Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
142 results about "Turbo encoder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
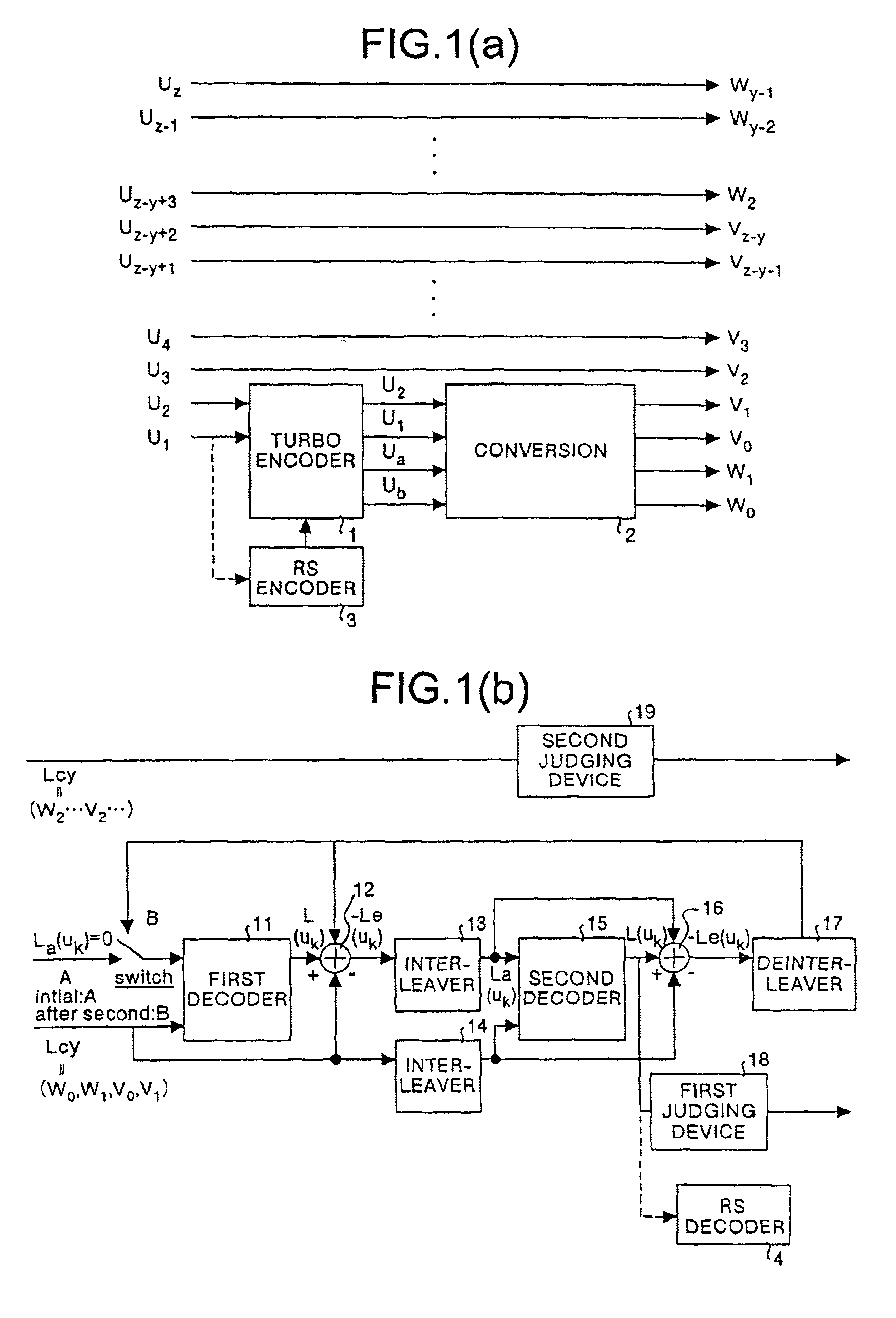
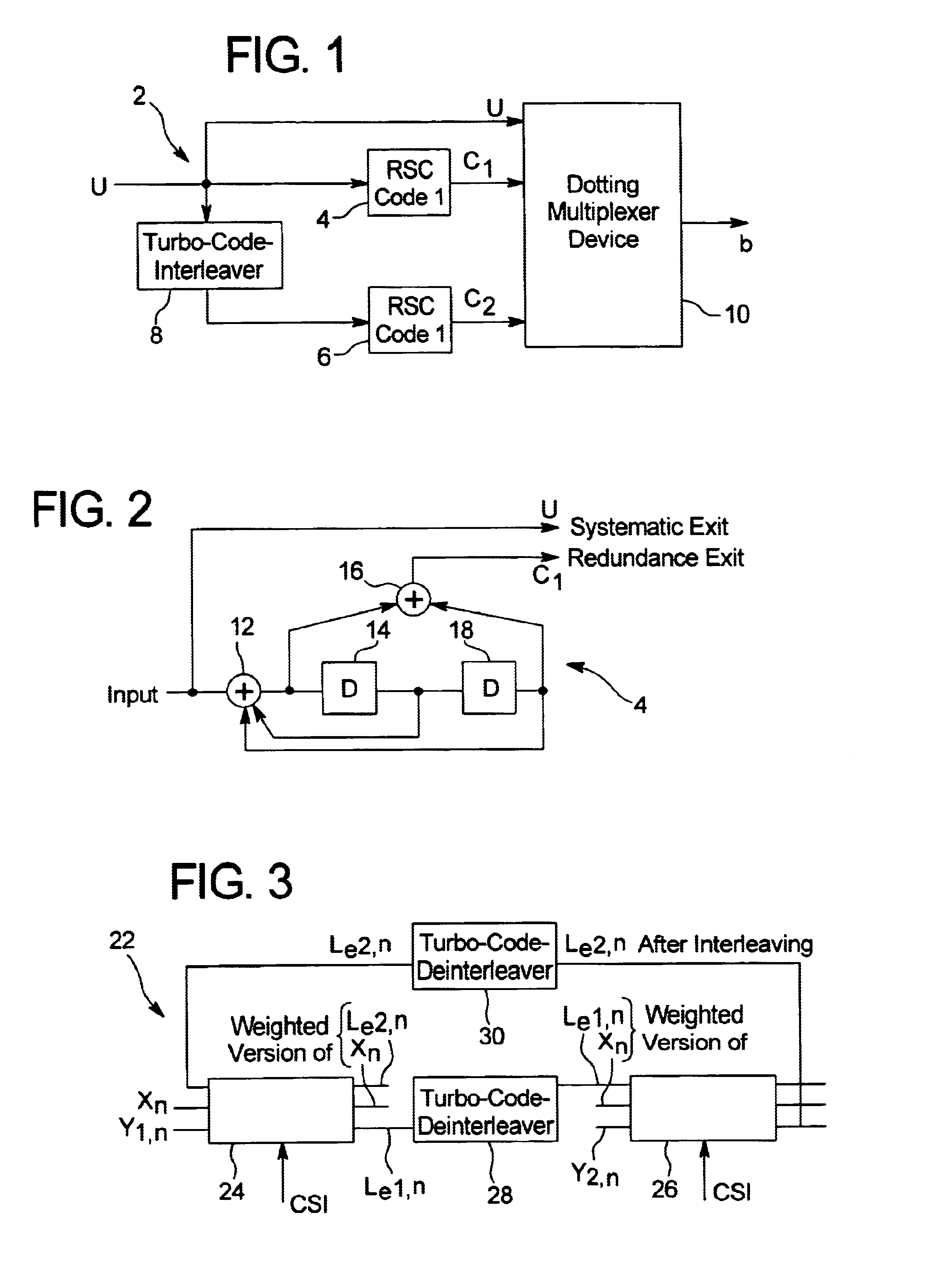
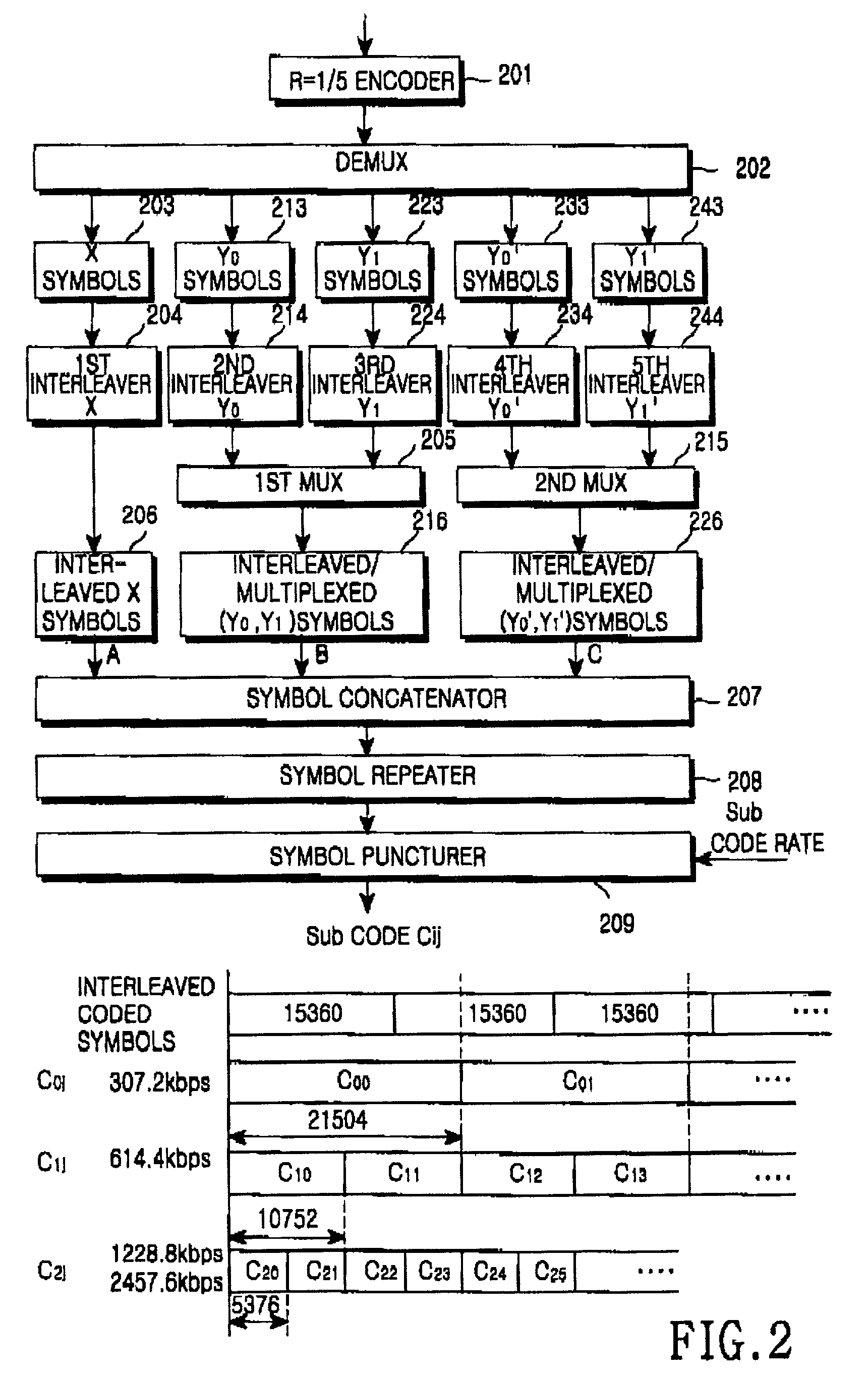
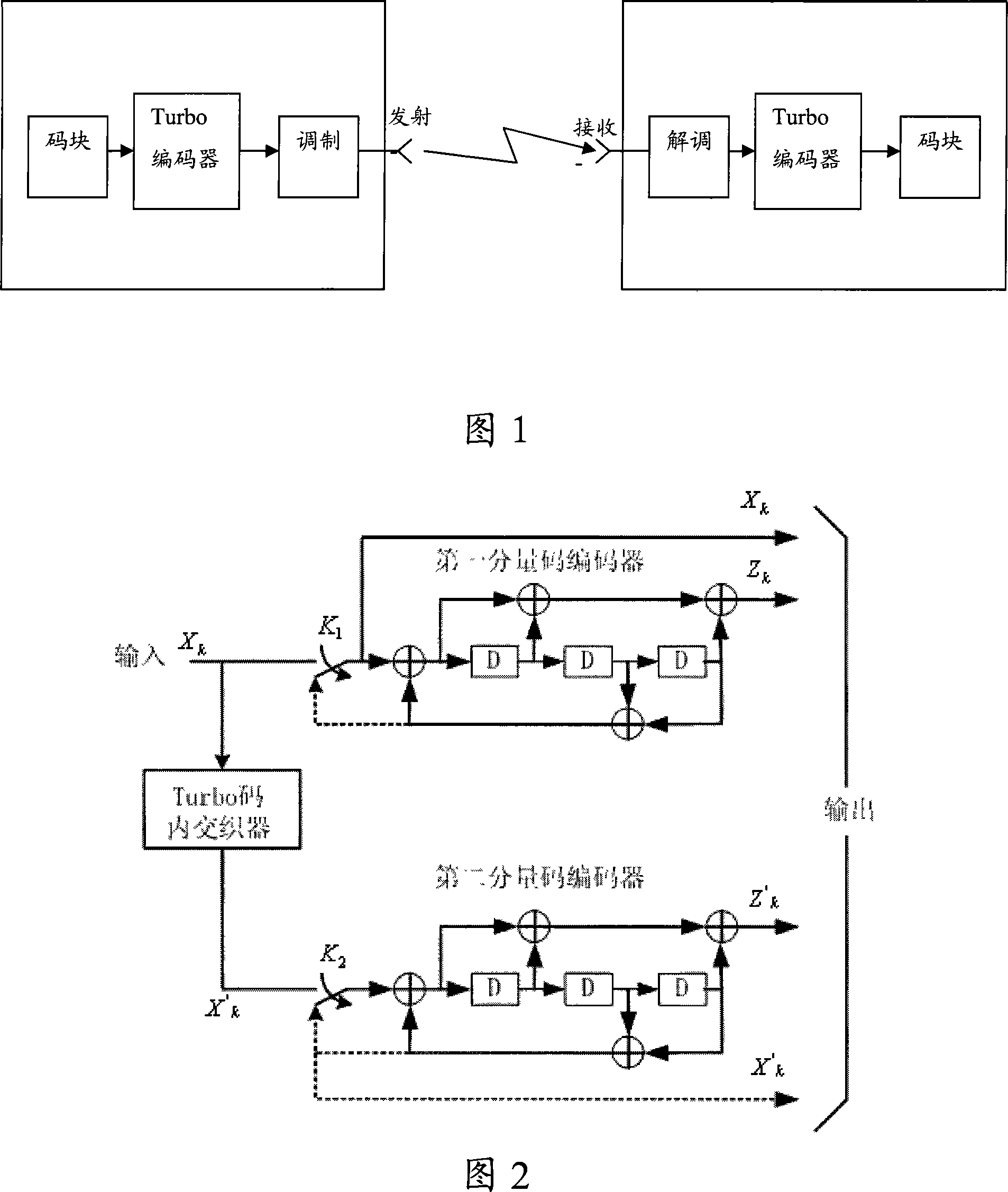
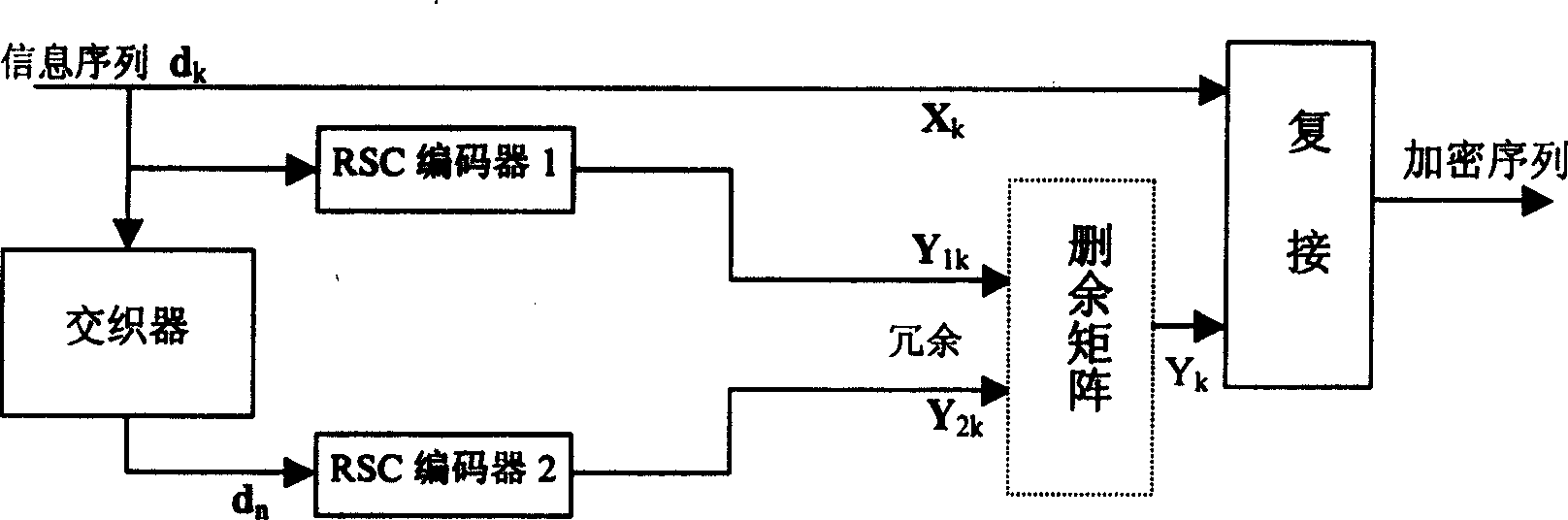
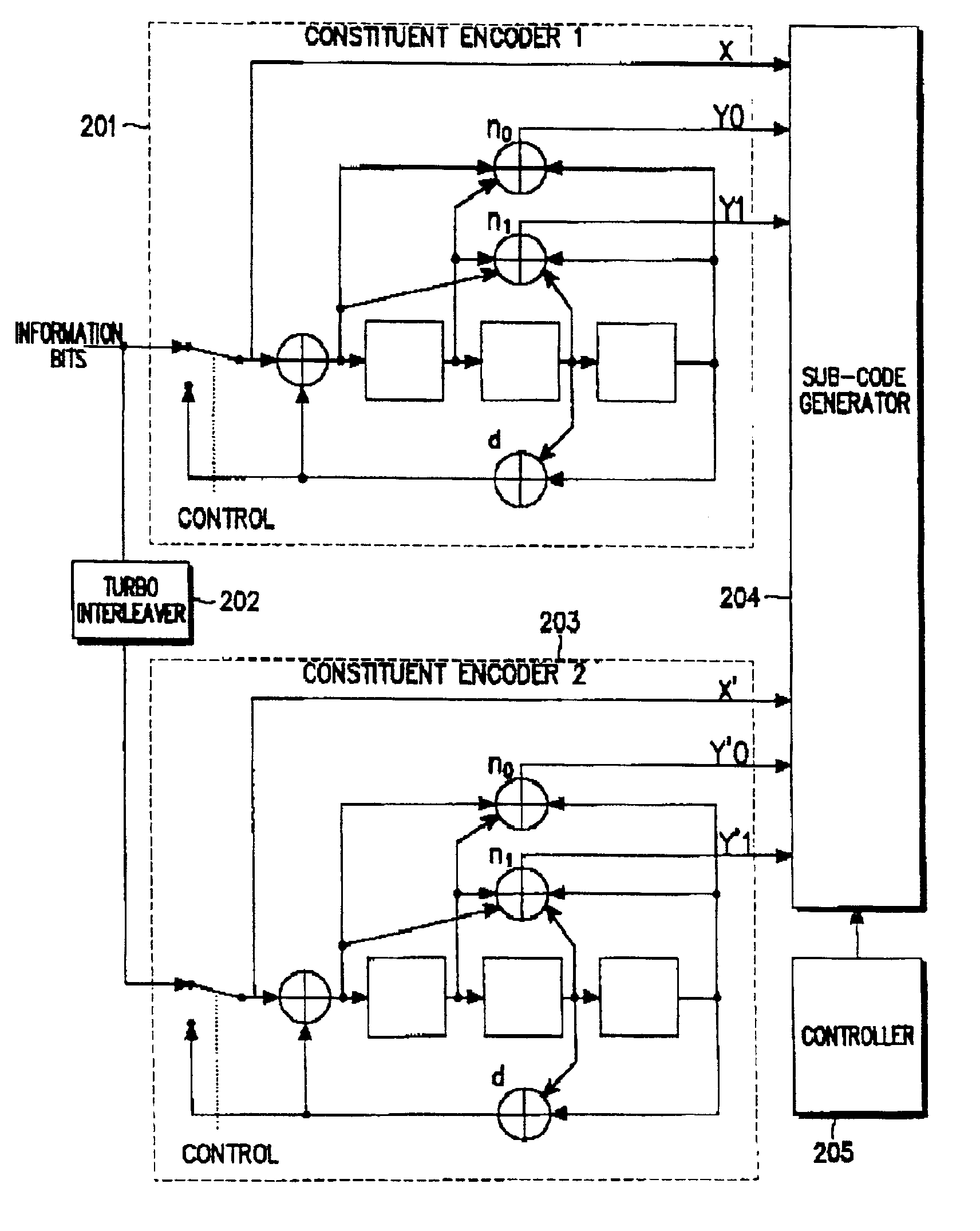
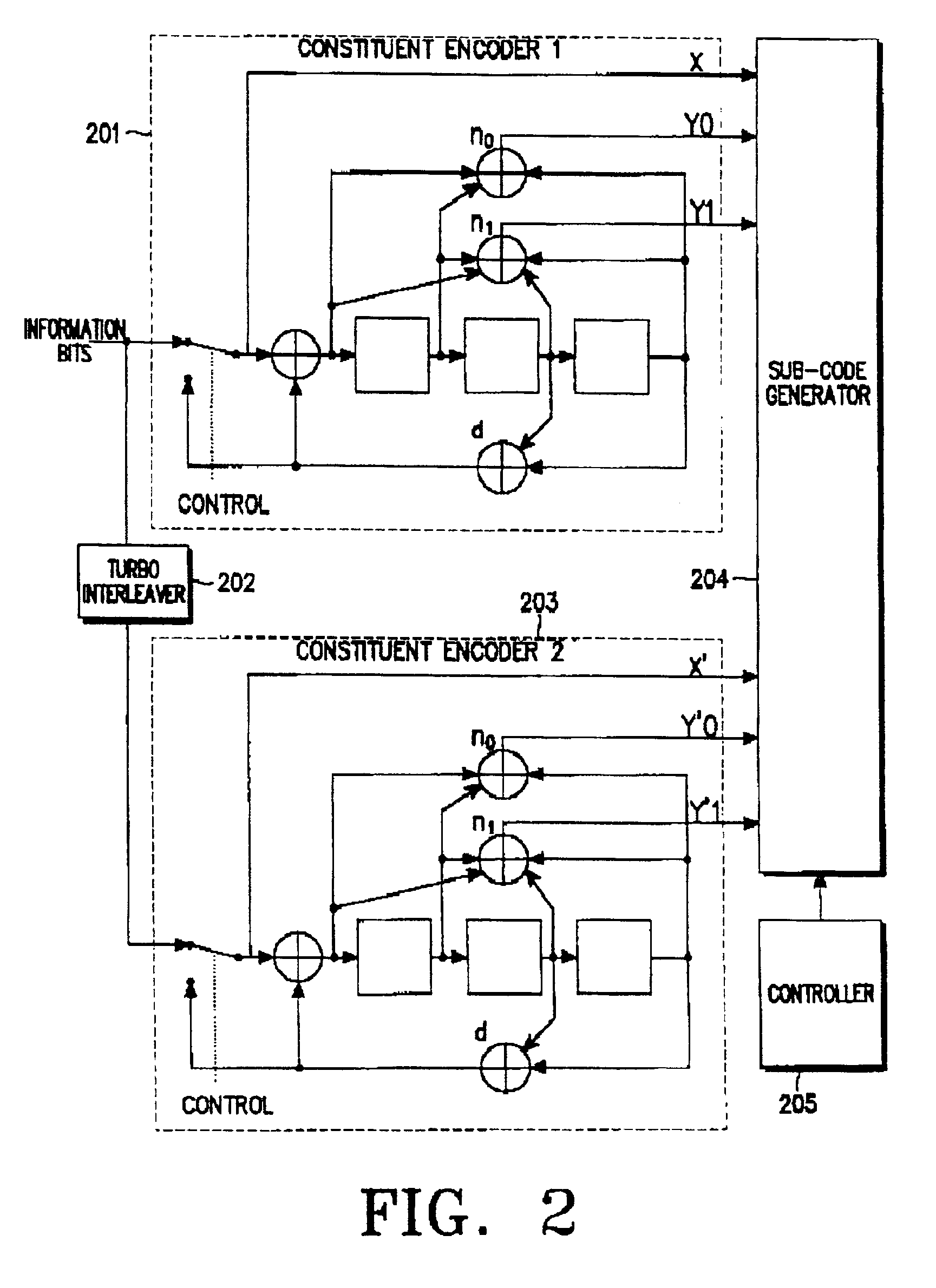
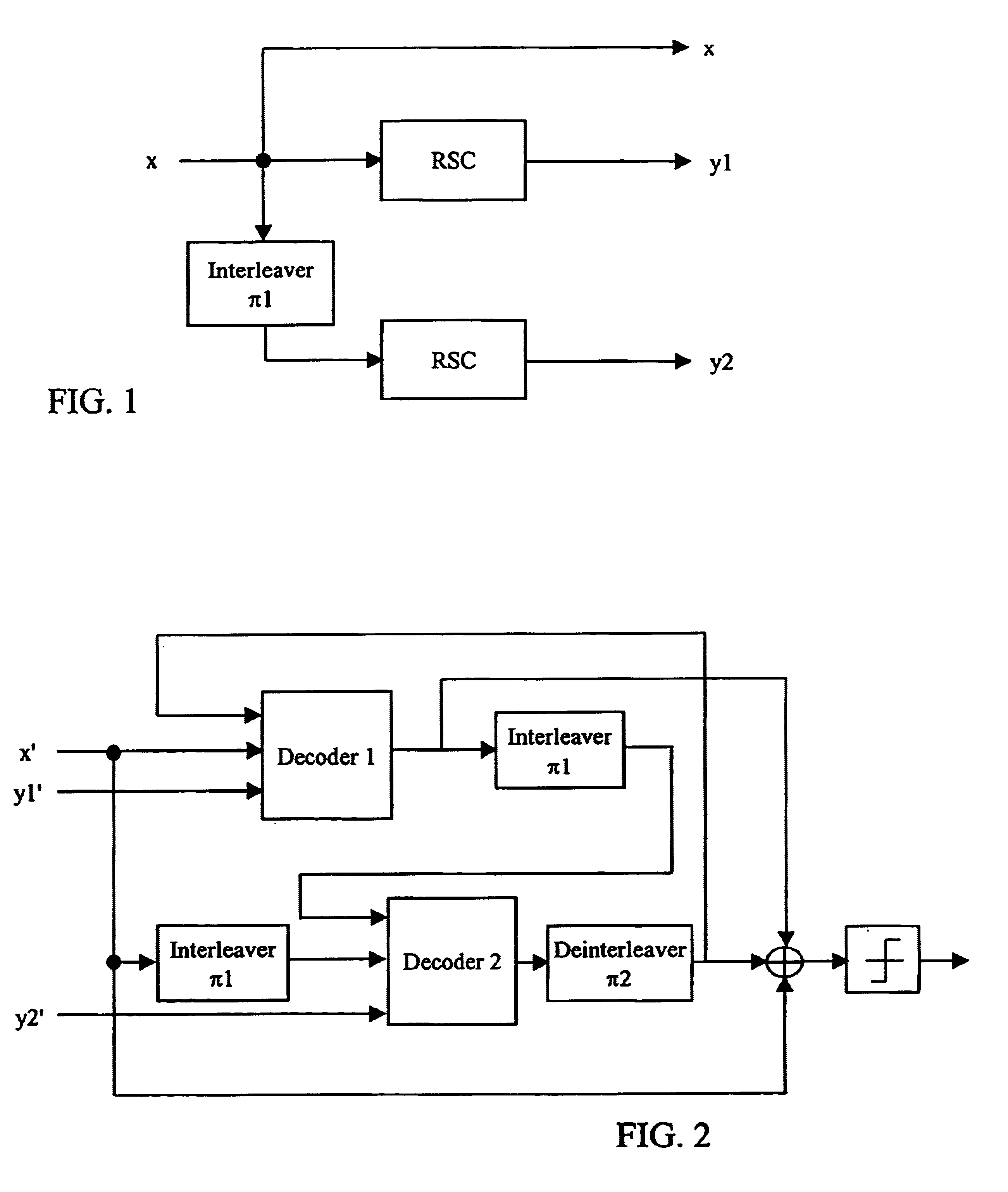
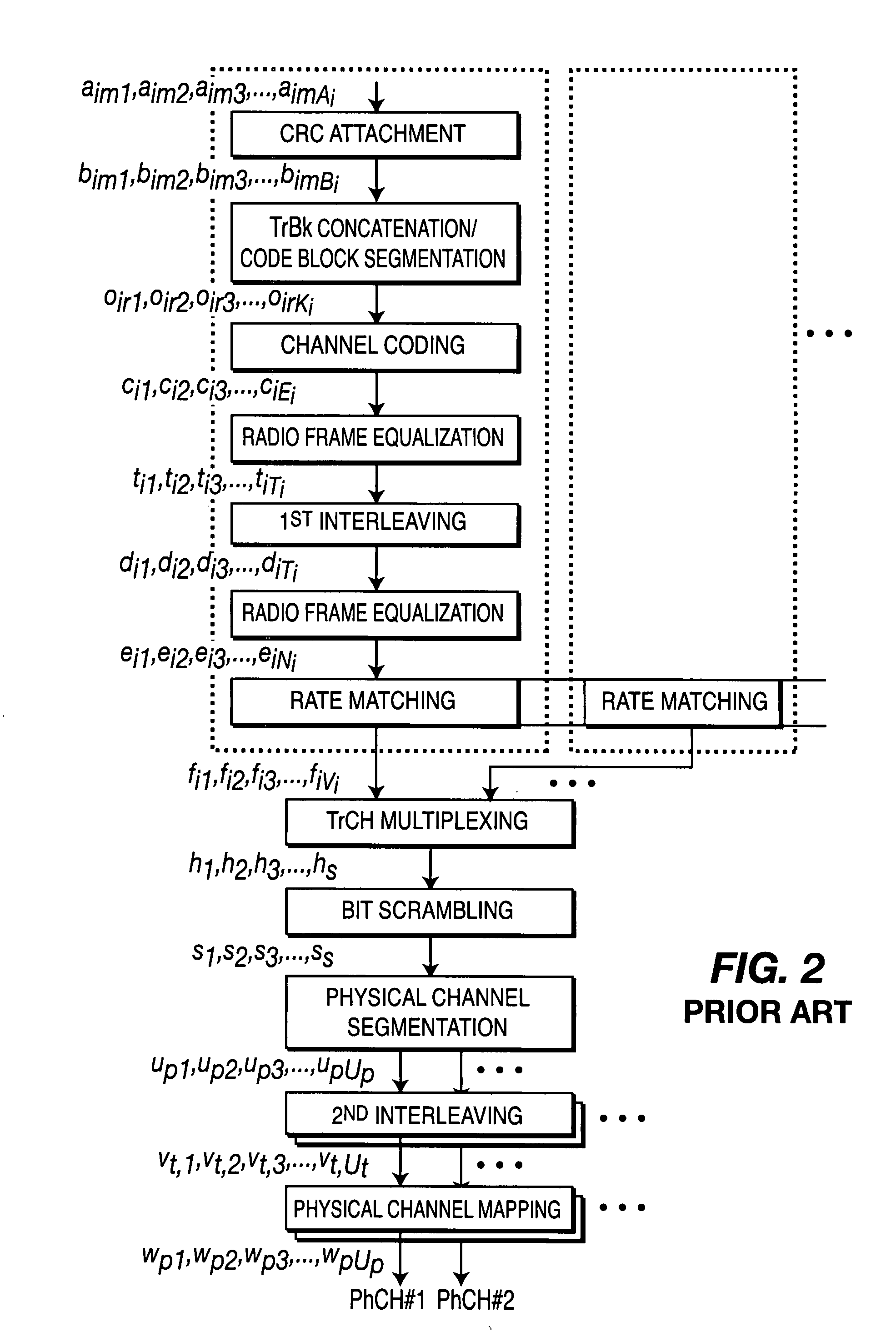
The Turbo Encoder block encodes a binary input signal using a parallel concatenated coding scheme. This coding scheme employs two identical convolutional encoders and one internal interleaver. Each constituent encoder is independently terminated by tail bits.
Flexible rate split method for MIMO transmission
InactiveUS20050111376A1Wide diversityReduce error rateSpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsMimo transmissionSelection system
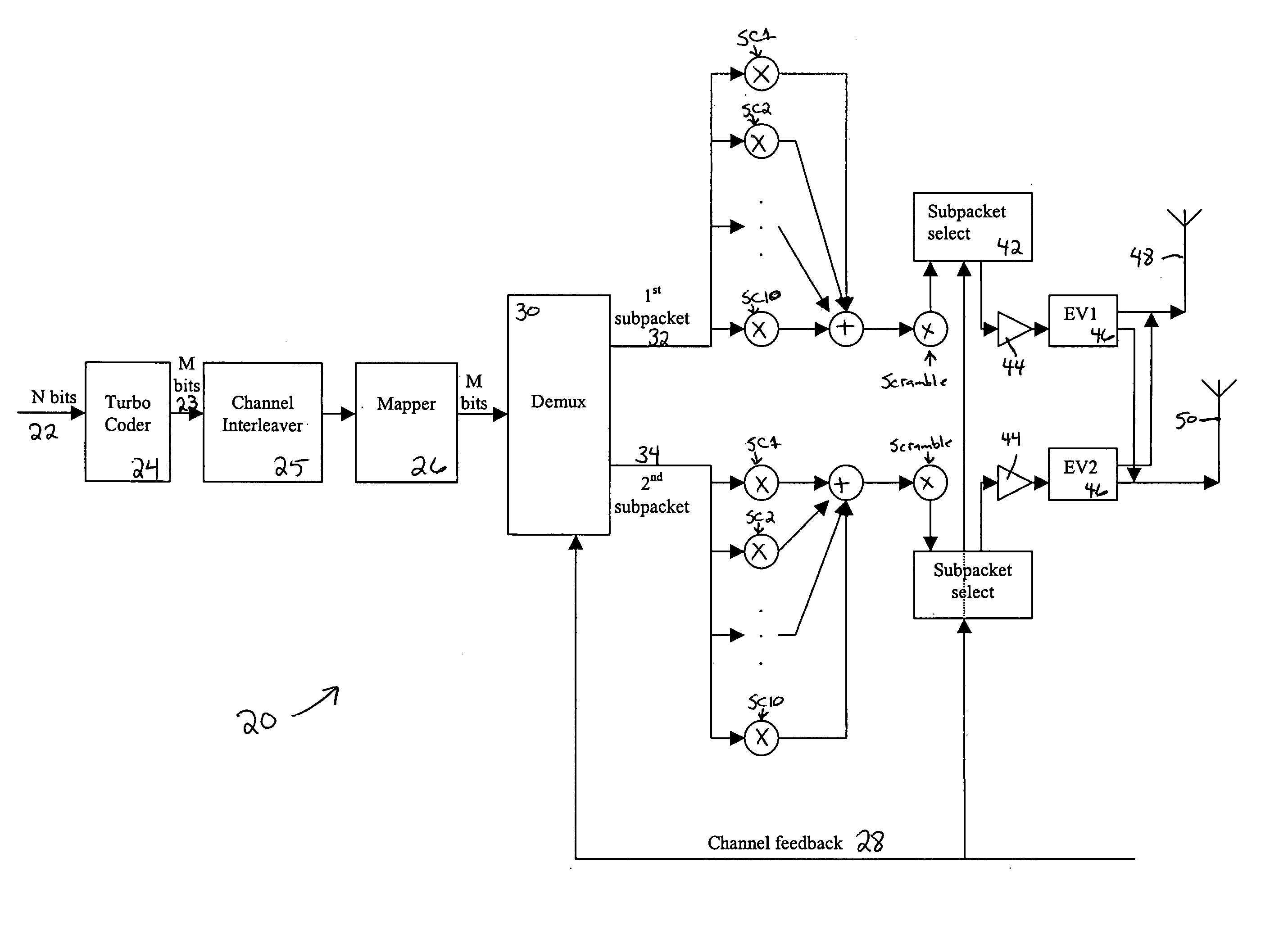
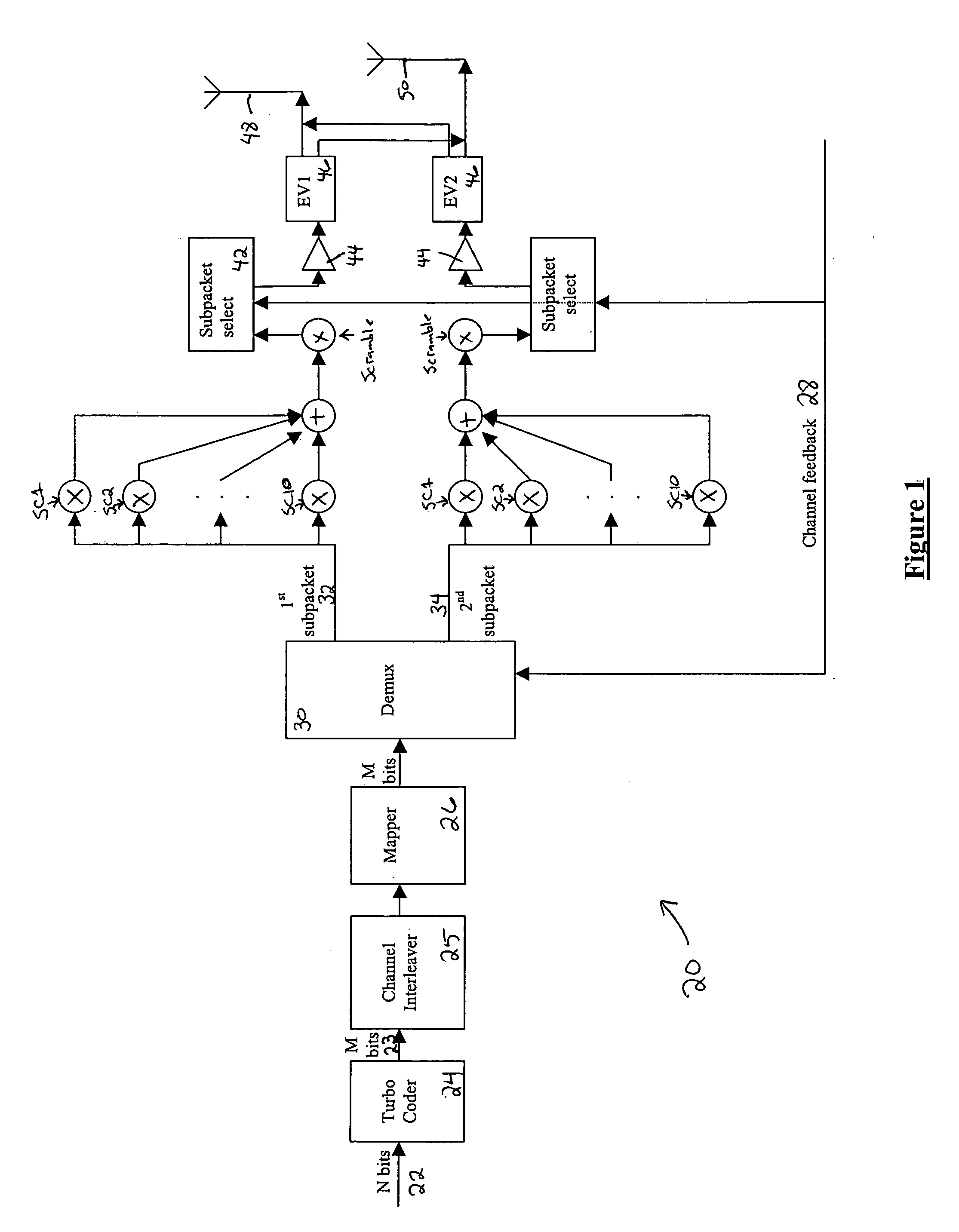
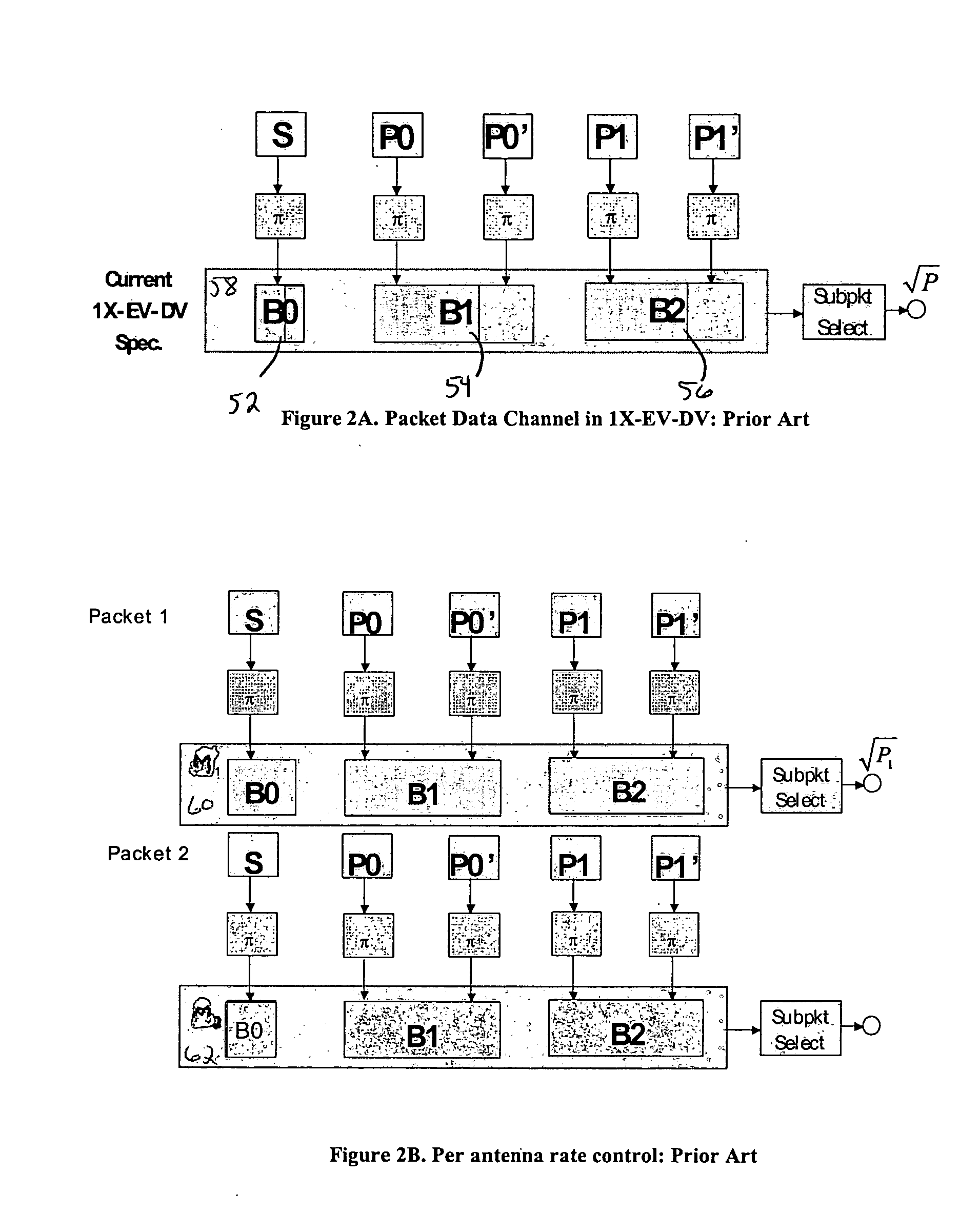
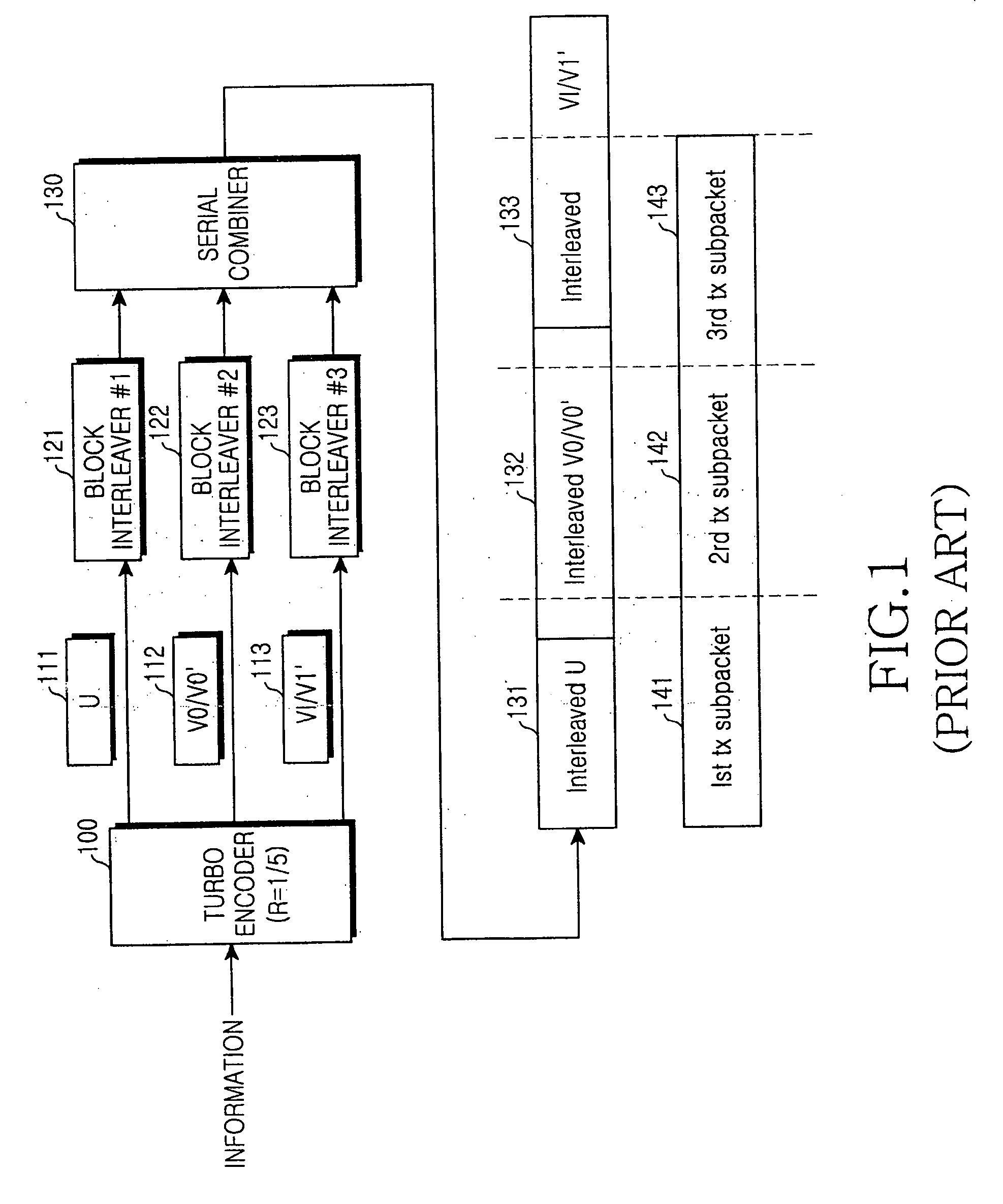
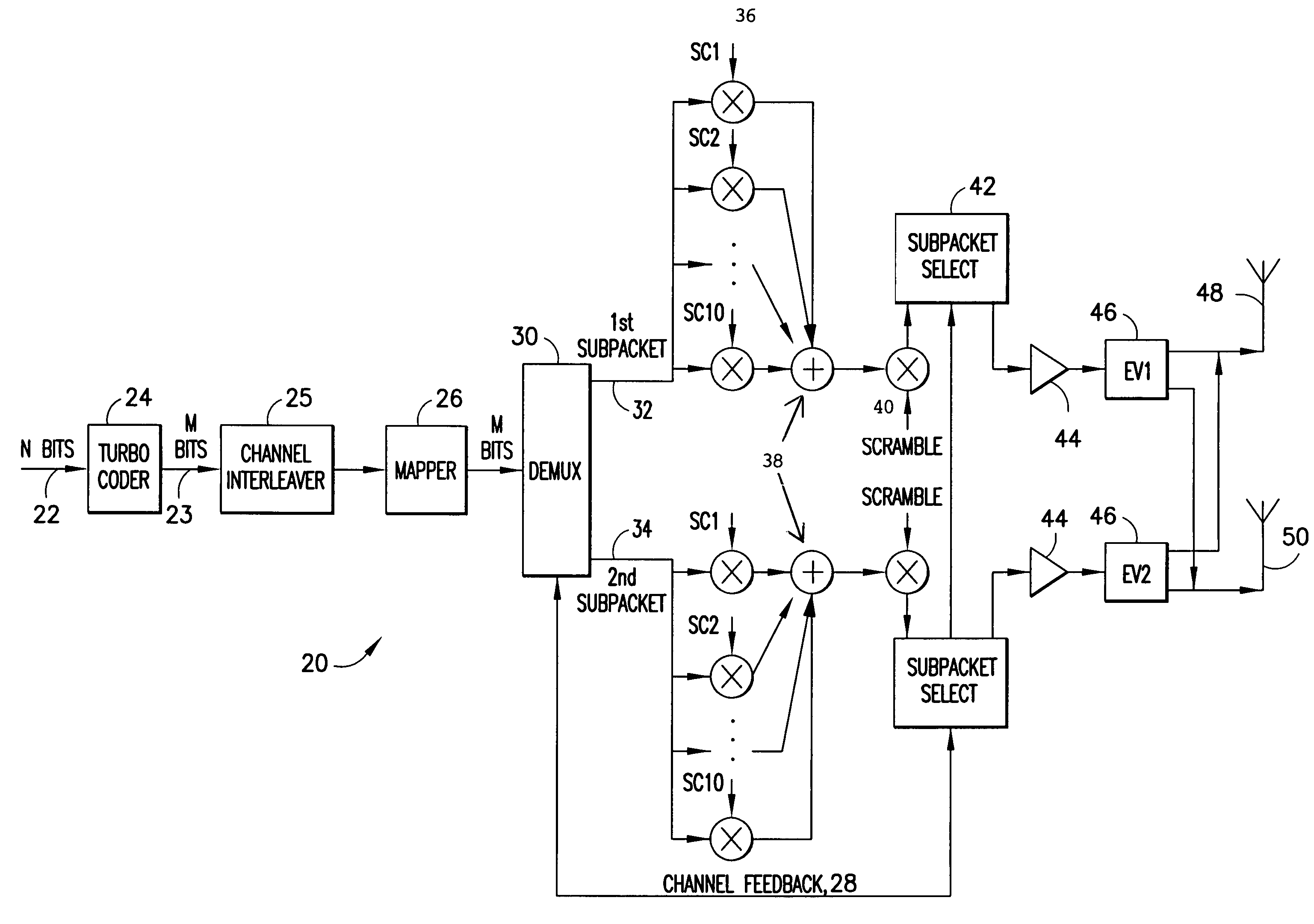
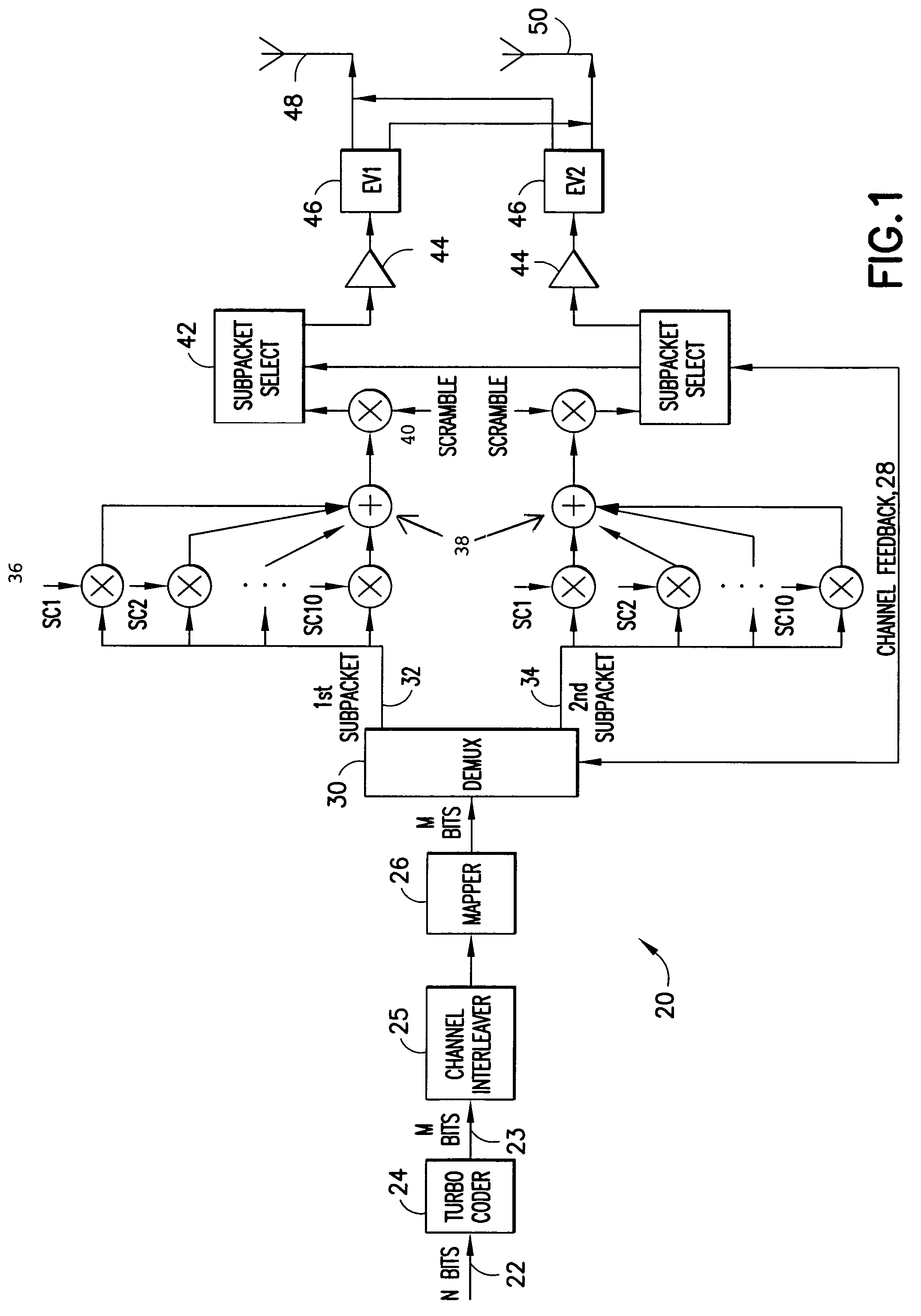
A method for transmitting a packet of N input bits includes encoding all of the N bits as a single entity, such as with an interleaver of length N within a turbo coder, outputting M encoded bits, channel interleaving the M bits, splitting the M encoded bits into a parallel first and second portion, and transmitting them over separate channels to achieve spatial diversity. The size of the first and second portion is determined based on a closed feedback loop that provides some knowledge of the channel, preferably a measure of channel capacity. The feedback loop may also provide channel knowledge to a subpacket selector associated with each transmit antenna, which determines an appropriate rate for that channel and selects subpackets to fill a transmission packet for that channel. The subpacket selectors choose a subpacket of systematic bits and fill the remaining transmission packet size with subpackets of parity bits. Eigenvectors may be employed to transmit each transmission packet over more than one channel with a power disparity between the channels. A transmitter according to the present invention is also described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Pre-decoder for a turbo decoder, for recovering punctured parity symbols, and a method for recovering a turbo code
InactiveUS6910170B2Improve decoding performanceReduce the number of iterationsError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesTurbo encoderTurbo coded
A pre-decoder applied to a turbo decoder for decoding a punctured turbo code. The turbo code consists of a data bit stream and a plurality of parity bit streams, parts of which are punctured. The pre-decoder has an arithmetic unit for calculating estimated parity bit streams by carrying out, with respect to the data bit stream, the same algorithm used by a turbo encoder to produce the parity bit streams, a comparison unit for comparing the plurality of parity bit streams with the estimated parity bit streams, and a recovery unit for substituting estimated parity symbols for corresponding punctured parts of the parity symbol streams when related non-punctured bits of the parity bit streams are identical with corresponding estimated non-punctured parity bits. The punctured parity symbols are recovered by the pre-decoder completely, or at least partially, and provided to the turbo decoder. Accordingly, the decoding performance of the turbo decoder is enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for retransmitting high-speed data in a CDMA mobile communication system
ActiveUS7283509B2Improve radio communication performanceEfficiently transmitting/receivingError prevention/detection by using return channelModulated-carrier systemsTurbo encoderMobile communication systems
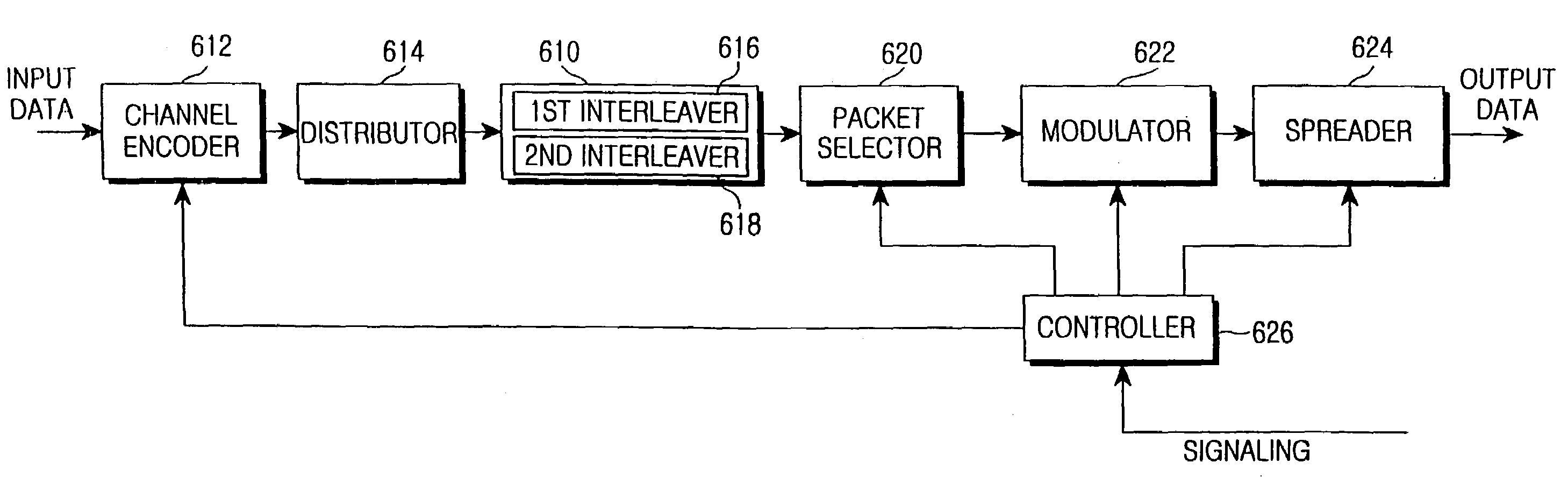
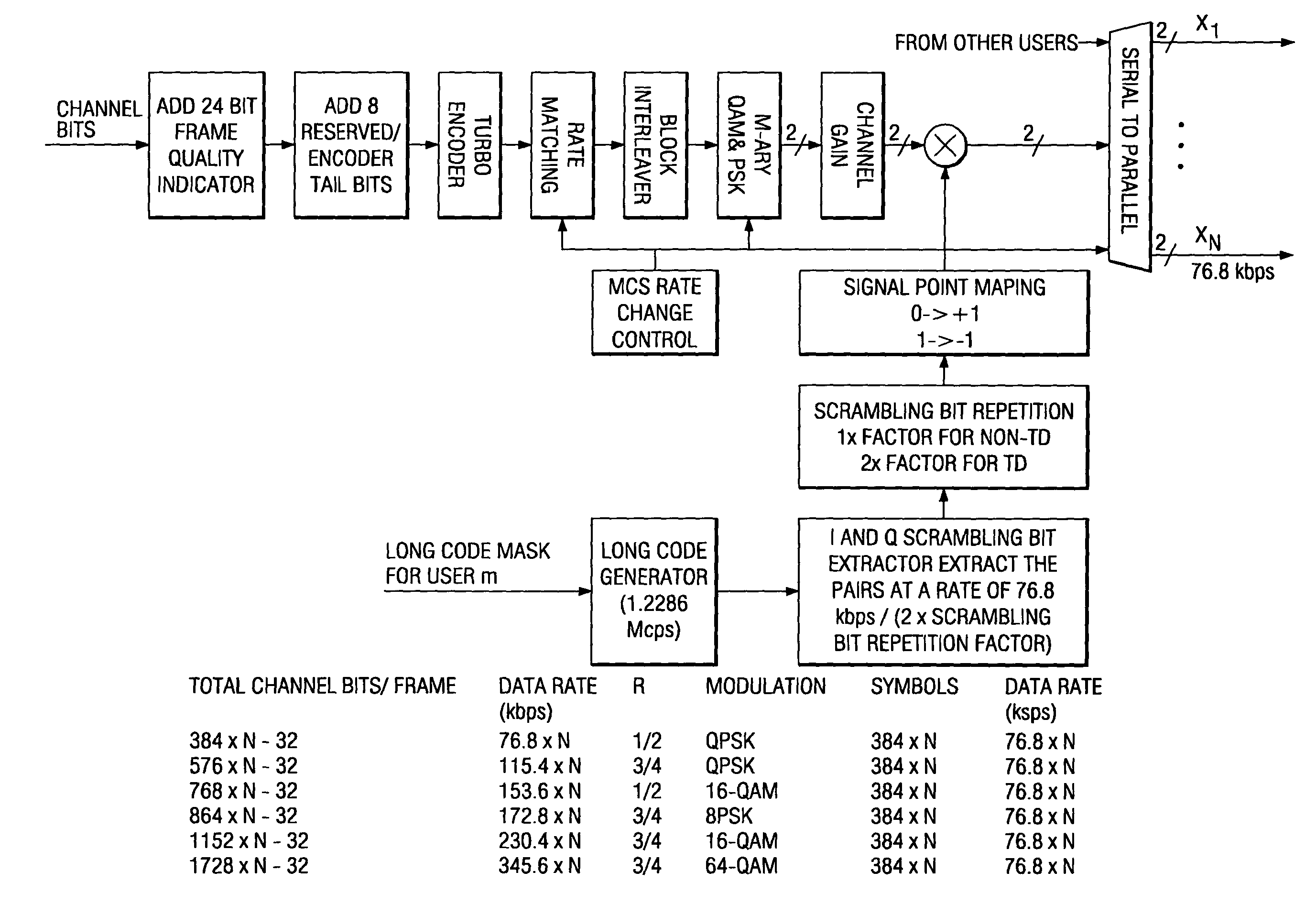
An apparatus for retransmitting data at a retransmission request from a receiver by a transmitter in a CDMA mobile communication system including a turbo encoder with a given coding rate and initially transmitting systematic bits and parity bits obtained by encoding the data by the turbo encoder using one modulation mode among a plurality of modulation modes. A controller determines a modulation mode to be used between the transmitter and the receiver in response to the retransmission request. A distributor distributes coded bits obtained by encoding the data at the coding rate into systematic bits and parity bits. A selector selects coded bits transmittable by the determined modulation mode among the systematic bits and the parity bits at the initial transmission, if the determined modulation mode is different from the modulation mode used at initial transmission. A modulator modulates the transmittable coded bits into modulated symbols according to the determined modulation mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Communication device and communication method
InactiveUS7260768B1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareTurbo encoder
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method of rate matching for link adaptation and code space management
InactiveUS20050050427A1Reduce constraintsUnequal/adaptive error protectionCode conversionComputer hardwareRound complexity
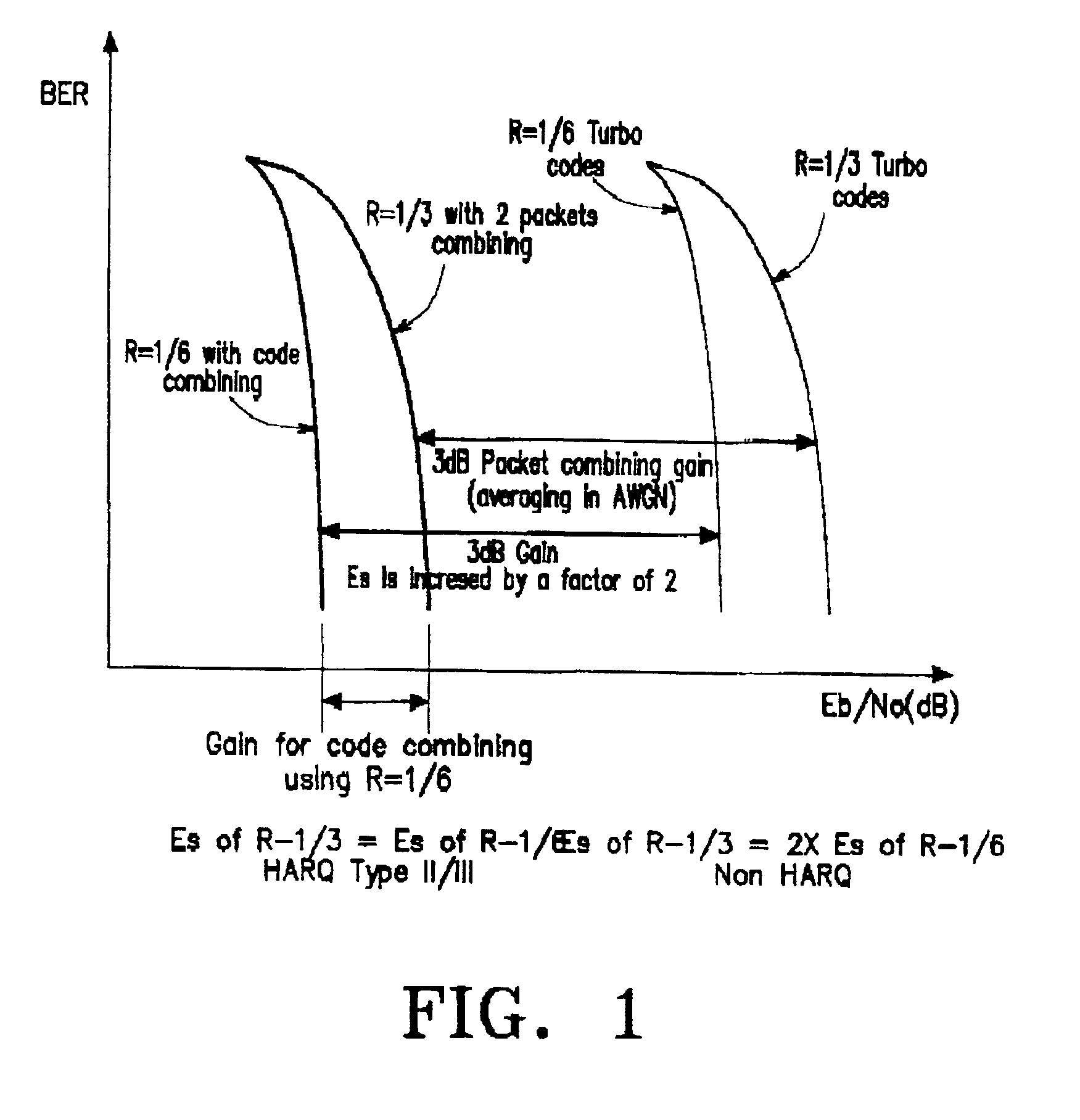
A method of symbol combining and incremental redundancy for link adaptation and code space management was proposed. In order to reduce constraints on the Walsh codes allocation, MCS level change, as well as frame duration change for the initial transmission and re-transmissions, a “rate matching” stage is proposed between the Turbo encoder and block interleaver on the transmitter. In the initial transmission, the Turbo encoded symbols are interleaved with or without any puncturing or repeating (i.e. puncture / repeat factor is set to 1). The coded symbols are also stored in the memory for possible retransmissions. In the re-transmission, the transmitter first determines the number of Walsh codes available for this user and MCS level and frame duration according to the C / I feedback values from MS. The stored coded symbols are then punctured or repeated according to “rate matching factors”. On the receiver side, “rate matching factors” can be derived from the number of code channels, MCS level and frame duration of current re-transmissions and initial transmission. Then, de-puncturing / de-repeating is performed before coded symbol combining. A similar rate matching based IR / symbol combining scheme can be used to design different IR using different rate matching algorithms. It has low implementation complexity and is easily made backward compatible.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of transmitting or receiving a data packet in packet data communication system using hybrid automatic repeat request
InactiveUS20080043777A1High gainIncrease the coding gainError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemTurbo encoder
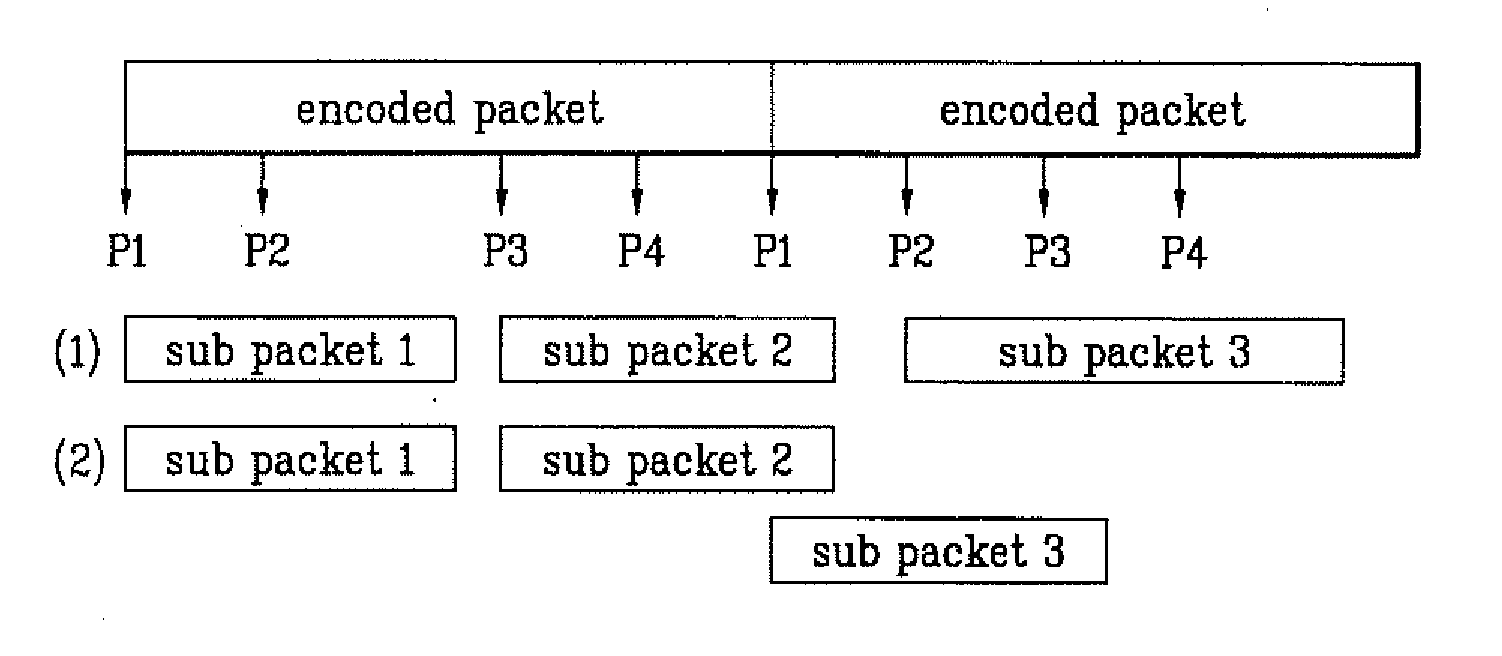
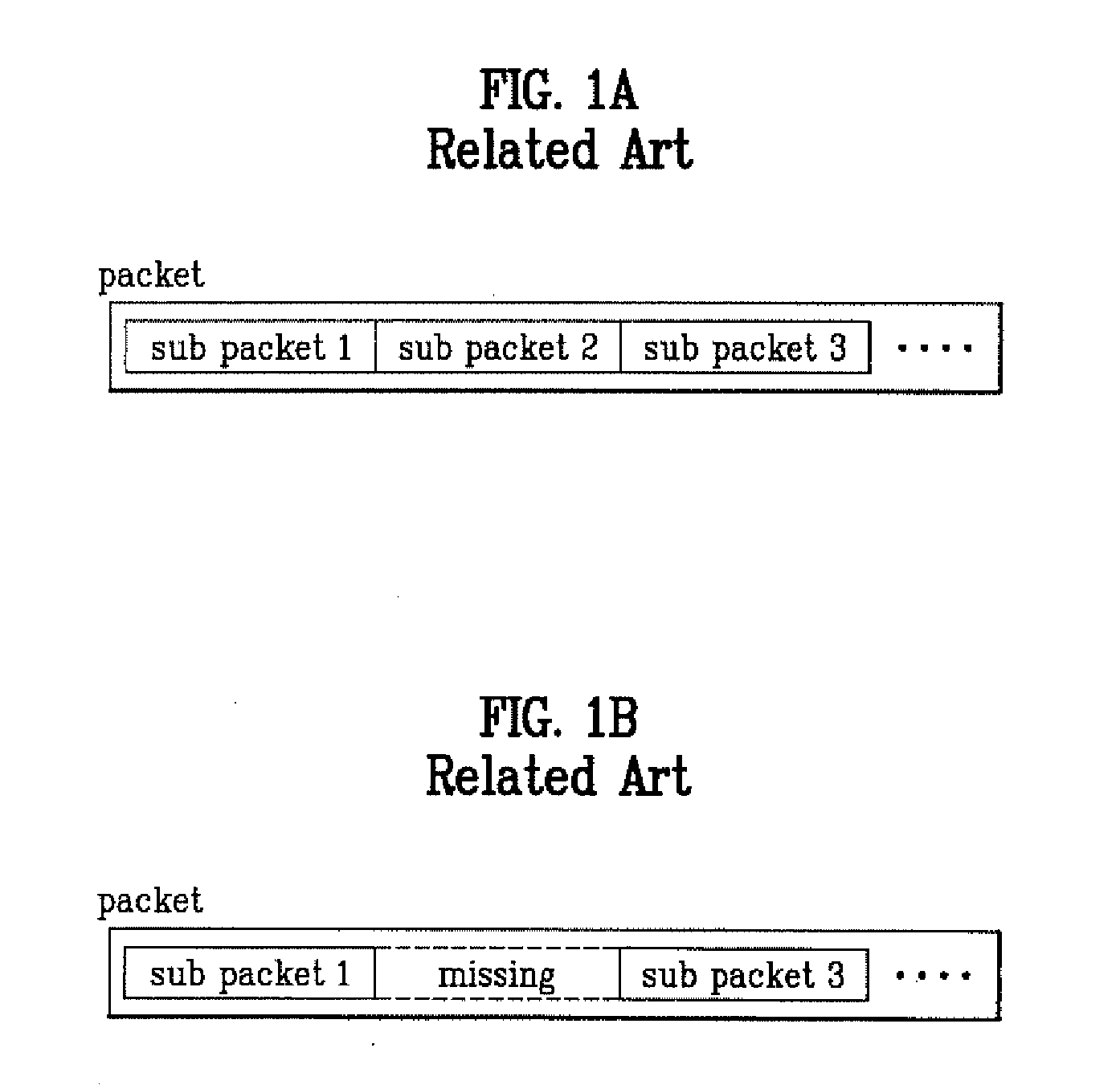
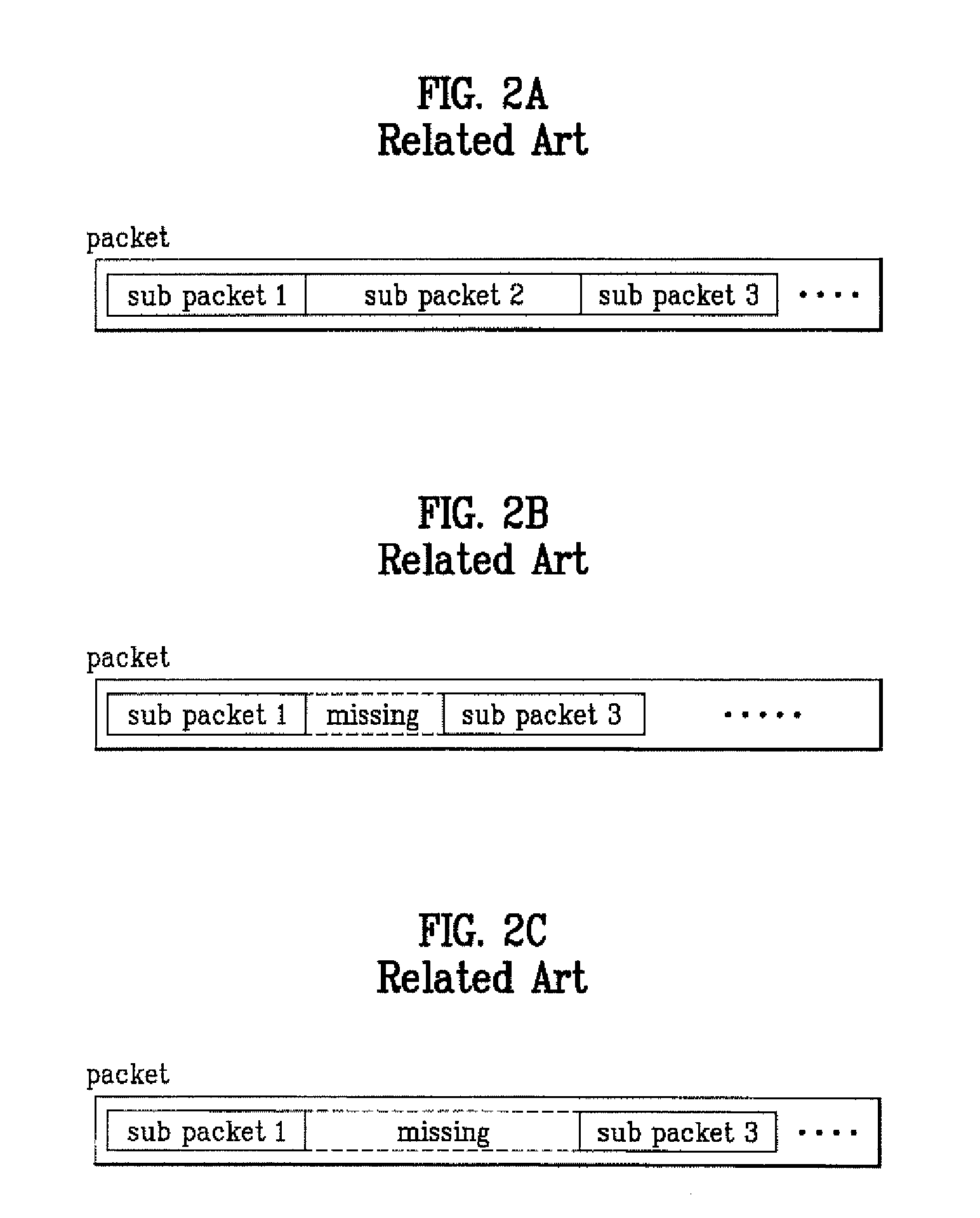
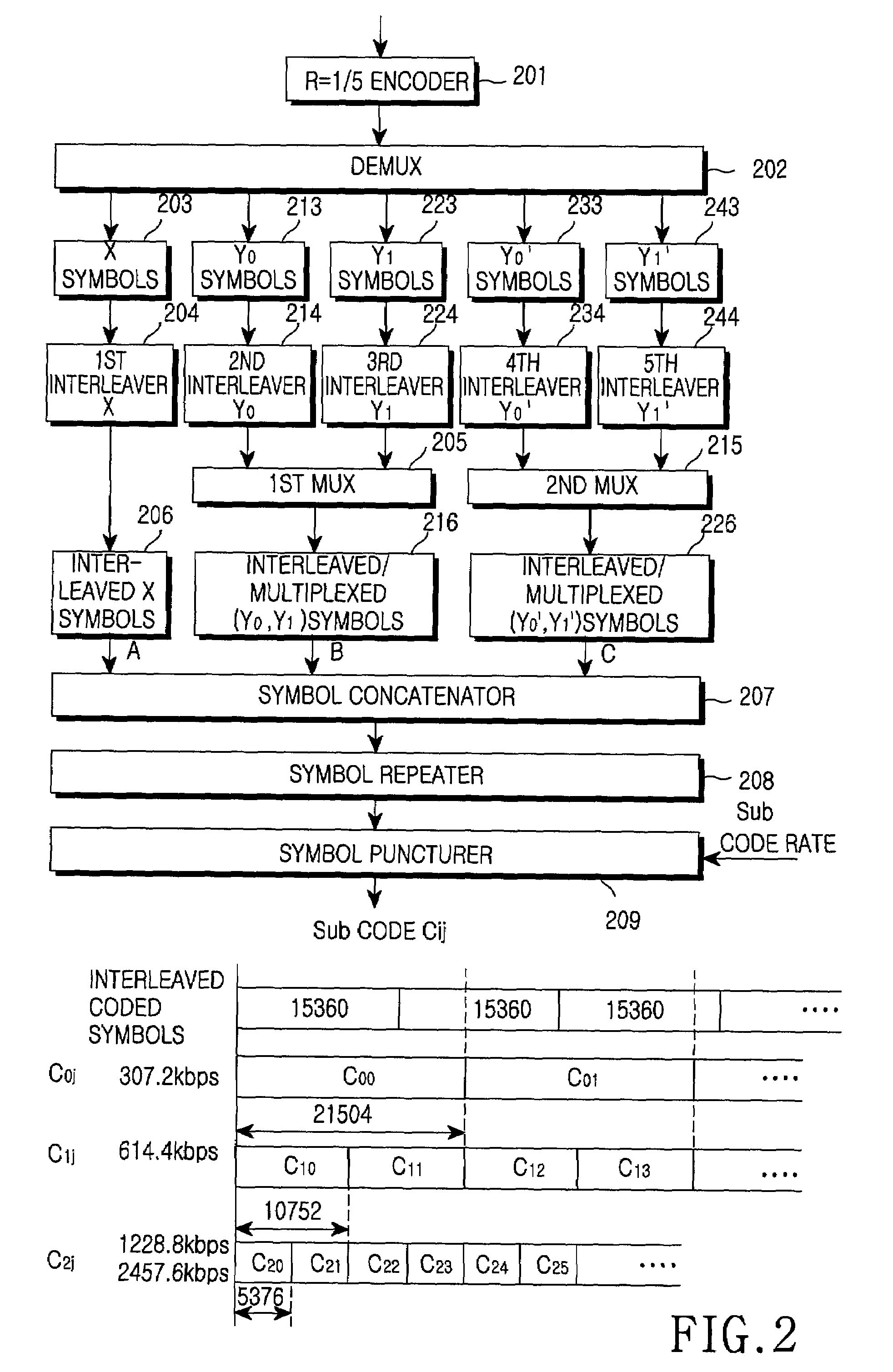
A method of transmitting / receiving a packet using a hybrid automatic repeat request in the mobile communication system is disclosed. The packet data transmitting method includes transmitting at least one sub packet divided from plurality of encoded packets generated by repeating a bit stream that is made by encoding information desired to be transmitted with ⅕ rate turbo encoder, and transmission start point information of the sub packet through the sub packet identifier field on the accompanying control channel.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for transmitting data in a digital transmission system given a packet-switched service
InactiveUS6625179B1Easy to determineIncrease ratingsError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsEstimation methodsTurbo encoder
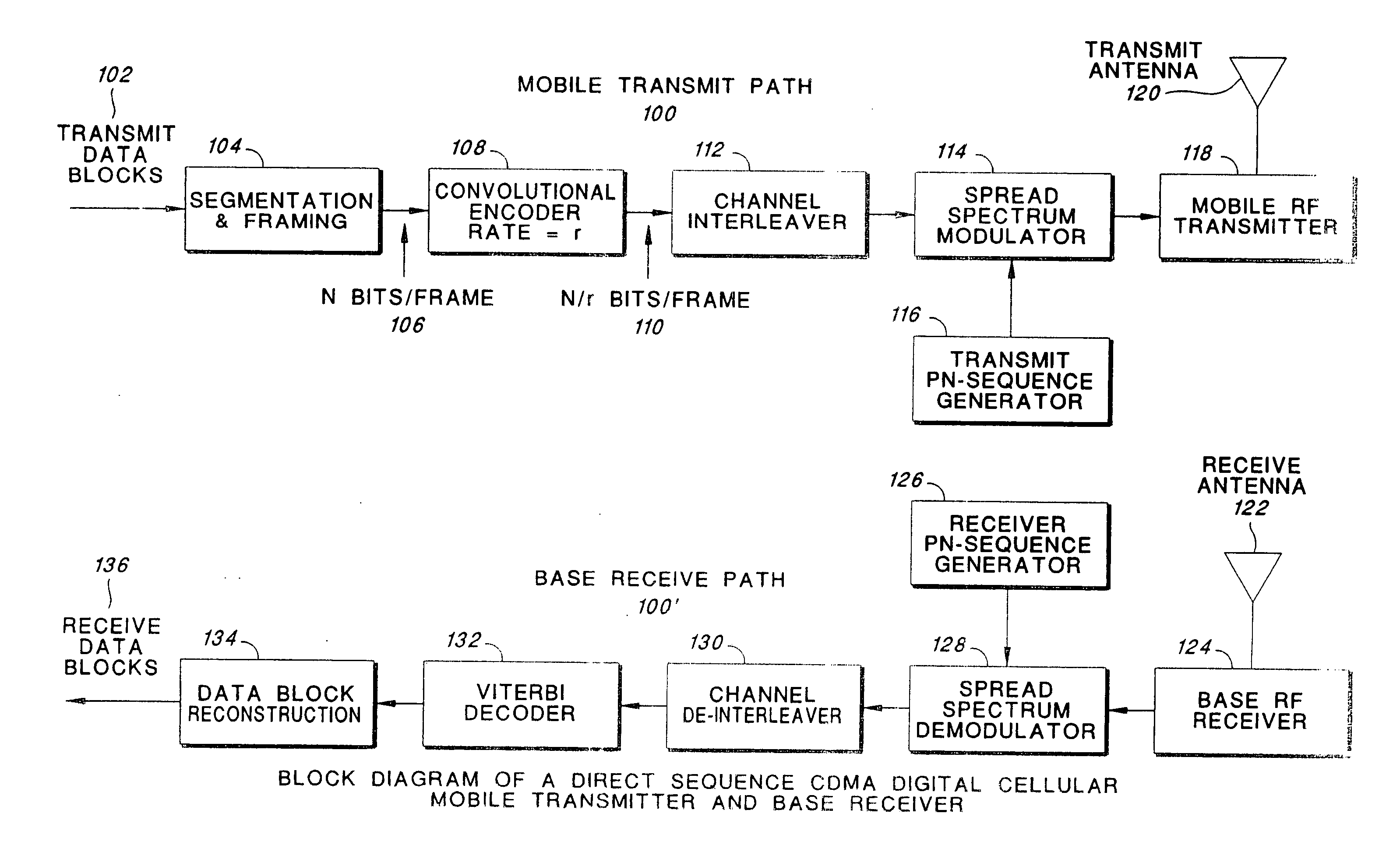
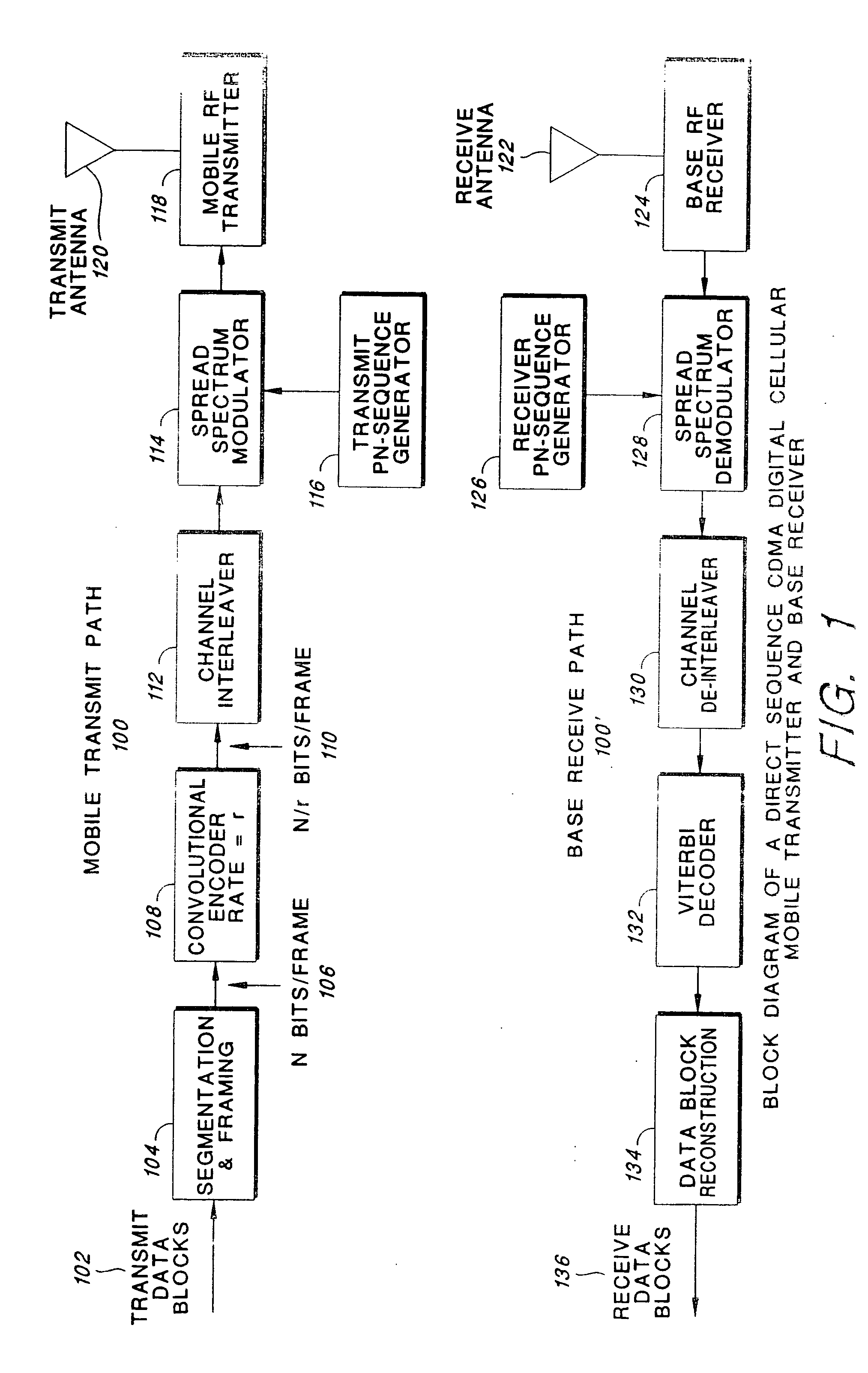
In a method for transmitting data in a digital transmission system given packet-switched service, for purposes of channel coding, a turbo-coding is performed in a turbo-coder at the sender side and a turbo-decoding with soft decision output signals is performed in a turbo-decoder at the receiver side. To trigger an ARQ, the channel quality is estimated by a parameter estimation method; the variances of the soft decision output signals at the turbo-decoder are determined; the correctness or respectively, defectiveness of the transmitted packet is inferred from the channel quality and the variances; and a retransmission of at least a part of defective packet is triggered. In the retransmission of the information of a defective packet, at least part of the information suppressed by the dotting in the precious transmission is sent. This additional information is [. . .] inserted into the already existing information at the receiver side, and this complete information is decoded again.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG +1
Apparatus and method for generating and decoding codes in a communication system
ActiveUS7200181B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionComputer hardwareCommunications system
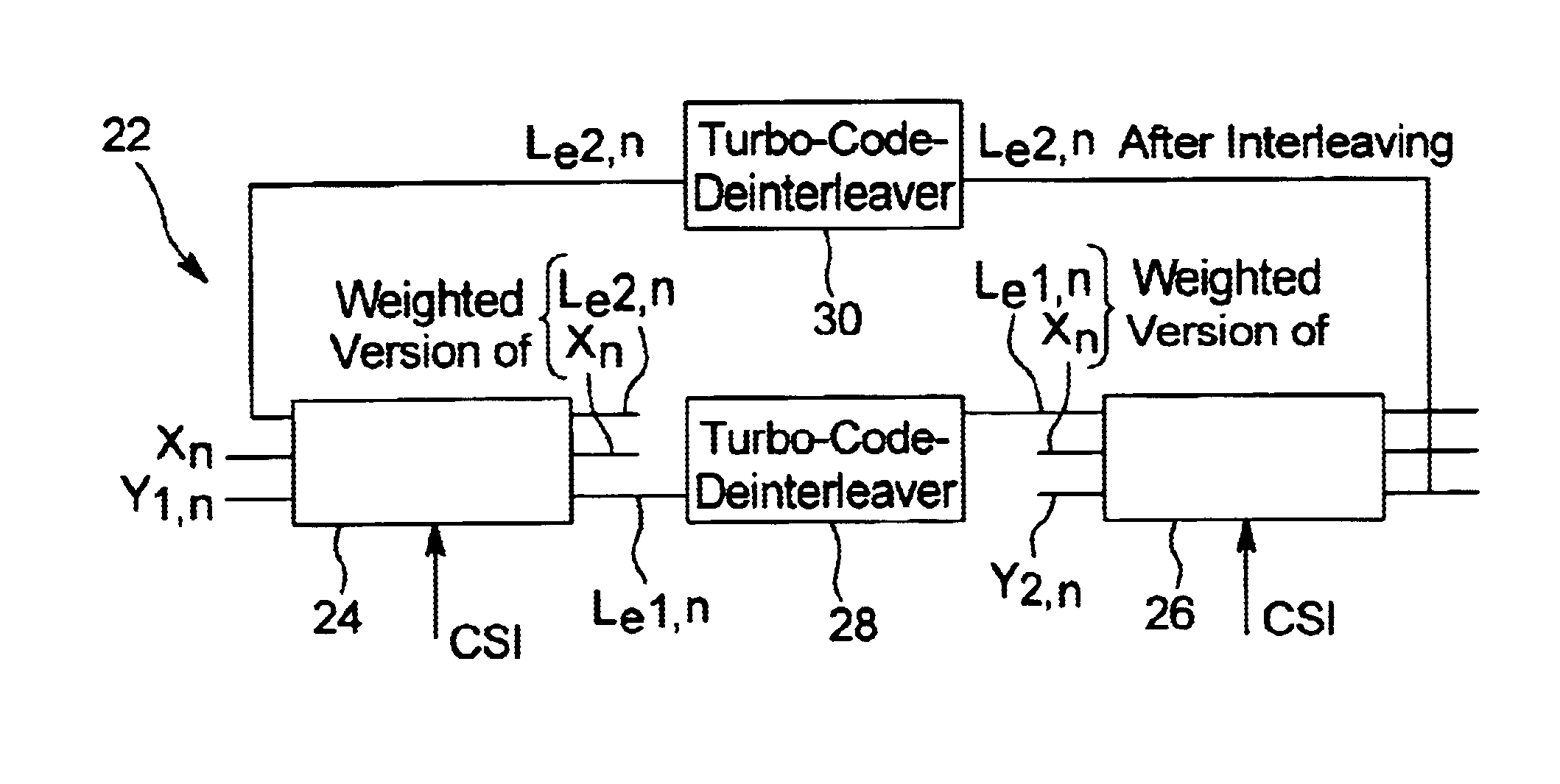
An apparatus generates quasi-complementary turbo codes in a communication system. The apparatus includes a turbo encoder, an interleaver for interleaving symbols output from the turbo encoder according to a given rule, and a code generator for generating the quasi-complementary turbo codes by puncturing and repeating the interleaved symbols from the interleaver. Further, an apparatus decodes quasi-complementary turbo codes in the communication system. The decoding apparatus includes a code decoder for generating code symbols according to a code rate transmitted through depuncturing sub-codes of quasi-complementary turbo codes transmitted from a transmitter and soft combining the sub-codes, a deinterleaver for deinterleaving the symbols output from the code decoder, and a turbo decoder for decoding an output of the deinterleaver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Sets of rate-compatible universal turbo codes nearly optimized over various rates and interleaver sizes
InactiveUS20050172202A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionHigh rateTurbo encoder
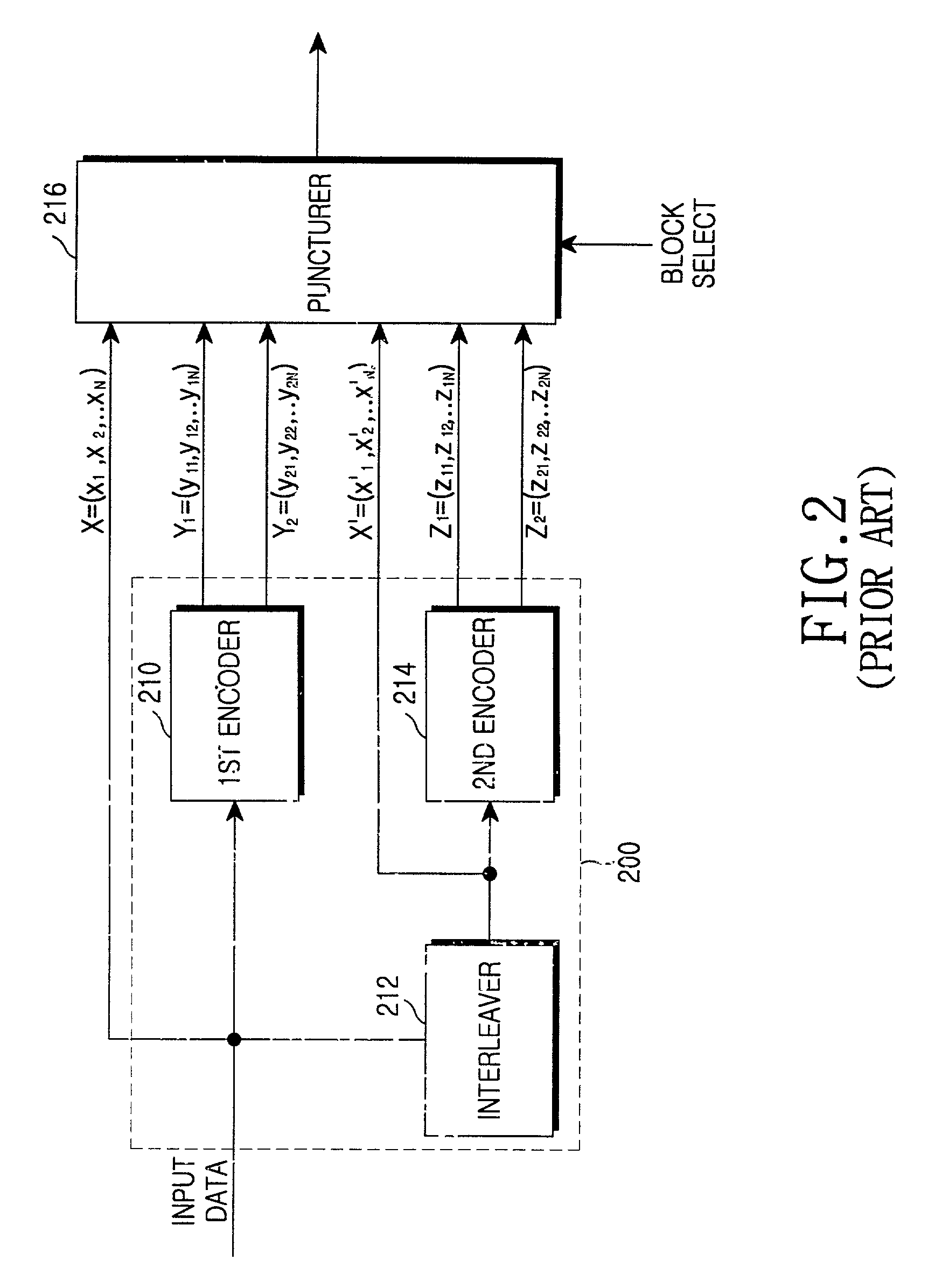
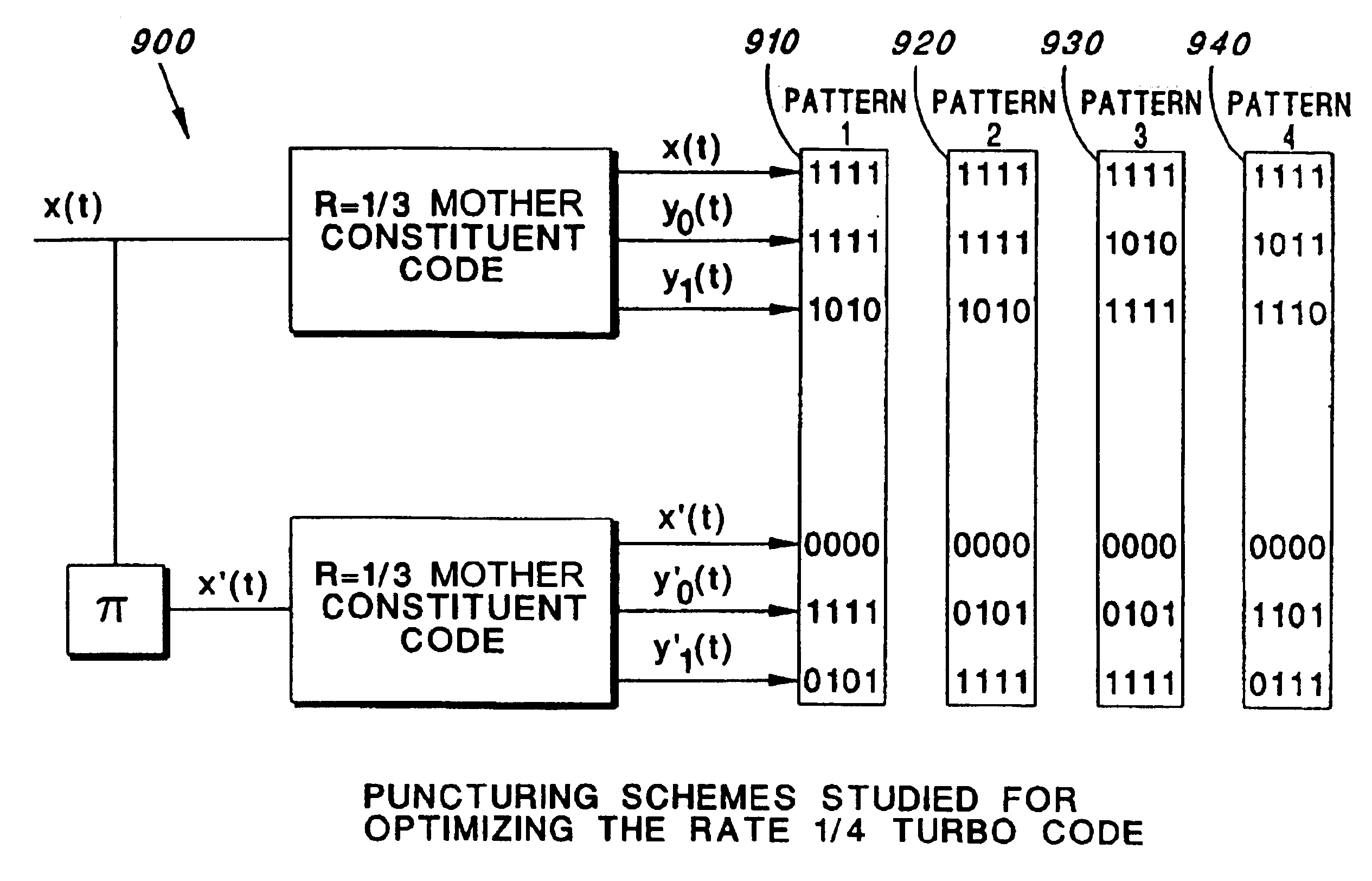
A method and apparatus for Turbo encoding uses a set of rate-compatible Turbo Codes optimized at high code rates and derived from a universal constituent code. The Turbo Codes have rate-compatible puncturing patterns. The method comprises: encoding a signal at a first and second encoder using a best rate 1 / 2 constituent code universal with higher code rates, the first encoder and the second encoder each producing a respective plurality of parity bits for each information bit; puncturing the respective plurality of parity bits at each encoder with a higher rate best puncturing patterns; and puncturing the respective plurality of parity bits at each encoder with a lower rate best puncturing pattern. In a variation, the best rate 1 / 2 constituent code represents a concatenation of polynomials 1+D2+D3 (octal 13) and 1+D+D3 (octal 15), D a data bit. A Turbo Encoder is provided which has hardware to implement the method.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
Apparatus and method for generating codes in communication system
InactiveUS7093185B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemTurbo encoder
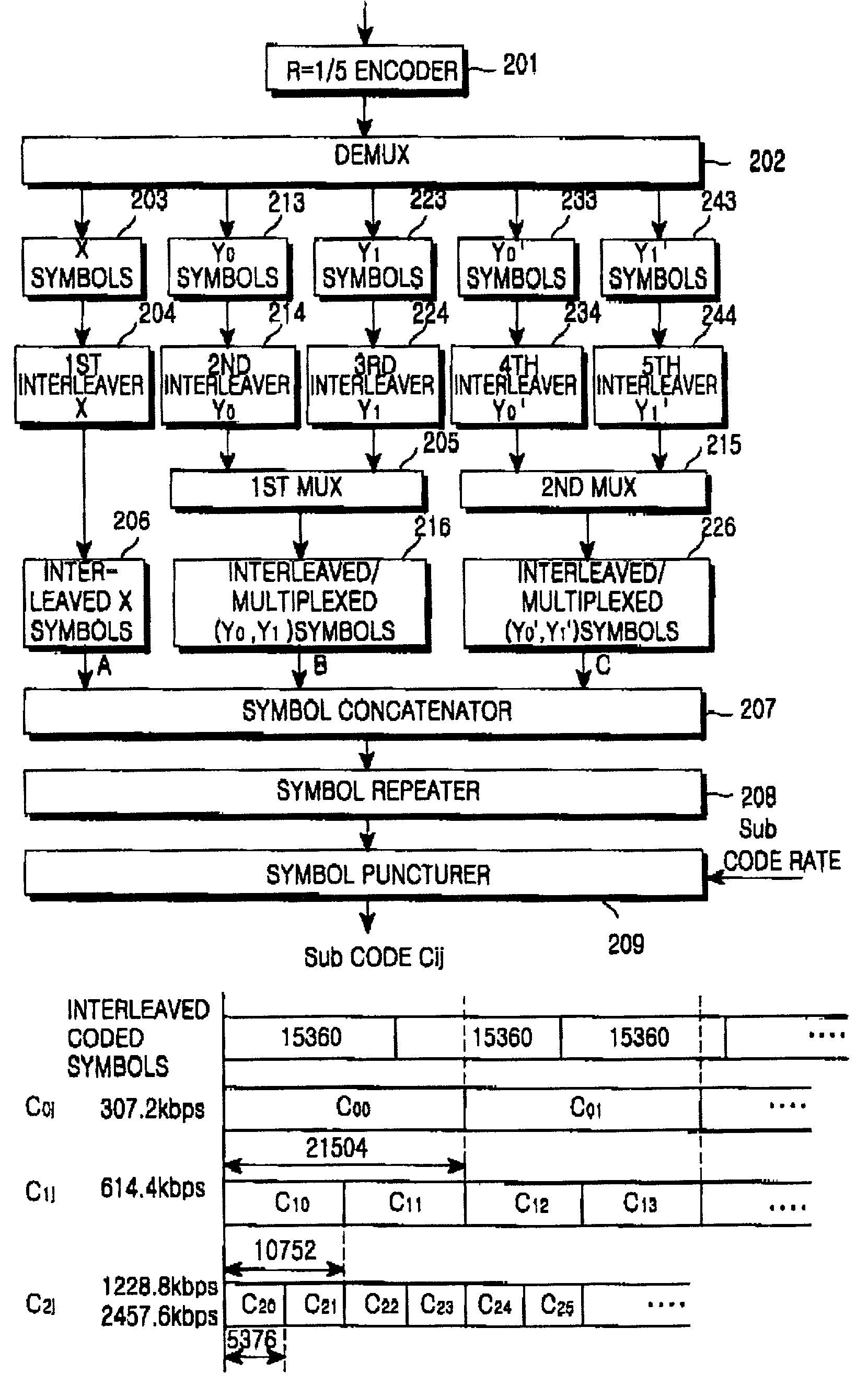
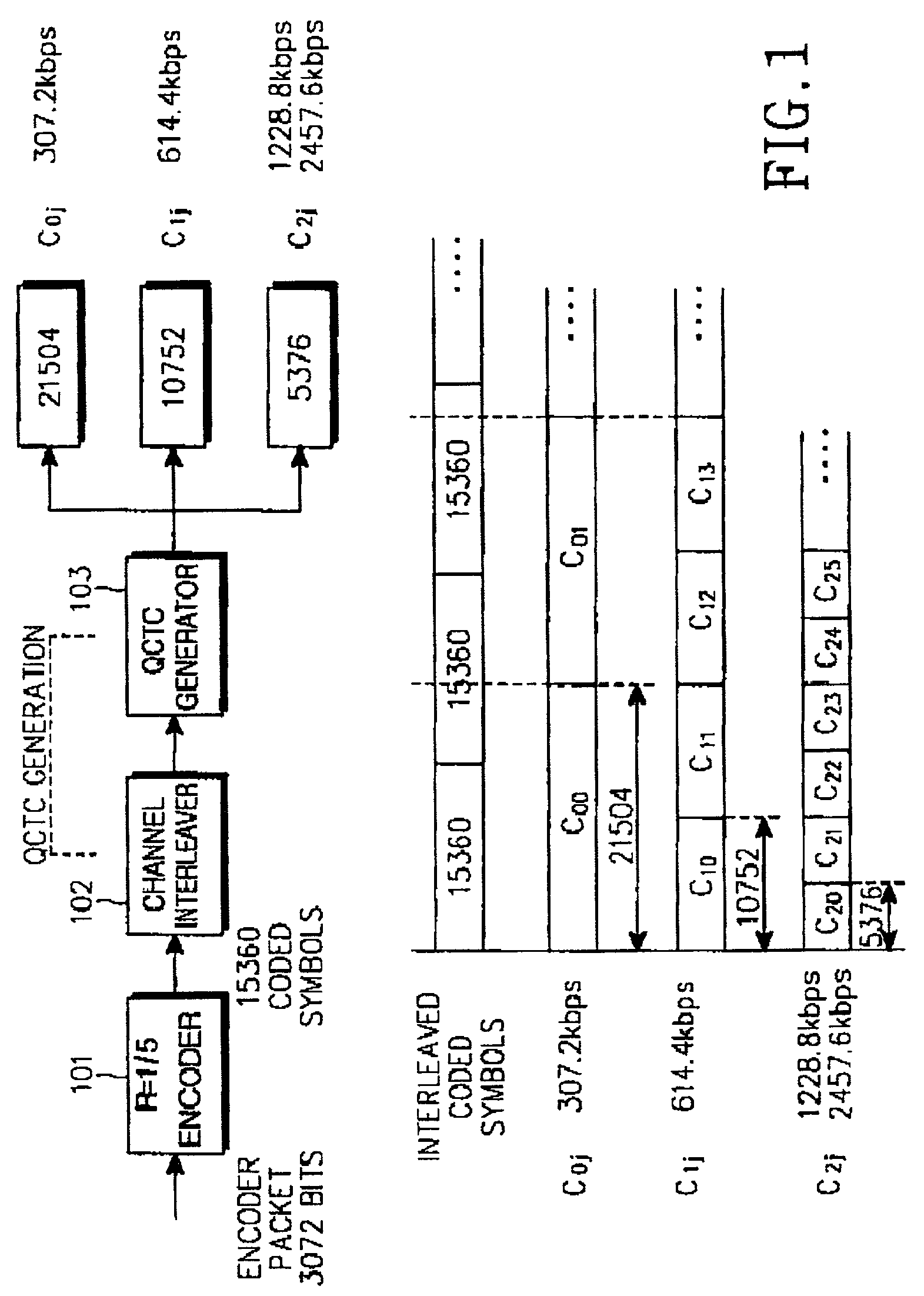
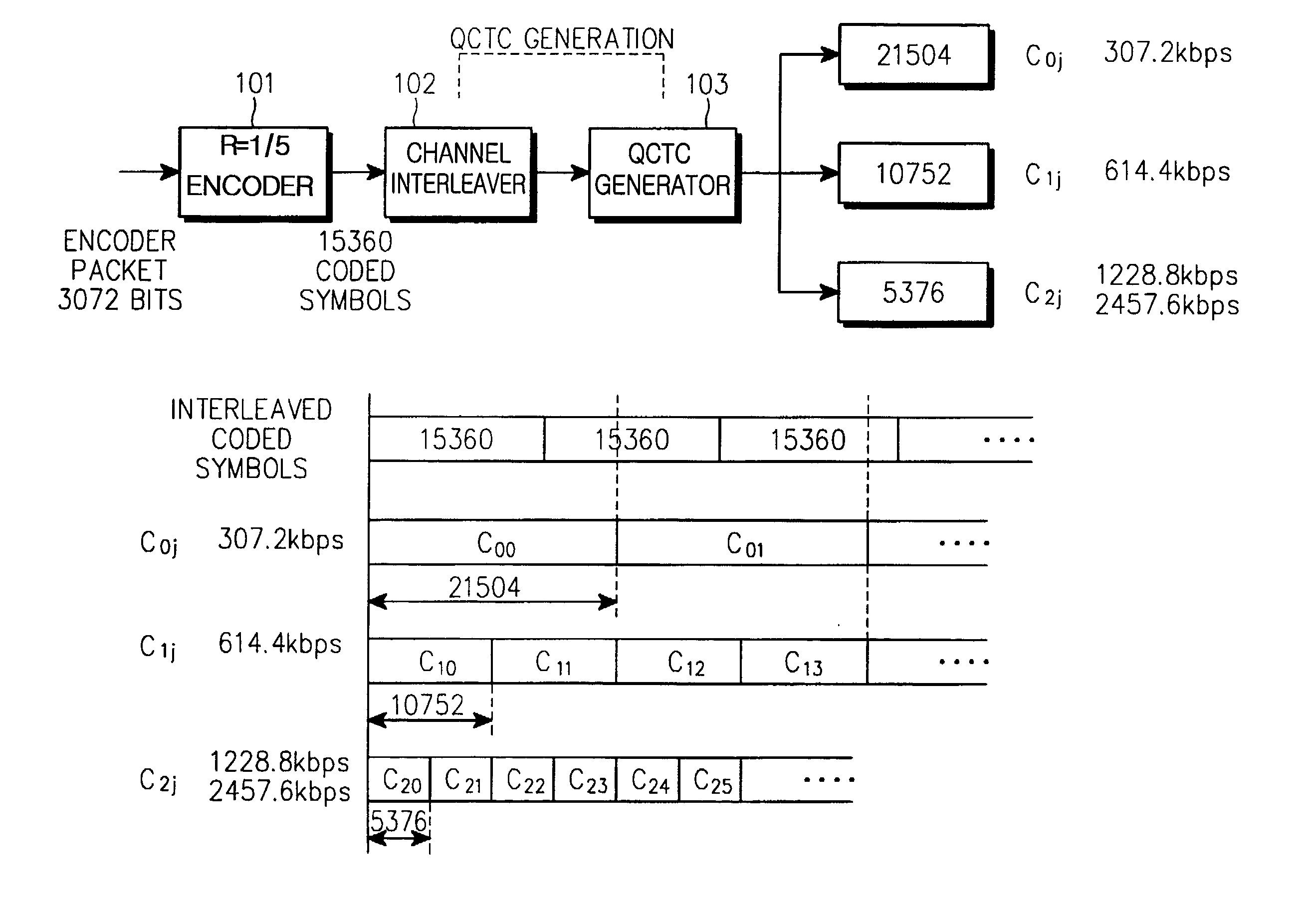
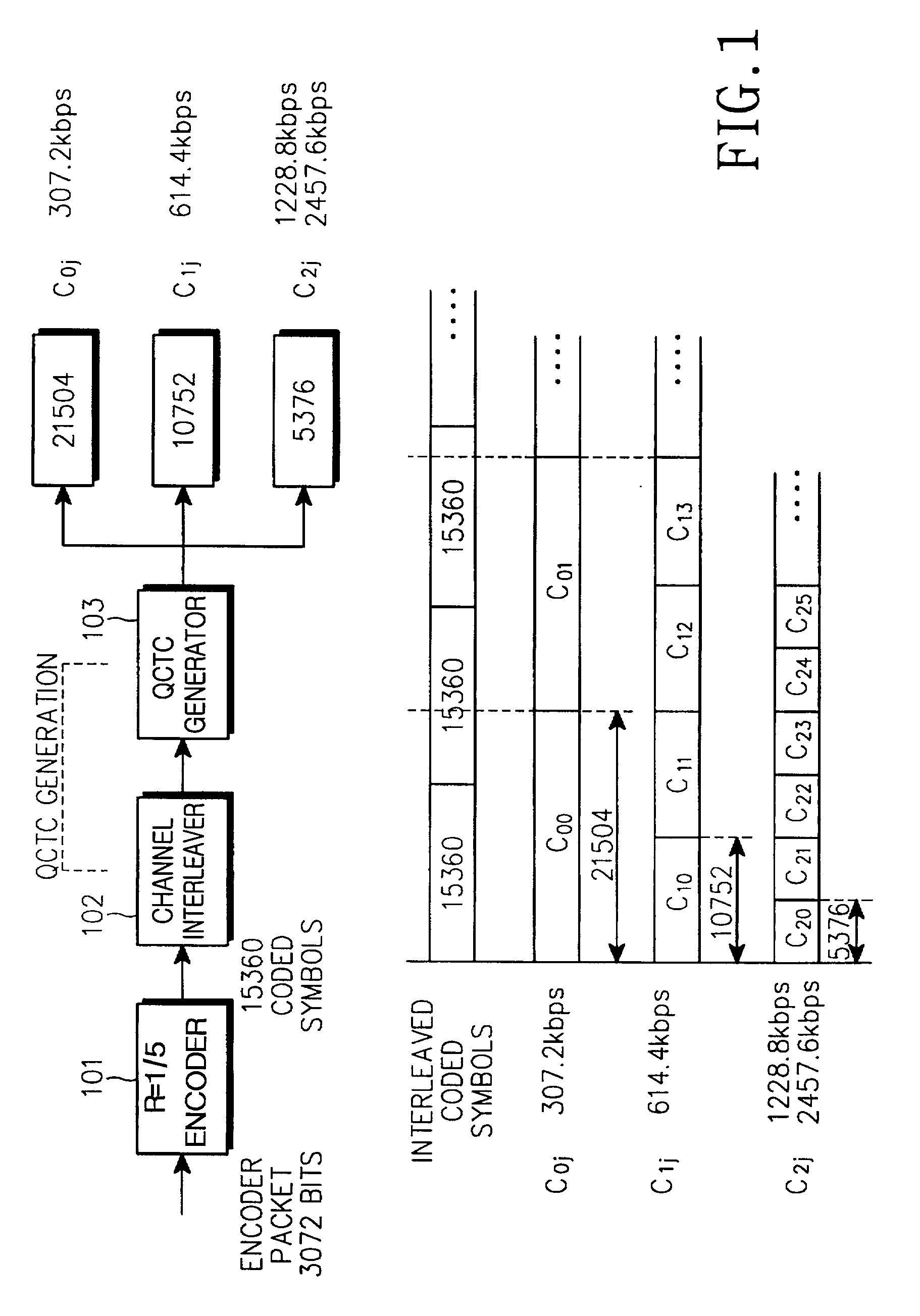
A QCTC (Quasi-Complementary Turbo Code) generating apparatus having: a turbo encoder for generating an information symbol sequence and a plurality of parity symbol sequences by encoding the information symbol sequence; a channel interleaver for individually interleaving the symbol sequences, generating new parity symbol sequences by multiplexing the symbols of parity symbol sequences with the same priority levels, and serially concatenating the information symbol sequence and the new parity symbol sequences; and a QCTC generator for generating a sub-code with a given code rate by recursively selecting a predetermined number of symbols from the concatenated symbol sequence at a given starting position.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Turbo code velocity matching and code bit reading method
InactiveCN101159513AImplementing Orthogonal RetransmissionReduce overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelComputer hardwareTurbo encoder
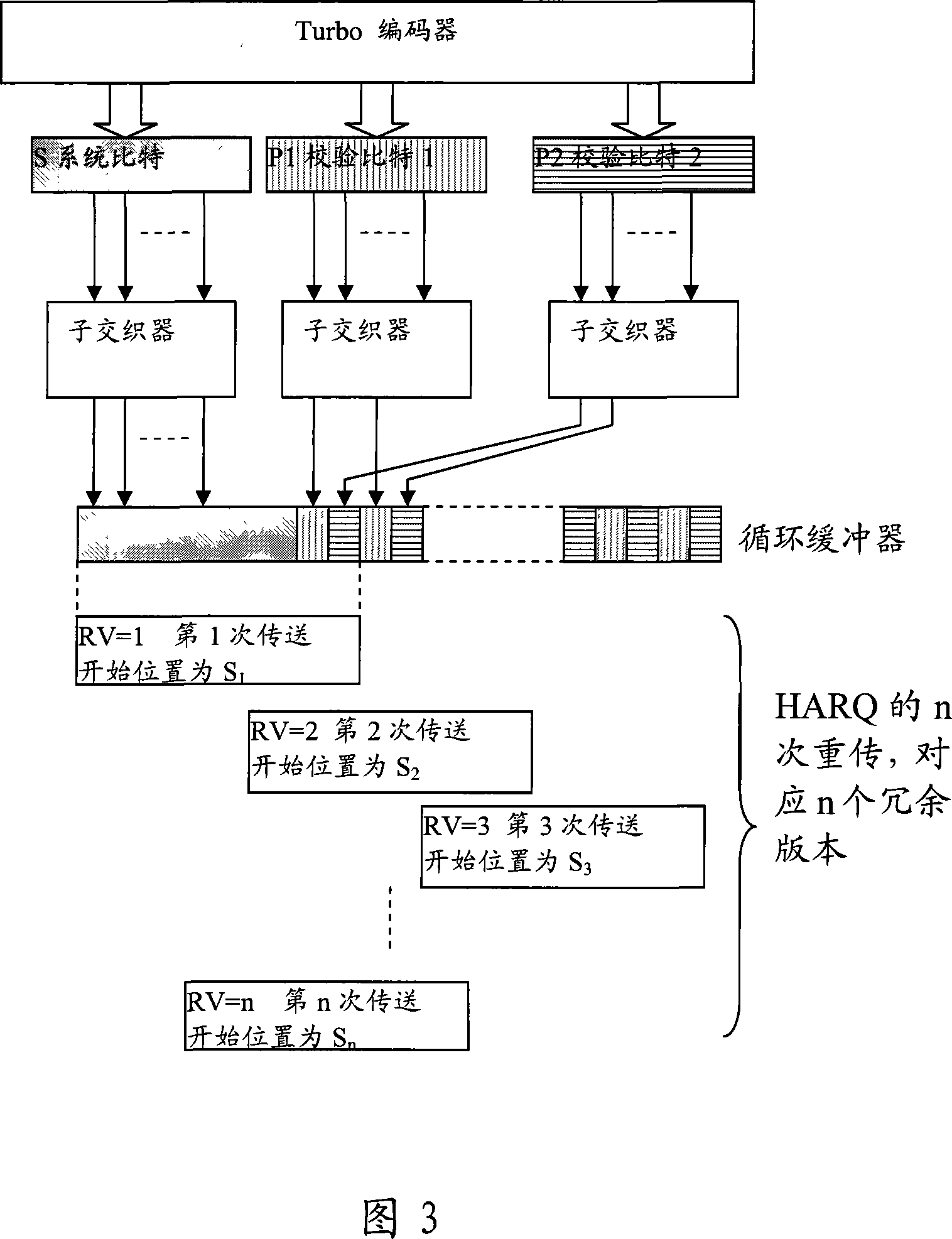
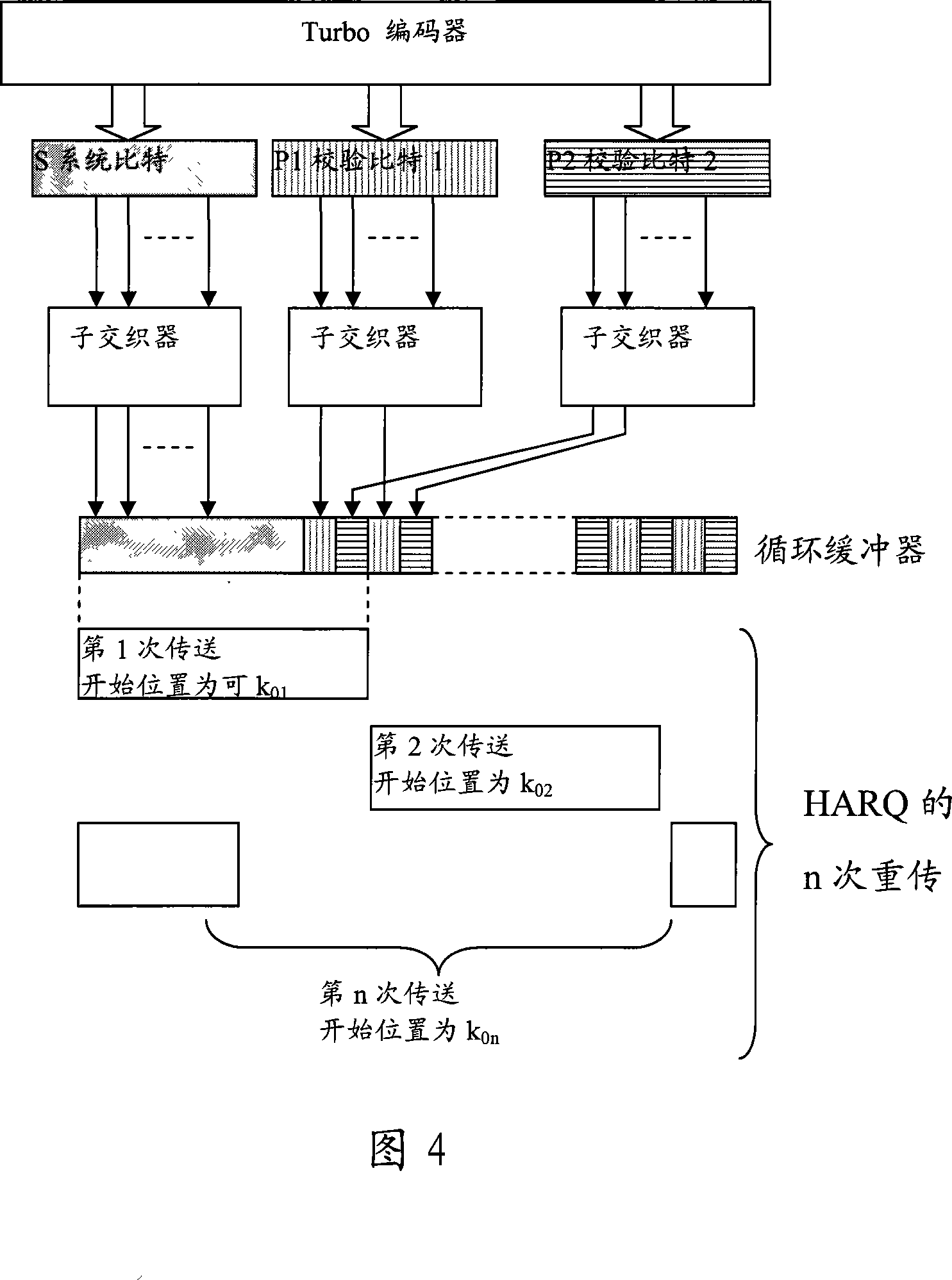
The invention provides a turbo code rate matching method, which comprise the following steps: (a) sending the information in groups to a turbo code encoder with a code rate of 1 / r to generate a system bit stream and (r-1) checked bit streams; (b) interleaving the system bit stream and the checked bit streams coded by the turbo code encoder via the individual sub-interleavers thereof, laying the system bit stream in the inside front part of a circular buffer and laying the checked bit streams behind the system bit stream in a staggered manner, to form a circular buffer zone; (c) sequentially reading E code bits required in each HARQ transmission from the circular buffer zone to form a HARQ sub-pack. The inventive method can completely realize the orthogonal retransmission of Turbo codes without defining redundant version number, thereby saving the signaling costs.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Sets of rate-compatible universal turbo codes nearly optimized over various rates and interleaver sizes
A method and apparatus for Turbo encoding uses a set of rate-compatible Turbo Codes optimized at high code rates and derived from a universal constituent code. The Turbo Codes have rate-compatible puncturing patterns. The method comprises: encoding a signal at a first and second encoder using a best rate ½ constituent code universal with higher code rates, the first encoder and the second encoder each producing a respective plurality of parity bits for each information bit; puncturing the respective plurality of parity bits at each encoder with a higher rate best puncturing patterns; and puncturing the respective plurality of parity bits at each encoder with a lower rate best puncturing pattern. In a variation, the best rate ½ constituent code represents a concatenation of polynomials 1+D2+D3 (octal 13) and 1+D+D3 (octal 15), D a data bit. A Turbo Encoder is provided which has hardware to implement the method.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
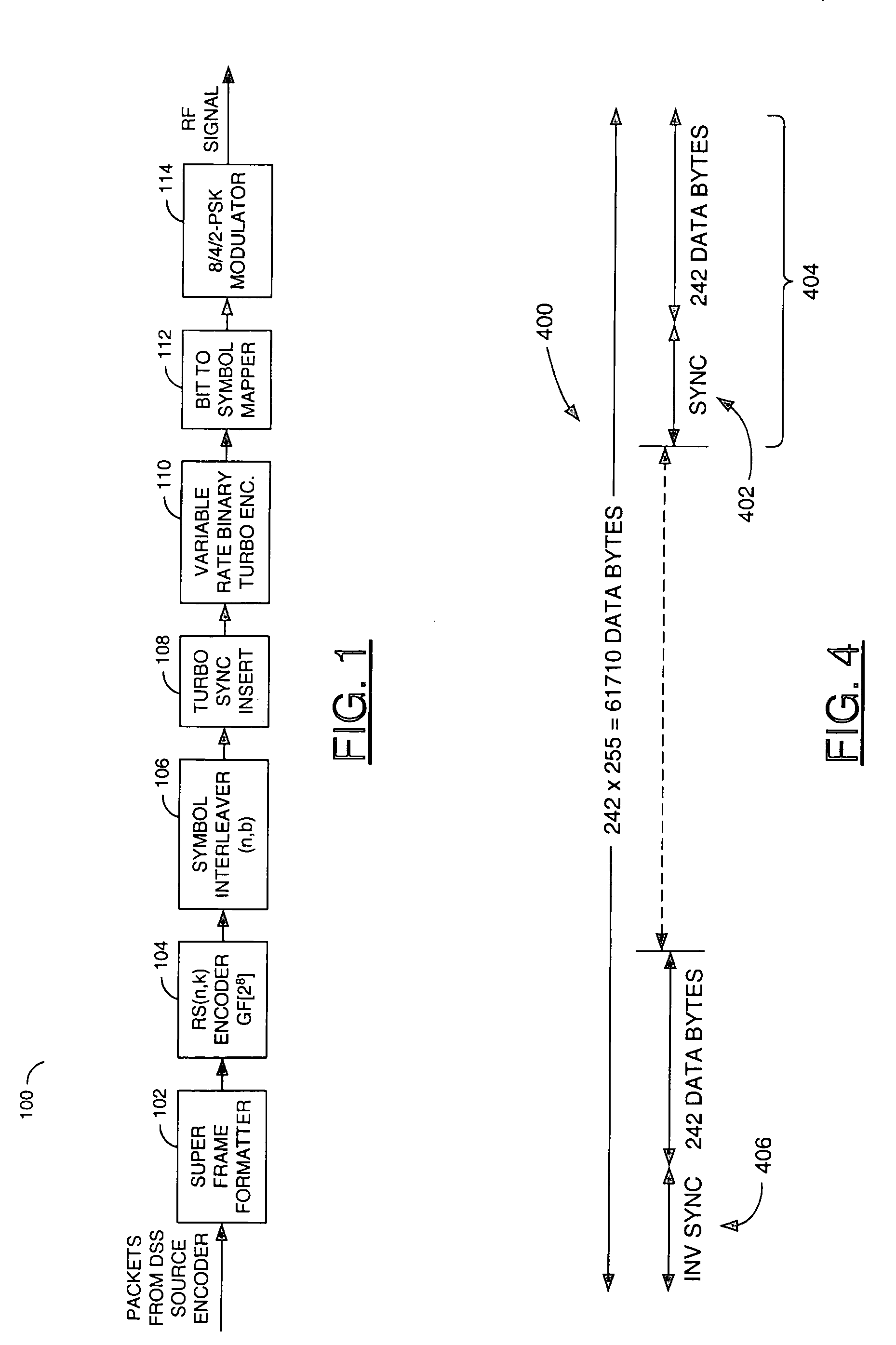
System to efficiently transmit two HDTV channels over satellite using turbo coded 8PSK modulation for DSS compliant receivers
InactiveUS6987543B1Television system detailsModulated-carrier systemsHigh-definition televisionComputer hardware
A channel encoding system and a channel decoding system for use in transmitting multiple high definition television programs in a single satellite channel. The channel encoding system may comprise a frame formatter that may be configured to format a transport stream to produce a block stream. An error correction encoder may be configured to encode the block stream to produce an error protected block stream. An interleave module may be configured to interleave the error protected block stream to produce a data stream. A turbo encoder may be configured to encode the data stream to produce an encoded stream. A bit-to-symbol mapper may be configured to map the encoded stream to produce a symbol stream capable of at least eight different symbols. Finally, a modulator may be configured to modulate the symbol stream.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
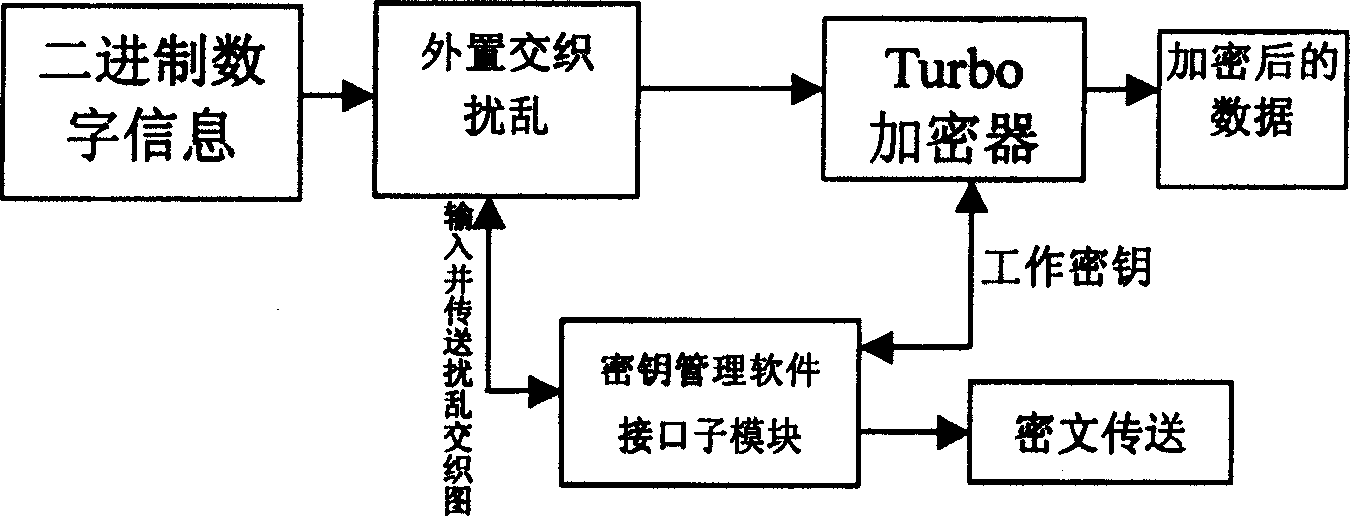
Digital information anti-interference soft encrypted method and system based on Turbo code-encode
InactiveCN1585321AReduce correlationGood scrambling effectMultiple keys/algorithms usageError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareTurbo encoder
The invention uses software encryption, the interleaver and recursive system code submodule in Turbo coding structure to make up cipher key that can encrypt the information source. Its system consists of an encryption module, an anti-interference decryption module and a cipher management software interface module. The encryption module is composed of the external interleaving scramble submodule, the Turbo encipher and cipher management submodule. Turbo encoder is adopted in the encryption module. The noise and other interference are reduced in the transmission of the encrypted information. The invention can be applied in secret information encryption like military intelligence.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
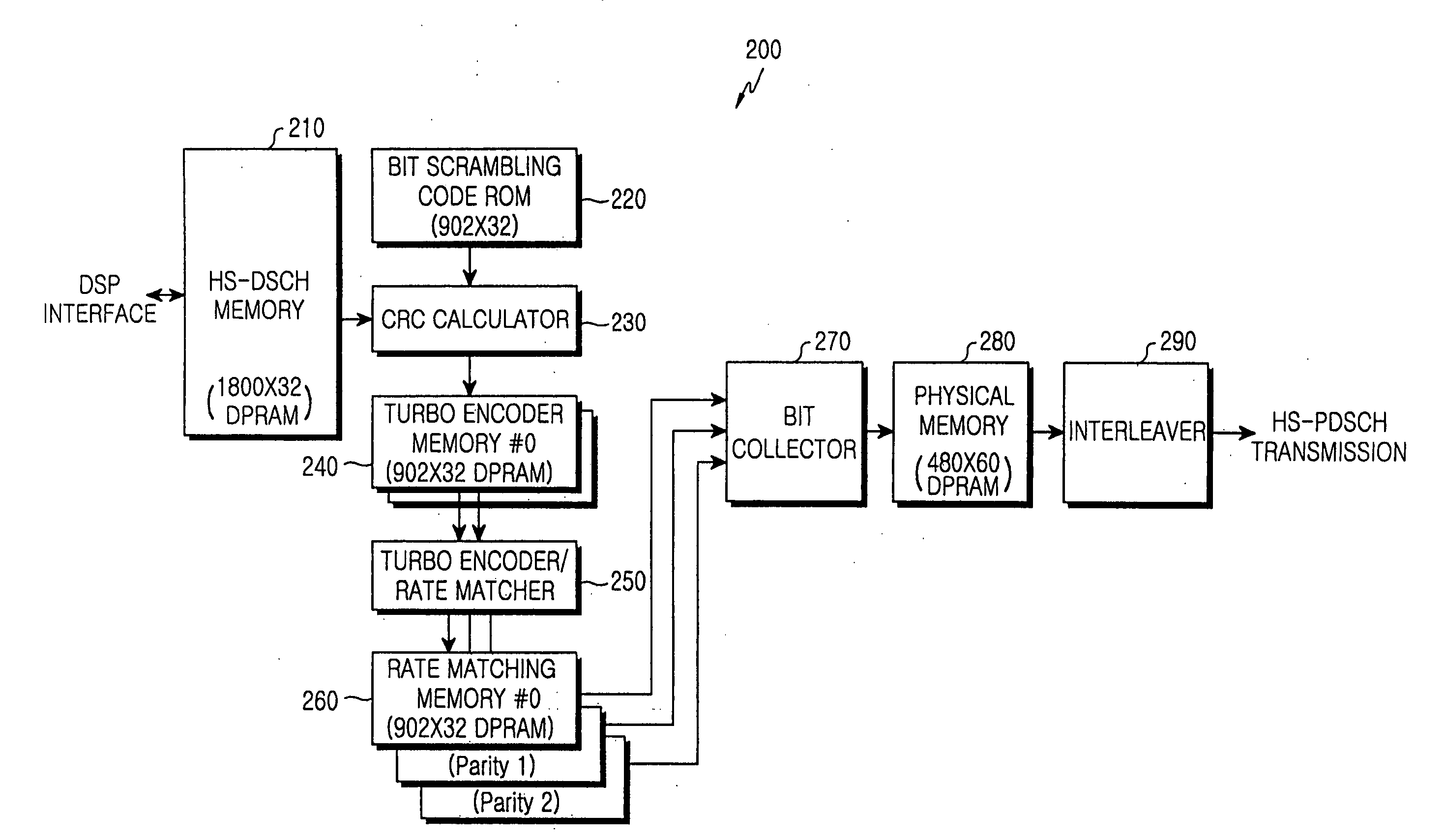
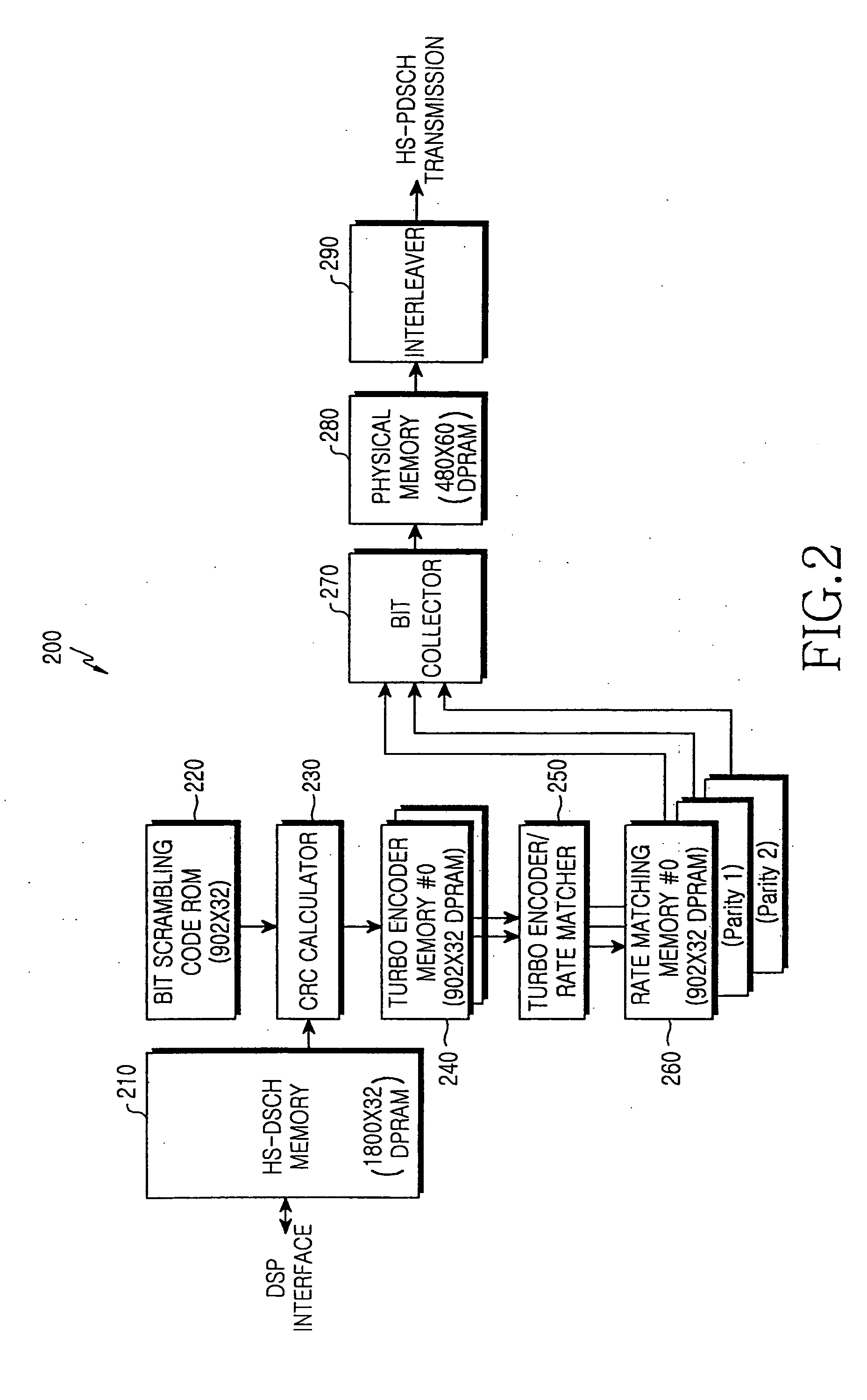
HS-DSCH transmitter and CRC calculator therefor in a W-CDMA system
An HS-DSCH transmitter in a W-CDMA system is provided. In the HS-DSCH transmitter, a memory stores input transmission data. A bit scrambling code ROM stores random sequences for bit scrambling of the input data. A CRC calculator generates a bit scrambled sequence by attaching a CRC to the input transmission data and multiplying the CRC-attached data by a random sequence read from the bit scrambling code ROM. First and second turbo encoder input memories store the bit scrambling sequence. A turbo encoder & rate matcher reads the same bit scrambling sequence from the first and second encoder input memories, generates a systematic sequence, a first parity sequence, and a second parity sequence by turbo-encoding the read bit scrambling sequence, and rate-matches the sequences. First, second and third rate matching memories store the rate-matched sequences, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Distributed video coding apparatus and method capable of controlling encoding rate
InactiveUS20090147841A1Simply bit rateReduce in quantityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareVideo encoding
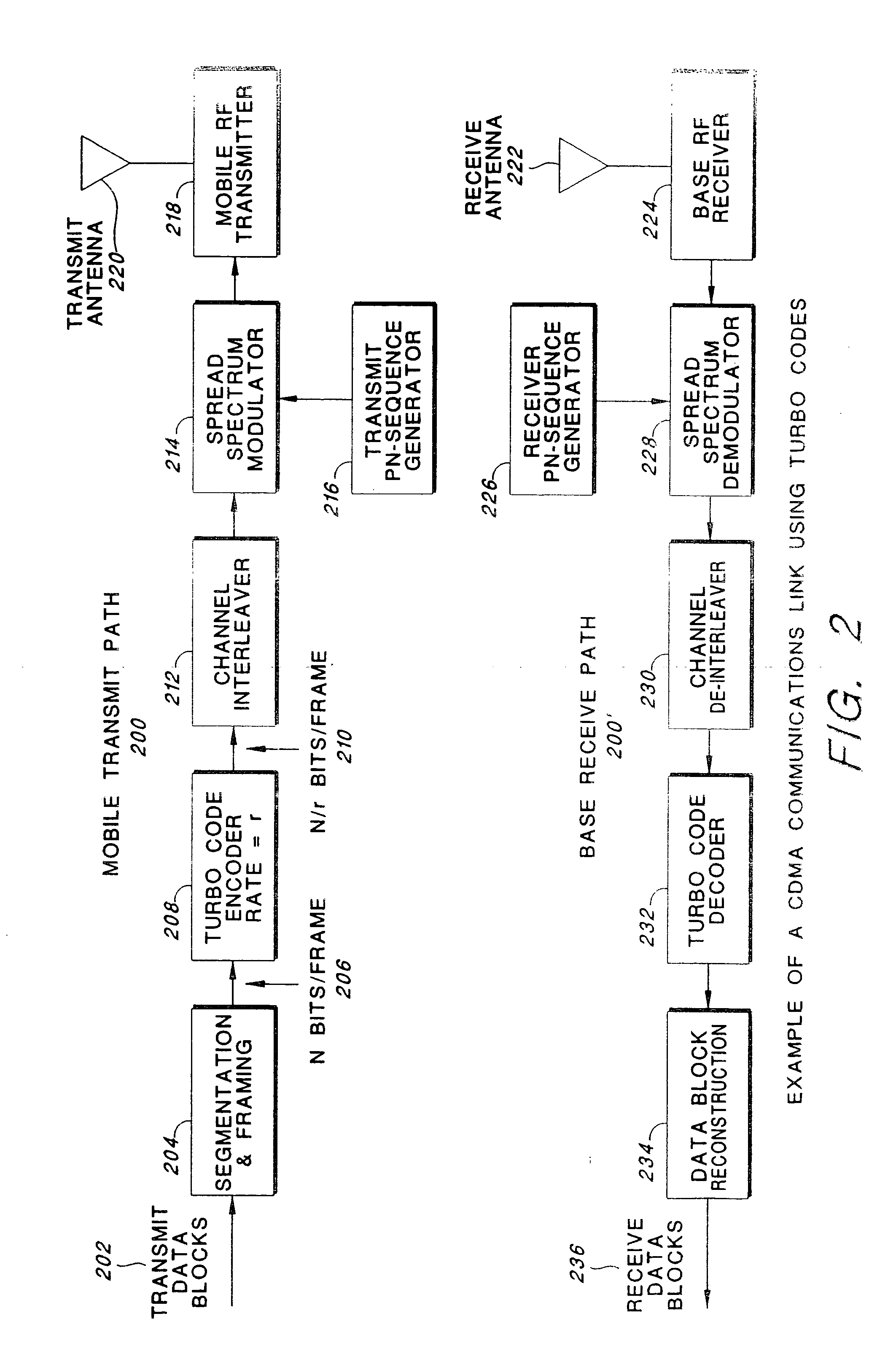
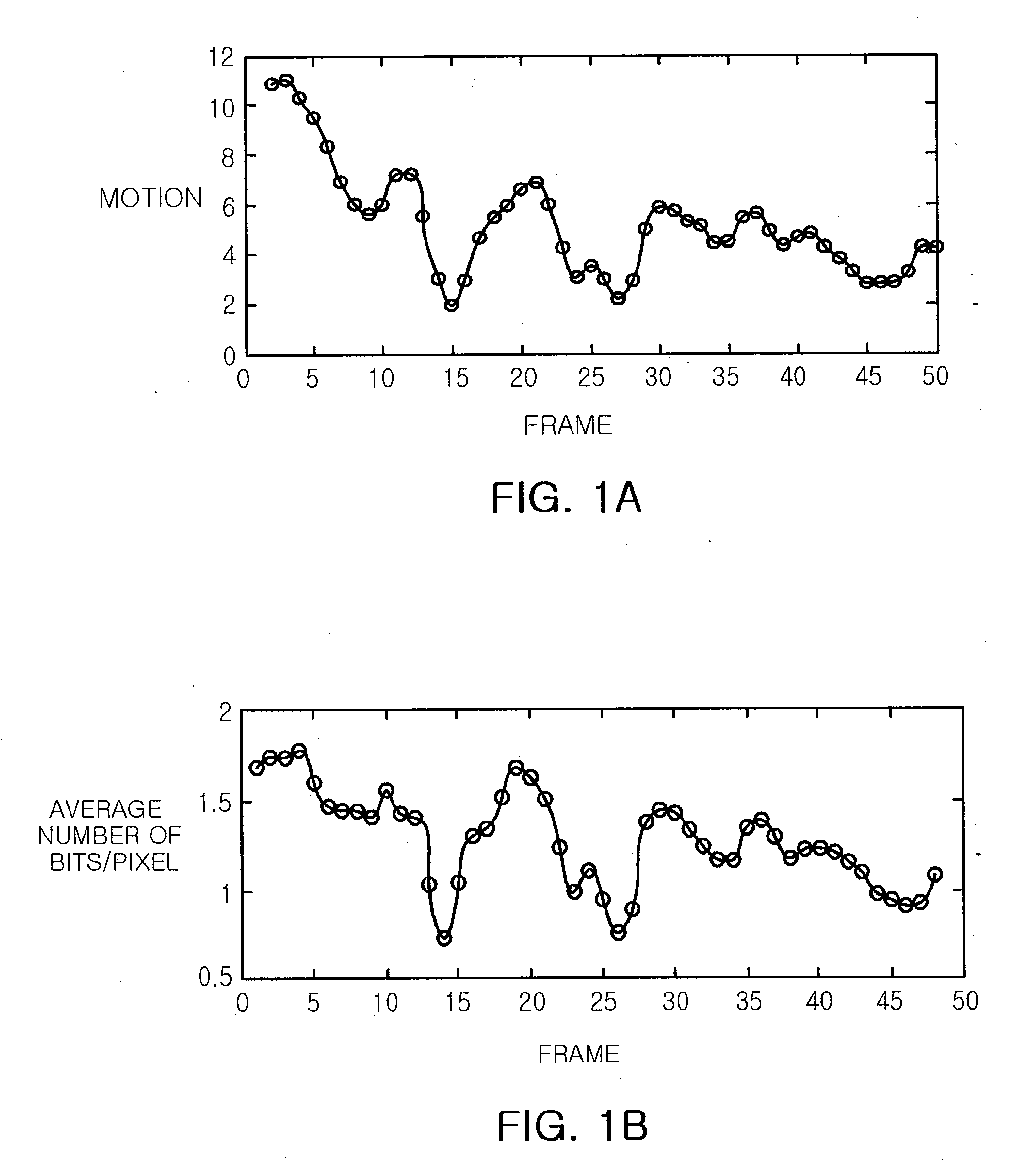
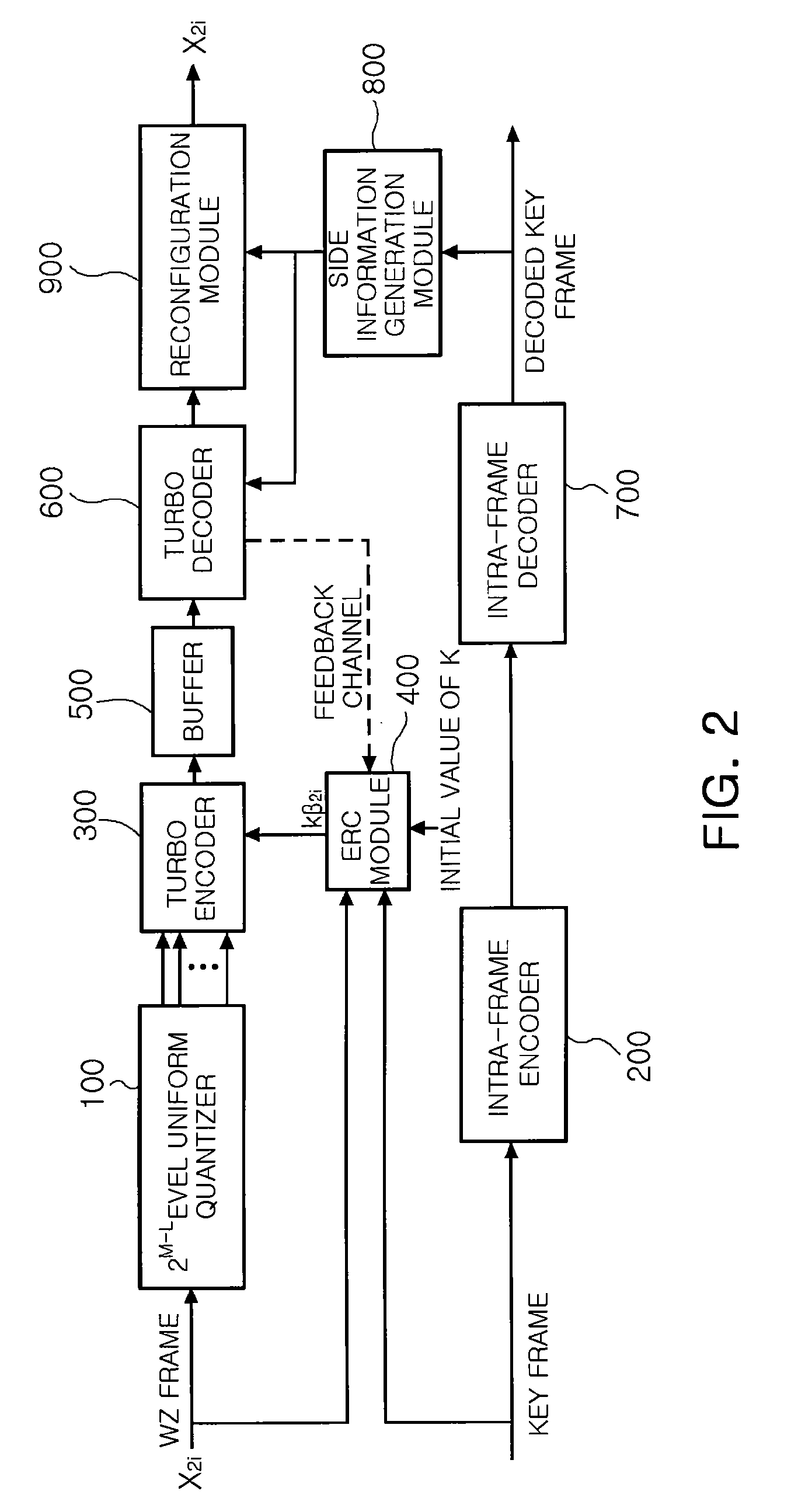
There are provided a distributed video coding apparatus and method capable of controlling an encoding rate, the apparatus including: an intra-frame encoder encoding a key frame and outputting a bit stream of the encoded key frame; an encoder rate control (ERC) module calculating a bit rate according to motion complexity of a present Wyner-Ziv (WZ) frame by using a correlation between the motion complexity and the bit rate; and a turbo encoder encoding the present WZ frame by the bit rate calculated at the ERC module and outputting the encoded WZ bit stream.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Apparatus and method for generating sub-codes to a turbo-encoder
InactiveUS6877130B2Improve bindingError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using convolutional codesCommunications systemAlgorithm
Provided is an apparatus and method for generating an initial puncturing matrix from which a first sub-code is produced in a communication system. The apparatus includes a turbo encoder for generating information symbols and first and second parity symbols for the input of an information bit stream and a sub-code generator for generating sub-codes from the information symbols and the first and second parity symbols using puncturing matrices. The method comprises the steps of selecting as many information symbols as a number of columns in the initial puncturing matrix from the information symbols output from the turbo encoder, if a difference between the number Ns of selected symbols in the initial puncturing matrix and the number of the columns in the initial puncturing matrix is equal to or greater than a number of component encoders in the turbo encoder, and selecting as many first and second parity symbols as the difference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for interleaving channels in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20060156172A1Improve reliabilityImproving channel performanceTransmission path divisionError detection/correctionCommunications systemTurbo encoder
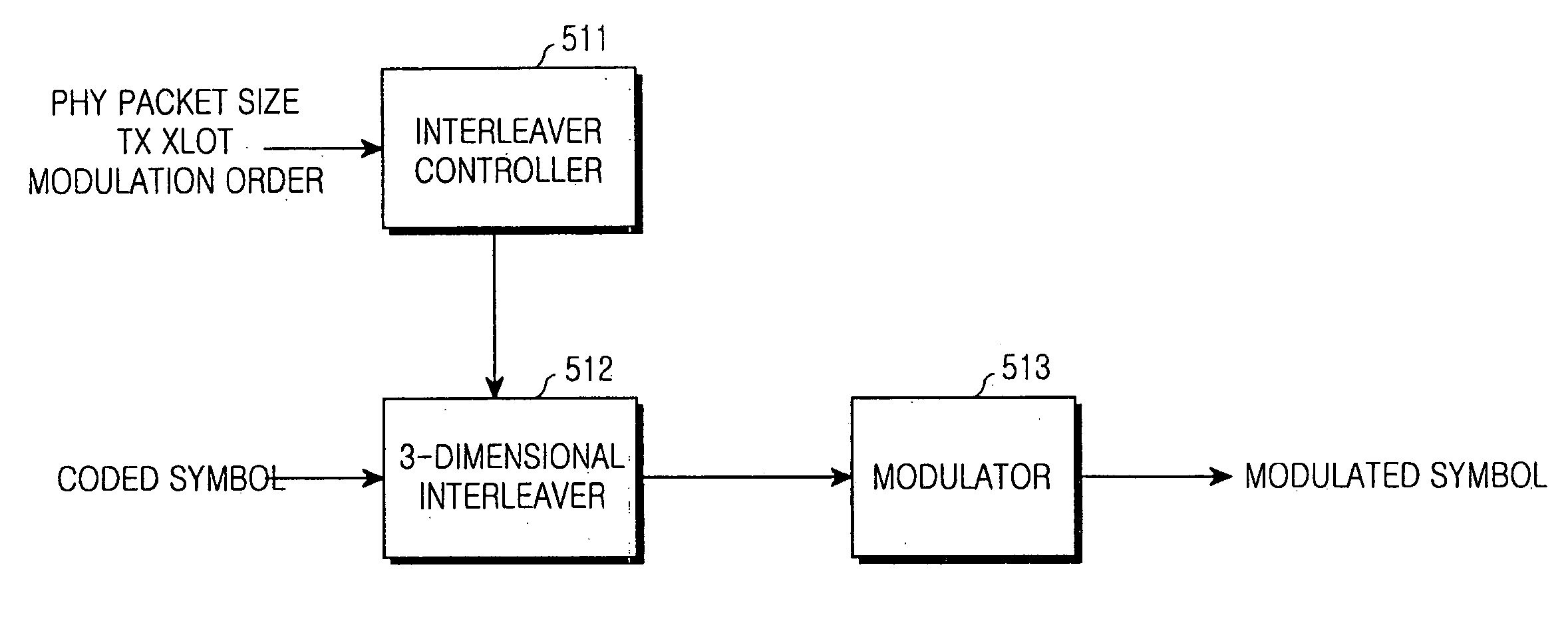
An apparatus and method interleaving symbols coded by a turbo encoder in a communication system that uses the turbo encoder for encoding transmission information into coded systematic symbols and at least one parity symbol pair, and maps the coded symbols using a second or higher modulation order before transmission. An interleaver controller performs a control operation of cyclic-shifting the systematic symbols among the symbols coded by the turbo encoder depending on a size of a physical packet to be transmitted, the number of transmission slots, and the modulation order, using an equation of (K×c+k) mod R, and cyclic-shifting redundancy symbols constituting the remaining size of the coded symbols to be transmitted, using an equation of floor{(K×c+k) / D}mod R. An interleaver cyclic-shifts input symbols under the control of the interleaver controller.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmission method and device for physical layer data in satellite two-way communication
InactiveCN102386996AFlexible length settingReduce complexityError preventionRadio transmissionError floorTwo-way communication
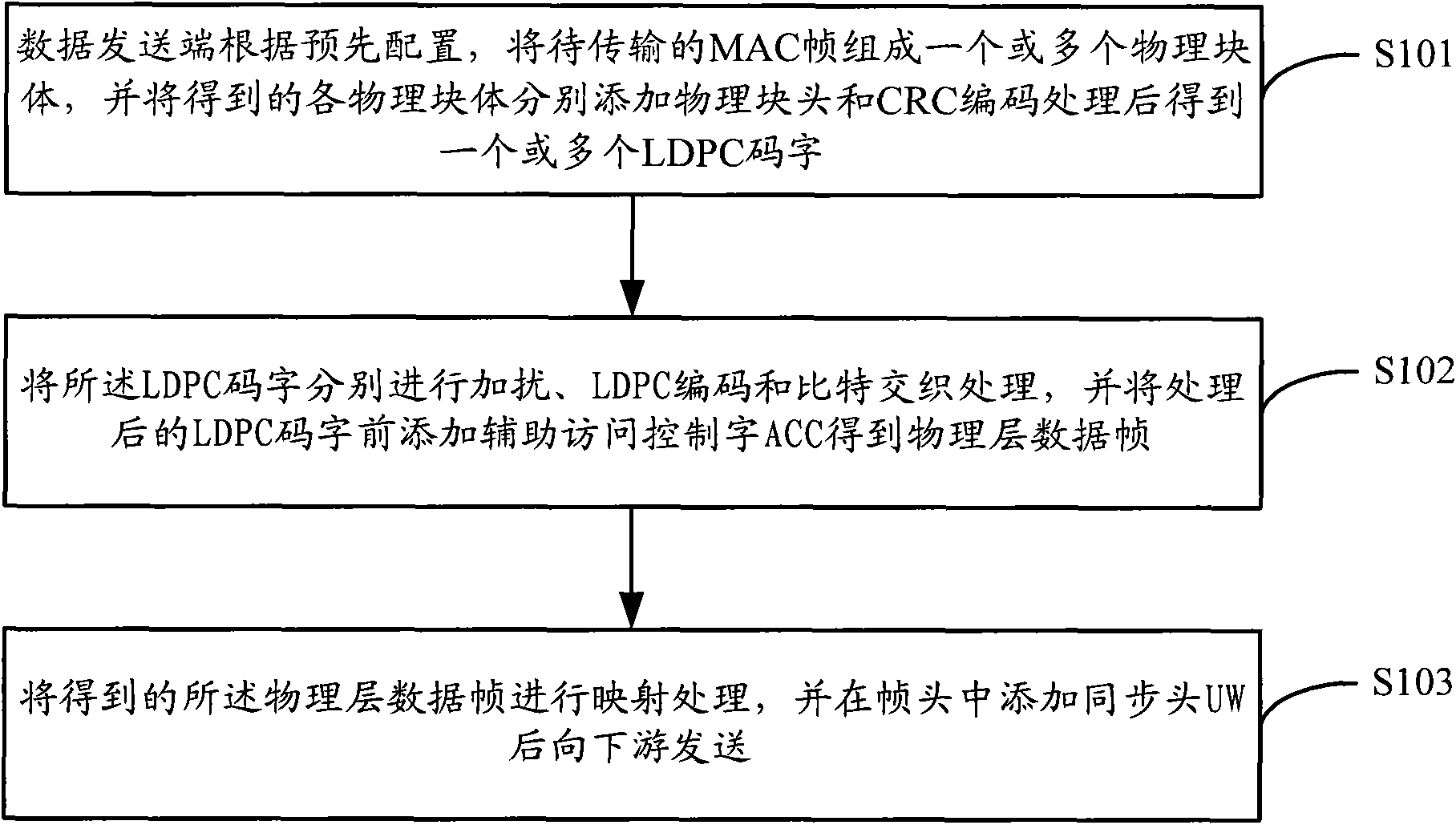
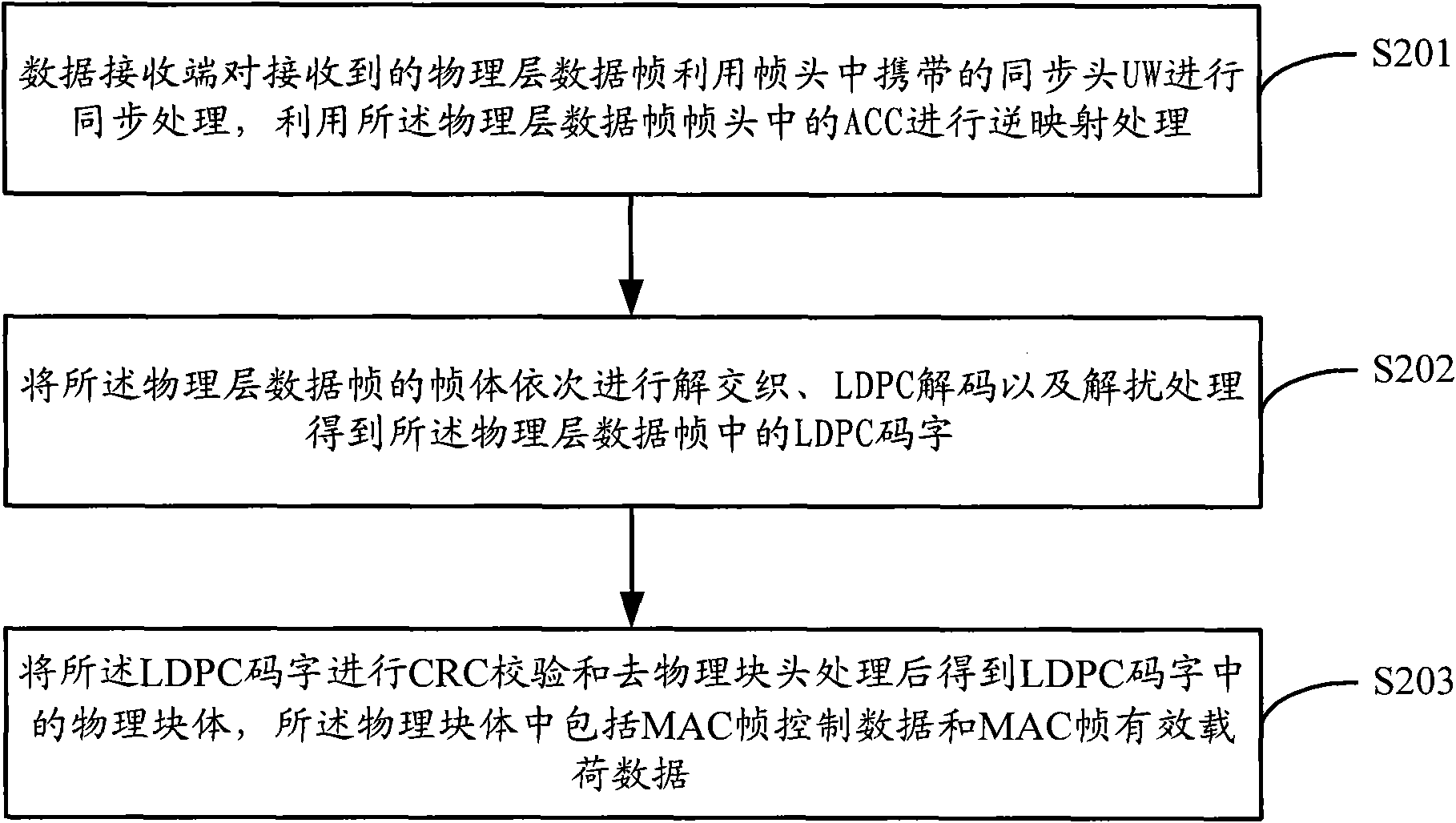
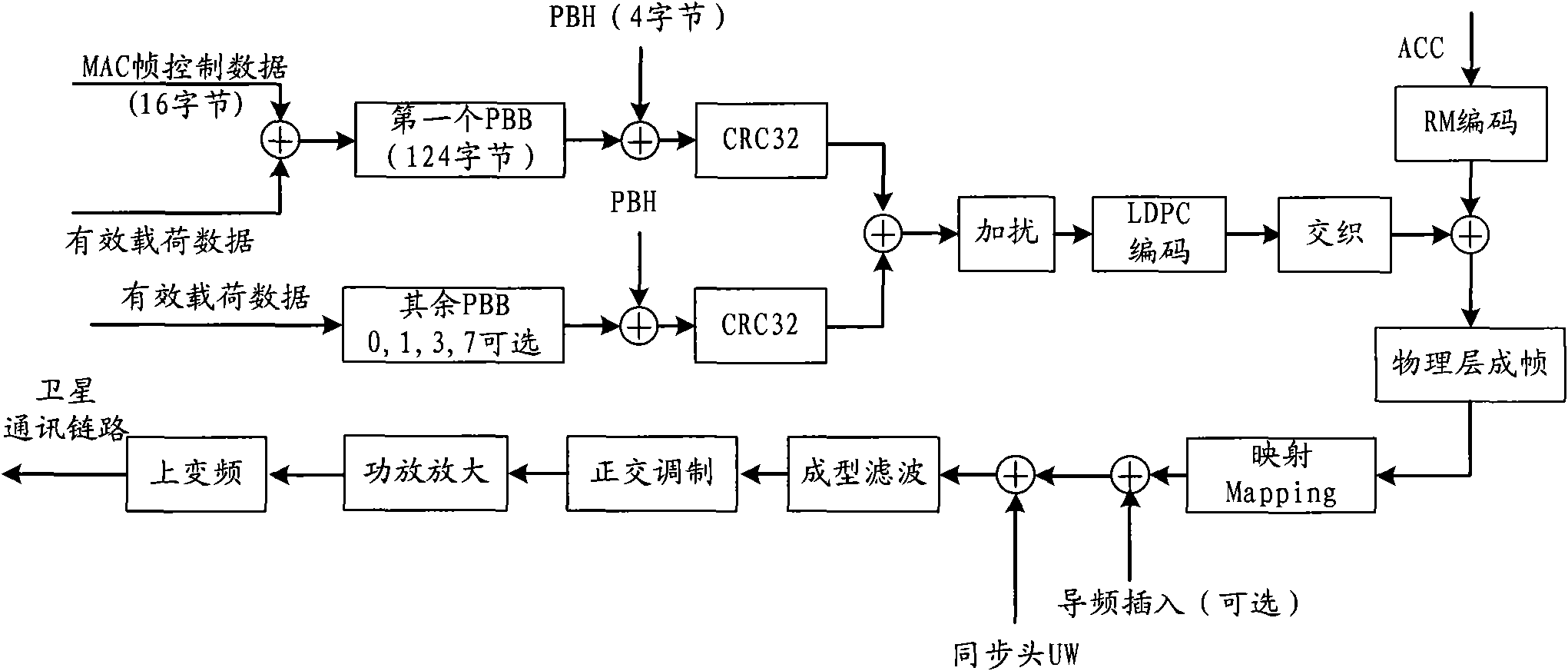
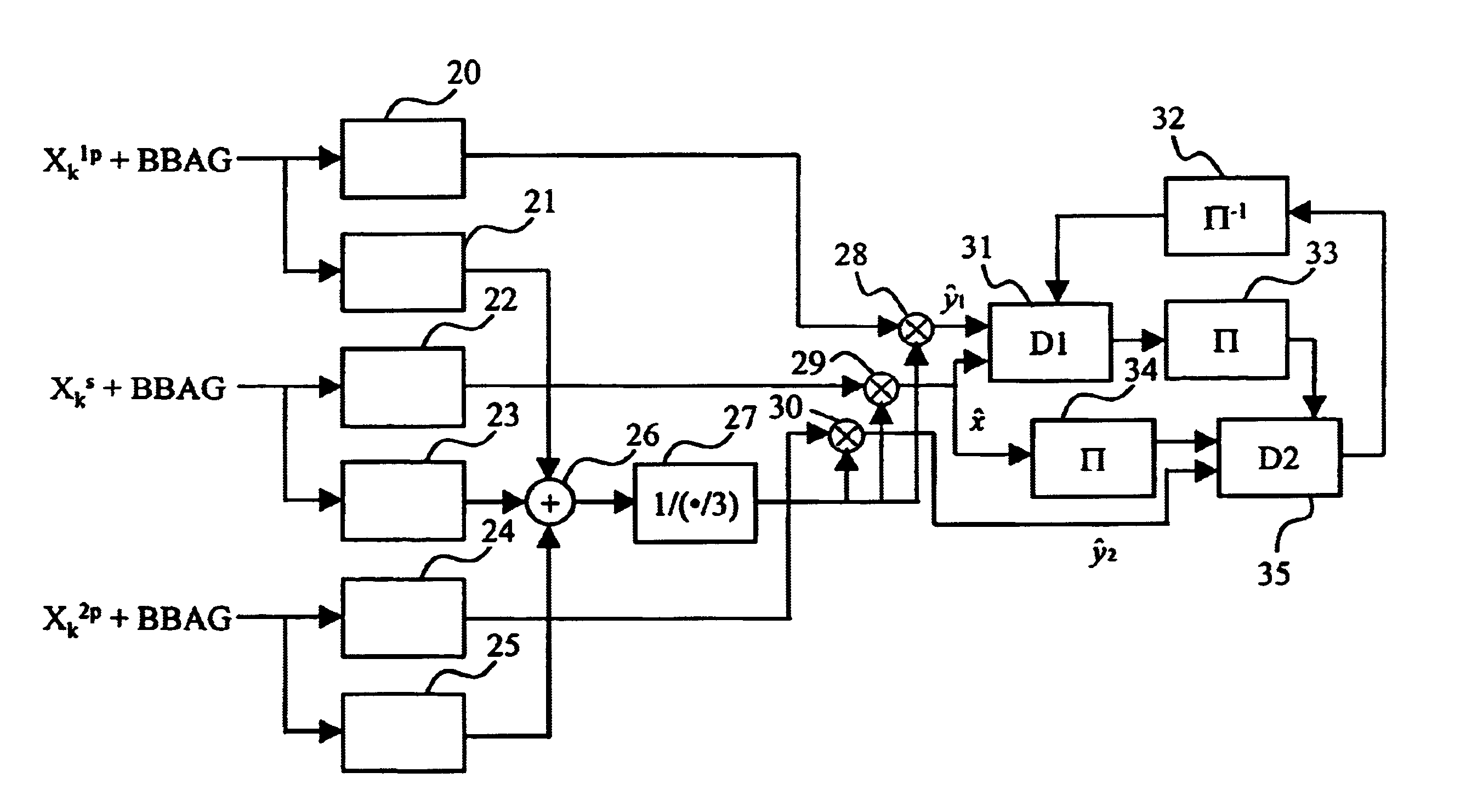
The invention discloses a transmission method and a device for physical layer data in satellite two-way communication. The transmission method includes that media access control (MAC) frames to be transmitted form one or a plurality of physical block bodies through a data sending end according to predefined configurations, and one or a plurality of low density parity check (LDPC) code words are obtained after physical block heads and cyclic redundancy check (CRC) codes are added on each obtained physical block body. The physical block bodies at least comprise control data of the MAC frames, and the control data respectively performs scrambling, LDPC encoding and bit interweaving processing on the LDPC code words and adds advanced audio codes (ACCs) in front of the processed LDPC code words to obtain physical layer data frames. The obtained physical layer data frames are conducted with mapping processing and sent to the downstream after synchronous heads UW are added in frame heads. The transmission method and the device for physical layer data in satellite two-way communication solves the problems of high complexity and error floor in coding and the like caused by the fact that the existing frame control data adopts an independent Turbo coder in the prior art.
Owner:ACAD OF BROADCASTING SCI SARFT
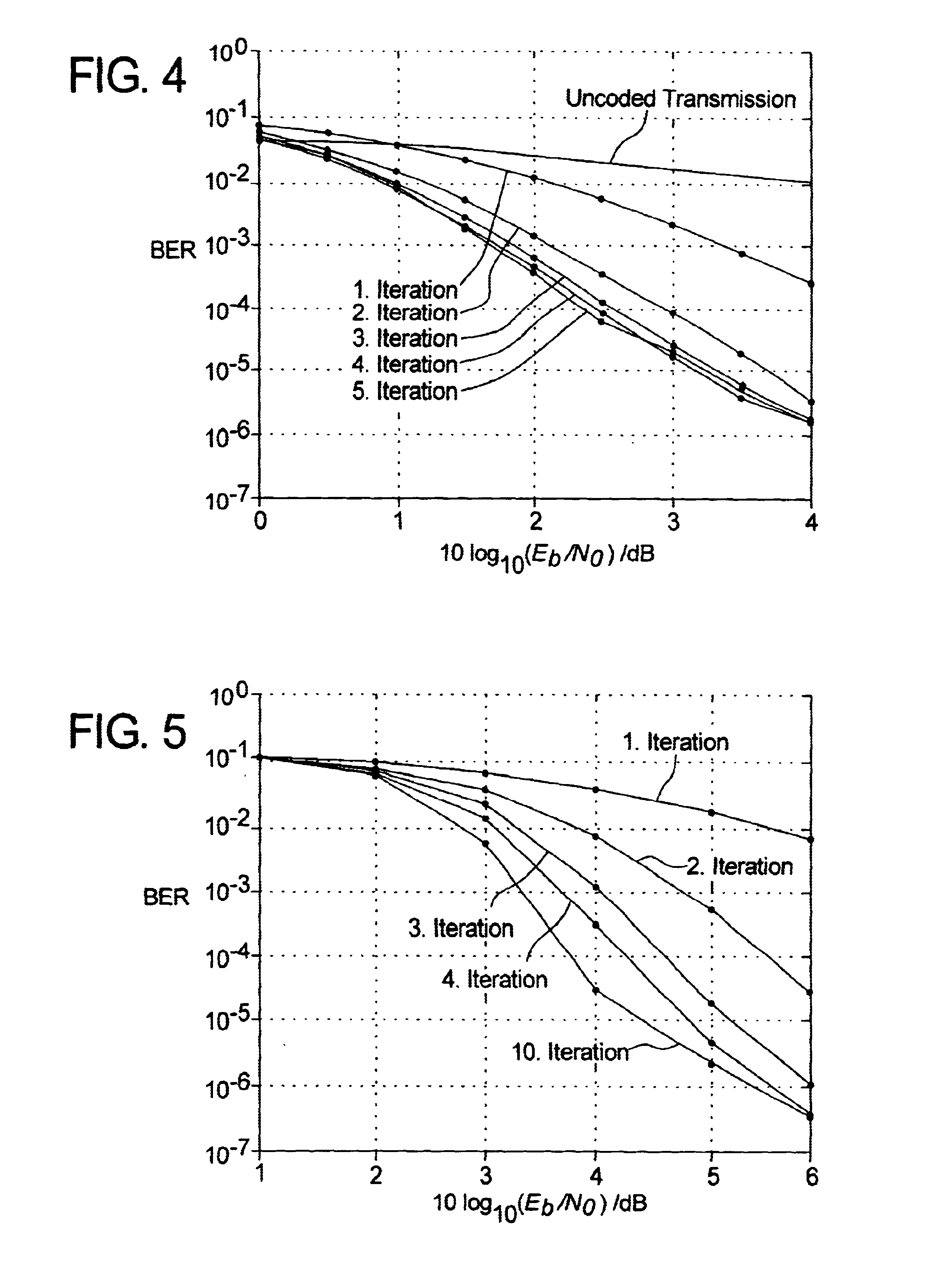
Method and device for evaluating the noise associated with turbocodes, and systems using them
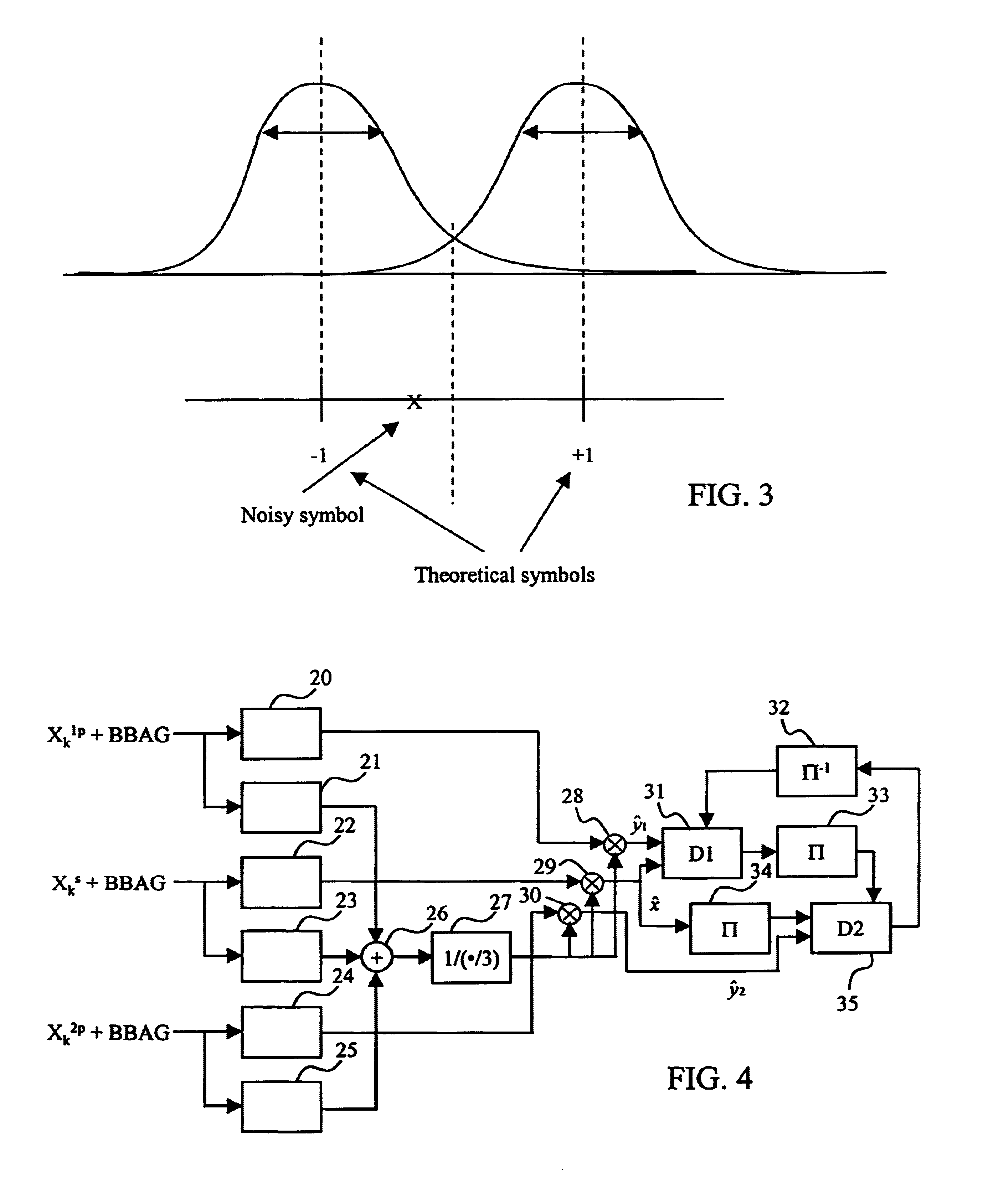
InactiveUS6898251B2Improve decoding performanceEasy to implementData representation error detection/correctionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesTurbo encoderNoise estimation
In order to evaluate the noise related to data issuing from a turbo-encoder, estimates of the noise related to its systematic output, to the data issuing from its first elementary encoder, and to the data issuing from its second elementary encoder are determined. At least two of the estimates of the noise related to the systematic output, to the data issuing from the first encoder, and to the data issuing from the second encoder, are added. The results of these additions are divided by the number of augends added, and then inverted, so as to obtain a noise factor, and the noise factor is multiplied with the data issuing from at least one of the first encoder, second encoder, and systematic output.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus of turbo encoder
InactiveUS7490282B2Data representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemReal-time data
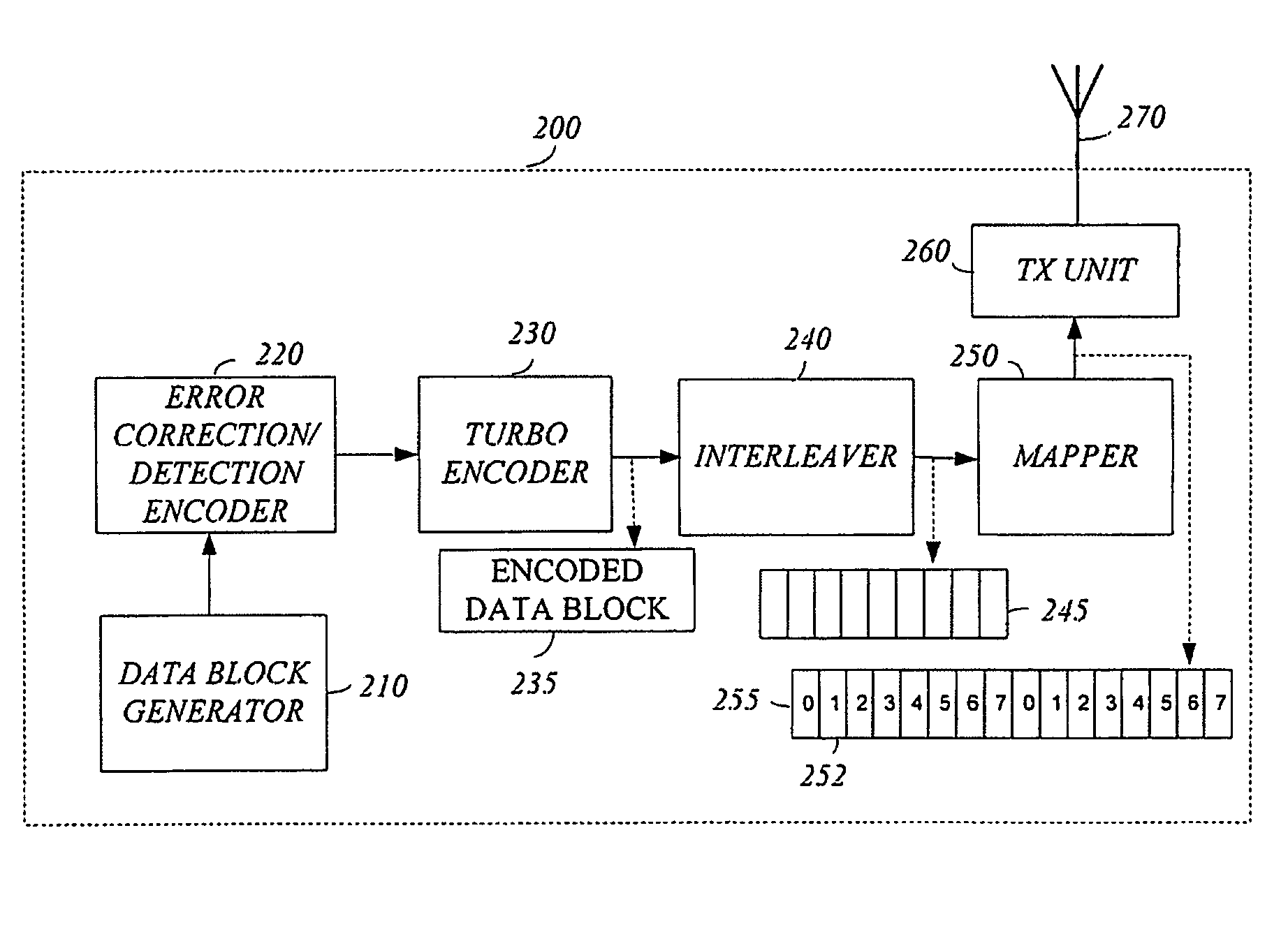
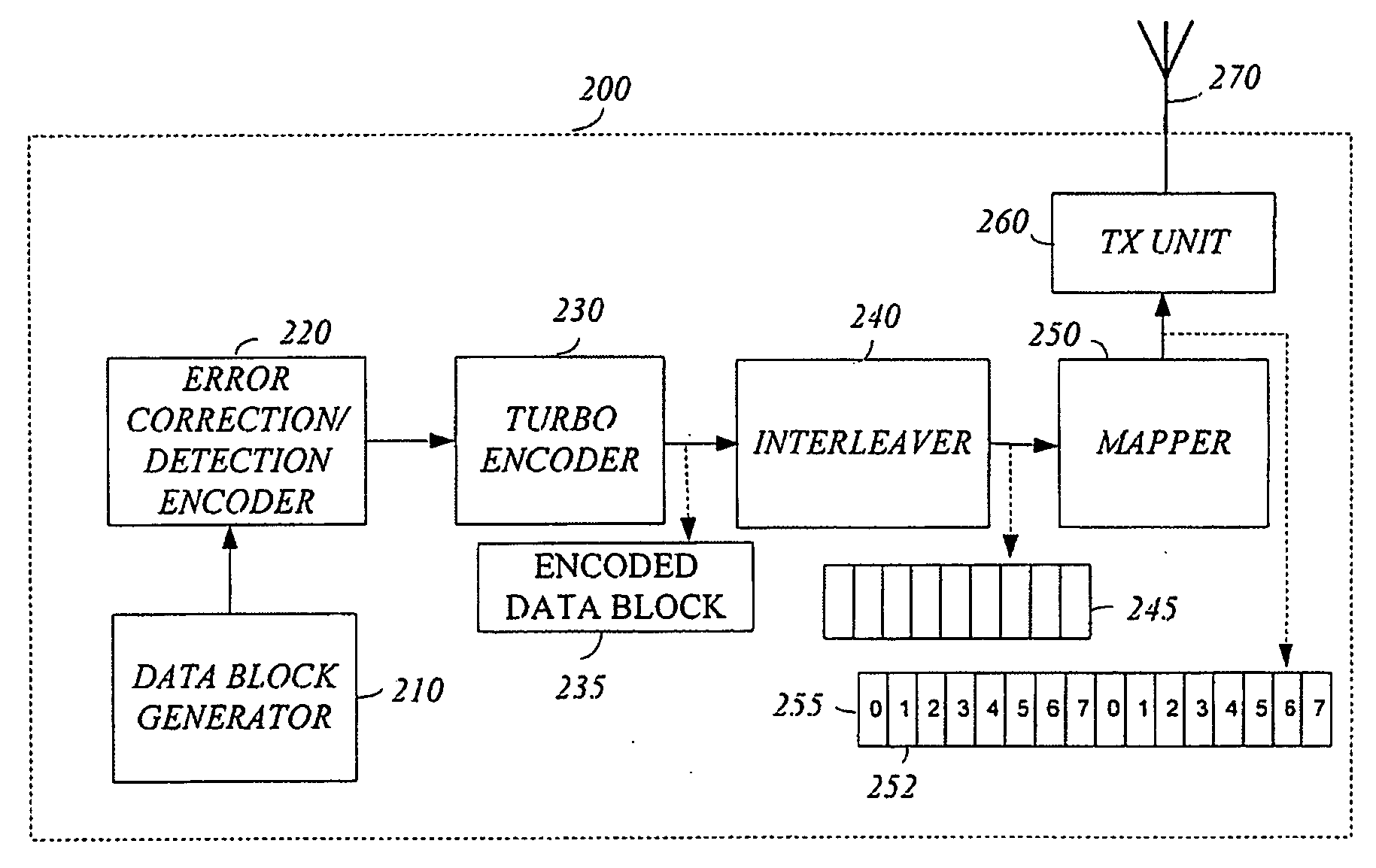
Briefly, an apparatus, a method and a wireless communication device are provided. The wireless communication device includes a turbo encoder to generate an encoded data block and a transmitter to transmit a data sub-block of the encoded data block in a time slot of a physical channel of the wireless communication system. The encoded data block includes real time data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Detection, avoidance and/or correction of problematic puncturing patterns in parity bit streams used when implementing turbo codes
ActiveUS7293217B2Data representation error detection/correctionUnequal/adaptive error protectionComputer architectureTurbo encoder
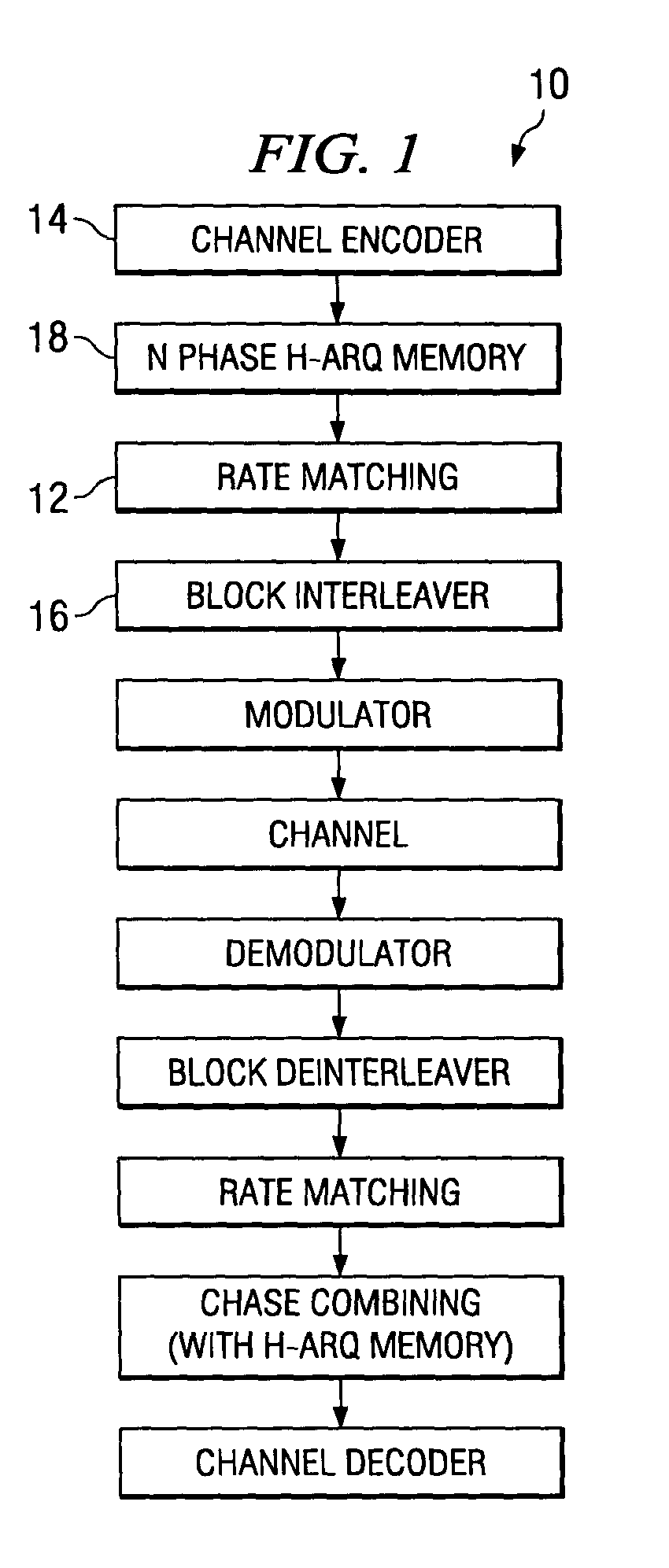
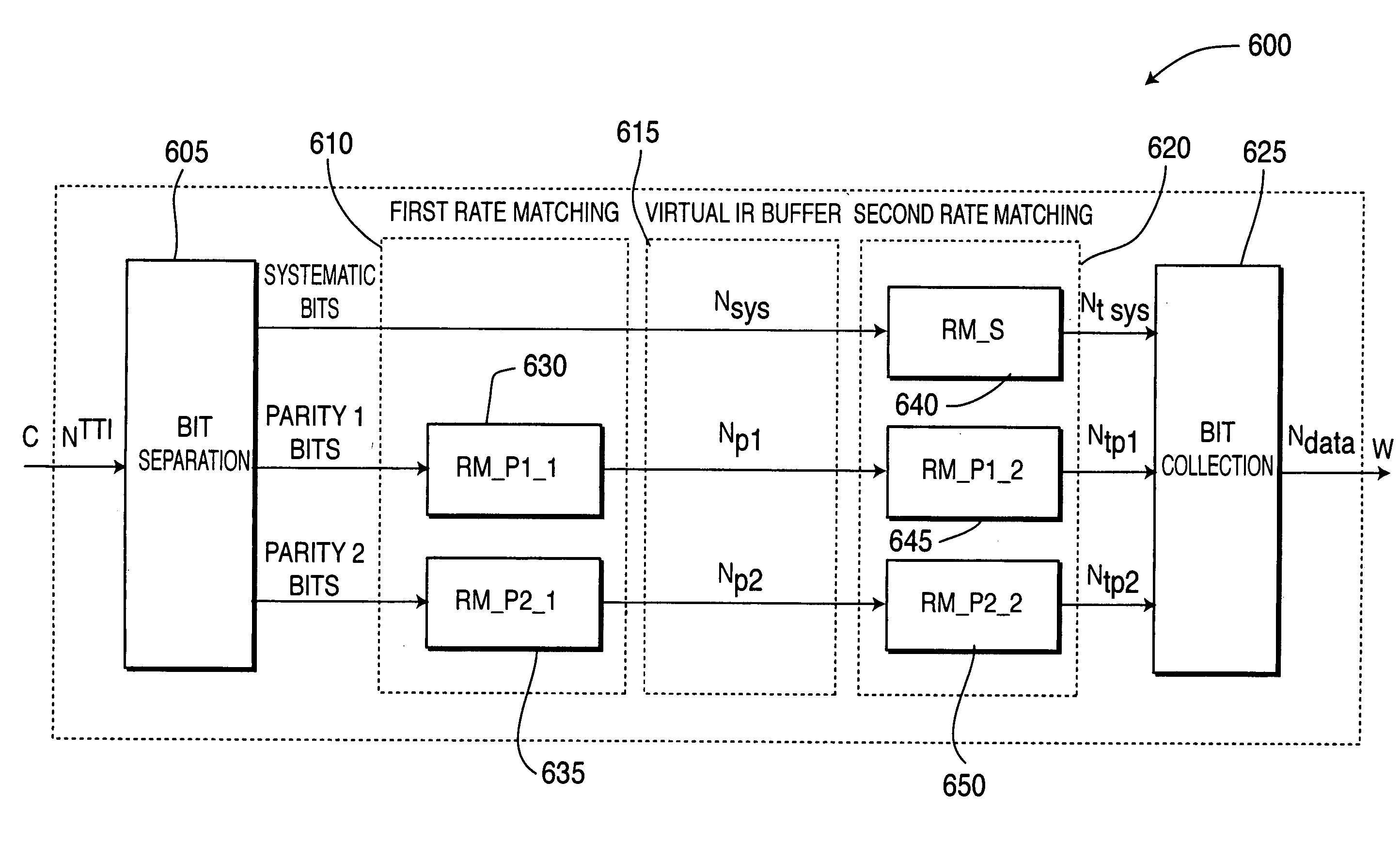
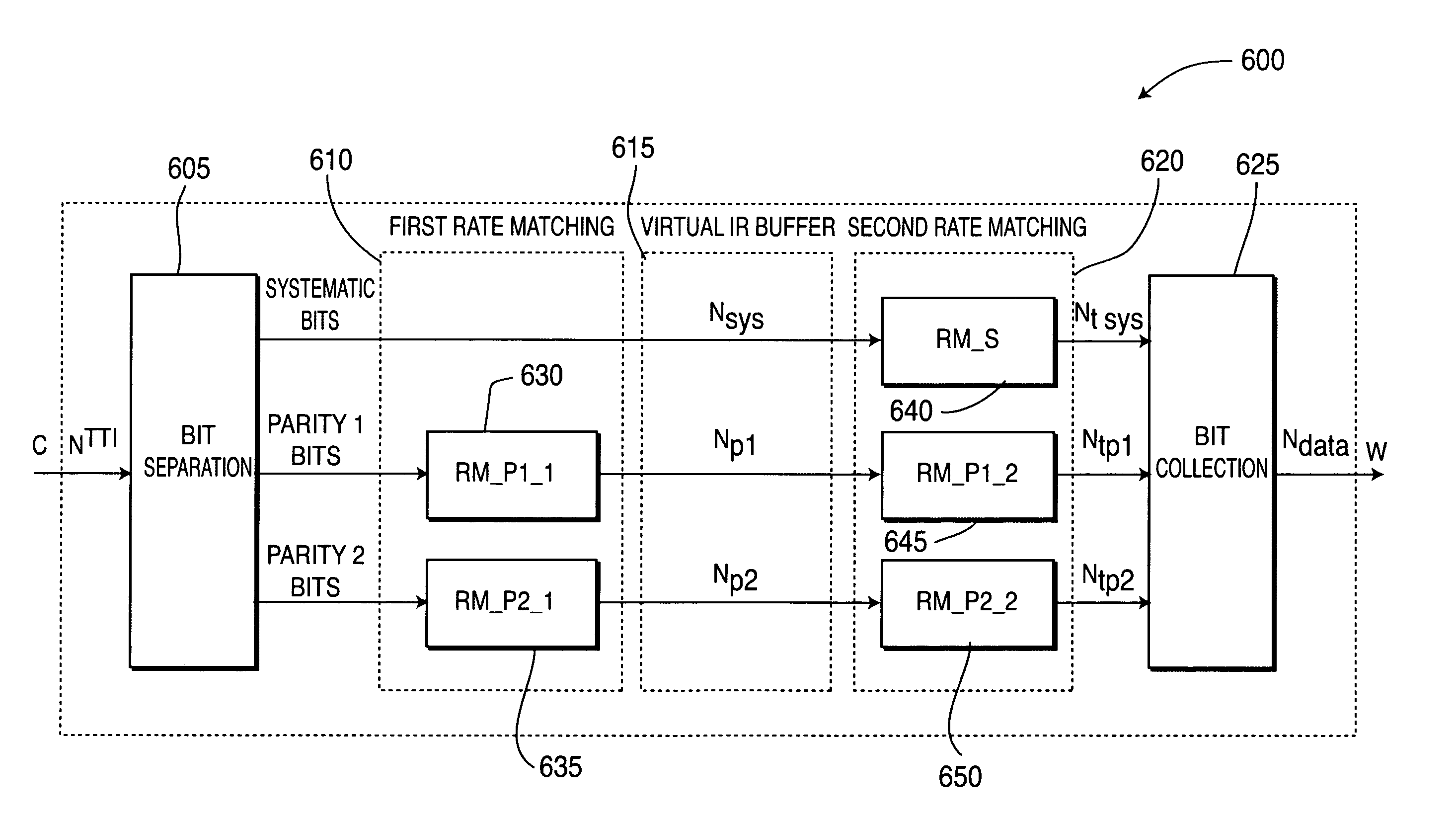
Detecting, avoiding and / or correcting problematic puncturing patterns in parity bit streams used when implementing punctured Turbo codes is achieved without having to avoid desirable code rates. This enables identification / avoidance of regions of relatively poor Turbo code performance. Forward error correction comprising Turbo coding and puncturing achieves a smooth functional relationship between any measure of performance and the effective coding rate resulting from combining the lower rate code generated by the Turbo encoder with puncturing of the parity bits. In one embodiment, methods to correct / avoid degradations due to Turbo coding are implemented by puncturing interactions when two or more stages of rate matching are employed.
Owner:PANTECH WIRELESS LLC
Flexible rate split method for MIMO transmission
InactiveUS7746800B2Wide diversityReduce error rateSpatial transmit diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsMimo transmissionTurbo encoder
A method for transmitting a packet of N input bits includes encoding all of the N bits as a single entity, such as with an interleaver of length N within a turbo coder, outputting M encoded bits, channel interleaving the M bits, splitting the M encoded bits into a parallel first and second portion, and transmitting them over separate channels to achieve spatial diversity. The size of the first and second portion is determined based on a closed feedback loop that provides some knowledge of the channel, preferably a measure of channel capacity. The feedback loop may also provide channel knowledge to a subpacket selector associated with each transmit antenna, which determines an appropriate rate for that channel and selects subpackets to fill a transmission packet for that channel. The subpacket selectors choose a subpacket of systematic bits and fill the remaining transmission packet size with subpackets of parity bits. Eigenvectors may be employed to transmit each transmission packet over more than one channel with a power disparity between the channels. A transmitter according to the present invention is also described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and apparatus of turbo encoder
InactiveUS20060095827A1Data representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemReal-time data
Briefly, an apparatus, a method and a wireless communication device are provided. The wireless communication device includes a turbo encoder to generate an encoded data block and a transmitter to transmit a data sub-block of the encoded data block in a time slot of a physical channel of the wireless communication system. The encoded data block includes real time data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Interleaving order generator, interleaver, turbo encoder, and turbo decoder
InactiveUS20050154954A1Increase in circuit scaleEasy to followError correction/detection using convolutional codesTransmission systemsData seriesHigh speed memory
In various multi-media services, an enormous memory capacity need not be prepared even when it is necessary to prepare a plenty of types of interleaving patterns. For example, when decoding reception data series of 2 Mbps or above with configuration such as 8-iteration, there is no need of preparing a high-speed memory capacity for temporarily storing the generated interleaving pattern. Furthermore, when the generated pattern needs to be transferred to an interleaving RAM in a turbo decoder actually performing processing, there is no need of preparing such a large amount of transfer data that the interface becomes a bottle neck. It is possible to provide an interleaving order generator, an interleaver, a turbo encoder, and a turbo decoder which can be realized by a minimum parameter transfer never promoting bottle neck on the Interface even when a variable rate function is provided and the interleave length changes frequently and solves the problem that the transfer rate in the multi-media service cannot be followed.
Owner:NEC CORP
Detection, avoidance and/or correction of problematic puncturing patterns in parity bit streams used when implementing turbo codes
ActiveUS20080046800A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesUnequal/adaptive error protectionTurbo encoderEngineering
Detecting, avoiding and / or correcting problematic puncturing patterns in parity bit streams used when implementing punctured Turbo codes is achieved without having to avoid desirable code rates. This enables identification / avoidance of regions of relatively poor Turbo code performance. Forward error correction comprising Turbo coding and puncturing achieves a smooth functional relationship between any measure of performance and the effective coding rate resulting from combining the lower rate code generated by the Turbo encoder with puncturing of the parity bits. In one embodiment, methods to correct / avoid degradations due to Turbo coding are implemented by puncturing interactions when two or more stages of rate matching are employed.
Owner:PANTECH WIRELESS LLC
Apparatus and method for generating codes in communication system
InactiveUS20020129314A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemTurbo encoder
A QCTC (Quasi-Complementary Turbo Code) generating apparatus having: a turbo encoder for generating an information symbol sequence and a plurality of parity symbol sequences by encoding the information symbol sequence; a channel interleaver for individually interleaving the symbol sequences, generating new parity symbol sequences by multiplexing the symbols of parity symbol sequences with the same priority levels, and serially concatenating the information symbol sequence and the new parity symbol sequences; and a QCTC generator for generating a sub-code with a given code rate by recursively selecting a predetermined number of symbols from the concatenated symbol sequence at a given starting position.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
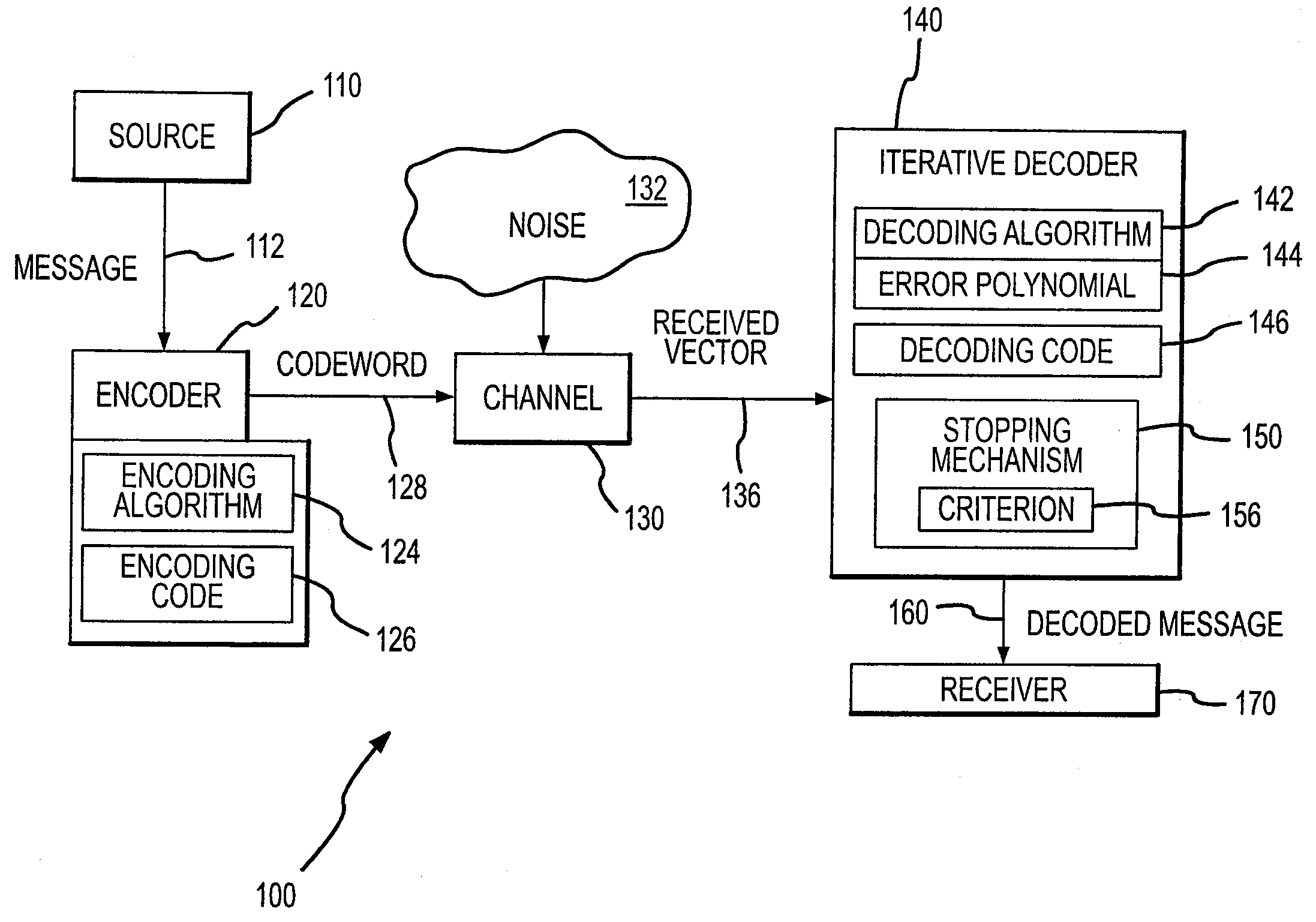
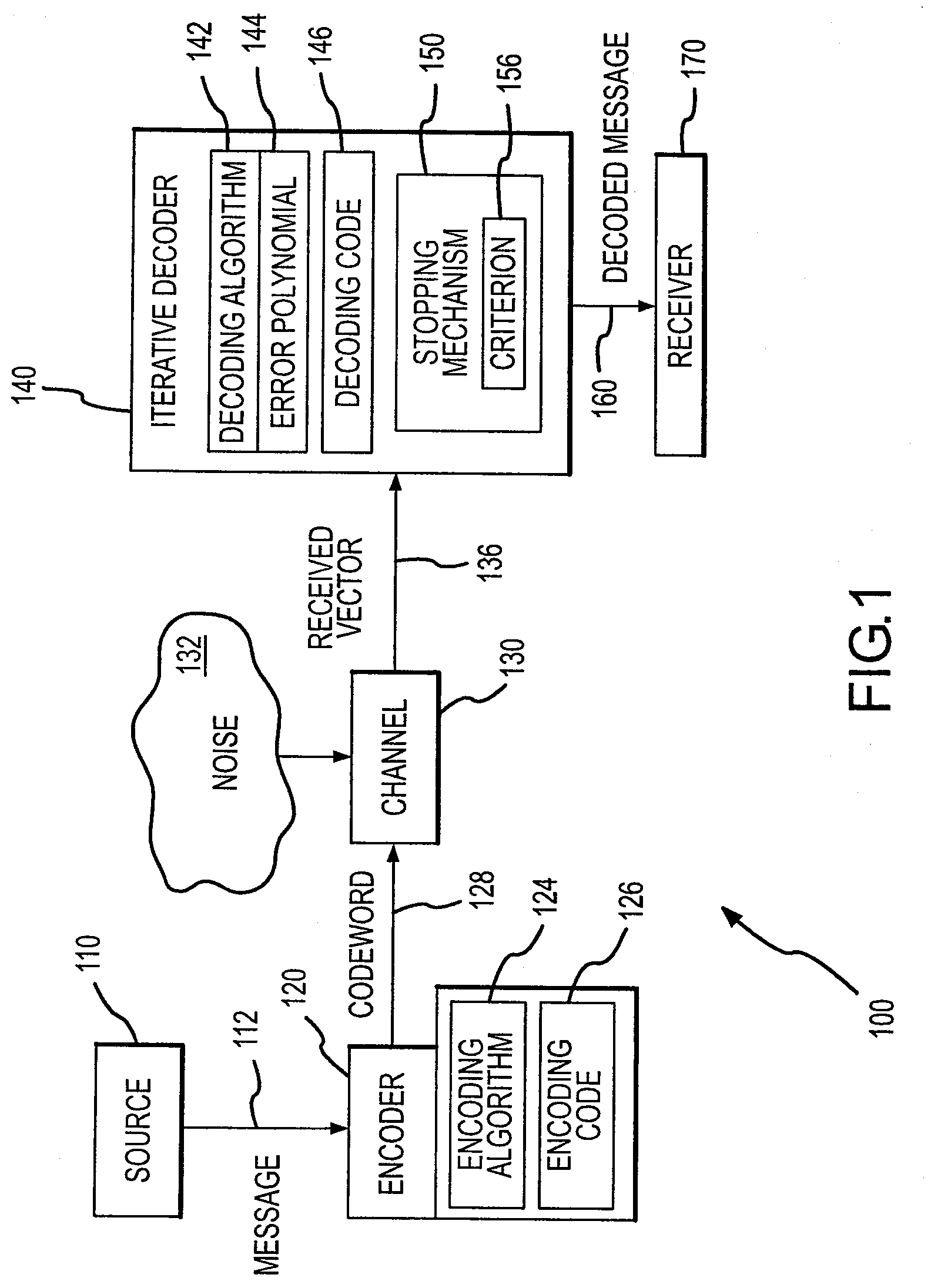
Iterative decoder with stopping criterion generated from error location polynomial
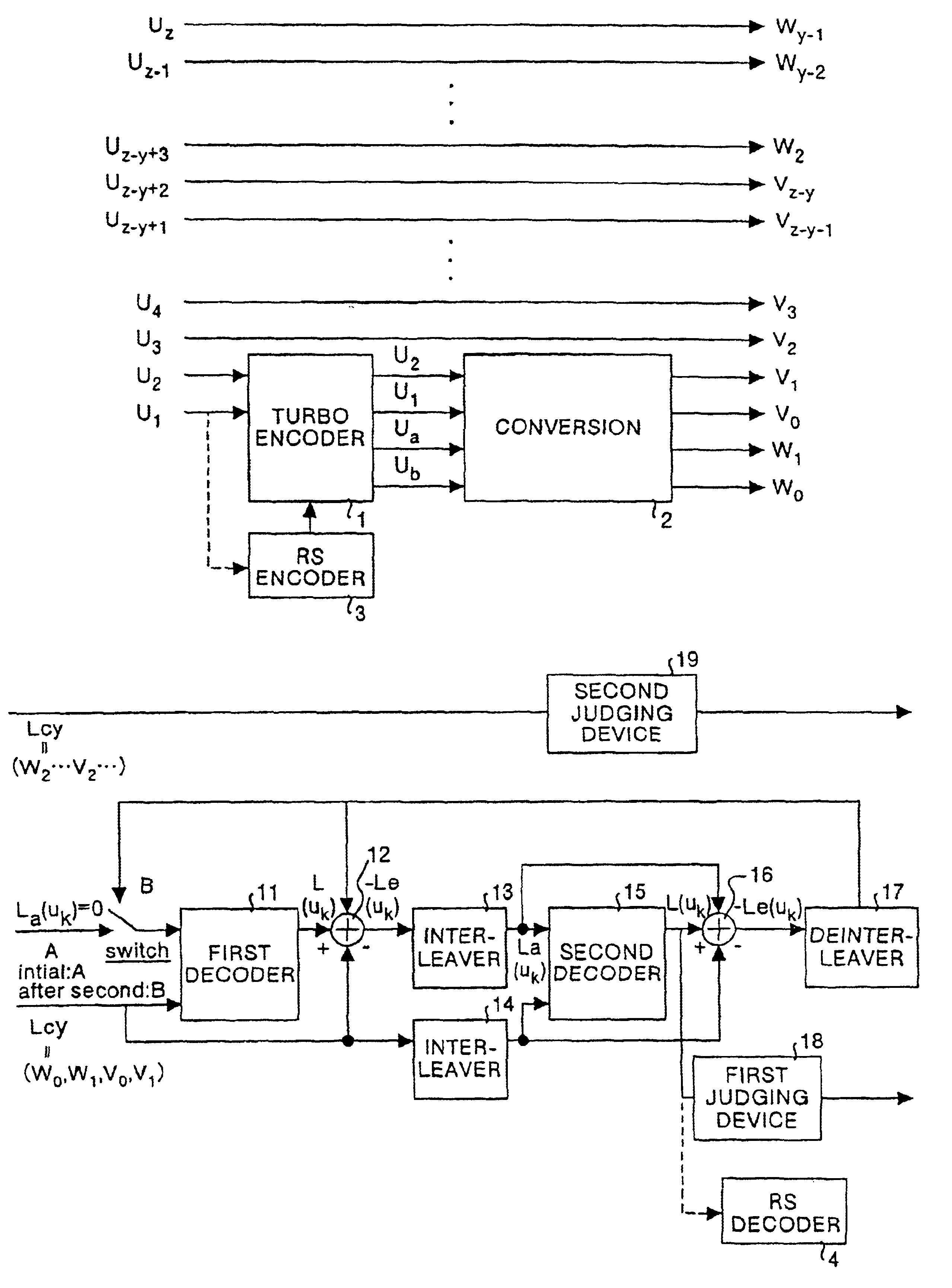
InactiveUS7904795B2Reduce in quantityEnhanced stopping criterionData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer hardwareTurbo encoder
A decoder for error correction an encoded message, such as one encoded by a turbo encoder, with reduced iterations due to an improved stopping criterion. The decoder includes an error correction loop that iteratively processes a message that is encoded prior to transmittal over a communication channel. The error correction loop generates, such as with a Reed-Solomon decoder, an error location polynomial in each iterative process. A stopping mechanism in the decoder allows an additional iteration of the message decoding based on the error location polynomial, such as by obtaining the degree of the error location polynomial and comparing it to a threshold. In one example, the threshold is the maximum number of symbol errors correctable by the Reed-Solomon code embodied in the decoder. The stopping mechanism allows additional iterations when the stopping criterion (or polynomial degree) is greater than the maximum number of symbol errors correctable by the Reed-Solomon code.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Interleaving order generator, interleaver, turbo encoder, and turbo decoder
InactiveUS7210076B2Improve scaleEasy to followError correction/detection using convolutional codesTransmission systemsTurbo encoderData rate
Owner:NEC CORP
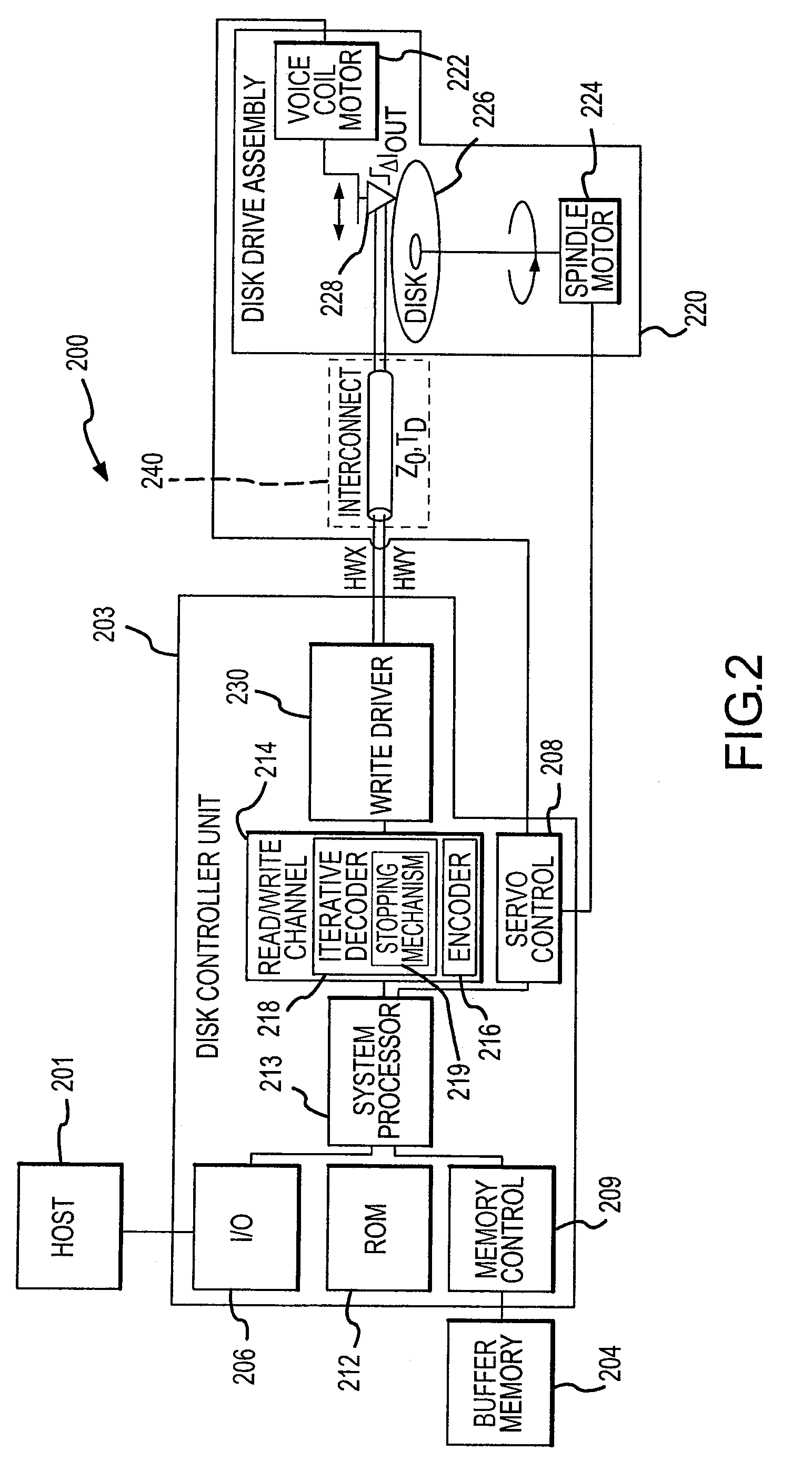
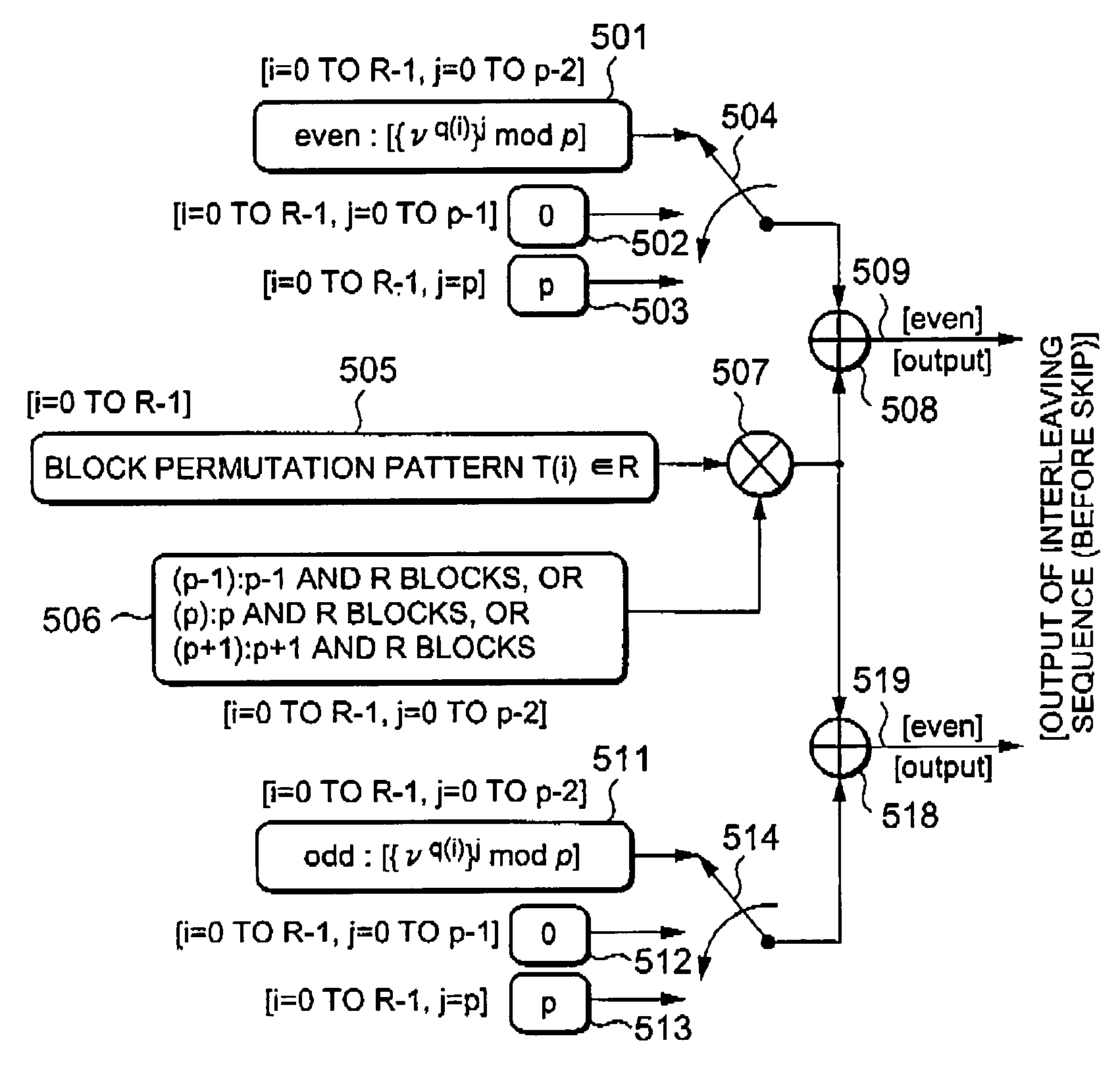
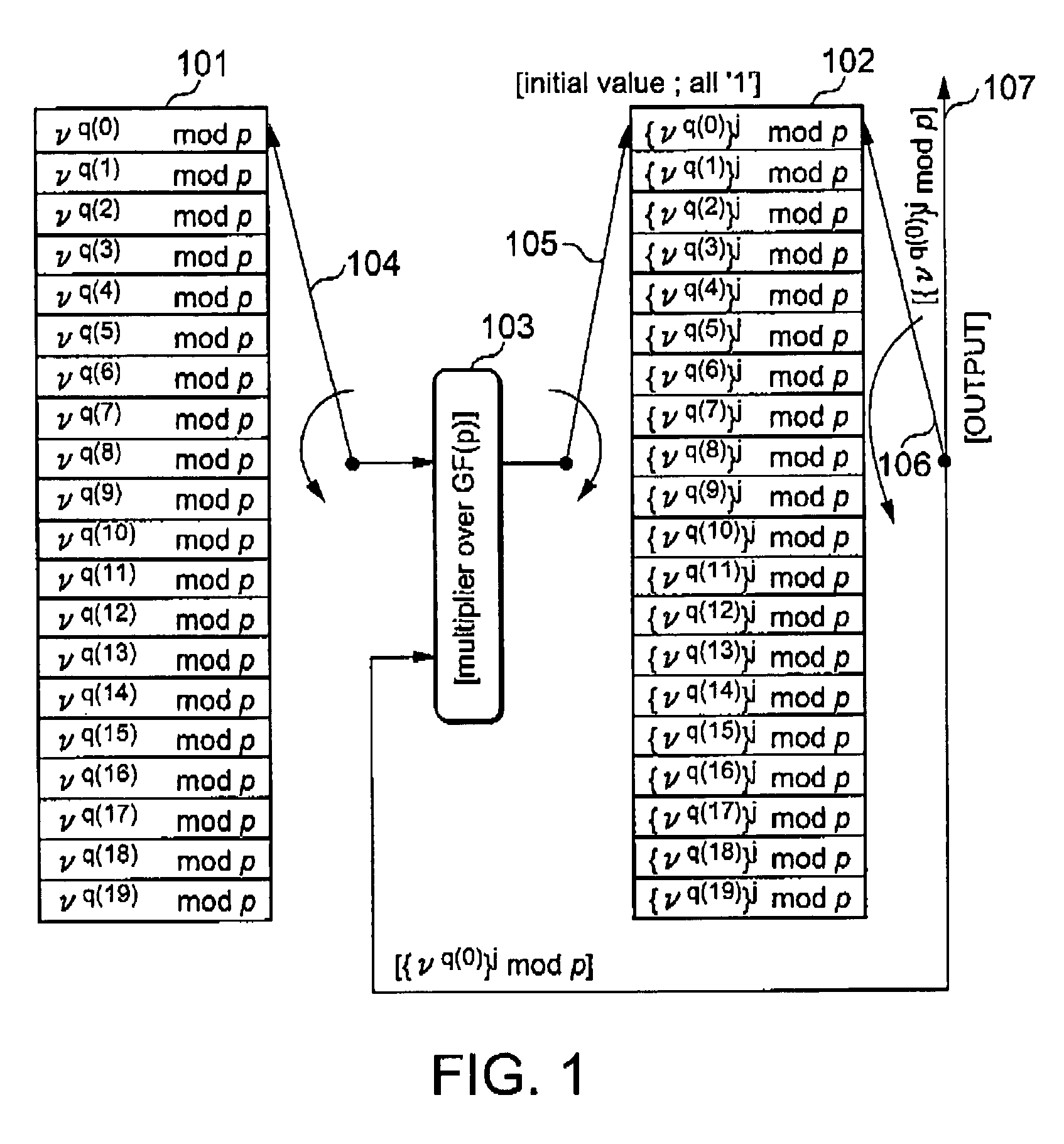
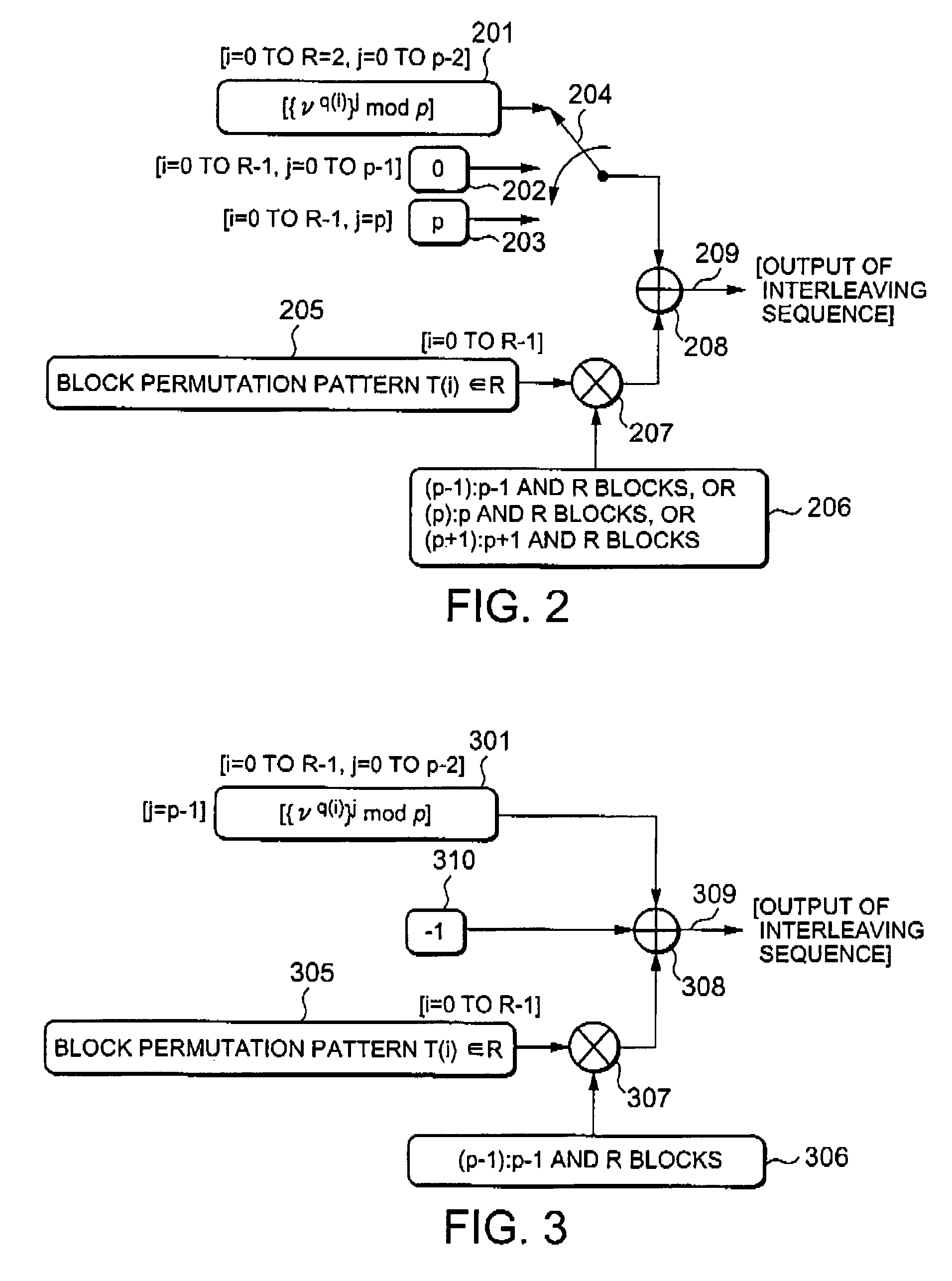
Addresses generation for interleavers in turbo encoders and decoders
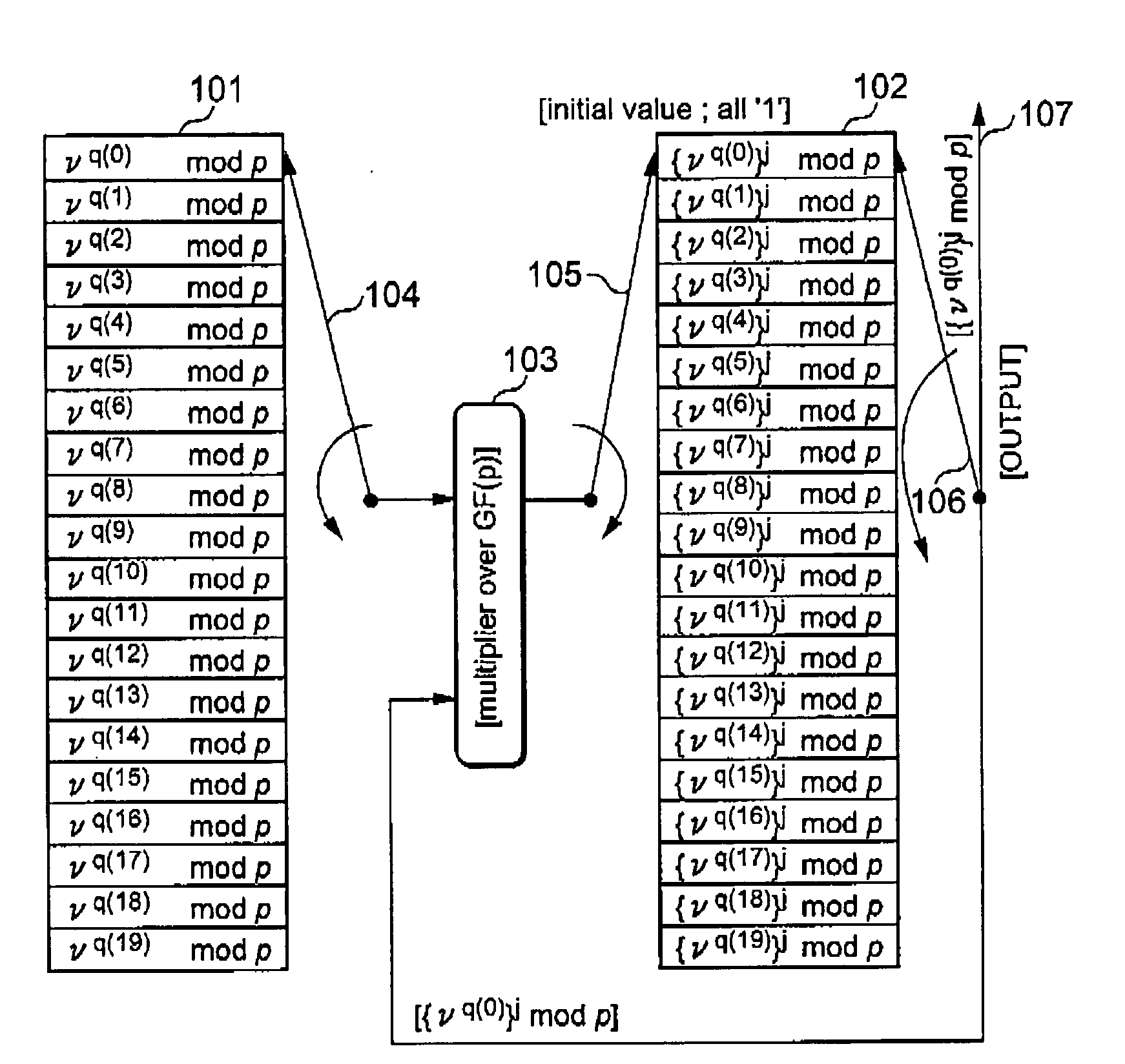
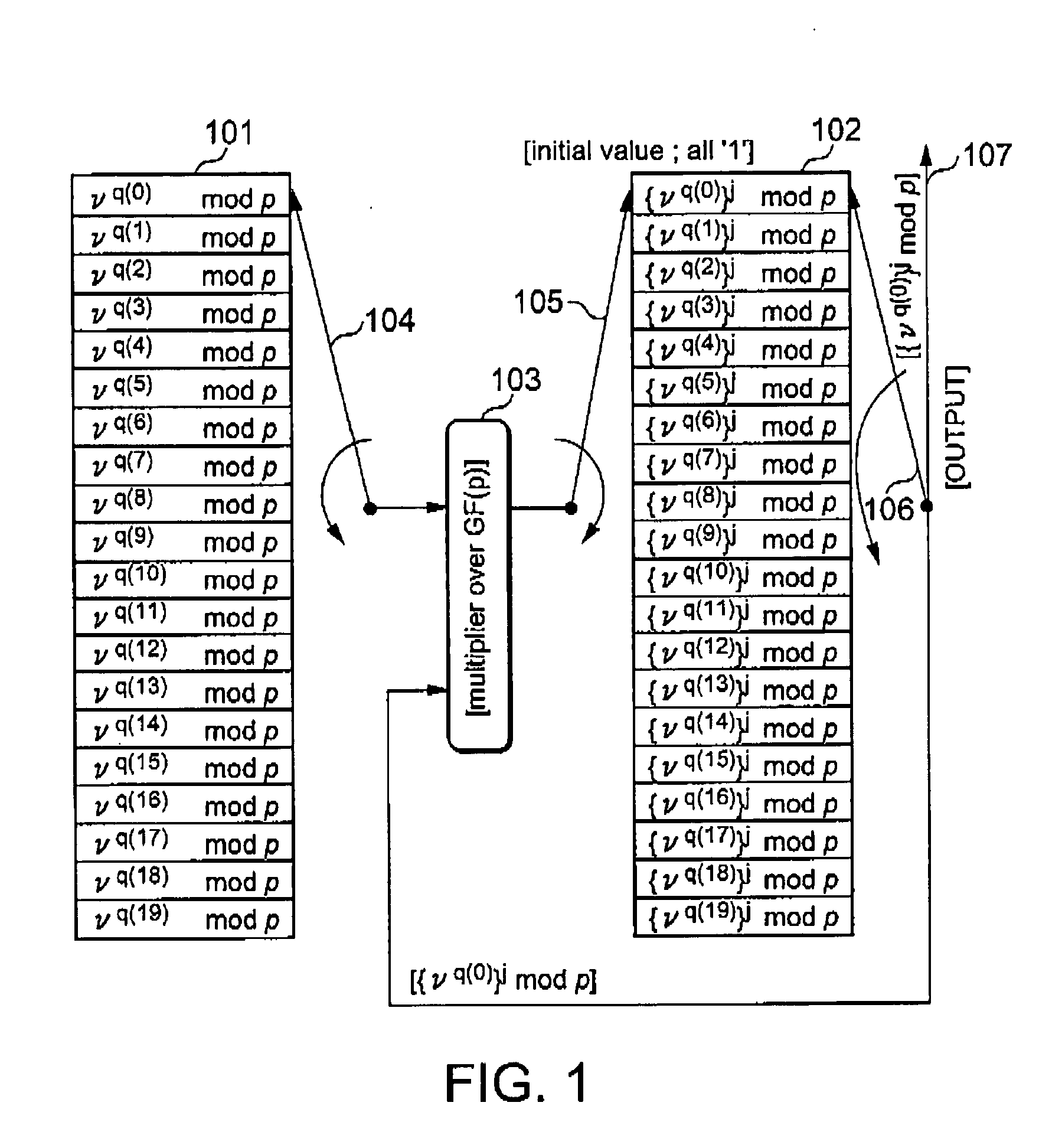
InactiveUS7170432B2Adapt quicklyAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsInterleave sequenceTurbo encoder
An arrangement for generating addresses for interleaving / de-interleaving sequences (X1, X2, X3, . . . , XK) including a given number (K) of items, wherein each value for said given number (K) identifies a corresponding set of interleaving parameters (R, C, p, v). The arrangement has at least one memory unit wherein a plurality of records are stored, each record being indicative of a respective set of parameters (R, C, p, v) corresponding to at least one value for said given number (K). Sets of interleaving parameters (R, C, p, v) are thus available in the memory unit to be promptly and directly retrieved for all possible values of said given number of items (K). A preferred use is in turbo encoders / decoders for advanced telecommunications applications such as UMTS.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com