Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
85results about "Amplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneously" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
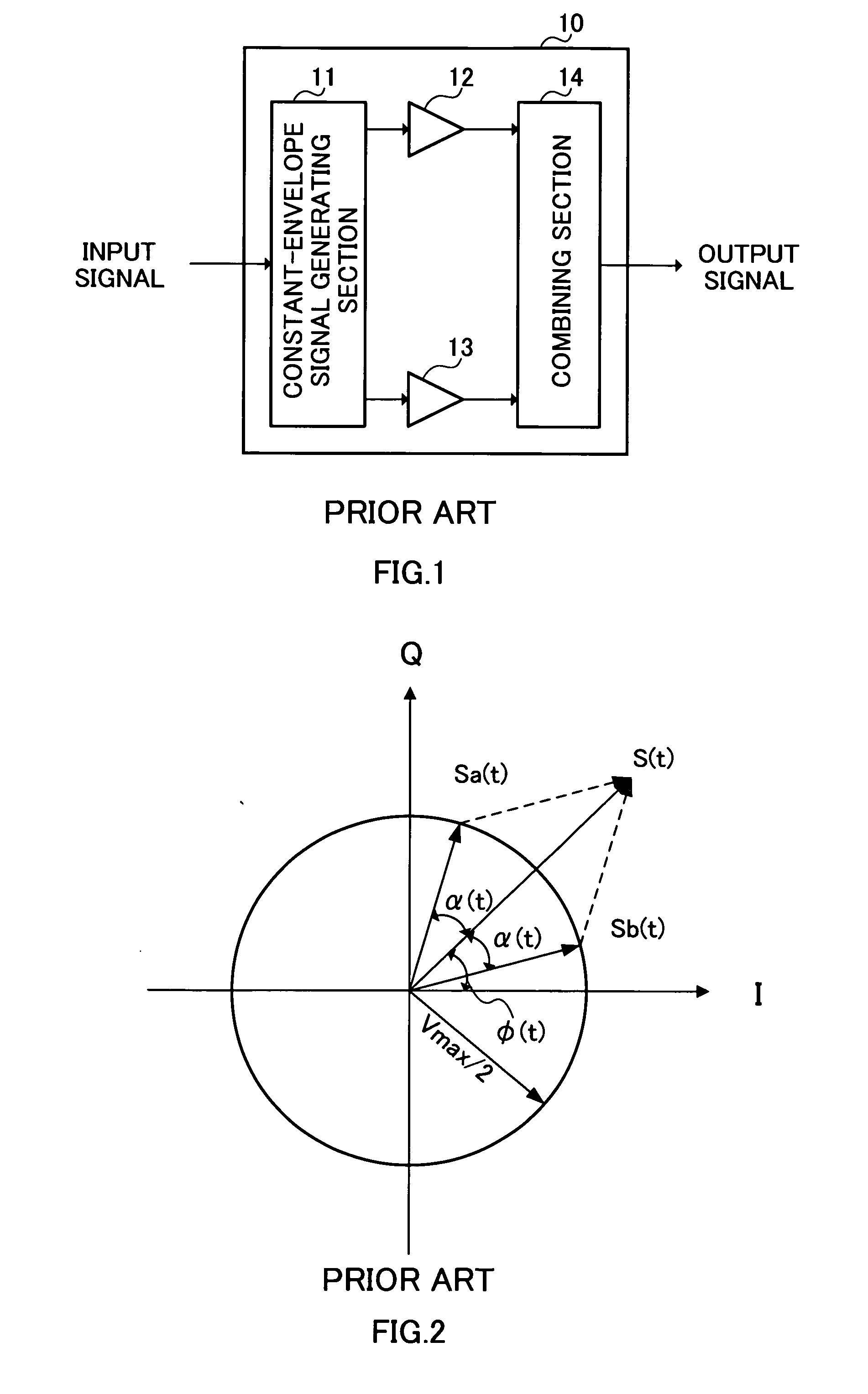
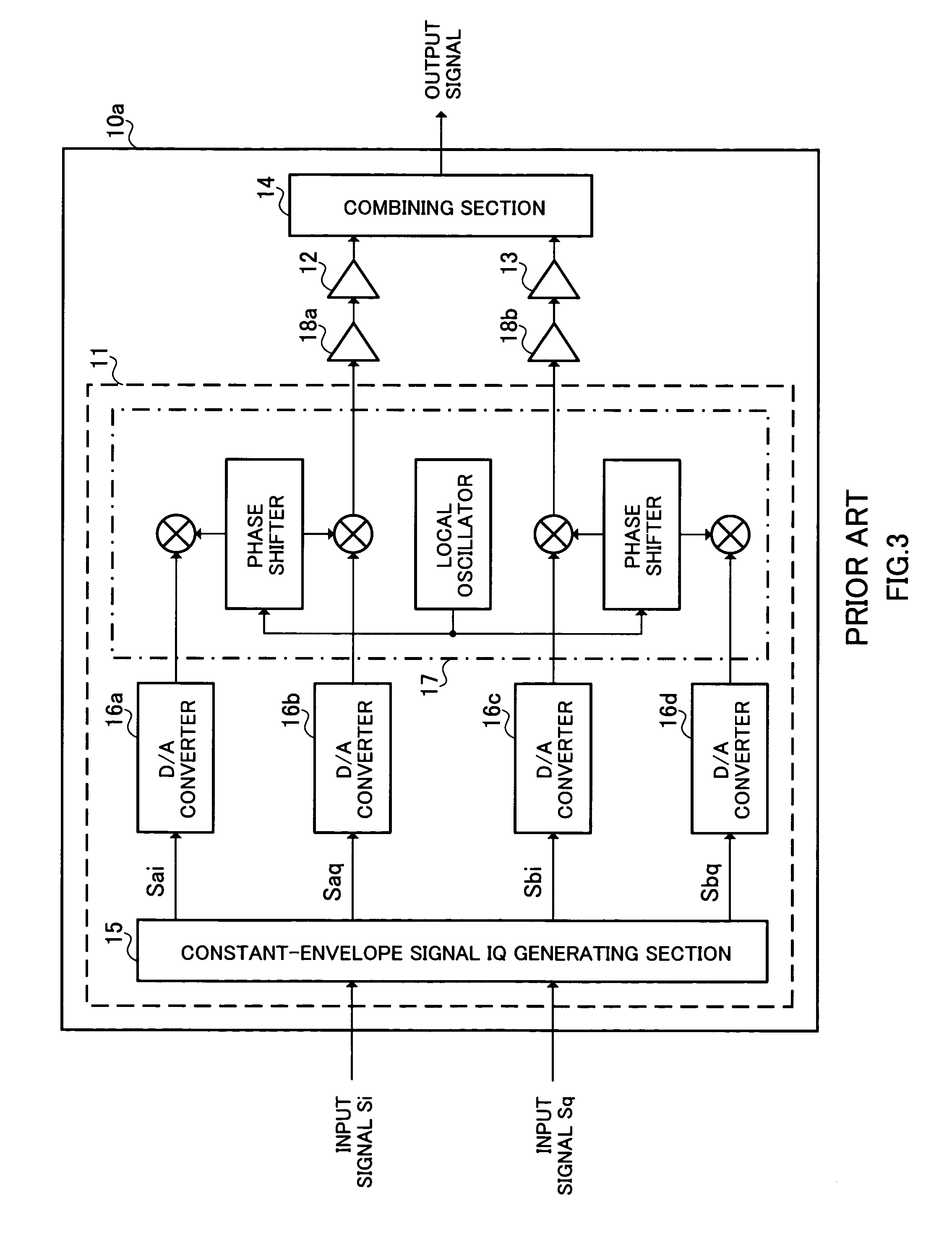
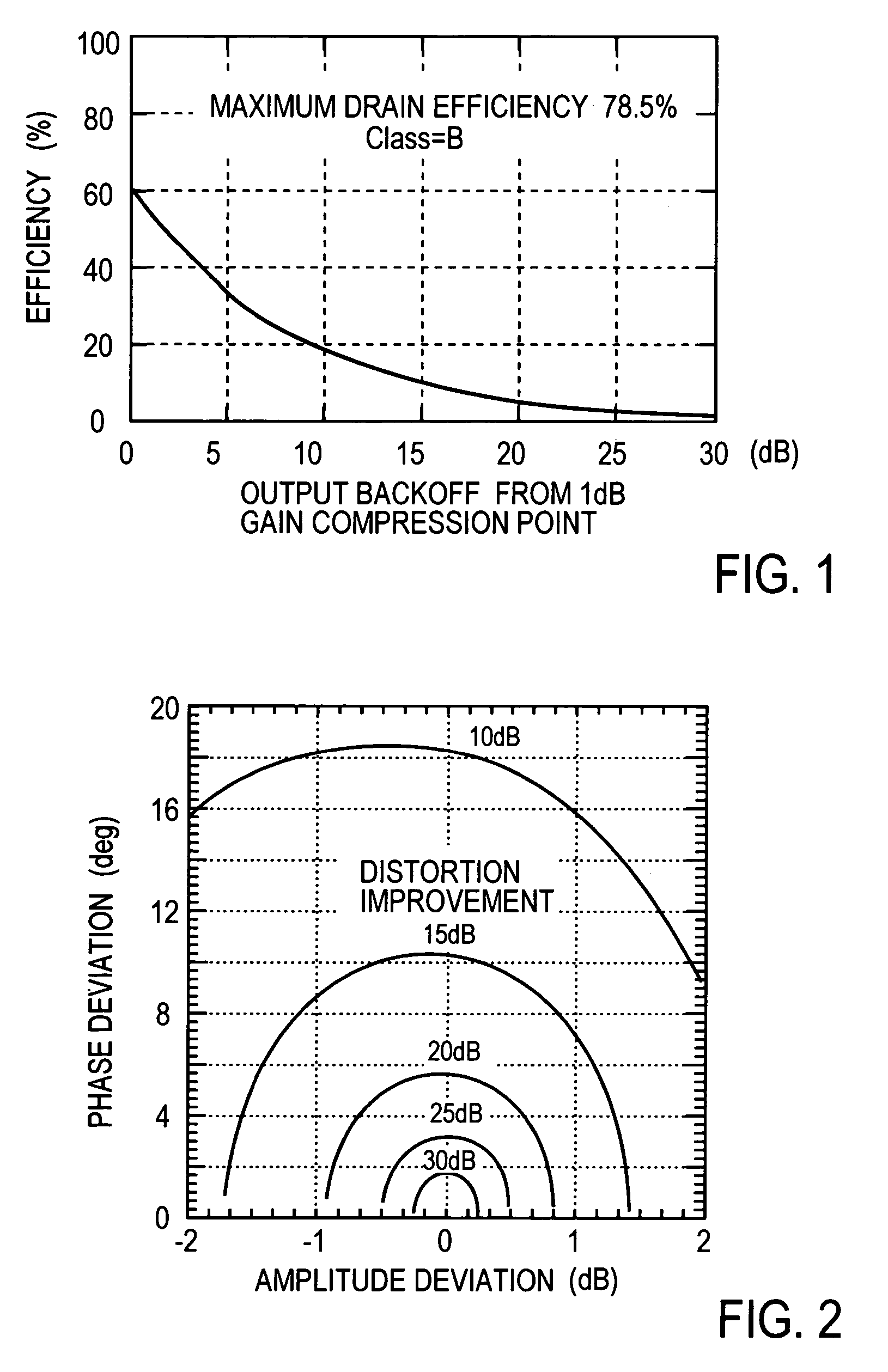
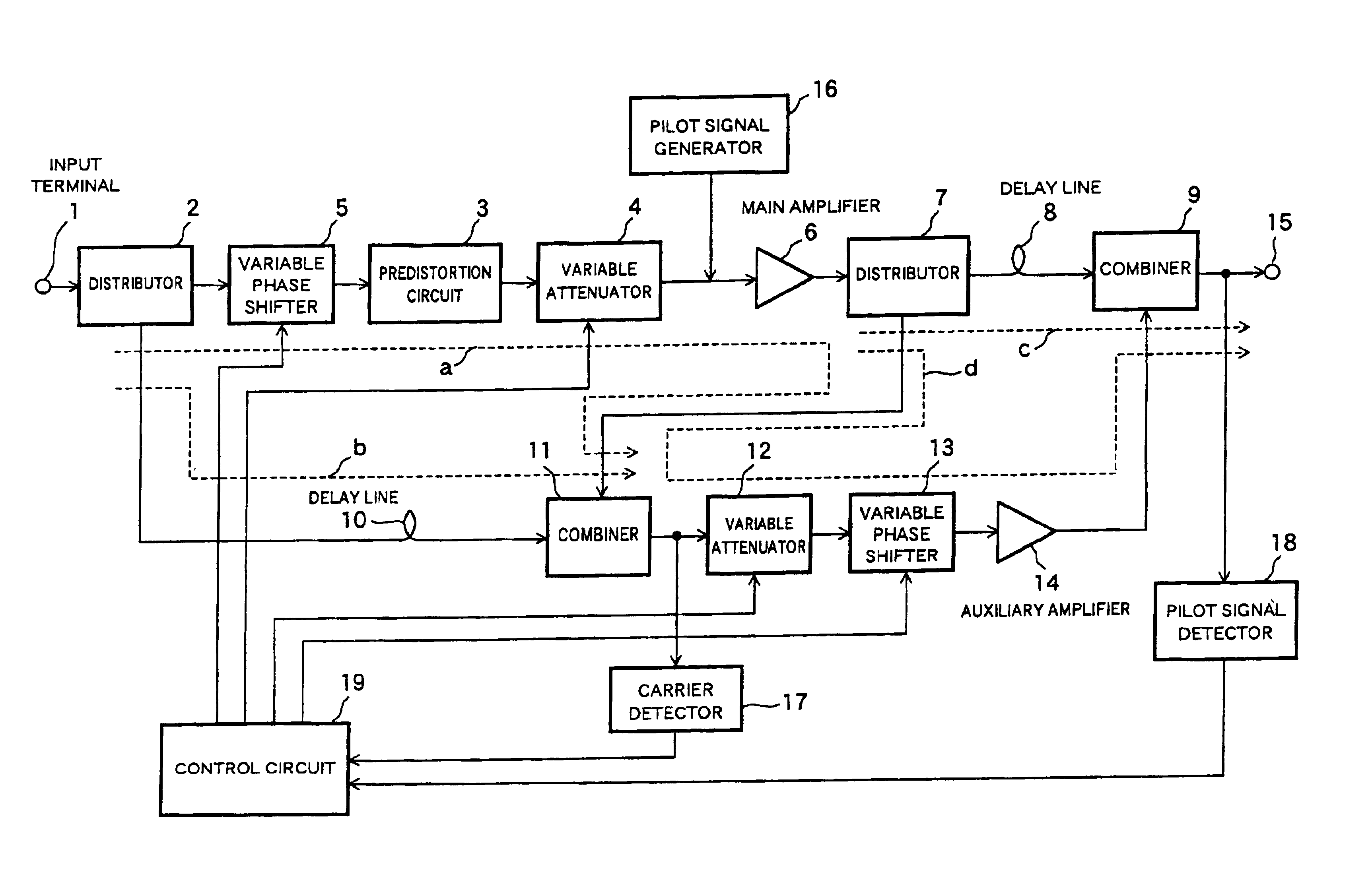
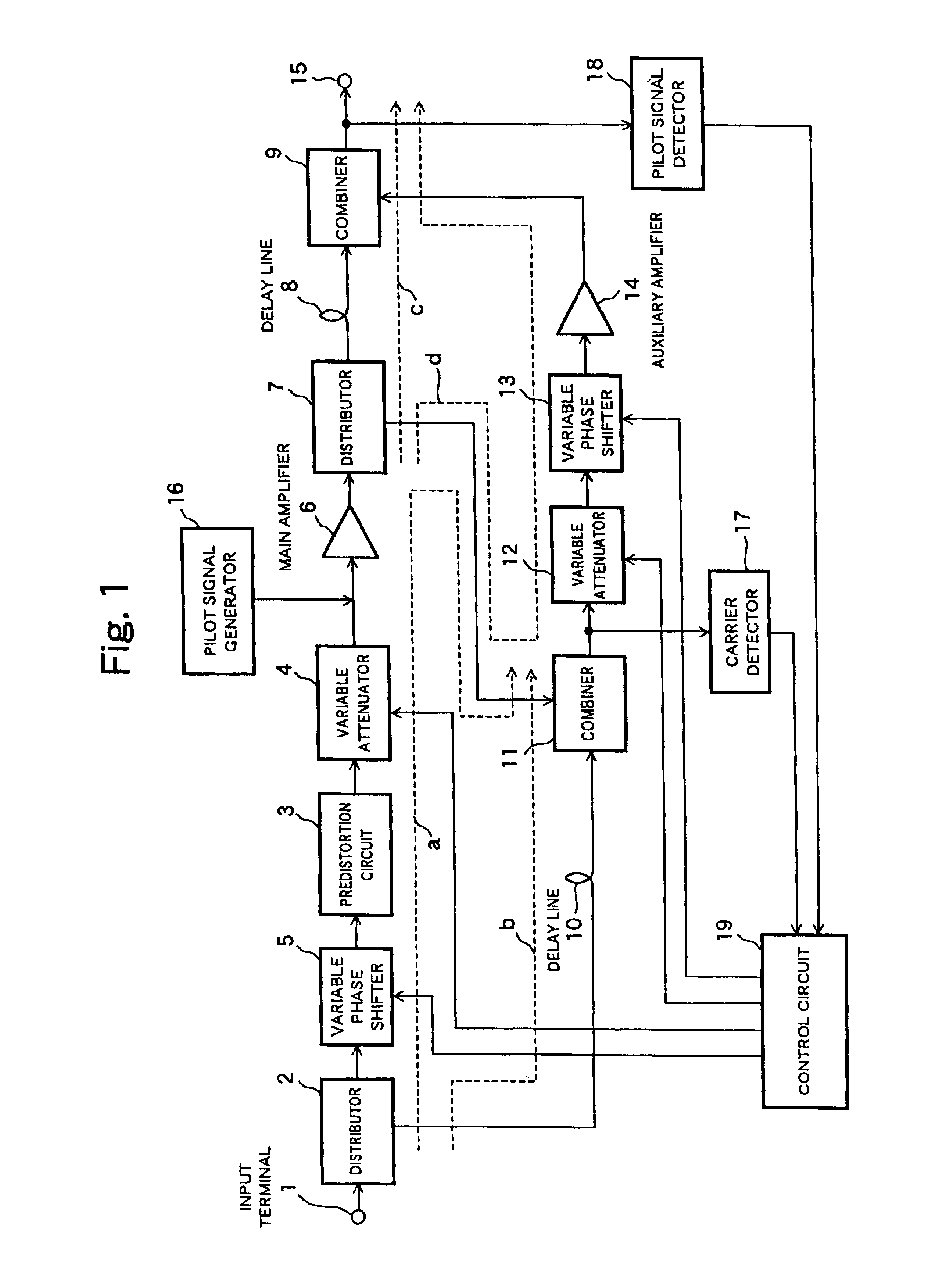
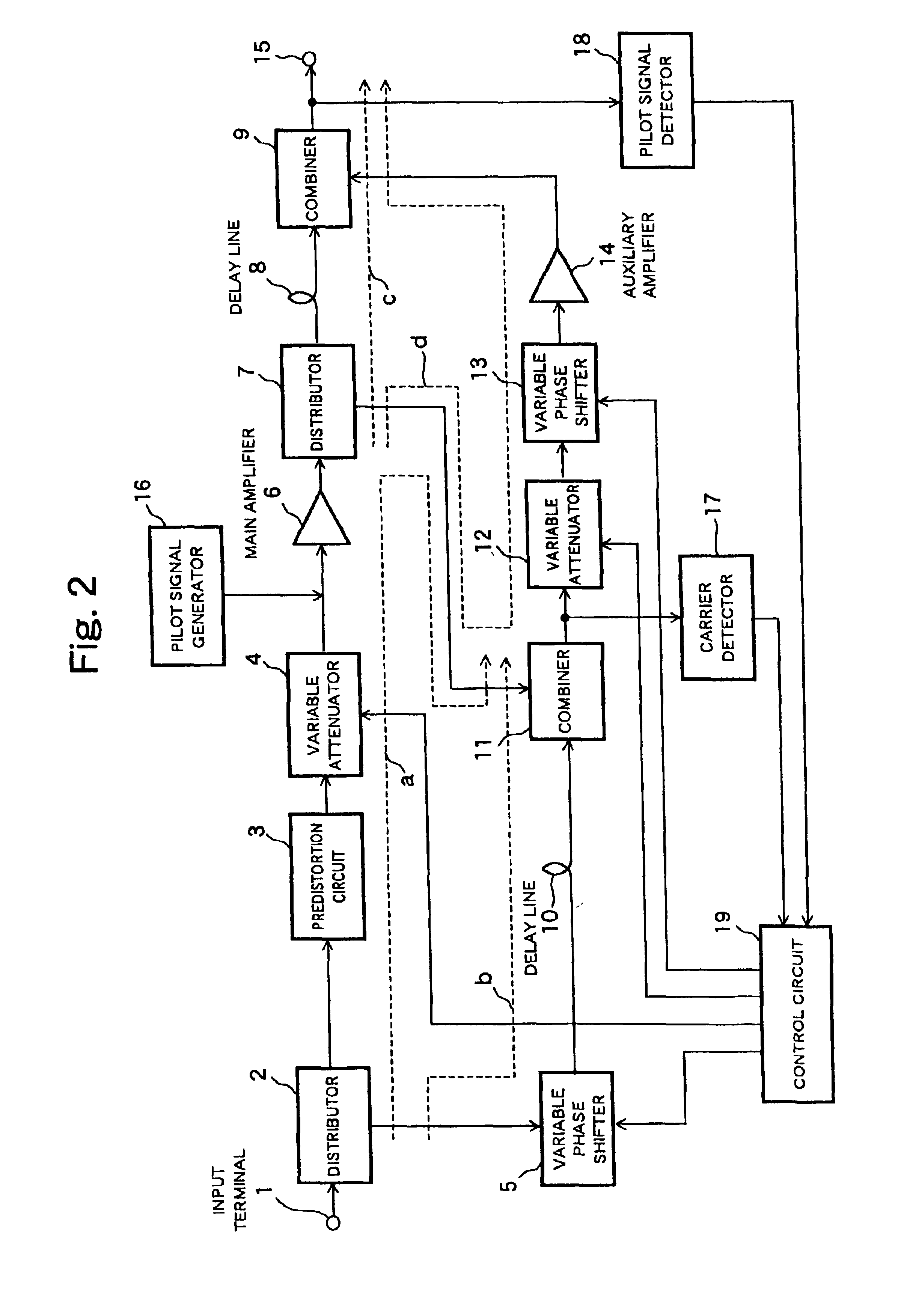
High-efficiency linear power amplifier
ActiveUS7042283B2Achieve linearityHigh-efficiency power amplificationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersDigital analog converterAudio power amplifier
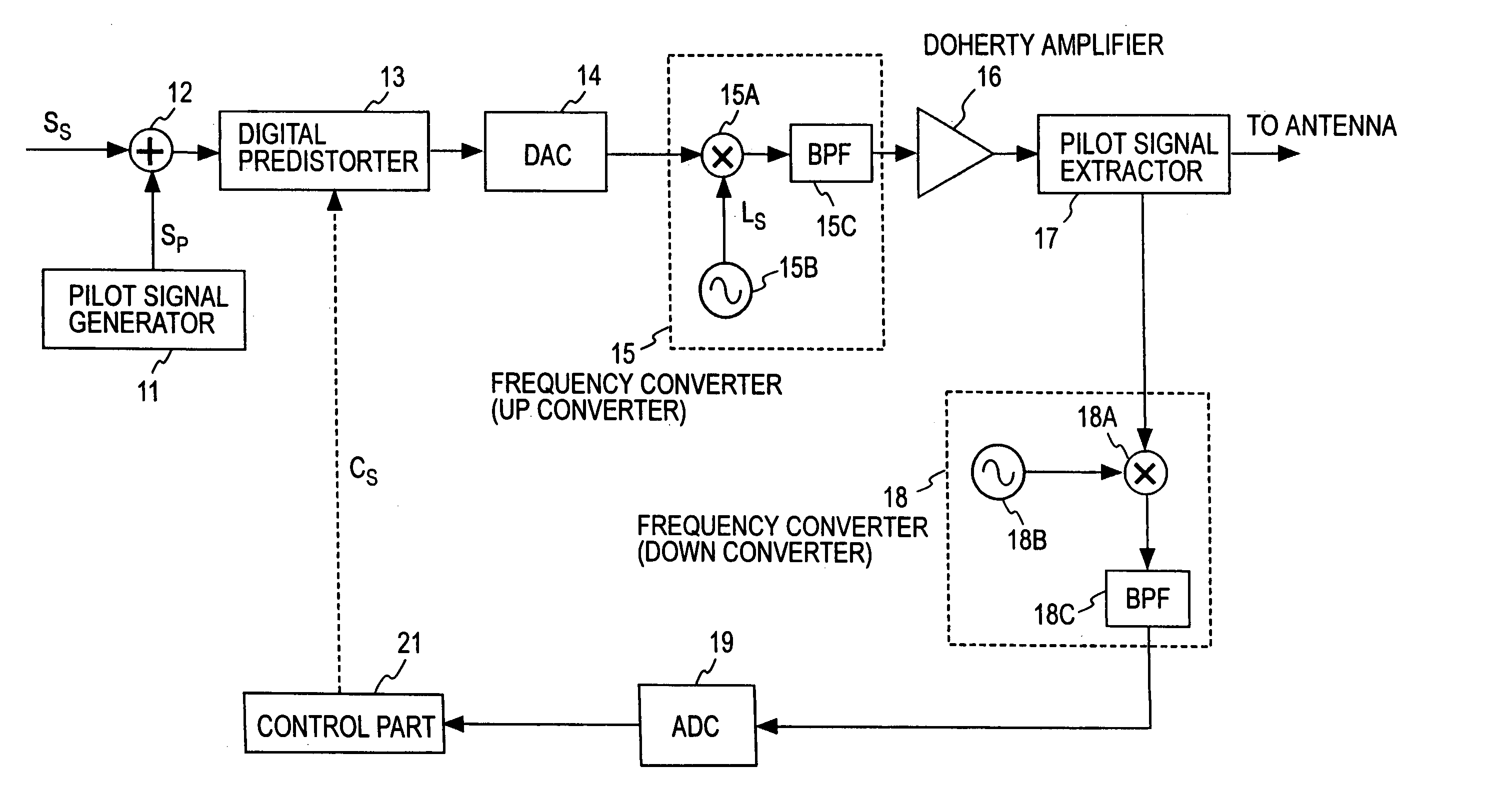
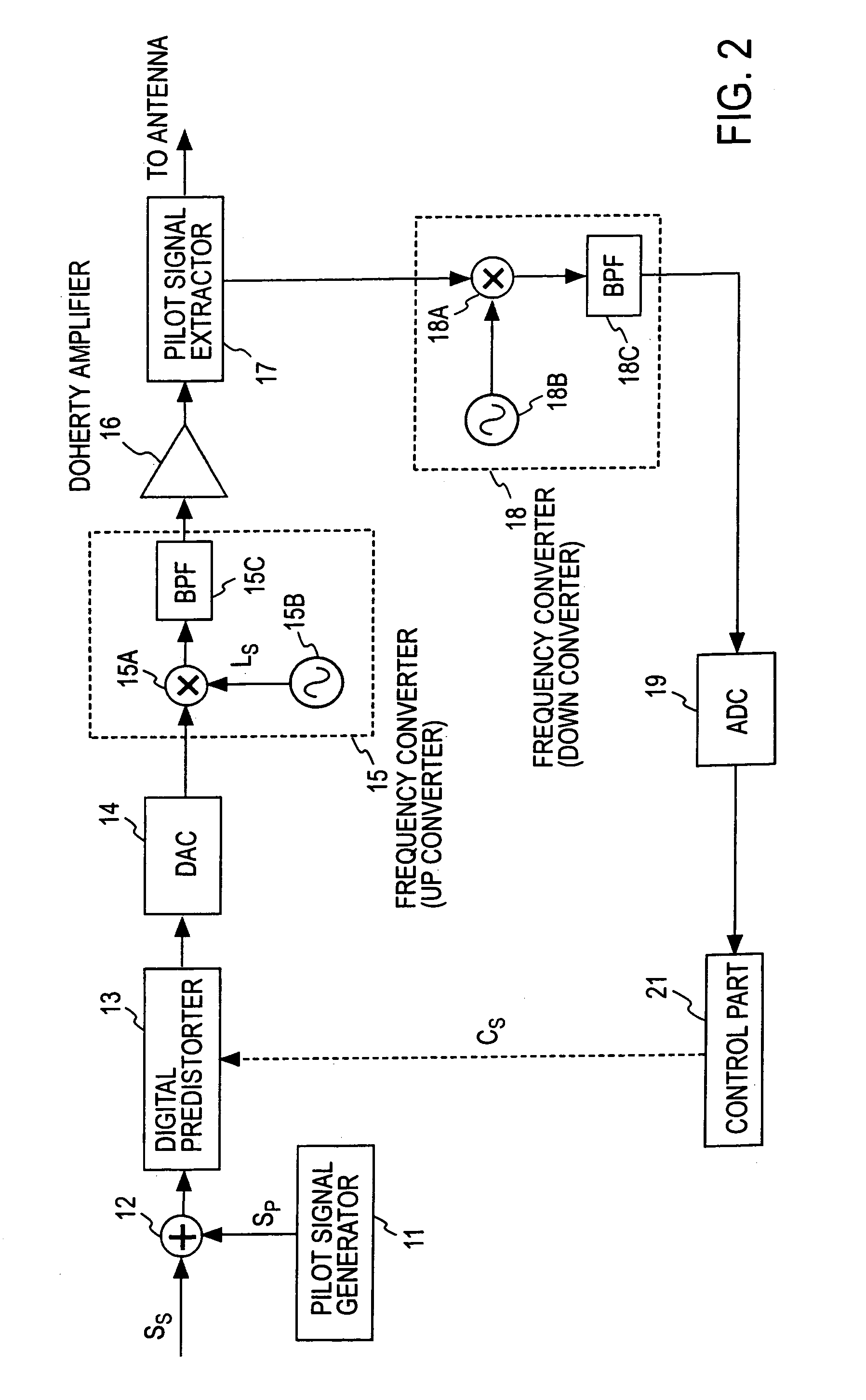
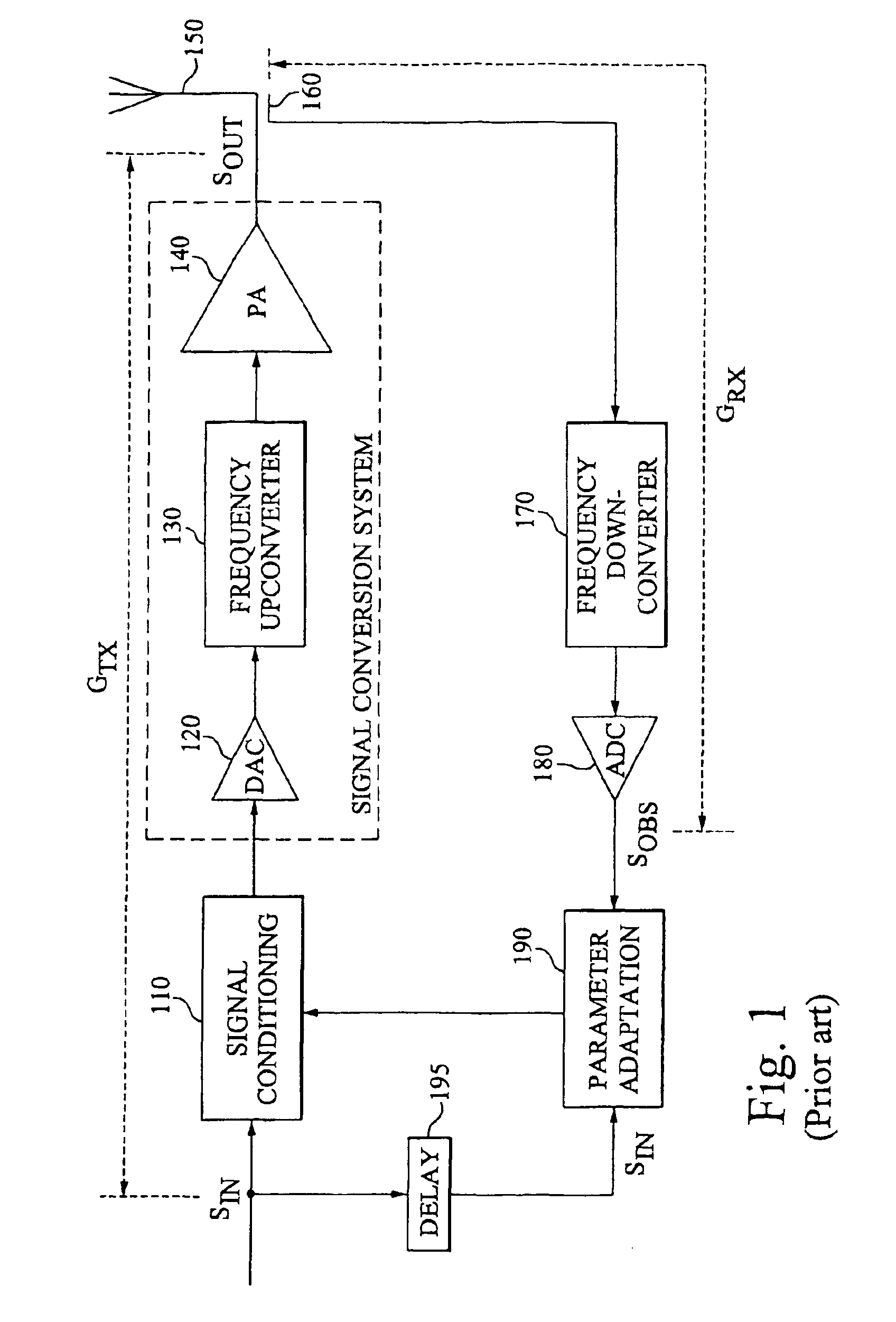
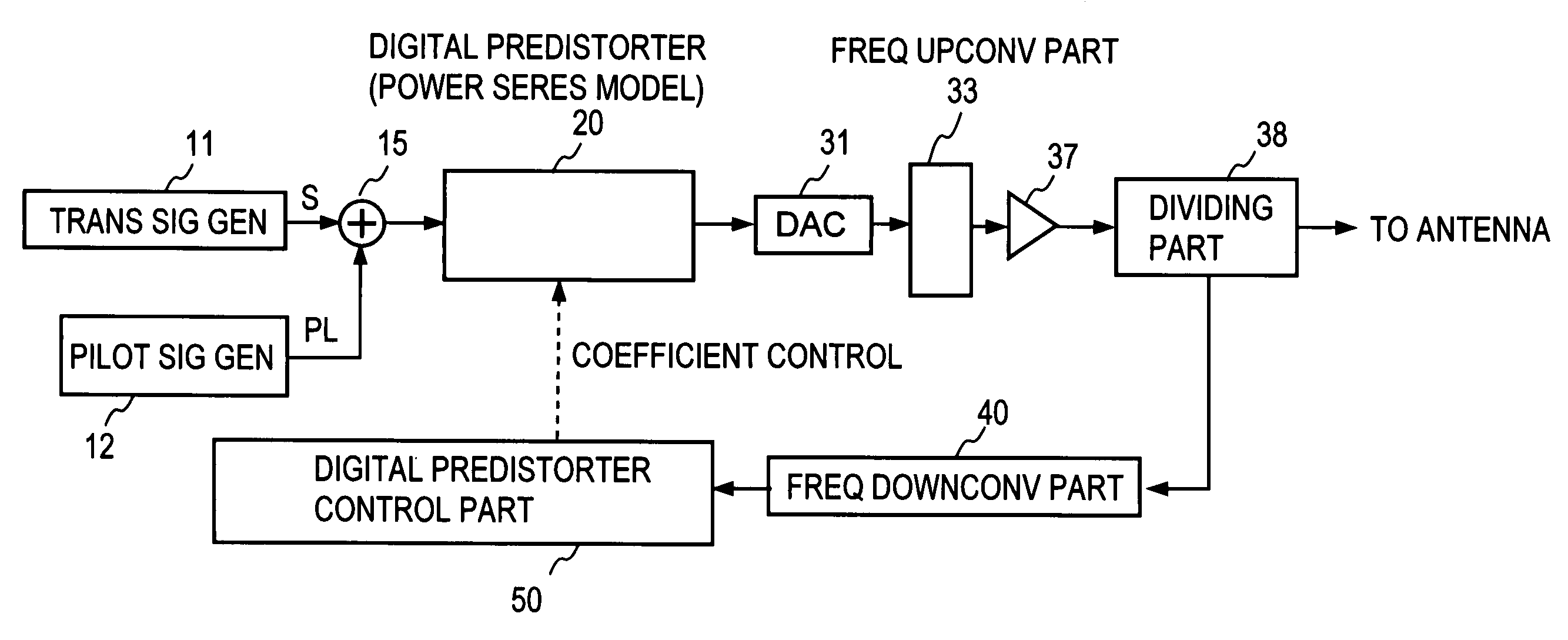
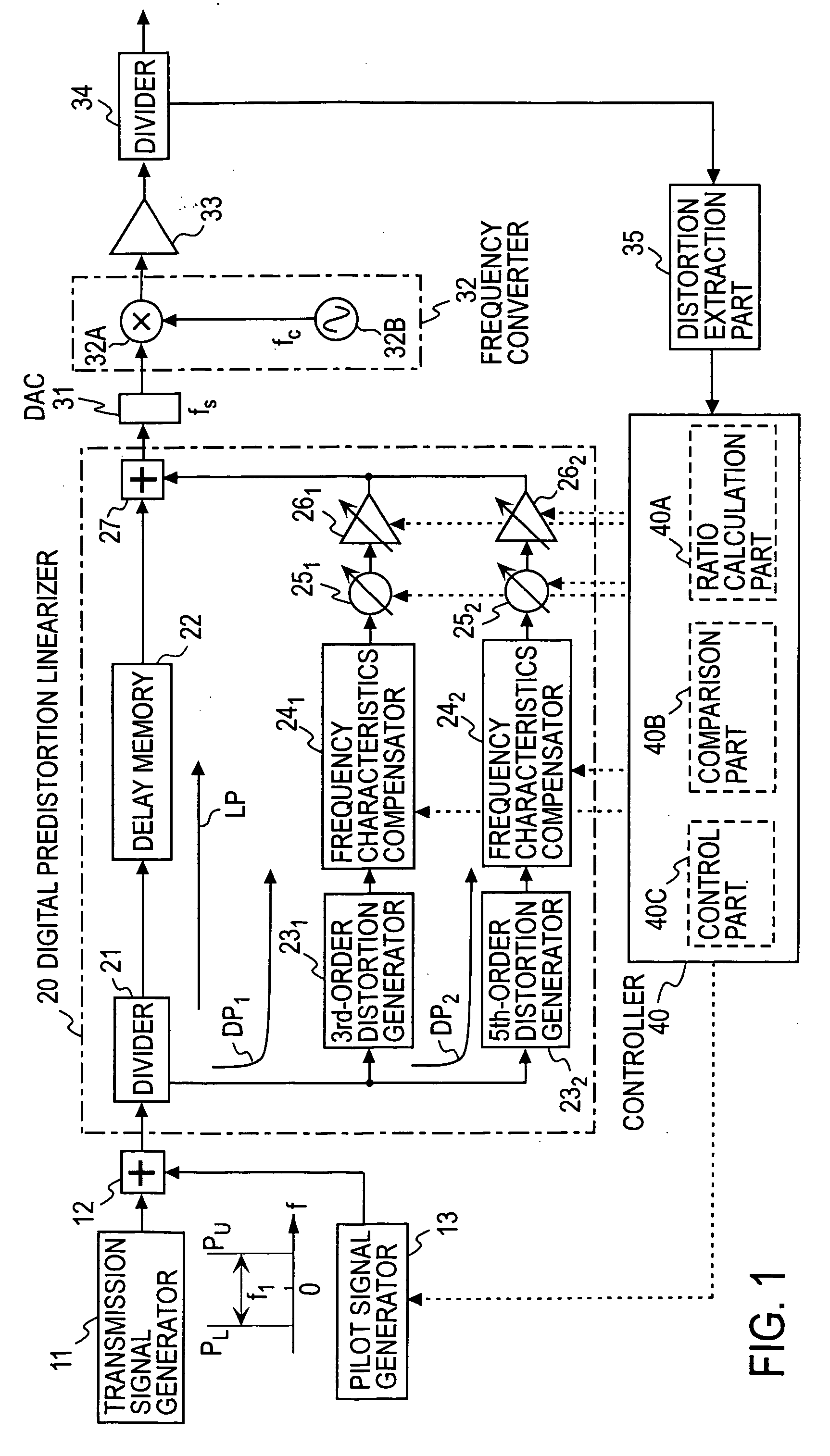
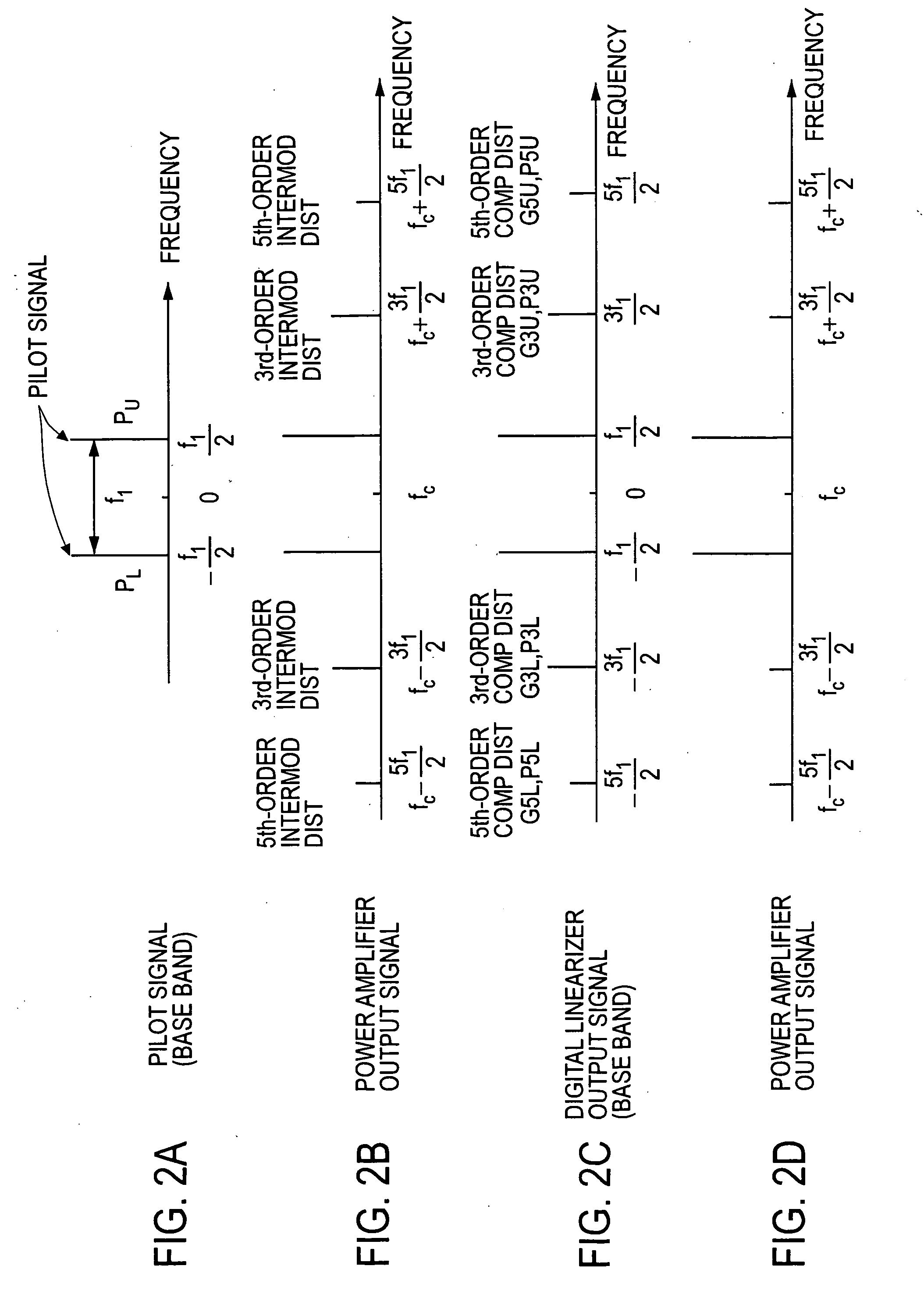
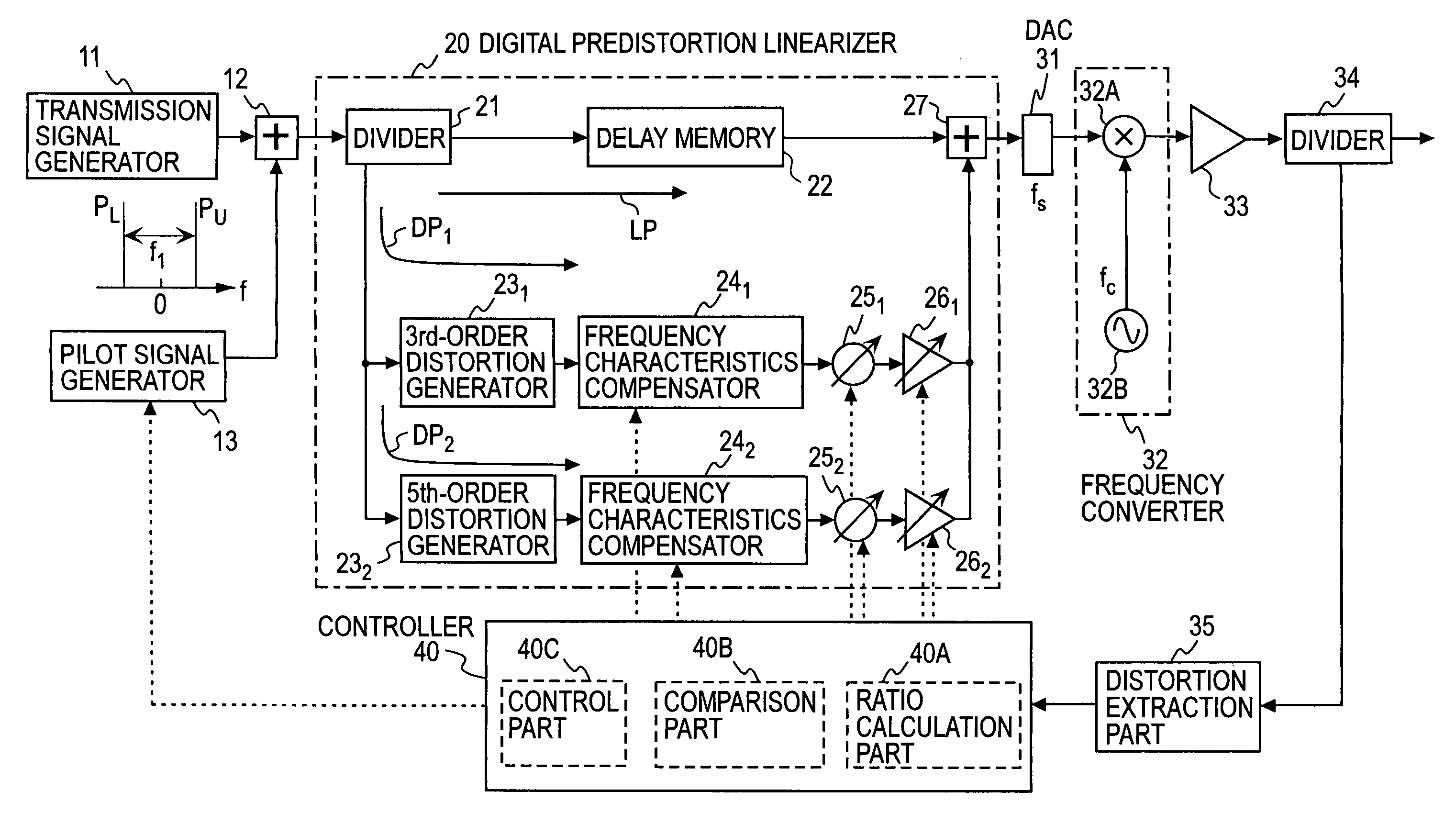
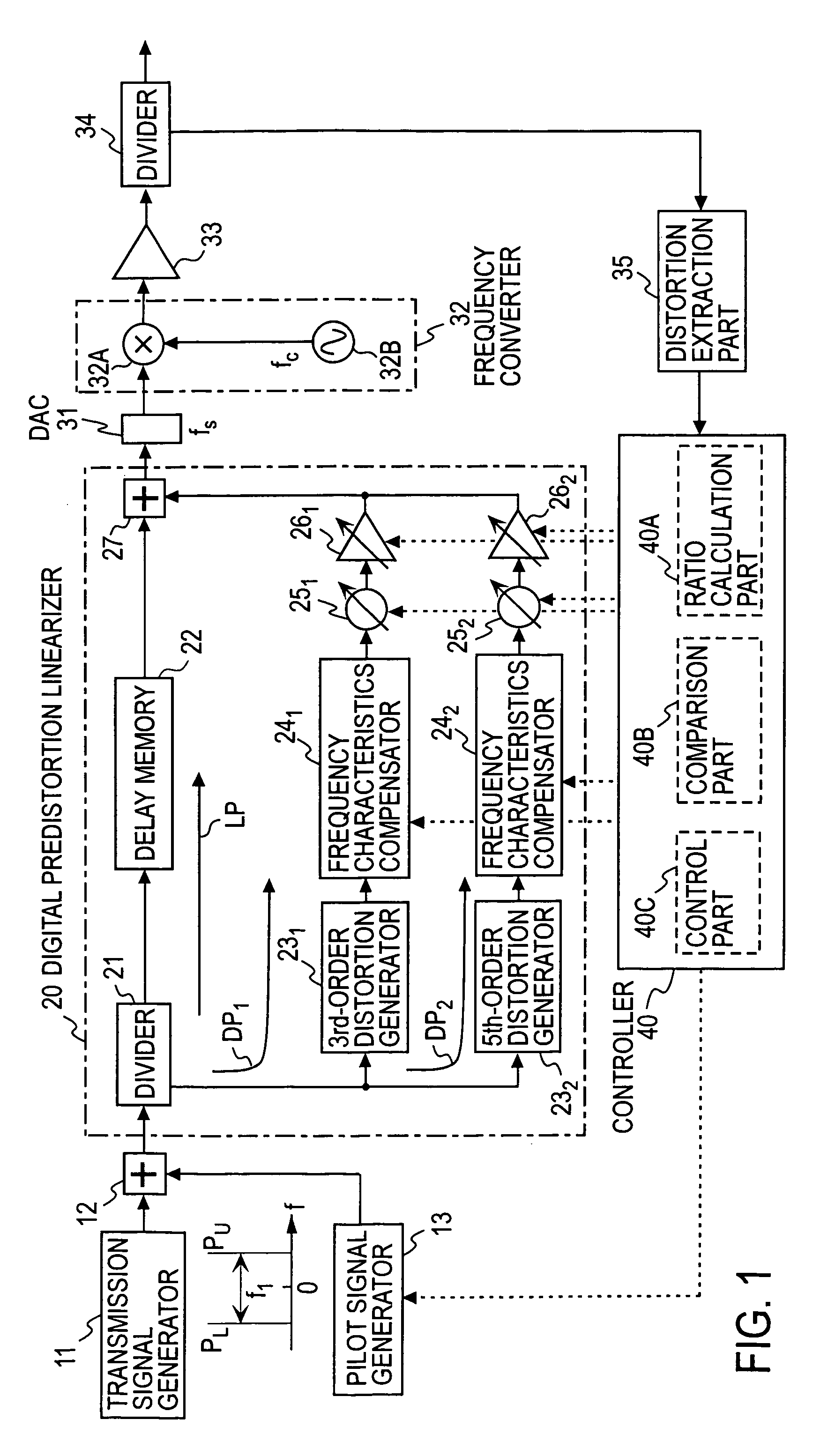
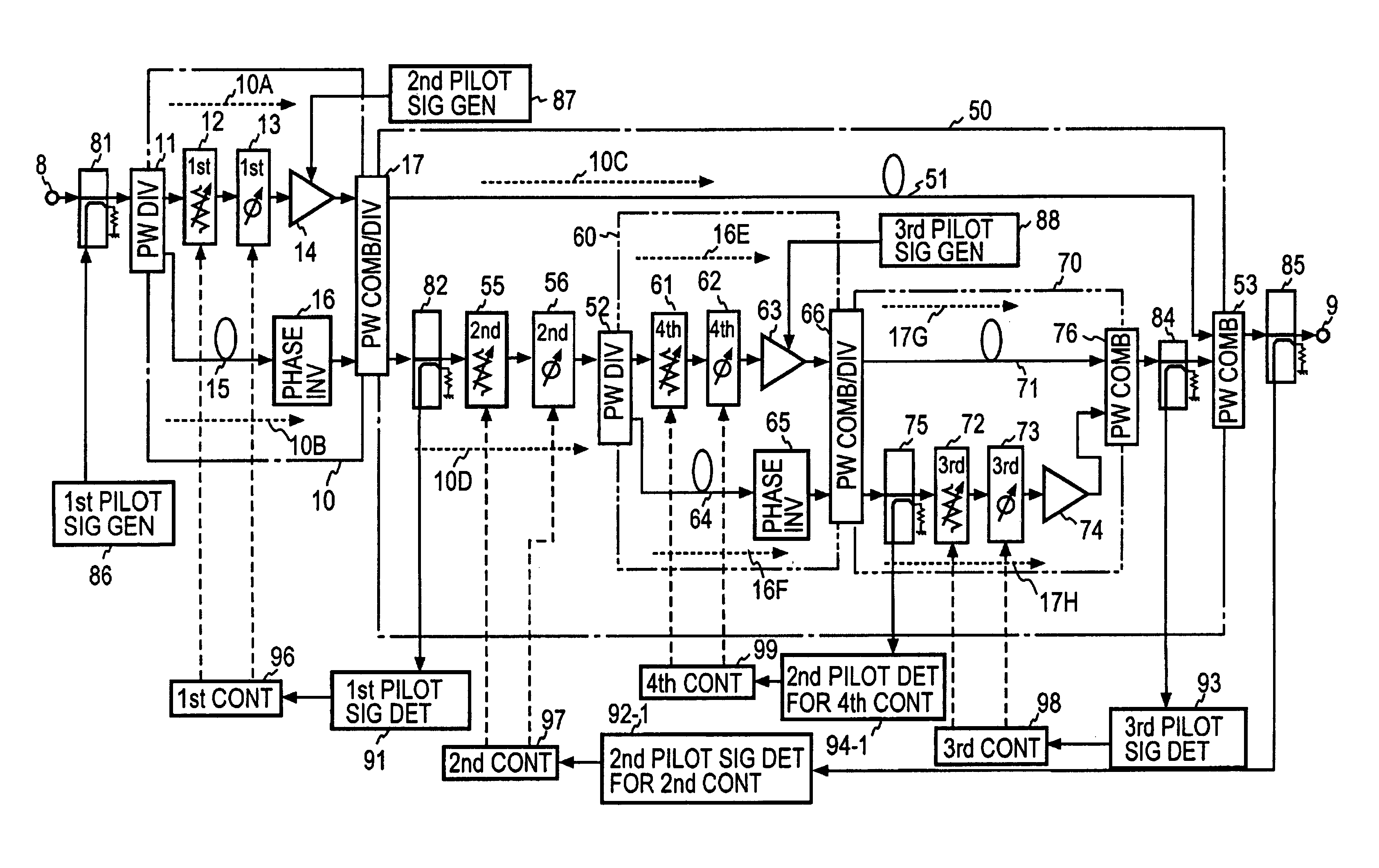
A transmission signal and a pilot signal are predistorted by a digital predistorter 13 by use of a power-series model, and the predistorted output is converted by a digital-analog converter 14 to an analog signal. The analog signal is up converted by a frequency converter 15 to an RF-band signal, which is transmitted after being power-amplified by a Doherty amplifier 16. The pilot signal is extracted by a pilot signal extractor 17 from the output from the Doherty amplifier, and the extracted pilot signal is down converted by a frequency converter 18 to a baseband signal. The baseband pilot signal is converted by an analog-digital converter 19 to a digital pilot signal. A control part 21 detects an odd-order distortion component from the digital pilot signal, and based on the detected result, controls parameters of the digital predistorter.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Calibration of an adaptive signal conditioning system
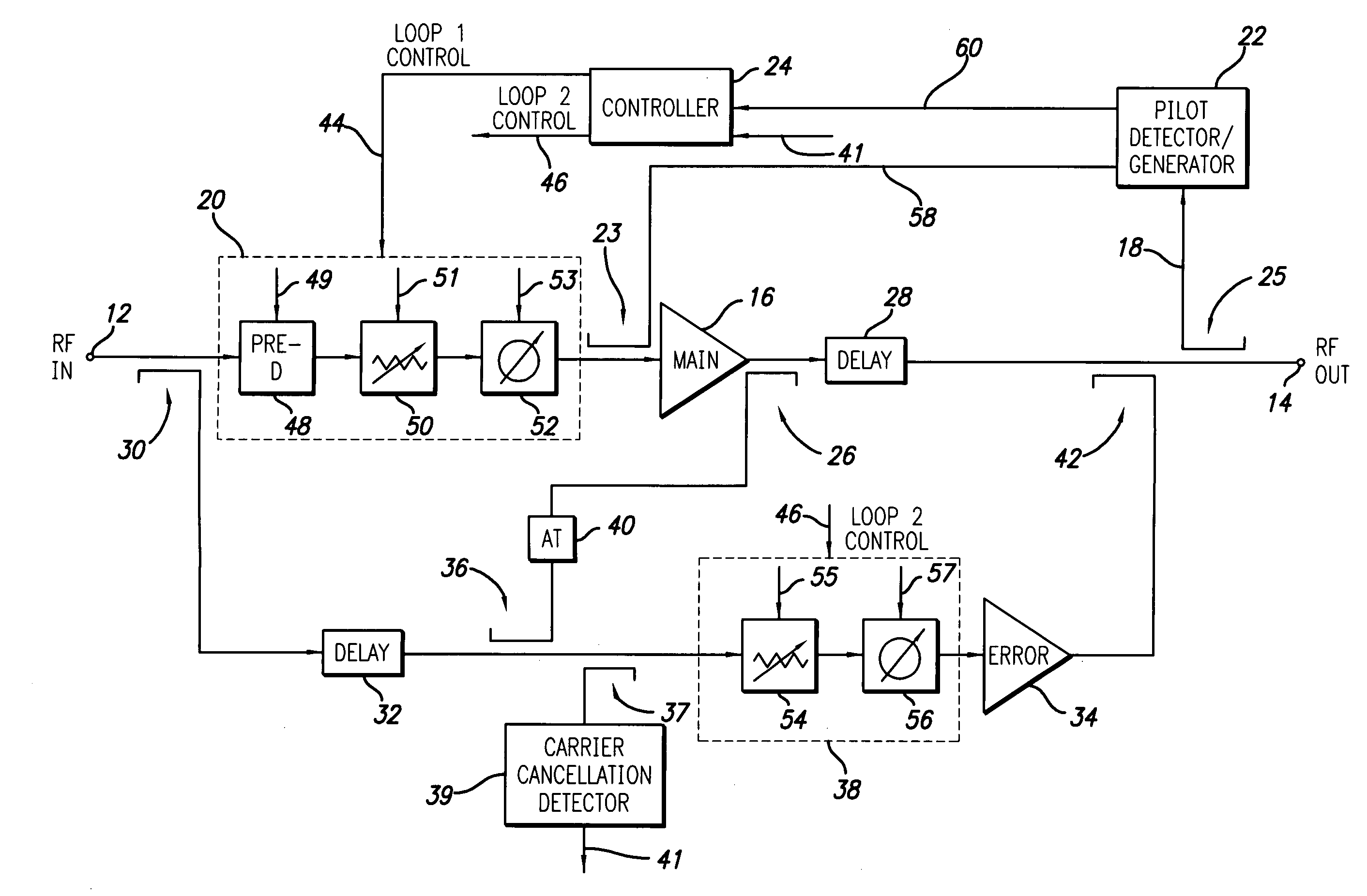
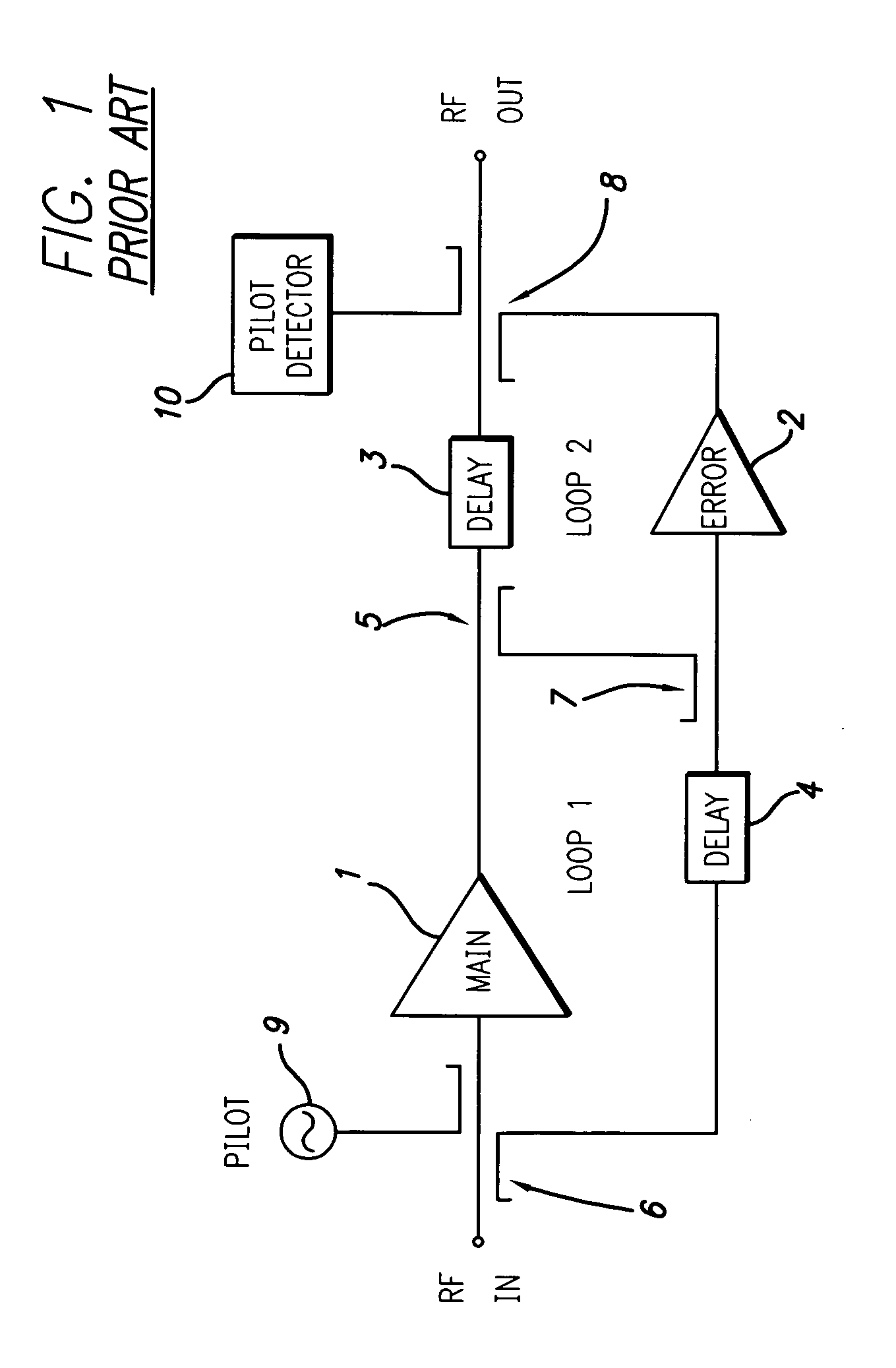
InactiveUS6943627B2Robust and efficient calibrationAccurate conditionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric devicesSignal conditioningEngineering
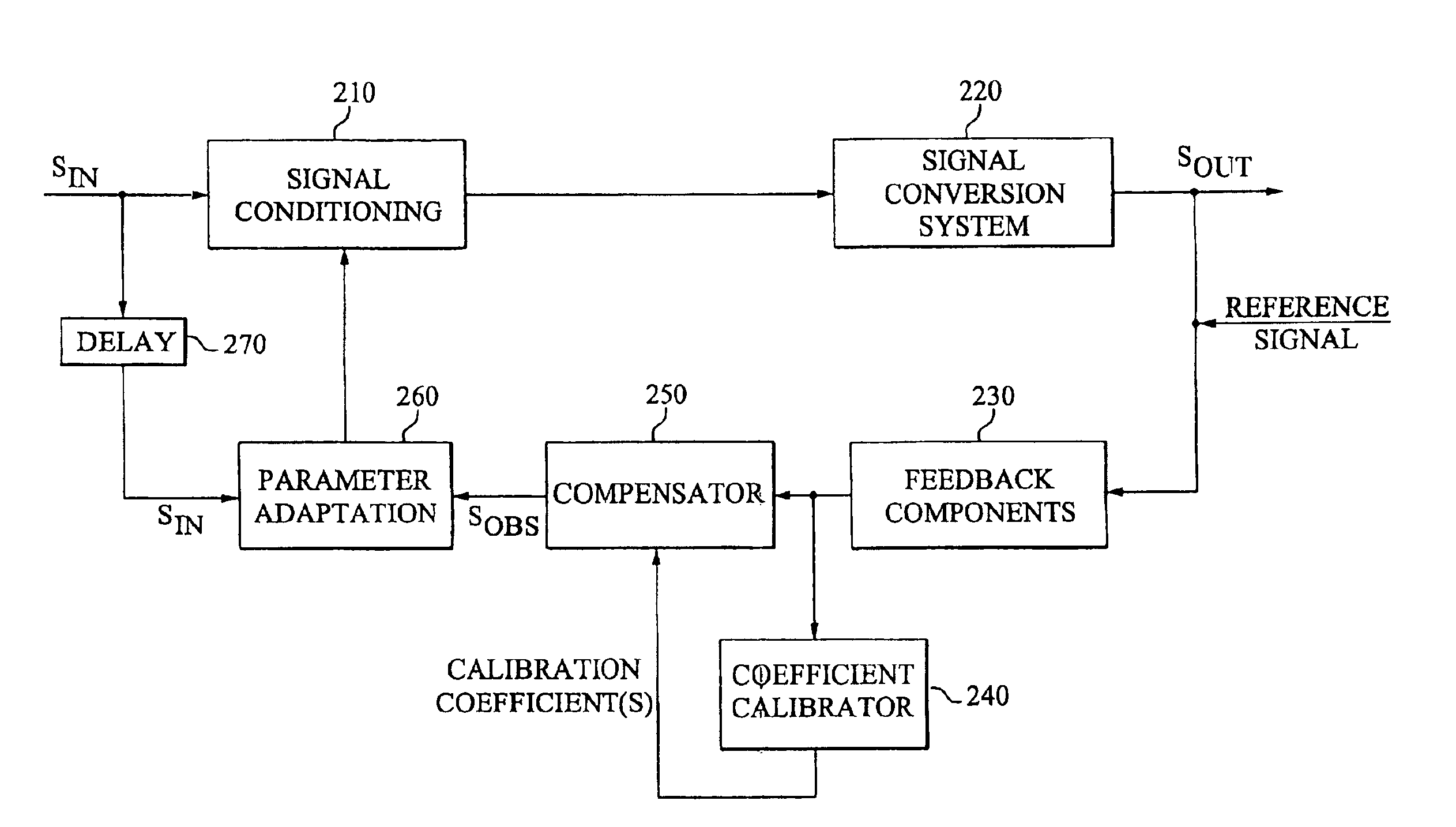
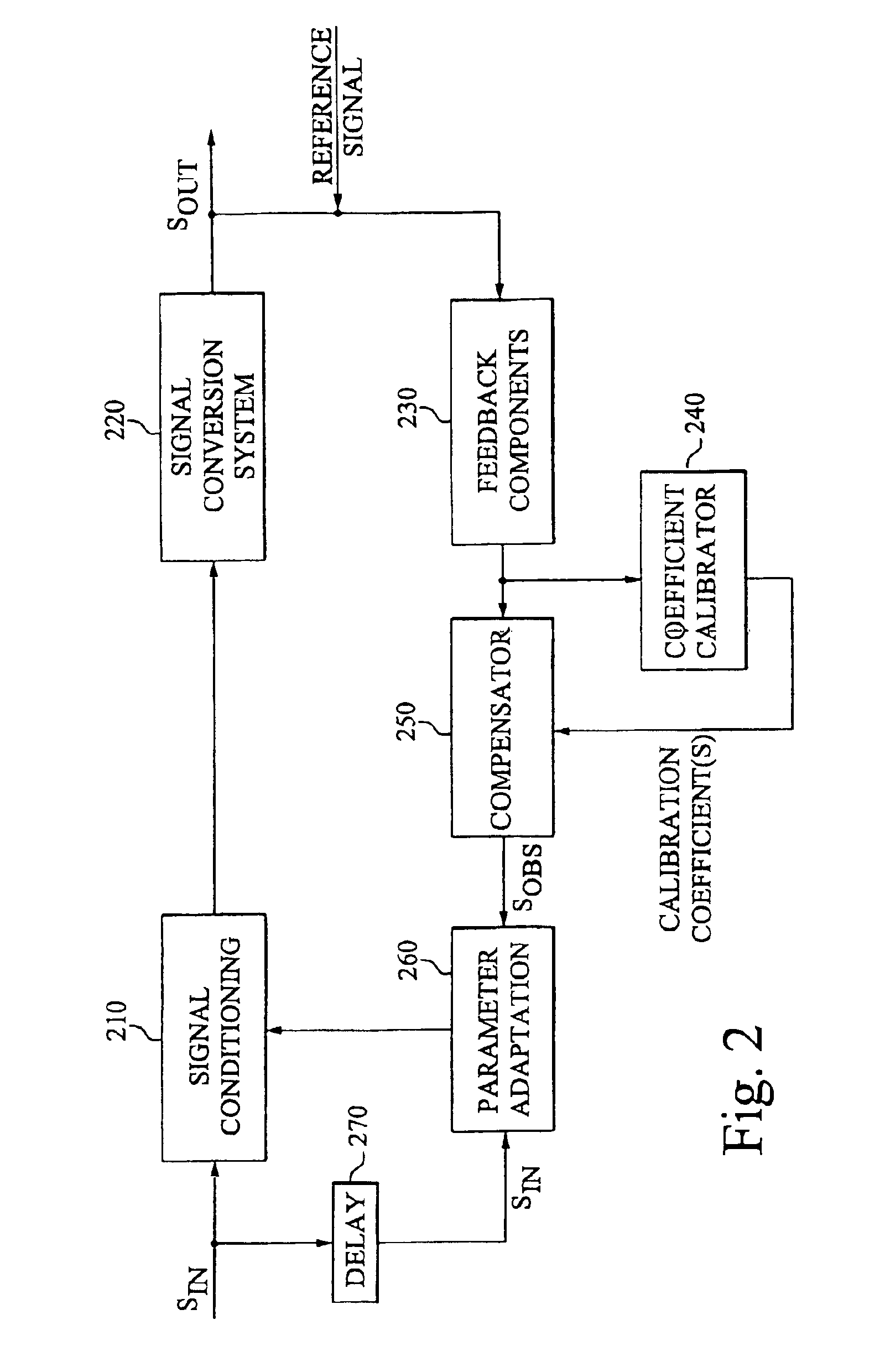
The invention provides robust and non-invasive calibration of an adaptive signal conditioning system having a signal conditioning block in the signal path to a signal conversion system, and a feedback path with a number of feedback components for enabling adaptation, by means of a parameter adaptation block, of the parameters used in the signal conditioning. In order to calibrate the feedback path, a well-defined reference signal is inserted into the feedback path, and an appropriate calibration coefficient is then determined by a coefficient calibrator in response to the received reference signal. The calibration coefficient is provided to a compensator, which effectively compensates for changes in the transfer characteristics of the feedback path due to factors such as variations in ambient temperature and component aging. Accordingly, the feedback signal transferred over the calibrated feedback path will be an accurate representation of the output signal of the signal conversion system, thus allowing accurate adaptive signal conditioning.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Modulator-amplifier
InactiveUS7109789B2Minimize switching-induced distortionMinimize distortionSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyAudio power amplifierSoftware engineering
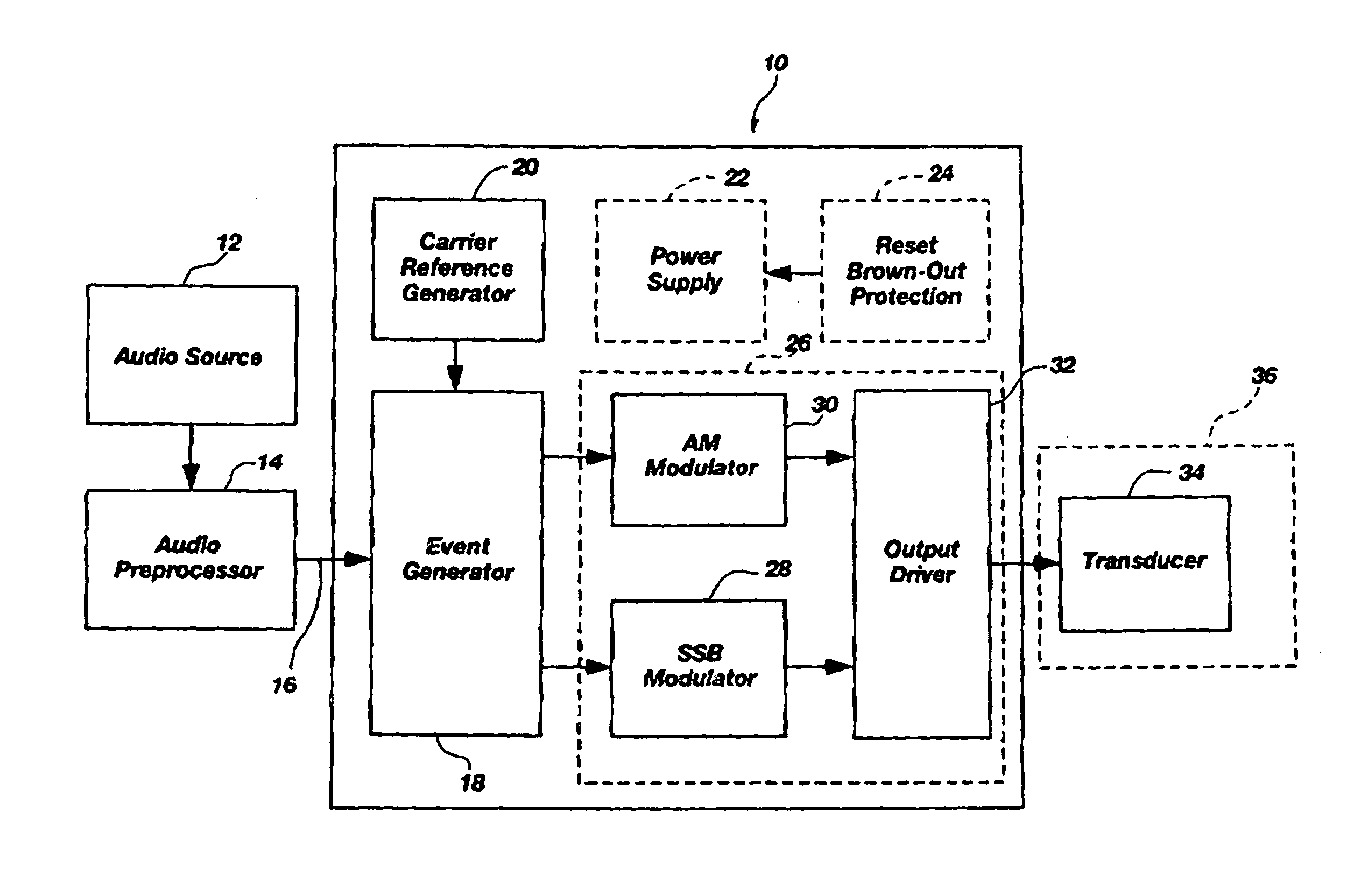
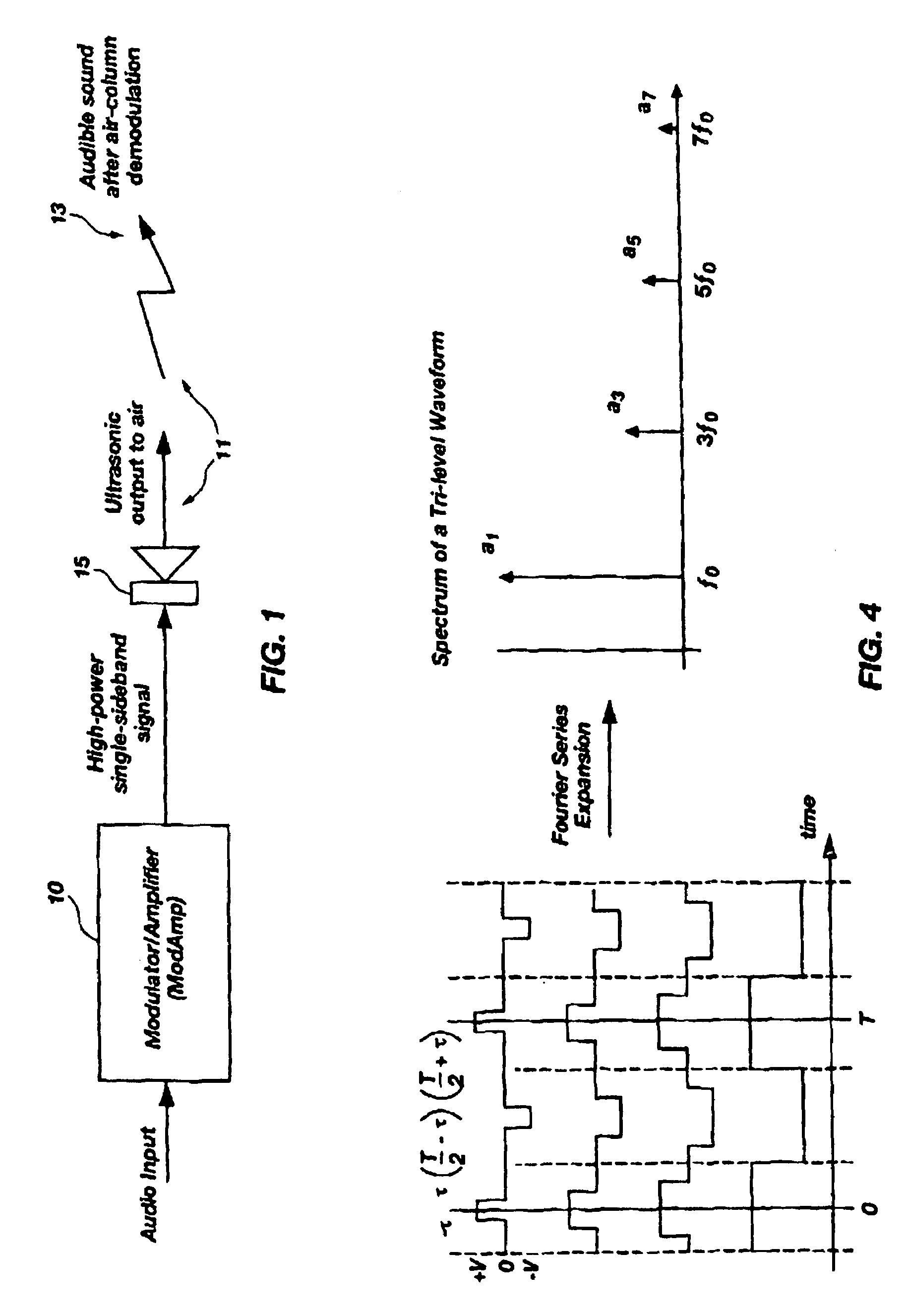
A modulator-amplifier configured for use in parametric sound reproduction systems, including an input configured for receiving at least one input signal, a reference signal generator configured for generating a reference signal, and a comparator stage coupled to the input and the reference signal generator, the comparator stage configured for detecting relationships between a first signal based on the input signal and the reference signal. A switching power stage coupled to the comparator is configured to receive a second signal derived from a combination of an output from the comparators and the input signal, wherein there is a non-linear relationship between the input signal and the timing of state transitions in the switching power stage for the purpose of generating an output that has been shifted in frequency relative to a frequency of the input signal, and which includes at least one sideband.
Owner:TURTLE BEACH
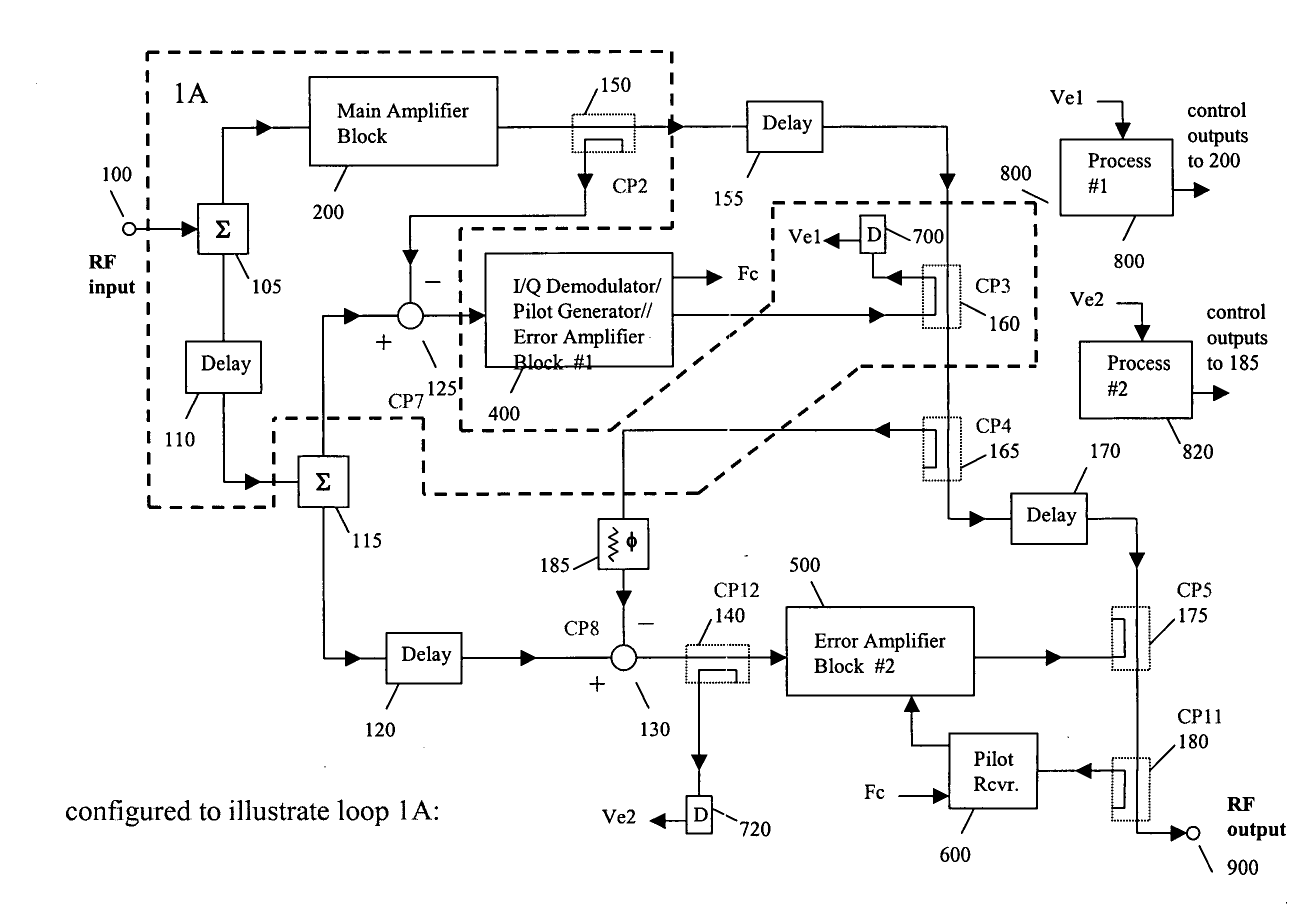
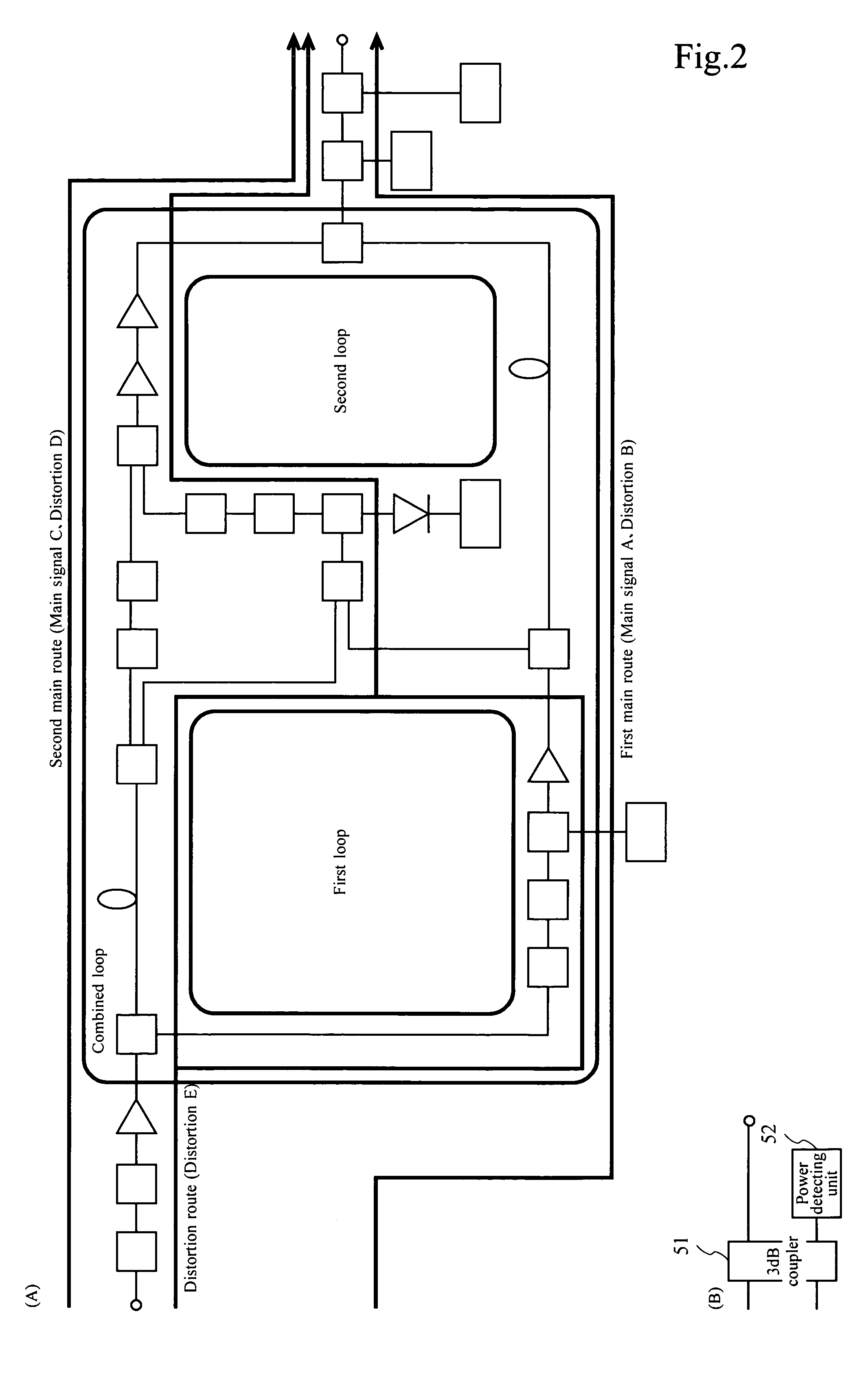
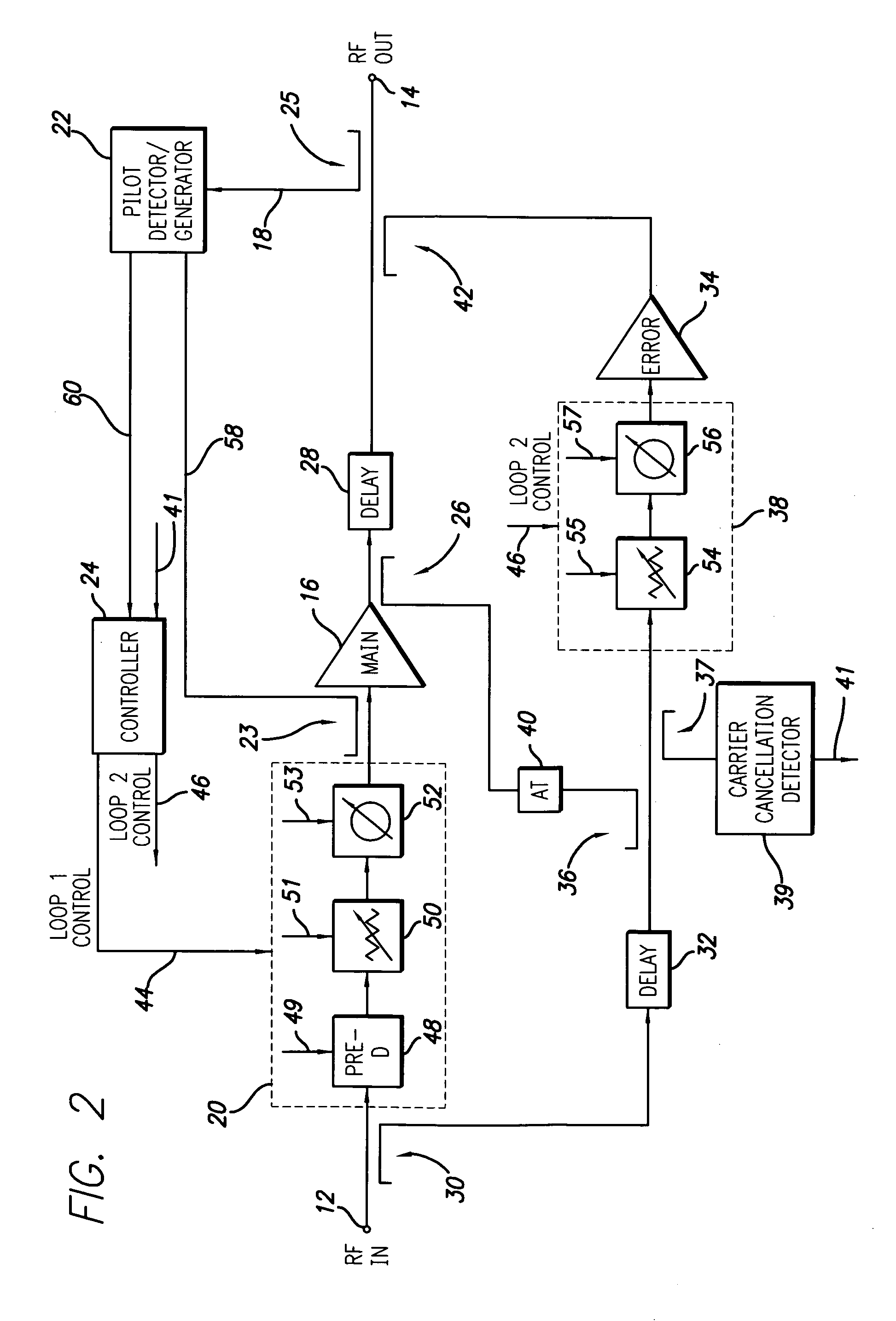
System and method of carrier reinjection in a feedforward amplifier
InactiveUS20050113052A1Signal distortion is smallAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
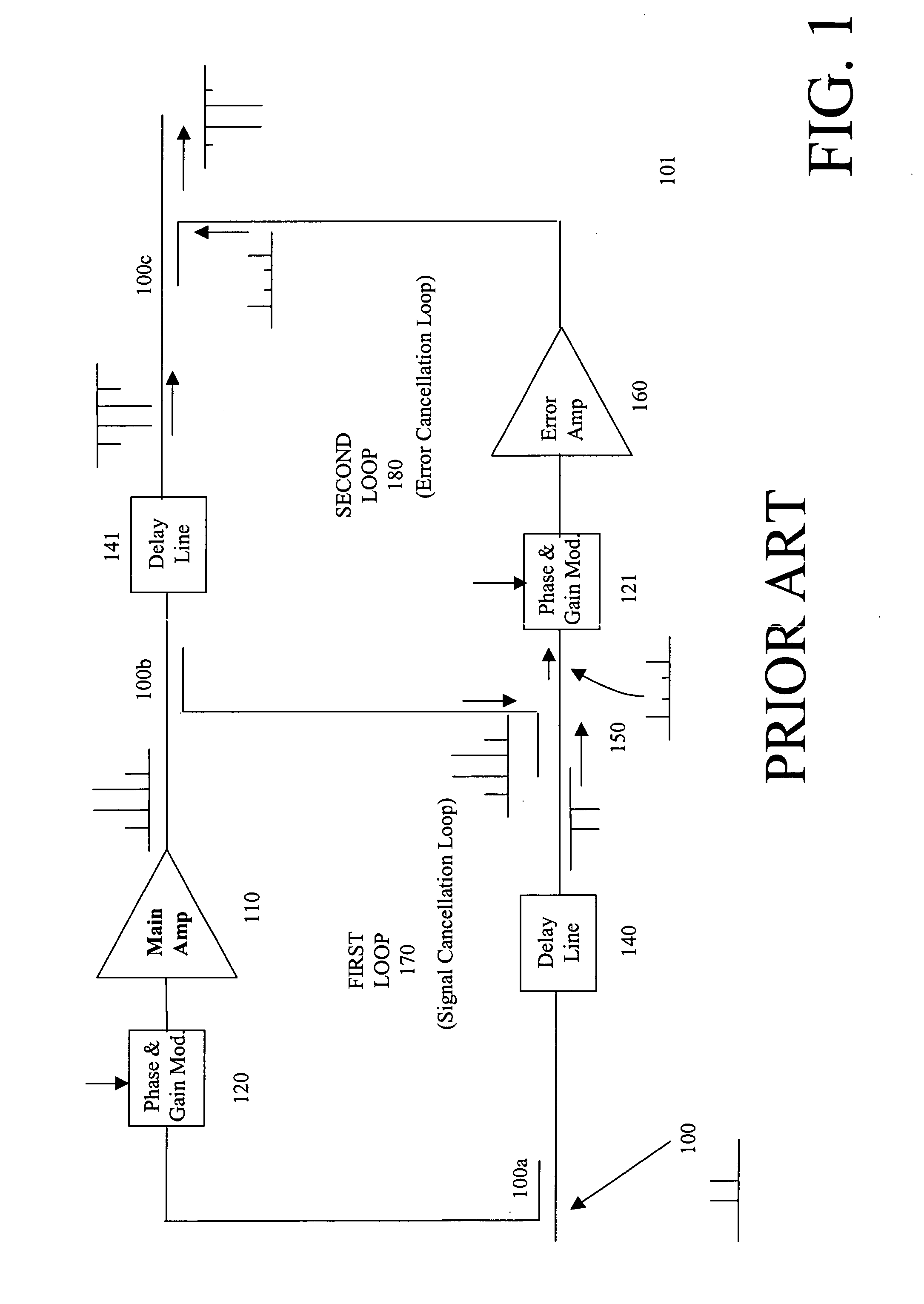
A dual loop feedforward power amplifier. A dual loop feedforward power amplifier, comprising an input that provides a multicarrier signal; a first feedforward power amplifier; and a second feedforward power amplifier, wherein the first feedforward power amplifier serves as a main amplifier gain block in the second feedforward power amplifier, wherein the first feedforward power amplifier comprises a carrier cancellation loop and a first error amplifier loop, and wherein the second feedforward power amplifier comprises a third loop and a fourth loop that cancel small signal distortions that are not reduced by the first feedforward amplifier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Amplifier circuit and amplifying method
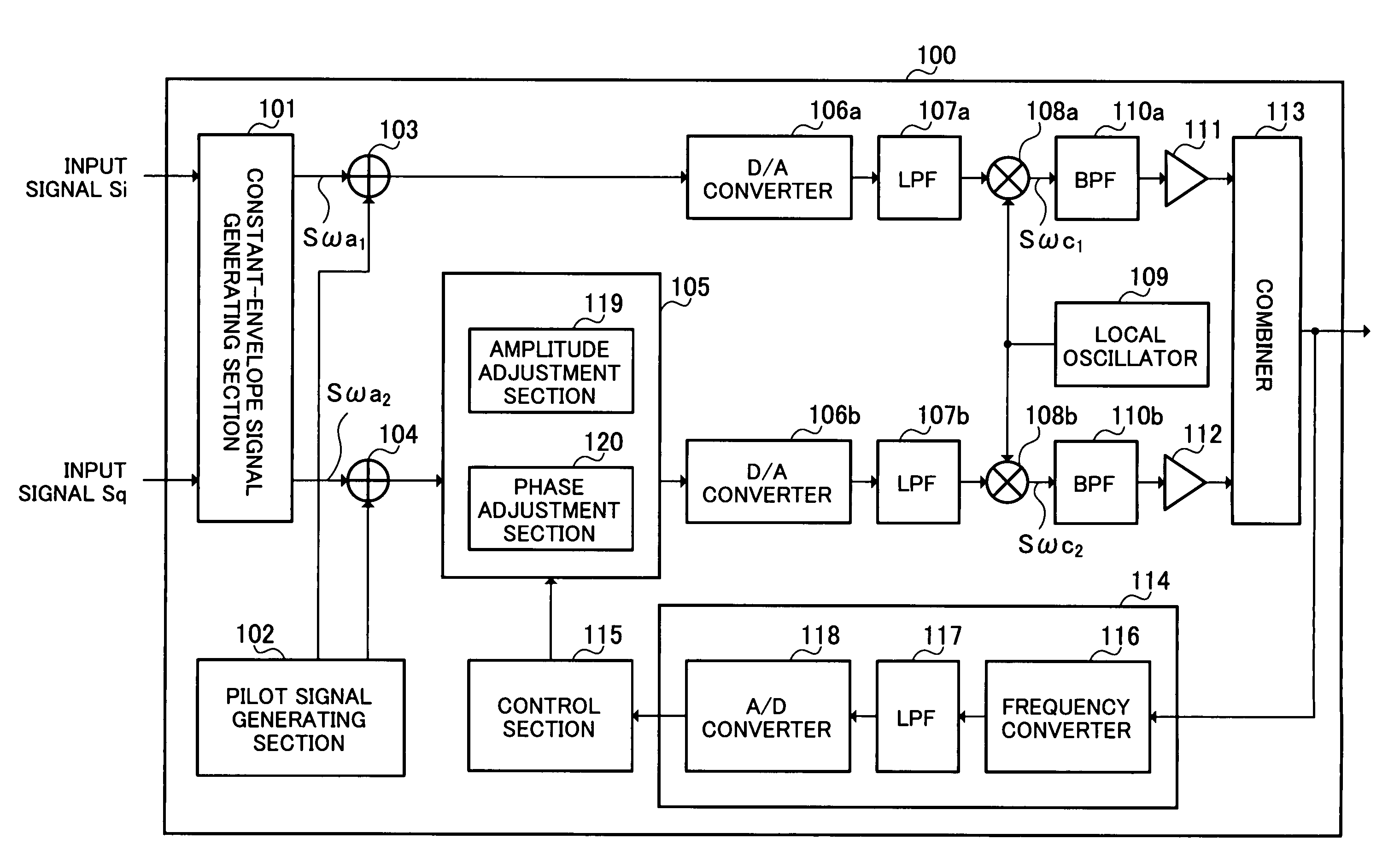
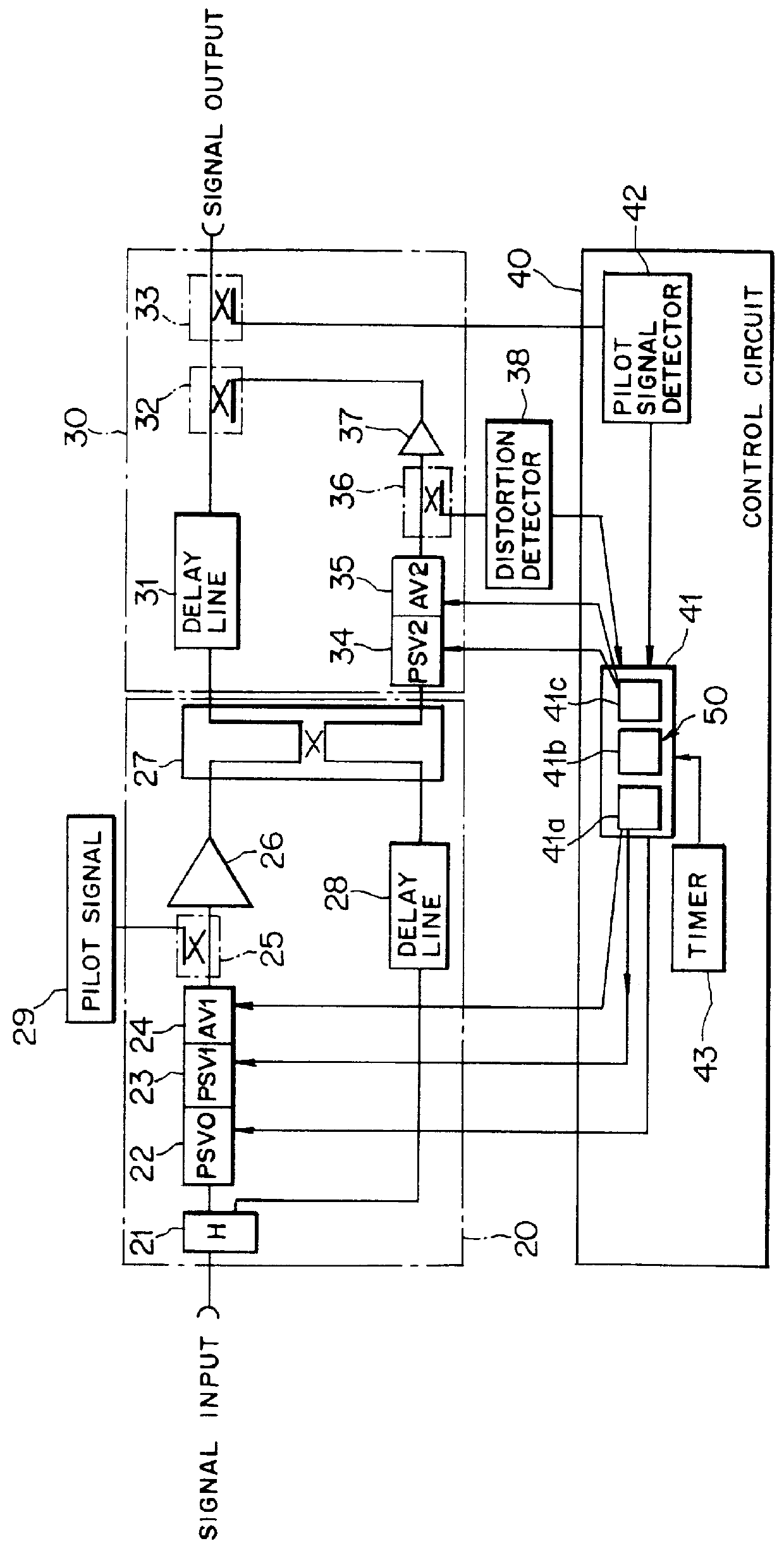
InactiveUS20070076814A1Suppress circuit scale of circuitImprove power efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierConstant envelope
An amplifier circuit capable of suppressing the circuit scale thereof and obtaining an output signal with high power efficiency and little distortion is disclosed. In this circuit, constant-envelope signal generating section (101) generates a plurality of constant-envelope signals from an input signal. Pilot signal generating section (102) generates a plurality of pilot signals associated with the generated plurality of constant envelope signals, the plurality of pilot signals having predetermined amplitudes, predetermined phases and predetermined frequencies, respectively, the phases and frequencies being different from each other. First addition section (103) and second addition section (104) add the plurality of pilot signals to the generated plurality of constant-envelope signals. First amplifier (111) and second amplifier (112) amplify the plurality of constant-envelope signals to which the plurality of pilot signals are added. Vector adjustment section (105) corrects the amplitude or phase of one of the generated plurality of constant-envelope signals using a signal component included in the amplified plurality of constant-envelope signals and corresponding to the plurality of pilot signals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
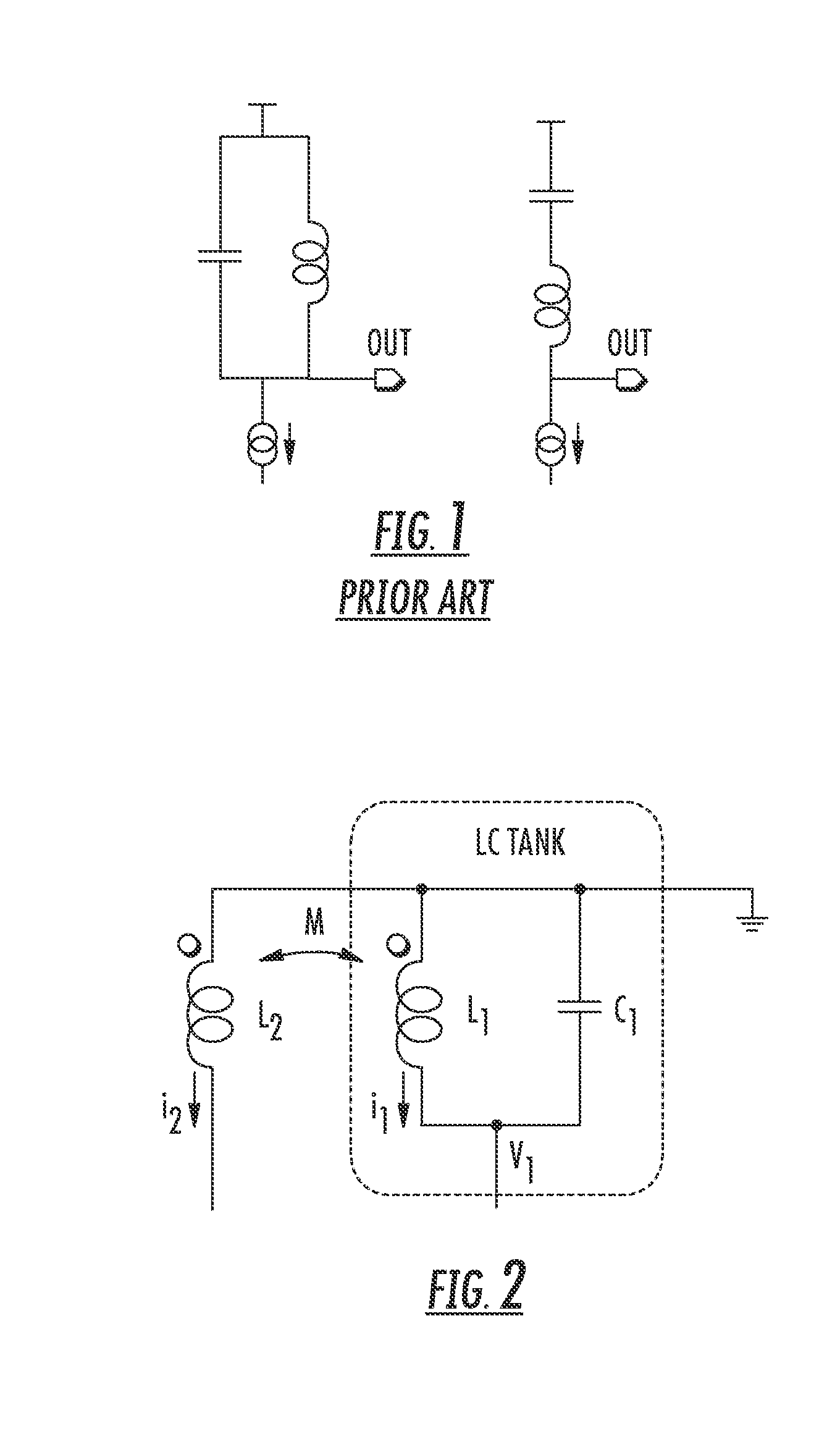
Method of adjusting the resonance frequency of an l-c resonant circuit and resonant circuit
ActiveUS20080174378A1Multiple-port networksAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyResonanceInductor
An L-C resonant circuit with an adjustable resonance frequency, having a capacitor and a first inductor electrically coupled together and a second inductor magnetically coupled to the first inductor. Additionally, there is a control circuit to sense a signal representing a first current flowing through the first inductor and to force through the second inductor a second current that is a replica of the first current for setting the adjustable resonance frequency of the L-C resonant circuit.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
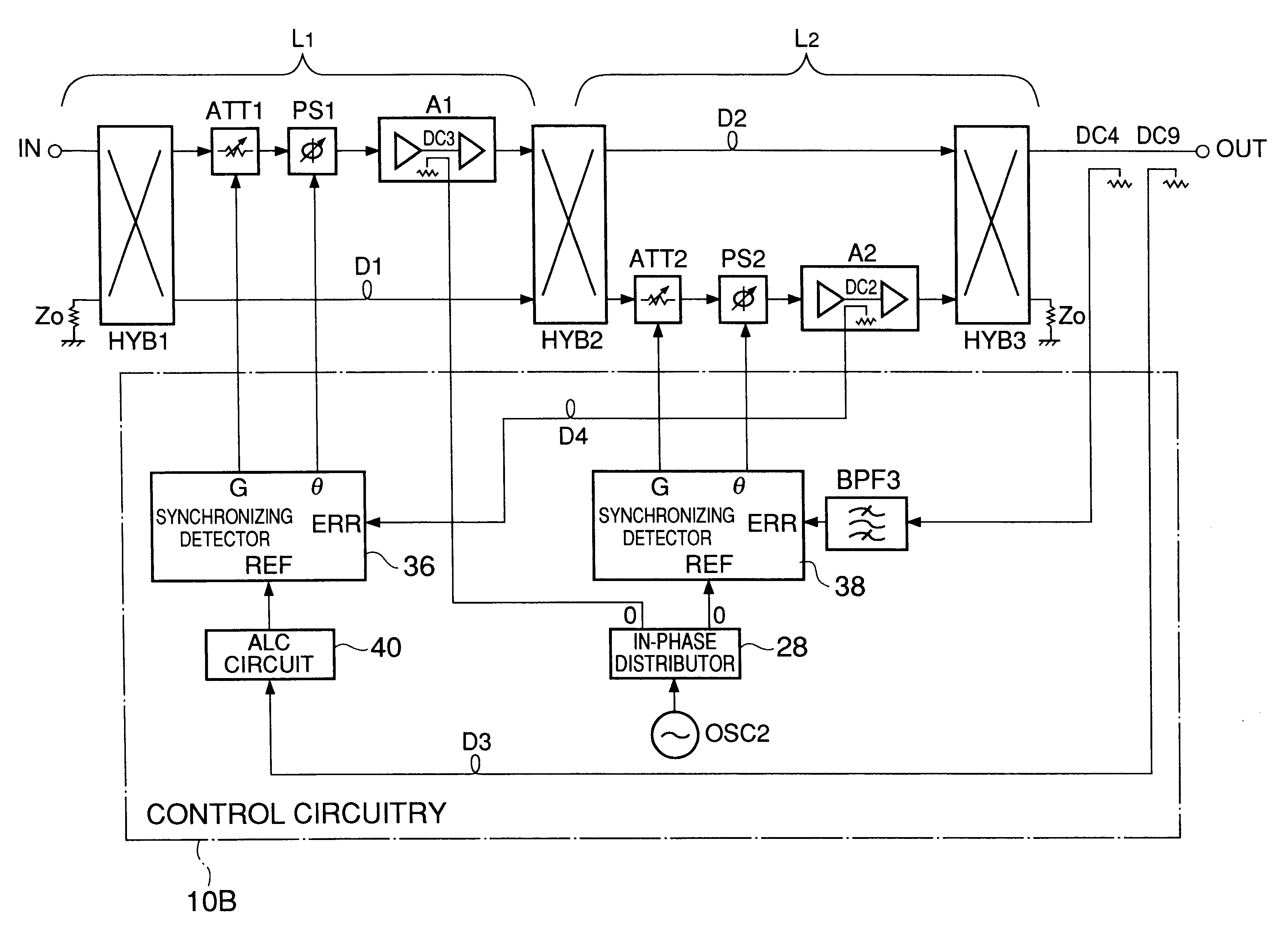
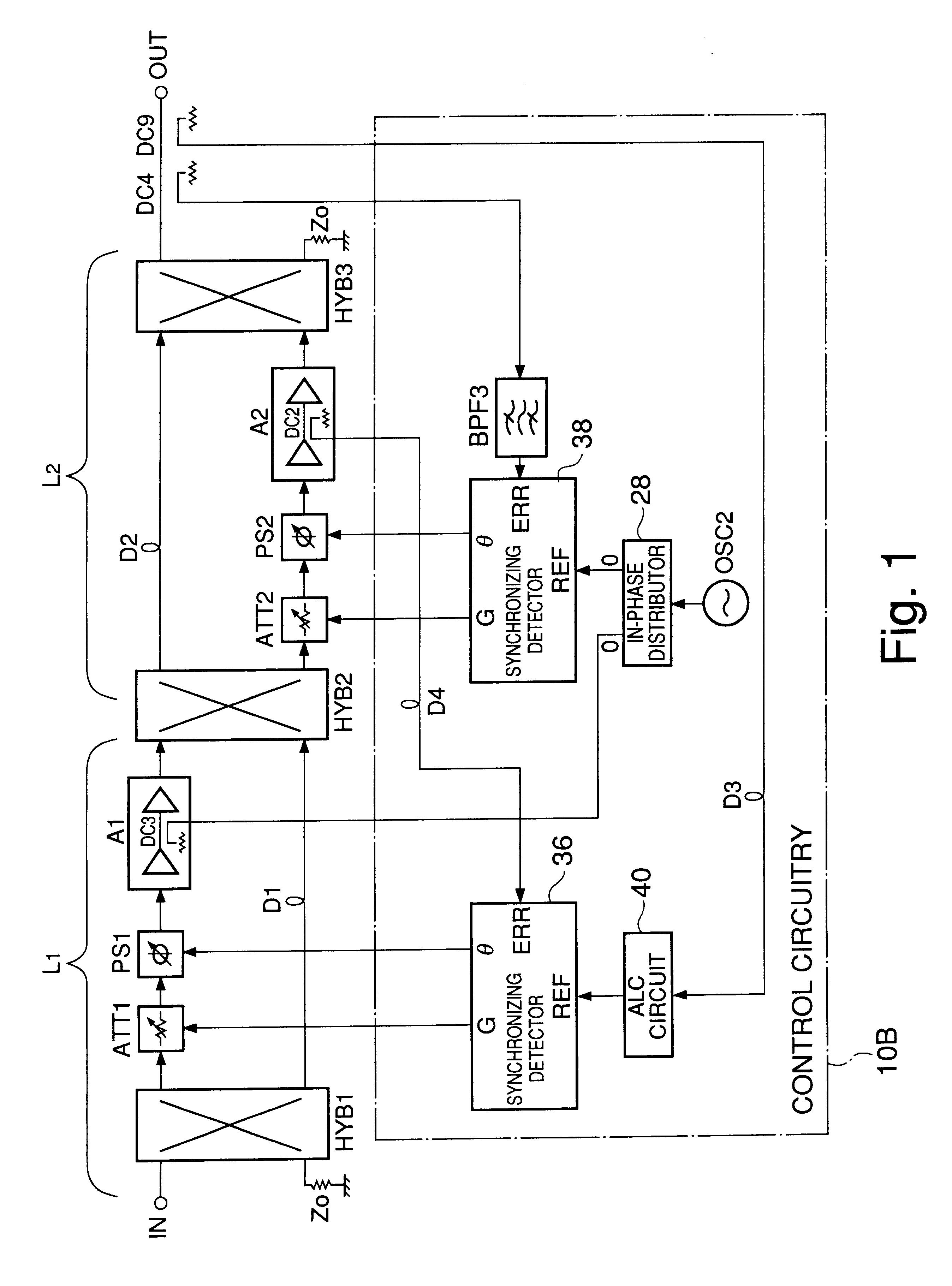
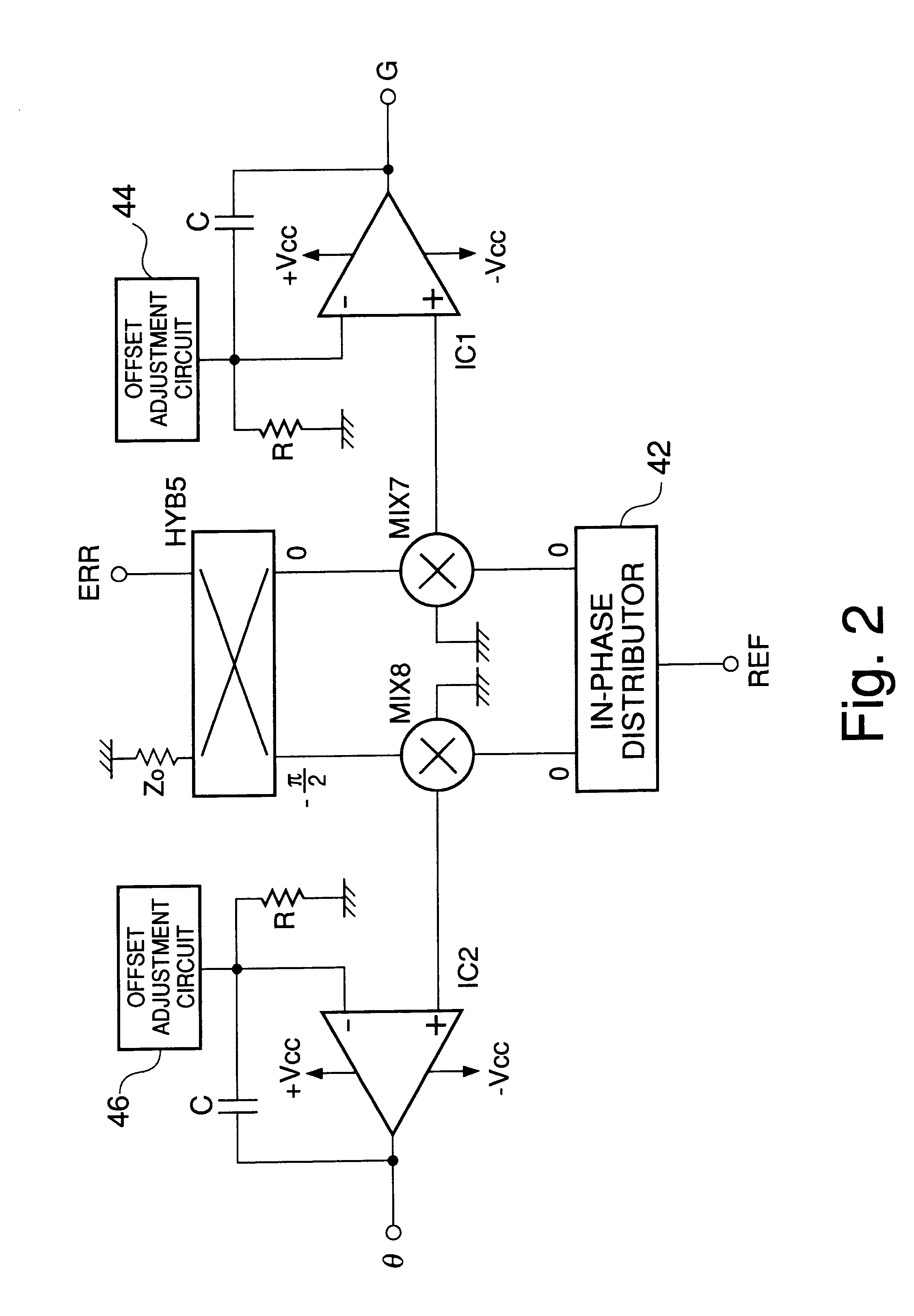
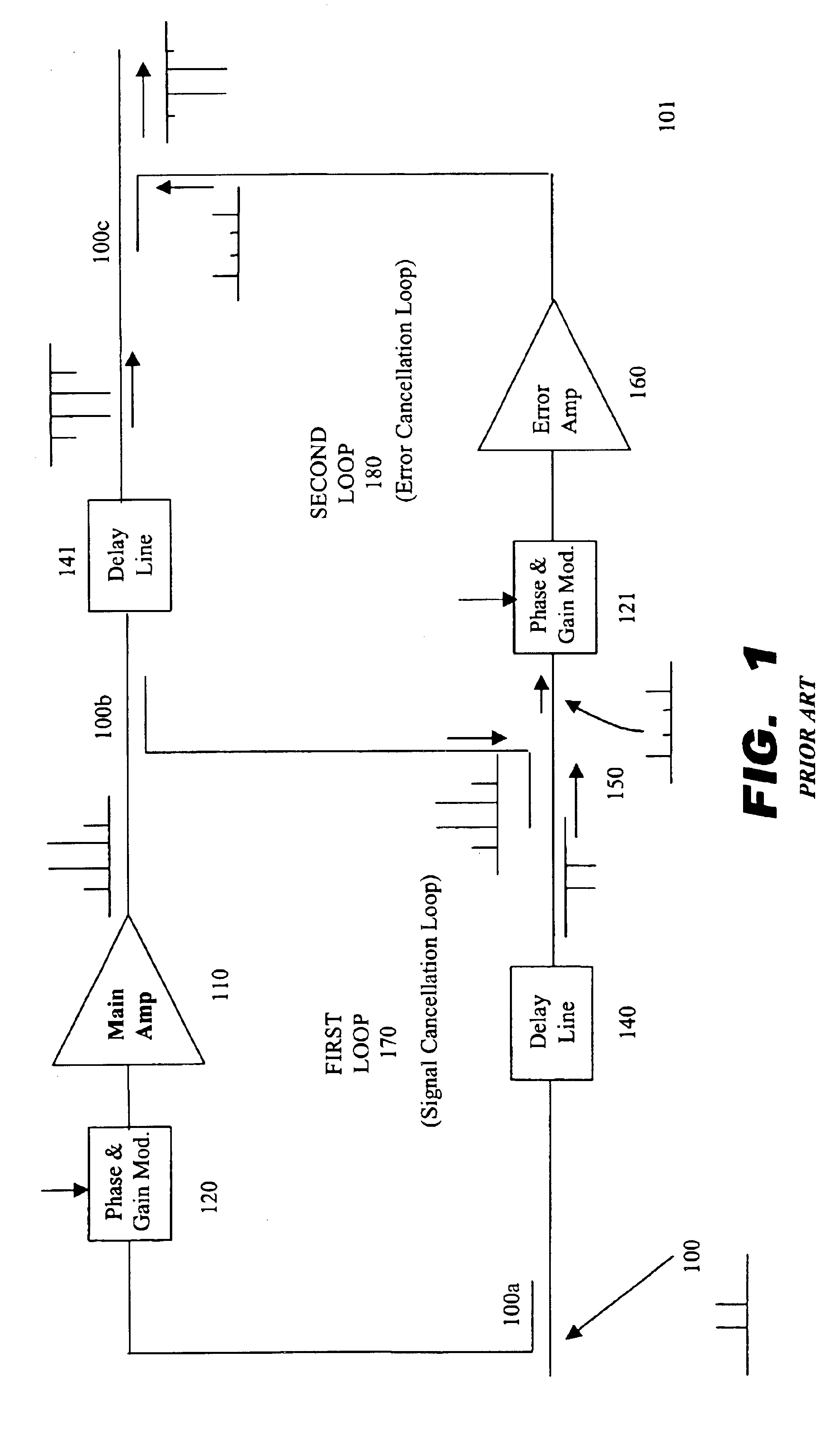
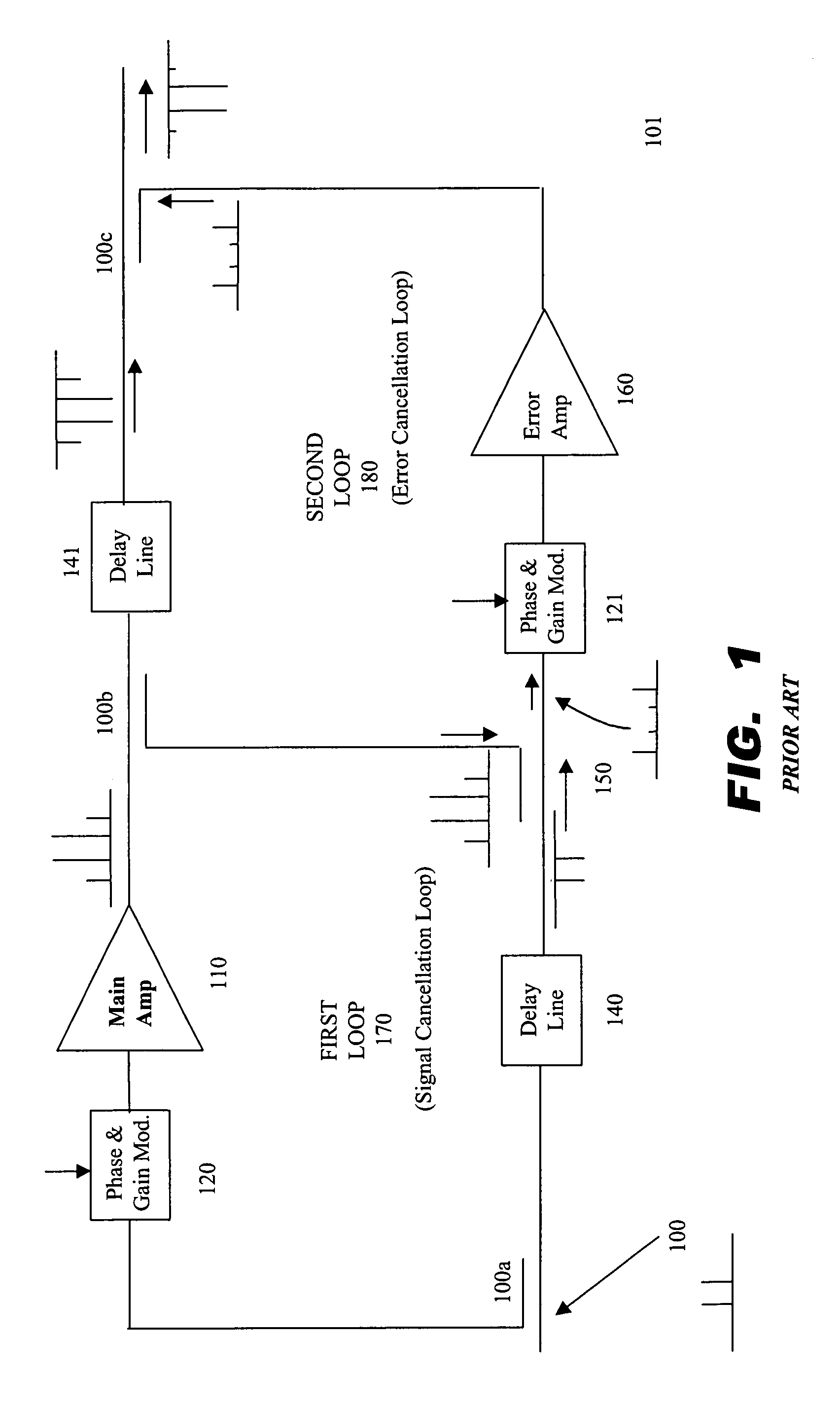
Amplifier with feedforward loops for rejecting non-linear distortion
InactiveUS6172560B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
An amplifier with feedforward loops for rejecting non-linear distortion and control circuitry for such amplifier and employing a distortion compensation method. A signal from a dominant path is input into a synchronizing detector via an ALC circuit as a reference signal. Using this reference signal, an error signal output from a distortion rejection loop is subjected to synchronizing detection. An offset voltage of a mixer inside the synchronizing detector can be prevented from varying due to change in local level. Outputs from synchronizing detectors are used for control to optimize corresponding loops. As a pilot signal for a distortion detection loop can be eliminated, undesirable spurious effects due to such a pilot signal is avoided. The acquisition time of each of the loops can be shortened because an optimizing control using a step-by-step procedure under CPU control can be eliminated.
Owner:JAPAN RADIO CO LTD
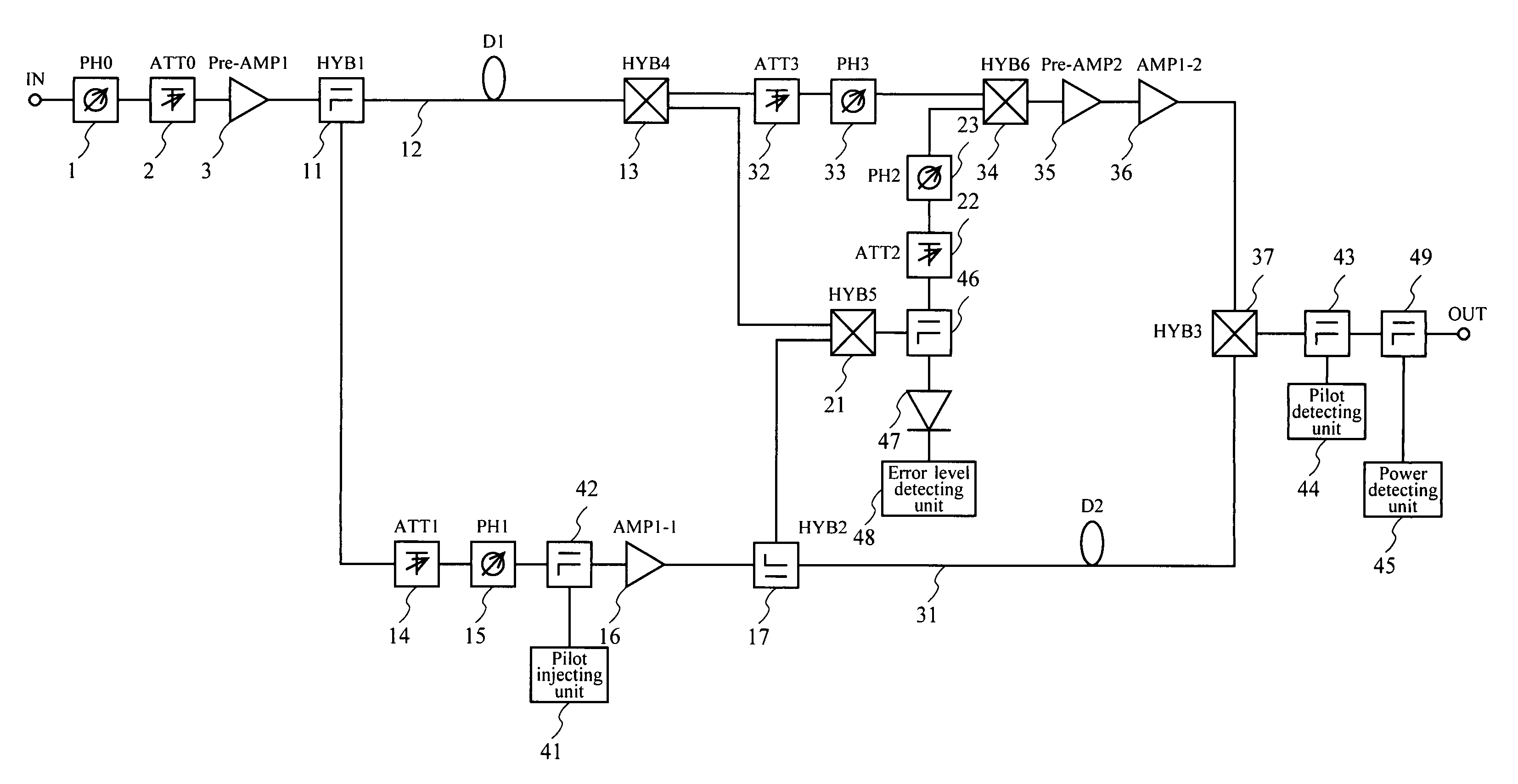
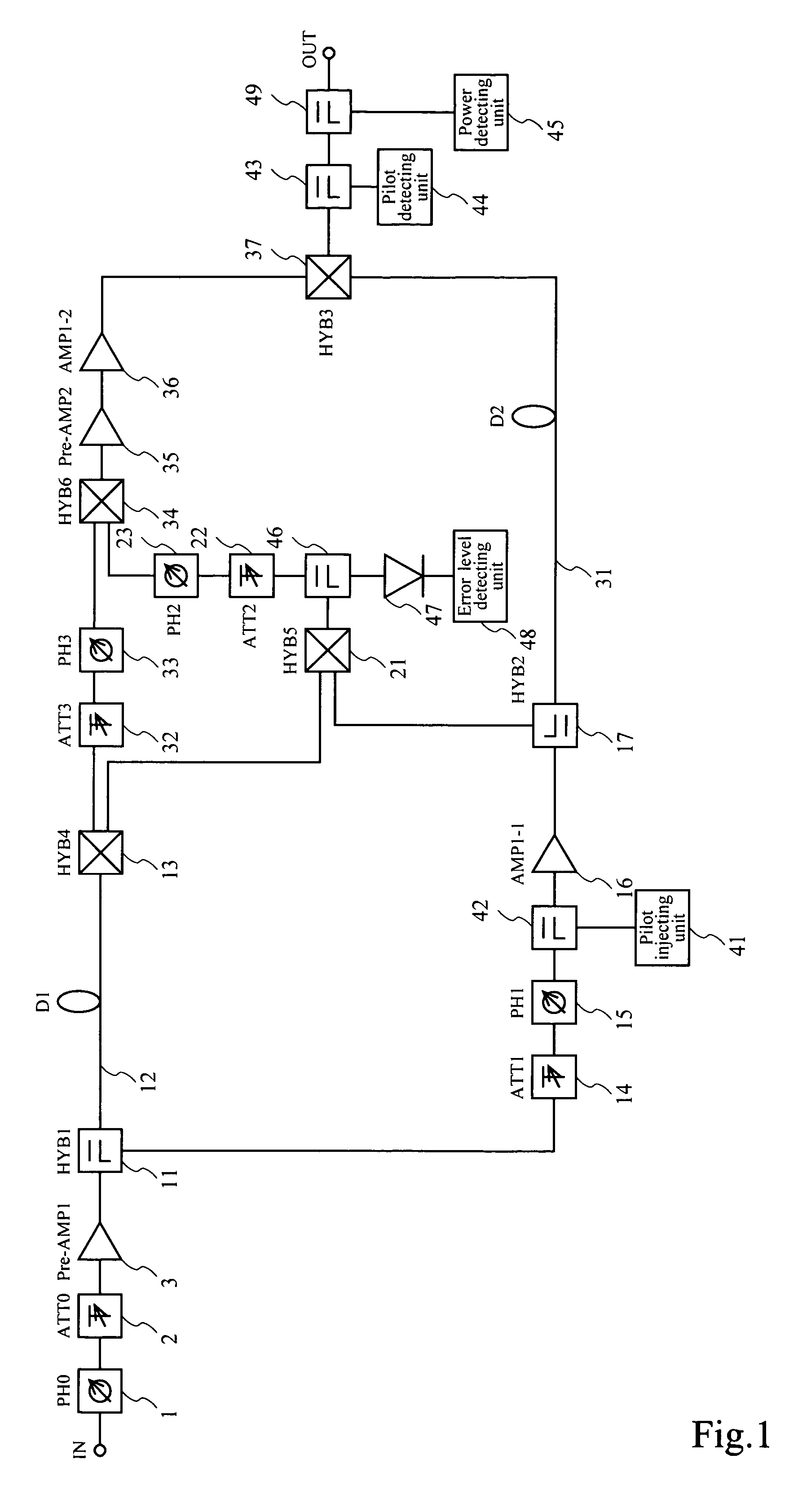
Linear power amplification method and linear power amplifier
ActiveUS7170342B2Excellent distortion compensation performanceGood compensationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierLinear power amplifier
A combined signal of a digital pilot signal and a digital transmission signal is applied to a digital predistorter (20), wherein it is added with odd-order distortions based on a power series model to generate a predistorted signal, then the predistorted signal is converted by a DA converter (31) to an analog signal, then the analog signal is upconverted by a frequency upconverting part (33) to a send frequency band, and the upconverted signal is output after being amplified by a power amplifier (37). A pilot signal component is extracted from the power amplifier output, then odd-order distortion components of the power series model are extracted by a digital predistorter control part (50) from the pilot signal component, and the odd-order distortions in the digital predistorter (20) are controlled to decrease the levels of the distortion components.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
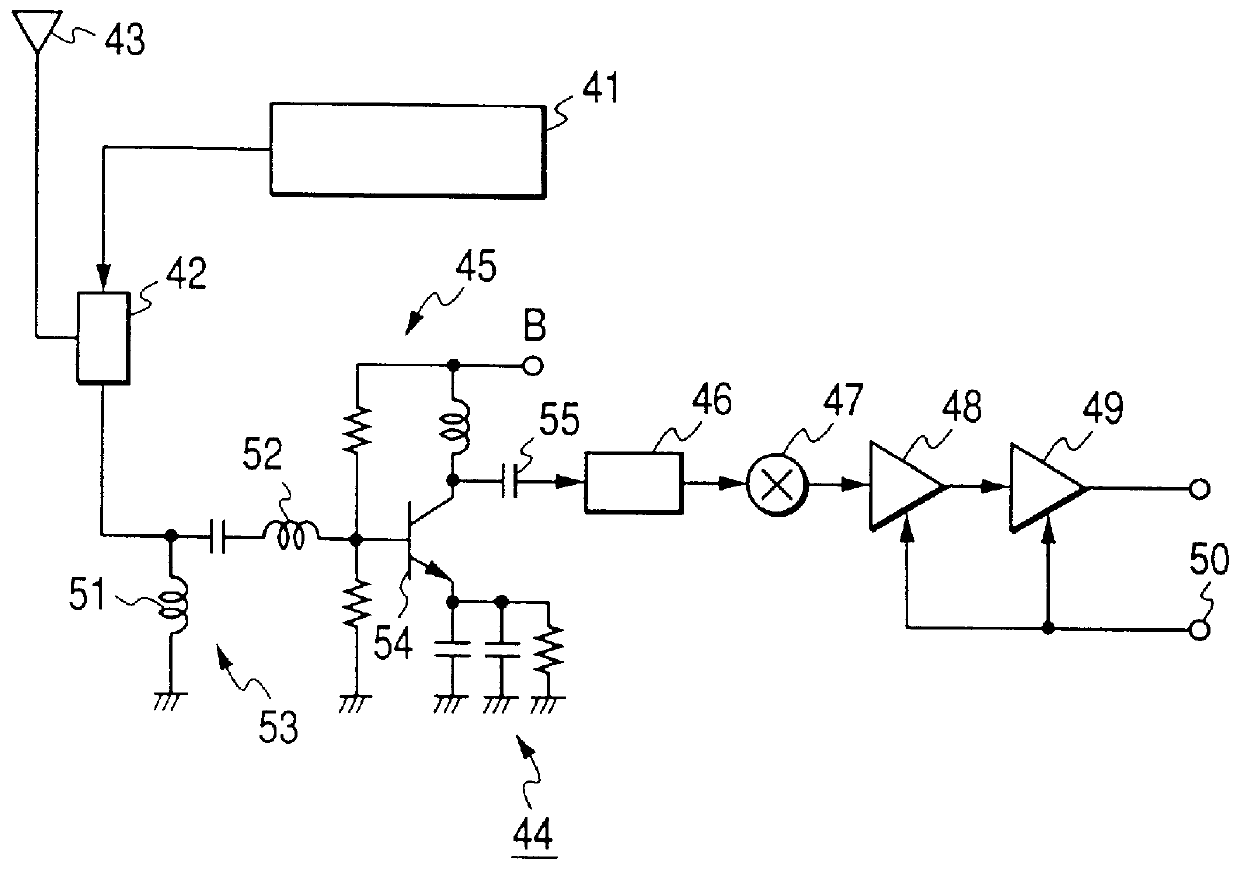
Reception circuit for cellular telephone
InactiveUS6141561AReduce gainGain controlAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyAudio power amplifierTime division multiple access
A reception circuit for a cellular telephone according to the present invention shares the use of a code division multiple access system and a frequency division multiple access system, comprises: an amplifier circuit at the forefront stage; a bypass circuit connected to the amplifier circuit at the forefront in parallel therewith, having lower gain than the amplifier circuit at the forefront stage; and a common processing circuit connected to the latter stages of the amplifier circuit at the forefront and the bypass circuit, and when the level of a received signal is not higher than predetermined voltage, induces the received signal to the processing circuit through the amplifier circuit at the forefront while when the level of the received signal exceeds the predetermined voltage, the received signal is induced to the processing circuit through the bypass circuit.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Method and apparatus for control of predistortion linearizer based on power series
InactiveUS20050189990A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationFrequency characteristicLow frequency
A gain adjuster and a phase adjuster of a distortion generation path are set so that an extracted distortion component becomes small, the extracted component is compared with a reference value. When an upper-frequency distortion component of a pilot signal is larger than the reference value, the gain and phase of a frequency characteristic compensator of the distortion generation path are controlled so that the upper-frequency distortion component of the pilot signal becomes smaller than a value preset in the controller. When a lower-frequency distortion component of the pilot signal is larger than a reference value, the gain and phase of the frequency characteristic compensator of the distortion generation path are controlled so that the lower-frequency distortion component of the pilot signal becomes smaller than a value preset in the controller.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
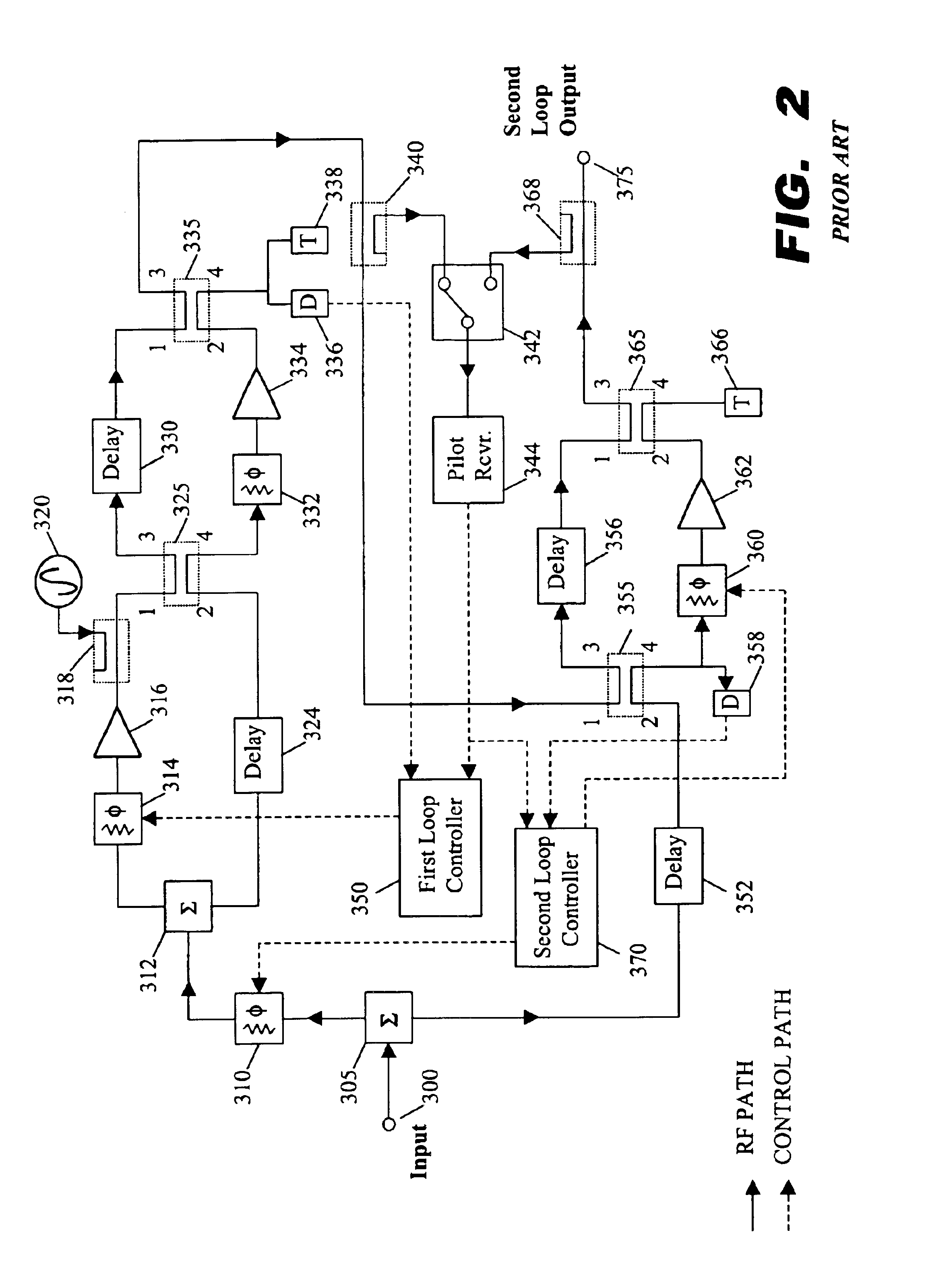
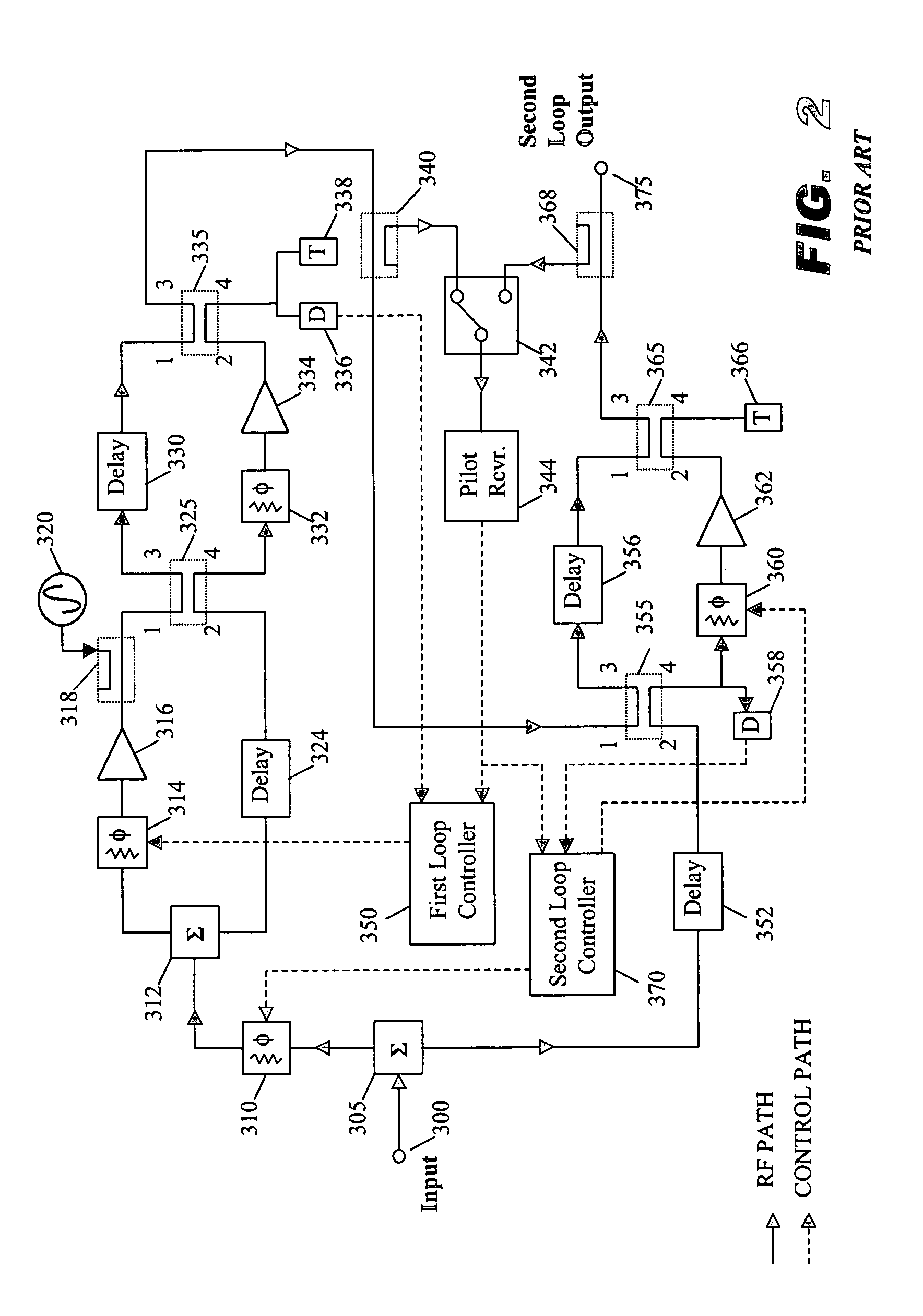
Dual loop feedforward power amplifier
InactiveUS6958647B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
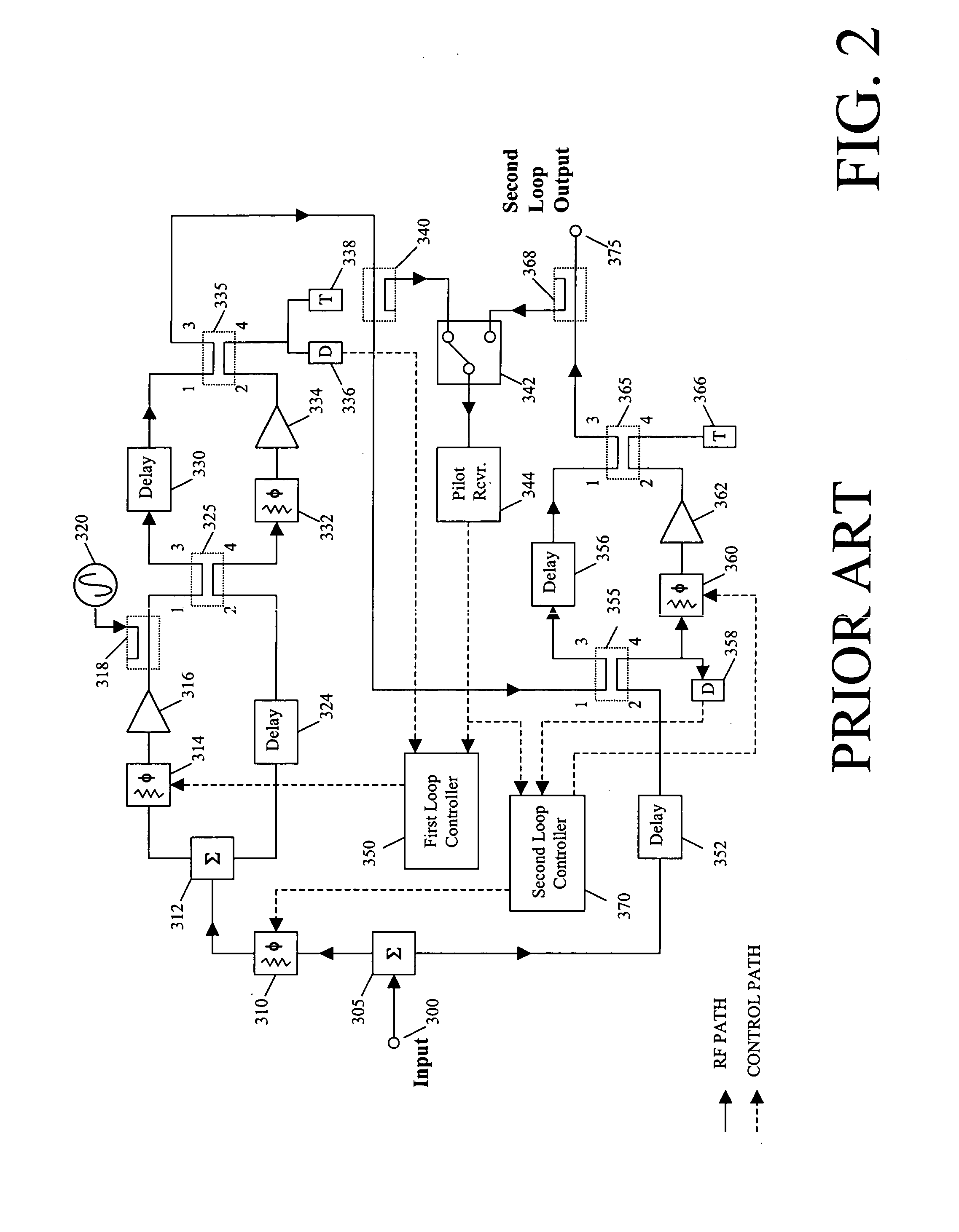
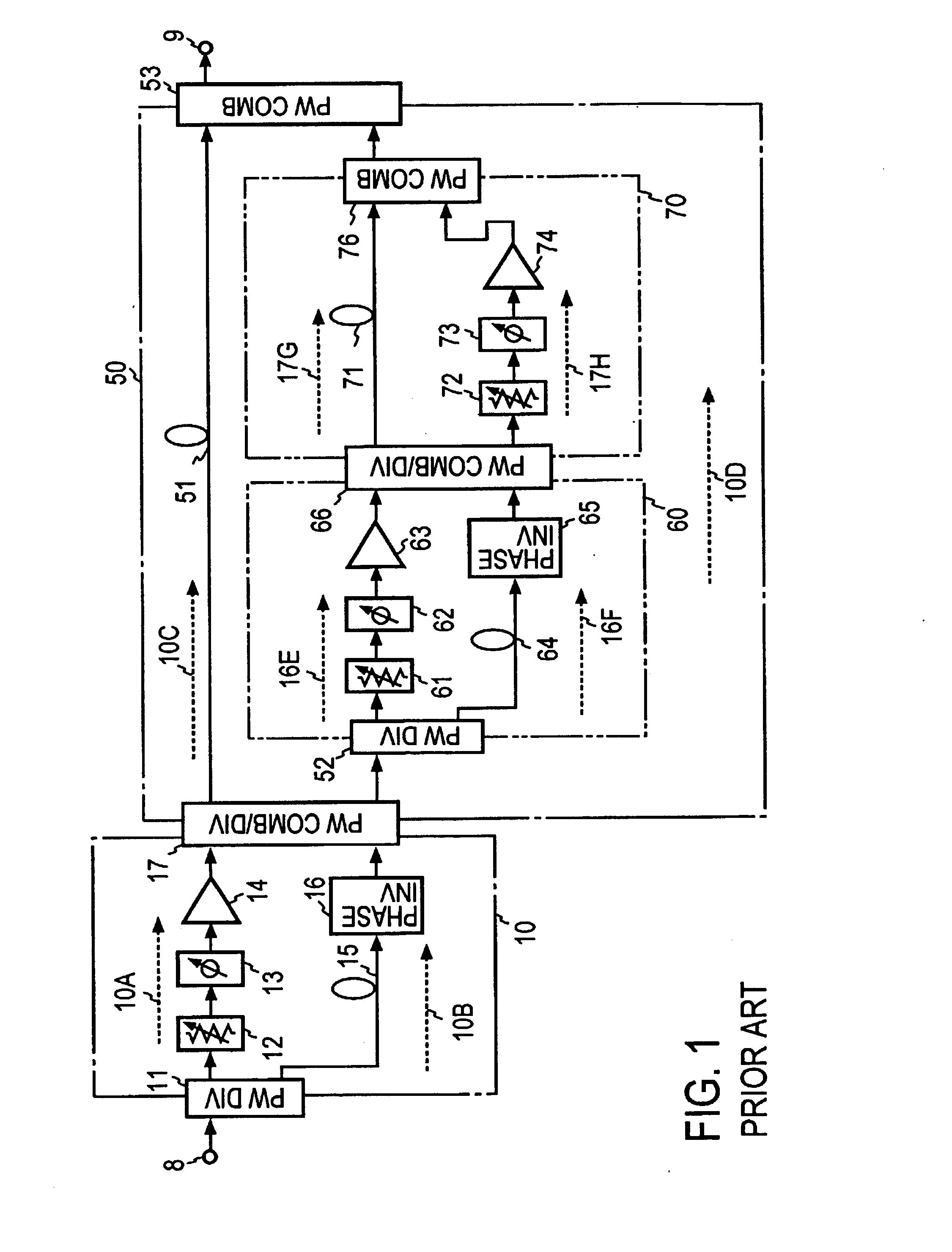
A feedforward amplifier. The present invention therefore provides a feedforward amplifier, comprising: a pilot reference generator that generates a pilot signal; a first carrier cancellation loop; a first error amplifier loop including a first error amplifier, wherein the pilot signal is utilized to provide gain stabilization in the first error amplifier a third loop; a second carrier cancellation loop that includes a first phase and amplitude adjuster in module and a second amplitude and phase adjuster disposed between module and module, wherein the pilot signal is utilized to control the adjustment of the second carrier cancellation loop.
Owner:INTEL CORP
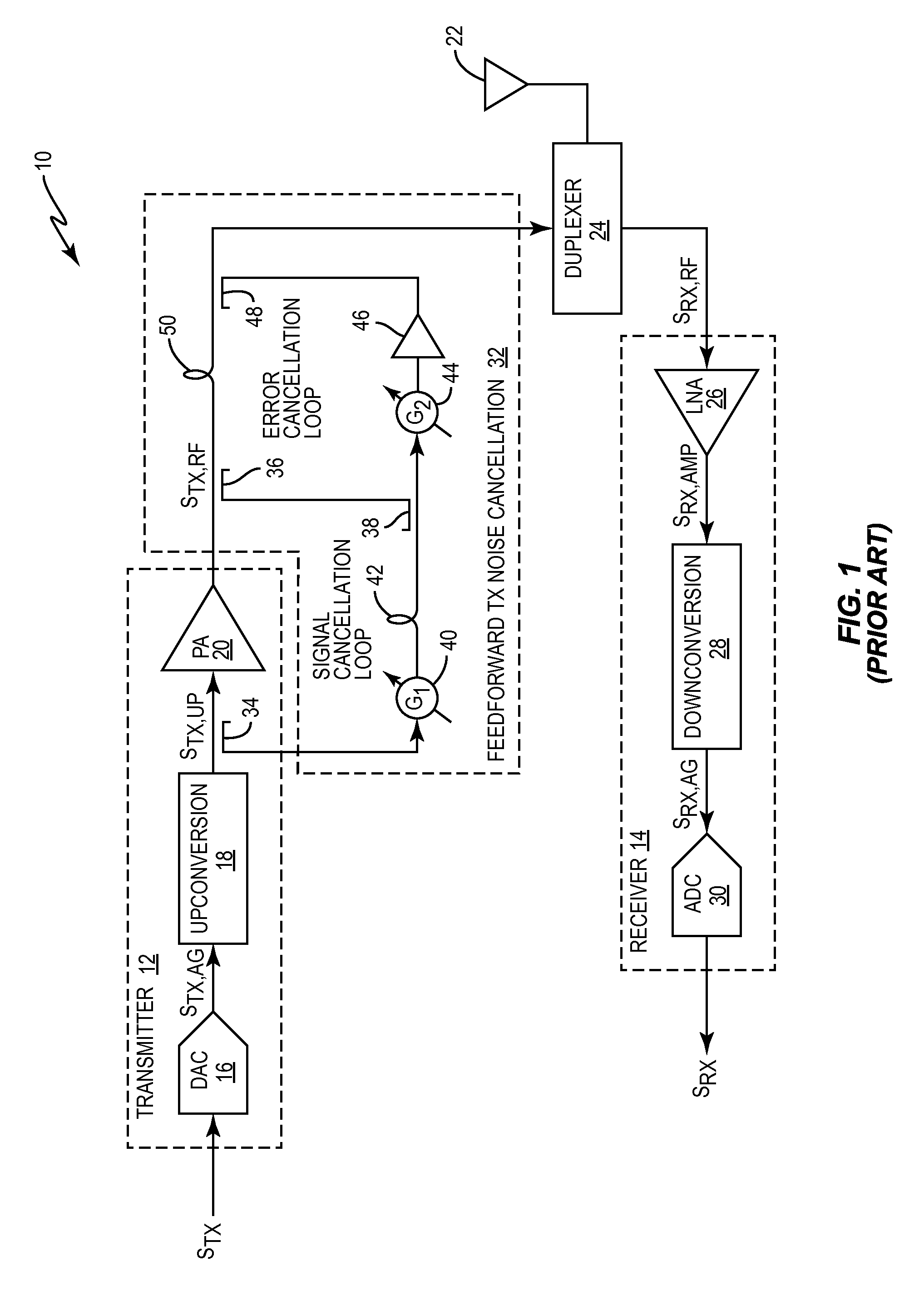
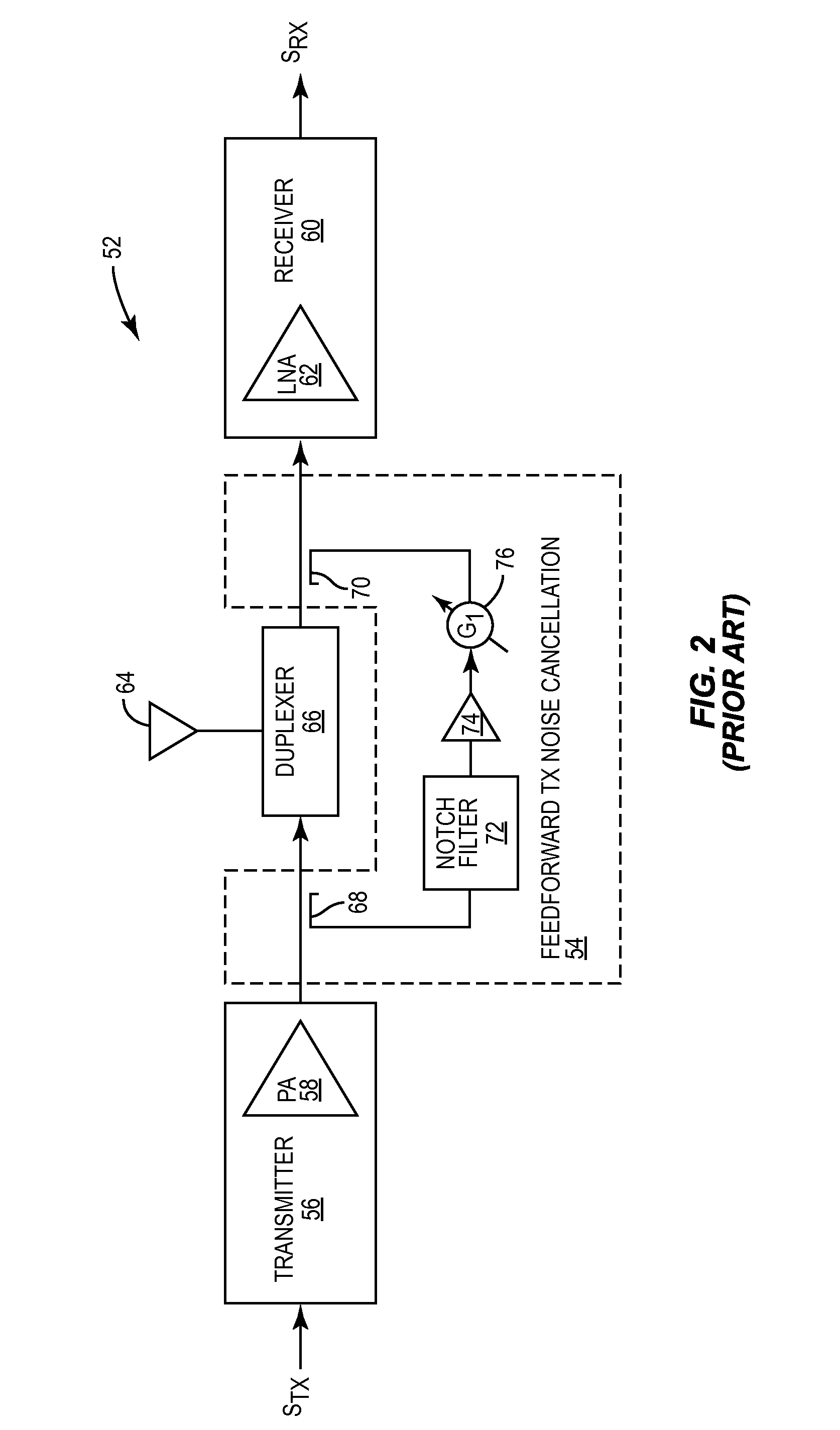
Transmitter noise suppression in receiver
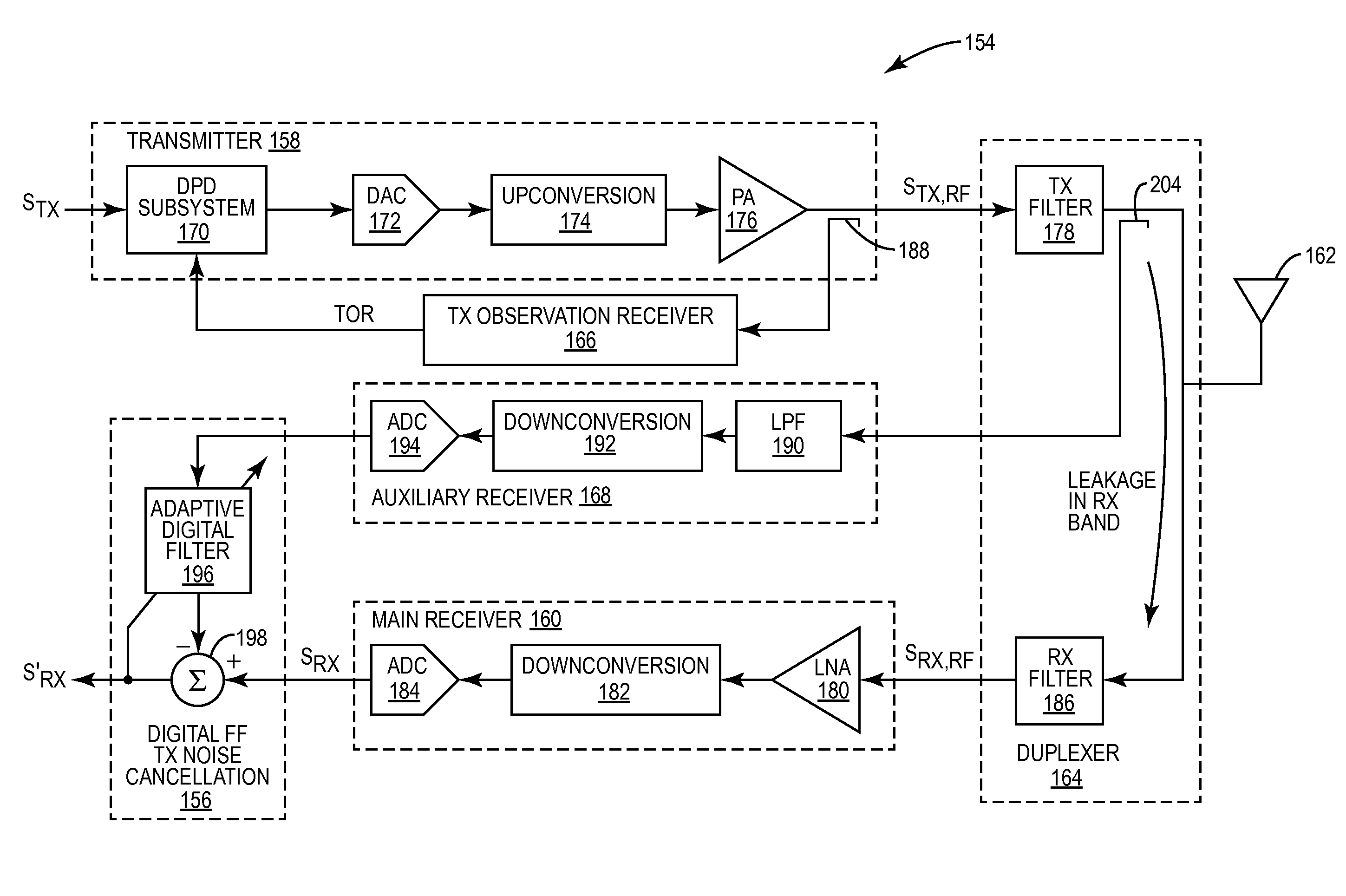
ActiveUS8995932B2Suppressing transmitter noiseMultiple-port networksError preventionNoise suppressionWide band
Systems and methods for suppressing transmitter noise in a receive band of a co-located receiver that are suitable for wideband applications are disclosed. In one embodiment, an analog radio frequency transmit signal output by a transmitter includes a desired signal in a transmit band of the transmitter and transmitter noise in a receive band of a main receiver. A secondary receiver obtains a secondary receiver input signal that is representative of at least the transmitter noise in the receive band of the main receiver and outputs a digital feedforward signal. A digital feedforward transmit noise cancellation subsystem generates a digital transmitter noise cancellation signal that is representative of the transmitter noise in the receive band based on the digital feedforward signal and subtracts the digital transmitter noise cancellation signal from a digital receive signal output by the main receiver to thereby provide a compensated digital receive signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
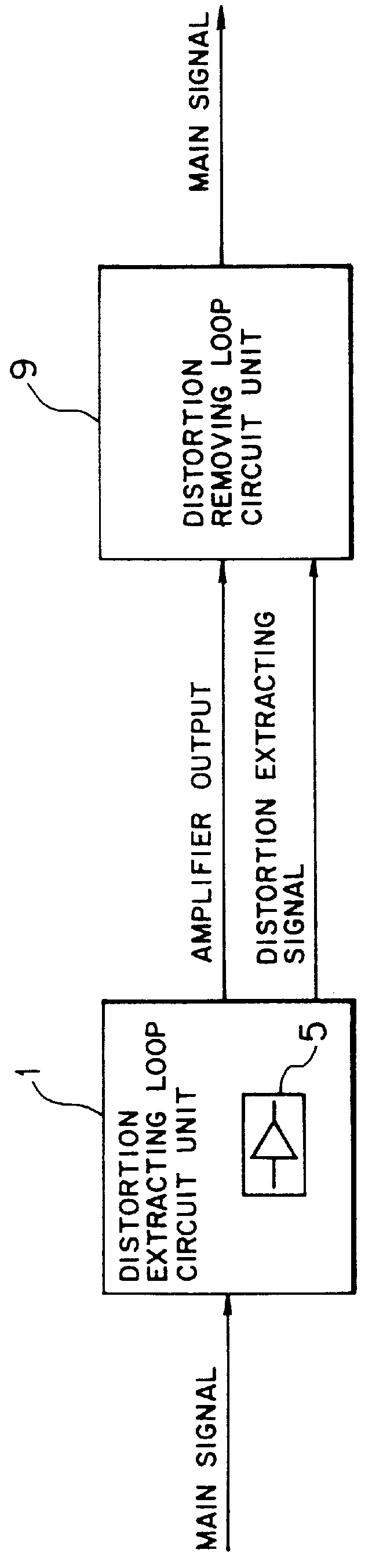
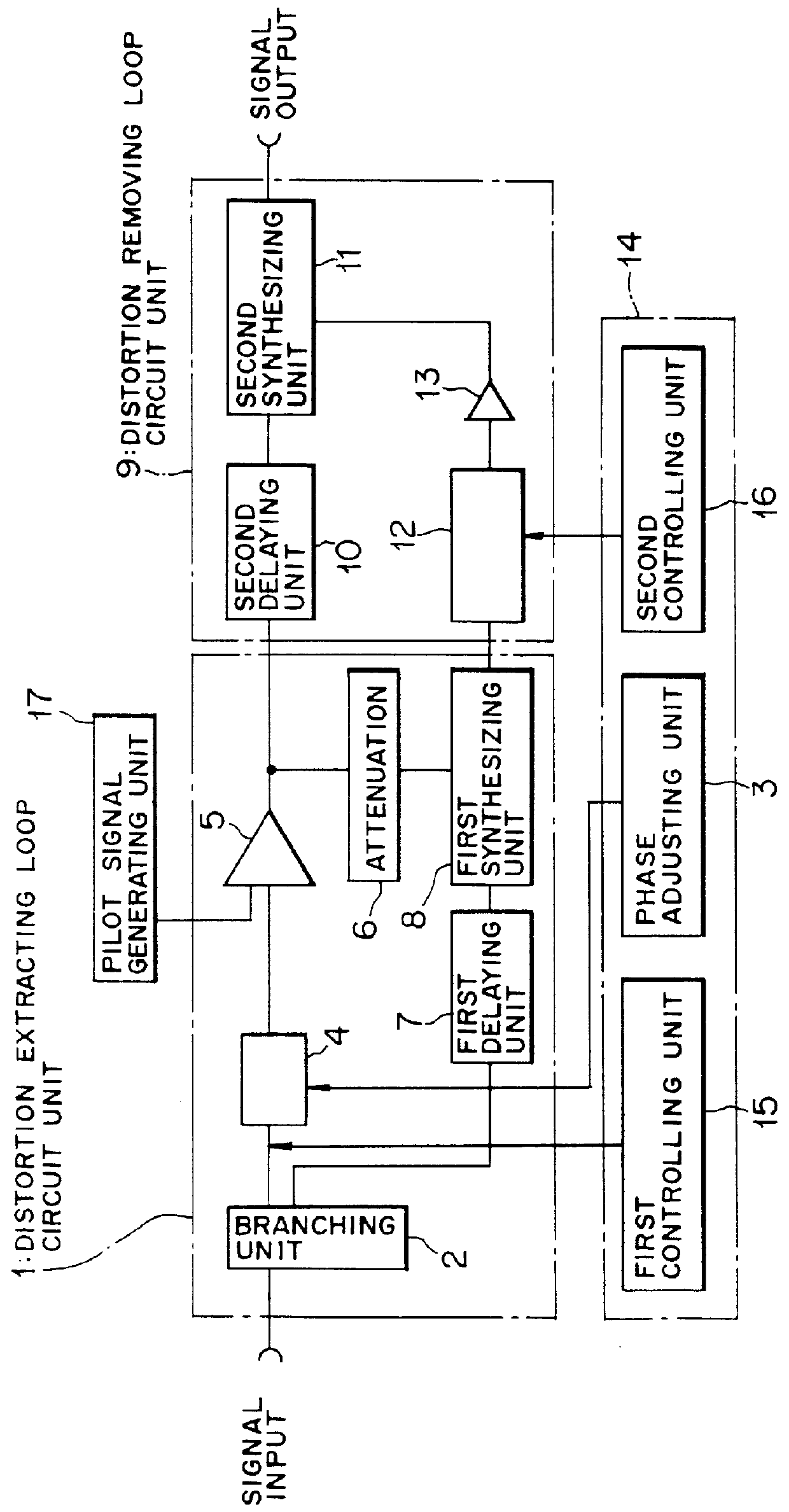
Feed-forward amplifying device and method of controlling the same and base station with feed-forward amplifying device
InactiveUS6148185AAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionTransmitters monitoringCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a feed-forward amplifying device suitable for radio communication systems such as digital automobile telephone. In the feed-forward amplifying device which includes a distortion extracting loop circuit unit including a main amplifier which amplifies a main signal in a main signal system, the distortion extracting loop circuit unit creating a distortion extracting signal by controlling the phase of the main signal the distortion extracting signal obtained by canceling the main signal component of an output from the main amplifier; and a distortion removing loop circuit unit arranged at the rear stage of the main amplifier, the distortion removing loop circuit unit producing only the main signal component from a signal in the main signal system at the rear stage of the main amplifier using the distortion extracting signal obtained by canceling the main signal component, the distortion extracting loop circuit unit executes phase control by shifting a phase control point where the main signal can be most canceled, thus creating the distortion extracting signal. This device can improve the power efficiency with a small back-up of the amplifier and stably produce a low-distortion amplified signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
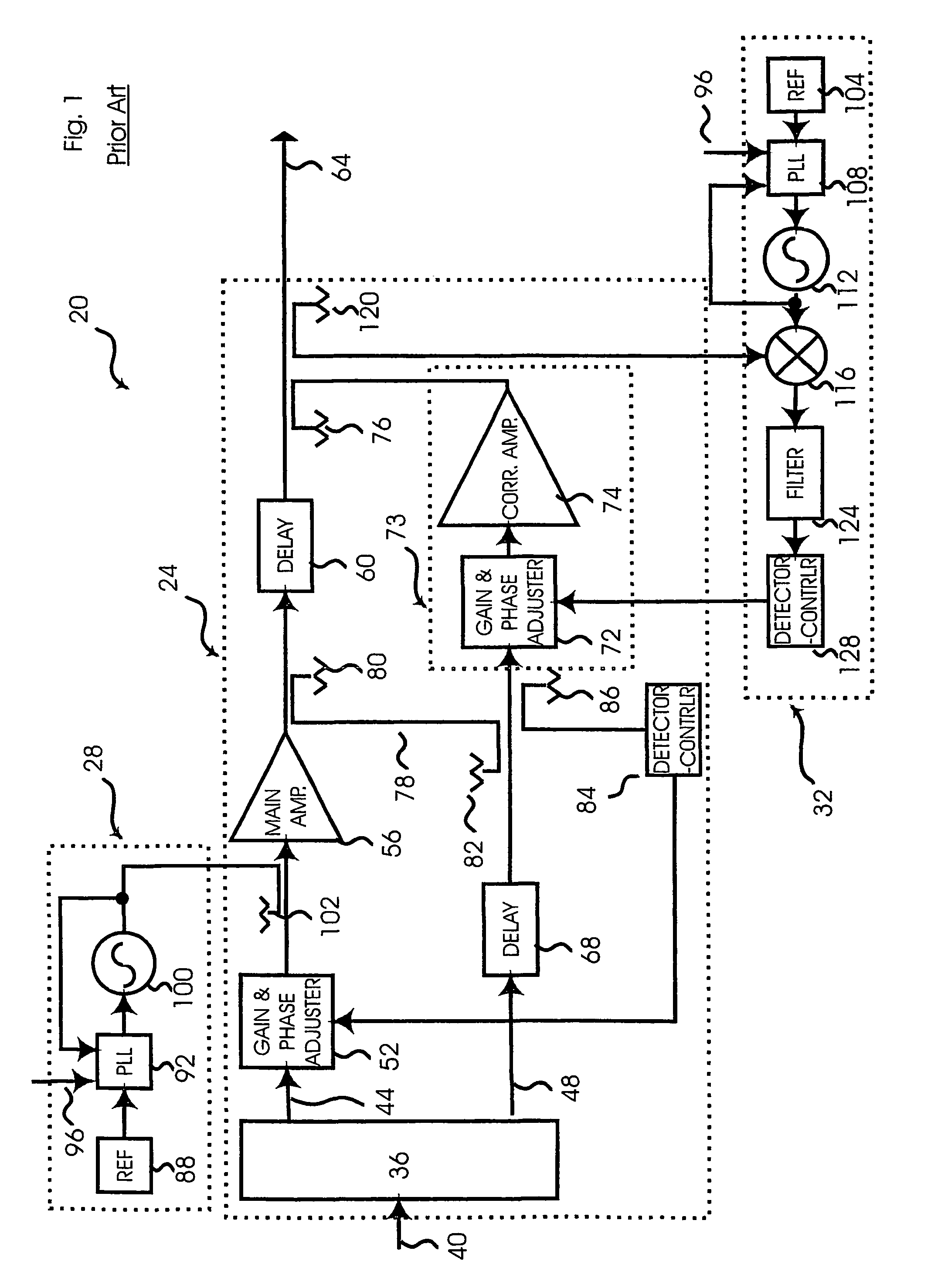
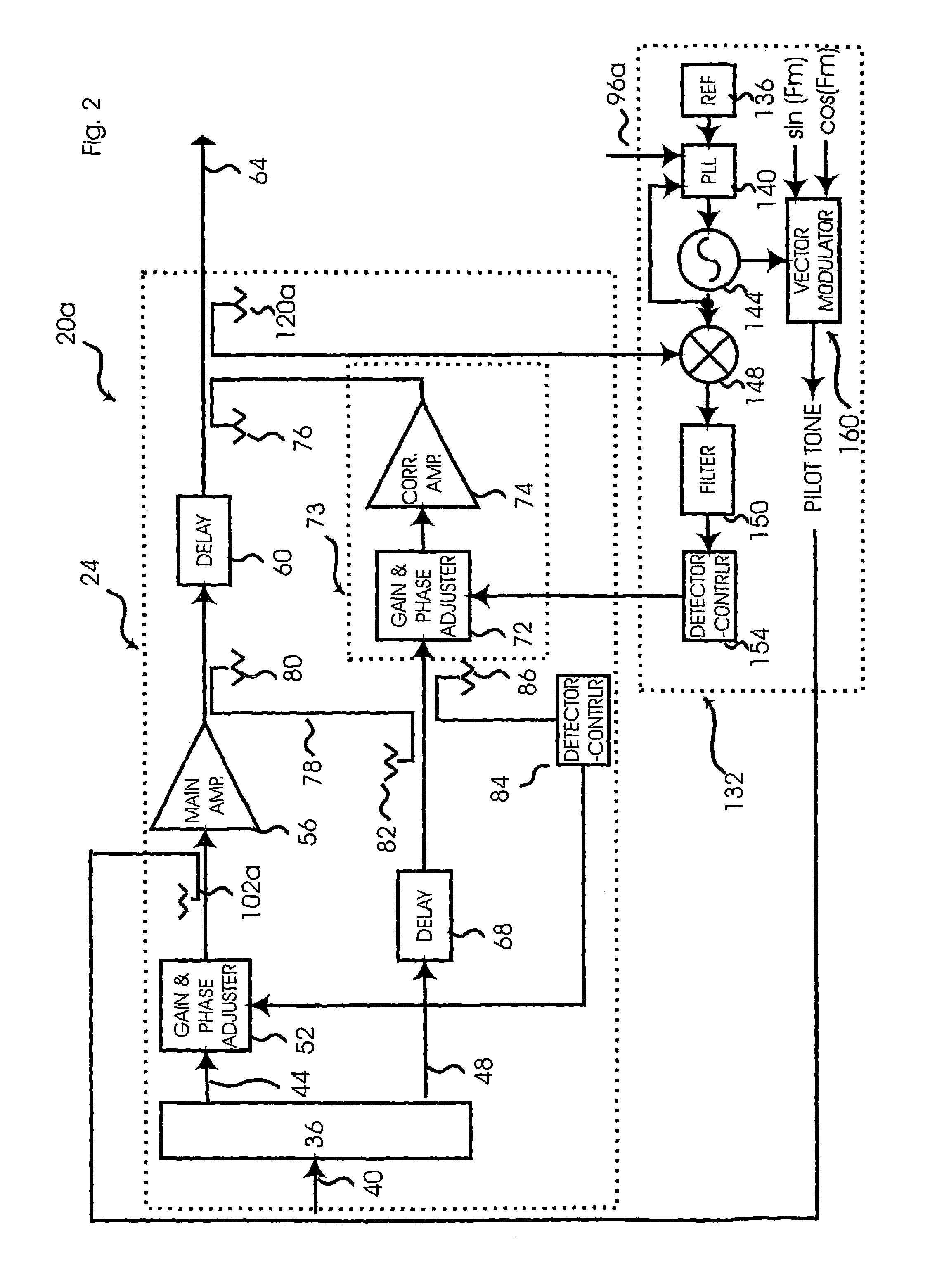
Apparatus and method for controlling adaptive circuits
InactiveUS7218172B2Fast convergenceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier with control circuitsPhase shift controlAudio power amplifier
A feed-forward amplifier having a signal cancellation loop including a cancellation node that includes a gain controller and a phase controller. Each controller provides a discrete tap steering signal and modulates the corresponding tap steering signal with a discrete tracer signal that takes on a preselected sequence of values. The sequence chosen so that the tracer signal is mutually orthogonal to each other tracer signal over a preselected period. A gain and phase adjuster connected to the outputs of the controllers provides a controlled gain change and phase shift in the signal cancellation loop, the magnitude of the gain change and phase shift controlled by the corresponding tap steering signals presented to the gain and phase adjuster by the controllers. A detector, the input of which is connected to the cancellation node and the output of which is connected to the controllers, outputs a measure of the envelope of the signal at the cancellation node. After the preselected period new values for the tap steering signals presented to the gain and phase adjuster by the controllers are obtained by multiplying detector output by the respective tracer signal, each over the respective preselected period, summing each resulting series of values, and changing the tap steering signals to be modulated and presented to the gain and phase adjuster in accordance with the values of the respective sums.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
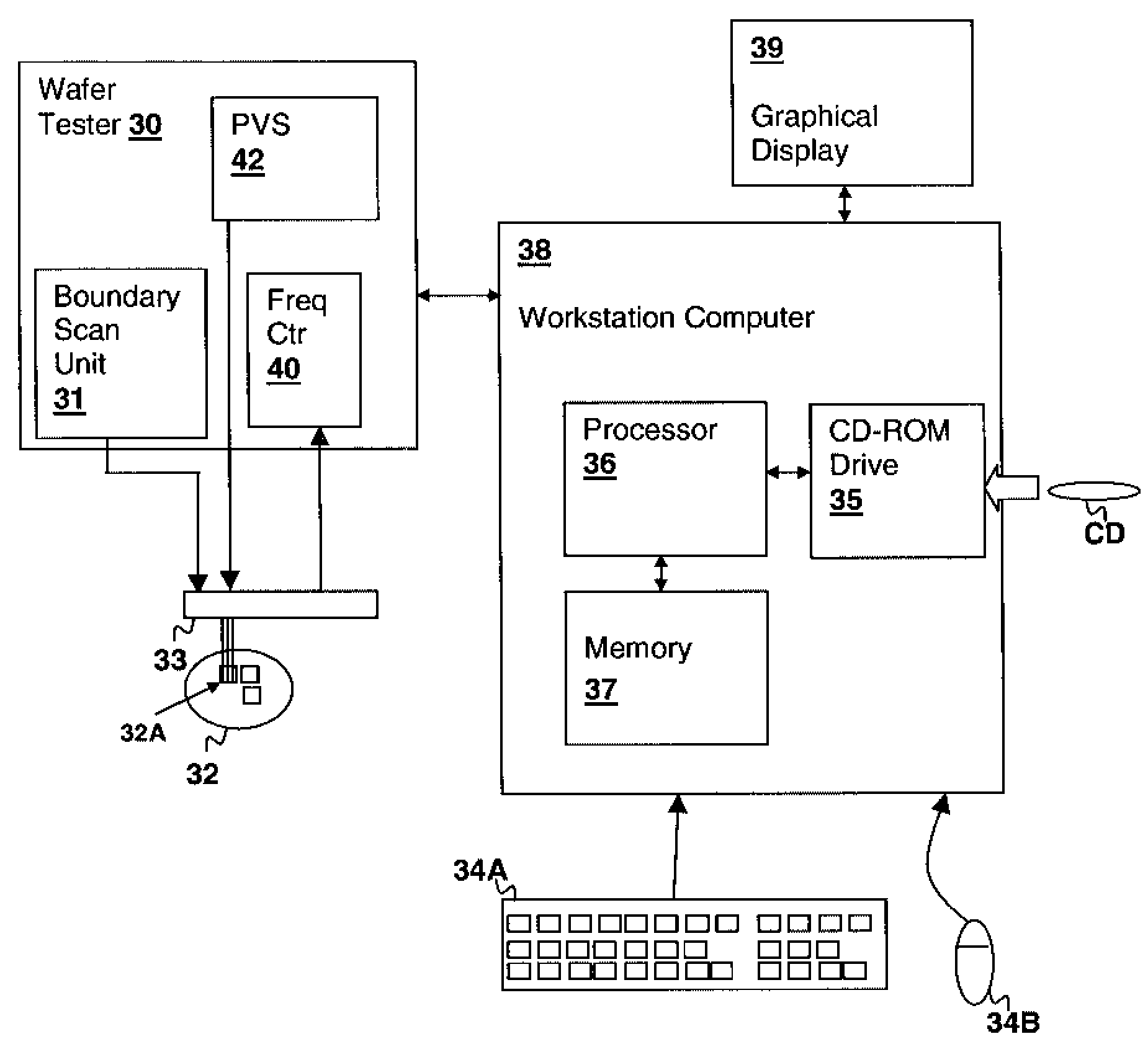
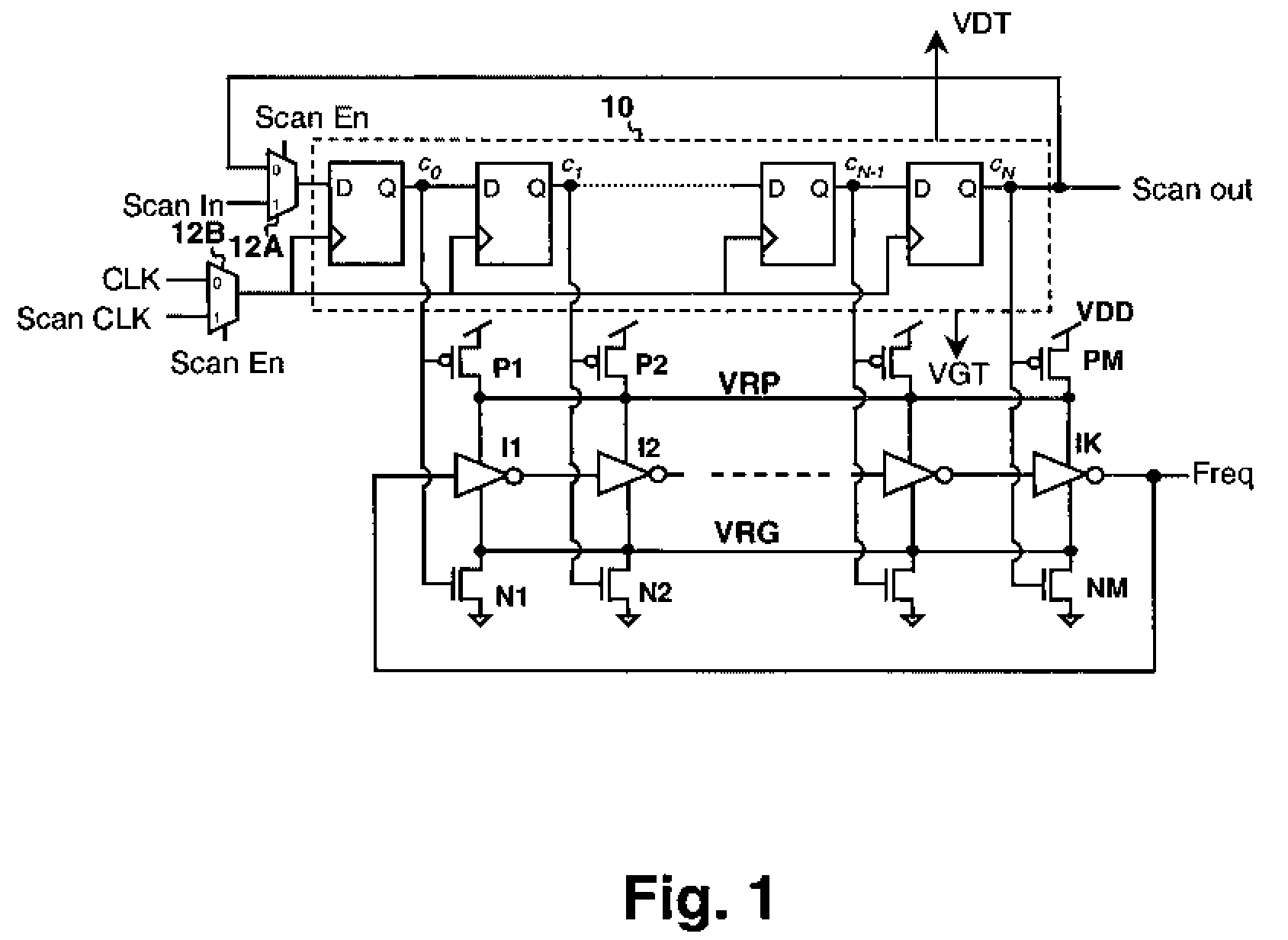
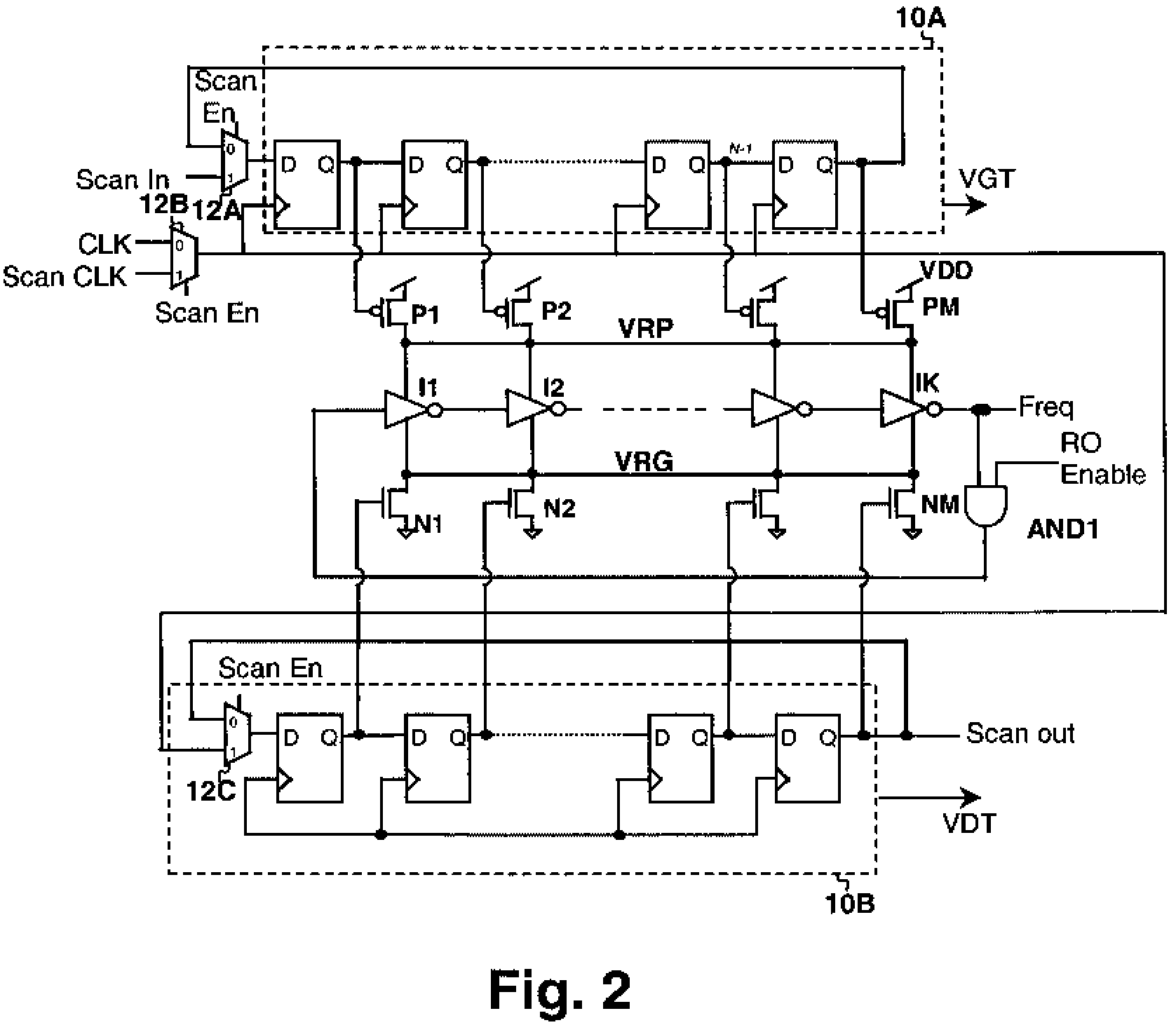
Scannable virtual rail method and ring oscillator circuit for measuring variations in device characteristics
InactiveUS7532078B2Pulse automatic controlAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyFrequency measurementsSystematic difference
A scannable virtual rail method and ring oscillator circuit for measuring variations in device characteristics provides the ability to study random device characteristic variation as well as systematic differences between N-channel and P-channel devices using a ring oscillator frequency measurement. The ring oscillator is operated from at least one virtual power supply rail that is connected to the actual power supply rail by a plurality of transistors controlled by a programmable source. The transistors are physically distributed along the physical distribution of the ring oscillator elements and each can be enabled in turn and the variation in ring oscillator frequency measured. The ring oscillator frequency measurements yield information about the variation between the transistors and N-channel vs. P-channel variation can be studied by employing positive and negative virtual power supply rails with corresponding P-channel and N-channel control transistors.
Owner:IBM CORP
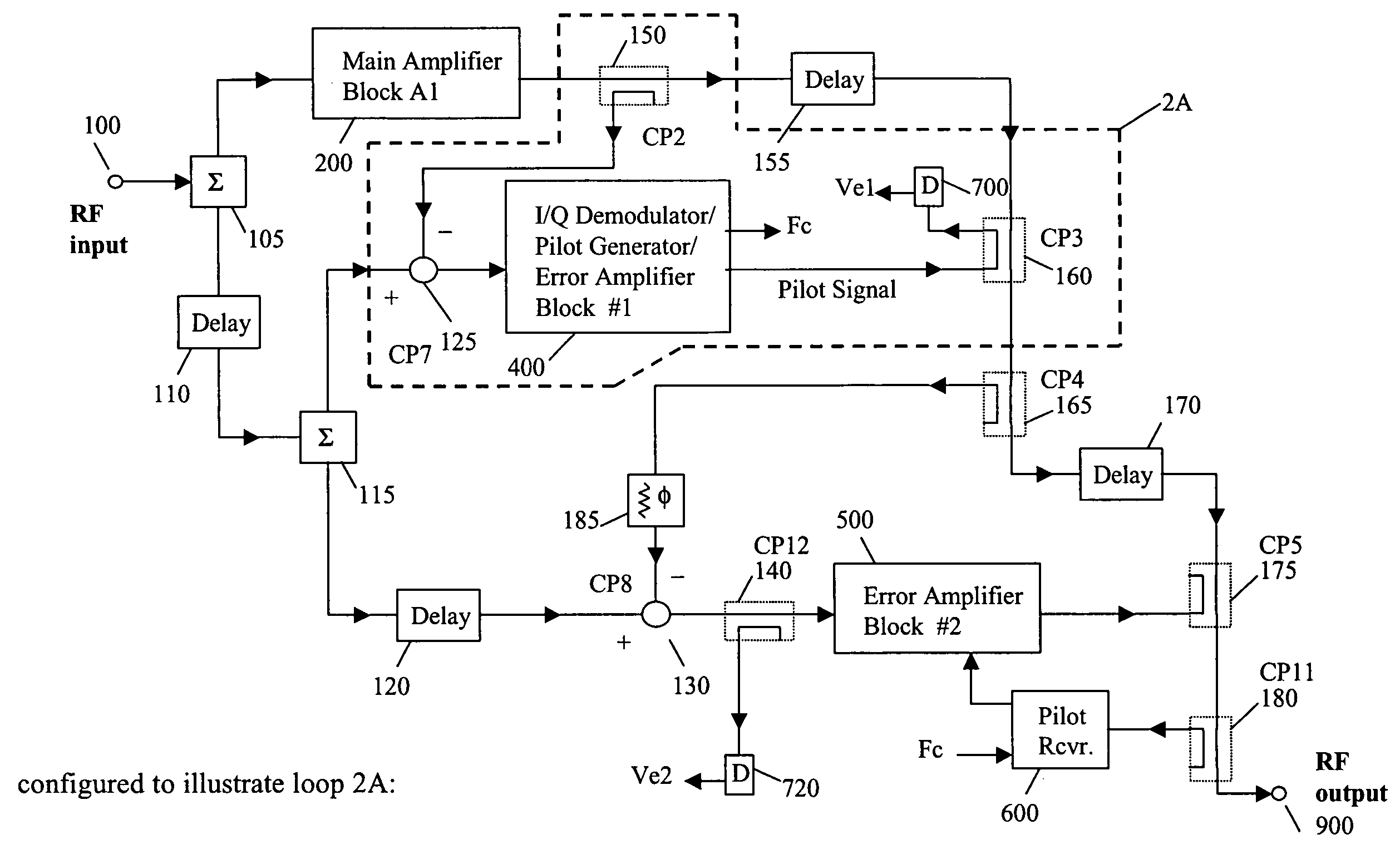
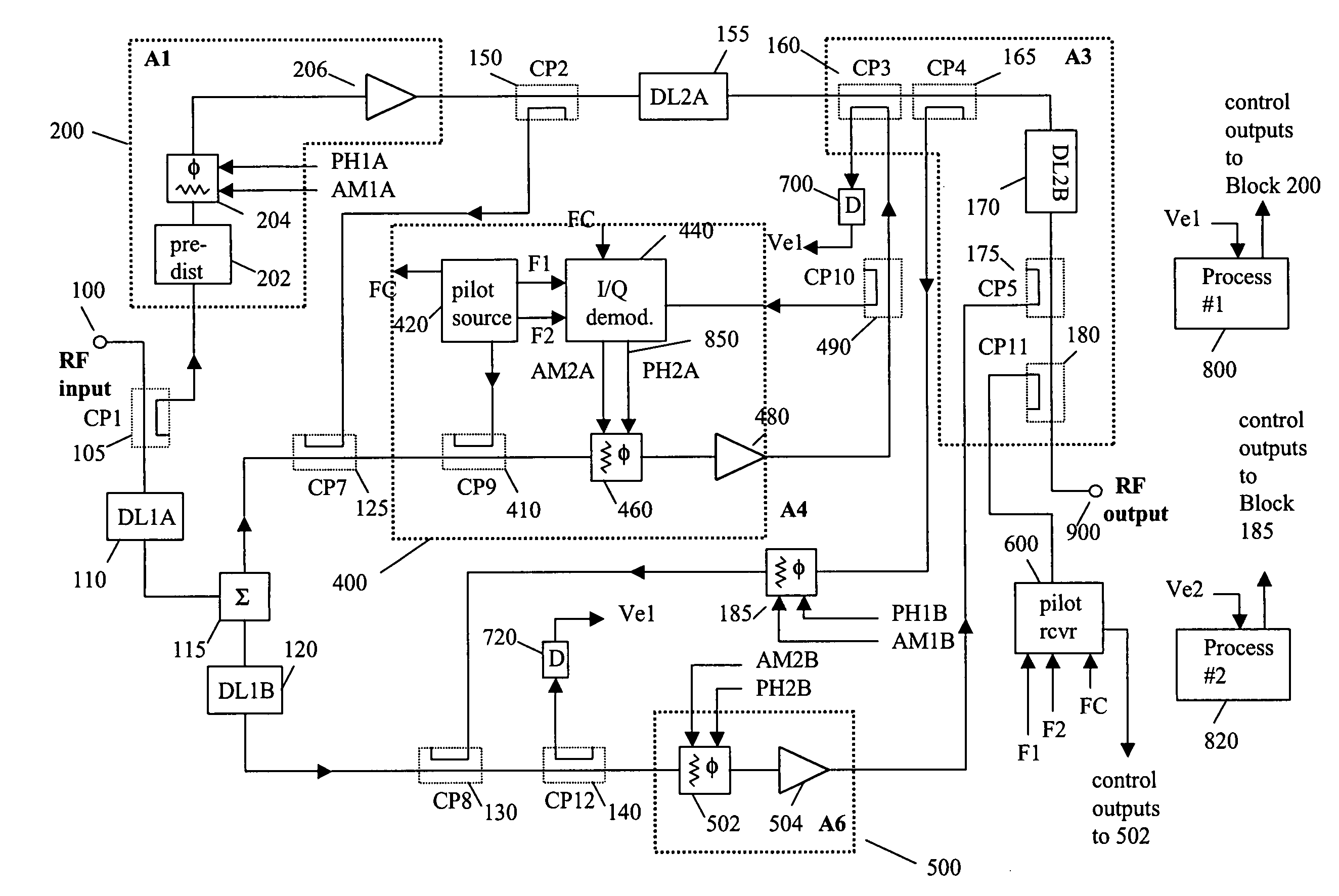
System and method of pilot tone reuse in a feedforward amplifier
ActiveUS20050110567A1Cancel intermodulation distortionReduce distortion problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
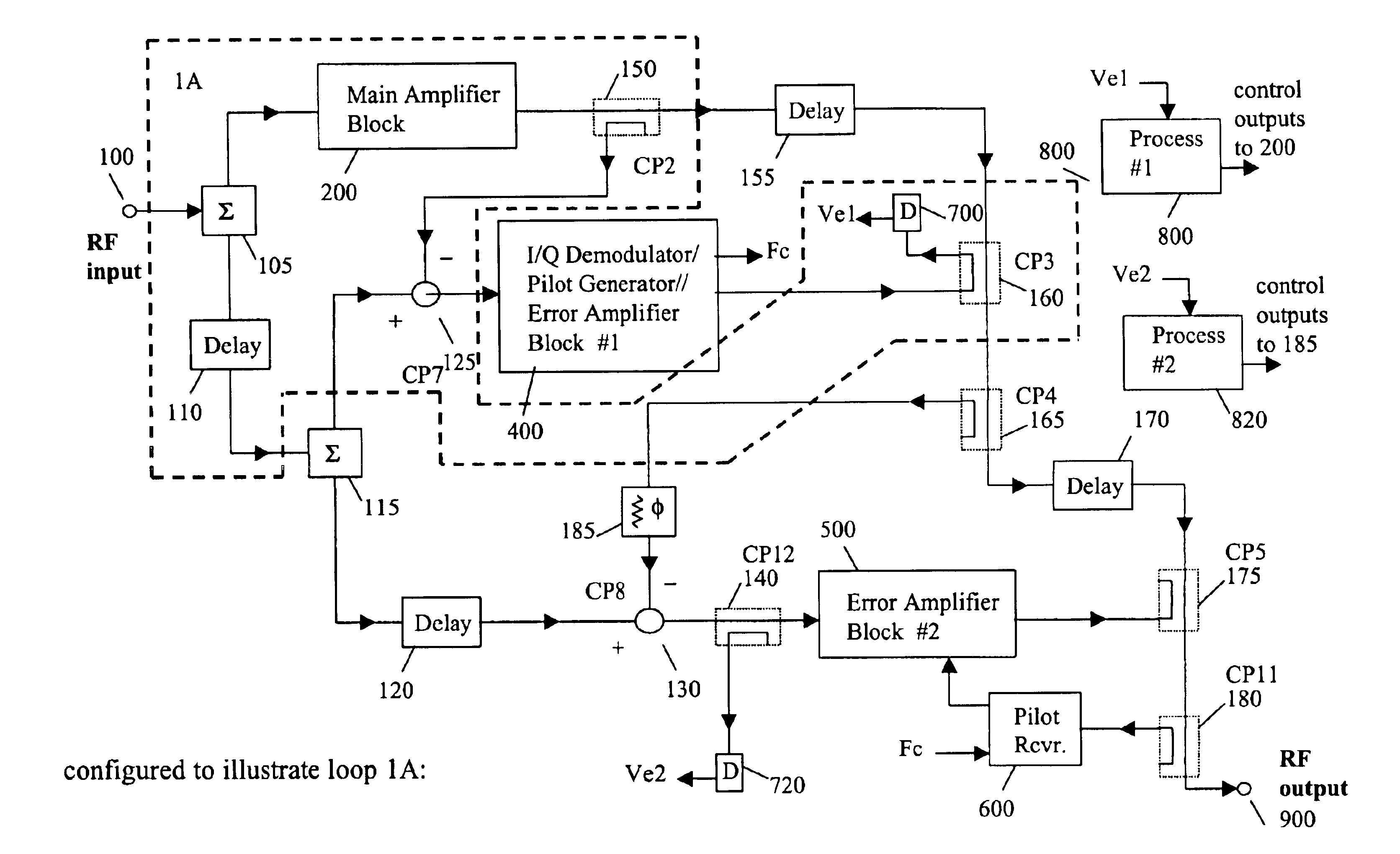
A system and method of pilot tone reuse. The present invention therefore provides a feedforward amplifier, comprising: an input that accepts a radio frequency signal having multiple carriers; a first control loop including a main amplifier block and a detector, wherein the first control loop generates a first carrier cancelled signal; a second control loop including a pilot generator, I / Q demodulator, vector modulator and first error amplifier block, wherein the pilot generator, I / Q demodulator and first error amplifier block amplify the first carrier cancelled signal and generates a pilot signal; a third control loop comprising a vector modulator and a second carrier cancellation detector; and a fourth control loop comprising of vector modulator, a second error amplifier block, and a pilot signal receiver for receiving the pilot signal generated by the pilot generator in the second error amplifier block such that the pilot signal is reused by the fourth control loop to thereby further cancel intermodulation distortion in the output of the main amplifier block.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for control of predistortion linearizer based on power series
InactiveUS7196576B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationControl theoryFrequency characteristic
A gain adjuster and a phase adjuster of a distortion generation path are set so that an extracted distortion component becomes small, the extracted component is compared with a reference value. When an upper-frequency distortion component of a pilot signal is larger than the reference value, the gain and phase of a frequency characteristic compensator of the distortion generation path are controlled so that the upper-frequency distortion component of the pilot signal becomes smaller than a value preset in the controller. When a lower-frequency distortion component of the pilot signal is larger than a reference value, the gain and phase of the frequency characteristic compensator of the distortion generation path are controlled so that the lower-frequency distortion component of the pilot signal becomes smaller than a value preset in the controller.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
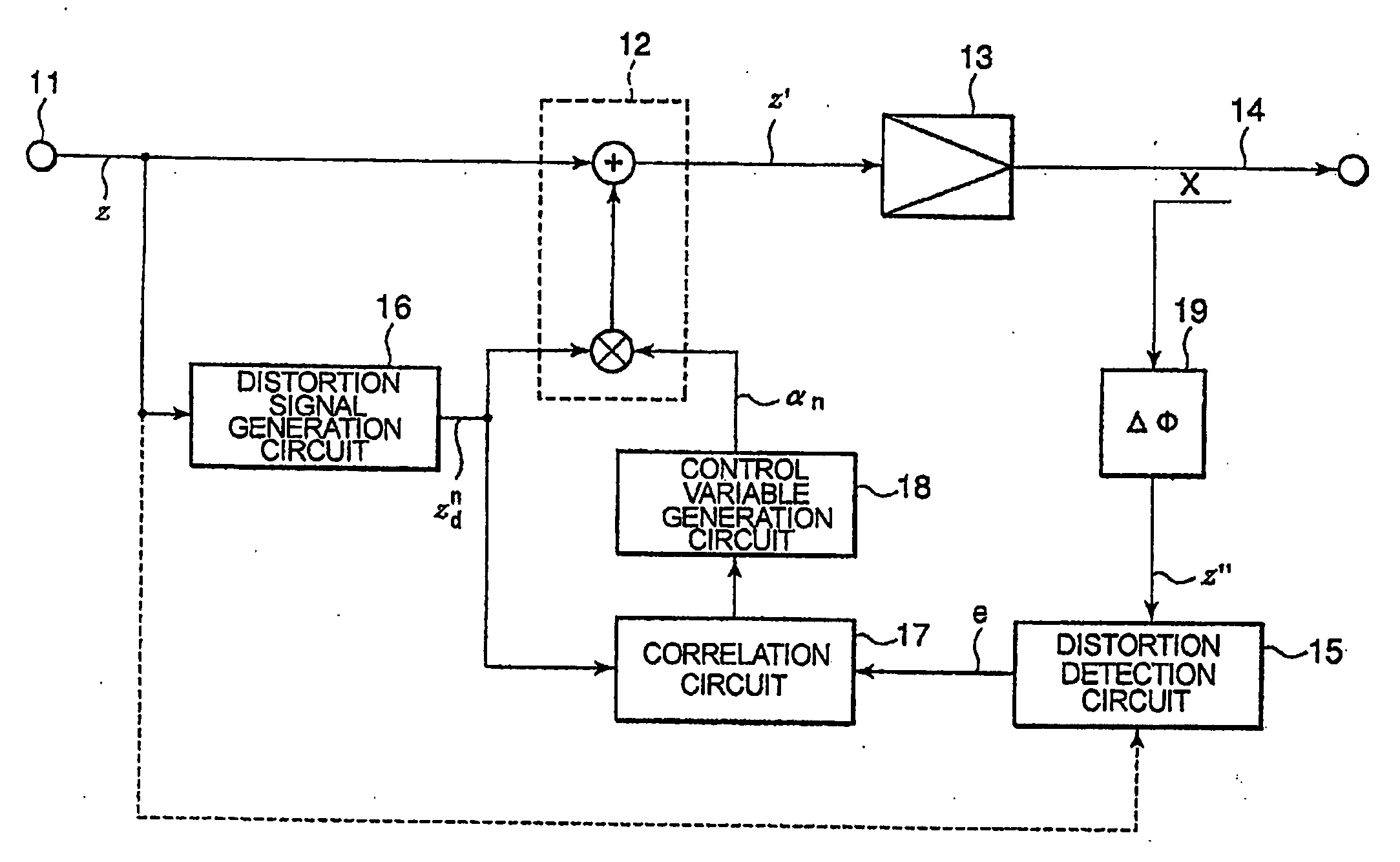
Distortion compensation device for use in high-frequency power amplifier
InactiveUS8175551B2Good compensationShorten the time periodAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
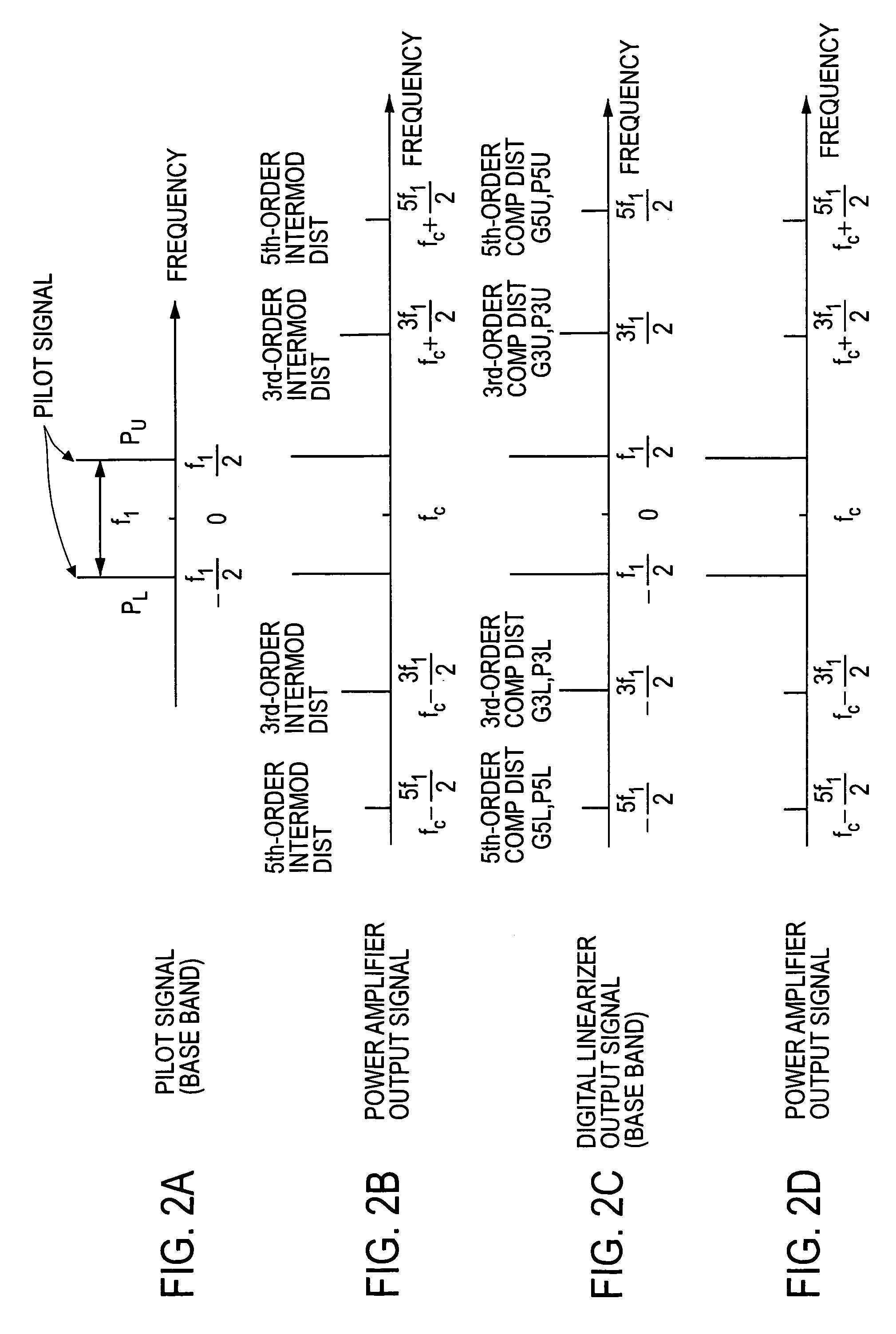
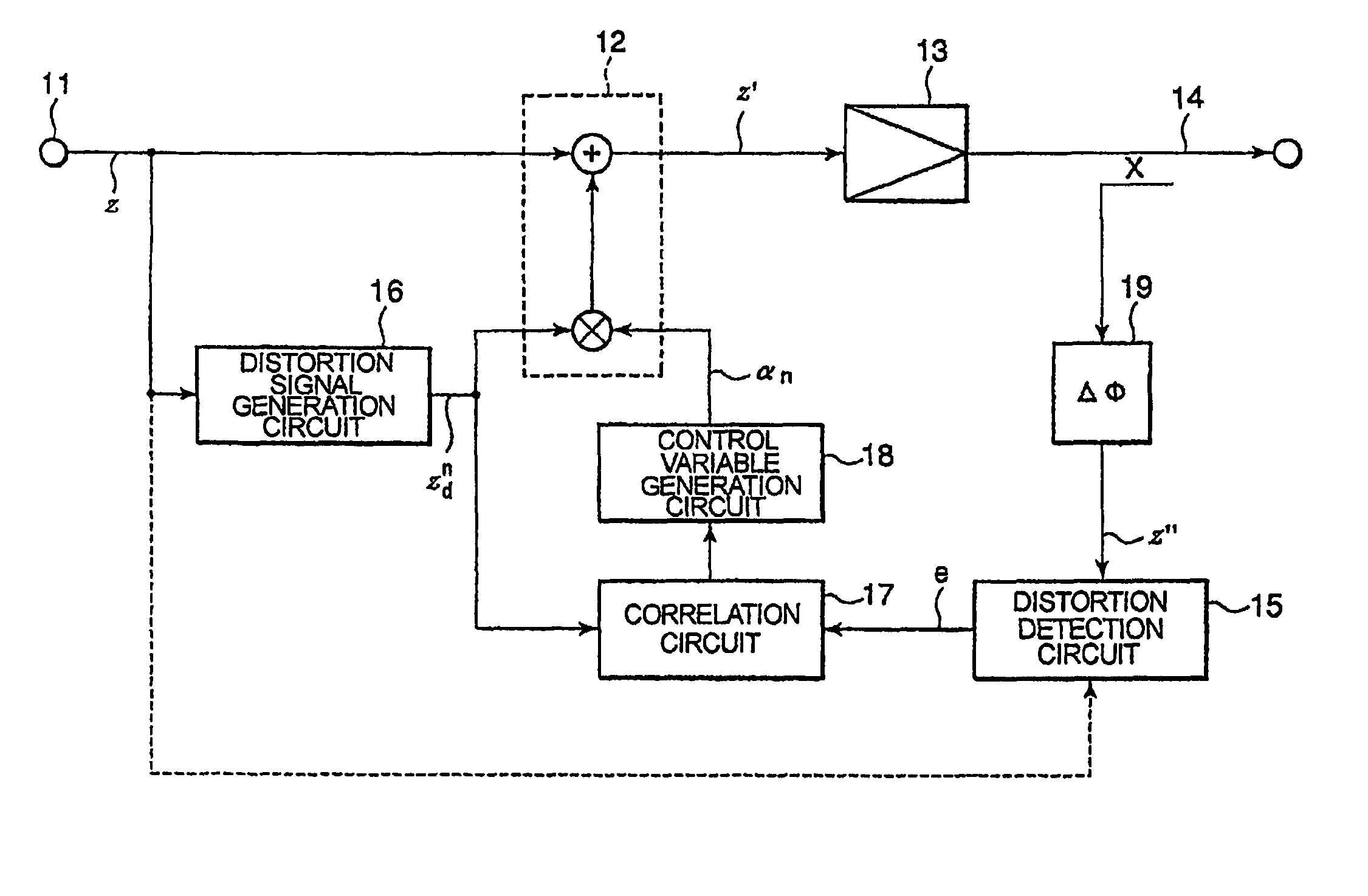
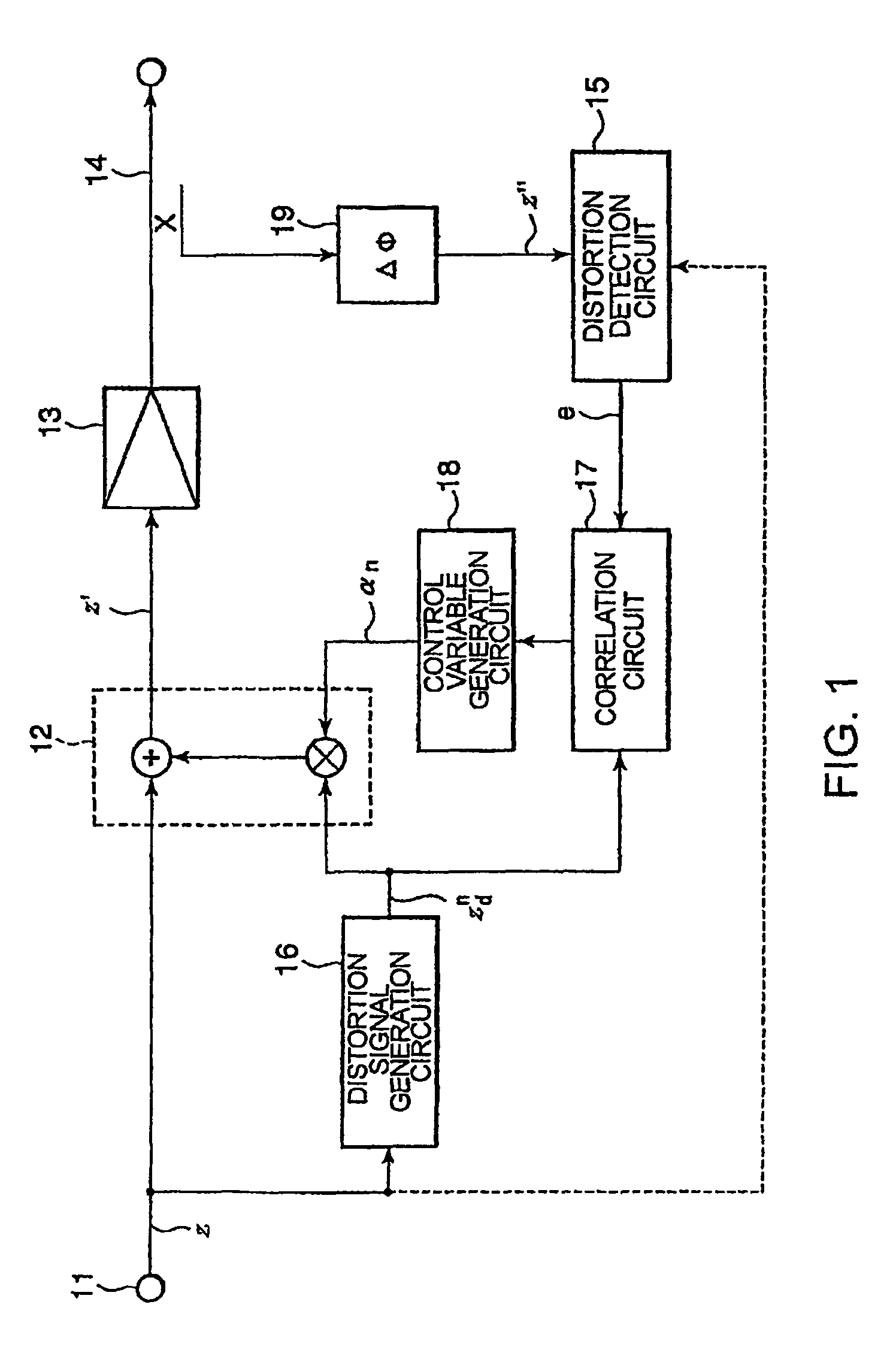
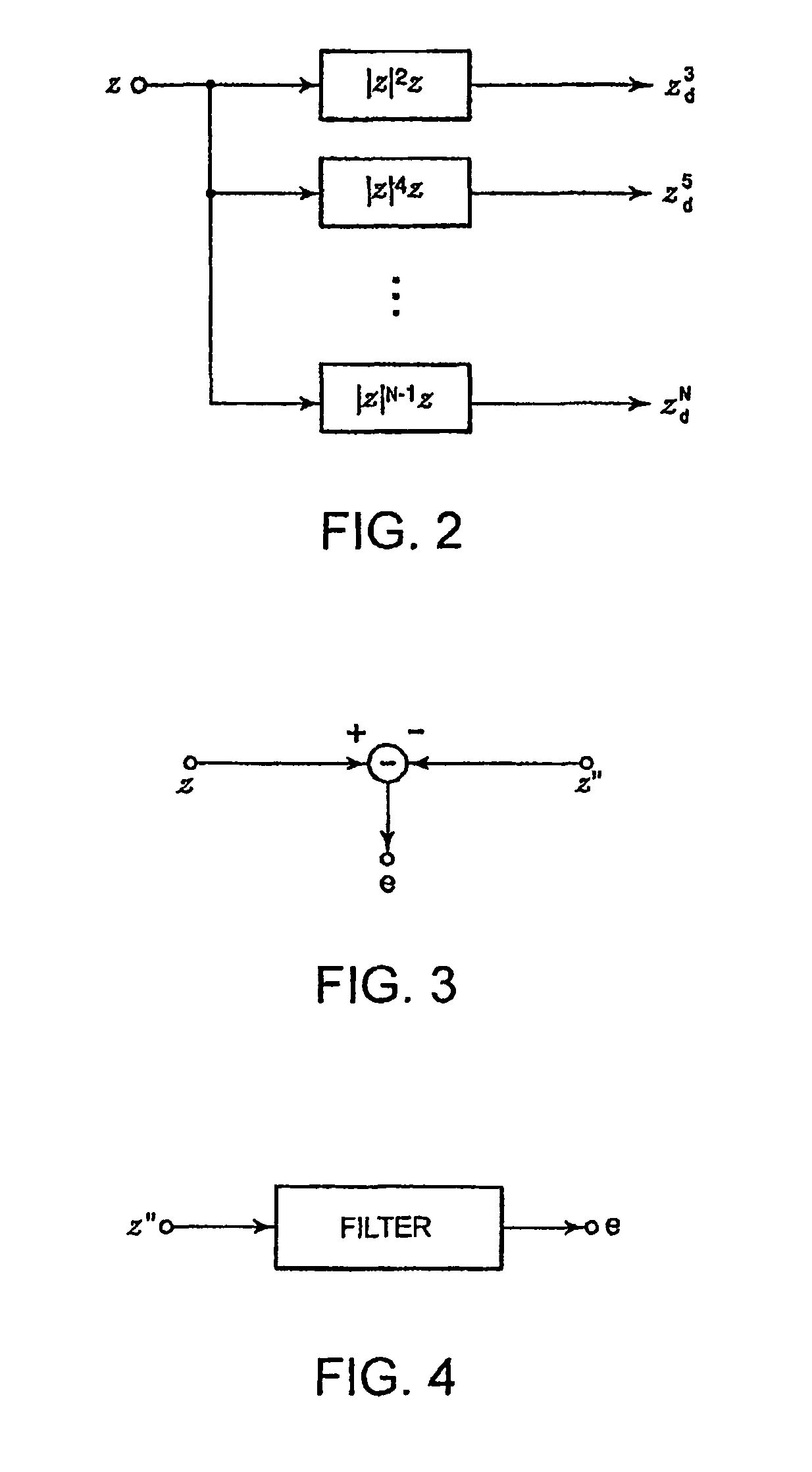
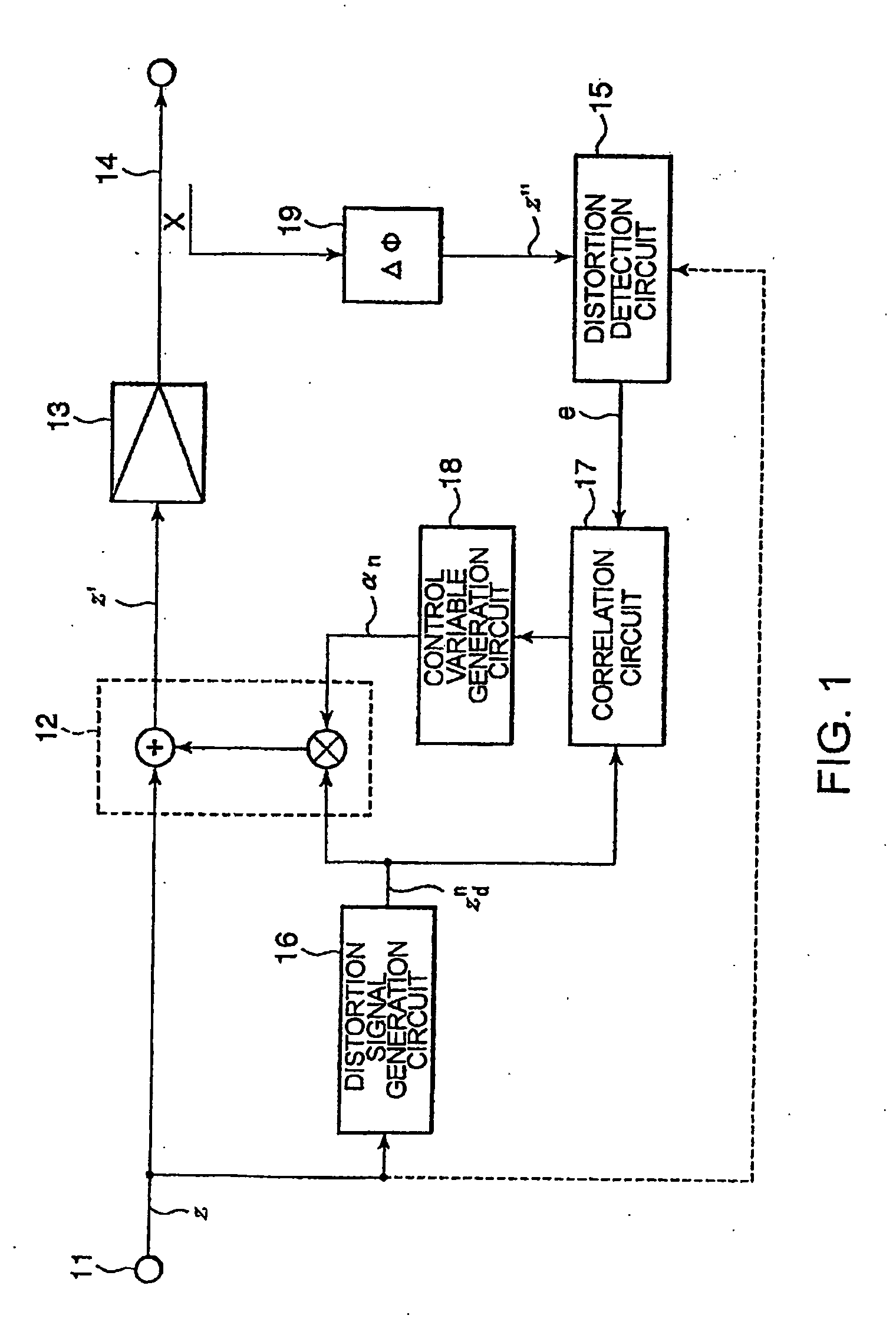
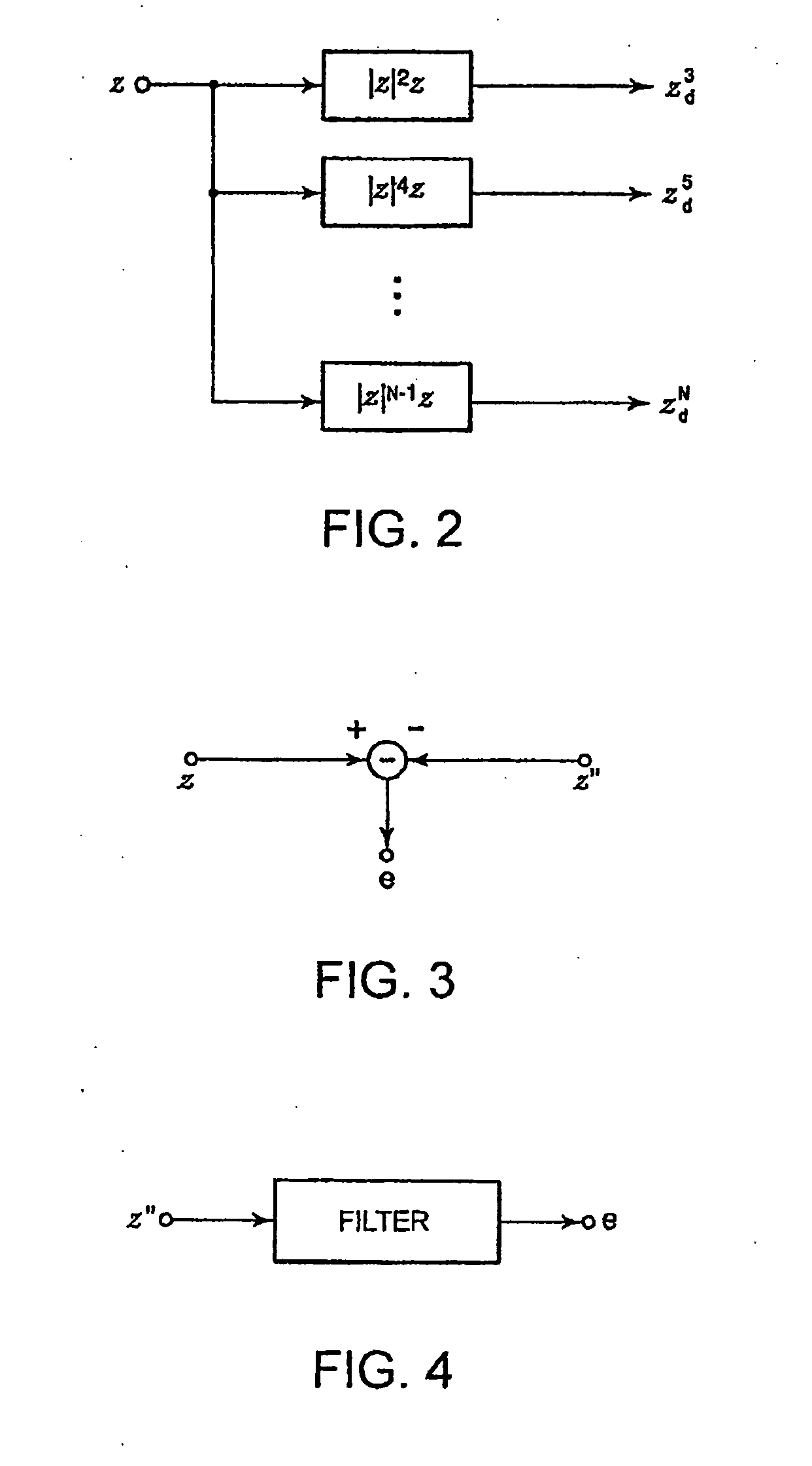
A non-linear distortion signal contained in output signal components from a high-frequency power amplifier is detected, while a non-linear distortion signal is generated from a high-frequency signal to be amplified. Correlation between this non-linear distortion signal and the detected non-linear distortion signal is determined, and a control variable is calculated based on the signal thus obtained. The obtained control variable is multiplied by the generated non-linear distortion signal to generate a distortion compensation signal, which is added to the signal to be amplified. This provides a distortion compensation device capable of automatically maintaining optimum distortion compensation characteristics and rapidly achieving desirable distortion compensation.
Owner:NEC CORP
Audio signal correction and calibration for a room environment
ActiveUS20140161281A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive resonant transducersHigh frequency amplifiersSignal correctionFilter tuning
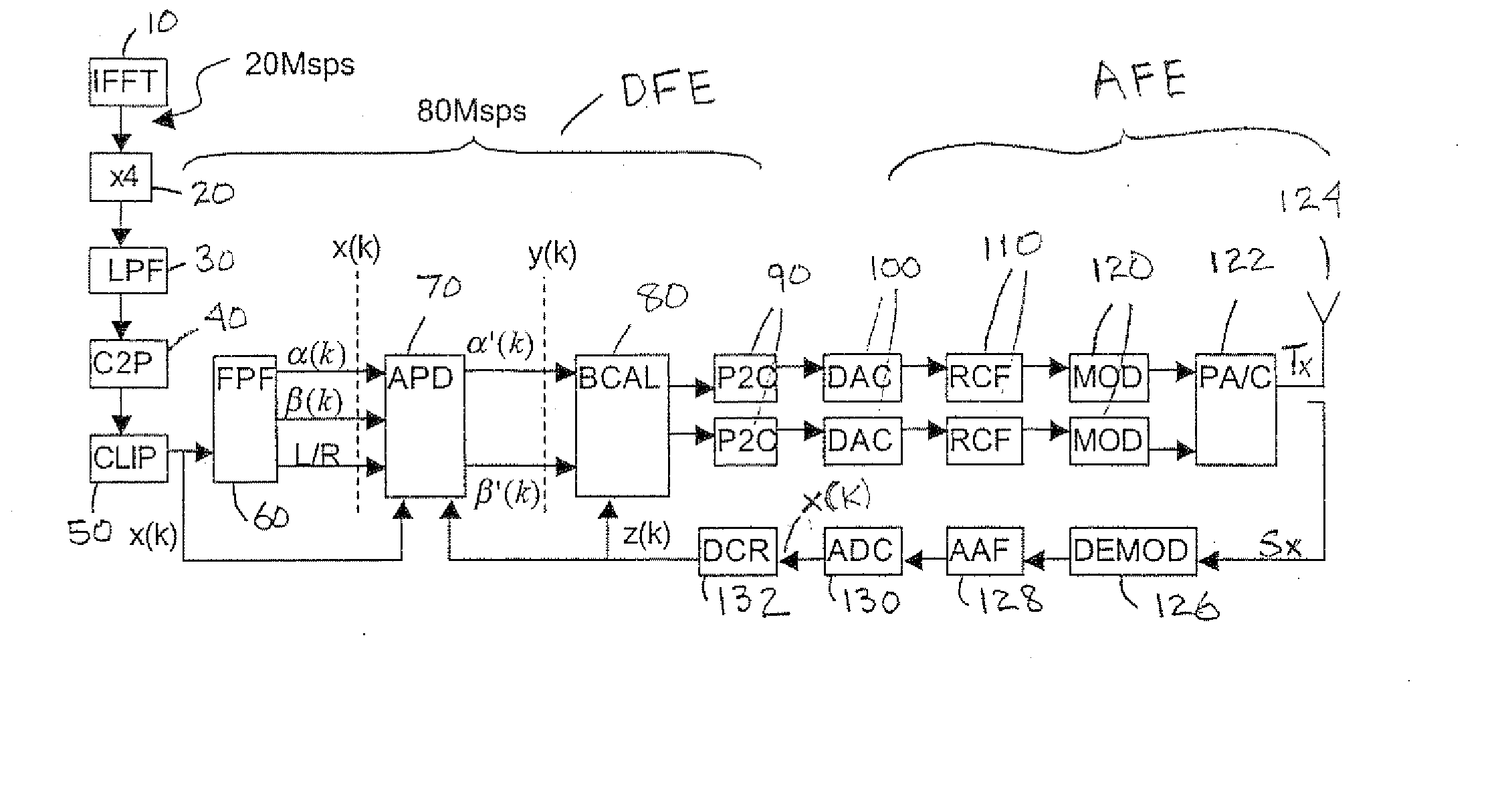
Disclosed are an apparatus and method of processing an audio signal to optimize audio for a room environment. One example method of operation may include recording the audio signal generated within a particular room environment and processing the audio signal to create an original frequency response based on the audio signal. The method may also include identifying a target sub-region of the frequency response which has a predetermined area percentage of a total area under a curve generated by the frequency response, determining whether the target sub-region is a narrow energy region, creating a filter to adjust the frequency response, and applying the filter to the audio signal.
Owner:HARMAN PROFESSIONAL INC
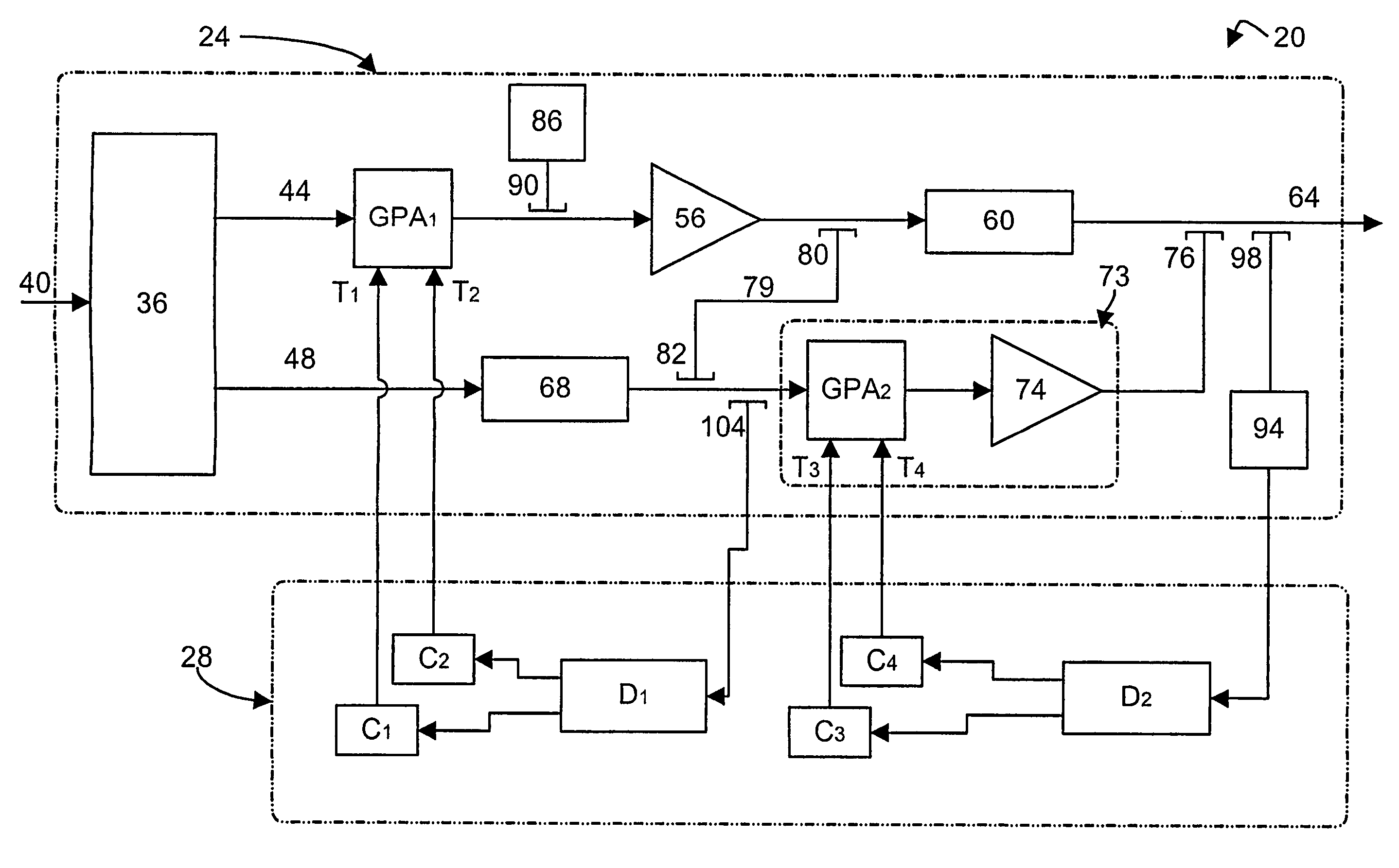
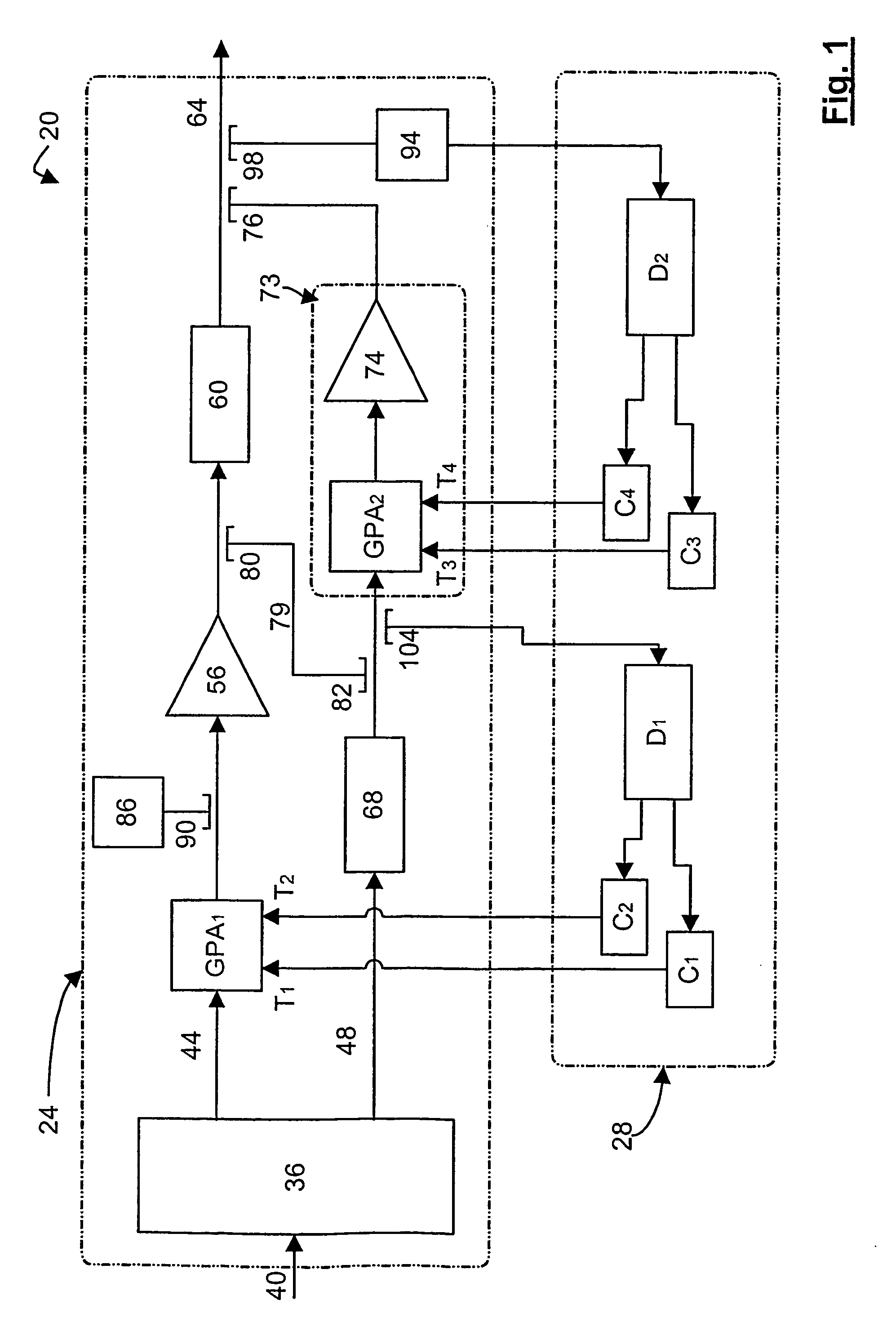
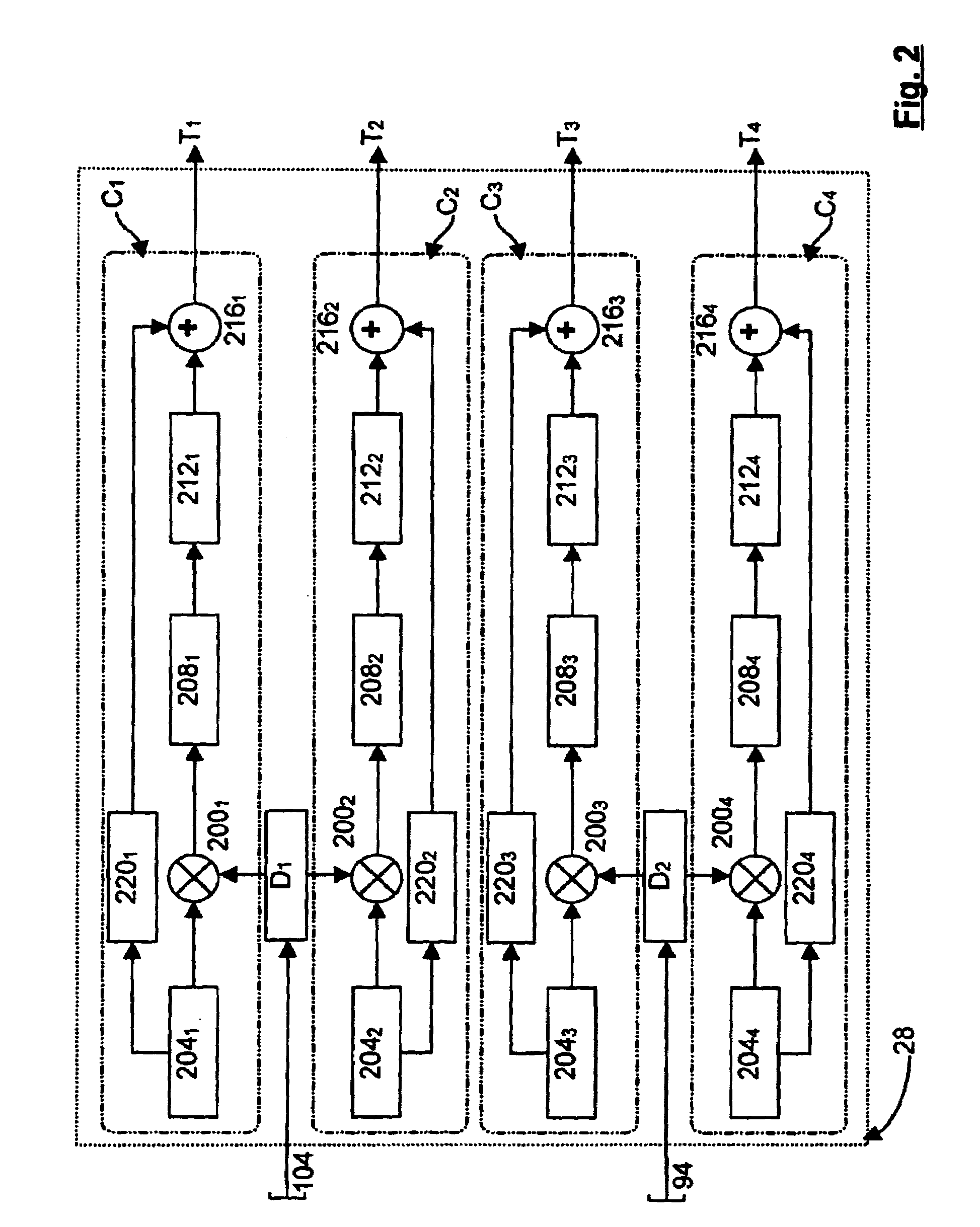
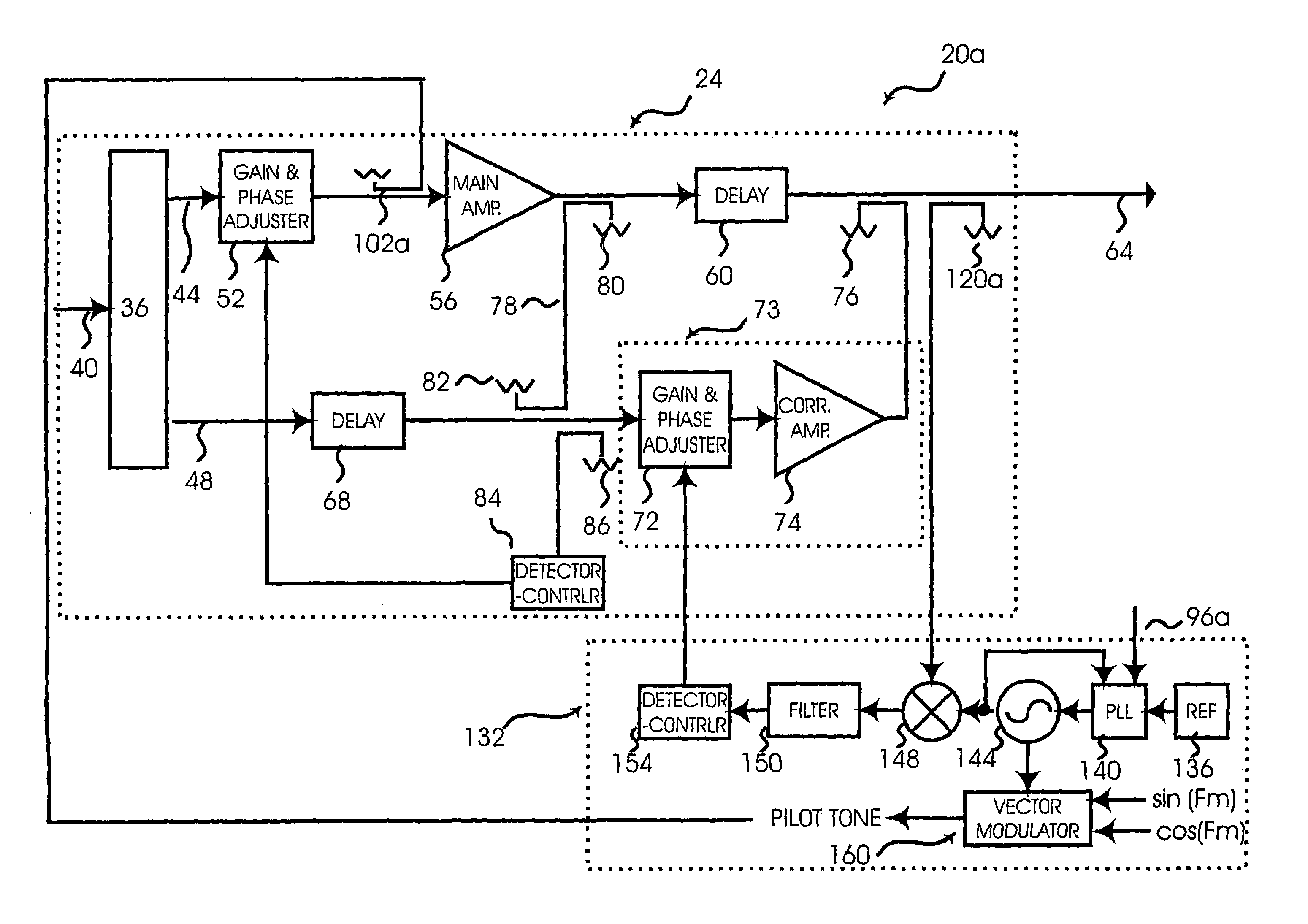
Distortion compensating amplifier
InactiveUS7680467B2Highly efficient distortion compensatingGood compensationResonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierDistortion
In a distortion compensating amplifier that compensates for distortion occurring in main amplifiers, a first amplifying unit amplifies, with a first main amplifier, a first signal consisting of a main signal to be amplified and detects distortion occurring in the first main amplifier, a distortion adjusting unit subjects the distortion detected by the first amplifying unit to vector adjustment, a second amplifying unit combines a second signal consisting of the main signal to be amplified and the distortion supplied from the distortion adjusting unit and amplifies a combined signal with a second main amplifier, and a combining unit combines an amplified signal supplied from the first amplifying unit and an amplified signal supplied from the second amplifying unit.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Feedforward amplifier circuitry
InactiveUS6774716B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
The present invention is intended to provide a feedforward amplifier circuitry which is capable of changing a location or placement of each section constituting the feedforward circuitry, in particular a feedforward amplifier circuitry which is capable of changing an interposing location of a variable phase shifter. In the feedforward amplifier circuitry, a variable phase shifters (5, 12) can be disposed on a location other than a post-stage of a predistortion circuits (3, 20), as a result of which it is advantageously possible to provide a designer with more flexibility in changing the locations of variable shifters, regardless of the conventional arrangement of the variable phase shifters disposed on the post-stages of the distortion circuits, when the feedforward amplifier is actually designed.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Distortion compensation device for use in high-frequency power amplifier
InactiveUS20100201442A1Shorten the time periodImprove featuresAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationNonlinear distortionHigh frequency power
A non-linear distortion signal contained in output signal components from a high-frequency power amplifier is detected, while a non-linear distortion signal is generated from a high-frequency signal to be amplified. Correlation between this non-linear distortion signal and the detected non-linear distortion signal is determined, and a control variable is calculated based on the signal thus obtained. The obtained control variable is multiplied by the generated non-linear distortion signal to generate a distortion compensation signal, which is added to the signal to be amplified. This provides a distortion compensation device capable of automatically maintaining optimum distortion compensation characteristics and rapidly achieving desirable distortion compensation.
Owner:NEC CORP
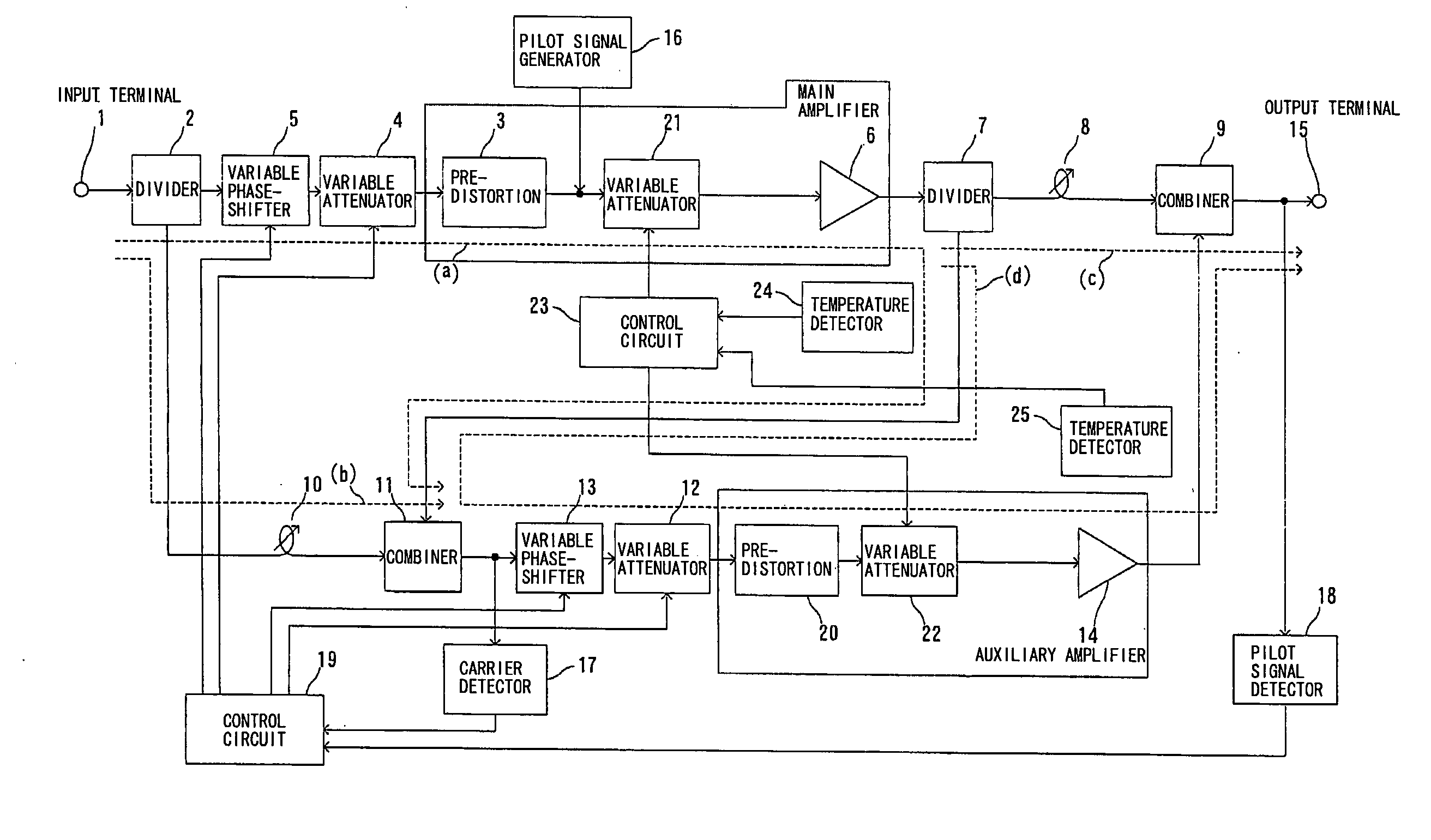
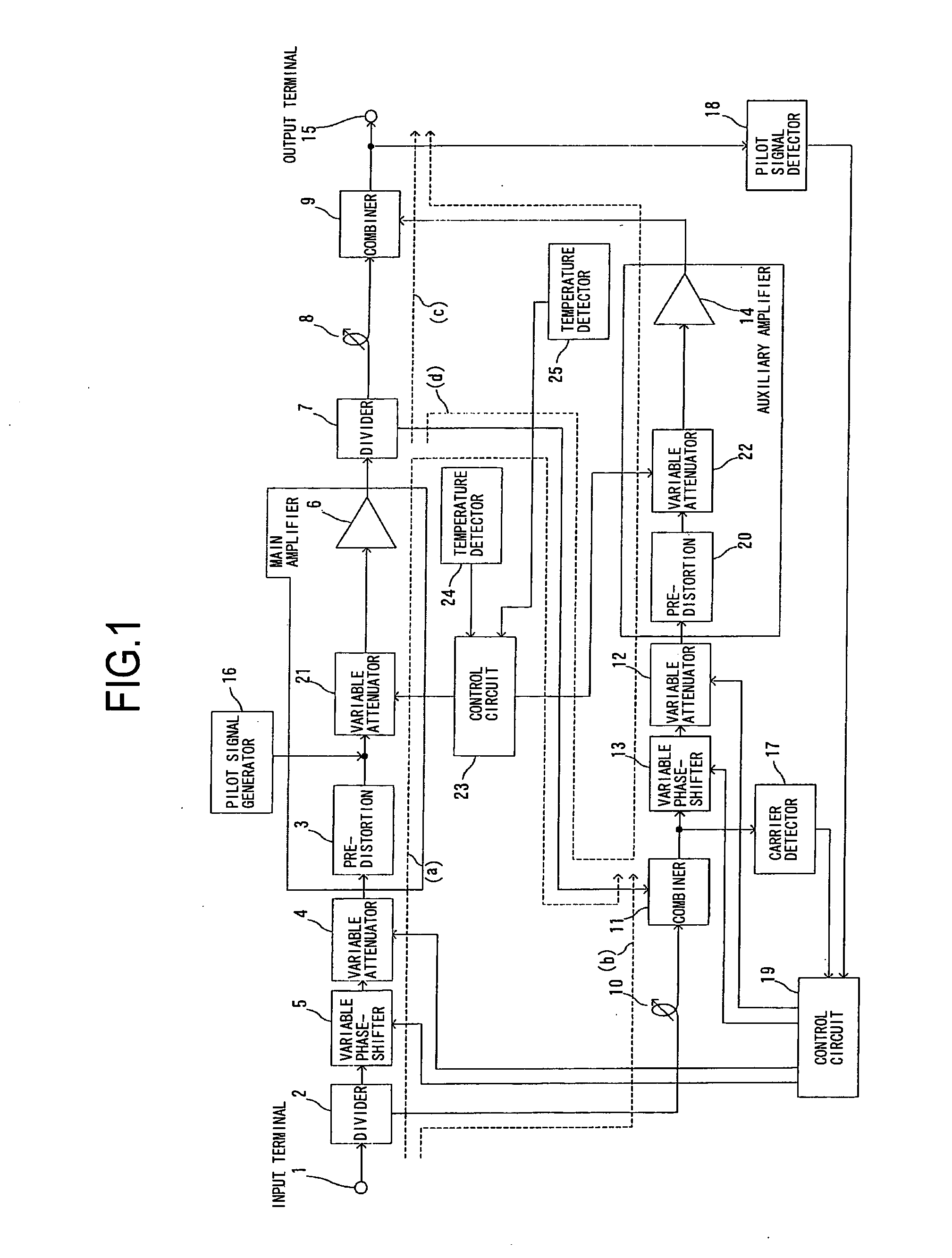
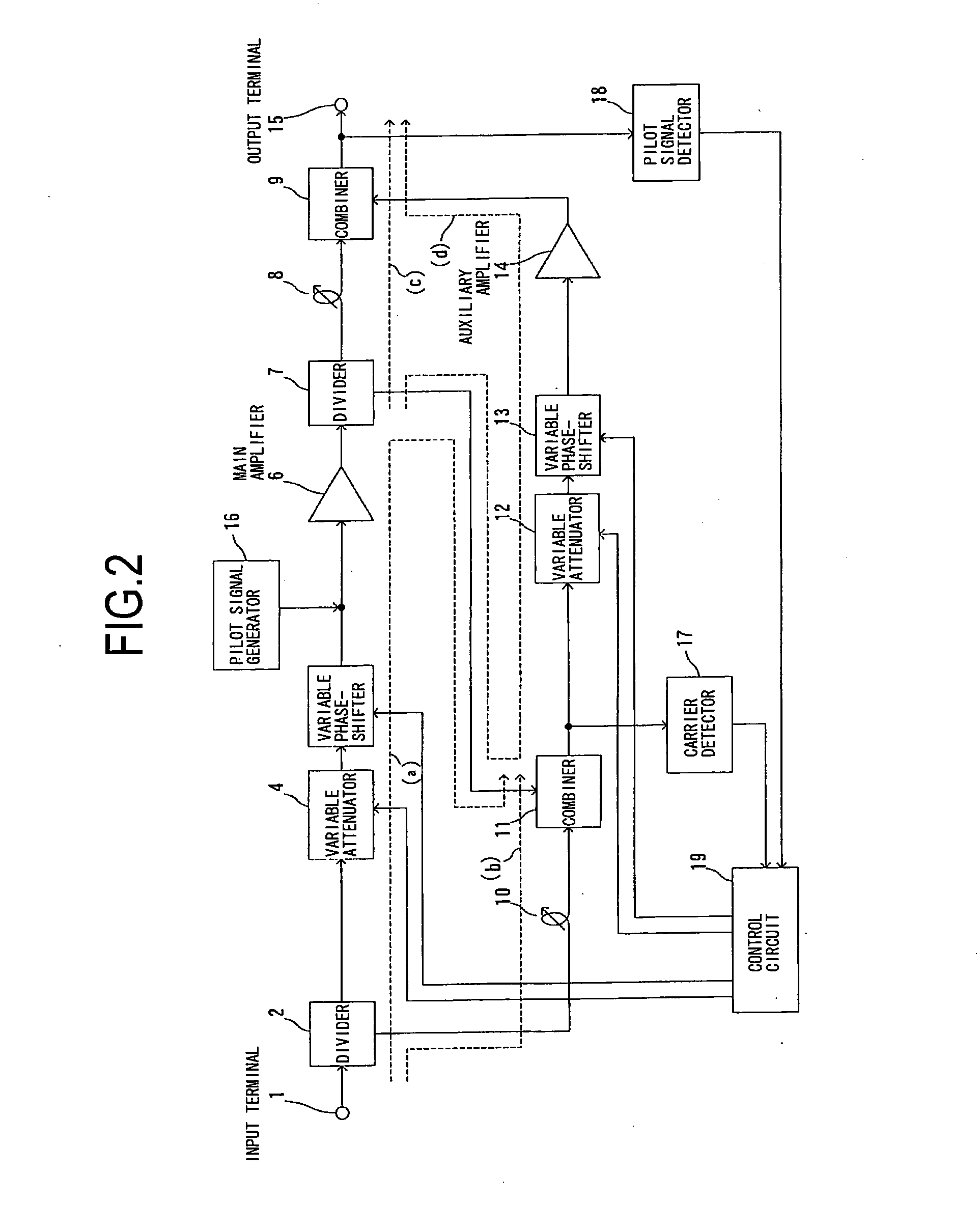
Feed-forward amplifier
InactiveUS7646239B2Sufficient distortion compensation effectMinimize distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
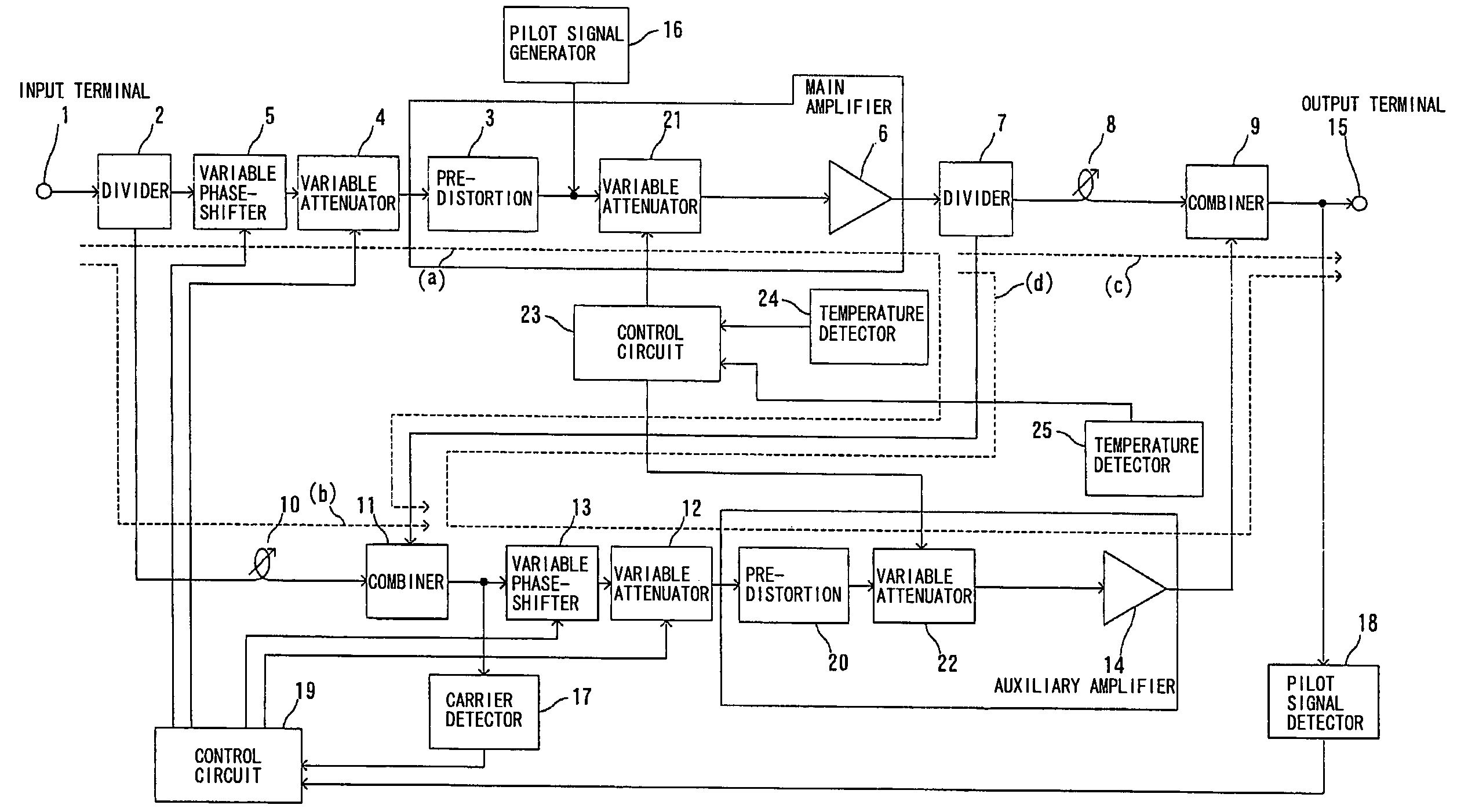
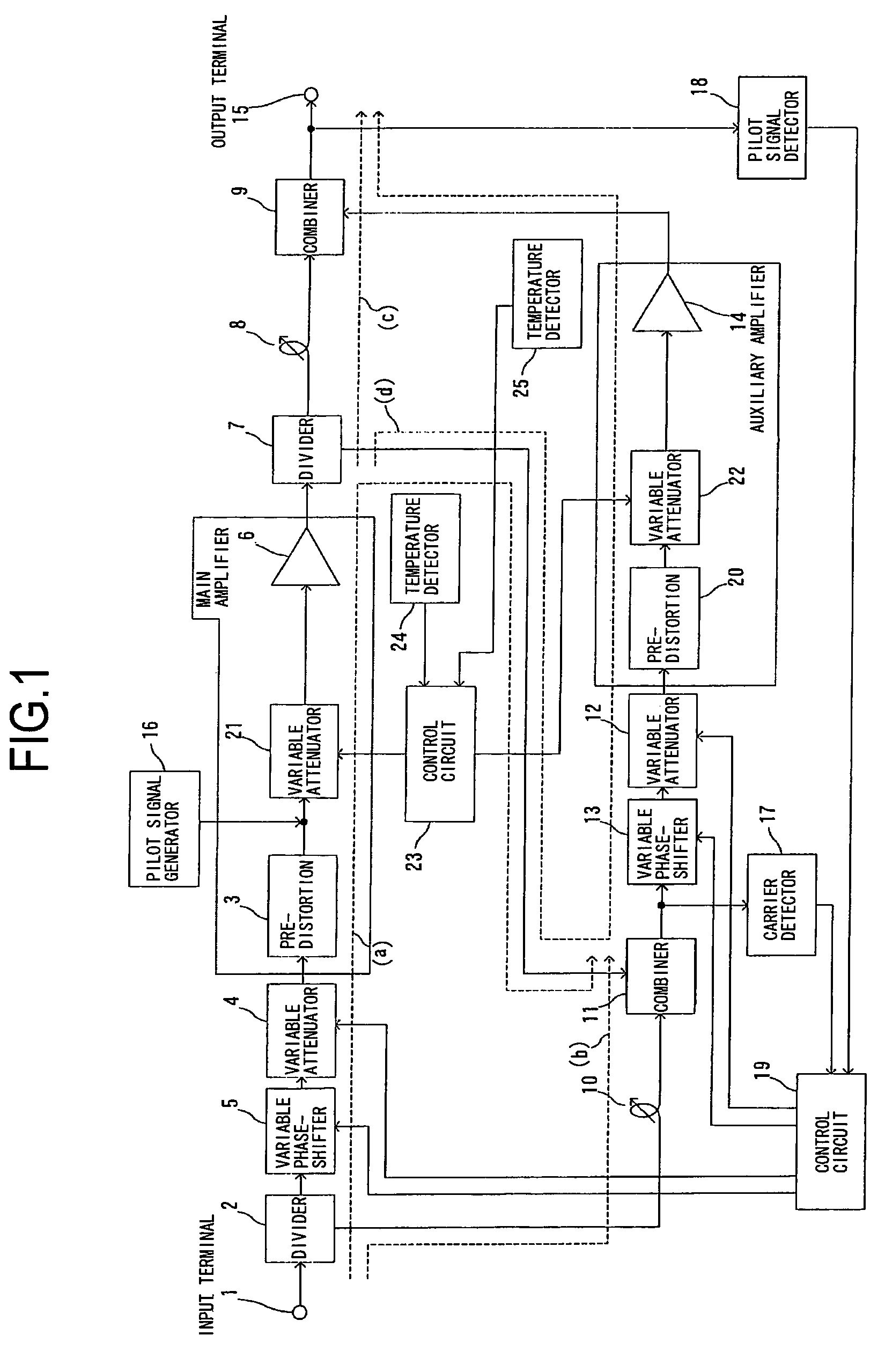
There is provided a feed-forward amplifier which enables a predistortion circuit to obtain sufficient distortion compensation effects even if ambient temperature or the like changes. The feed-forward amplifier includes a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation of a signal input to a main amplifier, a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to a change in the ambient temperature of the main amplifier, a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation of a signal input to an auxiliary amplifier, and a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to a change in the ambient temperature of the auxiliary amplifier, wherein a control circuit controls the variable attenuators to reduce the amount of attenuation according to the reduced gain of the main amplifier and the reduced gain of the auxiliary amplifier, and a control circuit controls the variable attenuators to optimize the amount of attenuation according to the ambient temperature of the main amplifier and the ambient temperature of the auxiliary amplifier.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
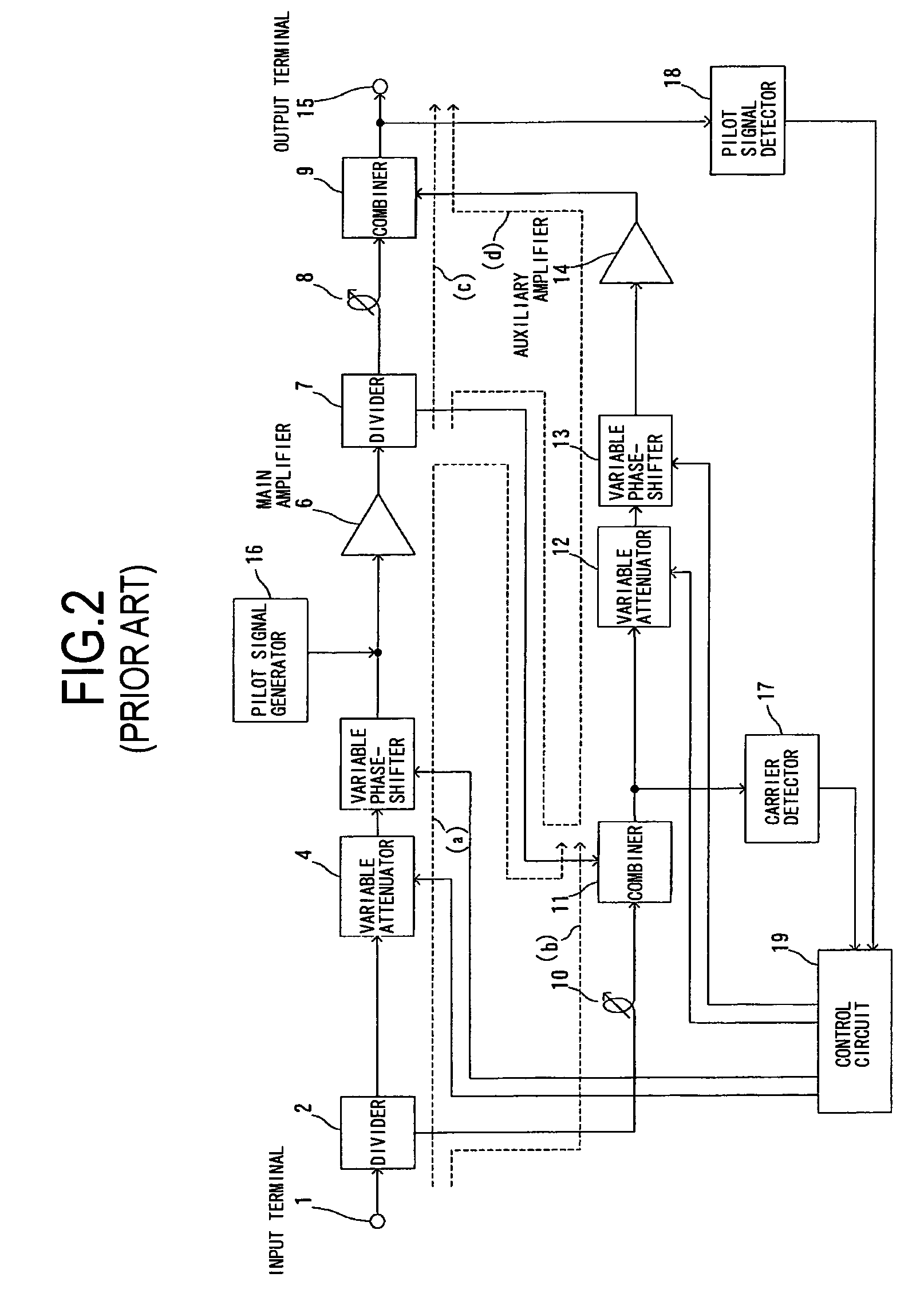
Feed forward amplifier
InactiveUS7053702B2Reduce expensesReduce complexityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyTelecommunicationsAudio power amplifier
The present invention provides a novel feed forward amplifier (“FFA”) and a pilot tone generator-receiver therefor. In an embodiment of the invention, the feed forward amplifier only requires a single oscillator to operate both the pilot tone generator and pilot tone receiver used in conjunction with the amplifier circuitry of the FFA. In another embodiment of the invention, a method is provided of generating and detecting a pilot tone from a single oscillating signal.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Feedforward amplifier with dual loop
InactiveUS6838934B2Easy balance controlAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
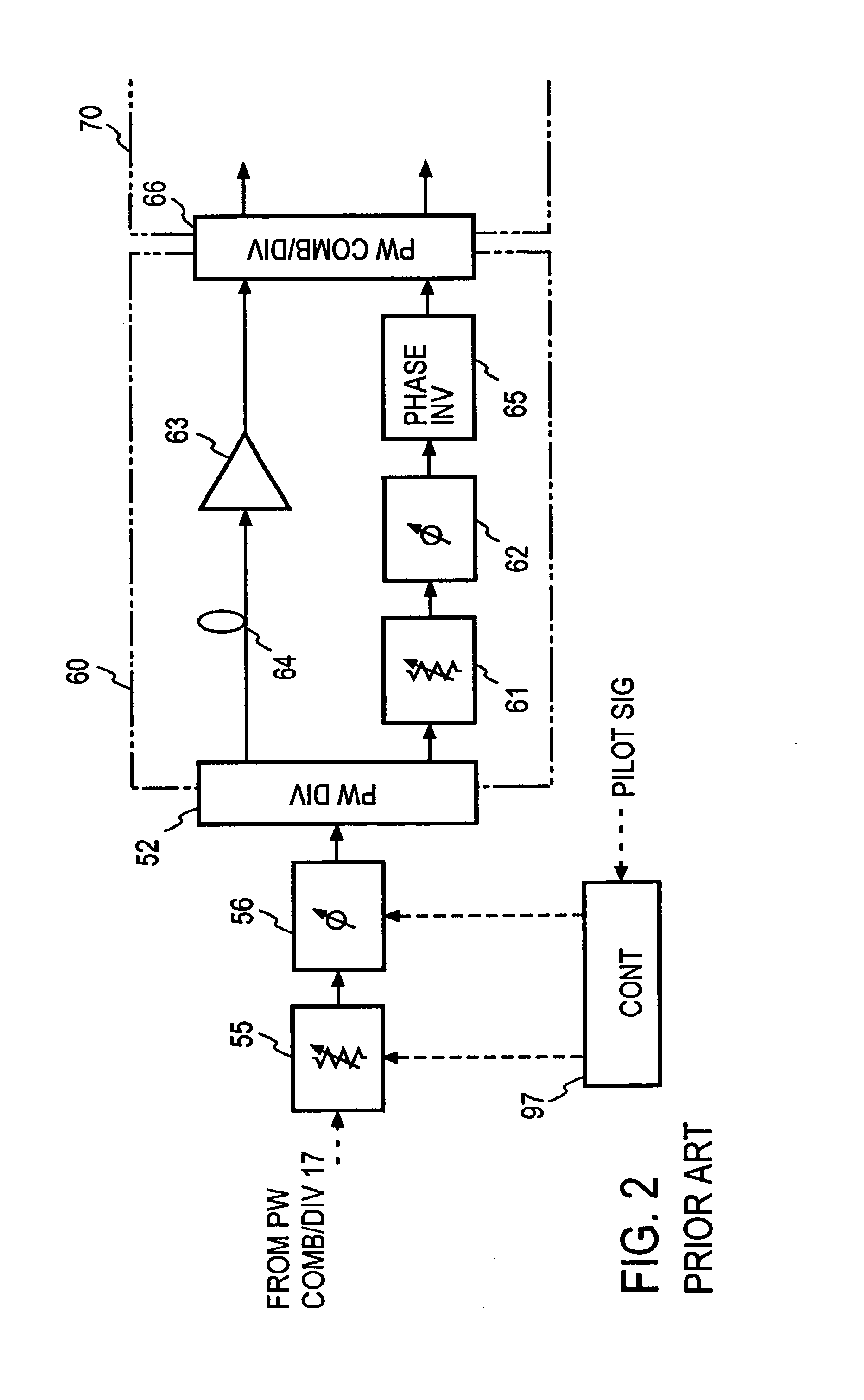
In a feedforward amplifier with a dual loop in which a distortion injection path of a distortion elimination circuit 50 is provided as a feedforward configuration composed of a first auxiliary amplifier distortion elimination circuit 60 and a first auxiliary amplifier distortion elimination circuit, a second variable attenuator 55 and a second variable phase shifter 56 are provided preceding the distortion detection circuit 60, a second pilot signal injected between stages of a main amplifier 14 is detected by a directional coupler 85, and the second variable attenuator 55 and the second variable phase shifter 56 are controlled by a second controller 97 to minimize the level of the detected second pilot signal, thereby bringing the distortion elimination circuit and the first auxiliary distortion detection circuit into balance at the same time.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Digital branch calibrator for an RF transmitter
InactiveUS20070291863A1Significant to useImprove efficiencyMultiple-port networksError preventionTransmitterTransposer
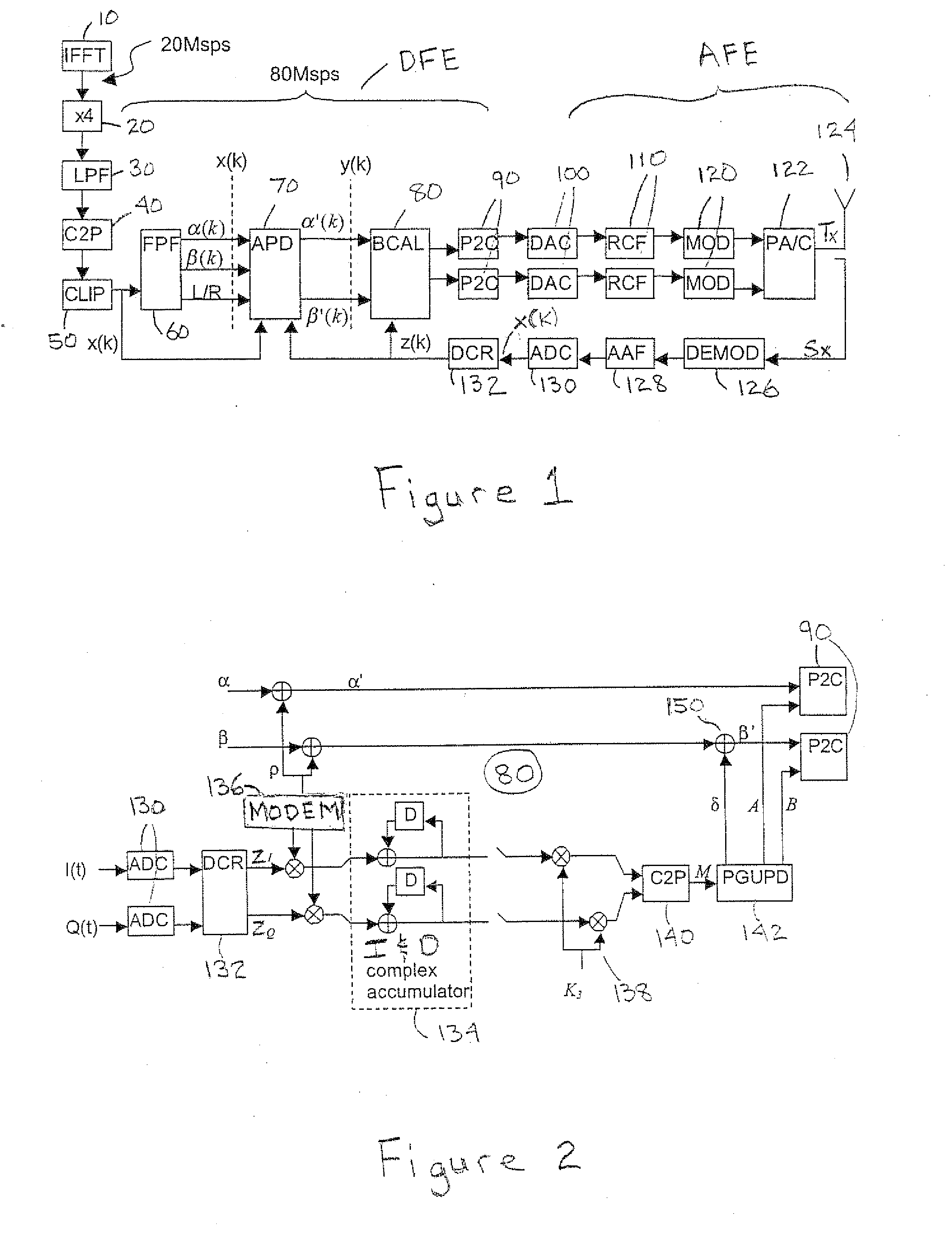
The present invention provides a digital (computational) branch calibrator which uses a feedback signal sensed from an RF transmit signal path following the combining stage of LINC circuitry of a transmitter to compensate for gain and phase imbalances occurring between branch fragment signals leading to the combiner. The calibrator feeds a quiet (zero) base band signal through the transmit path during the calibration sequence (i.e. a period when data is not transmitted) and adjusts the phase and gain of the phasor fragment signals input thereto by driving the sensed output power to zero. The calibration is performed by alternating phase and gain adjustments with predetermined (programmable) and multiple update parameters stages (speeds). A baseband modulation is preferably used to distinguish false leakage (e.g. due to local oscillator, LO, feed through and DC offset in the base band Tx) from imbalance leakage.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Feed forward amplifier employing positive feedback pilot generation with automatic level control
InactiveUS20060176113A1Lower Level RequirementsLarge levelAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
A feed forward amplifier and method of amplification are disclosed. The amplifier output is used to generate a pilot signal via feedback using uncancelled noise in the amplifier output. An automatic level control circuit maintains the pilot signal at a substantially constant level when the detected uncancelled noise in the amplifier output is above a threshold level. The generated pilot signal strength is allowed to vary when the detected uncancelled noise in the amplifier output is below the threshold and disappears automatically when the amplifier is aligned.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Feed-forward amplifier
InactiveUS20080136518A1Sufficient distortion compensation effectMinimize distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
There is provided a feed-forward amplifier which enables a predistortion circuit to obtain sufficient distortion compensation effects even if ambient temperature or the like changes. The feed-forward amplifier includes a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation of a signal input to a main amplifier, a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to a change in the ambient temperature of the main amplifier, a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation of a signal input to an auxiliary amplifier, and a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to a change in the ambient temperature of the auxiliary amplifier, wherein a control circuit controls the variable attenuators to reduce the amount of attenuation according to the reduced gain of the main amplifier and the reduced gain of the auxiliary amplifier, and a control circuit controls the variable attenuators to optimize the amount of attenuation according to the ambient temperature of the main amplifier and the ambient temperature of the auxiliary amplifier.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
System and method of carrier reinjection in a feedforward amplifier
InactiveUS7173484B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
A dual loop feedforward power amplifier. A dual loop feedforward power amplifier, comprising an input that provides a multicarrier signal; a first feedforward power amplifier; and a second feedforward power amplifier, wherein the first feedforward power amplifier serves as a main amplifier gain block in the second feedforward power amplifier, wherein the first feedforward power amplifier comprises a carrier cancellation loop and a first error amplifier loop, and wherein the second feedforward power amplifier comprises a third loop and a fourth loop that cancel small signal distortions that are not reduced by the first feedforward amplifier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
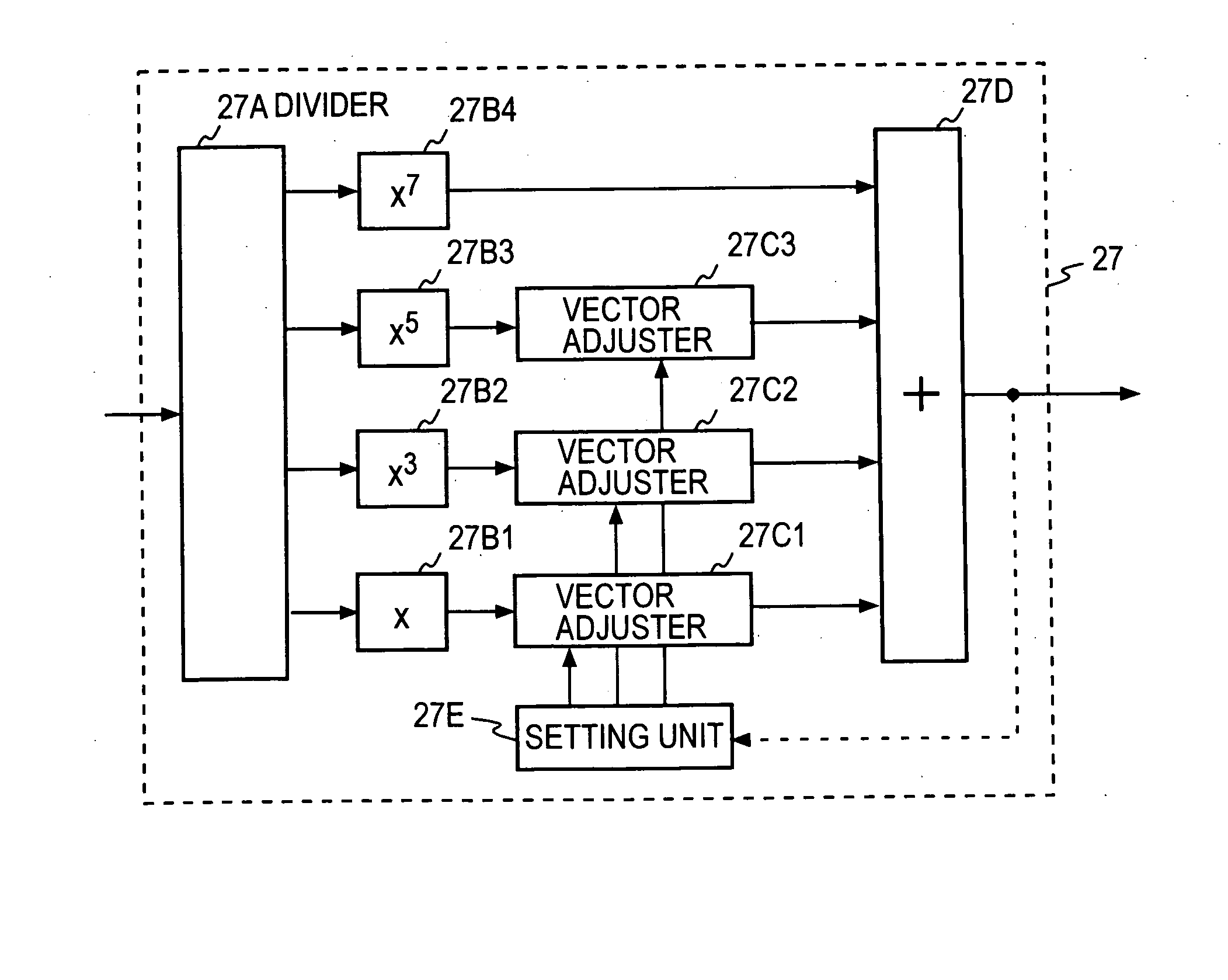
Digital predistorter and predistortion method therefor
InactiveUS20060088124A1Easy to adjustAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLinearityPredistortion
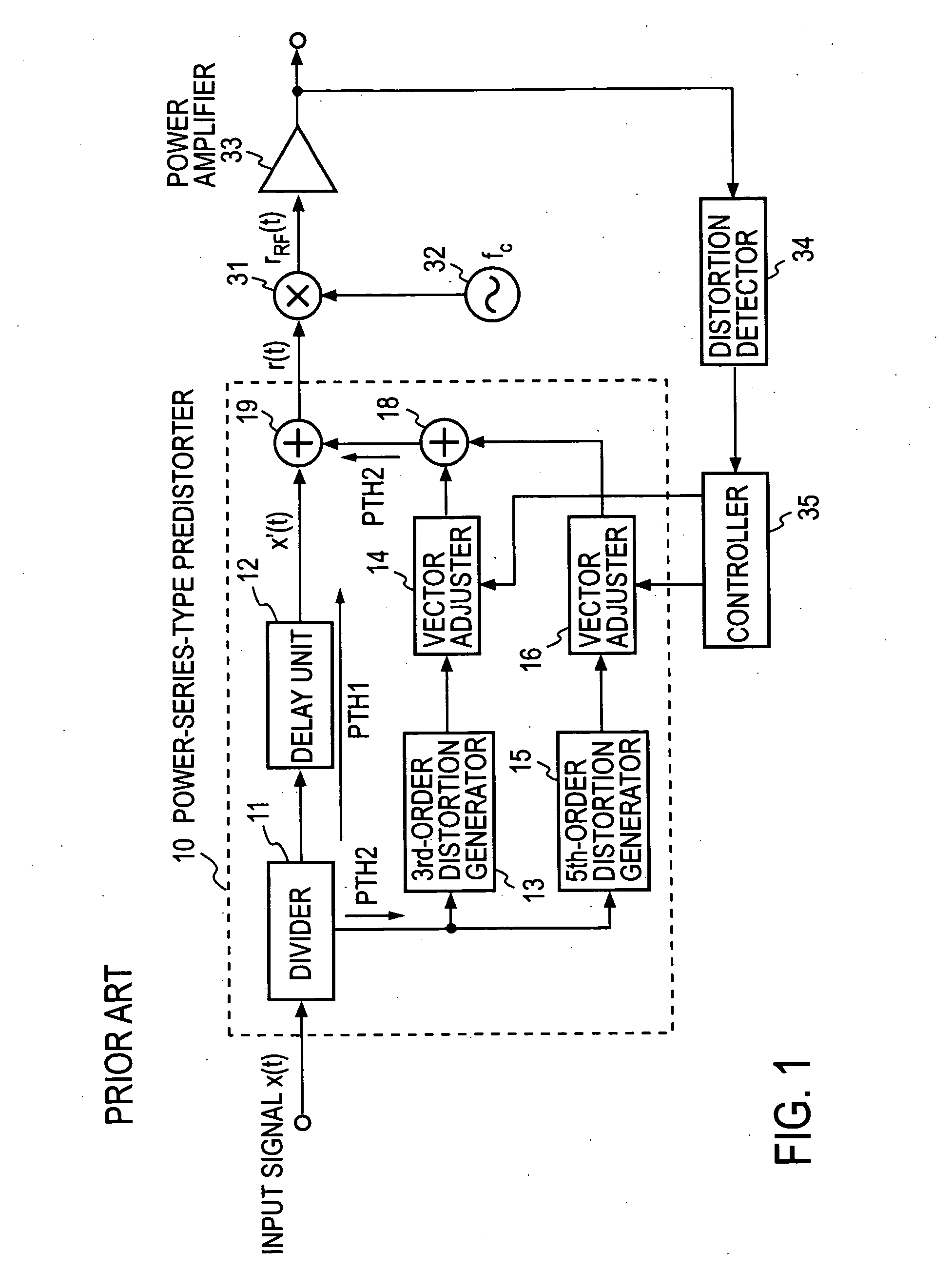
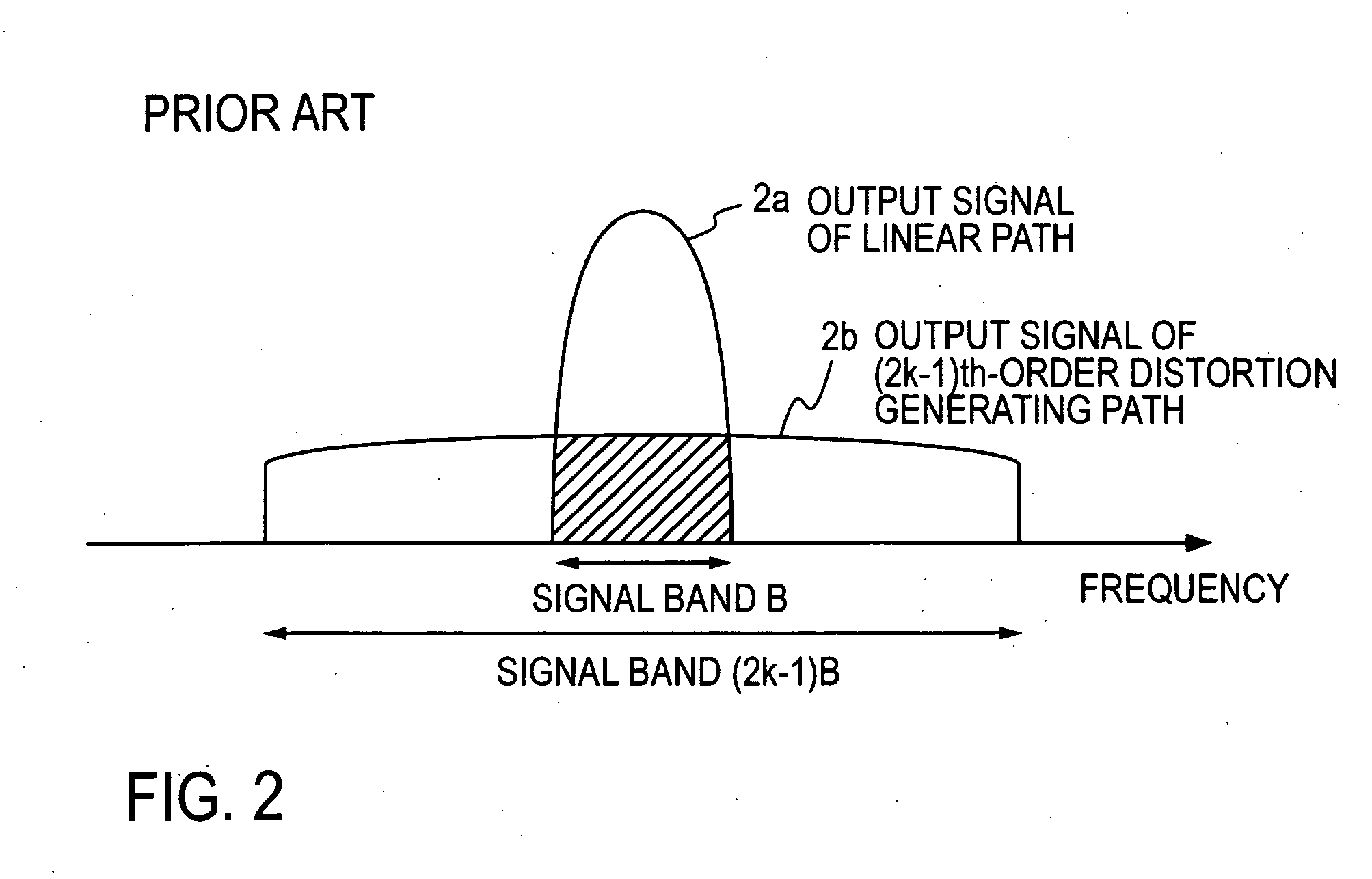
A predistorter includes: a divider that divides an input signal and supplies the divided input signal to a linear transmission path and a distortion generating path; a (2k−1)th-order distortion generator that raises the signal supplied to the distortion generating path to the (2k−1)th power to generate a distortion component; a vector adjuster that adjusts the amplitude and phase of the output of the (2k−1)th-order distortion generator; and an adder that sums up the output of the vector adjuster and the output of the linear transmission path to generate a predistorted signal r(t), in which the (2k−1)th-order distortion generator comprises: a (2k−1)th-order multiplier (27B4) that raises the divided signal to the (2k−1)th power; a lower-than-(2k−1)th-order multiplier (27B3, 27B2, 27B1) that raises the divided signal to the 5th, 3rd and 1st power, respectively; a vector adjuster (27C3, 27C2, 27C1) that adjusts the amplitude and phase of the output of the lower-than-(2k−1)th-order multiplier; and an adder (27D) that sums up the output of the vector adjuster and the output of the (2k−1)th-order multiplier.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com