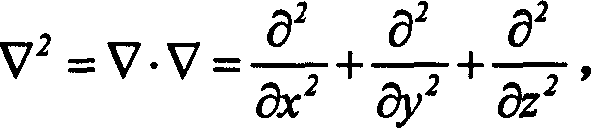Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87 results about "Traffic balancing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
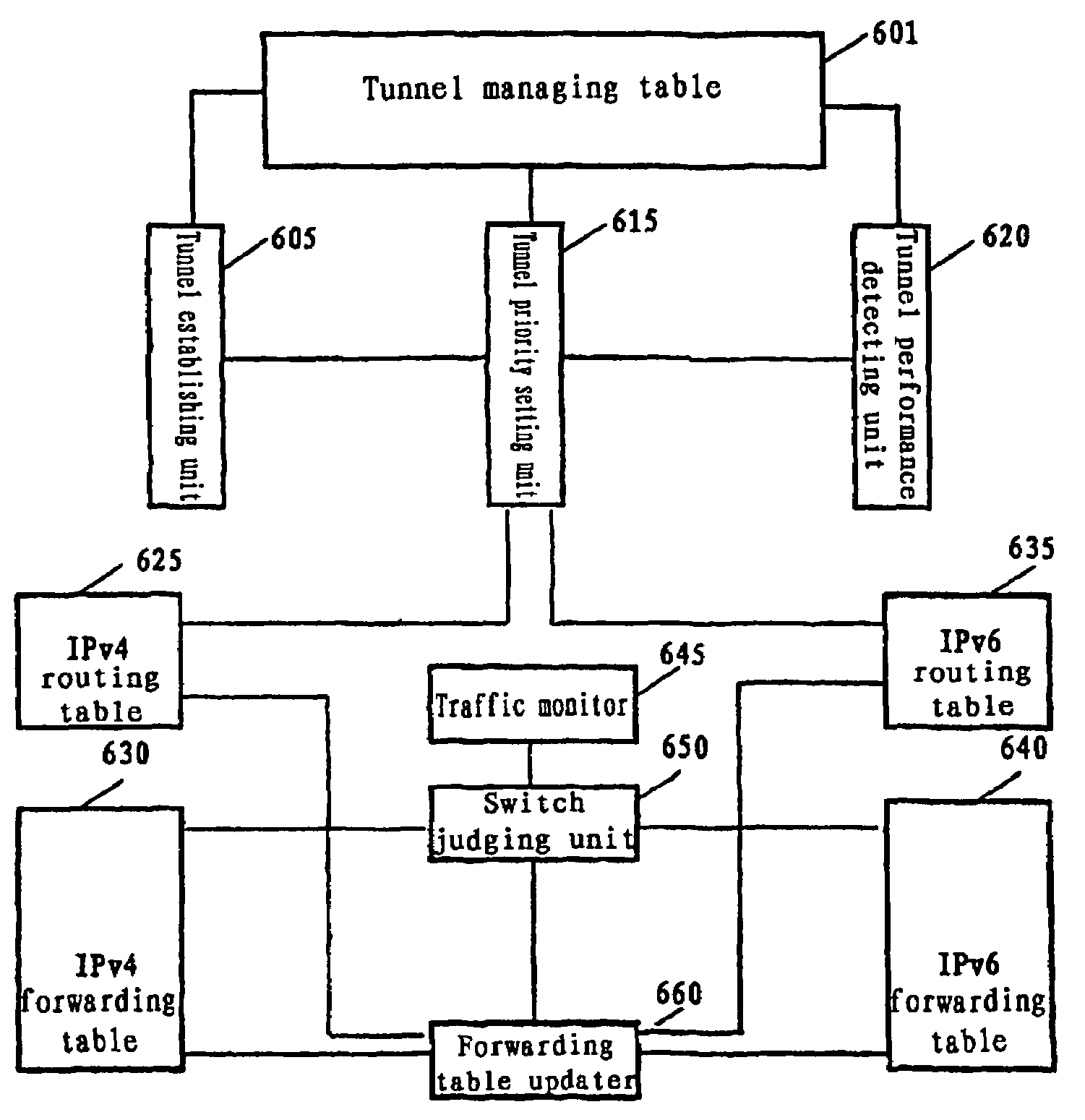
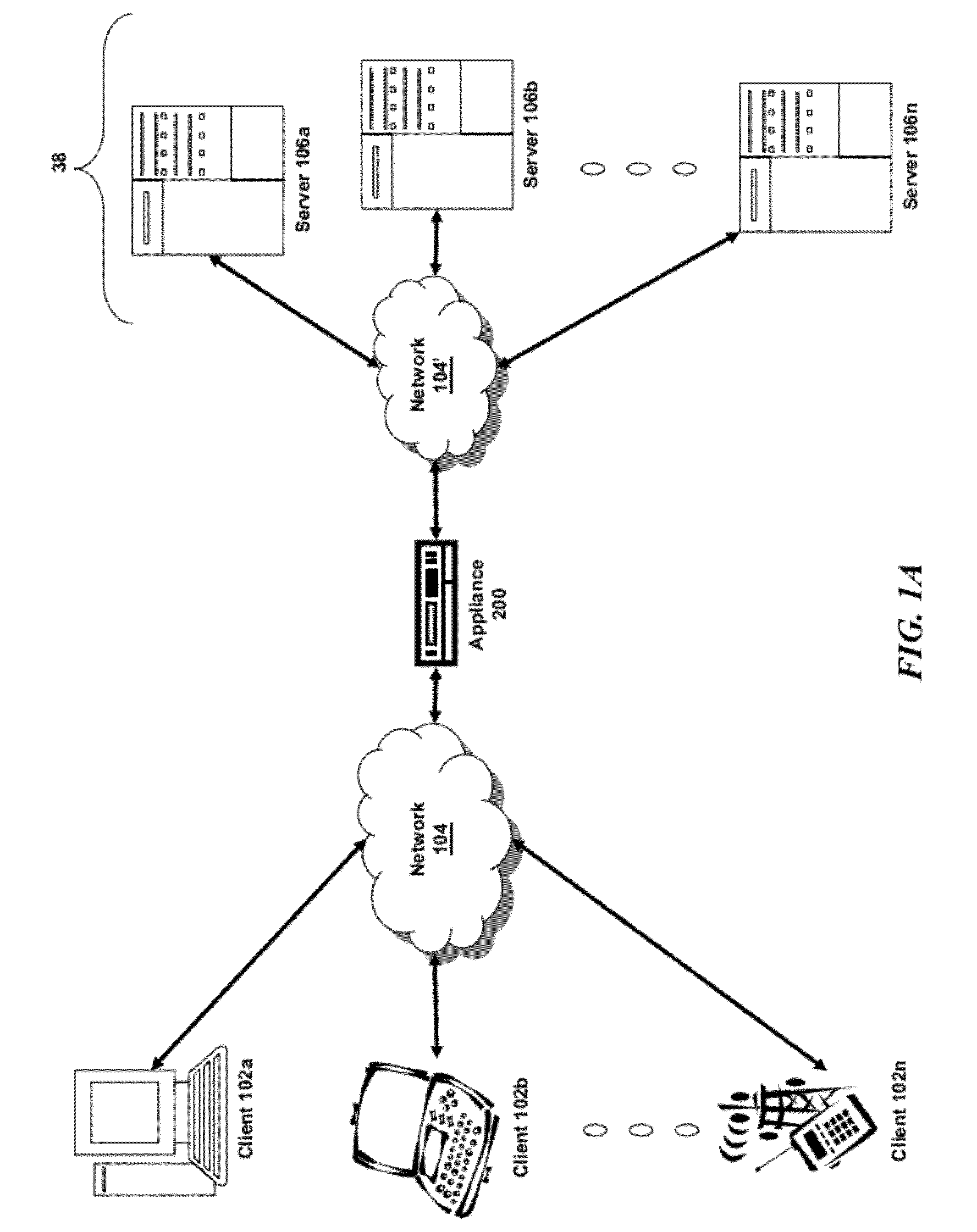
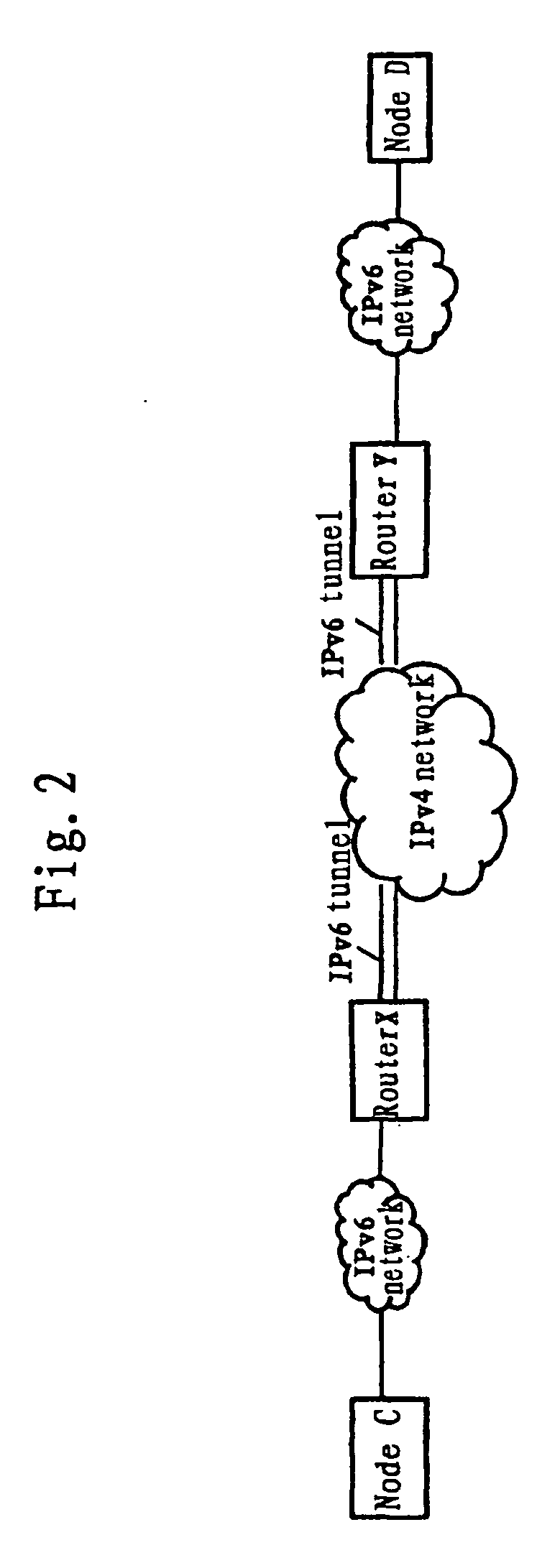
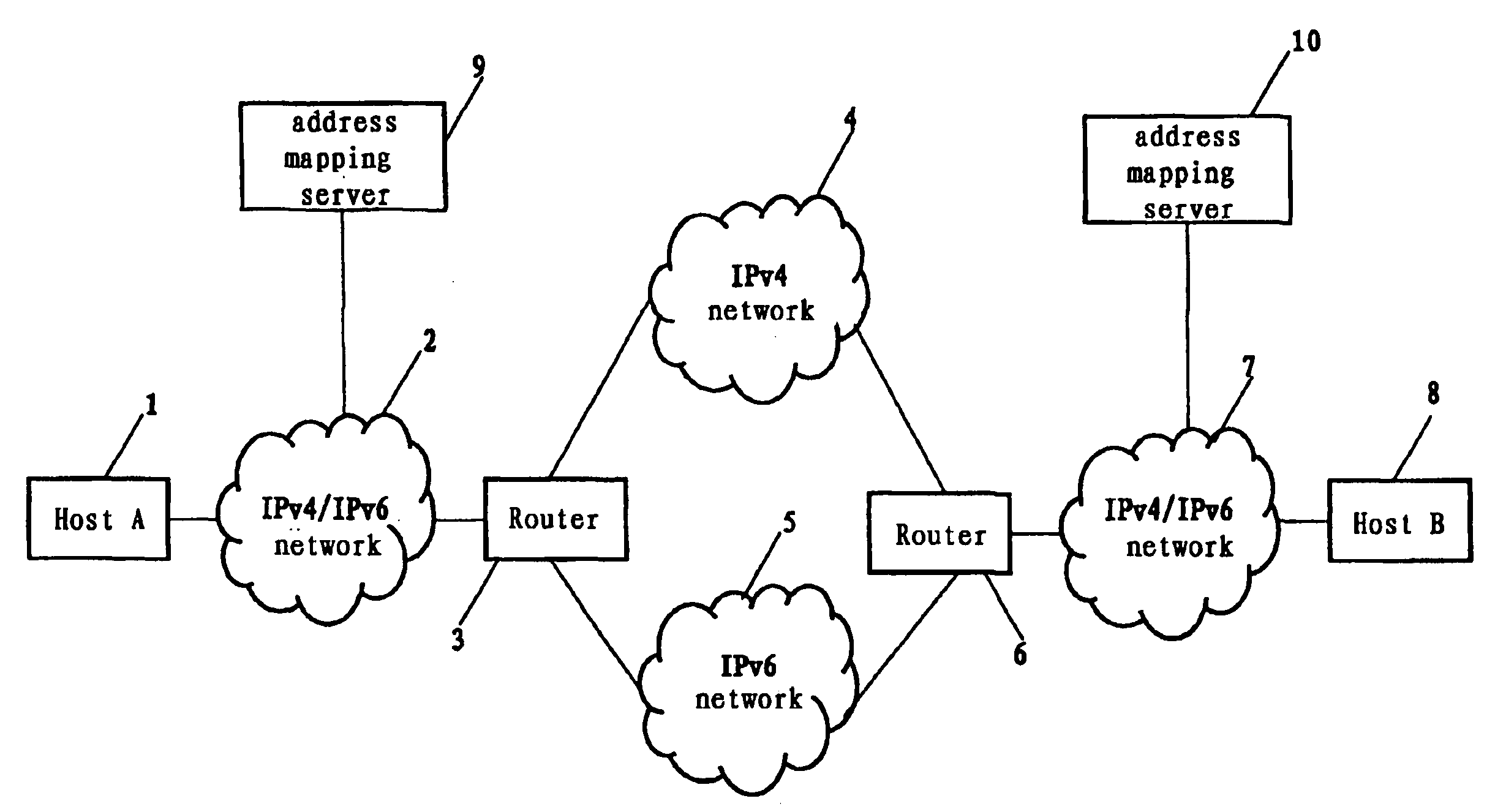
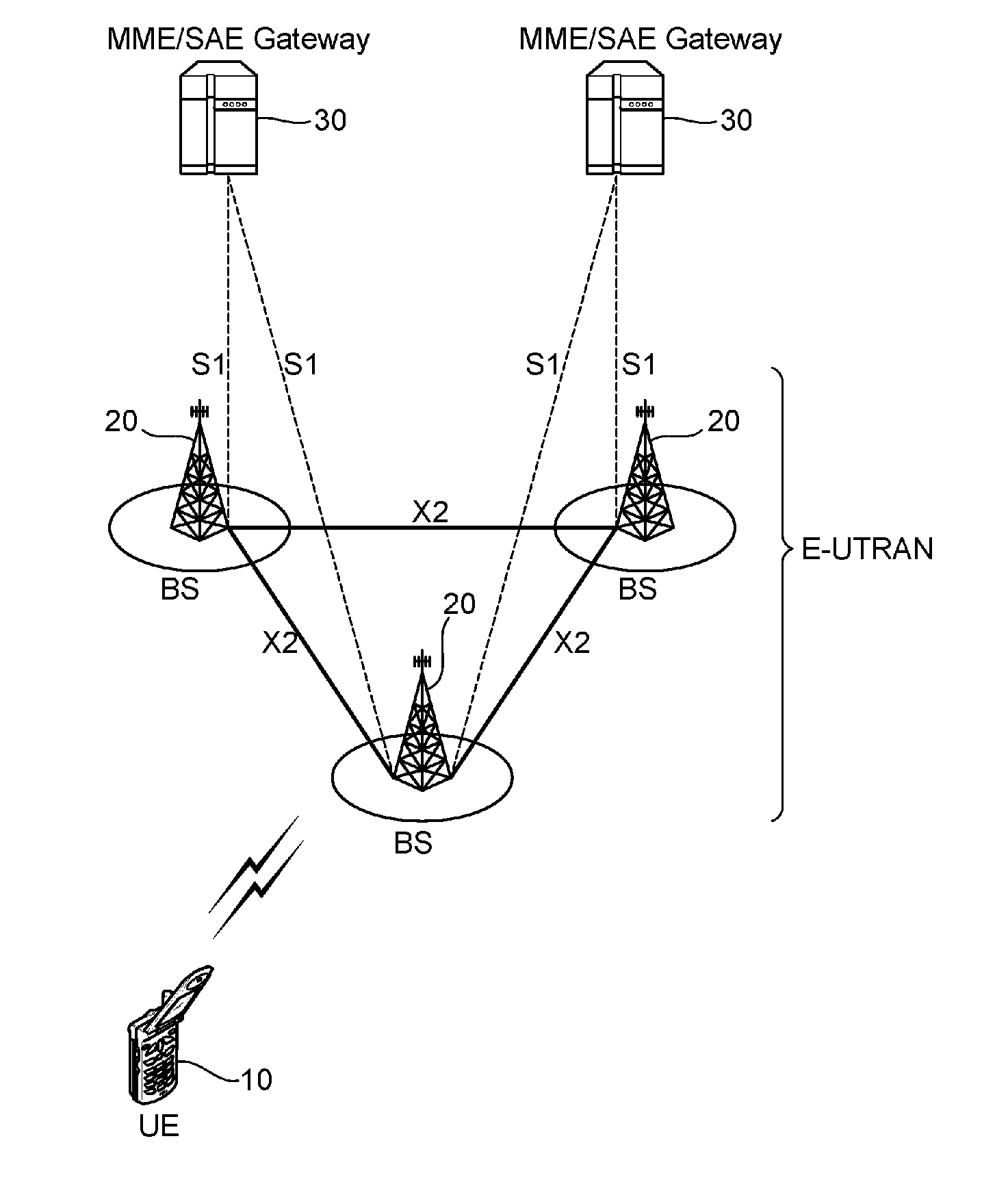
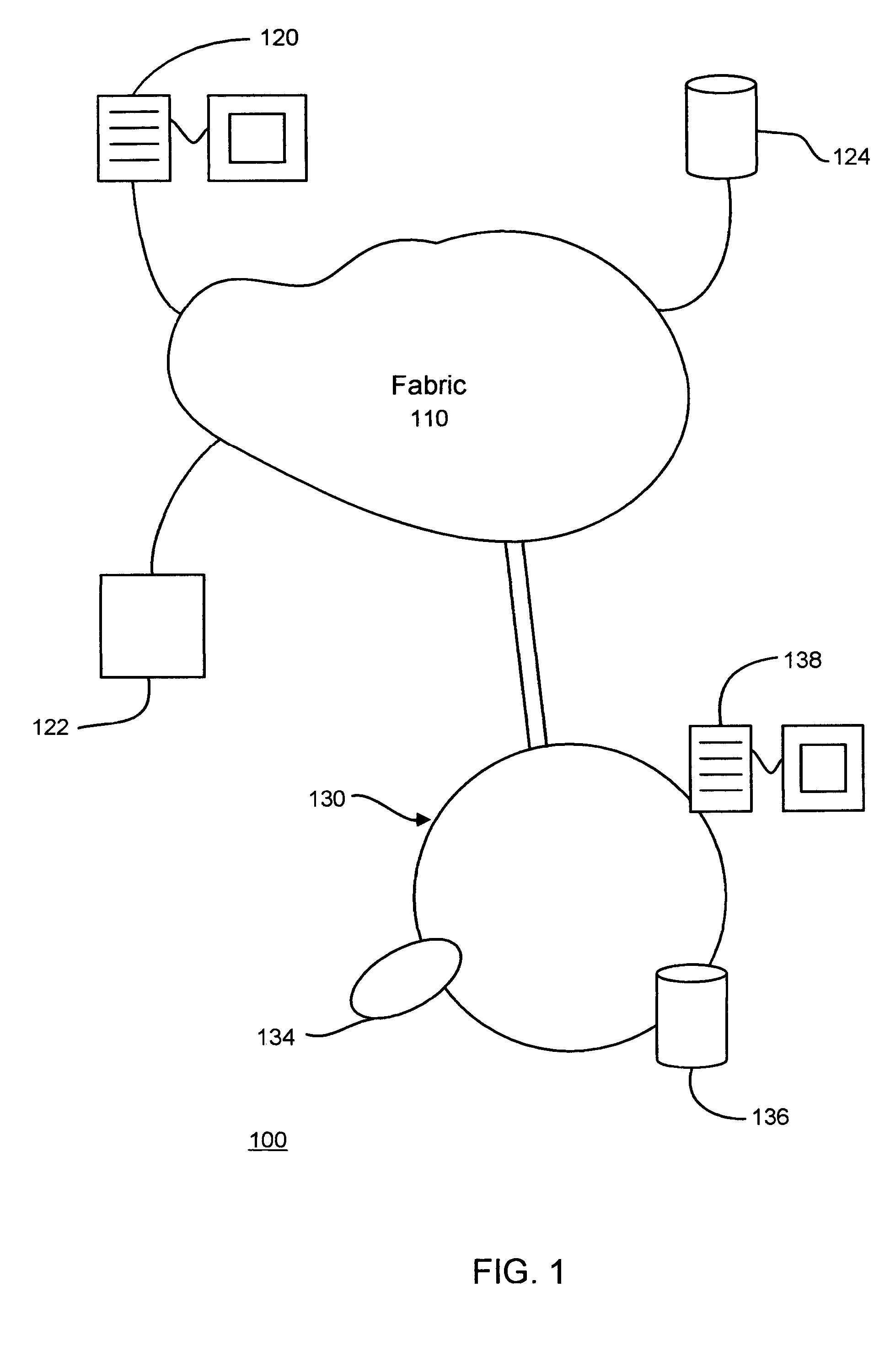
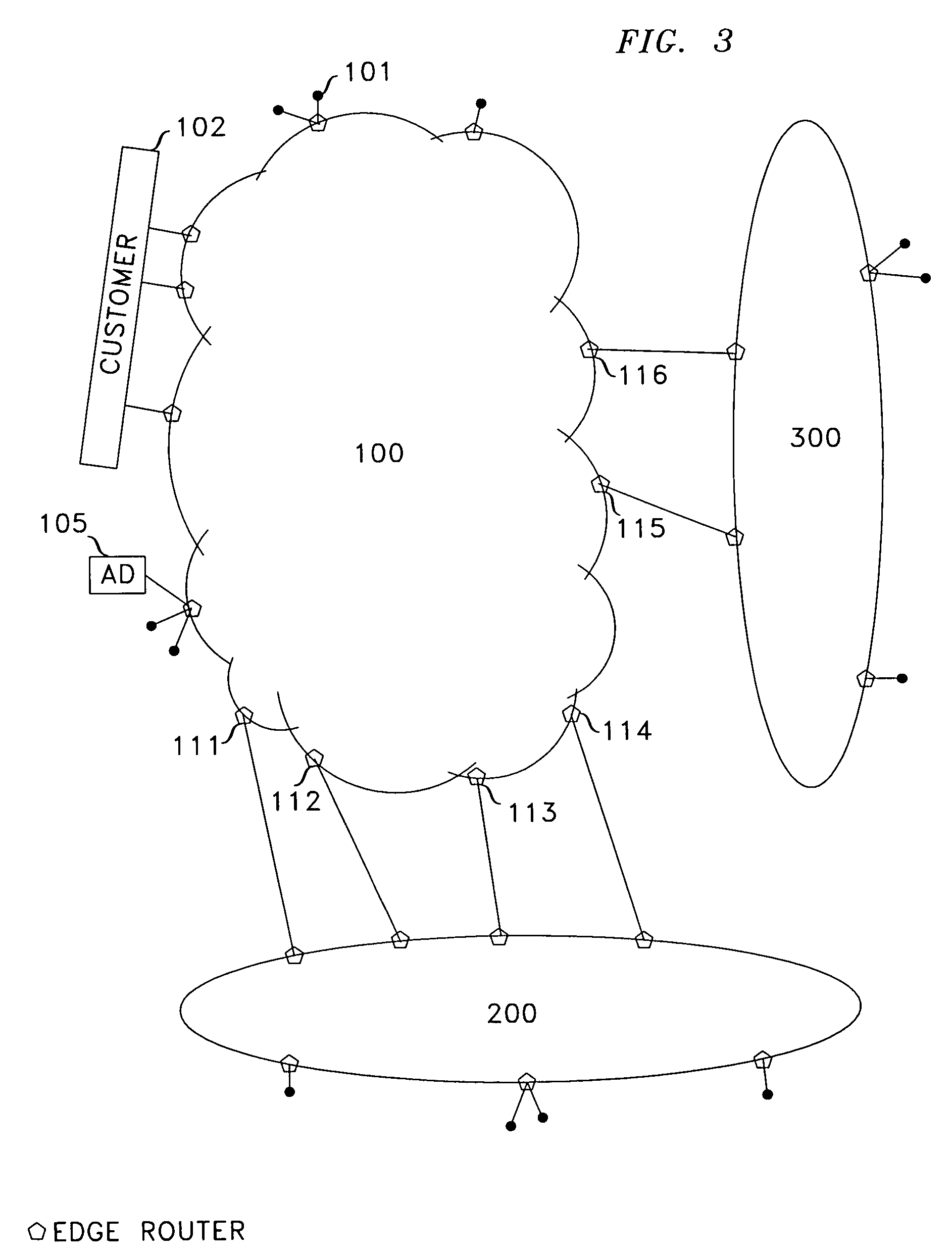
Network system, traffic balancing method, network monitoring device and host
ActiveUS8194553B2Traffic balance in the networksControl balanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityIp address
A traffic balancing system, traffic balancing device and traffic balancing method that converts IP packets by switching IP address of the destination host between the dual stack hosts communicating with each other, in order to control traffic balancing in the networks.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Skypoint for mobile hotspots
A system and method for dynamically planning a network is presented. One method may begin by determining network parameters for connecting nodes to a network and decision variables associated with radios and / or nodes in the network. Constraints may be established to narrow possible values of the network parameters and / or the decision variables. The constraints may be based on one or more of: values associated with connecting a radio to a node in the network, values associated with connecting two nodes in the network together over a communication link, whether a node can connect to a GIG node and a flow balance in the GIG node. To find possible links in the network that are optimal, the method may minimize an equation based on the network parameters, constraints and decision variables to determine optimal communication links between pairs of nodes in the network, pairs of nodes and radios and / or pairs of radios.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Traffic balancing apparatus and method, and network forwarding apparatus and method using the same
InactiveUS7492708B2Reduce the burden onBalance of the loads of different networks can be maintainedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityResource utilization
The present invention reduces the burden of the network having heavier load, maintains the load balance among different networks, and improves the overall resource utilization efficiency and transmission qualities of the networks, by providing a network forwarding apparatus for selectively distributing the IP packets to be forwarded to the network having less traffic for transmission by monitoring in real-time the traffic in the different networks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Decentralized industrial process simulation system
ActiveUS20110131017A1Accurately solves massAccurately flow balanceProgramme controlAnalogue computers for control systemsMass storageParallel computing
A high fidelity distributed plant simulation technique includes a plurality of separate simulation modules that may be stored and executed separately in different drops or computing devices. The simulation modules communicate directly with one another to perform accurate simulation of a plant, without requiring a centralized coordinator to coordinate the operation of the simulation system. In particular, numerous simulation modules are created, with each simulation module including a model of an associated plant element and these simulation modules are stored in different drops of a computer network to perform distributed simulation of a plant or a portion of a plant. At least some of the simulation modules, when executing, perform mass flow balances taking into account process variables associated with adjacent simulation modules to thereby assure pressure, temperature and flow balancing (i.e., conservation of mass flow) through the entire simulation system. In a dynamic situation, a transient mass storage relay technique is used to account for transient changes in mass flow through any non-storage devices being simulated by the simulation modules. Moreover, adjacent simulation modules located in different drops communicate directly with one another using a background processing task, which simplifies communications between adjacent simulation modules without the need for a central coordinator.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
Oil pipeline network leakage intelligent self-adaptation monitoring system and method based on big data
InactiveCN103939749ASimple methodHigh sensitivityFluid-tightness measurementPipeline systemsTraffic capacityMonitoring system
The invention provides an oil pipeline network leakage intelligent self-adaptation monitoring system and method based on big data, and belongs to the technical field of pipeline network internal detection methods. By means of the system and method, a large number of data collected on site can be effectively analyzed in reasonable time, the state of a pipeline network can be obtained by means of an intelligent self-adaptation method, and accordingly a topological structure of the pipeline network is obtained. By means of a flow balance method and with the combination of an information consistency theory, whether the pipeline network leaks is analyzed, and the method is visual, simple, high in sensitivity and low in false alarm rate. Besides, precise warning is well carried out on detection of small leakage amount and slow leakage. By means of a generalized regression neural network, leakage positioning of the pipeline network is carried out, and accuracy of a result is improved. Accordingly, leakage detection and positioning problems of the pipeline network are solved by means of strategies based on the big data and the intelligent self-adaptation method, and meanwhile the aims of high precision and high accuracy can be achieved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
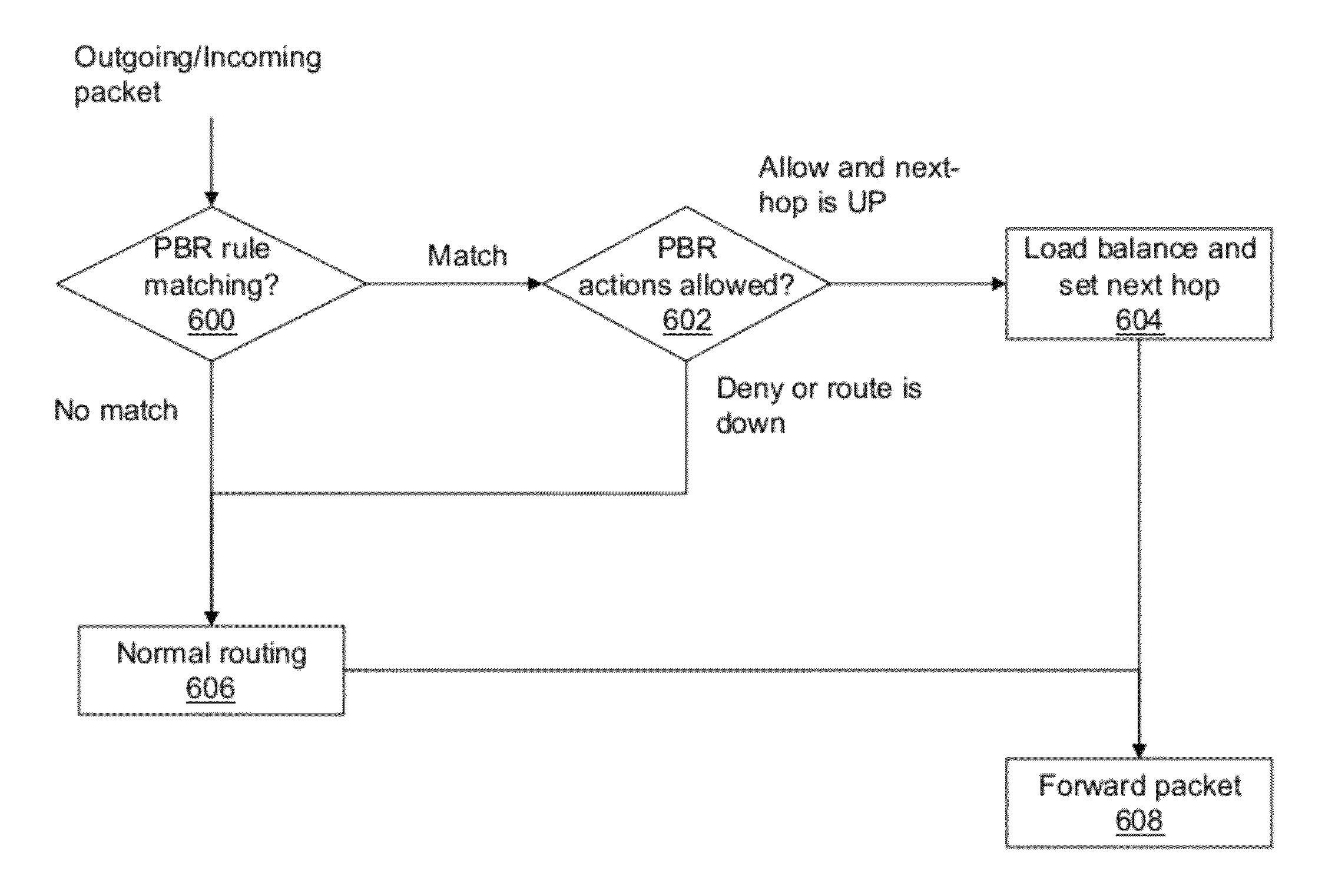
Systems and Methods for Policy Based Routing for Multiple Hops
ActiveUS20120163180A1Provide reliabilityBalance traffic loadError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic characteristicIp address
The present application is directed towards policy based routing for intelligent traffic management via multiple next hops. In some embodiments, the systems and methods disclosed herein may provide management of inbound and outbound traffic across multiple network links, and may further provide reliability in case of link failure, and provide balancing of traffic, responsive to the latency and bandwidth requirements of various applications. Accordingly, these systems and methods may provide intelligent policy-based routing and network and port address translation, sensitive to application traffic types, protocols, source IP addresses and ports, destination IP addresses and ports, or any combination thereof, and can balance traffic loads among multiple available paths based on multiple traffic characteristics. The routing may performed on a packet-by-packet basis, a transaction-by-transaction basis, or a session-by-session basis, and the systems and methods may include capabilities for application-aware health monitoring of available network paths.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method of performing cell reselection in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20110053597A1Improve service satisfactionSatisfaction level can be enhancedWireless communicationTraffic volumeTraffic balancing
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Traffic balancing apparatus and method, and network forwarding apparatus and method using the same
InactiveUS20060233175A1Reduce the burden onBalance of load of differentError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsResource utilizationTraffic balancing
The present invention reduces the burden of the network having heavier load, maintains the load balance among different networks, and improves the overall resource utilization efficiency and transmission qualities of the networks, by providing a network forwarding apparatus for selectively distributing the IP packets to be forwarded to the network having less traffic for transmission by monitoring in real-time the traffic in the different networks.
Owner:IBM CORP
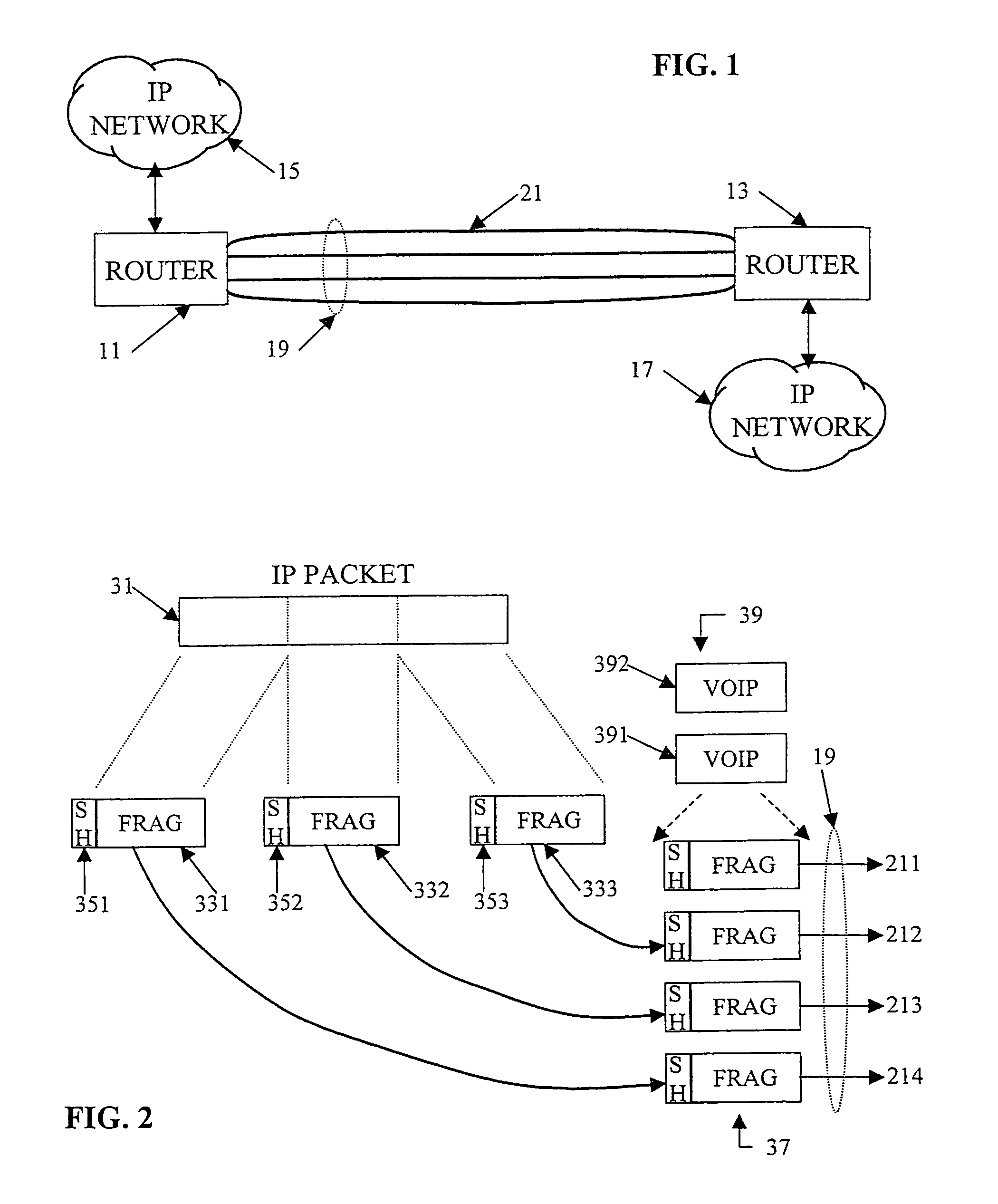
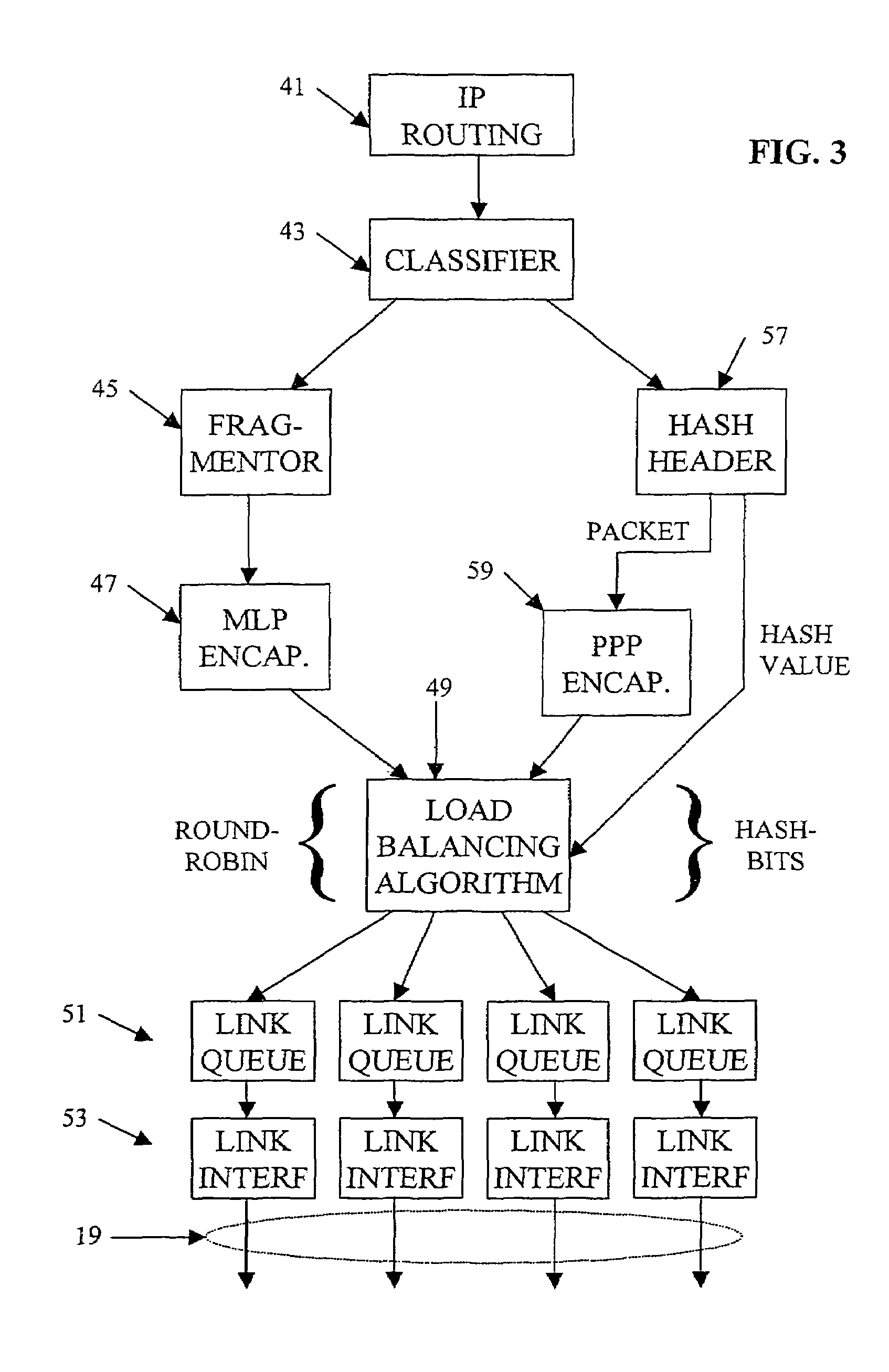
Combining multilink and IP per-destination load balancing over a multilink bundle
InactiveUS7613110B1Prevents differential delayAvoid uneven loadEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityProtocol processing
Load balanced transport of best efforts traffic together with delay-bounded traffic over a multilink bundle combines fragmentation and fragment distribution for best efforts packets with per-flow balancing for delay-bounded traffic. In the preferred embodiments, the best efforts packets receive Multilink Protocol treatment, including fragmentation and addition of sequence headers. Fragments of packets for one such communication go over the various links within the bundle, as appropriate for load balancing on the links. For each delay-bounded flow, such as for a VOIP service, the sending node hashes the packet header data and applies all packets for the flow to one of the links, assigned as a function of the hash value. Different flow headers produce different hash results; therefore the node sends different flows over the different links in a substantially balanced manner.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Systems and methods for policy based routing for multiple next hops
ActiveUS9178805B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic characteristicIp address
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Self-organization method of municipal traffic control signal based on fluid dynamics
InactiveCN101515407AWith autonomous collectionDisposableControlling traffic signalsInformation processingOrganizational control
The invention relates to a self-organization method of urban traffic control signal based on fluid dynamics, belonging to the technical field of traffic engineering. The invention takes an urban traffic control signal system as transportation network processing, and every crossing is taken as an intelligent body having the functions of autonomous collection and information processing and simultaneously has two sets of cellular automaton for evolution to realize dynamic decision of the traffic signal control at every crossing; on the other hand, by utilizing the natural similarity between traffic flow and fluid flow, the fluid dynamics is introduced based on the cellular automaton to set up equilibrium model of the traffic flow; meanwhile, urban traffic signal self-organization control regulation based on quaternary-phase sequence switch is set out, and traffic crossing phase position decision rule is correspondingly set out, thereby realizing real time decision of a traffic system signal mode. The invention solves the problems of nondeterminacy and unbalanced traffic flow existing in the urban traffic control, so as to improve the performance and real-time property of the urban traffic control system.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
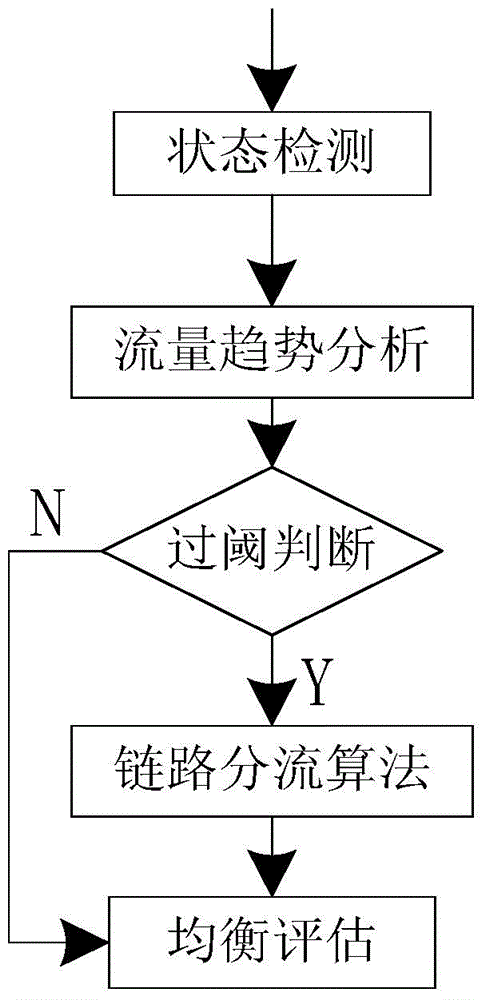
Traffic balancing method for electric power communication network based on traffic prediction
ActiveCN104410582AEliminate hidden dangers in advanceReduce load rateData switching networksTraffic capacityTraffic prediction
The invention relates to a traffic balancing method for an electric power communication network based on traffic prediction. The traffic balancing method comprises the following steps: firstly, detecting a node link state to acquire node traffic data, and setting a load threshold of the node; secondly, analyzing the state of the traffic data at certain time and predicting the traffic during the future certain time slot; meanwhile, judging whether the possibility of overload exists or not; performing link shunting processing on a link which is predicted to possibly exceed a threshold; finally, dynamically counting and adjusting the load degree of the whole network and enabling the whole network to operate at an optimized state. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the node traffic can be reasonably limited, and the operation efficiency of the link is greatly improved; the selection of a node threshold is controlled by analyzing the balance degree of the whole network, so that the distribution of a data flow is developed towards the integral optimization of the network.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +4
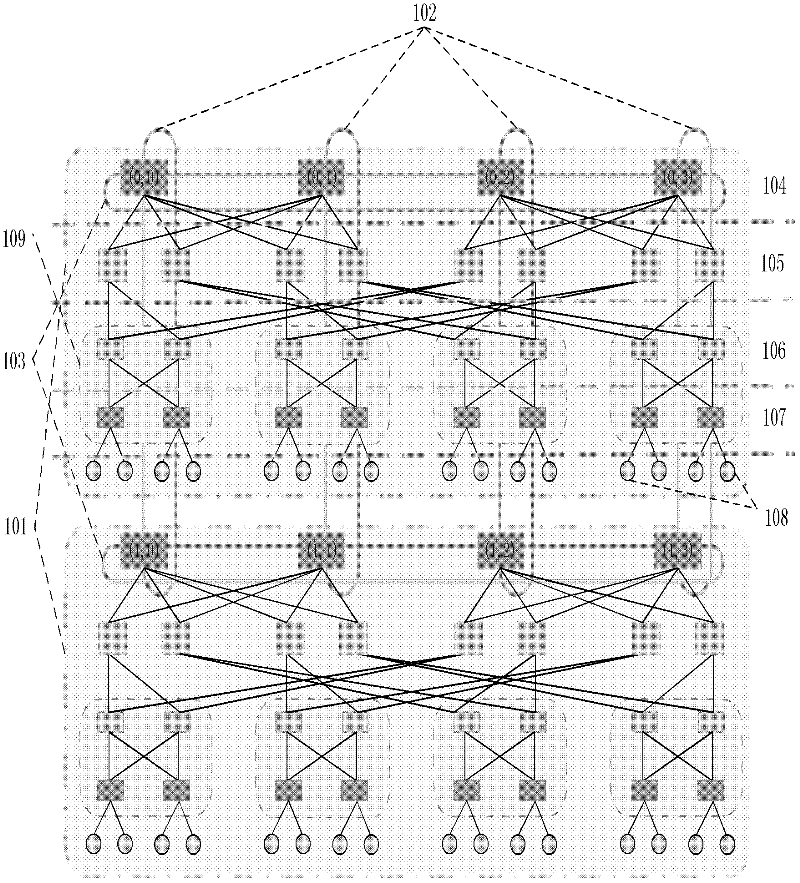
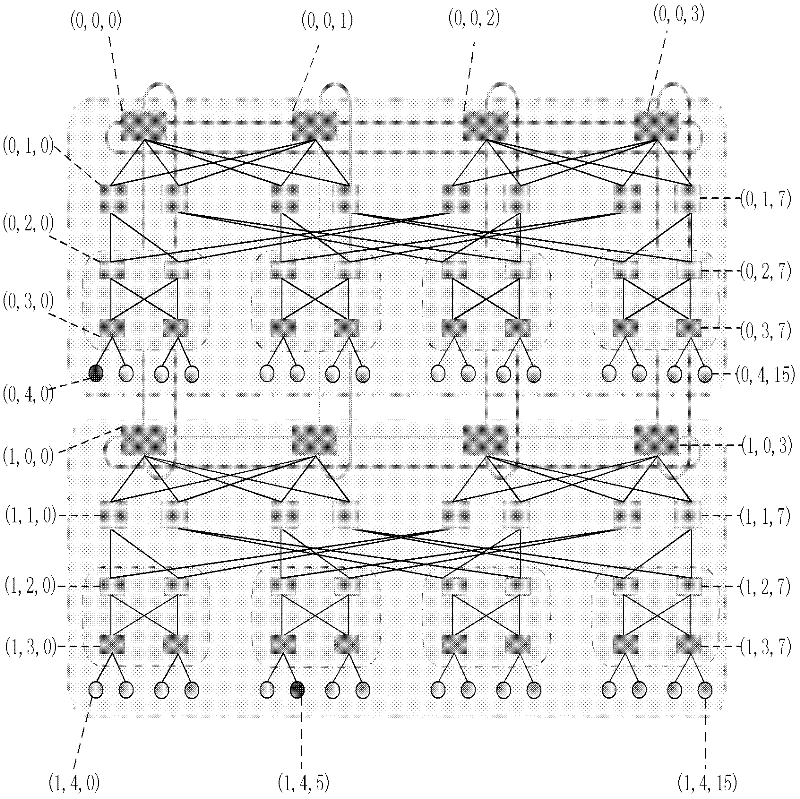
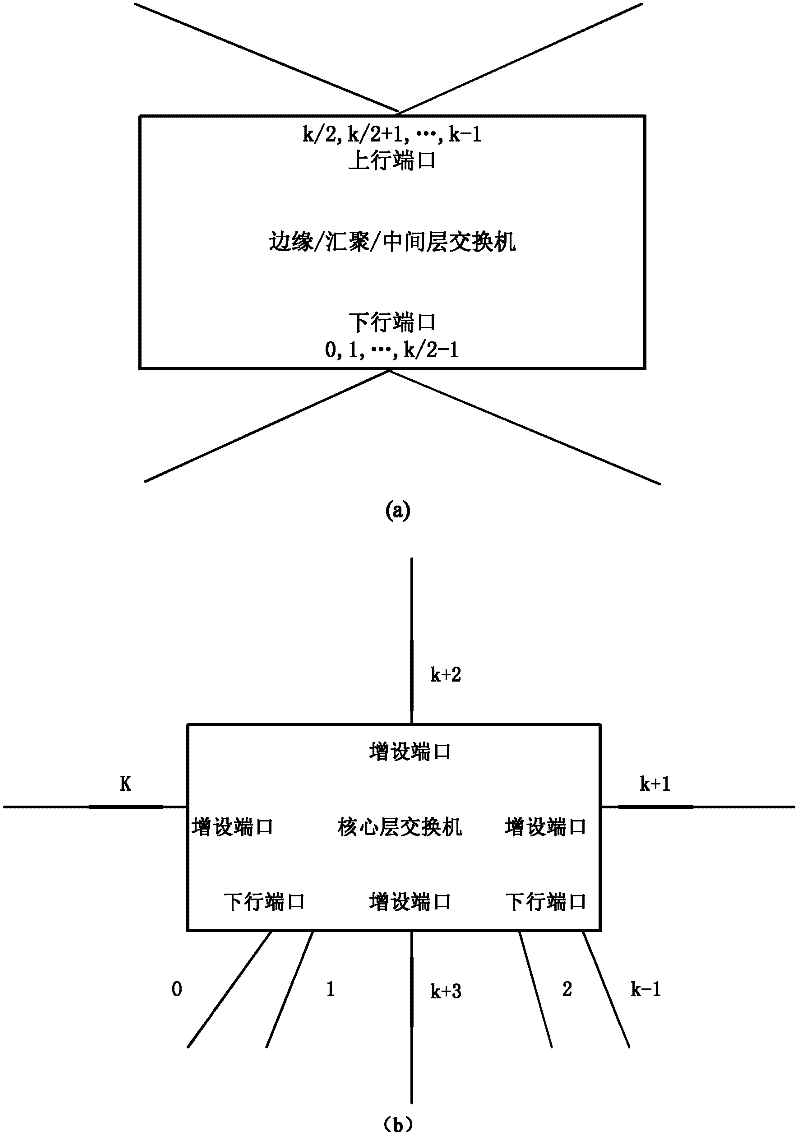
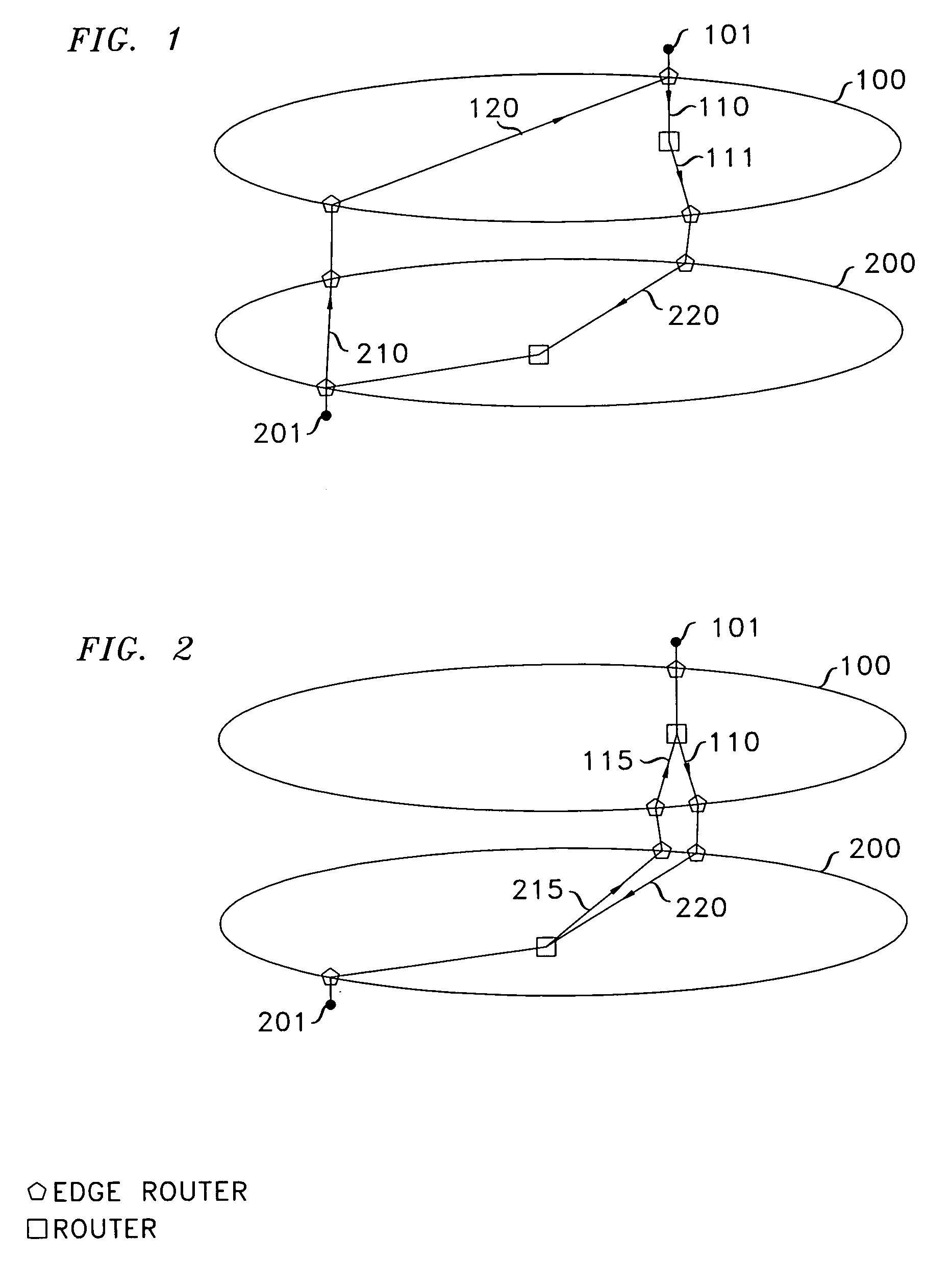
Routing method for module-expansion-based data center network topology system
InactiveCN102420775AImprove addressing efficiencySave storage spaceData switching networksTraffic capacityData center
The invention discloses a routing method for a module-expansion-based data center network topology system, and mainly aims to solve the problem that the conventional routing methods in the Ethernet and a data center tree network cannot be well applied to the module-expansion-based data center network topology system. The method is implemented by the following steps of: (1) performing initialization, and identifying each piece of network equipment in the topology system by adopting a hierarchical addressing mechanism; (2) reading the addressing information of current network equipment, and judging the type of the current network equipment; (3) generating data, and transmitting the data to edge layer switches by using a source server; (4) determining data output ports according to the destination address of the data and a port with the data by using the edge layer switches, convergence layer switches and intermediate layer switches; and (5), determining a data output port according to the destination address of the data, the hop number of a path hop number and the cache information of the port by using core layer switches. The method has the advantages that: network throughput is improved; traffic balancing is realized; the method can be used for the path selection of a data center network and the provision of high-efficiency data transmission service; and the shortcomings of static routing are overcome.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
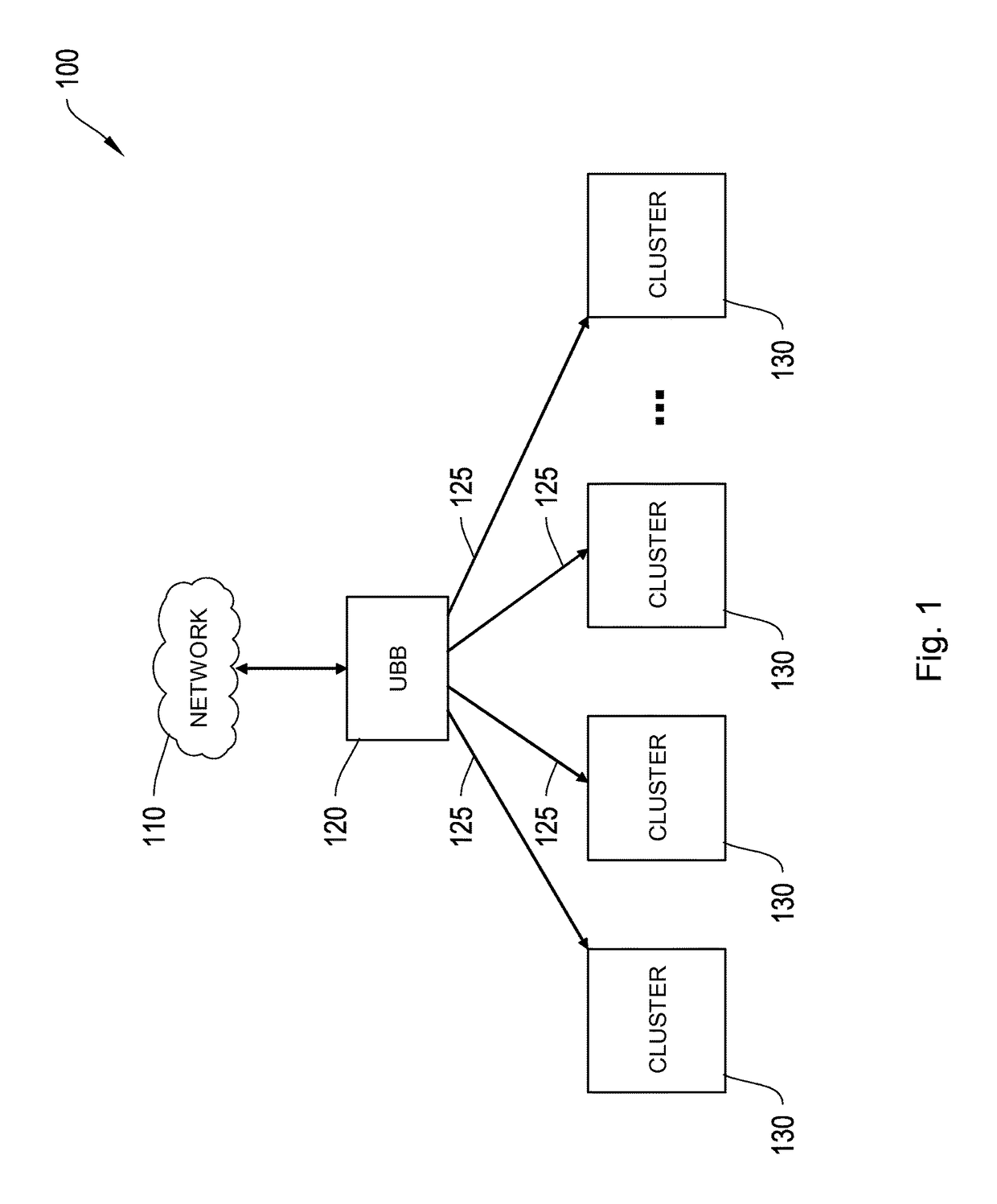
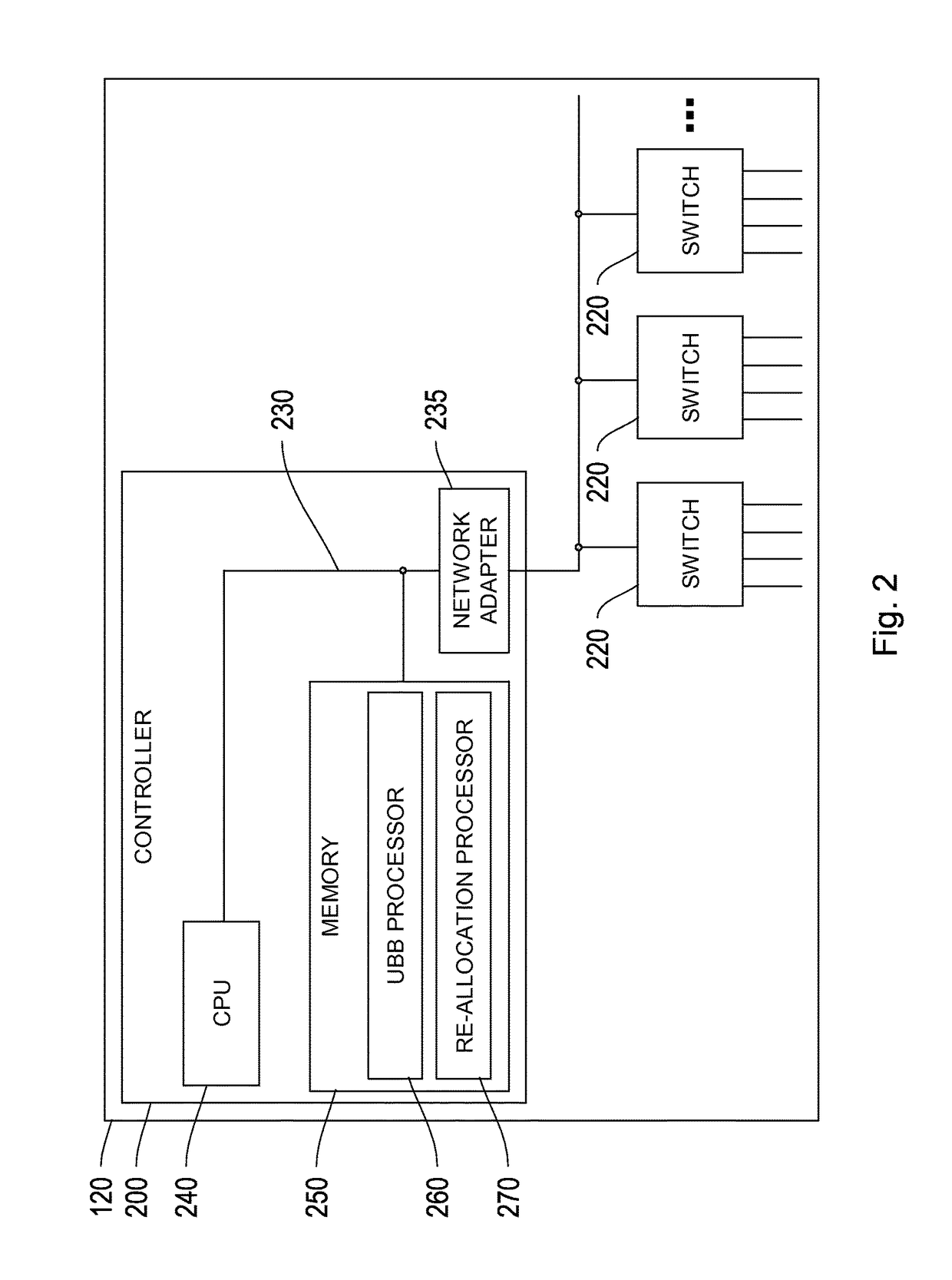
Network system, traffic balancing method, network monitoring device and host
ActiveUS20080273461A1Traffic controlControl balanceError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityIp address
A traffic balancing system, traffic balancing device and traffic balancing method that converts IP packets by switching IP address of the destination host between the dual stack hosts communicating with each other, in order to control traffic balancing in the networks.
Owner:IBM CORP
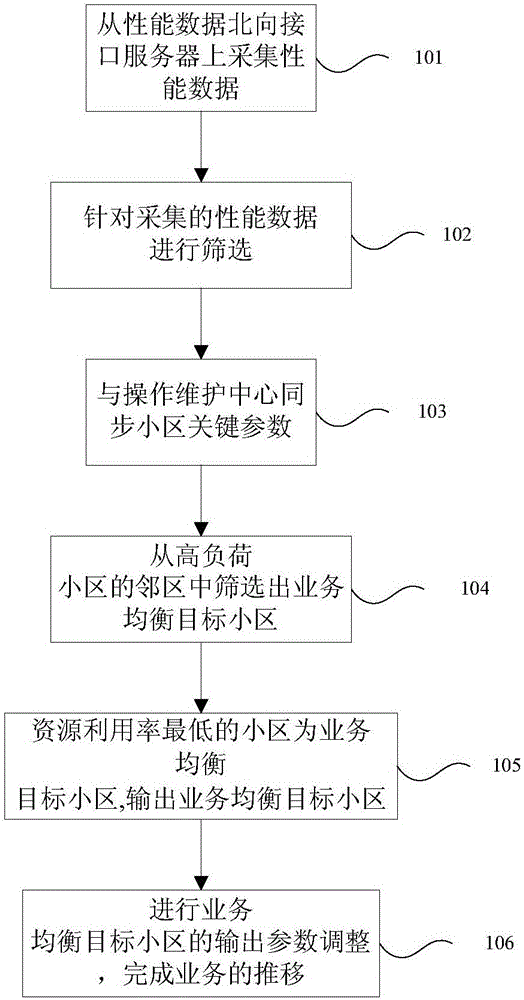
Load-based automatic optimization method for LTE neighbor cell parameters
InactiveCN106851736AImprove efficiencyImprove convenienceNetwork traffic/resource managementComplete transpositionResource utilization
The invention discloses a load-based automatic optimization method for LTE neighbor cell parameters which belongs to the technical field of mobile communication. The optimization method comprises: collecting wireless performance indexes of to-be-optimized LTE cells to acquire high load cells needing to be handled; synchronizing key parameters of the cells; screening corresponding low traffic load balancing target cells from neighbor cells of the high load cells and outputting a list of traffic balancing target cells; determining the cell of the lowest resource utilization ratio as a traffic balancing target cell; and automatically carrying out an adjustment on the output parameters of the traffic balancing target cell or the high load cells to complete transposition of the traffic. According to the method, automatic optimization of neighbor cell parameters of the LTE cells is realized and awareness of the cells is improved efficiently based on real-time performance data. Compared with a manual optimization method, the method brings a substantial improvement in optimization efficiency and optimization effect of resource utilization ratios as well as user numbers and throughput indexes of the cells and also meets application requirement of users better.
Owner:BEIJING TUOMING COMM TECH
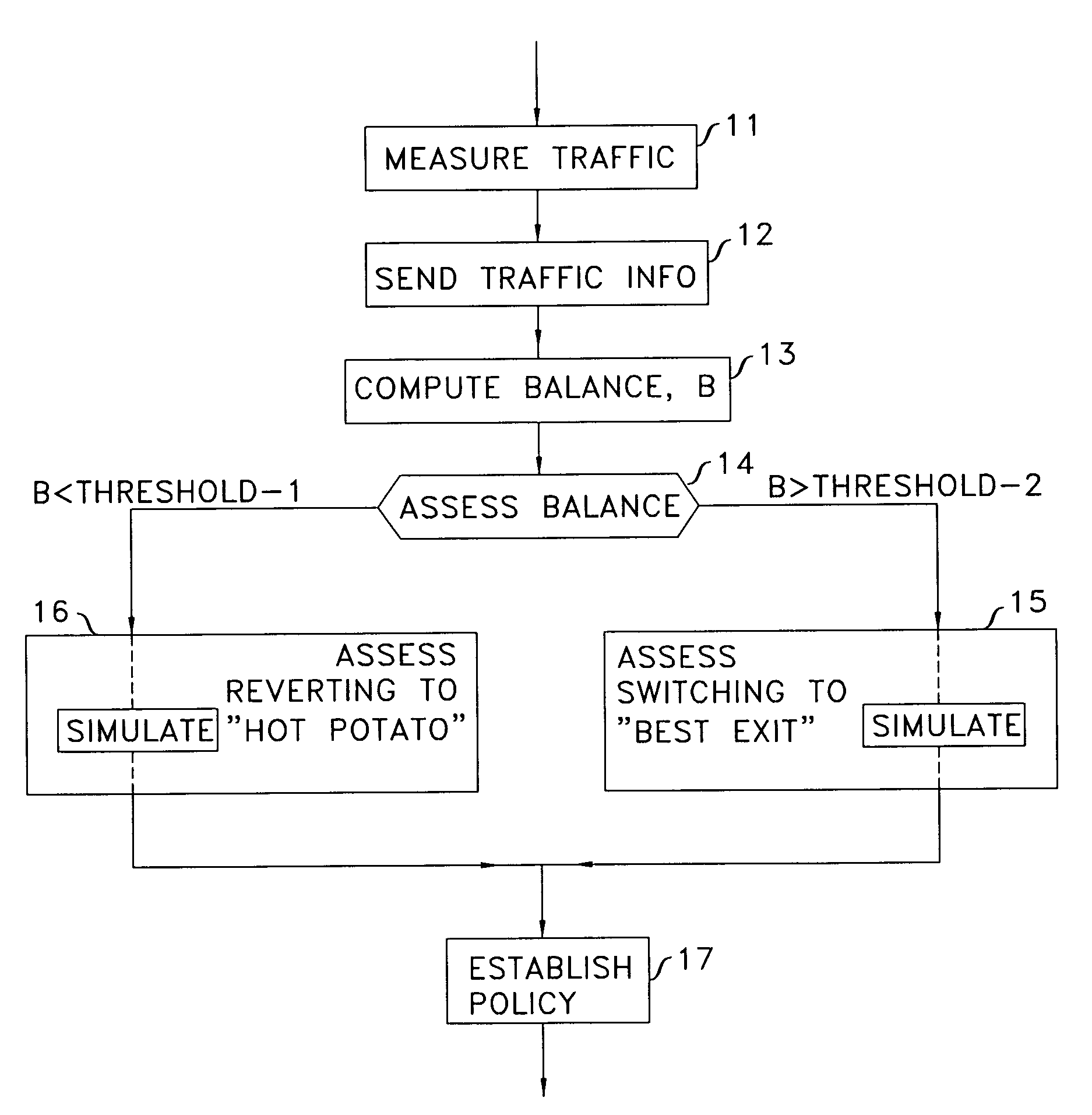
Method for controlling traffic balance between peering networks
InactiveUS20090185486A1Improve artError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityTraffic balancing
A method that measures ratio, relative to a peering network, of traffic burden of incoming traffic to traffic burden of outgoing traffic, where traffic burden takes into account traffic volume and distance that the traffic traverses through the network. A determination is made from this ratio as to whether an imbalance exists with the peering network. With the assistance of a simulation of changes in routing policy and their effects, an existing or impending imbalance is remedied by changing the routing policy relative to particular customers, for example from a “hot potato” routing policy to a “best exit” routing policy.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
System and methods for utilization-based balancing of traffic to an information retrieval system
ActiveUS9641431B1Avoid OverloadingReduce in quantityDigital computer detailsProgram controlTraffic capacityTraffic balancing
Systems and methods for, among other things, a utilization based load balancing system which controls the distribution of queries to an information retrieval system made up of a network of server clusters. In one embodiment, a server cluster allocates computational resources among computational tasks. These computational tasks are replicated across a given server cluster, typically such that those computational tasks requested more frequently have more replicas, and more resources allocated to them to fulfill the requests. The system applies a utilization metric to determine how much capacity a given task has available and uses this determination to determine the capacity available for the cluster as a whole. Load balancing is achieved by re-directing queries to another cluster in response to the utilization value for a given cluster reaching a threshold.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
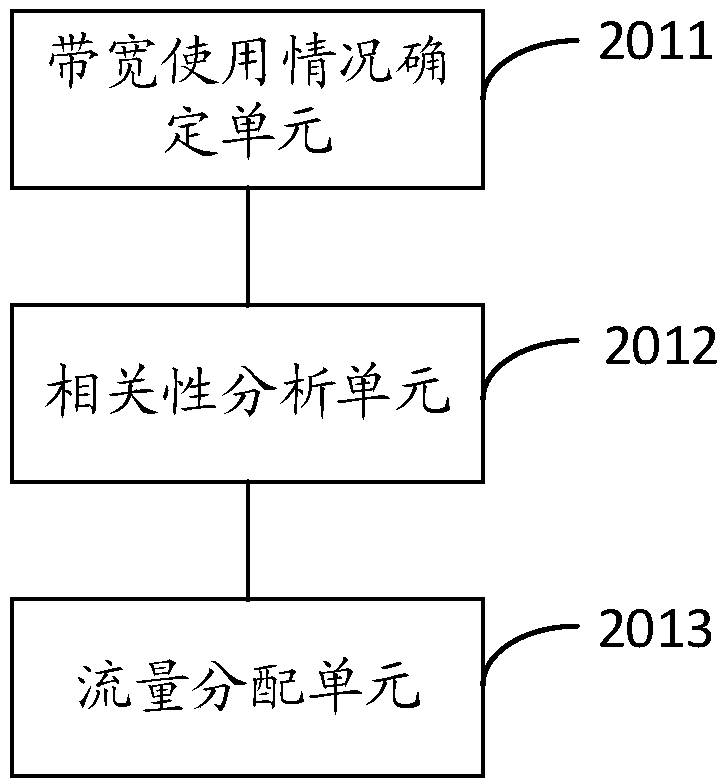
Bandwidth resource scheduling methods and devices
The invention provides bandwidth resource scheduling methods and devices, and relates to the field of computer networks. The methods and the devices solve the problems that existing inter-node trafficbalancing technology cannot adapt to actual network cases, node utilization efficiency is low, and user experience is poorer. The method includes: determining a bandwidth multiplexing strategy of each service node according to full-period bandwidth size data of all types of services corresponding to each user identifier; determining the number of resolution result IP addresses, which are providedby all the service nodes, according to the bandwidth multiplexing strategy when a domain name resolution request sent by a local domain name system (DNS) server is received; and selecting a corresponding number of IP addresses from corresponding service nodes according to the number of the resolution result IP addresses, which are provided by all the service nodes, to use the same as a resolutionresult to return the same to a local DNS. The technical solution provided by the invention is suitable for use in DNS traffic scheduling, and realizes inter-service-node traffic balancing adapting tonetwork service bearing cases.
Owner:GUIZHOU BAISHANCLOUD TECH CO LTD
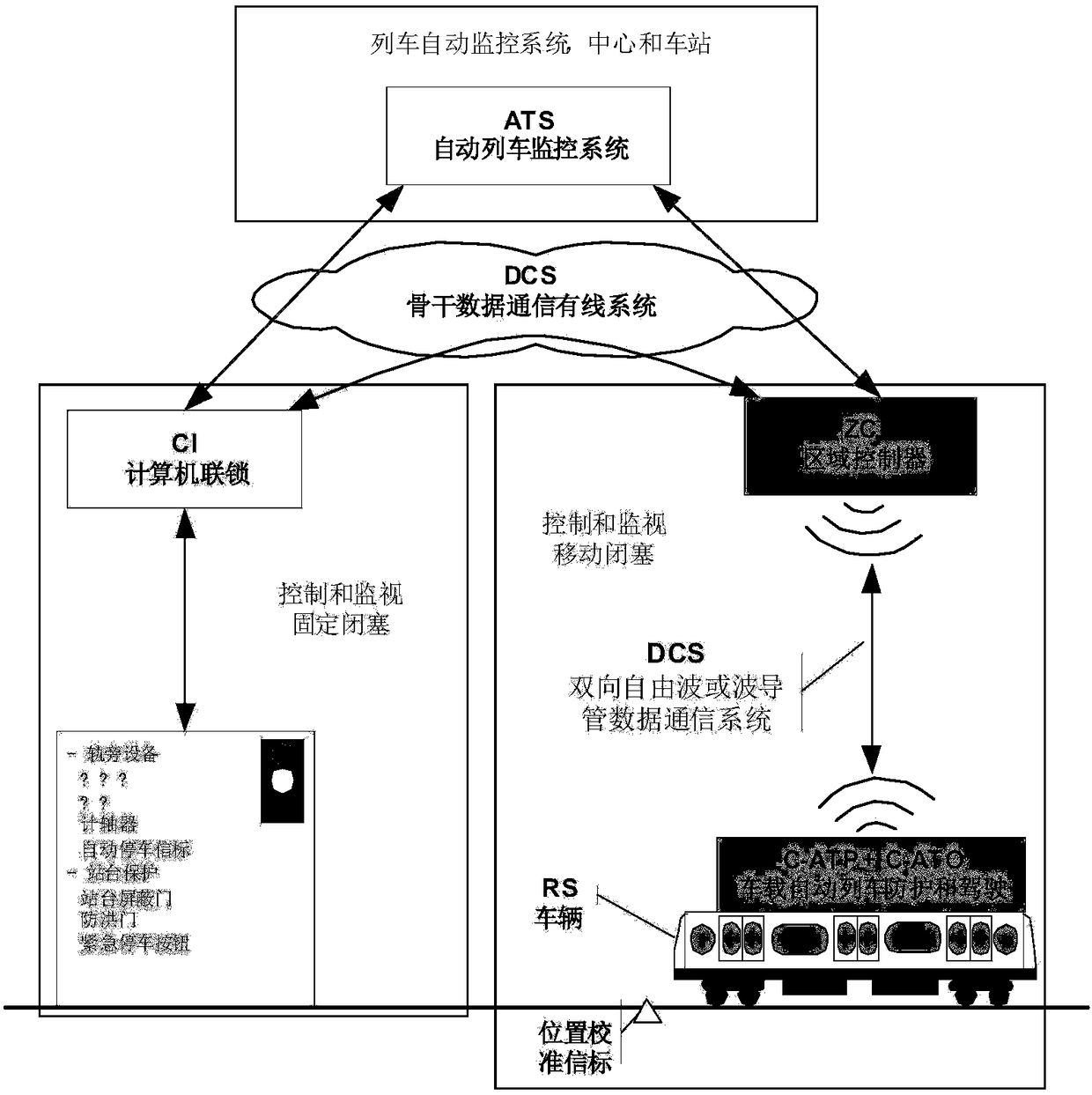
Operation method for coping with tidal passenger flow by adopting communication based train control (CBTC) system
ActiveCN108146471AClose range trackingImprove operational efficiencyRailway traffic control systemsTraffic capacityCoupling
The embodiment of the invention discloses an operation method for coping with a tidal passenger flow by adopting a communication based train control (CBTC) system. The operation method comprises the following steps that in a preset time period after the morning peak or the evening peak, trains depart from a first area to a second area according to a first departure interval, and trains depart fromthe second area to the first area according to a second departure interval, wherein the first departure interval is smaller than the second departure interval; and in the process that the trains depart from the second area to the first area, a virtual coupling mode based on train-train communication is adopted to enable the multiple trains to be in virtual coupling operation, so that the actual train flow from the second area to the first area is increased, two-way train flow balance is maintained. The multiple trains are in virtual coupling operation, so that closer-range tracking of the trains is achieved; and meanwhile, the operation mode is more flexible, the passenger carrying characteristics of the tidal passenger flow of urban rail traffic is coped with through the two-way asymmetric rapid and slow train operation measure and the two-way asymmetric passenger flow operation measure, thus the cost is lower, and the train operation efficiency is higher.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
Construction method of urban traffic signal self-organization rule based on fluid dynamics
The invention relates to a method for structuring city traffic signal automatically organize rule based on fluid dynamics in the field of traffic project technology. The invention uses city traffic signal control system as traffic network processing, each intercross as intelligent body with auto collecting and processing function; each intercross possesses two suits of cell salve robot to achieve the dynamic resolution of each intercross traffic signal control; it uses the resemblance between traffic flow and fluid flow to introduce fluid dynamics to establish the balance model of traffic flow and sets city traffic signal automatically organize and control rule based on four phases switching at the same time; it sets traffic intercross phase quoting rule to achieve the real time resolution of traffic system signal model.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Load balancing method for multi-type exit gateway
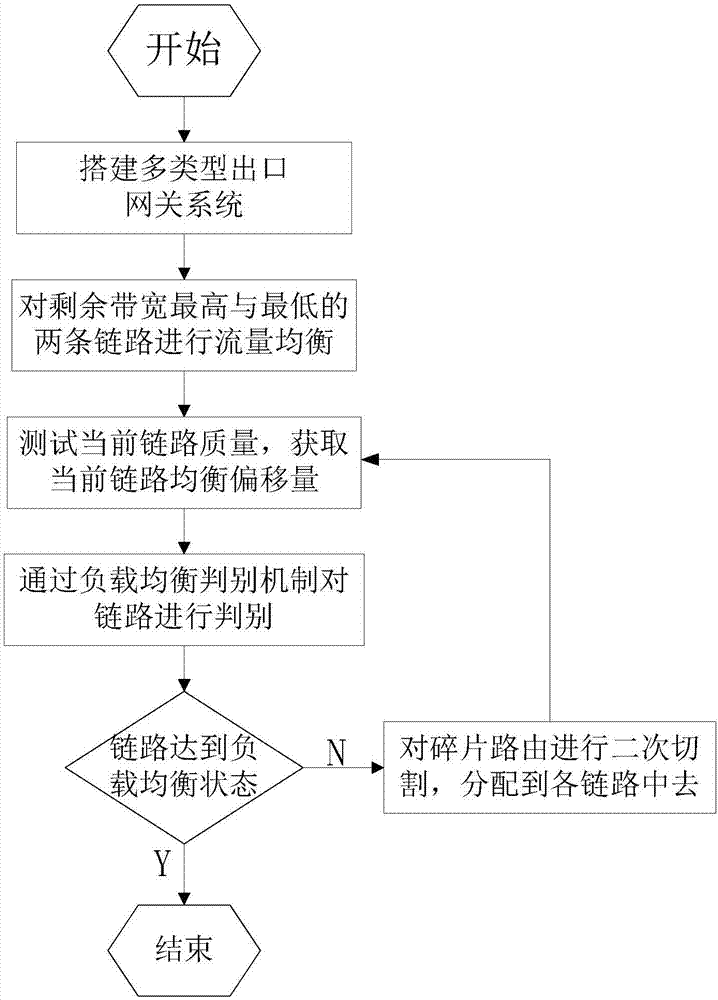
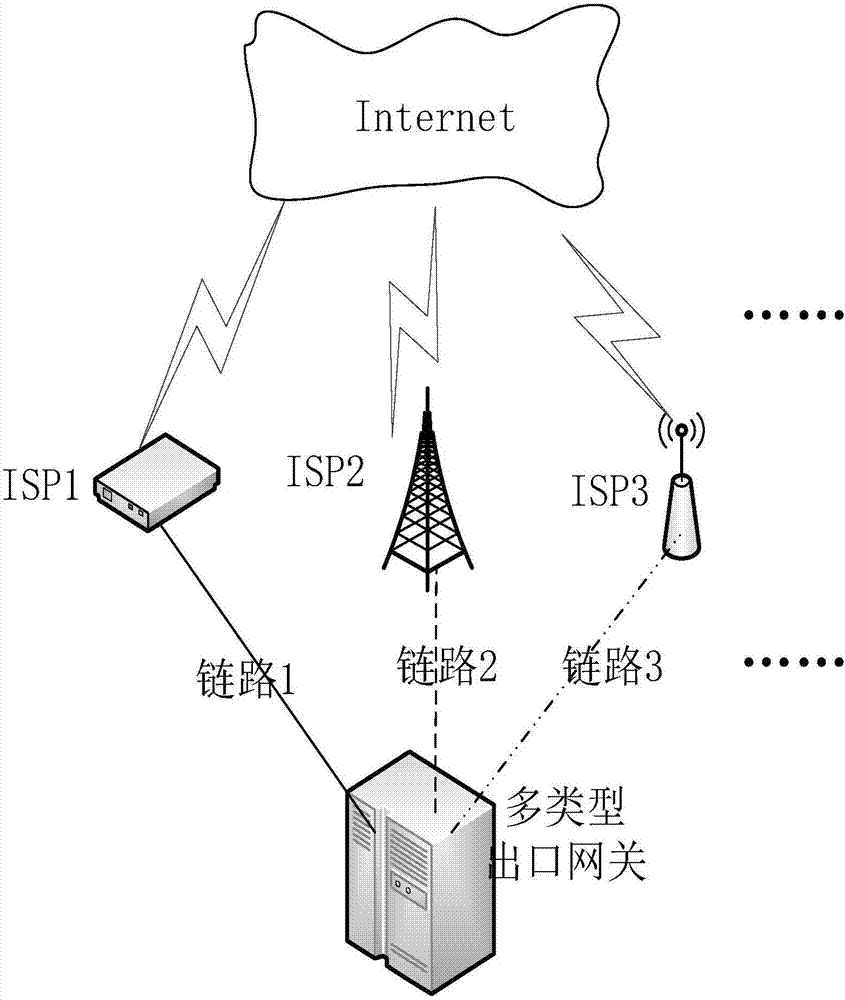
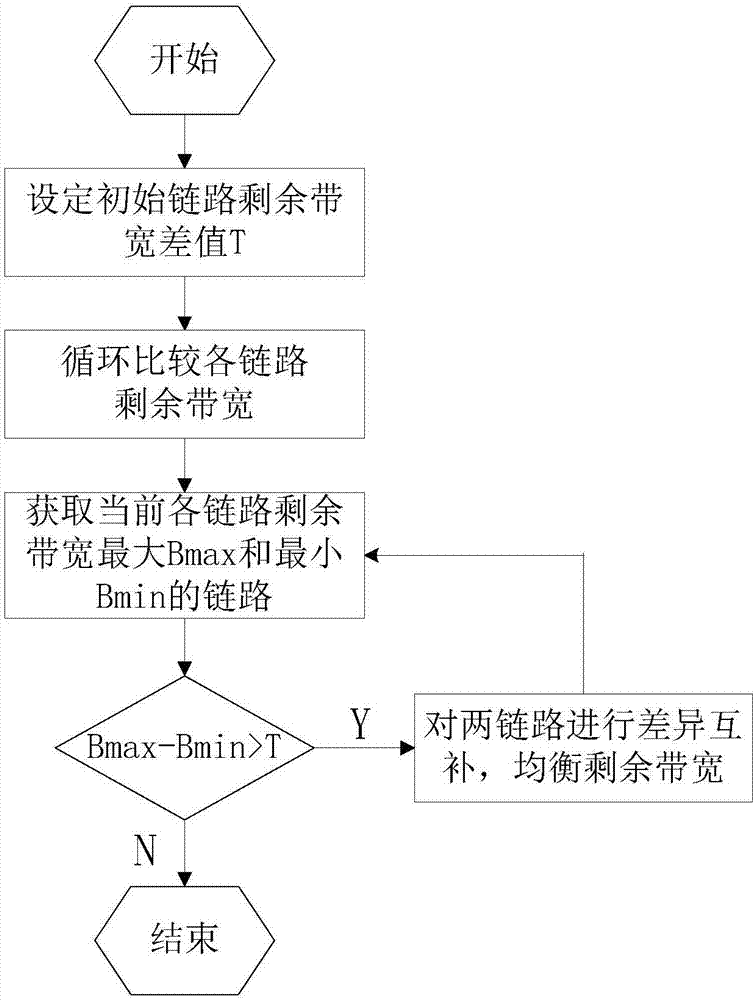
ActiveCN107294868AQuantitative analysis is accurate and reliableAchieve load balancing effectData switching networksTraffic capacityTraffic balancing
The invention discloses a load balancing method for a multi-type exit gateway, which mainly solves the problems of unreasonable traffic distribution, high transmission delay and low network throughput when the existing multi-type exit gateway transmits big data on multiple links. According to the solution, the method comprises the steps of: 1) setting up a multi-type exit gateway system; 2) preprocessing links, and performing traffic balancing on the two links having the highest and lowest remaining bandwidths; 3) introducing a load balancing judgment mechanism, calculating the quality of the current link, and judging whether the link is in a load balancing state by comparing with an initial target threshold; and 4) when the load of the link does not reach a balancing state, performing secondary cutting by adopting a routing fragment, allocating the traffic to each link, then performing judgment, and so on, till the links of the multi-type exit gateway are in the load balancing state. The method reduces the transmission delay, improves the network throughput, and can be applied to a gateway system having great outlet link network environment difference.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Load economical allocation control method based on flow balance
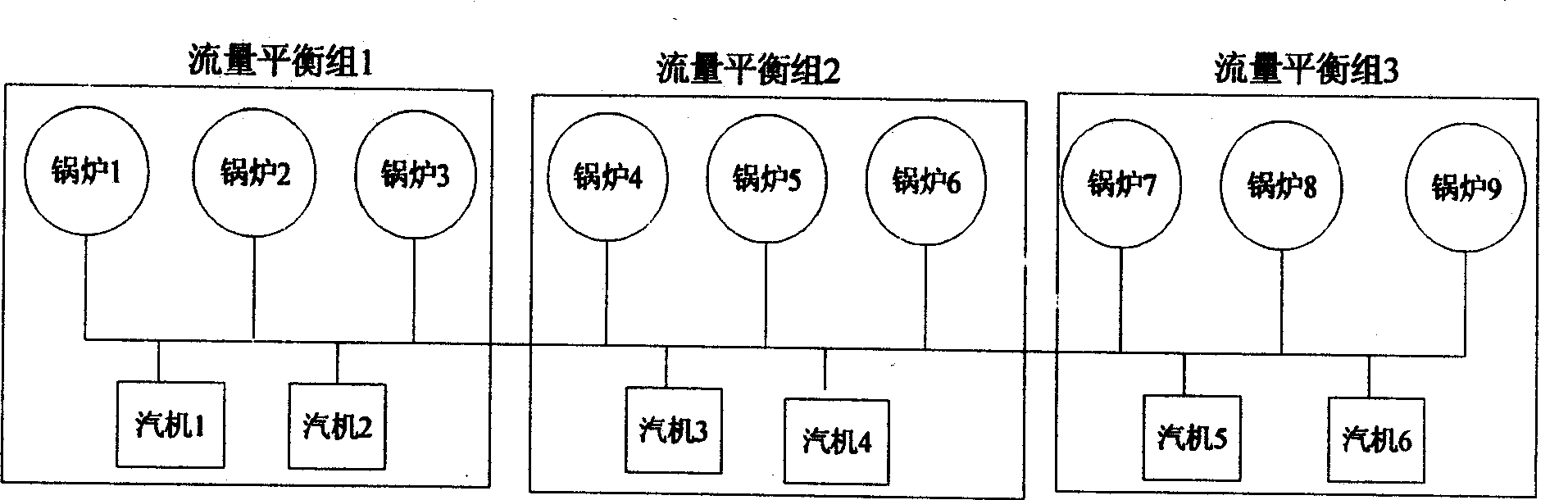
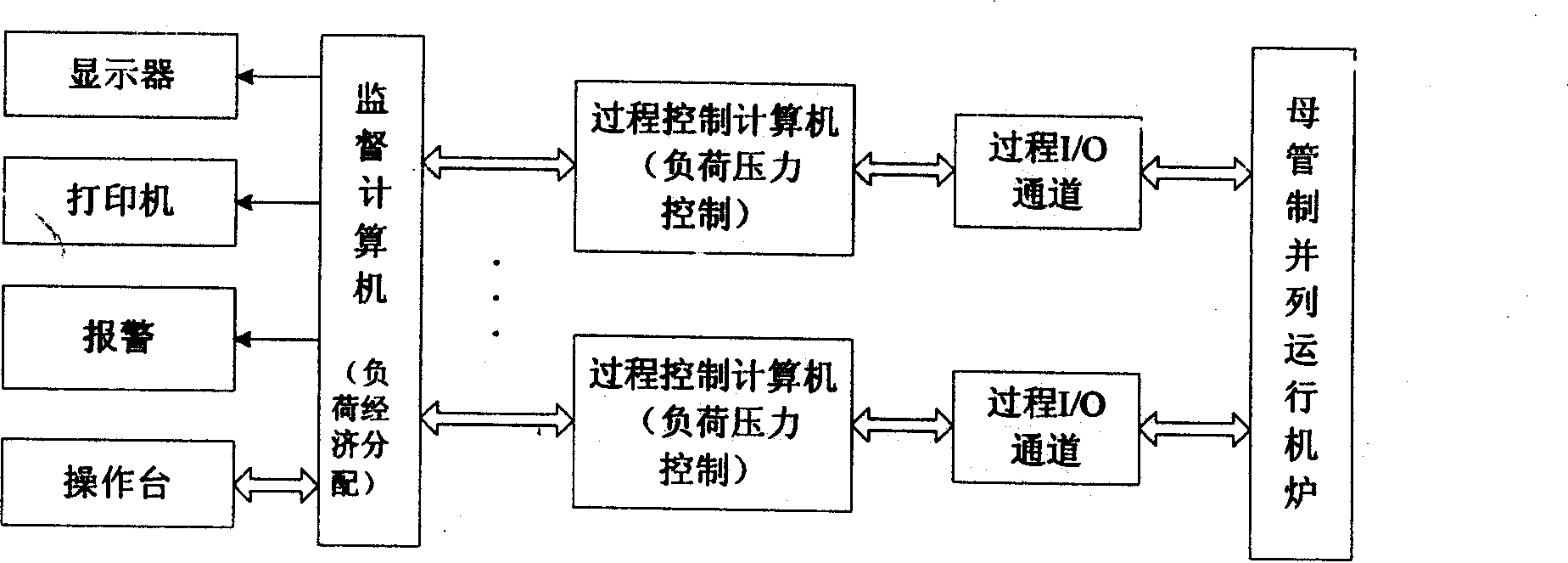
InactiveCN101373383AReasonable distributionReduce distributionTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlDistribution controlEngineering
A load economic distribution control method based on a flow balance group is used for the economic distribution control of the load of a boiler and a stream turbine group in a piping-main scheme parallel operation mode, can be conveniently realized by supervising and controlling a two-stage computer system structure, and has the characteristics of good rapidity of distribution control, small pressure fluctuation of a main pipe, remarkable reduction of coal consumption and the like. When a control system in a piping-main scheme thermal power plant conducts load distribution on a parallel operation machine set, the control method comprises the following steps: (1) dividing a flow supply and demand balance group in the principle of proximity at the moment of each timing load distribution; (2) executing an overall situation load economic distribution task according to a given load demand at the moment of each timing load distribution; (3) judging whether a new lifting load demand appears or not in the stable operation process; (4) judging whether a malfunction and blowing-out signal appears or not in the operation process; (5) judging whether a malfunction and stopping signal appears or not in the operation process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of performing cell reselection in wireless communication system
InactiveUS8467798B2Improve service satisfactionImprove the level ofWireless communicationTelecommunicationsCommunications system
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Distributed direct drive excavator hydraulic system with servo motor-driven double variable pumps
PendingCN108425893ASmall pressure lossLow calorific valueServomotor componentsAccumulator installationsDistributed intelligenceTransmitted power
The invention provides a distributed direct drive excavator hydraulic system with servo motor-driven double variable pumps, wherein a first bidirectional variable pump, a second bidirectional variablepump and a servo motor are directly connected to independently drive a hydraulic cylinder, the flow balance of the hydraulic cylinder is realized by the first bidirectional variable pump and the second bidirectional variable pump, and meanwhile the servo motor is adopted for driving, so that the distributed intelligent control of transmitting power by a wire instead of a hydraulic pipeline is achieved; a main loop of the system is short and is not provided with a throttling element, so the pressure loss is small, the heat generation is small, a cooling device is not needed, the throttling loss and the overflow loss of the system are avoided, the system efficiency is relatively high, and in case of negative load, the system can also convert potential energy fed back by the load into electrical energy and store the electrical energy in a power supply device for reuse, thus saving energy.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
Traffic forwarding method and devices
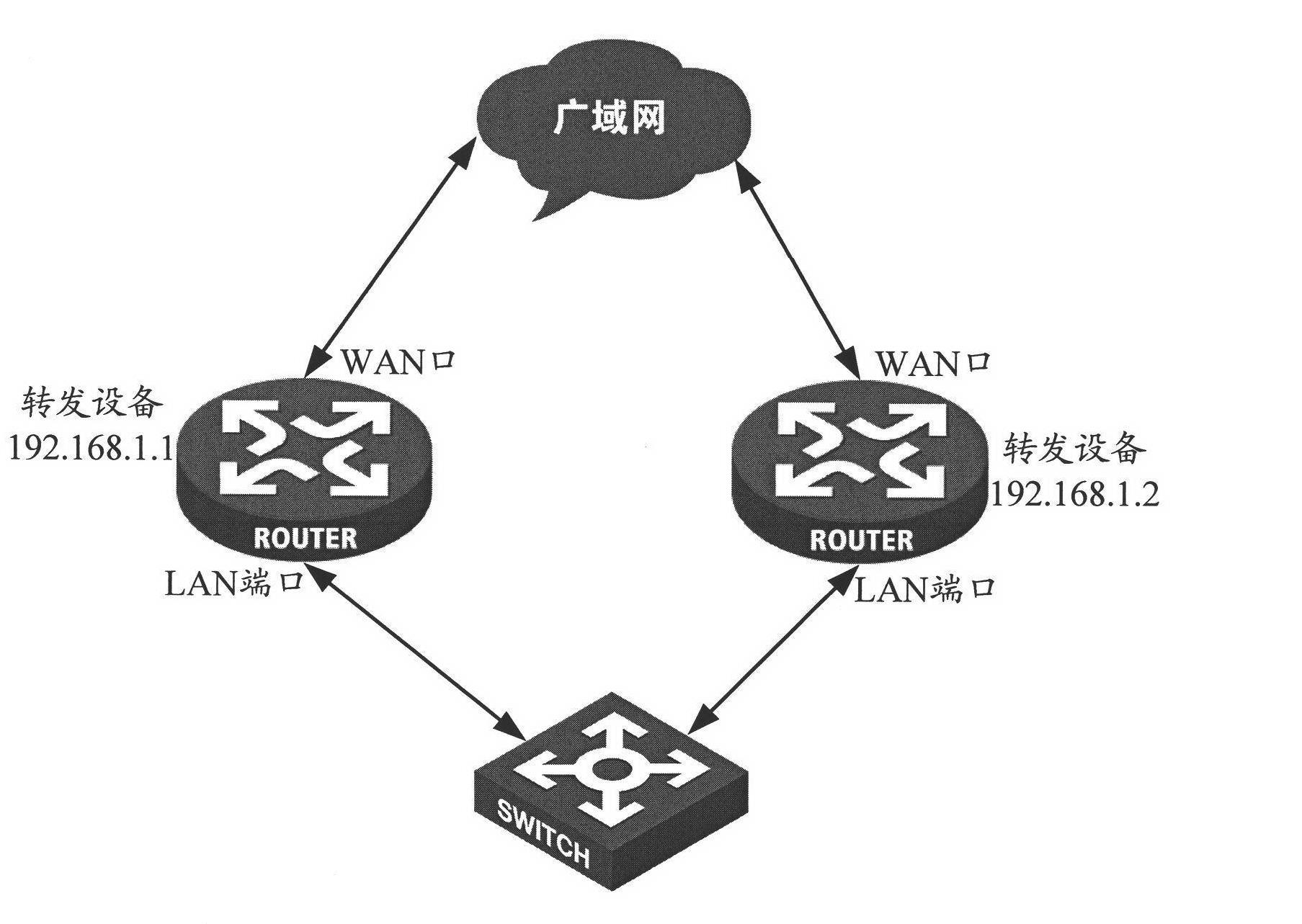
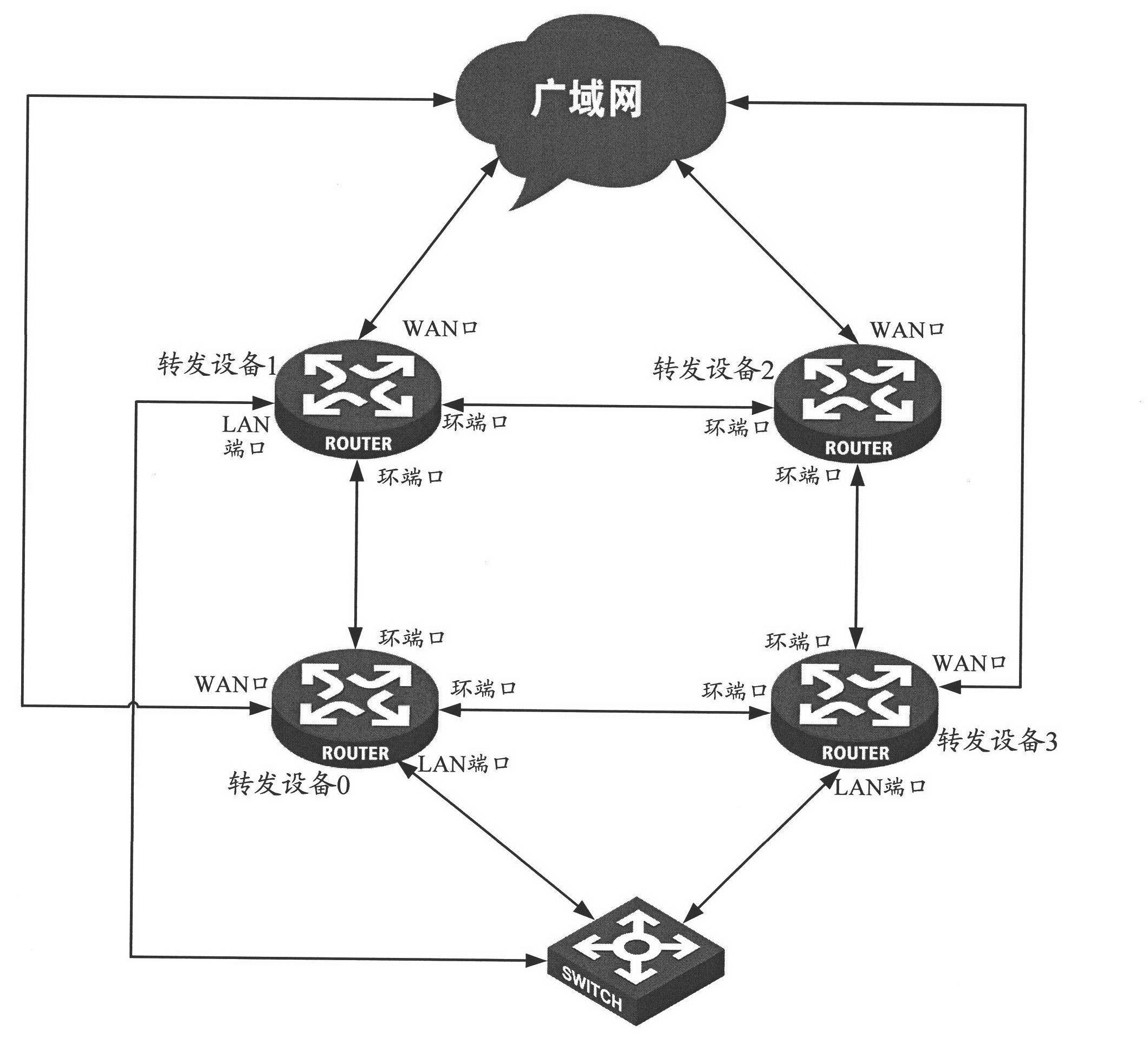
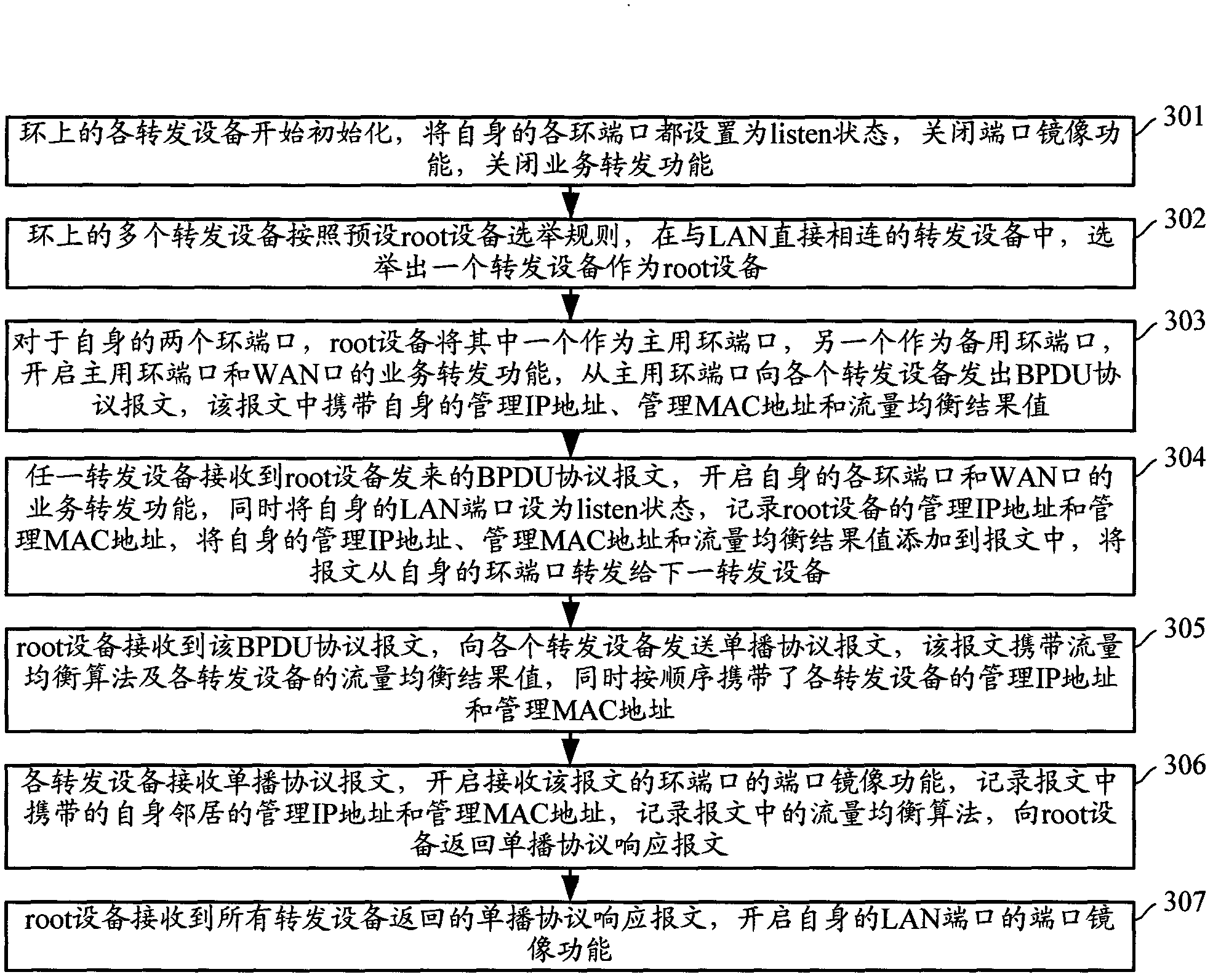
ActiveCN102209035AUniform flowImplement hot backupData switching networksTraffic capacityTraffic balancing
The invention discloses a traffic forwarding method and devices. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting a plurality of forwarding devices between a WAN (wide area network) and a LAN (local area network) into a ring, taking one forwarding device on the ring as a root device, using one of two ring ports of the root device as a primary ring port while using the other as a secondary ring part; setting the secondary ring port in a state of forbidding service forwarding, setting an LAN port of one of the forwarding devices in the state of allowing the service forwarding, and setting the LAN ports of other forwarding devices in the state of forbidding the service forwarding; when traffic from the LAN reaches any forwarding device of the ring, mirroring the traffic to the other ring port by the forwarding device; meanwhile, judging whether the traffic can be forwarded to the WAN per se according to a predetermined traffic balancing algorithm or not; if so, forwarding the traffic to the WAN. The forwarding devices between the LAN and the WAN can be used for balancing the traffic in the invention.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
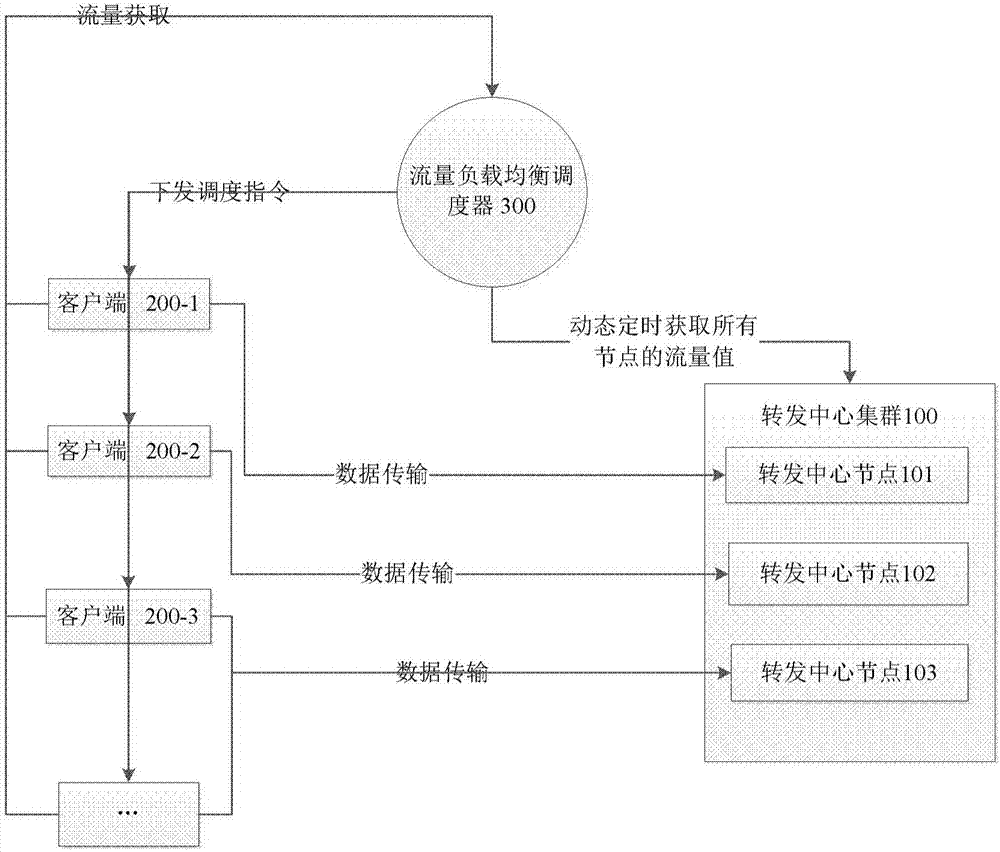
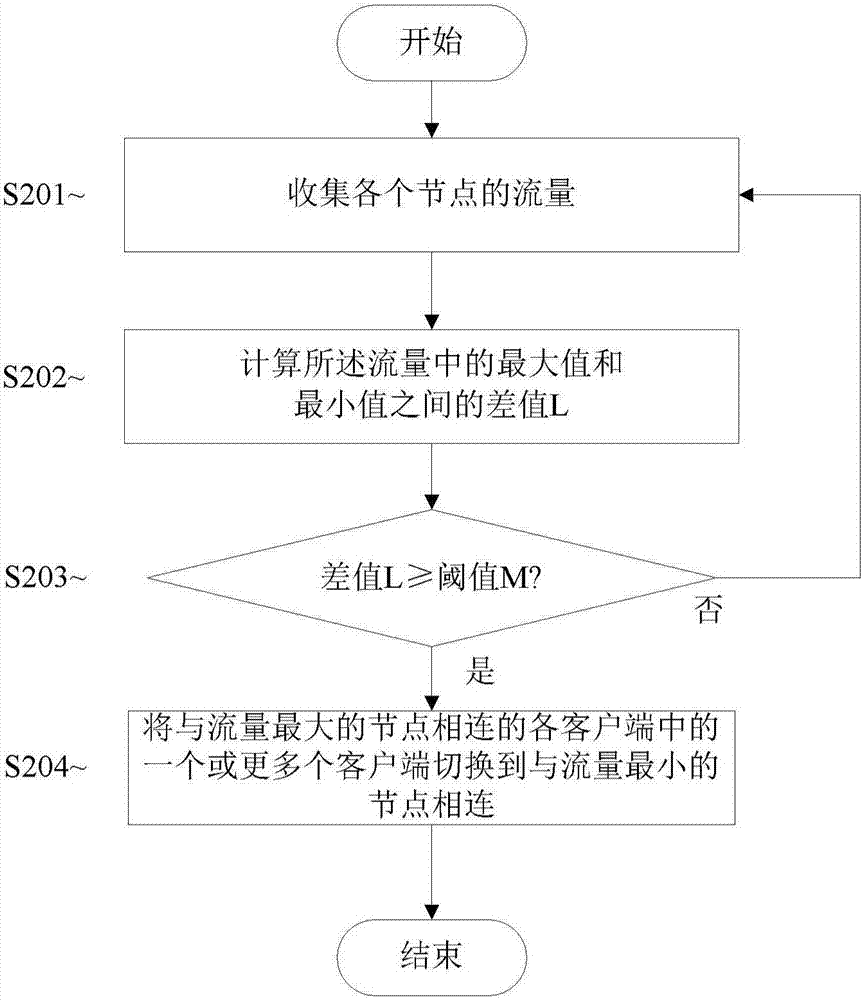
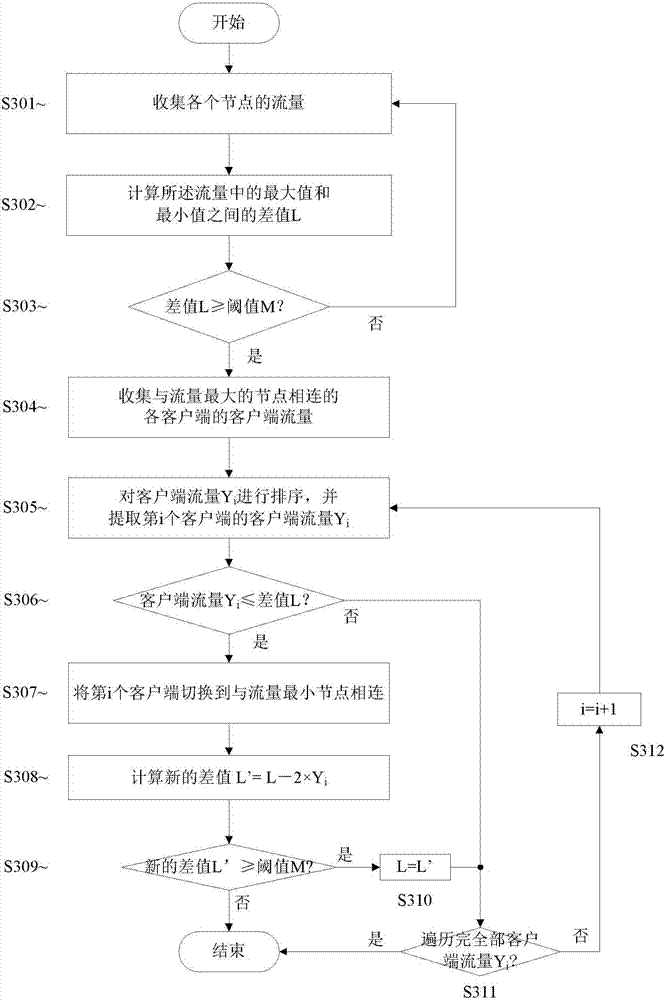
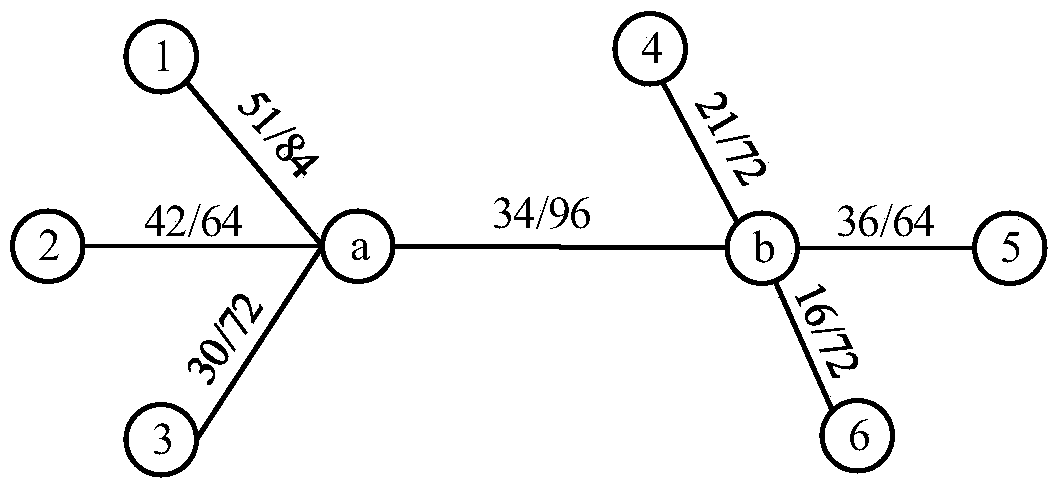
Traffic load balancing method and system
The invention provides a method for carrying out traffic load balancing in a multi-node network. The method may comprise the steps of collecting the traffic of each node; calculating a difference value L between the maximum value and the minimum value in the traffic; determining whether the difference value L is greater than or equal to a preset traffic balancing threshold value M; and in response to the fact that the difference value L is determined to be greater than or equal to the preset traffic balancing threshold value M, switching one or more of clients connected with the node with the maximum traffic to be connected with the node with the minimum traffic.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG SHANGKE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
Power communication network routing method for joint balance of load traffic and service risks
ActiveCN108809828ALoad balancingAchieving Joint EquilibriumData switching networksElectric power systemBalance strategy
The invention belongs to the technical field of power system communication, and particularly relates to a power communication network routing method for joint balance of load traffic and service risks. In terms of load traffic balancing, the link channel occupancy condition and the node traffic admission condition are considered in the power communication network routing method provided by the invention, and then a load weight function of the link is designed; in terms of service risk balancing, modelling is performed on the availability of an optical fiber link of a power communication network, and then a balancing strategy considering the service priority and the service risks that the link has carried is designed; and finally, a balancing factor is introduced to construct a link cost function that comprehensively considers the load and the risks so as to achieve the joint balance of the carrying capacity and the service risks. According to the power communication network routing method provided by the invention, the balancing factor can be adjusted according to the importance of the service, the network blocking rate and the service risks of the network can be reduced at the same time, the link load traffic and the risk value are balanced, and finally the network reaches the optimal performance.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
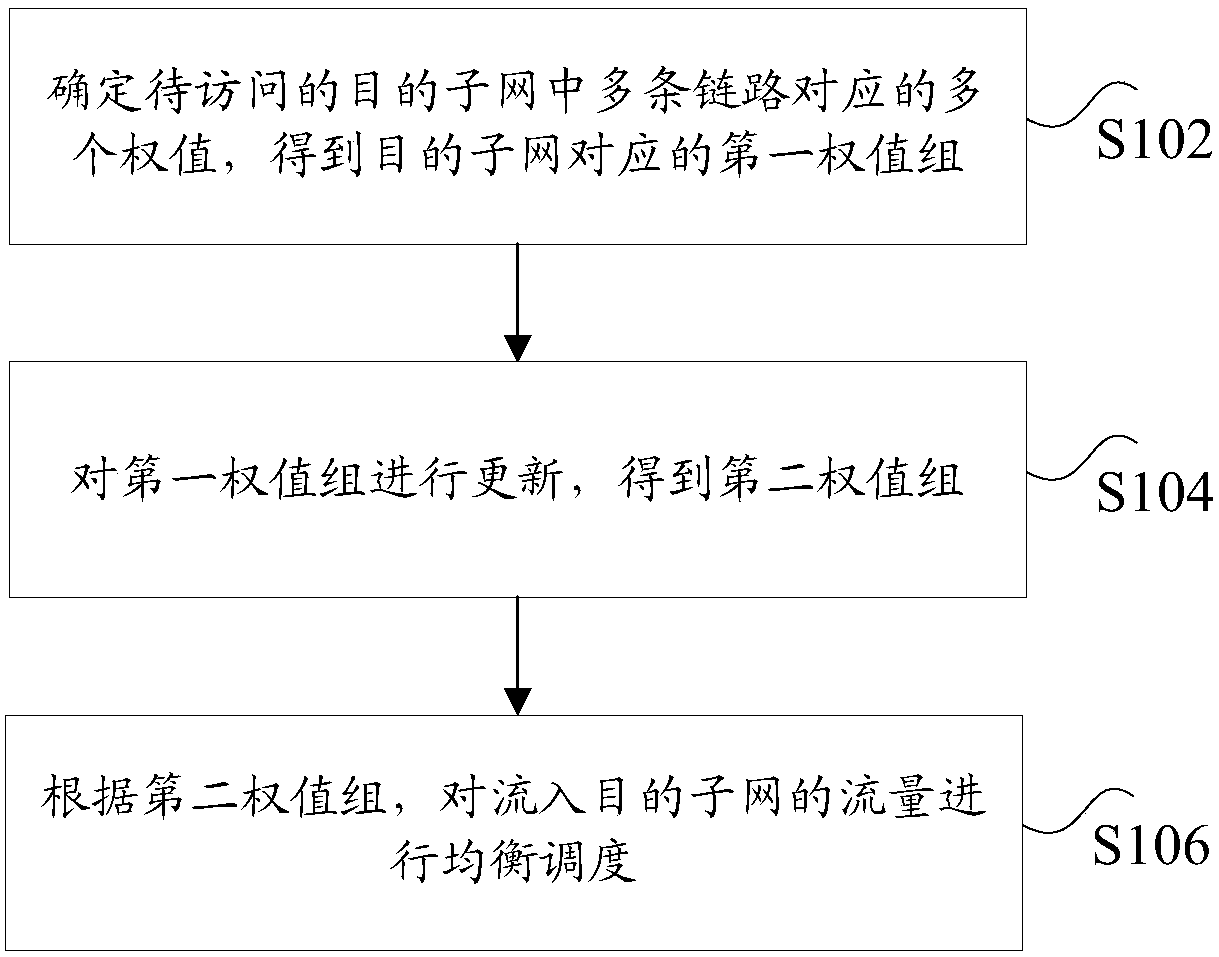
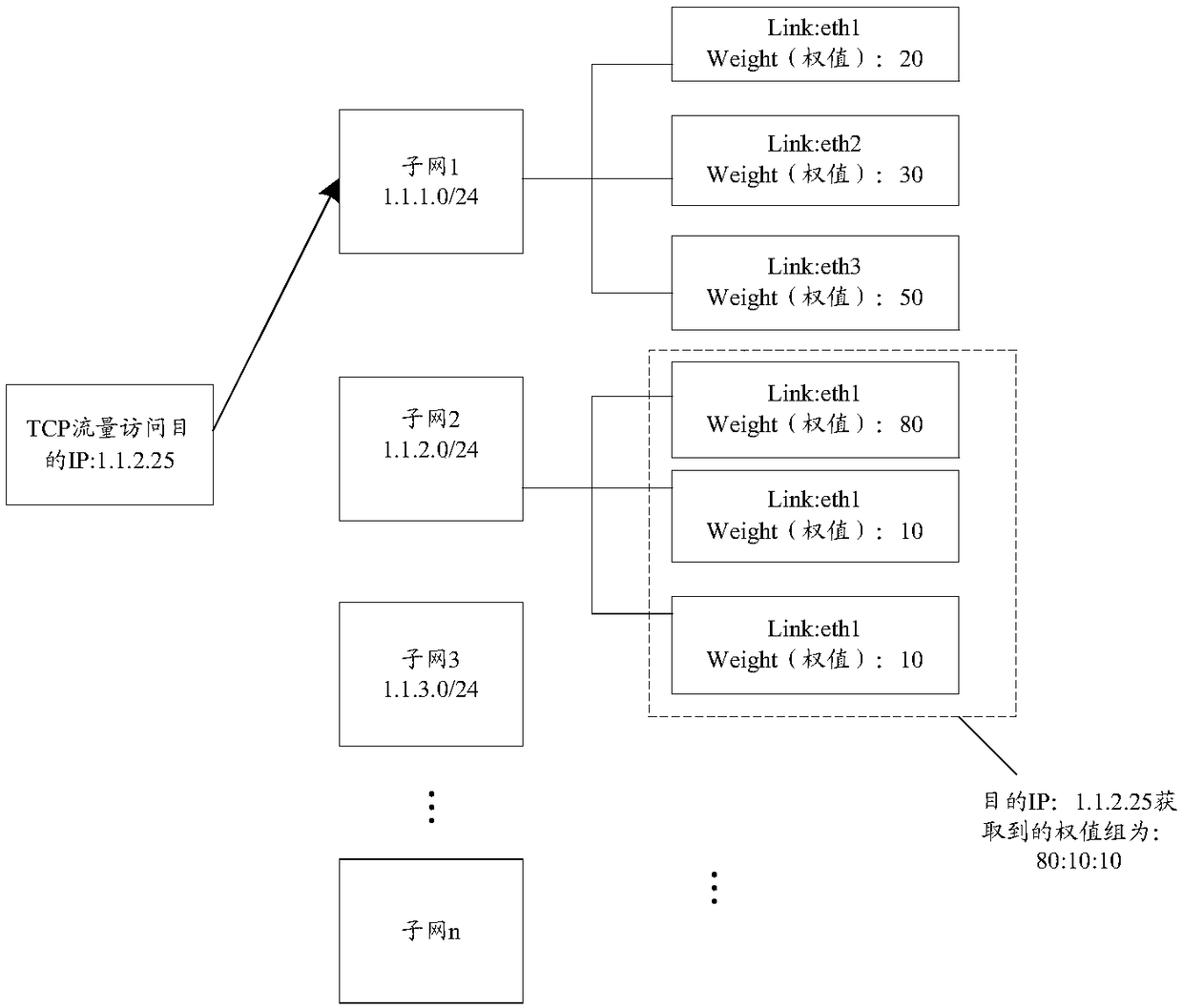
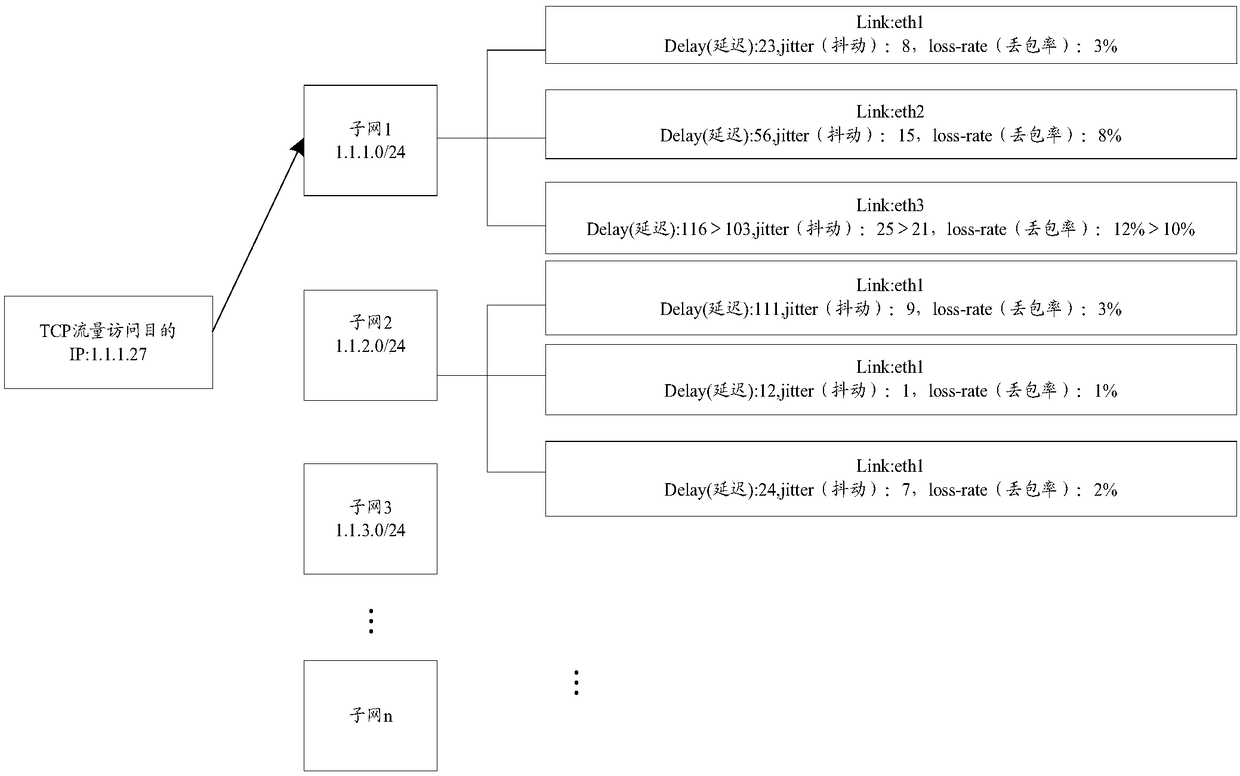
Traffic balancing scheduling method and apparatus
InactiveCN108337184AImprove network qualityImprove Internet experienceData switching networksTraffic capacityTraffic balancing
The invention discloses a traffic balancing scheduling method and apparatus. The method comprises the following steps: determining a plurality of weights corresponding to a plurality of links in a destination subnet to be accessed to obtain a first weight group corresponding to the destination subnet; updating the first weight group to obtain a second weight group; and performing balancing scheduling on the traffics flowing into the destination subnet according to the second weight group. By adoption of the traffic balancing scheduling method and apparatus, the technical problem that the network quality of the egress traffic in the multi-egress link is poor in the related art is solved, the network quality of the egress traffic is improved, and the user experience is also improved.
Owner:HILLSTONE NETWORKS CORP
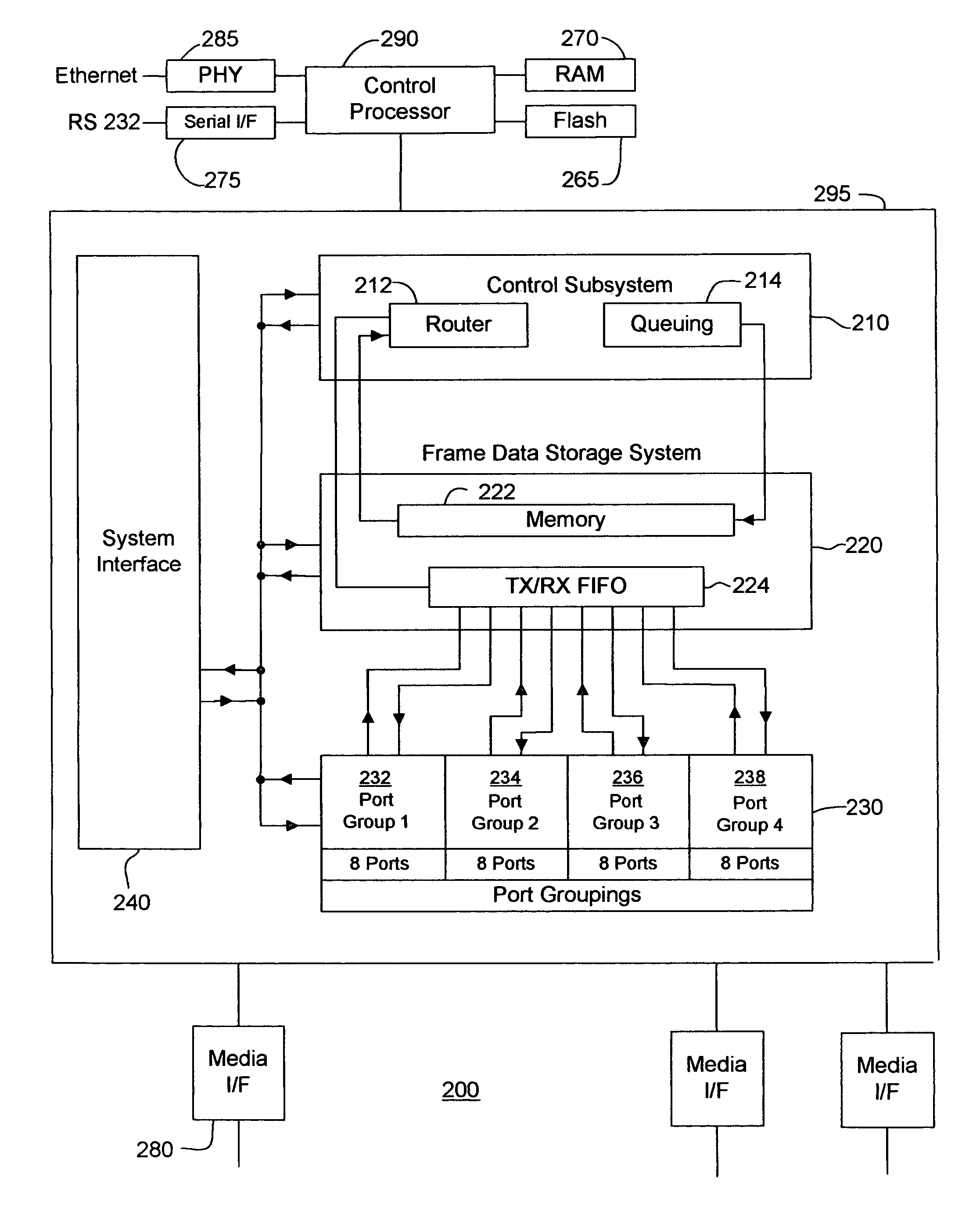
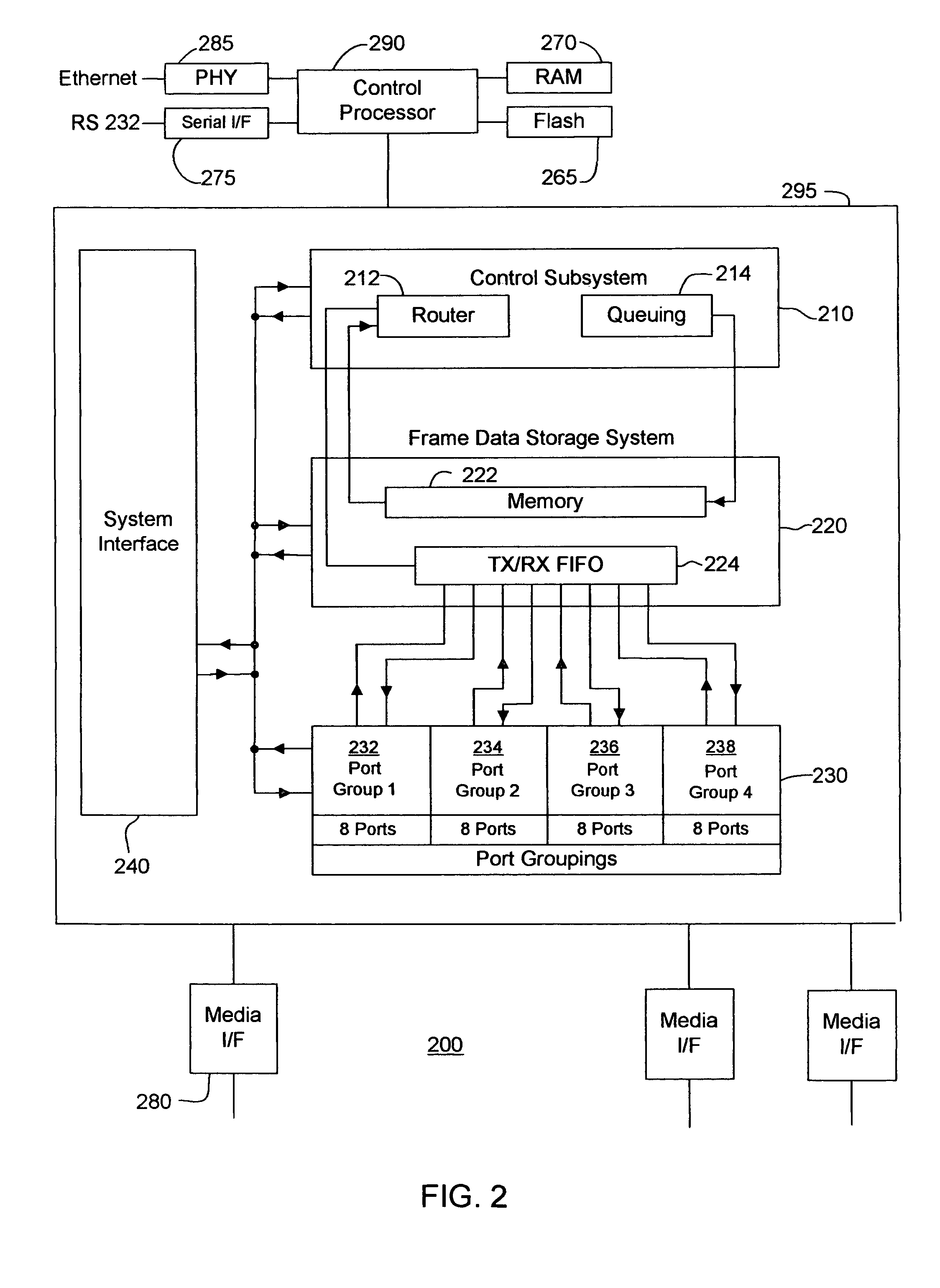
Frame traffic balancing across trunk groups
Embodiments of methods, apparatuses and / or systems for balancing flow across trunk groups are disclosed. For example, a method of routing a flow of frames may include receiving at least one frame; selecting an exit port of a switch for the at least one frame to exit based, at least in part, on balancing flow across trunk groups; and transmitting the at least one frame.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for controlling traffic balance between peering networks
A method that measures ratio, relative to a peering network, of traffic burden of incoming traffic to traffic burden of outgoing traffic, where traffic burden takes into account traffic volume and distance that the traffic traverses through the network. A determination is made from this ratio as to whether an imbalance exists with the peering network. With the assistance of a simulation of changes in routing policy and their effects, an existing or impending imbalance is remedied by changing the routing policy relative to particular customers, for example from a “hot potato” routing policy to a “best exit” routing policy.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com