Method for separating copper from lead copper matte
A lead matte, 2SO4 technology, applied in the field of copper separation, can solve the problems of improper roasting temperature control, high maintenance cost, large oxygen consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of improving metal leaching rate, low equipment material requirements, and safe and reliable operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
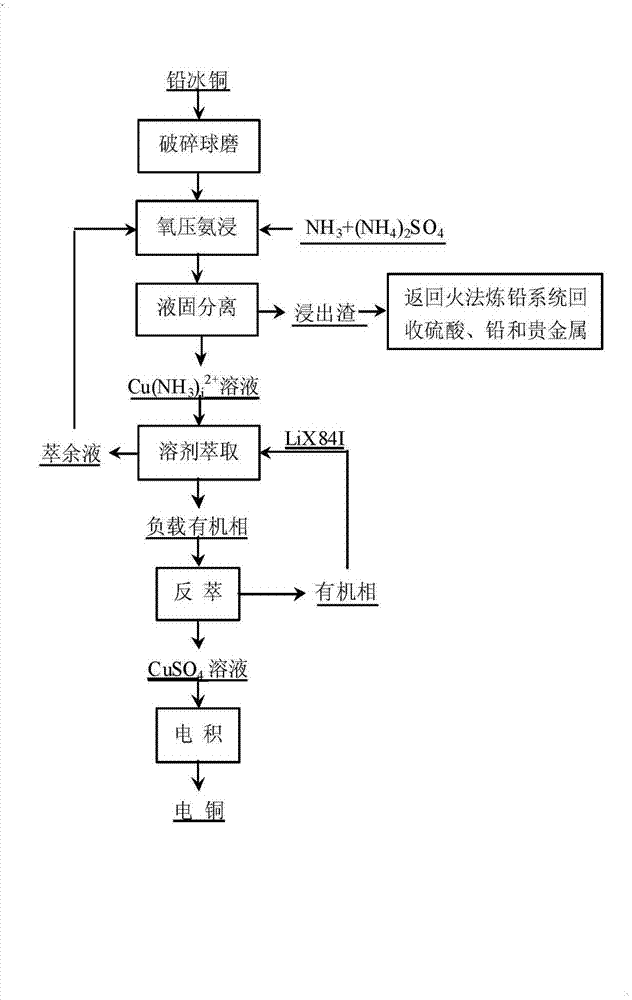
[0024] A method for separating copper from lead matte can be specifically realized through the following method steps:
[0025] ①The chemical composition of lead matte is (%): Cu 44.13, Pb 18.21, Fe 4.68, S 15.80, As 0.94, Zn 0.16, Si 0.16, Ag 0.166, crush the lead matte block, and use a ball mill to grind it to the particle size Below 140 mesh;
[0026] ②After ball milling, use NH 3 -(NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 Leaching, continuously feed oxygen during the leaching process; the process conditions of this step are: liquid-solid ratio 10:1; NH 3 with (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 molar ratio n [NH3] :n [(NH4)2SO4] = 5:1; total ammonia to copper molar ratio n [(NH3)T] :n [CuT] = 8:1; oxygen partial pressure 1.5Mpa; leaching temperature 120°C; leaching time 7h;
[0027] ③ After the leaching process is completed, liquid-solid separation is carried out; the leaching residue and Cu(NH 3 ) i 2+ The leaching solution and the leaching slag are returned to the pyro-method lead smelting system to rec...
Embodiment 2
[0031] A method for separating copper from lead matte can be specifically realized through the following method steps:
[0032] ①The chemical composition of lead matte is (%): Cu 30.65, Pb 5.89, Fe 28.12, S 21.72, As 0.85, Zn 0.36, Si 3.25, Ag 0.085, Au 36g / t, the lead matte block is broken, Use a ball mill to grind to a particle size below 100 mesh;
[0033] ②After ball milling, use NH 3 -(NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 Leaching, oxygen is continuously introduced during the leaching process; the process conditions of this step are: liquid-solid ratio 3:1; NH 3 with (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 molar ratio n [NH3] :n [(NH4)2SO4] = 6:1; total ammonia to copper molar ratio n [(NH3)T] :n [CuT] = 7:1; oxygen partial pressure 1.0Mpa; leaching temperature 200°C; leaching time 2h;
[0034] ③ After the leaching process is completed, liquid-solid separation is carried out; the leaching residue and Cu(NH 3 ) i 2+ The leaching solution and the leaching slag are returned to the pyro-method lead smelting ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A method for separating copper from lead matte can be specifically realized through the following method steps:
[0039] ① The chemical composition of lead matte is (%): Cu 26.21, Pb 8.04, Fe 15.70, S 9.02, As 2.72, Zn 0.65, Si 5.34, Ag 0.118, Au 18g / t, which will break the lead matte block , use a ball mill to grind to a particle size below 120 mesh;
[0040] ②After ball milling, use NH 3 -(NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 Leaching, continuously feed oxygen during the leaching process; the process conditions of this step are: liquid-solid ratio 5:1; NH 3 with (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 molar ratio n [NH3] :n [(NH4)2SO4] = 4:1; total ammonia to copper molar ratio n [(NH3)T] :n [CuT] = 10:1; oxygen partial pressure 0.3Mpa; leaching temperature 150°C; leaching time 5h;
[0041] ③ After the leaching process is completed, liquid-solid separation is carried out; the leaching residue and Cu(NH 3 ) i 2+ The leaching solution and the leaching slag are returned to the pyro-method lead smelting ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com