Random copolymer based on polyphosphoester as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of random copolymers and polyphosphates, which can be used in medical preparations of non-active ingredients, drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., and can solve problems such as no reports of phosphate ester copolymers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
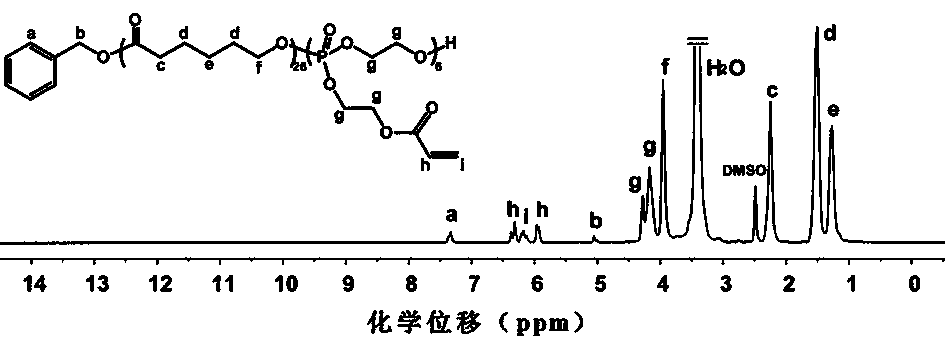
[0050] Example 1: Random copolymer Poly(CL) with side groups having carbon-carbon double bonds 26 - co -OPEA 6 )Synthesis
[0051] Initiation of the monomer ε-caprolactone (ε-CL) and the phosphate monomer 2-acrylate ethyloxy-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphospholane (OPEA) with benzyl alcohol Ring-opening copolymerization to prepare a random copolymer Poly(CL 26 - co -OPEA 6 ).
[0052] Dry the branched round-bottomed flask with a stirring bar in an oven at 120 °C for at least 24 hours, plug it with a glass stopper, connect it with an oil pump through a latex tube, and pump it to room temperature, then introduce high-purity argon gas, and then evacuate it. After repeating three times, it was filled with argon.
[0053] Benzyl alcohol (0.10 g, 0.93 mmol), ε-caprolactone (ε-CL) (4.51 g, 39.43 mmol), OPEA (2.24 g, 10.08 mmol), toluene (10 mL ) and stannous octoate [Sn(Oct) 2 ] (12 mg). After the reaction flask was filled with argon, the reaction was stirred in an oil bath at 90°C fo...
Embodiment 2
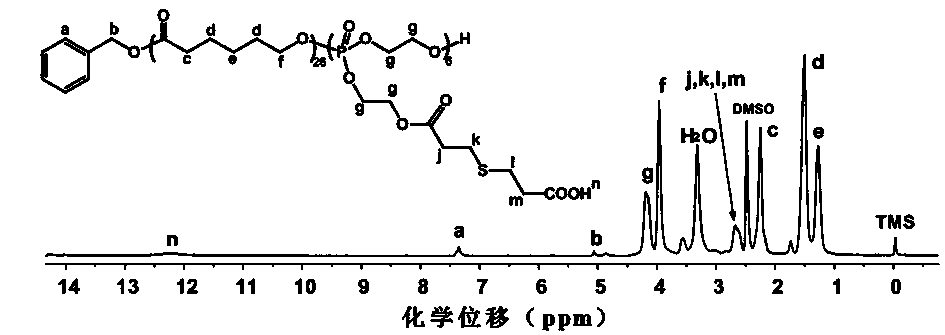
[0054] Example 2: Random copolymer Poly[CL with carboxyl groups in side groups 26 - co -(OPEA -COOH ) 6 ]Synthesis
[0055] The Poly(CL of embodiment one preparation 26 - co -OPEA 6 ) and mercaptopropionic acid, a mercapto reagent, were subjected to a mercapto-ene addition reaction under the irradiation of 365 nm ultraviolet light to obtain a random copolymer Poly[CL 26 - co -(OPEA -COOH ) 6 ].
[0056] Add Poly(CL 26 - co -OPEA 6 ) (0.52 g, 0.12 mmol), added chloroform to dissolve, then added mercaptopropionic acid (0.12 g, 1.08 mmol) and photoinitiator benzoin dimethyl ether (DMPA) (1 mg) in sequence, placed in a 365 nm ultraviolet lamp The reaction was carried out for 30 minutes. Shake the reaction dish gently every 5 minutes during the reaction to complete the reaction. After the reaction was finished, the reaction mixture was precipitated with 100 mL of ice anhydrous ether, and the ether was poured off to obtain a colorless viscous substance. The crude pro...
Embodiment 3
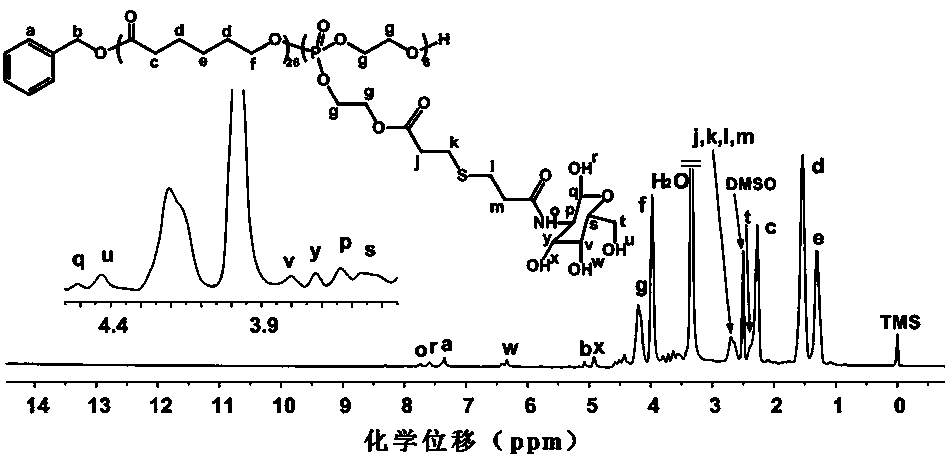
[0057] Example 3: Random copolymer Poly[CL with galactose groups in side groups 26 - co -(OPEA -Gal ) 6 ]Synthesis
[0058] Using galactosamine hydrochloride as the amino reagent, in 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC·HCl) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS ) in the presence of Poly[CL 26 - co -(OPEA -COOH ) 6 ] carboxyl group to undergo amidation reaction to obtain a random copolymer Poly[CL with liver cell targeting and biodegradability 26 - co -(OPEA -Gal ) 6 ].
[0059] In a 25 mL dry three-necked flask, add Poly[CL 26 - co -(OPEA-COOH) 6 ] (0.23 g, 0.05 mmol), 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC·HCl) (0.16 g, 0.83 mmol) and N-hydroxysuccinyl Imine (NHS) (0.08 g, 0.69 mmol), dissolved in 10 mL of dry dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), was activated for 12 hours. Triethylamine (0.07 g, 0.69 mmol) and galactosamine hydrochloride (0.11 g, 0.51 mmol) were dissolved in 5 mL of DMSO, and added dropwise to the reaction flas...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com