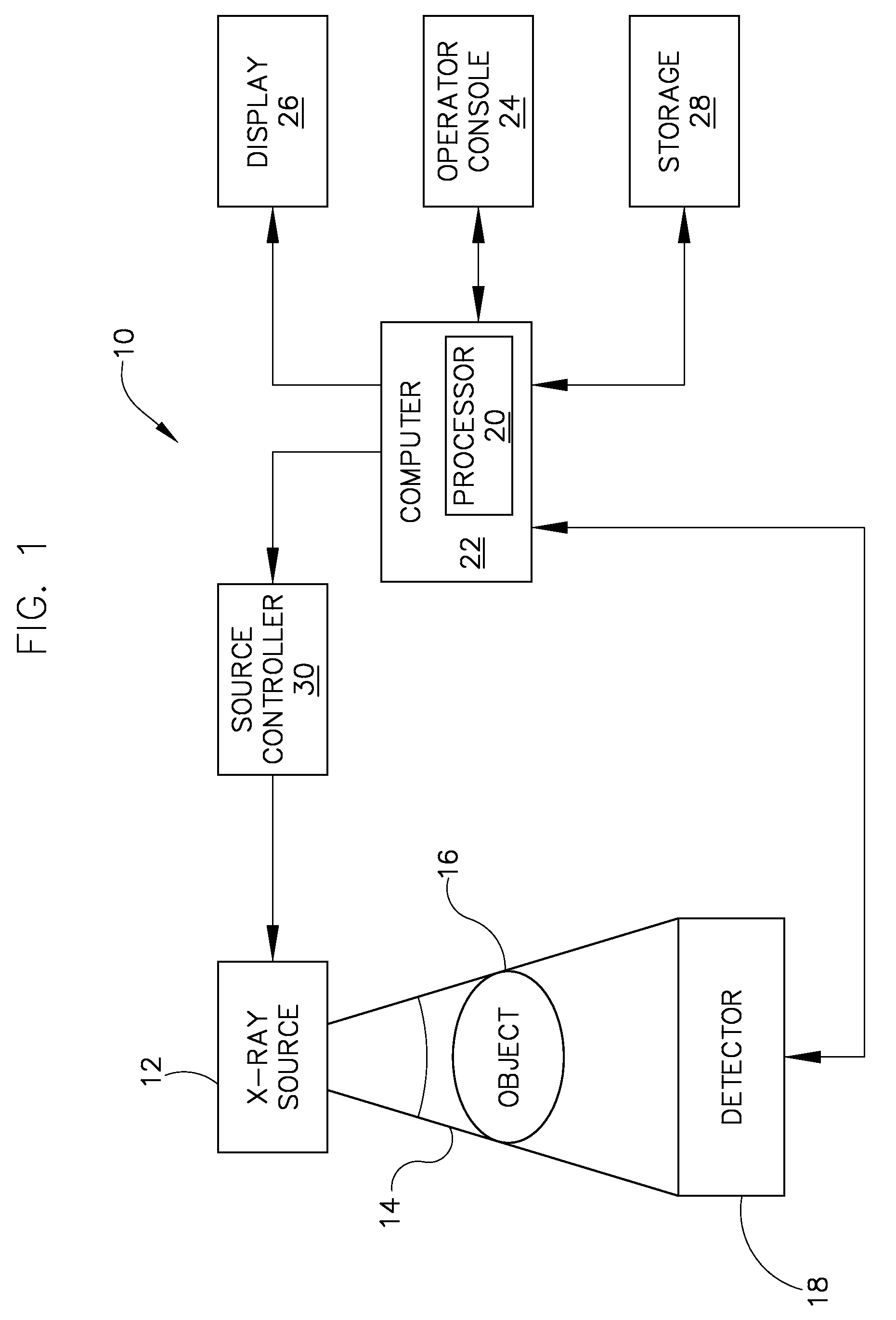
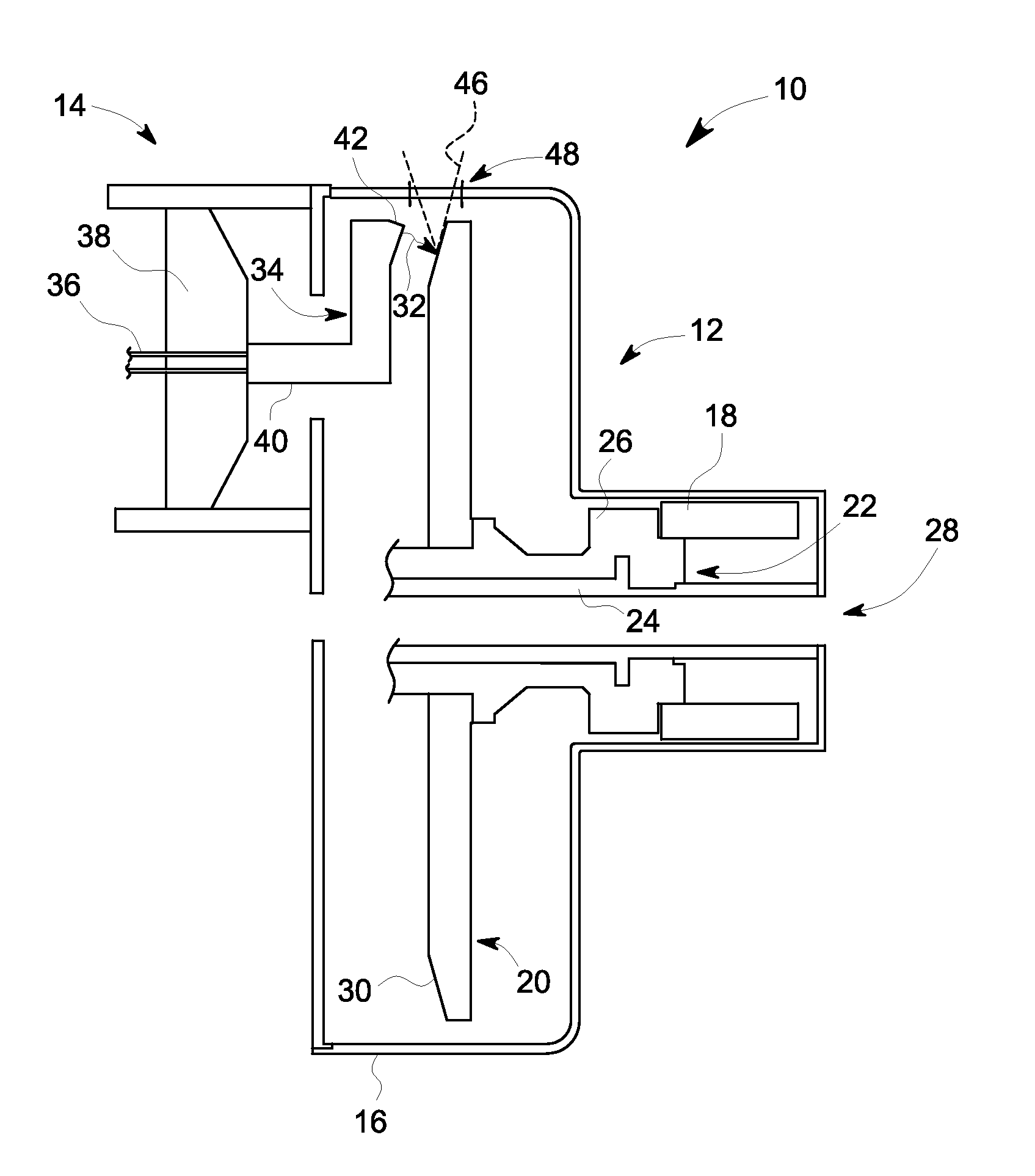
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50results about "X-ray tube bearing assembly cooling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
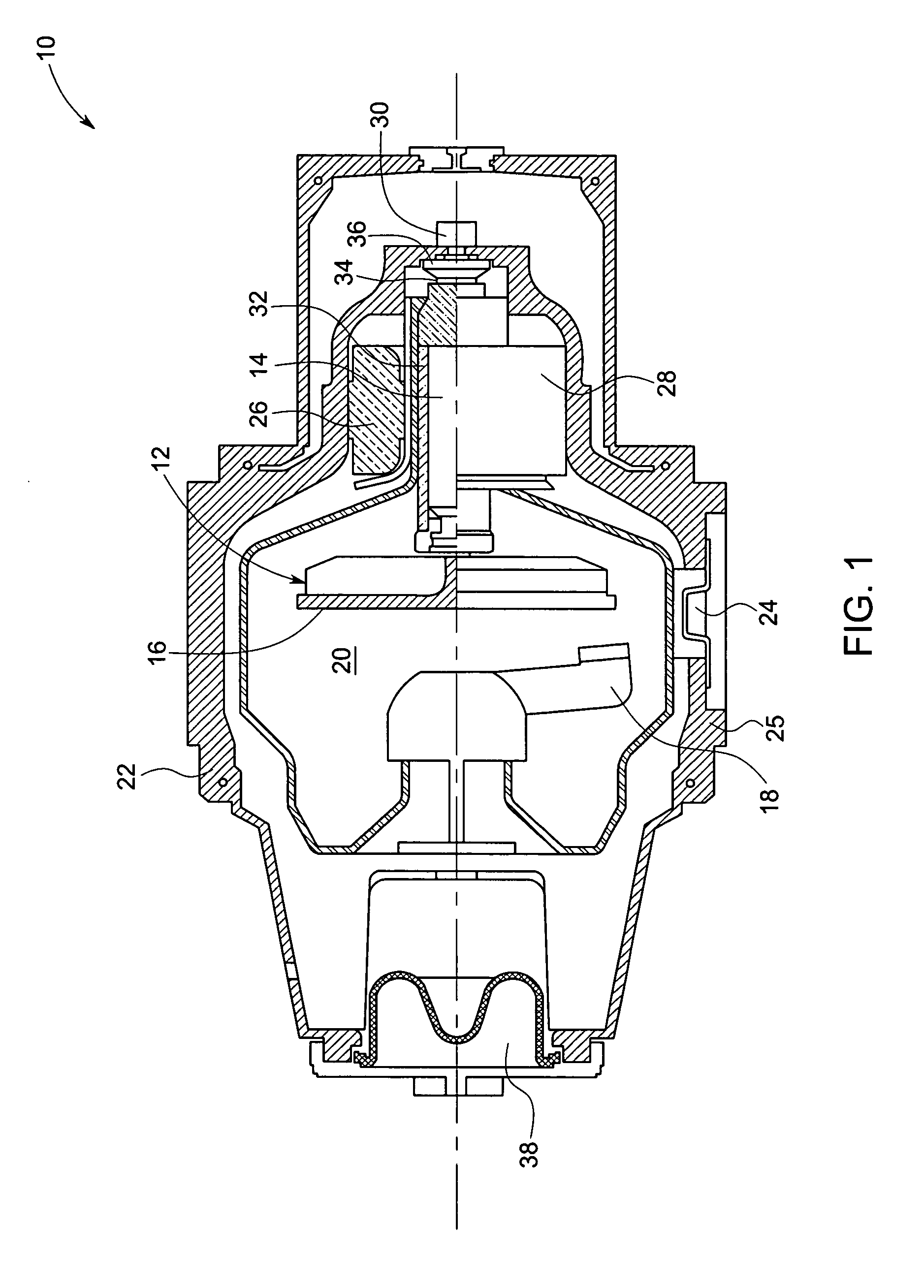
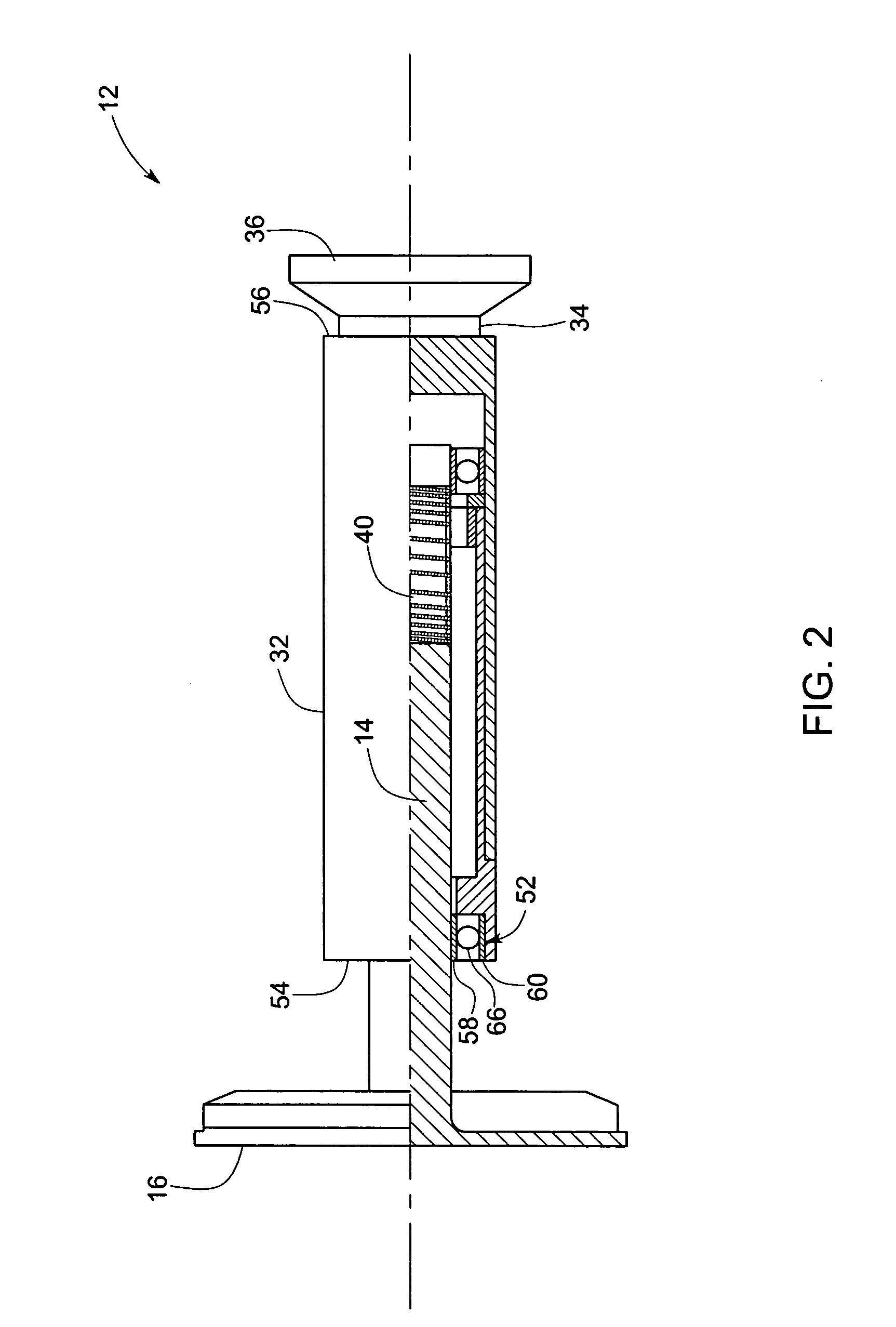
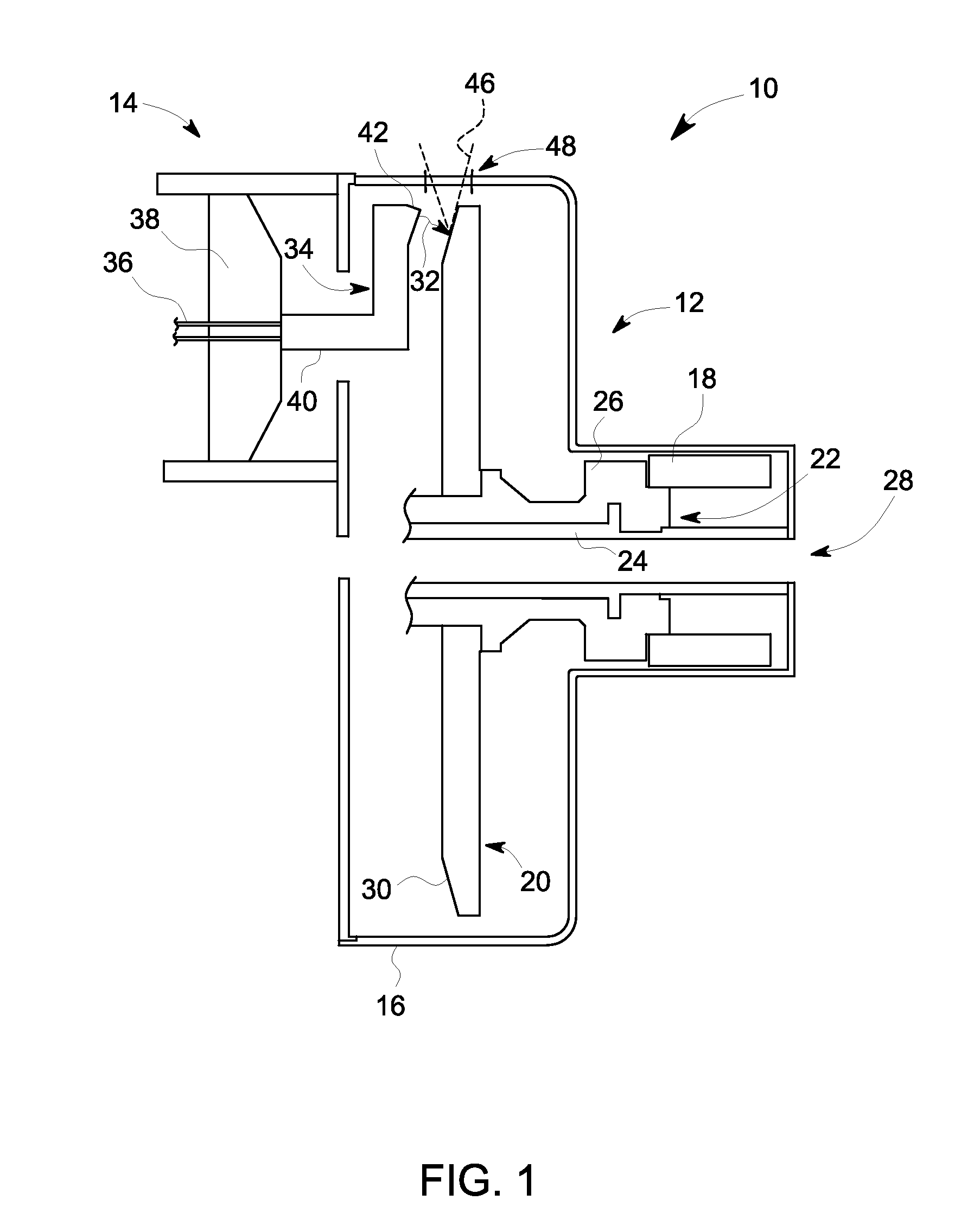
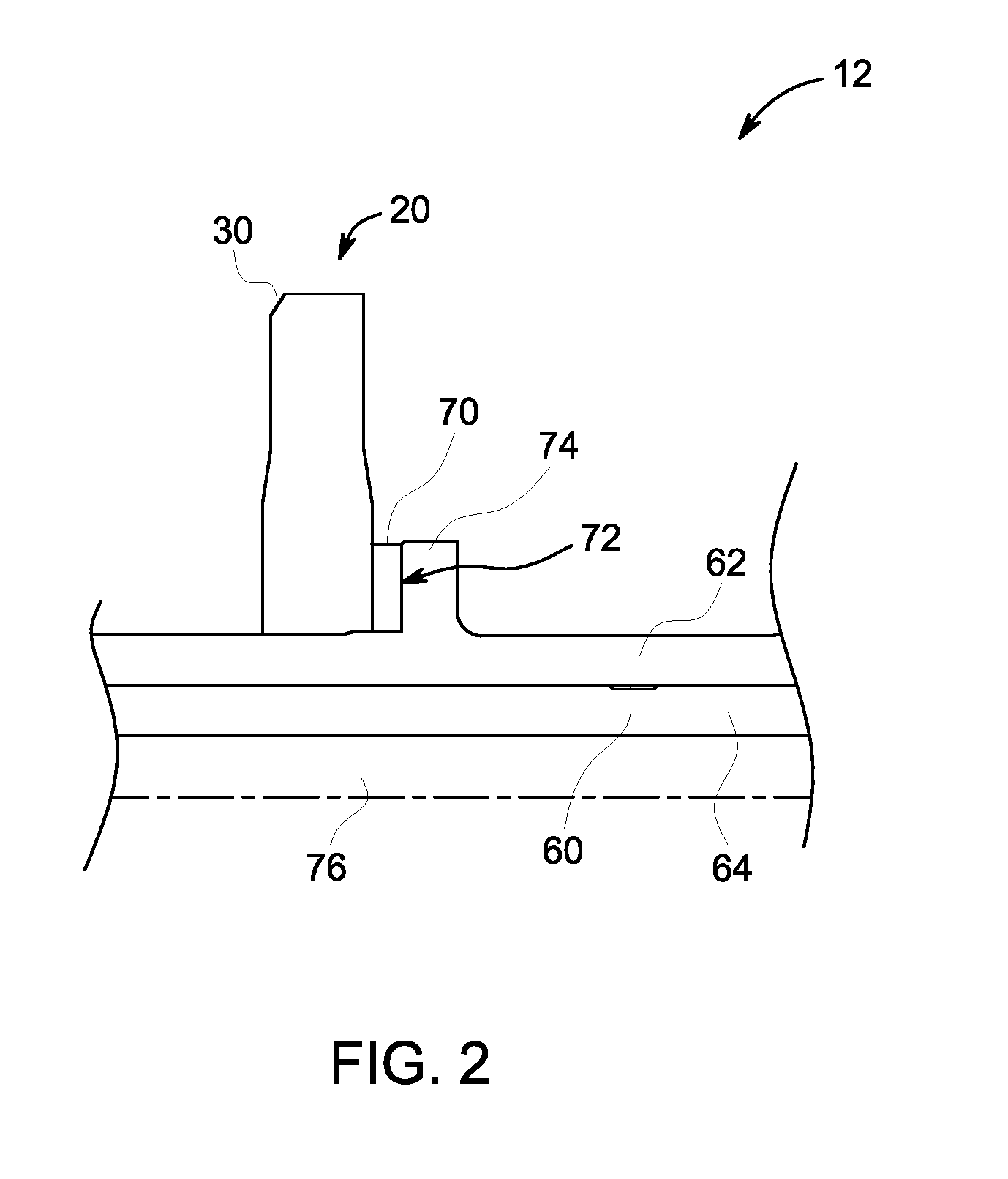
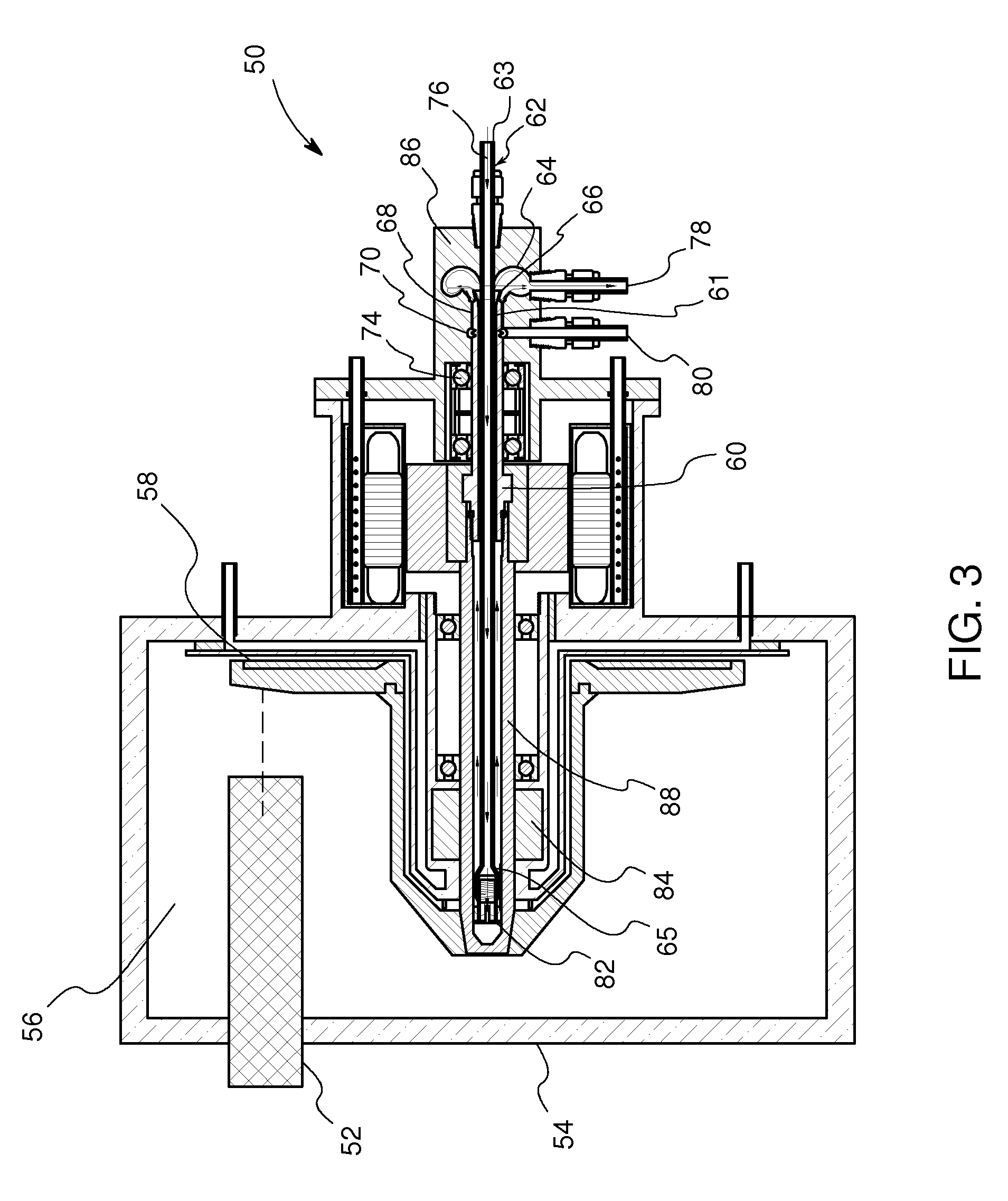
Welded Spiral Groove Bearing Assembly
ActiveUS20160133431A1Structure miniaturizationLow costBearing assemblyX-ray tube electrodesSpiral groove bearingEngineering
A structure and associated method for forming a liquid metal or spiral groove bearing assembly for an x-ray tube is illustrated that utilizes a unitary sleeve and a thrust ring or seal each formed of a weldable, non-refractory material. The sleeve and the thrust seal are welded to one another to provide an improved construction for minimizing leaks of the liquid metal bearing fluid. The structure of the sleeve and the thrust seal are formed with deformation restricting features that maintain the integrity of the bearing surfaces of the assembly when the thrust seal is secured within the sleeve and welded thereto to form the bearing assembly.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus with a rotationally driven body in a fluid-filled housing
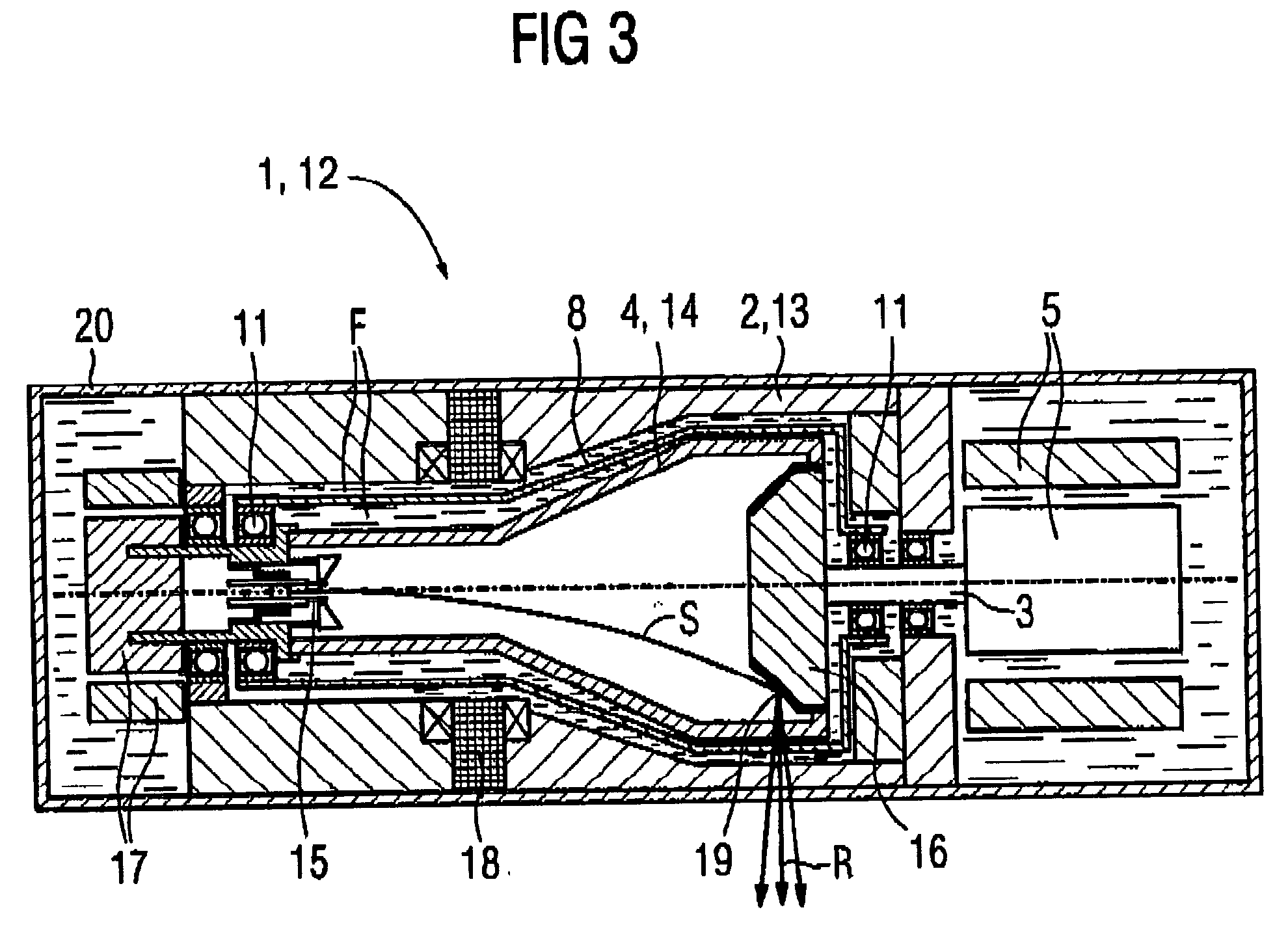
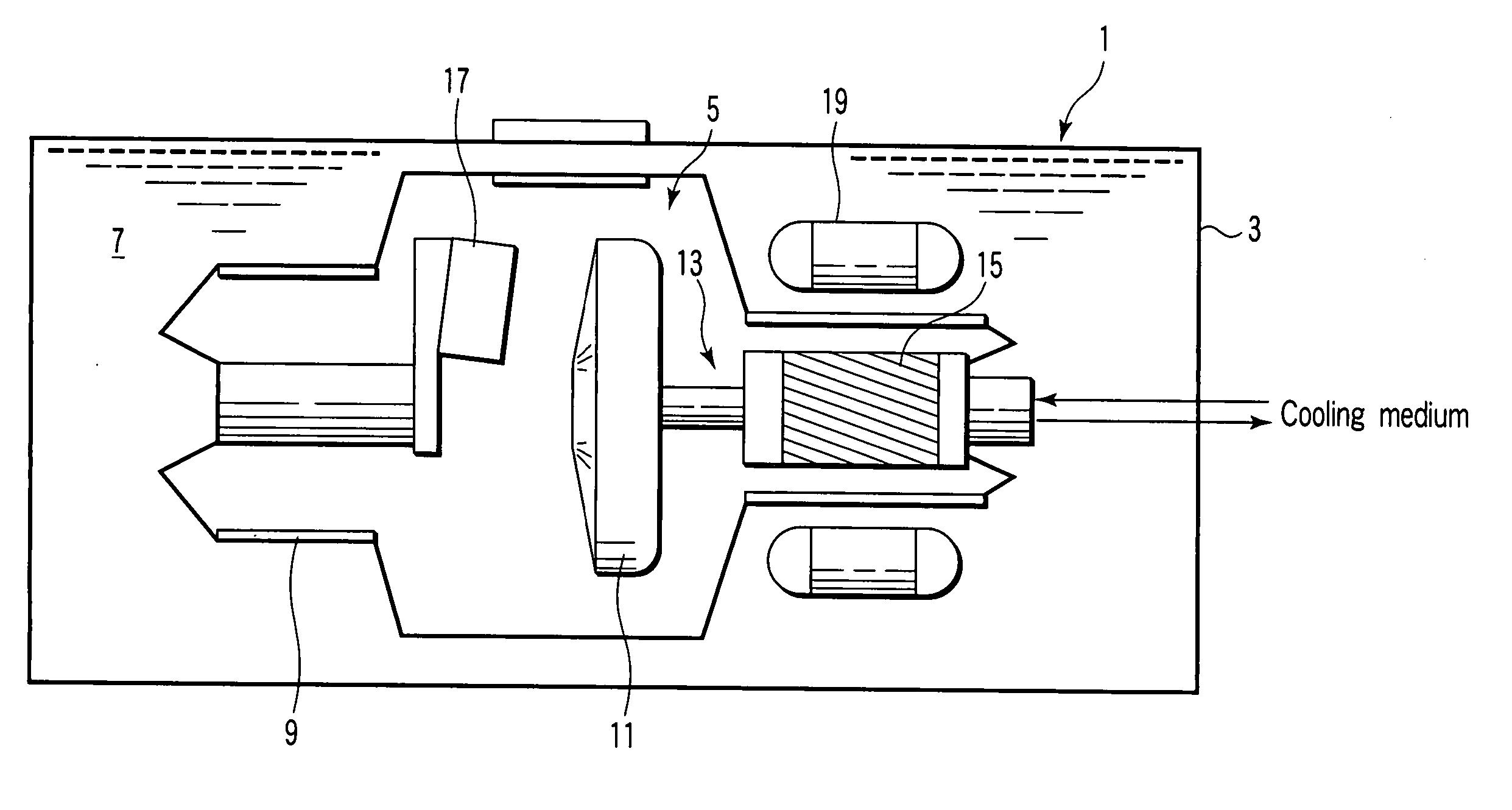
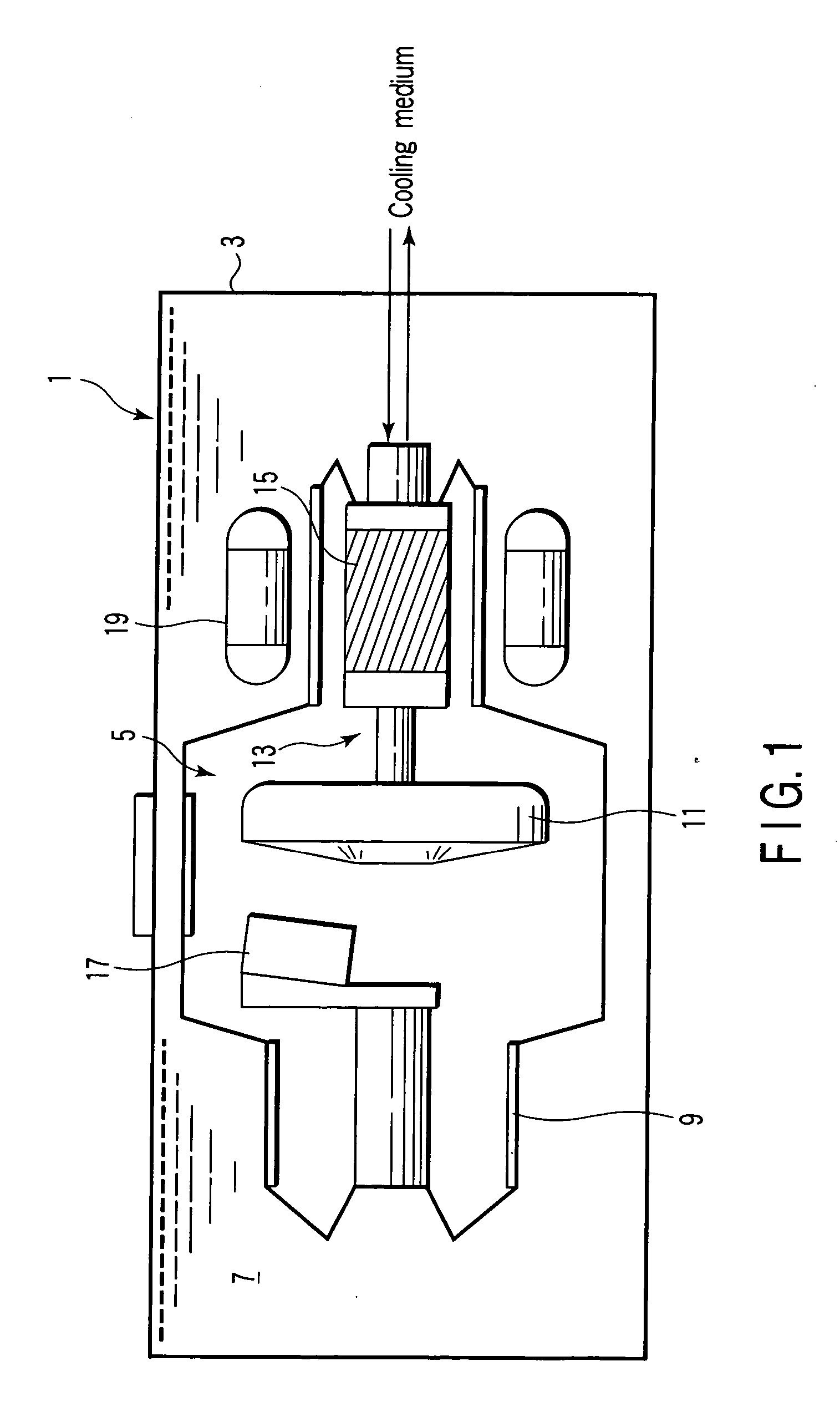
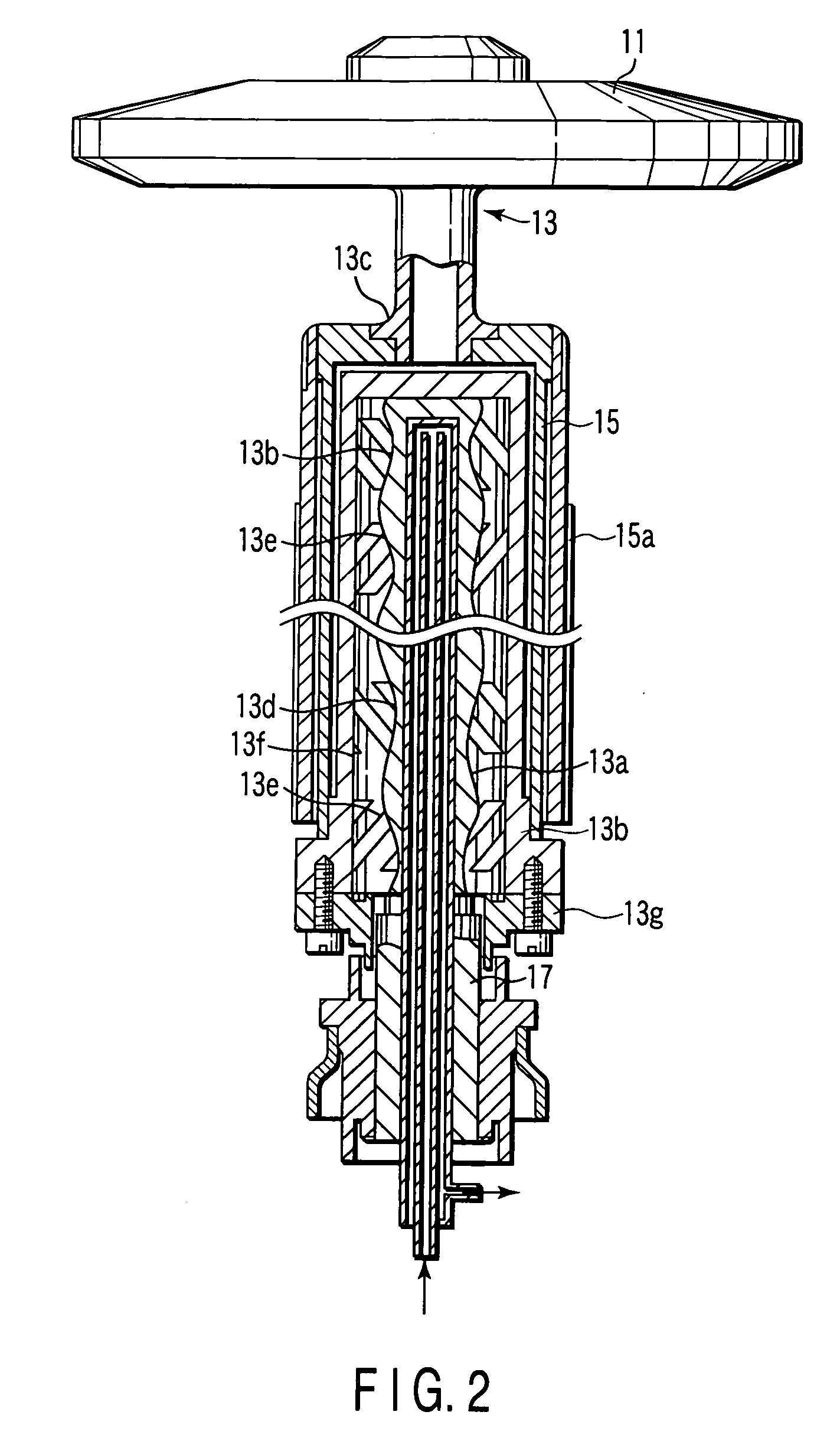
ActiveUS7025502B2Reduce lossReduce rotational powerX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingX-ray tube electrodesX-rayEngineering
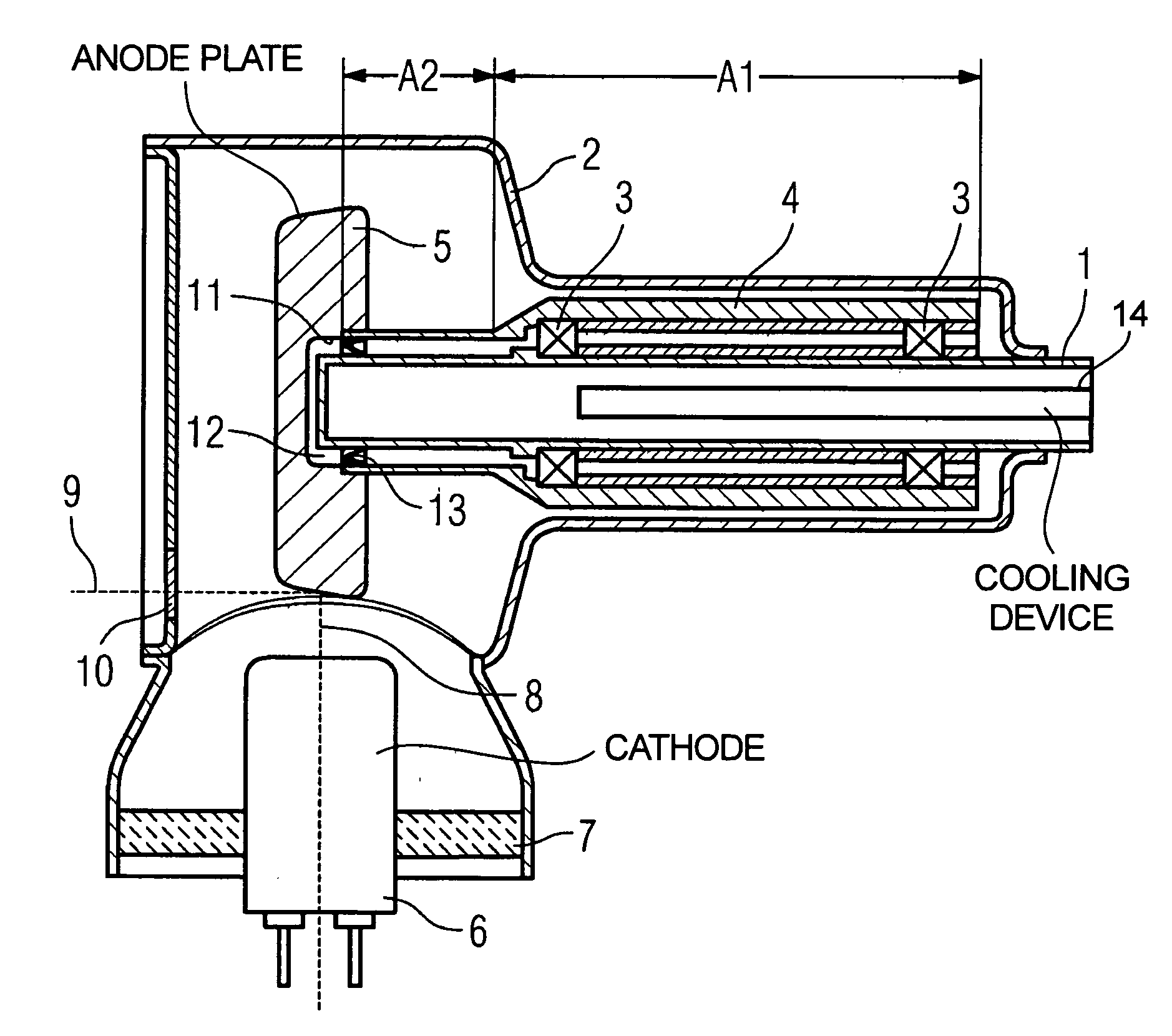
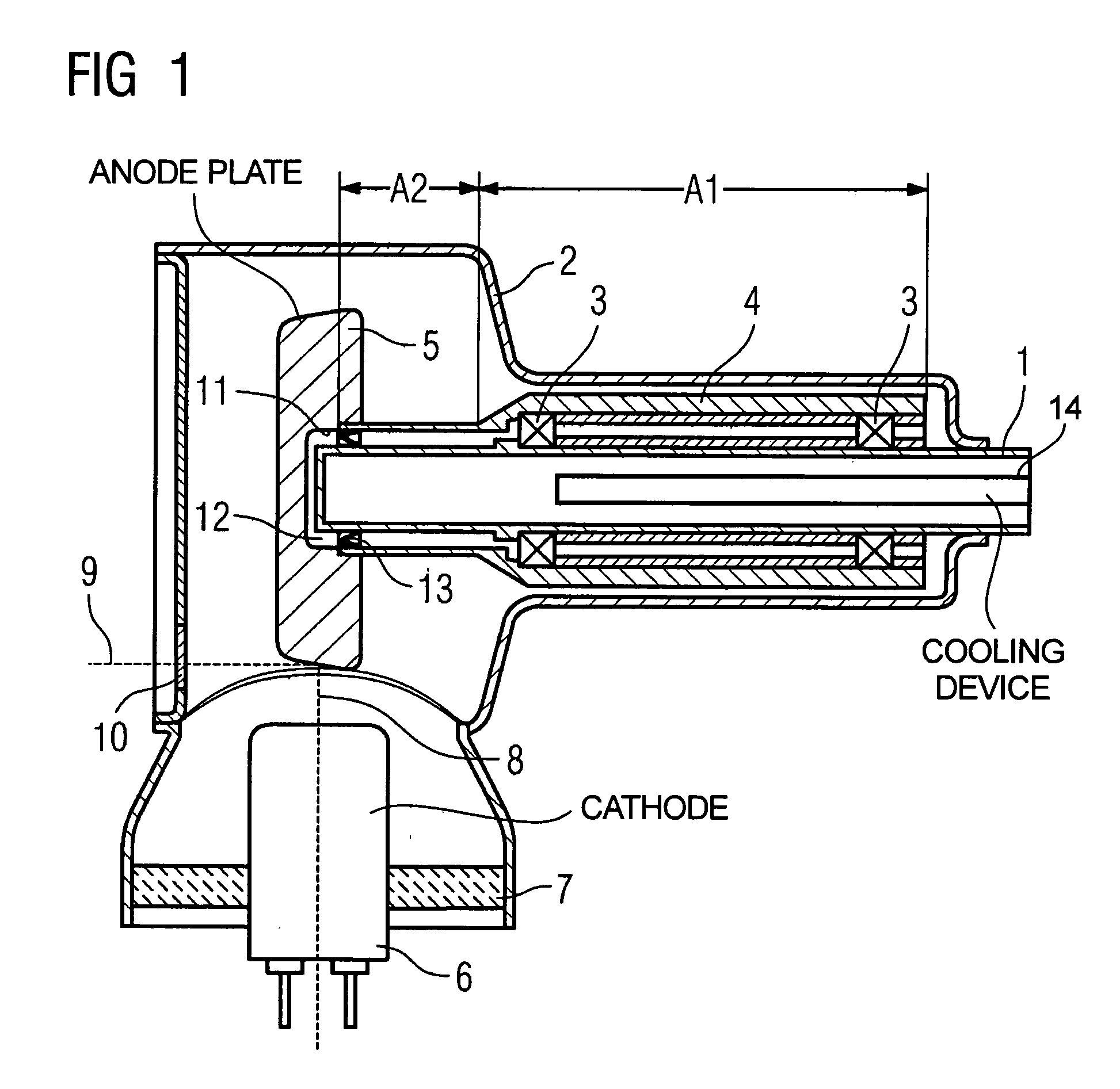
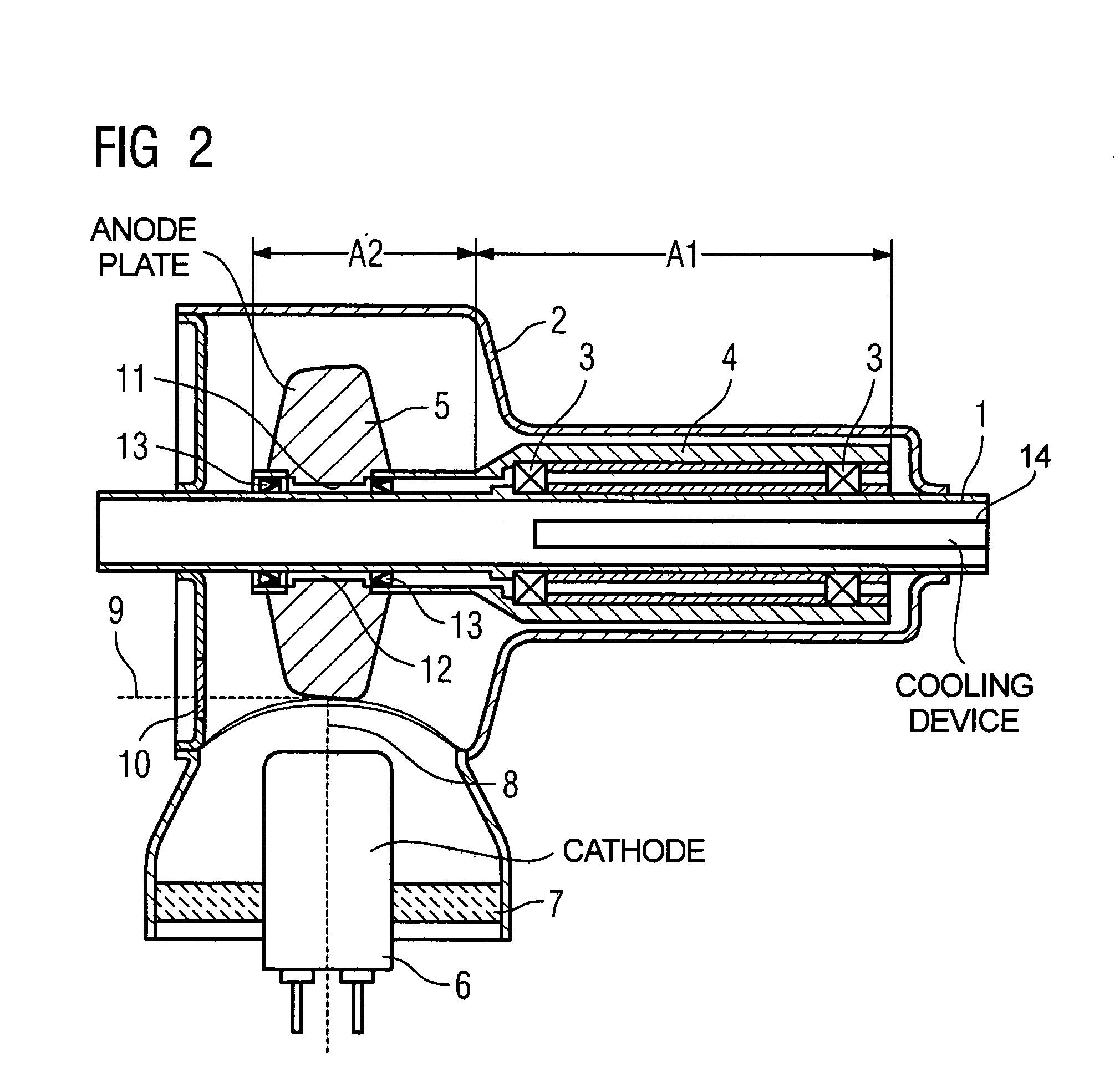
To reduce the rotational power, an apparatus with a rotational body that is rotationally driven in a fluid-filled housing a rotational directing body is provided between the rotational body and the housing, which is rotatably supported coaxially with respect to the rotational body. The rotational directing body is configured such that in operation it rotates at an intermediate rotational frequency in comparison to the housing and the rotational body. The apparatus is particularly an X-ray radiator having a cathode and anode that are mounted in a vacuum tube in a spatially fixed manner in relation to the tube, the vacuum tube being rotationally driven as a rotational body in a coolant housing.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
X-ray apparatus
ActiveUS20060193439A1Improved heat radiation characteristicIncrease heatX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingX-ray tube electrodesX-rayLiquid metal
The present invention is characterized by supporting a stator to generate a magnetic field and an anode target by a dynamic pressure plain bearing using a liquid metal, and cooling at least the inside of the dynamic pressure plain bearing and an enclosure containing an anode target by circulating one kind of cooling medium, in a rotary X-ray tube apparatus which obtains X-rays by impinging an electron on an anode by rotating an anode target.
Owner:CANON ELECTRON TUBES & DEVICES CO LTD
X-ray tube having liquid lubricated bearings and liquid cooled target
An x-ray tube having a liquid lubricated bearing assembly and a liquid cooled anode target. The anode target and bearing assembly having increased lubrication and cooling to withstand higher power, higher temperature and higher load applications.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray tubes and methods of making the same
A rolling contact bearing assembly is provided. The bearing assembly includes an inner ring and an outer ring concentrically disposed about the inner ring. The bearing assembly further includes a plurality of rolling contact elements disposed between the inner and outer rings, where at least one of the inner ring, the outer ring and the rolling elements having a solid lubricant coating disposed thereon. The bearing assembly further includes a gallium-based cooling solution disposed between the inner and outer rings and in contact with the rolling contact elements.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
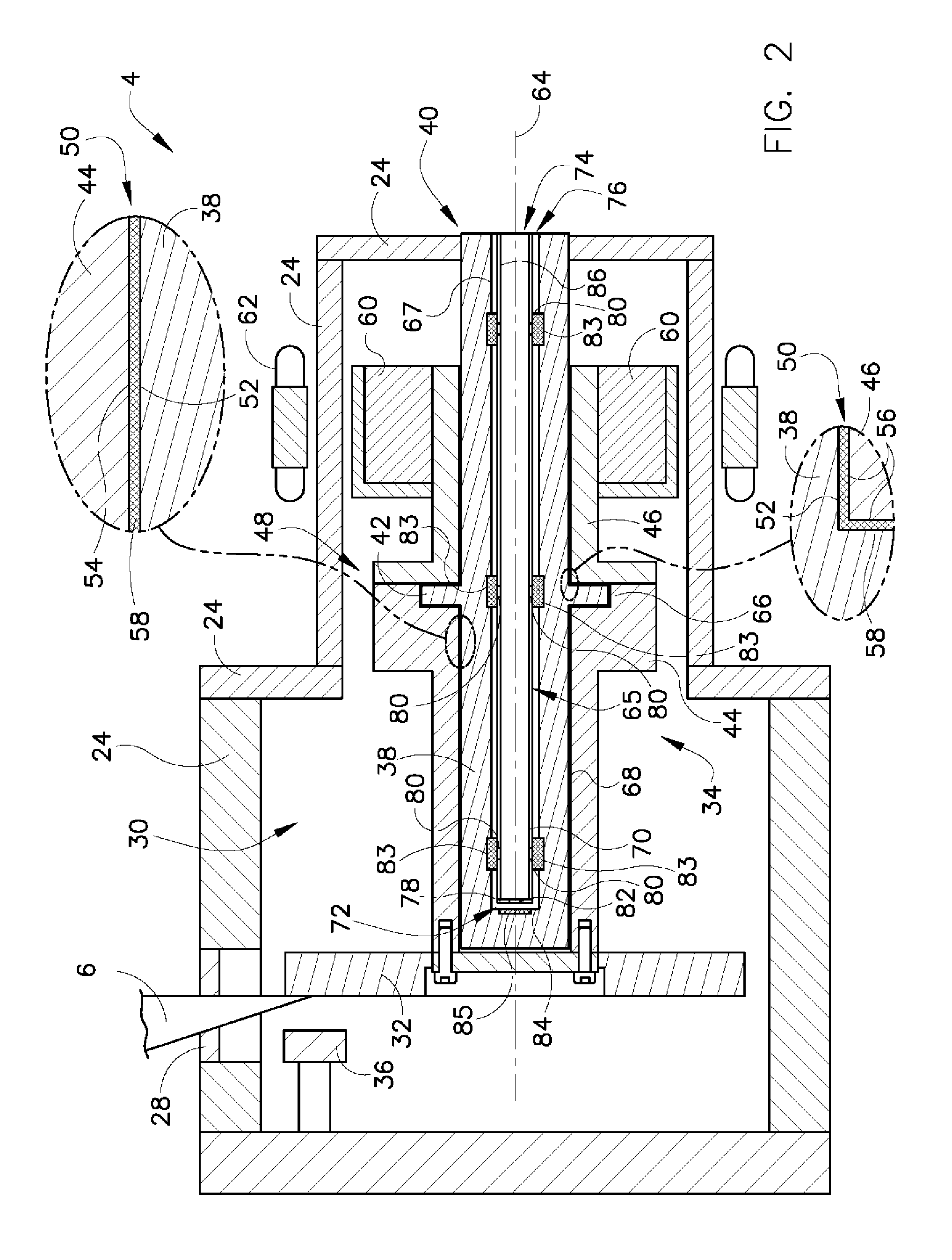
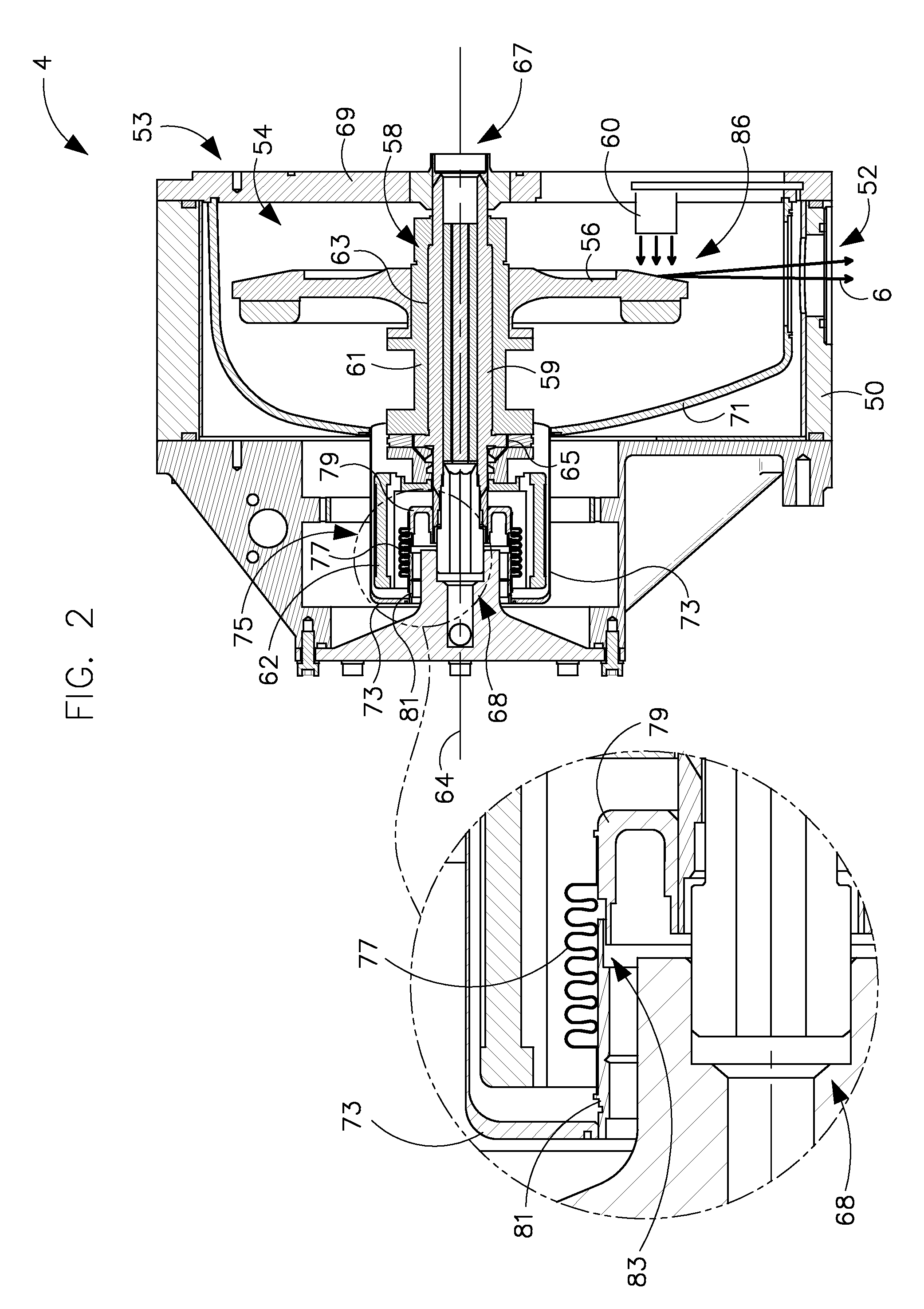
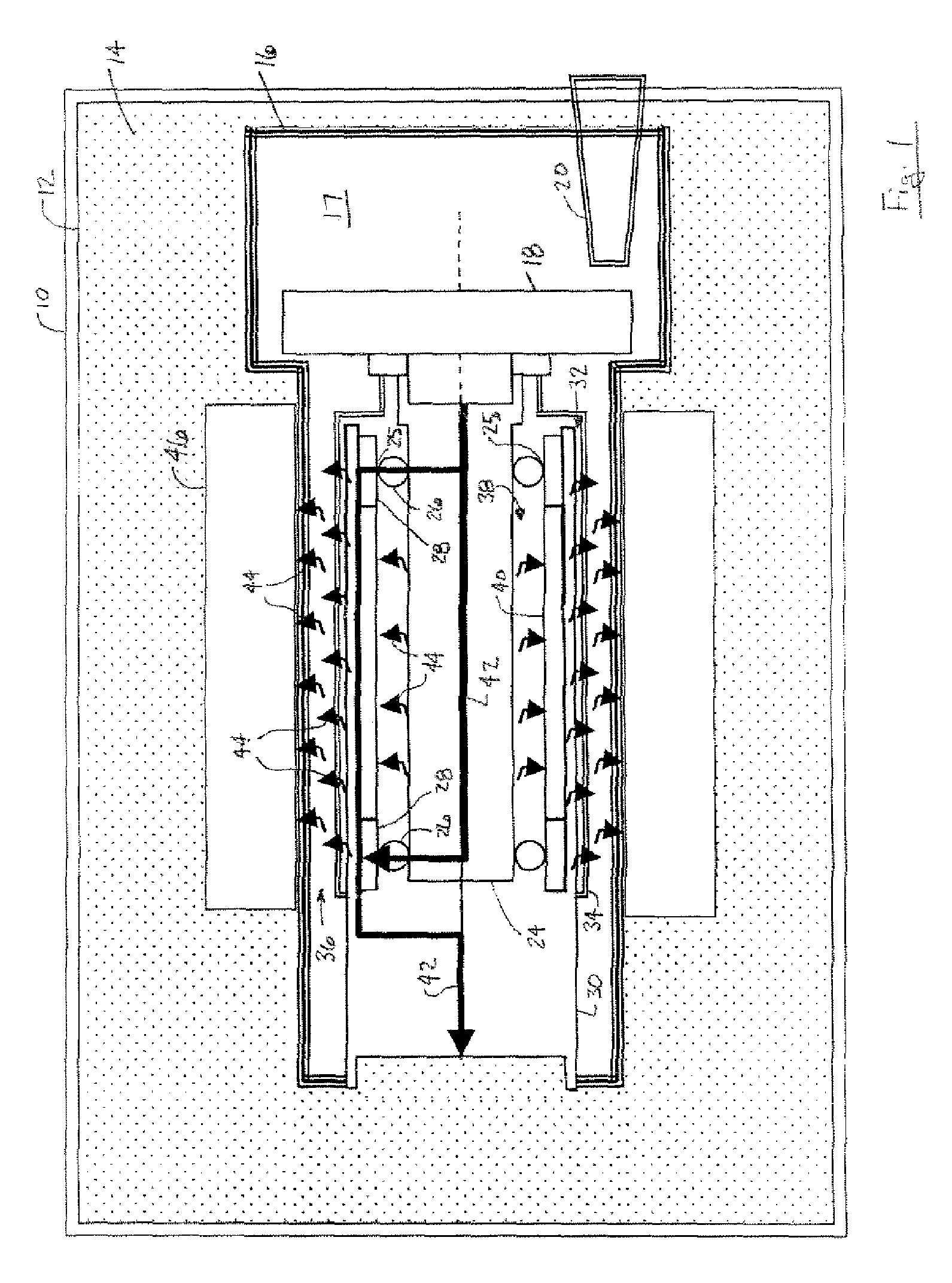
Apparatus and method of cooling a liquid metal bearing in an x-ray tube
An x-ray tube includes a center shaft having an inner surface and an outer surface, the inner surface forming a portion of a cavity therein, a mount having an inner surface, the mount having an x-ray target attached thereto, and a liquid metal positioned between the outer surface of the center shaft and the inner surface of the mount. The x-ray tube further includes a flow diverter positioned in the cavity, the flow diverter having a wall with an inner surface, and a plurality of jets passing through the wall, wherein the plurality of jets are configured such that when a fluid is flowed into the flow diverter and passes along its inner surface, a portion of the fluid passes through the plurality of jets and is directed toward the inner surface of the center shaft.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus for ultra high vacuum thermal expansion compensation and method of constructing same
ActiveUS9305739B2Reduce mechanical stressOvercomes drawbackX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingElectron sourceUltra-high vacuum
An x-ray tube includes a frame forming a first portion of a vacuum enclosure, a rotating subsystem shaft positioned within the vacuum enclosure and having a first end and a second end, wherein the first end of the rotating subsystem shaft is attached to a first portion of the frame, a target positioned within the vacuum enclosure and attached to the rotating subsystem shaft between the first end and the second end, the target positioned to receive electrons from an electron source positioned within the vacuum enclosure, and a thermal compensator mechanically coupled to the second end of the rotating subsystem shaft and to a second portion of the frame, the thermal compensator forming a second portion of the vacuum enclosure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
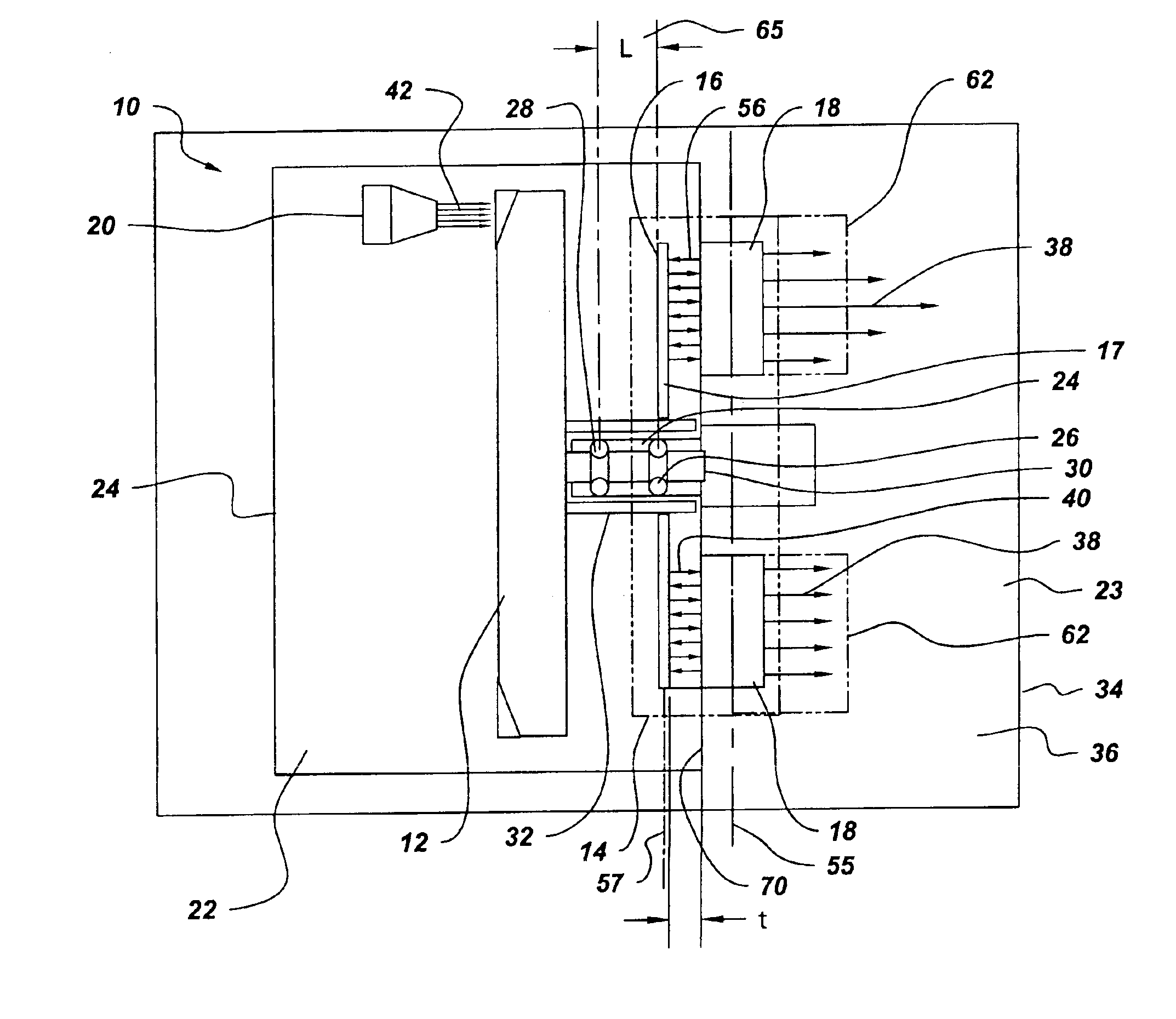
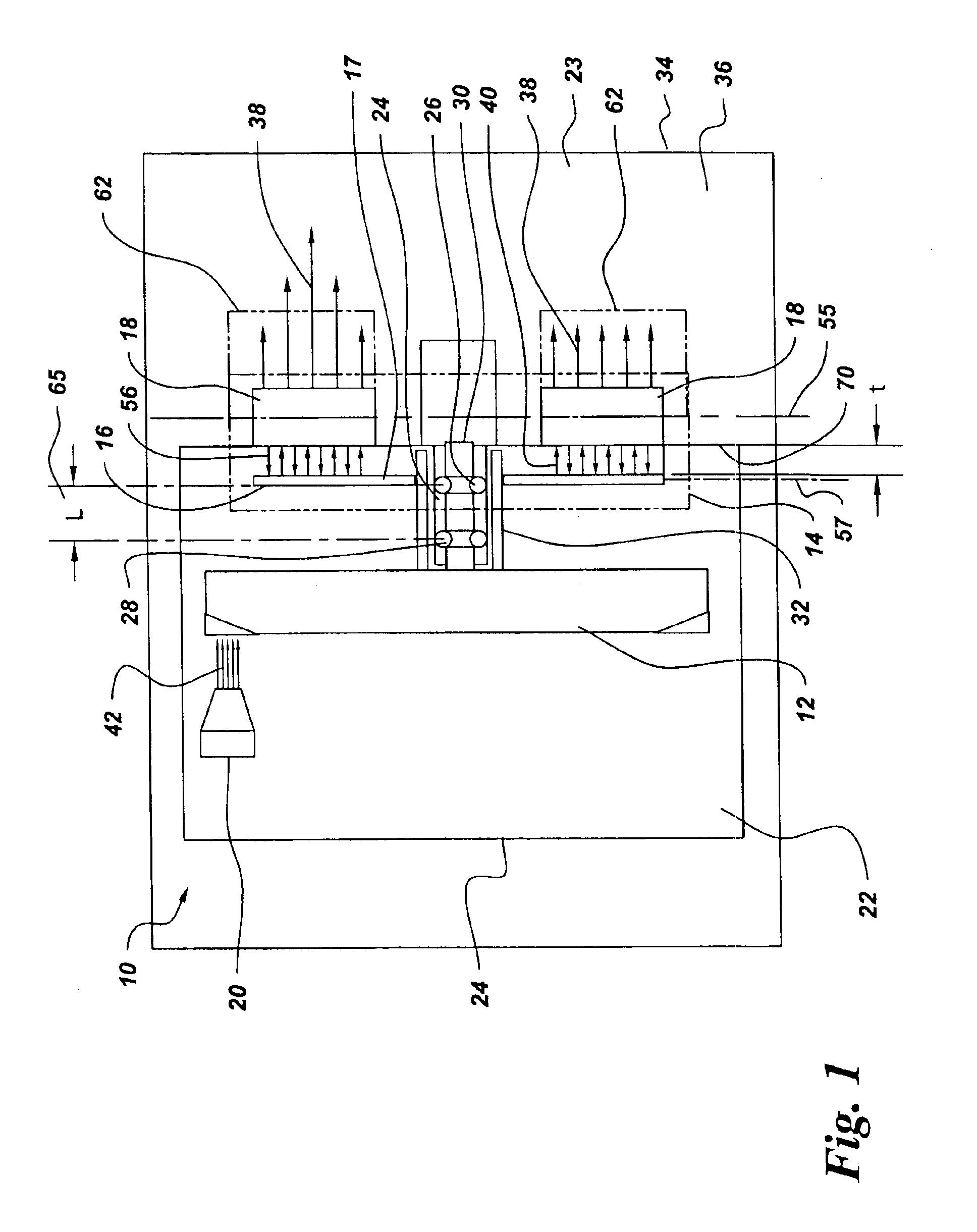
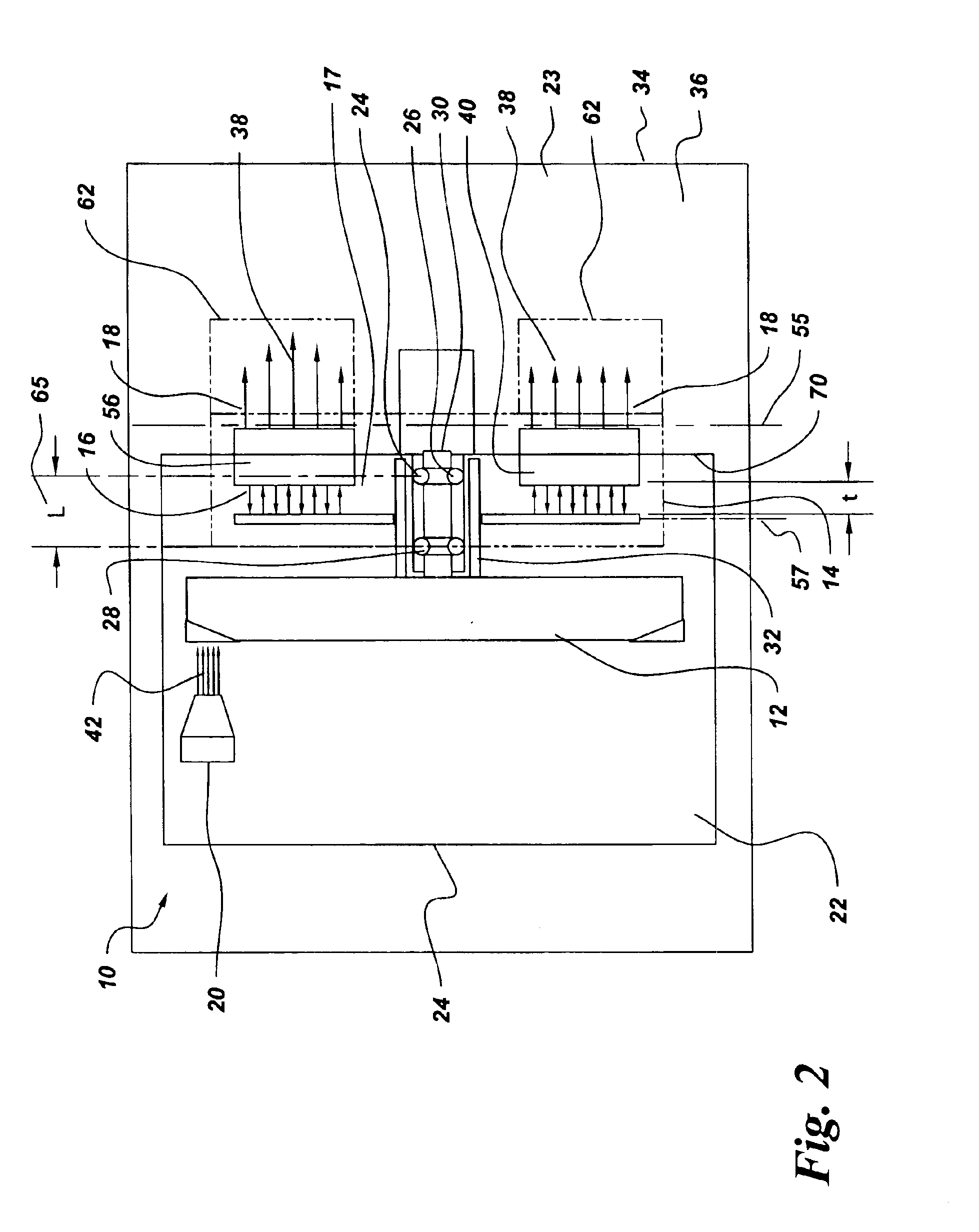
Axial flux motor driven anode target for x-ray tube
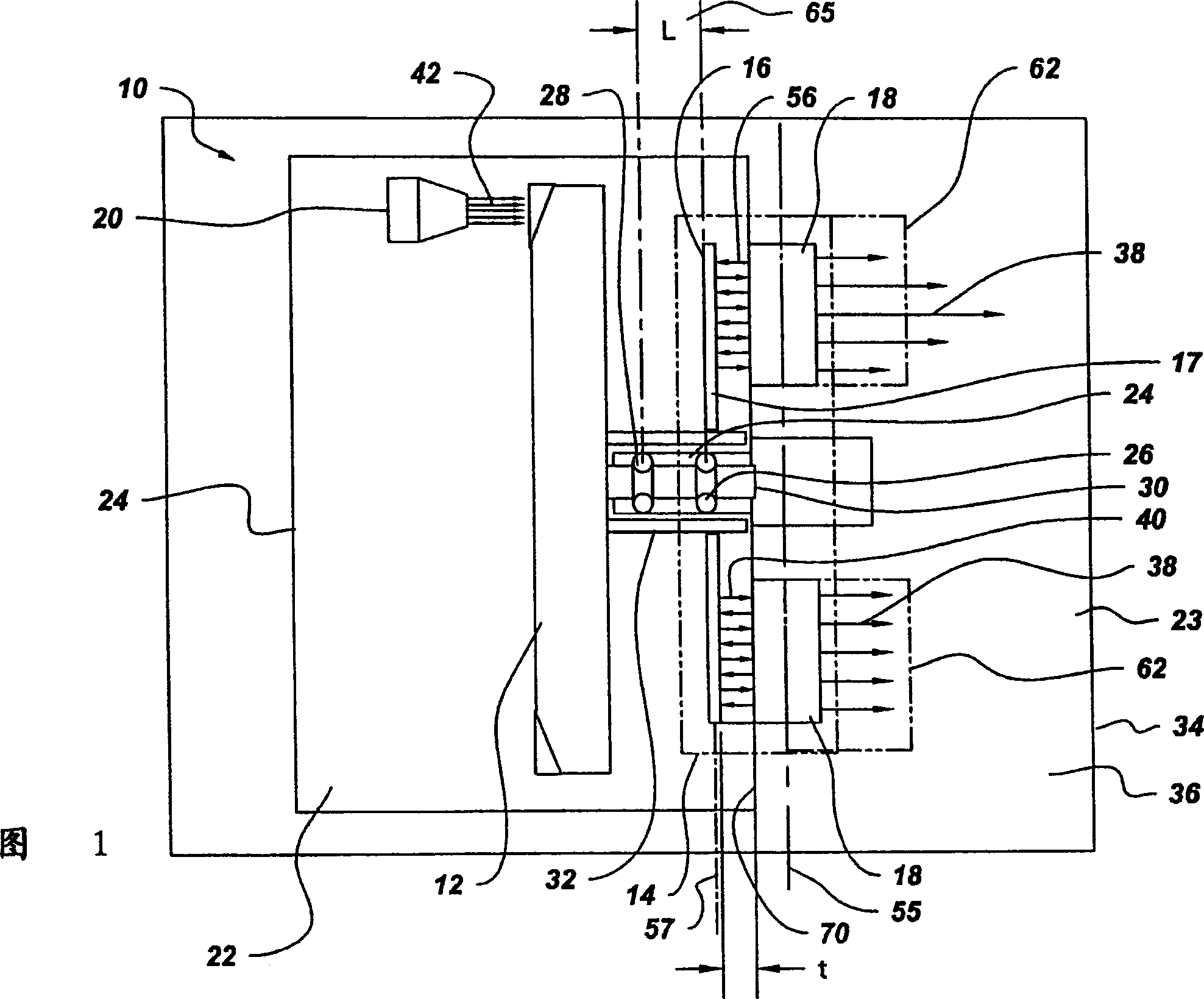
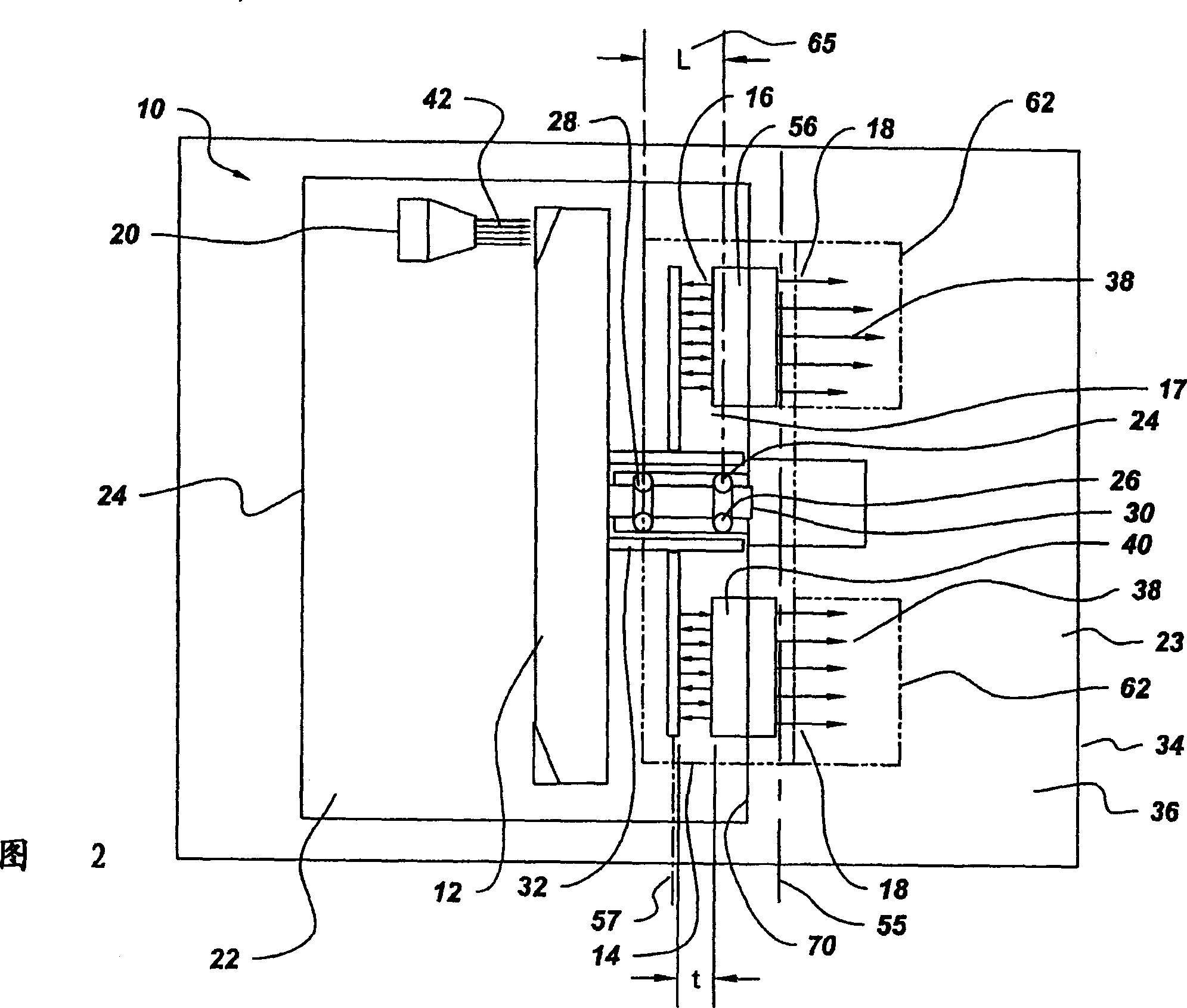
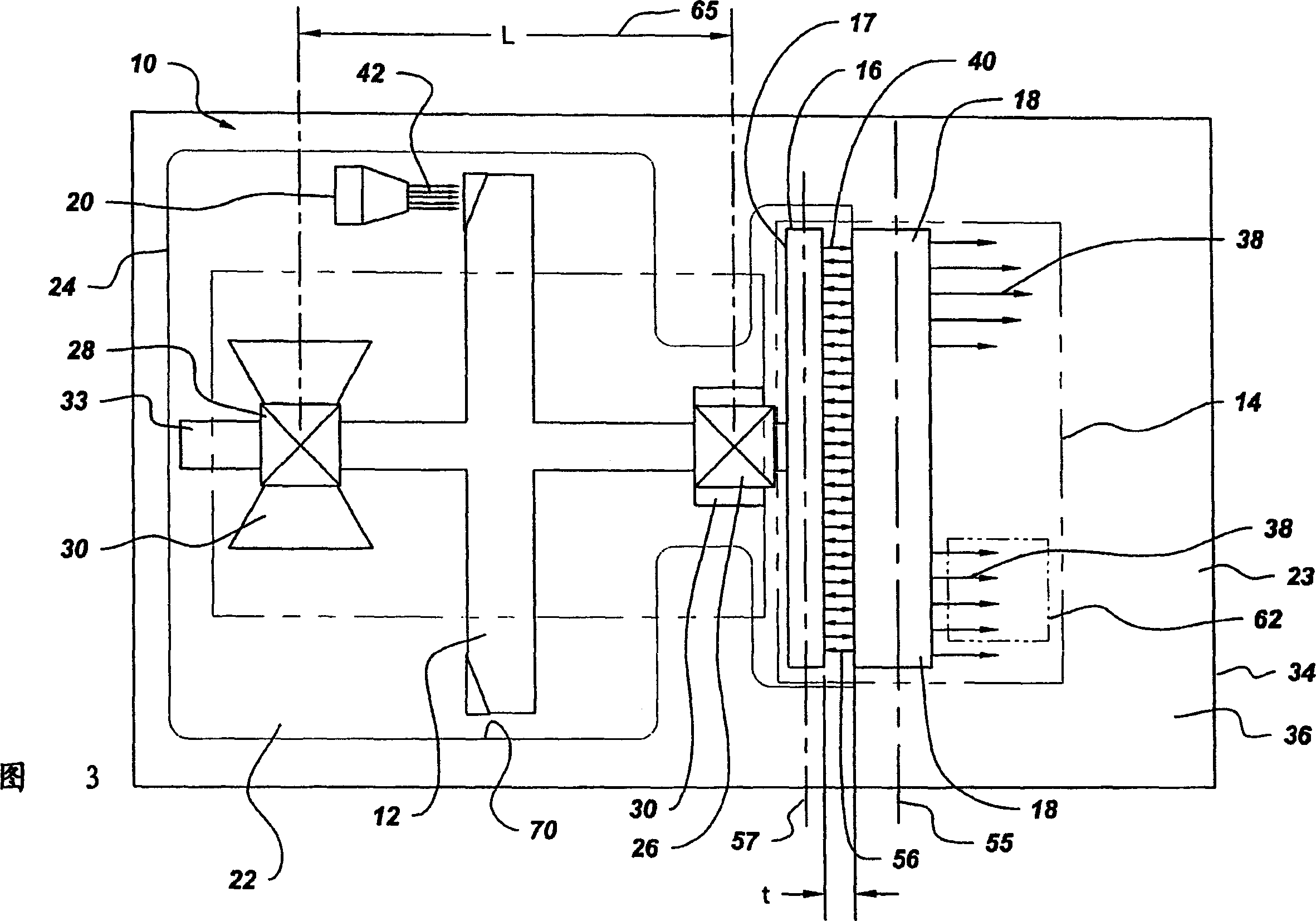
The X-ray tube(10) includes a cathode(20), rotor target assembly(12), and axial flux type motor(14) having a rotor(16) and stator(18). The stator(18) is arranged along with a lateral axial line(55) parallel to a rotor axial line(57). The rotor(16) and stator(18) are connected to the anode target assembly(12). The cathode(20) generates an electron beam(42) and makes the electron beam(42) collide on the anode target assembly(12). The vacuum housing(22) surrounds the anode target assembly(12), cathode(20), and rotor(16) to make the collision of the electron beam(42) possible.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
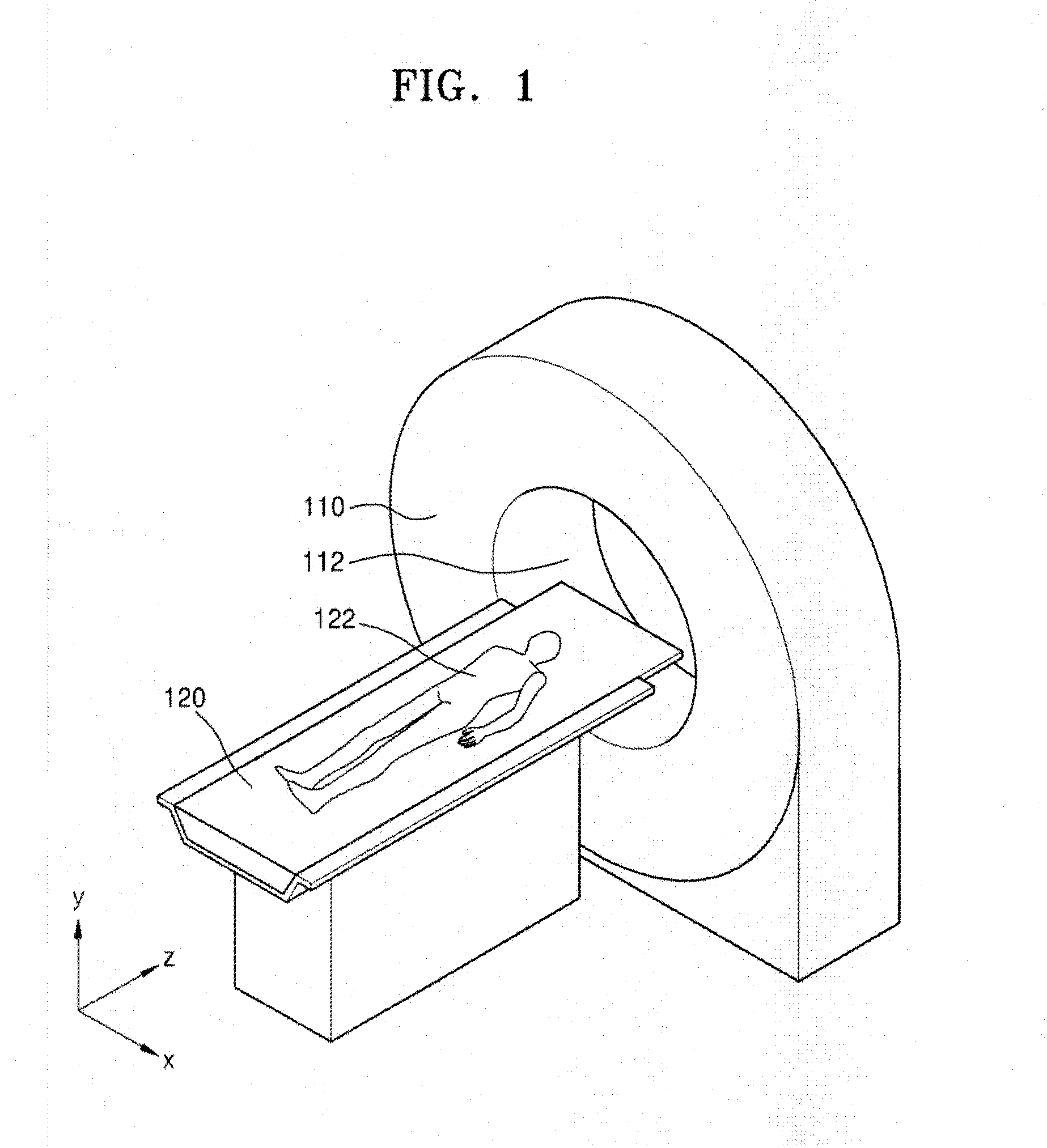
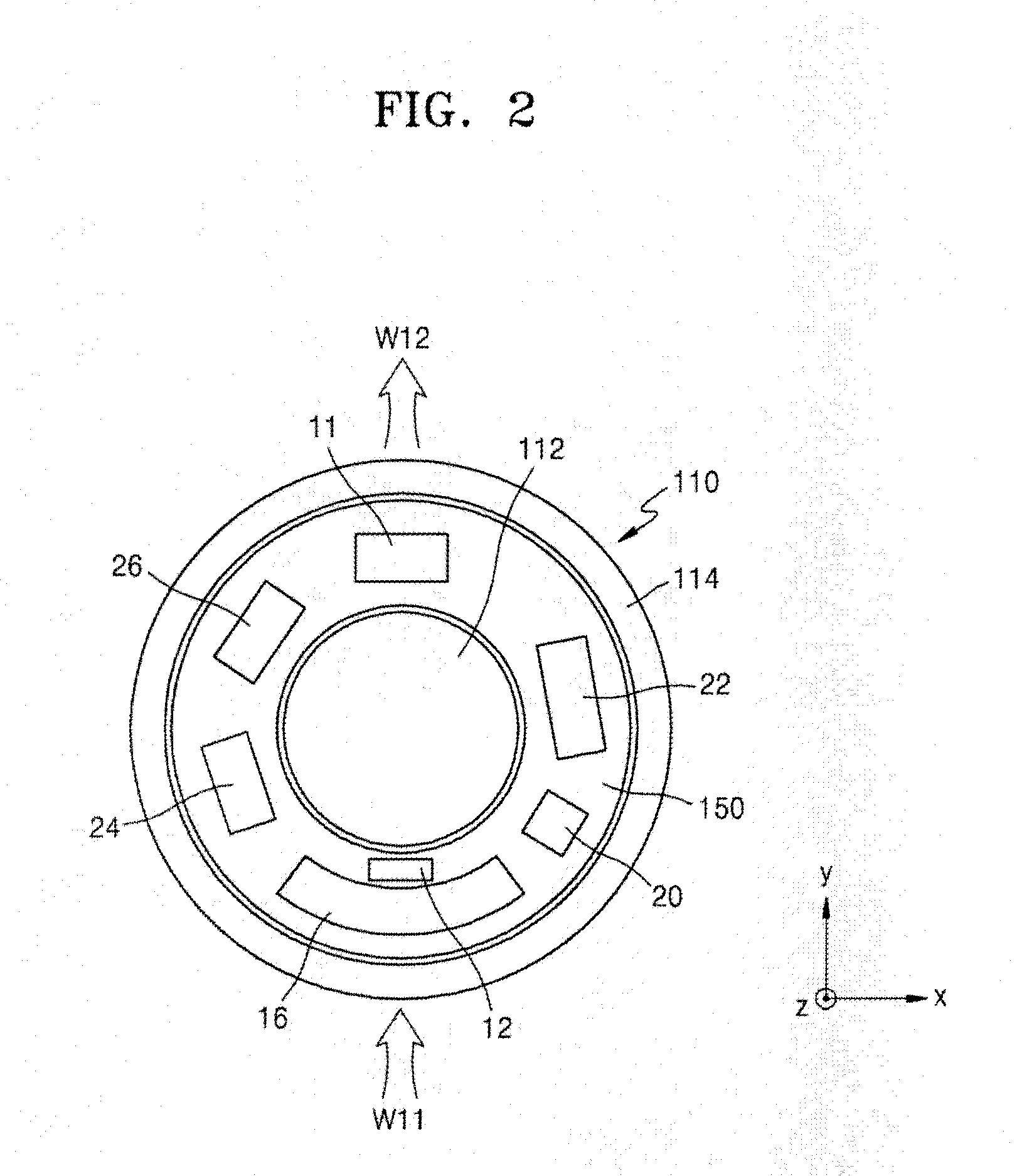
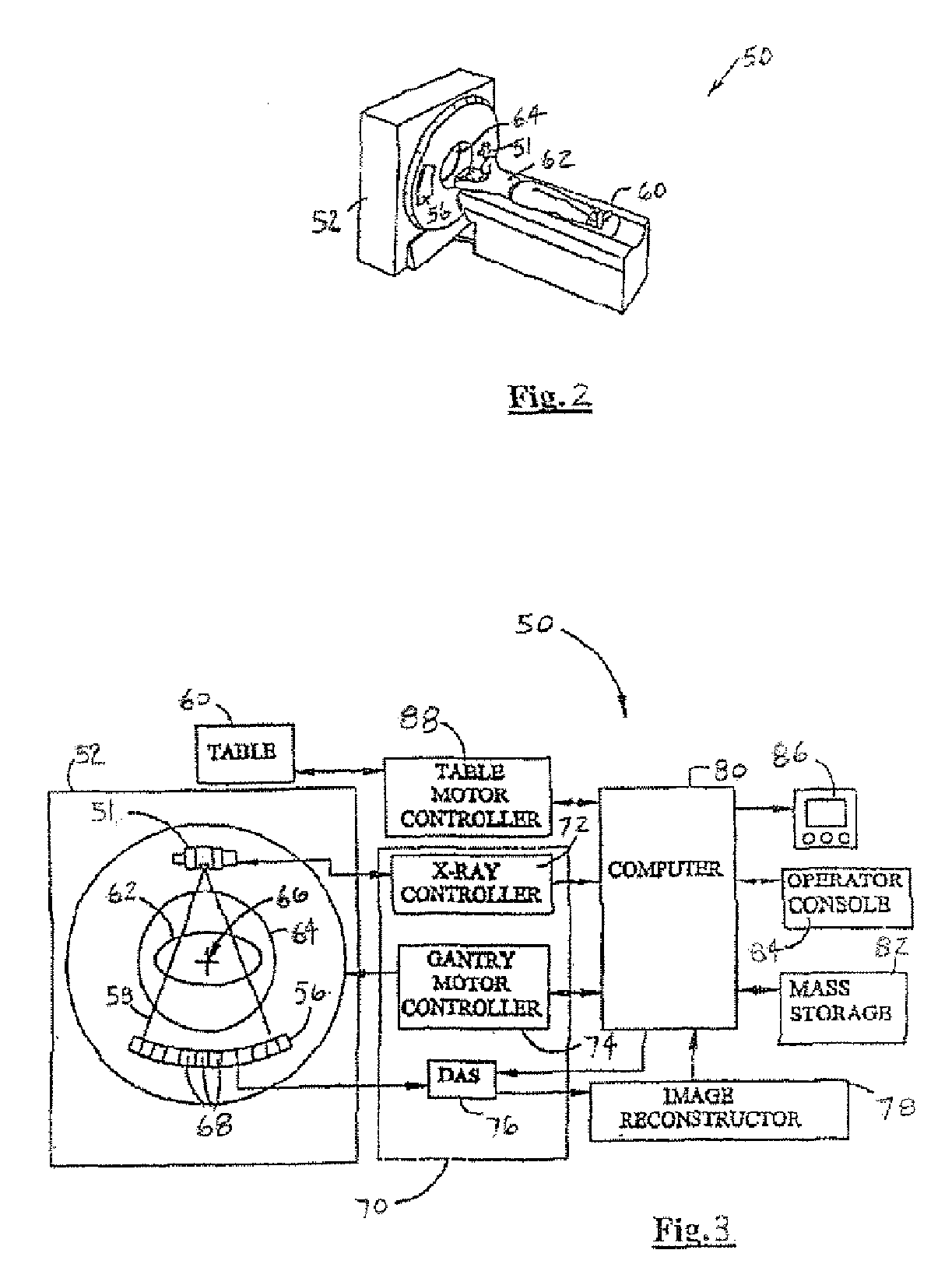
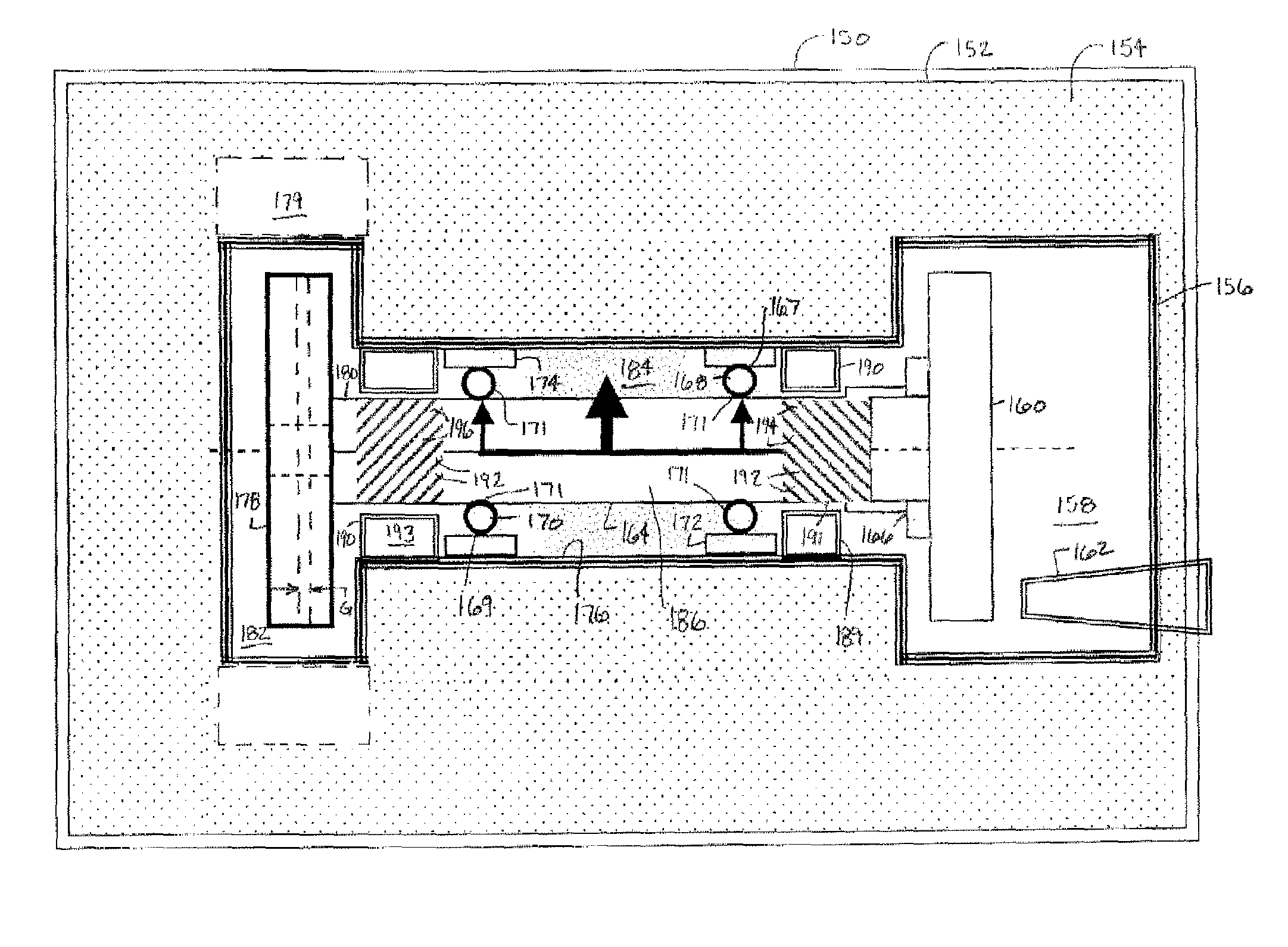
Computed tomography system having cooling system
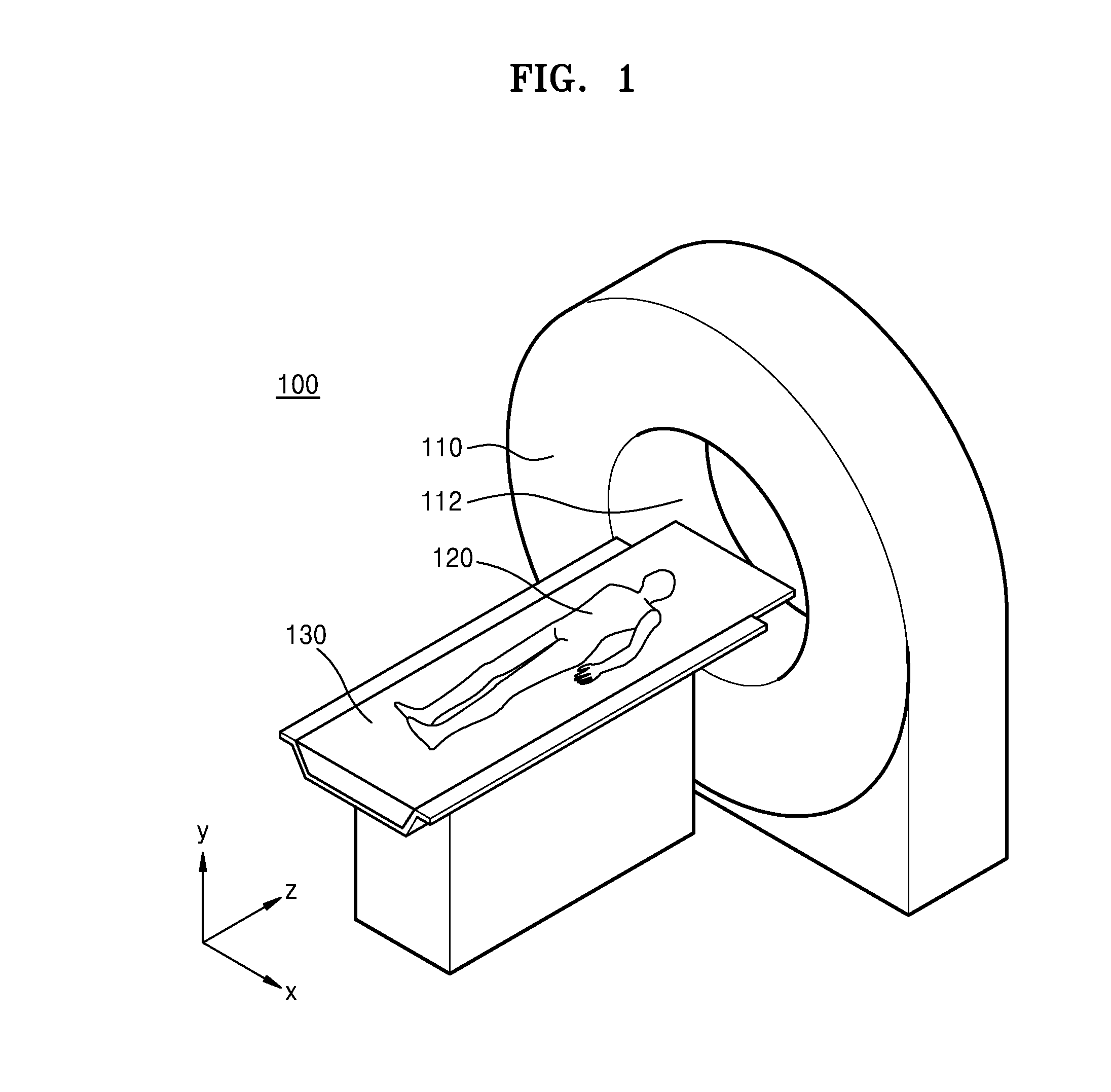
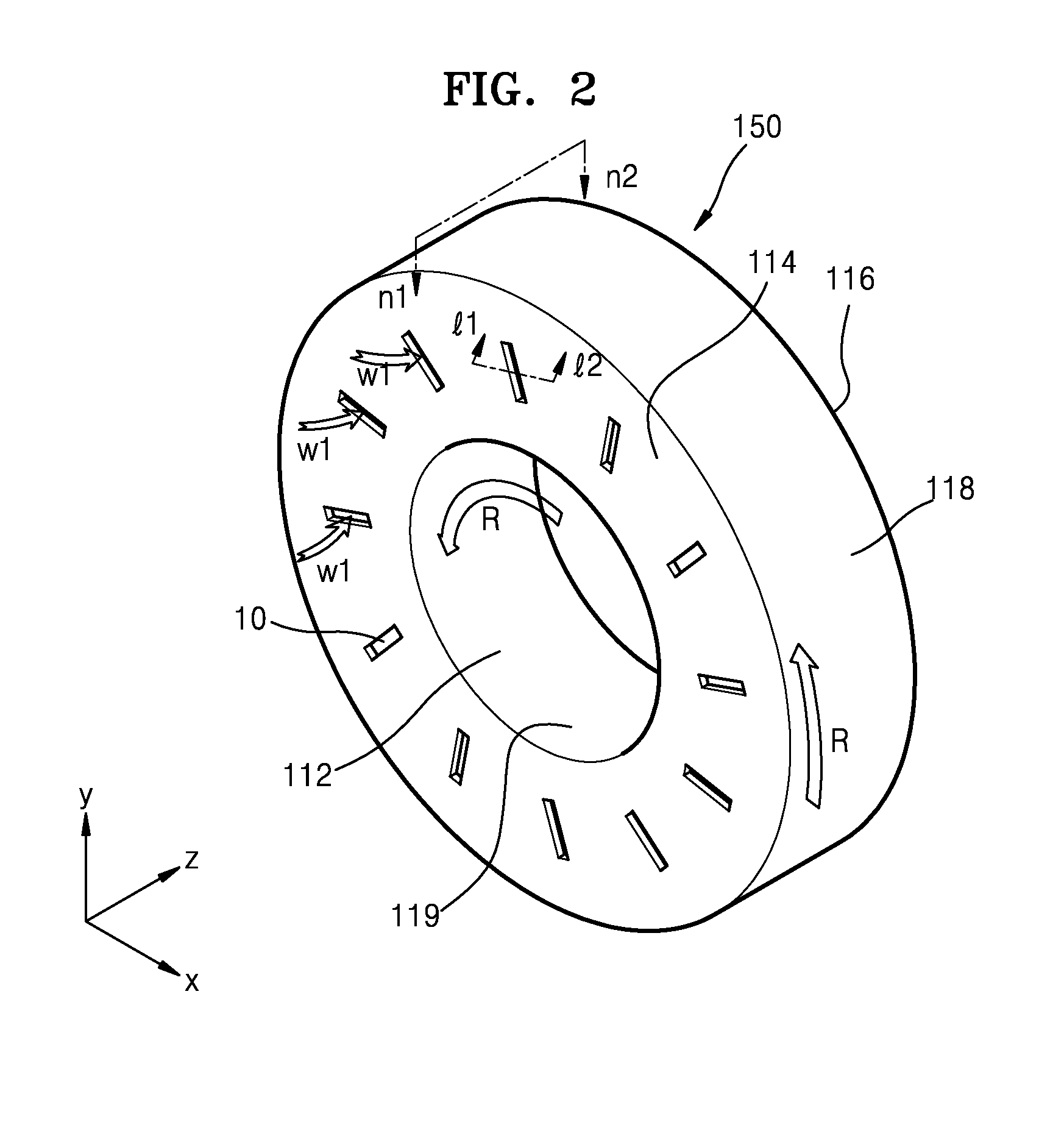
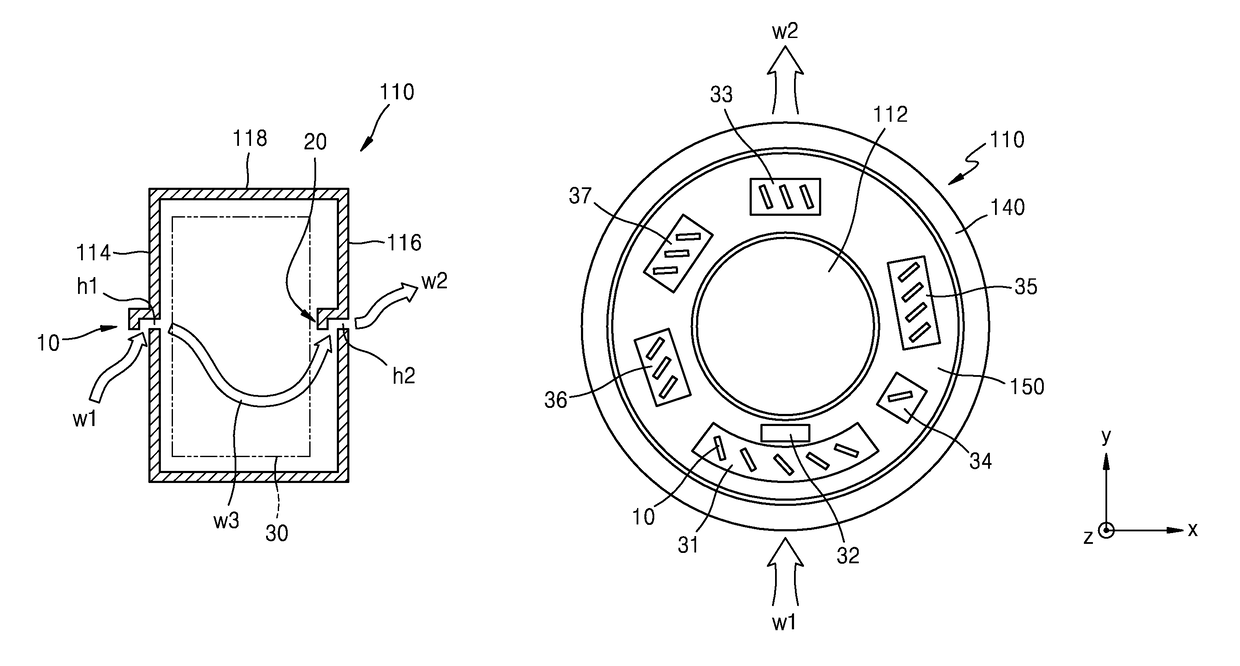
ActiveUS20160235378A1X-ray tube bearing assembly coolingPatient positioning for diagnosticsComputed tomographyOperational system
A cooling system of a computed tomography (CT) system provides for a more efficient operation than known heretofore. The cooling system of the CT system includes a gantry and a table that moves an object into a bore of the gantry. The gantry includes part boxes mounted therein, and blade elements are formed in regions of the part boxes. The cooling system of the CT system includes a cooling method that includes a multiple cooling method including a stand-by mode and an operating mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
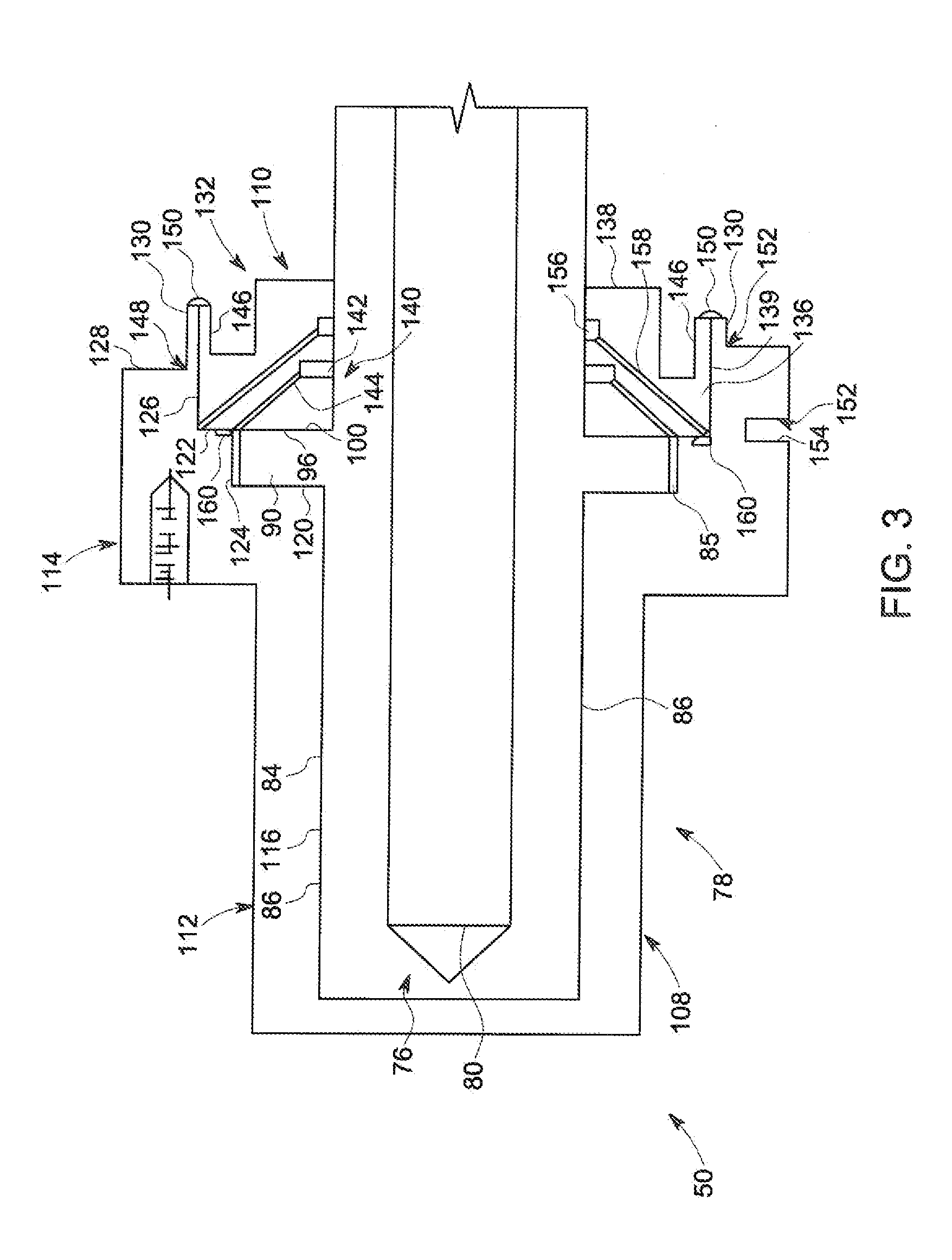
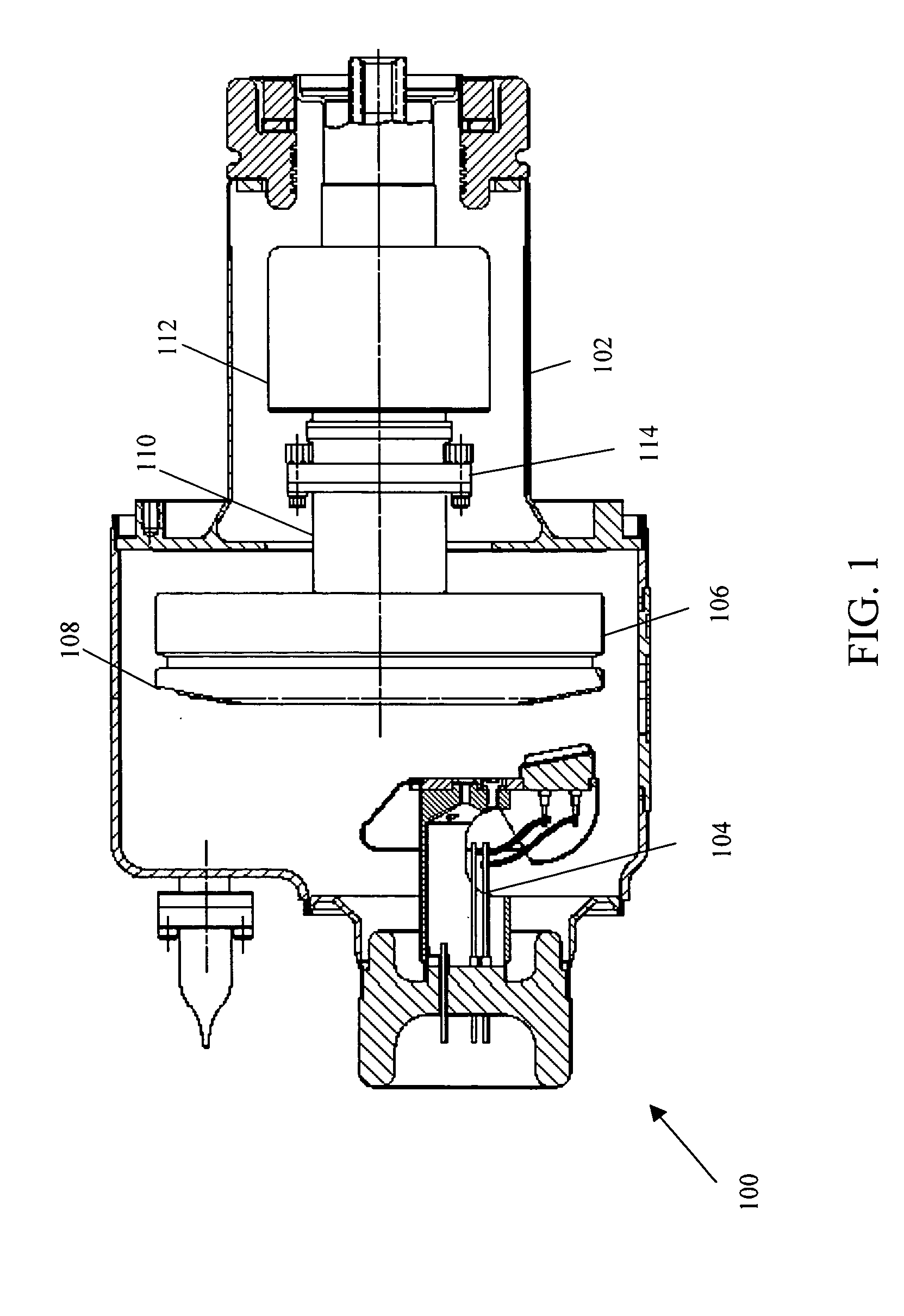
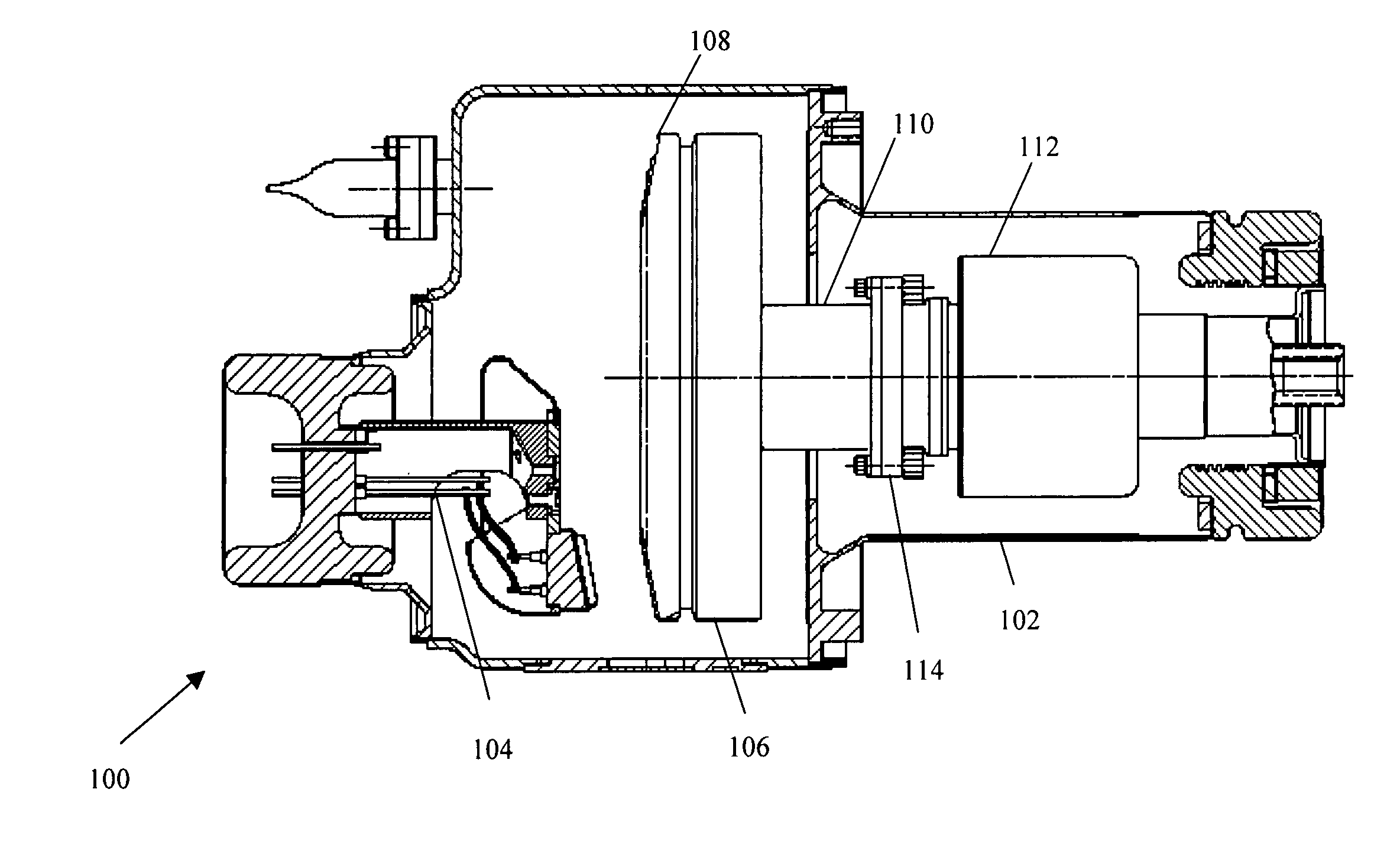
Liquid cooled bearing housing with greased lubricated rotating anode bearings for an x-ray tube
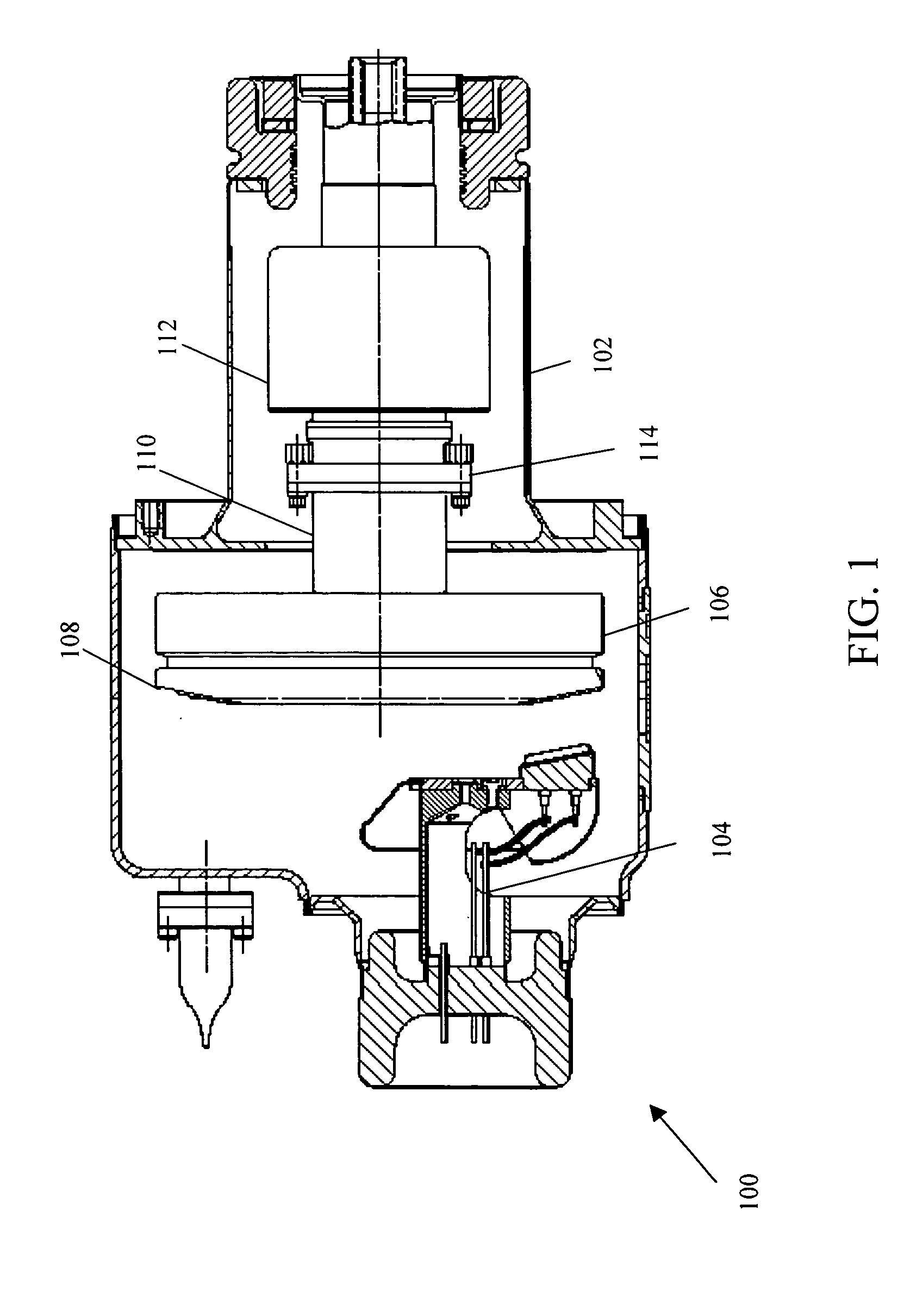
InactiveUS20060159228A1Improve heat transfer efficiencyLower operating temperatureX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingX-ray tube electrodesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A rotating anode bearing housing includes an x-ray tube frame (106) that has a vacuum chamber (108). An anode (110) resides within the vacuum chamber (108) and rotates on a shaft (114) via a bearing (117). The bearing (117) is attached to an interior surface (126) of the x-ray tube frame (106). The bearing (117) transfers thermal energy from the shaft (114) to the x-ray tube frame (106).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
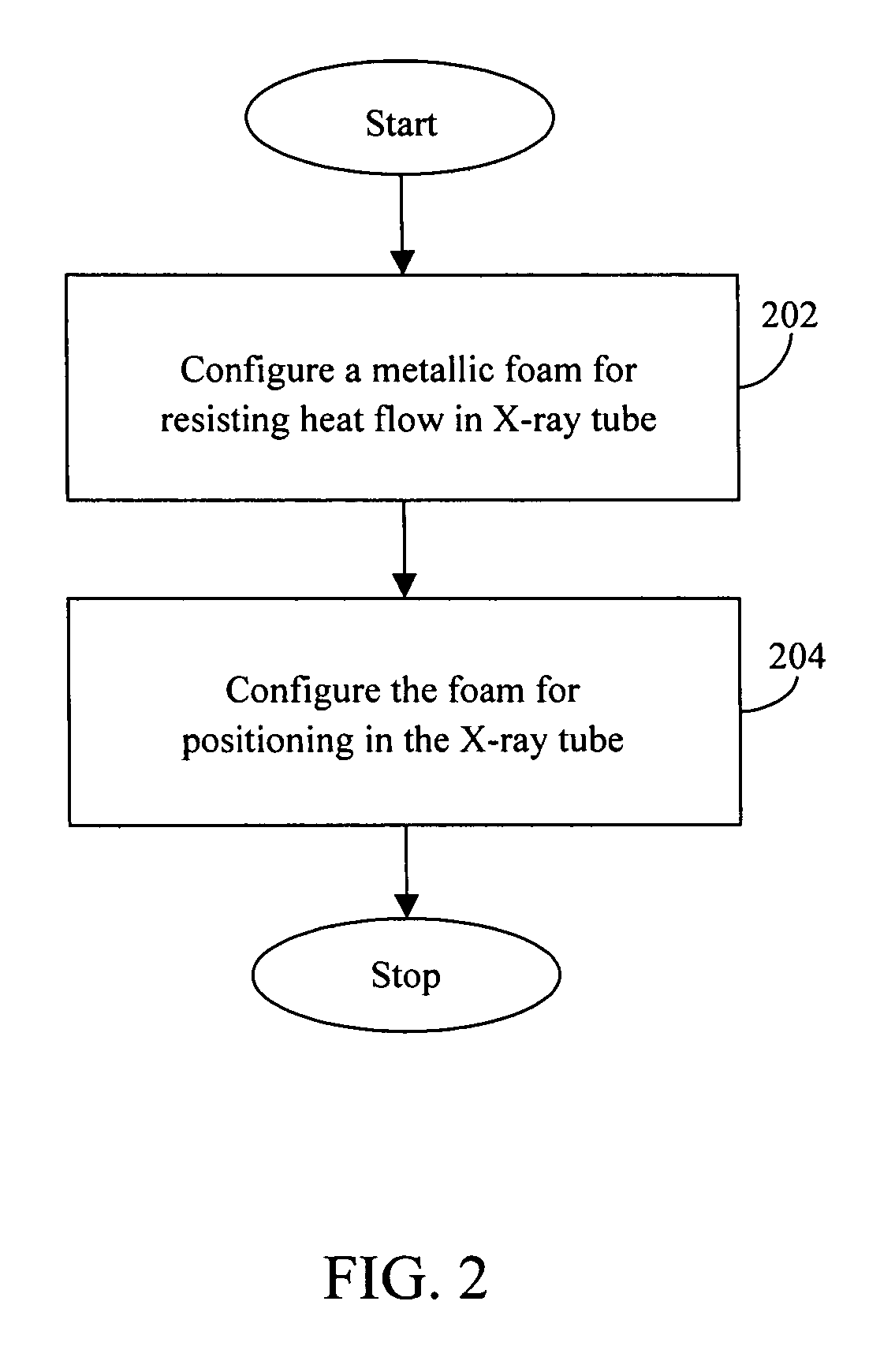
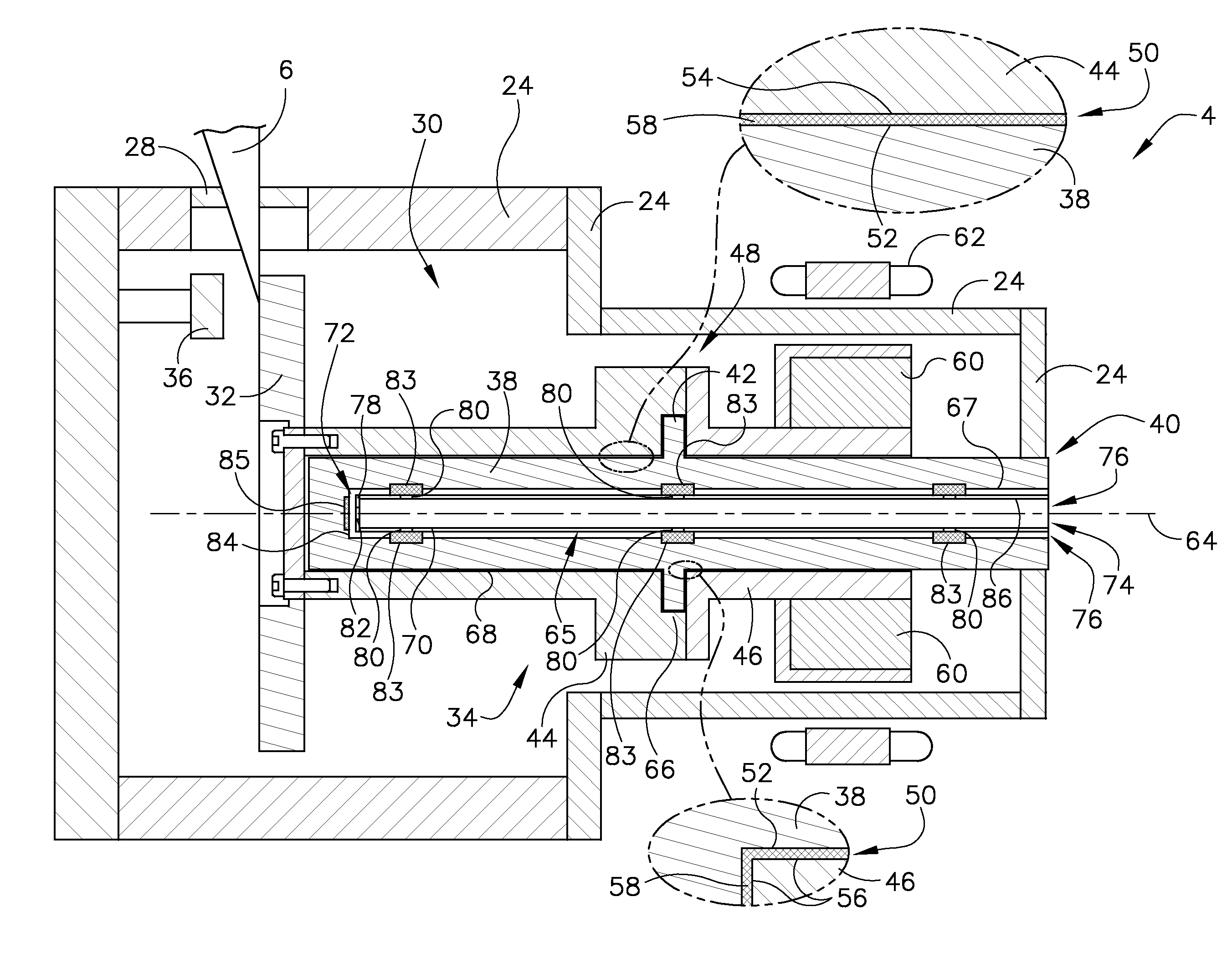
Method and system for thermal control in X-ray imaging tubes
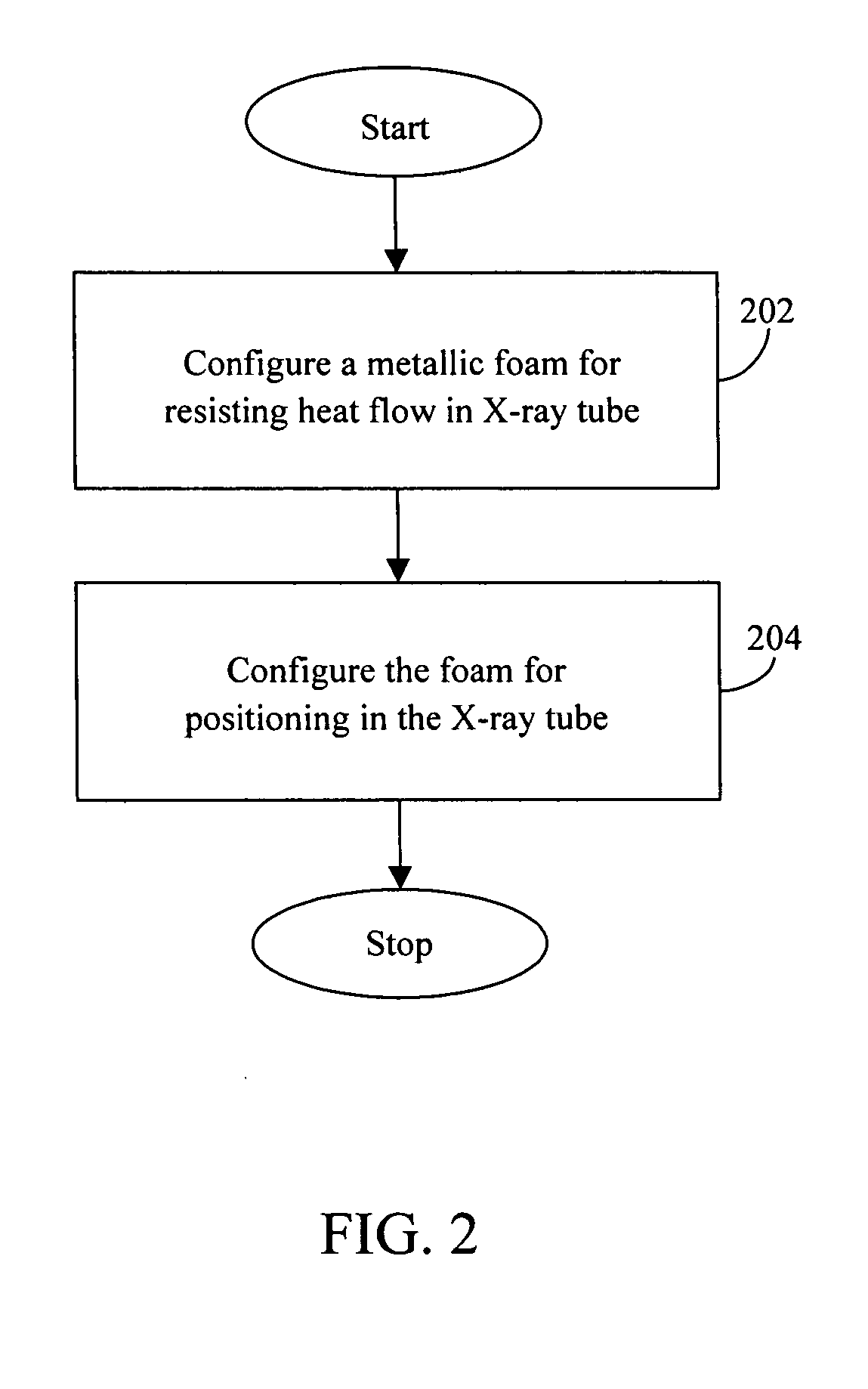
InactiveUS7561669B2X-ray tube bearing assembly coolingX-ray tube electrodesHeat flowThermal insulation
Methods and systems for providing thermal insulation in an X-ray tube are provided. The method includes configuring a metallic foam to resist the heat flow in an X-ray tube. The method further comprises configuring the metallic foam for positioning in the X-ray tube to resist heat flow to bearings in the X-ray tube.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
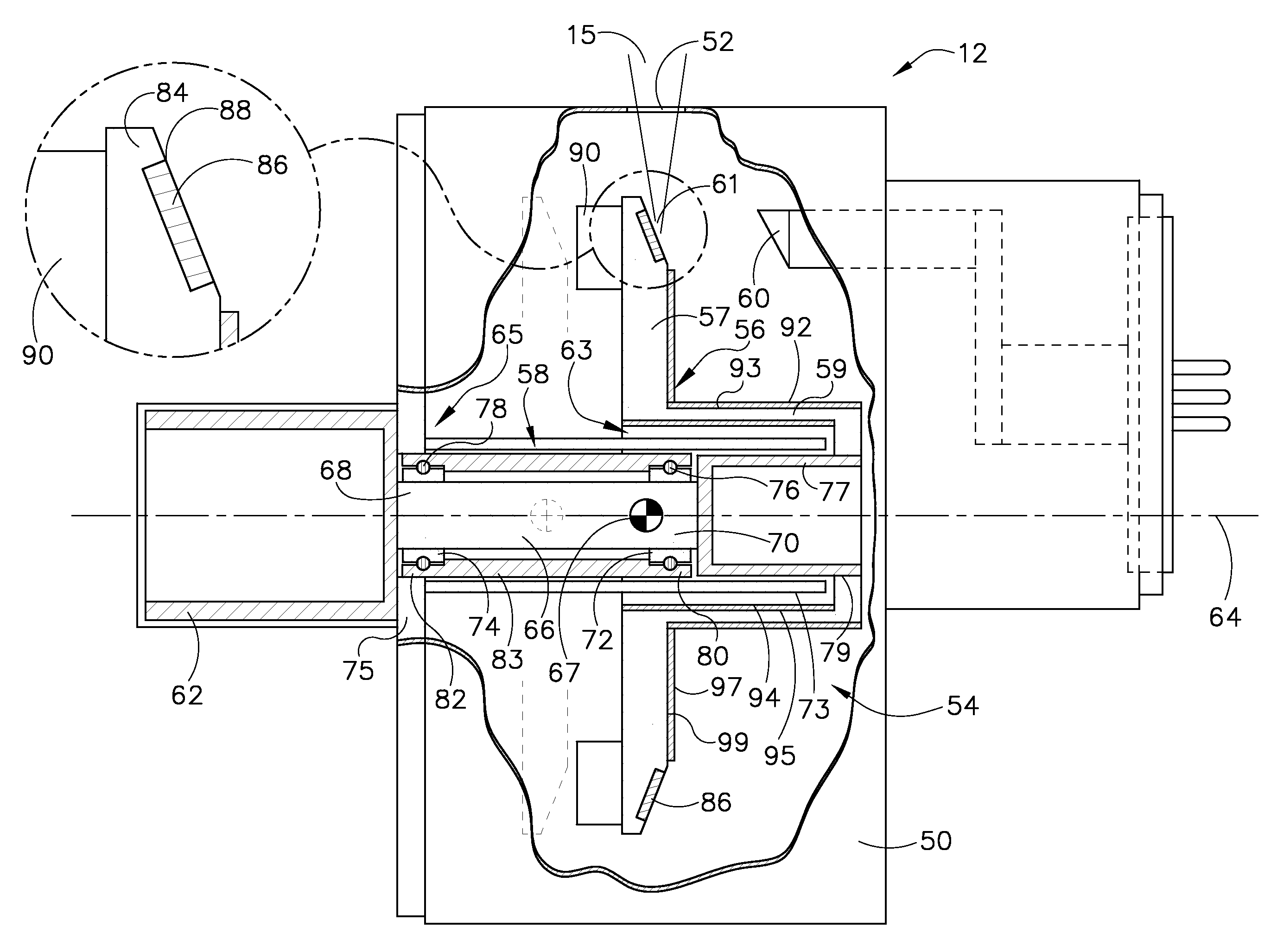
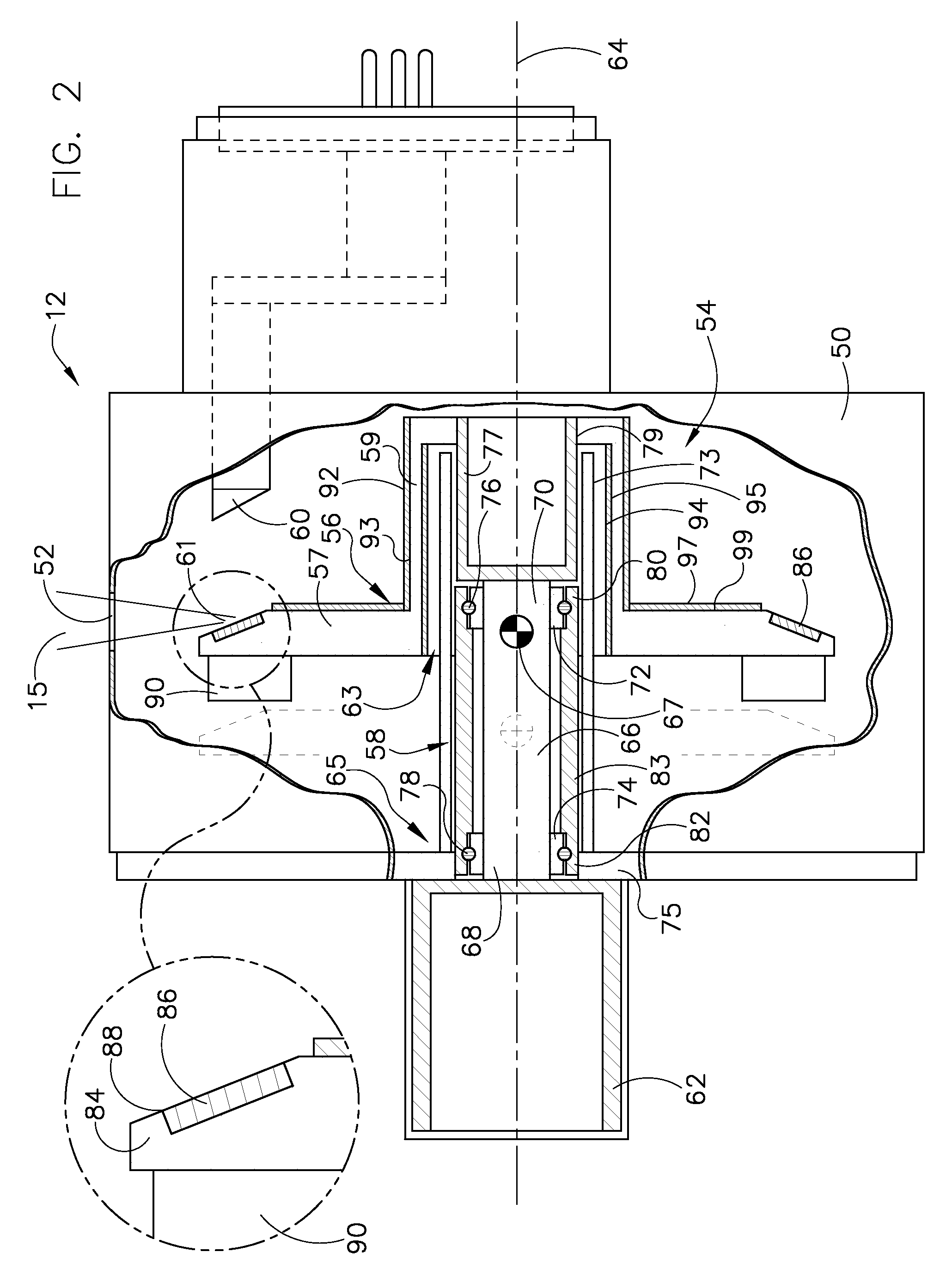
Method and apparatus for increasing heat radiation from an x-ray tube target shaft
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray tube with bonded target and bearing sleeve
The embodiments disclosed herein relate to the thermal regulation of components within an X-ray tube by transferring heat between the anode and the rotary mechanism to which the anode is attached. For example, in one embodiment, an X-ray tube is provided. The X-ray tube generally includes a fixed shaft, a rotating bearing sleeve disposed about the fixed shaft and configured to rotate with respect to the fixed shaft via a rotary bearing, and an electron beam target disposed about the bearing sleeve and configured to rotate with the bearing sleeve. The electron beam target is permanently bonded to the bearing sleeve.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
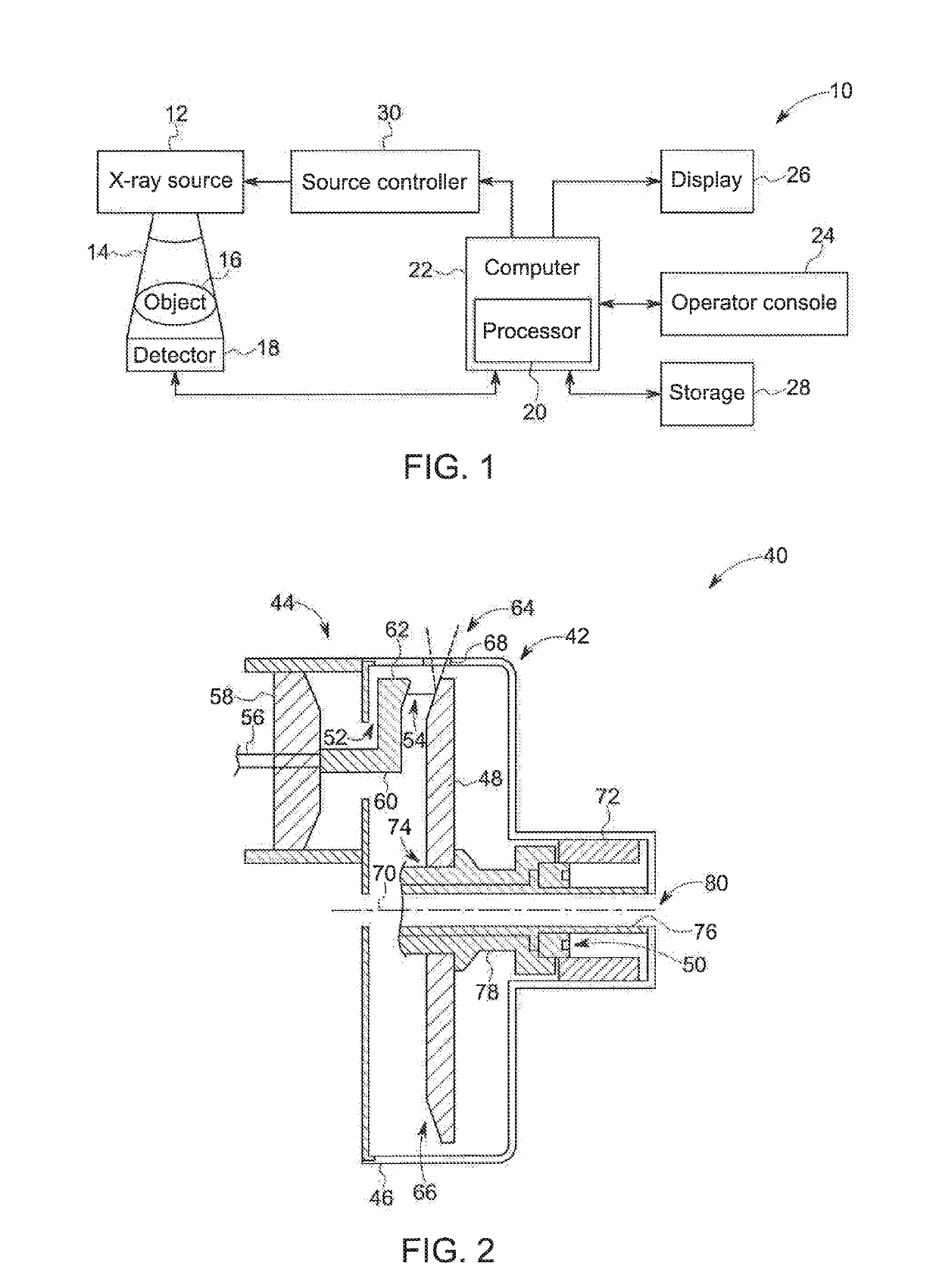
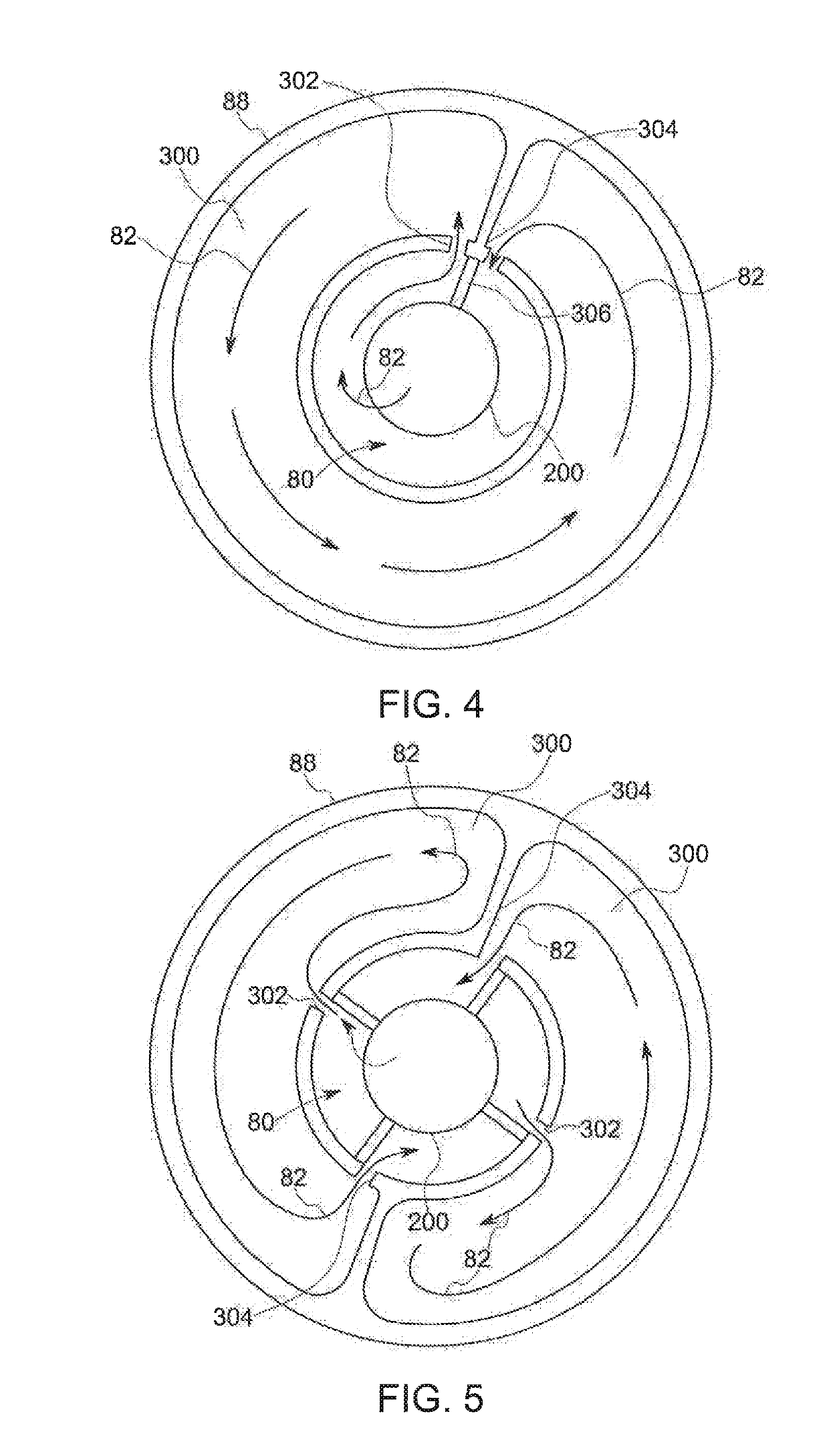
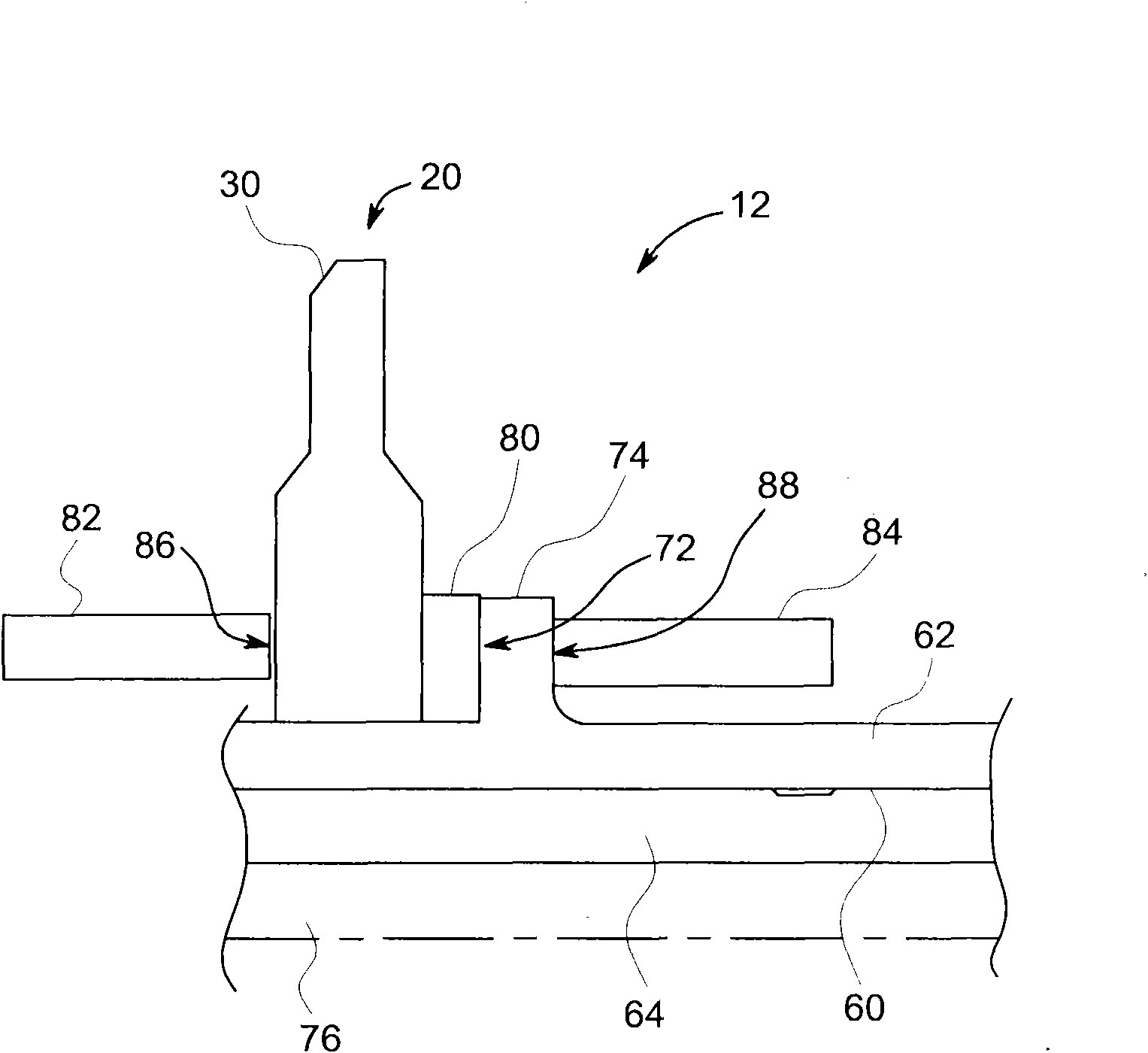
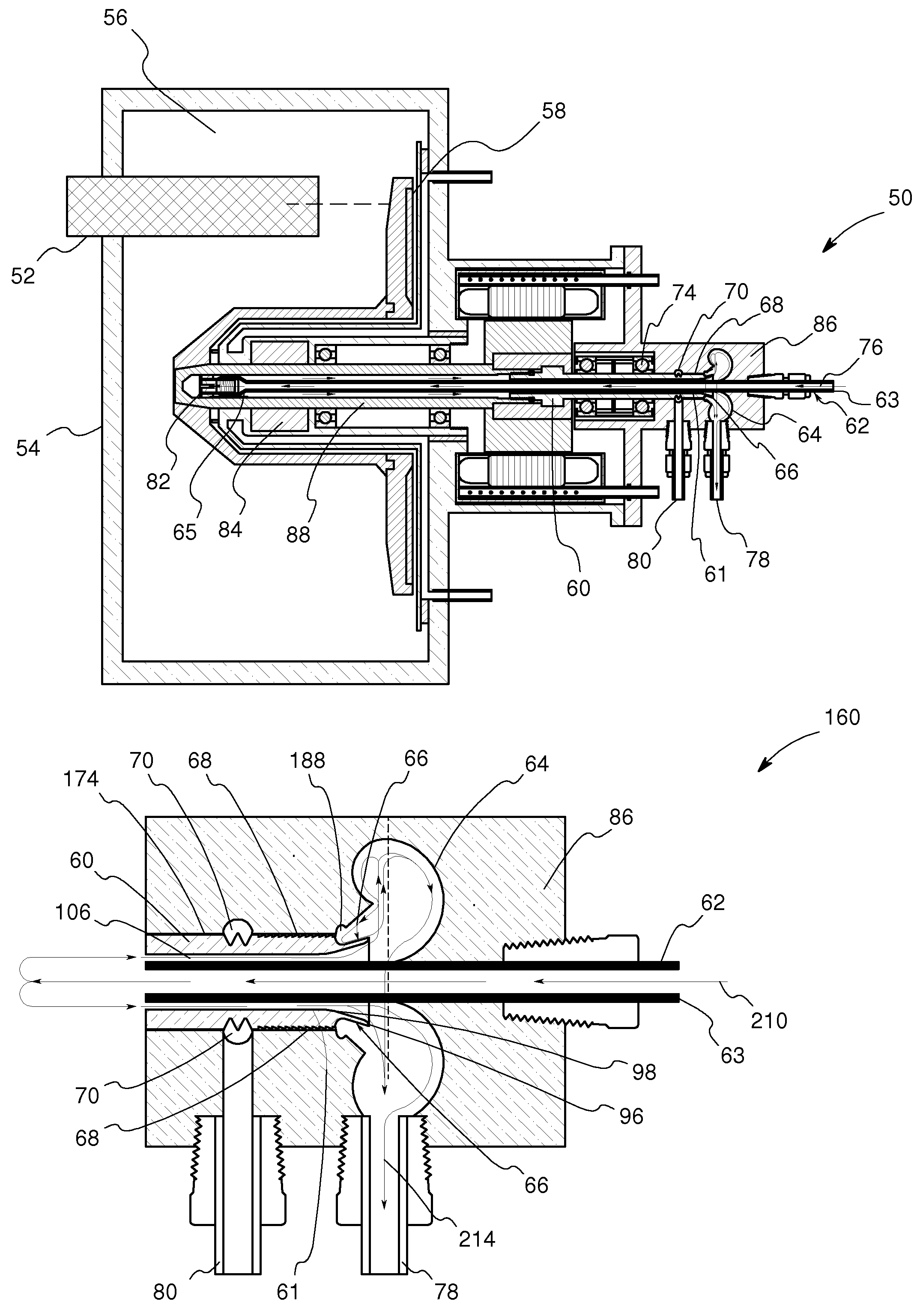
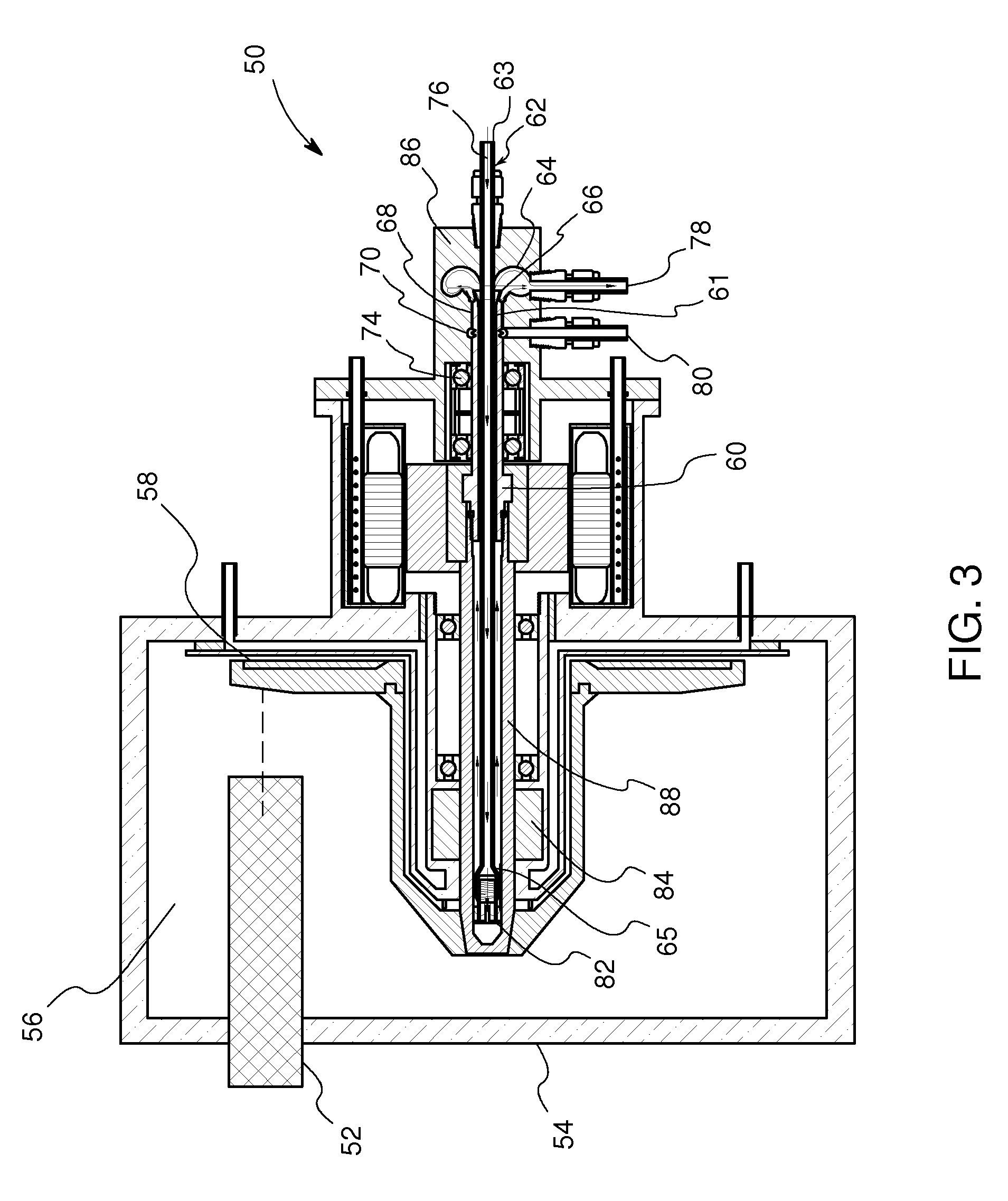
Rotating union for a liquid cooled rotating X-ray target
A rotating union for an X-ray target is provided. The rotating union for the X-ray target comprises a housing, a coolant-slinging device comprising a rotating shaft having an inner diameter and an outer diameter, a proximal end and a distal end, and a bore therein, one or more slingers coupled to a proximal end of the rotating shaft; a drain annulus coupled to the one or more slingers, wherein the one or more slingers are configured to direct a coolant to the drain annulus and the drain annulus is configured to direct the coolant through a primary coolant outlet; and a stationary tube having a first end and a second end, wherein at least a portion of the stationary tube is disposed within the bore of the rotating shaft.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Axial flux motor driven anode target for X-ray tube
An X-ray tube comprises a cathode, an anode target assembly and an axial flux motor having a rotor and a stator. The stator is positioned along a transverse axis parallel to the rotor axis. The rotor and the stator are configured to be coupled to the anode target assembly. A cathode generates an electron beam for impingement upon the anode target assembly and a vacuum housing surrounds the anode target assembly, the cathode and the rotor to enable the electron beam impingement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for increasing heat radiation from an x-ray tube target shaft
A target for generating x-rays includes a target substrate, a target shaft attached to the target substrate, and a radiation emissive coating applied to at least one of the target substrate and the target shaft, wherein a center-of-gravity of the target is positioned between a front bearing assembly and a rear bearing assembly of an x-ray tube.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for thermal control in X-ray imaging tubes
Methods and systems for providing thermal insulation in an X-ray tube are provided. The method includes configuring a metallic foam to resist the heat flow in an X-ray tube. The method further comprises configuring the metallic foam for positioning in the X-ray tube to resist heat flow to bearings in the X-ray tube.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray apparatus
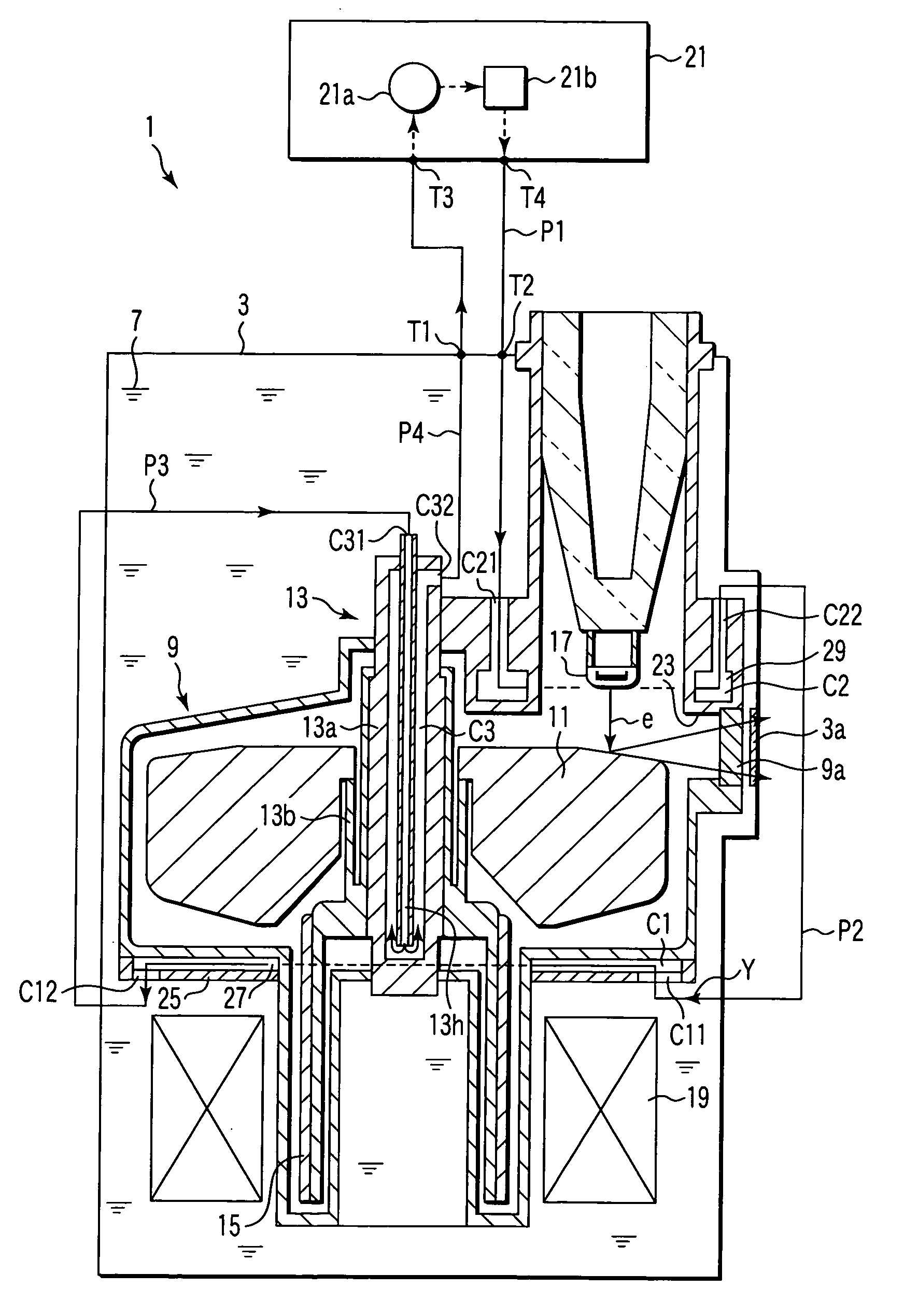
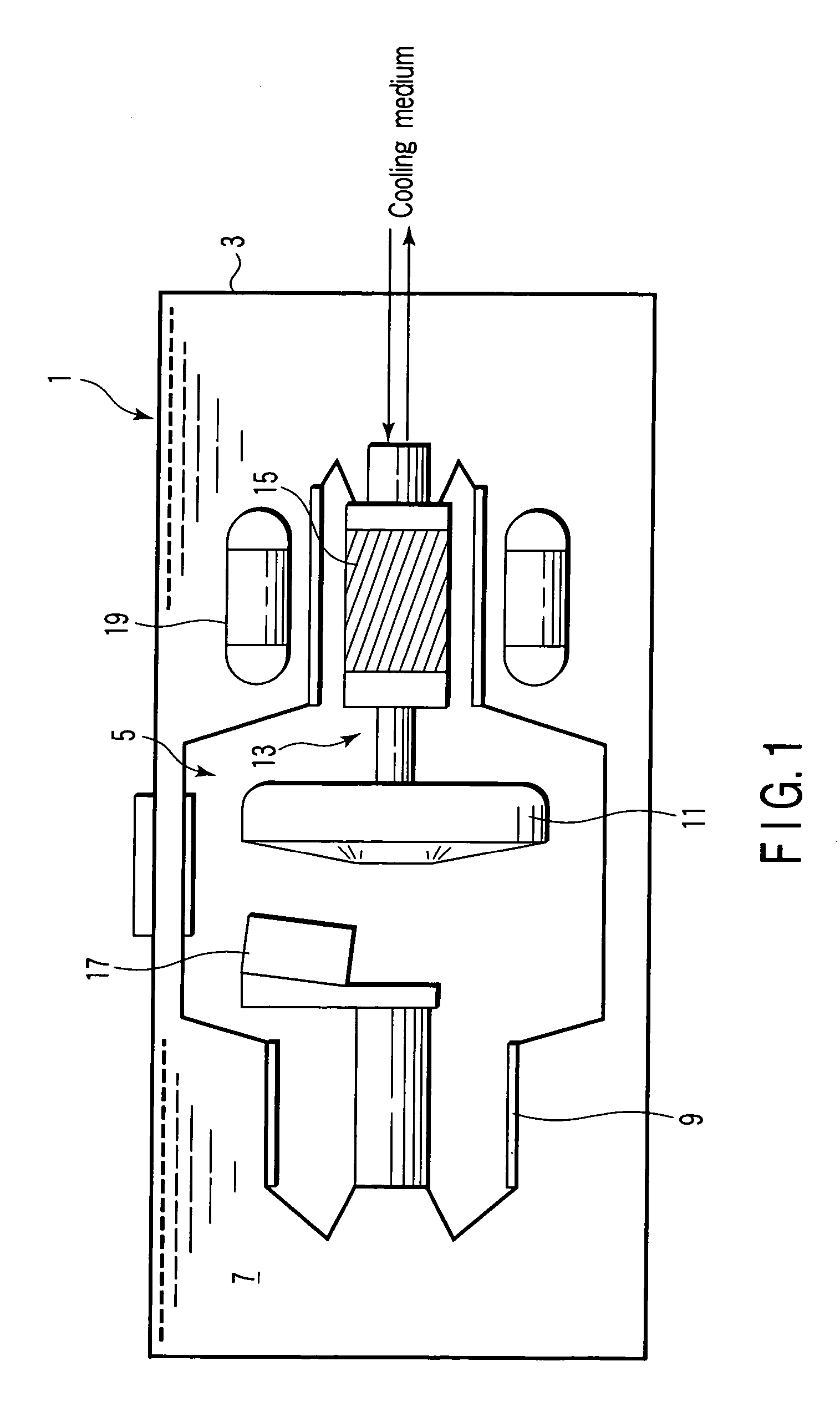
ActiveUS7197118B2Increase heatStable outputX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingX-ray tube electrodesX-rayLiquid metal
The present invention is characterized by supporting a stator to generate a magnetic field and an anode target by a dynamic pressure plain bearing using a liquid metal, and cooling at least the inside of the dynamic pressure plain bearing and an enclosure containing an anode target by circulating one kind of cooling medium, in a rotary X-ray tube apparatus which obtains X-rays by impinging an electron on an anode by rotating an anode target.
Owner:CANON ELECTRON TUBES & DEVICES CO LTD
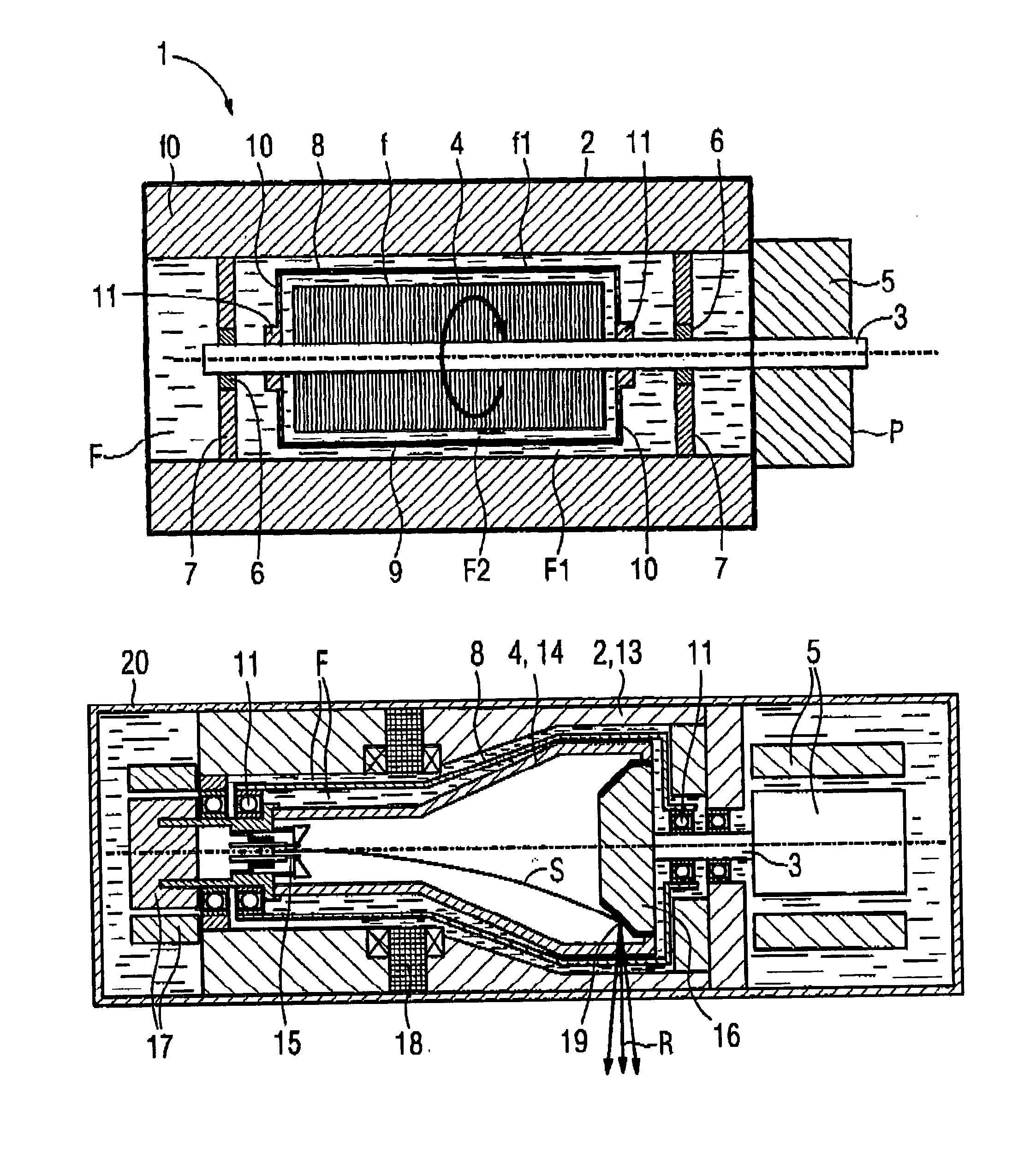
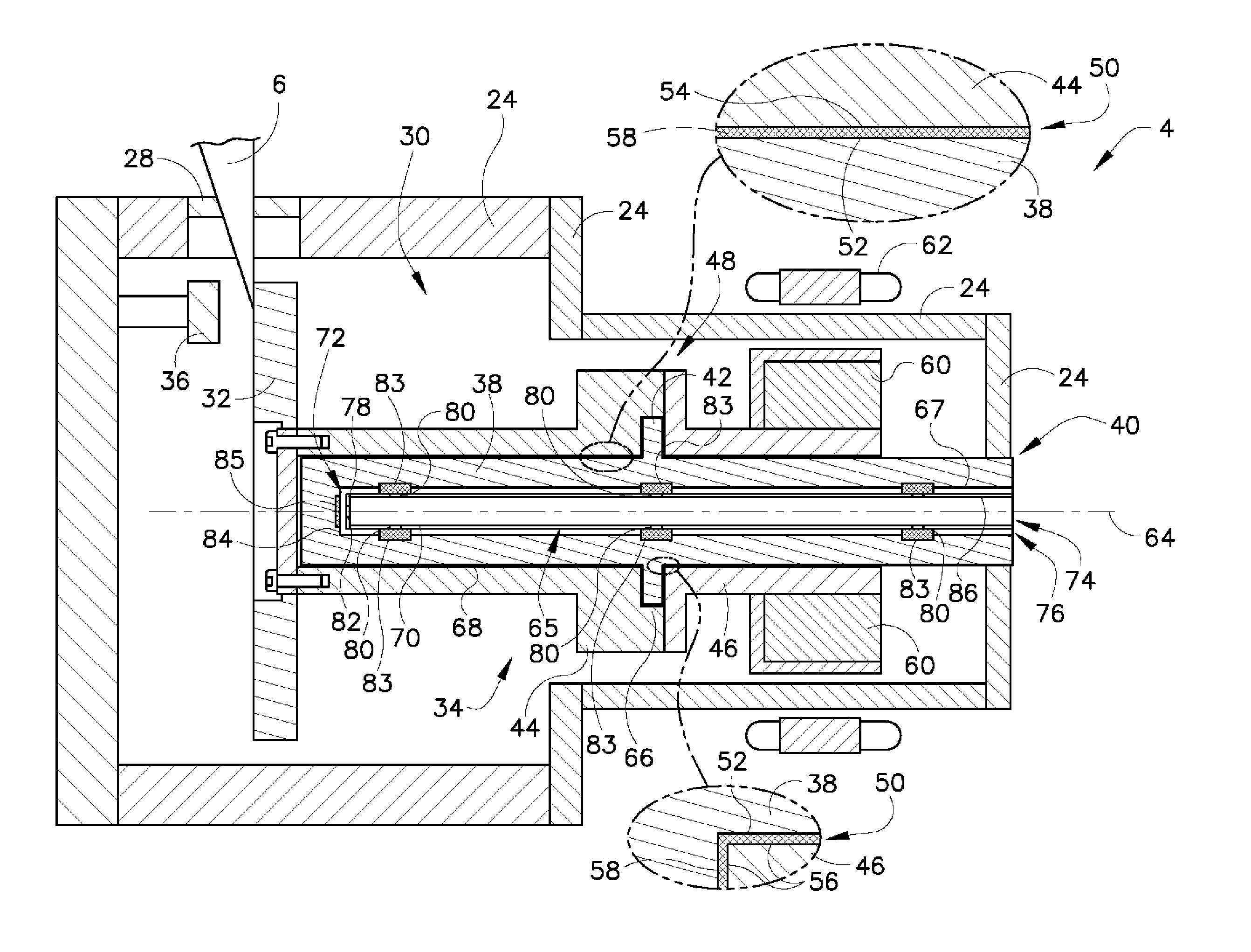
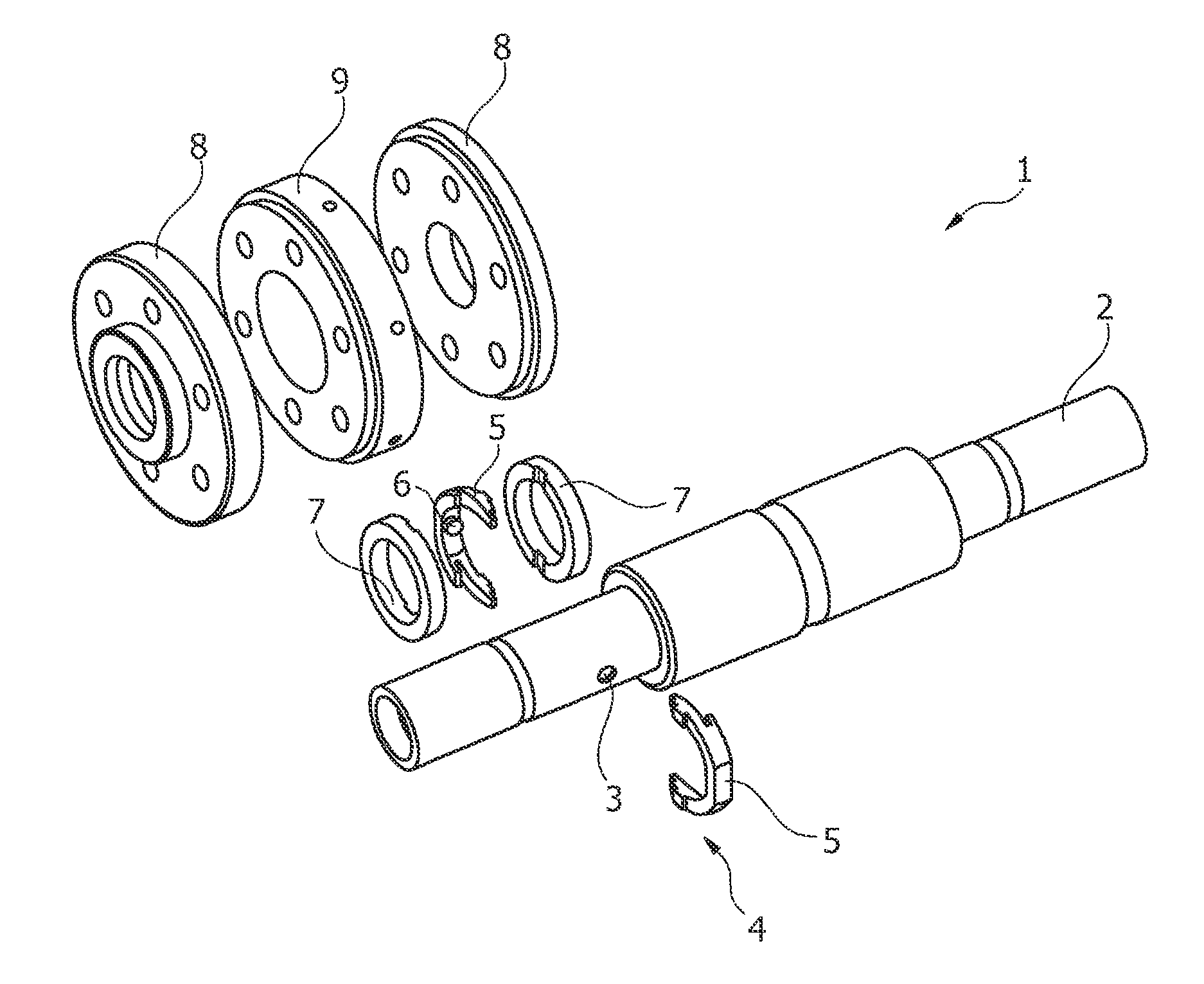
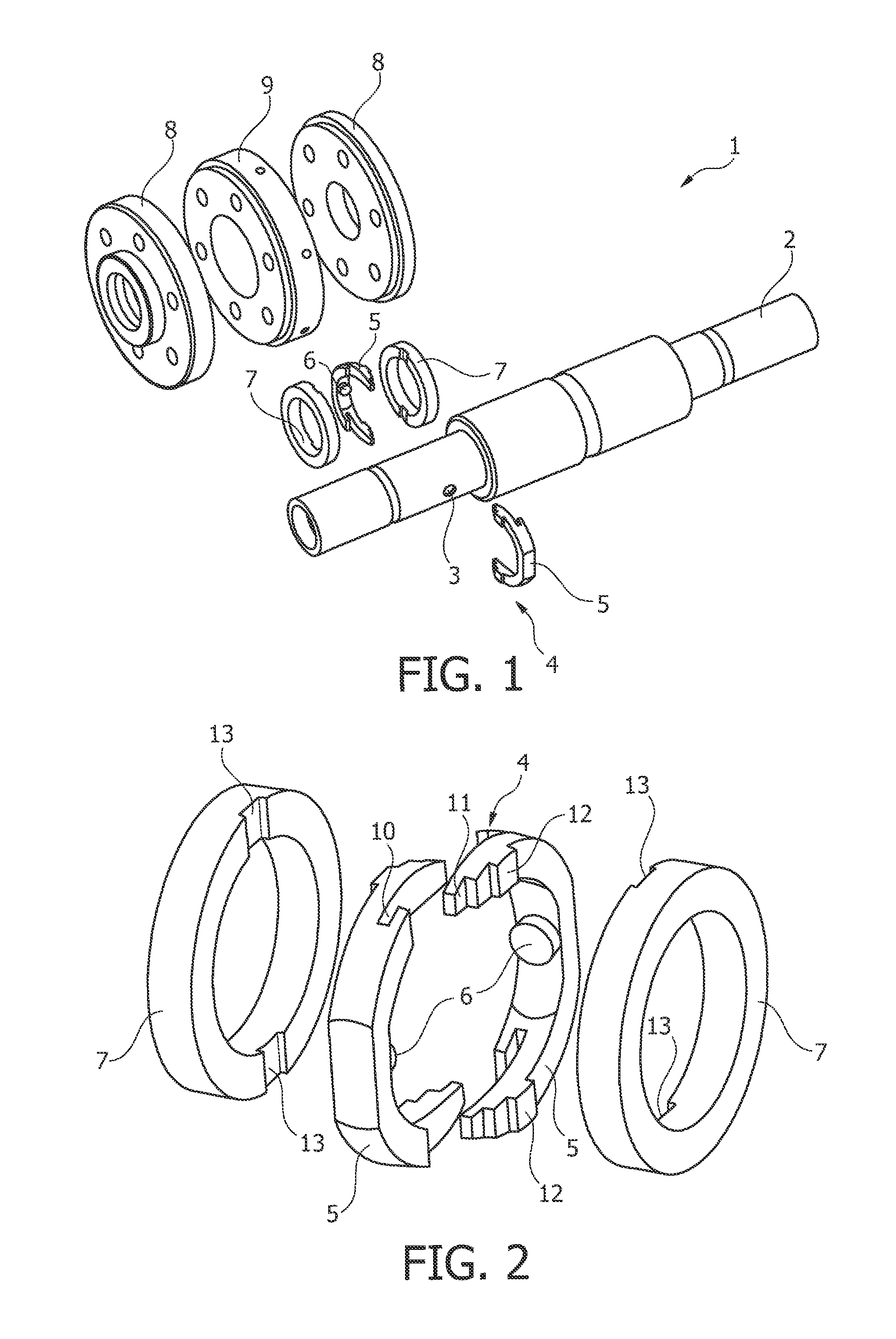
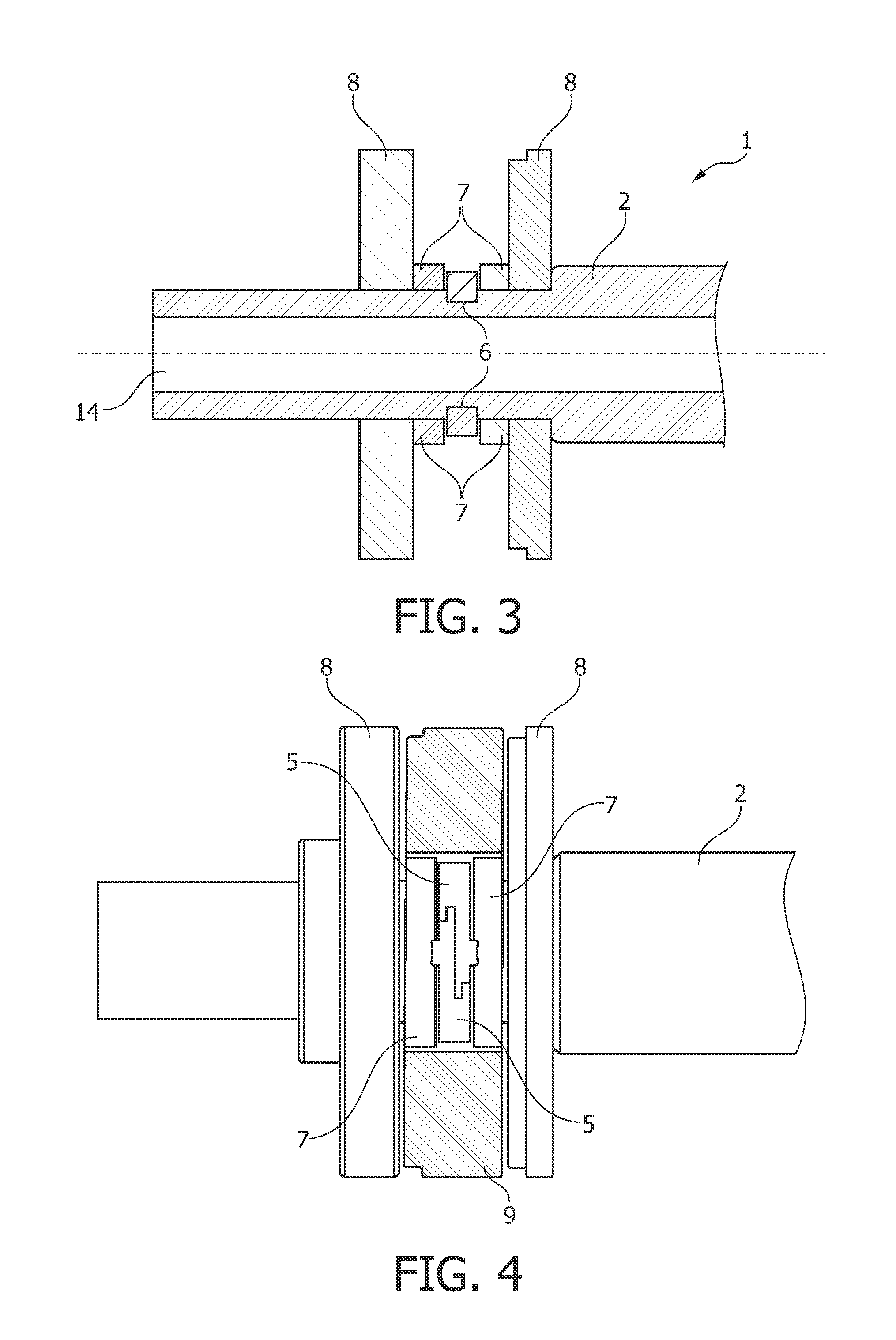
Bearing system for a rotary anode of an X-ray tube
ActiveUS8964941B2Maintain stabilityEasy to disassembleX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingMechanical engineeringX-ray tube
The present invention relates to a bearing system (1) for a rotary anode (24) of an X-ray tube (23). The bearing system comprises a shaft (2) for supporting the rotary anode (24), the shaft being surrounded by two swash rings (7). Further, a gimbal ring (4) surrounding the shaft (2) and being arranged in between the two swash rings (7) is provided. This gimbal ring (4) is hingeably connected with the shaft (2) such that the gimbal ring (4) is tiltable relative to a longitudinal axis of the shaft (2). Further, the invention relates to an X-ray tube (19) and an imaging system (15) having such a bearing system (1).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
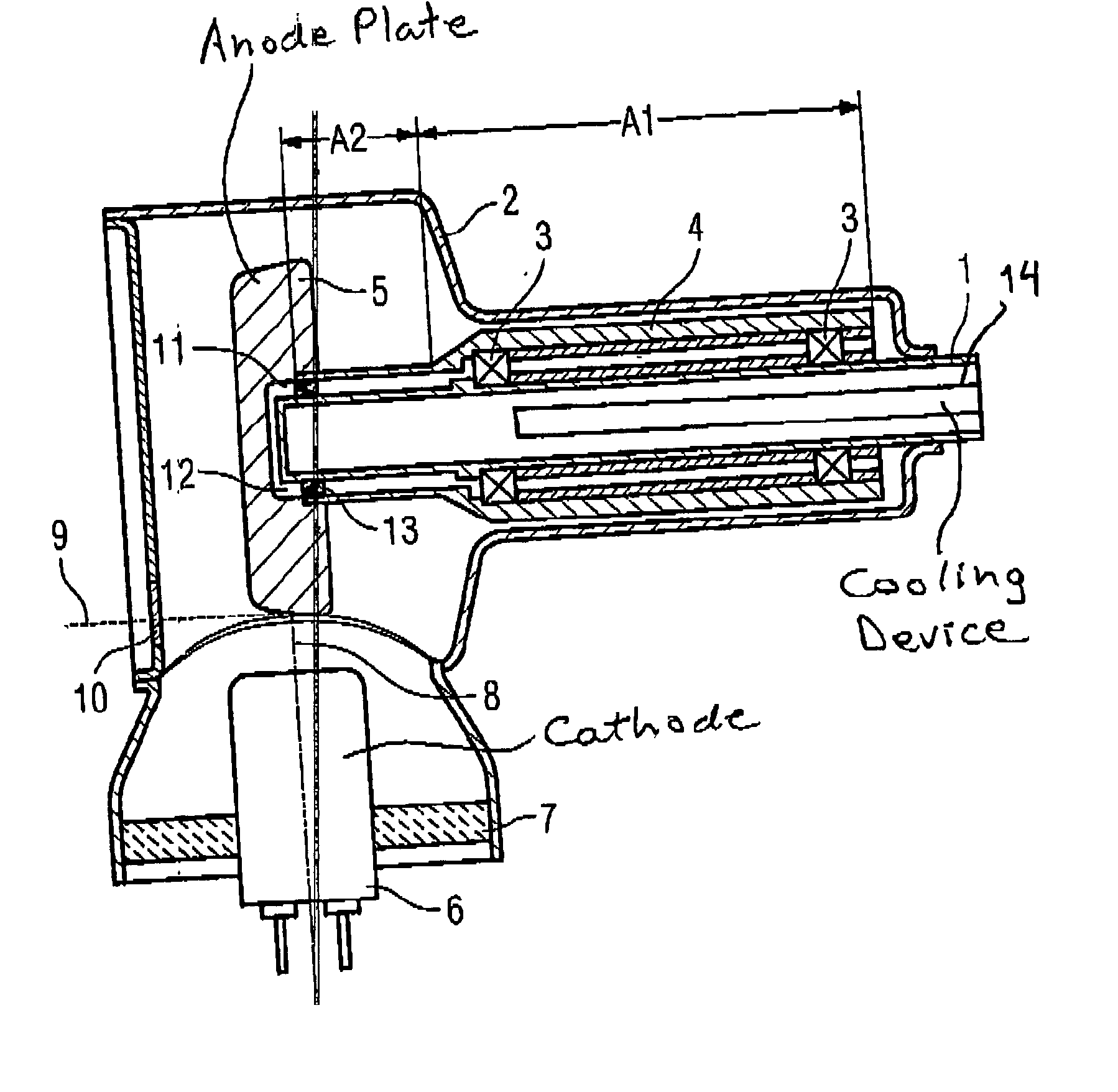
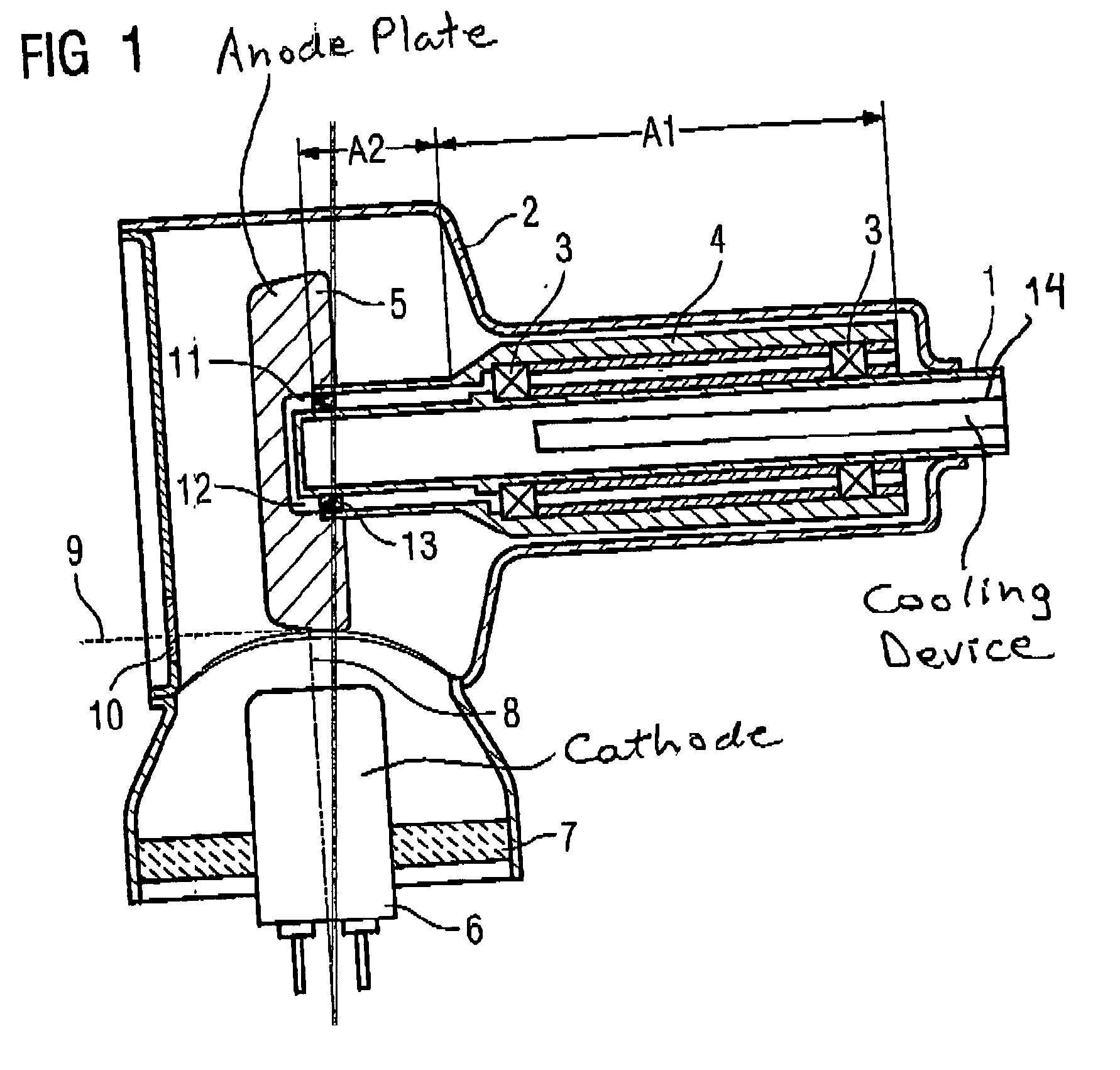
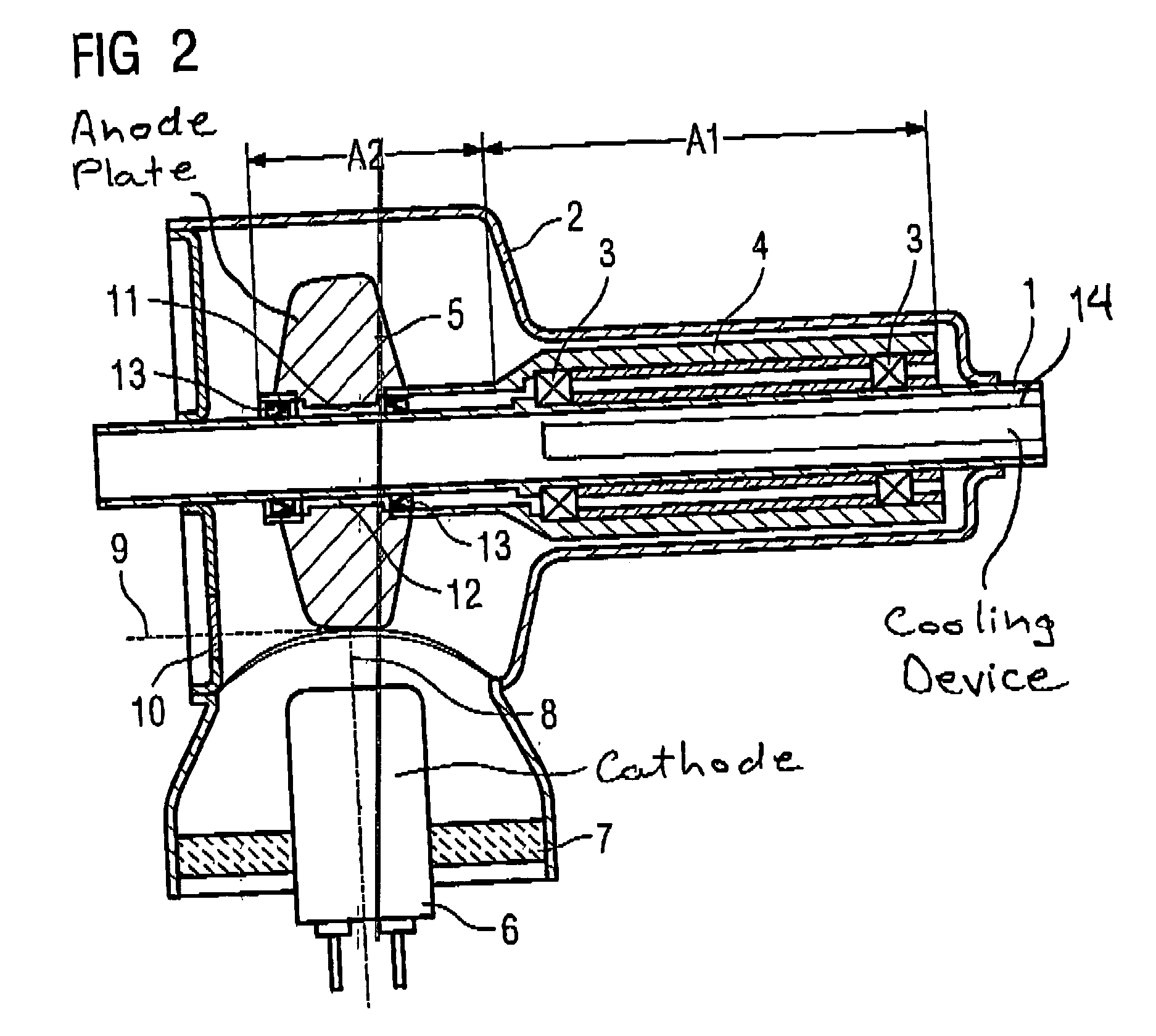
X-ray tube with rotary anode
InactiveUS20050157845A1Improve performanceSuper cost-effectiveX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesMaterials scienceX-ray tube
An x-ray tube has an anode plate connected to an anode tube that is mounted such that it can rotate around a rigid anode shaft. To improve the heat dissipation from the anode plate, a liquid for dissipation of heat to the anode shaft is accommodated in an intervening space formed between the anode shaft and the anode plate.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
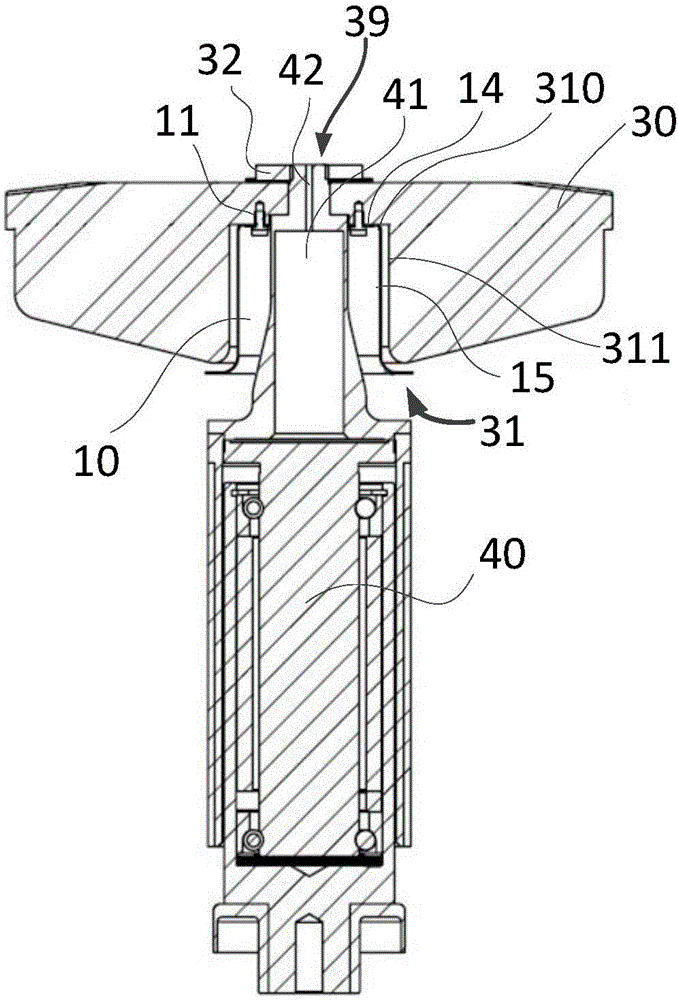
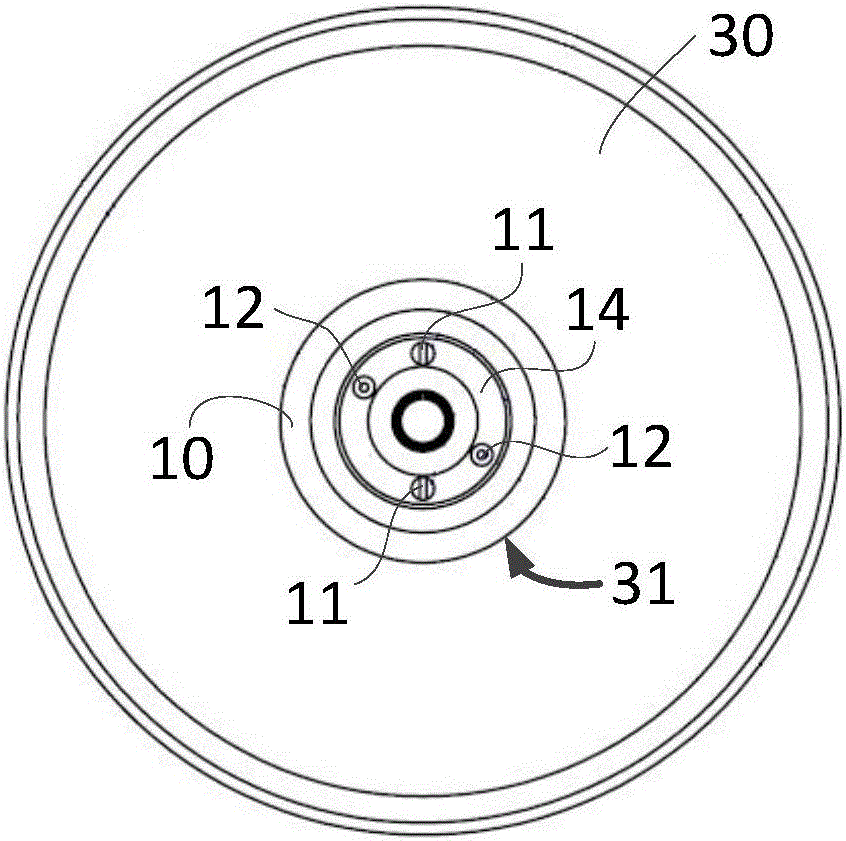
X-ray bulb tube
ActiveCN106356270AReduce temperature conductionHigh strengthX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingX-ray tube electrodesTarget surfaceX-ray
The invention relates to an X-ray bulb tube. The X-ray bulb tube comprises a target disc and a rotating part used or driving the target disc to rotate, wherein the target disc comprises a target surface which can produce X rays under impact of electrons, and a locating slot is also limited at central axis of the target disc at a side opposite to the target surface, so that an annular gap is defined between the locating slot and the circumferential side wall of the rotating part when the rotating part is fixedly arranged on the target disc, a heat-resistant plate is also arranged between the rotating part and the target disc, and the heat-resistant plate is fixedly arranged on the target disc in the annular gap. According to the invention, the heat-resistant plate of the X-ray bulb tube is fixedly arranged on the target disc and is not in surface contact with the rotating part, so that strength of the rotating part can be strengthened, and conduction of temperature of a reflecting piece onto a fixed shaft is also effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
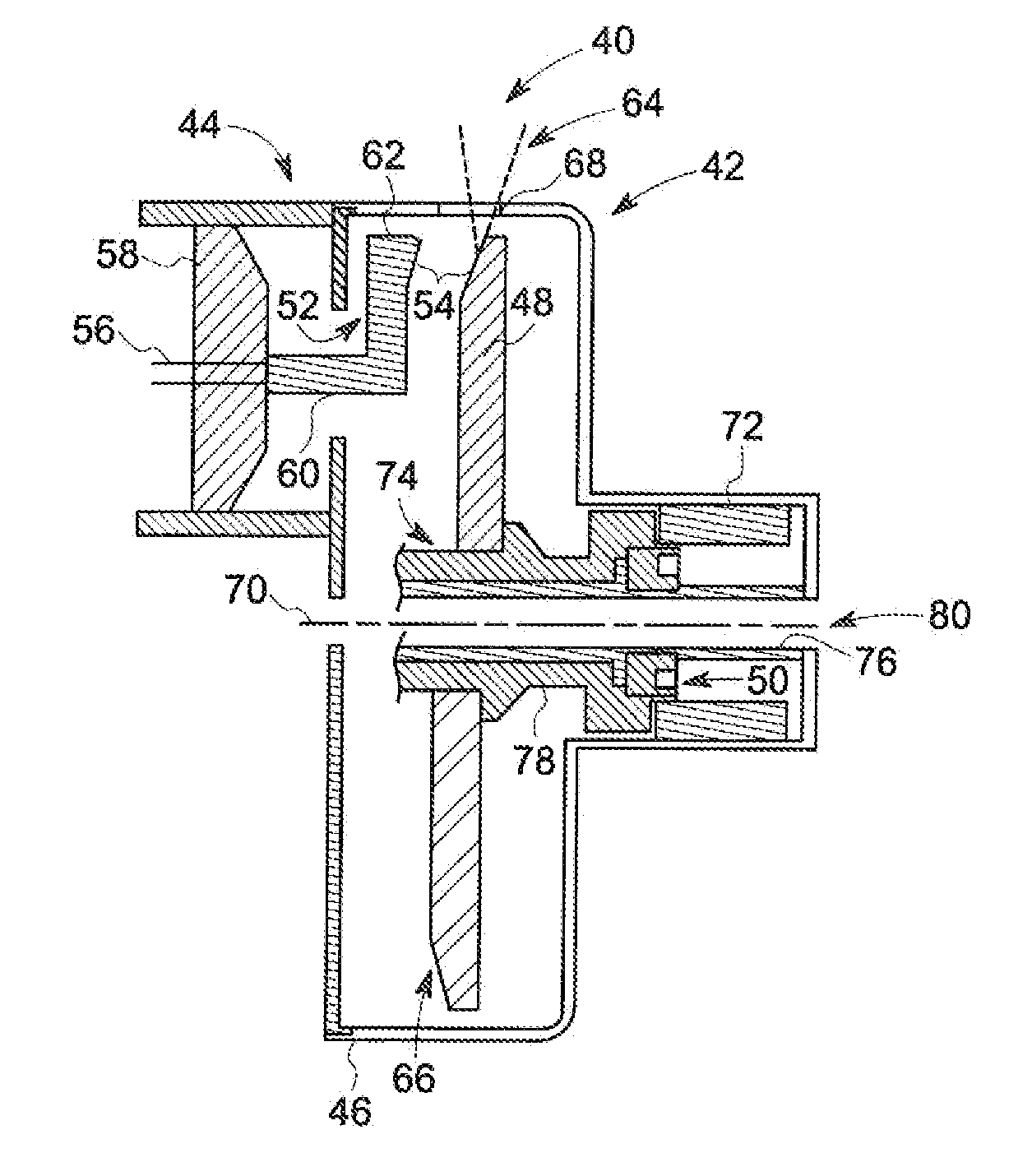
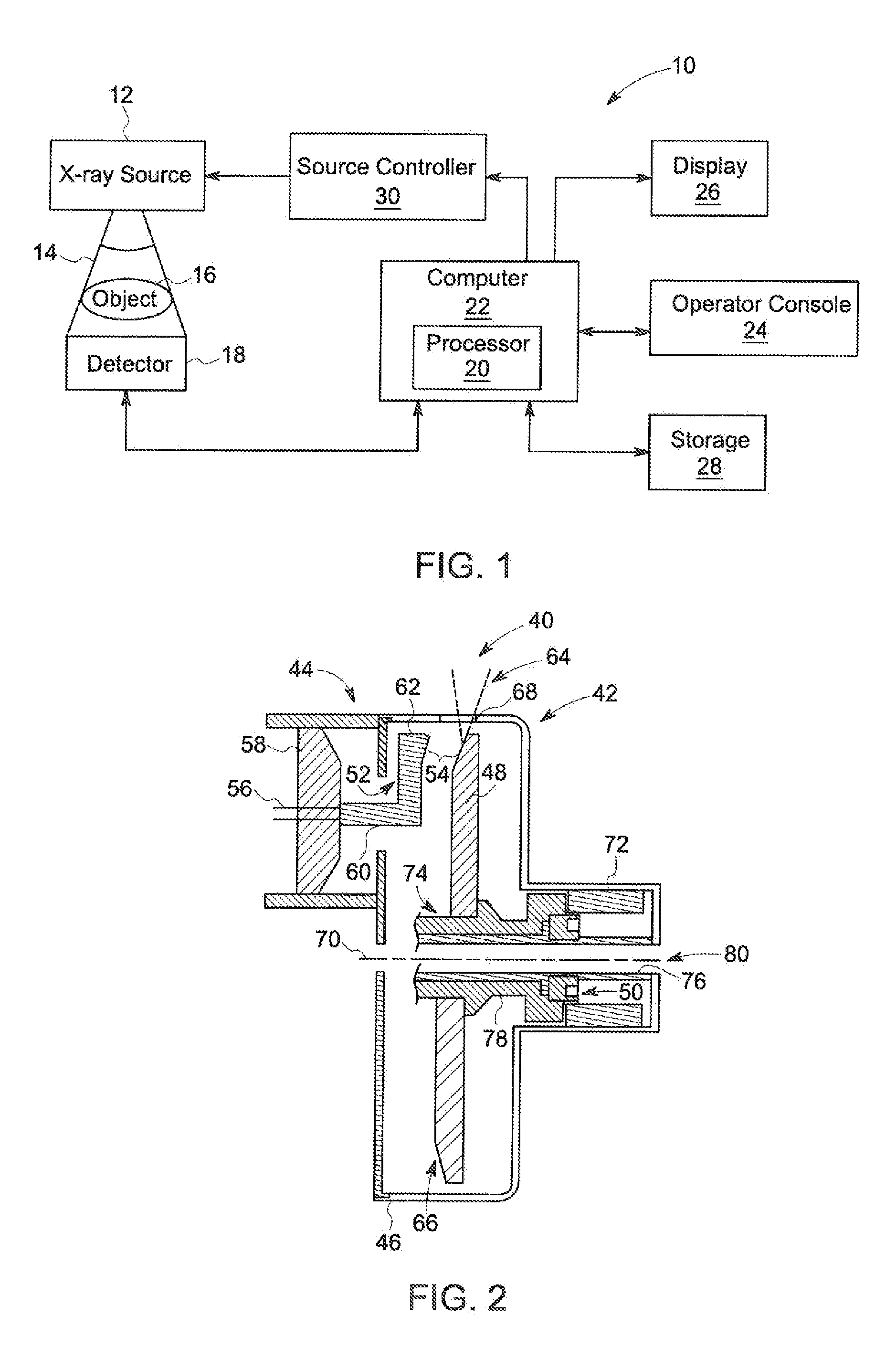
Apparatus and method of cooling a liquid metal bearing in an x-ray tube
An x-ray tube includes a center shaft having an inner surface and an outer surface, the inner surface forming a portion of a cavity therein, a mount having an inner surface, the mount having an x-ray target attached thereto, and a liquid metal positioned between the outer surface of the center shaft and the inner surface of the mount. The x-ray tube further includes a flow diverter positioned in the cavity, the flow diverter having a wall with an inner surface, and a plurality of jets passing through the wall, wherein the plurality of jets are configured such that when a fluid is flowed into the flow diverter and passes along its inner surface, a portion of the fluid passes through the plurality of jets and is directed toward the inner surface of the center shaft.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
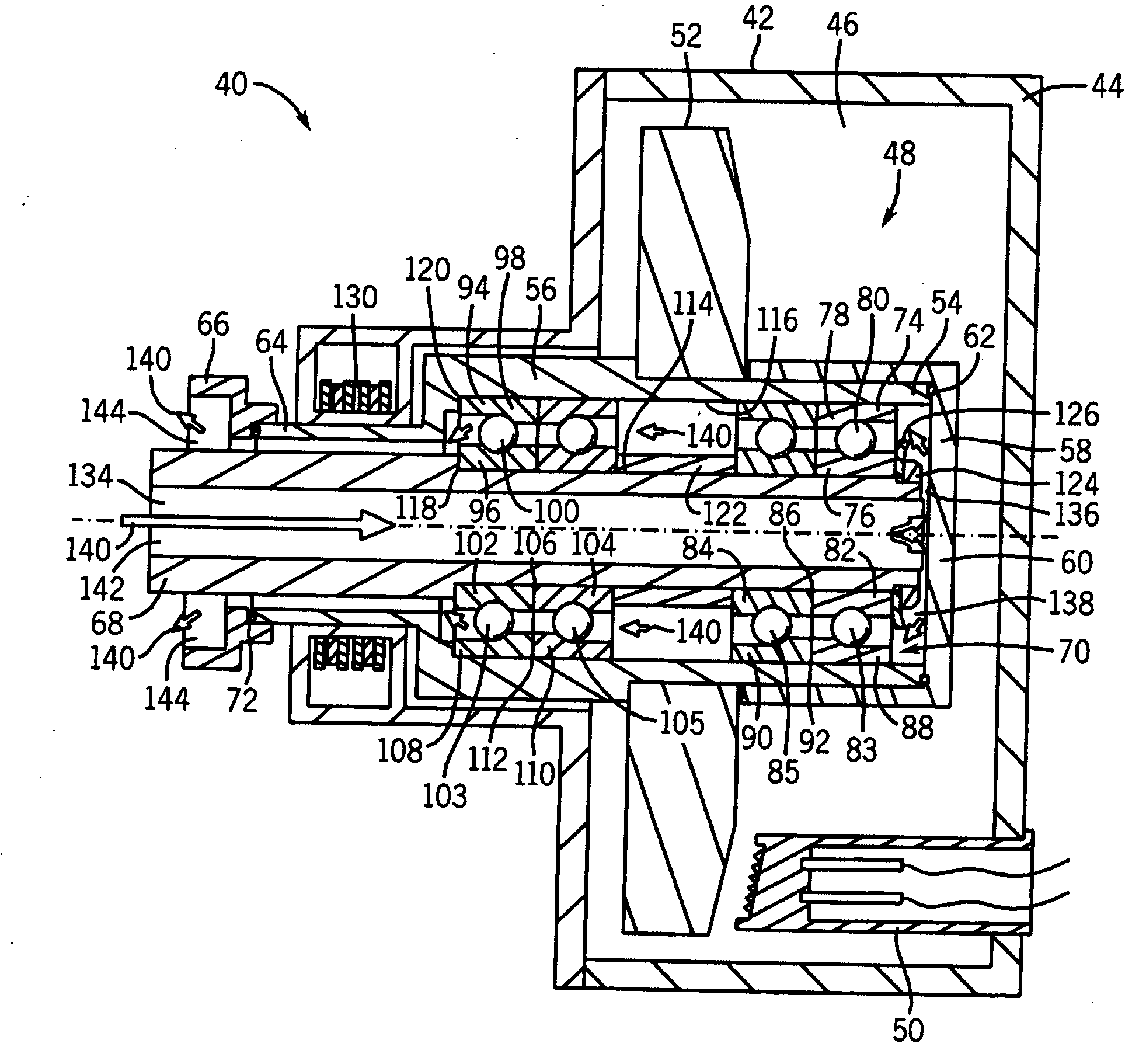
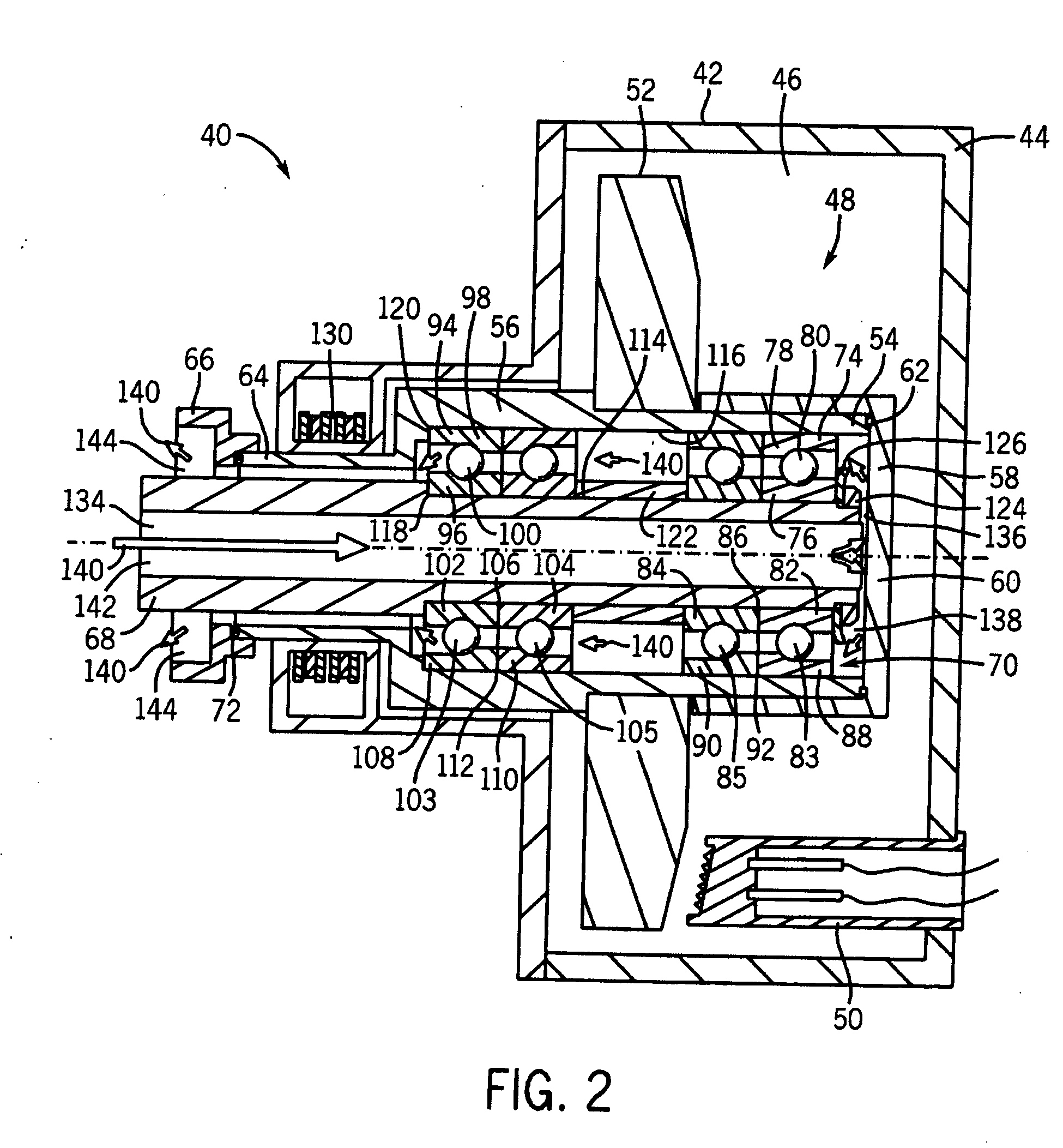
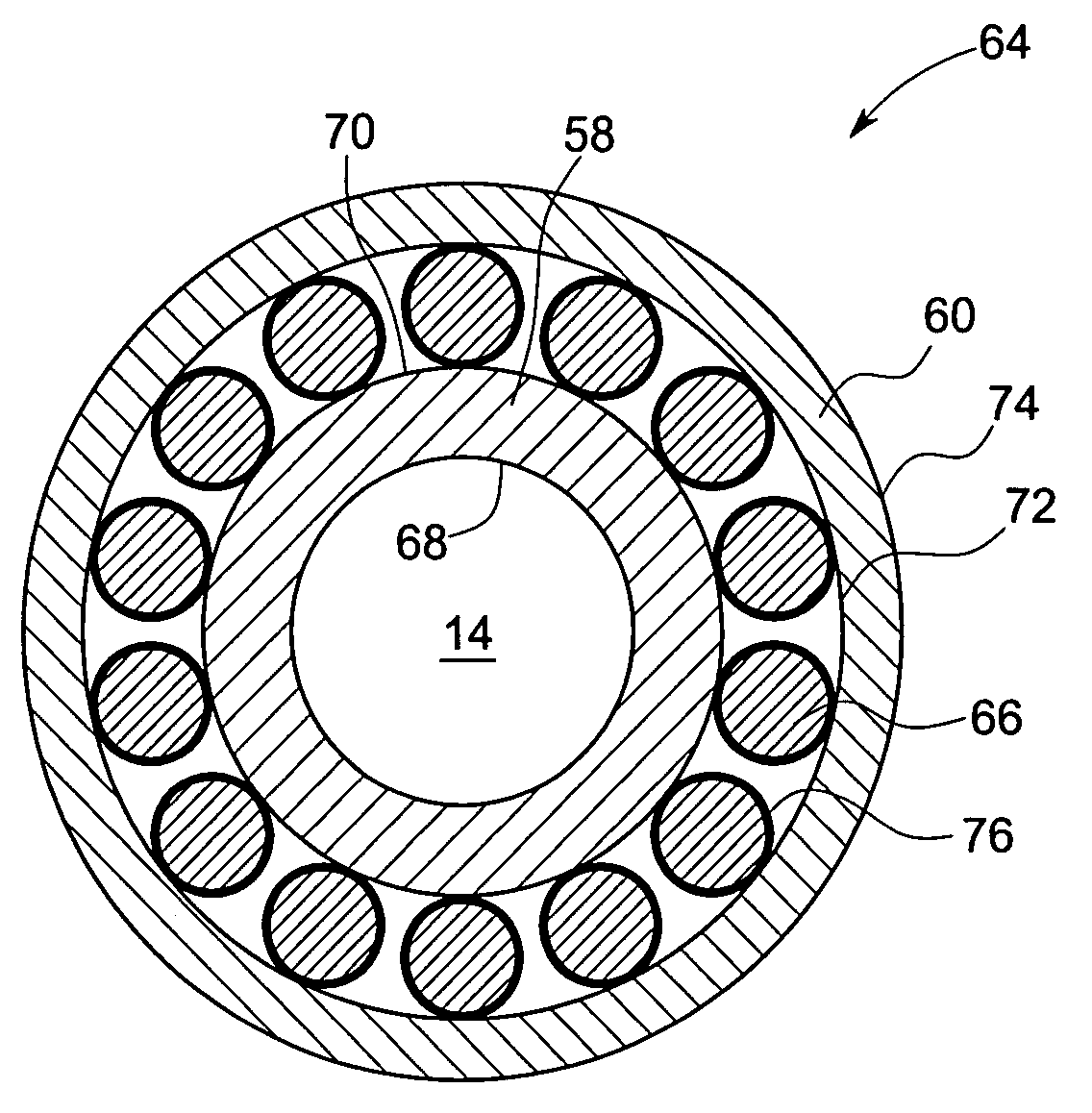
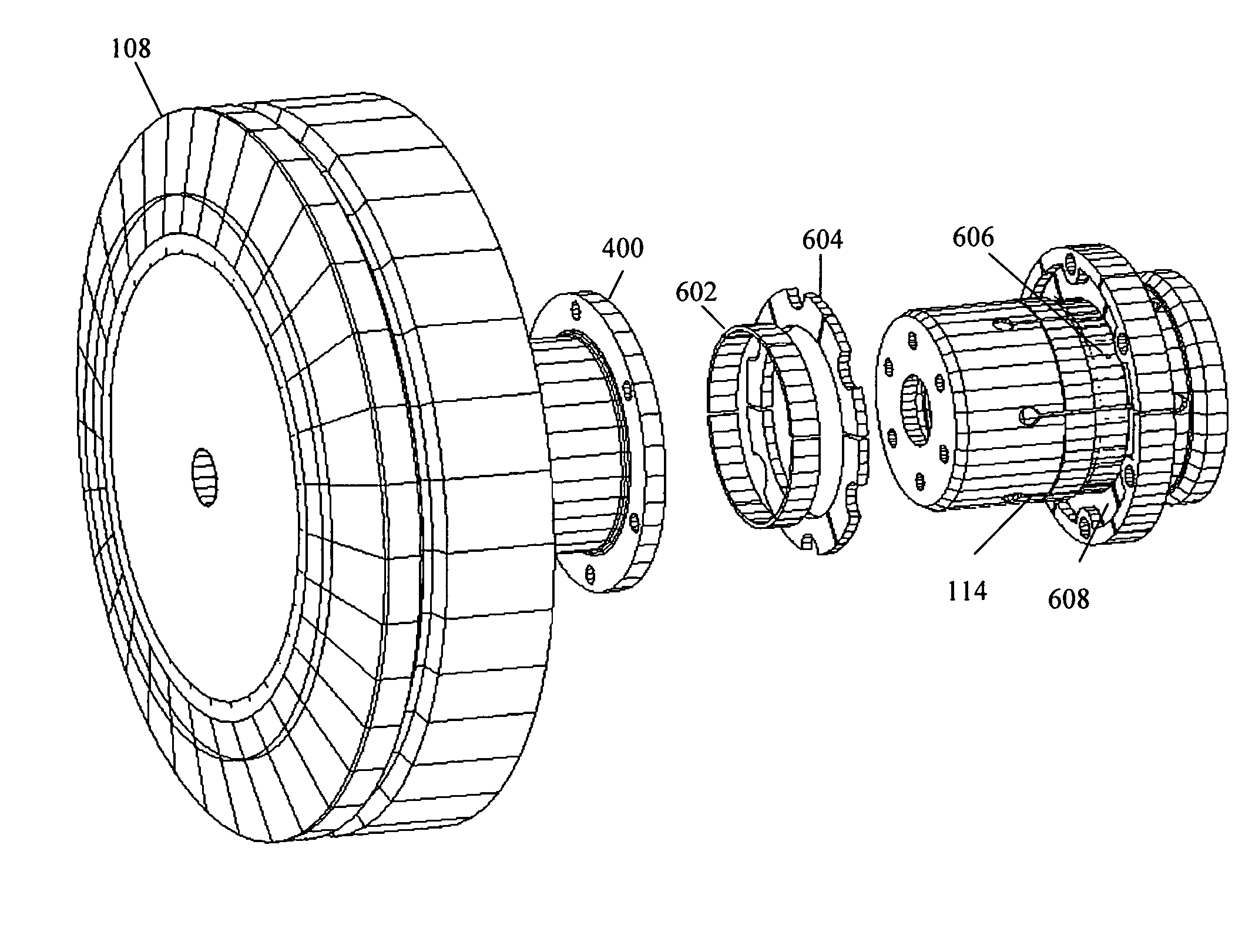
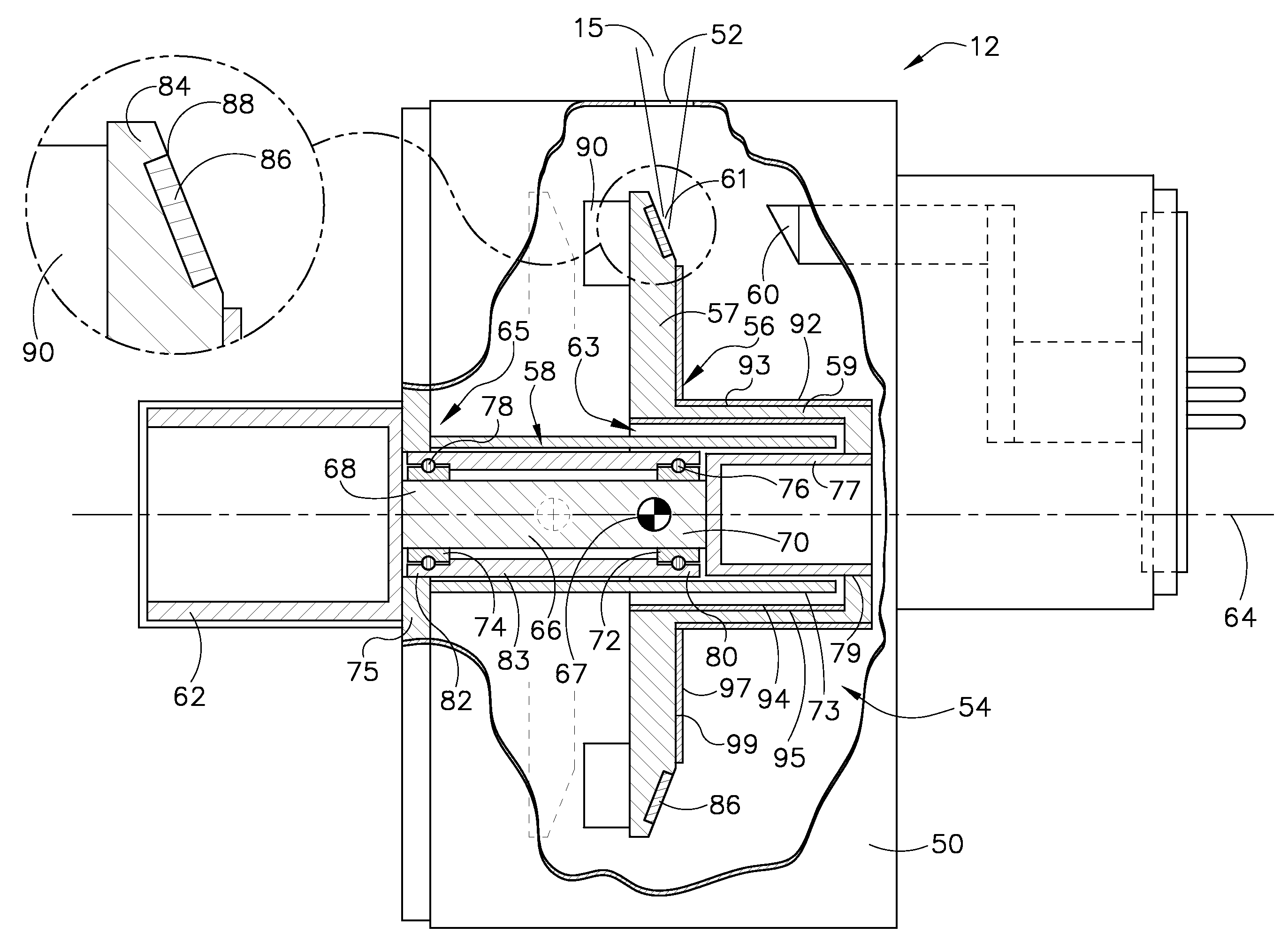
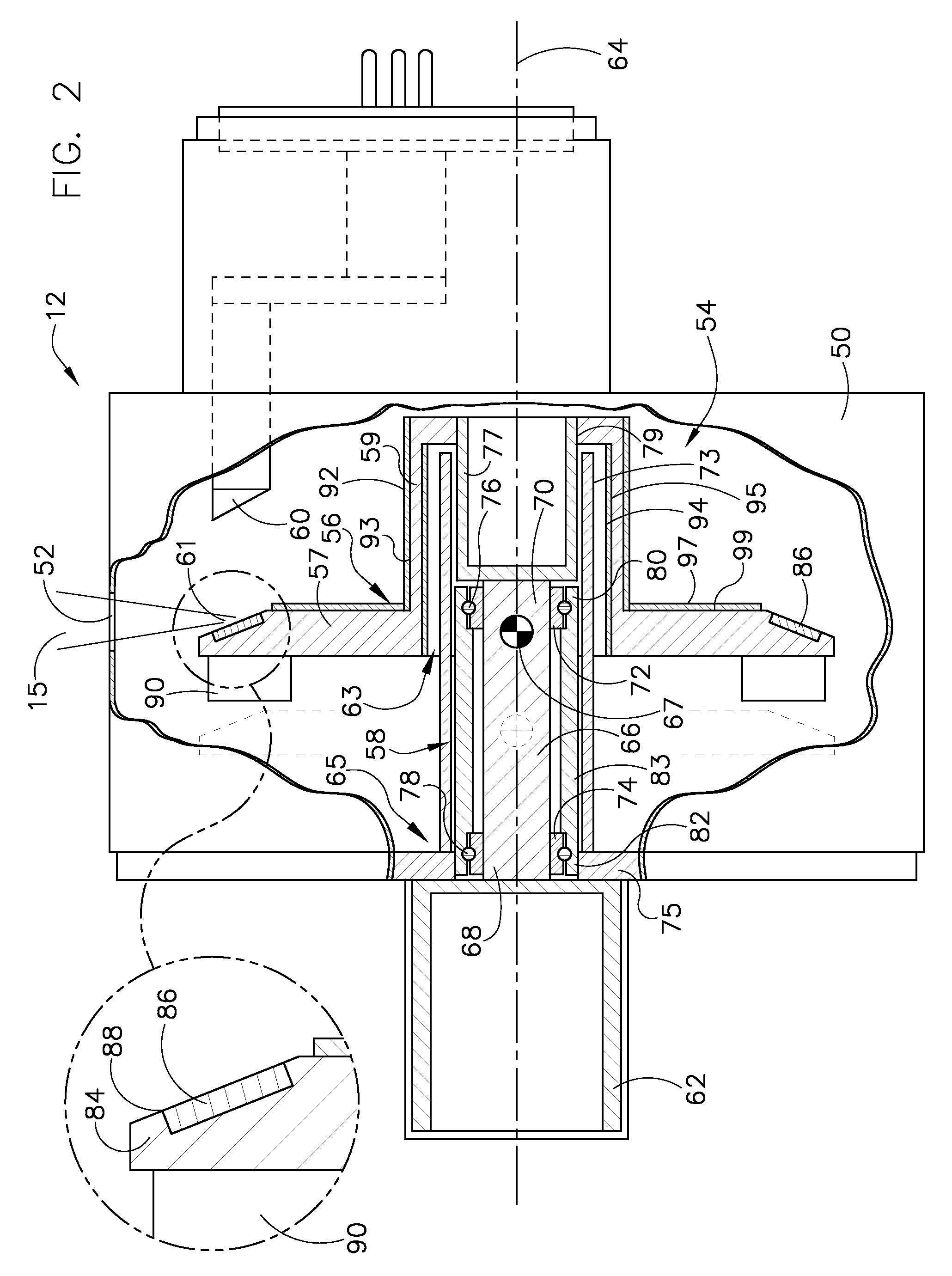
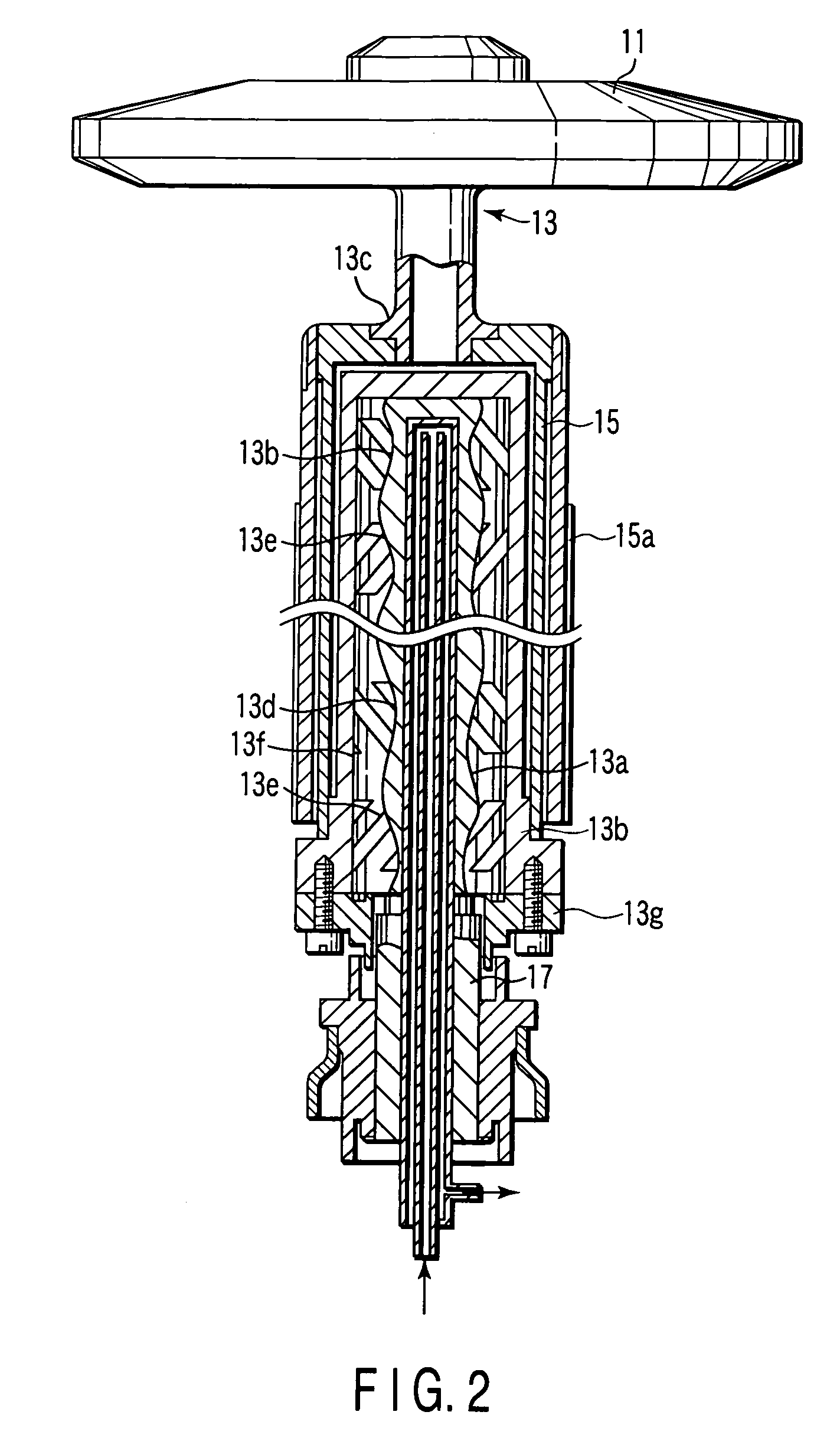
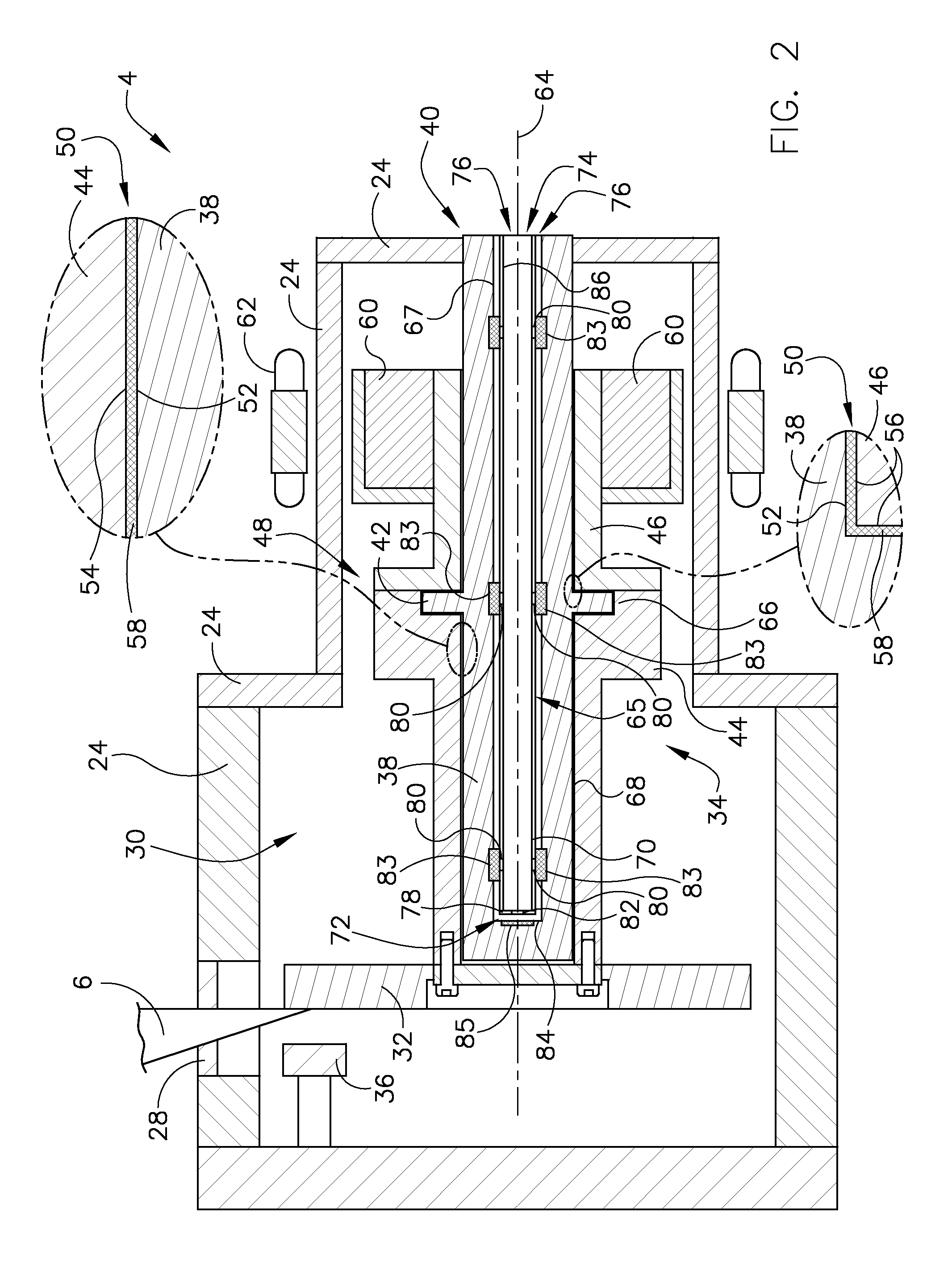
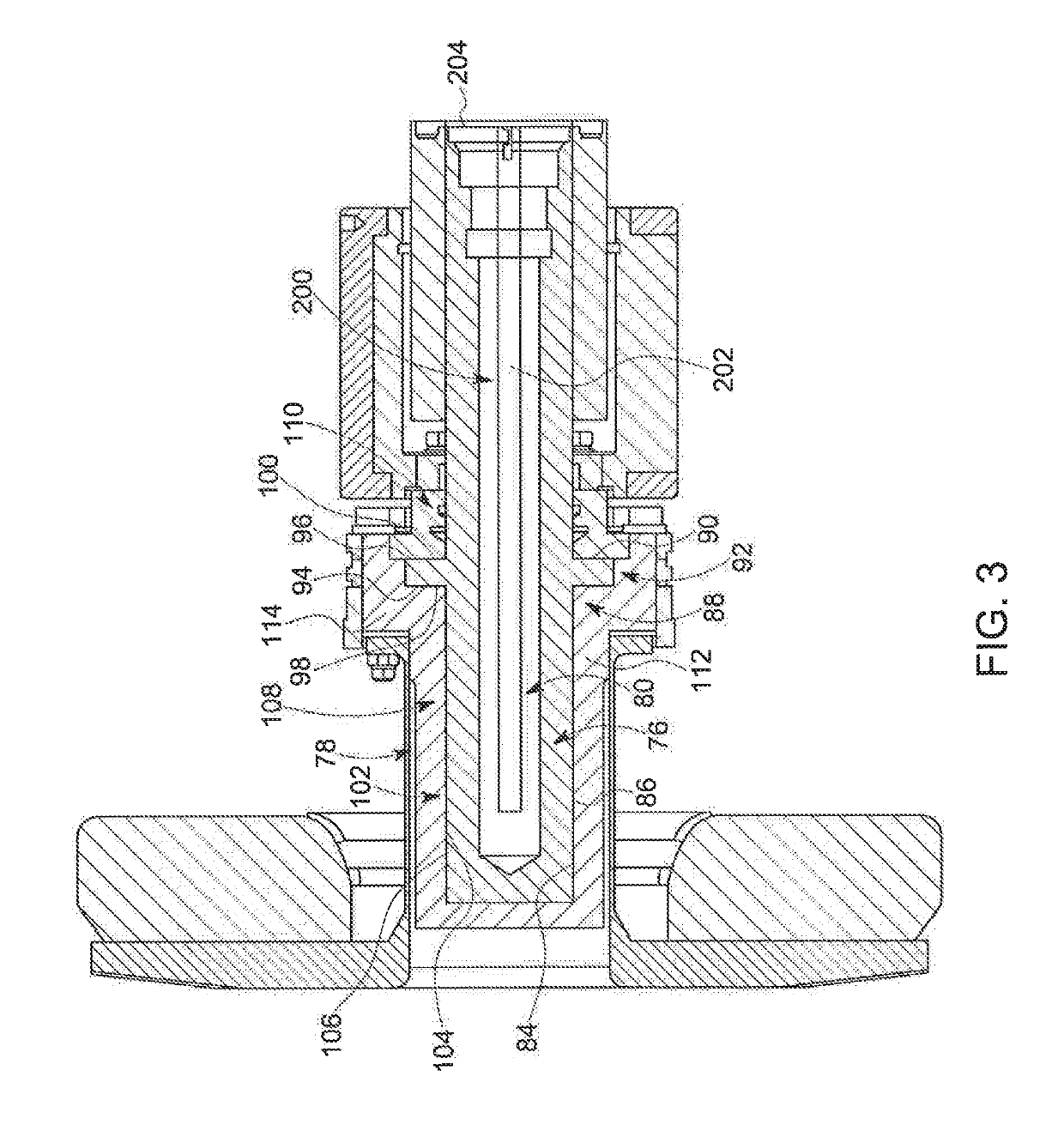
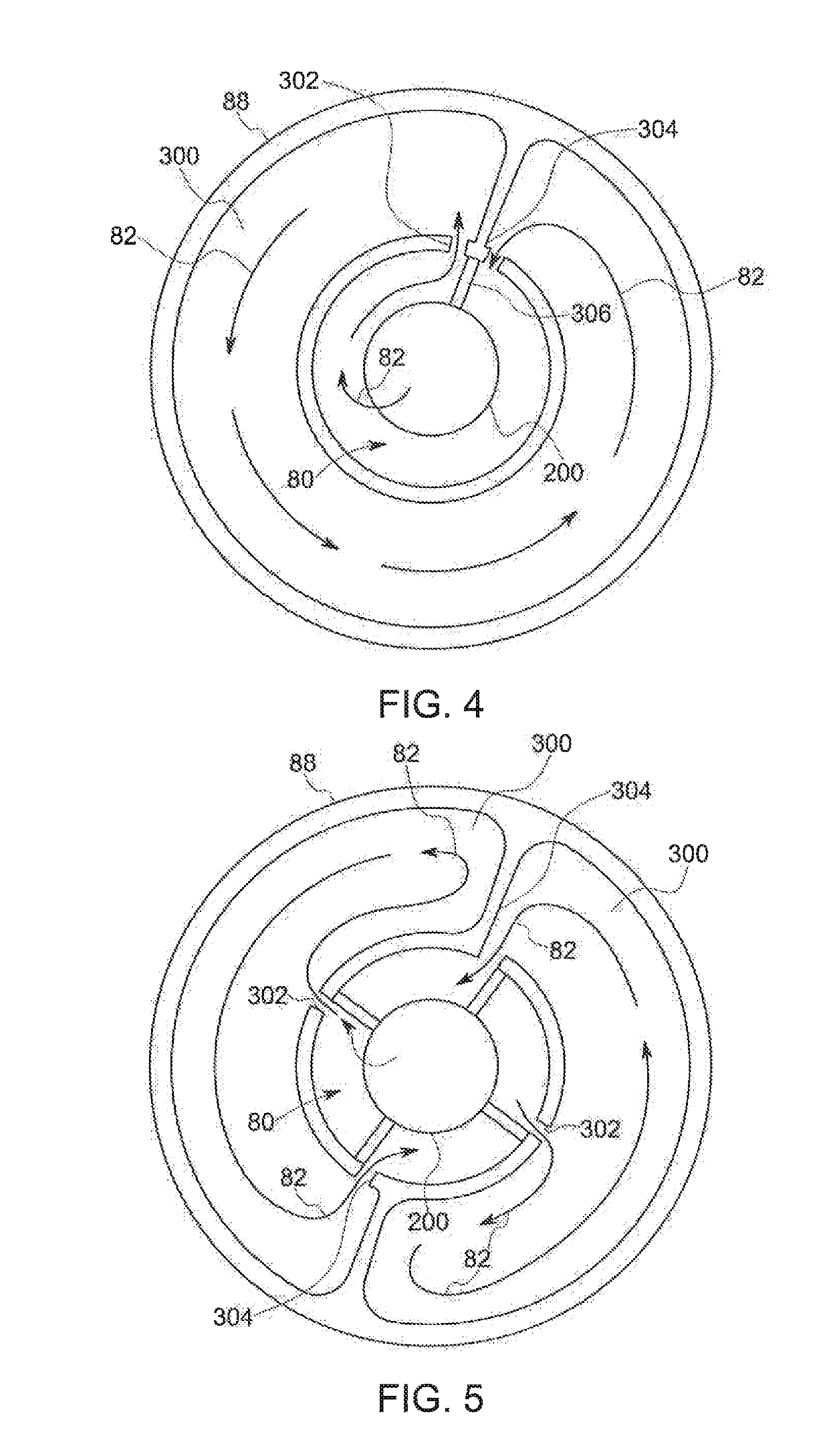
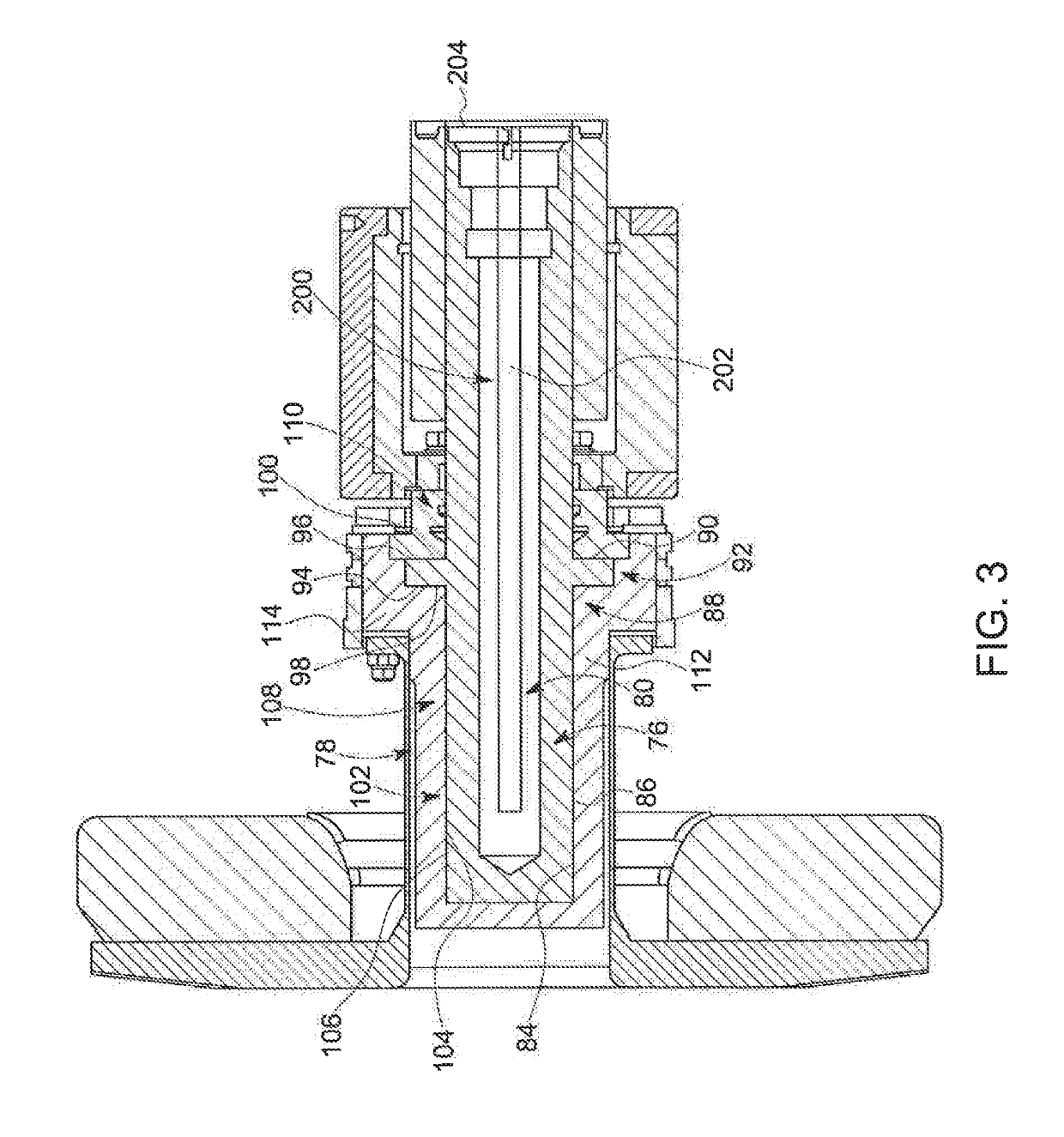
Thrust flange for x-ray tube with internal cooling channels
ActiveUS10438767B2Maximize heat transferReduce thermal deformationX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingThermal deformationThrust bearing
A bearing structure for an X-ray tube is provided that includes a journal bearing shaft with a radially protruding thrust bearing flange encased within a bearing housing or sleeve. The sleeve includes a thrust seal that is engaged with the sleeve in a manner to maintain coaxiality for the rotating liquid metal seal formed in the sleeve about the shaft. The shaft includes a central bore containing a cooling tube that directs coolant within the bore to maximize the heat transfer from the shaft to the coolant, allowing materials with lower thermal conductivities, such as steel, to be used to form the bearing shaft. The thrust flange on the shaft is formed with channel(s) therein that enable the coolant and / or the liquid metal to effect greater heat transfer on the components of the sleeve through the thrust flange, thereby reducing thermal deformation of the bearing components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Liquid cooled bearing housing with greased lubricated rotating anode bearings for an x-ray tube
InactiveUS7113568B2Improve heat transfer efficiencyLower operating temperatureX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingX-ray tube electrodesVacuum chamberMechanical engineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Thrust Flange For X-Ray Tube With Internal Cooling Channels
ActiveUS20190164716A1Maximize heat transferReduce thermal deformationX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingThrust bearingThermal deformation
A bearing structure for an X-ray tube is provided that includes a journal bearing shaft with a radially protruding thrust bearing flange encased within a bearing housing or sleeve. The sleeve includes a thrust seal that is engaged with the sleeve in a manner to maintain coaxiality for the rotating liquid metal seal formed in the sleeve about the shaft. The shaft includes a central bore containing a cooling tube that directs coolant within the bore to maximize the heat transfer from the shaft to the coolant, allowing materials with lower thermal conductivities, such as steel, to be used to form the bearing shaft. The thrust flange on the shaft is formed with channel(s) therein that enable the coolant and / or the liquid metal to effect greater heat transfer on the components of the sleeve through the thrust flange, thereby reducing thermal deformation of the bearing components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray tube with bonded target and bearing sleeve
The embodiments disclosed herein relate to the thermal regulation of components within an X-ray tube by transferring heat between the anode and the rotary mechanism to which the anode is attached. For example, in one embodiment, an X-ray tube is provided. The X-ray tube generally includes a fixed shaft, a rotating bearing sleeve disposed about the fixed shaft and configured to rotate with respect to the fixed shaft via a rotary bearing, and an electron beam target disposed about the bearing sleeve and configured to rotate with the bearing sleeve. The electron beam target is permanently bonded to the bearing sleeve.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rotating union for a liquid cooled rotating x-ray target
A rotating union for an X-ray target is provided. The rotating union for the X-ray target comprises a housing, a coolant-slinging device comprising a rotating shaft having an inner diameter and an outer diameter, a proximal end and a distal end, and a bore therein, one or more slingers coupled to a proximal end of the rotating shaft; a drain annulus coupled to the one or more slingers, wherein the one or more slingers are configured to direct a coolant to the drain annulus and the drain annulus is configured to direct the coolant through a primary coolant outlet; and a stationary tube having a first end and a second end, wherein at least a portion of the stationary tube is disposed within the bore of the rotating shaft.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray tube with rotary anode
InactiveUS7116757B2Improve performanceSuper cost-effectiveX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingMaterials scienceX-ray tube
An x-ray tube has an anode plate connected to an anode tube that is mounted such that it can rotate around a rigid anode shaft. To improve the heat dissipation from the anode plate, a liquid for dissipation of heat to the anode shaft is accommodated in an intervening space formed between the anode shaft and the anode plate.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
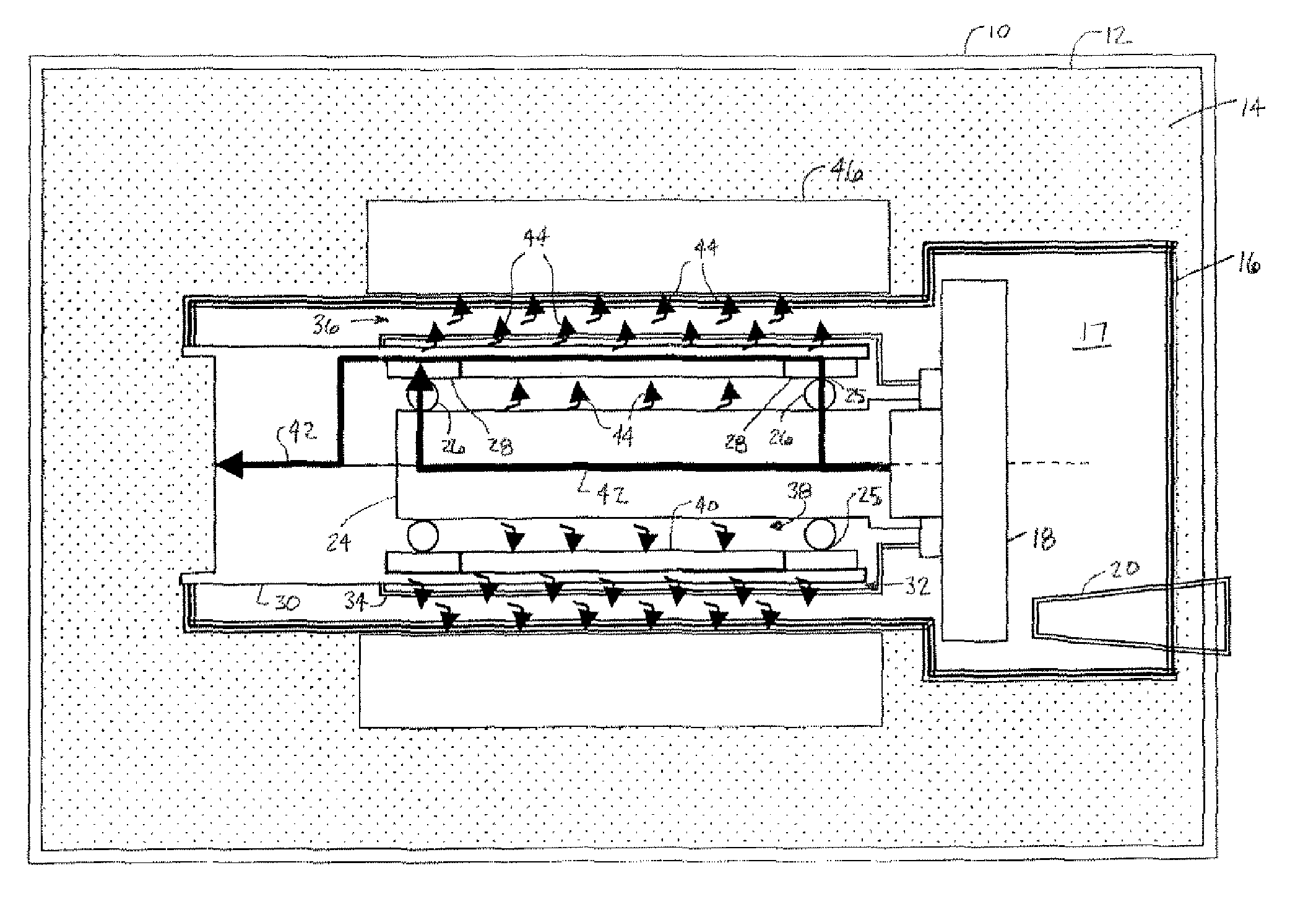
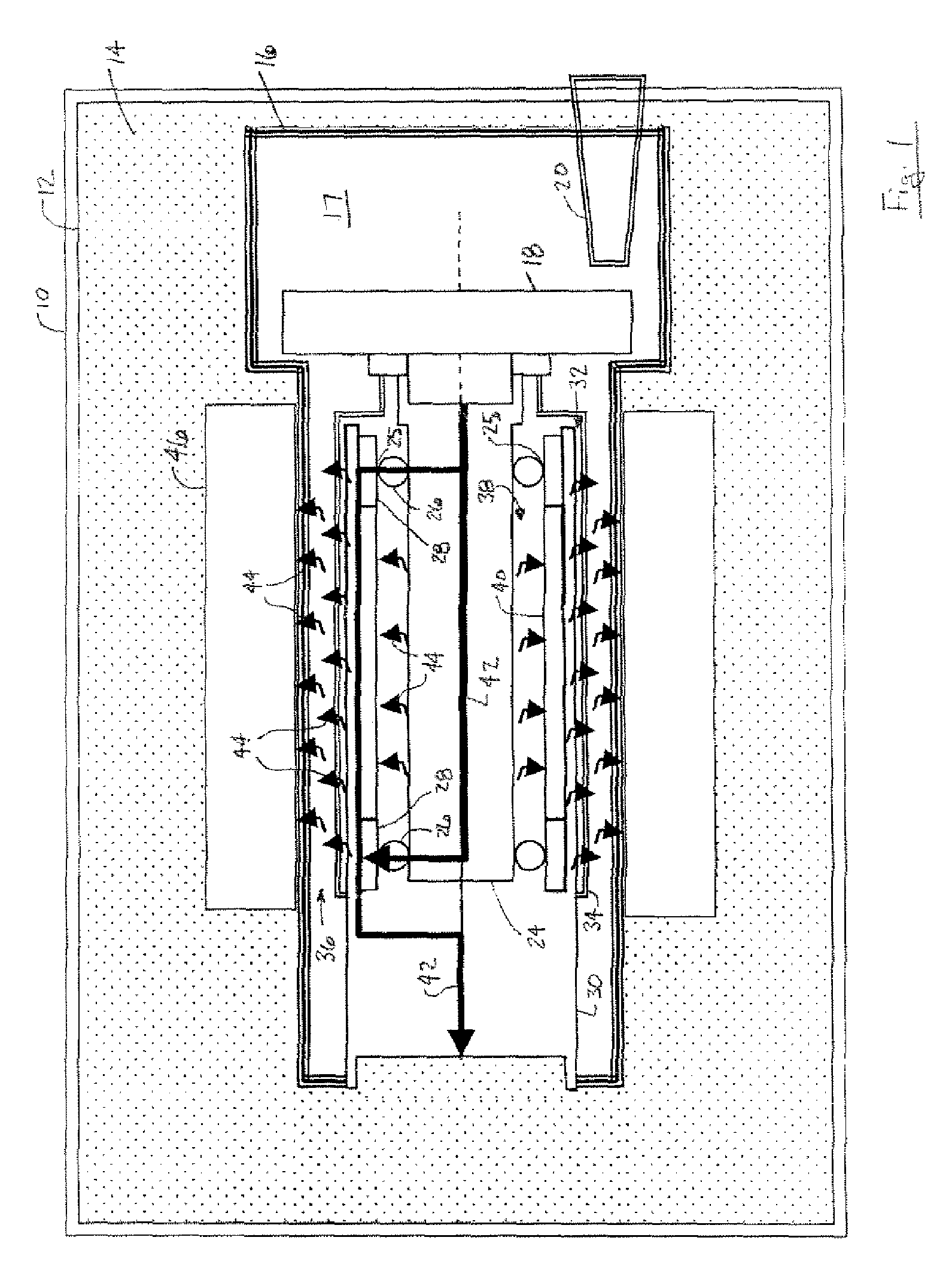
Computed tomography system having cooling system
InactiveUS20170042493A1Radiation diagnostic image/data processingX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingComputed tomographyEngineering
Provided is a CT system having a cooling system. The CT system may include a gantry unit including: a rotor; and an assembly component; an intake provided on a first surface of the rotor; and an outtake provided on a second surface opposite to the first surface of the rotor, wherein the gantry unit is cooled by air moving through the intake and the outtake due to a rotation force or a centrifugal force generated by a rotation movement of the rotor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Computed tomography system having cooling system
InactiveUS10064590B2Radiation diagnostic image/data processingX-ray tube bearing assembly coolingComputed tomographyEngineering
A computed tomography (CT) system having a cooling system includes: a gantry unit, including a rotor and an assembly component; an intake provided on a first surface of the rotor; and an outtake provided on a second surface opposite to the first surface of the rotor; wherein the gantry unit is cooled by air moving through the intake and the outtake due to a rotation force or a centrifugal force generated by a rotation movement of the rotor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com