A kind of preparation method of mutually immiscible copper-carbon supersaturated solid solution
A technology of mutual insolubility and solid solution, applied in the field of surface processing of materials, can solve the problems of reduced powder sintering performance, low interface bonding force, poor compatibility, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding oxidation or nitriding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] S1. Put copper powder (200 mesh) and carbon powder (200 mesh) into the ball mill according to the weight ratio of 100:6 for ball milling and mixing. The ball milling time is 2 hours; the powder after mixing is poured into the laminating machine, and the Pressed under a pressure of 30MPa for 18 hours; then put it into a vacuum sintering furnace for sintering, the sintering condition is to raise the temperature to 400°C at 5°C / min, keep the temperature for 30min after reaching 400°C, and then raise the temperature to 800°C at 10°C / min, and finally Incubate at 800°C for 60 minutes.
[0027] S2. Grinding and polishing the Cu-C composite material substrate with a specification of 10×10×10 cm to complete the pretreatment. The sandpaper used is 400, 800, 1000, 1200 mesh sandpaper, and the particle size of the diamond polishing agent is 0.5 μm.
[0028] S3. Carry out HCPEB irradiation treatment on the pretreated Cu-C composite material; according to the technical requirements o...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Same as Example 1, only change the number of times of electron beam irradiation in S3, select the electron beam energy as 27KeV according to the technical requirements of HCPEB equipment, and the energy density is 4J / cm 2 , the target-source distance is 15cm, and the sample is irradiated 5 times.
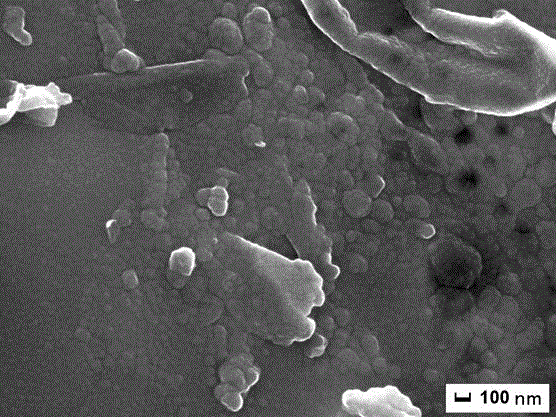
[0034] Carry out SEM observation to the sample surface after irradiation; image 3 It shows that the superfine grain structure is also formed locally on the surface of the sample after 5 irradiation treatments.
[0035] TEM observation of the irradiated samples showed that abundant vacancy cluster defects were formed after 5 irradiations.
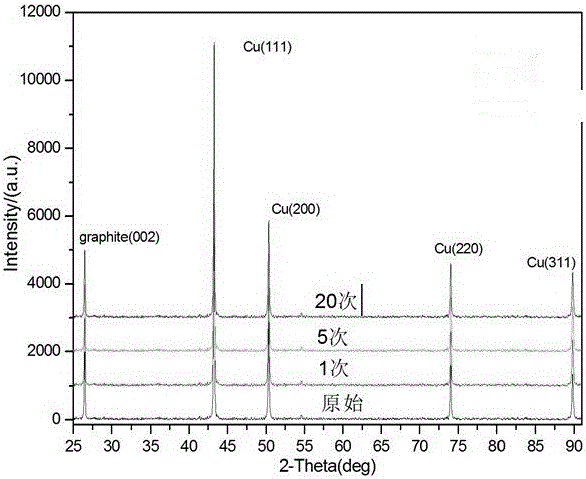
[0036] The structural changes of the material surface were analyzed by X-ray diffraction; the results showed that after 5 irradiation treatments, the diffraction peak intensity of (111) Cu increased compared with that of 1 irradiation, and it shifted to the left compared with the unirradiated sample shifted, but shifted to the right compar...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Same as Example 1, only change the number of times of electron beam irradiation in S3, select the electron beam energy as 27KeV according to the technical requirements of HCPEB equipment, and the energy density is 4J / cm 2 , the distance between the target and the source is 15cm, and the sample is irradiated 20 times.
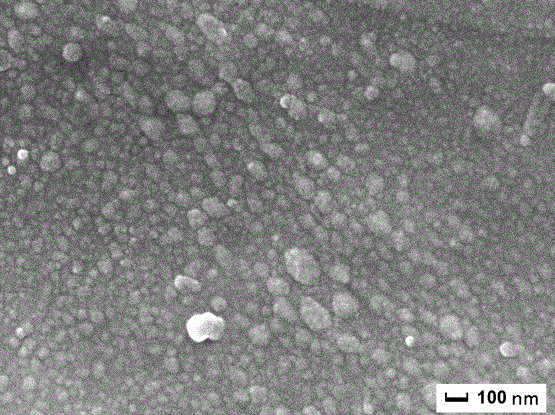
[0039] attached Figure 4 SEM observation was carried out on the surface of the sample after irradiation; the results showed that a large number of ultra-fine grain structures were locally distributed on the surface of the material after 20 irradiation treatments, and the size was between 70 and 100 nm. Spectrum (EDS) analysis, the results show that there are two elements of Cu and C, as attached Figure 5 shown.
[0040] TEM observation of the irradiated sample shows that after 20 times of irradiation, black spot defects (point defects) with a high density are formed.
[0041] The structural changes of the material were analyzed by X-ray diffraction; ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com