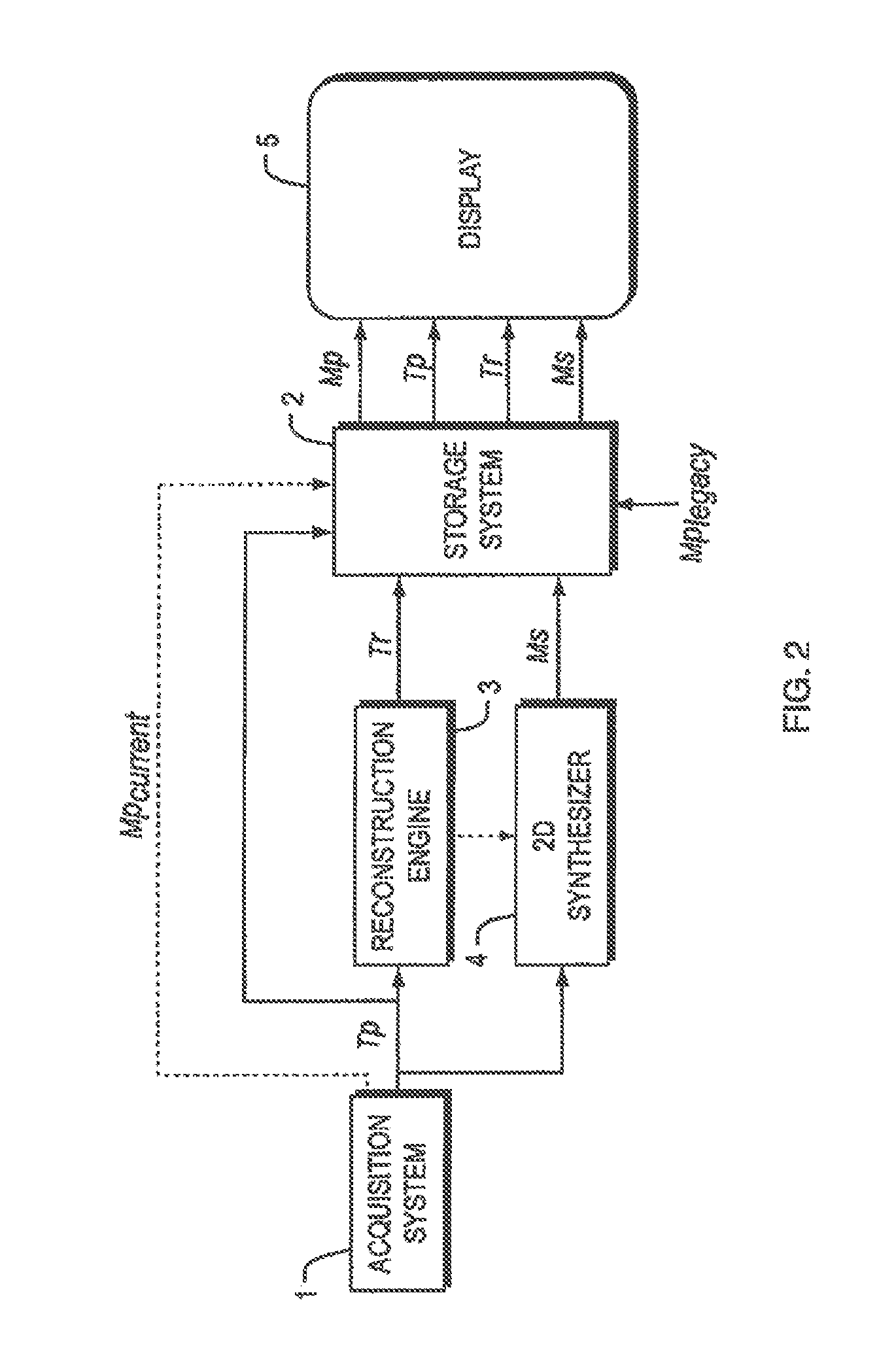
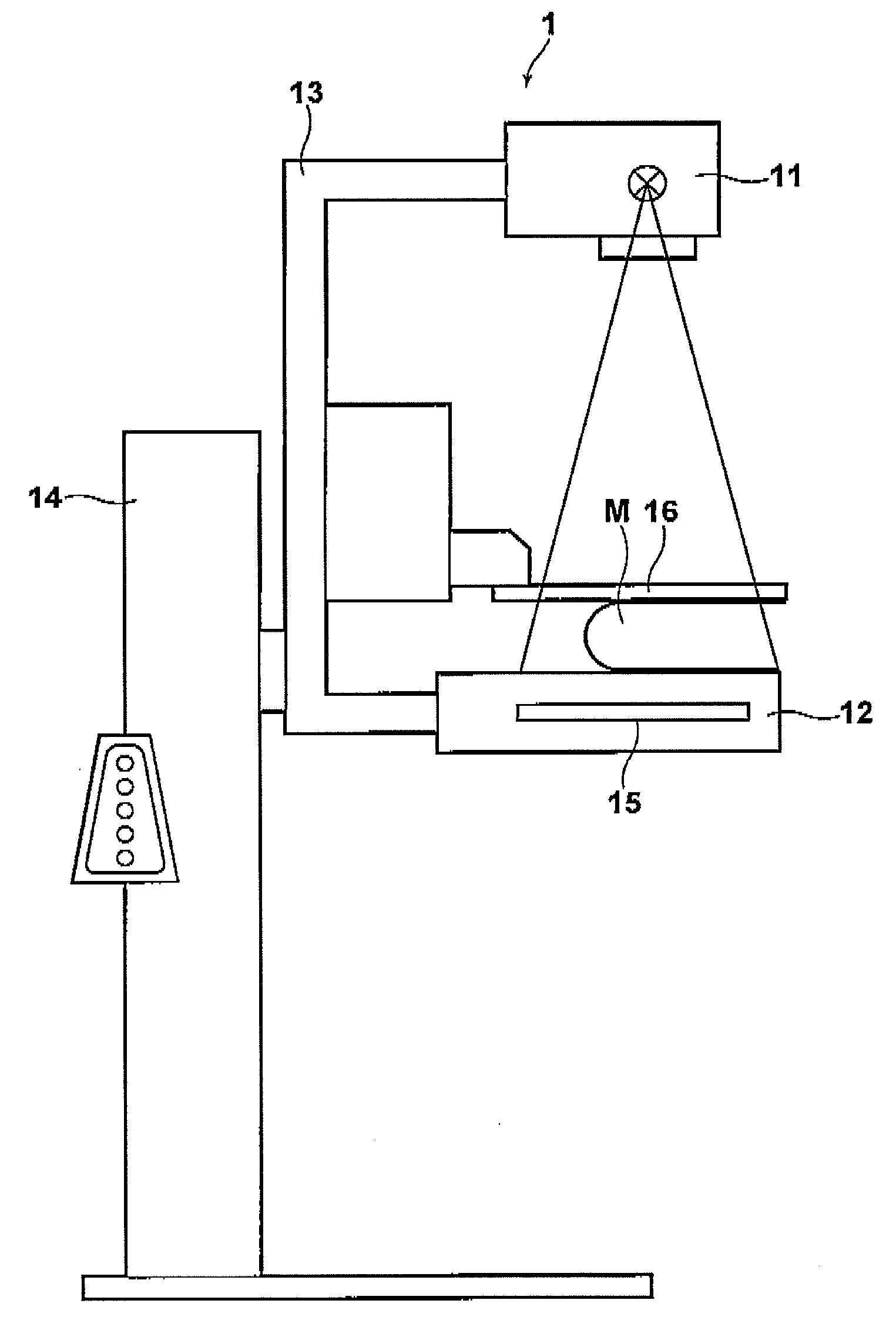
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "Xeromammogram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
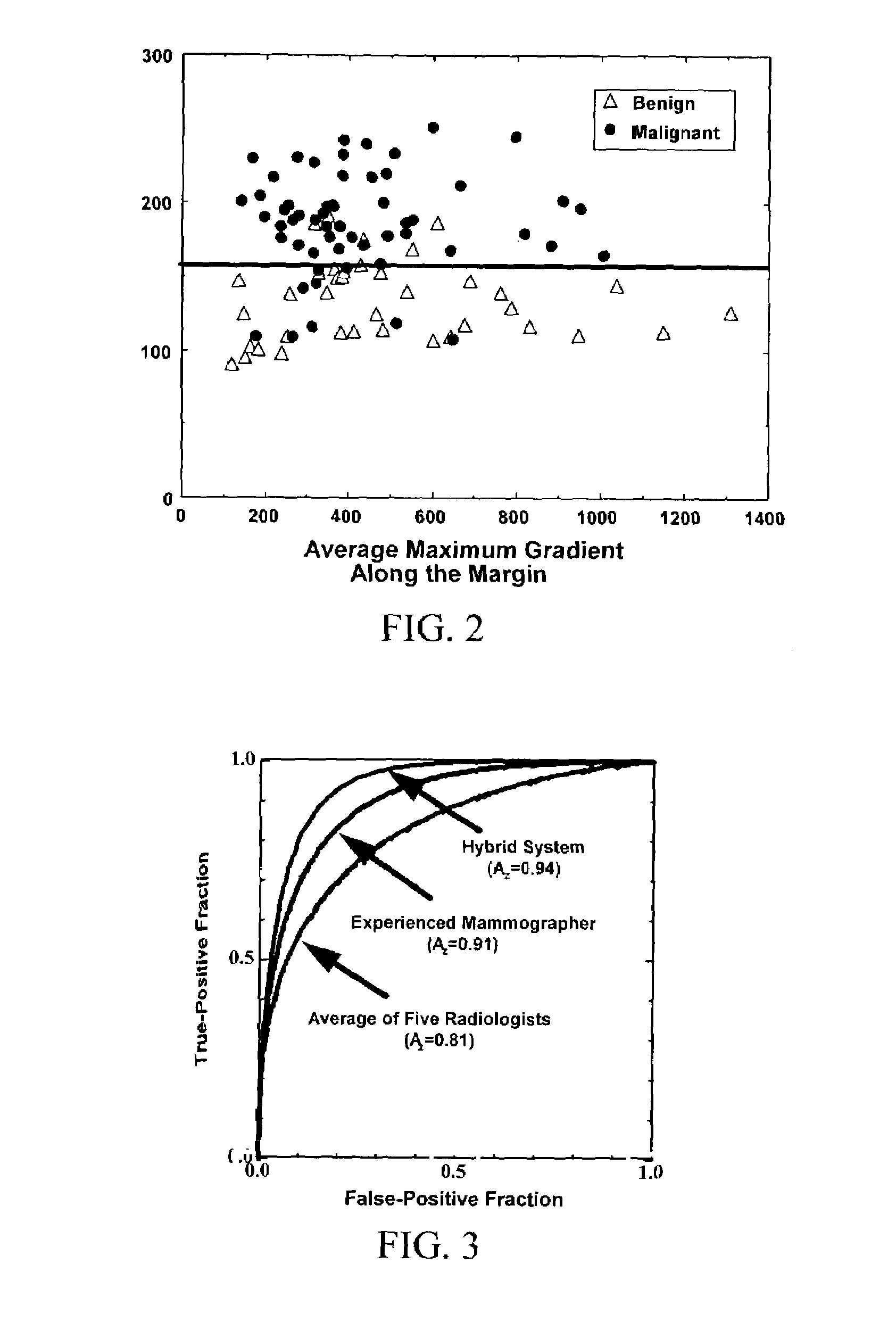
Method and system for risk-modulated diagnosis of disease
ActiveUS7123762B2Well representedEasy diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementRadiologyLesion feature
A method of calculating a disease assessment by analyzing a medical image, comprising (1) extracting at least one lesion feature value from the medical image; (2) extracting at least one risk feature value from the medical image; and (3) determining the disease assessment based on the at least one lesion feature value and the at least one risk feature value. The method employs lesion characterization for characterizing the lesion, and risk assessment based on the lesion's surroundings, i.e., the environment local and distal to the lesion. Computerized methods both characterize mammographic lesions and assess the breast parenchymal pattern on mammograms, resulting in improved characterization of lesions for specific subpopulations, combining the benefits of both techniques.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
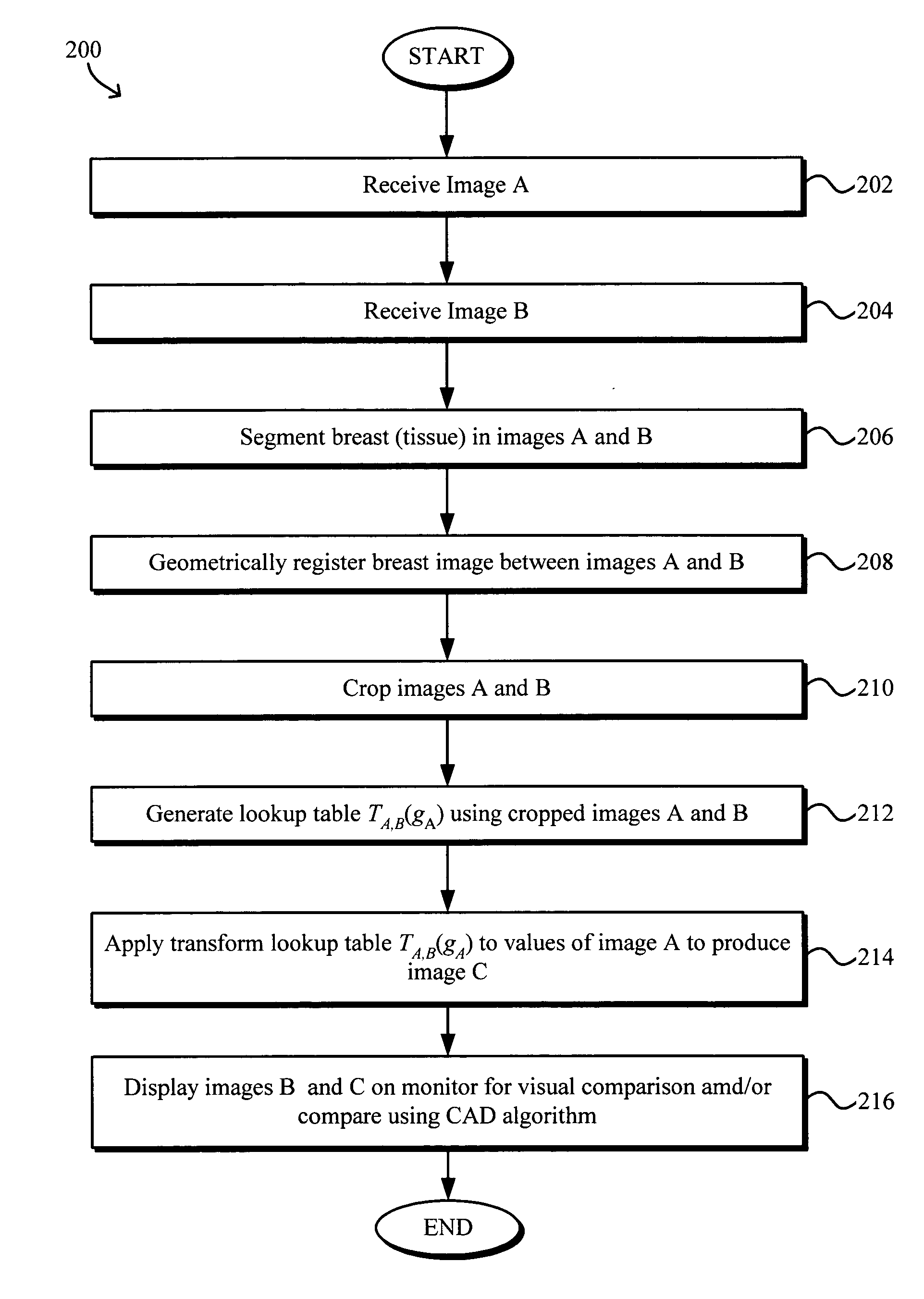
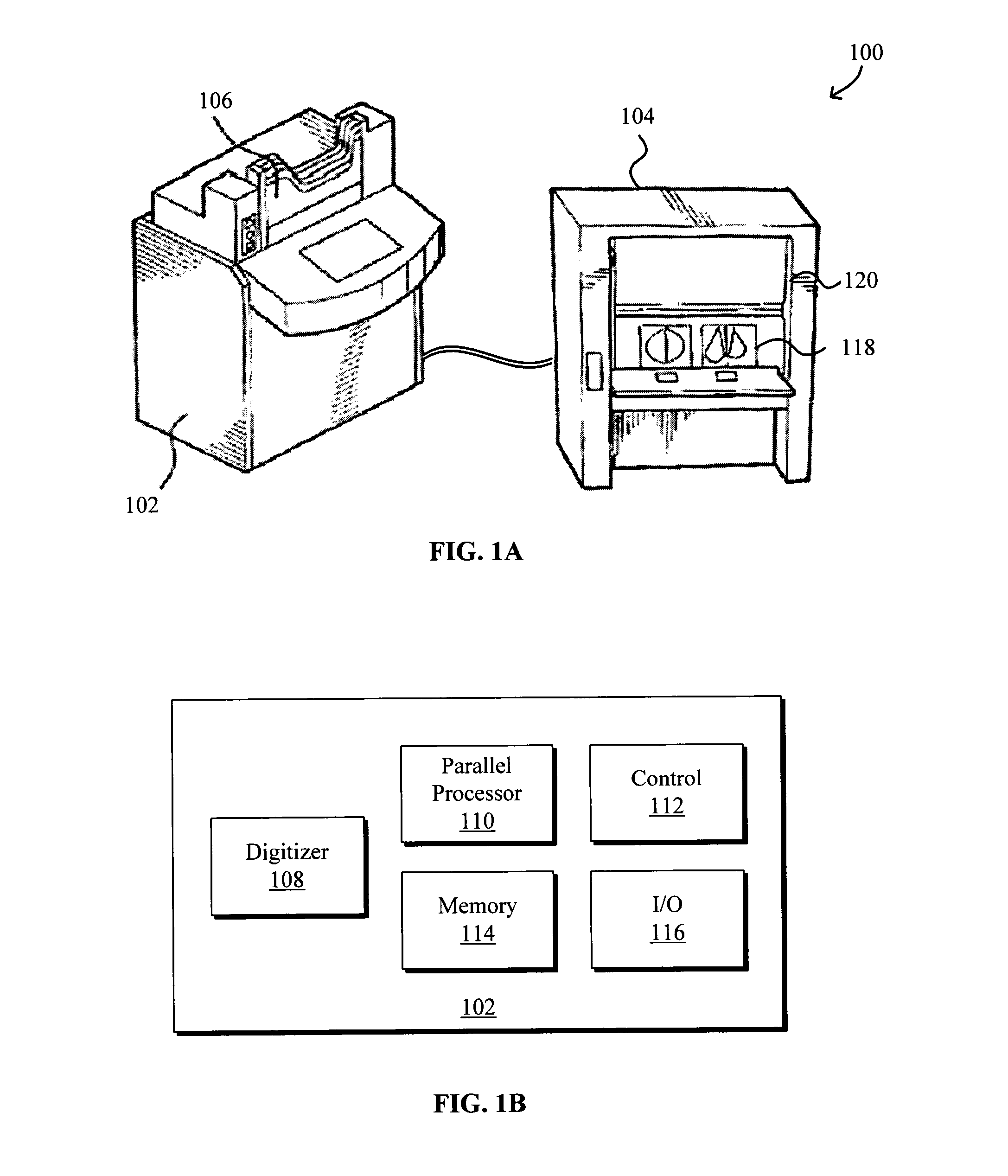
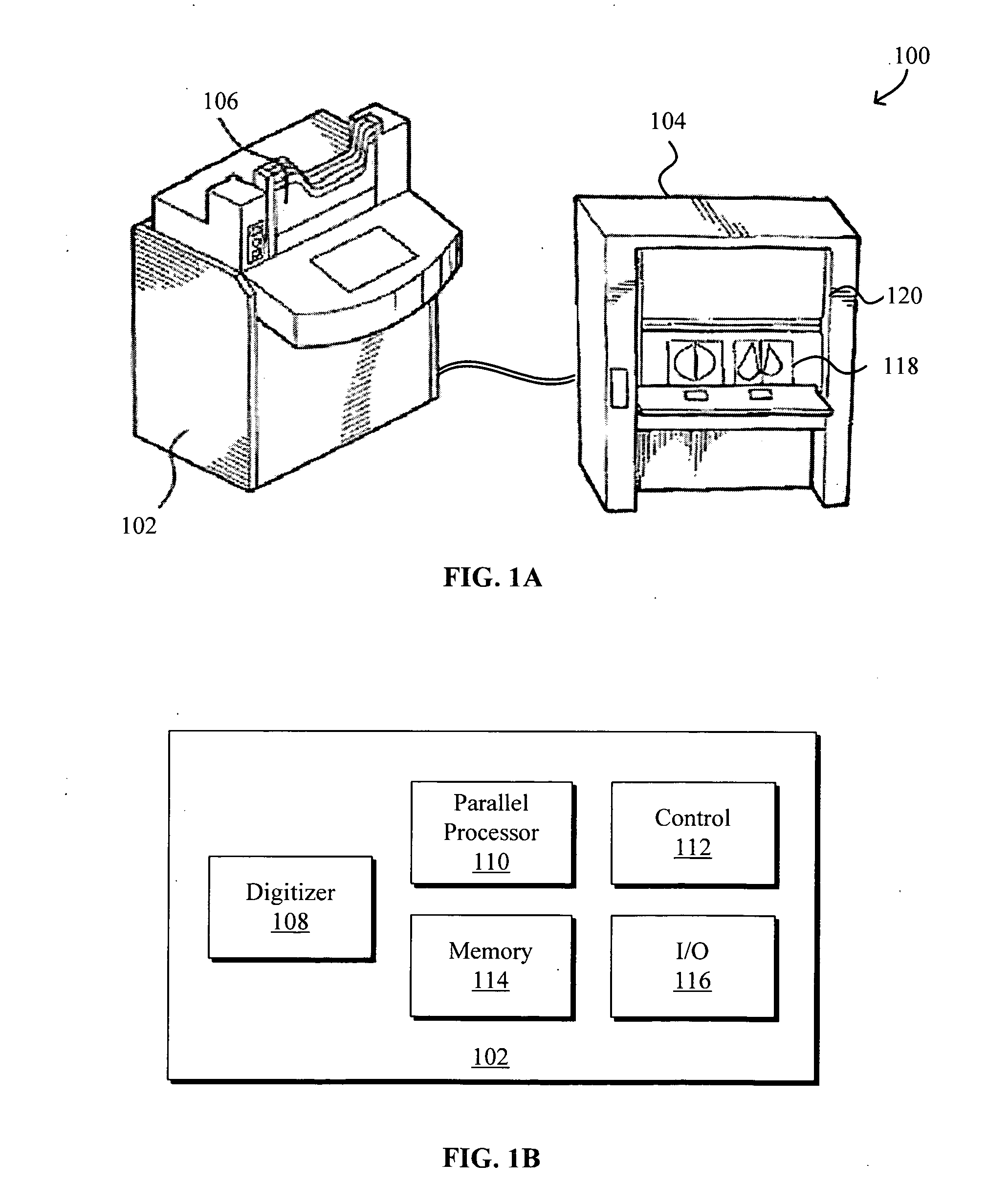
Model-based grayscale registration of medical images
ActiveUS20050013471A1Increase speedImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisPixel value differenceVisual perception
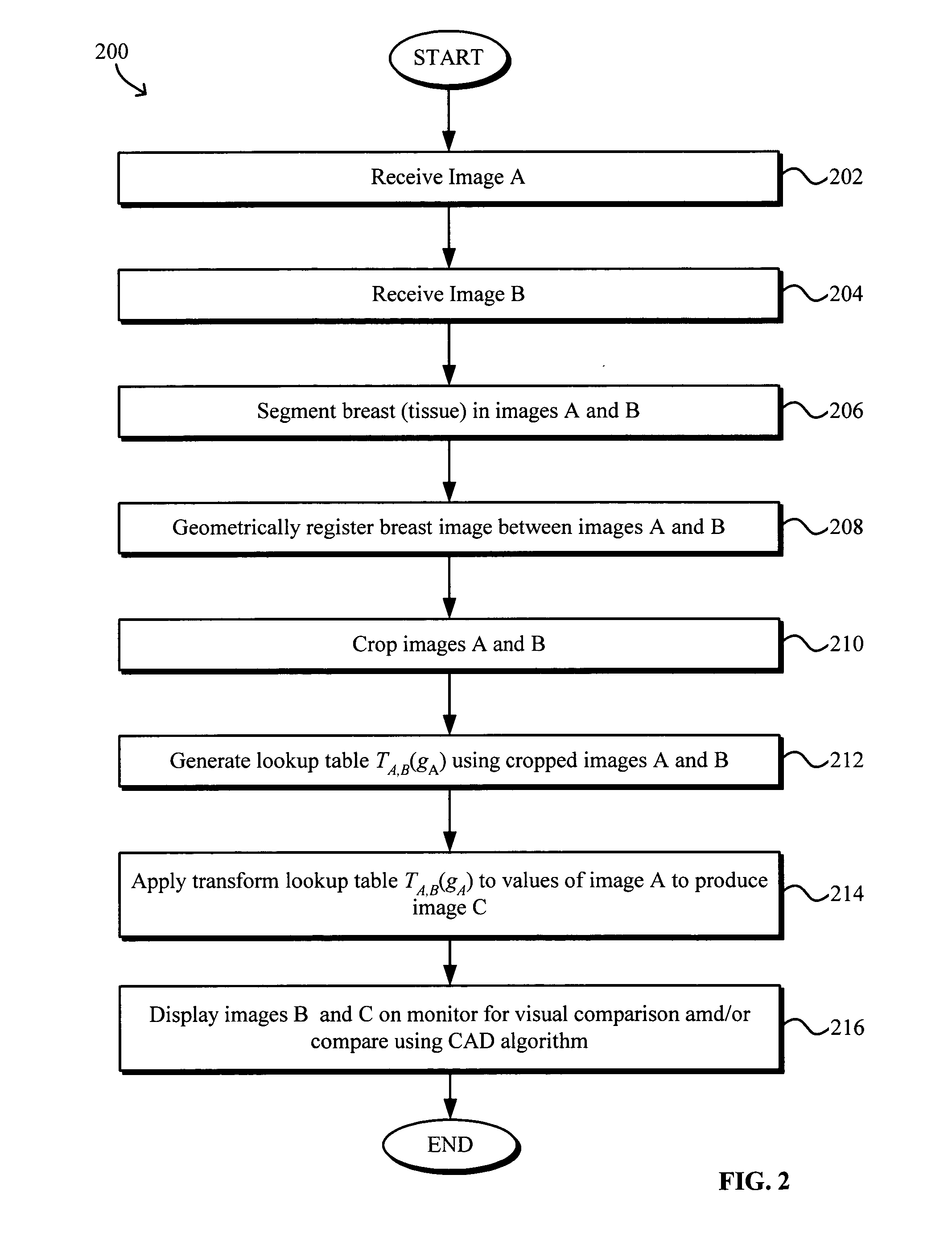
Numerical image processing of two or more medical images to provide grayscale registration thereof is described, the numerical image processing algorithms being based at least in part on a model of medical image acquisition. The grayscale registered temporal images may then be displayed for visual comparison by a clinician and / or further processed by a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system for detection of medical abnormalities therein. A parametric method includes spatially registering two images and performing gray scale registration of the images. A parametric transform model, e.g., analog to analog, digital to digital, analog to digital, or digital to analog model, is selected based on the image acquisition method(s) of the images, i.e., digital or analog / film. Gray scale registration involves generating a joint pixel value histogram from the two images, statistically fitting parameters of the transform model to the joint histogram, generating a lookup table, and using the lookup table to transform and register pixel values of one image to the pixel values of the other image. The models take into account the most relevant image acquisition parameters that influence pixel value differences between images, e.g., tissue compression, incident radiation intensity, exposure time, film and digitizer characteristic curves for analog image, and digital detector response for digital image. The method facilitates temporal comparisons of medical images such as mammograms and / or comparisons of analog with digital images.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
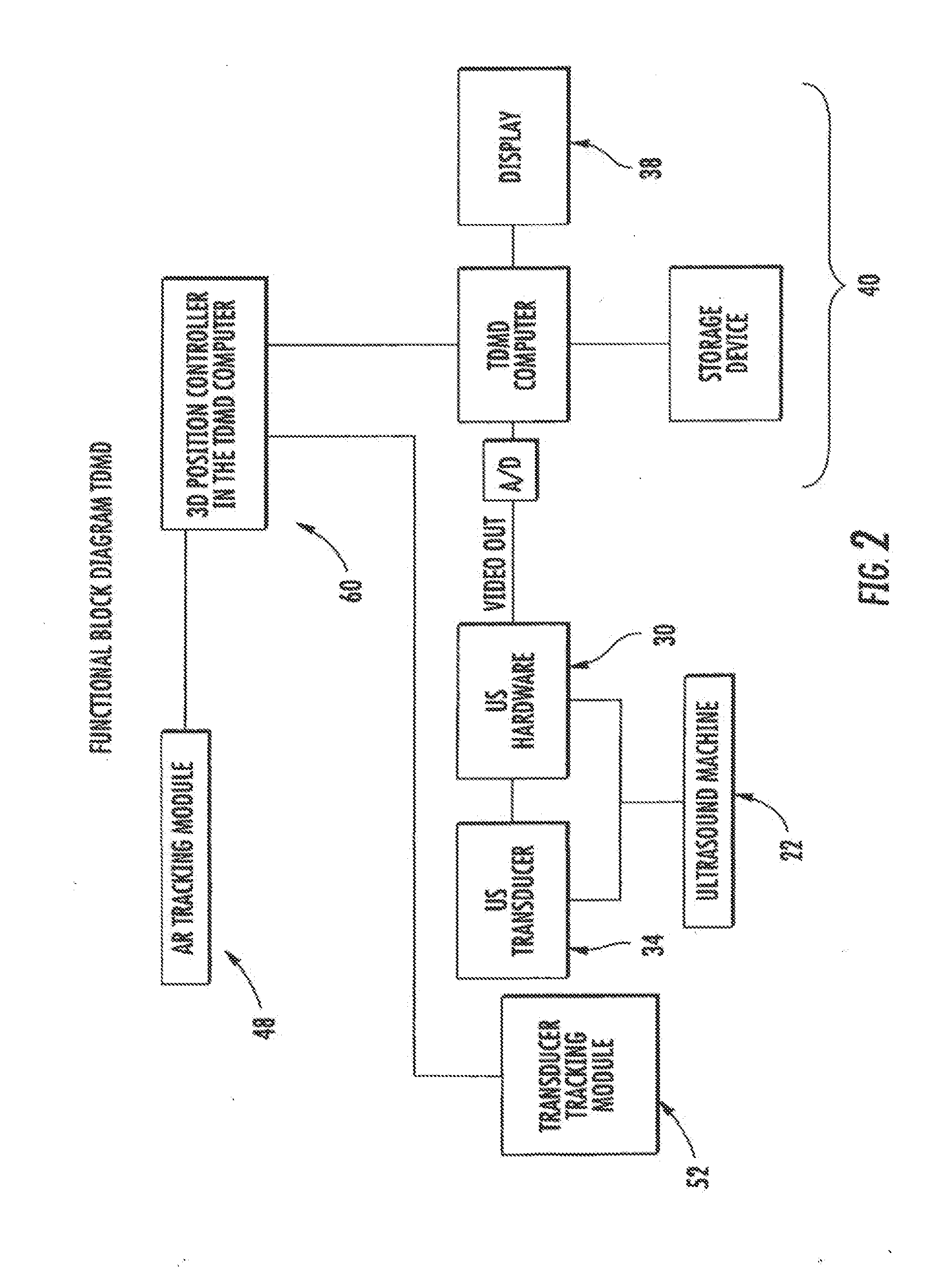
Three dimensional mapping display system for diagnostic ultrasound machines and method
ActiveUS20090124906A1Shorten the timeTime-consuming to eliminateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLocal control/monitoringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityUltrasonic sensor
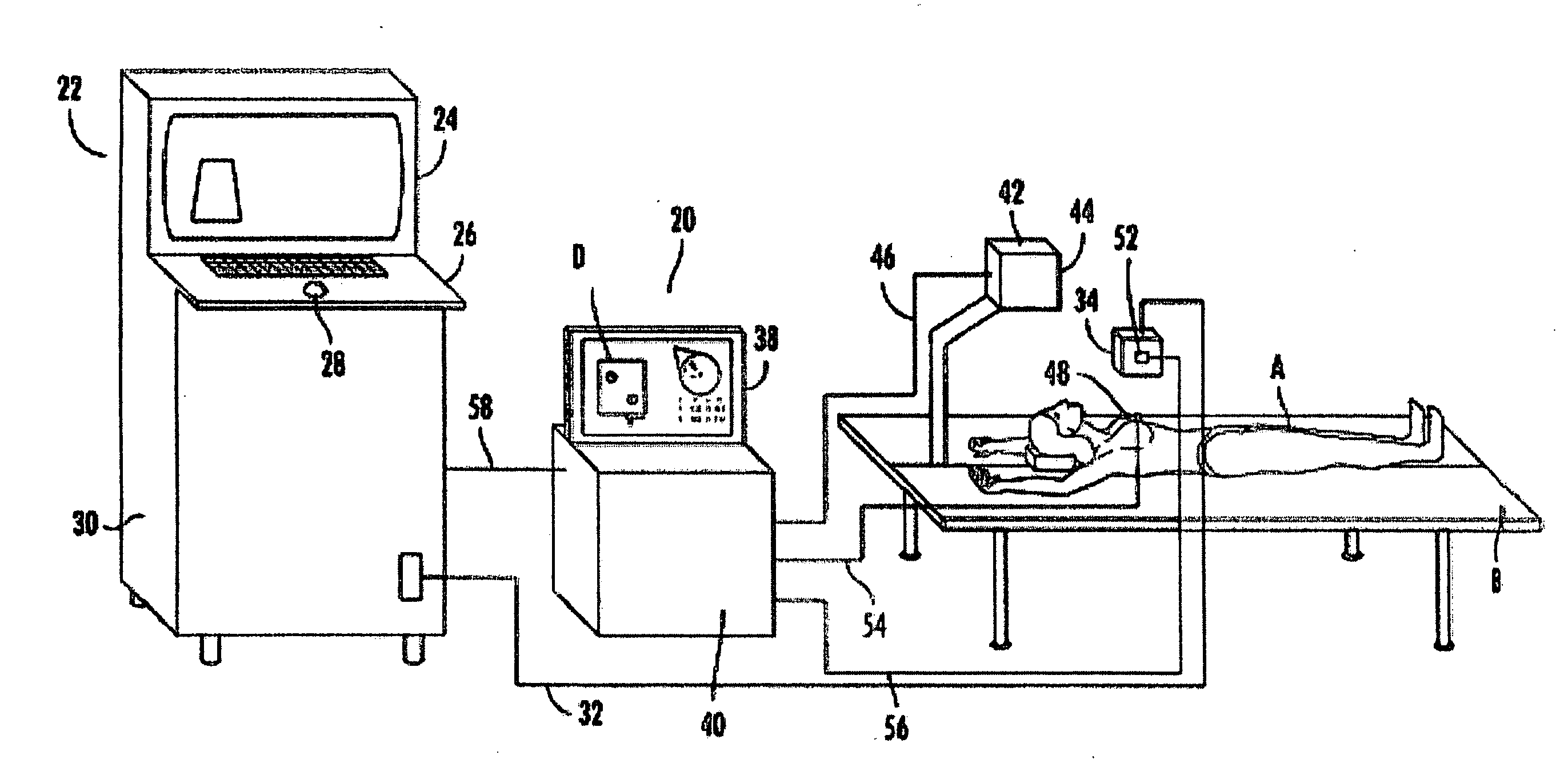
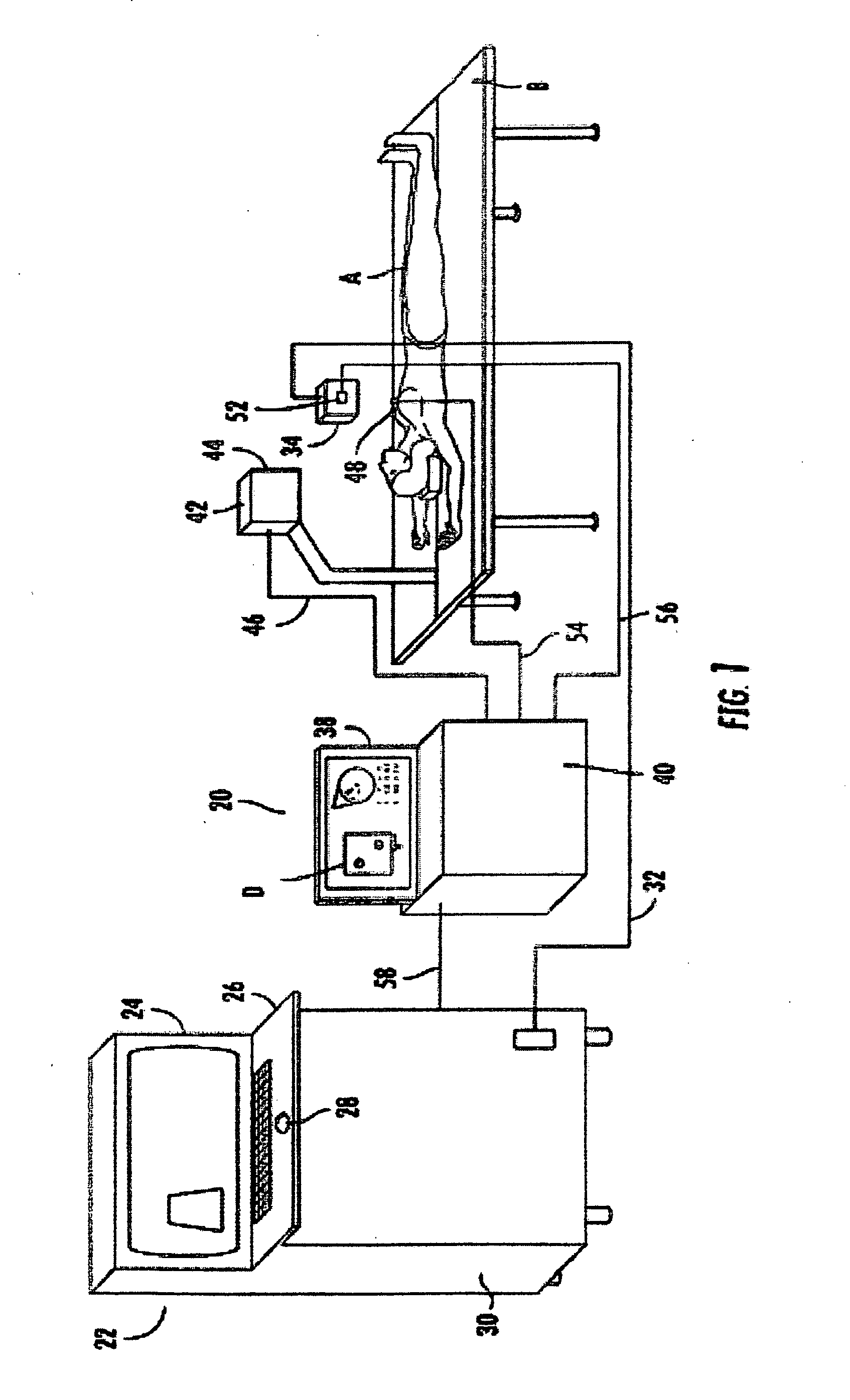
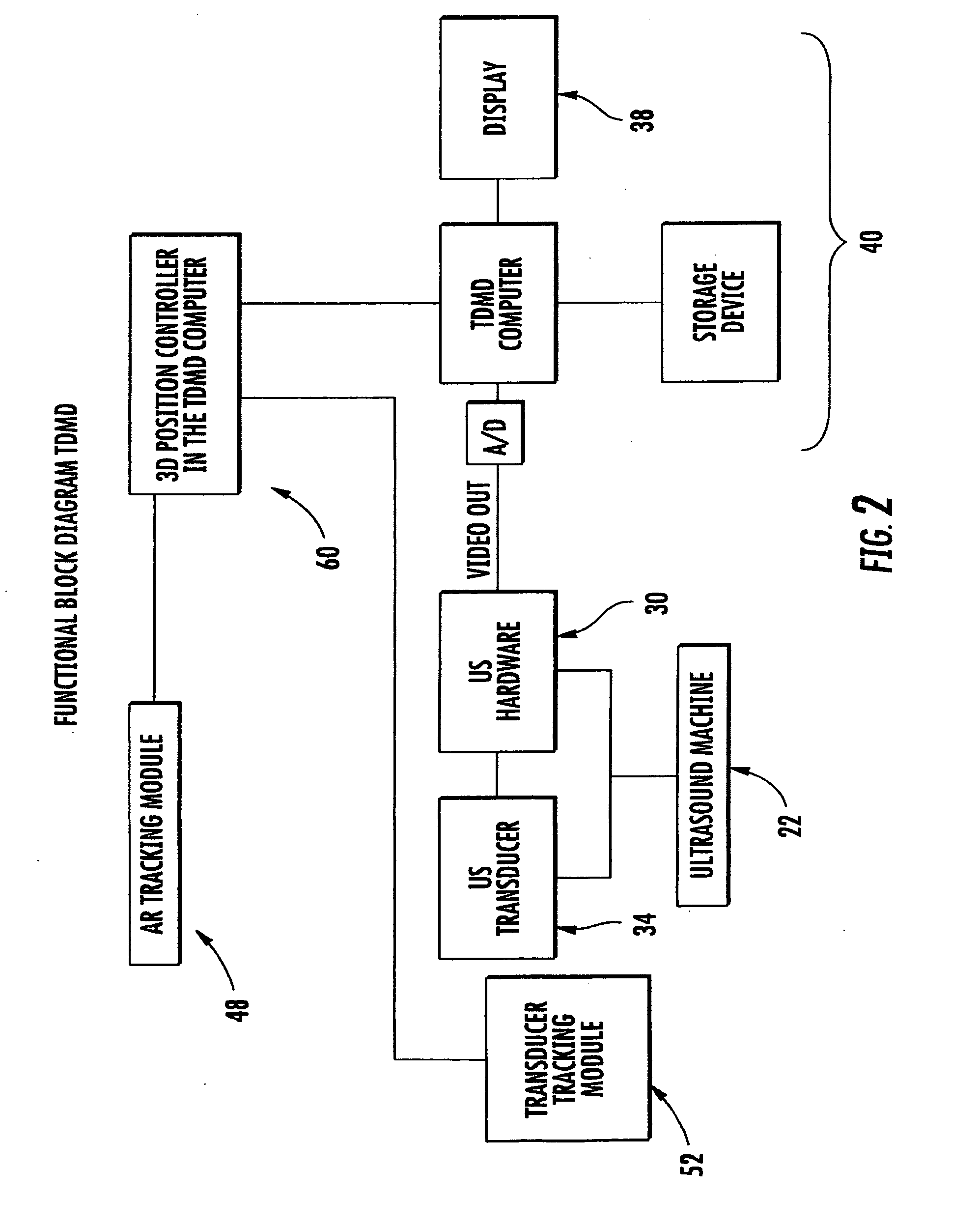
An apparatus, system, and method where the ultrasound transducer position registration is automated, calculates the position of each pixel in the ultrasound image in reference to the predetermined anatomical reference points (AR) and can store the information on demand. The graphic interface associated with the ultrasound image allows for the instant display of selected targets position coordinates relative to anatomical reference points, in the ultrasound images. This system would significantly reduce the ultrasound examination time, by eliminating the time consuming manual labeling of images and speeding up the target finding at subsequent examinations, enhance correlation capability with other diagnostic imaging modalities like CT scans, MRI, mammograms, decrease human errors and fatigue, provide an easy, uniform, method of communicating the target position among healthcare providers.
Owner:METRITRACK
X-ray image processing
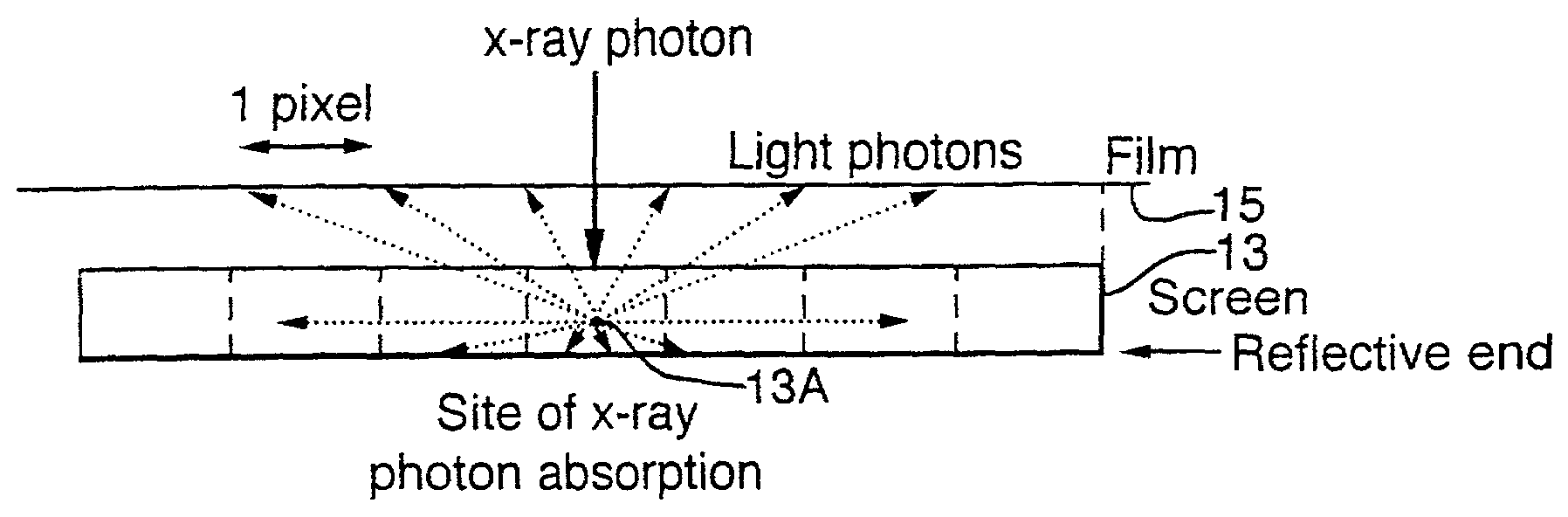
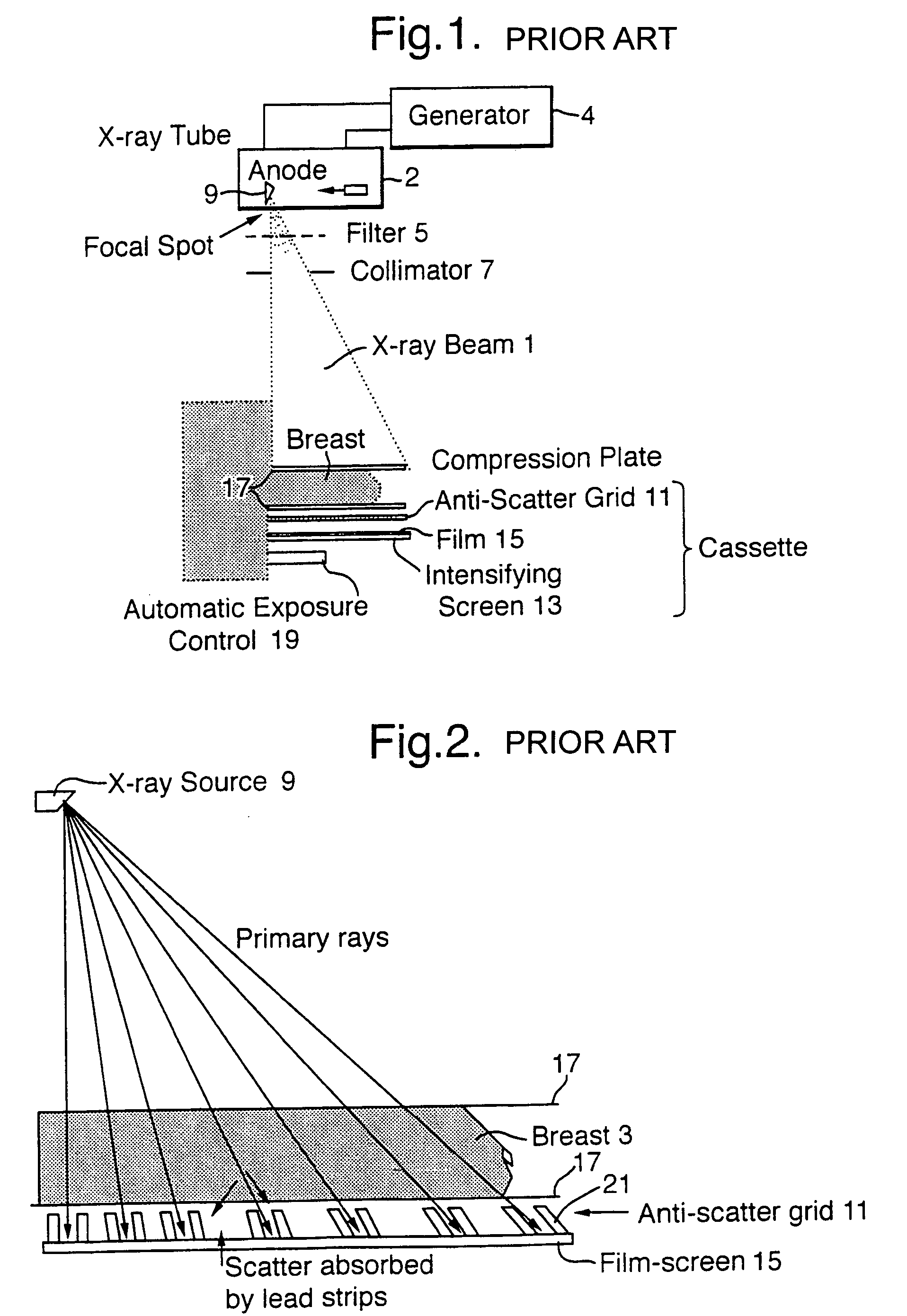
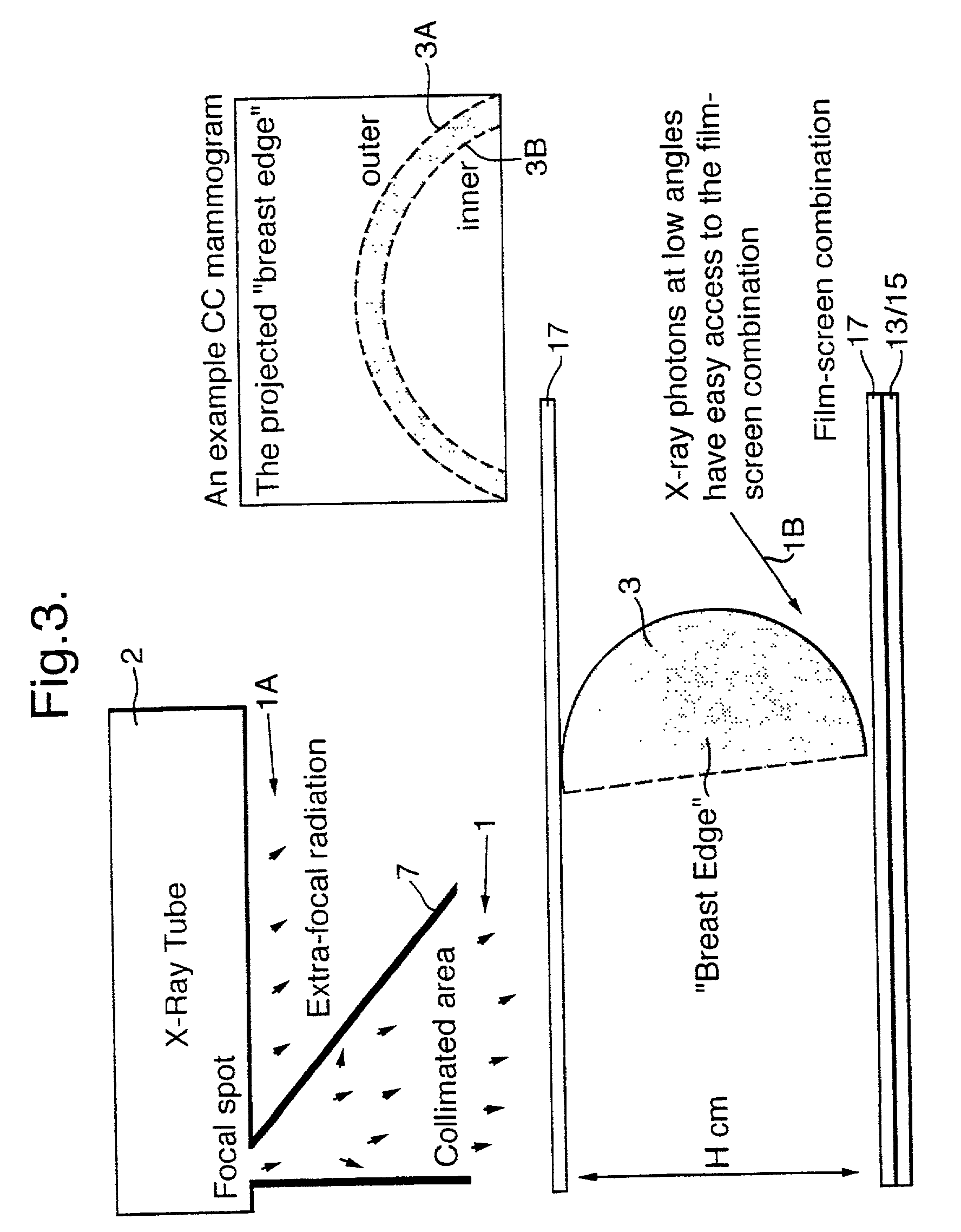
A method of enhancing and normalizing x-ray images, particularly mammograms, by correcting the image for digitizer blur, glare from the intensifying screen and the anode-heel effect. The method also allows the calculation of the compressed thickness of the imaged breast and calculation of the contribution to the mammograms of the extra focal radiation. The correction of the image for glare from the intensifying screen allows the detection of noise, such as film shot noise, in the image, and in particular the differentiation between such noise and microcalcifications.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
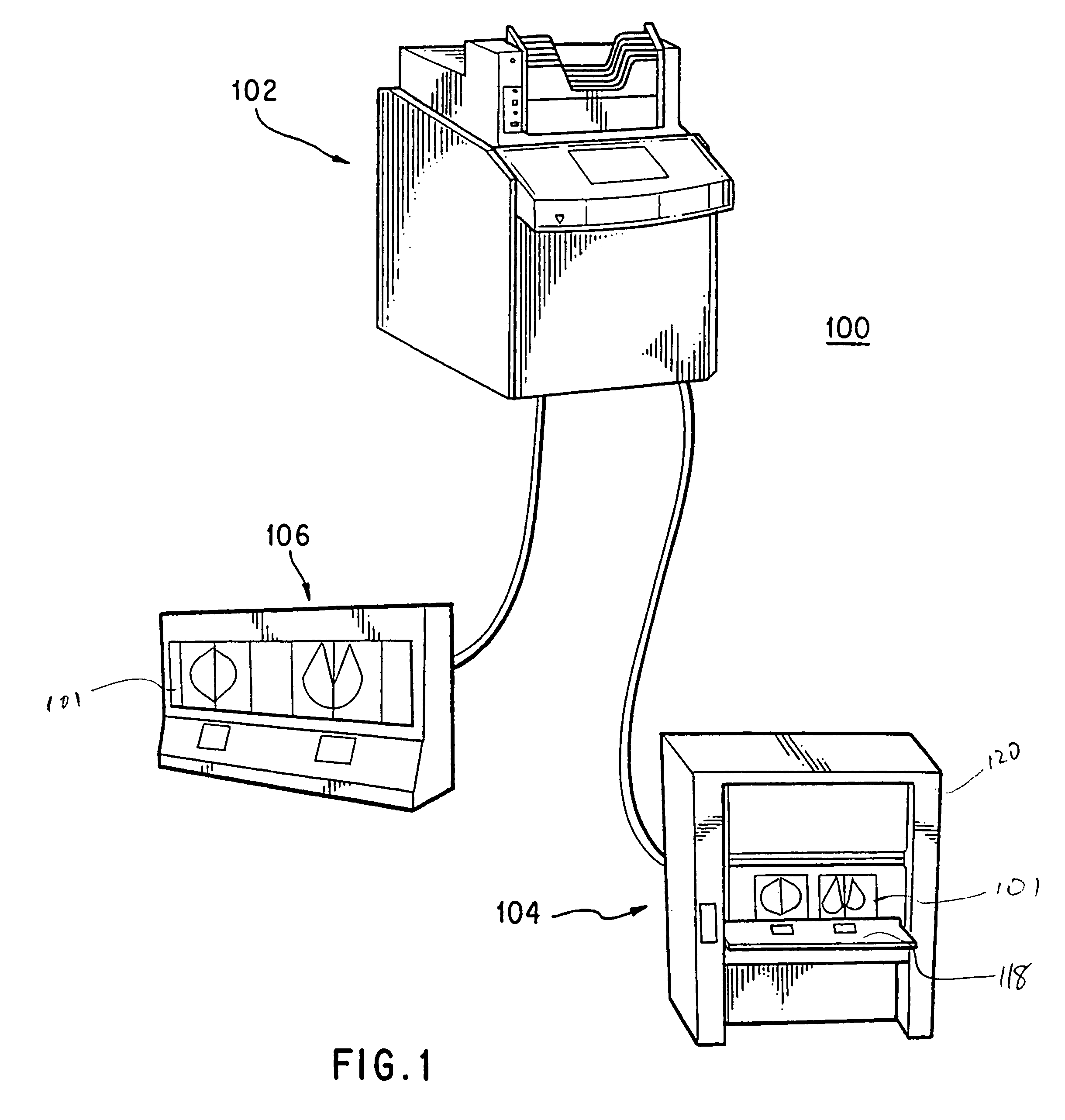
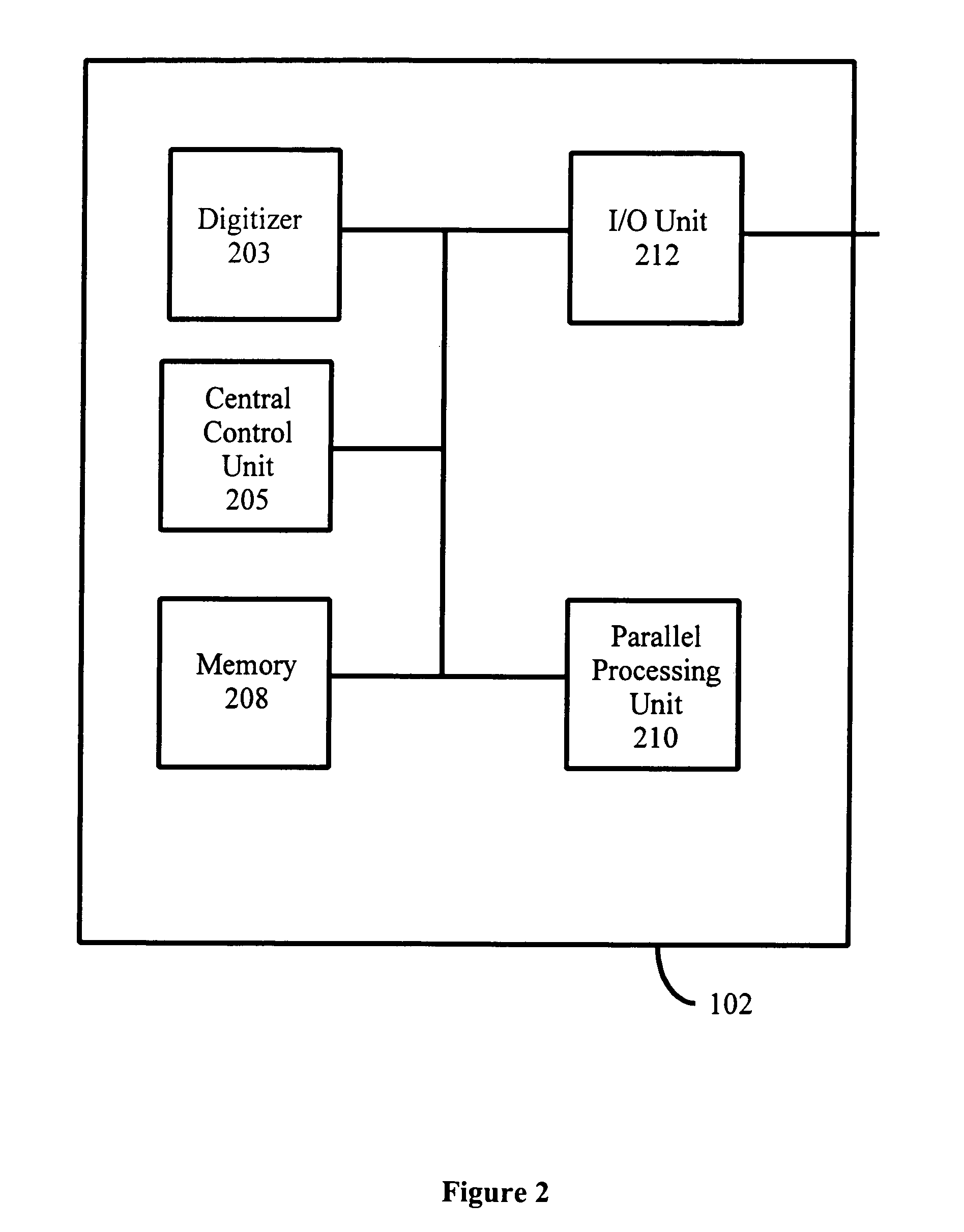
Method and system for automatic identification and orientation of medical images
InactiveUS7146031B1Reduce errorsShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammogramDisplay device
A method and system for computer-aided detection of abnormal lesions in digital mammograms is described, wherein digital films are processed using an automated and computerized method of detecting the order and orientation of a set of films. In one embodiment, anatomic features are used to detect the order, orientation and identification of a film series. In another embodiment of the invention, a technologist feeds films into the system in any order and orientation. After processing, the system provides an output on a display device to a radiologist that is in an order and orientation preferred by the radiologist. In yet another embodiment of the invention, films from one case are distinguished from films of another case. In this manner and through the use of a bulk loader, a large number of films can be stacked together and fed into the system at one time.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
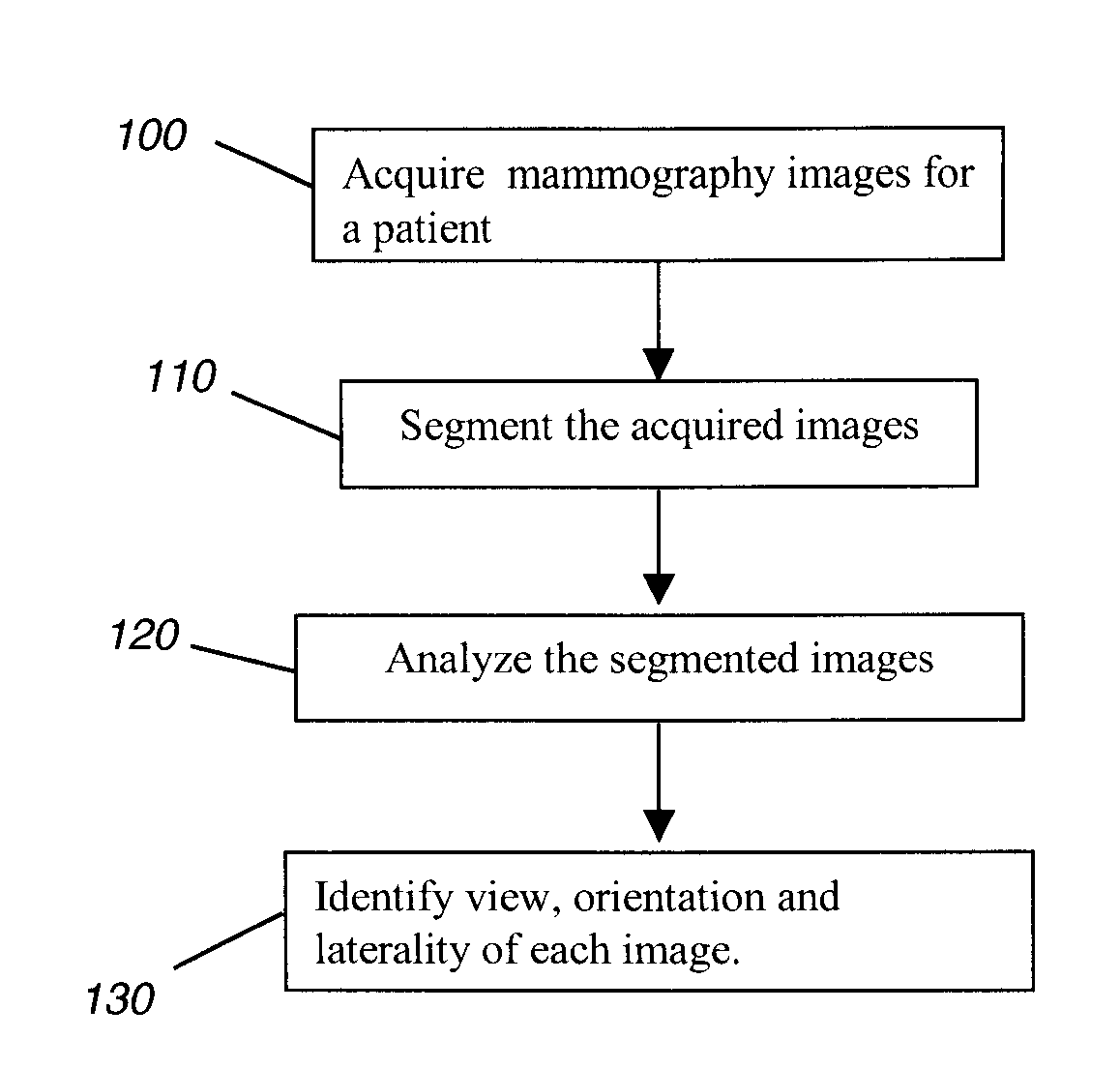
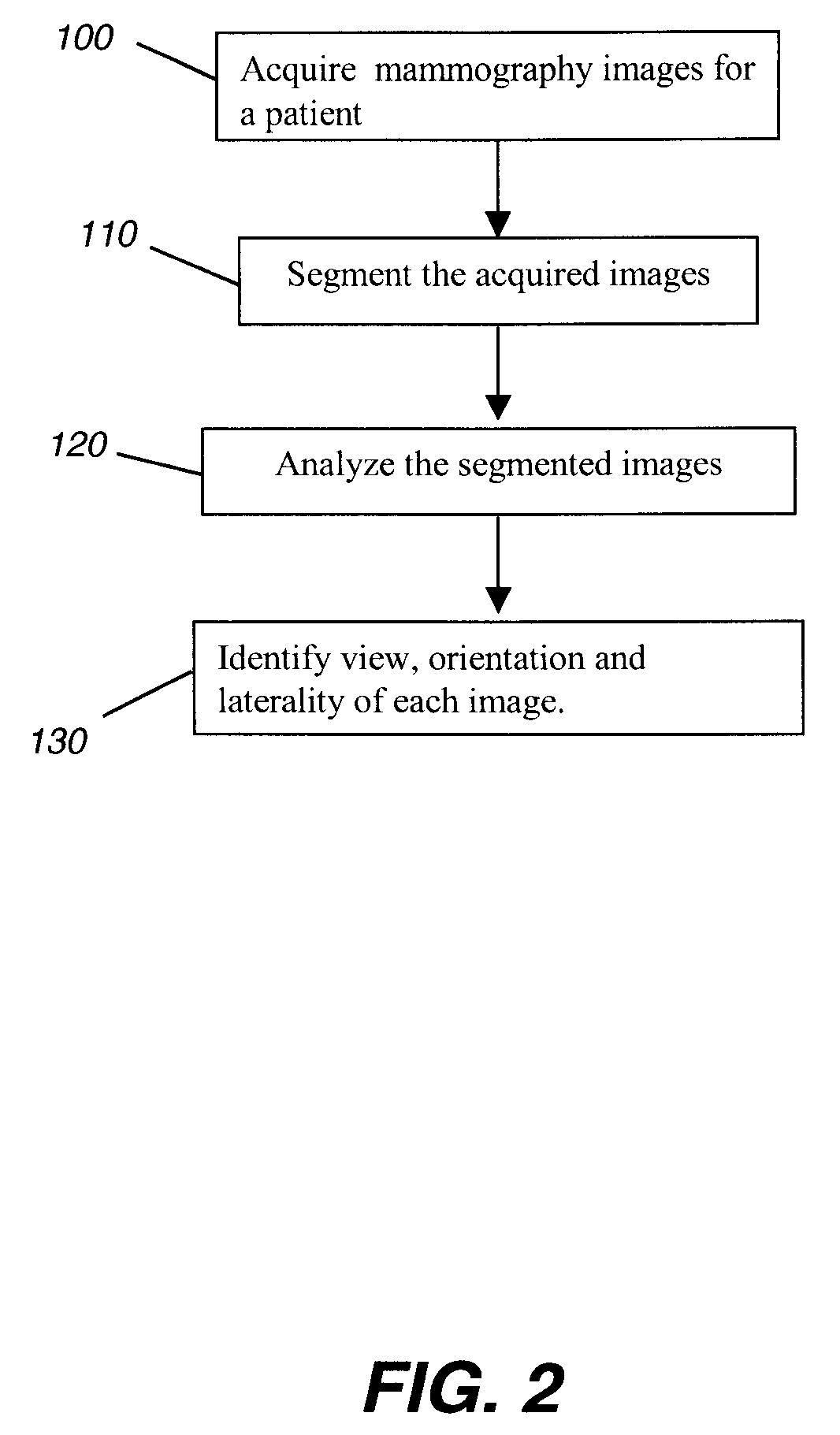
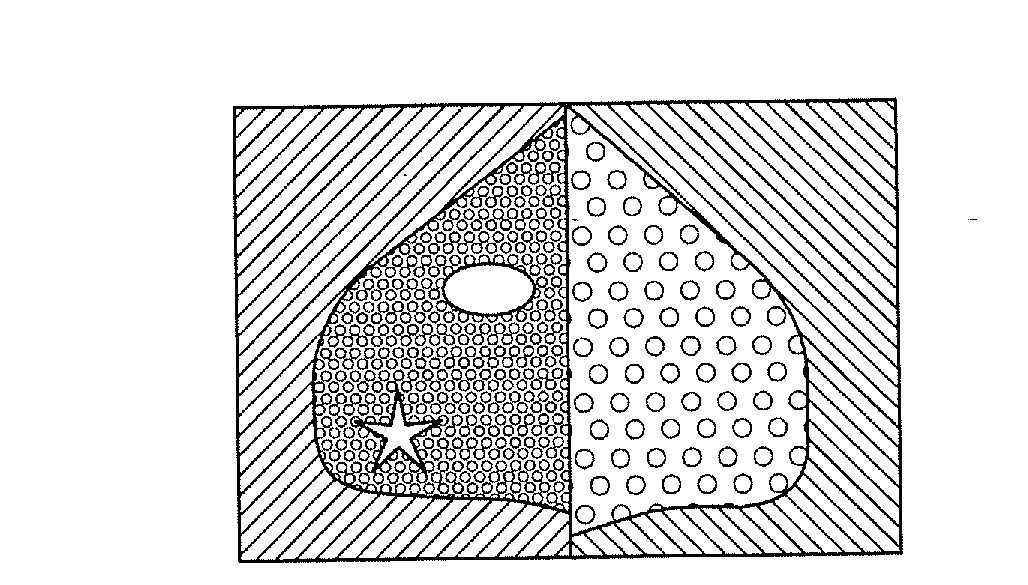
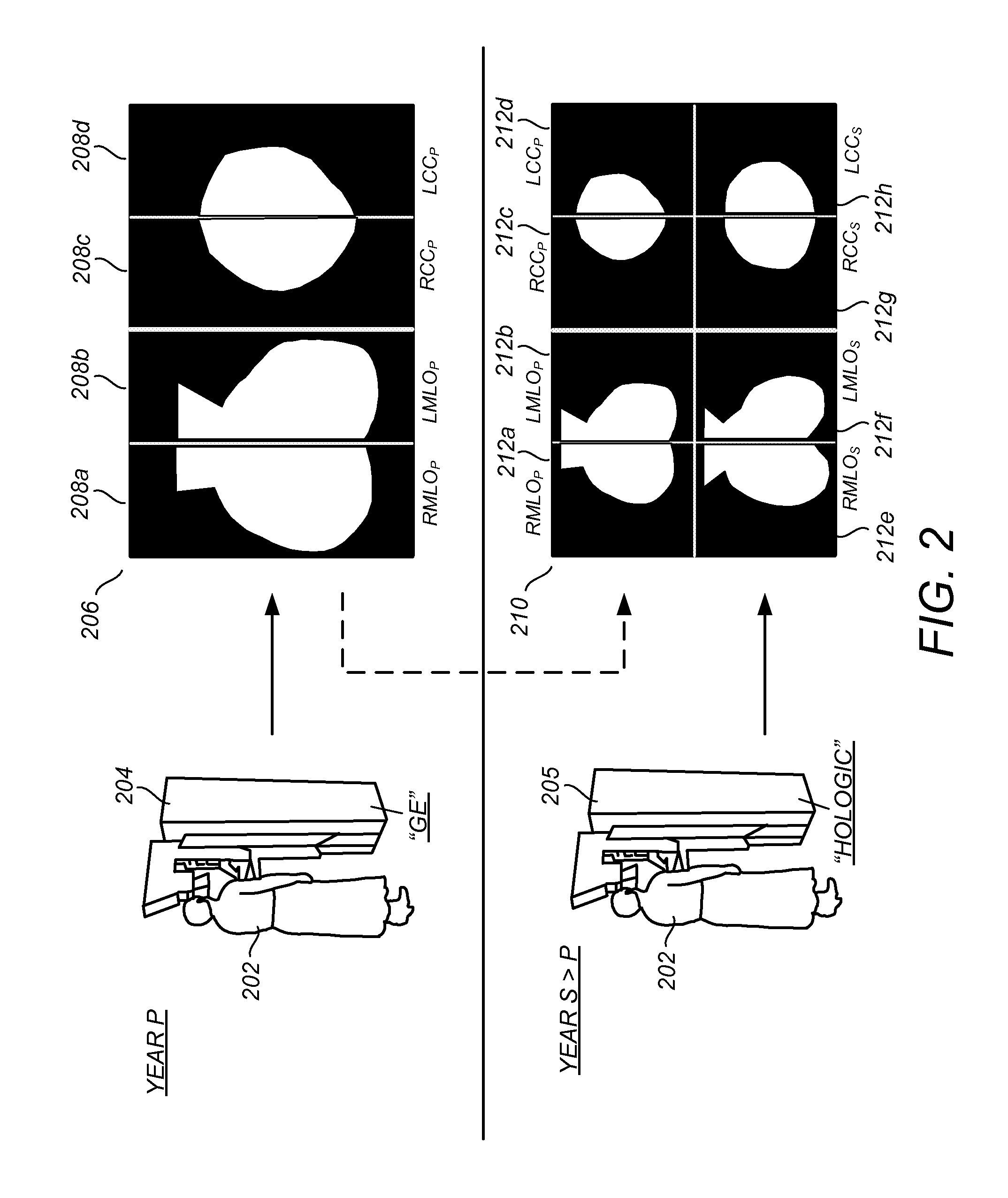
Determining mammographic image view and laterality
A method for displaying a mammography image. Digital data of the mammography image is obtained. The mammography image is segmented to identify at least a first diagnostically relevant region comprising an image of the breast tissue and a second diagnostically relevant region. A view type is assigned for the image, either cranio-caudal or medio-lateral oblique view, according to a symmetry index calculated from the segmented first diagnostically relevant region. Right or left laterality is assigned to the image according to a laterality feature calculated according to the relative position of at least the second diagnostically relevant region within the image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Synchronized viewing of tomosynthesis and/or mammograms
ActiveUS20080152086A1Facilitate diagnostic reviewCathode-ray tube indicatorsMammographyTomosynthesisData set
Systems and methods that visualize medical data having image rendering circuits configured to substantially concurrently display a first image view of breast tissue using a stack of primary tomosynthesis image data and a second image view of breast tissue using a reference image data set, the second image view rendered from at least one of a 2D X-ray mammogram reference image data set or a reference stack of tomosynthesis image data. The first view is visualized based on: (a) anatomical and / or geometric position properties of the reference image data set of the patient; (b) properties of a current view of the reference image data set of the patient; or (c) anatomical and / or geometric position properties of the reference image data set and properties of a current view of the reference image data set.
Owner:PHILIPS AB
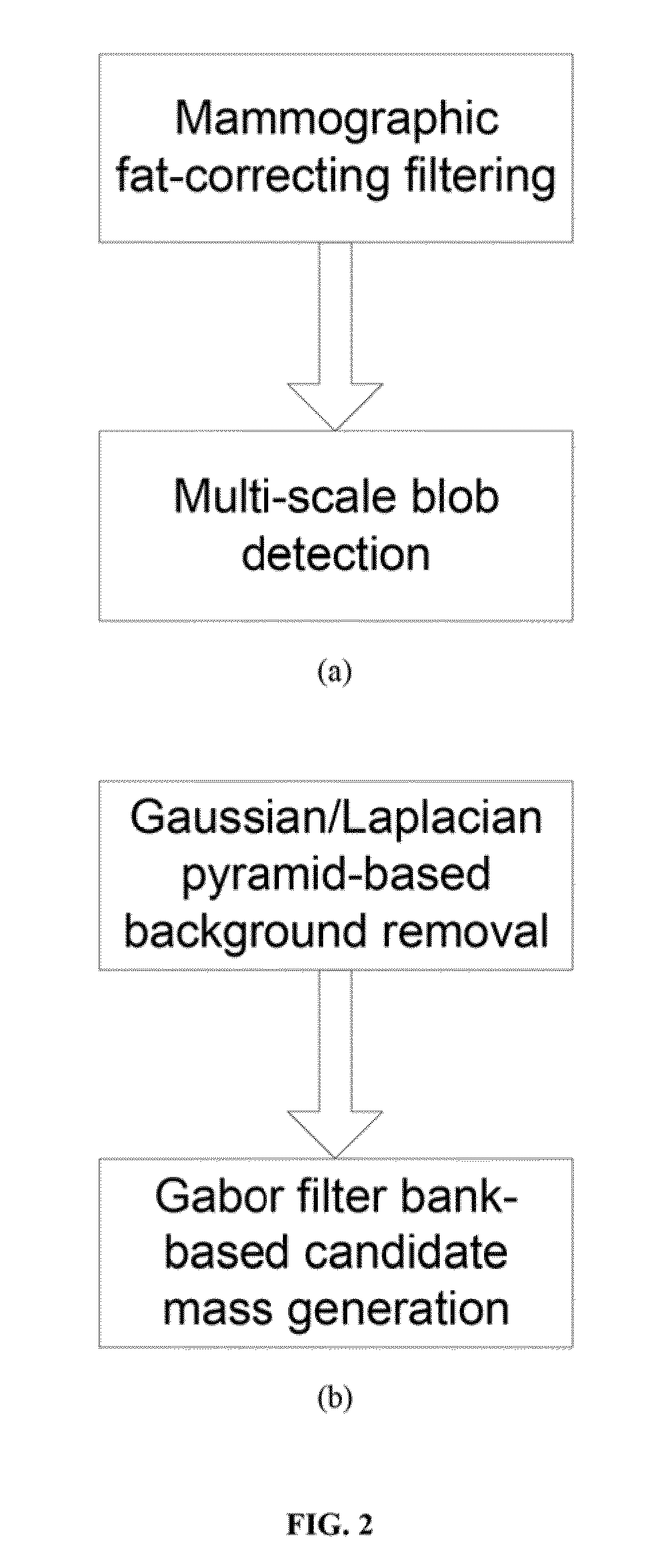
Method for Mass Candidate Detection and Segmentation in Digital Mammograms
A basic component of Computer-Aided Detection systems for digital mammography comprises generating candidate mass locations suitable for further analysis. A component is described that relies on filtering either the background image or the complementary foreground mammographic detail by a purely signal processing method on the one hand or a processing method based on a physical model on the other hand. The different steps of the signal processing approach consist of band-pass filtering the image by one or more band pass filters, multidimensional clustering, iso-contouring of the distance to centroid of the one or more filtered values, and finally candidate generation and segmentation by contour processing. The physics-based approach also filters the image to retrieve a fat-corrected image to model the background of the breast, and the resulting image is subjected to a blob detection filter to model the intensity bumps on the foreground component of the breast that are associated with mass candidates.
Owner:AGFA NV
Texture analysis for mammography computer aided diagnosis
InactiveUS20080031506A1MinimizesMinimizes under-samplingImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammogramAided diagnosis
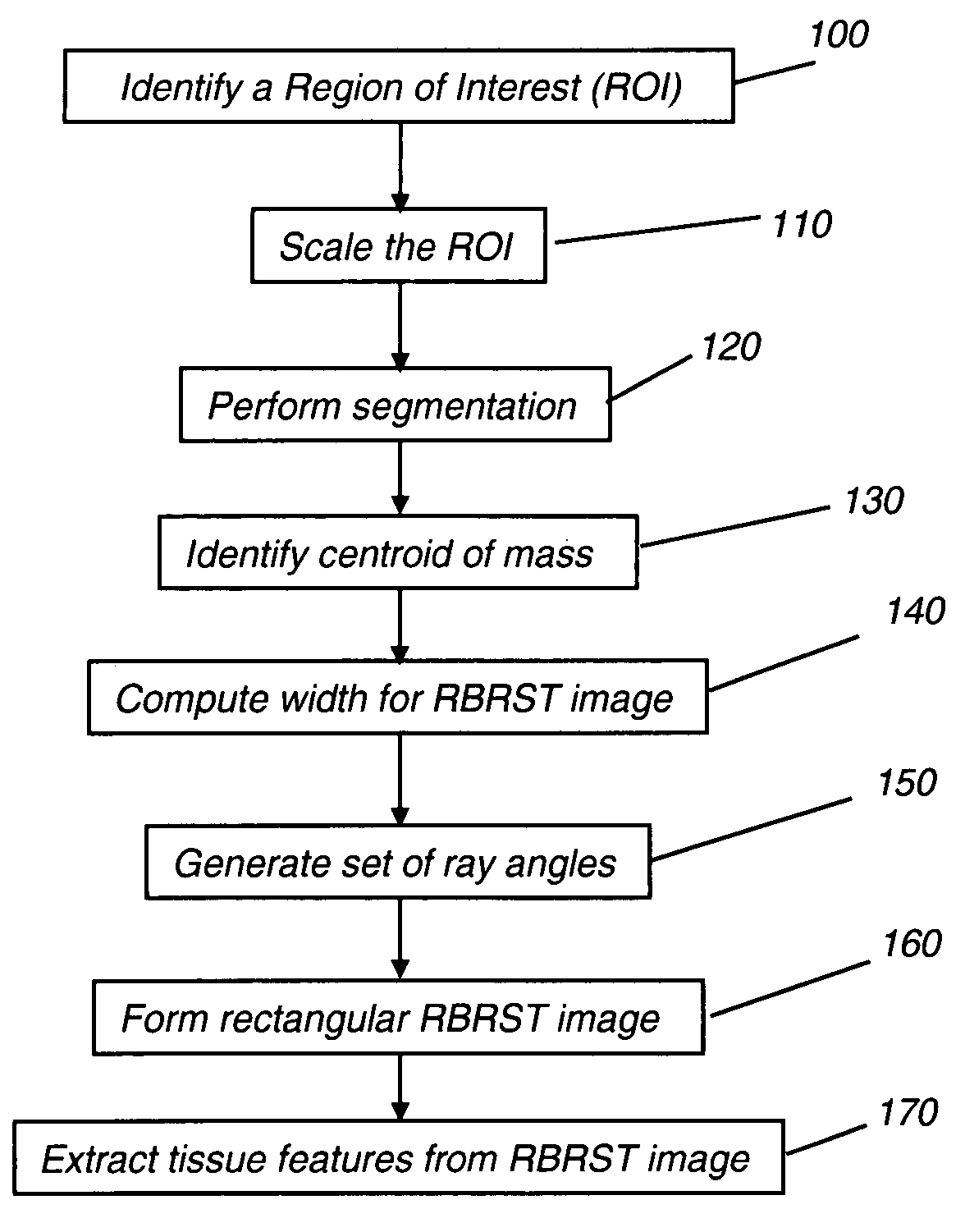
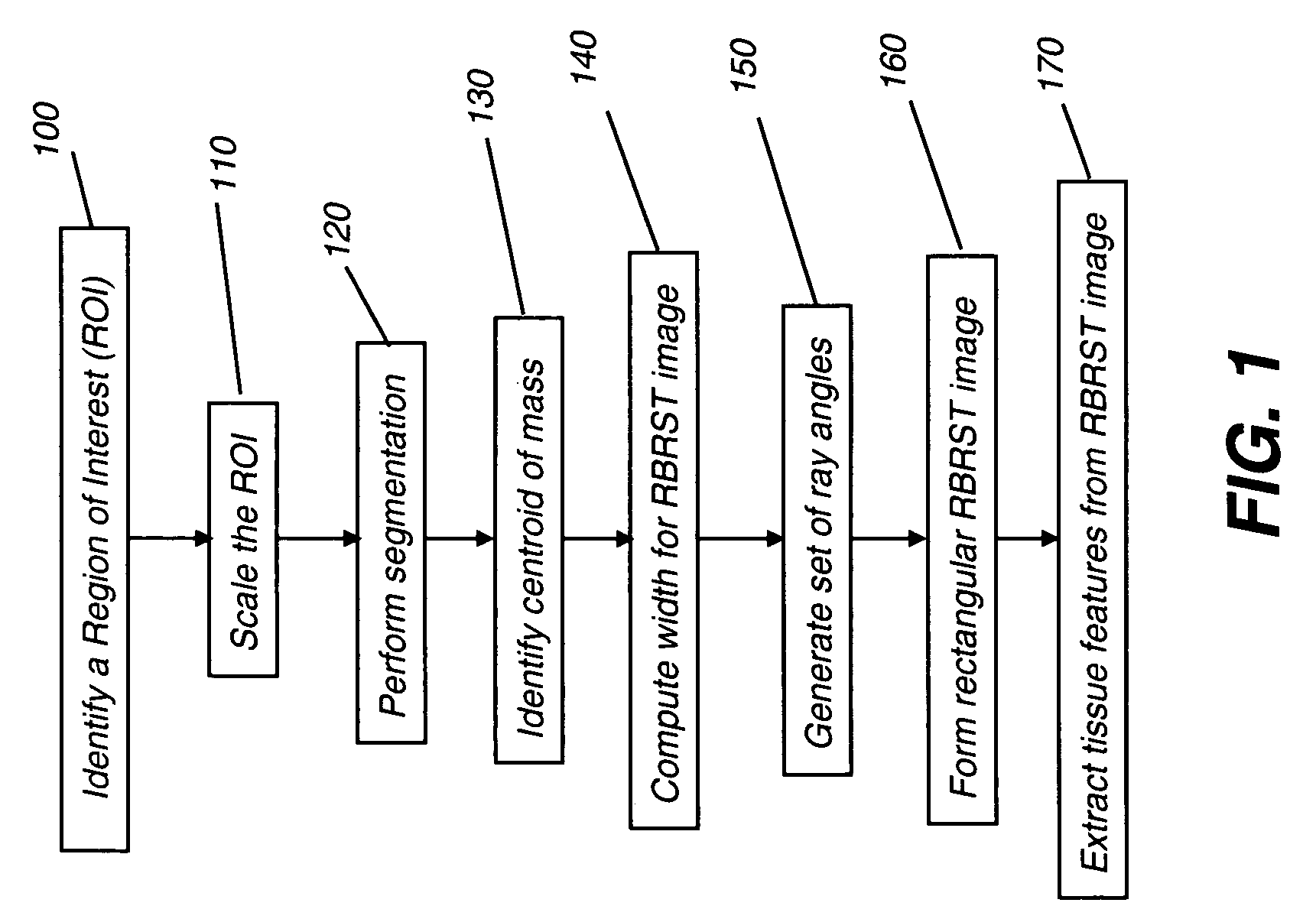
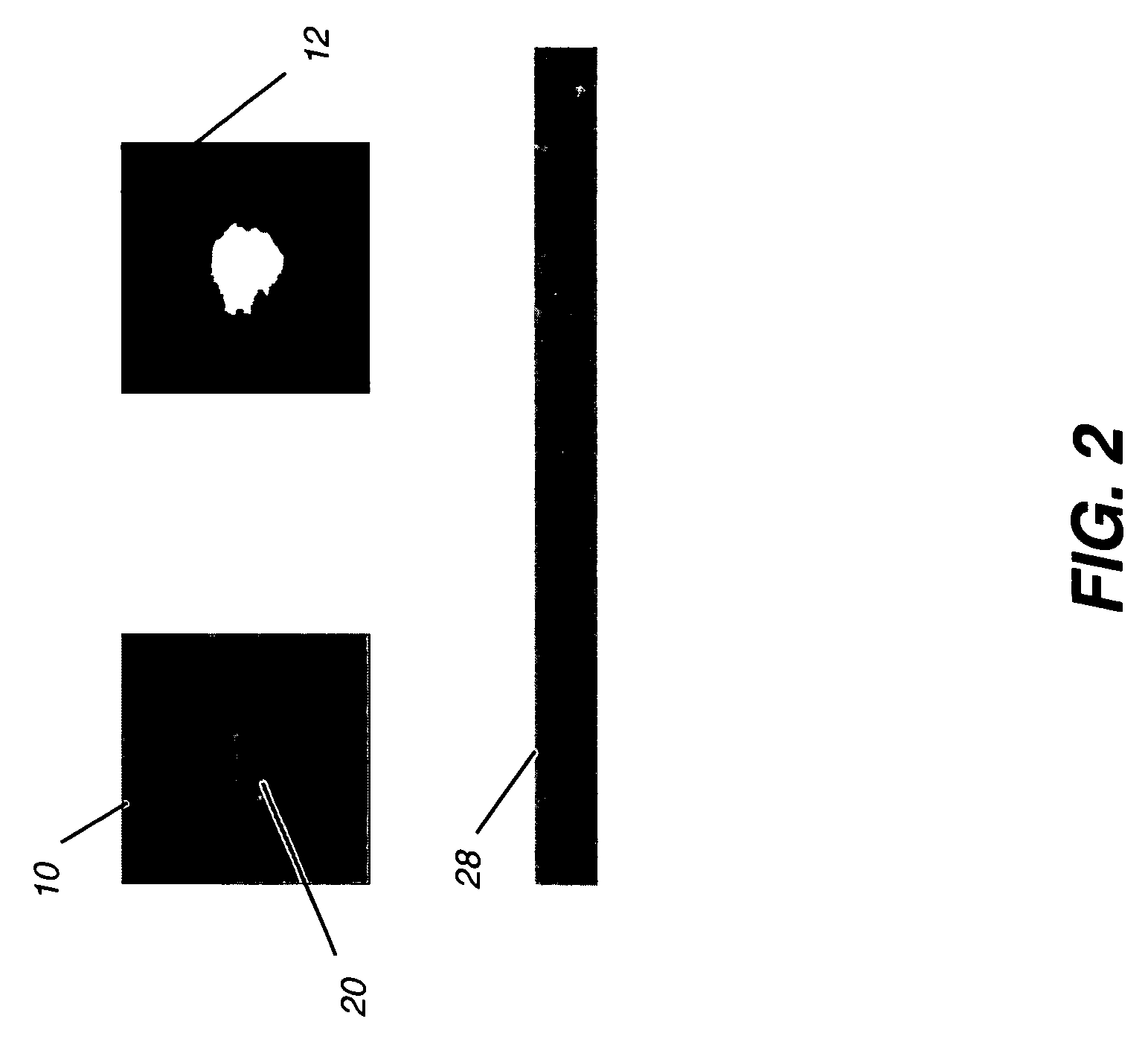
A method of characterizing a mass within a digital mammogram. A region of interest is identified that includes the mass and surrounding tissue. A border outline of the mass is identified. A rectangular image is formed wherein each column of the image is formed by repetition of steps. A vector is employed for each of a set of ray angles, wherein the vector extends from a central point of the mass and intersects the border outline at an intersection point. A starting pixel along the vector is identified, between the intersection point and the central point, at a first distance before the intersection point. An ending pixel along the vector is identified at a second distance beyond the intersection point. Pixels along the vector, from the starting pixel to the ending pixel, are remapped as the respective column in the rectangular image. Texture features are extracted from the formed rectangular image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
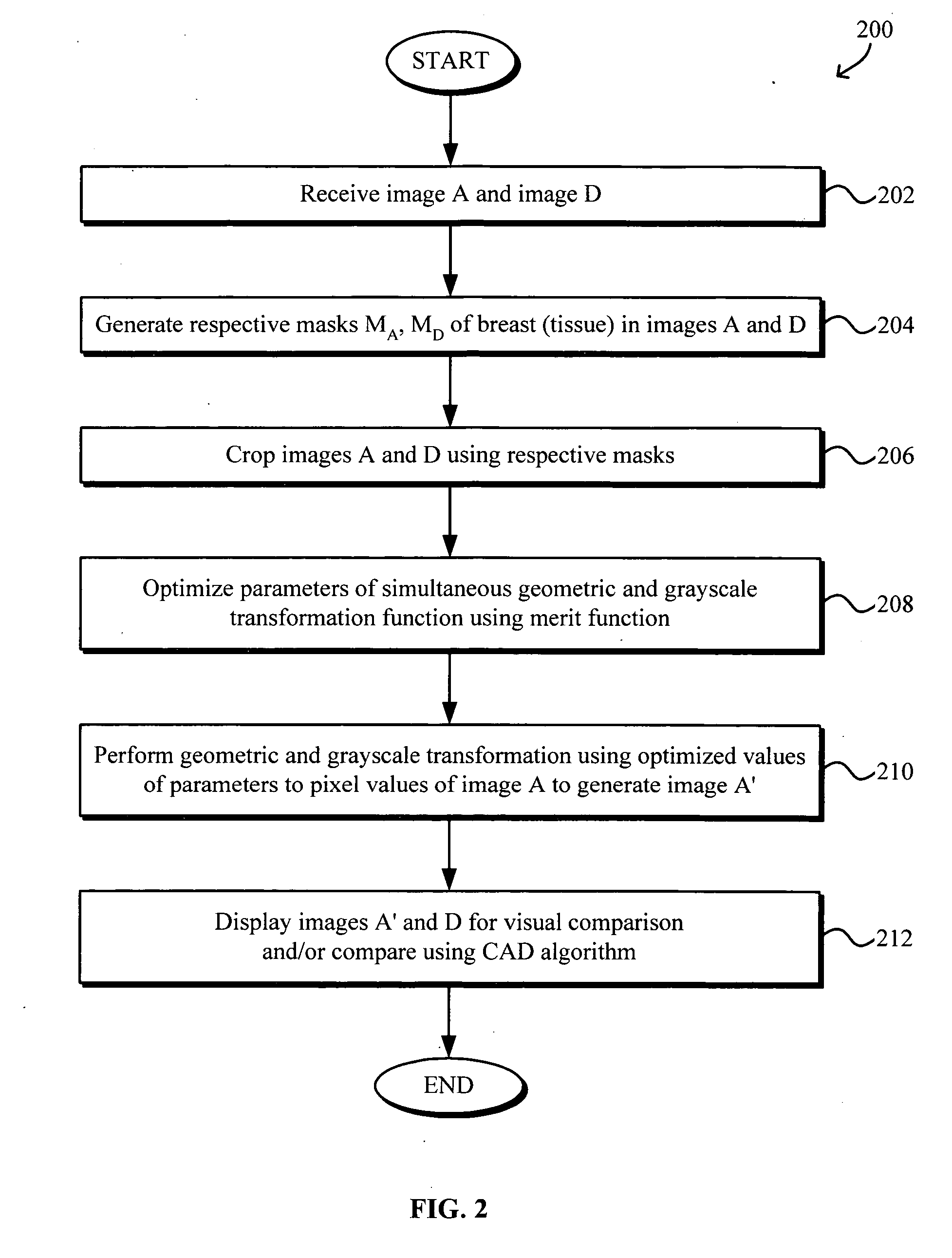
Simultaneous grayscale and geometric registration of images
InactiveUS20050163360A1Improve reliabilityIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionAlgorithm
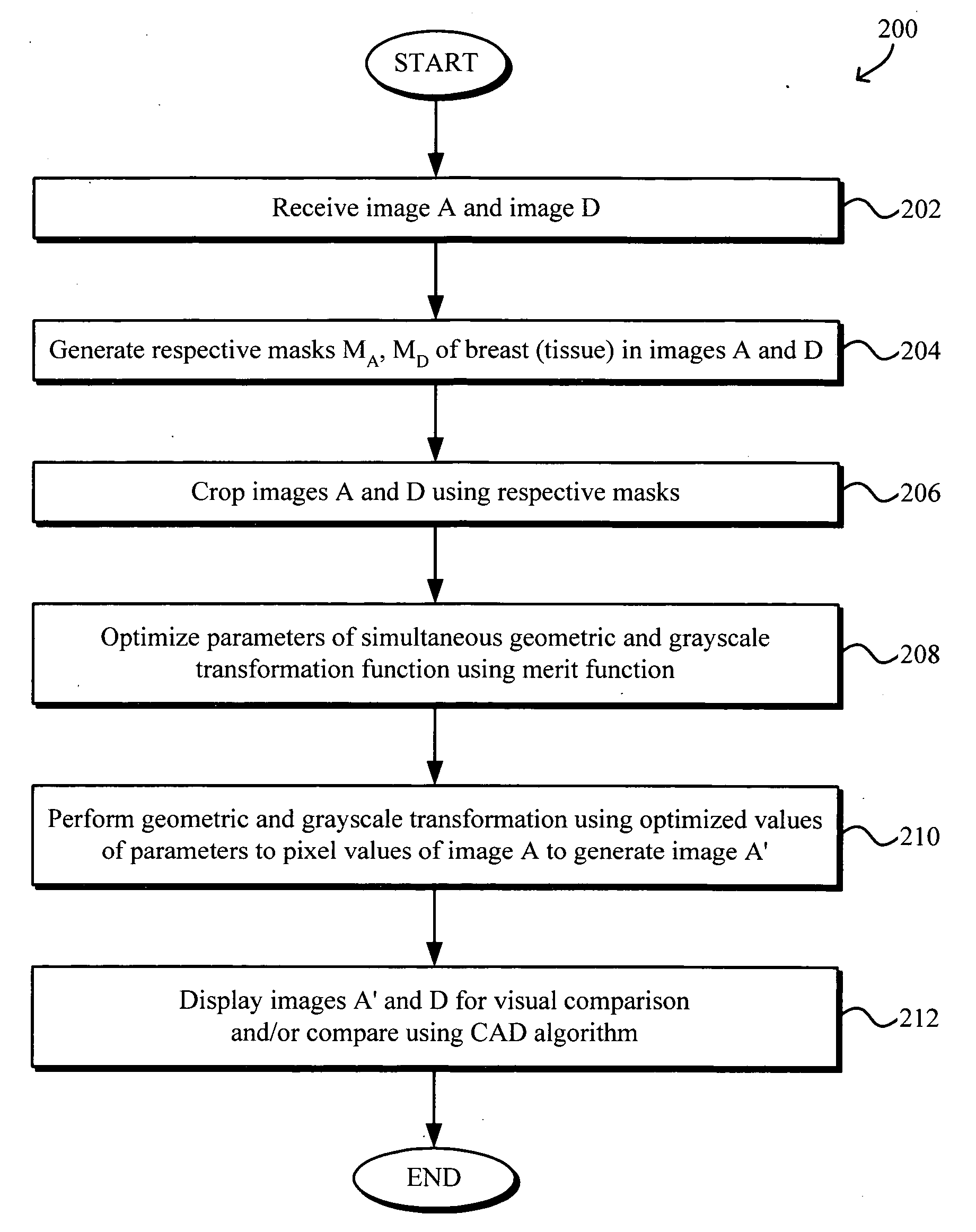
Simultaneous grayscale and geometric registration of images, such as mammograms, facilitates temporal comparison and enhances the speed and reliability of computer aided diagnosis (CAD) detection of medical abnormalities. The method generally includes optimizing a merit function, e.g., sum of squared errors, containing parameters associated with a transformation function for simultaneous geometric and grayscale registering of the images, the optimizing of the merit function being performed by determining optimal values of the parameters using data in the images and registering one image to the other by applying the geometric and grayscale transformation function using the optimal values of the parameters. The optimizing may be performed iteratively from coarse to fine resolutions using a modified Levenberg-Marquardt method for optimizing nonlinear parameters with linear regression for optimizing linear parameters. A final iteration may be performed after removing pixel value pairs from the images that correspond to outliers of a joint pixel value histogram.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
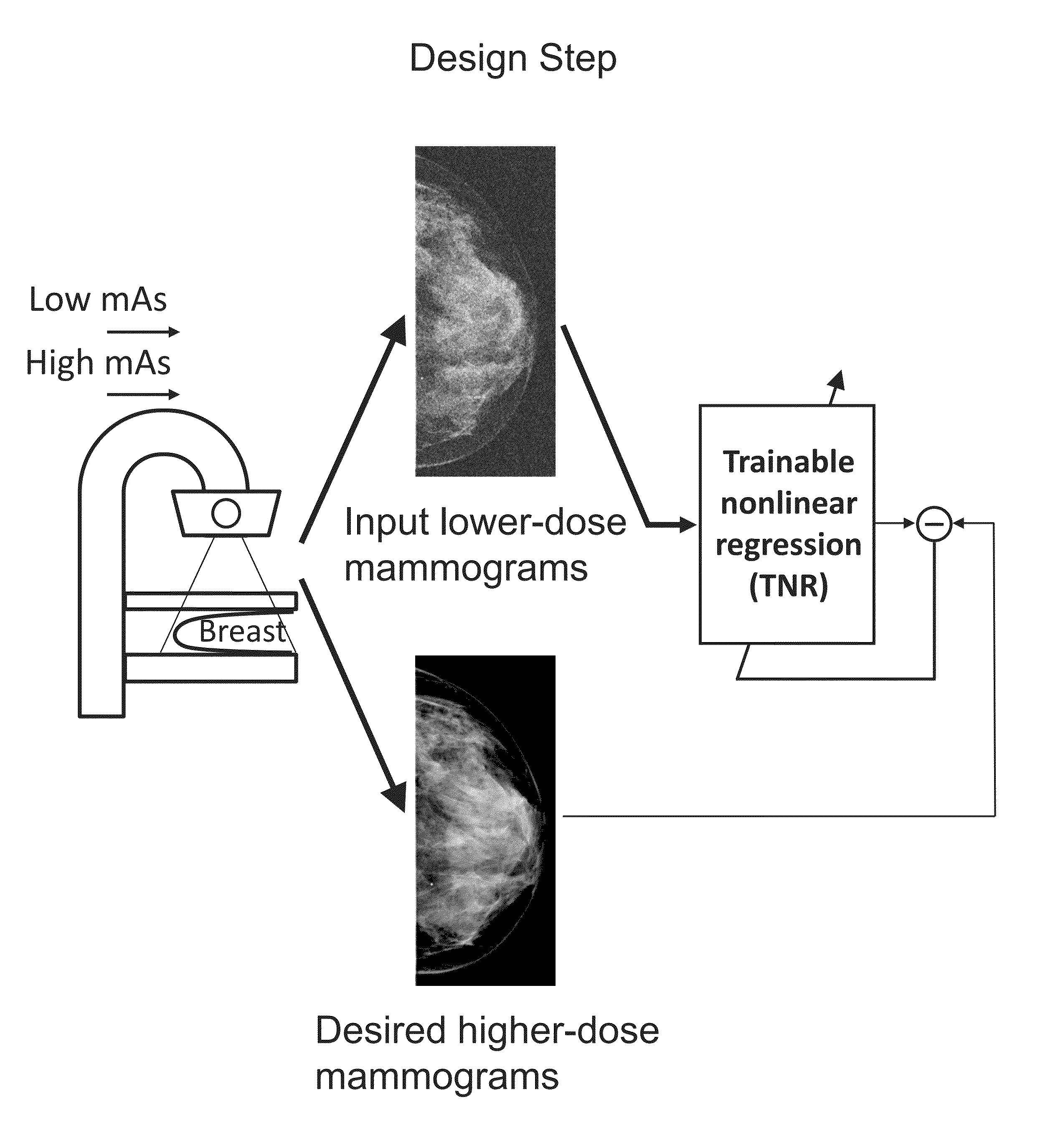
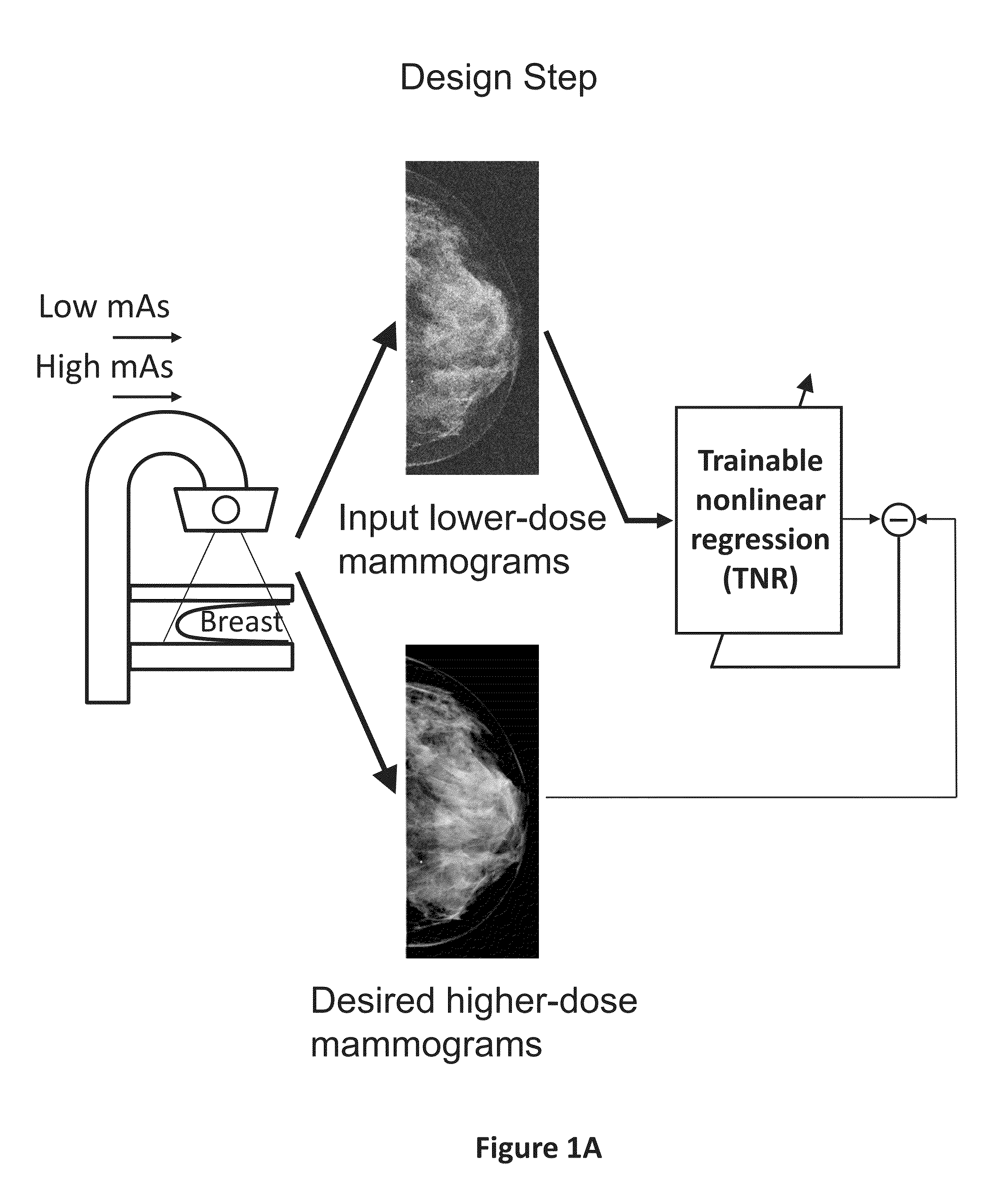
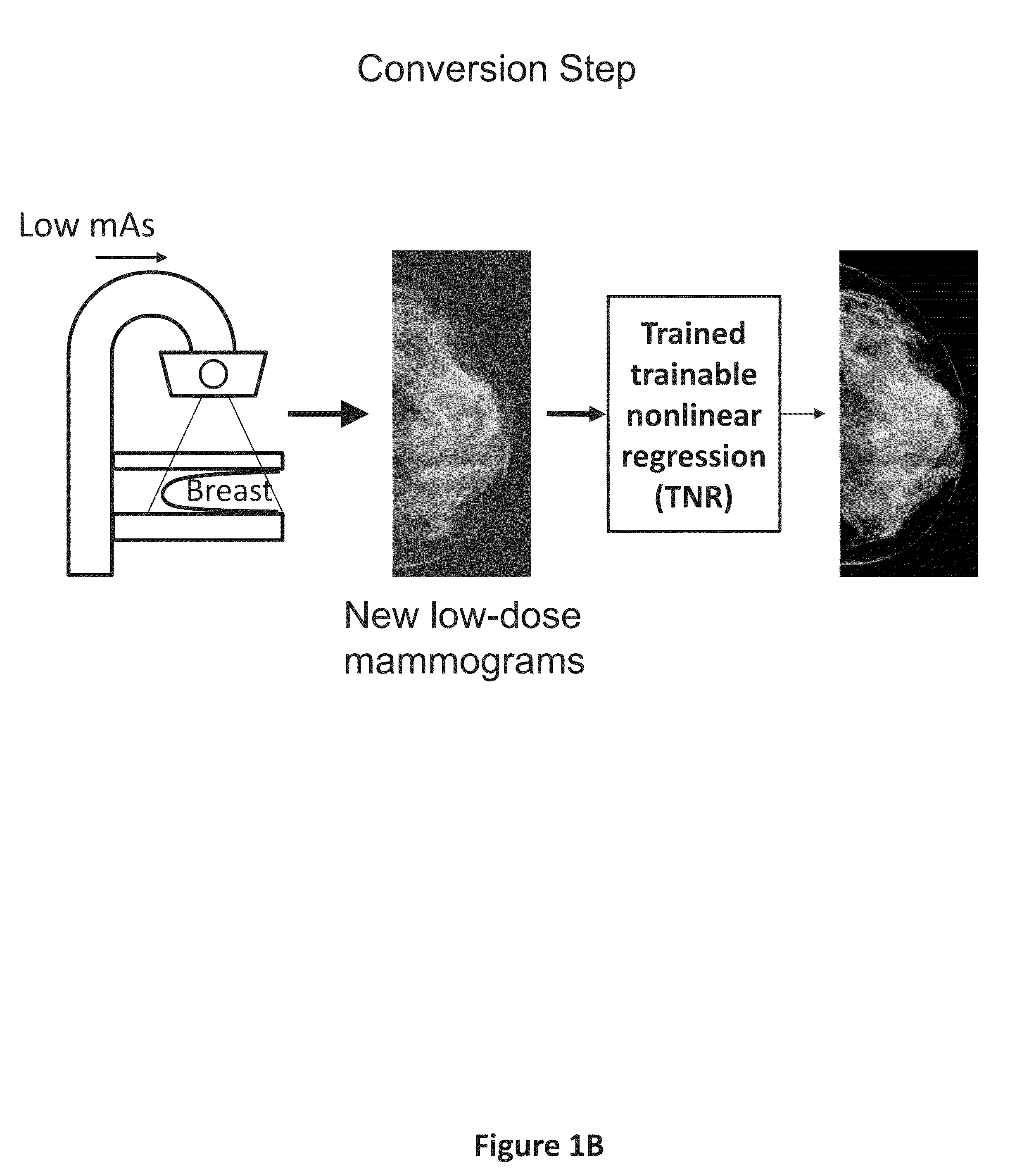
Converting low-dose to higher dose mammographic images through machine-learning processes
ActiveUS20150196265A1Improve image qualityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityX-ray
A method and system for converting low-dose mammographic images with much noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like mammographic images, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme, which can be called a call pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input mammogram acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of mammograms, inputting low-dose mammograms together with corresponding desired standard x-ray radiation dose mammograms (higher-dose), which are ideal images for the output images. Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose mammograms to high-dose-like mammograms. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose mammograms anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) mammogram is entered, the trained PTNR would output a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it would output high-dose-like mammograms or “virtual high-dose” mammograms where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. With the “virtual high-dose” mammograms, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
Methods and Apparatus for Computer Automated Diagnosis of Mammogram Images
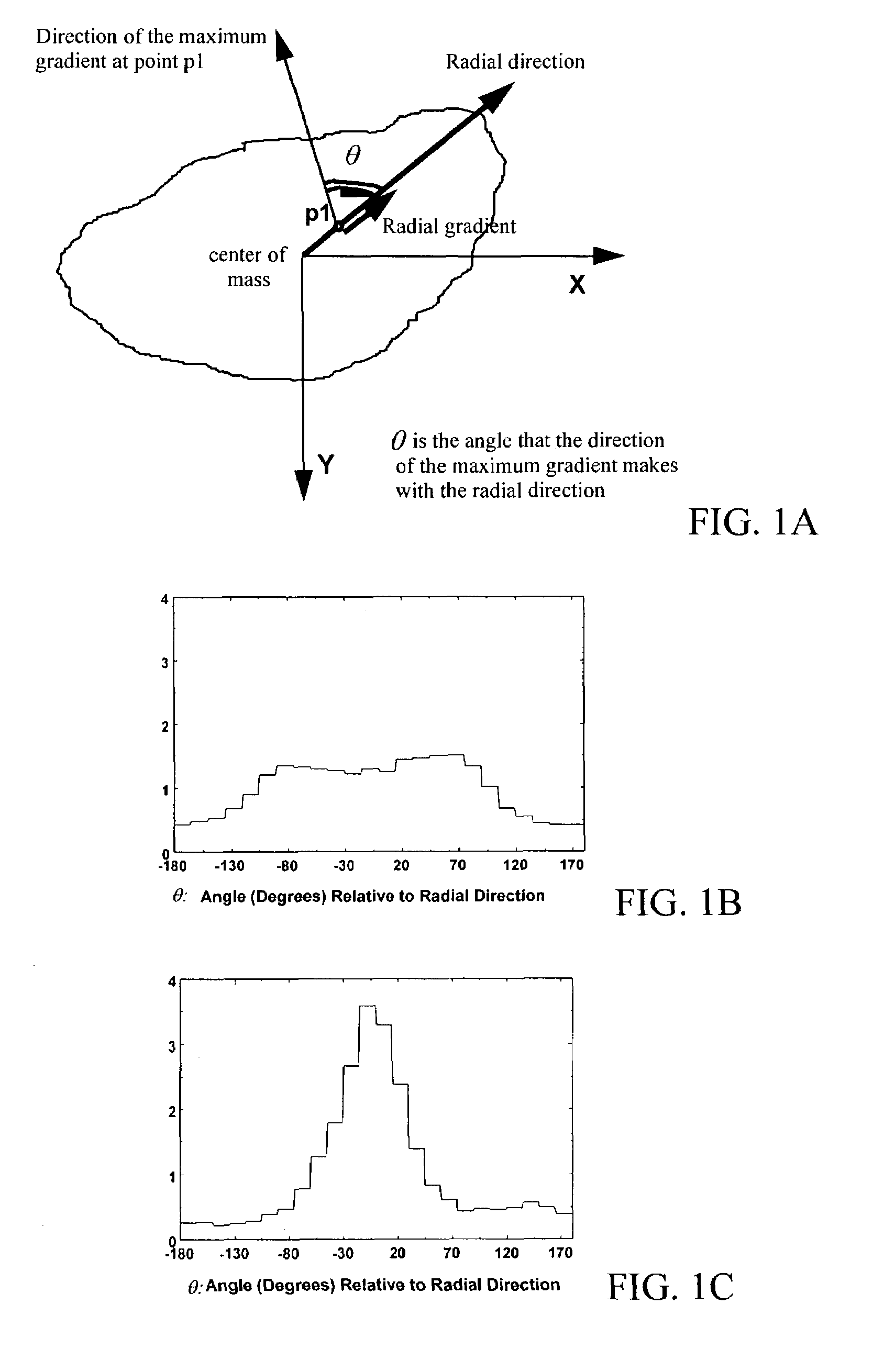
InactiveUS20070280525A1Accurately determineReduce or eliminate false positive findingsImage enhancementImage analysisXeromammogramPhysician roles
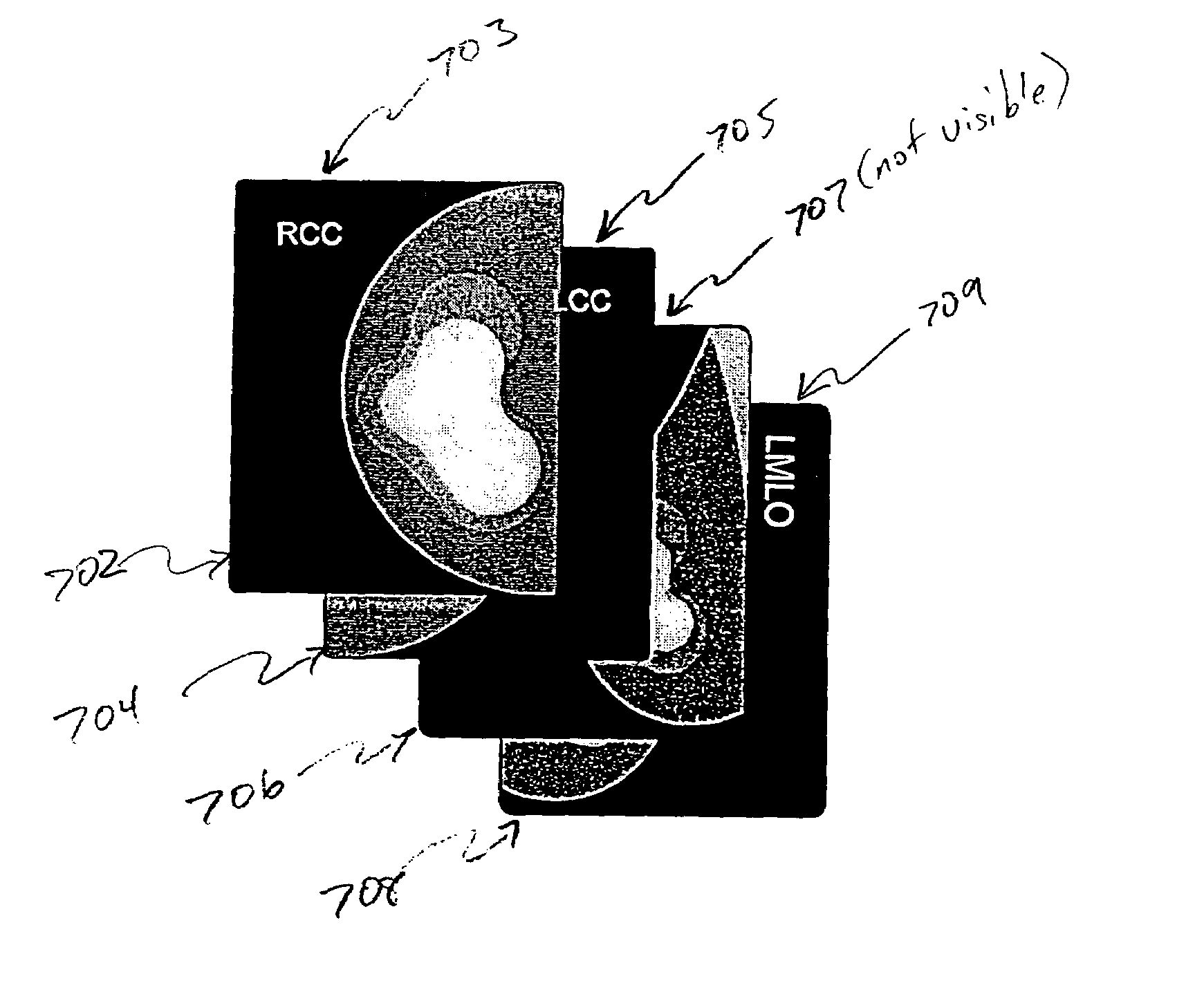
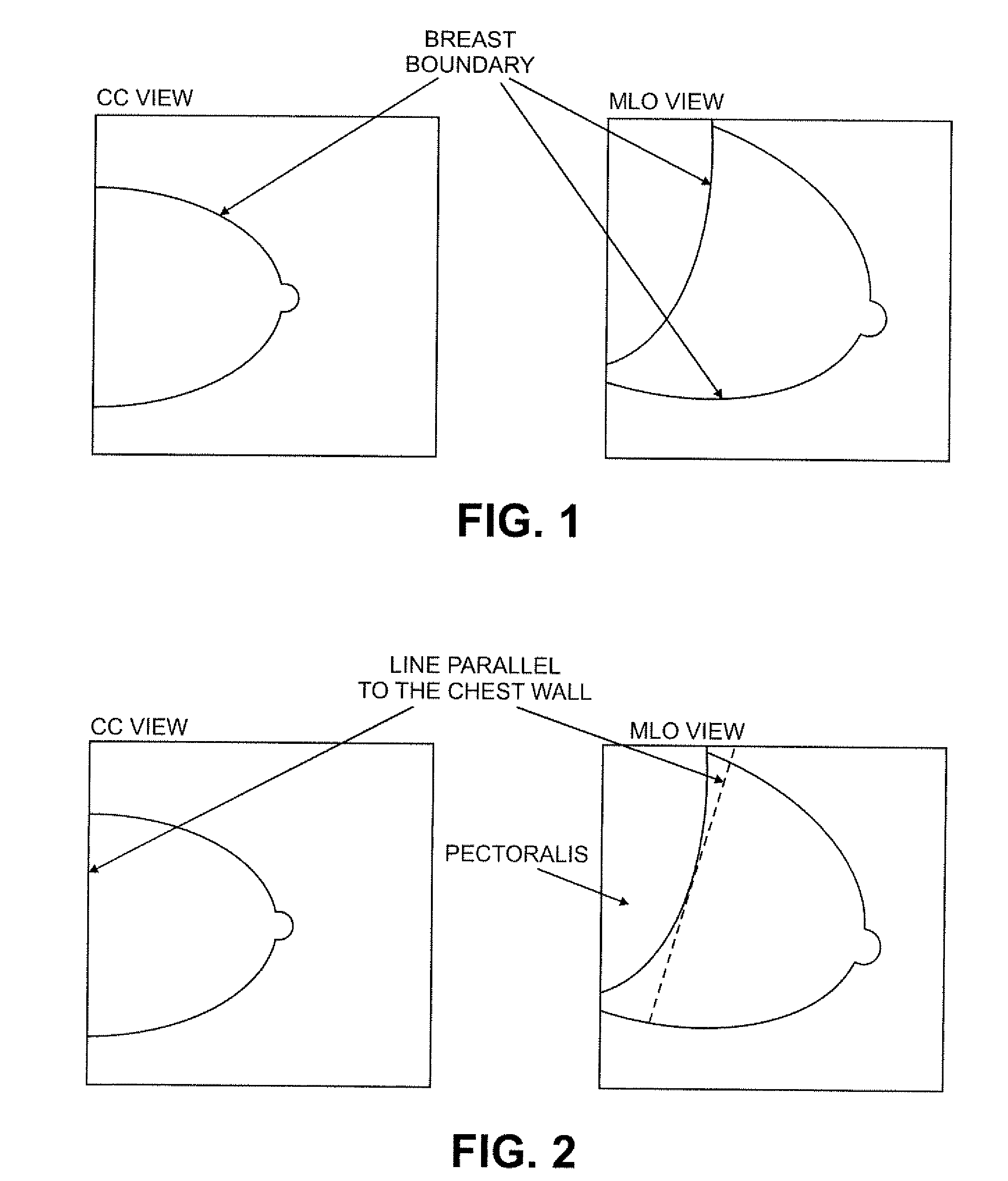
A system, method, and computer program product for computer analysis of lesions in digitized film-based and / or digital mammograms is described, wherein diagnostic information is combined from two different 2-D mammographic views with the information obtained from one view (or field of view) or mammographic position is processed with information obtained from a second (or a plurality of) related mammographic views to reduce false-positive findings (increase specificity) while preserving or improving diagnostic sensitivity. The digital mammograms or digitized film-based mammograms used, are those that are in current use, and those that conform to the requirements of the American College of Radiology and the Mammography Quality Standards Acts. In a preferred embodiment, a line constructed at the location of the chest wall (or parallel to the chest wall), the location of the nipple, and a line constructed perpendicular to the chest wall datum line and passing through the location of the nipple serve as reference datum across mammogram views. An algorithm locates suspicious lesions in each mammography view and evaluates the concordance of the 3-D spatial locations to rule out physically impossible false-positive findings, based on calculations of spatial relationships. Concordant findings are detected using anatomic landmarks and such findings are reported using terms that are currently in use by physicians and other health care providers in the field of mammography.
Owner:CAROLINA IMAGING SPECIALISTS
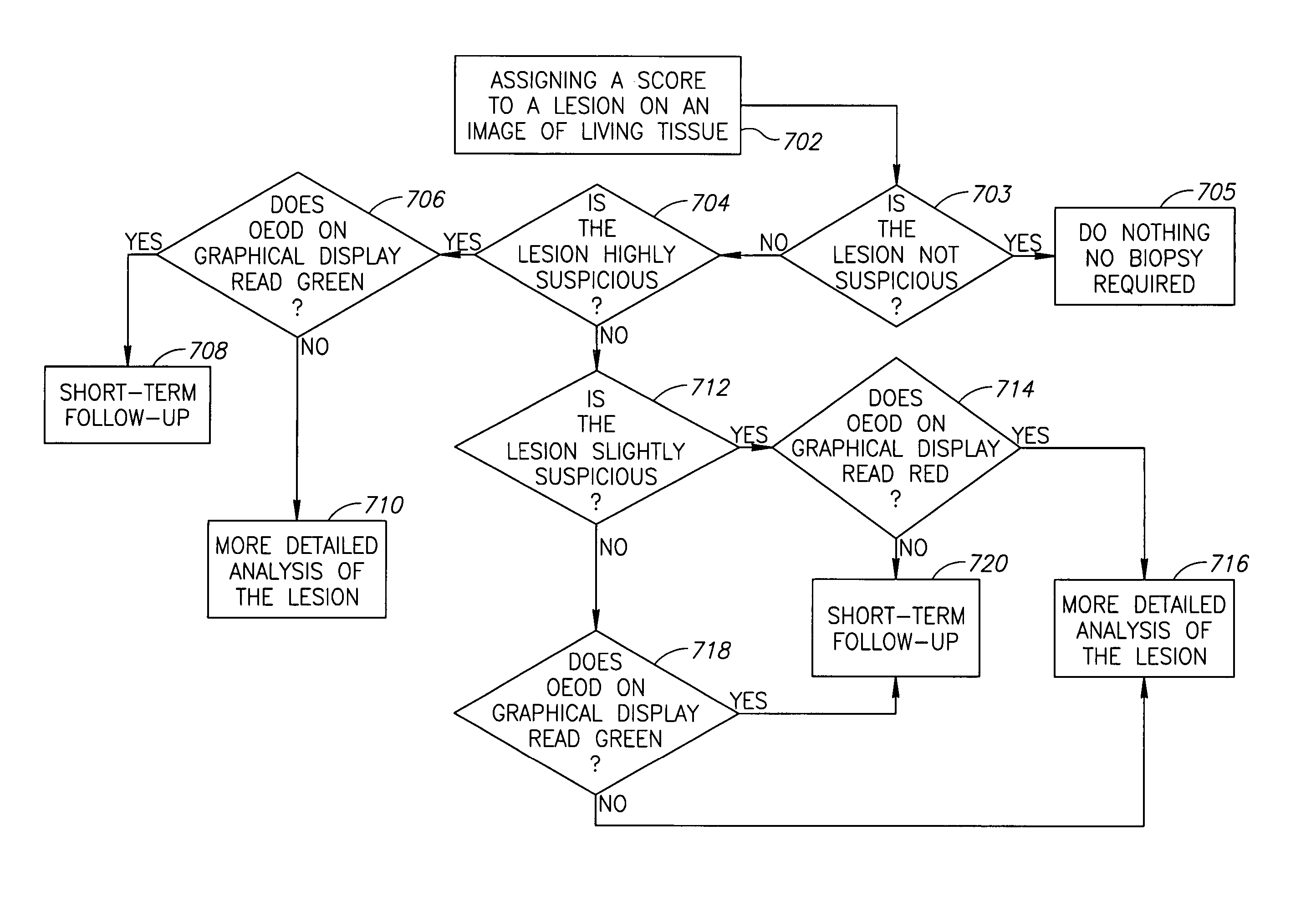
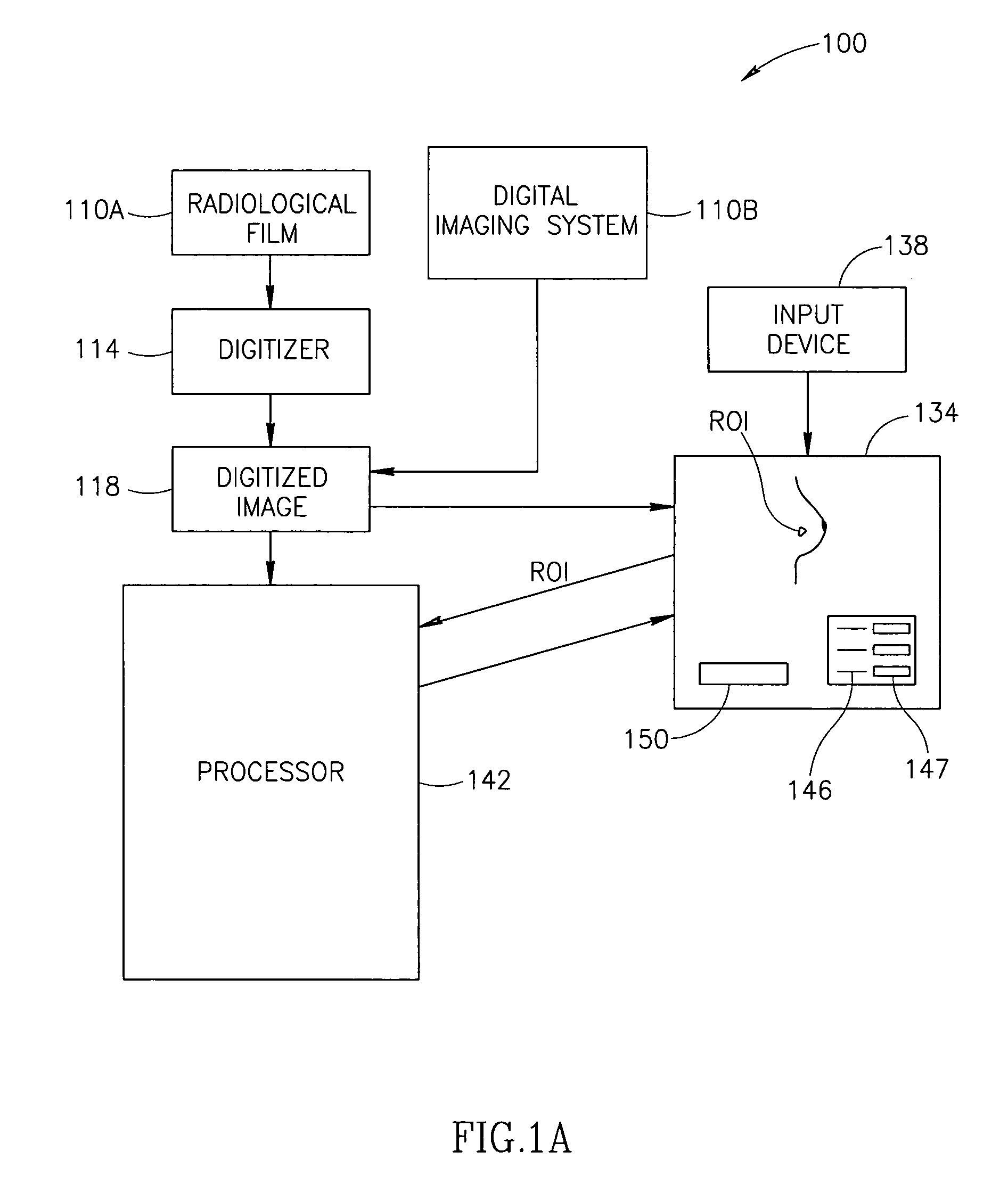
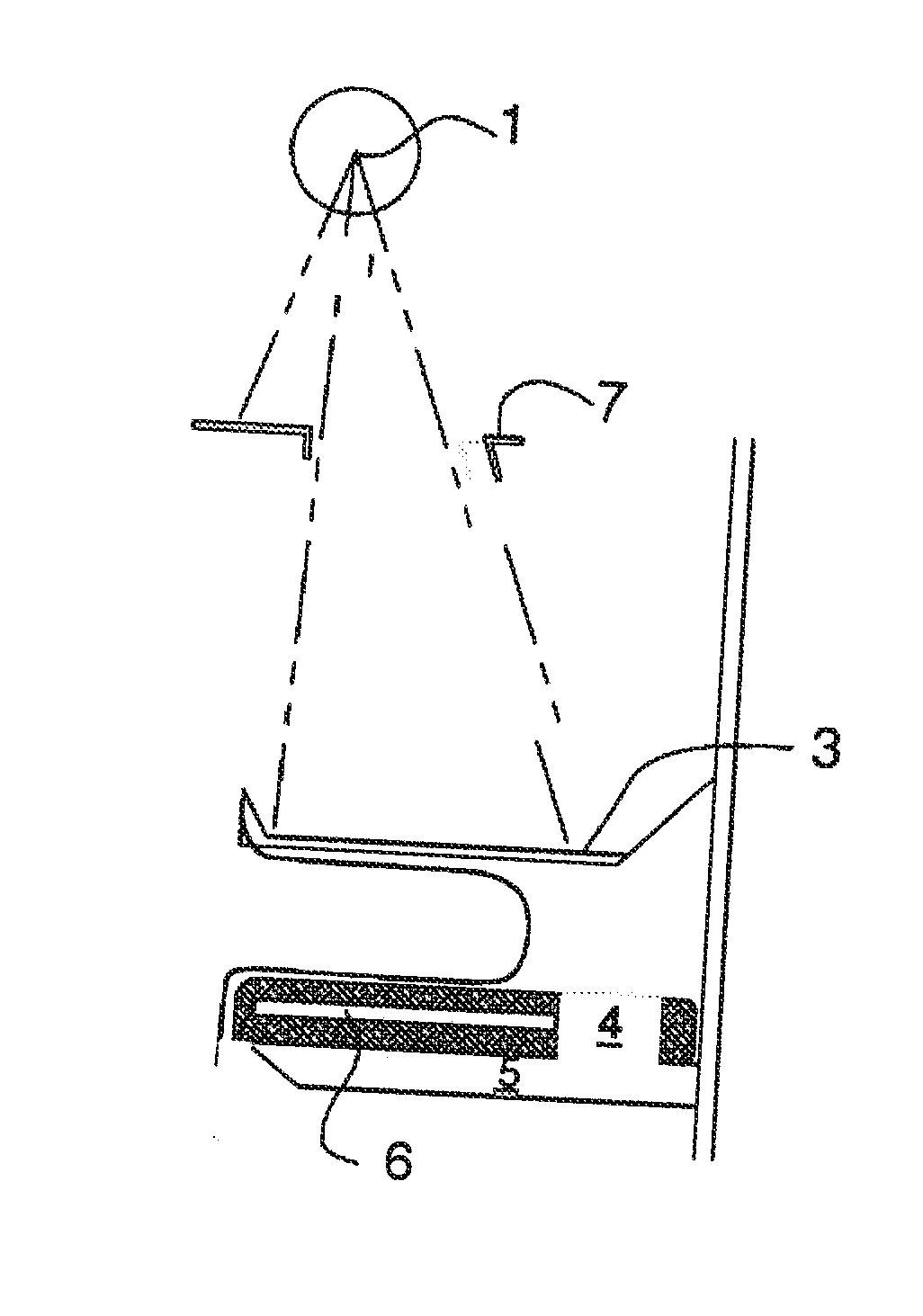
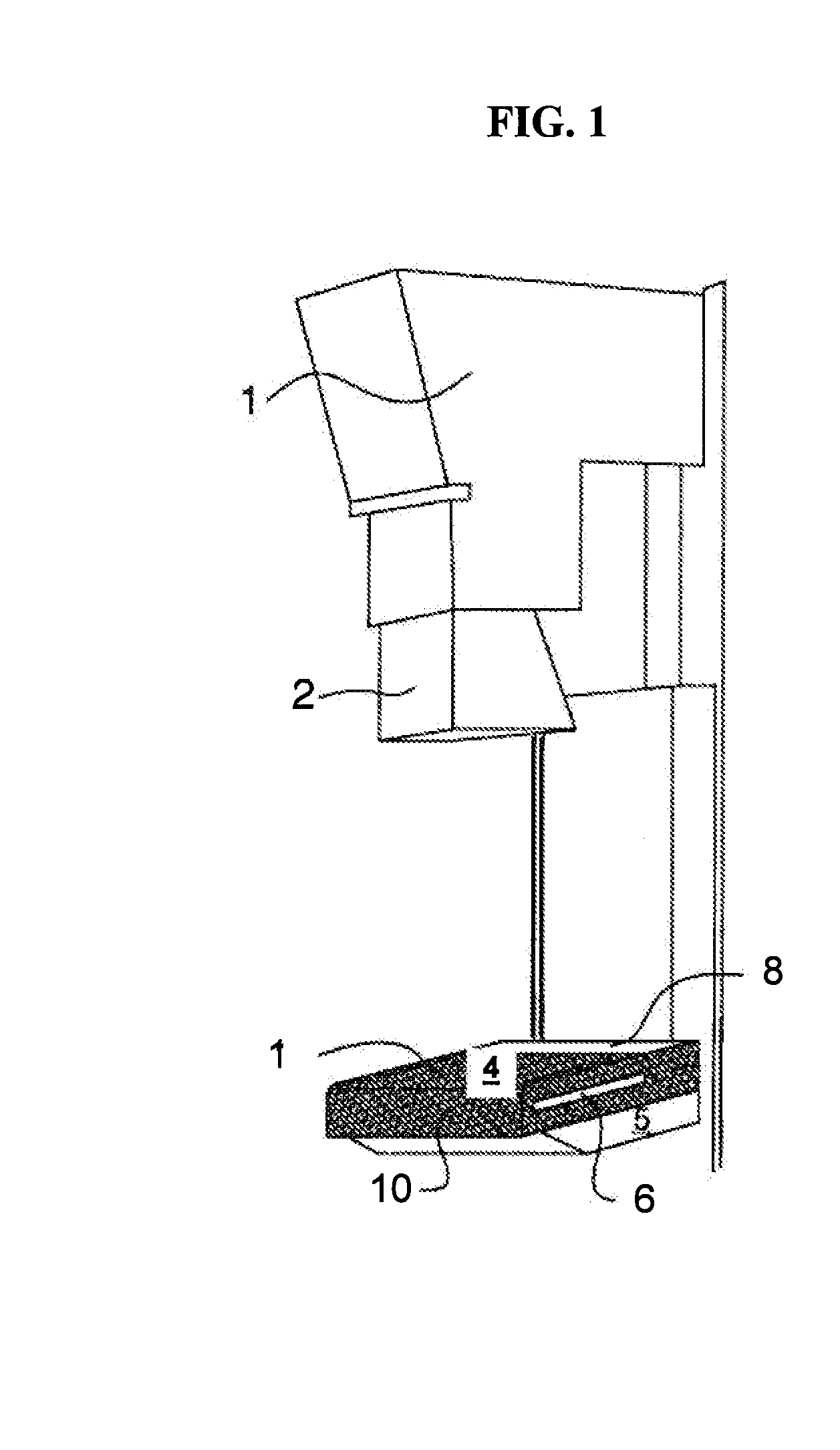
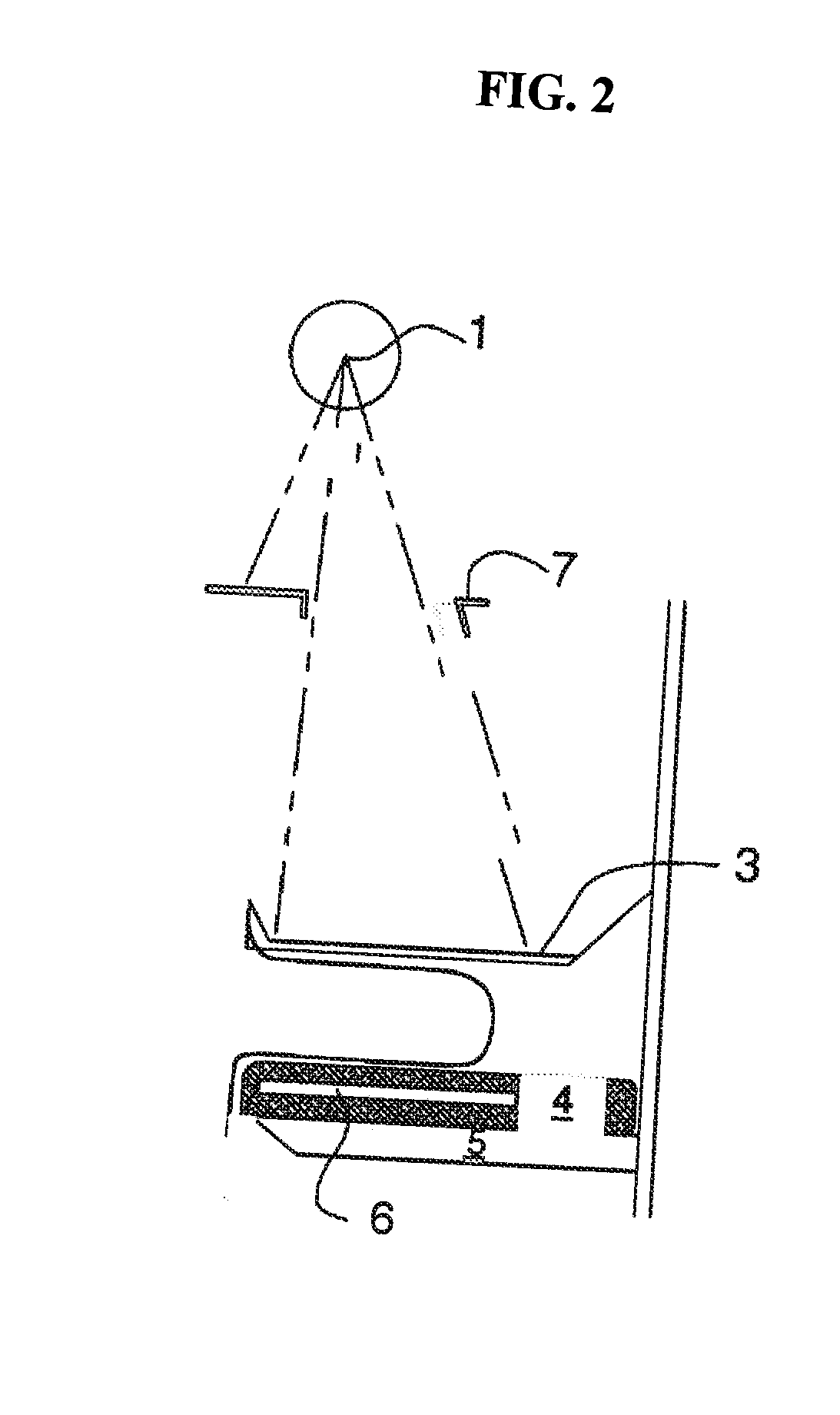
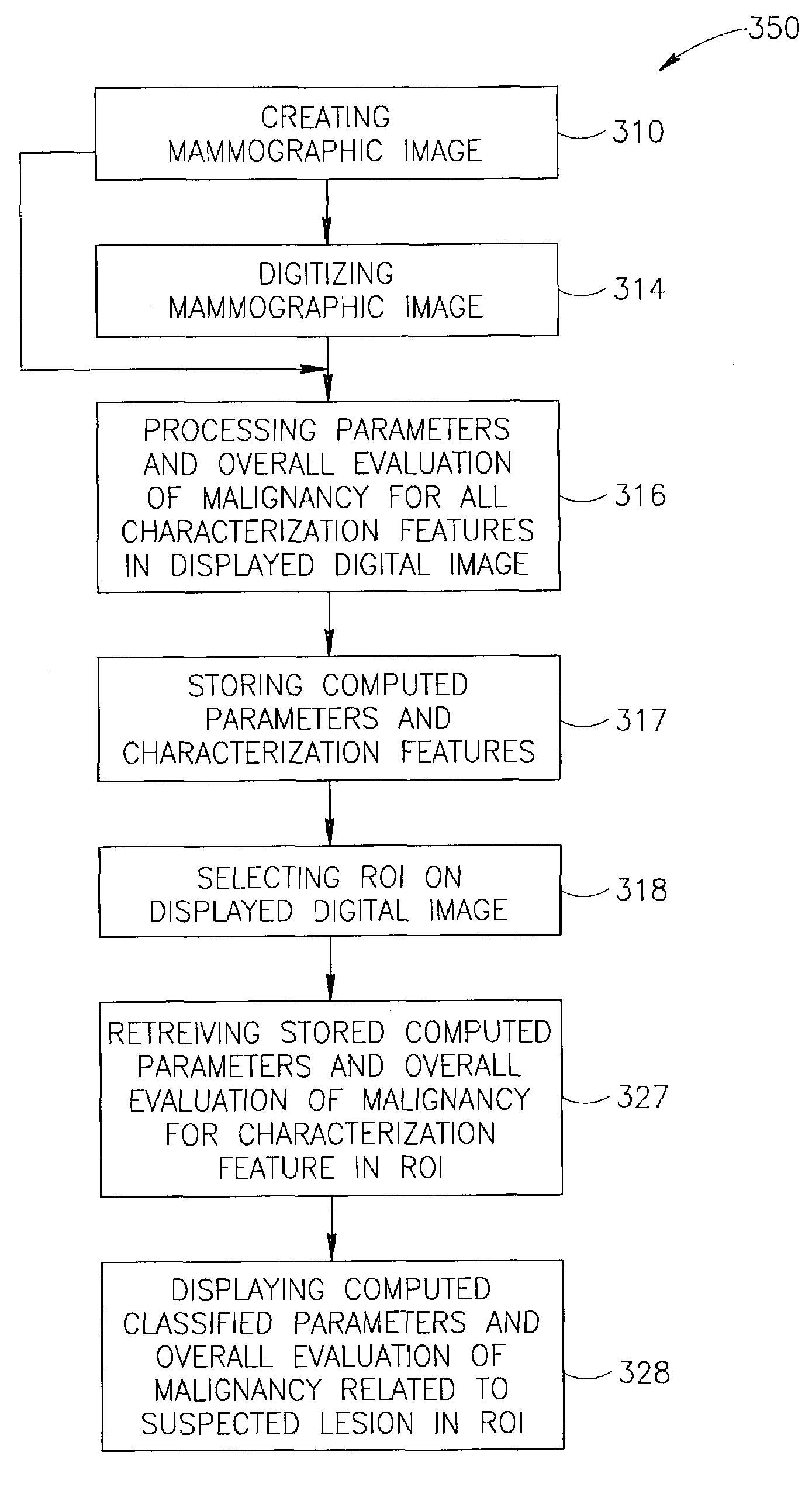
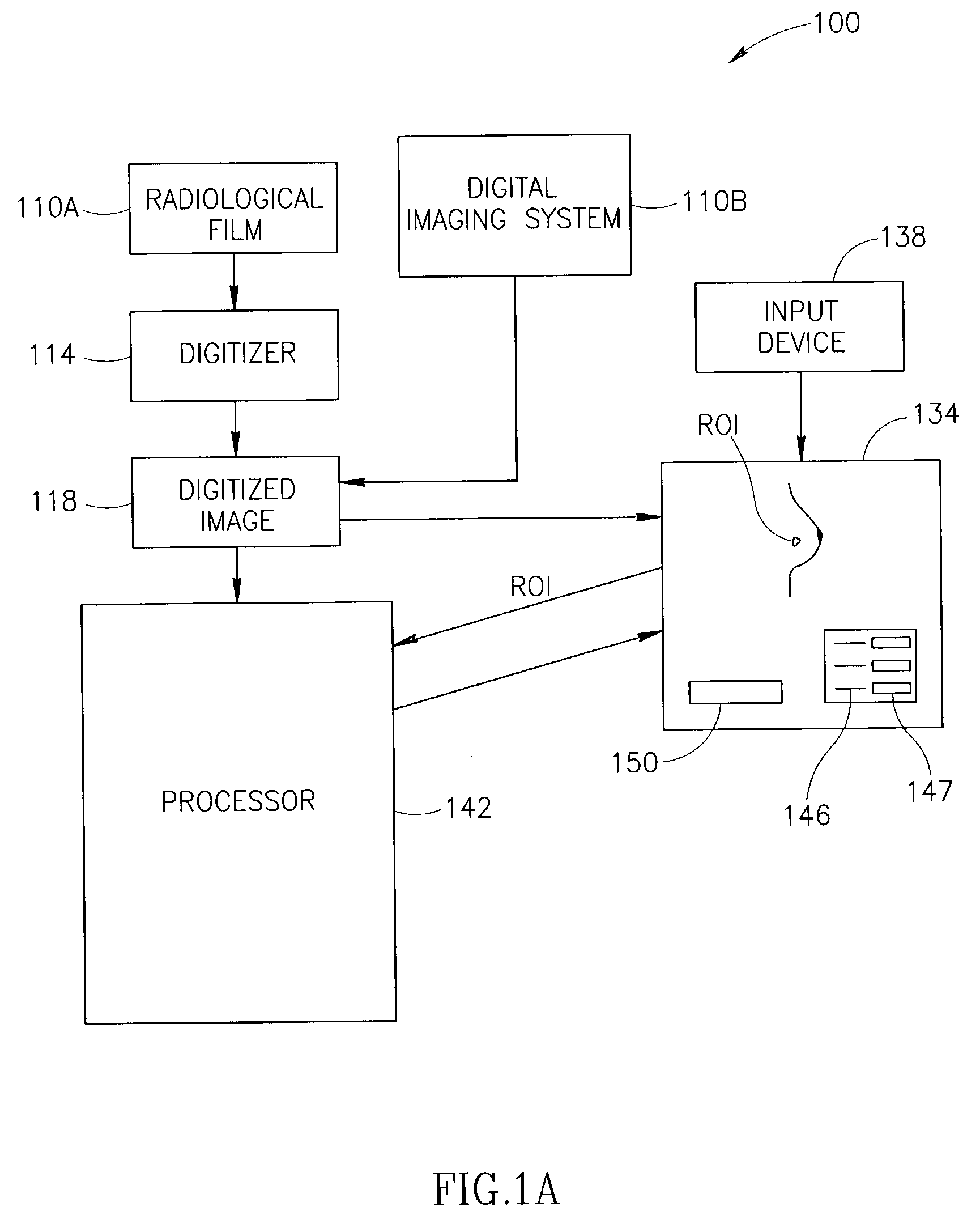
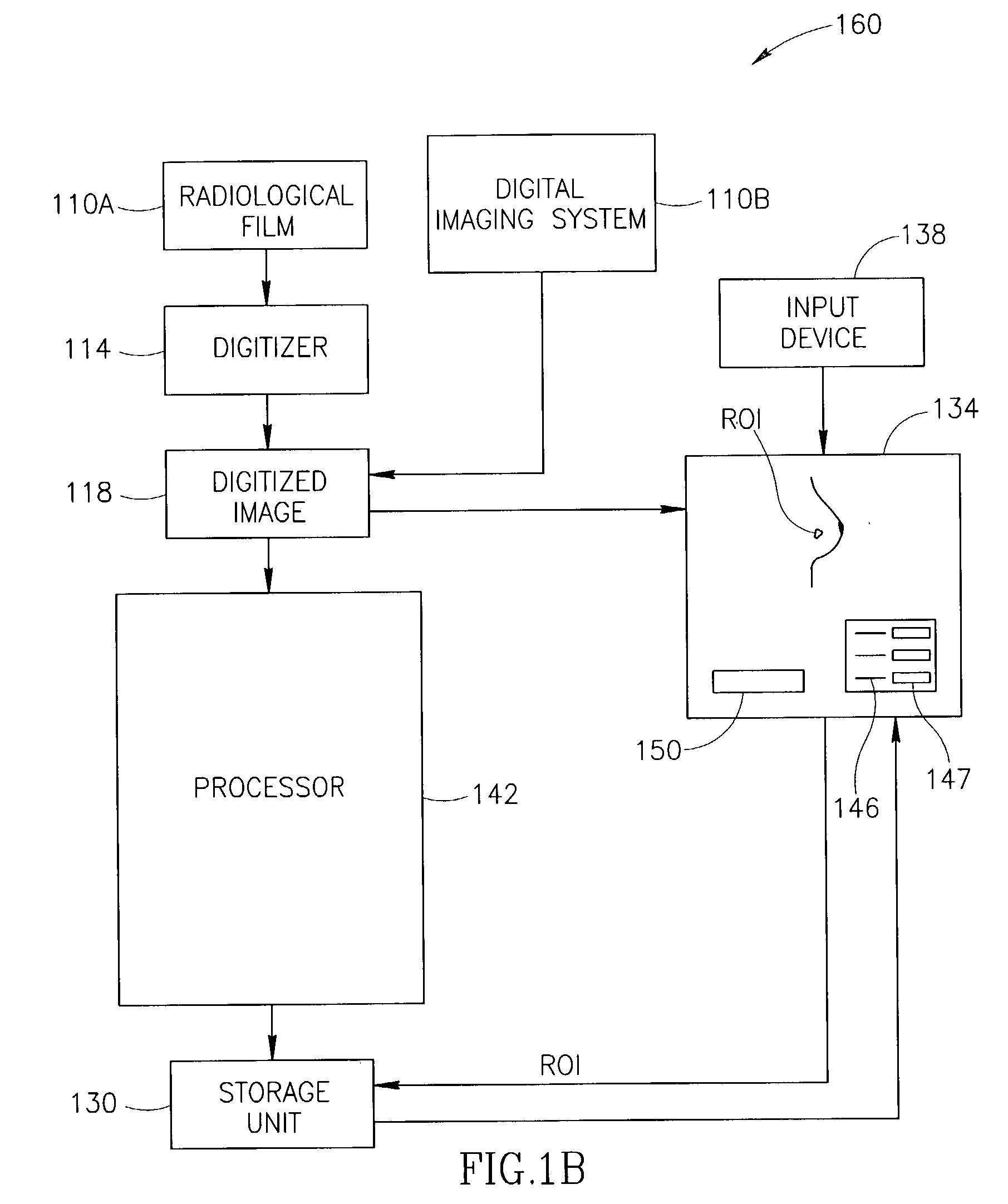
Display for computer-aided evaluation of medical images and for establishing clinical recommendation therefrom
InactiveUS7418119B2Aid in diagnosisHard to see or difficult to evaluate lesionsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer-aidedComputer aid
A method for displaying a computer-generated determination of the overall likelihood of malignancy in a mammogram lesion. The method requires providing a digitized image of a mammogram, displaying the digitized image, and selecting a region of interest directly on the displayed digitized image. The digitized image is then processed so that classifier data of the lesion in the user-selected region of interest are generated and displayed. The overall likelihood of malignancy is generated from the classifier data and also displayed. A clinical recommendation for further assessing the lesion is derived from the overall evaluation of malignancy and presented to the user. A system for displaying a determination of the overall likelihood of malignancy in a mammogram lesion and for presenting a clinical recommendation to the user is also provided. A method for integrating the overall likelihood of malignancy with a physician's independent score for the lesion is discussed.
Owner:SIEMENS COMP AIDED DIAGNOSIS
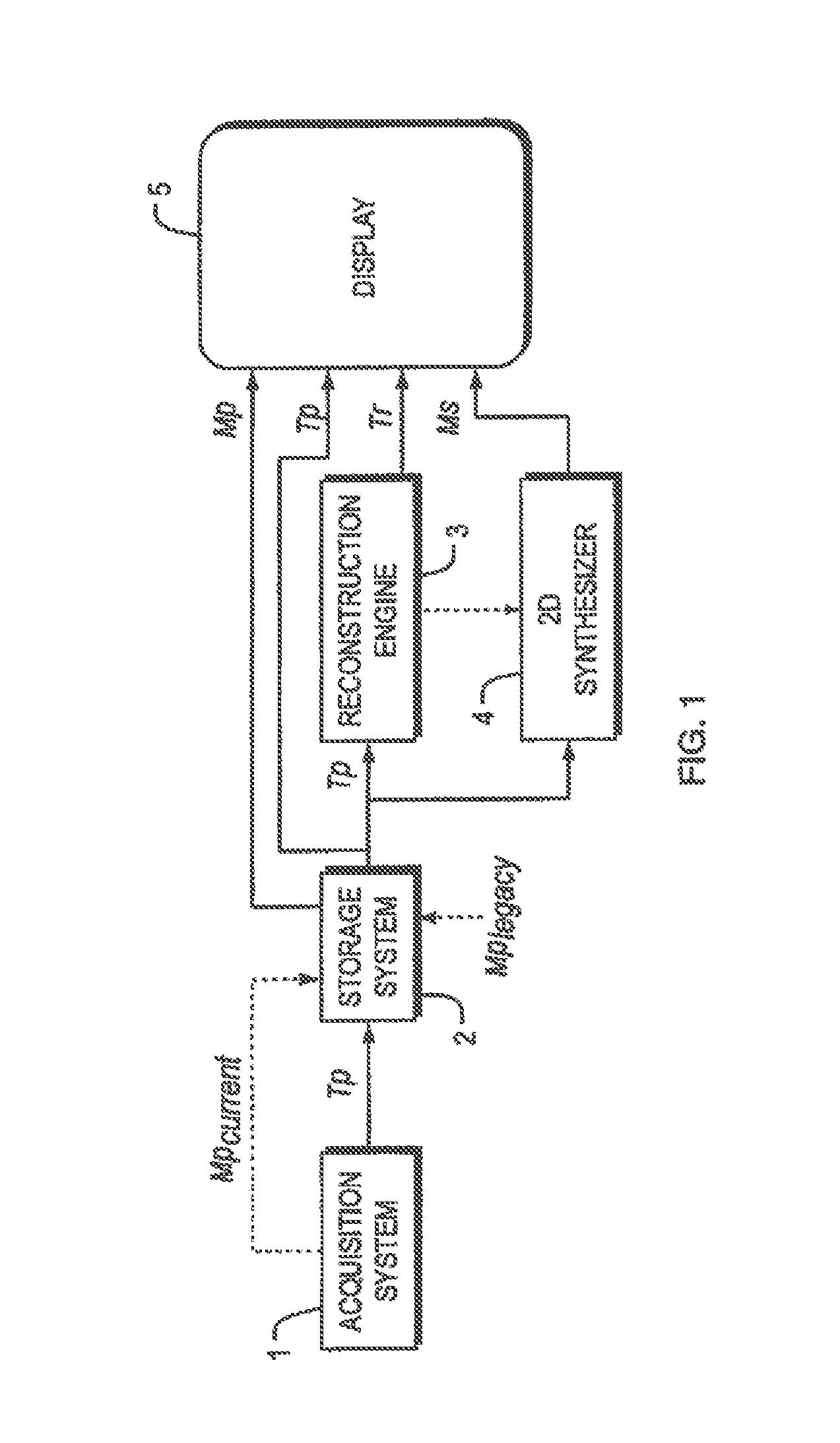
System and Method for Generating A 2D Image from a Tomosynthesis Data Set
InactiveUS20140086471A1Effective assessmentView effectivelyReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomosynthesisData set
A 2D mammogram image is synthesized from at least one of tomosynthesis projection images and / or the tomosynthesis reconstructed image data. In a simplest form, the mammogram may be synthesized by selecting one of the tomosynthesis projection images for display as a synthesized mammogram. Other methods of synthesizing a mammogram include re-projecting and filtering projection data and / or reconstructed data. The synthesized mammogram is advantageously displayed together with at least a portion of the reconstructed data to aid in review of the reconstructed data. The present invention thus provides a familiar image which may be used to facilitate review of a tomosynthesis data set.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
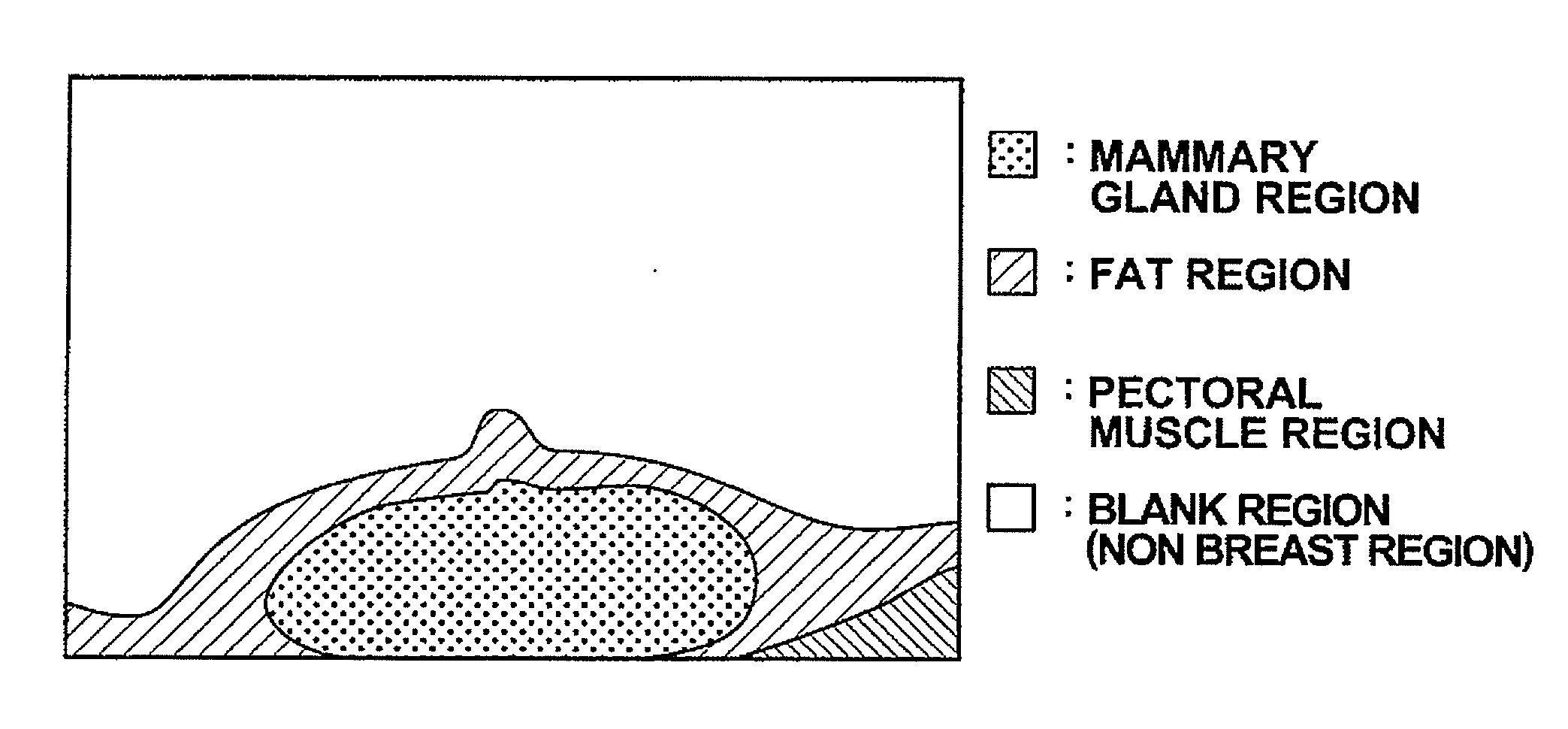
Breast image display apparatus and its program
InactiveUS20090086891A1Improve accuracyHigh precision diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisMammary gland structureComputer science
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Generating a synthetic two-dimensional mammogram
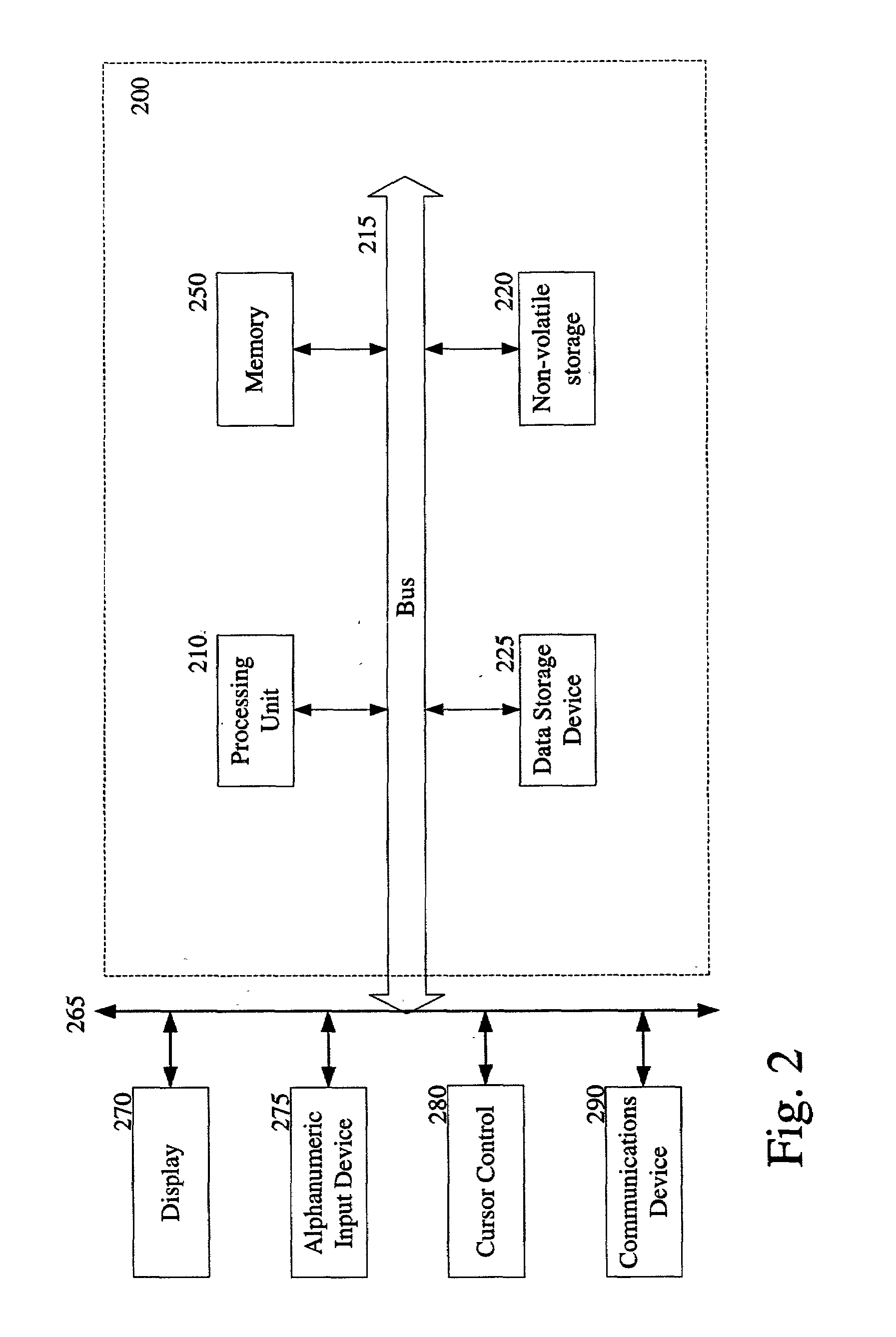
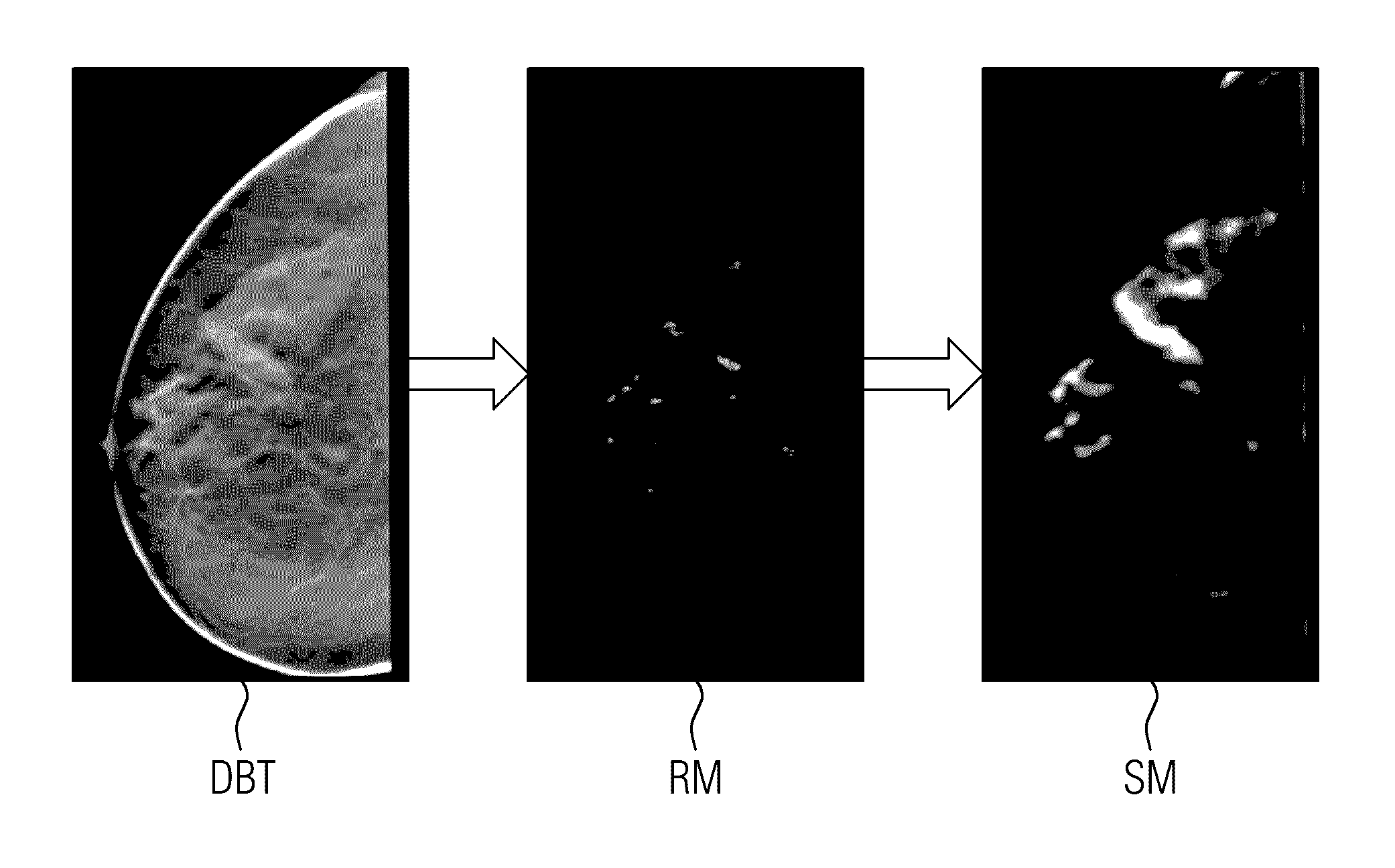
ActiveUS9792703B2Increase contrastImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionVoxelComputer science
A method for generating a synthetic two-dimensional mammogram with enhanced contrast for structures of interest includes acquiring a three-dimensional digital breast tomosynthesis volume having a plurality of voxels. A three-dimensional relevance map that encodes for the voxels the relevance of the underlying structure for a diagnosis is generated. A synthetic two-dimensional mammogram is calculated based on the three-dimensional digital breast tomosynthesis volume and the three-dimensional relevance map.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
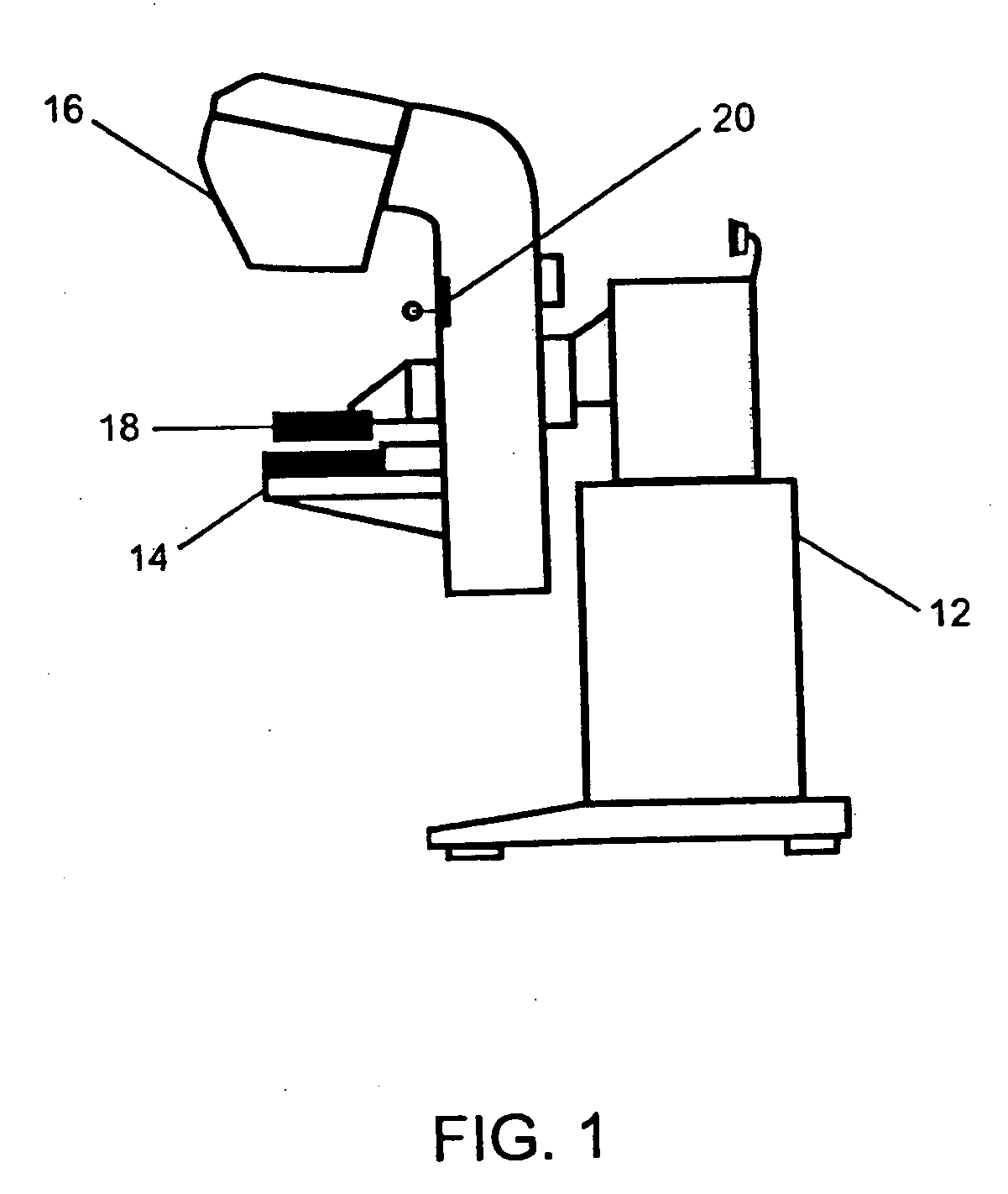
Mammogram recording and read-out apparatus
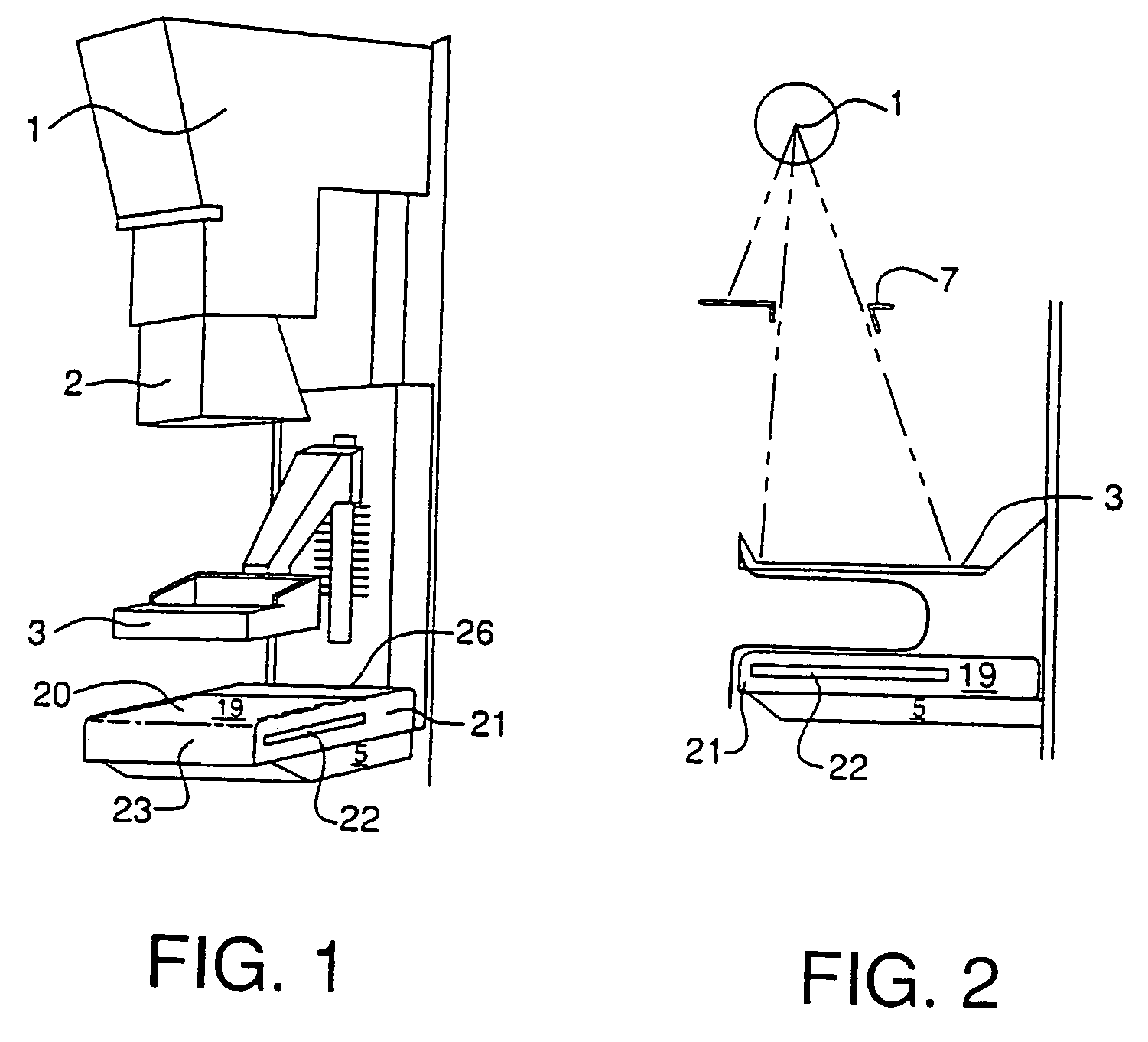
InactiveUS20050254620A1Appropriate performanceLow costTelevision system detailsSurgeryXeromammogramImage detector
A mammogram recording and read-out apparatus comprises a radiation image detector having a rectangular shape, a detector support section, and a breast support section. A support state of the detector support section is capable of being changed over between a first support state, in which the radiation image detector is supported in an orientation such that a short side of the radiation image detector stands facing the chest wall of an object, and a second support state, in which the radiation image detector is supported in an orientation such that a long side of the radiation image detector stands facing the chest wall of the object.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Device and method for the computer-assisted analysis of mammograms
ActiveUS20090220139A1Reduce areaFor automatic positioningImage enhancementImage analysisComputer-aidedNuclear medicine
A device for the computer-assisted analysis of mammograms. Said device comprises means for detecting a contour line that surrounds an object area of the mammogram, which is defined by an object. The device also comprises a means for positioning and scaling the mammogram. The device is configured to determine the contour line of the object area of the mammogram and to automatically position and scale the mammogram based on the contour line. A method for the computer-assisted analysis of mammograms is also disclosed. The disclosed device and method make it easier for a doctor to comparatively analyze and diagnose mammograms.
Owner:IMAGE DIAGNOST INT
Methods and apparatus for computer automated diagnosis of mammogram images
InactiveUS7865002B2Accurately determineReduce or eliminate false positive findingsImage enhancementImage analysisMammography viewComputer analysis
Owner:CAROLINA IMAGING SPECIALISTS
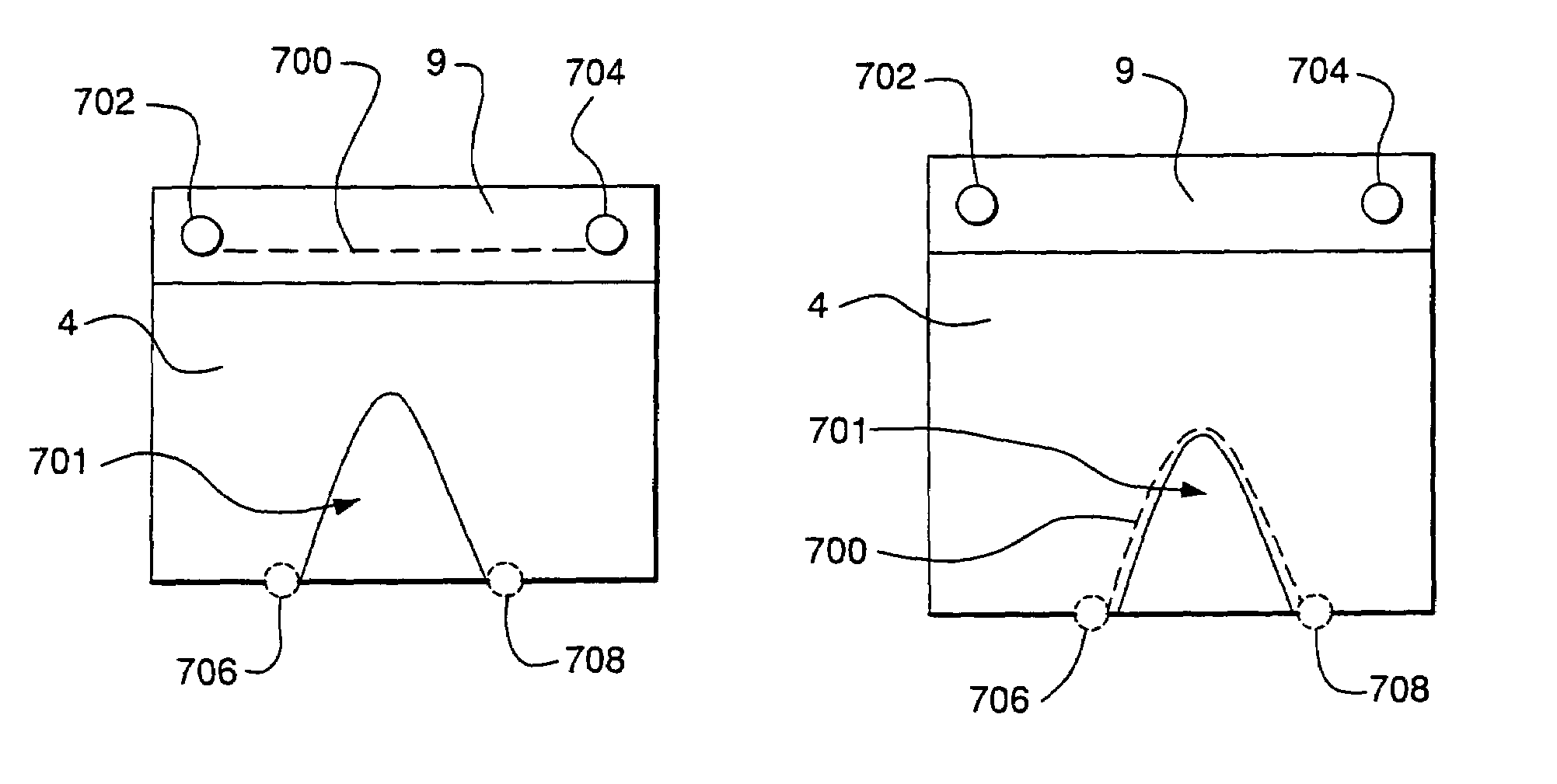
Method and apparatus for correction of mammograms for non-uniform breast thickness
A method and apparatus for correcting for a distortion in a mammogram. The method comprises classifying pixels as either likely fat or likely not-fat. The method further comprises identifying a candidate distortion and calculating a histogram of the likely fat and the likely not-fat pixels at the candidate distortion. The method further comprises evaluating a quality of the candidate distortion based on features of the histograms of pixel values in the fat and dense tissue classes. The distortion may be a two dimensional tilt of the plates or a three dimensional deformation of the plates as in a bend.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Generating a synthetic two-dimensional mammogram
ActiveUS20170011534A1Increase contrastImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionVoxelComputer science
A method for generating a synthetic two-dimensional mammogram with enhanced contrast for structures of interest includes acquiring a three-dimensional digital breast tomosynthesis volume having a plurality of voxels. A three-dimensional relevance map that encodes for the voxels the relevance of the underlying structure for a diagnosis is generated. A synthetic two-dimensional mammogram is calculated based on the three-dimensional digital breast tomosynthesis volume and the three-dimensional relevance map.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for determining peripheral breast thickness
InactiveUS20060167355A1Image analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringDigital mammogramComputerized system
A method, computer software product and computer system for analyzing digital mammograms. The method, computer software product and computer system involve a generating phantom thickness object; receiving a set of dimensions for a breast; and, transforming the phantom thickness object to conform to the set of dimensions for the breast to provide the three-dimensional breast thickness object.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK & WOMENS COLLEGE HEALTH SCI CENT
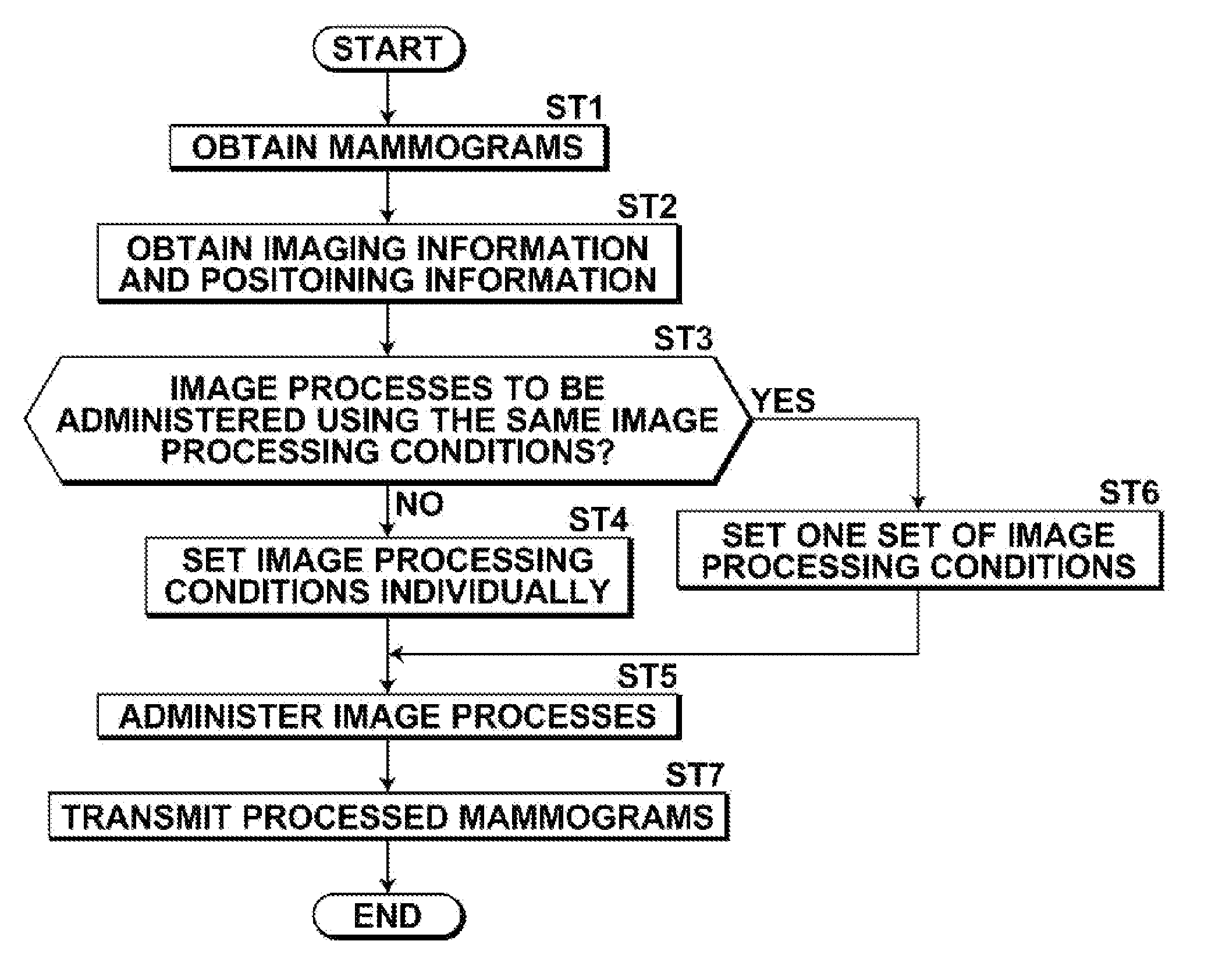
Radiation image processing apparatus, radiation image processing method, and radiation image processing program
InactiveUS20120014505A1Easy to observeImprove image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingComputer vision
An information obtaining means obtains imaging information related to states during imaging and positioning information related to positioning of breasts during imaging regarding a plurality of mammograms, which are targets of comparison. An image processing means administers image processes onto the plurality of mammograms based on predetermined image processing conditions. A judging means judges whether image processes are to be administered onto the plurality of mammograms according to the same image processing conditions, based on the imaging information and the positioning information.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
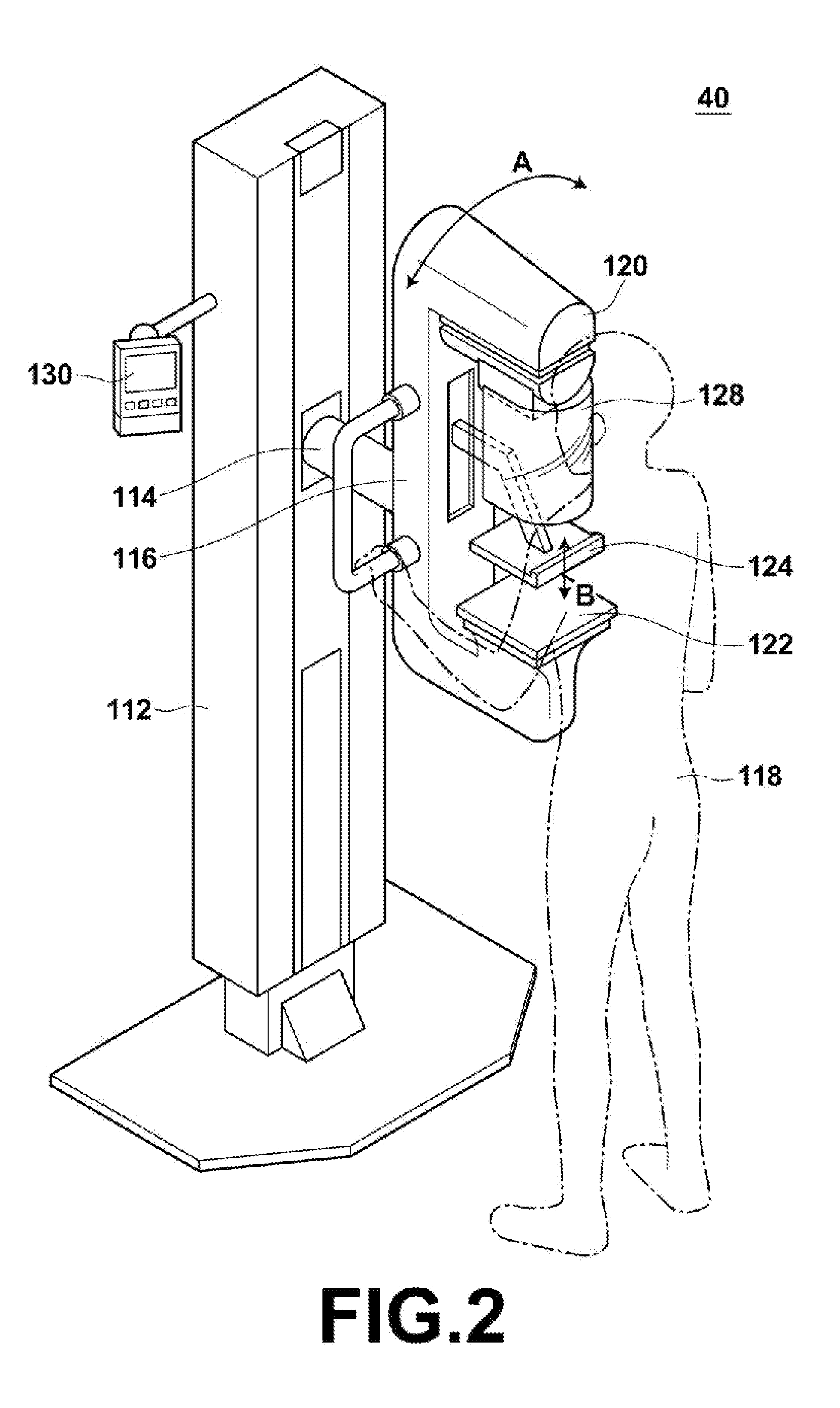
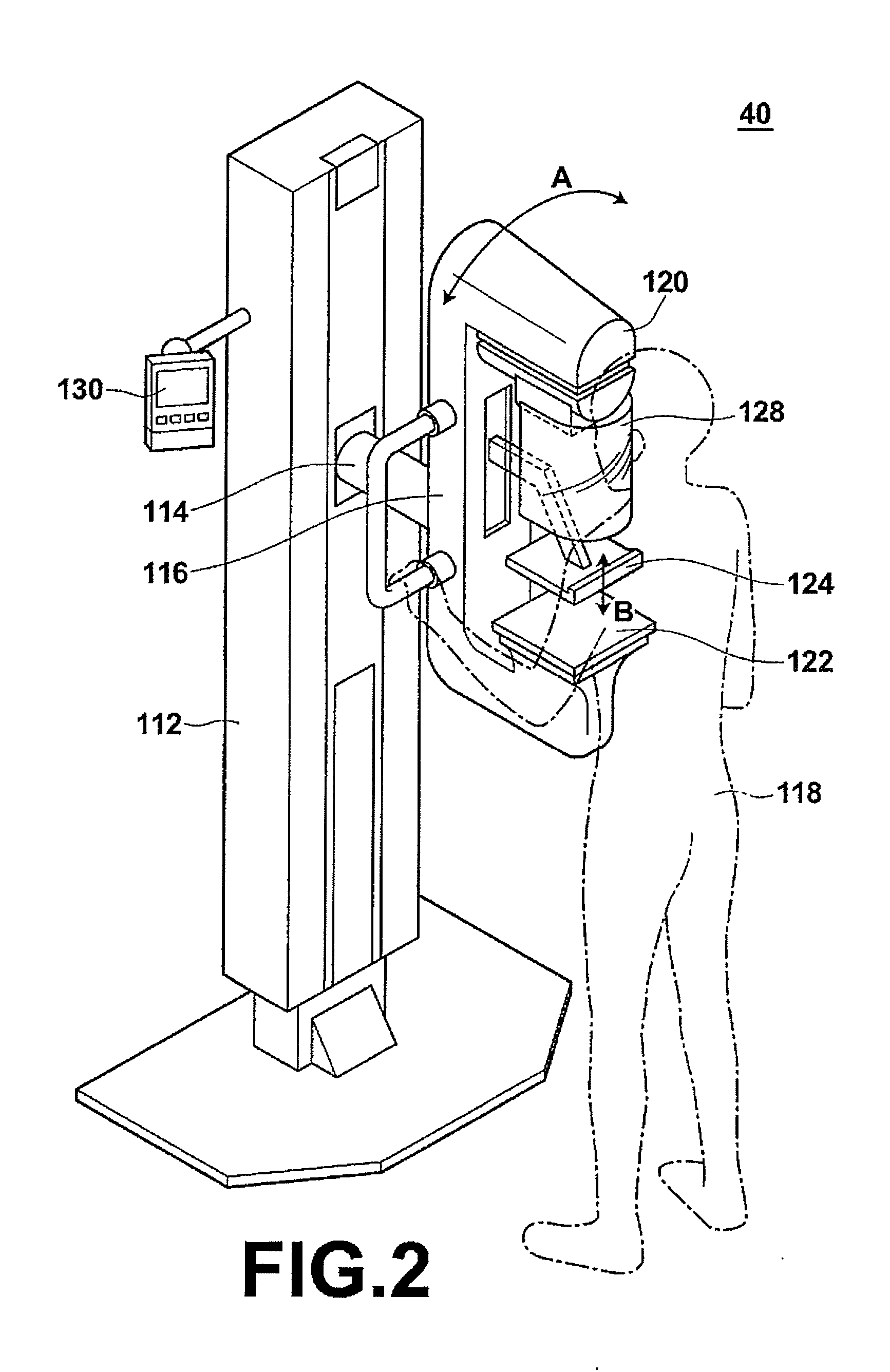
Mammography systems and methods, including methods utilizing breast sound comparision
InactiveUS20080240345A1Increase heightBreast motionStethoscopePatient positioning for diagnosticsSound detectionCompression device
Provided are systems using compression devices for a mammography unit, and methods of using the same, for example, in conjunction with imaging of a patient's breast. The instant mammography units can comprise at least one x-ray transparent inflatable chamber for containing a fluid. When fluid is introduced into the chamber, at least one surface of the chamber expands, breast motion is limited, and the breast and its vasculature are compressed. Fluid may also be released from the chamber, and as the chamber deflates, blood flow to the breast is restored, producing Korotkoff sounds that may be detected by a sound detection device. Sound data may be obtained with respect to both of a patient's breasts, and the sound data from a patient's first breast may be compared with the data obtained from the contralateral breast. The detected sounds, the comparison data, or both may be used to assist a radiologist in identifying regions of interest on a mammogram, and additionally or alternatively may be used to a enhance a computer-assisted detection (CAD) process by contributing additional data parameters.
Owner:GALKIN BENJAMIN M
Display for computer-aided diagnosis of mammograms
InactiveUS7203350B2Aid in diagnosisHard to see or difficult to evaluate lesionsImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay deviceMalignancy
A method for displaying a computer-generated determination of the likelihood of malignancy in a mammogram lesion. The method requires providing a digitized image of a mammogram, displaying the digitized image, and selecting a region of interest directly on the displayed digitized image. The digitized image is then processed so that classifier data of the lesion in the user-selected region of interest are generated and displayed. A system for displaying a determination of the likelihood of malignancy in a mammogram lesion. The system includes a display for presenting a digitized mammogram and an input device in communication with the display for selectably indicating a region of interest on the displayed mammogram. The system also includes a processor for generating classifier data related to a characterization feature within the region of interest. The classifier data is presented on the display.
Owner:SIEMENS COMP AIDED DIAGNOSIS
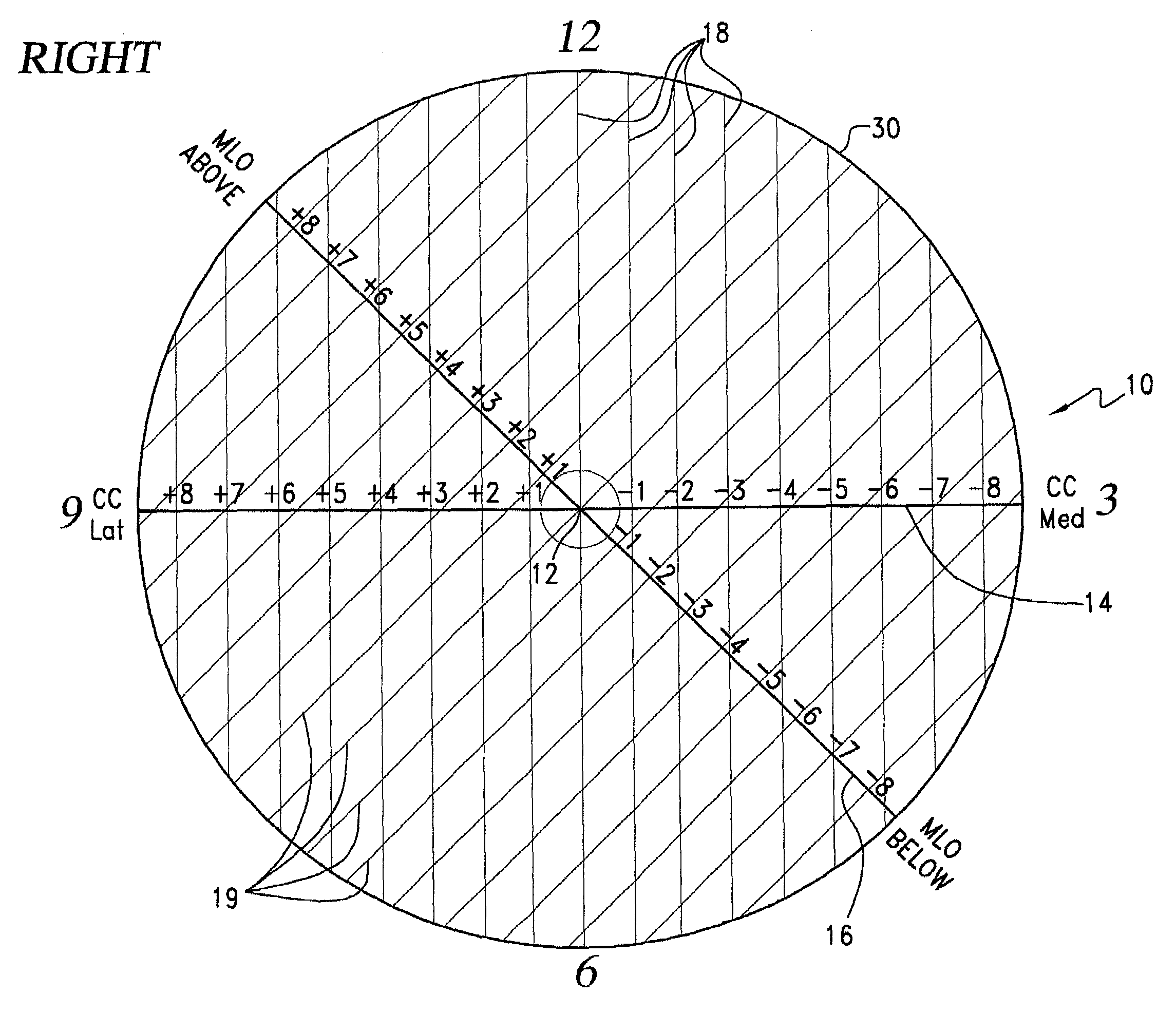
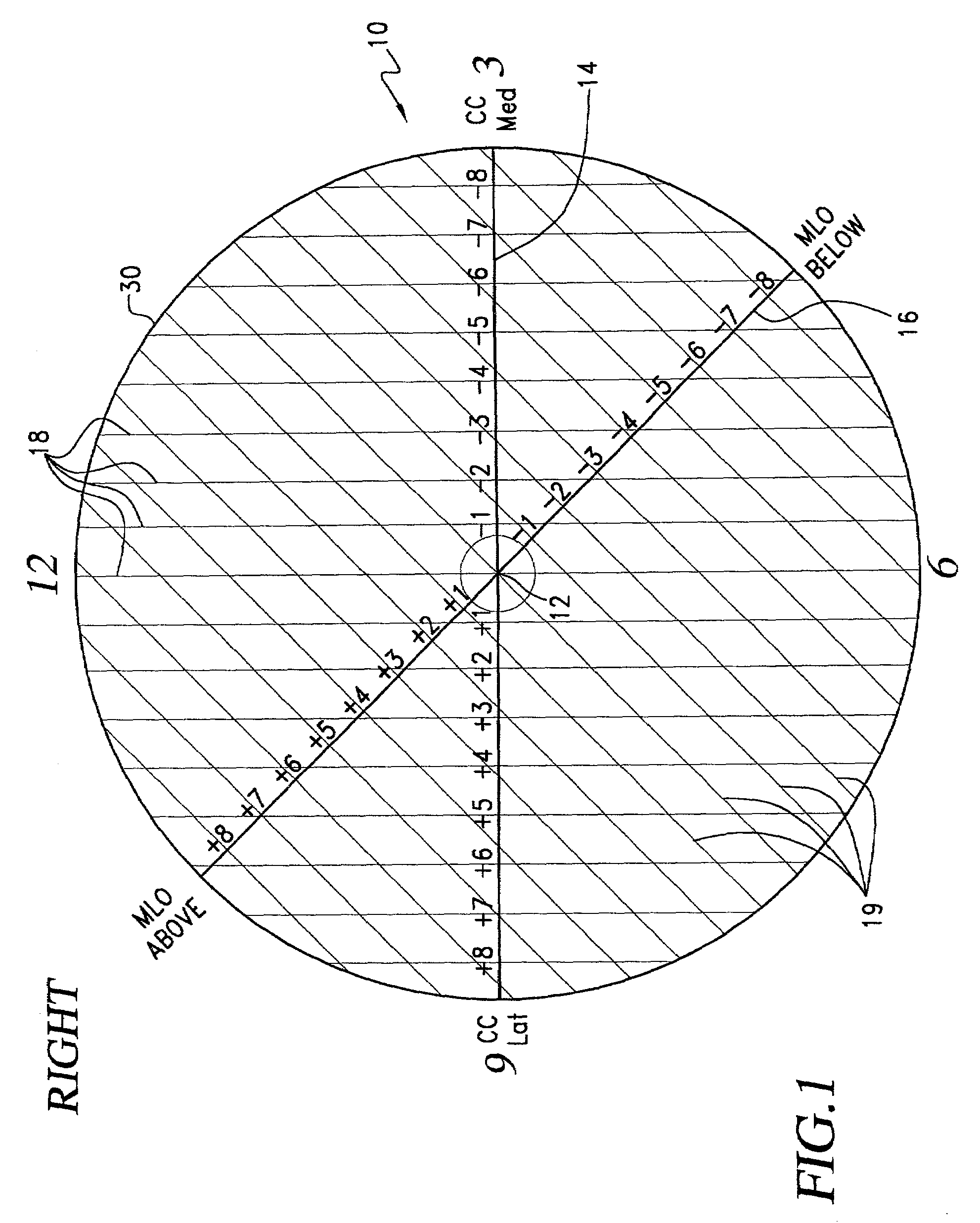
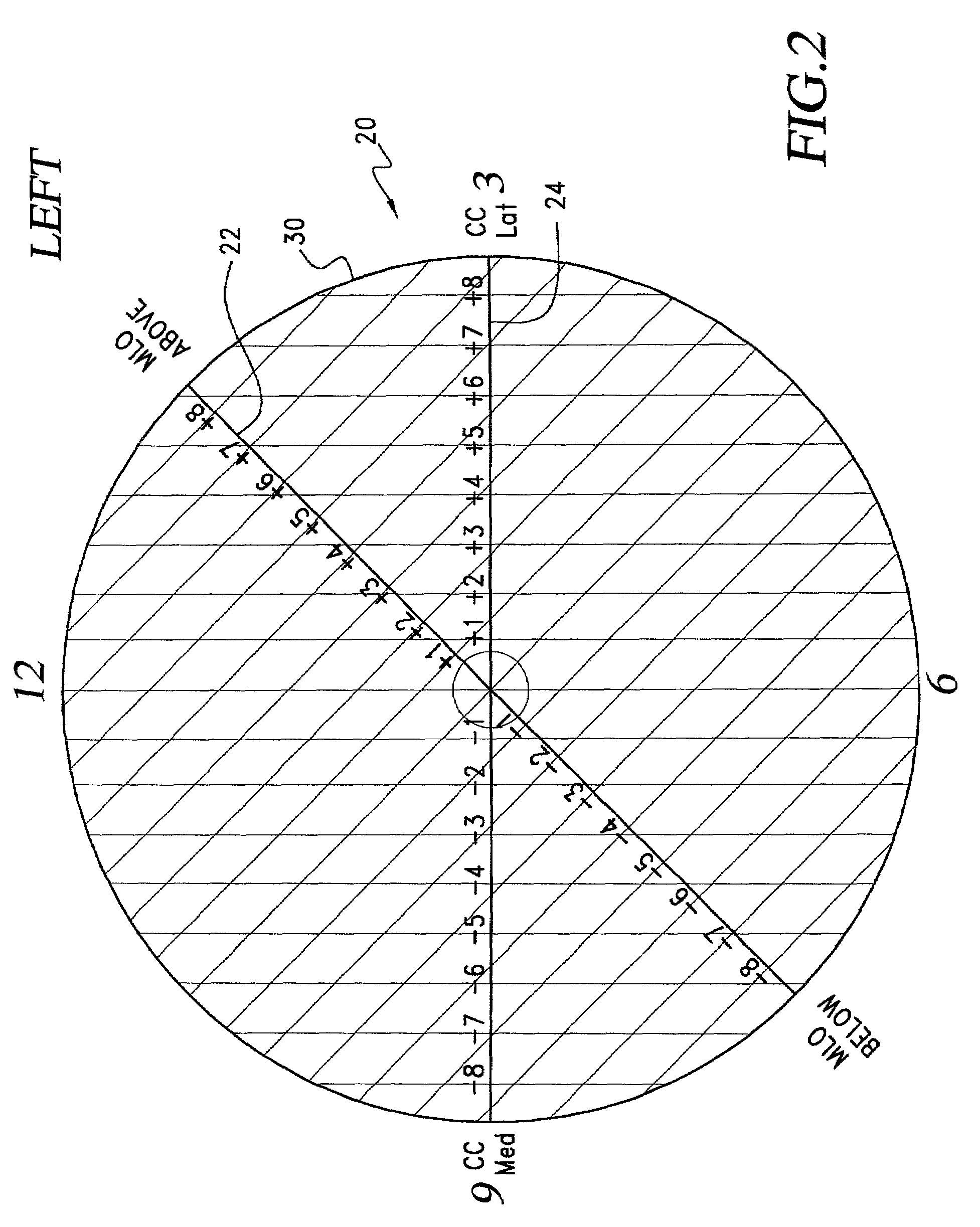
Template for the localization of lesions in a breast and method of use thereof
ActiveUS7124760B2Enhance self-confidenceFair degree of imprecision in localizing lesionsSurgeryPatient positioning for diagnosticsLeft breastRight breast
A template for the localization of lesions in a breast. The template includes a substrate of transparent material that includes a central marking; a horizontal line extending through the central marking; a first series of spaced lines, each line of the first series being perpendicular to the horizontal line and each line including marking indicia for indicating the distance of that line from the central marking; an oblique line extending approximately 45 degrees from the horizontal line and through the central marking; and, a second series of spaced lines, each line of the second series being perpendicular to the oblique line and each line including marking indicia for indicating the distance of that line from the central marking. There is a right breast template and a left breast template. The appropriate template is utilized and the CC and MLO views of a mammogram are used to define a CC line and an MLO line that are plotted on that template. The intersection of these two lines is indicative of the location of the lesion. The template can then be placed over the breast of the patient and a lesion-indicative marking can be placed on the patient's skin.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
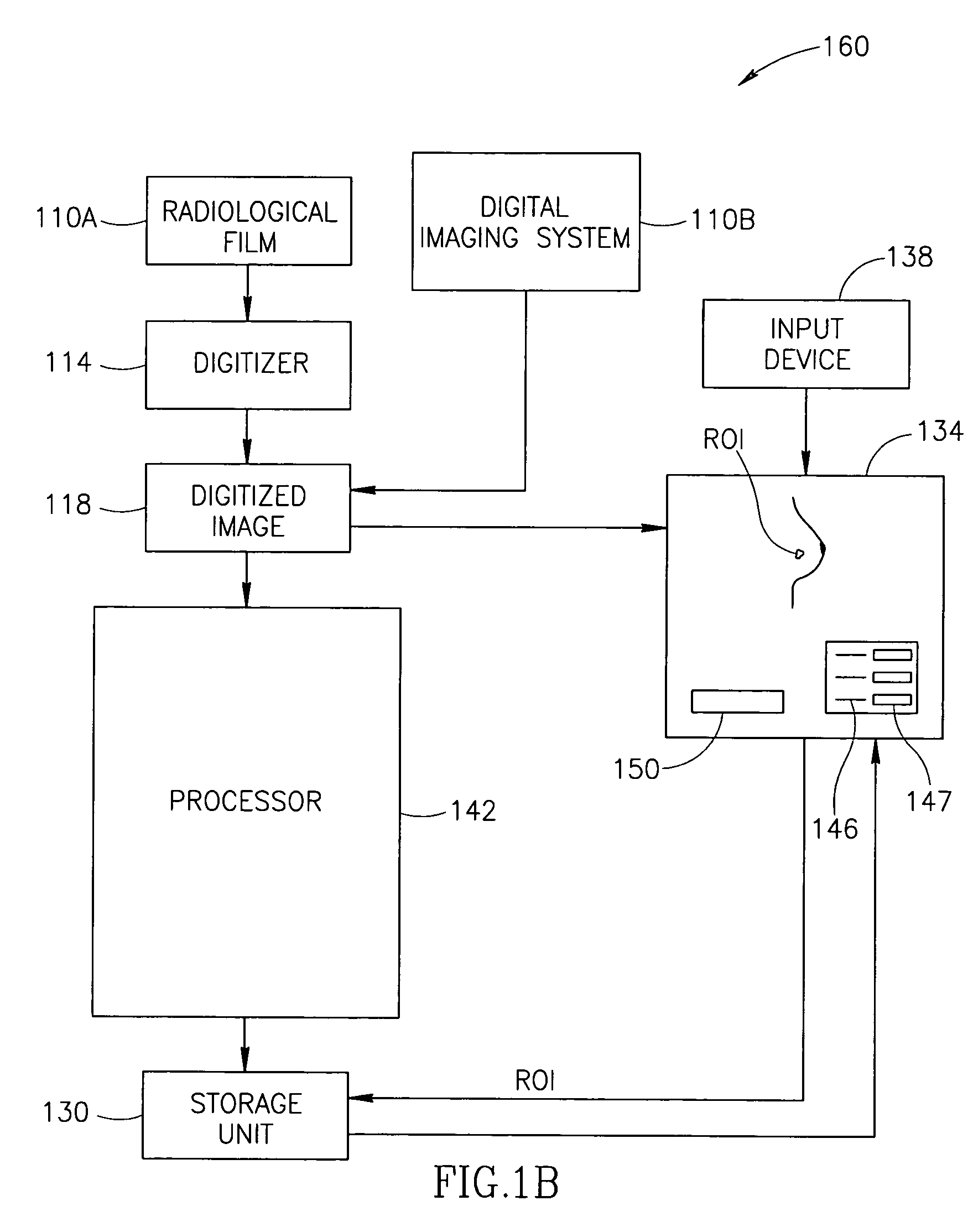
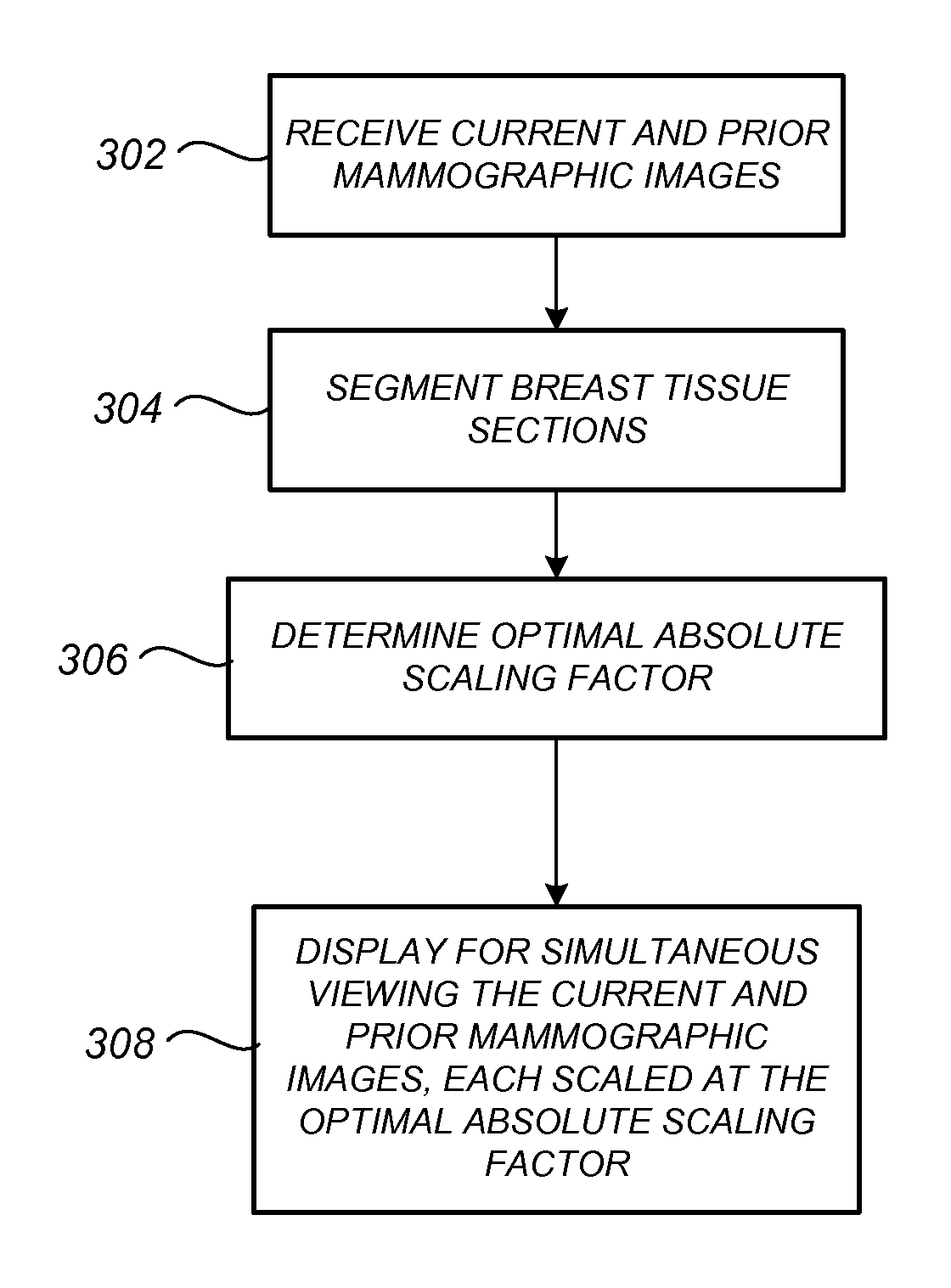
Facilitating Temporal Comparison of Medical Images
InactiveUS20110128289A1Facilitating temporal comparisonFacilitating temporal comparison of breast mammogramsImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay deviceComputer science
Methods, systems, and computer program products for facilitating temporal comparison of medical images is provided, with one exemplary application being for breast mammograms. In one embodiment, prior and subsequent mammographic images of a breast acquired using at least partially different mammogram acquisition systems are displayed for simultaneous viewing on a same mammogram display at an identical tissue distance per unit display distance without requiring a scale-adjusting viewer input. Also described are other embodiments for optimally scaling, windowing and / or otherwise advantageously processing and / or displaying prior and subsequent mammographic image sets in manners that facilitate temporal comparison therebetween.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Mammography cushioning devices and methods
InactiveUS7142631B2Less discomfortReducing patient discomfortPatient positioning for diagnosticsMammographyPatient comfortBiomedical engineering
A mammography comfort device comprises a compressible bolster and a separate x-ray transparent compressible pad. The bolster, affixed to the sides of a bucky, retains the pad on the imaging surface. A radiopaque identifier permanently affixed to the pad imparts information about the pad onto a mammogram. The comfort device can be used with an x-ray transparent disposable cover. A kit comprising at least two disposable covers and a comfort device can be supplied. A separate stretchable retainer holds a breast on the bucky and serves as an exposure equalizer. A compression paddle adapted with a bolster and a light transparent panel facilitates proper placement of a breast for compression. When the bolster comprises sections having different identification force deflection values the panel angles to the approximate shape of a compressed breast to distribute compression force more evenly. A vented panel provides for passage of warm air for patient comfort.
Owner:GALKIN BENJAMIN M
Three dimensional mapping display system for diagnostic ultrasound machines and method
ActiveUS20140163376A1Shorten the timeTime-consuming to eliminateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityUltrasonic sensor
An apparatus, system, and method where the ultrasound transducer position registration is automated, calculates the position of each pixel in the ultrasound image in reference to the predetermined anatomical reference points (AR) and can store the information on demand. The graphic interface associated with the ultrasound image allows for the instant display of selected targets position coordinates relative to anatomical reference points, in the ultrasound images. This system would significantly reduce the ultrasound examination time, by eliminating the time consuming manual labeling of images and speeding up the target finding at subsequent examinations, enhance correlation capability with other diagnostic imaging modalities like CT scans, MRI, mammograms, decrease human errors and fatigue, provide an easy, uniform, method of communicating the target position among healthcare providers.
Owner:METRITRACK
Radiation image processing apparatus, radiation image processing method, and radiation image processing program
InactiveUS20120014585A1Ensure correct executionImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingMulti resolution
A multiple resolution converting means administers multiple resolution conversion on a plurality of radiation images, which are targets of comparison, to generate a plurality of band images having different frequency bands. An image processing means administers image processes on the plurality of band images having corresponding frequency bands to match the appearances thereof, based on anatomical information of structures included in the mammogram MA reconstructing means reconstructs the band images, on which the image processes have been administered, to generate processed radiation images.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com