Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75results about "Closures with oxygen absorbers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
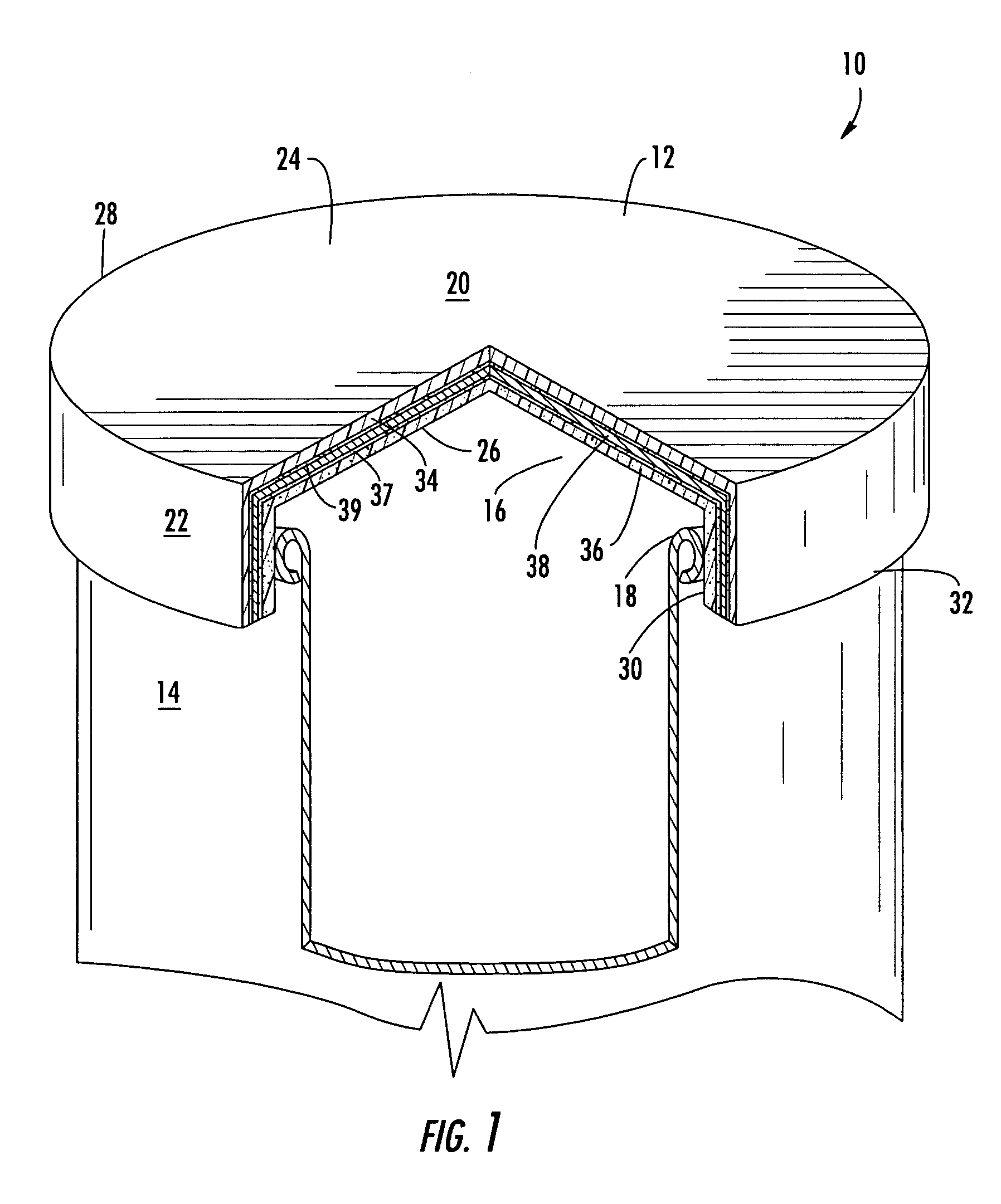
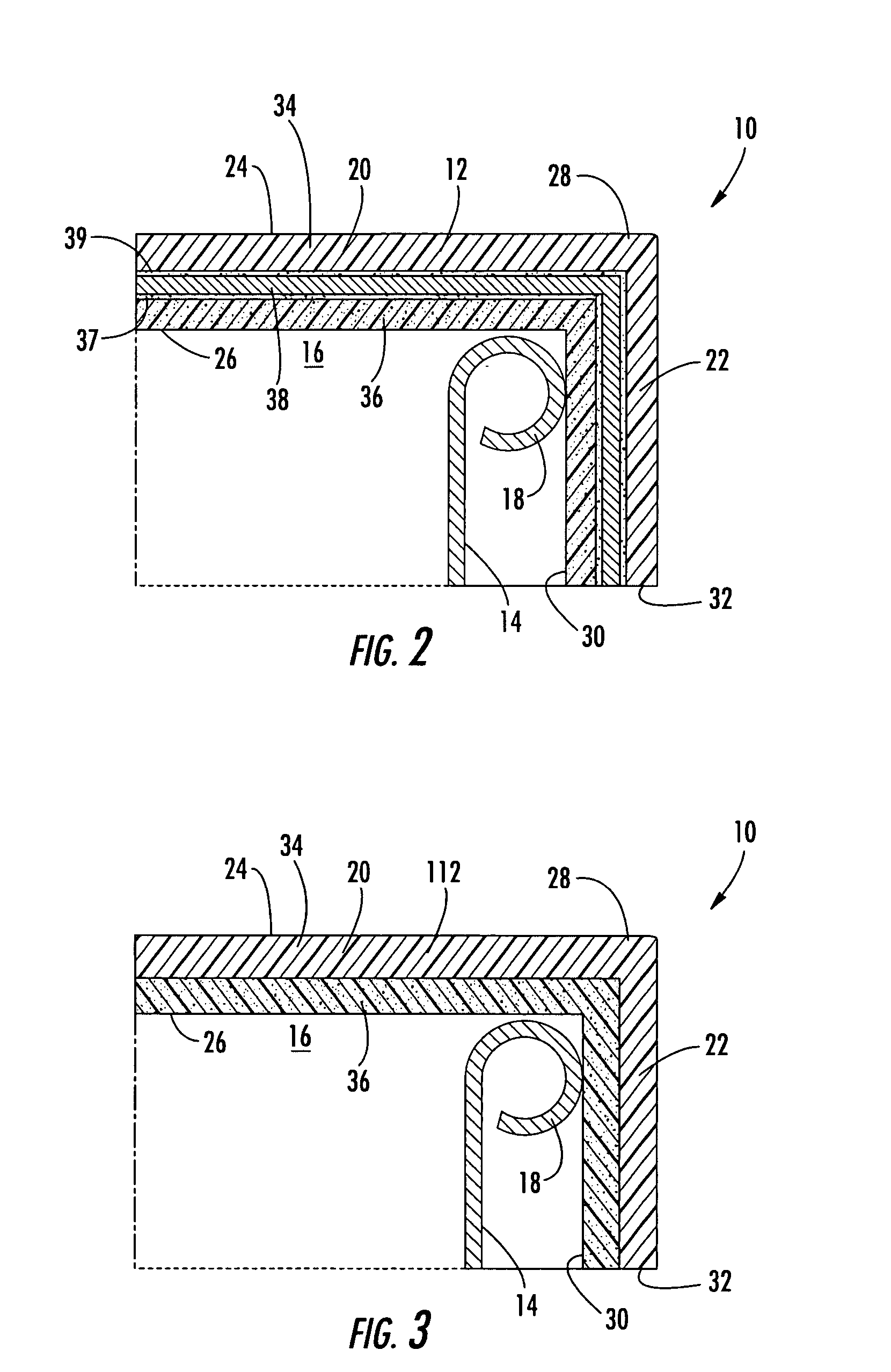
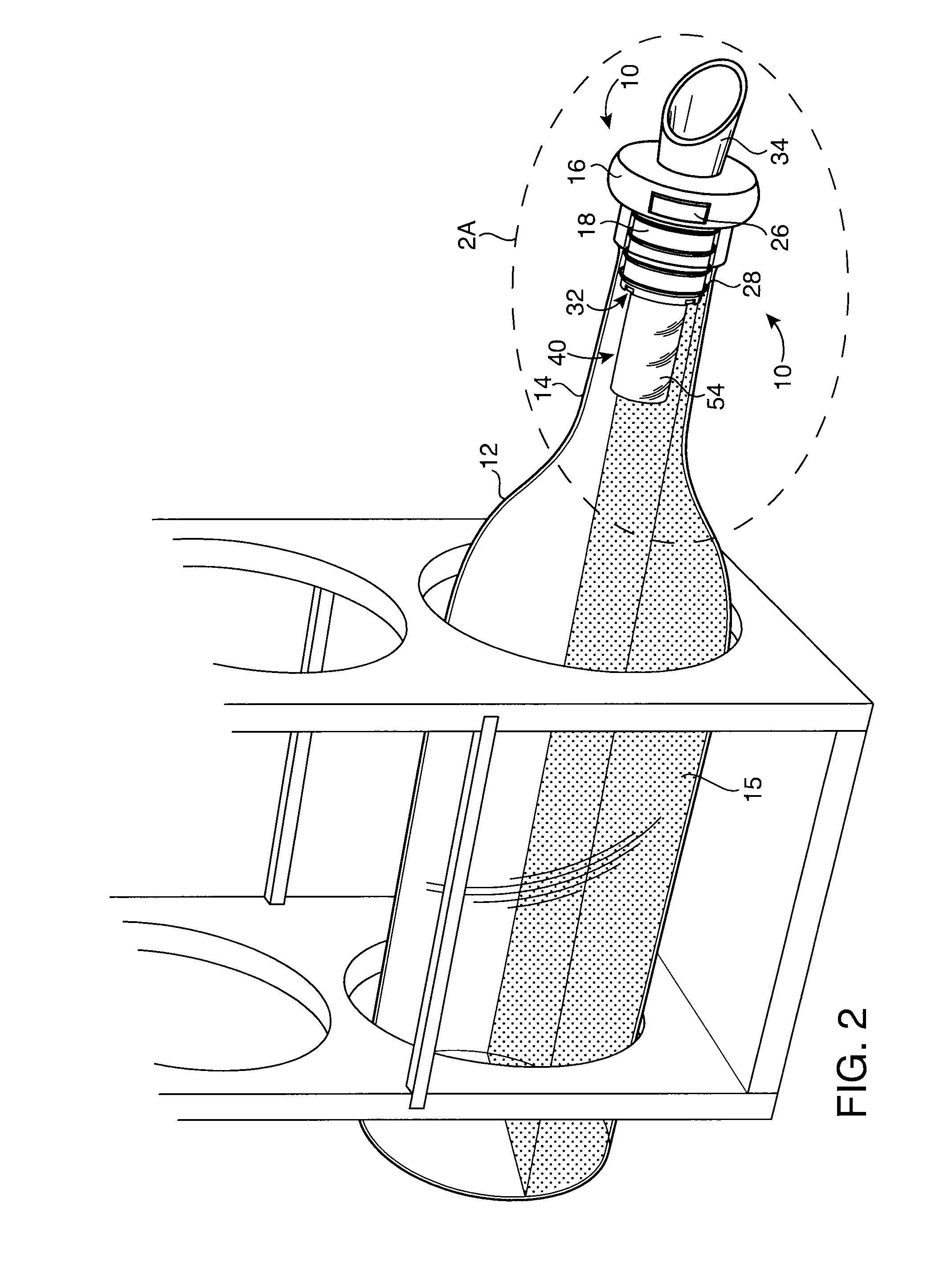
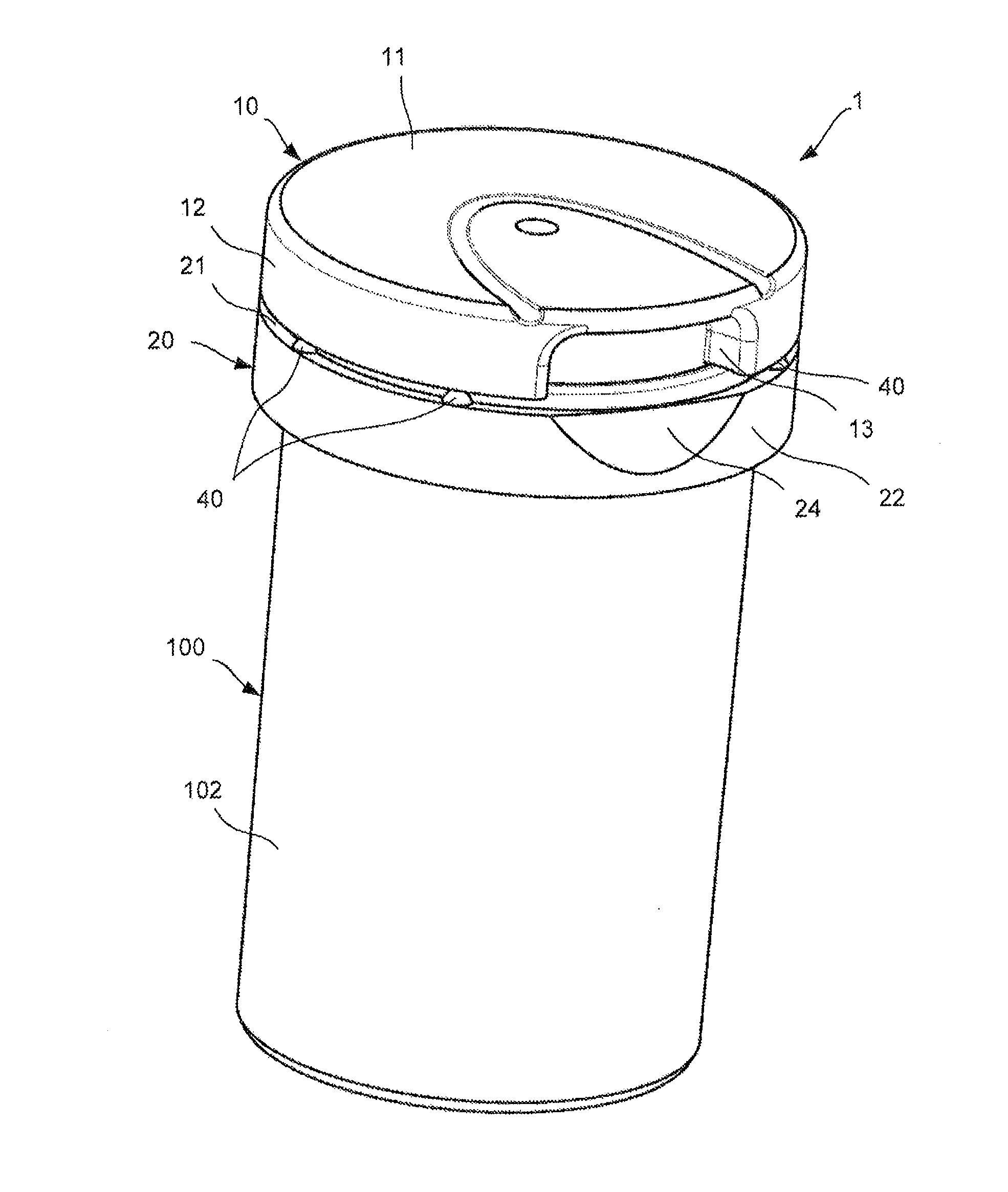
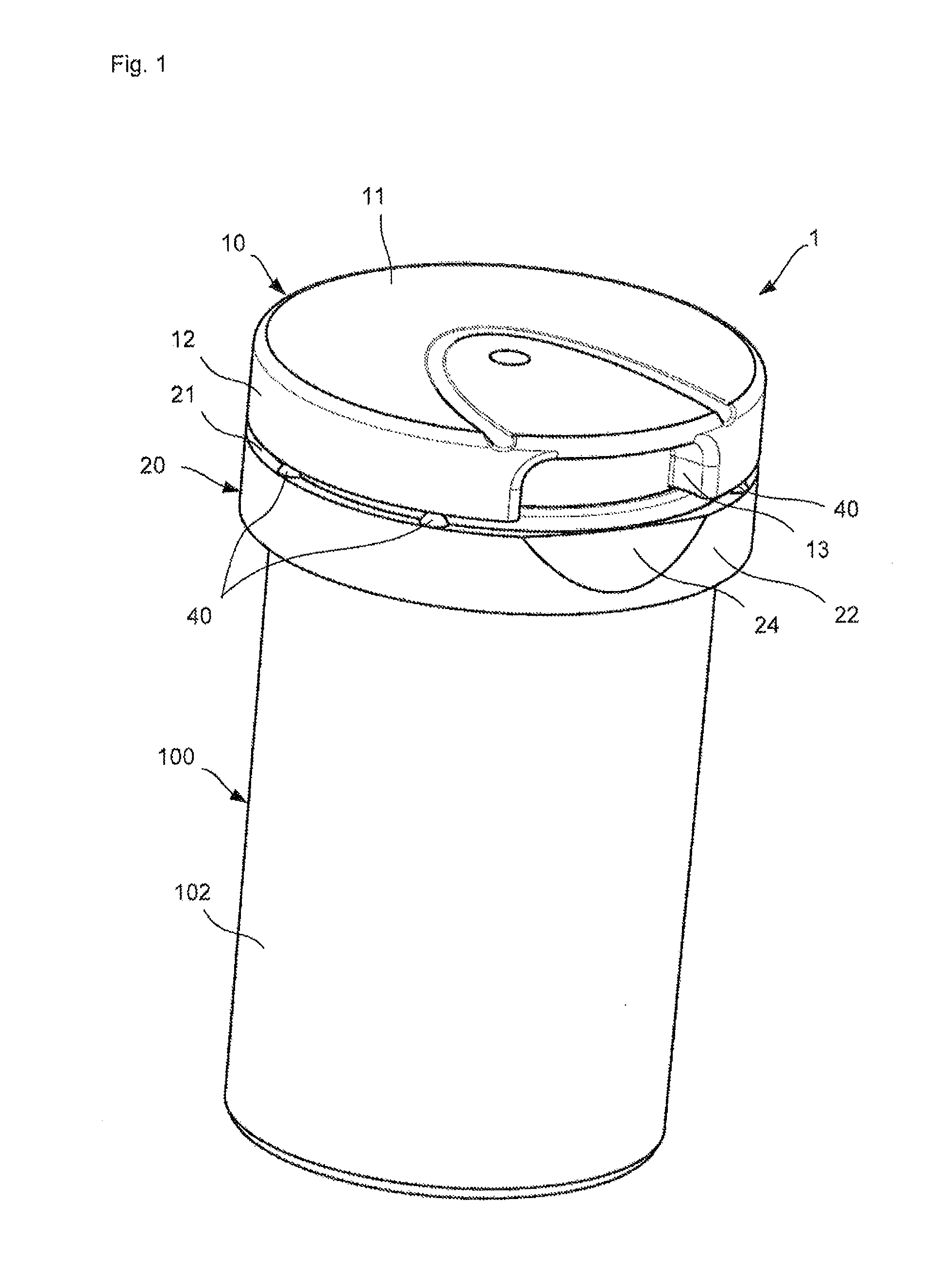
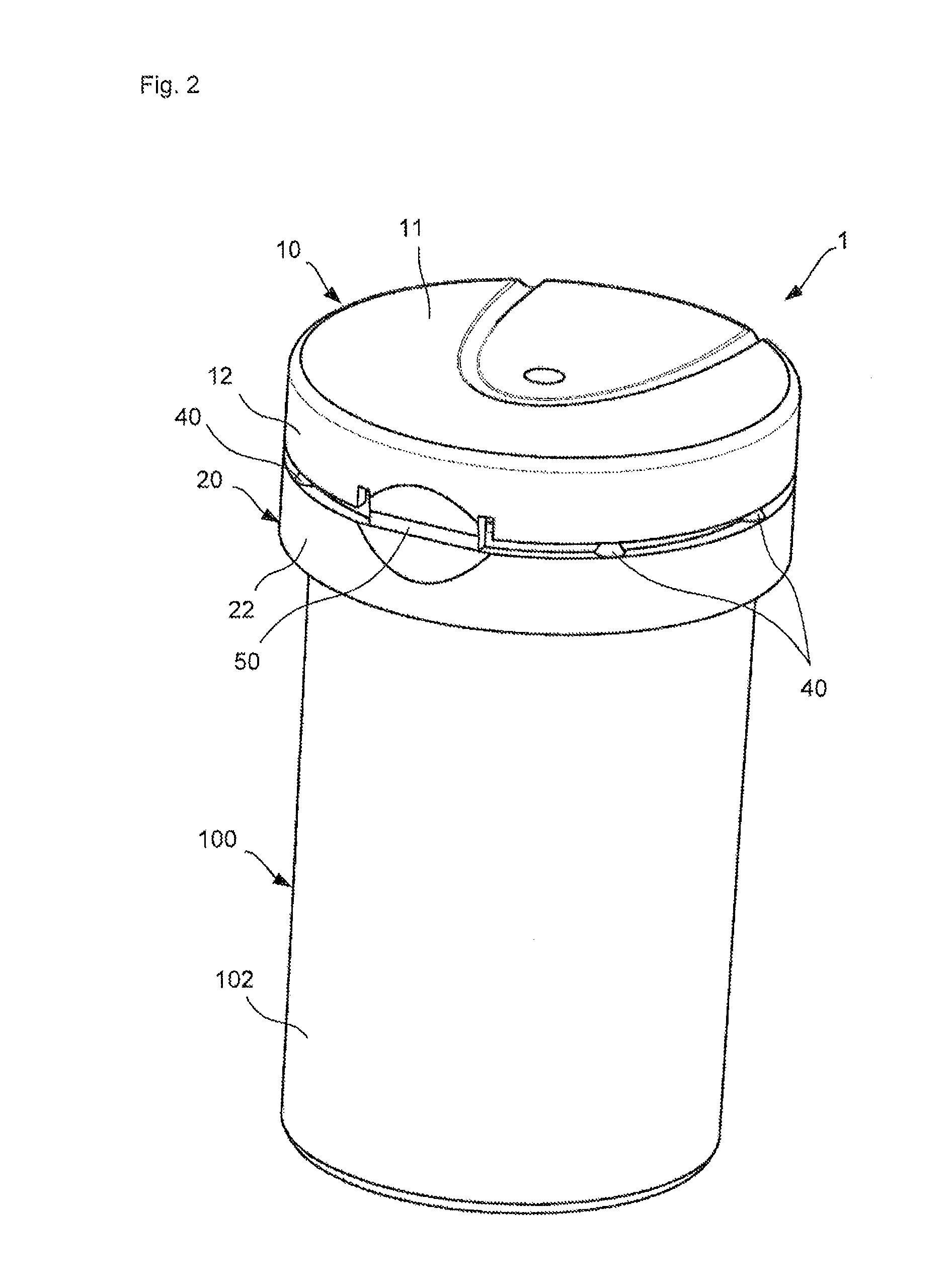
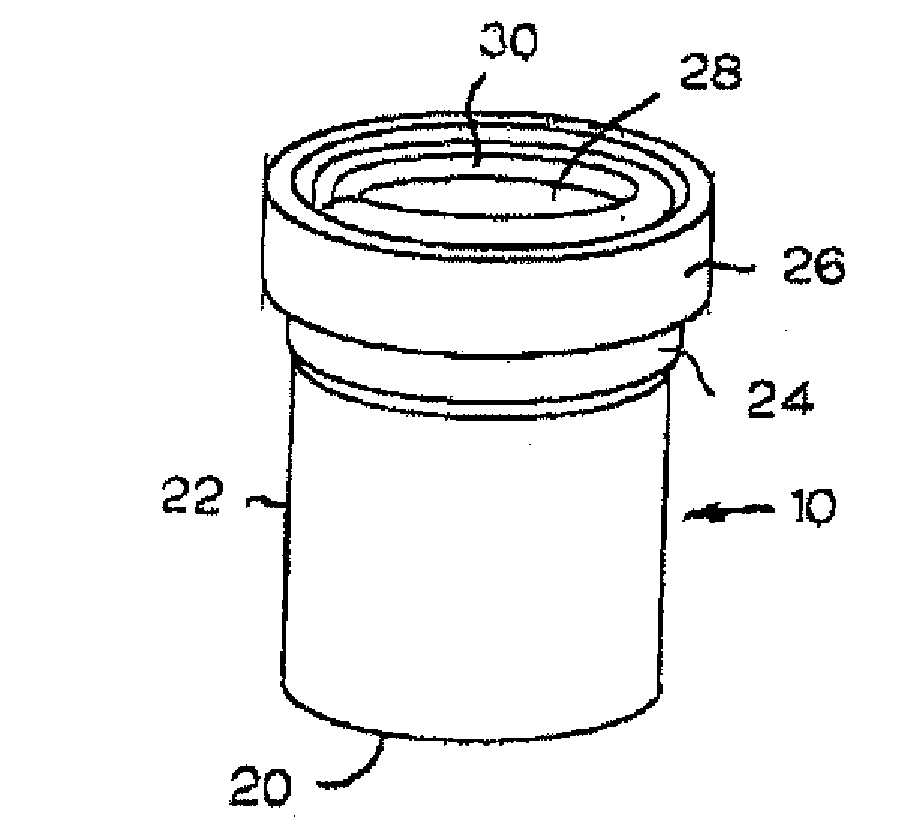
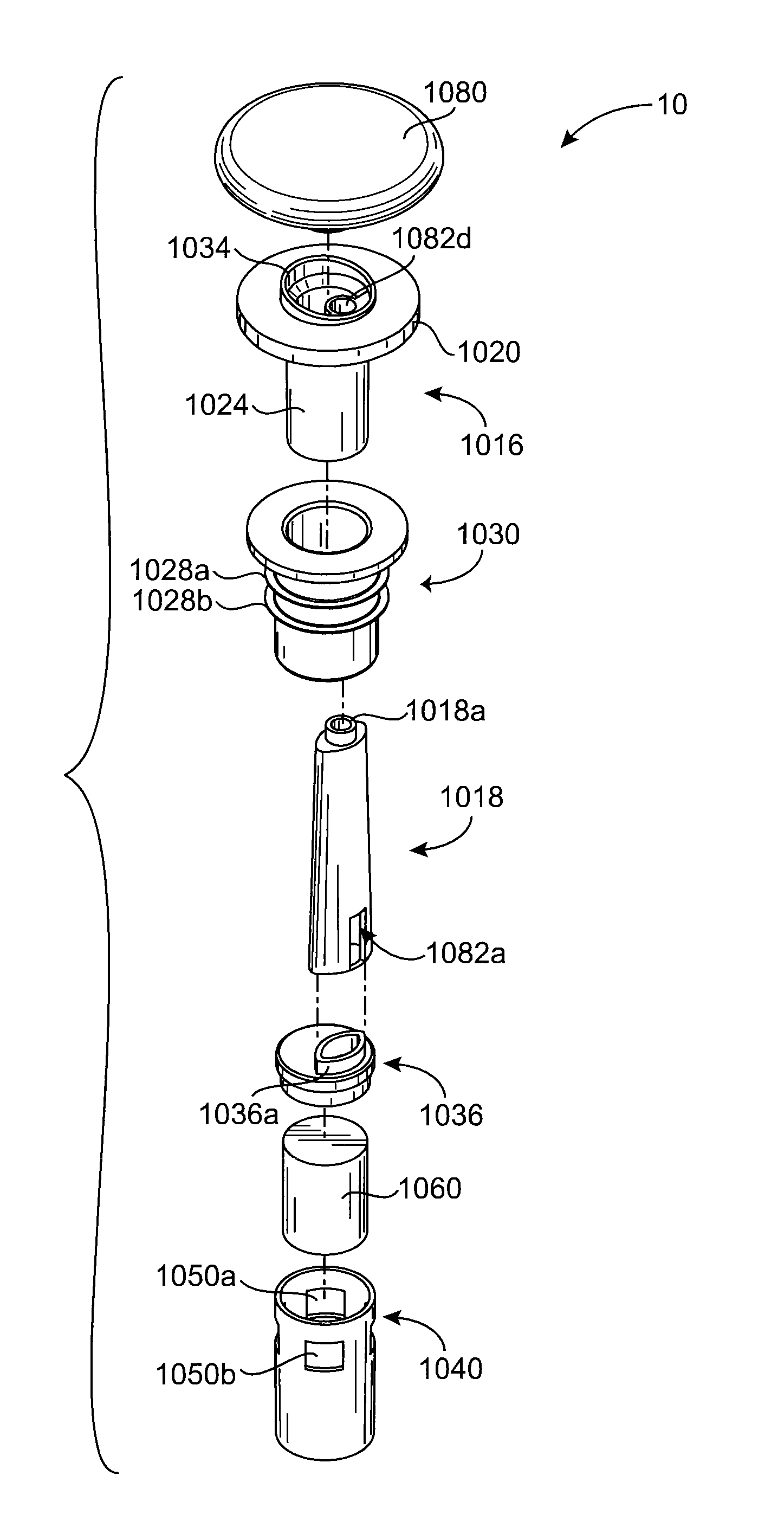
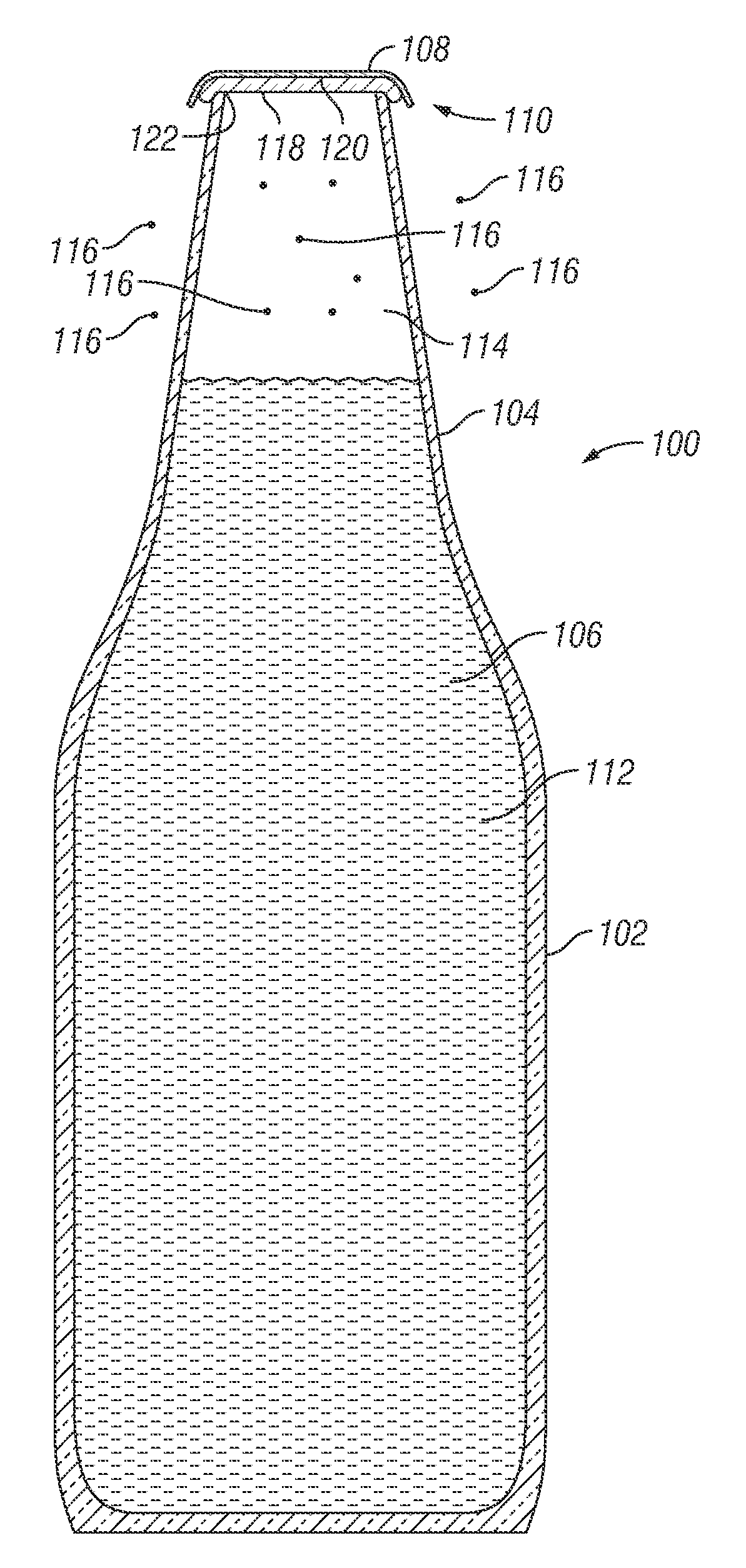
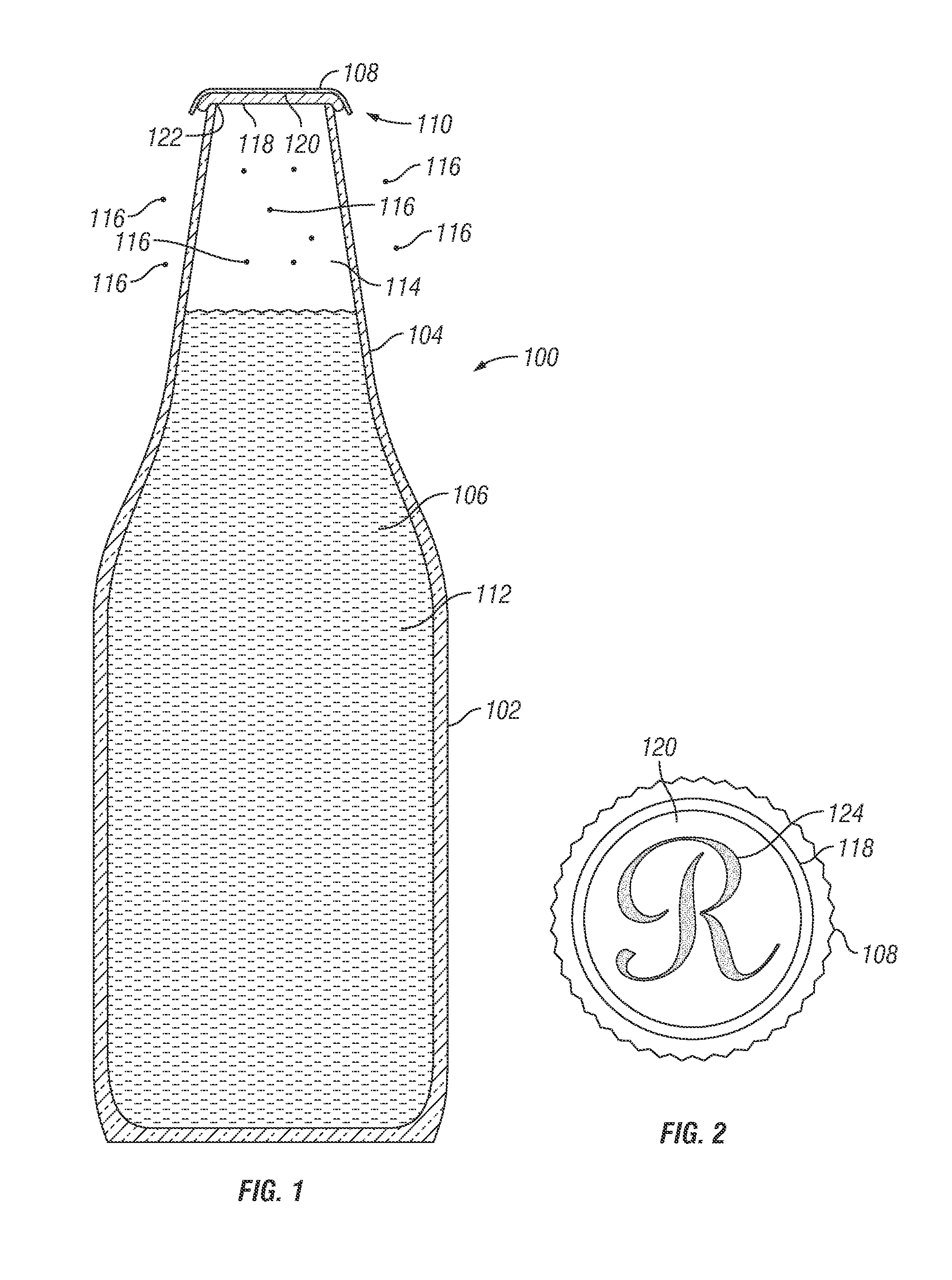
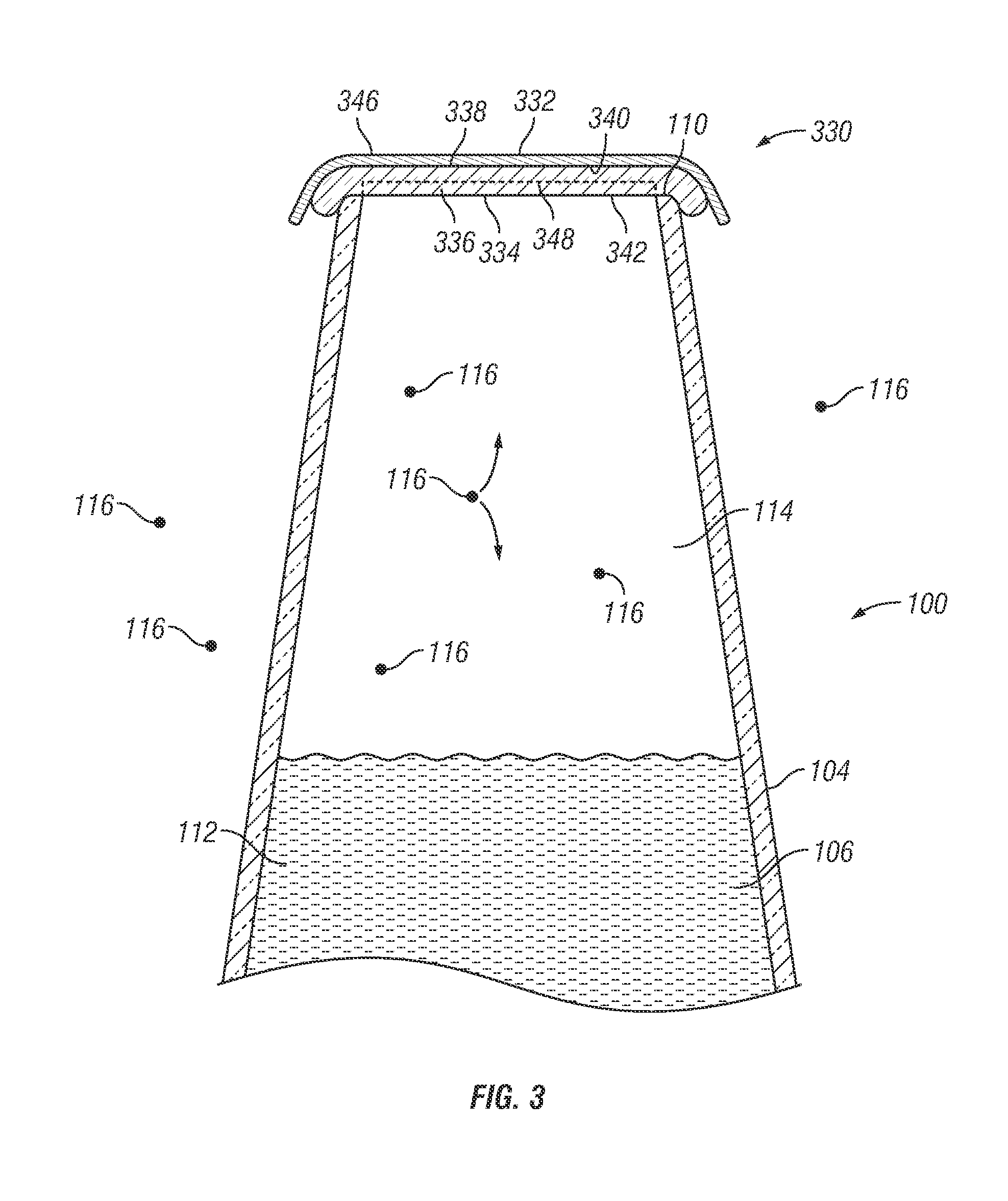
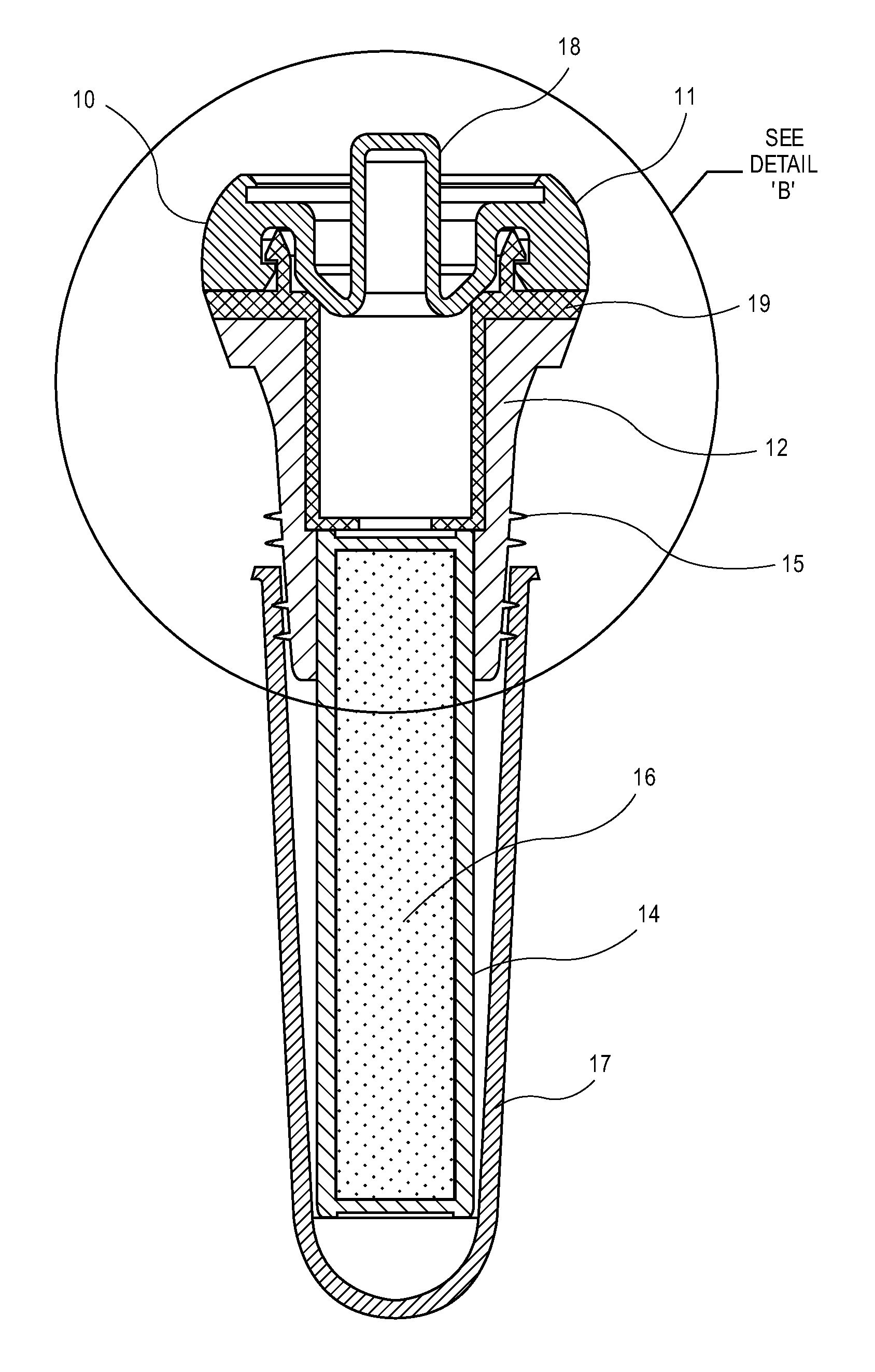
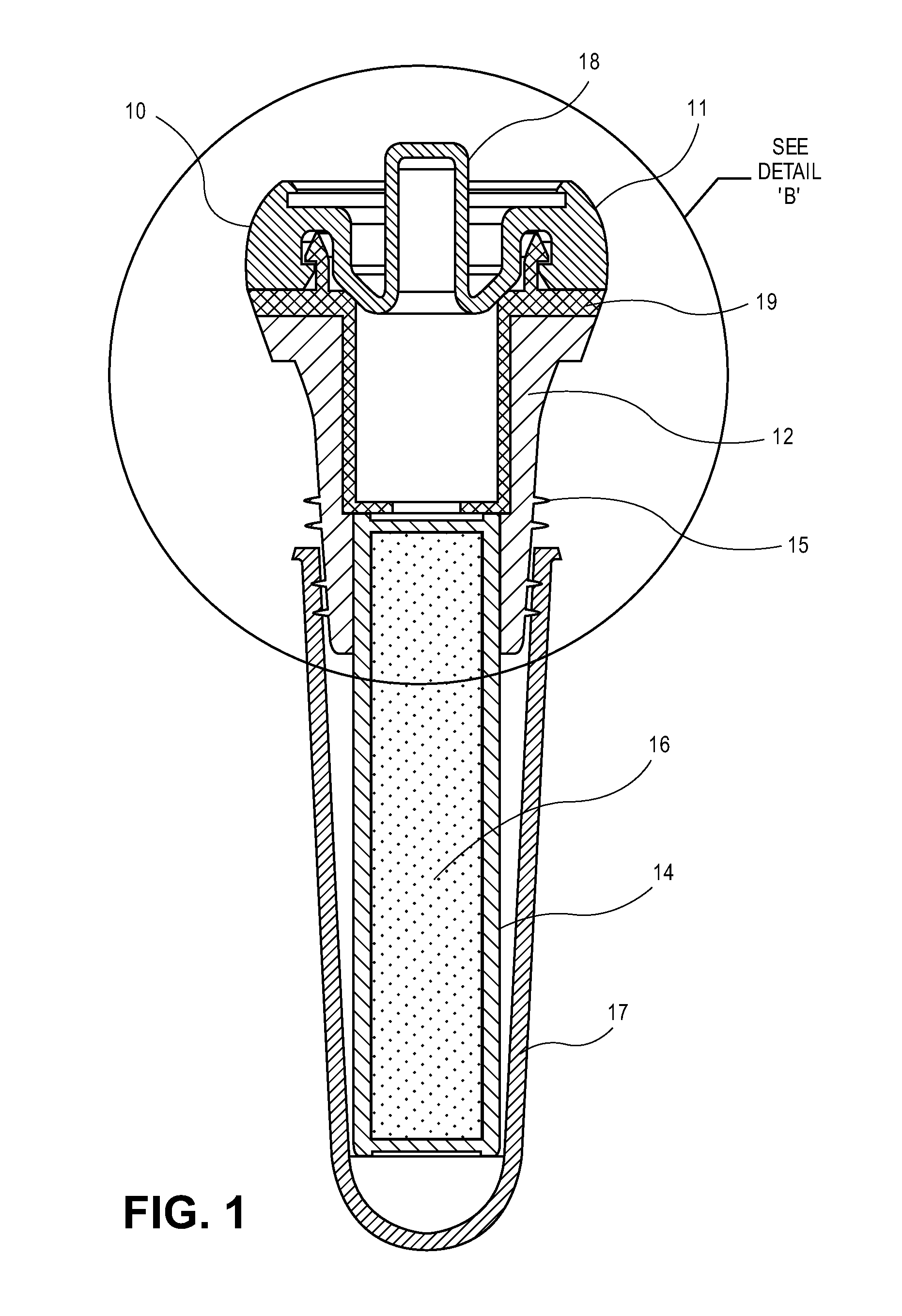
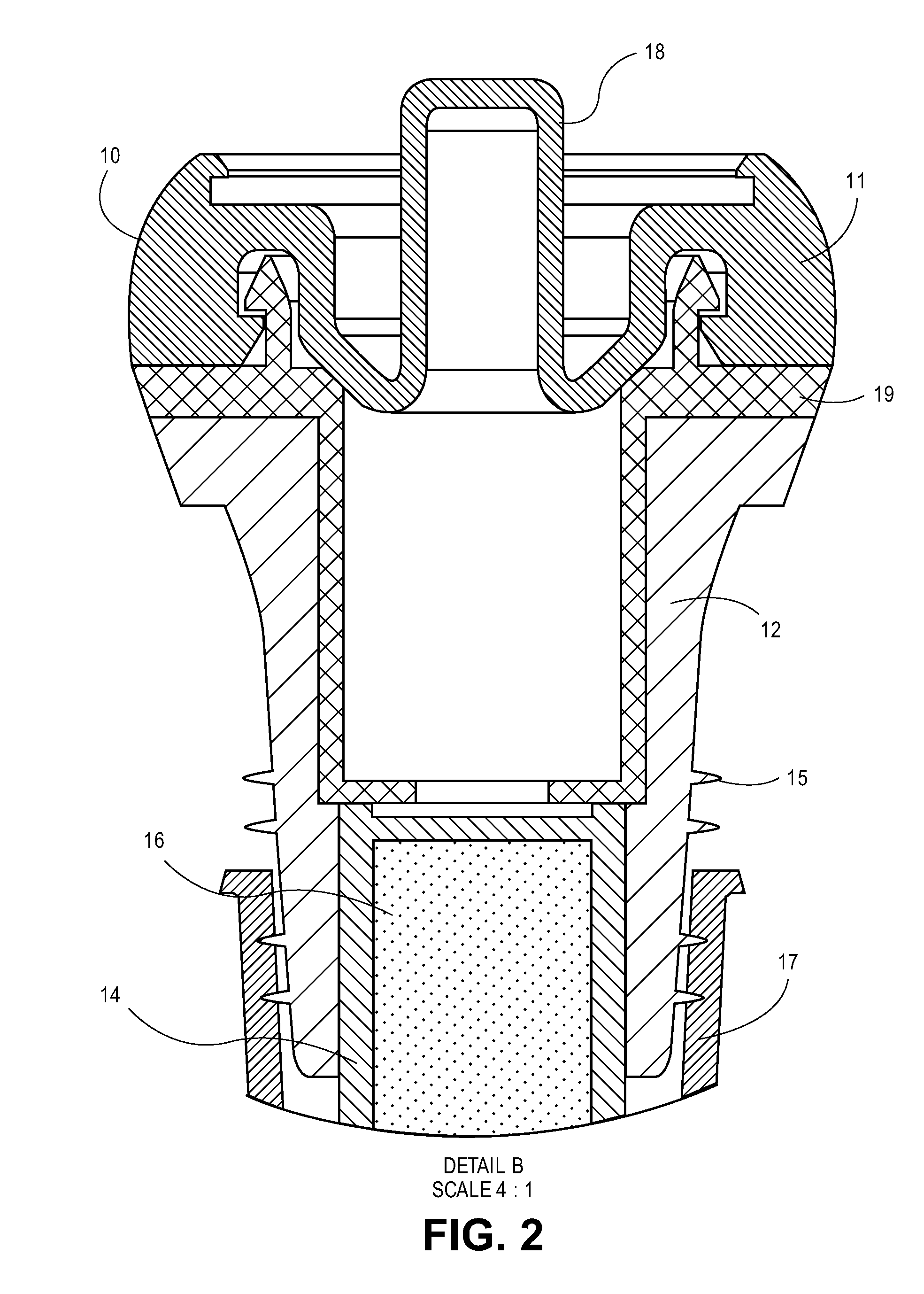
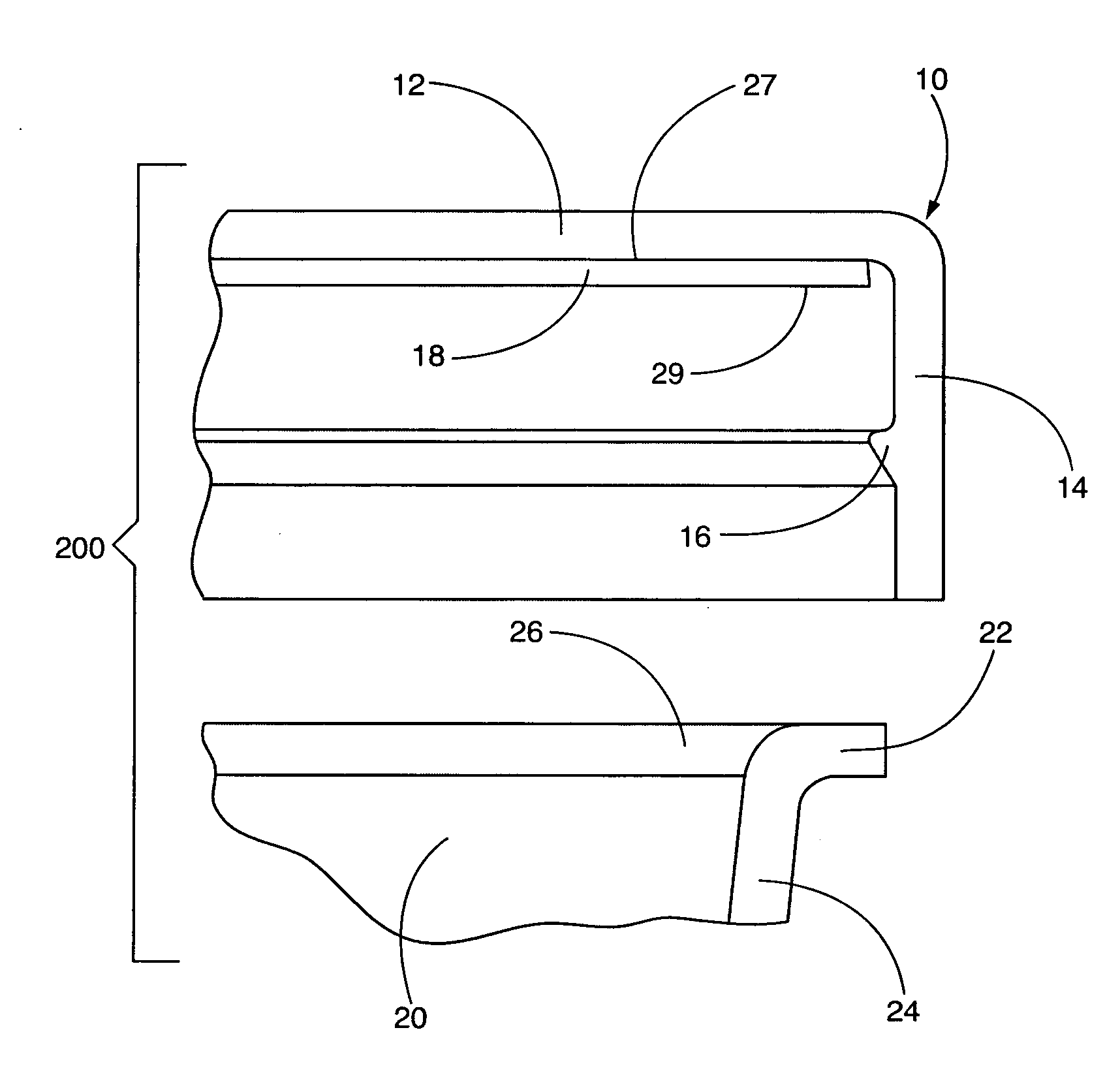
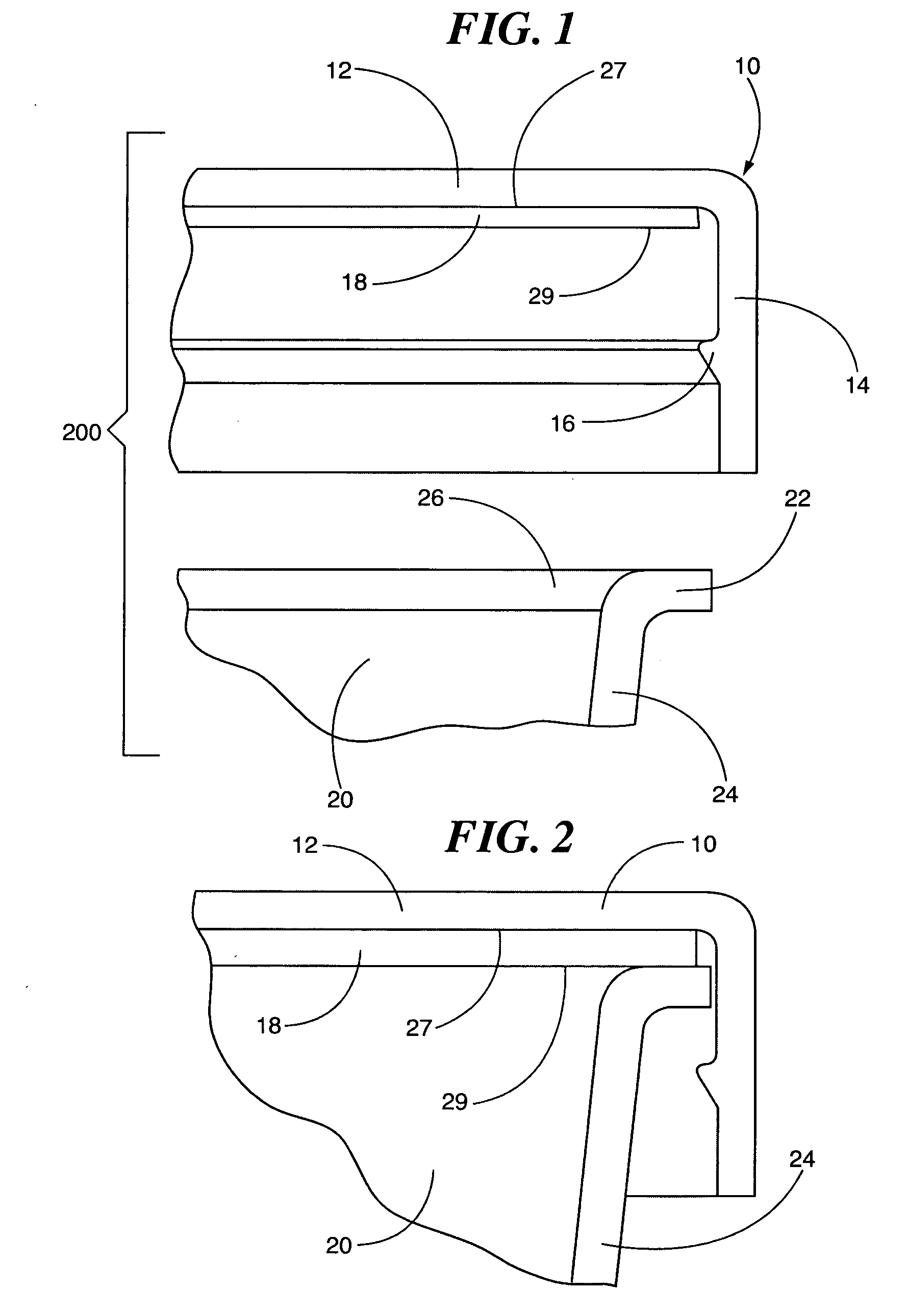
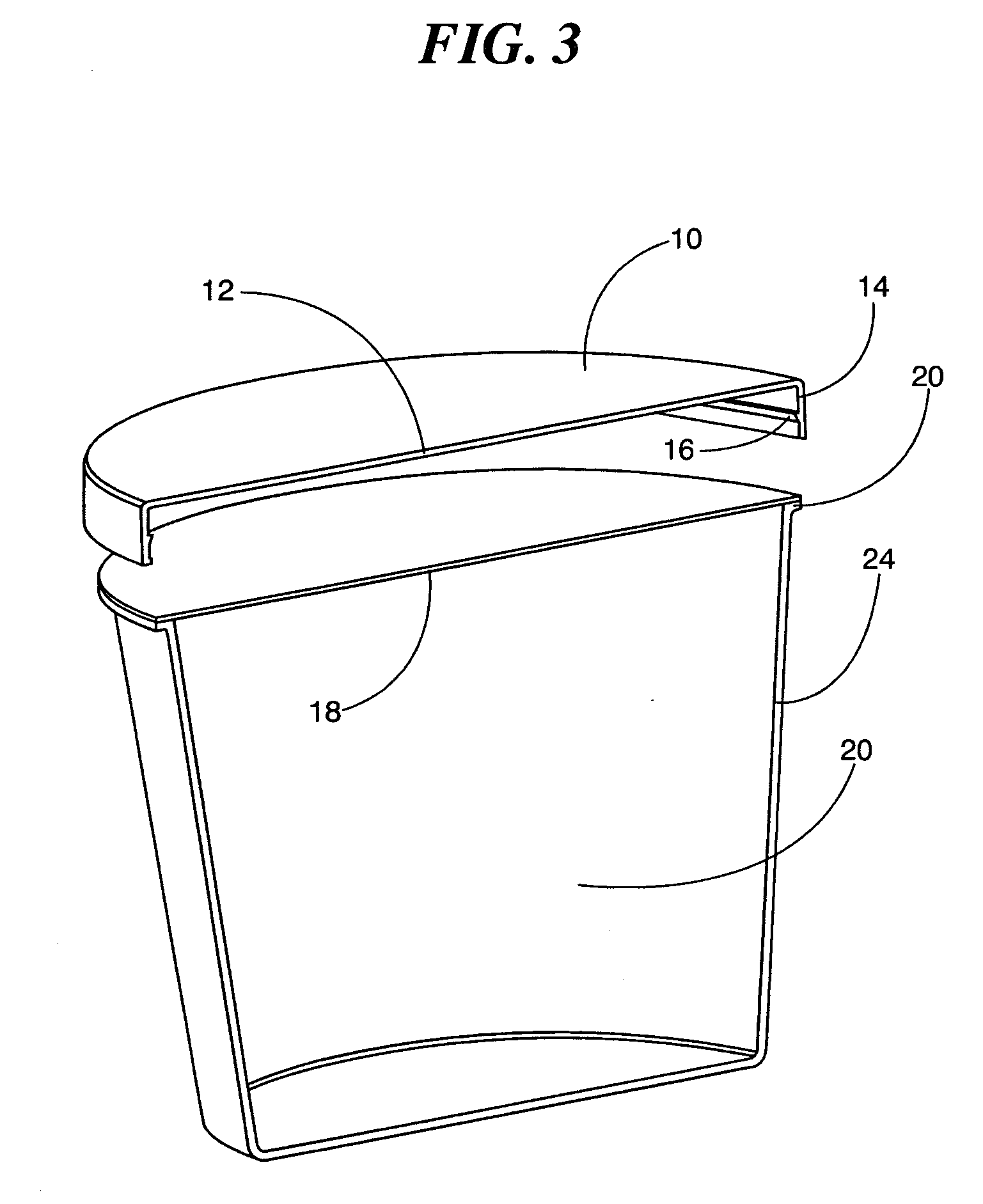
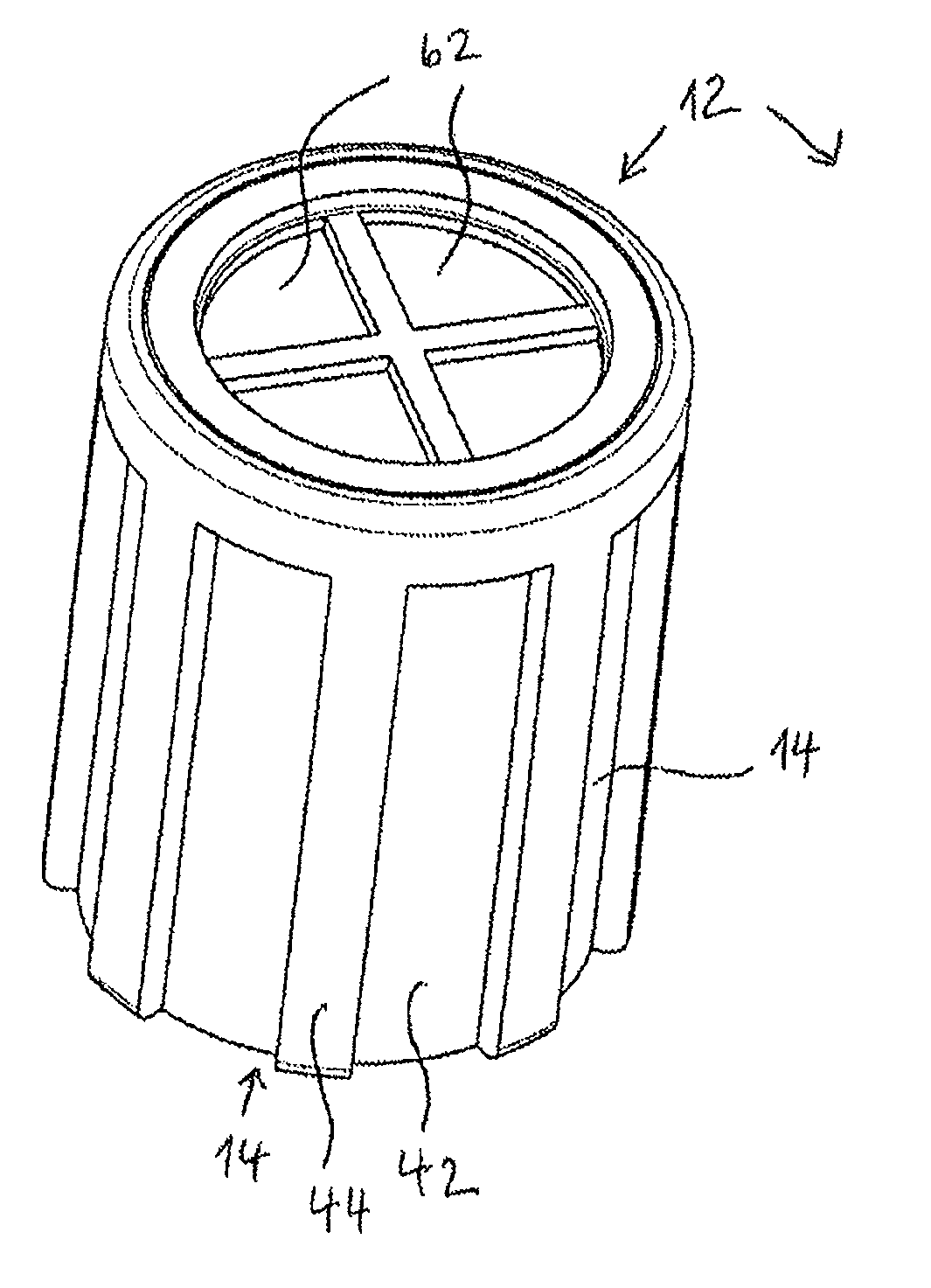
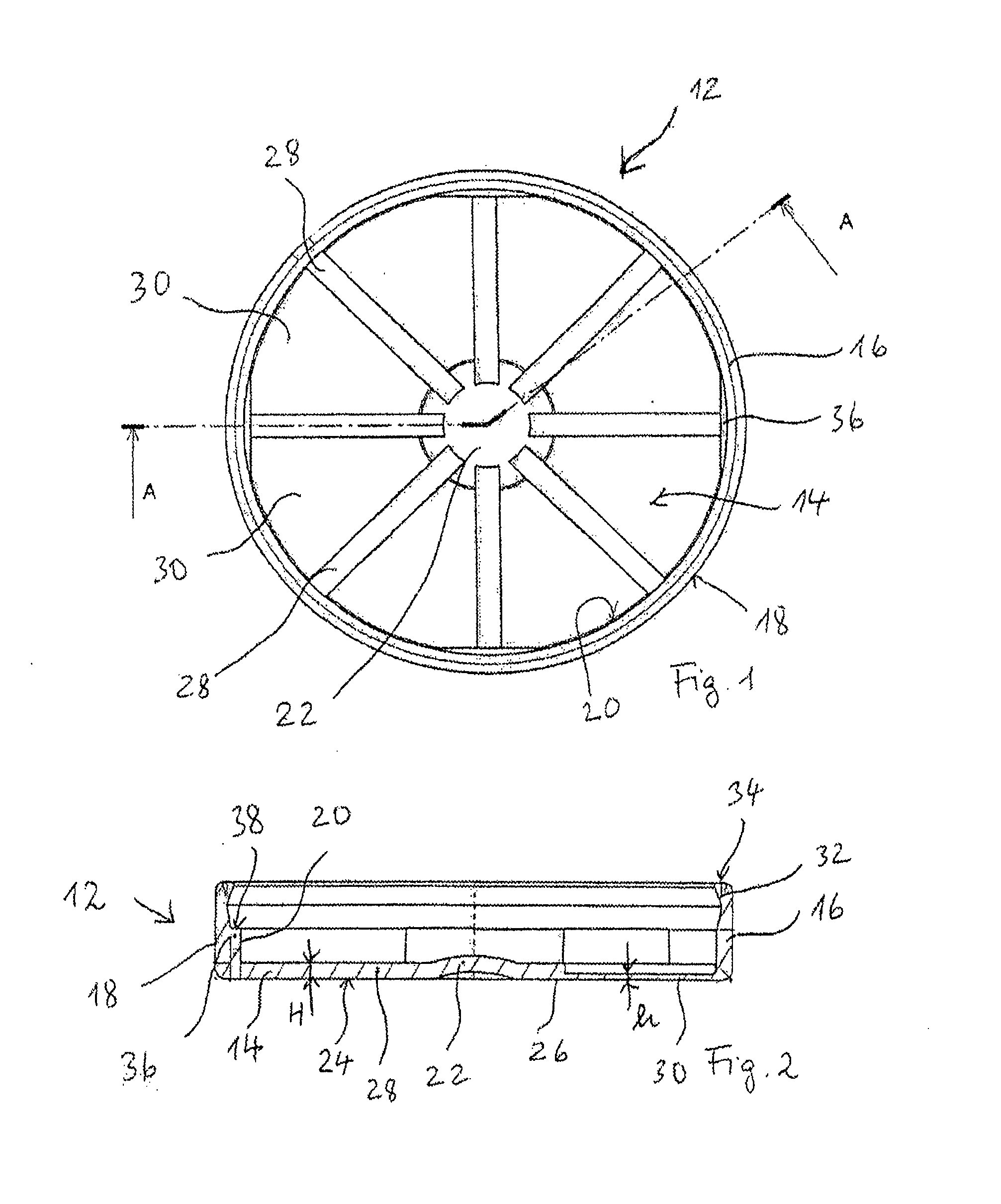
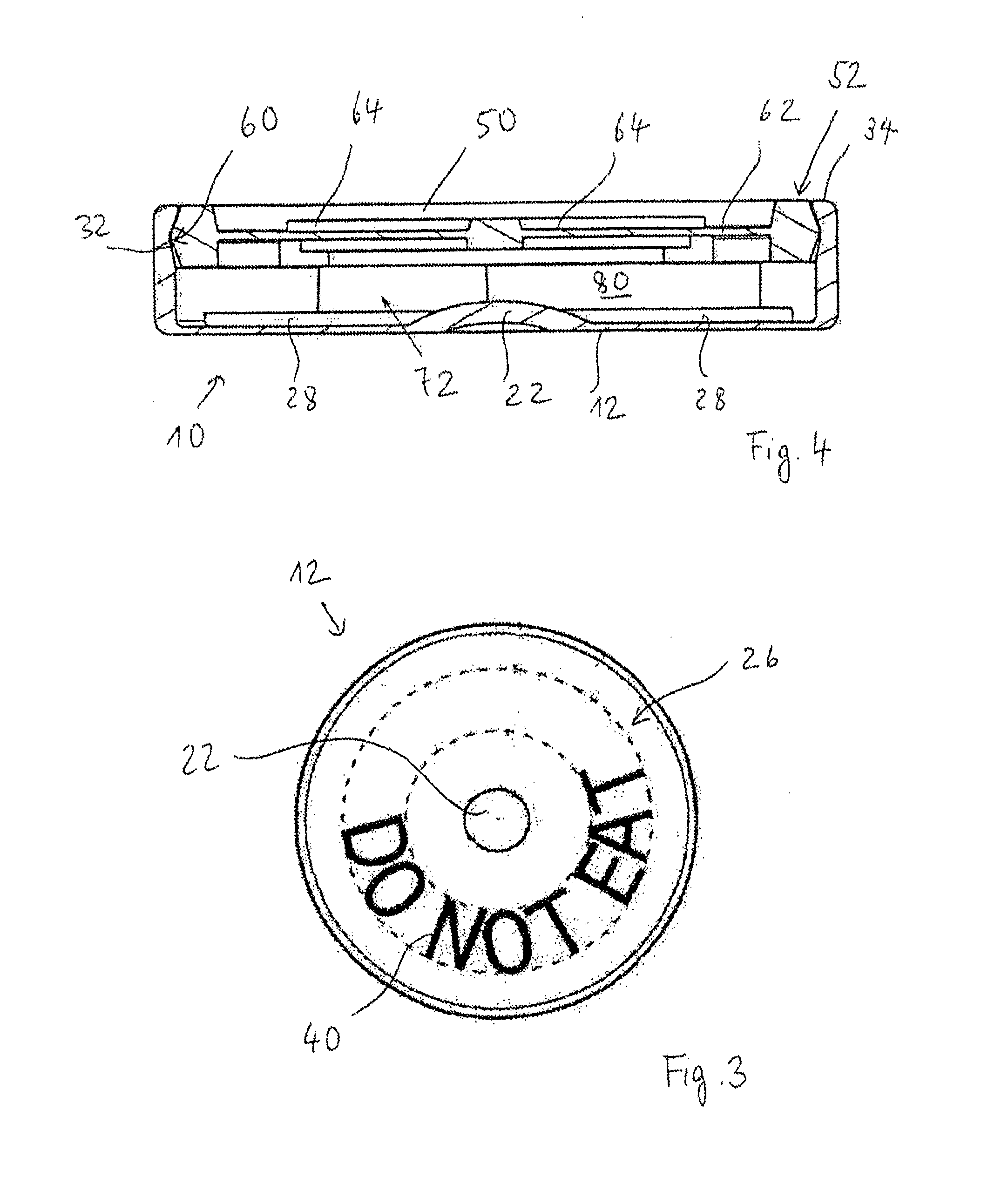
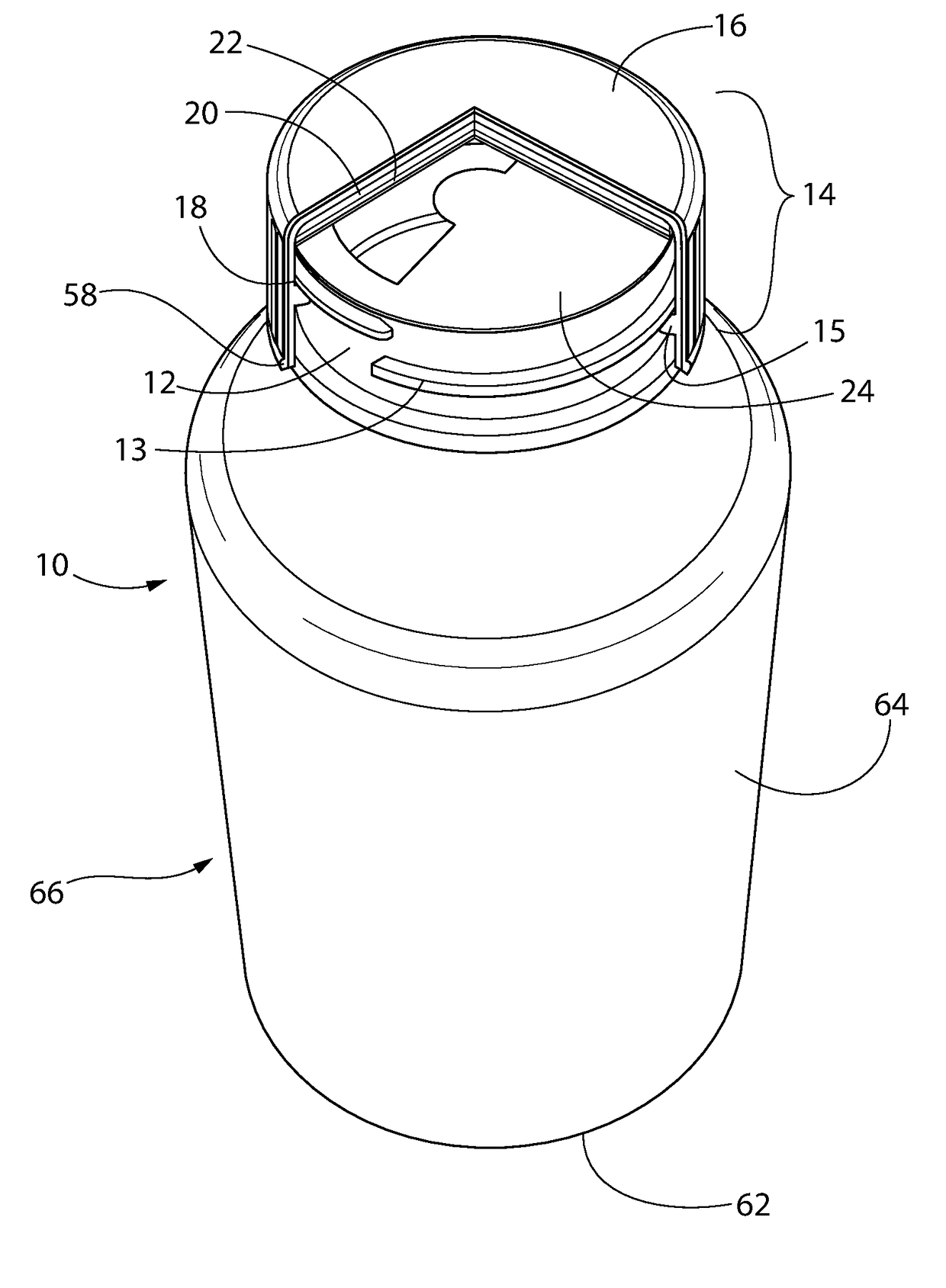
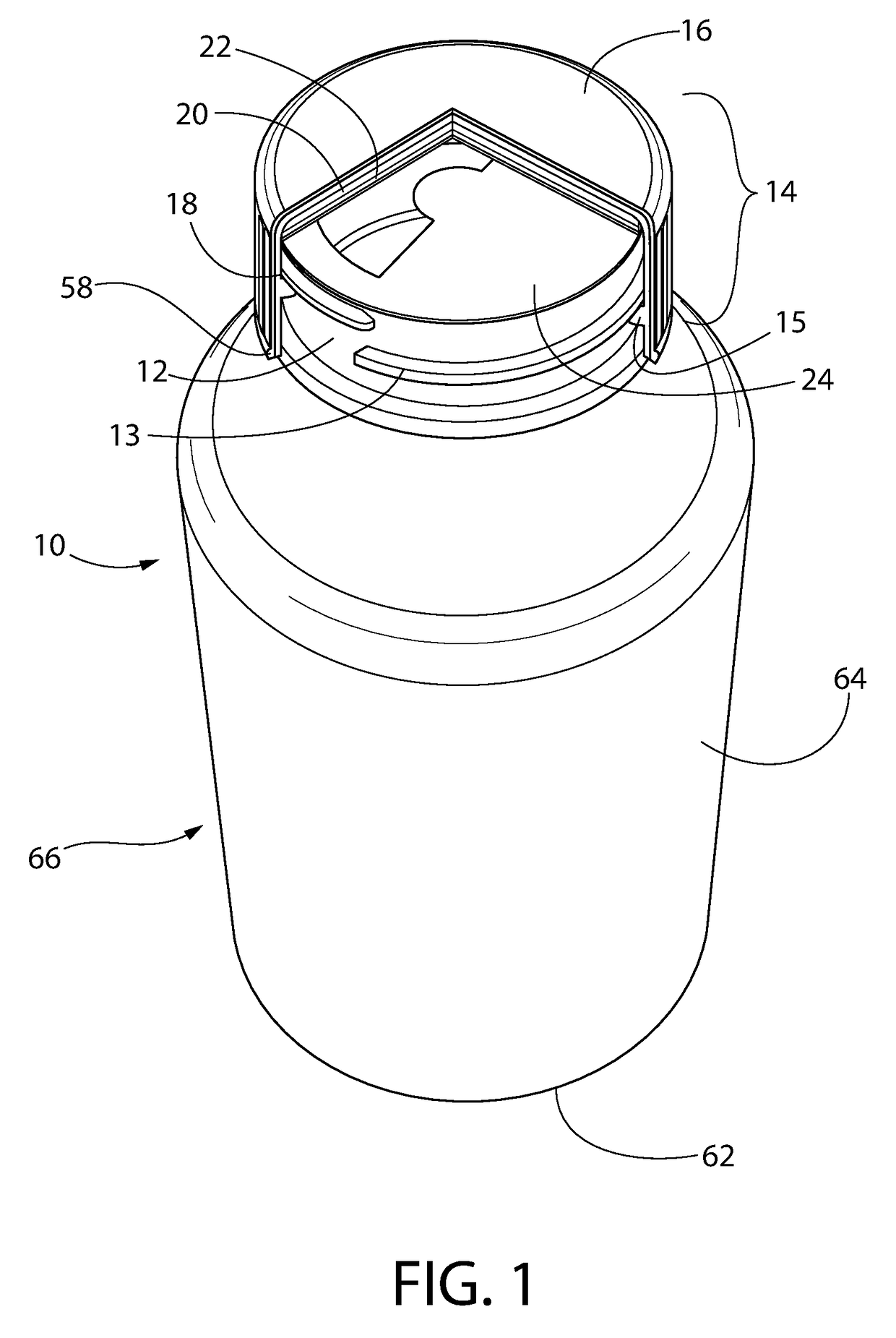
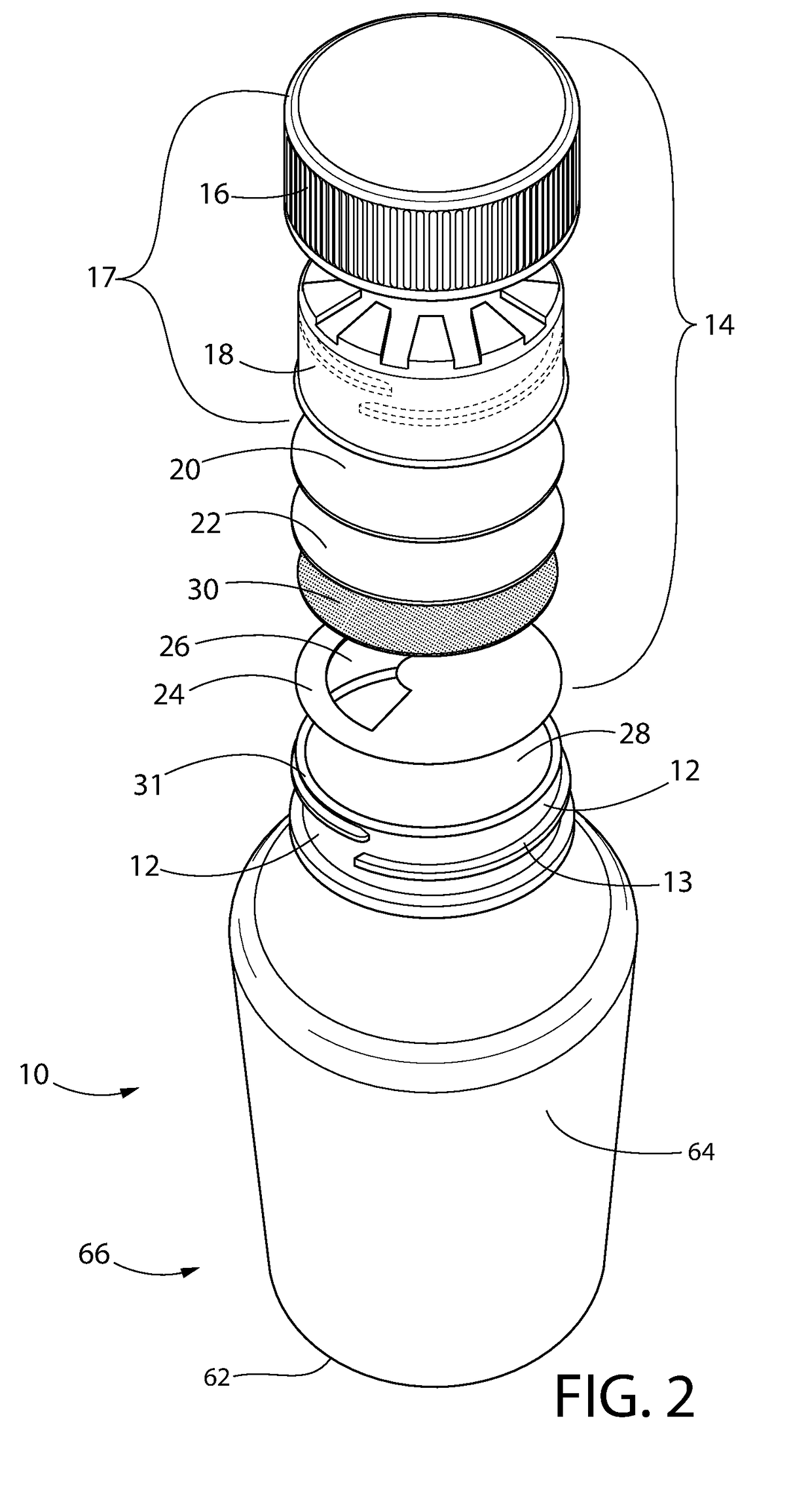
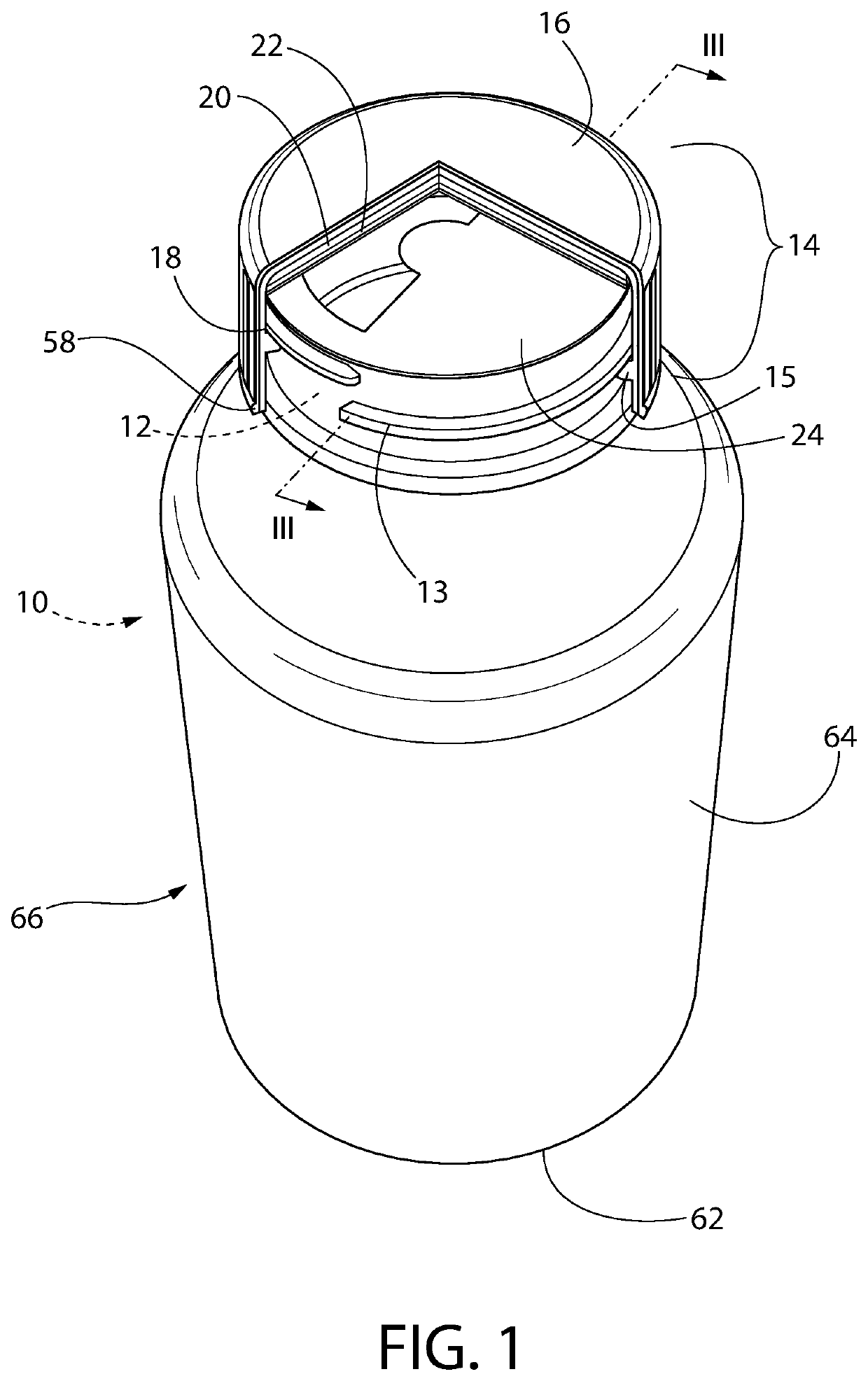
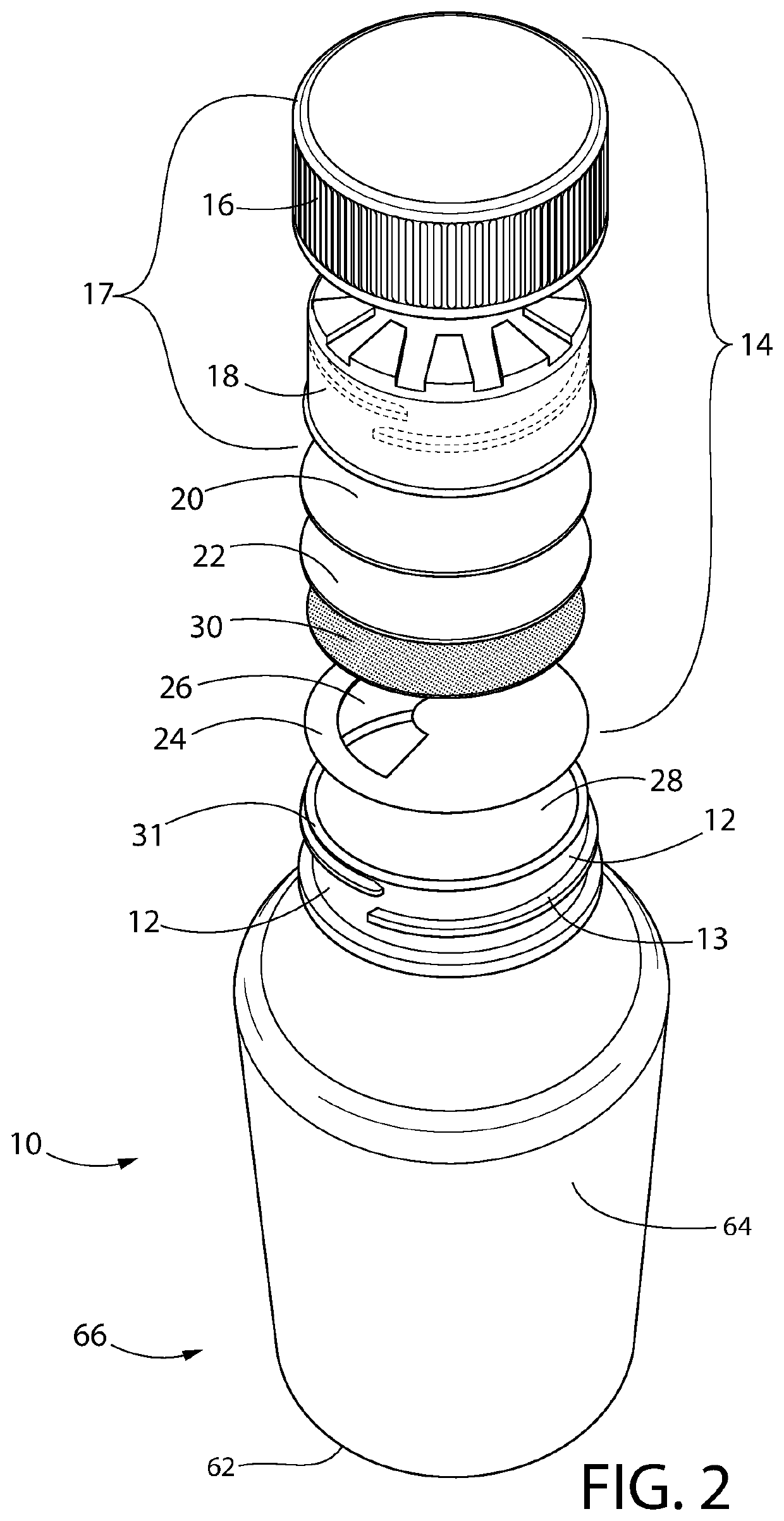
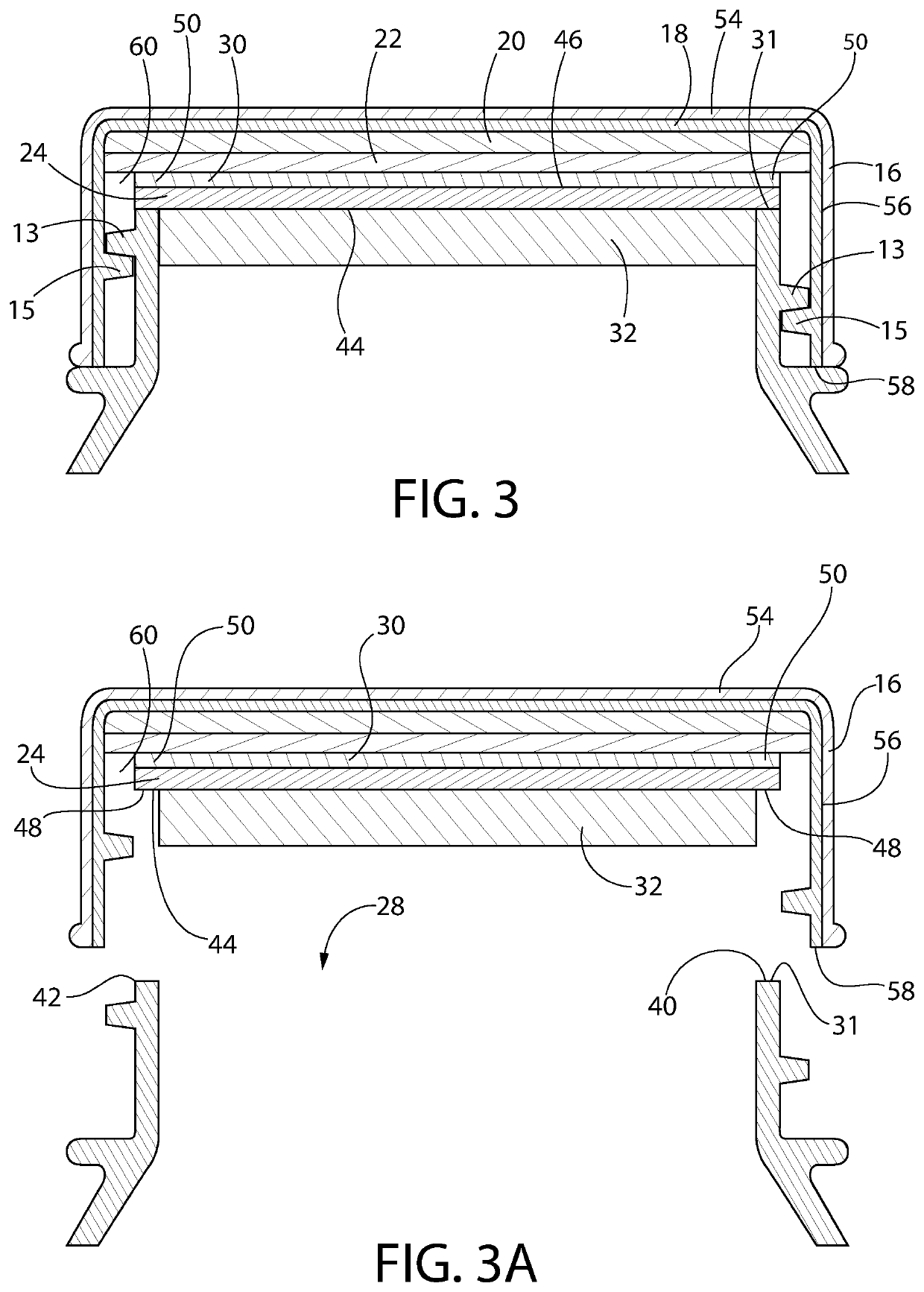
Bottle Stopper
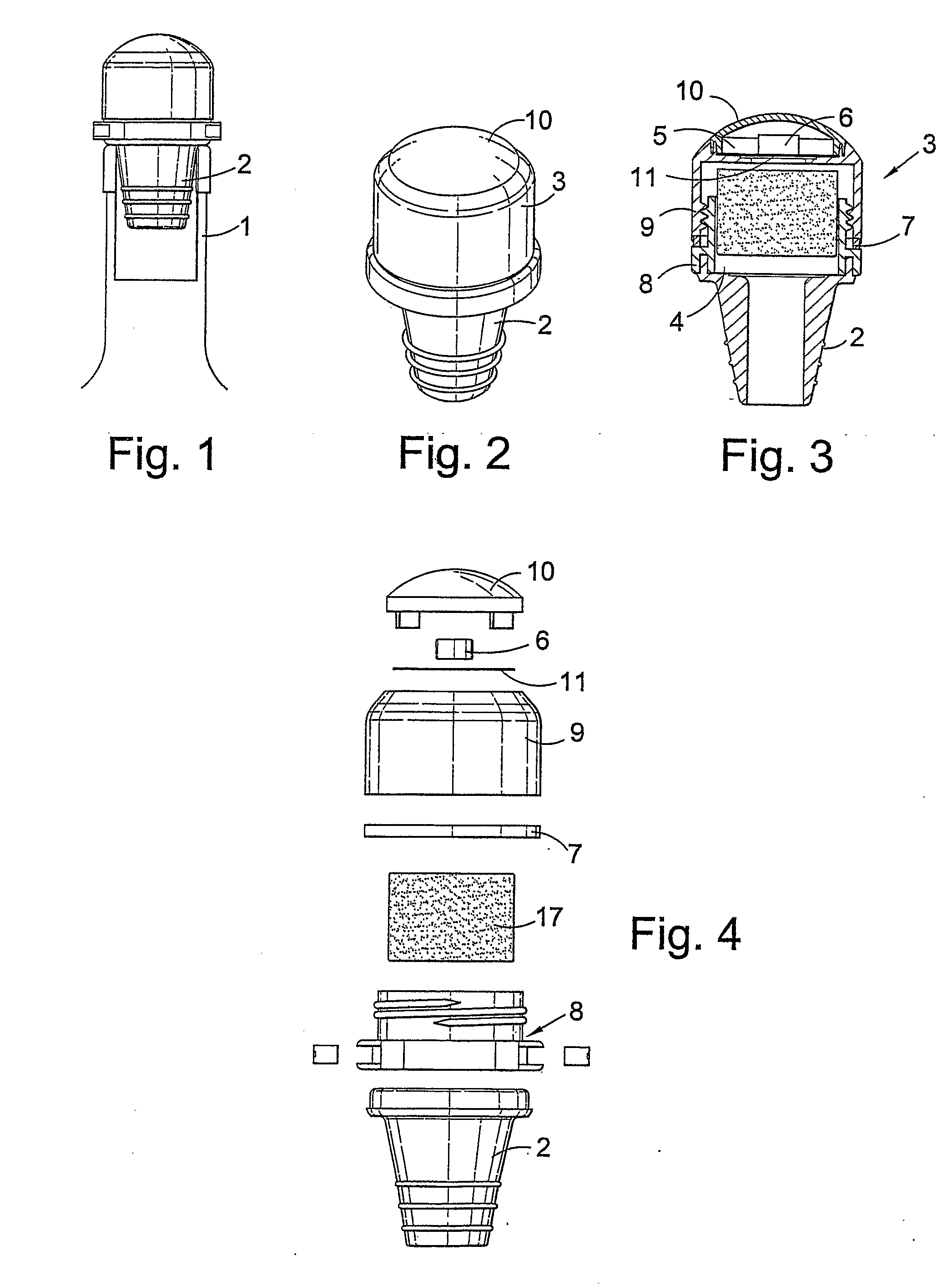
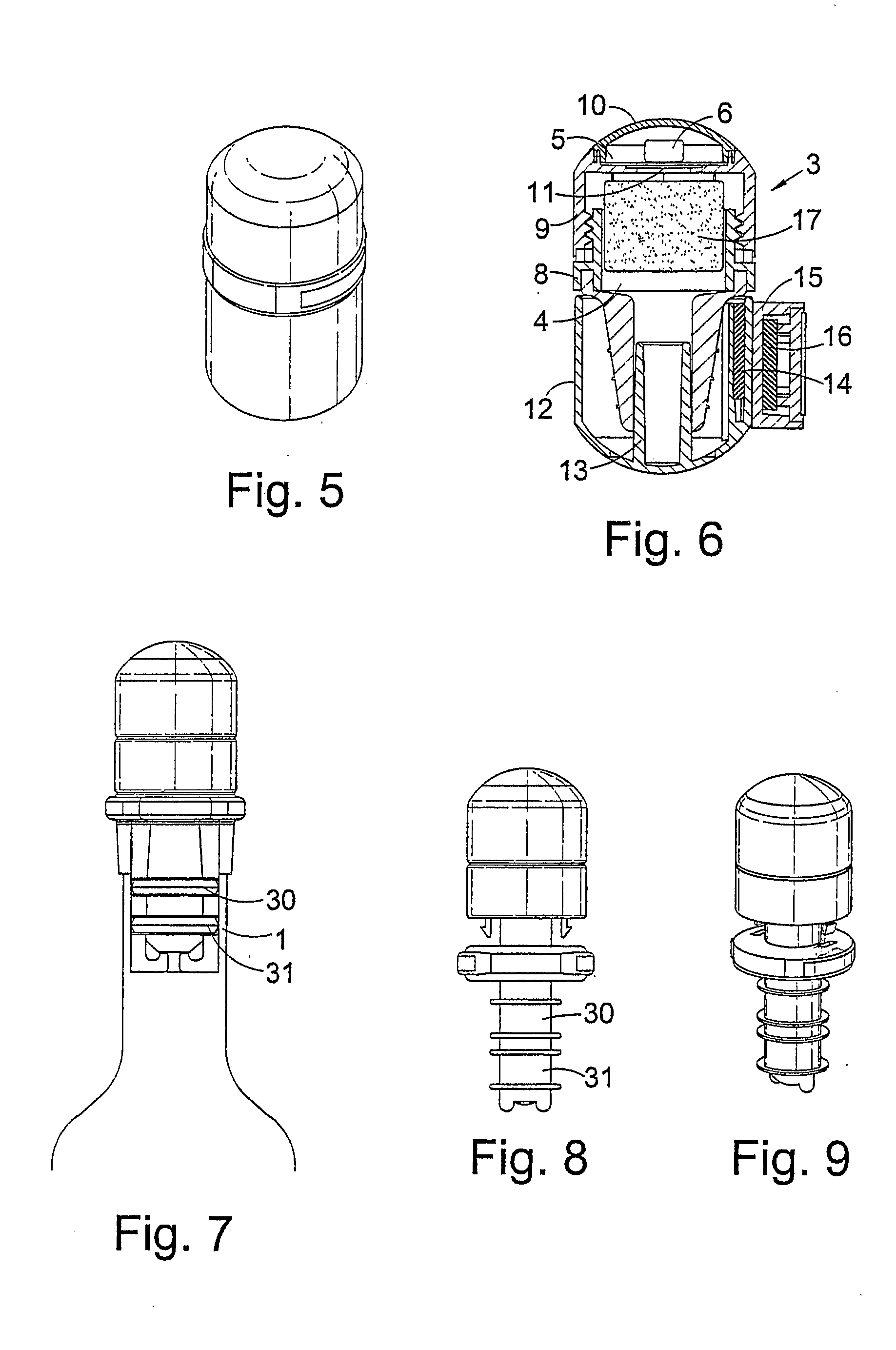
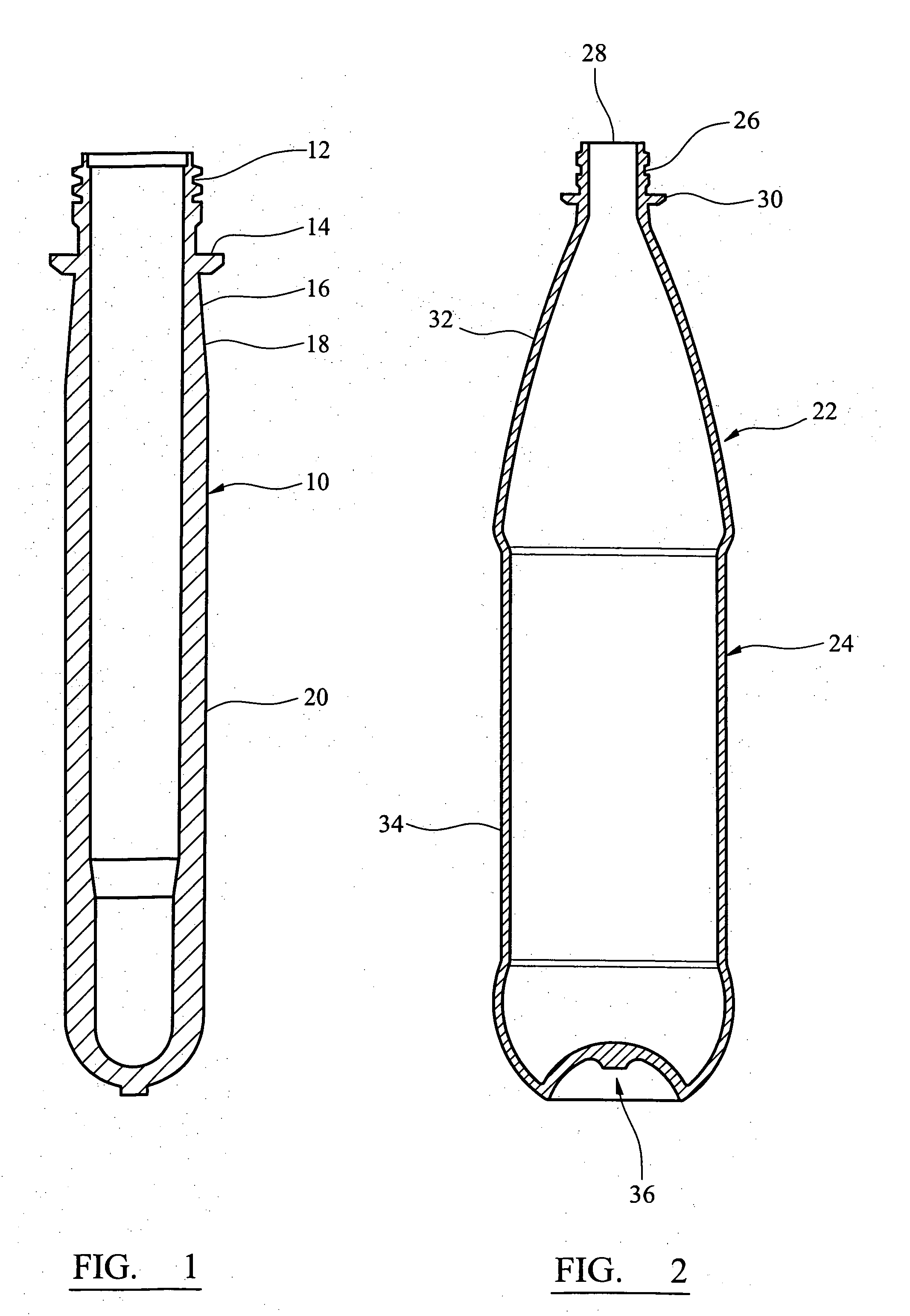
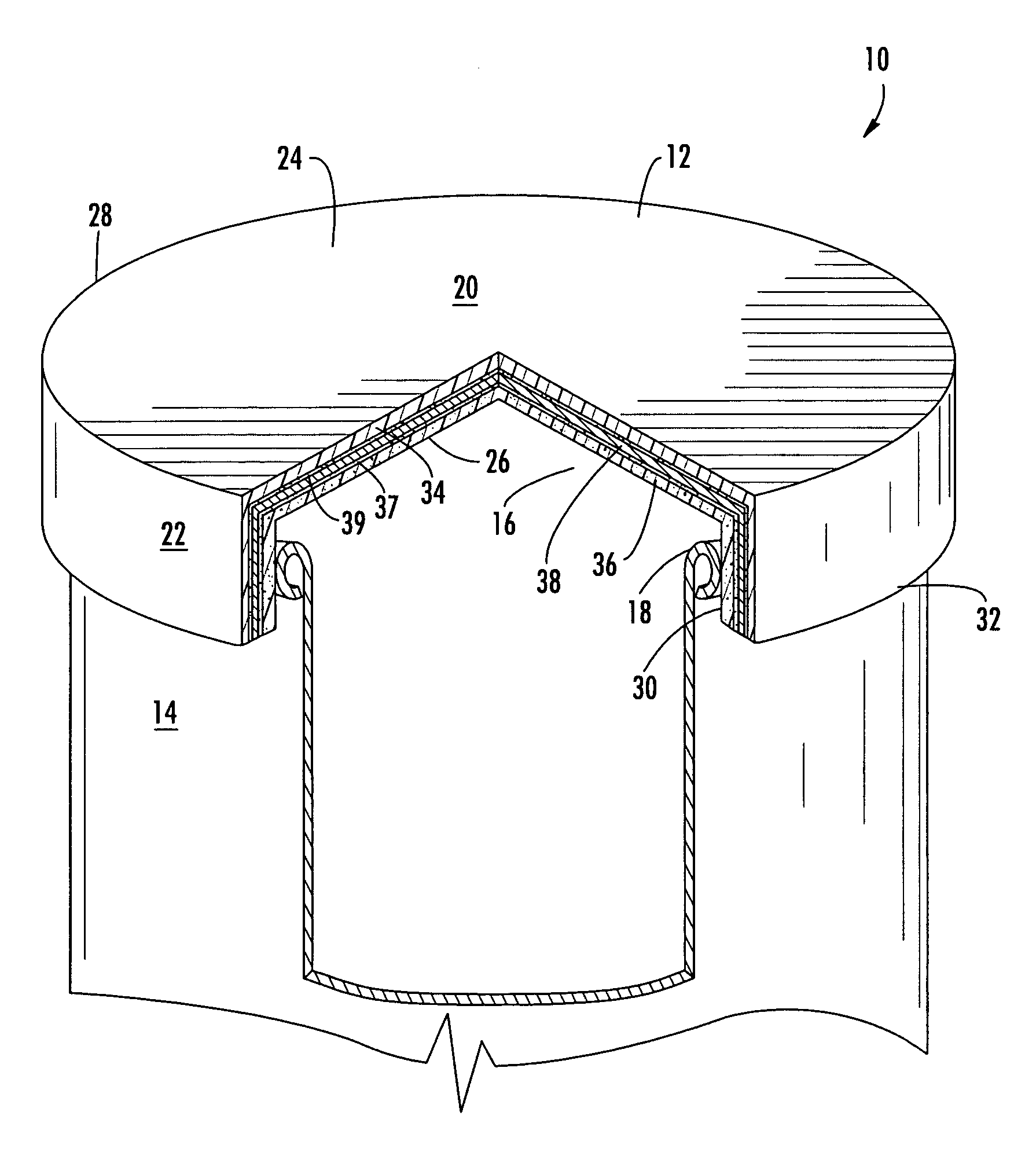
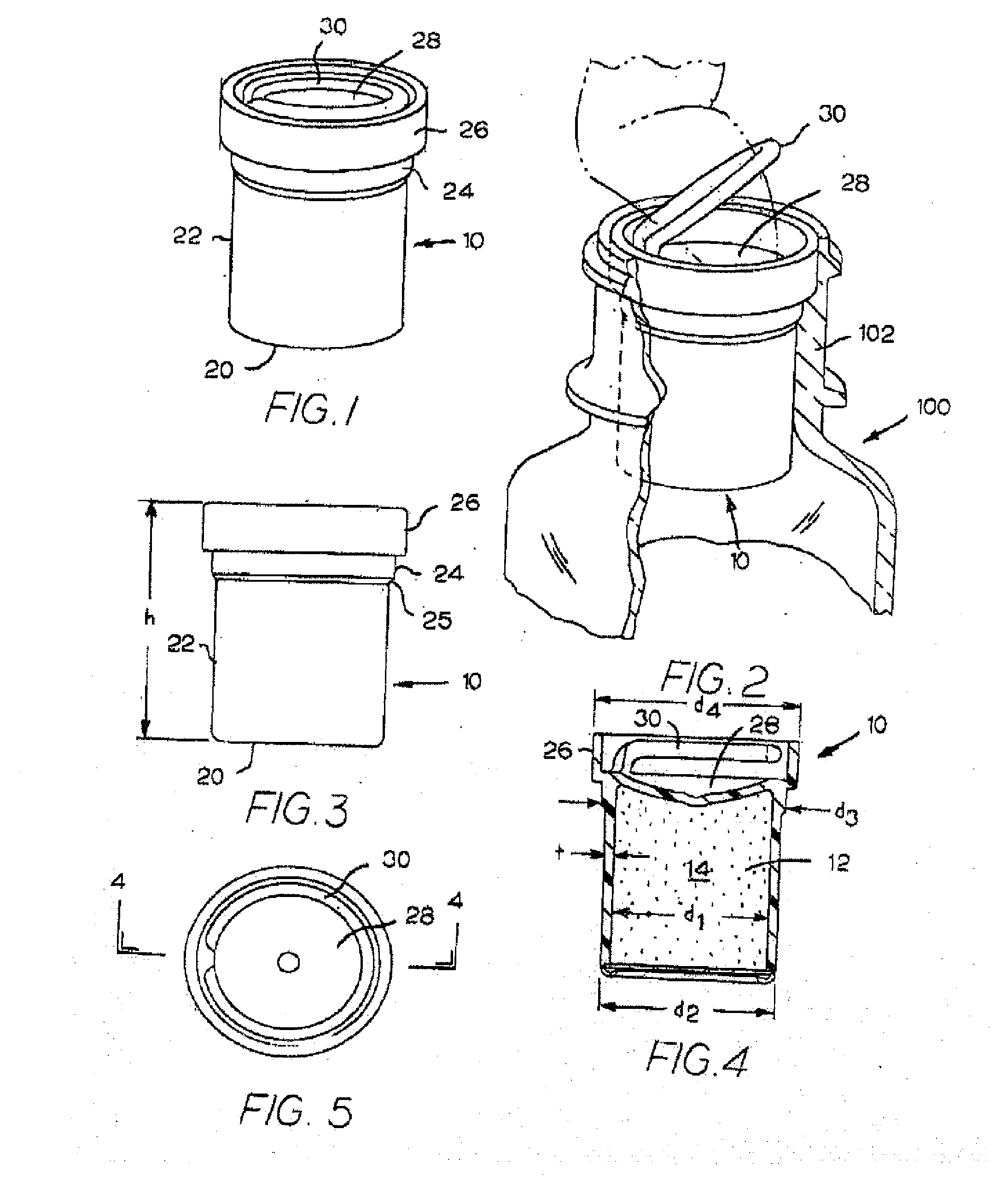
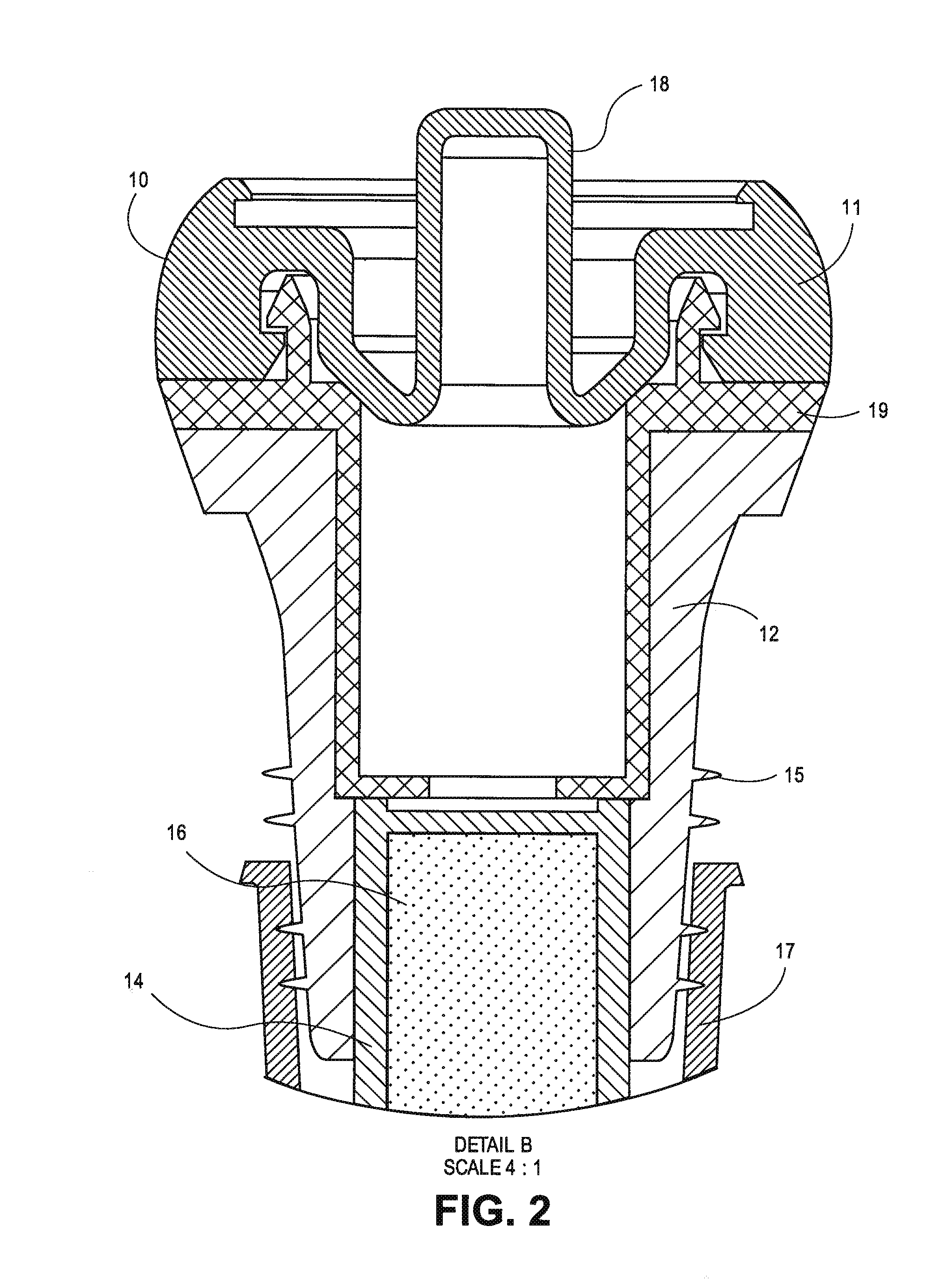
In one aspect the invention provides a bottle stopper for a wine bottle or the like, which bottle stopper comprises a body having a sealing member which sits within the peck (1) of the bottle in use and which extends radially outwardly from the body of the stopper to seal the bottle neck, the stopper further having a passageway extending upwardly therethrough to communicate with the interior of the bottle and which incorporates or communicates with a chamber within the stopper in which is housed an oxygen-scavenging medium. In a further aspect the invention provides a bottle stopper for a wine bottle or the like, which bottle stopper comprises a body having a sealing member (30, 31) which sits within the neck of the bottle in use and which extends radially outwardly from the body of the stopper to seal the bottle neck, the bottle stopper further having a mechanism for compressing the sealing member substantially axially of the stopper to expand the sealing member laterally / substantially radially of the stopper into sealing contact with the neck of the bottle.
Owner:LAPORTA GIOVANNI MARIA
Scavenging oxygen
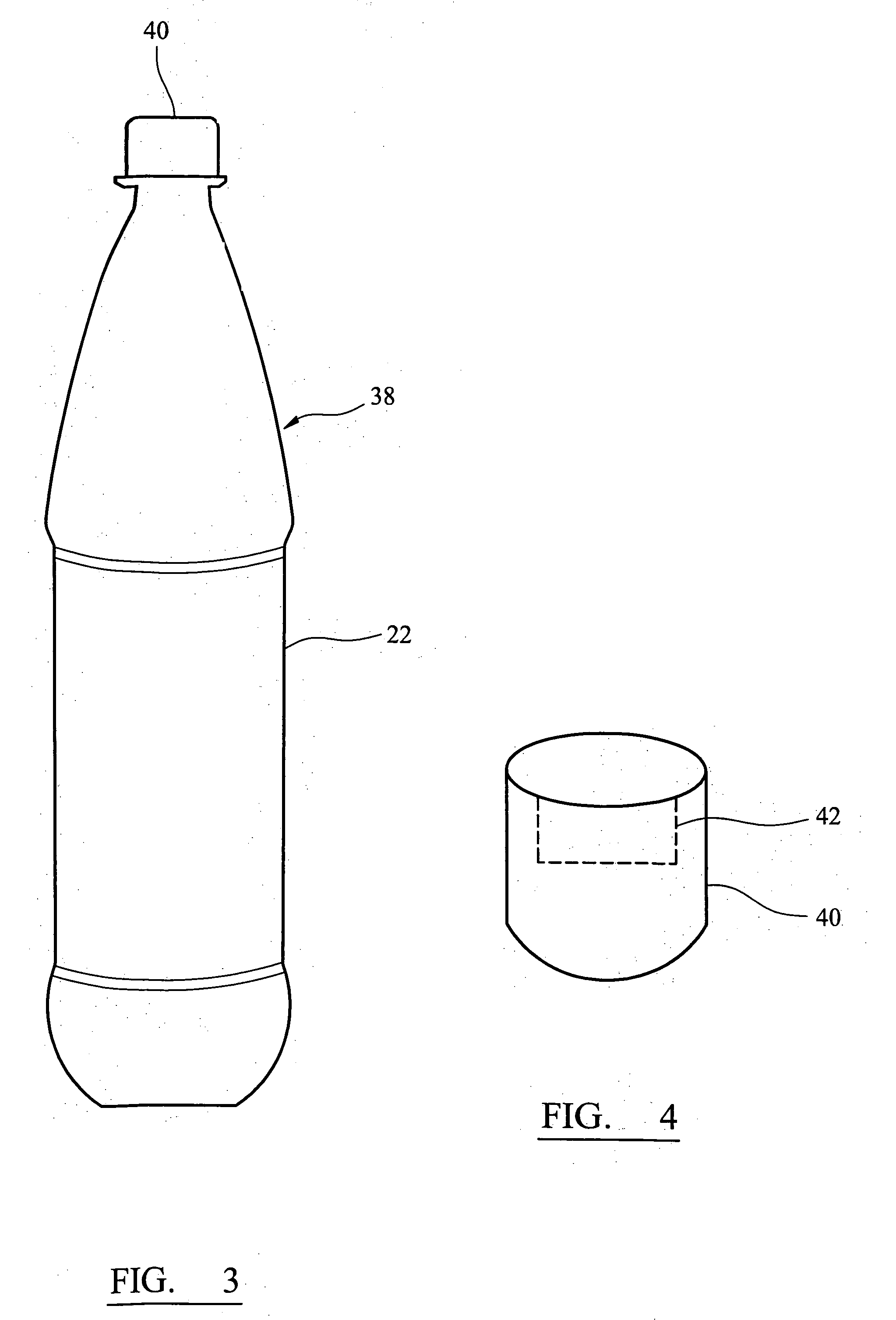
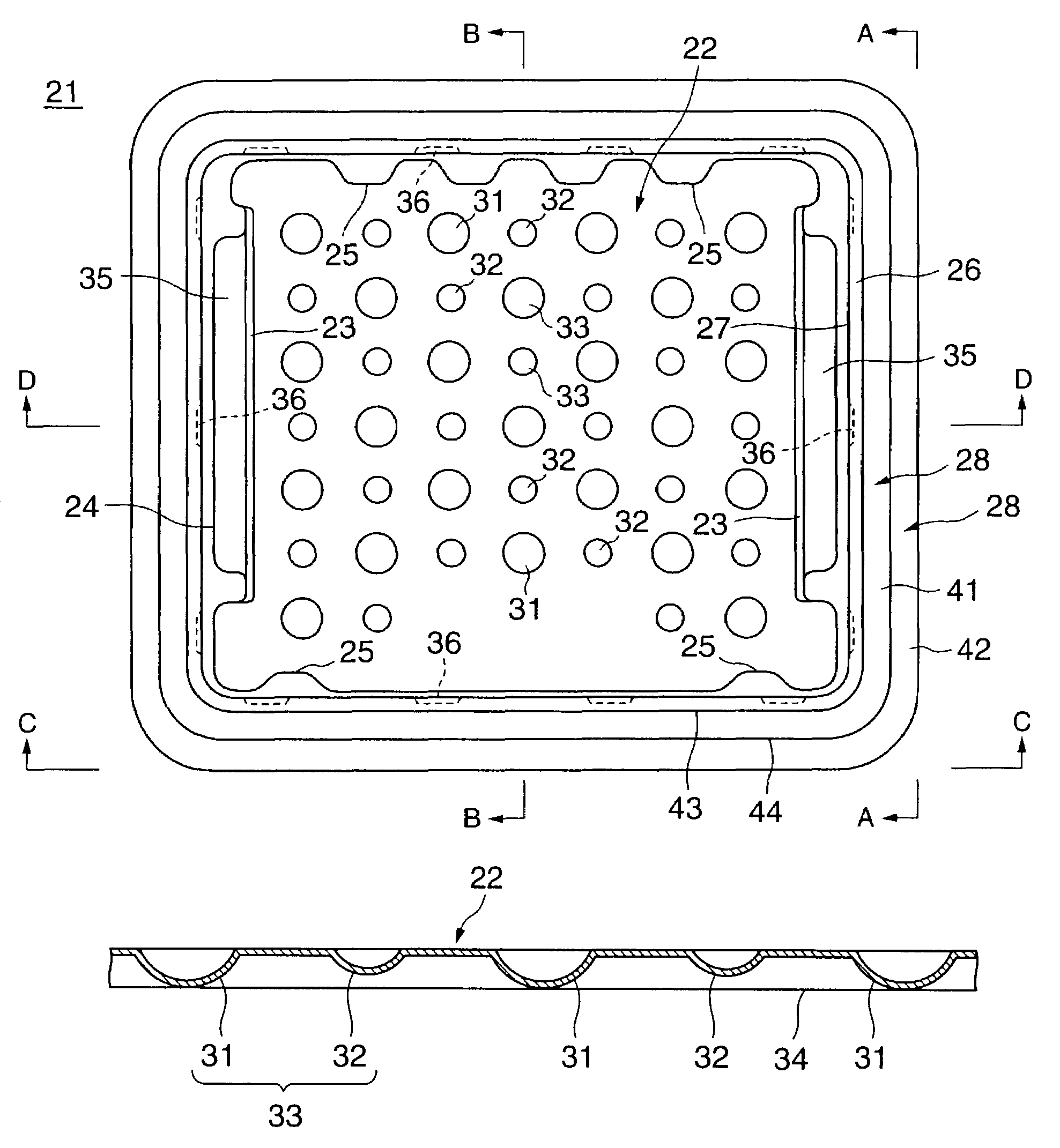
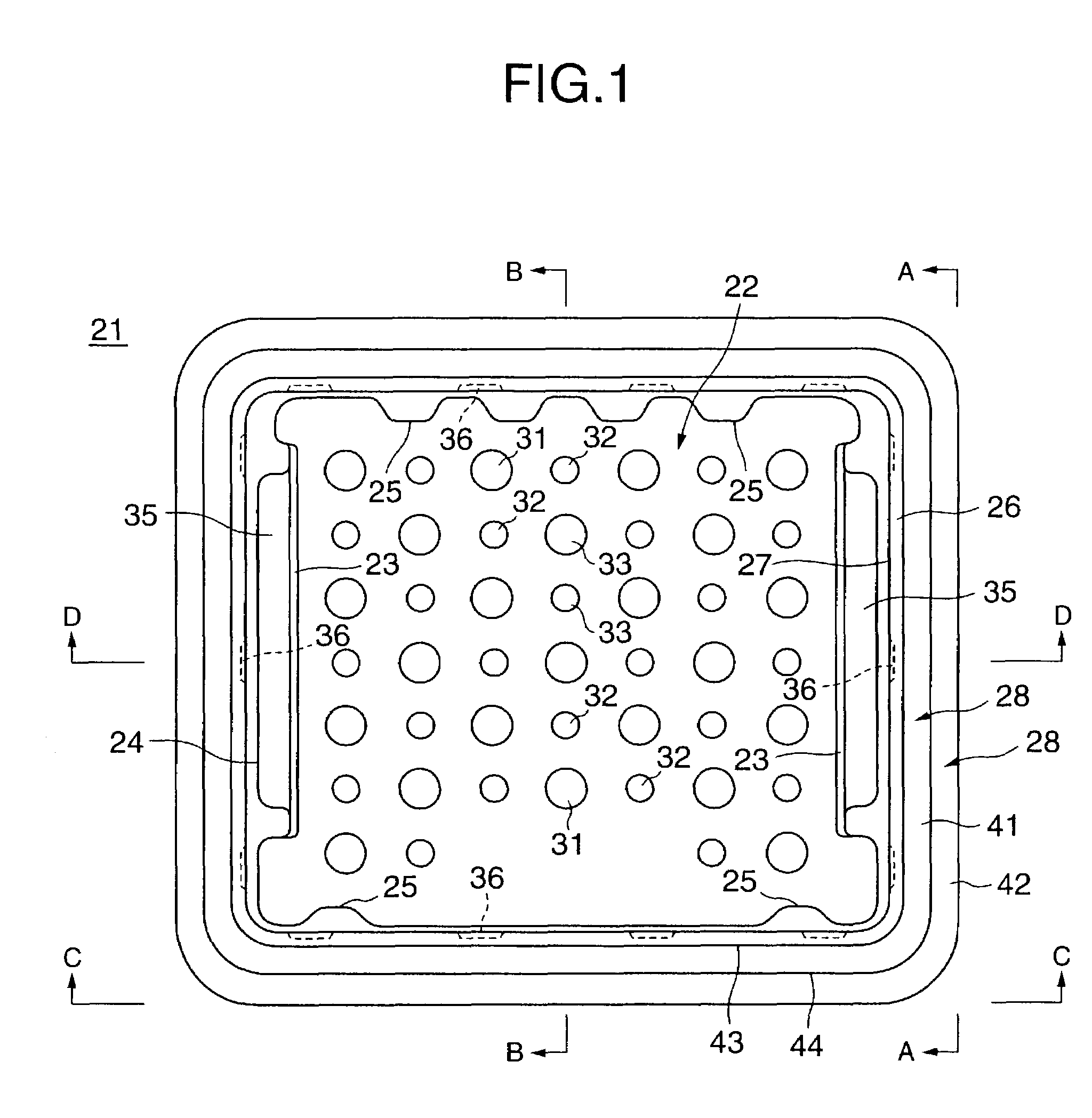
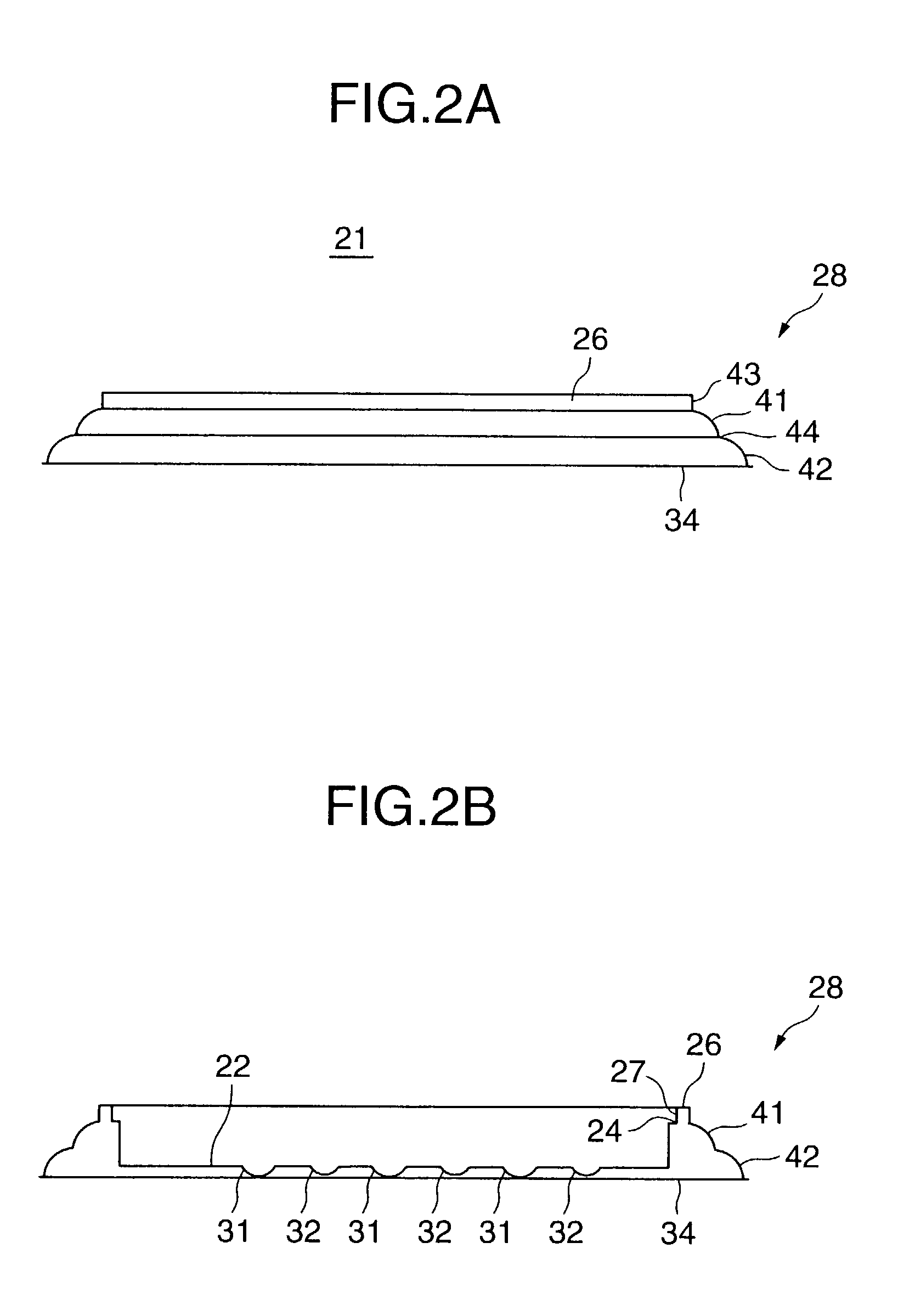
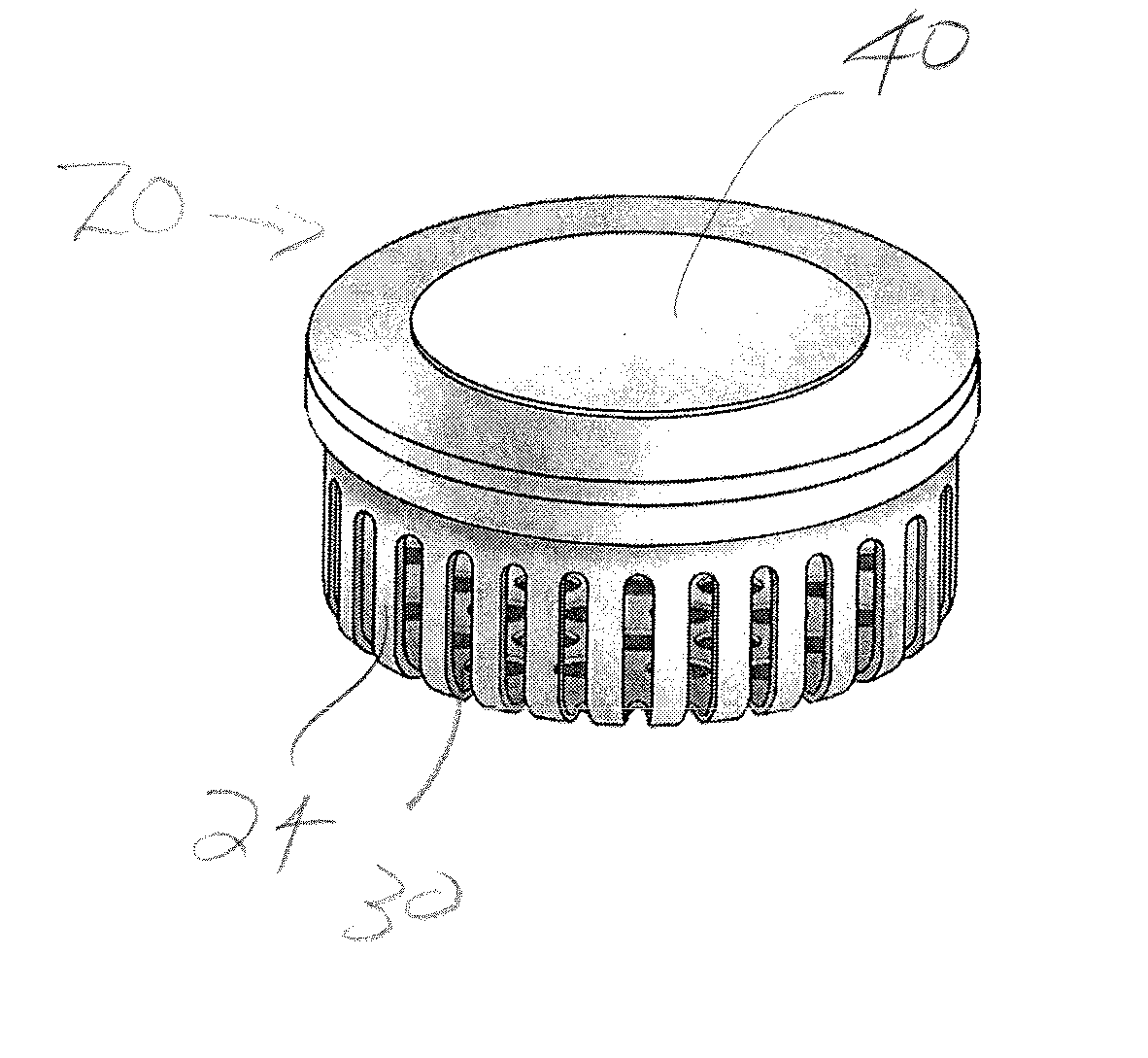
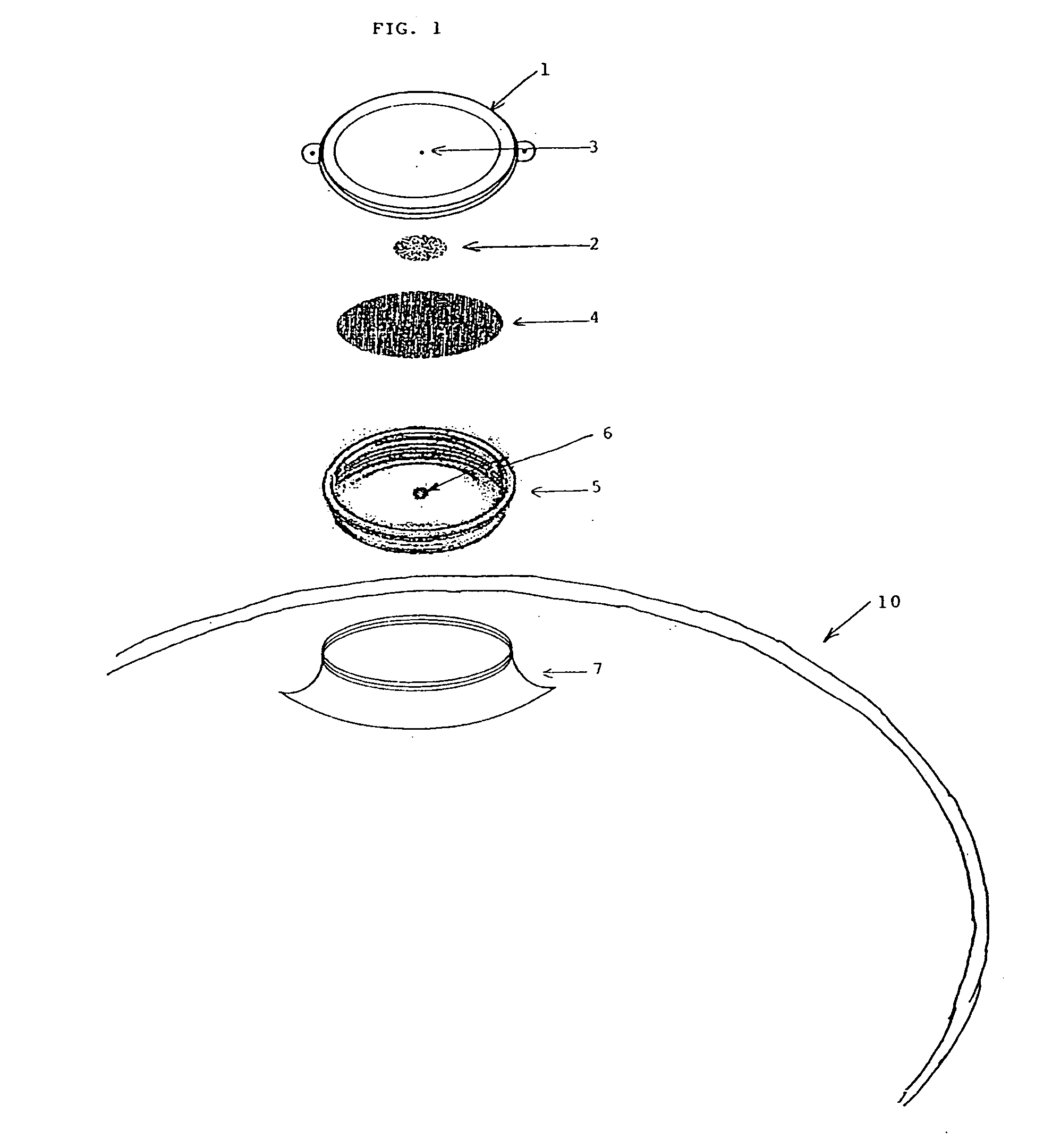
InactiveUS20100028499A1Increase response rateSmall amountClosures with oxygen absorbersFruit and vegetables preservationWater vaporPalladium catalyst
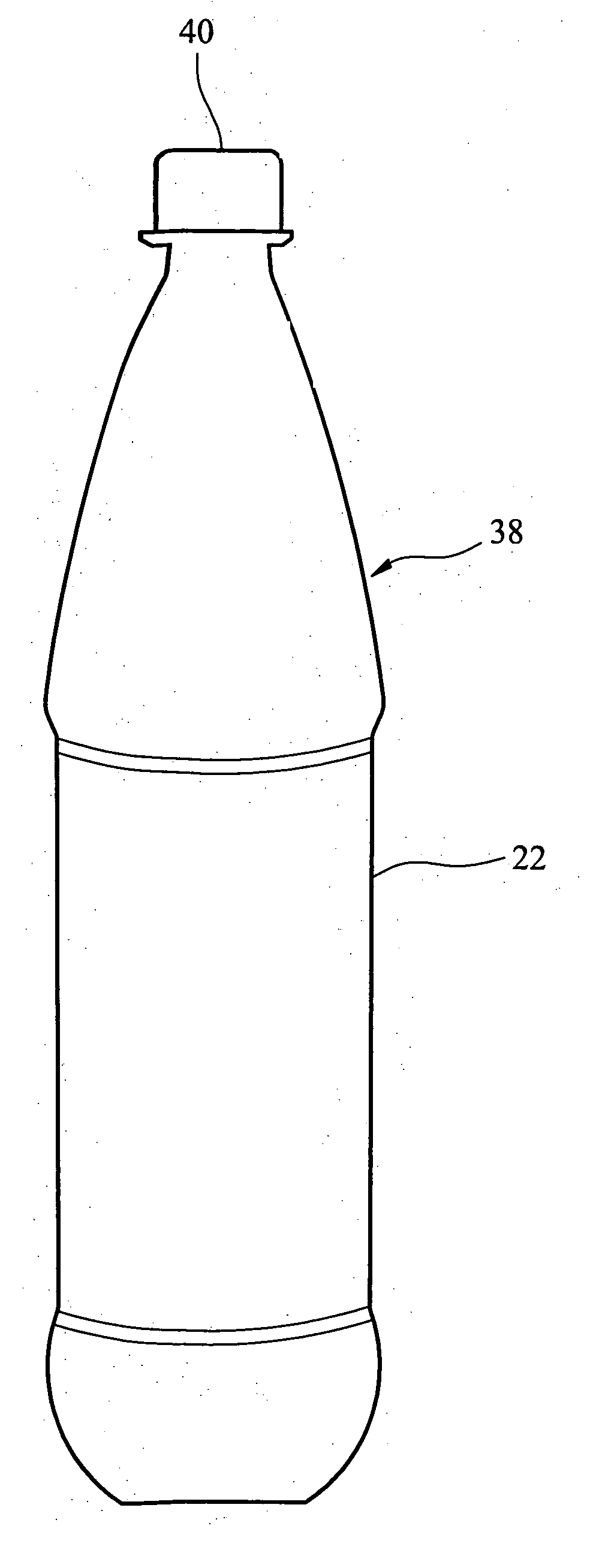
A container (22) includes a shell (24) made from a polymer, for example PET, and incorporating a catalyst, for example a palladium catalyst. A closure (40) incorporates a plug which includes a source of hydrogen, for example a hydride. In use, with container (22) including a beverage and closure (40) in position, the headspace in the container will be saturated with water vapor. This vapor contacts the hydride associated with plug (42) and as a result the hydride produces molecular hydrogen which migrates into the polymer matrix of shell (24) and combines with oxygen which may have entered the container through its permeable walls. A reaction between the hydrogen and oxygen takes place, catalysed by the catalyst, and water is produced. Thus, oxygen which may ingress the container is scavenged and the contents of the container are protected from oxidation.
Owner:COLORMATRIX HLDG
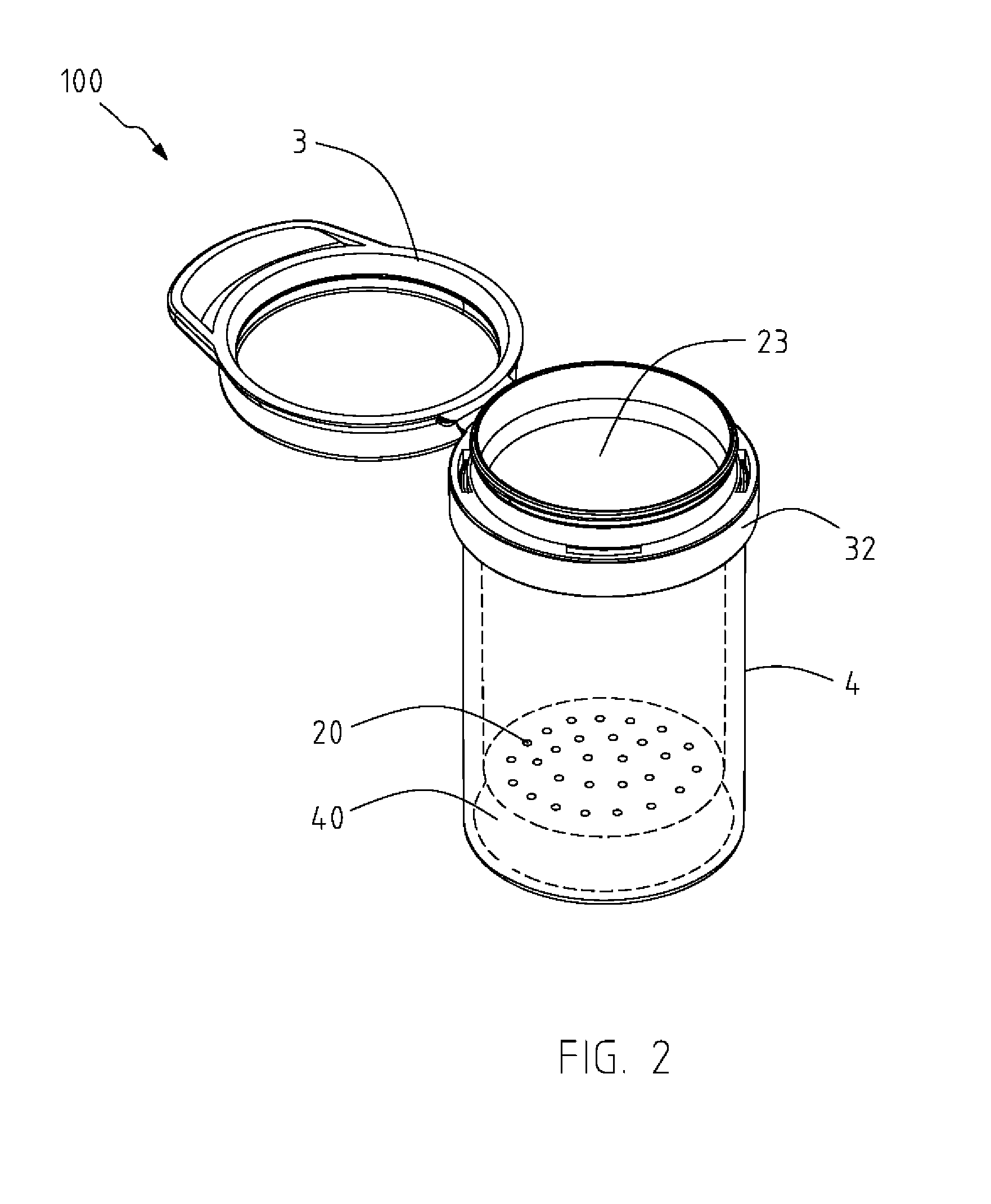
Tray pack and packaging structure
InactiveUS7093717B2Effective elastic deformationShock diffusion effectContainers to prevent mechanical damageTray containersEngineeringSynthetic resin
The object of the invention is to construct a simple packaging structure having few components and capable of protecting a contained product against shock impacts coming from all directions. To this end, the packaging structure according to the present invention is made of synthetic resin with an elastic quality molded into a sheet form, and includes a first tray pack and a second tray pack which face each other and are adjoined to hold the contained product securely in place; wherein the first and second tray packs are provided with sustaining portions sustaining the periphery of the contained product.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
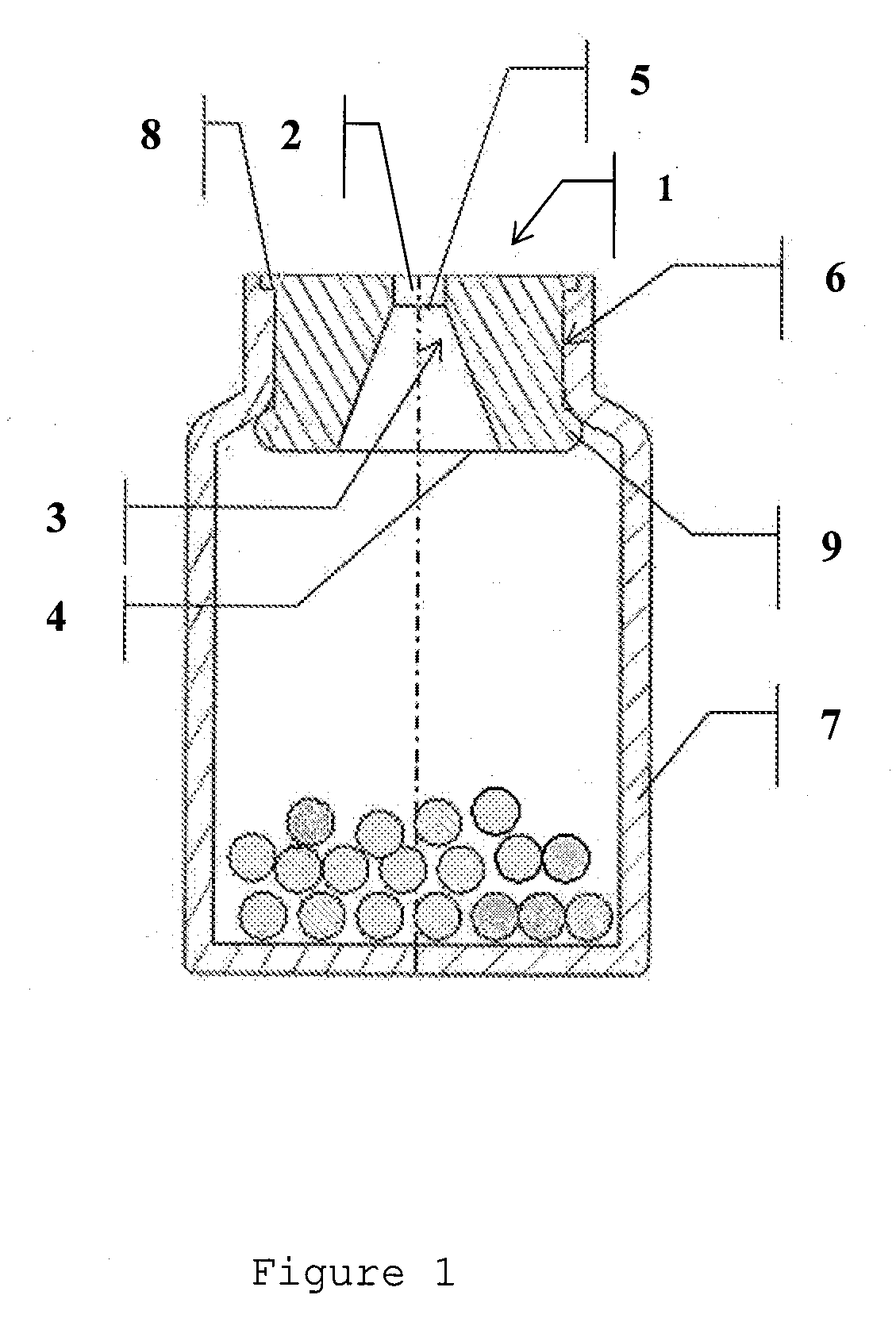
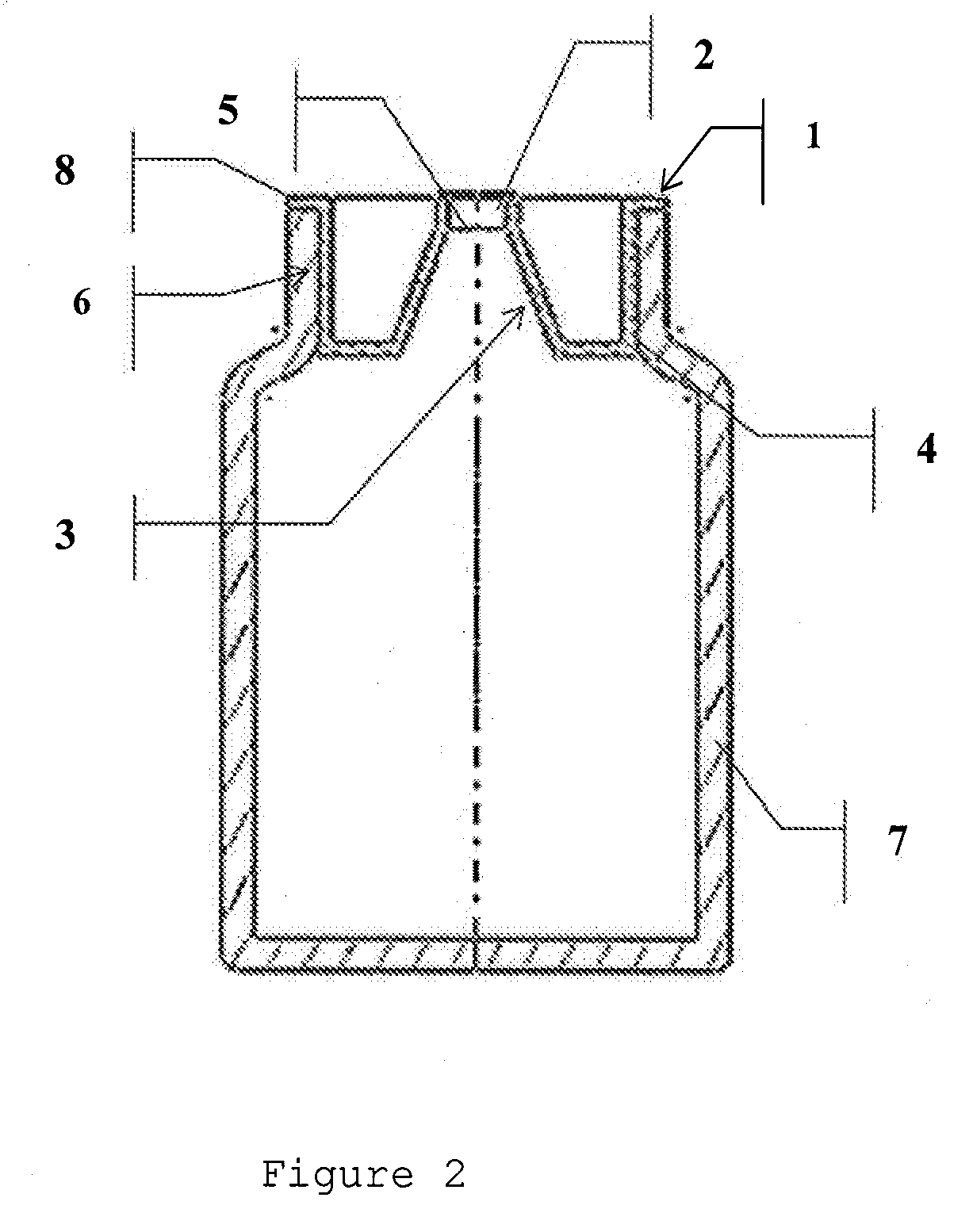
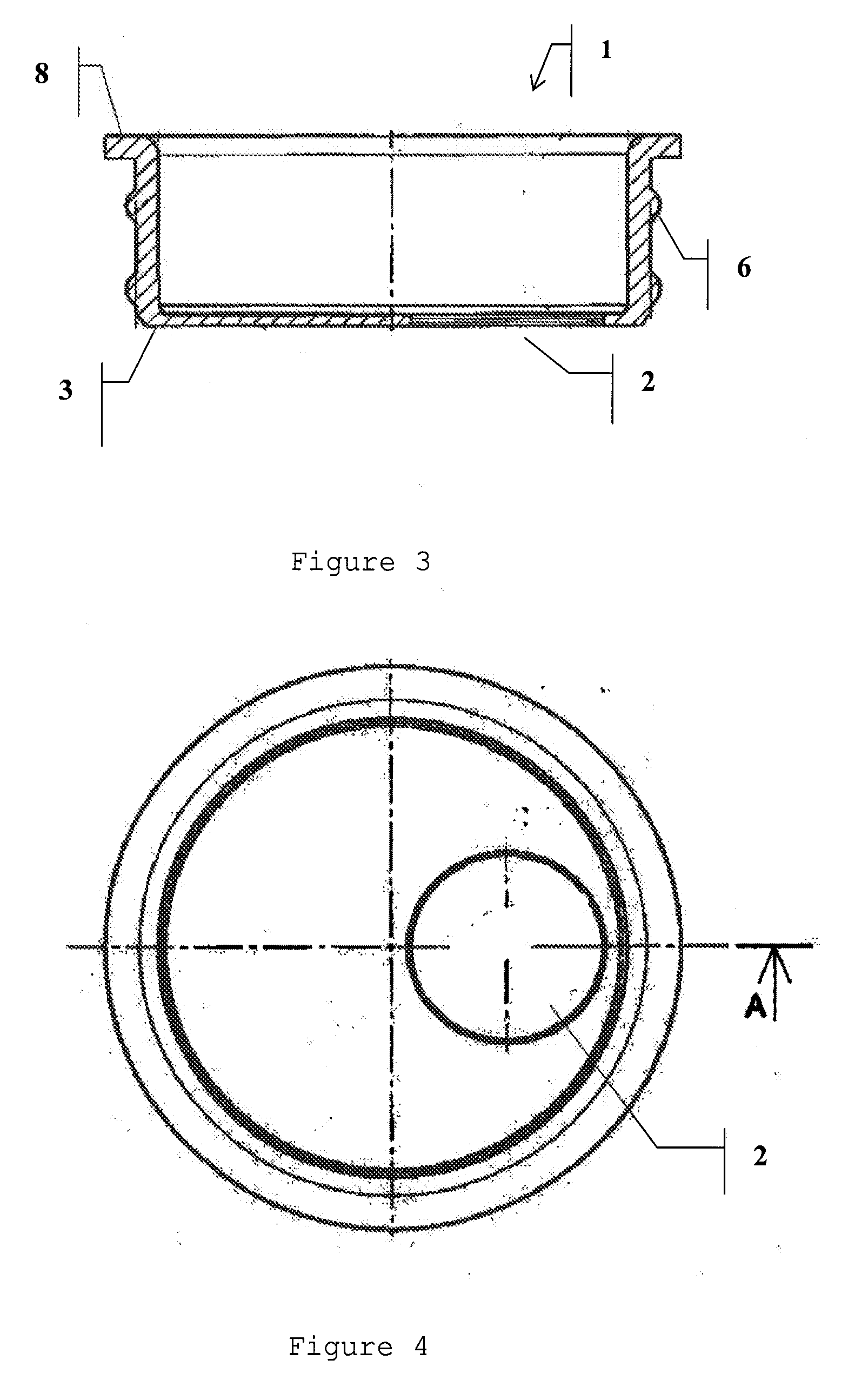
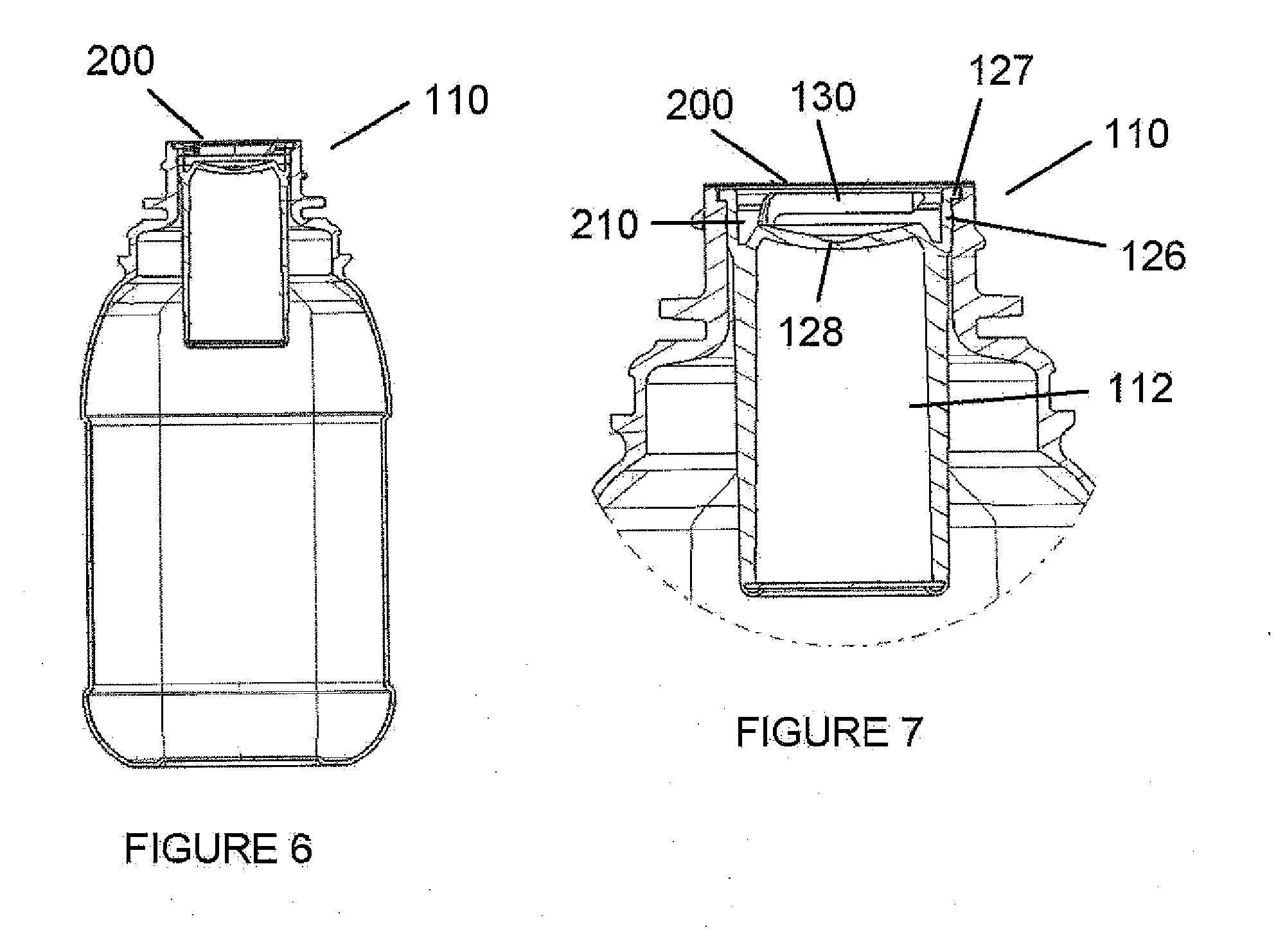
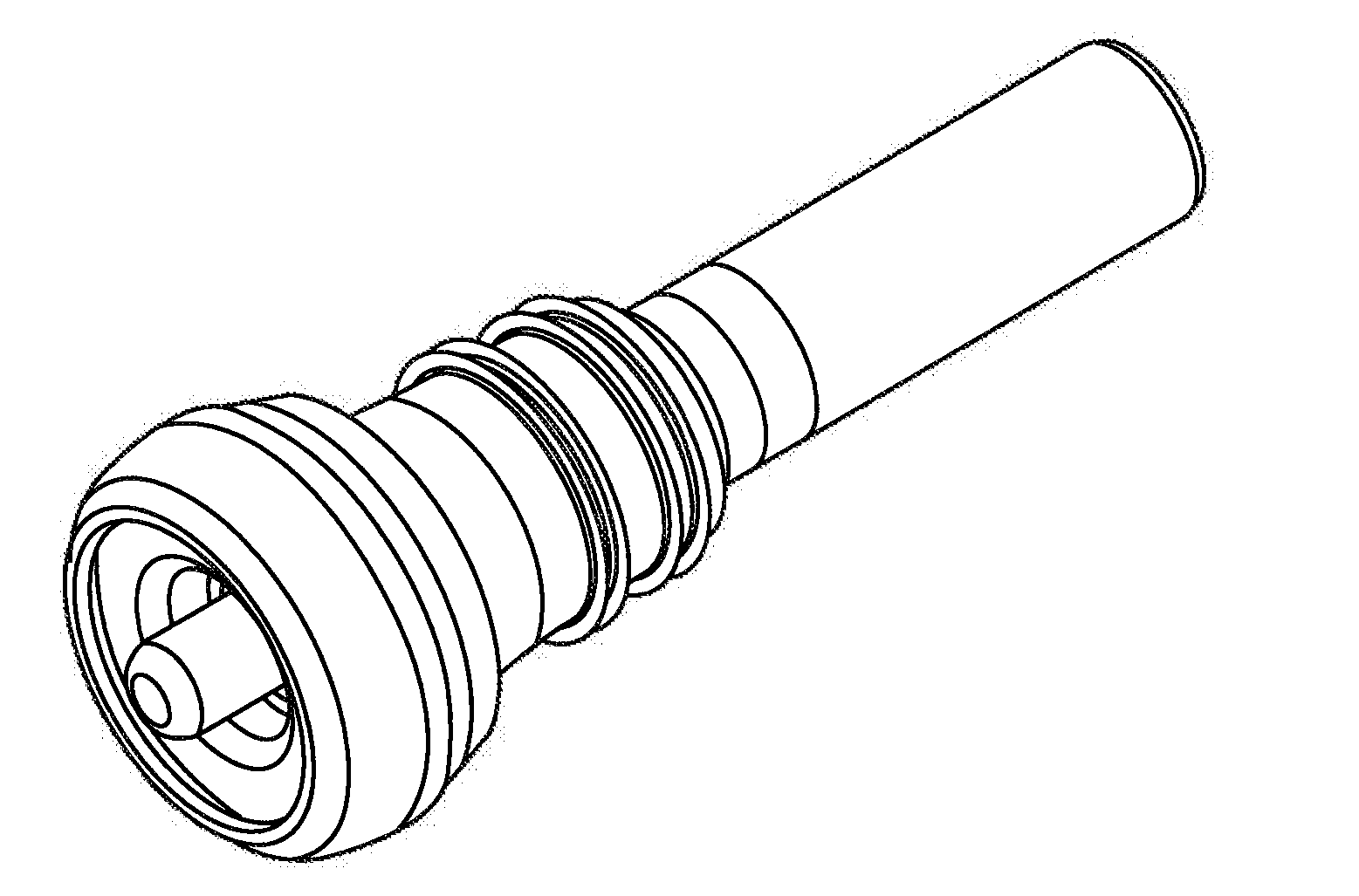
Container oxygen-scavenging apparatus and methods of use
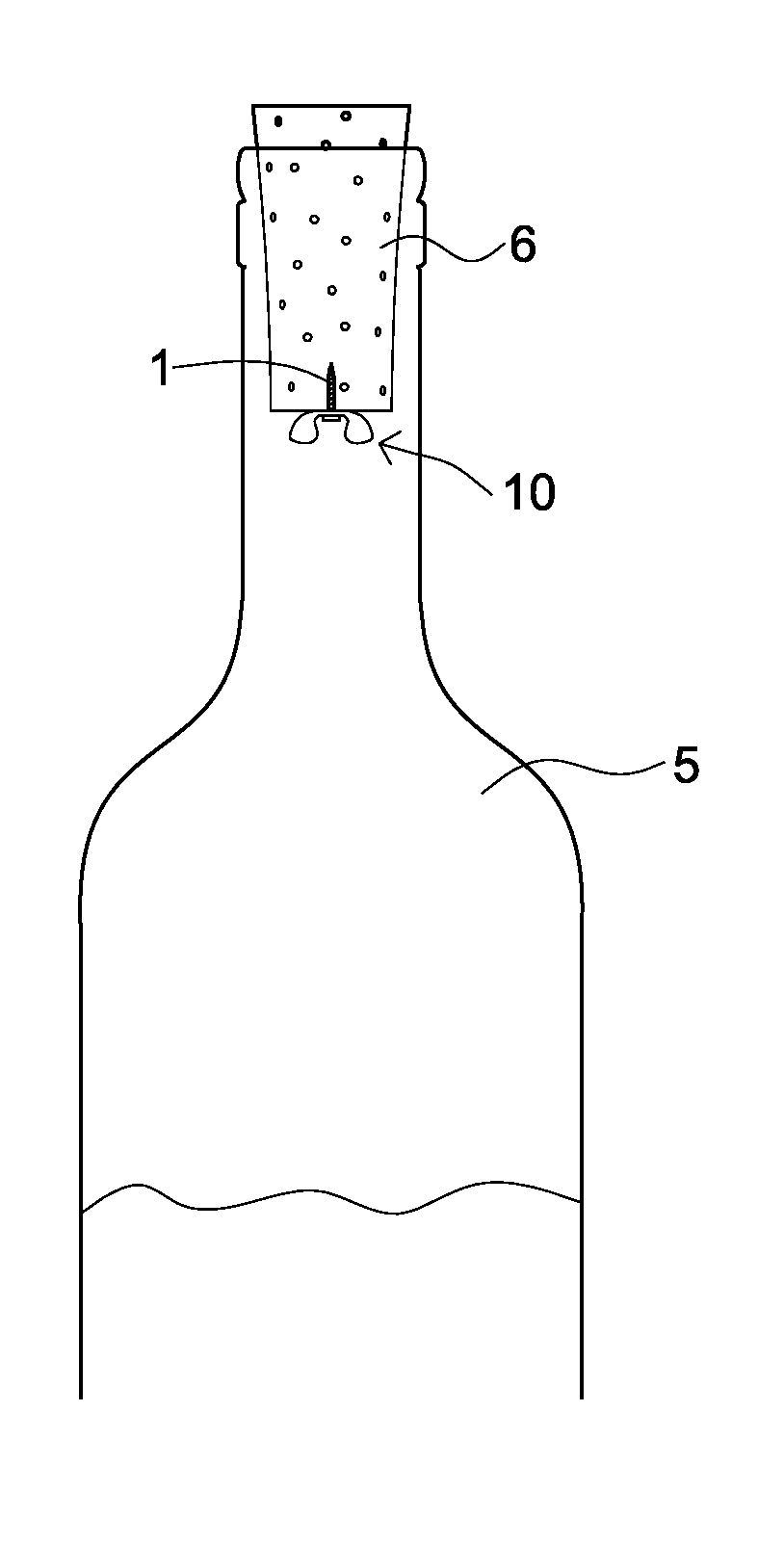
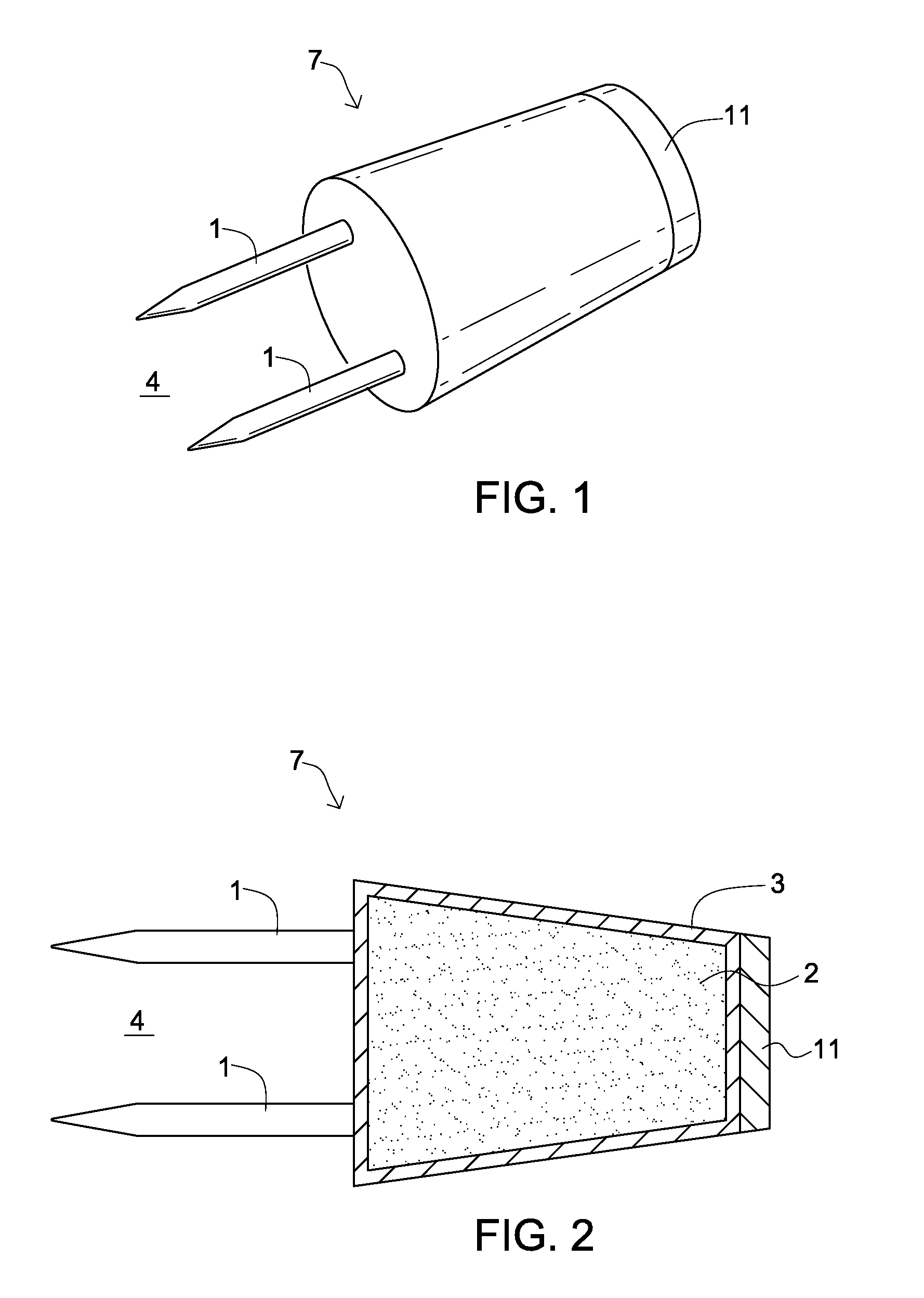
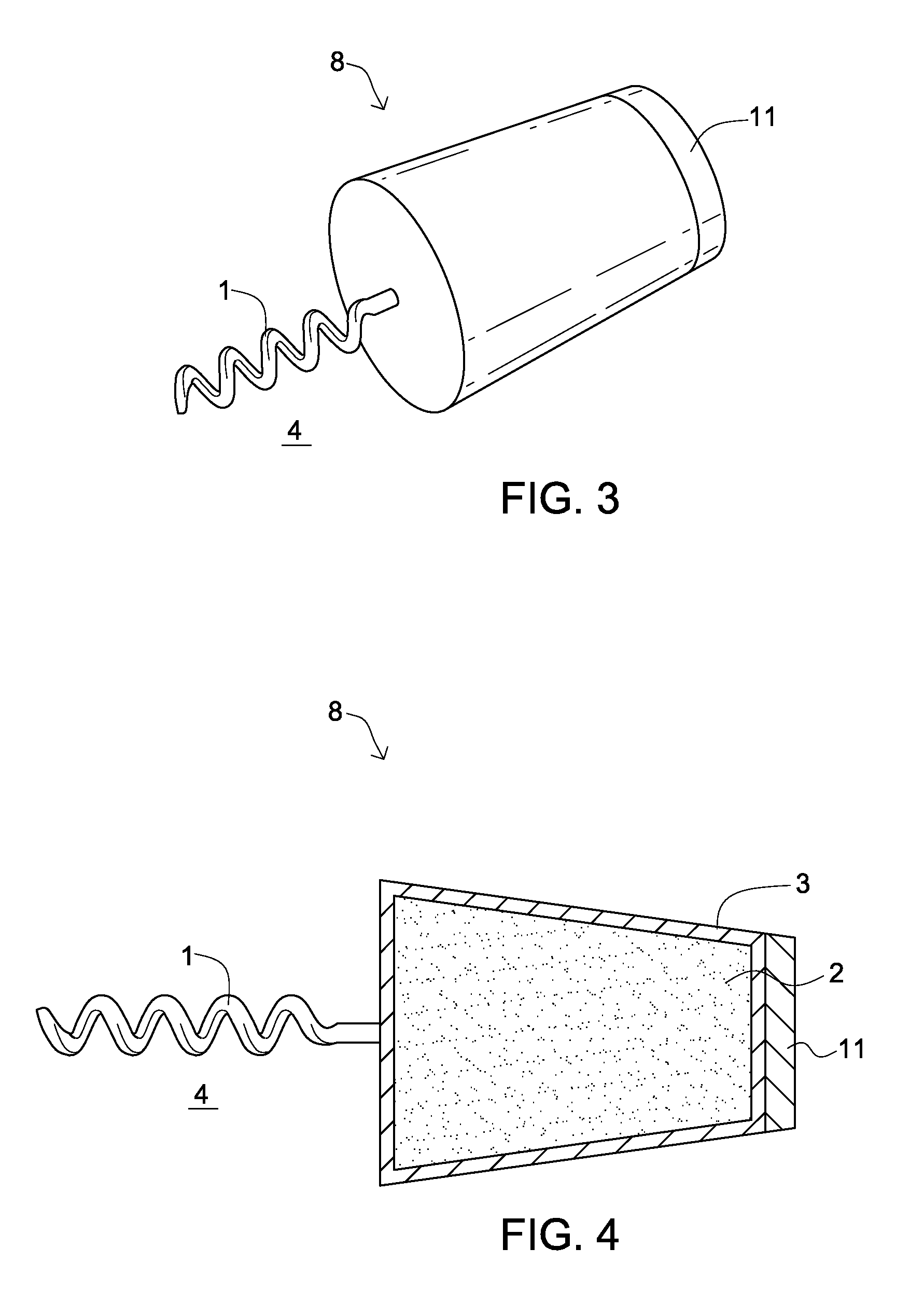
An oxygen-scavenging apparatus is disclosed that can easily be applied by an end user to the bottom of a wine-bottle cork, or other food or beverage container that is sealed with a container-stopper device, such as a synthetic cork or a screw-type cap. The oxygen-scavenging apparatus is easily attachable and detachable, and relies on a friction-based fastener for its coupling to the container stopper. In some embodiments, the apparatus can serve a dual purpose by both scavenging oxygen and by absorbing moisture by using both oxygen-scavenging compound and desiccant material. The oxygen-scavenging apparatus is simple in design and thus relatively easy and cost-effective to manufacture.
Owner:VJP
Container overcap with drying agent layer
InactiveUS7185780B2Reduce moistureImprove crispnessClosures with oxygen absorbersCapsDesiccantAdhesive
There is provided an overcap for a resealable container that includes a drying agent layer. The drying agent layer is included in a top portion of the overcap and is positioned below a top layer of the top portion such that the drying agent layer is exposed to the interior of the container. The overcap may be formed from a multilayered coextruded sheet having a top layer of polymer material and a drying agent layer mixed with a polymer material. The multilayered coextruded sheet may also include a barrier layer, a polymer layer, and / or additional drying agent layers. Alternatively, the drying agent layer may be joined to the overcap by an injection molding process or by an adhesive. The drying agent layer is exposed to moisture in the interior of the container such that the drying agent layer is operable to absorb moisture from the air that enters the interior of the container during the opening and resealing of the container.
Owner:SONOCO DEV INC
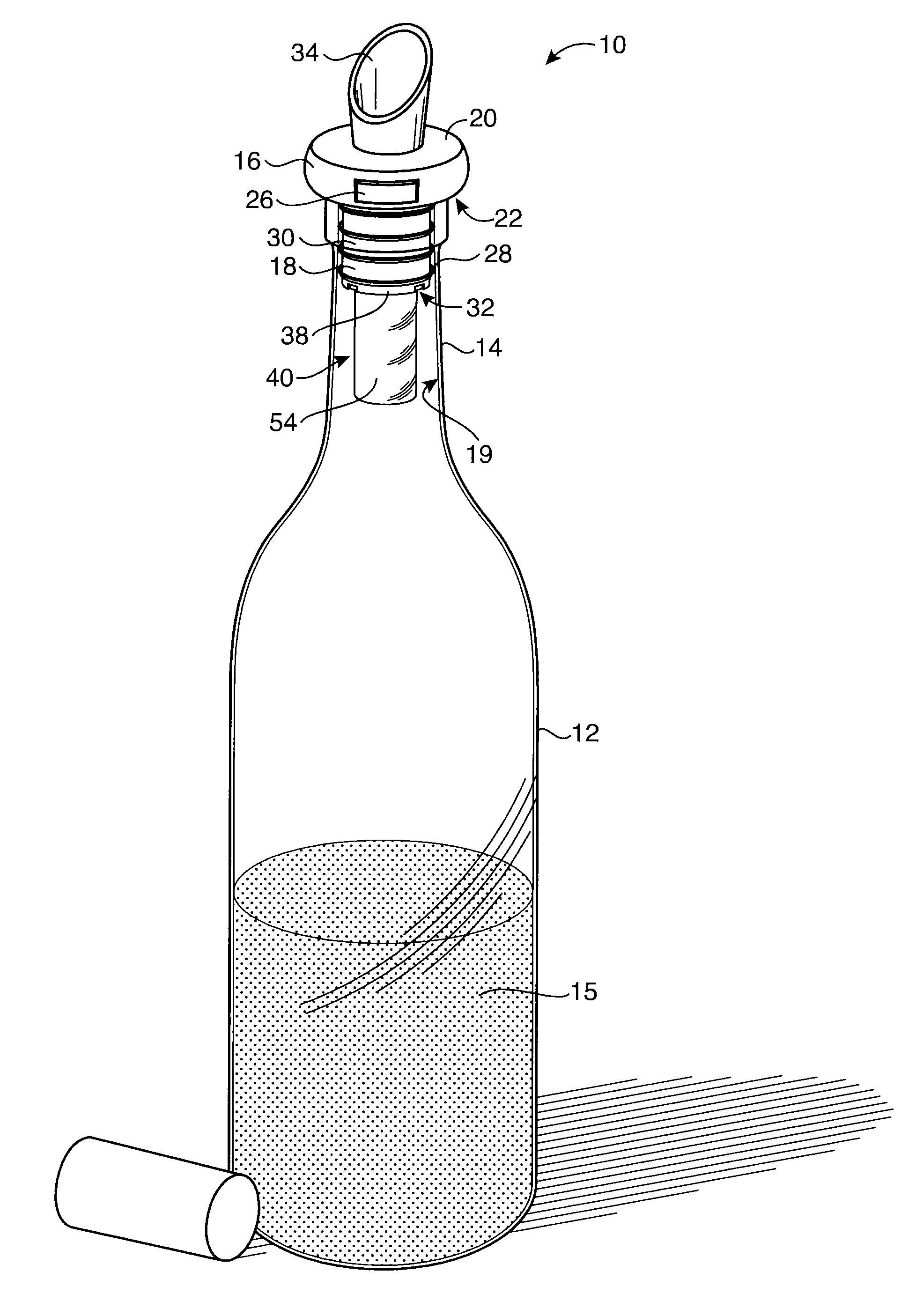
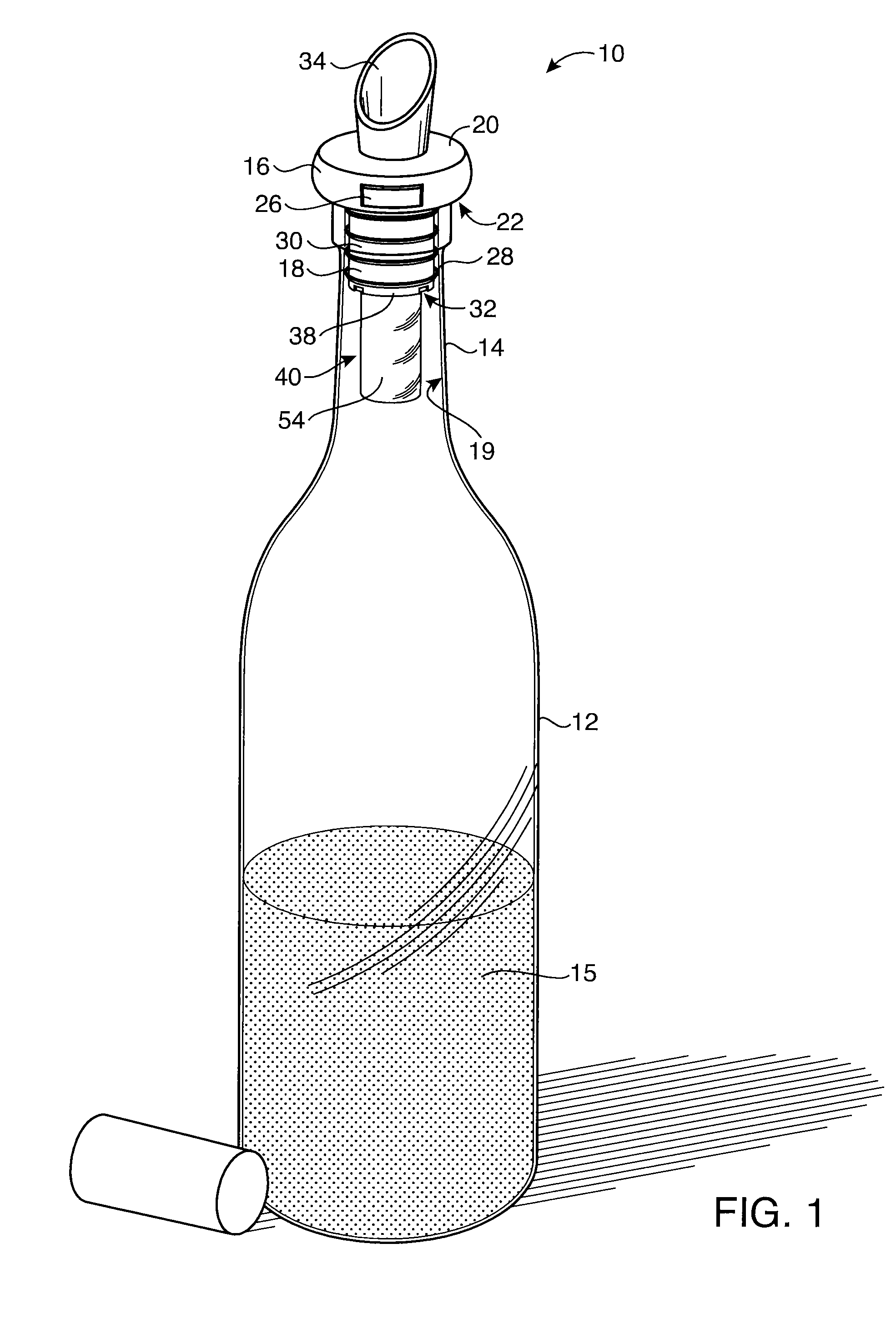
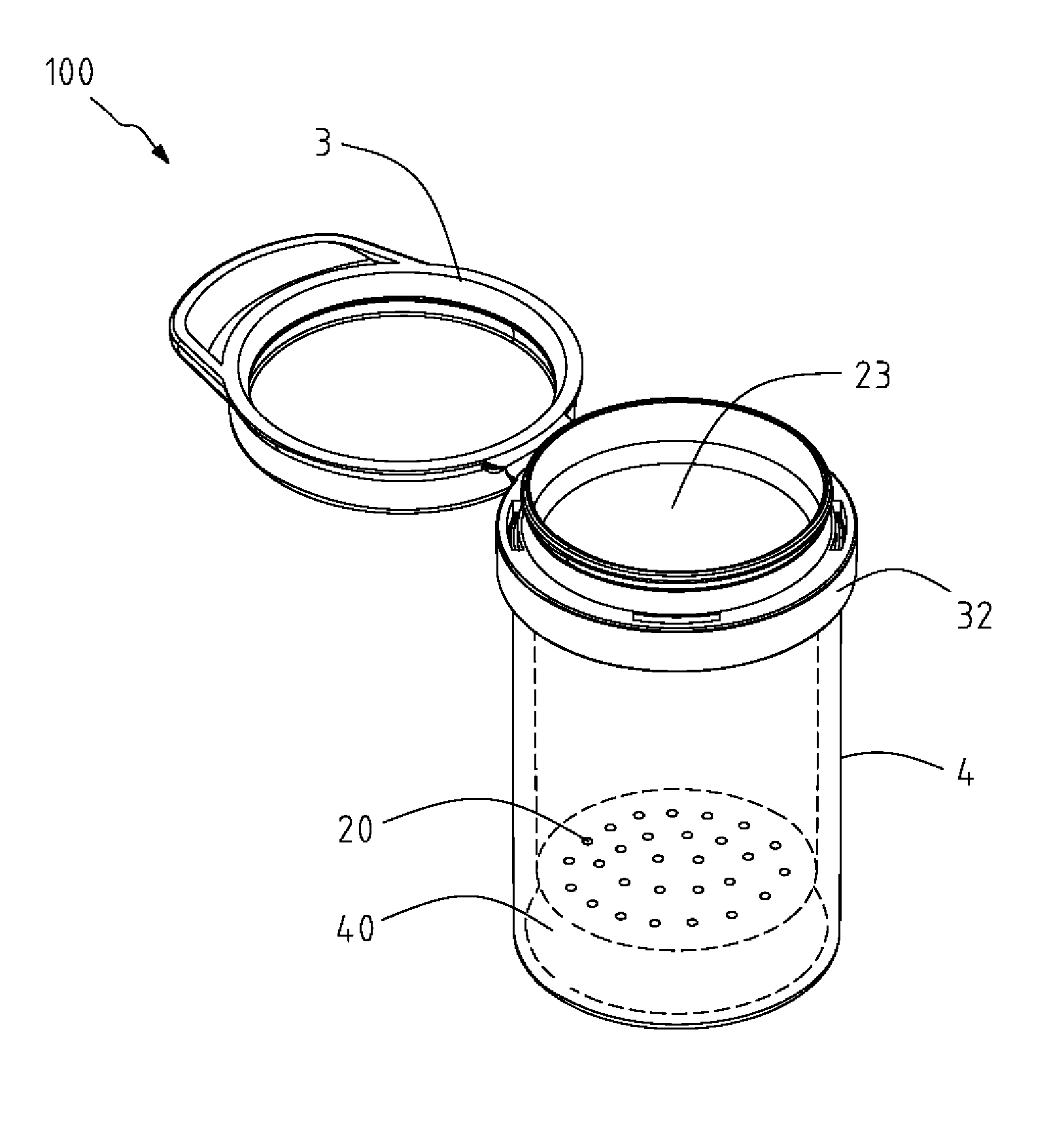
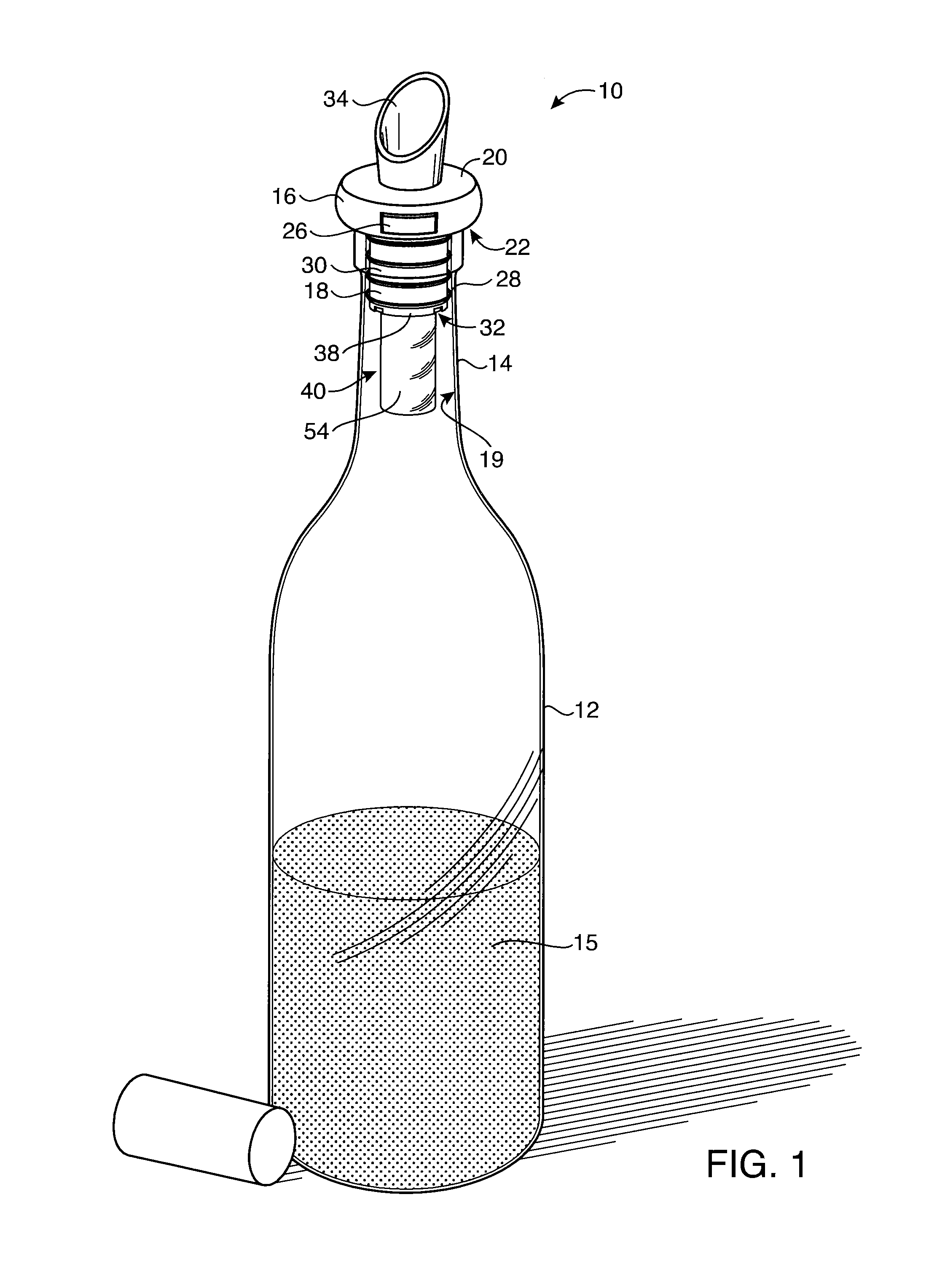
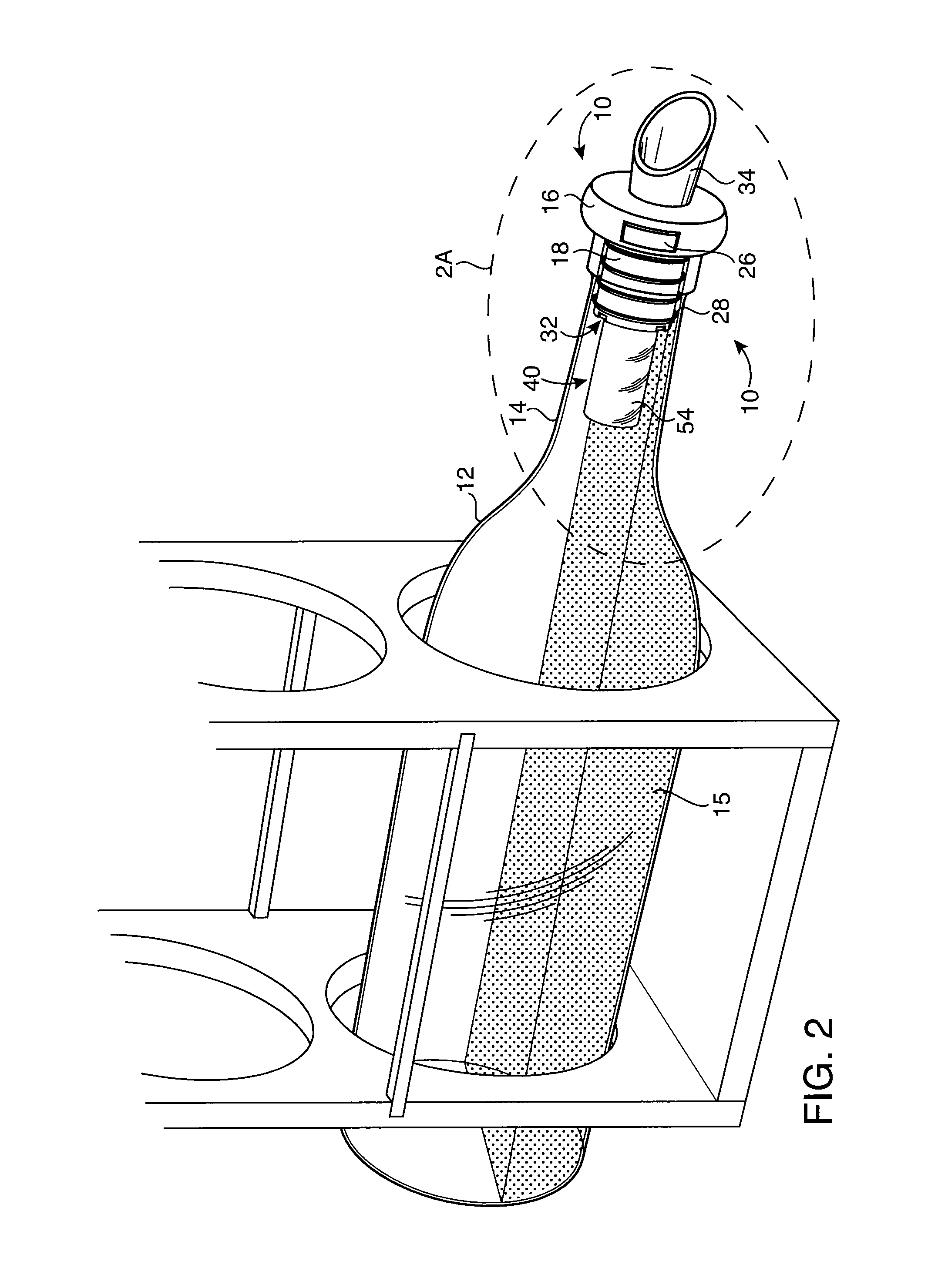
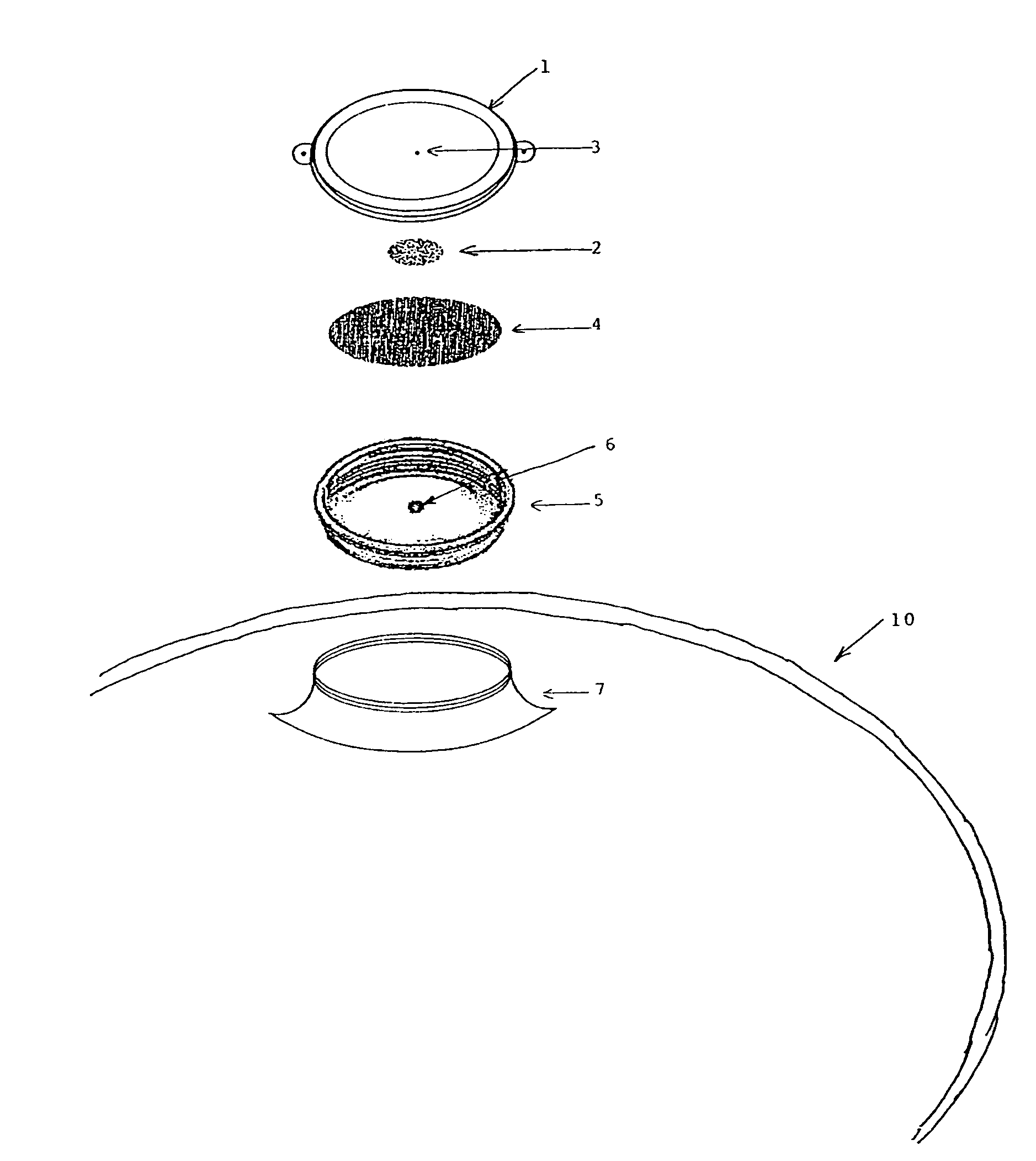
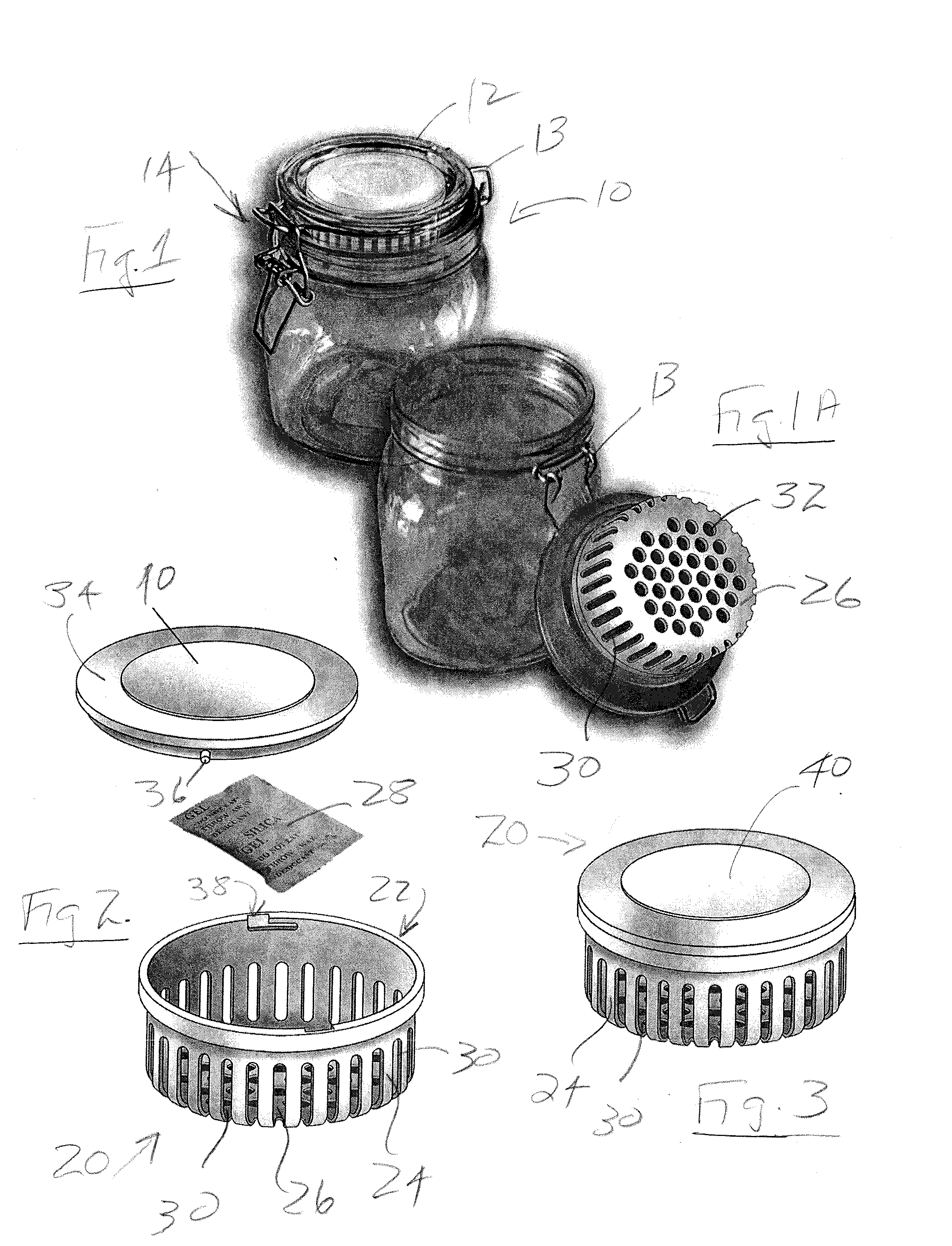
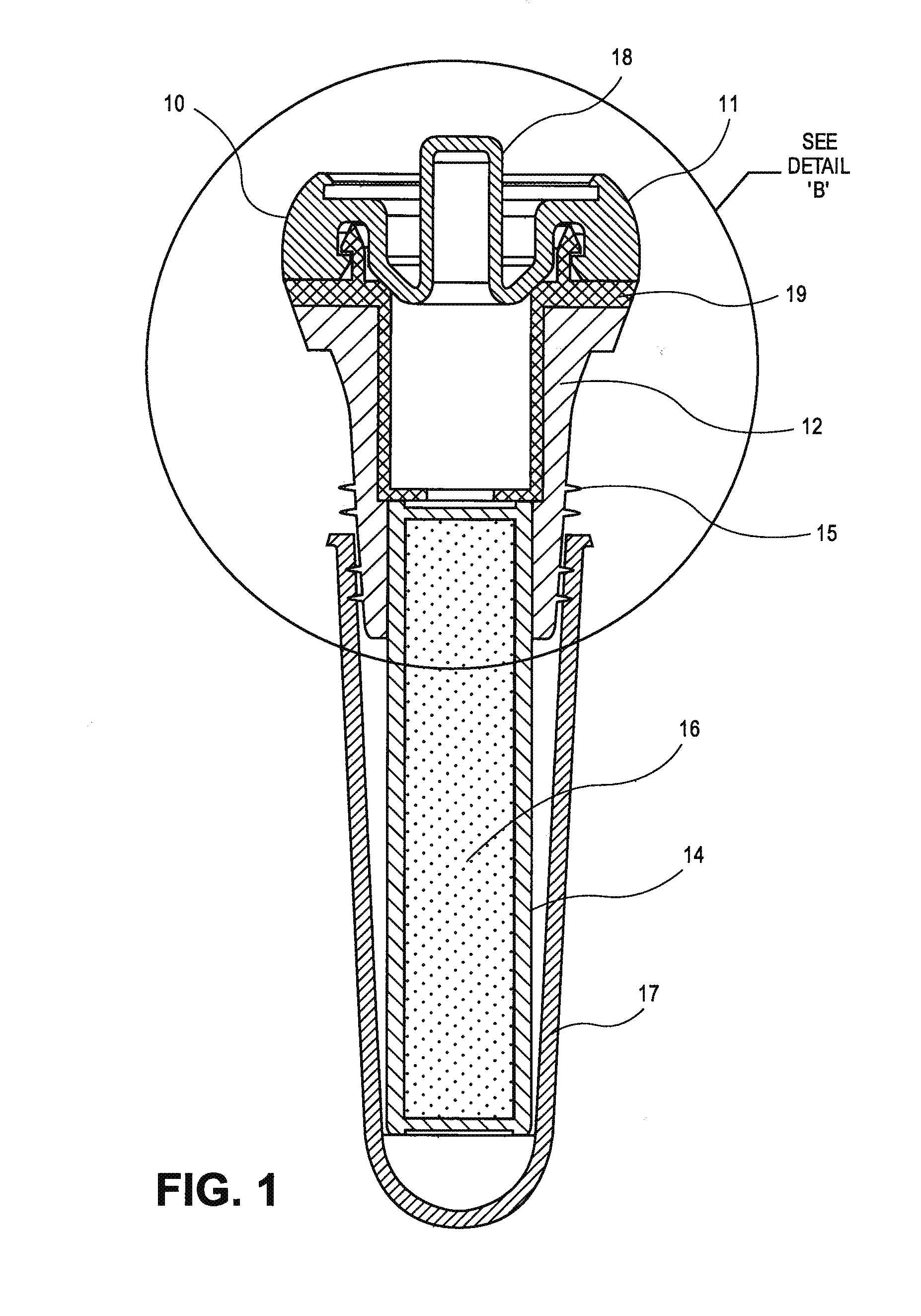
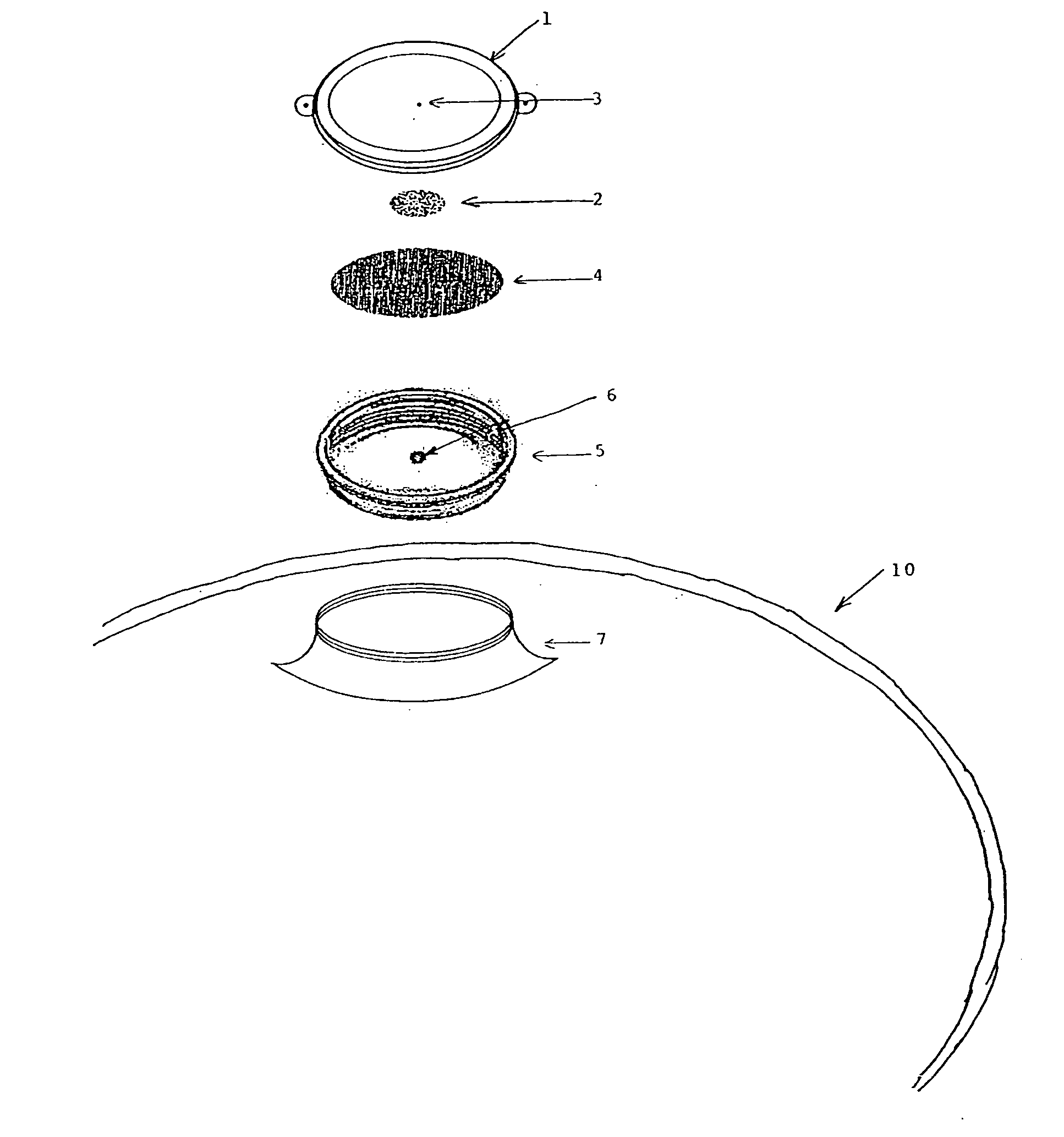
Preservation Device
A preservation device are used to preserve liquids and other items, such as foodstuffs, which spoil when exposed to oxygen for a period of time. The preservation devices are configured to form an air tight seal when disposed on a bottle and / or a vessel. The devices include a container, and disposed within the container is an oxygen absorber, which removes oxygen remaining in the bottle or vessel after it is sealed by the preservation device. Either the container or the oxygen absorber has a gas permeable, liquid impermeable membrane. The preservation device may also include a flow control mechanism that enables a liquid to be dispensed from the bottle without requiring the removal of the entire stopper device from the bottle. The preservation device may alternatively include an air channel system to control the flow of the liquid to be dispensed from the bottle without requiring the removal of the entire stopper device from the bottle. Such arrangements enable the liquid to be dispensed while only allowing a minimal amount of oxygen to enter the bottle, thus improving preservation.
Owner:SELLO LLC
Oxygen-Absorbable Resin Composition, Oxygen-Absorbable Barrier Resin Composition, Oxygen-Absorbable Molded Article, Packaging Material Comprising the Molded Article, and Packaging Container
InactiveUS20100187137A1Release bad smellNo problem in metal detectionClosures with oxygen absorbersOther chemical processesVitrificationShell molding
[Problem to be Solved] To provide an oxygen-absorbable resin composition that does not require any metal incorporated thereinto and has excellent oxygen absorbability even at room temperature, an oxygen-absorbable barrier resin composition also exhibiting excellent gas-barrier property, oxygen-absorbable molded article comprised of the resin composition, an oxygen-absorbable packaging material comprised of the molded article, and an oxygen-absorbable packaging container.[Means for Solving Problems] THE oxygen-absorbable resin composition comprises an oxygen-absorbable resin (A) having a cycloene structure in the molecule and a softener (B) and has a glass transition temperature of not higher than 30° C. The oxygen-absorbable barrier resin composition comprises a barrier resin (C) in addition to (A) and (B). The oxygen-absorbable resin (A) having a cycloene structure in the molecule is preferably a cyclized product of a conjugated diene polymer having an unsaturated bond reduction ratio of at least 60%. The softener (B) is preferably liquid paraffin or polybutene.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Device for Distributing and/or Controlling the Discharge of Unitary Products, Fitted Onto a Container, and For the In-Situ Treatment of its Internal Atmosphere
The present invention relates to a device for distribution and / or controlling the discharge of unitary products, and for simultaneous in-situ treatment of the atmosphere of a container onto which it is fitted. The device comprises a lower surface provided with an entry opening, an upper surface provided with at least one main distribution opening, a guiding surface for the products to be distributed, and a means of securing the device. The device is made from a thermoplastic material comprising at least one thermoplastic polymer and at least one agent for treating gaseous pollutants present in the atmosphere of the container, by reaction with and / or adsorption of at least one existing gaseous pollutant and / or desorption of said agent in the atmosphere of the container.
Owner:AIRSEC S
Oxygen-absorbing resin, oxygen-absorbing resin compositions and oxygen-absorbing containers
ActiveUS20090098323A1Excellent oxygen absorption performanceImprove abilitiesClosures with oxygen absorbersThin material handlingHydrogen atomFluence
The invention aims at providing an oxygen-absorbing resin which has excellent oxygen absorption performance and which can dispense with the addition of a transition metal catalyst or the irradiation with a radiation. The invention provides an oxygen-absorbing resin which is obtained by polymerizing a raw material containing a monomer (A) having an unsaturated alicyclic structure bearing a carbon-carbon double bond wherein one carbon atom adjacent to the carbon-carbon double bond is bonded to an electron-donating substituent and a hydrogen atom and another carbon atom adjacent to the carbon atom is bonded to a heteroatom-containing functional group or a bonding group derived from the functional group with the electron-donating substituent and the functional or bonding group taking cis-configuration and which contains the unsaturated alicyclic structure in an amount of 0.5 to 10 meq / g; oxygen-absorbing resin compositions containing the above oxygen-absorbing resin; and oxygen-absorbing containers, characterized by having an oxygen-absorbing layer made from the resin or the compositions.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN KAISHA LTD
Cap for a container
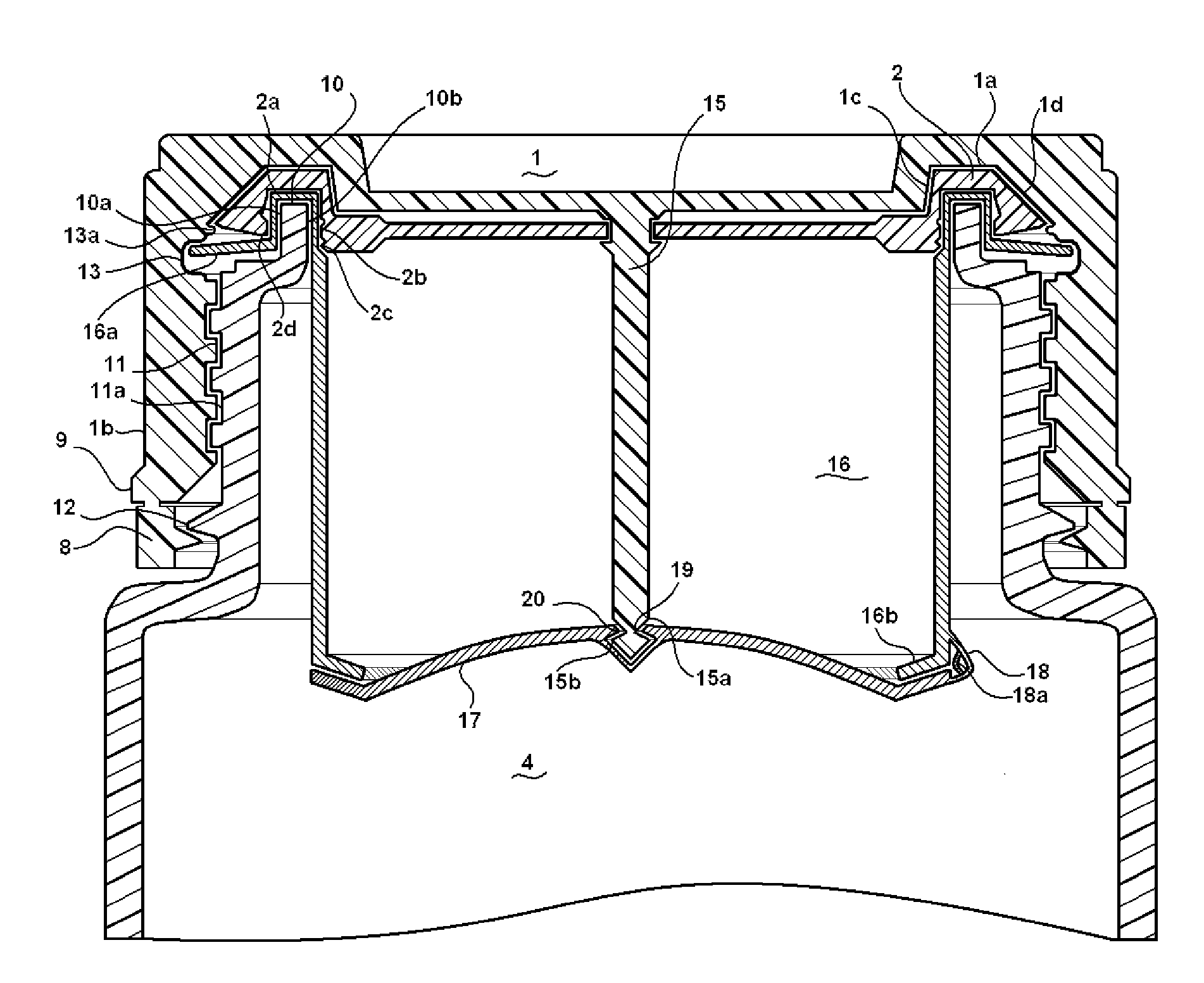
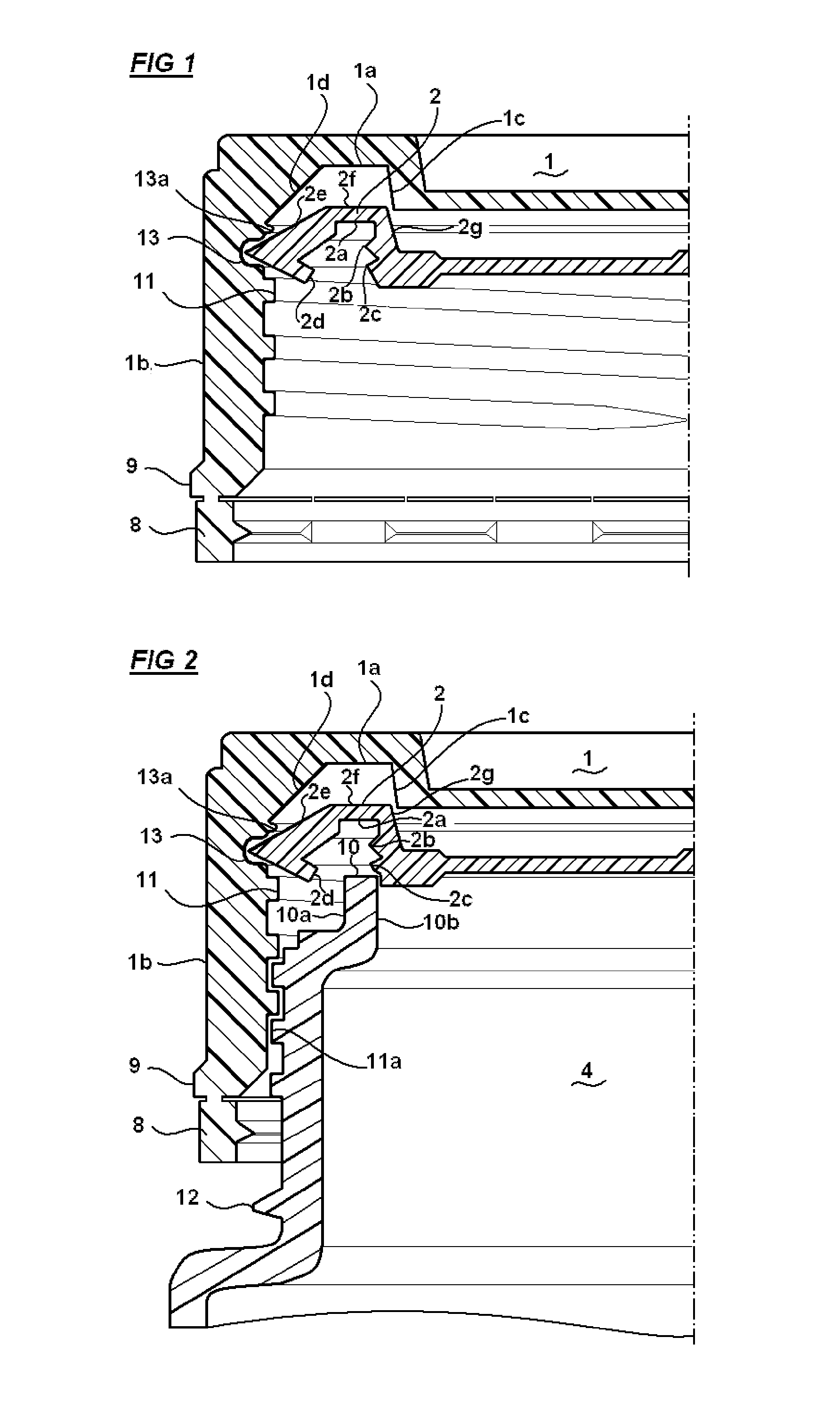
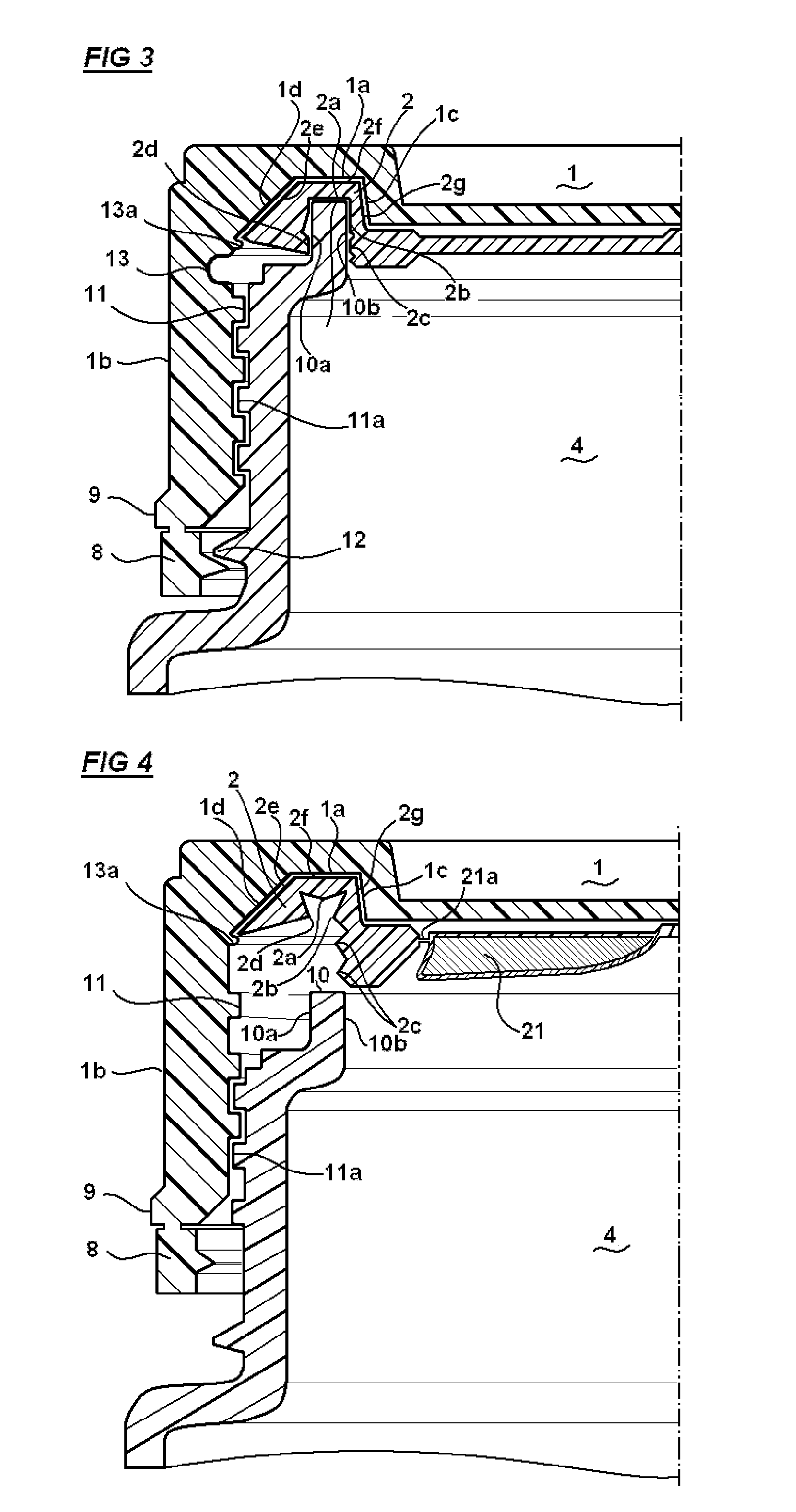
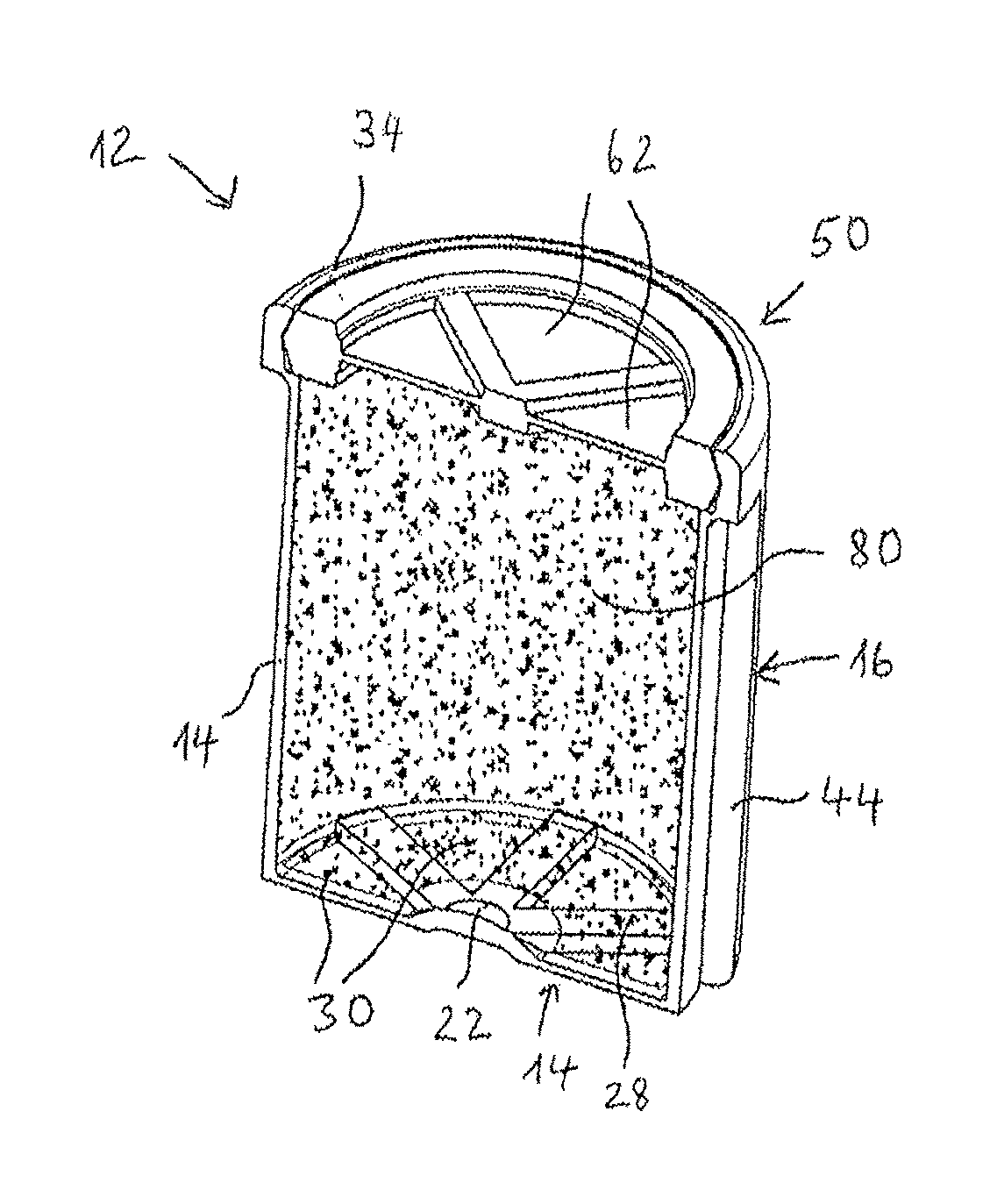
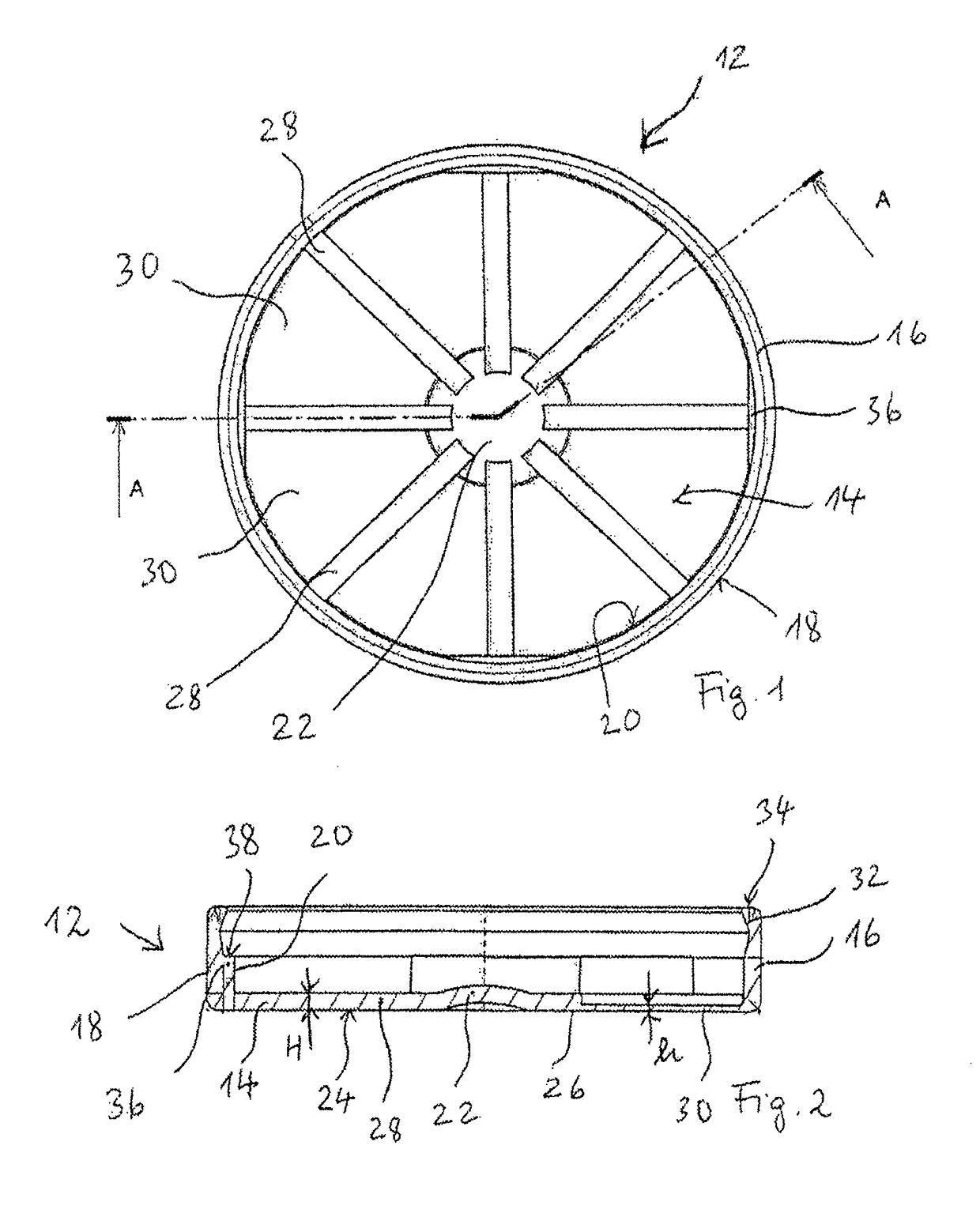
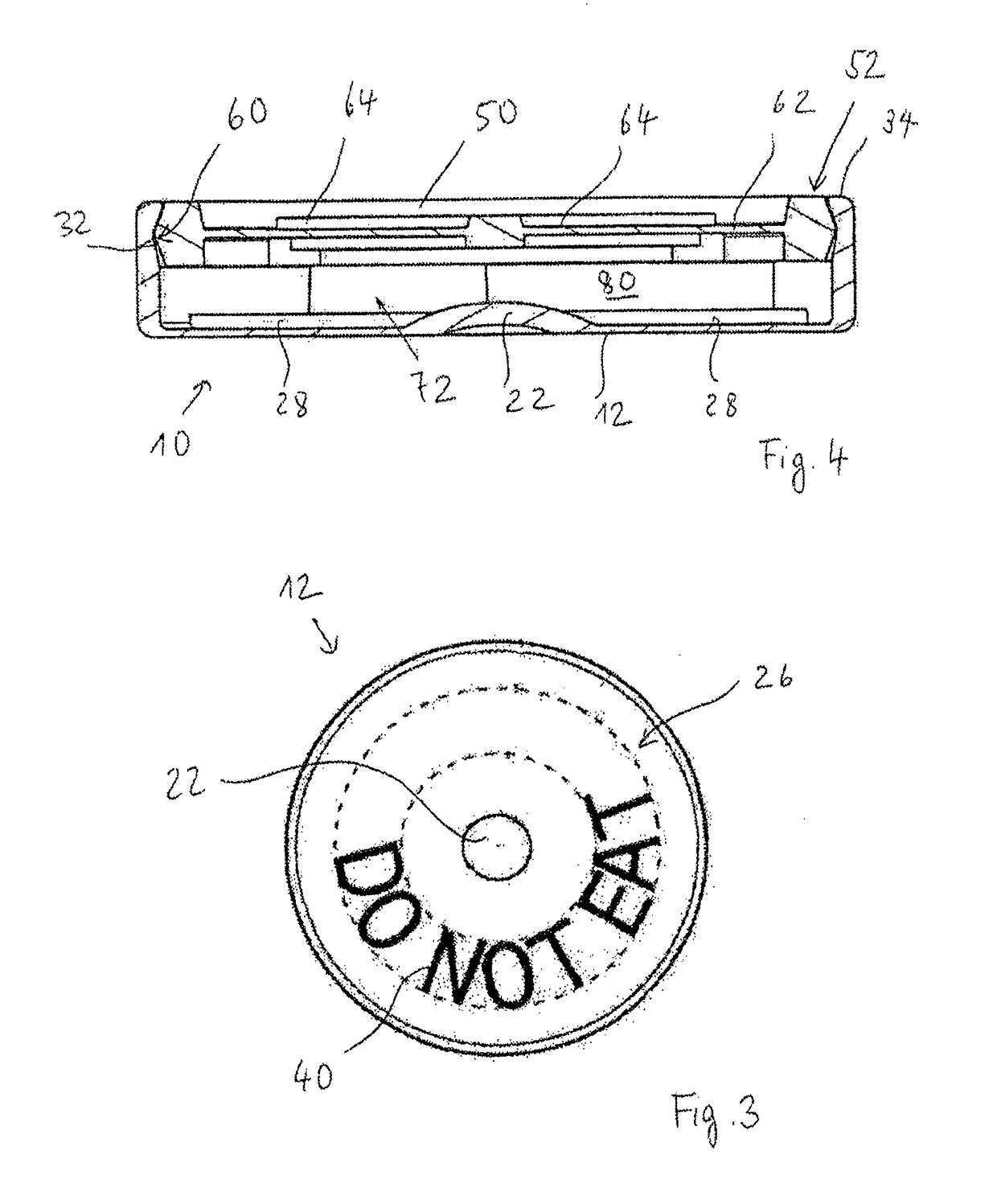
ActiveUS20160101914A1Increase storage capacityAvoid problemsClosures with oxygen absorbersClosure with auxillary devicesMechanical engineeringSolid product
Disclosed is a cap for a container and a container comprising such cap. This container typically accommodates loosely stored, solid products, such as strips, pills, tablets or the like. The cap includes a lid body with a top part and a peripheral wall, wherein the lid body includes a sealing skirt and an inner peripheral wall, which extend from the top part, and form a peripheral groove in between. At least one projection portion for partially covering the peripheral groove is integrally formed with the sealing skirt and the inner peripheral wall.
Owner:AIRNOV INC
Packaging Insert
InactiveUS20070257046A1Easy to openEasy to removeClosures with oxygen absorbersClosure with auxillary devicesEngineeringBottle
The present invention relates to a packaging insert that comprises a chamber that can be filled with an adsorbent. When the insert is positioned within a closed bottle, the adsorbent can entrap any moisture or gases generally targeted by the adsorbent selected. The insert is designed such that the container can be induction sealed with the insert positioned within the neck of the container.
Owner:SUD CHEM INC
Desiccant container structure
InactiveUS20150291338A1Preventing the objects from being affectedIncrease spaceClosures with oxygen absorbersContainer/bottle contructionDesiccantEngineering
A desiccant container structure includes a main body, a lid, and a desiccant storing element having at least a viewing portion made of a transparent material. The main body is formed with a plurality of through holes and an accommodation space for accommodating an object. The desiccant storing element is formed with a storing chamber for accommodating a desiccant and communicating with the main body through the plurality of through holes. The desiccant in the desiccant storing element is capable of absorbing moisture from the accommodation space through the plurality of through holes for maintaining the object in a dry state, and a state of the desiccant is capable of being viewed directly through the transparent viewing portion.
Owner:CHEN ERIK
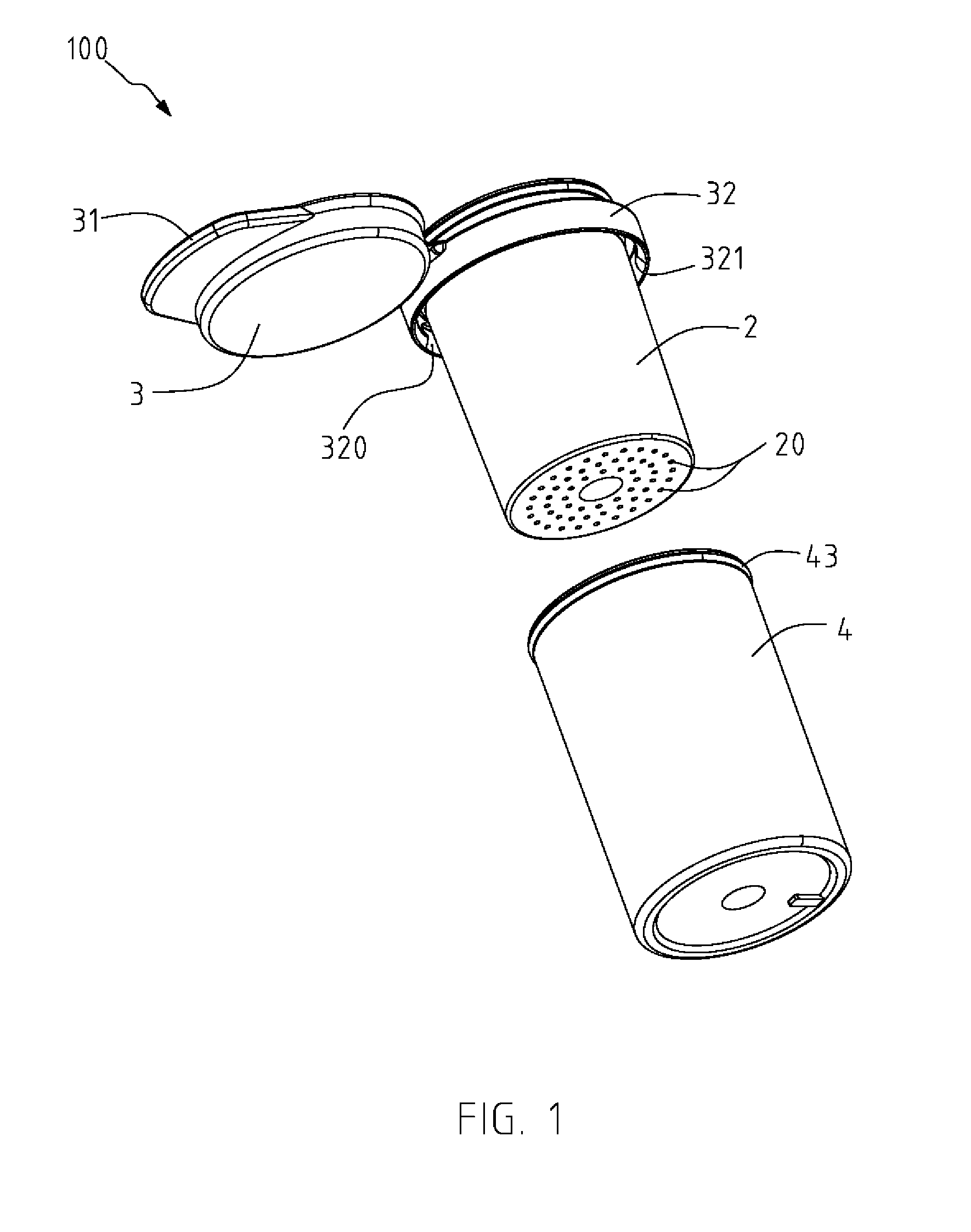
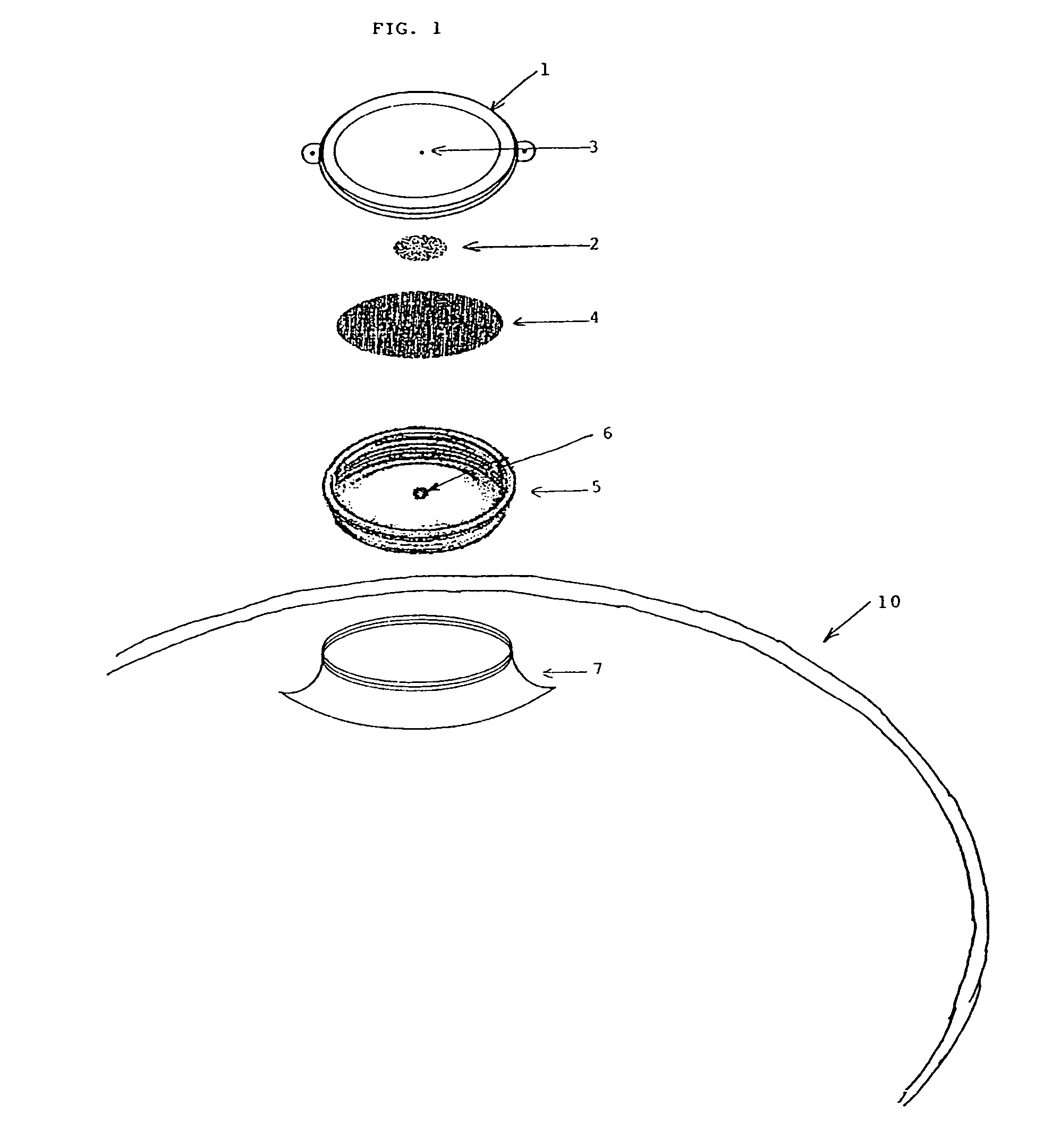
Preservation device
InactiveUS20160229604A1Avoid flowClosures with oxygen absorbersClosure with auxillary devicesEngineeringOxygen
A preservation device, configured to form an air tight seal when disposed on a bottle and / or a vessel, is used to preserve liquids and other items, such as foodstuffs, which spoil when exposed to oxygen for a period of time. The device comprises at least a container which contains an oxygen absorber to remove oxygen remaining in the bottle or vessel after it is sealed by the preservation device. The container or the oxygen absorber has a gas permeable, liquid impermeable membrane. The preservation device may include an air channel system to control the flow of the liquid to be dispensed from the bottle without requiring the removal of the entire stopper device from the bottle, to enable the liquid to be dispensed while only allowing a minimal amount of oxygen to enter the bottle, thus improving preservation.
Owner:SELLO LLC
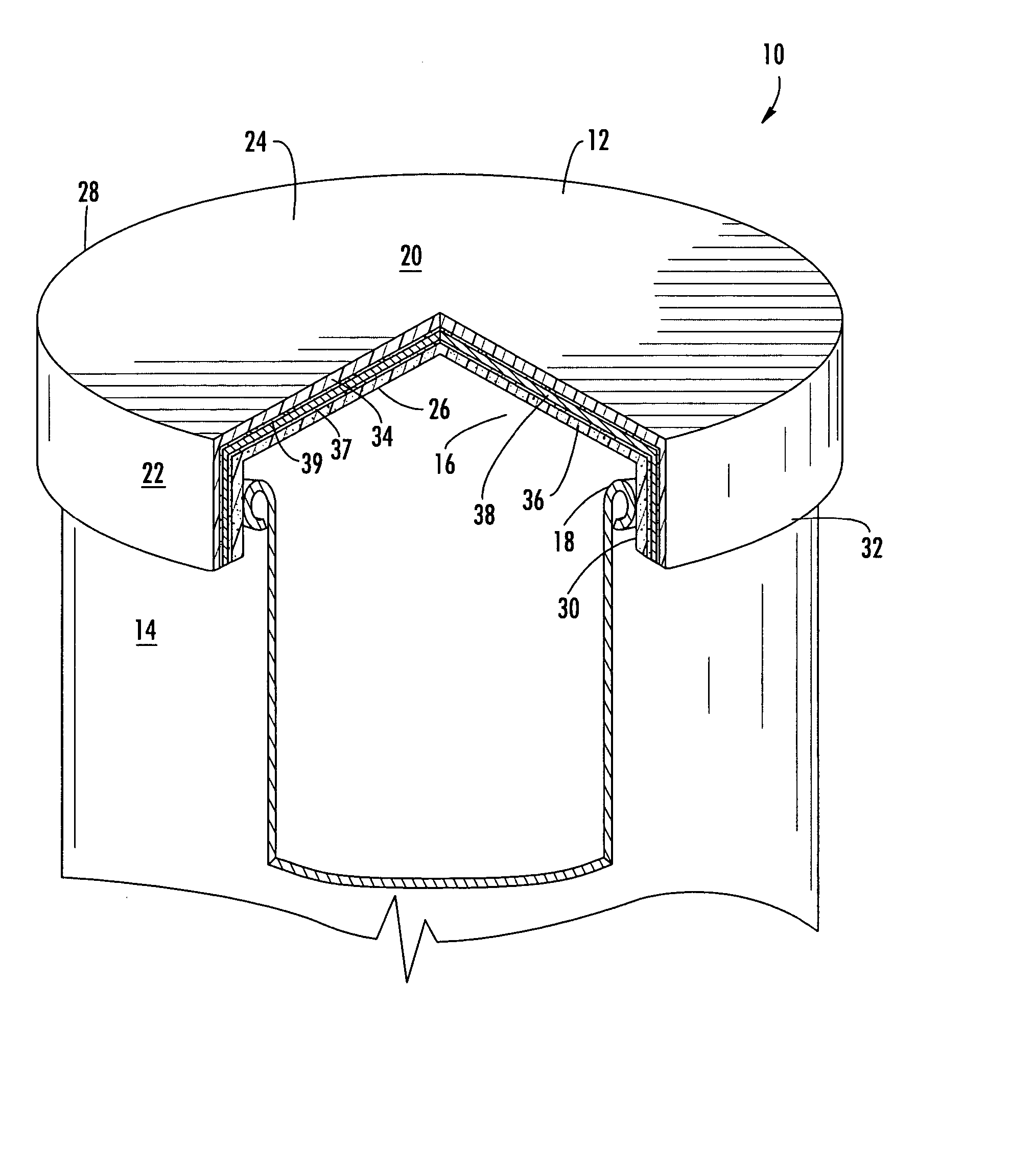
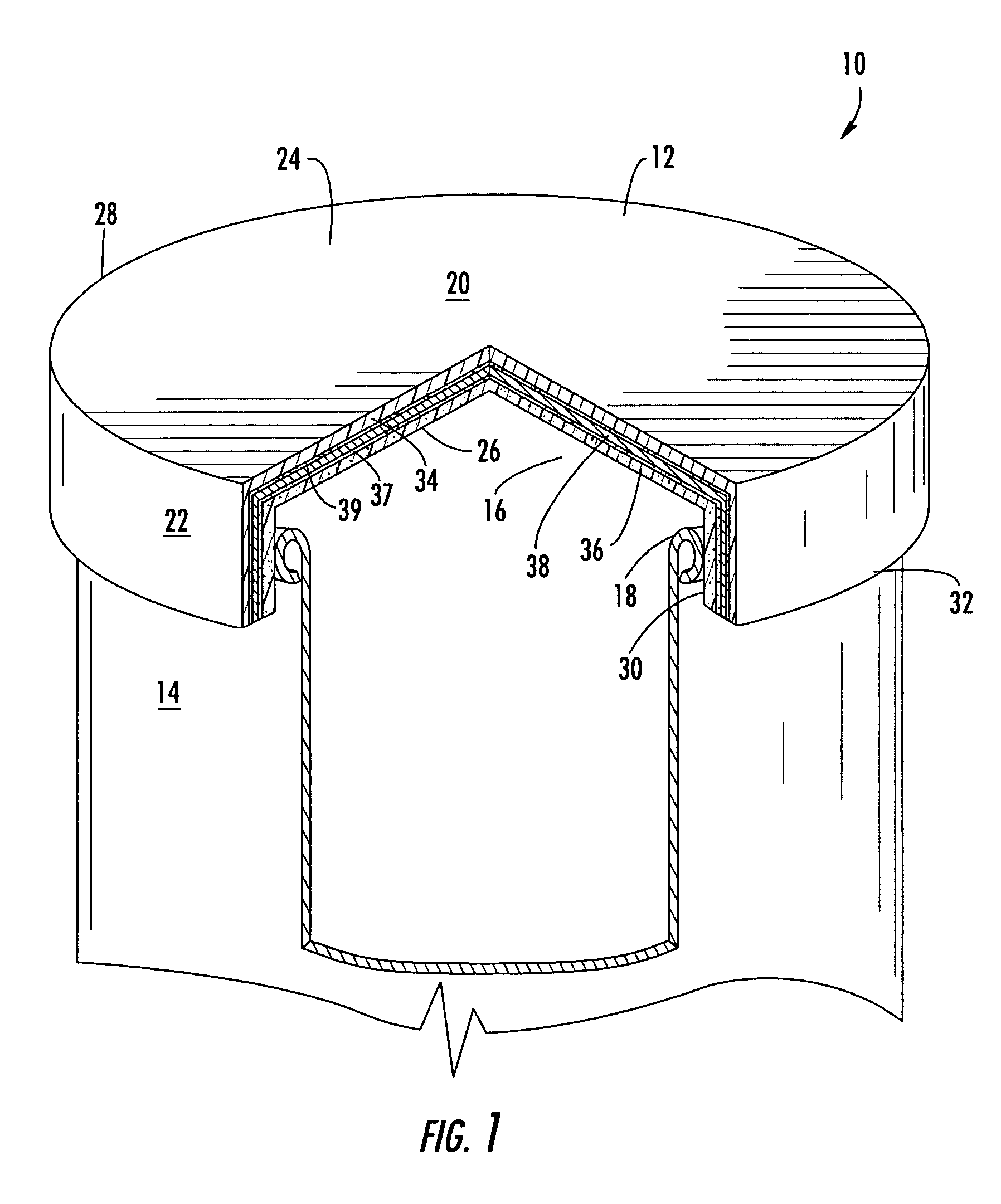
Container closure
A crown system includes a crown having a top surface and a bottom surface and a liner having a top surface that contacts a bottom surface of the crown. The liner is configured to absorb oxygen in a headspace and includes at least about 2.2 micromoles of sodium sulfite per cubic millimeter in a volume of the liner to a depth of about 0.003 millimeter from a bottom surface of the liner.
Owner:ANHEUSER BUSCH INC
Reusable closure
ActiveUS20150217912A1Avoid enteringAvoid exposureClosures with oxygen absorbersPackage recyclingEngineeringOxygen
A preservation apparatus and method for using the same are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the preservation apparatus comprising: a removable closure adapted to fit together in sealed relationship with a first container for containing an item, where the removable closure comprises a second container to contain a substance operable to collect oxygen molecules contained within the first container. The preservation apparatus also comprises a removable cap adapted to cover a portion of the removable closure including the second container, in order prevent the second container from being exposed to oxygen molecules outside the cap.
Owner:ZERO OXYGEN SOLUTIONS INC
Moisture absorbent scavenger and vacuum relief device for chemical containers
The invention is a vent for use with a container, such as commercial steel pails and drums, and a method for venting containers. The vent has a cap seal with one or more semipermeable membranes covering an orifice in the cap seal. The membrane prevents the passage of at least one atmospheric component, but allows the free passage of air. When a product is filled into the container at an elevated temperature and cools, a vacuum is formed within the container. The resulting vacuum opens a vacuum release device in the vent and pulls air through a hole in the cap seal, which is protected by a micro-porous membrane. The venting of air into the container relieves the vacuum without damage to the container or the product within the container.
Owner:LANXESS SOLUTIONS US INC
Storage container for holding desiccant and insert to convert standardized storage container to hold desiccant
InactiveUS20160304264A1Closures with oxygen absorbersClosure with auxillary devicesDesiccantAdhesive
A container with an insert for a desiccant has a lid, and the insert includes a housing having sidewall portions and a bottom portion with passages for receiving a desiccant to be used with contents of the container. The passages enable air to circulate within the housing, and a cover to be secured to the housing has an upper surface containing adhesive to enable said insert be held to the undersurface of the lid for the container. The insert can be used with traditional containers such as an apothecary glass jar or a glass jar with swing top lid that can be clamped.
Owner:ALWAYS HOME INT INC
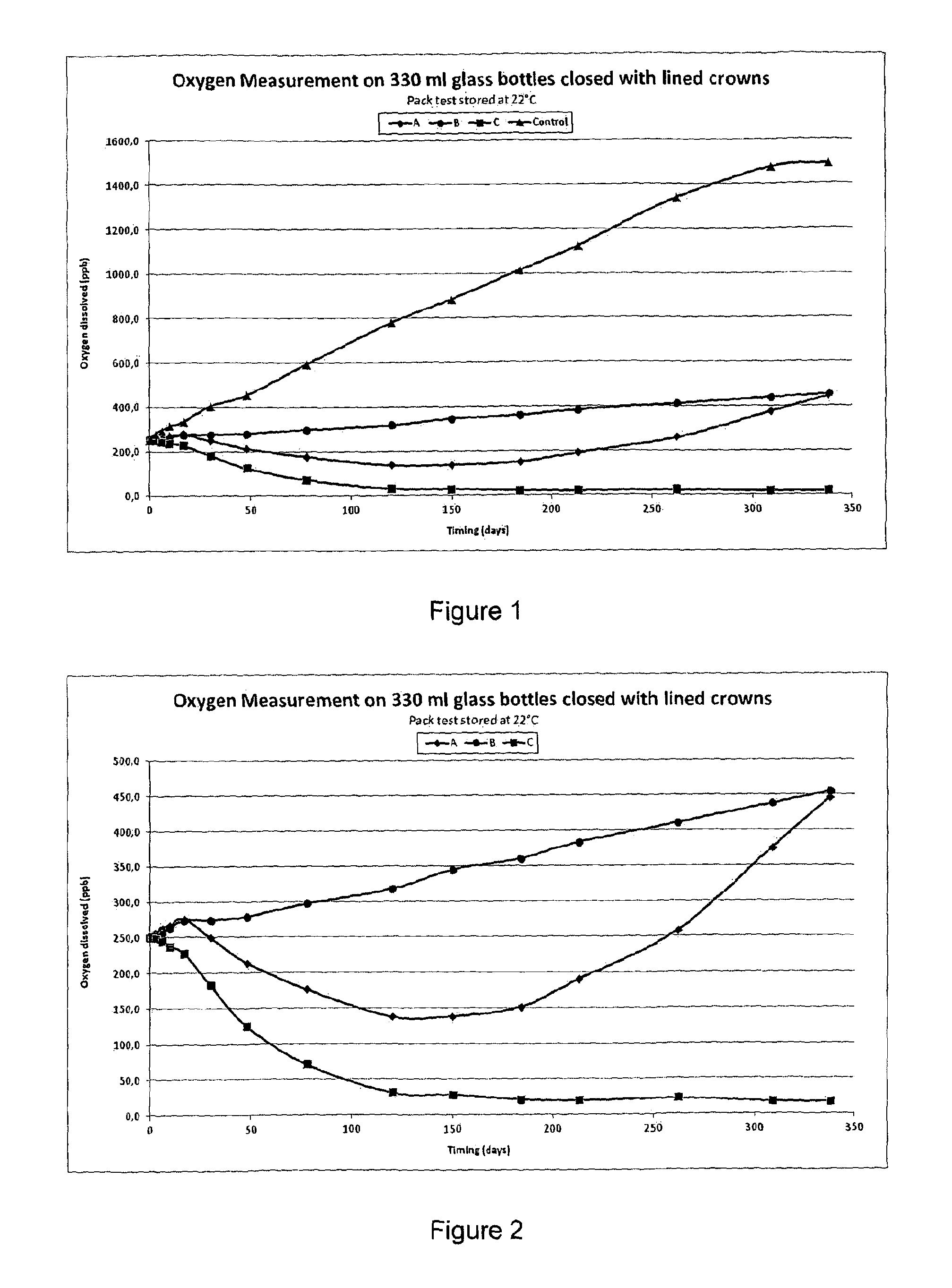
Closure Liner Composition With Improved Oxygen Reduction
InactiveUS20150118366A1Improve oxygen reduction performanceExtended shelf lifeClosures with oxygen absorbersCapsParticulatesOxygen
Disclosed is a closure liner composition comprising a mixture (or blend) of a thermoplastic polymer, an oxygen barrier polymer, and a particulate oxygen scavenging material. The oxygen barrier polymer preferably comprises polyisobutylene. The particulate oxygen scavenging material preferably is selected from the group consisting of an alkali metal salt of sulfite, ascorbate, isoascorbate, and a mixture of two or more of these materials. The closure liner composition may be used to fabricate a liner for a closure (e.g., a metal crown used to cap a bottle) that provides superior oxygen reduction properties and improved shelf life.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Container overcap with drying agent layer
InactiveUS20050127082A1Reduce moistureImprove crispnessClosures with oxygen absorbersCapsAdhesiveDesiccant
There is provided an overcap for a resealable container that includes a drying agent layer. The drying agent layer is included in a top portion of the overcap and is positioned below a top layer of the top portion such that the drying agent layer is exposed to the interior of the container. The overcap may be formed from a multilayered coextruded sheet having a top layer of polymer material and a drying agent layer mixed with a polymer material. The multilayered coextruded sheet may also include a barrier layer, a polymer layer, and / or additional drying agent layers. Alternatively, the drying agent layer may be joined to the overcap by an injection molding process or by an adhesive. The drying agent layer is exposed to moisture in the interior of the container such that the drying agent layer is operable to absorb moisture from the air that enters the interior of the container during the opening and resealing of the container.
Owner:SONOCO DEV INC
Systems and methods for de-oxygenation of a closed container
InactiveUS20190270560A1Improve sealingReduce partial pressureClosures with oxygen absorbersClosure using stoppersFlavorBottle
Systems and methods for preserving oxidizable substances such as liquids or foodstuffs are disclosed. These systems incorporate a sealing device and an oxygen scavenging chemical or agent coupleable to or contained within the system. The oxygen scavenging agent can remove the oxygen from the headspace of a container such as a bottle of wine without reducing the pressure in the headspace to the extent that the flavor of the wine is adversely affected.
Owner:LUTZ THOMAS R
Canister for containing an active material
ActiveUS20150321142A1Easy to assembleEasy to manufactureClosures with oxygen absorbersGas treatmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
A canister including a canister body containing a bottom wall and at least one sidewall with inner and outer sidewall surfaces and an upper rim, and a closing element containing a top wall with an outer surface and an inner surface, and a fixing portion surrounding the top wall. The top wall or the bottom wall or at least one sidewall include a membrane region with a predetermined permeability. The fixing portion includes an elevated or recessed snap portion around its outer periphery shaped to correspond to the inner sidewall surface of the sidewall of the cylindrical canister body and form a snap connection with the canister body. The closing element is fixed to the canister body such that the outer surface of the top wall does not extend beyond the upper rim of the sidewall of the canister body.
Owner:AIRNOV INC
Container orifice reducer with tamper evident seal
ActiveUS20170305613A1Easy to manufactureExtended shelf lifeSmall article dispensingClosures with oxygen absorbersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Containers with closures are disclosed. A closure may include at least a polymer orifice reducer configured to be permanently secured to a rim of an opening of a container and a flexible tamper evident seal disposed on the topside of the orifice reducer. The flexible tamper evident seal, optionally foil, covers one or more openings in the orifice reducer. Processes for permanently securing a closure to a container, optionally by forming a heat seal between the orifice reducer and container rim, are also disclosed.
Owner:CSP TECH INC
Closure with oxygen scavenger
InactiveUS20060102875A1Avoid enteringClosures with oxygen absorbersHydrogenPolymer sciencePolypropylene
A closure that is able to prevent oxygen from entering the container upon which the closure is attached. Preferably, the closure is comprised of one piece wholly molded of plastic, oxygen scavenging or anti-oxidant compounds, and catalysts homogenously mixed therein. More preferably, the closure is a composition of polypropylene or high-density polyethylene with an oxygen scavenger and catalyst integrated within the polypropylene or high-density polyethylene.
Owner:PHOENIX CLOSURES
Oxygen-absorbing resin, oxygen-absorbing resin compositions and oxygen-absorbing containers
ActiveUS7842361B2Excellent oxygen absorption performanceImprove abilitiesClosures with oxygen absorbersThin material handlingHydrogen atomFluence
The invention aims at providing an oxygen-absorbing resin which has excellent oxygen absorption performance and which can dispense with the addition of a transition metal catalyst or the irradiation with a radiation. The invention provides an oxygen-absorbing resin which is obtained by polymerizing a raw material containing a monomer (A) having an unsaturated alicyclic structure bearing a carbon-carbon double bond wherein one carbon atom adjacent to the carbon-carbon double bond is bonded to an electron-donating substituent and a hydrogen atom and another carbon atom adjacent to the carbon atom is bonded to a heteroatom-containing functional group or a bonding group derived from the functional group with the electron-donating substituent and the functional or bonding group taking cis-configuration and which contains the unsaturated alicyclic structure in an amount of 0.5 to 10 meq / g; oxygen-absorbing resin compositions containing the above oxygen-absorbing resin; and oxygen-absorbing containers, characterized by having an oxygen-absorbing layer made from the resin or the compositions.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN KAISHA LTD
Reusable closure with vent
A preservation apparatus and method for using the same are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the preservation apparatus comprises a removable closure adapted to fit together in a sealed relationship with a vessel for containing an item, the removable closure comprising a top portion having a first opening to enable pressure within the vessel to be transferred to an interior of the top portion; and a container operable to contain a substance operable to collect oxygen molecules contained within the vessel and render them harmless to the item, wherein the container comprises a lid with a second opening located in proximity to the first opening and having a vent through which the pressure from the vessel is transferred to the interior of the top portion.
Owner:ZERO OXYGEN SOLUTIONS INC
Three-part closure sealing and dispensing device for all types of Containers
A container closure device with a flexible three-dimensional formed sealing wad with a circumferential ridge, the closure body (1) is formed with a top wall and a cylindrical wall, wherein the top wall has a circumferential trapezoidal groove on the inner side of its rim, adjacent to the cylindrical wall. A sealing wad (2) is arranged below the inner side of the top wall of the closure body, whereby the ridge is located under the groove and has an internal circumferential recess in the ridge running around the perimeter of the underneath side of the sealing wad, serving to receive the edge of the spout forming the opening of the container, whereby the protruding ridge is oversized compared to the groove, the width of the recess is reduced and compressed when the ridge is forced into the groove. The recess has sealing fingers and on its inner and outer side walls which creates the seal with the container.
Owner:CLARKSON ARON JOSEPH
Container orifice reducer with tamper evident seal
ActiveUS10569937B2Extended shelf lifeClosures with oxygen absorbersSmall article dispensingMechanical engineeringPolymer
Containers with closures are disclosed. A closure may include at least a polymer orifice reducer configured to be permanently secured to a rim of an opening of a container and a flexible tamper evident seal disposed on the topside of the orifice reducer. The flexible tamper evident seal, optionally foil, covers one or more openings in the orifice reducer. Processes for permanently securing a closure to a container, optionally by forming a heat seal between the orifice reducer and container rim, are also disclosed.
Owner:CSP TECH INC
Moisture absorbent scavenger and vacuum relief device for chemical containers
The invention is a vent for use with a container, such as commercial steel pails and drums, and a method for venting containers. The vent has a cap seal with one or more semipermeable membranes covering an orifice in the cap seal. The membrane prevents the passage of at least one atmospheric component, but allows the free passage of air. When a product is filled into the container at an elevated temperature and cools, a vacuum is formed within the container. The resulting vacuum opens a vacuum release device in the vent and pulls air through a hole in the cap seal, which is protected by a micro-porous membrane. The venting of air into the container relieves the vacuum without damage to the container or the product within the container.
Owner:LANXESS SOLUTIONS US INC
Canister for containing an active material
ActiveUS9861926B2Easy to assembleEasy to manufactureClosures with oxygen absorbersCapsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A canister including a canister body containing a bottom wall and at least one sidewall with inner and outer sidewall surfaces and an upper rim, and a closing element containing a top wall with an outer surface and an inner surface, and a fixing portion surrounding the top wall. The top wall or the bottom wall or at least one sidewall include a membrane region with a predetermined permeability. The fixing portion includes an elevated or recessed snap portion around its outer periphery shaped to correspond to the inner sidewall surface of the sidewall of the cylindrical canister body and form a snap connection with the canister body. The closing element is fixed to the canister body such that the outer surface of the top wall does not extend beyond the upper rim of the sidewall of the canister body.
Owner:AIRNOV INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com