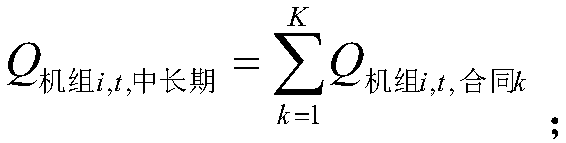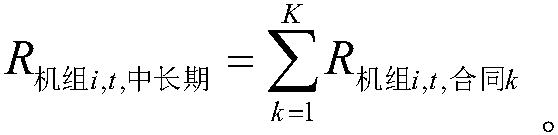Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Workload scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
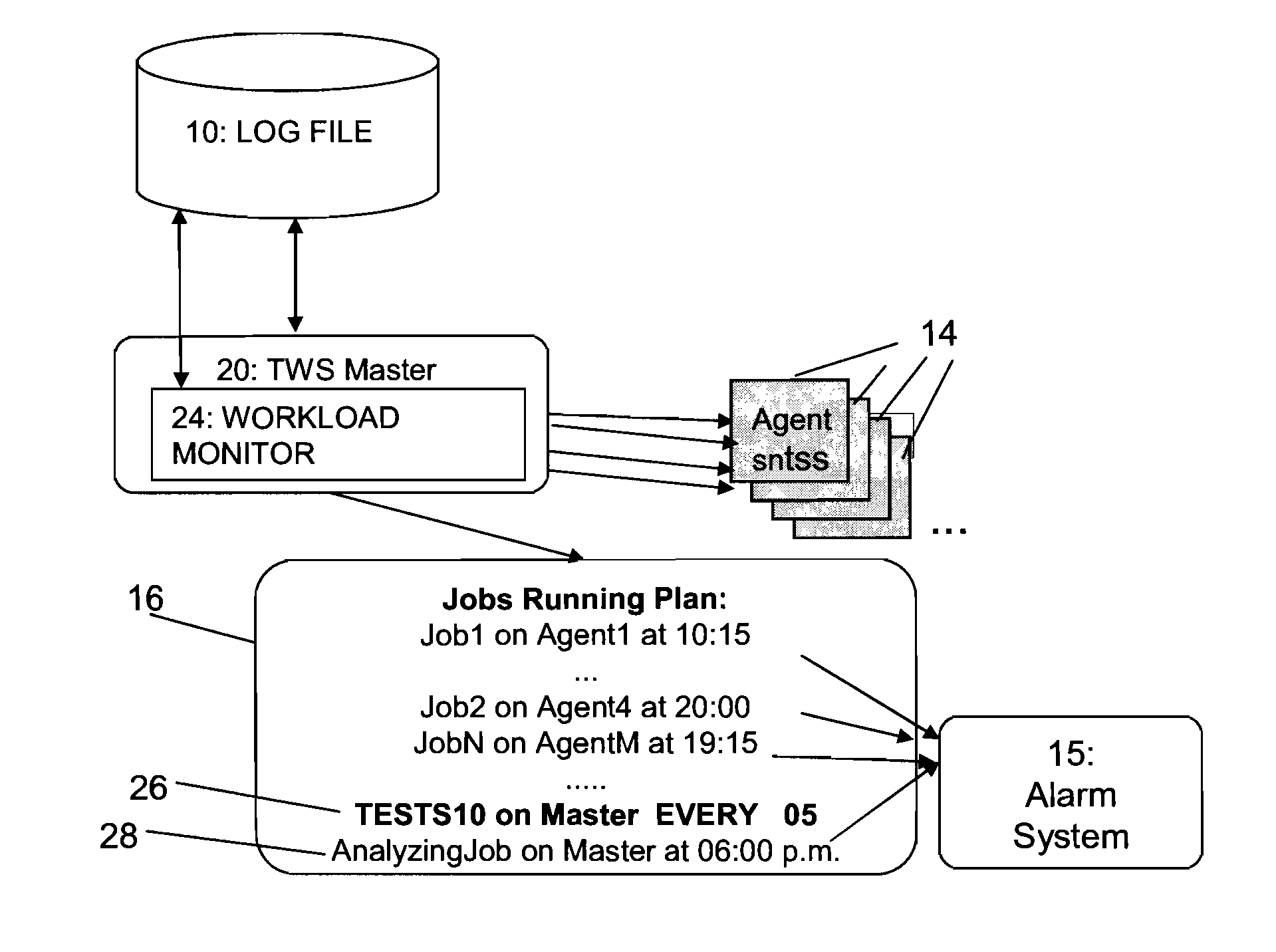
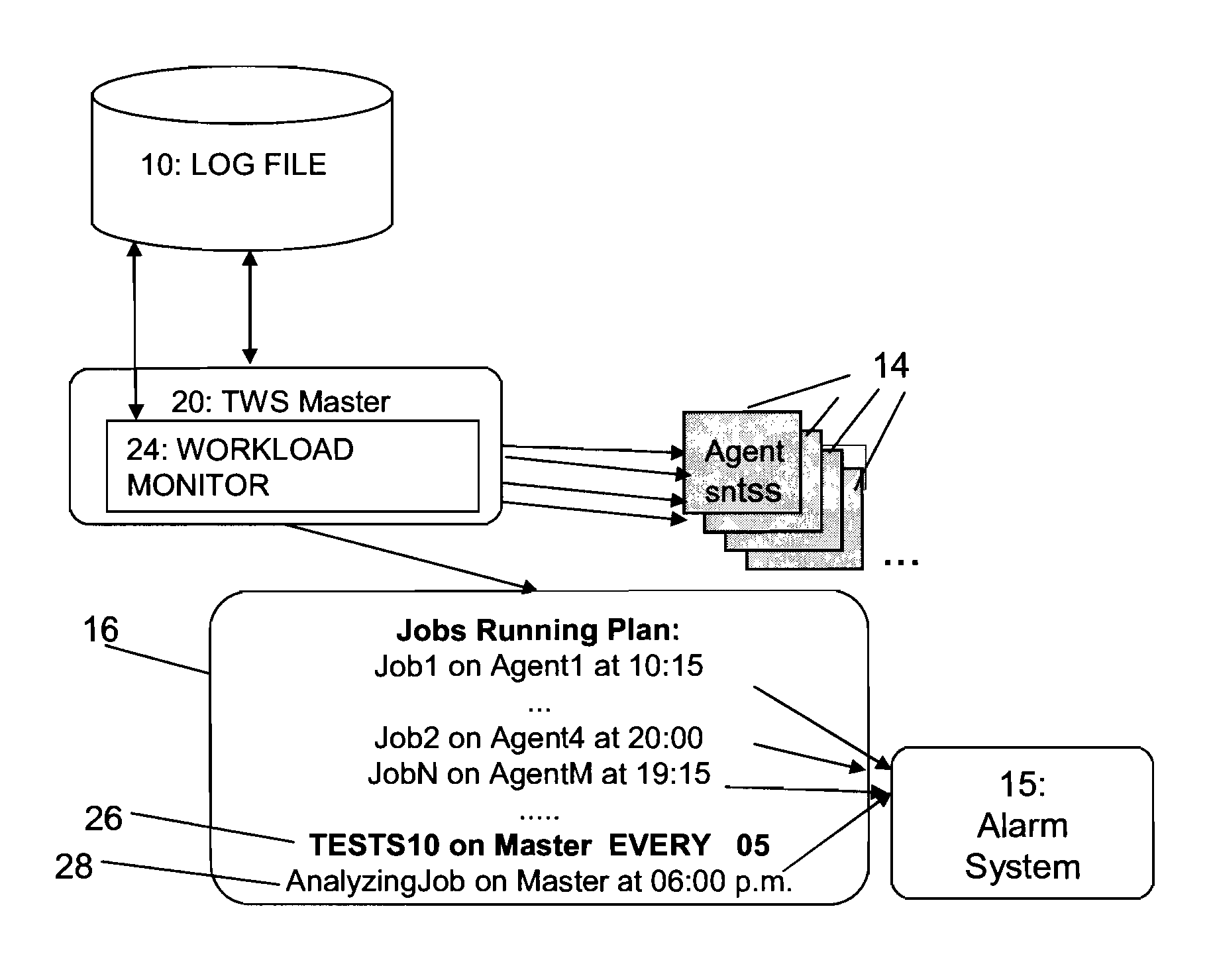
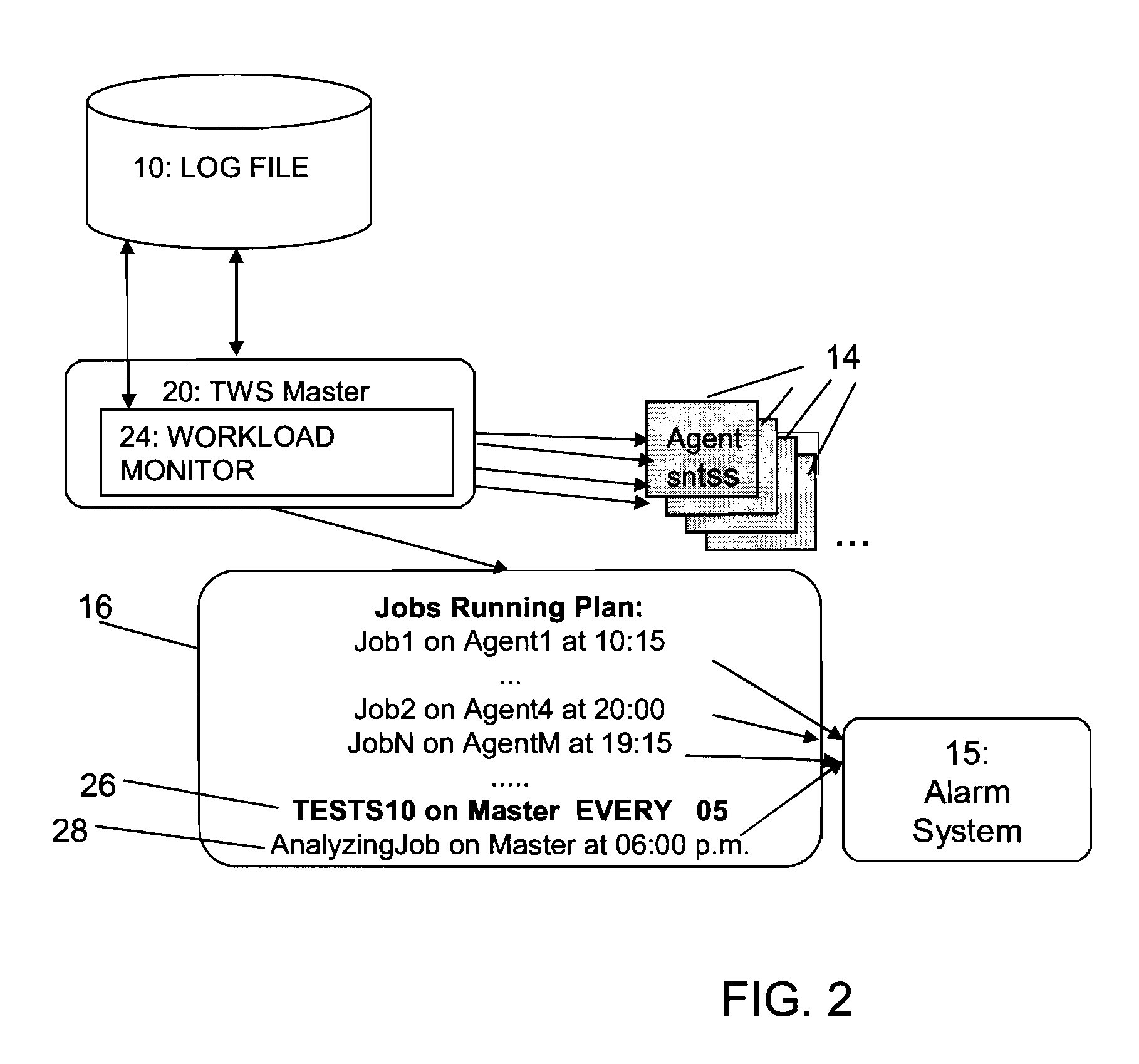
In the distributed computing world, scheduling means job scheduling, or more correctly, workload management. Workload management is not only about how a specific unit of work is submitted, packaged and scheduled, but it's also about how it runs, handles failures and returns results.
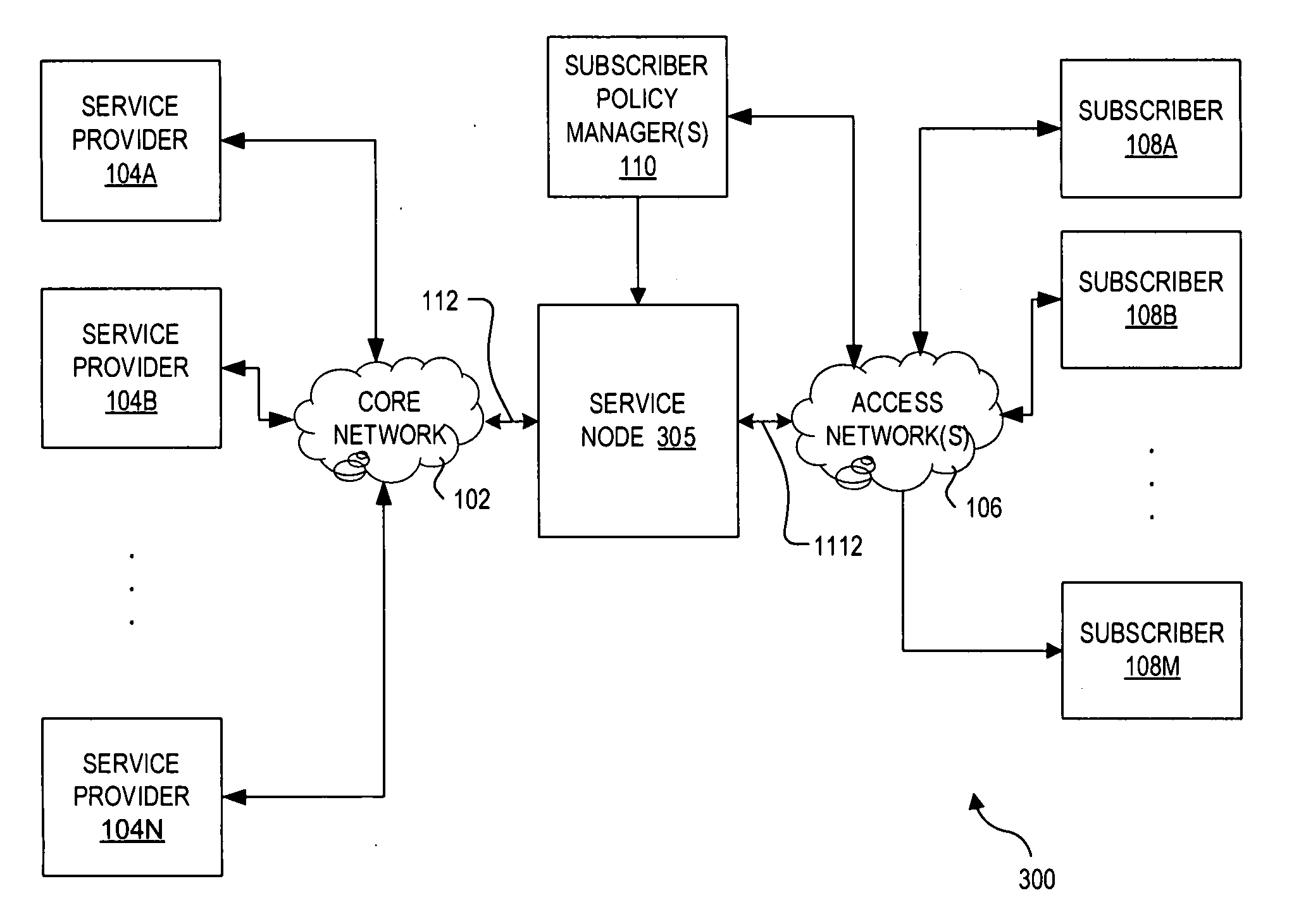
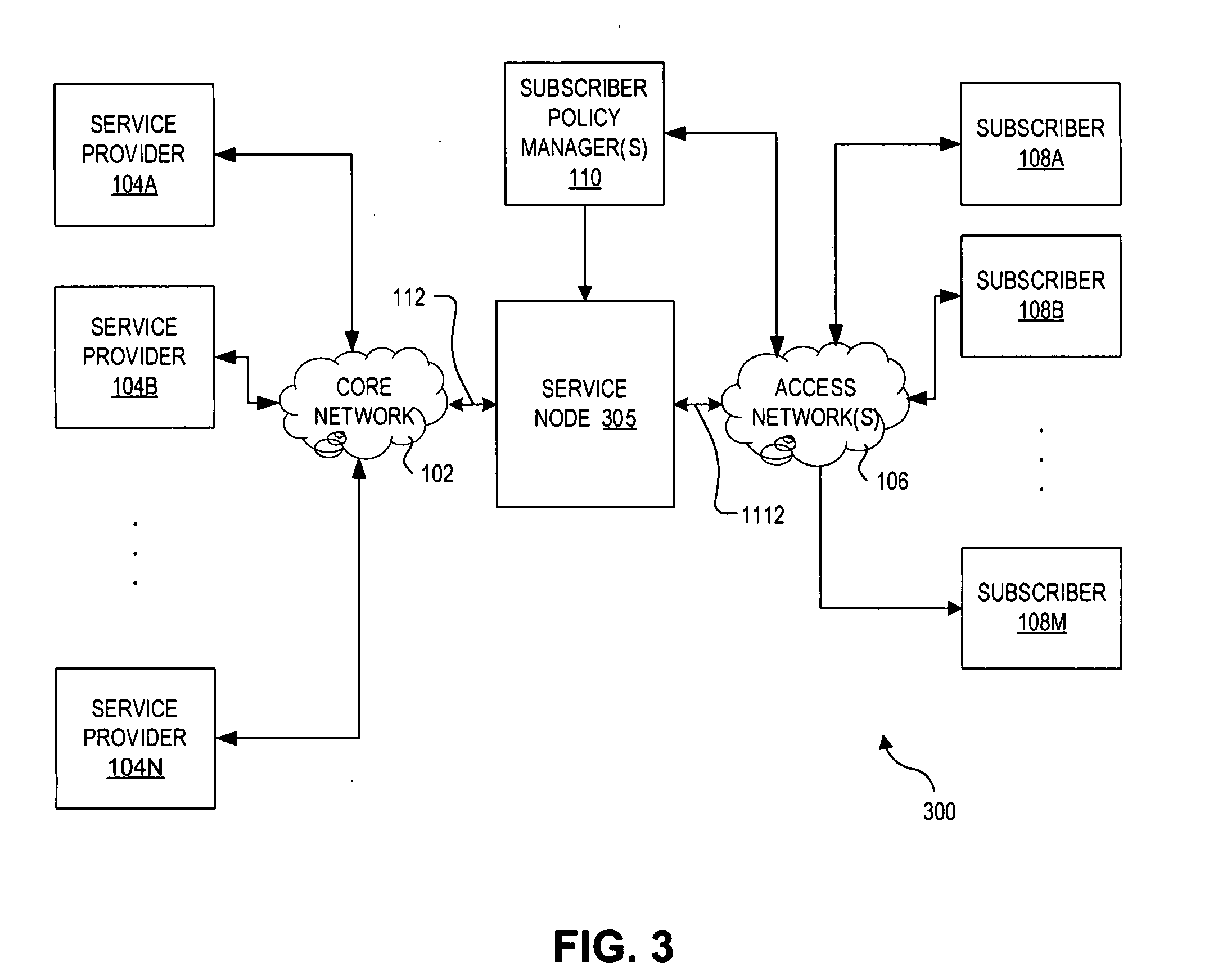
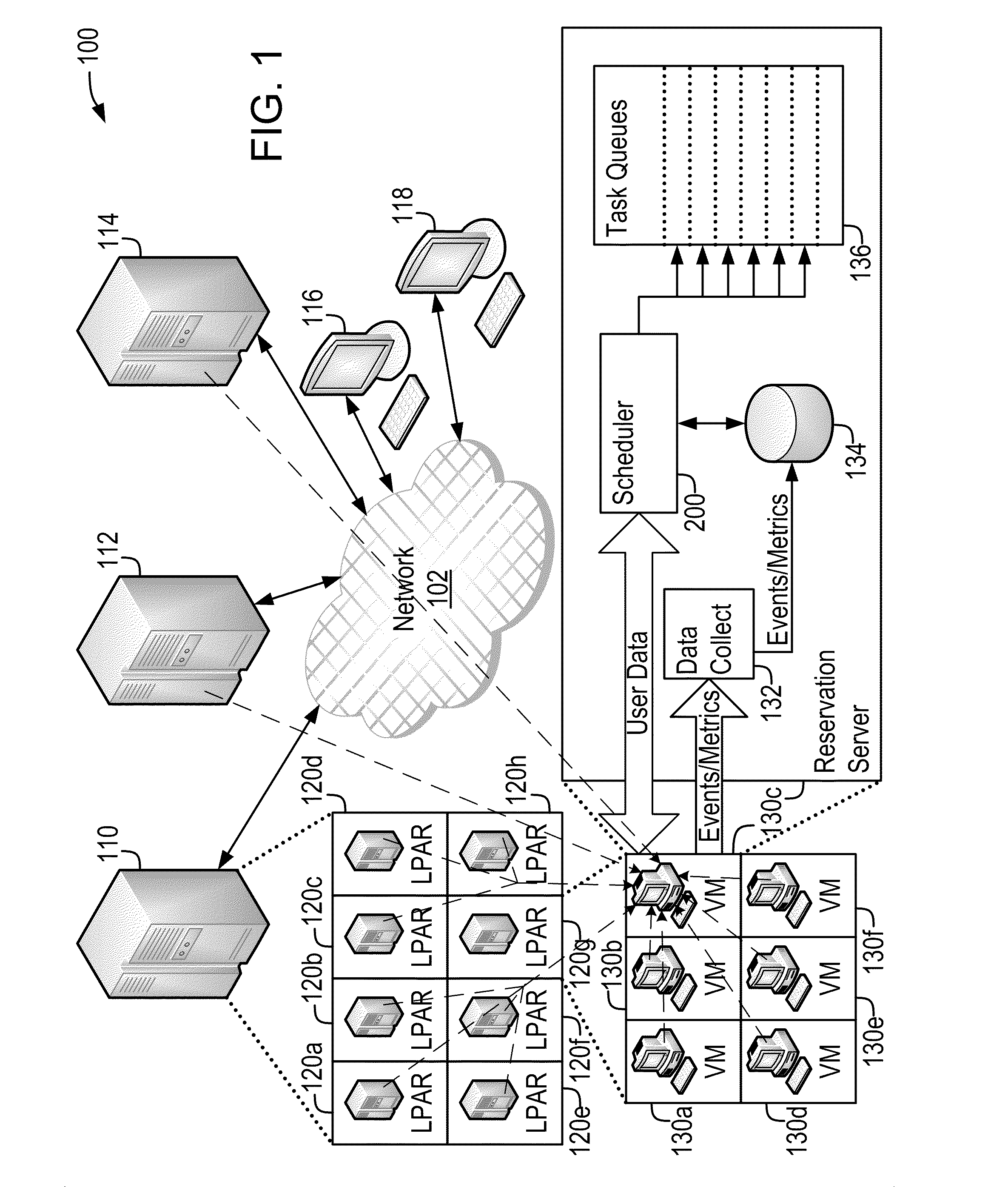
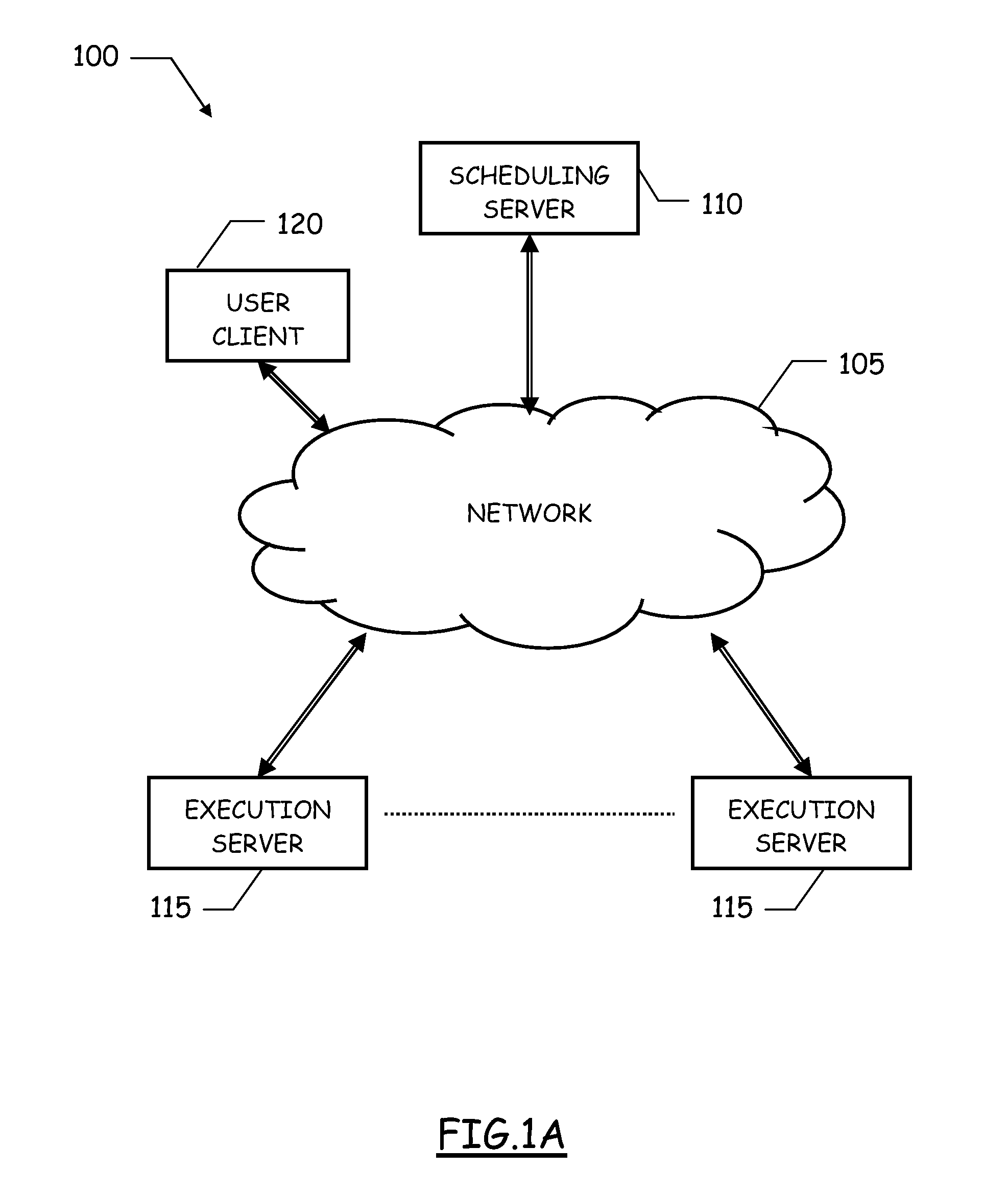
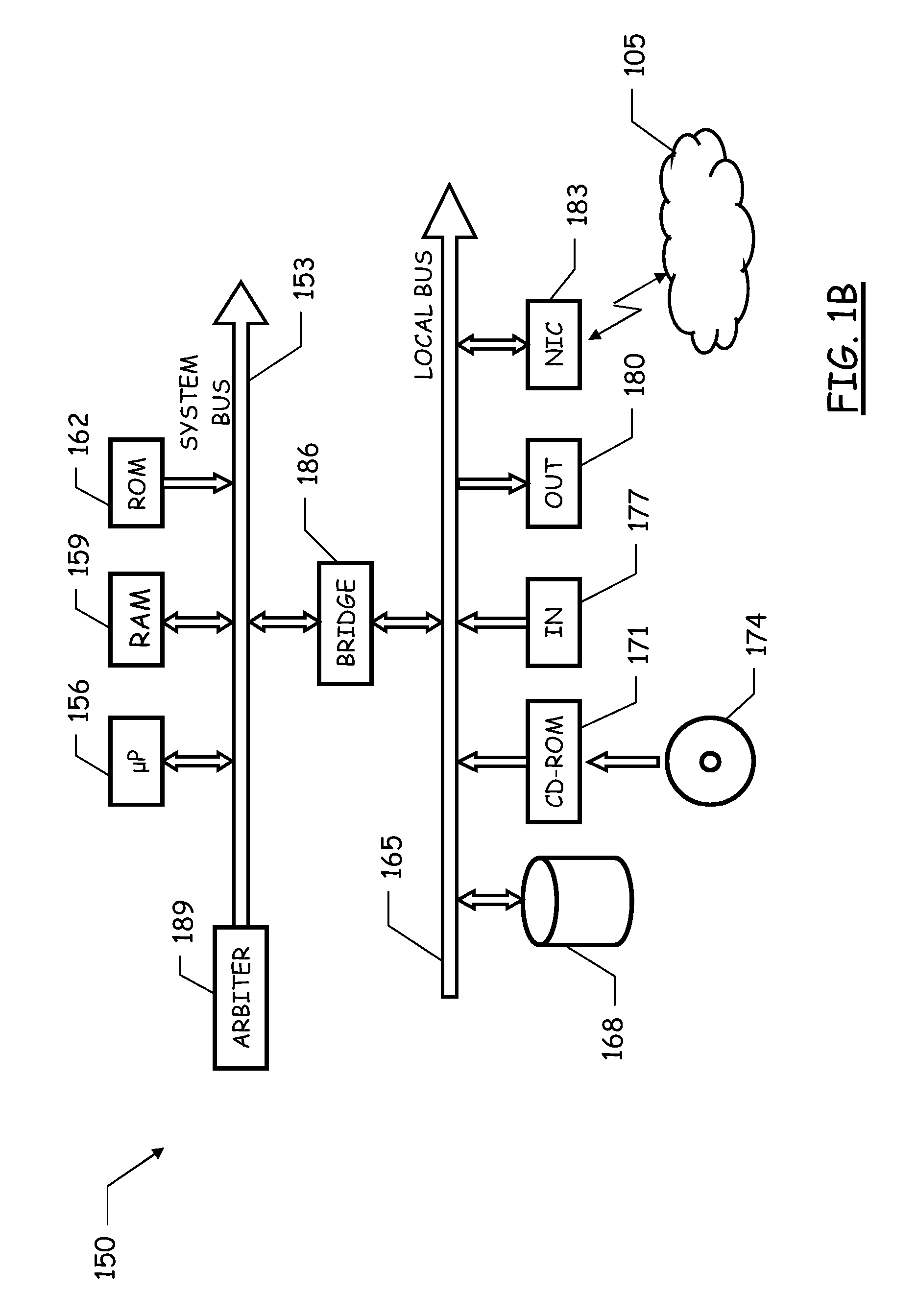
Scheduling of workloads in a distributed compute environment
A method of workload scheduling in a distributed compute environment includes assigning a subscriber of a network service to a first compute node instance (“CNI”) of a plurality of CNIs within a network node interposed between the subscriber and a provider of the network service. The subscriber traffic associated with the subscriber is processed at the first CNI. Subscriber specific data is generated at the first CNI related to the subscriber traffic. The subscriber specific data is then backed up to a second CNI of the network node that is designated as a standby CNI that will process the subscriber traffic if the first CNI fails.
Owner:TELLABS COMM CANADA
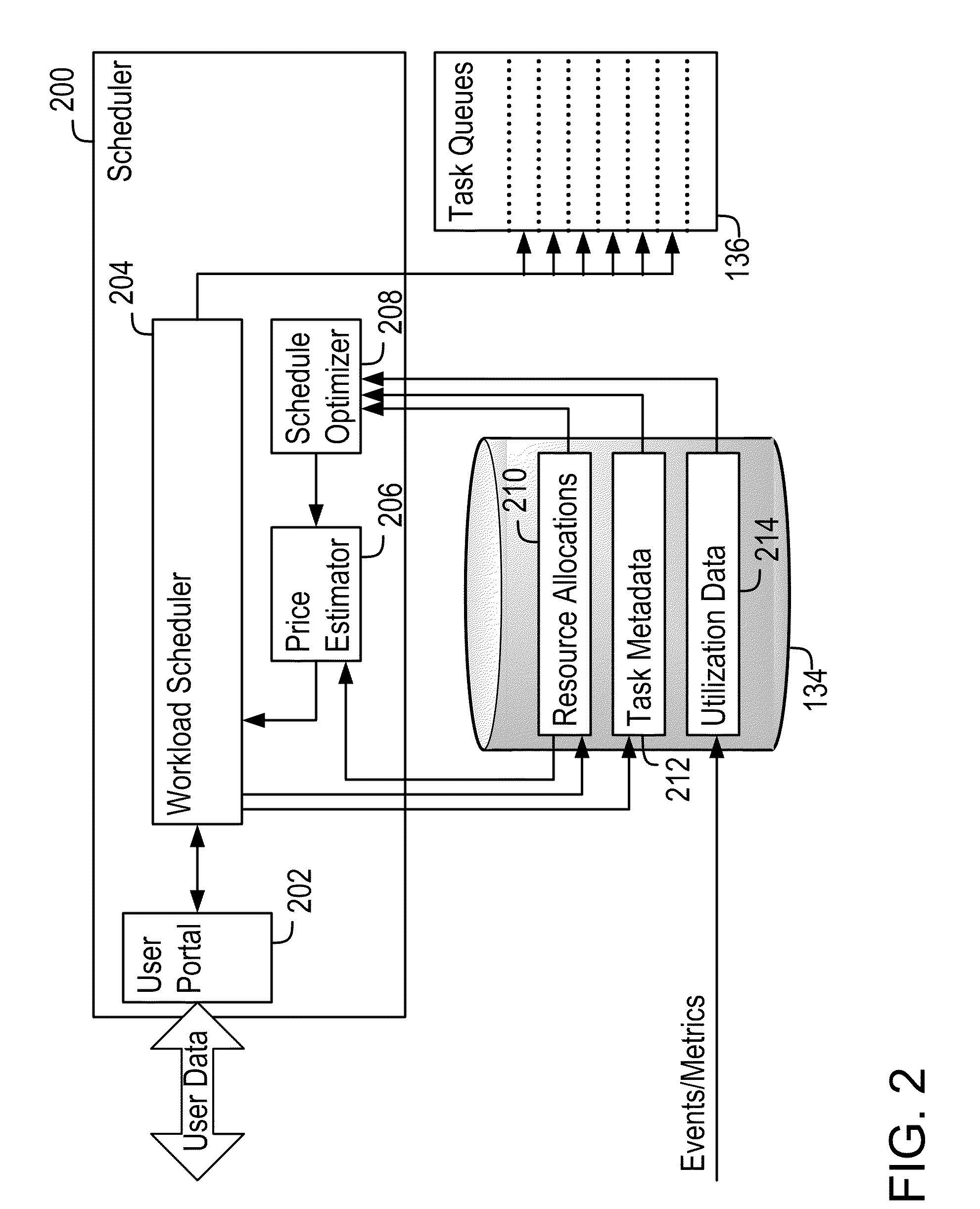
Demand-Driven Workload Scheduling Optimization on Shared Computing Resources
InactiveUS20110154353A1Low costHinder taskResource allocationMemory systemsTime scheduleProgram planning
Systems and methods implementing a demand-driven workload scheduling optimization of shared resources used to execute tasks submitted to a computer system are disclosed. Some embodiments include a method for demand-driven computer system resource optimization that includes receiving a request to execute a task (said request including the task's required execution time and resource requirements), selecting a prospective execution schedule meeting the required execution time and a computer system resource meeting the resource requirement, determining (in response to the request) a task execution price for using the computer system resource according to the prospective execution schedule, and scheduling the task to execute using the computer system resource according to the prospective execution schedule if the price is accepted. The price varies as a function of availability of the computer system resource at times corresponding to the prospective execution schedule, said availability being measured at the time the price is determined.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
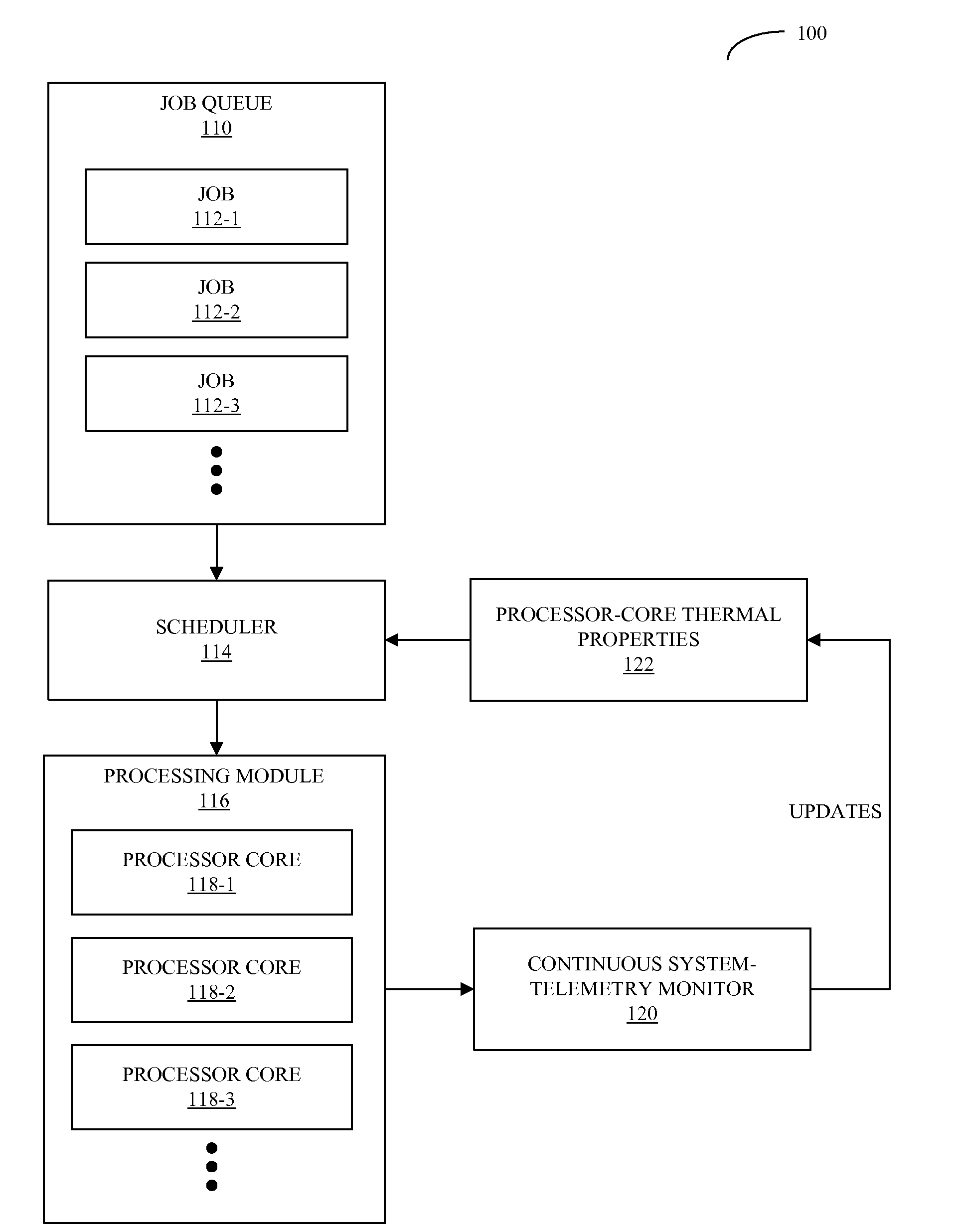
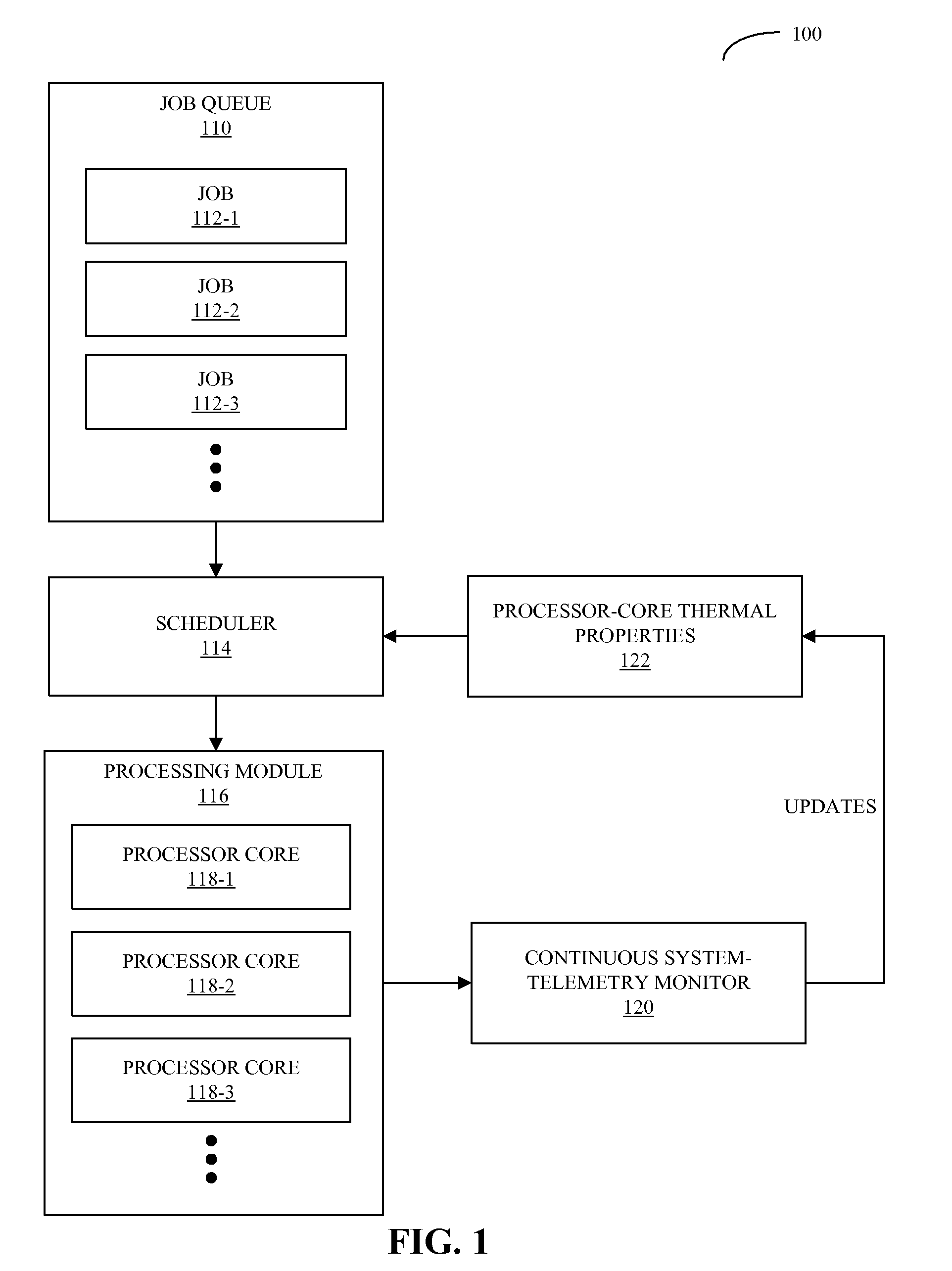
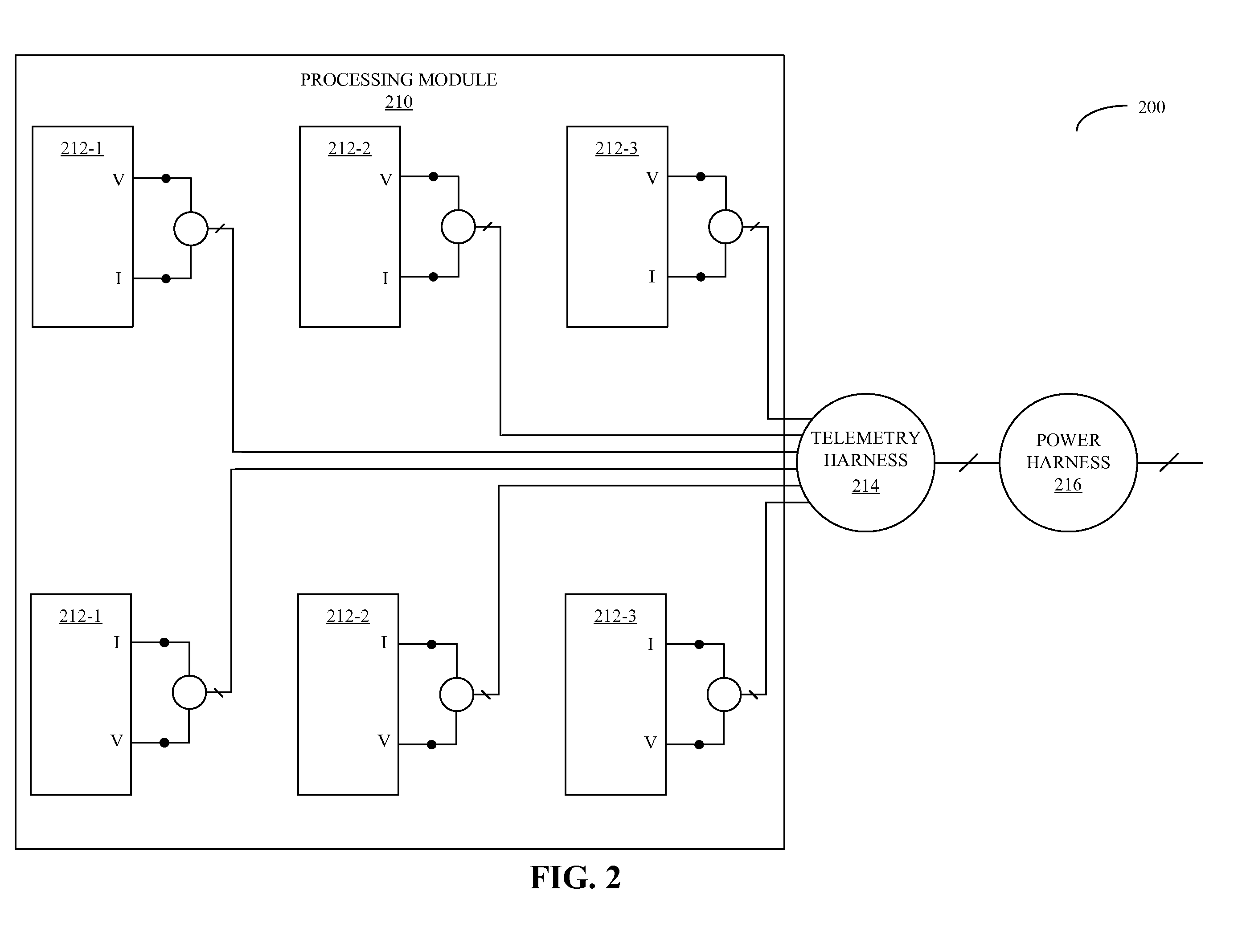
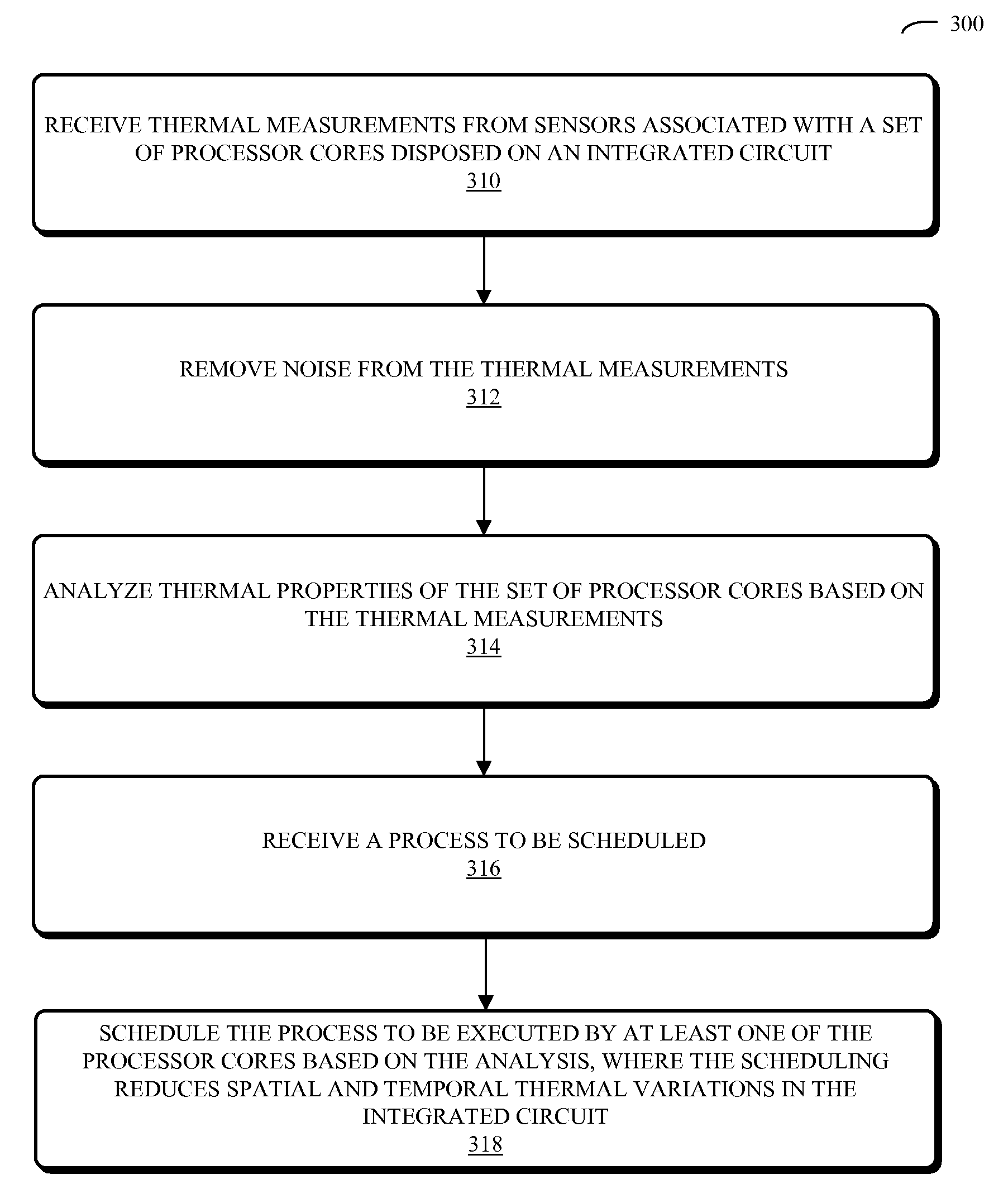
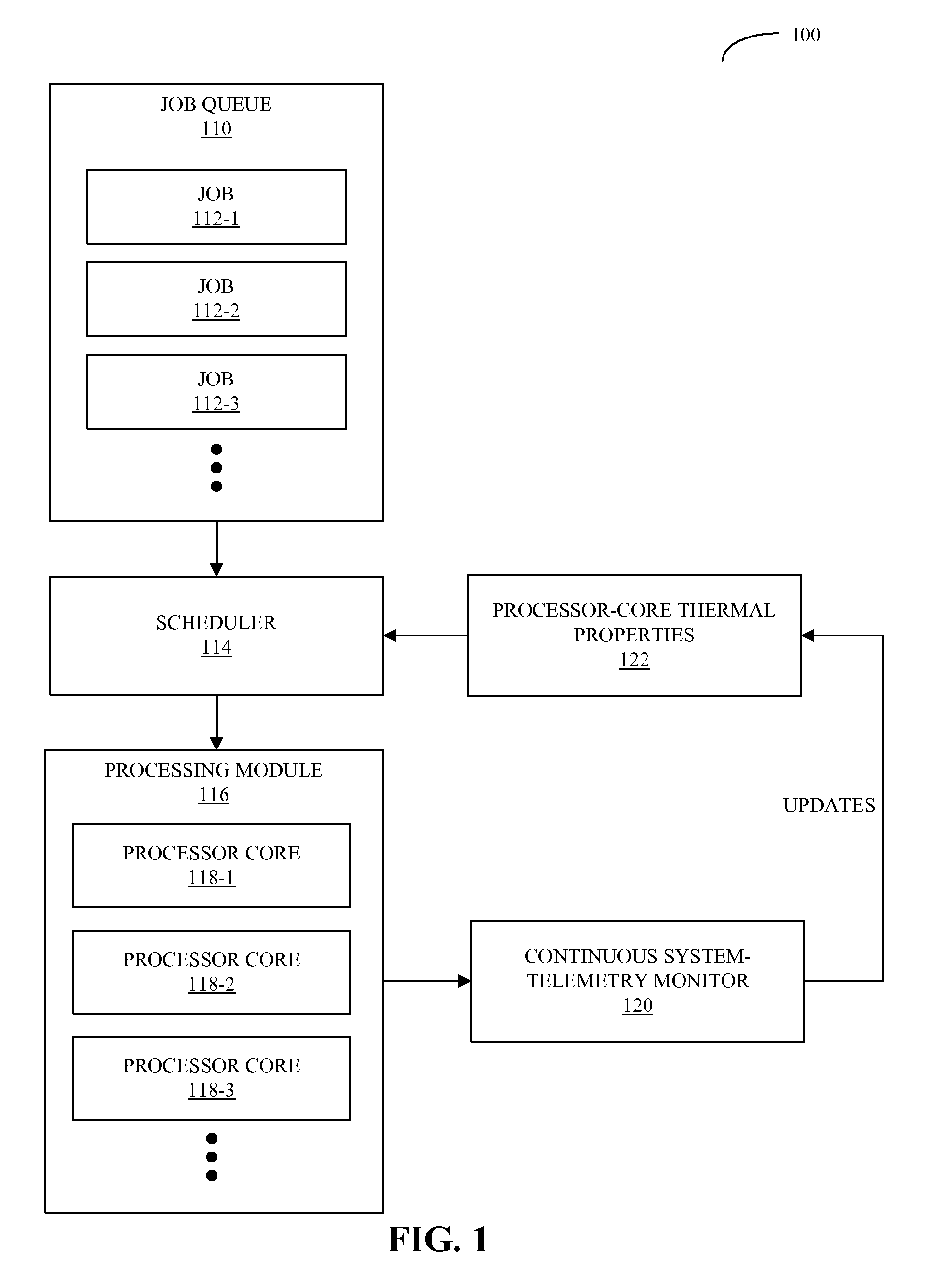
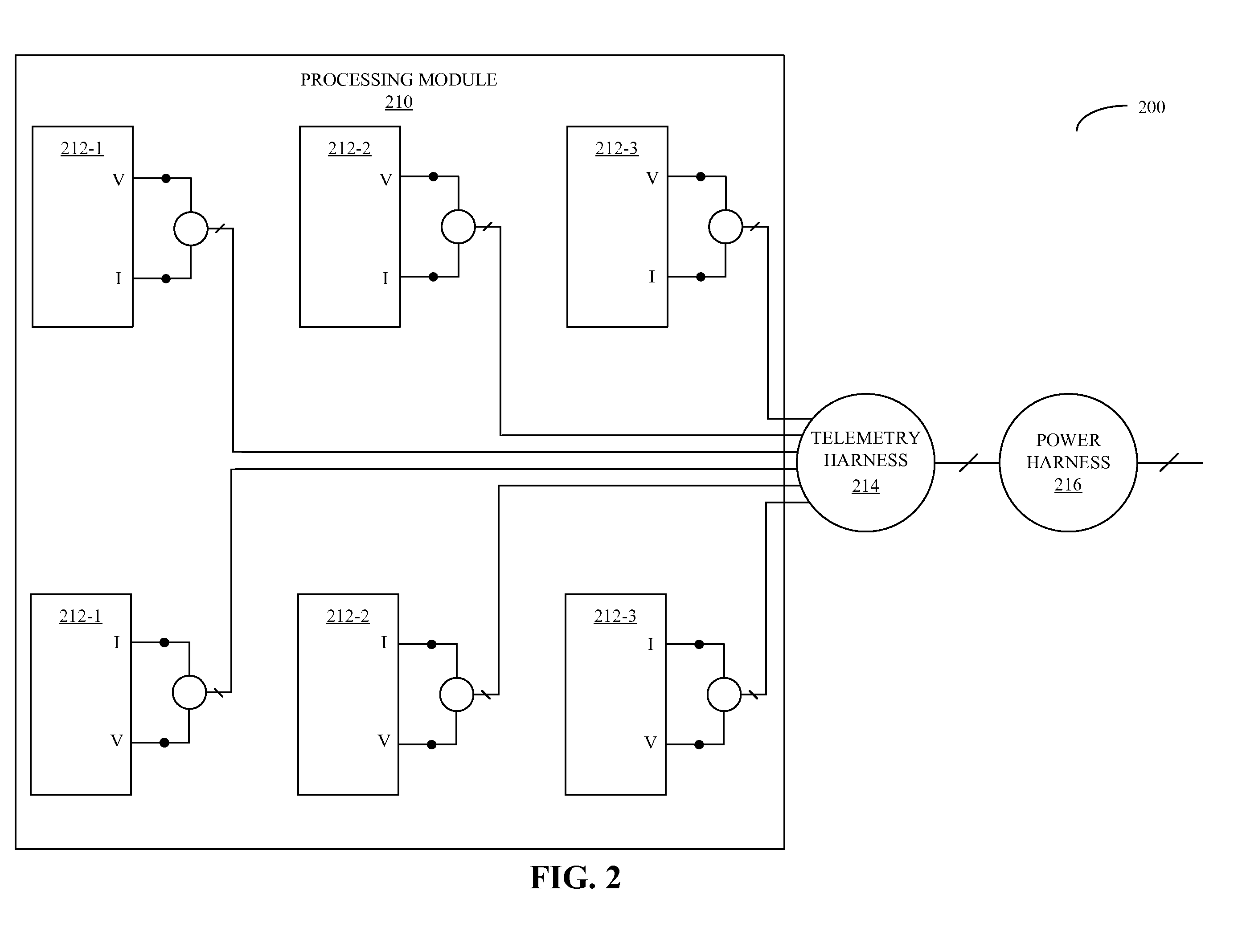
Workload scheduling in multi-core processors
ActiveUS20090271141A1Cancel noiseReduces spatial and temporal thermal variationThermometer detailsEnergy efficient ICTThermal variationComputerized system
A computer system that schedules loads across a set of processor cores is described. During operation, the computer system receives thermal measurements from sensors associated with the set of processor cores, and removes noise from the thermal measurements. Then, the computer system analyzes thermal properties of the set of processor cores based on the thermal measurements. Next, the computer system receives a process to be executed, and schedules the process to be executed by at least one of the processor cores based on the analysis. This scheduling is performed in a manner that reduces spatial and temporal thermal variations in the integrated circuit.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
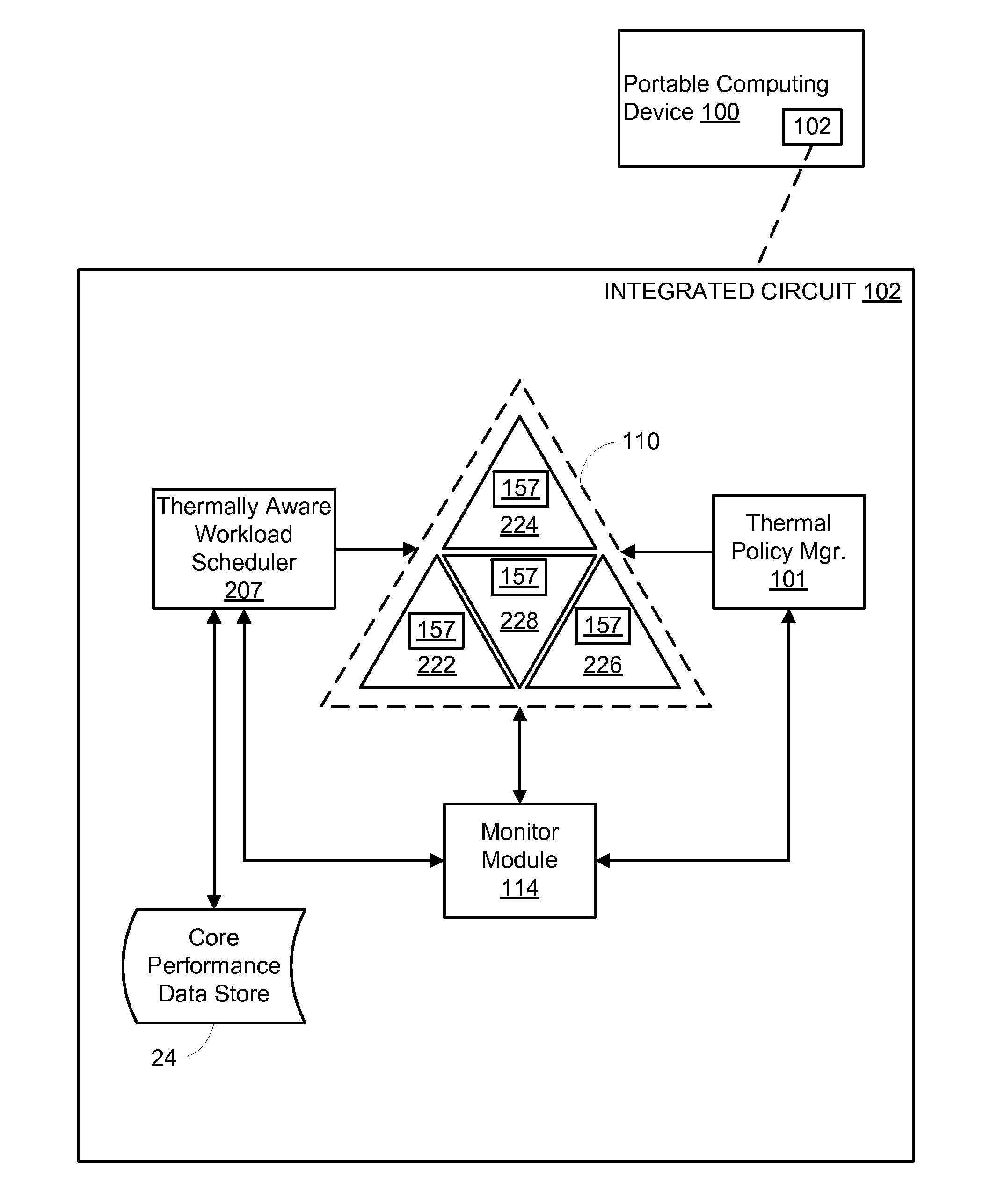
Thermally driven workload scheduling in a heterogeneous multi-processor system on a chip
ActiveUS20130132972A1Quality improvementHinder efficient processingEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionQuality of serviceHandling Code
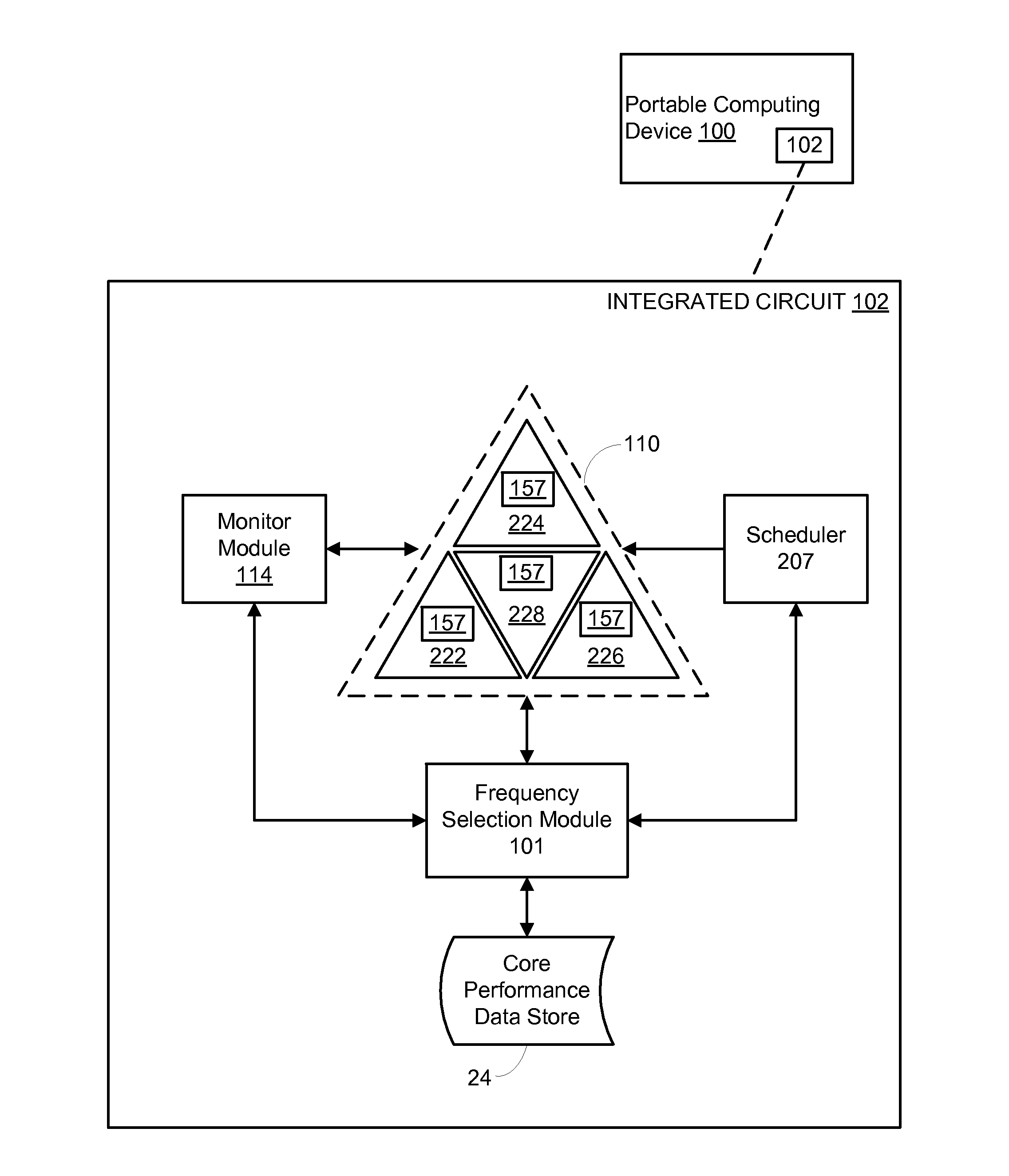
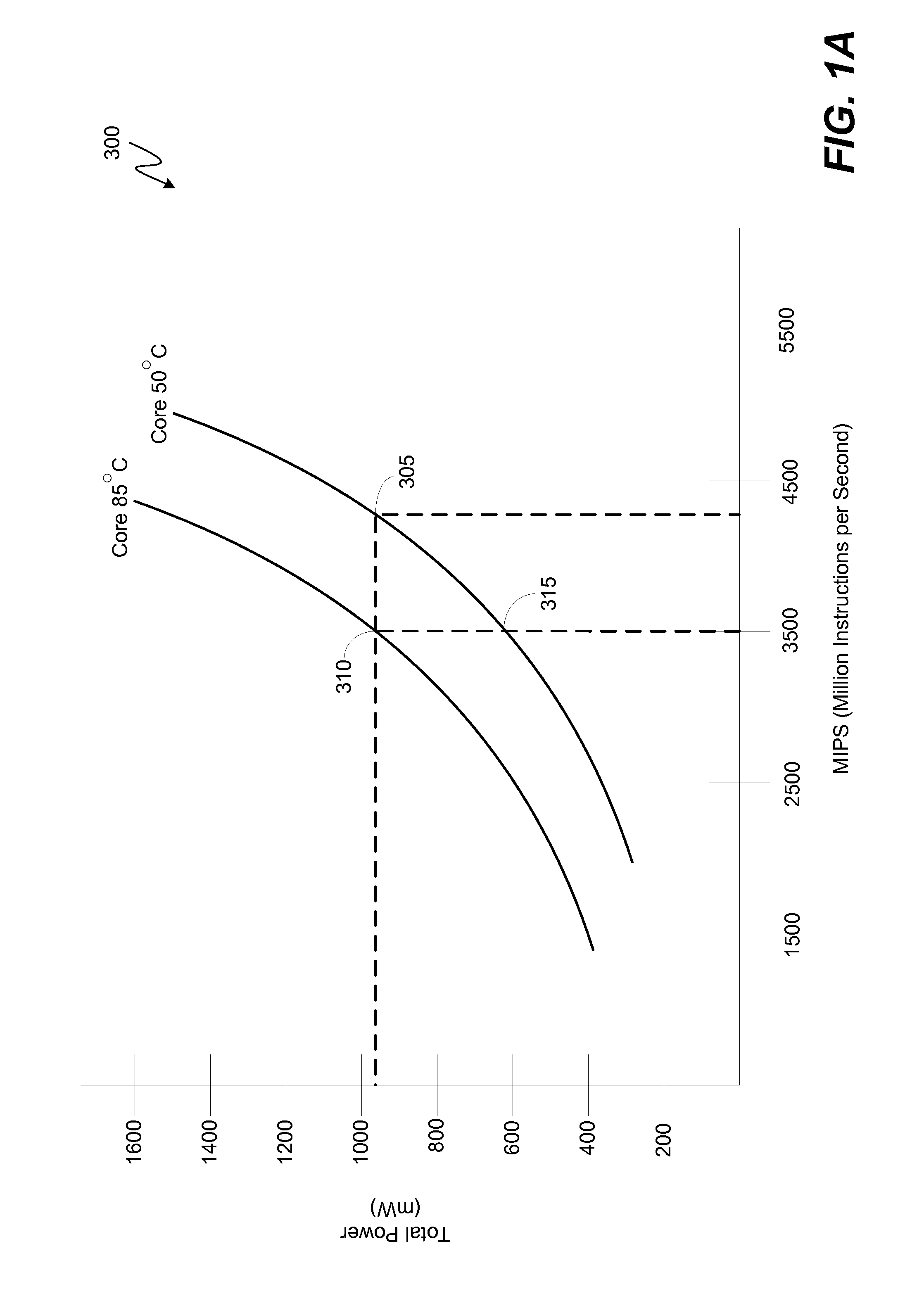
Various embodiments of methods and systems for thermally aware scheduling of workloads in a portable computing device that contains a heterogeneous, multi-processor system on a chip (“SoC”) are disclosed. Because individual processing components in a heterogeneous, multi-processor SoC may exhibit different processing efficiencies at a given temperature, and because more than one of the processing components may be capable of processing a given block of code, thermally aware workload scheduling techniques that compare performance curves of the individual processing components at their measured operating temperatures can be leveraged to optimize quality of service (“QoS”) by allocating workloads in real time, or near real time, to the processing components best positioned to efficiently process the block of code.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Optimizing energy use in a data center by workload scheduling and management
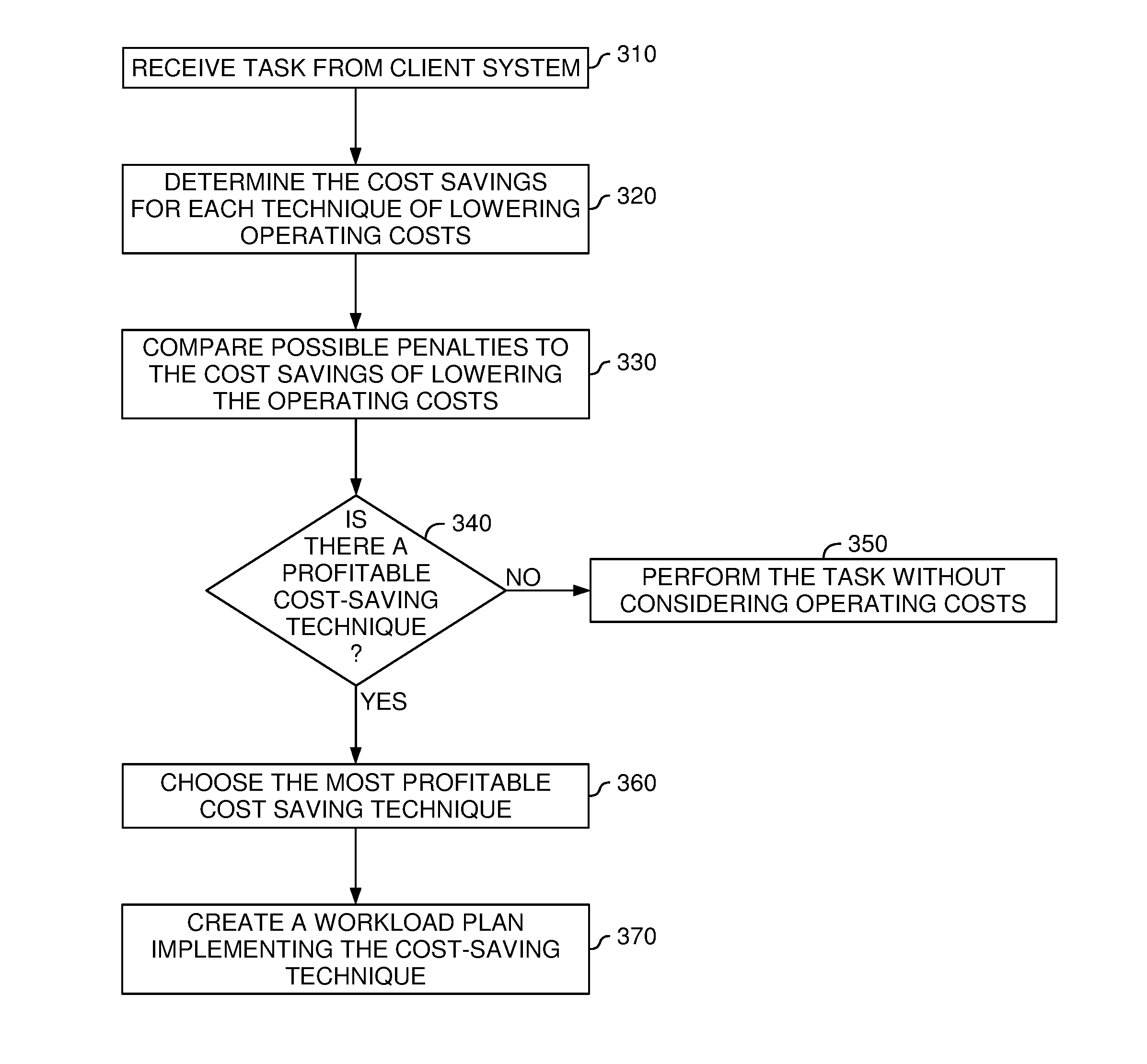
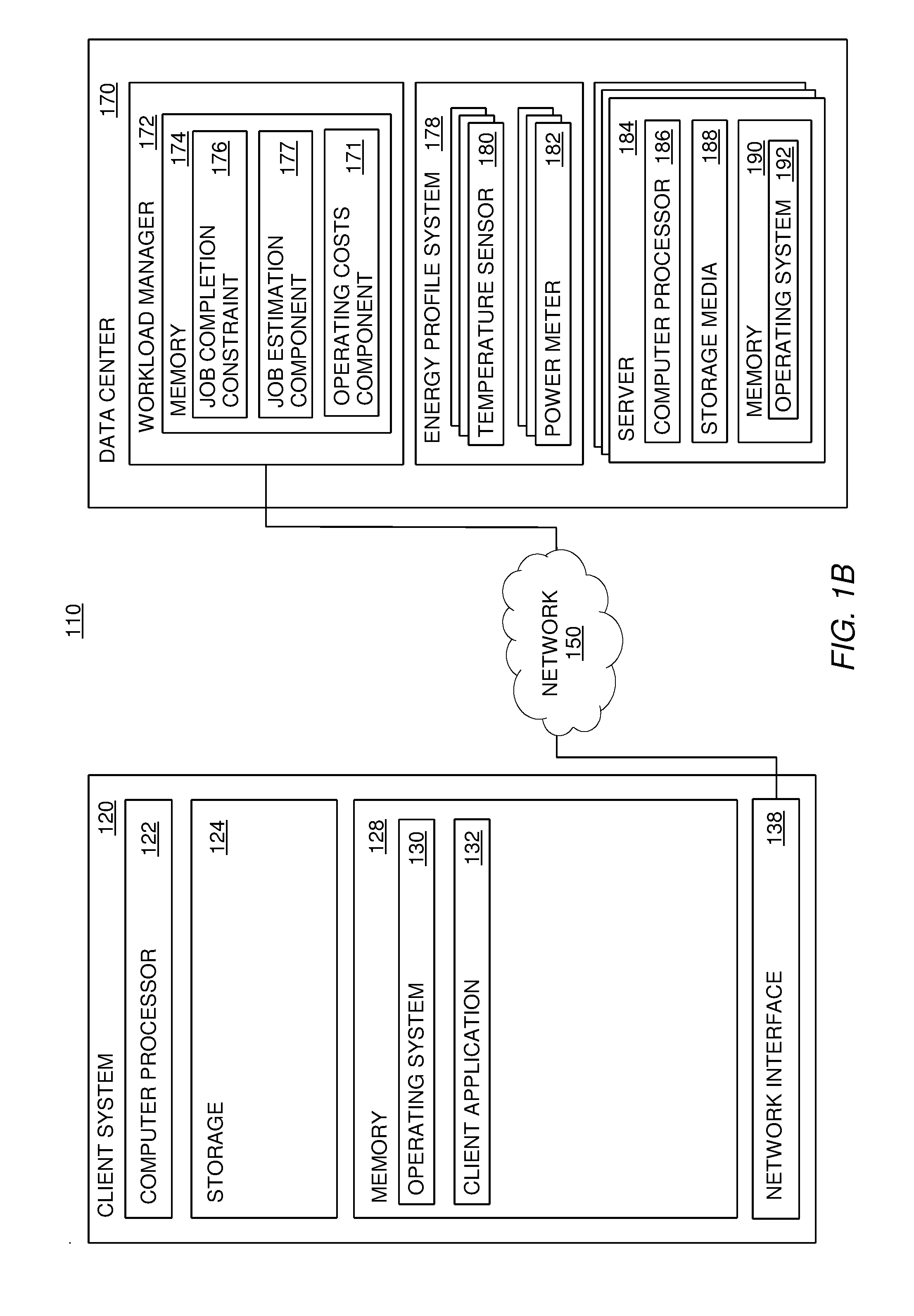
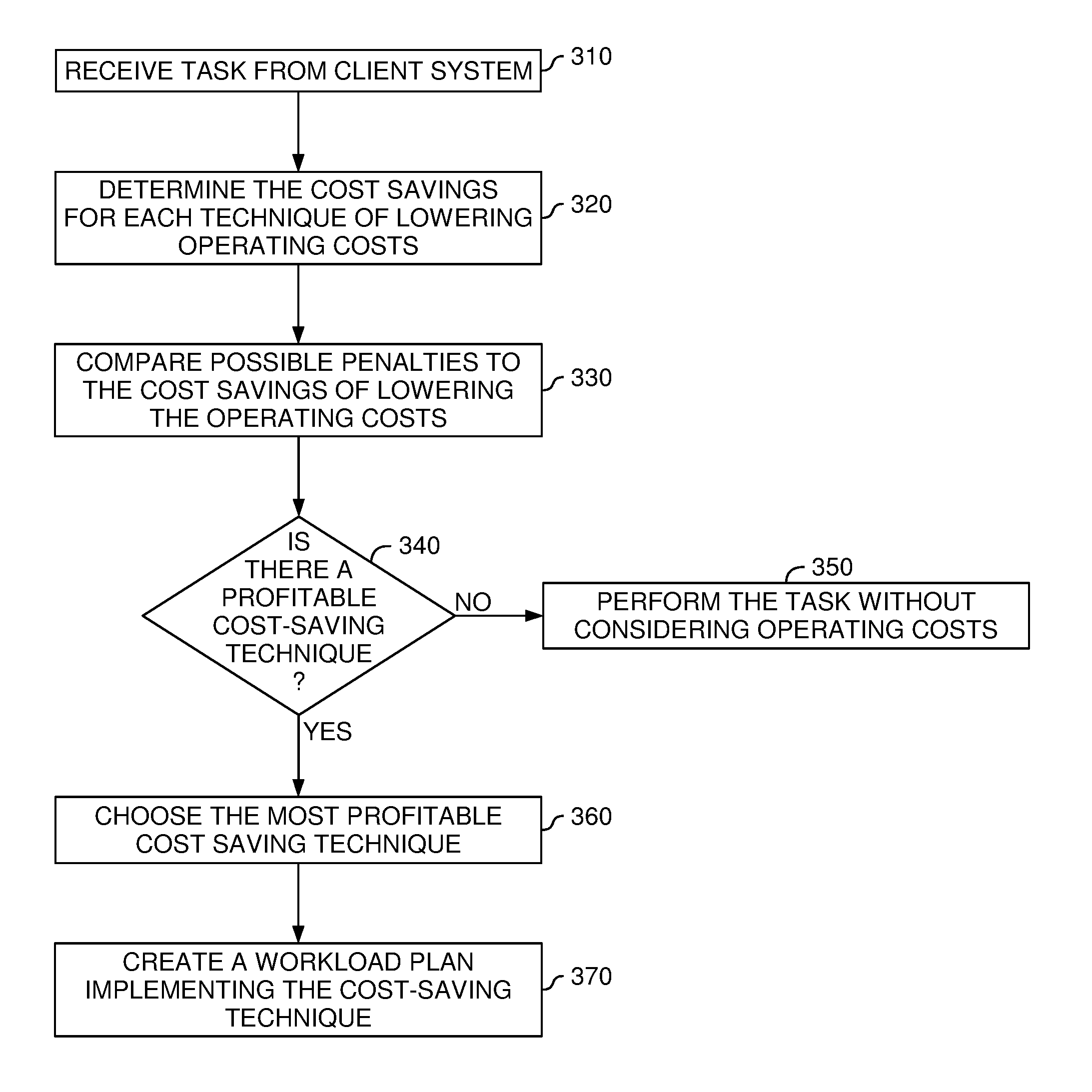
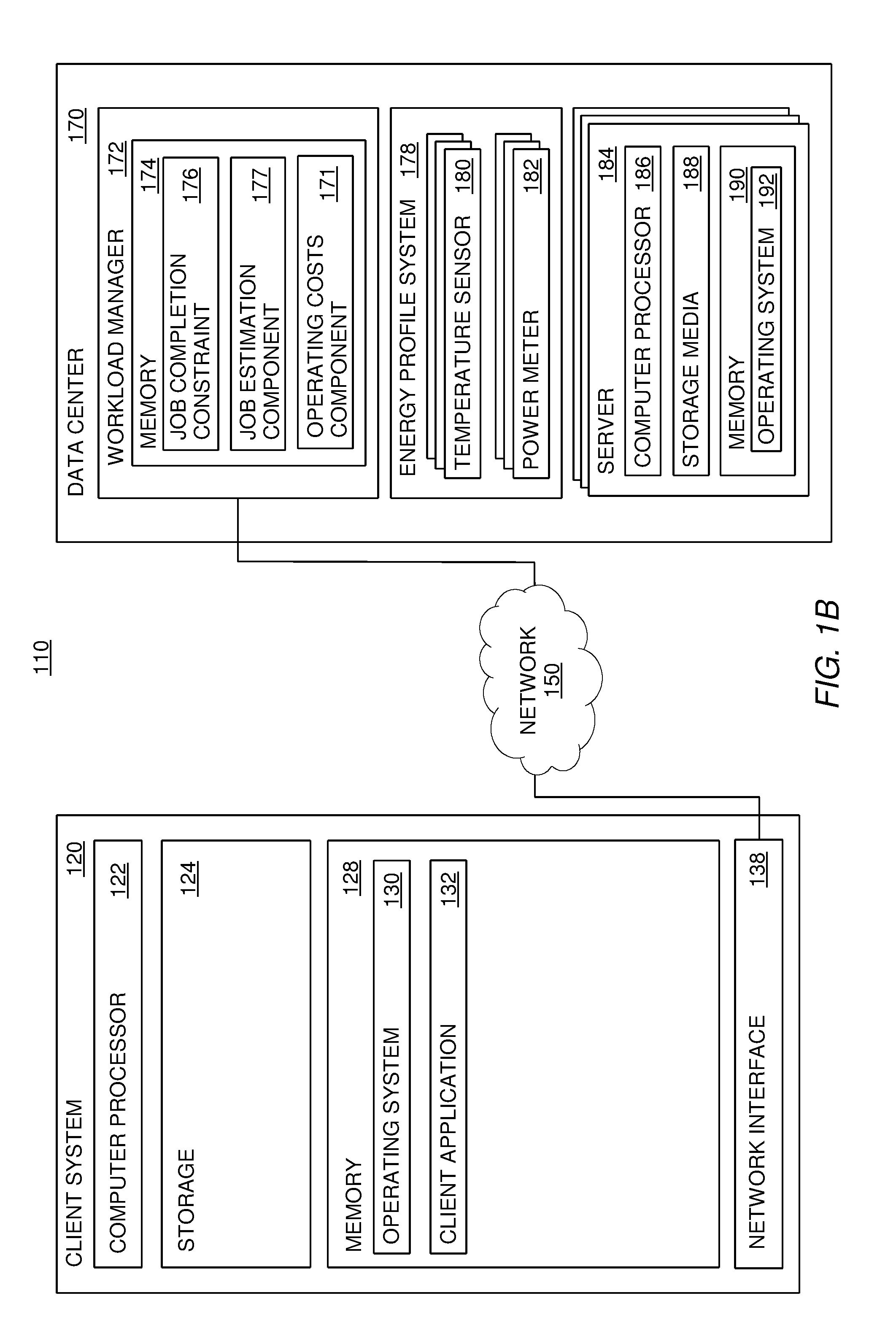
Techniques are described for scheduling received tasks in a data center in a manner that accounts for operating costs of the data center. Embodiments of the invention generally include comparing cost-saving methods of scheduling a task to the operating parameters of completing a task—e.g., a maximum amount of time allotted to complete a task. If the task can be scheduled to reduce operating costs (e.g., rescheduled to a time when power is cheaper) and still be performed within the operating parameters, then that cost-saving method is used to create a workload plan to implement the task. In another embodiment, several cost-saving methods are compared to determine the most profitable.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method, system and computer program for distributing a plurality of jobs to a plurality of computers
InactiveUS20090113442A1Avoid deploymentMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsWorkload schedulingComputer methods
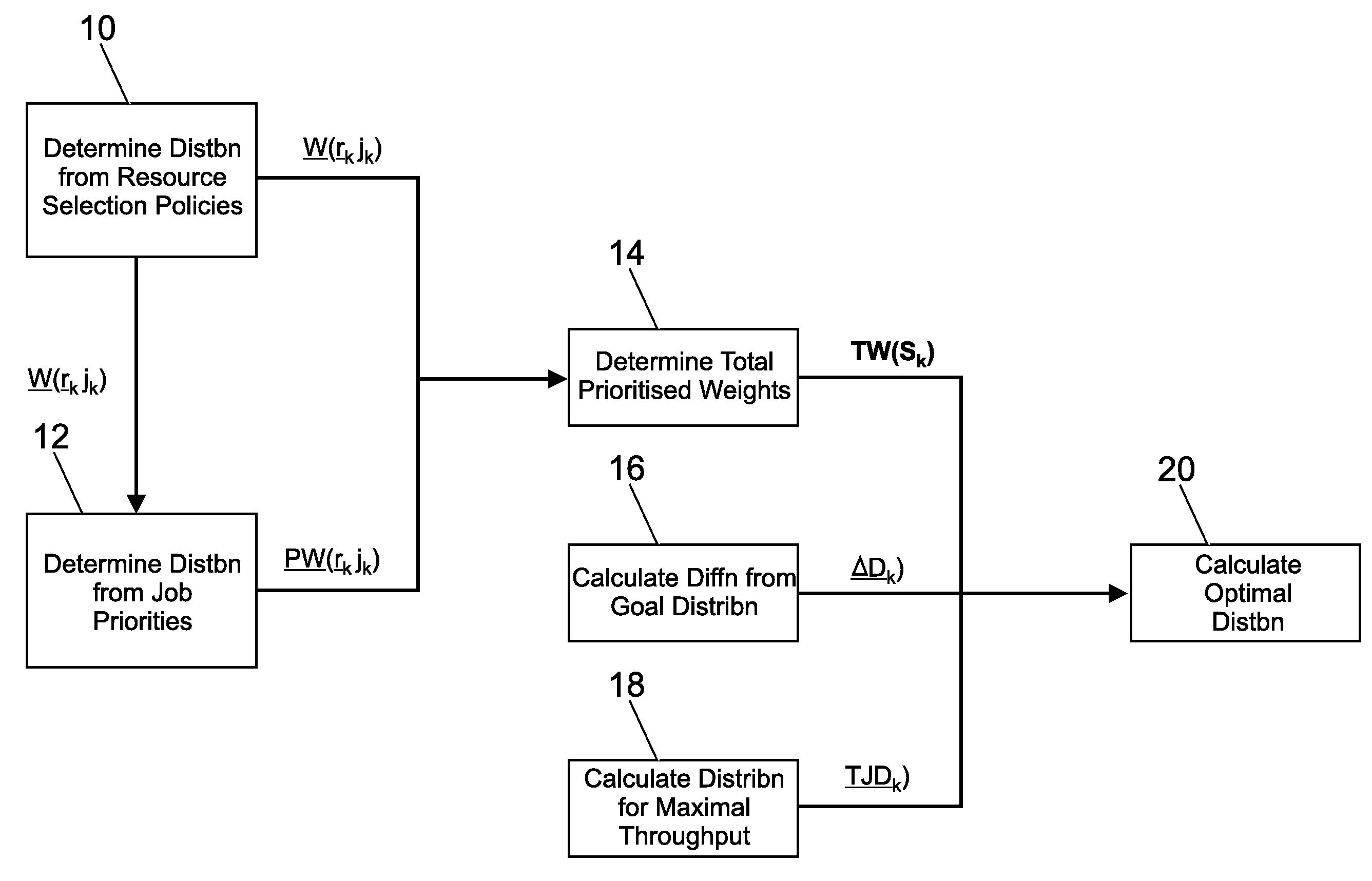
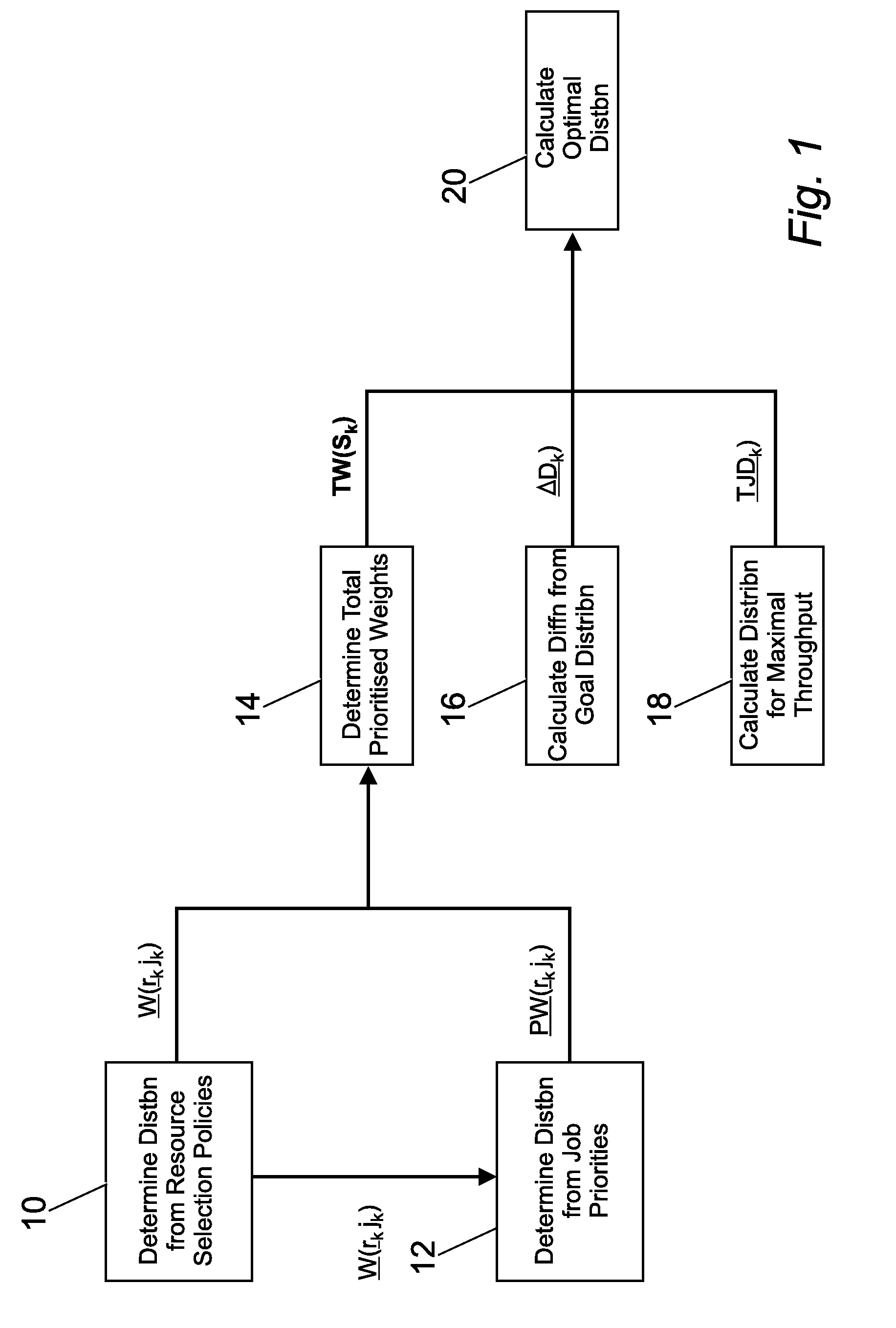
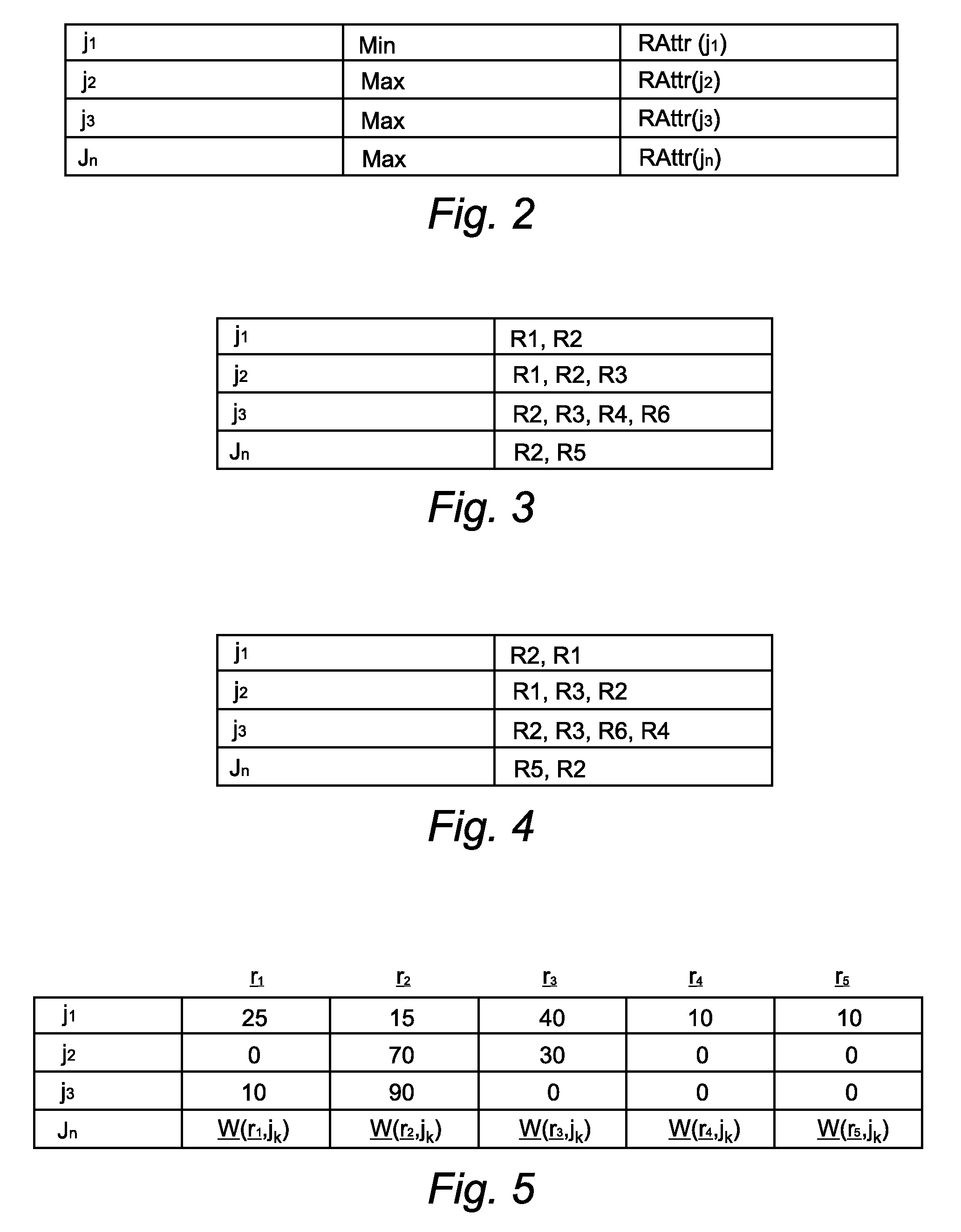
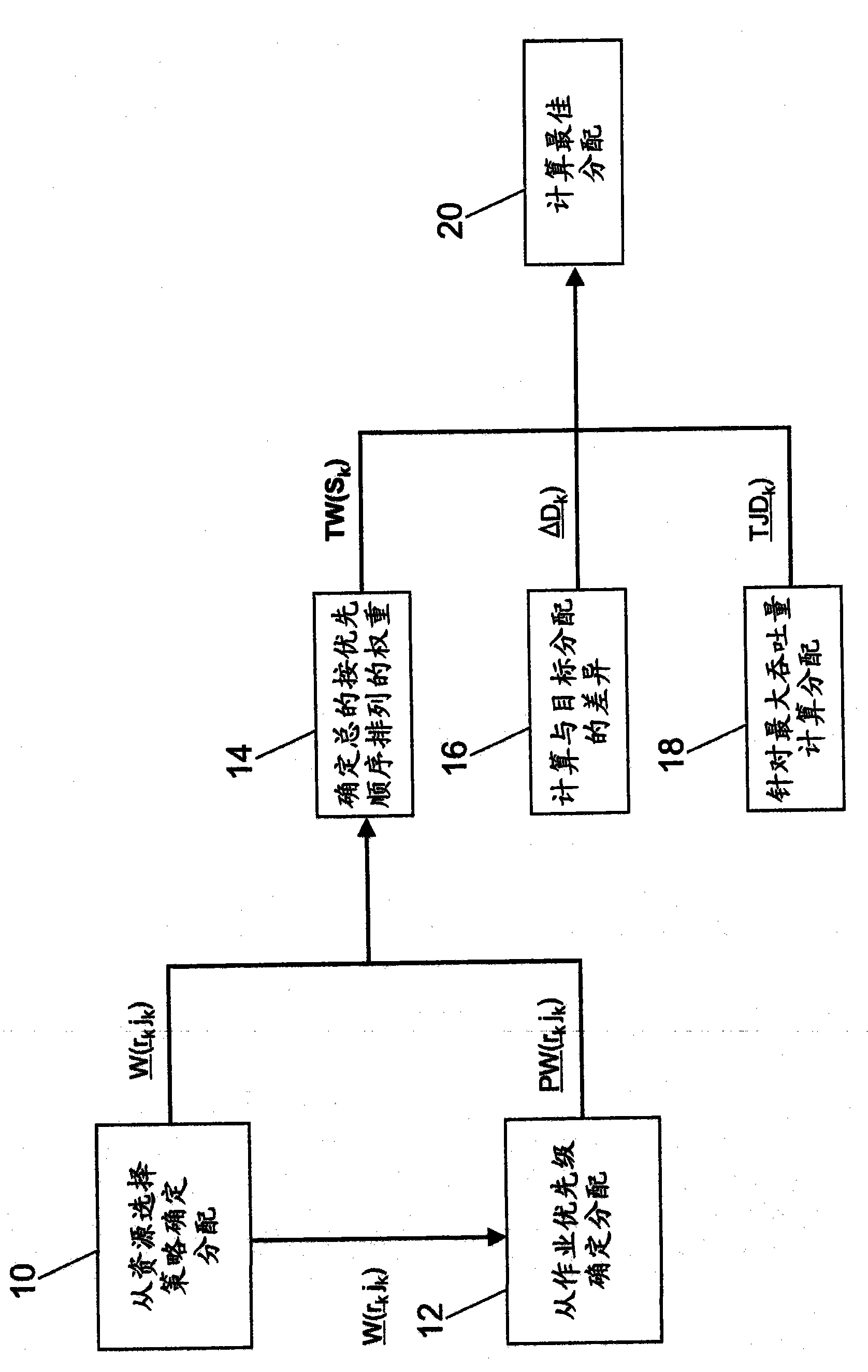
Method and system for providing a mechanism for determining an optimal workload distribution, from a plurality of candidate workload distributions, each of which has been determined to optimize a particular aspect of a workload-scheduling problem. More particularly, the preferred embodiment determines a workload distribution based on resource selection policies. From this workload distribution, the preferred embodiment optionally determines a workload distribution based on job priorities. From either or both of the above parameters, the preferred embodiment determines a workload distribution based on a total prioritized weight parameter. The preferred embodiment also determines a workload distribution which attempts to match the previously determined candidate workload distributions to a goal distribution. Similarly, the preferred embodiment calculates a further workload distribution which attempts to maximize job throughput.
Owner:IBM CORP
Redundant flexible datacenter workload scheduling
Owner:LANCIUM LLC
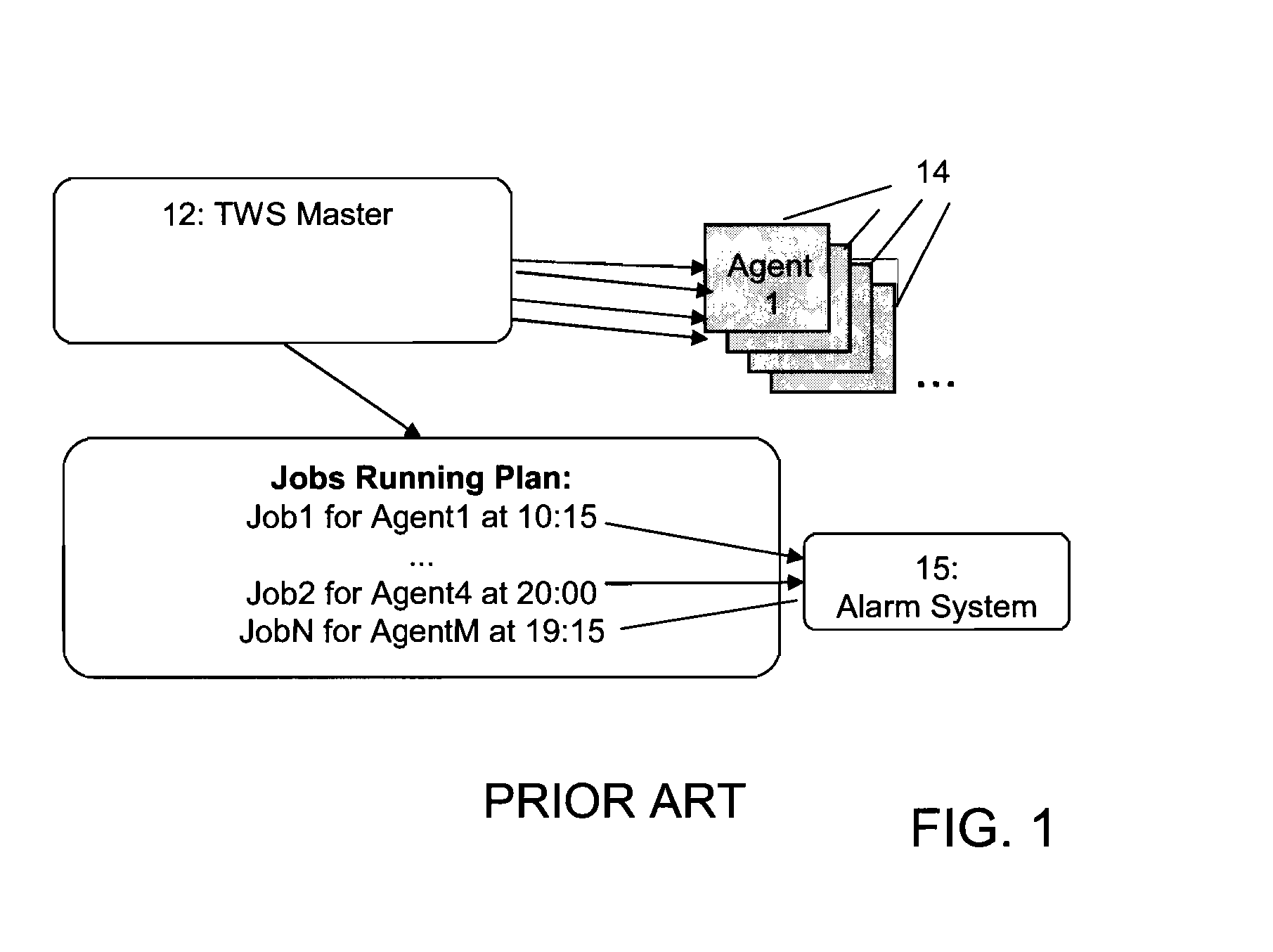
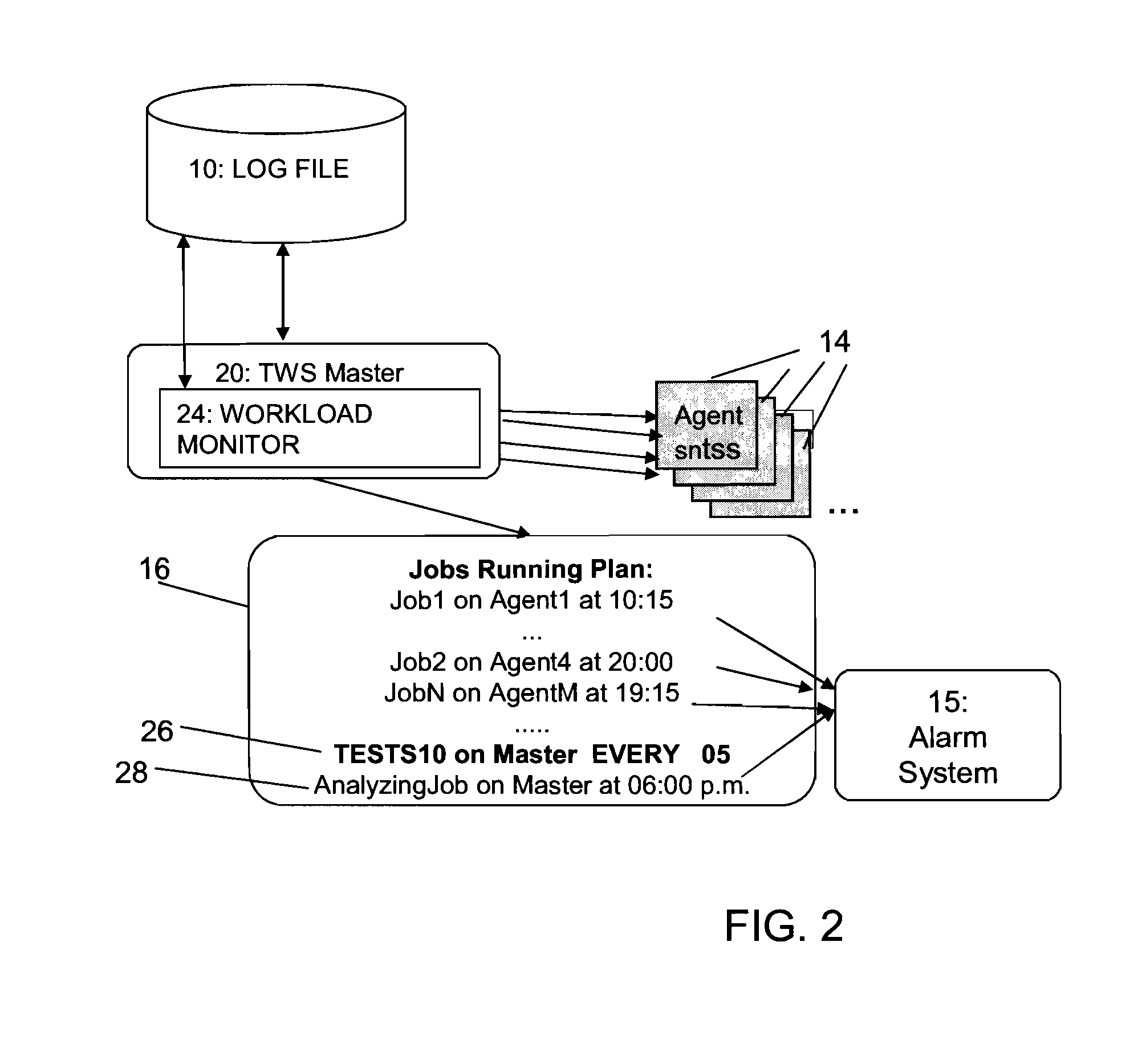
Monitoring performance on workload scheduling systems
ActiveUS20080189712A1Lower performance requirementsError preventionTransmission systemsTime rangeData processing system
The present invention relates to the field of enterprise network computing. In particular, it relates to a method and respective system for monitoring workload of a workload scheduler. Information defining a plurality of test jobs of low priority is received. The test jobs have respective launch times, and the test jobs are launched for execution in a data processing system in accordance with said launch times and said low execution priority. It is evaluated how many of said test jobs are executed within a pre-defined analysis time range. A performance decrease warning is issued, if the number of executed test jobs is lower than a predetermined threshold number. The workload scheduler discards launching of jobs having a low priority when estimating that a volume of jobs submitted with higher priority is sufficient to keep said scheduling system busy.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Adjunct partition work scheduling with quality of service attributes
ActiveUS8677356B2Multiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationQuality of serviceOperational system
Operating system-directed workload scheduling of an adjunct partition in a logically partitioned computer is selectively overridden to handle platform work requiring a Quality of Service (QoS) guarantee. Firmware may track outstanding requests for platform work for an adjunct partition, and in response to a request for platform work that requires a QoS guarantee, the firmware may assume or take over scheduling decisions for the adjunct partition from the operating system of an associated logical partition and schedule execution of the adjunct partition to ensure that the adjunct partition will be allocated sufficient execution resources to perform the platform work independent of the scheduling desires of the operating system. As a result, any platform work that potentially impacts the platform work of other adjunct partitions will not be held up as a result of an unwillingness or inability of the operating system to schedule execution of the adjunct partition.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
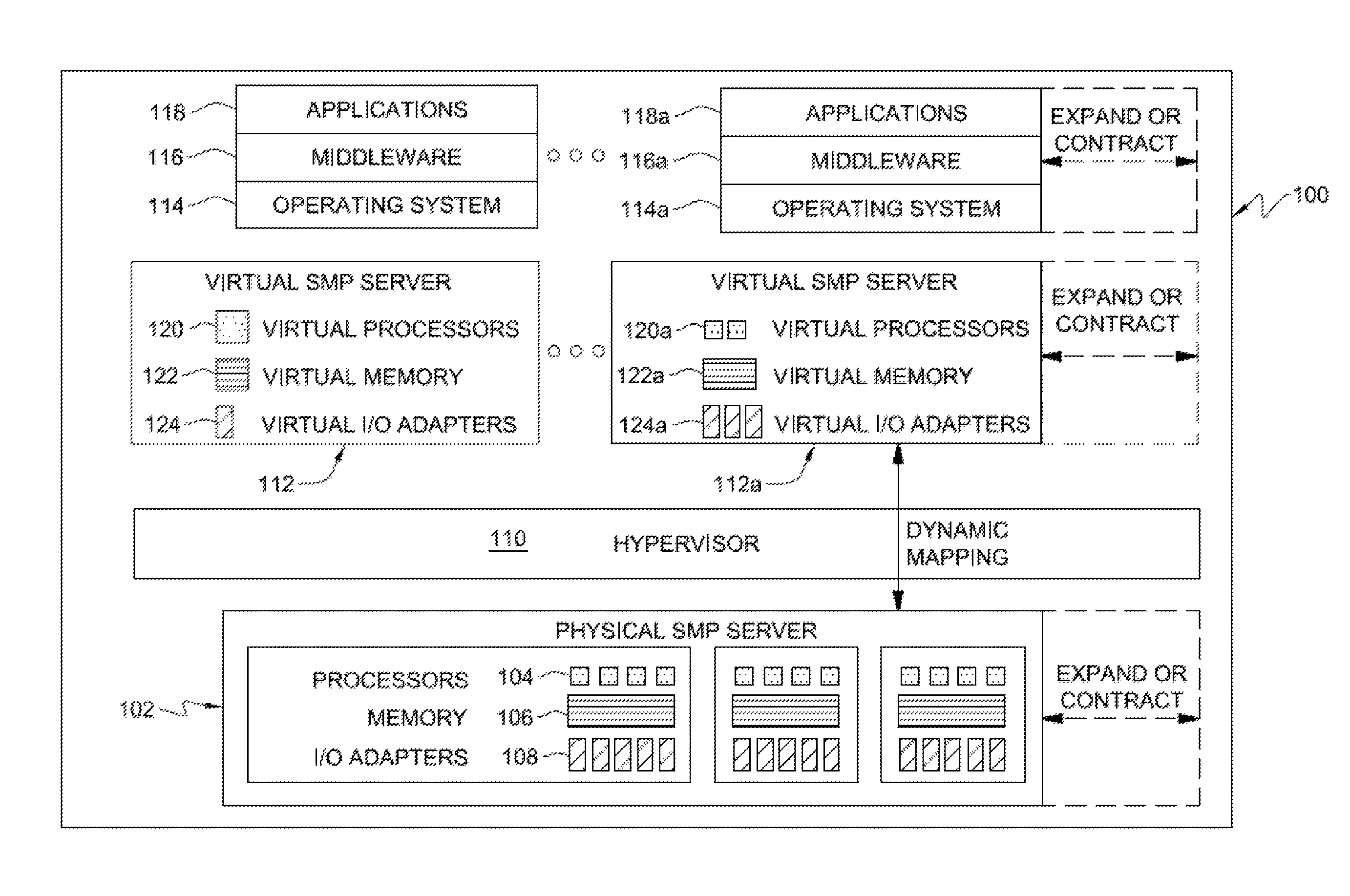
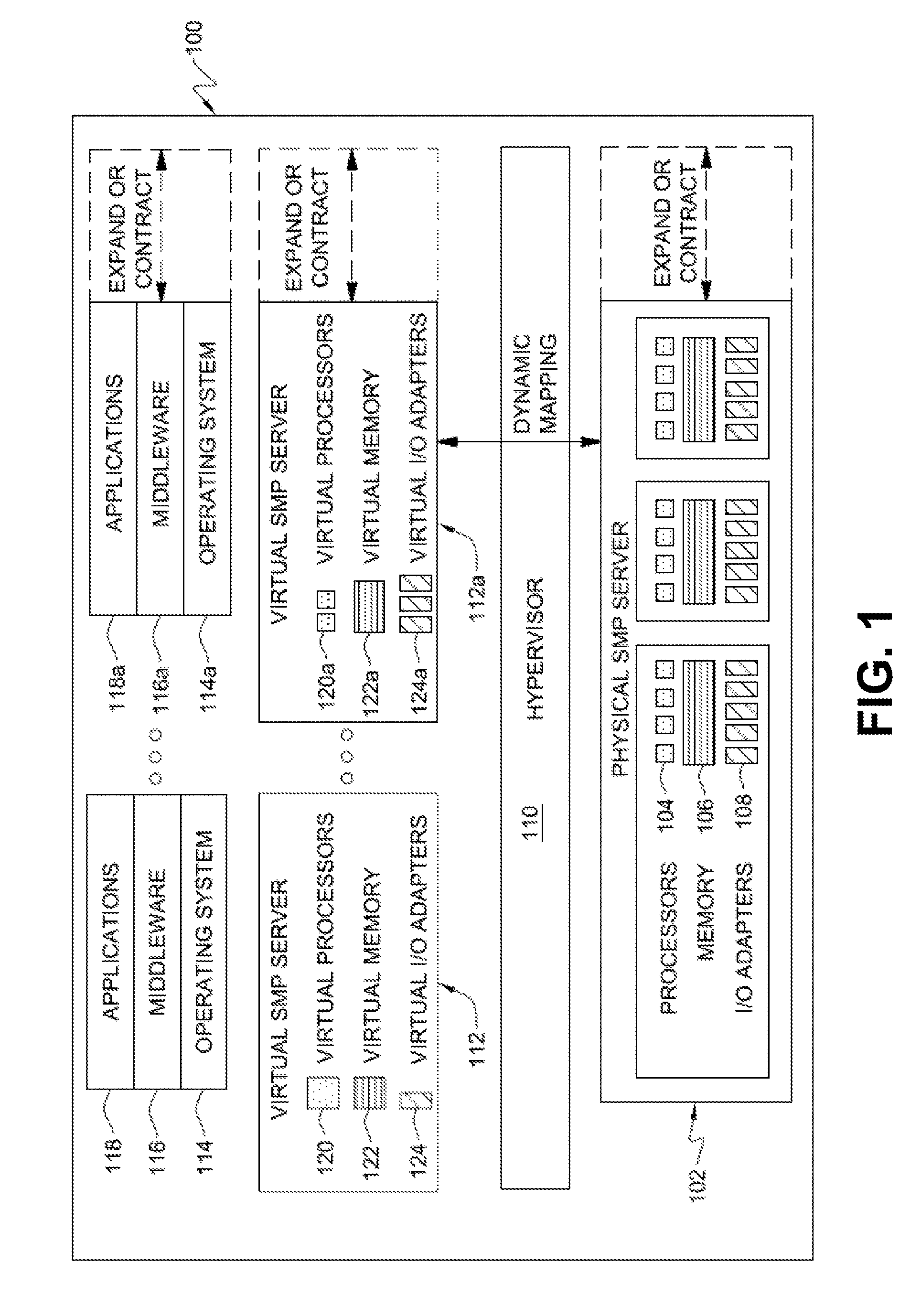
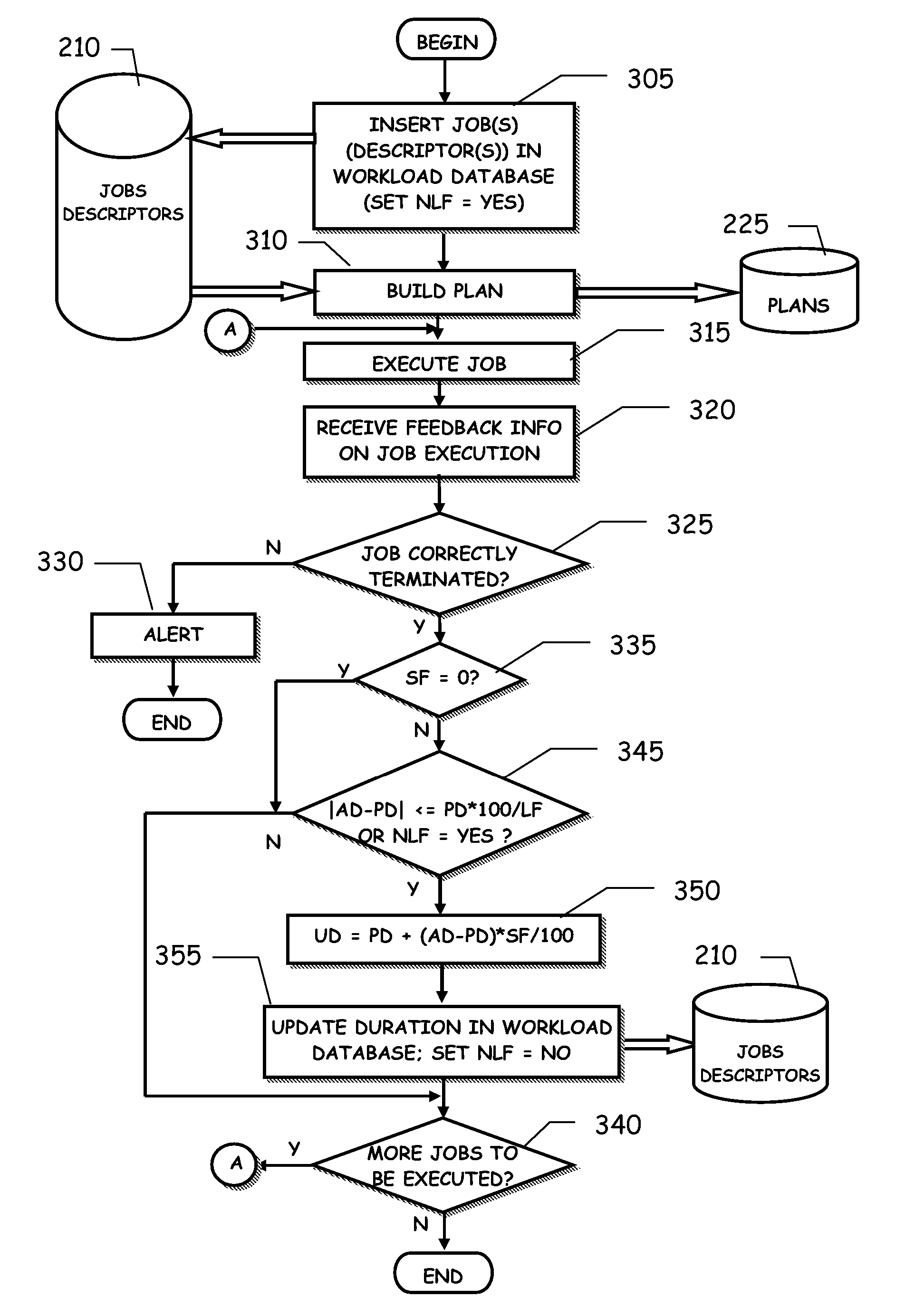
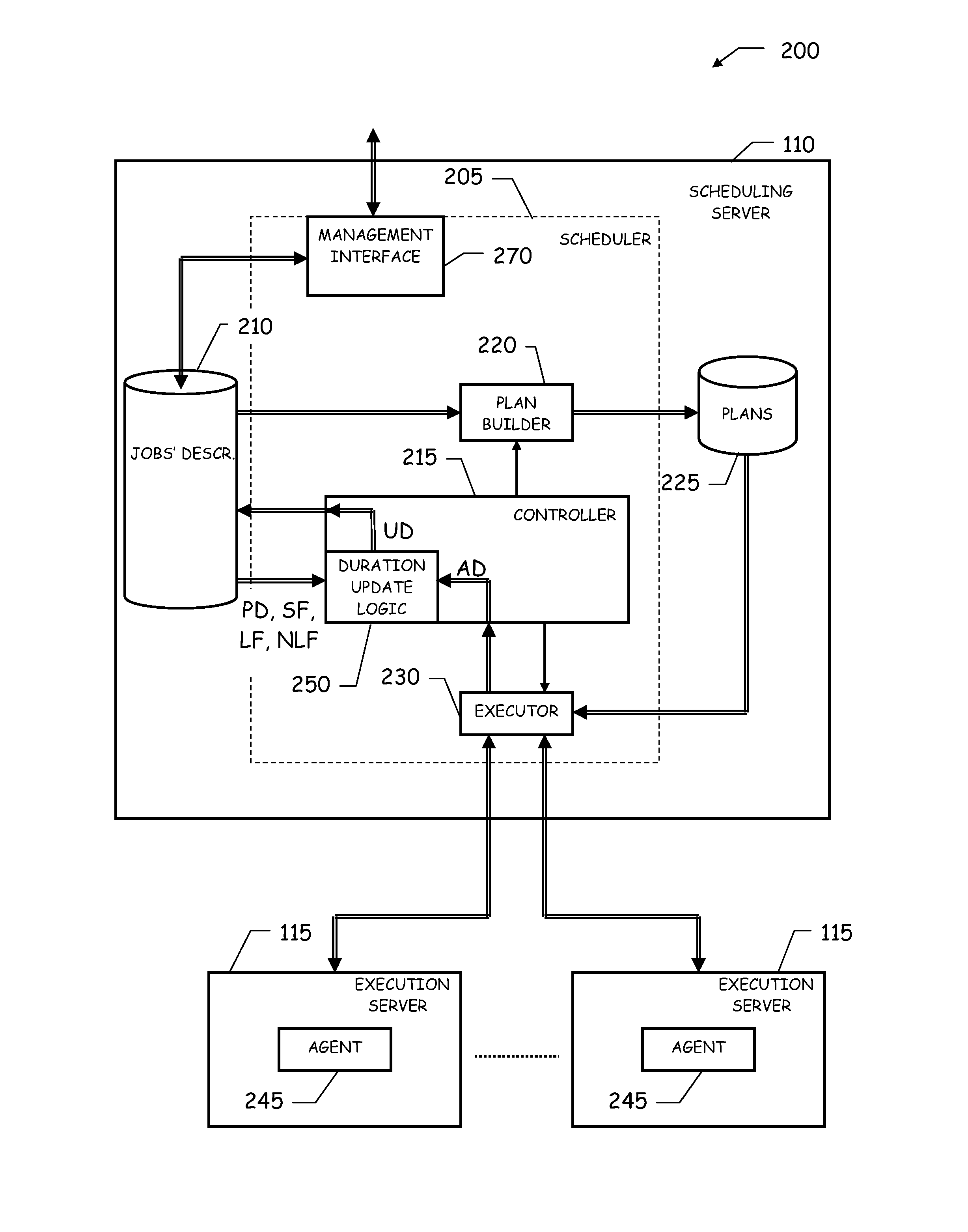
Workload scheduling method and system with improved planned job duration updating scheme
InactiveUS20060242648A1Simple methodMultiprogramming arrangementsResourcesData processing systemParallel computing
A method for scheduling execution of a work unit in a data processing system (100) comprises assigning to the work unit an expected execution duration (PD); executing the work unit (315); determining an actual execution duration (AD) of the work unit (320); determining a difference between the actual execution duration and the expected duration; and conditionally adjusting (345,350,355) the expected execution duration assigned to the work unit based on the measured actual execution duration, wherein the conditionally adjusting includes preventing the adjustment of the expected execution duration in case said difference exceeds a predetermined threshold (LF). The method further includes associating to the work unit a parameter (NLF) having a prescribed value adapted to provide an indication of unconditional adjustment of the expected execution duration: in case said parameter takes the prescribed value, the expected duration assigned with the work unit based on the measured actual execution duration even if the difference in durations exceeds the predetermined threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
Optimizing energy use in a data center by workload scheduling and management
InactiveUS20130104136A1Energy efficient ICTProgram initiation/switchingData centerWorkload scheduling
Techniques are described for scheduling received tasks in a data center in a manner that accounts for operating costs of the data center. Embodiments of the invention generally include comparing cost-saving methods of scheduling a task to the operating parameters of completing a task—e.g., a maximum amount of time allotted to complete a task. If the task can be scheduled to reduce operating costs (e.g., rescheduled to a time when power is cheaper) and still be performed within the operating parameters, then that cost-saving method is used to create a workload plan to implement the task. In another embodiment, several cost-saving methods are compared to determine the most profitable.
Owner:IBM CORP
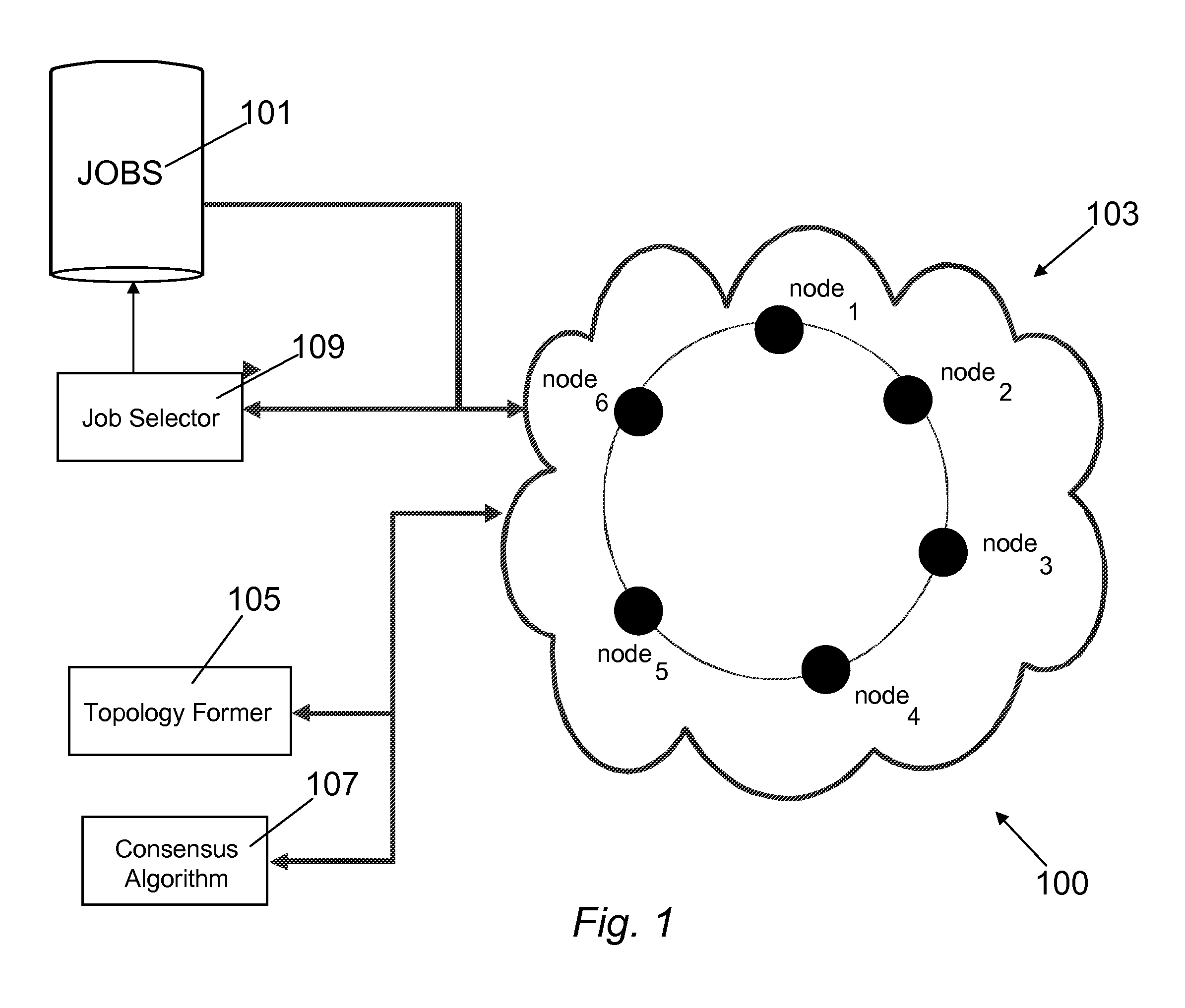
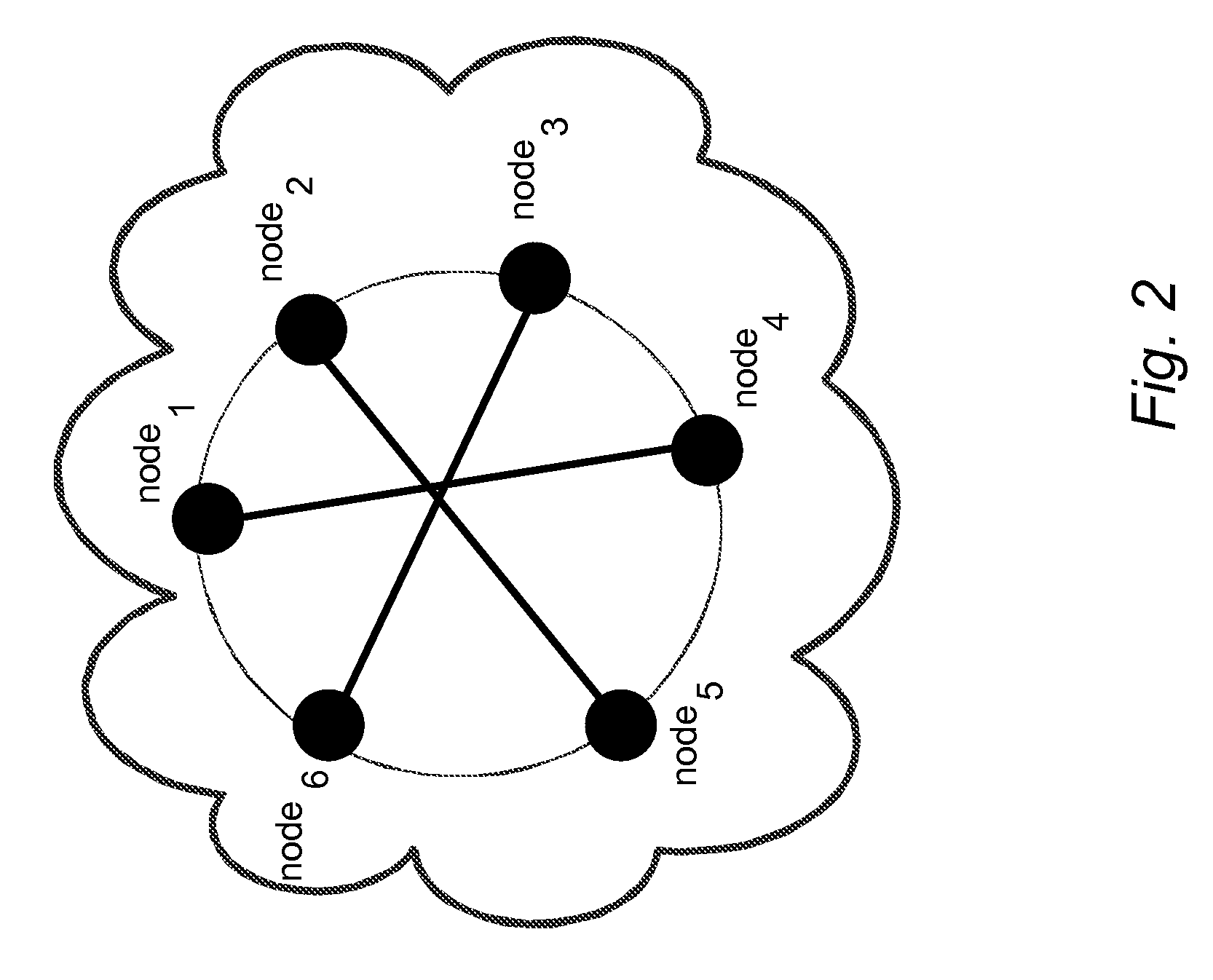
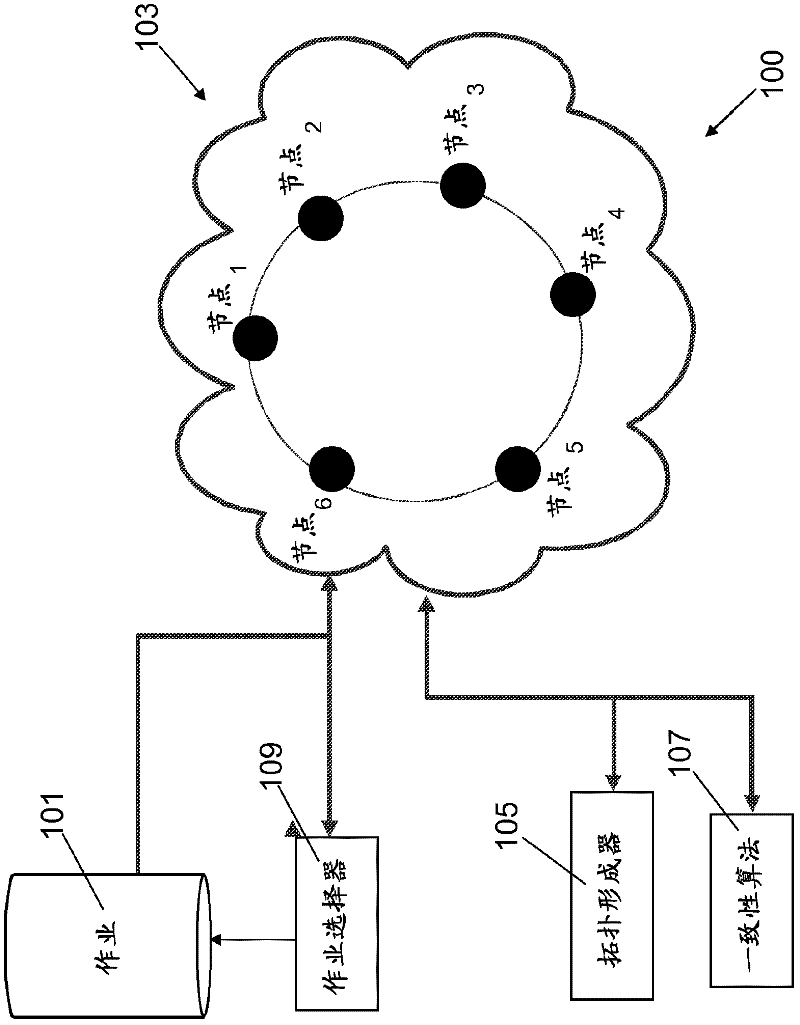
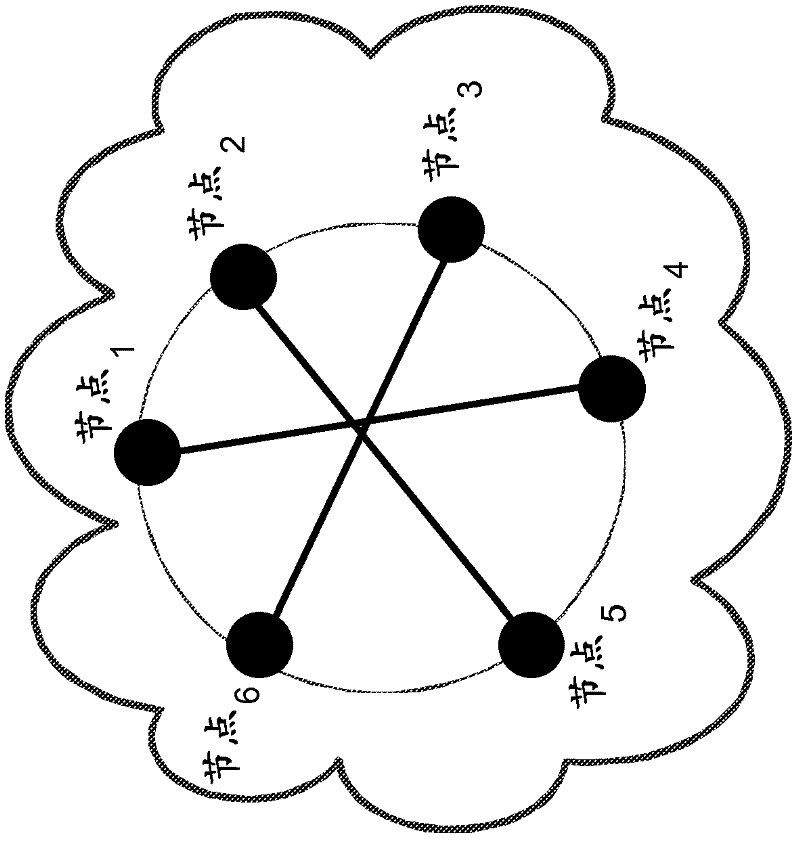
Method and System for Job Scheduling in Distributed Data Processing System with Identification of Optimal Network Topology
InactiveUS20110022706A1Optimize networkFast convergenceDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsDistributed Computing EnvironmentSmall worlds
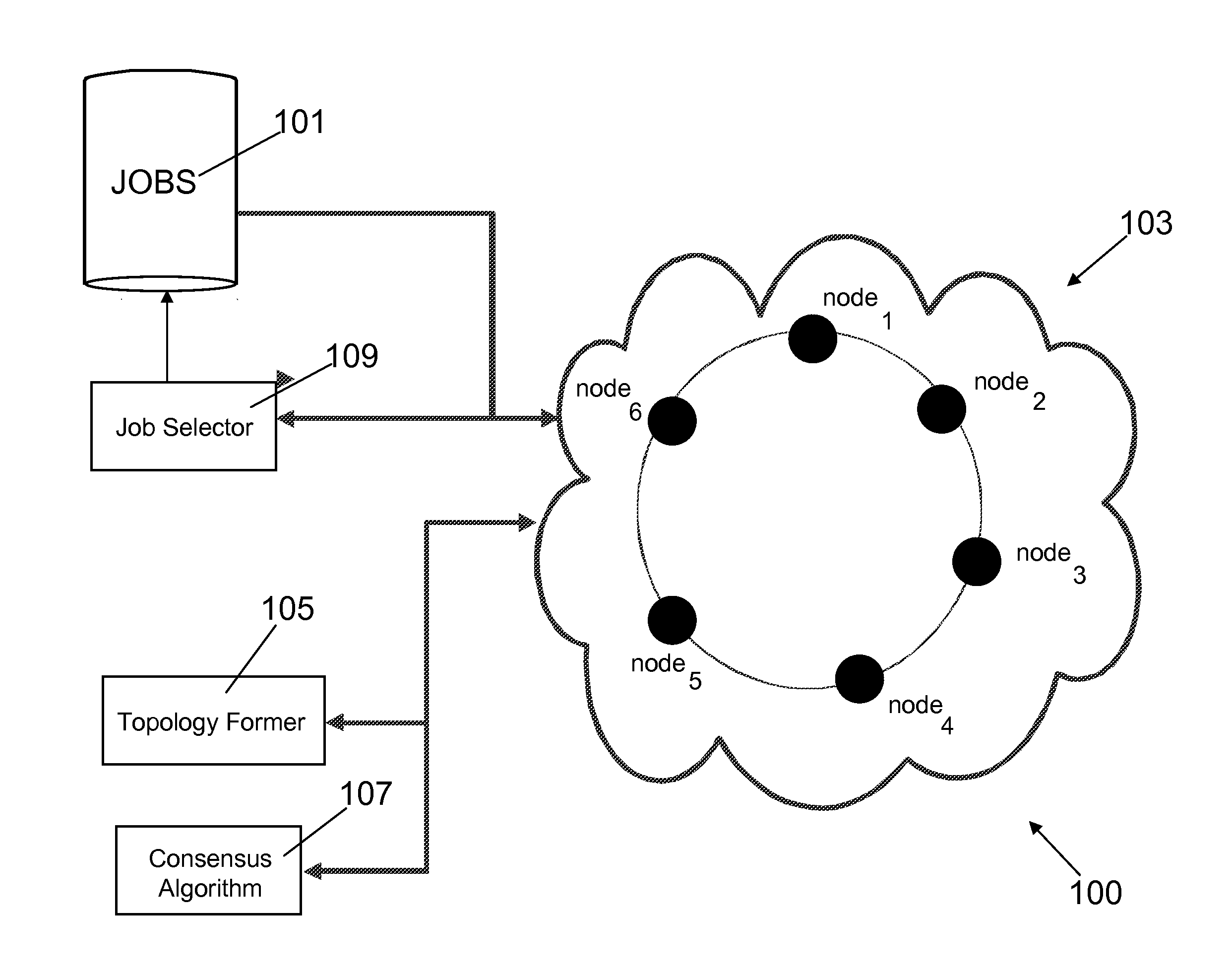
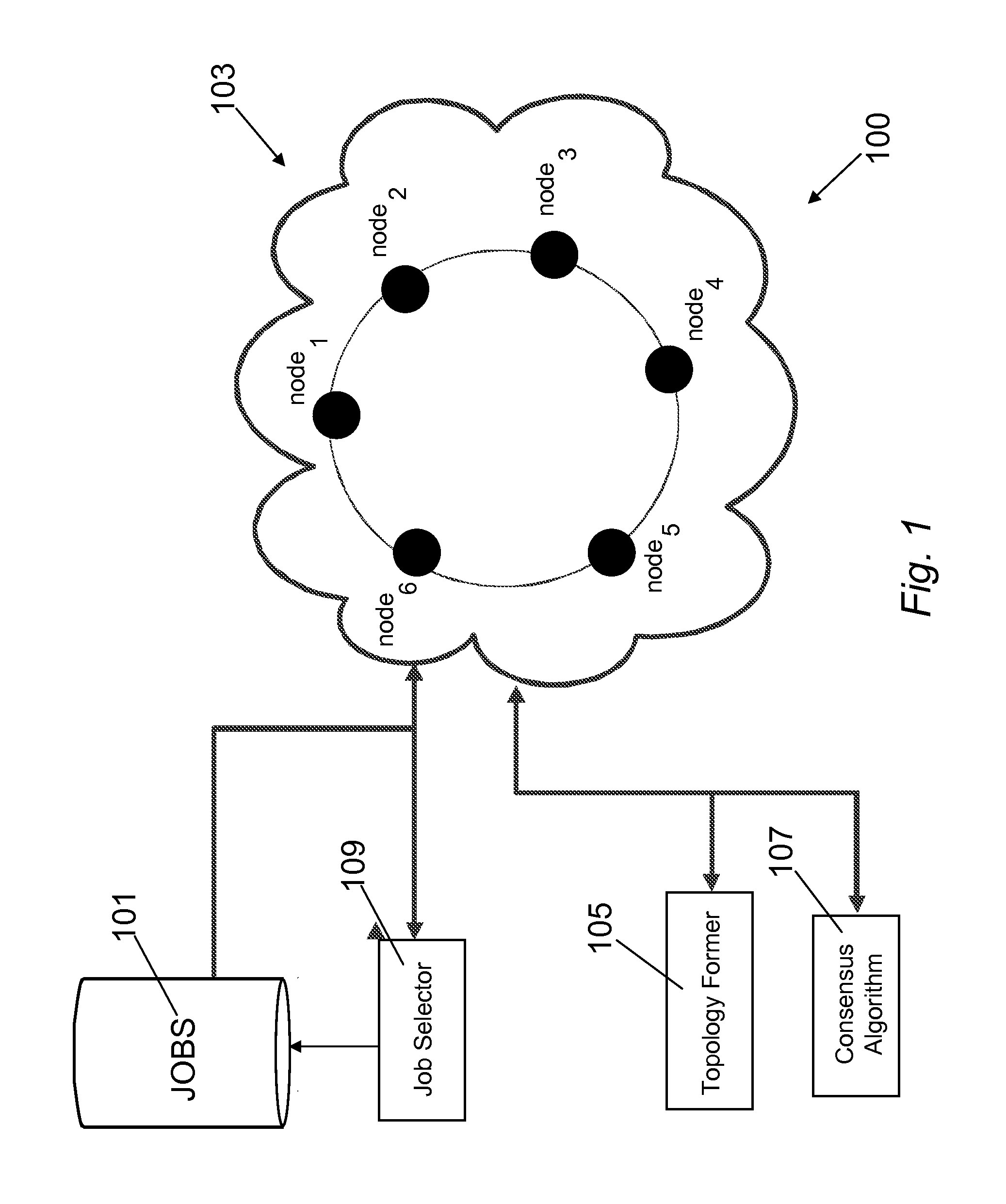
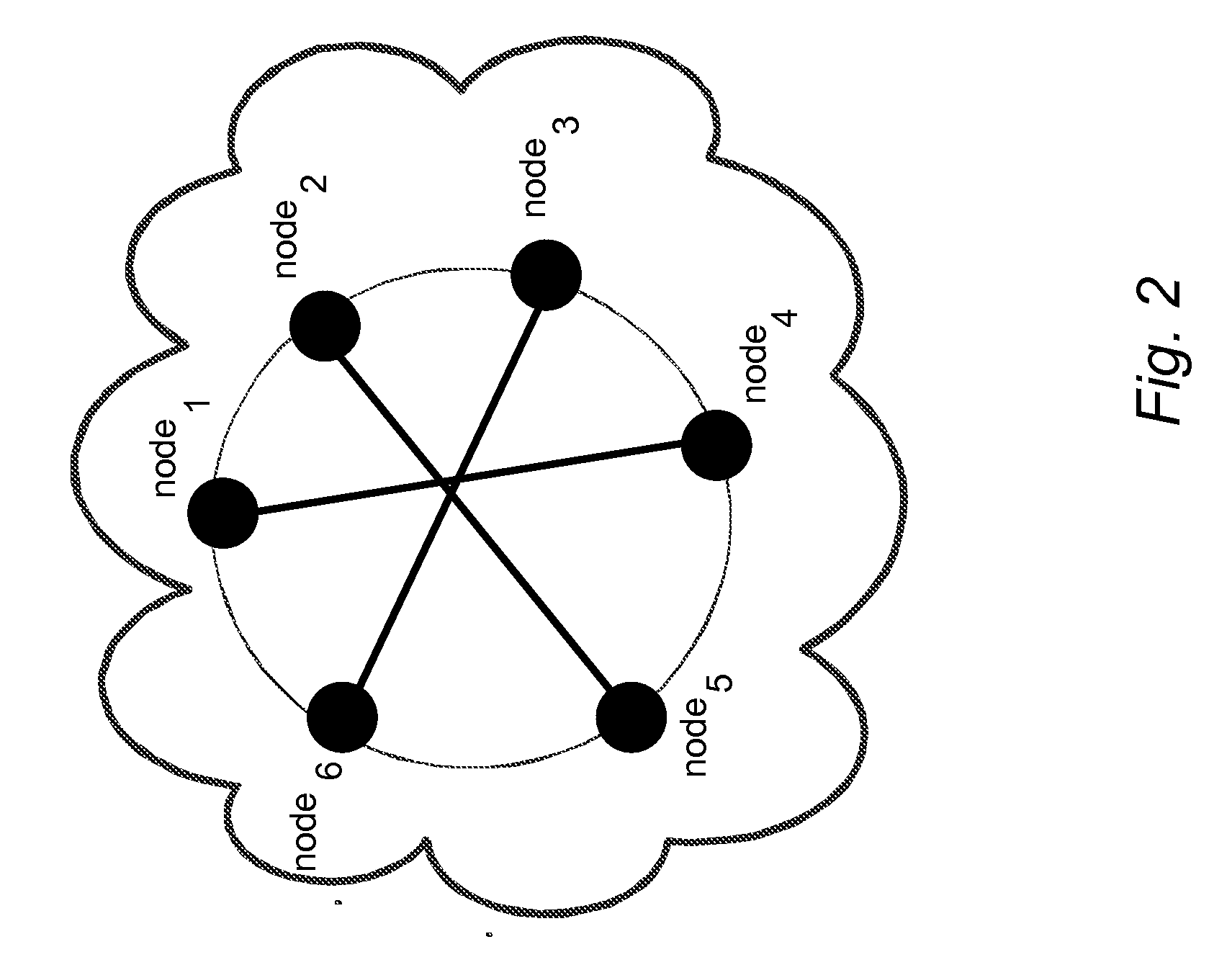
The method of the present invention provides an automatic and optimised selection of the network topology for distributing scheduling of jobs on the computers of the modified network topology. The automatic and optimised selection of the network topology starts from the current topology and a desired number of additional connections. In this way the method of the present invention provides a higher convergence speed for the modified consensus algorithm in comparison, e.g., to a simple ring network. The method exploits the so called small-world networks. Small-world networks are more robust to perturbations than other network architectures. The preferred embodiment provides a workload scheduling system which is highly scalable to accommodate increasing workloads within a heterogeneous distributed computing environment. A modified average consensus algorithm is used to distribute network traffic and jobs amongst a plurality of computers.
Owner:IBM CORP
Workload scheduling in multi-core processors
ActiveUS7716006B2Cancel noiseReduces spatial and temporal thermal variationThermometer detailsEnergy efficient ICTThermal variationComputerized system
A computer system that schedules loads across a set of processor cores is described. During operation, the computer system receives thermal measurements from sensors associated with the set of processor cores, and removes noise from the thermal measurements. Then, the computer system analyzes thermal properties of the set of processor cores based on the thermal measurements. Next, the computer system receives a process to be executed, and schedules the process to be executed by at least one of the processor cores based on the analysis. This scheduling is performed in a manner that reduces spatial and temporal thermal variations in the integrated circuit.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
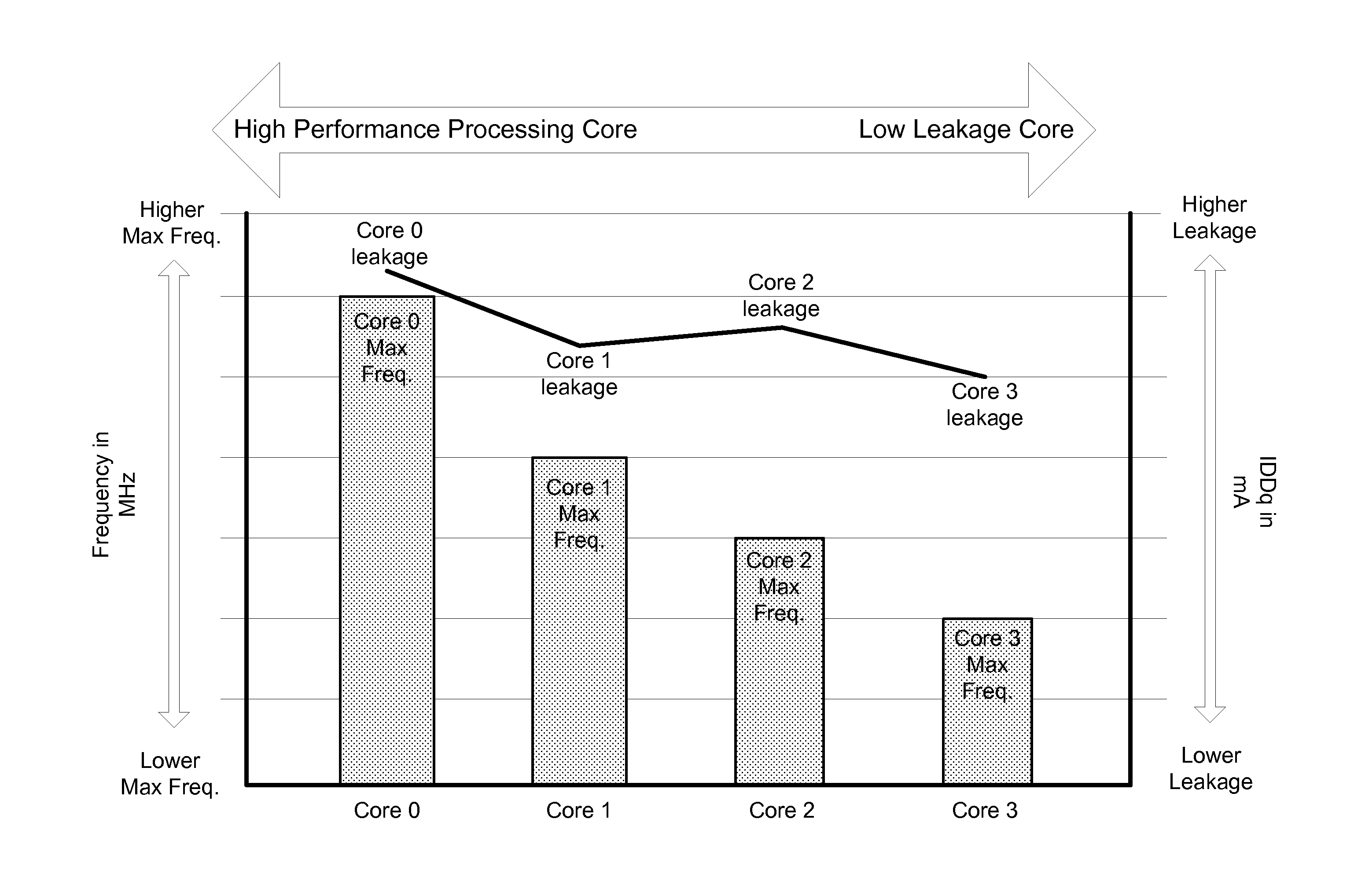
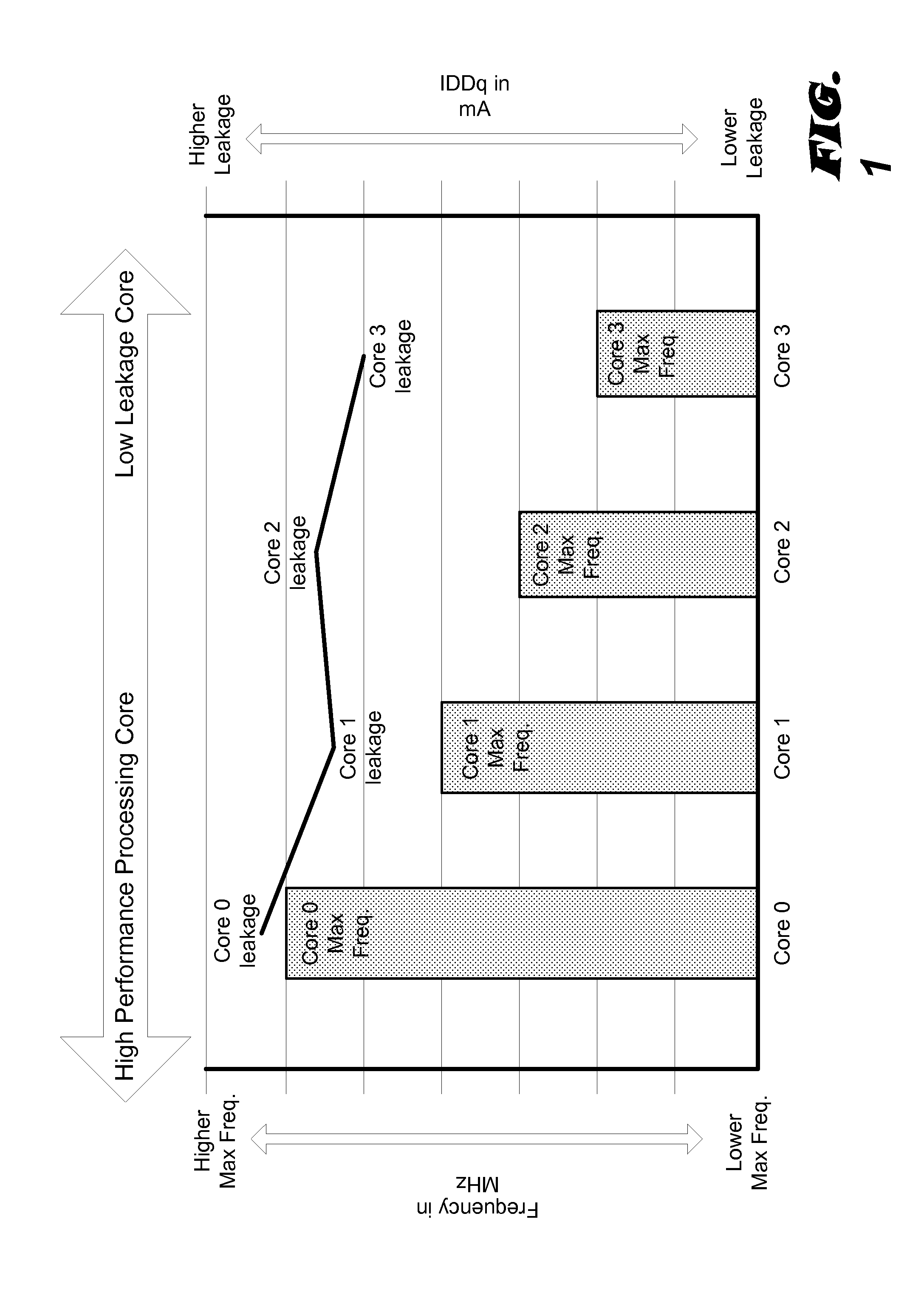
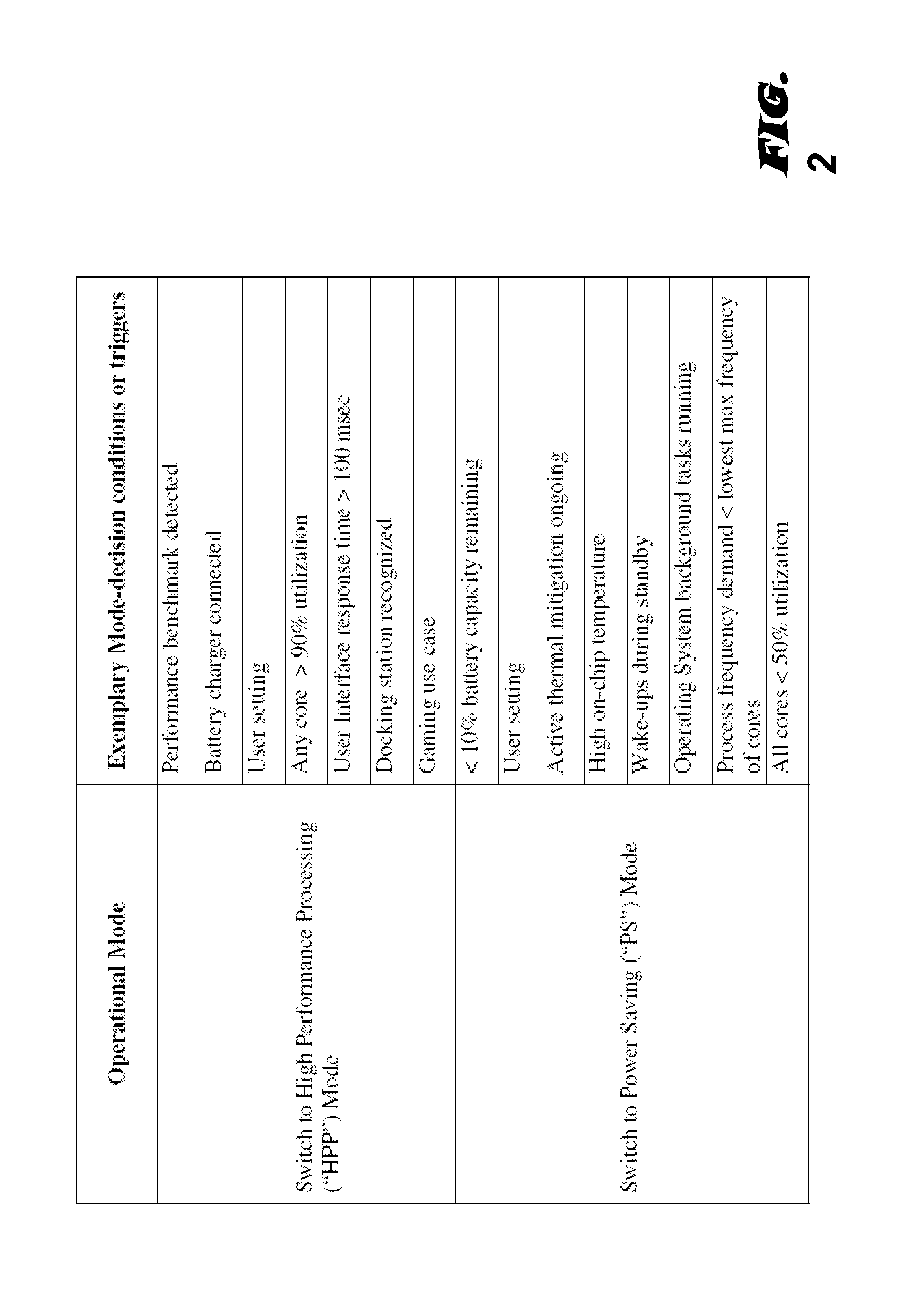
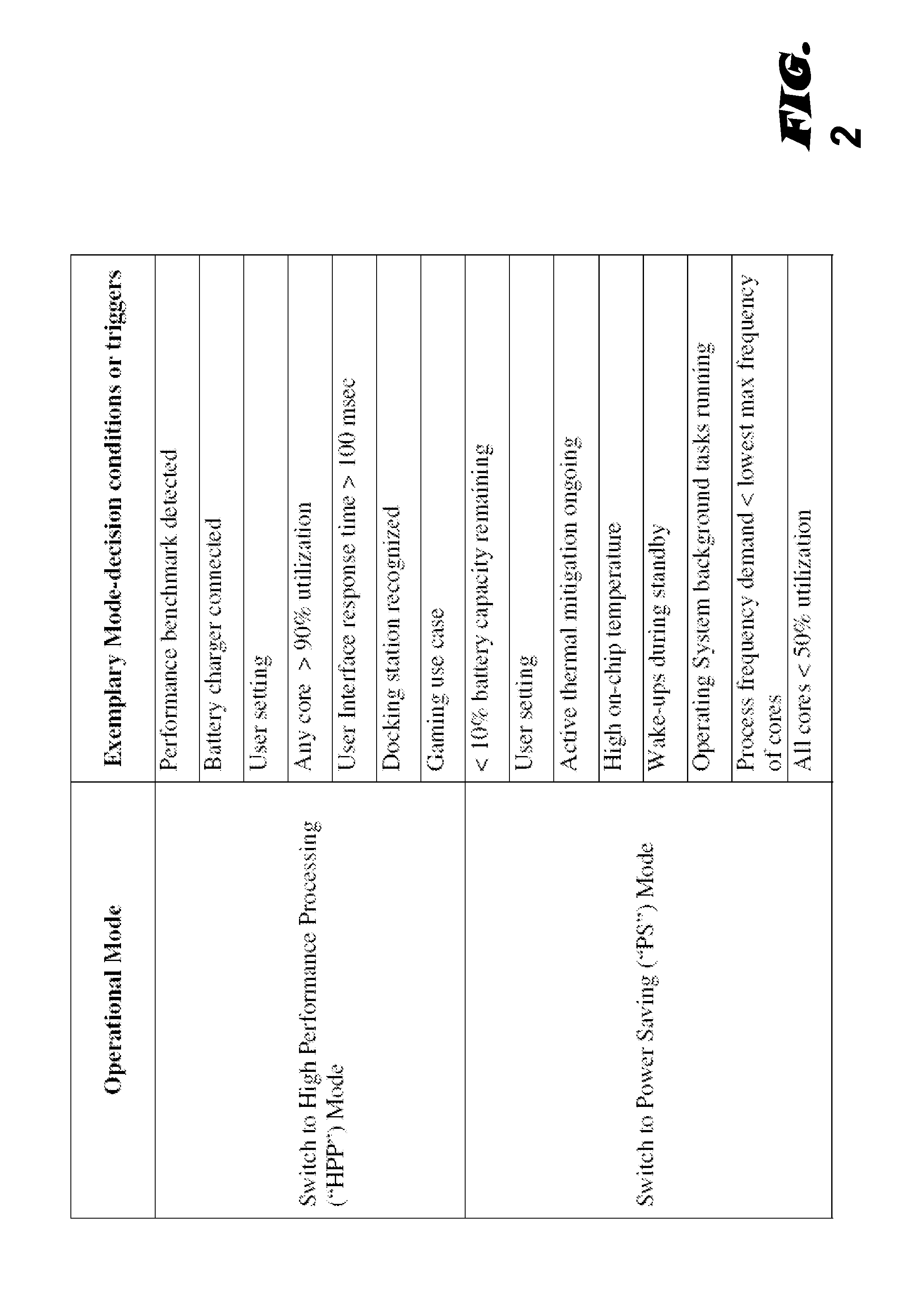
Modal workload scheduling in a heterogeneous multi-processor system on a chip
ActiveUS20140115363A1Quality improvementQuiescent supply currentEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementQuality of serviceMulti processor
Various embodiments of methods and systems for mode-based reallocation of workloads in a portable computing device (“PCD”) that contains a heterogeneous, multi-processor system on a chip (“SoC”) are disclosed. Because individual processing components in a heterogeneous, multi-processor SoC may exhibit different performance capabilities or strengths, and because more than one of the processing components may be capable of processing a given block of code, mode-based reallocation systems and methodologies can be leveraged to optimize quality of service (“QoS”) by allocating workloads in real time, or near real time, to the processing components most capable of processing the block of code in a manner that meets the performance goals of an operational mode. Operational modes may be determined by the recognition of one or more mode-decision conditions in the PCD.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
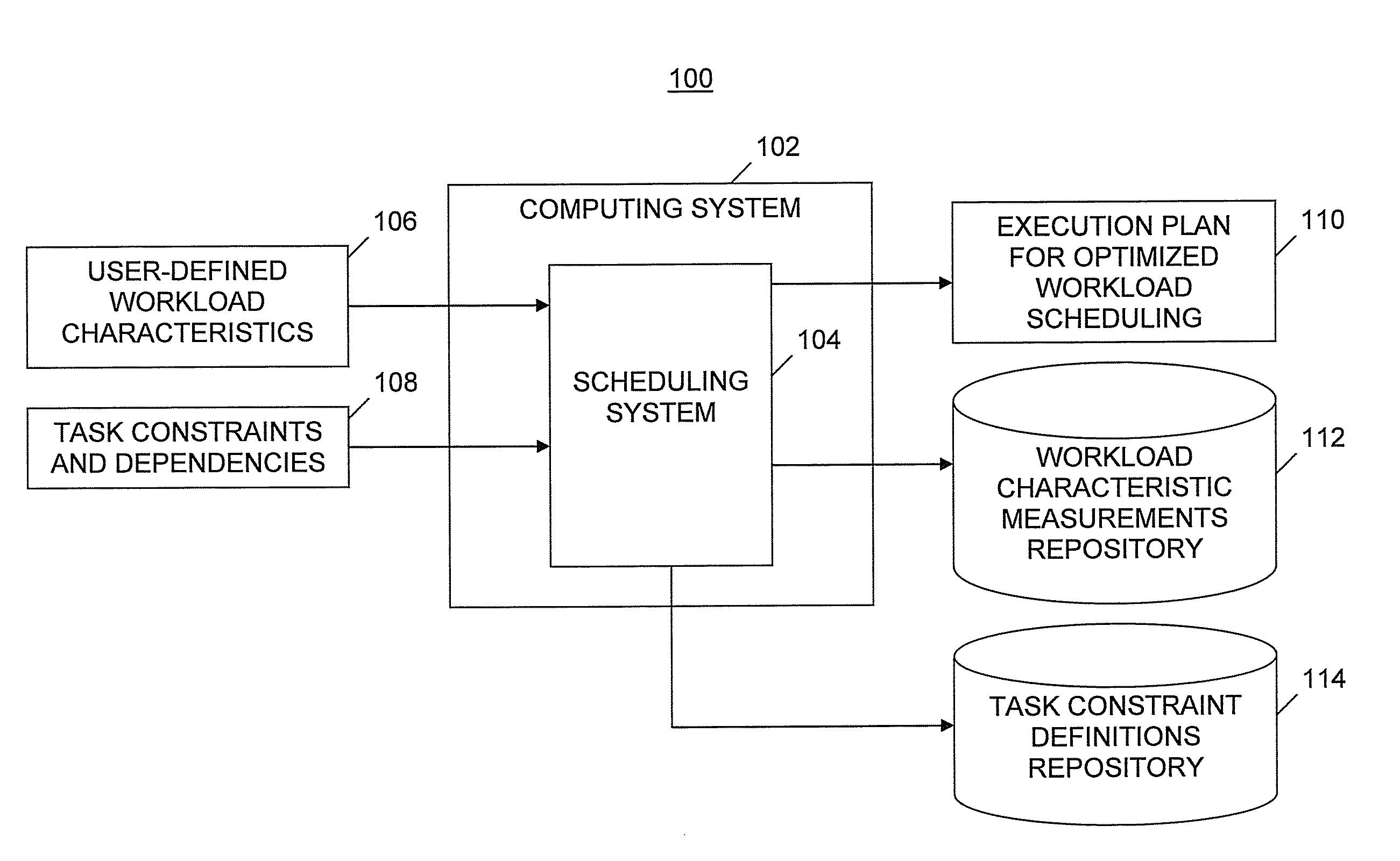
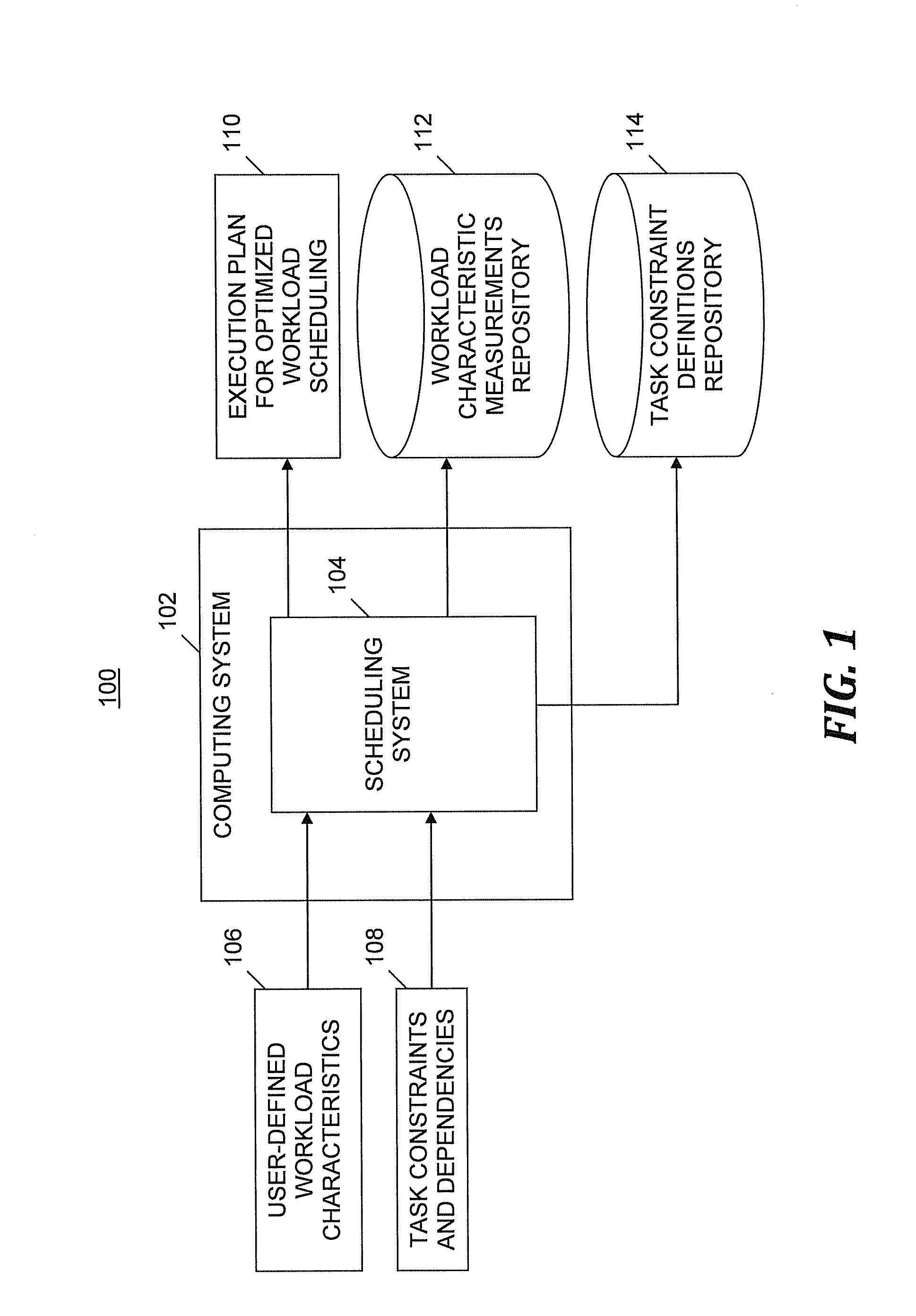
Autonomic workload planning
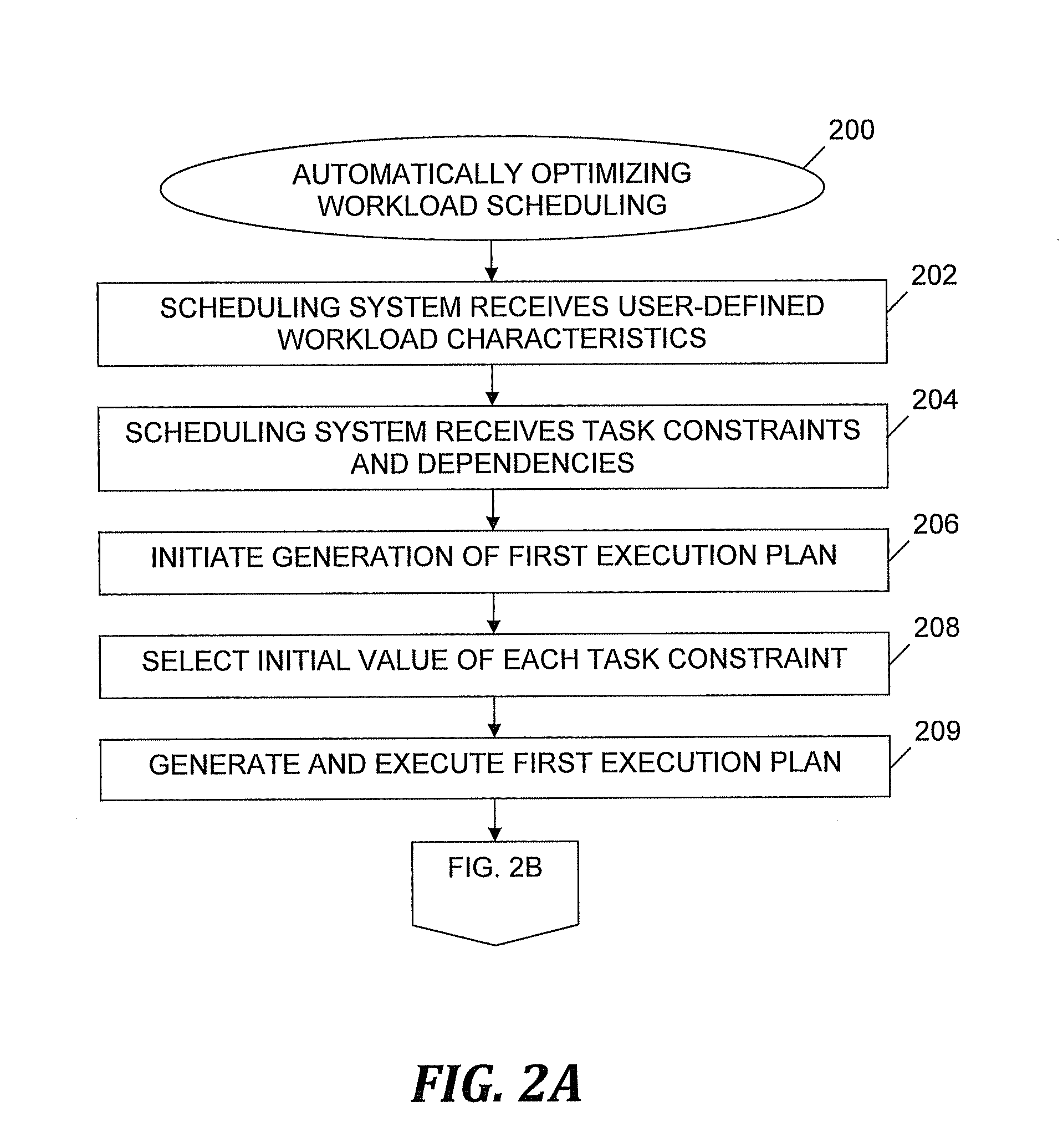
A method of automatically optimizing workload scheduling. Target values for workload characteristics and constraint specifications are received. Generation of a first execution plan is initiated. Initial constraint values conforming to the constraint specifications are selected. Each constraint value constrains tasks included in the workload. The first execution plan is executed, thereby determining measurements of workload characteristics. Contributions indicating differences between workload characteristic measurements and target values are determined and stored. Generation of a next execution plan is initiated. Modified constraint values conforming to the constraint specifications are selected. Changes in the workload characteristics based on the modified constraint values are evaluated. An optimal or acceptable sub-optimal solution in a space of solutions defined by the constraint specifications is determined, resulting in new values for the constraints. After replacing the initial values with the new values, the next execution plan is generated and executed.
Owner:IBM CORP
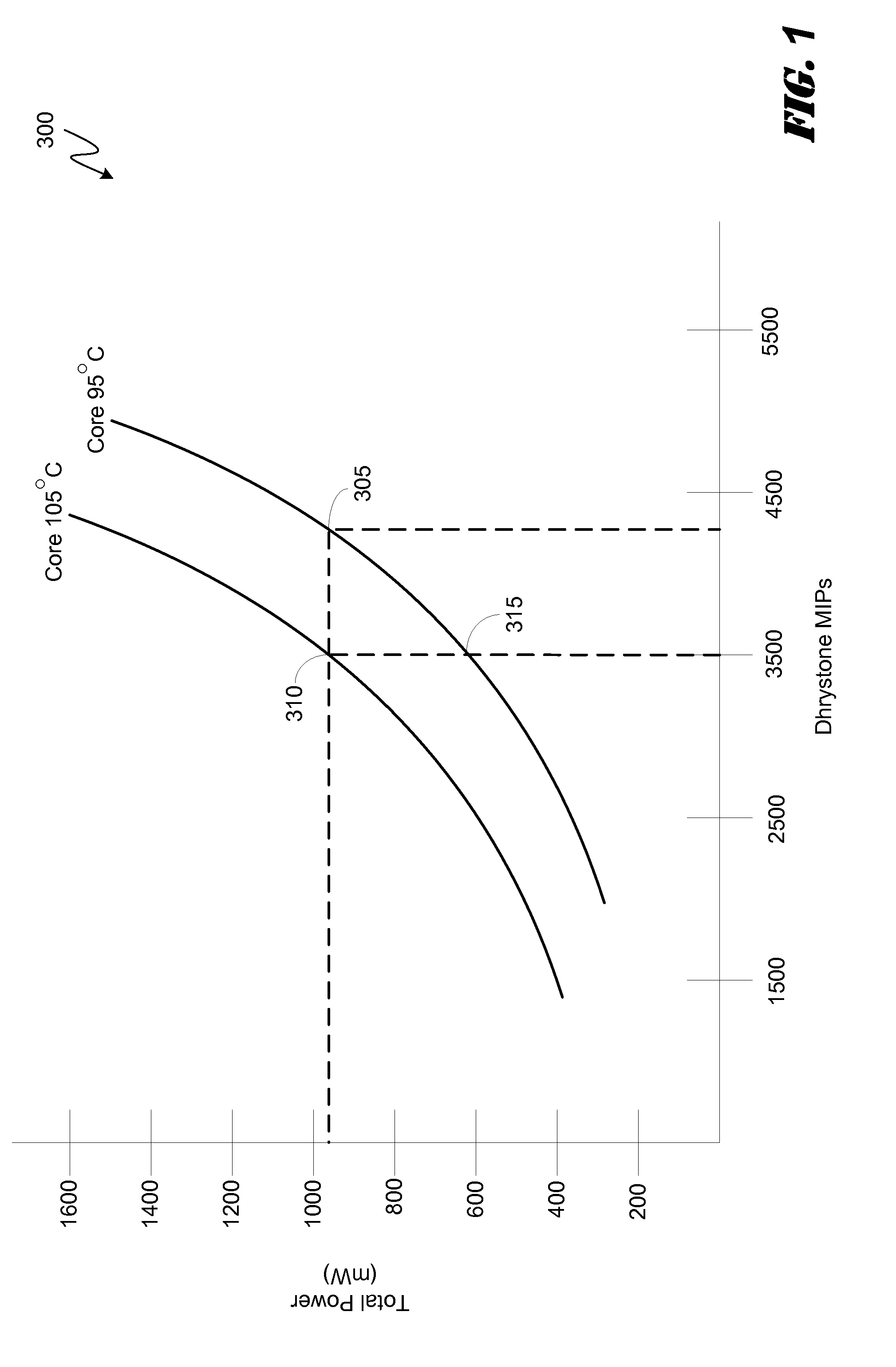
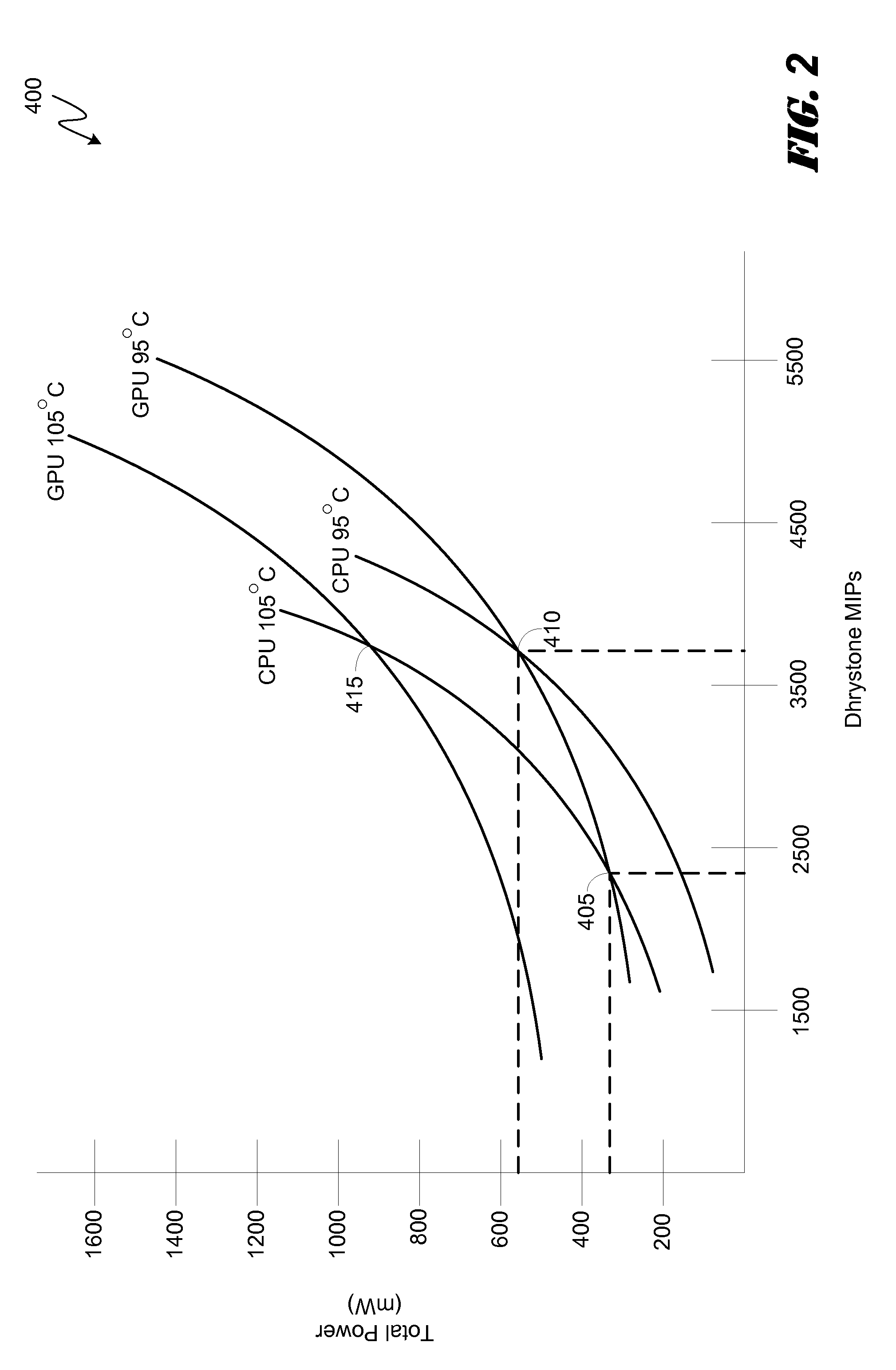
System and method for dynamic dcvs adjustment and workload scheduling in a system on a chip
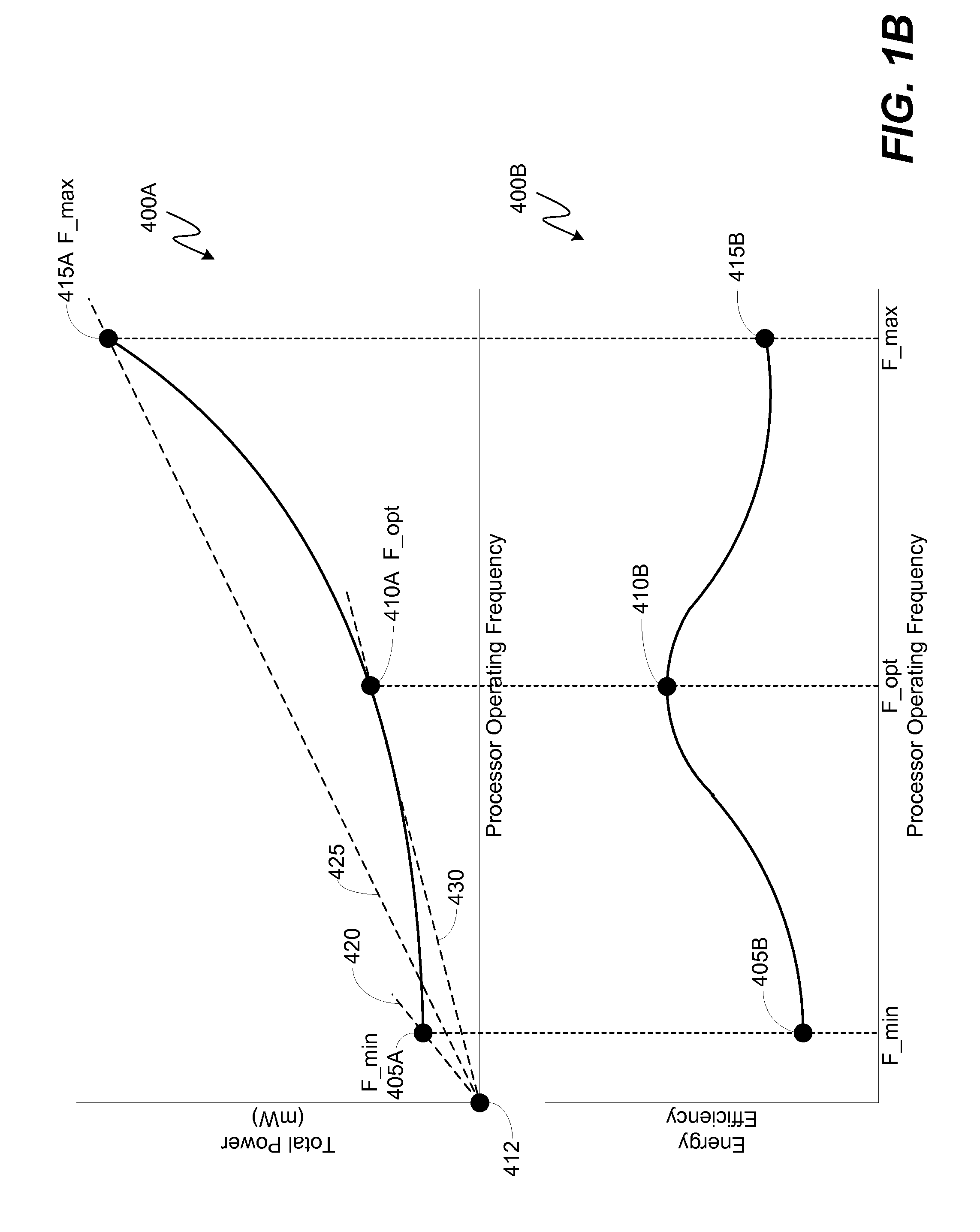
ActiveUS20150143142A1Minimize power consumptionRaise the ratioVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingPower modeWorkload scheduling
Various embodiments of methods and systems for dynamically adjusting operating frequency settings of one or more processing components in a portable computing device (“PCD”) are disclosed. One such method involves receiving a request to adjust an operating frequency setting of a processing component to a required frequency (“F_req”) to process a workload. Factor readings associated with the operating capacity of the processing component may be taken. Based on the readings, performance curves associated with the processing component may be queried. The performance curves are used to determine the optimal operating frequency (“F_opt”) for the processing component. The F_opt is compared to the F_req and, if the F_req is less than F_opt, the operating frequency setting of the processing component is set to F_opt. Advantageously, as compared to F_req, at F_opt workload processing may be more efficient and a low power mode may be entered sooner.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Decomposition settlement method for medium-long-term electric quantity finance contract in spot market
InactiveCN107845035AThe method is simple and practicalReduce the workload of scheduling transactionsFinanceDecompositionLong-running transaction
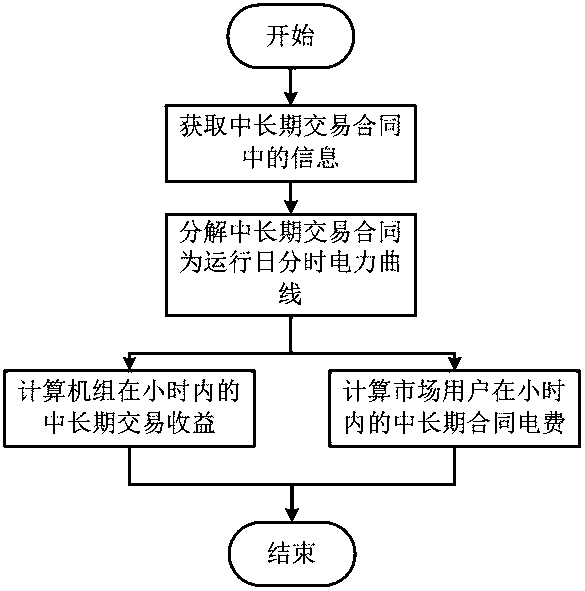
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric power market, and more specifically relates to a method for decomposing and settling medium and long-term electricity financial contracts in the spot market. Including the following steps: S1. Obtain the information in the medium and long-term transaction contract; S2. Calculate the time-of-use power curve of the operation day according to the information obtained in the step S1; S3. The medium and long-term transaction income of the computer group within each hour; S4. Calculate The medium and long-term contract electricity charges of market users within each hour. The present invention provides a method for decomposing and settling medium and long-term electricity financial contracts in the spot market, which is applied to the decomposition of electricity in financial contracts in the spot market. Combining the characteristics of financial electricity contracts, only settlement is required and no physical execution is required. The load-adjusting curve is used to decompose electricity. The method is simple and practical, which reduces the workload of scheduling transactions and makes it easier to connect with the spot market. It provides a feasible construction plan for the current power spot market.
Owner:广东电力交易中心有限责任公司
Workflow processing method based on micro-service architecture system
ActiveCN111858001AEasy to useProgram initiation/switchingInterprogram communicationWorkload schedulingProcess definition
The invention relates to the technical field of information, and provides a workflow processing method based on a micro-service architecture system. The objective of the invention is to solve the problems of data transmission and sharing between cross-application workflow applications and nodes in a micro-service system. According to the main scheme, a workflow micro-service management node manages workflow related workload scheduling and flow processing of all other micro-service application nodes in the micro-service system; after a user operates the process on each micro-service applicationnode, the workflow micro-service management node broadcasts a new process definition file in the micro-service system; a process engine provided by the workflow micro-service management node for themicro-service application node can automatically transmit task data of a workflow node of a previous micro-service application node to a corresponding workflow node of a next micro-service applicationnode; and then the process engine of the next micro-service application node processes the workflow task.
Owner:武汉众邦银行股份有限公司
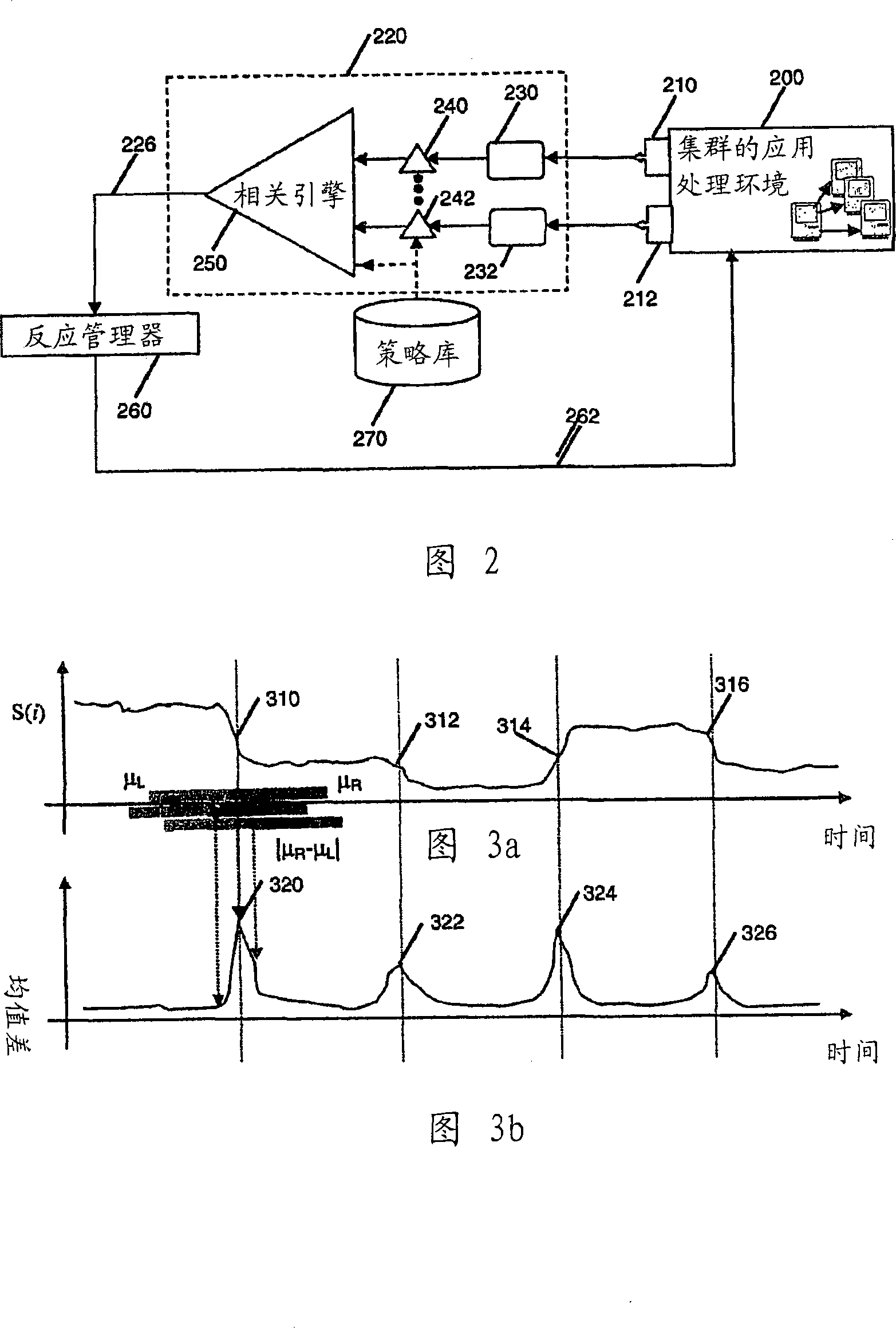
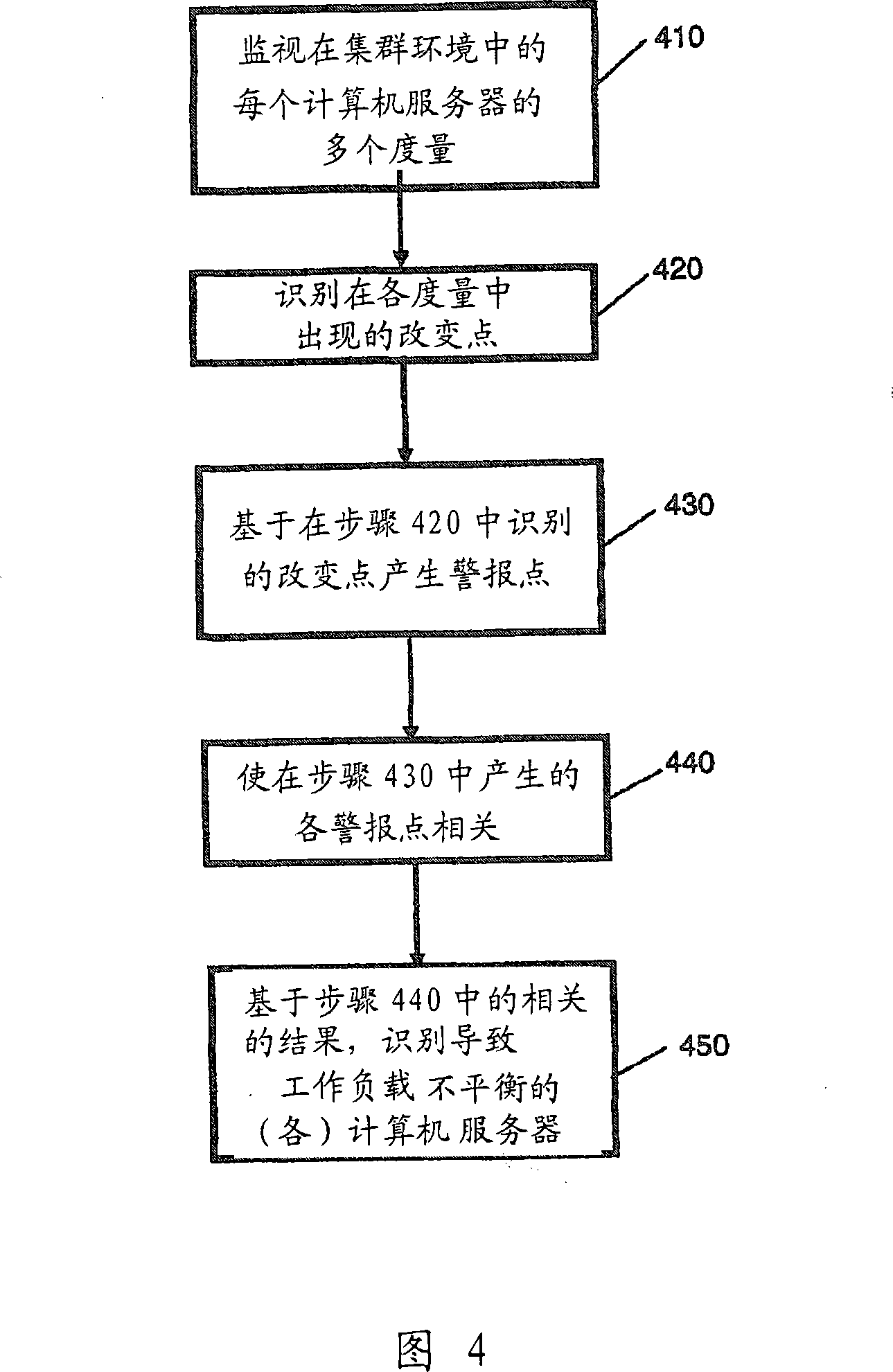
System and method for detecting imbalances in dynamic workload scheduling in clustered environments
A method, system and computer program product for detecting workload imbalance in a dynamically scheduled computer server cluster are disclosed. One such method comprises the steps of: monitoring a plurality of metrics at each of said computer servers; detecting change points in said plurality of metrics; generating alert points based on said detected change points; alarm points are correlated; and based on a result of said correlation, identifying one or more of said computer servers causing a workload imbalance. Systems and computer program products for practicing the methods described above are also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Monitoring performance on workload scheduling systems
ActiveUS8381219B2Lower performance requirementsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime rangeData processing system
The present invention relates to the field of enterprise network computing. In particular, it relates to a method and respective system for monitoring workload of a workload scheduler. Information defining a plurality of test jobs of low priority is received. The test jobs have respective launch times, and the test jobs are launched for execution in a data processing system in accordance with said launch times and said low execution priority. It is evaluated how many of said test jobs are executed within a pre-defined analysis time range. A performance decrease warning is issued, if the number of executed test jobs is lower than a predetermined threshold number. The workload scheduler discards launching of jobs having a low priority when estimating that a volume of jobs submitted with higher priority is sufficient to keep said scheduling system busy.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Adjunct partition work scheduling with quality of service attributes
ActiveUS20120180046A1Sufficient execution resourceMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationQuality of serviceDecision taking
Operating system-directed workload scheduling of an adjunct partition in a logically partitioned computer is selectively overridden to handle platform work requiring a Quality of Service (QoS) guarantee. Firmware may track outstanding requests for platform work for an adjunct partition, and in response to a request for platform work that requires a QoS guarantee, the firmware may assume or take over scheduling decisions for the adjunct partition from the operating system of an associated logical partition and schedule execution of the adjunct partition to ensure that the adjunct partition will be allocated sufficient execution resources to perform the platform work independent of the scheduling desires of the operating system. As a result, any platform work that potentially impacts the platform work of other adjunct partitions will not be held up as a result of an unwillingness or inability of the operating system to schedule execution of the adjunct partition.
Owner:IBM CORP
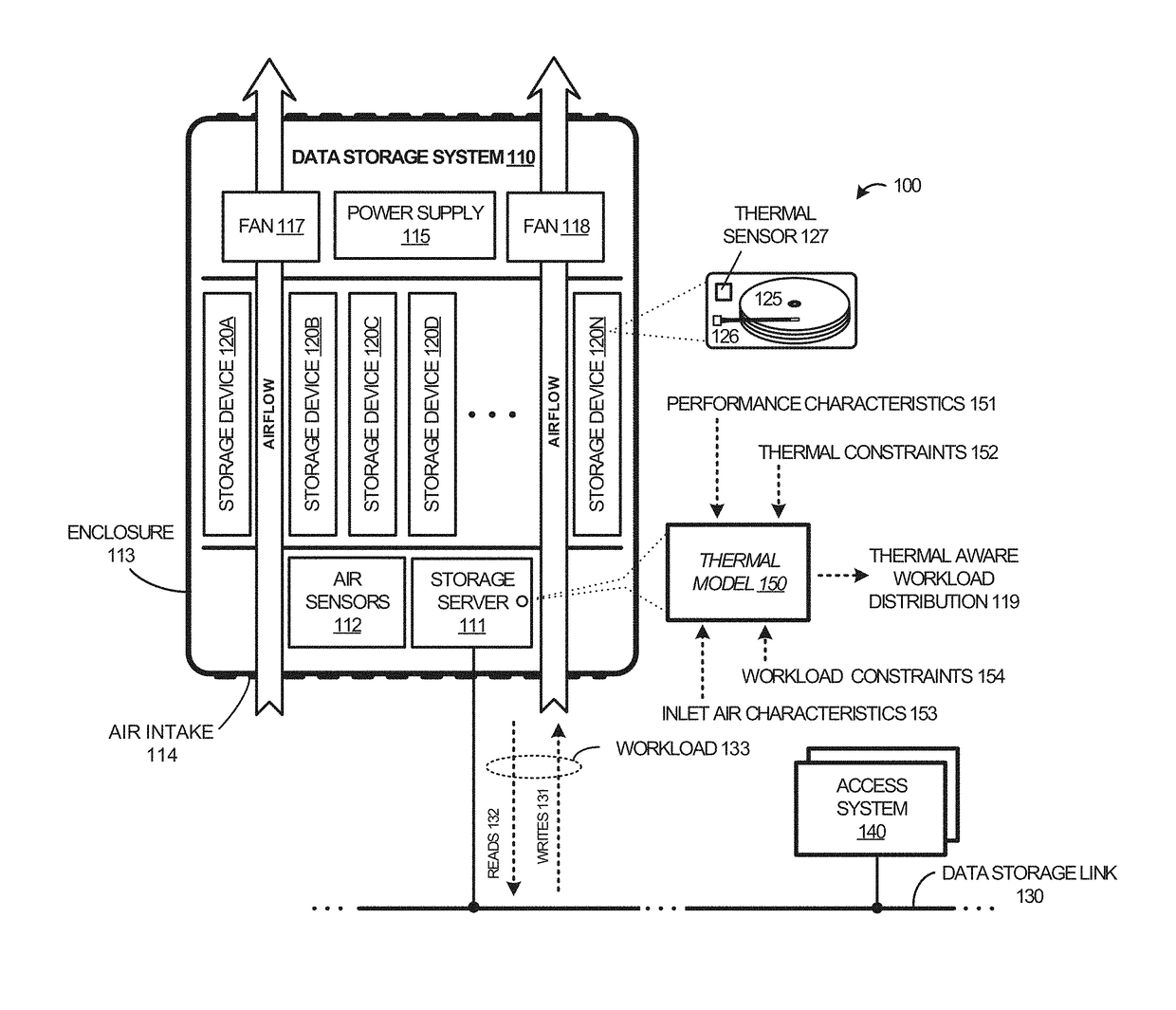
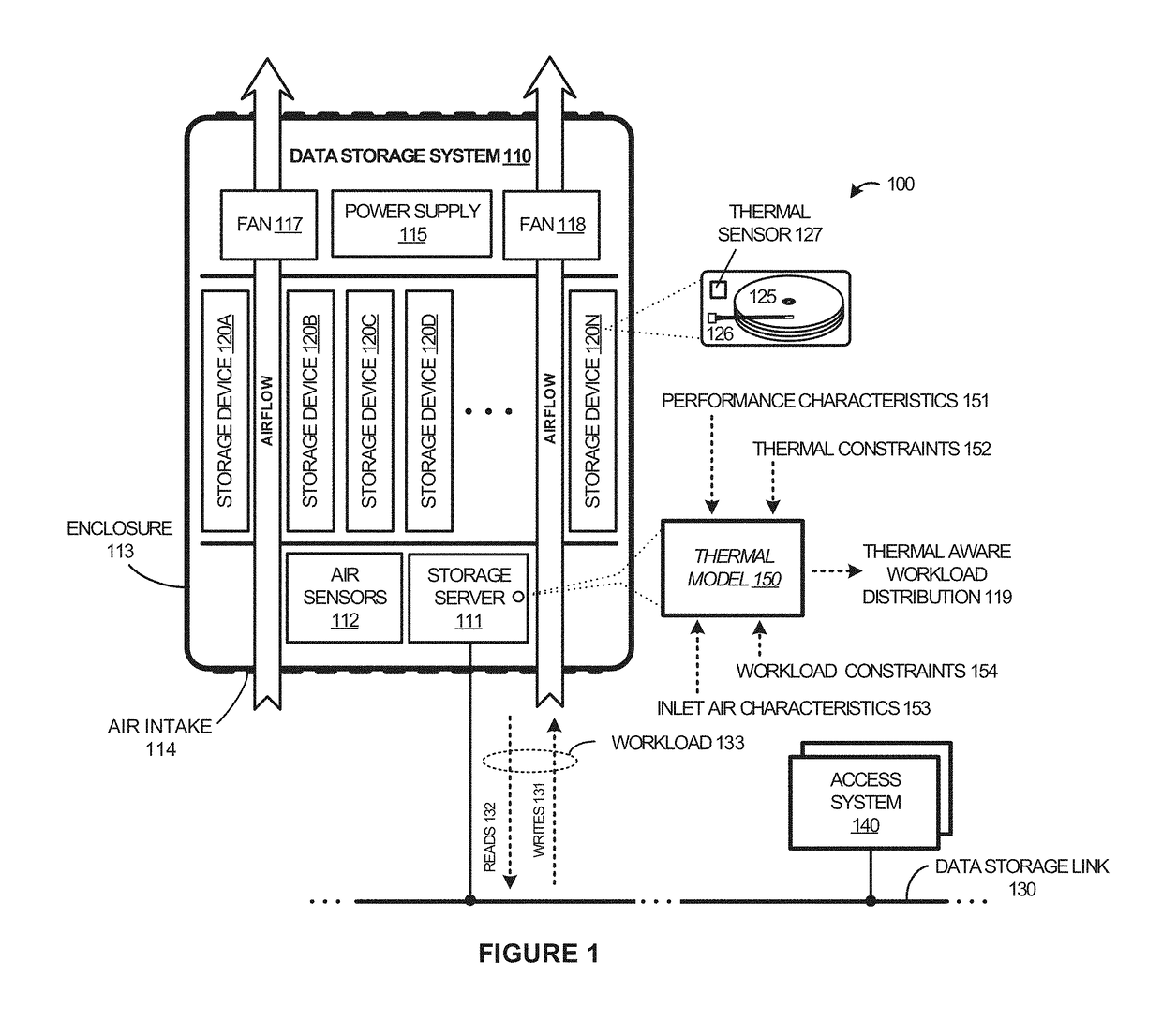
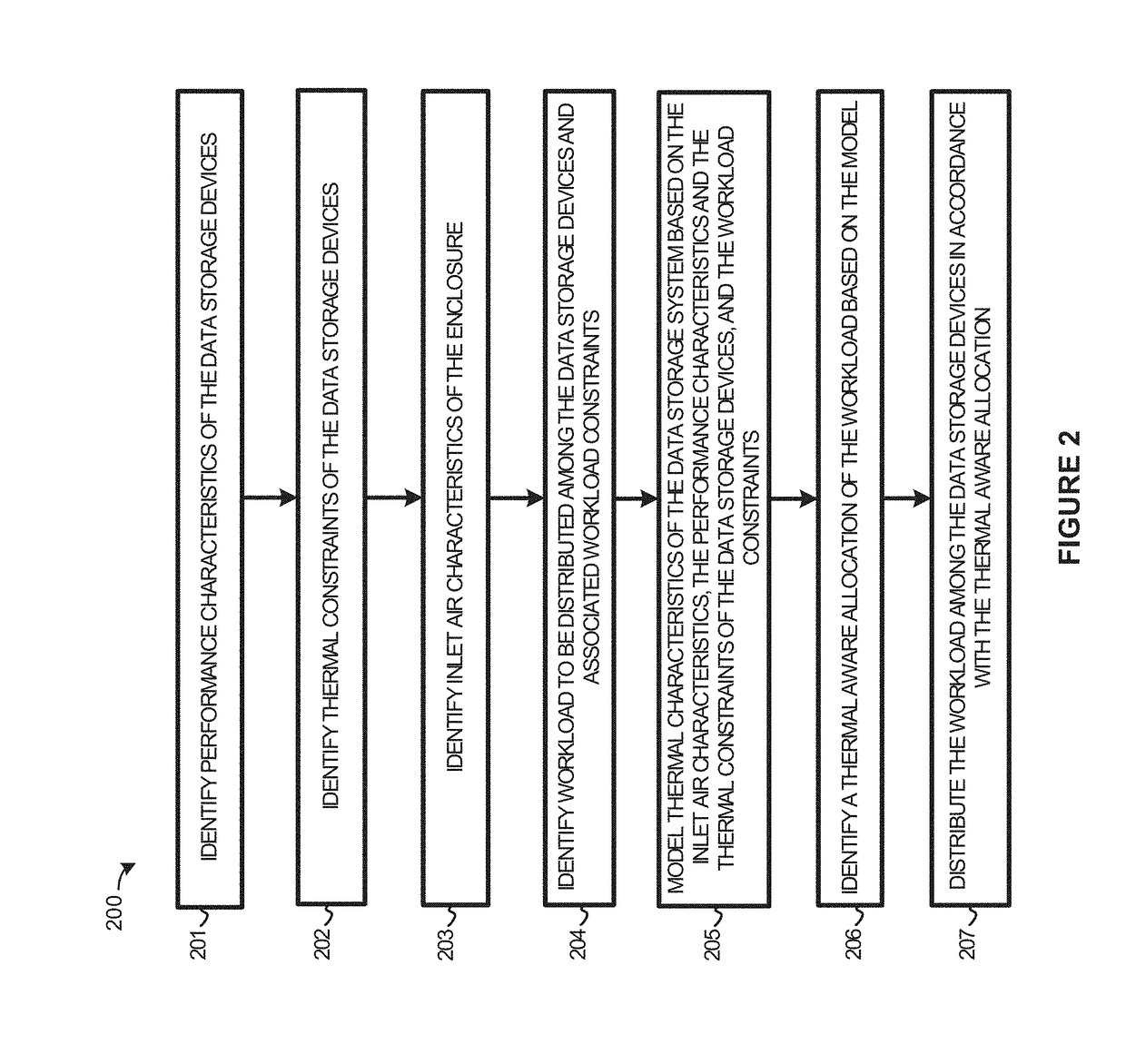
Thermal aware workload scheduling
ActiveUS20180004260A1Resource allocationDigital data processing detailsWorkload schedulingThermal aware
Systems, software, devices, and methods of distributing a workload among available data storage devices in a thermal aware manner are described herein. More specifically, the examples herein discuss distributing the workload among the available data storage devices in a thermal aware manner that optimizes collective IOPs of the data storage devices in an enclosure. The thermal aware distribution of the storage operations is determined by a thermal model that predicts thermal characteristics of the data storage system based on inlet air characteristics of the enclosure, performance characteristics and thermal constraints of the data storage devices, and constraints of the workload.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
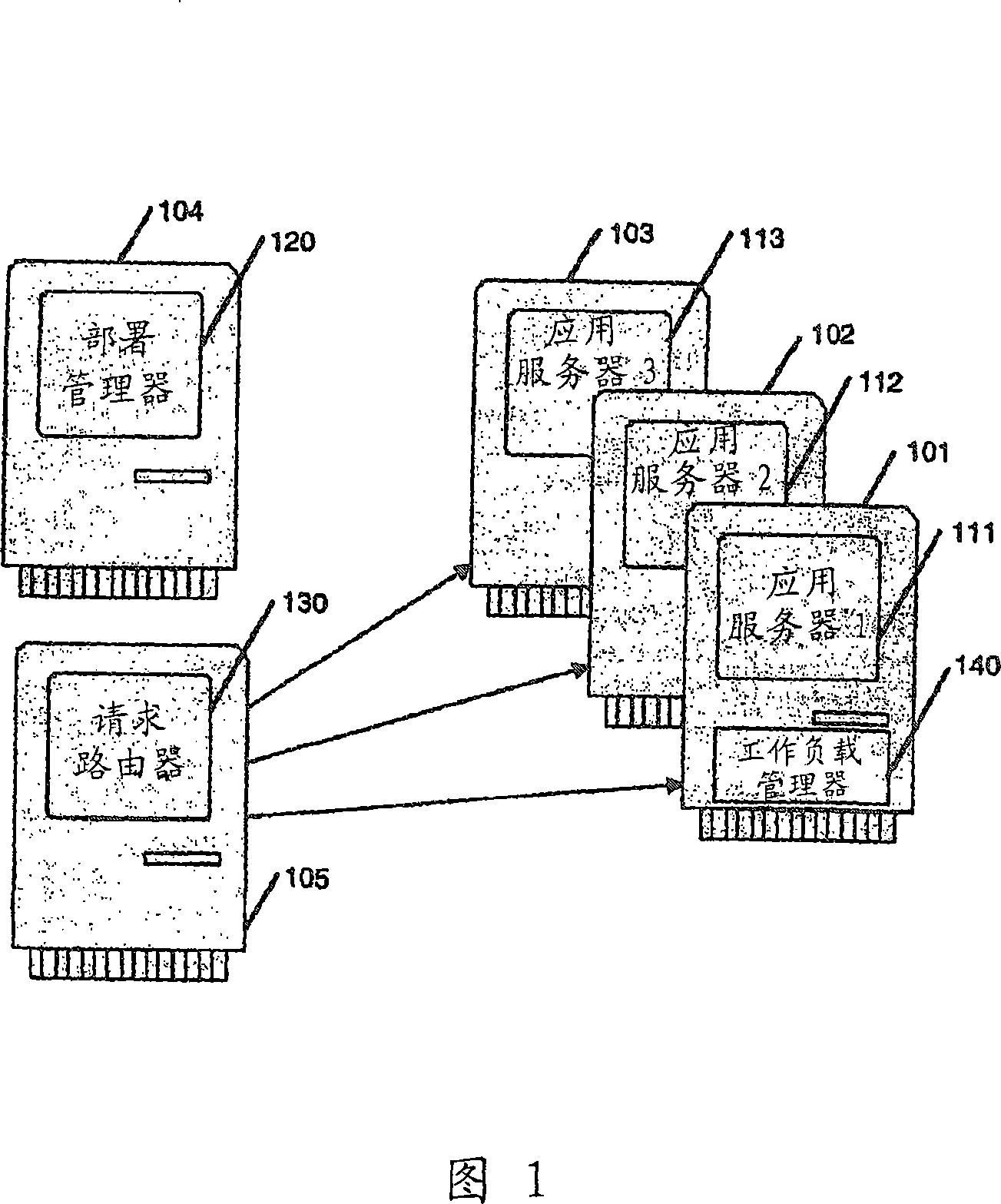
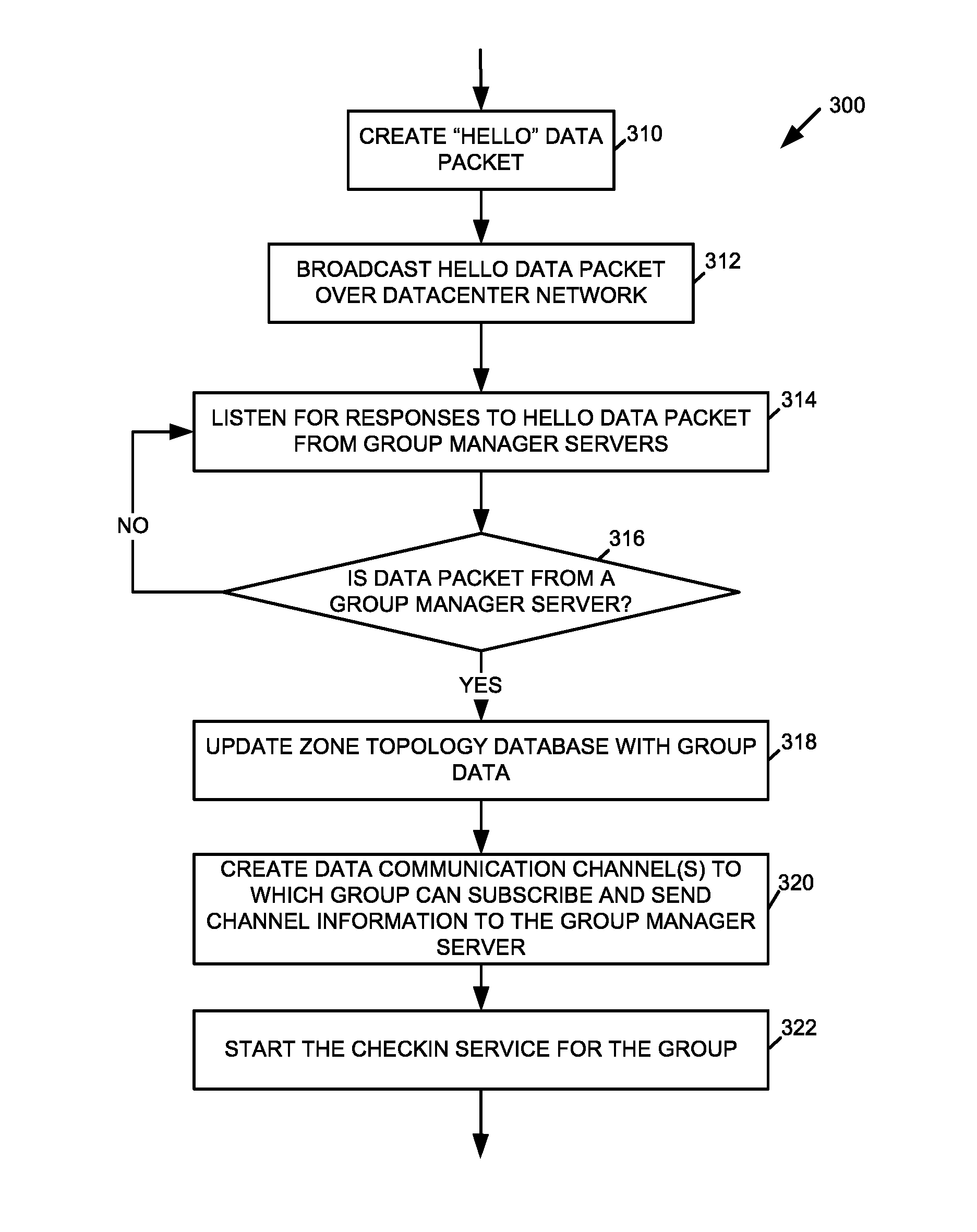
Method, system, and device for managing server hardware resources in a cloud scheduling environment
Owner:INTEL CORP
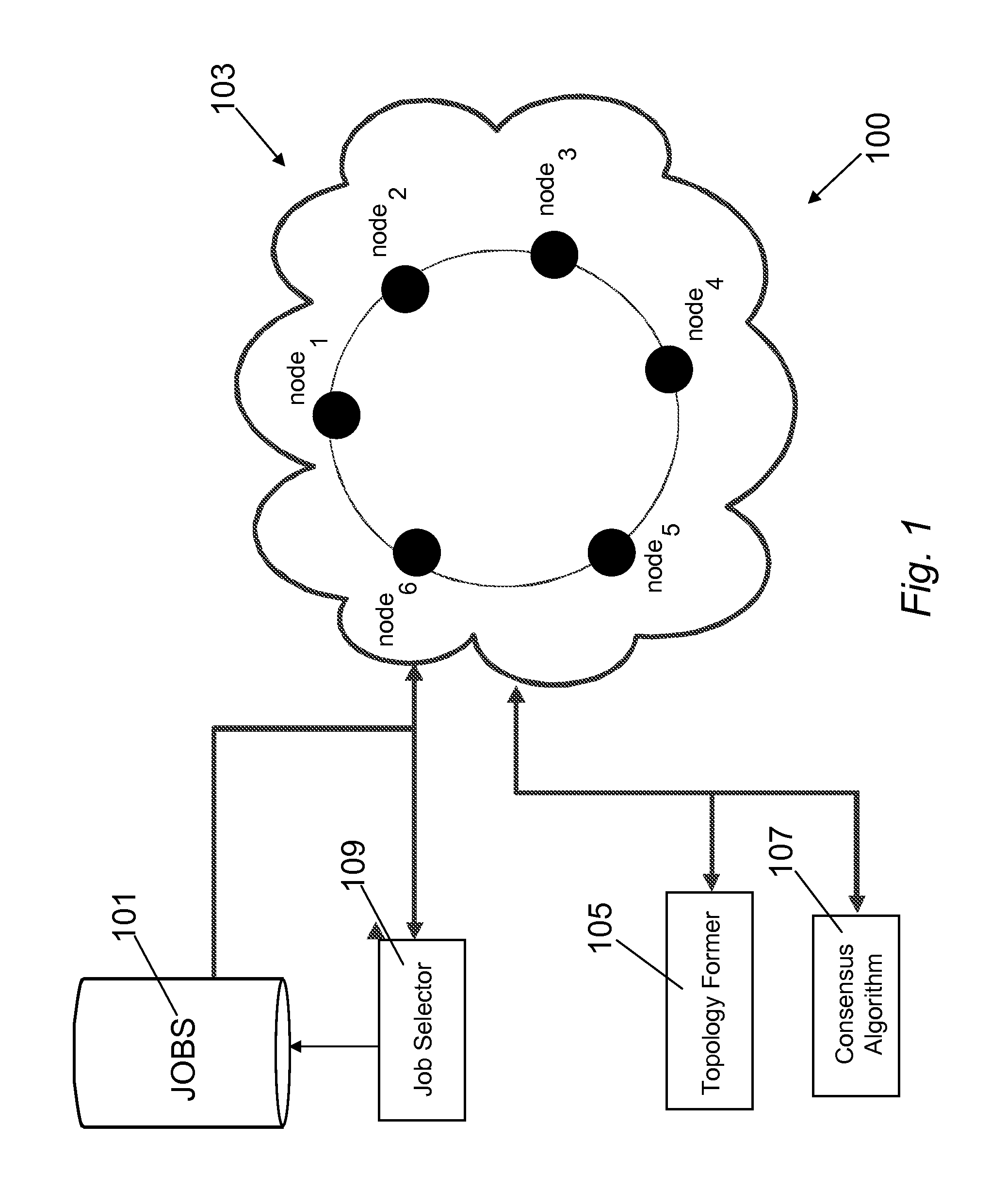
Method and system for job scheduling in distributed data processing system with identification of optimal network topology
InactiveUS8495206B2Fast convergenceRobust to perturbationDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsDistributed Computing EnvironmentSmall worlds
The method of the present invention provides an automatic and optimized selection of the network topology for distributing scheduling of jobs on the computers of the modified network topology. The automatic and optimized selection of the network topology starts from the current topology and a desired number of additional connections. In this way the method of the present invention provides a higher convergence speed for the modified consensus algorithm in comparison, e.g., to a simple ring network. The method exploits the so called small-world networks. Small-world networks are more robust to perturbations than other network architectures. The preferred embodiment provides a workload scheduling system which is highly scalable to accommodate increasing workloads within a heterogeneous distributed computing environment. A modified average consensus algorithm is used to distribute network traffic and jobs amongst a plurality of computers.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Workload scheduling method and system with improved planned job duration updating scheme
A method for scheduling execution of a work unit in a data processing system comprises assigning to the work unit an expected execution duration; executing the work unit determining an actual execution duration of the work unit; determining a difference between the actual execution duration and the expected duration; and conditionally adjusting the expected execution duration assigned to the work unit based on the measured actual execution duration, wherein the conditionally adjusting includes preventing the adjustment of the expected execution duration in case said difference exceeds a predetermined threshold. The method further includes associating to the work unit a parameter having a prescribed value adapted to provide an indication of unconditional adjustment of the expected execution duration: in case said parameter takes the prescribed value, the expected duration assigned with the work unit based on the measured actual execution duration even if the difference in durations exceeds the predetermined threshold.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method, system and computer program for distributing a plurality of jobs to a plurality of computers
The preferred embodiment provides a mechanism for determining an optimal workload distribution, from a plurality of candidate workload distributions, each of which has been determined to optimise a particular aspect of a workload-scheduling problem. More particularly, the preferred embodiment determines a workload distribution based on resource selection policies. From this workload distribution the preferred embodiment optionally determines a workload distribution based on job priorities. From either or both of the above parameters, the preferred embodiment determines a workload distributionbased on a total prioritised weight parameter. The preferred embodiment also determines a workload distribution which attempts to match the previously determined candidate workload distributions to agoal distribution. Similarly, the preferred embodiment calculates a further workload distribution which attempts to maximise job throughput.
Owner:IBM CORP
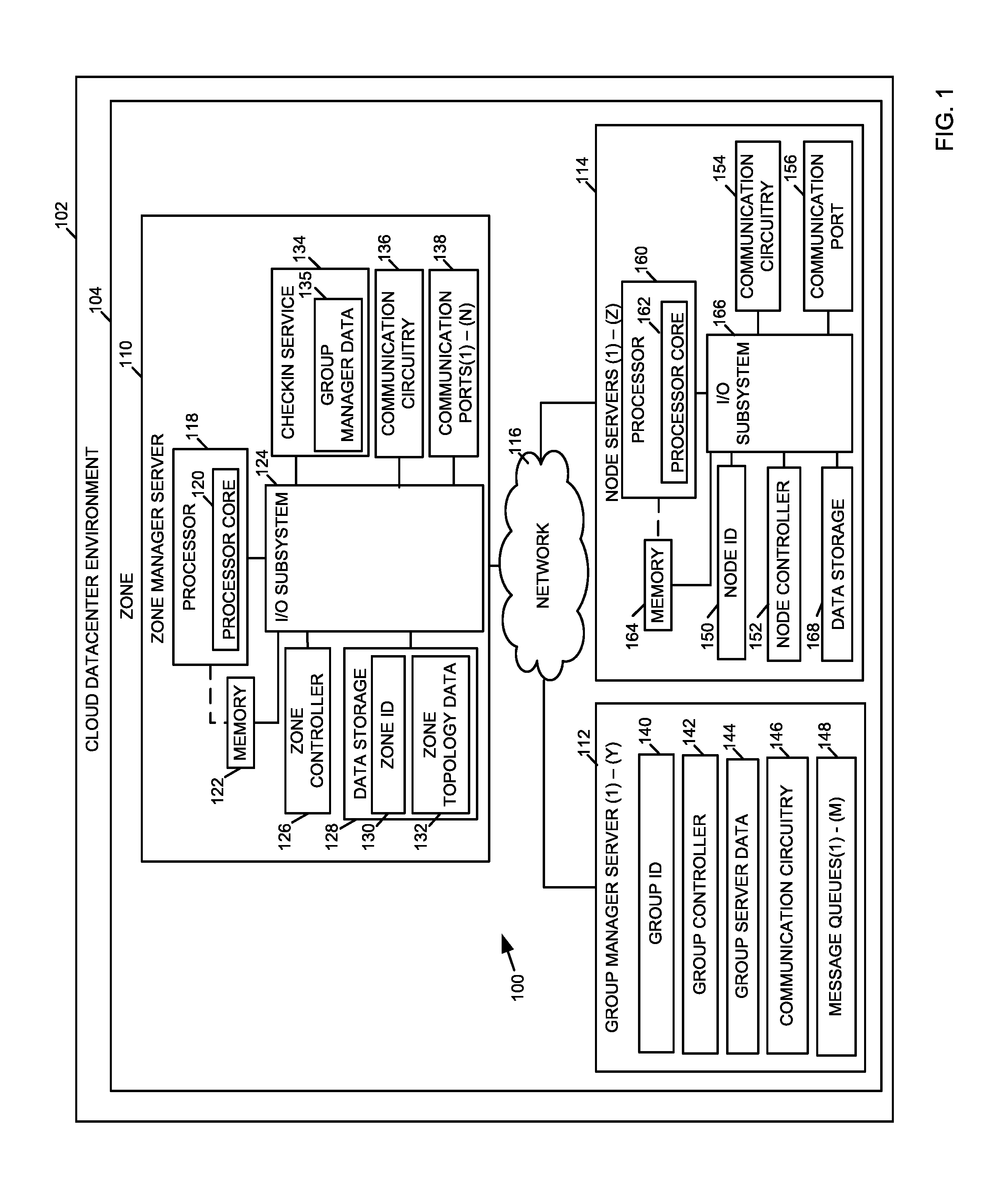
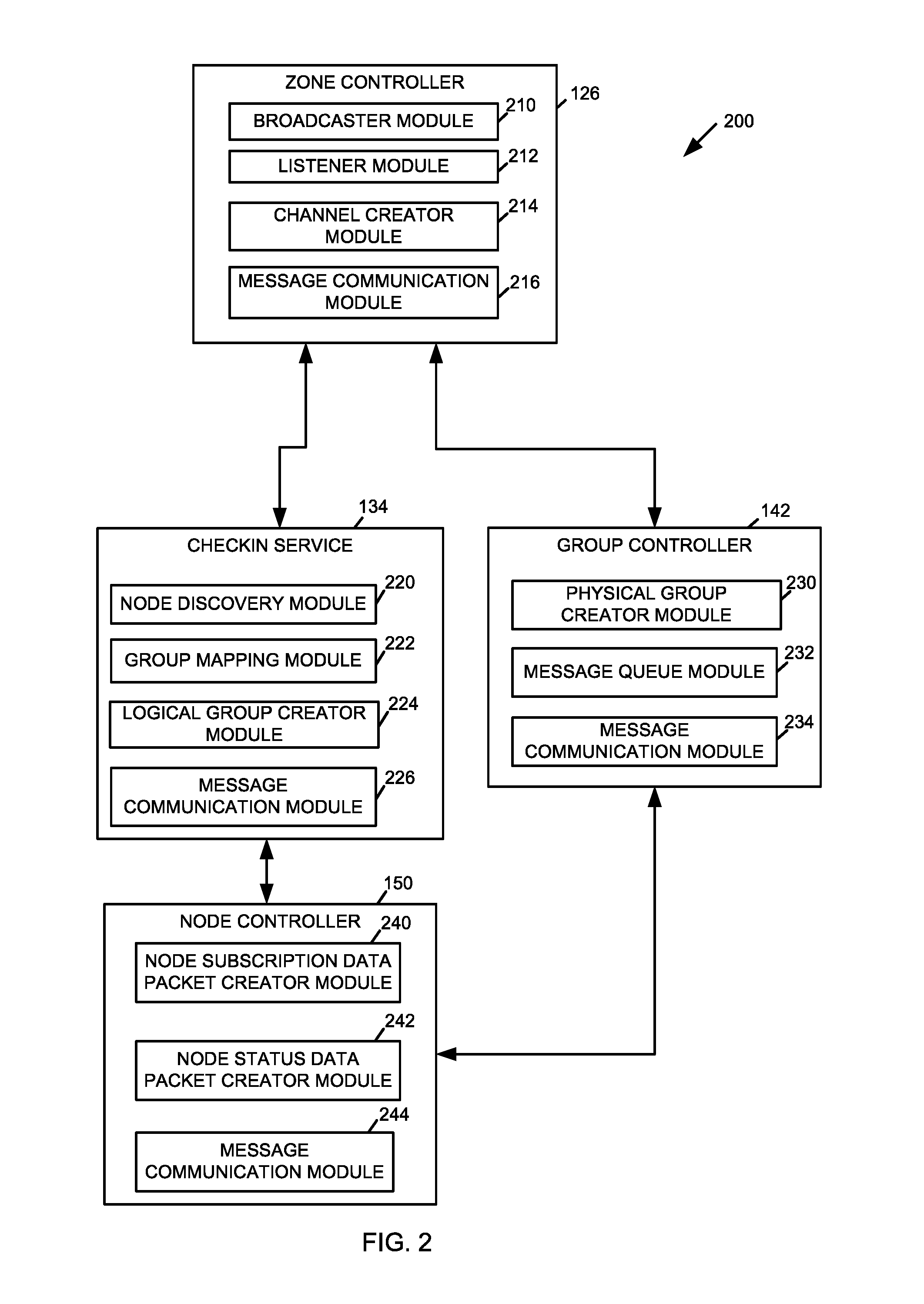
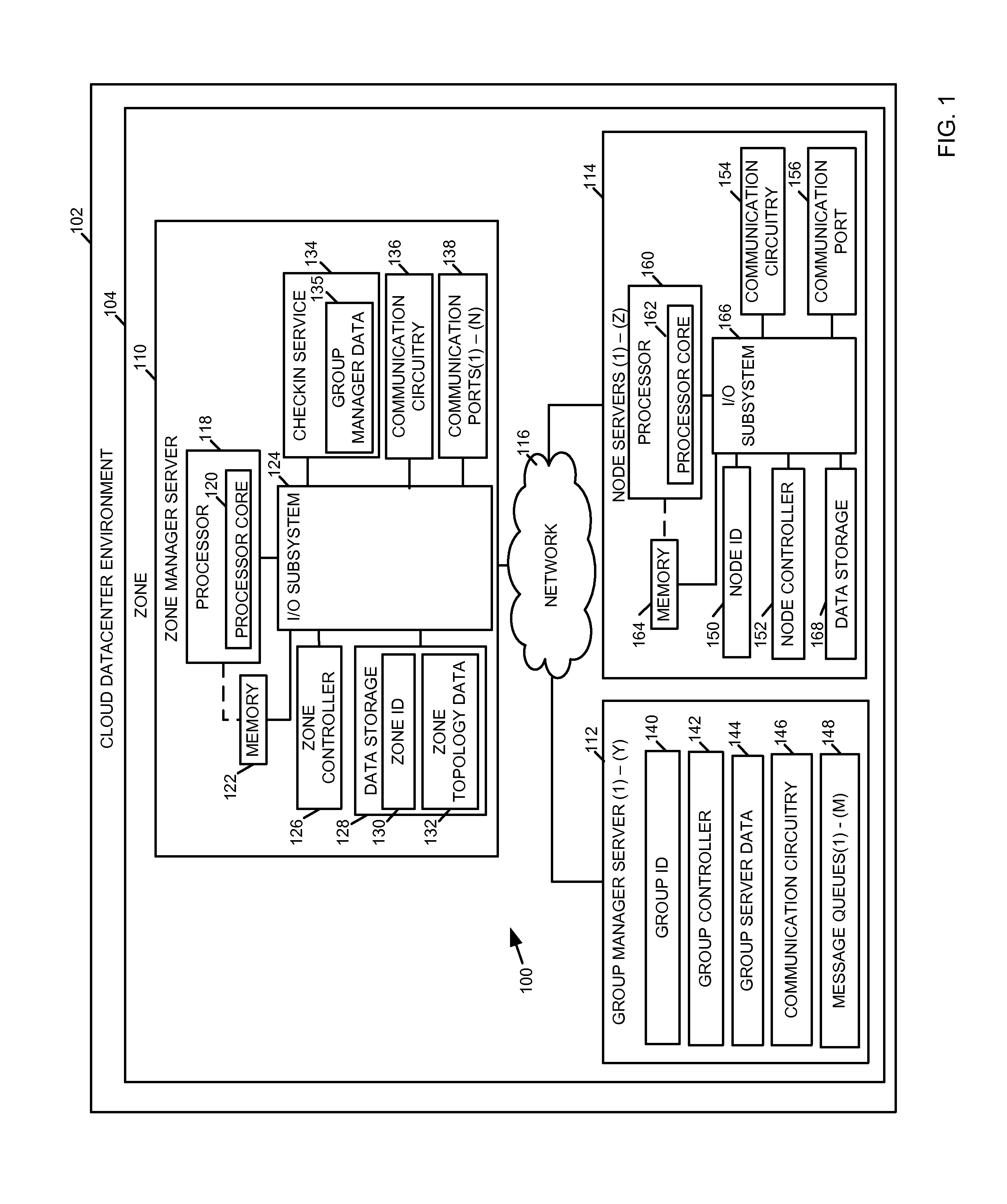
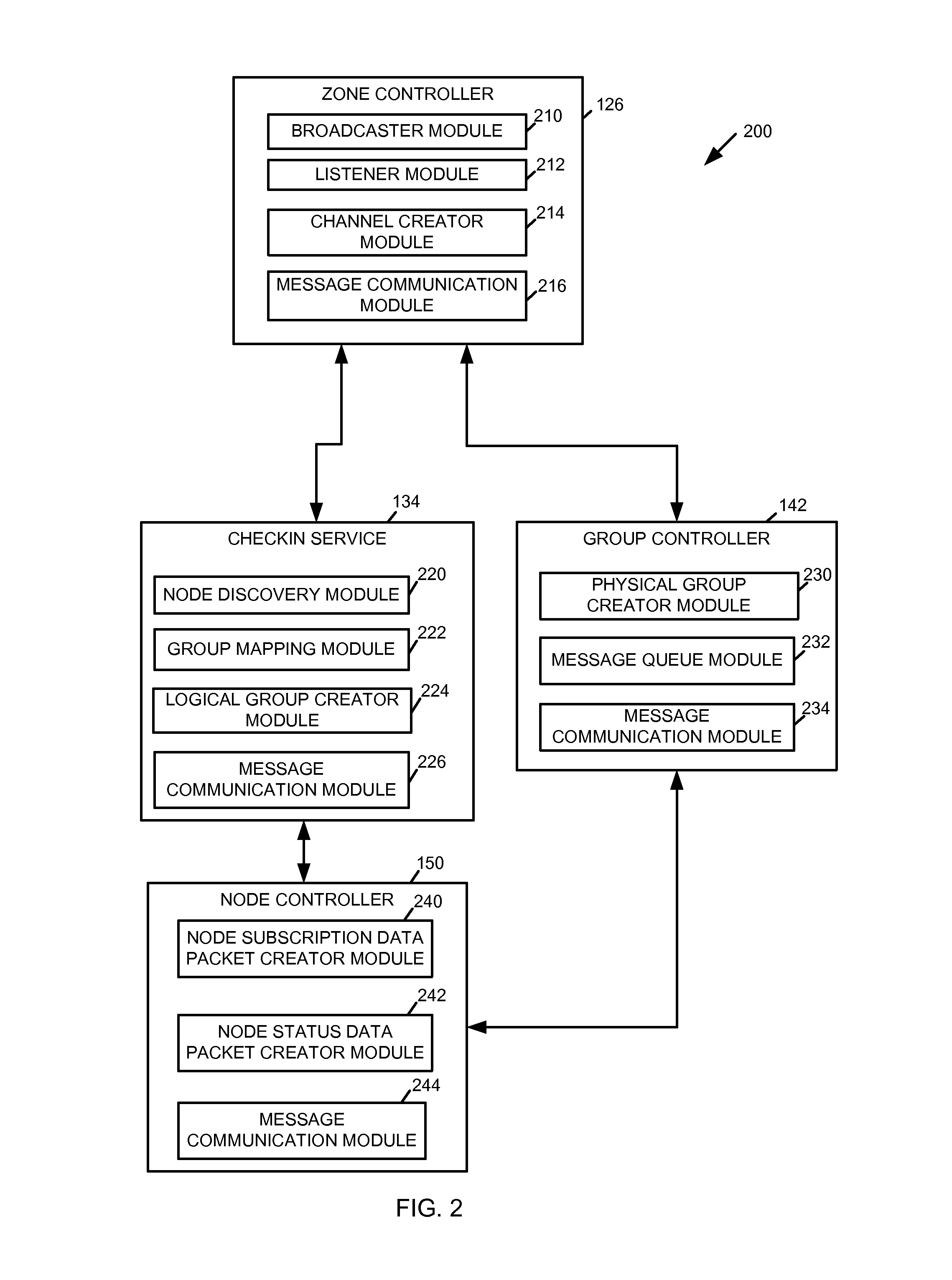
Method, system, and device for managing server hardware resources in a cloud scheduling environment
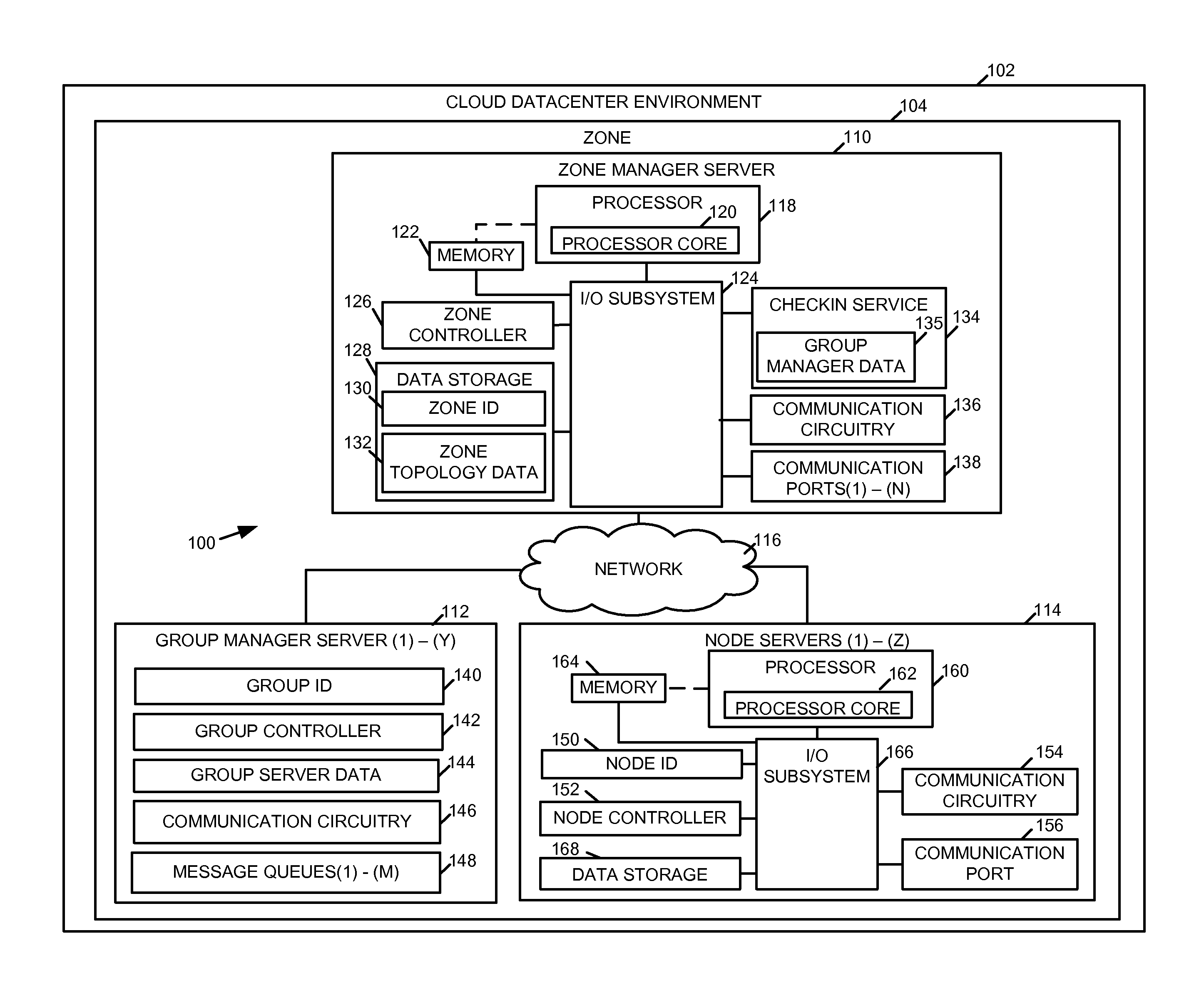
A method, system, and device for managing hardware resources in a cloud scheduling environment includes a zone controller. The zone controller can manage groups of node servers in a cloud datacenter using a checkin service. The checkin service allows server groups to be created automatically based on one or more hardware characteristics of the node servers, server health information, workload scheduling or facilities management parameters, and / or other criteria.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Modal workload scheduling in a heterogeneous multi-processor system on a chip
ActiveUS8996902B2Energy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingQuality of serviceMulti processor
Various embodiments of methods and systems for mode-based reallocation of workloads in a portable computing device (“PCD”) that contains a heterogeneous, multi-processor system on a chip (“SoC”) are disclosed. Because individual processing components in a heterogeneous, multi-processor SoC may exhibit different performance capabilities or strengths, and because more than one of the processing components may be capable of processing a given block of code, mode-based reallocation systems and methodologies can be leveraged to optimize quality of service (“QoS”) by allocating workloads in real time, or near real time, to the processing components most capable of processing the block of code in a manner that meets the performance goals of an operational mode. Operational modes may be determined by the recognition of one or more mode-decision conditions in the PCD.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
A method and system for job scheduling in distributed data processing system with identification of optimal network topology
InactiveCN102473116AImprove anti-disturbance abilityFast convergenceResource allocationDistributed Computing EnvironmentSmall worlds
The method of the present invention provides an automatic and optimised selection of the network topology for distributing scheduling of jobs on the computers of the modified network topology. The automatic and optimised selection of the network topology starts from the current topology and a desired number of additional connections. In this way the method of the present invention provides a higher convergence speed for the modified consensus algorithm in comparison e.g. to a simple ring network. The method exploits the so called small-world networks. Small-world networks are more robust to perturbations than other network architectures. The preferred embodiment provides a workload scheduling system which is highly scalable to accommodate increasing workloads within a heterogeneous distributed computing environment. A modified average consensus algorithm is used to distribute network traffic and jobs amongst a plurality of computers.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
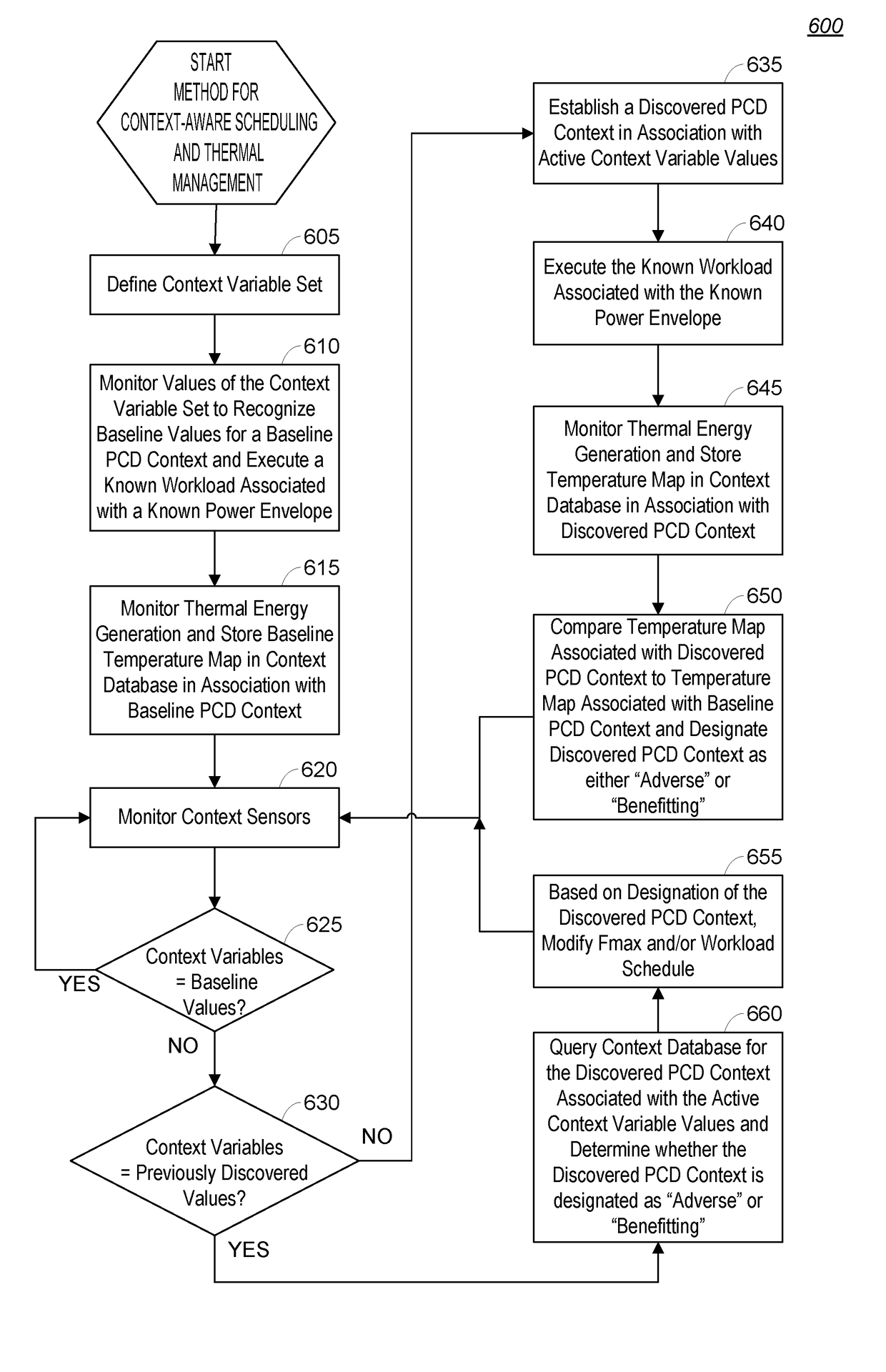
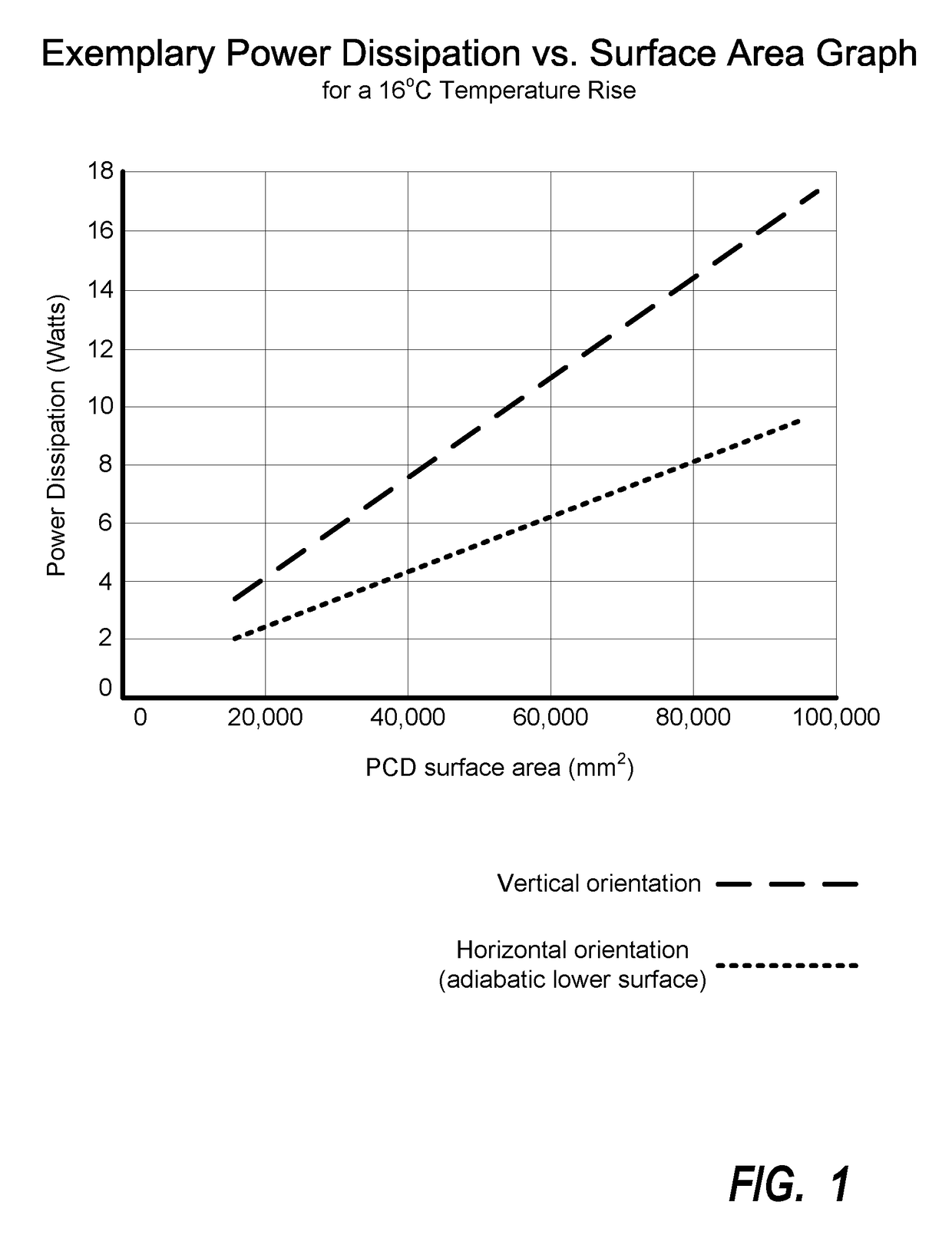
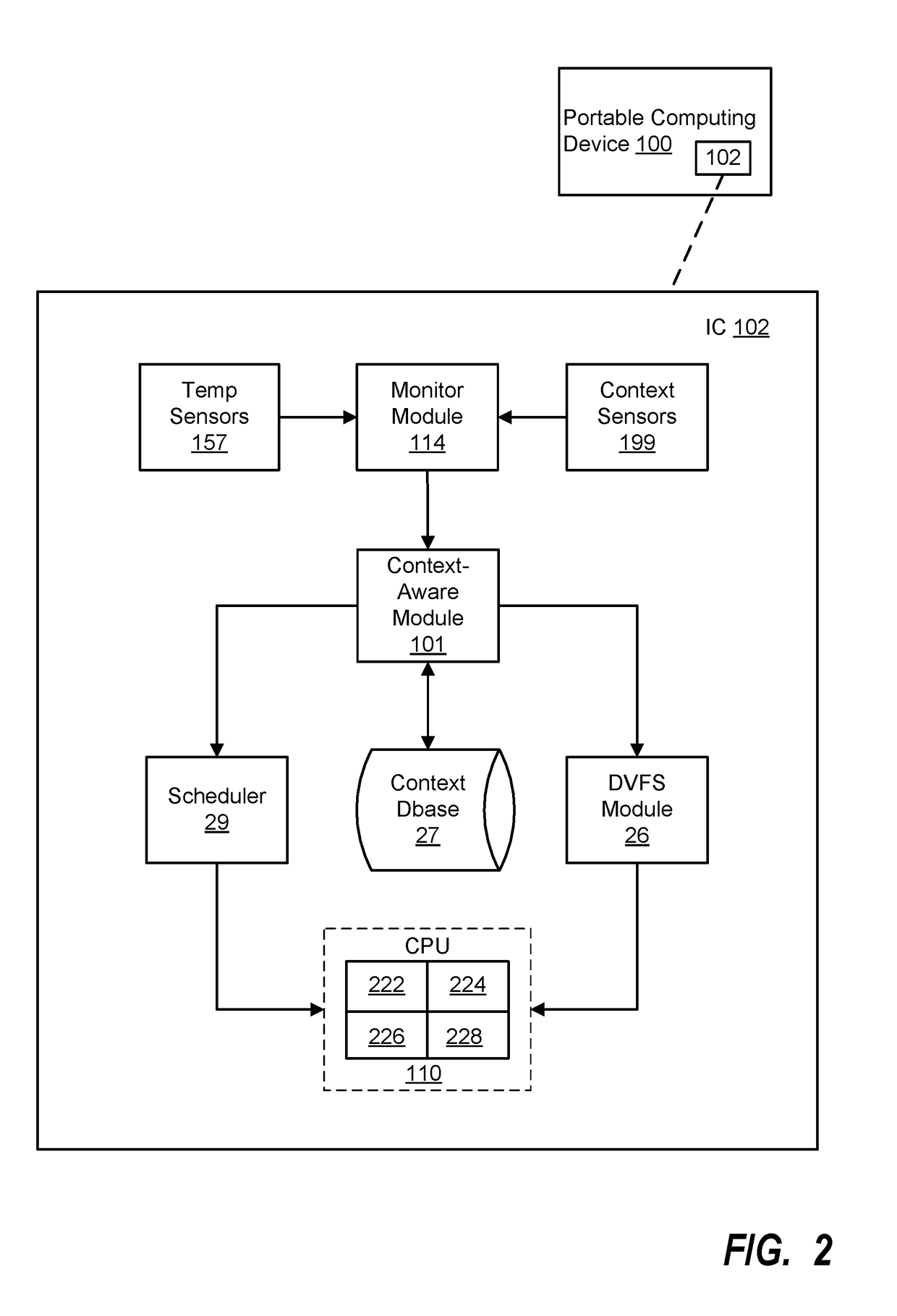
System and method for context-aware thermal management and workload scheduling in a portable computing device
ActiveUS20180210522A1Program initiation/switchingPower supply for data processingThermal energyWorkload scheduling
Various embodiments of methods and systems context-aware thermal management in a portable computing device (“PCD”) are disclosed. Notably, the environmental context to which a PCD is subjected may have significant impact on the PCD's thermal energy dissipation efficiency. Embodiments of the solution seek to leverage knowledge of a PCD's environmental context to modify or adjust thermal policy parameters applied within a PCD in response to a thermal event within the PCD.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com