Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110 results about "Dystrophy fuchs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fuchs’ dystrophy is a type of eye disease that affects the cornea. Your cornea is the dome-shaped outer layer of your eye that helps you see.
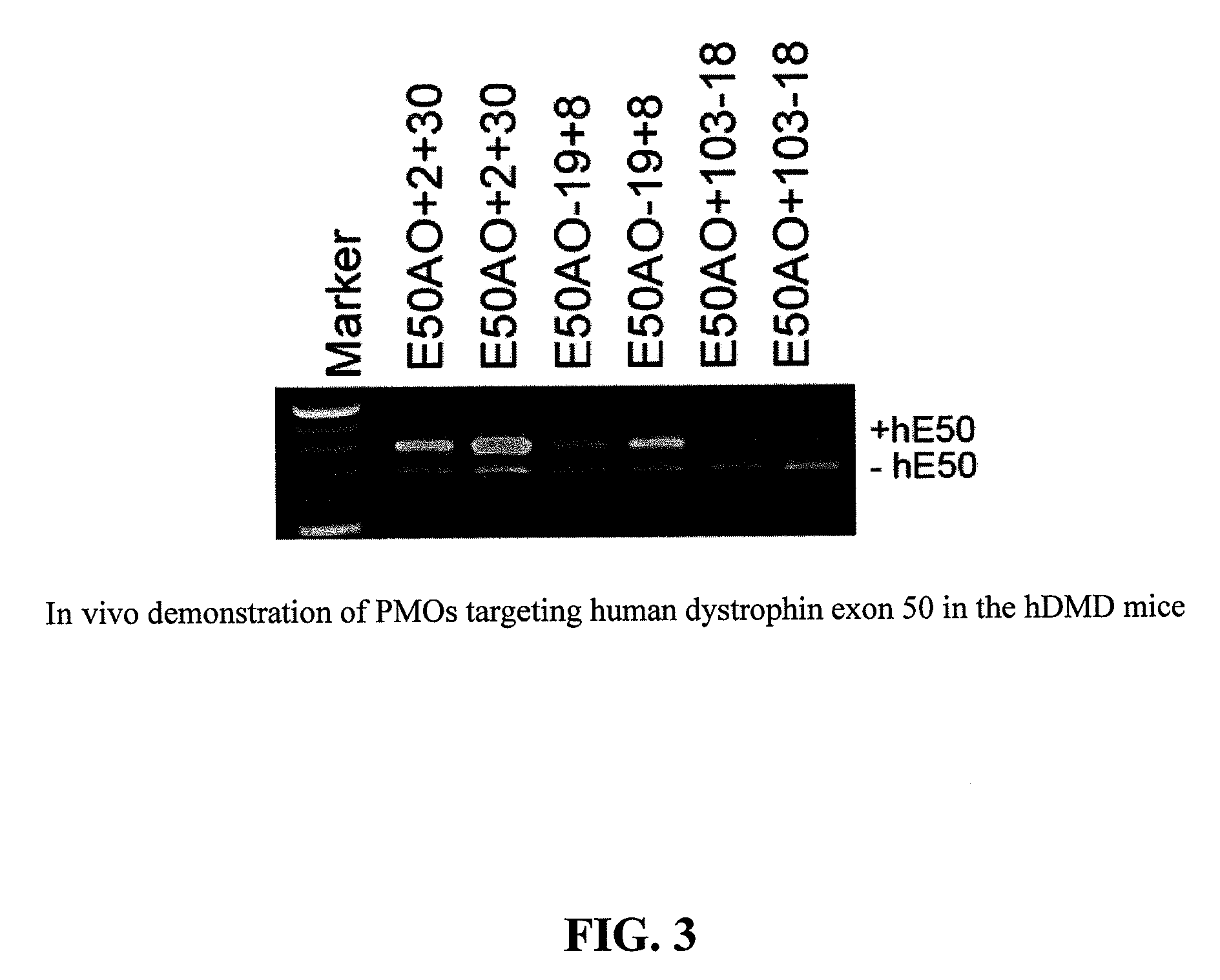
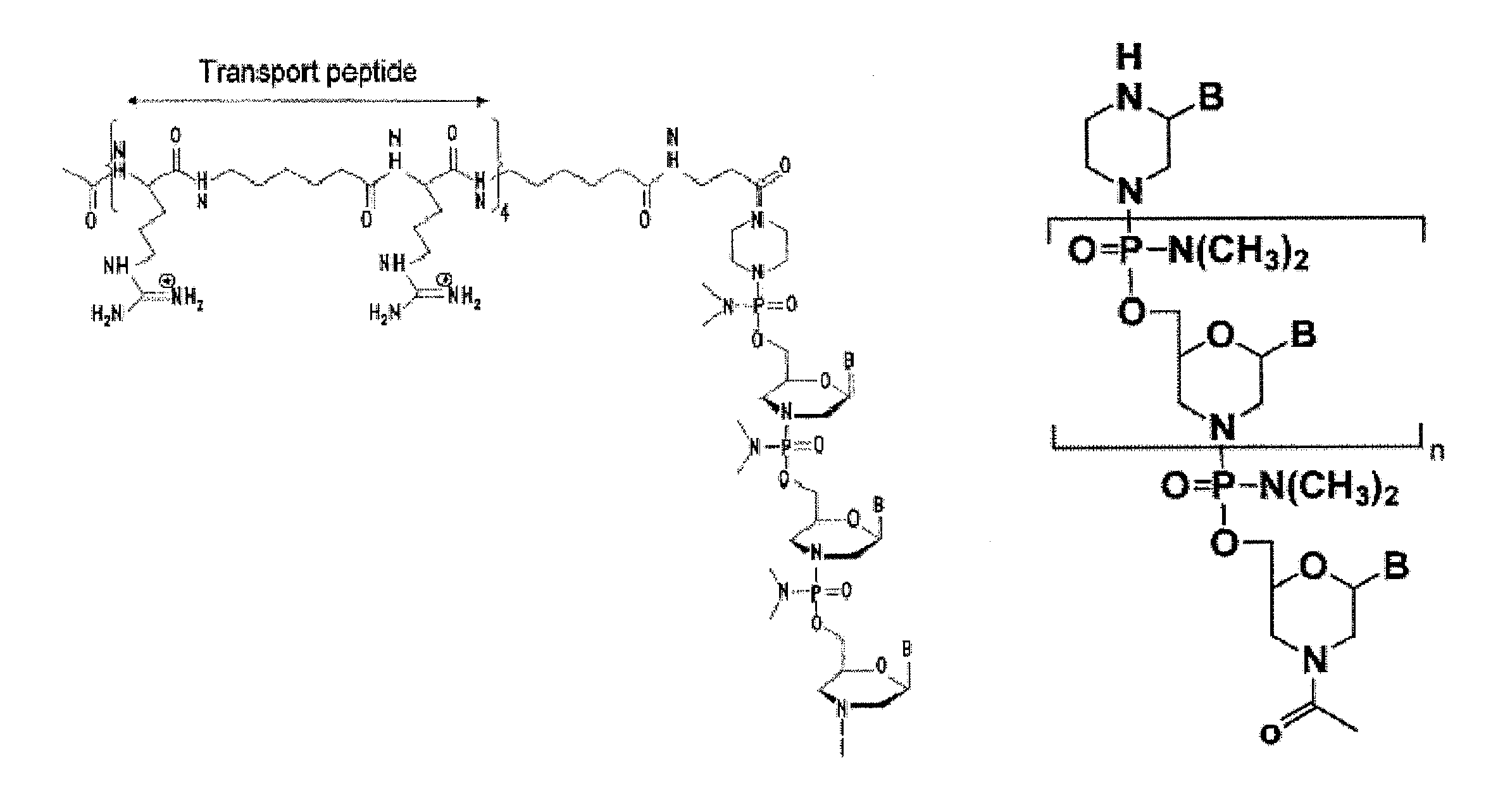
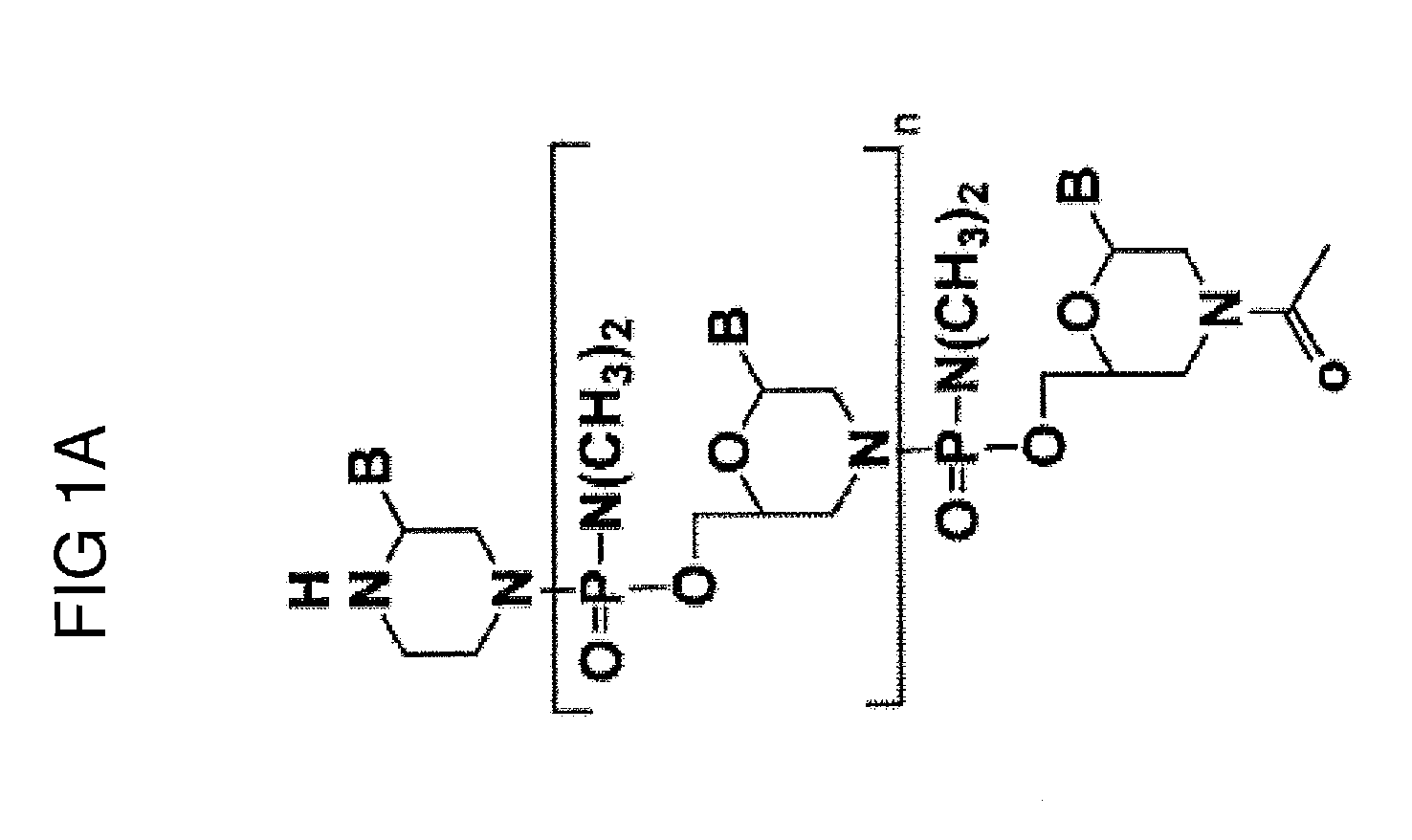
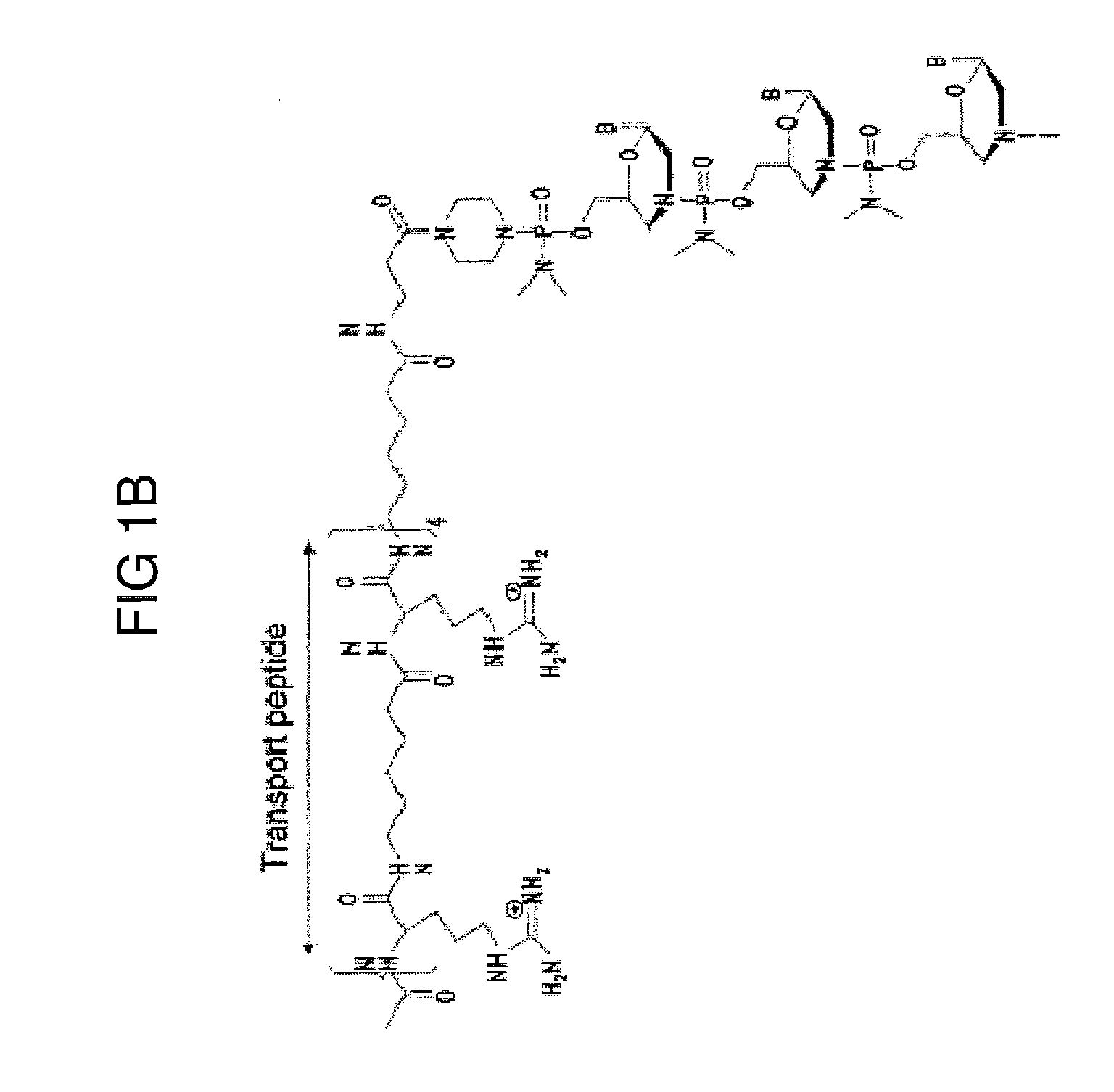
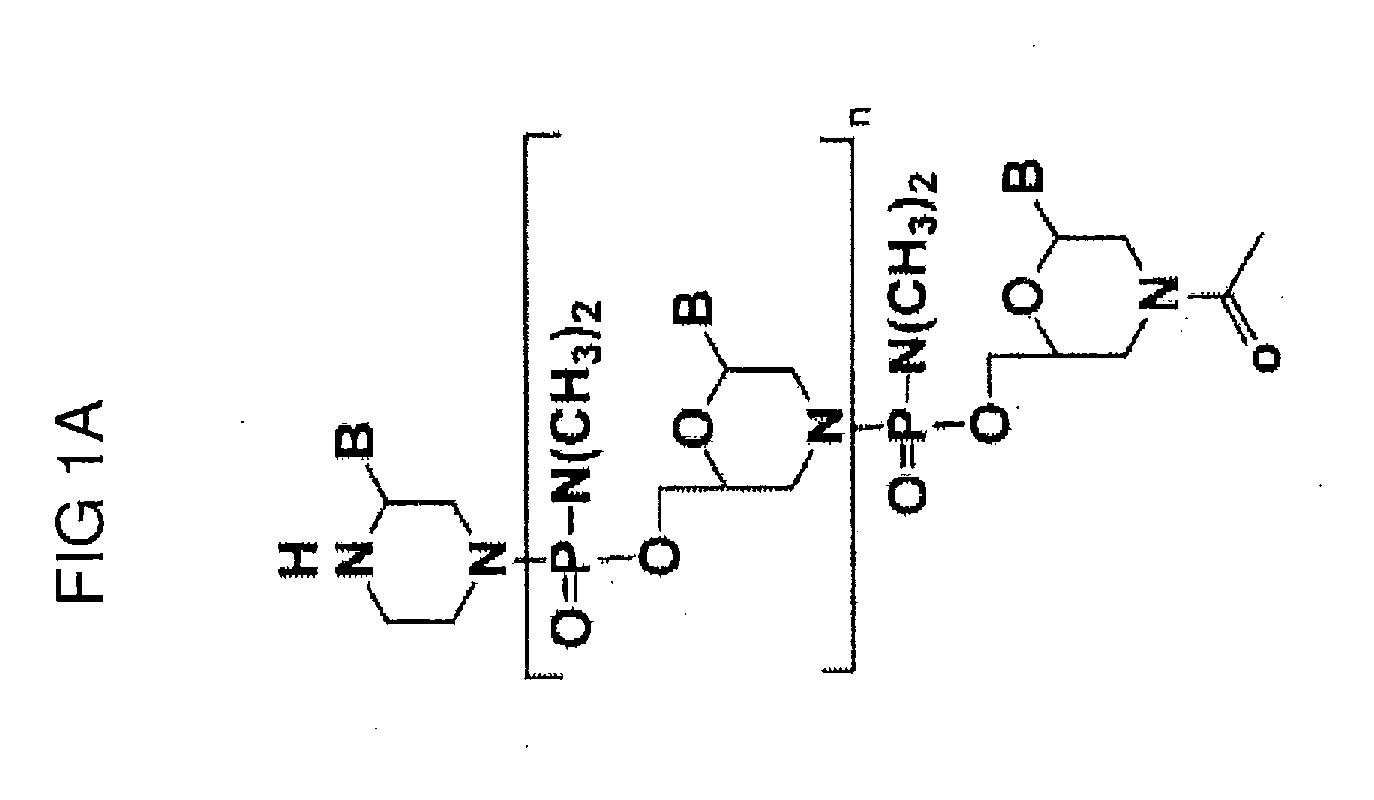
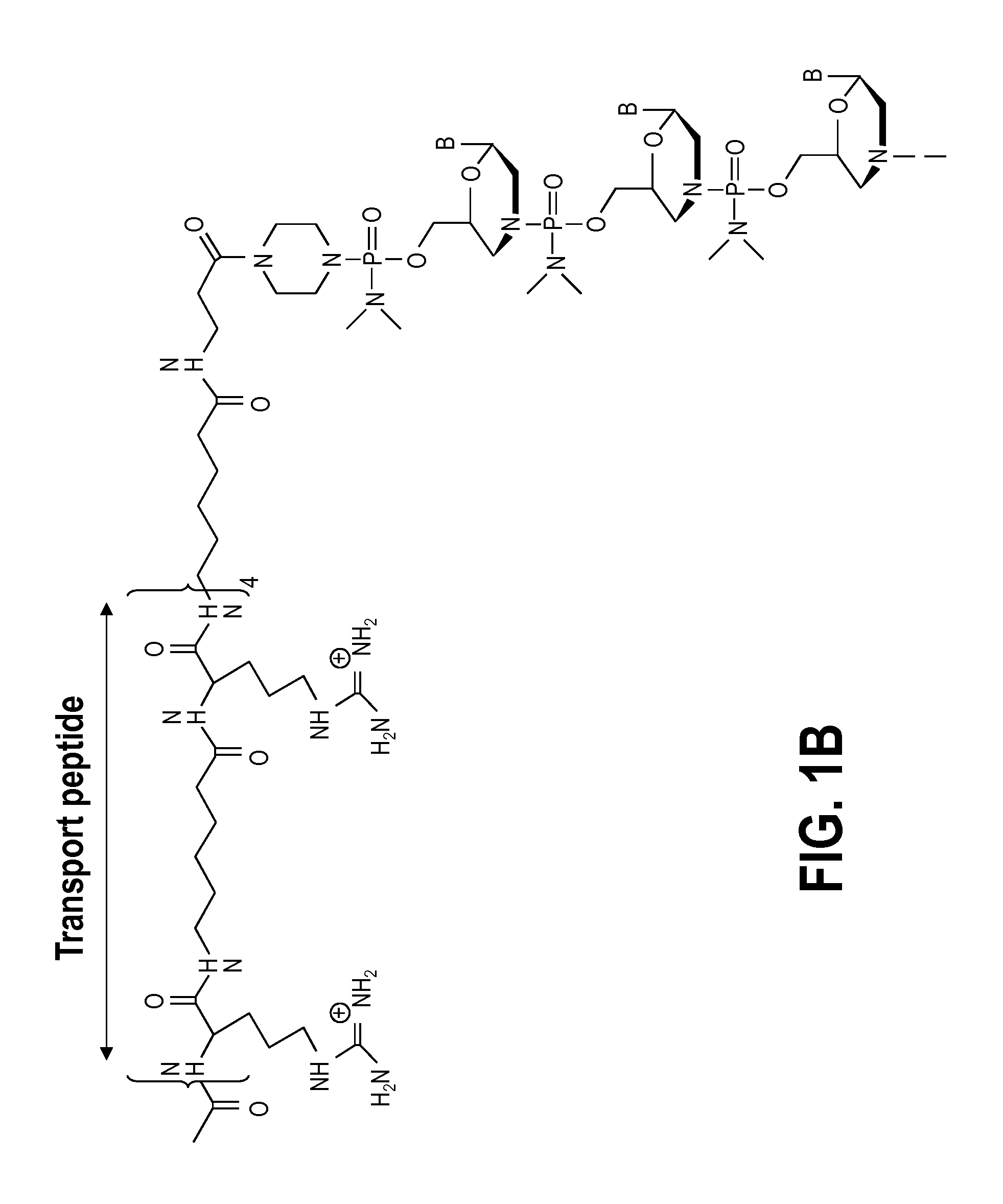
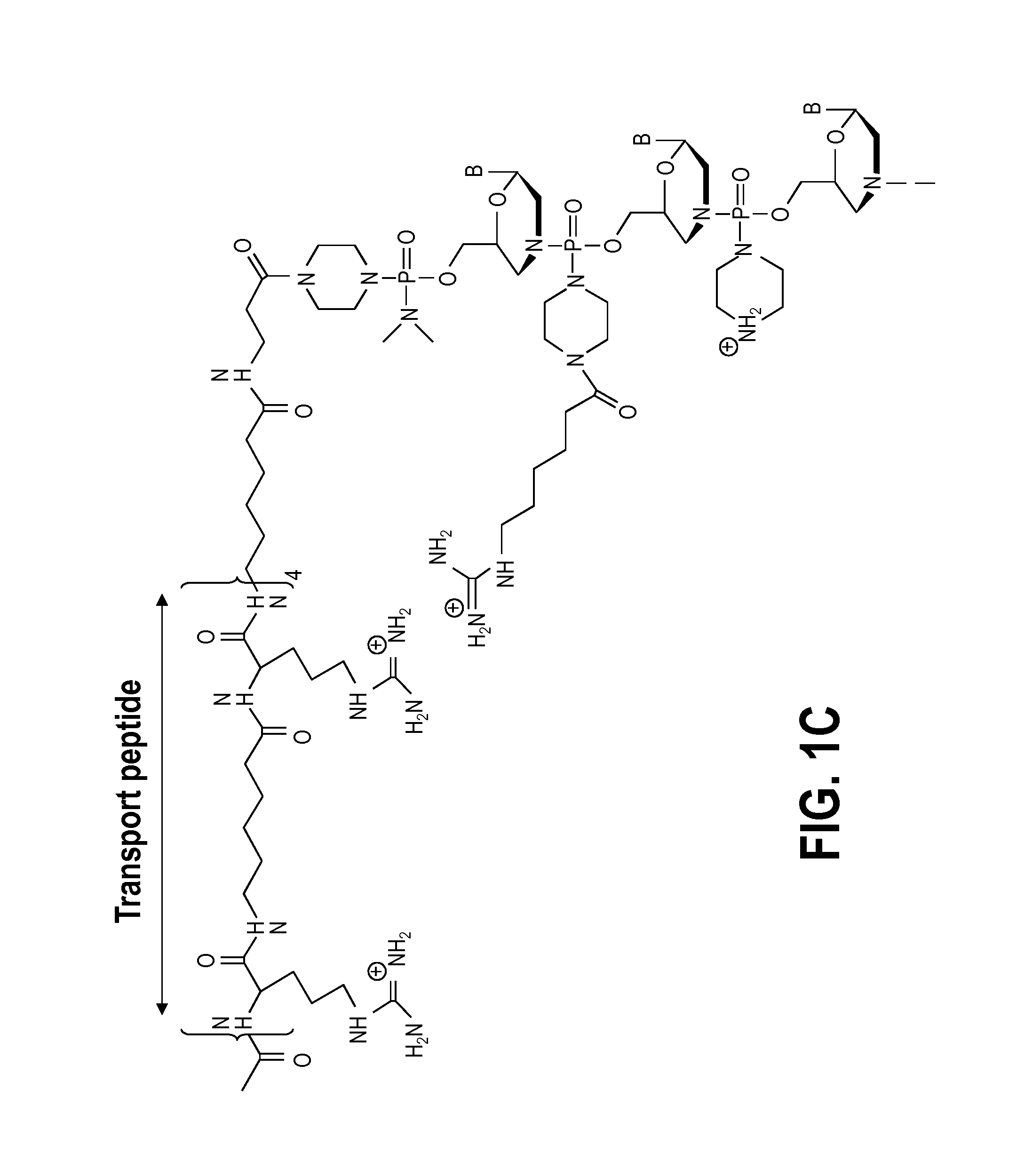
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor mediated gene transfer into muscle cells
InactiveUS20120122801A1Organic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryGlycoside formationMannose 6-phosphate receptor
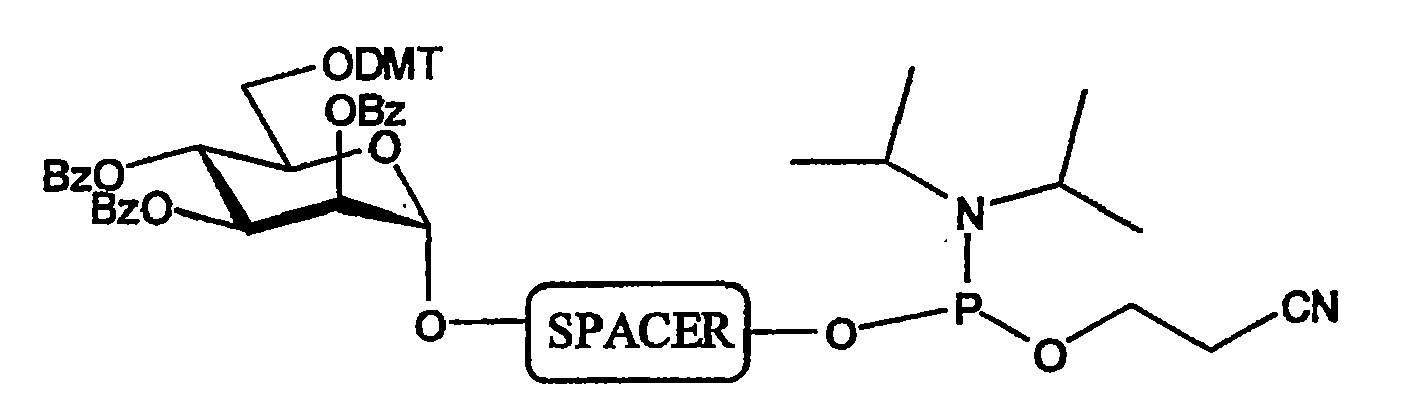
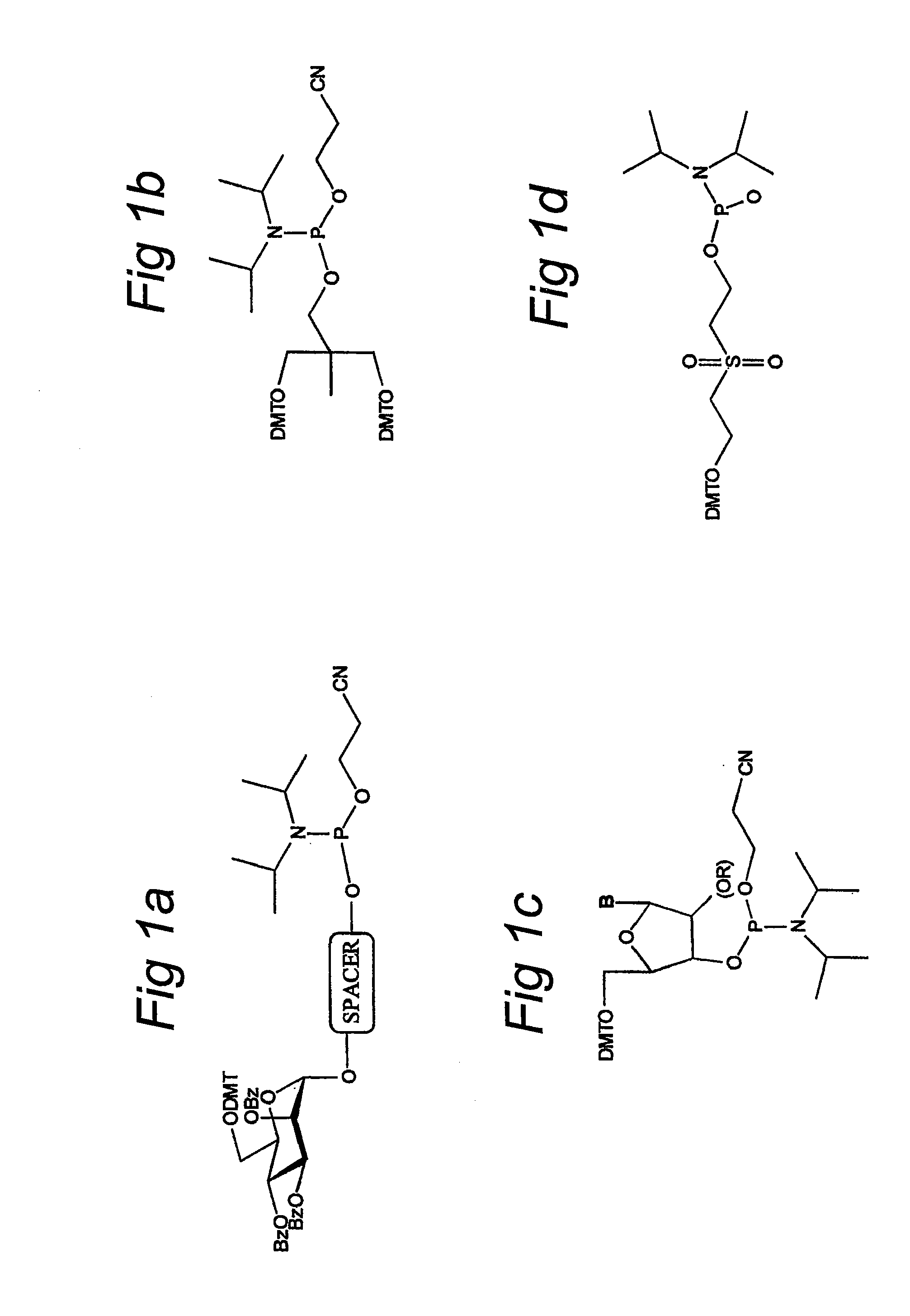
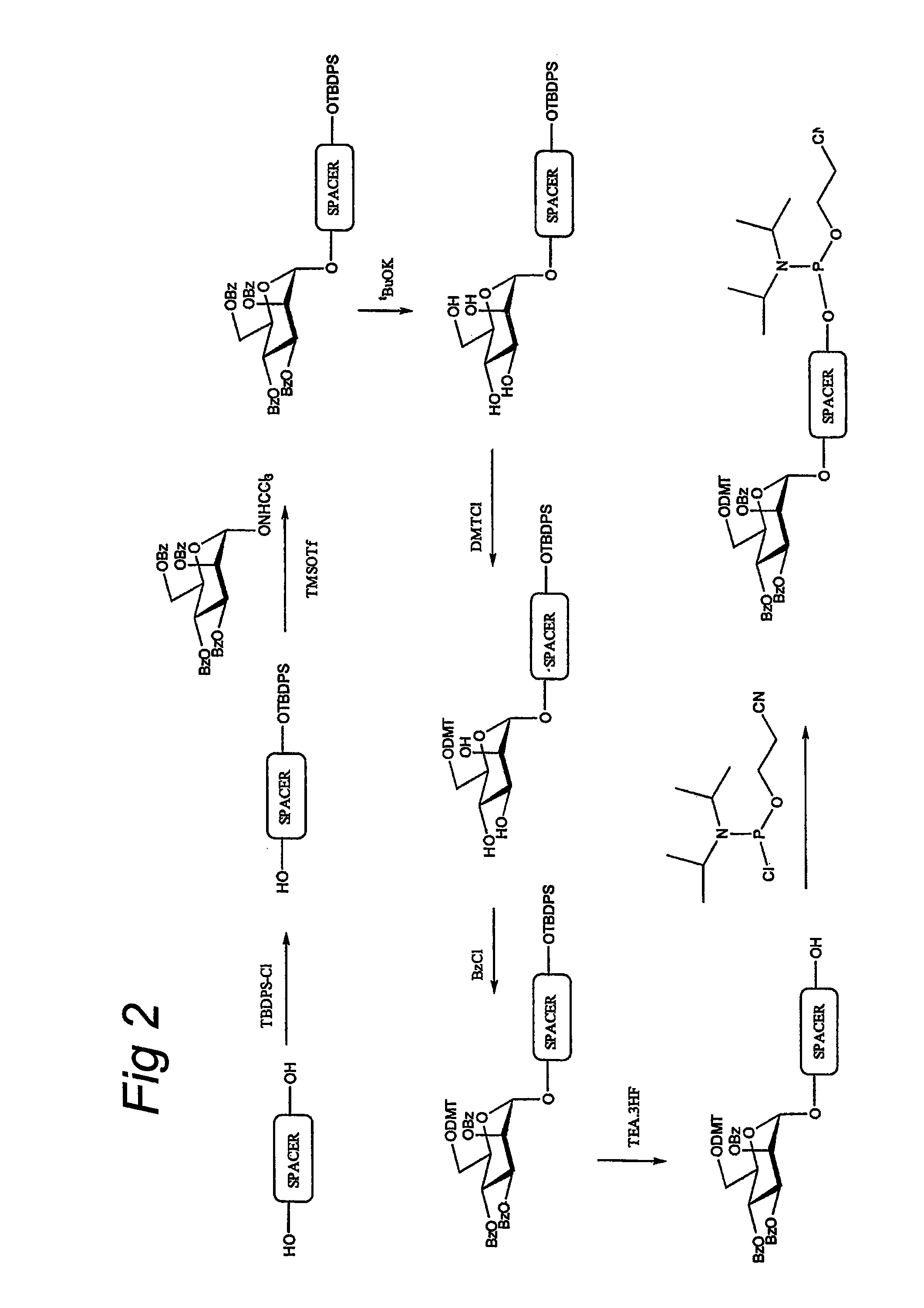
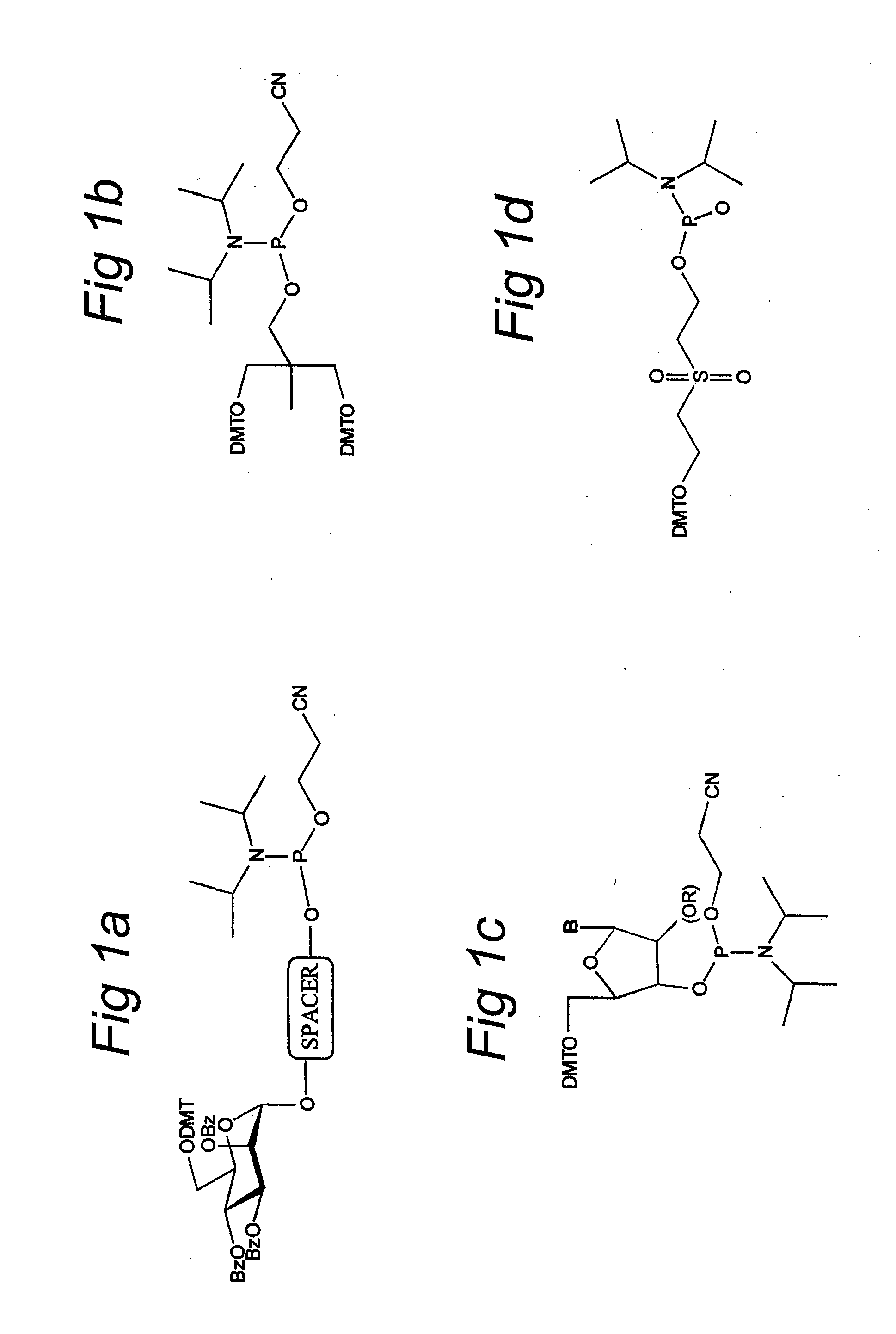
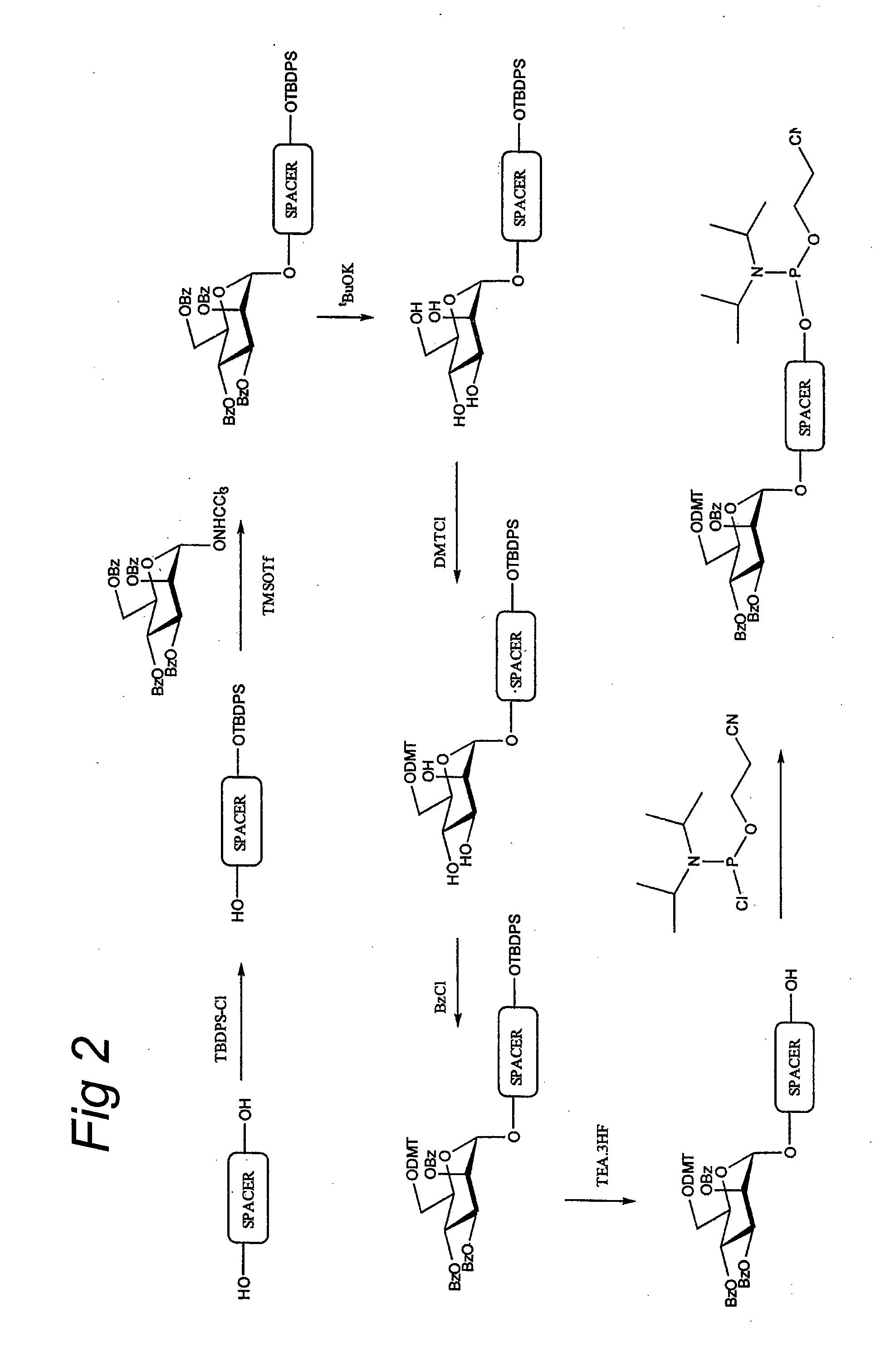
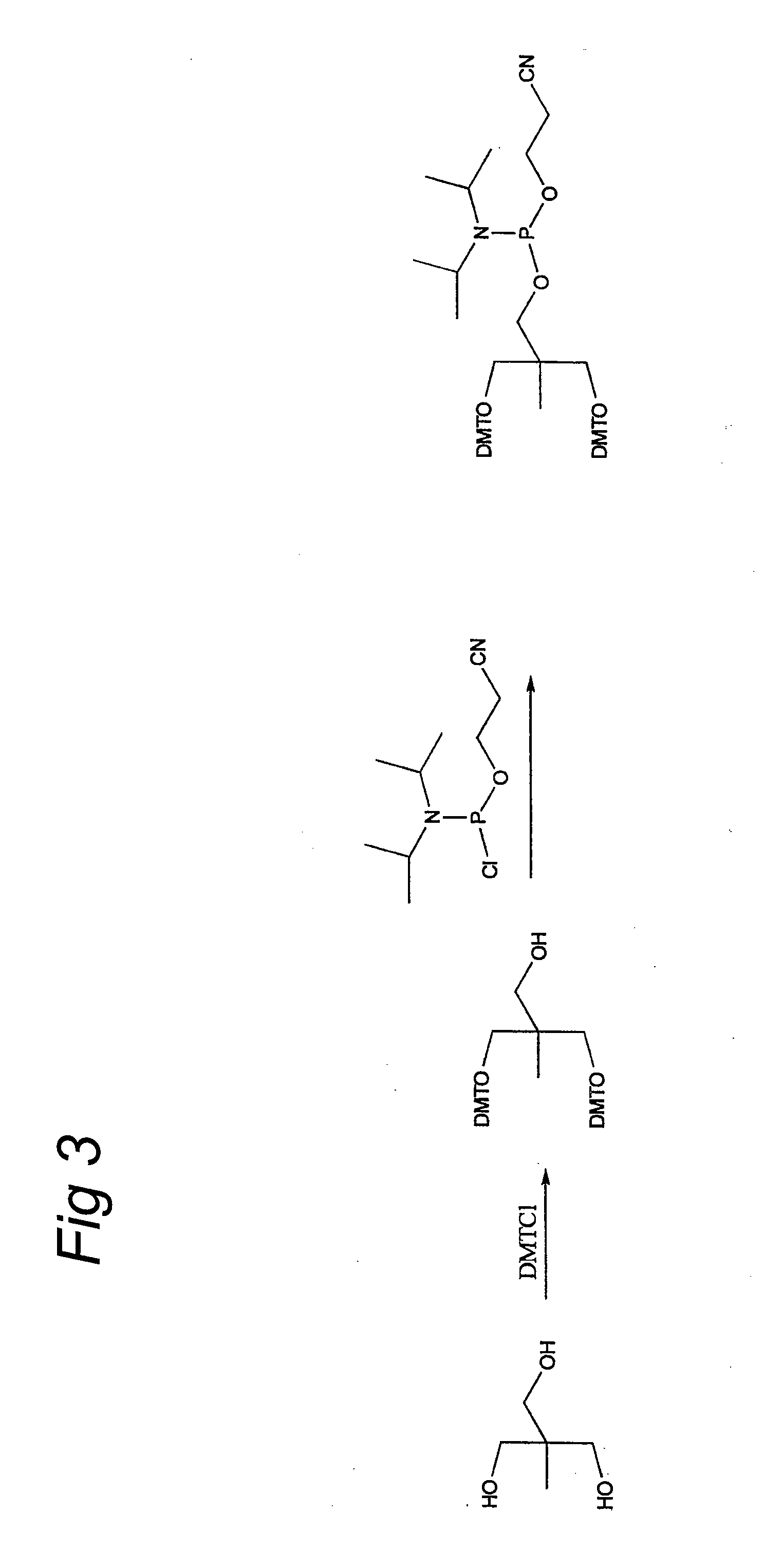
The invention relates to glycoside-compound conjugates for use in antisense strategies and / or gene therapy. The conjugates comprise a glycoside linked to a compound, in which the glycoside is a ligand capable of binding to a mannose-6-phosphate receptor of a muscle cell. For example the cells are muscle cells of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patient and the conjugate comprises an antisense oligonucleotide which causes ex on skipping and induces or restores the synthesis of dystrophin or variants thereof.
Owner:PROSENSA THERAPEUTICS
Recombinant adeno-associated virus delivery of alpha-sarcoglycan polynucleotides
ActiveUS9434928B2High transduction efficiencyIncrease volumePeptide/protein ingredientsOther blood circulation devicesFhit genePolynucleotide
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
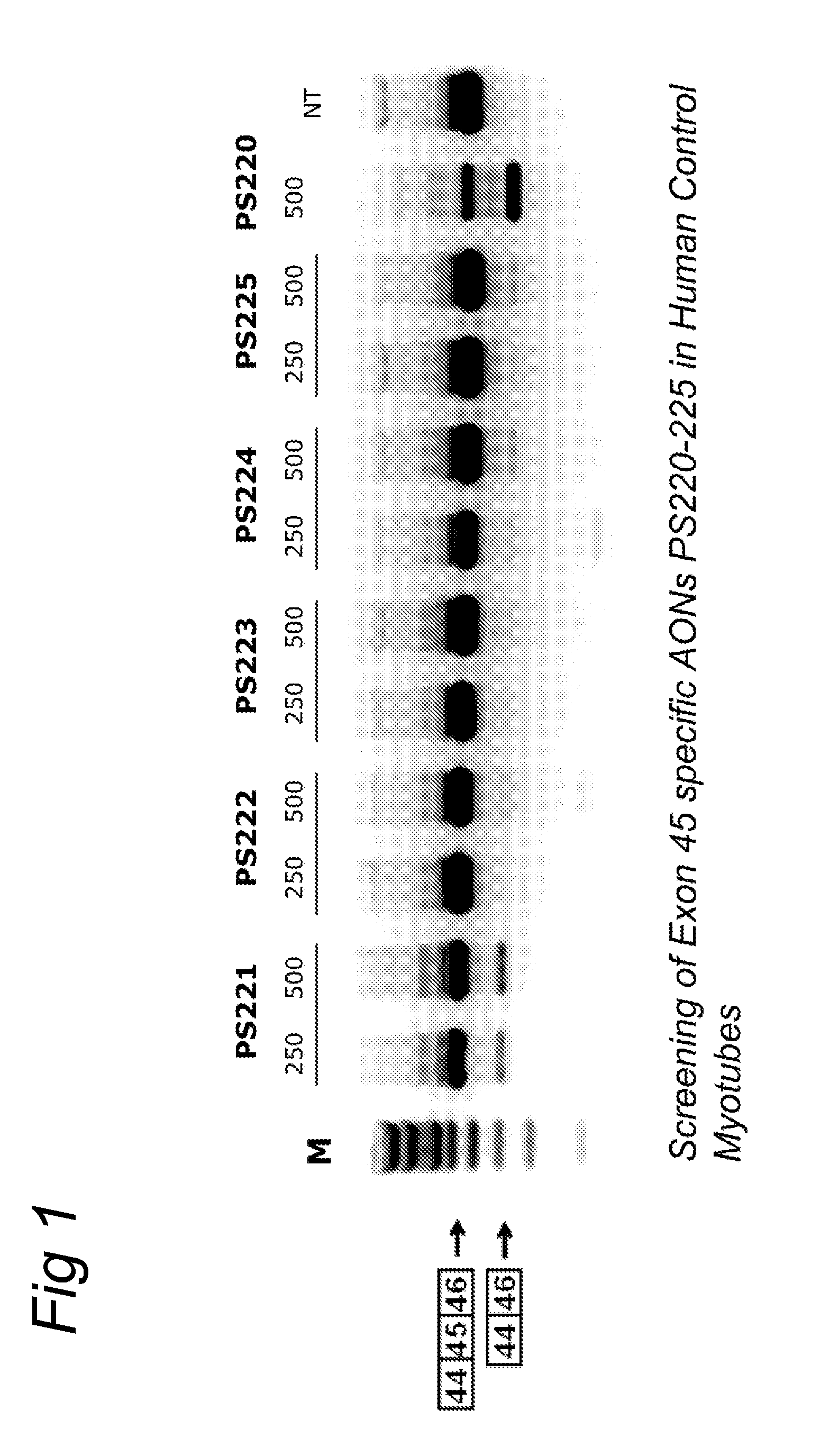
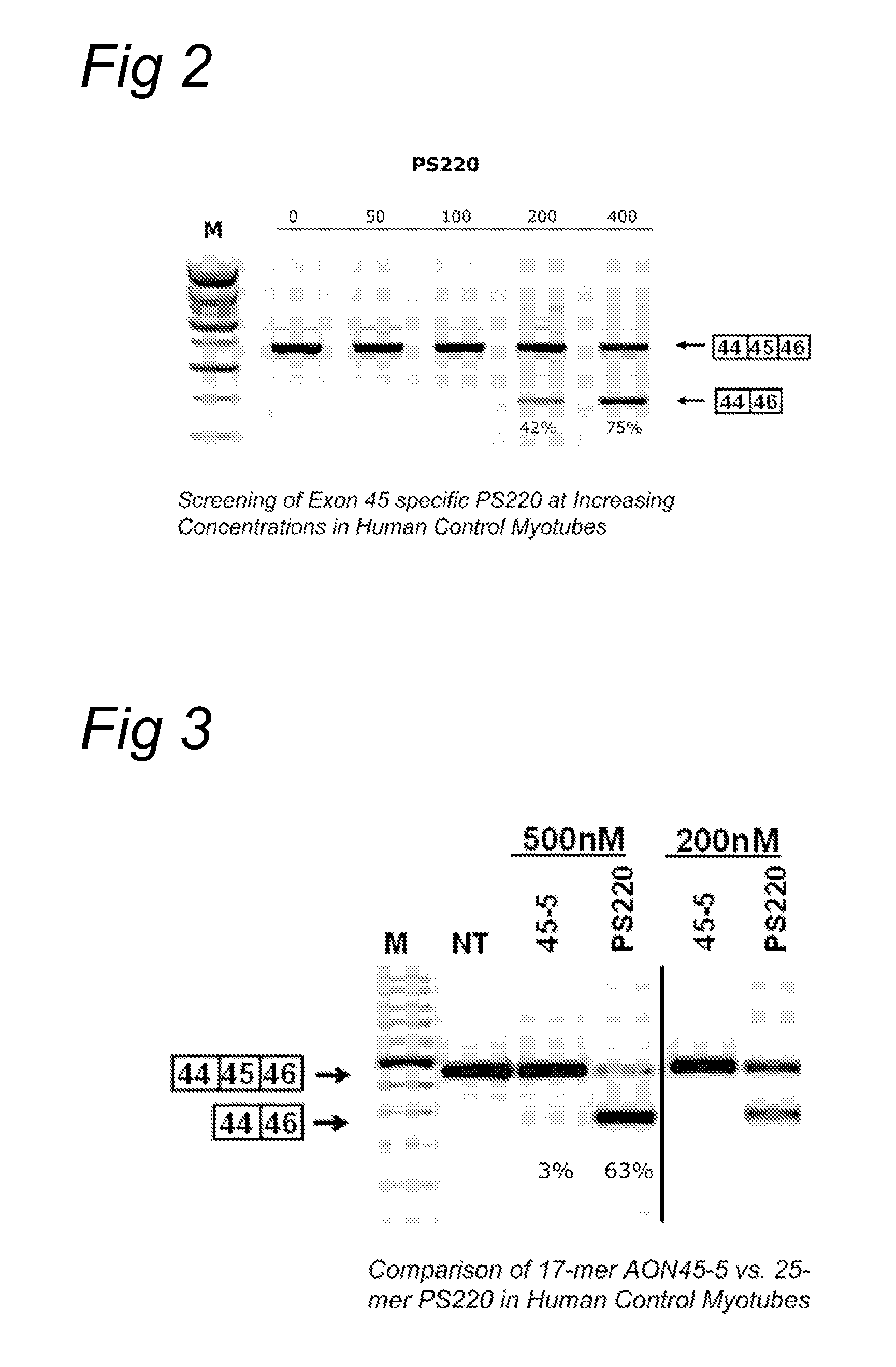
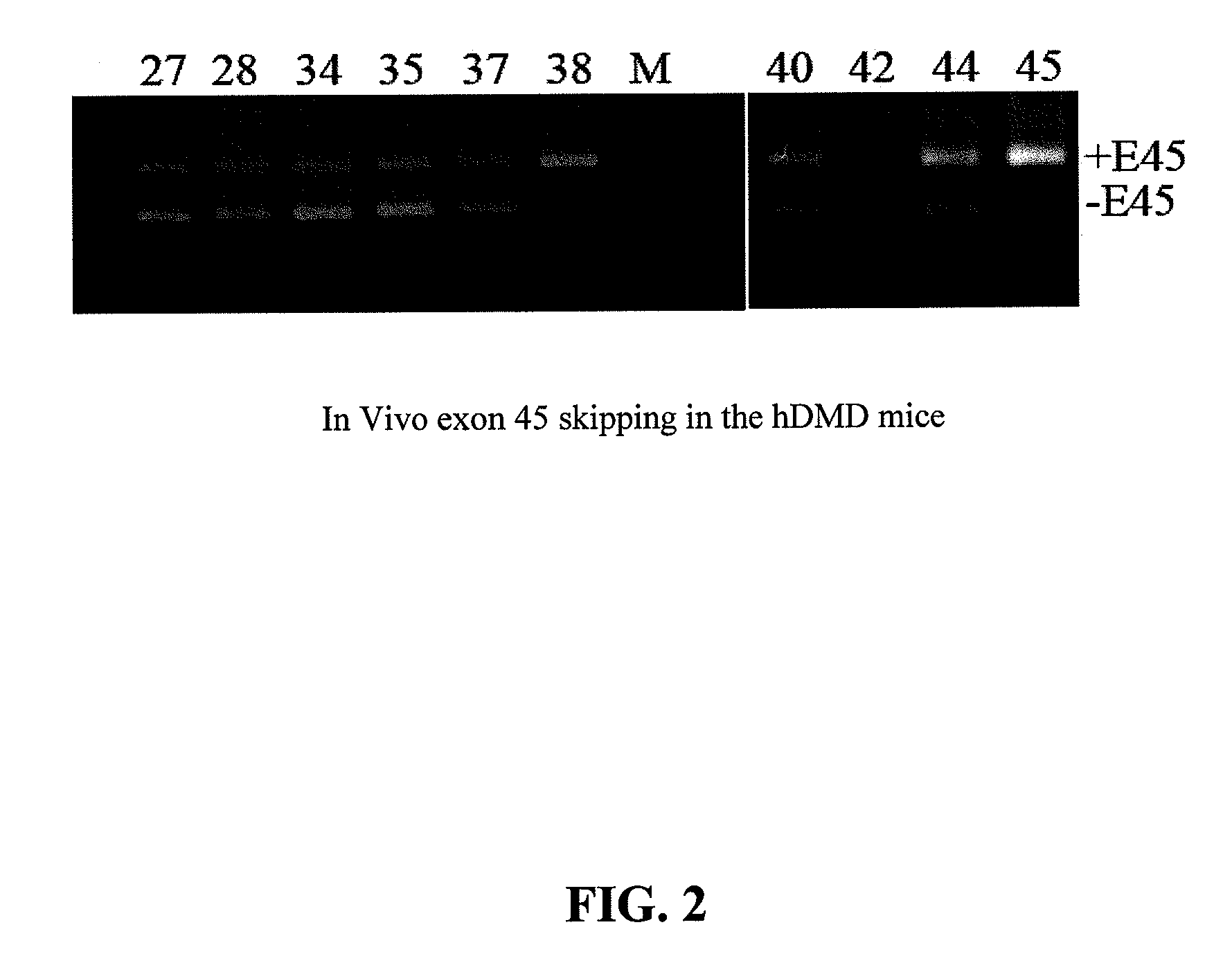
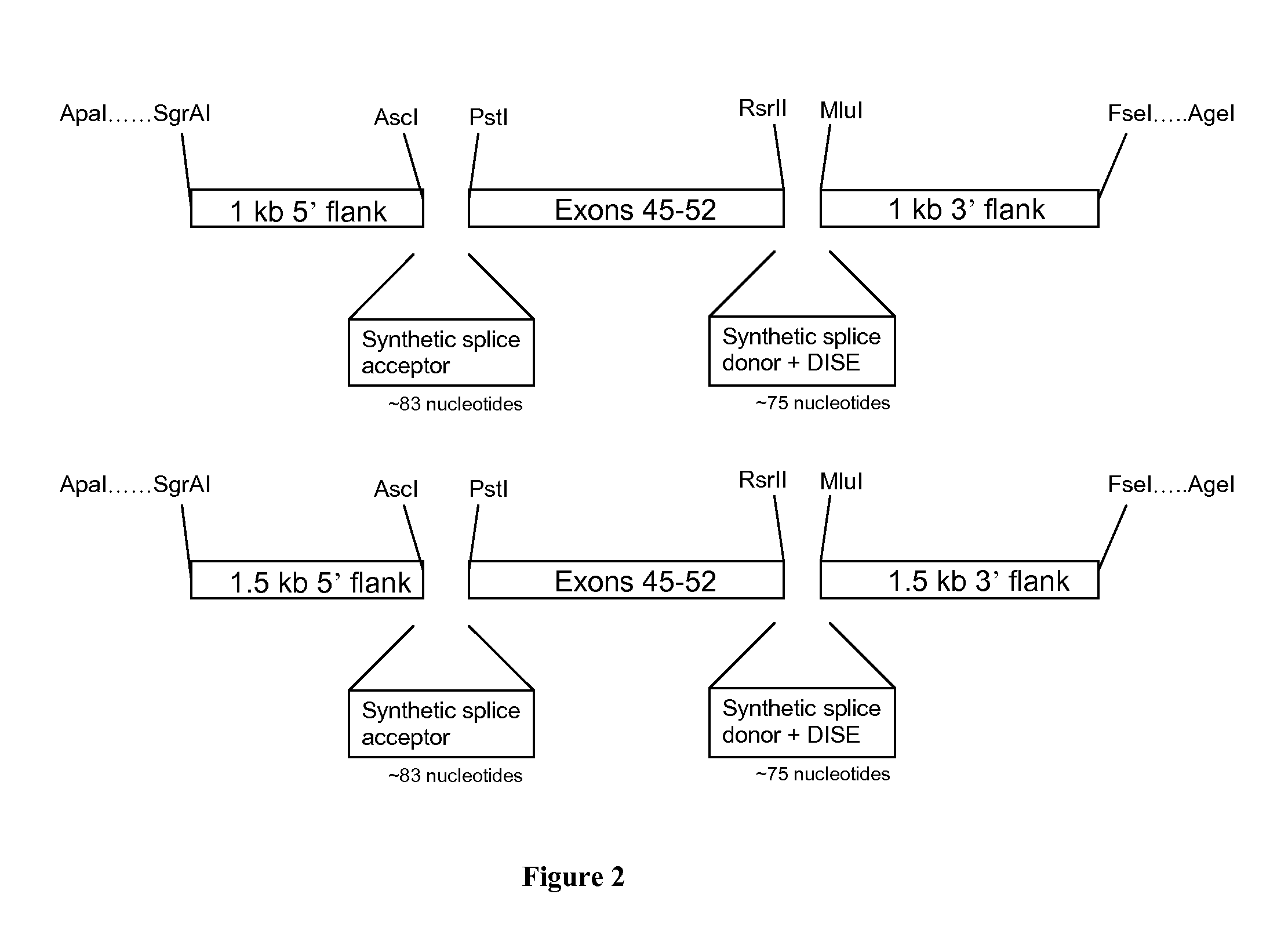
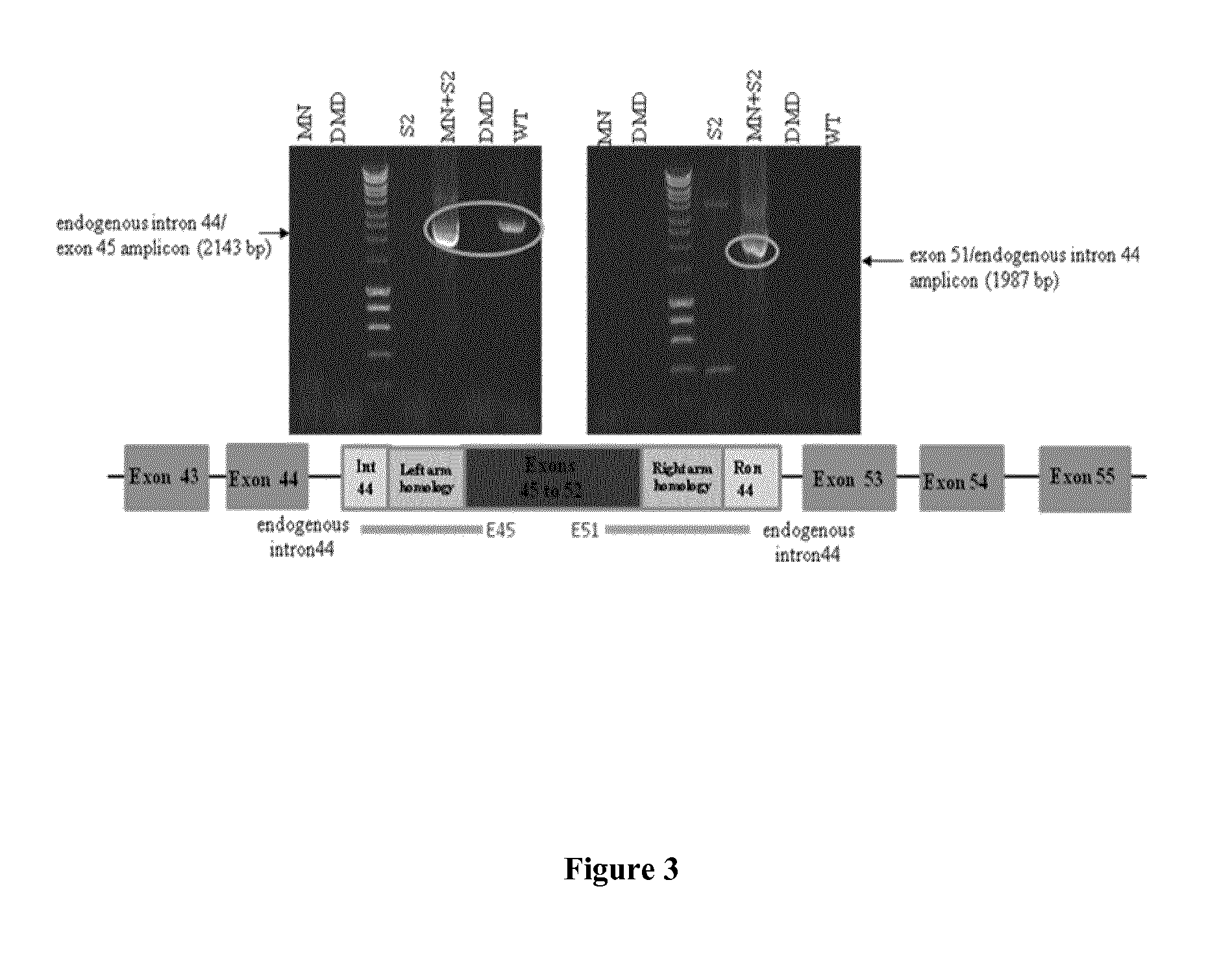
METHODS AND MEANS FOR EFFICIENT SKIPPING OF EXON 45 IN DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY PRE-mRNA
ActiveUS20120022134A1Reduced calcium uptake by muscle cellsReduce synthesisOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationNucleotidePrecursor mRNA
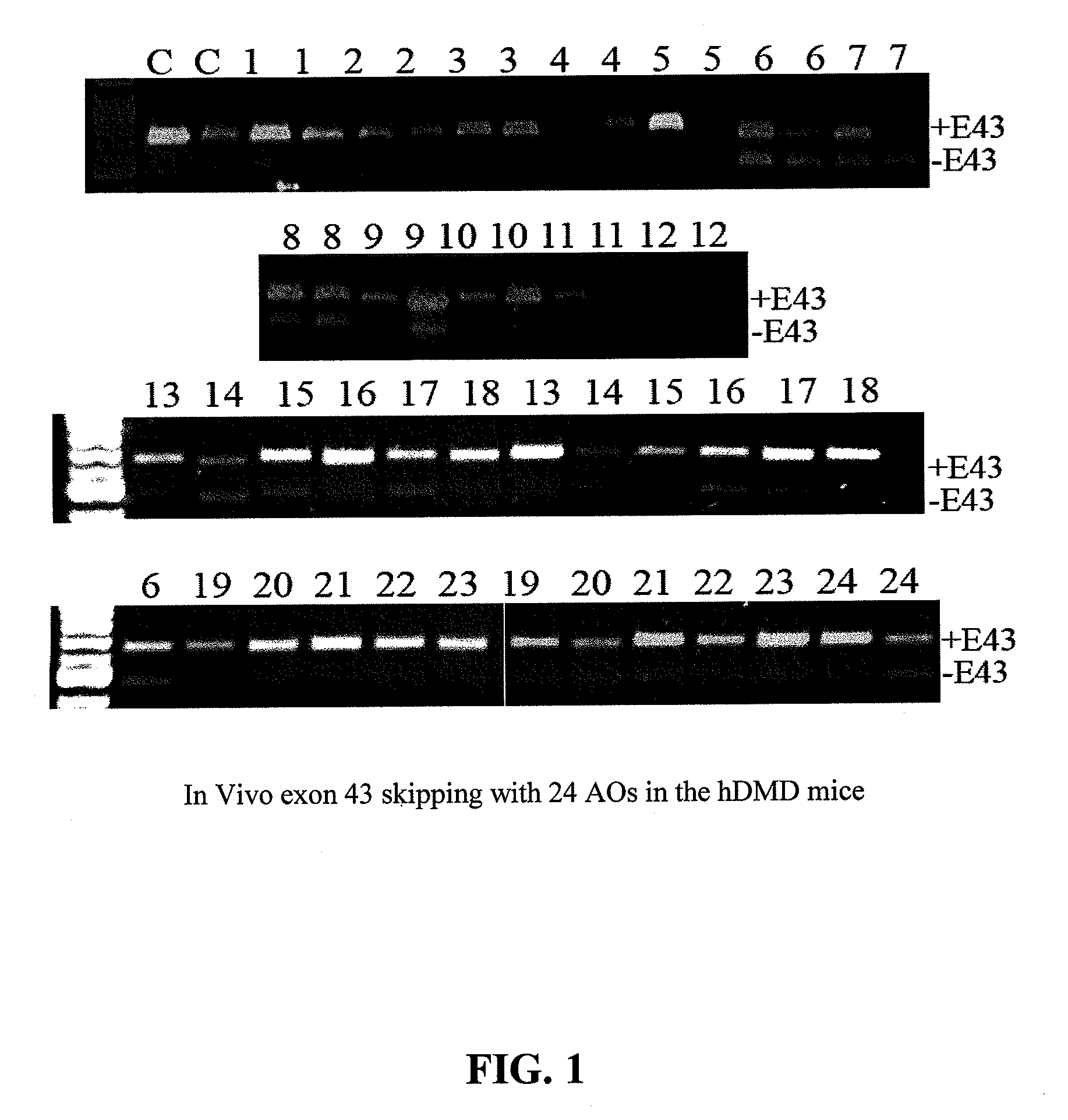
The invention relates to a method for inducing or promoting skipping of exon 45 of DMD pre-mRNA in a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patient, preferably in an isolated (muscle) cell, the method comprising providing said cell with a molecule that binds to a continuous stretch of at least 21 nucleotides within said exon. The invention further relates to such molecule used in said method.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV +2
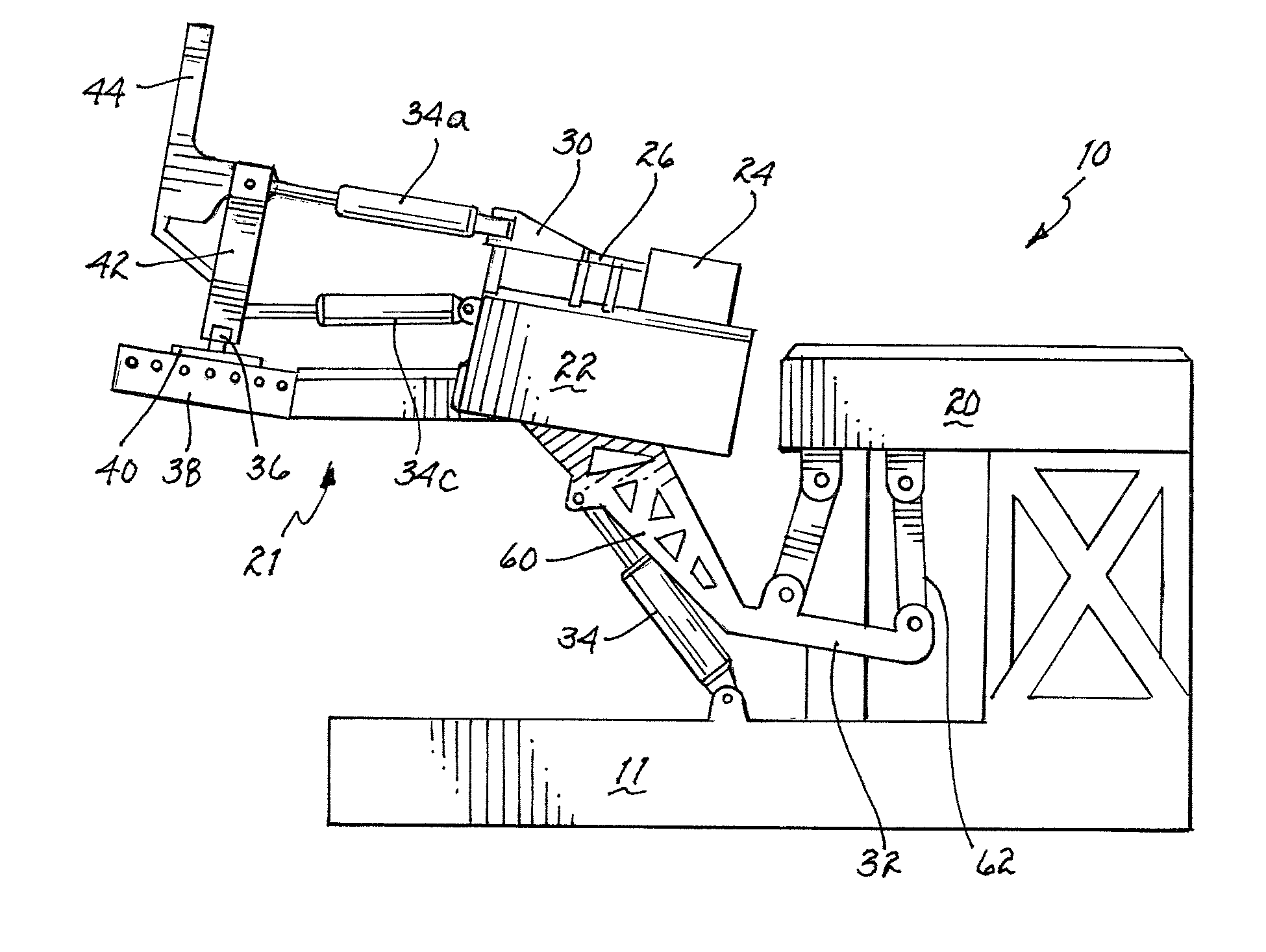
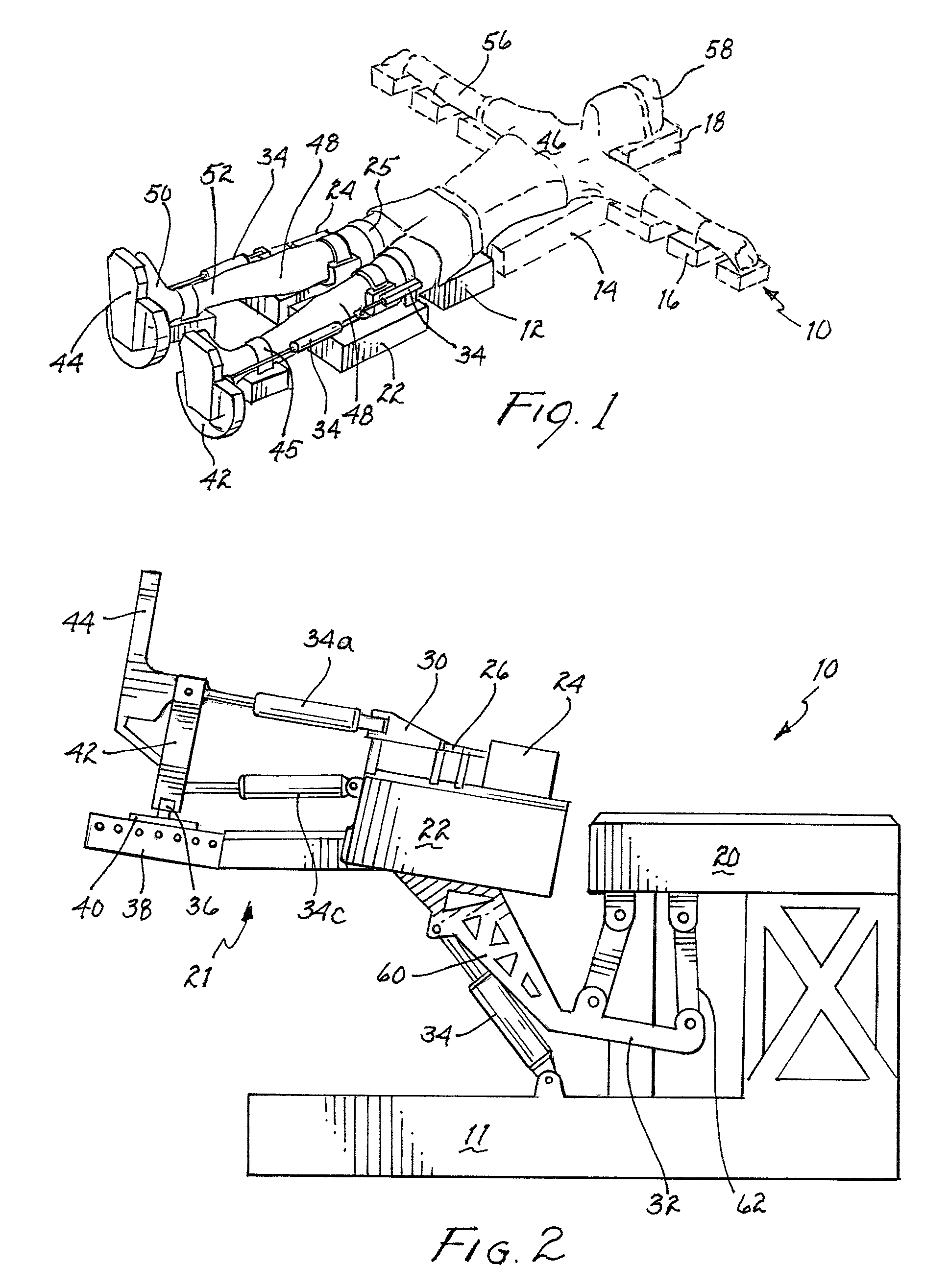
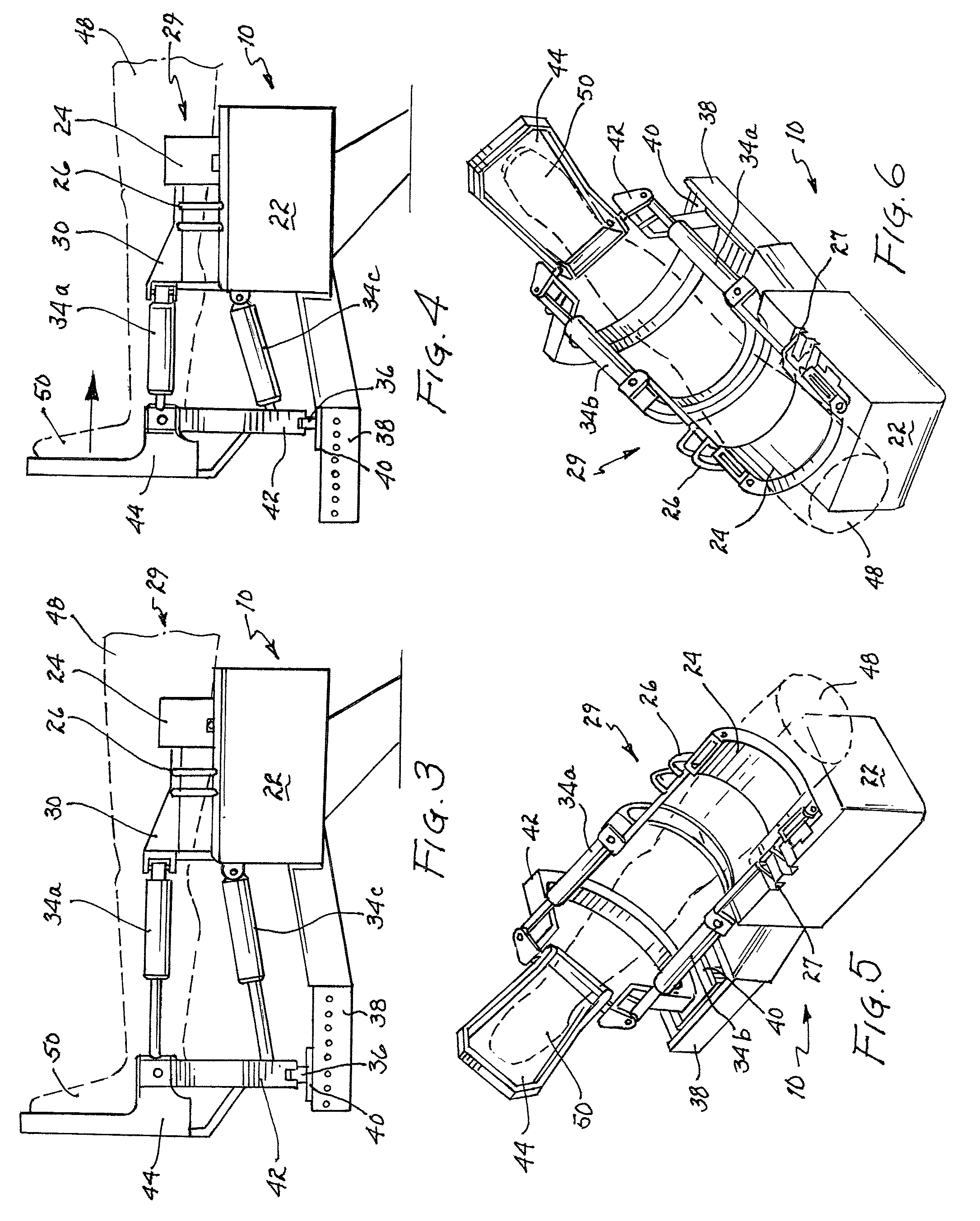
Automated therapy table for treating lower extremities and method therefor
An automated therapy table is disclosed. The automated therapy table may have various support portions capable of independent automatic actuation of a person's lower extremities through passive exercise. The automated therapy table allows a patient to perform leg elevation, approximation / decompression of the leg, internal / external rotation of the leg, ankle plantar flexion / dorsiflexion, and foot inversion / eversion movements. During each movement, the patient may be instructed to think in the direction of the movement. It has been found that doing so helps increase the healing effects. The disclosed table and method may be beneficial for patients after certain operations as well as for those suffering from various forms of debilitating illnesses, such as Multiple Sclerosis, Charcot-Marie-Tooth, and Muscular Dystrophy.
Owner:SCHAEFFER DWIGHT L
Exon skipping compositions for treating muscular dystrophy
InactiveUS20140315977A1Enhance the activity, cellular distribution, or cellular uptake of the antisense oligonucleotideOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDuchenne muscular dystrophyMuscular dystrophy
Antisense molecules capable of binding to a selected target site in the human dystrophin gene to induce exon 53 skipping are described.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
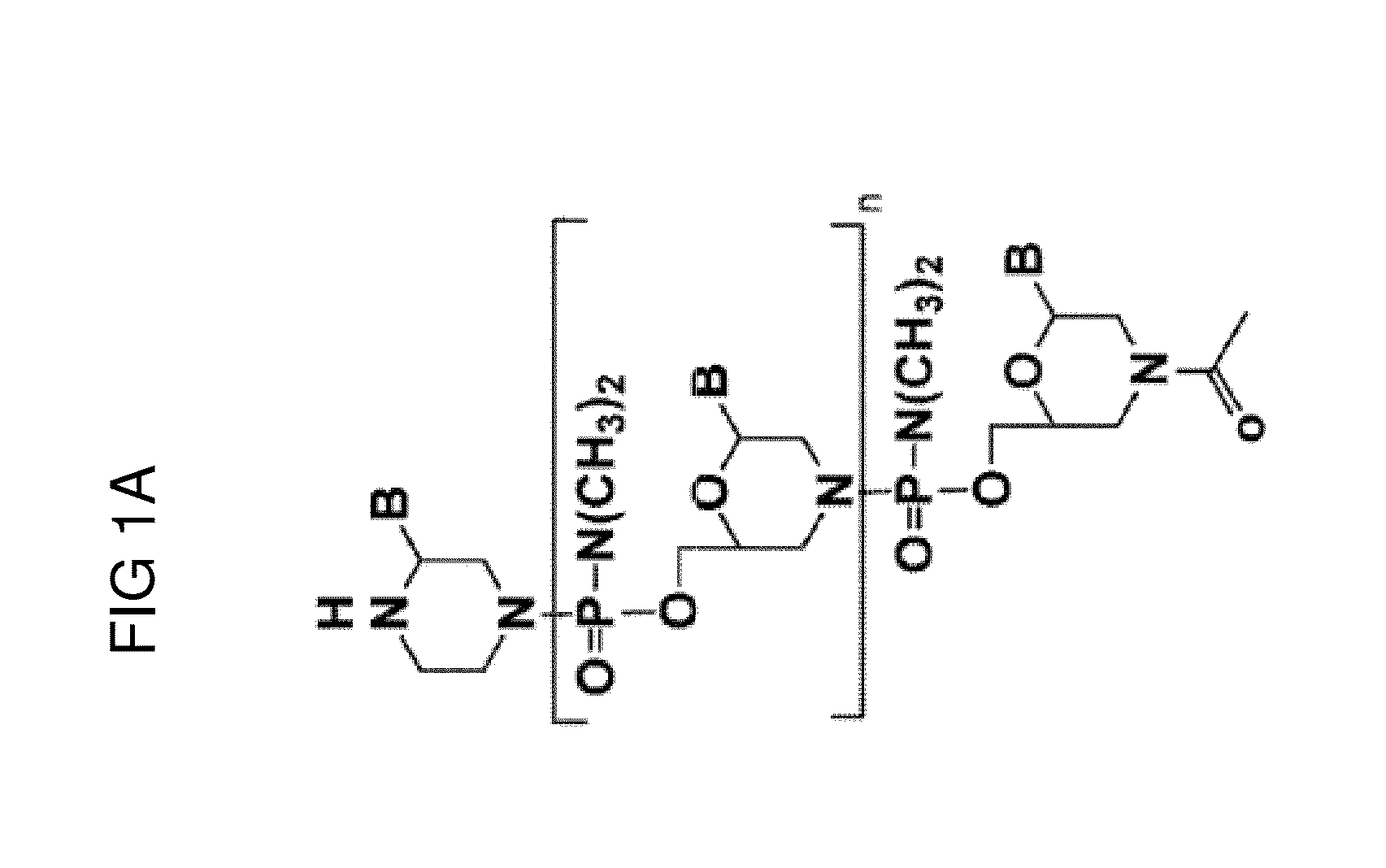
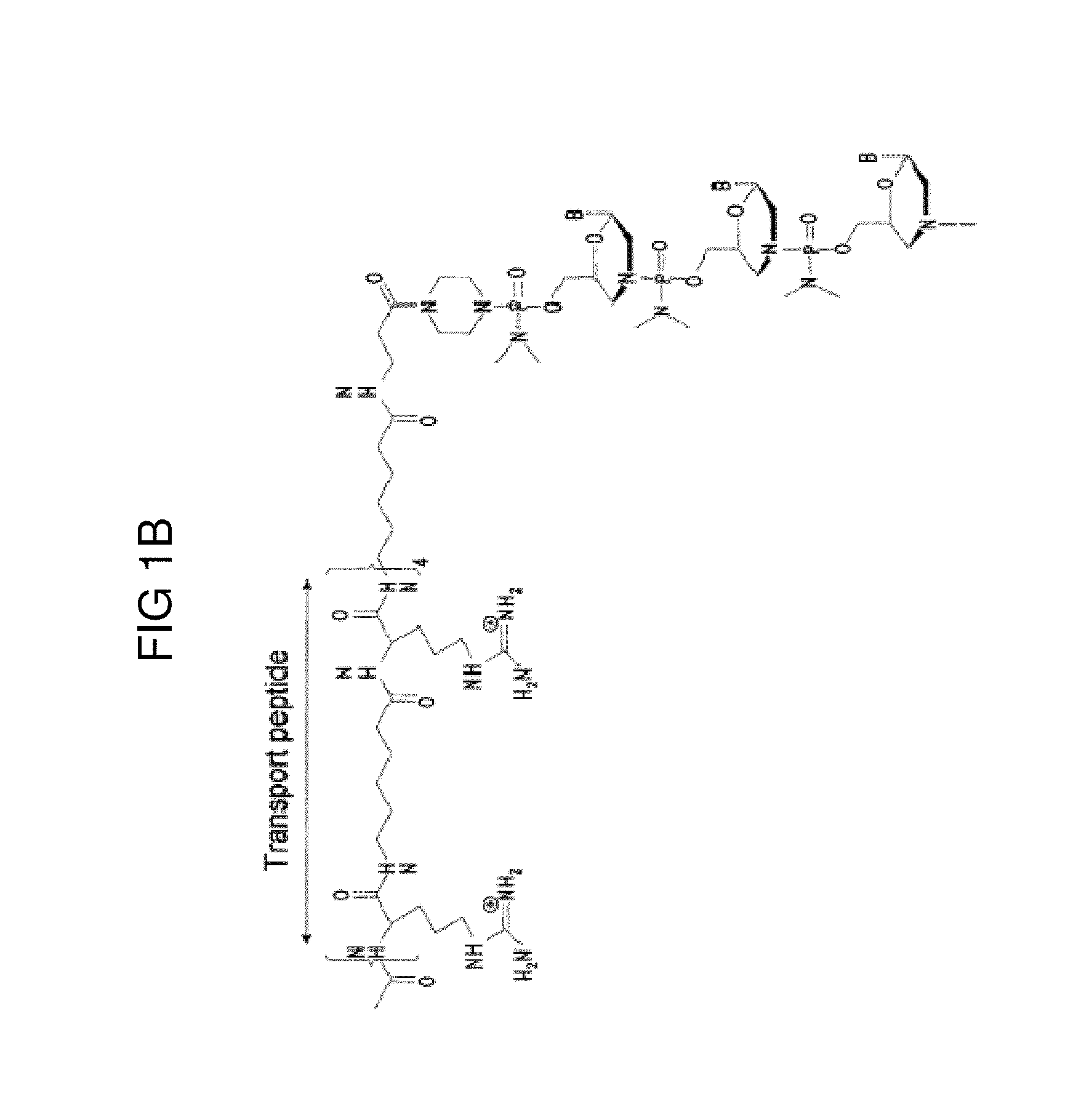
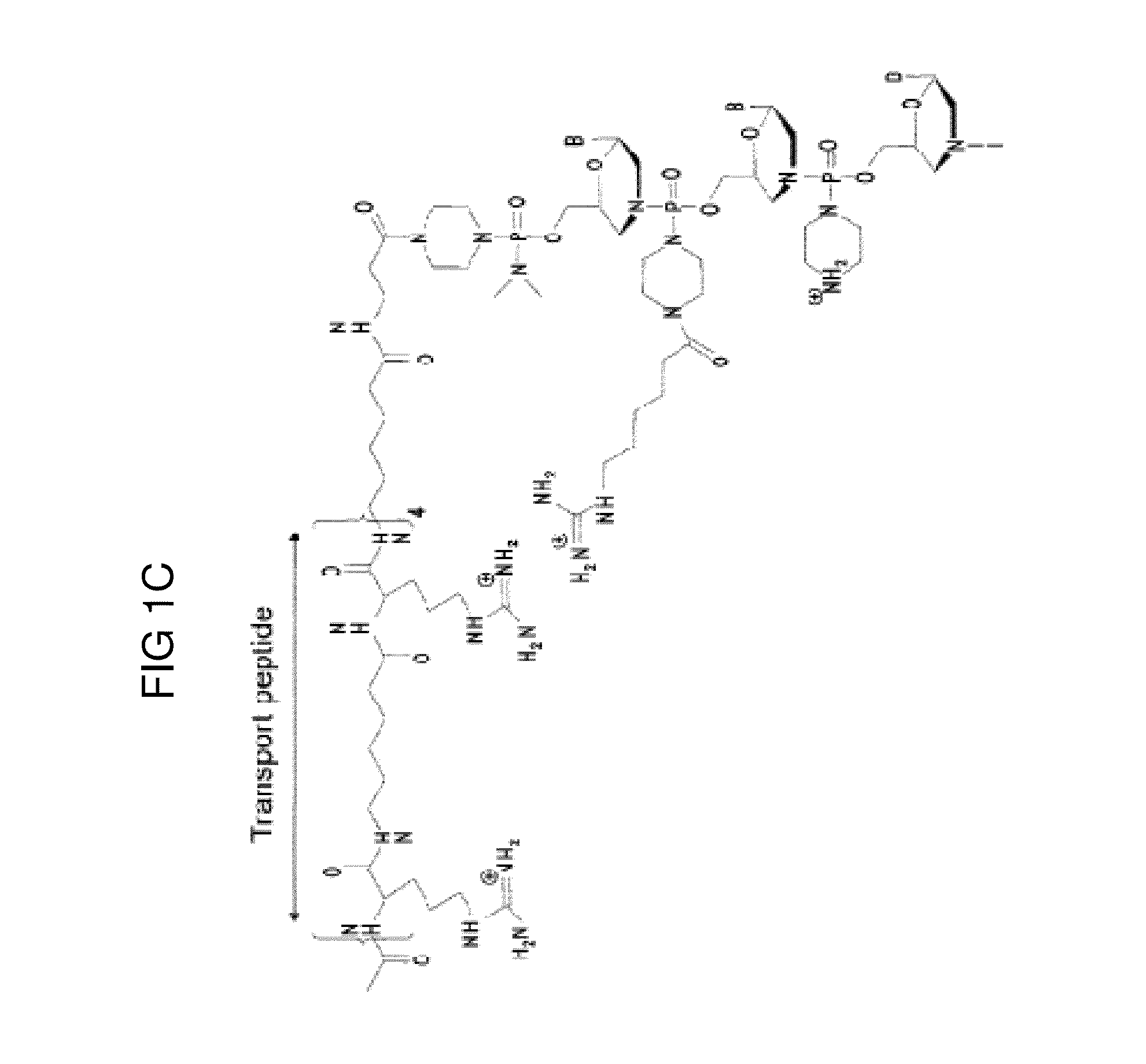
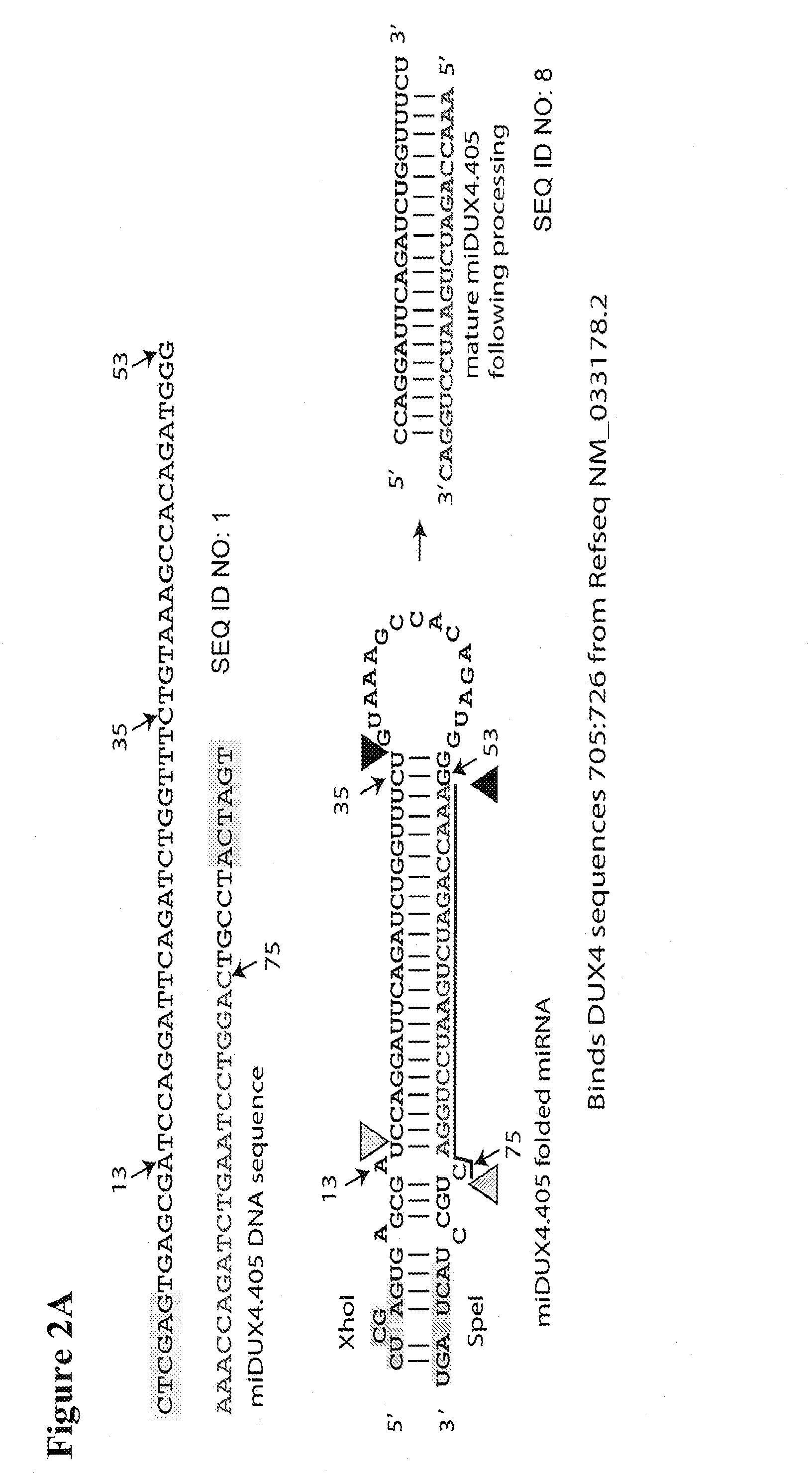
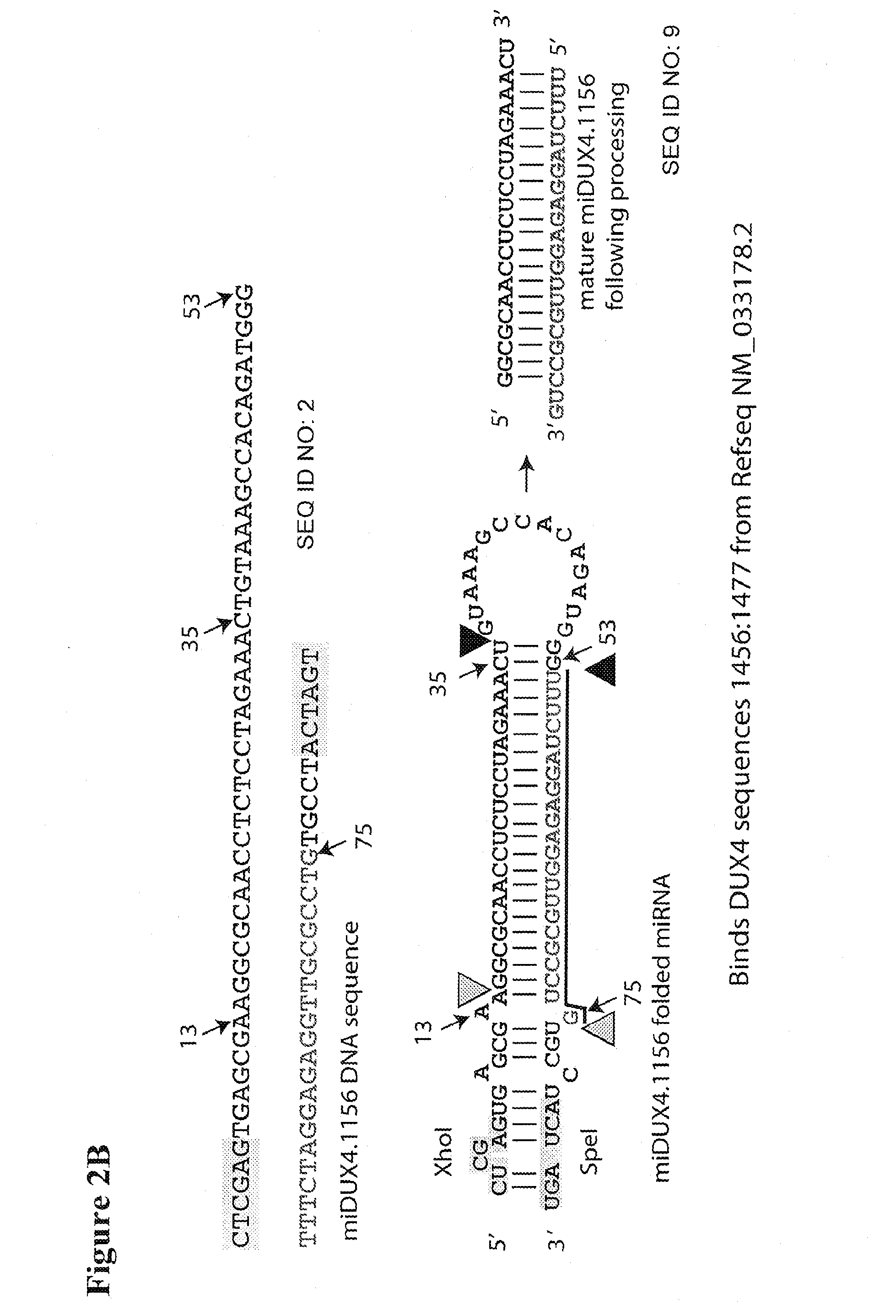
Recombinant Virus Products and Methods for Inhibition of Expression of DUX4
ActiveUS20140322169A1Ease of administrationEase of handlingBiocideSugar derivativesAdeno associate virusDna encoding
The present invention relates to RNA interference-based methods for inhibiting the expression of the DUX4 gene, a double homeobox gene on human chromosome 4q35. Recombinant adeno-associated viruses of the invention deliver DNAs encoding microRNAs that knock down the expression of DUX4. The methods have application in the treatment of muscular dystrophies such as facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy.
Owner:RES INST AT NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Exon skipping compositions for treating muscular dystrophy
InactiveUS20160040162A1Enhance the activity, cellular distribution, or cellular uptake of the antisense oligonucleotideOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDuchenne muscular dystrophyMuscular dystrophy
Antisense molecules capable of binding to a selected target site in the human dystrophin gene to induce exon 53 skipping are described.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor mediated gene transfer into muscle cells
InactiveUS20110110960A1Organic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryDystrophinMannose 6-phosphate receptor
The invention relates to glycoside-compound conjugates for use in antisense strategies and / or gene therapy. The conjugates comprise a glycoside linked to a compound, in which the glycoside is a ligand capable of binding to a mannose-6-phosphate receptor of a muscle cell. For example the cells are muscle cells of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patient and the conjugate comprises an antisense oligonucleotide which causes exon skipping and induces or restores the synthesis of dystrophin or variants thereof.
Owner:PROSENSA
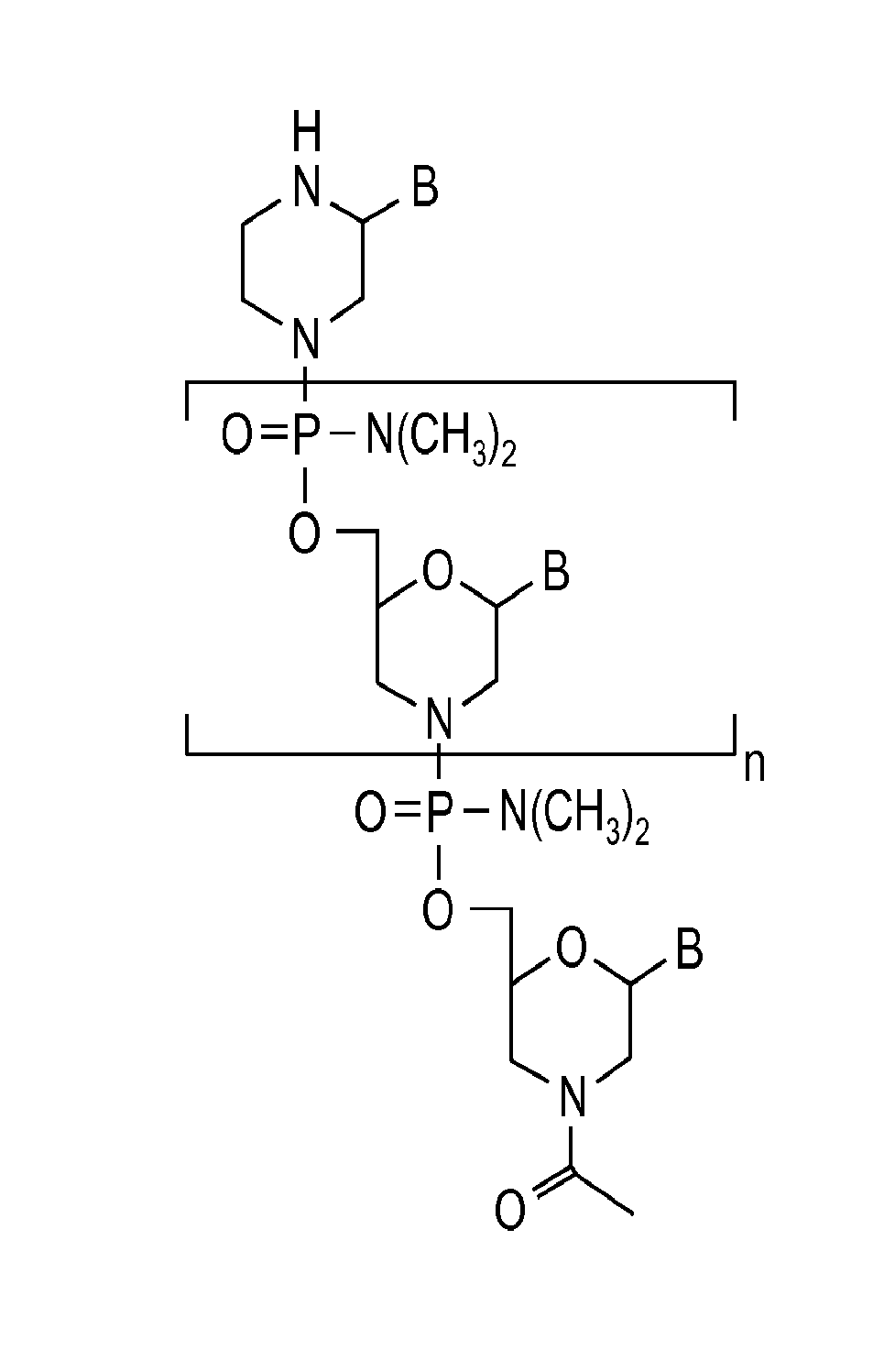
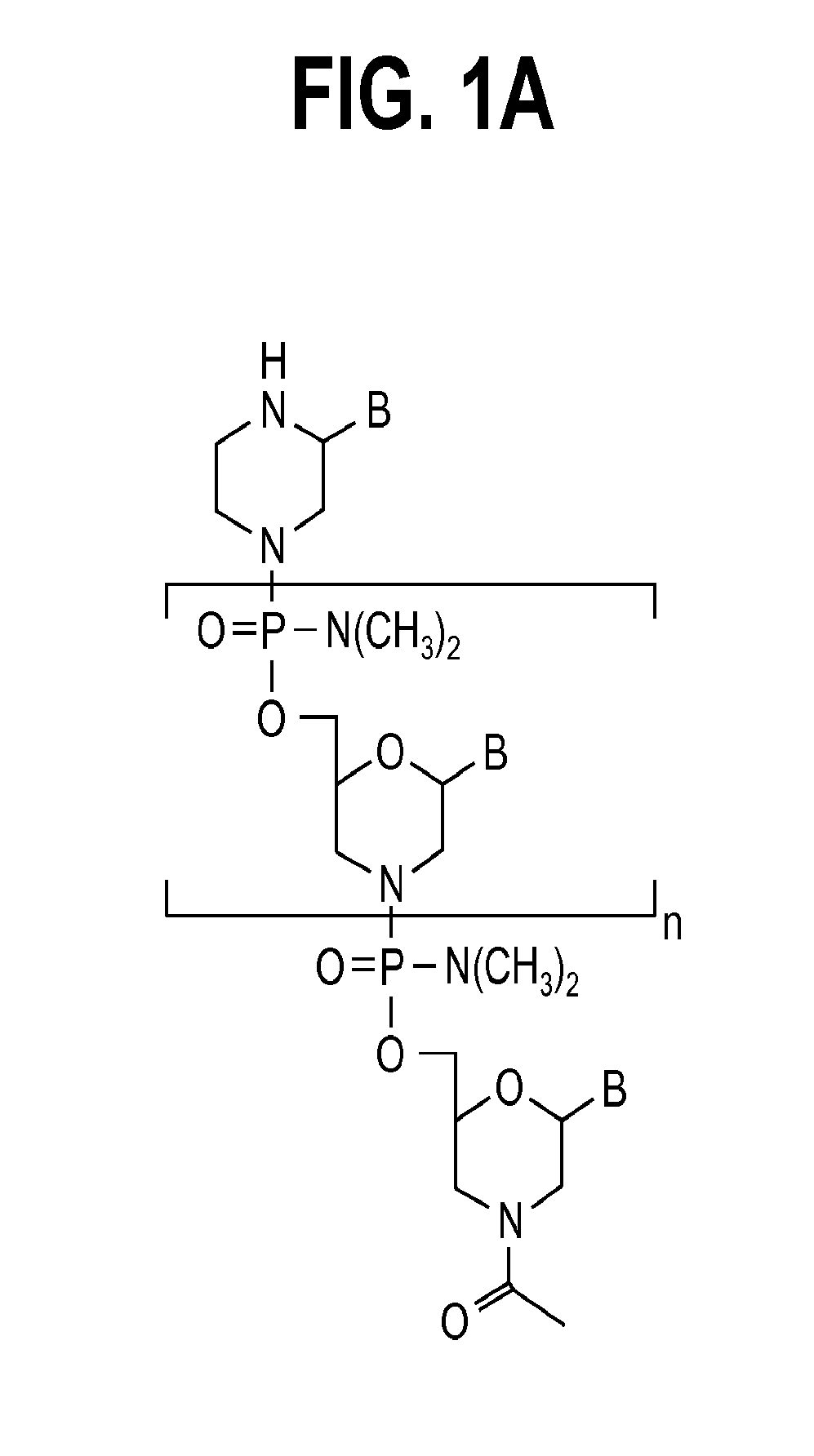
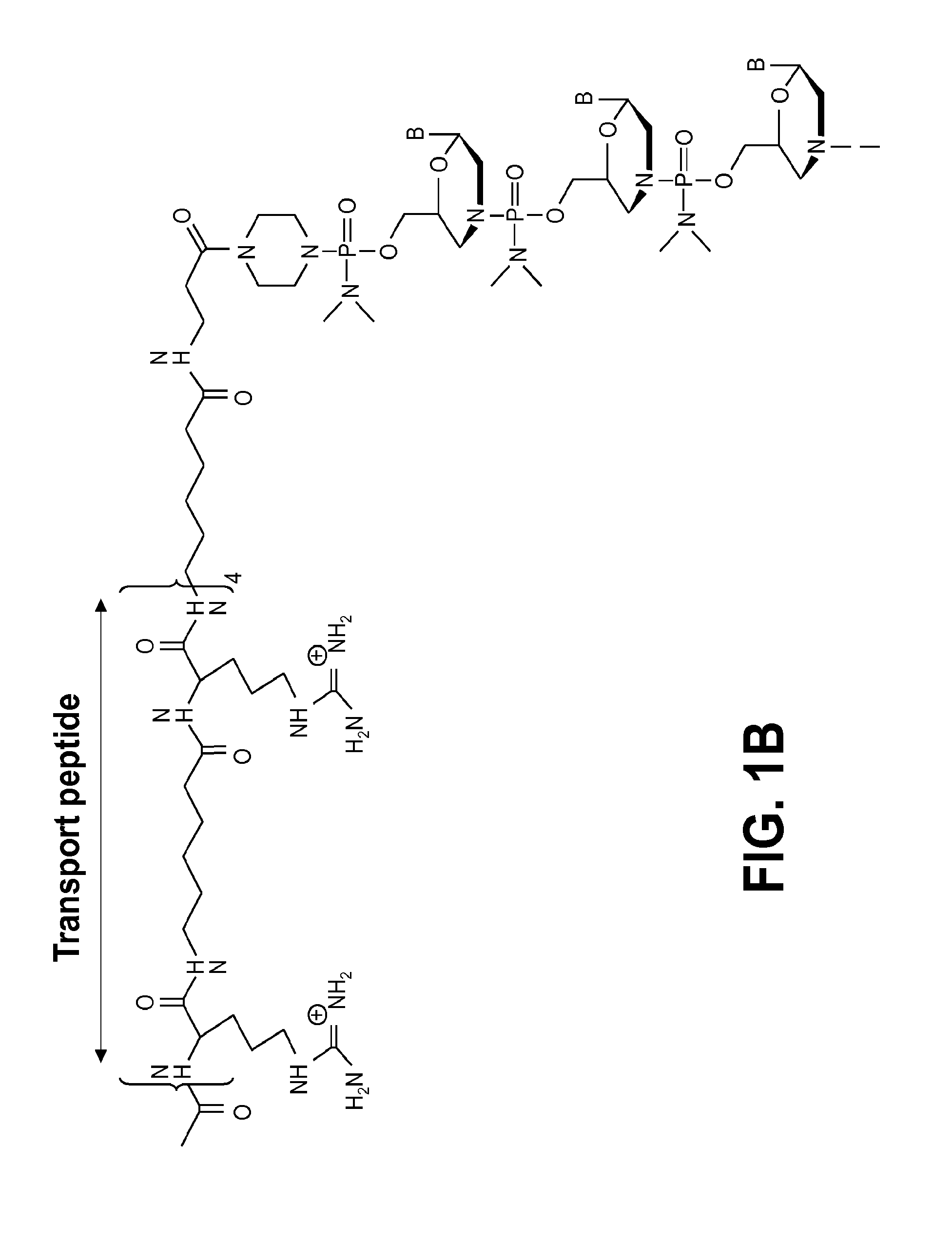
Antisense oligonucleotides
Embodiments of the present invention are directed generally to antisense compounds and compositions for the treatment of muscular dystrophy, and in particular, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). In one embodiment, the invention is directed to antisense oligonucleotide molecules, pharmaceutical compositions and formulations comprising antisense oligonucleotide molecules, and methods of treating muscular dystrophy related diseases and disorders wherein the antisense oligonucleotide molecules comprises a base sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 5-8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 24, 27, 28, 34, 35, 37, 40, 42, 44-46, 79, 97, 100, 101, and 116, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
Exon skipping compositions for treating muscular dystrophy
InactiveUS20140329881A1Enhance the activity, cellular distribution, or cellular uptake of the antisense oligonucleotideOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDuchenne muscular dystrophyMuscular dystrophy
Antisense molecules capable of binding to a selected target site in the human dystrophin gene to induce exon 44 skipping are described.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Exon skipping compositions for treating muscular dystrophy
InactiveUS20150361428A1Enhance the activity, cellular distribution, or cellular uptake of the antisense oligonucleotideSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDuchenne muscular dystrophyMuscular dystrophy
Antisense molecules capable of binding to a selected target site in the human dystrophin gene to induce exon 53 skipping are described.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Automated therapy table for treating lower extremities and method therefor
An automated therapy table is disclosed. The automated therapy table may have various support portions capable of independent automatic actuation of a person's lower extremities through passive exercise. The automated therapy table allows a patient to perform leg elevation, approximation / decompression of the leg, internal / external rotation of the leg, ankle plantar flexion / dorsiflexion, and foot inversion / eversion movements. During each movement, the patient may be instructed to think in the direction of the movement. It has been found that doing so helps increase the healing effects. The disclosed table and method may be beneficial for patients after certain operations as well as for those suffering from various forms of debilitating illnesses, such as Multiple Sclerosis, Charcot-Marie-Tooth, and Muscular Dystrophy.
Owner:SCHAEFFER DWIGHT L
Health food used for improving symptom of malnutrition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102742837ANutritional diversityEffective in preventing malnutritionFood preparationFood materialRed bean
The invention provides a health food used for improving the symptom of malnutrition. The health food comprises red dates, dangshen, bighead atractylodes rhizome, Indian bread, coix seeds, lotus seed pulp, Gorgon fruit, Chinese yam, white hyacinth beans, wolfberry, longan pulp, red beans, peanut kernels with red coats, brown granulated sugar, starch syrup, walnut kernels, sunflower seeds, pine nuts, raisin and black sesame. The health food provided in the invention is green and safe and has comprehensive nutrients since natural food materials and articles functioning both as a medicine and a food material are used as main raw materials for the health food. The health food supplements various nutritional components such as a variety of amino acids, unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and trace elements through adjusting the functions of the spleen and the stomach, can be used for preventing and controlling the symptom of malnutrition and is a purely natural tonifying health food suitable for long-term use.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Compositions and methods for duchenne muscular dystrophy gene therapy
InactiveUS20150196670A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDuchenne's Muscular DystrophyFhit gene
The present invention relates to a gene therapy method for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, or DMD.
Owner:ASSOC FRE CONTRE LES MYOPATHIES
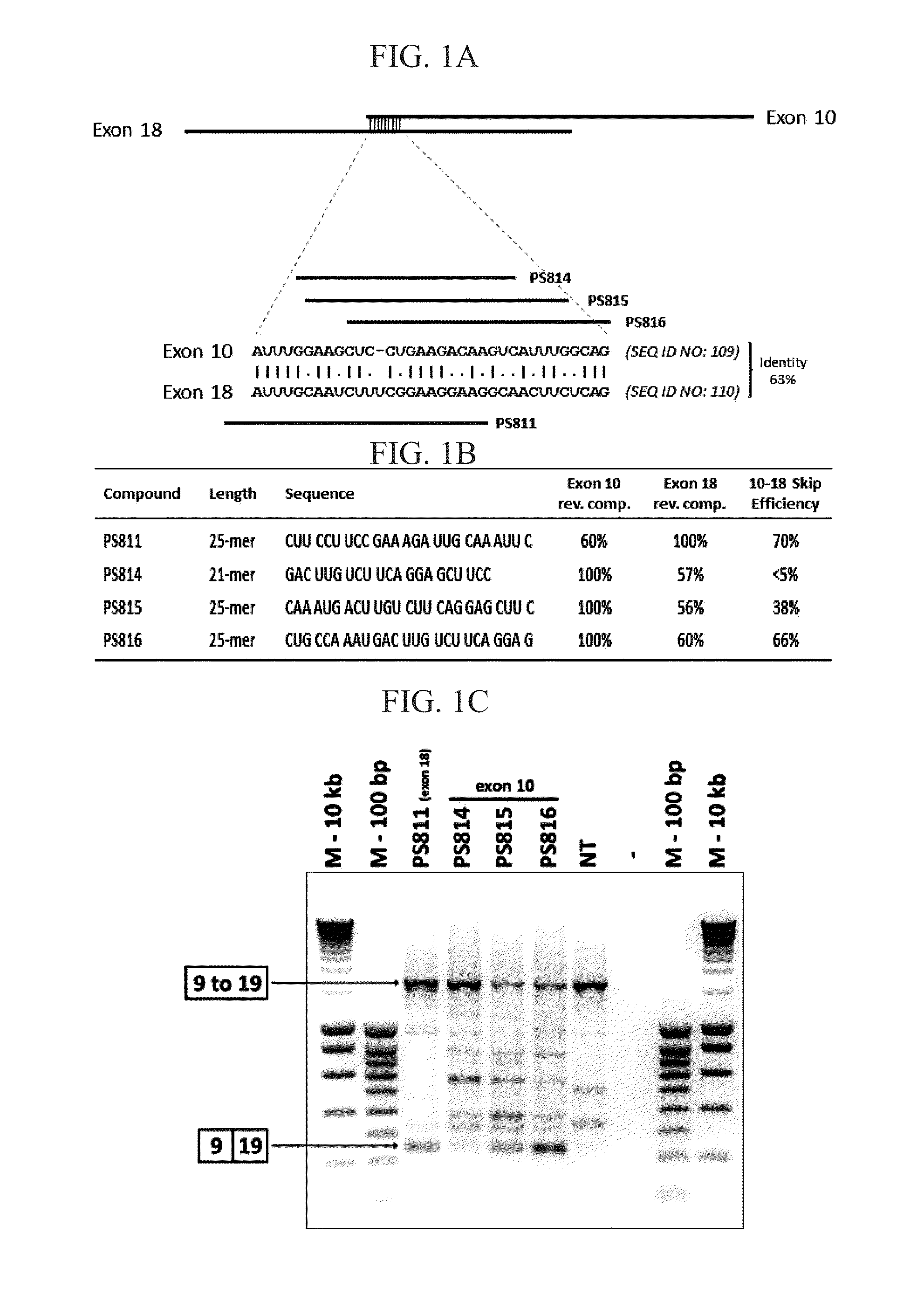
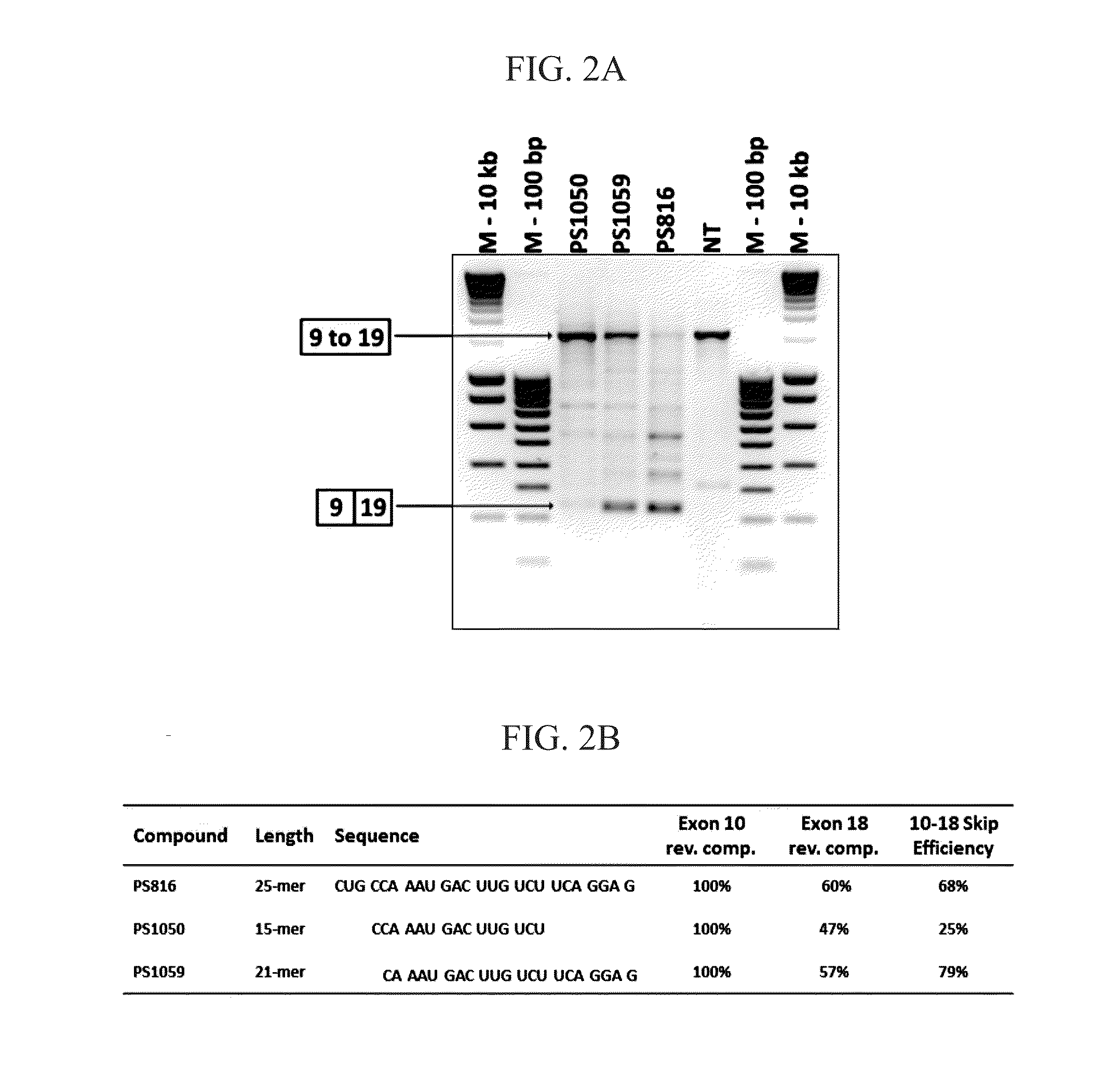
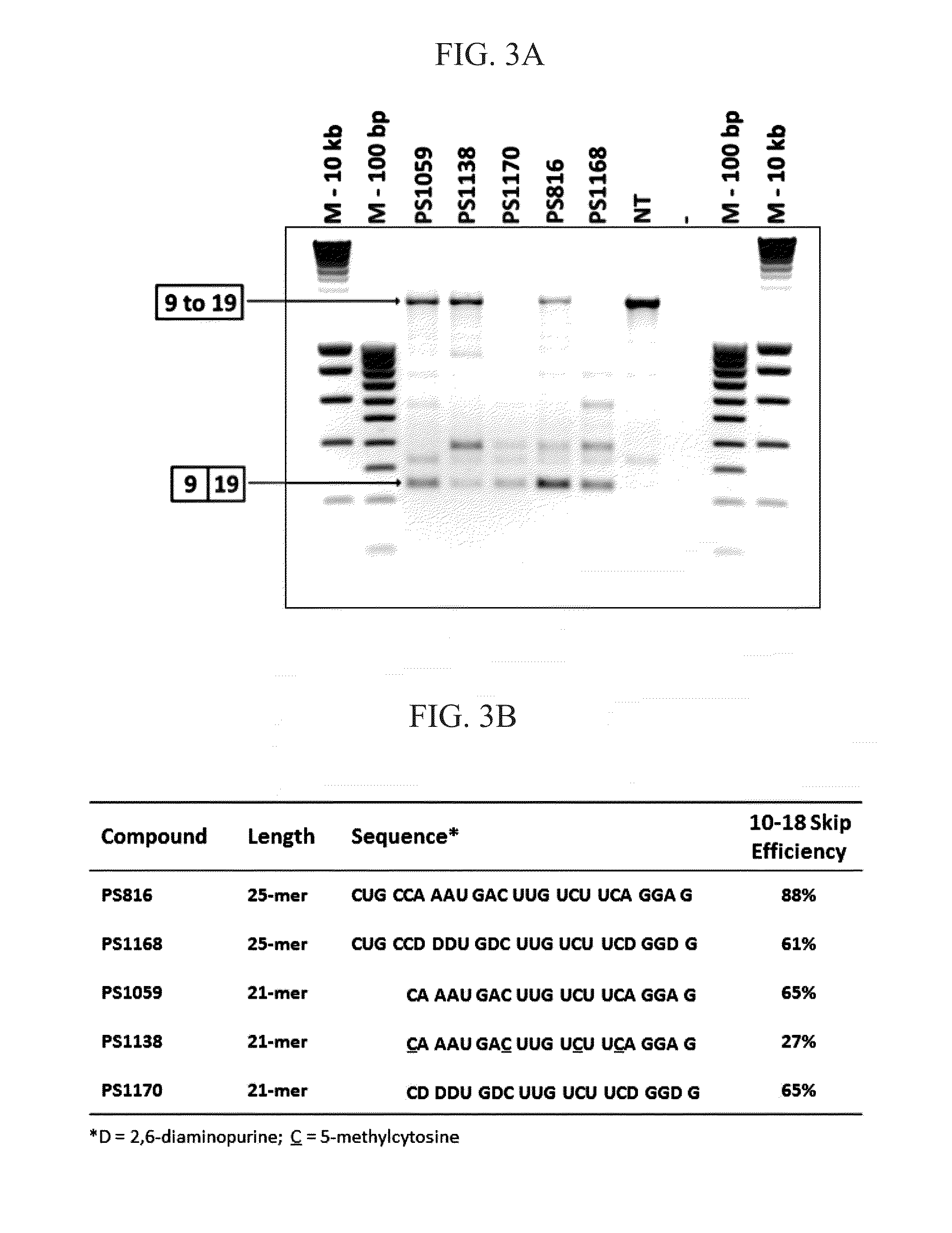
Oligonucleotide for the Treatment of Muscular Dystrophy Patients
InactiveUS20150191725A1Avoid or decrease a potential multimerisation or aggregationSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDystrophinExon
The invention relates to an oligonucleotide and to a pharmaceutical composition comprising said oligonucleotide. This oligonucleotide is able to bind to a region of a first exon from a dystrophin pre-mRNA and to a region of a second exon within the same pre-mRNA, wherein said region of said second exon has at least 50% identity with said region of said first exon, wherein said oligonucleotide is suitable for the skipping of said first and second exons of said pre-mRNA, and preferably the entire stretch of exons in between.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV
ActRIIB proteins and variants and uses therefore relating to utrophin induction for muscular dystrophy therapy
In certain aspects, the present invention provides compositions and methods for inducing utrophin expression in muscle with an ActRIIB protein as therapy for muscular dystrophy. The present invention also provides methods of screening compounds that modulate activity of an ActRIIB protein and / or an ActRIIB ligand.
Owner:ACCELERON PHARMA INC
Lipid raft, caveolin protein, and caveolar function modulation compounds and associated synthetic and therapeutic methods
The present invention is directed to the modulation of lipid rafts, caveolin proteins, or caveolar functions and processes by platinum(IV) compounds. Caveolae and / or lipid rafts are associated with cell transcription regulation, membrane and cellular transport, cell membrane receptor function, cellular trafficking, antigen presentation, cell differentiation and activation, cytokine modulation, membrane structure and function, and protein modulation. Caveolae, caveolin proteins and lipid rafts are known therapeutic targets for numerous biological functions. Diseases and disorders currently known to be therapeutically targeted through caveolae and / or lipid rafts include diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis, pulmonary fibrosis, multiple sclerosis, viral and prion diseases, neuronal disorders, degenerative muscular dystrophies, and autoimmune disorders.
Owner:KAY HEIDI
Methods of diagnosis and prognosis for a muscular dystrophy
InactiveUS20090280517A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDuchenne muscular dystrophyMyopathy
The invention relates to the treatment, diagnosis, and prognosis of a muscular dystrophy or myopathy. The present inventors have found that the quantity of mu-crystallin is increased in a muscular dystrophy. In particular, the inventors have found that mu-crystallin is increased in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). Based on the inventors' findings, the invention provides a novel means for the treatment, diagnosis, and prognosis of a muscular dystrophy or myopathy.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Methods and materials for producing transgenic artiodactyls
ActiveUS20120220037A1Animal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological materialsHuman disease
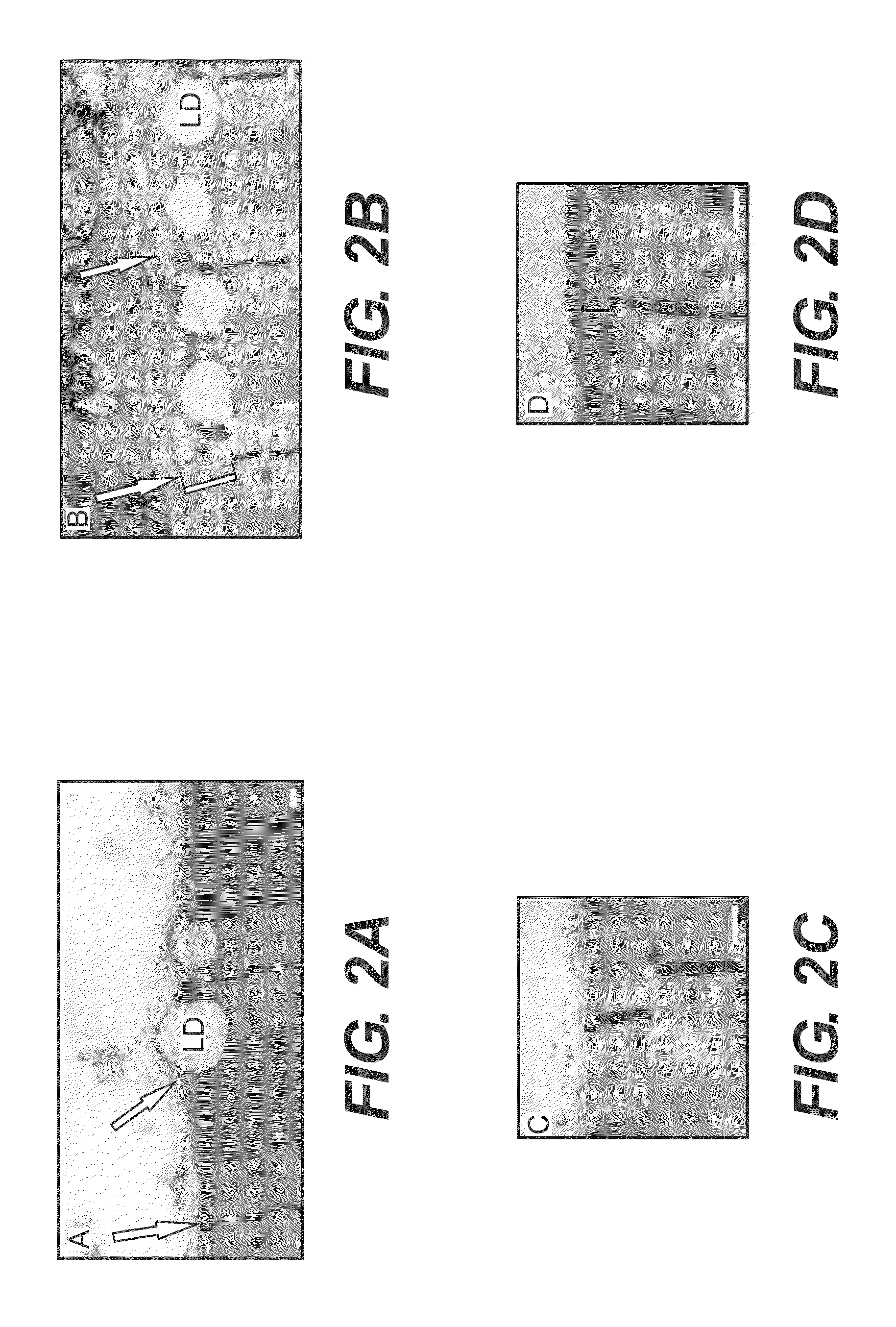
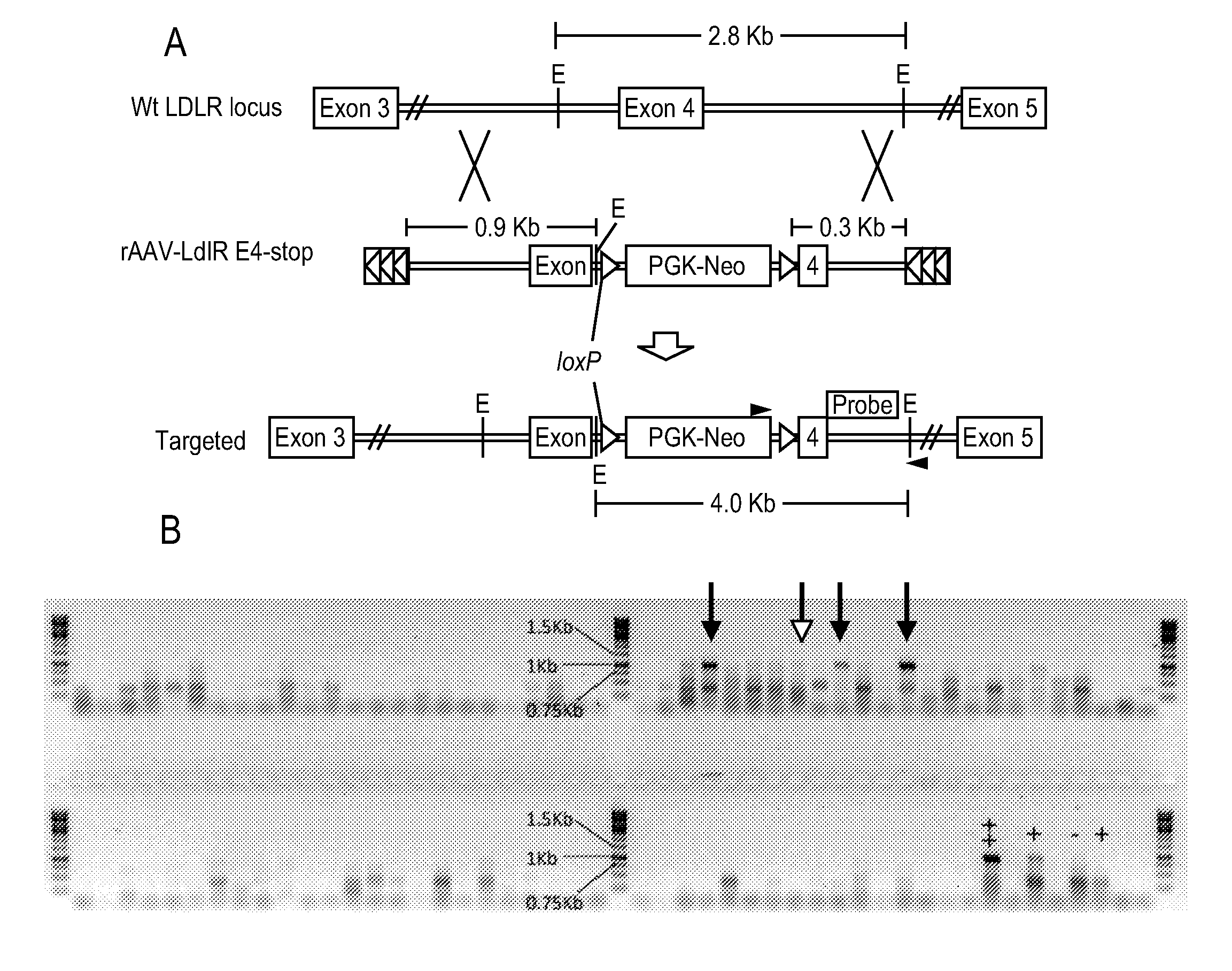
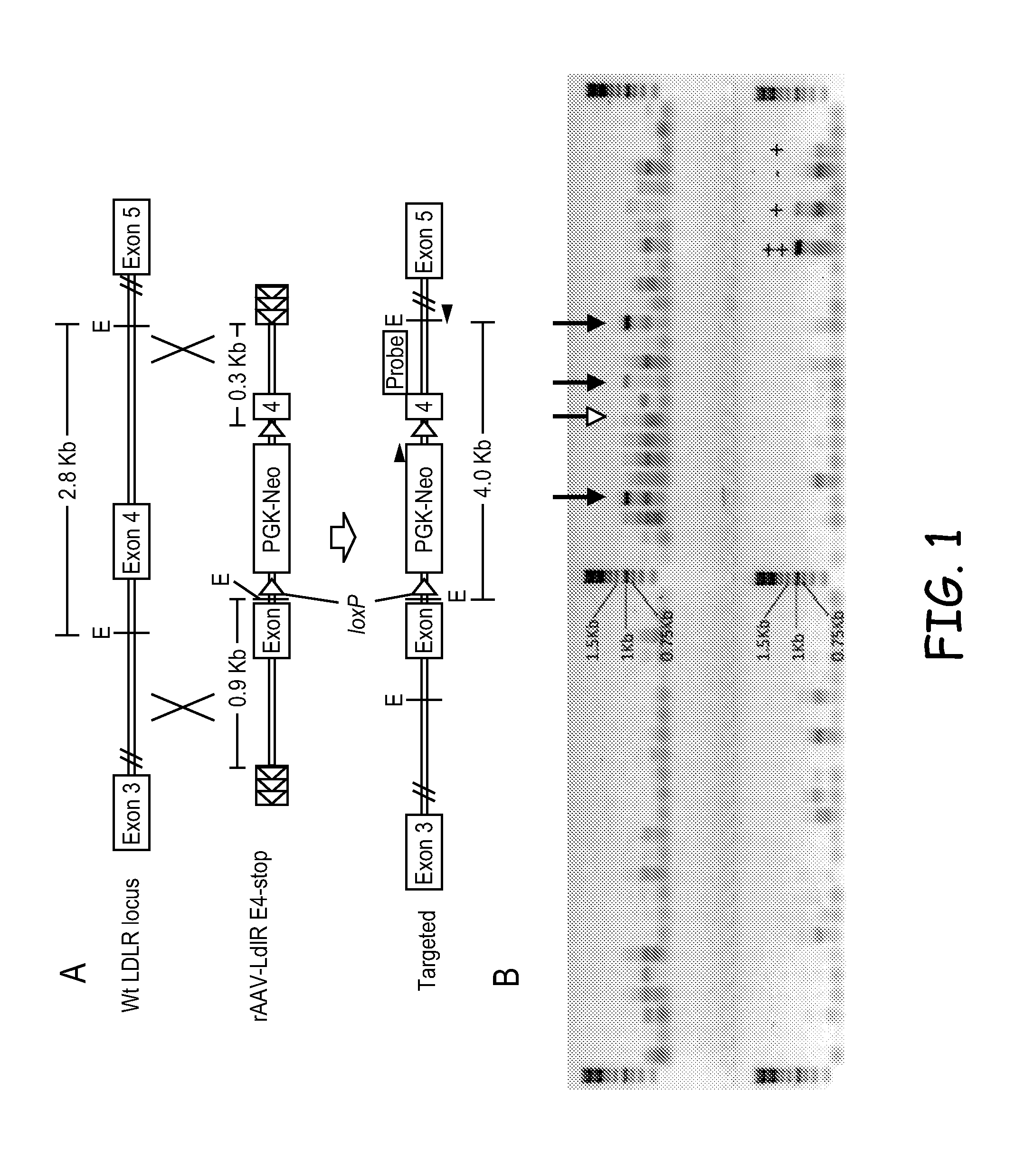
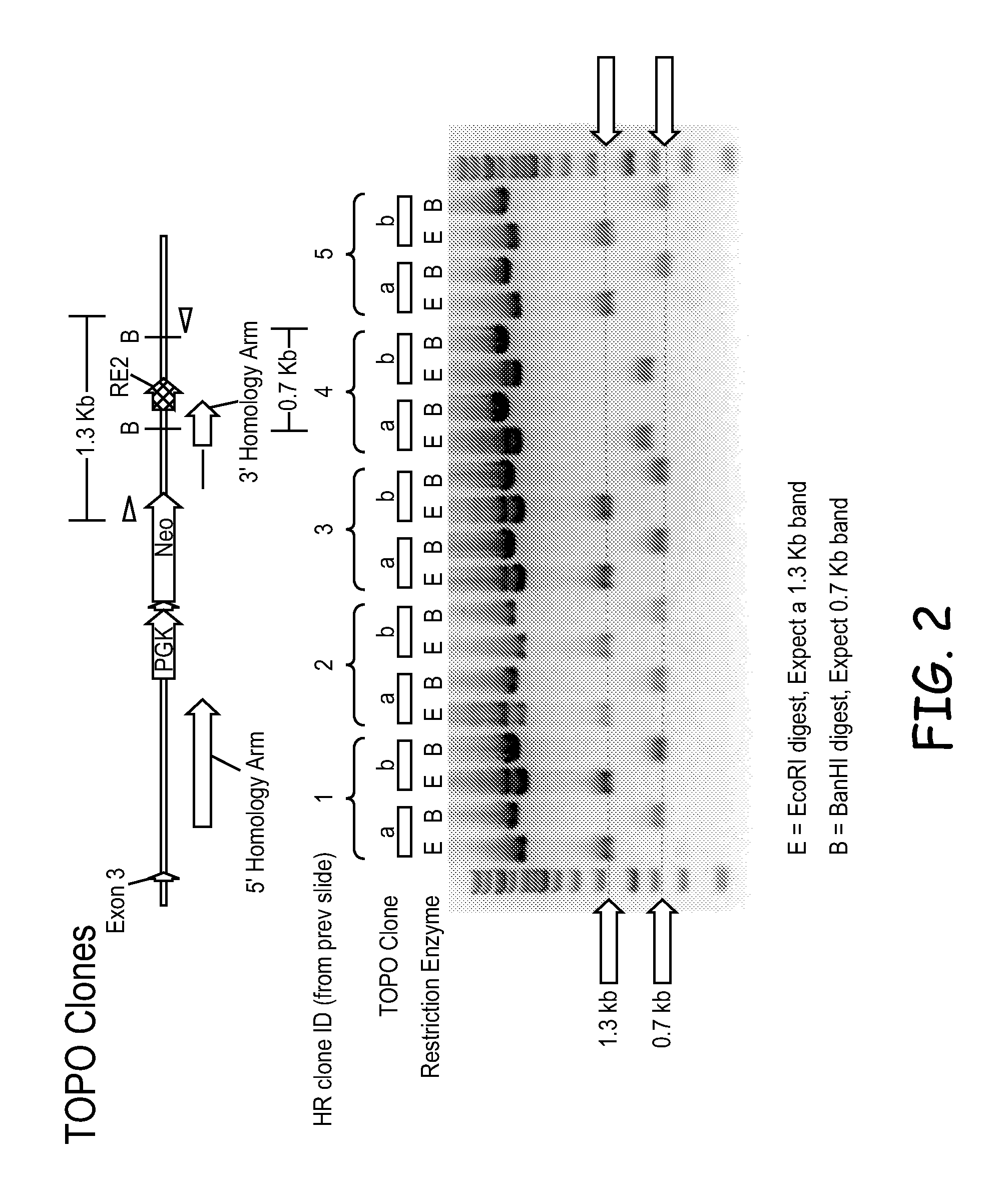
Swine animal models comprising a genomic disruption of an endogenous gene chosen from the group consisting of a Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor gene LDLR, Duchene's Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) gene, and hairless gene (HR). Methods of preparing transfected cells useful for making a transgenic animal comprising exposing a first group of cells to a transfection agent and reseeding the group with additional cells that have not been exposed to the agent. The transgenic animals are useful for medical and scientific animal models of human diseases and conditions, as well as sources for cells, tissues, and biomaterials.
Owner:RECOMBINETICS INC
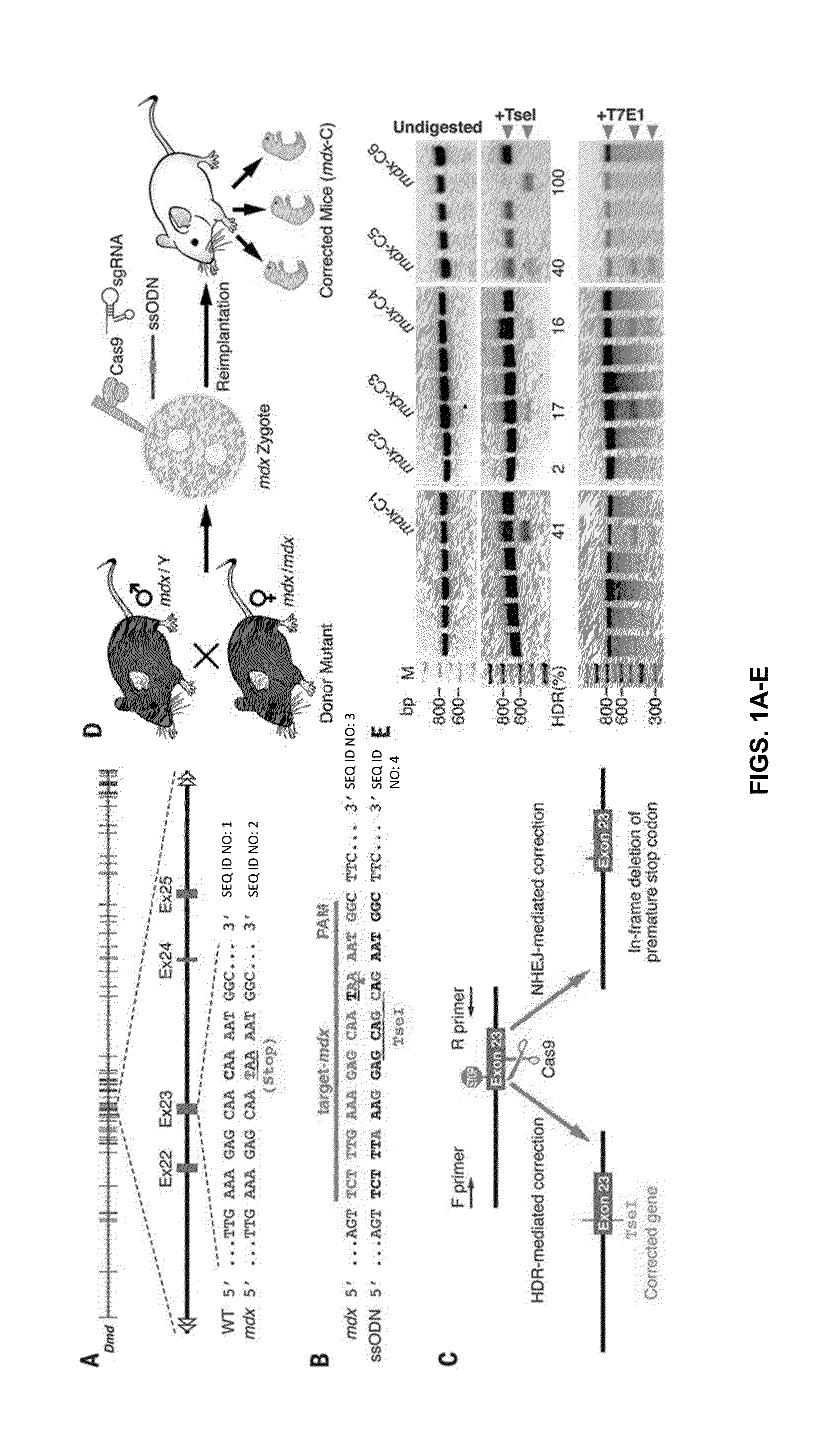
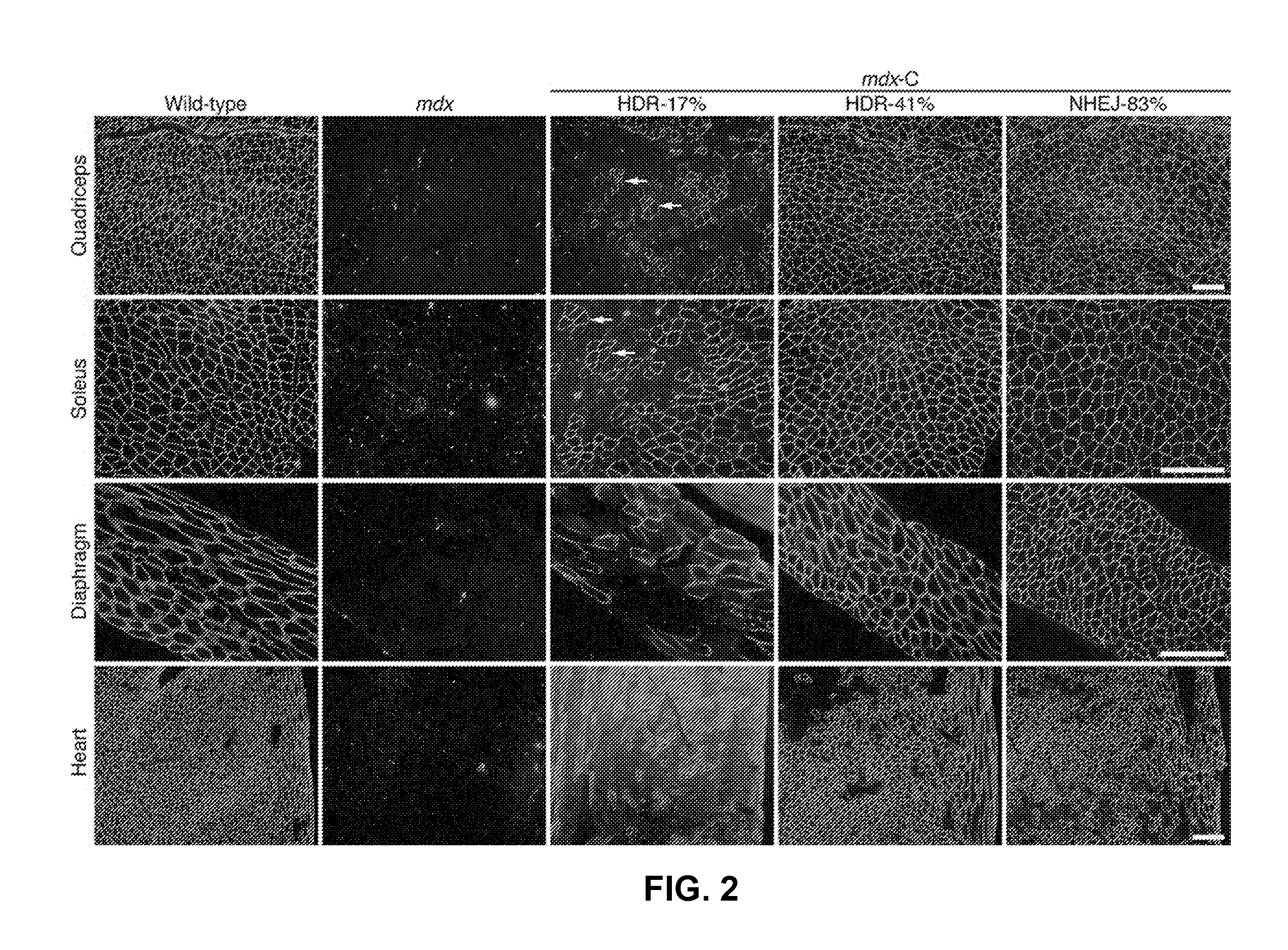
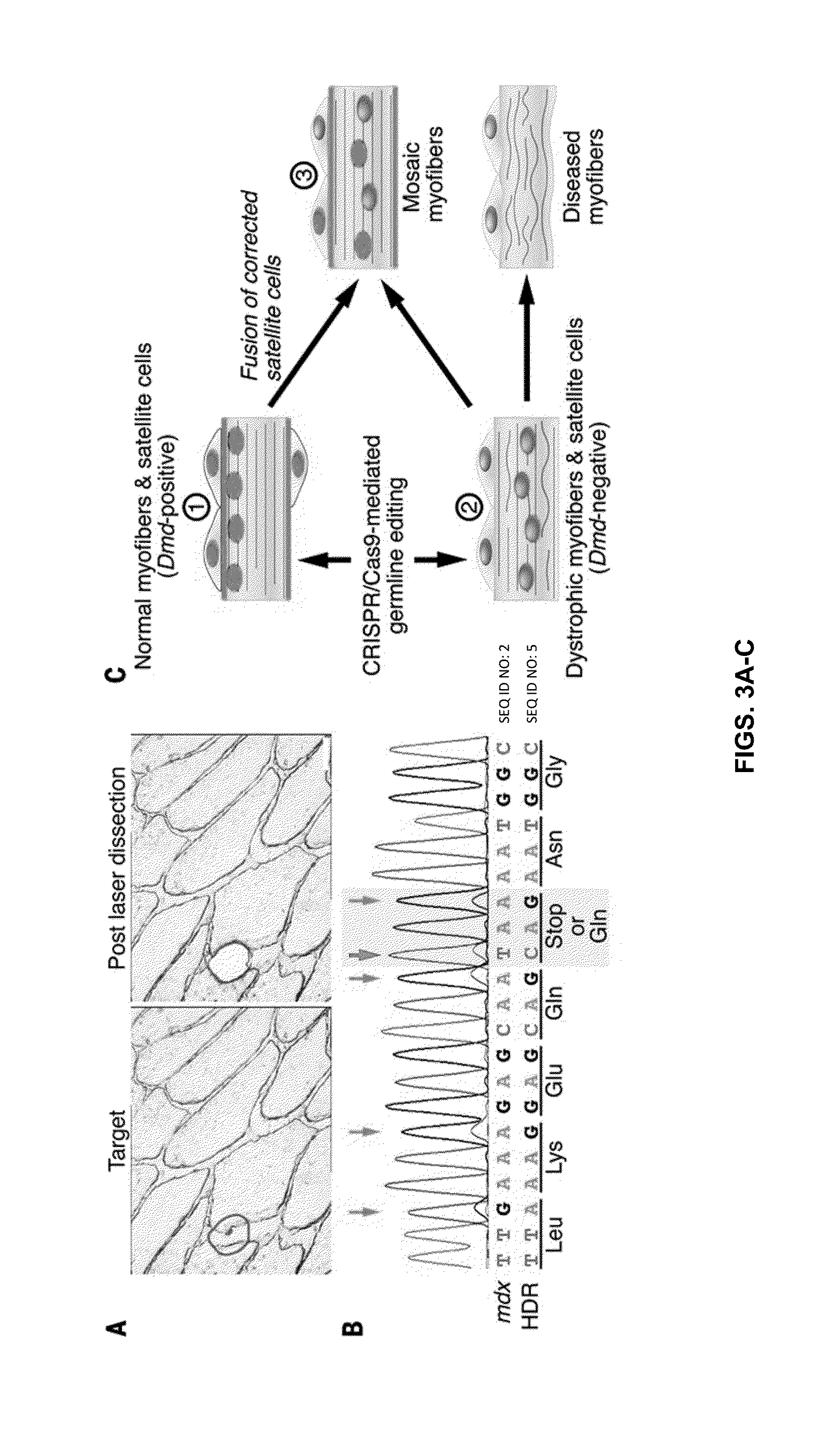
Prevention of muscular dystrophy by crispr/cas9-mediated gene editing
InactiveUS20160058889A1Lower Level RequirementsImprove grip strengthSplicing alterationPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseIn vivo
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is an inherited X-linked disease caused by mutations in the gene encoding dystrophin, a protein required for muscle fiber integrity. The disclosure reports CRISPR / Cas9-mediated gene editing (Myo-editing) is effective at correcting the dystrophin gene mutation in the mdx mice, a model for DMD. Further, the disclosure reports optimization of germline editing of mdx mice by engineering the permanent skipping of mutant exon (exon 23) and extending exon skipping to also correct the disease by post-natal delivery of adeno-associate virus (AAV). AAV-mediated Myo-editing can efficiently rescue the reading frame of dystrophin in mdx mice in vivo. The disclosure reports means of Myo-editing-mediated exon skipping has been successfully advanced from somatic tissues in mice to human DMD patients-derived iPSCs (induced pluripotent stem cells). Custom Myo-editing was performed on iPSCs from patients with differing mutations and successfully restored dystrophin protein expression for all mutations in iPSCs-derived cardiomyocytes.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Treatment of muscular dystrophy with cord blood cells
InactiveUS7452529B2Reduce rejectionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDuchenne muscular dystrophyVein
The invention features methods for treating a patient suffering from muscular dystrophy by administration of umbilical cord blood cells, e.g., by IV infusion.
Owner:VIACORD +1
Compositions and Methods for Characterizing and Treating Muscular Dystrophy
ActiveUS20130347136A1Reduced expression levelImprove expression levelMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDuchenne muscular dystrophyMedicine
Compositions and methods for identifying new treatments for Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD), and uses thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Pharmaco-cellular therapeutic method for the treatment of muscular dystrophies
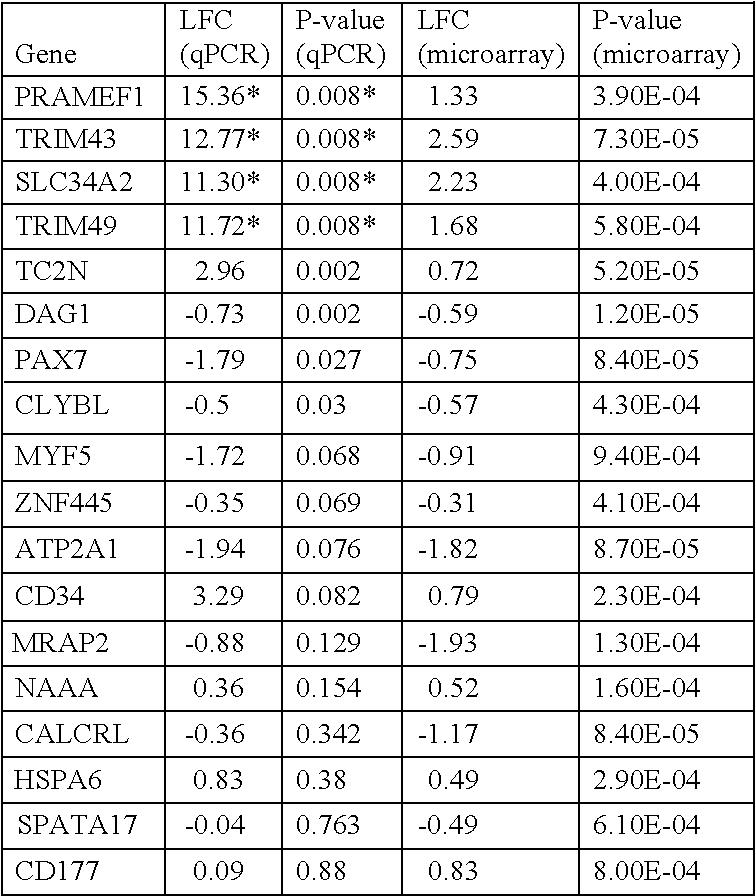
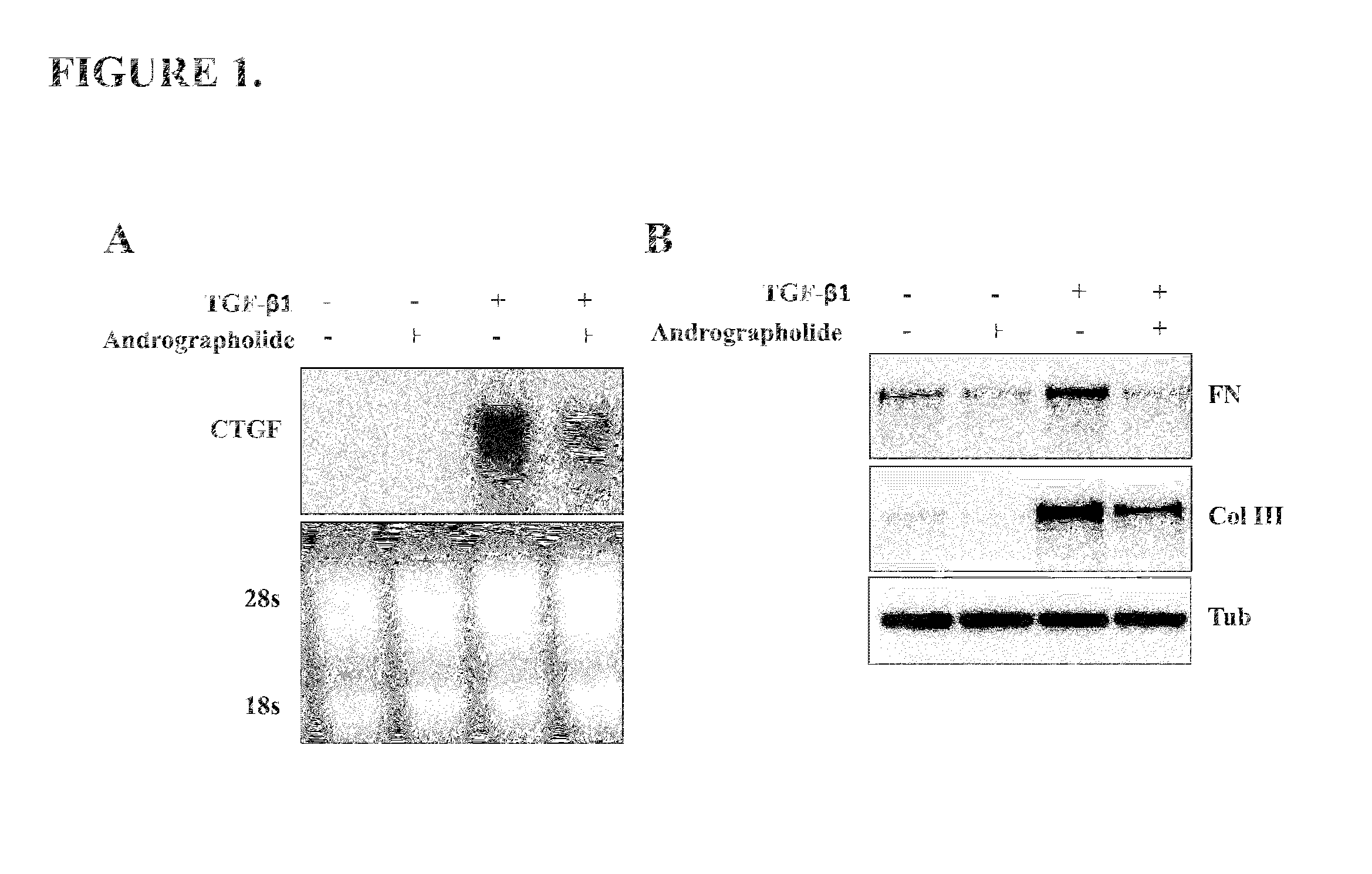
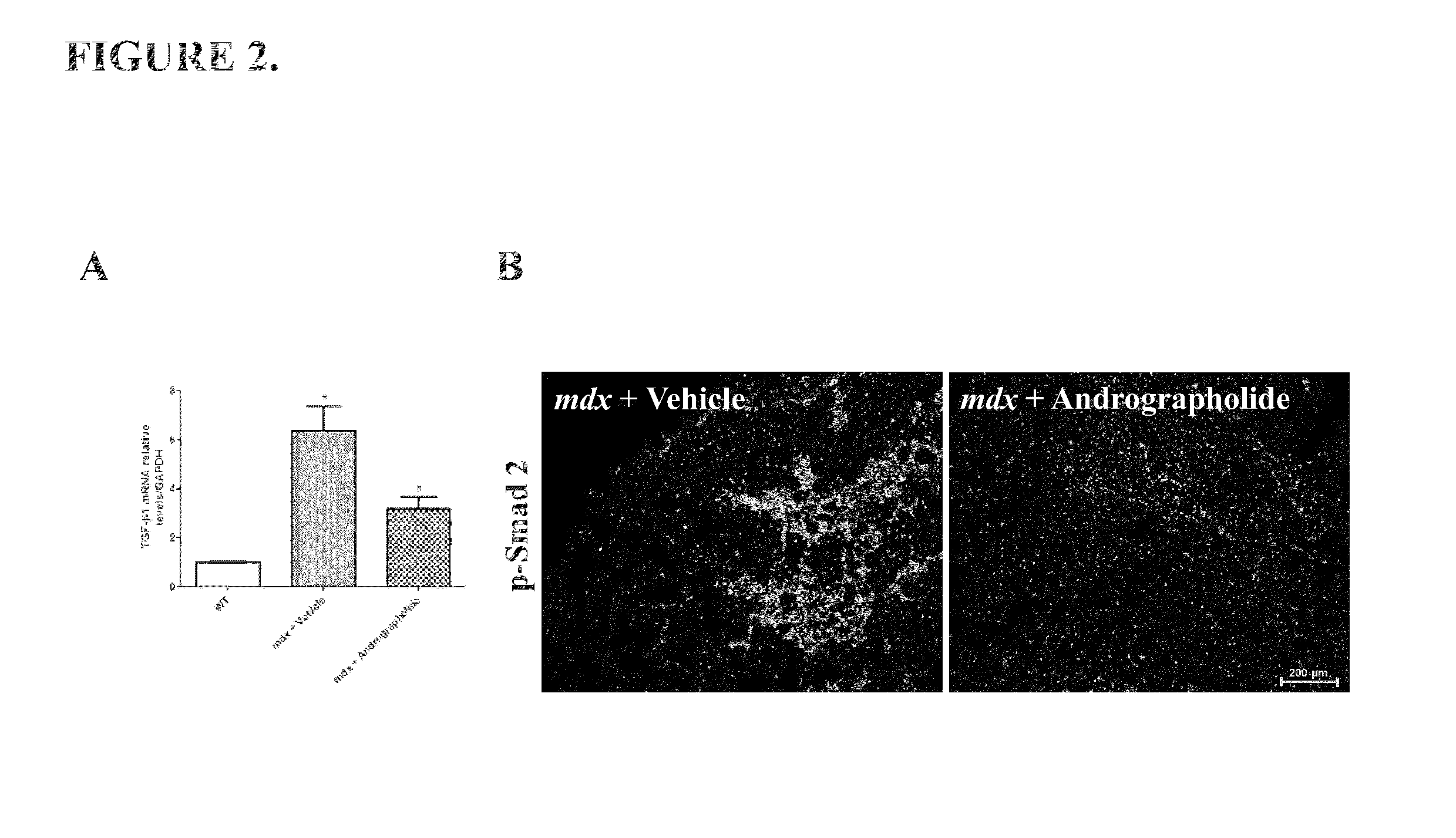
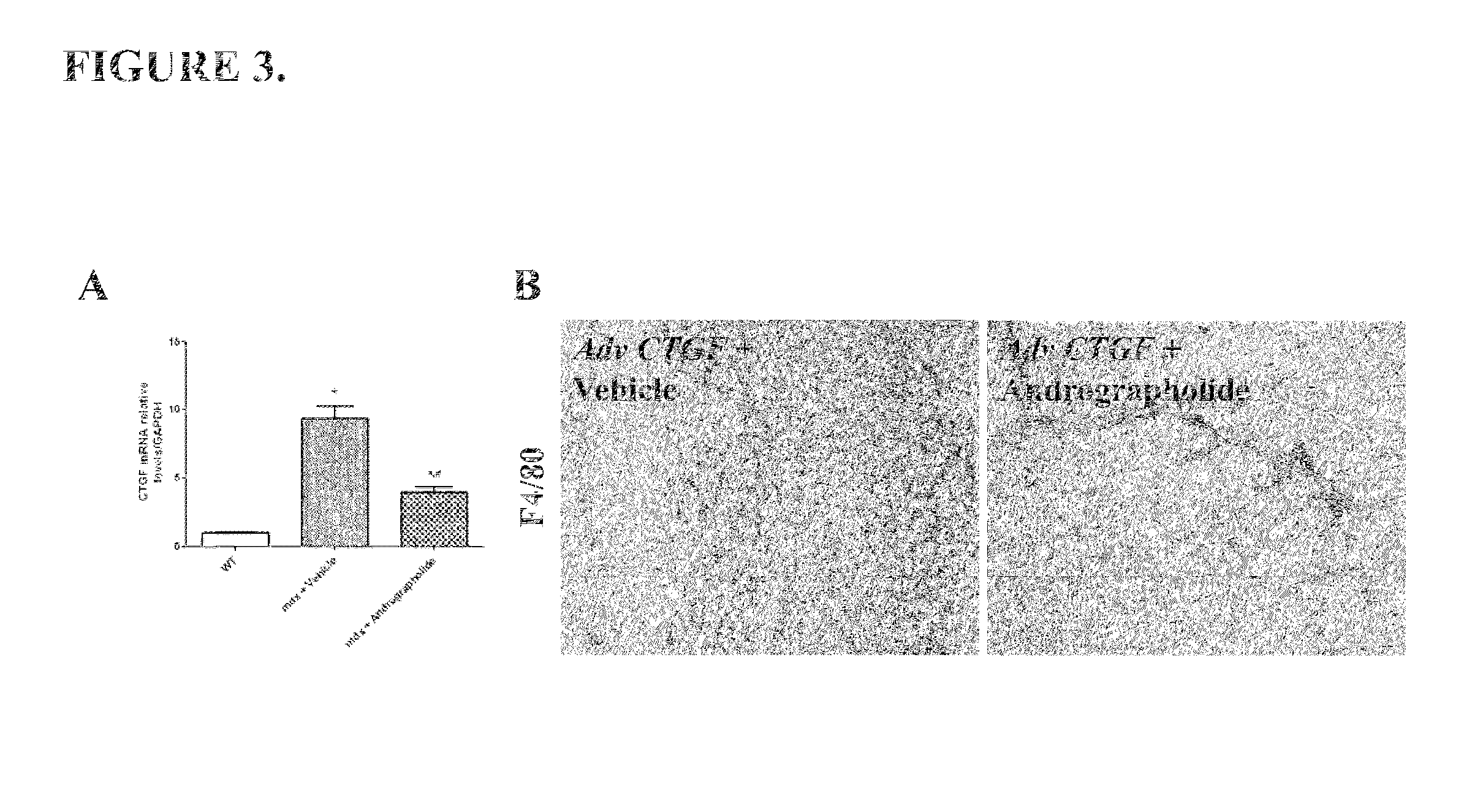
A method of treating a muscular dystrophy disease in a patient includes administering an effective amount of a botanical drug isolated from Andrographis paniculata in combination with cell therapy. The method improves skeletal muscle performance.
Owner:PONTIFISIA UNIVERSIDAD KATOLIKA DE CHILE
Methods for Treatment of Muscular Dystrophy
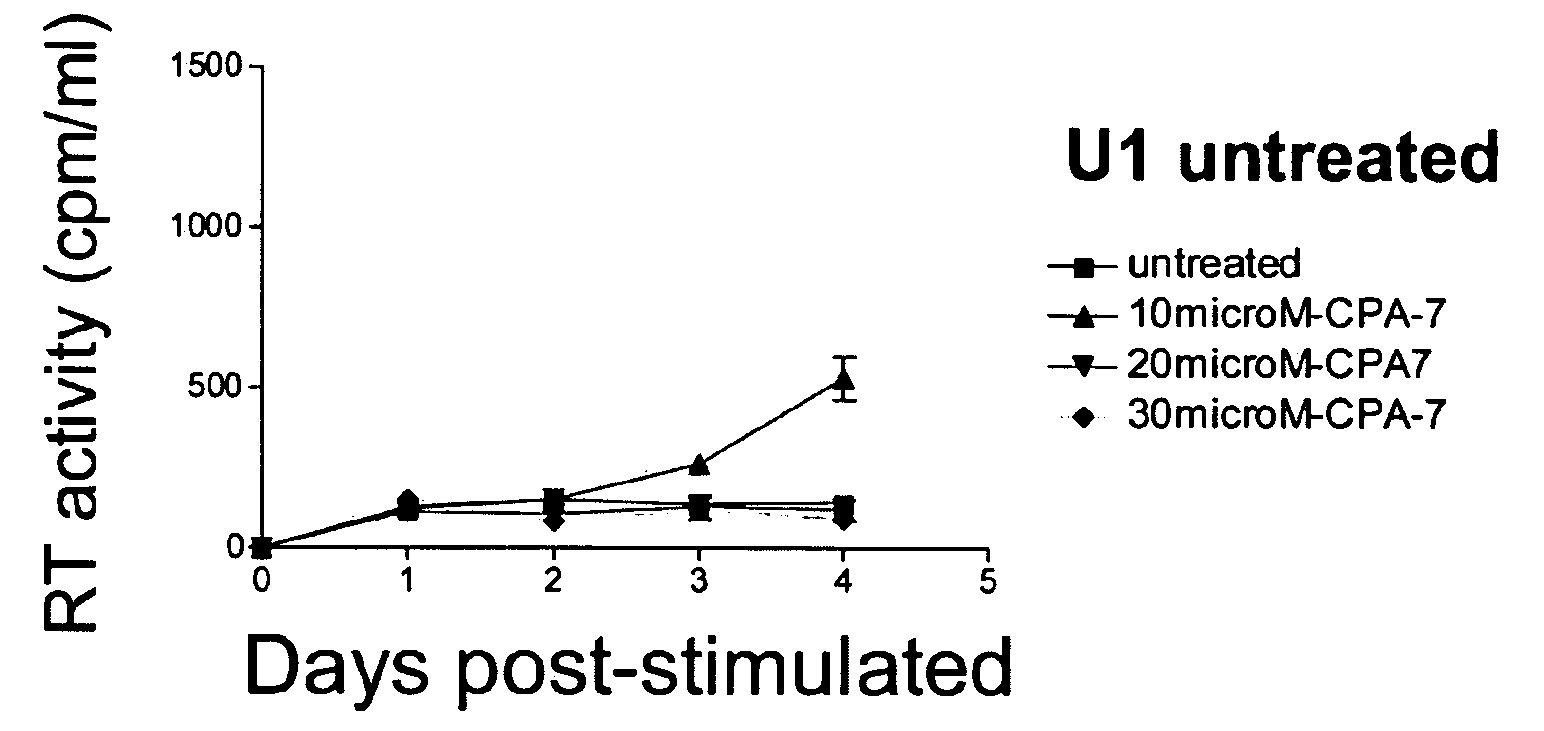
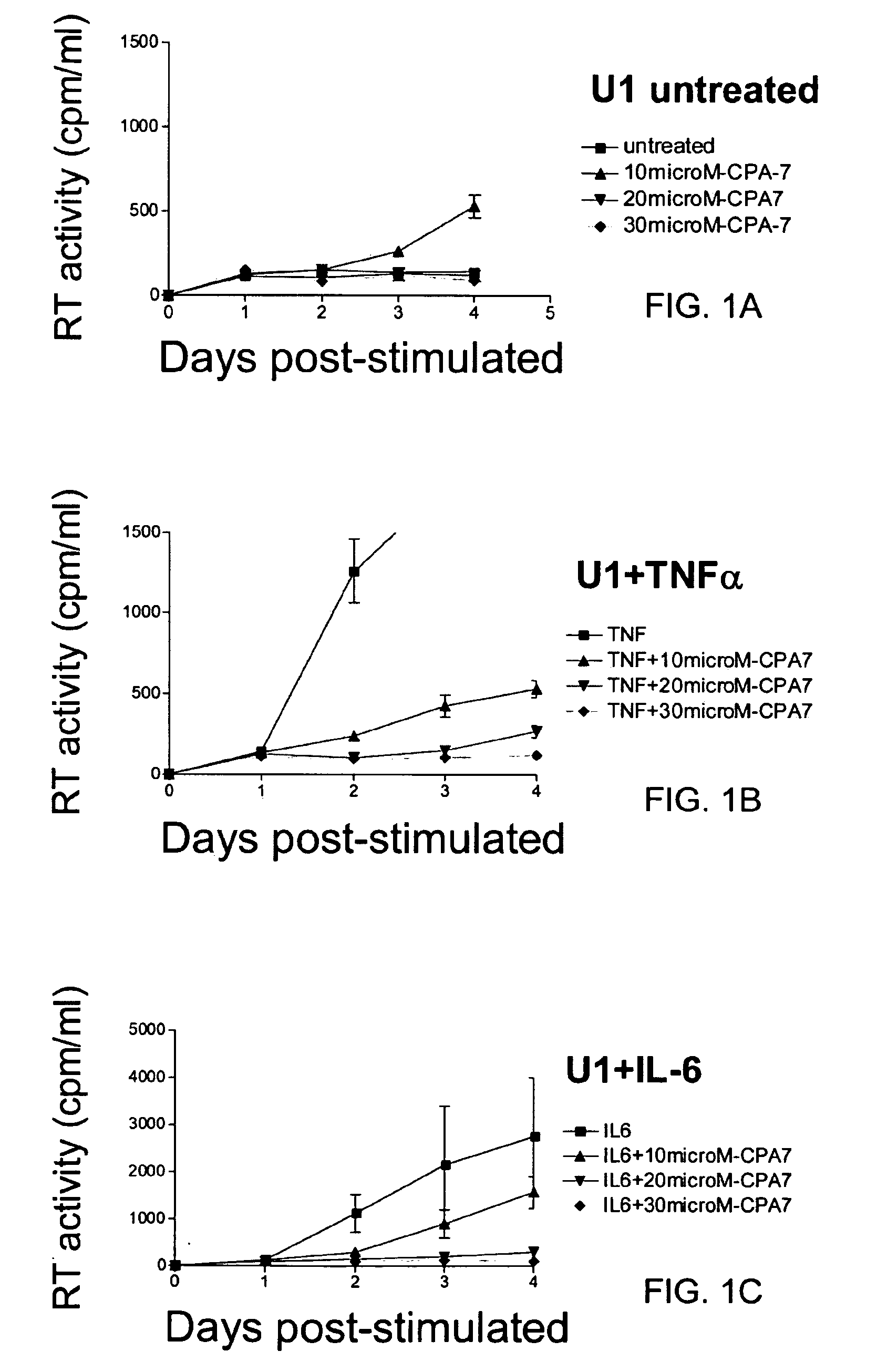
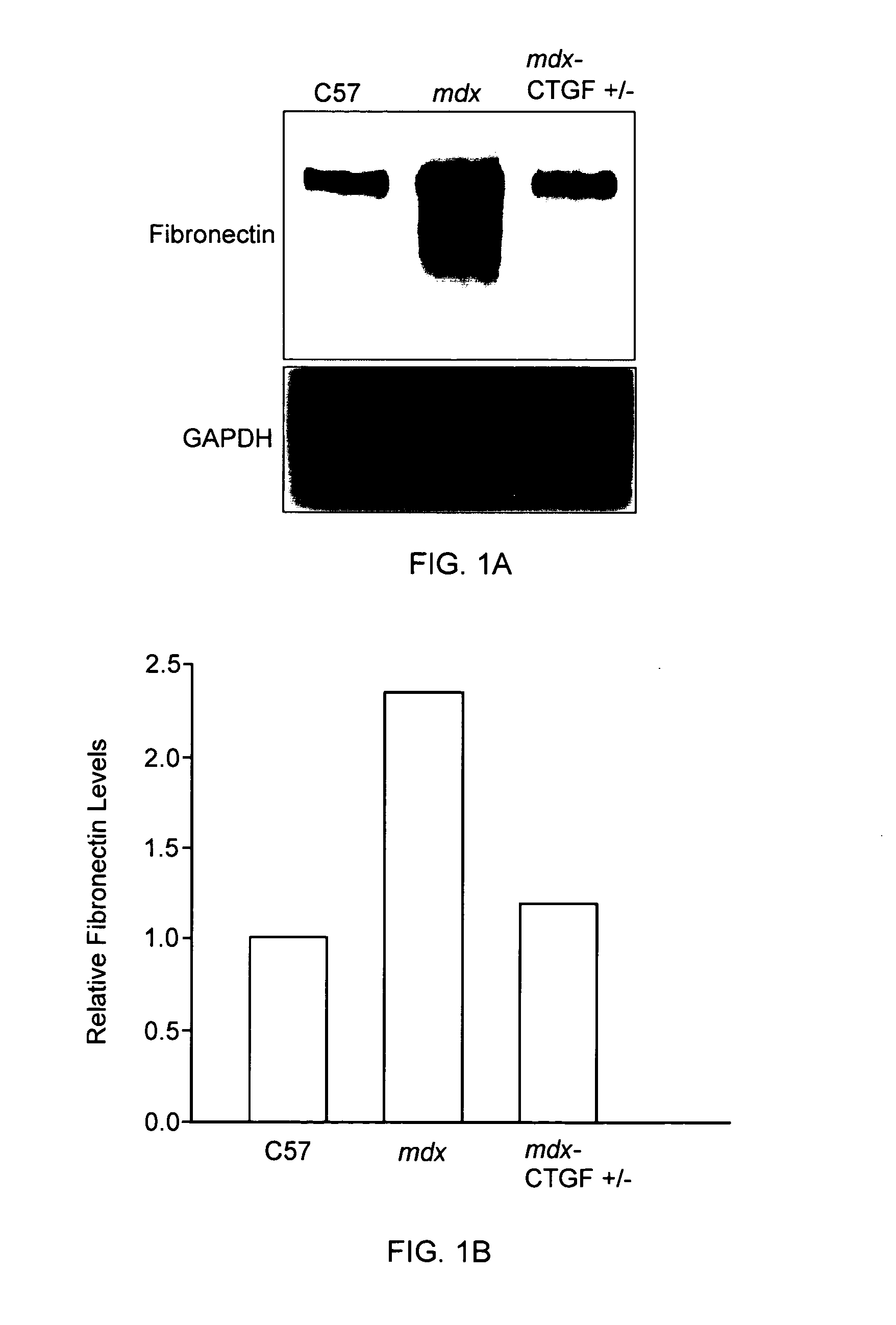
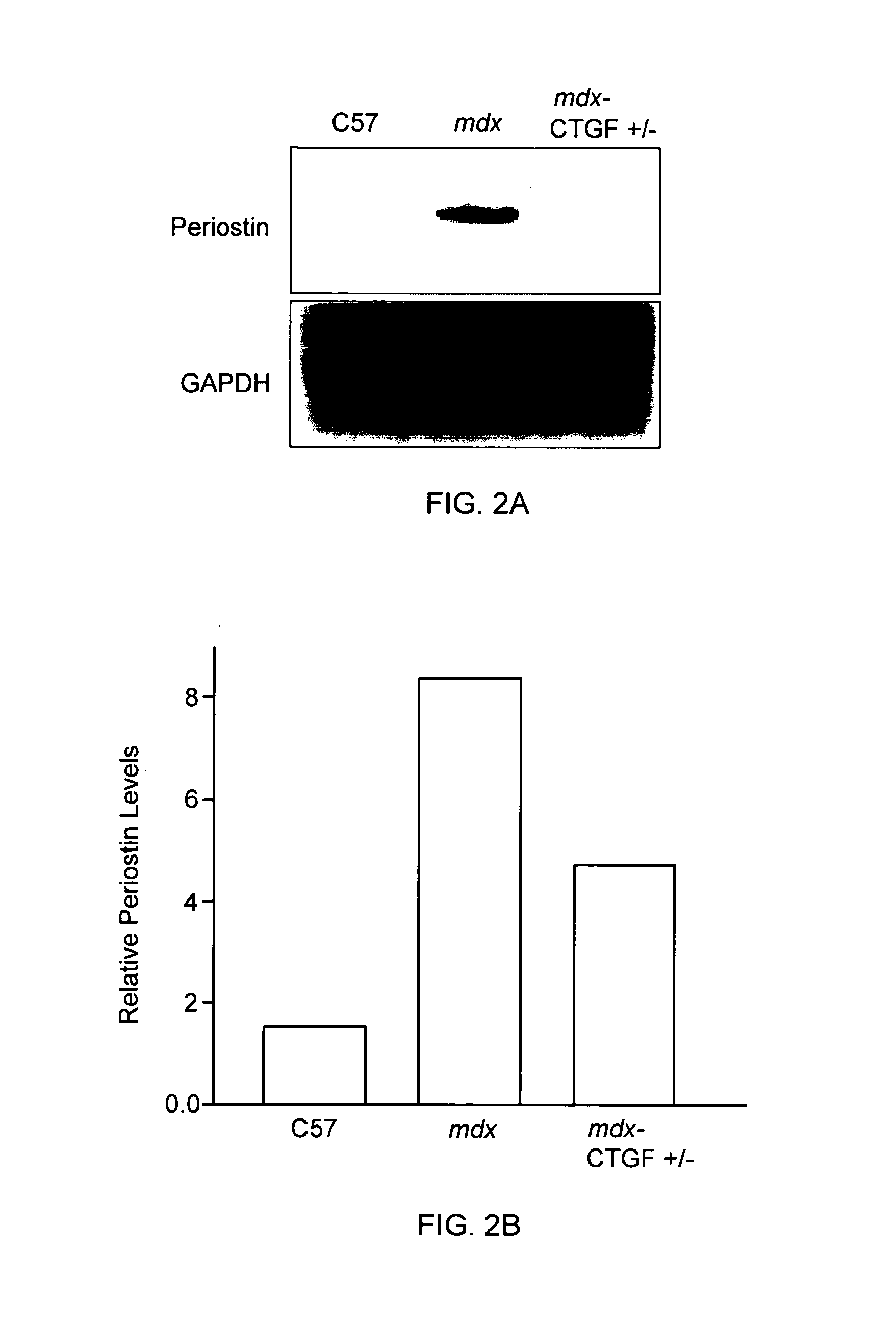
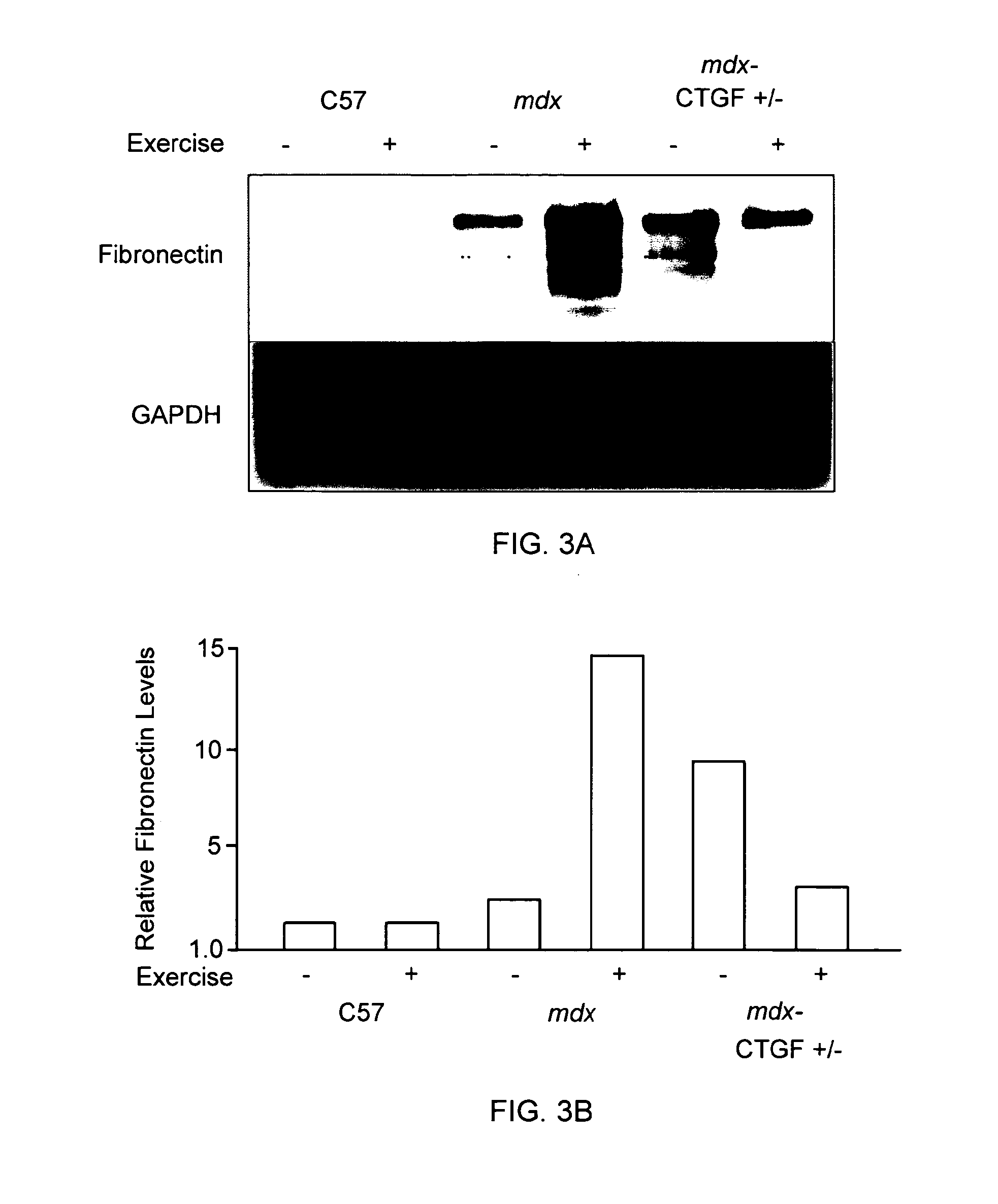
ActiveUS20120164151A1Improve muscle functionReduce decreaseOrganic active ingredientsMuscular disorderDystrophy fuchsMuscular dystrophy
The present invention relates to methods and agents useful for treating muscular dystrophy. Methods and agents for treating various physiological and pathological features associated with muscular dystrophy are also provided.
Owner:FIBROGEN INC
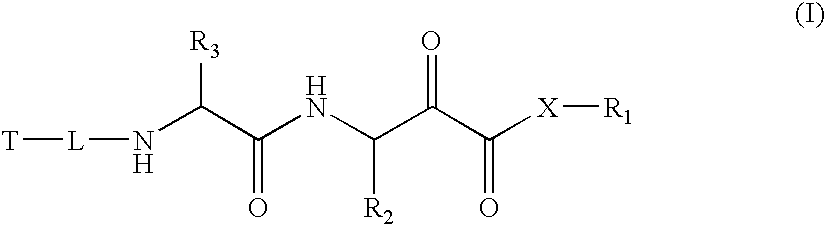
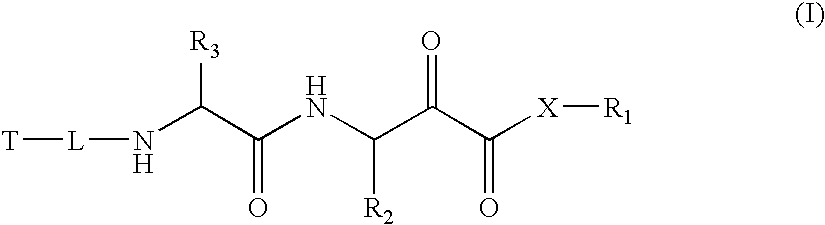
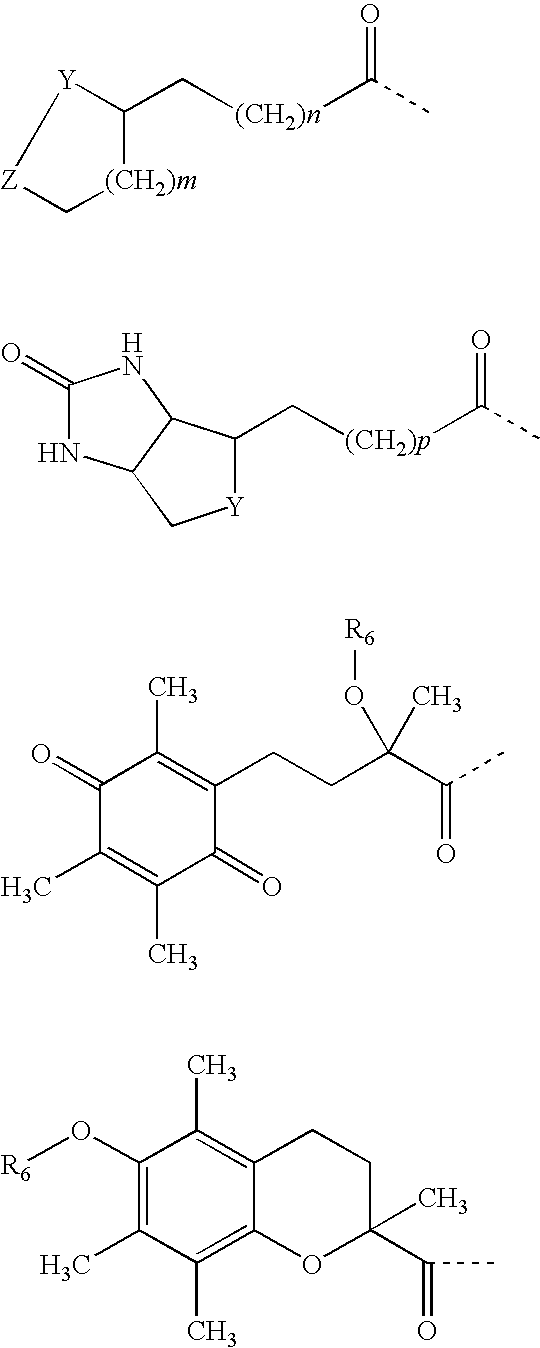
Alpha-keto carbonyl calpain inhibitors
InactiveUS20060258598A1Maintain good propertiesSenses disorderNervous disorderCathepsin HPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to novel α-keto carbonyl calpain inhibitors for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and neuromuscular diseases including Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Becker Muscular Dystrophy and other muscular dystrophies. Disuse atrophy and general muscle wasting can also be treated. Diseases of the eye, in particular cataract, can be treated as well. Generally all conditions where elevated levels of calpains are involved can be treated. The compounds of the invention may also inhibit other thiol proteases such as cathepsin B, cathepsin H, cathepsin L, papain or the like. Multicatalytic Protease (MCP) also known as proteasome may also be inhibited and the compounds can therefore be used to treat cell proliferative diseases such as cancer, psoriasis, and restenosis. The compounds of the present invention are also inhibitors of cell damage by oxidative stress through free radicals and can be used to treat mitochondrial disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, where elevated levels of oxidative stress are involved.
Owner:SANTHERA PHARMA SCHWEIZ
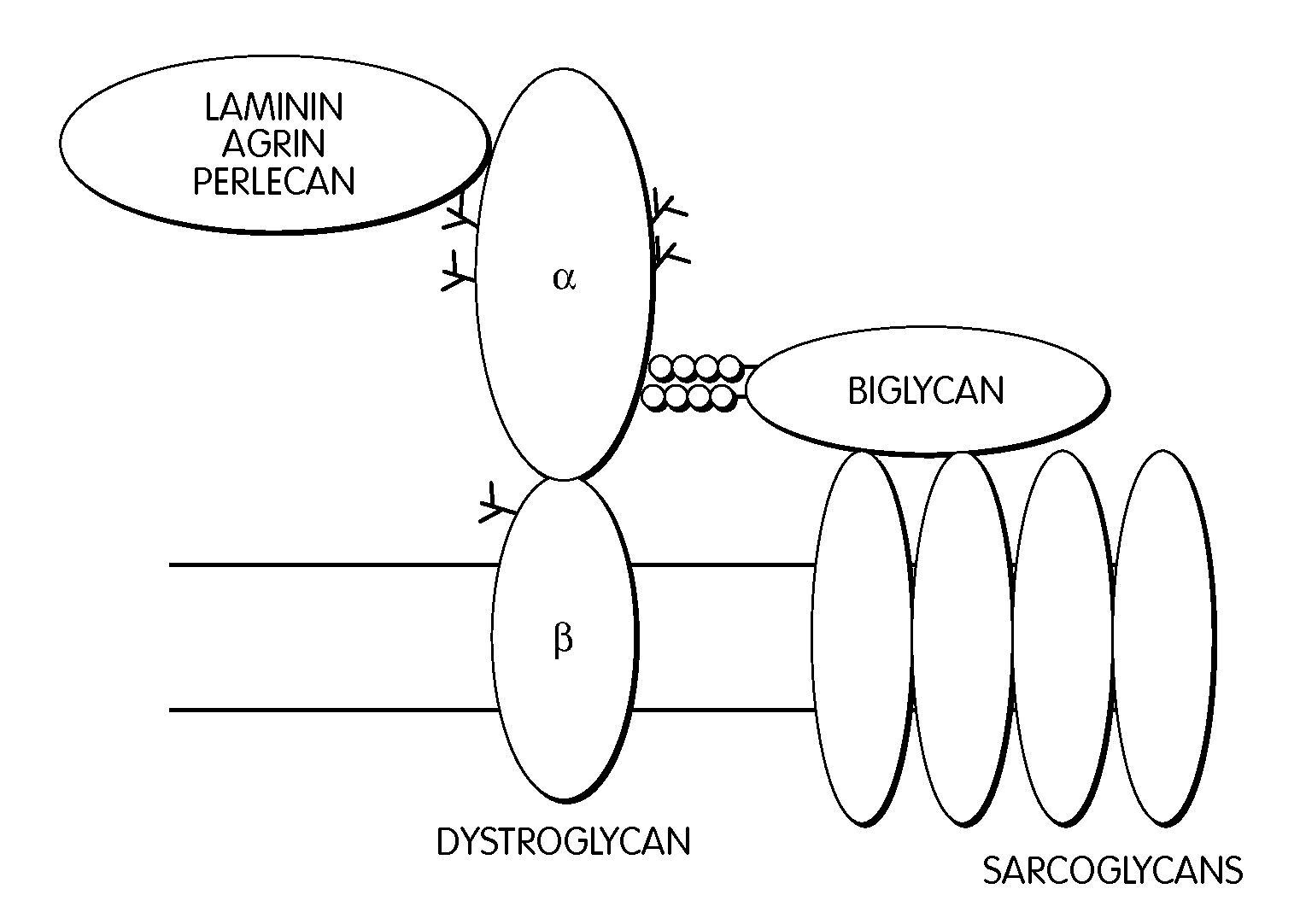
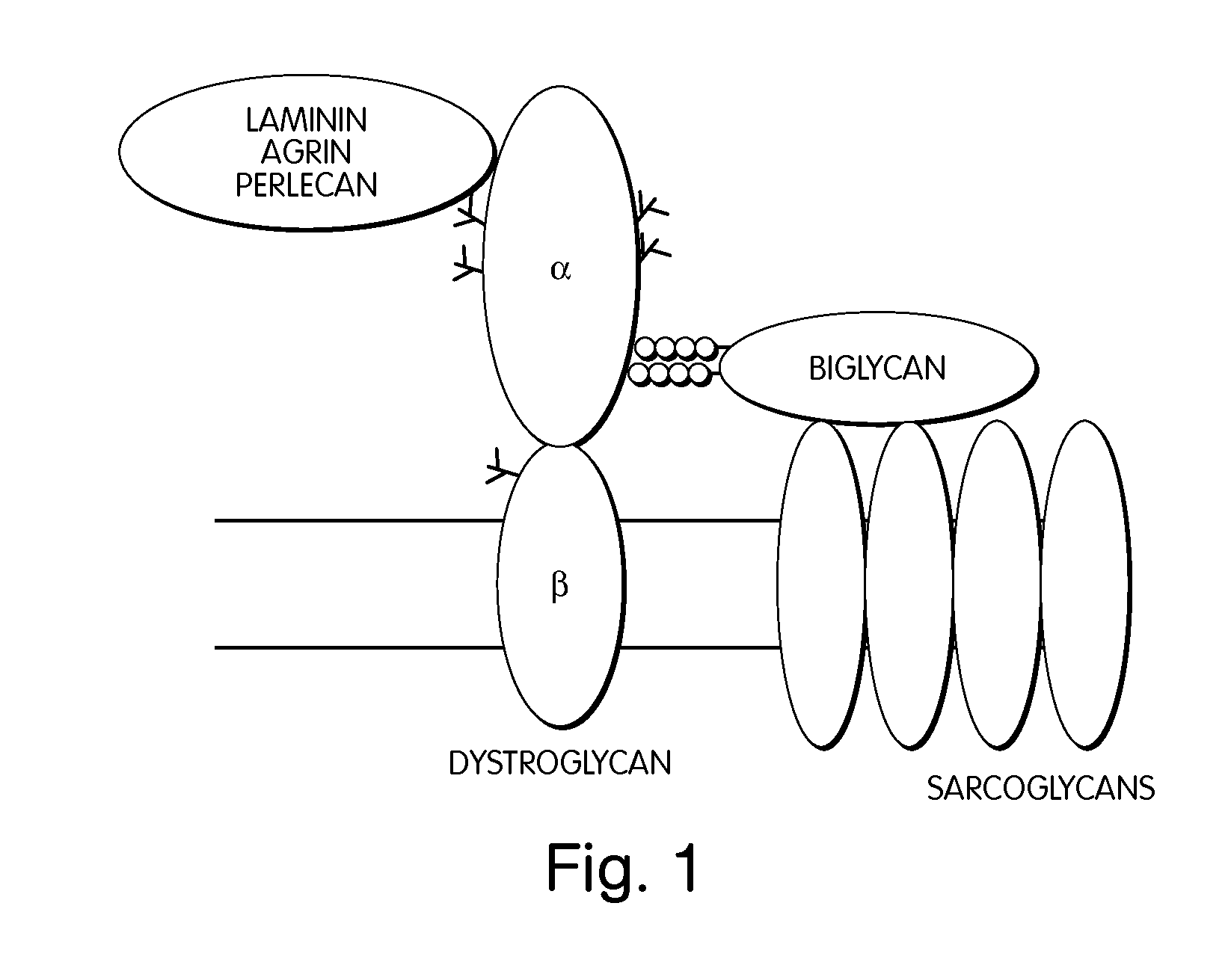
Treatment of muscular dystrophies and related disorders
InactiveUS20110053854A1Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderSynapseDisease
The invention provides, among other aspects, compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of collagen VI; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); and disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Diagnostics assay methods and amelioration of muscular dystrophy symptoms
InactiveUS6858395B2Ameliorating conditionAmeliorating mobilityPeptide/protein ingredientsIntegrin superfamilyMuscle tissueProtein C
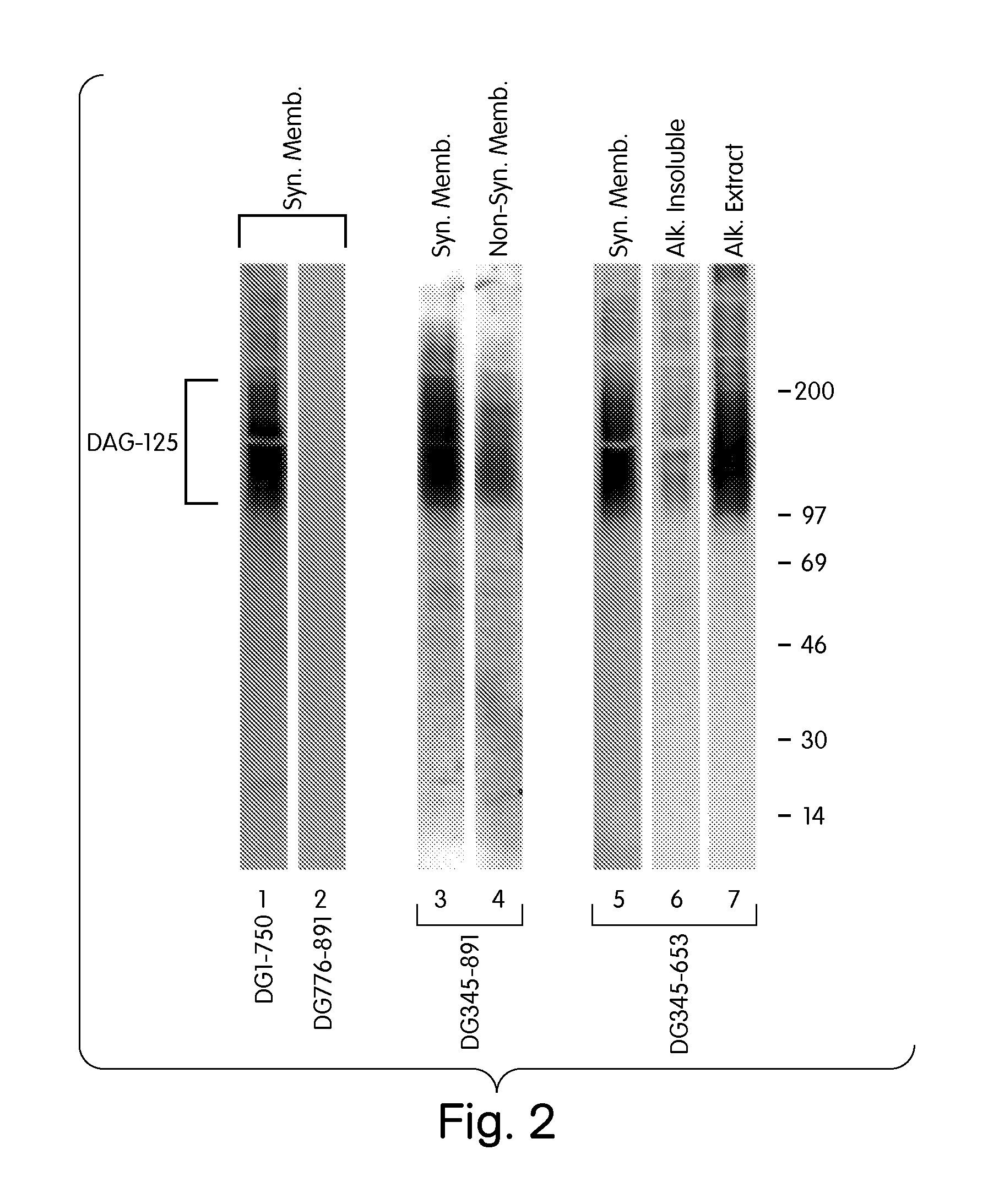
The present disclosure provides compositions and sequences for the diagnosis, genetic therapy of certain muscular dystrophies, especially muscular dystrophy resulting from a deficiency in dystrophin protein or a combined deficiency in dystrophin and utrophin, and methods and compositions for the identification of compounds which increase expression of the α7 integrin. Expression of the integrin αBX2 polypeptide in muscle cells results in better physical condition in a patient or an animal lacking normal levels of dystrophin or dystrophin and utrophin. The present disclosure further provides immunological and nucleic acid based methods for the diagnosis of scapuloperoneal muscular dystrophy, where there is a reduction in or absence of α7A integrin expression in muscle tissue samples and normal levels of laminin-2 / 4 in those same samples. The present disclosure further provides methods for identifying compositions which increase the expression of α7 integrin protein in muscle cells of dystrophy patients.
Owner:KAUFMAN STEPHEN J
Statins in the treatment of muscular dystrophies and myopathies
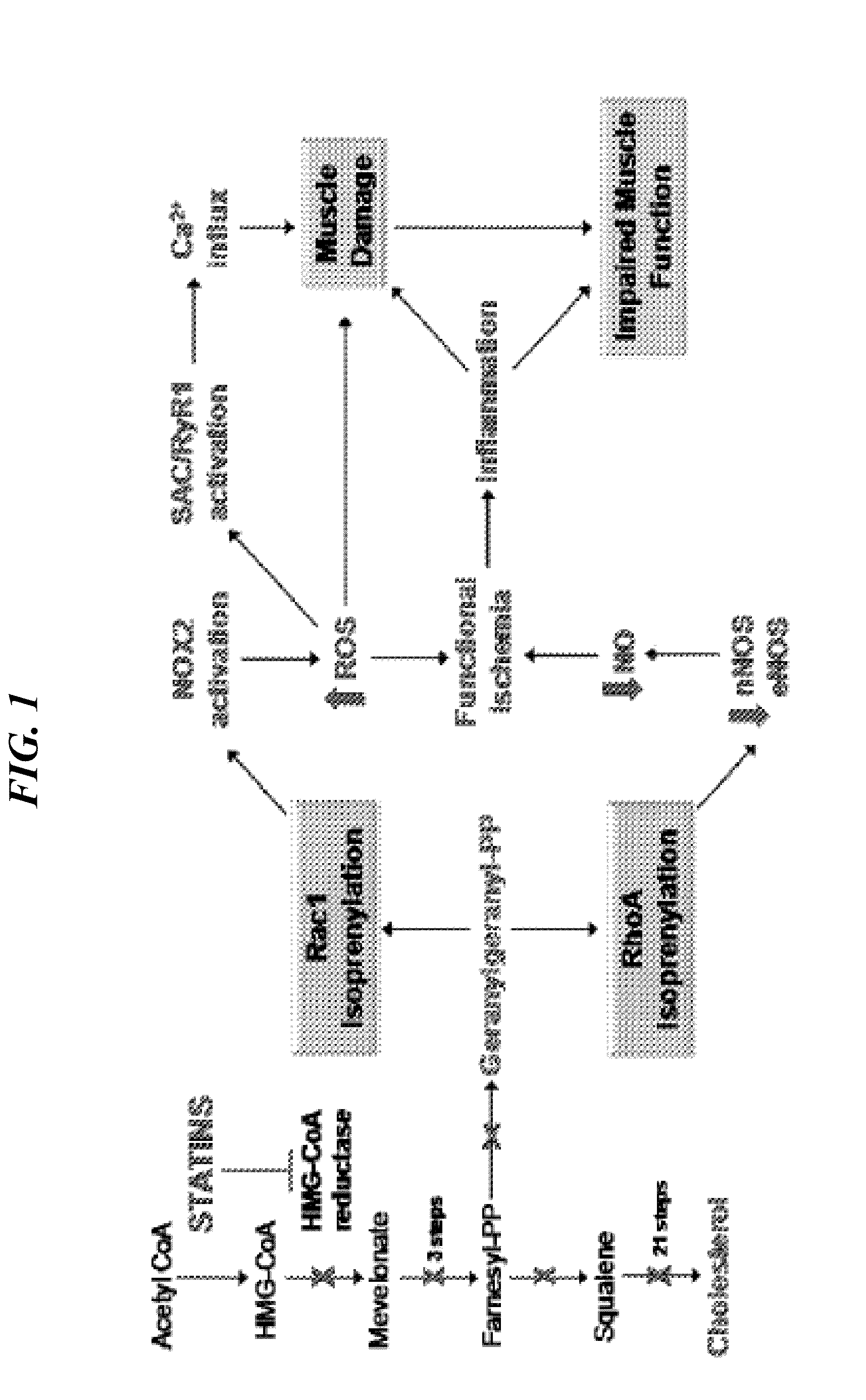
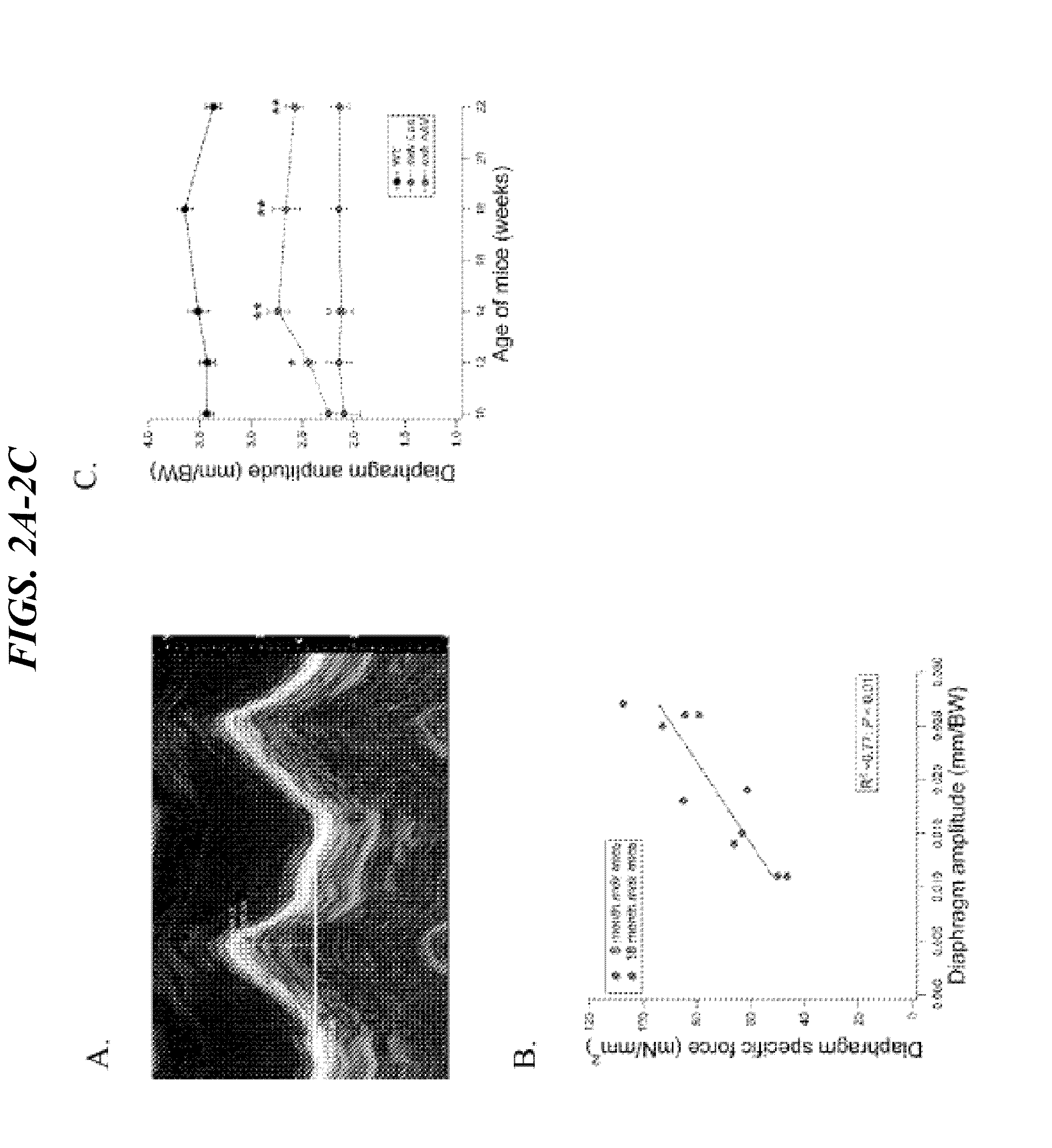
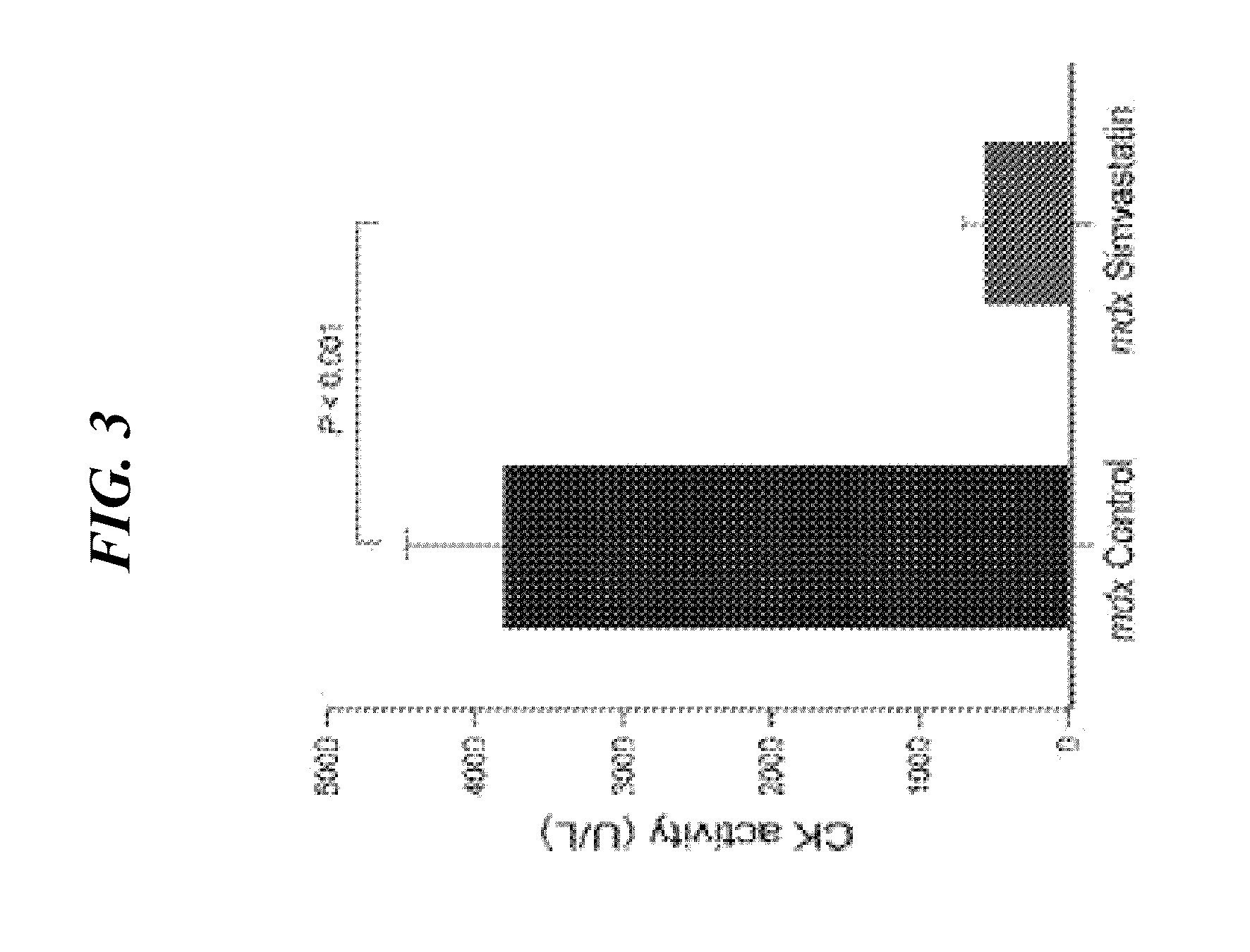
The invention provides methods and compositions for treating neuromuscular diseases including, but not limited to muscular dystrophies. It is demonstrated herein that statin drugs are therapeutic for neuromuscular disease, including, but not limited to muscular dystrophies.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method of early detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular disease
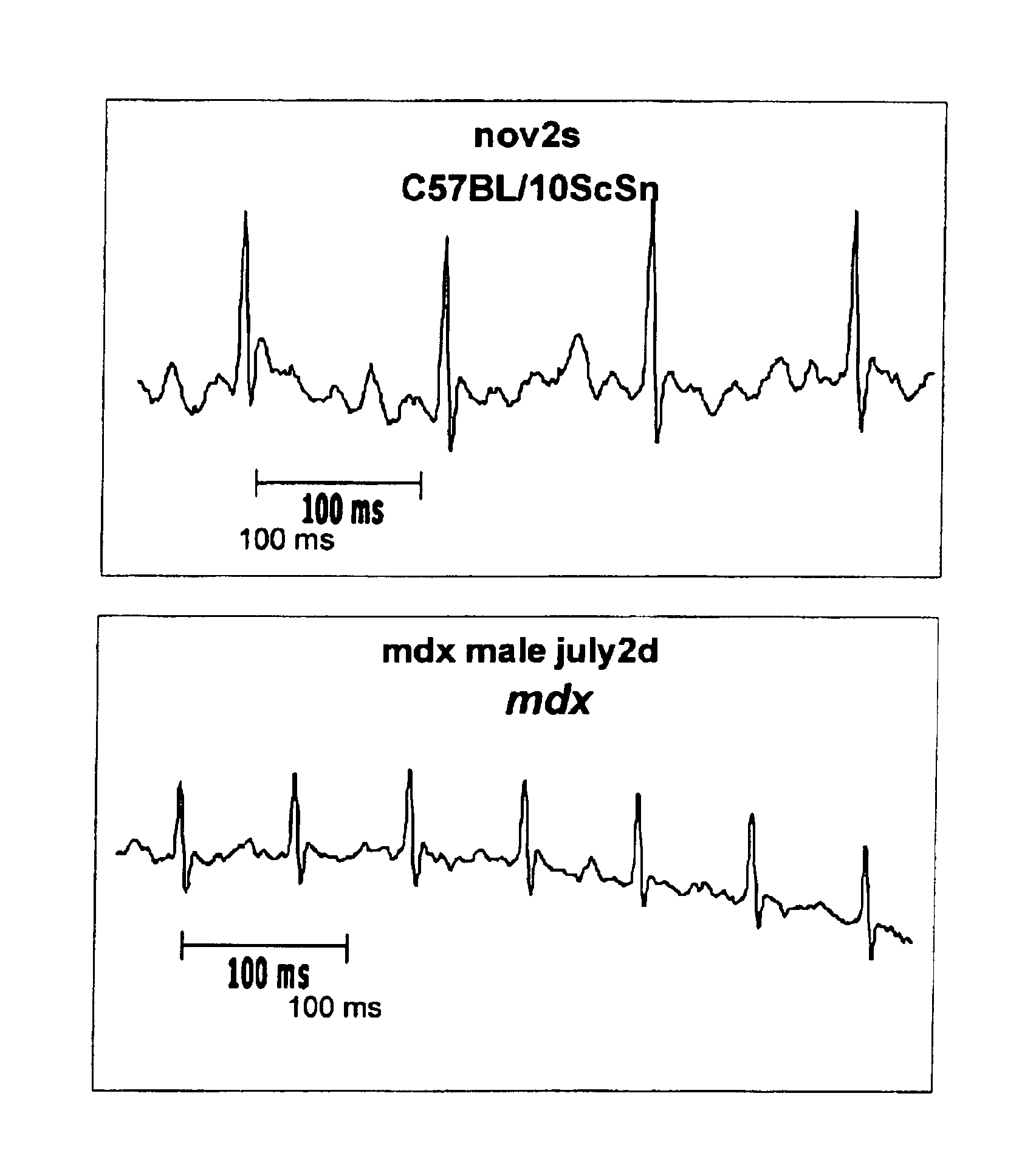
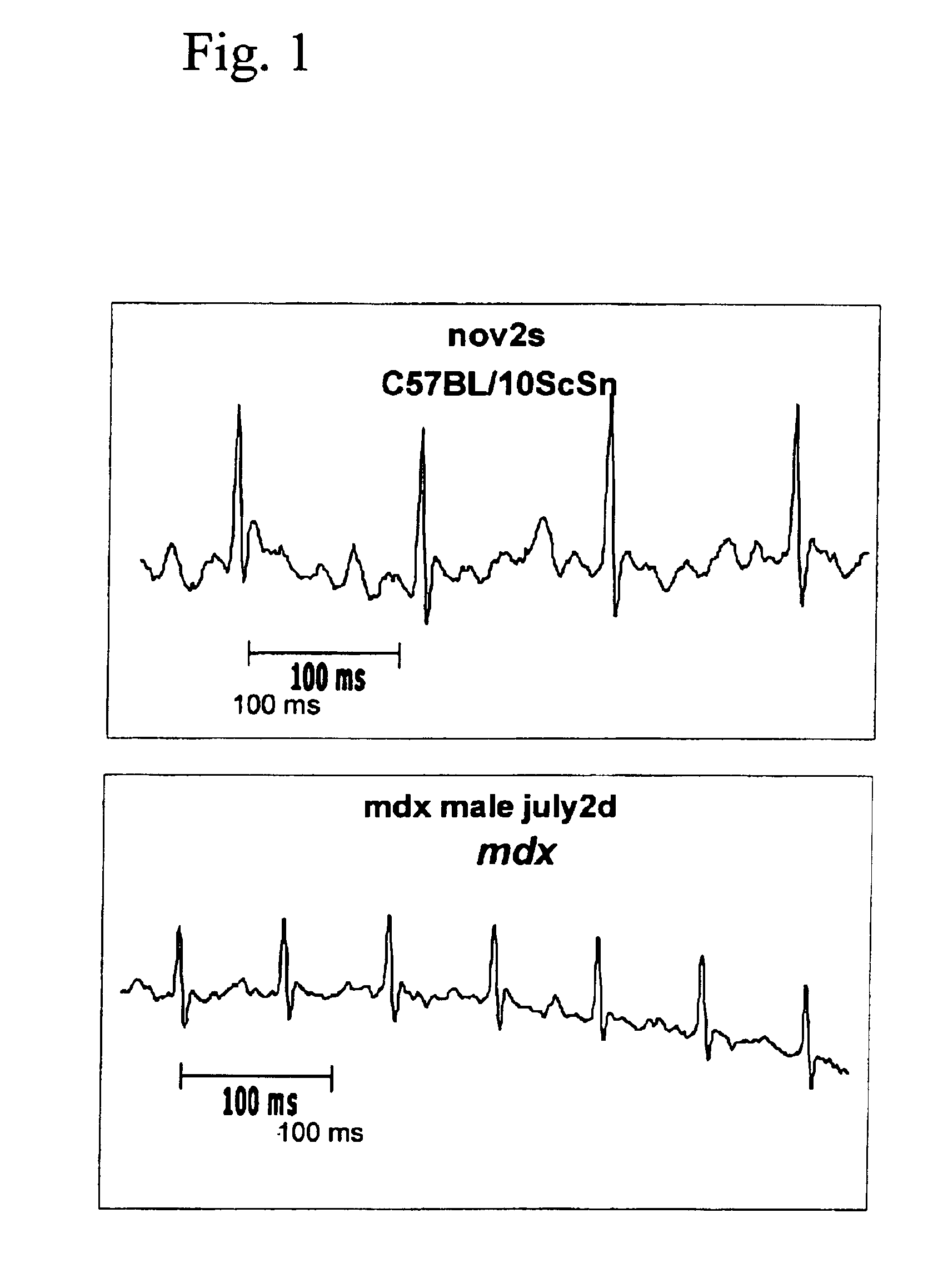
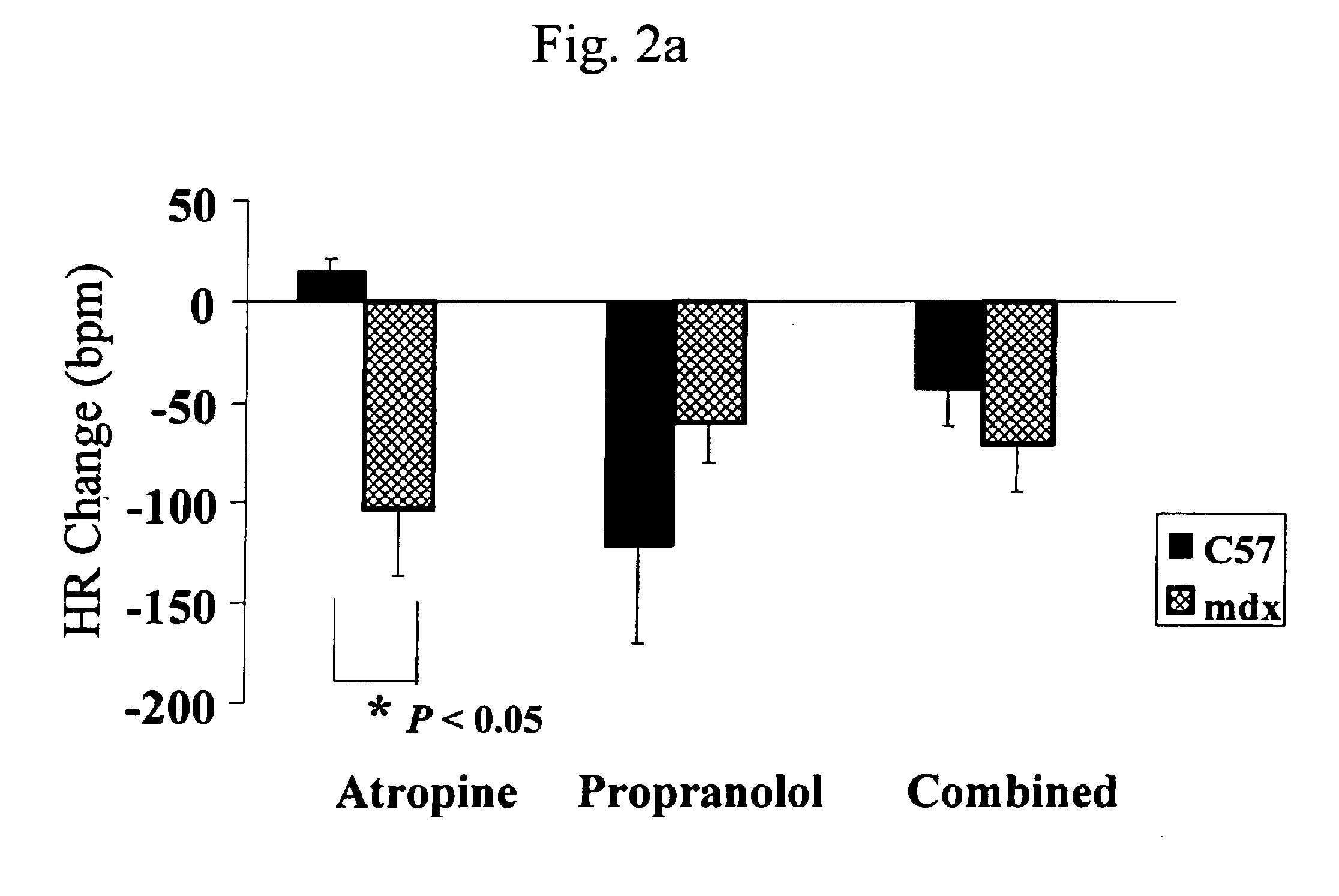
InactiveUS6875418B2Compounds screening/testingDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseDecreasing heart rate
The mdx mouse is a model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The present invention describes that mdx mice exhibited clinically relevant cardiac phenotypes. A non-invasive method of recording electrocardiograms (ECGs) was used to a study mdx mice (n=15) and control mice (n=15). The mdx mice had significant tachycardia, consistent with observations in patients with muscular dystrophy. Heart-rate was nearly 15% faster in mdx mice than control mice (P<0.01). ECGs revealed significant shortening of the rate-corrected QT interval duration (QTc) in mdx mice compared to control mice (P<0.05). PR interval duration were shorter at baseline in mdx compared to control mice (P<0.05). The muscarinic antagonist atropine significantly increased heart-rate and decreased PR interval duration in C57 mice. Paradoxically, atropine significantly decreased heart-rate and increased PR interval duration in all mdx mice. Pharmacological autonomic blockade and baroreflex sensitivity testing demonstrated an imbalance in autonomic nervous system modulation of heart-rate, with decreased parasympathetic activity and increased sympathetic activity in mdx mice. These electrocardiographic findings in dystrophin-deficient mice provide new bases for diagnosing, understanding, and treating patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Owner:MOUSE SPECIFICS
Compositions And Methods For The Treatment Of Muscular Dystrophy
InactiveUS20100292306A1Long-term treatmentLess efficaciousBiocideMuscular disorderDystrophinMuscle damage
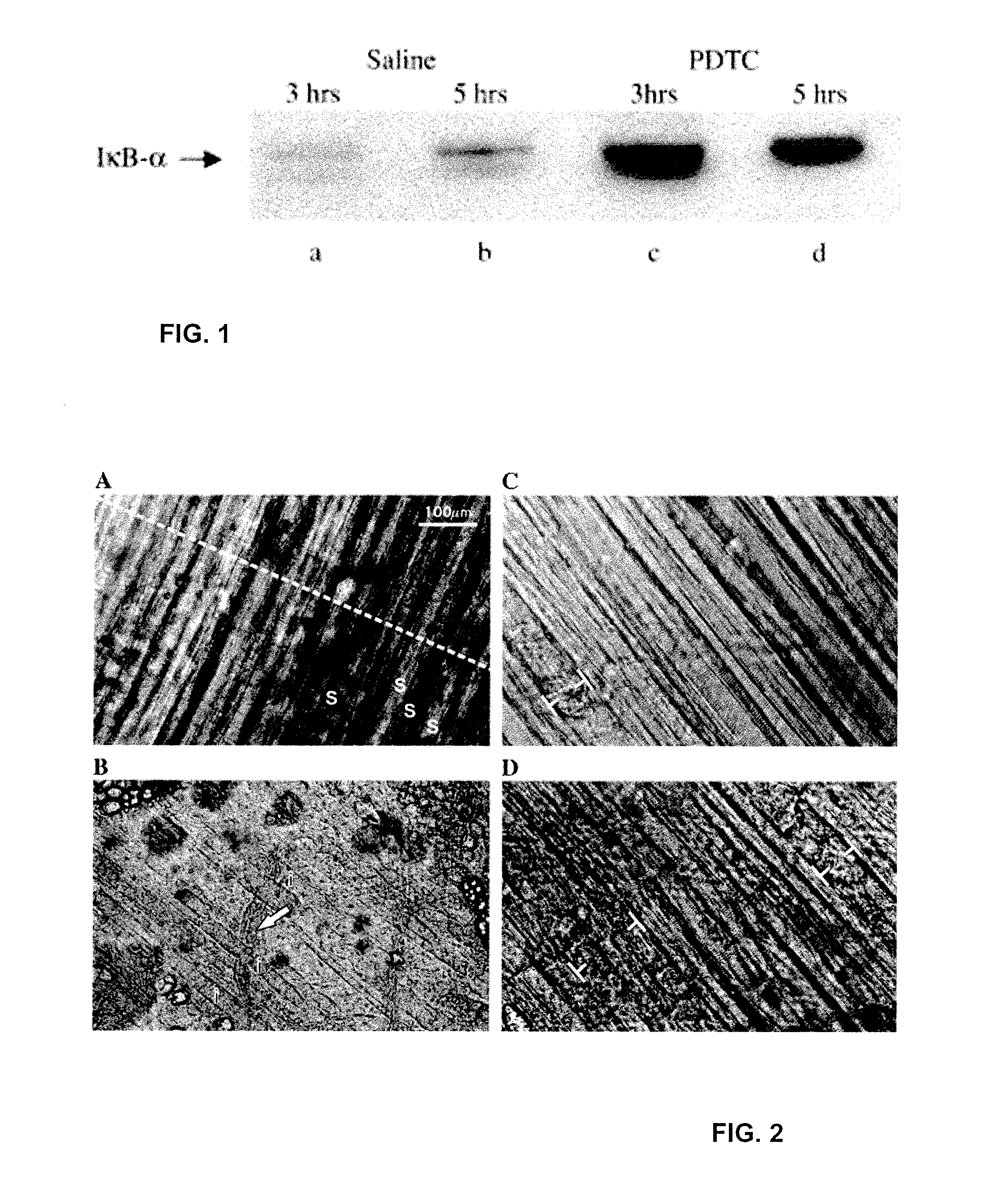
Compositions and methods for treatment of individuals diagnosed with a dystrophin deficiency are disclosed. In particular, inhibitors of NFκB transactivation and / or inhibitors that suppress p65 expression are used to prevent and / or reverse muscle damage in animals or humans lacking dystrophin. Such compositions and methods are useful in the treatment of individuals with muscular dystrophy.
Owner:A T STILL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com