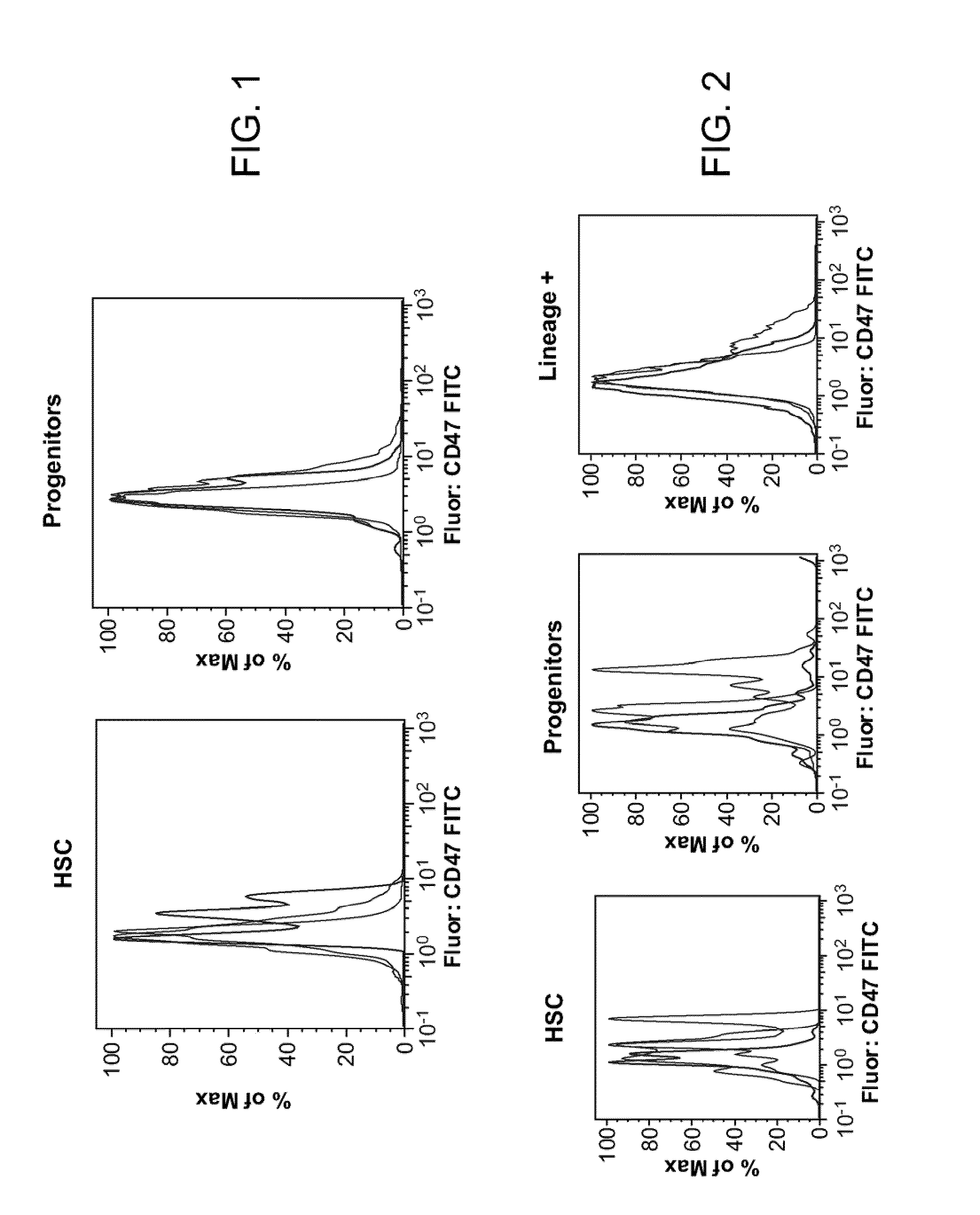
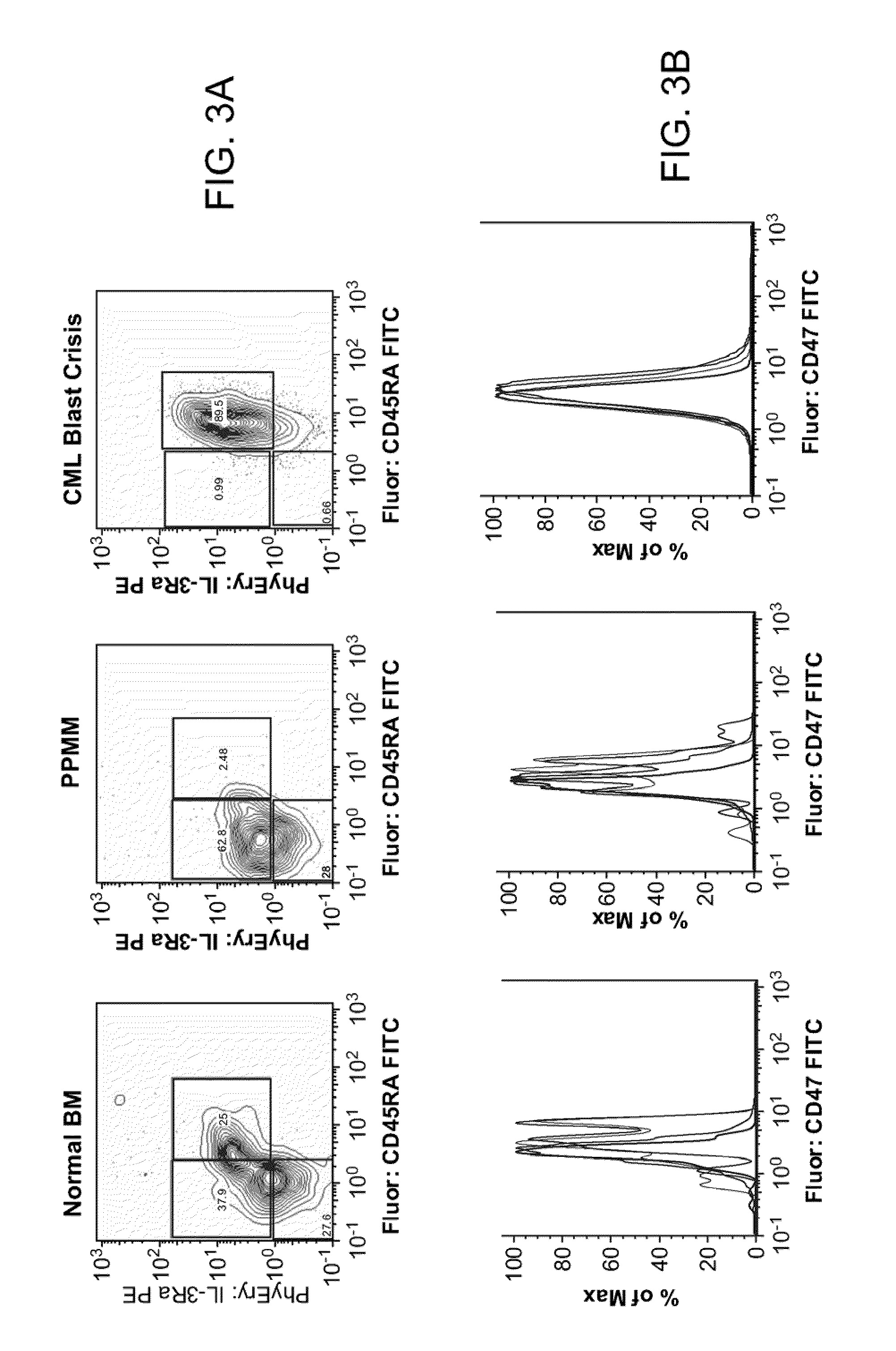
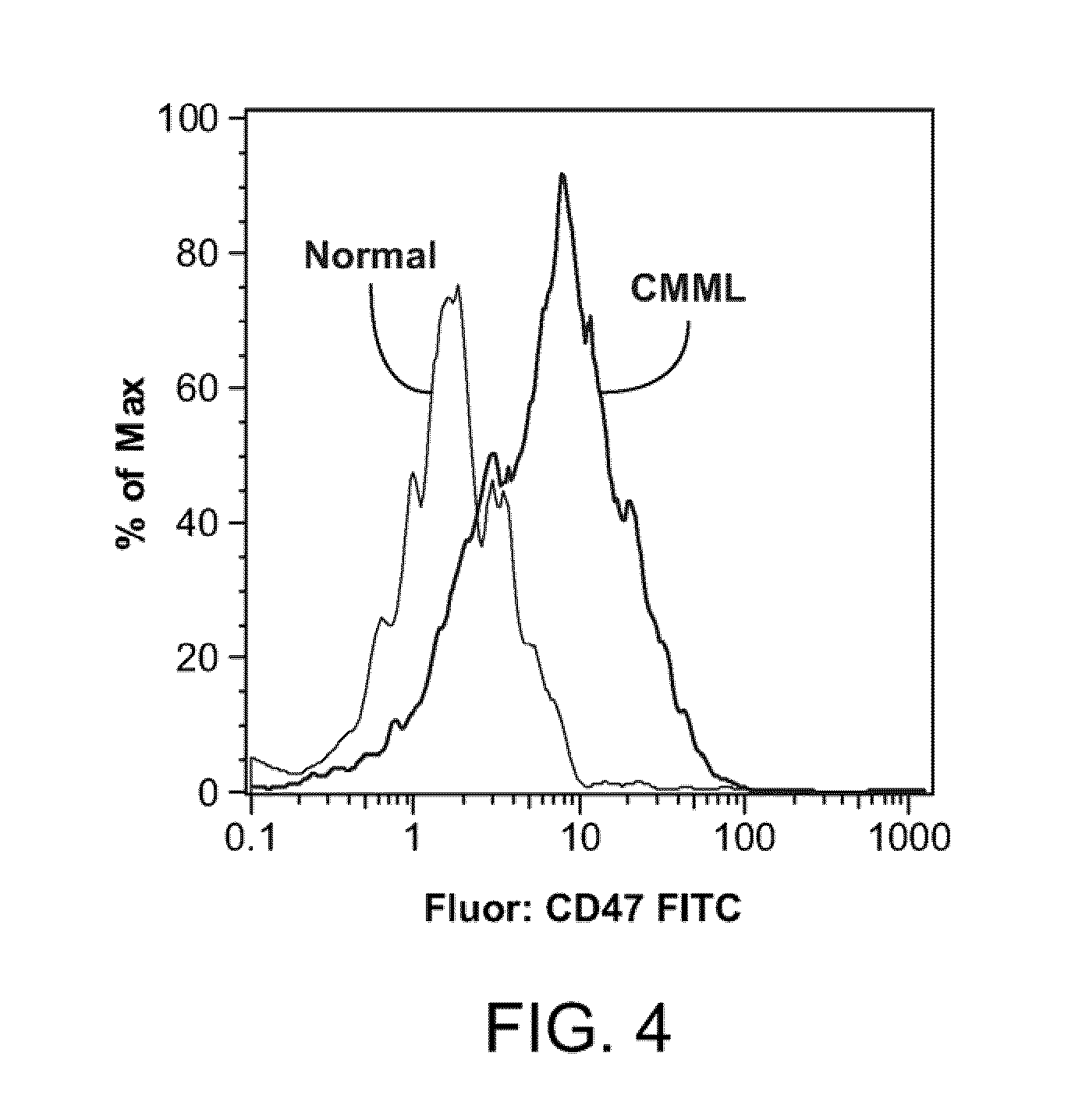
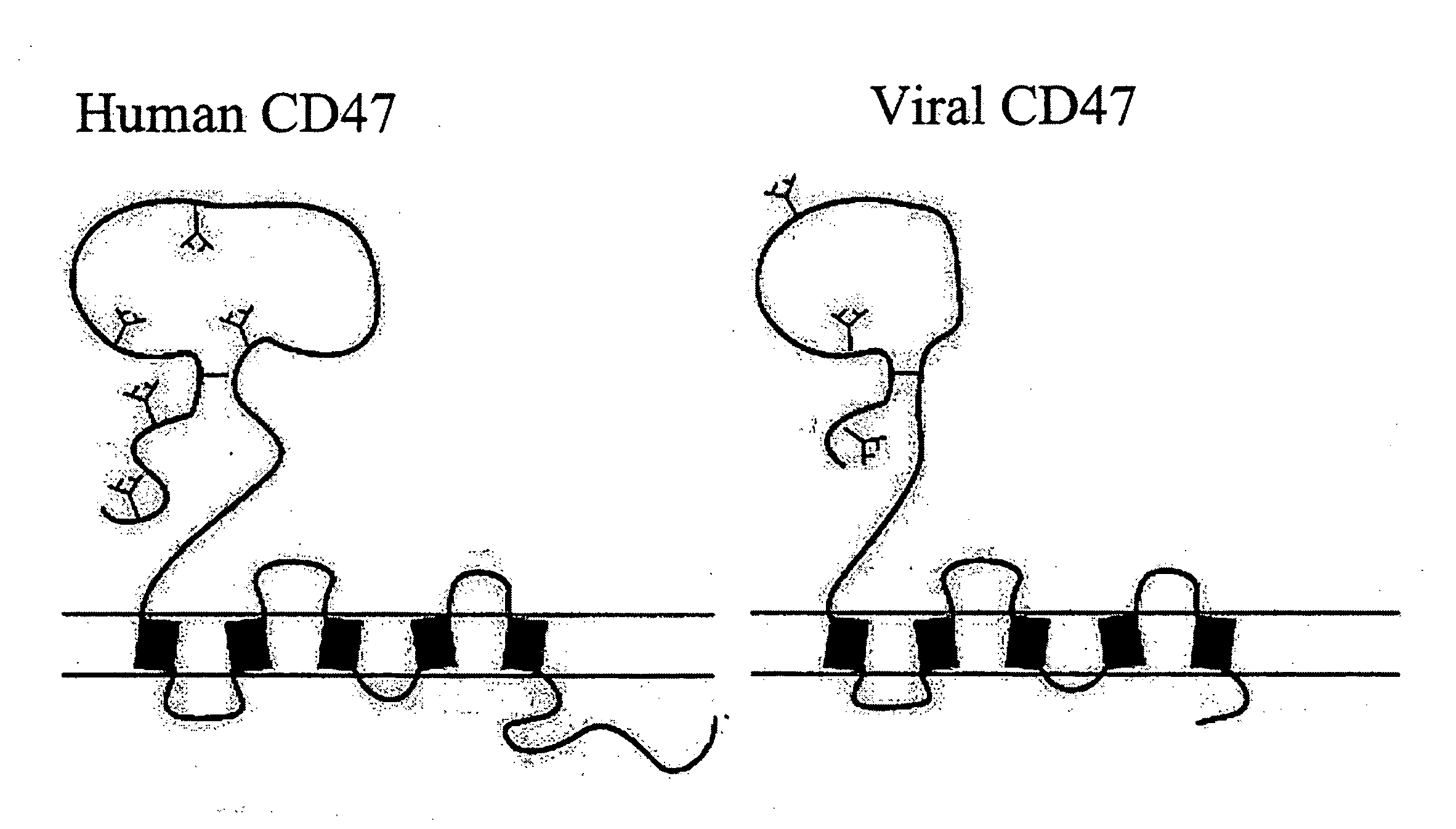
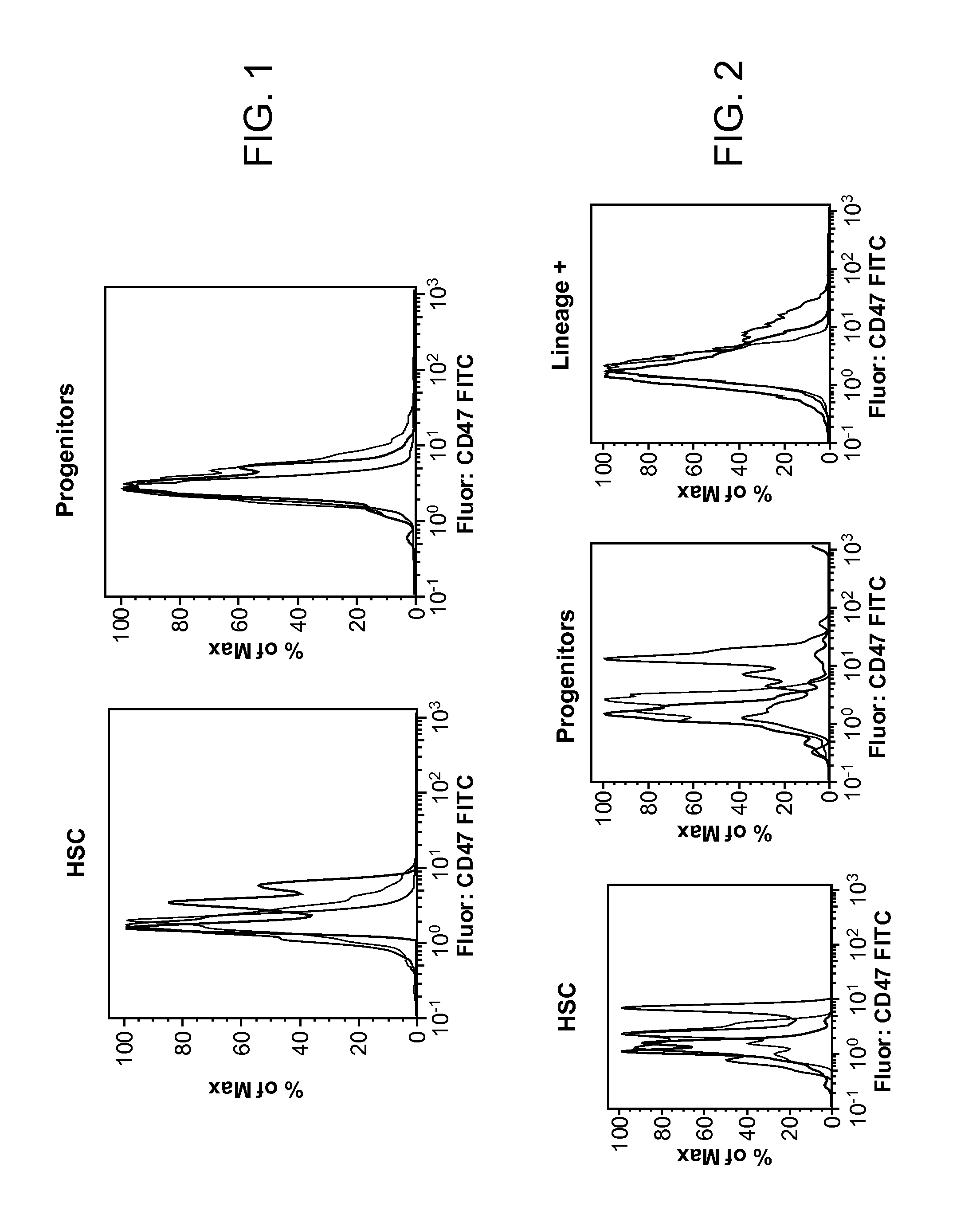
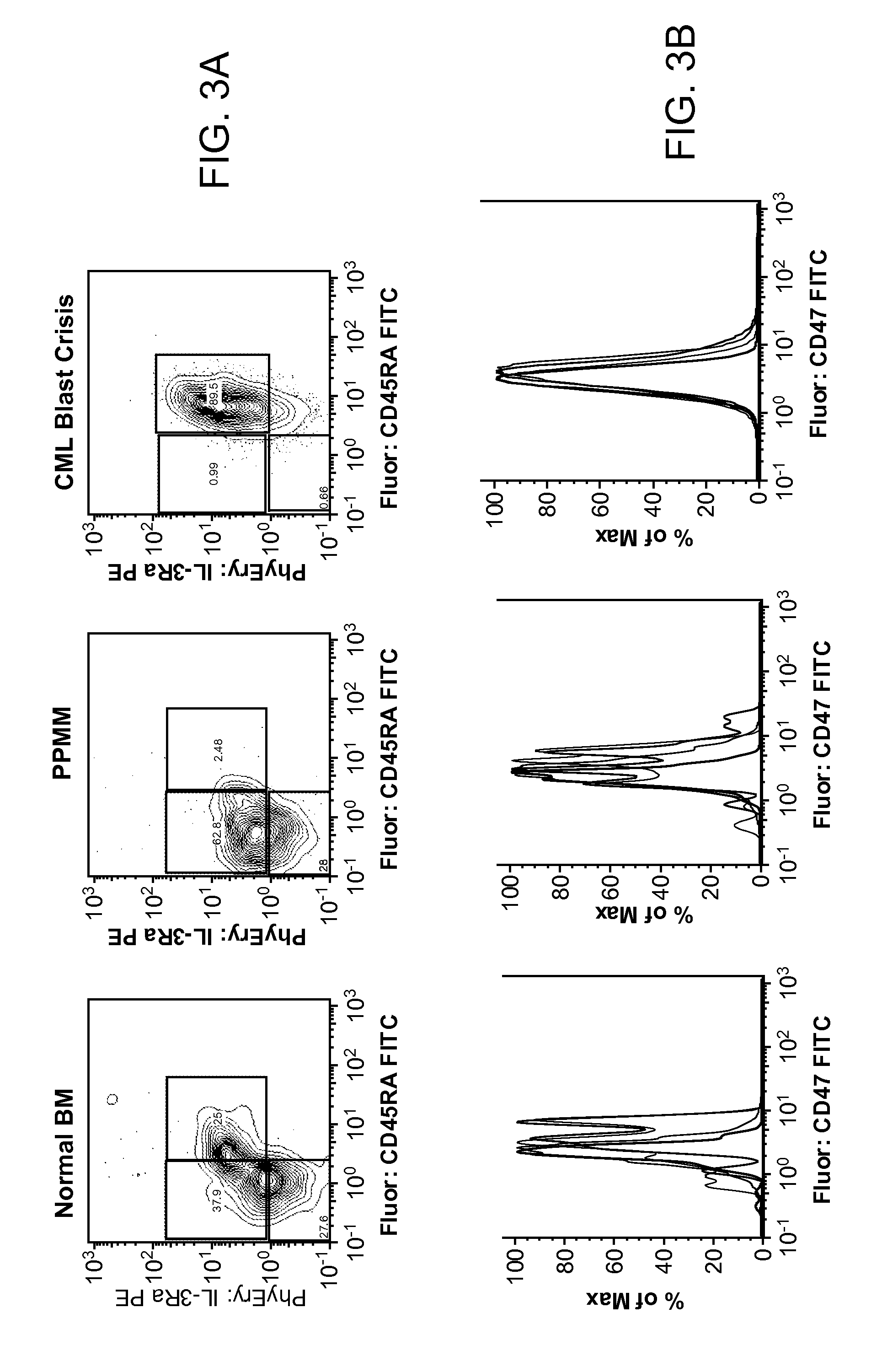
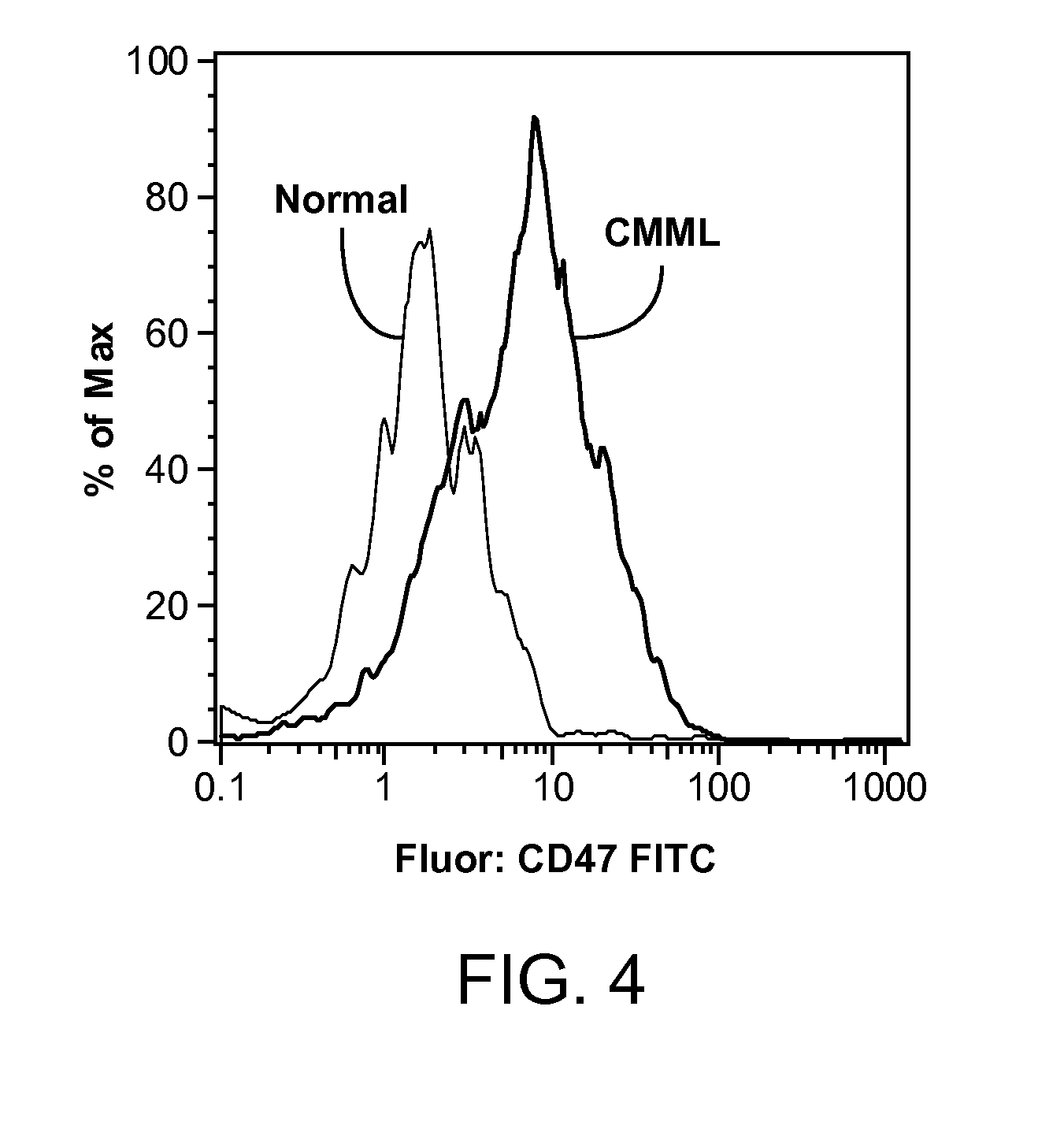
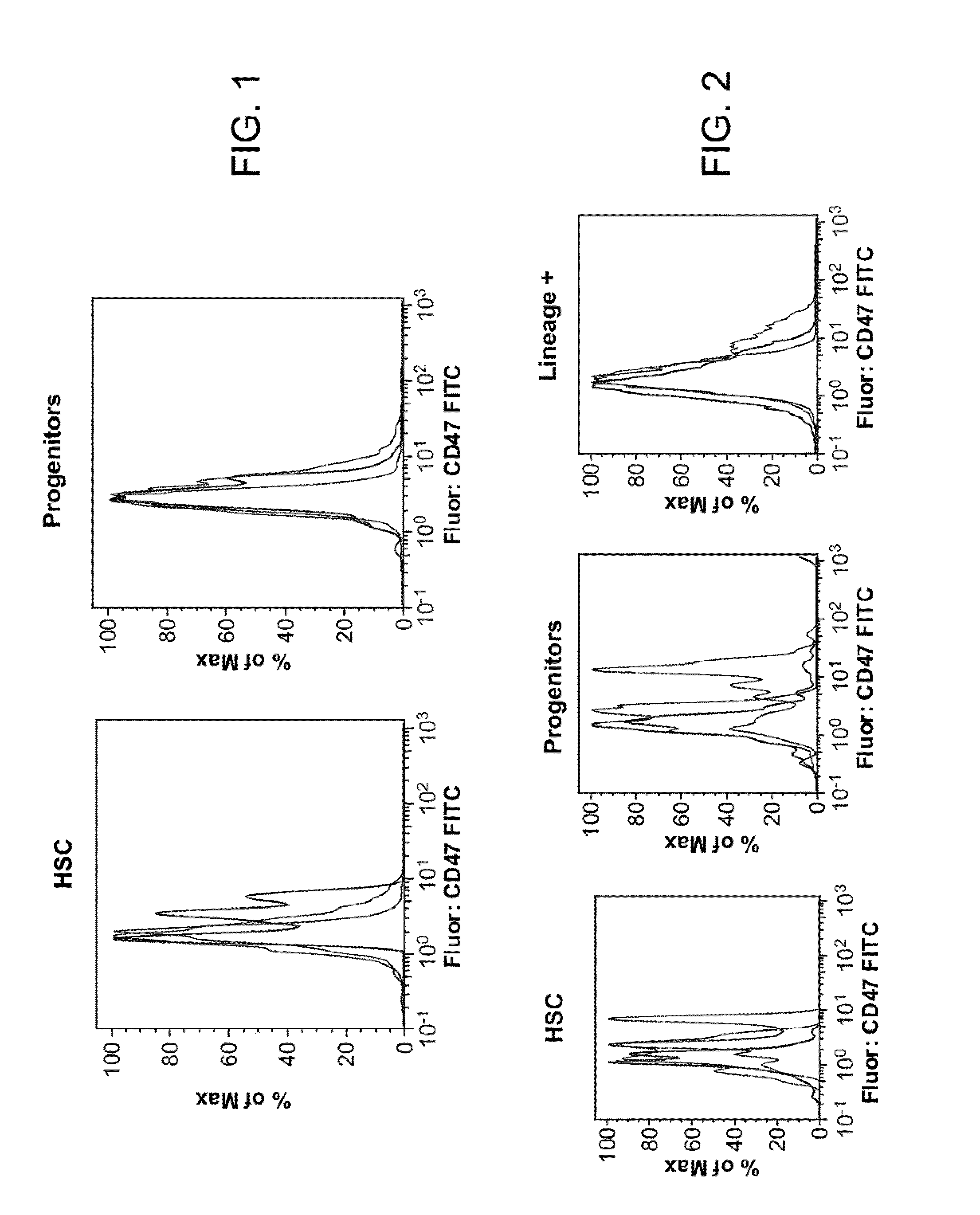
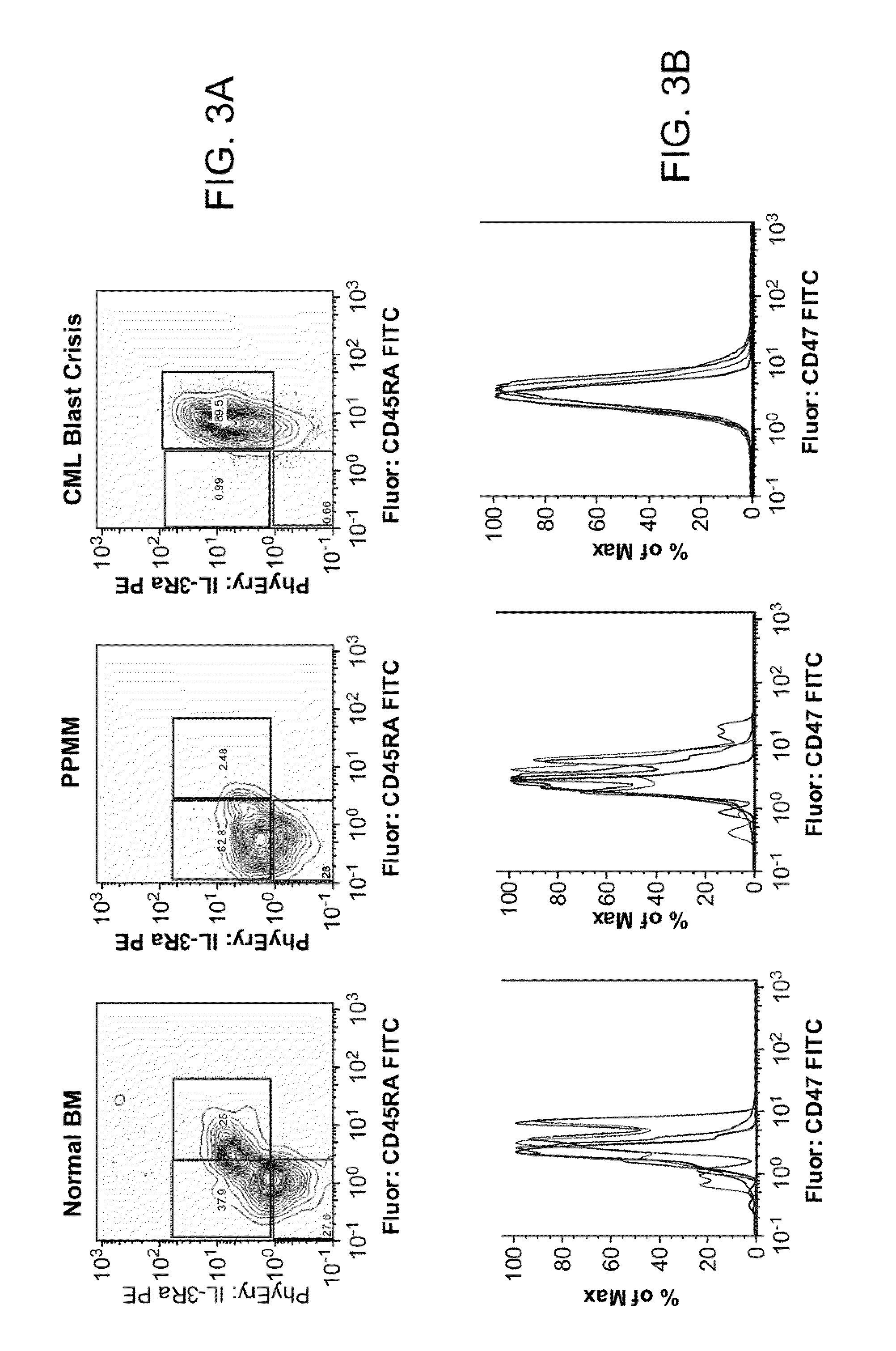
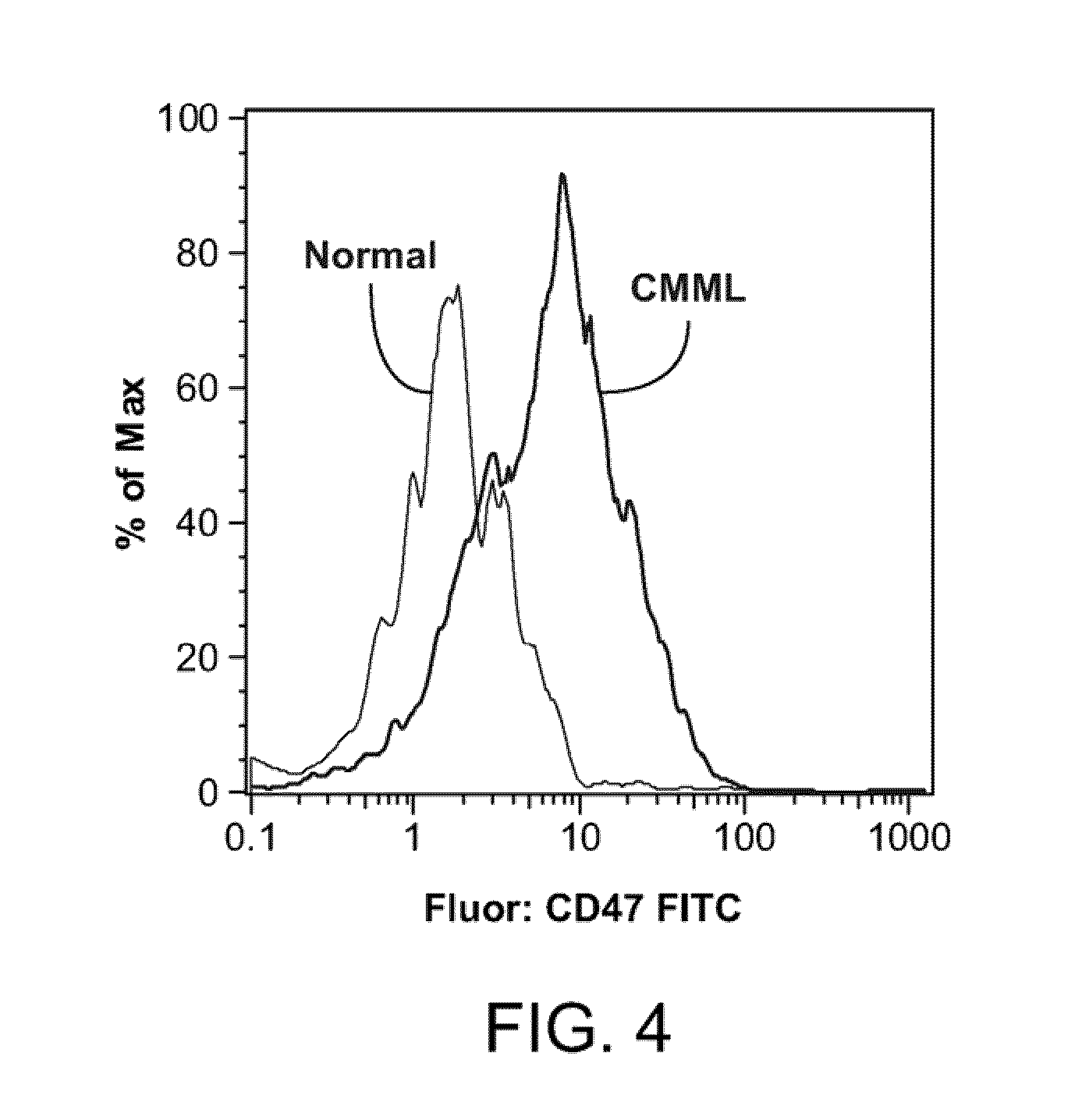
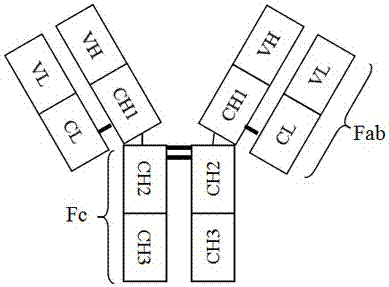
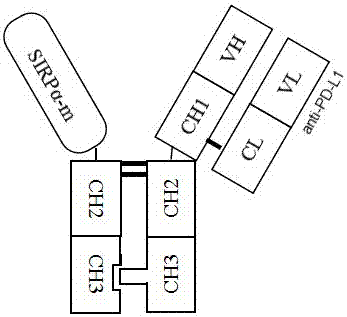
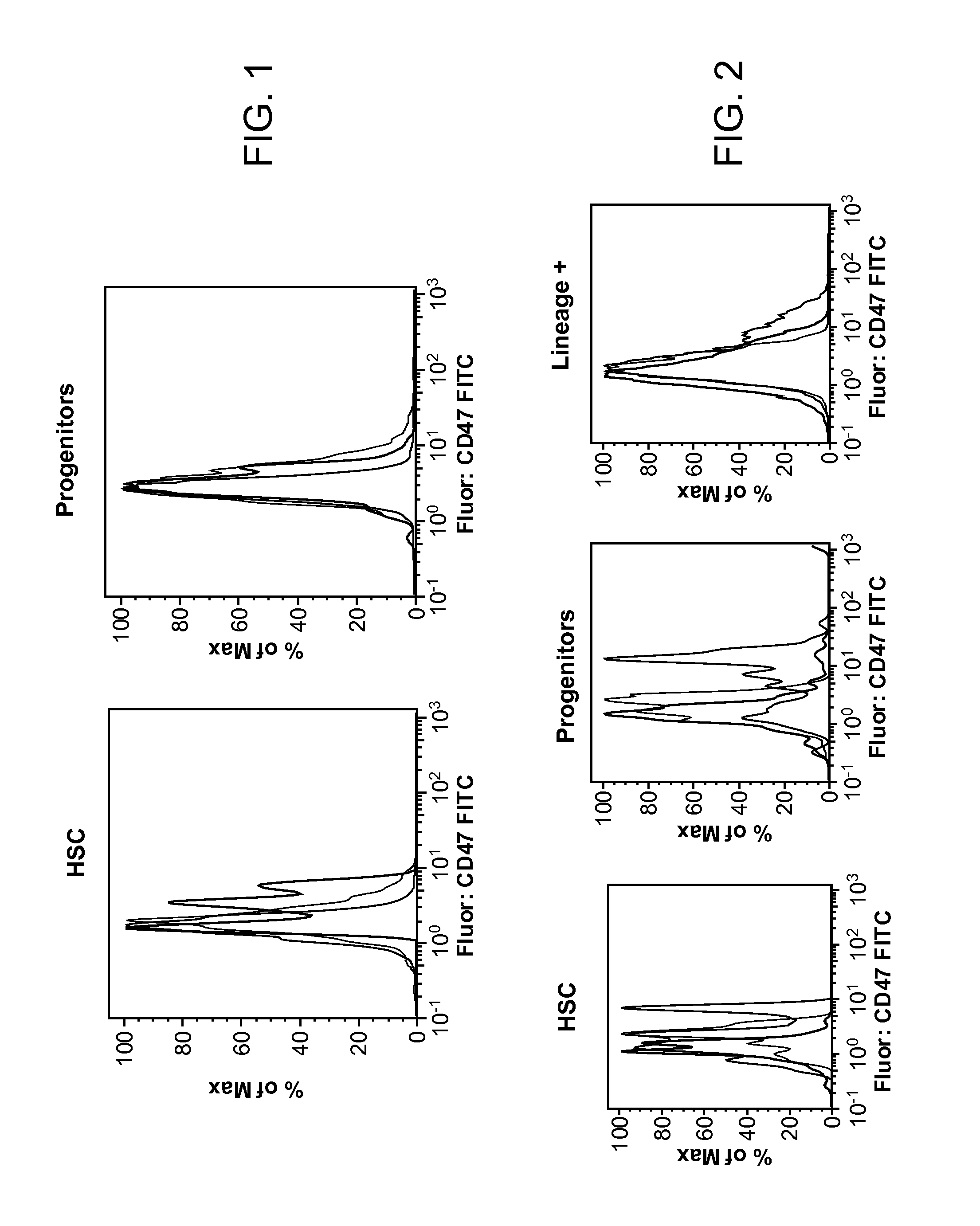
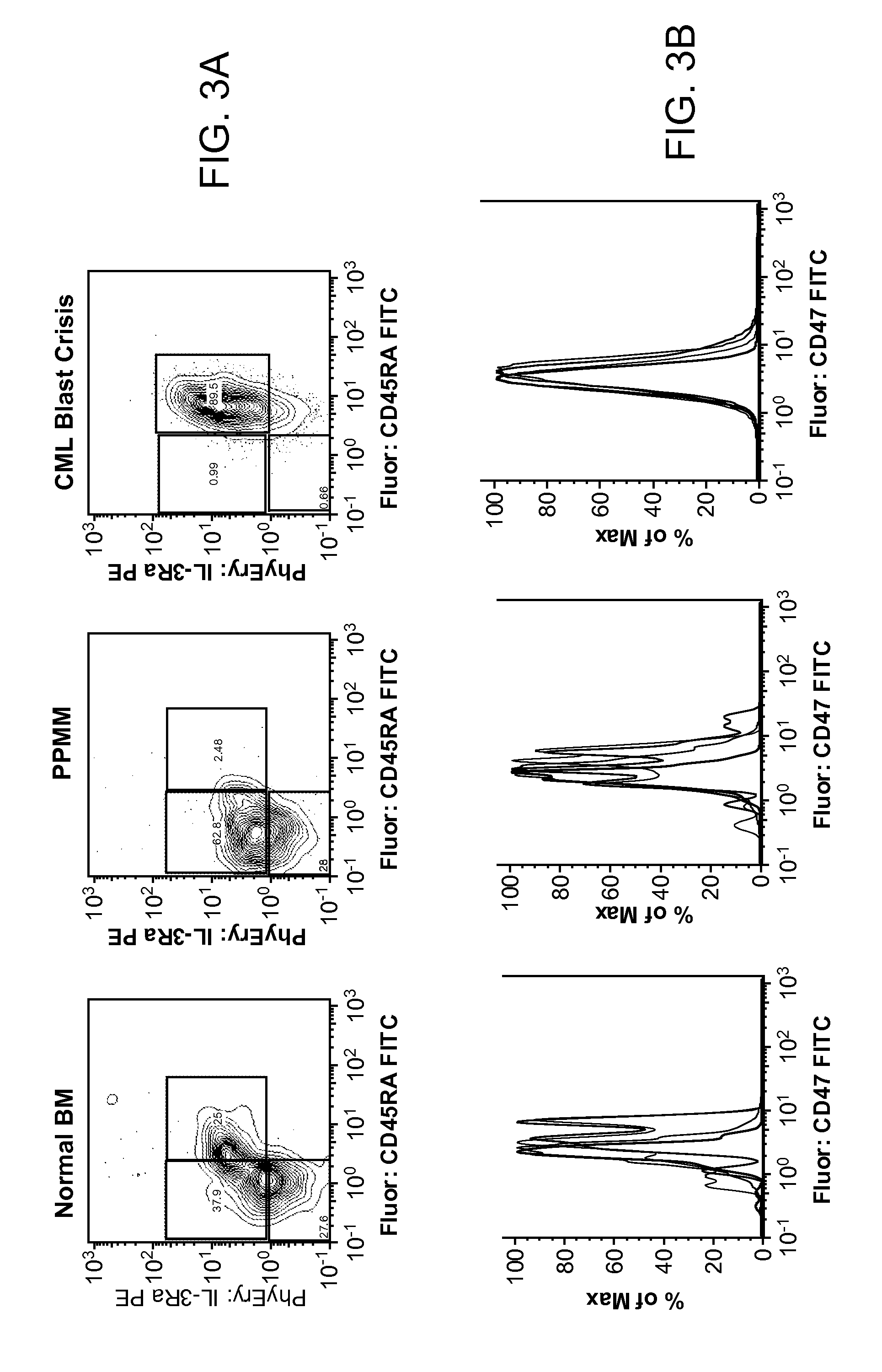
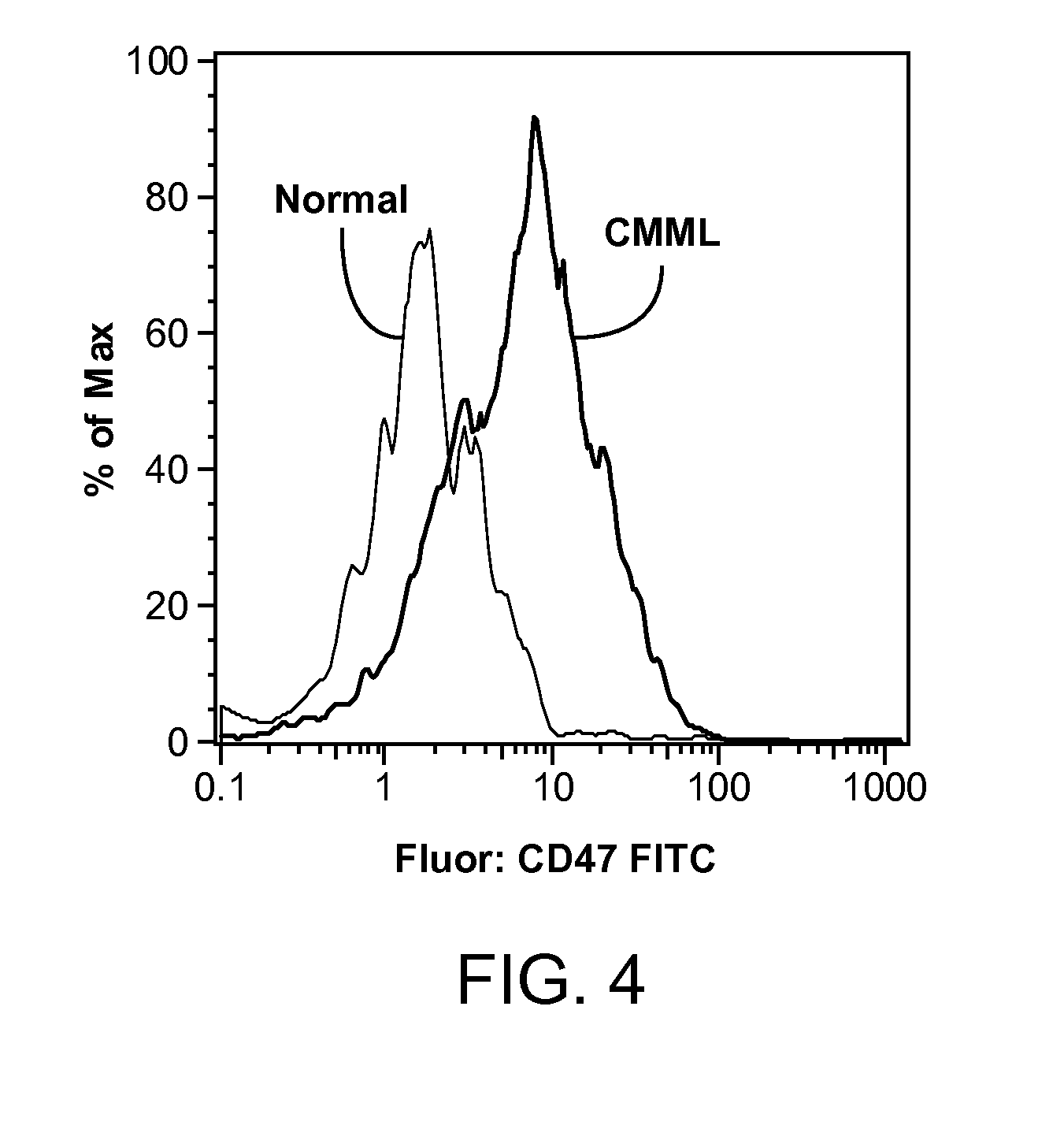
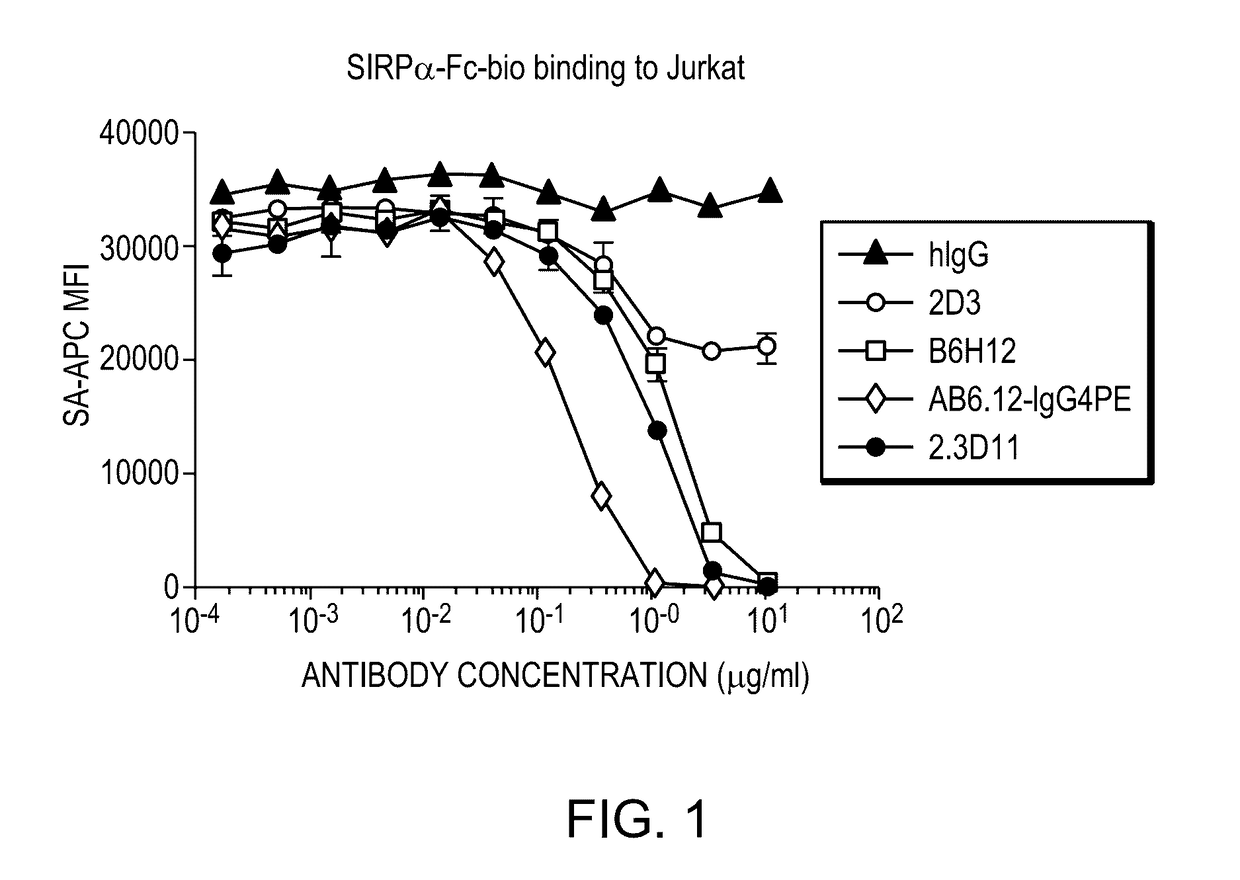
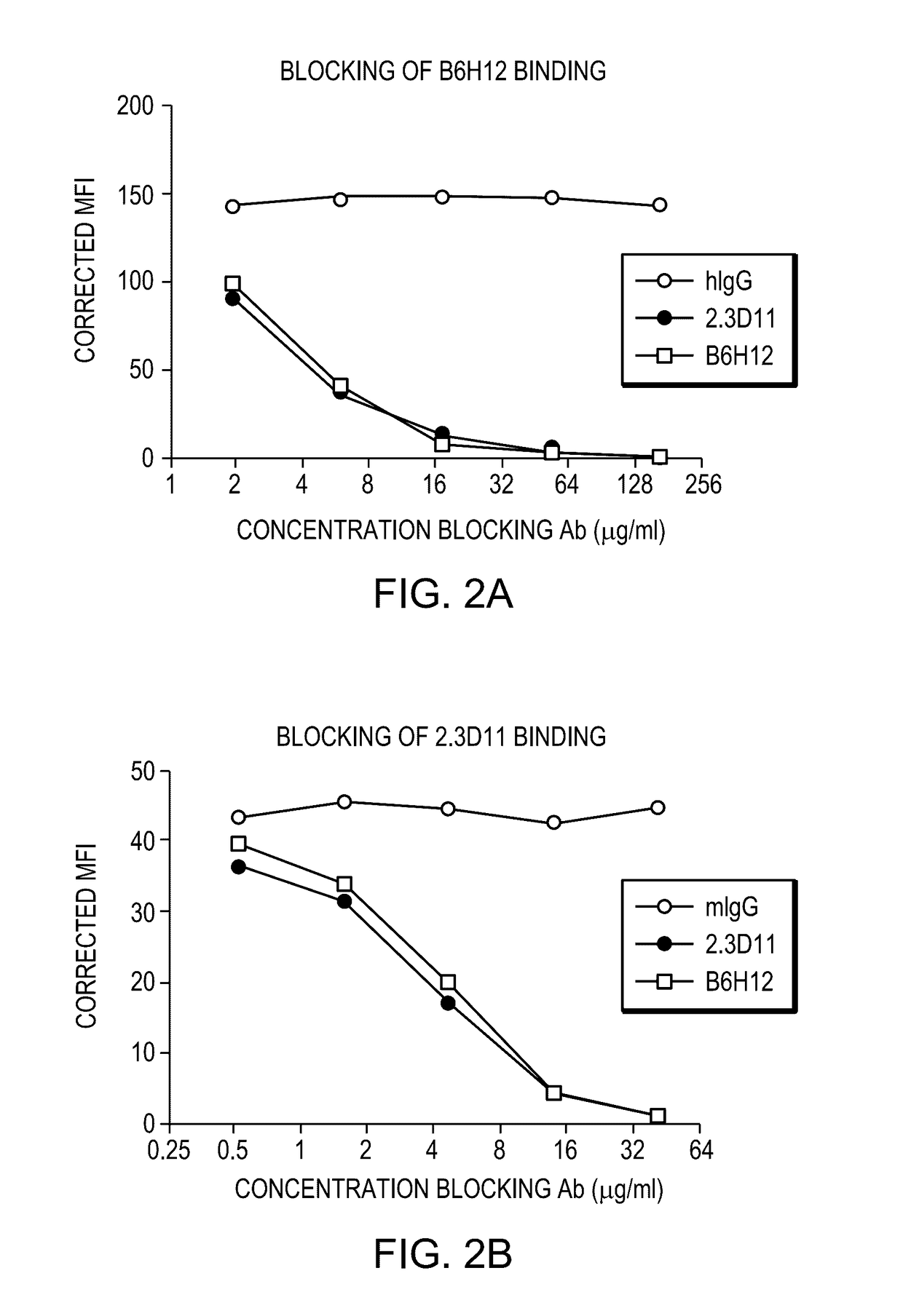
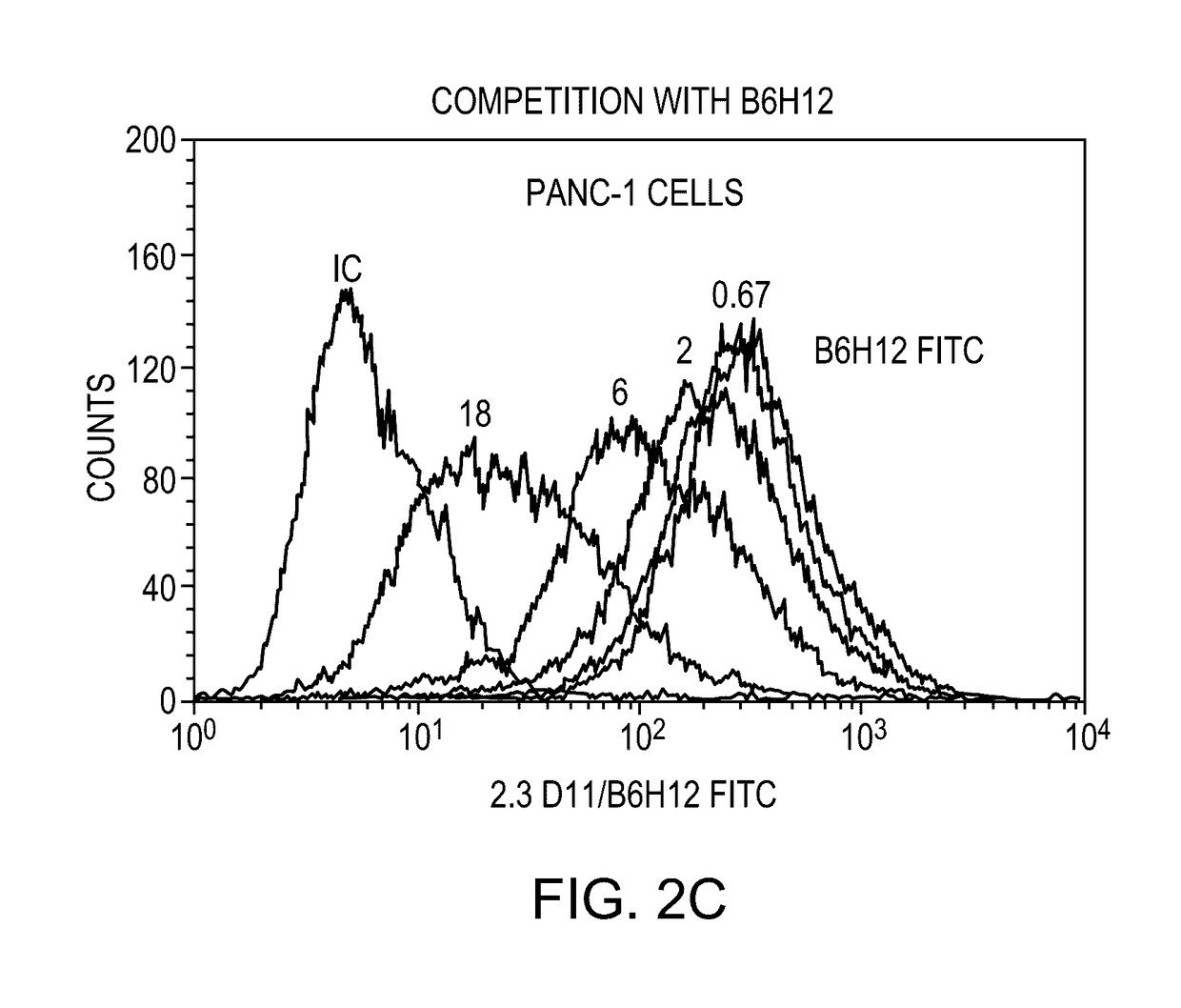
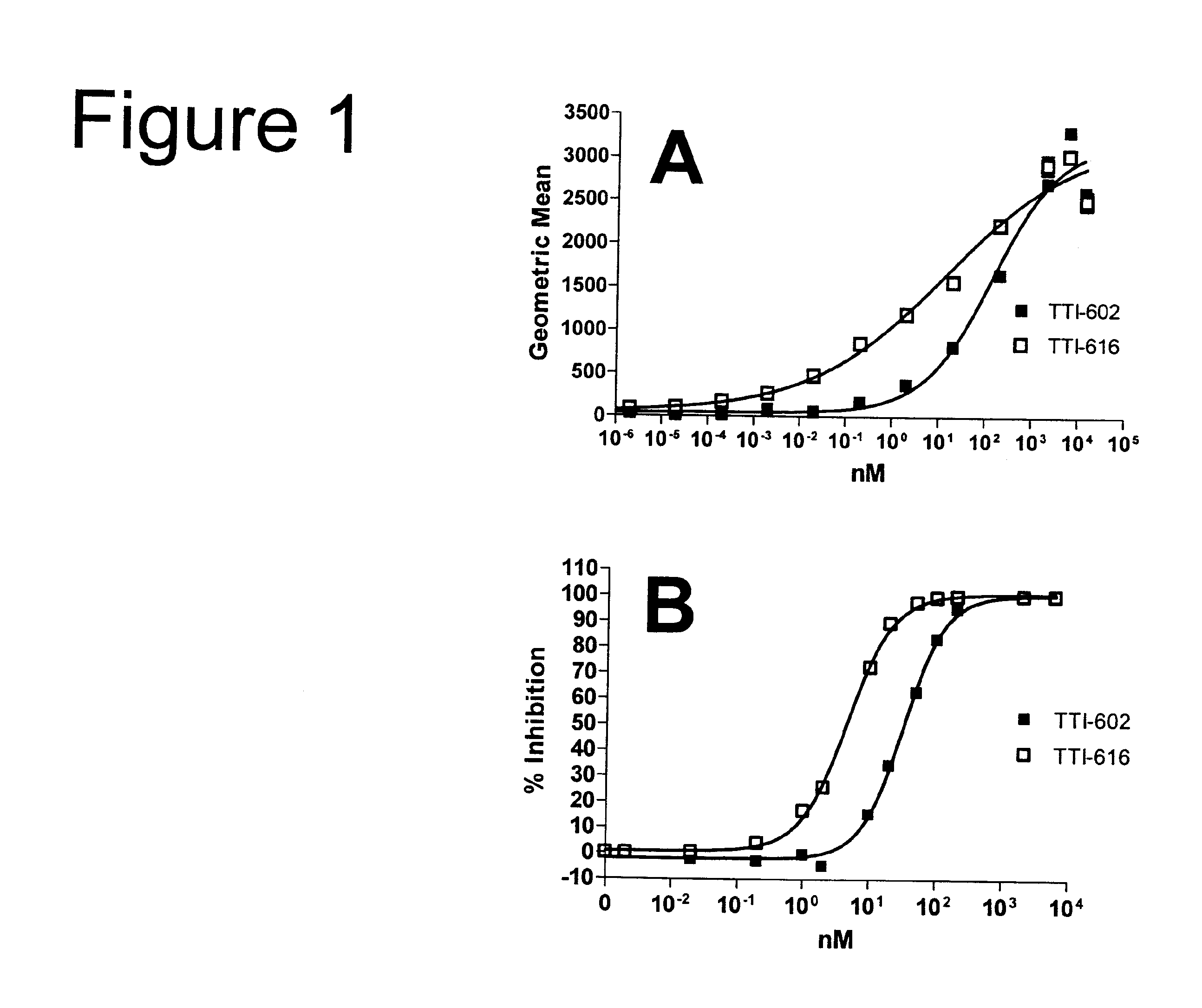
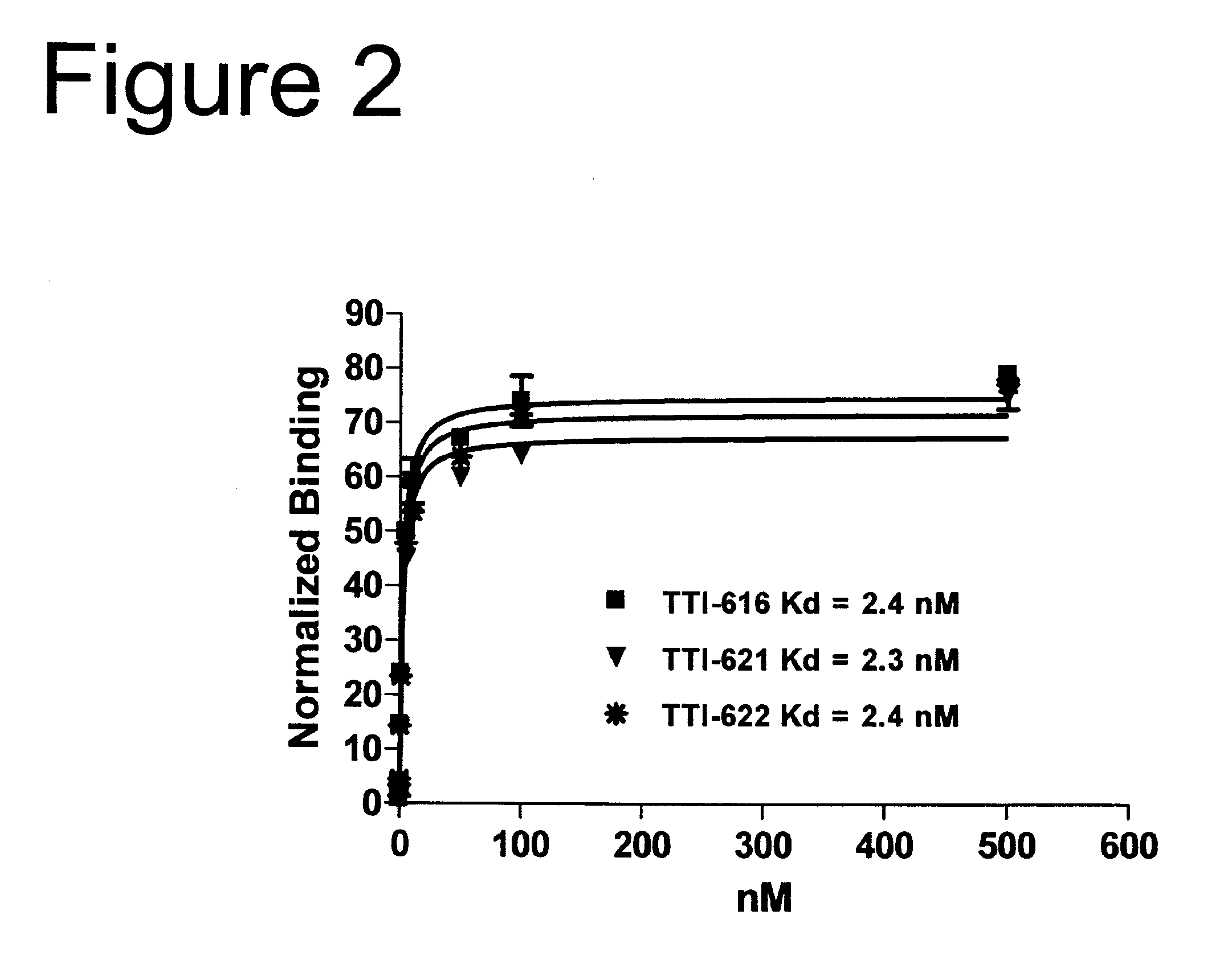
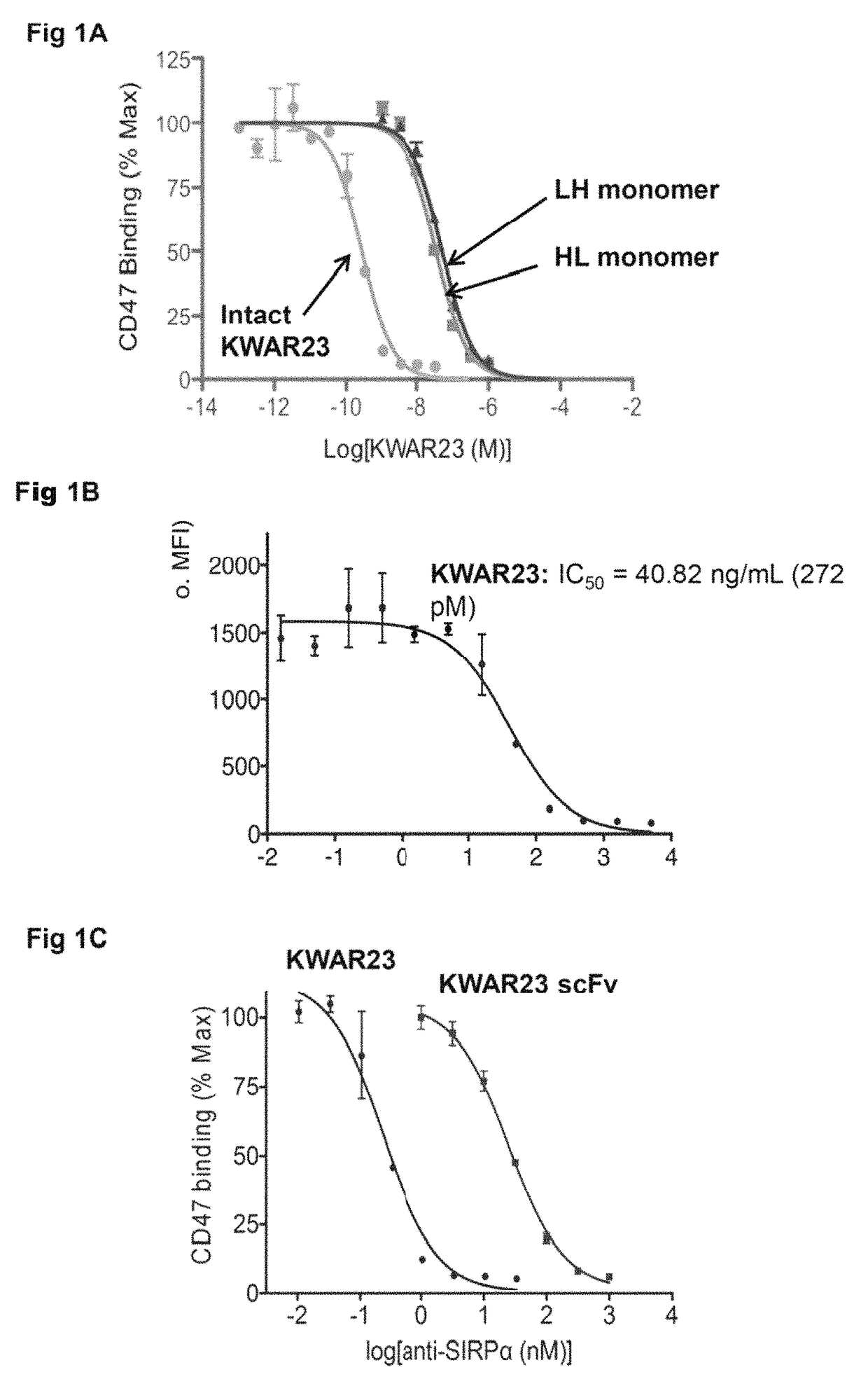
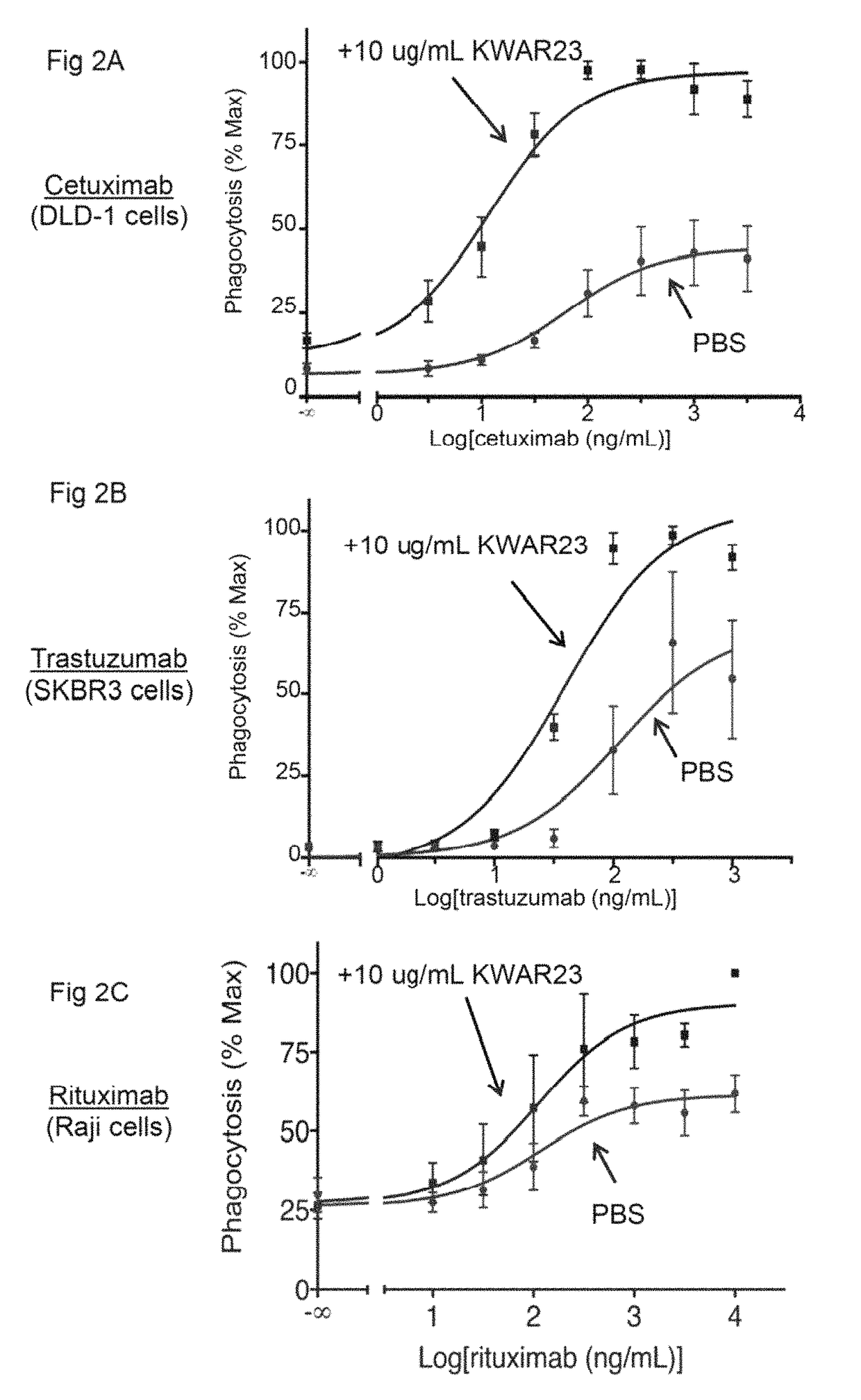
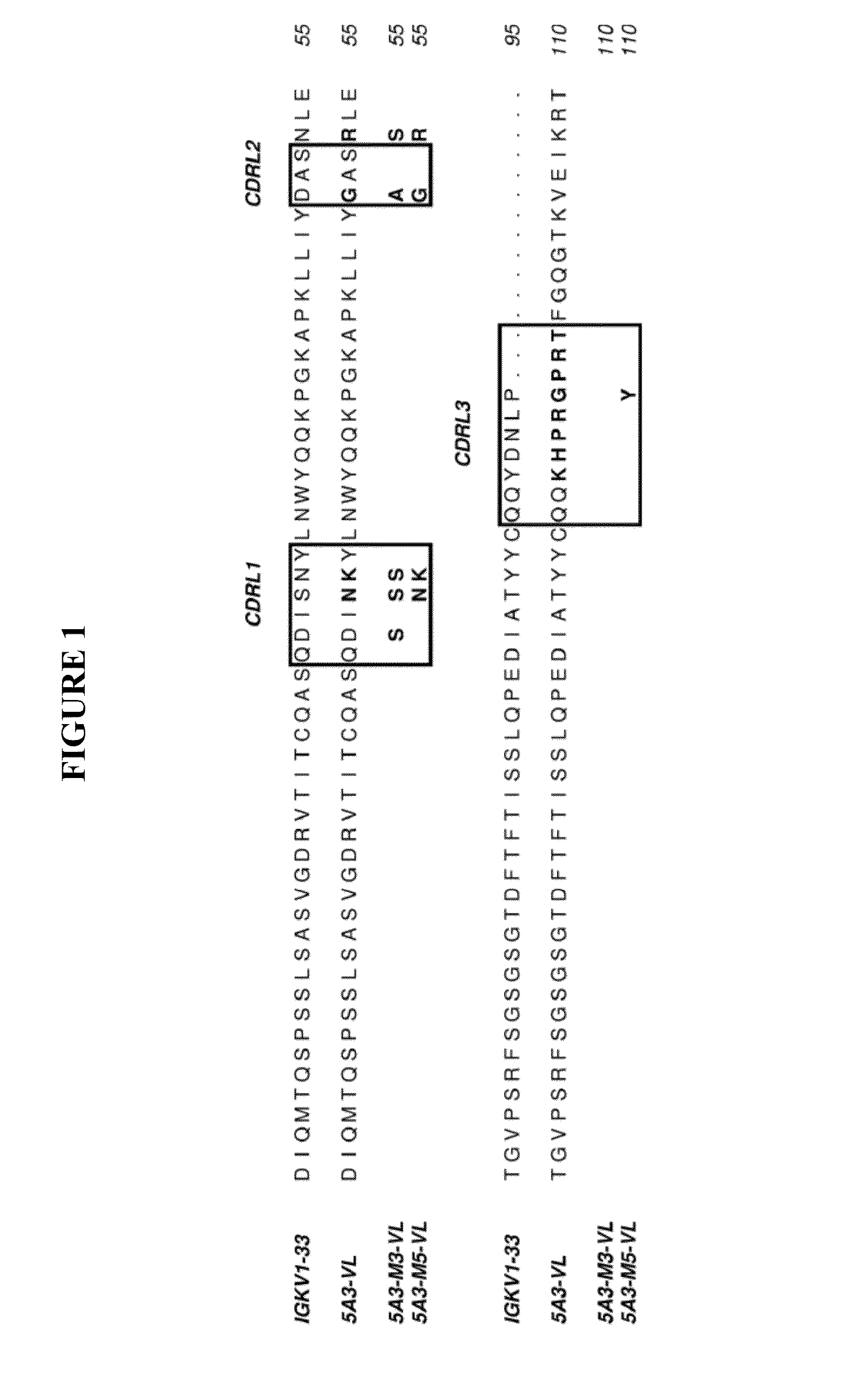
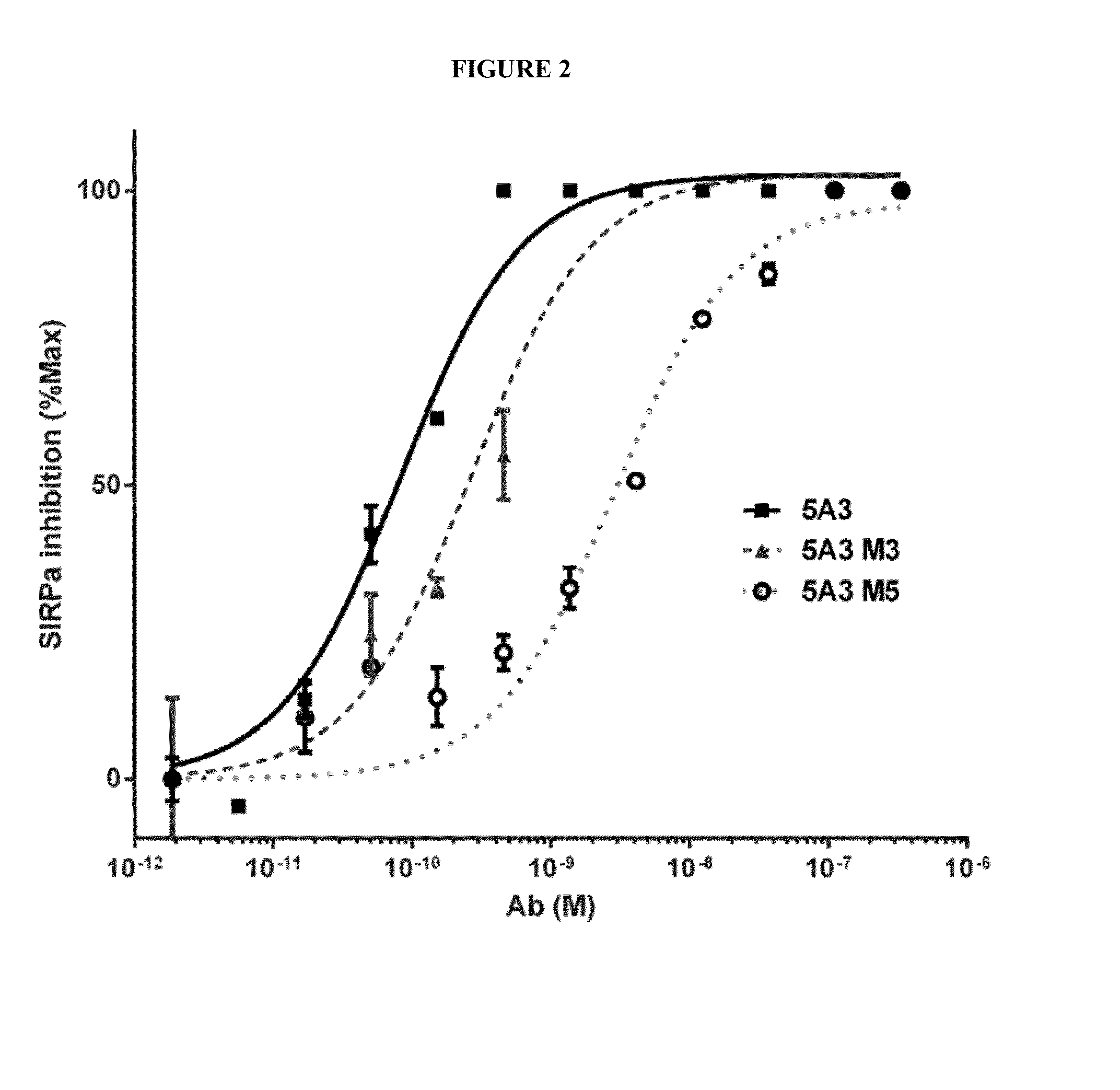
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
336 results about "CD47" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
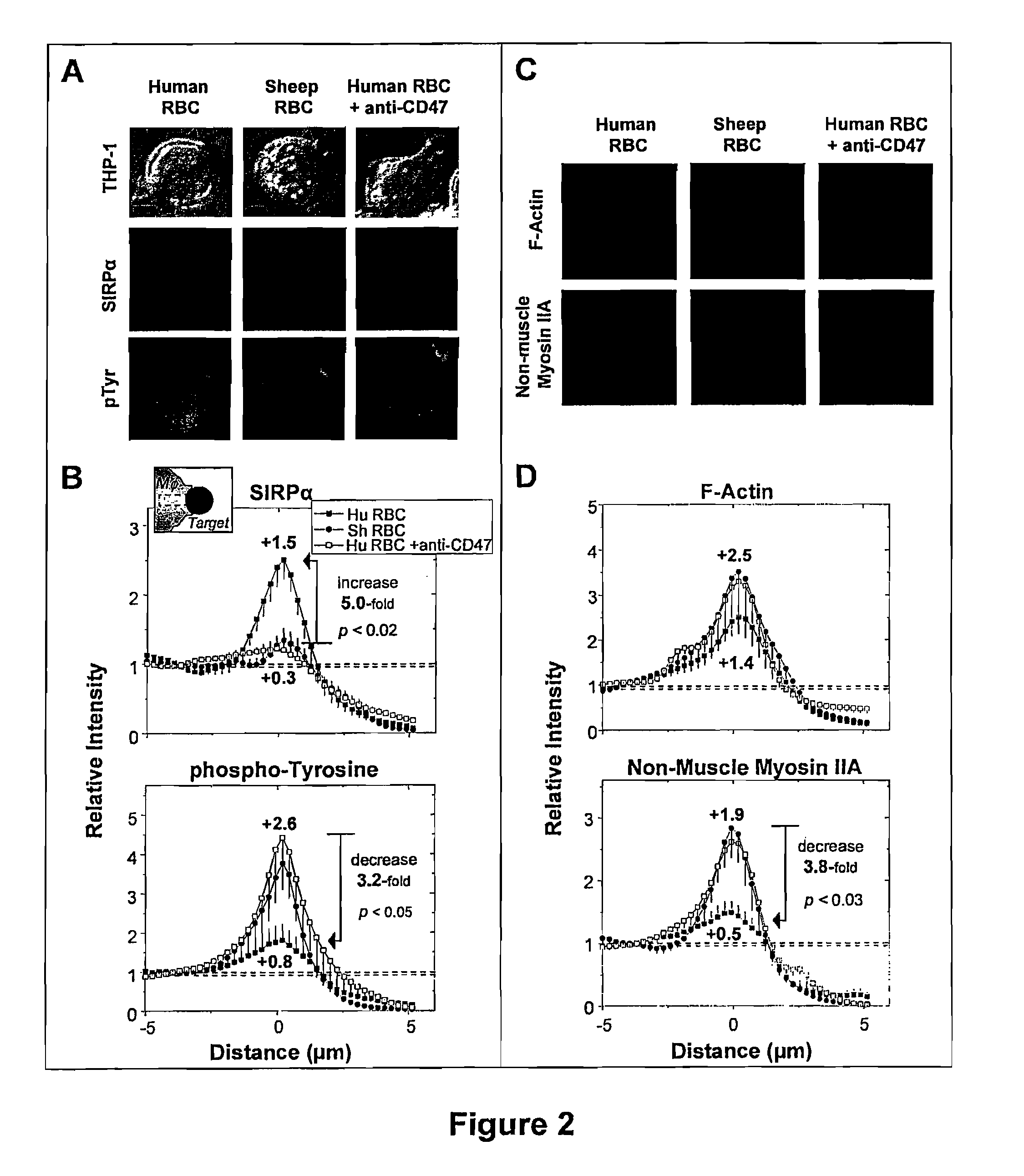
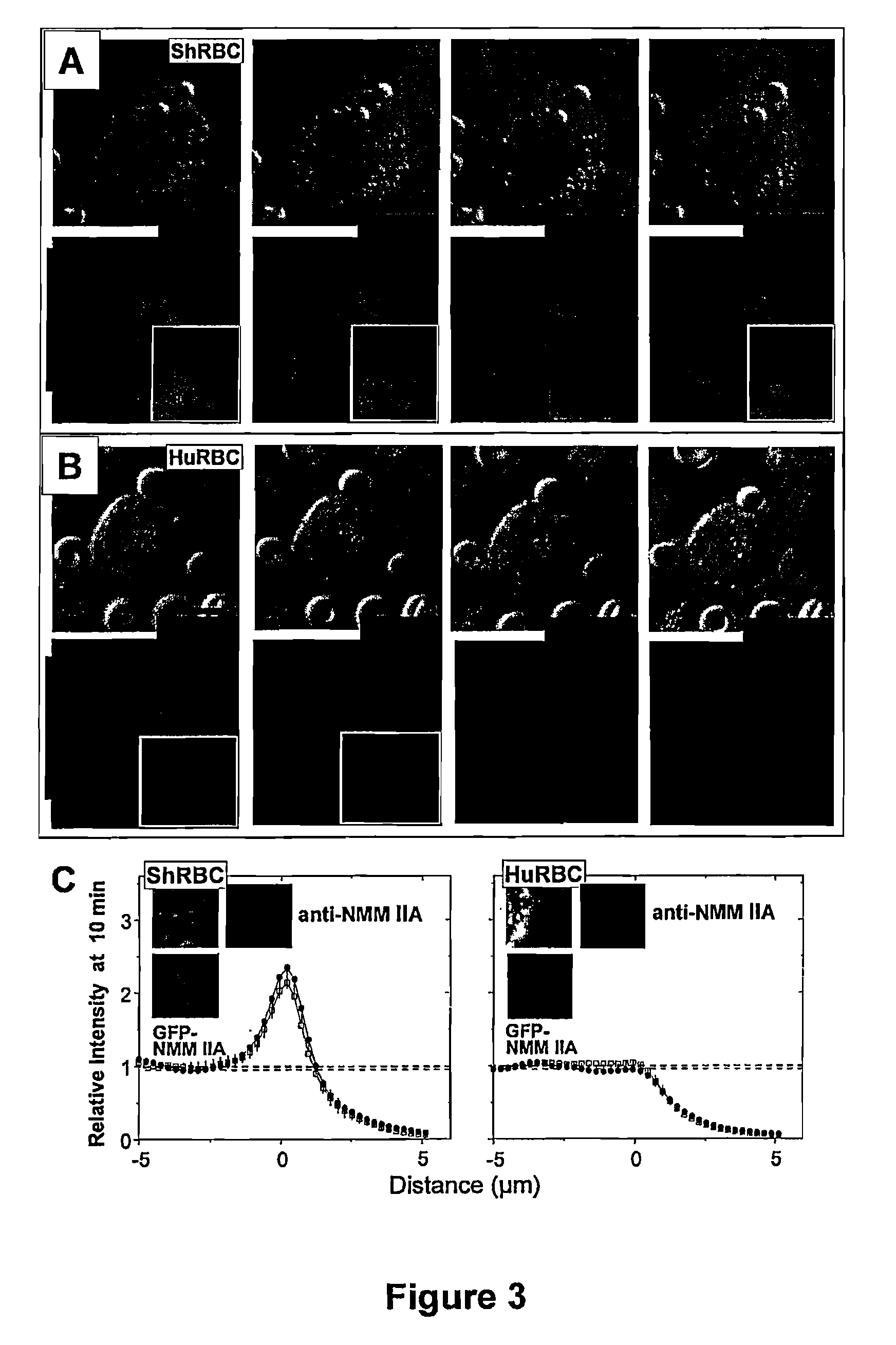
CD47 (Cluster of Differentiation 47) also known as integrin associated protein (IAP) is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the CD47 gene. CD47 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and partners with membrane integrins and also binds the ligands thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) and signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα). CD-47 acts as a don't eat me signal to macrophages of the immune system which has made it a potential therapeutic target in some cancers, and more recently, for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis.
Methods of treating acute myeloid leukemia by blocking CD47
ActiveUS8562997B2Increase the gapEasy to eliminateCompound screeningNervous disorderMyeloid leukemiaCancer cell
Methods are provided to manipulate phagocytosis of cancer cells, including e.g. leukemias, solid tumors including carcinomas, etc.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
CD47 related compositions and methods for treating immunological diseases and disorders
InactiveUS20080131431A1Lower capability requirementsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderImmune complex depositionImmune complex
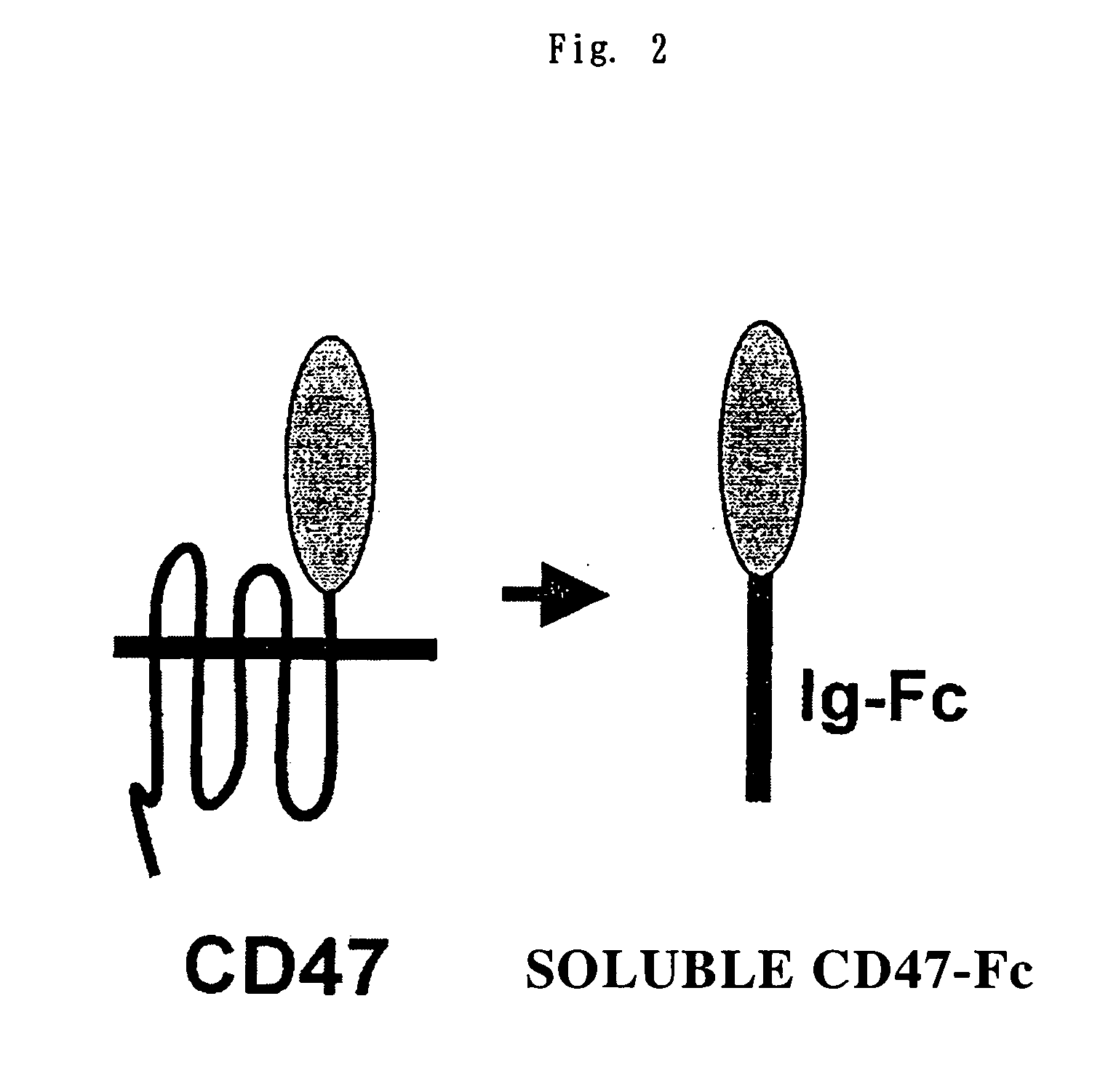
Provide herein are fusion polypeptides that comprise a CD47 extracellular domain or a variant thereof that is fused to a Fc polypeptide. The fusion polypeptides are useful for treating an immunological disease or disorder in a subject according to the methods described herein. The fusion polypeptides are capable of suppressing immunoresponsiveness of an immune cell, inhibiting production of proinflammatory cytokines, including inhibiting immune complex-induced production of cytokines.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
CD47 Related Compositions and Methods for Treating Immunological Diseases and Disorders
Provide herein are fusion polypeptides that comprise a CD47 extracellular domain or a variant thereof that is fused to a Fc polypeptide. The fusion polypeptides are useful for treating an immunological disease or disorder in a subject according to the methods described herein. The fusion polypeptides are capable of suppressing immunoresponsiveness of an immune cell, inhibiting production of proinflammatory cytokines, including inhibiting immune complex-induced production of cytokines.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for manipulating phagocytosis mediated by CD47
InactiveUS20090191202A1Enhance phagocytosisPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHematopoietic cellSolid tumor
Methods are provided to manipulate phagocytosis of cells, including hematopoietic cells, e.g. circulating hematopoietic cells, bone marrow cells, etc.; and solid tumor cells. In some embodiments of the invention the circulating cells are hematopoietic stem cells, or hematopoietic progenitor cells, particularly in a transplantation context, where protection from phagocytosis is desirable. In other embodiments the circulating cells are leukemia cells, particularly acute myeloid leukemia (AML), where increased phagocytosis is desirable.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Synergistic Anti-CD47 Therapy for Hematologic Cancers
ActiveUS20120282174A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRadioactive preparation carriersSurface markerCD20
Methods are provided for treatment of hematologic cancers, particularly lymphomas and leukemias, including without limitation myelogenous and lymphocytic leukemias. A combination of antibodies specific for CD47; and specific for a cancer associated cell surface marker are administered to the patient, and provide for a synergistic decrease in cancer cell burden. The combination of antibodies may comprise a plurality of monospecific antibodies, or a bispecific or multispecific antibody. Markers of interest include without limitation, CD20, CD22, CD52, CD33; CD96; CD44; CD123; CD97; CD99; PTHR2; and HAVCR2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
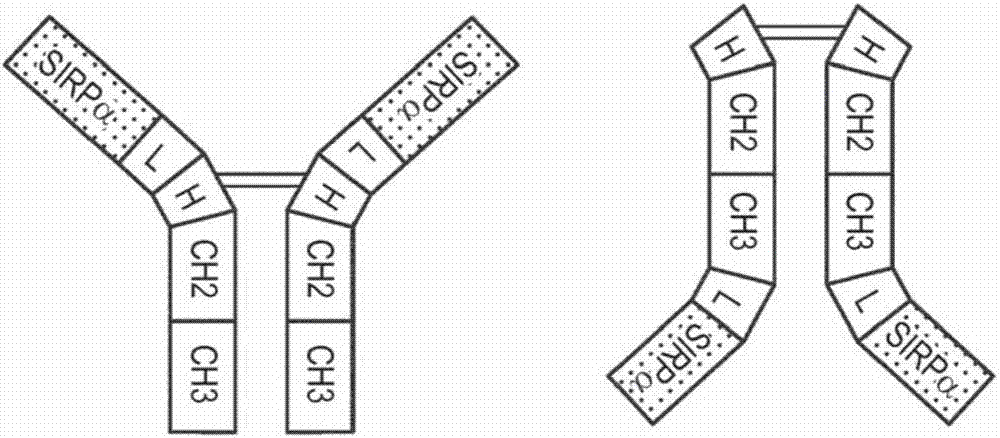
Antibodies and antibody fragments targeting sirp-alpha and their use in treating hematologic cancers
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO +2
Methods for Manipulating Phagocytosis Mediated by CD47
ActiveUS20110014119A1Increase the gapEasy to eliminateCompound screeningNervous disorderCancer cellSolid tumor
Methods are provided to manipulate phagocytosis of cancer cells, including e.g. leukemias, solid tumors including carcinomas, etc.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
CD47 and PD-L1 targeting bifunctional fusion protein
ActiveCN107459578AImprove targetingHigh activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDisulfide bondingBlood safety
The invention relates to a CD47 and PD-L1 targeting bifunctional fusion protein, belongs to the field of biomedicine, and solves the problems that anti-PD-1 / PD-L1 treatment is poor in a low-immunogenicity tumor treatment effect and anti-CD47 treatment is poor in a targeting ability. The fusion protein is composed of a CD47 binding part and a PD-L1 binding part which are linked by a disulfide bond, can block the binding of CD47 and SIRPalpha, can block the binding of PD-L1 and PD-1, can achieve the effects of activating macrophages to phagocytize tumor cells and promoting antigen presentation in natural immunity, can achieve an effect of promoting the activation of tumor specific T cells in acquired immunity, and has lower blood toxicity; and as compared with the single use of anti-PD-L1 or anti-CD47 for treatment, the fusion protein has better antitumor curative effects and blood safety.
Owner:TAIZHOU MABTECH PHARM CO LTD
Compositions and Methods for Treating Hematological Cancers Targeting the SIRPA CD47 Interaction
ActiveUS20120189625A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMyeloid leukemiaOncology
The invention relates to modulating the SIRPα-CD47 interaction in order to treat hematological cancer and compounds therefor. In some embodiments, there is provided methods and uses of SIRPα polypeptides, fragments and fusion proteins for treating hematological cancer, preferably human acute myeloid leukemia.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN +1
Synergistic anti-CD47 therapy for hematologic cancers
Methods are provided for treatment of hematologic cancers, particularly lymphomas and leukemias, including without limitation myelogenous and lymphocytic leukemias. A combination of antibodies specific for CD47; and specific for a cancer associated cell surface marker are administered to the patient, and provide for a synergistic decrease in cancer cell burden. The combination of antibodies may comprise a plurality of monospecific antibodies, or a bispecific or multispecific antibody. Markers of interest include without limitation, CD20, CD22, CD52, CD33; CD96; CD44; CD123; CD97; CD99; PTHR2; and HAVCR2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Anti-cd47 antibodies and methods of use
ActiveUS20170081407A1Little and no hemagglutinationProgression moreImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsSolid tumorCD47
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Treatment of CD47+ Disease Cells with SIRP Alpha-FC Fusions
ActiveUS20150329616A1Good effectHigh affinityAnimal cellsImmunoglobulin superfamilyCancer cellErythrocyte binding
CD47+ disease cells, such as CD47+ cancer cells, are treated with an agent that blocks signalling via the SIRPα / CD47 axis. The agent is a human SIRPα fusion protein that displays negligible CD47 agonism and negligible red blood cell binding. The fusion protein comprises an IgV domain from variant 2 of human SIRPα, and an Fc having effector function. The IgV domain binds human CD47 with an affinity that is at least five fold greater than the affinity of the entire extracellular region of human SIRPα. The fusion protein is at least 5 fold more potent than a counterpart lacking effector function.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Prevention of tissue ischemia, related methods and compositions
ActiveUS8236313B2Increase blood flowIncrease oxygenationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCoronary artery diseaseWhole body
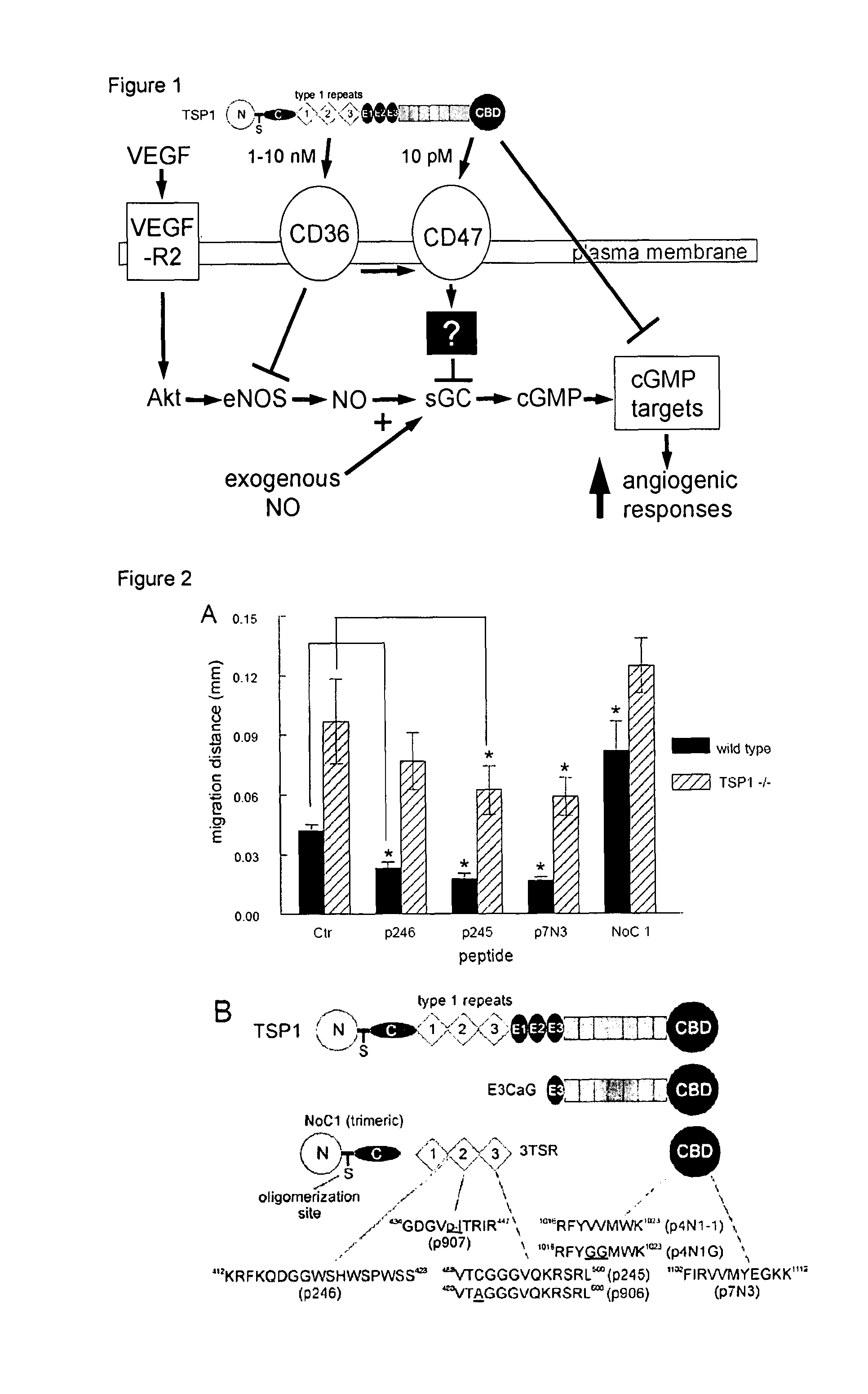
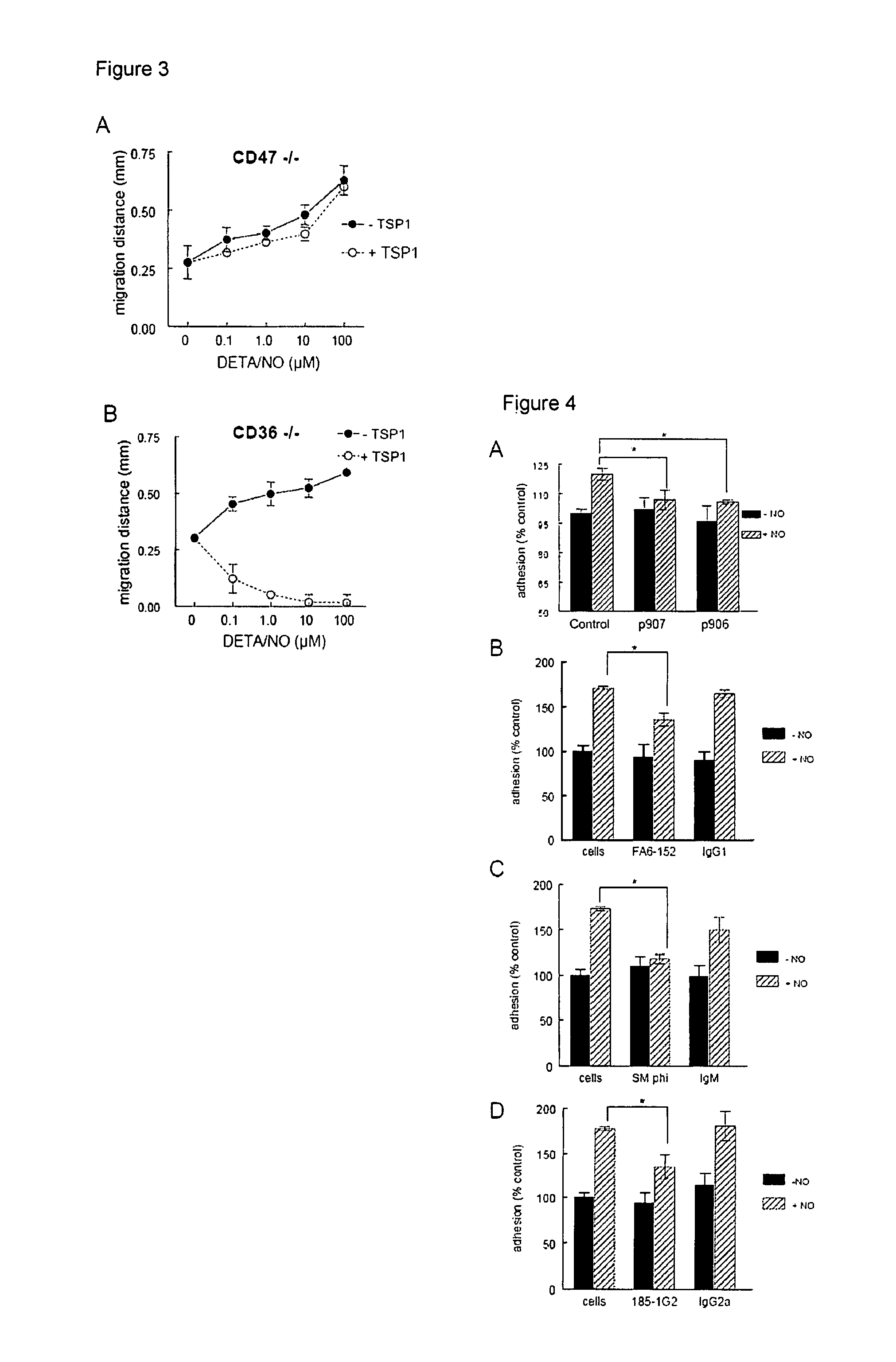
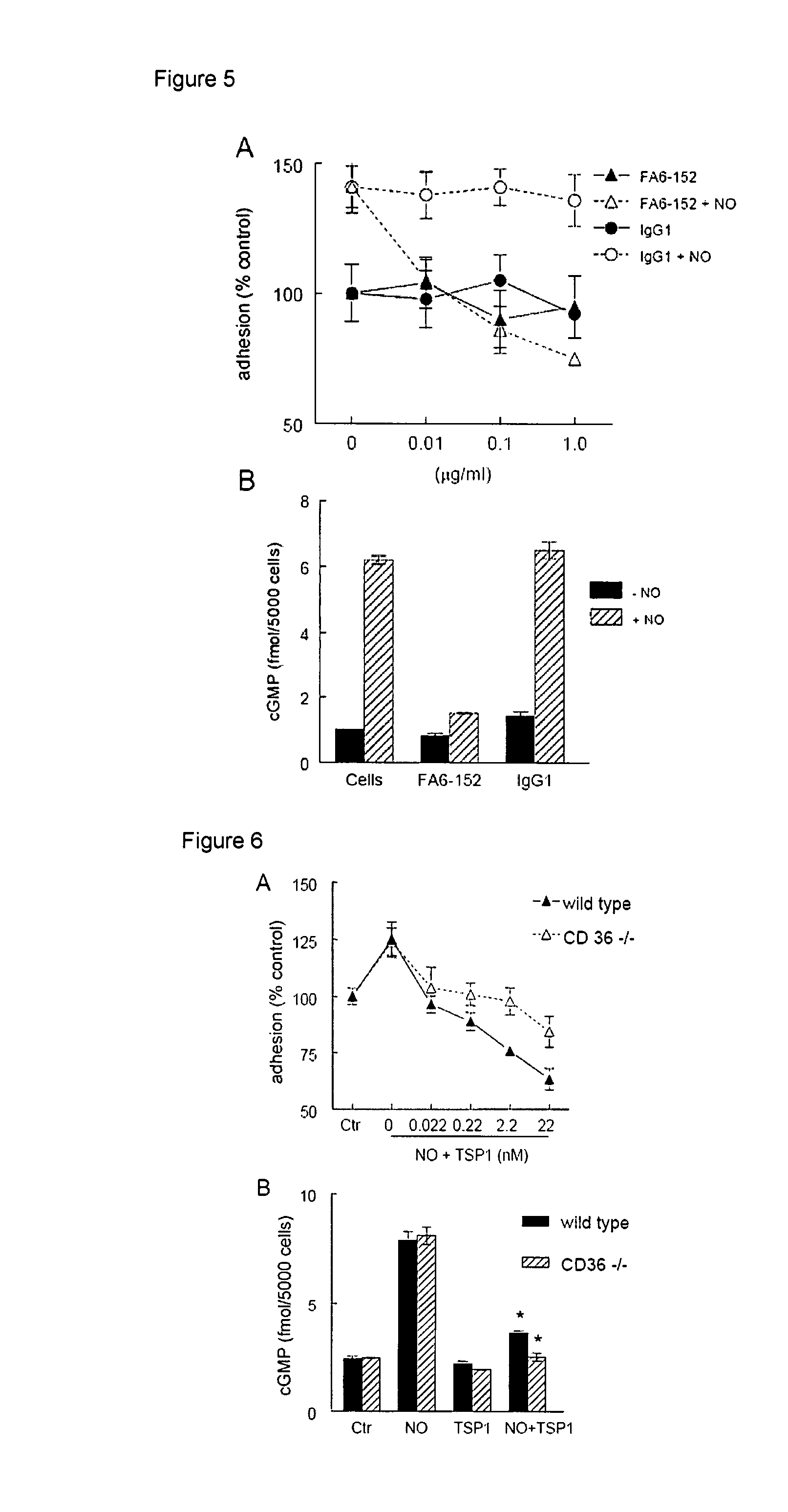
Provided herein are compositions and methods for preventing, ameliorating, and / or reducing tissue ischemia and / or tissue damage due to ischemia, increasing blood vessel diameter, blood flow and tissue perfusion in the presence of vascular disease including peripheral vascular disease, atherosclerotic vascular disease, coronary artery disease, stroke and influencing other conditions, by suppressing CD47 and / or blocking TSP1 and / or CD47 activity or interaction. Influencing the interaction of CD47-TSP1 in blood vessels allows for control of blood vessel diameter and blood flow, and permits modification of blood pressure and cardiac function. Under conditions of decreased blood flow, for instance through injury or atherosclerosis, blocking TSP1-CD47 interaction allows blood vessels to dilate and increases blood flow, tissue perfusion and tissue survival. This in turn reduces or prevents tissue necrosis and death. The therapeutics identified herein allow for precise regulation of blood flow to tissues and organs which need it, while substantially avoiding systemic complications. Methods and compositions described herein can be used to increase tissue survival under conditions of trauma and surgery, as well as conditions of chronic vascular disease. Also disclosed are methods for the treatment of elderly subjects using agents that affect TSP1 and CD47 and thereby affect tissue perfusion. Additionally, provided herein are compositions and methods for influencing blood coagulation, allowing for controlled increased or decreased blood clotting. Additionally, provided herein are compositions and methods for decreasing blood flow, as in the case of cancer through mimicking the effects of TSP1 and CD47 on blood vessel diameter and blood flow.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS +1
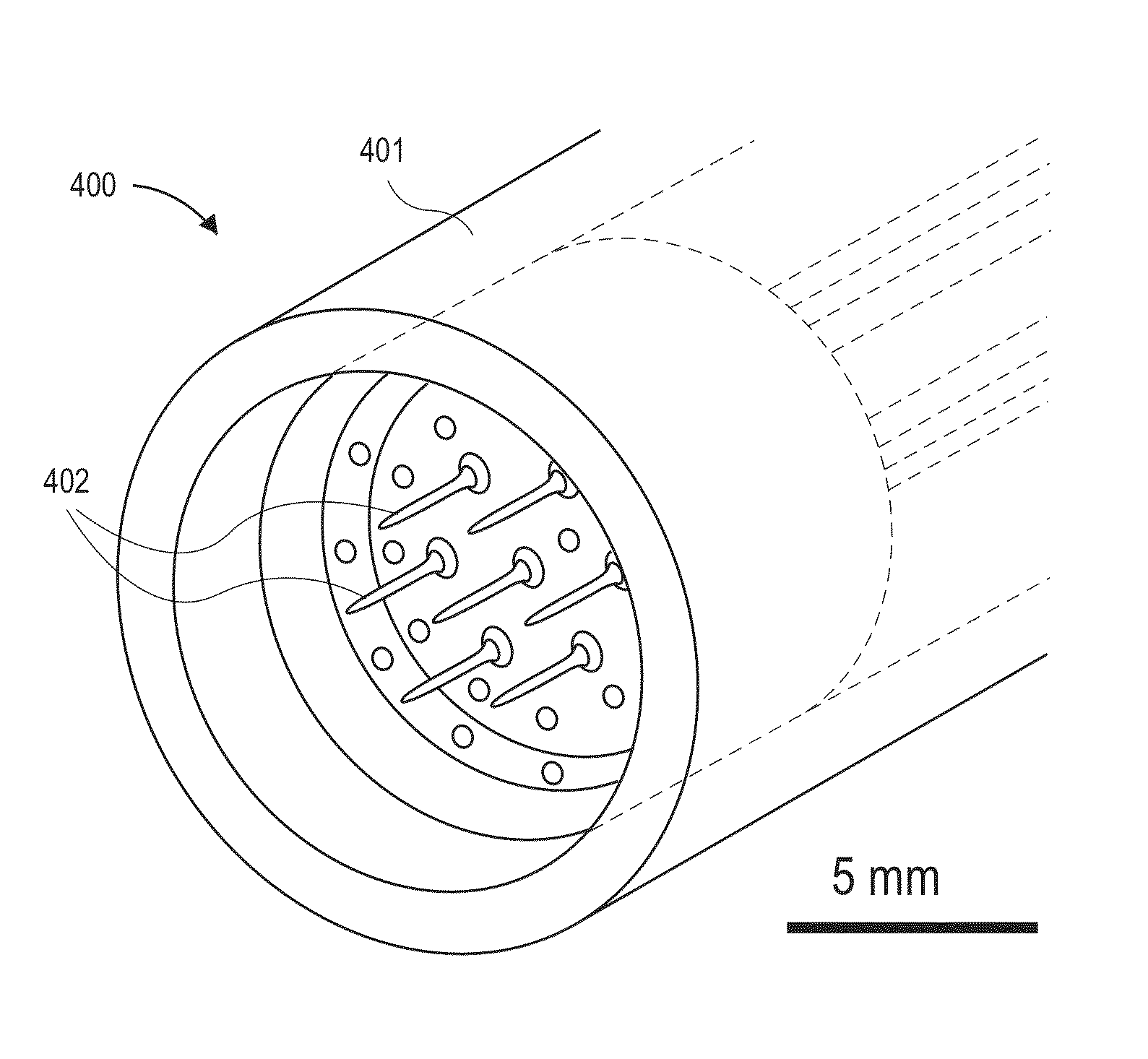
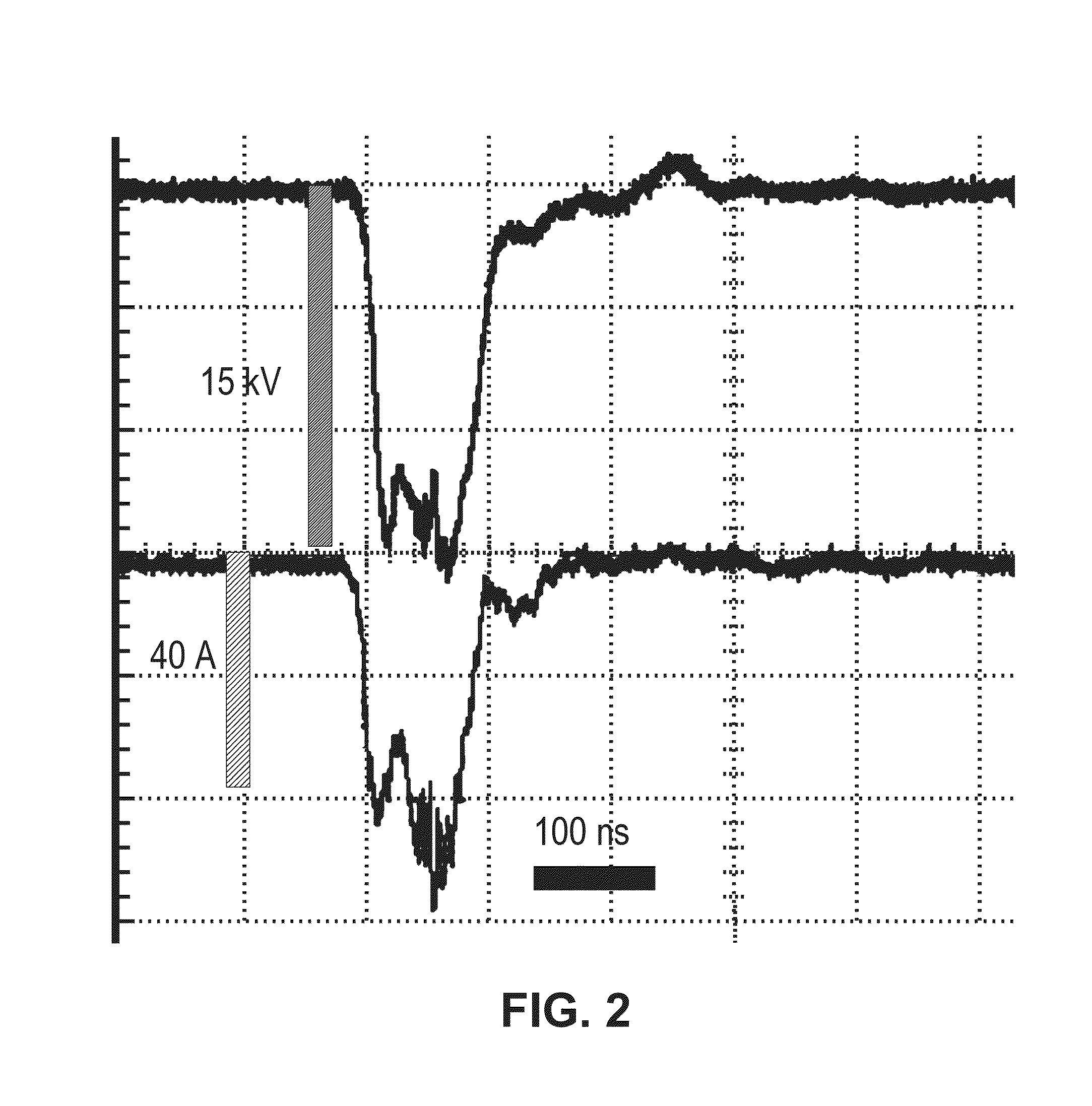
Methods and devices for stimulating an immune response using nanosecond pulsed electric fields
ActiveUS20140358066A1Reduce transferOrganic active ingredientsSurgical needlesNanosecondCalreticulin
Nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF) treatments of a tumor are used to cause the tumor to express calreticulin and stimulate an immune response against the tumor and other tumors in a subject. An immune response biomarker can be measured, and further nsPEF treatments can be performed if needed to stimulate or further stimulate the immune response. Cancers that have metastasized may be treated. The treatment can be combined with CD47-blocking antibodies, doxorubicin, CTLA-4-blocking antibodies, and / or PD-1-blocking antibodies. Electrical characteristics of nsPEF treatments can be based on the size, type, and / or strength of tumors and / or a quantity of tumors in the subject.
Owner:PULSE BIOSCI INC
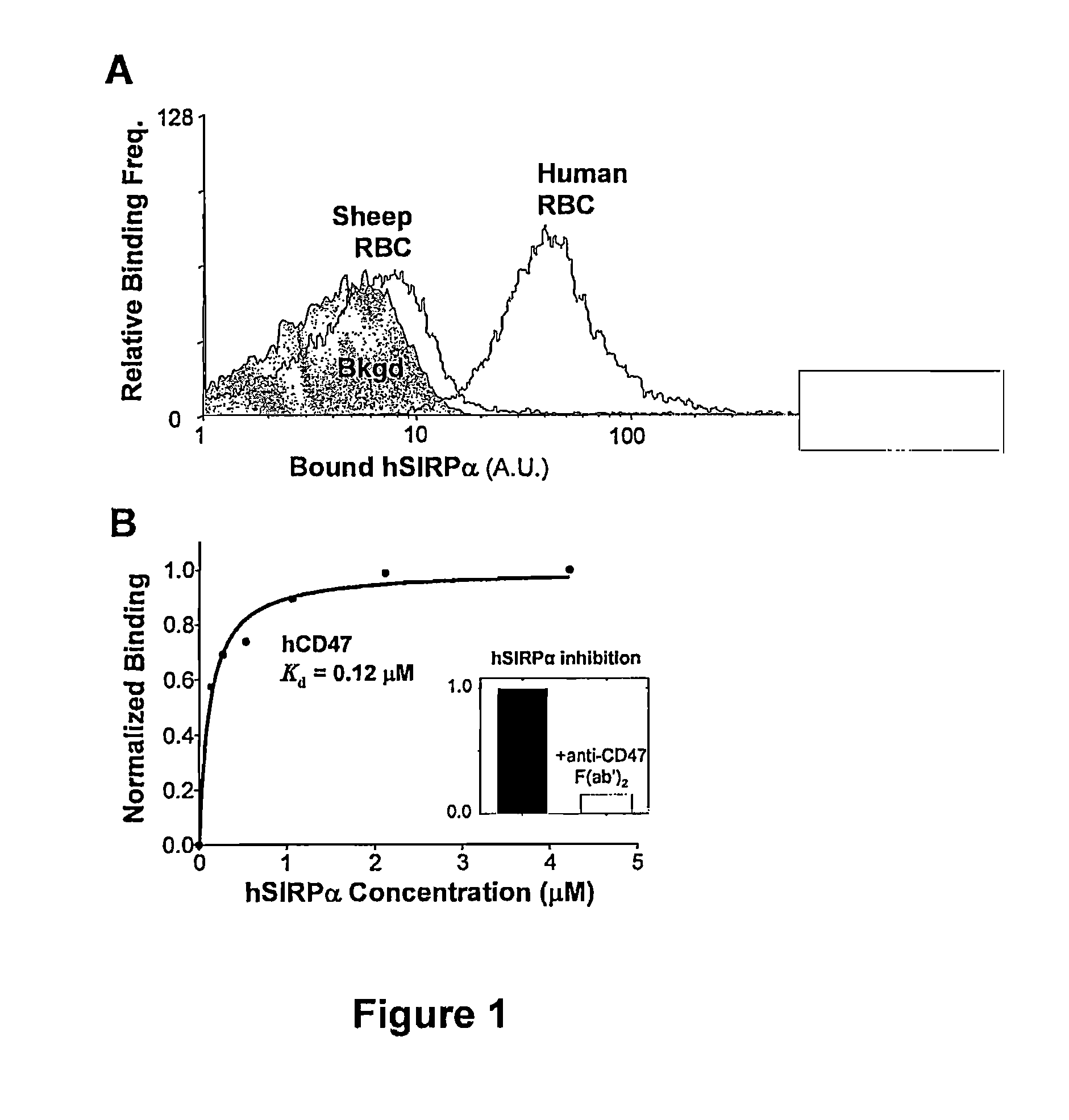
Polynucleotides and polypeptides relating to the modulation of SIRPalpha-CD47
InactiveUS7282556B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesPolynucleotideCell biology
Polypeptides that can modulate SIRPα-CD47 functions and methods of use of the polypeptides are presented. In addition, polynucleotides that encode the polypeptides referred to above are presented. Further, pharmaceutical compositions to treat conditions are presented.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Methods and devices for stimulating an immune response using nanosecond pulsed electric fields
ActiveUS9101764B2Reduce transferOrganic active ingredientsSurgical needlesAbnormal tissue growthNanosecond
Nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF) treatments of a tumor are used to cause the tumor to express calreticulin and stimulate an immune response against the tumor and other tumors in a subject. An immune response biomarker can be measured, and further nsPEF treatments can be performed if needed to stimulate or further stimulate the immune response. Cancers that have metastasized may be treated. The treatment can be combined with CD47-blocking antibodies, doxorubicin, CTLA-4-blocking antibodies, and / or PD-1-blocking antibodies. Electrical characteristics of nsPEF treatments can be based on the size, type, and / or strength of tumors and / or a quantity of tumors in the subject.
Owner:PULSE BIOSCI INC
Modulation of sirp-alpha - cd47 interaction for increasing human hematopoietic stem cell engraftment and compounds therefor
InactiveUS20100239578A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCD47Hematopoietic stem cell
The invention relates to modulating the SIRPα-CD47 interaction in order to increase hematopoietic stem cell engraftment and compounds therefor. In some embodiments, there is provided isolated SIRPα and CD47 polypeptides, fragments and fusion proteins for enhancing hematopoietic stem cell engraftment. Further there is provided methods for increasing hematopoietic stem cell engraftment through administration of the above polypeptides.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK +1
Novel recombinant bi-functional fusion proteins, preparation and use thereof
ActiveUS20150266942A1Inhibit bindingGrowth inhibitionSenses disorderBacteriaDiseaseVascular endothelium
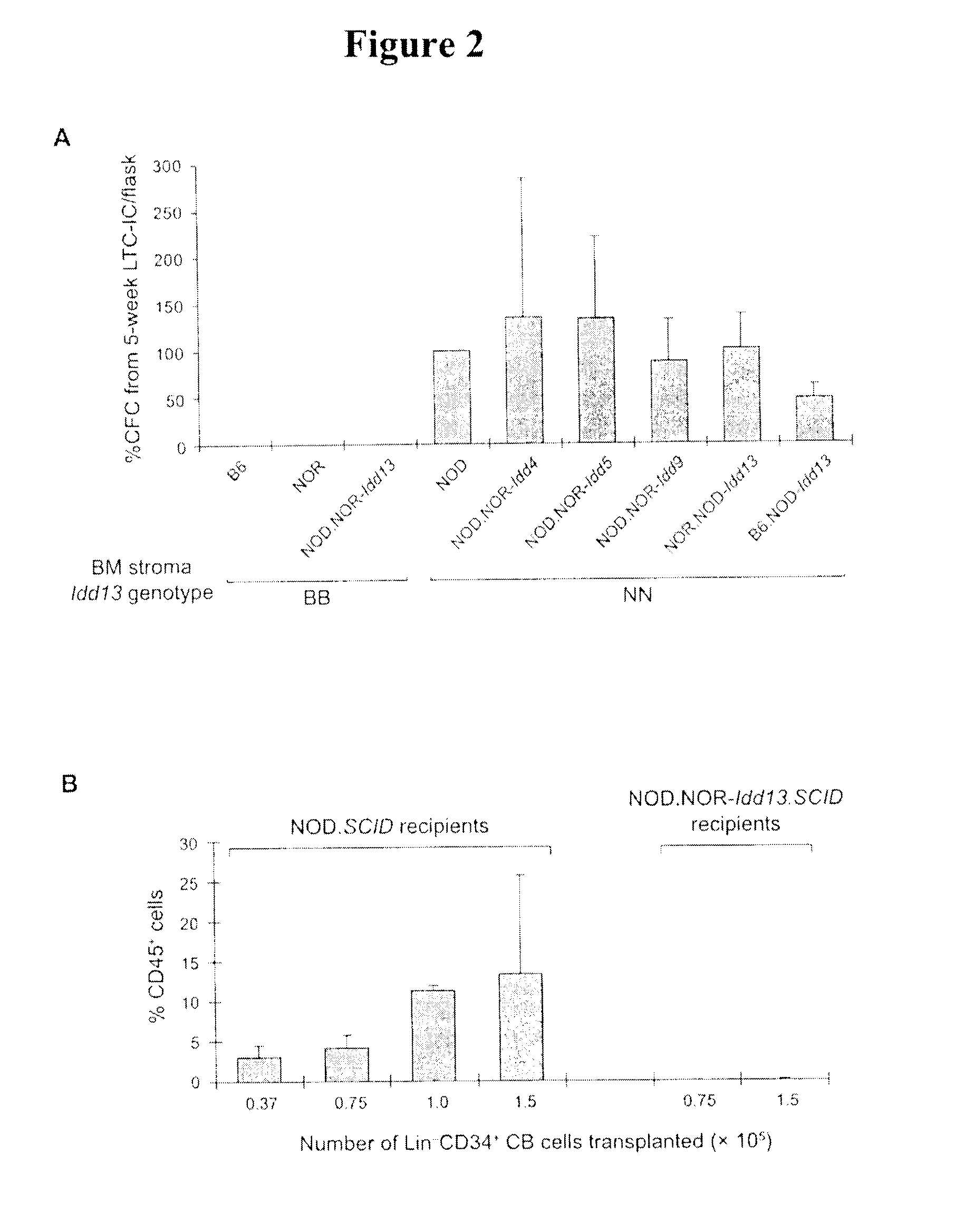
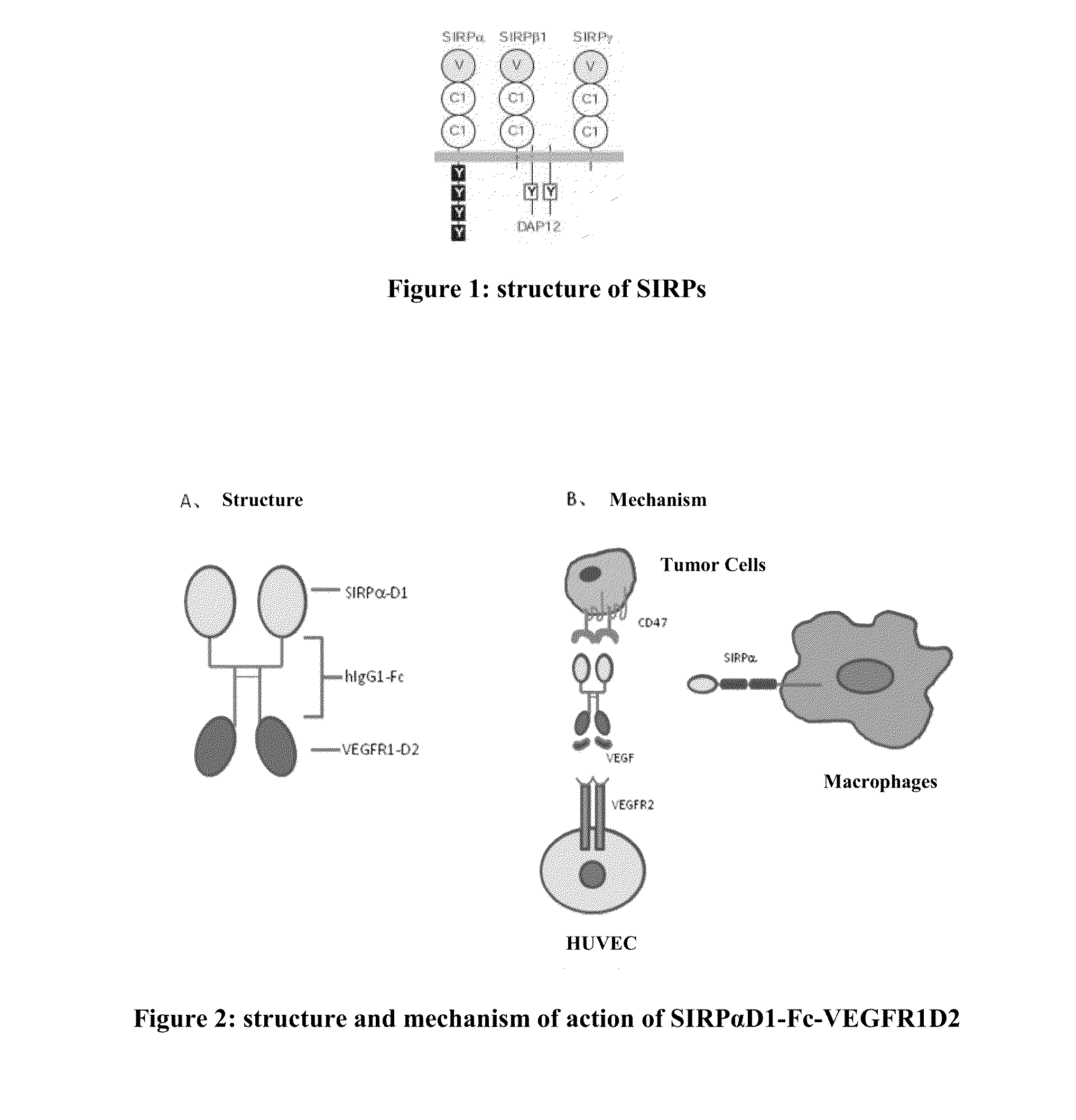
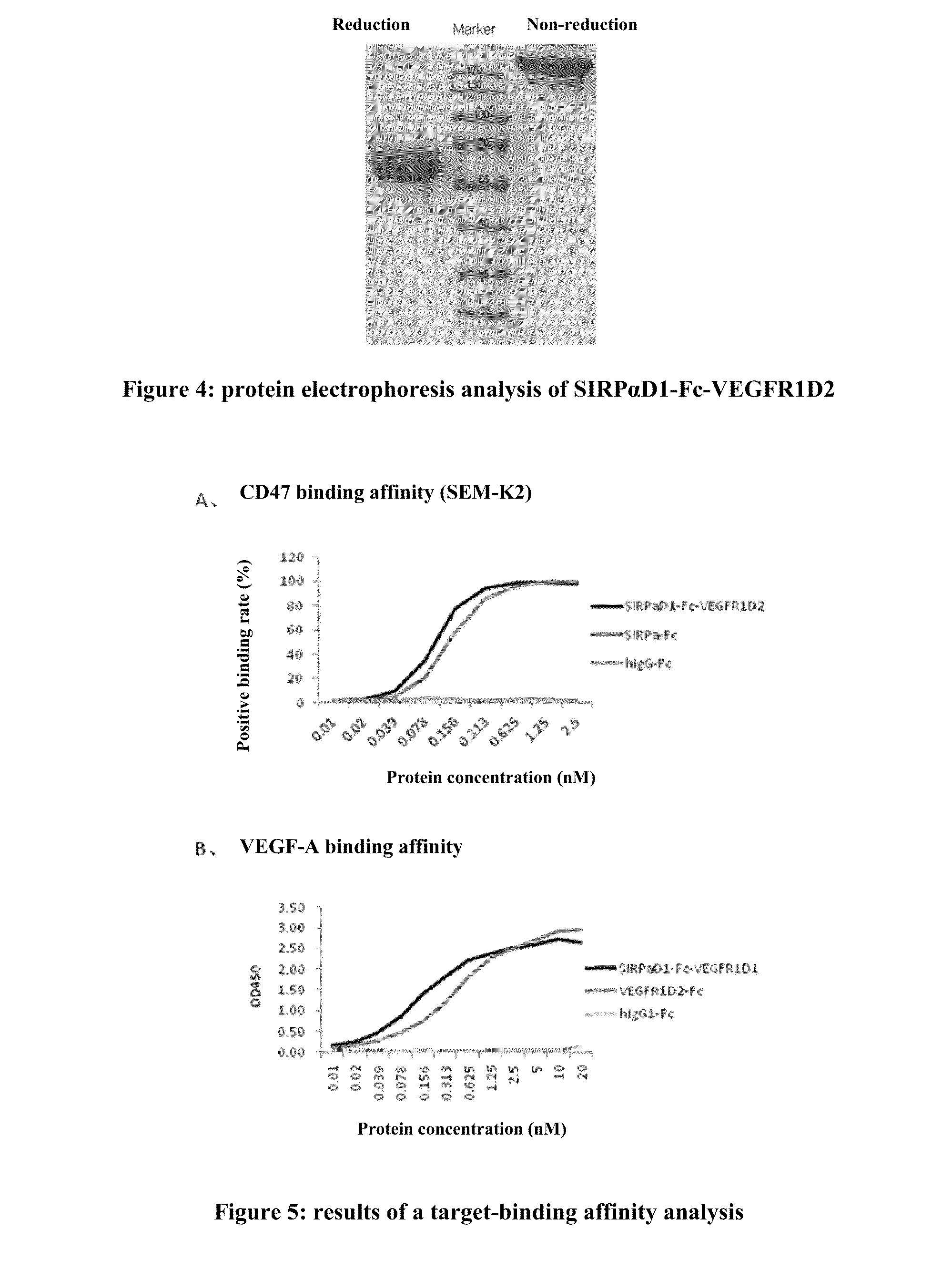
A recombinant bi-functional fusion protein, comprising an Ig region of an extracellular domain of a signal-regulator protein (SIRP), linked via a Fc fragment of an Ig, to an Ig region of an extracellular domain of VEGFR, wherein the protein can bind to CD47 and VEGF simultaneously, blocking the binding of CD47 with the SIRP on the cell surface of macrophages to stimulate the phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages, and inhibiting the growth of vascular endothelial cells induced by VEGF. The present application also provides a nucleic acid molecule encoding the recombinant bi-functional fusion protein and an expression vector expressing the protein, a method for producing the protein and a method for treating a disease over-expressing CD47 or VEGF.
Owner:MACROIMMUNE
Compositions for inhibiting macrophage activity
InactiveUS20030026803A1Reduce and eliminate effectFunctional relationshipNervous disorderDigestive systemDiseaseAutoimmune disease
Use of an agent capable of inhibiting the interaction between SIRP1alpha and CD47, in the preparation of a composition for the inhibition of macrophage involvement in autoimmune disease. The invention further relates to a method for the treatment of an autoimmune disease with macrophage involvement, comprising administering to a mammal an effective amount of an agent which inhibits the interaction between CD47 and SIRP1alpha. The invention also relates to a method for identifying an agent capable of inhibiting the interaction between CD47 and SIRP1alpha, comprising the steps of exposing one or more test compounds to CD47 and / or SIRP1alpha, and monitoring the ability of the test compound to inhibit their interaction.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Anti-SIRP-alpha antibodies and bispecific macrophage enhancing antibodies
Anti-SIRPα antibodies, including multi-specific anti-SIRPα antibodies, are provided, as are related compositions and methods. The antibodies of the disclosure bind to SIRPα and can block the interaction of CD47 on one cell with SIRPα on a phagocytic cell. Antibodies that are bispecific for SIRPα and a second antigen are termed Bi-specific Macrophage Enhancing (BiME) antibodies and have emergent properties. The subject anti-SIRPα antibodies find use in various therapeutic methods. Embodiments of the disclosure include isolated antibodies and derivatives and fragments thereof, pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more of the anti-SIRPα antibodies; and cell lines that produce the antibodies. Also provided are amino acid sequences of exemplary anti-SIRPα antibodies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Anti-CD47 Antibodies and Methods of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20140303354A1High selectivityHigh affinityHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBinding siteBispecific monoclonal antibody
The invention relates to monoclonal and / or monovalent antibodies that bind CD47. The invention relates to monoclonal and / or monovalent antibodies that bind CD19. The invention also relates to novel bispecific monoclonal antibodies carrying a different specificity for each binding site of the immunoglobulin molecule, where one of the binding sites is specific for CD47. The invention also relates to novel bispecific monoclonal antibodies carrying a different specificity for each binding site of the immunoglobulin molecule, where one of the binding sites is specific for CD19.
Owner:NOVIMMUNE
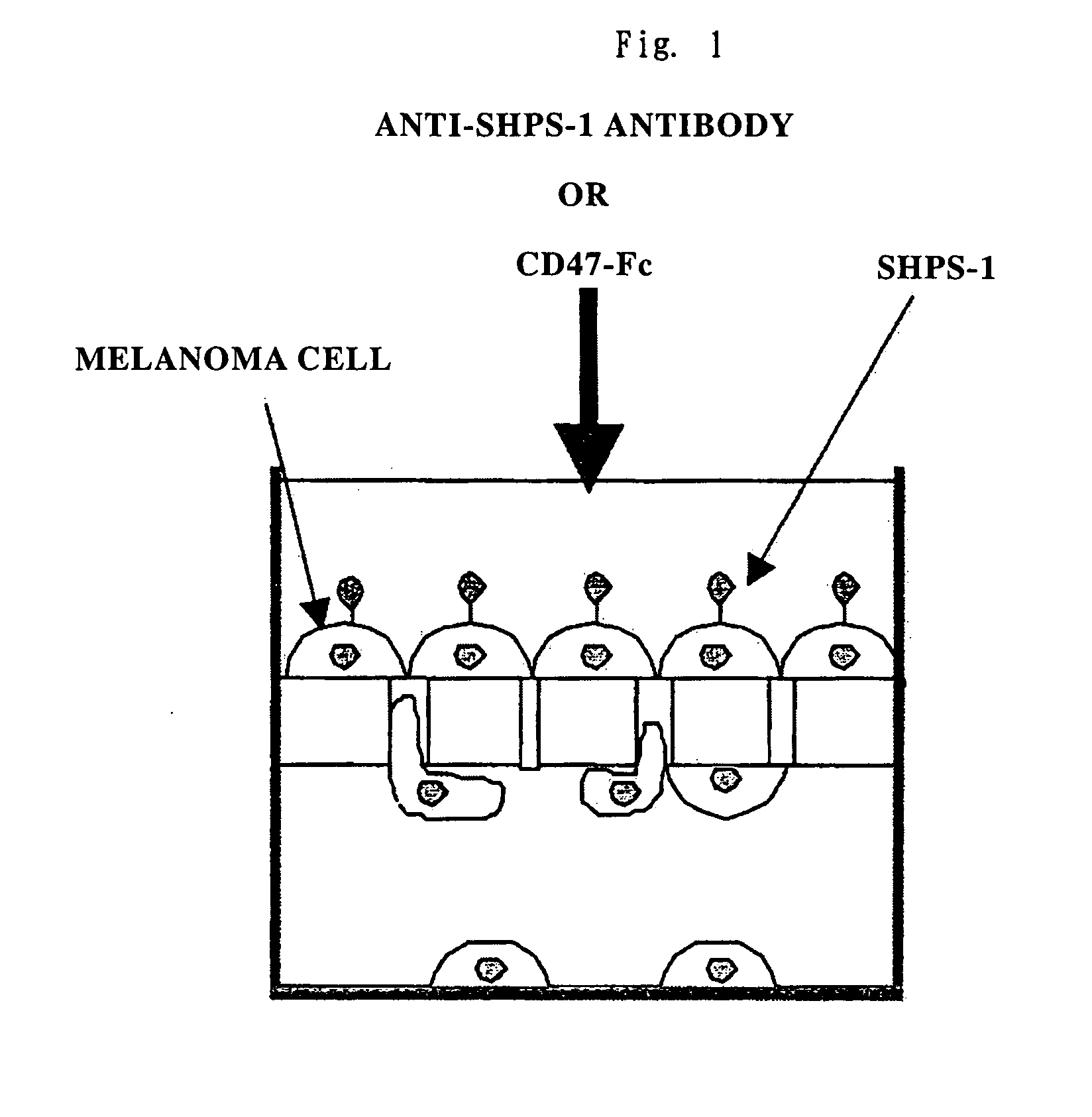
Cd47 partal peptdie and anti-shps-1 monoclonal antibody
A CD47 partial peptide which has an amino acid sequence constituting an extracellular region having an immunoglobulin-like structure of a CD47 protein, which is specifically bound to an N-terminal immunoglobulin-like structure of a dephosphorylation substrate protein SHPS-1 of an SH2 domain-containing protein, and which can act on a function of cell response mediated by SHPS-1, and an anti-SHPS-1 monoclonal antibody.
Owner:GUNMA UNIVERSITY
Methods for Manipulating Phagocytosis Mediated by CD47
Methods are provided to manipulate phagocytosis of cells, including hematopoietic cells, e.g. circulating hematopoietic cells, bone marrow cells, etc.; and solid tumor cells. In some embodiments of the invention the circulating cells are hematopoietic stem cells, or hematopoietic progenitor cells, particularly in a transplantation context, where protection from phagocytosis is desirable. In other embodiments the circulating cells are leukemia cells, particularly acute myeloid leukemia (AML), where increased phagocytosis is desirable.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
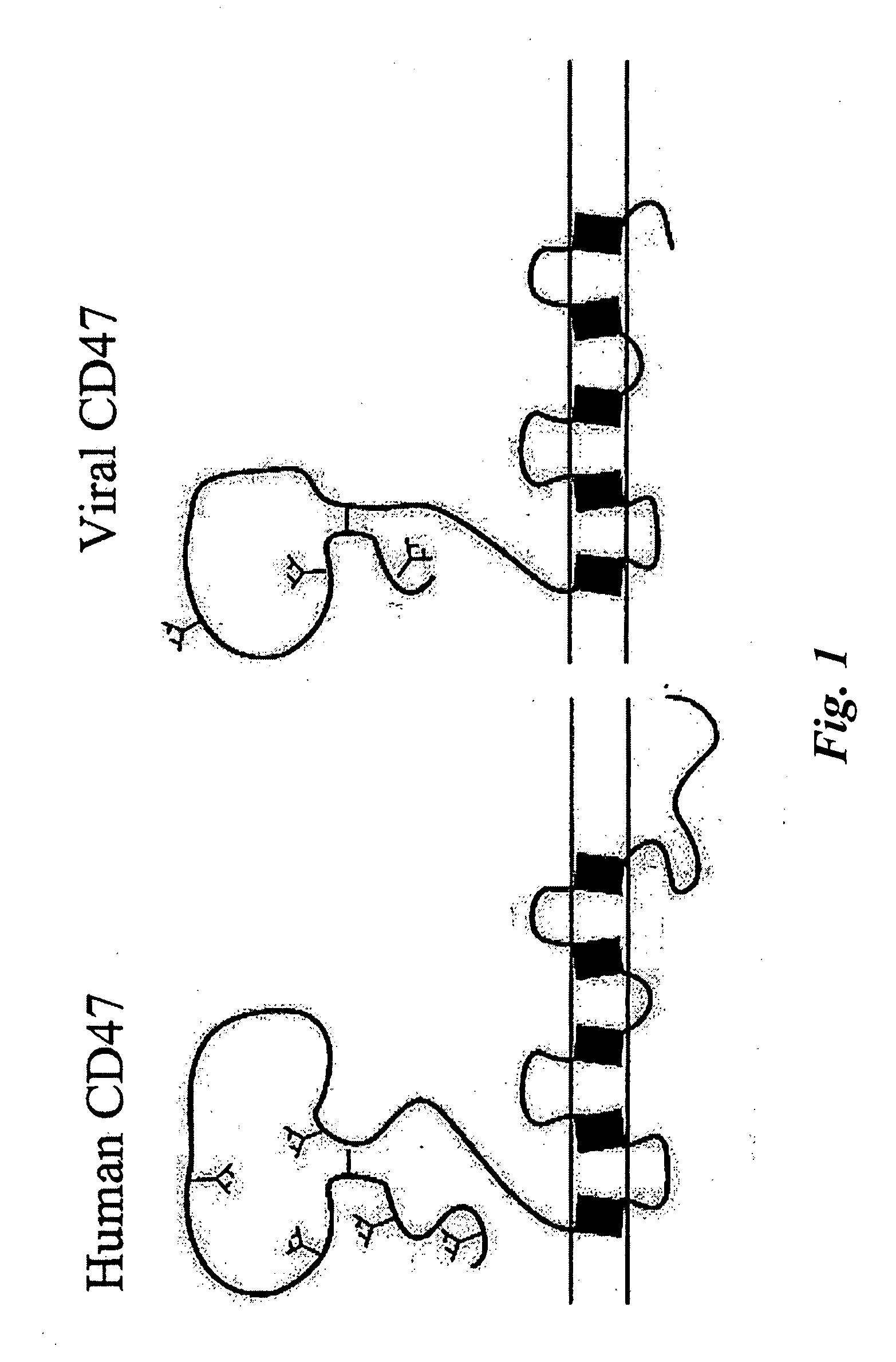
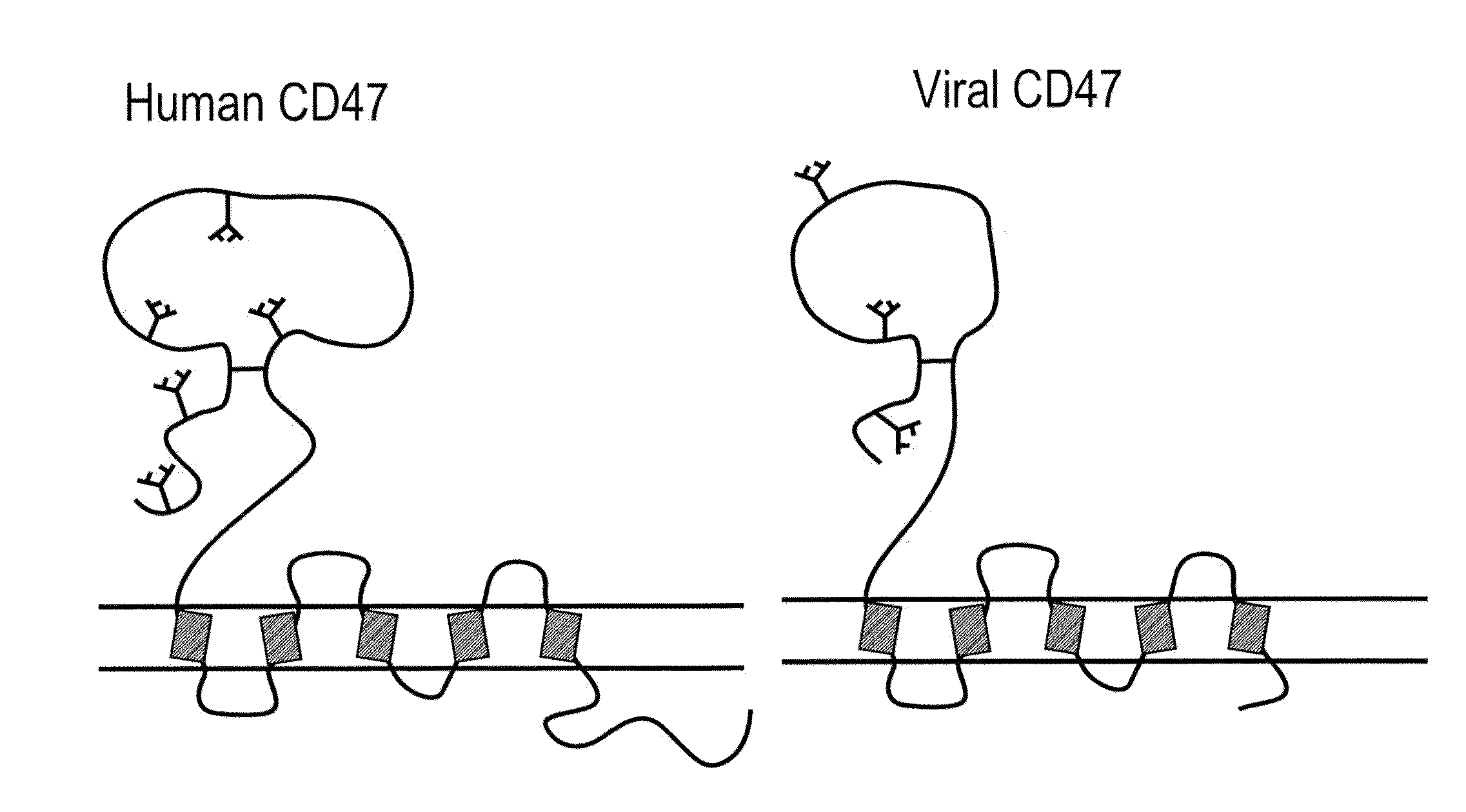
Protection of virus particles from phagocytosis by expression of CD47
The present invention relates to a viral particle. The viral particle has a radius of less than about 1 μm, and at least one peptide comprising at least a biologically active portion of CD47. The present invention also includes a method of increasing the life of a particle in vivo in a mammal. The method includes the steps of expressing at least one peptide comprising at least a biologically active portion of CD47 in a viral particle, and administering the viral particle having CD47 expressed to a mammal, wherein the administered viral particle has a longer half life in the mammal than an otherwise identical viral particle that does not have CD47 expressed thereon.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
CD47 related compositions and methods for treating immunological diseases and disorders
InactiveUS8377448B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmune complex depositionImmune complex
Provide herein are fusion polypeptides that comprise a CD47 extracellular domain or a variant thereof that is fused to a Fc polypeptide. The fusion polypeptides are useful for treating an immunological disease or disorder in a subject according to the methods described herein. The fusion polypeptides are capable of suppressing immunoresponsiveness of an immune cell, inhibiting production of proinflammatory cytokines, including inhibiting immune complex-induced production of cytokines.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Bispecific recombinant protein and application thereof
ActiveCN108864290AImprove securityAvoid killingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLow affinityTumor target
The invention discloses bispecific recombinant protein. The bispecific recombinant protein comprises a high-affinity tumor-targeted arm and a low-affinity fusion protein for blocking interaction of CD47 and SIRPalpha, wherein an antibody corresponding to the high-affinity tumor-targeted arm is not combined with the CD47, and the bonding affinity to target antigens on tumor cells is at least 6 times of the bonding affinity of the monomeric fusion protein and dimer corresponding to the low-affinity fusion protein for blocking the interaction of the CD47 and the SIRPalpha to the CD47 on the tumorcells; the low-affinity fusion protein for blocking mutual action of the CD47 and SIRPalpha contains SIRPalpha extracellular truncation. The invention also discloses a nucleic-acid molecule for encoding the recombinant protein and application of the recombinant protein and the nucleic-acid molecule in preparation of medicines for treating tumors. The bispecific recombinant protein disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the bonding abundance of tumor targeting saturation of the recombinant protein with the function of adjusting macrophage is obviously improved by the bispecific recombinant protein, the side effect of the non-tumor targeting is reduced and the application value is large clinically.
Owner:SHANGHAI JMT BIO INC
Treatment of CD47+ disease cells with SIRP alpha-Fc fusions
ActiveUS9969789B2High affinityGood curative effectImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellRed blood cell
CD47+ disease cells, such as CD47+ cancer cells, are treated with an agent that blocks signalling via the SIRPα / CD47 axis. The agent is a human SIRPα fusion protein that displays negligible CD47 agonism and negligible red blood cell binding. The fusion protein comprises an IgV domain from variant 2 of human SIRPα, and an Fc having effector function. The IgV domain binds human CD47 with an affinity that is at least five fold greater than the affinity of the entire extracellular region of human SIRPα. The fusion protein is at least 5 fold more potent than a counterpart lacking effector function.
Owner:PFIZER INC
CD47 nanobody and application thereof
ActiveCN110144009AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsMedicineAgglutination
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, discloses a CD47 nanobody and an application thereof, and particularly discloses a blocking type nanobody for integrin-associated protein (CD47) andderived protein thereof. Particularly, the invention discloses an integrin-associated protein (CD47) binding molecule and an application thereof, particularly in treatment and / or prevention or diagnosis of CD47 associated diseases such as tumor. The related CD47 nanobody can effectively block interaction between the CD47 and a ligand SIRPa thereof, and the antibody cannot cause human erythrocyte agglutination.
Owner:SHANGHAI NOVAMAB BIOPHARM CO LTD
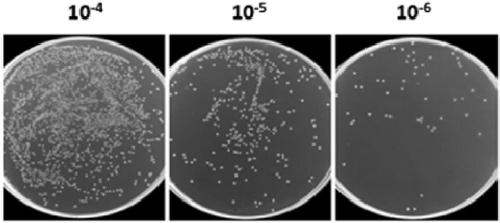
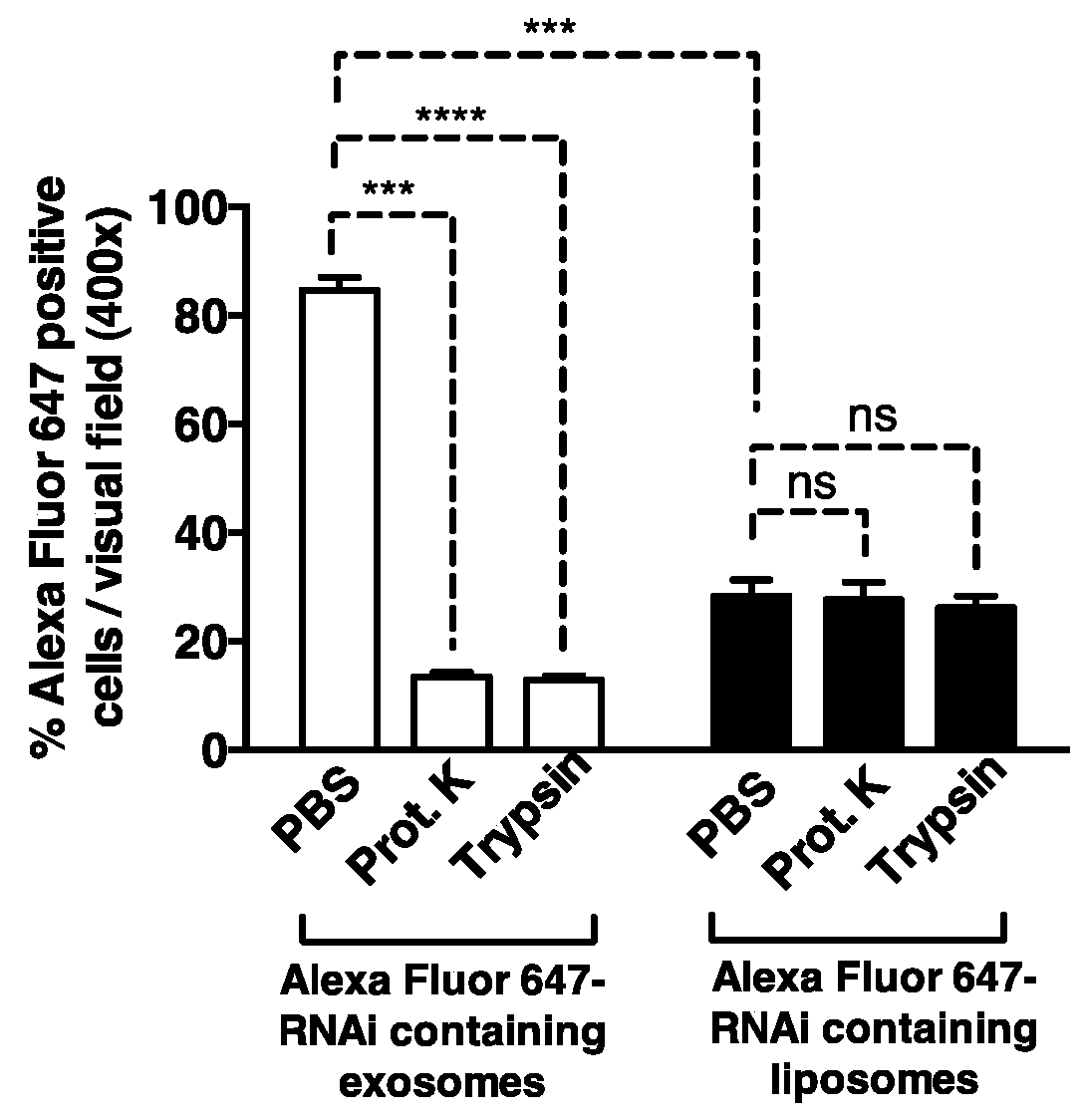
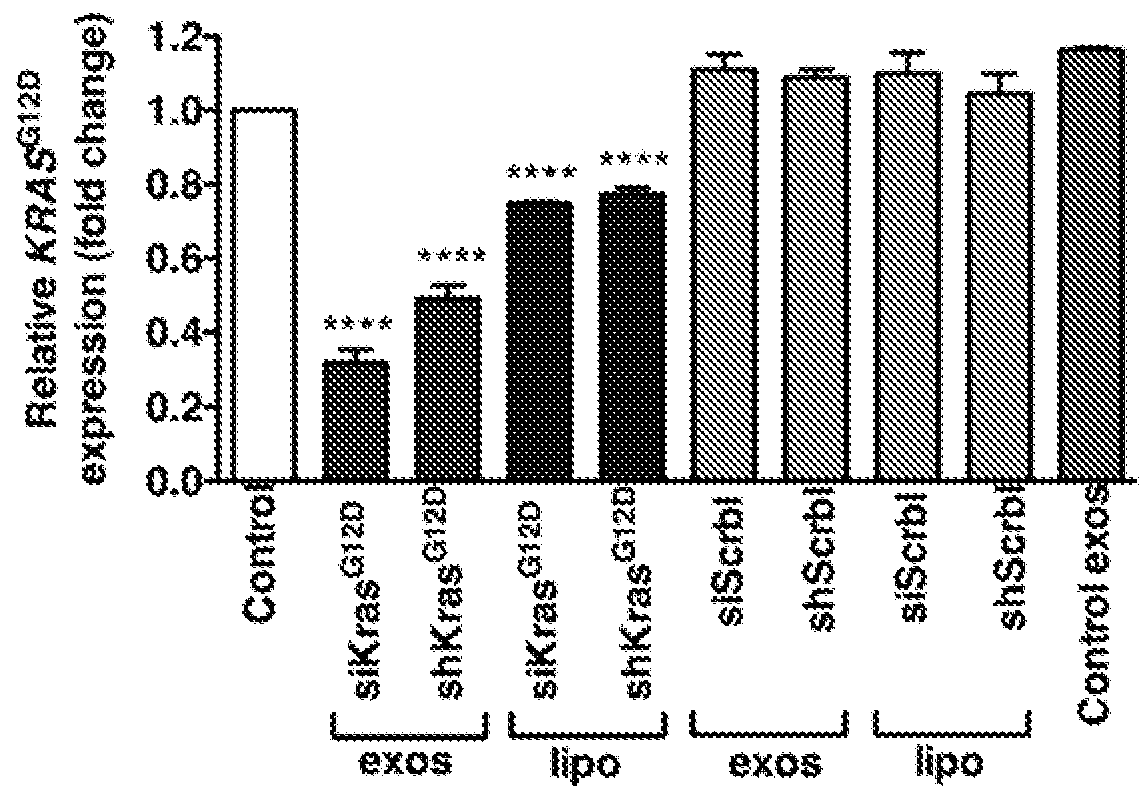
Use of exosomes for the treatment of disease
The present invention provides lipid-based nanoparticles (e.g., liposomes or exosomes) having CD47 on their surface and comprising a therapeutic agent (e.g., a therapeutic protein, an antibody, an inhibitory RNA, and / or a small molecule drug). Furthermore, the present invention provides for use of such lipid-based nanoparticles in therapy.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com