Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Delay and sum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
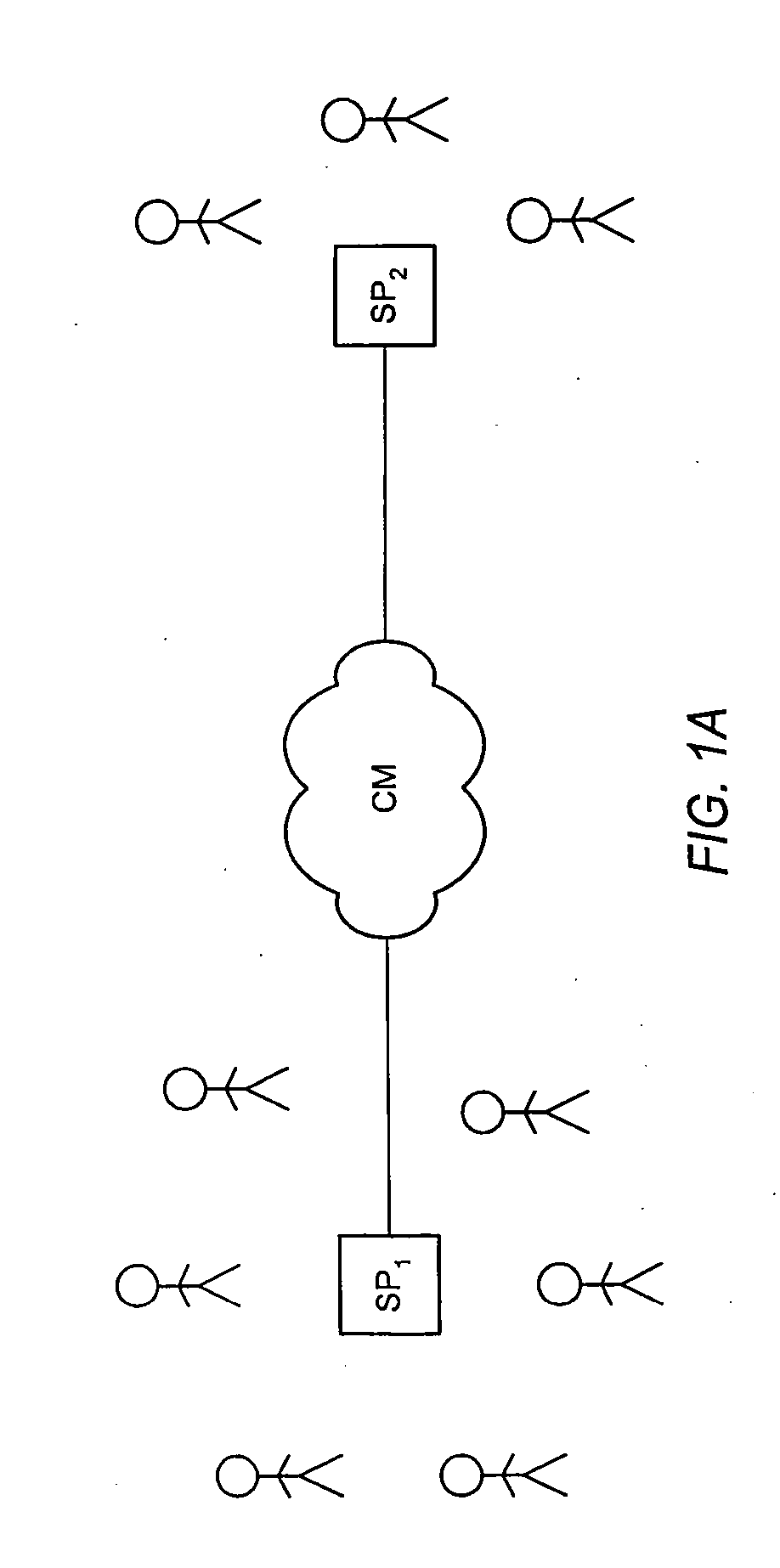
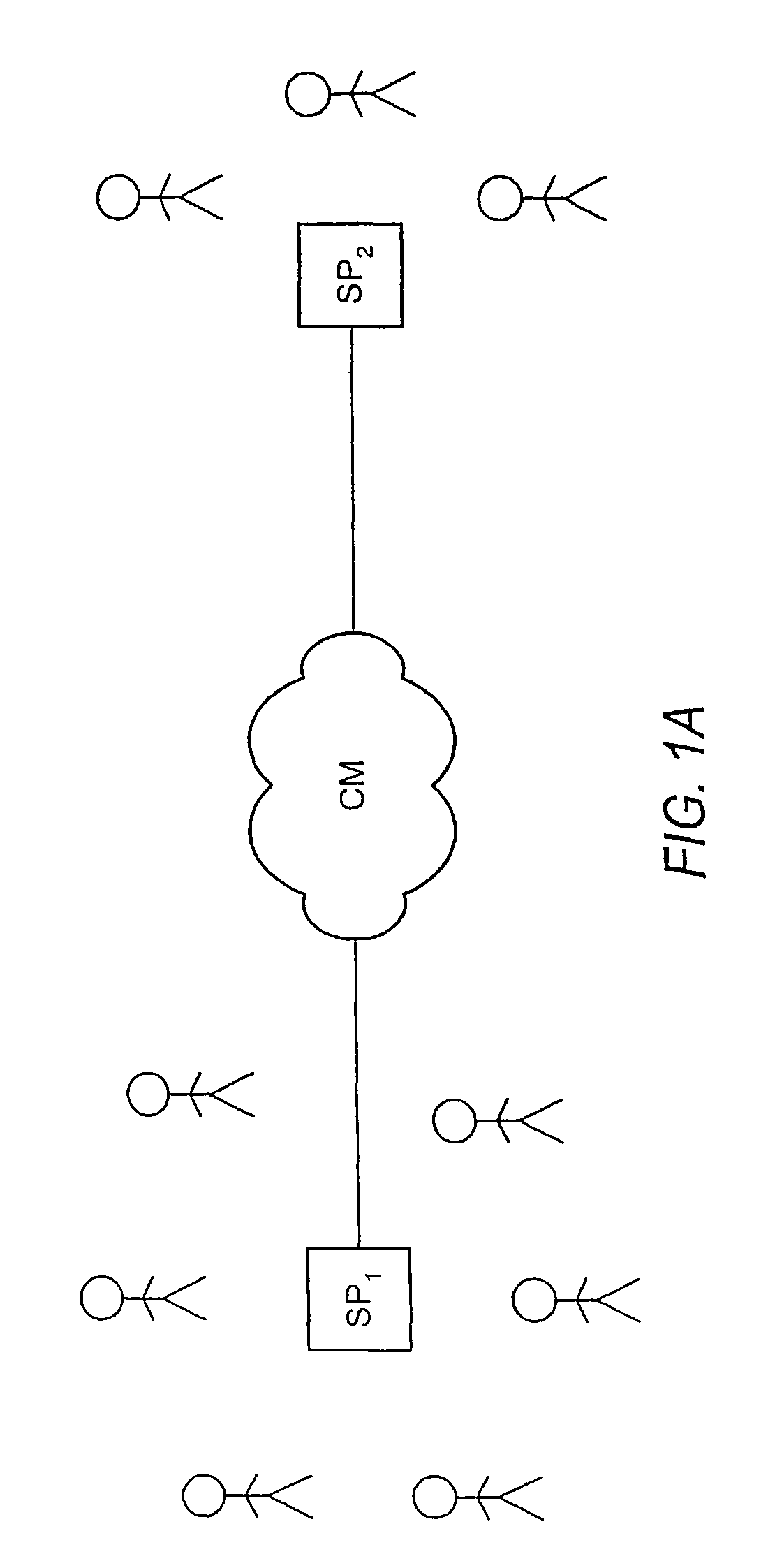
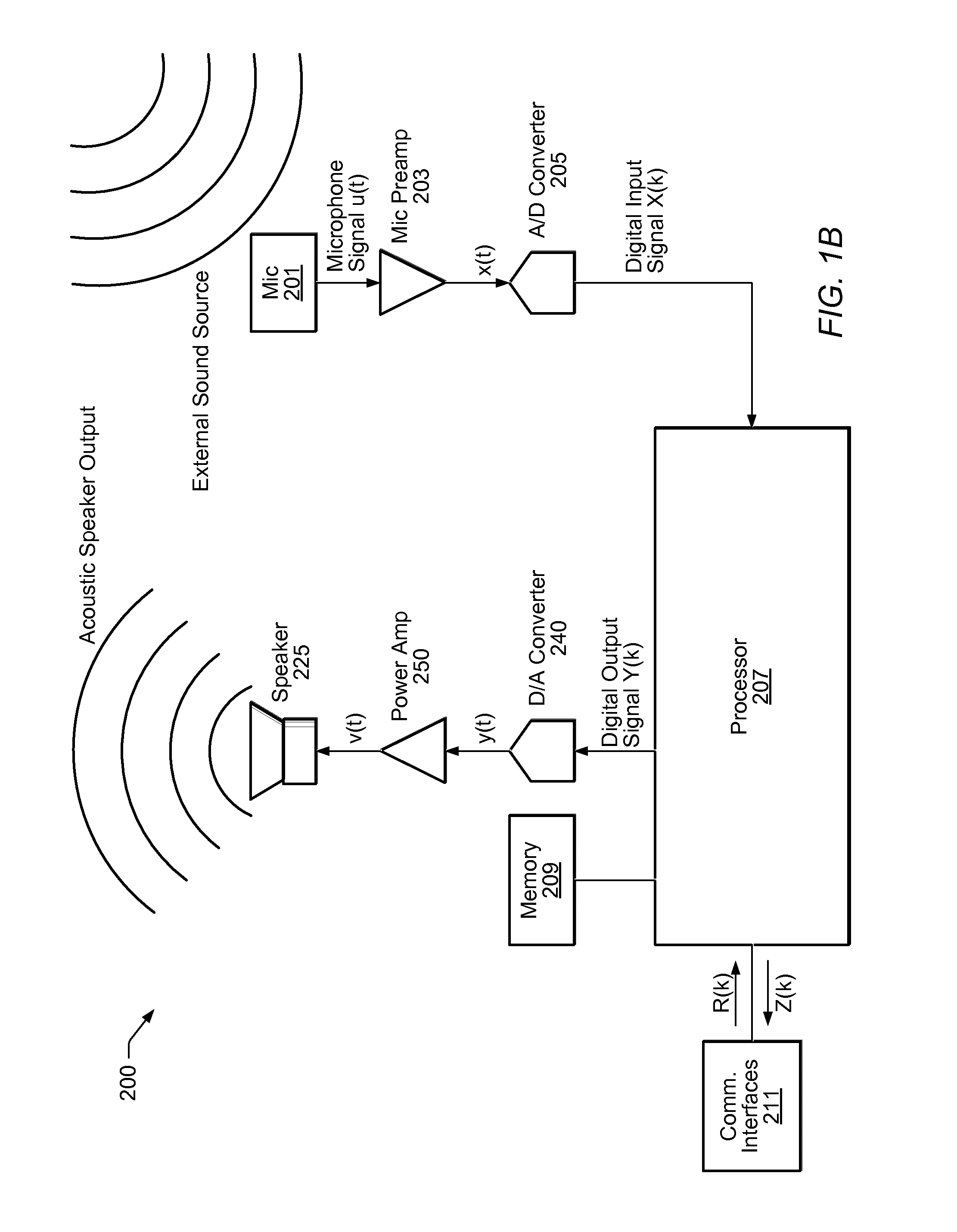
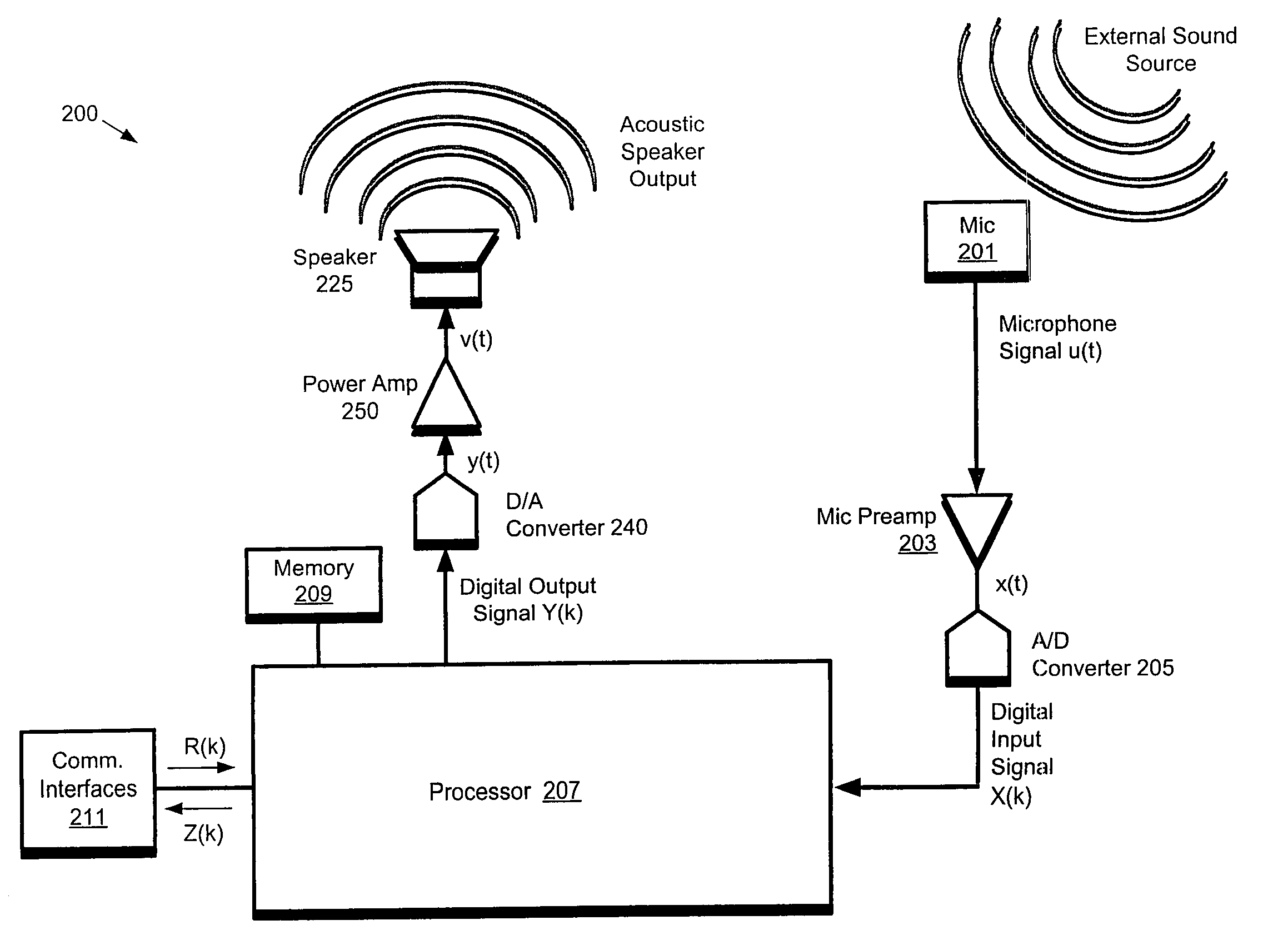
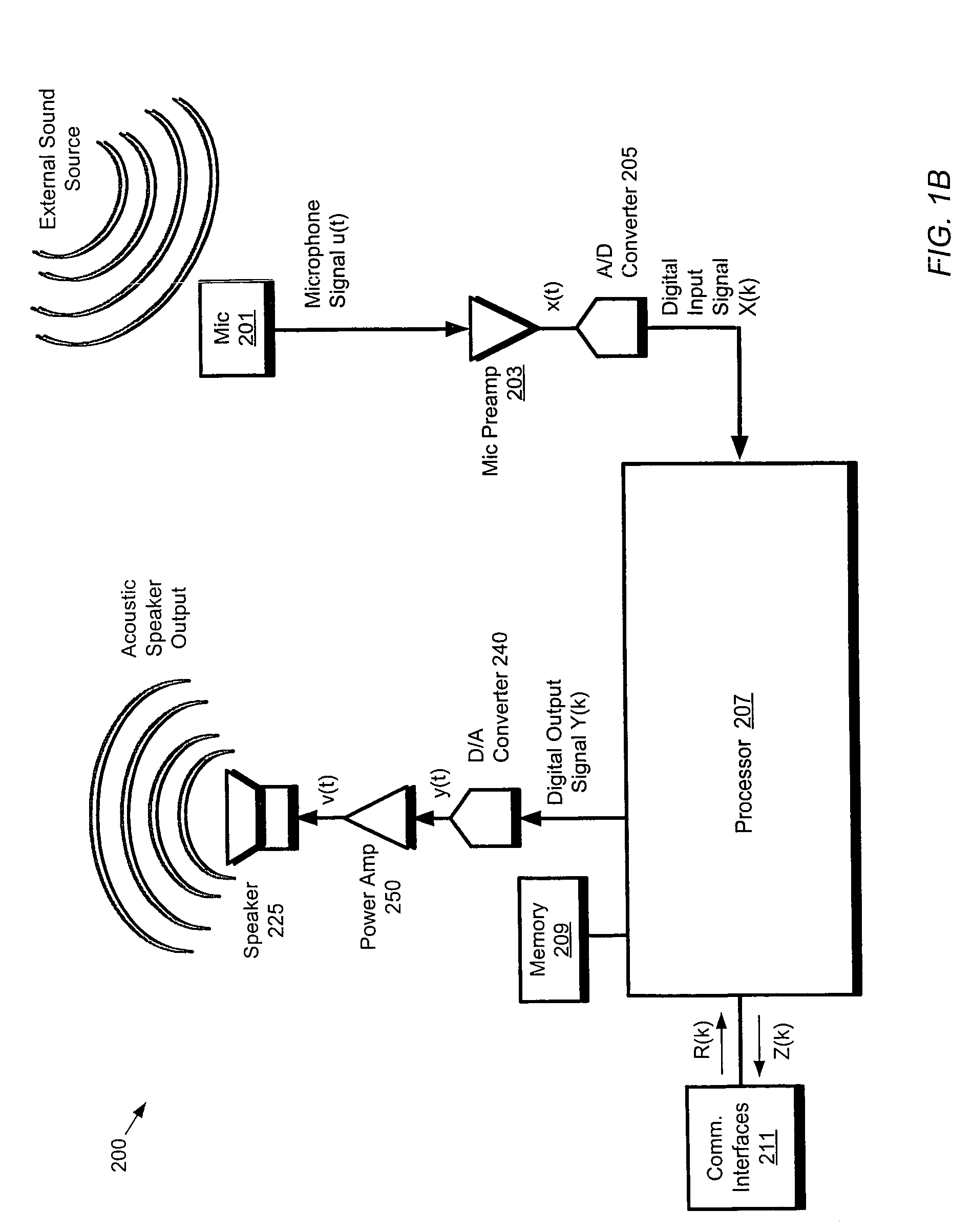
Forming beams with nulls directed at noise sources
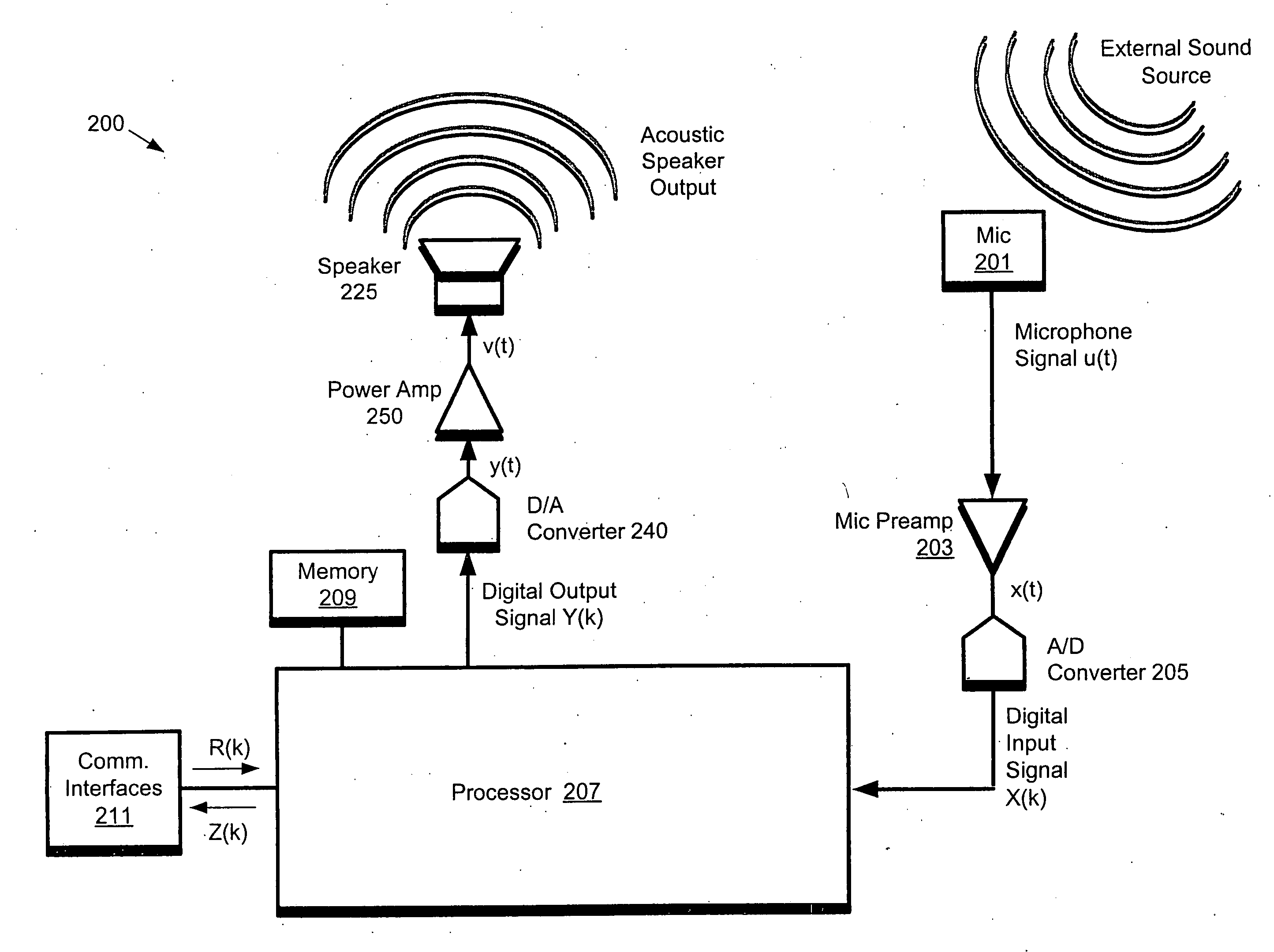
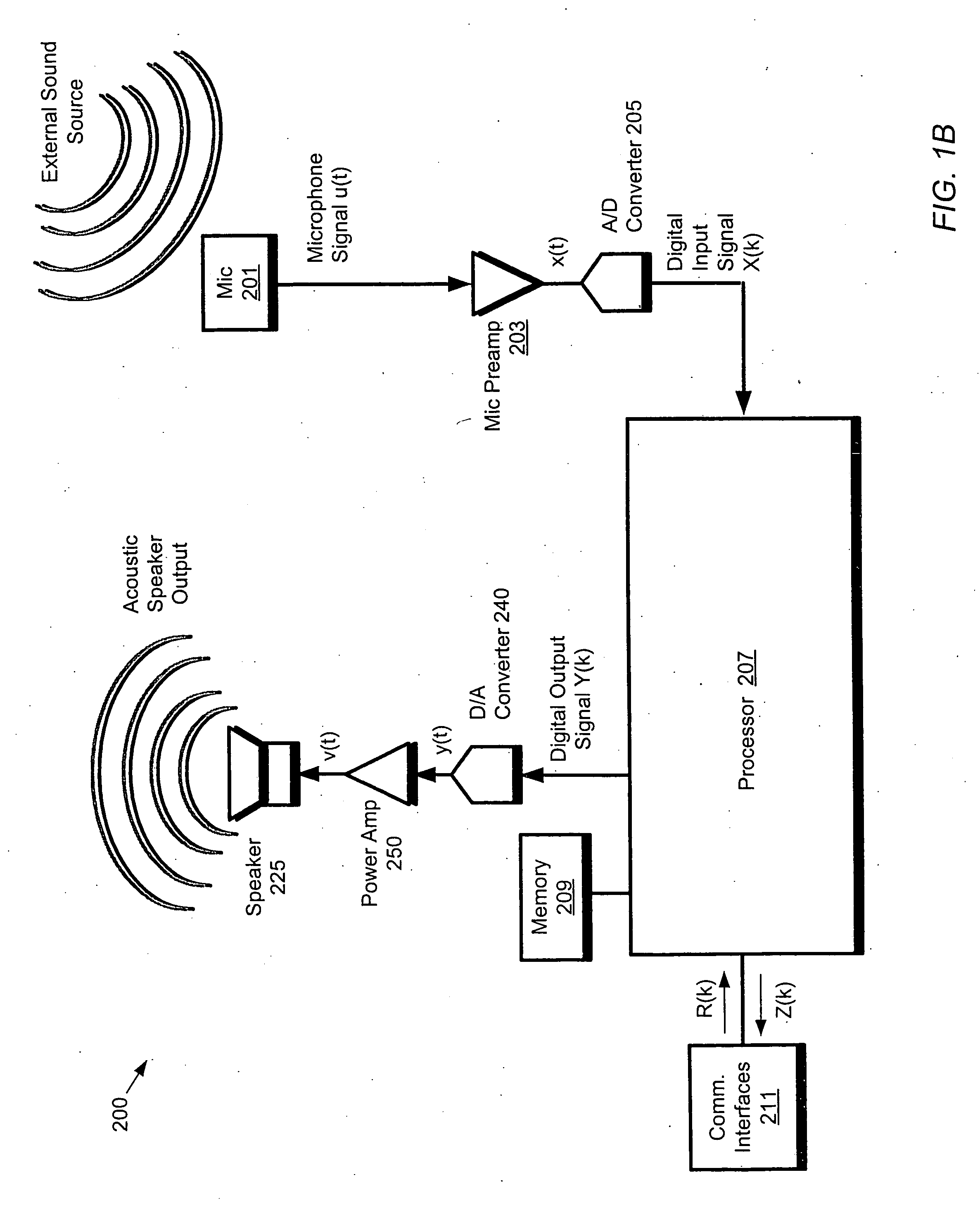
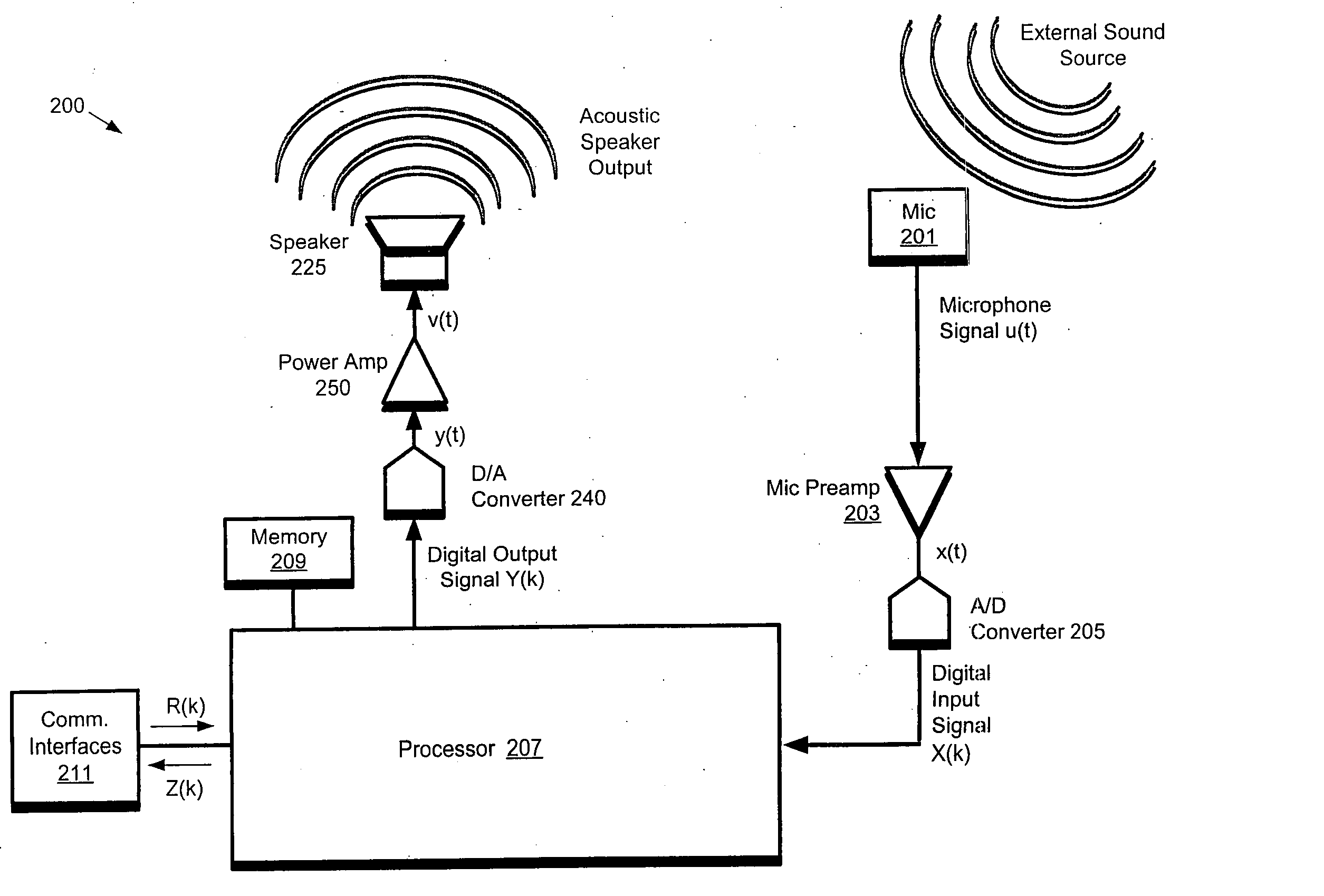
ActiveUS20060262943A1Signal processingMicrophones signal combinationCommunications systemSound sources
A communication system (e.g., a speakerphone) includes an array of microphones, a speaker, memory and a processor. The processor may perform a virtual broadside scan on the microphone array and analyze the resulting amplitude envelope to identify acoustic source angles. Each of the source angles may be further investigated with a directed beam (e.g., a hybrid superdirective / delay-and-sum beam) to obtain a corresponding beam signal. Each source may be classified as either intelligence or noise based on an analysis of the corresponding beam signal. The processor may design a virtual beam pointed at an intelligence source and having nulls directed at one or more of the noise sources. Thus, the virtual beam may be highly sensitive to the intelligence source and insensitive to the noise sources.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
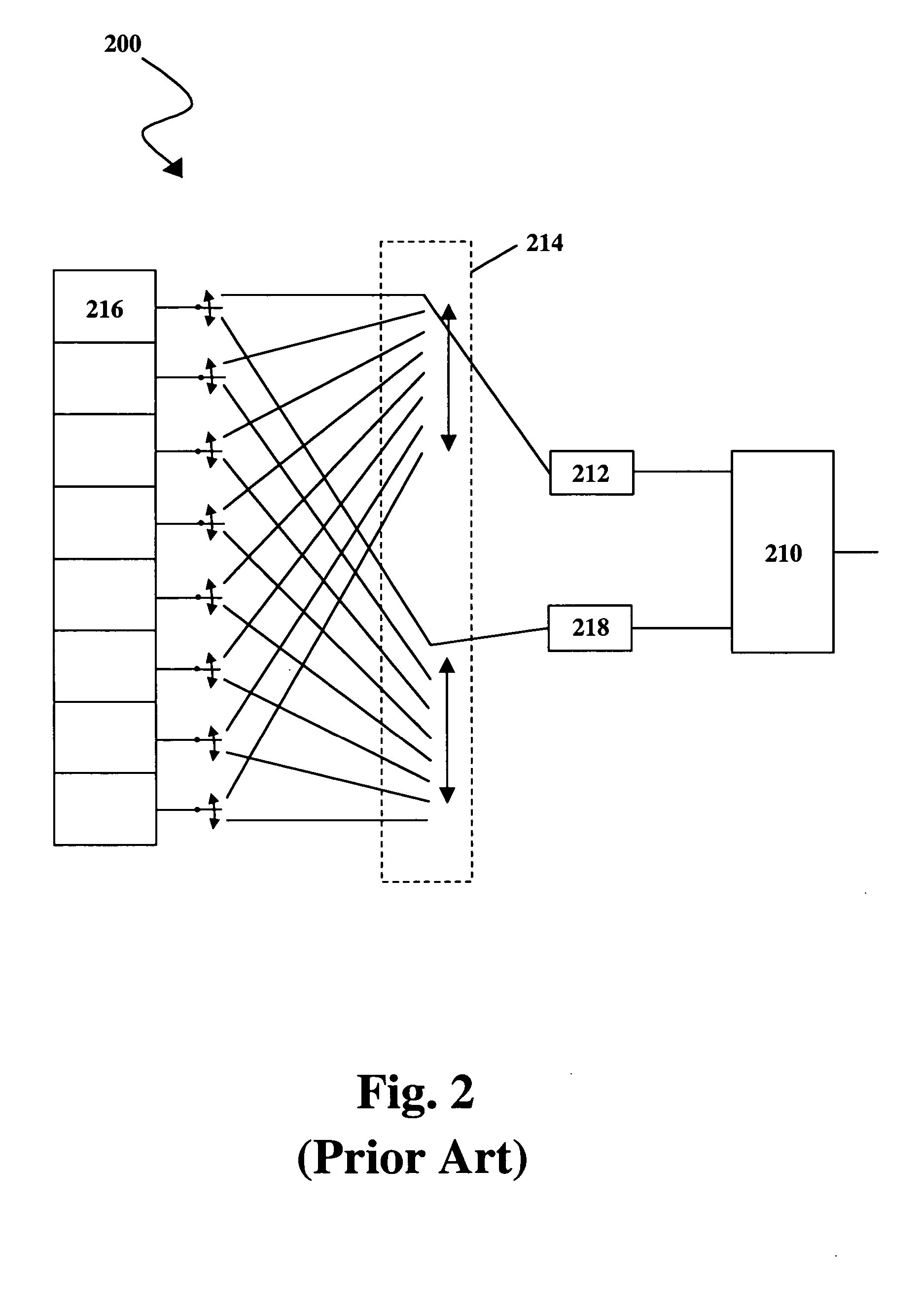
Apparatus and method for phased subarray imaging
InactiveUS7972271B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnostics3d imageImaging quality
An invention for coherent array image formation and restoration is taught. The invention is applicable for both 2D and 3D imaging using either 1D or 2D arrays, respectively. A transducer array is subdivided into subarrays, each subarray having a number of adjacent array elements. All elements of each subarray transmit and receive in parallel. The signals received from each subarray are delayed and summed to form scan lines, or beams. The low-beam-rate beams formed from each subarray are upsampled and interpolated prior to forming high-beam-rate images. Depending on the subarray geometry, a subarray-dependent restoration filter is also applied to the subarray beams. The restored beams from each subarray are combined to form the final high-beam-rate image. The invention significantly reduces the front-end hardware complexity compared to conventional methods such as full phased array imaging with comparable image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
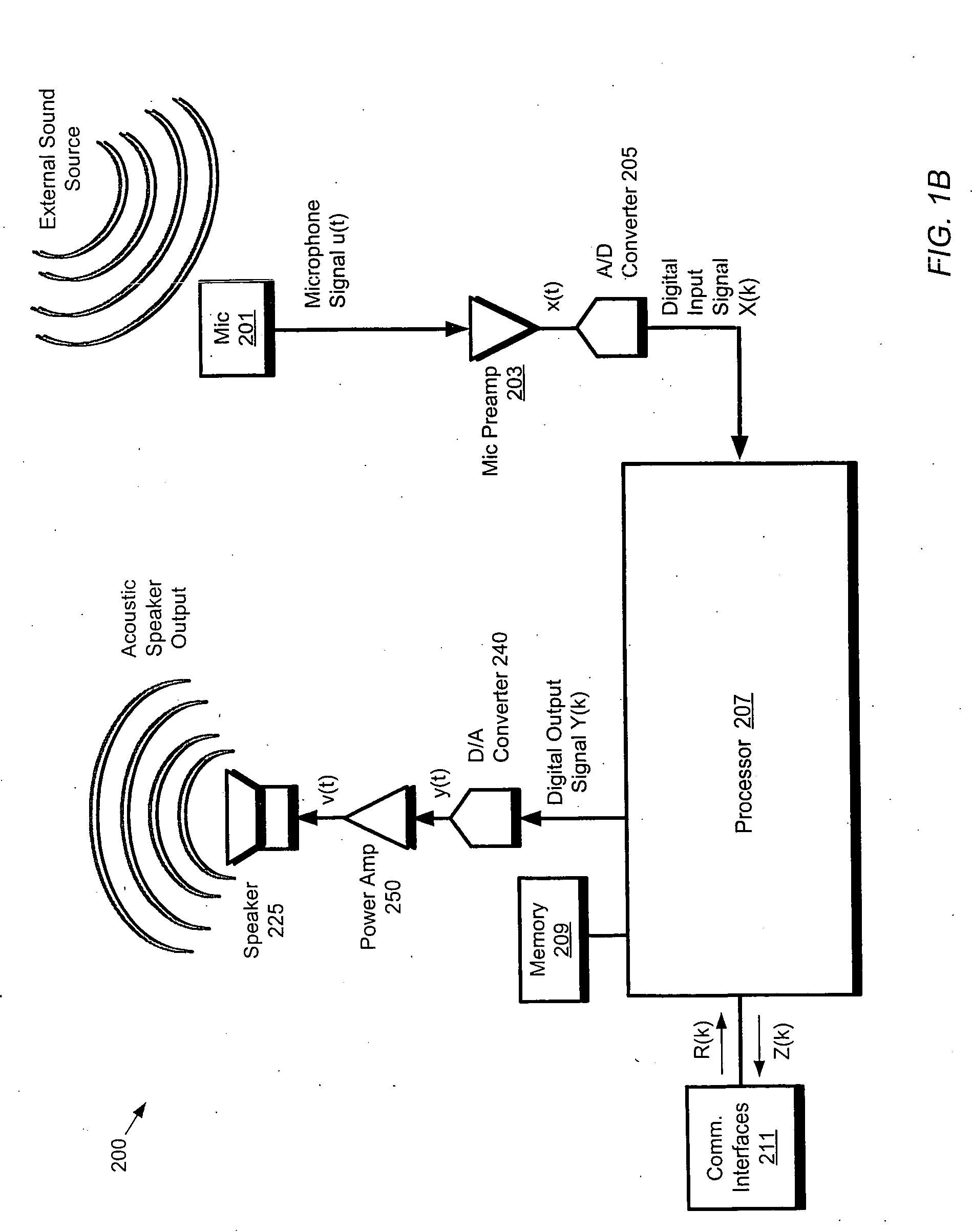
Hybrid beamforming
A system such as a speakerphone may include a processor, memory and an array of microphones. The processor may be configured (via program instructions stored in the memory) to perform automatic echo cancellation, self calibration and beam forming. In particular, the processor may receive input signals from the microphone array and operate on the input signals with a highly directed virtual beam which is a composite of two or more beams which are restricted to respective frequency ranges. The two or more beams may include beams of different kinds, e.g., superdirective beams and delay-and-sum beams.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
Apparatus and method for phased subarray imaging
InactiveUS20050101867A1Reduction front-end electronic complexityLow beam rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImaging quality3d image
An invention for coherent array image formation and restoration is taught. The invention is applicable for both 2D and 3D imaging using either ID or 2D arrays, respectively. A transducer array is subdivided into subarrays, each subarray having a number of adjacent array elements. All elements of each subarray transmit and receive in parallel. The signals received from each subarray are delayed and summed to form scan lines, or beams. The low-beam-rate beams formed from each subarray are upsampled and interpolated prior to forming high-beam-rate images. Depending on the subarray geometry, a subarray-dependent restoration filter is also applied to the subarray beams. The restored beams from each subarray are combined to form the final high-beam-rate image. The invention significantly reduces the front-end hardware complexity compared to conventional methods such as full phased array imaging with comparable image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Forming beams with nulls directed at noise sources
A communication system (e.g., a speakerphone) includes an array of microphones, a speaker, memory and a processor. The processor may perform a virtual broadside scan on the microphone array and analyze the resulting amplitude envelope to identify acoustic source angles. Each of the source angles may be further investigated with a directed beam (e.g., a hybrid superdirective / delay-and-sum beam) to obtain a corresponding beam signal. Each source may be classified as either intelligence or noise based on an analysis of the corresponding beam signal. The processor may design a virtual beam pointed at an intelligence source and having nulls directed at one or more of the noise sources. Thus, the virtual beam may be highly sensitive to the intelligence source and insensitive to the noise sources.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
Hybrid beamforming
A system such as a speakerphone may include a processor, memory and an array of microphones. The processor may be configured (via program instructions stored in the memory) to perform automatic echo cancellation, self calibration and beam forming. In particular, the processor may receive input signals from the microphone array and operate on the input signals with a highly directed virtual beam which is a composite of two or more beams which are restricted to respective frequency ranges. The two or more beams may include beams of different kinds, e.g., superdirective beams and delay-and-sum beams.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
Received data processing apparatus of photoacoustic tomography
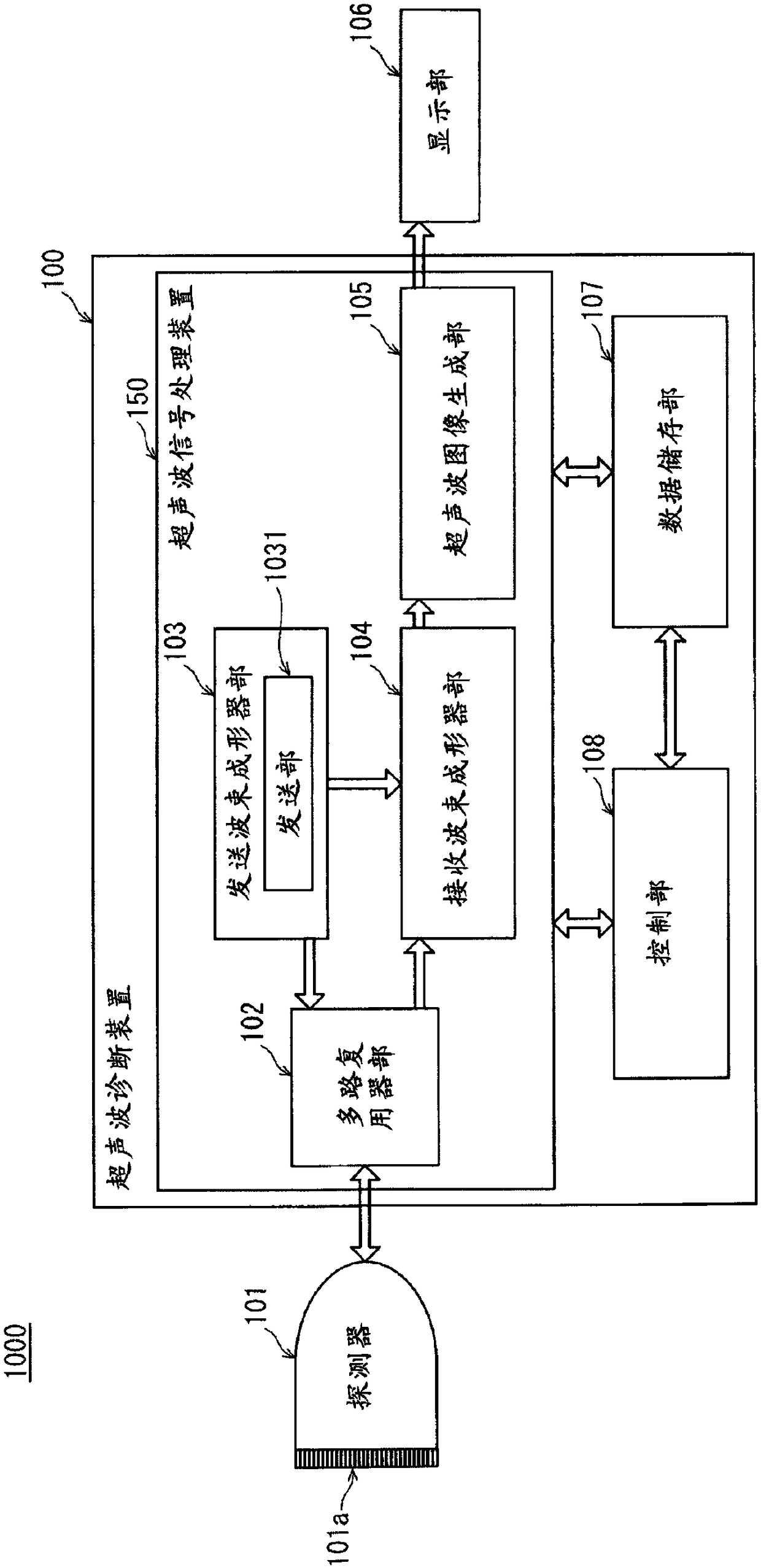
ActiveUS20110128816A1Increase in sizeIncrease equipment costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using tomographyDelay and sumAcoustic wave
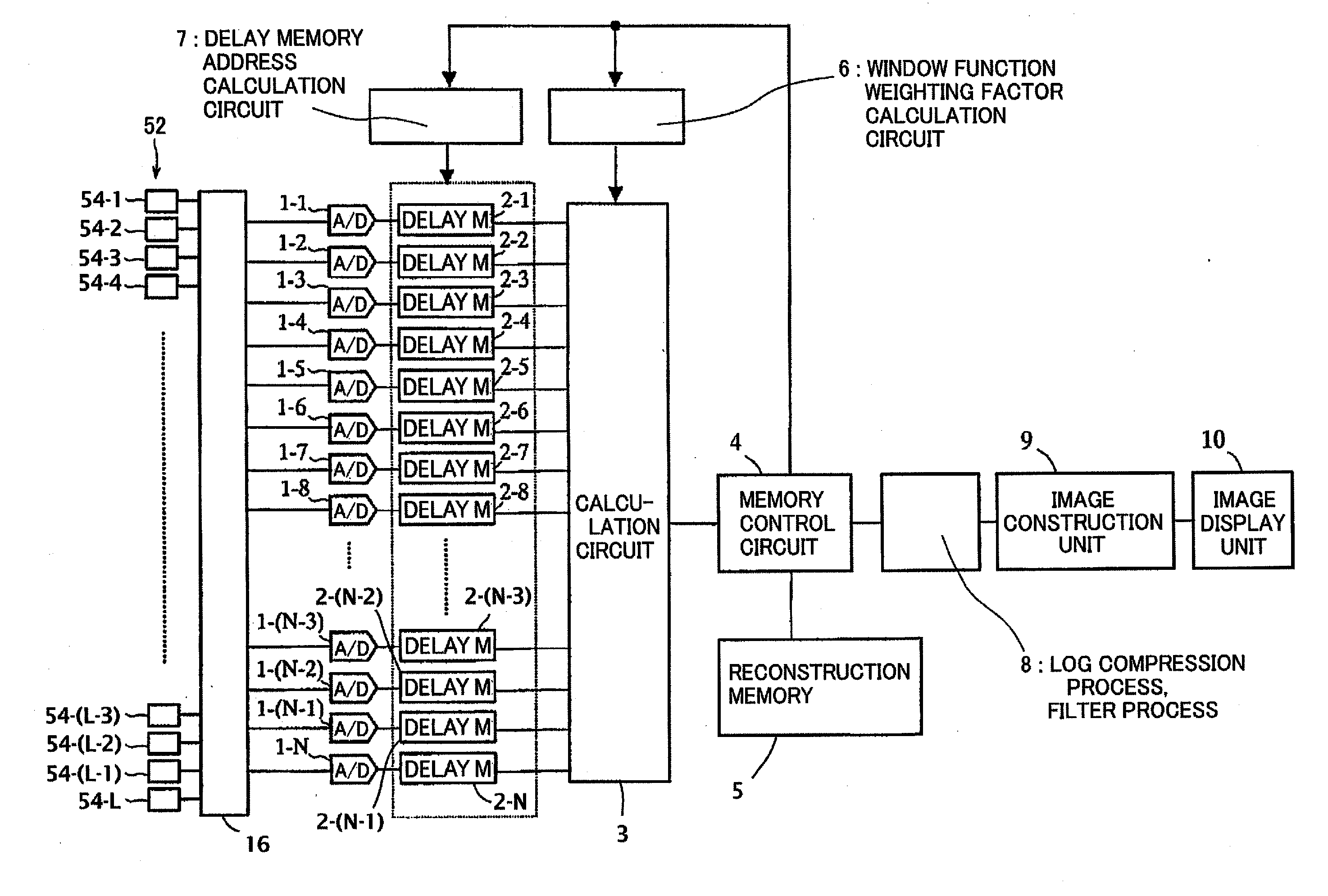
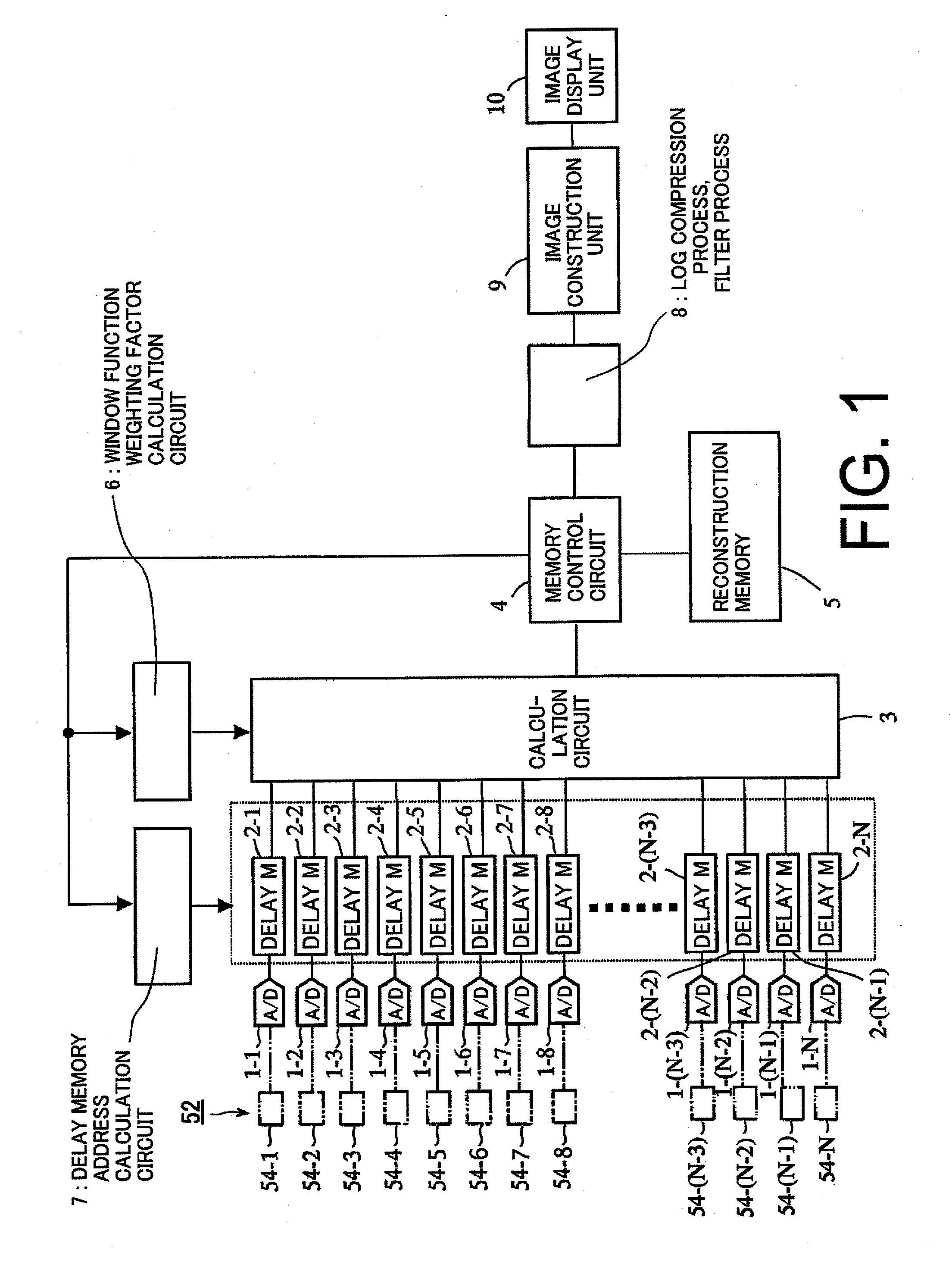
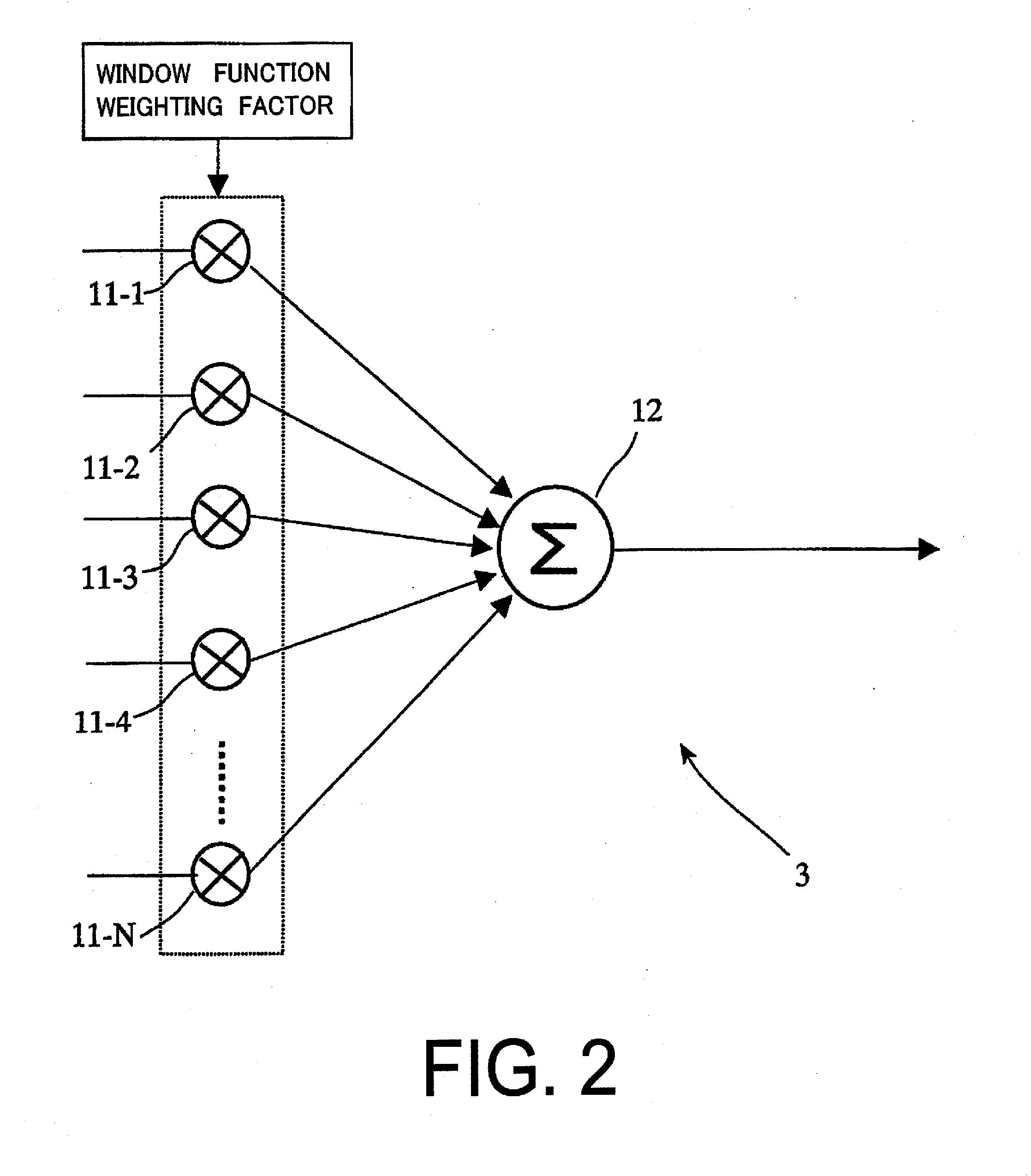
There is provided a received data processing apparatus of photoacoustic tomography including a minimum constitution unit data composition unit that sequentially reads receiving digital signals from first storage units and composes minimum constitution unit data of the acoustic wave of the minimum constitution units by performing a delay-and-sum process; a second storage unit that stores the minimum constitution unit data of the entire region of the specimen; an image construction unit that constructs an image of the specimen based on the minimum constitution unit data stored in the second storage unit; and a control unit that sequentially stores the minimum constitution unit data calculated by the minimum constitution unit data composition unit in the second storage unit and reads the stored minimum constitution unit data of the entire region of the specimen to transmit the minimum constitution unit data to the image construction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
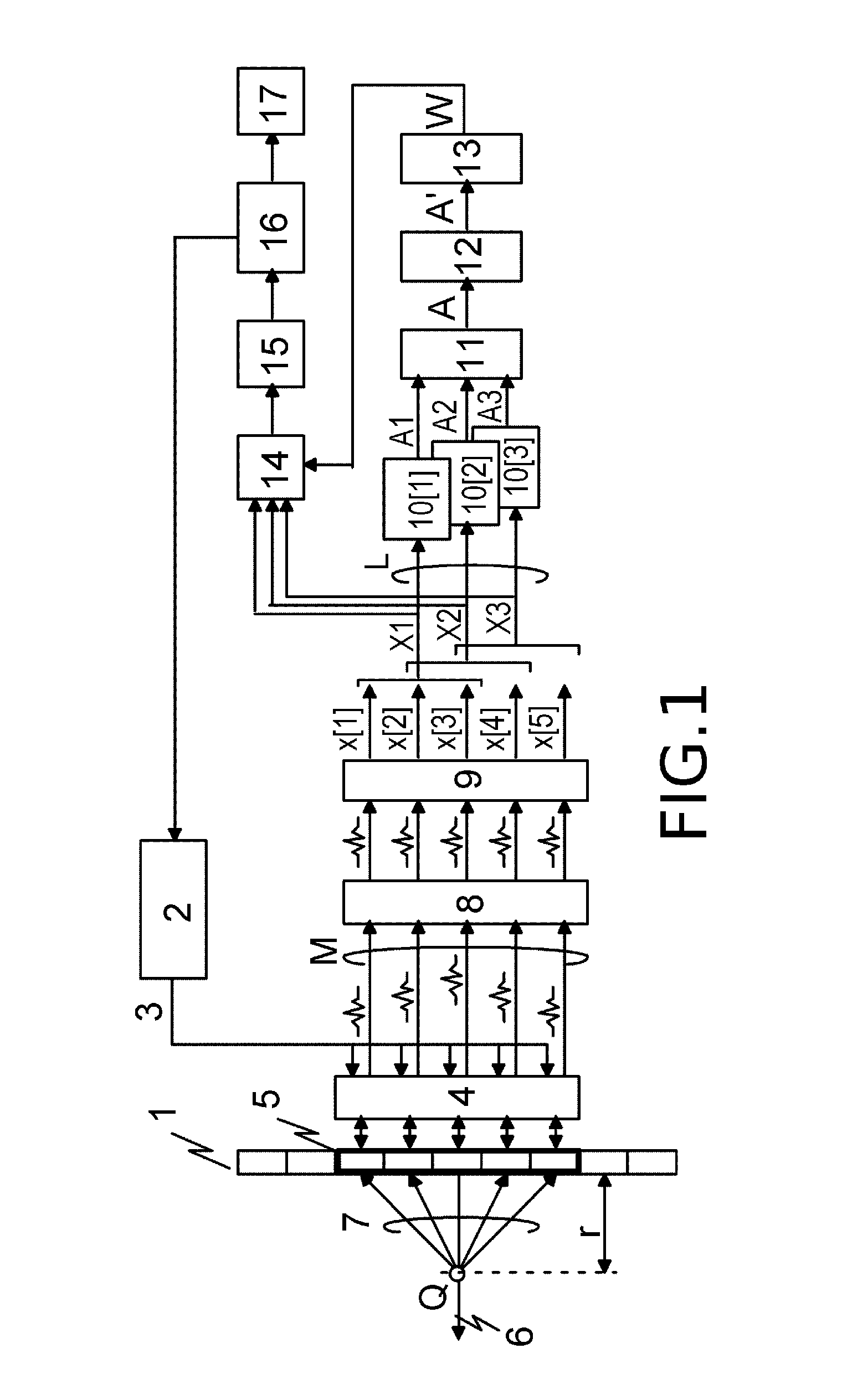
Measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20120044785A1Improve imaging resolutionSimple structureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImaging processingMeasurement device
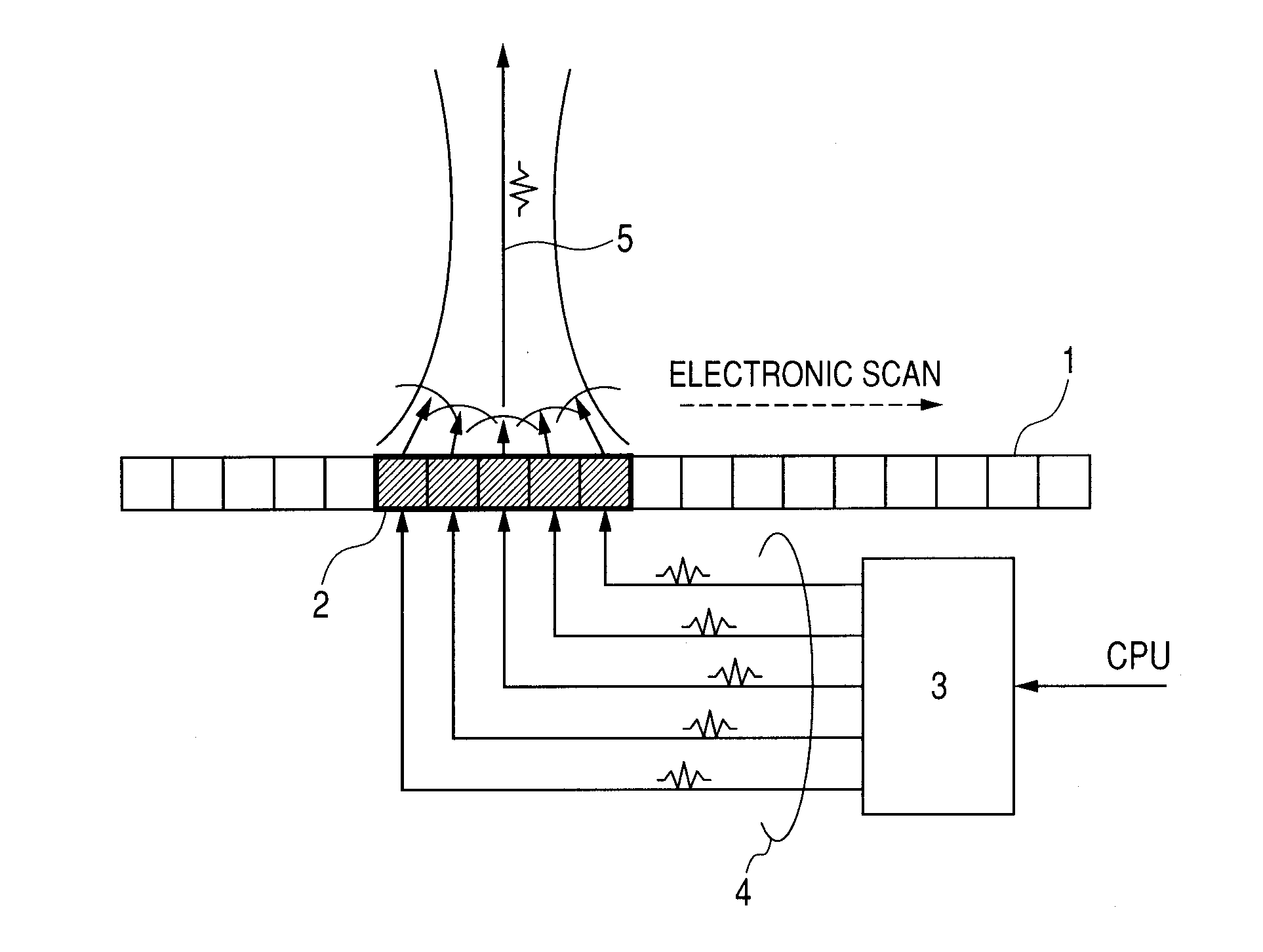
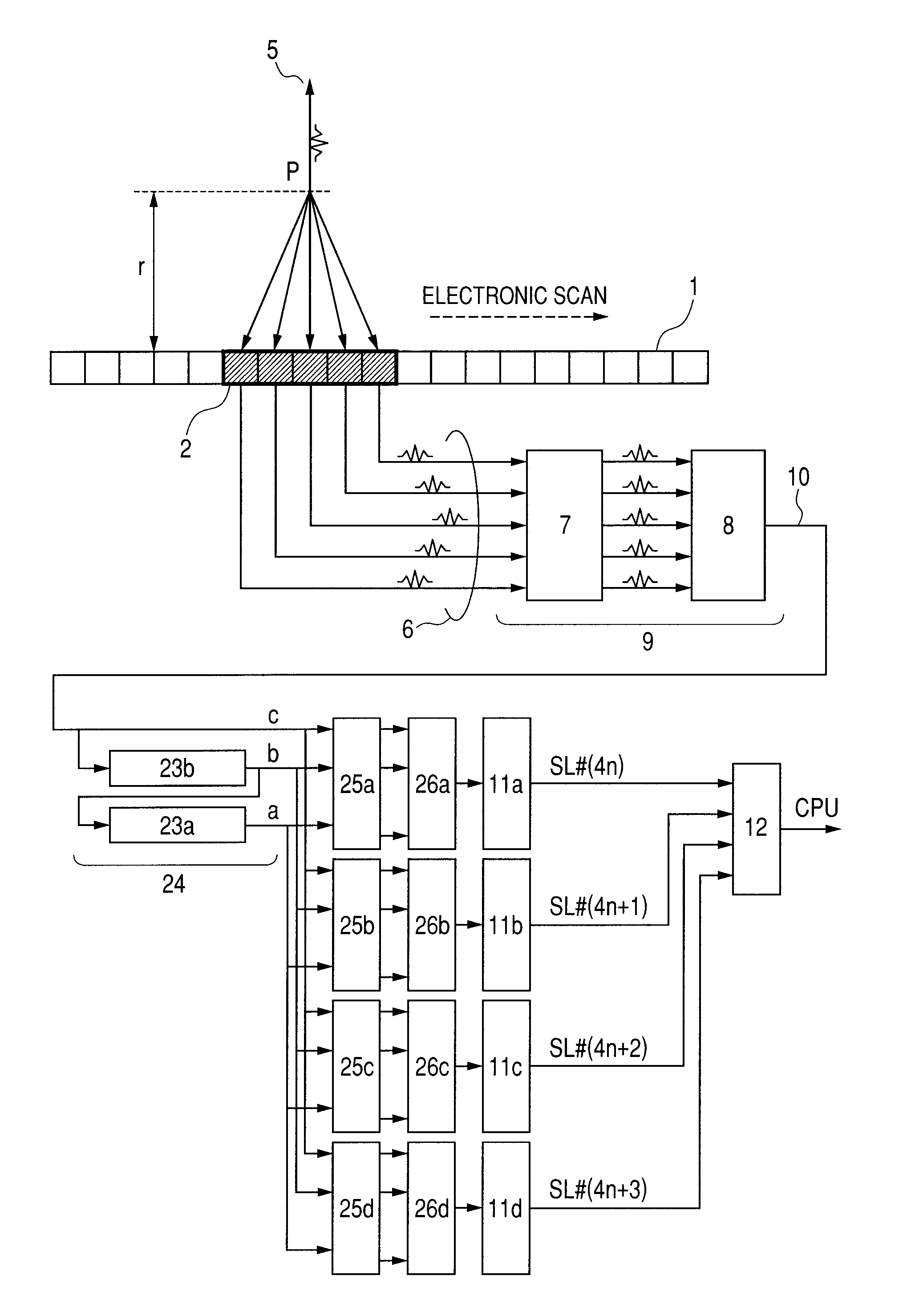
Provided is a measuring apparatus, including: a moving mechanism for moving a probe in an elevation direction; a first delay and sum circuit for performing delay and sum of reception signals at individual positions along the elevation direction to output a first add signal; a signal extraction circuit for letting an output of the first delay and sum circuit to pass through delay circuits to output in parallel first add signals obtained at different positions; a second delay and sum circuit for performing delay and sum of the first add signals output from the signal extraction circuit to output a second add signal; and an image processing circuit for generating image data by using the second add signal. Accordingly, image resolution in the elevation direction may be improved with a simple structure without deteriorating an image obtaining speed in the measuring apparatus for obtaining an ultrasonic image.
Owner:CANON KK
Sound source direction positioning method based on difference array
The invention relates to a sound source direction positioning method based on a difference array. The sound source direction positioning method based on a difference array includes the steps: utilizing a plane microphone array to record input signals, and calculating a covariance matrix; further performing decomposition of characteristic constants to acquire the characteristic vector of the maximum characteristic constant and take the characteristic vector of the maximum characteristic constant as the target sound source, and calculating the covariance matrix of the target sound source; designing two orthogonal N-step dual difference array wave beam forming; based on the weight of wave beam forming and the covariance matrix of the target sound source, calculating the sound source direction candidate item; utilizing the sound source direction candidate item to calculate the sound source direction candidate items in other three quadrants, and forming a sound source direction candidate item group together; and utilizing the wave beam forming method for delay-and-sum to perform wave beam forming, and comparing the energy of the wave beams formed by the four sound source direction candidate items, and selecting the sound source direction candidate item with the maximum energy as the target sound source direction. The sound source direction positioning method based on a difference array has the advantages of high efficiency, low computational complexity and high accuracy, and is a new positioning method.
Owner:UNISOUND SHANGHAI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD +1
Dual focusing beam forming method and device based on virtual array elements
ActiveCN102727256AIncrease the amount of informationHigh energyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImage resolutionSynthesis methods
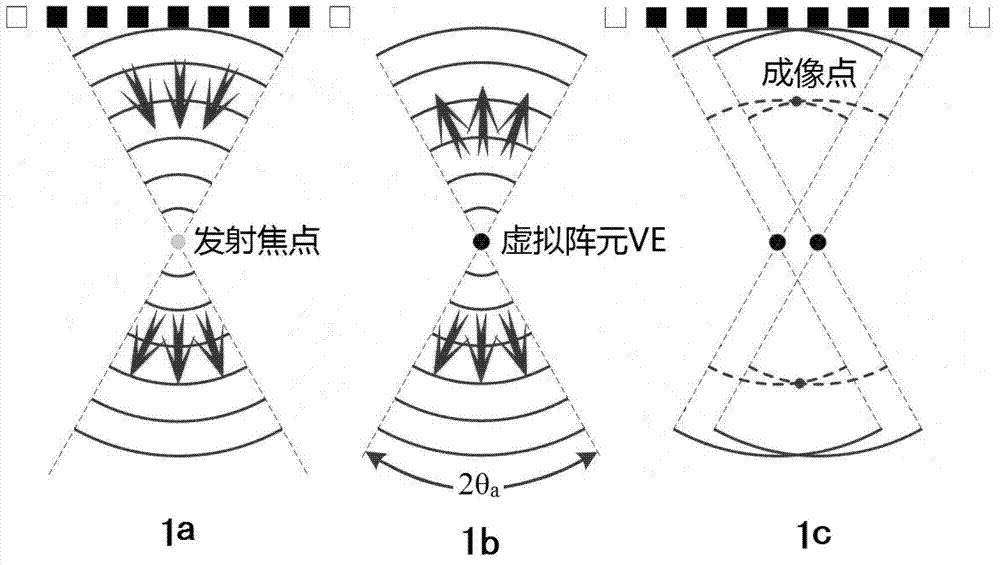
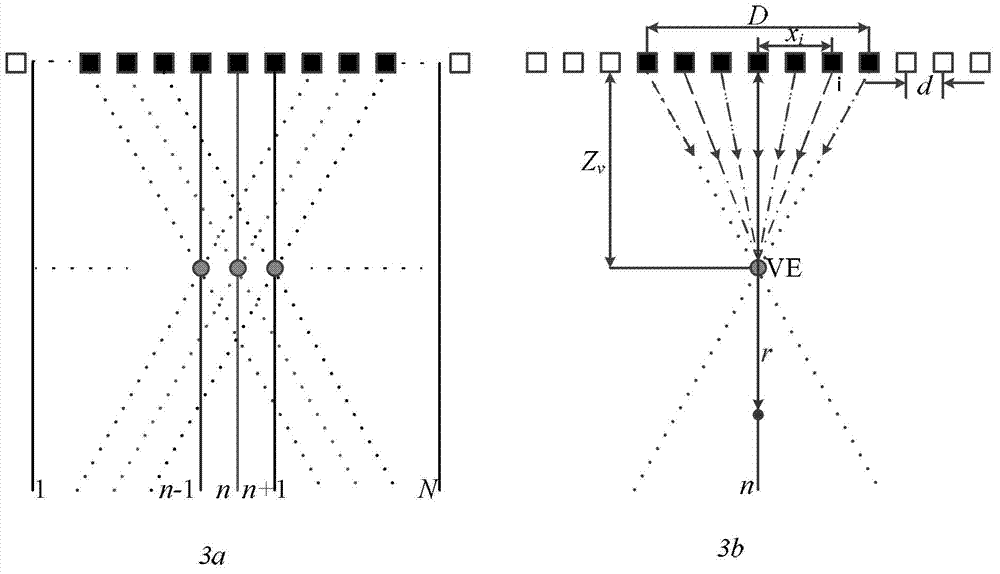
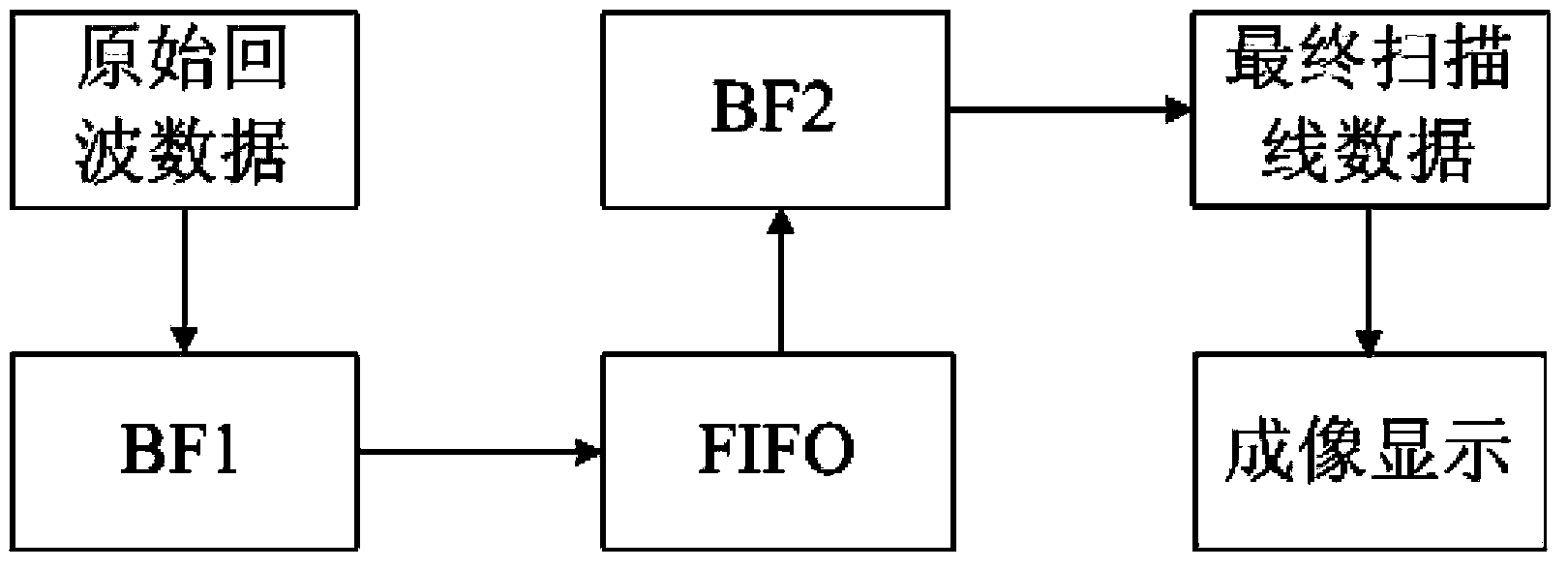
The invention discloses a dual focusing beam forming method and device based on virtual array elements. The method comprises the following steps of: performing primary focusing by using a single fixed focus; calculating a delay parameter of secondary focusing by using the concept of the virtual array elements; and performing secondary focusing according to the principle of delay-and-sum (DAS) beam forming and the dynamic focusing technology to acquire finally imaged scanning line data. Dual focusing beam forming ultrasonic imaging is realized by introducing the virtual array element technology to an ultrasonic imaging system, using a DAS beam synthesis method and performing DAS twice. The method is characterized in that related valid information of a plurality of superposed sound fields is extracted by performing DAS twice, so that information quantity and energy of sound wave signals are increased, and the imaging effect is greatly improved. According to the method, two beam formers BF1 and BF2 and a first in first outlet (FIFO) buffer are used and DAS is performed twice, so that a large quantity of low-resolution echo data is not required to be stored.
Owner:CHONG QING BORN FUKE MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Apparatus and method for phased subarray imaging
ActiveUS20070208254A1Reduction front-end electronic complexityLow beam rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImaging quality3d image
An invention for coherent array image formation and restoration is taught. The invention is applicable for both 2D and 3D imaging using either 1D or 2D arrays, respectively. A transducer array is subdivided into subarrays, each subarray having a number of adjacent array elements. All elements of each subarray transmit and receive in parallel. The signals received from each subarray are delayed and summed to form scan lines, or beams. The low-beam-rate beams formed from each subarray are upsampled and interpolated prior to forming high-beam-rate images. Depending on the subarray geometry, a subarray-dependent restoration filter is also applied to the subarray beams. The restored beams from each subarray are combined to form the final high-beam-rate image. The invention significantly reduces the front-end hardware complexity compared to conventional methods such as full phased array imaging with comparable image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Object information acquiring apparatus
ActiveUS20130308850A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionElectricityDelay and sum
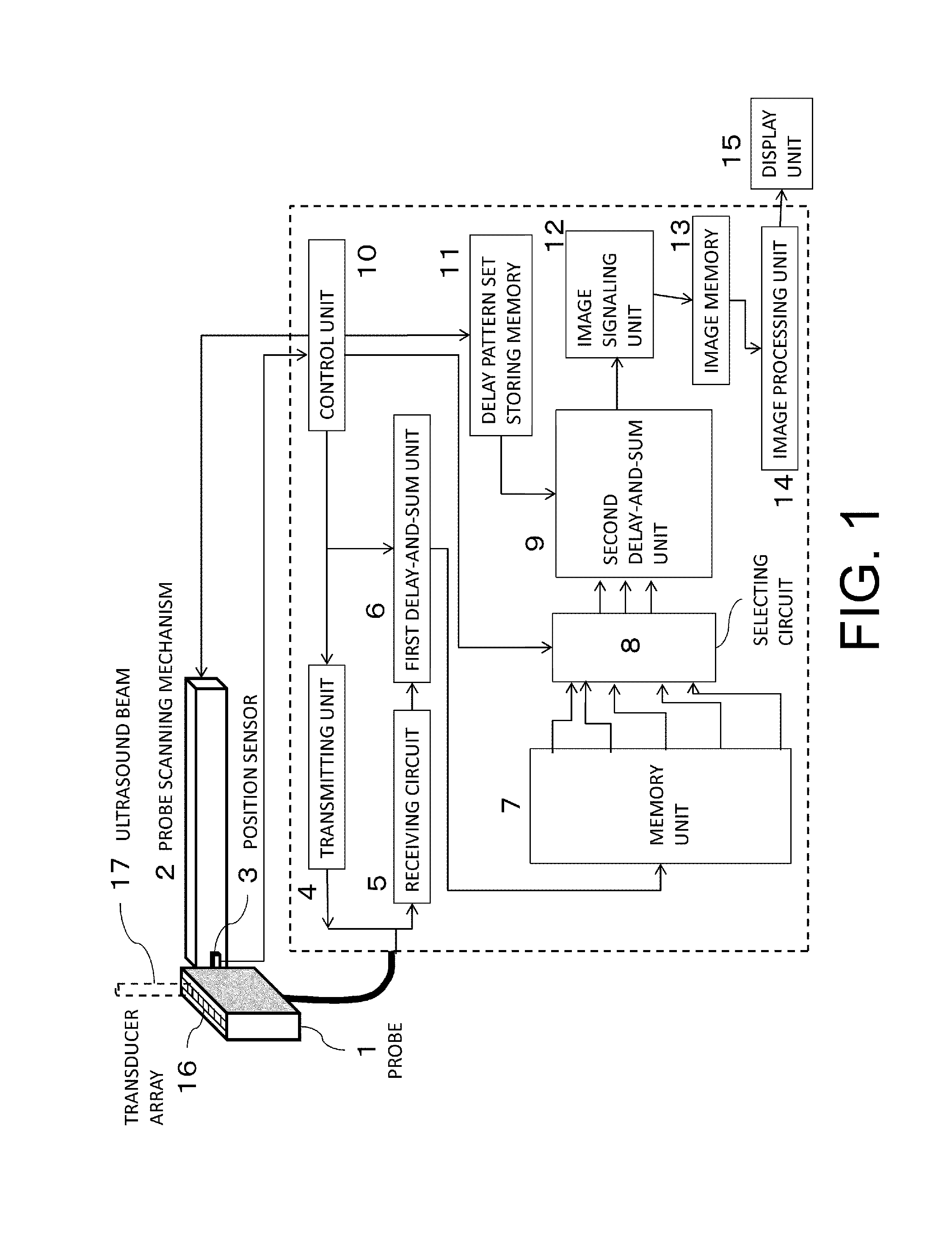
There is used an object information acquiring apparatus including a probe for electrically scanning an object in first direction and mechanically scanning in second direction intersecting with the first direction, a first delay-and-sum unit for operating a delay-and-sum on a received signal, a memory for storing a first delay-and-sum signal for each plane in the second direction, a selecting unit for selecting signals corresponding to M sectional planes from among the stored signals, a second delay-and-sum unit for operating a delay-and-sum on the selected signals in the second direction, and a unit for acquiring image in the object from the second delay-and-sum signal, the second delay-and-sum unit switching, according to the mechanical scanning, a first case in which M signals are fixed and a delay pattern is varied and a second case in which a set of the M signals is varied and the delay pattern is fixed.
Owner:CANON KK
Acoustic velocity correction method for photoacoustic imaging
InactiveCN103445765A2D-image generationDiagnostic recording/measuringSimultaneous equationsPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
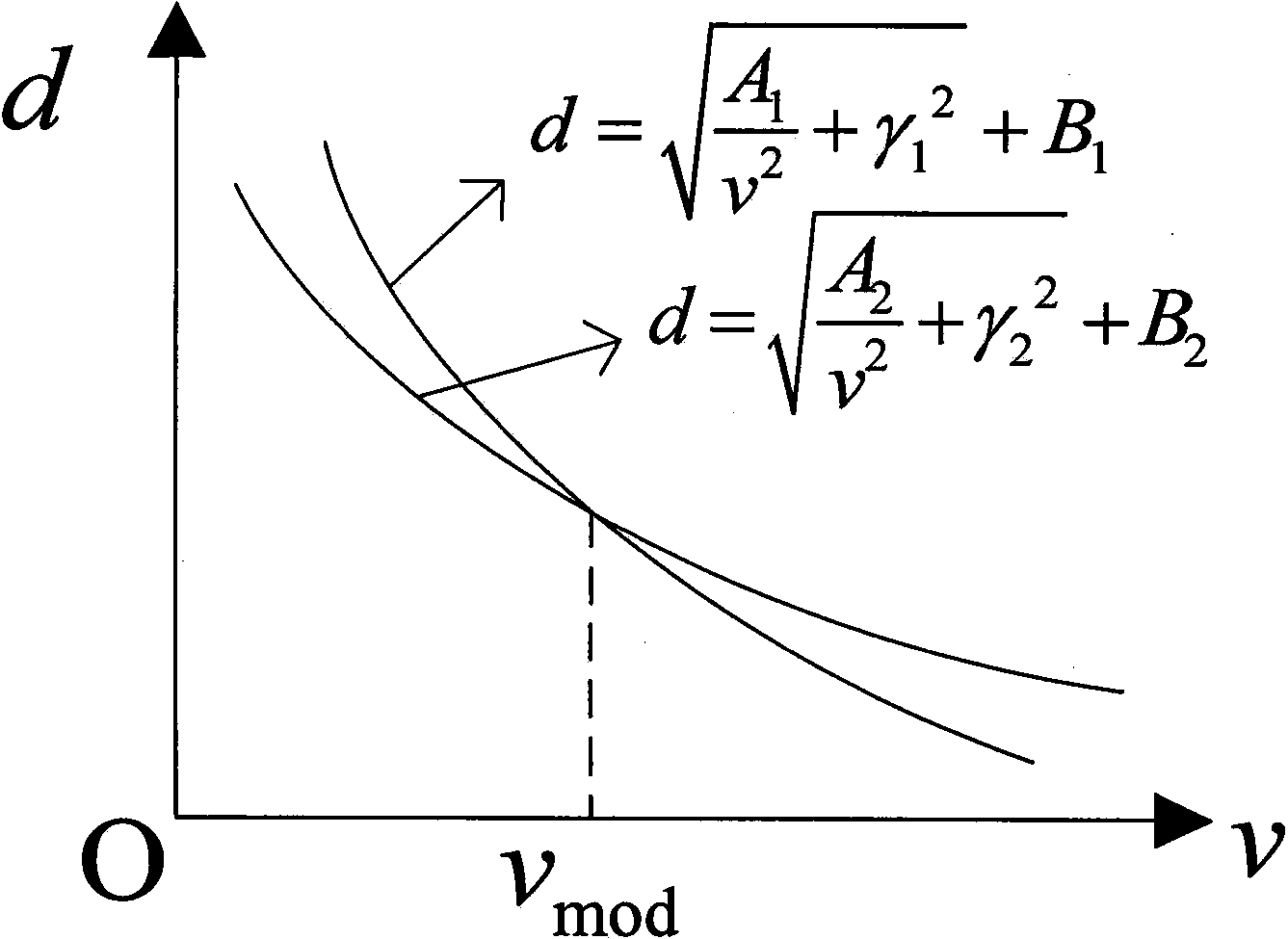
The invention discloses an acoustic velocity correction method for photoacoustic imaging. The method includes the steps of irradiating tissue under test by laser in a photoacoustic imaging system; using a linear sensor to acquire ultrasonic signals emitted by the irradiated tissue; determining a focus evaluation standard, and selecting a focus position; adjusting the acoustic velocity and delay compensation, rebuilding an image by means of delay and sum process, and focusing a selected point; fitting curves of relation between the acoustic velocity and delay compensation according to the relation between the acoustic velocity and delay, and determining curve parameters; performing simultaneous solution on the curves of relation of different focus depths to obtain the corrected acoustic velocity and delay compensation. The linear sensor is used for acquiring signals; the image is rebuilt by means of delay and sum process; a relation equation for the focused acoustic velocity and delay compensation is obtained by adjusting the target acoustic velocities and delay compensations of different positions; the corrected acoustic velocity is acquired by a simultaneous equation; accordingly, operation is simple.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Ultrasound diagnostic device and control method for the same
ActiveUS20160245905A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationMeasurement point
An ultrasound diagnostic device to which an ultrasound probe having a plurality of transducer elements is connectable. The ultrasound diagnostic device includes ultrasound signal processing circuitry operating as: a delay-and-sum processor; a determiner; and a velocity value calculator. The determiner determines whether adjustment of a velocity value for a partial area in a subject is necessary, based on acoustic line signal intensities for a specific measurement point in the partial area and other measurement points in the partial area. The specific measurement point is selected from among measurement points in the partial area based on acoustic line signals for the measurement points in the partial area. The velocity value calculator, when the determiner determines that velocity value adjustment is necessary, calculates an adjusted velocity value for the partial area by using the acoustic line signal for the specific measurement point.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Subject information obtaining apparatus, subject information obtaining method, and program
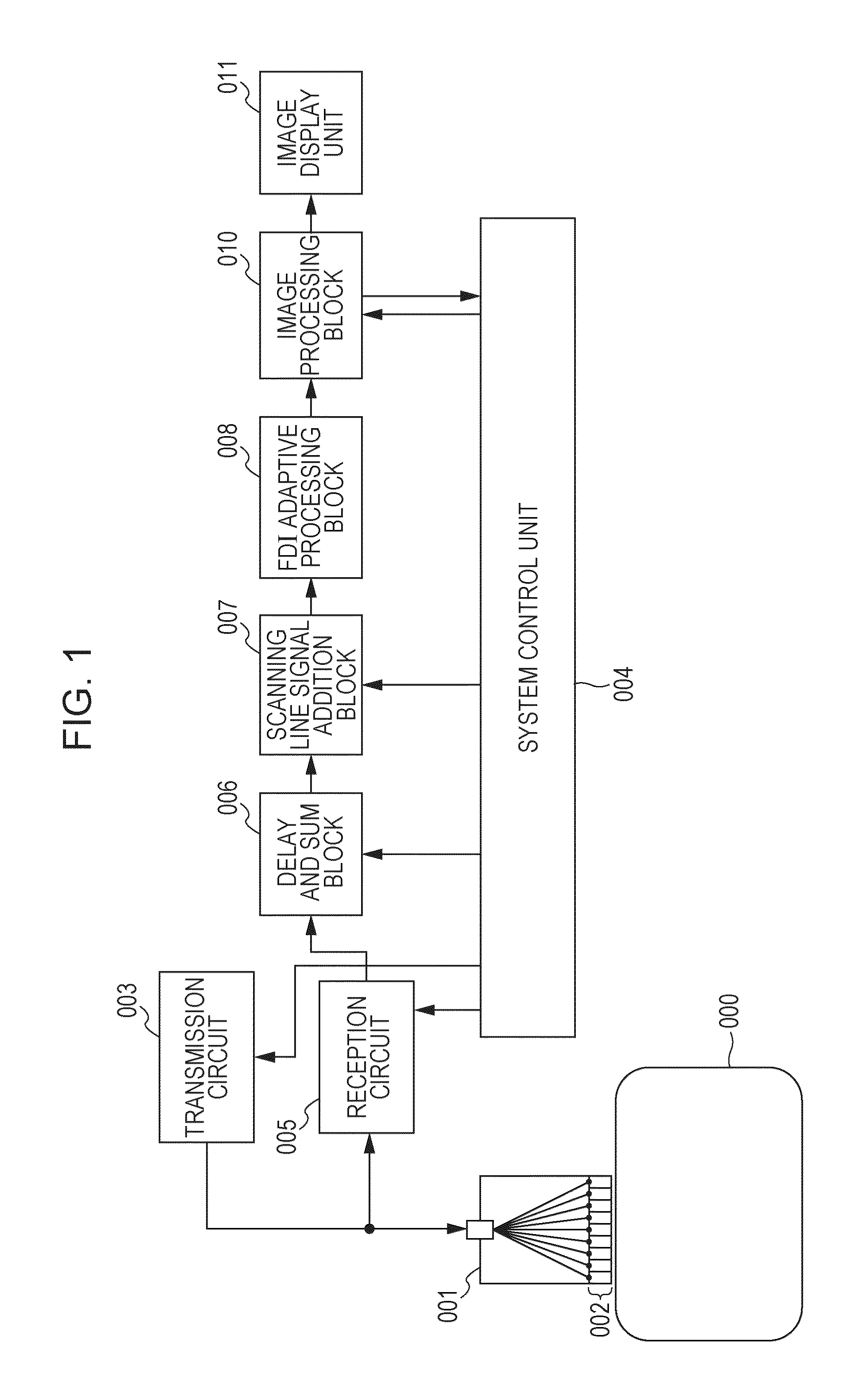
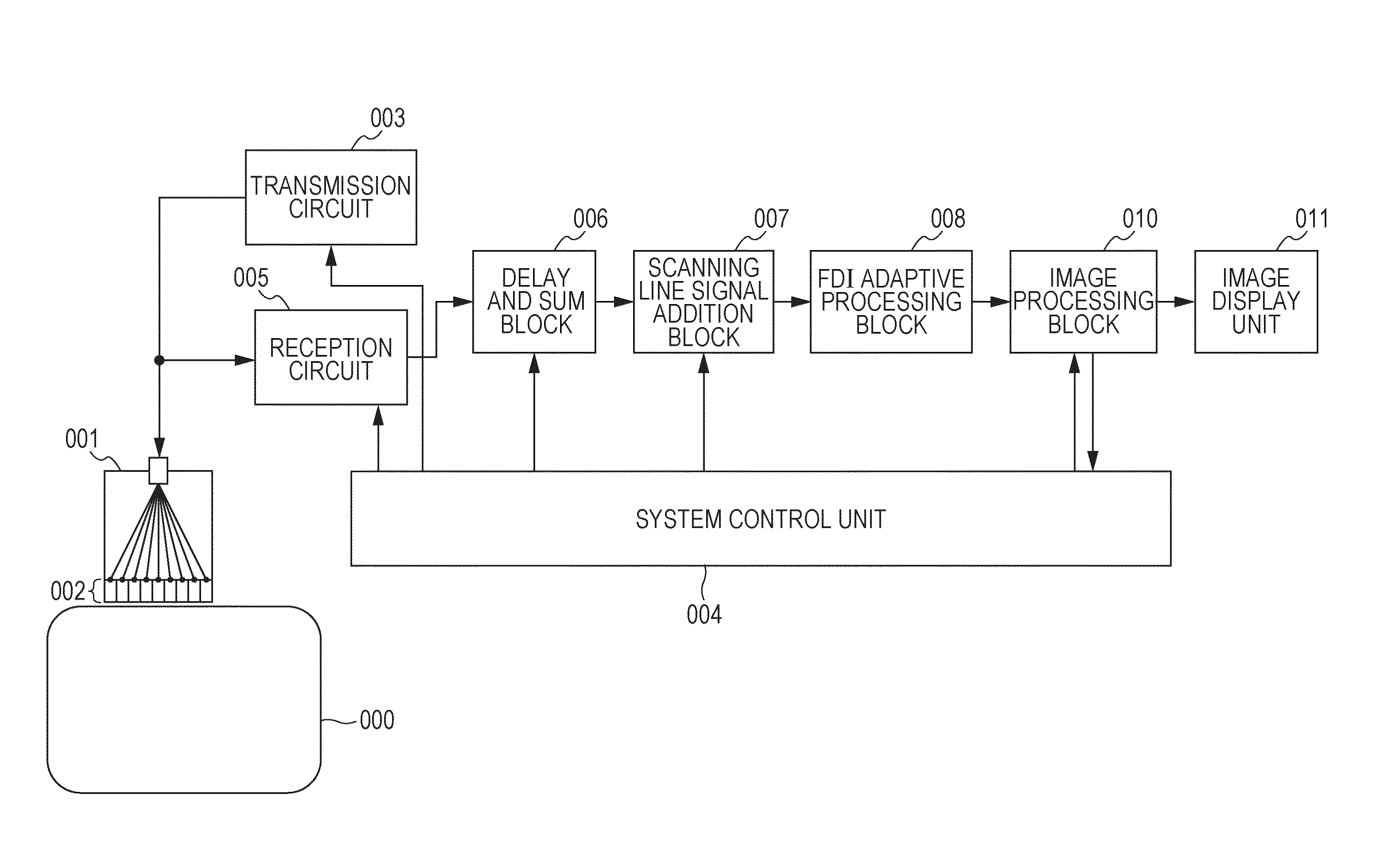
ActiveUS9304191B2Reduce impactOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDelay and sumPower intensity
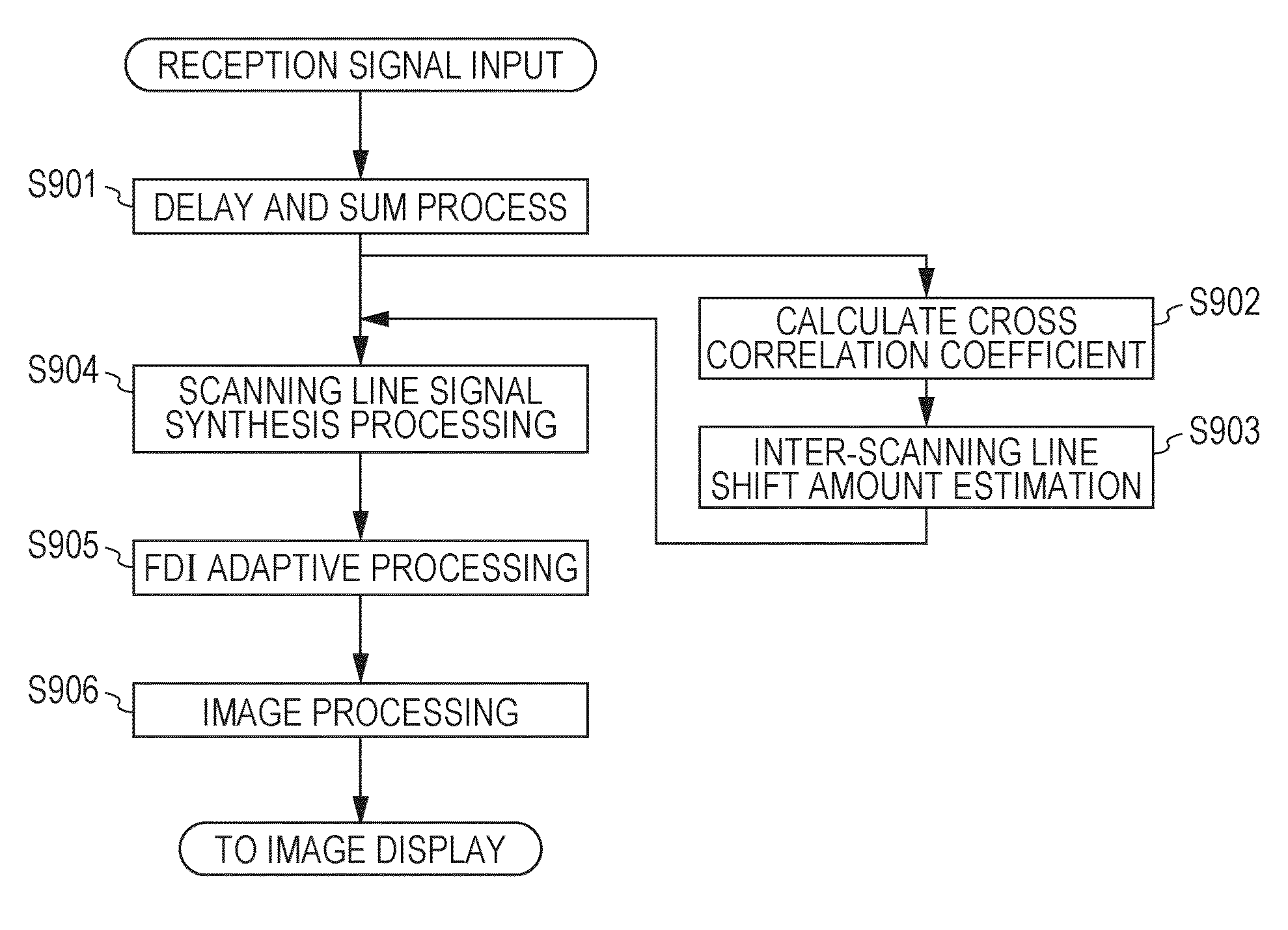
A subject information obtaining apparatus according includes: plurality of conversion elements configured to convert an elastic wave from a subject into a plurality of reception signals, a delay and sum unit configured to perform a delay and sum process by using the plurality of reception signals and output a plurality of scanning line signals, a scanning line synthesis unit configured to add the plurality of scanning line signals between adjacent scanning lines and output a plurality of synthesis scanning line signals, and an FDI adaptive processing unit configured to perform a frequency domain interferometry and an adaptive signal processing by using the plurality of synthesis scanning line signals and obtain a power intensity distribution.
Owner:CANON KK
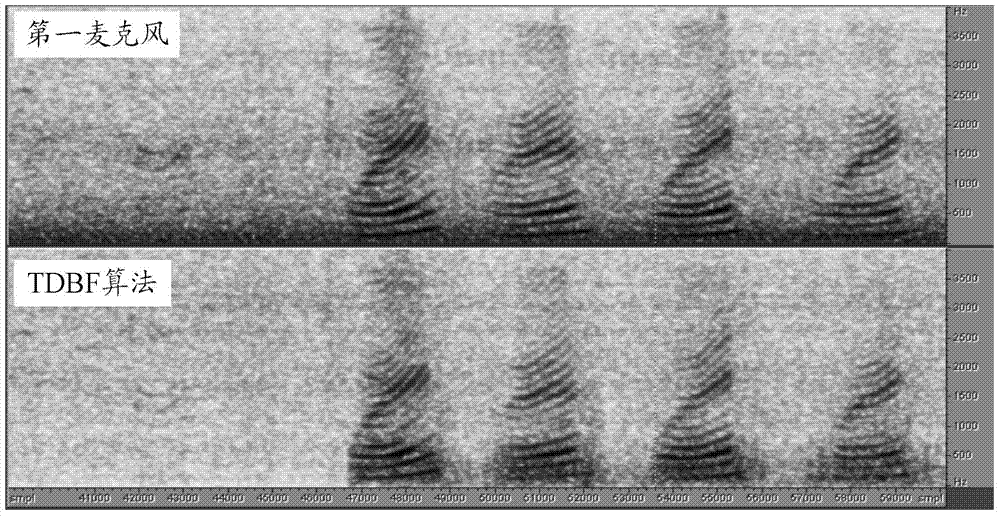
Double-microphone noise inhibiting method and system
The invention provides a double-microphone noise inhibiting method and system, and in particular relates to connection of the time-domain beam forming method and the frequency domain after-processing method. The method is that one delay-and-sum is added and treated as an assistant signal; whether to select the original path or add a new path is determined according to a voice activating detector. With the adoption of the method, that the large steady noise (fuzzy voice) included in voice cannot be treated in the traditional method can be avoided, the voice articulation and subjective feeling of the improved voice can be obviously improved.
Owner:MORNINGCORE HLDG CO LTD +1
Object information acquiring apparatus, information processing apparatus and object information acquiring method
ActiveUS20140058262A1High resolutionImprove robustnessDiagnostic recording/measuringInfrasonic diagnosticsInformation processingDelay and sum
An object information acquiring apparatus is provided that includes: a plurality of receiving elements which receive an acoustic wave that propagates from an object, and which convert the acoustic wave to a reception signal; an adaptive beamformer that performs adaptive beamforming of adjusting reception directionality in accordance with the reception signal in use of the reception signal; a delay-and-sum beamformer that performs delay-and-sum beamforming having preset directionality in use of the reception signal; an amplitude modulator that uses one output signal of one of the adaptive beamformer and the delay-and-sum beamformer, to perform amplitude modulation on an output signal of the other one of the beamformers; and a generator that, on the basis of a signal outputted by the amplitude modulator, generates image data on the interior of the object.
Owner:CANON KK
Ultrasound signal processing device, ultrasound signal processing method, and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium
ActiveUS20150025378A1Suppressing increase in memory sizeAvoid quality lossOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationTransducer
Preceding decoders each convolve a corresponding one of a plurality of transducer elements constituting a transducer element array of an ultrasound probe with an impulse response waveform, while varying a filter coefficient corresponding to time side lobes for each transmission event. A succeeding decoder stores, in a memory, a reception beam signal that is output from a reception beam former. When a new reception beam signal is output, the succeeding decoder performs delay-and-sum on the new reception beam signal and the reception beam signal, which has been output immediately before the new reception beam signal and is stored in the memory.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Ultrasound signal processing device, ultrasound diagnostic device, and ultrasound signal processing method
InactiveUS20180055486A1Easy to useReduce in quantityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationMeasurement point
Ultrasound signal processing device performing transmission events of transmitting converging ultrasound beams to subject using ultrasound probe having transducer elements, receiving ultrasound reflection from the subject, generating acoustic line signal, and including ultrasound signal processing circuitry configured to operate as: transmitter varying focal point defining position where ultrasound beams converge between transmission events and performing each transmission event; receiver generating, for each transmission event, receive signal sequences for the transducer elements based on ultrasound reflection; and delay-and-sum calculator generating acoustic line signal for each measurement point by performing processing for specifying measurement point signal for each transmission event and performing weighted delay-and-summing of measurement point signals for the transmission events, the processing including identification of transducer element on straight line passing through the measurement point and the focal point and specification of, as the measurement point signal, receive signal for the transducer element from the sequence for the transducer element.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Doped multi-rate spread spectrum composite code
ActiveUS7526010B1Preserve energyAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringParallel computingExclusive or
A composite code is made for example by exclusive-OR'ing each real element of a first constituent code A with each element of a second constituent code B to obtain a basic composite code. To suppress autocorrelation, differing numbers of doping code elements are inserted between code segments made from combining each element of code A with an element of code B. A matched filter first stage removes from its input the A code and any doping code added to it, summing the elements of code A. A matched filter second stage removes from its input the B code and any doping code added at the second level. The summed elements of code B are the input to the first stage. Optionally, the summed elements of the doping code at any level may be delayed and summed with the elements of the A code in the first stage.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
Subject information obtaining apparatus, subject information obtaining method, and program
ActiveUS20140219060A1Reduce the impactReduce impactUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsEngineeringDelay and sum
A subject information obtaining apparatus according includes: plurality of conversion elements configured to convert an elastic wave from a subject into a plurality of reception signals, a delay and sum unit configured to perform a delay and sum process by using the plurality of reception signals and output a plurality of scanning line signals, a scanning line synthesis unit configured to add the plurality of scanning line signals between adjacent scanning lines and output a plurality of synthesis scanning line signals, and an FDI adaptive processing unit configured to perform a frequency domain interferometry and an adaptive signal processing by using the plurality of synthesis scanning line signals and obtain a power intensity distribution.
Owner:CANON KK
Ultrasound Diagnostic Apparatus and an Ultrasound Signal Processing Method
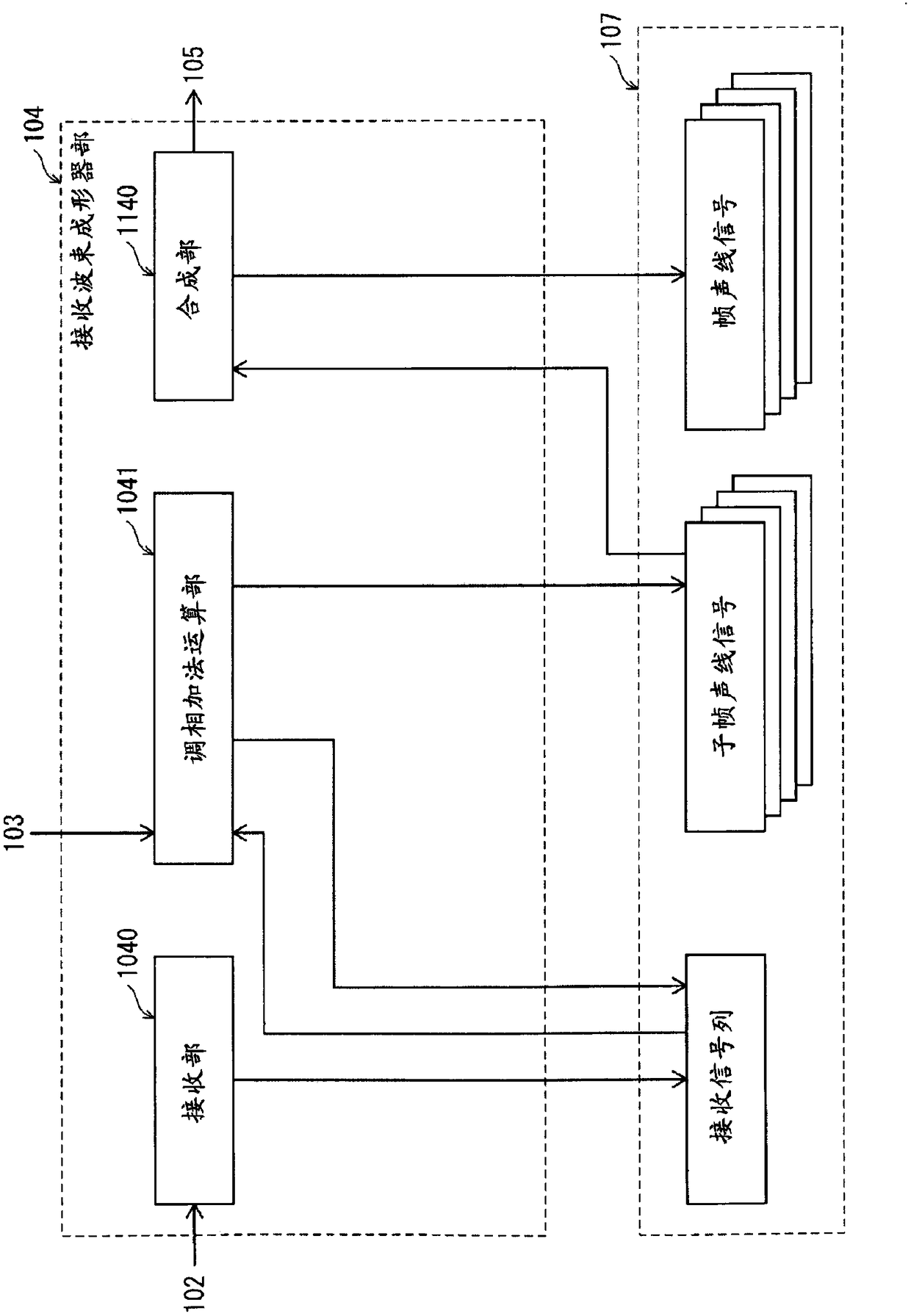
ActiveUS20180303461A1Reduce the amount of calculationPrevent degradationOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsRe sequencingSonification
An ultrasound diagnostic apparatus that transmits an ultrasound beam using an ultrasound probe including transducers and generates acoustic line signal subframe data, includes: a transmitter that causes transmission transducer arrays to transmit the ultrasound beam; a receiver that generates a reception signal sequence; and a delay-and-sum part that performs delay-and-sum operation, wherein the receiver includes part receivers, the delay-and-sum part includes: part delay-and-sum parts that perform delay-and-sum to generate an acoustic line signal so as to generate acoustic line signal partial subframe data; part folding parts that extract an acoustic line signal sequence and arrange the acoustic line signals to generate acoustic line signal partial subframe folded data; a main summing part that sums the acoustic line signal partial subframe folded data to generate acoustic line signal subframe folded data; and a re-sequence part that re-sequences the acoustic line signals to generate the acoustic line signal subframe data.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Ultrasound signal processing device, ultrasound signal processing method, and ultrasound diagnostic device
ActiveCN108209971AReduce spatial resolutionReduce in quantityInfrasonic diagnosticsTomographyMeasurement pointImage resolution
The invention provides an ultrasound signal processing device that enables reducing delay-and-sum computation amount in a synthetic aperture method utilizing converging-type transmission beam formingwhile suppressing decrease in spatial resolution and S / N ratio, an ultrasound diagnostic device, and an ultrasound diagnostic method. The ultrasound signal processing device includes ultrasound signalprocessing circuitry that operates as: a transmitter that causes an ultrasound probe to transmit ultrasound beams to an ultrasound main irradiation area defined by two straight lines each connectinga focal point and a different end of a transmission transducer element array; a receiver that generates receive signal sequences; a delay-and-sum calculator that sets first and second target areas inthe ultrasound main irradiation area, and performs delay-and-summing of receive signal sequences based on ultrasound reflection from measurement points in the first and second target areas thereby togenerate sub-frame acoustic line signals, the first target area is an entirety of an area located at or shallower than a focal depth, the second target area is part of an area located deeper than thefocal depth; and a synthesizer that synthesizes sub-frame acoustic line signals to generate a frame acoustic line signal.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Object information acquiring apparatus
ActiveUS9364152B2Easy to useOrgan movement/changes detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionElectricityDelay and sum
Owner:CANON KK
Received data processing apparatus of photoacoustic tomography
ActiveUS9247923B2Increase speedOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostics using tomographyAcoustic waveDelay and sum
There is provided a received data processing apparatus of photoacoustic tomography including a minimum constitution unit data composition unit that sequentially reads receiving digital signals from first storage units and composes minimum constitution unit data of the acoustic wave of the minimum constitution units by performing a delay-and-sum processing. A second storage unit stores the minimum constitution unit data of the entire region of the specimen, and an image construction unit constructs an image of the specimen based on the minimum constitution unit data stored in the second storage unit. A control unit sequentially stores the minimum constitution unit data calculated by the minimum constitution unit data composition unit in the second storage unit and reads the stored minimum constitution unit data of the entire region of the specimen to transmit the minimum constitution unit data to the image construction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Measuring apparatus
ActiveUS9116225B2Improve imaging resolutionSimple structureOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsImaging processingSonification
Provided is a measuring apparatus, including: a moving mechanism for moving a probe in an elevation direction; a first delay and sum circuit for performing delay and sum of reception signals at individual positions along the elevation direction to output a first add signal; a signal extraction circuit for letting an output of the first delay and sum circuit to pass through delay circuits to output in parallel first add signals obtained at different positions; a second delay and sum circuit for performing delay and sum of the first add signals output from the signal extraction circuit to output a second add signal; and an image processing circuit for generating image data by using the second add signal. Accordingly, image resolution in the elevation direction may be improved with a simple structure without deteriorating an image obtaining speed in the measuring apparatus for obtaining an ultrasonic image.
Owner:CANON KK
Dual focusing beam forming method and device based on virtual array elements
ActiveCN102727256BIncrease the amount of informationHigh energyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImage resolutionUltrasonic imaging
The invention discloses a dual focusing beam forming method and device based on virtual array elements. The method comprises the following steps of: performing primary focusing by using a single fixed focus; calculating a delay parameter of secondary focusing by using the concept of the virtual array elements; and performing secondary focusing according to the principle of delay-and-sum (DAS) beam forming and the dynamic focusing technology to acquire finally imaged scanning line data. Dual focusing beam forming ultrasonic imaging is realized by introducing the virtual array element technology to an ultrasonic imaging system, using a DAS beam synthesis method and performing DAS twice. The method is characterized in that related valid information of a plurality of superposed sound fields is extracted by performing DAS twice, so that information quantity and energy of sound wave signals are increased, and the imaging effect is greatly improved. According to the method, two beam formers BF1 and BF2 and a first in first outlet (FIFO) buffer are used and DAS is performed twice, so that a large quantity of low-resolution echo data is not required to be stored.
Owner:CHONG QING BORN FUKE MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Eigenvalue decomposition-fused low-complexity minimum variance ultrasound imaging method
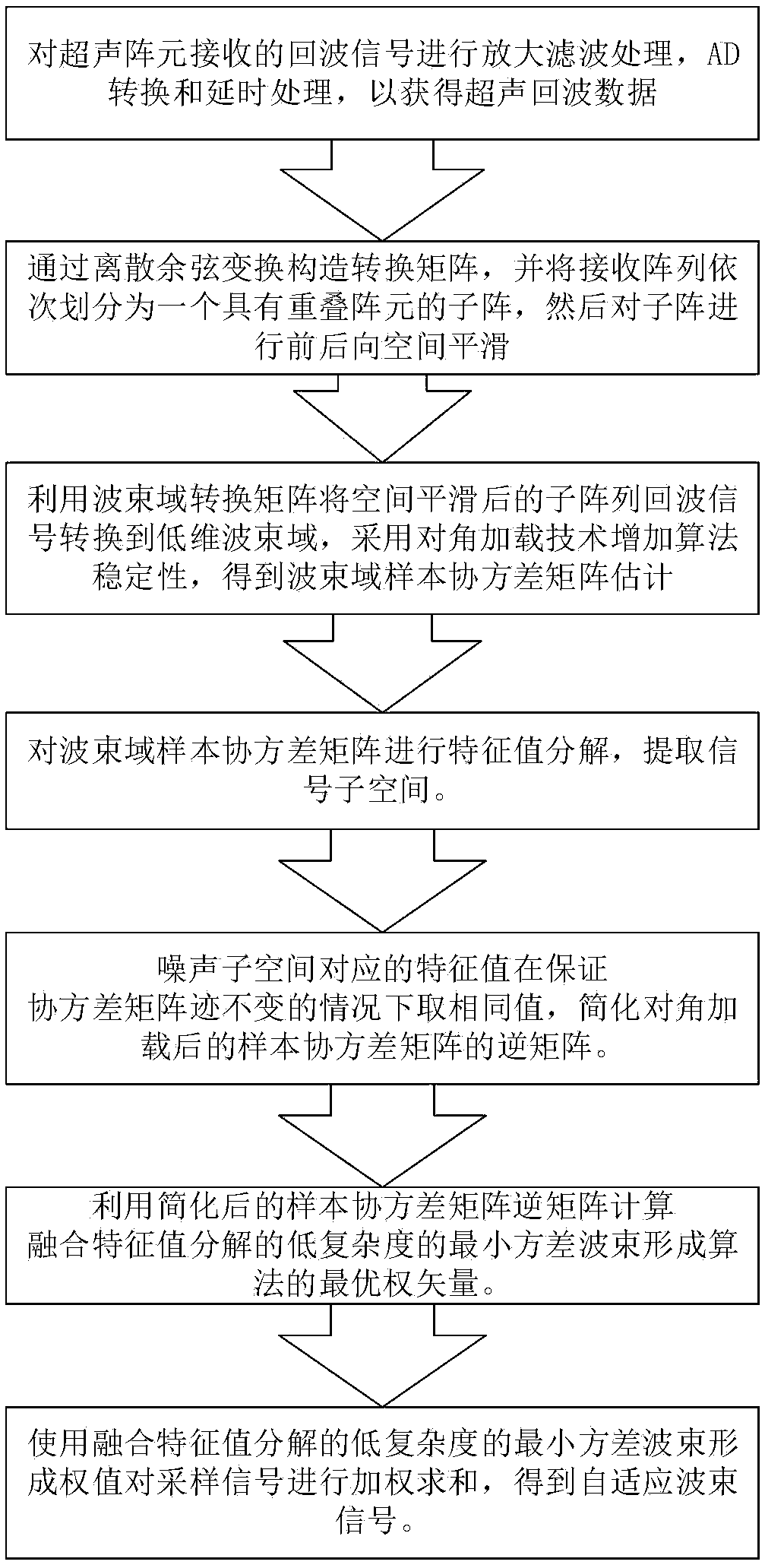
ActiveCN109187771AReduce complexityHigh-resolutionProcessing detected response signalSonificationDecomposition
The invention relates to an eigenvalue decomposition-fused low-complexity minimum variance ultrasound imaging method, and belongs to the field of ultrasound imaging. Firstly, echo data is converted toa beam domain with fewer dimensions by means of discrete cosine transform; and then a sample covariance matrix is subjected to eigenvalue decomposition to extract signal subspaces, a maximum eigenvalue and an eigenvector corresponding to the maximum eigenvalue are selected, remaining eigenvalues are the same value on the condition that it is guaranteed that a trace of the sample covariance matrixis invariable, and inversion of the matrix is simplified into multiplication of a vector. According to the algorithm, the operation time can be obviously shorter than that of an eigenvalue decomposition-based minimum variance algorithm, the good robustness is achieved on noise, and the imaging effect is obviously better than that of a traditional delay and sum algorithm, minimum variance algorithm and beam domain minimum variance algorithm.
Owner:STATE GRID EAST INNER MONGOLIA ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD MAINTENANCE BRANCH +1
Dual-microphone noise suppression method and system
The invention provides a double-microphone noise inhibiting method and system, and in particular relates to connection of the time-domain beam forming method and the frequency domain after-processing method. The method is that one delay-and-sum is added and treated as an assistant signal; whether to select the original path or add a new path is determined according to a voice activating detector. With the adoption of the method, that the large steady noise (fuzzy voice) included in voice cannot be treated in the traditional method can be avoided, the voice articulation and subjective feeling of the improved voice can be obviously improved.
Owner:MORNINGCORE HLDG CO LTD +1
Ultrasound diagnostic device and control method for the same
ActiveUS10080547B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationMeasurement point
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com