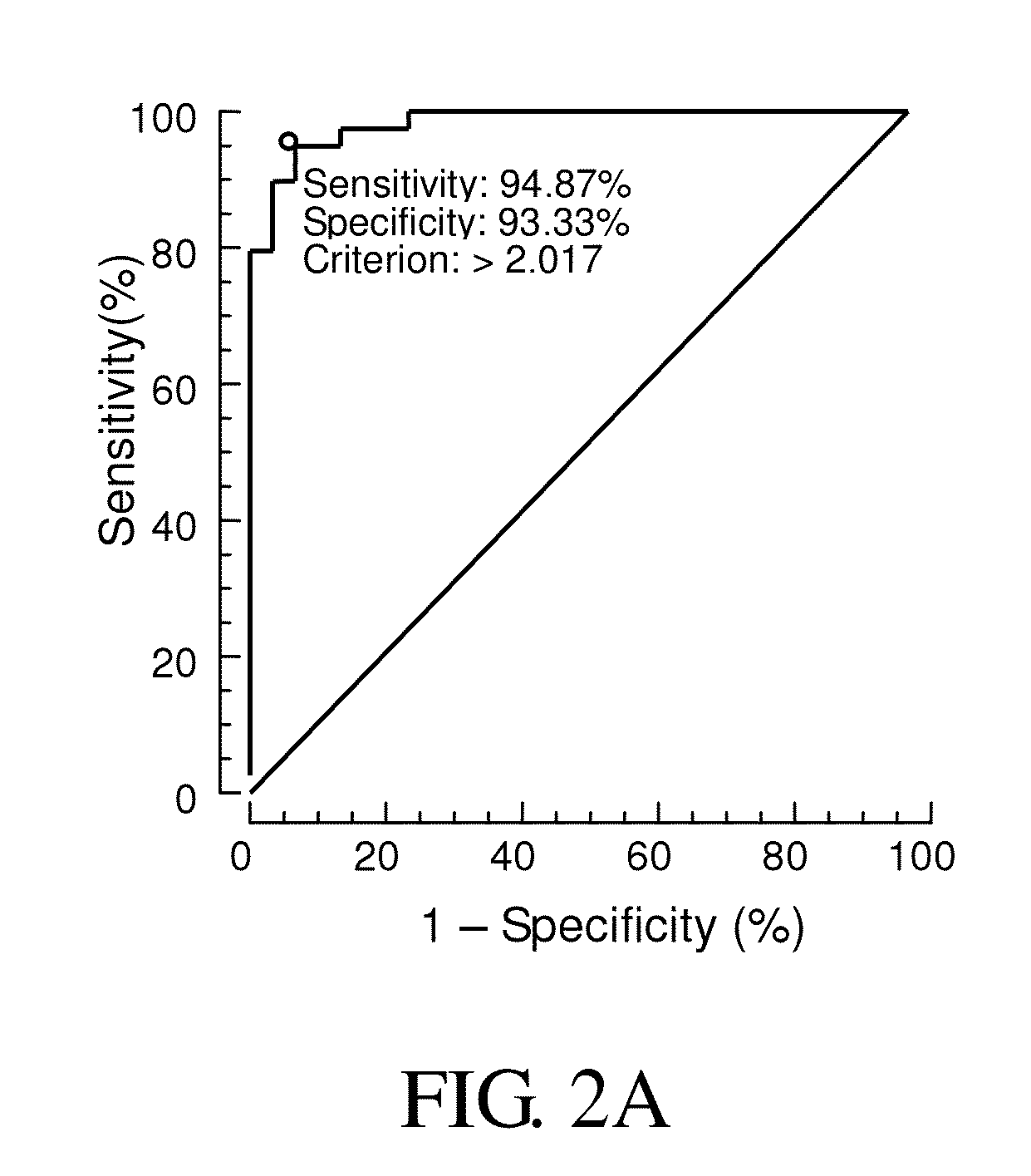
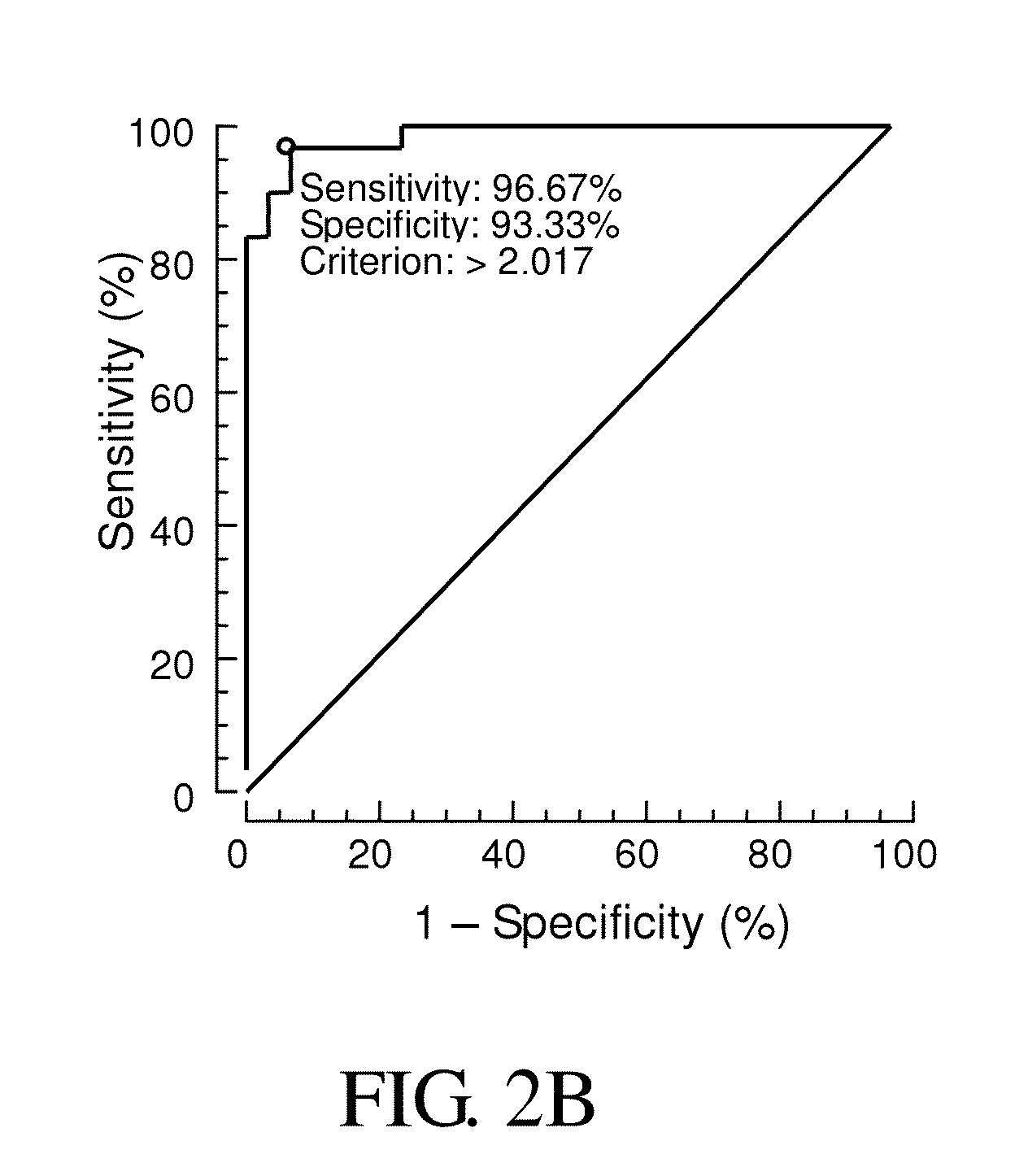
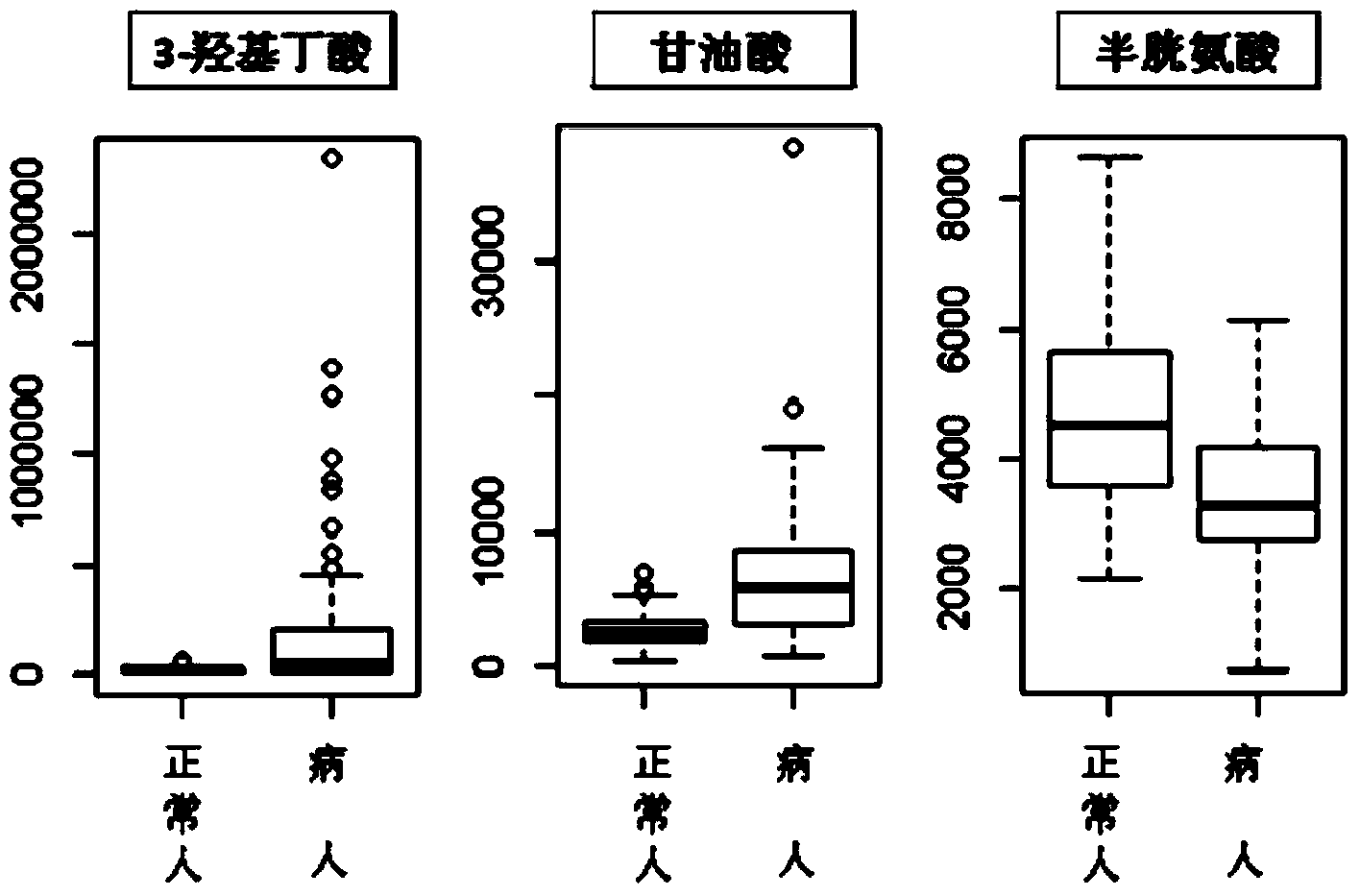
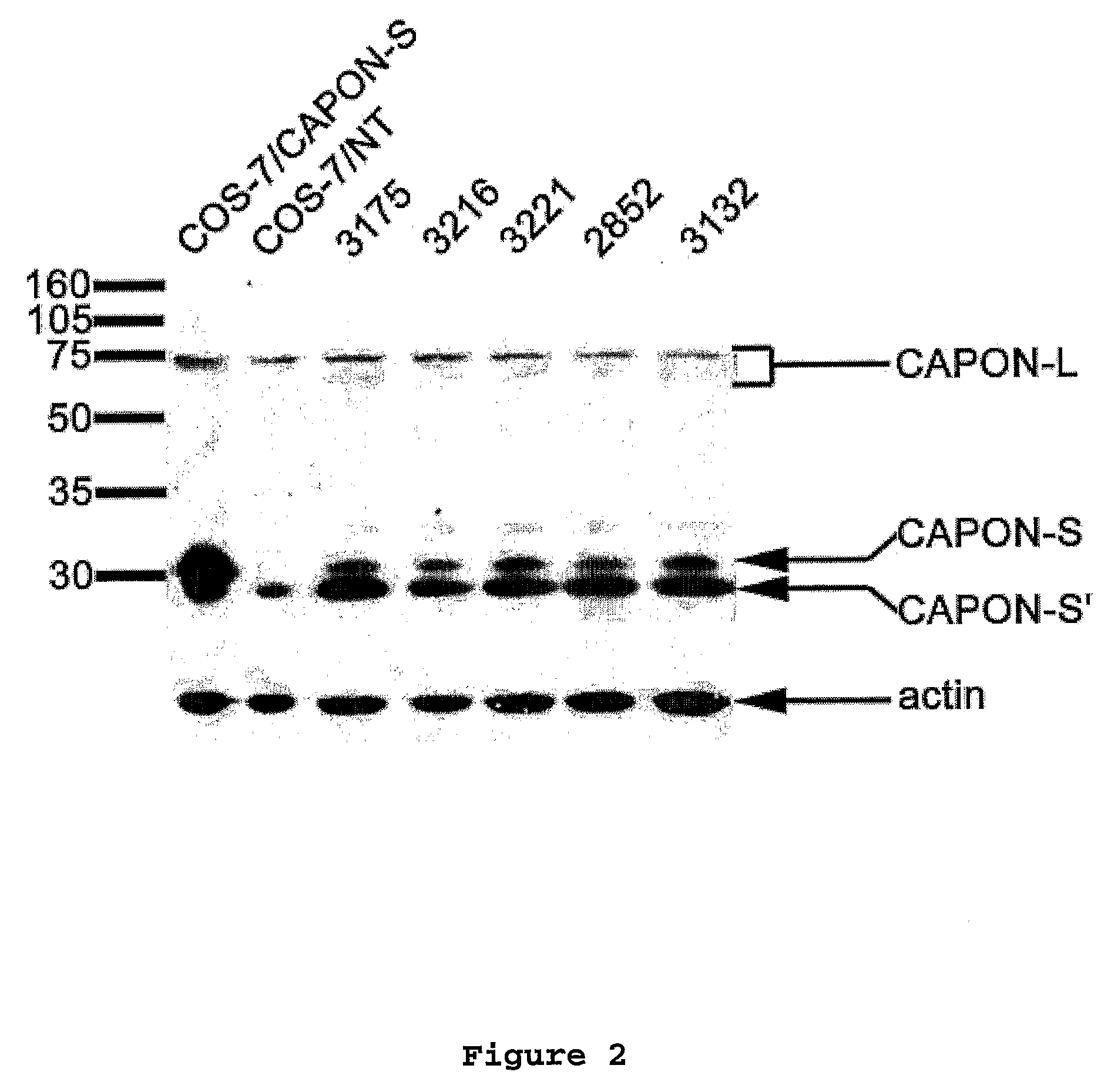
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Diagnosis of schizophrenia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The diagnosis of schizophrenia is based on criteria in either the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, version DSM-5, or the World Health Organization's International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, the ICD-10. Clinical assessment is performed by a mental health professional based on observed behavior, reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. Symptoms associated with schizophrenia occur along a continuum in the population and must reach a certain severity and level of impairment before a diagnosis is made.
Use Of Genes As Molecular Markers In Diagnosis Of Schizophrenia And Diagnostic Kit For The Same
InactiveUS20080274455A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative Real Time PCRScreening method
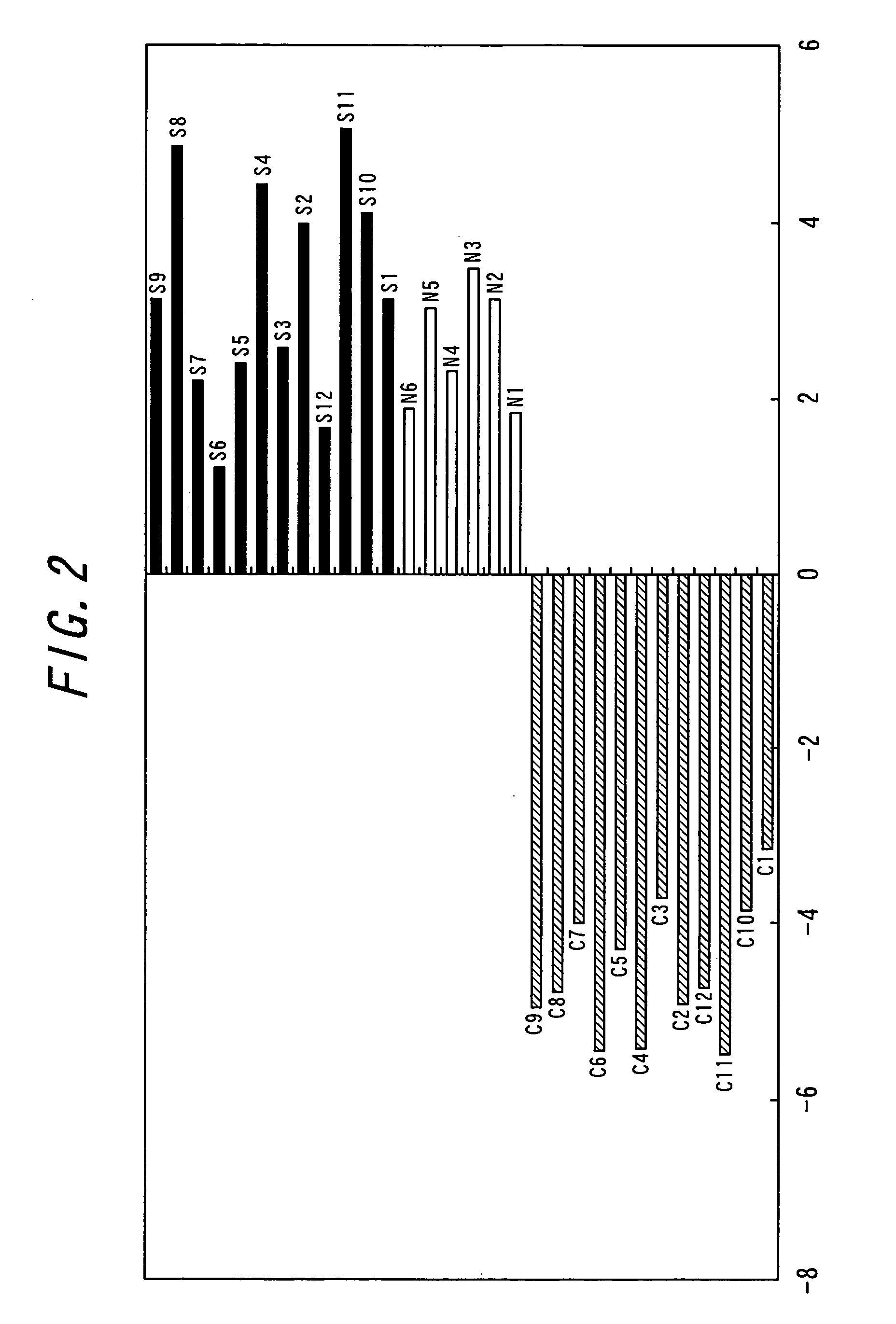
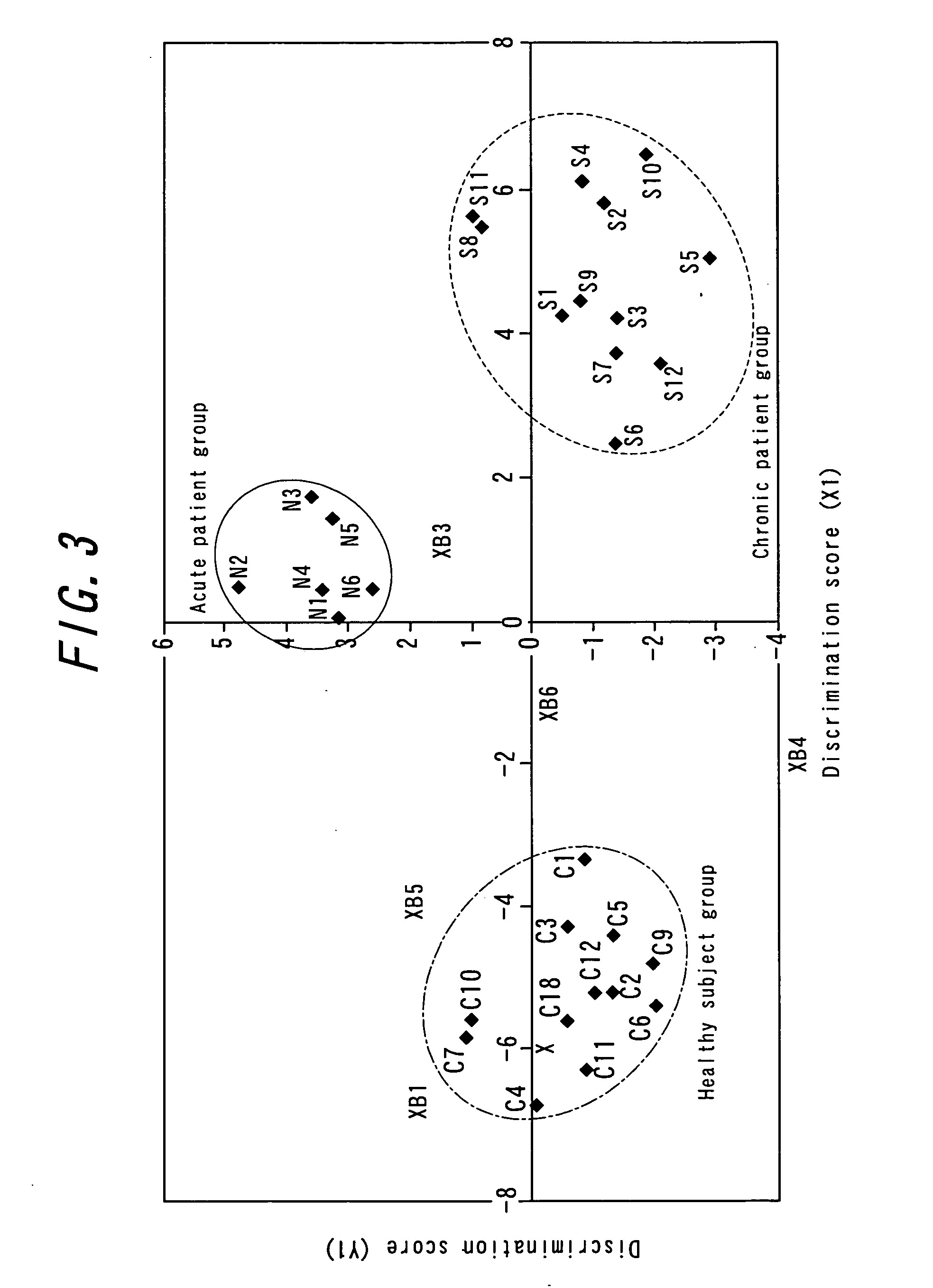
Drug-naive and drug-free schizophrenic PBL were screened to identify additional markers that are differentially expressed compared to healthy individuals using microarray and quantitative real-time PCR (QRT-PCR) techniques. Genes for dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) and inwardly rectifying potassium channel (Kir2.3) were found to be overexpressed in microarray analysis. Increased mRNA levels were confirmed by QRT-PCR using SybrGreen method and dual labeled TaqMan probes.The invention relates to a method for diagnosing schizophrenia in a subject comprising assessing the level or the expression level of at least one of the following genes or proteins: Kir2.3 or DRD2 or a gene encoding Kir2.3 or DRD2. The invention further relates to agents and uses thereof, said agents specifically binding to said proteins or nucleic acids encoding them, diagnostic kits and screening methods.Use of both molecular markers allow prediction of schizophrenia and help to follow efficiency of drugs in therapy in order to provide a more tailored medication for schizophrenic patients.
Owner:THE BIOLOGICAL RES CENT OF THE HUNGARIAN ACAD OF SCI
Method of diagnosing integration dysfunction syndrome using blood
InactiveUS20060099593A1Reliable methodForcing riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical psychologyHealthy subjects
An object of the present invention is. to provide an objective method for diagnosis of schizophrenia using gene expression in mononuclear cells of peripheral blood as an index, and this invention provide a method for diagnosing whether a test subject suffers from schizophrenia or not. The method according to this invention is a method for diagnosing whether a test subject suffers from schizophrenia or not, the method comprising the steps of; obtaining mononuclear cells in blood containing nucleic acid from said subject, measuring the content of at least one nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of nucleic acid(s) (containing its fragment and a nucleic acid complementary to the nucleic acid) defining gene(s) exhibiting altered expression by occurrence of schizophrenia or nucleic acid(s) (containing its fragment and a nucleic acid complementary to the nucleic acid) defining gene(s) exhibiting altered expression by progression of schizophrenia in said mononuclear cells, and determining alteration of the quantified level(s) of the gene(s) in said test subject is statistically significant in comparison with the quantified level(s) of said nucleic acid(s) defining gene(s) exhibiting altered expression by occurrence of schizophrenia or said nucleic acid(s) defining gene(s) exhibiting altered expression by progression of schizophrenia in healthy subjects or schizophrenic patients, thereby diagnosing whether said subject is suffering from schizophrenia or not.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Schizophrenia marker
InactiveCN107746874AEasy diagnosisLife improving treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCitrobacterSuccinivibrio
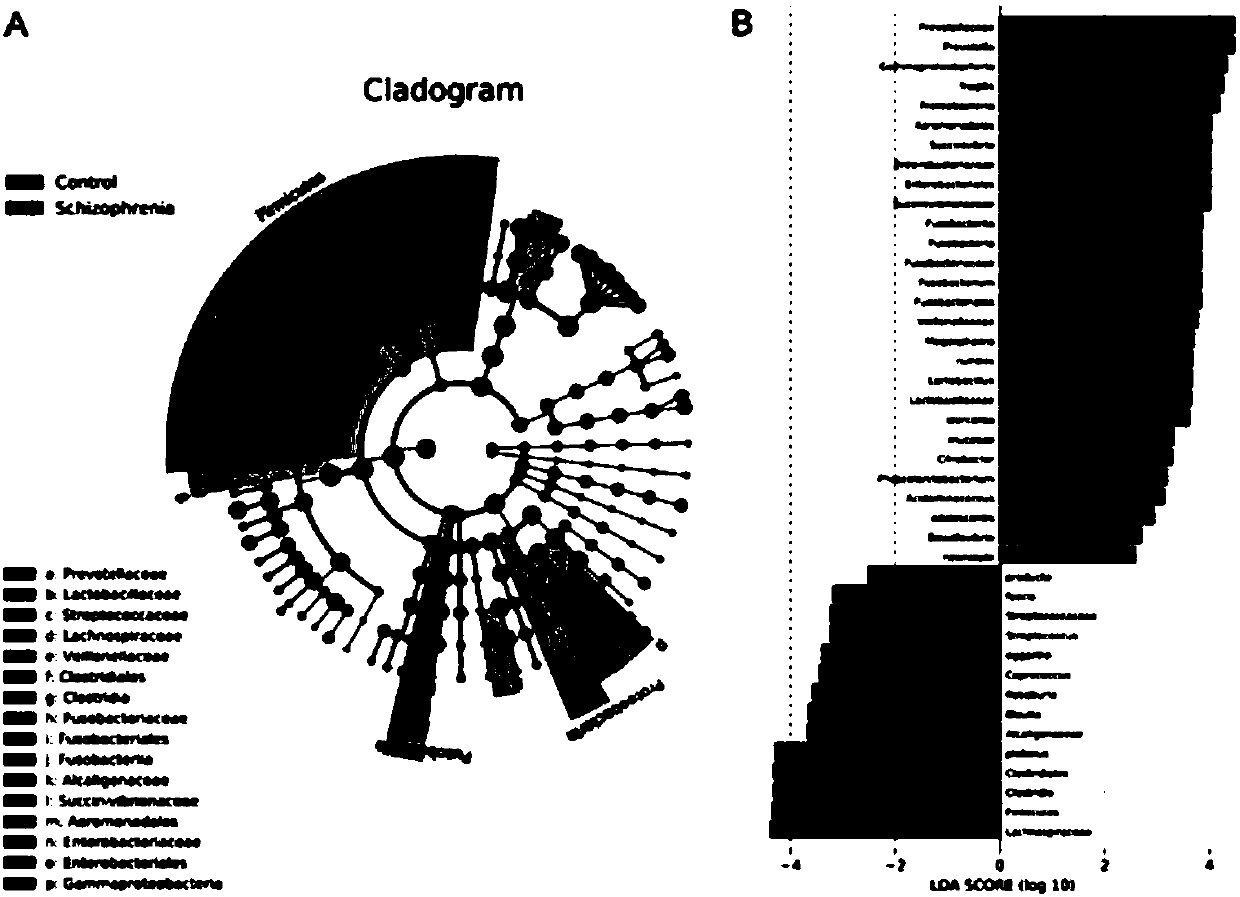
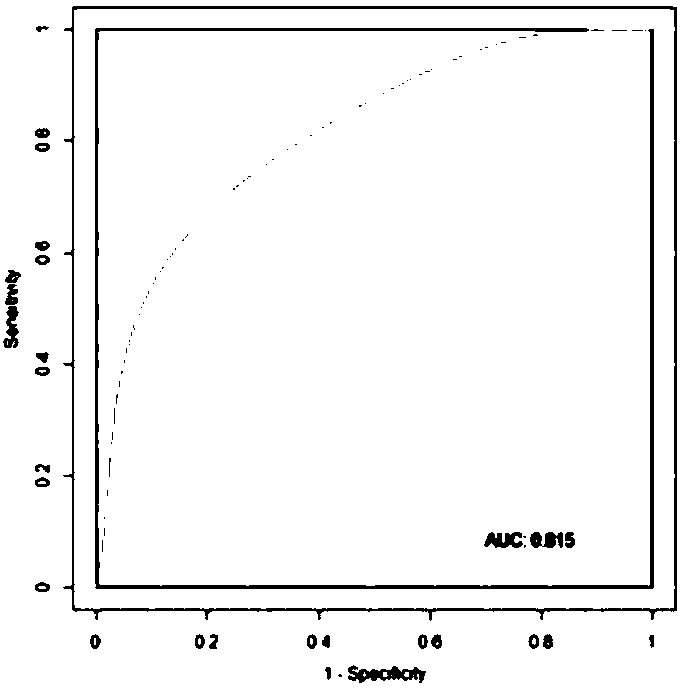
The invention relates to the fields of genetic engineering and biomedicine, and more specifically relates to a biomarker of schizophrenia and its application. The invention discloses a marker of schizophrenia and its application in preparing a kit for diagnosing schizophrenia, and also discloses a kit for detecting the marker. The schizophrenia markers disclosed in the present invention include Prevotella, Succinivibrio, Fusobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Megasphaera , Acidaminococcus, Citrobacter, Phascolarctobacterium, Coprococcus, Roseburia, Blautia 11 species At least 5 of the microorganisms. The marker provided by the invention can judge schizophrenia and normal people, the AUC is above 0.81, has good diagnostic efficiency, and can be used to prepare a kit for effectively diagnosing schizophrenia.
Owner:张猛 +1
Biomarker of schizophrenia and use method and application thereof
InactiveCN103512890ARealize detectionAvoid potential dangerOptically investigating flaws/contaminationTrue positive rateSchizophrenia
The invention discloses a group of biomarkers for diagnosis of schizophrenia, and the biomarkers can be applied to preparation of detection reagents or detection kits for diagnosis of schizophrenia. Based on the markers, the invention also provides a detection kit, a detection reagent and a chip or array for the diagnosis of schizophrenia, and a method for the diagnosis of schizophrenia by using the markers. The method of the present invention is simple and practical, has reliable diagnosis results and gives consideration to both sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & RES INST
Compositions and methods for diagnosis of schizophrenia
InactiveUS20140171413A1Good sensitivity and specificityElevationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGene productIncreased risk
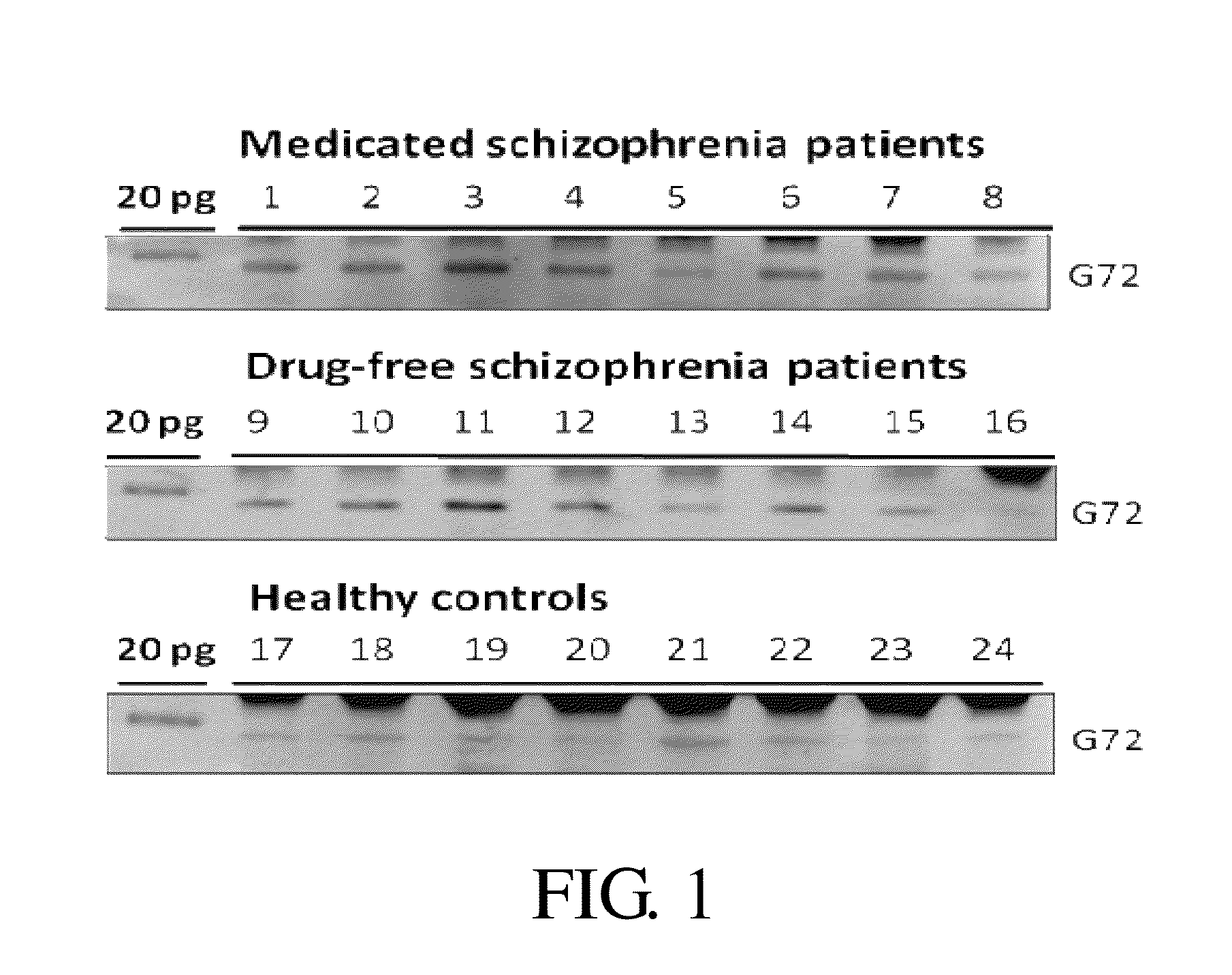
Provided is a method for diagnosis of schizophrenia, which comprises: detecting G72 gene product in a body fluid sample from a subject by an assay to determine G72 expression level; comparing said G72 expression level to a baseline G72 expression; and relating the G72 expression level to the patient's risk of schizophrenia by assigning an increased risk of schizophrenia when said G72 expression level is greater than said baseline G72 expression. Through detecting G72 expression level in a peripheral sample, the method can be simply performed by an in vitro assay and accurately predict or diagnose a subject with schizophrenia.
Owner:CHINA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY(TW)
Biomarker of schizophrenia and usage method and application thereof
InactiveCN103512972ASensitive and Specific DiagnosisComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansClinical psychologyTrue positive rate
The invention discloses a group of biomarkers for diagnosis of schizophrenia, and the biomarkers can be applied to preparation of detection reagents or detection kits for diagnosis of schizophrenia. Based on the markers, the invention also provides a detection kit, a detection reagent and a chip or array for the diagnosis of schizophrenia, and a method for the diagnosis of schizophrenia by using the markers. The method of the present invention is simple and practical, has reliable diagnosis results and gives consideration to both sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Brain network classification method combining node attributes and multi-level topology
PendingCN112634214AImprove classification performanceImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionBrain network
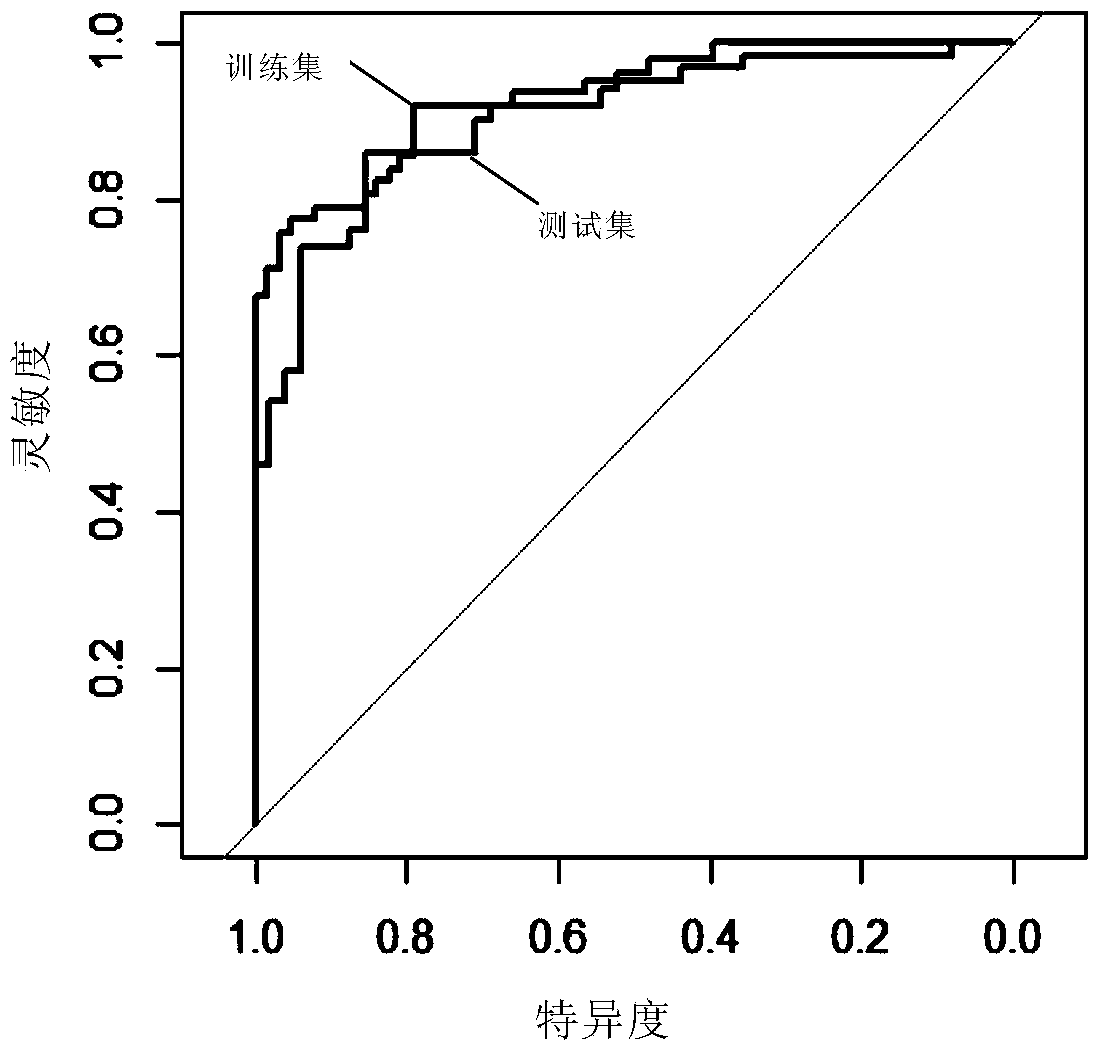
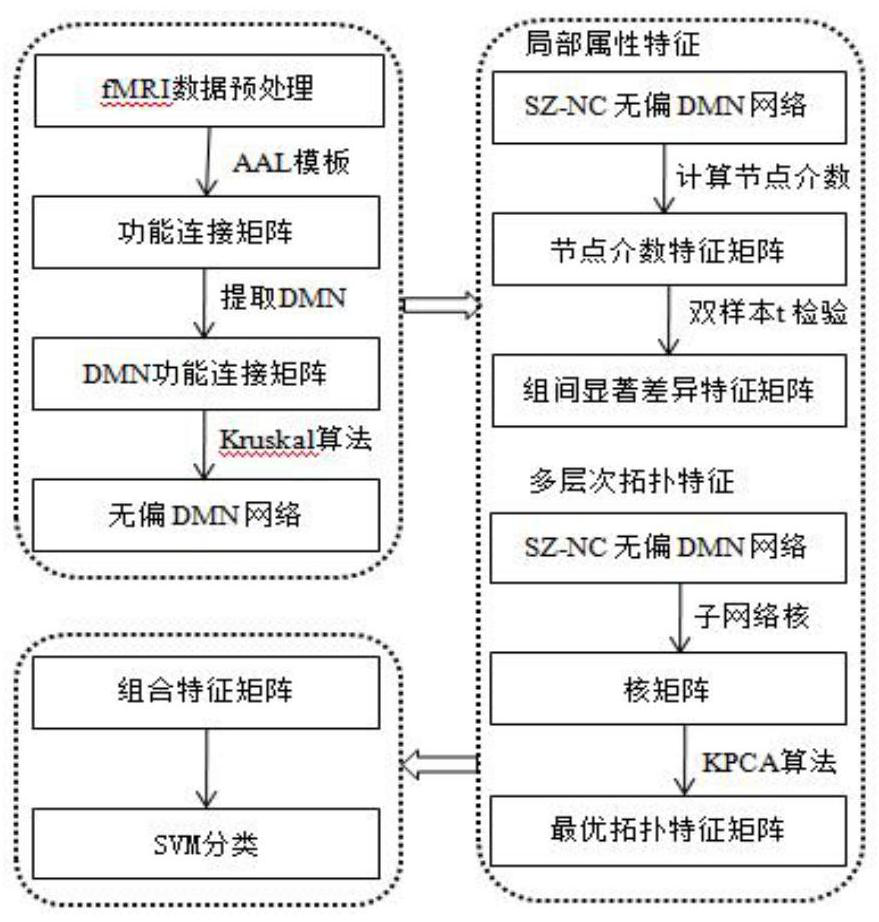
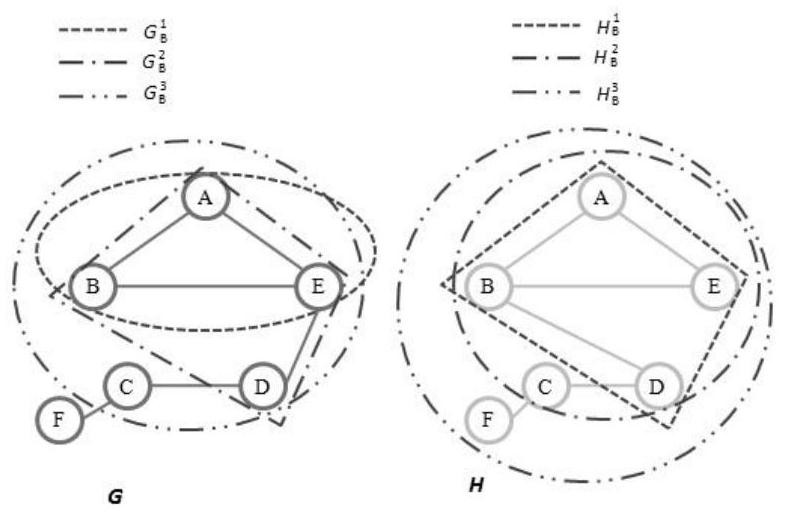
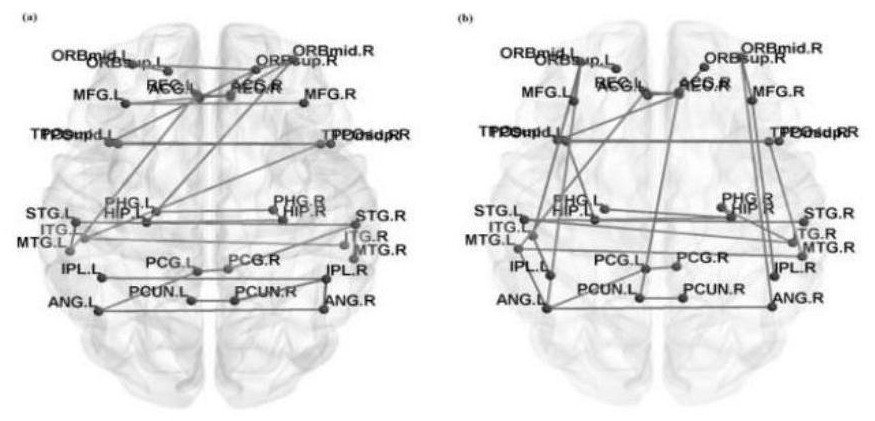
The invention discloses a brain network classification method combining node attributes and multi-level topology, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining functional magnetic resonance brain image data, and carrying out the preprocessing; S2, based on the preprocessed data, generating a whole-brain network function connection matrix by using an automatic anatomical marking template, and constructing an unbiased brain network by using a Kruskal algorithm and taking DMN as a region of interest; S3, extracting brain region node betweenness from the unbiased brain network to serve as local attribute features, and extracting brain region features with inter-group significant differences by using a double-sample t test method; S4, extracting multi-level topological features on the unpartial brain network by using sub-network kernels, generating a sub-network kernel matrix, and extracting optimal topological features by using a kernel principal component analysis method. According to the method, the classification performance is remarkably improved, an abnormal brain area can be found, multi-level topological characteristics of brain area nodes can be captured, and the method has important significance in clinical auxiliary diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
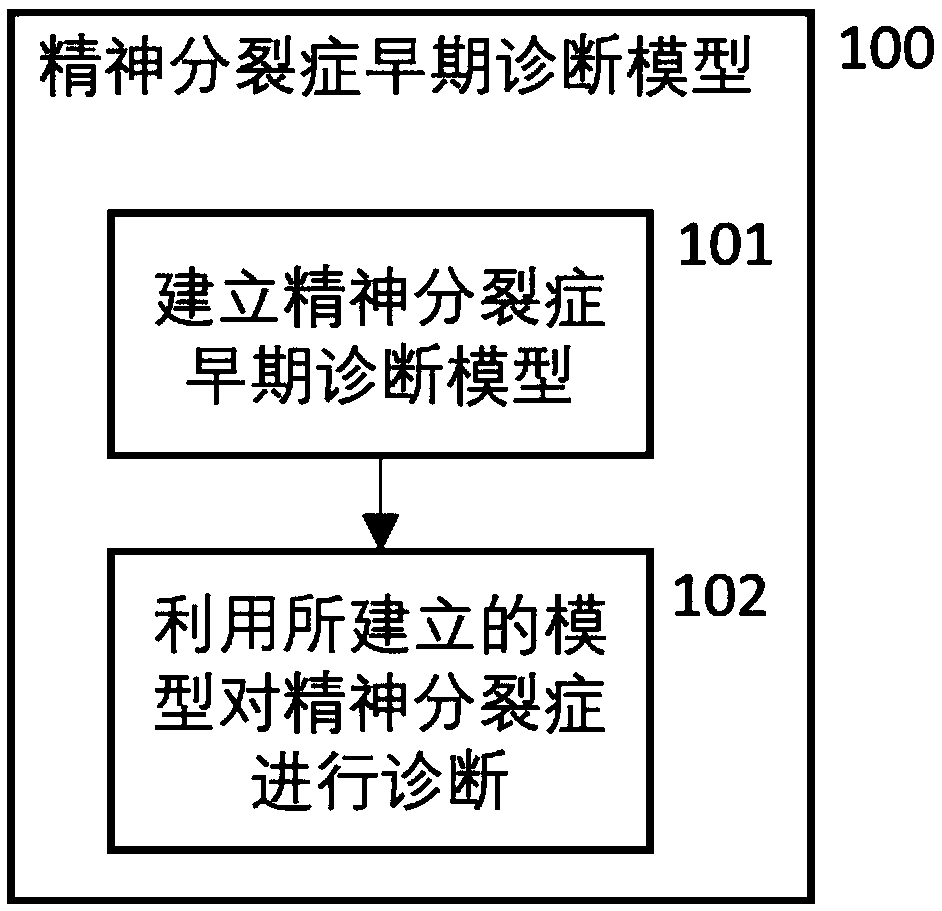
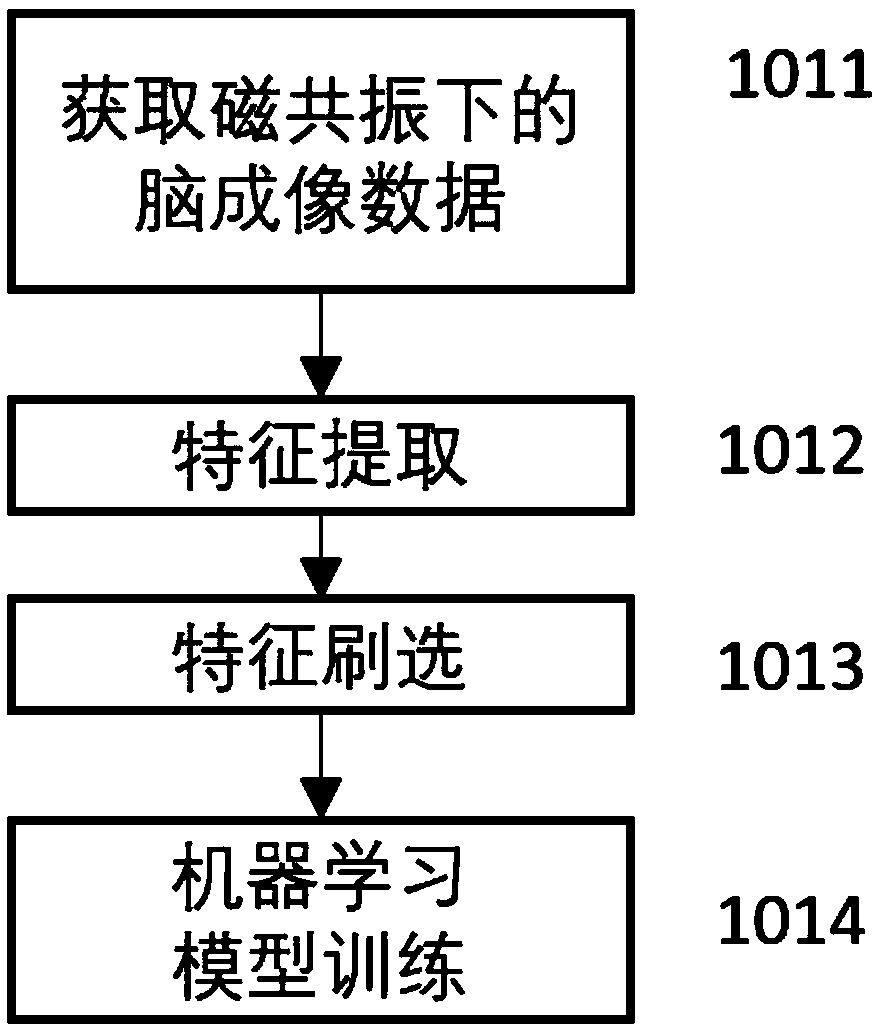
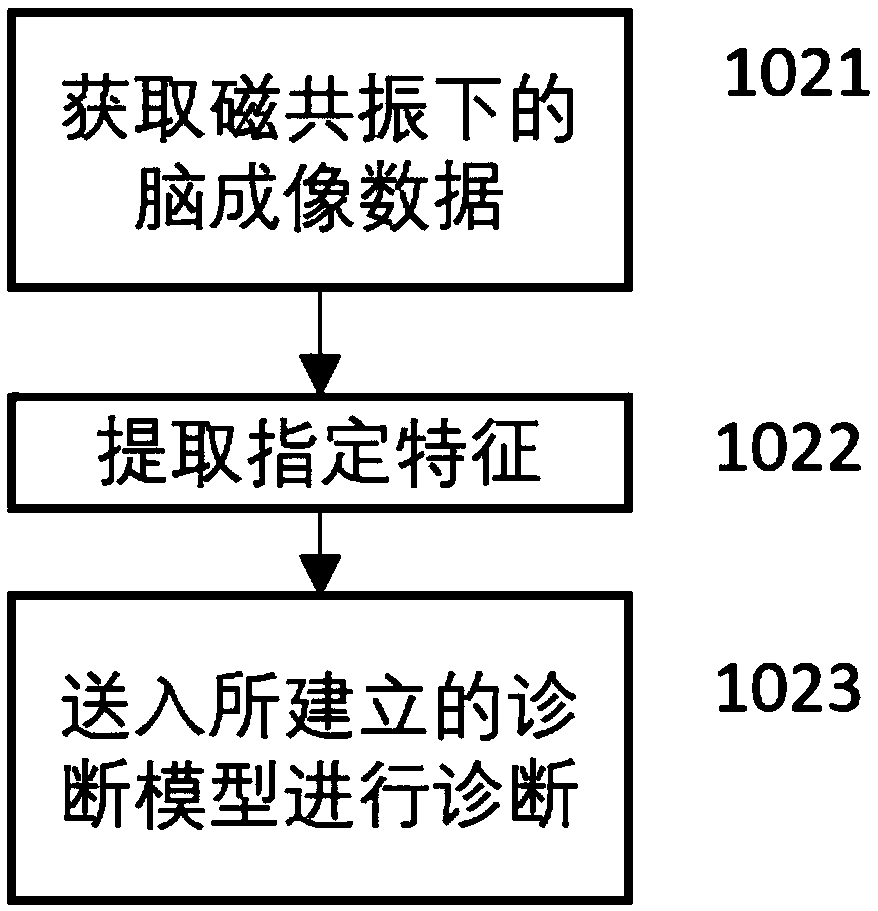
Schizophrenia early diagnosis model based on face expression recognition magnetic resonance imaging and application thereof
ActiveCN109359403ADelay social function impairmentEasy to identifyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseStudy methods
The invention relates to the technical field of early diagnosis of schizophrenia, in particular to a schizophrenia early diagnosis model based on face expression recognition magnetic resonance imagingand application thereof. The method includes: obtaining the brain imaging data under the magnetic resonance as the training data of the model; extracting features from training data; screening the extracted features; establishing an early diagnosis model of schizophrenia by using the screened features and supervised machine learning method for model training. Schizophrenia is a serious psychiatric disease.Patients with schizophrenia suffer from severe social dysfunction, and those with severe schizophrenia often have impulse, self-injury and wounding behavior.Improving the recognition rate ofschizophrenia is helpful to postpone the social dysfunction of schizophrenia patients and lighten the burden of family and society. The invention successfully constructs a multidimensional early diagnosis model of schizophrenia through feature screening according to different dimensional indexes of brain function and brain structure, and improves the recognition rate and diagnosis rate of schizophrenia patients.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
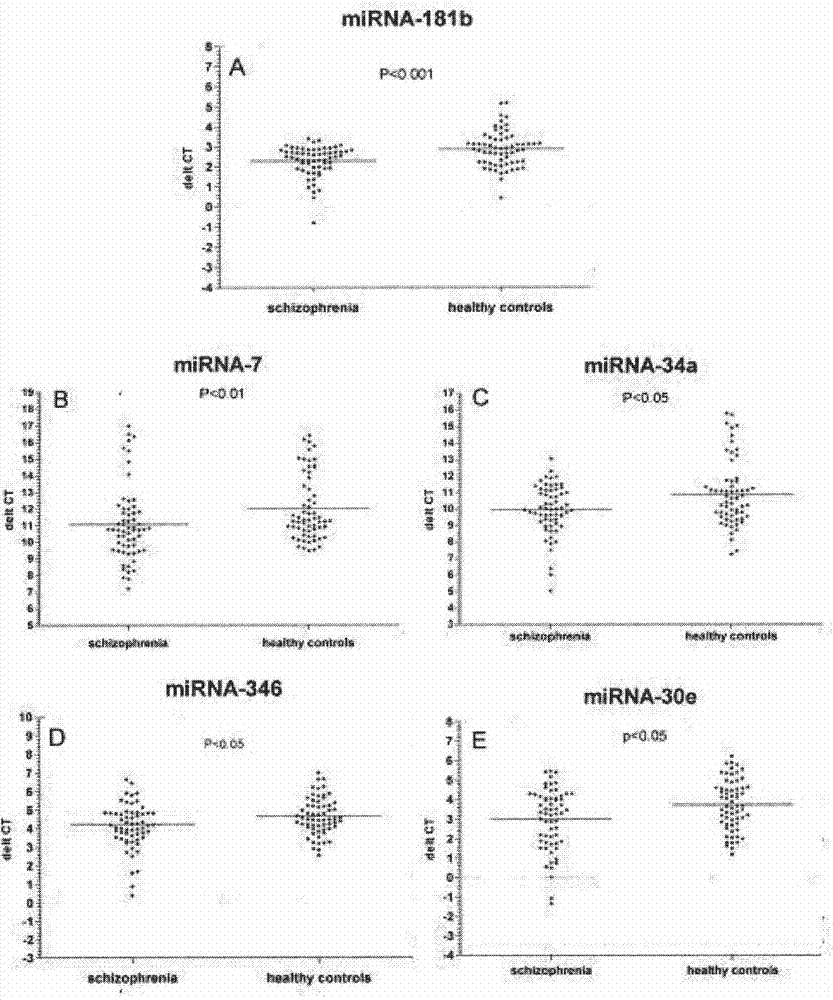
Schizophrenia biomarker, detection method and kit
InactiveCN104745680AImprove diagnostic accuracySimplify the diagnostic processMicrobiological testing/measurementSchizophreniaBioinformatics
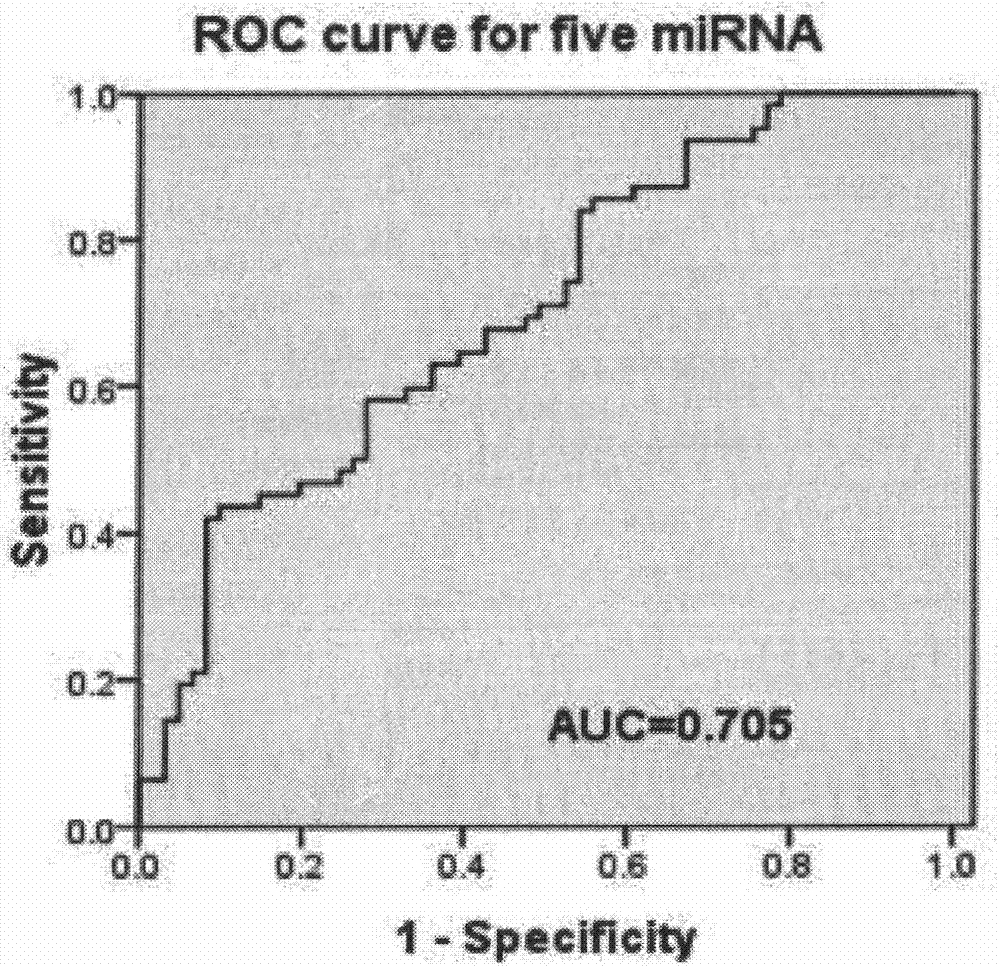
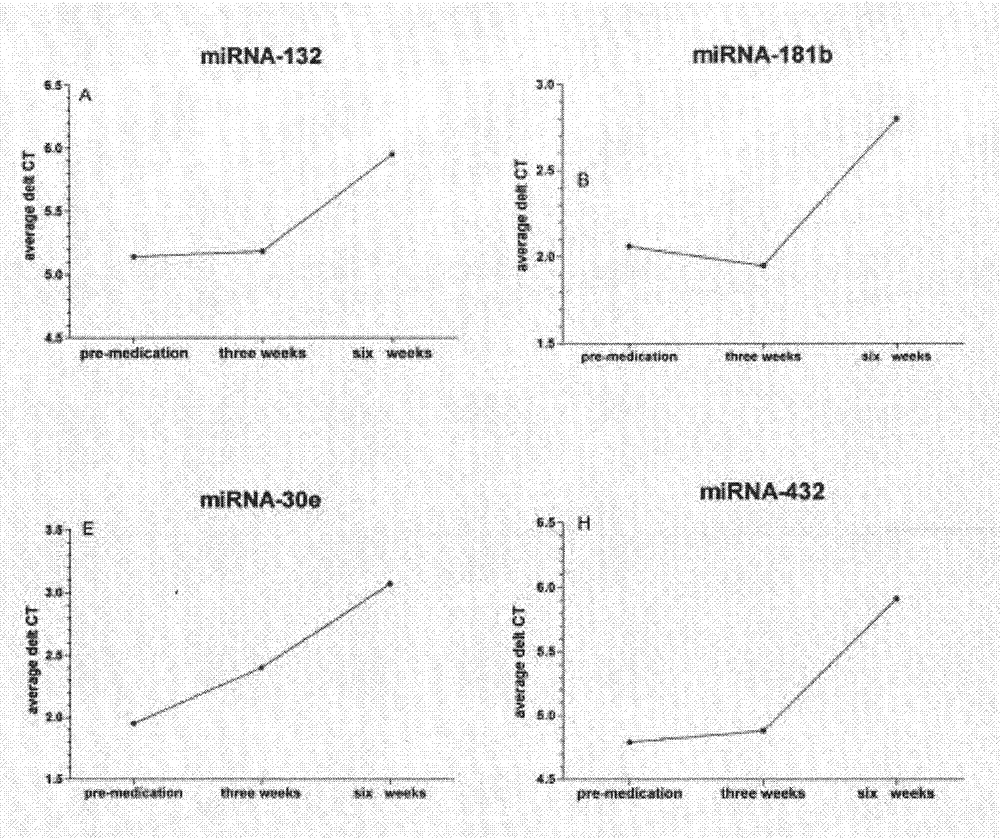
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a schizophrenia biomarker, a detection method and a kit. The invention provides a schizophrenia biomarker, a detection method thereof and a kit for detecting the content of the biomarker, wherein the biomarker comprises miRNA-30e, miRNA-181b, miRNA-346, miRNA-34a and miRNA-7. The invention further provides a schizophrenia outcome biomarker, a detection method of the marker, and a kit for detecting the content of the marker, wherein the schizophrenia outcome biomarker comprises miRNA-30e, miRNA-181b, miRNA-132 and miRNA-432. The beneficial effects are of providing the biomarker for the diagnosis and outcome of the schizophrenia, the biomarker has higher specificity and higher diagnosis reference values.
Owner:张理义 +1
Proteins related to schizophrenia and uses thereof
Presenilin Associated Membrane Protein (PAMP), and nucleic acids encoding this protein, are provided. PAMP and PAMP nucleic acids provide diagnostic and therapeutic tools for evaluating and treating or preventing neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. In a specific embodiment, mutations in PAMP are diagnostic for schizophrenia. The invention further relates to screening, particularly using high-throughput screens and transgenic animal models, for compounds that modulate the activity of PAMP and presenilins. Such compounds, or gene therapy with PAMP, can be used in treating neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders, particularly schizophrenia. In addition, the invention provides PAMP mutants, nucleic acids encoding for PAMP mutants, and transgenic animals expressing PAMP mutants, which in a preferred aspect result in biochemical, morphological, or neuropsychological changes similar to those associated with schizophrenia.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
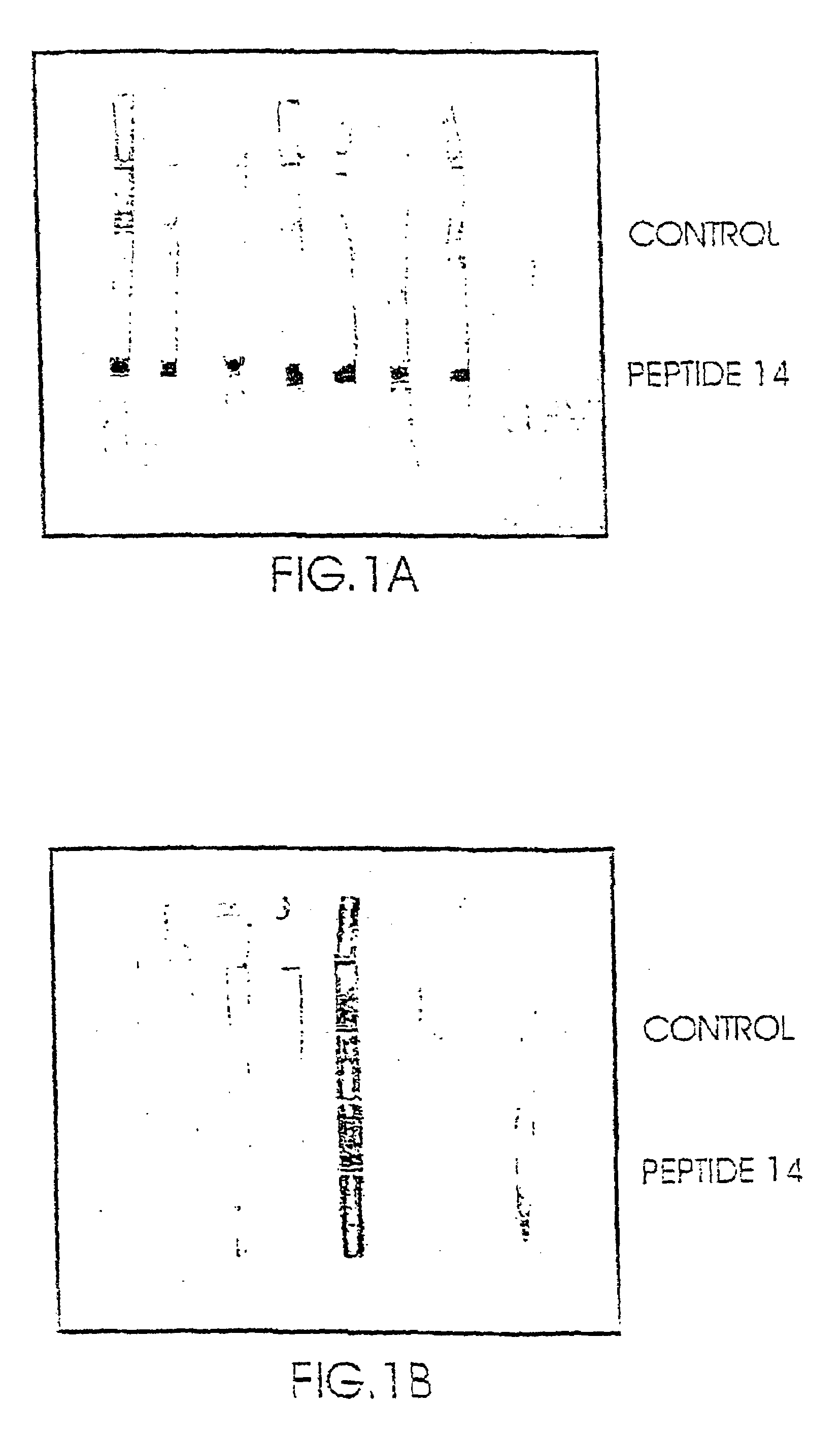
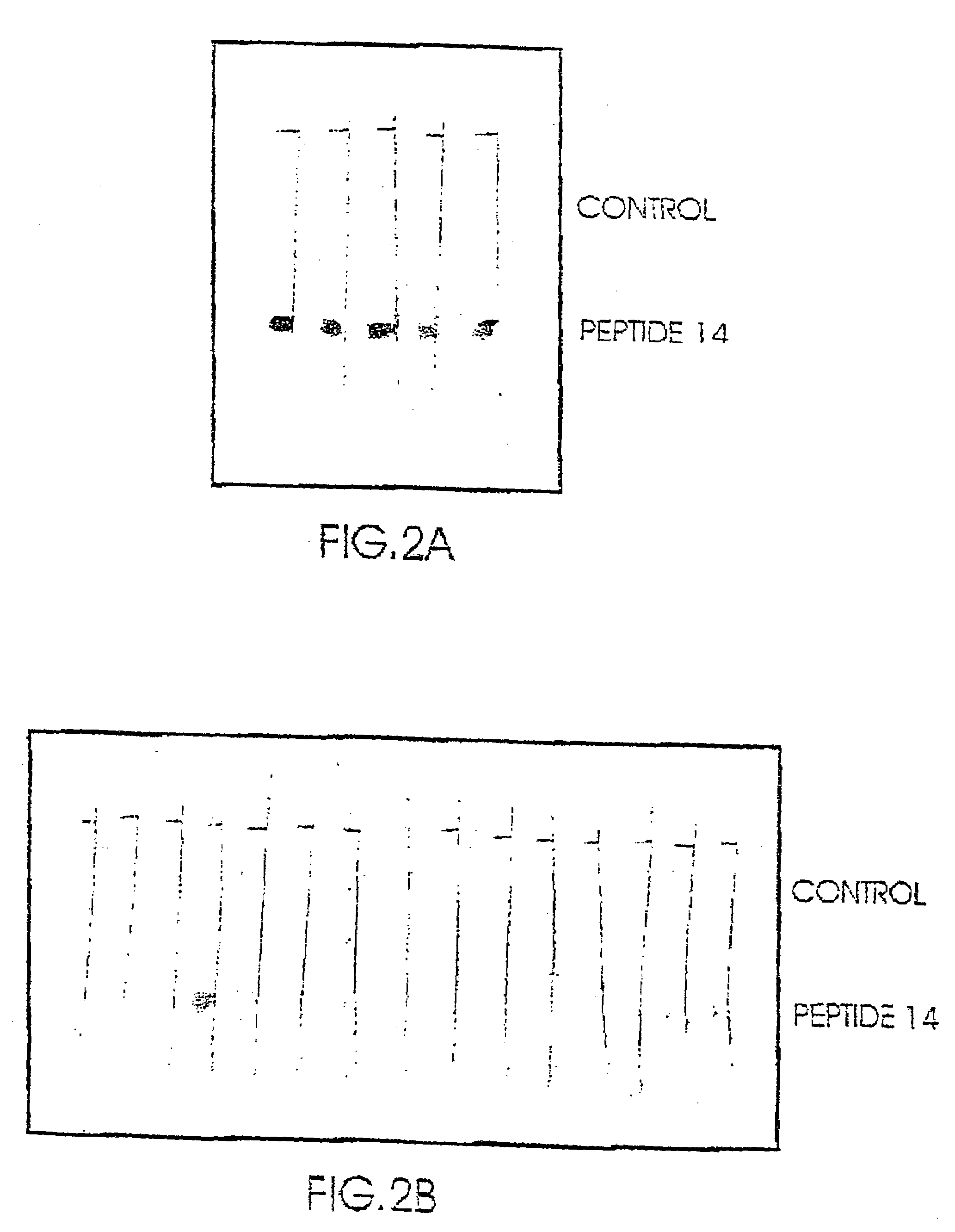
Novel peptides for the diagnosis of schizophrenia
InactiveUS20050089927A1Increase heightReduce the binding forcePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesMedicineBinding site
Short peptides are provided, which bind to a body fluid sample obtained from a schizophrenic patient at a substantively higher level than to a body fluid sample obtained from a non-schizophrenic individual. The peptides are no more than 10 amino acids long and comprise a continuous sequence of at least 5 amino acids which consists of at least one positively charged amino acid at one of its ends. The provided peptides, which are the putative binding sites of autoantibodies found in high levels in schizophrenic individuals, are thus useful in diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
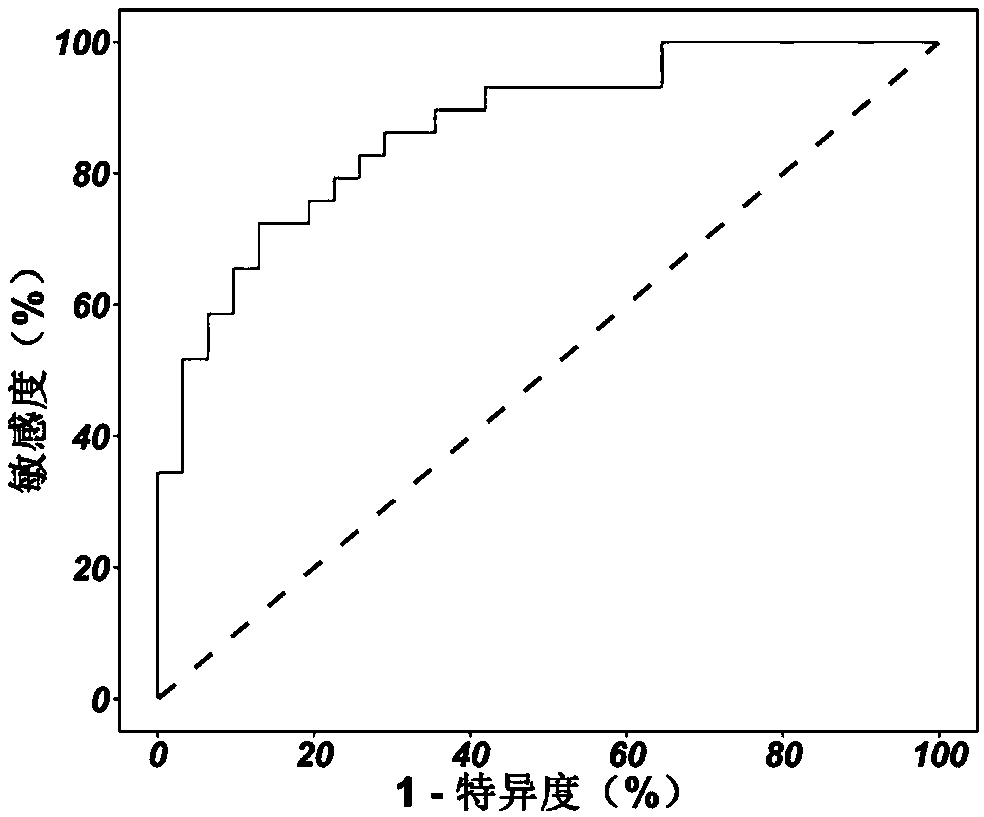
Diagnosis index, diagnosis model and diagnosis system for schizophrenia
PendingCN112168187AHigh diagnostic valueMedical automated diagnosisSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFixation point
The invention provides a diagnosis index, a diagnosis model and a diagnosis system for schizophrenia. The diagnosis model comprises four key diagnosis indexes of fixed-point staring skewness peak time, face region fixation time, face region entering times and face region first fixation point fixation time. Compared with the prior art, the diagnosis model has the advantages that the diagnosis accuracy of schizophrenia is greatly improved, and a treatment scheme can be better formulated clinically.
Owner:BEIJING ANDING HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Methods and systems for facilitating the diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia
InactiveUS20070072233A1Improved psychiatric functionLower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMedicineCompound (substance)
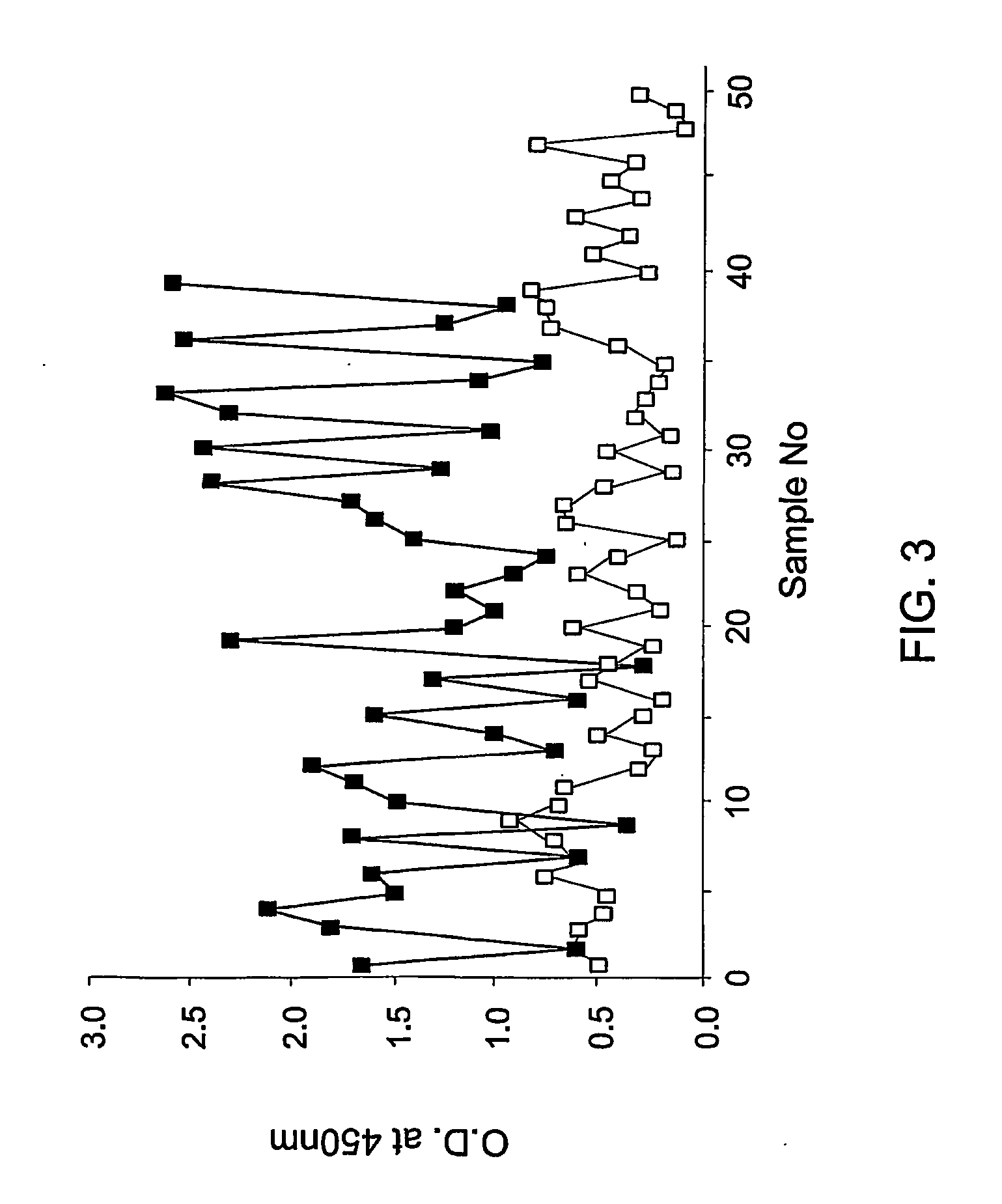
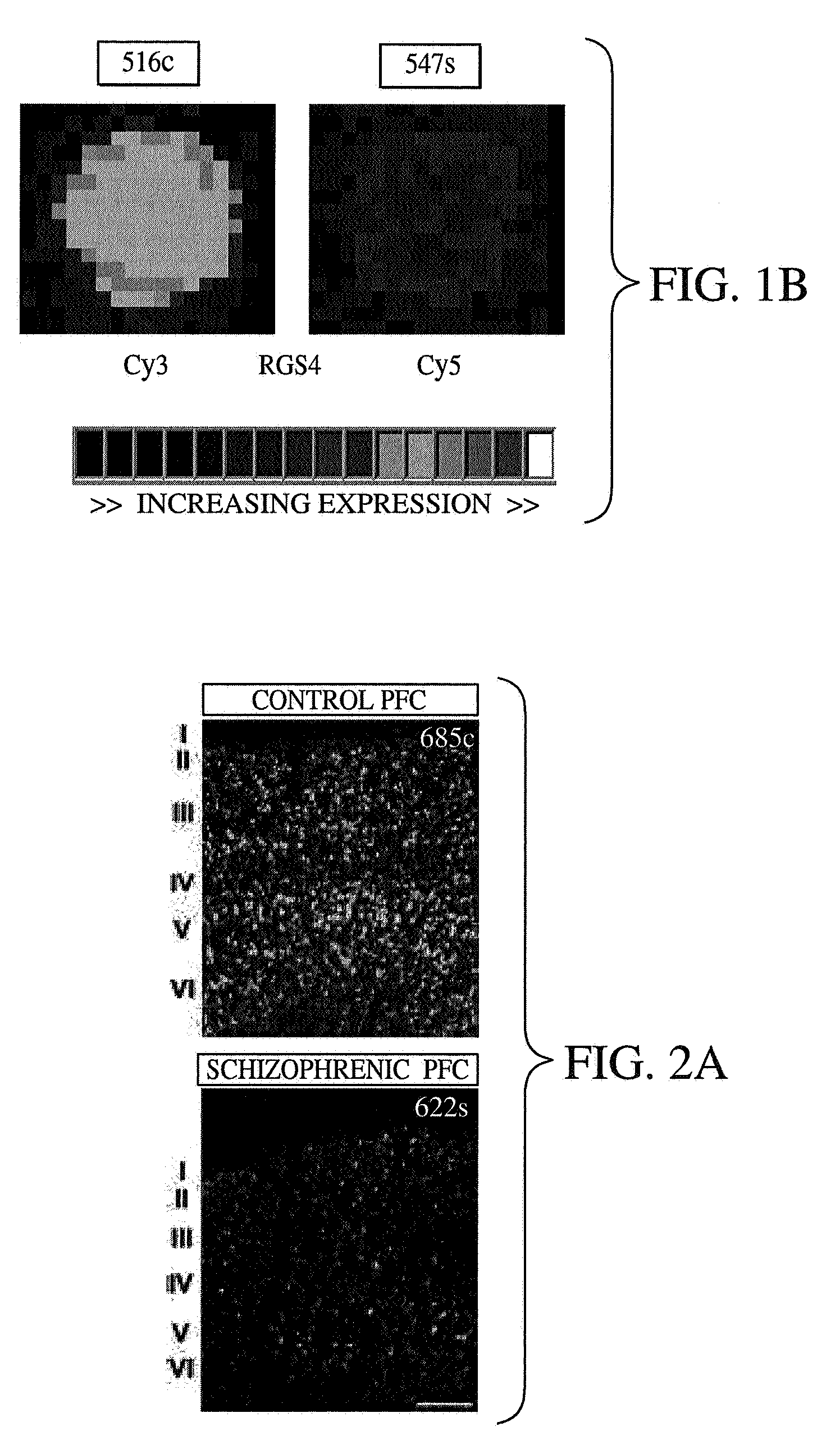
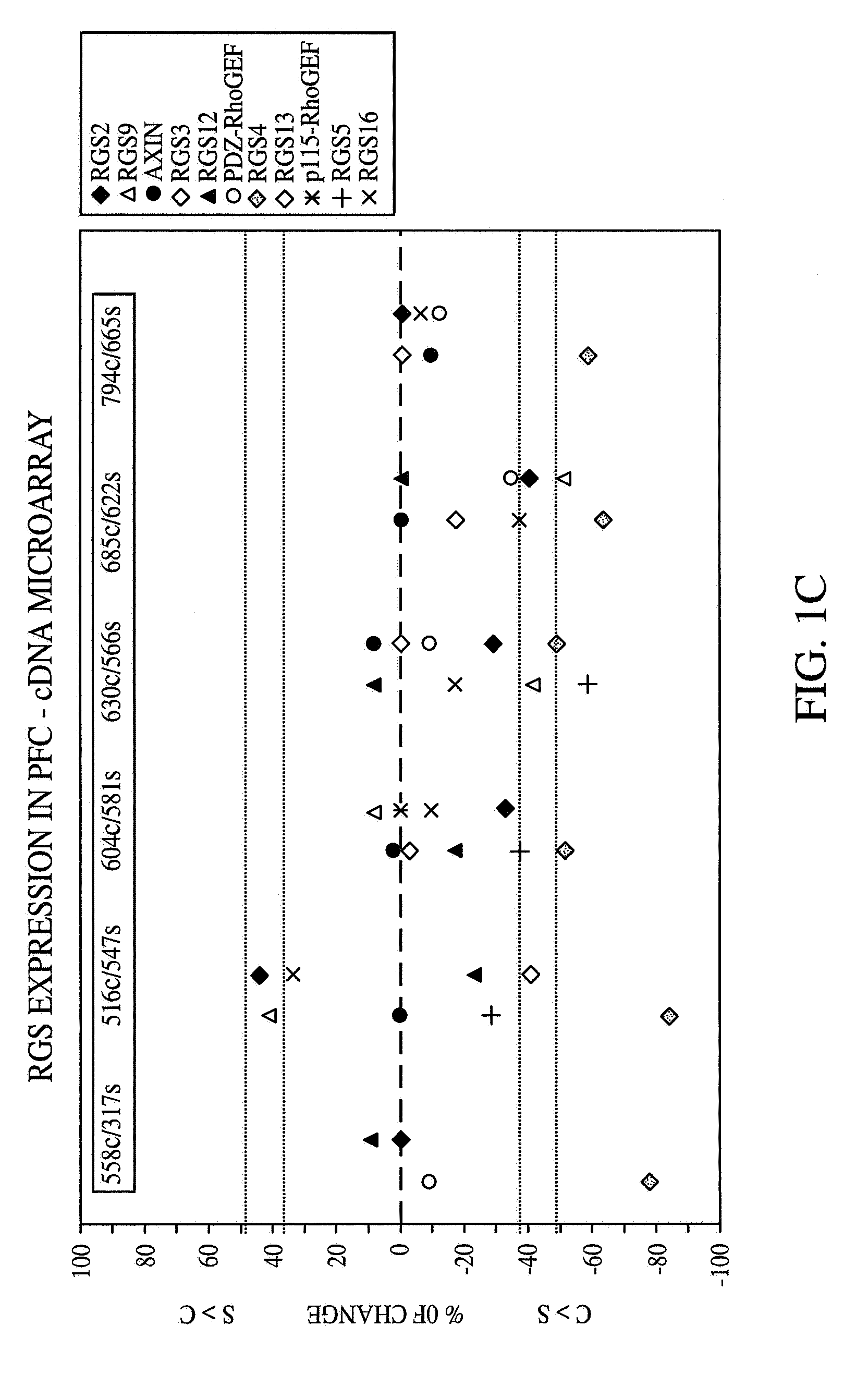
A method of diagnosing, assessing susceptibility, and / or treating schizophrenia involving the observation of regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) levels in a subject. Embodiments of the present invention include increasing RGS4 expression levels in the cortex, either by chemical means or by genetic complementation (e.g. gene therapy).
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
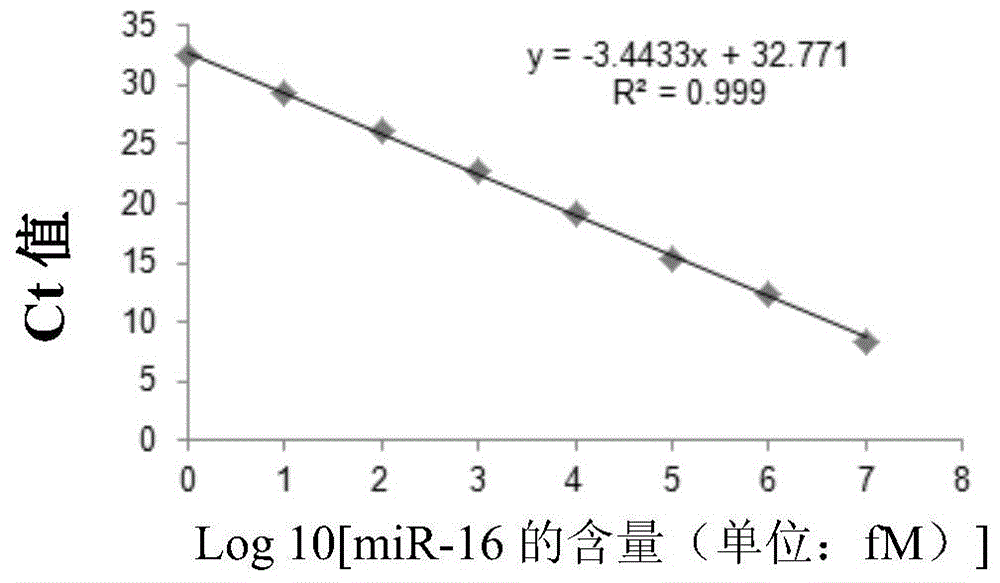
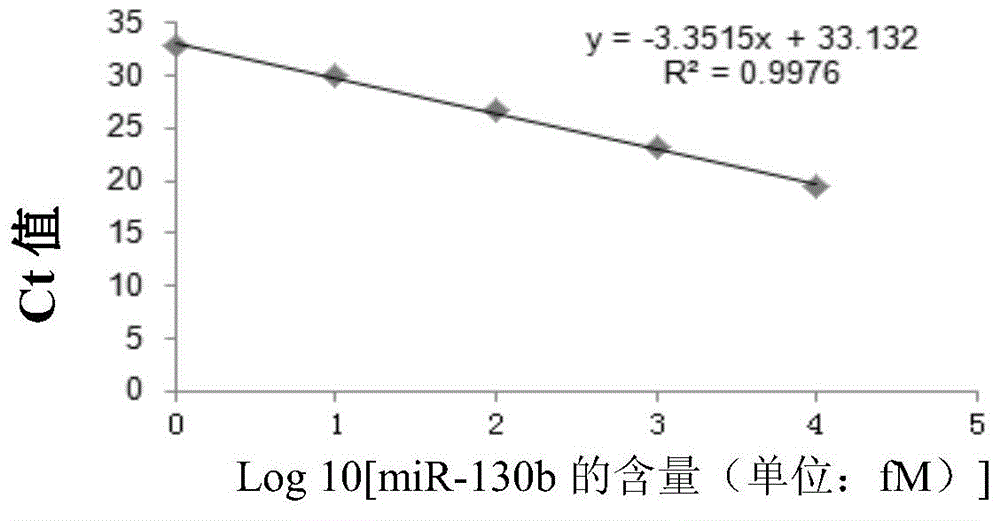
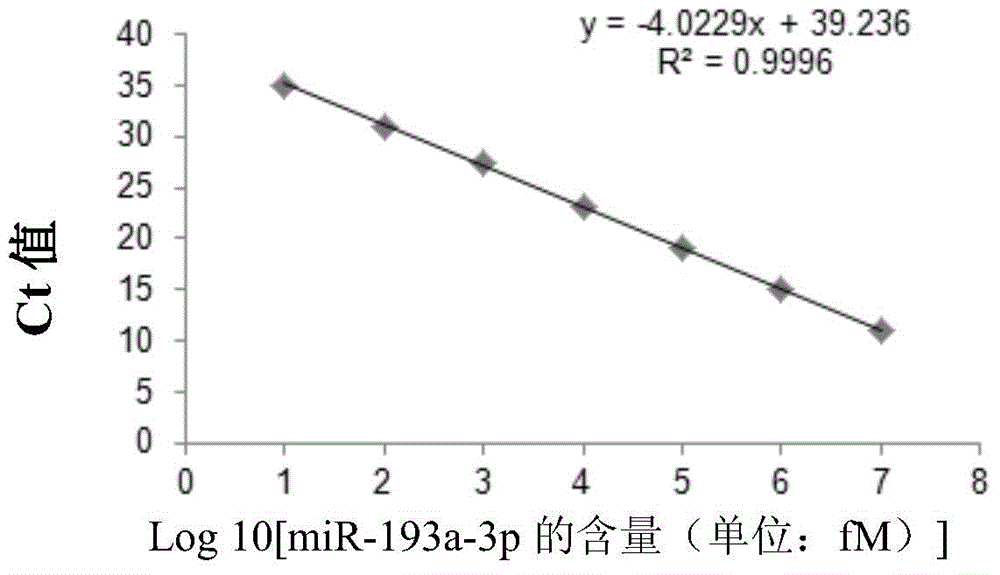
Use of miRNA molecules in diagnosis and prognosis of schizophrenia
The invention relates to a use of miRNA molecules in diagnosis and prognosis of schizophrenia, especially relates to a use of miR-130b and miR-193a-3p in diagnosis and prognosis of schizophrenia, and also relates to a use of one or more primers and / or probes for specifically detecting the content of the miR-130b or the miR-193a-3p in blood plasma in preparation of reagents for diagnosis or prognosis of schizophrenia patients.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
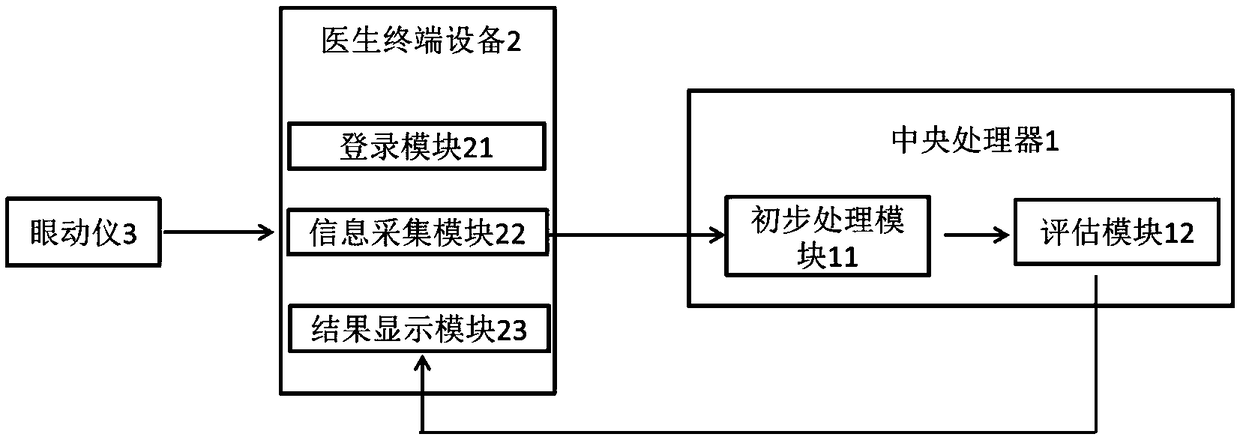
System for diagnosing schizophrenia by utilizing eye movement index
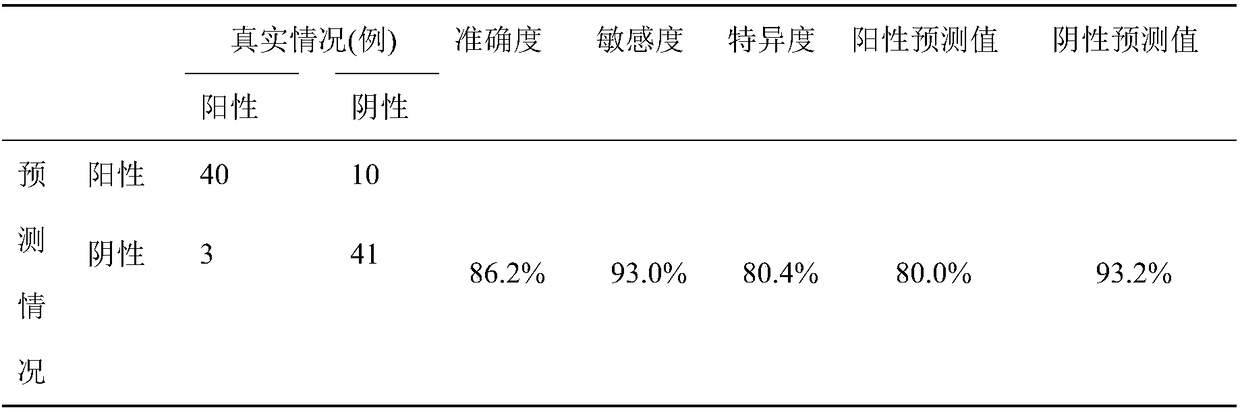
InactiveCN109480865AImprove diagnostic accuracyFully automatedSensorsPsychotechnic devicesTerminal equipmentSchizophrenia
The invention discloses a system for diagnosing schizophrenia by utilizing an eye movement index. The system comprises an eye tracker, a doctor terminal device and a central processing unit connectedin sequence. The system utilizes the eye movement index to establish an assessment model and executes schizophrenia diagnosis. By utilizing the system, the diagnosis accuracy of 80% can be achieved, and the system is suitable for clinic popularization and use.
Owner:BEIJING ANDING HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Methods and kits for diagnosis of schizophrenia
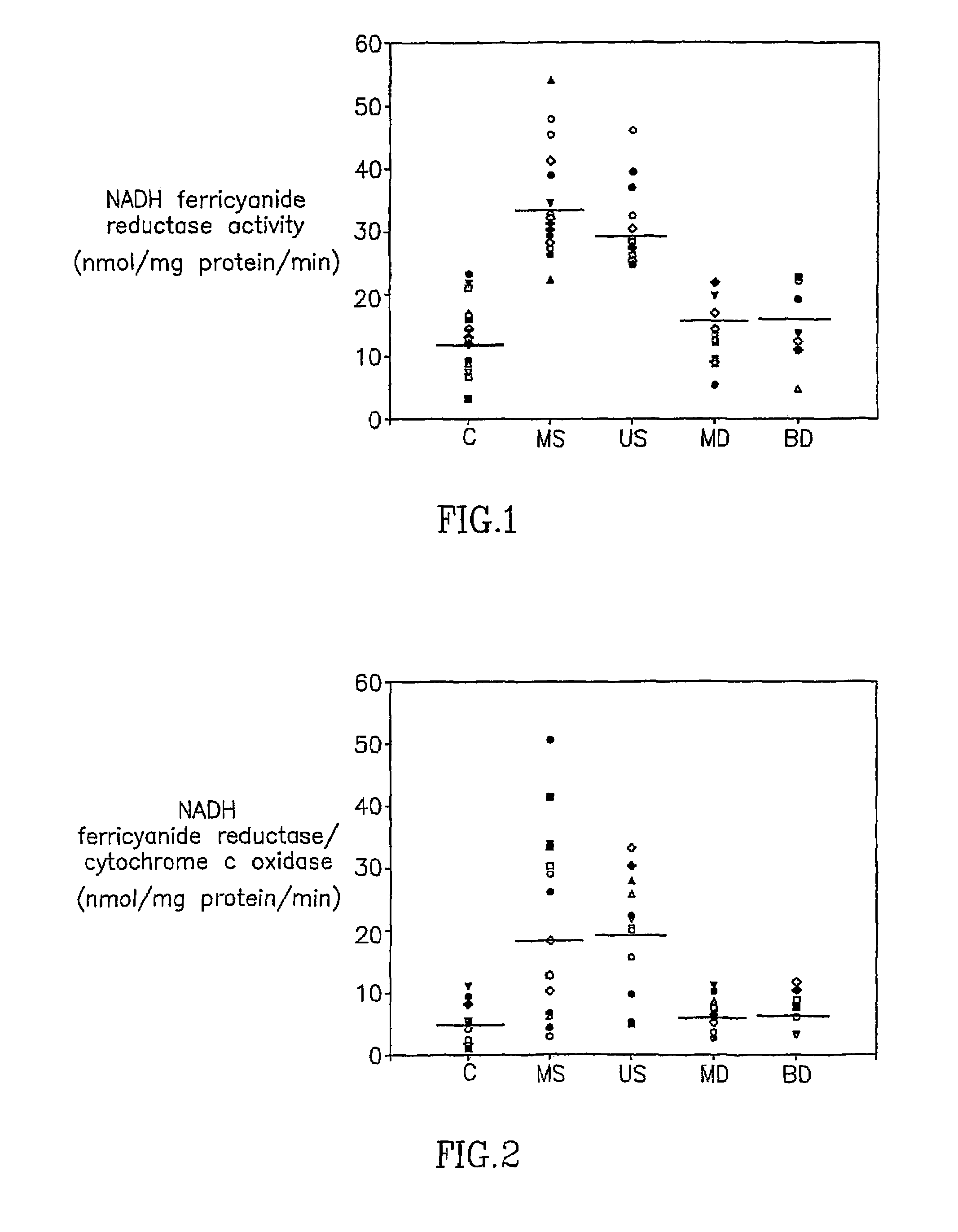
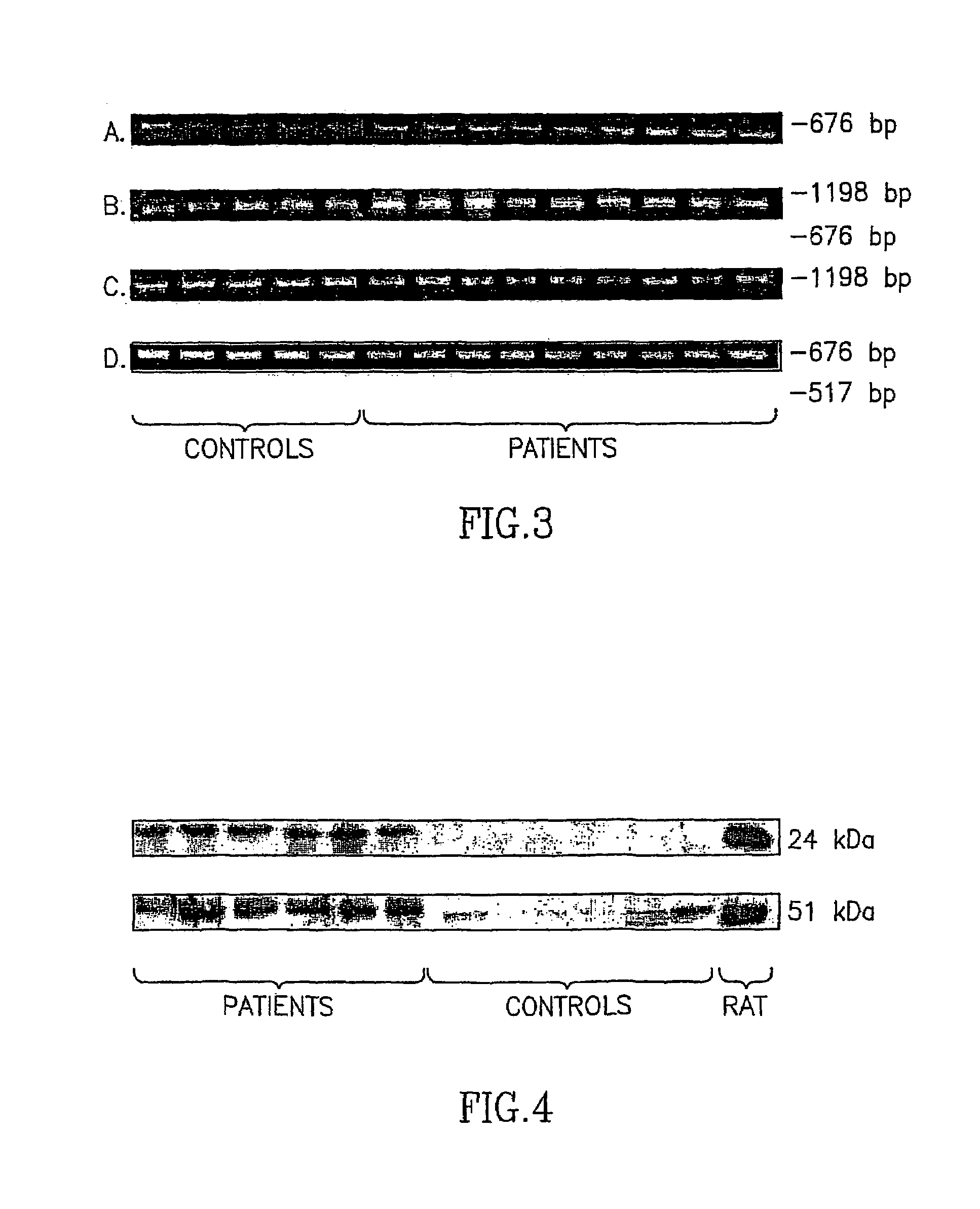
InactiveUS7442496B2Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisMitochondrial Complex ISchizophrenia
The present invention provides methods and kits for the diagnosis of schizophrenia, which employ mitochondrial complex I as a peripheral biological marker for schizophrenia. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method for diagnosing schizophrenia in a subject by determining the level of activity of a mitochondrial complex I enzyme in a sample obtained from the subject, and comparing the level of activity in the sample with a normative value of mitochondrial complex I enzyme activity, wherein an altered level of activity of mitochondrial complex I enzyme in the sample compared with the normative value is indicative of the subject having schizophrenia. In another embodiment, the present invention provides a method for diagnosing schizophrenia in a subject by determining the level of m-RNA or protein of mitochondrial complex I in a sample obtained from the subject, and comparing the level m-RNA or protein of mitochondrial complex I in the sample with a normative value of mitochondrial complex I m-RNA or protein, wherein an altered level of mitochondrial complex I m-RNA or protein in the sample compared with the normative value is indicative of the subject having schizophrenia. Kits for diagnosing schizophrenia using the methods of the present invention are also disclosed.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Schizophrenia related nucleic acid sequence
InactiveCN1737140AEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringNucleic acid sequencingSchizophrenia
The invention relates to a Schizophrenia related nucleic acid sequence, which comprises sequences represented in SEQ ID No.1-12 in the sequence table, wherein the existence of mononucleotide polymorphism at No.26 is G, and is A equivalent site on the DNA compatible chains, and if the existence of mononucleotide polymorphism at No.26 is C, and is T equivalent site on the DNA compatible chains.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
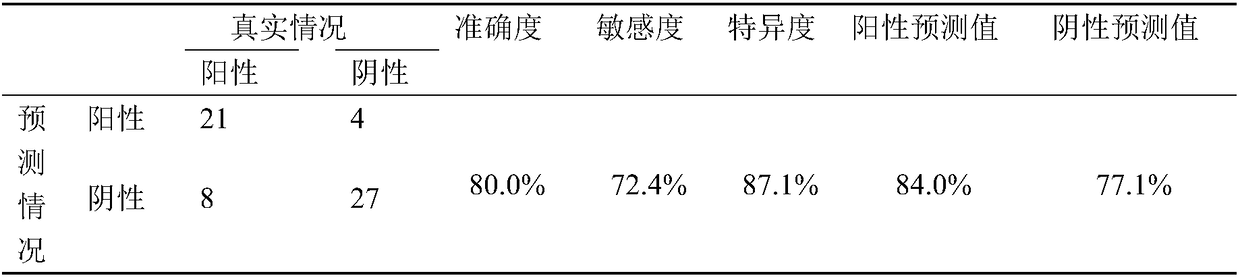
System for diagnosing schizophrenia by utilizing cognitive indexes
PendingCN109473170AEasy programmingAchieving processing powerHealth-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisMedicinePerformed Diagnosis
The invention discloses a system for diagnosing schizophrenia by utilizing cognitive indexes. The system comprises a doctor terminal device and a central analyzer. The system collects the cognitive indexes of a subject by using the doctor terminal device and transmits the cognitive indexes to the central analyzer, and the central analyzer performs diagnosis of schizophrenia by using a diagnosis model constructed according to cognitive indexes. By means of the system, the diagnosis accuracy of 86% can be achieved, and the system is suitable for clinical popularization and application.
Owner:BEIJING ANDING HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
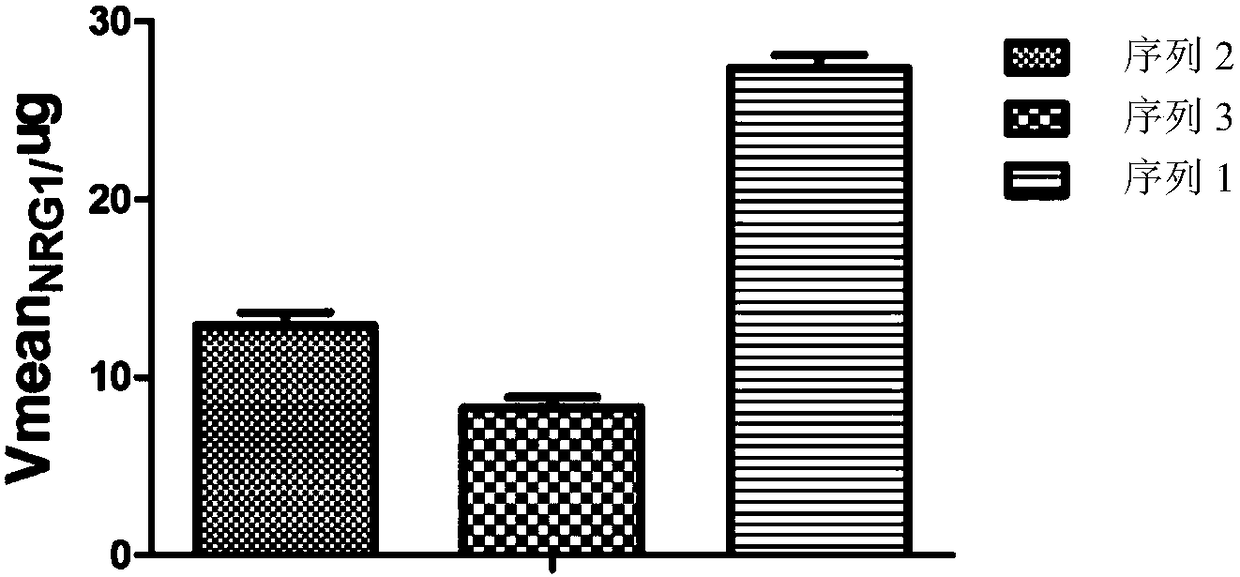
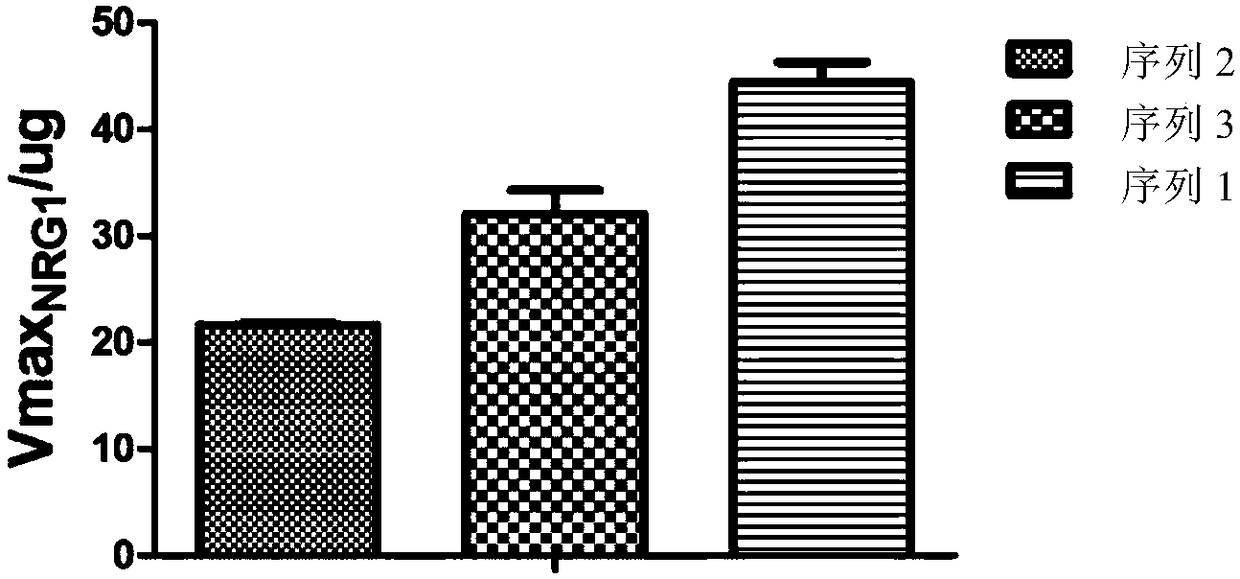
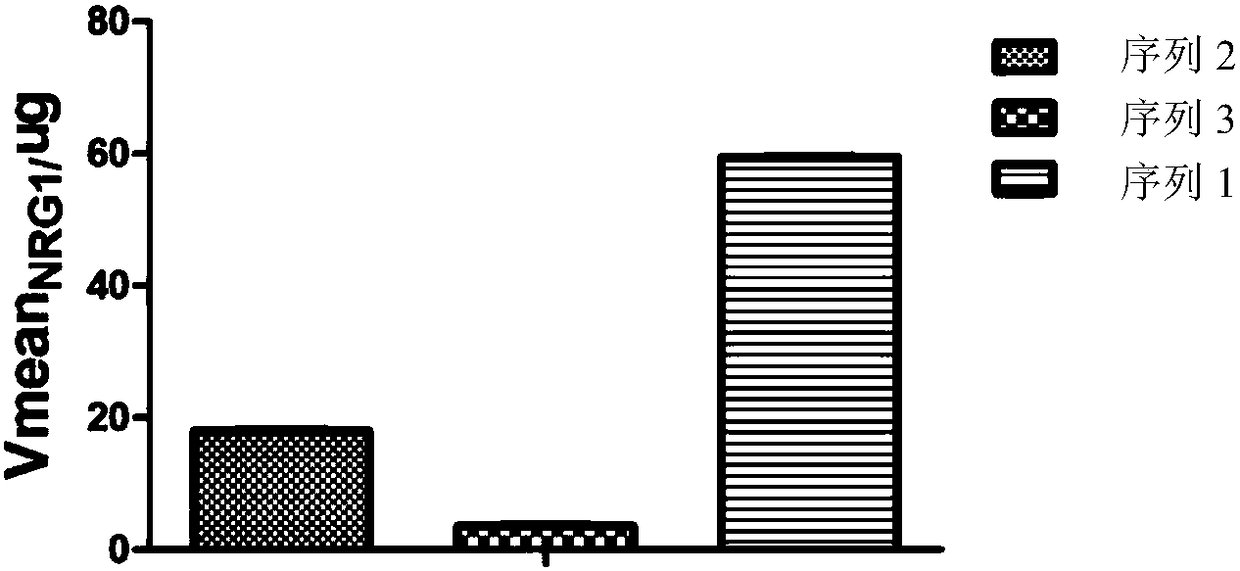
Detection method for measuring BACE1 enzyme digestion NRG1 activity and kit thereof
BACE1 can perform enzyme digestion on NRG1 in specific sequences among EF and ME areas in the 10-residue distance to a transmembrane region of NRG1, so that the invention finds that activity of BACE1enzyme is closely related to schizophrenia morbidity, disease courses and severity degrees. On the basis, the invention provides a BACE1 enzyme digestion polypeptide substrate containing an EFME sequence, compound containing the substrate, a kit and application of the substrate in detecting BACE1 enzyme digestion NRG1 activity of a detected sample. The application can be used for diagnosing schizophrenia, and the problem that existing schizophrenia diagnosis lacks an effective molecule diagnosis standard is solved.
Owner:BEIJING ANDING HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Schizophrenia-related voltage-gated ion channel gene and protein
InactiveUS20080184381A1Altered level of expressionCostly and time-consume to developBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiDiseaseBipolar mood disorder
The invention concerns the genomic DNA, cDNA, and polypeptide sequences of CanIon, a novel voltage gated ion channel protein. The invention also concerns biallelic markers of the CanIon gene. The CanIon gene may be used as a biological target for the treatment and diagnosis of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other diseases and conditions.
Owner:SERONO GENETICS INST SA
Molecular marker for detecting/evaluating curative effect of premature schizophrenia and application of molecular marker
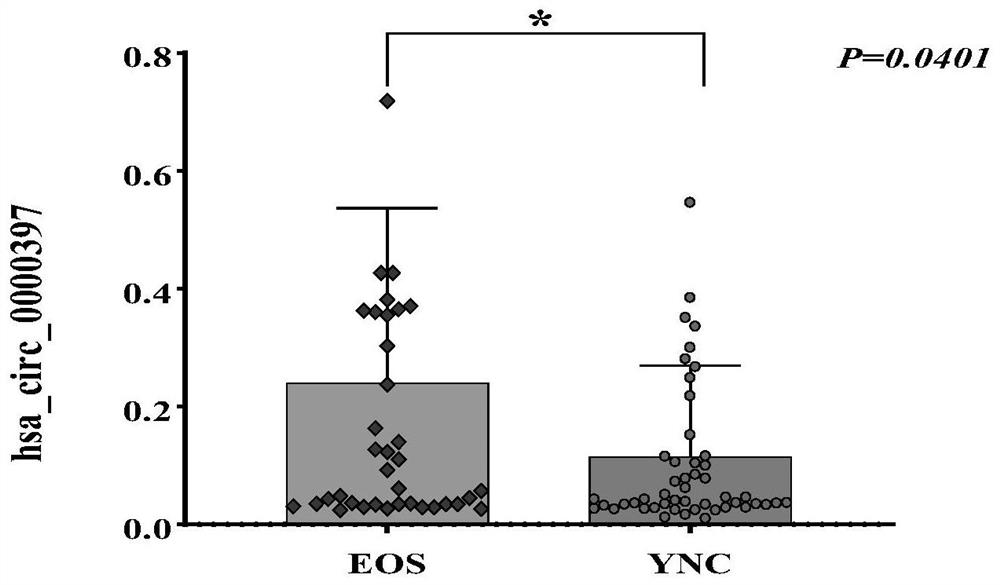
PendingCN113355408ARealize Auxiliary DiagnosisStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTherapeutic evaluationPhysiology
The invention discloses a molecular marker for detecting / evaluating curative effect of premature schizophrenia and application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker is hsa_circ_0000397, and the nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The molecular marker has a correlation relationship with the schizophrenia, can quickly, simply and accurately realize auxiliary diagnosis of the schizophrenia, and provides a basis for schizophrenia diagnosis and curative effect evaluation index selection.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL OF SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV +3
Targets, methods, and reagents for diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia
The present invention provides targets, methods, and reagents for the diagnosis and treatment of schizophrenia and related conditions. The invention provides methods for the diagnosis of schizophrenia and susceptibility to schizophrenia by detection of polymorphisms, mutations, variations, alterations in expression, etc., in calcineurin genes or calcineurin interacting genes, or polymorphisms linked to such genes. The invention provides oligonucleotides, arrays, and antibodies for detection of polymorphisms and variants. The invention provides transgenic mice having alterations in such genes. The invention also provides methods of treating schizophrenia by administering compounds that target these genes. The invention further provides screening methods for identifying such compounds and compounds obtained by performing the screens.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV +1
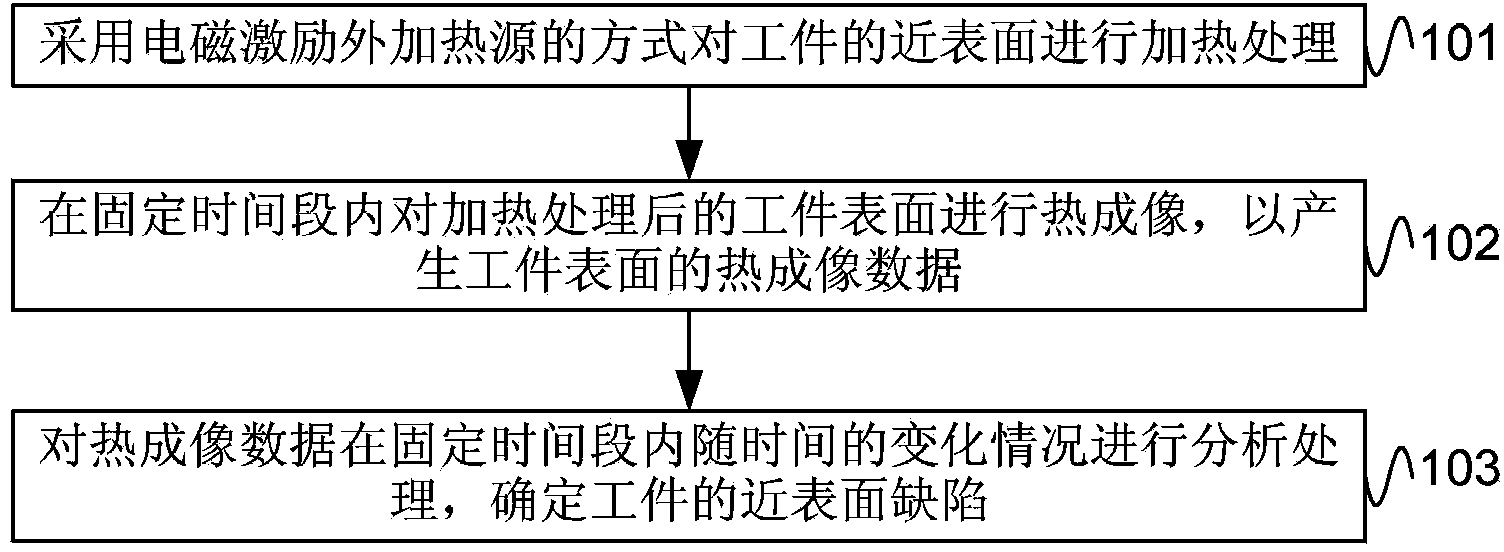
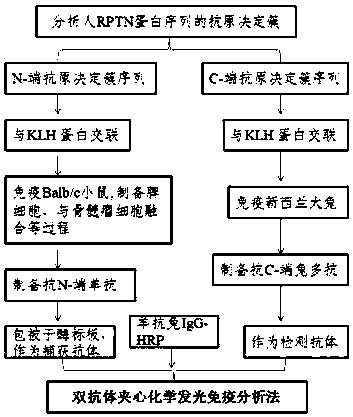
Double-antibody sandwich chemiluminescence immune assay method
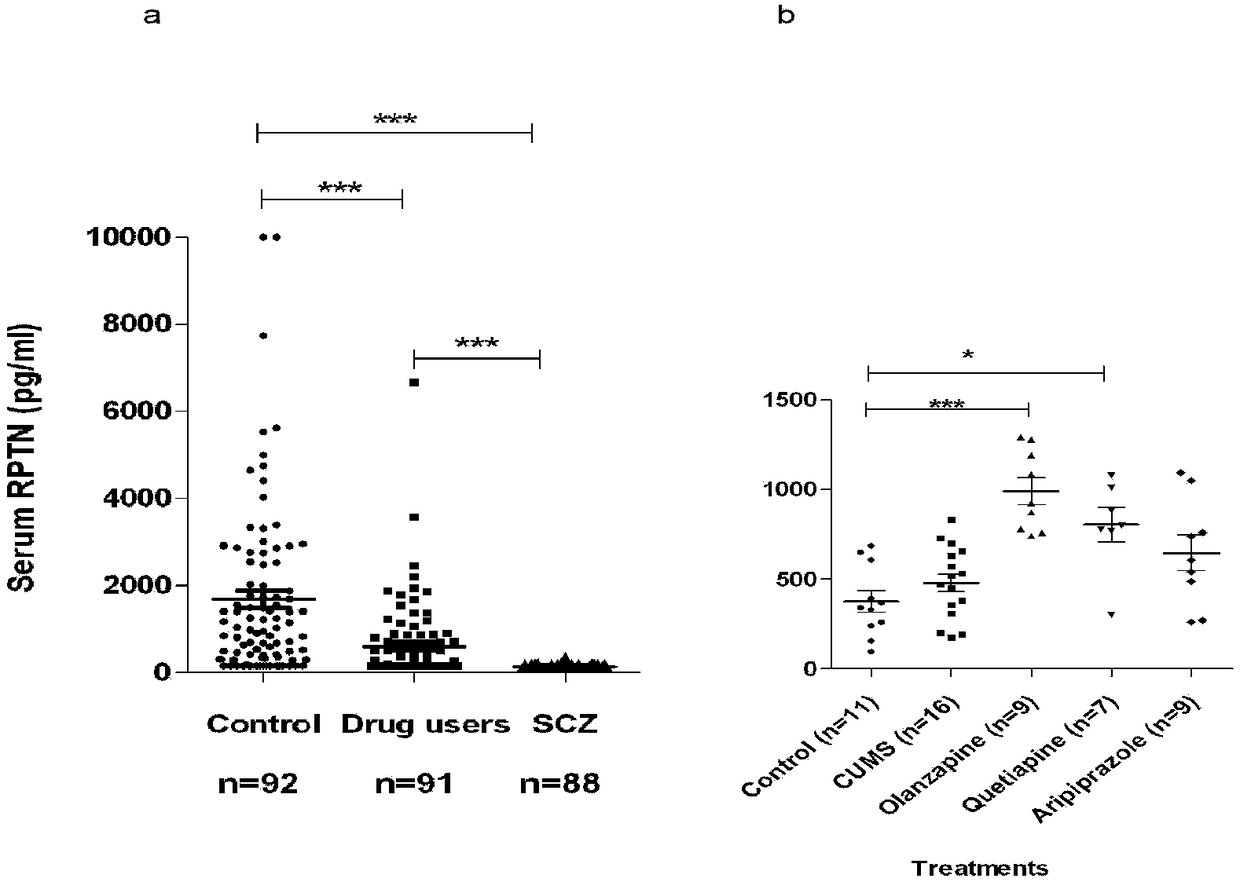
InactiveCN108387747AThe phenomenon of serum reduction was foundBiological testingNeuropsychiatric diseaseTherapeutic effect
The invention belongs to biomedical field, and relates to a double-antibody sandwich chemiluminescence immune assay method. The method comprises the following steps: adopting an anti-RPTN N-terminal mouse monoclonal antibody as a capturing antibody coated on an elisa plate, adding serum to be measured or RPTN standard after washing, and adding an RPTN C-terminal rabbit polyclonal antibody as a detection antibody after washing; adding goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP after washing, and adding a luminal reaction solution after washing; and measuring chemiluminiscence (RLU) on a chemiluminiscence immuneanalyzer after washing, wherein the intensity of RLU represents the content of RPTN. The method firstly discovers the phenomenon that the RPTN inside the serum of a schizophrenic patient is reduced, an RPTN chemiluminescence immune method is further developed and the normal range of the RPTN inside the serum is detected and determined, and a novel method is provided for diagnosis and therapeutic effect evaluation of schizophrenia; and a novel tool is provided for the research of other neuropsychiatric diseases and the research and development of antipsychotic drugs.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Schizophrenia Related Gene and Protein
InactiveUS20080199883A1Inhibit expressionFungiNervous disorderBipolar mood disorderCandidate Gene Association Study
Owner:SERONO GENETICS INST SA
Methods and Compositions for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Schizophrenia
Compositions and methods relating to the diagnosis and treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorders, and bipolar disorders are disclosed. Also provided are methods for screening therapeutic agents having efficacy for the treatment of such disorders.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
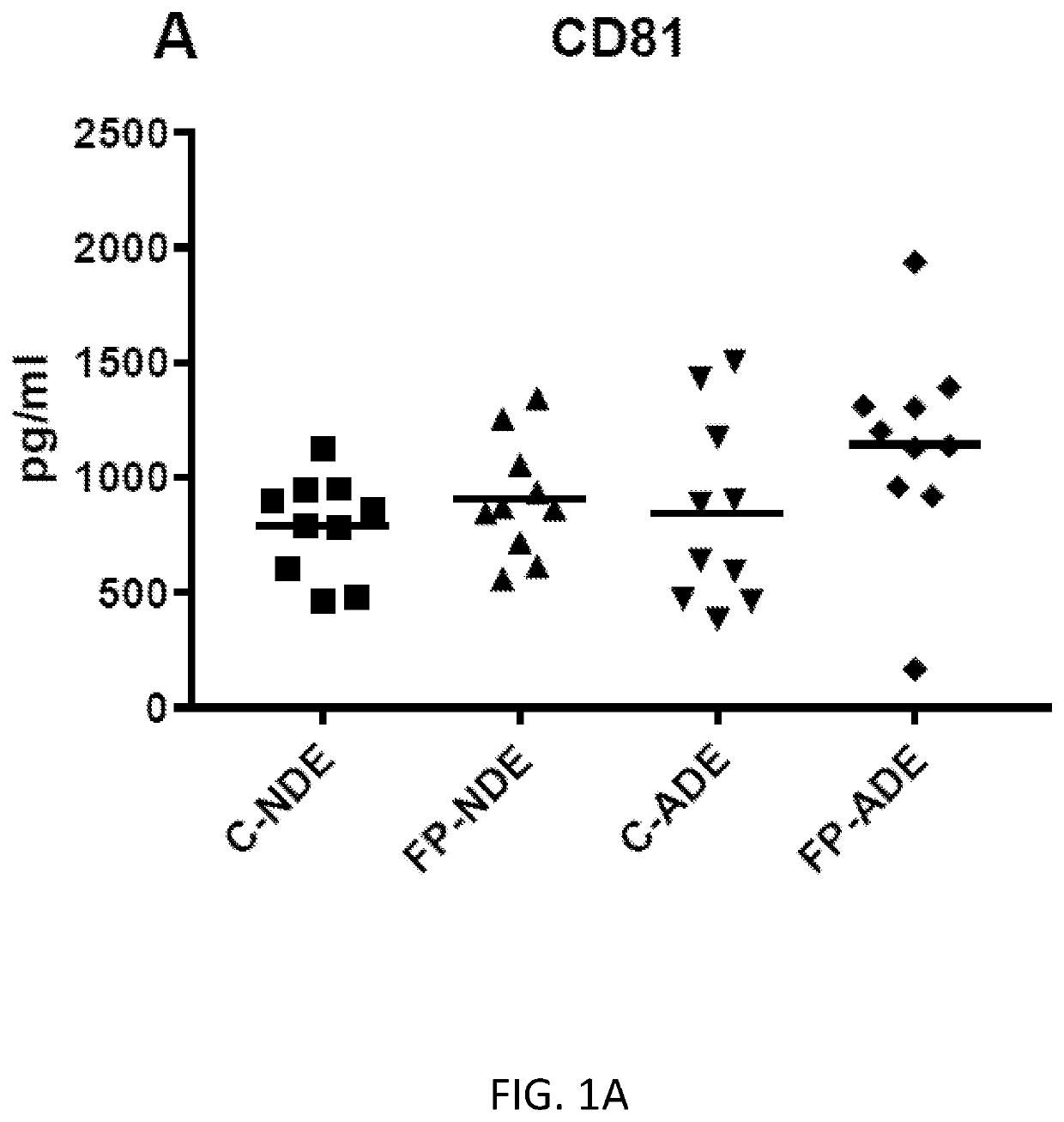
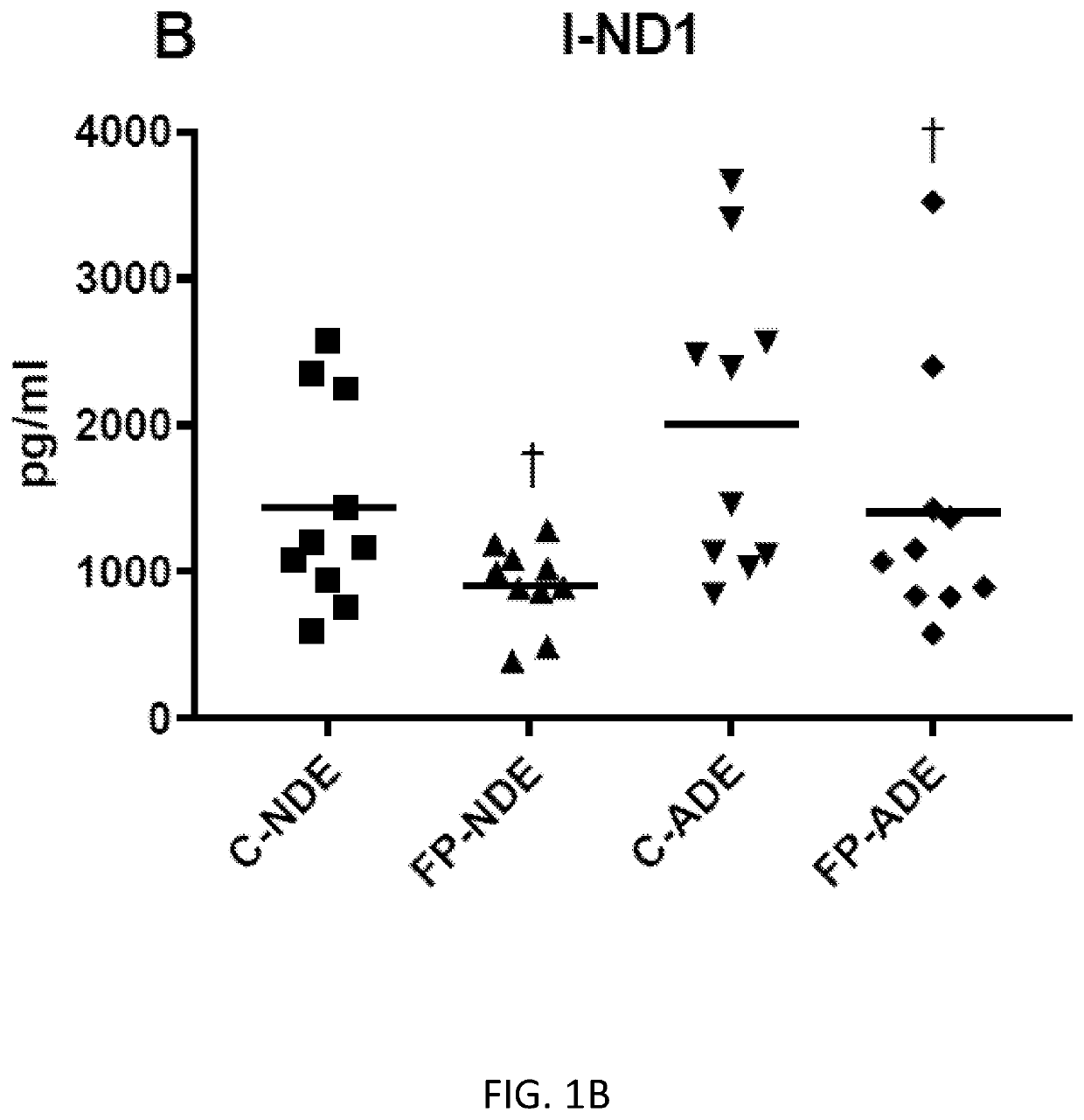
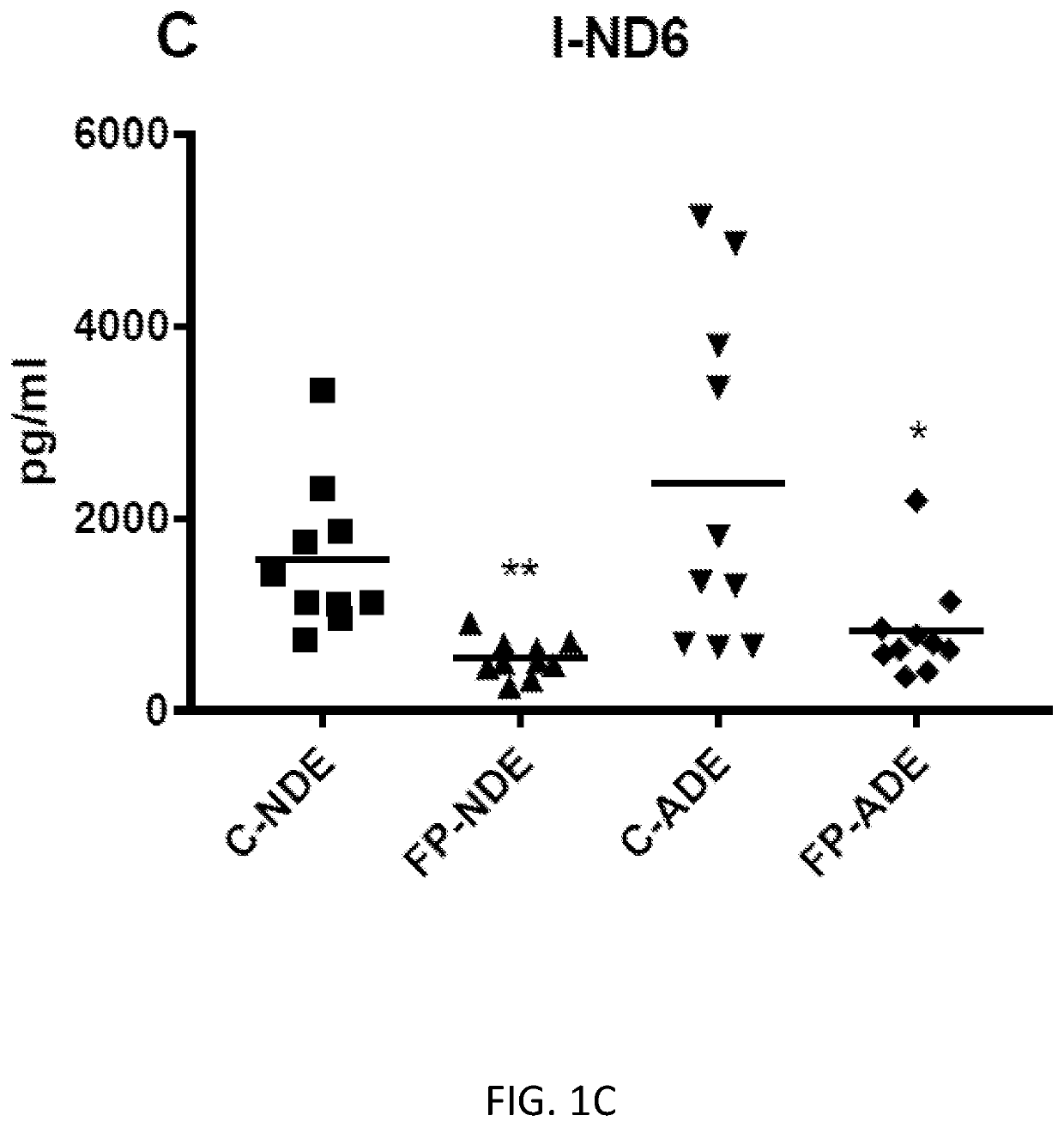
Exosome assay for depression and psychosis and methods and agents for treating depression, psychosis and schizophrenia
The present disclosure relates to exosomal complement mediators, cytokines, and mitochondrial electron transport biomarkers and diagnostic and prognostic methods for depression, psychosis and schizophrenia. The disclosure also provides compositions for detecting exosomal complement mediators, cytokines, and mitochondrial electron transport biomarkers in biological samples as well as compositions and methods useful for treating depression, psychosis and schizophrenia.
Owner:GOETZL EDWARD J
Polymorphism site and use of schizophrenia relative gene TTR
InactiveCN1683559AEasy to solveFacilitate early diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideExon
The present invention discloses one schizophrenia relative gene TTR and its polymorphism site and their use in detecting schizophrenia. The present invention also provides method of detecting mononucleotide polymorphism of the TTR gene. In the said method, the present invention detects four new mononucleotide polymorphism sites and one nonanucleotide deletion site in the site-293 of SEQ ID No. 1 sequence and the site-224, site-265, site-322 and site 352 of SEQ ID No. 2 of the TTR gene. Of them, the SNP1T¿ñA mutation located in the second exon of site-293 will make the amino acid sequence change from glutamic acid to valine and cause change in protein structure and function. The allelic site A, or the allelic site T on the DNA complementary strand is one danger allelic site of leading to schizophrenia and may be used in the diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Schizophrenia related gene
InactiveUS7220581B2Inhibit expressionFungiNervous disorderBipolar mood disorderAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to polynucleotides of the PAPAP gene, polypeptides encoded by the PAPAP gene, and antibodies directed specifically against such polypeptides. The invention also concerns methods for the treatment or diagnosis of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder or related CNS disorder. The invention also concerns the interaction of PAPAP with schizophrenia candidate gene g34872.
Owner:SERONO GENETICS INST SA
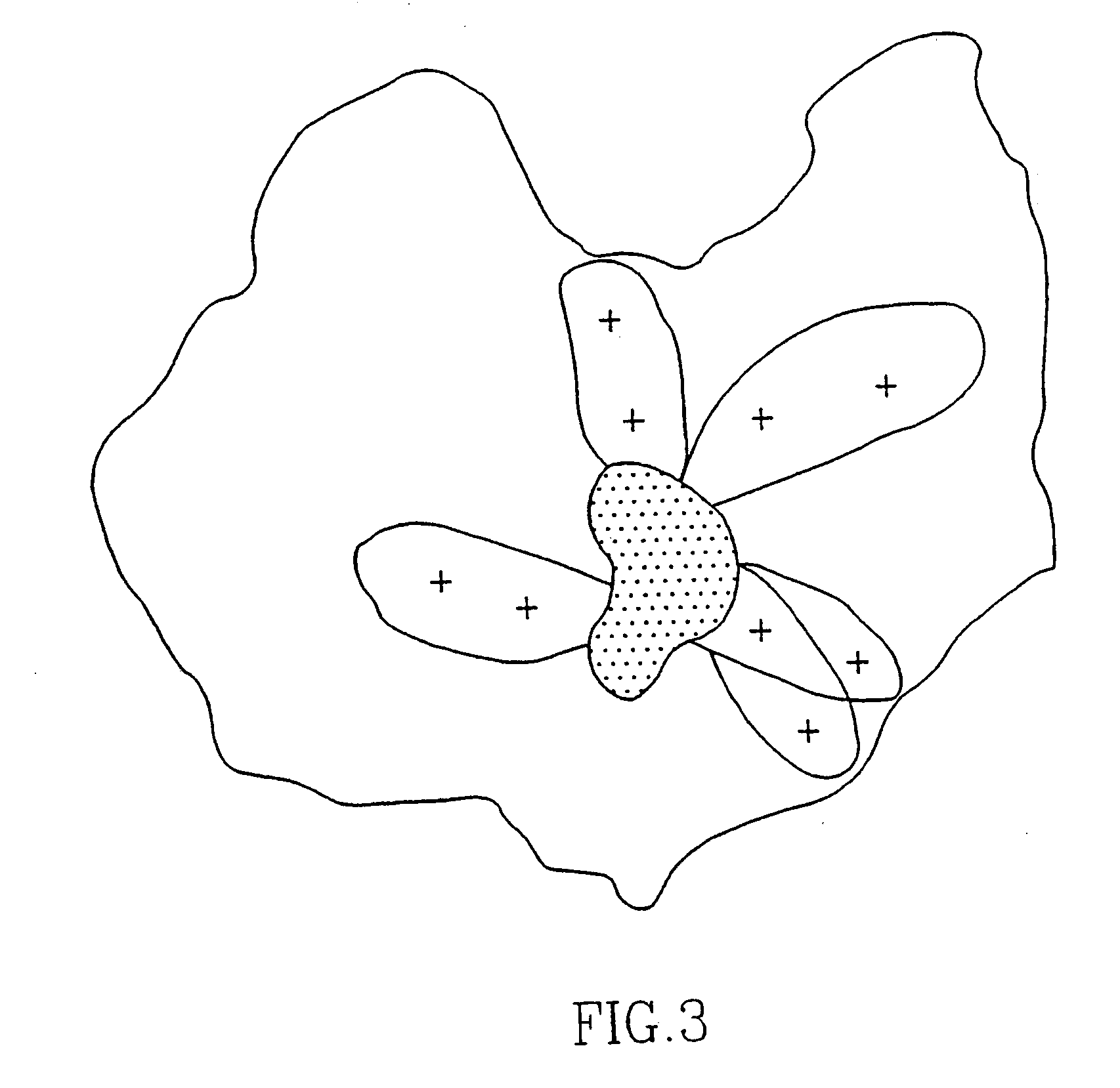
Assay for the diagnosis of schizophrenia based on a new peptide
The invention concerns peptides which bind antibodies that are found in elevated levels in body fluids of schizophrenic patients and are found at a lower level or not found at all in body fluids of non-schizophrenic individuals. Using a computerized program, the antigenic epitope of the peptides of the invention is predicted as having a core of hydrophobic amino acids which is surrounded by positively charged amino acids. The peptides of the invention are useful in the diagnosis of schizophrenia in an individual.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Use of the shank3 fragment sequence methylation detection reagent in the preparation of a diagnostic kit for schizophrenia
ActiveCN113667734BElevated levels of CG methylationMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicinePromoter
The invention provides the use of a SHANK3 fragment sequence methylation detection reagent in the preparation of a diagnostic kit for schizophrenia, and belongs to the technical field of in vitro diagnostic reagents. The present invention finds that the 144bp fragment sequence of the SHANK3 gene promoter can be used as a biomarker for diagnosing schizophrenia. Compared with healthy people, the methylation levels of the 83rd and 84th CGs and the 109th and 110th CGs of this fragment sequence were significantly increased in patients with schizophrenia. Therefore, the fragment sequence methylation detection reagent with a length of 144bp of the SHANK3 gene promoter can be used to prepare a schizophrenia diagnostic kit for early diagnosis of schizophrenia, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com