Coxsackie virus a16 strain and its application
A Coxsackie virus, A16 technology, applied in the direction of viruses, virus peptides, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problem that there is no standard strain of Coxsackie virus detection, and achieve the effect of good immunogenicity and high titer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1 Preliminary Screening of Coxsackievirus A16 Type Strain
[0084] Processing of clinical samples:
[0085] In a biological safety cabinet, 0.25 ml of each sample (pharyngeal and anal test sub-sample that has been tested positive for Coxsackievirus A16 by fluorescent quantitative PCR) was added to a centrifuge tube. Add 2.5 μl of penicillin and streptomycin solution, mix well, and place overnight at 4°C. Centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 20 min, and store the supernatant at 2-8°C for inoculation.
[0086] Virus isolation and culture:
[0087] Take the prepared healthy and non-contaminated RD cells grown to 80-90% density, and discard the cell culture medium. Inoculate 0.2ml / well of the processed sample into a 6-well plate, inoculate 1 well for each sample, and add 0.2ml / well of virus culture solution at the same time, place at 35°C 5% CO 2 Adsorption in the incubator for 1h. After that, add 3.5ml of virus culture solution to each well, and place at 35°C 5% CO 2 c...
Embodiment 2
[0157] Example 2 Plaque purification
[0158] The virus dilutions of the primary screened strains were inoculated in 6-well cell culture plates for purification.
[0159] (1) Cell preparation: RD cells that had grown into a monolayer were washed and digested and inoculated in a 6-well cell culture plate, 7×10 5 cells / well, supplemented with RD cell culture medium, placed in 5% CO 2 Incubate at 37±1°C in an incubator until a dense monolayer grows. Discard the original culture medium, wash the cell surface, and wash away the residual bovine serum and dead cells.
[0160] (2) Virus preparation: Dilute the virus solution by an appropriate multiple.
[0161] (3) Virus adsorption: inoculate the diluted virus solution, 0.4ml / well, set the virus solution control and cell control at the same time, and place in 5% CO 2 Adsorb in an incubator at 35°C for 1 to 2 hours, during which time the cell plate was gently shaken several times every 15 to 20 minutes to make it touch the entire c...
Embodiment 3
[0166] Example 3 Determination of Detecting Candidate Virus Strains
[0167] The virus strain purified by three plaques was amplified to the 5th generation to establish the original seed, and the relevant identification research and passage stability research were carried out on it. Strains with a high degree of infection were used as candidate strains for detection. Unless otherwise specified, see Example 1 for the specific research method operation steps.
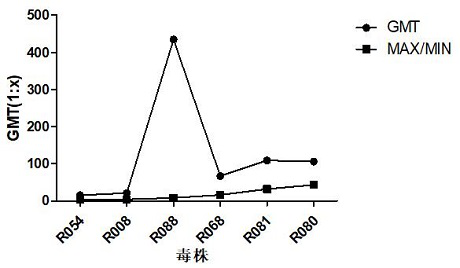
[0168] The identification research of original seed strains mainly includes immunogenicity, virus titration, genome sequencing analysis, and cross-neutralization ability research.
[0169] The research on the stability of subculture is mainly to subculture the original seed virus solution on RD cells in a certain proportion until the 15th generation, and carry out virus titration and genome sequence analysis on each generation of strains during the subculture process.
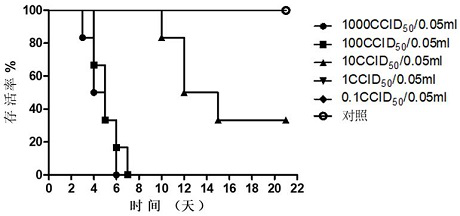
[0170] The results of the strain test show that th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com