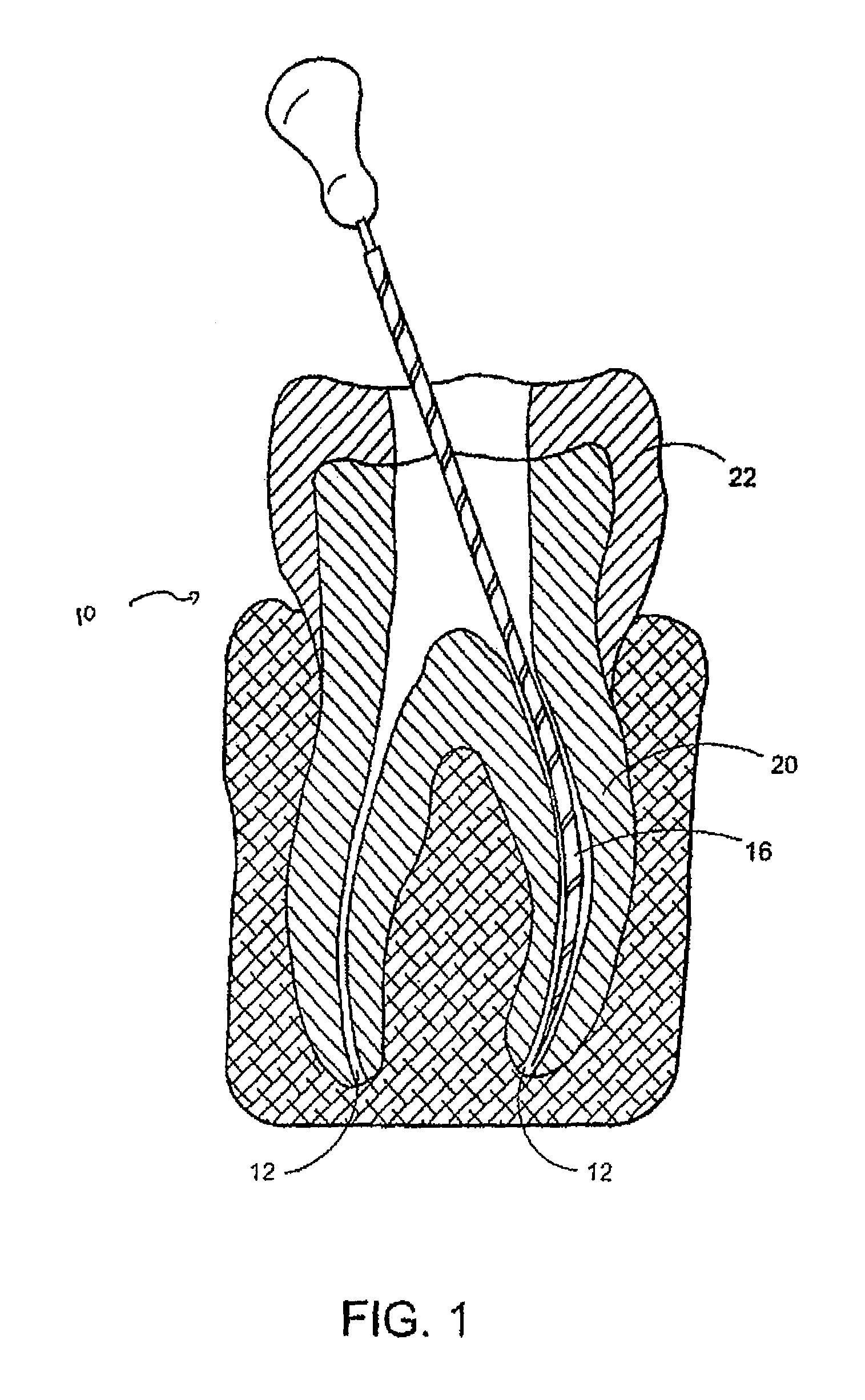
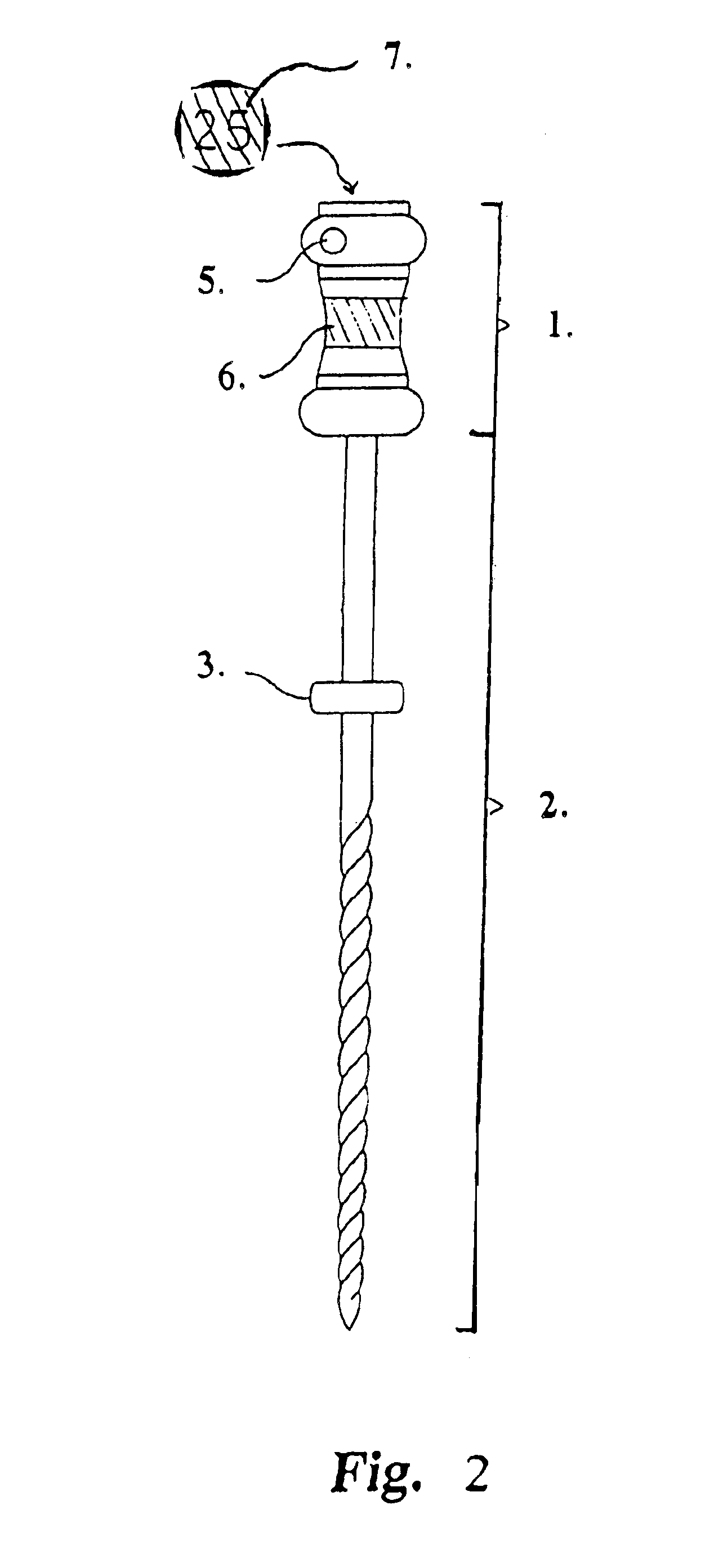
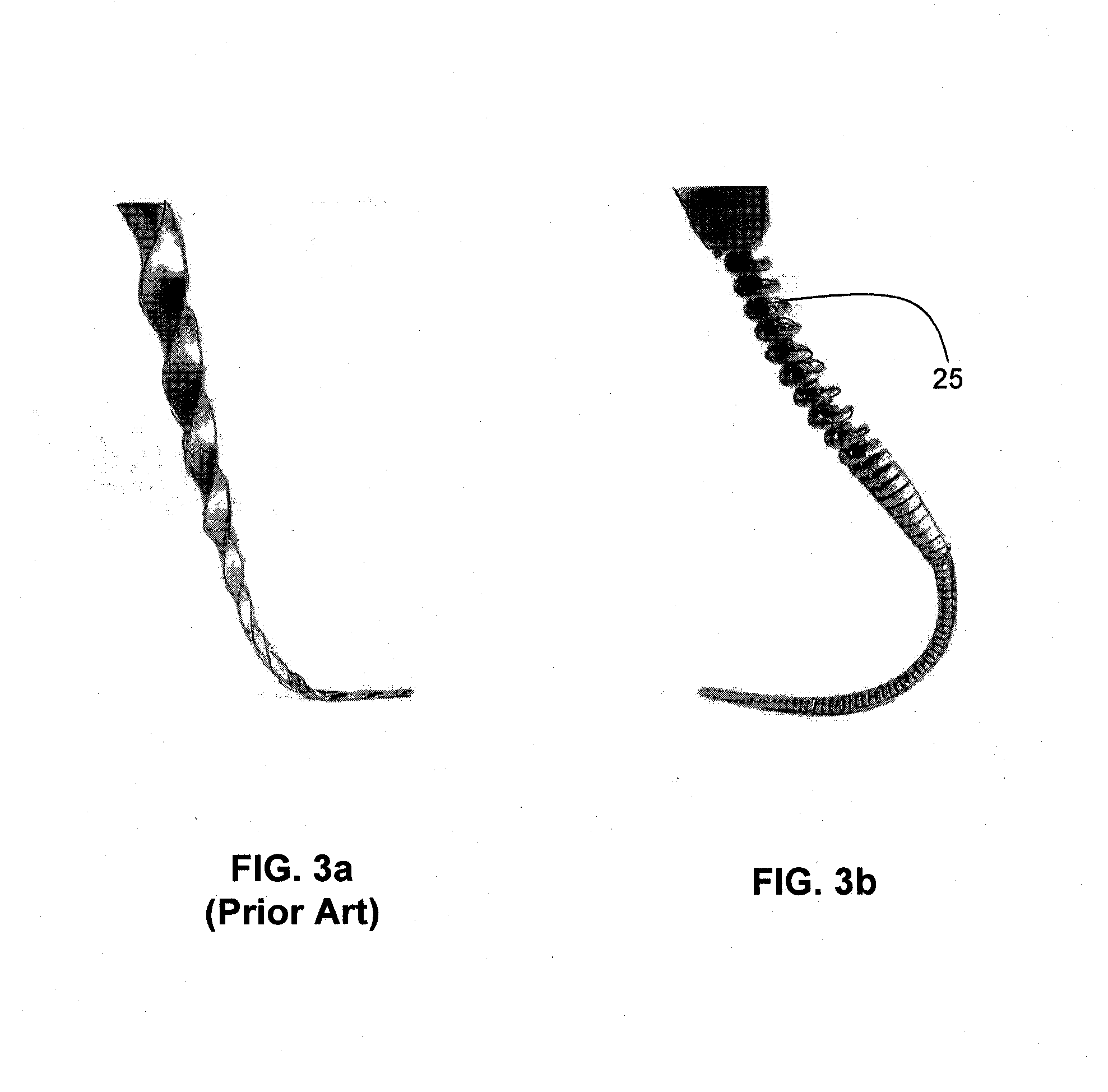
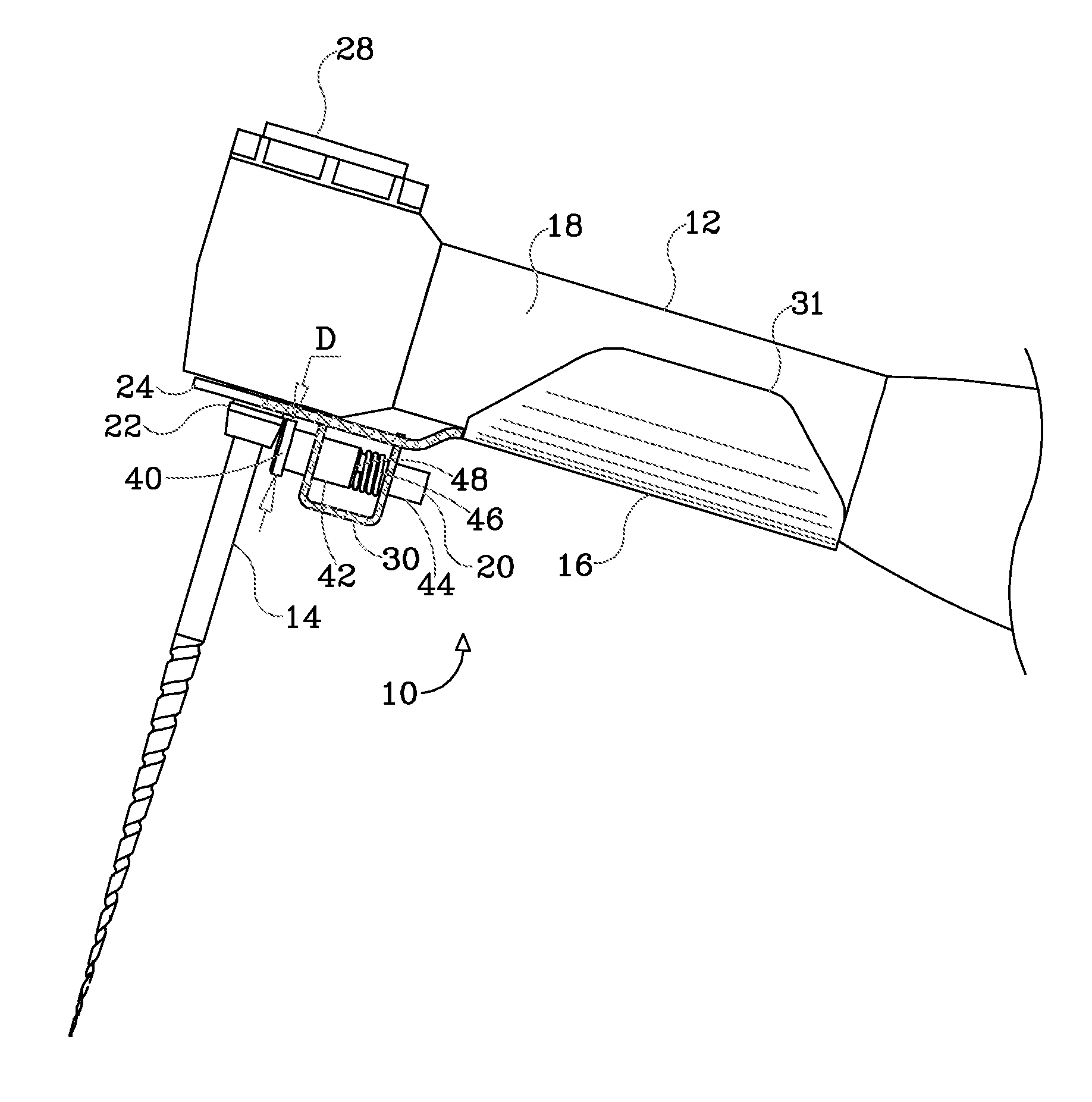
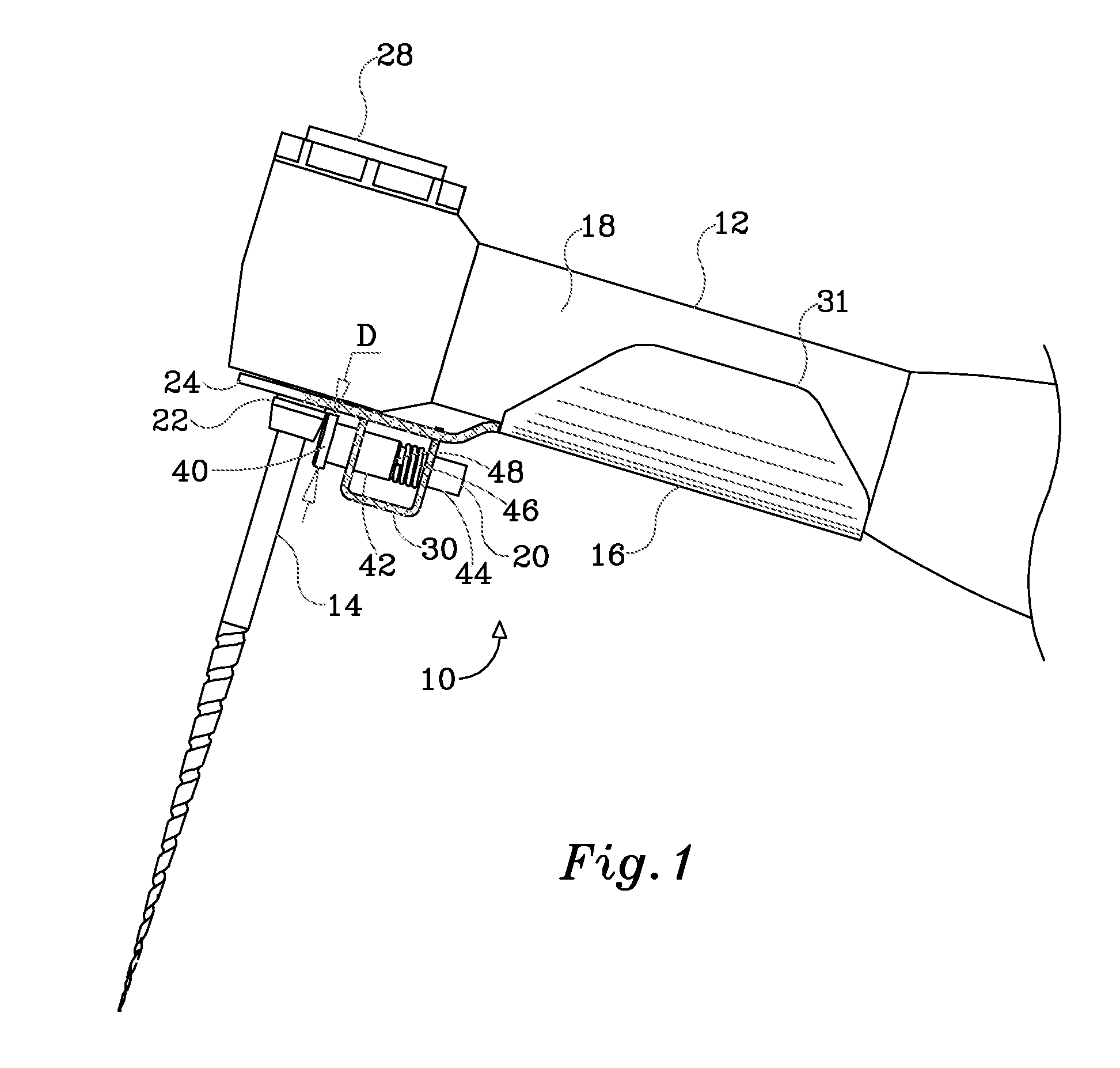
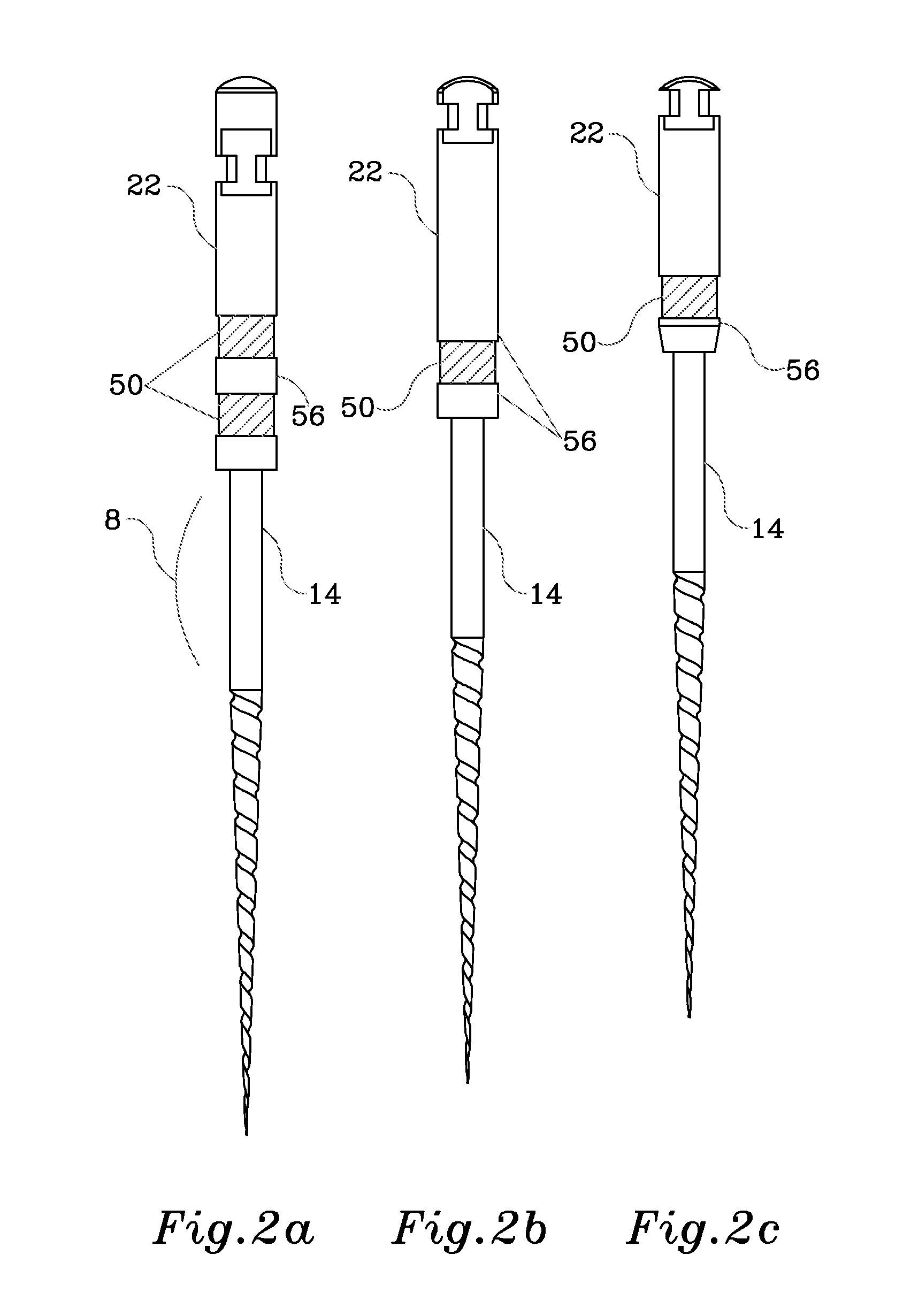
Endododontic file with multi-tapered flutes
ActiveUS20060228668A1Reduce torque loadIncreasing and reducing flexibilityTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsFluteEndodontic files
A multi-tapered endodontic file is provided, formed from shaft of material having a shaft. The shaft includes a working portion having one or more tissue-removing edges, points and / or surfaces. The working portion includes at least a first flute and a second flute. The first flute is tapered along its length in accordance with a first predetermined taper function. The second flute is tapered along its length in accordance with a second predetermined taper function.
Owner:MAILLEFER INSTR HLDG
Endodontic instrument having notched cutting surfaces
InactiveUS20050266375A1Trend downGood curative effectTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsFile designRasp
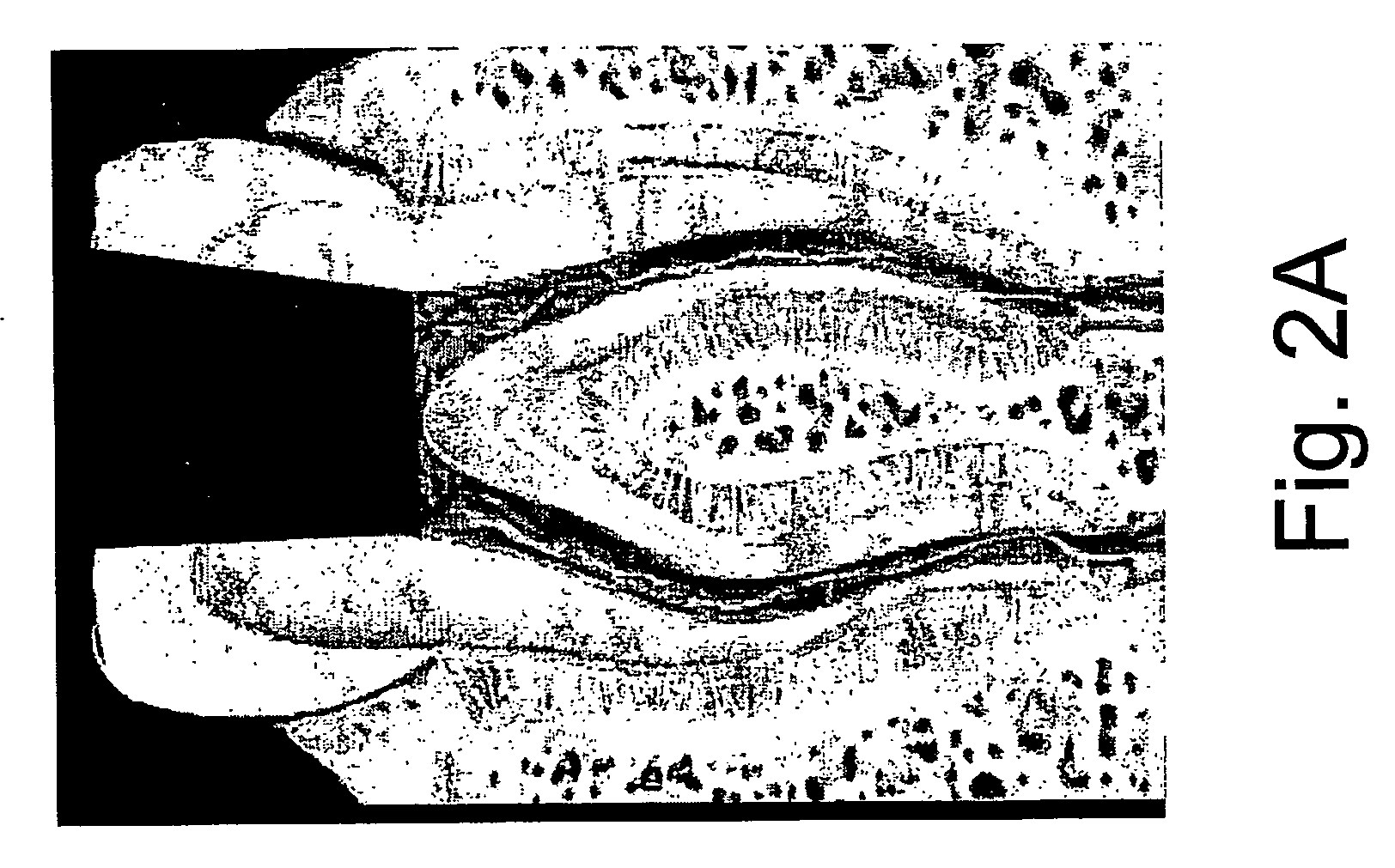
A fluteless endodontic file is provided, formed from a tapered shaft of material having a prismatic shape generally defined by three or more side surfaces and three or more interposed corners. A plurality of notches are cut into one or more corners defining cutting surfaces, points and / or edges. The notched cutting surfaces are formed such that the file, when rotated and / or reciprocated within a root canal, effectively cuts / debrides hard tissue (known in the art as dentin) as well as soft tissue, thus, forming an optimal canal shape. The cutting surfaces are also preferably formed at an angle to the centerline of the instrument to provide optimal cutting efficiency and material removal. The fluteless file design exhibits increased efficacy, with less tendency to bind and break within the root canal and also significantly reduces manufacturing and capital equipment costs.
Owner:BROCK G MATTHEW +1
Precision cast dental instrument
InactiveUS20070184406A1Resistance to breakageResistance to wearTransportation and packagingWristbandsDental structureInstrumentation
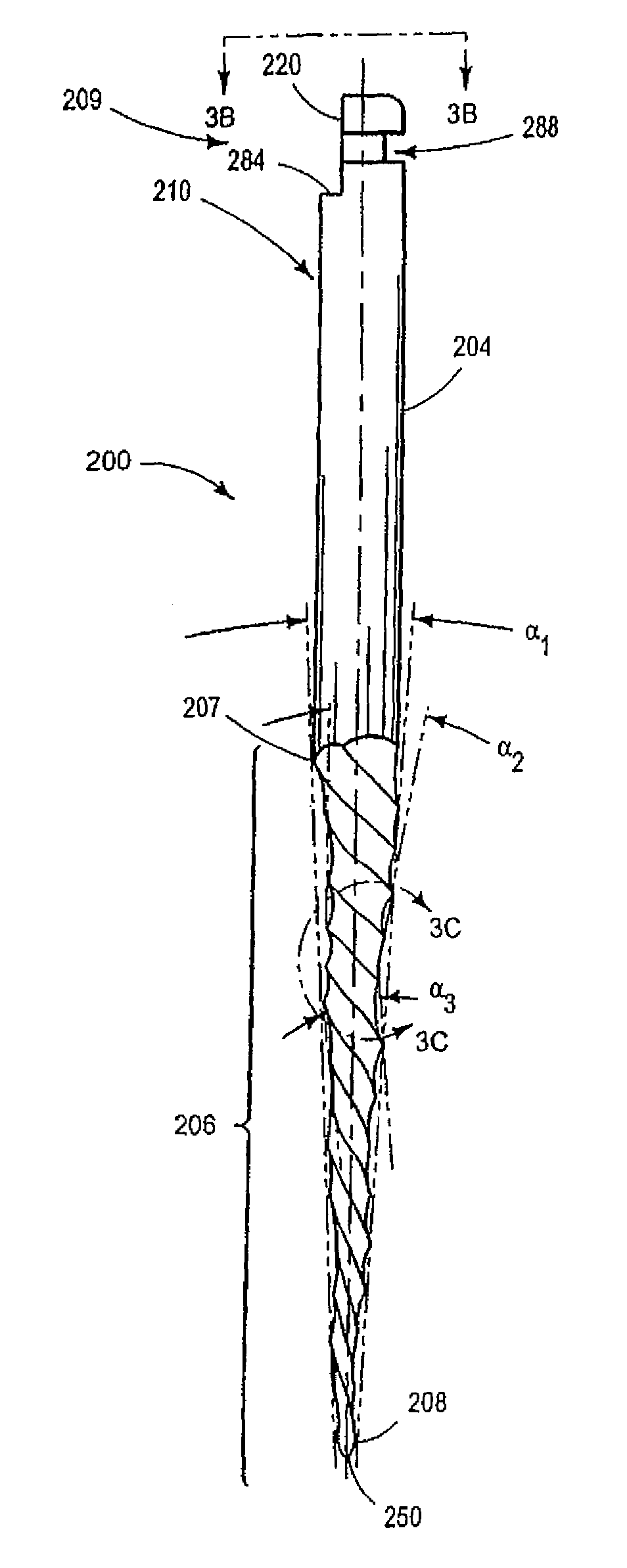
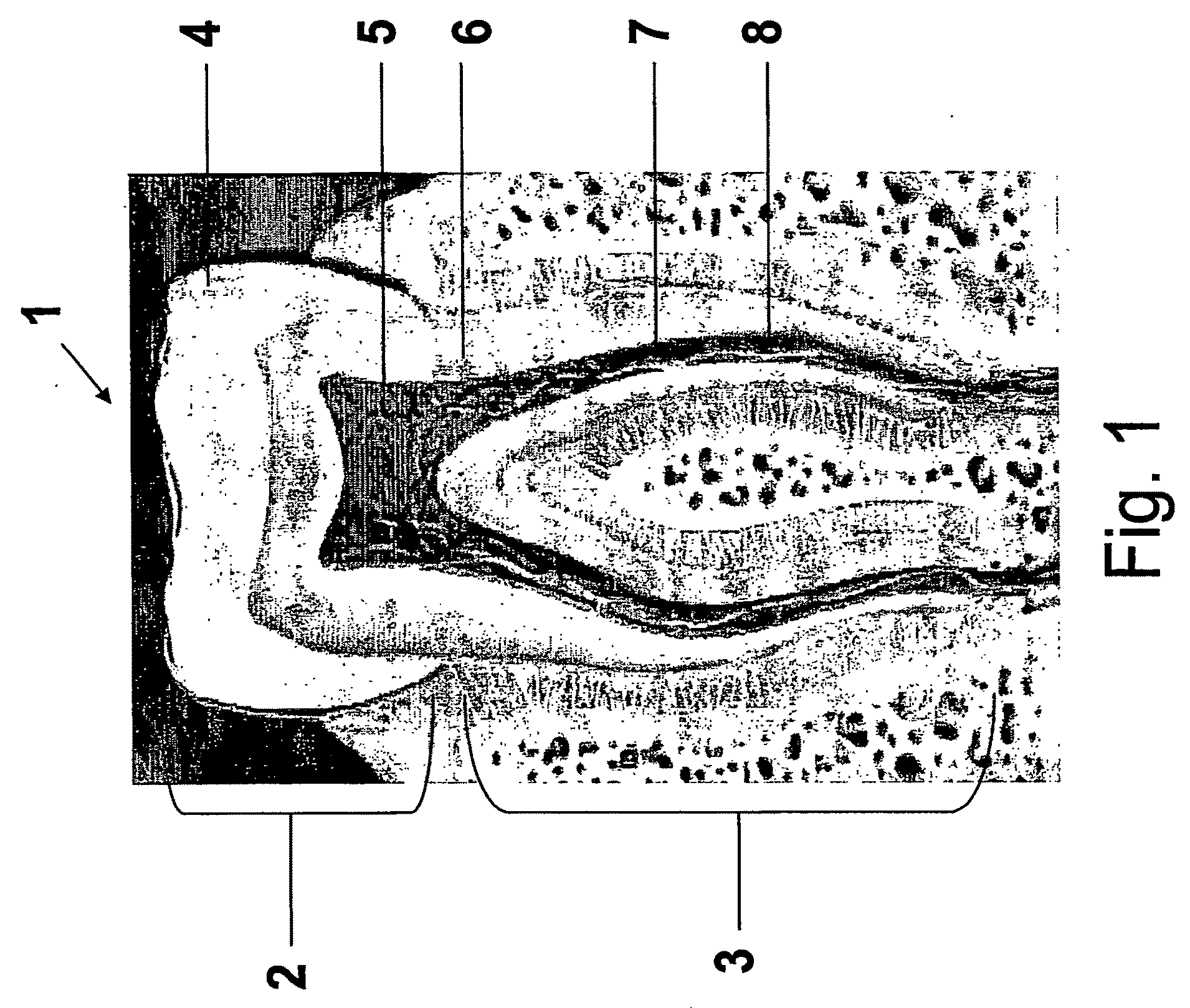
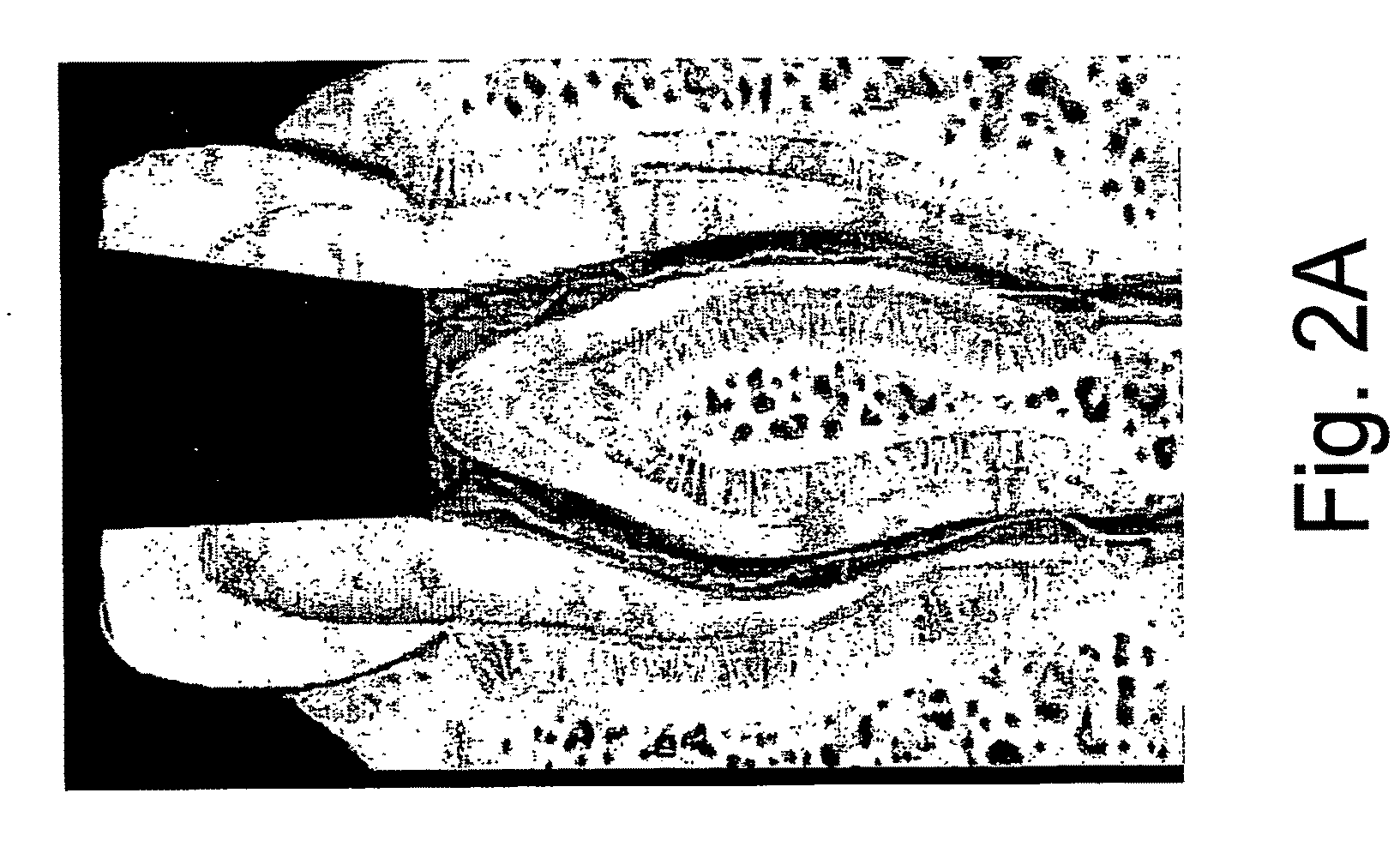
An endodontic file (200) is provided particularly adapted for the removal of tooth structure, decayed or damaged nerve tissues or dentine material on the interior walls of a root canal or dentine and / or enamel from the external tooth wall. The endodontic instrument includes a shaft (202) having a shank portion (204) and a generally elongated working portion (206). The working portion preferably includes cutting or abrading features (232) adapted upon rotation and / or reciprocation of the instrument to cut, abrade or remove tissue from the interior walls of a root canal or dentine and / or enamel from the external tooth wall. The working portion extends from a proximal end (207) adjacent the shank portion to a distal end (208) terminating at a tip (250). The entire instrument and / or at least the working portion thereof is formed of an amorphous or essentially amorphous material having no or essentially no detectable crystalline structure and / or from a nanocrystalline material having an average crystalline grain size less than about 1 μm. The instrument may be formed by conventional grinding operations or by direct casting, forging or molding, in a manner producing an integral as-molded instrument having one or more sharp cutting edges. The instrument is inexpensive to manufacture and exhibits improved cutting-edge sharpness, wear resistance, lubriciousness and resistance to breakage.
Owner:CLOUDLAND INST
Instruments having Anti-microbial coating
InactiveUS20070259307A1Eliminating and preventing and retarding and minimizing growthIncreased durabilityGum massageSurgerySurgical drillDental instruments
The present invention relates to dental instruments including dental burs, dental discs, tapes, endodontic files, surgical drills and taps, scalers, mirrors, intra-oral light sources, handpieces, perioscopes, covers for dental instruments and other tools having anti-microbial and / or medicament coatings which may be in a substantially permanent covalent manner or in a substantially non-permanent manner. The anti-microbial coating may be made from a variety of anti-microbial substances and other appropriate constituents to promote its fixing to the surface of the dental instrument and to promote its anti-microbial activity either during use or during storage. The substrate of the instruments may also include sources of anti-microbial agents, either by embedding, filling or mixing into the substrate.
Owner:DISCUS DENTAL LLC
Precipitation hardenable stainless steel endodontic instruments and methods for manufacturing and using the instruments
InactiveUS6514076B1Resistant to wearEasy to useTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsEndodontic filesChromium nickel
Precipitation hardenable stainless steel endodontic files and methods for their manufacture, wherein the most preferred precipitation hardenable stainless steel is 17-4PH and aging is preferably not one of the manufacturing steps. Precipitation hardenable stainless steels used in embodiments of this invention are iron-chromium-nickel grades that have the desired properties of flexibility, strength, hardness, wear resistance, stiffness, resistance to permanent deformation, resistance to variable torque, and biocompatibility for endodontic files.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
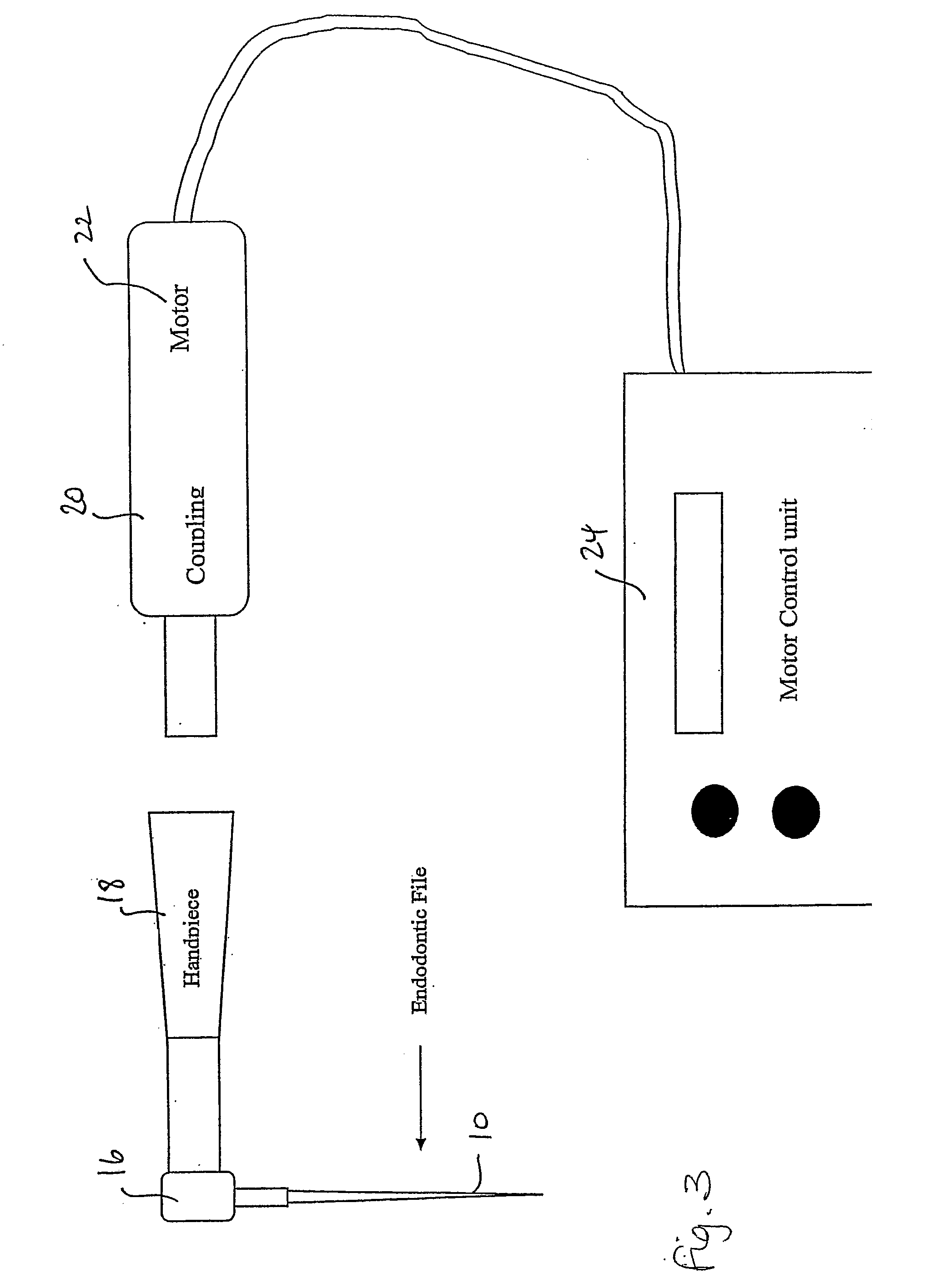
Motor control system for endodontic handpiece providing dynamic torque limit tracking of specific file fatigue
InactiveUS6955536B1Exact reproductionImprove accuracyAdditive manufacturing apparatusDental toolsElectric machineryEndodontic files
A system for establishing a cumulative history of stress factors encountered during use of an endodontic file and keeping track of such for a plurality of files so that the files can be re-used with confidence that a given file is as safe to use as a new file. Cost of file maintenance is significantly reduced and the likelihood of file breakage in use is minimized.
Owner:BUCHANAN L STEPHEN
Dental instruments having durable coatings
InactiveUS20060269901A1Extended service lifeUseful for wearTooth pluggers/hammersTeeth cappingSurgical drillDental insert
The present invention relates to dental instruments used in tooth restoration and replacement including dental burs, dental discs, tapes, endodontic files, surgical drills and taps, having abrading working surfaces coated or embedded with diamond particles or chips onto the substrate or shank, the abrading surfaces having a flexible diamond-like carbon (DLC) coating. The substrate may be flexible or the shank may be made of a relatively hard substrate and diamond particles or chips may be coated or embedded onto the substrate or shank through the use of polymeric bonding agents, through embedding in a nickel or nickel alloy matrix, or through chemical vapor deposition, or even direct coating if polymeric substrates are used. The abrading surface may also be formed through the formation of cutting edges or surfaces on the substrate. The present invention further relates to a dental tip, which may be part of an ultrasonic dental insert may be made of a metallic or polymeric substrate which is coated with a flexible and durable coating. The coated tip is bent or can be bent to a desired configuration. The coating is made of a diamond-like-carbon (DLC) coating having at least about 5 atomic percent of hydrogen. The coated abrading surfaces or tips are longer lasting than uncoated surfaces and the coating may also serve as a wear indicator. Further, the coating is present on the surface of the bur or tip during use without obstructing the abrasive function of the dental instruments.
Owner:DISCUS DENTAL LLC
Self adjusting instrument
ActiveUS20070054238A1Easy to cleanGreat dimensionDental toolsTeeth cappingEndodontic filesRoot canal procedure
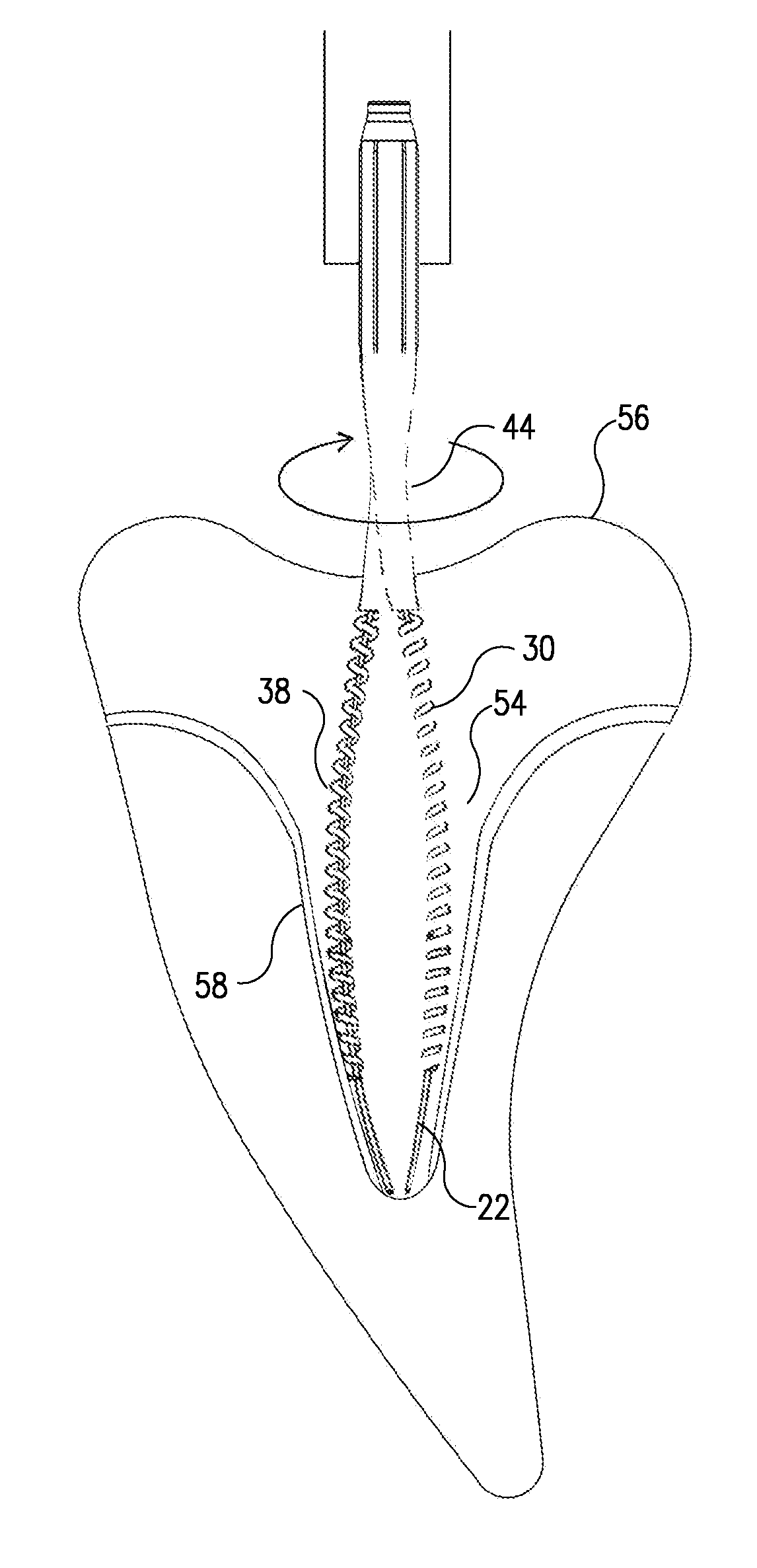
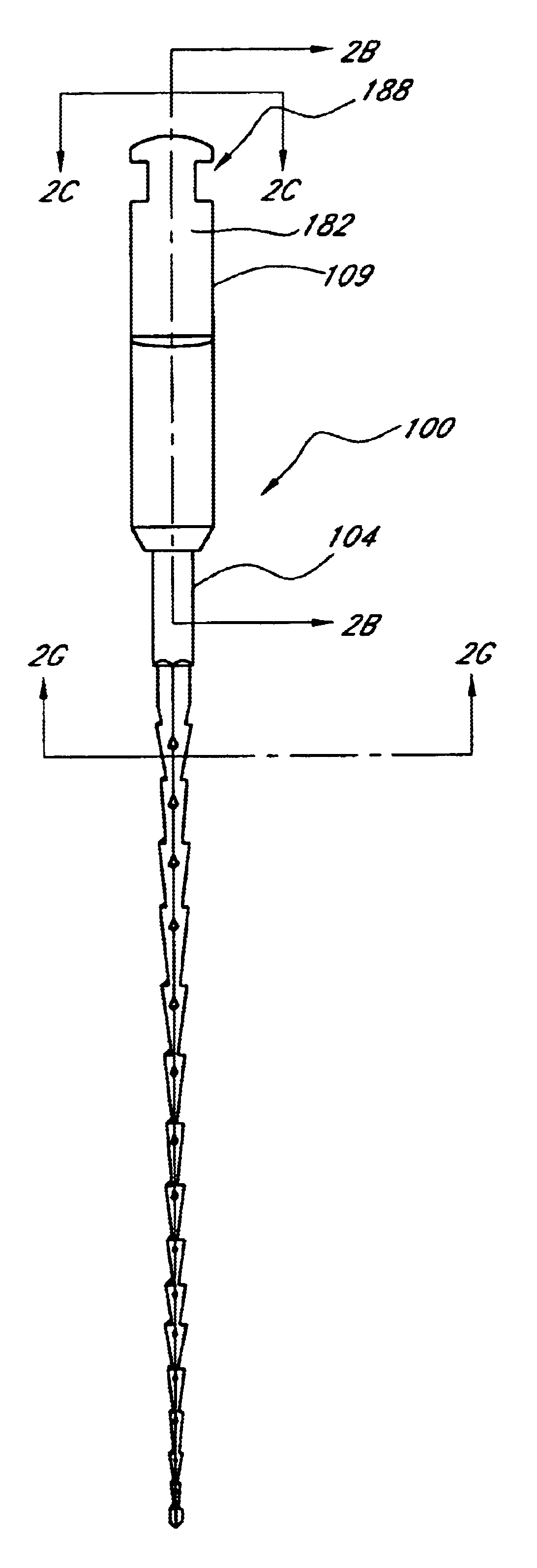
The invention is an instrument for cleaning and / or shaping and / or widening a channel that exists in or through a solid object. The design of the instrument the superelastic and shape memory properties of the material from which it is made, allow the inner volume enclosed by the instrument, its outer contour, or both to change as a result of the forces exerted upon it while working, thereby shaping the instrument to the three-dimensional contour of the channel. A preferred embodiment of the instrument is an endodontic file for use in the cleaning, shaping, and widening stages of a root canal procedure.
Owner:REDENT NOVA LTD
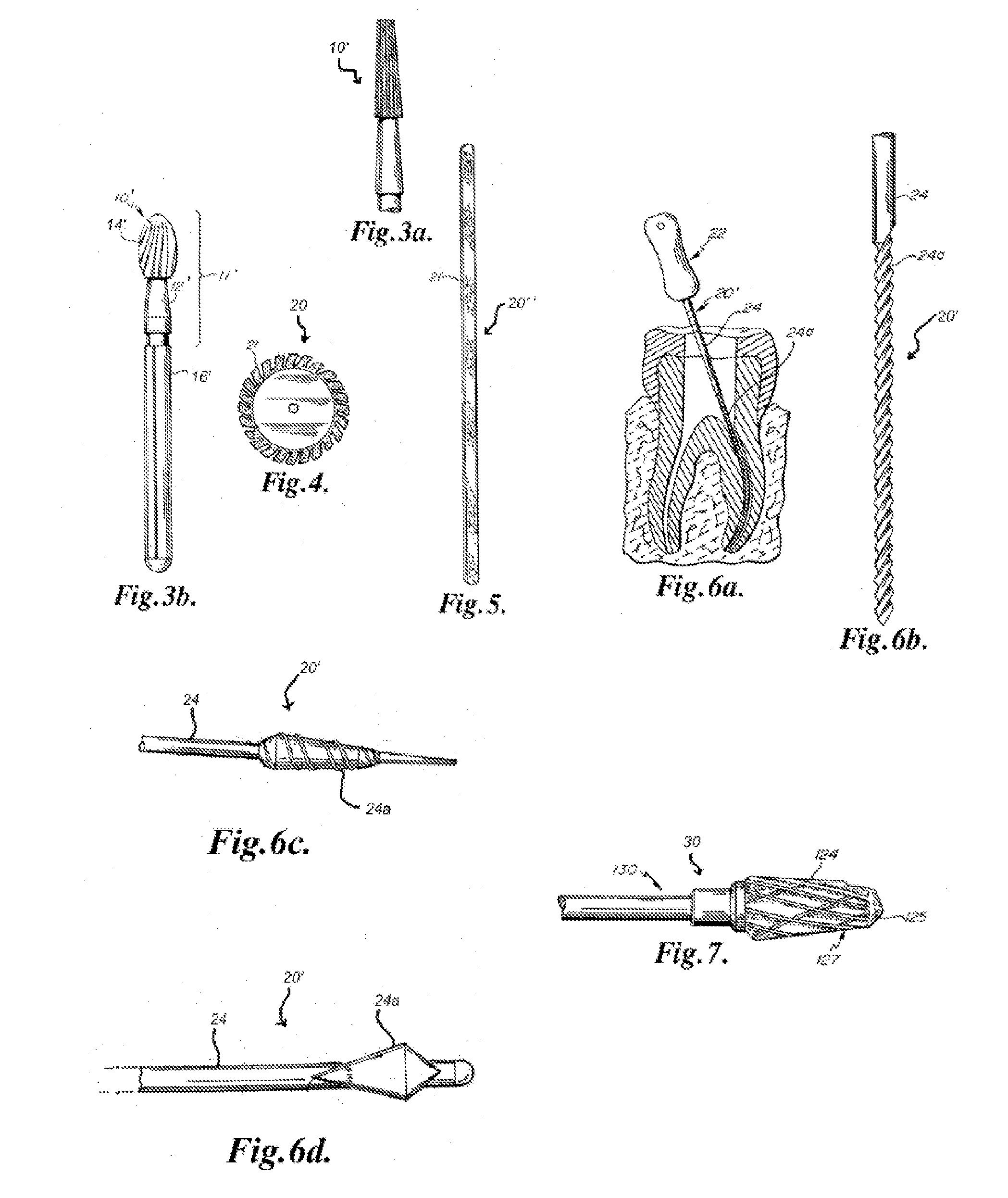
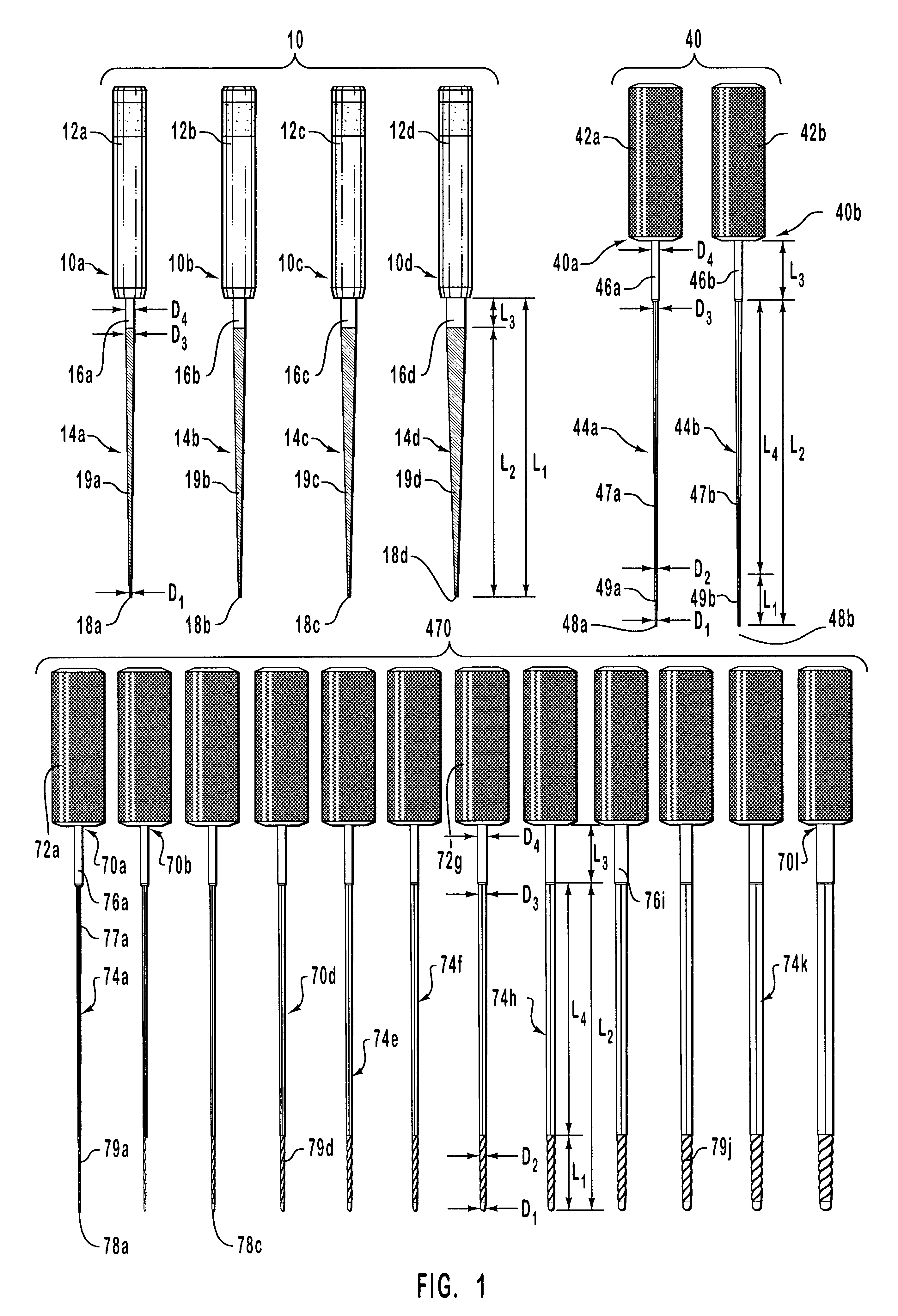
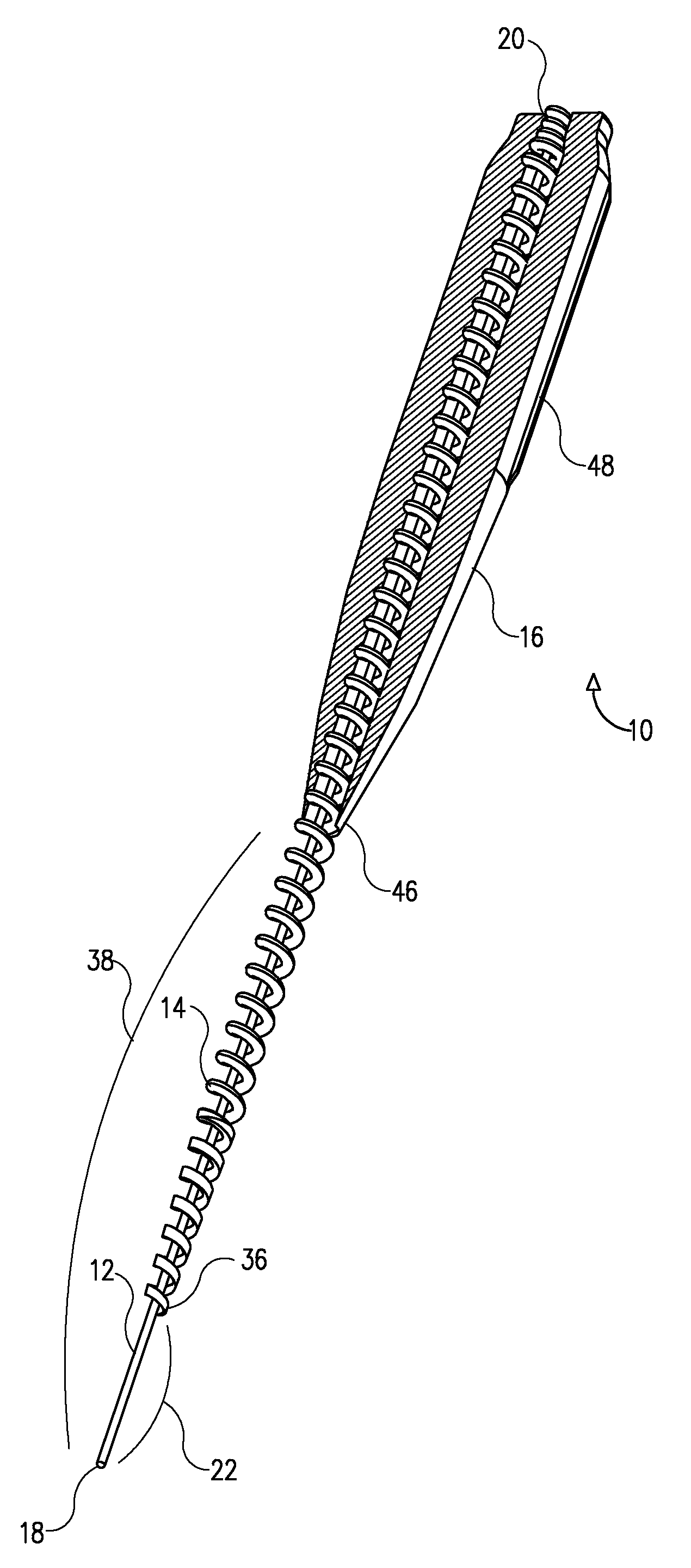
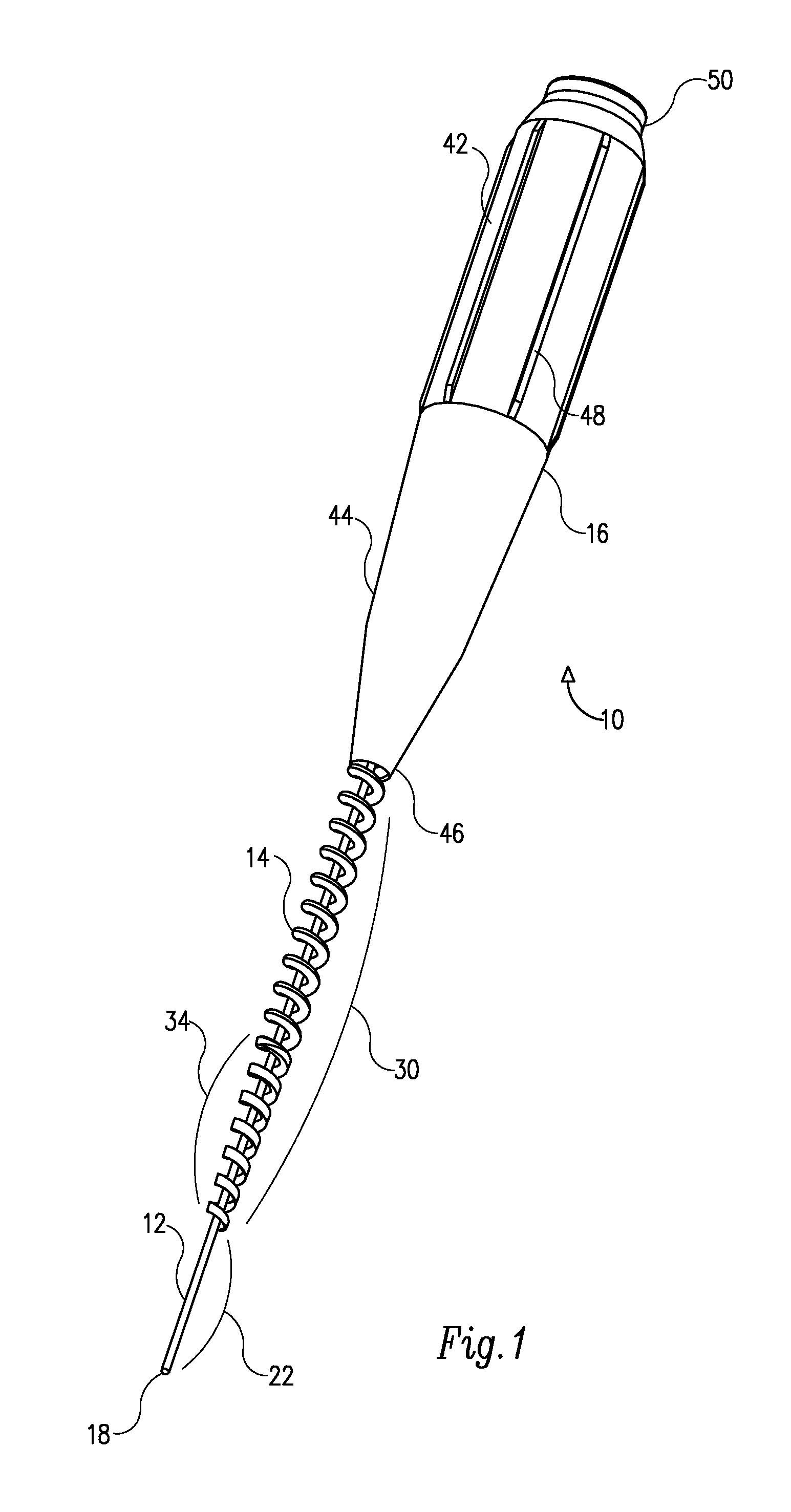
Rotary endodontic file with frictional grip
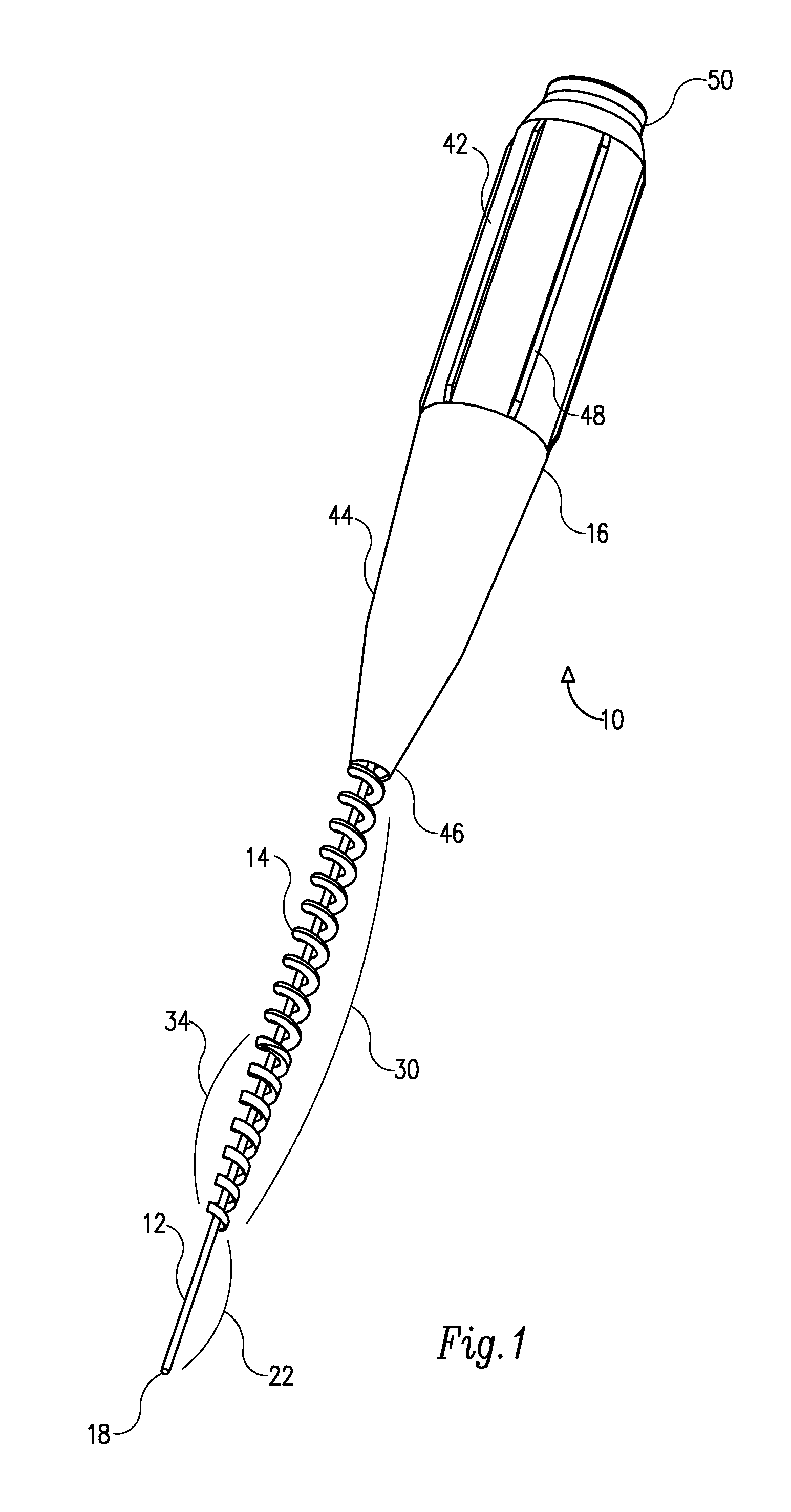
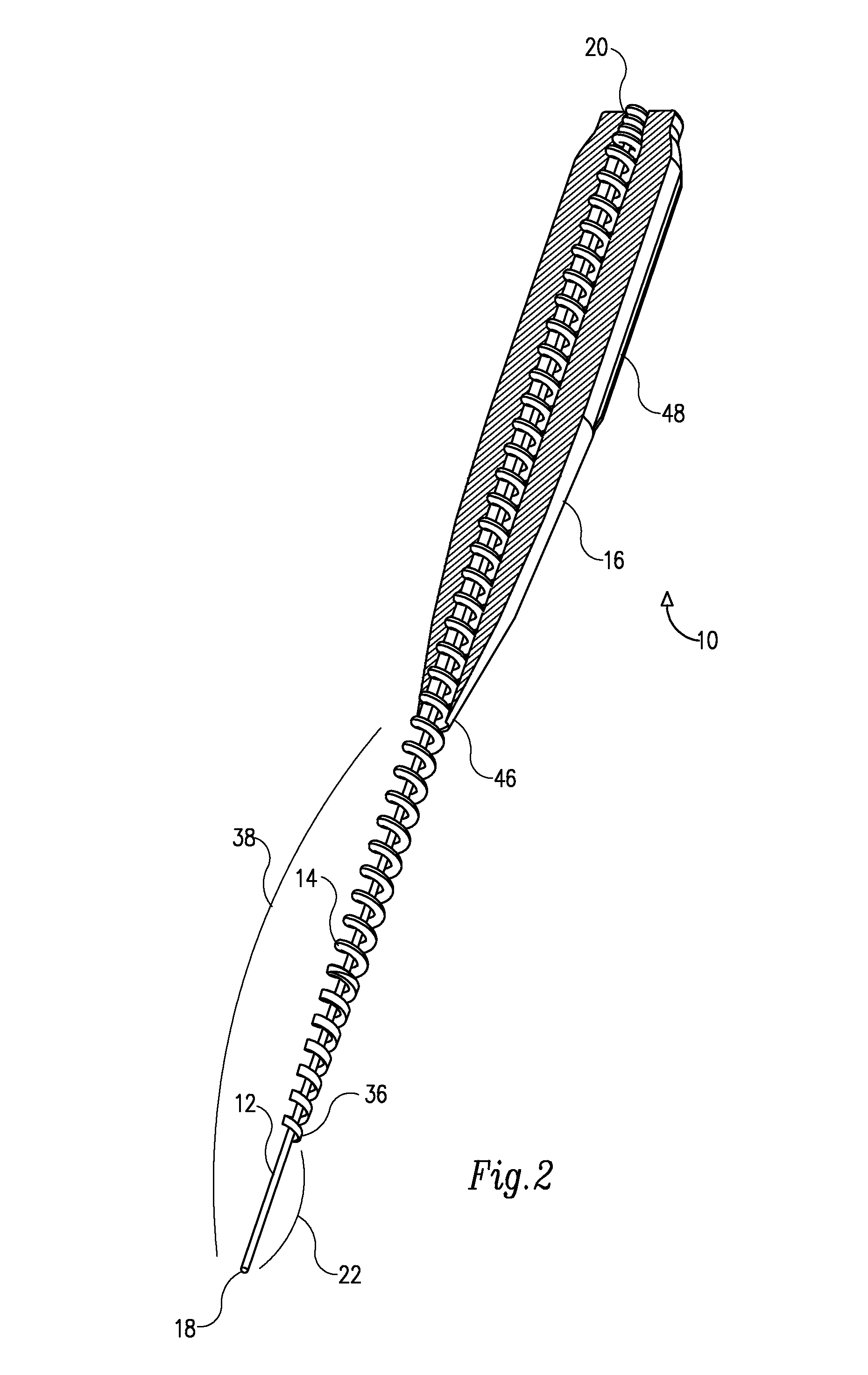
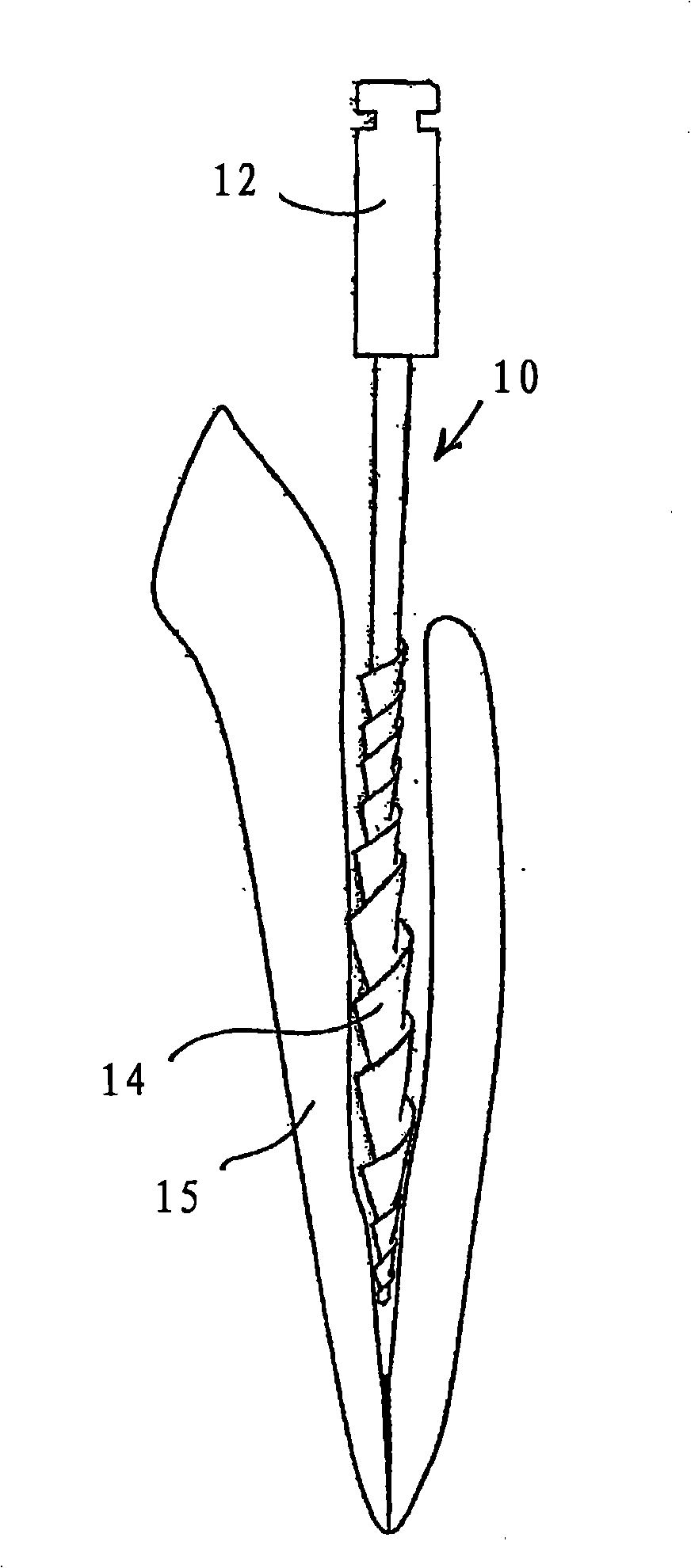
An endodontic file has at least a central longitudinal cord, a helically wound wire at least partially surrounding the cord and an elastomeric grip partially covering the helically wound wire near a first end thereof. The elastomeric grip has an outer diameter that is slightly wider than an internal diameter of a barrel of a dental instrument whereby on insertion into the barrel it is supported therein only by friction.
Owner:MDT MICRO DIAMOND TECH LTD
Endodontic files having variable helical angle flutes
ActiveUS7270541B1Reduce feed rateSmall surface areaTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsFluteRotational axis
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Endodontic instrument having notched cutting surfaces
InactiveUS6966774B2Trend downQuickly and economically manufacturedTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsFile designEndodontic files
A fluteless endodontic file is provided, formed from a tapered shaft of material having a prismatic shape generally defined by three or more side surfaces and three or more interposed corners. A plurality of notches are cut into one or more corners defining cutting surfaces, points and / or edges. The notched cutting surfaces are formed such that the file, when rotated and / or reciprocated within a root canal, effectively cuts / debrides hard tissue (known in the art as dentin) as well as soft tissue, thus, forming an optimal canal shape. The cutting surfaces are also preferably formed at an angle to the centerline of the instrument to provide optimal cutting efficiency and material removal. The fluteless file design exhibits increased efficacy, with less tendency to bind and break within the root canal and also significantly reduces manufacturing and capital equipment costs.
Owner:CLOUDLAND INST
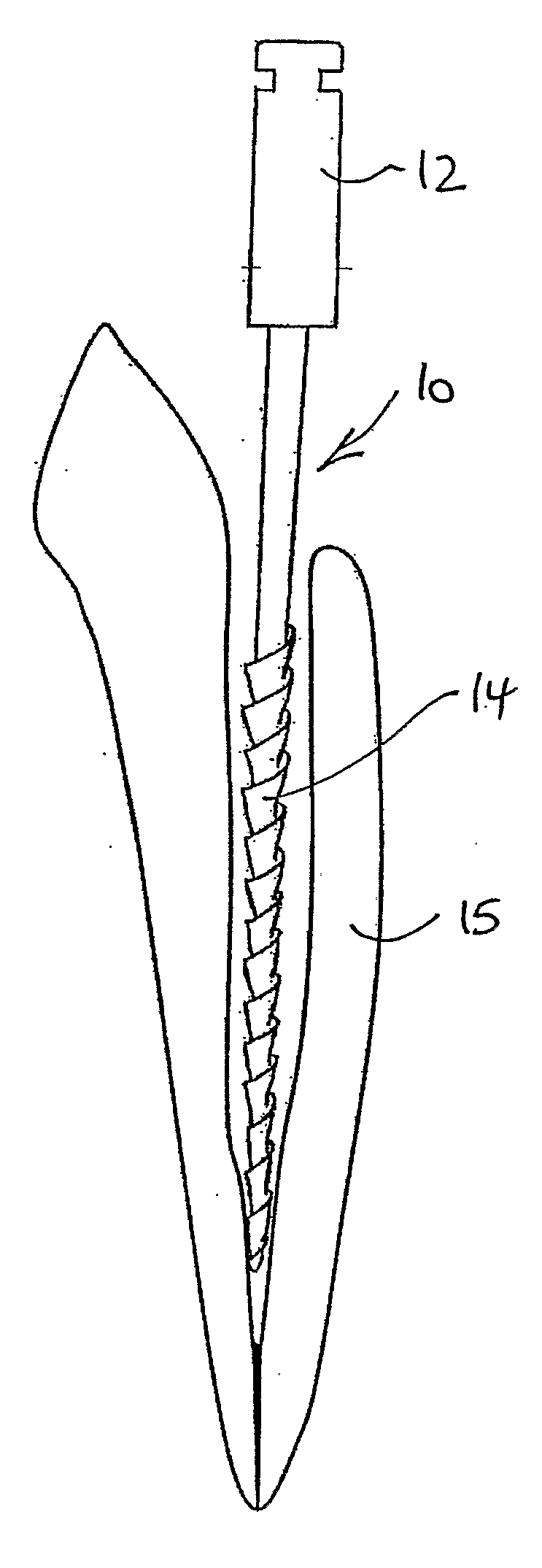
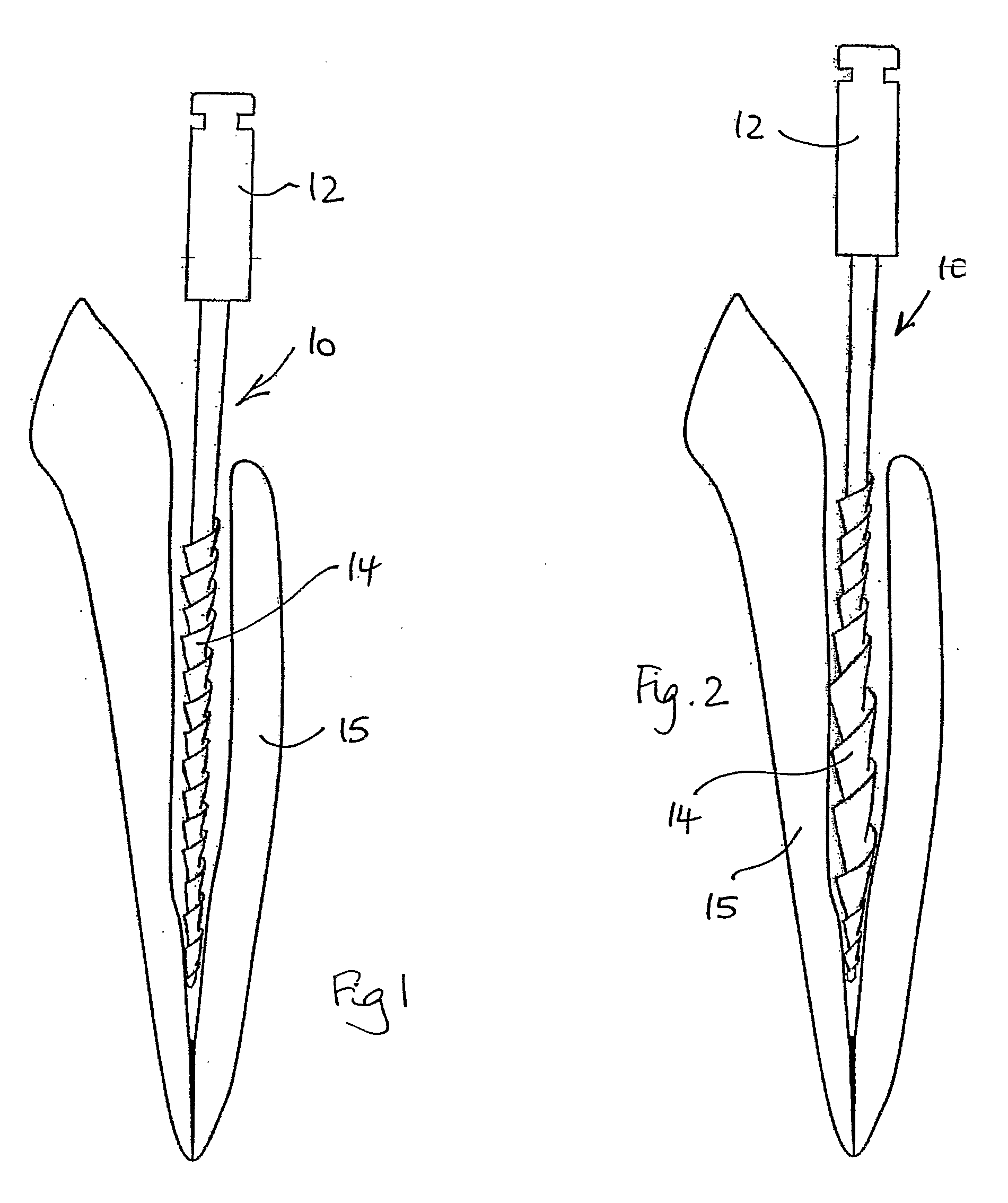
Endodontic file and method
An endodontic file comprising a conductive shank, and a generally non-conductive portion circumscribing the conductive shank and longitudinally extending along the conductive shank. A method for conducting an endodontic procedure comprising providing an endodontic file assembly having a conductive shank electrically engaged to an electronic device for furnishing current to the conductive shank. A generally non-conductive portion circumscribes the conductive shank. The conductive shank including the non-conductive portion passes into a root canal of a tooth for conducting an endodontic procedure.
Owner:AHANI HESSAM
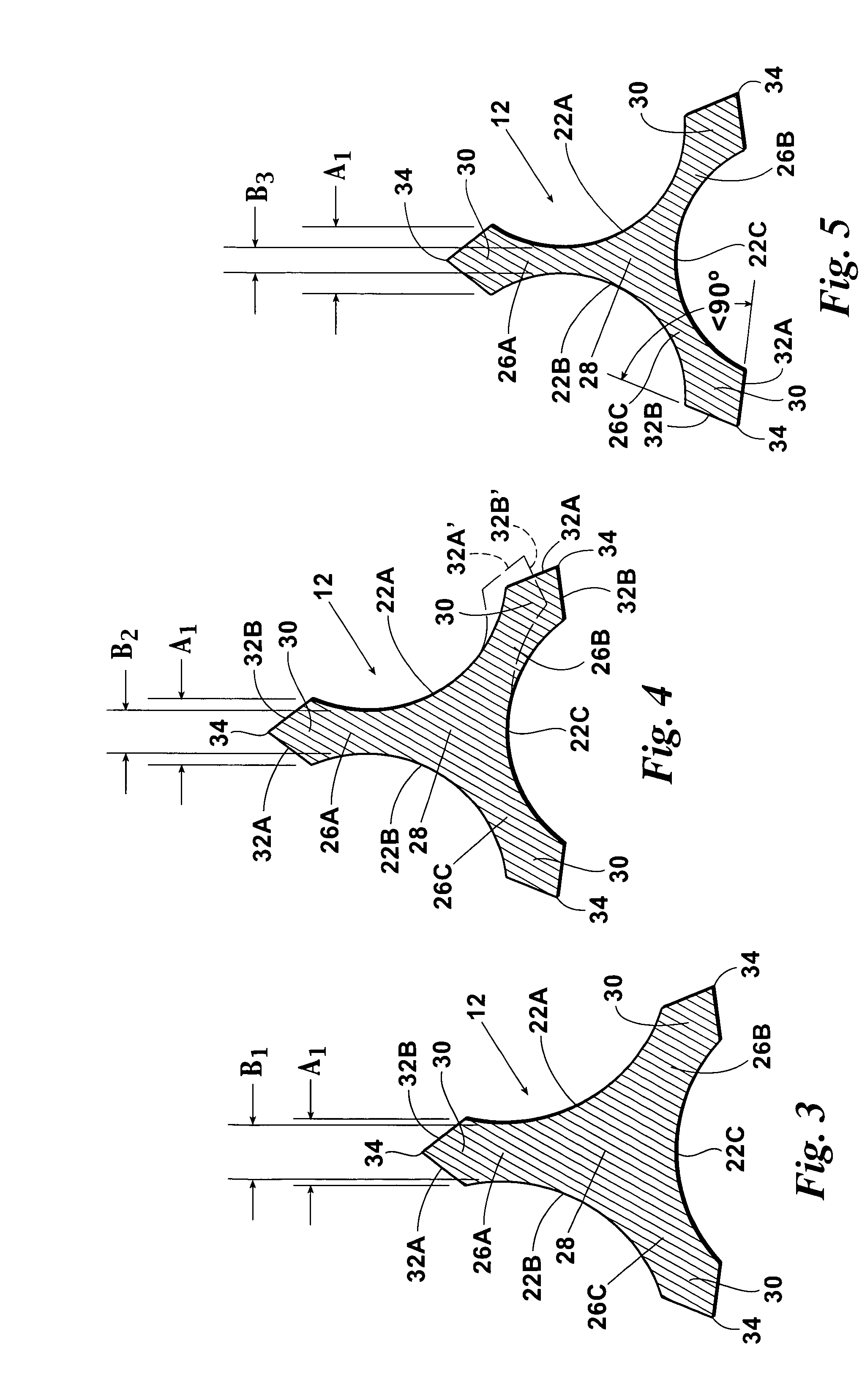
Endodontic files having improved lateral and torsional flexibility
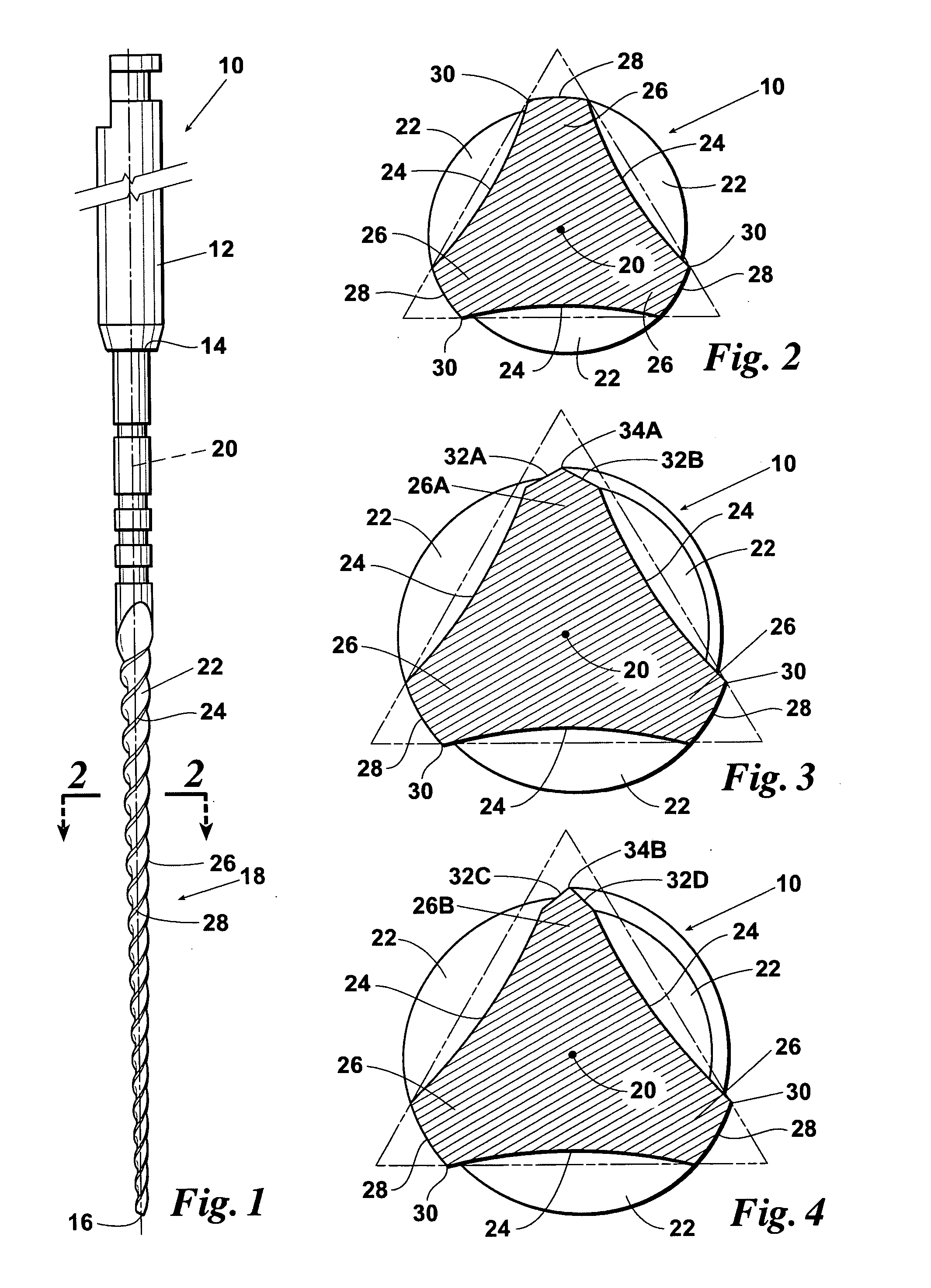
InactiveUS20060246394A1Reduce widthIncrease flexibilityTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsFluteEndodontic files
A dental reamer / file instrument having an elongated shank having a proximal end portion, a distal end and an intermediate tapered working portion, the external surface of the shank working portion having three continuous equally spaced helical flutes forming three spiral flanges, each of which, in a plane perpendicular to the length of the shaft is defined in part by a triangular outer working portion having a base width of “A”, an apex of each triangular outer portion forming a cutting / scraping edge, each triangular outer working portion being integrally connected to the central core portion by a reduced width neck portion of width “B” and wherein “A” is greater than “B”, the triangular outer working portions being rotational flexibility within elastic limits relative to the shaft central core portion.
Owner:CANTATORE GIUSEPPE +2
System for endodontic treatment
ActiveUS20120122055A1Reduce material fatigueEasy to controlTeeth cappingBoring toolsEndodontic therapyEndodontic files
Provided is a system for endodontic treatment of a root canal. The system includes a handpiece containing a rotary motor adapted to rotate an endodontic file secured by the handpiece. A control unit executes a regime of motion of the motor to produce a regime of file motion in which episodes of oscillation of the file are separated by a rotation of the file. When the arc of a rotation is less than the arc of the oscillation that preceded the rotation, the arcs of the episodes of oscillation overlap and the formation of ridges in the root canal is avoided.
Owner:FORUM ENG TECH 96
Multi-planar pre-curved rotary endodontic file
ActiveUS9078722B2Reduce torqueEffective maintenanceTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsEndodontic filesComputer science
An improved rotary endodontic file includes a multi-planar pre-curved apical portion having a first and a second curvature. The pre-curved apical portion begins at about one-third to one-quarter of the working length as measured from the tip end of the endodontic instrument. The first and second curvature permit the file to continually search and engage the walls of a tooth root canal in a forced inside-forced outside manner. As the file works its way down, it breaks free of any ledges encountered, probes lateral- and delta-type openings, and does not allow the file to stray from the curvature of the canal.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Rotary endodontic file with frictional grip
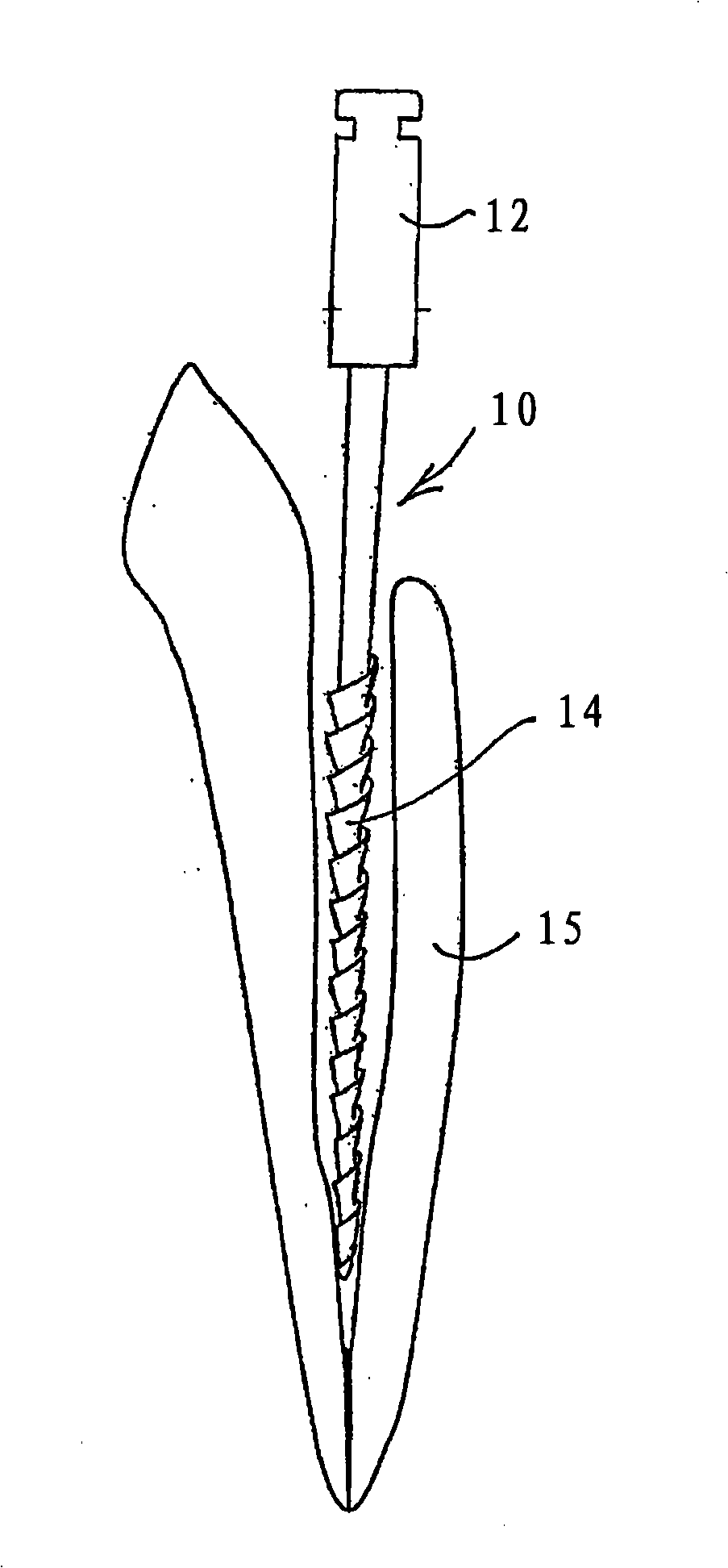
An endodontic file (10) has at least a central longitudinal cord (12), a helically wound wire (14) at least partially surrounding the cord and an elastomeric grip (16) partially covering the helically wound wire near a first end thereof and having an outer diameter that is slightly wider than an internal diameter of a barrel of a dental instrument whereby on insertion into the barrel it is supported therein only by friction.
Owner:MDT MICRO DIAMOND TECH LTD
Dental apparatus for shaping and cleaning a root canal
Apparatus is disclosed for use in cleaning dental root canals using an endodontic file. The file is mounted in a drill head driven by an electric motor. The motor is normally driven in one, forward direction, but periodically, the motor rotation is reversed for a very short time. The duration of the motor reversal is so short that although the motor rotates in the reverse direction, the inertia and backlash in the transmission between the motor output shaft and the drill head is such that the direction of rotation of the file in the root canal is not changed.
Owner:MICRO MEGA INT MFG SA
Reciprocal reverse rotation endodontic file
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
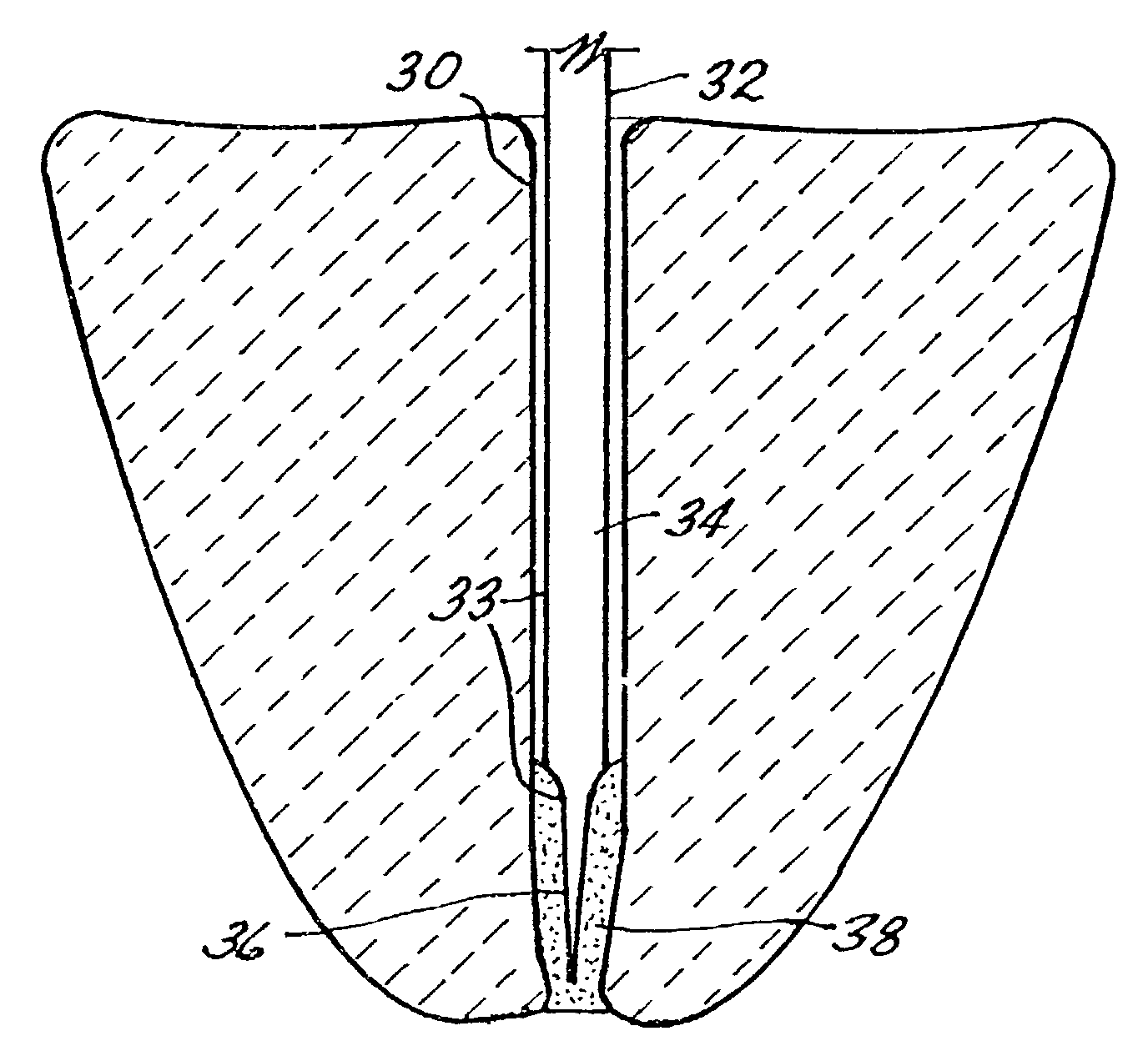
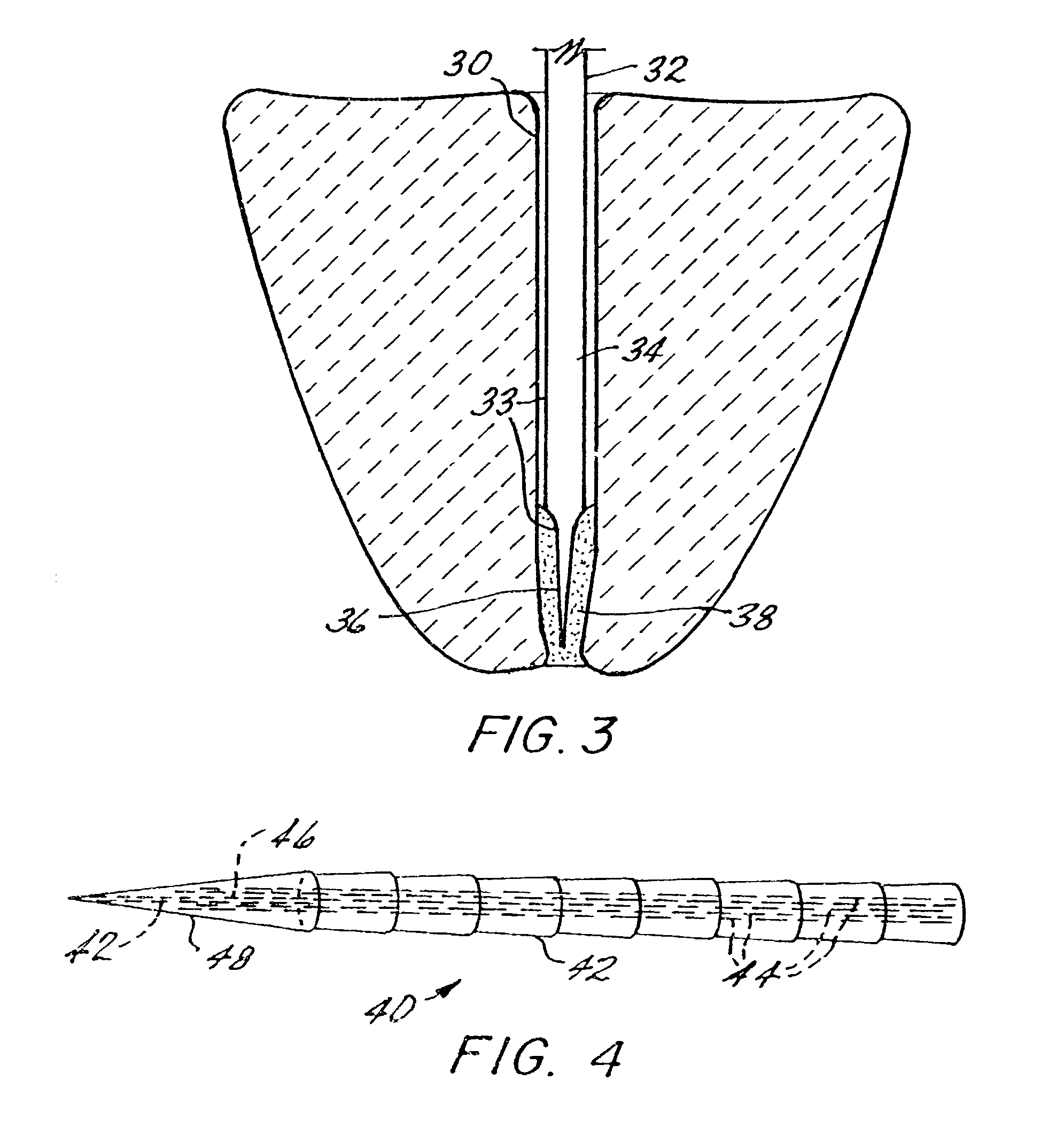
Endodontic File
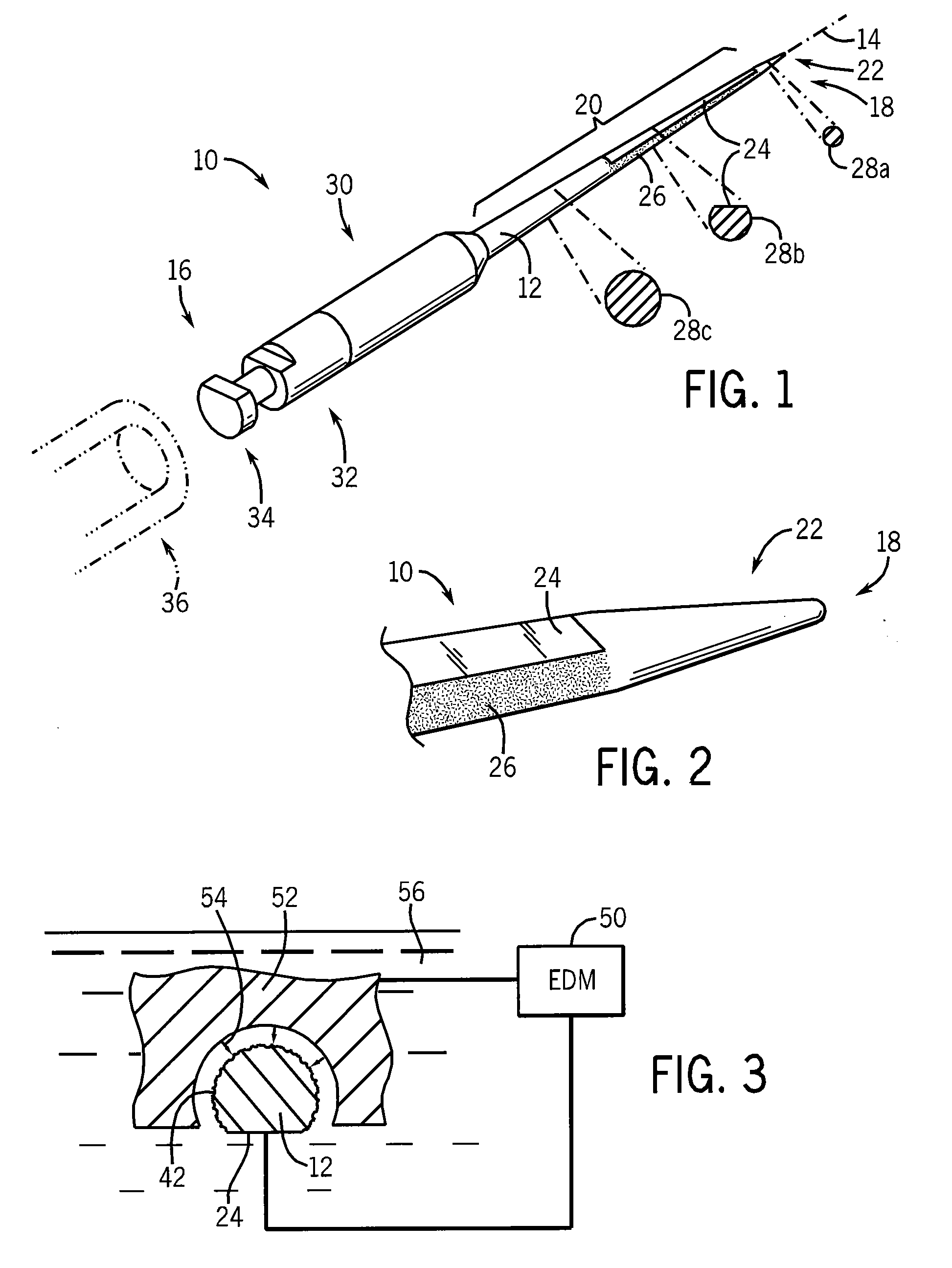
An endodontic instrument eliminates the need for conventional flutes by employing a tapered tip having an axially extending relief surface such as a flat permitting the passage of liquid and the ejection of debris from the tooth. In one embodiment, an abrasive surface of the tapered tip is produced by electrical discharge machining which provides randomly arrayed microscopic pits directly in the metallic surface of the instrument.
Owner:PLASTIC DENTAL CORP
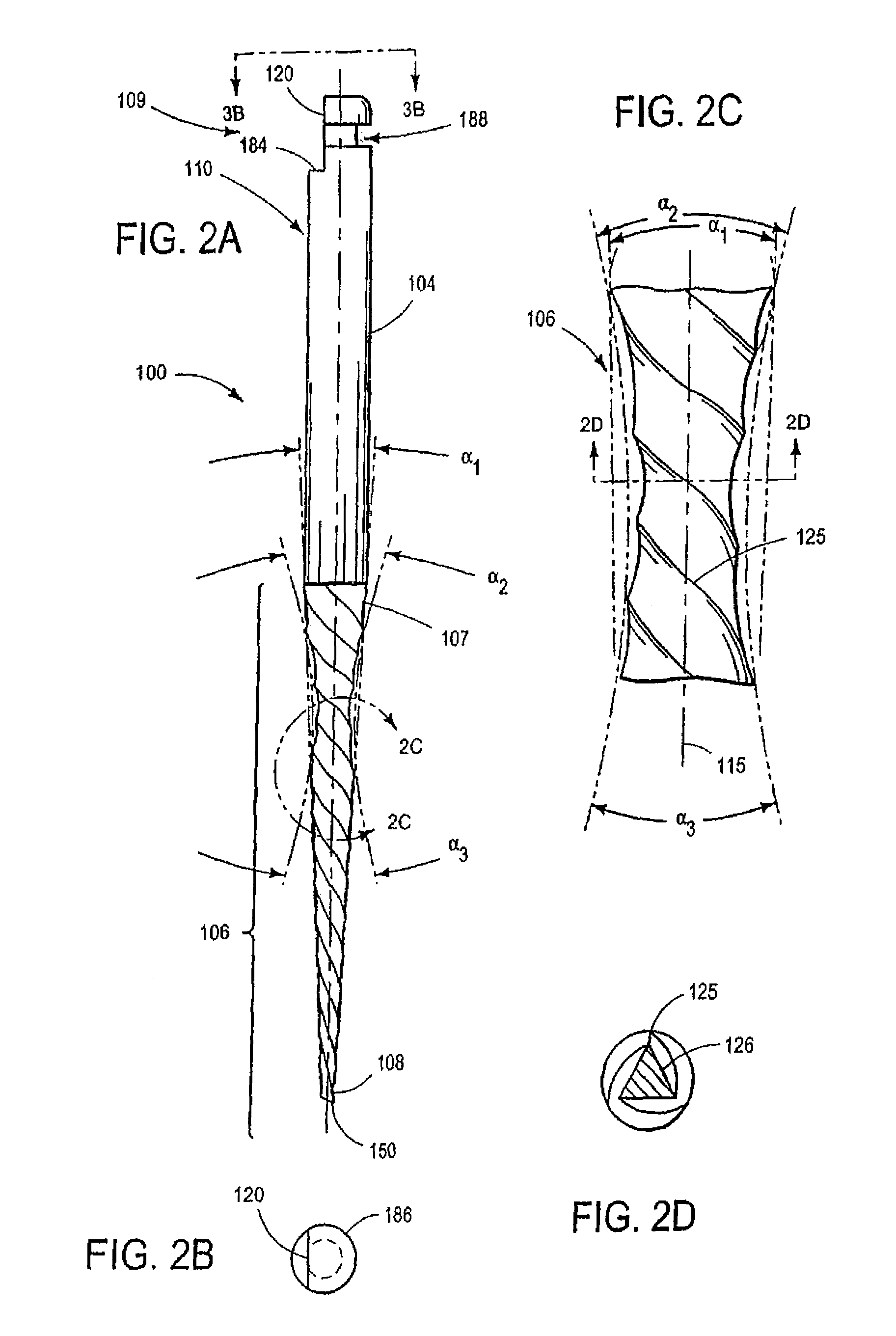
Endodontic files having variable helical angle flutes
ActiveUS20070207438A1Reduce feed rateSmall surface areaTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsFluteRotational axis
A rotatable endodontic file for cleaning / shaping a tooth root canal, comprising an elongated shaft having a proximal end portion, a distal end and a tapered working portion having a rotational axis, the working portion extending from the proximal portion to the distal end, the external surface of the shaft working portion having a plurality of at least two spiraled, spaced apart continuous helical flutes, the flutes having therebetween an equal number of spiraled, spaced apart flanges, each flange having in a plane perpendicular the rotational axis an outer end surface forming a continuous spiraled scraping / cutting edge extending the length of the shaft working portion, the flutes having helical angles relative to the rotational axis of between 10° and 30° and wherein the helical angles vary at selected longitudinal locations.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Precision cast dental instrument
InactiveUS7677296B2Resistance to breakageResistance to wearTransportation and packagingWristbandsInstrumentationPrecision casting
An endodontic file (200) is provided particularly adapted for the removal of tooth structure, decayed or damaged nerve tissues or dentine material on the interior walls of a root canal or dentine and / or enamel from the external tooth wall. The endodontic instrument includes a shaft (202) having a shank portion (204) and a generally elongated working portion (206). The working portion preferably includes cutting or abrading features (232) adapted upon rotation and / or reciprocation of the instrument to cut, abrade or remove tissue from the interior walls of a root canal or dentine and / or enamel from the external tooth wall. The working portion extends from a proximal end (207) adjacent the shank portion to a distal end (208) terminating at a tip (250). The entire instrument and / or at least the working portion thereof is formed of an amorphous or essentially amorphous material having no or essentially no detectable crystalline structure and / or from a nanocrystalline material having an average crystalline grain size less than about 1 μm. The instrument may be formed by conventional grinding operations or by direct casting, forging or molding, in a manner producing an integral as-molded instrument having one or more sharp cutting edges. The instrument is inexpensive to manufacture and exhibits improved cutting-edge sharpness, wear resistance, lubriciousness and resistance to breakage.
Owner:CLOUDLAND INST
Endodontic post system
InactiveUS7086864B2Strengthen toothPrevent subsequent root fracturesTeeth fillingFastening prosthesisGutta-perchaEndodontic files
An endodontic post comprising a combined endodontic post and filling material tip in a single unit. To use the post unit, the device is placed in an oven or heater to heat and soften the thermoplastic material. The device will then be placed in a root canal that has been opened to a predetermined dimension by use of endodontic files, to seal the apical end. If necessary, the gutta percha can be compacted toward the apex, while it is still in the softened state, to ensure the apex is adequately sealed. The post is then cemented into place by lining the canal walls with a bonding agent and filling the interface between the post and the walls of the canal with a dual cure resin cement. This will result in a coronal seal of the canal via resin restorative material and an apical seal of the canal by means of gutta percha and sealant. The remaining portion of the post, extending supra-gingivally, will be used to build a core around it. Any excess will be cut off. One length of the device will be longer to accommodate the longer roots in anterior teeth. Another length will be shorter to accommodate smaller roots in the molar region.
Owner:PENTRON CLINICAL TECH
Dental apparatus for shaping and cleaning a root canal
Apparatus is disclosed for use in cleaning dental root canals using an endodontic file. The file is mounted in a drill head driven by an electric motor. The motor is normally driven in one, forward direction but periodically the motor rotation is reversed for a very short time. The duration of the motor reversal is so short that although the motor rotates in the reverse direction, the inertia and backlash in the transmission between the motor output shaft and the drill head is such that the direction of rotation of the file in the root canal is not changed.
Owner:MICRO MEGA INT MFG SA
Endododontic file with multi-tapered flutes
ActiveUS7731498B2Reduce torque loadTrend downTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsFluteEndodontic files
Owner:MAILLEFER INSTR HLDG
Endodontic file with a metallic conductor as part of the plastic handle to facilitate use of electronic apex locators
InactiveUS6872075B2Prevent short-circuitingEasy accessDental toolsTeeth cappingEndodontic filesElectrical conductor
This invention modifies hand root canal files used in dentistry by placing metallic contact areas on the plastic handle. This change makes using electronic apex locators to determine the length of the root canal much faster and easier.
Owner:REGAN JOHN EDWARD
Dental handpiece
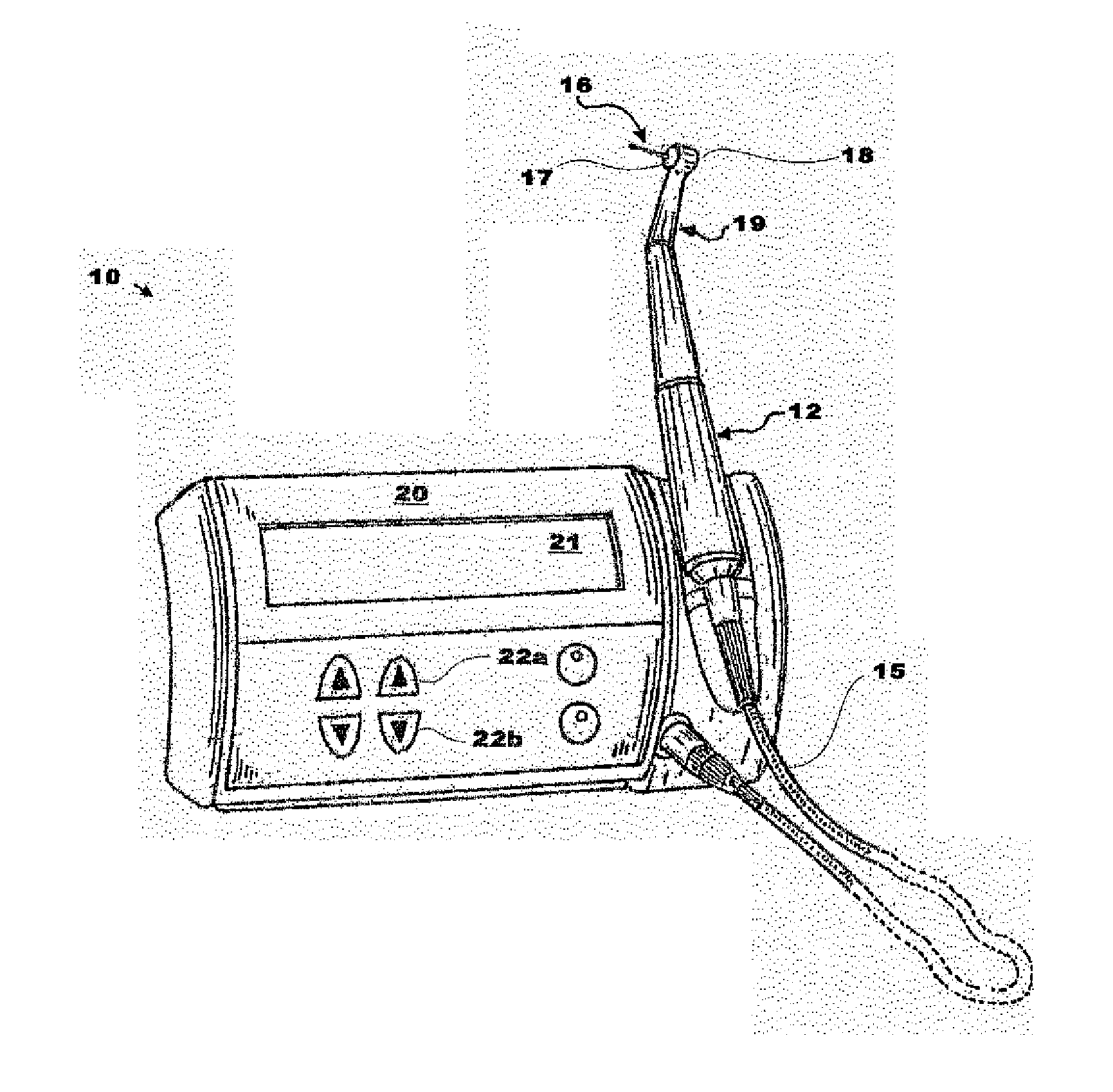
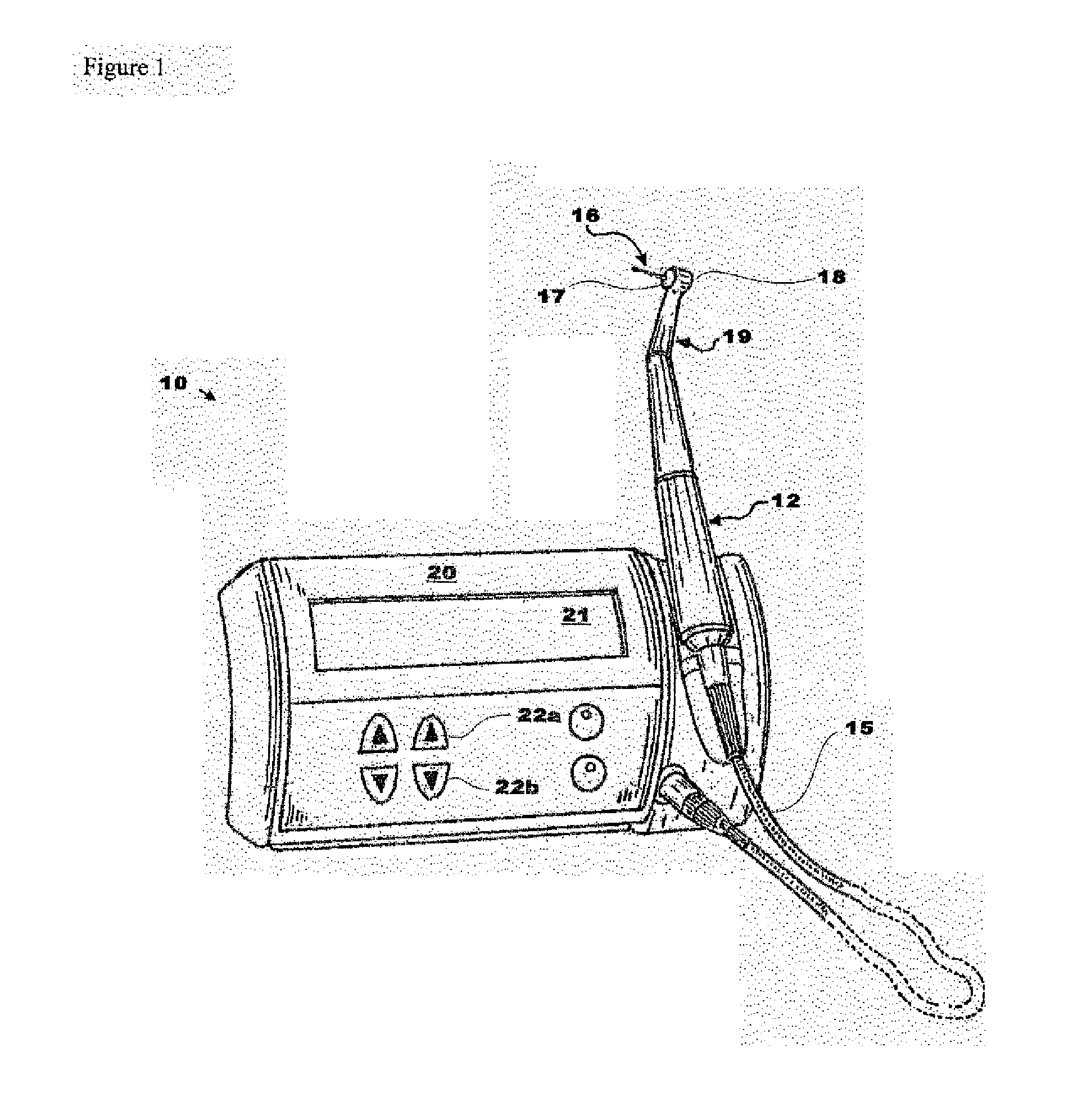
ActiveUS20150342702A1Risk minimizationCompact and lightweightDental toolsNerve needlesData streamEndodontic files
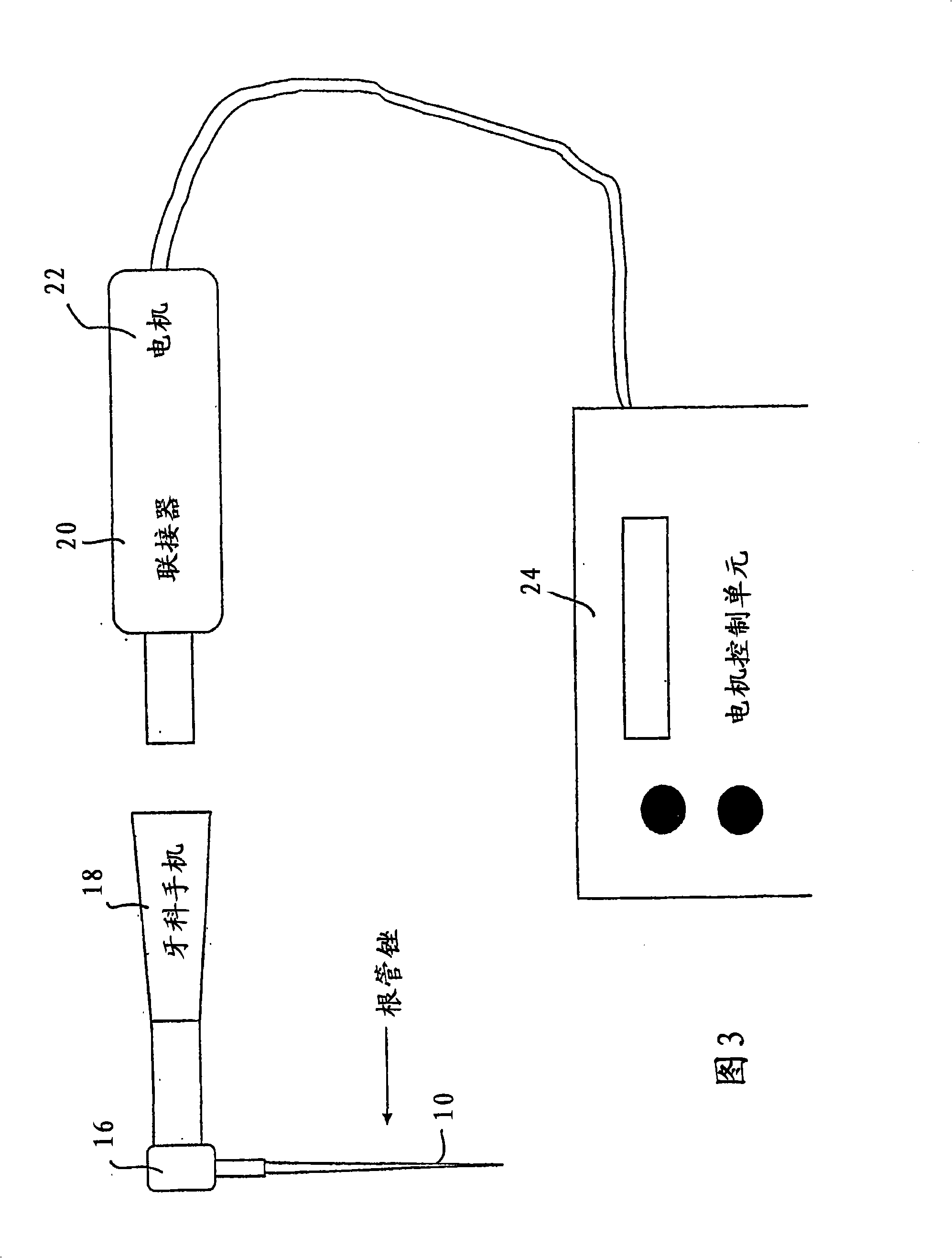
Described herein is a dental handpiece for the endodontic treatment of a root canal, including a chuck for attaching and holding an endodontic file, an electric motor having a shaft for driving the endodontic file, and a control unit for controlling the motor, which receives a stream of input data. While monitoring the stream of input data, the control unit determines the current absorbed by the electric motor, and controls the motor so that the file alternates the direction of rotation at a frequency of from 1 to 20 Hz between a first direction and a second direction opposite to the first direction, and whereby the control unit controls the electric motor so that the file continuously rotates in the second direction when the monitored data fulfils a predetermined torque threshold condition during rotation in the first direction.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Self Adjusting Instrument
ActiveUS20090130638A1Easy to cleanGreat dimensionDental toolsTeeth cappingEndodontic filesRoot canal procedure
The invention is an instrument for cleaning and / or shaping and / or widening a channel that exists in or through a solid object. The design of the instrument the superelastic and shape memory properties of the material from which it is made, allow the inner volume enclosed by the instrument, its outer contour, or both to change as a result of the forces exerted upon it while working, thereby shaping the instrument to the three-dimensional contour of the channel. A preferred embodiment of the instrument is an endodontic file for use in the cleaning, shaping, and widening stages of a root canal procedure.
Owner:REDENT NOVA LTD
Endodontic file having an outer spiral cord
ActiveUS20140329199A1Easy to prepareIncrease flexibilityTeeth cappingBoring toolsEndodontic filesEngineering
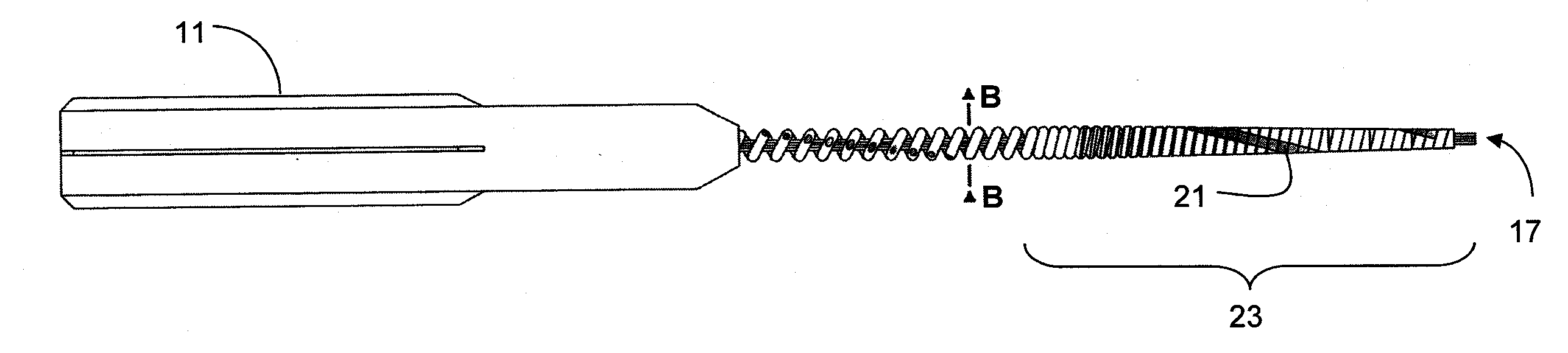
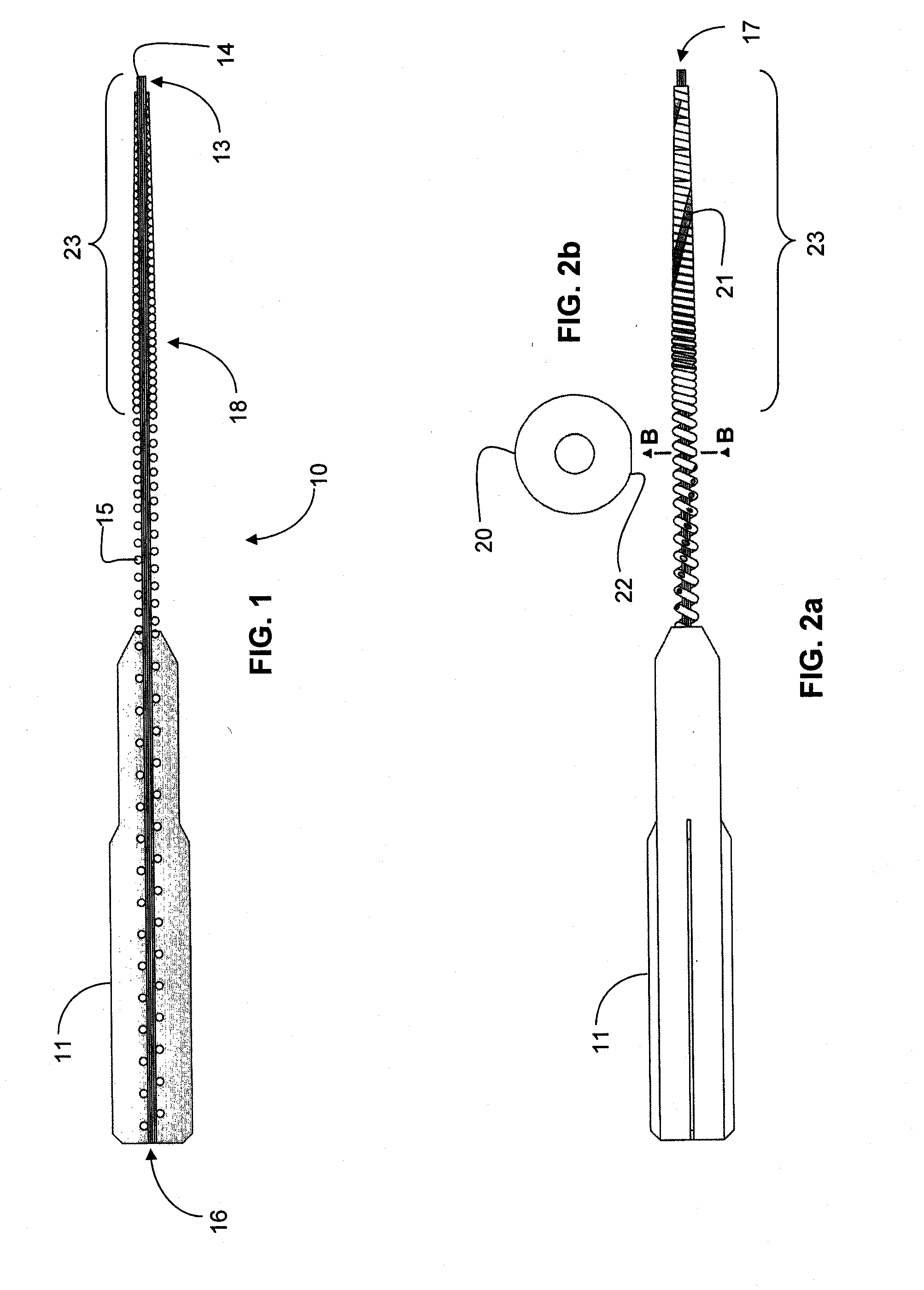
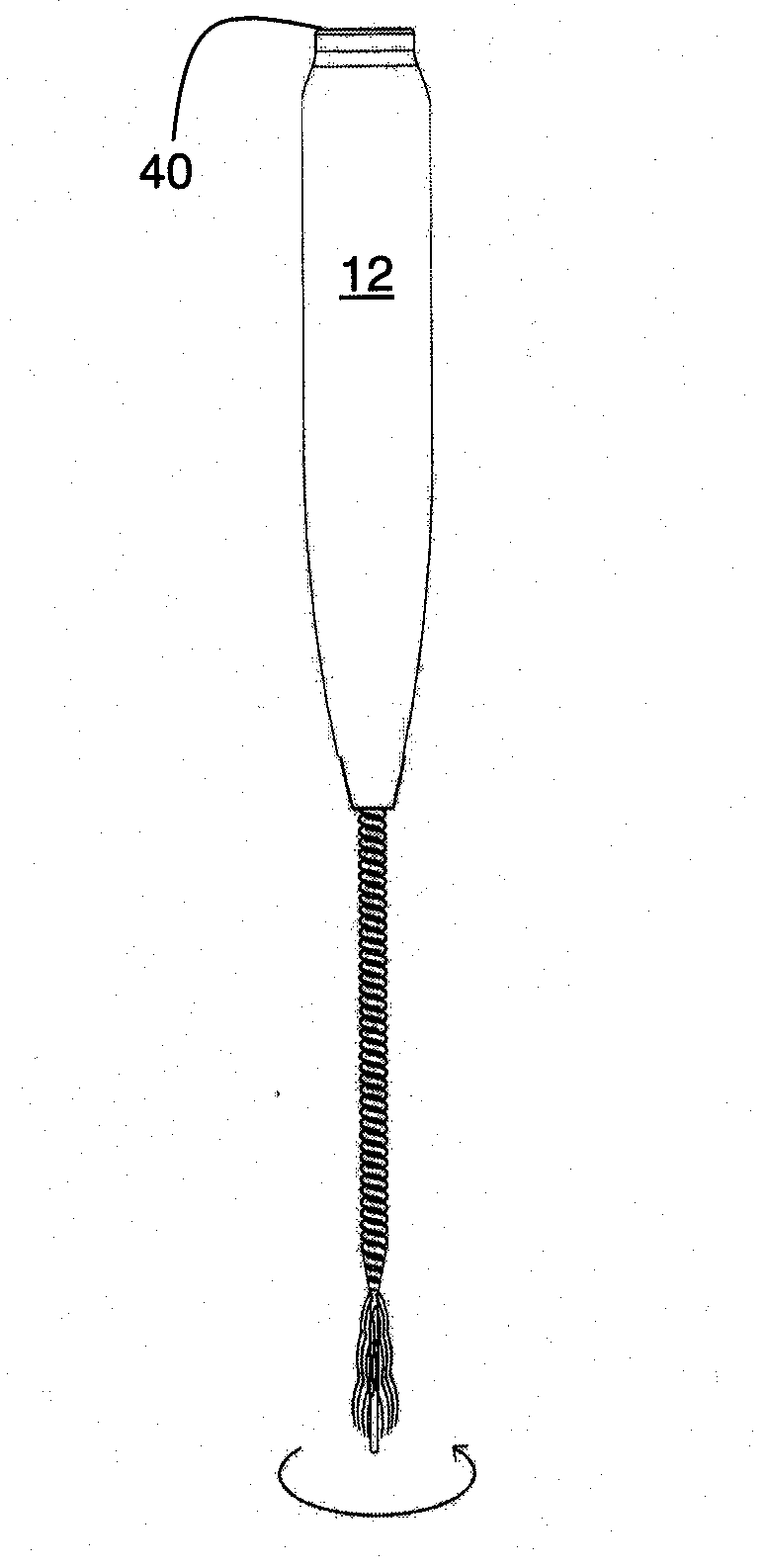
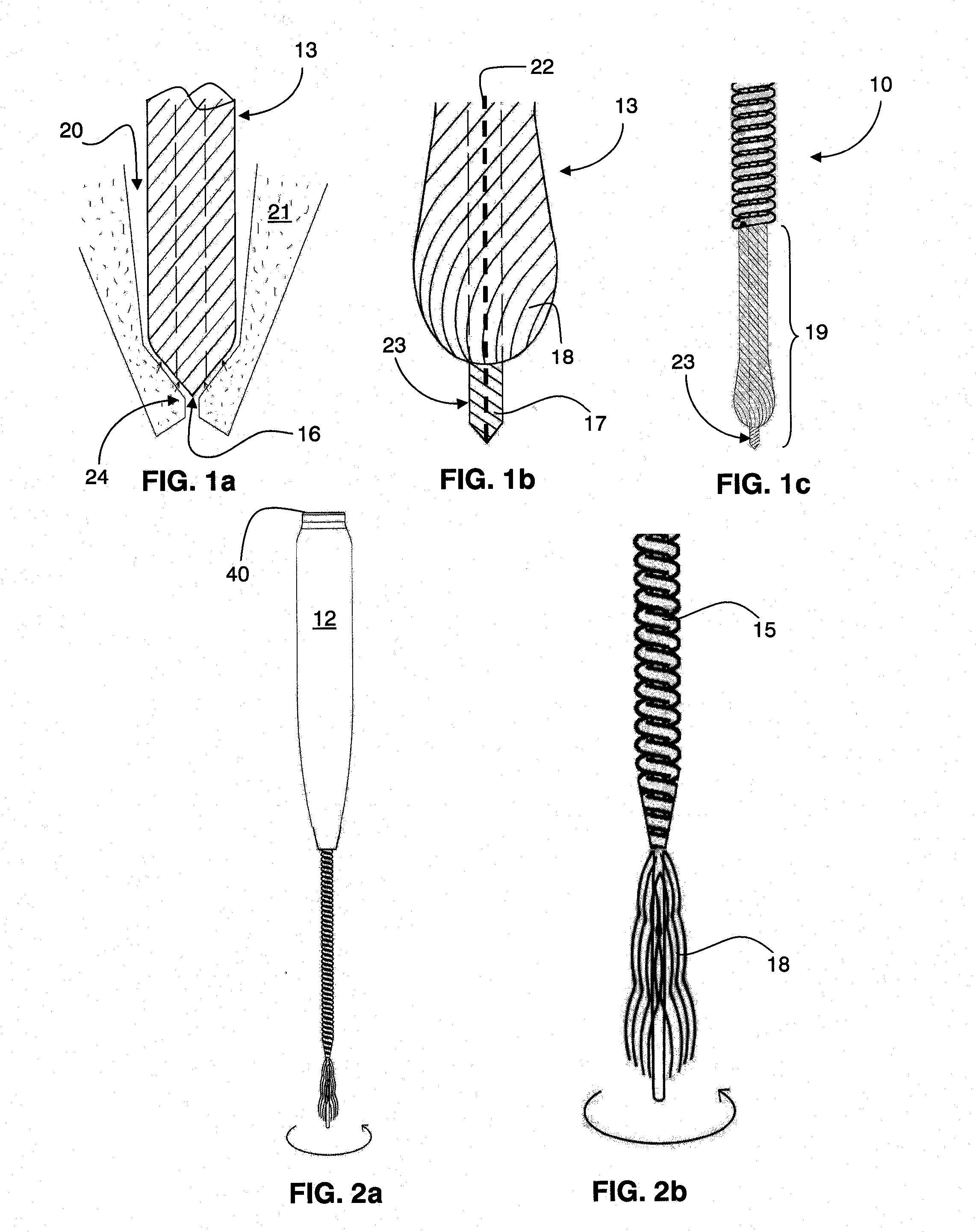
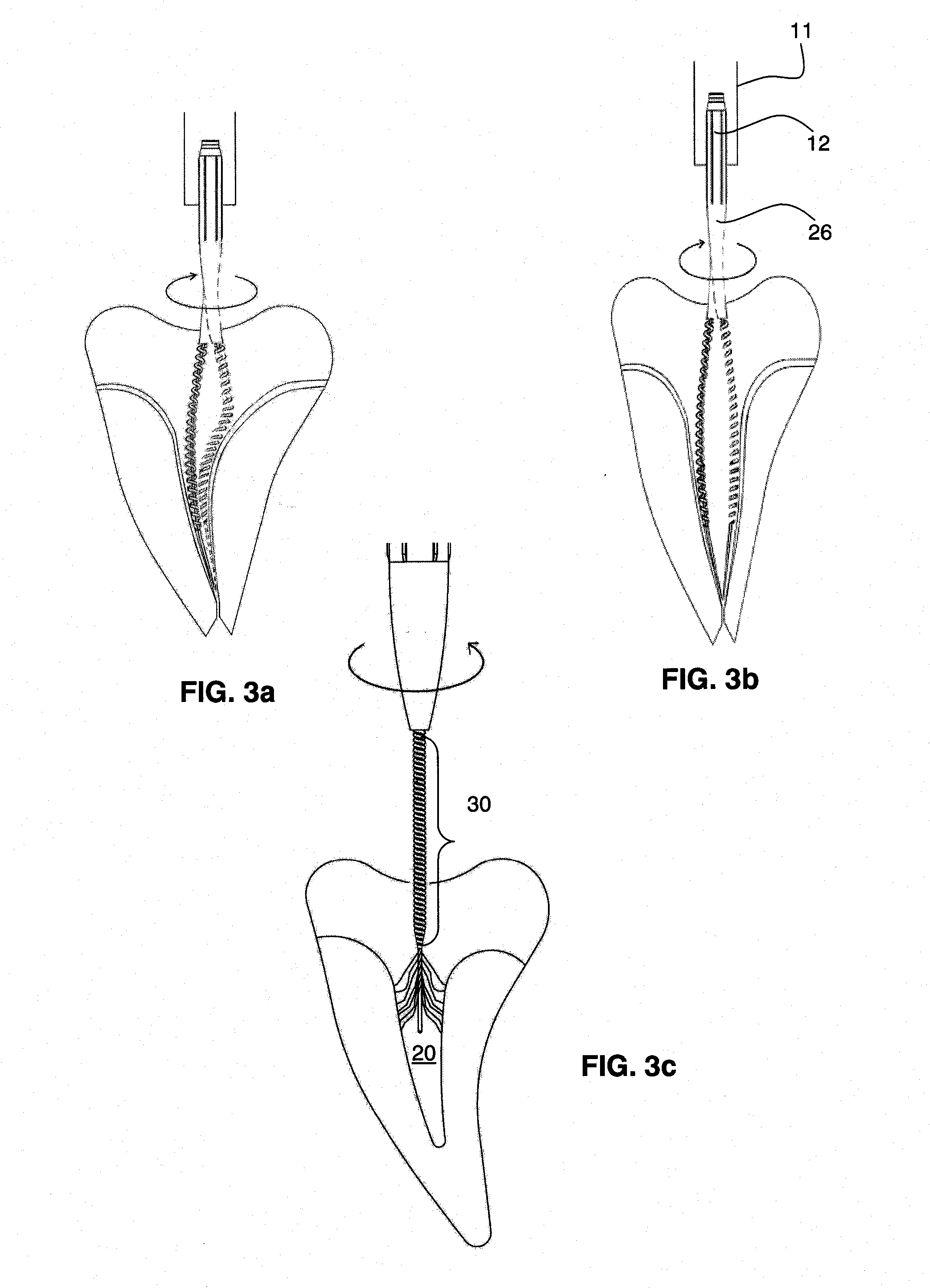
An endodontic file (10) has a handle (11) and a spiral cord (15) of helically wound metallic wire wound in a predetermined direction around a central metallic cord (13) formed between opposite ends of the central cord so as to form an integrated structure (18) of generally conical cross-section including a narrow tip end (17) and an opposite wider upper end (16) supported at the upper end by the handle. A flexible conical reinforcement (26, 31) supported by the handle covers an outermost layer of an upper portion of the spiral cord remote from the tip end, its lower end being of sufficiently low diameter to enter the root canal and dimensioned at its upper end to limit bending of the upper portion. An outer surface (20) of the spiral cord is configured for removing material from inside the root canal when the endodontic file is rotated in the predetermined direction.
Owner:MDT MICRO DIAMOND TECH LTD
Root canal length measurement device
InactiveUS20120088207A1Minimal interferenceTeeth fillingTeeth cappingEndodontic filesMeasurement device
A root canal length measurement device configured for detachable support on a neck of a dental handpiece and having a generally cylindrical electrical contact element that, in use, is resiliently biased by a spring toward an endodontic file rotatably mounted in the handpiece so that a flat surface of the contact element maintains a steady electrical connection with a shank portion of the endodontic file proximate its point of attachment to the handpiece.
Owner:MEDIC NRG
Endodontic file
An endodontic file for a motorized rotary handpiece includes a coupler element for coupling to the handpiece, a central longitudinal flexible core including a central flexible cable supported by the coupler element, and a helical wire surrounding the core and extending toward a tip of the core opposite the handle end. The flexible core includes a first plurality of inner strands twisted together in a first direction and surrounded by a second plurality of outer strands twisted in an opposite direction. The tip of the core is chamfered and unbonded and protrudes beyond the helical wire at the tip whereby in use reversing a direction of rotation of the endodontic file after the tip of the core reaches the apex of the root canal, unwinds the outer strands, which operate as a brush during removal of the endodontic file from the root canal.
Owner:MDT MICRO DIAMOND TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com