Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30results about How to "Low seed setting rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Castration method for rice hyberdization
InactiveCN103733984AImprove efficiencyLabor savingPlant genotype modificationPollinationResearch worker
The invention discloses a castration method for rice hyberdization, belongs to the technical field of crop breeding and particularly relates to a new castration method for rice hyberdization based on spikelet clipping and water spraying. The castration method for rice hyberdization comprises the following steps: 1, determining reasonable sowing time; 2, selecting rice plants; 3, pruning spikes of whole plants; 4, performing castration based on spikelet clipping and water spraying; and 5, performing pollination timely and efficiently. According to the castration method disclosed by the invention, the problems of high labor intensity, incomplete castration and hyberdization failure due to pistil damage in the past rice hyberdization work are solved, and the technology used in the castration method has the advantages of labor and cost economy, simplicity and convenience in operation, high hyberdization success rate, economy, environment friendliness and the like, and is highly popular among scientific research workers on breeding, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:江苏丰收种业有限公司 +1
Use of miR397 in drought resistance plant cultivation
InactiveCN101487021AImprove drought resistancePromote growthVector-based foreign material introductionFood safetyPlant cultivation
The invention discloses application of miR397 in the cultivation of drought-resistant plants, and by realizing the drought processing of paddy rice and detecting the miRNA expression level of processed samples, the invention discovers that the miR397 expression of the samples after the drought processing lies in a significant increasing trend, and the miR397 expression rise after the drought processing within 5 hours is more significant than the miR397 expression rise after the drought processing within 12 hours. The invention constructs a miR397 over-expression paddy rice mutant strain, which has better growth situation than wide paddy rice at relatively lower temperature and does not have obvious burliness difference with wide paddy rice, and results of simulated draught and post-draught recovery processing show that the paddy rice mutant strain has better drought resistance than wide paddy rice. The results provide a novel, simple and effective method for cultivating drought-resistant paddy rice and plants, which can be applied into large-scale popularization and application, does not cause environmental pollution and ensures food safety.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Tissue culture technique of plumbago auriculata
InactiveCN104686353ALow seed setting rateHigh proliferation rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyShoot
The invention discloses a tissue culture technique of plumbago auriculata. As plumbago auriculata is low in setting percentage, the seeds of plumbago auriculata are relatively expensive, plumbago auriculata is further low in expanding propagation to result in that the existing traditional propagation method cannot meet the application requirements of plumbago auriculata any more, however, the tissue culture technique of plumbago auriculata is capable of overcoming the shortcomings of the traditional propagation method and capable of producing good-quality plumbago auriculata variety on a large scale in relatively short time. According to the tissue culture technique, a plumbago auriculata in-vitro regeneration system is established by taking the tender twigs of plumbago auriculata as the explants and by virtue of the processes of explant processing, single bud induction, multiple shoot proliferation, rooting, acclimatization and transplant and the like; as a result, the proliferation ratio of plumbago auriculata can be greatly increased, and technical support is provided for the industrialized production of the tissue culture of plumbago auriculata.
Owner:刘祖英
Rice hybridization and castration method
InactiveCN104885928AImprove efficiencyLabor savingPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceHigh intensity
The invention provides a rice hybridization and castration method, belongs to the technical field of crop breeding, and particularly relates to a novel rice hybridization and emasculation-water spraying-castration method. The rice hybridization and castration method comprises the following steps: 1, selection of a reasonable sowing date; 2, selection of rice plants; 3, pruning of rice ears; 4, emasculation, water spraying and castration; 5, timely and efficient pollination. Through the adoption of the rice hybridization and castration method, the problem that the conventional rice hybridization work fails due to high labor intensity, incomplete castration and damage to pistil is solved; the rice hybridization and castration method has the advantages that the labor consumption and the cost are reduced, the operation is simple and convenient, the hybridization success rate is high, and the economical and environment-friendly effect is achieved, is deeply welcomed by scientific research breeding workers, and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:ANHUI HUIDA AGRO
Wheat mutation breeding method
InactiveCN103299900AIncrease frequency of chemical mutagenesisLittle physical damagePlant genotype modificationEthylmethane SulfonateChemical mutagens
The invention provides a wheat mutation breeding method and aims to improve the chemical mutagenesis efficiency, generate a relative high point mutation frequency and have relative little chromosomal aberration. The wheat mutation breeding method disclosed by the invention adopts a 0.5% EMS (Ethylmethane Sulfonate)-phosphoric acid buffering solution to treat wheat pollen to induce andro gametes to have variation so as to obtain variant seeds; the 0.5% EMS-phosphoric acid buffering solution takes a phosphoric acid buffering solution as a solvent and a chemical mutagen ethylmethane sulfonate EMS is diluted to the volume ratio concentration of 0.5%; the mol concentration of the phosphoric acid buffering solution is 1 / 15mol / L; the dosage of the 0.5% EMS-phosphoric acid buffering solution is 25-50 microliters on each floret; and the wheat pollen is pollen which is about to be ripe or pollen grains which are primarily ripe.
Owner:WHEAT RES INST OF AGRI SCI
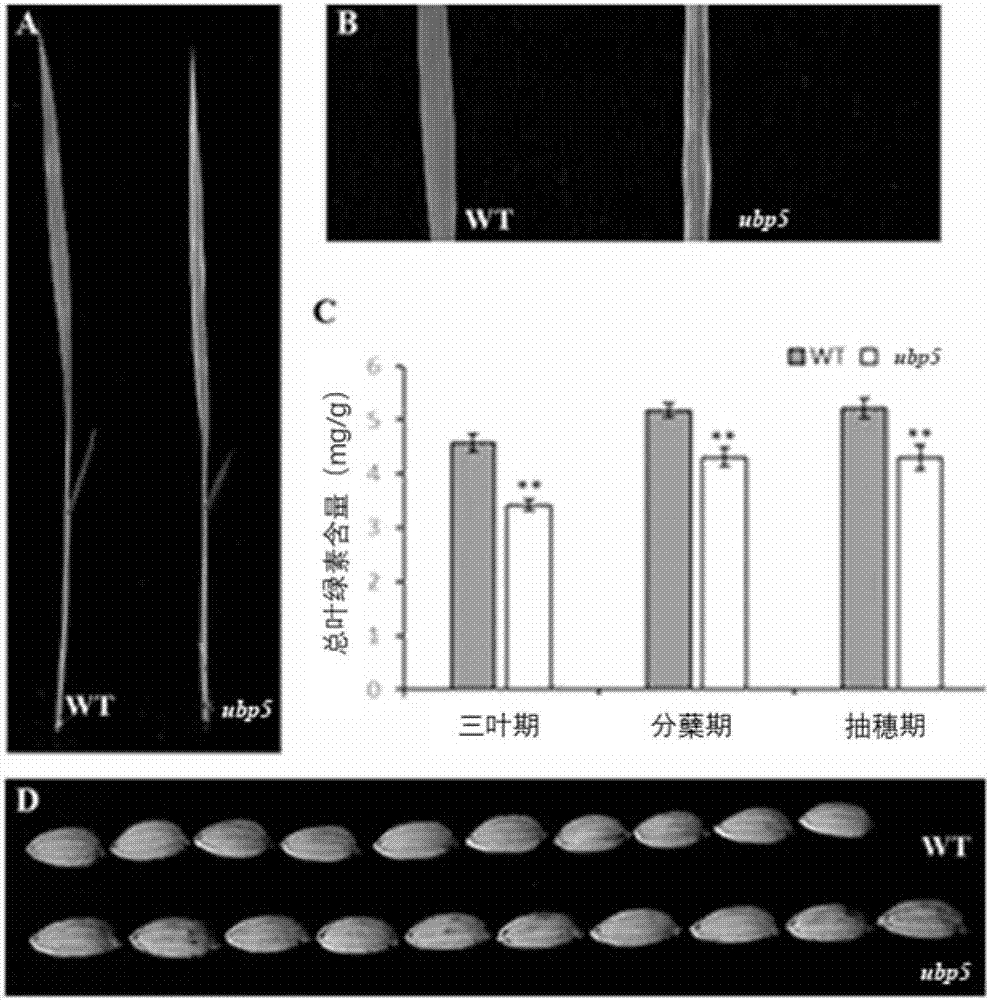
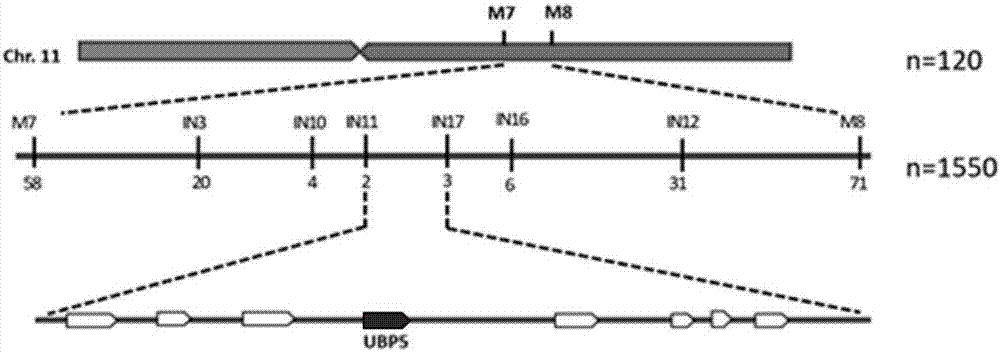
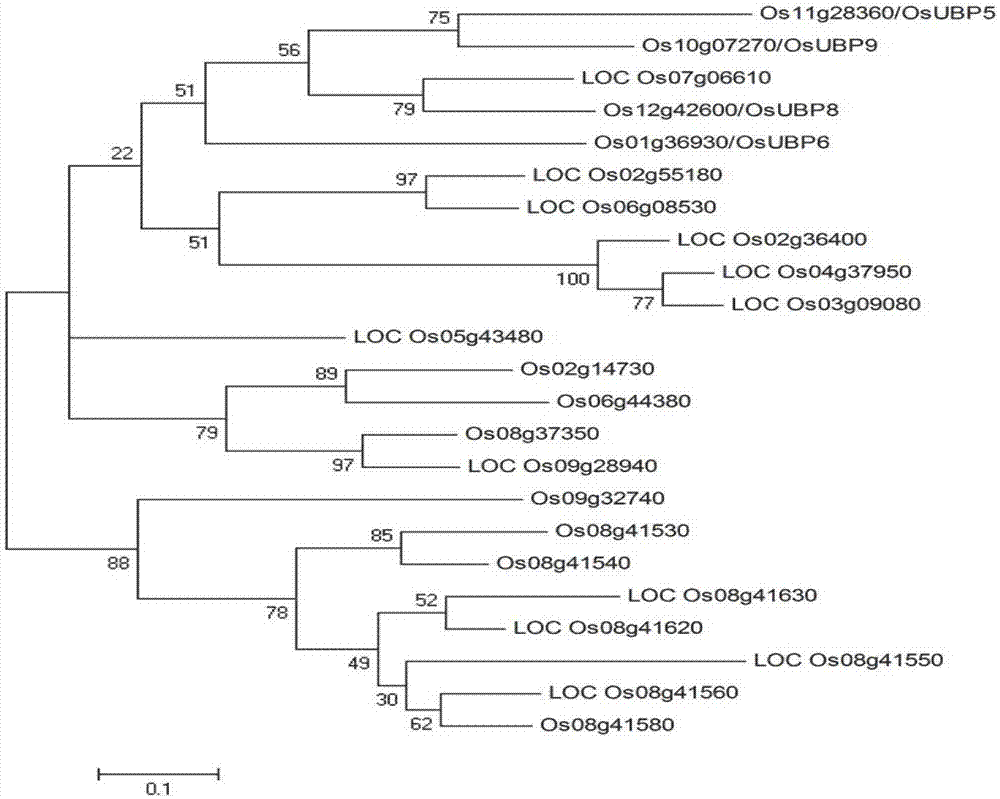
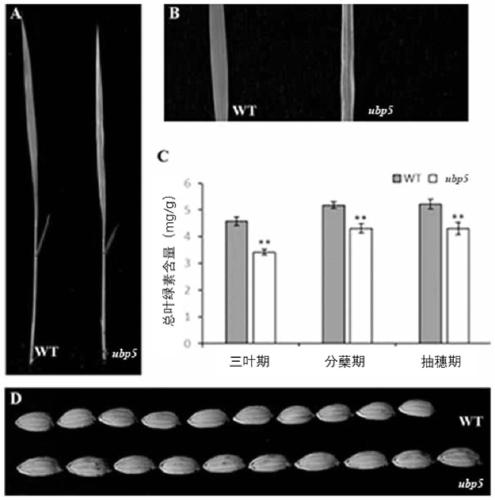
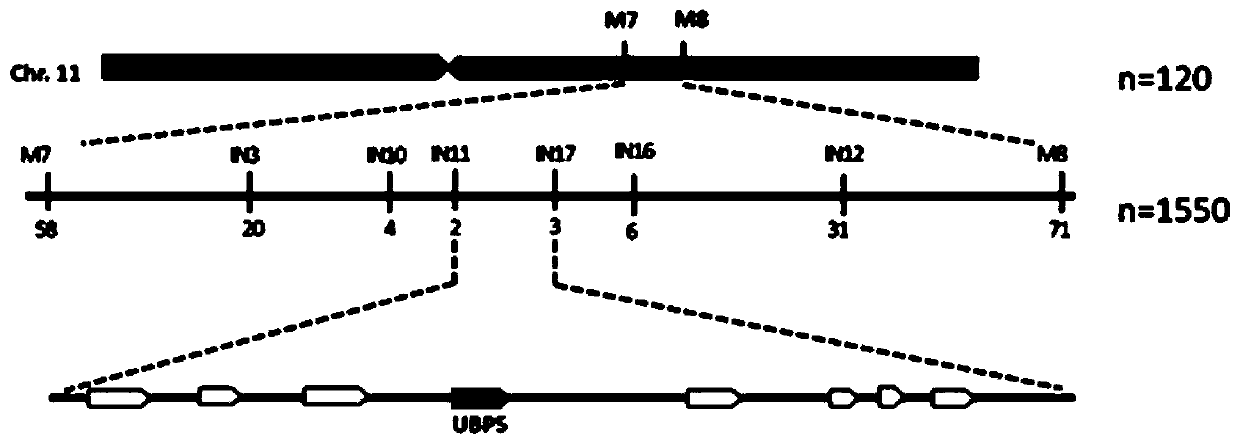
Deubiquitinating enzyme gene UPB5 for regulating and controlling grain shape and leaf color of rice and application thereof
InactiveCN107326035ALow seed setting rateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionProtein proteinGrain shape
The invention provides a deubiquitinating enzyme gene UPB5 for regulating and controlling a grain shape and leaf color of rice. The deubiquitinating enzyme gene UPB5 has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 in the description. The invention further provides a protein with a UBP5 gene code of the rice, and the protein has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.3 in the description. The experiment proves that the deubiquitinating enzyme gene UPB5 of the rice can cause the leaf blade color and seed shape of the rice to change; the invention further finds that after the ubiquitination enzyme gene UPB5 of the rice mutates, the leaf blades of the rice show the shape of a stripe; the seeds are elongated; the ripening rate becomes lower; the total content of chlorophyll is obviously reduced. The invention provides the application of the UBP5 gene and the mutant of the UBP5 gene to genetic improvement breeding of rice germplasm resources, thereby having a relatively good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Light effective agent
InactiveCN1425305AImprove photosynthesis efficiencyLow costBiocideAnimal repellantsSchizonepetaStemona
The light effective agent is used for raising the efficiency of plant's photosynthesis. It is prepared with astragalus root and other vital energy invigorating Chinese medicine materials, wolfberry fruit and other Yin-nourishing Chinese medicinal materials, eucommia bark and other Yang invigorating Chinese medicinal materials, sessile stemona root and other cough-relieving and phlegm-eliminating Chinese medicinal materials, acanthopanax bark and other diuresis Chinese medicinal materials and schizonepeta herb and other surfacial evil-expelling Chinese medicinal materials and through mixing with red sugar and alcohol and decoction. It is used to spray crop to obtain high yield and high quality variety.
Owner:广西光合绿神生物有限公司
Manglietiastrum sinicum Law bending pruning reproduction seedling culture method
InactiveCN105248225ALow seed setting rateIncrease success rateCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsPlant propagationManglietiastrum sinicum
The invention discloses a manglietiastrum sinicum Law bending pruning propagation seedling culture method, belonging to the field of plant propagation. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a 3 to 4-year-old manglietiastrum sinicum Law branch, and ringing the branch for one circle respectively at upper and lower positions, away from a trunk by 8 to 12cm, on the base of the branch, wherein the two circles have the width of 2 to 3cm and are deep into a xylem; peeling of a bark, then sleeving with a proper bamboo section, fixing the bamboo section on the branch, filling the bamboo section with a wet rooting medium prepared in advance, keeping the wetness of the medium in the bamboo section, and timely replenishing water for the medium in the bamboo section, wherein rooting is started after 30 days, and after 180 days the branch can be sawn off to serve as a seedling for field planting. The invention provides the bending pruning seedling culture method for a rare plant, i.e., manglietiastrum sinicum Law; the method greatly increases the seedling culture success rate of the manglietiastrum sinicum Law, and achieves an aim of quick cultivation for propagation expanding.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Light effective agent
InactiveCN1225173CImprove photosynthesis efficiencyLow costBiocideAnimal repellantsSchizonepetaPhotosynthesis
The light effective agent is used for raising the efficiency of plant's photosynthesis. It is prepared with astragalus root and other vital energy invigorating Chinese medicine materials, wolfberry fruit and other Yin-nourishing Chinese medicinal materials, eucommia bark and other Yang invigorating Chinese medicinal materials, sessile stemona root and other cough-relieving and phlegm-eliminating Chinese medicinal materials, acanthopanax bark and other diuresis Chinese medicinal materials and schizonepeta herb and other surfacial evil-expelling Chinese medicinal materials and through mixing with red sugar and alcohol and decoction. It is used to spray crop to obtain high yield and high quality variety.
Owner:广西光合绿神生物有限公司
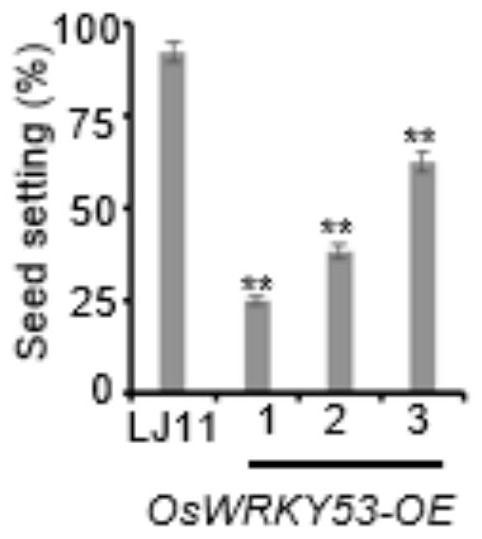
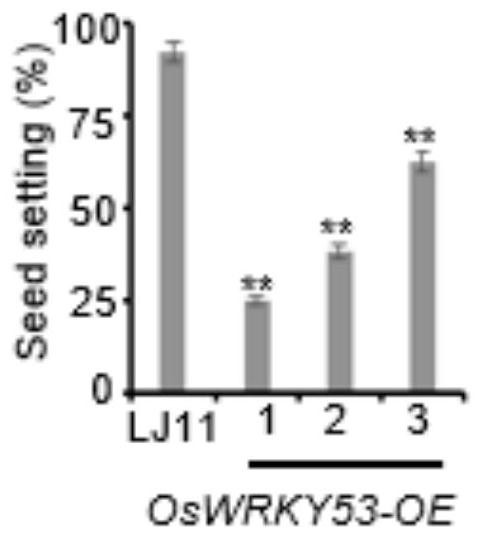
Application of rice transcription factor OsWRKY53 in negative regulation and control of cold tolerance of rice in booting stage
ActiveCN112592394AImproving Cold Tolerance of Rice at Booting StageNegative regulation of GA contentPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringTranscriptional activityMutant
The invention discloses an application of a rice transcription factor OsWRKY53 in negative regulation and control of cold tolerance of rice in a booting stage, aims to provide the new application of the rice transcription factor OsWRKY53 in negative regulation and control of the cold tolerance of the rice in the booting stage, and provides an important theoretical basis for increasing the yield ofthe rice under a low-temperature stress. According to the invention, a new function that the OsWRKY53 participates in regulating and controlling the cold tolerance of the rice in the booting stage isdiscovered, and a molecular mechanism that the OsWRKY53 negatively regulates and controls the cold tolerance of the rice in the booting stage is analyzed. The low-temperature treatment can cause thereduction of the GA content in the rice anther, but the GA content in an oswry53 mutant is obviously higher than that in a wild type. Experiments show that the OsWRKY53 can be directly combined with and inhibit the transcriptional activity of GA related biosynthetic genes OsGA20ox1, OsGA20ox3 and OsGA3ox1, so that the GA content in the rice anther is negatively regulated and controlled, and the cold resistance of the rice in the booting stage is negatively regulated and controlled.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
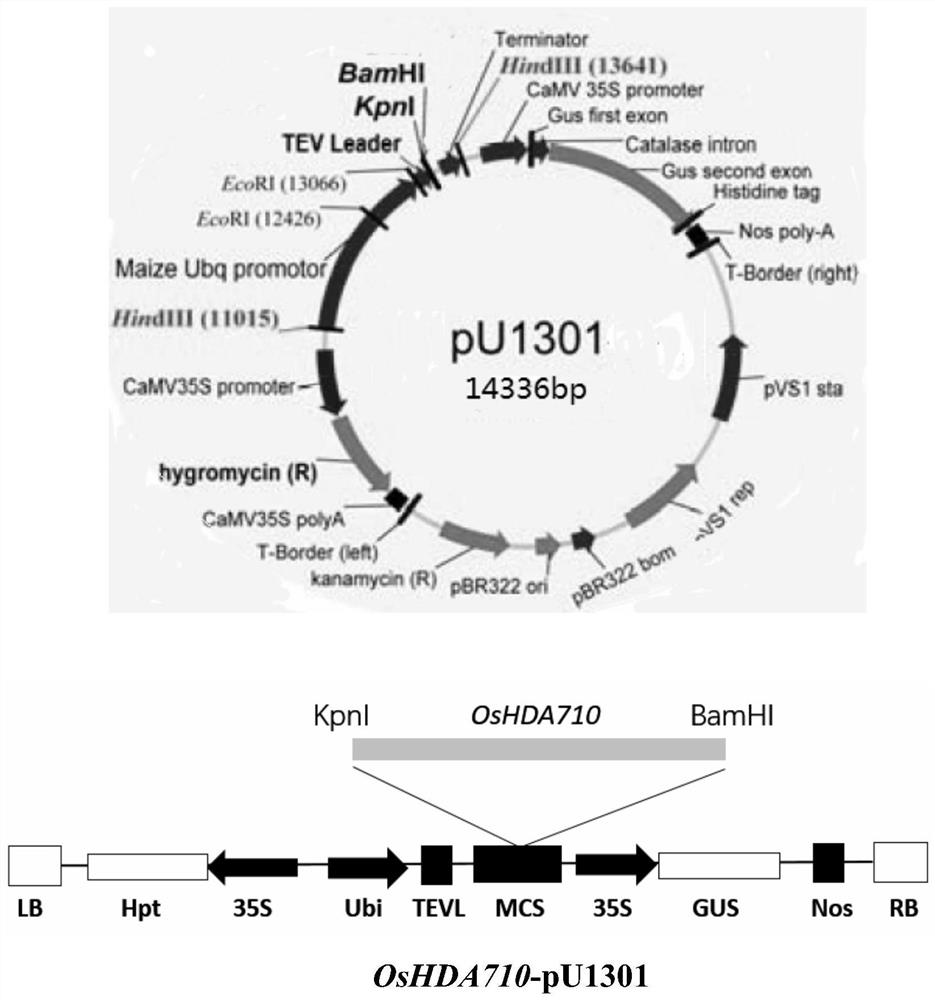
Application of OsHDA710 epigenetic regulatory factor gene in rice development and stress resistance
InactiveCN112322645AExpand the planting areaIncreased scale of industrializationHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyPlant hormone
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to application of an OsHDA710 epigenetic regulatory factor gene in rice development and stress resistance. TheOsHDA710 epigenetic regulatory factor gene is an HDAC family histone deacetylase gene related to stress resistance, and the nucleotide sequence of the OsHDA710 epigenetic regulatory factor gene is asshown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The gene is induced by adversity such as drought simulation, cold, salt and heat shock and plant hormones such as ABA, NAA, 6-BA, JA and IAA. The setting percentage of a gene mutant is remarkably reduced under natural conditions. NaCl and ABA are used for treating overexpression, mutants and wild type plant seedlings, it is found that the mutants of the gene are resistant to NaCl and ABA, and meanwhile growth and the seed germination rate of overexpression plants of the gene are both affected by exogenous ABA. After ABA treatment, the expression level detection of stress resistance related genes of transgenic family plants of different mutants shows that the gene has an important regulation and control function in the rice resistance process.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Rice hybridization emasculation method
A rice hybridization emasculation method belongs to the field of crops breeding technology and specifically relates to a new method for rice hybridization spikelets-shearing water-spraying emasculation. The rice hybridization emasculation method of the invention comprises the following steps: 1, reasonable sowing time; 2, rice plant selection; 3, pruning and panicle trimming; 4, spikelets-shearing water-spraying emasculation; and 5, timely and efficient pollination. Problems of previous rice hybridization work, such as high labor intensity, halfway emasculation and hybridization failure caused by damage to pistil are solved. The technology of the invention is labor-saving and cost-saving, is simple to operate, has high success rate of hybridization, is economic and environment friendly, is deeply popular with breeding researchers, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:安徽富牧通生物科技有限公司
UCH320 protein and application of coding gene thereof in adjusting and controlling plant growth and development
The invention discloses UCH320 protein and an application of encoding code thereof in adjusting and controlling plant growth and development. The application provided by the invention is an application of protein consisting of amino acid sequences shown by a sequence 1 in a sequence table or coding genes thereof in adjusting and controlling the plant growth and development. The plant growth and development is specifically embodied in at least one of (1) and (2): (1) the fructification rate of the seed; (2) the weight of the seed. Proven by experiment, in the development process of rice, the expression level of UCH320 protein in the rice is reduced by an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference technology, the rice seed can be caused to show the following phenotype: compared with the wild type rice seed, the fructification rate is reduced, the fertile seed is also long and thin, and the weight of the seed is also obviously reduced. The invention lays foundation for finding out simpler ideas and methods for creating crops with high-yield characters.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
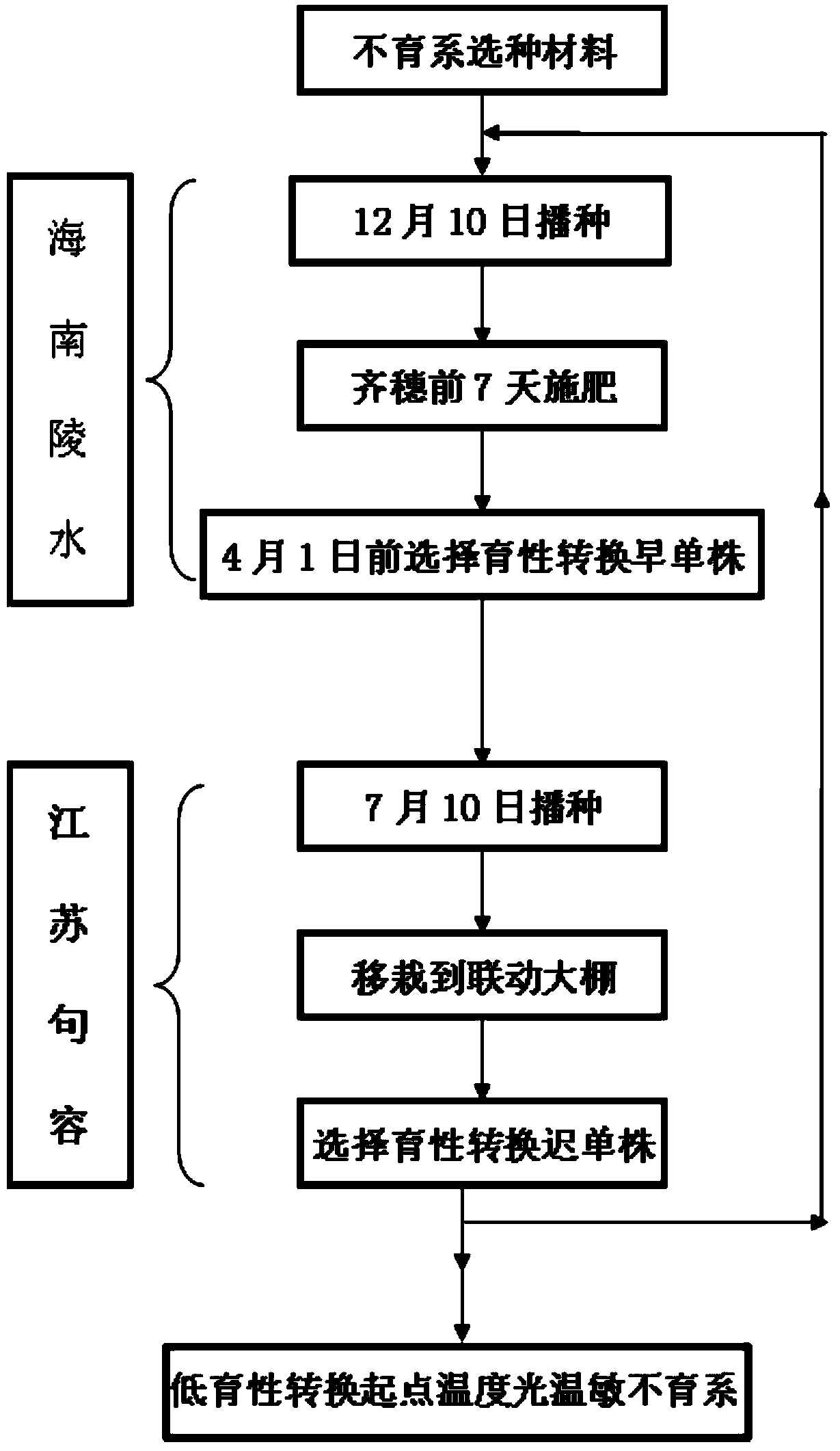
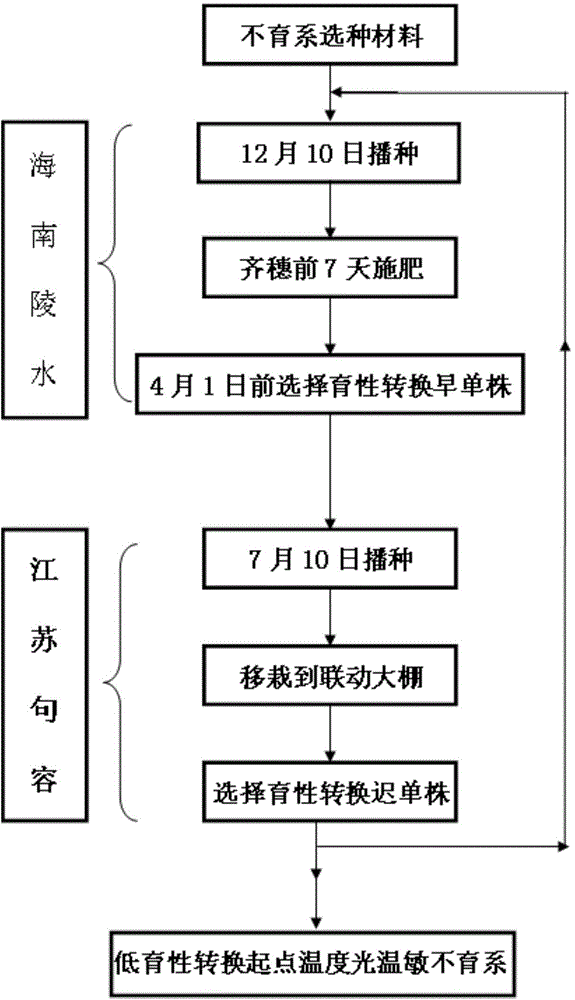
Low-fertility-transition-starting-point-temperature photo-thermo-sensitive sterile line breeding method
ActiveCN103461042ALow combining abilityImprove the coordination effectPlant genotype modificationRice cultivationAgricultural scienceLow fertility
The invention discloses low-fertility-transition-starting-point-temperature photo-thermo-sensitive sterile line breeding method, which comprises the steps that sterile line seed selection materials are sown in Lingshui of Hainan Province on December 10, and individual plants or single ears with early fertility transition are selected for reserving seeds; the seeds are sown in Jurong of Jiangsu Province on July 10, and entire individual plants with late fertility transition are selected for reserving seeds. By adopting the method, low-fertility-transition-starting-point-temperature photo-thermo-sensitive sterile lines can be simply and conveniently obtained, the bred two sterile lines have the advantages of outstanding comprehensive agronomic characters such as good combining ability, strong tillering ability and high percentage of ear-bearing tillers, the effect of saving labor and cost is effectively obtained and the goal of improving the breeding efficiency is achieved.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
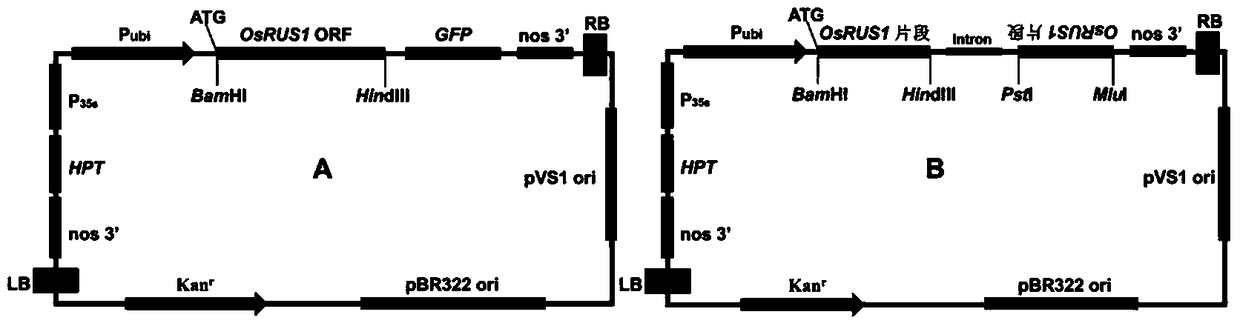
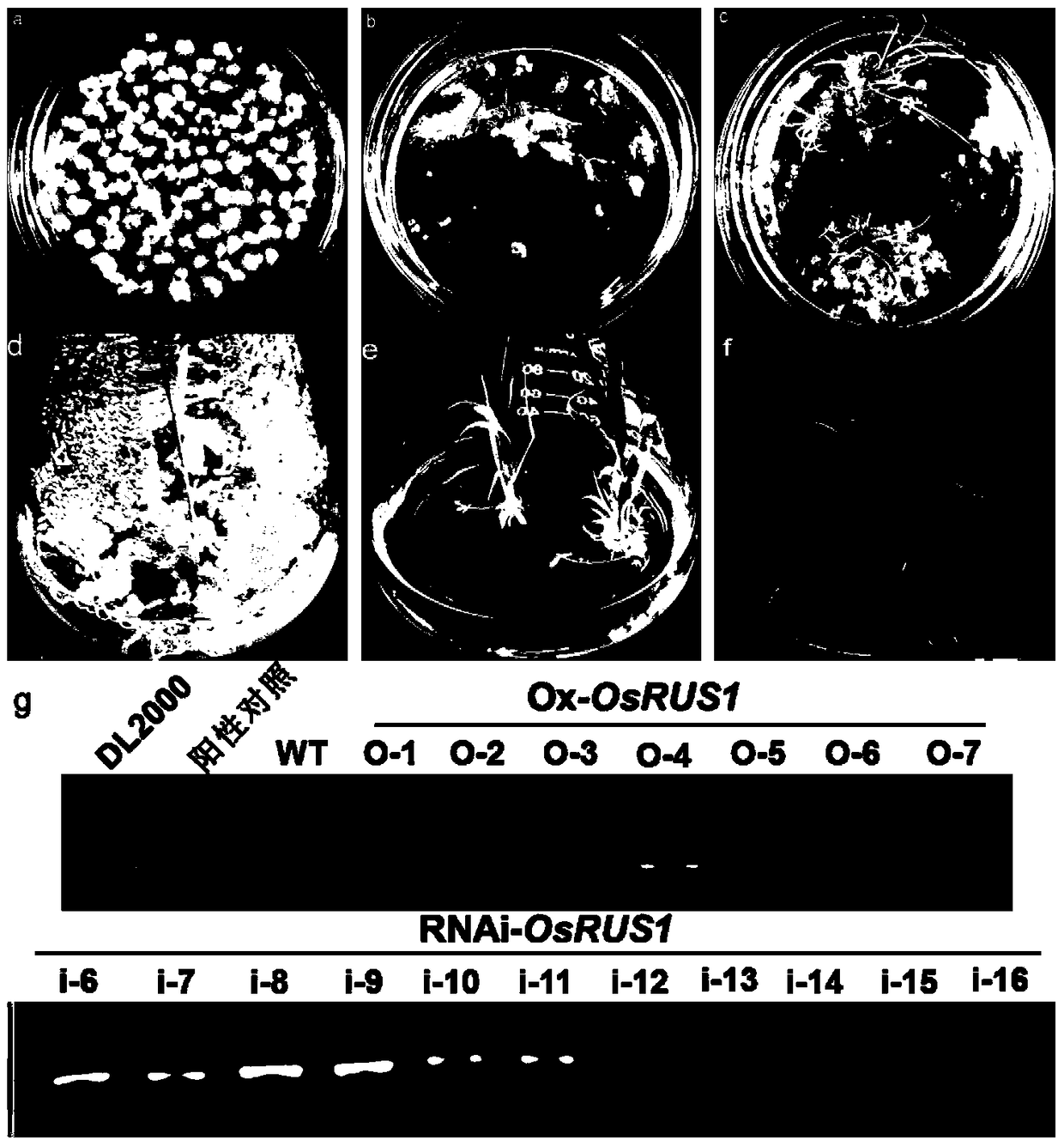
OsRUS1 protein and application of encoding genes thereof in control of tiller angle and tiller number of rice
The invention discloses an OsRUS1 protein and an application of encoding genes thereof in control of tiller angle and tiller number of rice. The amino acid sequence of the OsRUS1 protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the encoding genes of the OsRUS1 protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The inventor finds that the OsRUS1 protein has a function of controlling the tiller angle and tiller number of rice, and according to overexpression, plant type looseness, tiller reduction and rice ear lengthening are caused. According to the OsRUS1 protein and the encoding genes thereof, the tillering mechanism or signal path of rice can be further researched; and rice varieties with loose or compact plant types can be obtained by inhibiting or promoting the expression quantity of the OsRUS1 protein.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Application of rice transcription factor oswrky53 in negative regulation of cold tolerance at rice booting stage
ActiveCN112592394BNegative regulation of GA contentDecreased fertilityPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyBiosynthetic genes
The application of rice transcription factor OsWRKY53 in negatively regulating the cold tolerance of rice booting stage, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a new application of rice transcription factor OsWRKY53 in negatively regulating the cold tolerance of rice booting stage, which provides a basis for improving the yield of rice under low temperature stress. an important theoretical basis. The present invention discovers the new function of OsWRKY53 involved in regulating the cold tolerance at the booting stage of rice, and analyzes the molecular mechanism of OsWRKY53 negatively regulating the cold tolerance at the booting stage of rice. Low temperature treatment resulted in a decrease in GA content in rice anthers, but the GA content in the oswrky53 mutant was significantly higher than that in the wild type. Experiments have shown that OsWRKY53 can directly bind to and inhibit the transcriptional activity of GA-related biosynthetic genes OsGA20ox1, OsGA20ox3, and OsGA3ox1, thereby negatively regulating the GA content in rice anthers and negatively regulating the cold tolerance of rice at booting stage.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
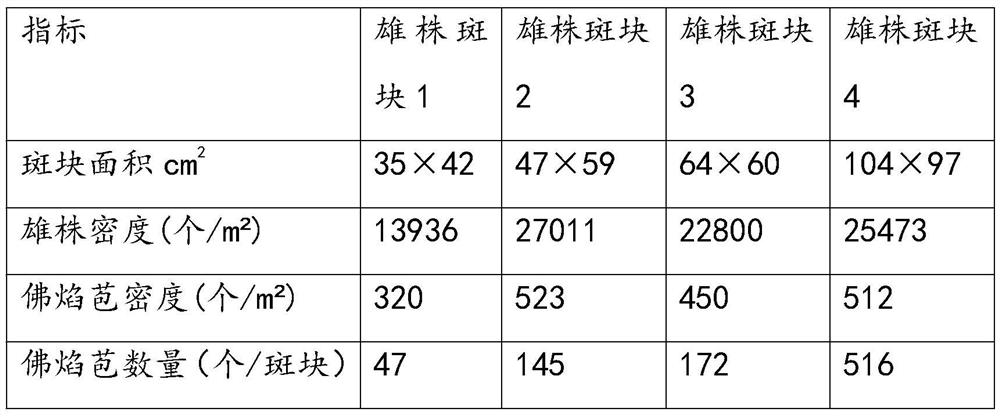
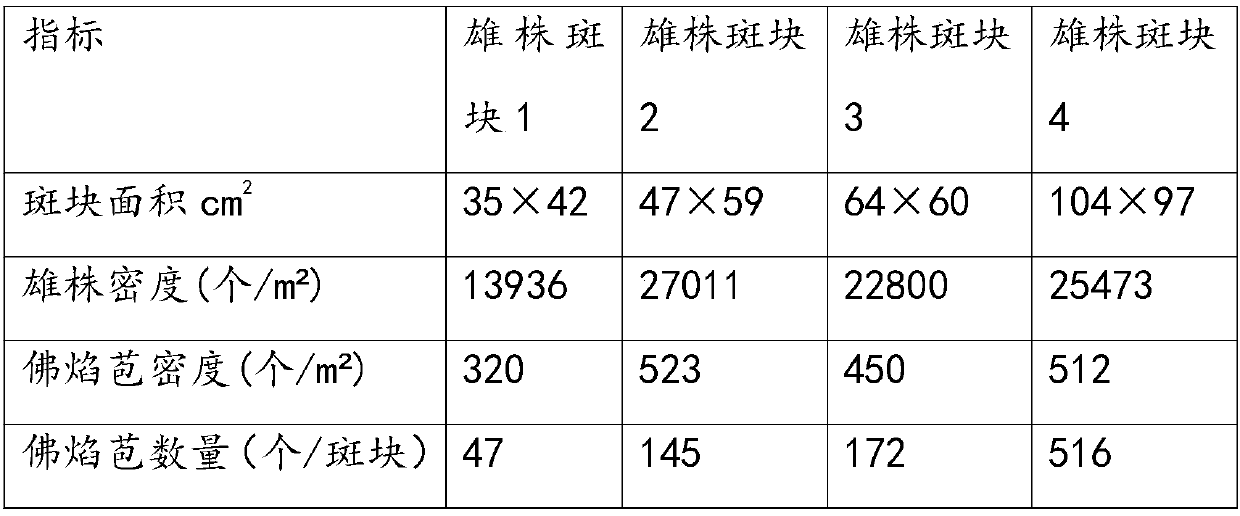
A kind of field effective harvesting method of red fiber shrimp seaweed fruit
The invention relates to a method for effectively harvesting red fiber shrimp seaweed fruit in the field. On the basis of accurately locating the position of the male plant patch in the population at the full flowering stage, within the effective pollination radius circle (20m) of the female flower around the male plant patch Collect female spathes with a fruit size of >2mm in length and >3.5mm in width, place them in a 40-mesh net bag, hang them in seawater for 15 days, and retrieve them after they are fully mature. Under the conditions of light and temperature in natural sea areas, the present invention utilizes male plants to locate and limit the water area and the size of fruit picking, thereby achieving a high harvest rate of red fiber shrimp seaweed fruit under the conditions of low cost and low labor intensity .
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Wild effective harvesting method of phyllospadix iwatensis fruit
The invention relates to a wild effective harvesting method of a phyllospadix iwatensis fruit. The method includes the steps: collecting female spathes of fruits with the length of 2mm and the width of 3.5mm in an effective pollination radius ring (20m) of female flowers on the peripheries of male plant patches based on accurate positioning of the male plant patches in population at a full-bloom stage; placing the female spathes into a 40-mesh net bag; locally hanging the net bag in sea water for 15 days; taking out the net bag after the female spathes completely mature. Under the conditions of light, temperature and the like in a natural sea area, the male plants are positioned, and a fruit picking water area and fruit picking size are limited, so that high harvesting rate of the phyllospadix iwatensis fruit is achieved under the conditions of low cost and labor intensity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
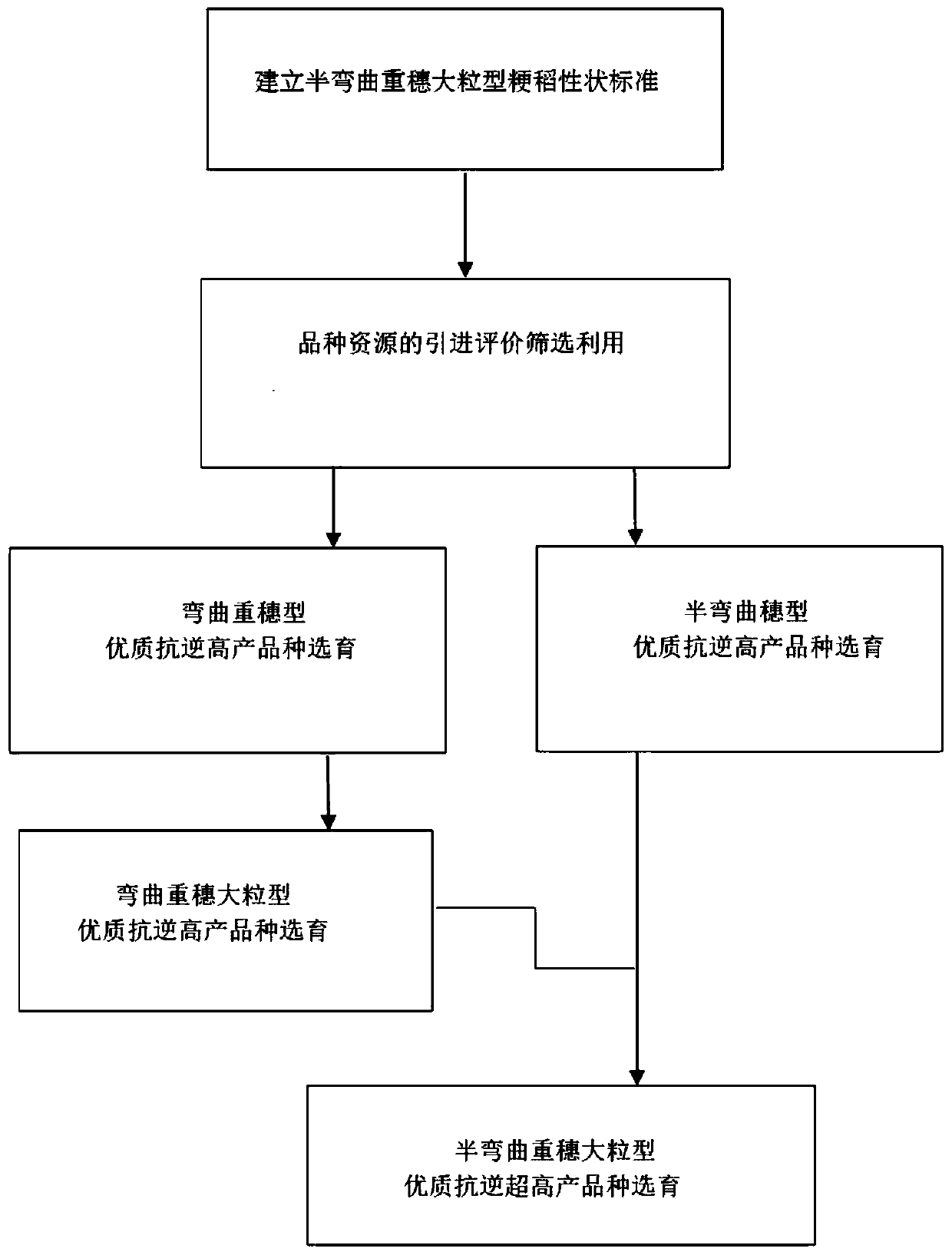
Method for breeding half-bending heavy-panicle large-grain type japonica rice
PendingCN111011209AGood ventilation and light transmissionImprove uprightnessPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention relates to a method for breeding half-bending heavy-panicle large-grain type japonica rice. The method comprises implementation steps of (I) establishing the property standard of the half-bending heavy-panicle large-grain type japonica rice; (II) performing introduction, evaluation, screening and utilization of variety resources; (III) performing breeding of bending heavy-panicle type superior-stress-tolerance high-yield varieties and half-bending panicle type superior-stress-tolerance high-yield varieties; (IV) performing breeding of bending heavy-panicle large-grain type superior-stress-tolerance high-yield varieties; and (V) performing breeding of half-bending heavy-panicle large-grain type superior-stress-tolerance extra-high-yield varieties. Through the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the bred varieties concurrently have double advantages of erect-panicle type varieties and bending-panicle type varieties, comprehensive stress tolerance polymerization is realized, breeding objectives of being superior, tolerant to stress and extra-high in yield are achieved, the selection efficiency and the probability of directionally breeding objective traitsare greatly improved, and the application effects are quite significant.
Owner:天津市优质农产品开发示范中心
Application of osrus1 protein and its coding gene in controlling rice tiller angle and tiller number
The invention discloses an OsRUS1 protein and an application of encoding genes thereof in control of tiller angle and tiller number of rice. The amino acid sequence of the OsRUS1 protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the encoding genes of the OsRUS1 protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The inventor finds that the OsRUS1 protein has a function of controlling the tiller angle and tiller number of rice, and according to overexpression, plant type looseness, tiller reduction and rice ear lengthening are caused. According to the OsRUS1 protein and the encoding genes thereof, the tillering mechanism or signal path of rice can be further researched; and rice varieties with loose or compact plant types can be obtained by inhibiting or promoting the expression quantity of the OsRUS1 protein.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
UCH320 protein and application of coding gene thereof in adjusting and controlling plant growth and development
The invention discloses UCH320 protein and an application of encoding code thereof in adjusting and controlling plant growth and development. The application provided by the invention is an application of protein consisting of amino acid sequences shown by a sequence 1 in a sequence table or coding genes thereof in adjusting and controlling the plant growth and development. The plant growth and development is specifically embodied in at least one of (1) and (2): (1) the fructification rate of the seed; (2) the weight of the seed. Proven by experiment, in the development process of rice, the expression level of UCH320 protein in the rice is reduced by an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference technology, the rice seed can be caused to show the following phenotype: compared with the wild type rice seed, the fructification rate is reduced, the fertile seed is also long and thin, and the weight of the seed is also obviously reduced. The invention lays foundation for finding out simpler ideas and methods for creating crops with high-yield characters.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
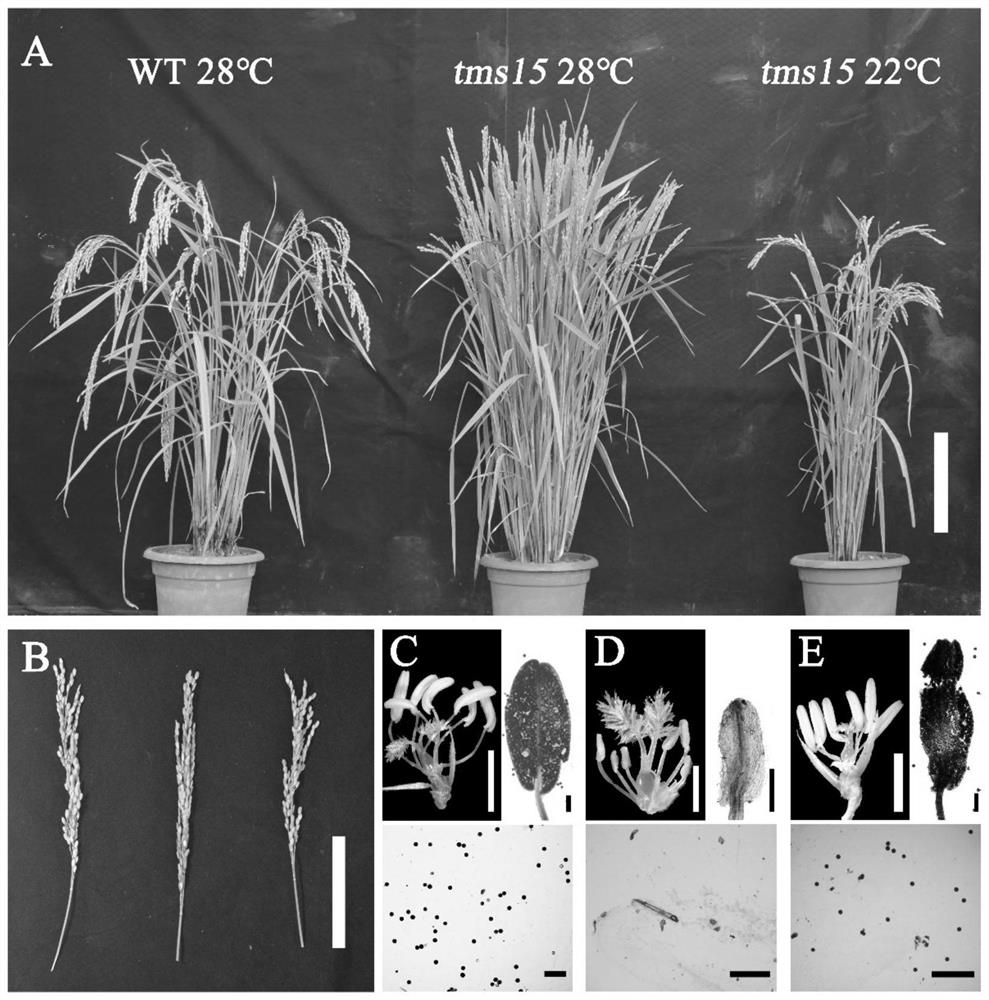
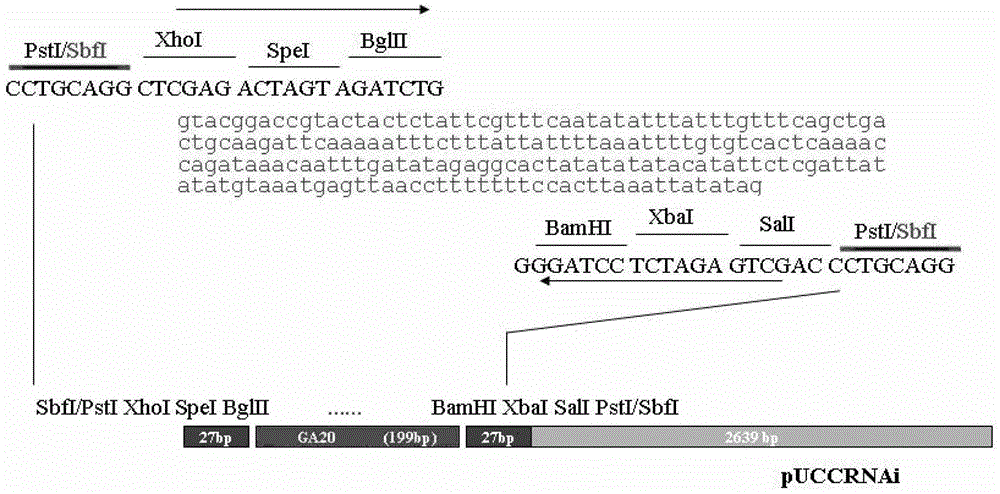
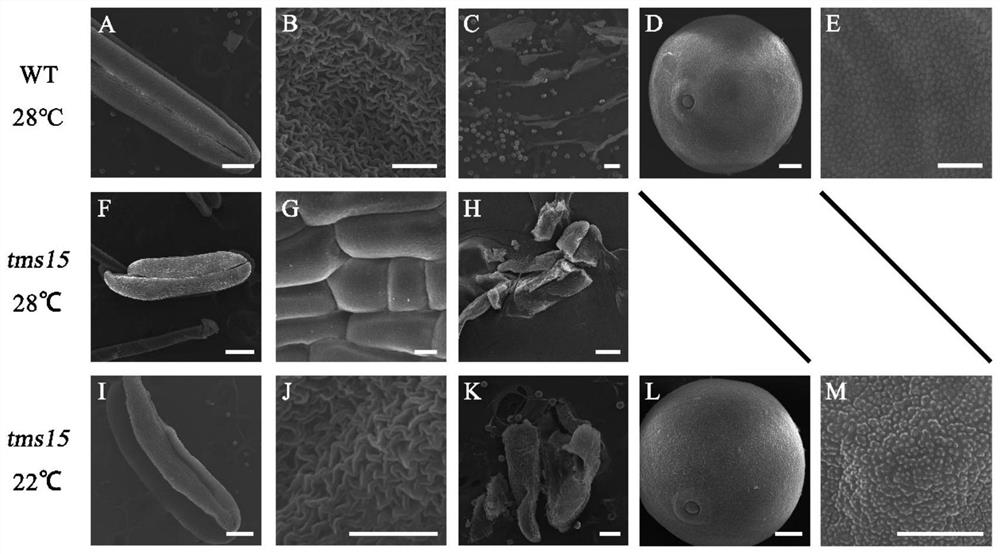
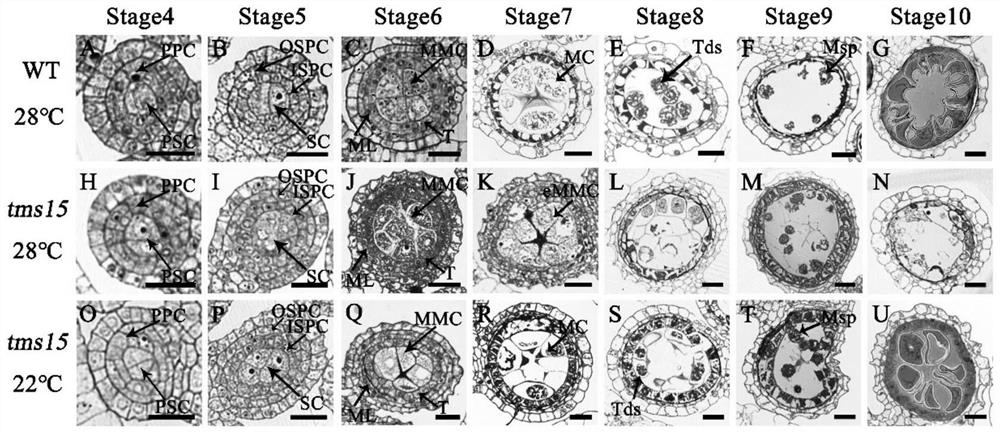
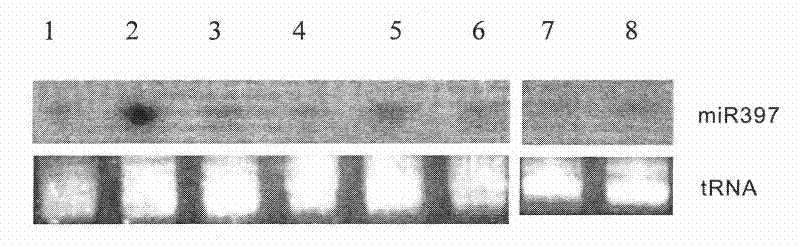
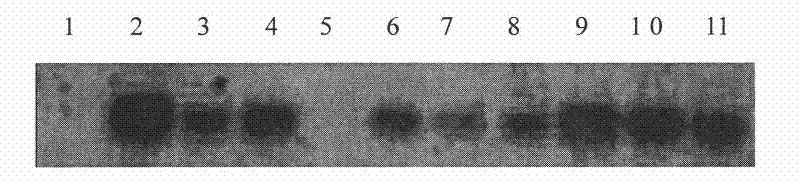
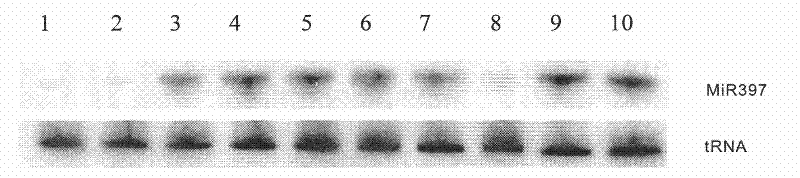
Plant temperature-sensitive sterile mutant tms15 and application thereof
ActiveCN114480419AGood sterility performanceLow seed setting rateMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyTapetum
The invention discloses a plant temperature-sensitive sterile gene mutant tms15 and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the plant temperature-sensitive sterile gene mutant tms15 comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table. The inventor carries out EMS mutagenesis on the middle flower 11 to screen a thermo-sensitive genic male sterile line tms15, and the thermo-sensitive genic male sterile line tms15 is subjected to EMS mutagenesis under a high temperature condition (gt; the male sterility phenotype is shown under the low-temperature condition (22-24 DEG C), and the fertility is recovered under the low-temperature condition (22-24 DEG C). Cytology results show that spore-forming cells in tms15 at high temperature are excessively proliferated, tapetum cells are also abnormally vacuolated, and normal pollen cannot be formed. After low-temperature treatment, normal proliferation of spore-forming cells and normal development of tapetum cells are recovered to a certain extent. The mutation of one basic group in the LRR section in the coding region of the gene enables the amino acid coded at the site to be changed from valine to glutamic acid, and the mutation enables the expression of the TMS15 gene to be obviously up-regulated compared with that of a wild type. The unique characteristic of the gene can provide new theoretical basis and application value for cross breeding of two lines.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Use of miR397 in drought resistance plant cultivation
InactiveCN101487021BImprove drought resistanceDoes not slow down growthVector-based foreign material introductionFood safetyPlant cultivation
The invention discloses application of miR397 in the cultivation of drought-resistant plants, and by realizing the drought processing of paddy rice and detecting the miRNA expression level of processed samples, the invention discovers that the miR397 expression of the samples after the drought processing lies in a significant increasing trend, and the miR397 expression rise after the drought processing within 5 hours is more significant than the miR397 expression rise after the drought processing within 12 hours. The invention constructs a miR397 over-expression paddy rice mutant strain, which has better growth situation than wide paddy rice at relatively lower temperature and does not have obvious burliness difference with wide paddy rice, and results of simulated draught and post-draught recovery processing show that the paddy rice mutant strain has better drought resistance than wide paddy rice. The results provide a novel, simple and effective method for cultivating drought-resistant paddy rice and plants, which can be applied into large-scale popularization and application, does not cause environmental pollution and ensures food safety.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
A method for propagating and raising seedlings of canopy wood ring branches
InactiveCN105248225BLow seed setting rateIncrease success rateCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsPlant propagationManglietiastrum sinicum
The invention discloses a manglietiastrum sinicum Law bending pruning propagation seedling culture method, belonging to the field of plant propagation. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a 3 to 4-year-old manglietiastrum sinicum Law branch, and ringing the branch for one circle respectively at upper and lower positions, away from a trunk by 8 to 12cm, on the base of the branch, wherein the two circles have the width of 2 to 3cm and are deep into a xylem; peeling of a bark, then sleeving with a proper bamboo section, fixing the bamboo section on the branch, filling the bamboo section with a wet rooting medium prepared in advance, keeping the wetness of the medium in the bamboo section, and timely replenishing water for the medium in the bamboo section, wherein rooting is started after 30 days, and after 180 days the branch can be sawn off to serve as a seedling for field planting. The invention provides the bending pruning seedling culture method for a rare plant, i.e., manglietiastrum sinicum Law; the method greatly increases the seedling culture success rate of the manglietiastrum sinicum Law, and achieves an aim of quick cultivation for propagation expanding.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Low-fertility-transition-starting-point temperature photo-thermo-sensitive sterile line breeding method
ActiveCN103461042BIntensified selection pressureLow combining abilityPlant genotype modificationRice cultivationAgricultural scienceLow fertility
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
Depleted grassland repairing method
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
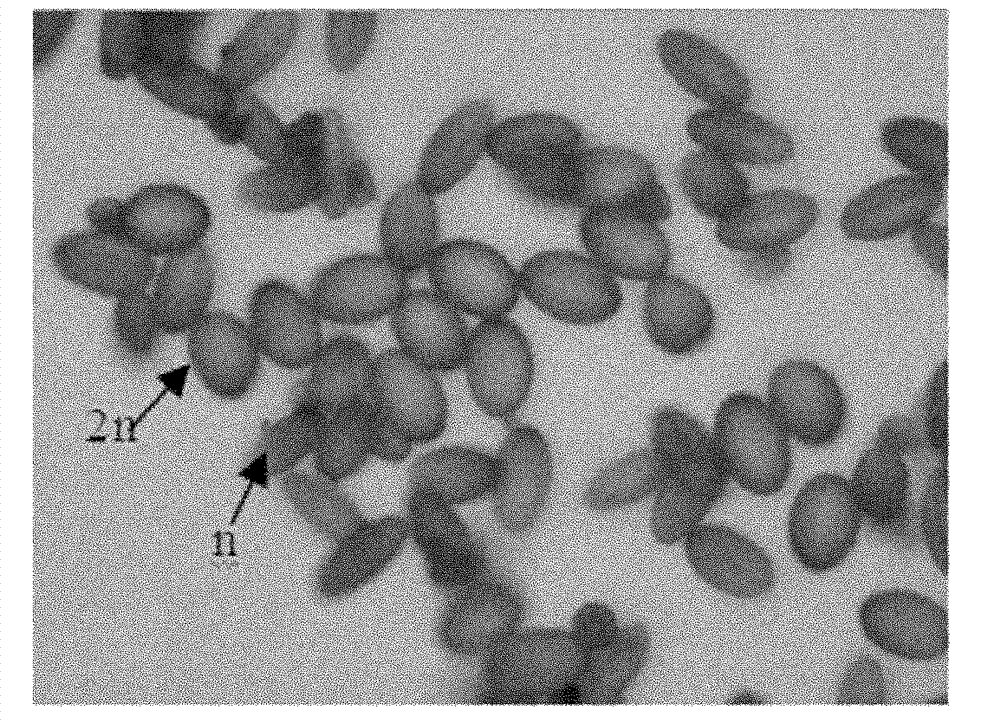
Sexual polyploidization breeding method of tetraploid Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis Makino
InactiveCN101946696BExtensive genetic diversityImprove seed setting ratePlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsDiseaseGenetic diversity
The invention belongs to the field of crop breeding and discloses a sexual polyploidization breeding method of tetraploid Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis Makino. The method comprises the following steps of: treating flower buds by using solution of colchicine in the bolting period of the Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis Makino to induce the flower buds to generate 2n male gametes; and performing manual sexual polyploidization cross breeding on a tetraploid male sterile line serving as a female parent and 2n male gamete-containing diploid obtained by the induction of the solution of colchicine serving as a male parent in a blooming period to obtain the tetraploid Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis Makino. In the method, a sexual polyploidization breeding approach of hybridizing the male sterile line of the tetraploid Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis Makino with the diploid Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis Makino which generates 2n gametes after induction is used for the first time to obtain a new species of the tetraploid Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis Makino which has wider genetic diversity and higher seed setting rate compared with the autotetraploid of asexual polyploidization. The new tetraploid of the invention has the characteristics of polyploid such as largeness, disease resistance and cold resistance, high quality, and the properties of a diploid male parent.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A deubiquitinase gene ubp5 regulating rice grain shape and leaf color and its application
InactiveCN107326035BLow seed setting rateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention provides a deubiquitinating enzyme gene UPB5 for regulating and controlling a grain shape and leaf color of rice. The deubiquitinating enzyme gene UPB5 has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 in the description. The invention further provides a protein with a UBP5 gene code of the rice, and the protein has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.3 in the description. The experiment proves that the deubiquitinating enzyme gene UPB5 of the rice can cause the leaf blade color and seed shape of the rice to change; the invention further finds that after the ubiquitination enzyme gene UPB5 of the rice mutates, the leaf blades of the rice show the shape of a stripe; the seeds are elongated; the ripening rate becomes lower; the total content of chlorophyll is obviously reduced. The invention provides the application of the UBP5 gene and the mutant of the UBP5 gene to genetic improvement breeding of rice germplasm resources, thereby having a relatively good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Secondary shaping method of platanus acerifolia
InactiveCN108684421AStrong growthBeautiful treeCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsComputer scienceSeedling
The invention discloses a secondary shaping method of platanus acerifolia. The shaping method includes the steps of (1) platanus acerifolia trunk determination, (2) primary shaping, and (3) secondaryshaping. The method solves the related problems that existing platanus acerifolia seedlings cultured by trimming are poor in growth vigor and low in ornamental value and cannot meet the demand of themarket for improved varieties of trees.
Owner:SUQIAN AGRI SCI RES INST JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preventing sorghum ear bagging mildewing
InactiveCN105052727ALow seed setting rateImprove seed setting ratePlant genotype modificationMedicineSorghum
The invention discloses a method for preventing sorghum ear bagging mildewing. The method includes the step that at the time after nine of one fine day before sorghum blooms, bagging is carried out through transparent sulfuric-acid paper bags. As bagging is carried out at the time point, ear mildewing commonly generated after the sorghum is bagged can be effectively prevented.
Owner:有限会社林平
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com