Processing method of non-magnetic electric heater based on MEMS technology
A processing method and heater technology, applied in the process of producing decorative surface effects, microstructure technology, piezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devices, etc., to solve the problem of electrical insulation and reduce the effect of magnetic field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
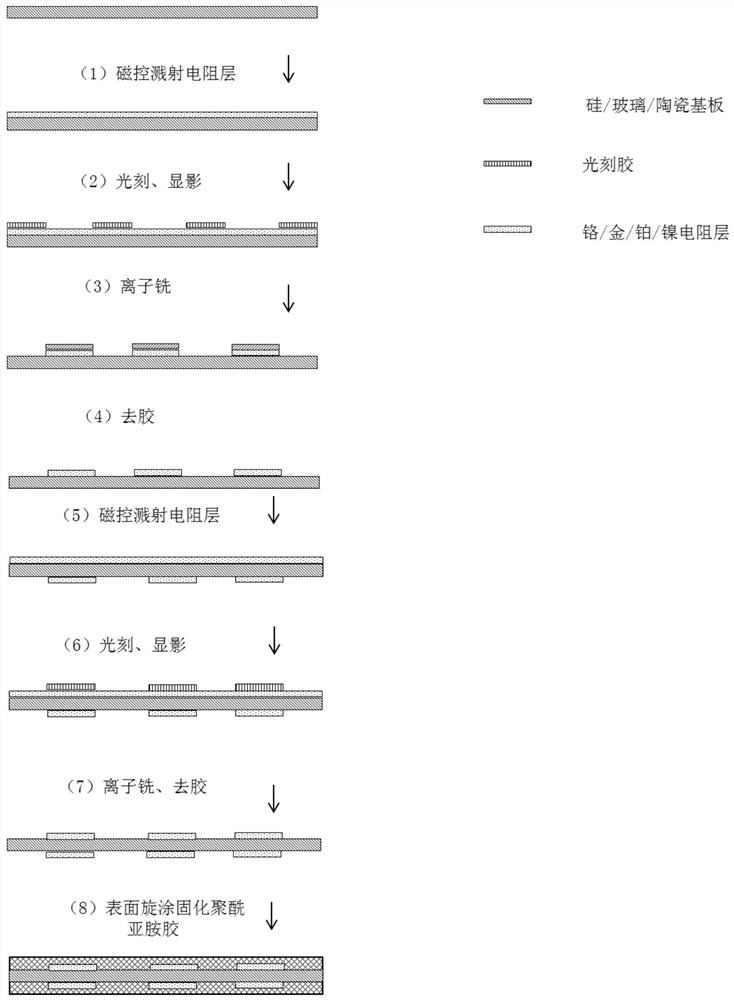
[0031] The first step is to process a resistance layer on the surface of a single crystal silicon wafer or ceramic or glass substrate: Magnetron sputtering of chromium / gold resistance layer on the surface of a single crystal silicon wafer or ceramic or glass, in which metal chromium is sputtered as an adhesion layer, gold as a resistive layer;
[0032] The second step, photolithography and development: pattern the surface of the substrate after sputtering the resistance layer, spin-coat a 5-micron-thick positive photoresist by using a positive resist process and perform a pre-baking process. Expose in the engraving machine, and finally develop and pattern in the developer;
[0033] The third step, ion milling: the patterned substrate is placed in an ion etching machine for ion milling process. Since the unpatterned area of the surface after removing the photoresist still has a chromium / gold seed layer, it is necessary to use a dry The excess metal layer is removed by French...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that in the first step, the chromium with excessive adhesion function in the resistance layer is replaced by metal titanium with higher adhesion function, the thickness is 30-80nm, and the thickness of the gold conductive layer is 100- 500nm; in the second step, a positive photoresist with a thickness of 10 microns and a line width of 20-300um is spin-coated by the positive resist process and pre-baked; in the third step, the resistive device layer is patterned by the ion milling process.
Embodiment 3
[0039] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that in the first step, the chromium with excessive adhesion function in the resistance layer is replaced by metal titanium with higher adhesion function, the thickness is 30-80nm, and gold is replaced by platinum as the resistance layer. The thickness is 100-3000nm; in the second step, a positive photoresist with a thickness of 10 microns and a line width of 20-300um is spin-coated in the second step and pre-baked; graphics.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com