Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Diffusion weighting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
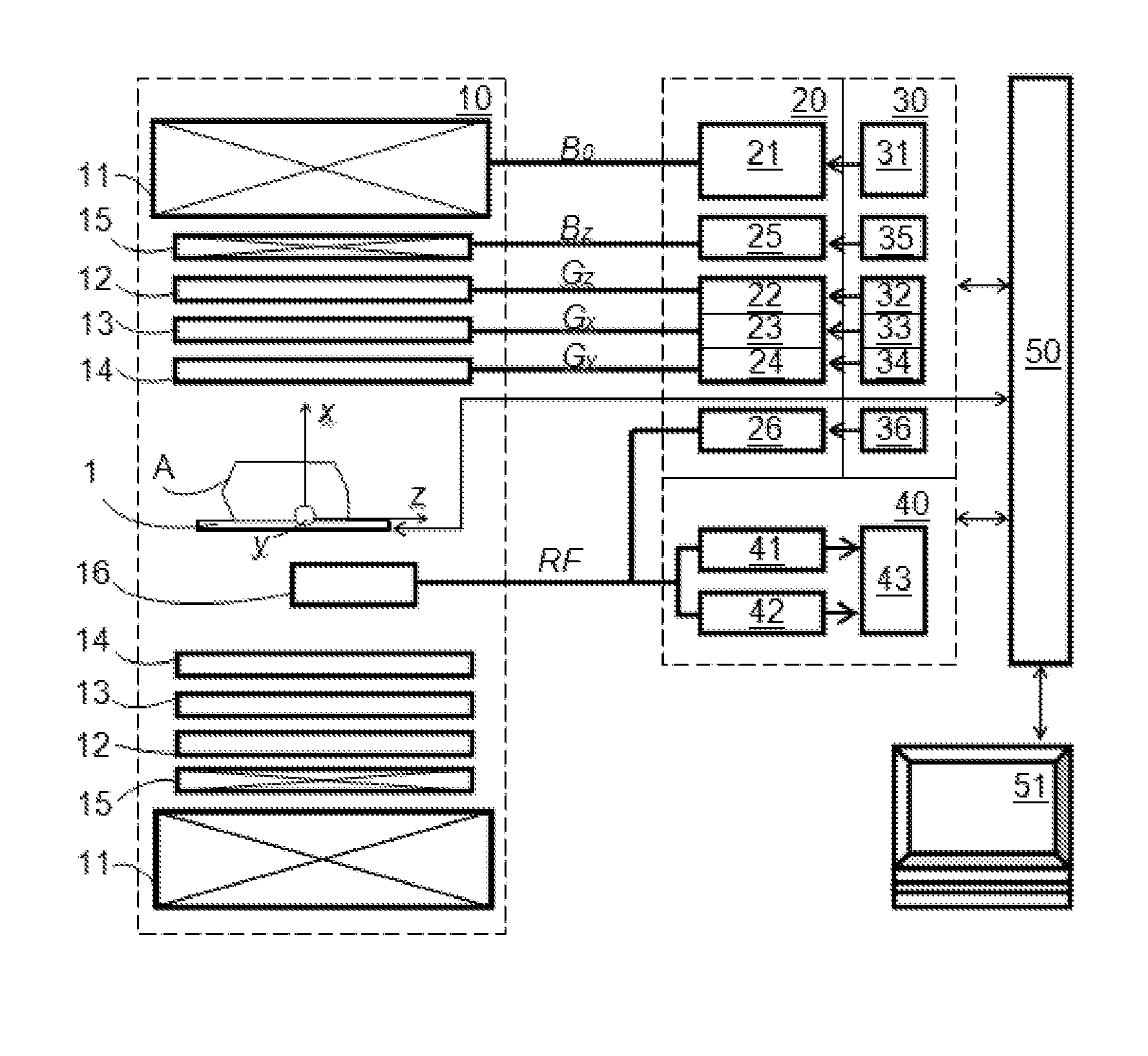
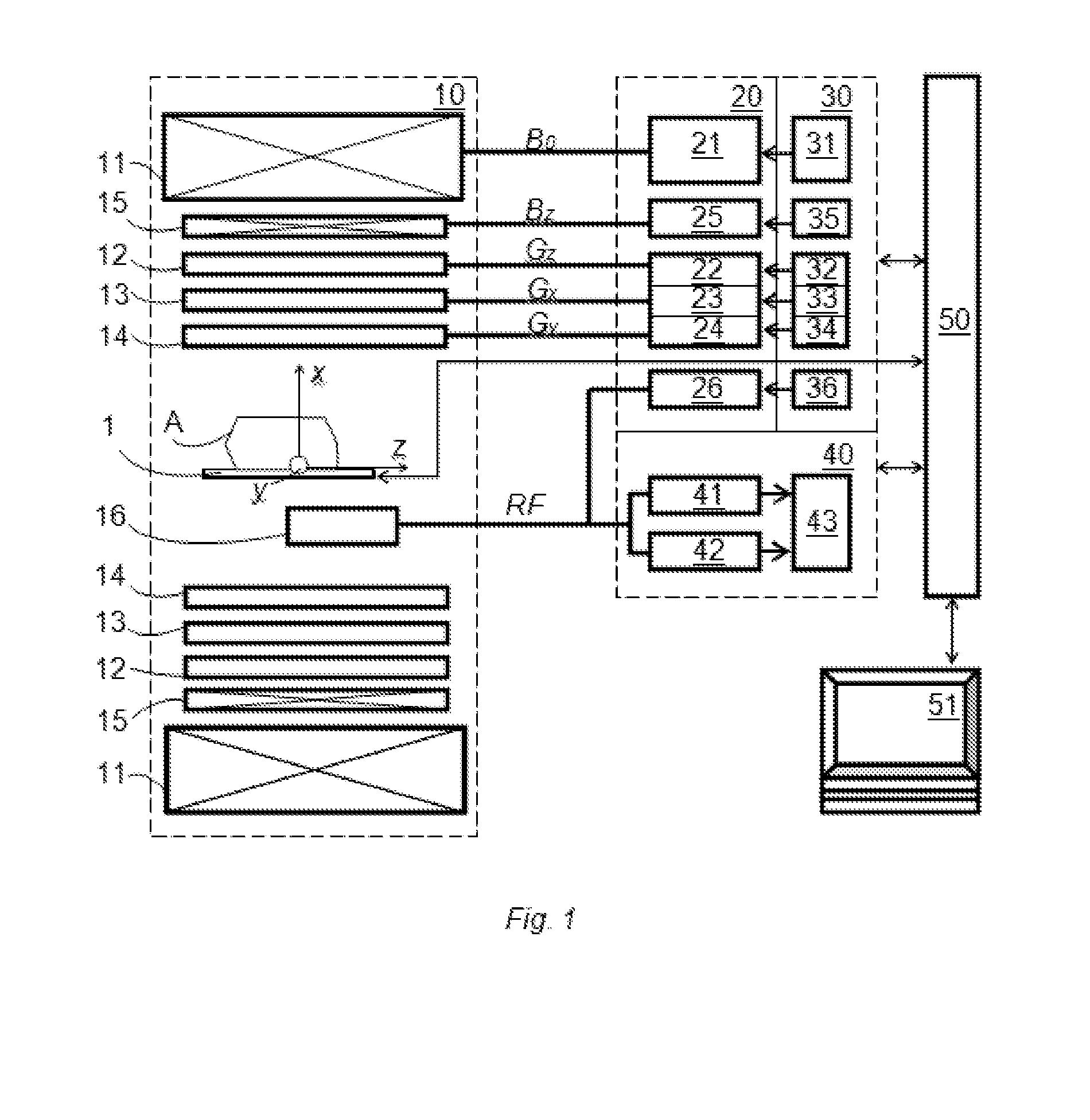
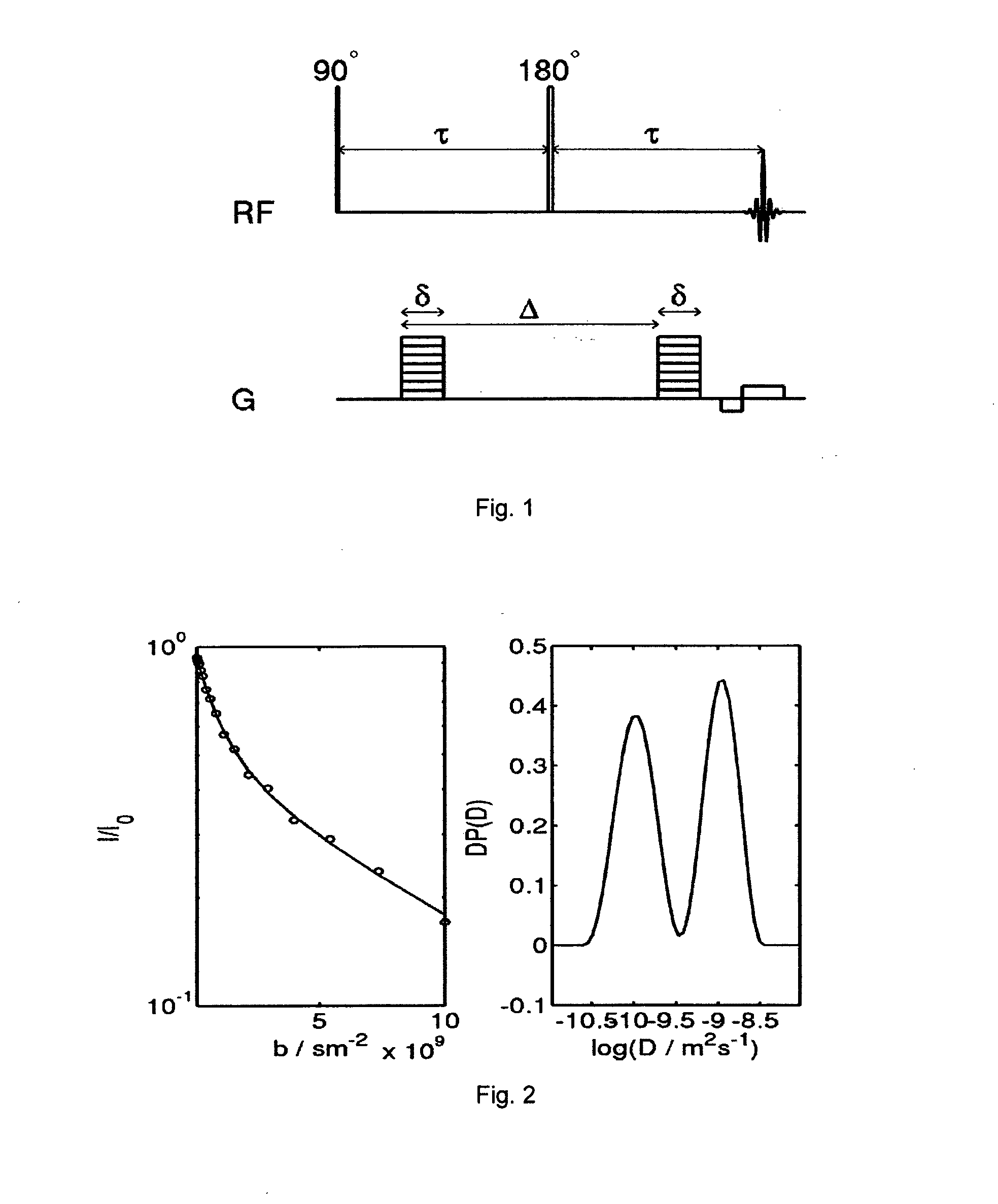
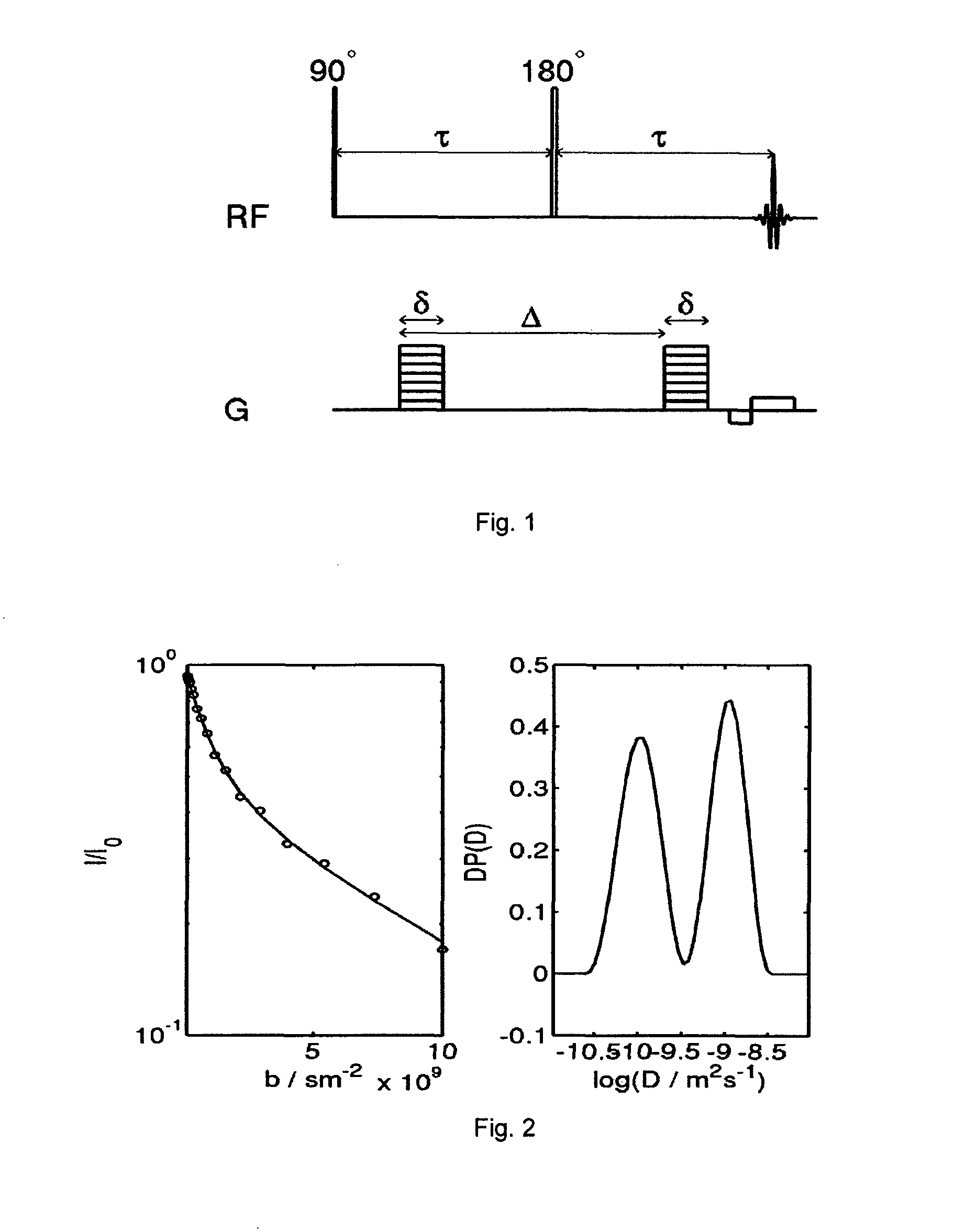
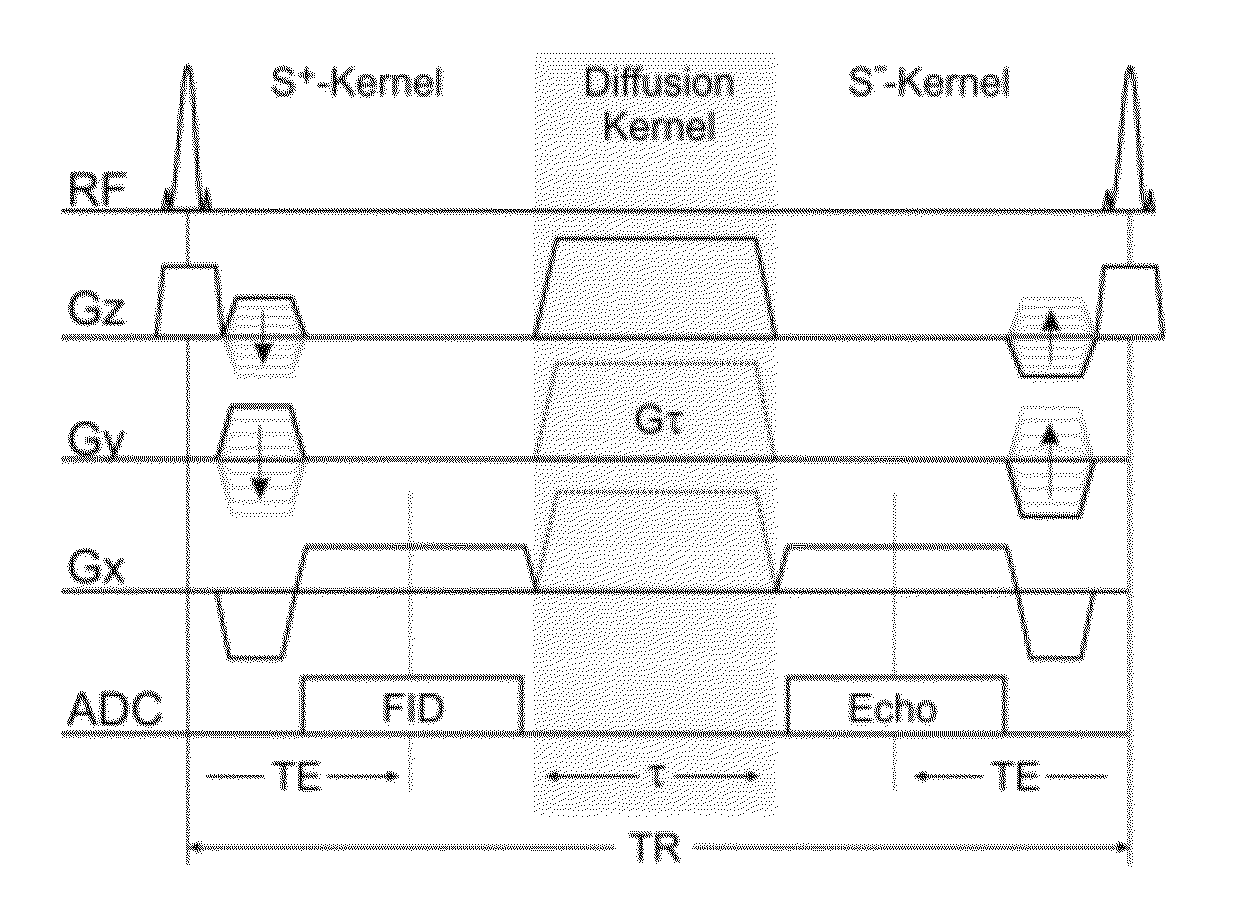
Diffusion weighting derives from applying diffusion gradients to each side of a 180° pulse. The higher the b-factor the greater the diffusion weighting. The b-factor depends on the characteristics of the diffusion gradients (amplitude, duration, spacing).
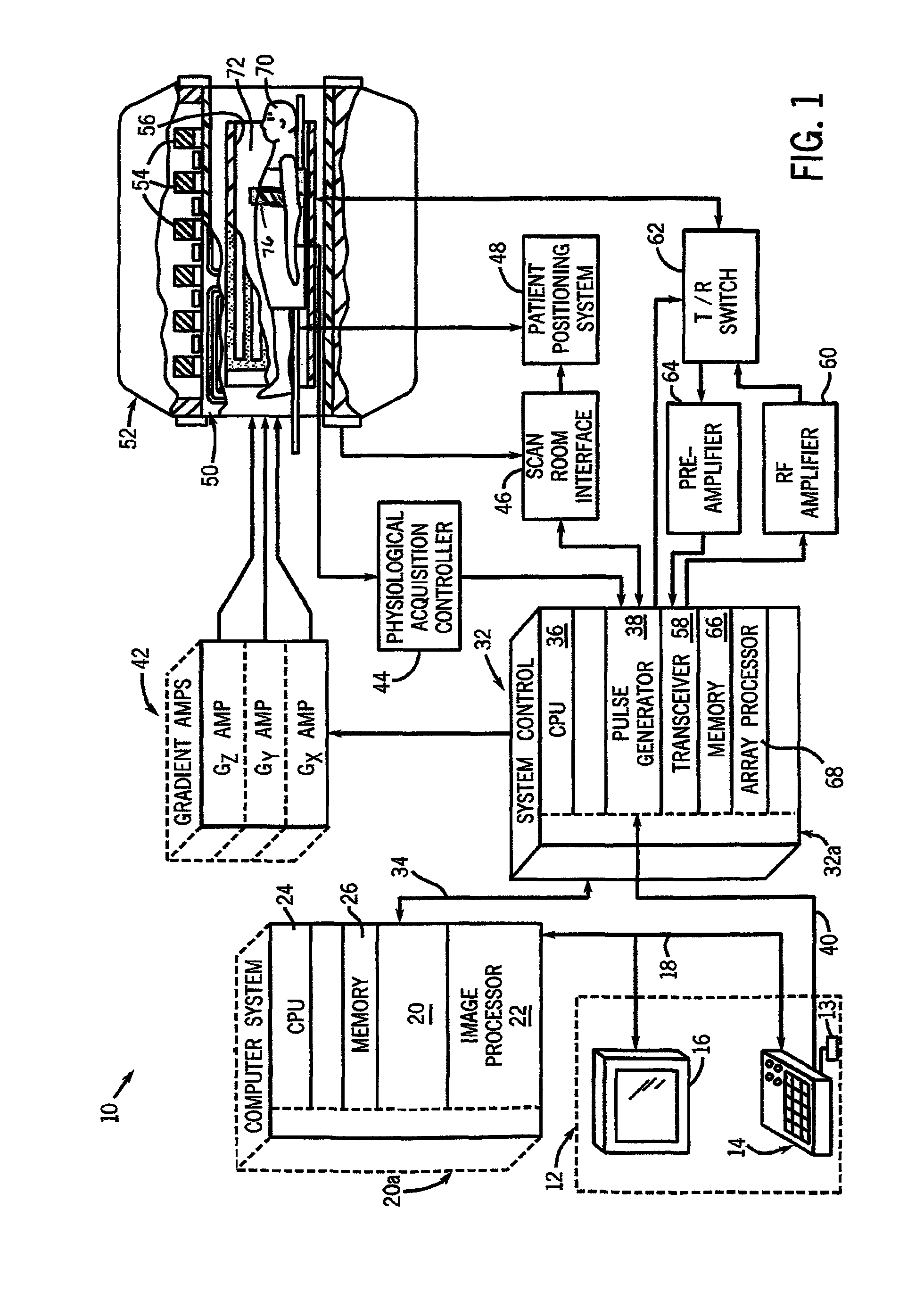
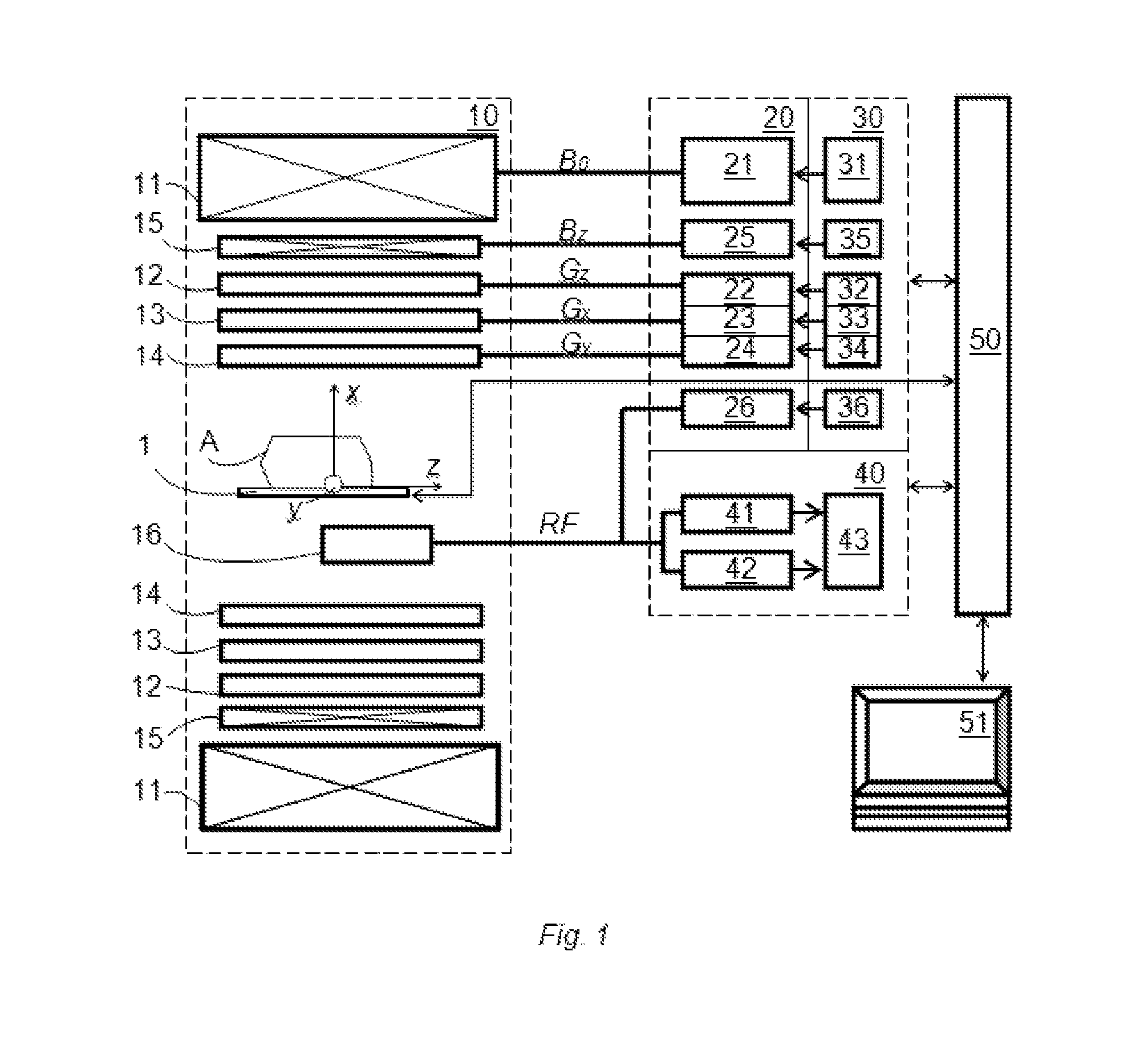
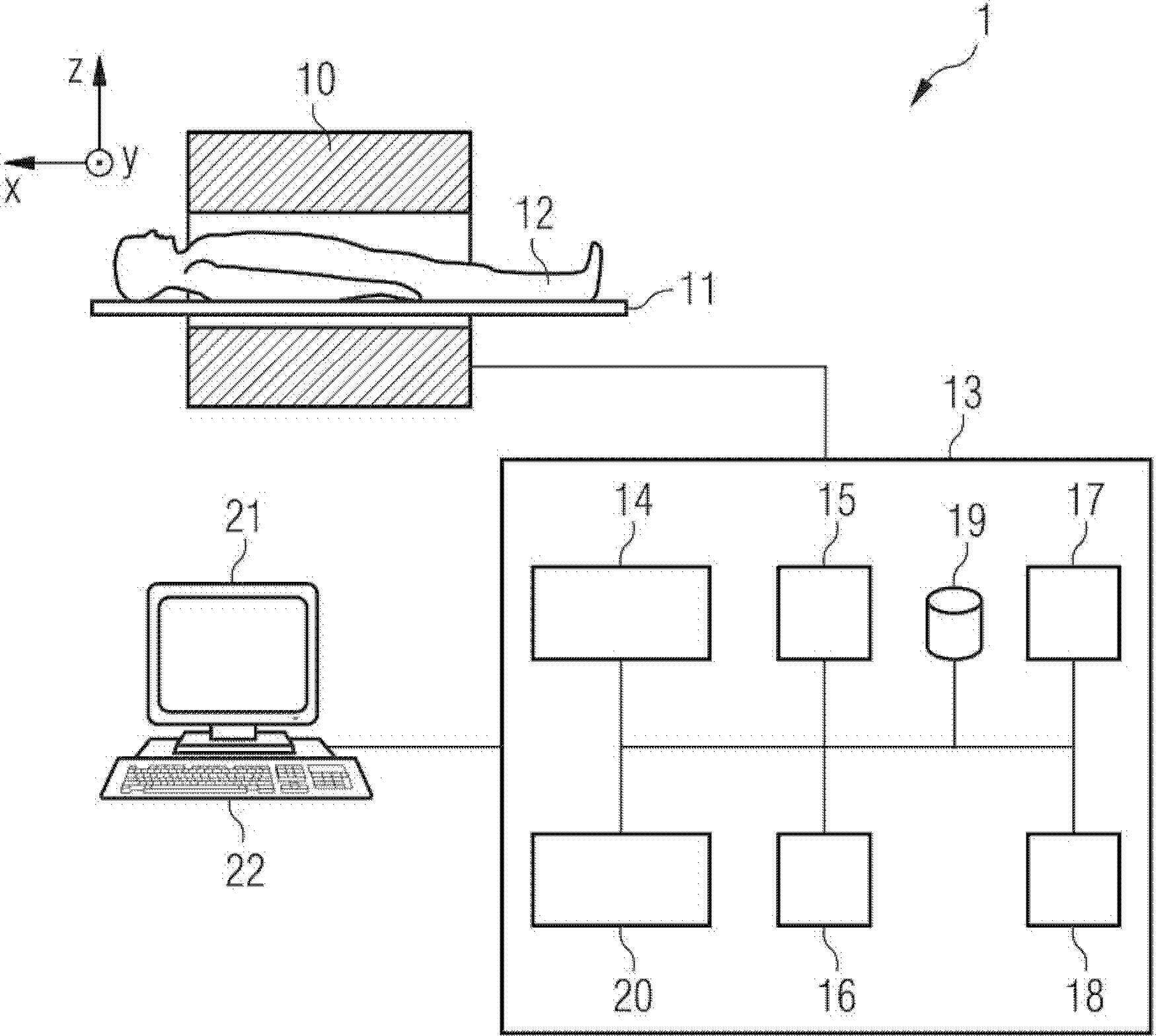
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20140266195A1Reduce sensitivityReduce scan timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase shiftedResonance
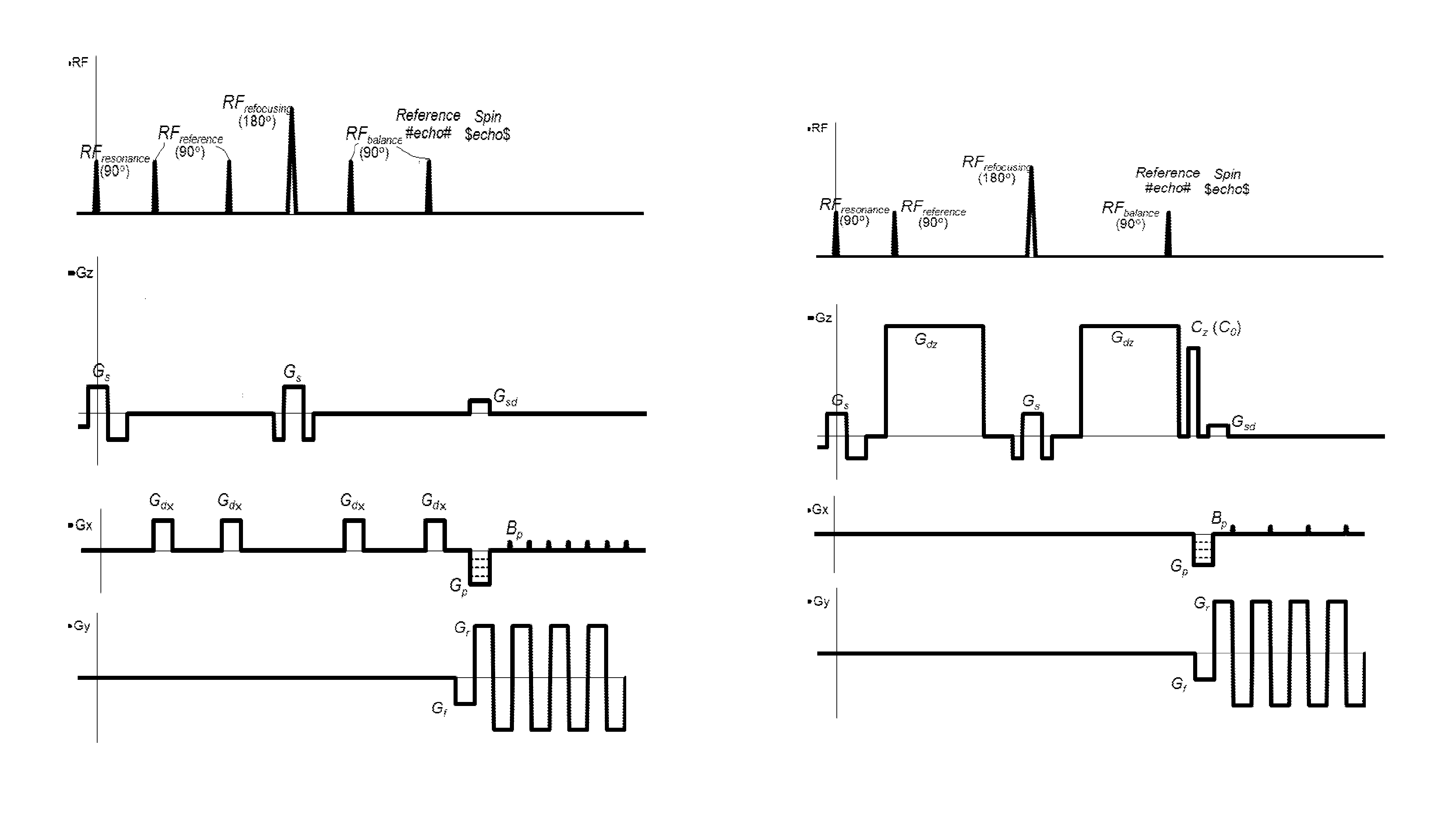
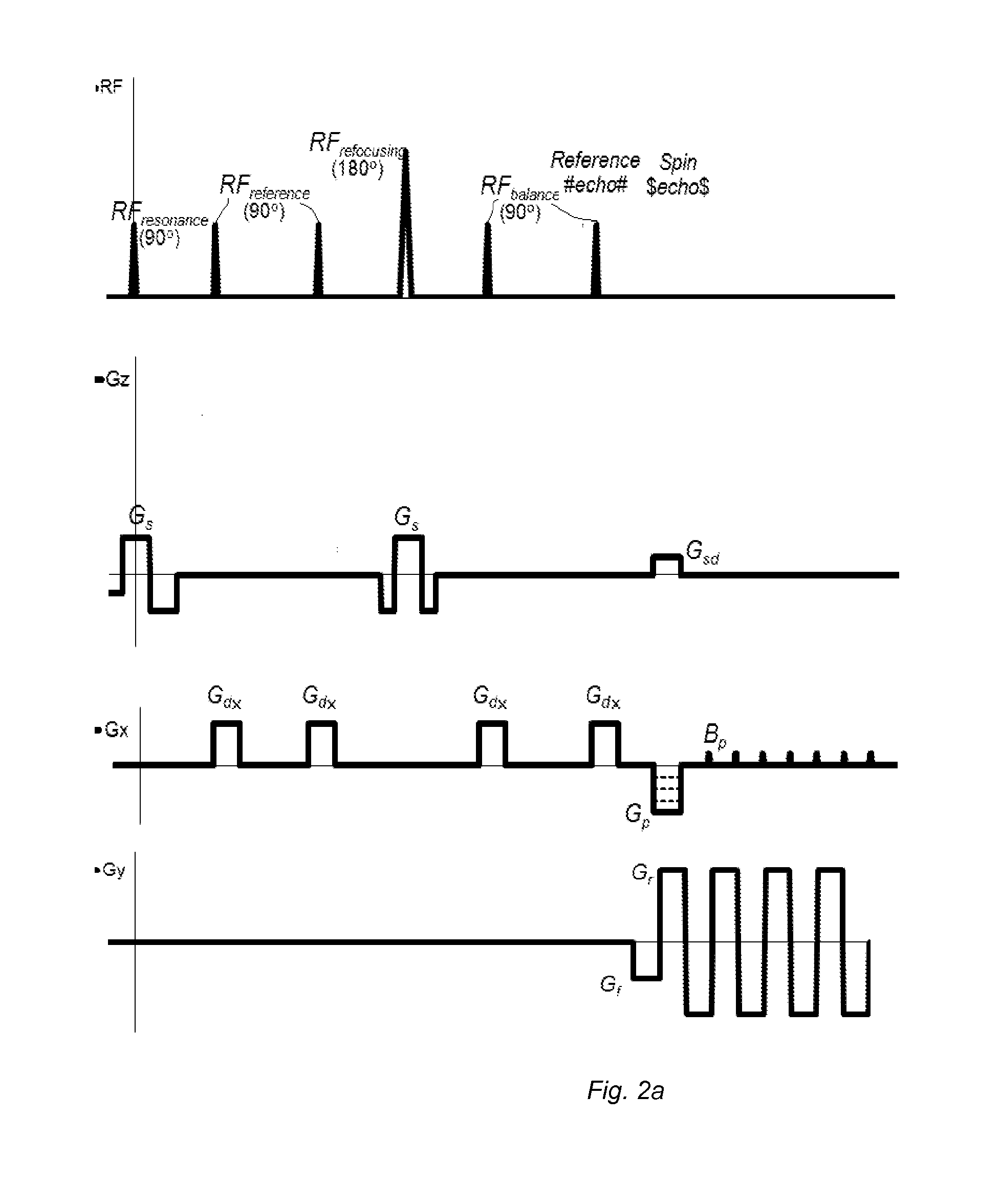
The method and system for correcting motion-induced phase errors in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) use a phase shift of the non-phase encoded reference echo-signal accumulated during the diffusion-weighting in order to characterize bulk motion and tissue deformation and to compensate their effect for correcting the diffusion / perfusion-weighted image. The sequences unbalanced with respect to the first motion derivative are used for distinguishing the perfusion component. The MRI apparatus provides additional excitation resonance-frequency ranges for forming the reference echo signals.
Owner:VAPOSUN
Fast-diffused magnetic resonance imaging and restoring method
InactiveCN102928796AReduced imaging timeImprove sampling efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDiffusionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a fast-diffused magnetic resonance imaging and restoring method. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) conducting signal collection to a detected target in N diffusion weighting directions through a plurality of channel coils; (S2) merging the obtained complementary k space data so as to obtain fully-sampled k space data KC; (S3) conducting primary restoration based on images of different diffusion weighting directions corresponding to the k space data and images corresponding to the fully-sampled k space data KC so as to obtain a primary image; and (S4) conducting regularization restoration based on the primary image, iterating to convergence so as to obtain the final needed images (I1,....IN). The description gives a specific realization mode of the method. Common information among images in different diffusion weighting directions are utilized, so that not only the sampling efficiency is improved, but also the resolution and signal to noise ratio of the images can be enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Sweeping real-time single point fiber
InactiveUS6859203B2Increase computing speedSuperfluous imageImage enhancementImage analysisFiberVoxel
An imaging method for imaging a subject (18) including fibrous / anisotropic structures (102) includes acquiring three-dimensional image representations without and with a plurality of different diffusion weighting and directions. When a user (56) hovers a selection device over a voxel of the image, a fiber representation (54) is extracted in substantially real time. The representation is generated by following a direction of a major eigenvector e1 from voxel to voxel. A human-viewable display of the fiber representation is produced (210).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for correcting motion in multi-shot diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20080310696A1Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiffusion-Weighted MR ImagingData acquisition
A method for performing motion correction in an autocalibrated, multi-shot diffusion-weighting MR imaging data acquisition includes performing motion correction on k-space data in an autocalibration region for each shot individually and then combining the motion-corrected k-space data from each shot to form a motion-corrected reference autocalibration region. Uncorrected source k-space data points are “trained to” the motion-corrected k-space data from the motion-corrected reference autocalibration region to determine coefficients that are used to synthesize motion-corrected k-space data in the outer, undersampled regions of k-space. Similarly, acquired k-space lines in the outer, undersampled regions of k-space may also be replaced by motion-corrected synthesized k-space data. The motion-corrected k-space data from the motion-corrected reference autocalibration region may be combined with the synthesized motion-corrected k-space data for the outer, undersampled regions of k-space to reconstruct motion-corrected images corresponding to each coil element. The motion corrected images corresponding to each coil element may be combined into a resultant image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for diffusion magnetic resonance imaging with the effects of eddy currents compensated
ActiveUS20070052417A1High precisionEffect of eddy current can be minimizedMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionResonance
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
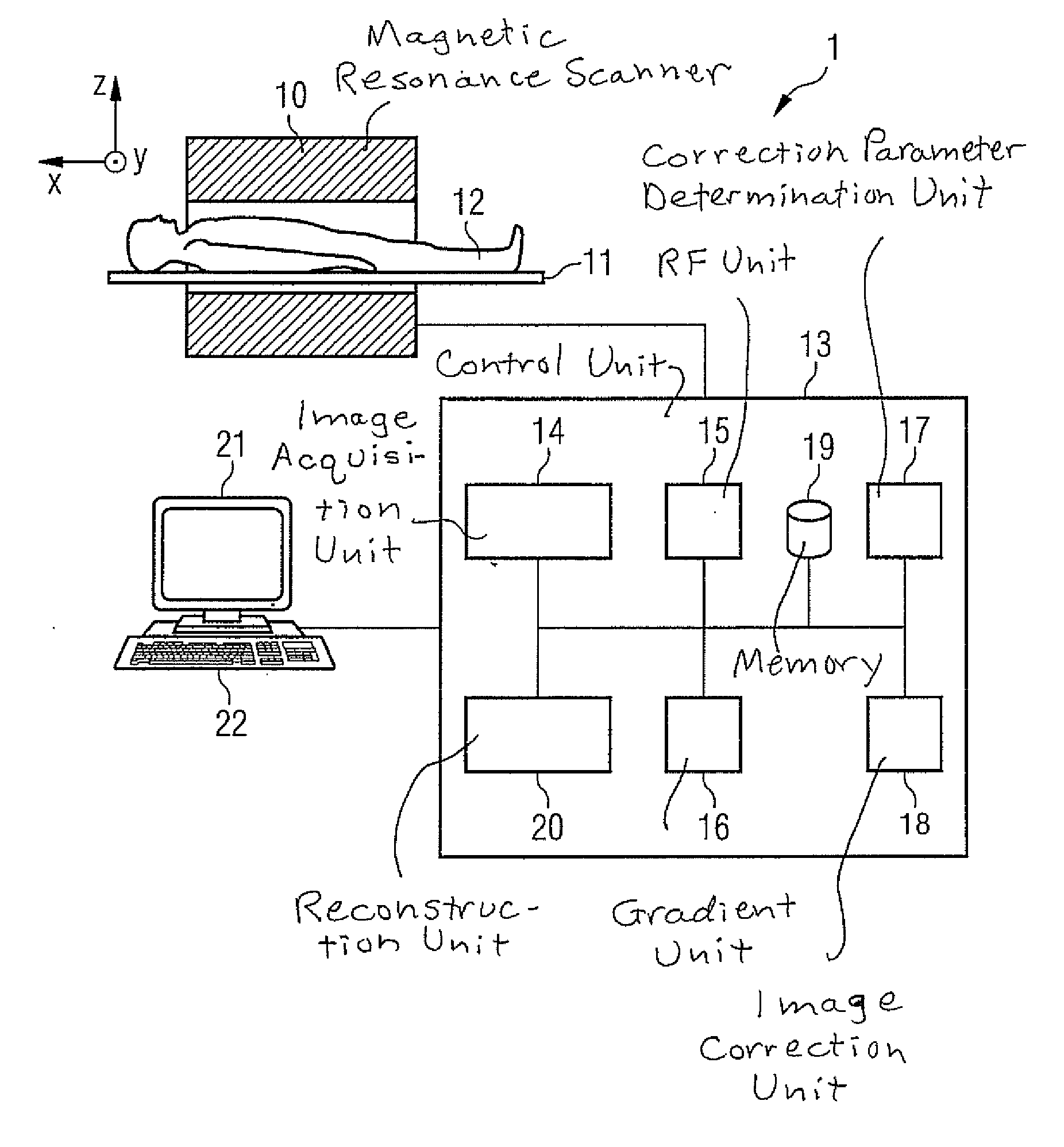
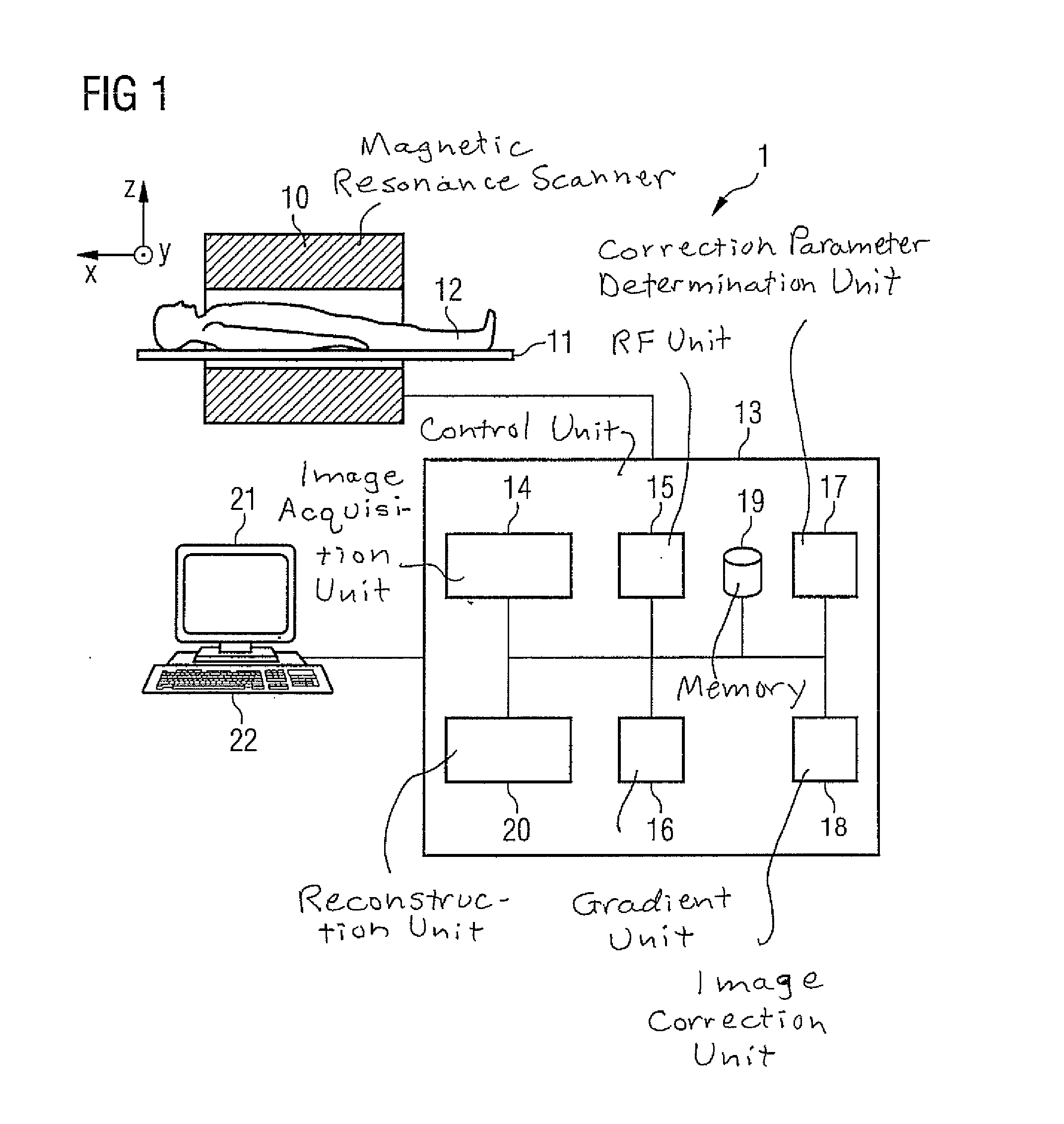
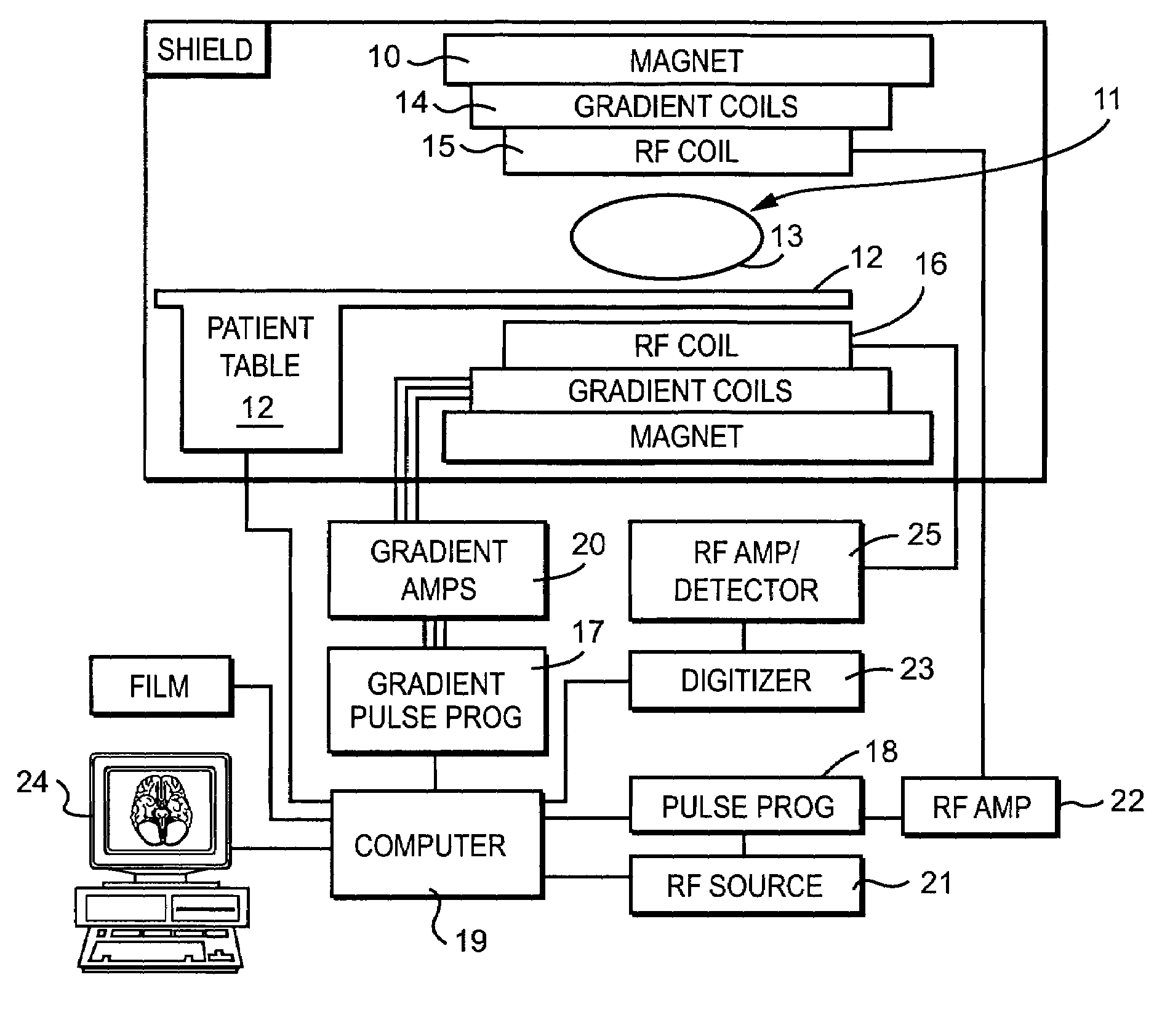
Method and magnetic resonance system to reduce distortions in diffusion imaging
ActiveUS20110187367A1Reduce distortion problemsSufficiently quickElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRDiffusionResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus to reduce distortions in magnetic resonance diffusion imaging, a magnetic resonance data acquisition system is operated to acquire magnetic resonance data in a first measurement with a first diffusion weighting, and to acquire magnetic resonance data in a second measurement with a second, different diffusion weighting. A non-linear, system-specific distortion-correcting function is determined on the basis of system-specific information that is specific to said magnetic resonance data acquisition system. Correction parameters are calculated to correct distortions in subsequently-acquired diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images, based on the data acquired in the first and second measurements with the system-specific distortion-correcting function applied thereto. The subsequently-acquired diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images are corrected using the correction parameters to at least reduce distortions therein.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
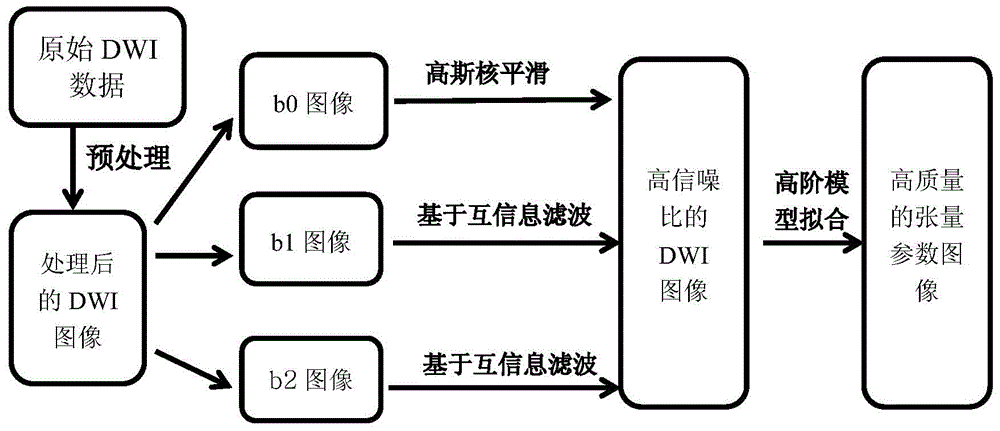
Multi-b-value DWI (diffusion weighted image) noise reduction method based on mutual information
ActiveCN104574298AReduce mistakesLess singular valueImage enhancementDiagnostic recording/measuringHead movementsImaging quality
The invention discloses a multi-b-value DWI (diffusion weighted image) noise reduction method based on mutual information. The method comprises steps as follows: acquiring to-be-tested multi-b-value DWIs in multiple diffusion sensitive gradient directions by a magnetic resonance scanner; performing preprocessing such as head movement correction, eddy current correction and the like on the images; estimating different b-value image signal-to-noise ratios; performing noise reduction processing on the images through setting parameters of an optimal noise reduction algorithm so as to acquire DWIs with higher signal-to-noise ratios. The method fully considers features of different images, and three-dimensional structural features of the processed images are reserved as many as possible while noises are eliminated. During establishment of a high-order complex model, different b images have higher image quality, so that acquired high-order parameter images can have smaller errors and fewer singular values. The method can be better applied to preprocessing of a high-order model imaging technology and plays an active role in further research on white matter fiber structures.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
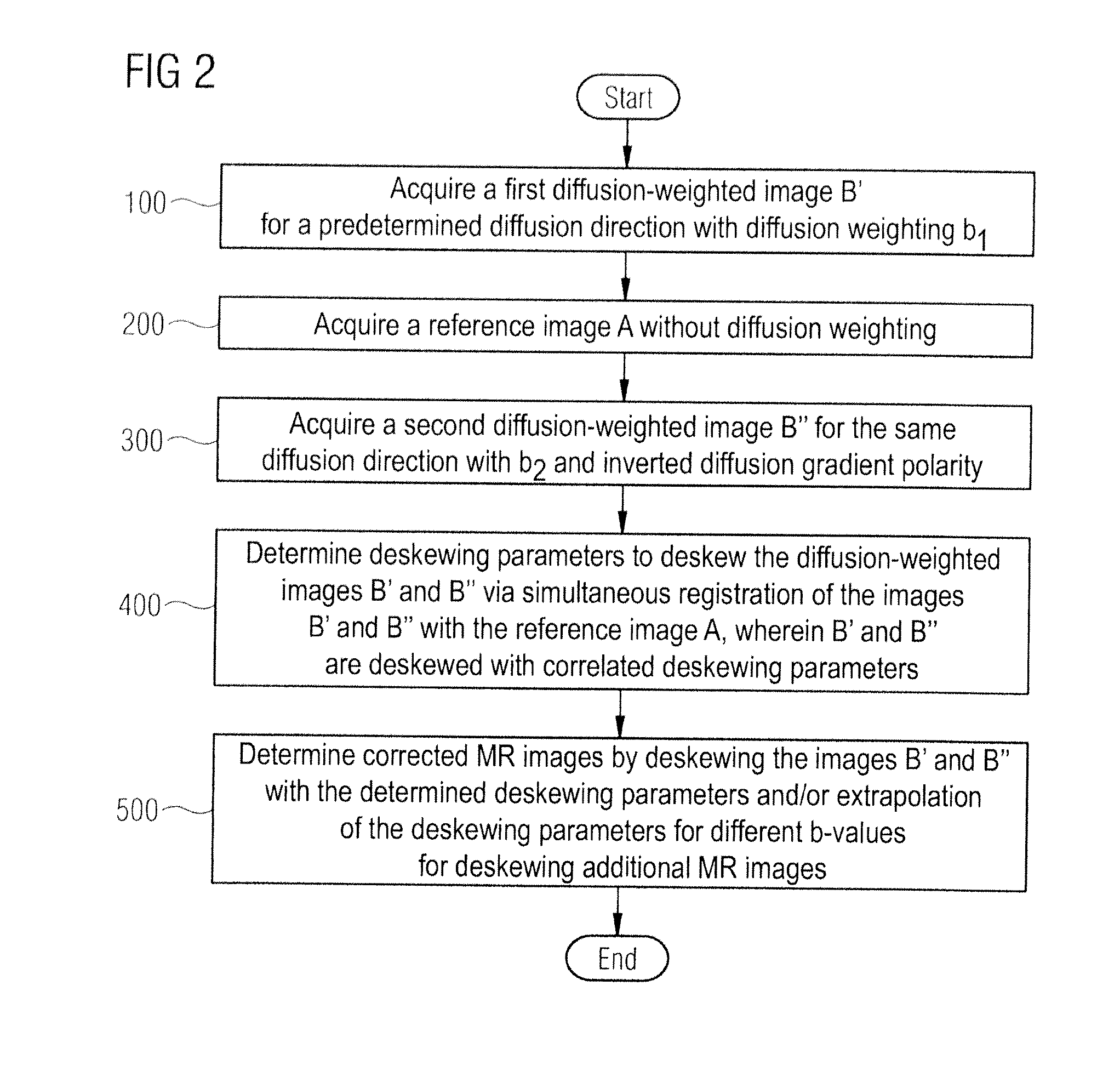
Correction of distortions in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110085722A1Easy to correctCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceReference image
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for correction of image distortions that occur in acquisition of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images of an examination subject, a reference image is acquired without diffusion weighting, a first diffusion-weighted image is acquired for a diffusion direction, a second diffusion-weighted image is acquired for the same diffusion direction, with the acquisition of the second diffusion-weighted image taking place at least with a different diffusion weighting or a different diffusion gradient polarity than the acquisition of the first diffusion-weighted image. Distortion parameters for the correction of image distortions in the acquired diffusion-weighted images are acquired, and the first diffusion-weighted image is deskewed with a first set of deskewing parameters, and the second diffusion-weighted image is deskewed with a second set of deskewing parameters. The first set and second set of deskewing parameters are correlated, and the deskewing parameters are determined by simultaneous minimization of differences between the deskewed first image and the reference image and differentiation between the deskewed second image and the reference image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
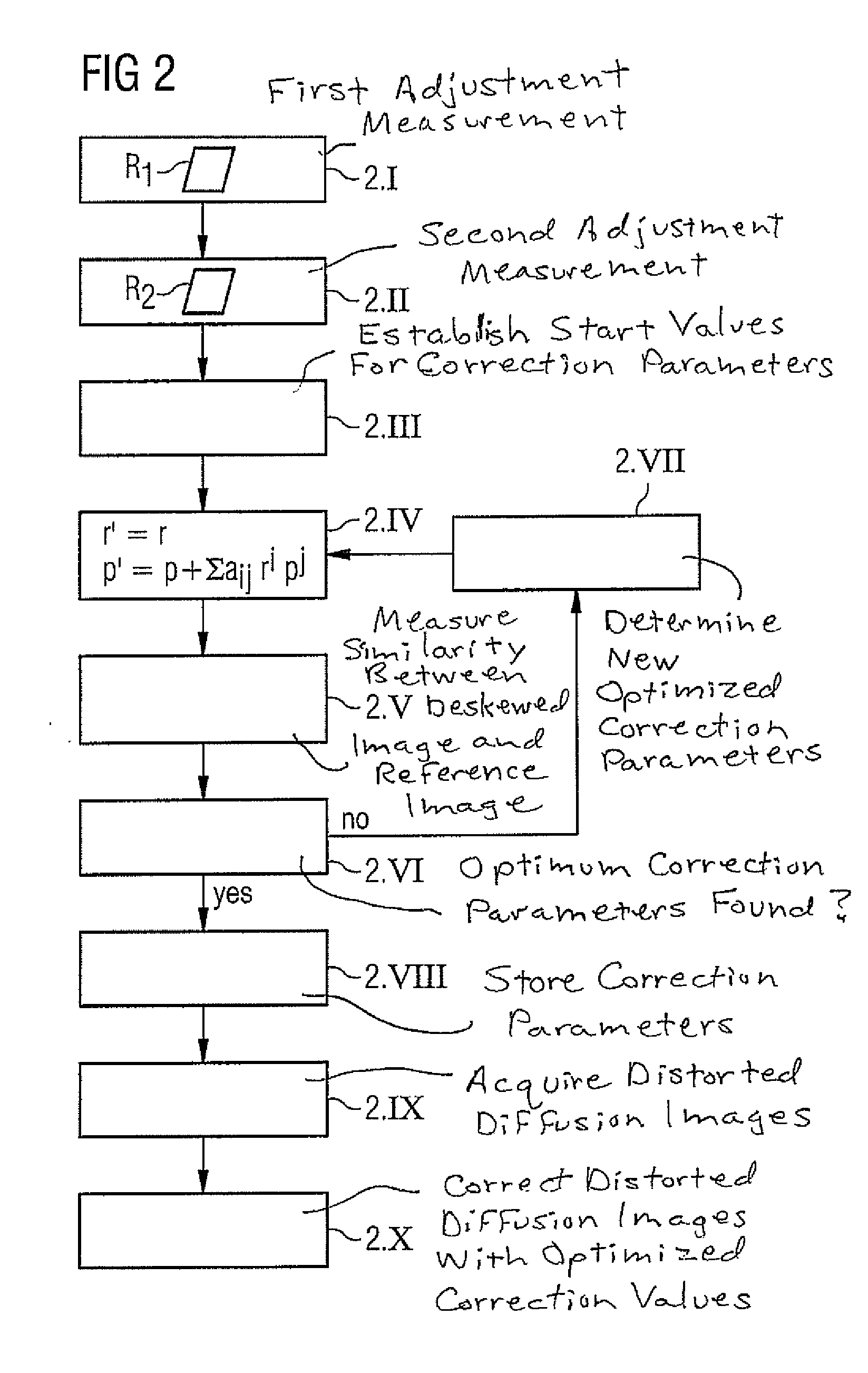
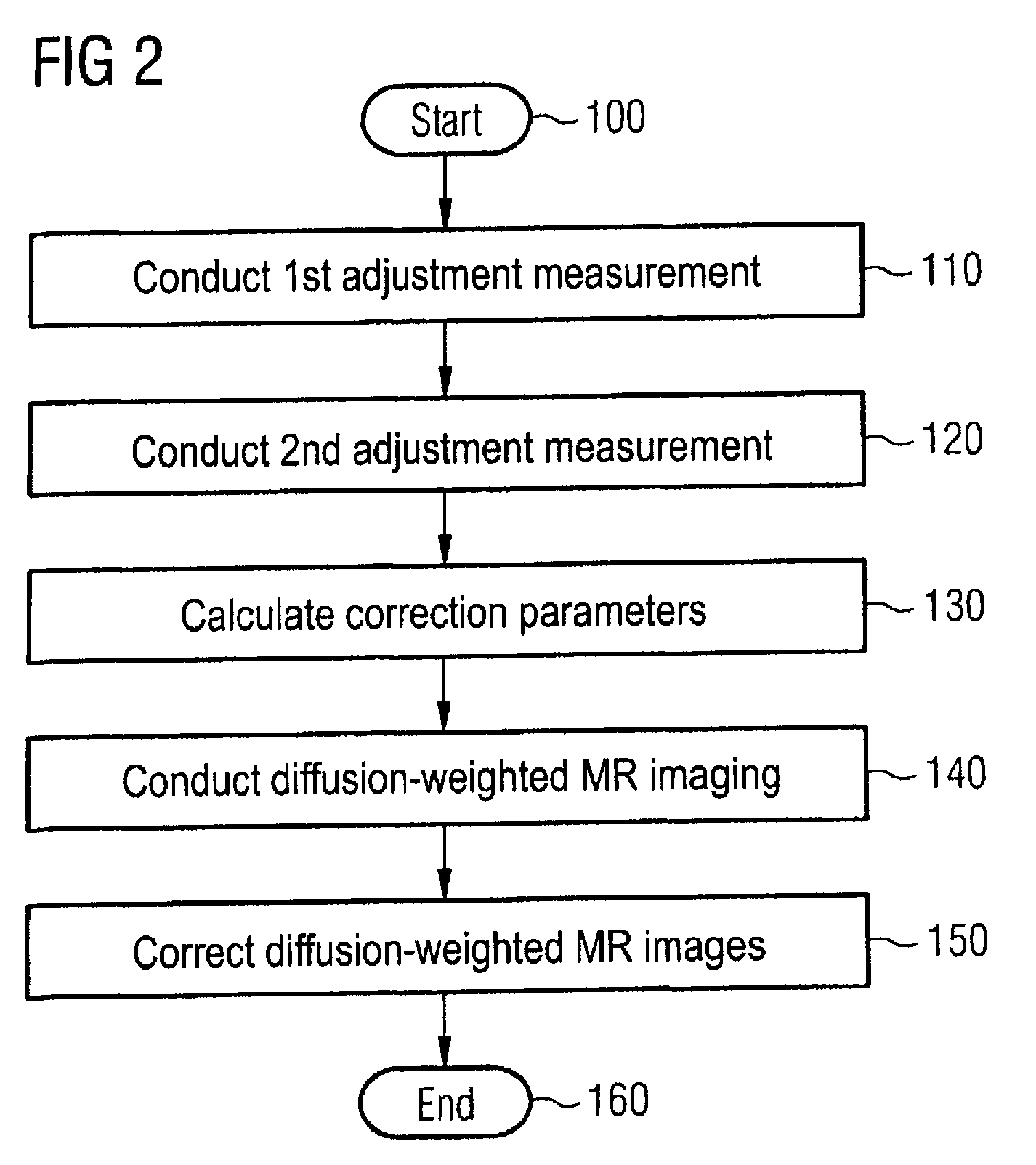
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus to reduce distortions in diffusion imaging
ActiveUS20100171498A1Improved correction methodMinimize scopeCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringDiffusionResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) system for correction of image distortions that occur in acquisitions of diffusion-weighted MR images of an examination subject a first adjustment measurement with a first diffusion weighting is implemented, a second adjustment measurement with a second diffusion weighting is implemented and correction parameters to de-skew diffusion-weighted MR images are automatically calculated in a computer on the basis of the two adjustment measurements. One of the two adjustment measurements is implemented with a predetermined diffusion weighting in three orthogonal diffusion directions, and correction parameters are determined for the three orthogonal diffusion directions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for correcting motion in multi-shot diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7860291B2Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiffusion-Weighted MR ImagingData acquisition
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and magnetic resonance system to correct distortions in image data
InactiveUS20110052031A1Easy to correctAvoid disadvantagesCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringDiffusionResonance
In a method for correction of distortions in image data in a diffusion imaging, the image data are acquired with an imaging MRT measurement for a predetermined diffusion weighting and map a predetermined image segment. A diffusion model for the image segment is determined. Output image data are determined for the image segment such that the output image data are essentially free of distortions caused by diffusion weighting. Reference image data are estimated for the predetermined diffusion weighting for the image segment based on the output image data and the diffusion model. The acquired image data are compared with the reference image data and the acquired image data are corrected based on the comparison.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for diffusion magnetic resonance imaging with the effects of eddy currents compensated
ActiveUS7218110B2High precisionEffect of eddy current can be minimizedMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionResonance
A method and a system for acquiring diffusion magnetic resonance images with compensation of the effects of eddy currents induced by the diffusion weighting (DW) gradient pulses. Prescan data are first acquired using the same DW sequence to be used for imaging. The prescan data are used to obtain eddy current parameters that model the effects of DW-induced eddy currents under the exact conditions under which DW images are to be acquired. The DW imaging sequence is then slightly modified according to the eddy current parameters and used to acquire DW image data with the effects of DW-induced eddy currents compensated.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS9513358B2Reduce sensitivityReduce scan timeAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPerfusionMR - Magnetic resonance
The method and system for correcting motion-induced phase errors in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) use a phase shift of the non-phase encoded reference echo-signal accumulated during the diffusion-weighting in order to characterize bulk motion and tissue deformation and to compensate their effect for correcting the diffusion / perfusion-weighted image. The sequences unbalanced with respect to the first motion derivative are used for distinguishing the perfusion component. The MRI apparatus provides additional excitation resonance-frequency ranges for forming the reference echo signals.
Owner:VAPOSUN
Method and system for diffusion magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20100152567A1Shorten the durationShort timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePulse sequence
A method, system, computer-readable medium, use, and pulse sequence for magnetic resonance imaging or nuclear magnetic resonance is provided for determining the rate of molecular exchange between components with different diffusion characteristics. The present invention encodes the magnetic resonance signal for exchange utilizing judiciously designed protocols for varying the parameters of a pulse sequence comprising a pair of diffusion weighting blocks separated by a mixing time.
Owner:RANDOM WALK IMAGING AB
Method and system for diffusion magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8565854B2Shorten the durationShort timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiffusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method, system, computer-readable medium, use, and pulse sequence for magnetic resonance imaging or nuclear magnetic resonance is provided for determining the rate of molecular exchange between components with different diffusion characteristics. The present invention encodes the magnetic resonance signal for exchange utilizing judiciously designed protocols for varying the parameters of a pulse sequence comprising a pair of diffusion weighting blocks separated by a mixing time.
Owner:RANDOM WALK IMAGING AB
System for Detecting Malignant Lymph Nodes Using an MR Imaging Device
A system detects malignant lymph nodes using an MR imaging device, for, in the absence of a contrast agent, acquiring in a patient anatomical volume of interest including lymph nodes, (a) a first image using a variable flip angle, lymph node enhanced contrast, MR image acquisition process, (b) a second image using a susceptibility weighting imaging acquisition process and (c) a third image using a diffusion weighting imaging acquisition process. In the presence of a contrast agent absorbed by benign lymph nodes, MR imaging device acquires in the patient anatomical volume of interest, (d) a fourth image using a susceptibility weighting imaging acquisition process. A display processor processes data representing the first, second, third and fourth images for display of malignant and benign lymph nodes on a reproduction device.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus to reduce distortions in diffusion imaging
ActiveUS8283925B2Improved correction methodMinimize scopeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiffusionResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) system for correction of image distortions that occur in acquisitions of diffusion-weighted MR images of an examination subject a first adjustment measurement with a first diffusion weighting is implemented, a second adjustment measurement with a second diffusion weighting is implemented and correction parameters to de-skew diffusion-weighted MR images are automatically calculated in a computer on the basis of the two adjustment measurements. One of the two adjustment measurements is implemented with a predetermined diffusion weighting in three orthogonal diffusion directions, and correction parameters are determined for the three orthogonal diffusion directions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Analysis for quantifying microscopic diffusion anisotropy
ActiveUS20150130458A1Controlled diffusionRobust and fast quantificationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiffusion AnisotropyUltrasound attenuation
The present invention describes a method for quantifying microscopic diffusion anisotropy and / or mean diffusivity in a material by analysis of echo attenuation curves acquired with two different gradient modulations schemes, wherein one gradient modulation scheme is based on isotropic diffusion weighting and the other gradient modulation scheme is based on non-isotropic diffusion weighting, and wherein the method comprises analyzing by comparing the signal decays of the two acquired echo attenuation curves.
Owner:RANDOM WALK IMAGING AB
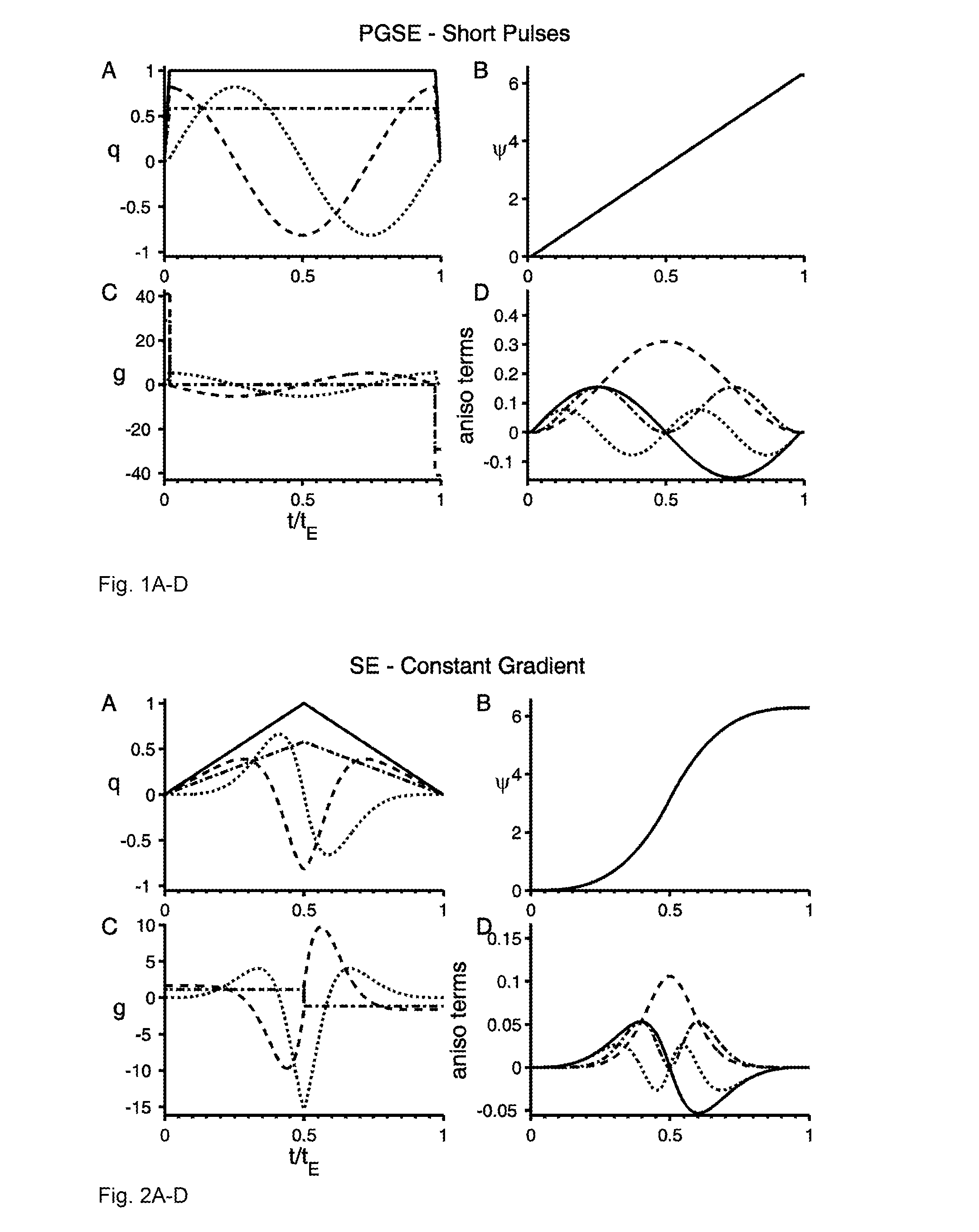
Pulse sequence method for MRI
ActiveUS20150115957A1Reduced and comparable demandShorten the timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionUltrasound attenuation
The present invention describes a method for magnetic resonance (MR) and / or MR imaging, comprising acquisition of signals and MR images originating from a RF and gradient sequence causing isotropic diffusion weighting of signal attenuation, wherein the isotropic diffusion weighting is achieved by one time-dependent dephasing vector q(t) having an orientation, wherein the isotropic diffusion weighting is proportional to the trace of a diffusion tensor D, and wherein the orientation of the time-dependent dephasing vector q(t) is either varied discretely in more than three directions in total, or changed continuously, or changed in a combination of discretely and continuously during the gradient pulse sequence, 0≦t≦echo time, where t represents the time. The method may be performed during a single shot (single MR excitation).
Owner:RANDOM WALK IMAGING AB
Method and magnetic resonance system to reduce distortions in diffusion imaging
ActiveCN102144923AQuick fixAccurate correctionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiffusionResonance
Provided is a method of reducing distortions in a magnetic resonance diffusion imaging, comprising the steps of executing at least one first measurement (R1) having a first diffusion weighting, and executing at least one second measurement (R2) having a second diffusion weighting. A non-linear, system-specific distortion-correcting function is determined on the basis of system-specific information that is specific to the magnetic resonance data acquisition system. Correction parameters are calculated to correct distortions in subsequently-acquired diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images, based on the data acquired in the first and second measurements with the system-specific distortion-correcting function applied thereto. The subsequently-acquired diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images are corrected using the correction parameters to at least reduce distortions therein. A magnetic resonance system is also provided, and by means of the magnetic resonance system, the above method can be executed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for ductal tube tracking imaging for breast cancer detection and diagnosis, and product
ActiveUS20110038521A1Low costEliminate discomfortMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelFat suppression
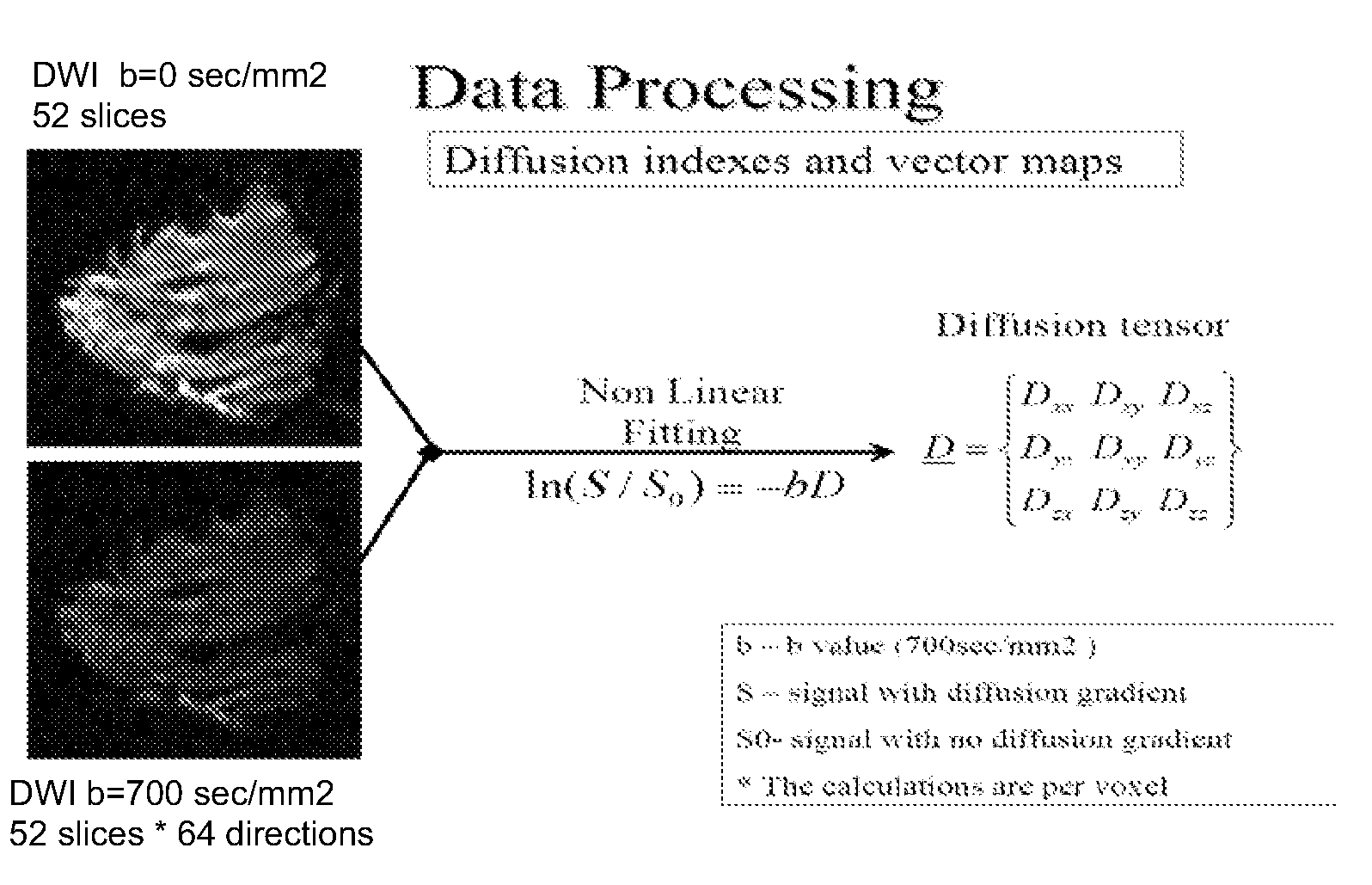
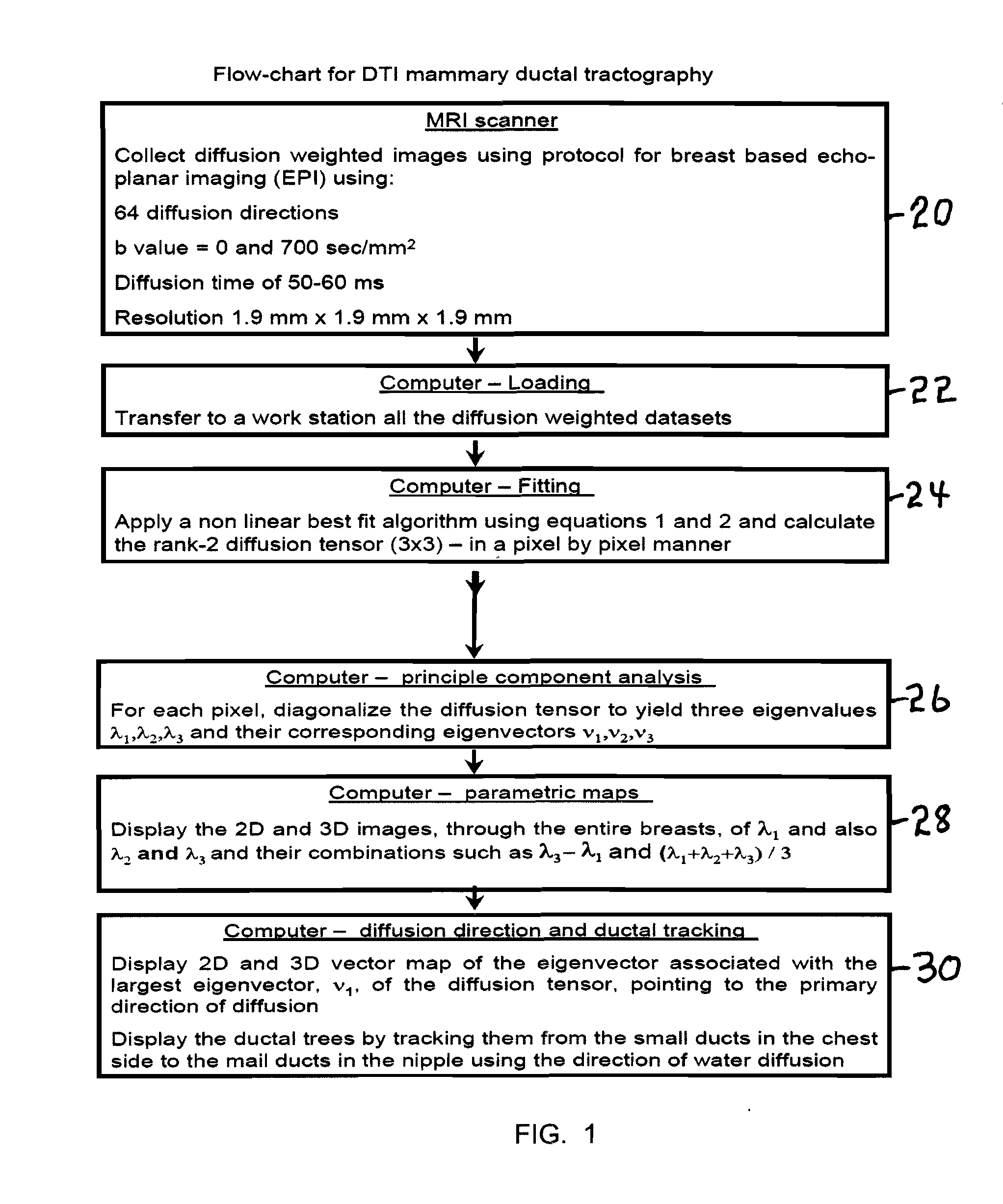
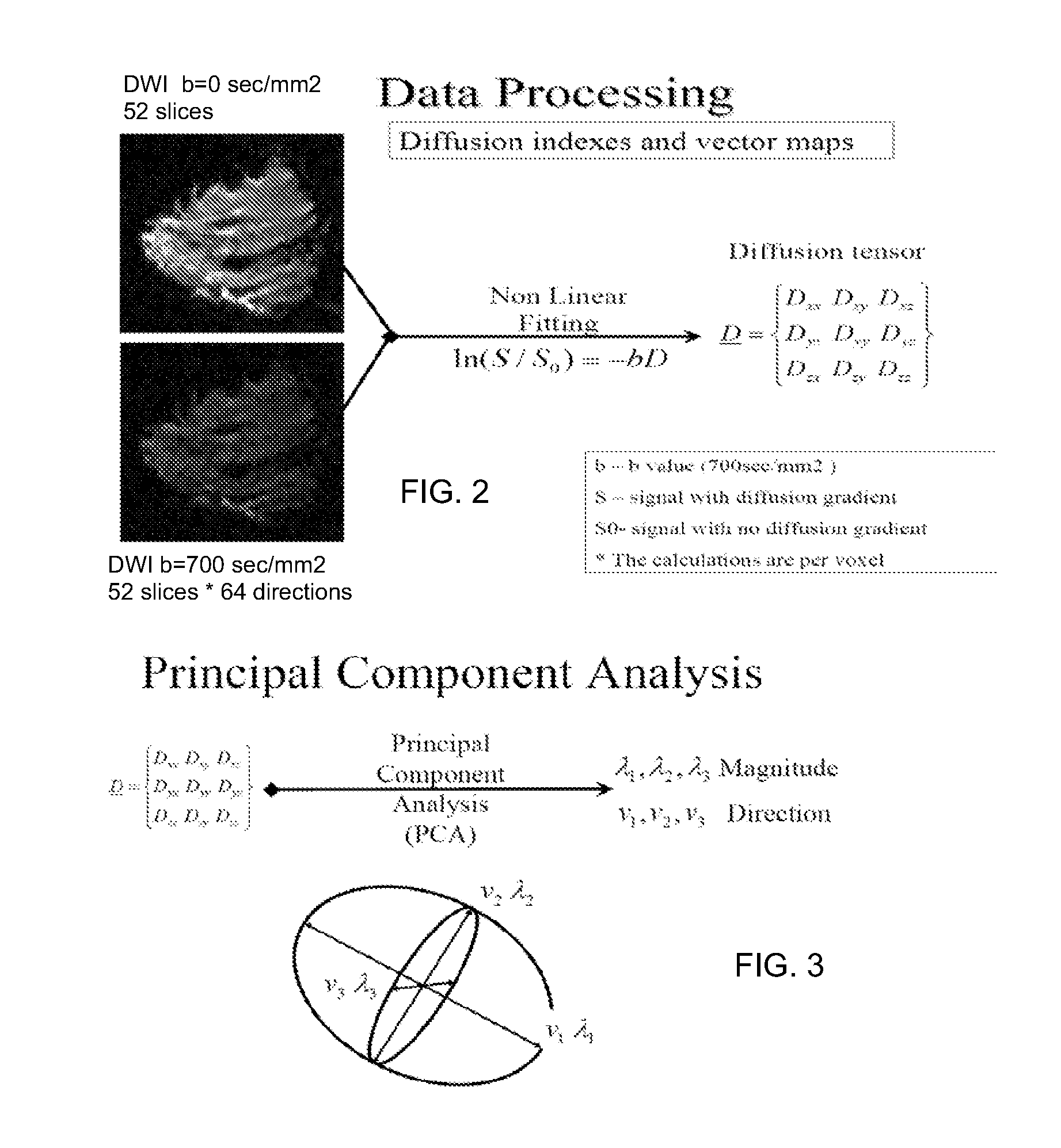
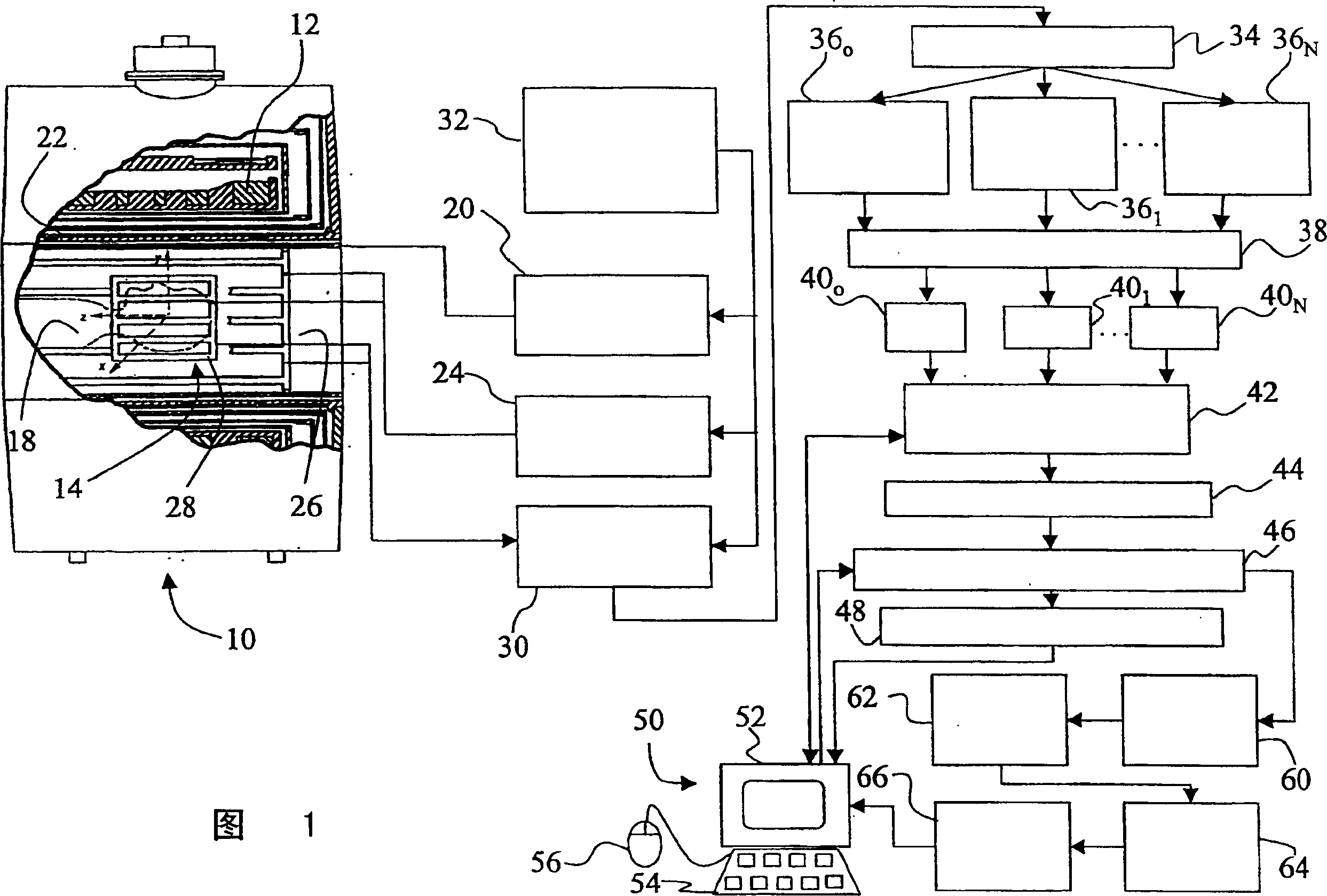
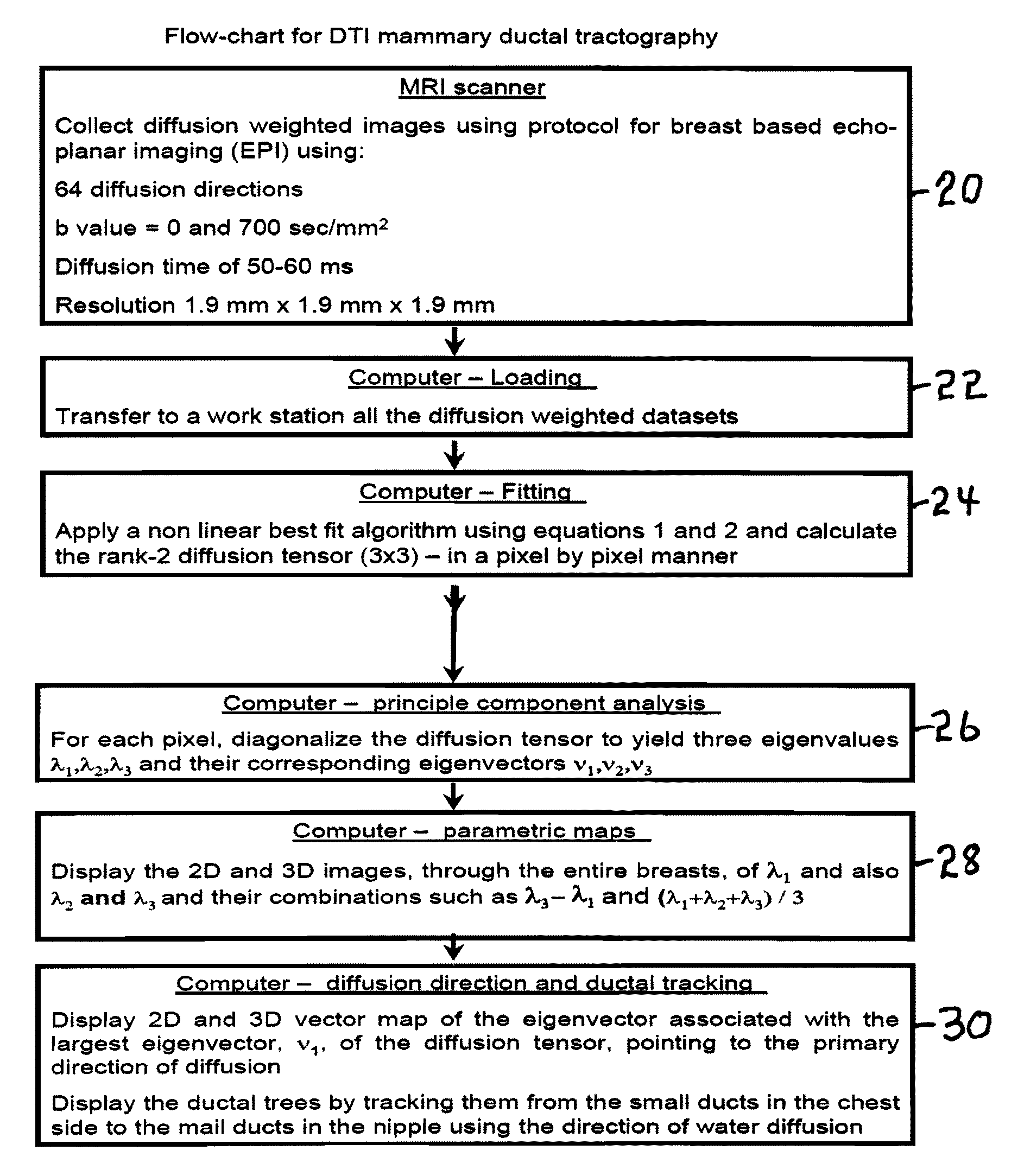
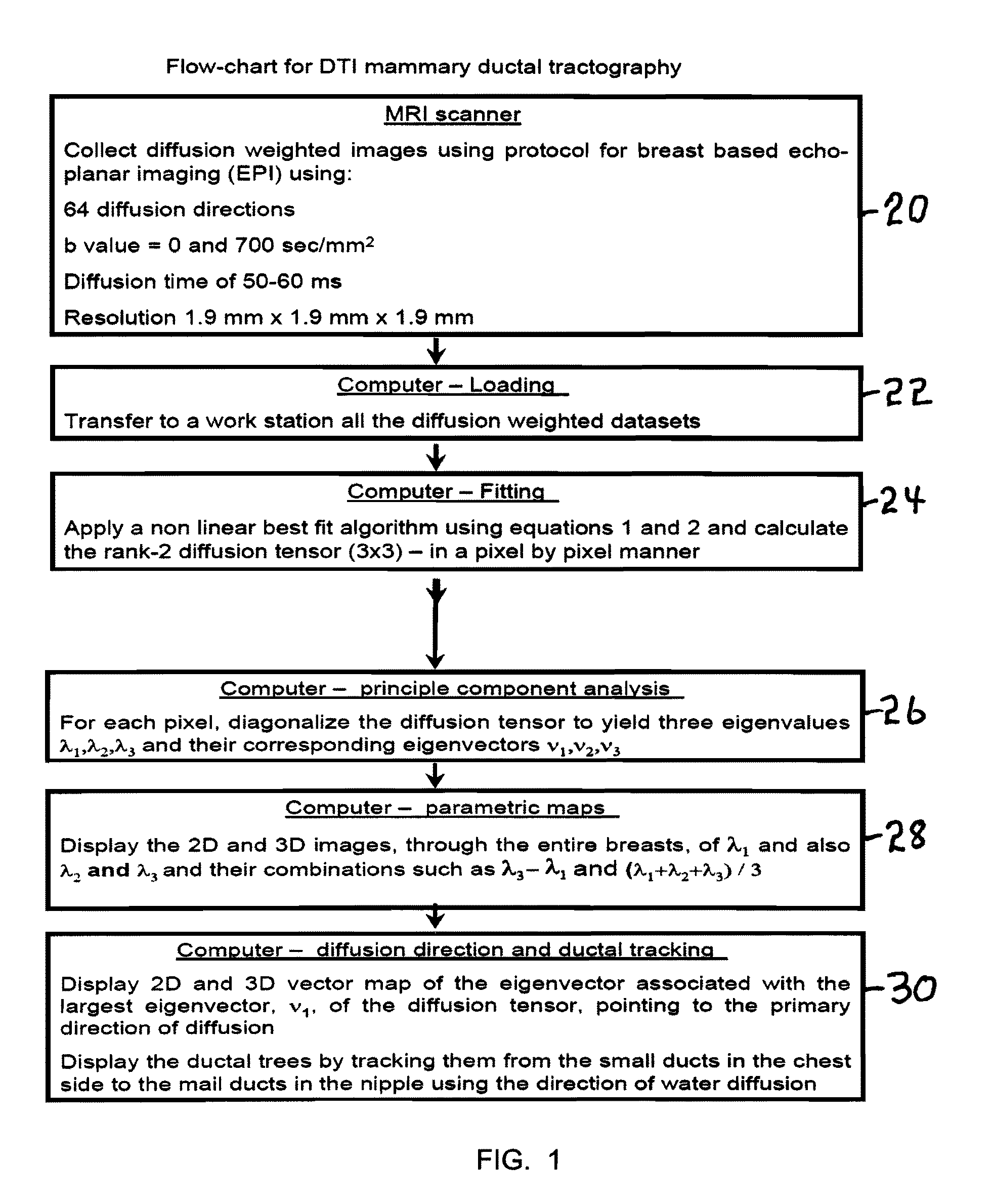
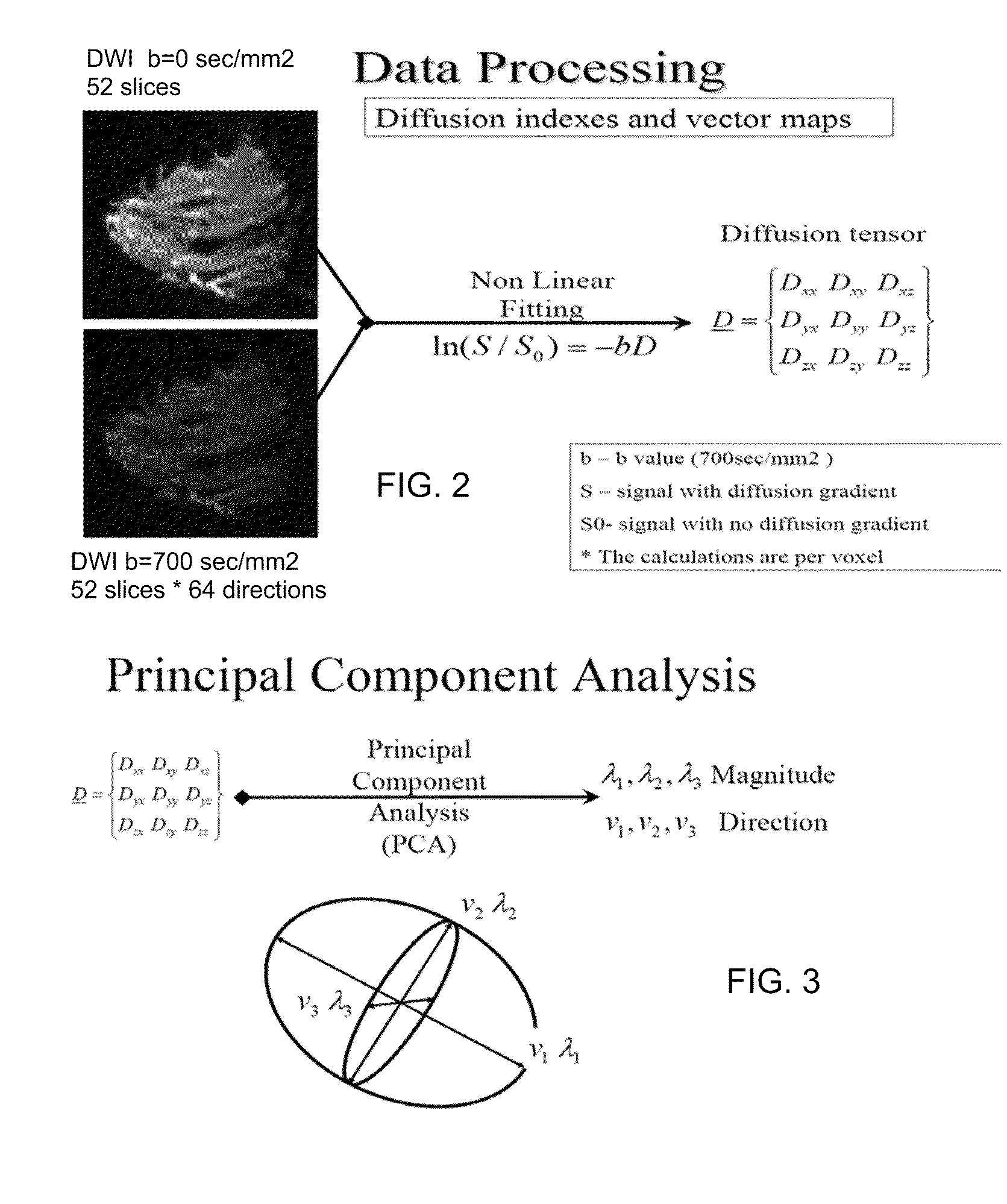
A method apparatus and computer product for imaging a human breast to map the breast ductal tree is disclosed. First, a breast is diffusion tensor imaged with high spatial resolution. Then the breast ductal tree is tracked using a protocol for breast based on echo-planar imaging (EPI) diffusion designed for optimizing diffusion weightings (b values), number of non-collinear directions for tensor calculations, diffusion, echo and repetition times, spatial resolution, signal to noise, scanning time and a sequence for fat suppression. The diffusion tensor is calculated by a non-linear best fit algorithm and then diagonalized with principal component analysis to three eigen vectors and their corresponding eigen values. A vector field map is obtained for tracking of breast ducts of the ductal trees along the direction of the 1st eigenvector v1 and the ductal tree is displayed on a voxel by voxel basis in parametric images using color coding and vector pointing.
Owner:DDE MRI SOLUTIONS LTD
Magnetic resonance method for quantification of molecular diffusion using double echo steady state sequences
ActiveUS20120242334A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDouble echo steady stateDiffuse Lesion
Disclosed is a magnetic resonance method for the quantification of molecular diffusion. The method uses a diffusion-weighted (dw) double echo steady state sequence (DESS). In particular, the method allows direct quantification of molecular diffusion from two steady state scans with differing diffusion weighting such as one with diffusion-weighting and preferably one without diffusion weighting. Such a quantification of molecular diffusion allows for rapid and / or quantitative measurements of physiological and / or functional parameters of living tissue. Quantitative measurements are often a prerequisite for pre-clinical and clinical research as well as for clinical trials in drug research performed at different sites. Especially for the early diagnosis of subtle or diffuse pathological changes, quantitative MR promises to have a very significant impact.
Owner:UNIV HOSPITAL OF BASEL
Real-time tractography
InactiveCN1653350AReal-time structure implementationCalculation speedImage enhancementImage analysisTractographyFiber
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for ductal tube tracking imaging for breast cancer detection and diagnosis, and product
ActiveUS8526698B2Less expensiveShort timeMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelFat suppression
A method apparatus and computer product for imaging a human breast to map the breast ductal tree is disclosed. First, a breast is diffusion tensor imaged with high spatial resolution. Then the breast ductal tree is tracked using a protocol for breast based on echo-planar imaging (EPI) diffusion designed for optimizing diffusion weightings (b values), number of non-collinear directions for tensor calculations, diffusion, echo and repetition times, spatial resolution, signal to noise, scanning time and a sequence for fat suppression. The diffusion tensor is calculated by a non-linear best fit algorithm and then diagonalized with principal component analysis to three eigen vectors and their corresponding eigen values. A vector field map is obtained for tracking of breast ducts of the ductal trees along the direction of the 1st eigenvector v1 and the ductal tree is displayed on a voxel by voxel basis in parametric images using color coding and vector pointing.
Owner:DDE MRI SOLUTIONS LTD
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for reducing distortion in diffusion imaging
ActiveCN102279375AReduced feed phenomenonMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiffusionResonance
The invention relates to a method for reducing distortions in diffusion imaging, comprising the steps of: carrying out at least one first measurement (R1) with a first diffusion weight each for a plurality of spatially separated layers; A plurality of spatially separated layers each carry out at least one second measurement (R2) with a second diffusion weight; determining a distortion correction function and determining correction parameters from said measurements (R1, R2) for weighting the diffusion Distortion correction is performed on the magnetic resonance image of the MRI image, wherein the image information and / or correction parameters of different layers are correlated with each other; and the distortion correction of the diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance image is performed based on the distortion correction function and the correction parameter. Furthermore, the invention proposes a magnetic resonance system (1) that can be used to carry out such a method.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Digital halftoning method utilizing diffused weighting and class matrix optimization
InactiveUS20100033764A1Execution efficiency is highError diffusionDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsMatrix optimizationAlgorithm
The present invention discloses a digital halftoning method. The method comprises steps of: (a1) dividing an original image into non-overlapping blocks; (a2) obtaining a Least-Mean-Square trained (LMS-trained) filter by comparing at least a training image and a halftone result corresponding to the training image (a3) optimizing a class matrix with the LMS-trained filter, which involves the diffused area and the diffused weightings; and (a4) processing the non-overlapping blocks by performing a dot diffusion procedure with the optimized class matrix and the diffused weightings to generate a halftone image corresponding to the original image. A detailed class matrix optimizing method as in the above-mentioned step (a3) is also disclosed.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Magnetic resonance method for quantification of molecular diffusion using double echo steady state sequences
ActiveUS8497680B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDouble echo steady stateDiffuse Lesion
Disclosed is a magnetic resonance method for the quantification of molecular diffusion. The method uses a diffusion-weighted (dw) double echo steady state sequence (DESS). In particular, the method allows direct quantification of molecular diffusion from two steady state scans with differing diffusion weighting such as one with diffusion-weighting and preferably one without diffusion weighting. Such a quantification of molecular diffusion allows for rapid and / or quantitative measurements of physiological and / or functional parameters of living tissue. Quantitative measurements are often a prerequisite for pre-clinical and clinical research as well as for clinical trials in drug research performed at different sites. Especially for the early diagnosis of subtle or diffuse pathological changes, quantitative MR promises to have a very significant impact.
Owner:UNIV HOSPITAL OF BASEL
System for detecting malignant lymph nodes using an MR imaging device
A system detects malignant lymph nodes using an MR imaging device, for, in the absence of a contrast agent, acquiring in a patient anatomical volume of interest including lymph nodes, (a) a first image using a variable flip angle, lymph node enhanced contrast, MR image acquisition process, (b) a second image using a susceptibility weighting imaging acquisition process and (c) a third image using a diffusion weighting imaging acquisition process. In the presence of a contrast agent absorbed by benign lymph nodes, MR imaging device acquires in the patient anatomical volume of interest, (d) a fourth image using a susceptibility weighting imaging acquisition process. A display processor processes data representing the first, second, third and fourth images for display of malignant and benign lymph nodes on a reproduction device.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus to reduce distortions in diffusion images
ActiveUS8487617B2Reduce distortion problemsReduced measurement timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionResonance
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
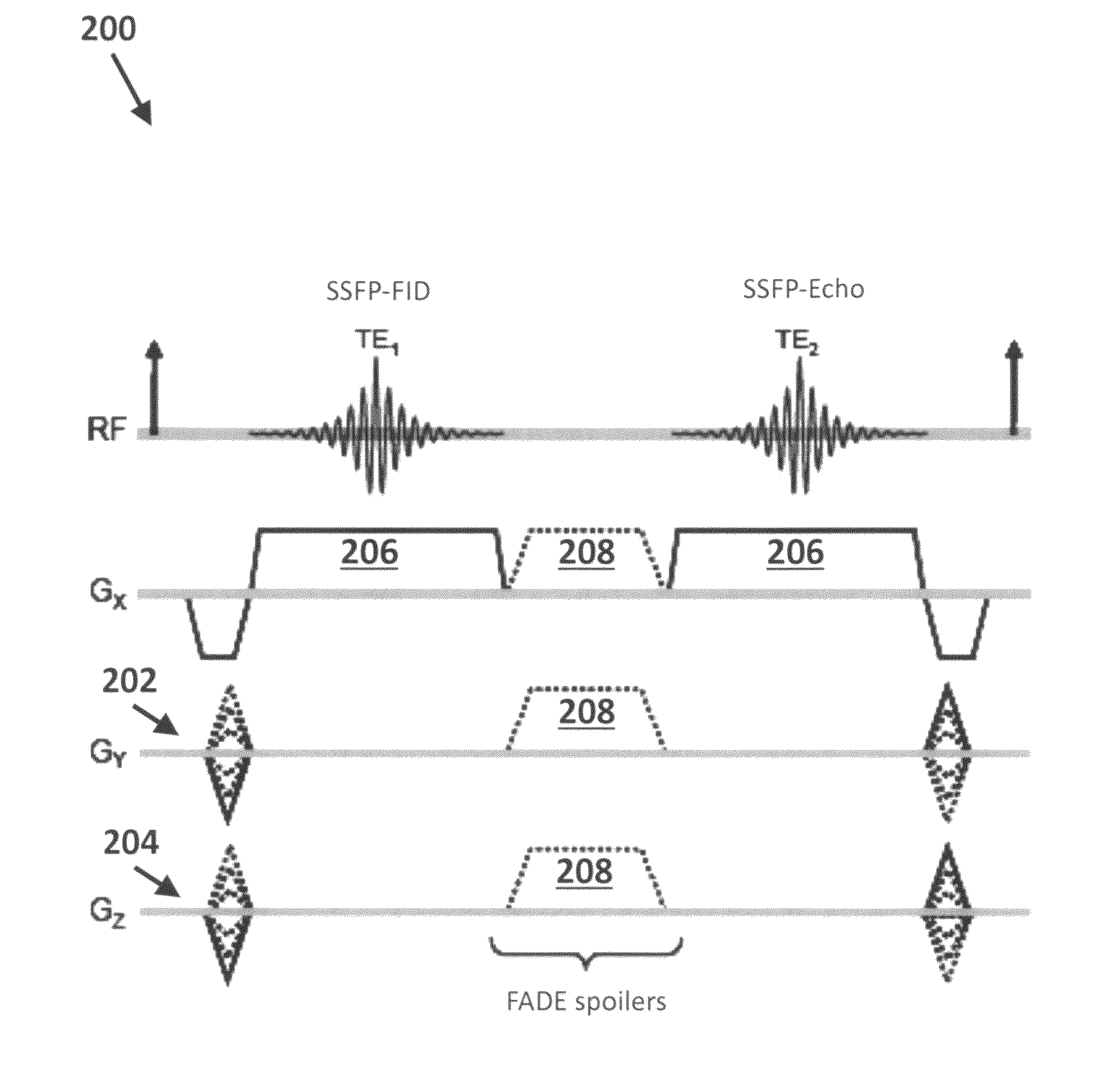
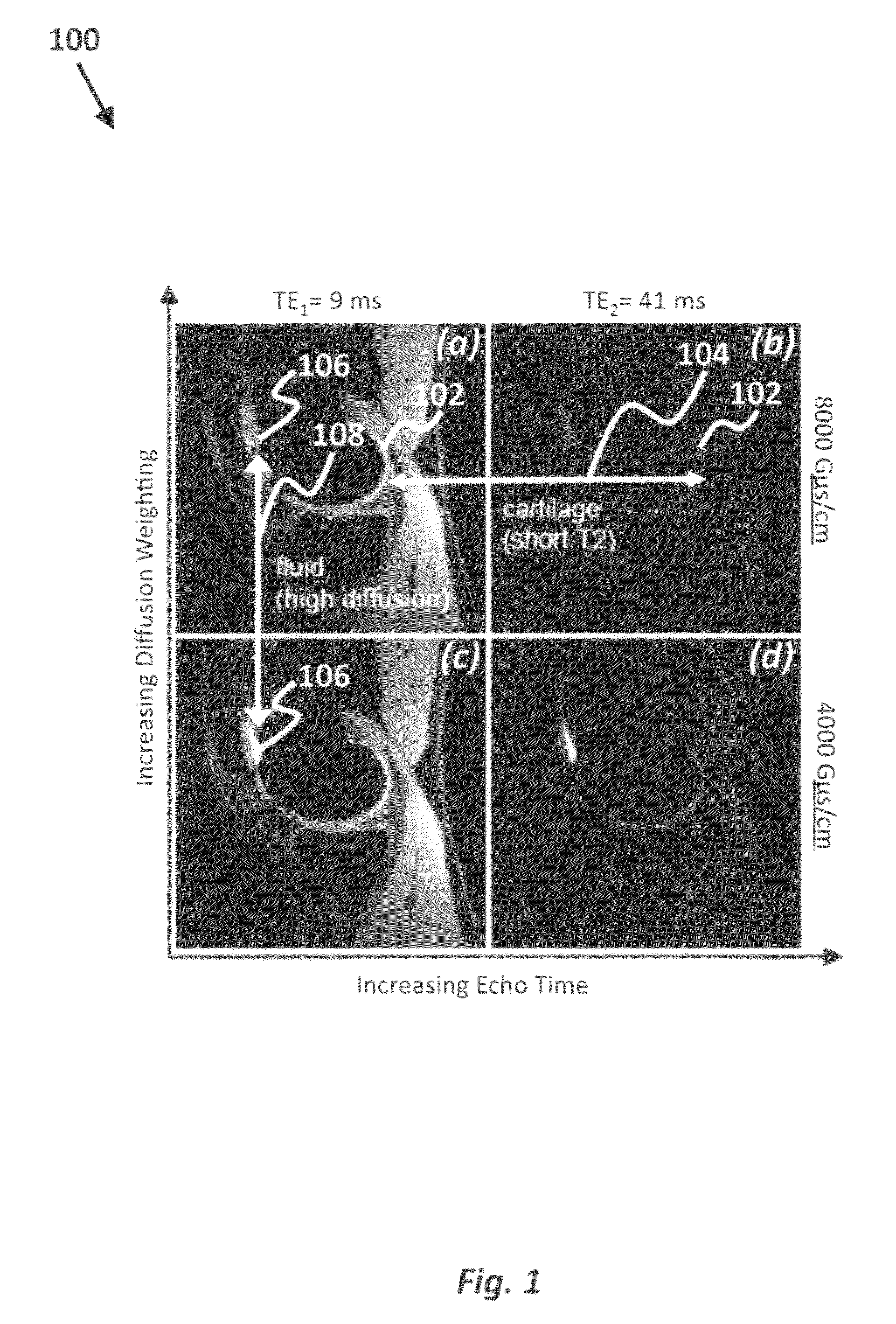
T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted imaging using fast acquisition with double echo (FADE)
ActiveUS8508225B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionT2 weightingData acquisition
A method of acquiring T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted images is provided. The method includes acquiring a first image and a second image in a single magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, where the first image and the second image have different echo times (TE). The single MRI scan includes a series of repeated RF excitation pulses, where the echo signal for the first image and the echo signal for the second image are acquired between a pair of RF excitation pulses. A spoiler gradient is disposed to provide a first diffusion weighting to the first image and a second diffusion weighting to the second image, where the first image and the second image have different T2 weightings and different diffusion weightings.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com