Ultrasound signal processing device, ultrasound signal processing method, and ultrasound diagnostic device
A signal processing device and ultrasonic technology, which are applied in ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosis, structure of ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosis equipment, and sonic diagnosis, etc. The problem of poor ultrasonic utilization efficiency, etc., achieves the effect of reducing the amount of calculation and the number of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0041]
[0042] Hereinafter, the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus 100 according to Embodiment 1 will be described with reference to the drawings.
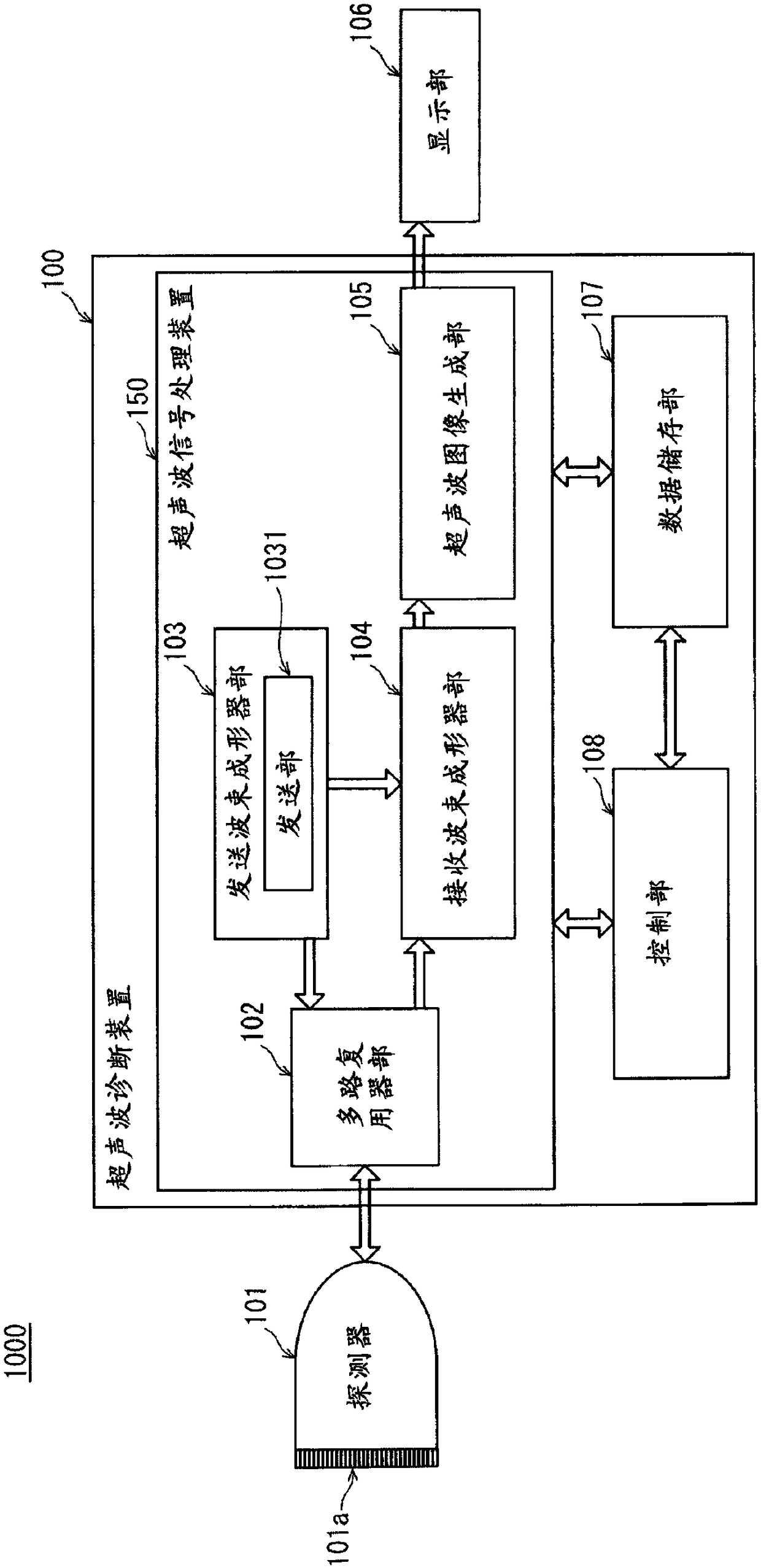
[0043] figure 1 It is a functional block diagram of the ultrasonic diagnostic system 1000 according to the first embodiment. Such as figure 1 As shown, the ultrasonic diagnostic system 1000 has: a probe 101, which has a plurality of vibrators 101a that transmit ultrasonic waves toward the subject and receive their reflected waves; The output signal of 101 generates an ultrasonic image, and the display unit 106 displays the ultrasonic image on the screen. The probe 101 and the display unit 106 are respectively configured to be connectable to the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus 100 . figure 1 A state in which the probe 101 and the display unit 106 are connected to the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus 100 is shown. In addition, the probe 101 and the display unit 106 may be located inside the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus 100 . ...
example 1
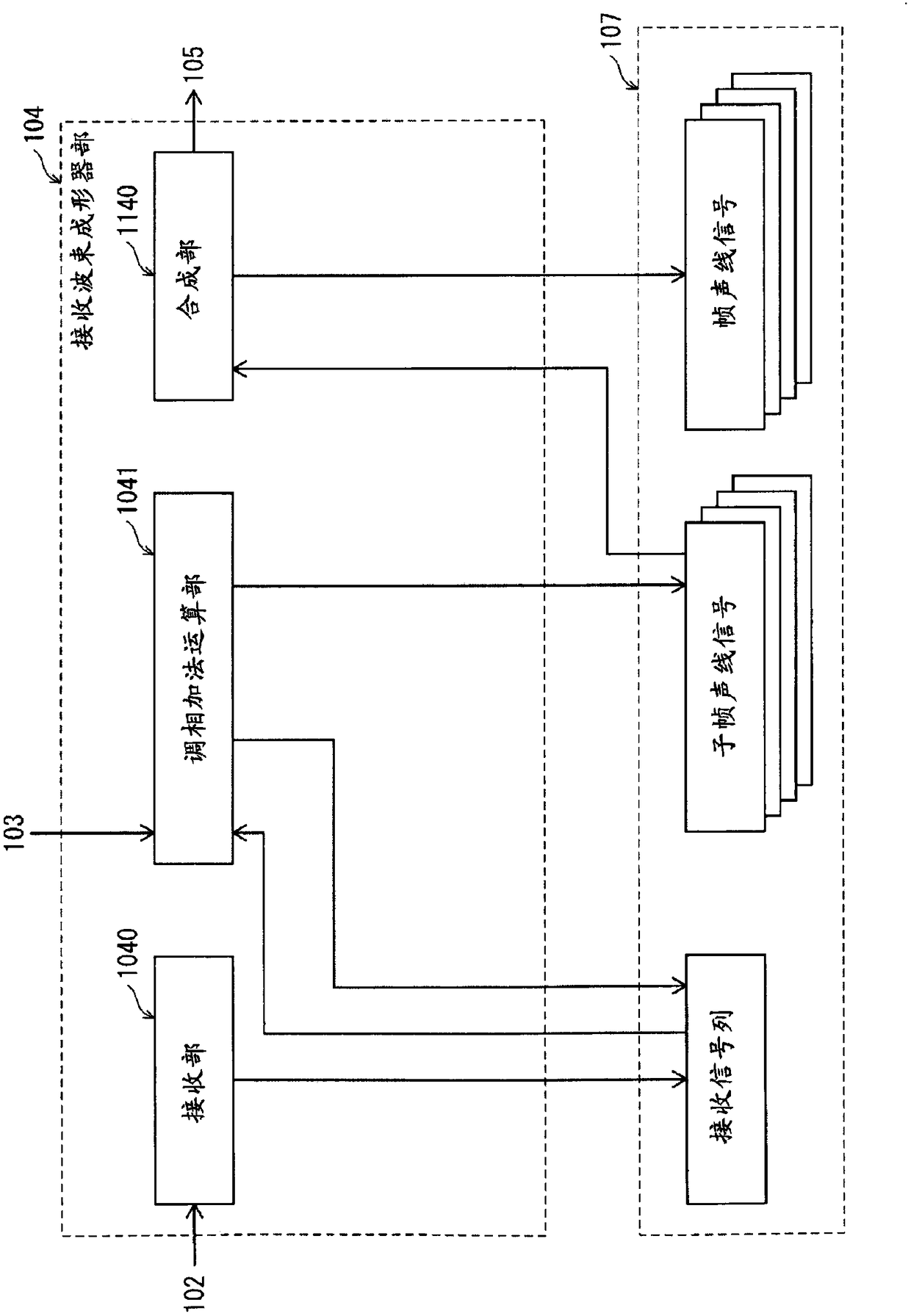
[0148] In the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus 100 according to Embodiment 1, the receiving aperture setting unit 1043 is configured to select the receiving aperture Rx so as to match the transducer whose column center is spatially closest to the observation point P. However, the reception aperture Rx can be calculated based on the total propagation time until the ultrasonic wave transmitted from the transmission aperture Tx is reflected at the observation point Pij in the target area Bx via the transmission focus F and reaches the reception transducer Rk of the reception aperture Rx. It is only necessary to generate sound ray signals for all observation points Pij in the target area Bx by controlling the delay of the propagation path, so the configuration of the receiving aperture Rx can be appropriately changed.
[0149] Modification 1 differs from Embodiment 1 in that it includes a transmission-synchronous reception aperture setting unit (hereinafter referred to as “Tx recept...
example 2
[0160] In the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatuses of Embodiment 1 and Modification 1, the shape of the second target region Bx2 is narrowed by n times in the column direction relative to the similar shape of the first target region Bx2 (1>n>0). shape. However, the shape of the second object area Bx may be the following patterns other than this.
[0161] Figure 17 A first setting example of the second target area Bx2 of Modification 2 is shown. Such as Figure 17 As shown, the second target area Bx2 is a portion corresponding to the inner side of a rectangle whose base is the transmission opening Tx, among the deeper than focus portions in the ultrasonic main irradiation area Ax. Therefore, when the depth of focus is Df, the shape overlaps with the first target region Bx1 within the range of depth from Df to 2×Df. On the other hand, the region whose depth is deeper than 2×Df is a strip-shaped region whose width in the column direction matches the width of the transmission op...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com