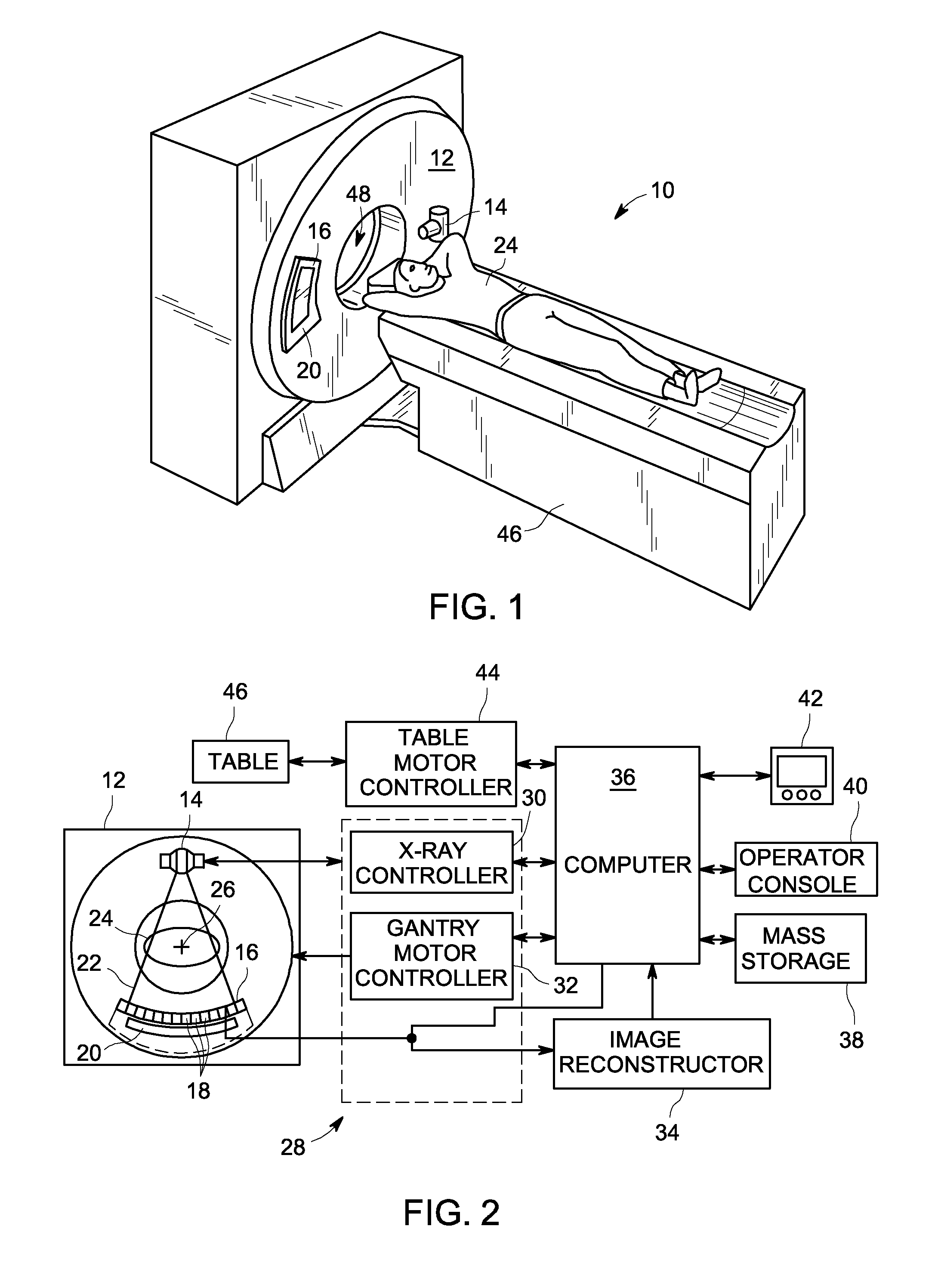
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67results about "X-ray tube vessel cooling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
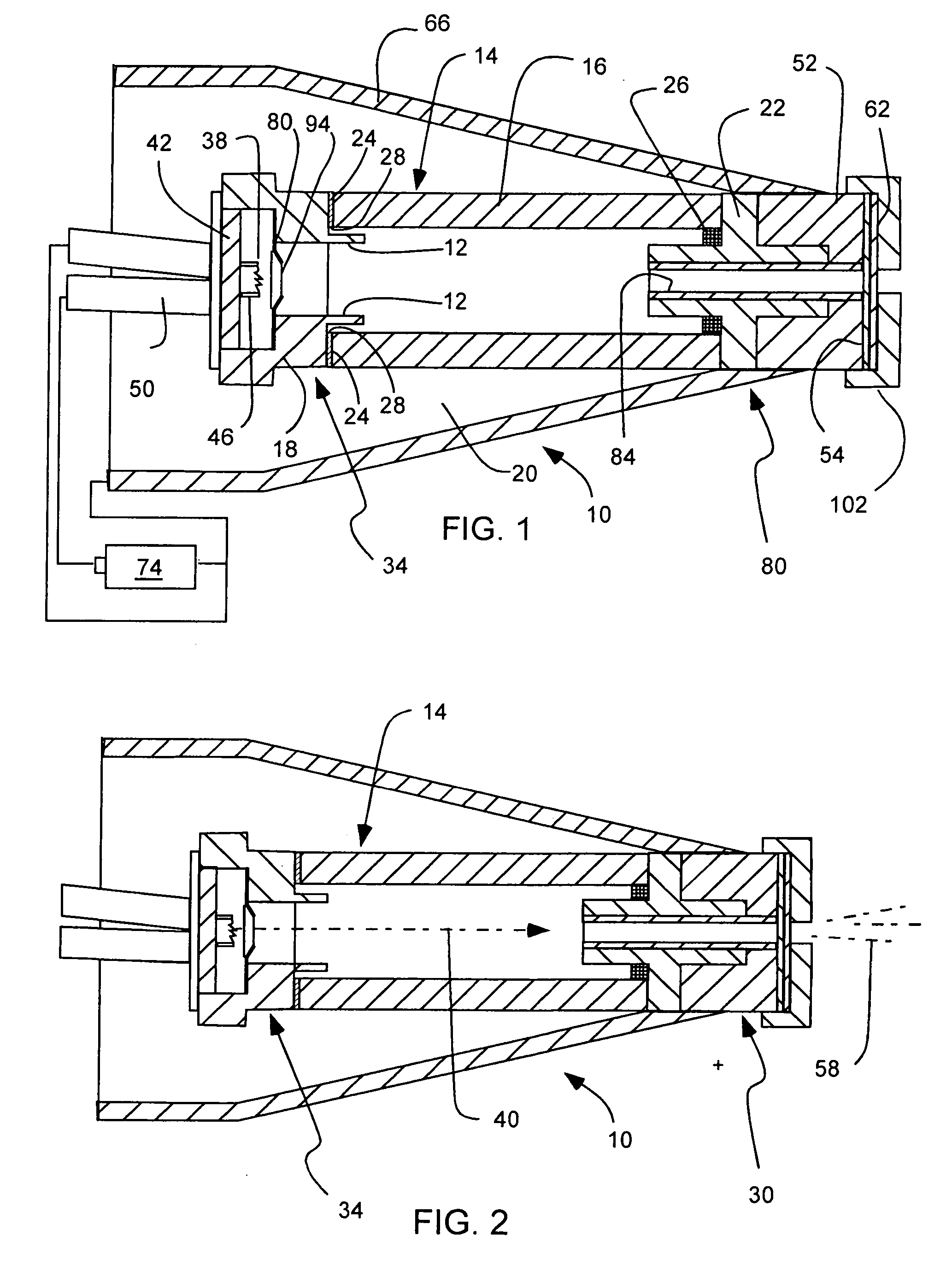
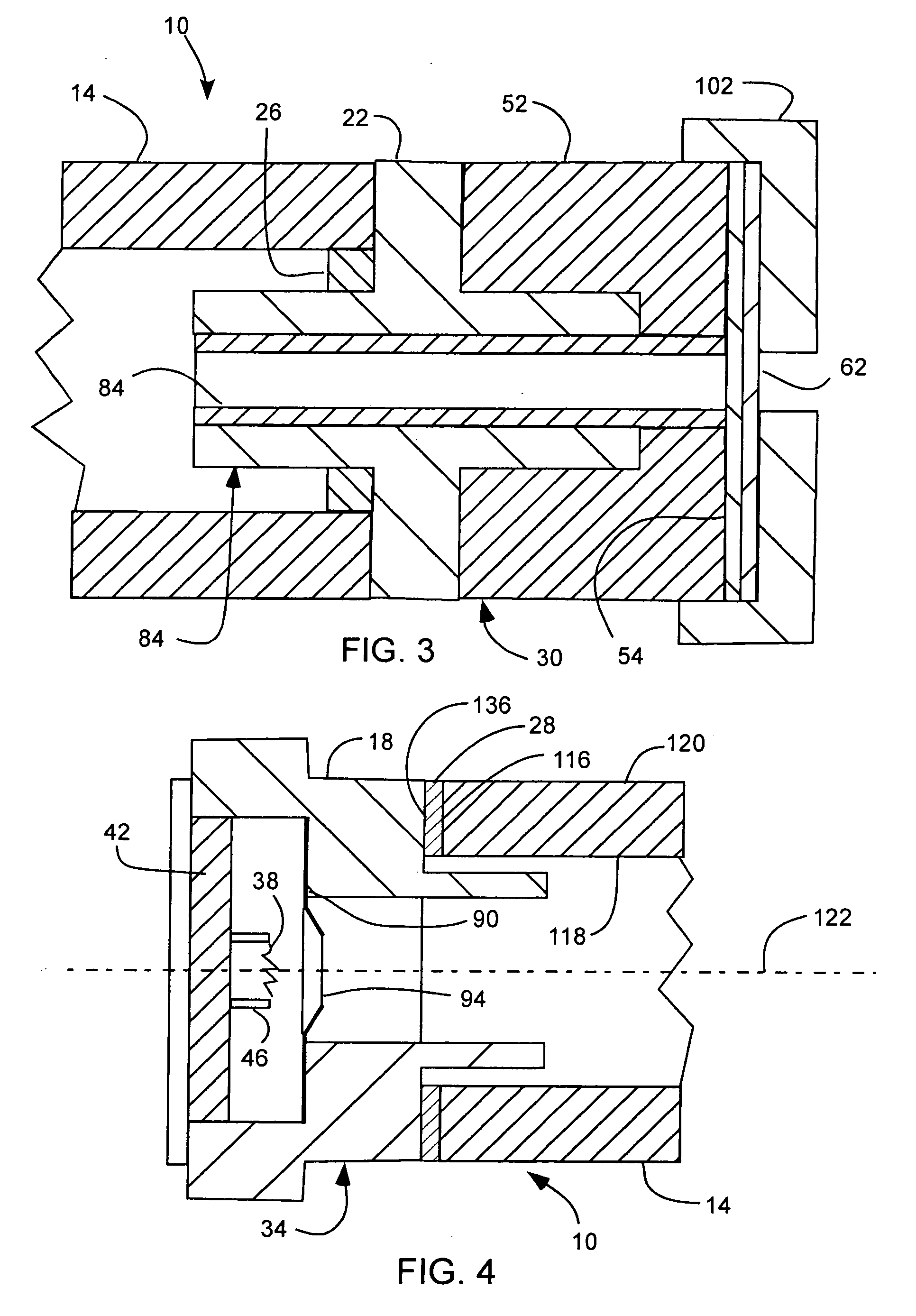
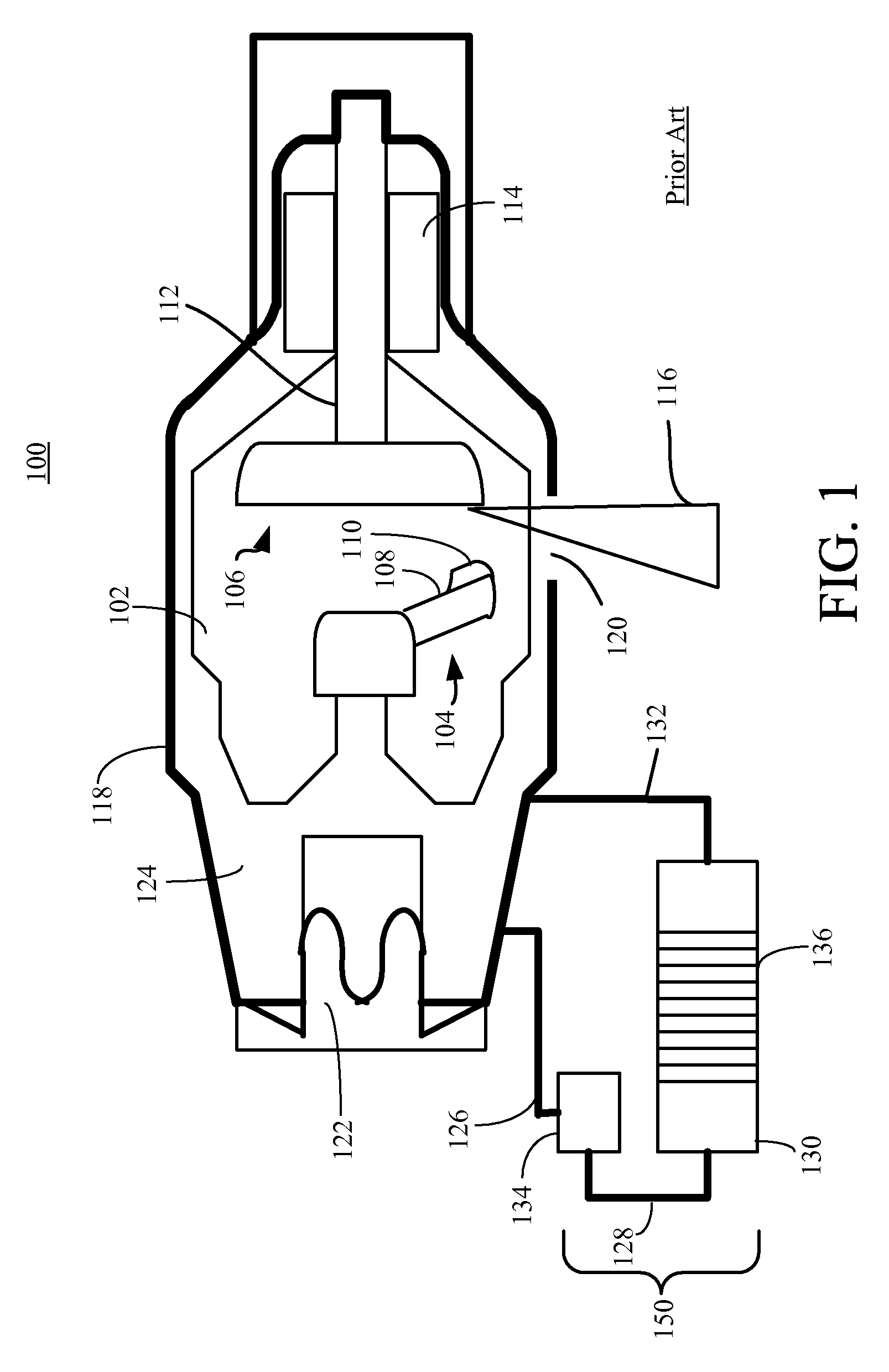
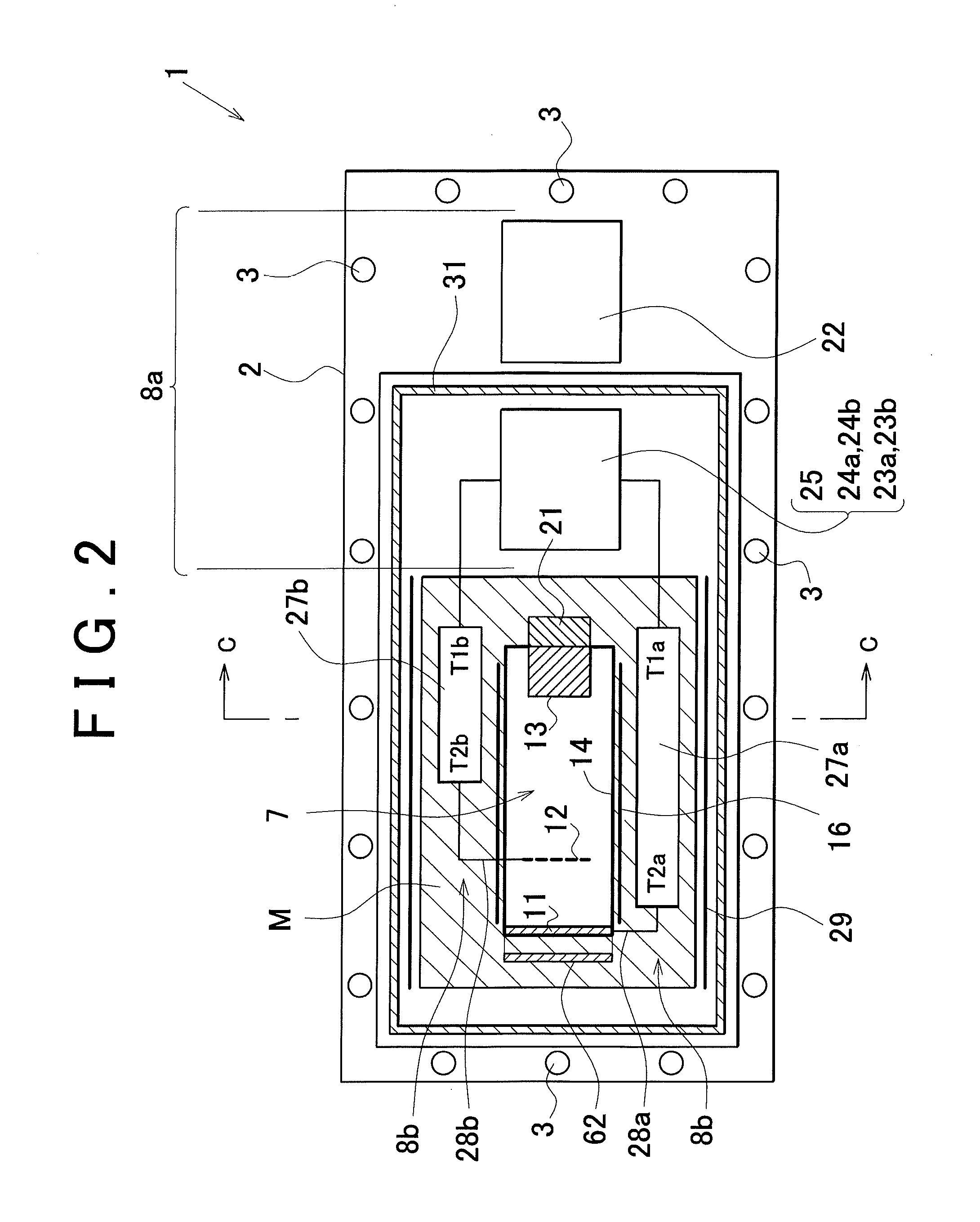
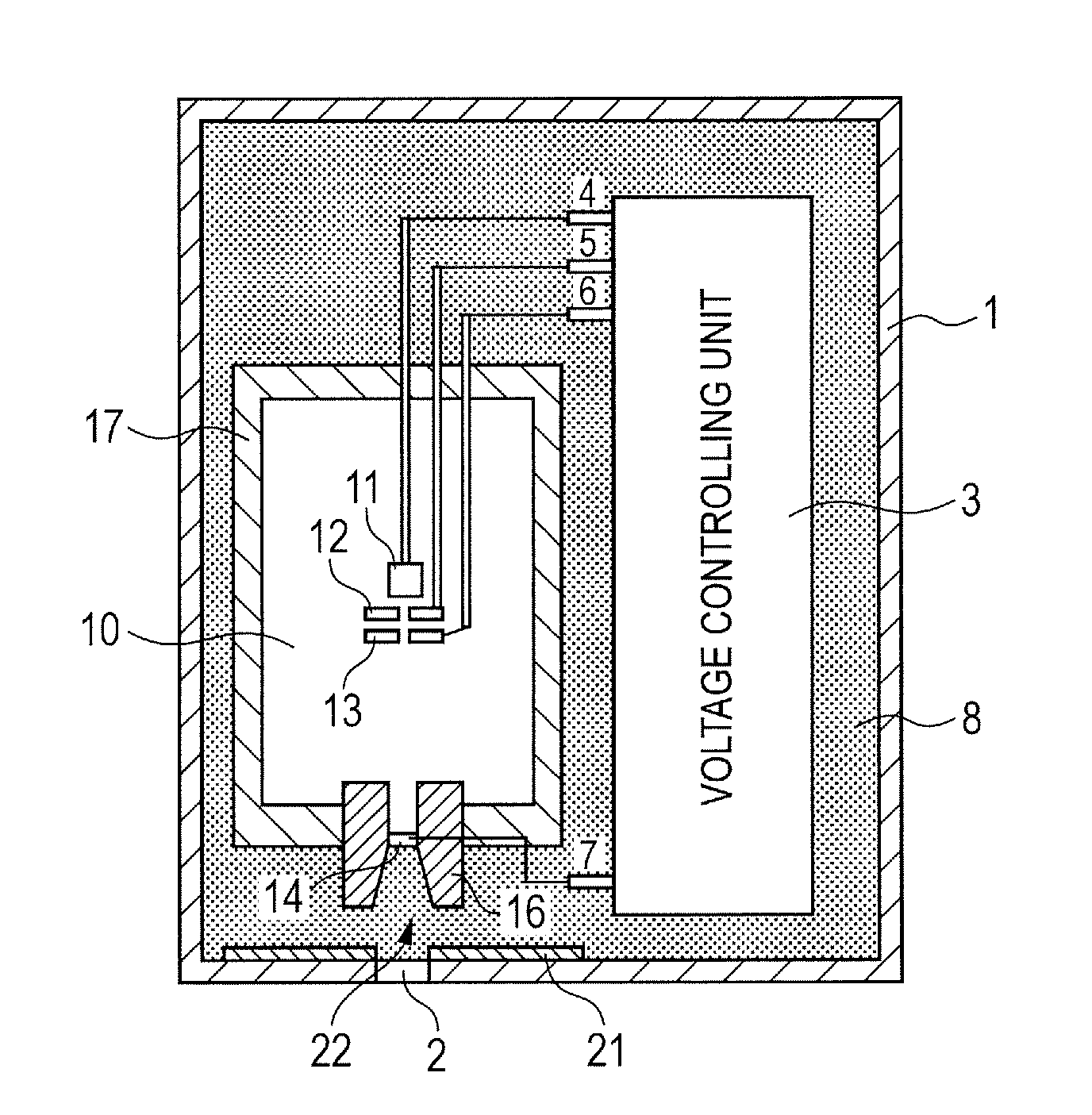
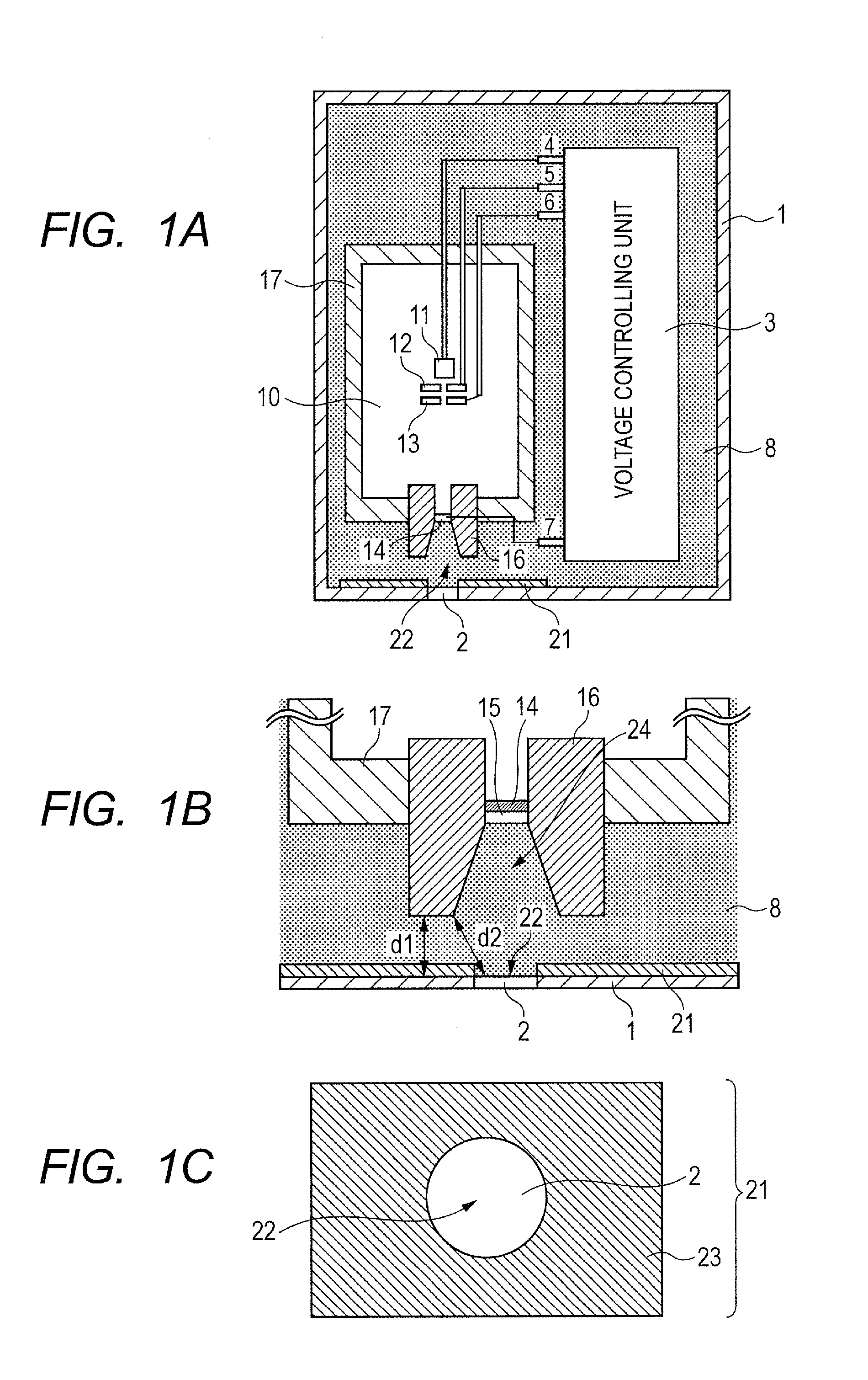
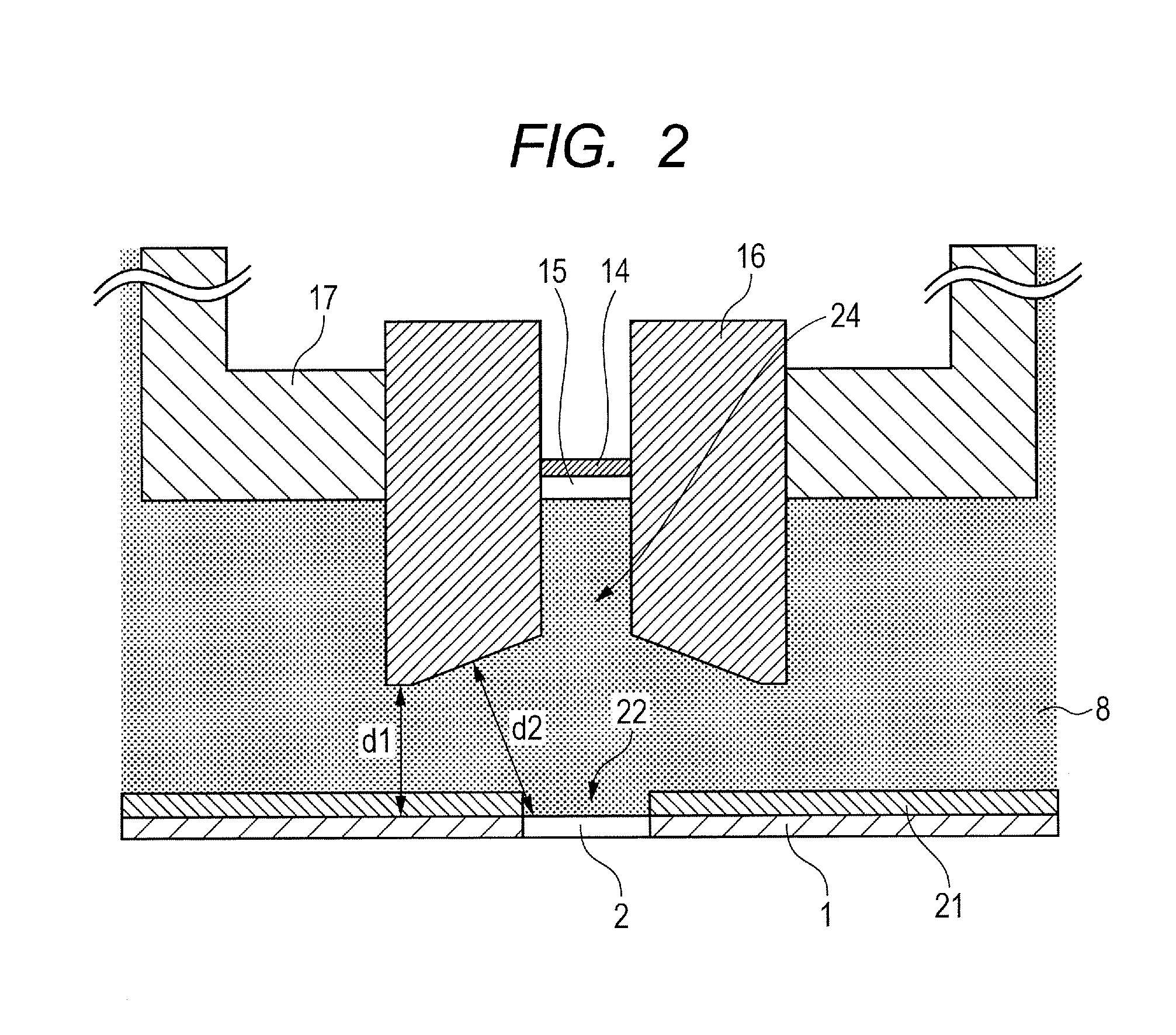
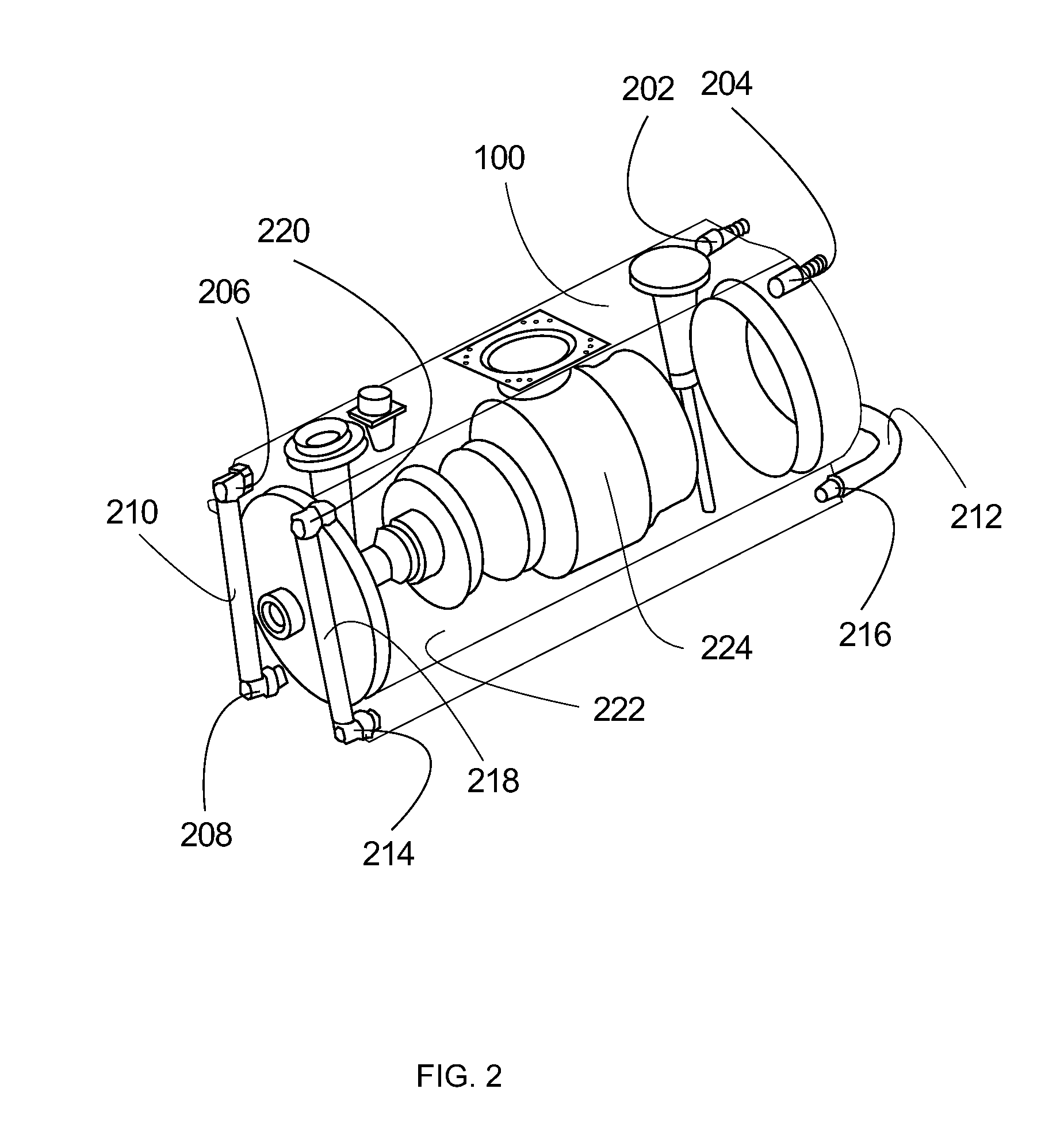
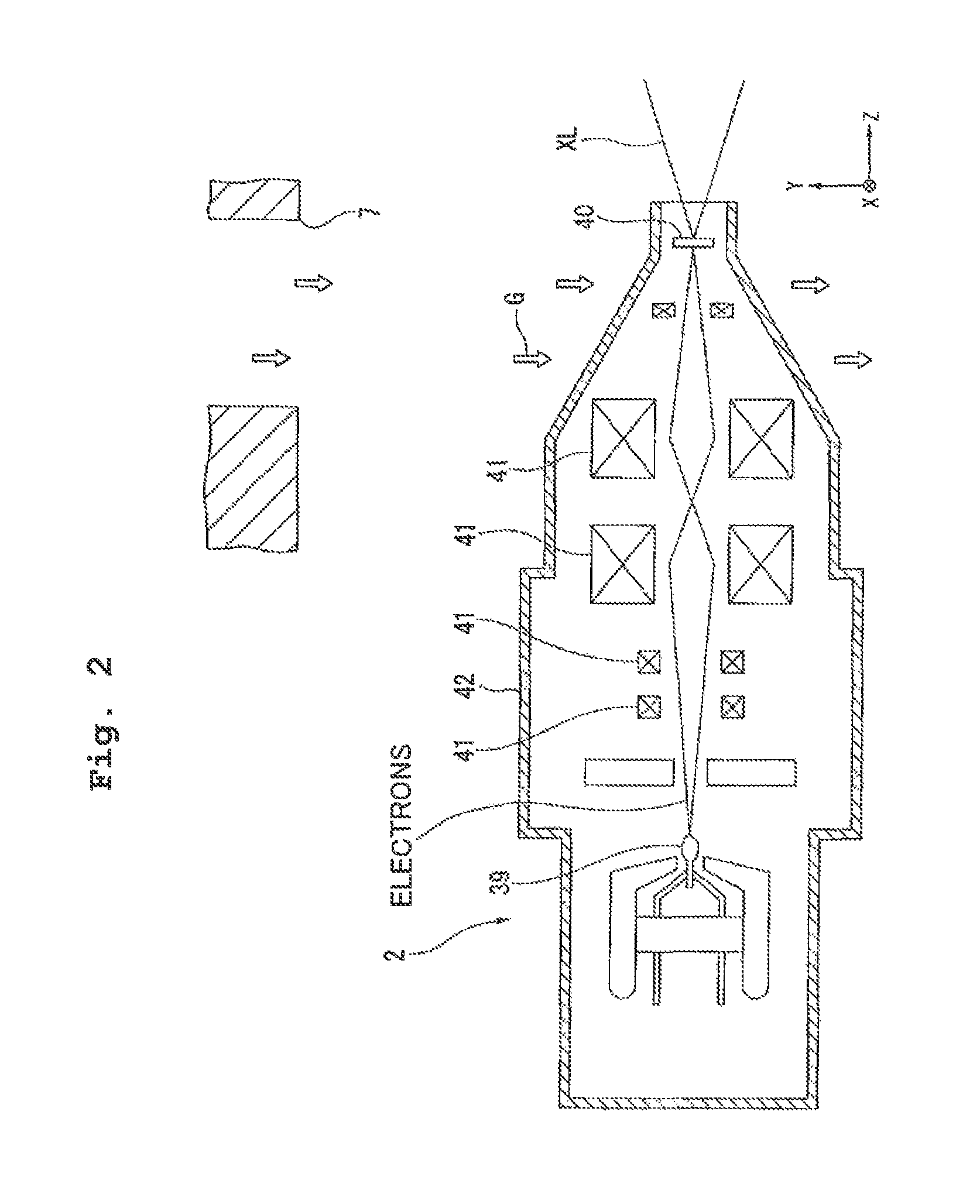
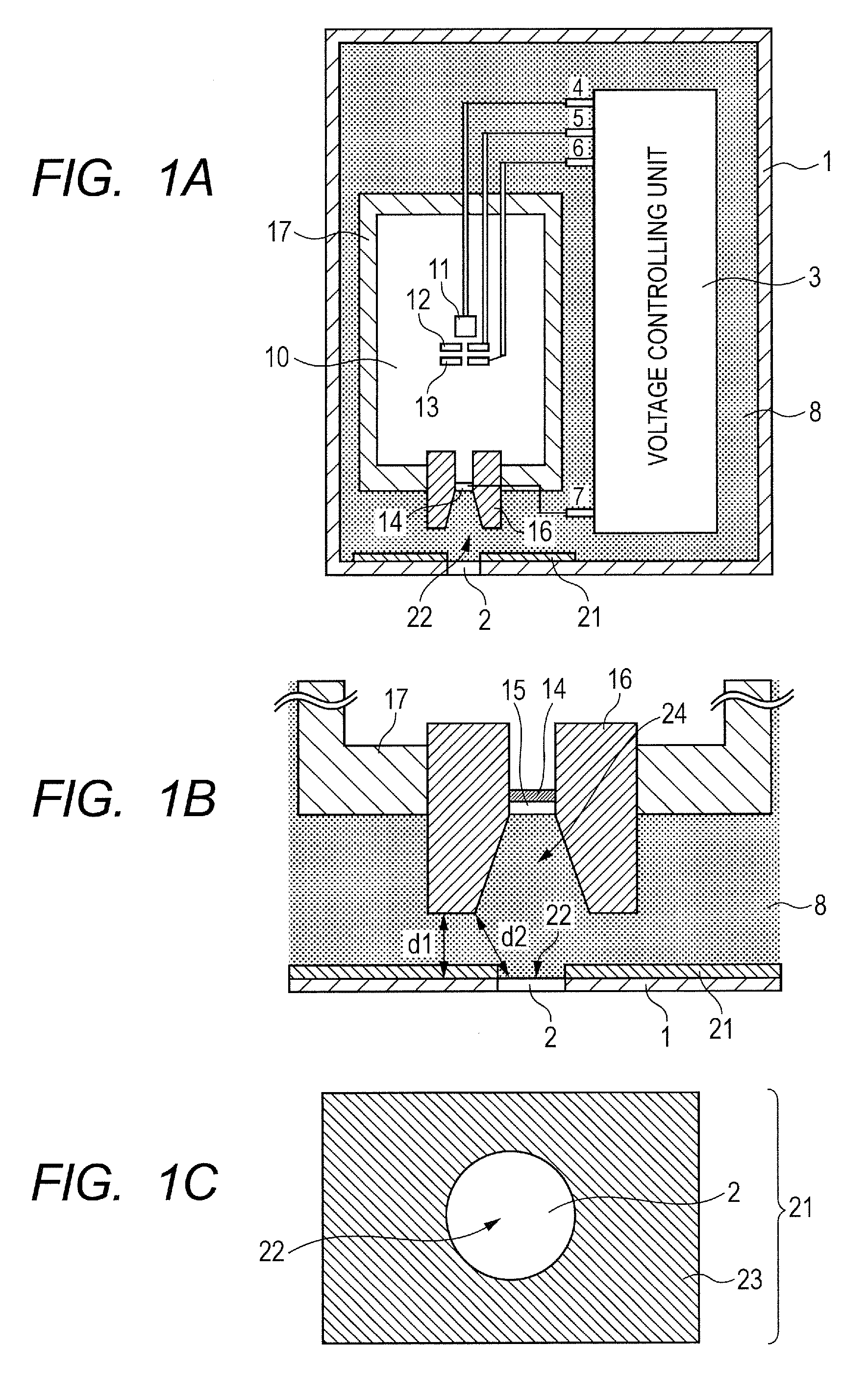
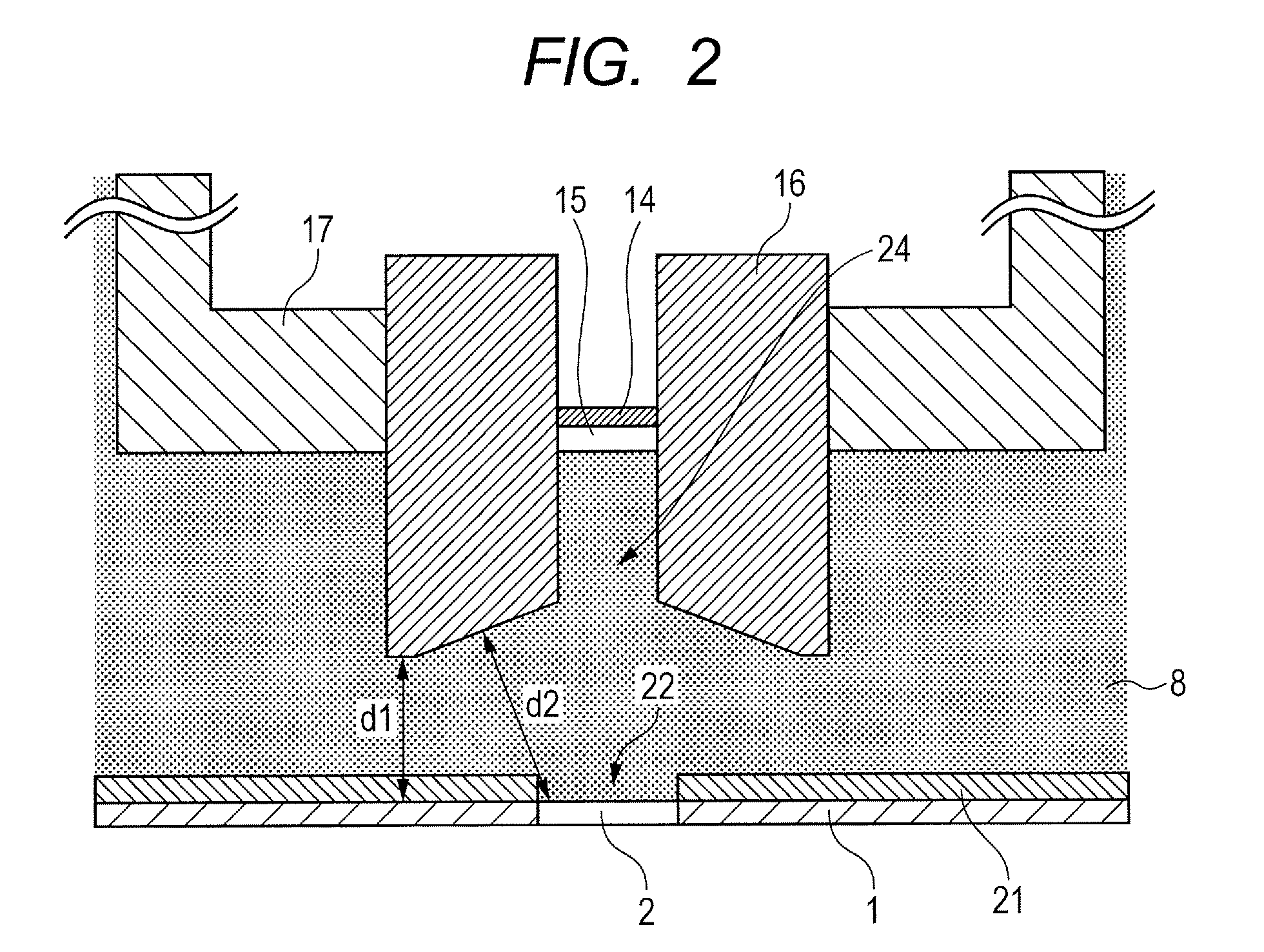
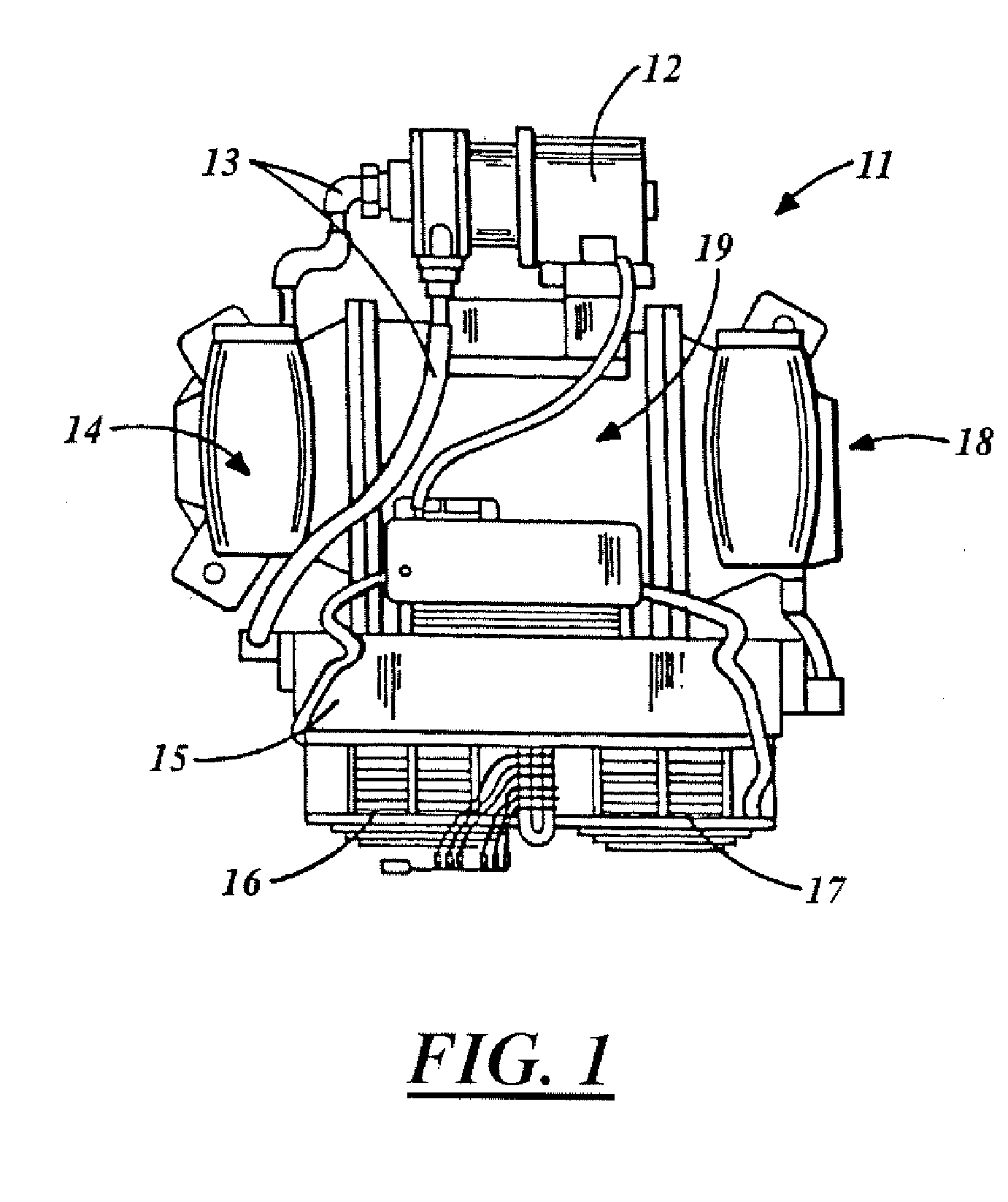
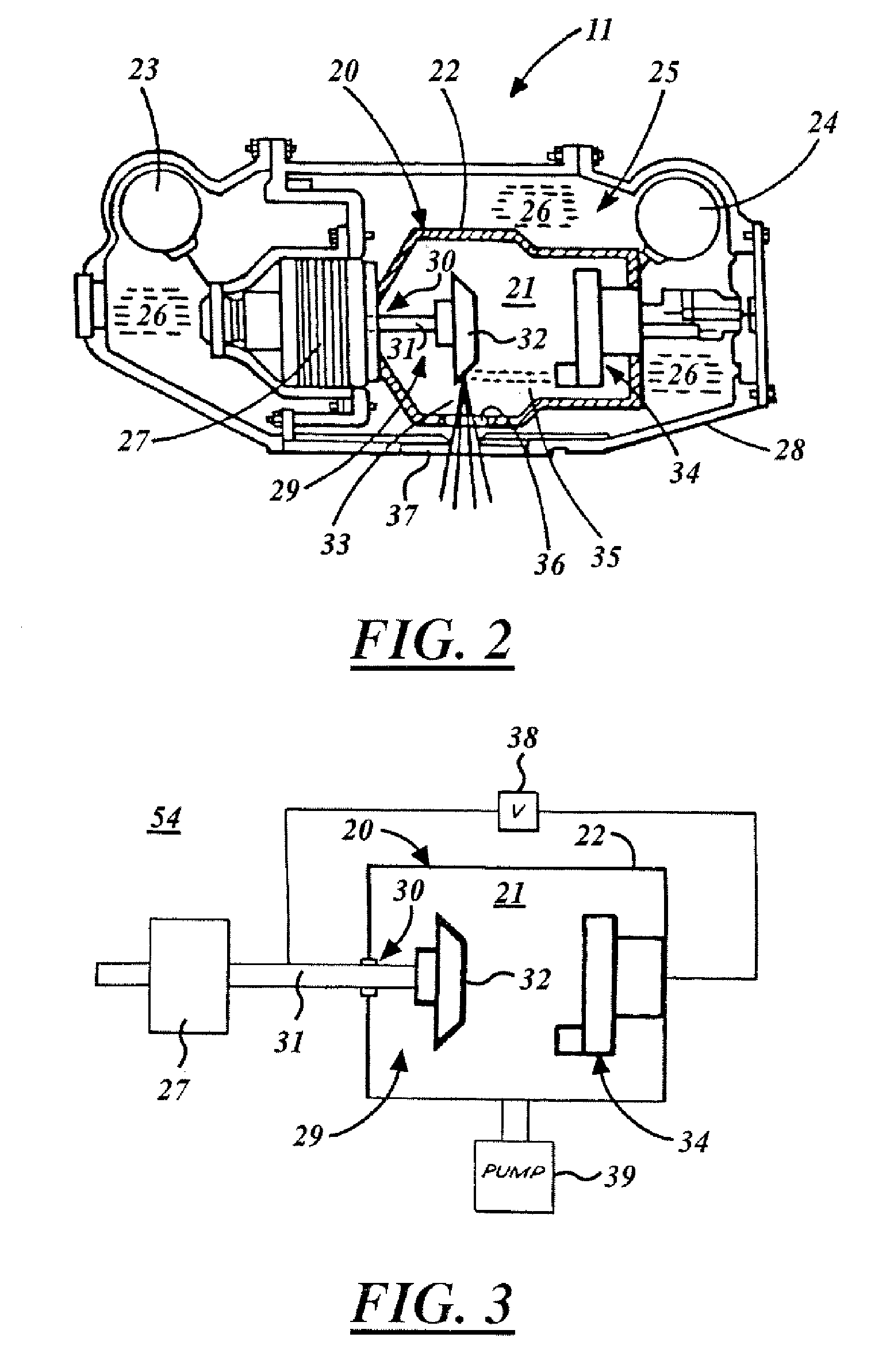
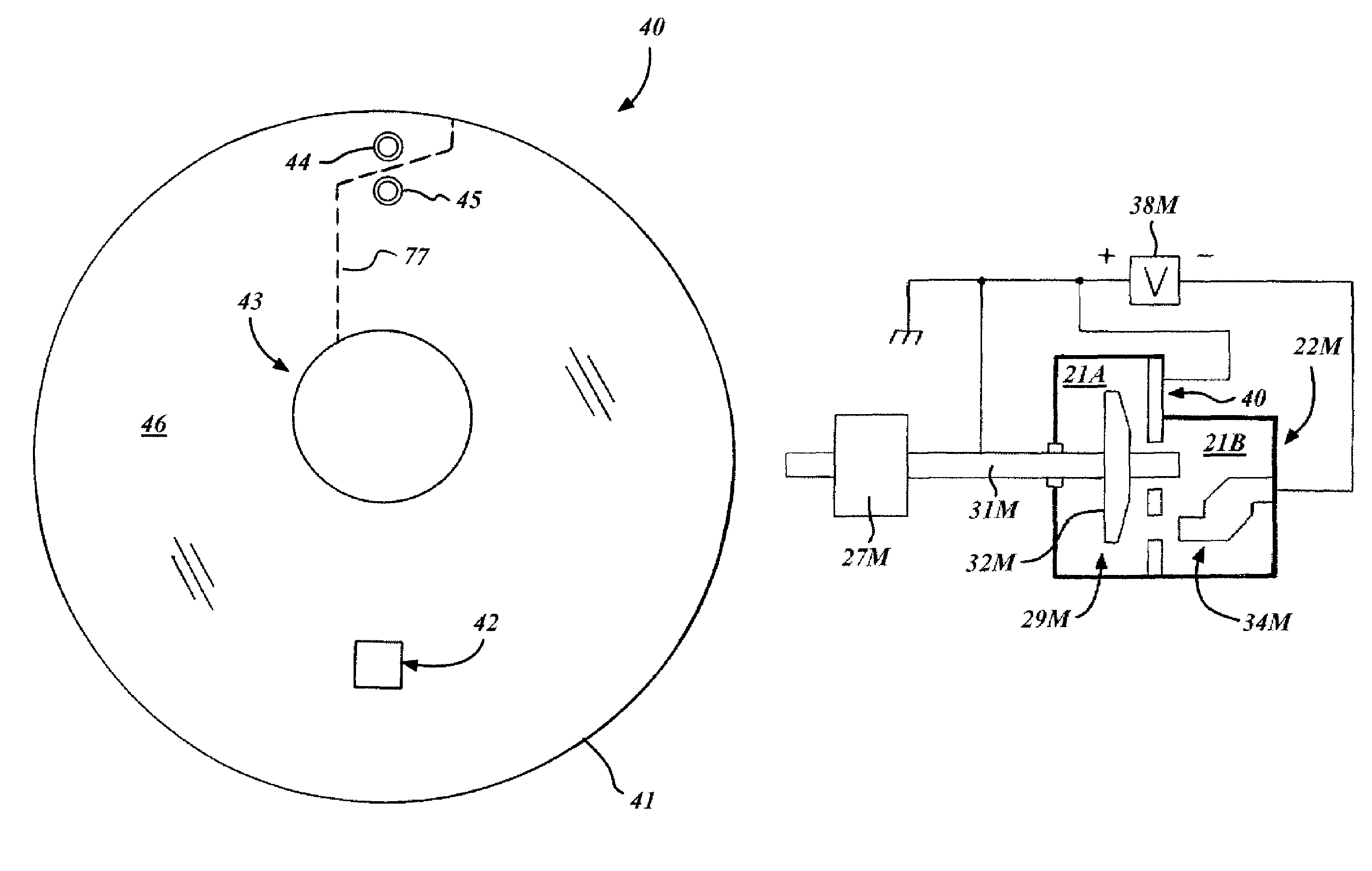
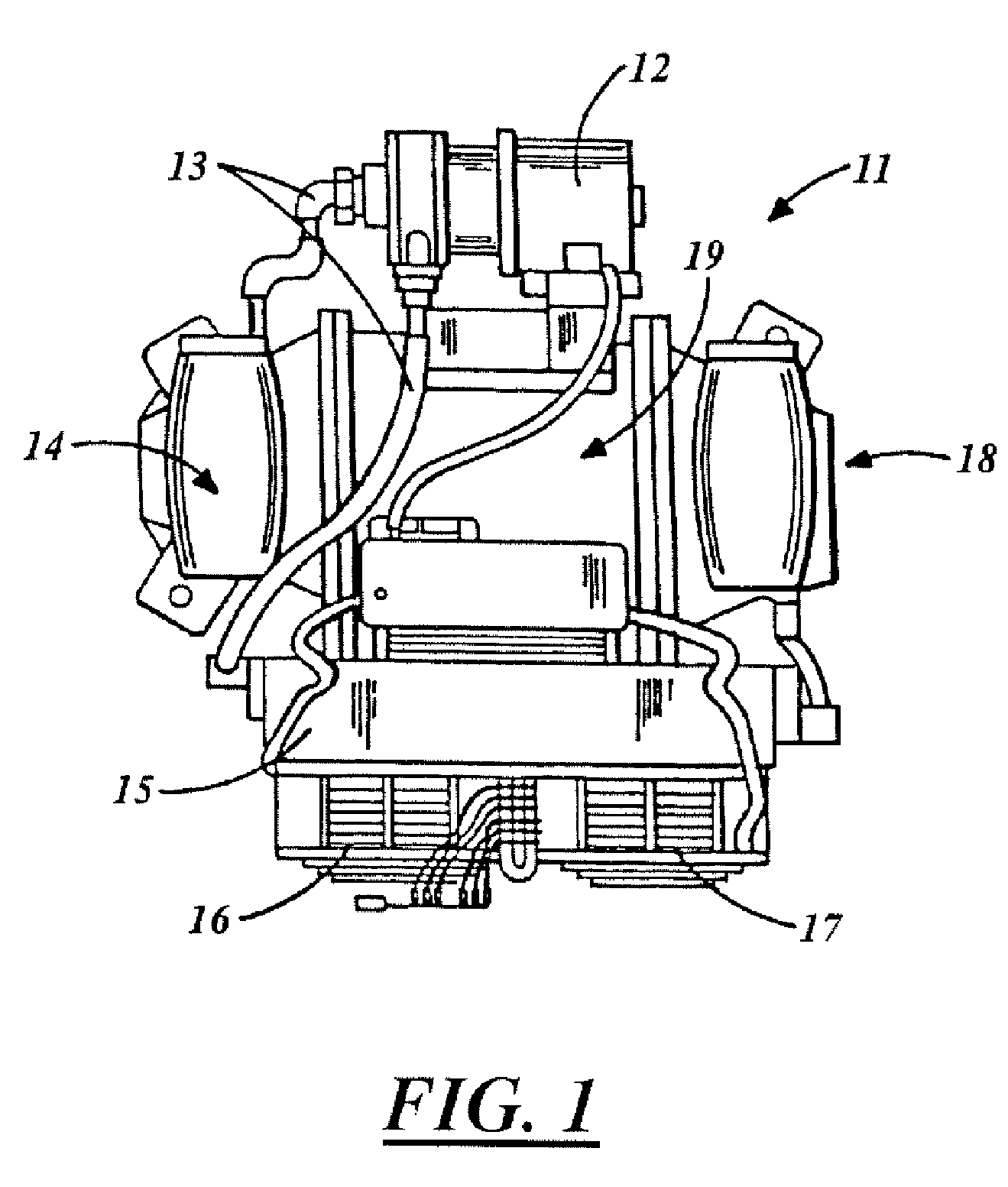
X-ray tube cathode with reduced unintended electrical field emission
ActiveUS7382862B2Easy to controlFocusX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingSoft x rayX-ray
An x-ray source has an evacuated tube. An anode is disposed in the tube and includes a material configured to produce x-rays in response to impact of electrons. A cathode is disposed in the tube opposing the anode configured to produce electrons accelerated towards the anode in response to an electric field between the anode and the cathode. A flange extends from the cathode toward the anode, and has a smaller diameter than the evacuated tube. The flange extends closer to the anode than an interface between the cathode and the tube thus forming a reduced-field region between the evacuated tube and the flange.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
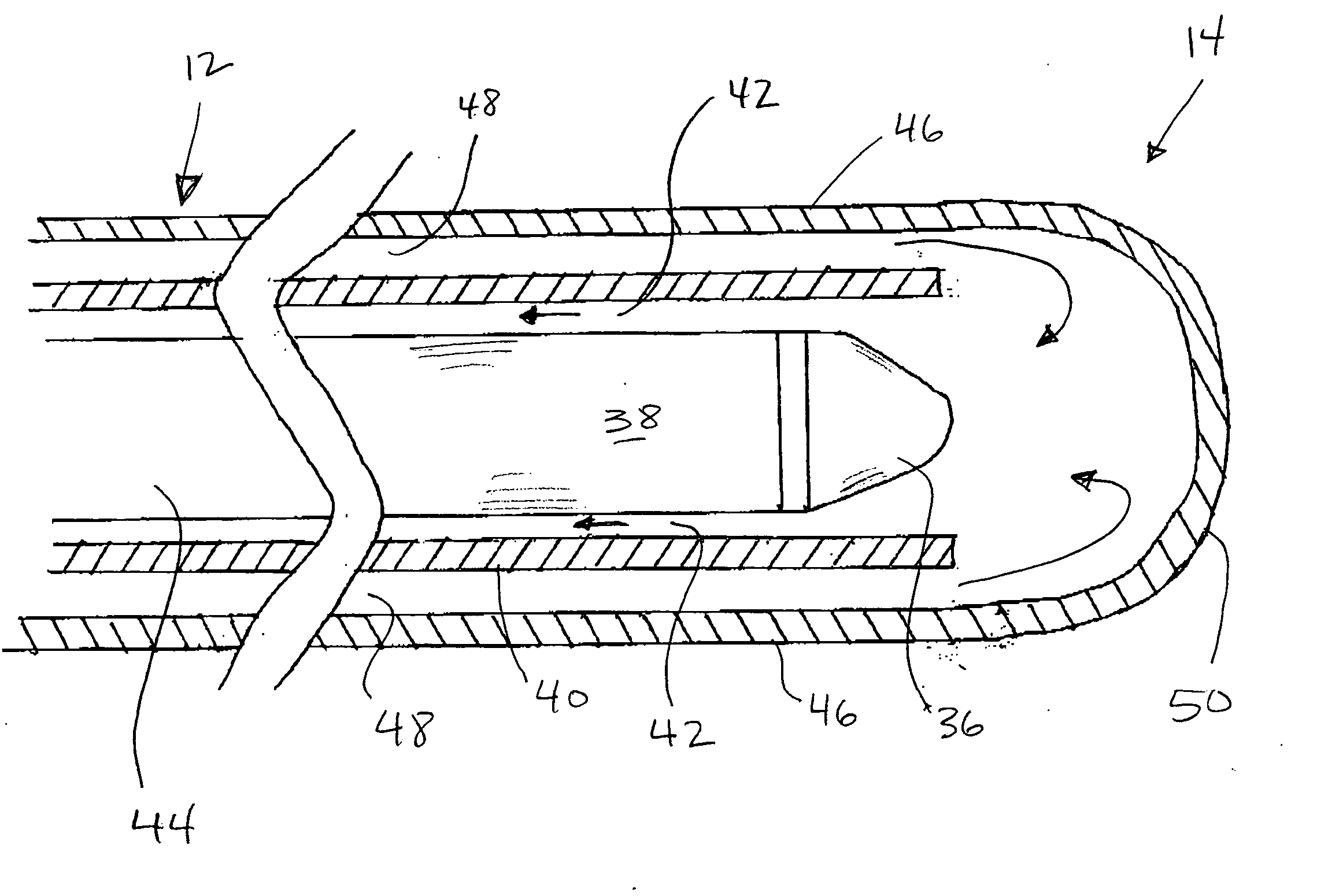
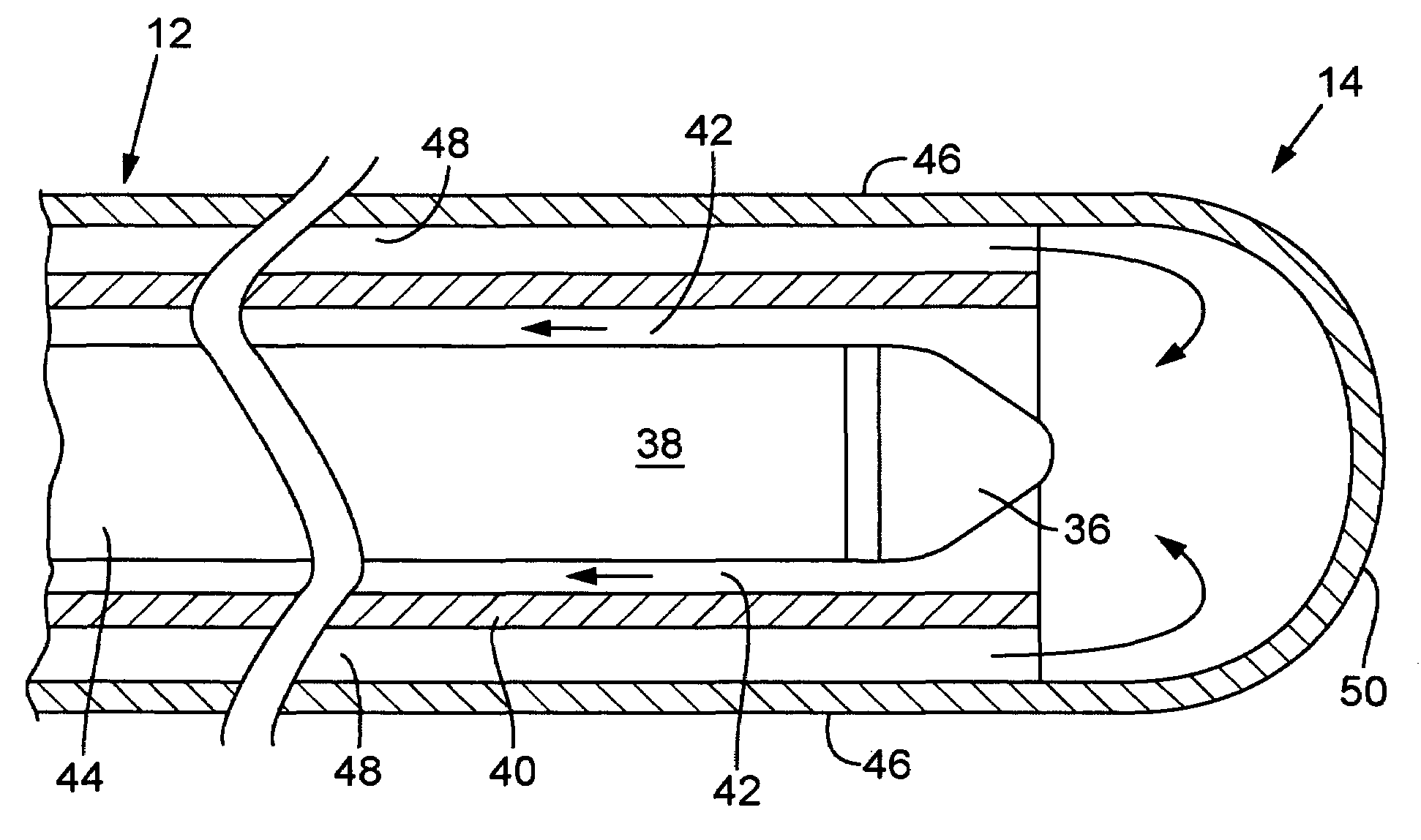
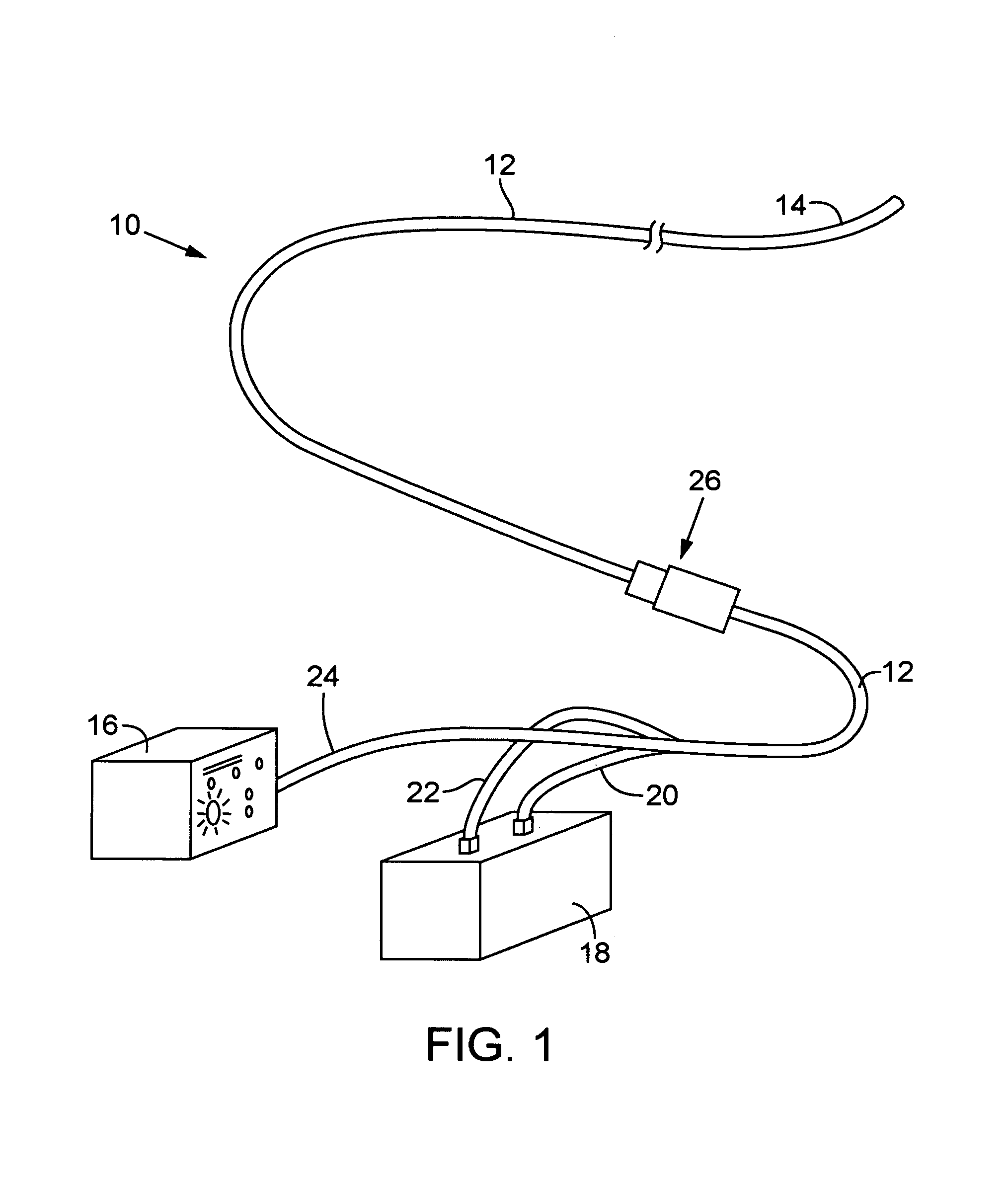
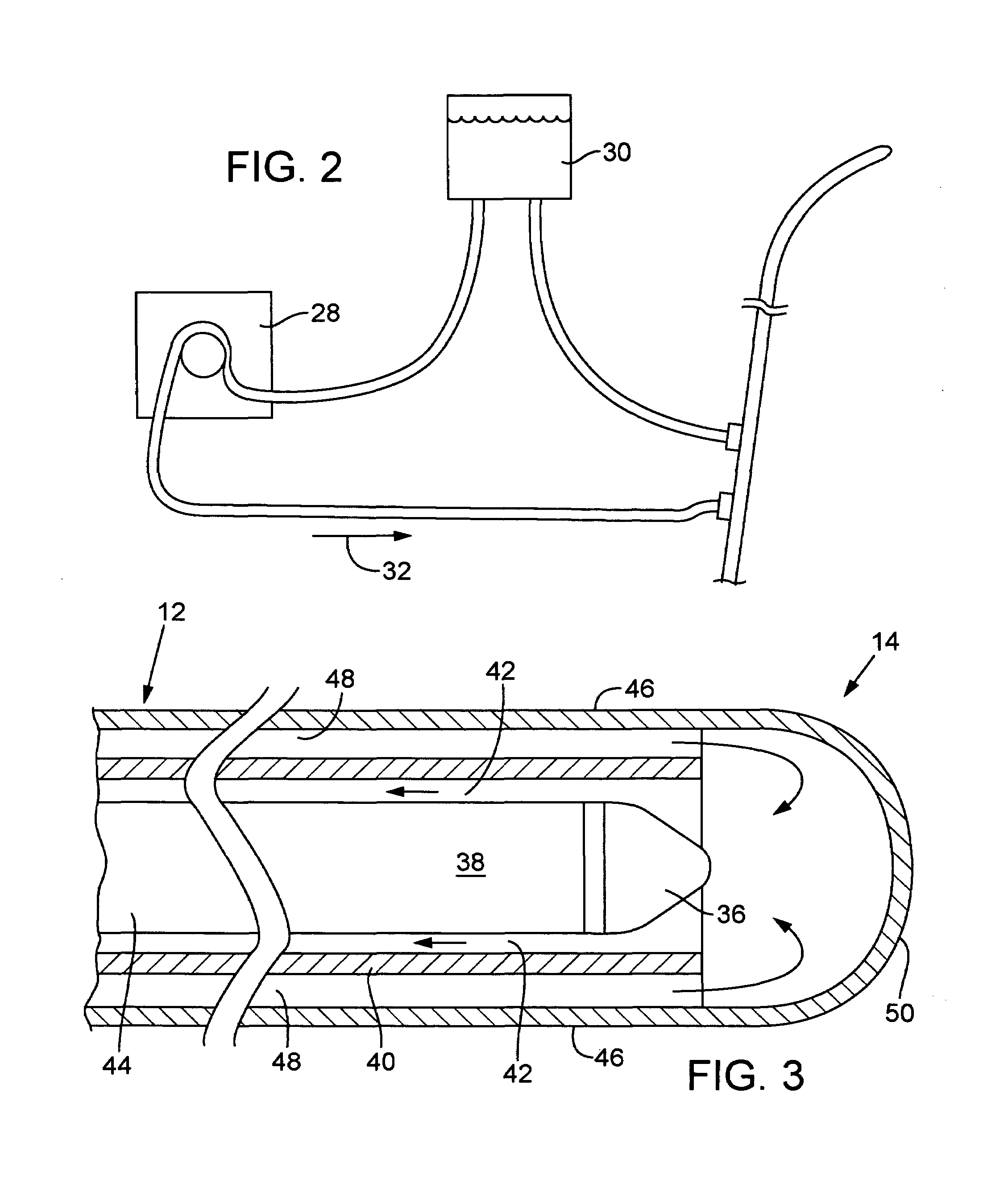
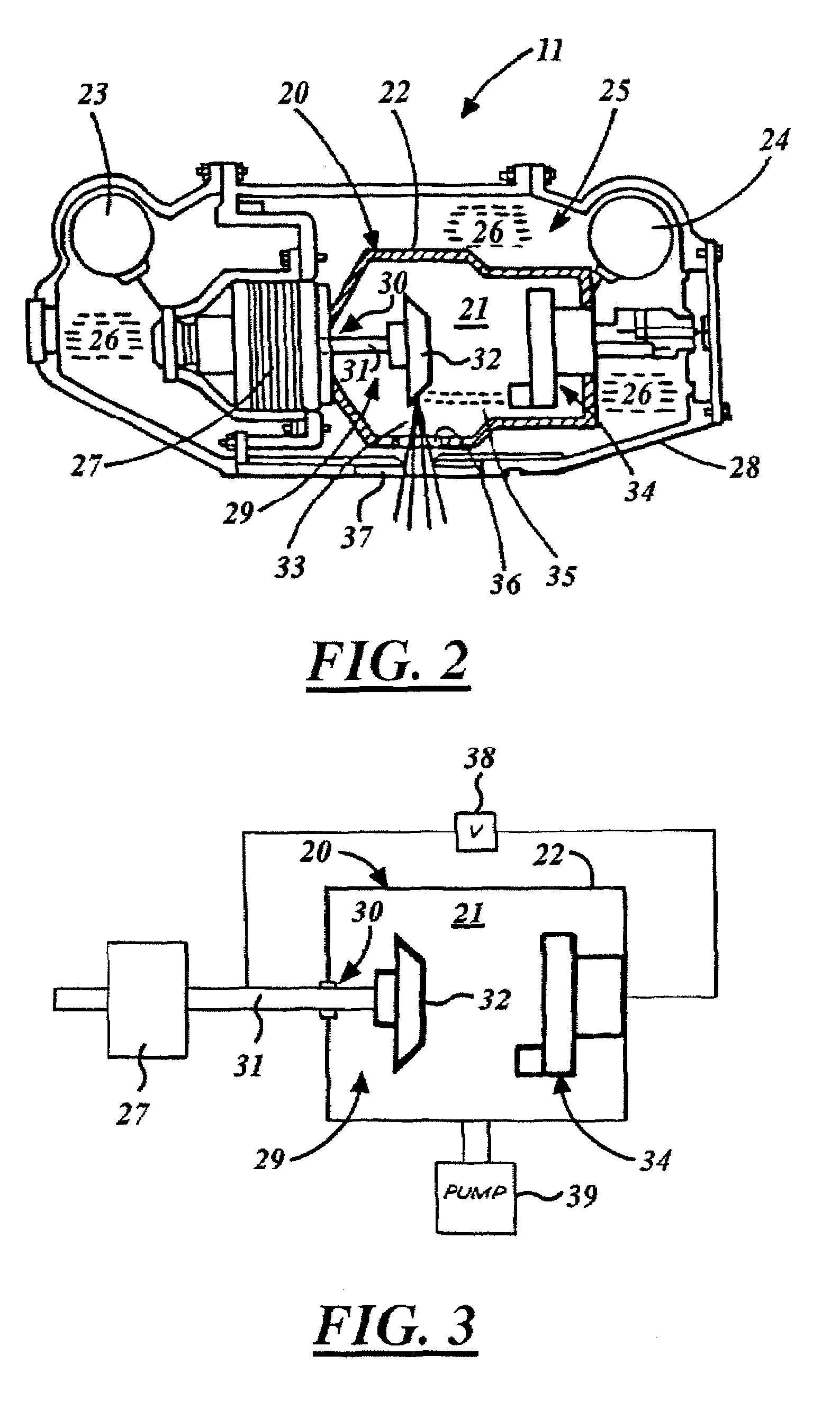
Miniature x-ray tube cooling system
ActiveUS20060171506A1Improve heat transfer performanceReduce surface tensionStentsBalloon catheterSoft x rayX-ray
A miniature x-ray tube is cooled using a catheter preferably having multiple small lumens for inflow and outflow of coolant. Inflow may be through an outer lumen(s) in a concentric-extrusion catheter, the liquid turning back at the distal end of the catheter to a proximal flow over the anode end of the x-ray tube and through an inner lumen within which the x-ray tube is positioned. A coolant distribution head may engage with the anode end of the x-ray tube, with small orifices so as to distribute coolant essentially evenly over the anode surface. Temperature and flow rate of the inflowing coolant liquid are balanced so as to optimize heat transfer while efficiently carrying coolant through small lumens without the need for high pressures. Some embodiments use the inflation liquid in an applicator balloon as the coolant, with the liquid actively flowing or, in a simplified system, with the liquid static.
Owner:XOFT MICROTUBE
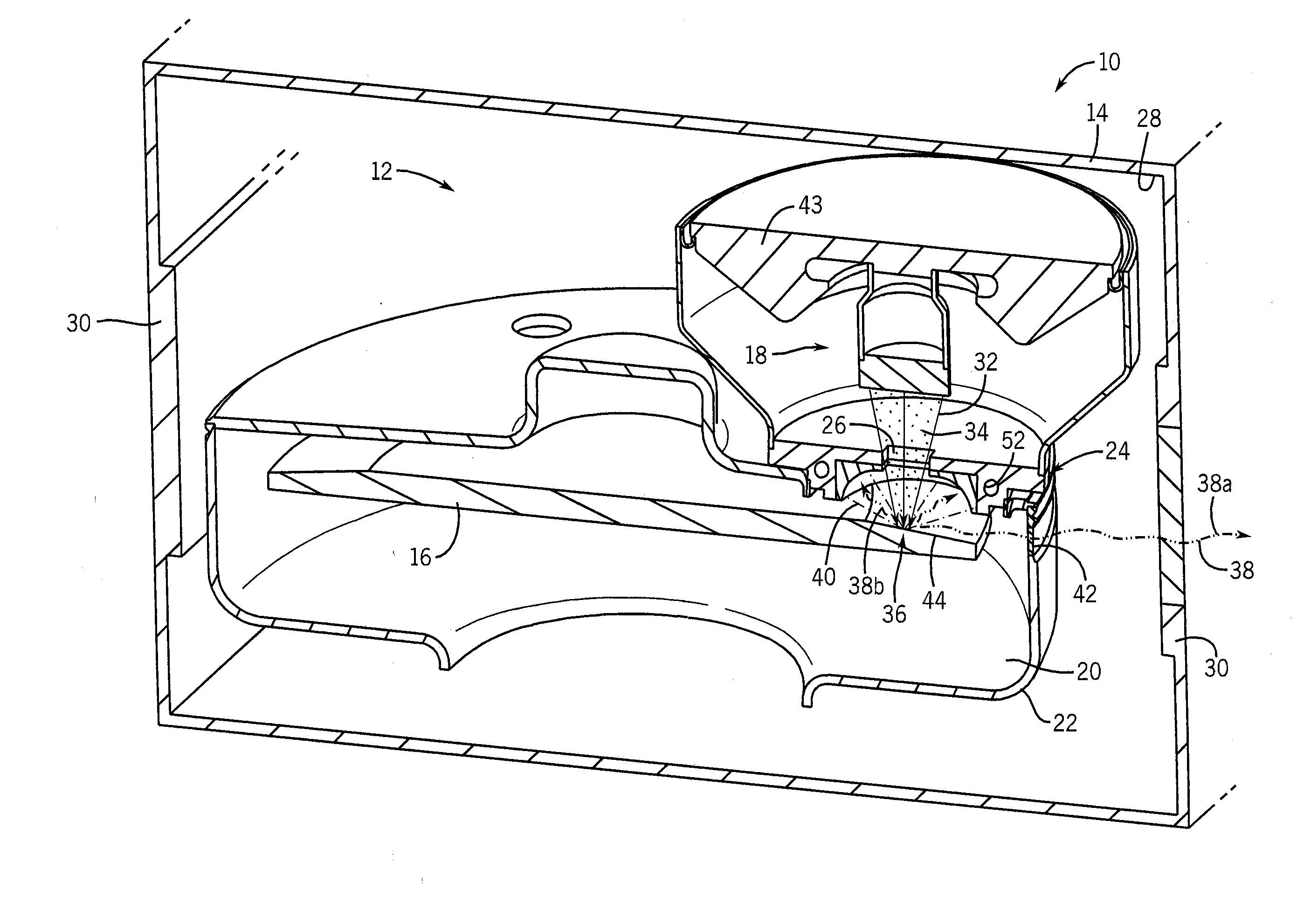
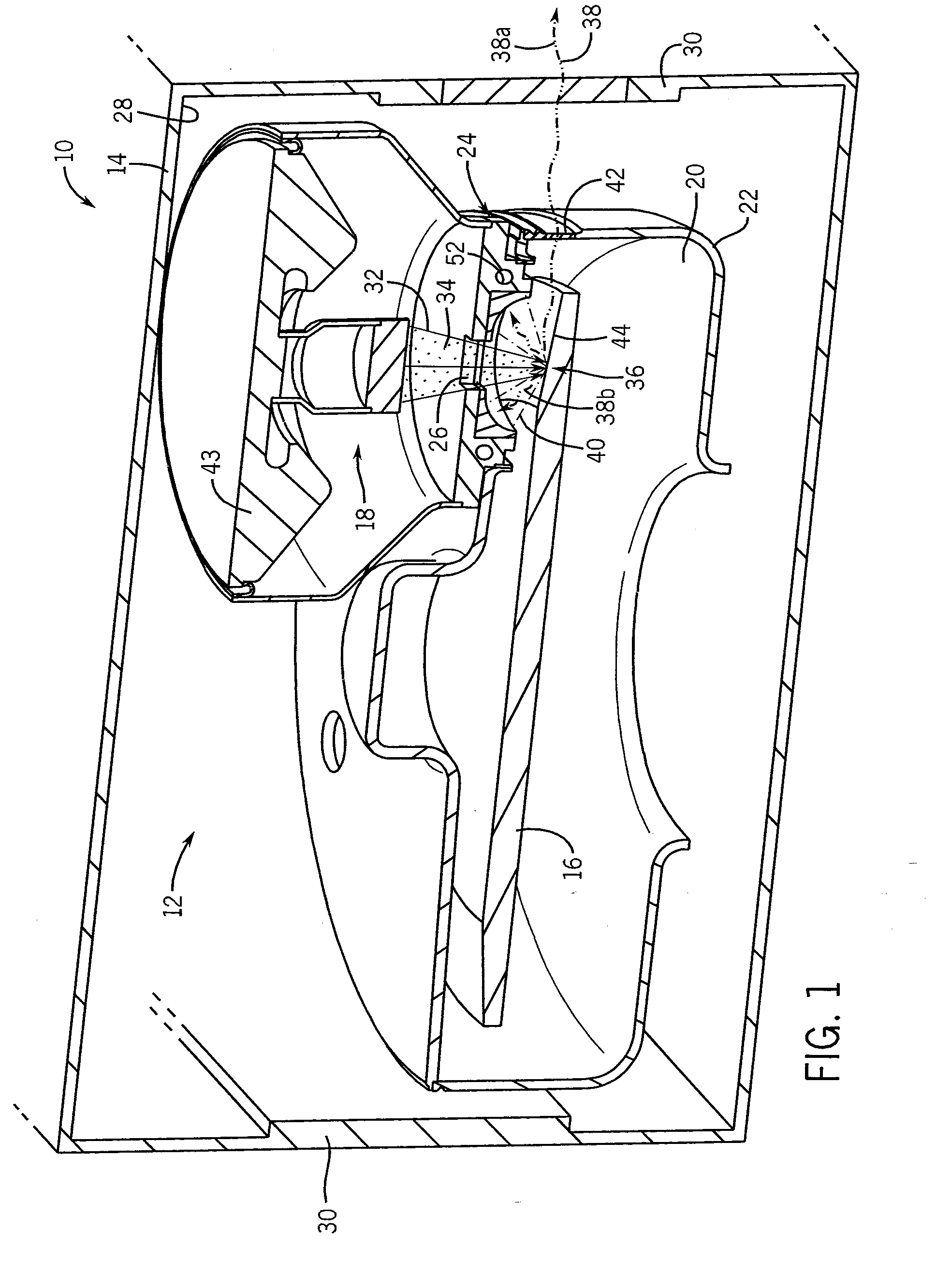
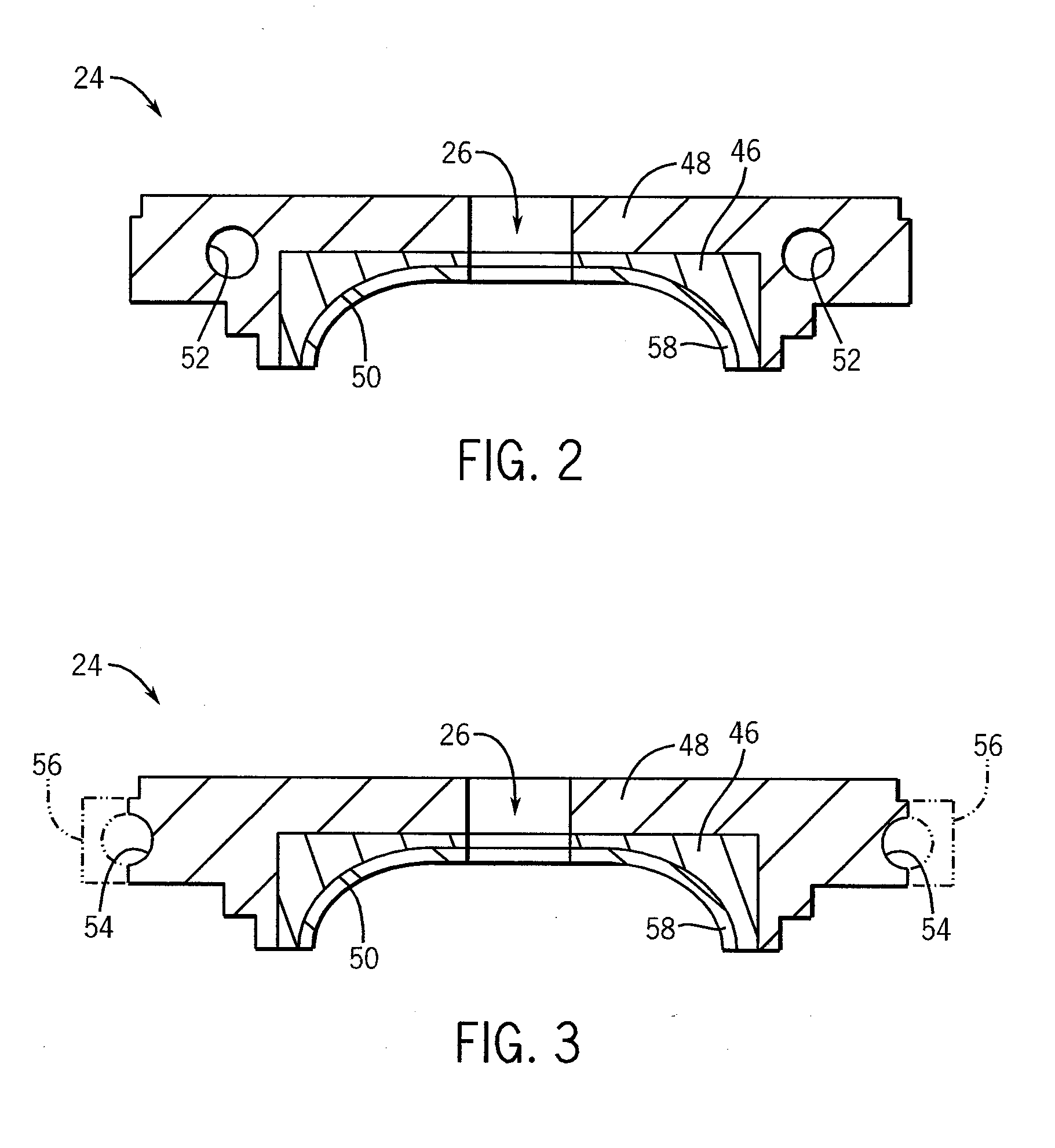
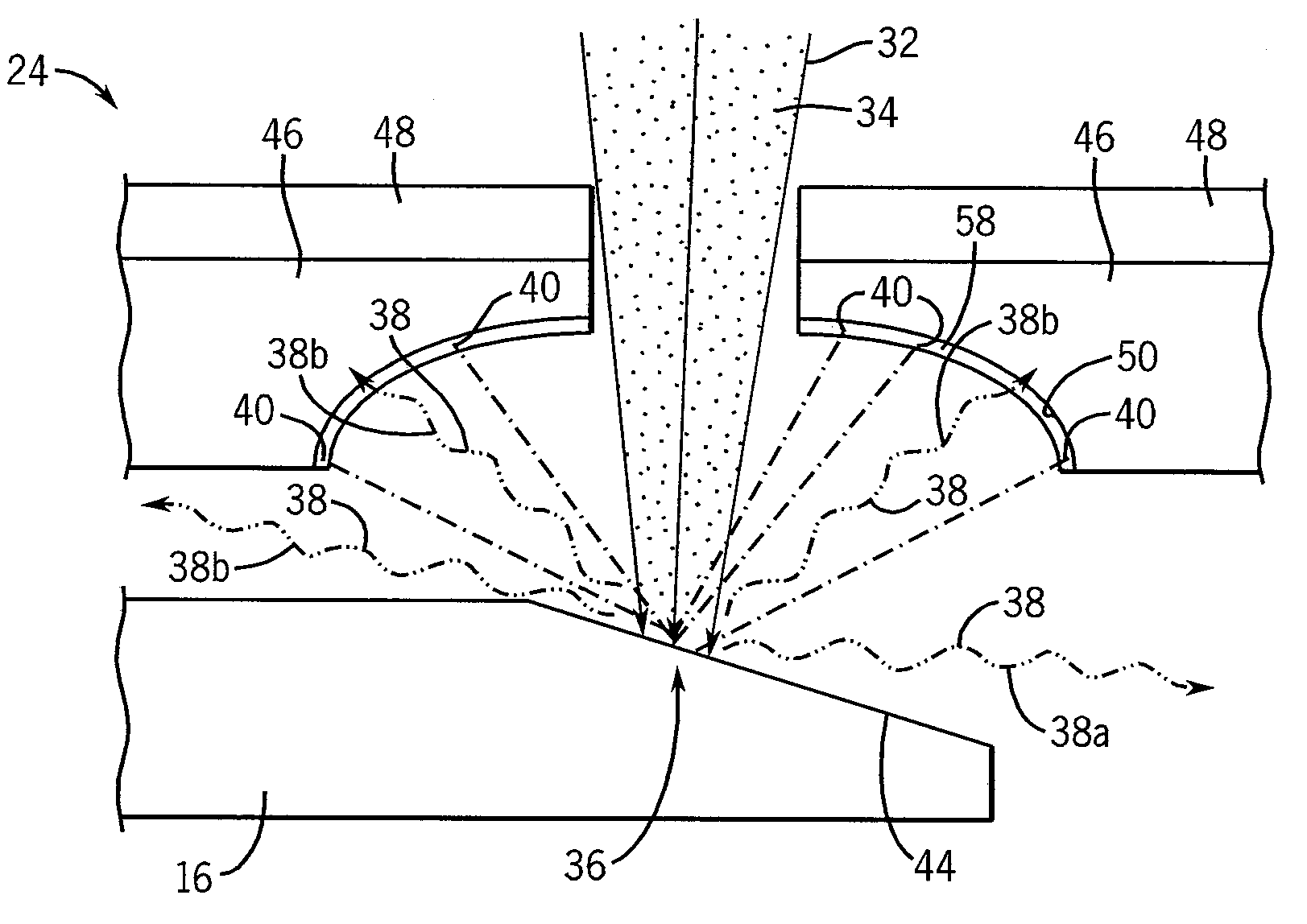
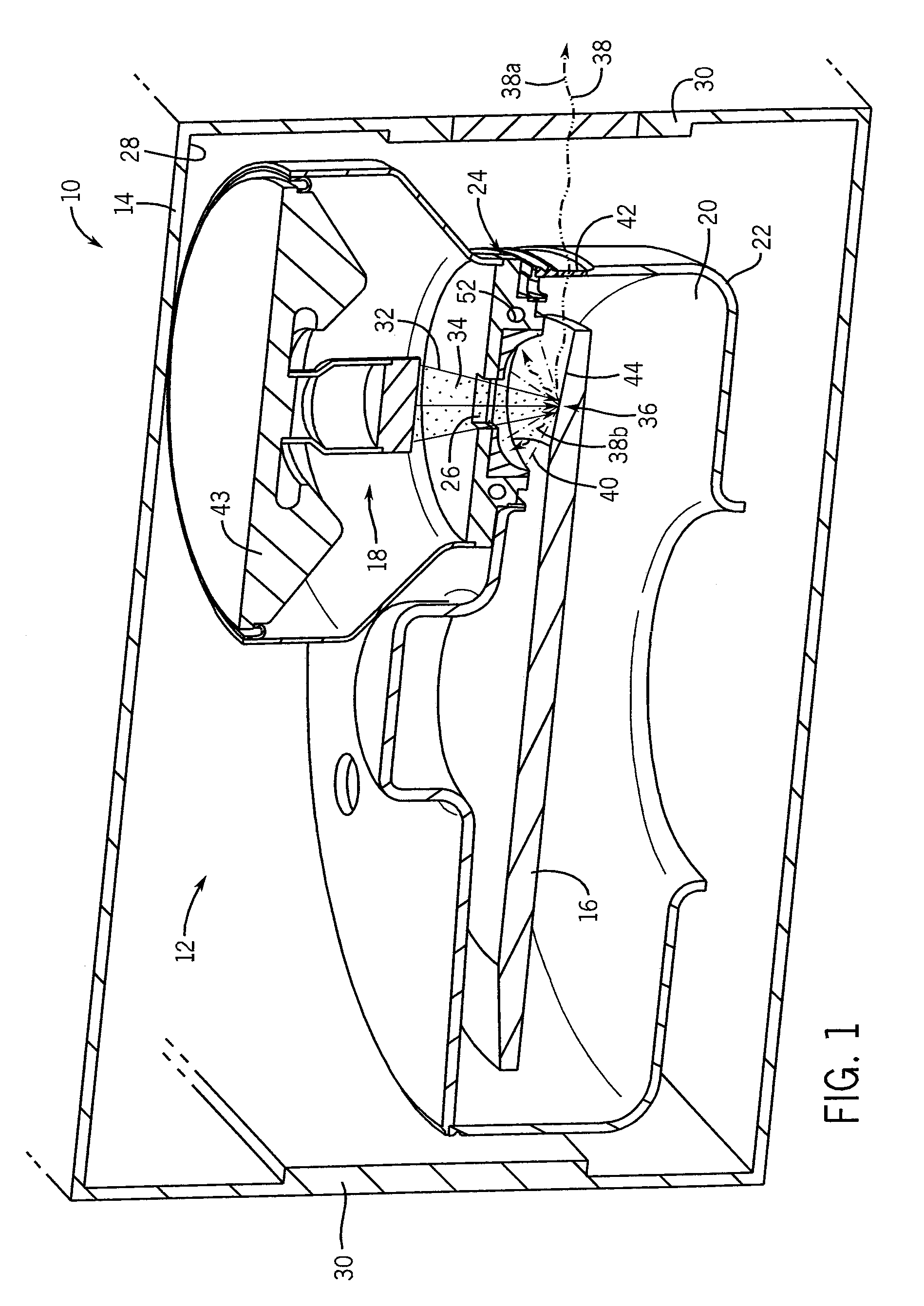
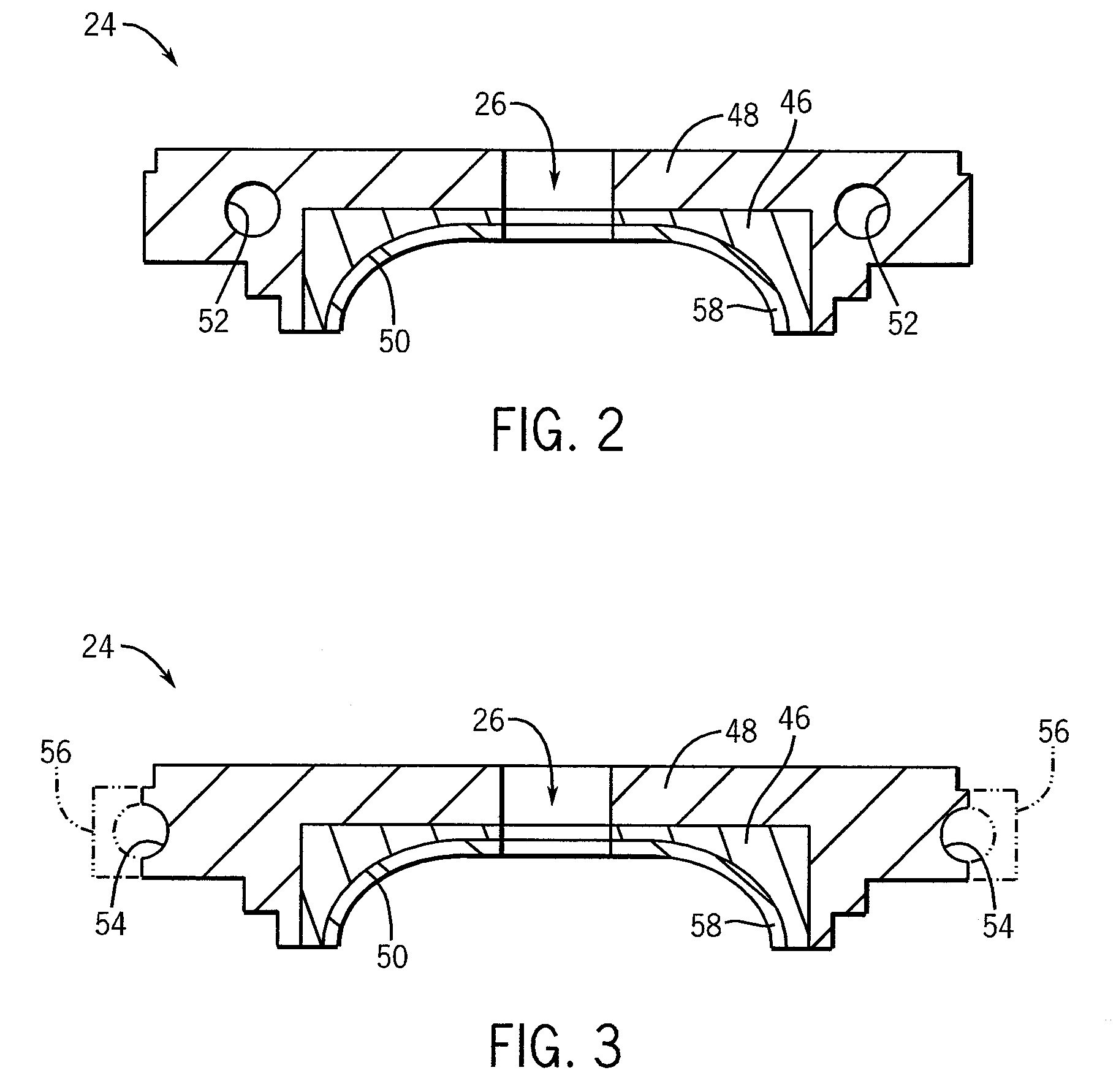
Large surface area x-ray tube shield structure
InactiveUS6519318B1Effective coolingImprove heat transfer performanceX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerElectron sourceCooling effect
An improved x-ray tube cooling system is disclosed. The system utilizes a shield structure that is connected between a cathode cylinder and an x-ray tube housing and is disposed between the electron source and the target anode. The shield includes a plurality of cooling fins to improve overall cooling of the x-ray tube and the shield so as to extend the life of the x-ray tube and related components. When immersed in a reservoir of coolant fluid, the fins facilitate improved heat transfer by convection from the shield to the to the coolant fluid. The cooling effect achieved with the cooling fins is further augmented by a convective cooling system provided by a plurality of fluid passageways formed within the shield, which are used to provide a fluid path to the coolant. In particular, a cooling unit takes fluid from the reservoir, cools the fluid, then circulates the cooled fluid through the fluid passageways. One or more depressions of "V" shaped cross section defined on the surfaces of the fluid passageways serve to facilitate nucleate boiling of the coolant in the passageway, and thereby materially increase the heat flux through the passageway to the coolant. Additionally, one or more extended surfaces disposed on the surfaces of the fluid passageways also facilitate a relative increase in the rate of heat transfer from the shield structure to the coolant. After flowing through the fluid passageway, the coolant is then discharged from the fluid passageways and directed over the cooling fins. In some embodiments, the fluid passageways are oriented so as to provide a greater heat transfer rate in certain sections of the shield than in other sections. Also disclosed is an improved braze joint for connecting the shield to the x-ray tube housing.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
X-ray tube cathode with reduced unintended electrical field emission
ActiveUS20070076849A1Minimize adverse triple point-related phenomenonEasy to controlCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-ray tube vessel coolingSoft x rayX-ray
An x-ray source has an evacuated tube. An anode is disposed in the tube and includes a material configured to produce x-rays in response to impact of electrons. A cathode is disposed in the tube opposing the anode configured to produce electrons accelerated towards the anode in response to an electric field between the anode and the cathode. A flange extends from the cathode toward the anode, and has a smaller diameter than the evacuated tube. The flange extends closer to the anode than an interface between the cathode and the tube thus forming a reduced-field region between the evacuated tube and the flange.
Owner:MOXTEK INC
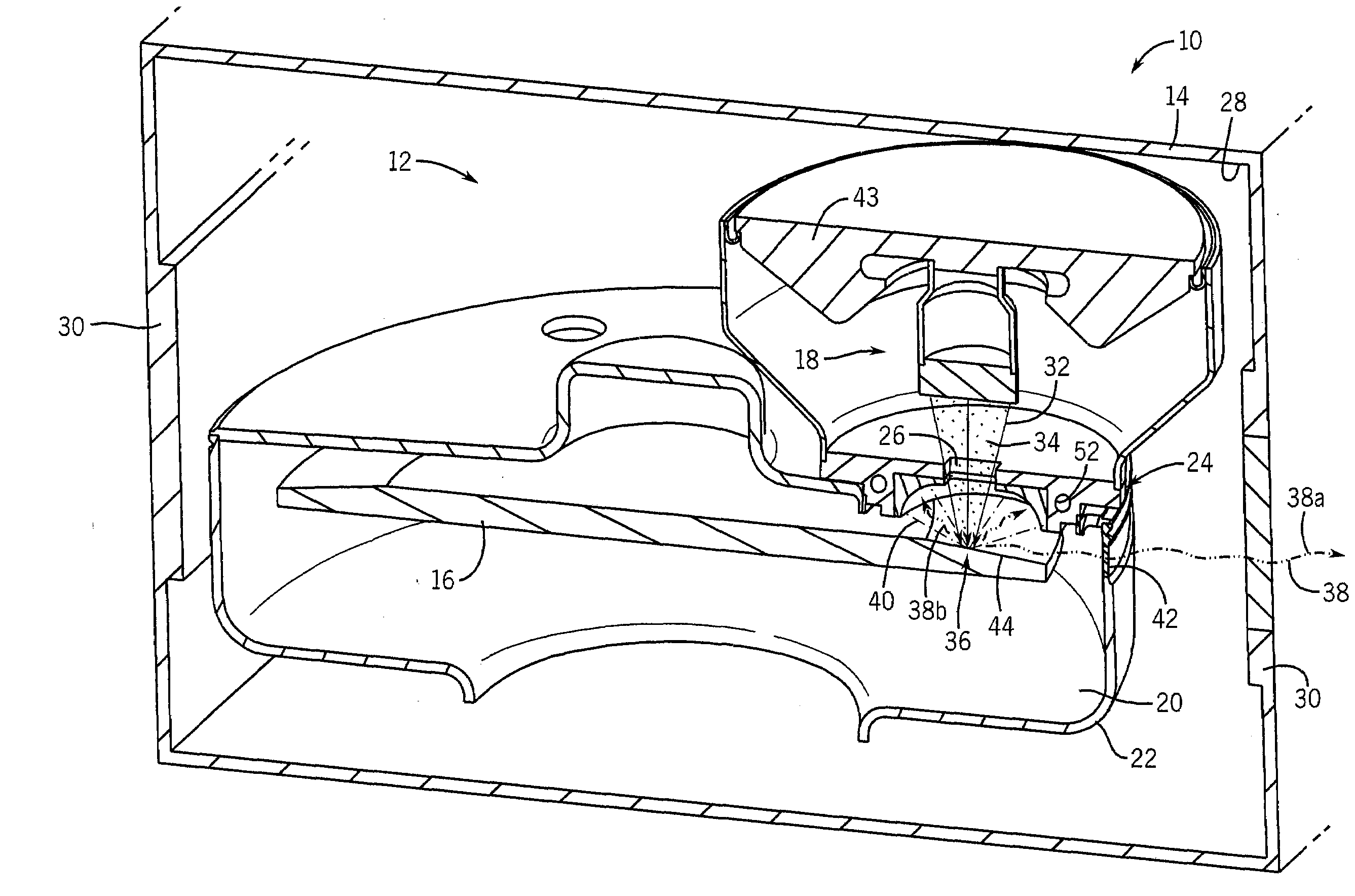
Electron absorption apparatus for an x-ray device
A shield assembly for an x-ray device is disclosed herein. The shield assembly includes a radiation shielding layer comprised of a first material; and a thermally conductive layer attached the radiation shielding layer. The thermally conductive layer is comprised of a second material. The shield assembly also includes an electron absorption layer attached to the radiation shielding layer. The electron absorption layer is comprised of a third material. The electron absorption layer is configured to absorb backscattered electrons.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Radiation generating apparatus and radiation imaging apparatus
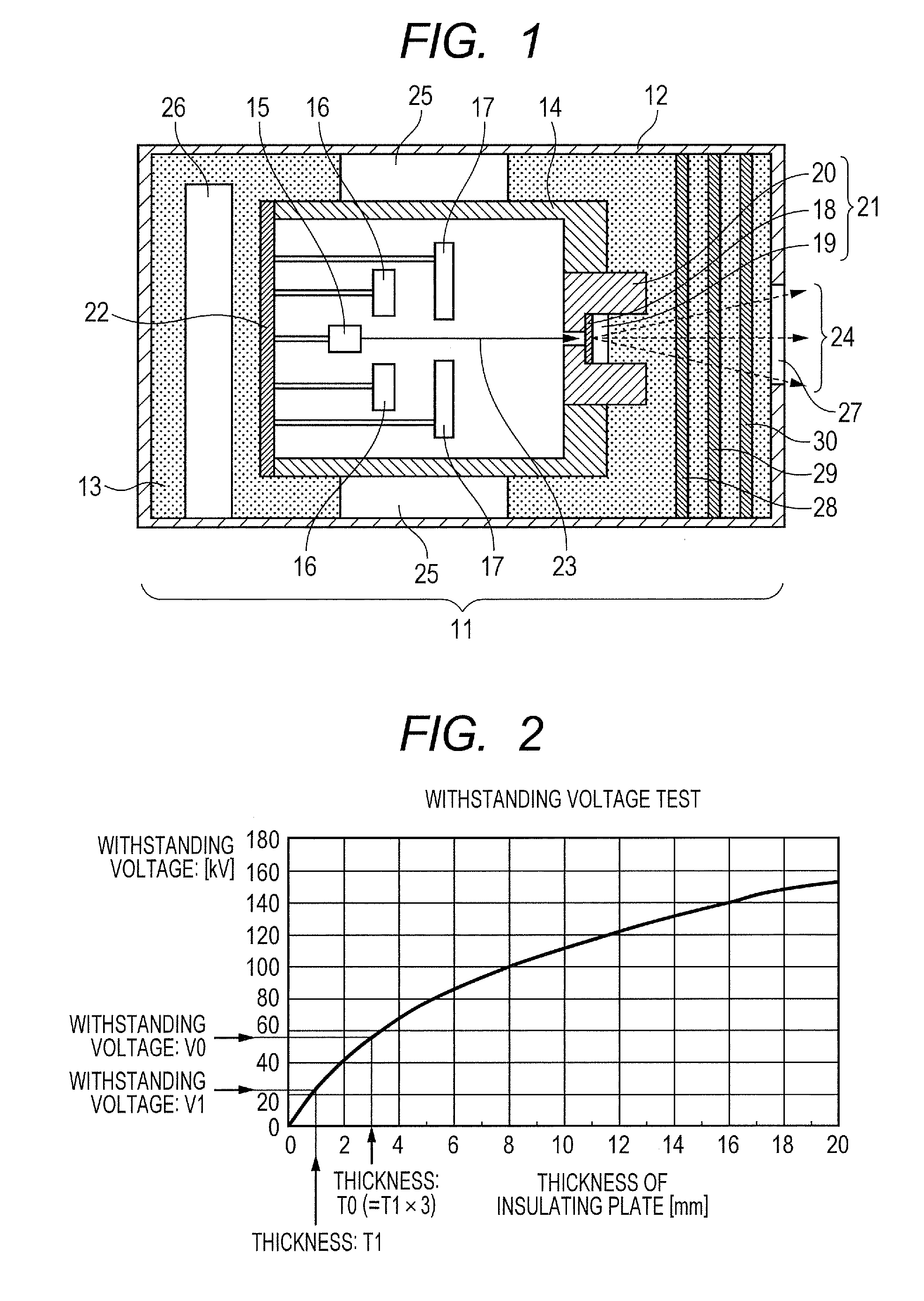
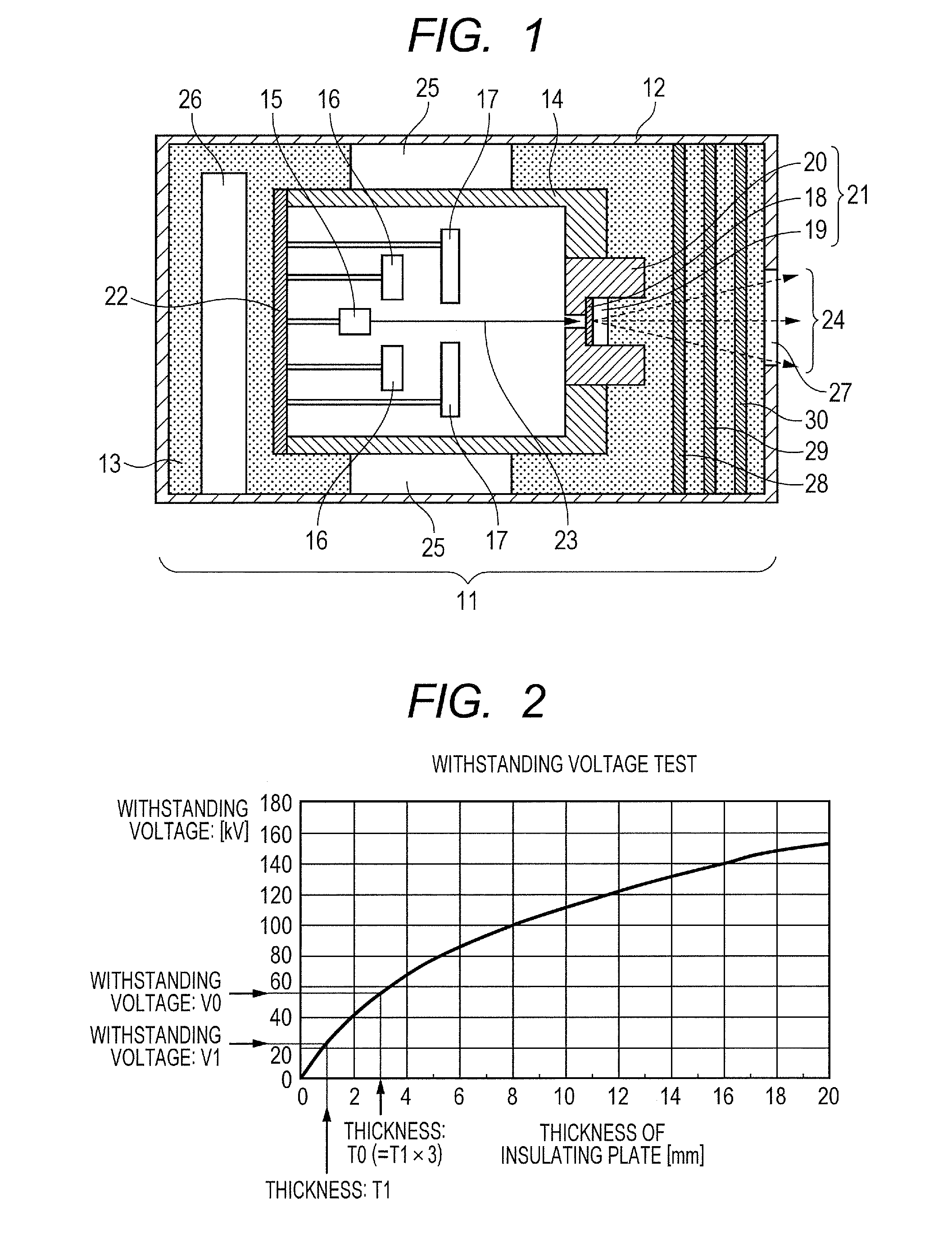
ActiveUS20130034207A1Secure withstanding voltage characteristicStabilize radiation outputX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesRadiation imagingVoltage
The present invention relates to a radiation generating apparatus which includes an envelope provided with a first window through which radiation is transmitted, a radiation tube housed in the envelope and provided with a second window through which the radiation is transmitted, the second window being located at a position opposite the first window, and an insulating fluid adapted to fill between the inner wall of the envelope and the radiation tube. Plural plates are arranged side by side between the first window including its periphery and the second window including its periphery by overlapping one another via gaps. The gaps is formed among the plates, thereby the withstanding voltage between the first window and second window is made larger.
Owner:CANON KK
X-ray tube aperture body with shielded vacuum wall
ActiveUS20130195253A1Reduce failure rateExtended service lifeCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-ray tube vessel coolingElectronAtomic physics
X-ray tube aperture body with shielded vacuum wall. In one example embodiment, an aperture body for use in an x-ray tube having an anode and a cathode includes an electron shield and a vacuum wall. The electron shield is configured to intercept backscattered electrons from the anode. The vacuum wall is separated by a gap from the electron shield and is shielded from the backscattered electrons by the electron shield. The aperture body also includes an electron shield aperture defined in the electron shield and a vacuum wall aperture defined in the vacuum wall through which electrons may pass between the cathode and the anode.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
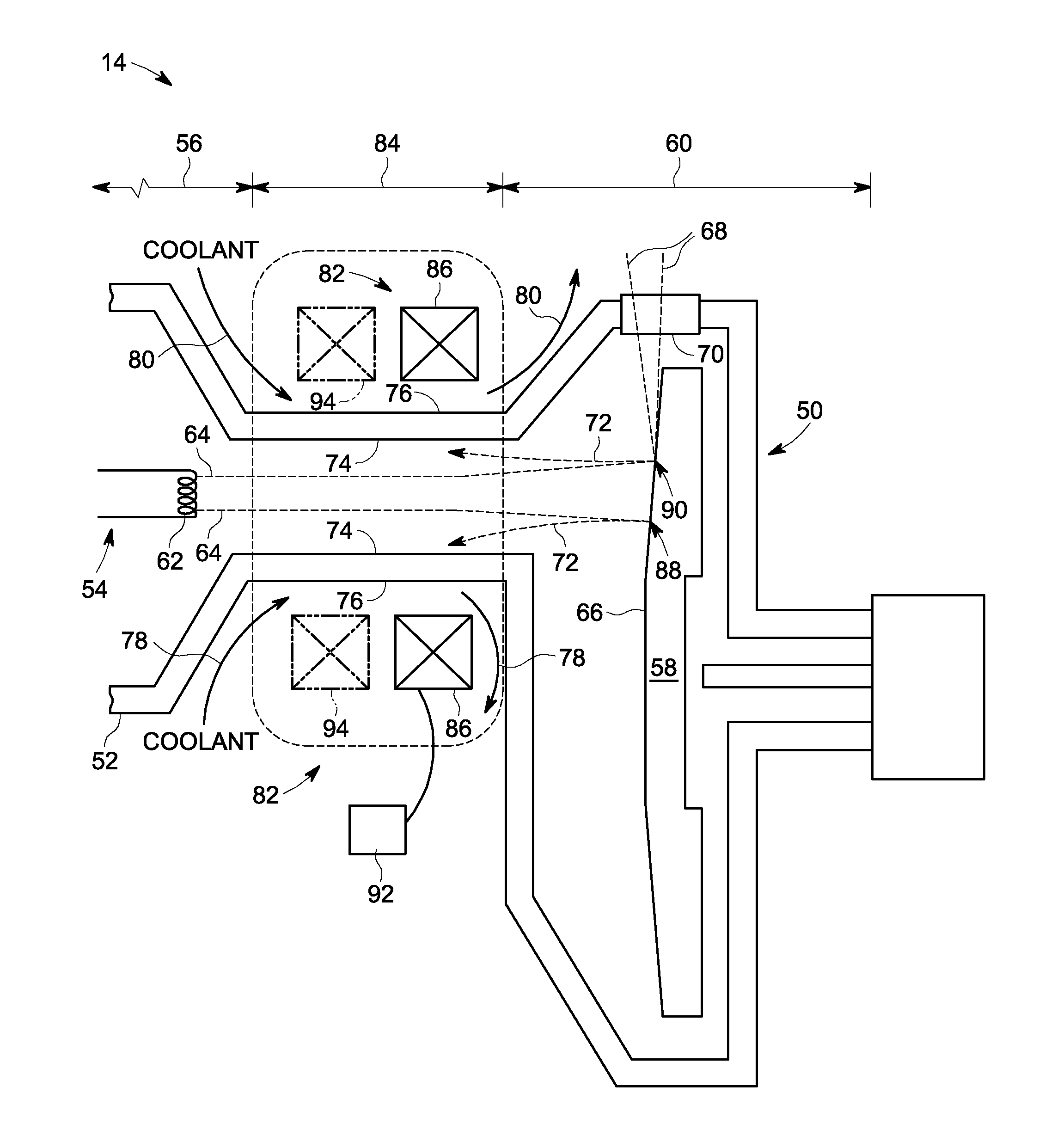
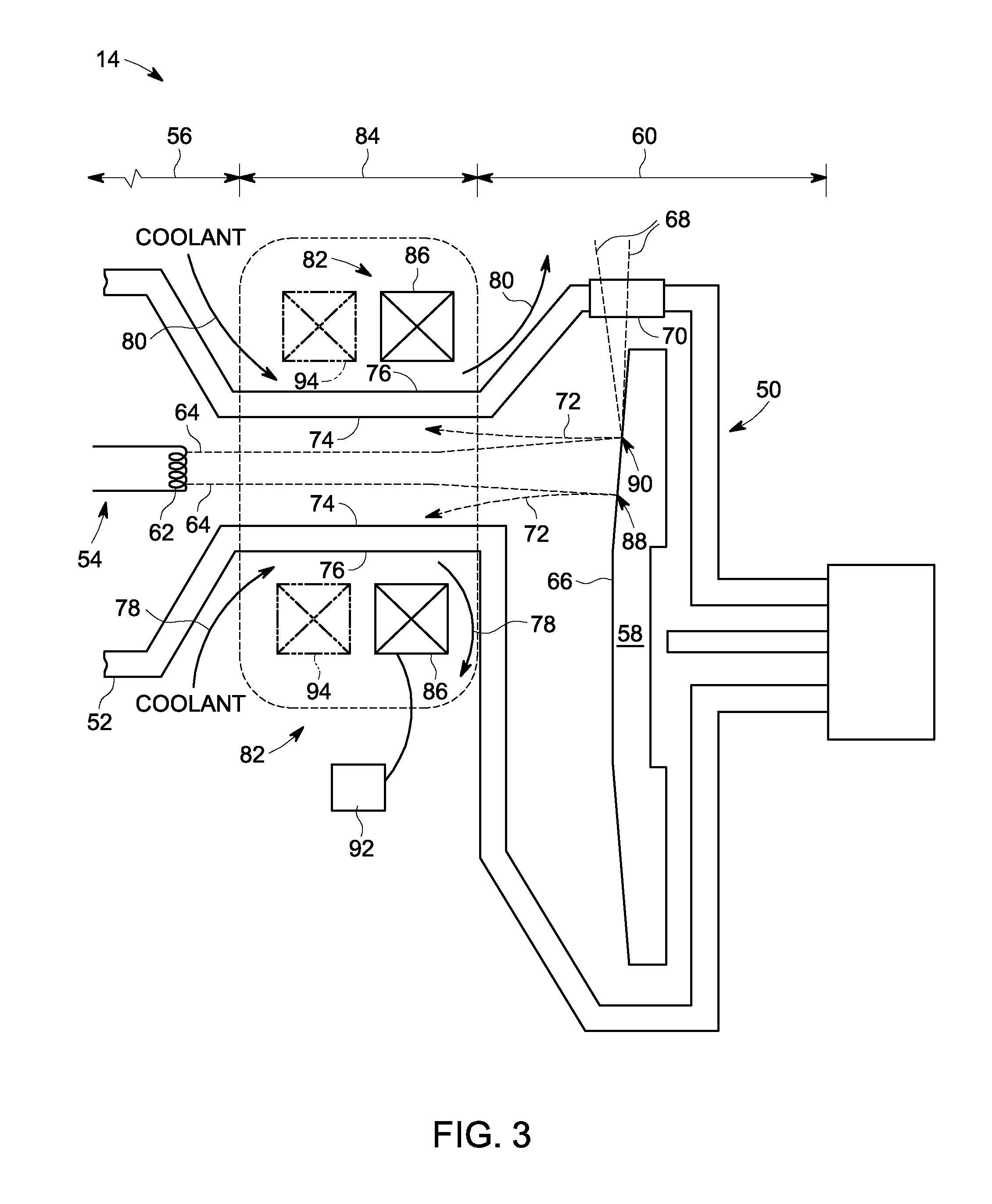
Systems and apparatus for integrated X-Ray tube cooling
ActiveUS7236571B1Improve heat transfer performanceX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerWorking fluidBeam source
An X-Ray tube is provided. The X-Ray tube includes a frame structure surrounding at least a portion of an electron beam source and an electron beam target. The frame structure has a cooling system integrated therein. The cooling system includes at least one air / fin layer; and a sub-cooled working fluid in thermal contact with the at least one air / fin layer, the sub-cooled working fluid being adapted to undergo a phase change in response to heat introduced to the frame structure by one or more of the electron beam source and the electron beam target, wherein the phase change facilitates transfer of the heat to the at least one air / fin layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
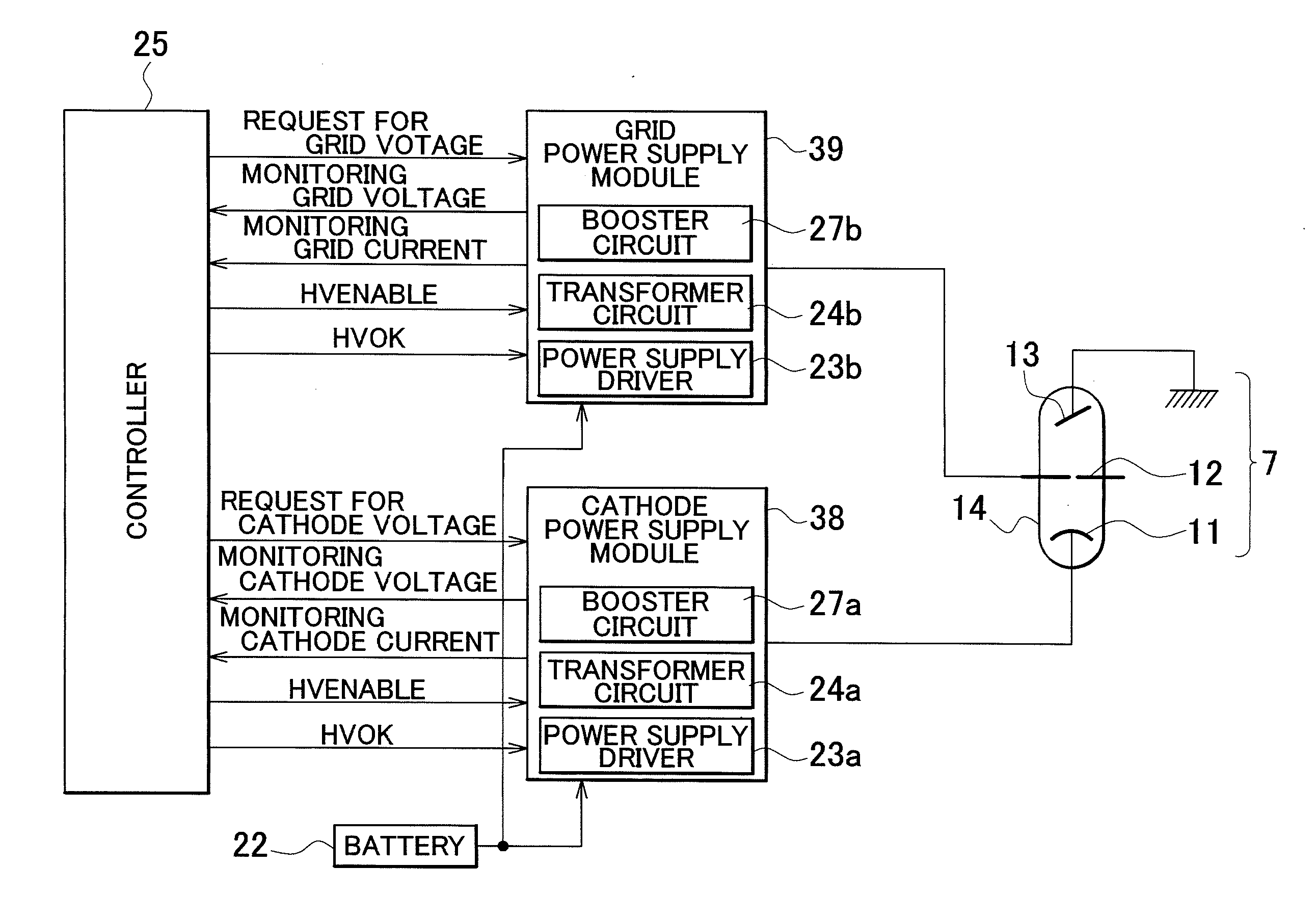
Industrial x-ray generator
ActiveUS20120027179A1Avoid heatSmall regionX-ray tube vessel coolingX-ray tube vessels/containerLow voltageHigh pressure
An X-ray generator includes a booster circuit formed by sequentially connecting a plurality of boosting steps extending from a low-voltage terminal to a high-voltage terminal of its own.The booster circuit is arranged in a lateral region of the X-ray tube so as to make the low-voltage terminal of its own correspond to the anode of the X-ray tube and the high-voltage terminal of its own correspond to the cathode of the X-ray tube. A lead wire extending from the cathode to the outside of the X-ray tube is connected to the high-voltage terminal of the booster circuit. A molded member containing insulating resin is formed to shield at least a cathode side end part of the X-ray tube, the lead wire outwardly extending from the cathode side end part and a high-voltage terminal side end part of the booster circuit.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
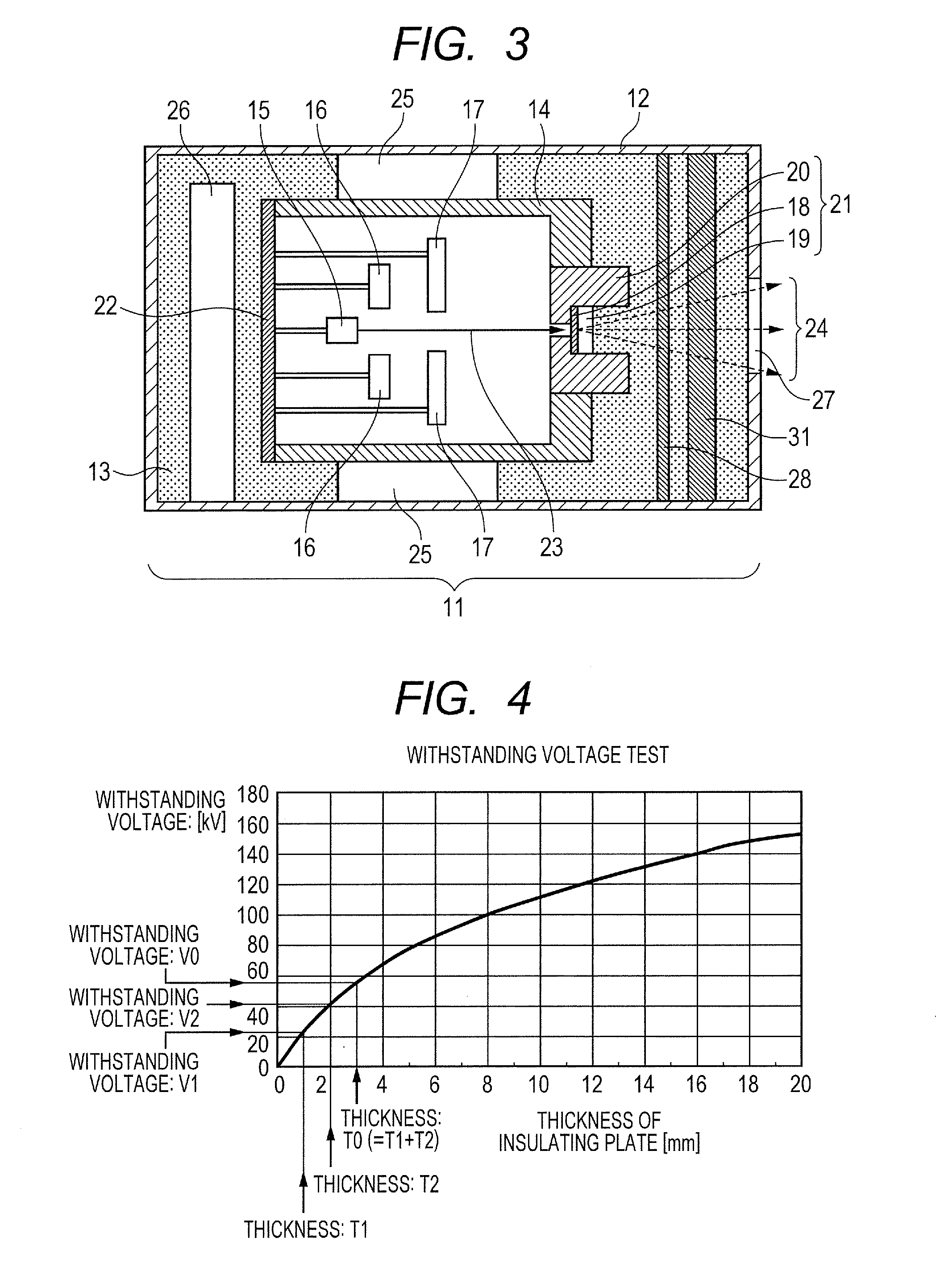
Radiation generating apparatus and radiation imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20130016810A1Small sizeReduce weightX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesSolid massShortest distance
In a radiation imaging apparatus which comprises an envelope which has a first window for transmitting a radiation and is filled with an insulating liquid, a radiation tube in the envelope which has, at a position facing the first window, a second window for transmitting the radiation, and a shielding member, a solid insulating member is arranged between the shielding member and the inner wall of the envelope, an opening is formed at a position on the insulating member corresponding to the first window, and a shortest distance from the shielding member to the first window or the inner wall of the envelope through the opening of the insulating member without the insulating member is made longer than a shortest distance from the shielding member to the first window or the inner wall of the envelope through the insulating member, thereby improving withstand voltage performance without reducing an radiation amount.
Owner:CANON KK
Stationary cathode in rotating frame x-ray tube
An x-ray tube includes a stationary base and a passage therein. The x-ray tube includes an anode frame having an anode positioned adjacent to a first end and having a neck at a second end, the neck extends into the passage, wherein the anode frame is configured to rotate about a longitudinal axis of the passage. A hermetic seal is positioned about the neck between the neck and the stationary base.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Shield assembly apparatus for an x-ray device
InactiveUS20080112540A1Reduces requisite massX-ray tube vessels/containerX-ray tube vessel coolingX-rayEngineering
A shield assembly for an x-ray device is disclosed herein. The shield assembly includes a radiation shielding layer comprised of a first material. The radiation shielding layer defines a collection surface. The shield assembly also includes a thermally conductive layer attached the radiation shielding layer. The thermally conductive layer is comprised of a second material. The shield assembly also includes a passage defined by the radiation shielding layer and / or the thermally conductive layer. The passage generally conforms to the size and shape of an electron beam when it passes through the passage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems, methods and apparatus for X-ray tube housing
An X-ray tube housing with integrated cooling passages in the walls of the X-ray tube housing, through which a liquid or gas coolant is circulated and the heat is transferred from the X-ray tube housing to an external cooler. The integrated cooling passages are created around the perimeter of the X-ray tube housing as the X-ray tube housing is formed. For a rotating anode X-ray tube using an oil coolant, the path of heat transfer is from the anode to the glass insert and oil by the means of radiation. The oil that is in contact with the glass insert conducts heat away form the insert to the X-ray tube housing which is then cooled by the integrated cooling passages located within the X-ray tube housing through which fluid is passed to an external fluid cooling system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
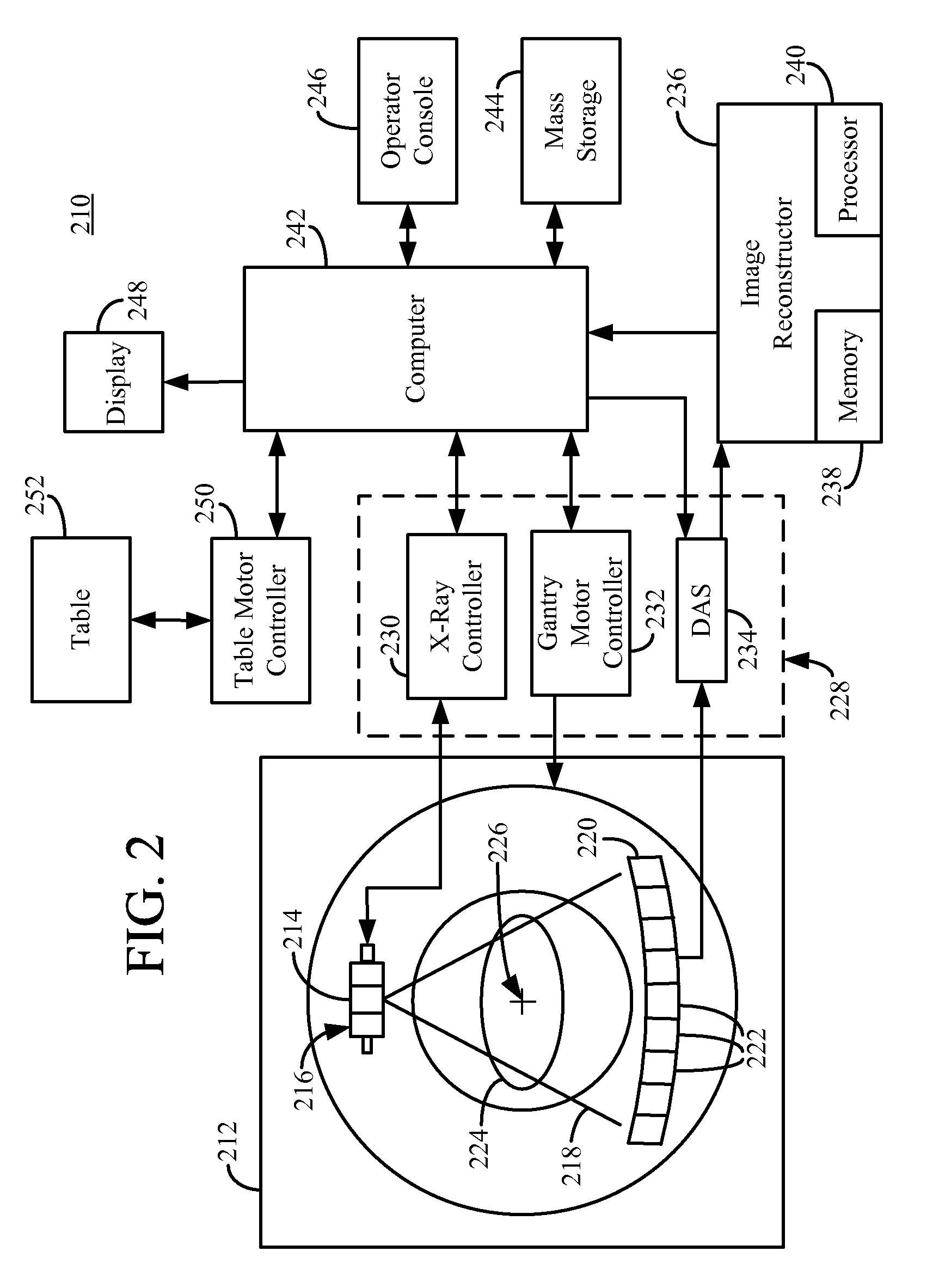
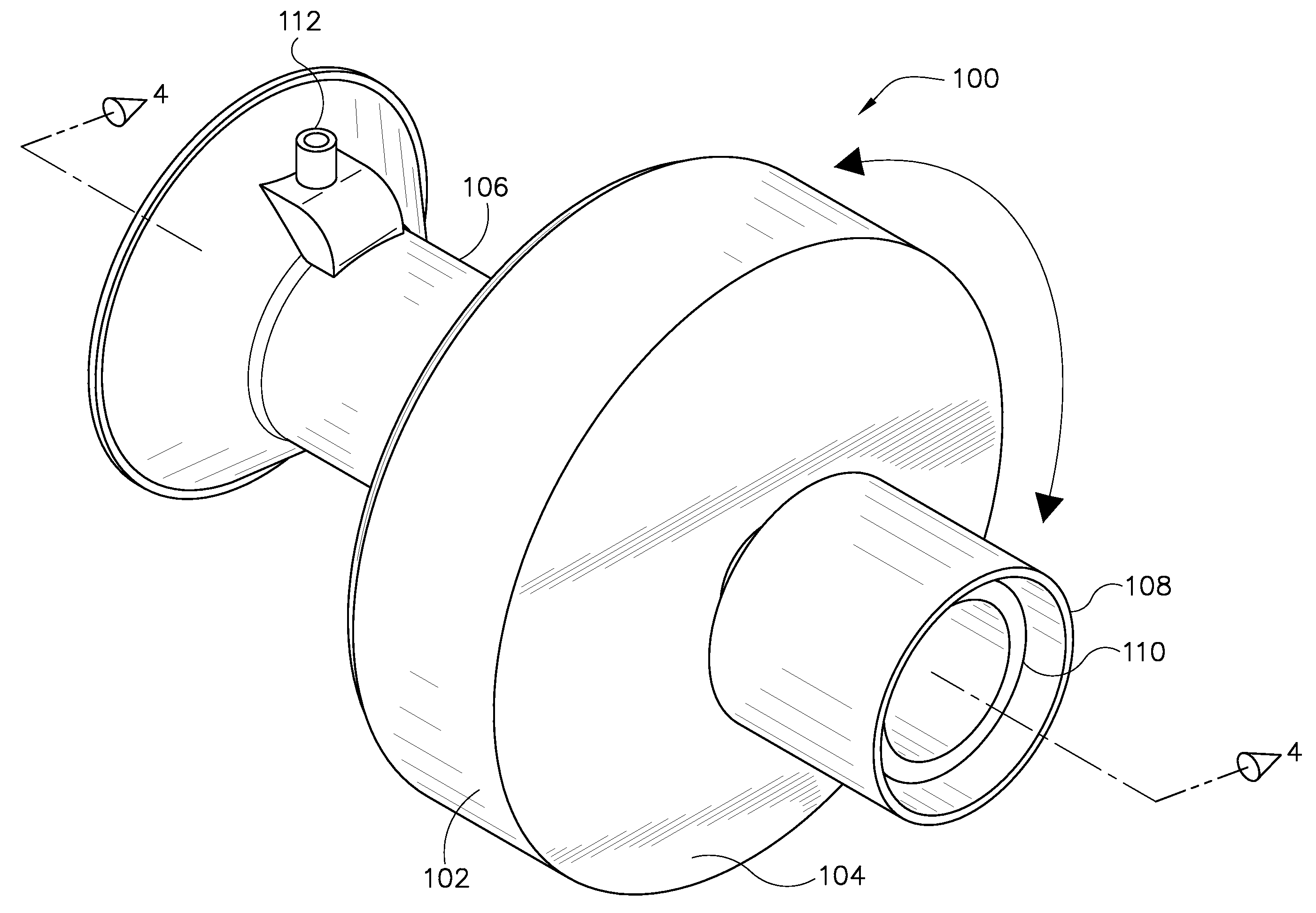
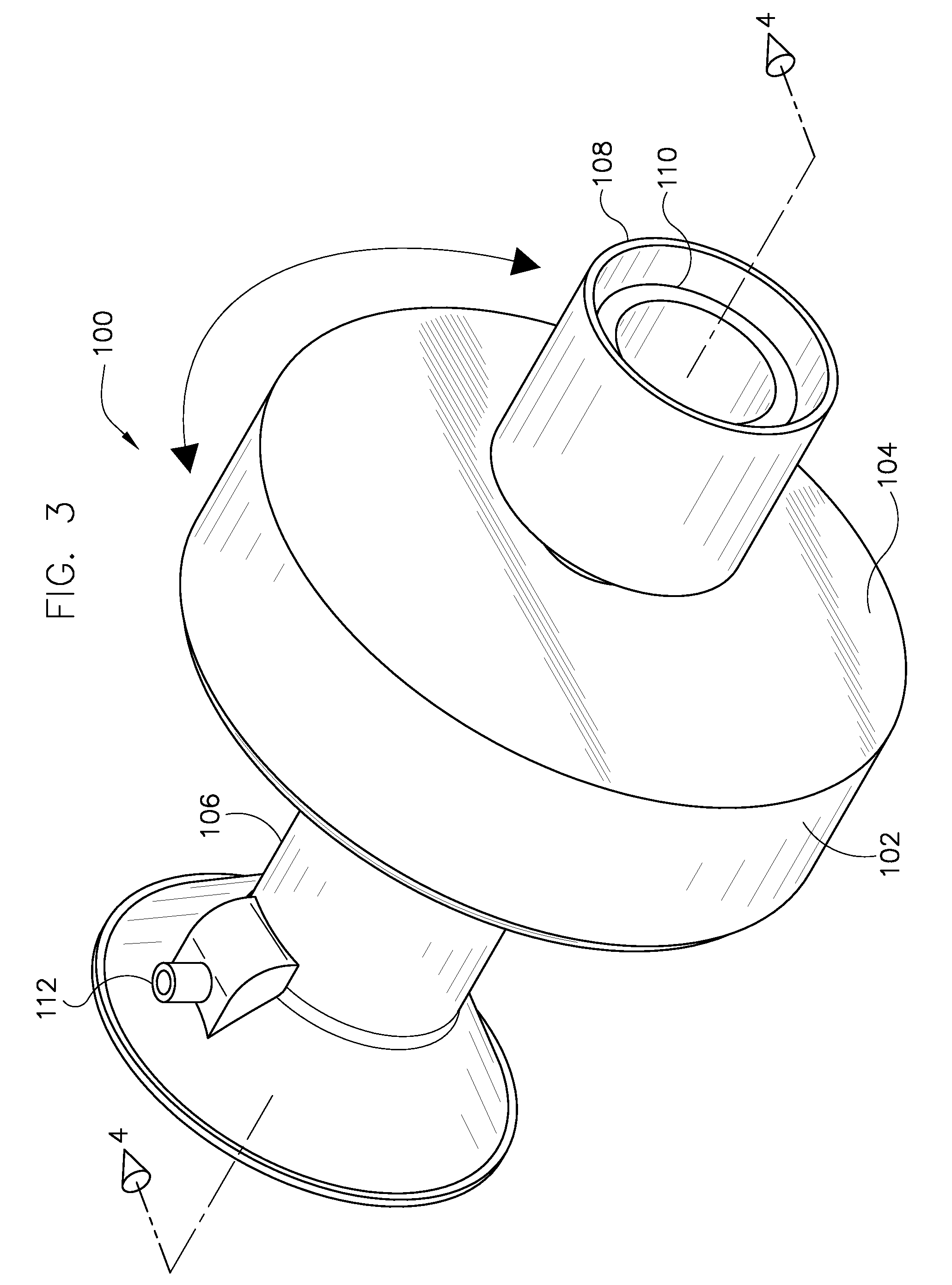
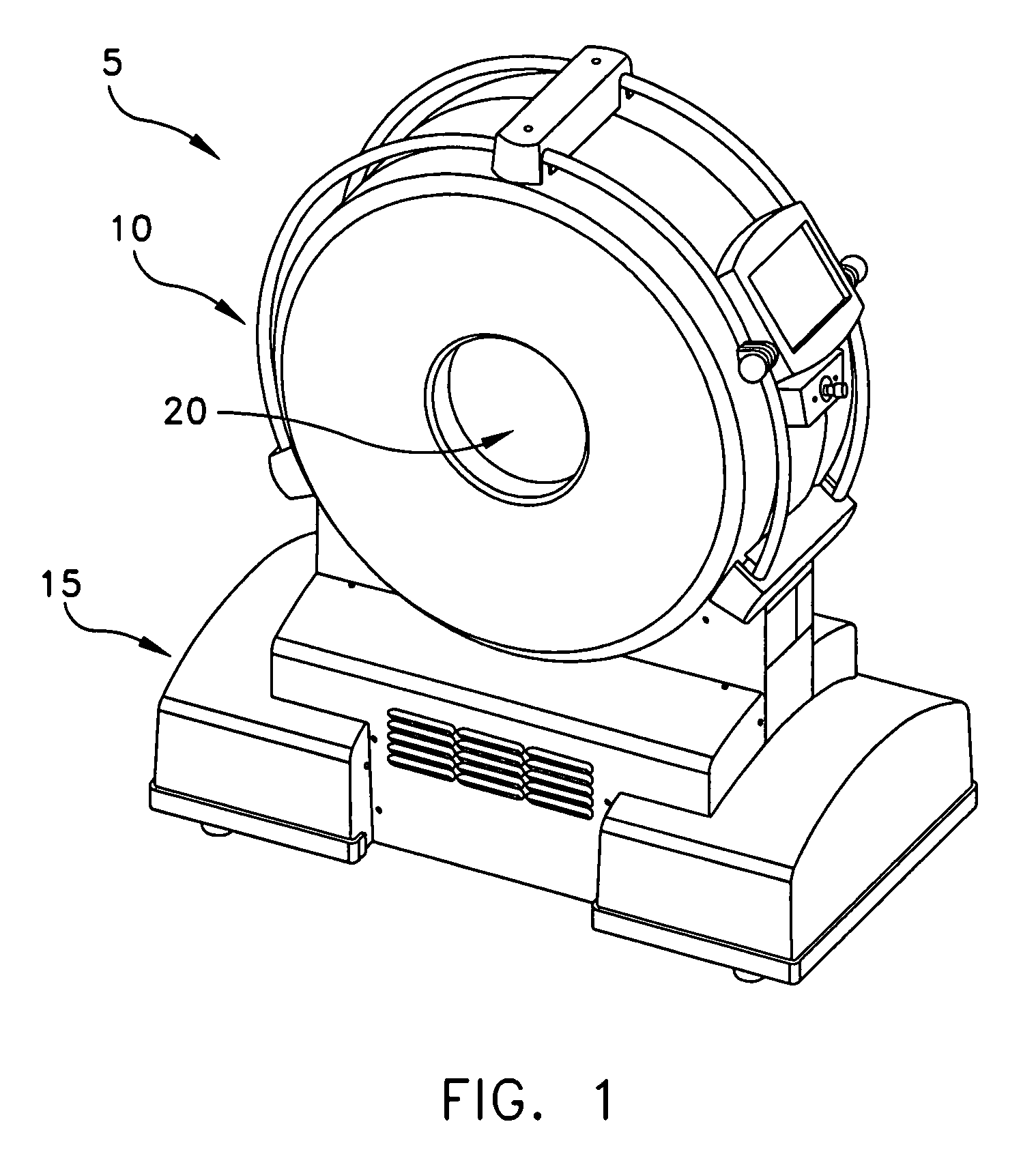
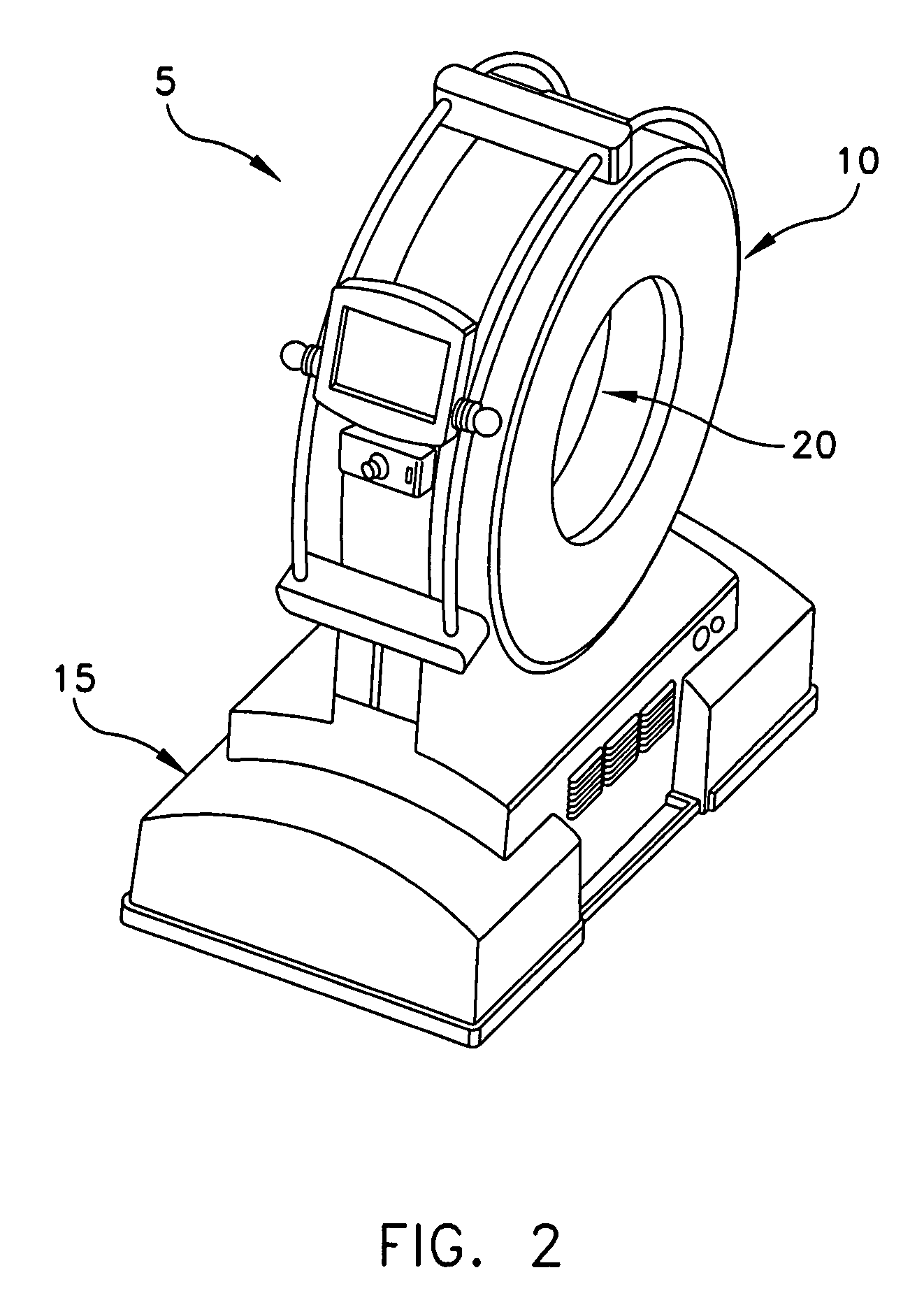
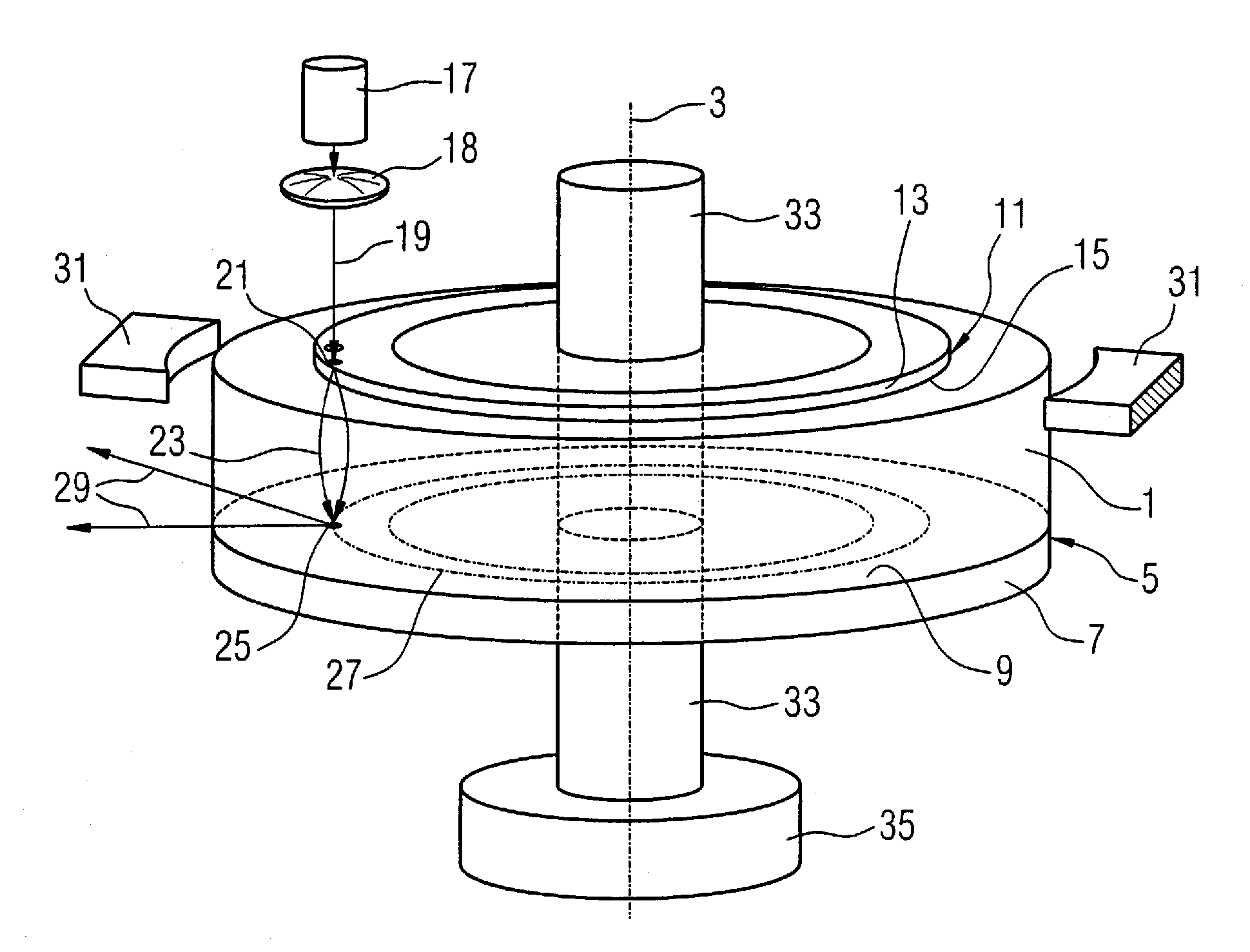
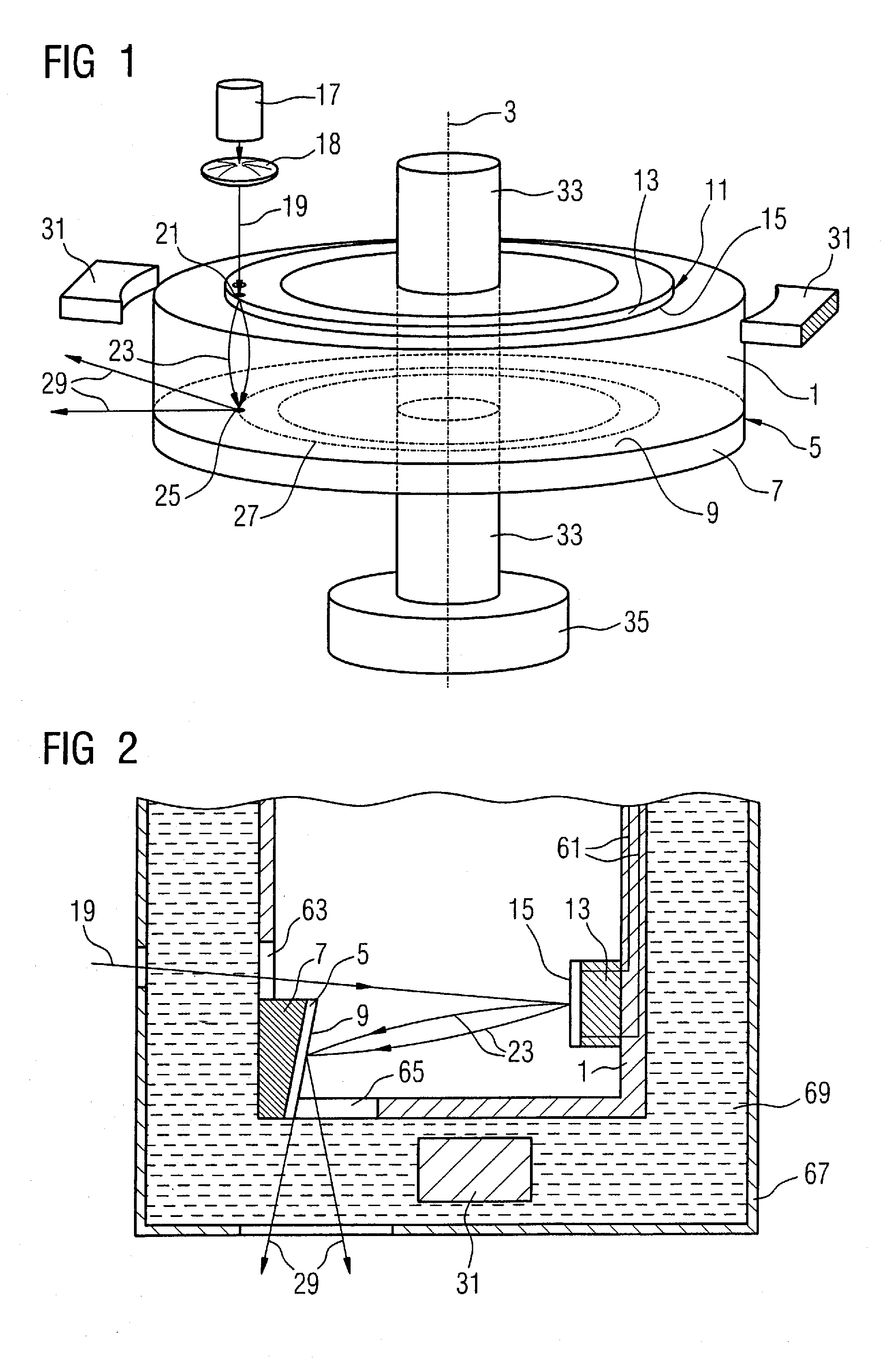
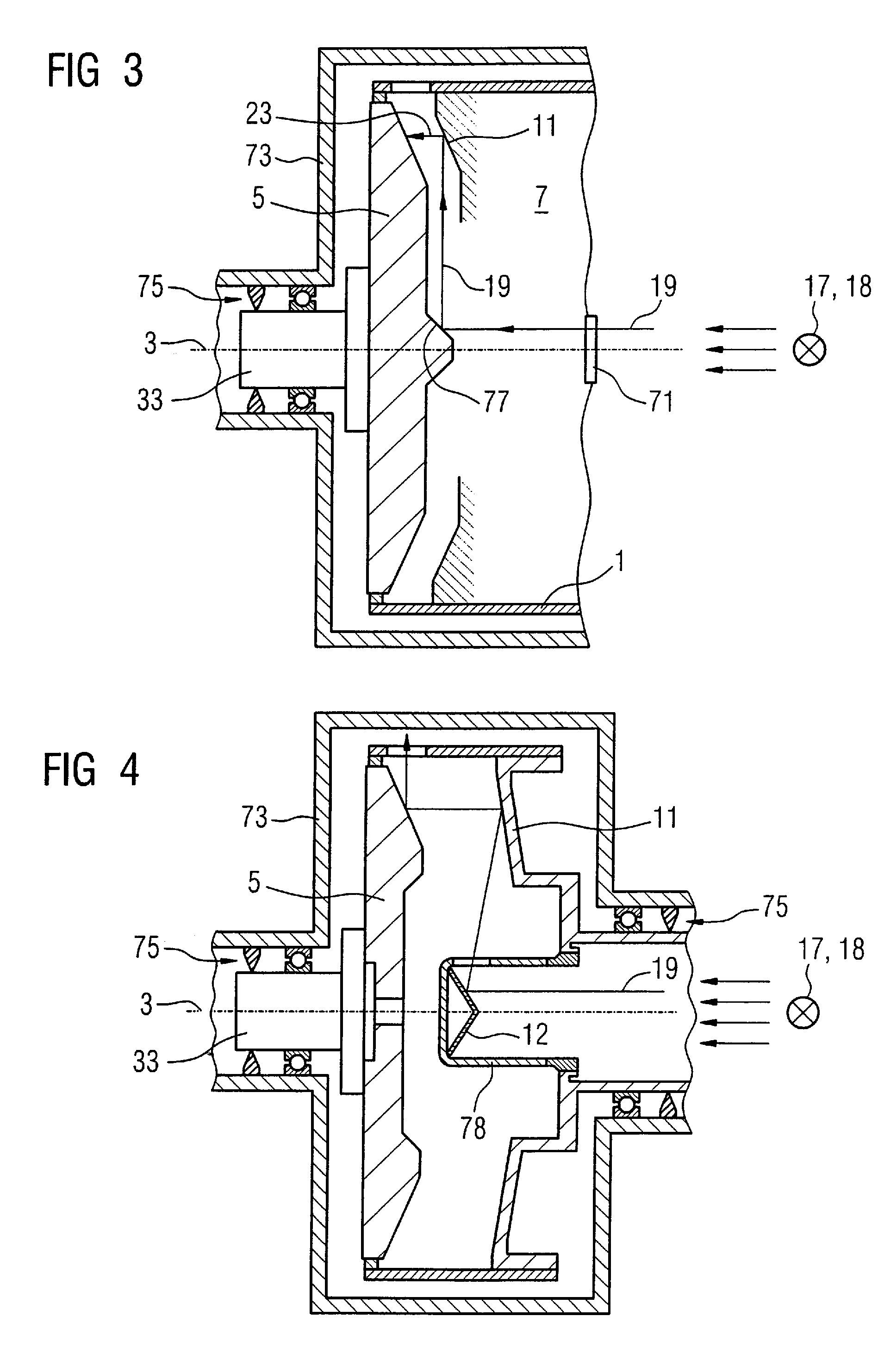
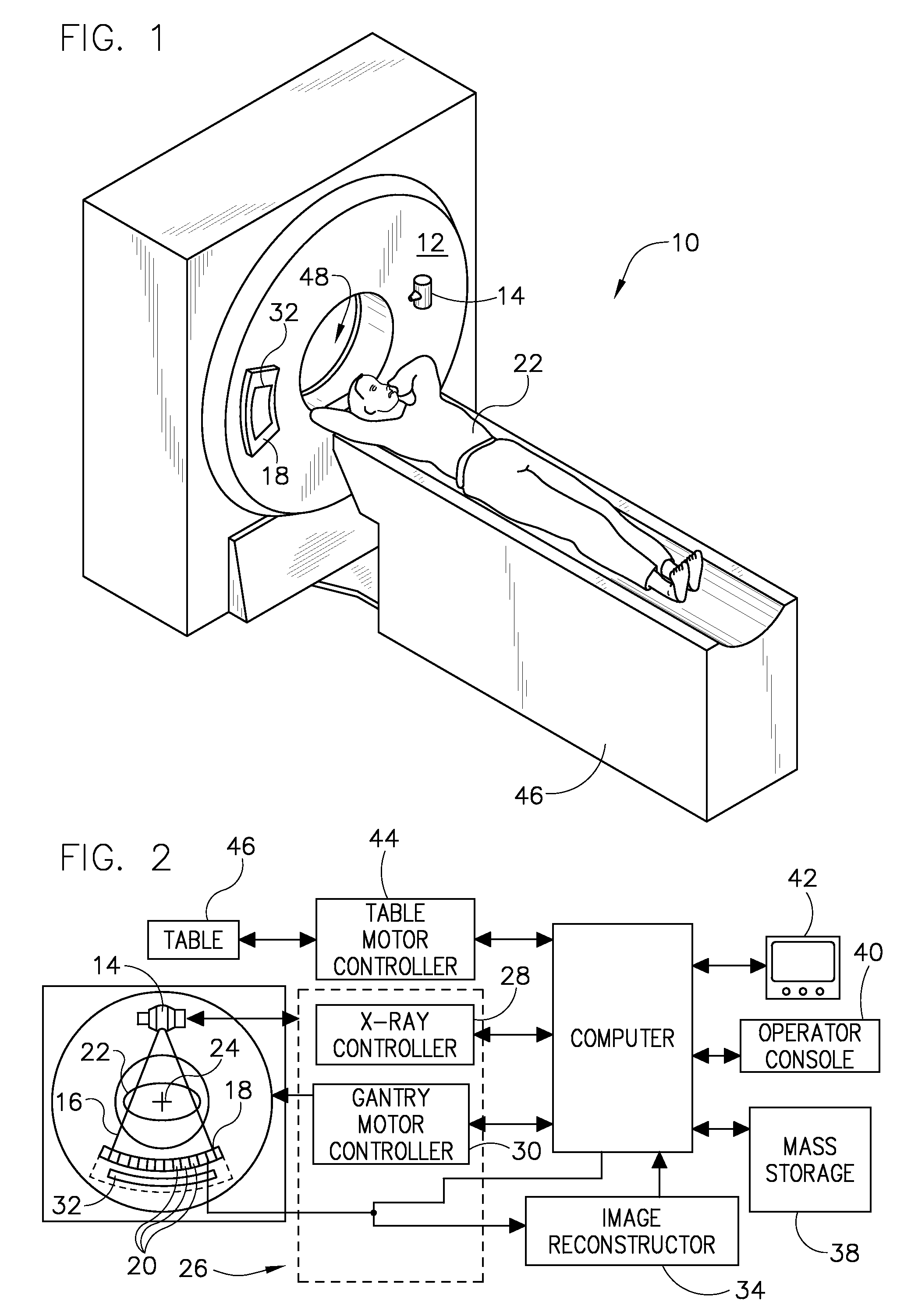
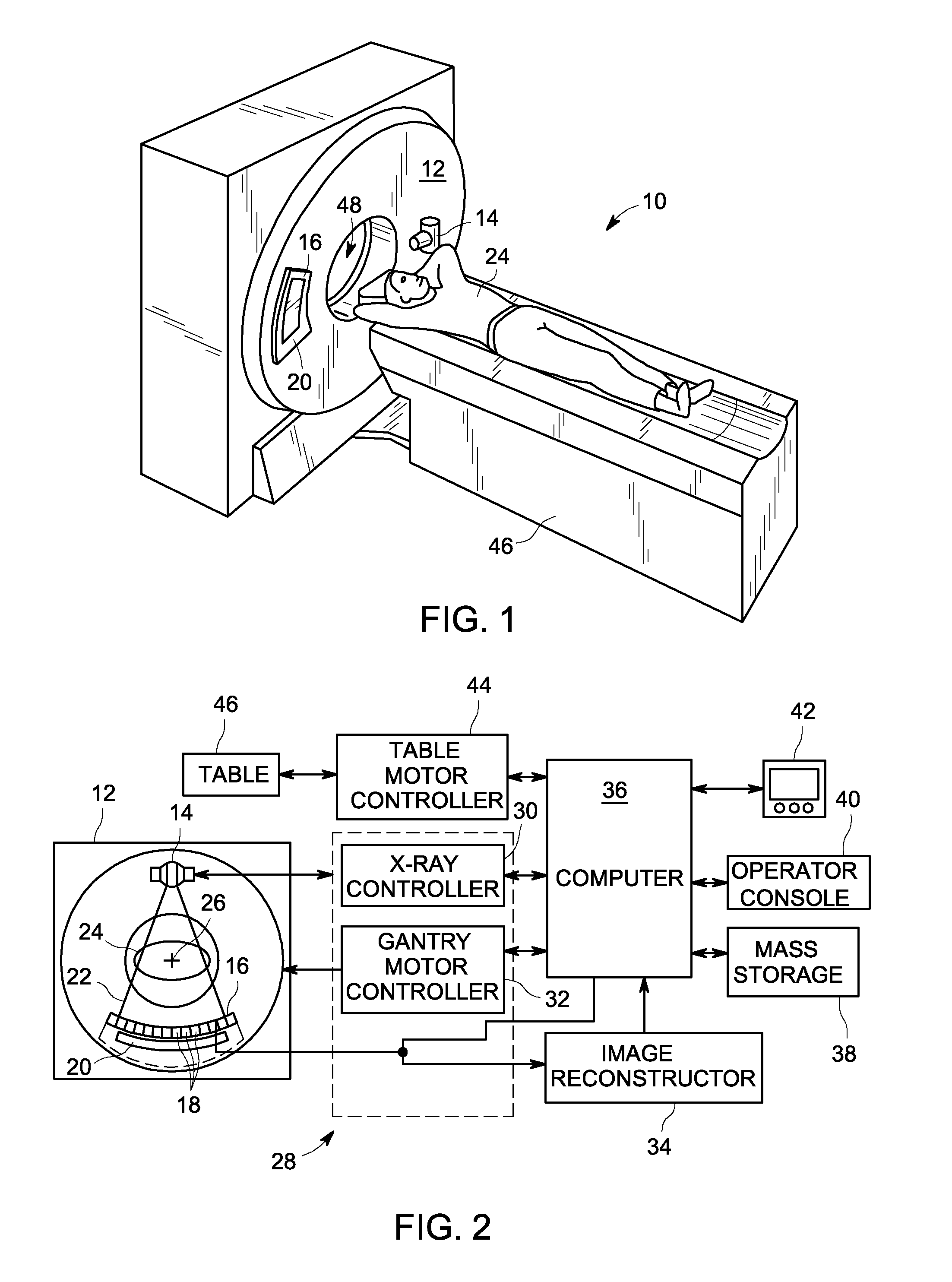
Computerized tomography (CT) imaging system with monoblock X-ray tube assembly
ActiveUS7396160B2Small sizeReduce weightMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayX-ray
A system for cooling an X-ray tube in a CT machine comprising a heat sink for drawing heat away from the X-ray tube and a collimator connected to the heat sink and adapted to collimate the X-rays emitted by the X-ray tube and “focus” those X-rays on an X-ray detector, the heat sink body being formed out of the same material as the emitter of the X-ray tube, such that the emitter opening of the X-ray tube will remain aligned with both the heat sink window and the collimator opening even when the emitter of the X-ray tube undergoes thermal expansion.
Owner:NEUROLOGICA CORP
Radiation generating apparatus and radiation imaging apparatus
InactiveUS9058958B2Reduce equipmentSecure withstanding voltage characteristicX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesRadiation imagingOptoelectronics
The present invention relates to a radiation generating apparatus which includes an envelope provided with a first window through which radiation is transmitted, a radiation tube housed in the envelope and provided with a second window through which the radiation is transmitted, the second window being located at a position opposite the first window, and an insulating fluid adapted to fill the space between the inner wall of the envelope and the radiation tube. Plural plates are arranged side by side between the first window including its periphery and the second window including its periphery, and overlapping one another with gaps between them. The gaps are formed among the plates, and thereby the withstanding voltage between the first window and second window is made larger.
Owner:CANON KK
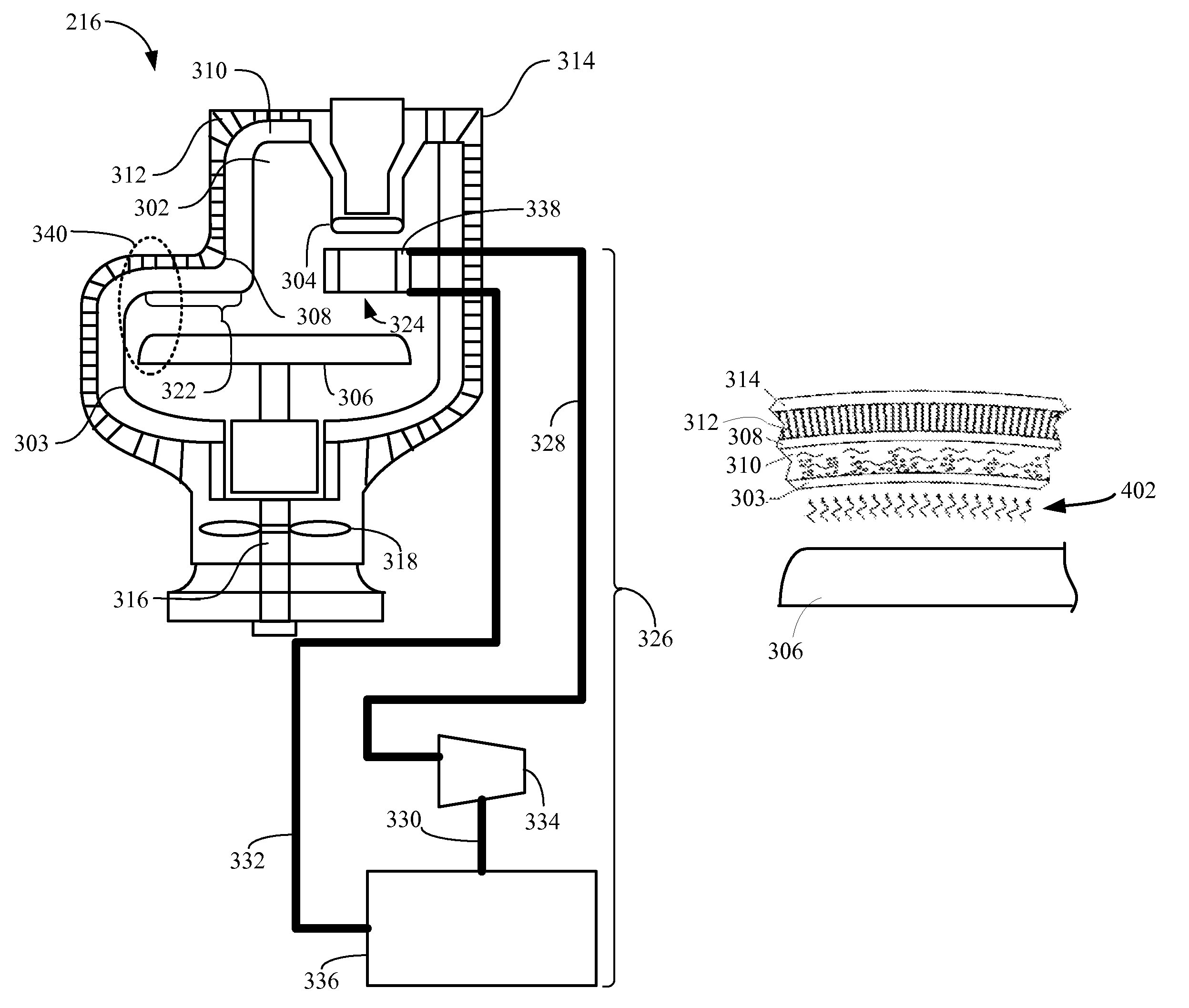
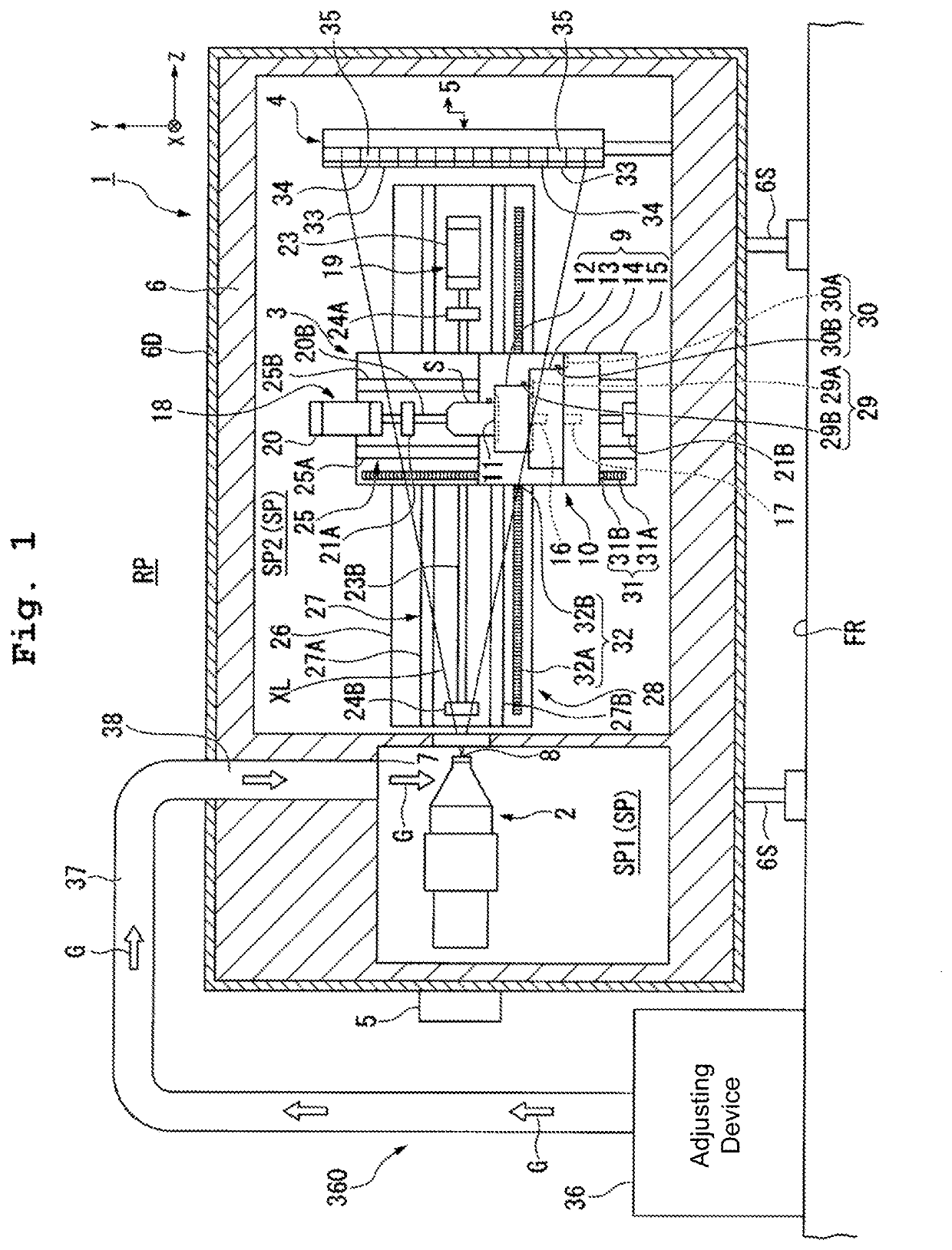
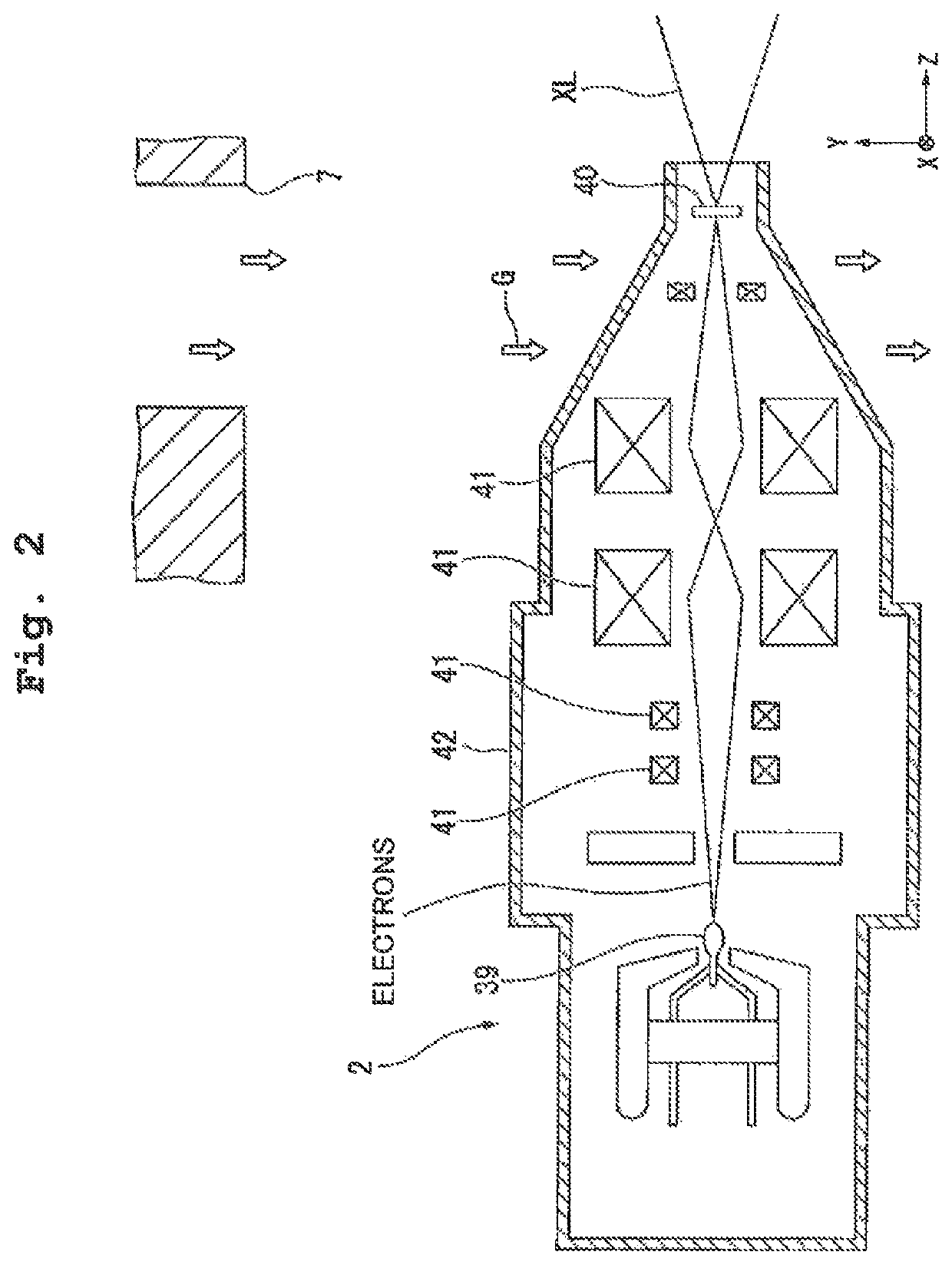
Apparatus, X-ray irradiation method, and structure manufacturing method
ActiveUS9234855B2Improve accuracyX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesTemperature controlX-ray
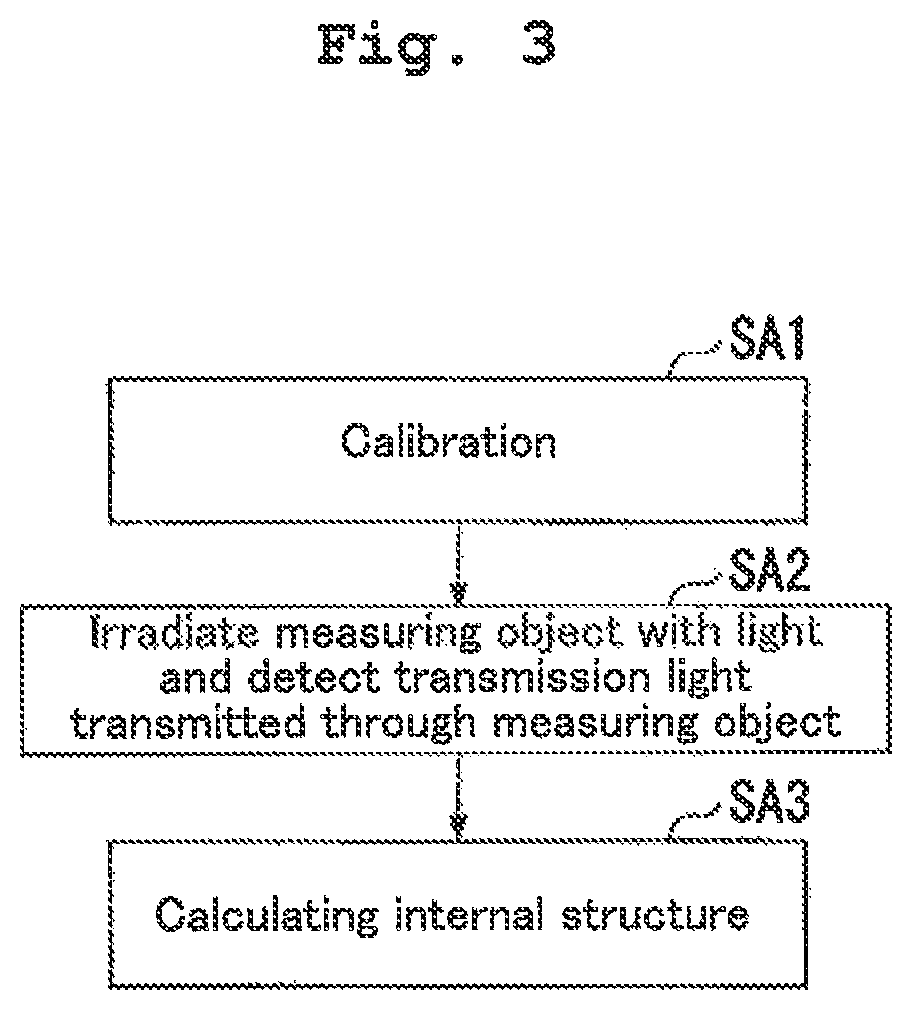
There is provided an apparatus configured to irradiate an object with an X-ray and detect a transmission X-ray transmitted through the object, including: a chamber member defining a first space; and a first supply port arranged in the first space to supply a temperature-controlled gas to a part of an X-ray source configured to irradiate the object with the X-ray.
Owner:NIKON CORP
X-ray radiator with a photocathode irradiated with a deflected laser beam
InactiveUS20070274453A1Suitable for industryFlexible and suitableX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerPhotocathodeX-ray
An x-ray radiator has an anode that emits x-rays, a cathode that thermionically emits electrons upon irradiation thereof by a laser beam, a voltage source for application of a high voltage between the anode and the cathode for acceleration of the emitted electrons toward the anode to form an electron beam, a vacuum housing, an insulator that is part of the vacuum housing and that separates the cathode from the anode, an arrangement for cooling components of the x-ray radiator, a deflection and arrangement that deflects the laser beam from a stationary source, that is arranged outside of the vacuum housing, to a spatially stationary laser focal spot on the cathode.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Miniature x-ray tube cooling system
ActiveUS7127033B2Improve heat transfer performanceReduce surface tensionStentsBalloon catheterSoft x rayX-ray
A miniature x-ray tube is cooled using a catheter preferably having multiple small lumens for inflow and outflow of coolant. Inflow may be through an outer lumen(s) in a concentric-extrusion catheter, the liquid turning back at the distal end of the catheter to a proximal flow over the anode end of the x-ray tube and through an inner lumen within which the x-ray tube is positioned. A coolant distribution head may engage with the anode end of the x-ray tube, with small orifices so as to distribute coolant essentially evenly over the anode surface. Temperature and flow rate of the inflowing coolant liquid are balanced so as to optimize heat transfer while efficiently carrying coolant through small lumens without the need for high pressures. Some embodiments use the inflation liquid in an applicator balloon as the coolant, with the liquid actively flowing or, in a simplified system, with the liquid static.
Owner:XOFT MICROTUBE +1
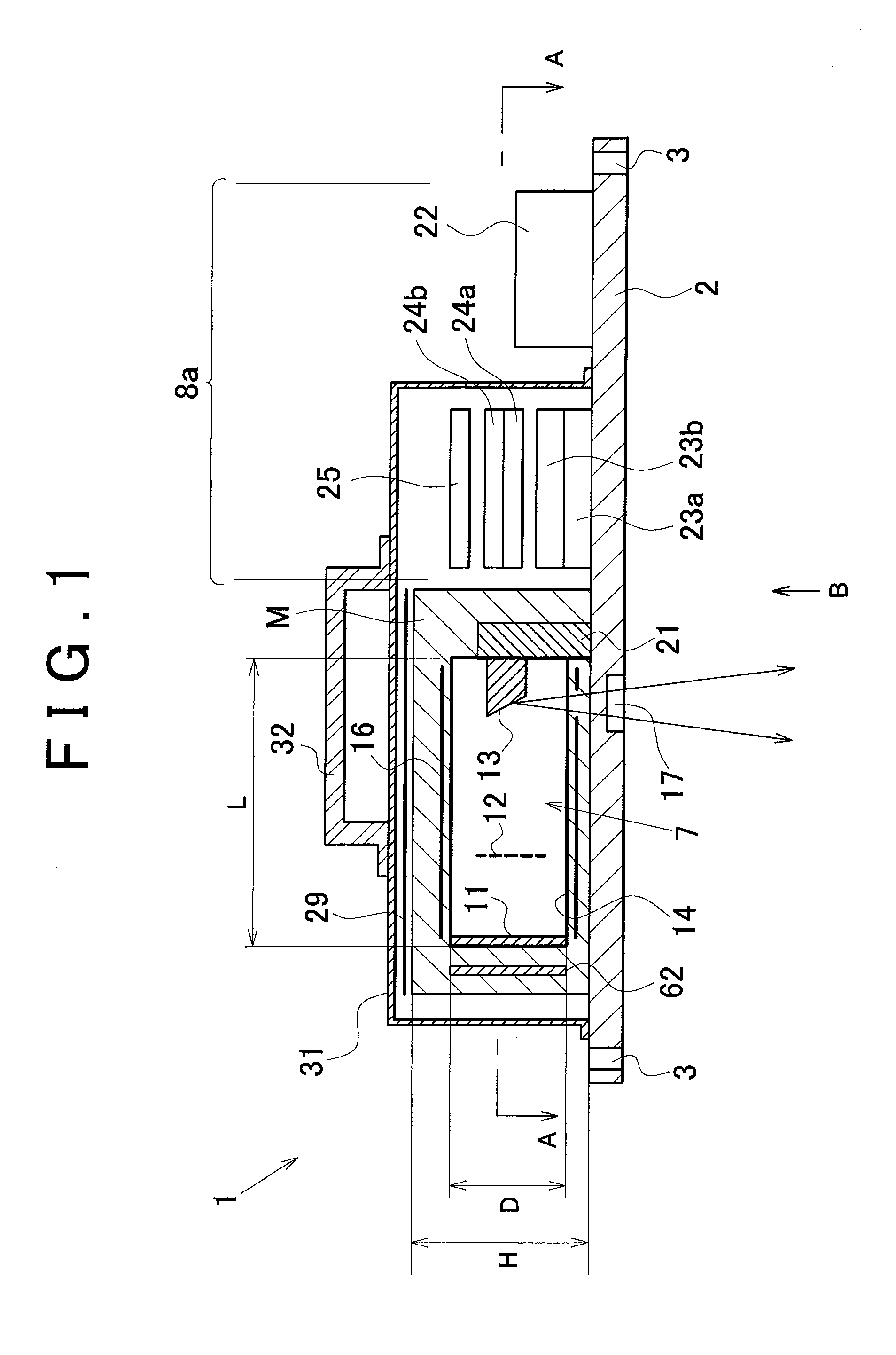
Industrial X-ray generator
ActiveUS8675817B2Small regionX-ray tube vessel coolingX-ray tube vessels/containerLow voltageEngineering
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Electron absorption apparatus for an x-ray device
A shield assembly for an x-ray device is disclosed herein. The shield assembly includes a radiation shielding layer comprised of a first material; and a thermally conductive layer attached the radiation shielding layer. The thermally conductive layer is comprised of a second material. The shield assembly also includes an electron absorption layer attached to the radiation shielding layer. The electron absorption layer is comprised of a third material. The electron absorption layer is configured to absorb backscattered electrons.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Radiation generating apparatus and radiation imaging apparatus
InactiveUS9070529B2Reduce the amount requiredSuppress a deterioration in the voltage-withstand performanceX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesShortest distanceRadiation imaging
In a radiation imaging apparatus, an envelope has a first window for transmitting radiation and is filled with an insulating liquid, and a radiation tube in the envelope has, at a position facing the first window, a second window for transmitting the radiation, and a shielding member. A solid insulating member is arranged between the shielding member and the inner wall of the envelope, and an opening is formed at a position on the insulating member corresponding to the first window. The shortest distance from the shielding member to the first window or the inner wall of the envelope through the opening of the insulating member without the insulating member is made to be longer than the shortest distance from the shielding member to the first window or the inner wall of the envelope through the insulating member, thereby improving withstand voltage performance without reducing an radiation amount.
Owner:CANON KK
X-ray radiator with a photocathode irradiated with a deflected laser beam
InactiveUS7508917B2Flexible and suitableReduce pollutionX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessel coolingPhotocathodeX-ray
An x-ray radiator has an anode that emits x-rays, a cathode that thermionically emits electrons upon irradiation thereof by a laser beam, a voltage source for application of a high voltage between the anode and the cathode for acceleration of the emitted electrons toward the anode to form an electron beam, a vacuum housing, an insulator that is part of the vacuum housing and that separates the cathode from the anode, an arrangement for cooling components of the x-ray radiator, a deflection and arrangement that deflects the laser beam from a stationary source, that is arranged outside of the vacuum housing, to a spatially stationary laser focal spot on the cathode.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
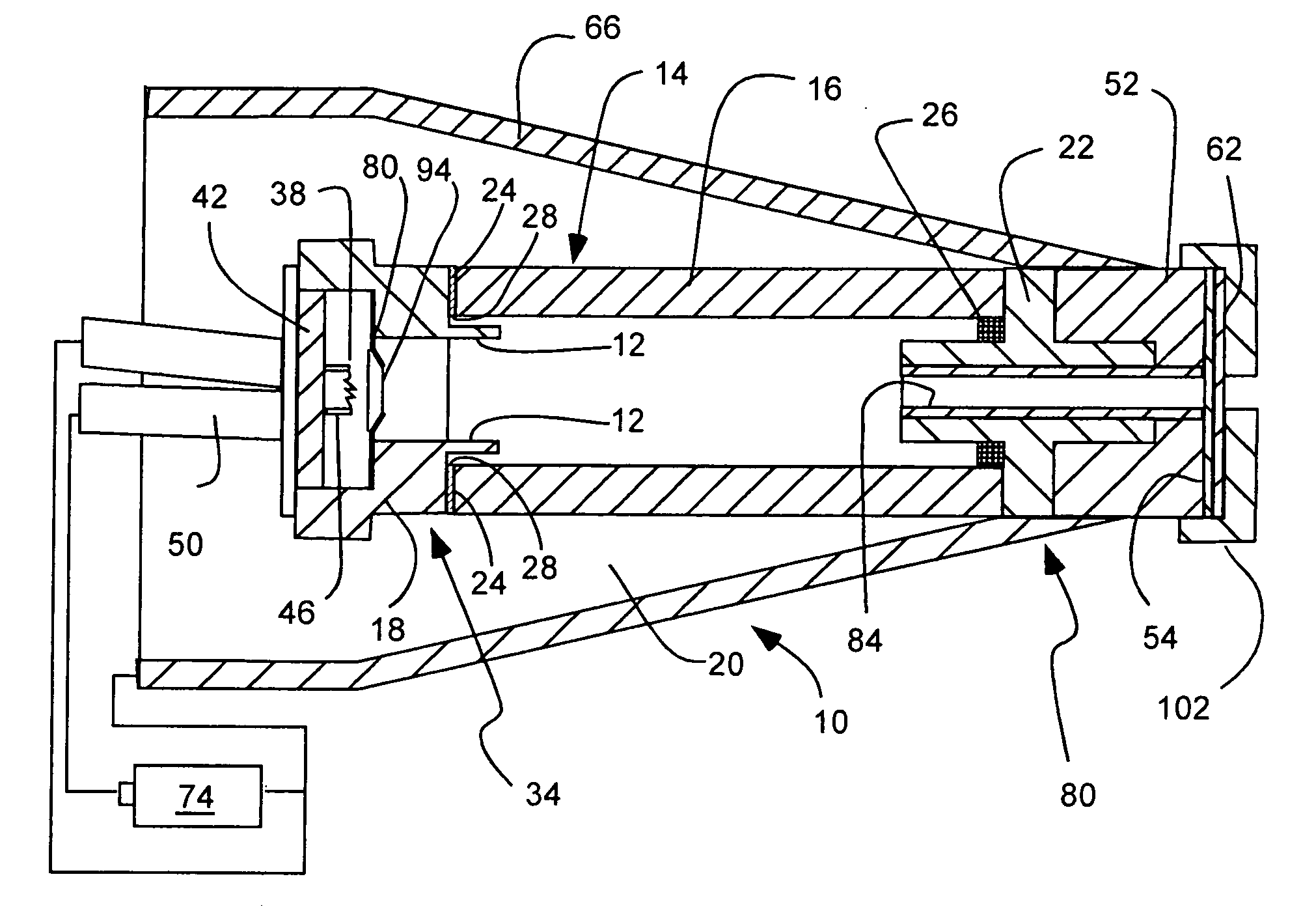
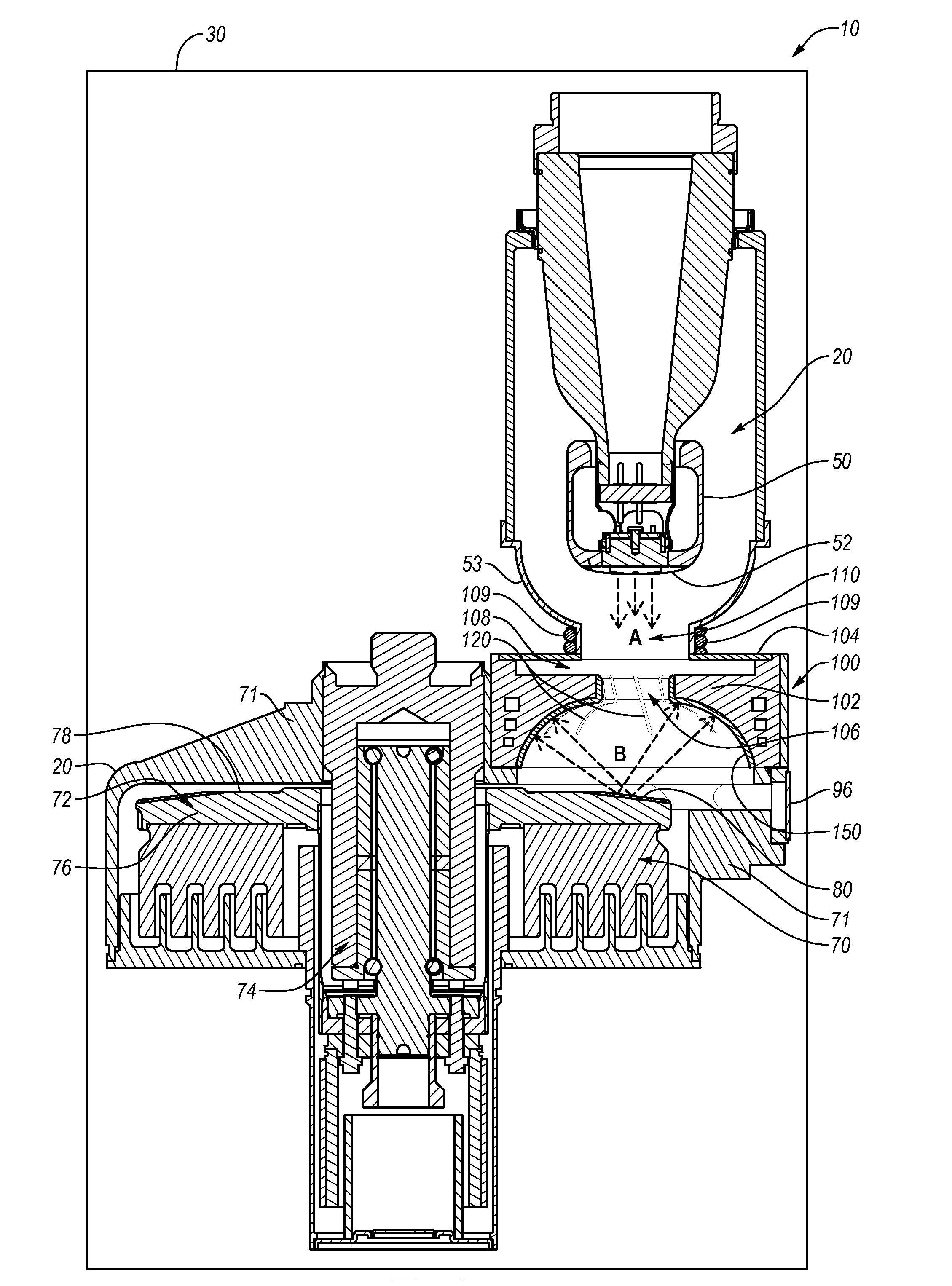
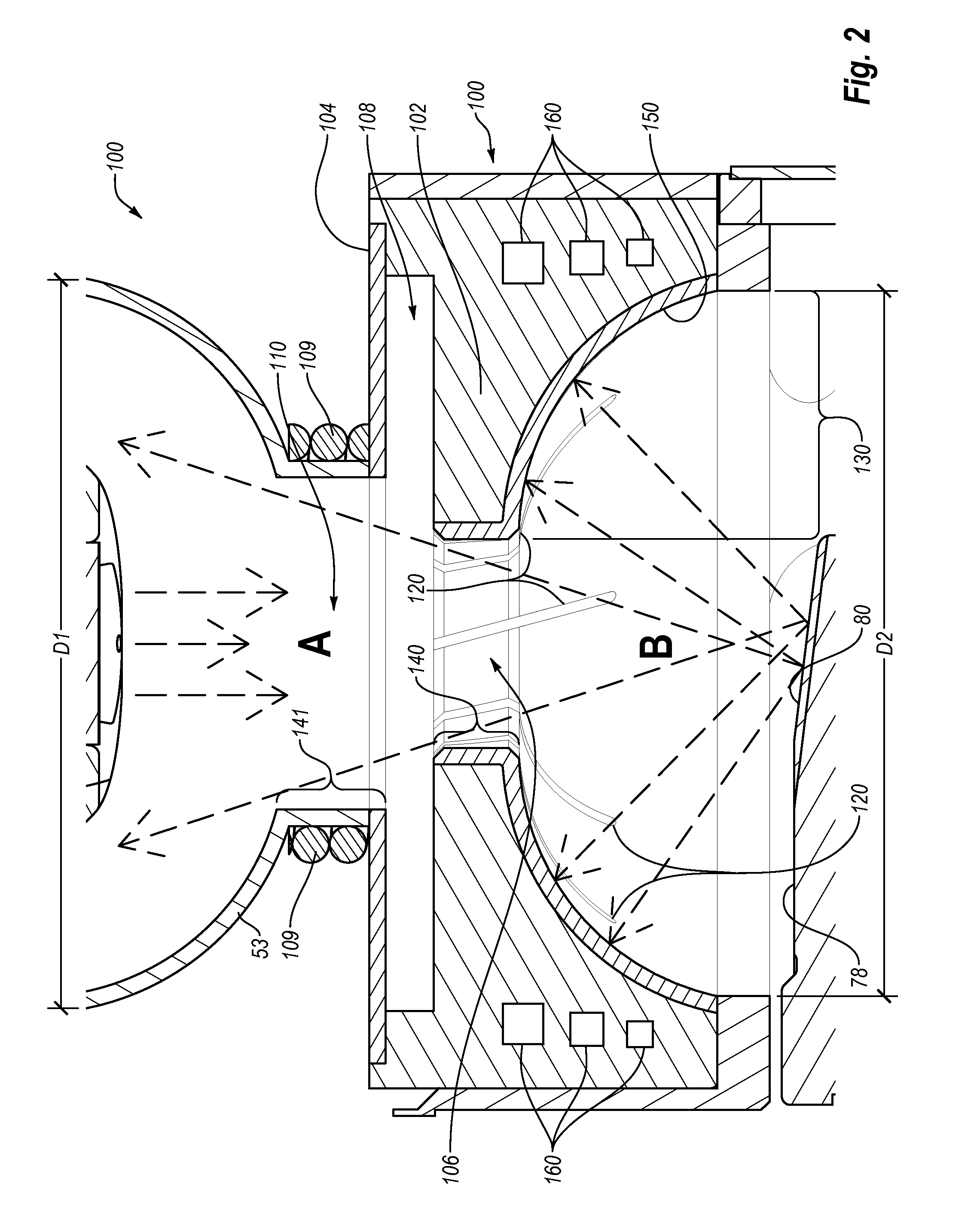
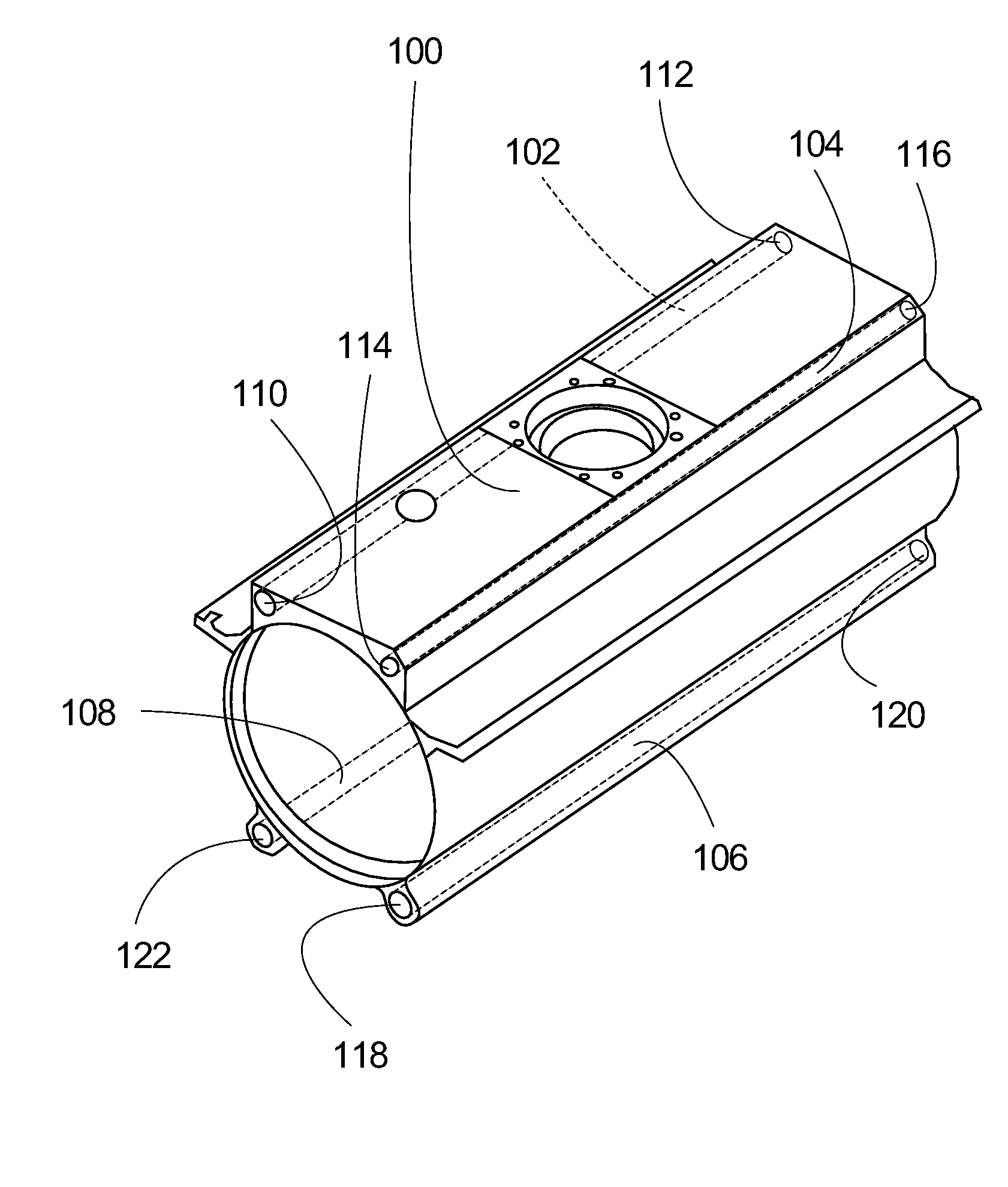
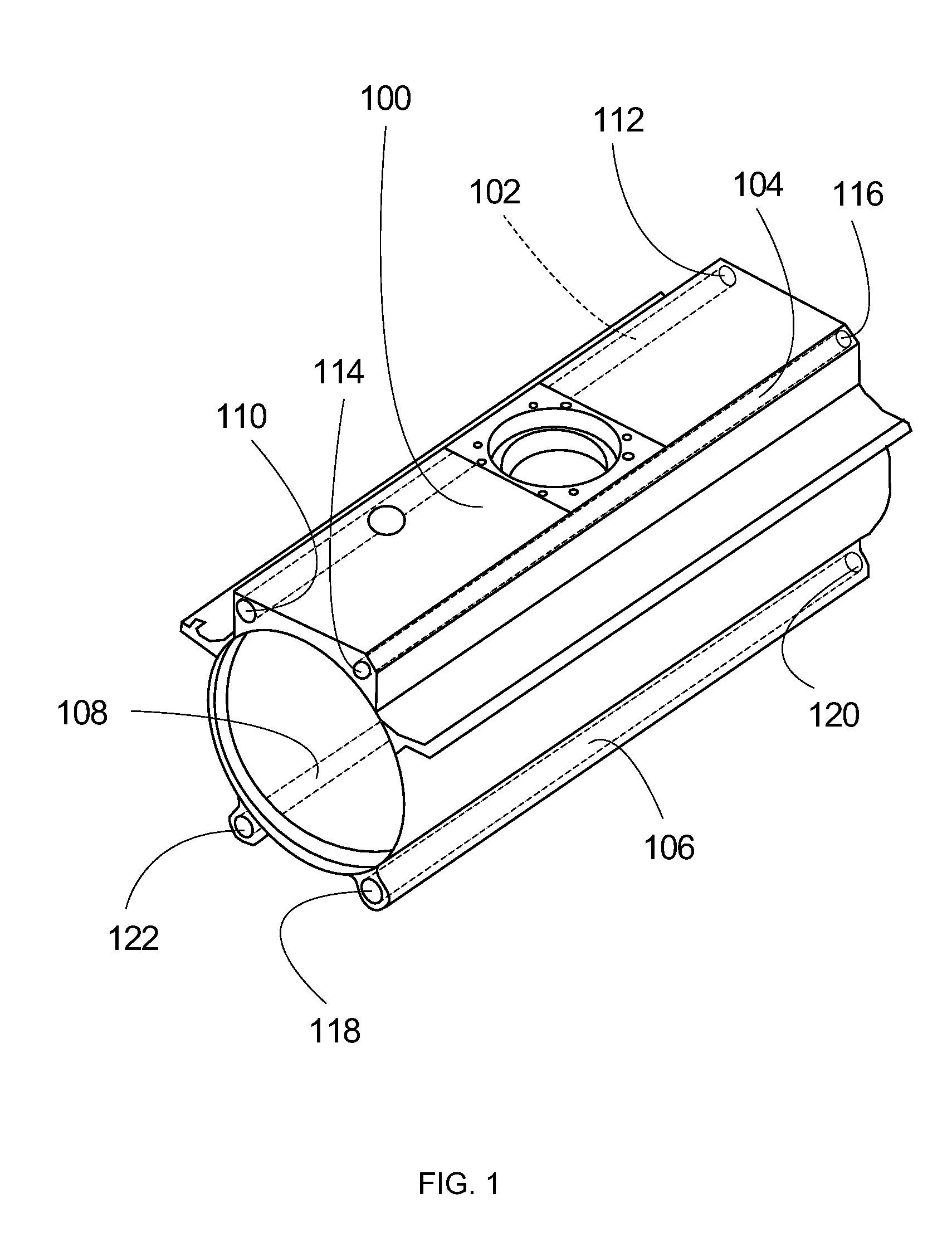
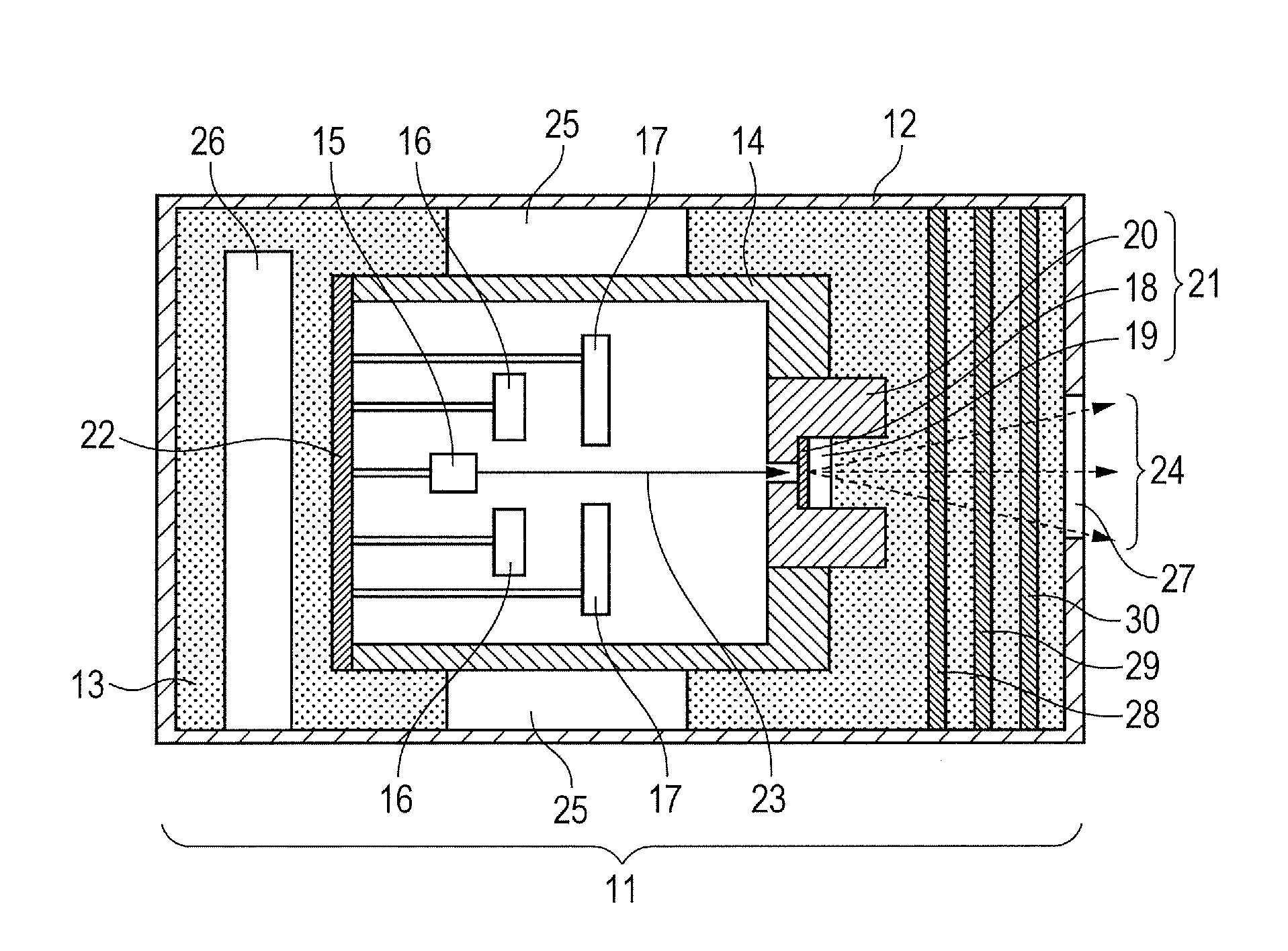
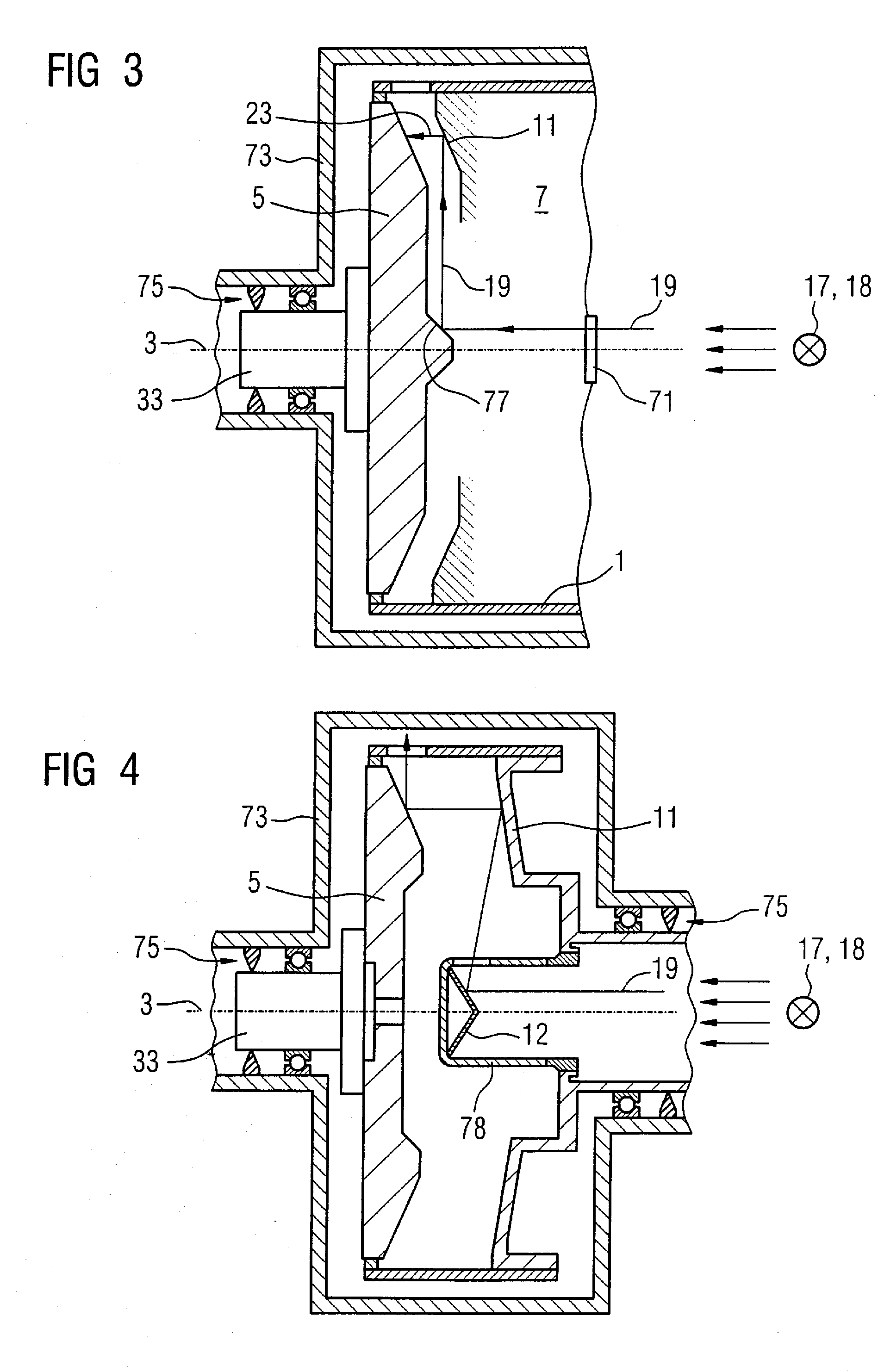
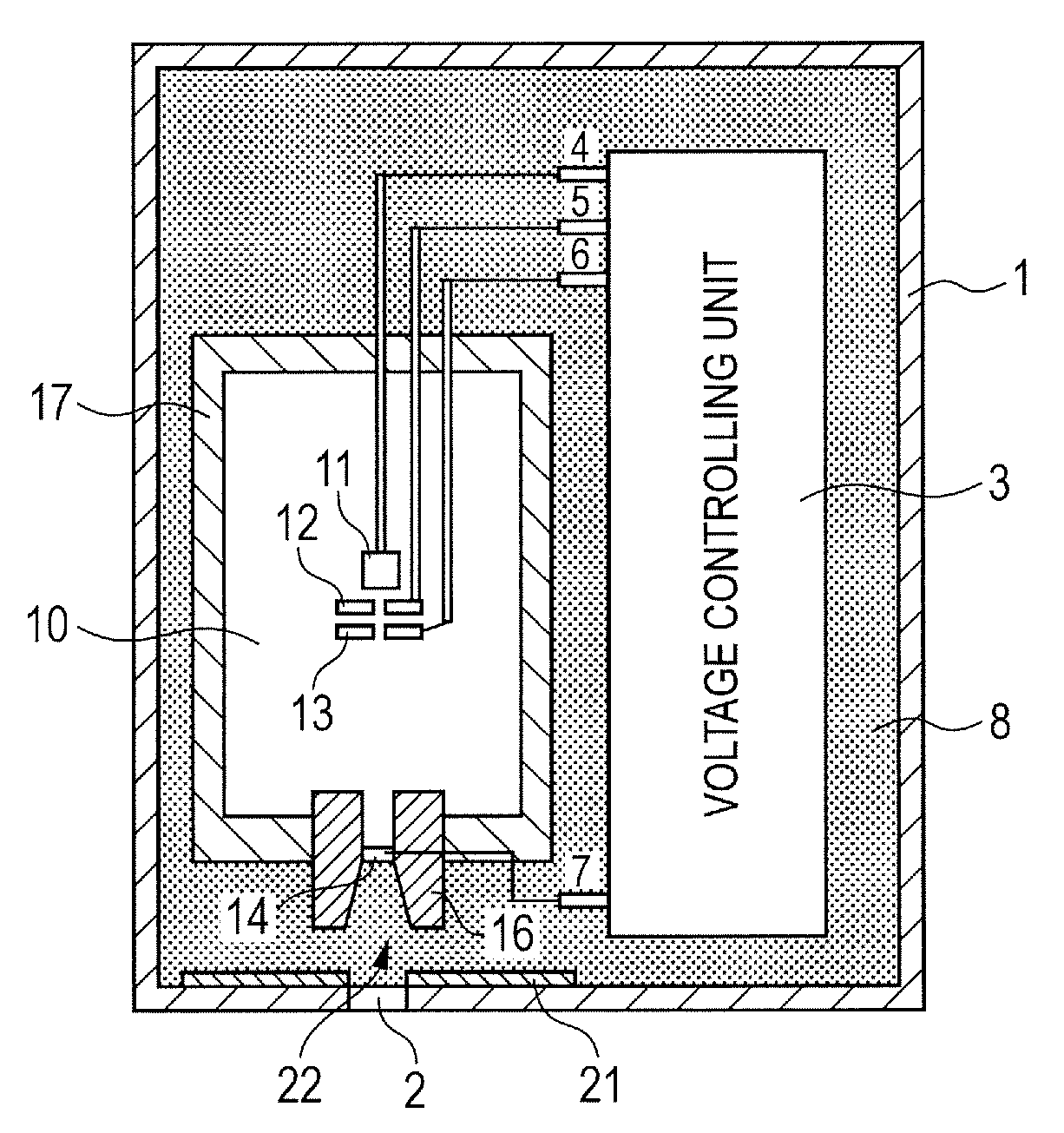
Apparatus and method for improved transient response in an electromagnetically controlled x-ray tube
ActiveUS20120099701A1Cathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-ray tube vessels/containerEngineeringElectron
An x-ray tube assembly includes a vacuum enclosure having a cathode portion, a target portion, and a throat portion comprising a non-electrically conductive tube. The throat portion has an upstream end coupled to the cathode portion and a downstream end coupled to the target portion. The x-ray tube assembly also includes a target positioned within the target portion of the vacuum enclosure, and a cathode positioned within the cathode portion of the vacuum enclosure. The cathode is configured to emit a stream of electrons through the throat portion toward the target.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
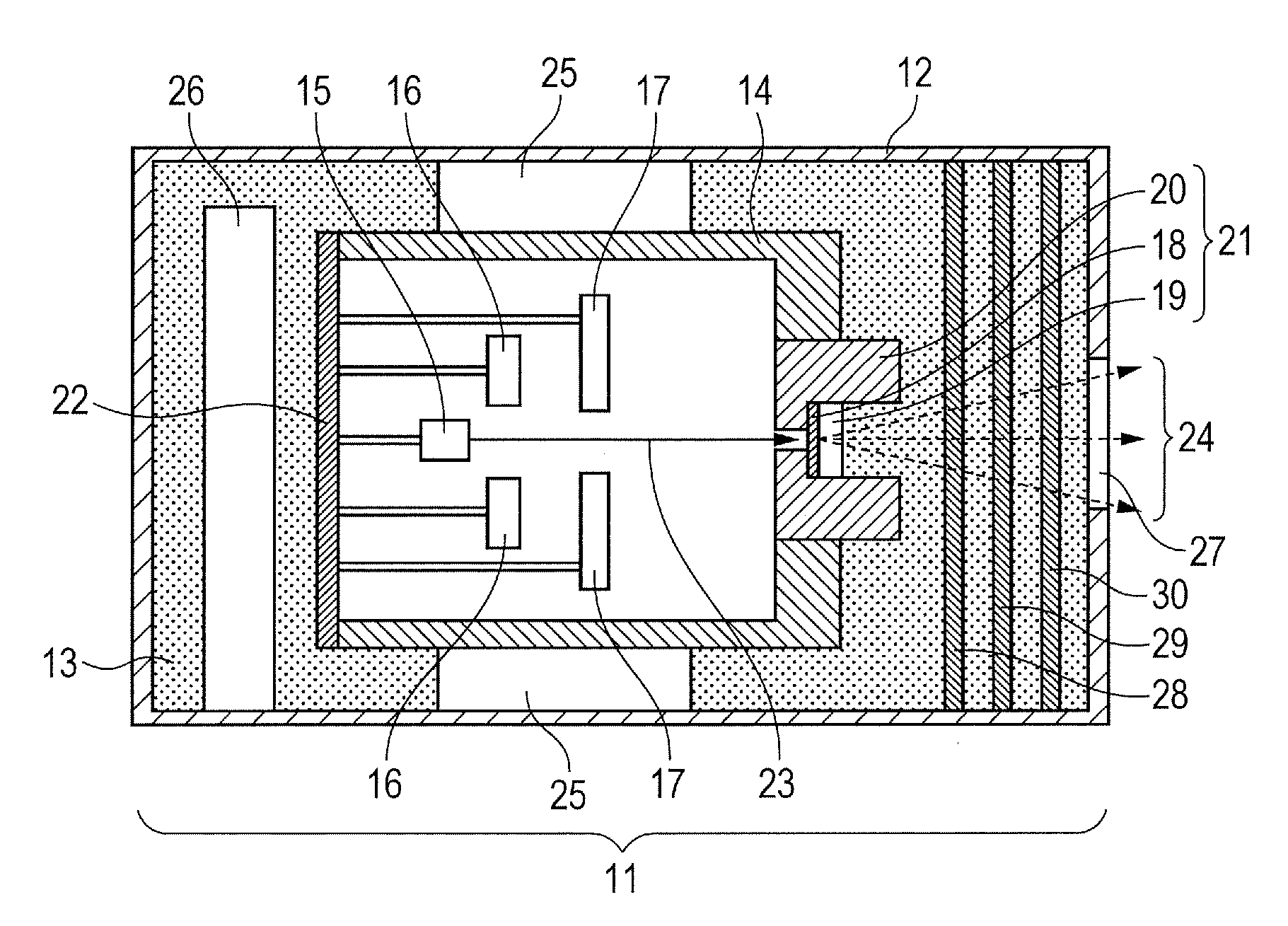
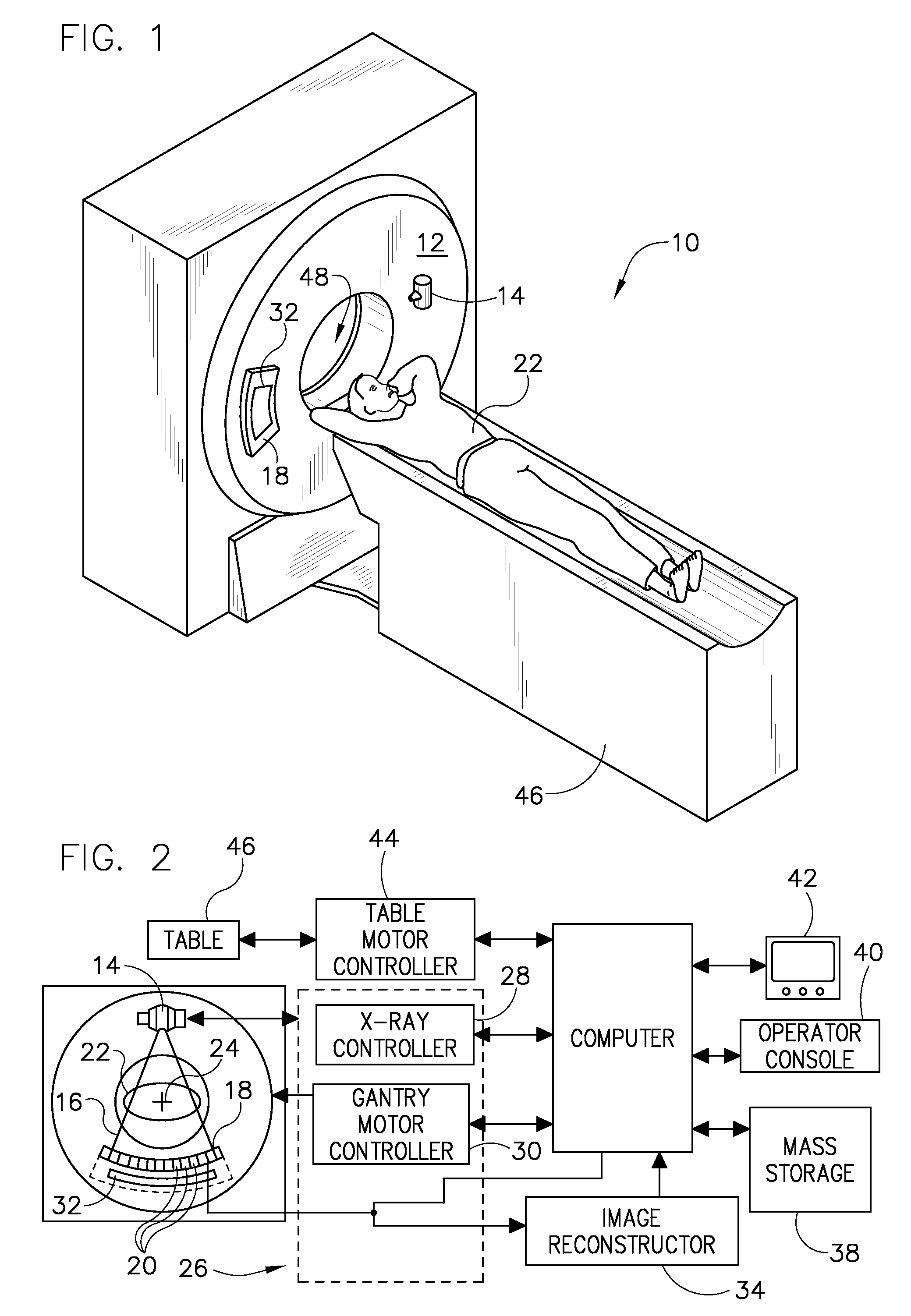
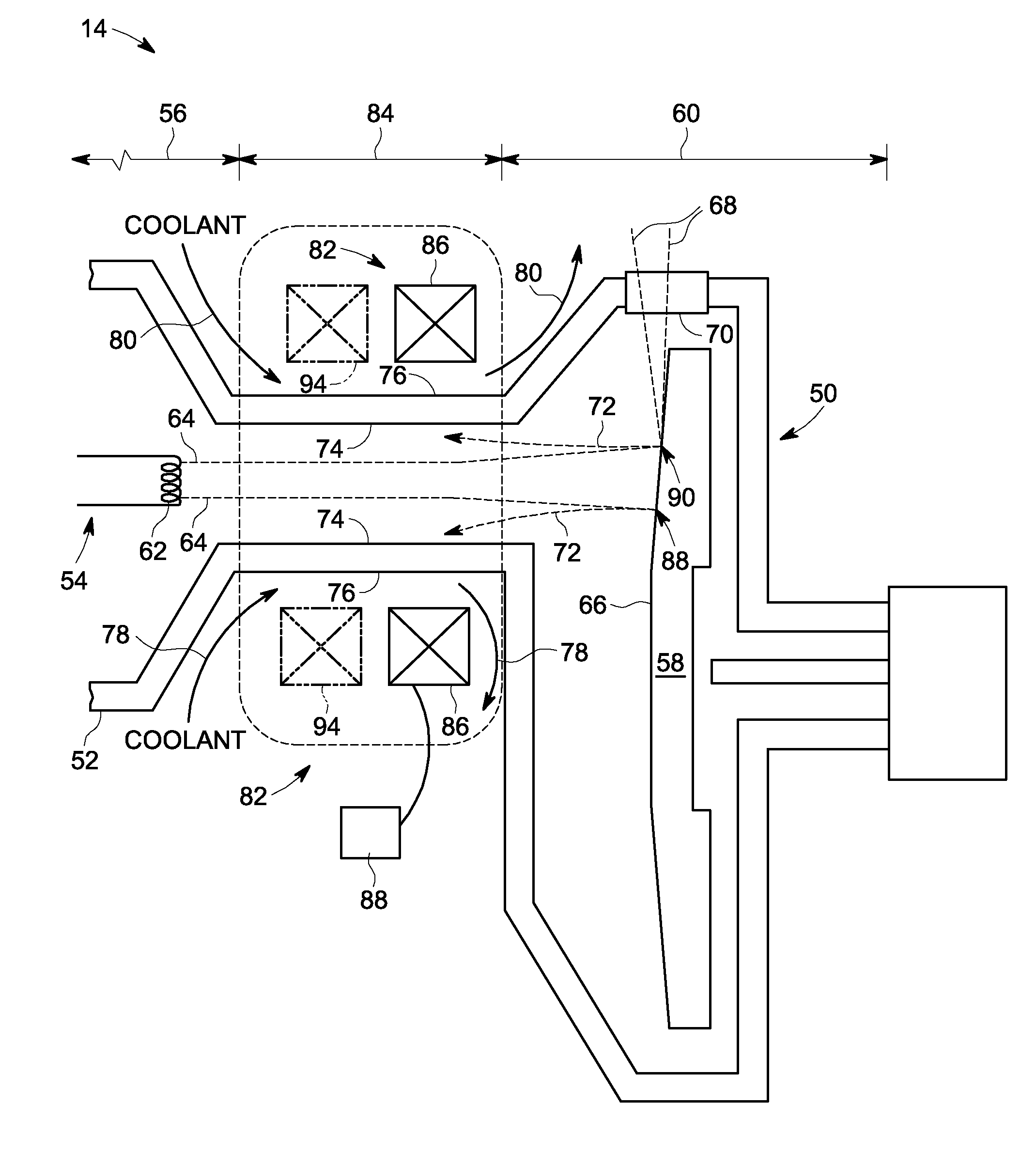
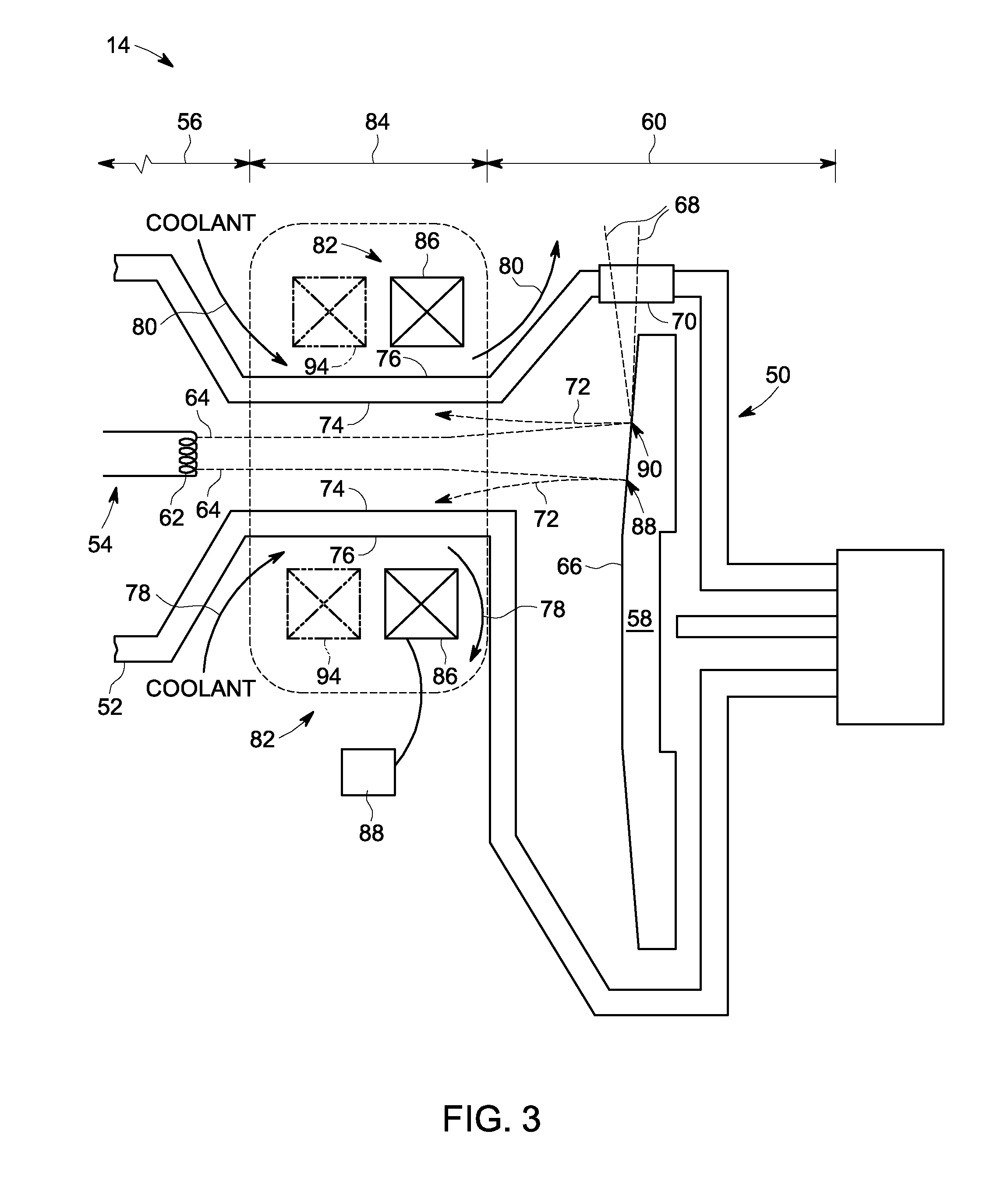
Computed tomography system having cooling system
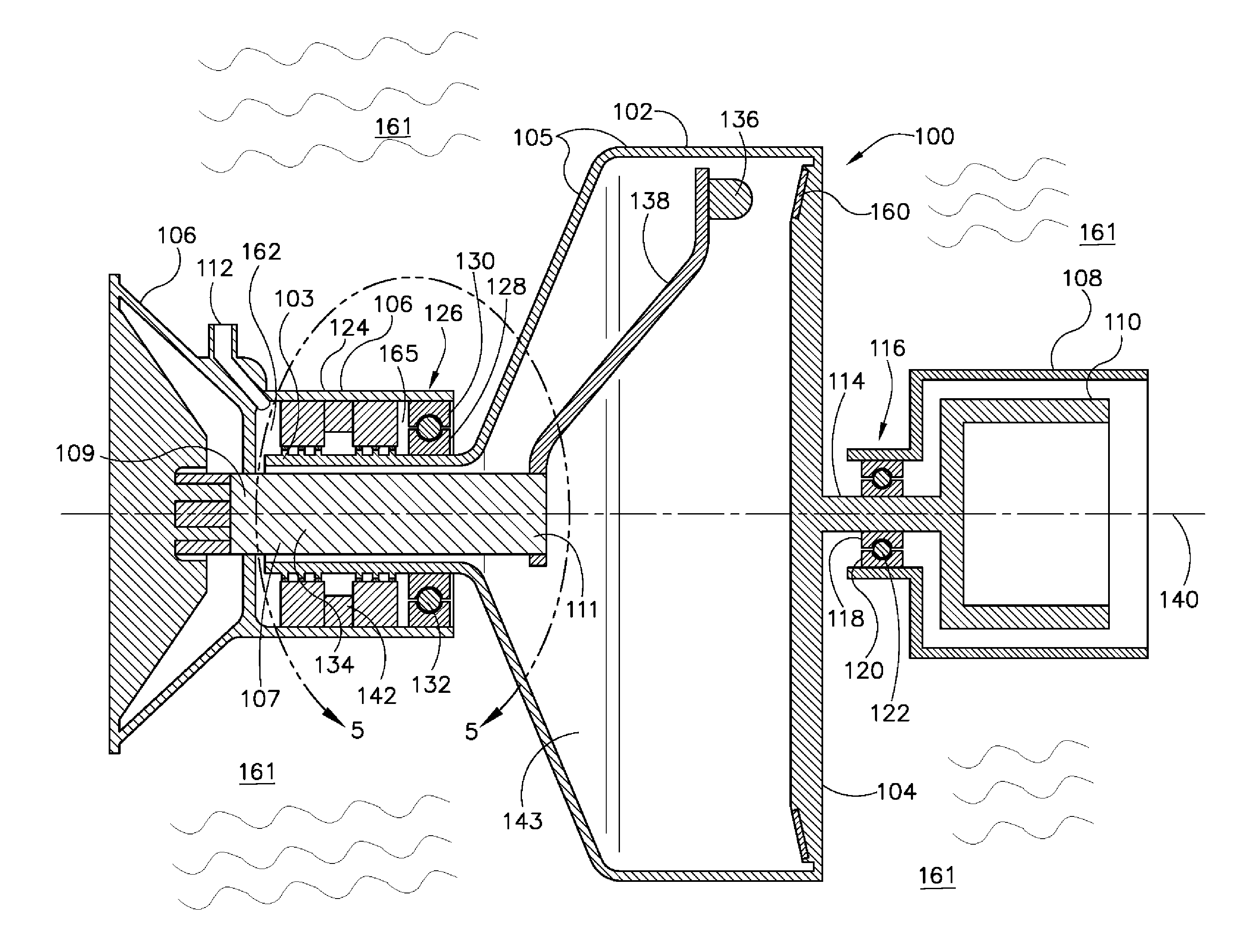
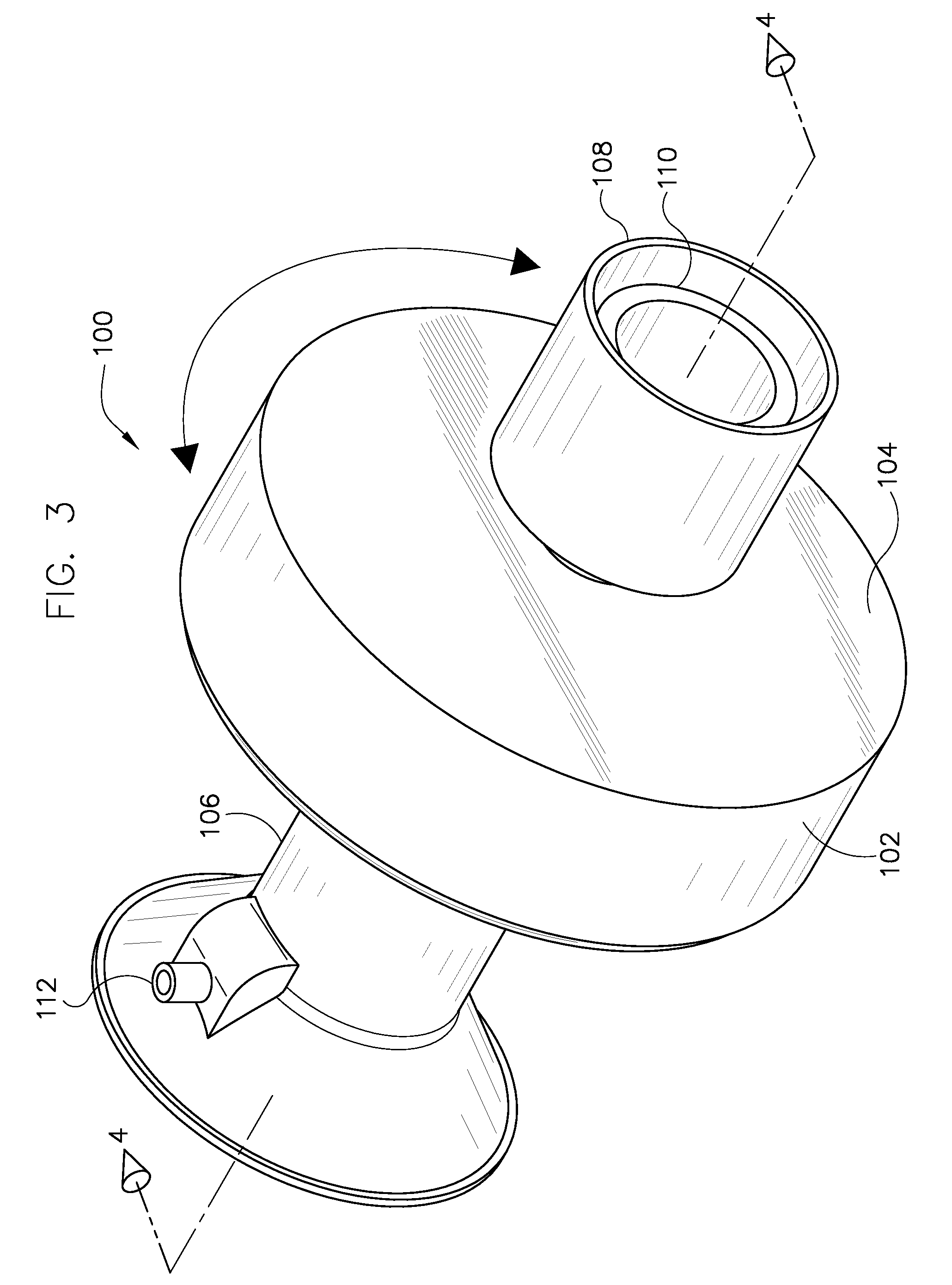
ActiveUS20160235378A1X-ray tube bearing assembly coolingPatient positioning for diagnosticsComputed tomographyOperational system
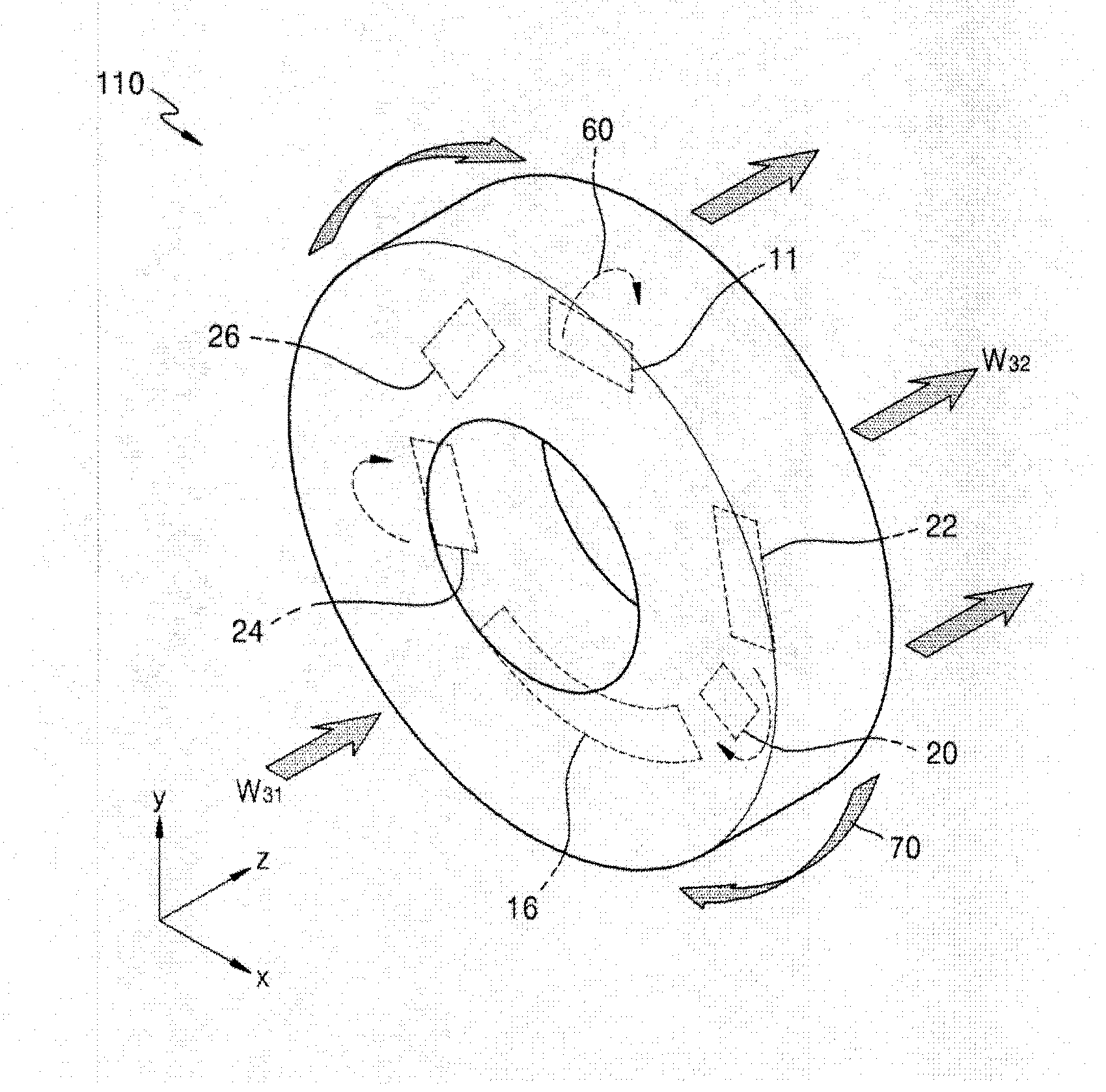
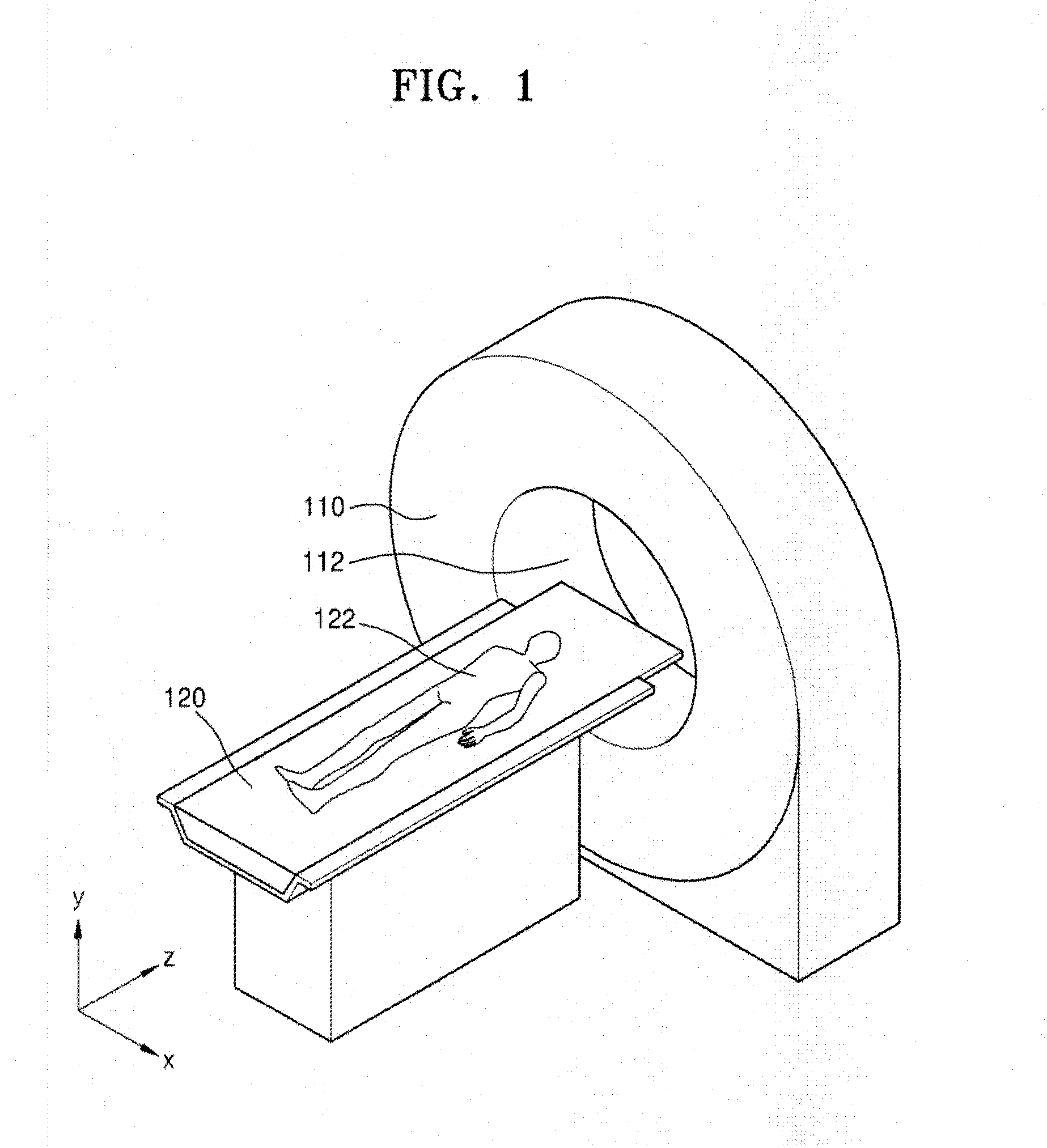
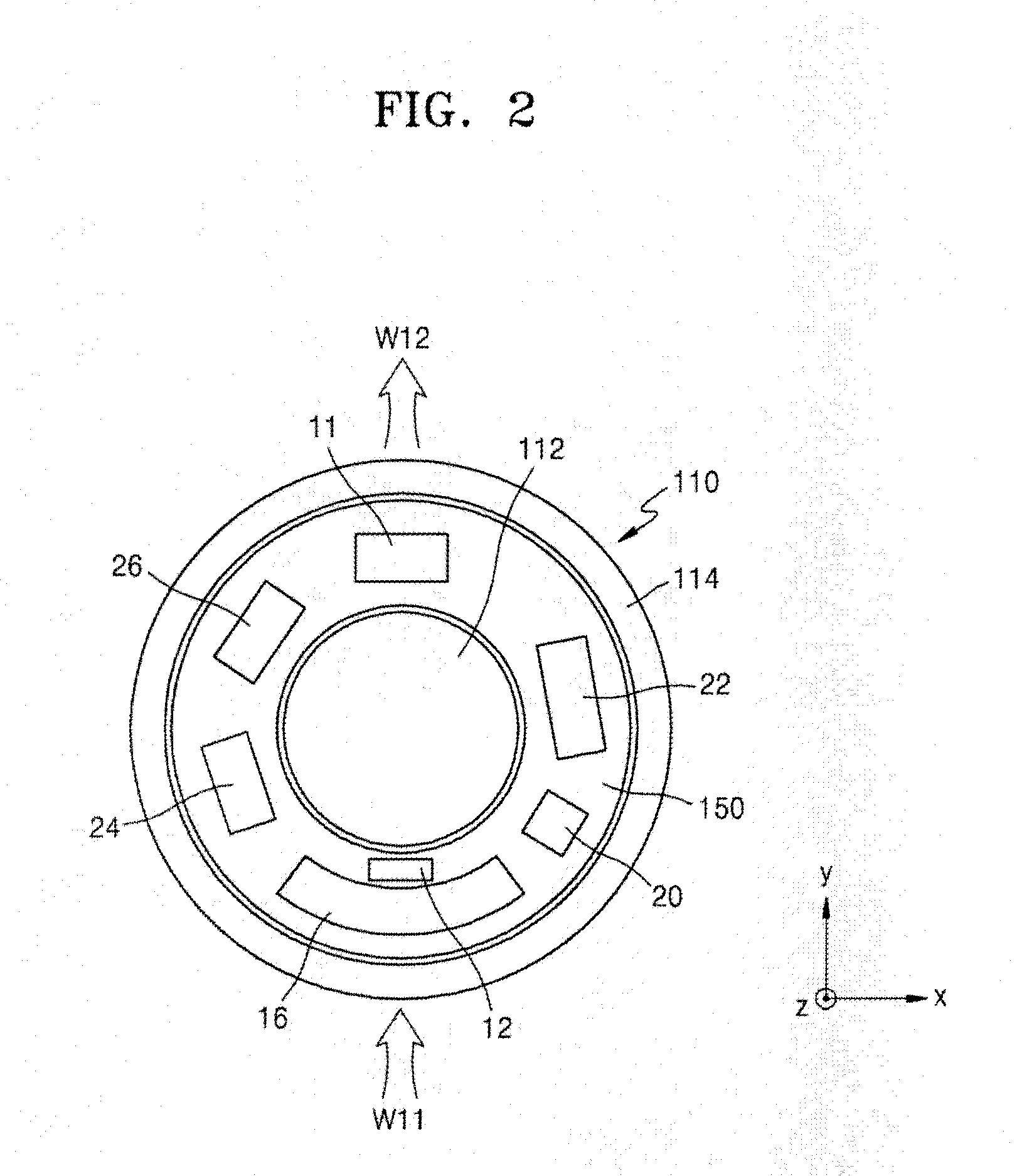
A cooling system of a computed tomography (CT) system provides for a more efficient operation than known heretofore. The cooling system of the CT system includes a gantry and a table that moves an object into a bore of the gantry. The gantry includes part boxes mounted therein, and blade elements are formed in regions of the part boxes. The cooling system of the CT system includes a cooling method that includes a multiple cooling method including a stand-by mode and an operating mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Structure for collecting scattered electrons
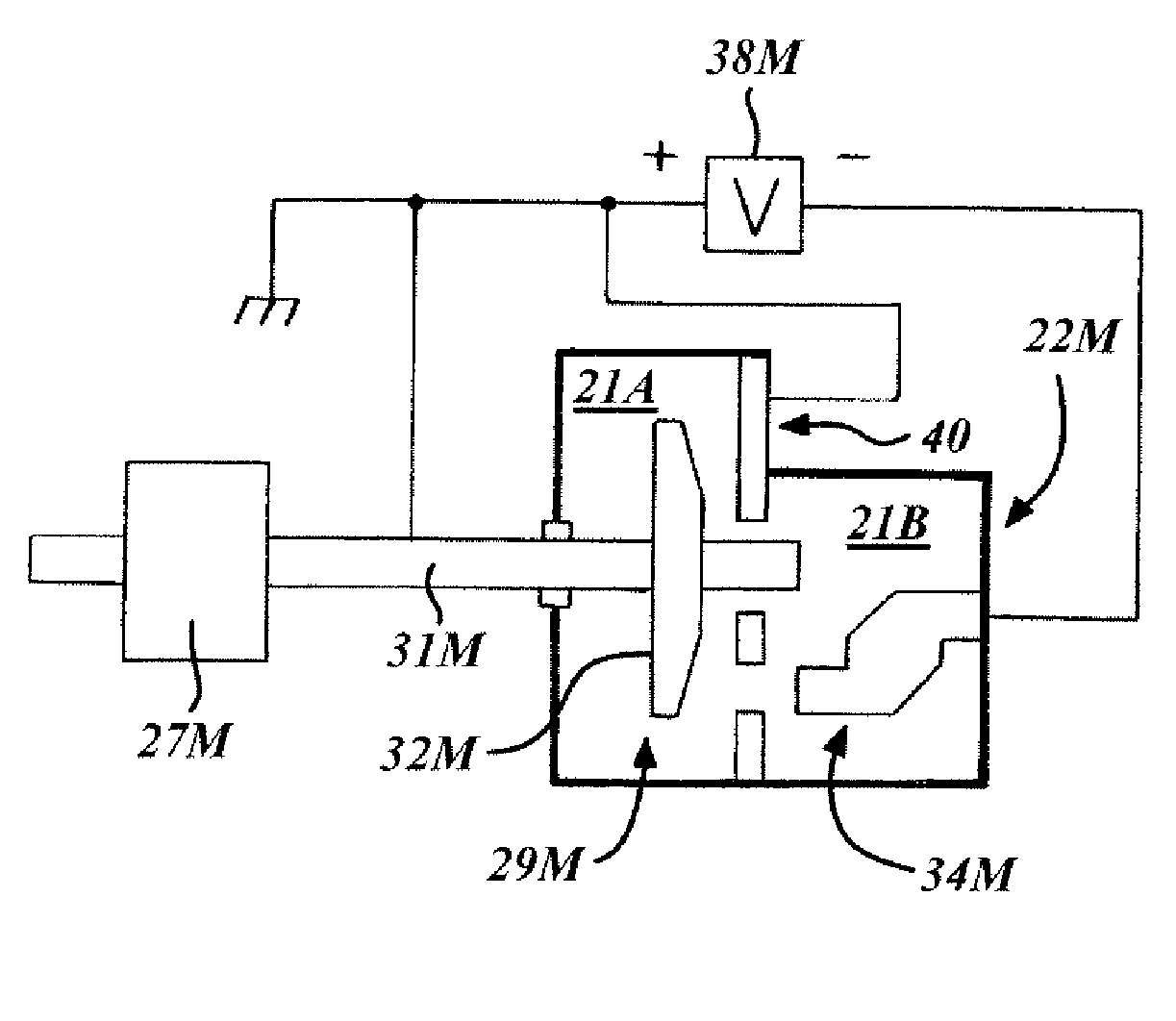
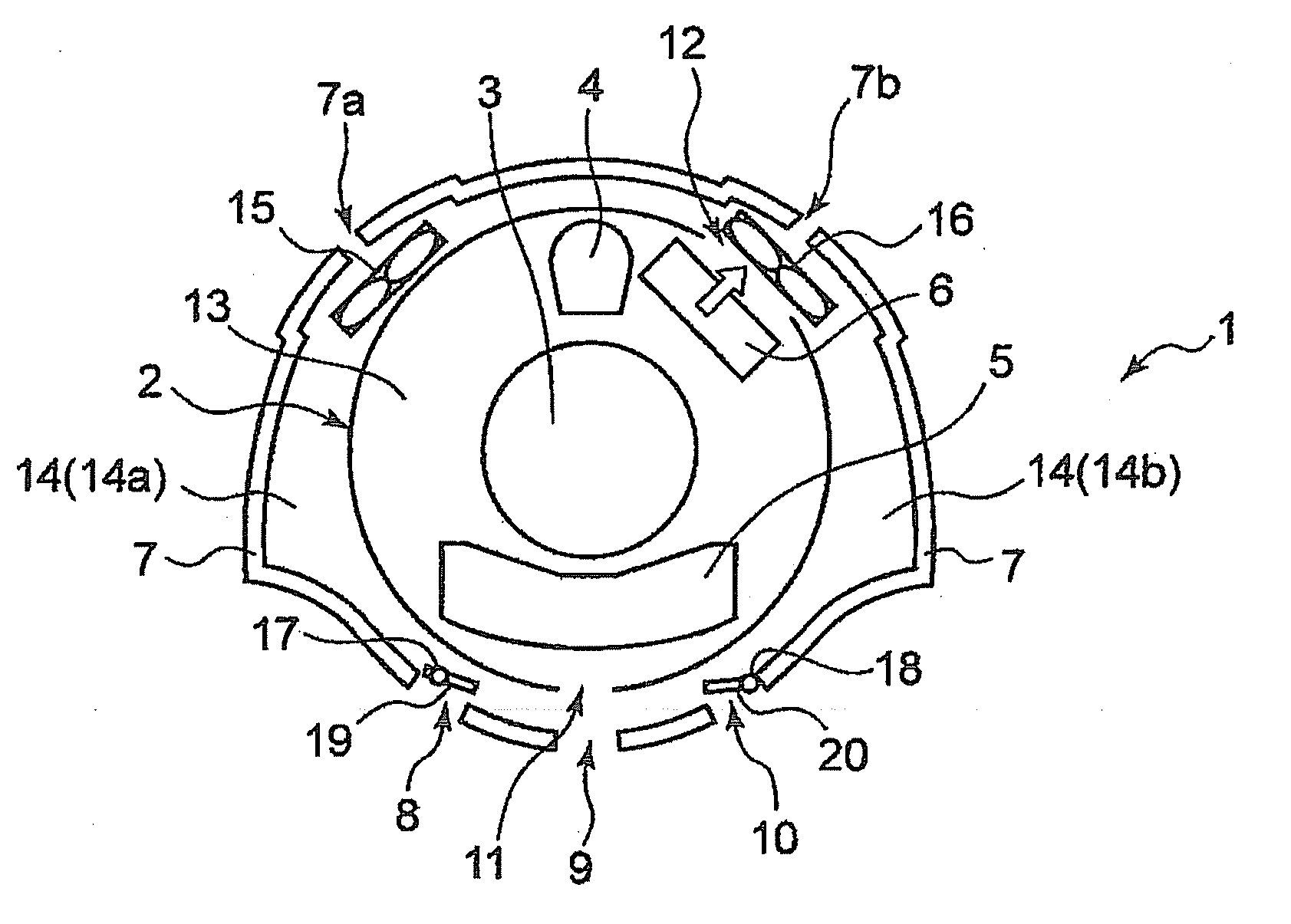
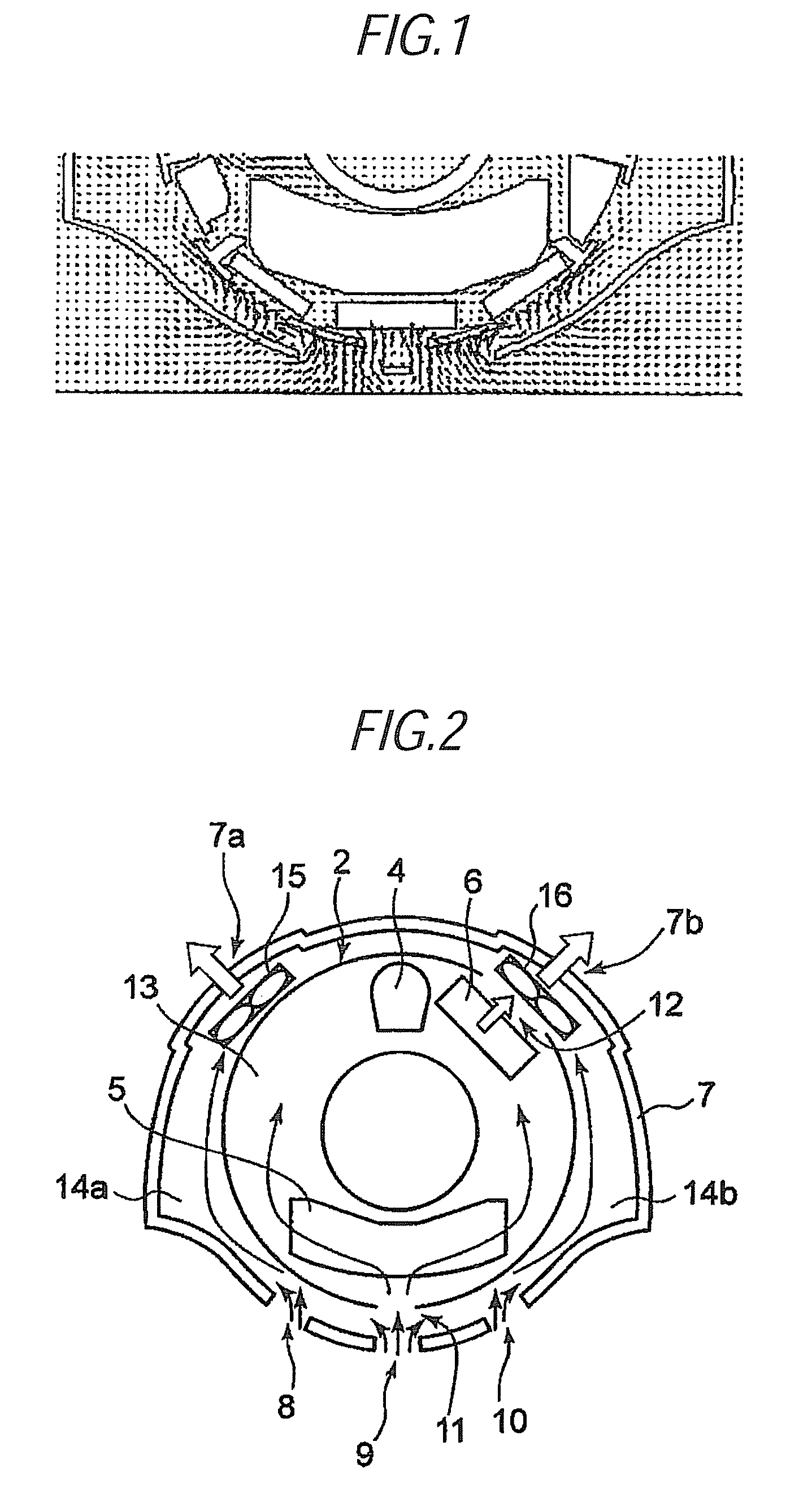
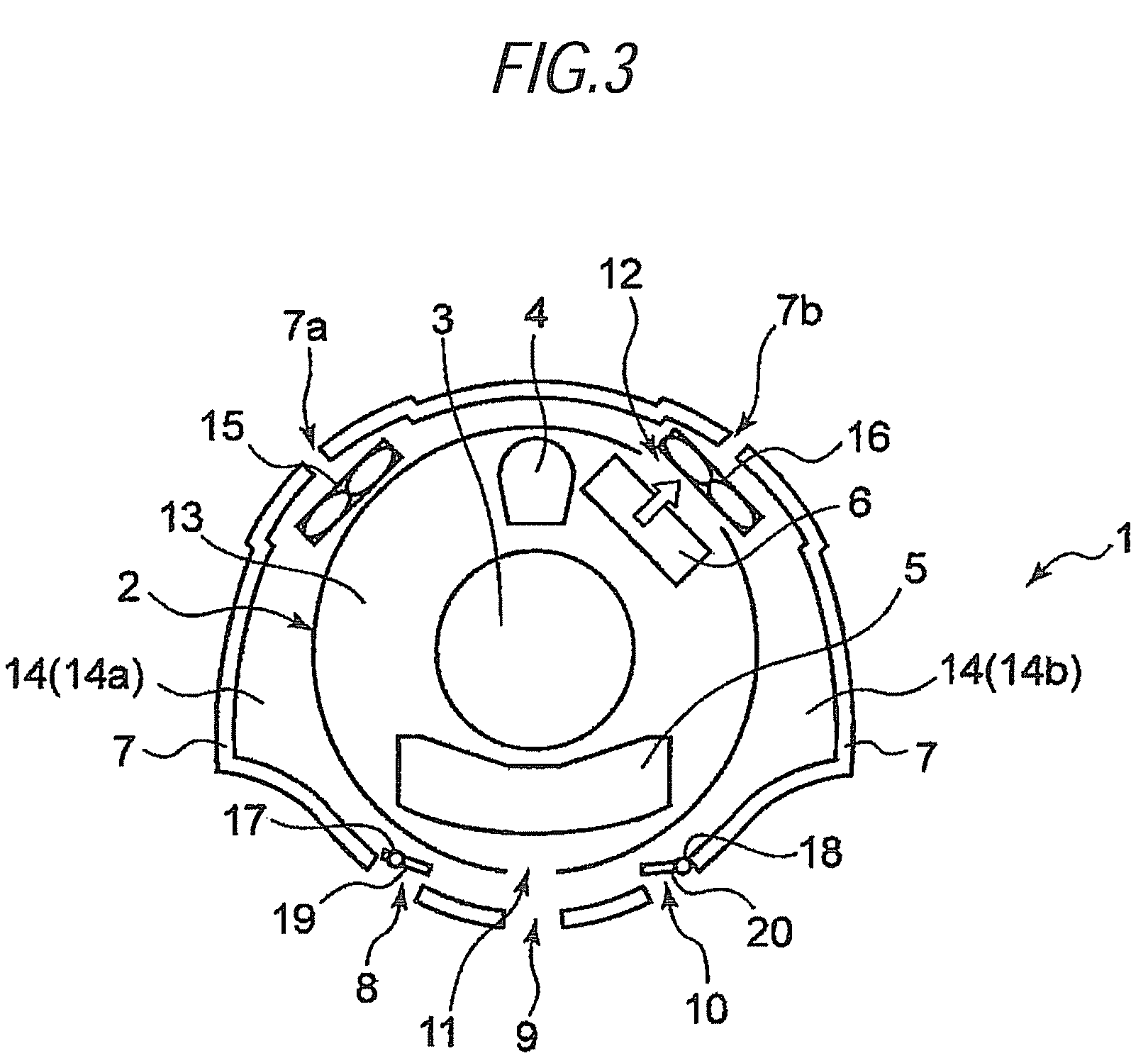
A structure for collecting scattered electrons within a substantially evacuated vessel containing both an electron-emitting cathode and an electron-attracting anode is disclosed herein. The electron-collecting structure includes a two-sided first plate, a two-sided second plate, a fluid inlet, and a fluid outlet. The first plate is both electrically conductive and thermally emissive and is mountable within the vessel so that its first side at least partially faces the anode. The second plate is also thermally emissive and has a first side that is substantially conterminous with the second side of the first plate. Furthermore, the second plate additionally has an internal conduit for conveying a heat-absorbing fluid within. Both the fluid inlet and the fluid outlet are in fluid communication with the conduit in the second plate. During operation, the structure is able to attract scattered electrons and transfer thermal energy attributable to the electrons away from the structure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Structure for collecting scattered electrons
InactiveUS7359486B2X-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerThermal energyThermionic emission
A structure for collecting scattered electrons within a substantially evacuated vessel containing both an electron-emitting cathode and an electron-attracting anode is disclosed herein. The electron-collecting structure includes a two-sided first plate, a two-sided second plate, a fluid inlet, and a fluid outlet. The first plate is both electrically conductive and thermally emissive and is mountable within the vessel so that its first side at least partially faces the anode. The second plate is also thermally emissive and has a first side that is substantially conterminous with the second side of the first plate. Furthermore, the second plate additionally has an internal conduit for conveying a heat-absorbing fluid within. Both the fluid inlet and the fluid outlet are in fluid communication with the conduit in the second plate. During operation, the structure is able to attract scattered electrons and transfer thermal energy attributable to the electrons away from the structure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS7806590B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayEngineering
According to the invention, an X-ray CT apparatus includes: an annular rotator including: an X-ray tube; an X-ray detector disposed oppositely to the X-ray tube; a radiator disposed in the vicinity of the X-ray tube and dissipating heat from the X-ray tube; an air outlet provided in the vicinity of the radiator; and an air inlet provided at a position oppositely to the air outlet, a gantry cover covering peripheral of the annular rotator and having an upper air vent and a plurality of lower air vents; a plurality of fans discharging to the outside air exist in a gap between the gantry cover and the annular rotator from the air outlet; and a baffle plate provided in the gap in the vicinity of the lower air vents and controlling an air flow passing through internal space of the annular rotator and an airflow passing through the gap.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Stationary cathode in rotating frame x-ray tube
An x-ray tube includes a stationary base and a passage therein. The x-ray tube includes an anode frame having an anode positioned adjacent to a first end and having a neck at a second end, the neck extends into the passage, wherein the anode frame is configured to rotate about a longitudinal axis of the passage. A hermetic seal is positioned about the neck between the neck and the stationary base.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for improved transient response in an electromagnetically controlled x-ray tube
ActiveUS20120099700A1Cathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-ray tube vessel coolingThroatEddy current
An x-ray tube assembly includes a vacuum enclosure including a cathode portion, a target portion, and a throat portion. The throat portion includes a magnetic field section, upstream section, and downstream section. The magnetic field section has a first susceptibility to generate eddy currents in the presence of a magnetic field intensity. The upstream section is coupled to the cathode portion and the magnetic field section and has a second susceptibility to generate eddy currents in the presence of the magnetic field intensity. The downstream section is coupled to the magnetic field section and has a third susceptibility to generate eddy currents in the presence of the magnetic field intensity. The first susceptibility to generate eddy currents is less than the second and third susceptibilities to generate eddy currents. The assembly includes a target within the target portion, and a cathode within the cathode portion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray device, X-ray irradiation method, and manufacturing method for structure
ActiveUS10705030B2Improve detection accuracySuppresses reduction in detection accuracyX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingInterior spaceNuclear engineering
Provided is an x-ray device capable of suppressing reduction in detection precision. The X-ray device irradiates x-rays on an object and detects X-rays that pass through the object. The X-ray device comprises: an X-ray source that emits X-rays; a stage that holds the object; a detection device that detects at least some of the x-rays that have been emitted from the X-ray source and have passed through the object; a chamber member that forms an internal space wherein the X-ray source, the stage, and the detection device are arranged; and a partitioning section that separates the internal space into a first space wherein the X-ray source is arranged and a second space wherein the detection device is arranged.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com