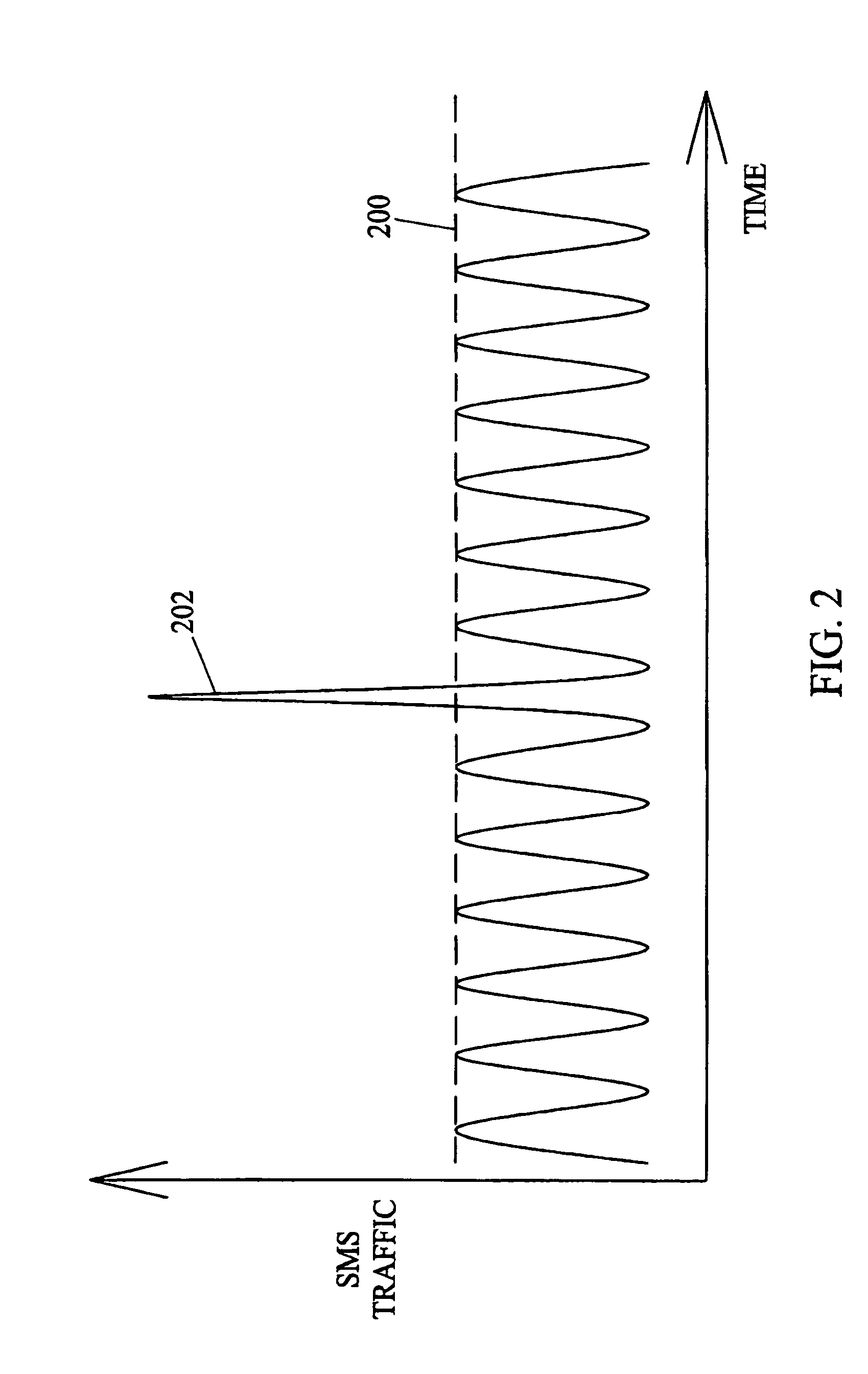
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
142 results about "Signal Transfer Point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
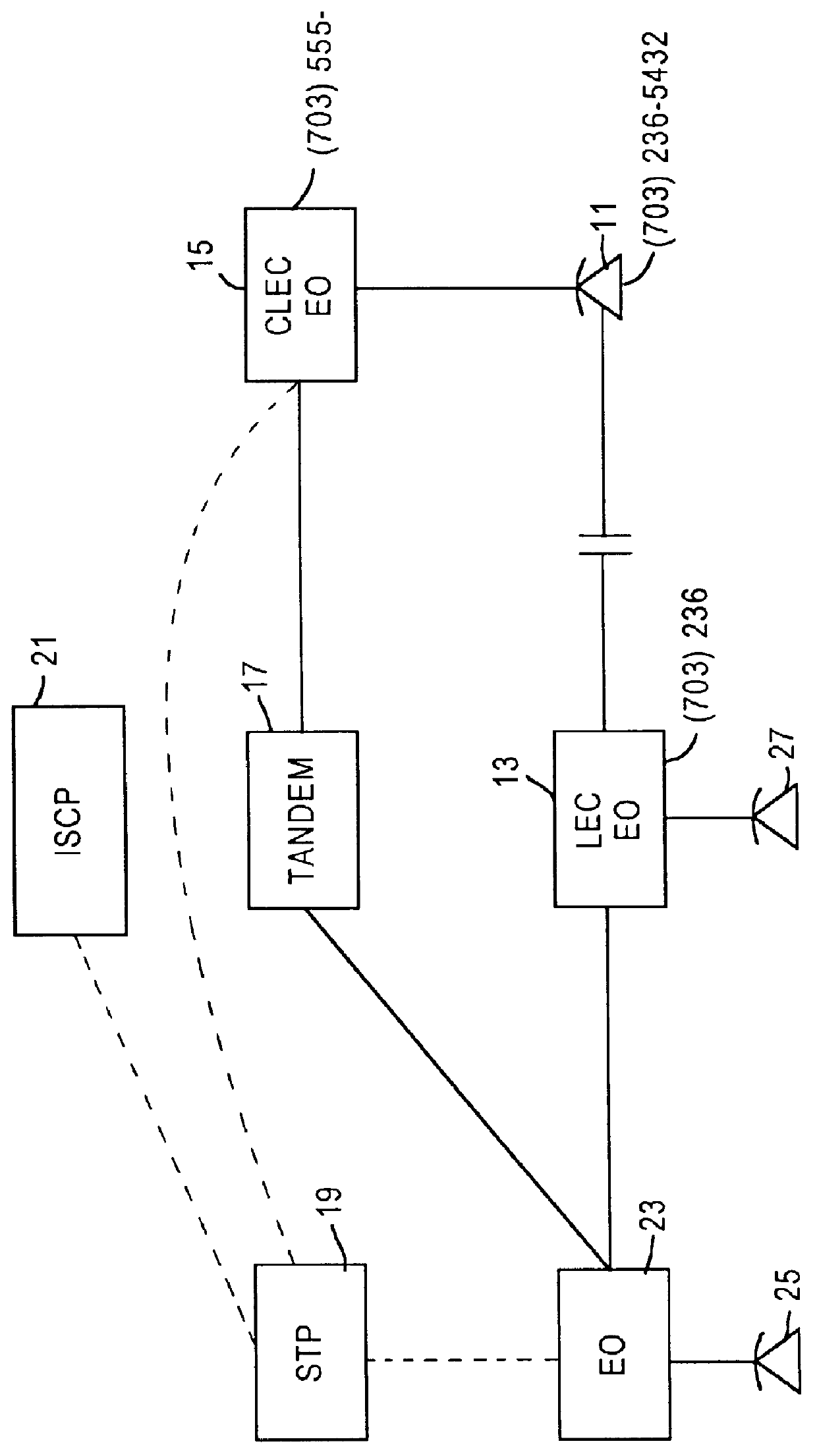
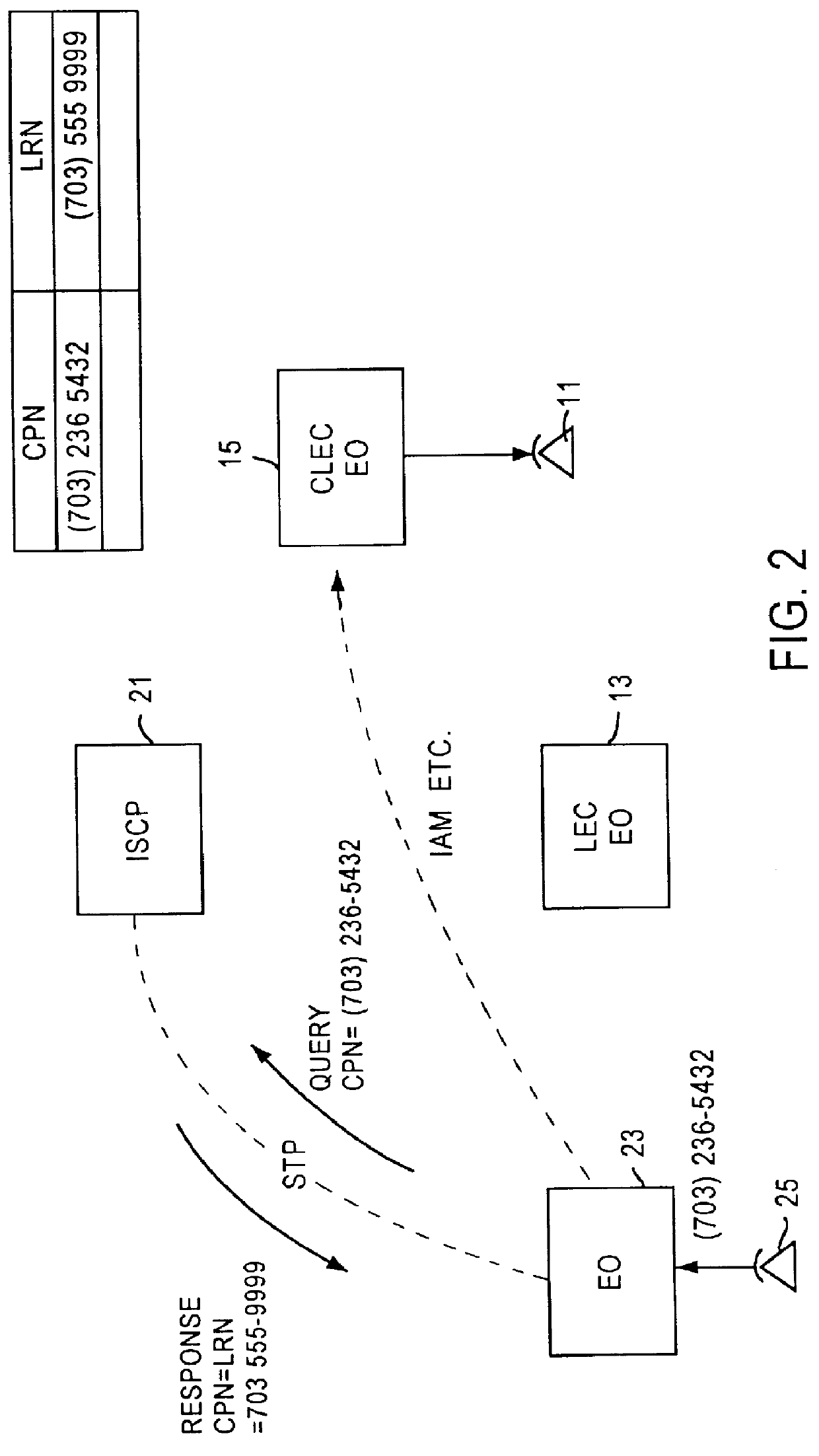
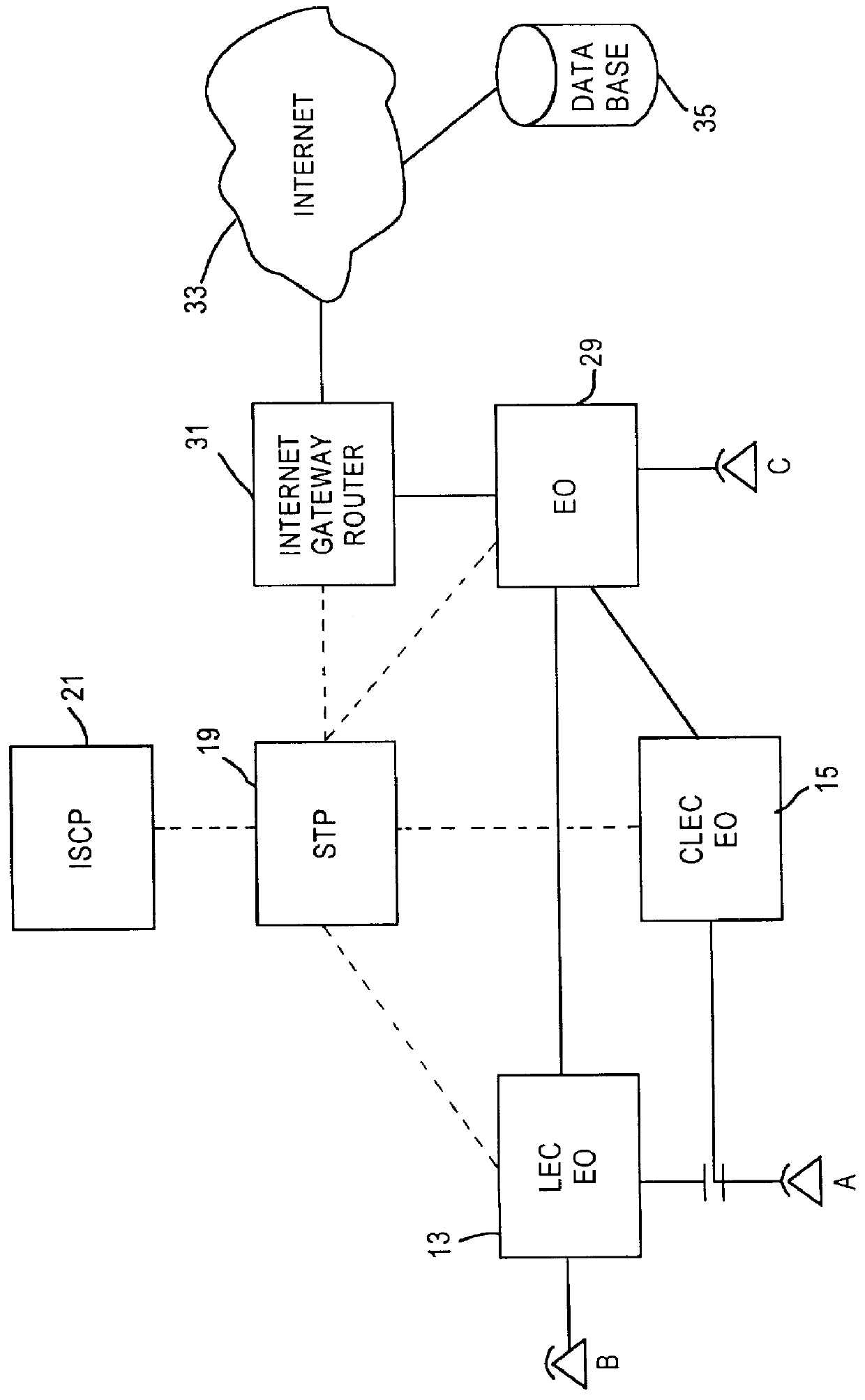
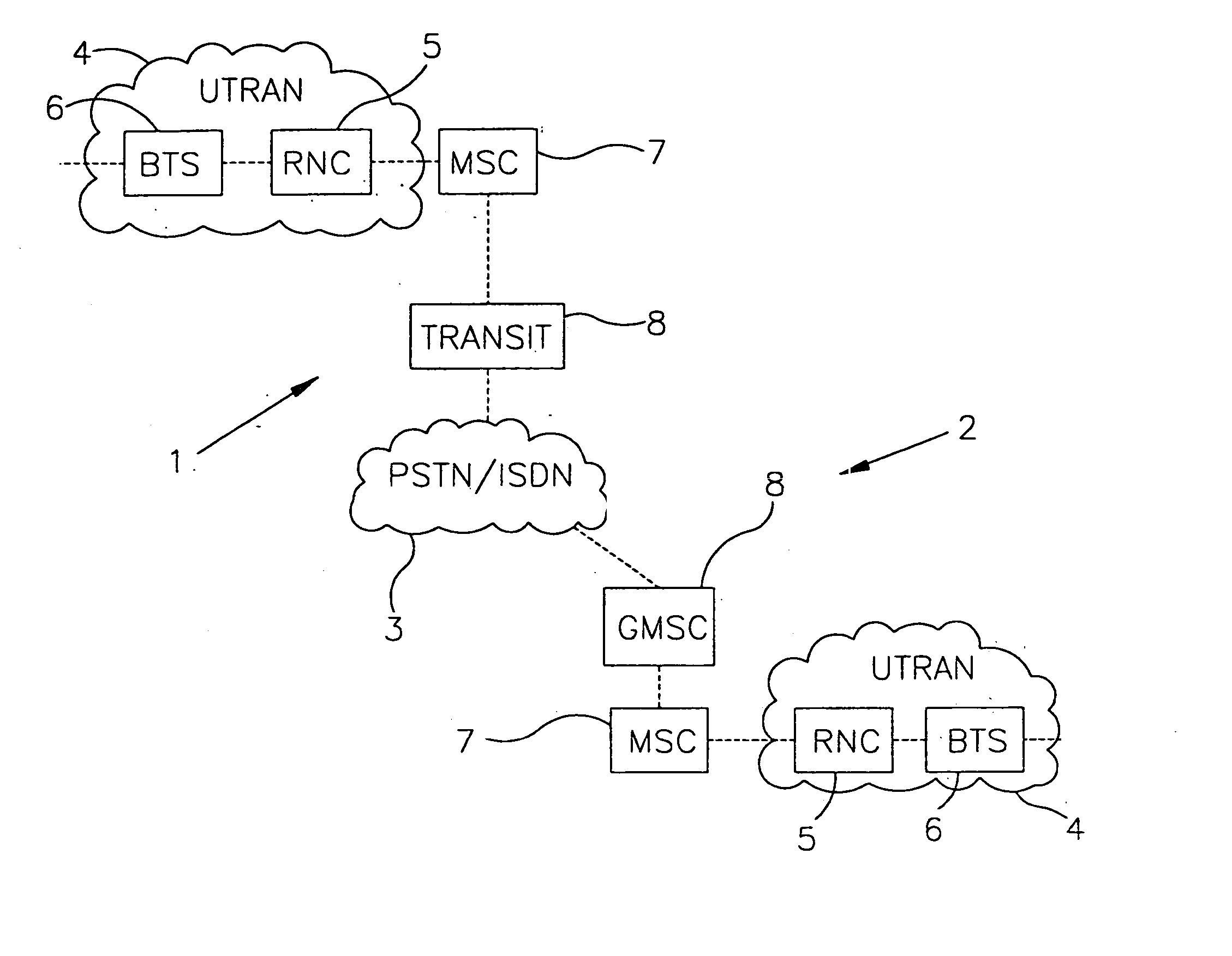
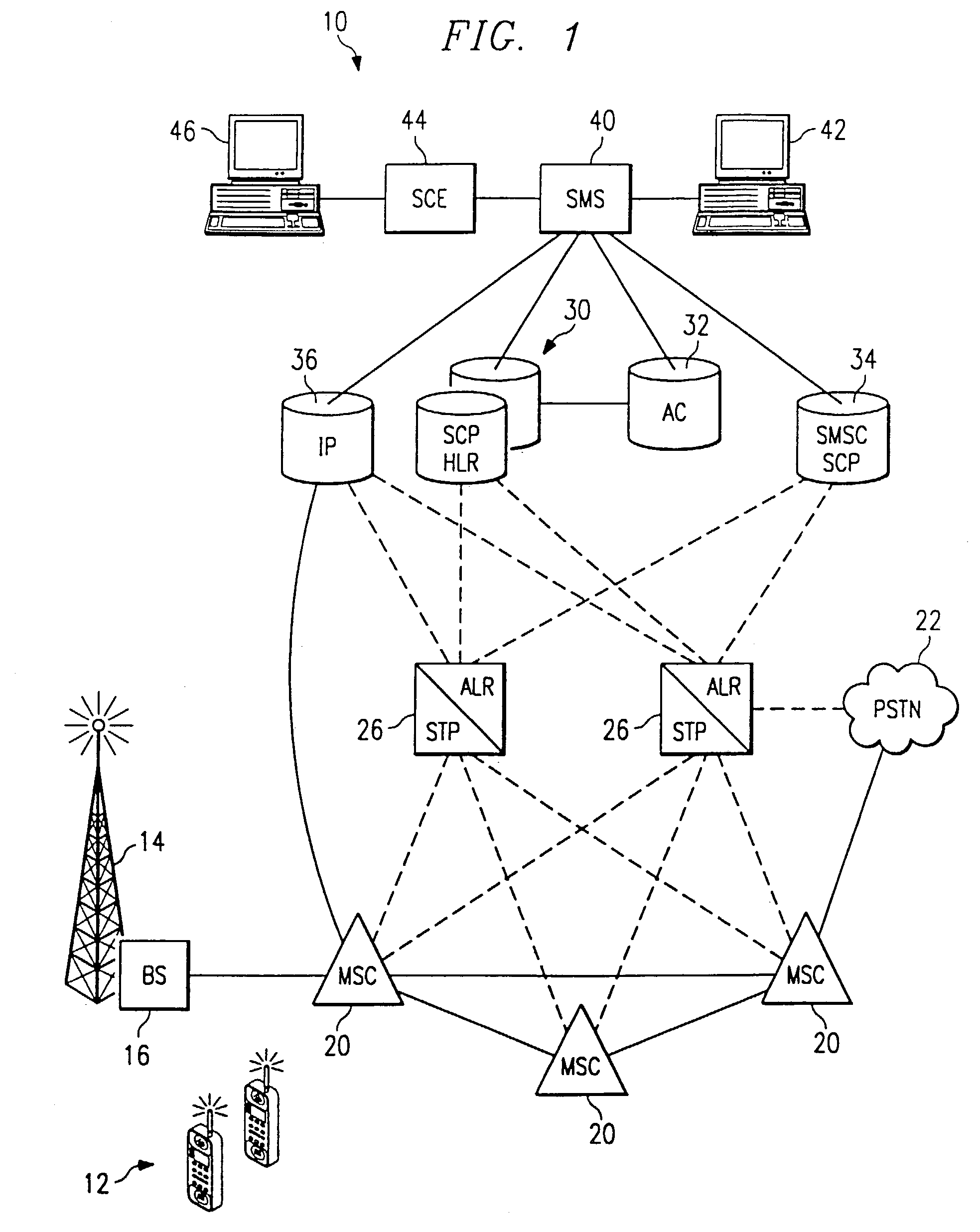
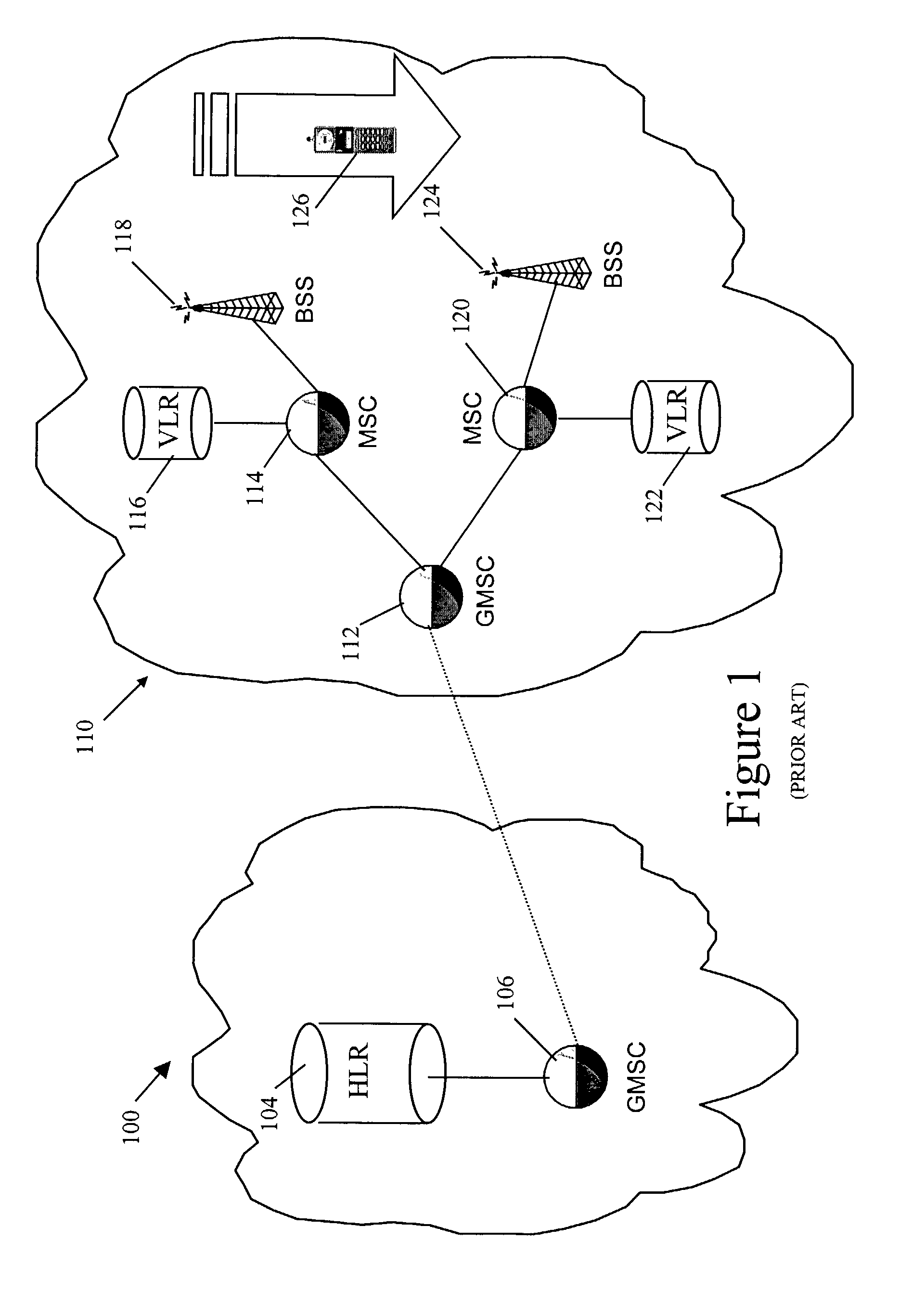
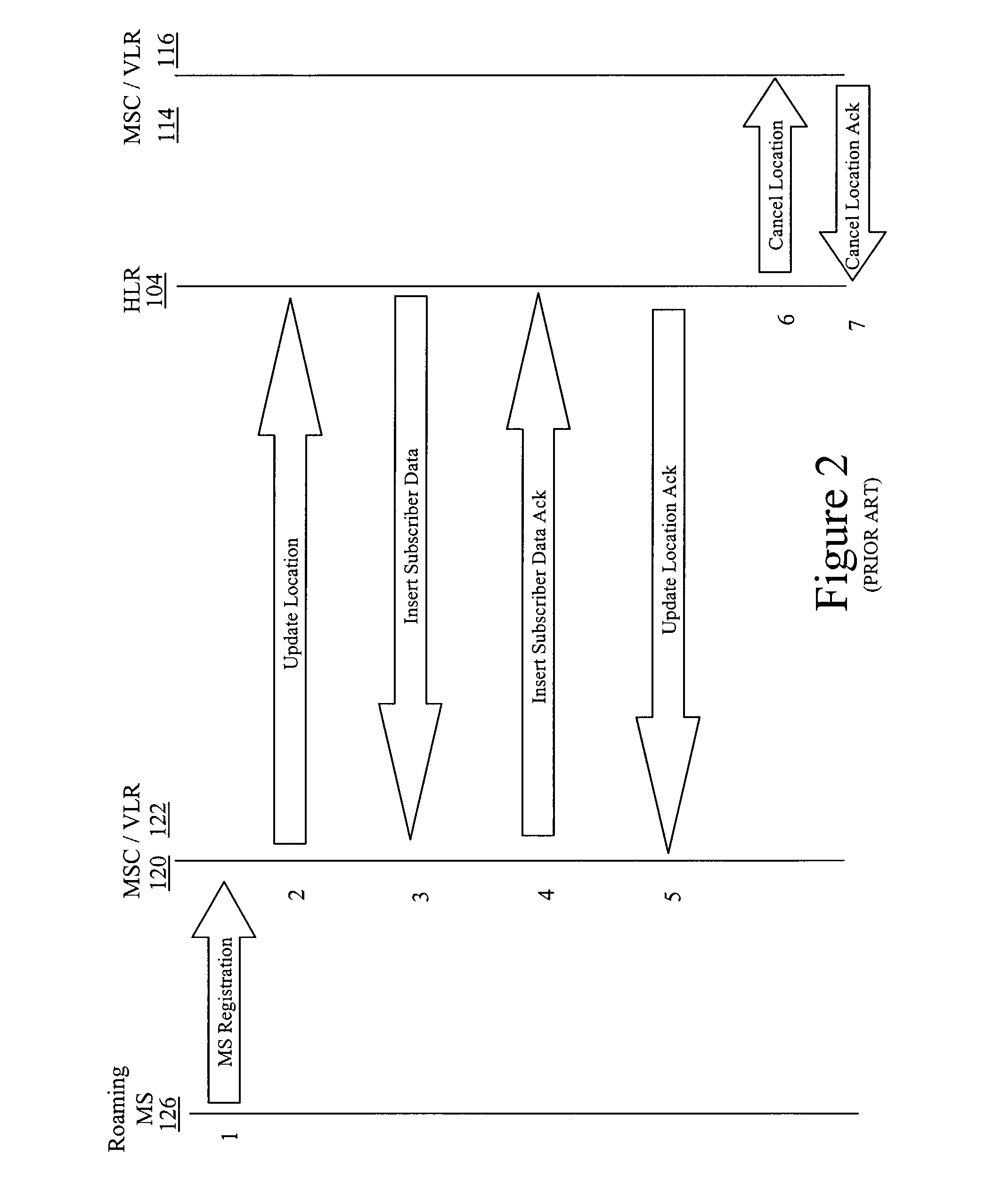
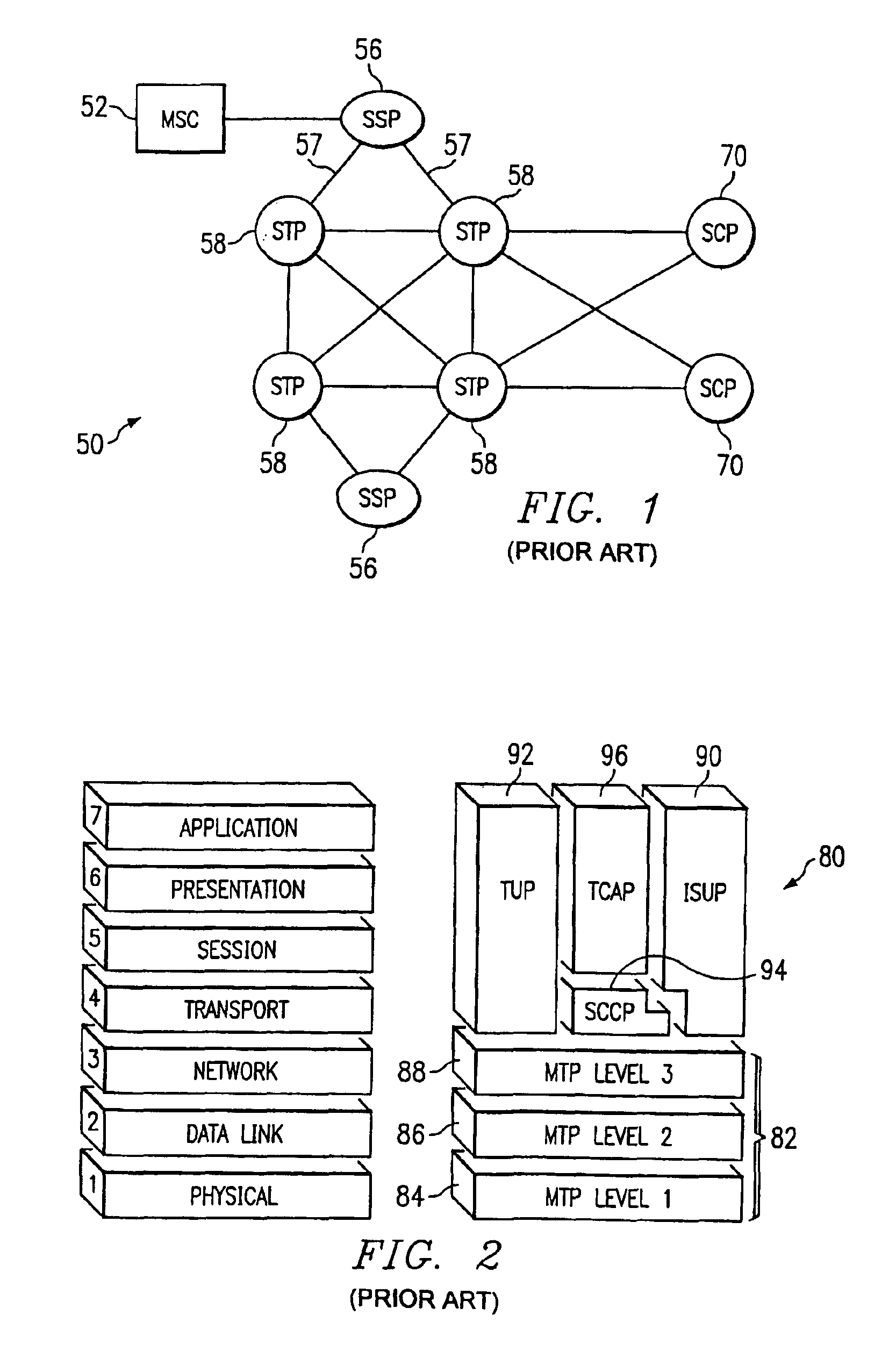
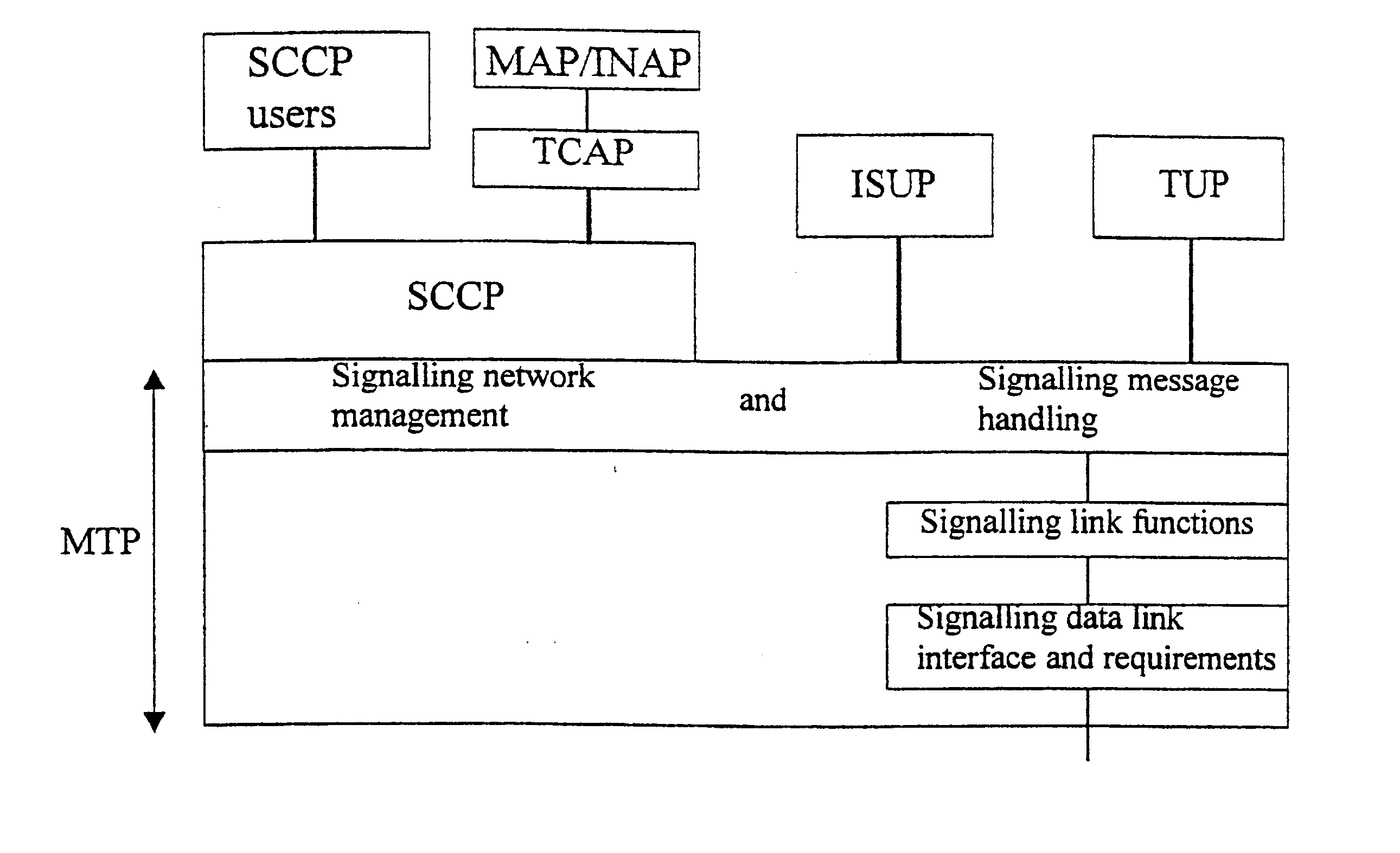
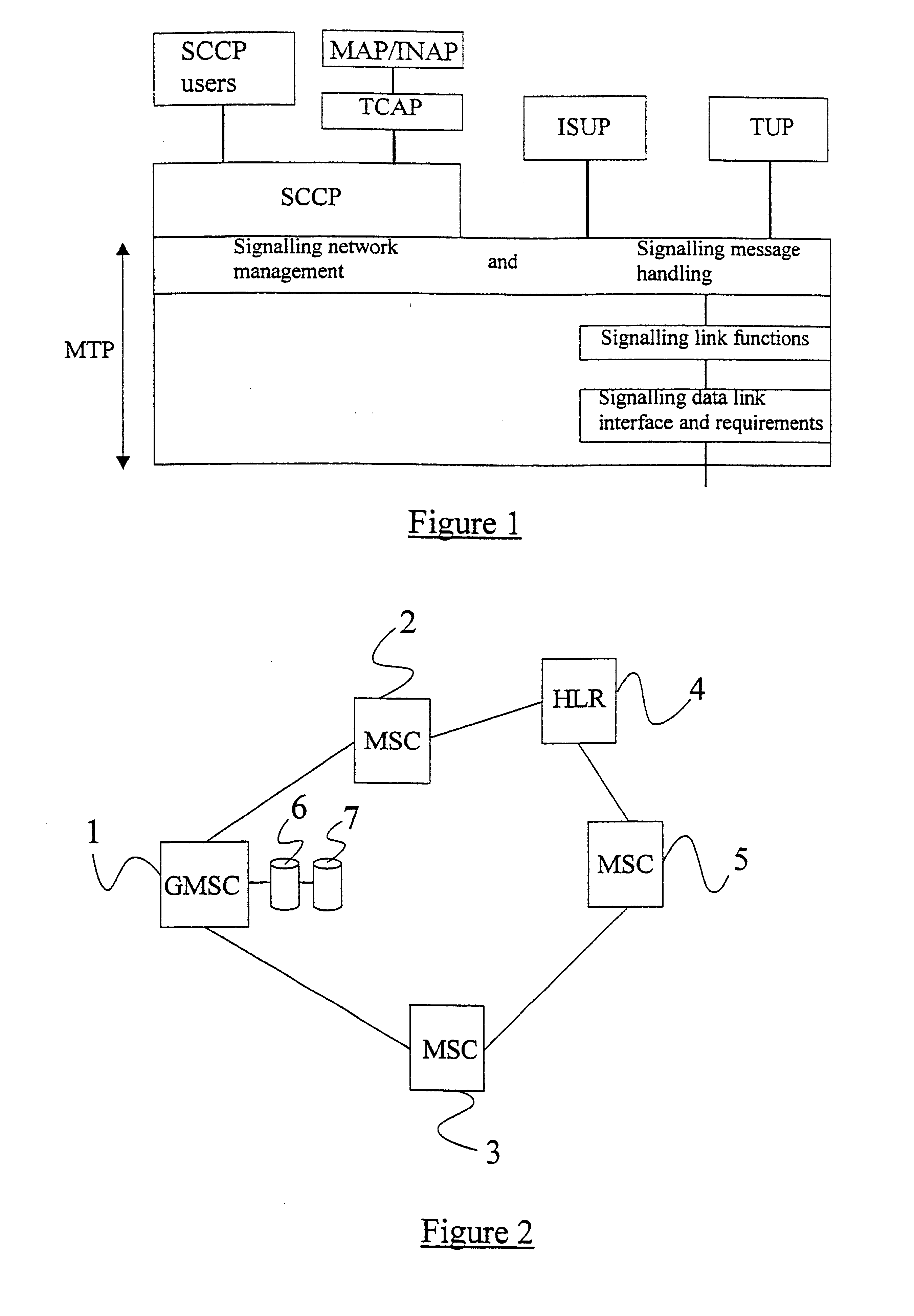
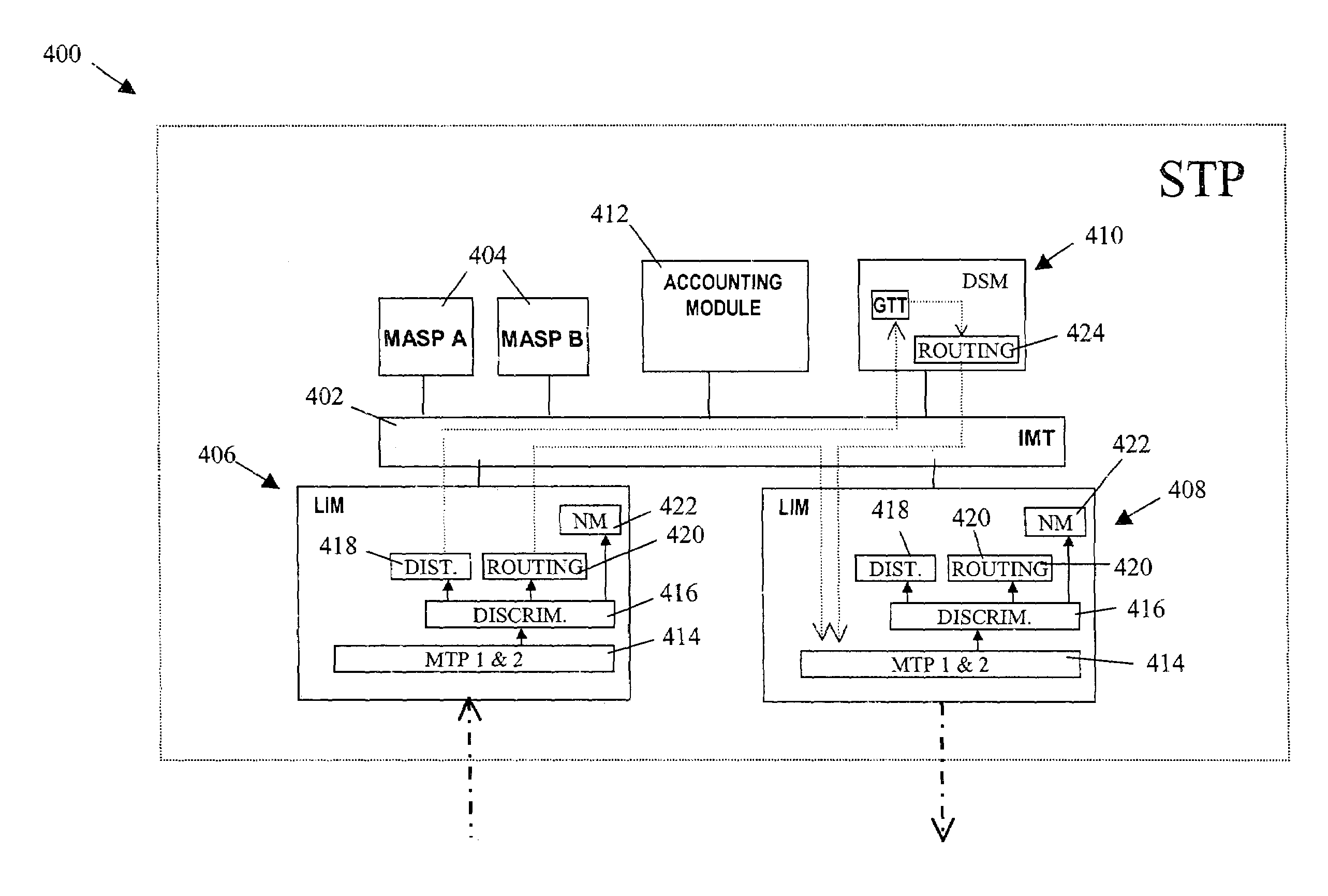
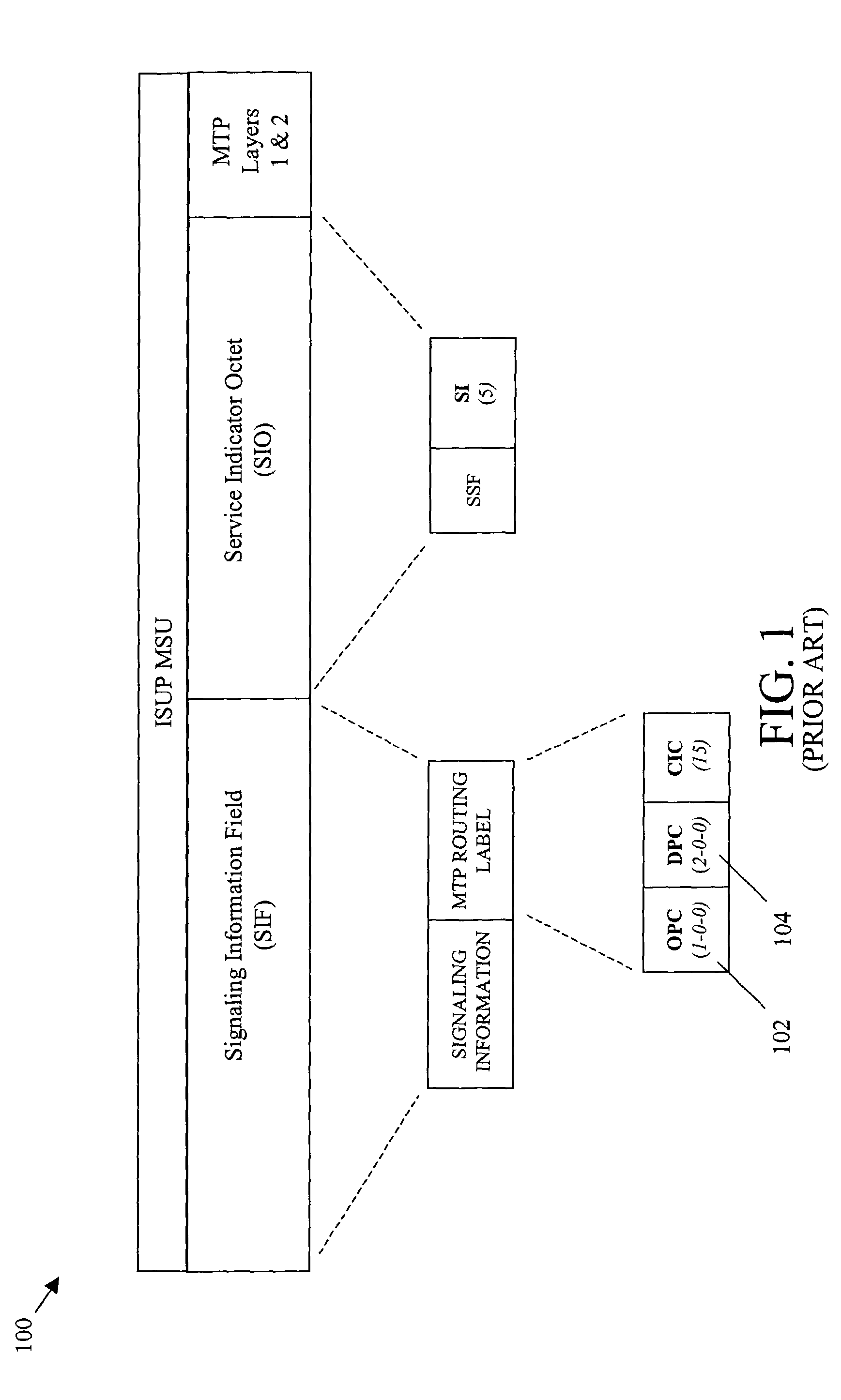
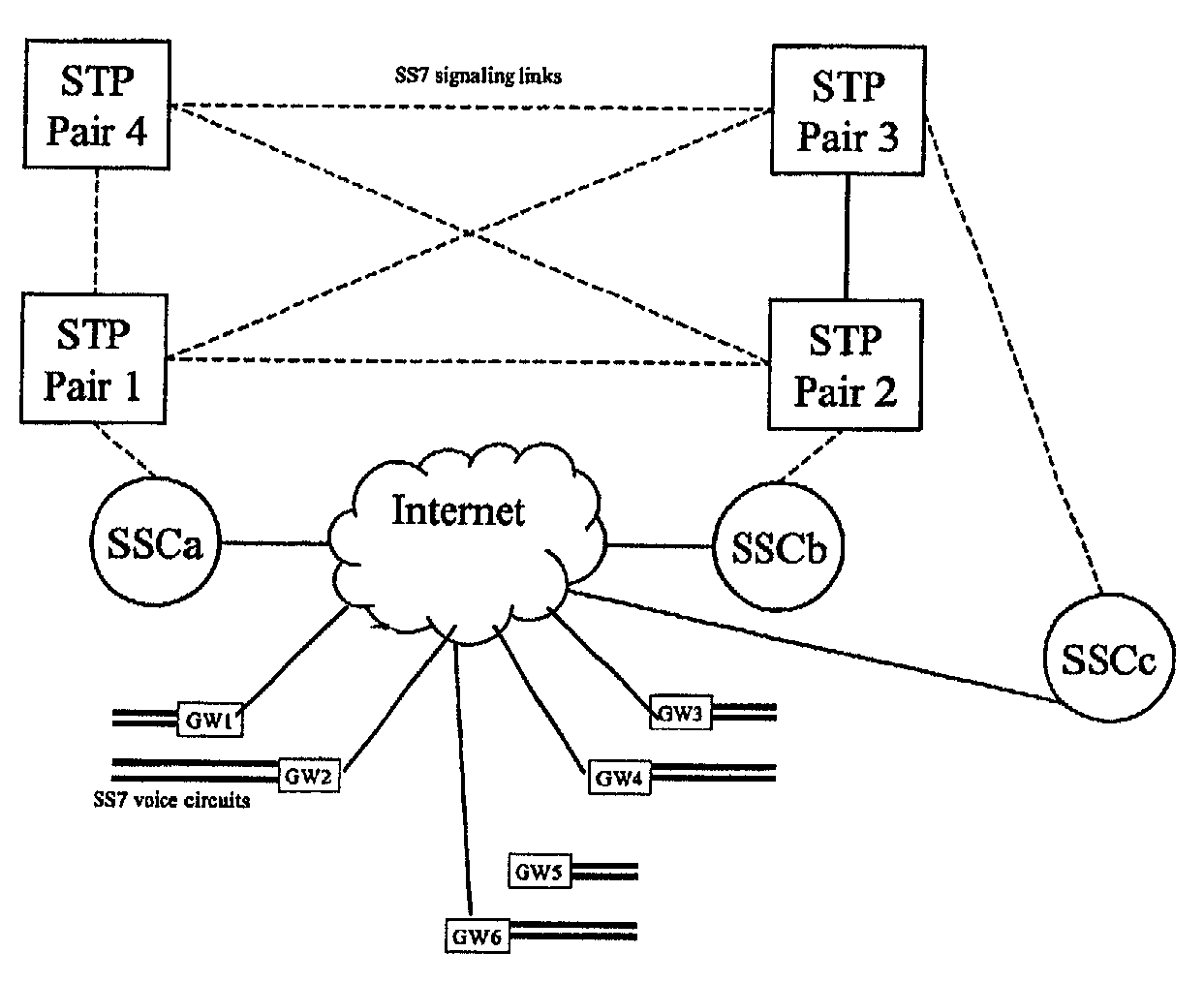
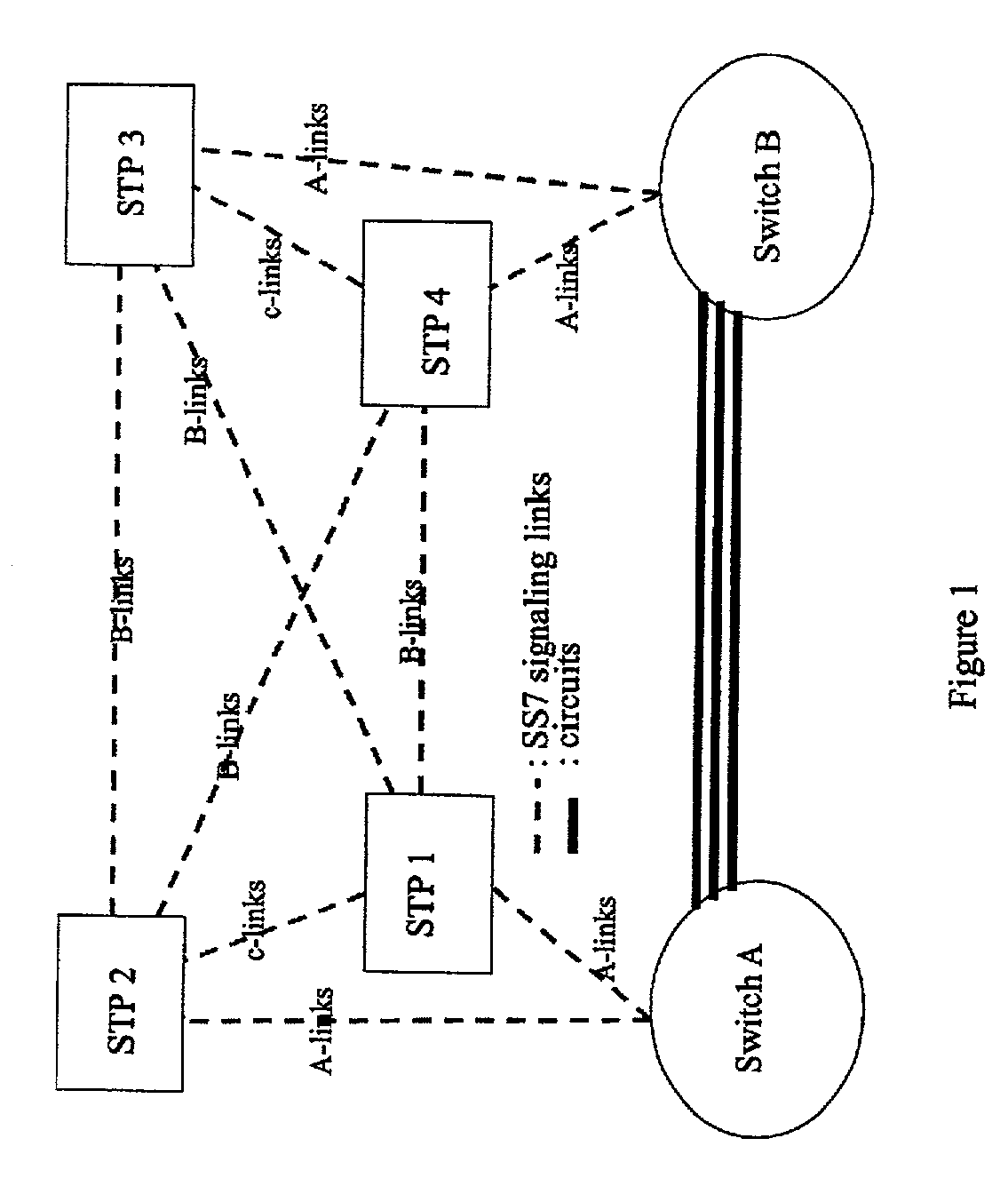
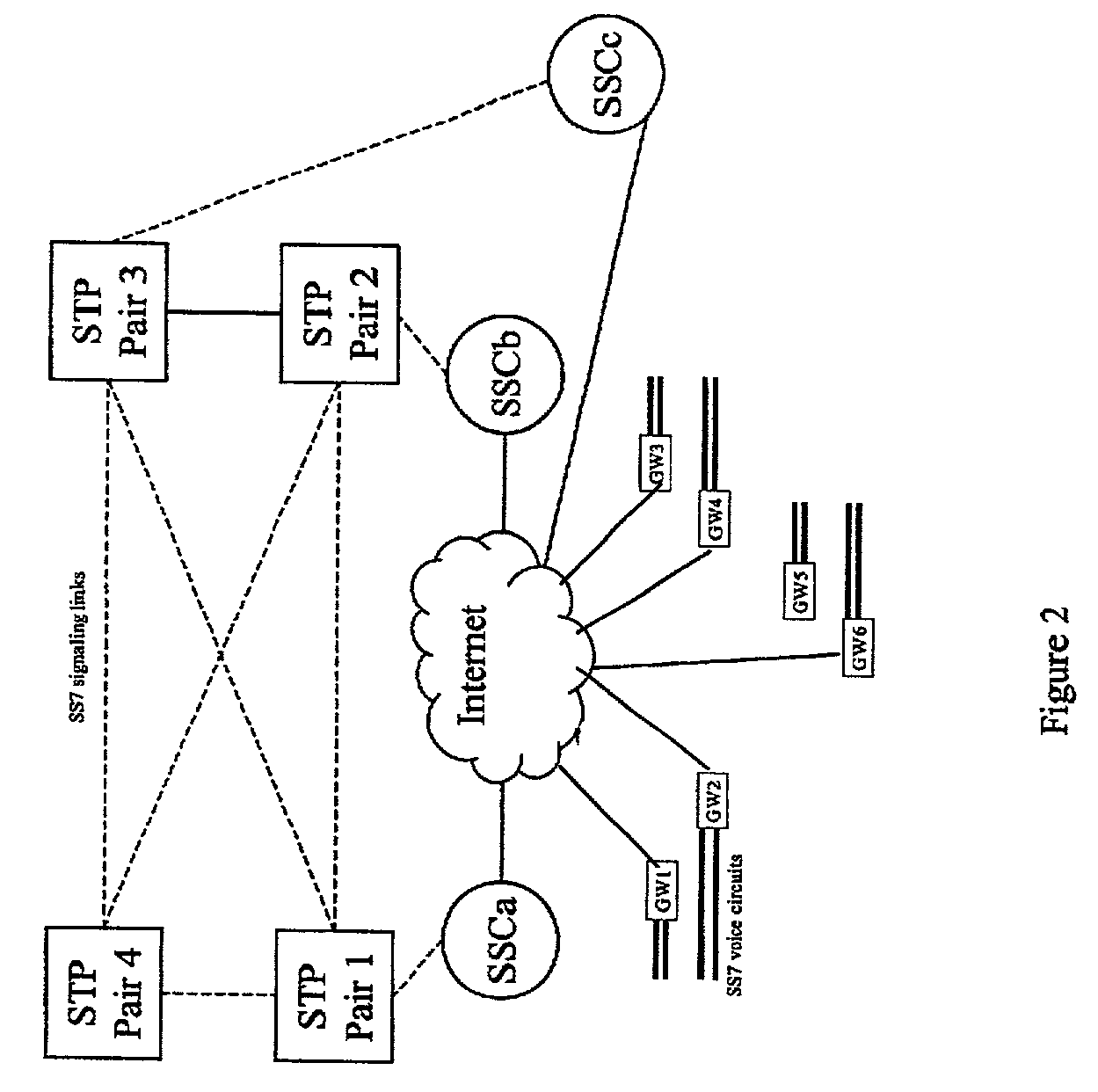
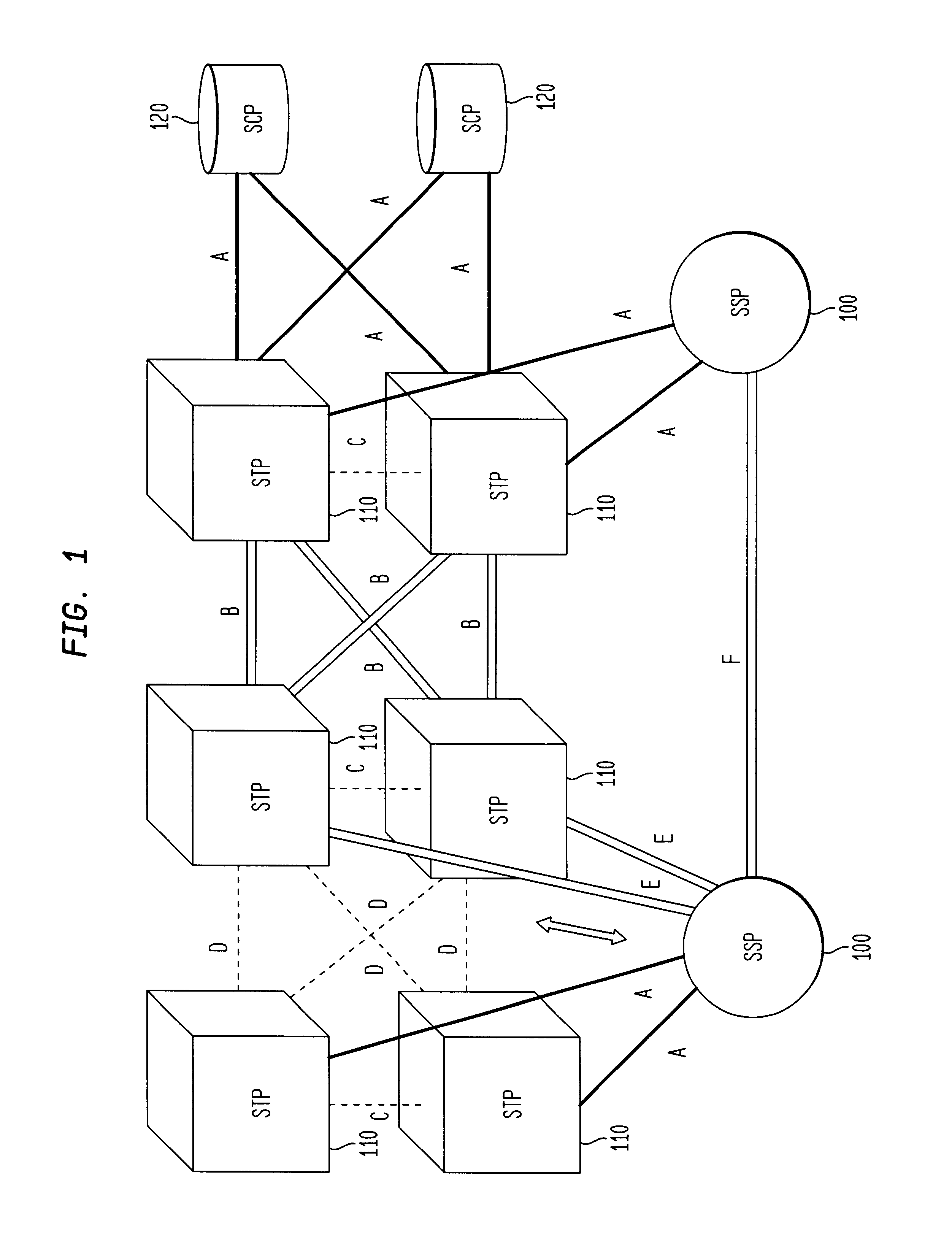
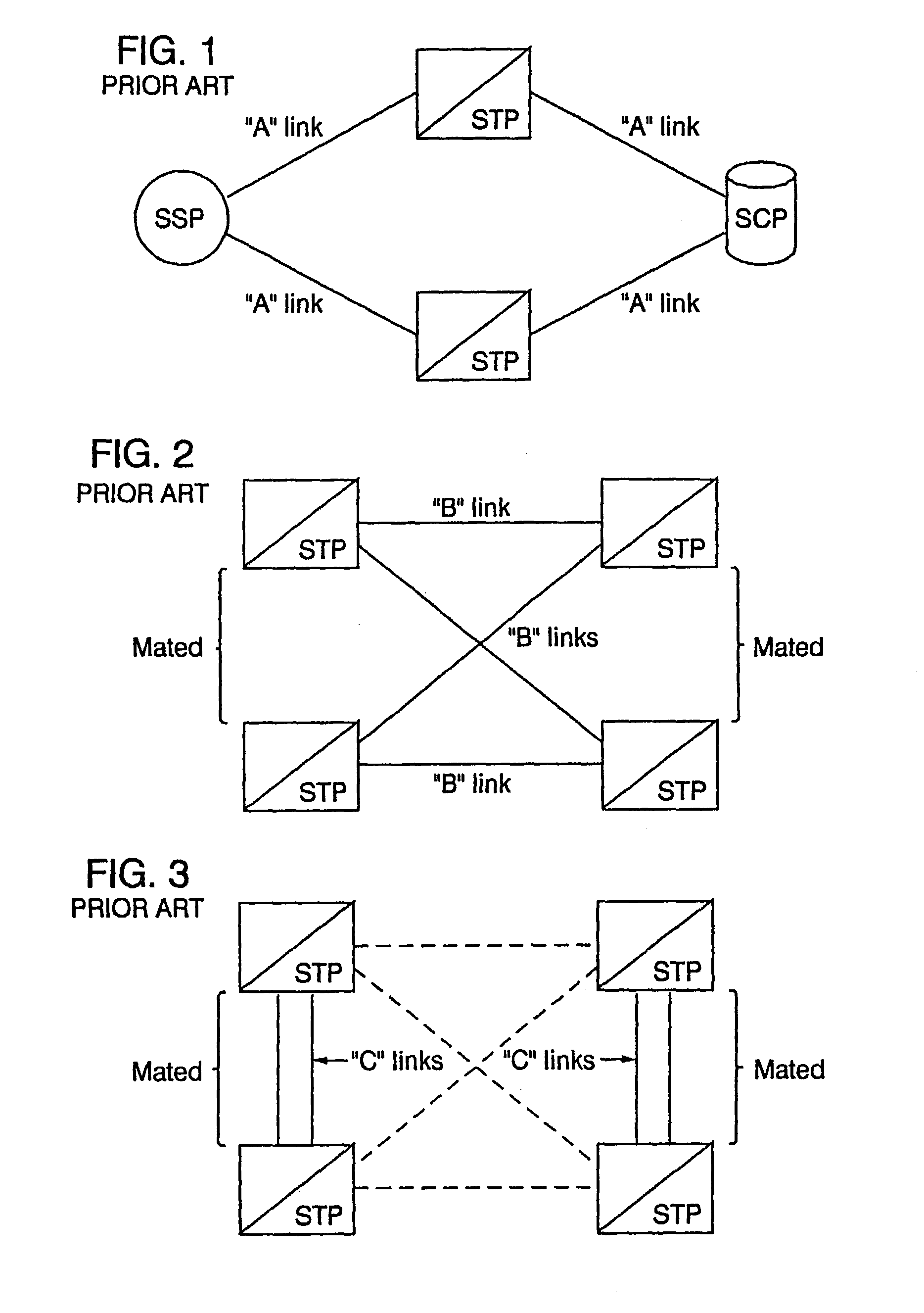
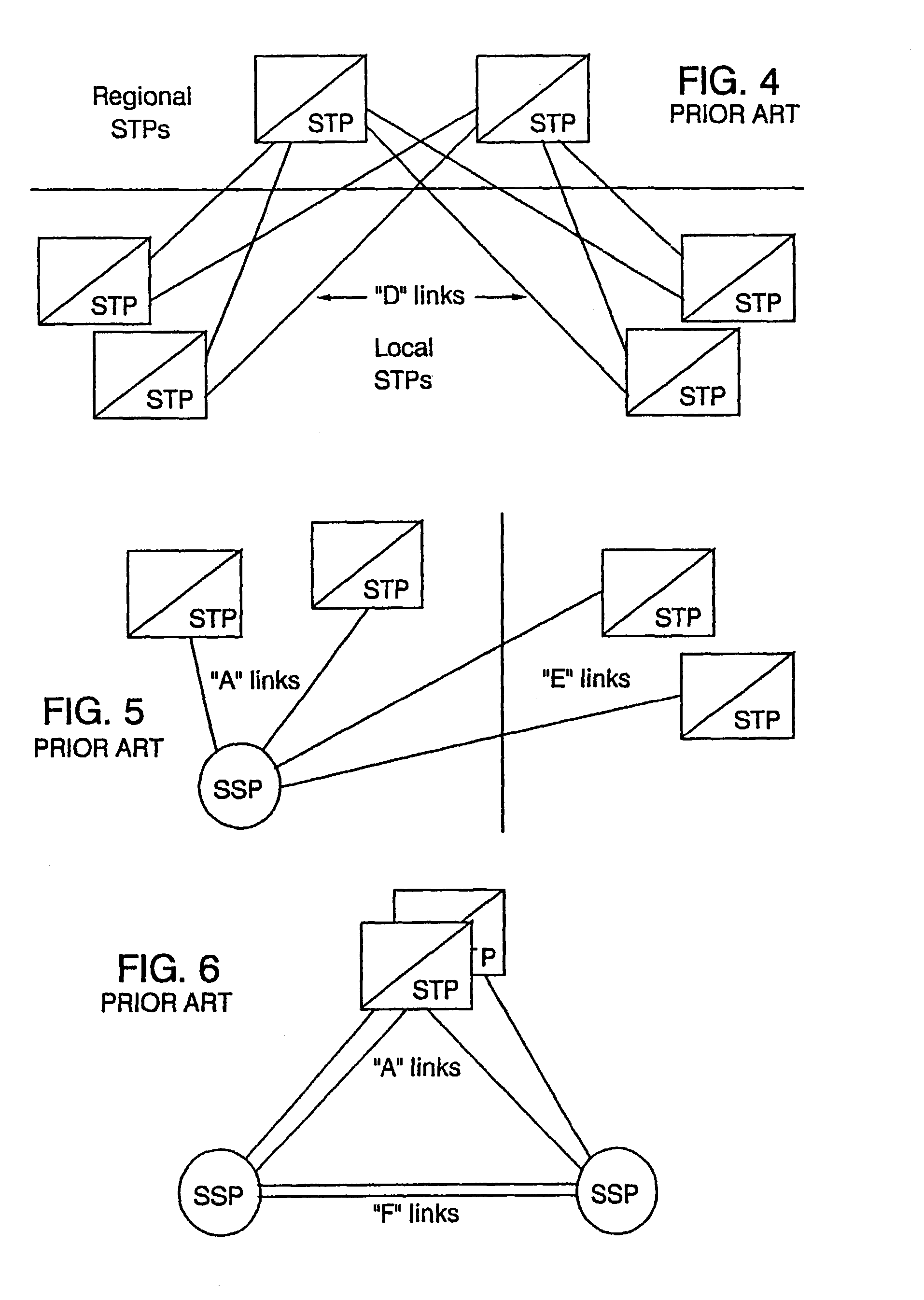
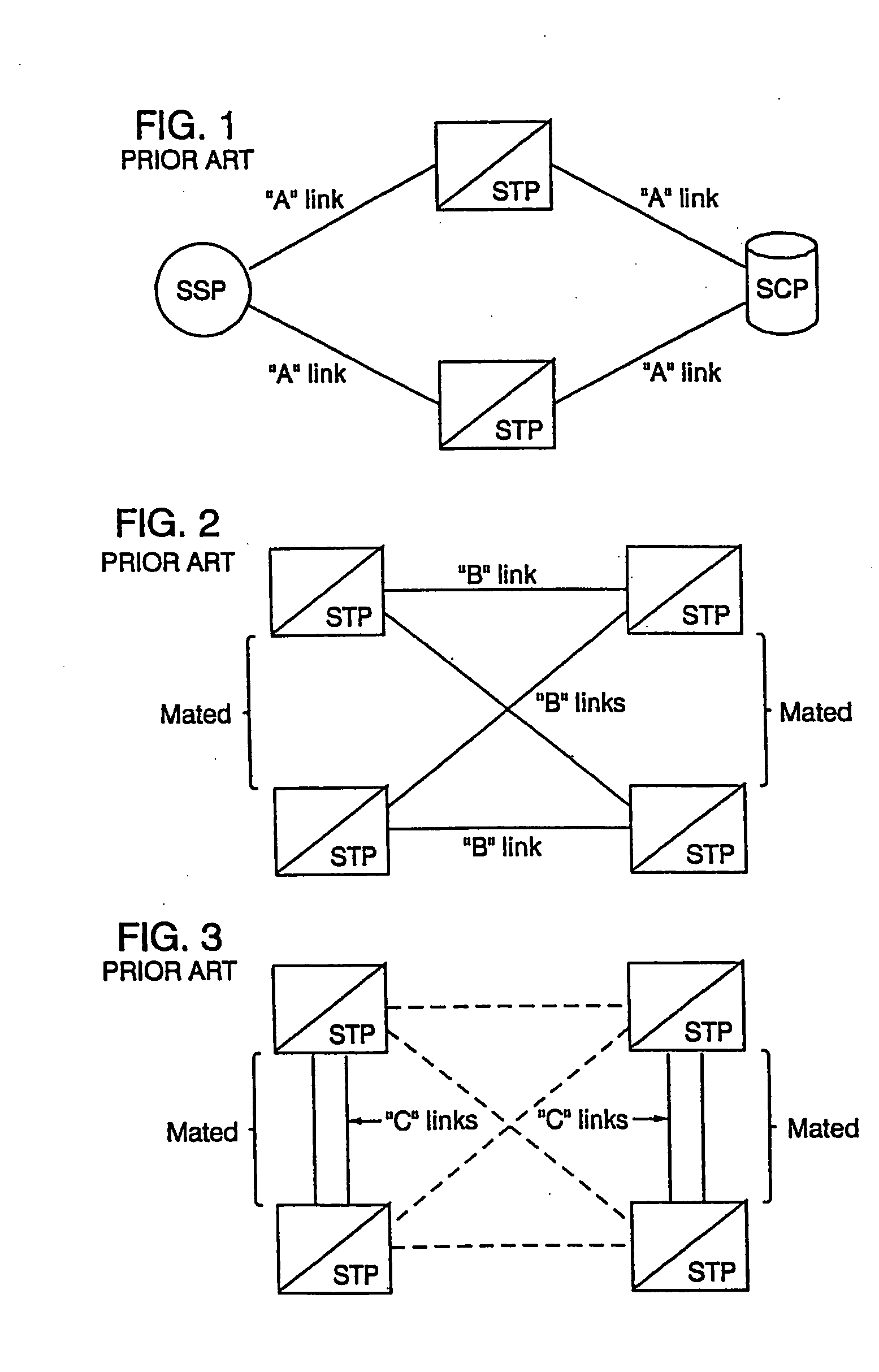
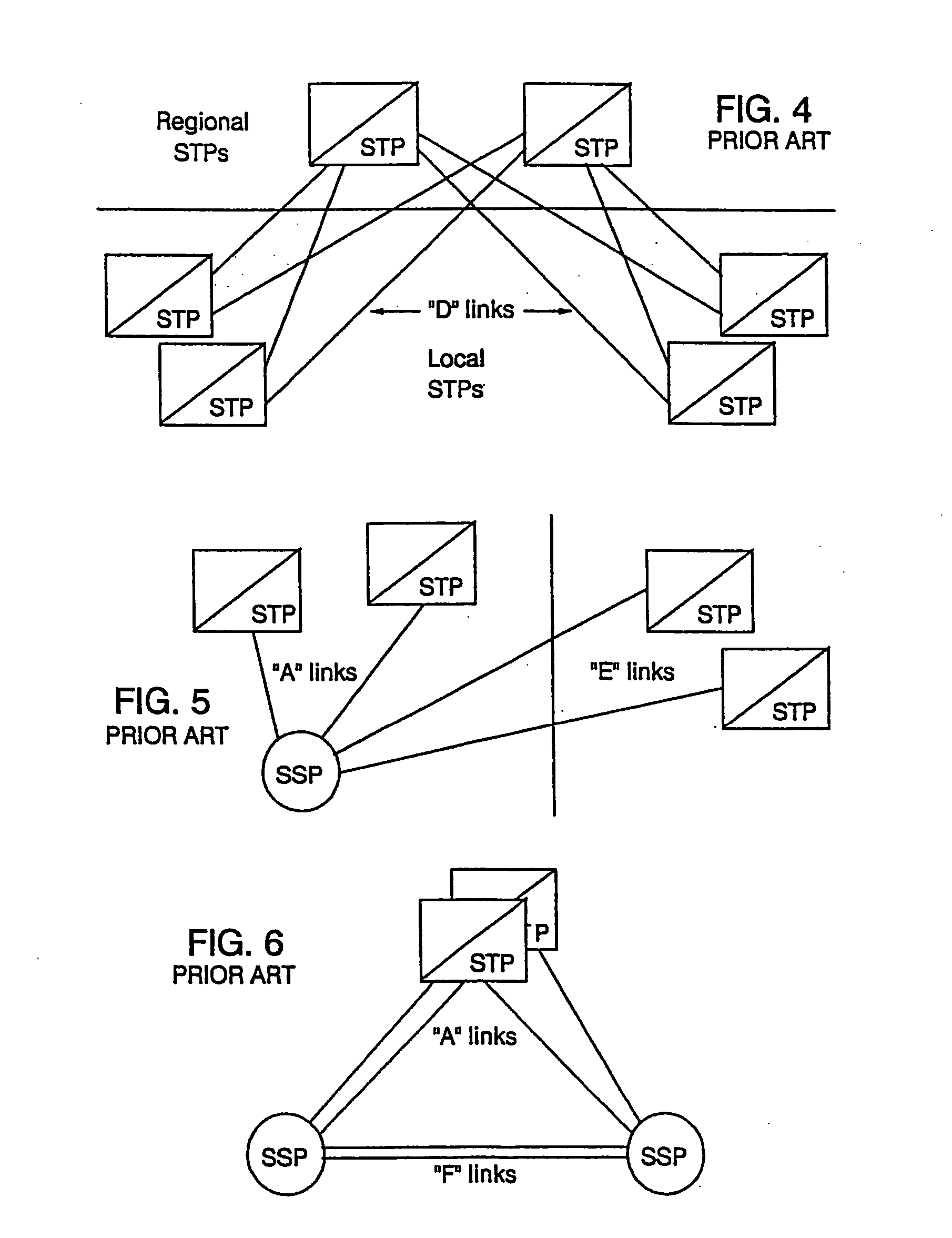
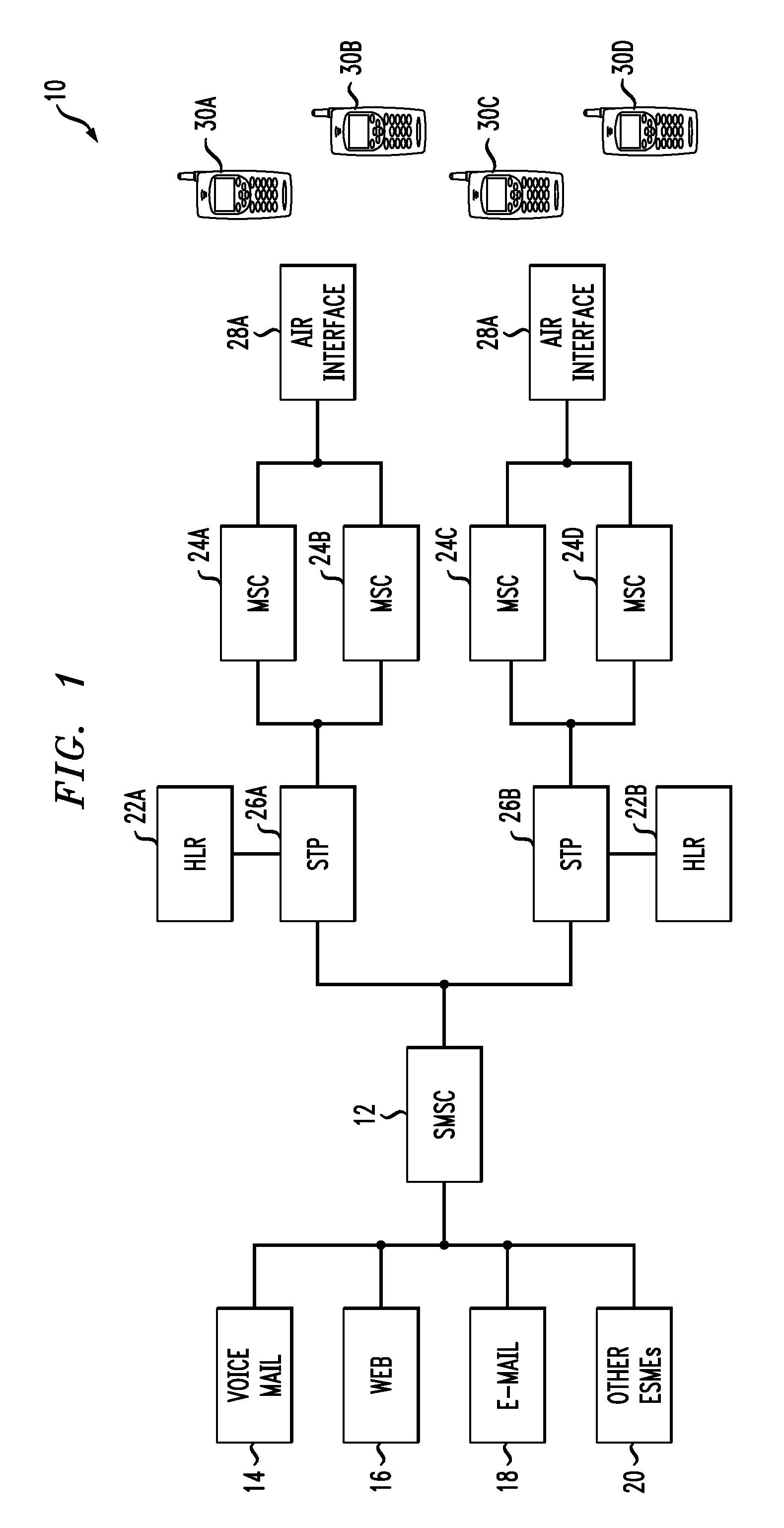
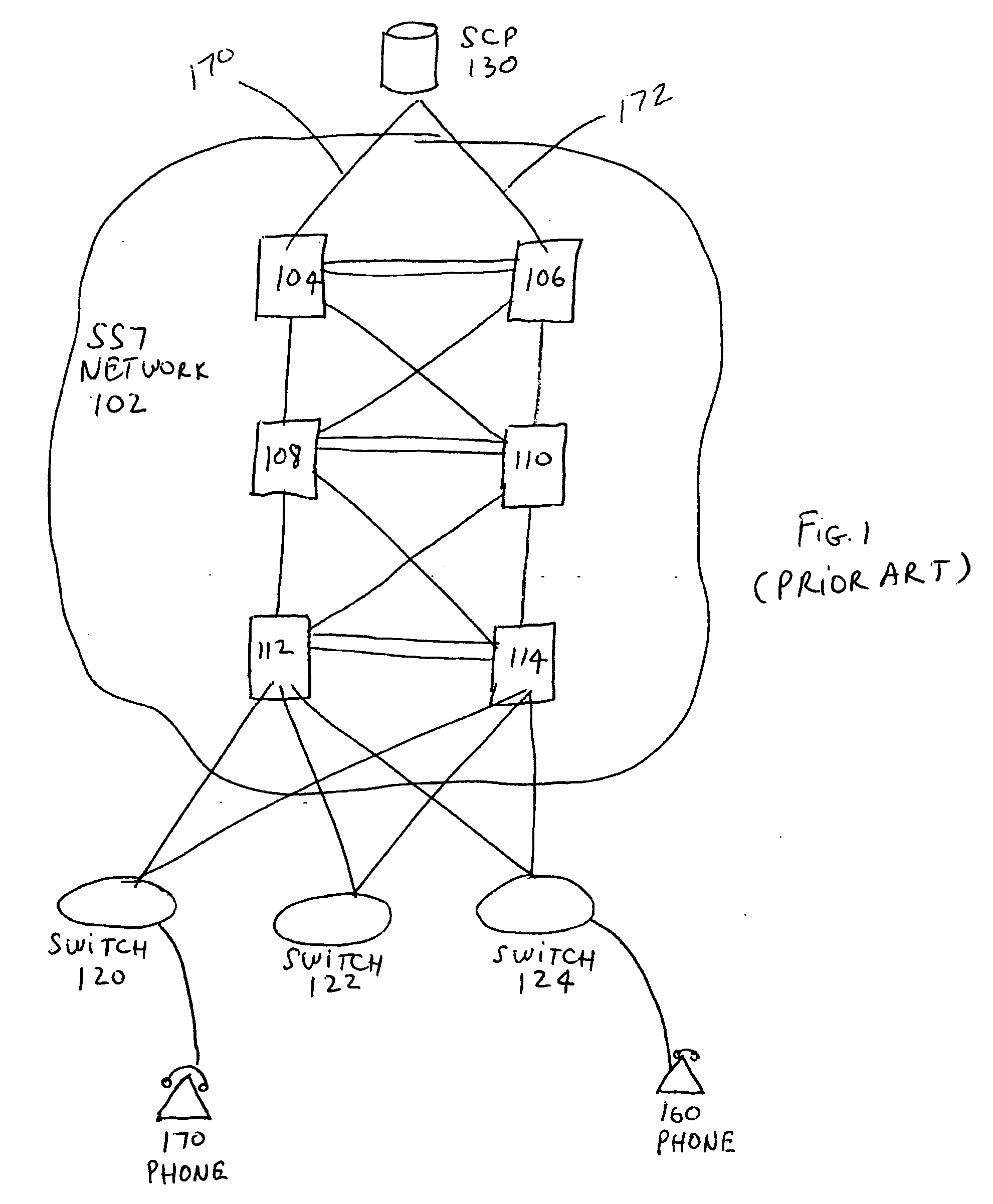
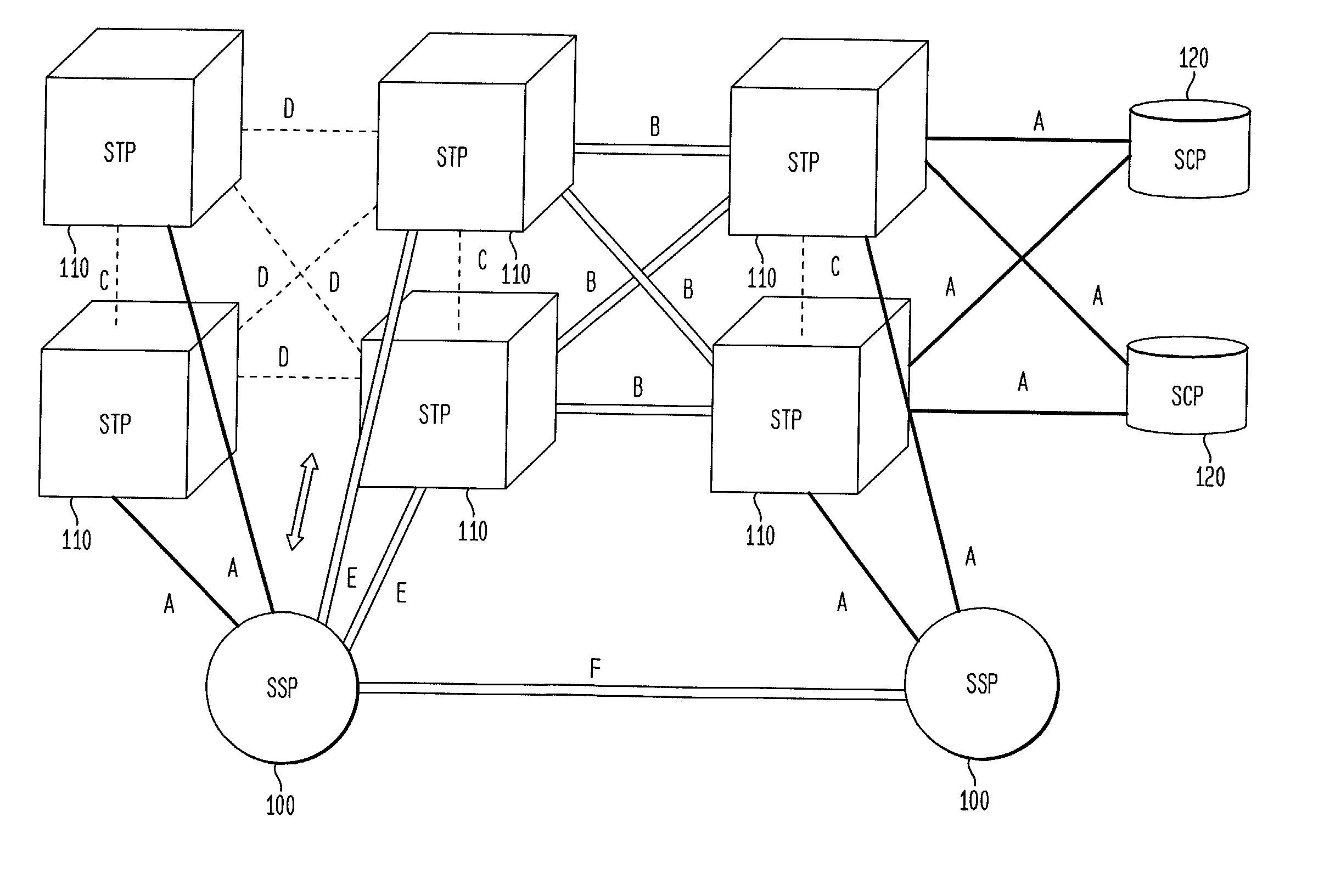
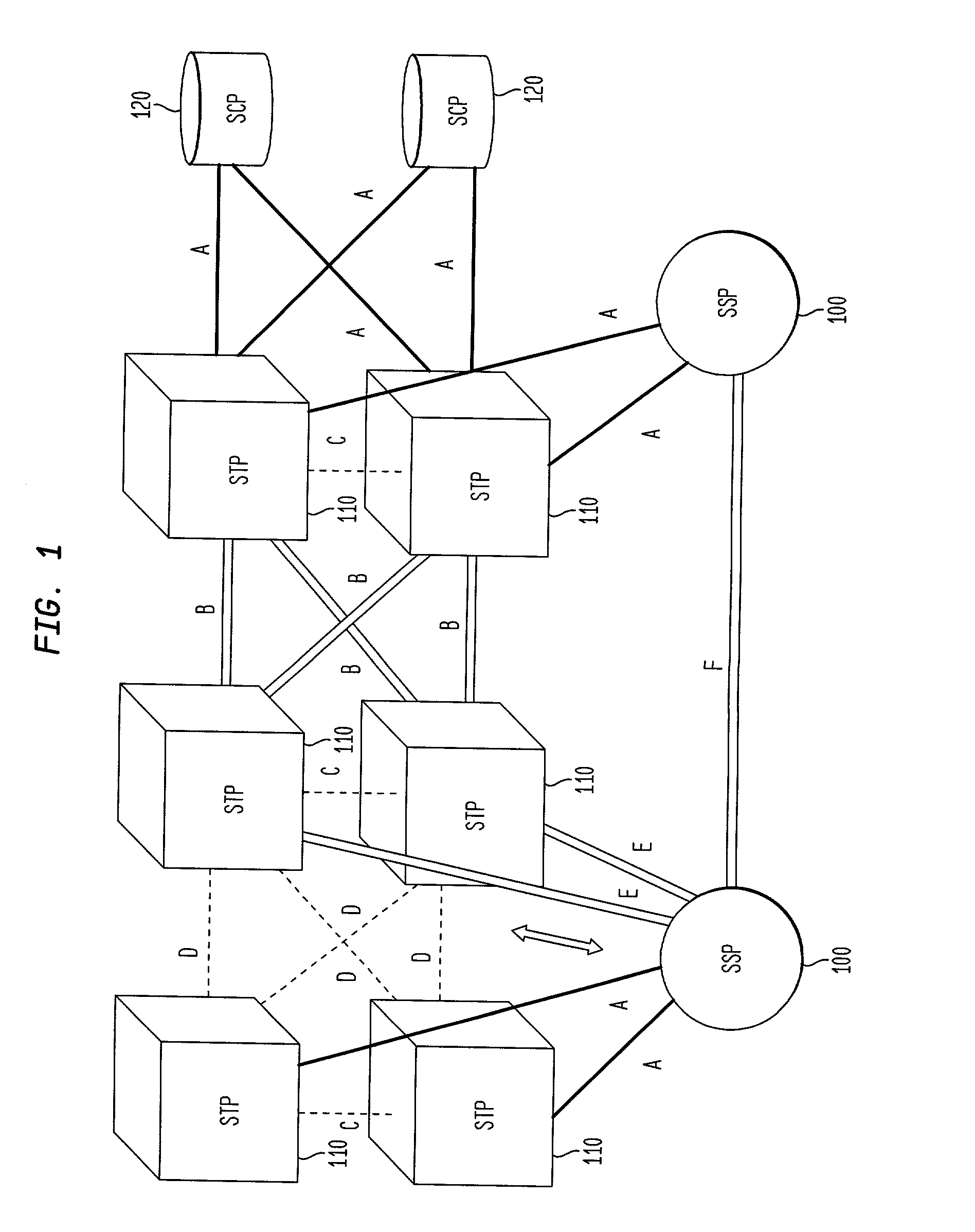
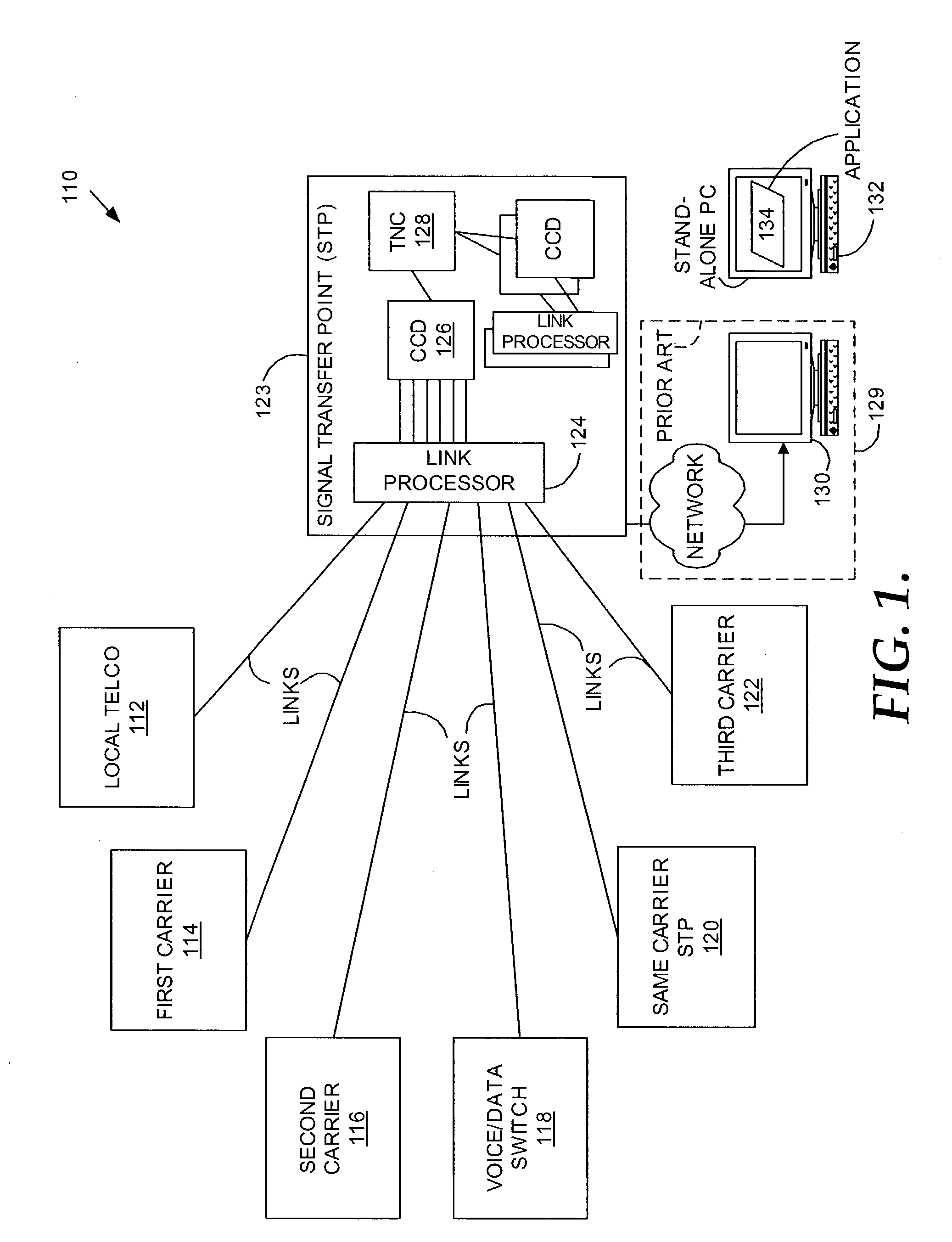
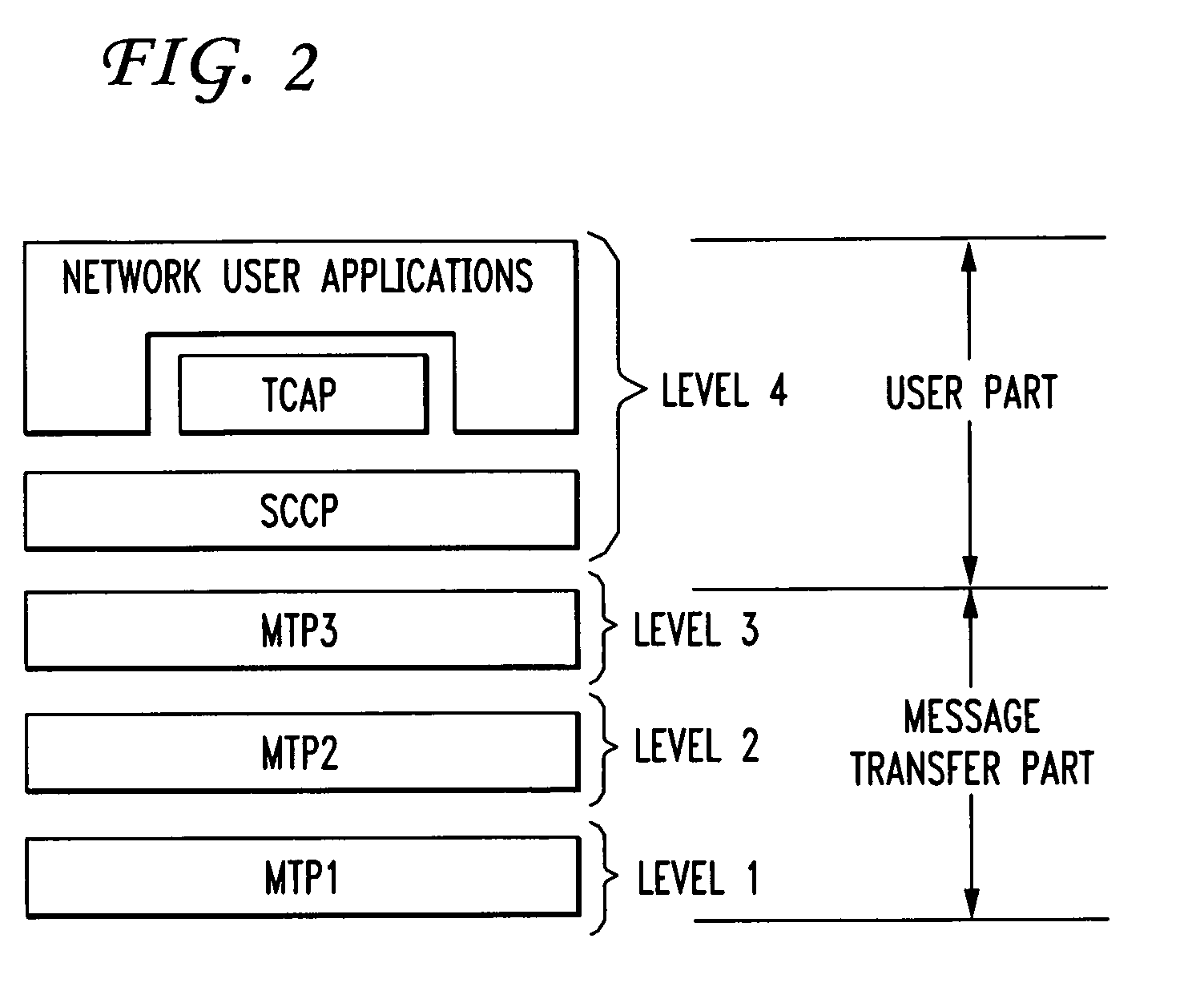
A Signal Transfer Point (STP) is a router that relays SS7 messages between signaling end-points (SEPs) and other signaling transfer points (STPs). Typical SEPs include service switching points (SSPs) and service control points (SCPs). The STP is connected to adjacent SEPs and STPs via signaling links. Based on the address fields of the SS7 messages, the STP routes the messages to the appropriate outgoing signaling link. Edge STPs can also route based upon message body content using deep packet inspection techniques, and can provide address translations and screen content to limit the transfer of messages with dubious content or sent from unreliable sources. To meet stringent reliability requirements, STPs are typically provisioned in mated pairs.
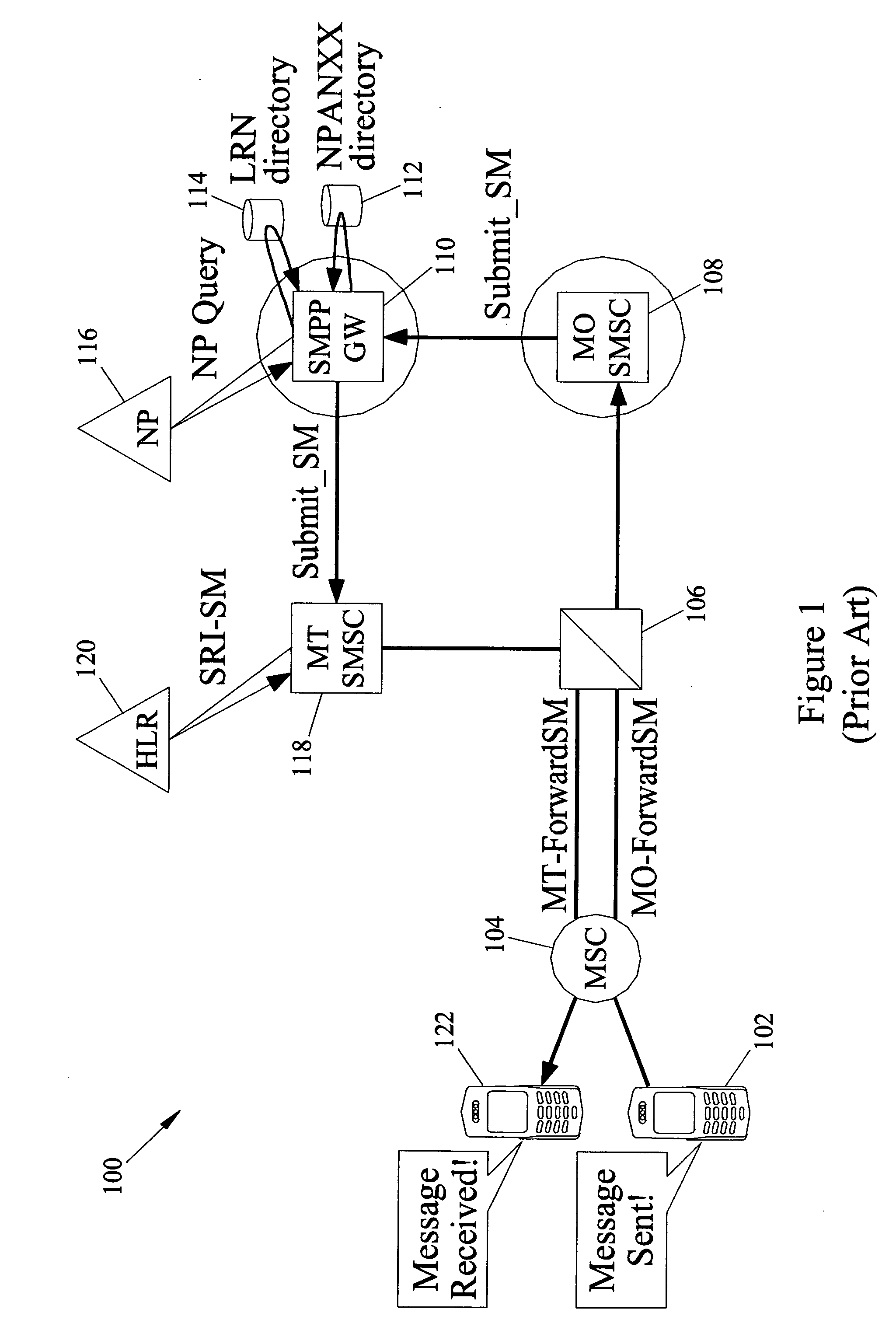
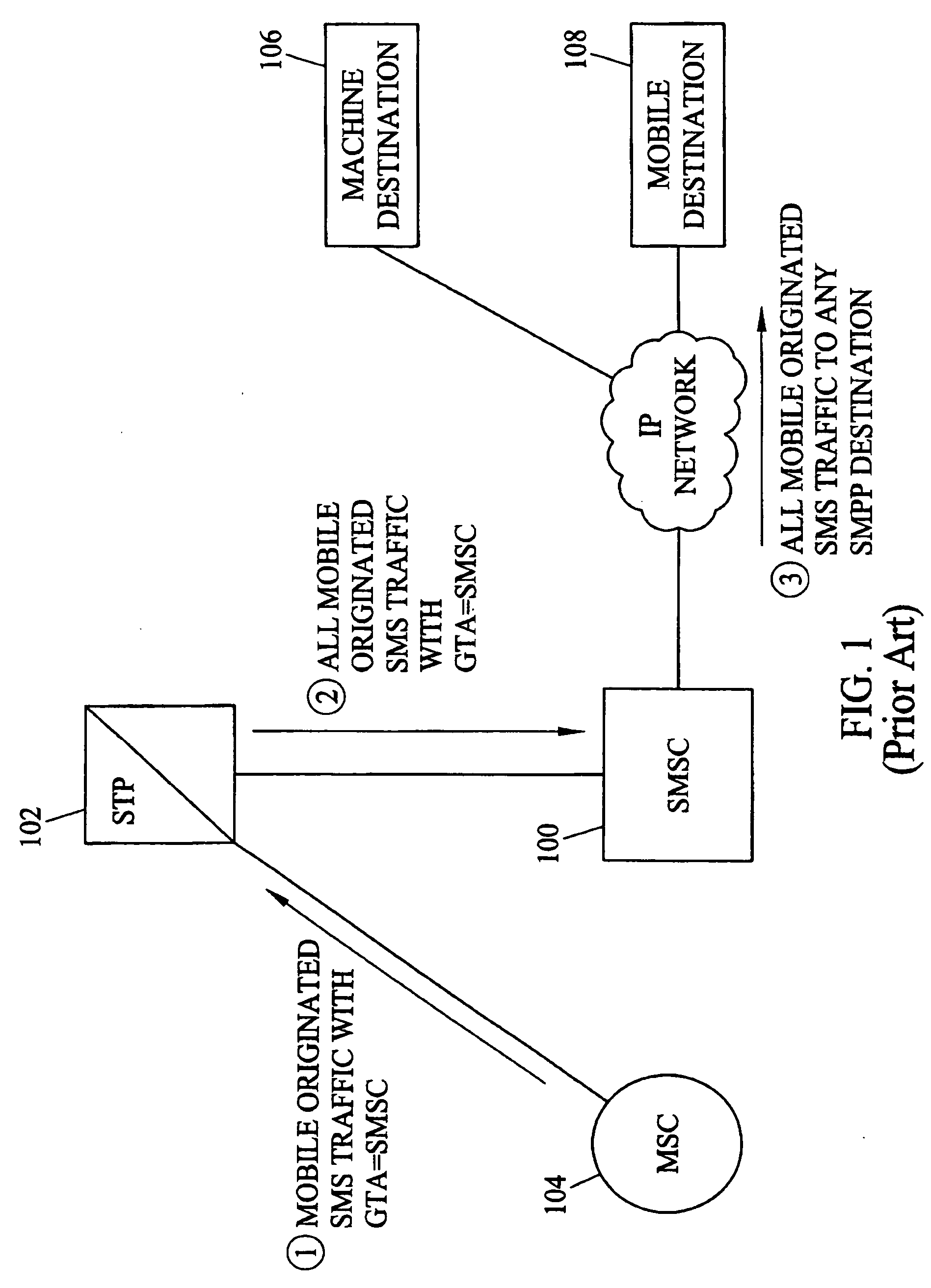
Telecommunication number portability
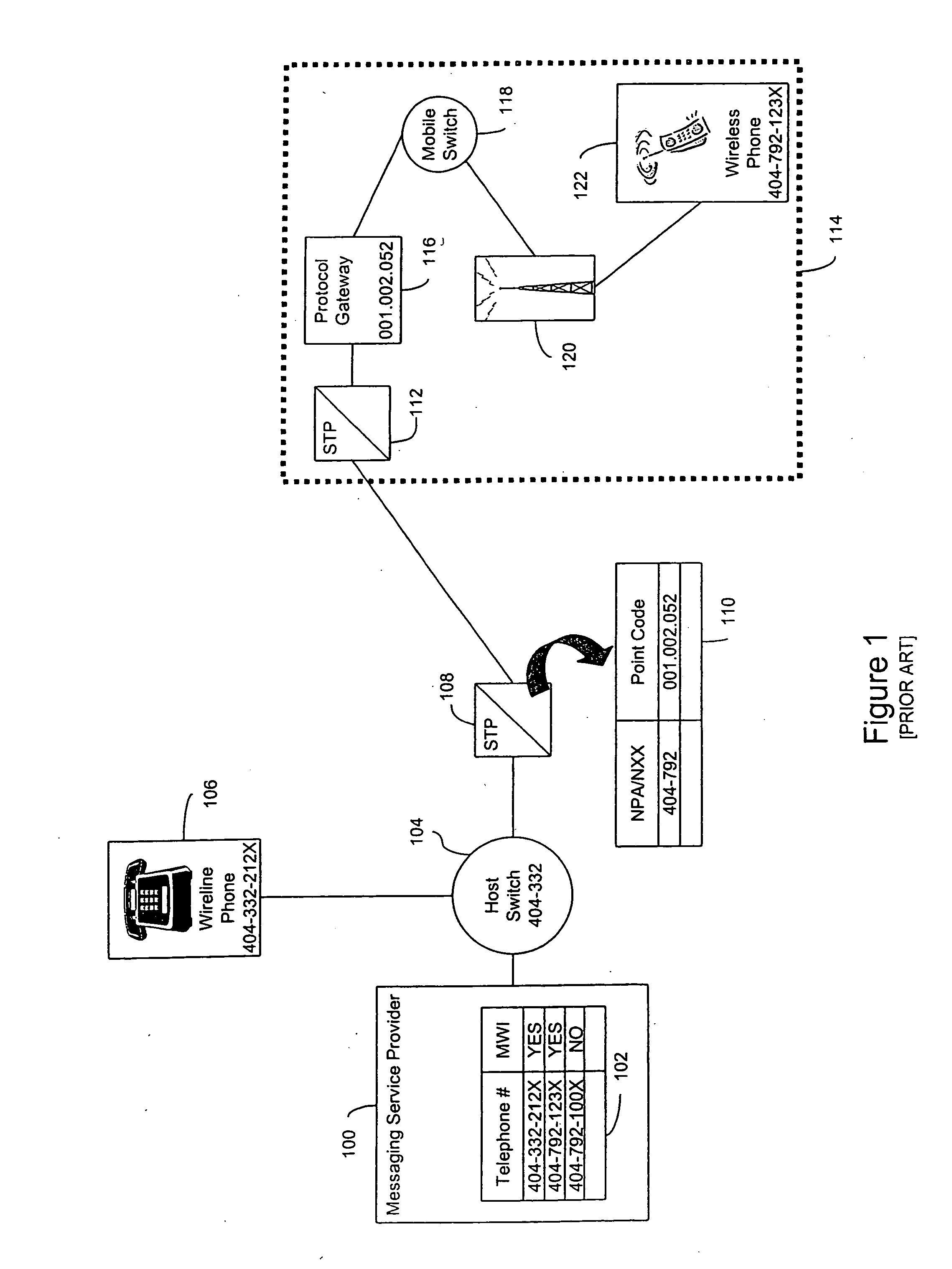
InactiveUS6021126AEfficient and economical number portabilityImprove comprehensive applicabilityInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersDomain nameIntelligent Network
A telecommunications system wherein the dialing of a directory number which has been ported triggers an intelligent network signal which is directed to the Internet. The signal is transmitted through the Internet to a database in the Internet. The database returns call set up directions which are used by the originating switching system to establish a voice link from the calling station to the station having the ported number. The intelligent network signal may be transmitted from the originating switching system to a signal transfer point (STP) and to the Internet. Within the Internet the signal is directed to an Internet database where a real number for the ported number is obtained. This is transmitted back to the signal switching point, which then uses the real number to complete the connection. In another embodiment, where a number has been ported to a station that is connected only to the Internet, the Internet database may provide a domain name address. This address is then used to establish a link through the Internet between the calling and called station. In this instance the Internet handles both the signaling and the voice connections.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
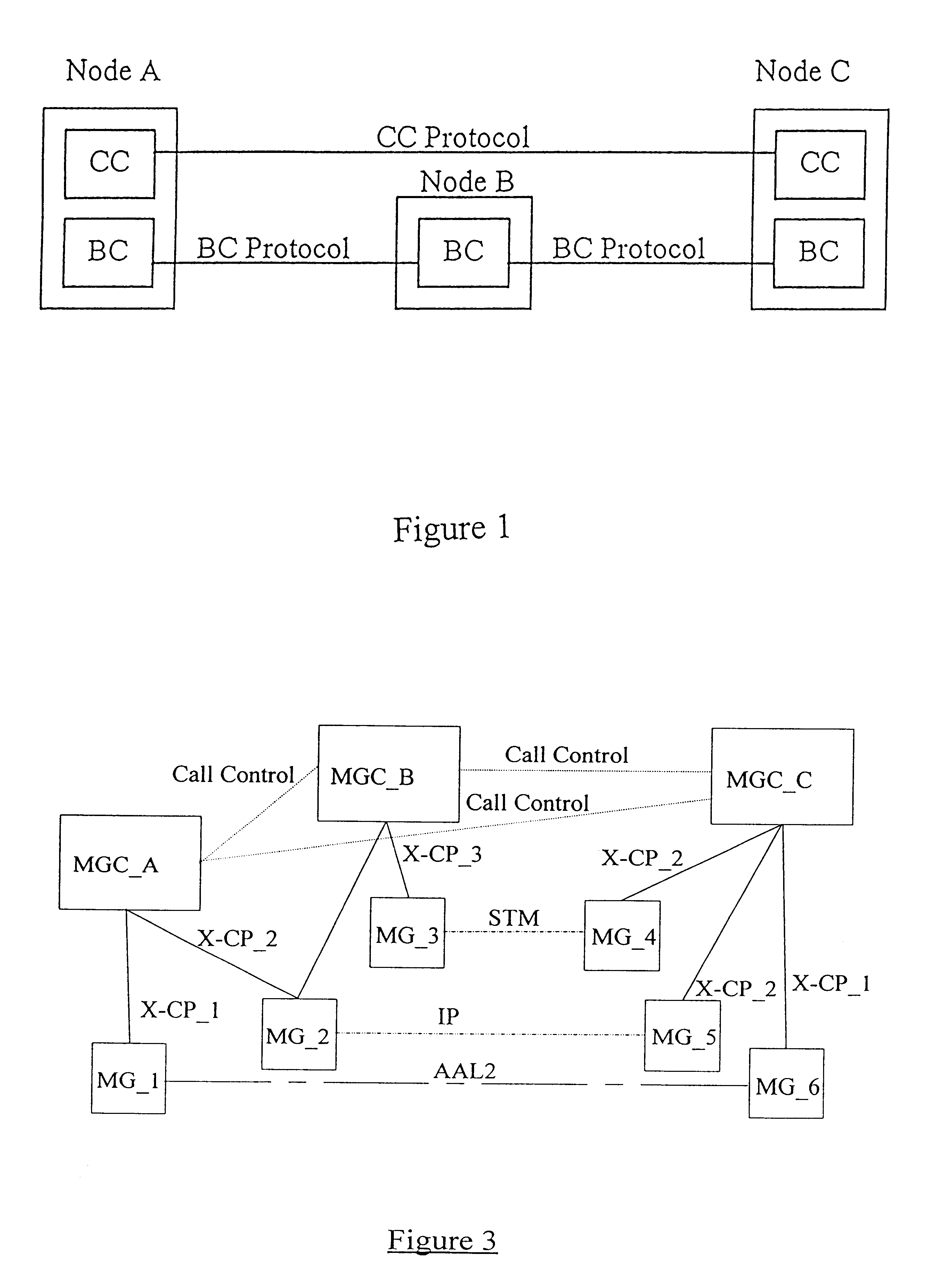
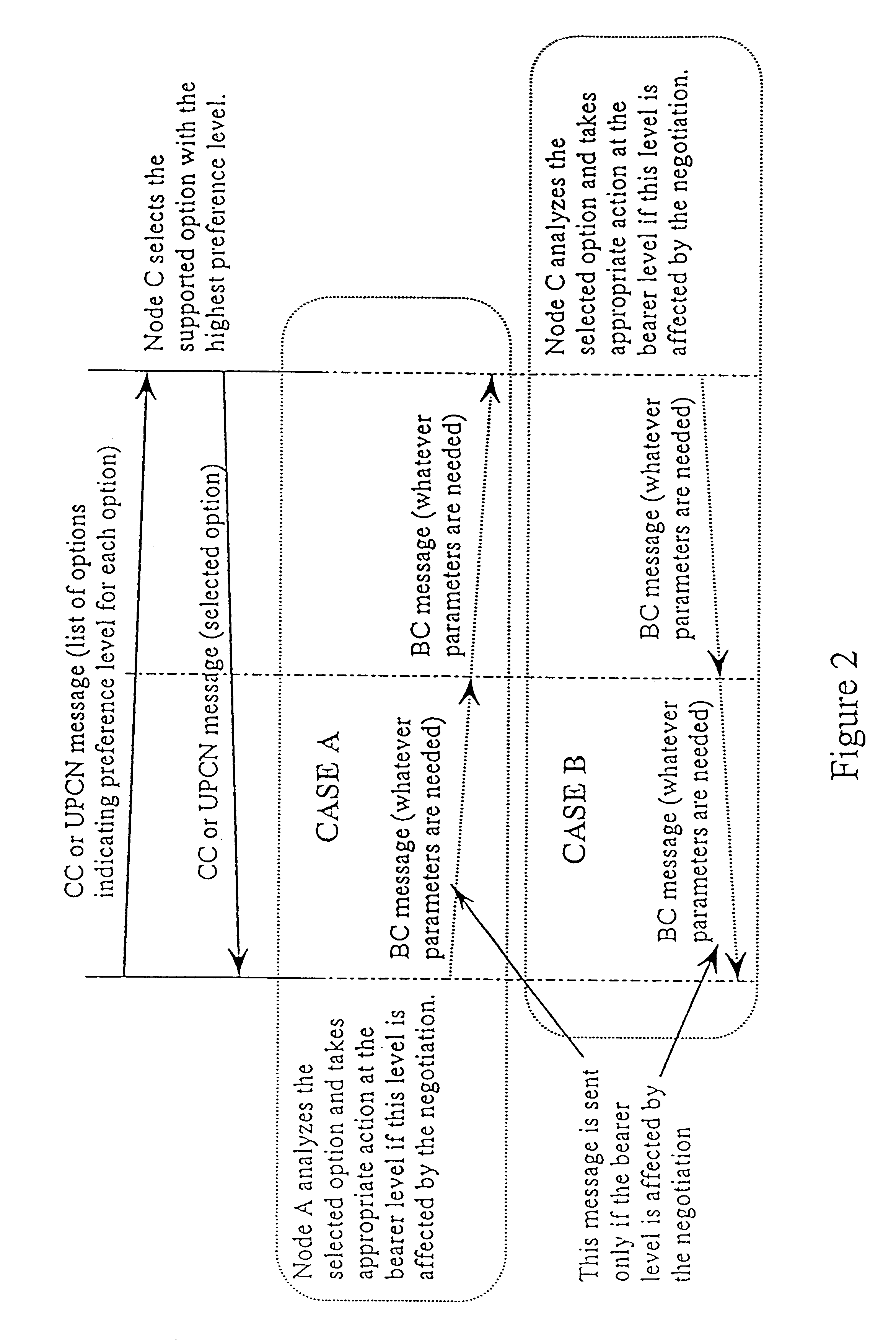
Capability negotiation in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6671367B1Smooth transferNetwork traffic/resource managementSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsTelecommunications linkCall control
A method of negotiating a call capability between signalling points in a telecommunications system. The method comprises sending a capability preference or prioritised list of preferences from an originating signalling point to a terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point, at the Call Control level. A capability acceptance is returned from the terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point to the originating signalling point at the Call Control level, if the terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point accepts a preference sent by the originating signalling point.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
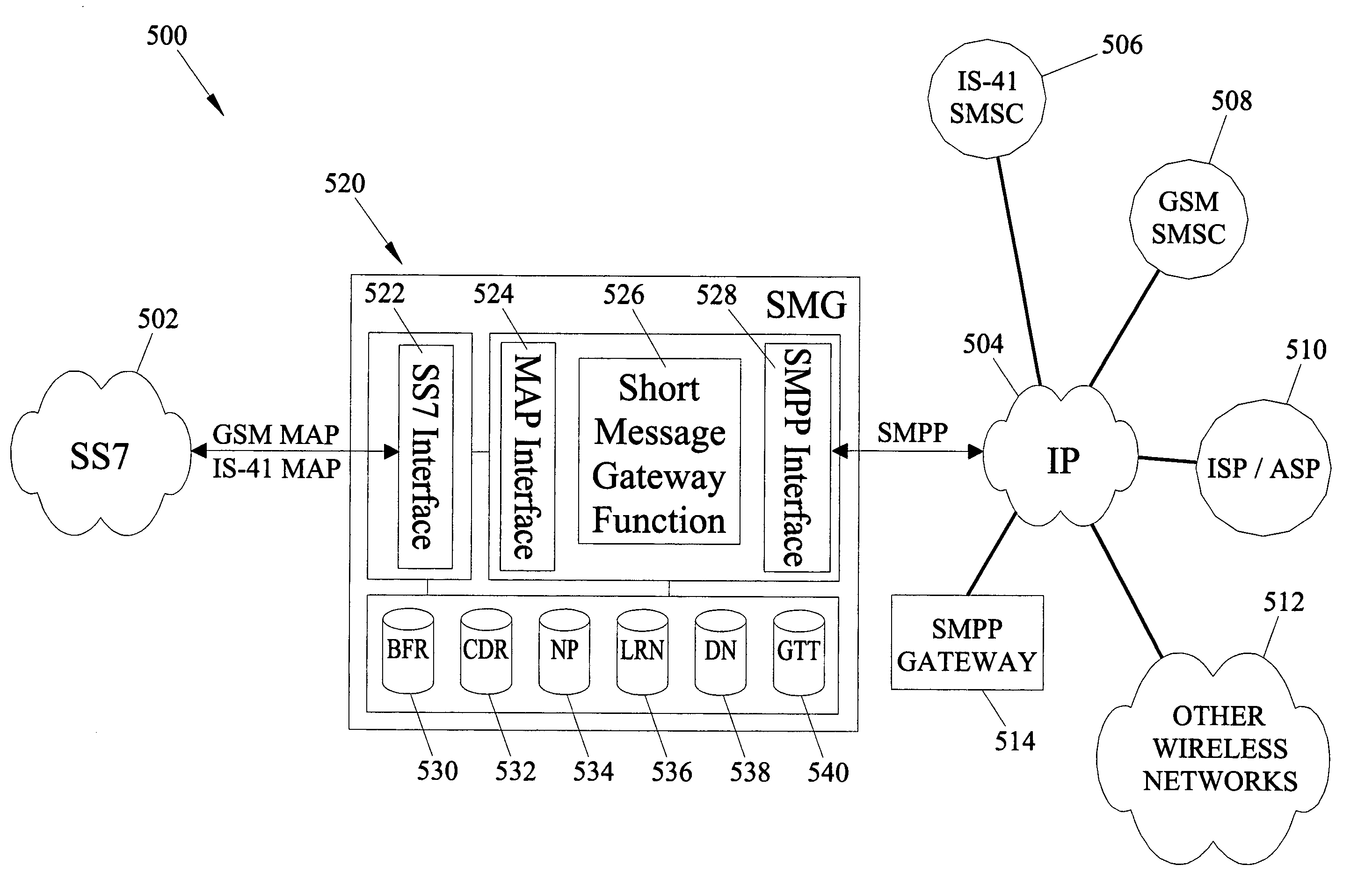
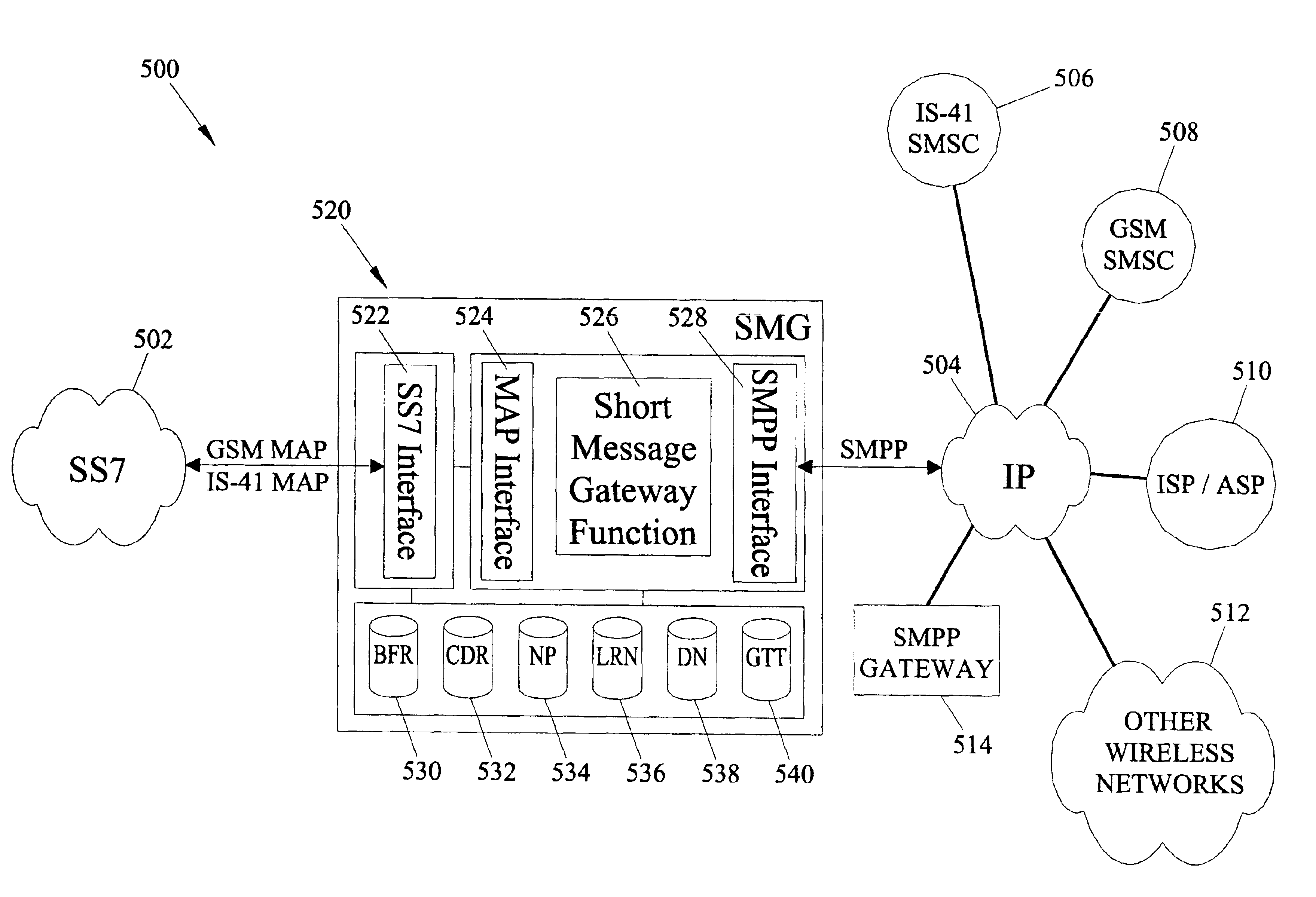
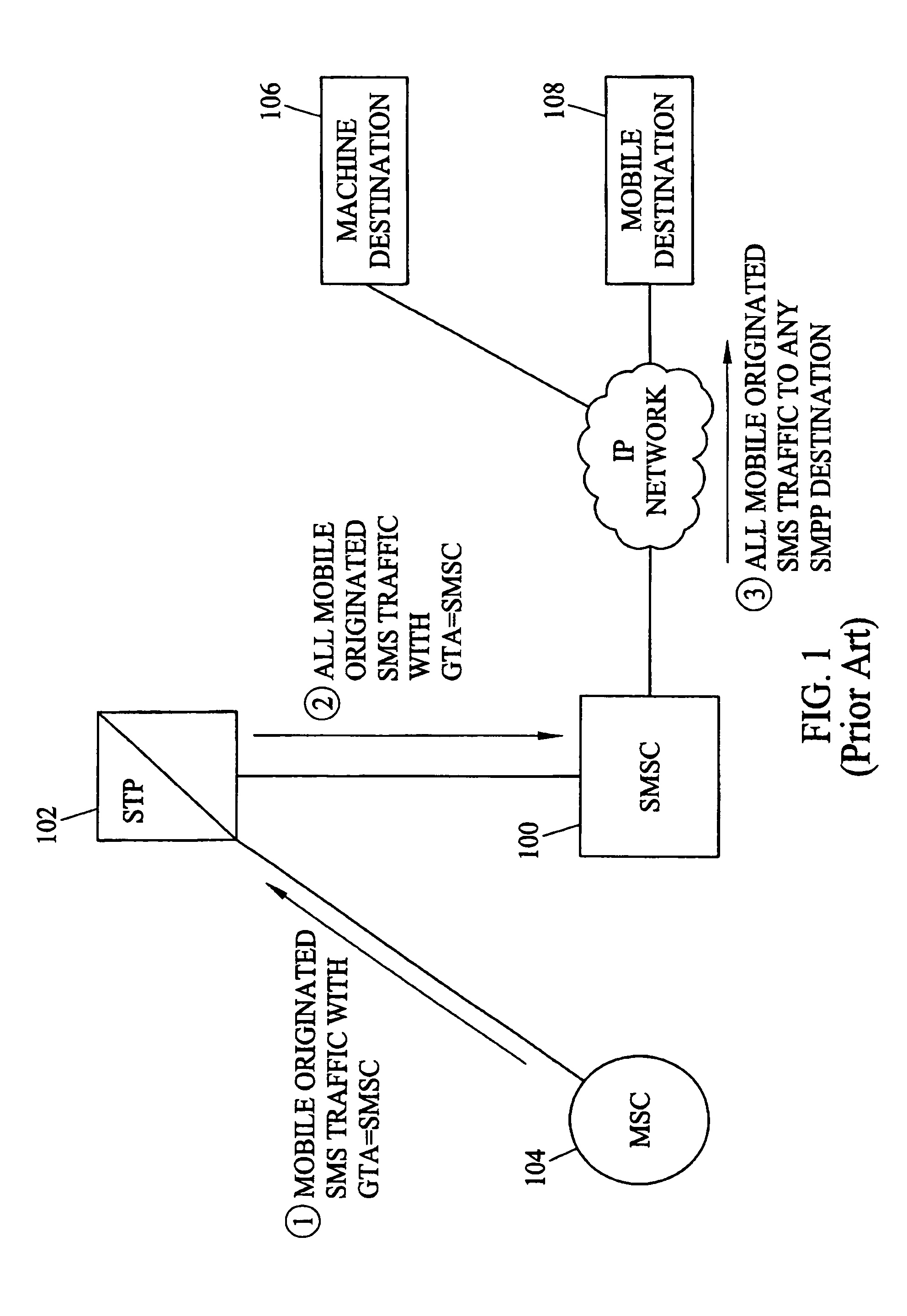
Methods and systems for providing short message gateway functionality in a telecommunications network
ActiveUS20050003838A1Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexMessage deliveryAddress resolution
A short message gateway may include signal transfer point (STP) functionality, mobile originating short message service center (SMSC) functionality, and short message delivery point-to-point (SMPP) gateway functionality. The short message gateway may receive an SS7 message including a short message payload. The short message gateway may formulate an SMPP message including the short message payload and access one or more internal address resolution and / or number portability databases to determine the destination address for the SMPP message. The short message gateway may then forward the SMPP message to its destination.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Capability negotiation in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS20040101125A1Smooth transferNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkCall control
A method of negotiating a call capability between signalling points in a telecommunications system. The method comprises sending a capability preference or prioritised list of preferences from an originating signalling point to a terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point, at the Call Control level. A capability acceptance is returned from the terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point to the originating signalling point at the Call Control level, if the terminating signalling point or signalling transfer point accepts a preference sent by the originating signalling point.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Methods and systems for providing short message gateway functionality in a telecommunications network
ActiveUS6885872B2Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkMessage delivery
A short message gateway may include signal transfer point (STP) functionality, mobile originating short message service center (SMSC) functionality, and short message delivery point-to-point (SMPP) gateway functionality. The short message gateway may receive an SS7 message including a short message payload. The short message gateway may formulate an SMPP message including the short message payload and access one or more internal address resolution and / or number portability databases to determine the destination address for the SMPP message. The short message gateway may then forward the SMPP message to its destination.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
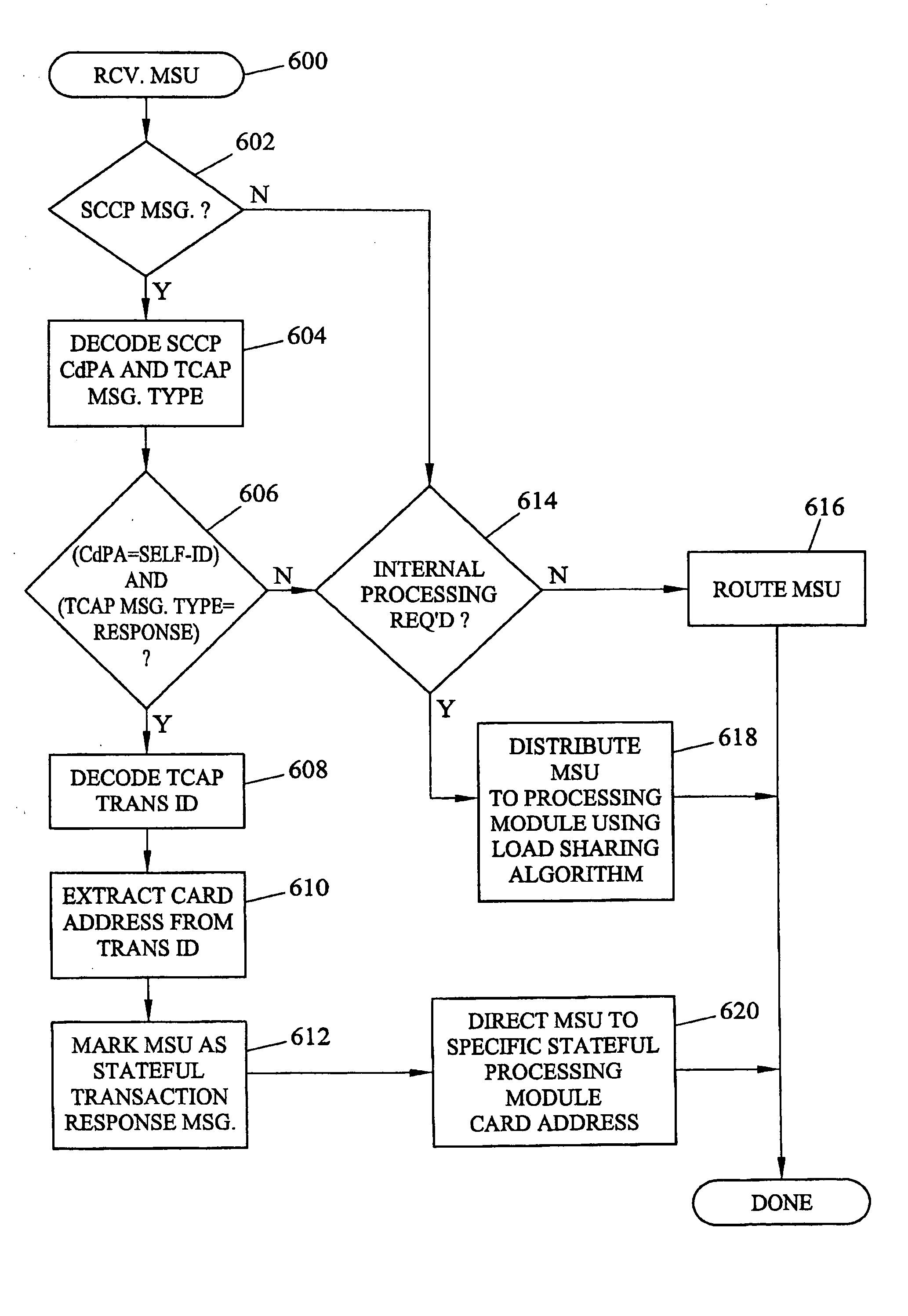
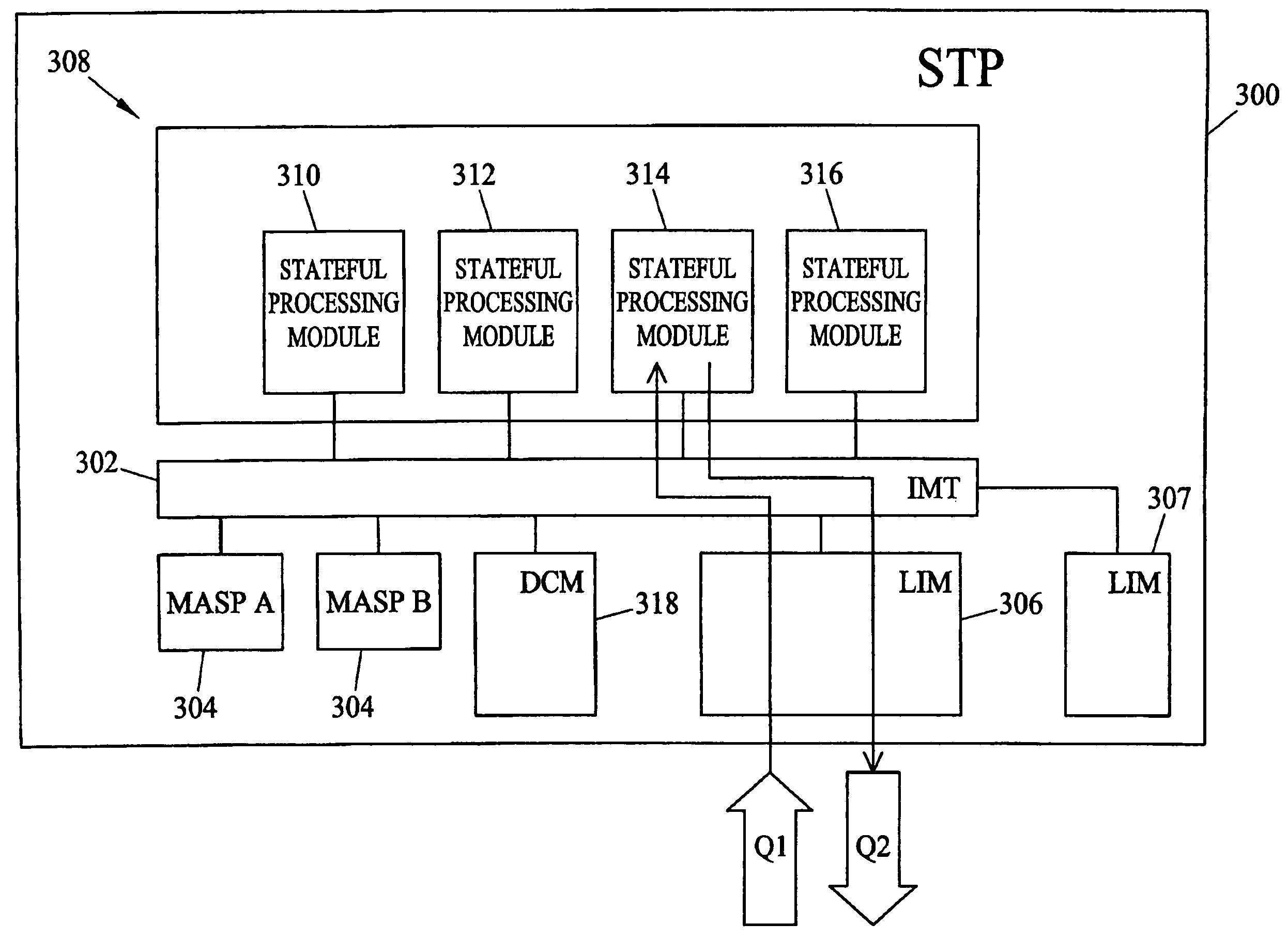
Systems and methods of performing stateful signaling transactions in a distributed processing environment
ActiveUS20050203994A1Efficient and reliable performanceAllocation is accurateMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationSignal Transfer PointDistributed computing
Methods and systems for performing stateful signaling transactions in a distributed processing environment are disclosed. A method for performing stateful signaling transactions in a distributed processing environment includes receiving a signaling message at a routing node, such as a signal transfer point. The signaling message is distributed to one of the plurality of stateful processing modules. The receiving stateful processing module buffers the signaling message and initiates a stateful transaction based on the signaling message. Initiating the stateful transaction may include generating a query message and inserting a stateful processing module identifier in the query message. The query message is sent to an external node, such as an SCP, which formulates a response. The SCP may insert the stateful processing module in the response and send the response back to the signal transfer point. The signal transfer point decodes the response and uses the stateful processing module identifier to forward the response to the correct stateful processing module.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
System and method for application location register routing in a telecommunications network
InactiveUS7079853B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentTelecommunications linkProcessor register
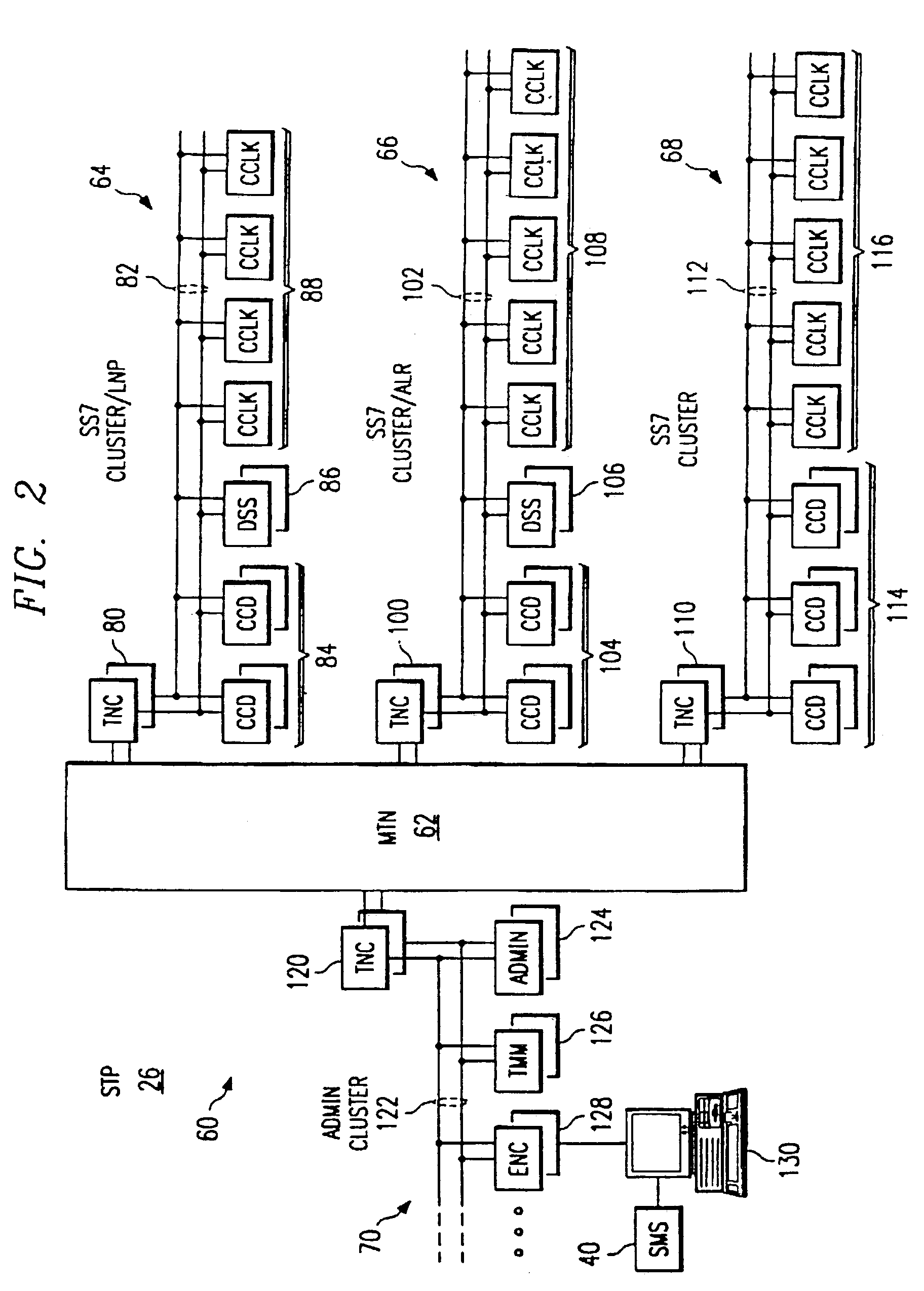
A system and method for application location register routing at a signal transfer point (26) are provided. The signal transfer point (26) includes processor clusters (64, 66, 68) and databases (236, 238) for processing queries including global title translation, local number portability, and application location register routing. A query message is received by the signal transfer point (26), a first database residing in the signal transfer point (26) is accessed to determine the location of a second database (238) also residing in the signal transfer point for processing the query message. The second database (238) is then accessed to obtain the network address of a home location register or short message service center, which is then used to deliver the query message to the network node specified by the network address.
Owner:ALCATEL USA SOURCING
Methods and systems for providing mobile location management services in a network routing node
InactiveUS7222192B2Reduce message trafficMultiple digital computer combinationsSubstation equipmentMobility managementMobile communication network
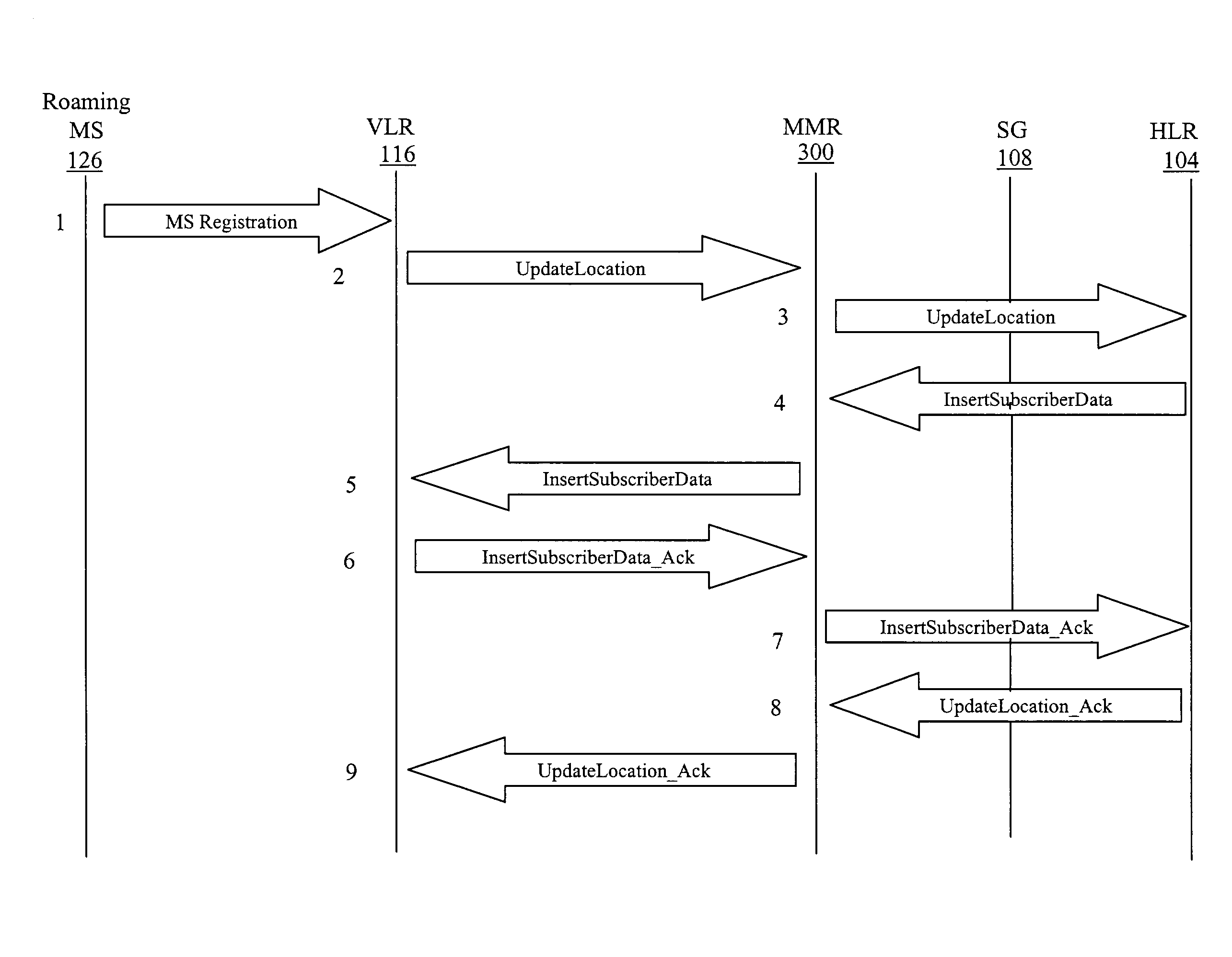
Disclosed is a mobility management routing (MMR) node that performs location management signaling operations associated with mobile subscribers. The MMR node may also perform the signaling message routing functionality typically provided by a network routing node, such as a signaling system 7 (SS7) signal transfer point (STP) or an SS7-over-Internet protocol signaling gateway (SG). The MMR node caches mobile subscriber information extracted from messages transmitted between an HLR and a VLR and responds to some of the messages using the cached information. As a result, signaling message traffic and call setup time in a mobile communications network are reduced.
Owner:TEKELEC
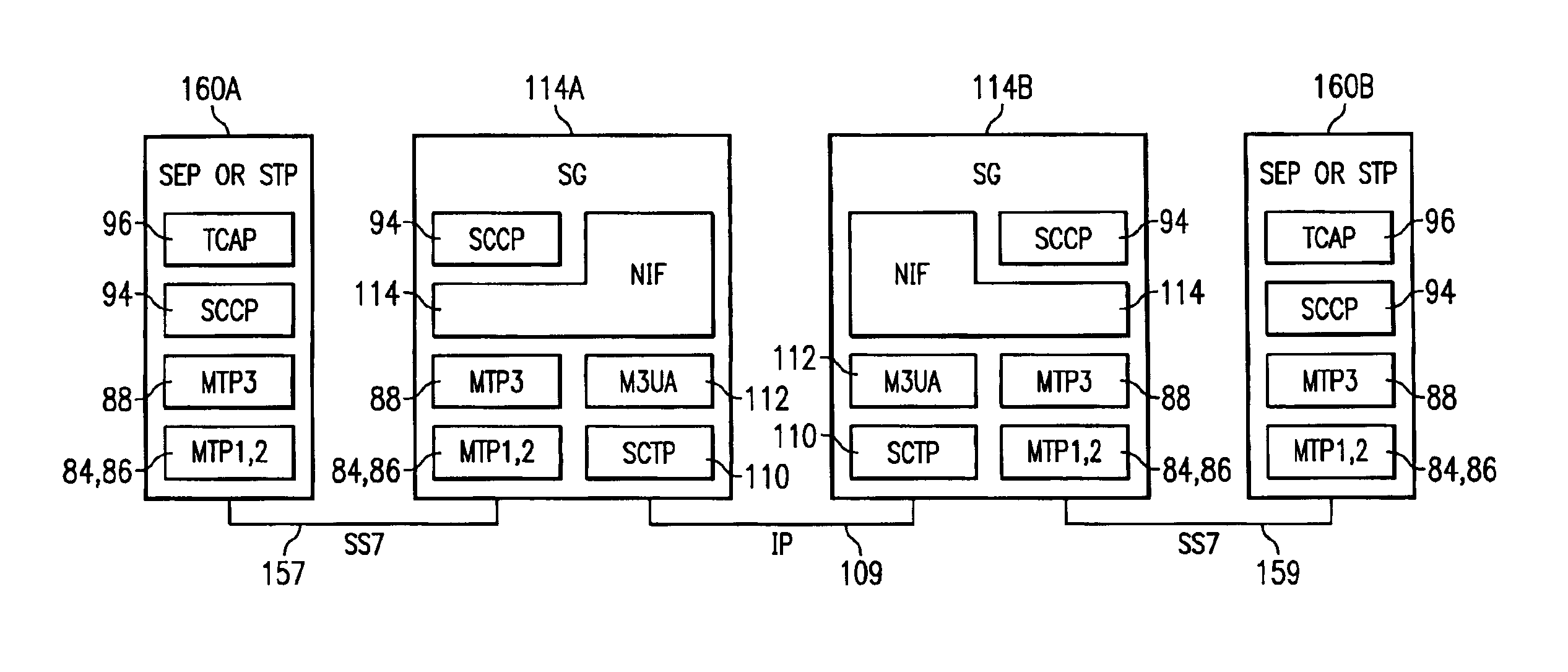
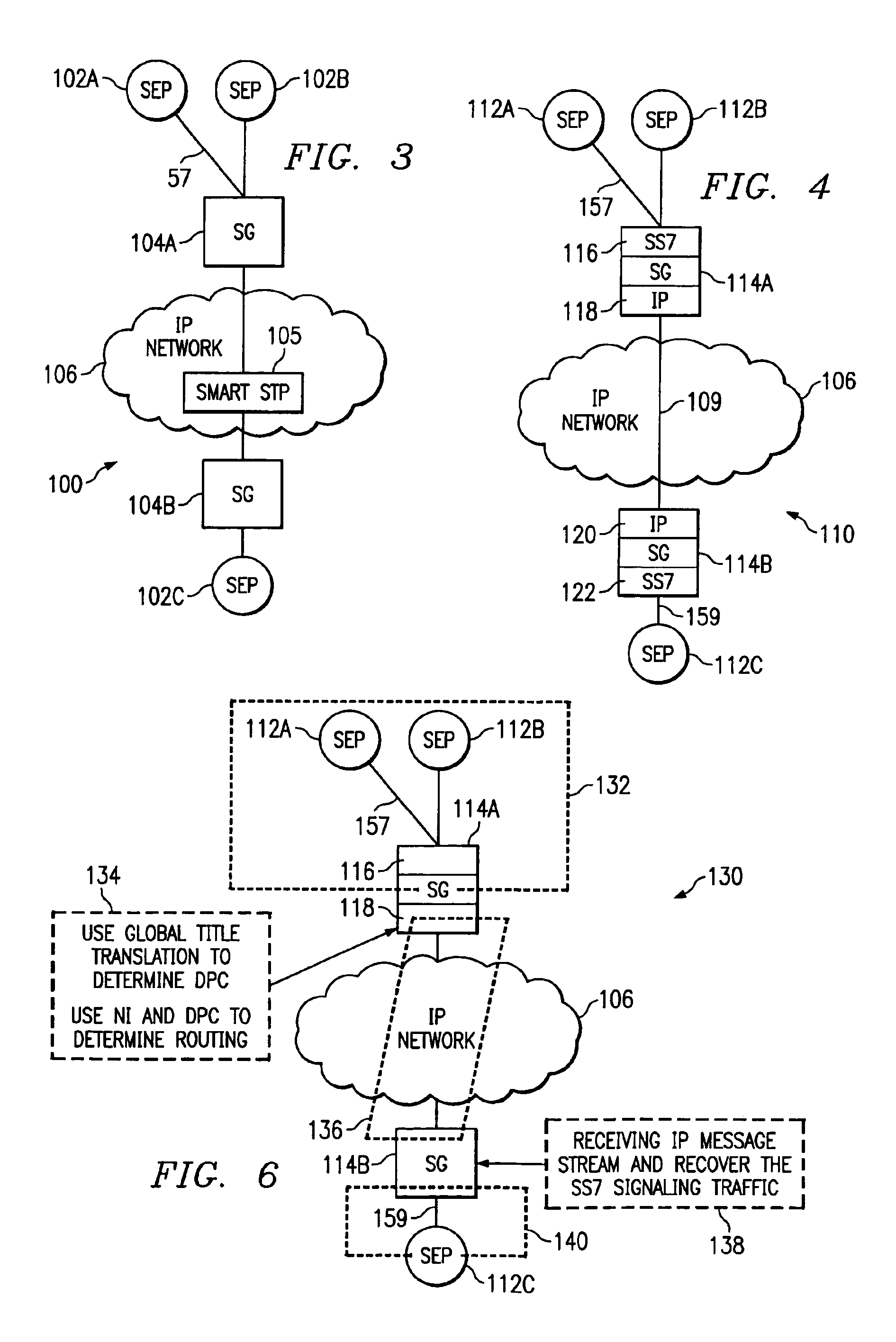
Method, system and signaling gateways as an alternative to SS7 signal transfer points
InactiveUS6920144B2Increase flexibilityHigh bandwidthTelephone data network interconnectionsTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityAlternative methods
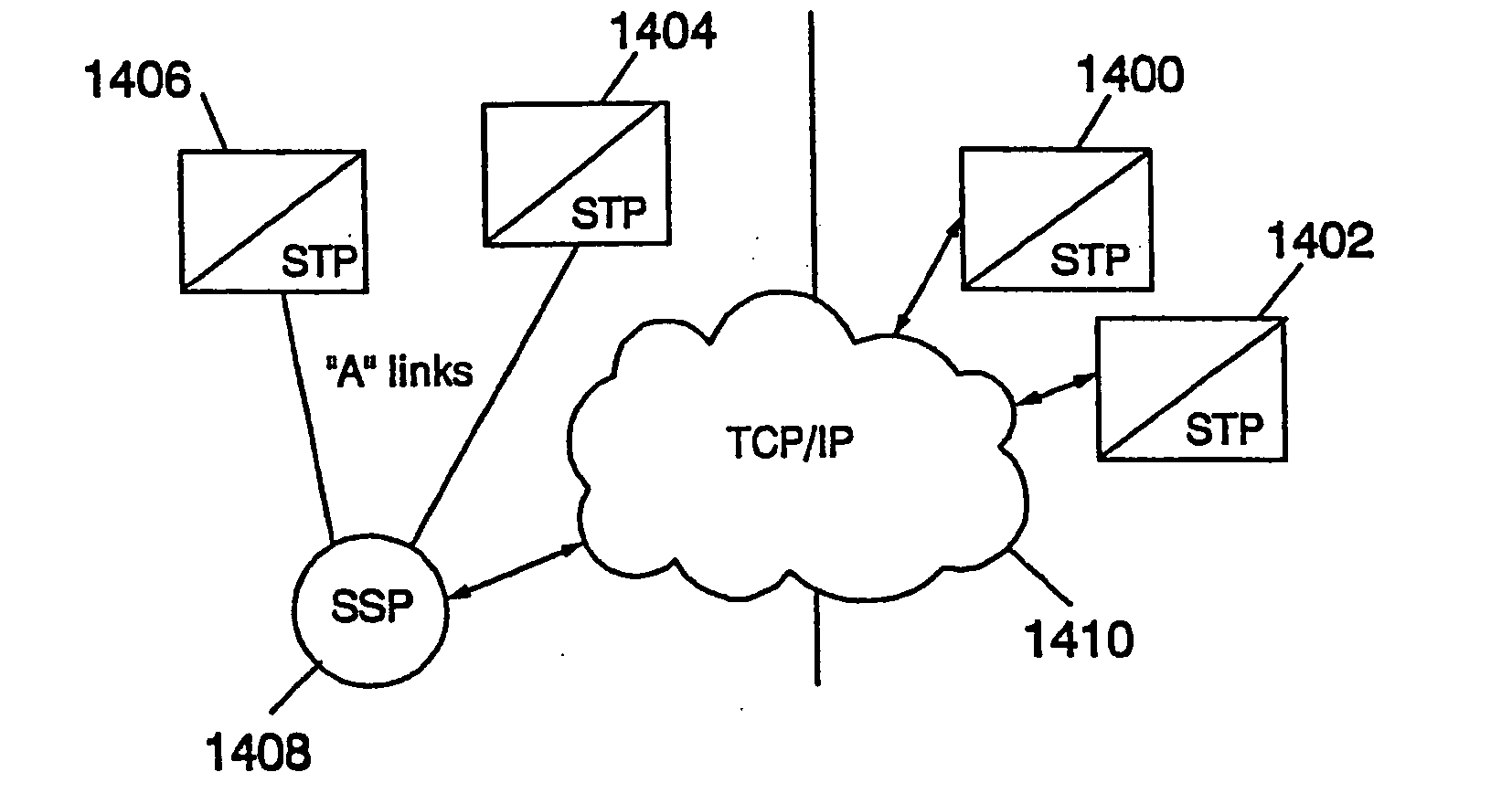
A system for routing Signaling System 7 (SS7) signaling traffic over an Internet Protocol (IP) network includes two or more signaling points, each signaling point capable of sending and receiving SS7 signaling traffic over an SS7 network and a first Signaling Gateway (SG) adapted for receiving SS7 signaling traffic from a first signaling point over the SS7 network. The first SG is configured to convert SS7 signaling traffic into an IP message stream and to route the IP message stream on the IP network to a second SG. The second SG is configured to receive the IP message stream via peer-to-peer IP communications over said IP network with said first SG and to recover the SS7 signaling traffic from the IP message stream. Peer-to-peer communications between the first and second SG is supported by conversion layers within the SG, in the form of an SCTP and M3UA protocols that allows peer IP signaling between the two SGs.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL) +1
Method and system for message routing
InactiveUS6842506B1Widens telephone serviceGood serviceMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsSignal Transfer PointService control
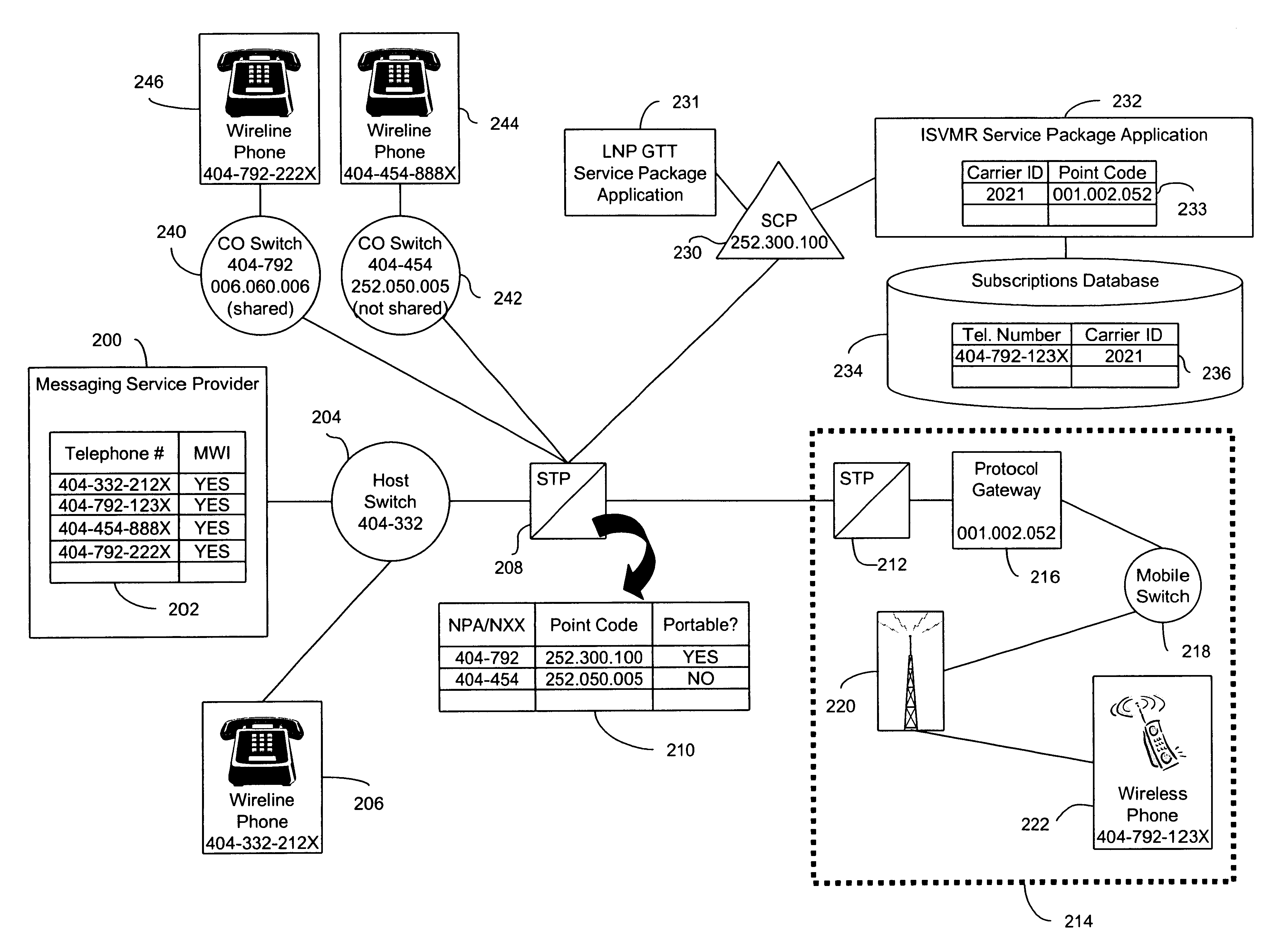
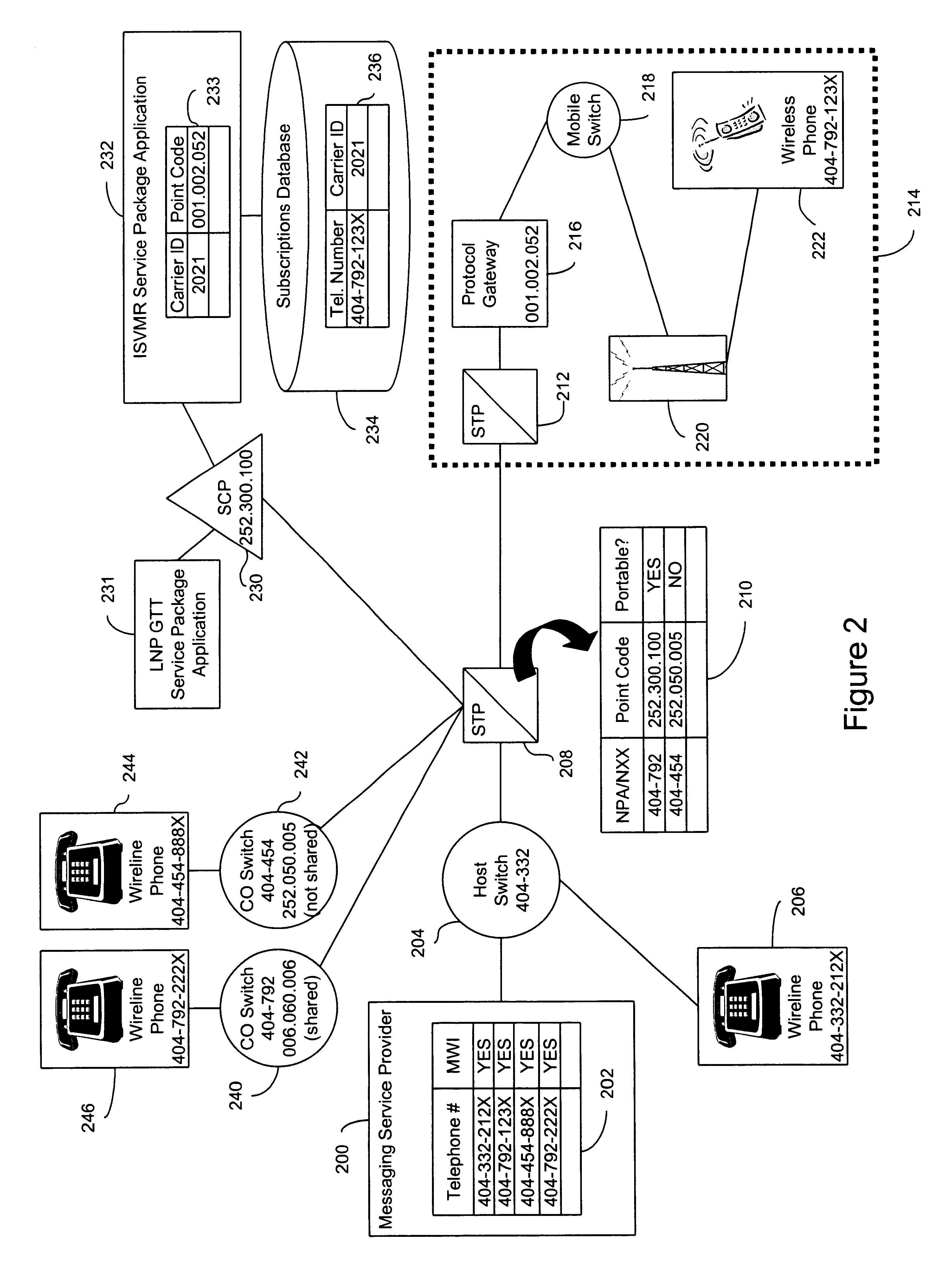
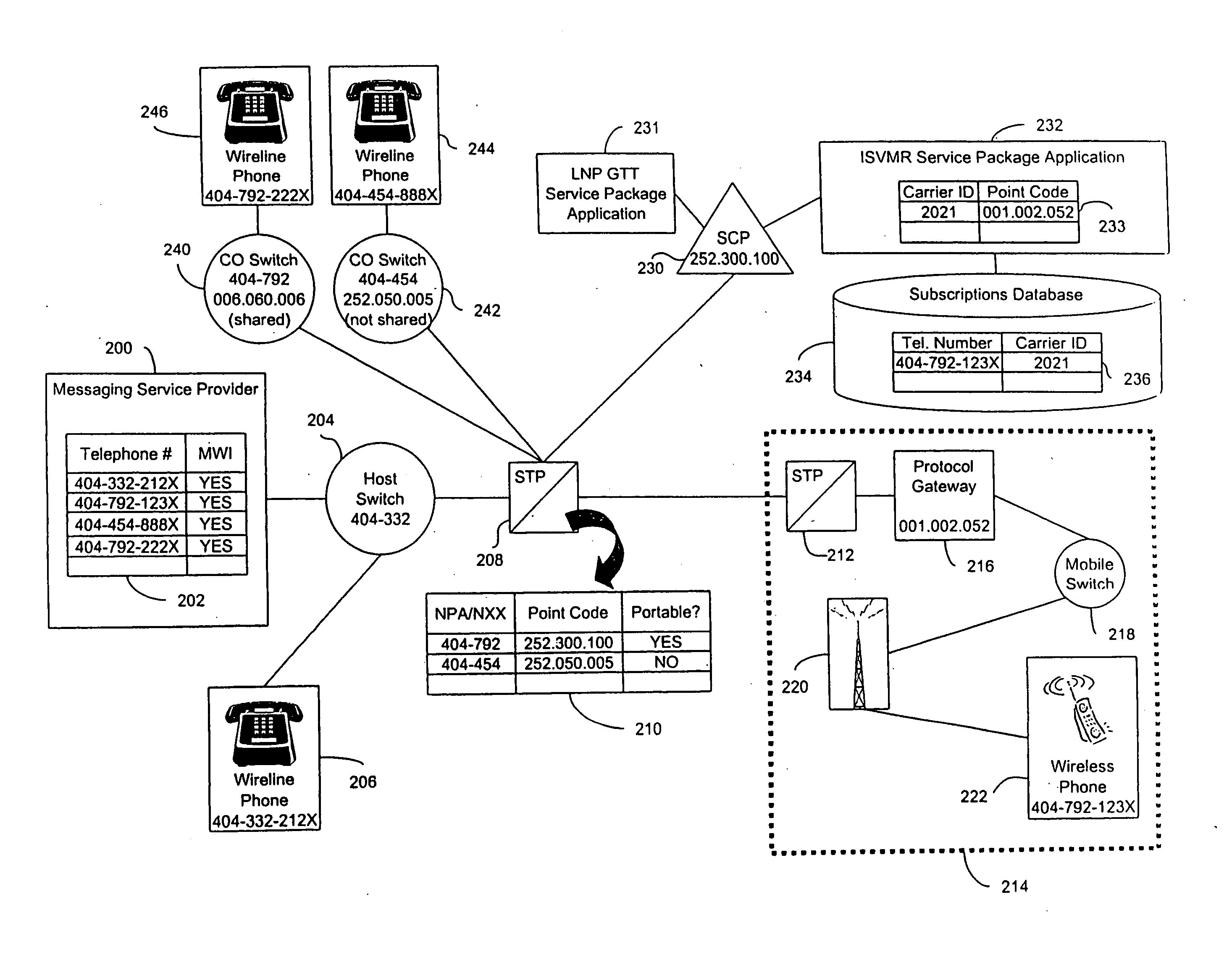
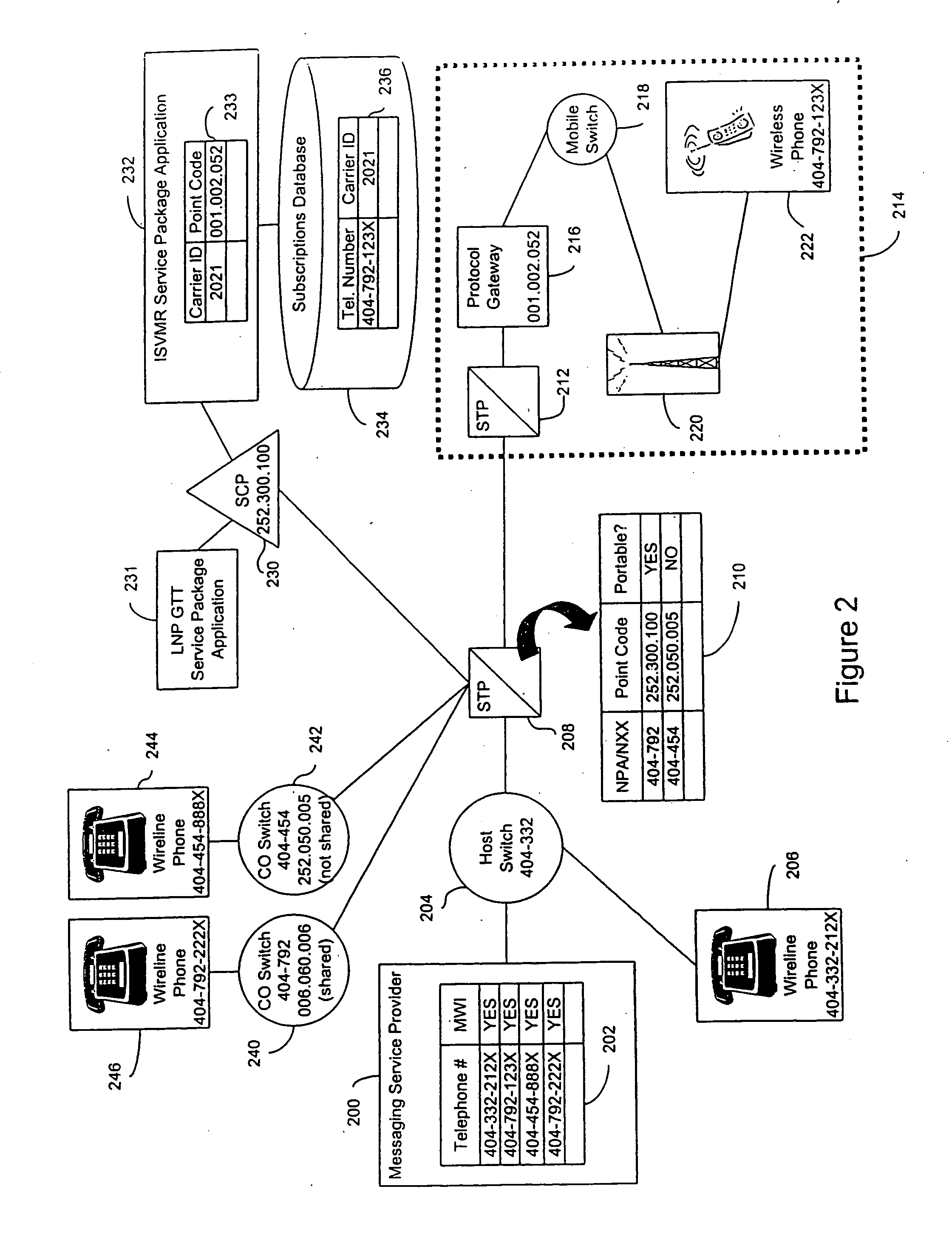
A method and system for forwarding information, such as a message waiting indicator (MWI) message, to a telephone number corresponding to a foreign network (e.g., a wireless network) and a shared NPA / NXX. The invention evaluates individual telephone numbers of shared NPA / NXXs to determine to what networks to send messages. A representative embodiment of the invention uses a service control point and service package application to deliver an MWI message from a messaging service provider to a wireless (i.e., foreign network) telephone number of a shared NPA / NXX. Shared NPA / NXXs are marked as “portable” in a signal transfer point for forwarding to the service control point, which determines whether the shared NPA / NXX telephone numbers require local number portability global title translation or should be forwarded to an inter-switch voicemail routing (ISVMR) service package application. The ISVMR service package application determines the point code to which the MWI message should be routed.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Global title translation with load sharing
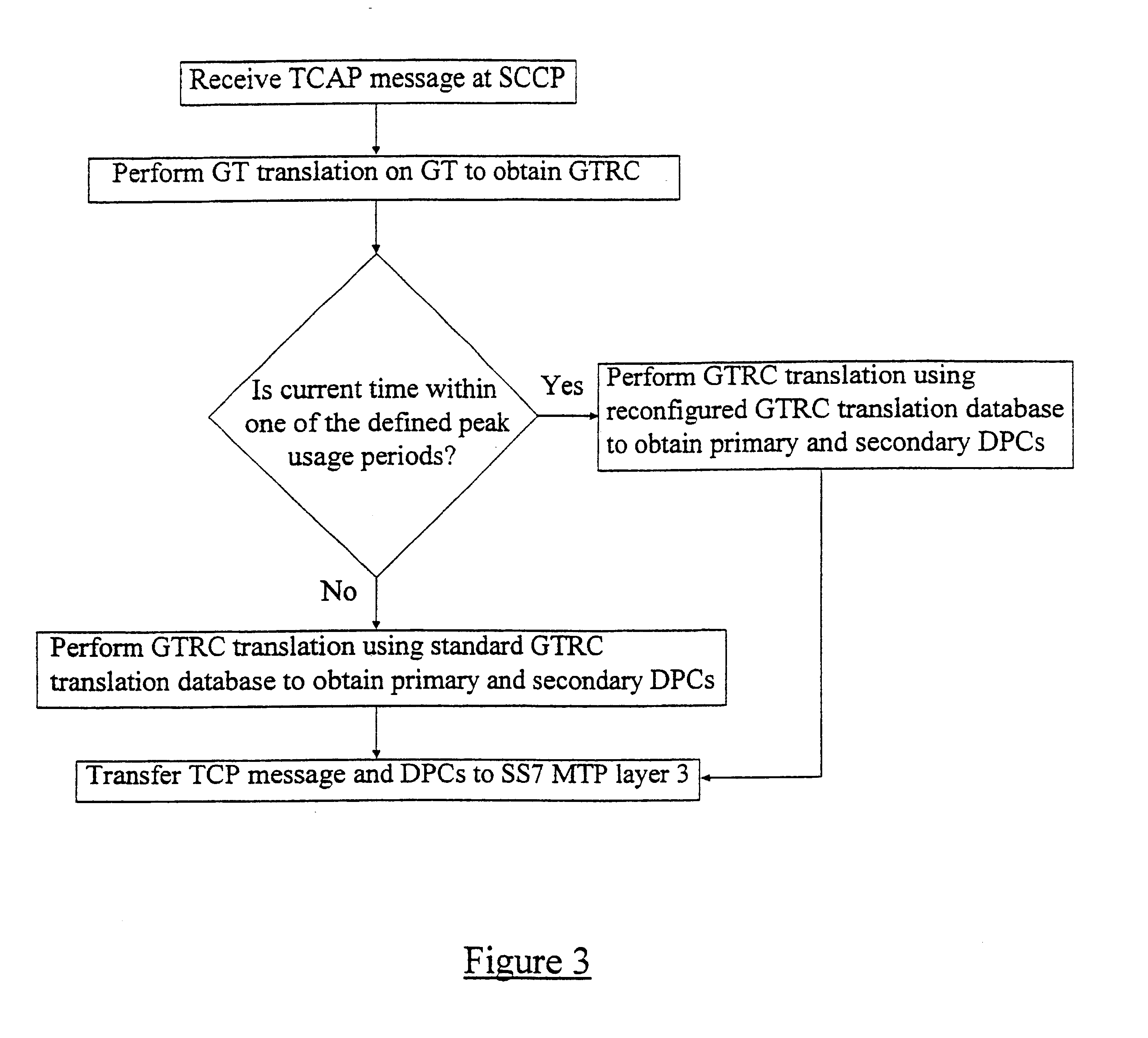
InactiveUS6785378B2Avoid or mitigate congestionReduce riskInterconnection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementPeak valueMajor and minor
A method of routing signalling information at a signalling transfer point of a telecommunication network. A Global Title Routing Case (GTRC) table is provided for mapping Global Titles to GTRCs, where each GTRC is allocated a primary and secondary destination signalling point. At least one peak time period is predefined, and said primary and secondary destination signalling points are swapped for a fraction of said GTRCs during said peak period to allow for load sharing during this period. For a signalling transfer request received at the signalling transfer point, the Global Title associated with the request is mapped to a GTRC using the GTRC table, and the destination signalling point is determined in dependence upon the primary and secondary destination signalling points allocated to the mapped GTRC and signalling point availability, and, in the case of said fraction of GTRCs, the time at which the request is received.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Methods and systems for routing signaling messages to the same destination over different routes using message origination information associated with non-adjacent signaling nodes
InactiveUS7088728B2Eliminate requirementsInterconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceNetwork addressing
Methods and systems for associating a plurality of different routes with the same destination and for routing signaling messages to the destination based on originating information associated with non-adjacent signaling nodes are disclosed. A routing database in a signal transfer point includes multiple routes to the same destination. The routes are distinguishable from each other in the routing database using message origination information associated with signaling nodes that are not adjacent to the signal transfer point. When a signaling message is received, origination and destination information in the signaling message are used in combination to select among multiple routes to a destination having a network address corresponding to the destination information in the signaling message. The signaling message is then routed over the route selected using the originating information. The selected route may be a high-speed route used to provide a particular quality of service.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
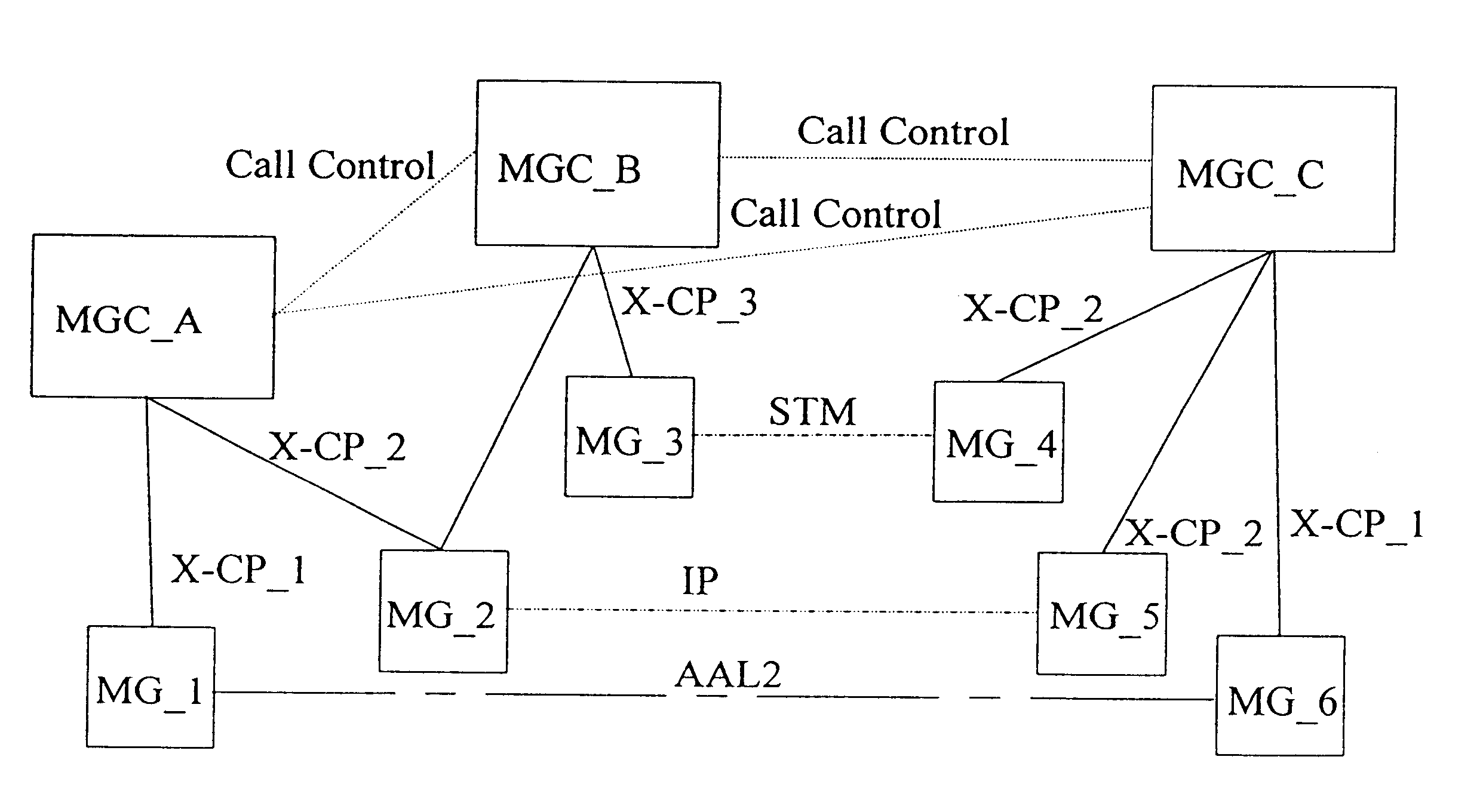
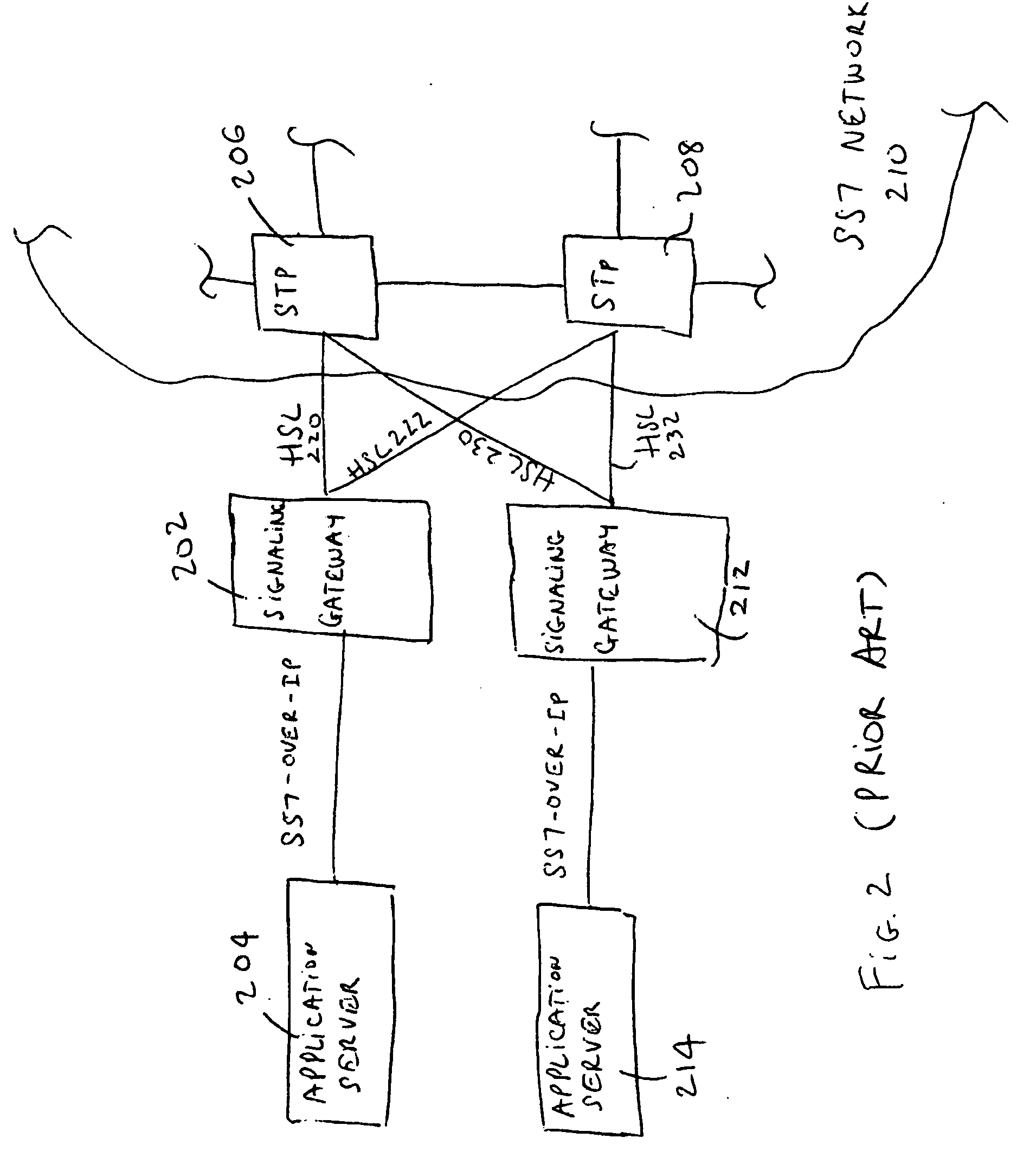
Method and architecture for redundant SS7 deployment in a voice over IP environment
InactiveUS7023794B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTelephone data network interconnectionsSoftswitchVoice over IP
18A method and system for controlling the switching and control operation of at least one of an Softswitch system, an Signal Transfer Points (STP) and a gateway (GW) (e.g., in a SS7 signaling environment). By providing support for redundancy, a second switch system can take over the routing and control operations of a first switch system when the first switch system experiences difficulty. Difficulty may be any one of several forms (e.g., switch crash, congestion, hardware failure).
Owner:NET2PHONE
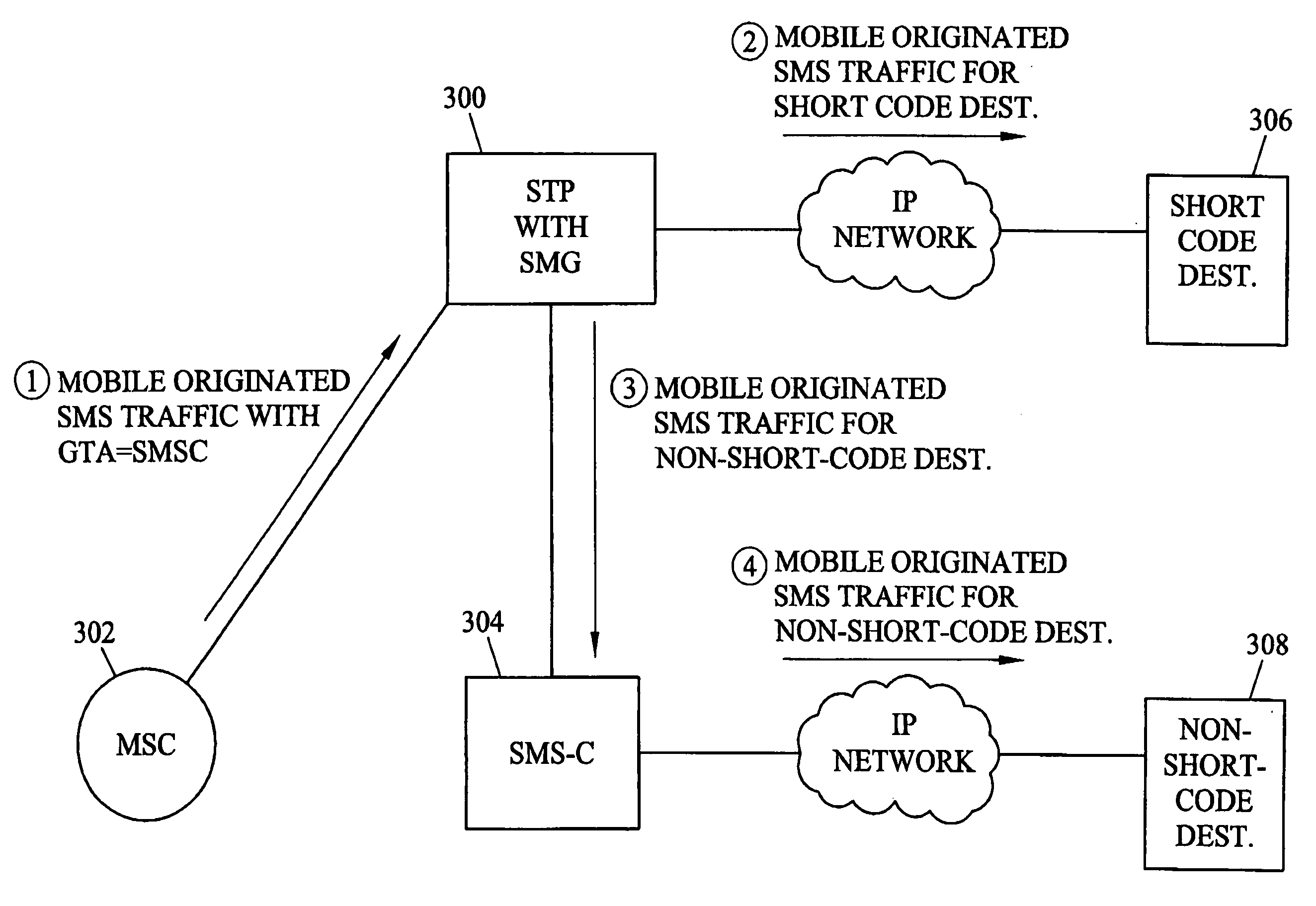
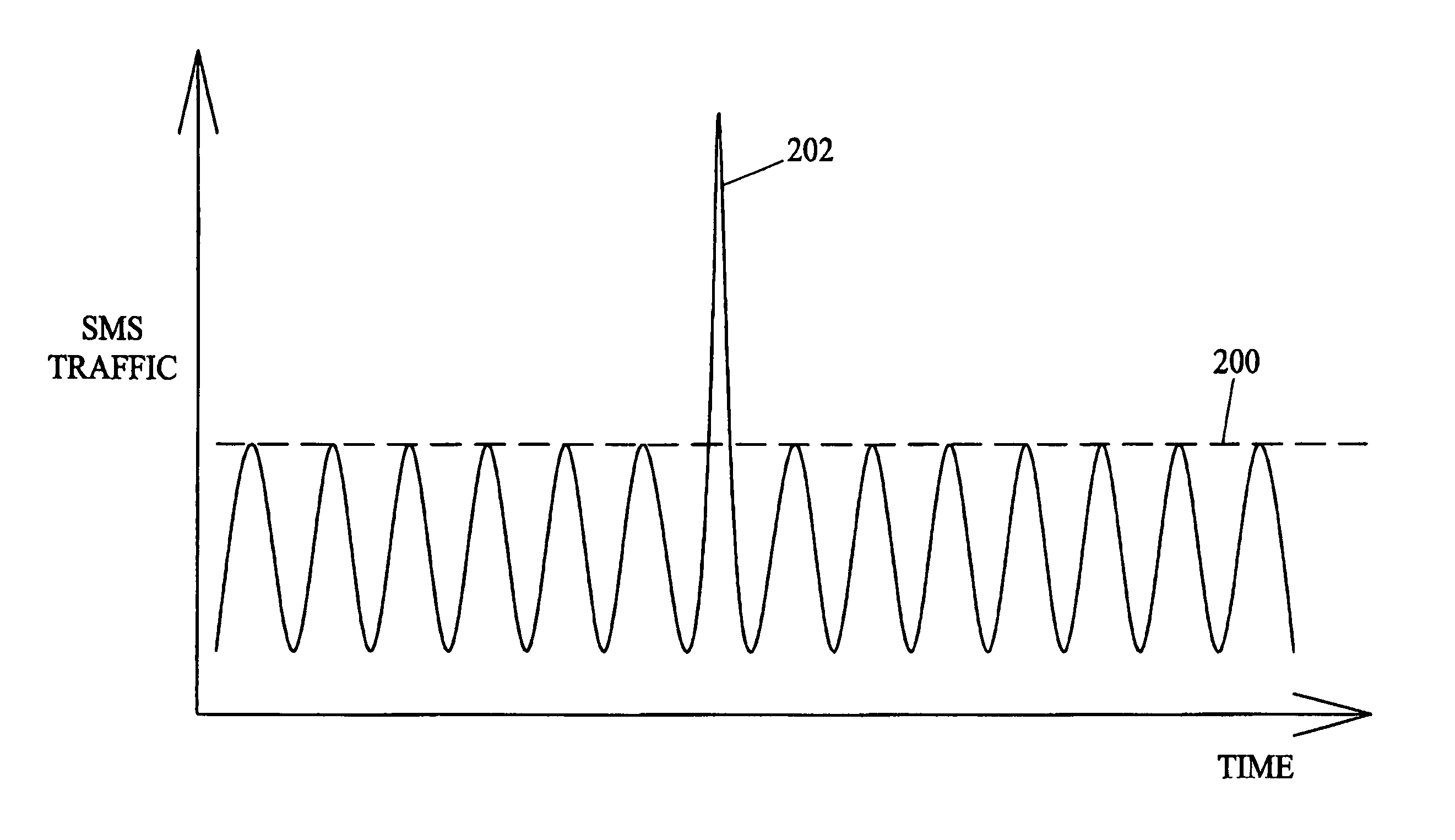
Methods and systems for automatically bypassing short message service center for short message service (SMS) messages destined for predetermined short message peer-to-peer (SMPP) destinations
ActiveUS20050176450A1Reduce needRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsShort Message Peer-to-PeerMessage routing
Methods and systems for automatically bypassing a short message service center for short message service (SMS) messages destined for predetermined SMPP destinations are disclosed. A signal transfer point may receive SMS messages that are global title addressed to a short message service center. The signal transfer point may internally route such messages to a short message gateway. The short message gateway may identify SMS messages destined for predetermined SMPP destinations and forward those messages to the destinations in a manner that bypasses the SMSC. For other SMS messages, the short message gateway may forward these messages to the SMSC for delivery.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
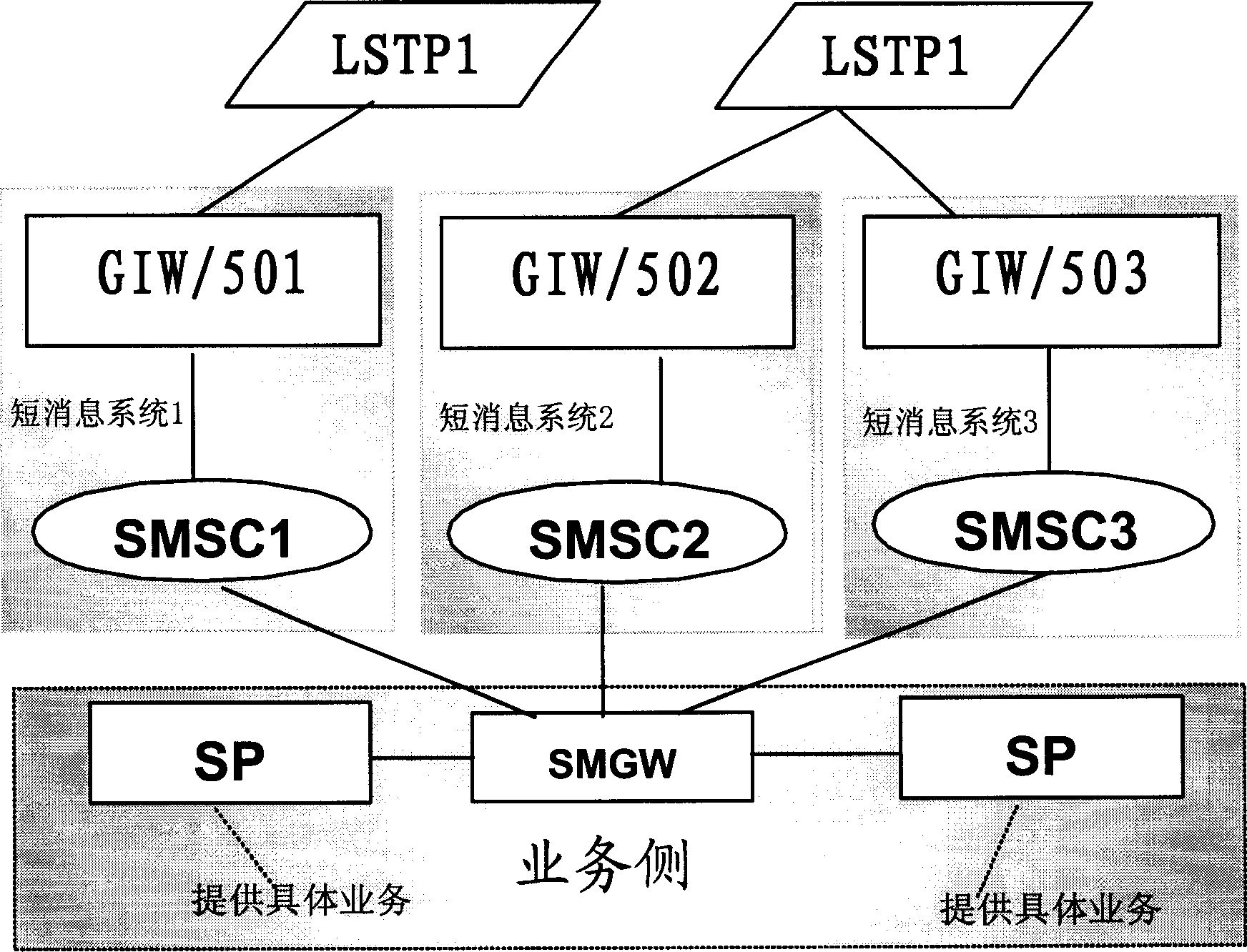
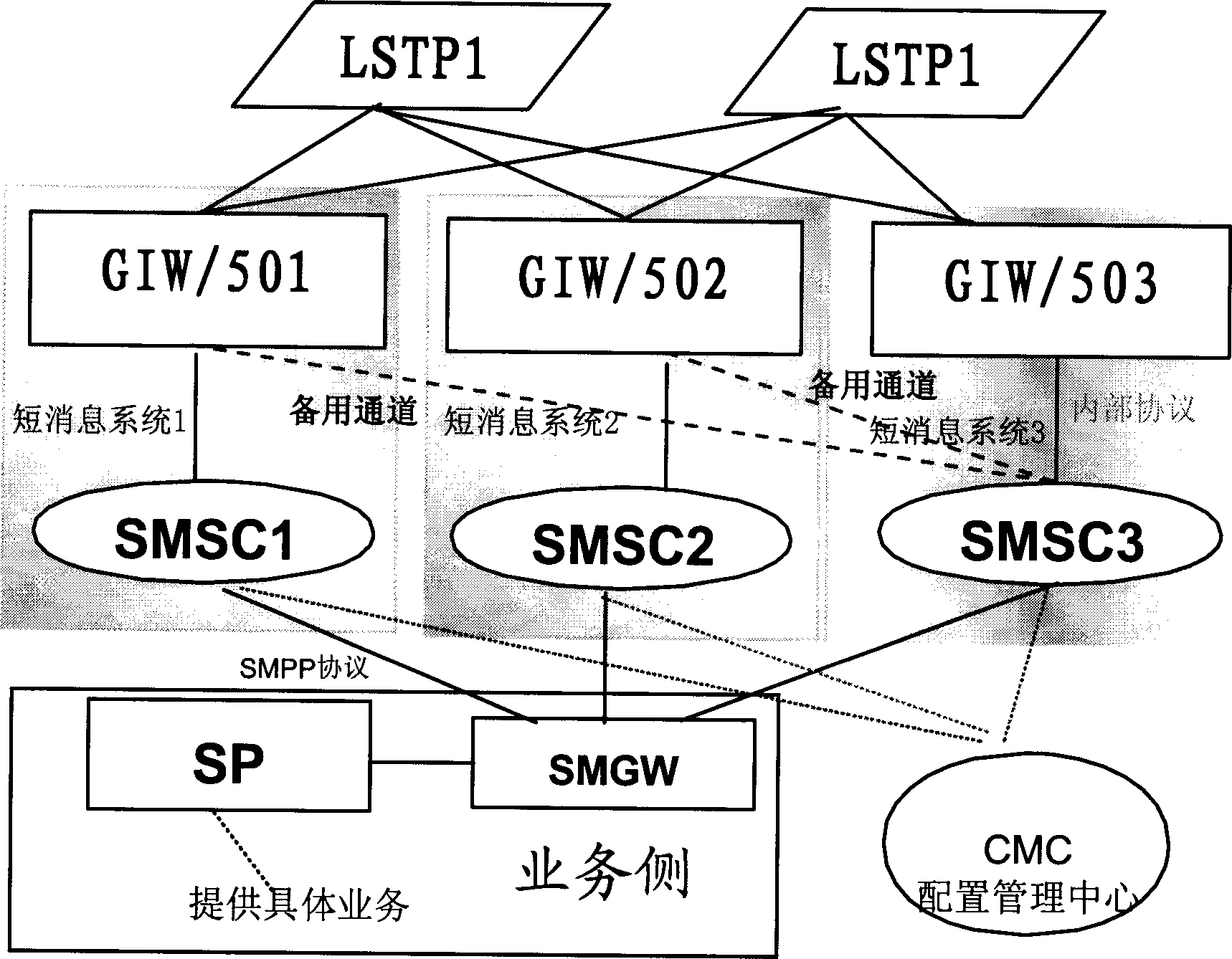
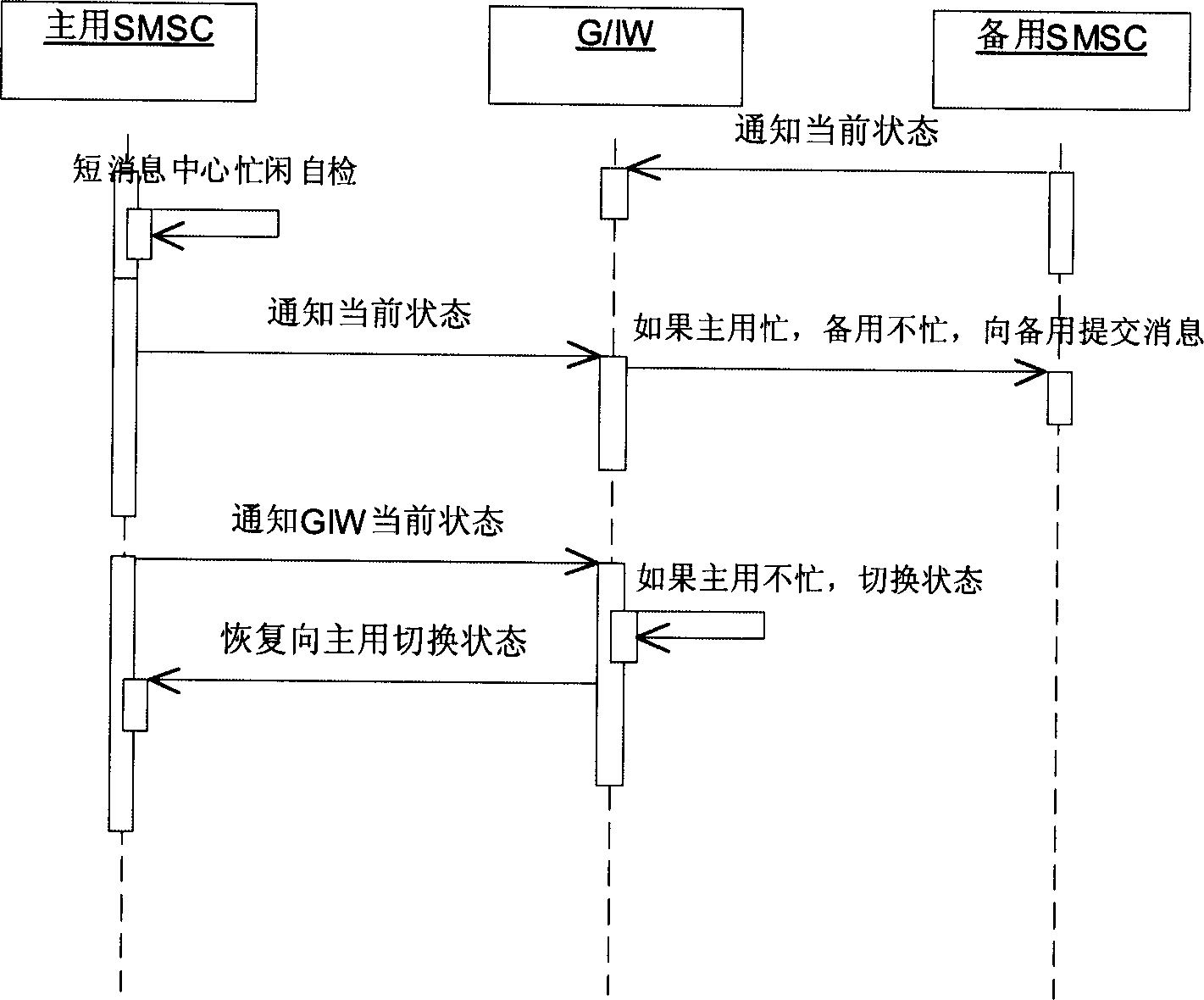
Short message system
InactiveCN1453979ASolve the problem of poor disaster toleranceImprove disaster toleranceSpecial service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsShort Message ServiceMobile Web
The system is featured as the follows. At least one short message gateway is connected to two or above two signaling transfer points of mobile network as well as to two or above two short message centres. It can be made a spare gateway for some other short message centre gateway since the short message centre gateway is connected with above one signaling transfer points so that chaining to be switched to preset backup short message centre can be ensured by utilizing global code address varying function when certain short message centre signaling gateway if fault. The same as above, short message can be retransmitted to spare short message centre for processing when certain short message centre is fault since short message gate way is also connected with spare short message centre in addition to its mainly used short message centre.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
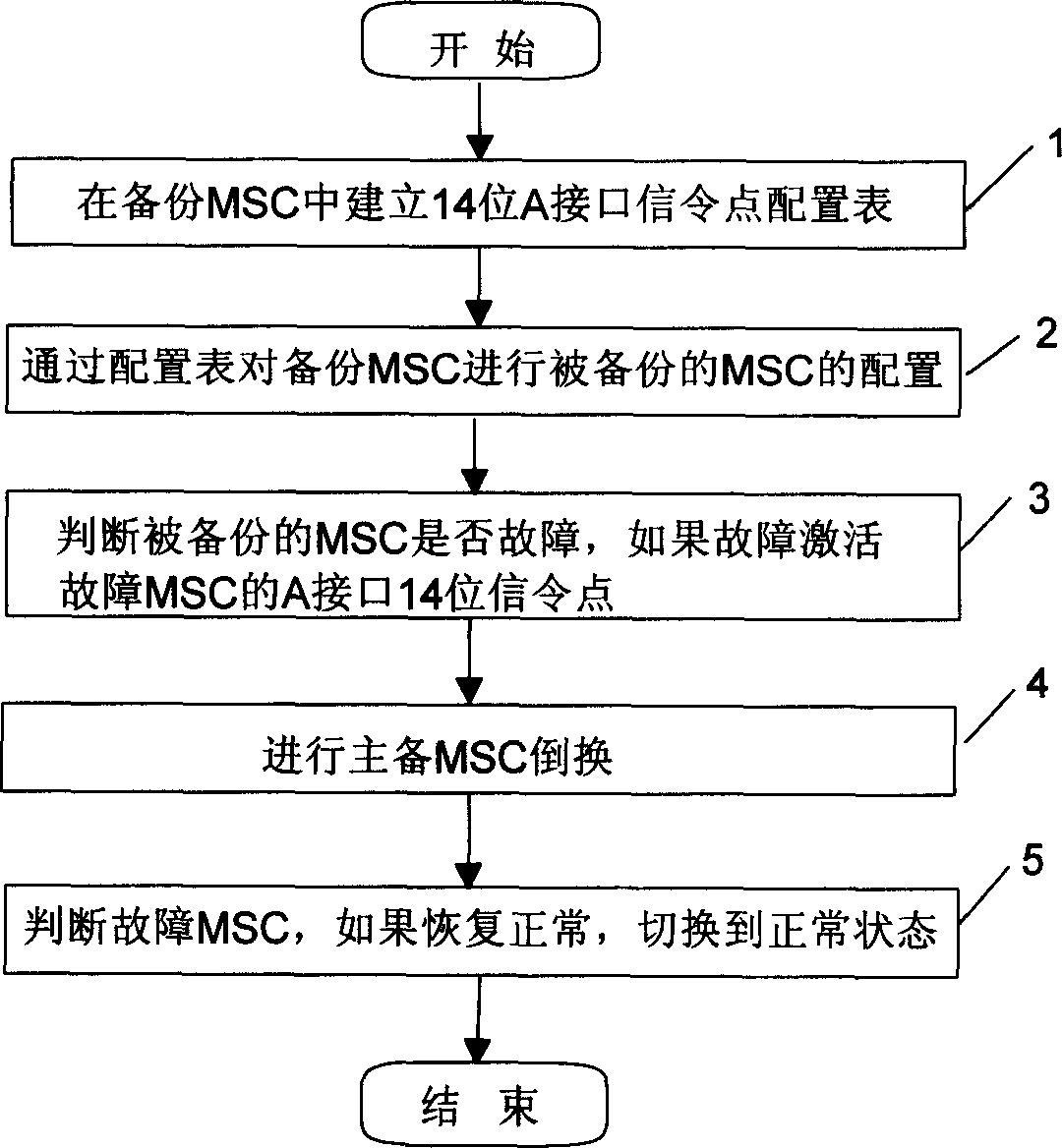
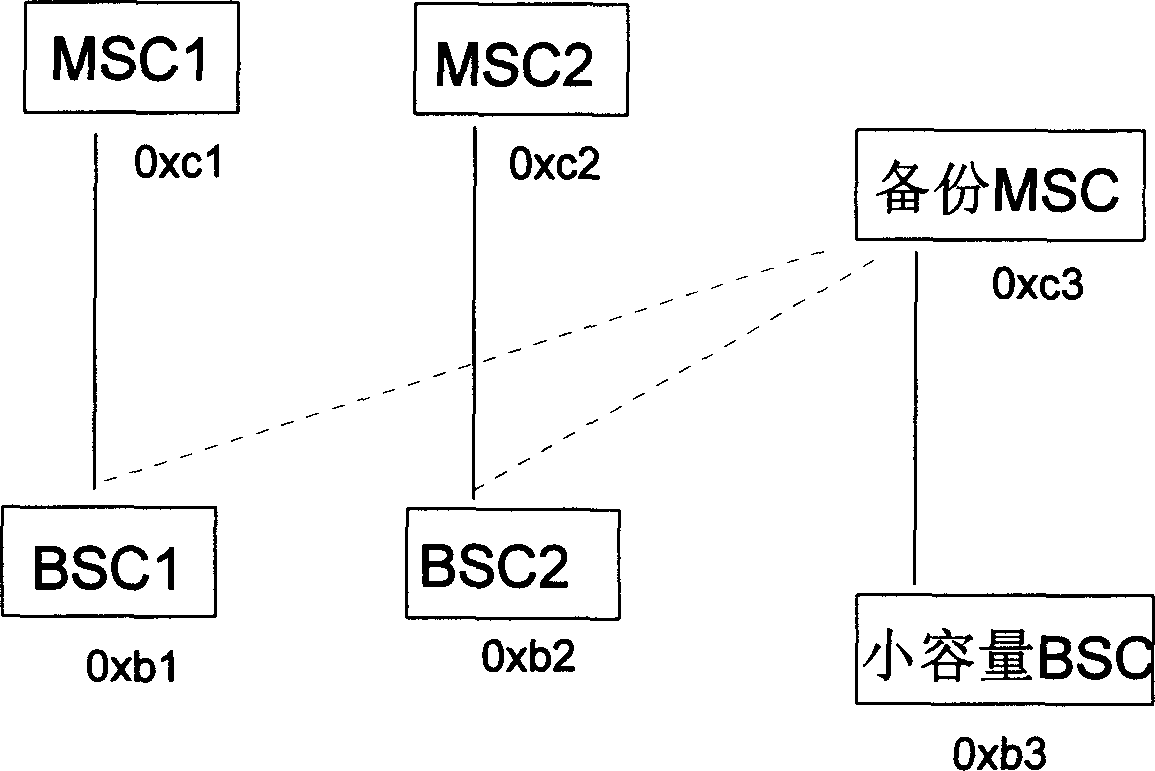
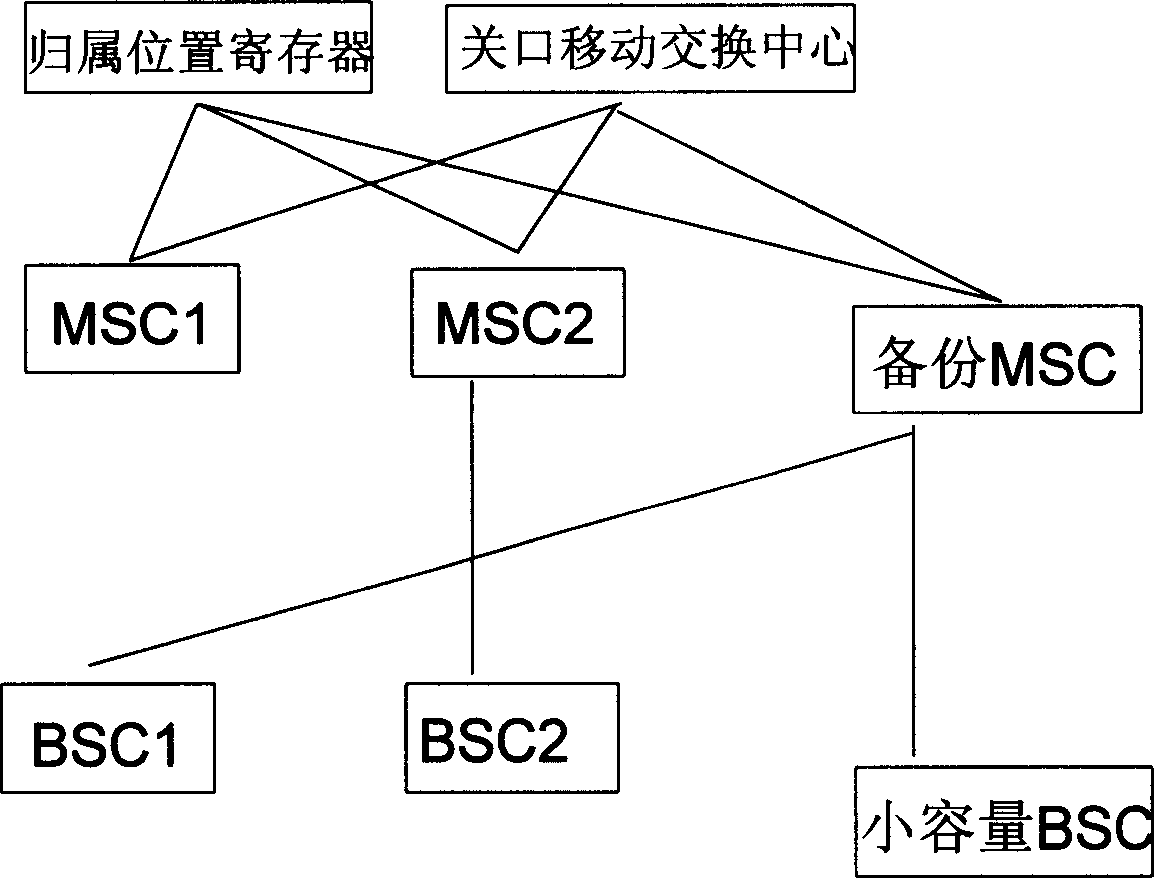
Backup method for mobile exchange center
InactiveCN1434574ASolve the one-to-one backup problemLess investmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionComputer architectureSignalling Connection Control Part
This invention discloses a backup method fo r a mobile exchange center including: applying 14 bit A interface signaling transfer points technology to allocate for them; judging if MCS at the fault stage and converting the master and backup MSC which replaces service of the fault MSC; judging if the fault has resumed mormal to deactivate MSC response MTP, signaling atate at sccp layer and relay toinform the resumed MSC to switch to normal state, which can support one-to-many MSC backup way to backup all MSC of homenet with only one backup MSC, no need to machine type nor influence to other network elements.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for sharing point codes in a network
InactiveUS6792100B2Not be burdened with service disruptionEliminate needTelephone data network interconnectionsTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityNetwork on
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC +1
Systems and methods of performing stateful signaling transactions in a distributed processing environment
ActiveUS7554974B2Accurate and fast positioningImprove versatilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationComputer networkParallel computing
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Method for processing an internet protocol (IP) encapsulated signaling system seven (SS7) user part message utilizing a signal transfer point (STP)
InactiveUS7031340B2Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexInternet protocol suiteTelecommunications
Methods and systems for transmitting user part messages between signaling system seven (SS7) signaling points over an internet protocol (IP) network include receiving, at a signal transfer point, a first SS7 user part message. The first SS7 user part message can be received from a first SS7 signaling point, such as a service switching point (SSP). The first SS7 signaling point is encapsulated in a first IP packet. The first IP packet is transmitted to a second SS7 signaling point over an IP network.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Methods and systems for communicating signaling system 7 (SS7) user part messages among SS7 signaling points (SPs) and internet protocol (IP) nodes using signal transfer points (STPs)
InactiveUS20060077978A1Reduce expensesImprove reliabilityInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsSignaling system
Methods and systems for transmitting user part messages between signaling system seven (SS7) signaling points over an internet protocol (IP) network include receiving, at a signal transfer point, a first SS7 user part message. The first SS7 user part message can be received from a first SS7 signaling point, such as a service switching point (SSP). The first SS7 signaling point is encapsulated in a first IP packet. The first IP packet is transmitted to a second SS7 signaling point over an IP network.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
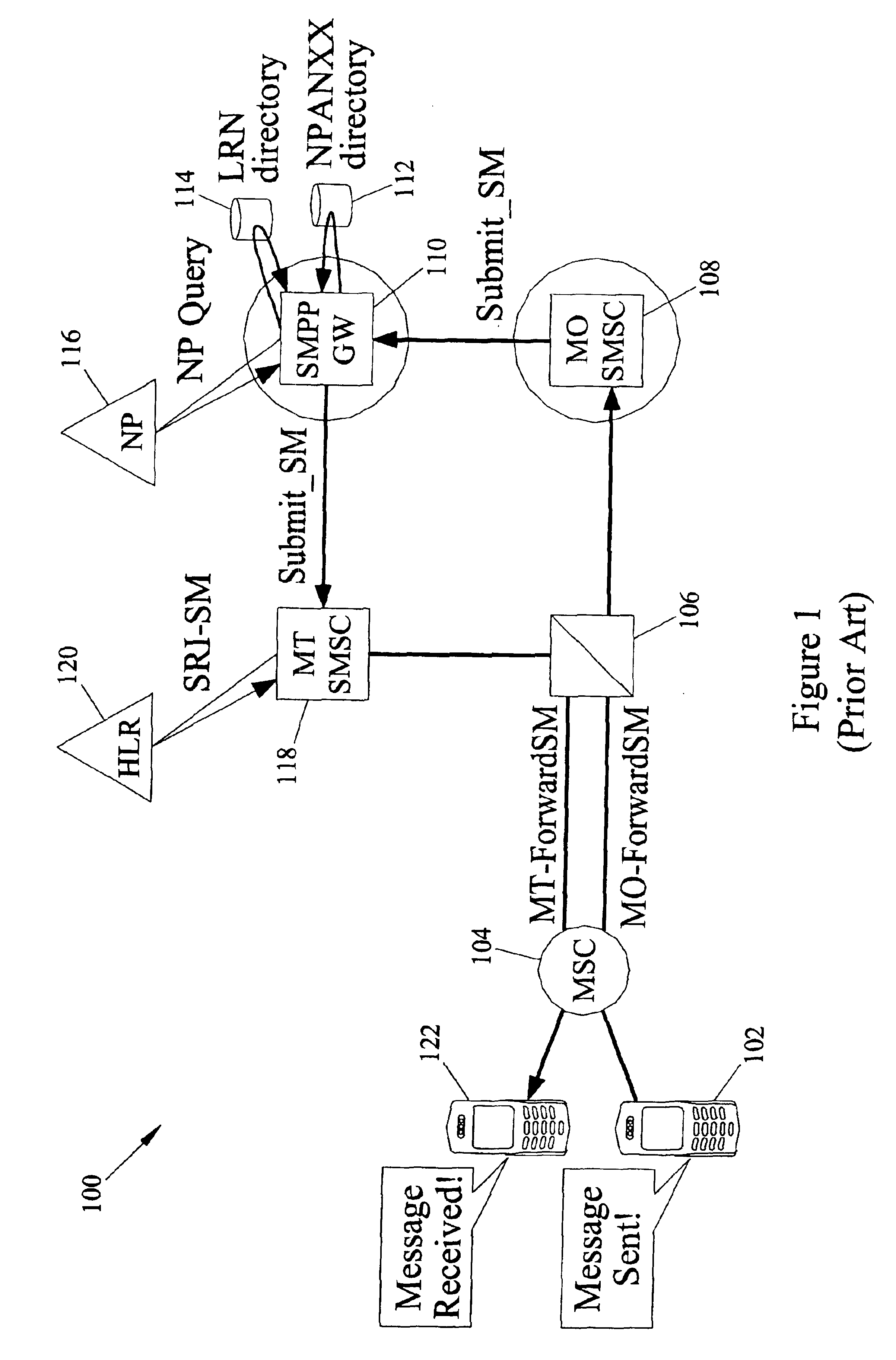
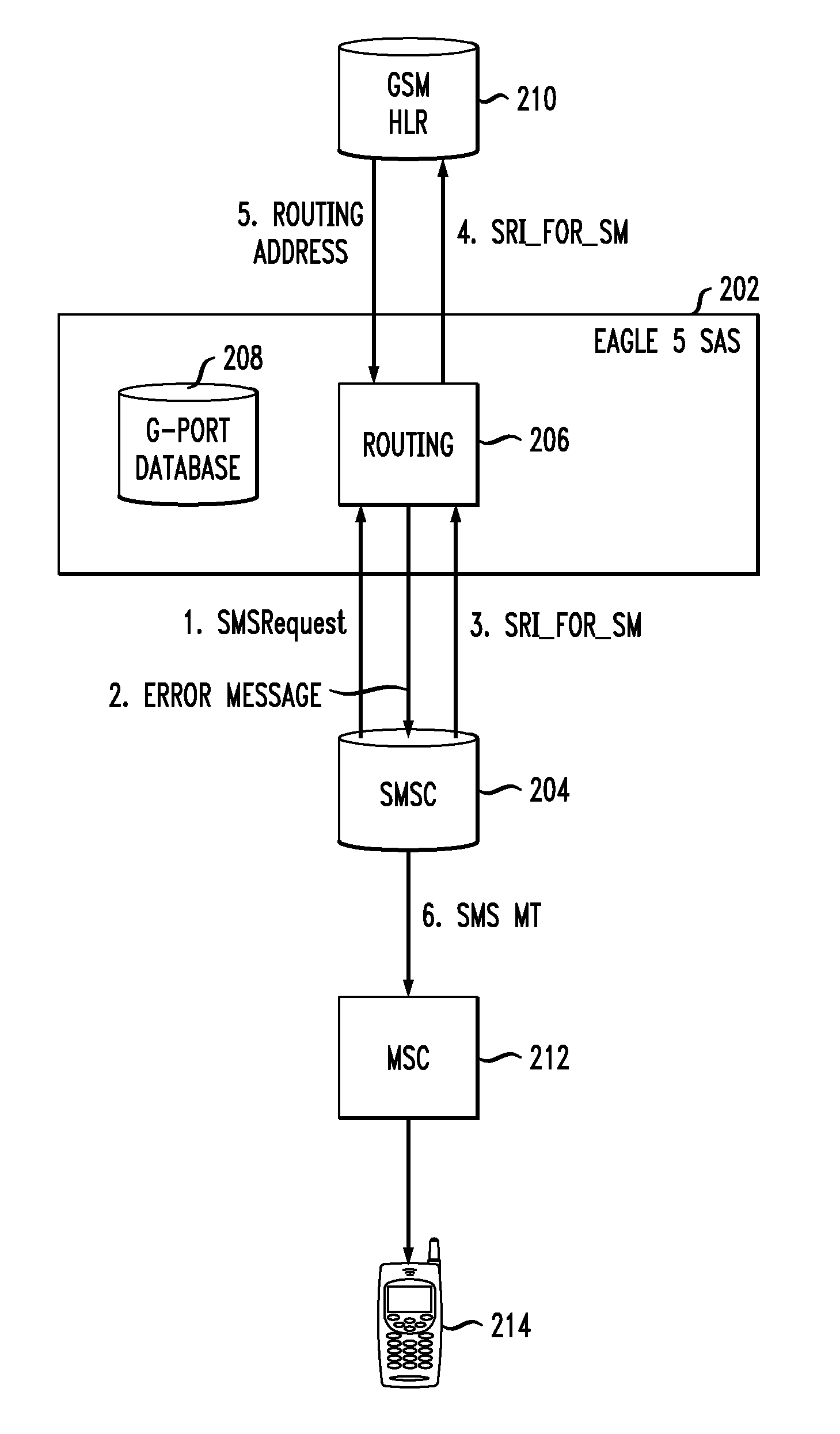
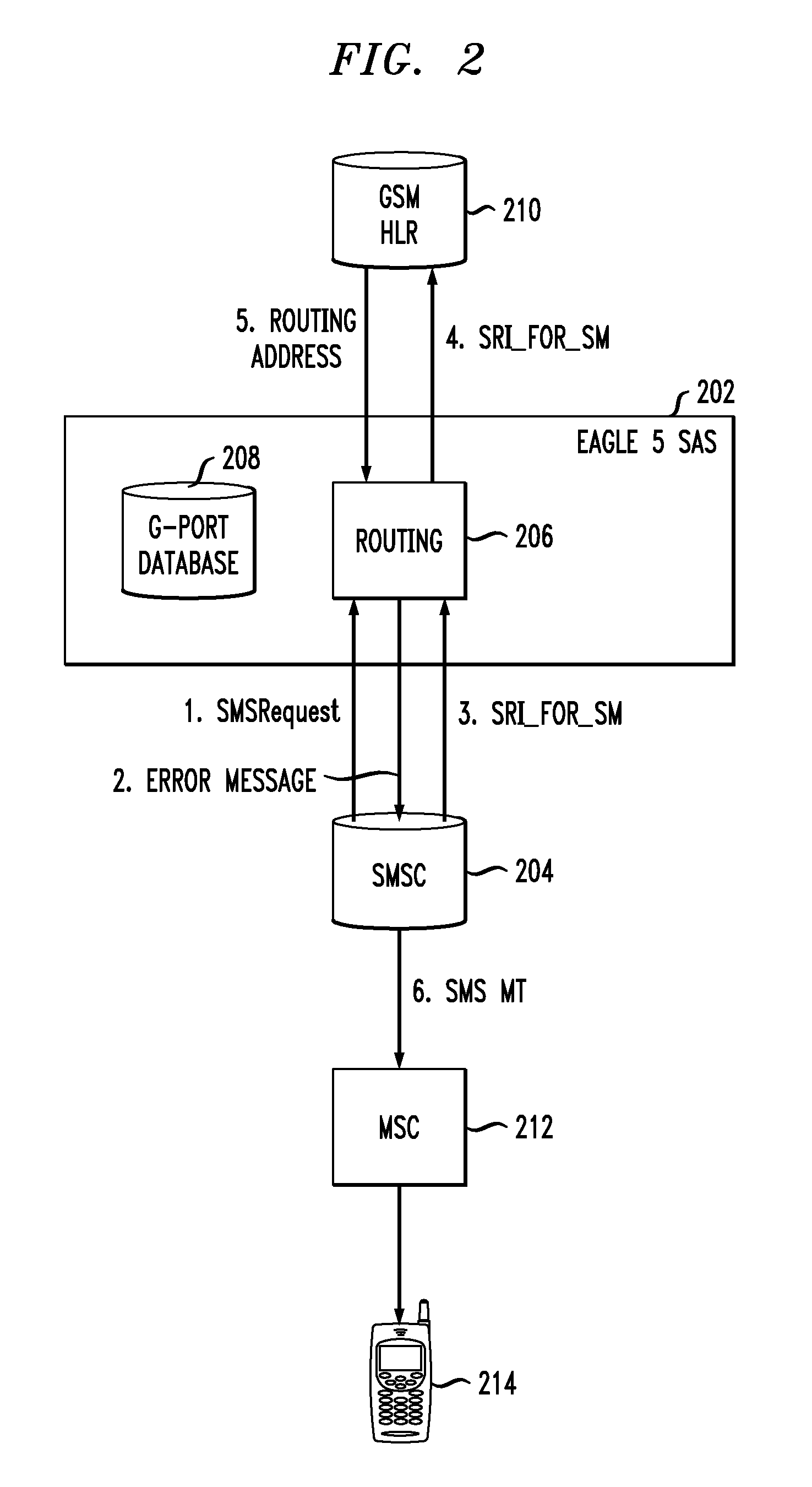
Method and apparatus for data message delivery to a recipient migrated across technology networks
A method of providing SMS delivery to recipients migrated across different technology networks. The method includes receiving a short message service (SMS) text message from a sender at a short message service center (SMSC), wherein the SMS text message includes a destination number for a recipient of the SMS text message. A first routing request is sent to a database in a first network for SMS routing information for the destination number via a first signal transfer point (STP). The first STP determines whether the destination number is a migrated or a non-migrated destination number based on data received from the first database. An an error indication is provided to the SMSC if the destination number and the first routing request are for different communication networks. Finally, a second routing request is sent to a second database in a second network for SMS routing information for the destination number via a second STP.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
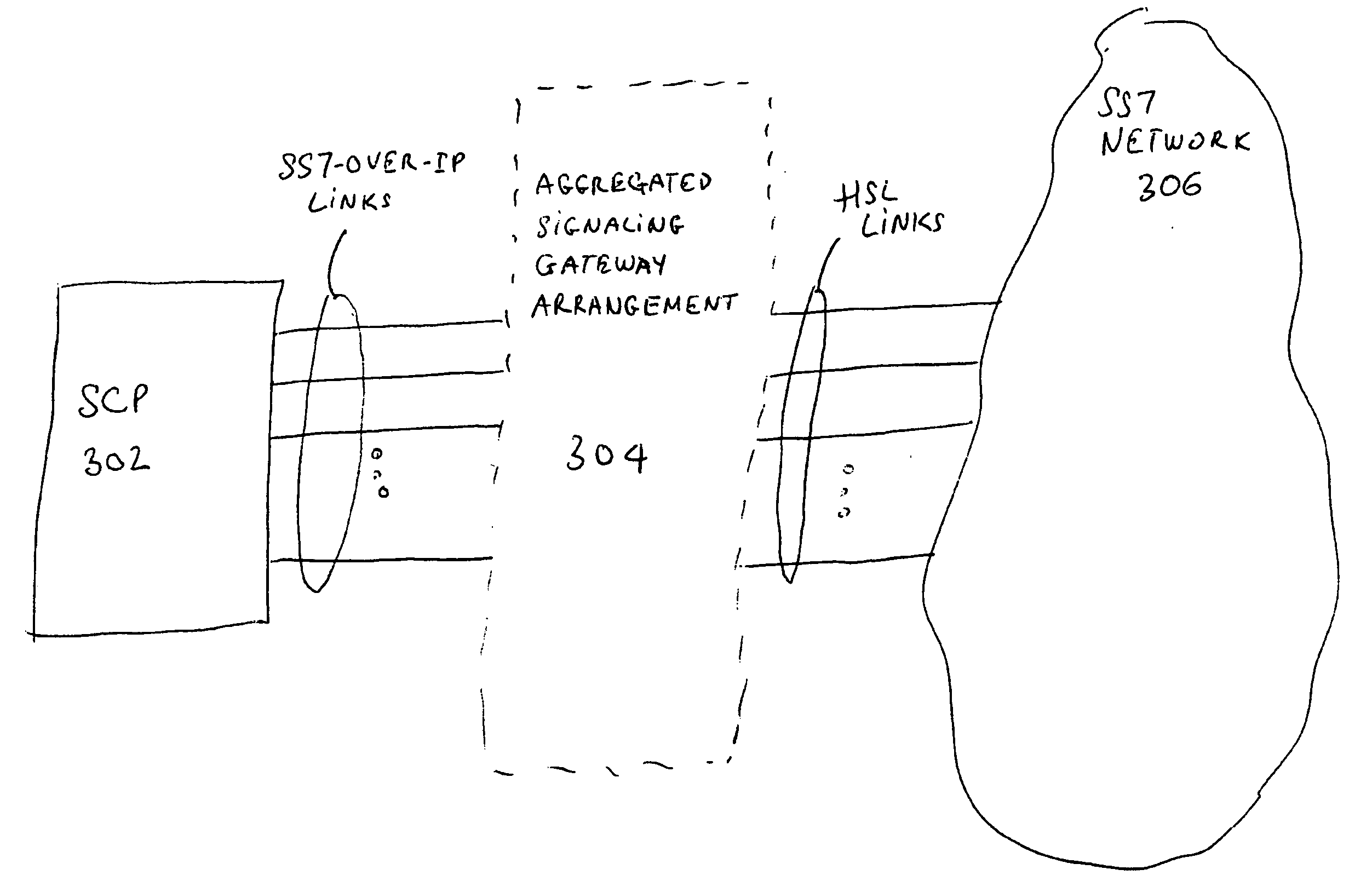
Signaling gateway aggregation
InactiveUS20050152383A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsComputer networkTransfer point
An arrangement for coupling a SCP (Signaling Control Point) and Signaling Transfer Point (STP) nodes of a SS7 network is disclosed. The arrangement includes an aggregated signaling gateway arrangement (ASGA), which includes at least a first signaling gateway and a second signaling gateway. The first signaling gateway is coupled between the SCP and a first STP node of the SS7 network. The second signaling gateway is coupled between the SCP and a second STP node of the SS7 network, the first signaling gateway and the second gateway being associated with a single SS7 point code.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
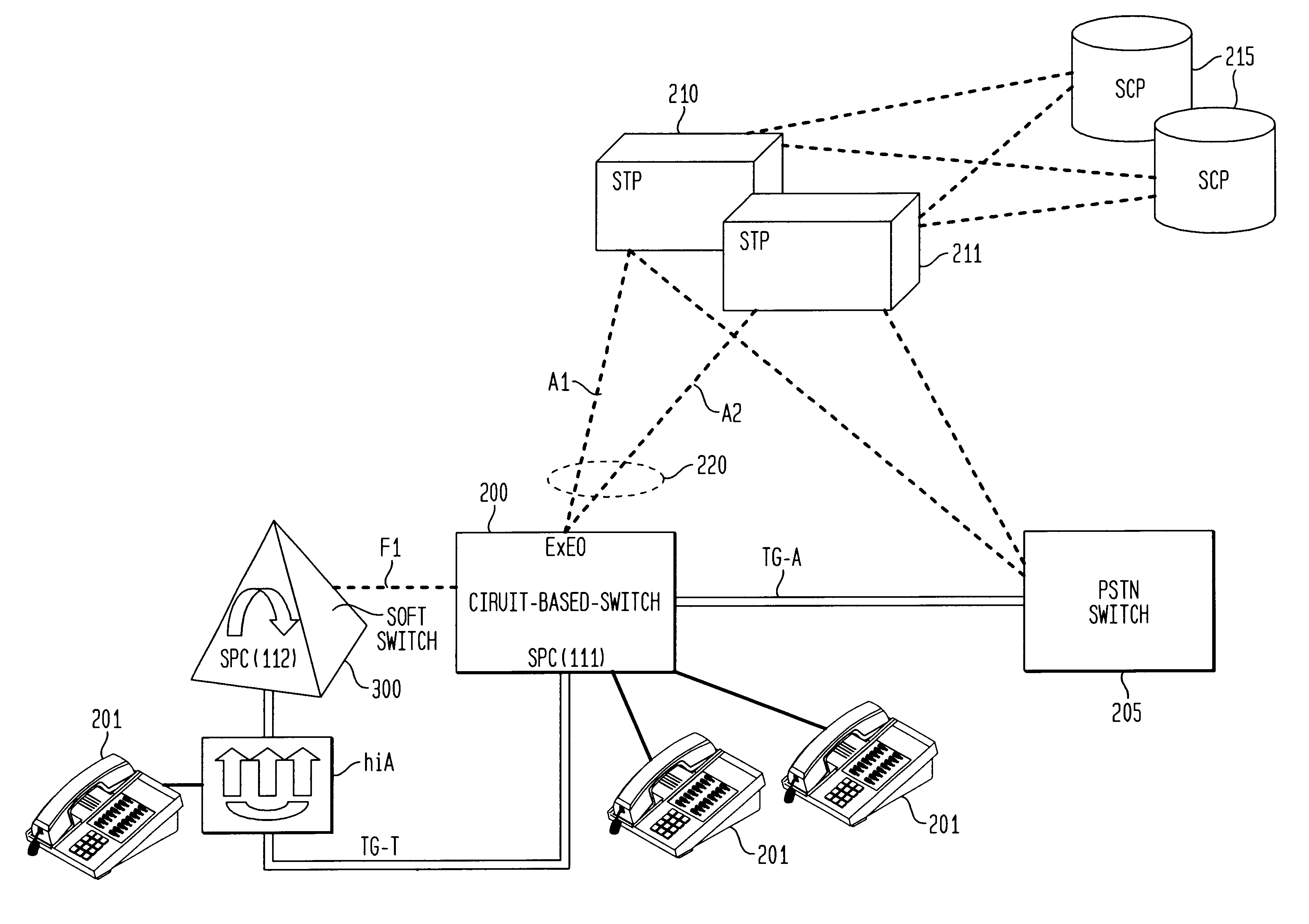
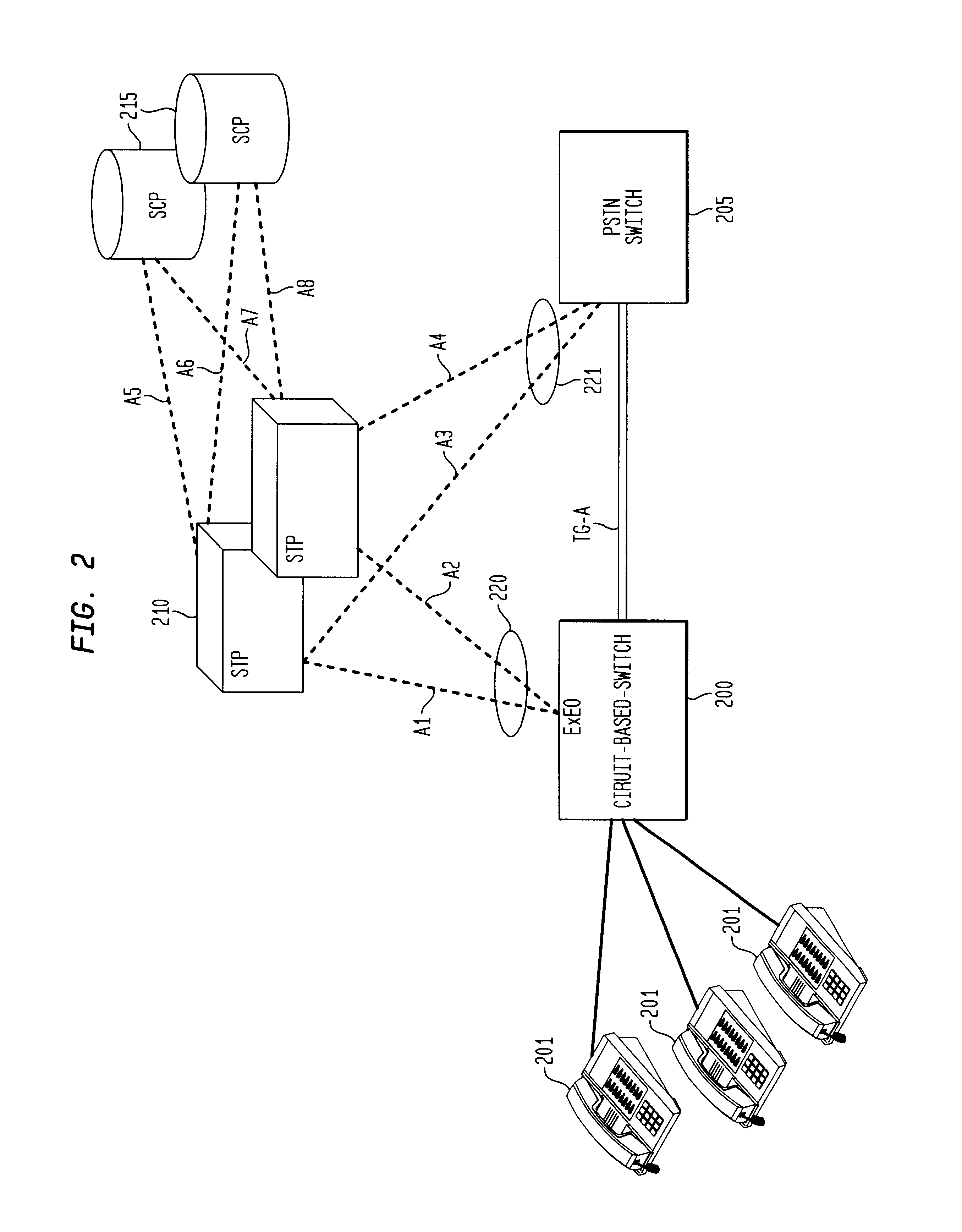
Method and apparatus for sharing point codes in a network
InactiveUS20030169867A1Not be burdened with service disruptionMinimal disruption and administrative changeTelephone data network interconnectionsTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityNetwork on
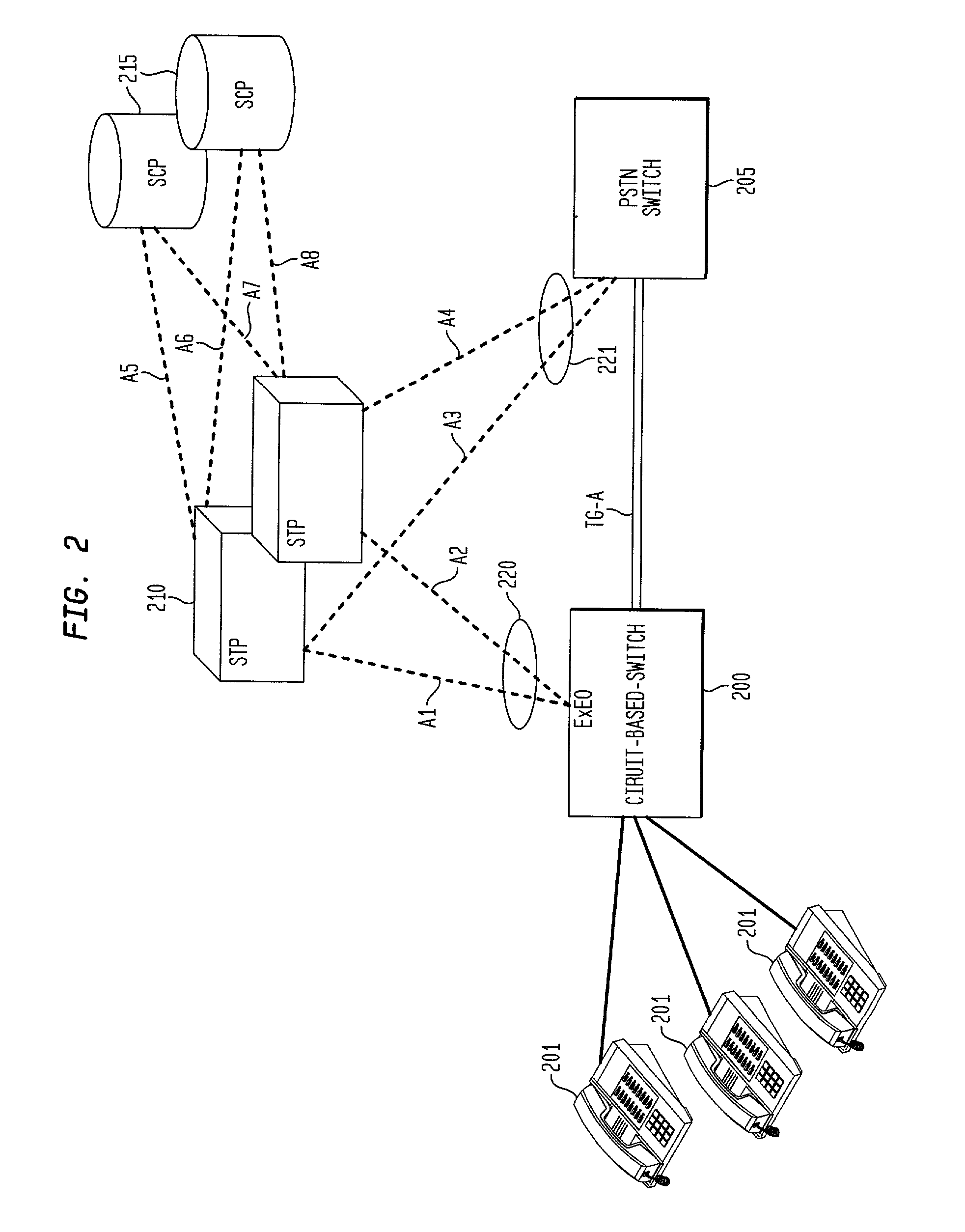
Migration of a circuit-based-switch to a packet-based-soft-switch in a SS7 telecommunications network is accomplished with no disruption to subscriber service and retains and reuses the assigned signaling point code (SPC) of the existing circuit-based-switch. The system and method inserts a new soft-switch between an SS7 signaling transfer point (STP) and the existing circuit-based-switch in a way where traffic is split incrementally off the circuit-based-switch to the soft-switch so that no administrative changes are required at either the STP or the existing circuit-based-switch. The soft-switch is gradually cutover to act as a proxy STP and tandem switch for the existing circuit-based-switch and routes all calls to and from the network on behalf of the existing switch. The system makes use of multiple internal networks of the soft-switch to accomplish the controlled routing of bi-directional traffic. The circuit-based-switch can eventually be removed from service after subscribers are migrated to the new soft-switch.
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC +1
Methods and systems for automatically bypassing short message service center for short message service (SMS) messages destined for predetermined short message peer-to-peer (SMPP) destinations
ActiveUS7110780B2Reduce needRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsShort Message Peer-to-PeerMessage routing
Methods and systems for automatically bypassing a short message service center for short message service (SMS) messages destined for predetermined SMPP destinations are disclosed. A signal transfer point may receive SMS messages that are global title addressed to a short message service center. The signal transfer point may internally route such messages to a short message gateway. The short message gateway may identify SMS messages destined for predetermined SMPP destinations and forward those messages to the destinations in a manner that bypasses the SMSC. For other SMS messages, the short message gateway may forward these messages to the SMSC for delivery.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
Method and system for message routing
InactiveUS20050053223A1Good serviceIncrease profitMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsService controlMessage routing
A method and system for forwarding information, such as a message waiting indicator (MWI) message, to a telephone number corresponding to a foreign network (e.g., a wireless network) and a shared NPA / NXX—The invention evaluates individual telephone numbers of shared NPA / NXXs to determine to what networks to send messages. A representative embodiment of the invention uses a service control point and service package application to deliver an MWI message from a messaging service provider to a wireless (i e., foreign network) telephone number of a shared NPA / NXX, Shared NPA / NXXs are marked as “portable” in a signal transfer point for forwarding to the service control point, which determines whether the shared NPA / NXX telephone numbers require local number portability global title translation or should be forwarded to an inter-switch voicemail routing (ISVMR) service package application. The ISVMR service package application determines the point code to which the MWI message should be routed.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
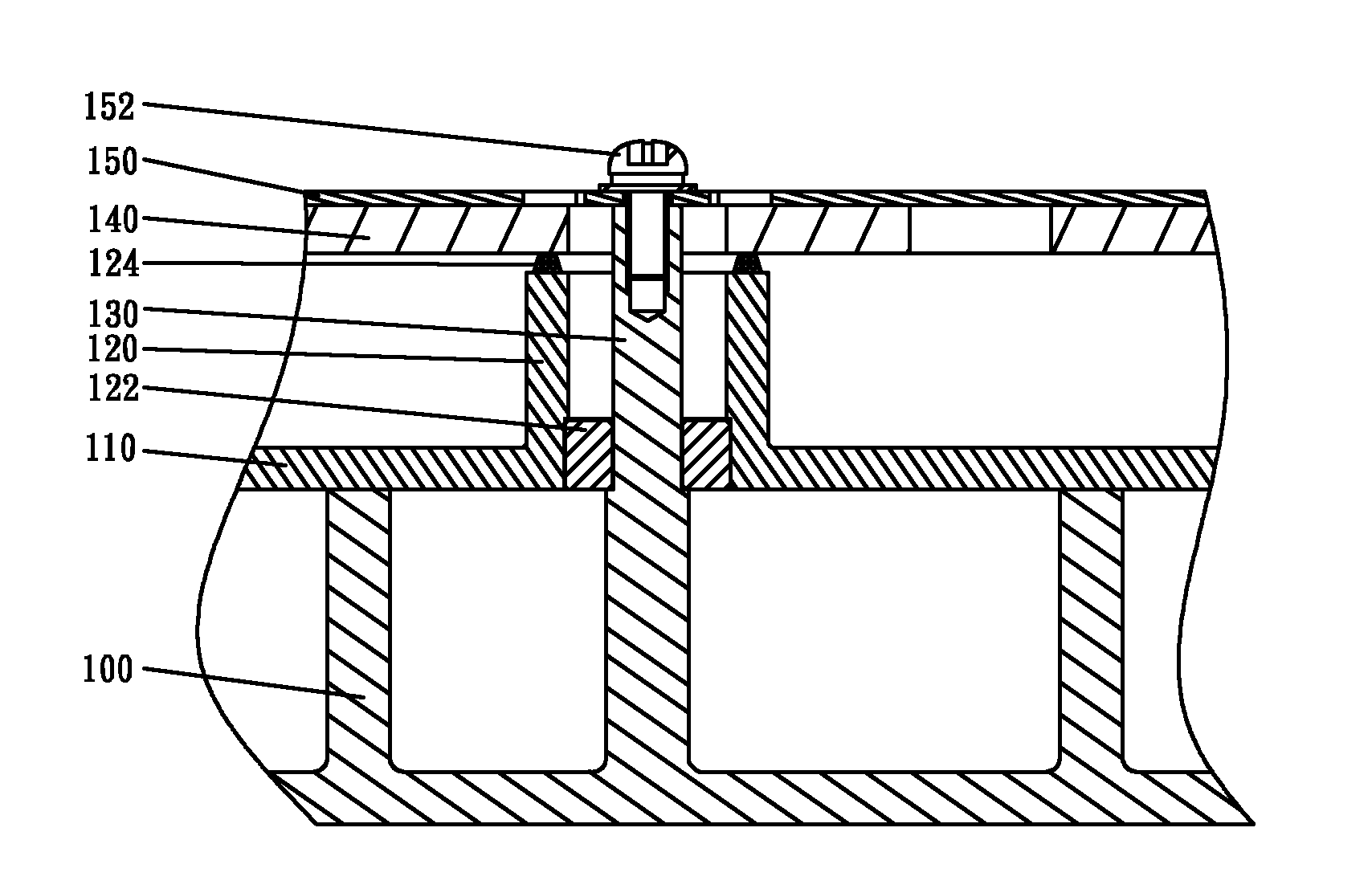
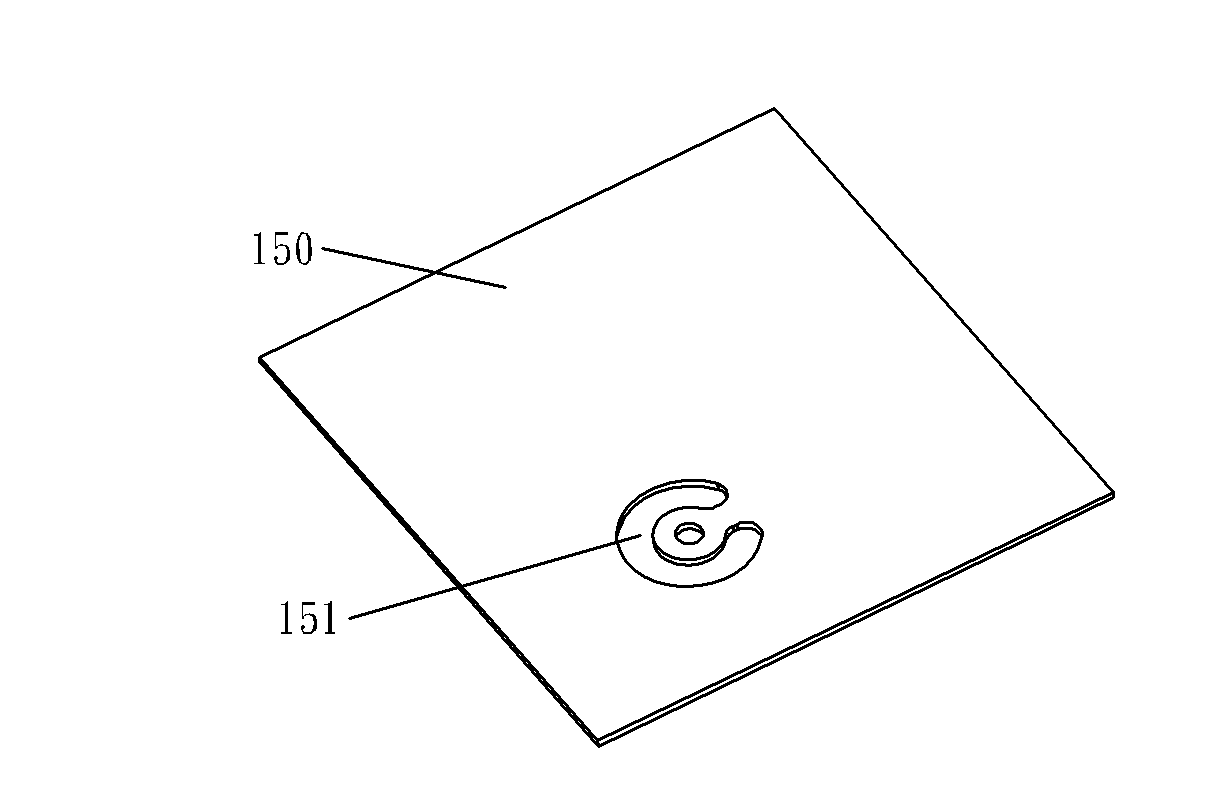
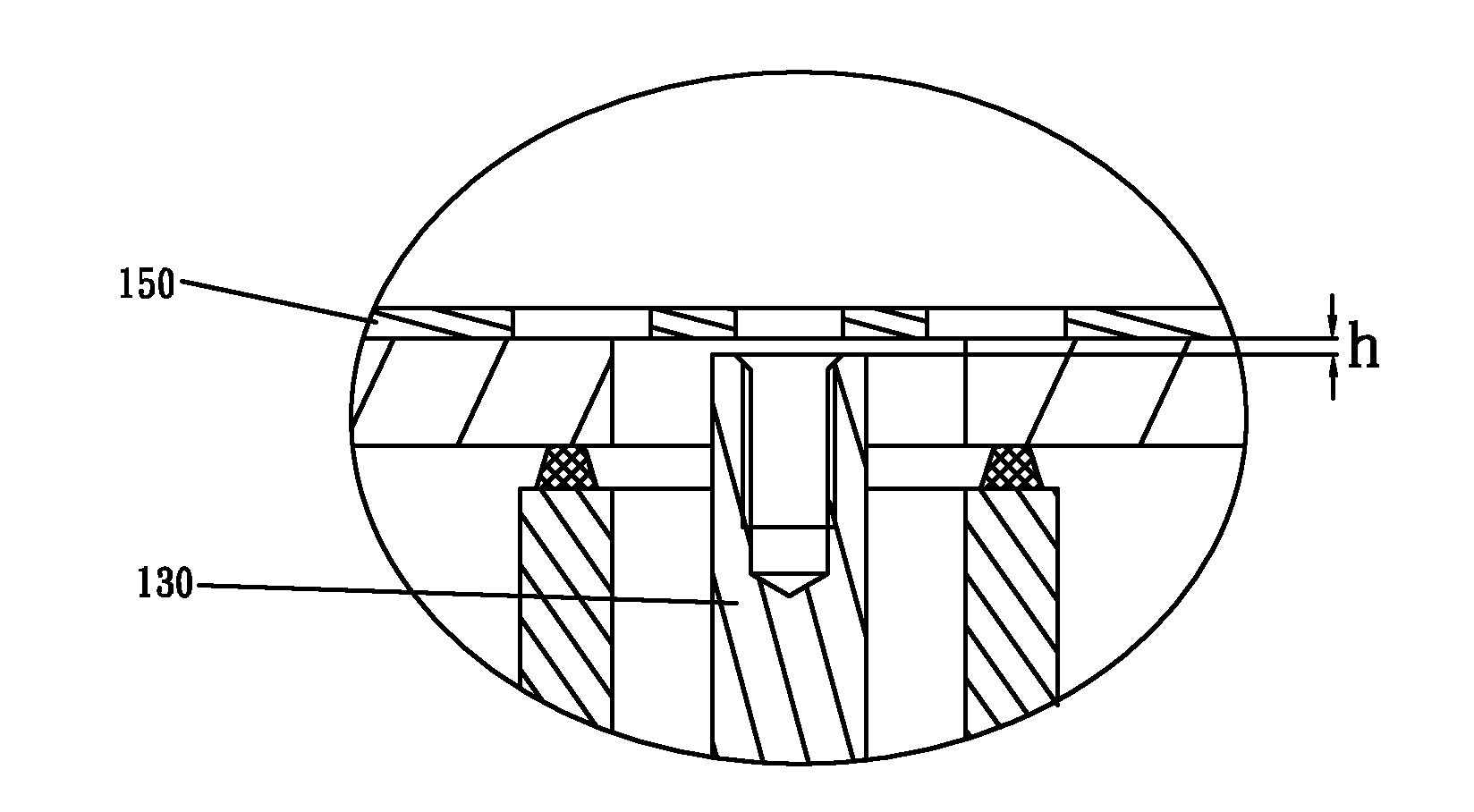
Cavity filter and communication equipment
ActiveCN102136616ANot easy to damageEliminate positioning errorsCoupling contact membersWaveguide type devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses a cavity filter. The cavity filter comprises a cavity body, a cover plate and an in-connector conductor, wherein the in-connector conductor is arranged in the cavity body and passes through the cavity body or the cover plate to connect a signal transfer point of an external circuit board of the cavity filter; the in-connector conductor comprises an elastic part; and the elasticity function of the elastic part is used for eliminating the relative position error between the in-connector conductor and the signal transfer point of the circuit board, ensuring good contact between the in-connector conductor and the signal transfer point of the external circuit board of the cavity filter, and avoiding the deformation damage of the circuit board in an installation process.
Owner:ANHUI TATFOOK TECH CO LTD
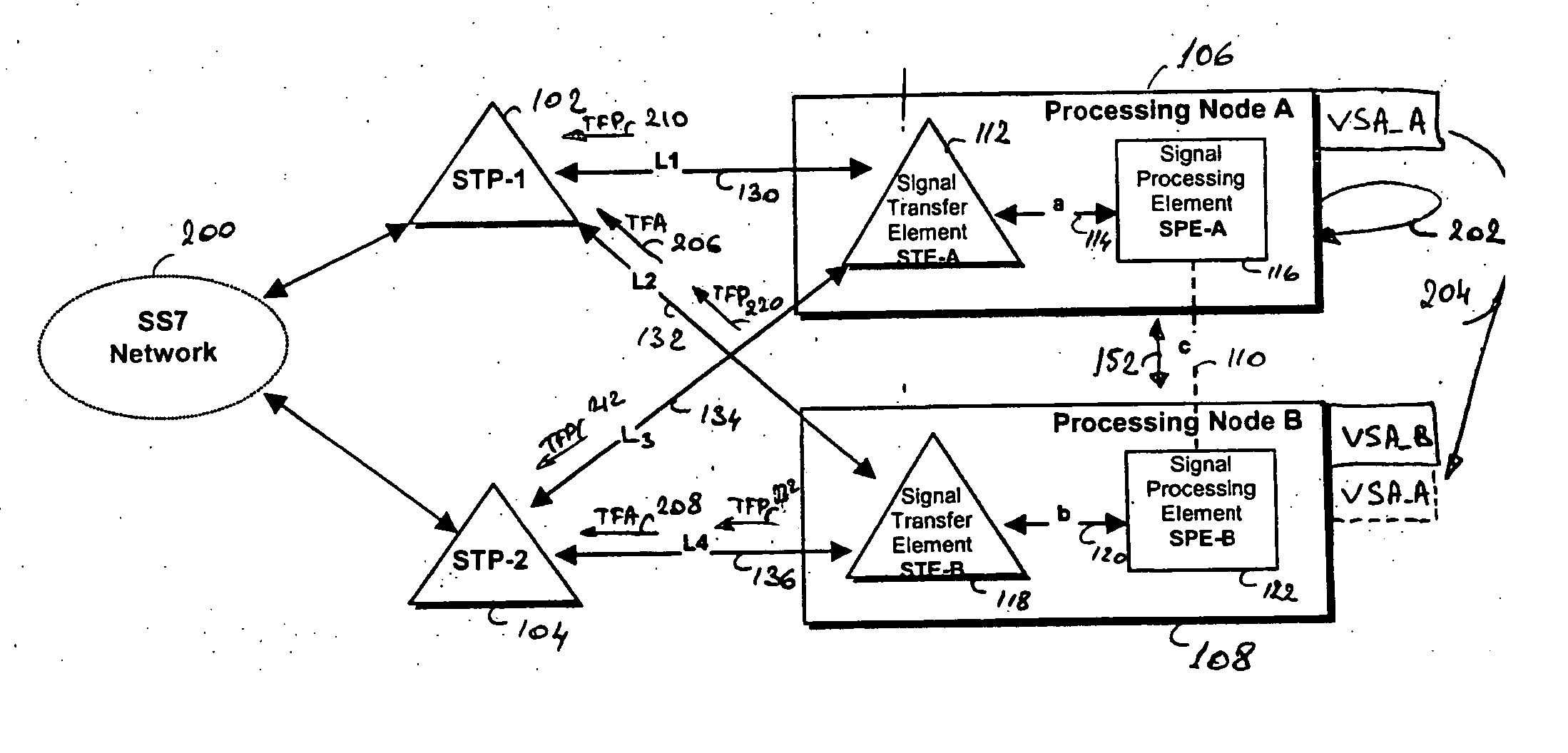
Method and system for service node redundancy
InactiveUS20050144316A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksDistributed computingUnavailability
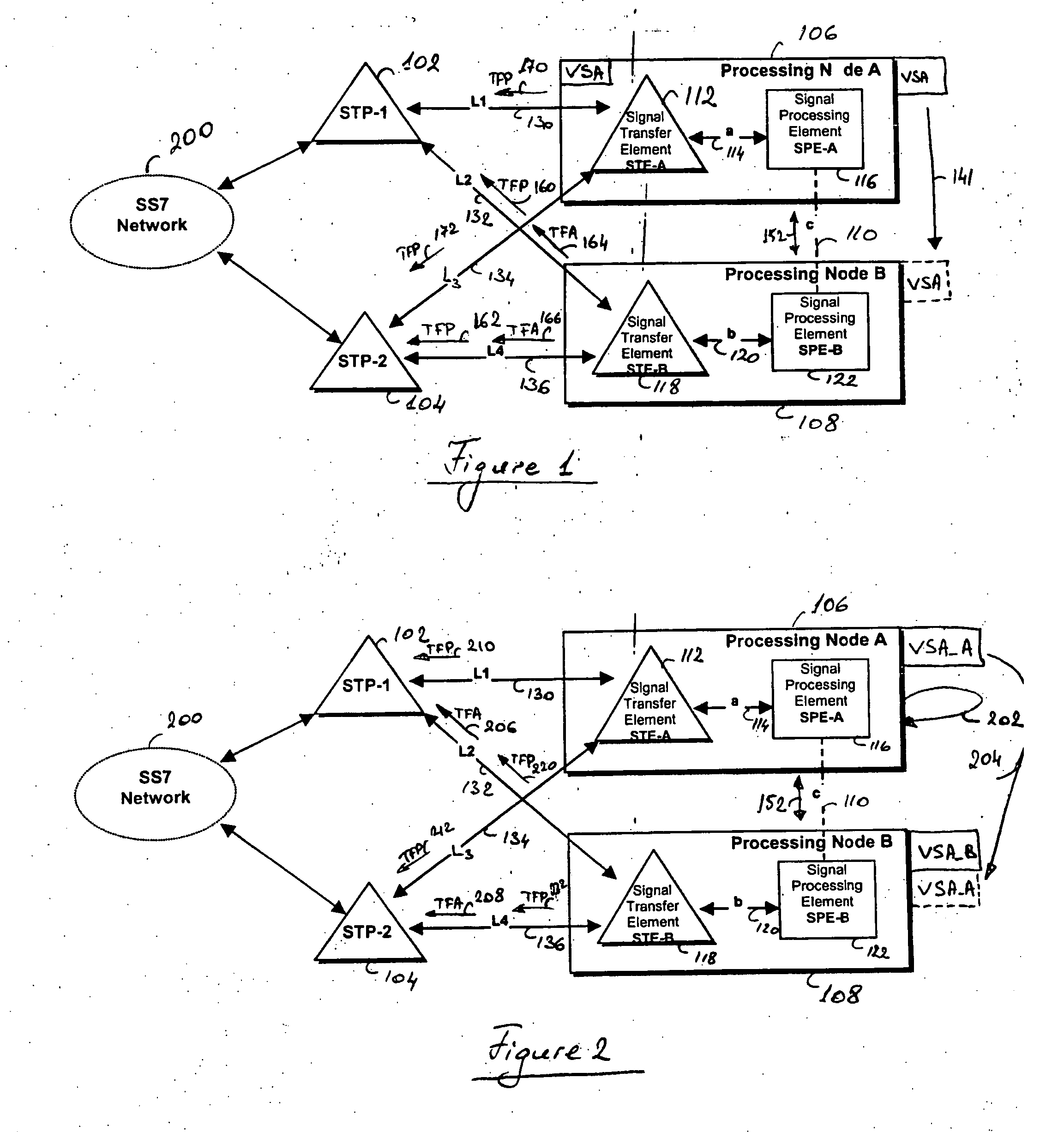
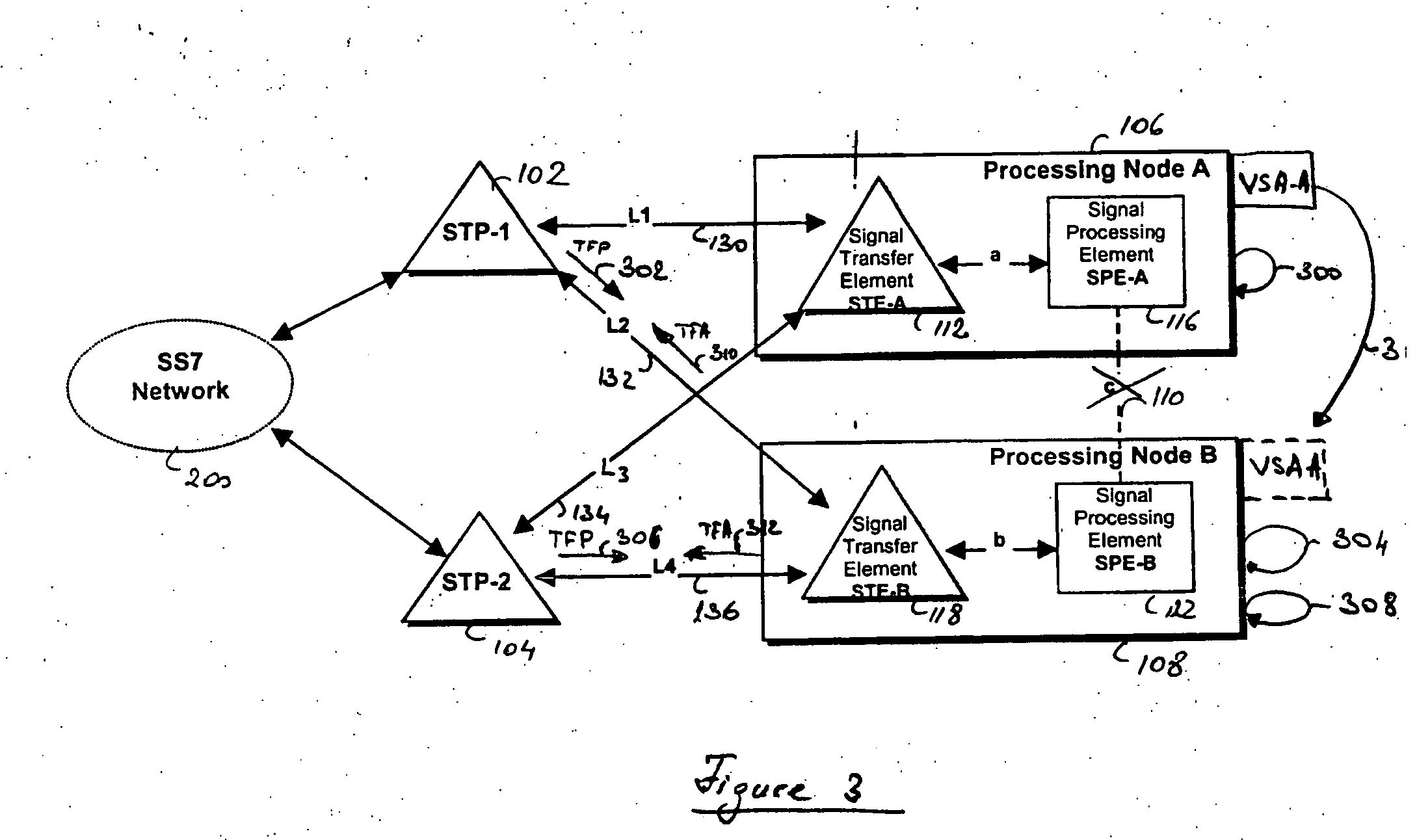
A method and processing node for processing node redundancy, wherein an unavailability of a primary processing node is first detected, and the linkset route to the unavailable node is inhibited by sending Transfer Prohibited (TFP) messages to Signal Transfer Point (STPs) adjacent to the unavailable node. Further, Transfer Allowed (TFA) messages are sent to the STPs in order to enable an alternate linkset route to the secondary processing node, i.e. the standby backup node. A Virtual Service Address (VSA) is reassigned from the unavailable primary node to the remaining node that takes over the processing of the unavailable node and thus becomes the primary processing node. The unavailability of the processing node may be detected via a heartbeat mechanism between the two redundant nodes, or via receipt of TFP messages from the adjacent STPs. The method and processing node may be used in a hot standby configuration or in a load sharing configuration.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
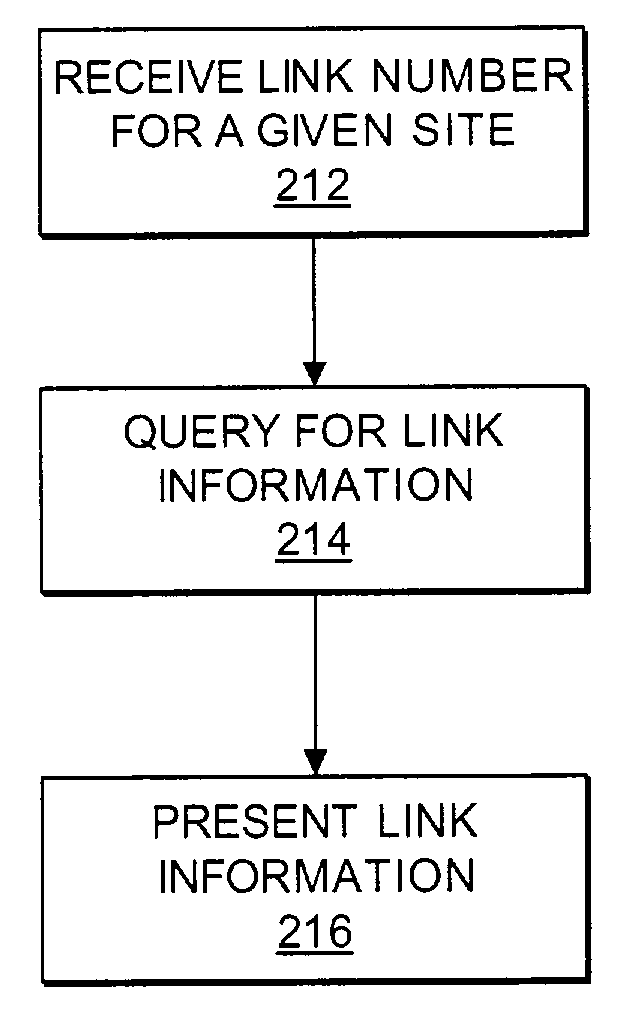
Method and system for presenting data stored within a network component
InactiveUS7092504B1Reduce troubleshooting timeInterconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTelecommunications linkDisplay device
A method, system, and medium for retrieving information stored within a telecommunications-network component is provided. The method includes presenting component information to a user in response to providing one or more links upon which to derive information. The present invention can optionally ensure integrity of the data provided and automatically present information about the communications links entered as well as other signal-transfer-point information. This information includes one or more processor components that service the link as well as all other links serviced by the processor(s). The query results are presented in an easy-to-understand format on a display device via a user interface.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
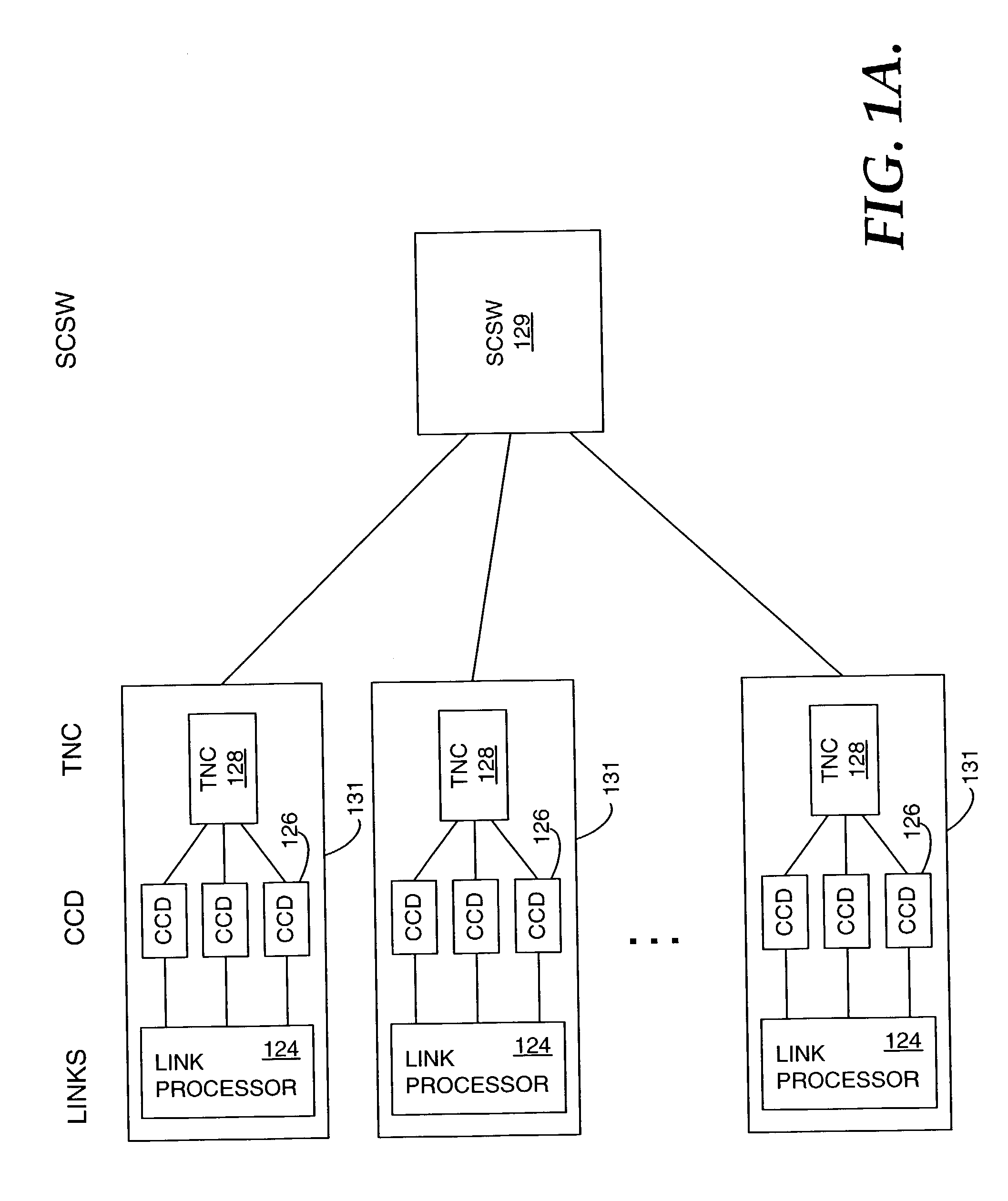
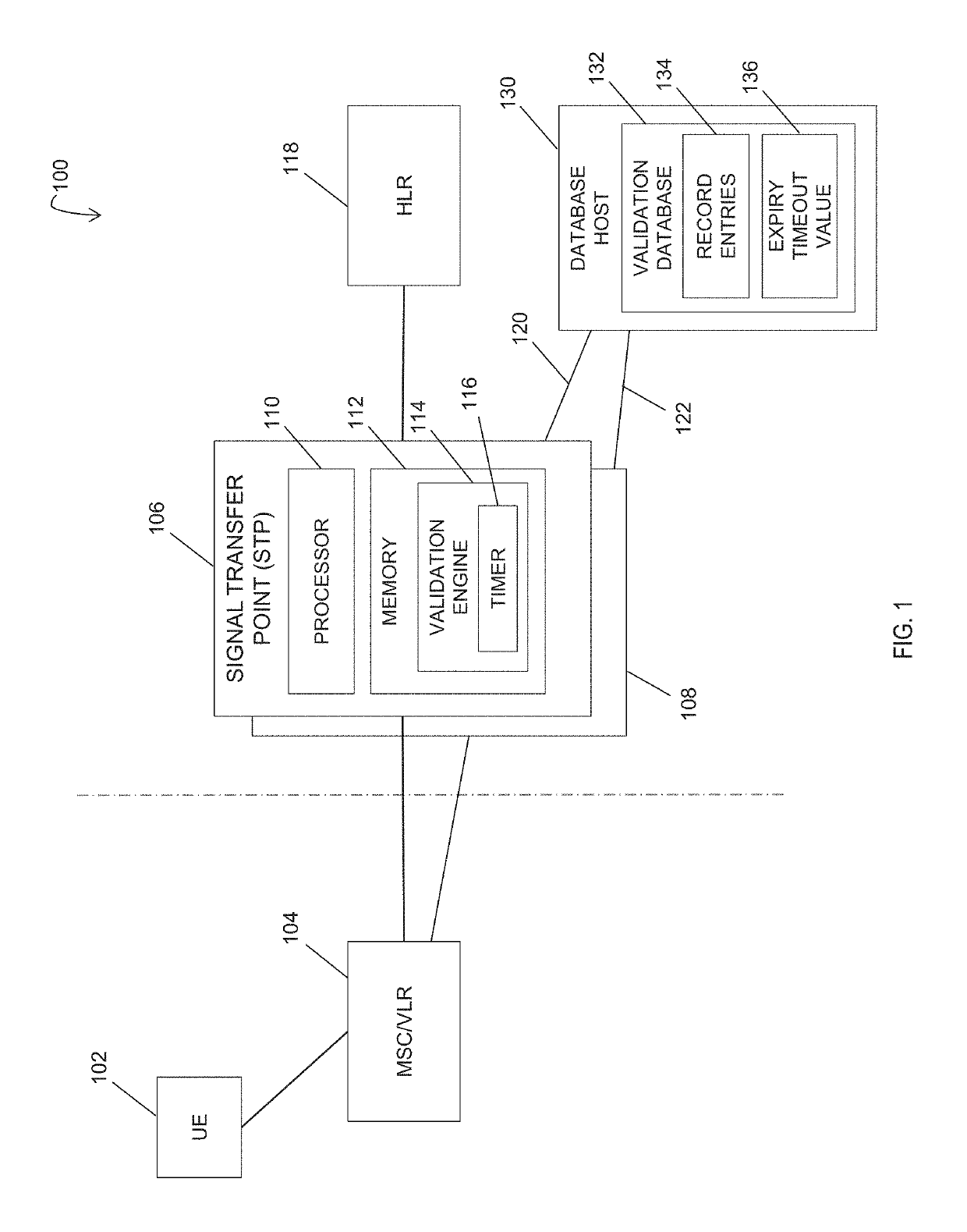
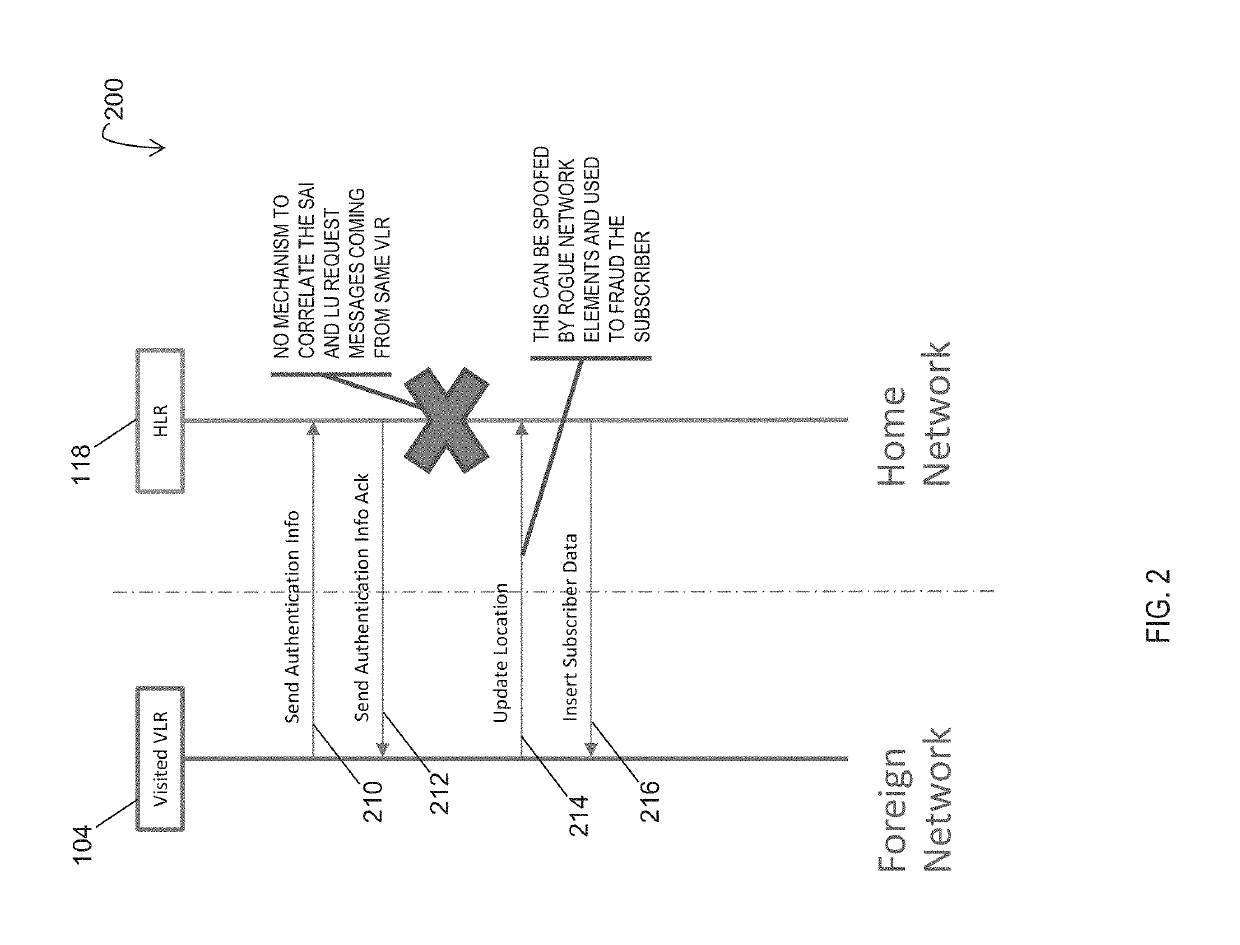
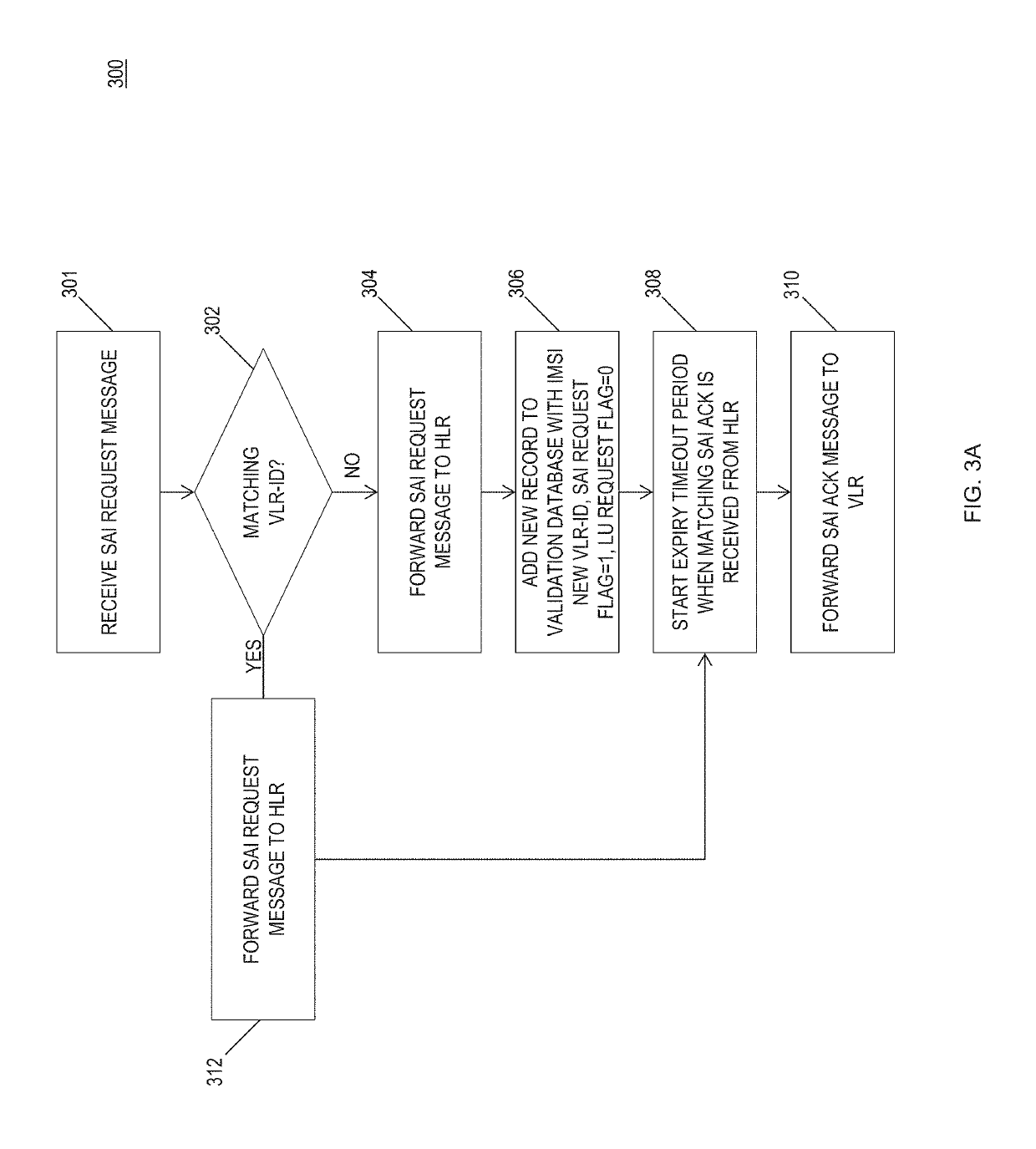
Methods, systems, and computer readable media for validating a visitor location register (VLR) using a signaling system No. 7 (SS7) signal transfer point (STP)
A method includes maintaining a VLR validation database accessible by an SS7 STP and receiving, by the STP, a MAP SAI request message. The method also includes determining that the MAP SAI request message includes a VLR identifier not recorded in the VLR validation database accessible by the STP and recording the VLR identifier in the VLR validation database. The method further includes receiving a first MAP LU request message and detecting a VLR identifier in the first MAP LU request message and determining that the VLR identifier read from the first MAP LU request message does not match the VLR identifier recorded for a subscriber in the VLR validation database. In response to determining that the VLR identifier does not match the VLR identifier recorded for the subscriber in the VLR validation database, the first MAP LU request message is rejected.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
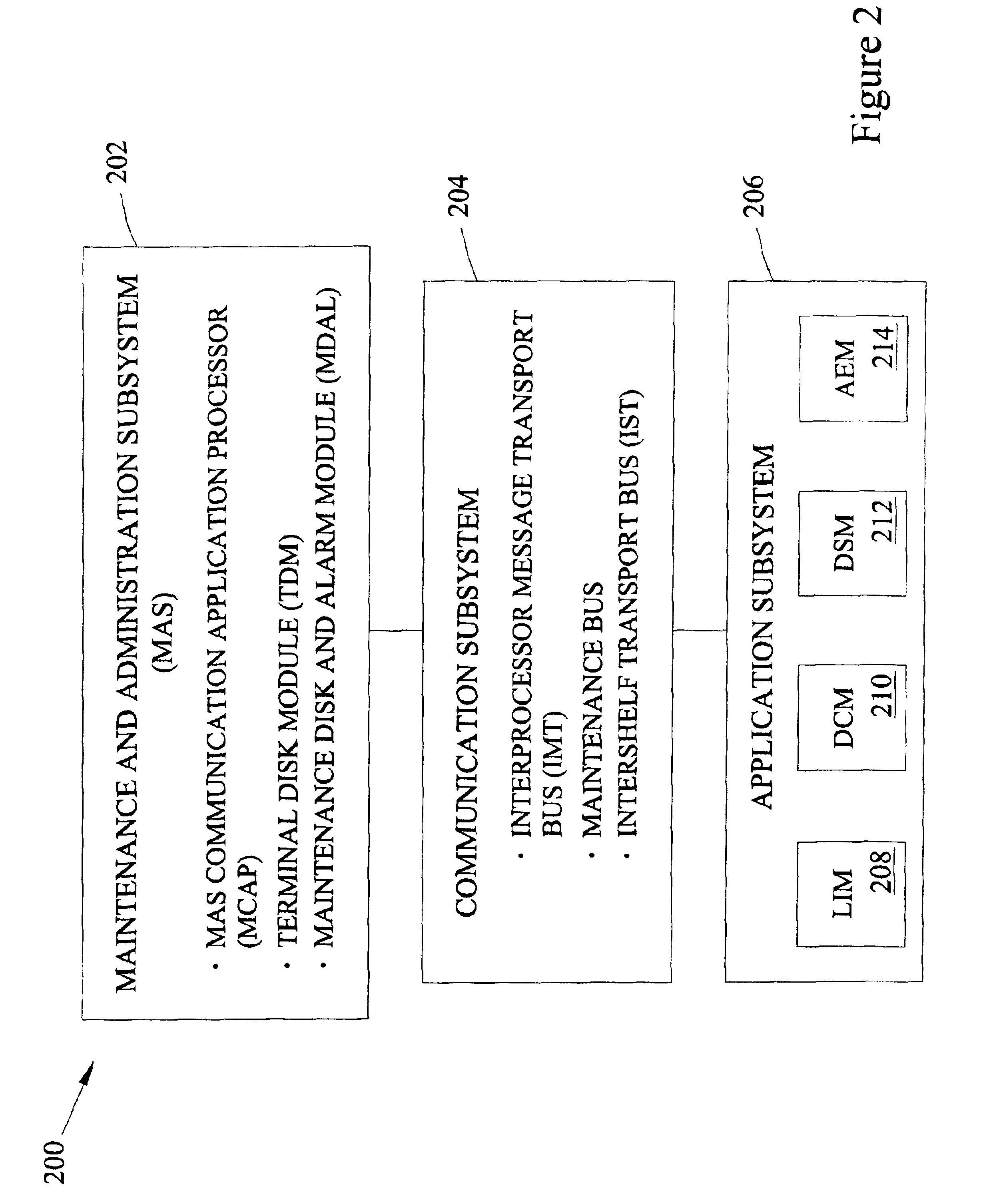
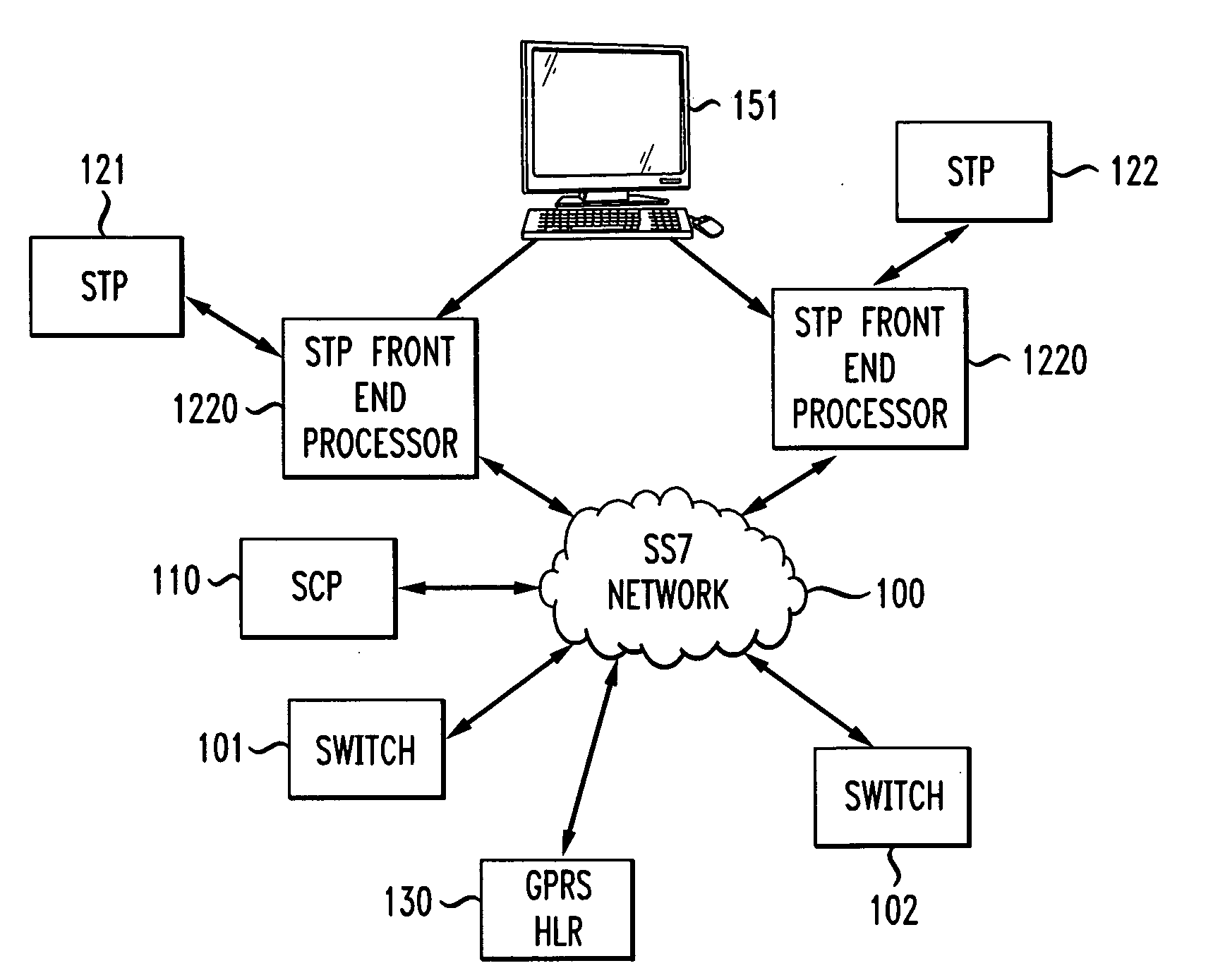
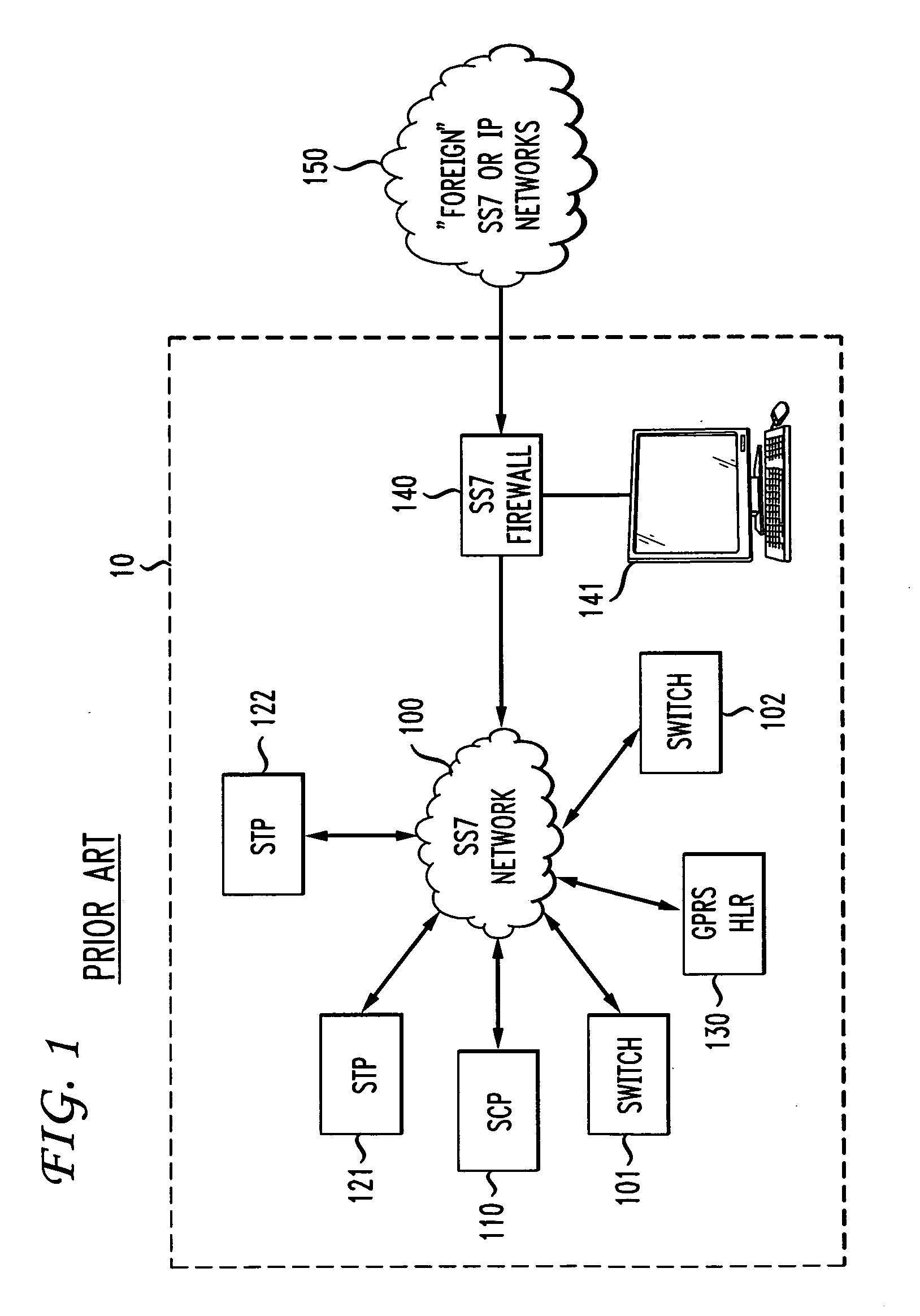
Signal transfer point front end processor
InactiveUS20110041176A1Improve the level ofInterconnection arrangementsDigital data processing detailsSecurity ruleProtocol stack
In an SS7 network, each of a plurality of Signal Transfer Points is fronted by a front-end processor (STP-FEP) that has a network presence. The STP-FEP implements at least the MTP2 layer of the SS7 protocol stack and implements security rules at the MTP2 and MTP3 layers.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com