Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Packet radio networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-hop packet radio networks
InactiveUS6965568B1Control rateIncrease probabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer networkTransceiver
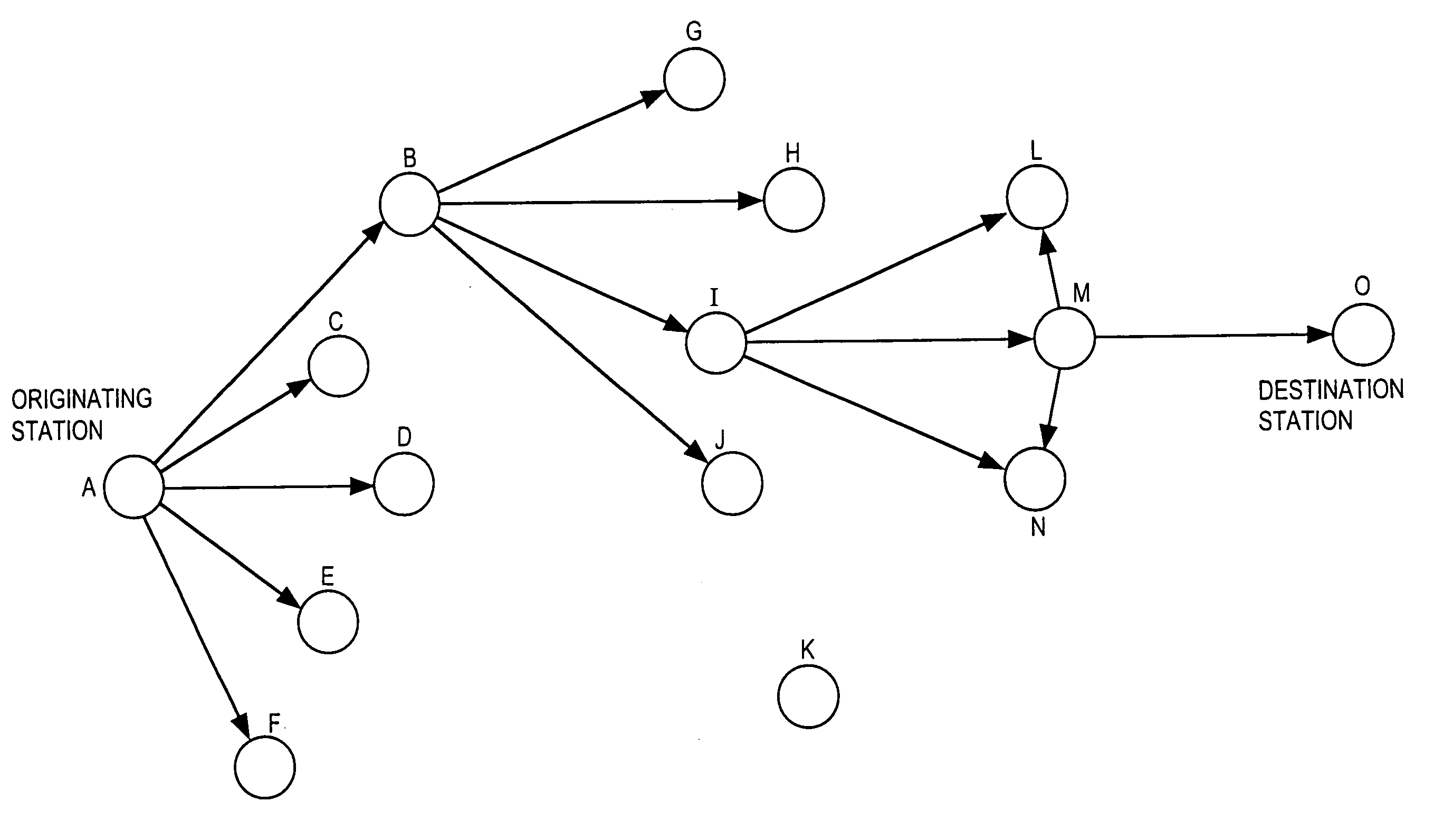
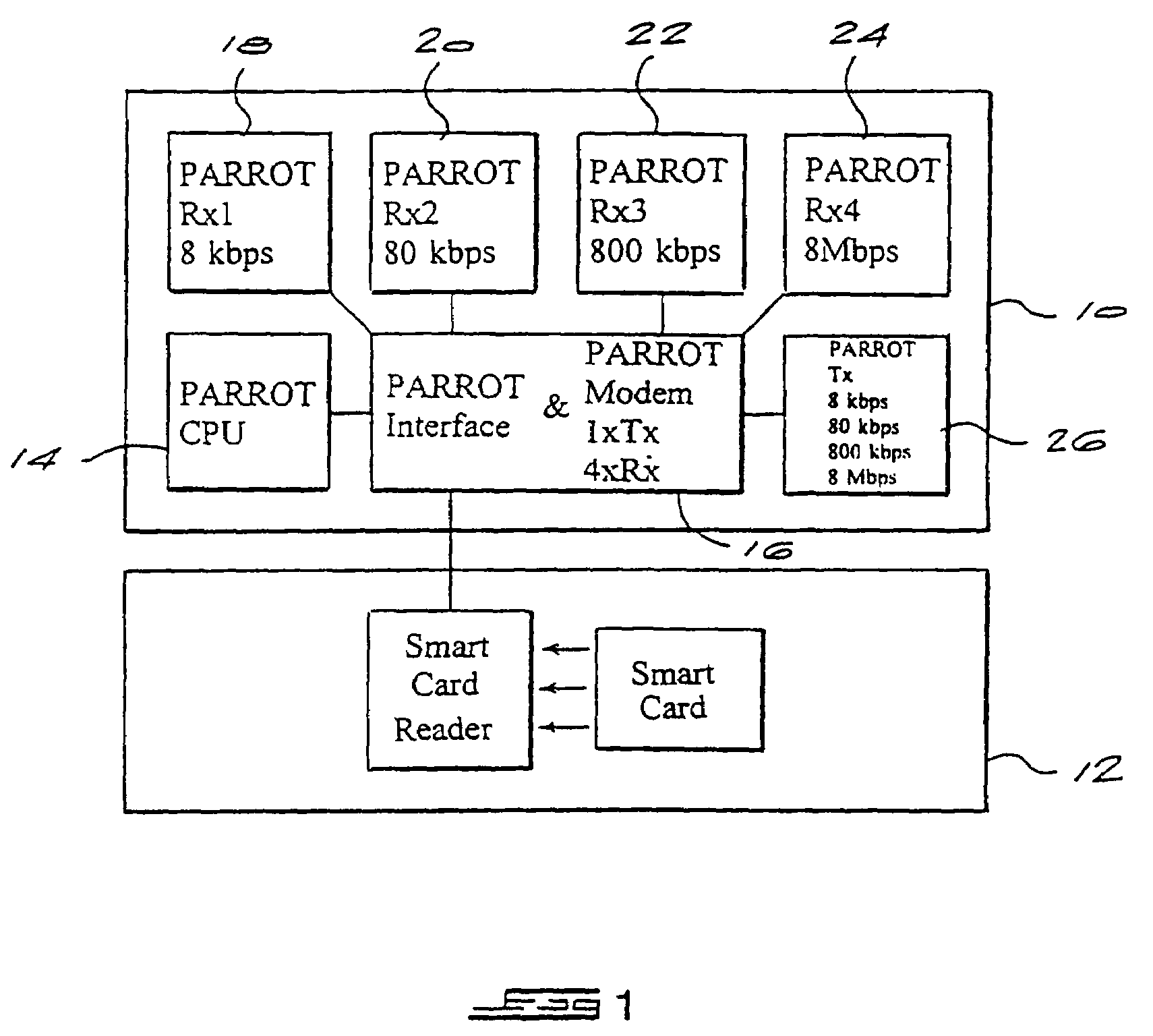
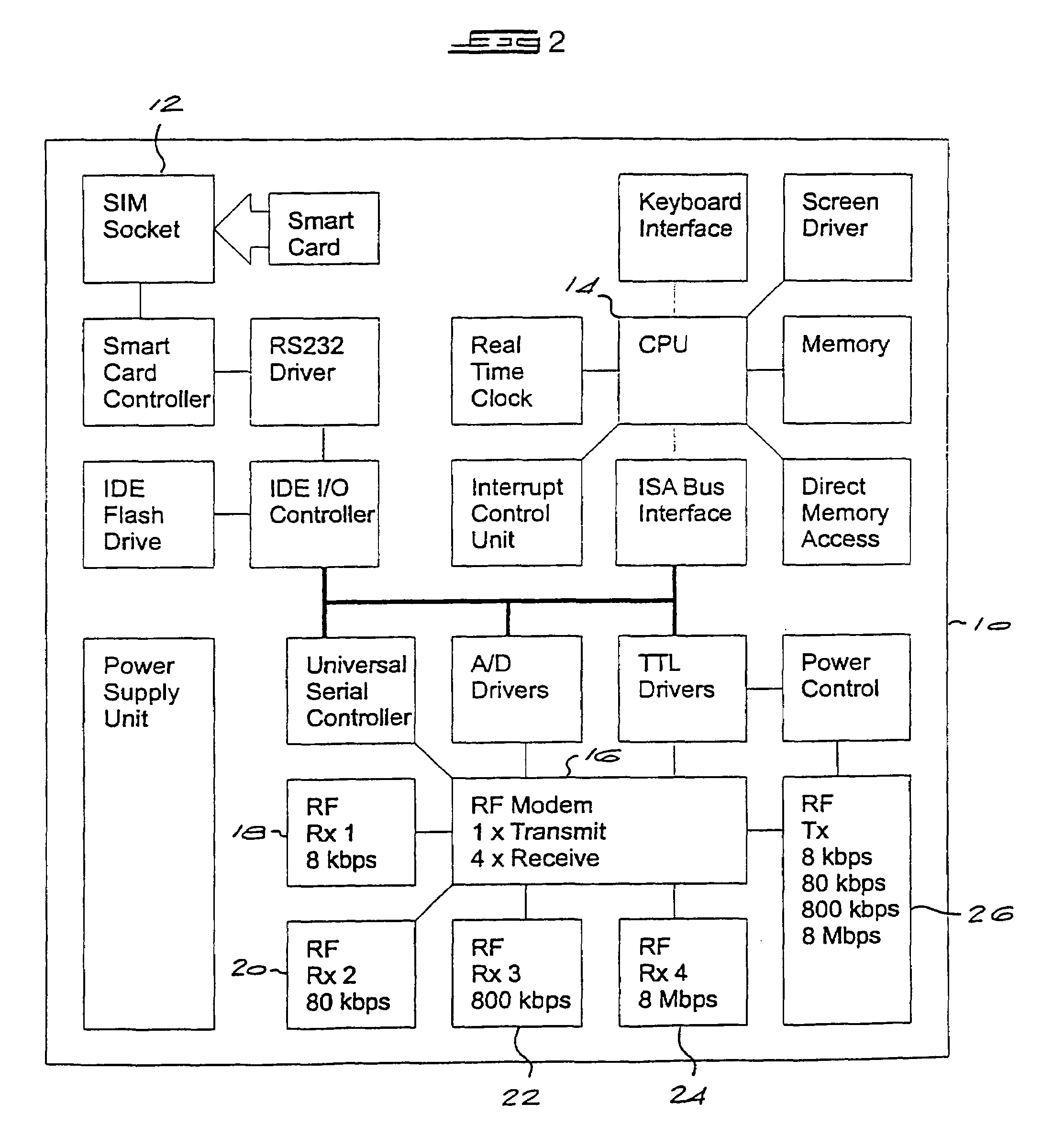
An adaptive communication system utilises opportunistic peak-mode transmissions to transmit data between originating and destination stations, via one or more intermediate stations. Each station monitors the activity of other stations in the network, storing connectivity information for use in subsequent transmissions. Each station also sends out probe signals from time to time, to establish which other stations are in range. Messages are then sent across the network from station to station, with confirmation data being transmitted back to the originating station, until the destination station is reached. Old messages, which would otherwise clog the network, are timed out and deleted. A communication network and transceiver apparatus for use in the network are also disclosed.
Owner:IWICS INC
Transporting QoS mapping information in a packet radio network
InactiveUS7167447B2Efficient reuseError preventionTransmission systemsRadio networksCommunications system
A method and a GGSN support node for sending data packets to a mobile station in a mobile communications system from an external communication system. The GGSN receives data packets from the external communication system in a first plurality of data flows which it maps to a second plurality of data flows in the mobile communications system. It establishes at least one filter for controlling the mapping and associates the filter with the mobile station. It also maps at least one of the data flows on the basis of the filter and configures the filter on the basis of information which preferably originates from the mobile station.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Transporting QoS mapping information in a packet radio network
InactiveUS20060126547A1Efficient reuseConnection managementData switching by path configurationCommunications systemData stream
A method and a GGSN support node for sending data packets to a mobile station in a mobile communications system from an external communication system. The GGSN receives data packets from the external communication system in a first plurality of data flows which it maps to a second plurality of data flows in the mobile communications system. It establishes at least one filter for controlling the mapping and associates the filter with the mobile station. It also maps at least one of the data flows on the basis of the filter and configures the filter on the basis of information which preferably originates from the mobile station.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
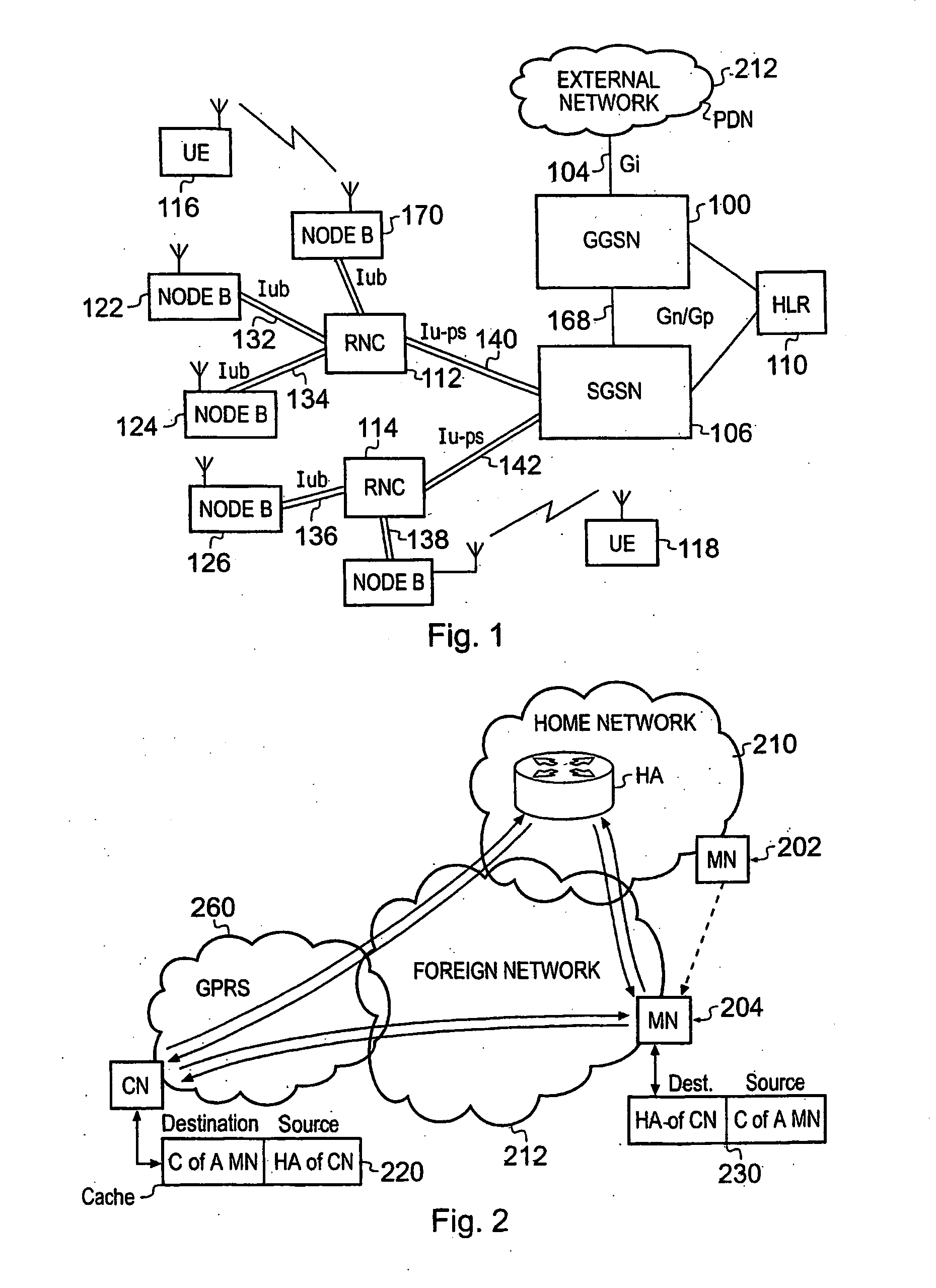
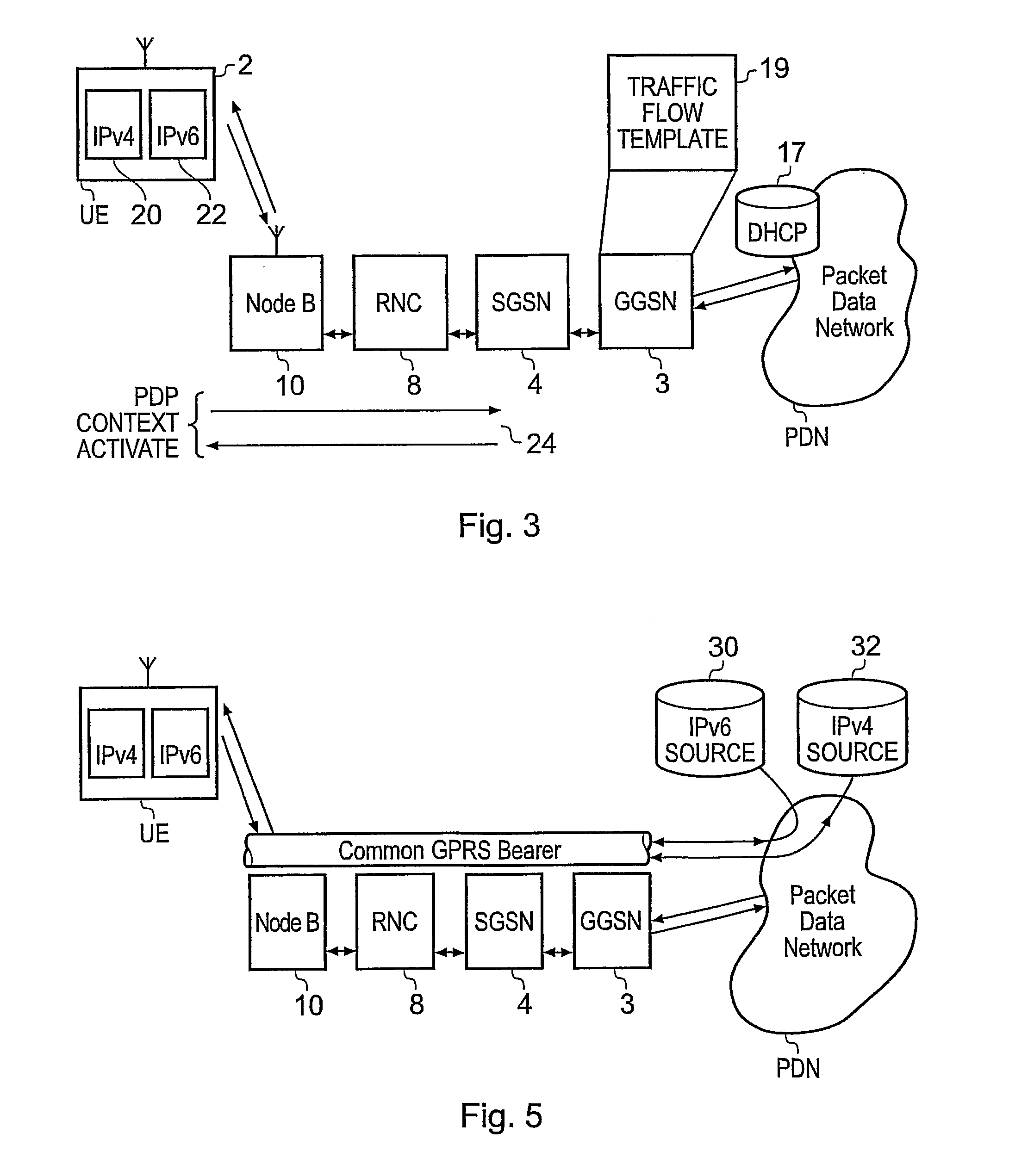
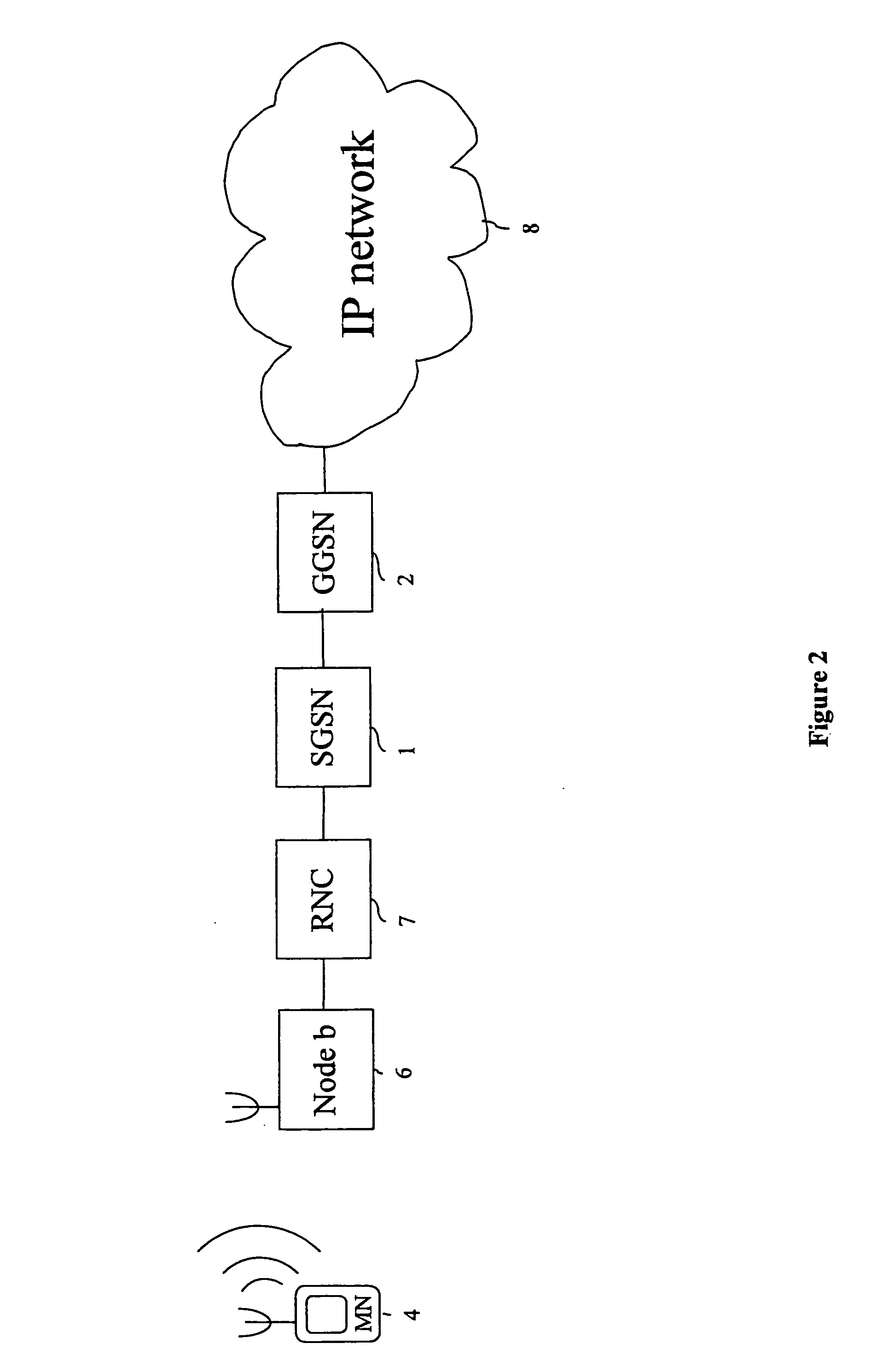
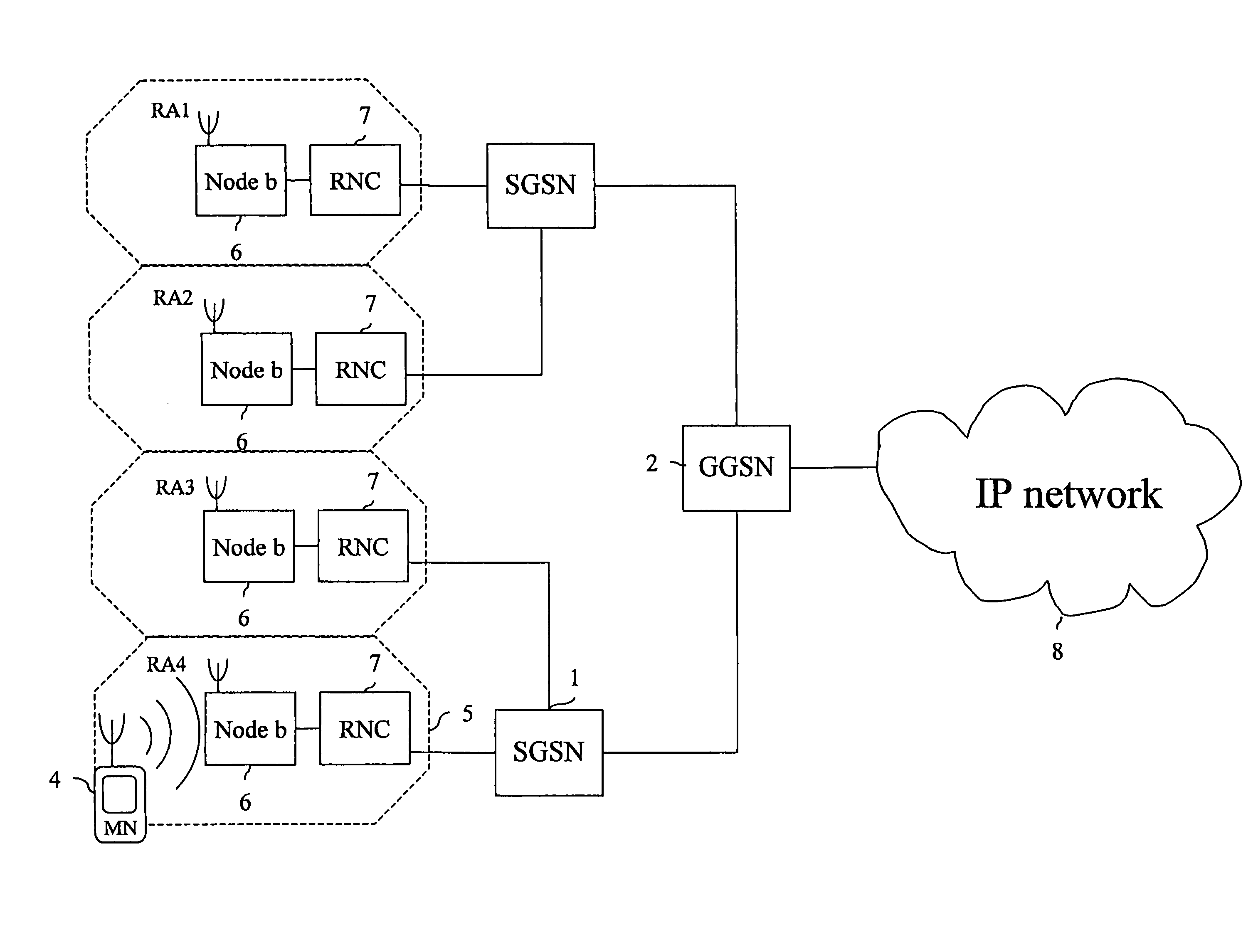
Packet radio network and method
ActiveUS20090175215A1Improve efficiencyEffective resourcesConnection managementWireless network protocolsComputer networkRadio networks
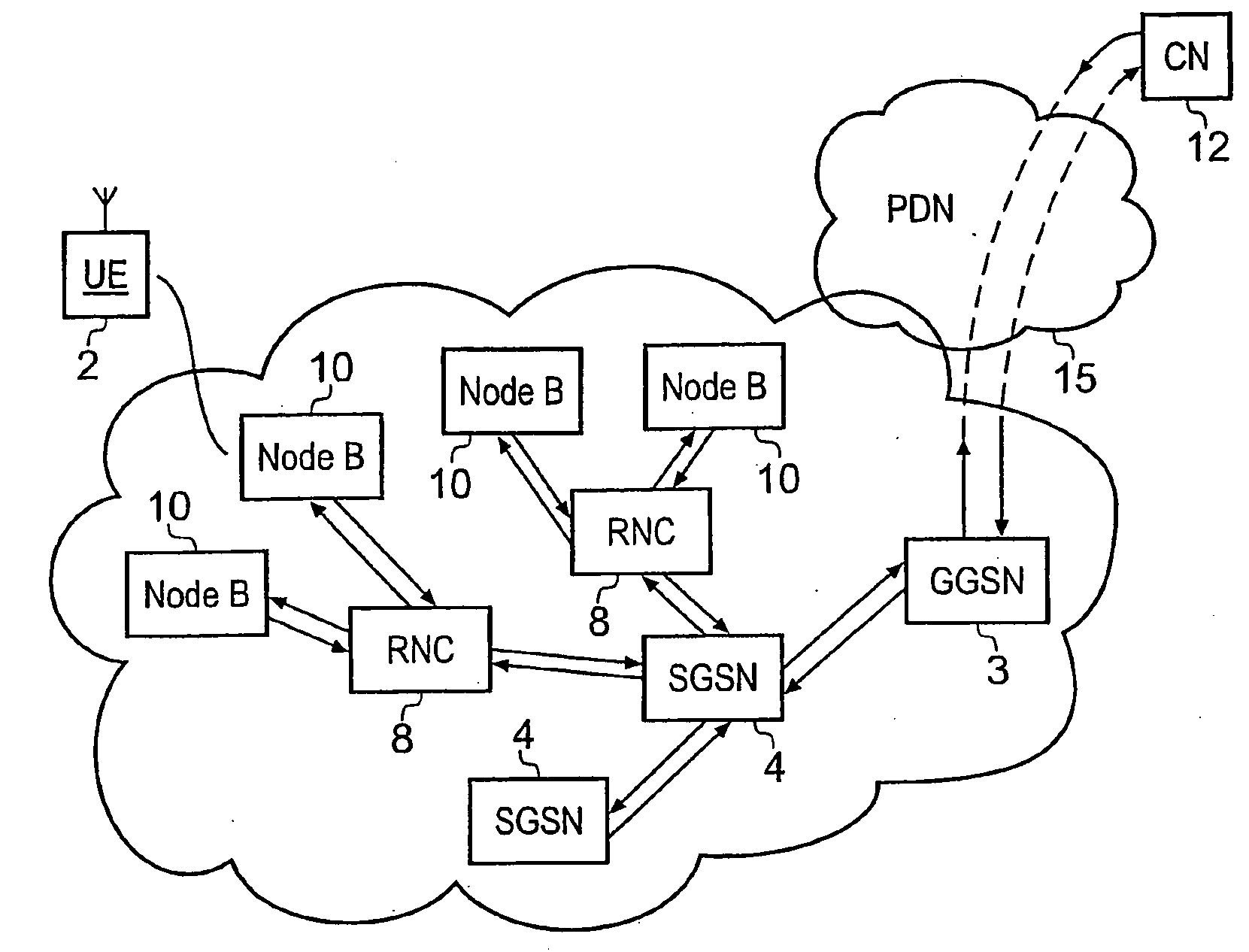
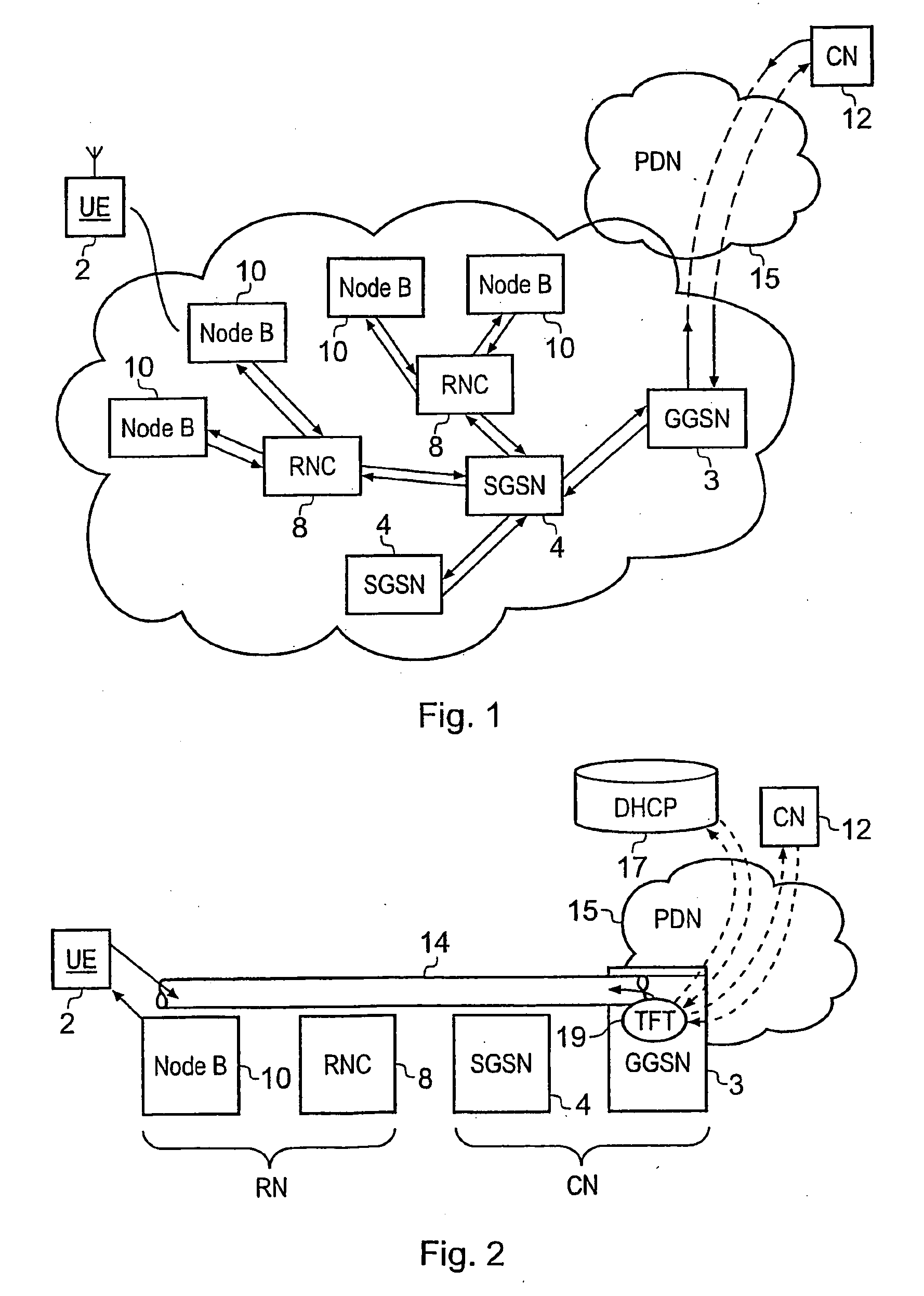
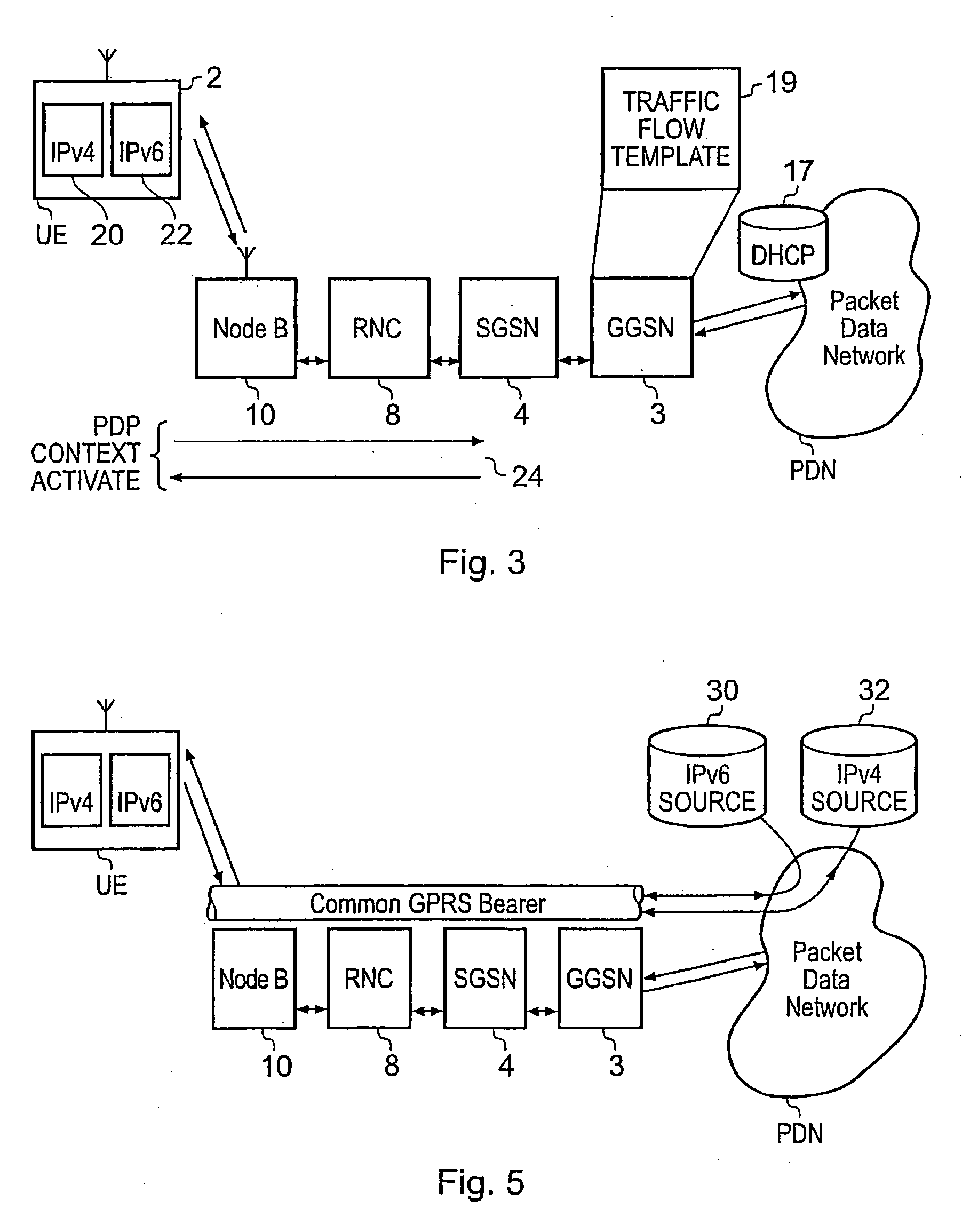
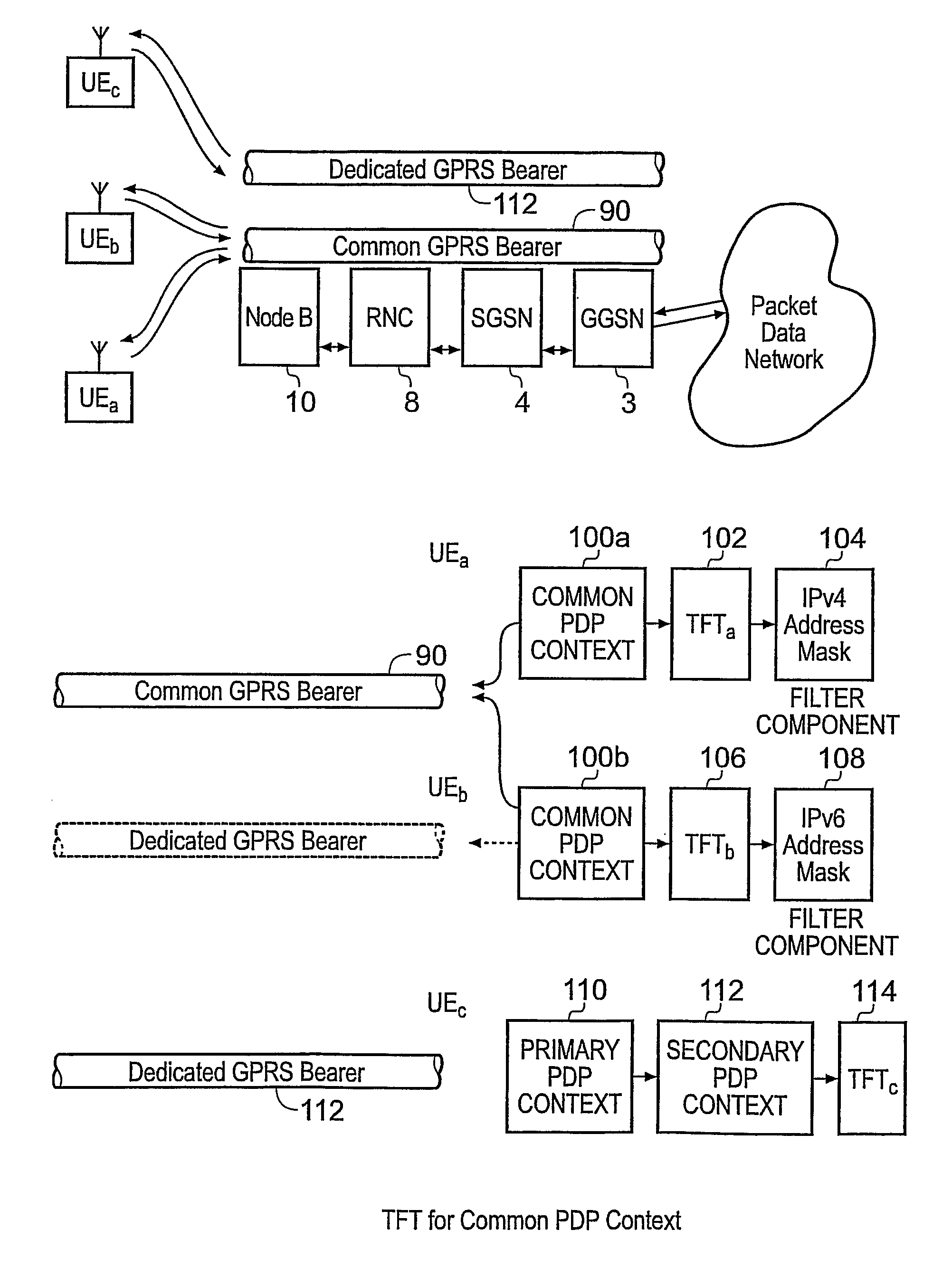
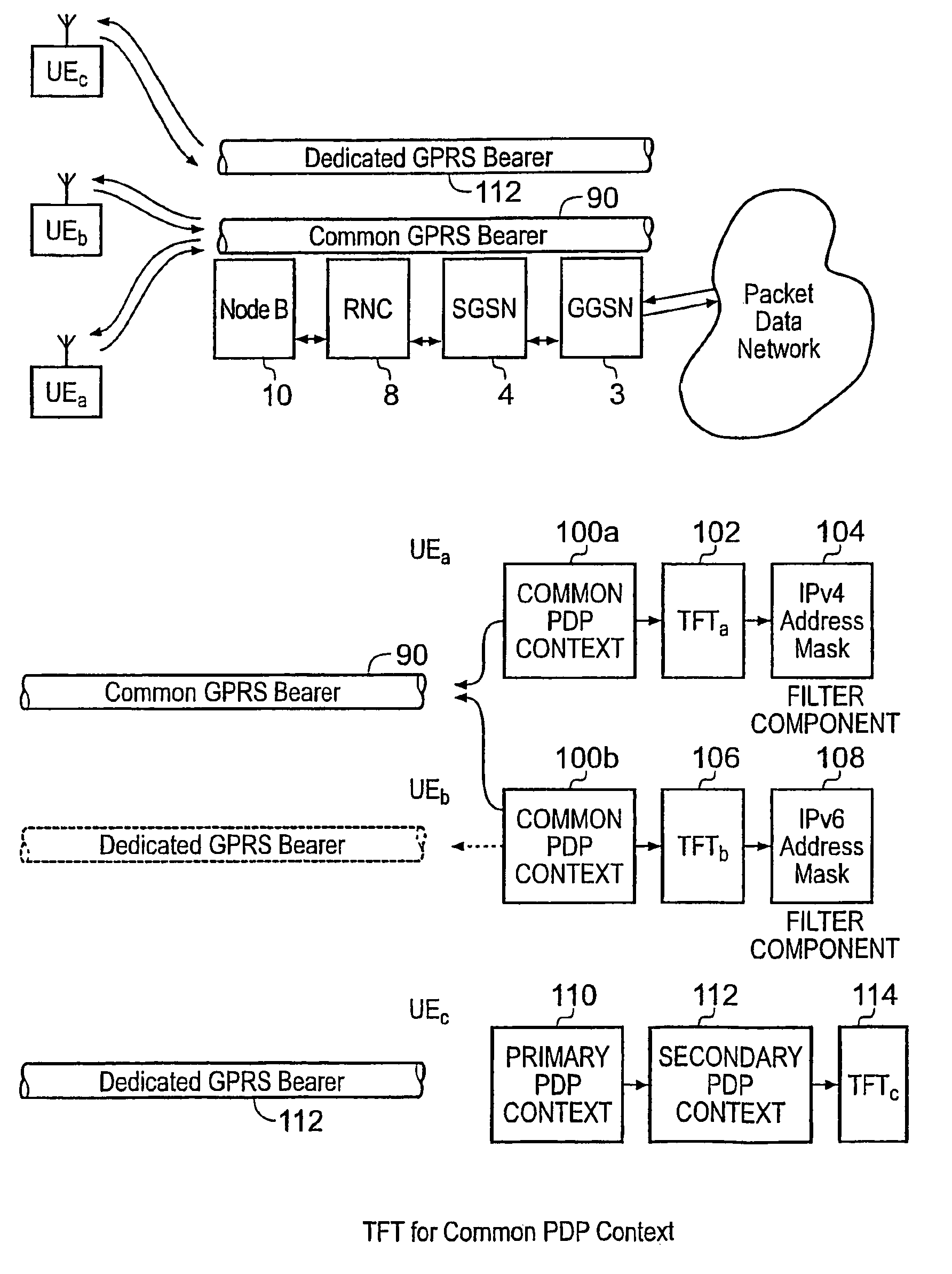
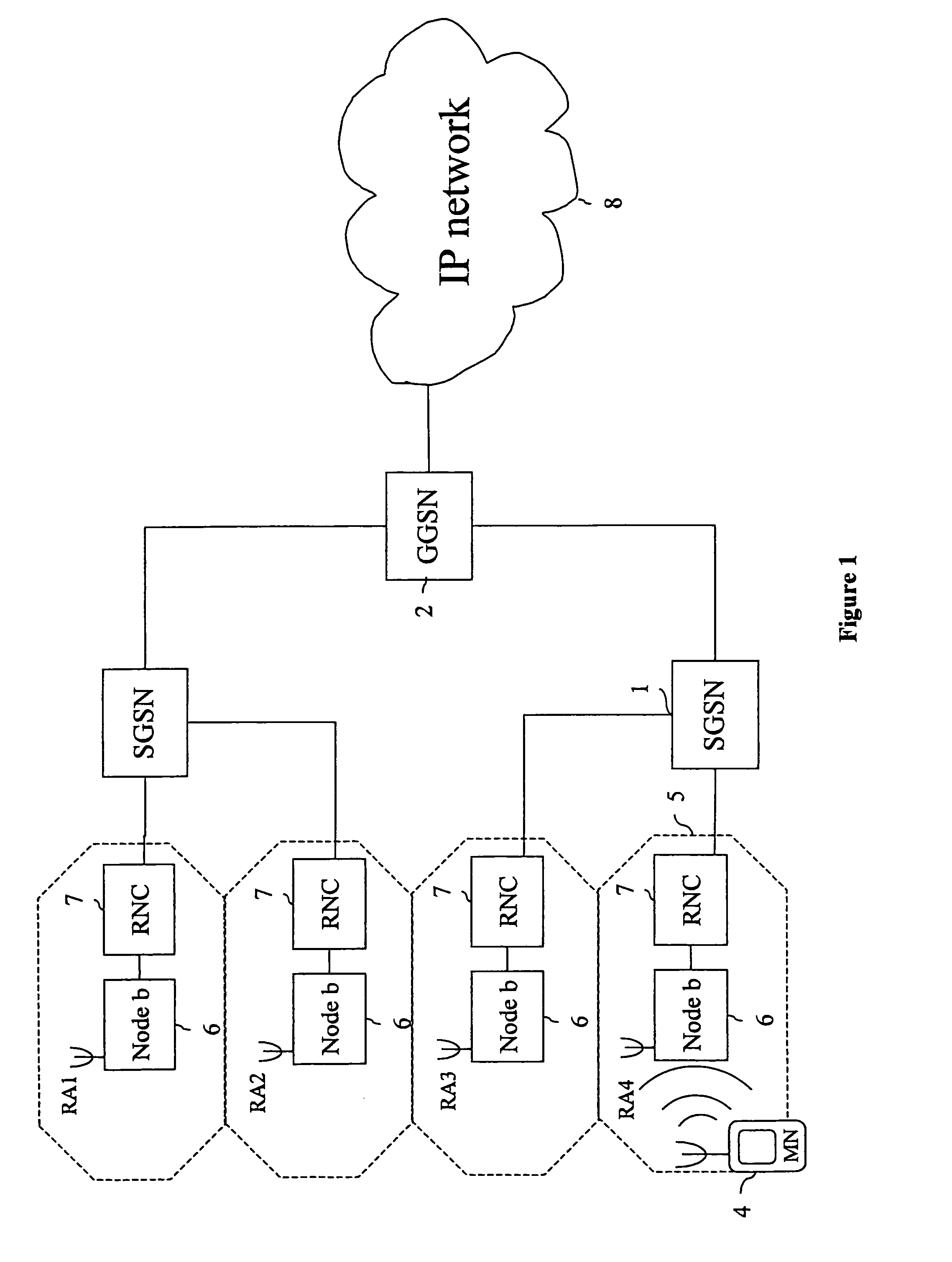
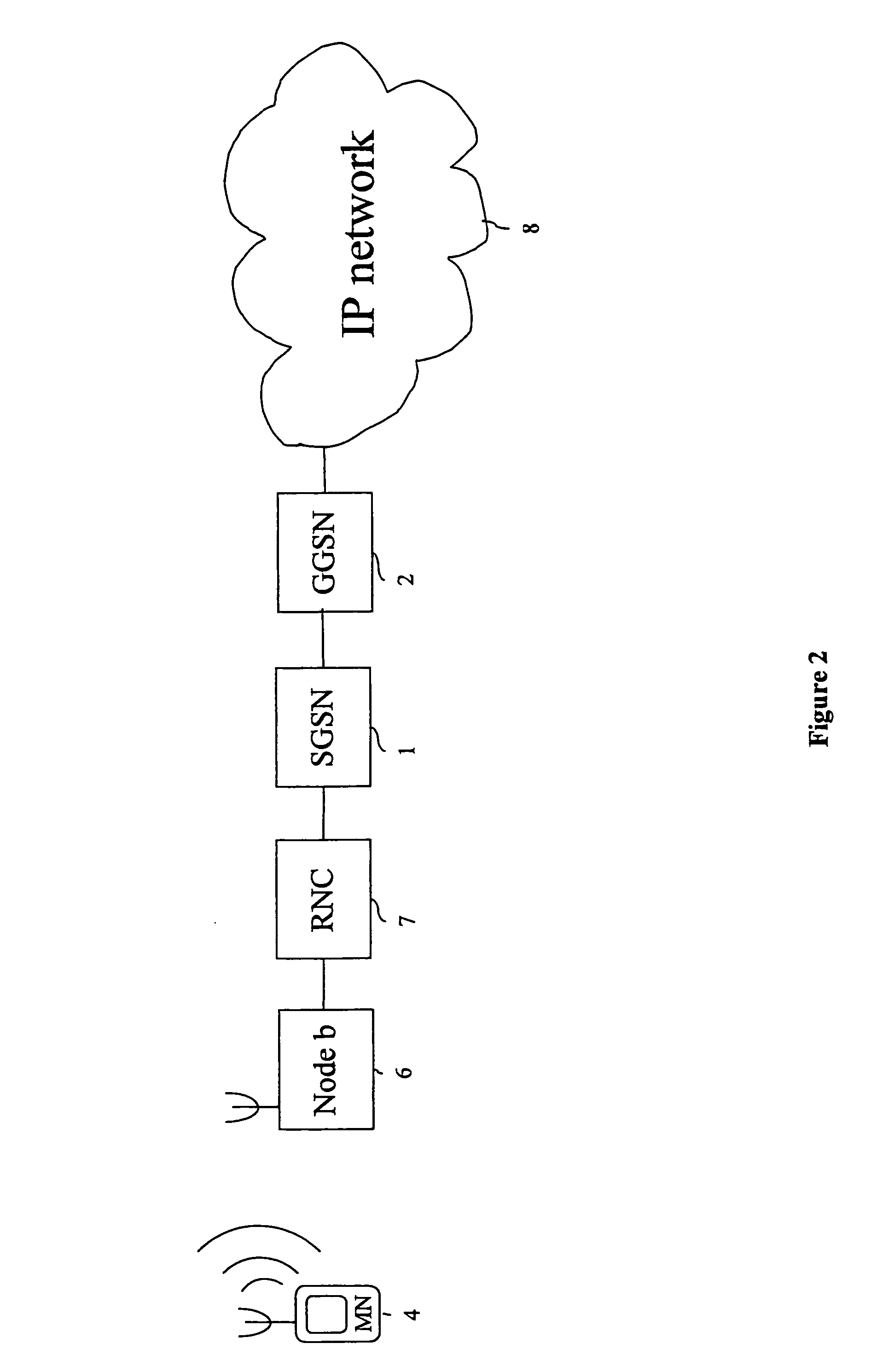
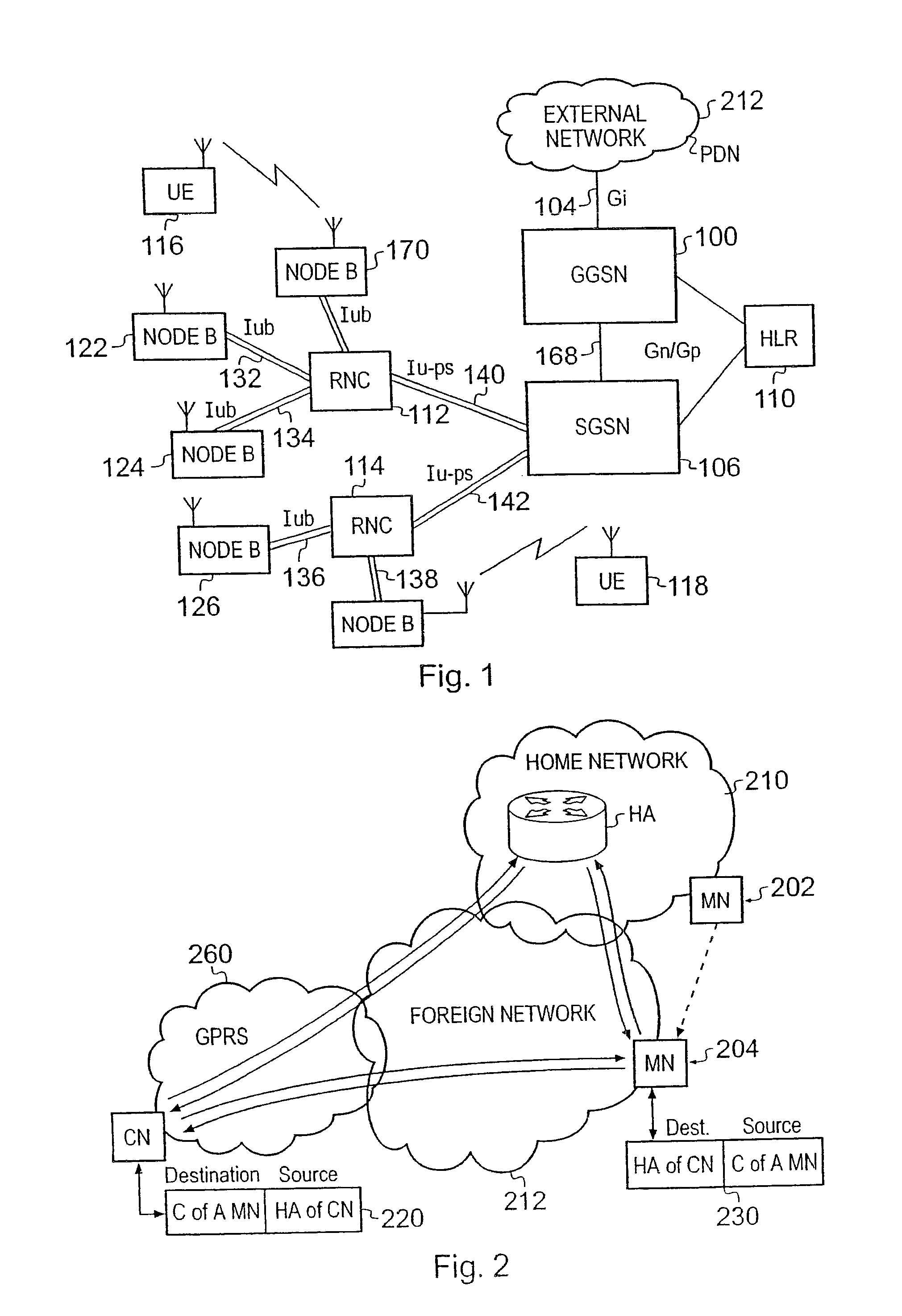
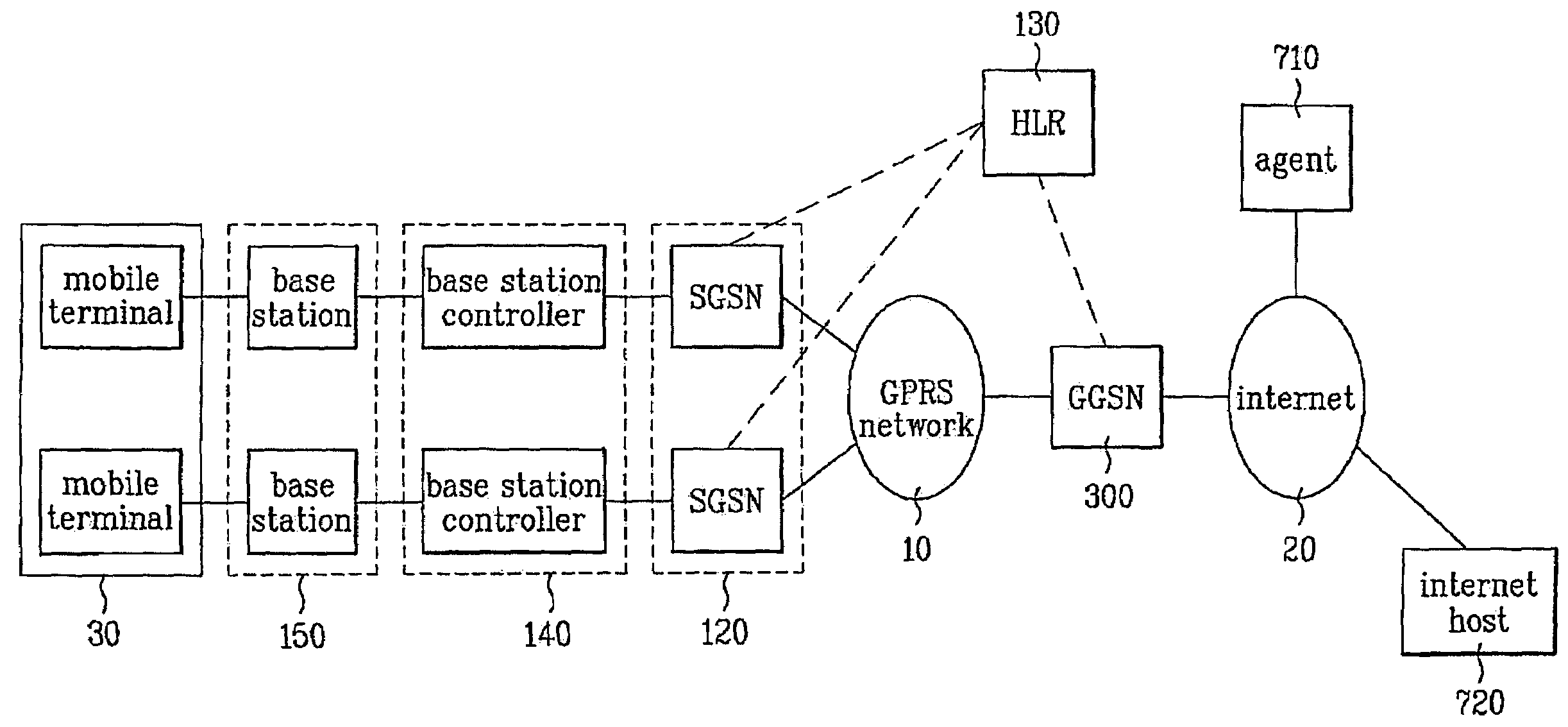
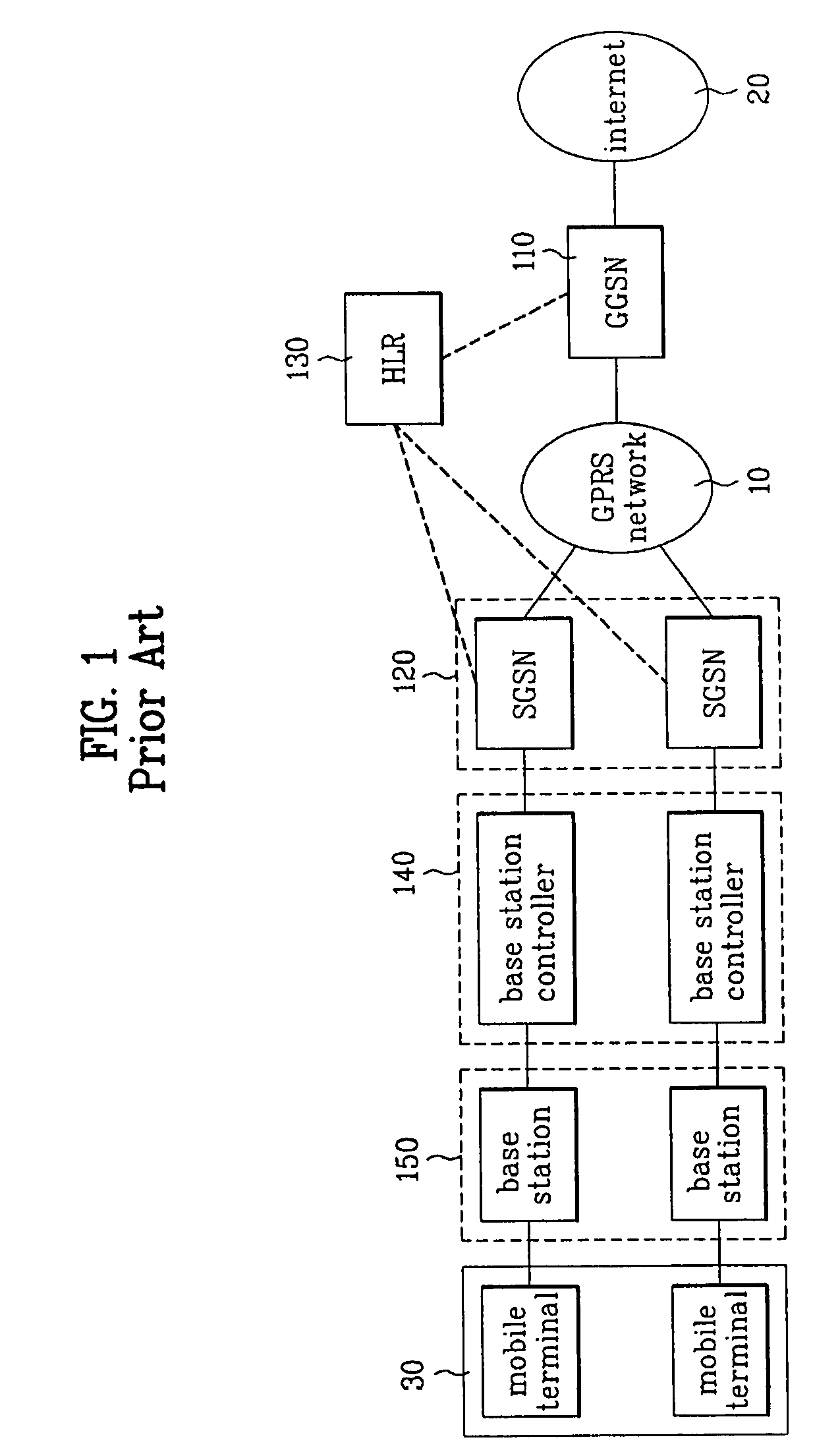
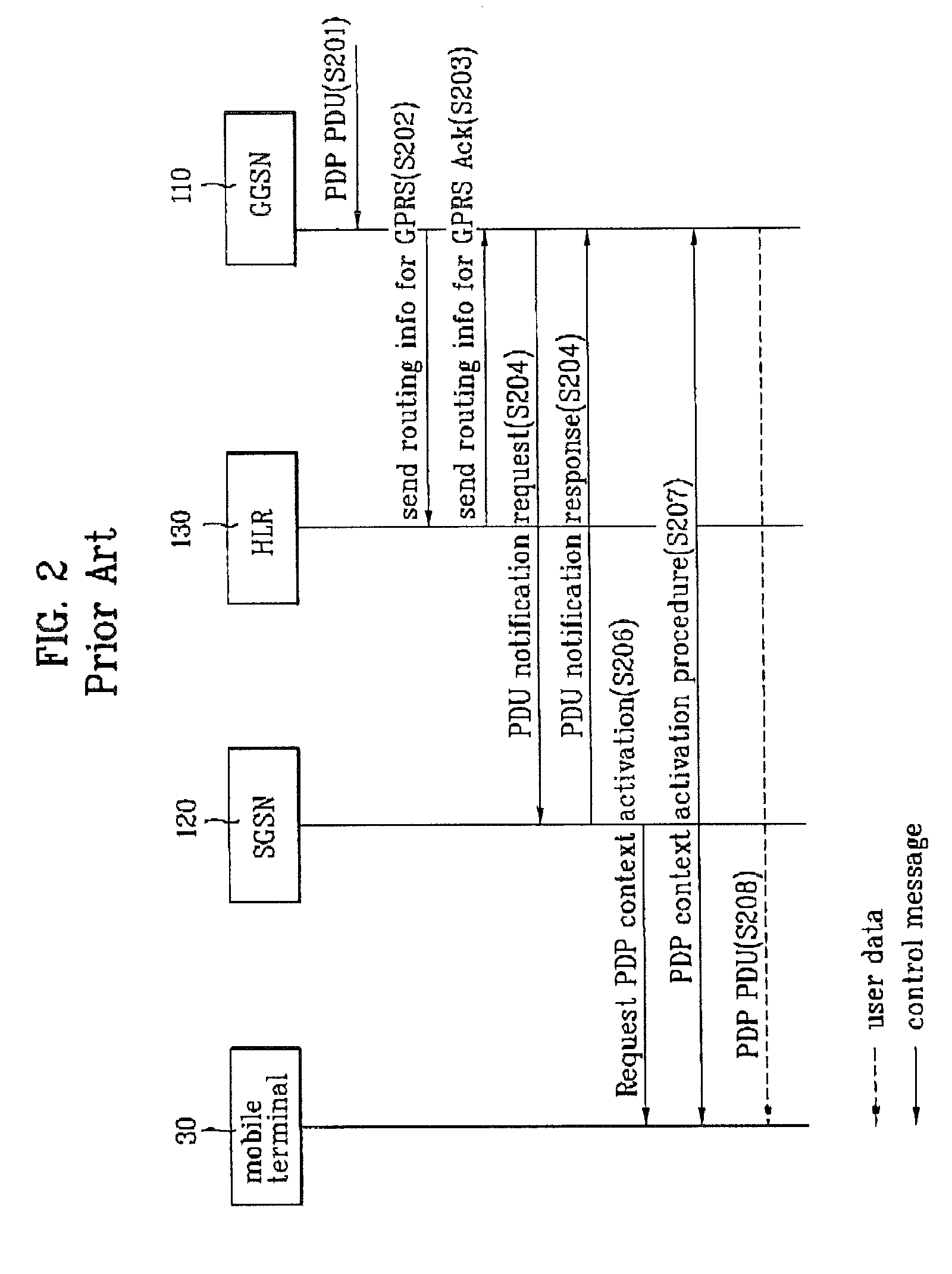
A packet radio network provides a facility for communicating internet packets to and / or from a mobile user equipment. The packet radio network comprises a gateway support node, a serving support node and a radio network controller. The gateway support node is operable to provide a packet data protocol context for controlling the communication of the internet packets to and / or from the packet radio network from and / or to the mobile user equipment via a packet communications bearer. The serving support node is connected to the gateway support node and is operable to control communications of the internet packets to and from the gateway support node to and / or from mobile user equipment to form the packet communications bearer. The radio network controller is operable to provide a radio access bearer for communicating the internet packets via a radio access interface to and / or from the mobile user equipment. In response to a packet data protocol activation request message requesting a common packet data protocol context, the serving support node is operable in combination with the gateway support node to establish a common packet data protocol context in association with a common packet communications bearer. The common packet data protocol context is established to communicate internet protocol packets via the common packet communications bearer. The common packet communications bearer is shared with at least one other communications session and is formed by the gateway support node and the serving support node using a common tunnelling protocol bearer. Therefore a packet radio network is provided which can provide a common communications bearer which can be shared between different communications sessions. As a result high-speed broadband communications, such as HSDPA can be supported efficiently, because more than one communications session shares common communications resources.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
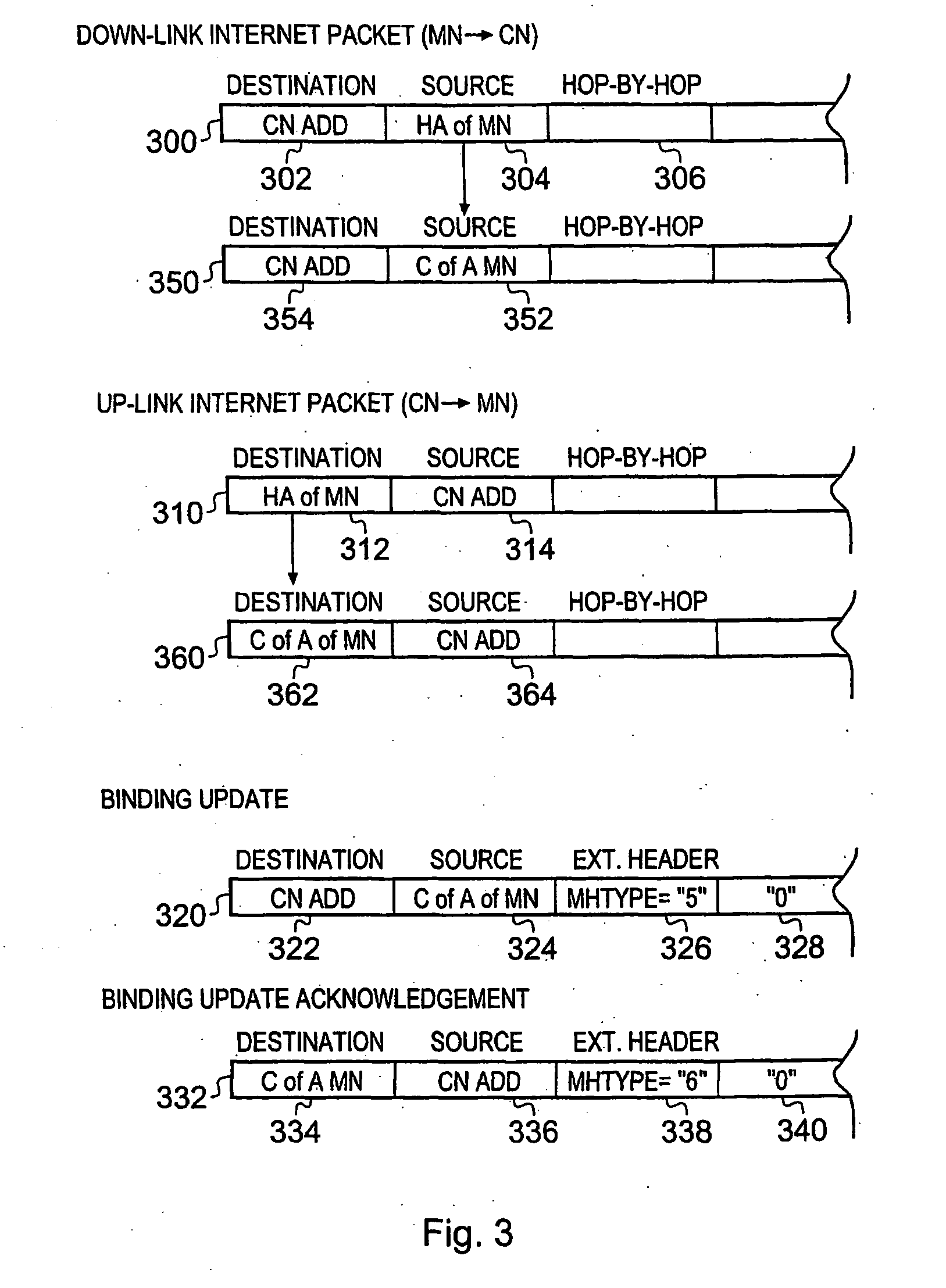
Telecommunications System And Method
ActiveUS20080117841A1Reduce the possibilityMultiplex communicationWireless network protocolsRadio networksTelecommunications network
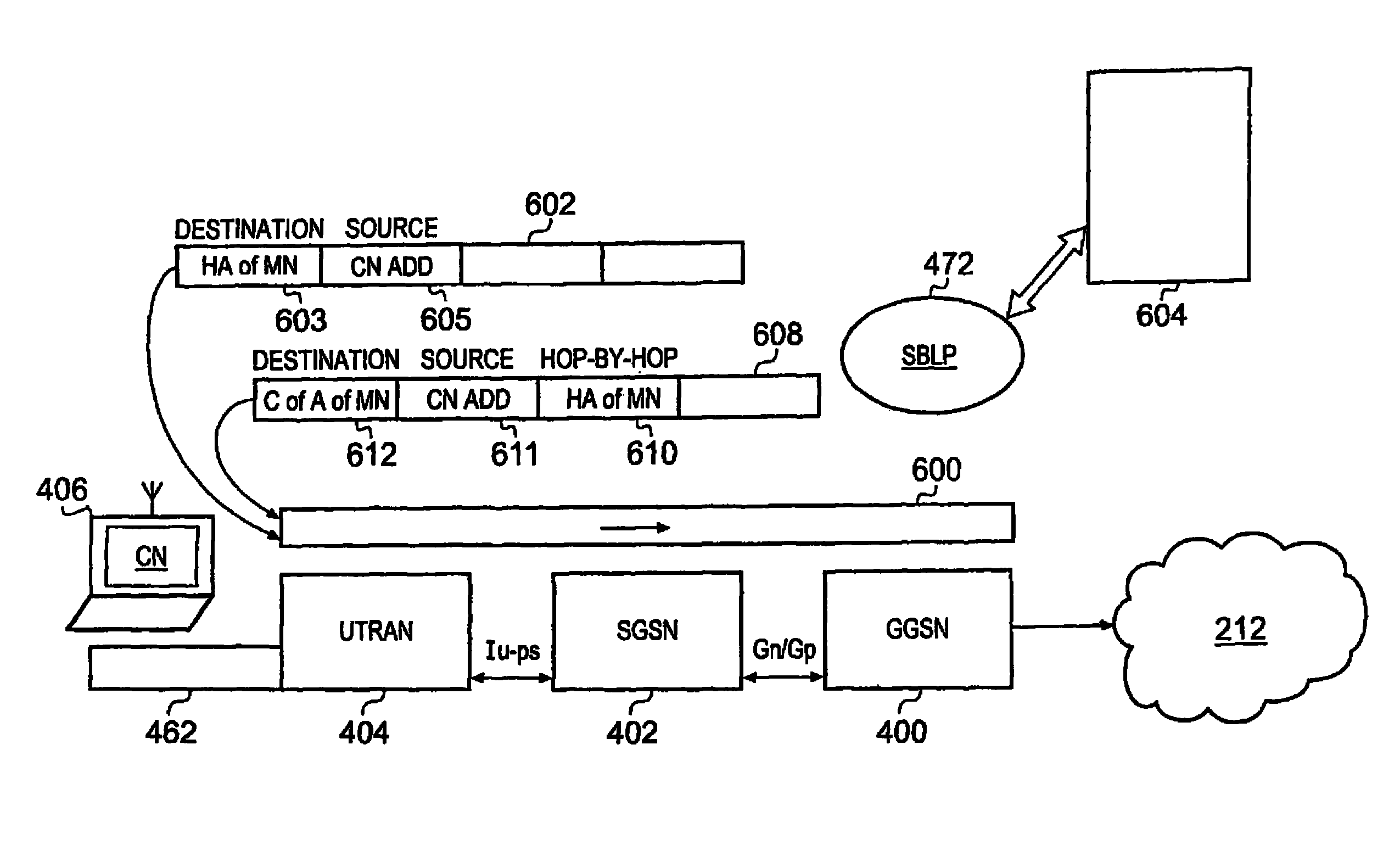
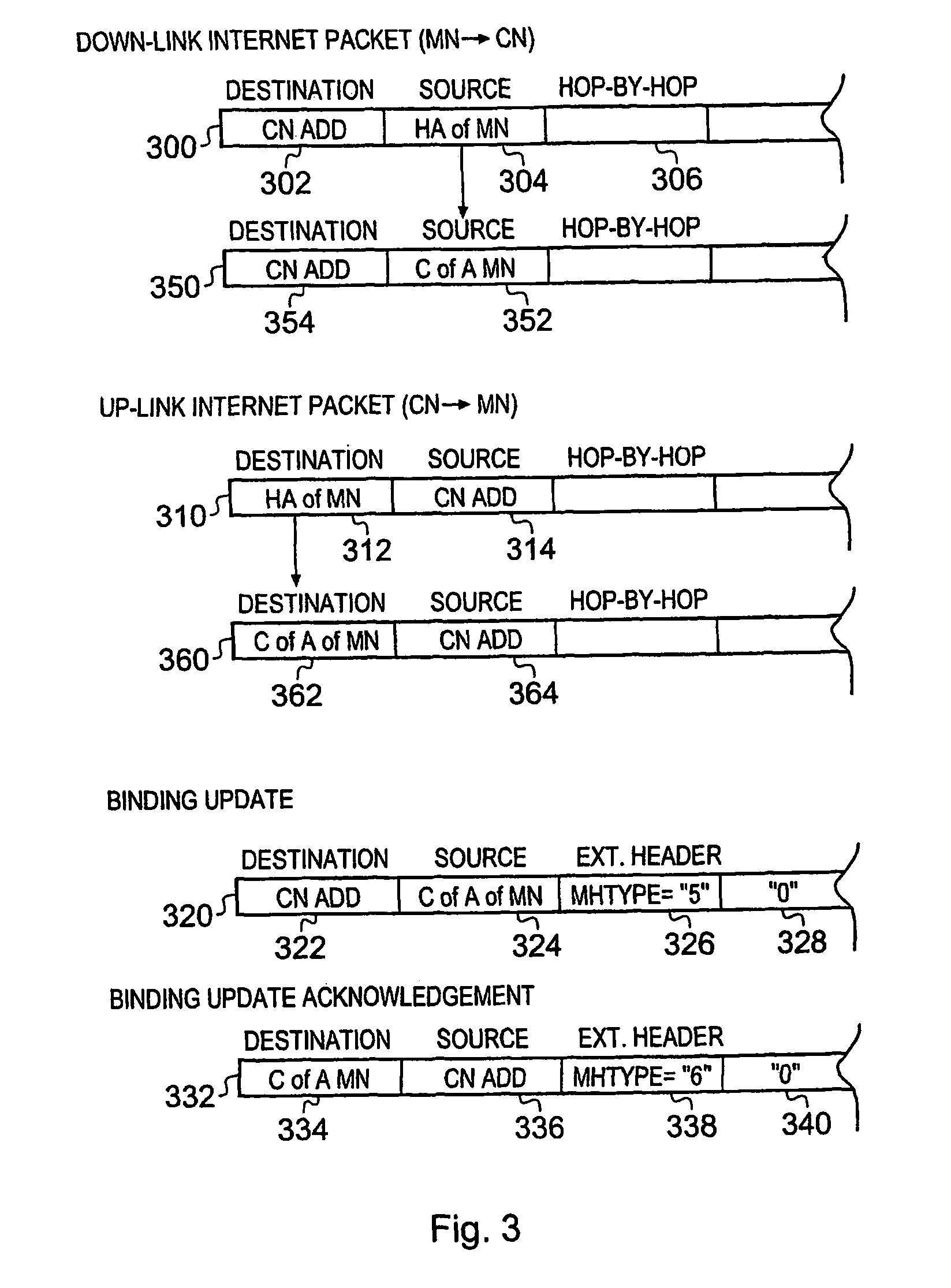
A telecommunications system for communicating internet packets between a mobile communications user equipment forming a correspondent node and a mobile node via an external packet data telecommunications network. The system comprises a packet radio network providing a plurality of packet data bearers for communicating internet packets with nodes attached to the packet radio network. Each of the bearers is defined with respect to a source address of the internet packets, the packet radio network including a gateway support node operable to provide an interface between the external network and, the packet radio network. The gateway support node (GGSN) is operable to detect (56) whether an internet packet is for providing a binding update to the correspondent node of a first source address of the mobile node to a care-of-address of the mobile node. If the internet packet is a binding update, the gateway support node allows (514) egress of internet packets sent from the correspondent node having the care-of-address of the mobile node as the destination address to the external network. By obtaining the care-of-address of the mobile node from the binding update and allowing egress of packets from the correspondent node having this care-of-address as the destination address in internet packet headers, a measure of security is provided, which can prevent or at least hinder theft of service. Theft of service may occur if an unscrupulous user uses an unauthorised destination address for IP data packets sent from the mobile user equipment acting as correspondent node and having a legitimate address in the hop-by-hop extension field and an unauthorised address in the destination field address.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
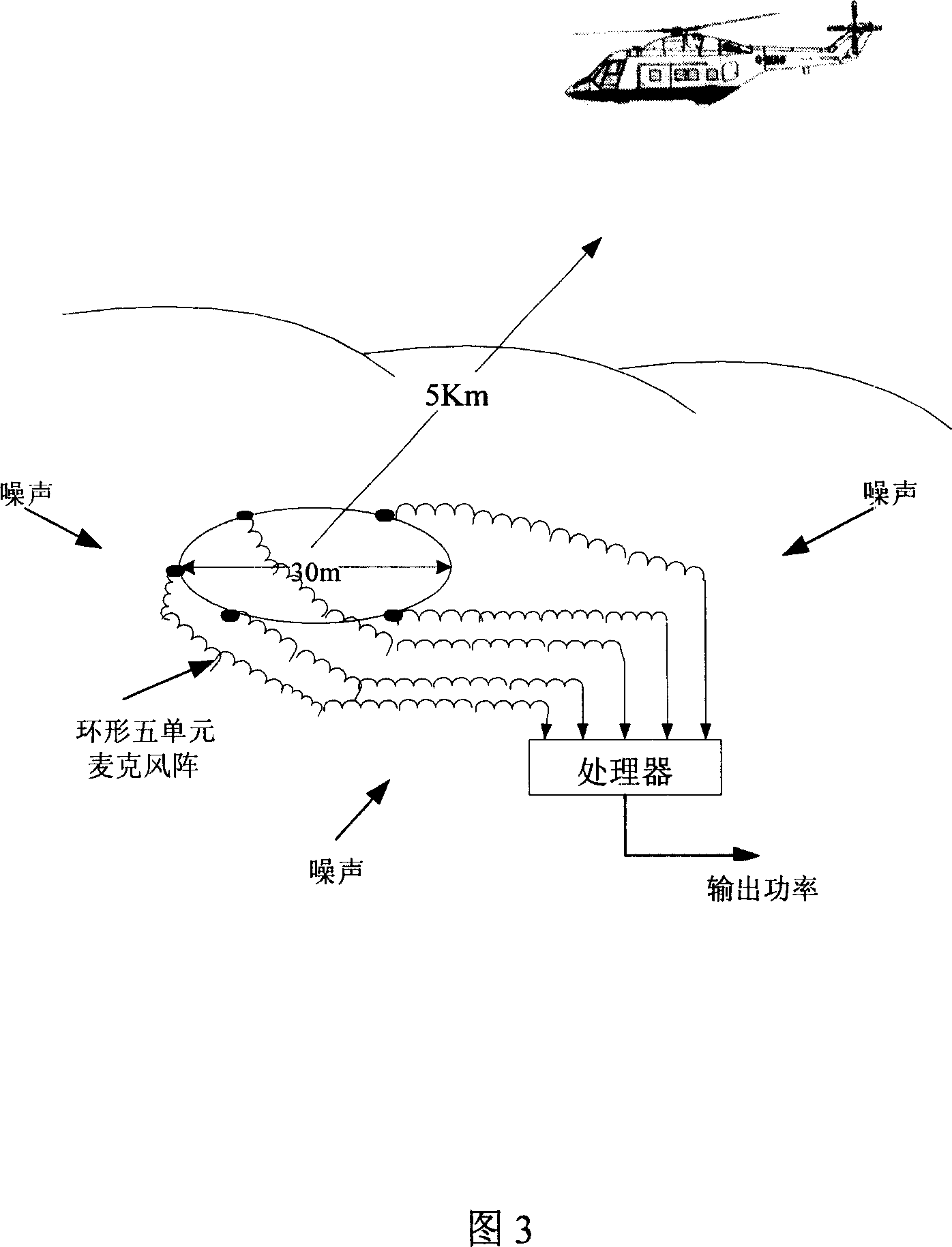
Low altitude target monitoring method based on microphones array network
ActiveCN101034158AReduce indicator requirementsReduce the difficulty of implementationPosition fixationAcoustic wave reradiationMultiple sensorControl delay
This invention discloses a low altitude targeted surveillance method which is on the basis of microphone array joint net. The invention belongs to low altitude targeted surveillance passive positioning technique field. Aim directly at requirement of administration blind area of remote area and monitoring uncooperation object, through microphone array of rational distribution, data merging system of multitude transmitters, low altitude targeted surveillance net of multitude subgroups wirdess network structure, compose single microphone array by means of space array through multitude transmitters, make every microphone receive sound wave signal of flying equipment shaking air radiation, through self-adaptation wave bunch treater, use algorithm such as wave beam shape, use wave beam control delay line, change delay amount of direction control delay line, measure wave direction of object; use multitude self-adaptation treater to superpose to construct self-adaptation transmitter array, make multitude microphone arrays process and obtain multi-target wave direction information by multitude self-adaptation transmitter arrays, merge information from multitude subgroups wirdess network structure to multi-transmitter data merging system, extract objective navigating information.
Owner:WISESOFT CO LTD +1
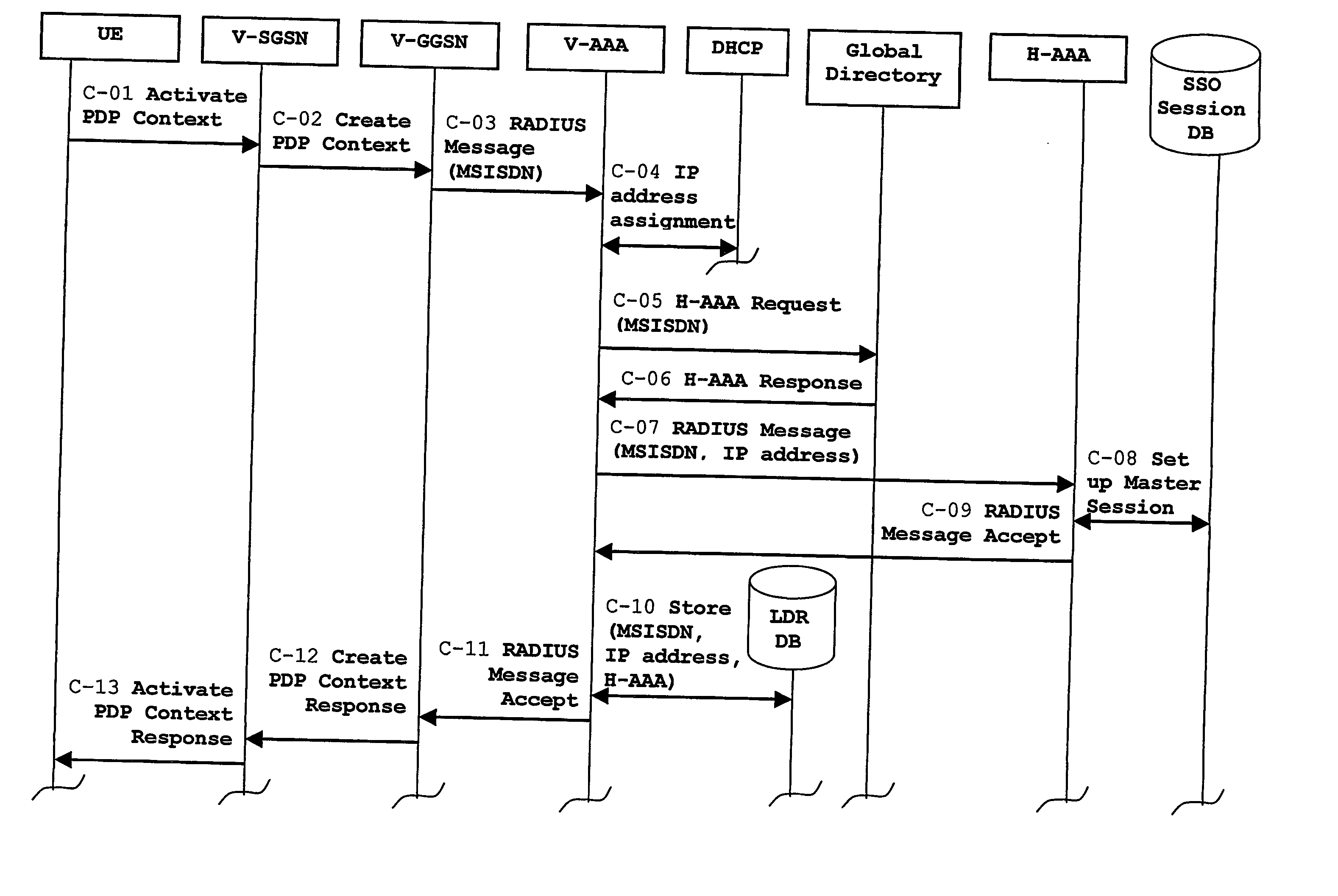
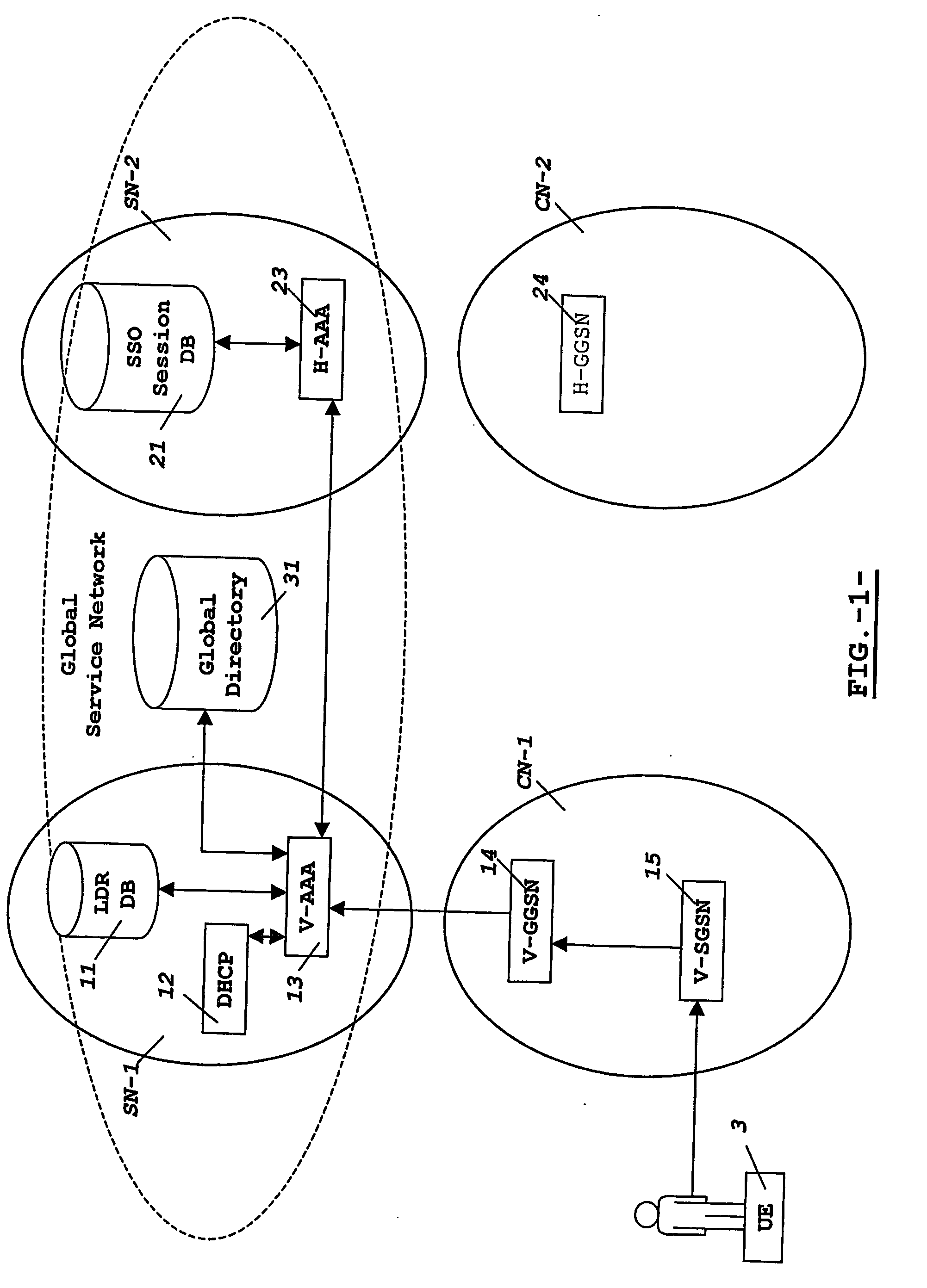
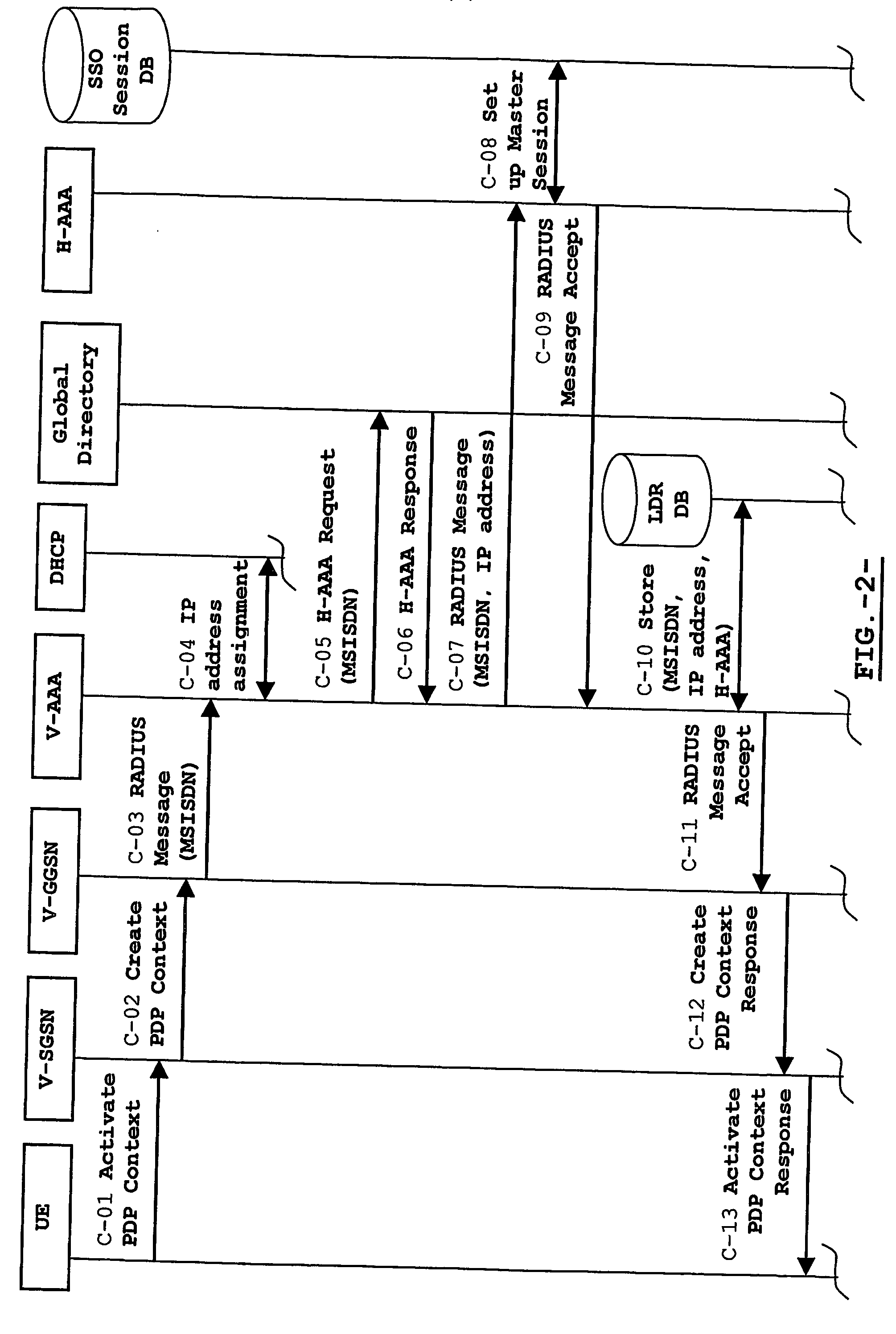
Single sign-on for users of a packet radio network roaming in a multinational operator network
InactiveUS20070127495A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexCyber operationsService protocol
The invention provides a system and a method basically oriented for providing Single Sign-On services for a user roaming in a packet radio network of a Multinational Mobile Network Operator that includes a federation of National Network Operators, one of these National Network Operators holding the user's subscription. In particular, the telecommunications system includes a number of Service Providers having service agreements with the Multinational Mobile Network Operator federation for offering Single Sign-On services to subscribers of any National Network Operator included in the federation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Systems and methods for constructing a virtual model of a multi-hop, multi-access network
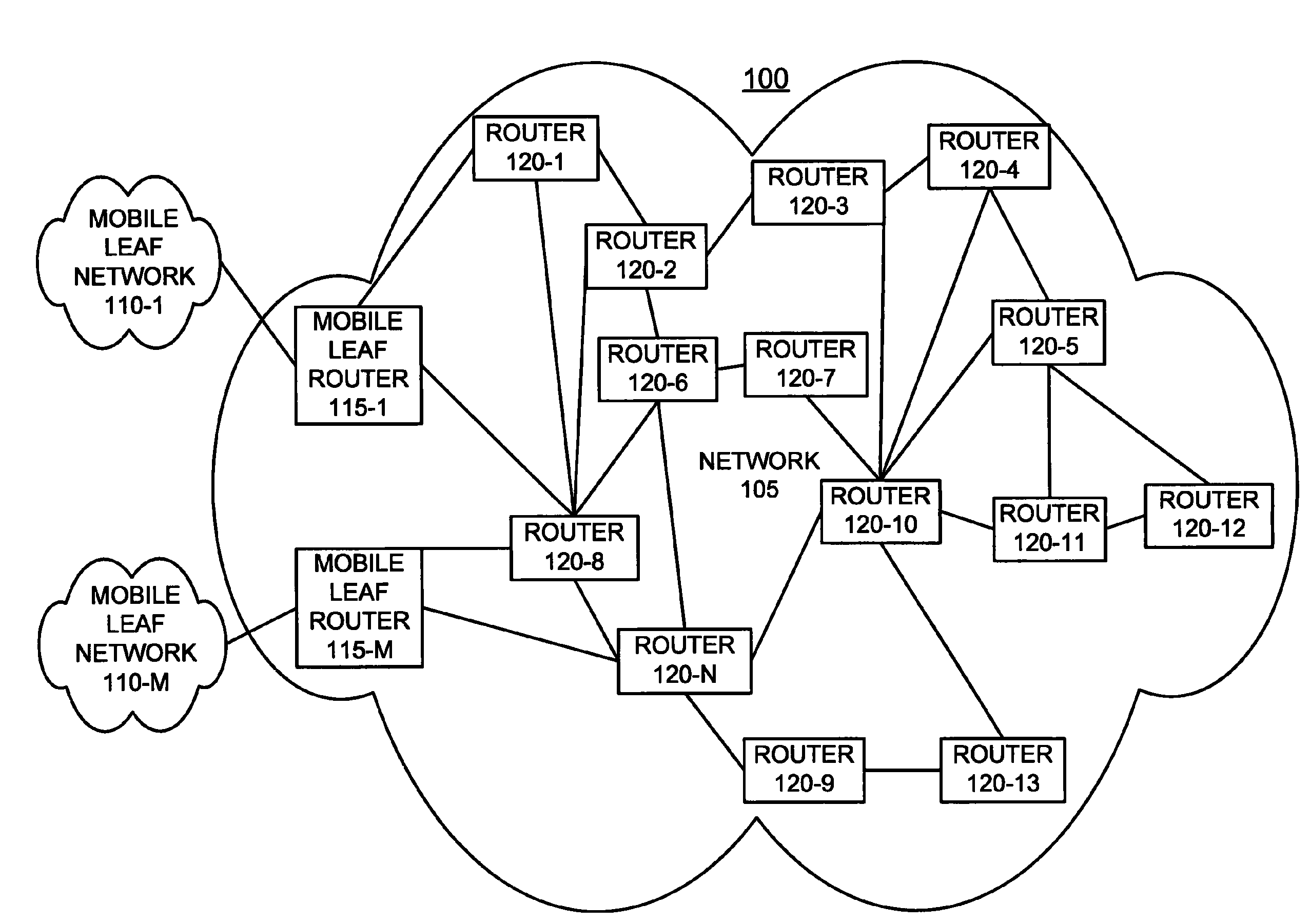
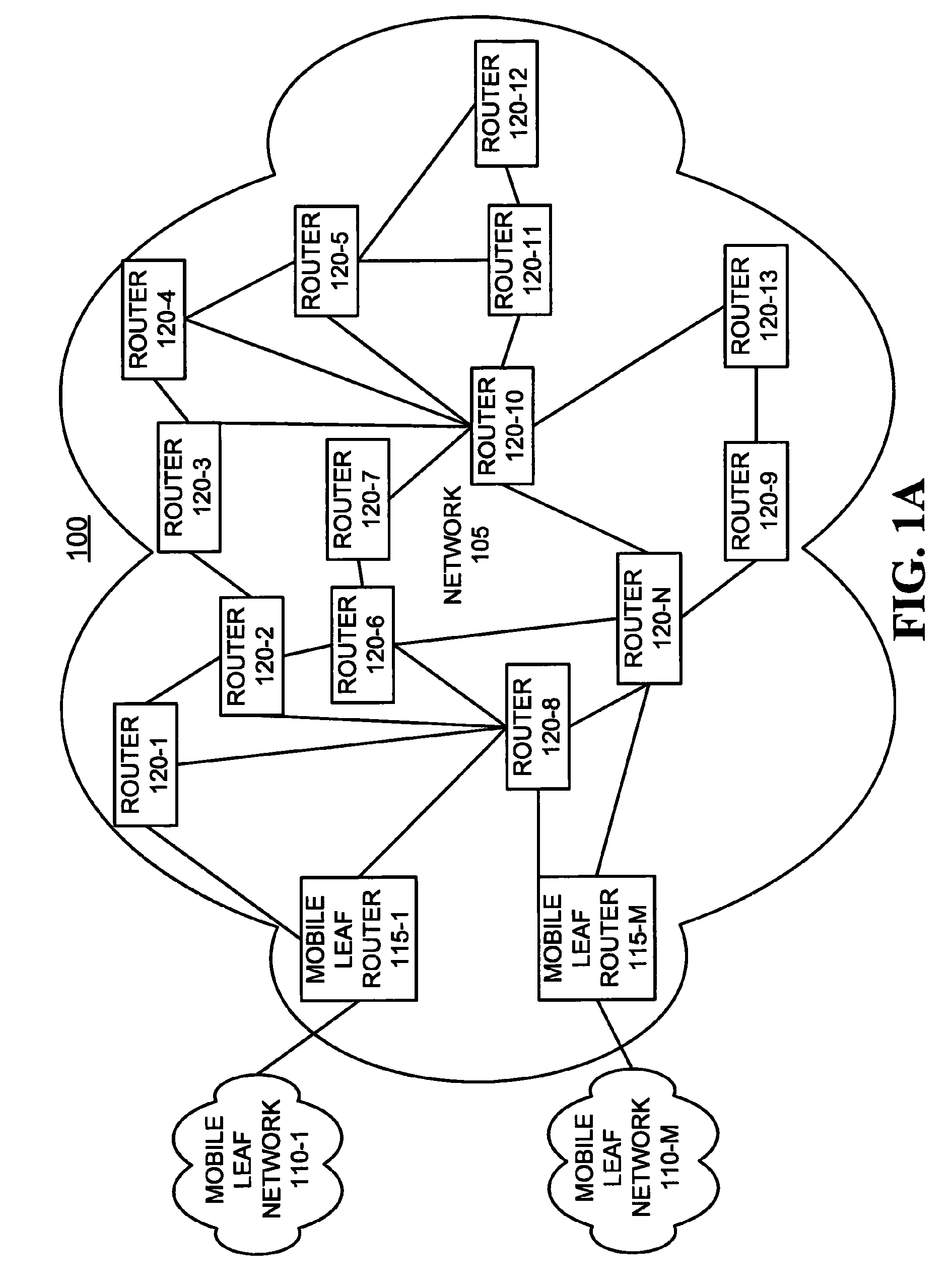
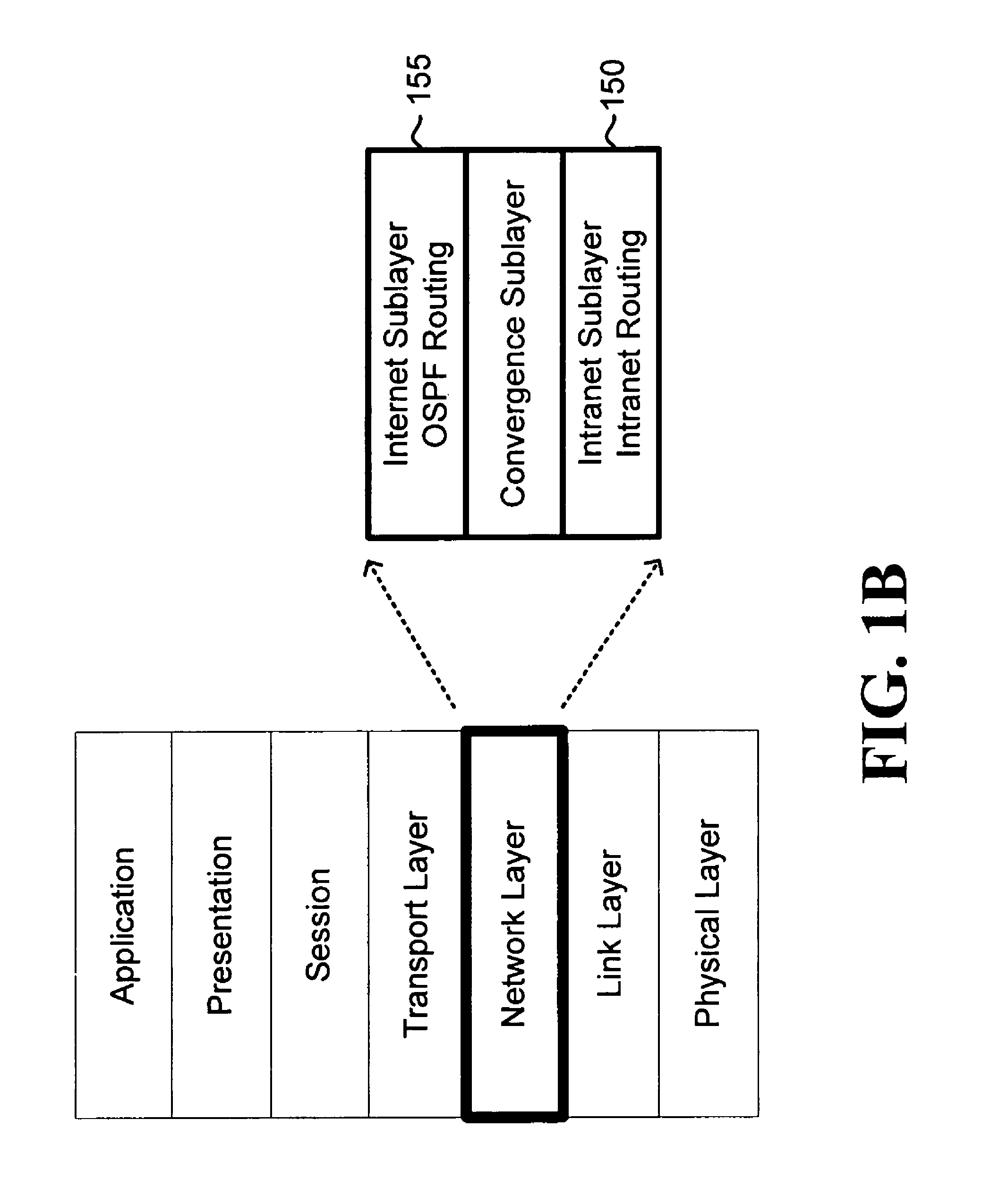
ActiveUS7983239B1Effective distributionMinimizes OSPF routing overheadError preventionTransmission systemsAccess networkRadio networks
A system constructs an OSPF-compatible virtual model of a multi-hop, multi-access packet radio network that includes a plurality of routers (120) and which includes its own private, internal routing system (150), in order to facilitate the incorporation of that packet radio network into an overall OSPF routing environment. The system determines a network graph identifying actual connectivity among the plurality of routers (120). The system constructs a virtual model (300) of the, wherein connectivity of the virtual model may be different than the actual connectivity of the network graph. The system represents the multi-hop, multi-access radio network in the virtual model as a set of multi-access links (305, 310), point-to-point links, AS-external routes, and area summary routes. The system employs the virtual model for routing purposes and advertises the virtual model to other OSPF routers for the same purpose.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
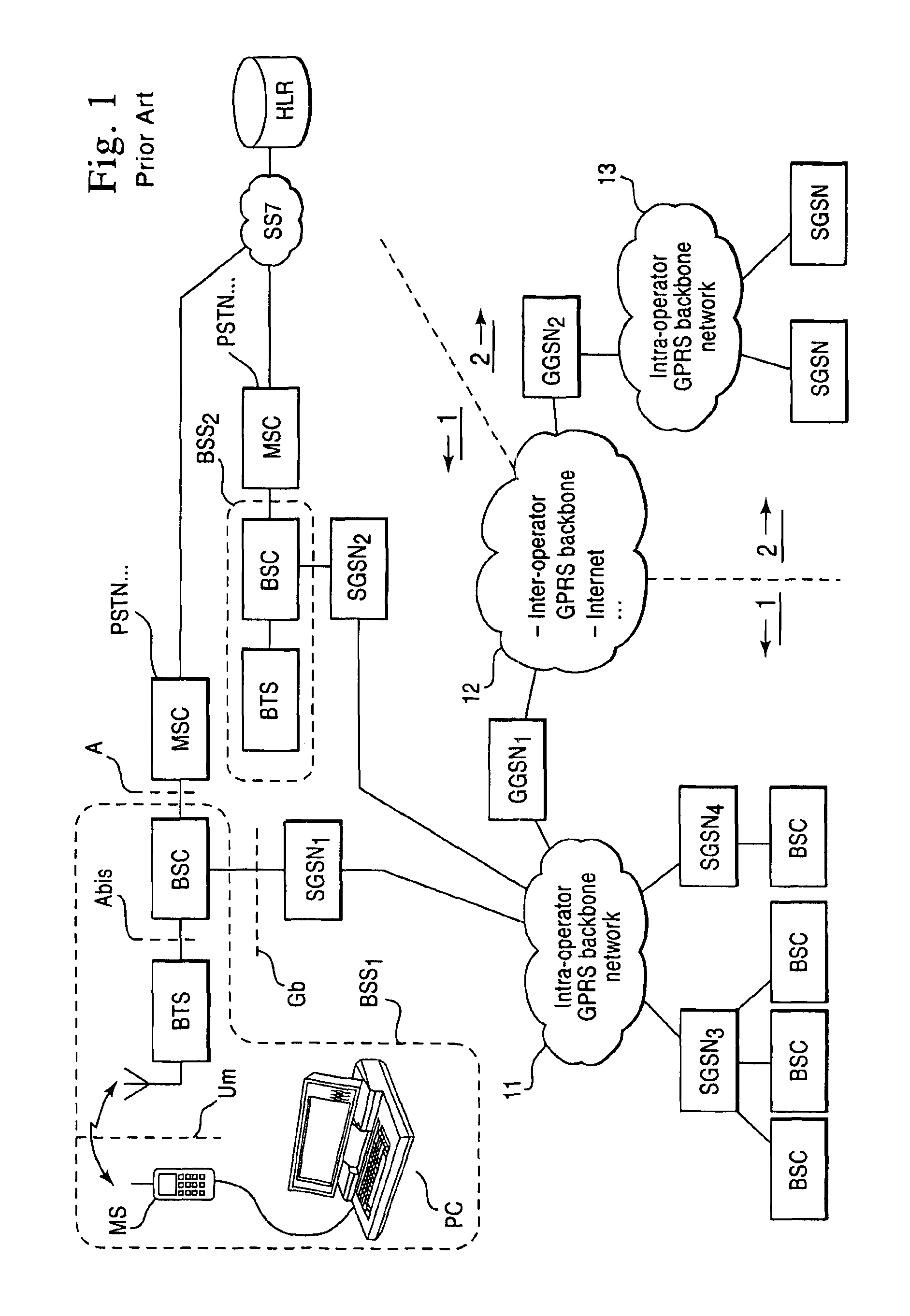
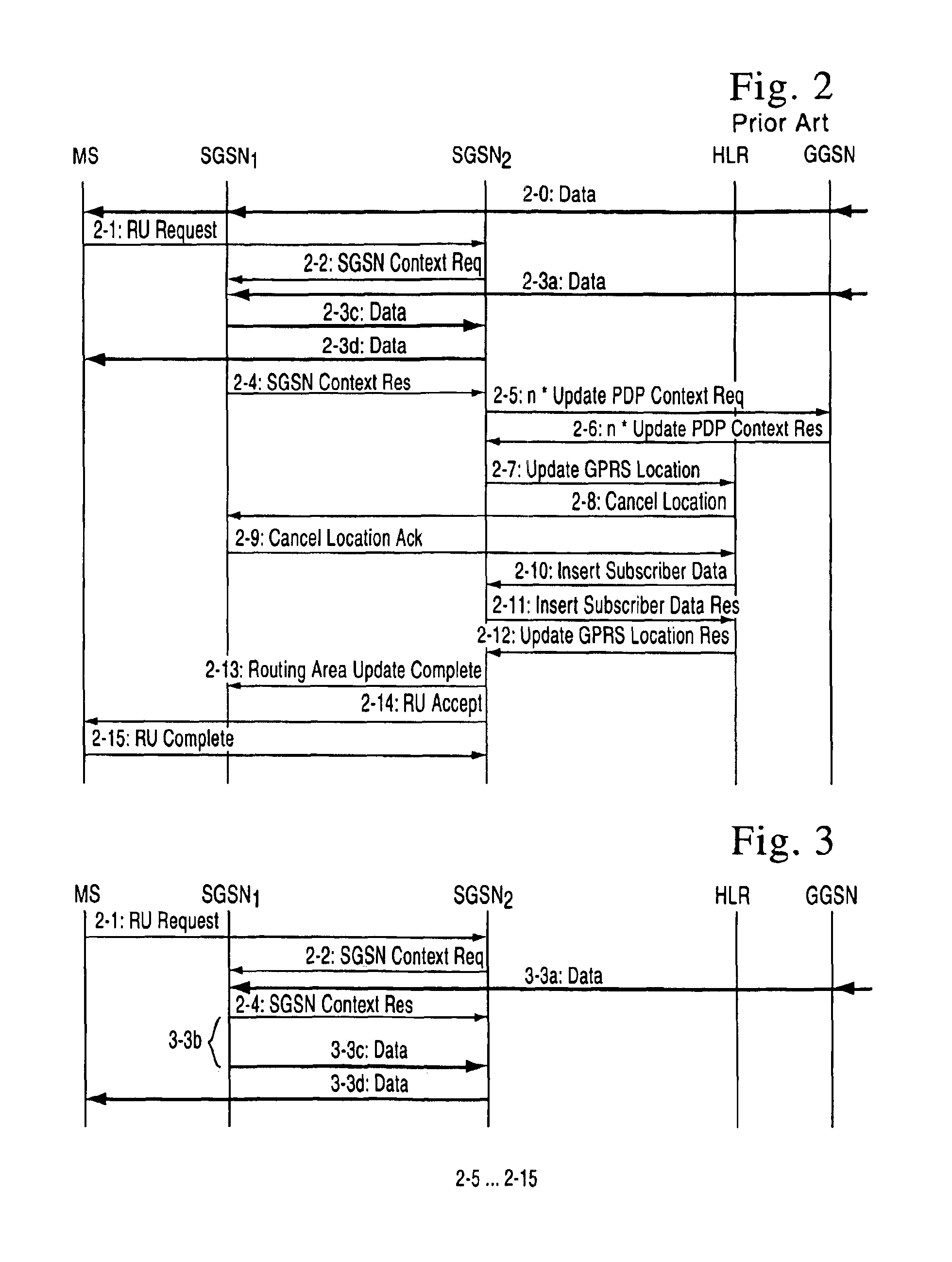
Routing area update in packet radio network
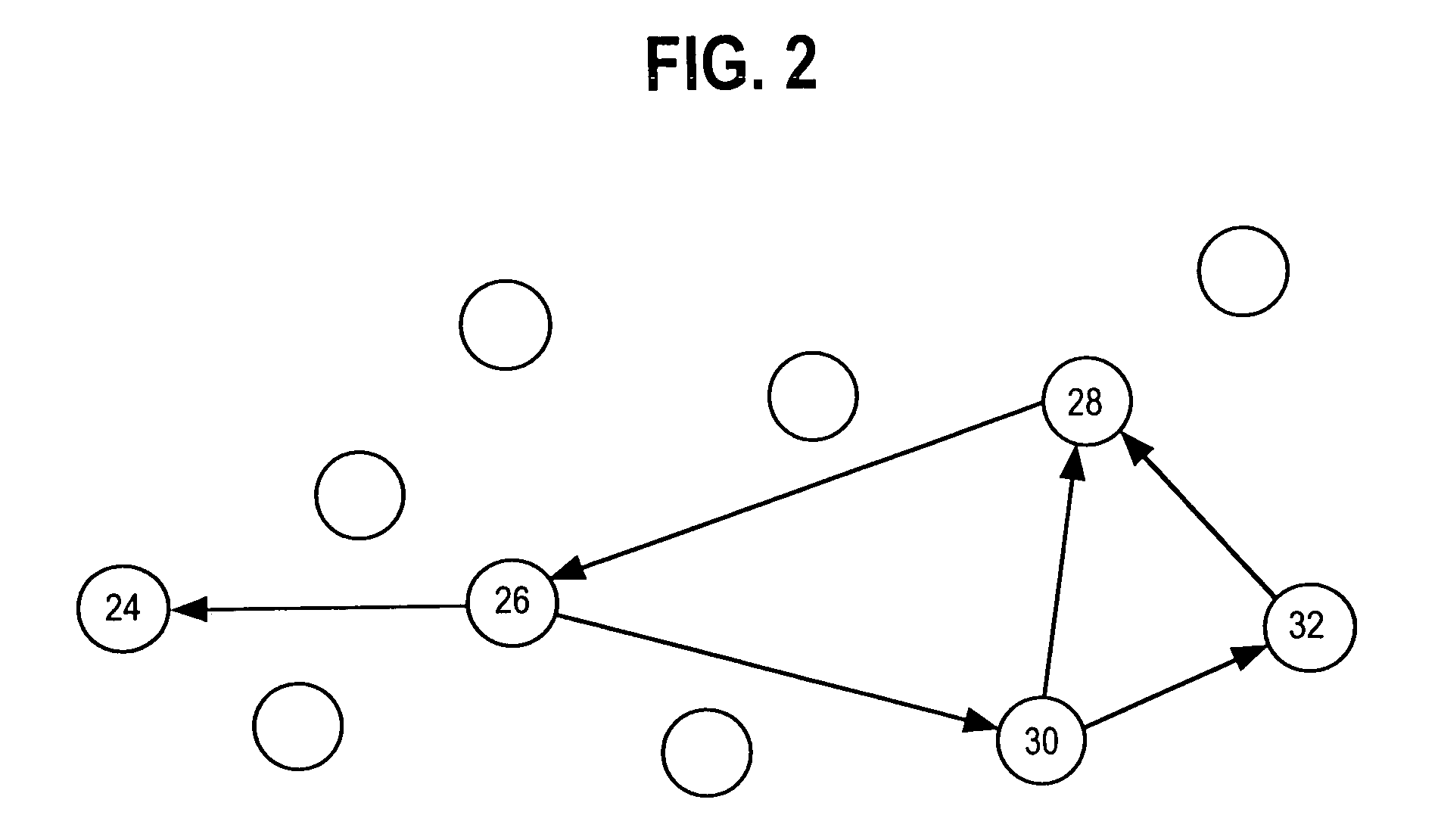
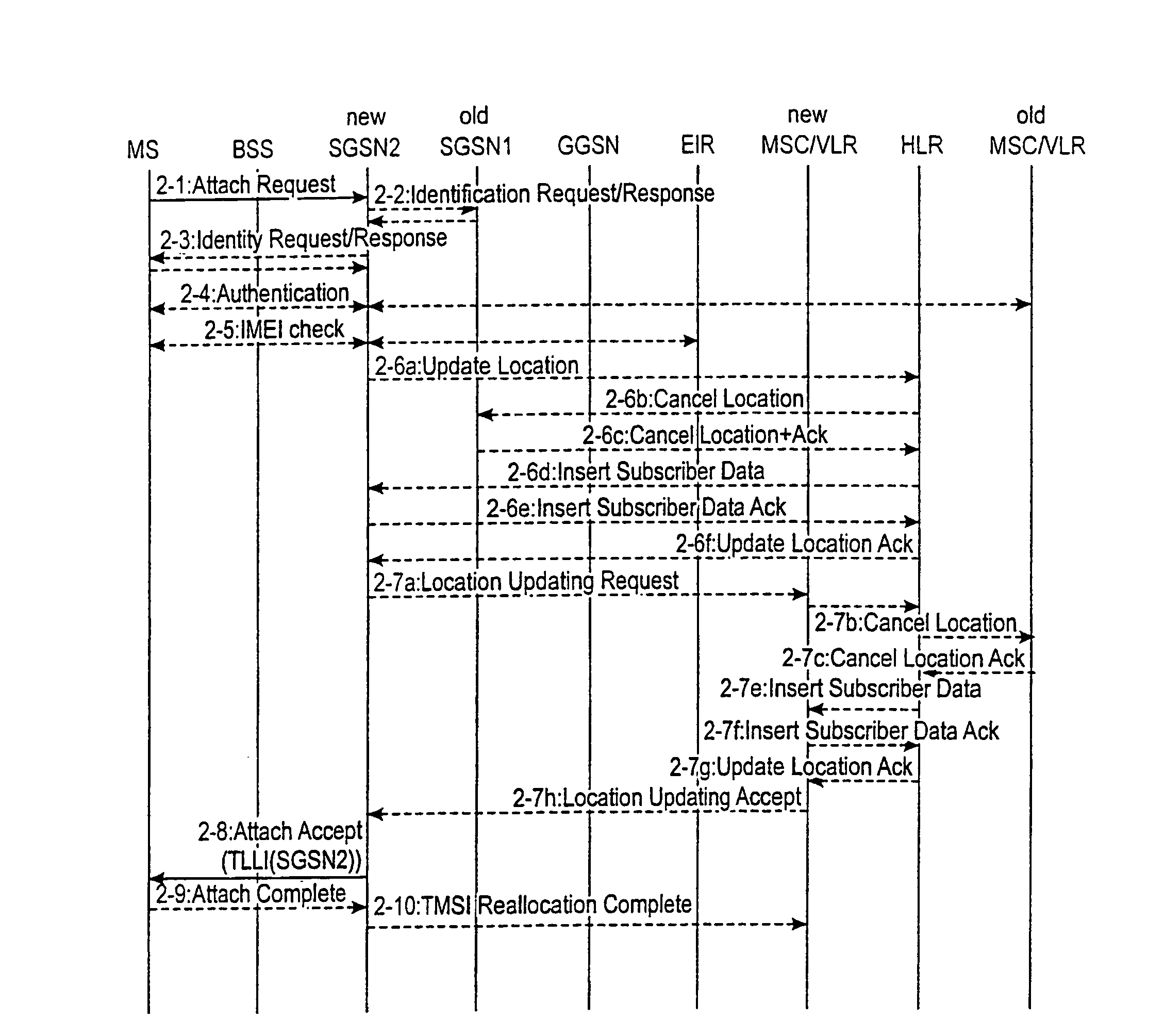
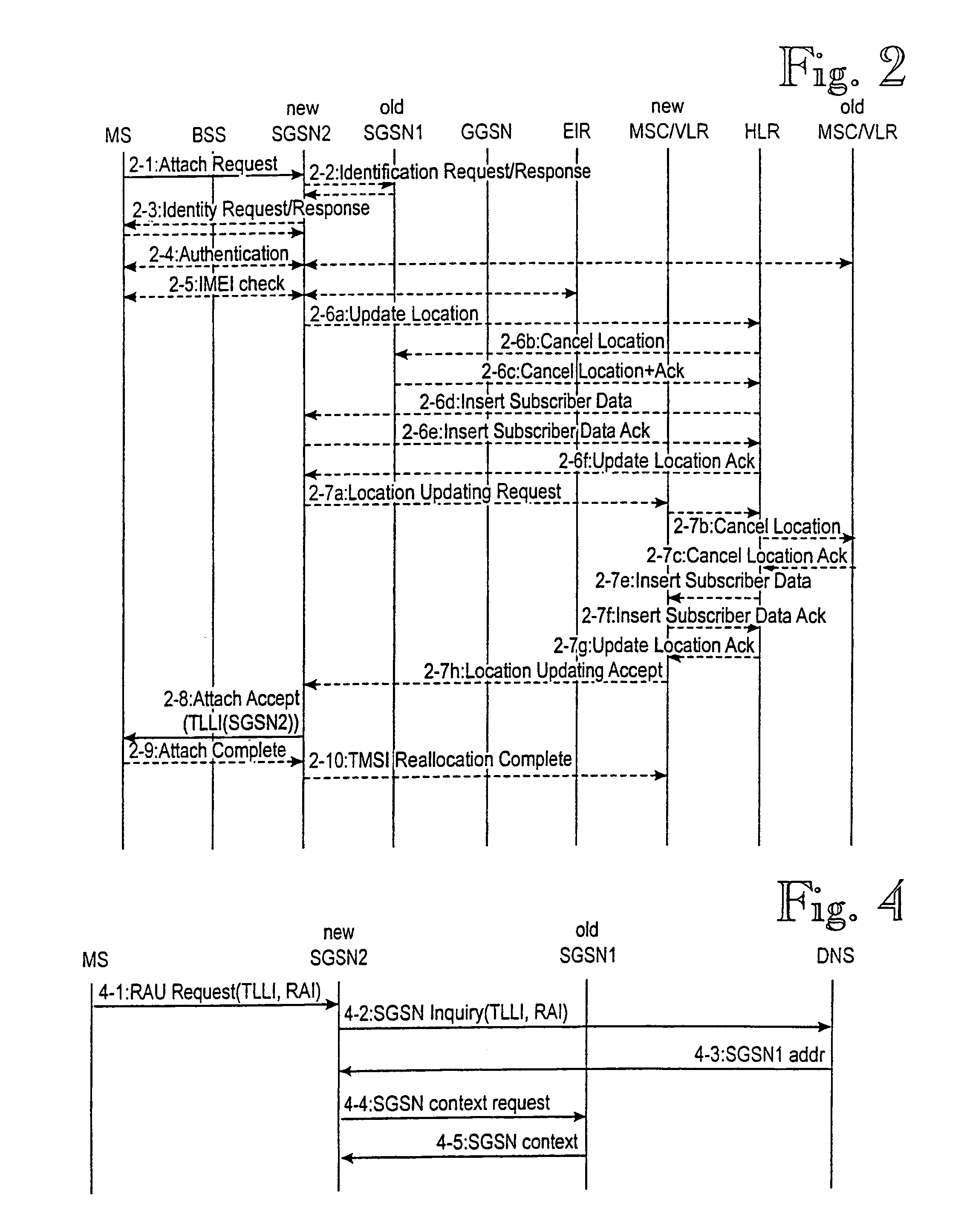
InactiveUS6870820B1Increases signaling loadSolve the real problemConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceRadio networks
A method of transmitting data in a packet radio network to a mobile station performing a routing area update. The packet radio network transmits data to the mobile station via a first support node. The mobile station sends a routing area update message to a second support node, which sends to the first support node a request for context data of the mobile station from the first support node. The first support node sends from its memory, end user data addressed to the mobile station to the second support node. It then waits for a predetermined period of time before sending the end user data to the second support node. The predetermined time may be fixed, depending preferably on the quality of service of the connection used by the mobile station. Alternatively the predetermined period of time expires when the second support note sends to the first support node a separate acknowledgement message indicating that the second support node has received the context data of the mobile station.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
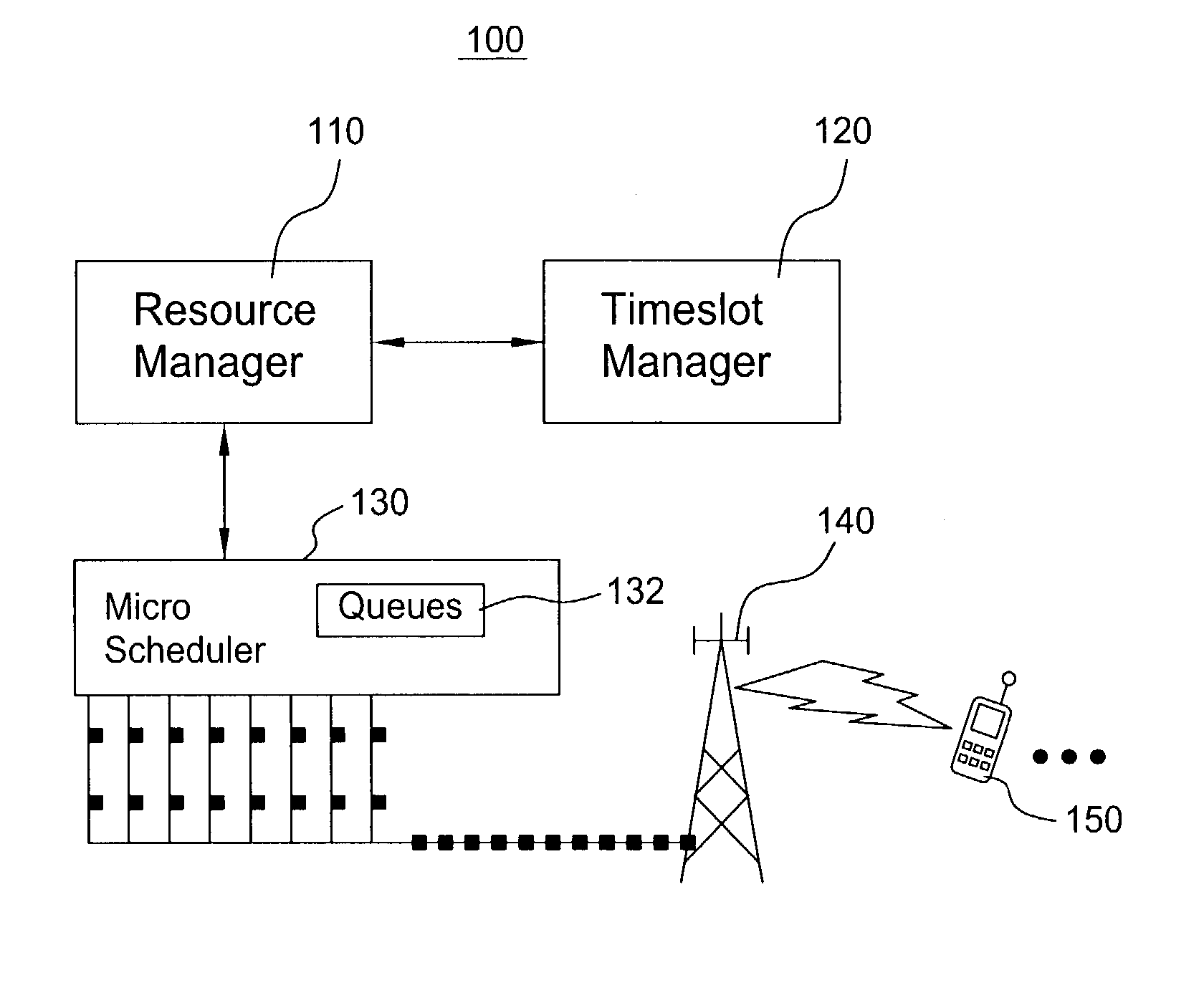
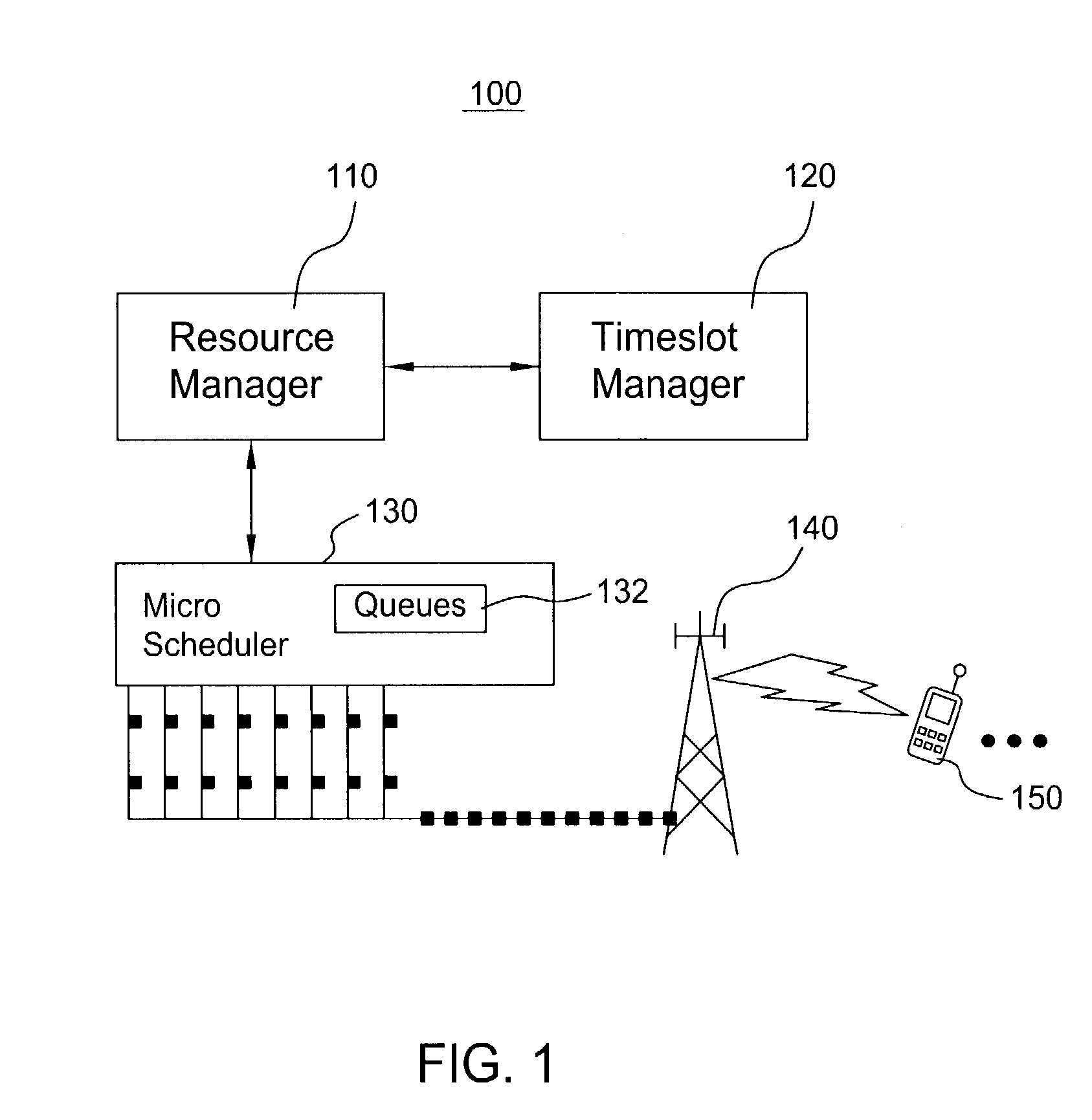
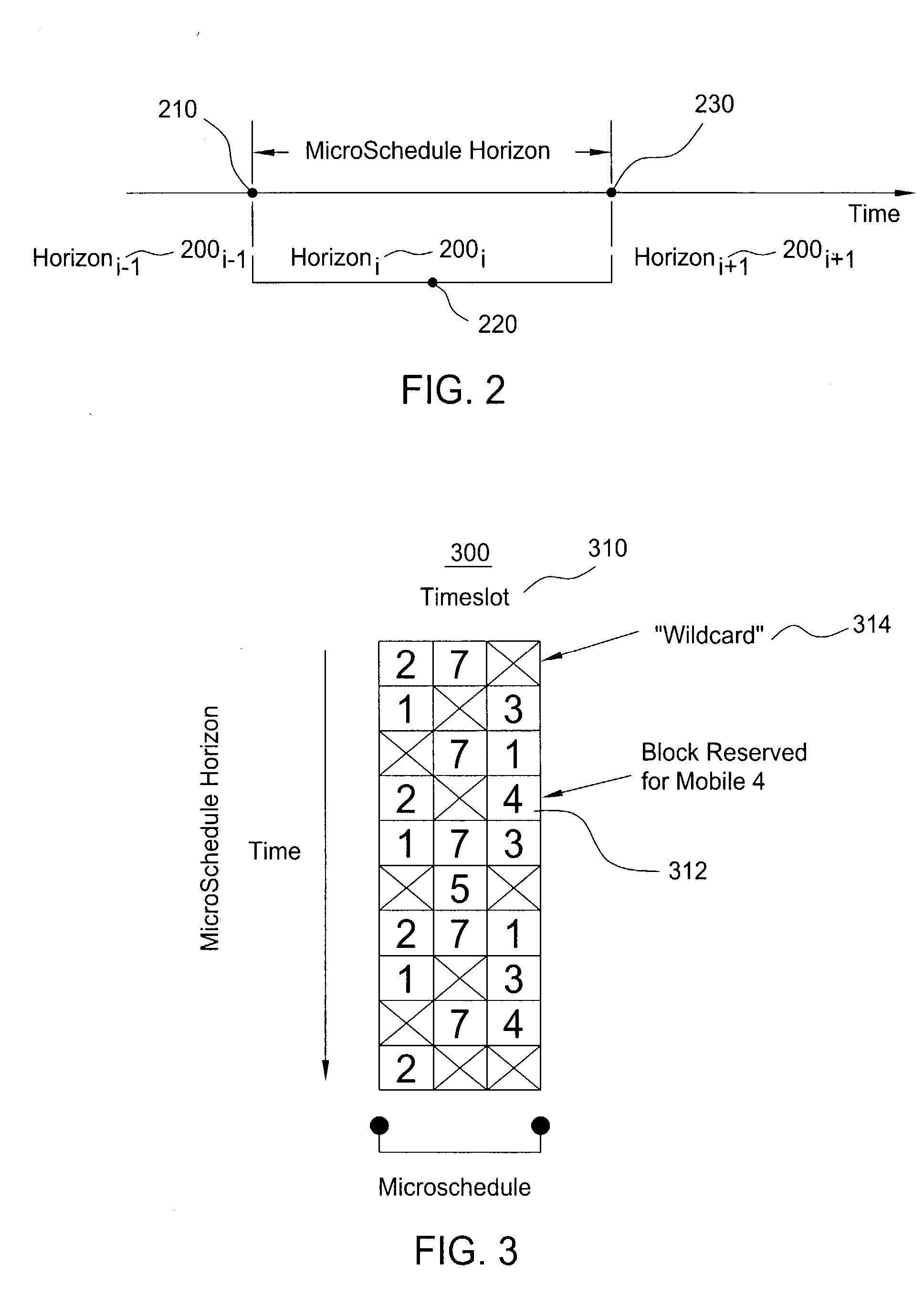
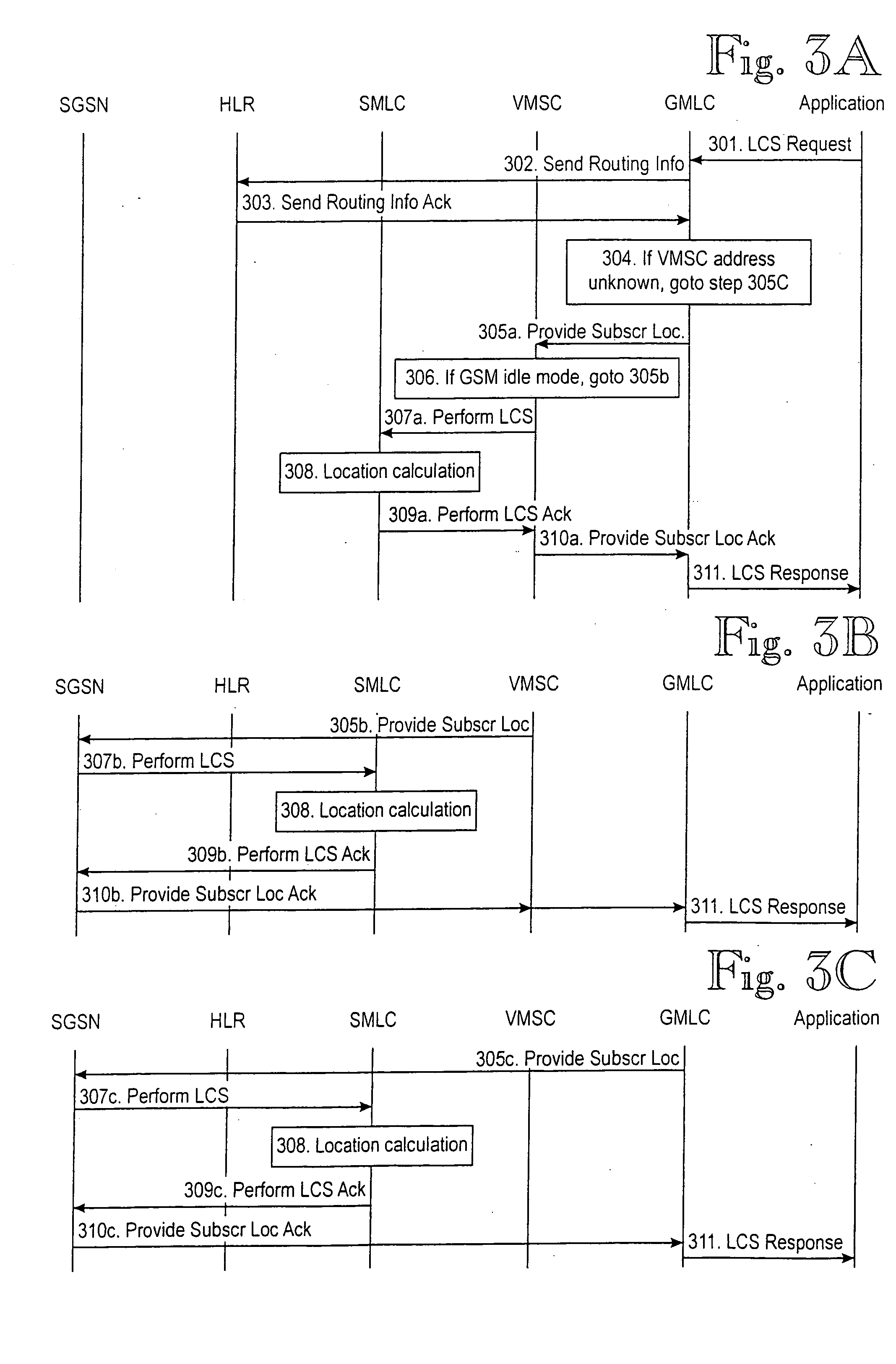
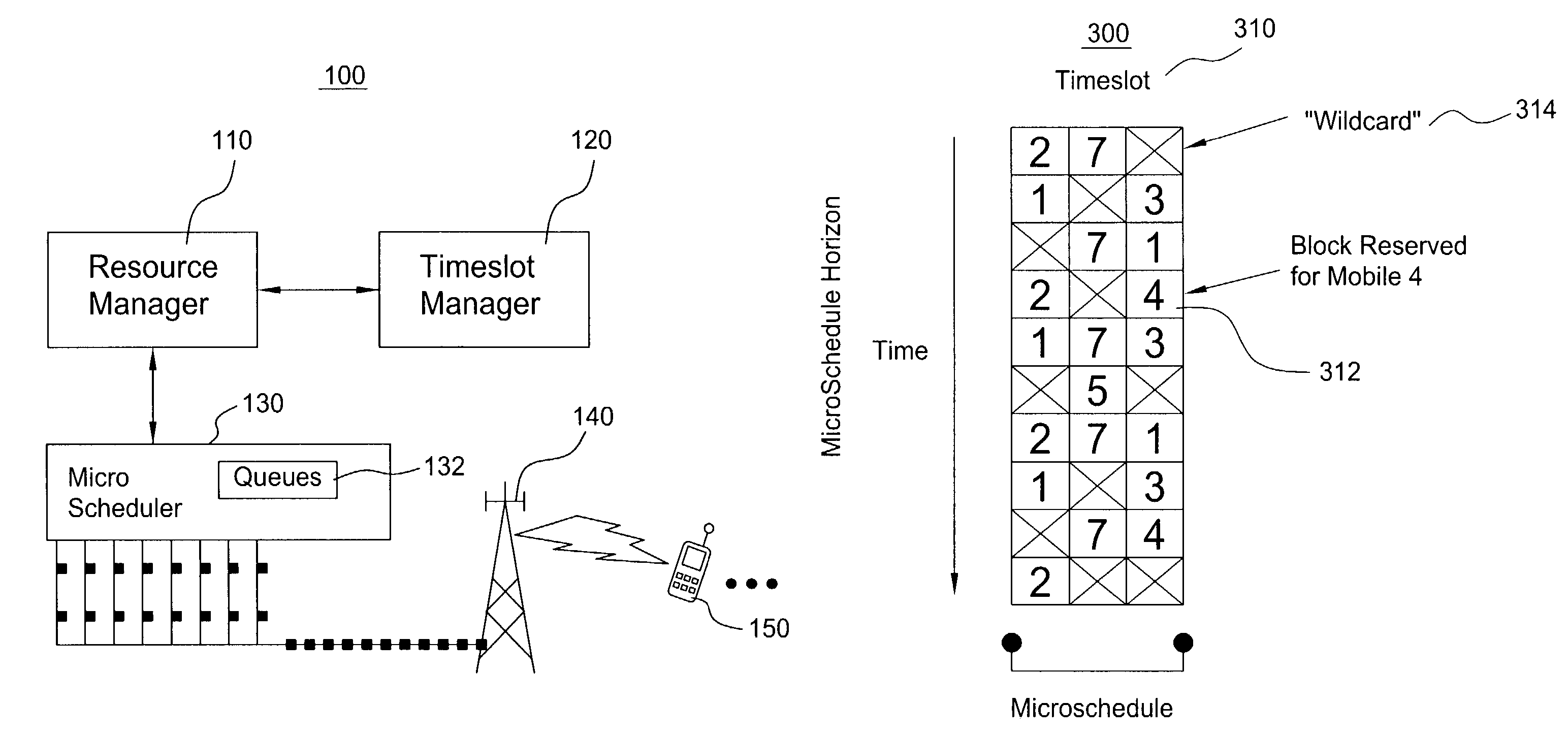
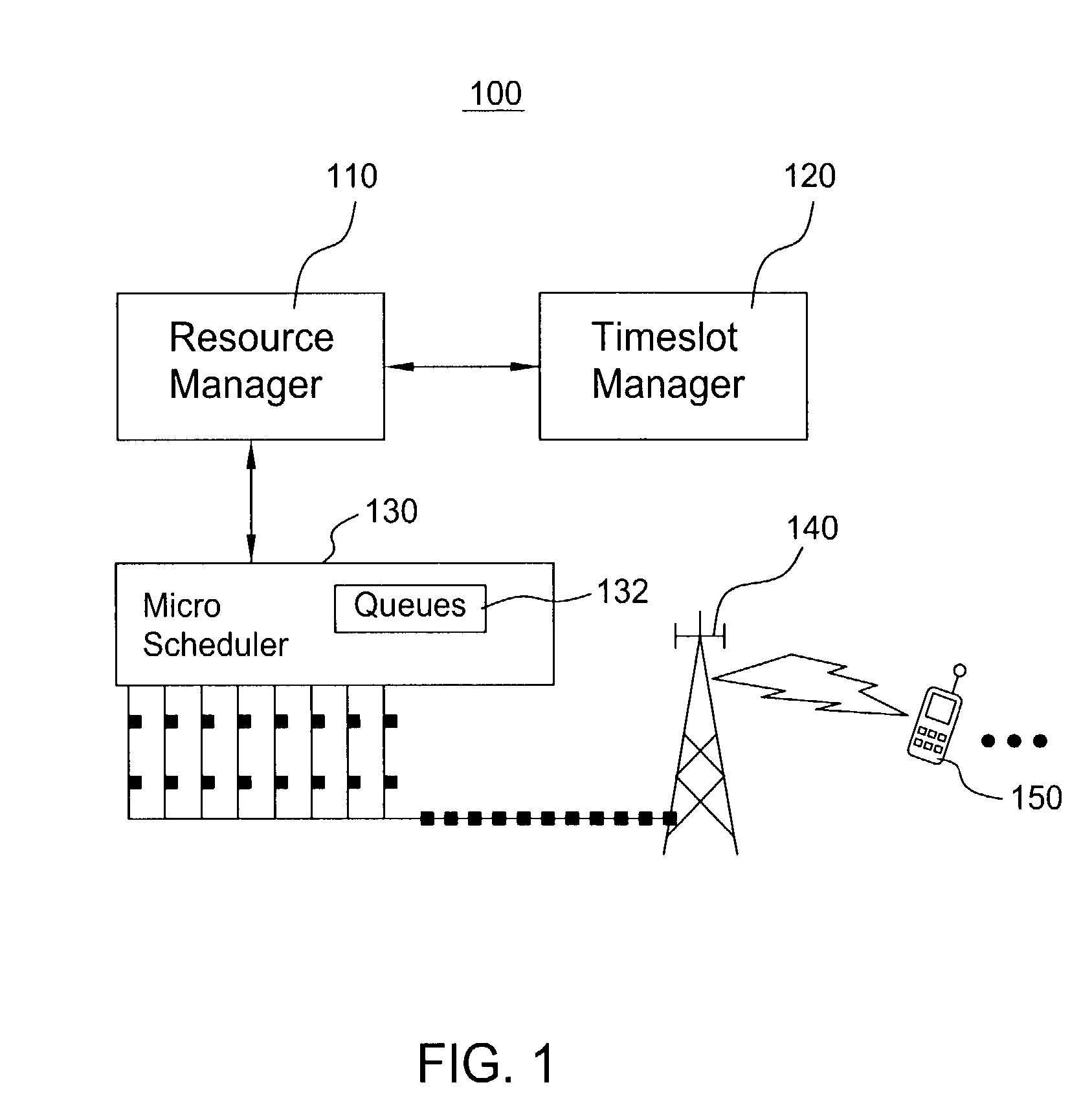
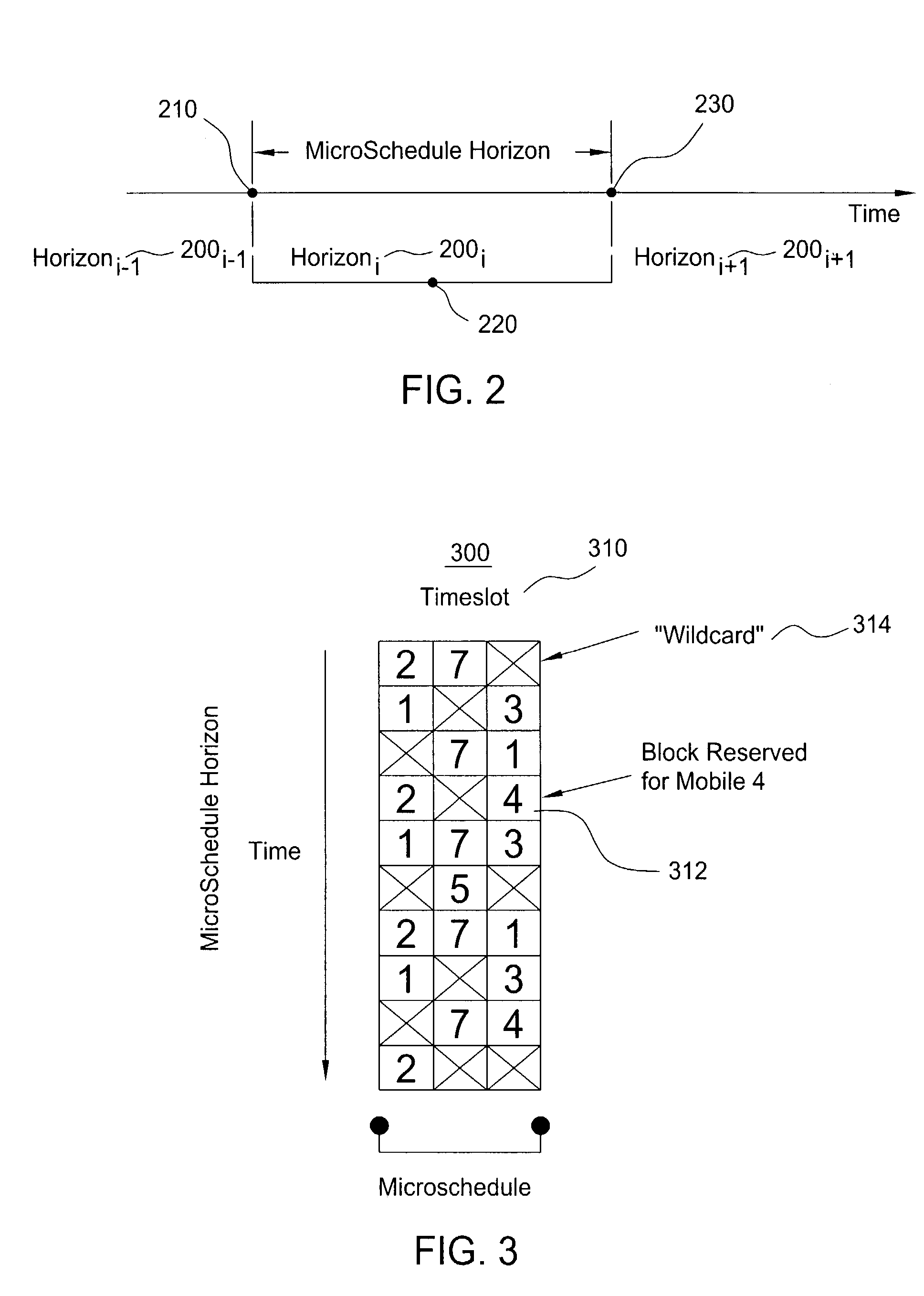
Scheduling method for quality of service differentiation for non-real time services in packet radio networks
ActiveUS20040228353A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQos quality of serviceComputer network
A method and apparatus for providing differentiated quality of service (QoS) within a GPRS / EGPRS network environment. The invention advantageously uses one or more of a microscheduling technique, a peak picking technique and other techniques and methodologies to provide differentiated quality of service levels to users while maximizing total network throughput.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
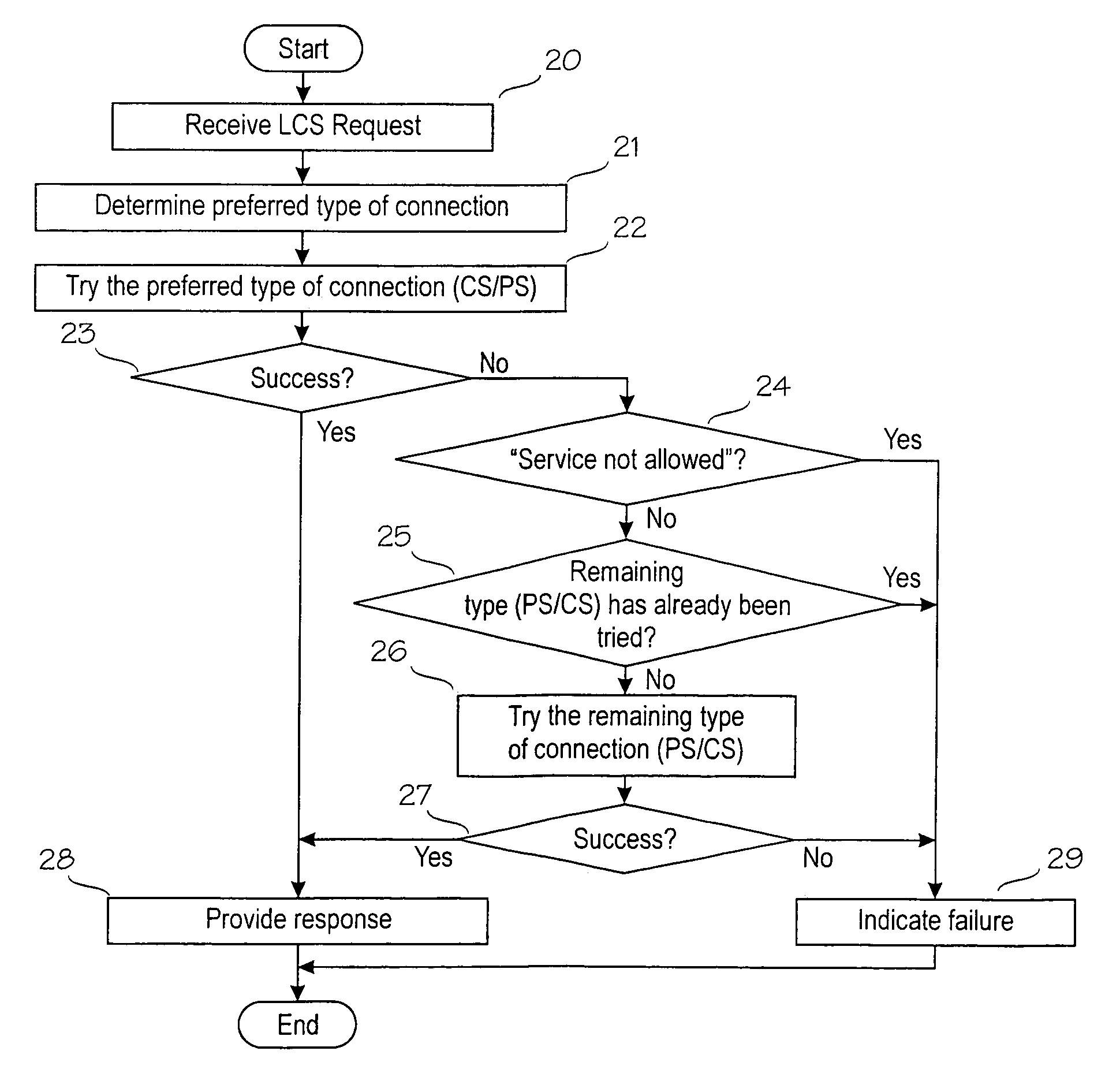
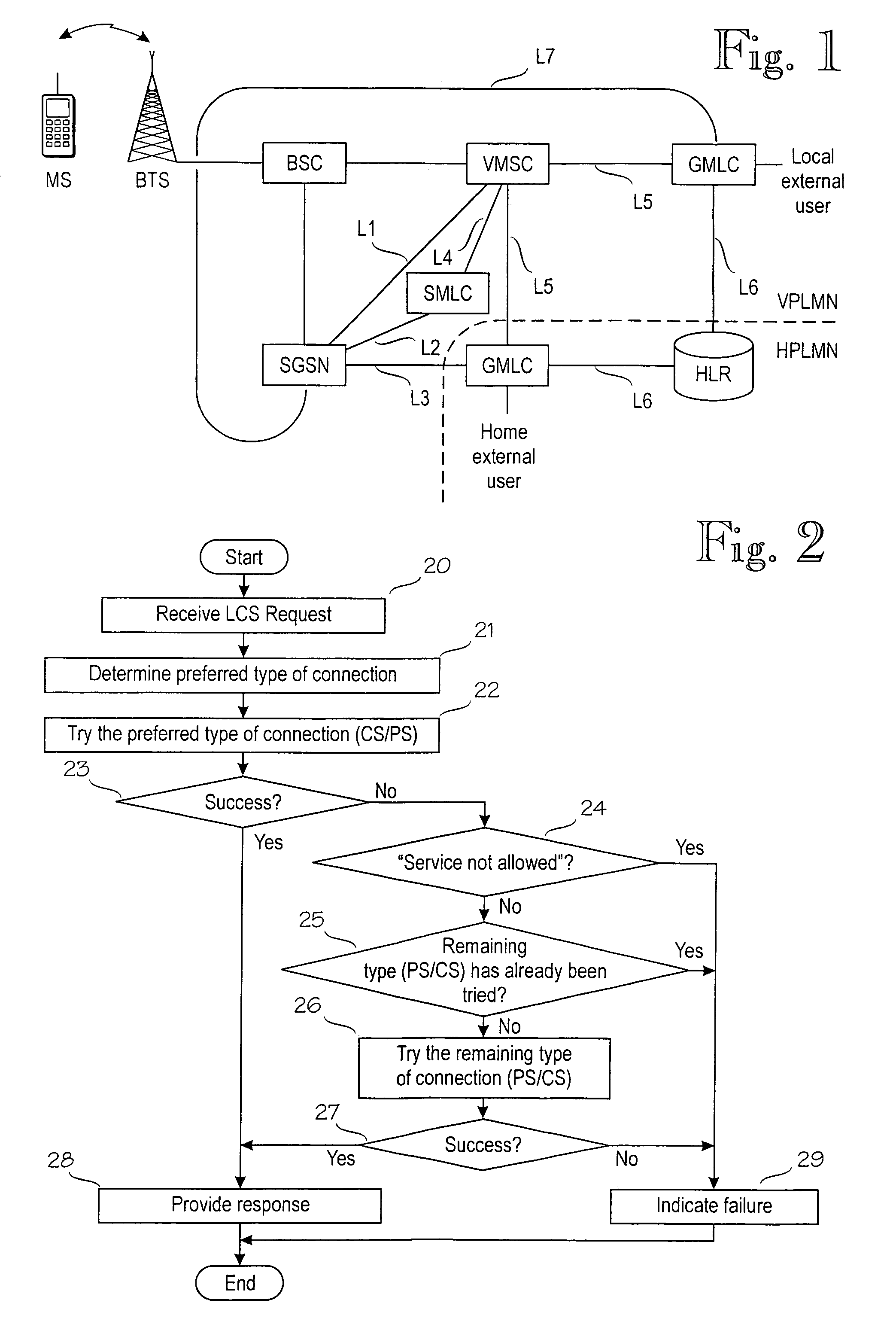
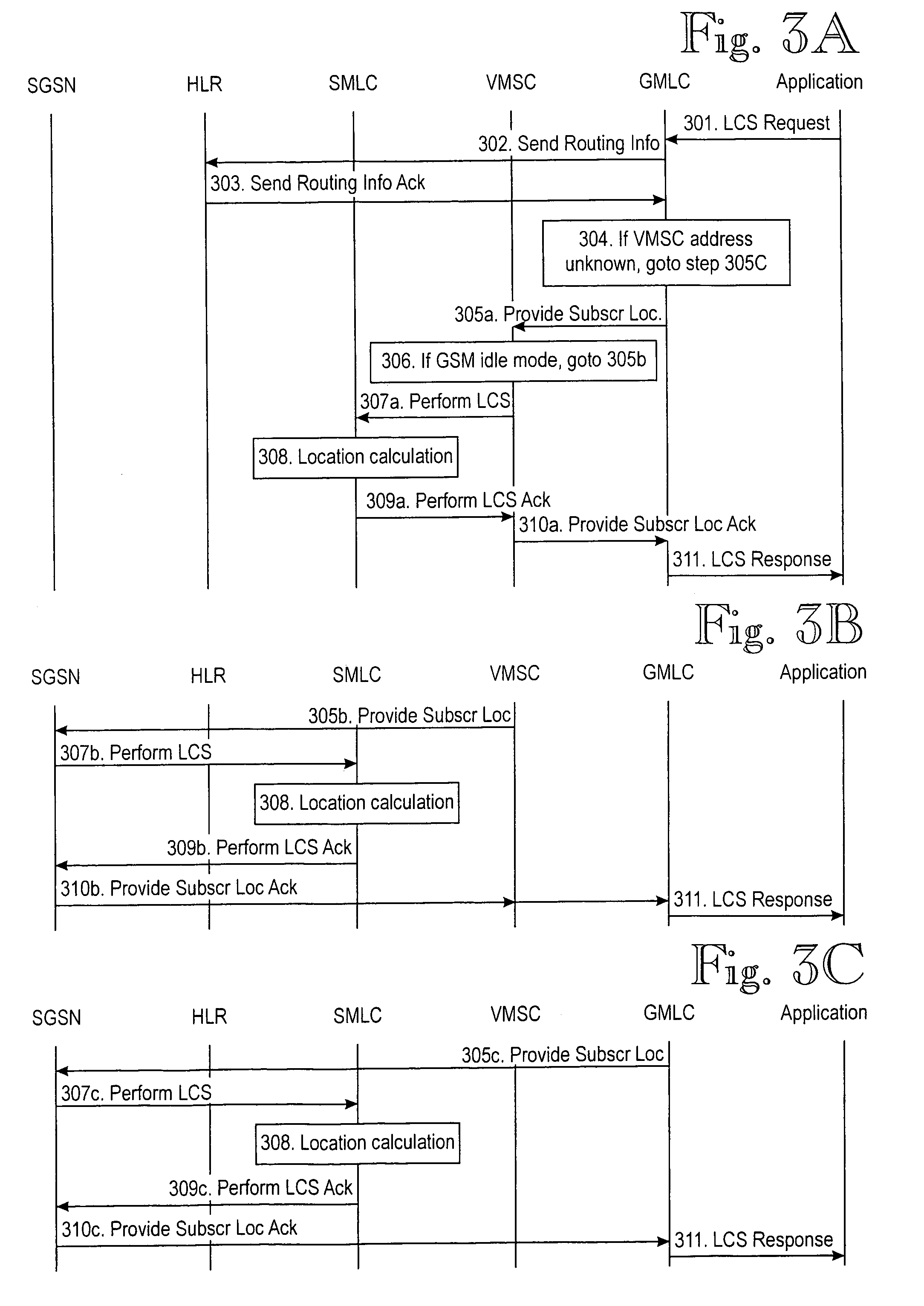
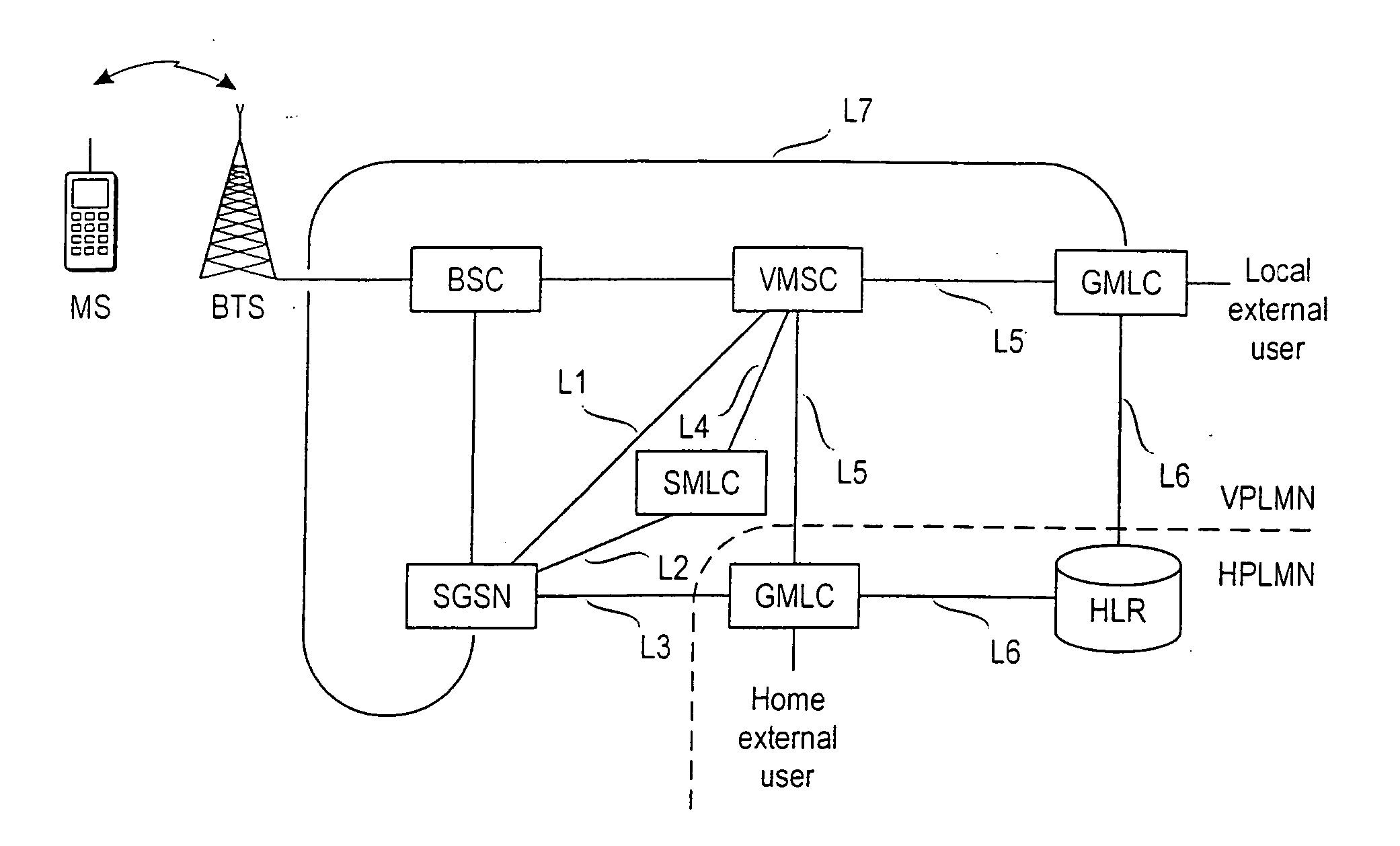
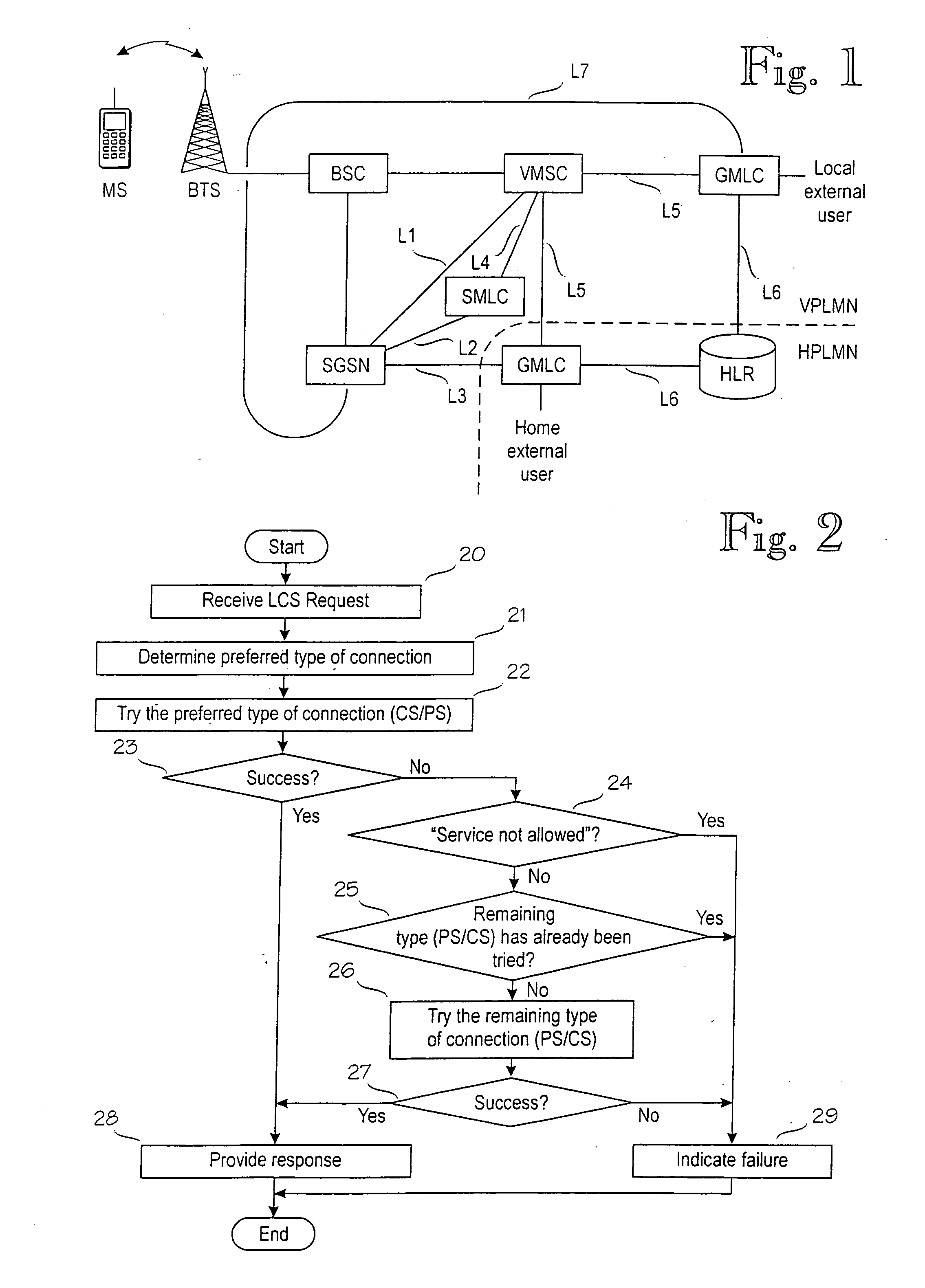
Location services in a packet radio network
InactiveUS7116984B1Reduce signaling overheadTime-division multiplexSubstation equipmentConnection typeCommunications system
A method for providing location service information related to a mobile station in a mobile communications system supporting connections of a first type, for example circuit-switched, and a second type, for example packet-switched. The method comprises receiving a request from a requesting entity; retrieving the location service information related to the mobile station; and providing a response to the request. The method further comprises determining a preferred type of connection for the retrieving based on a first set of predetermined criteria; and performing, in the retrieving, at least a first attempt via a preferred type of connection.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
Secure packet radio network
InactiveUS7068791B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsRadio networksTelecommunications
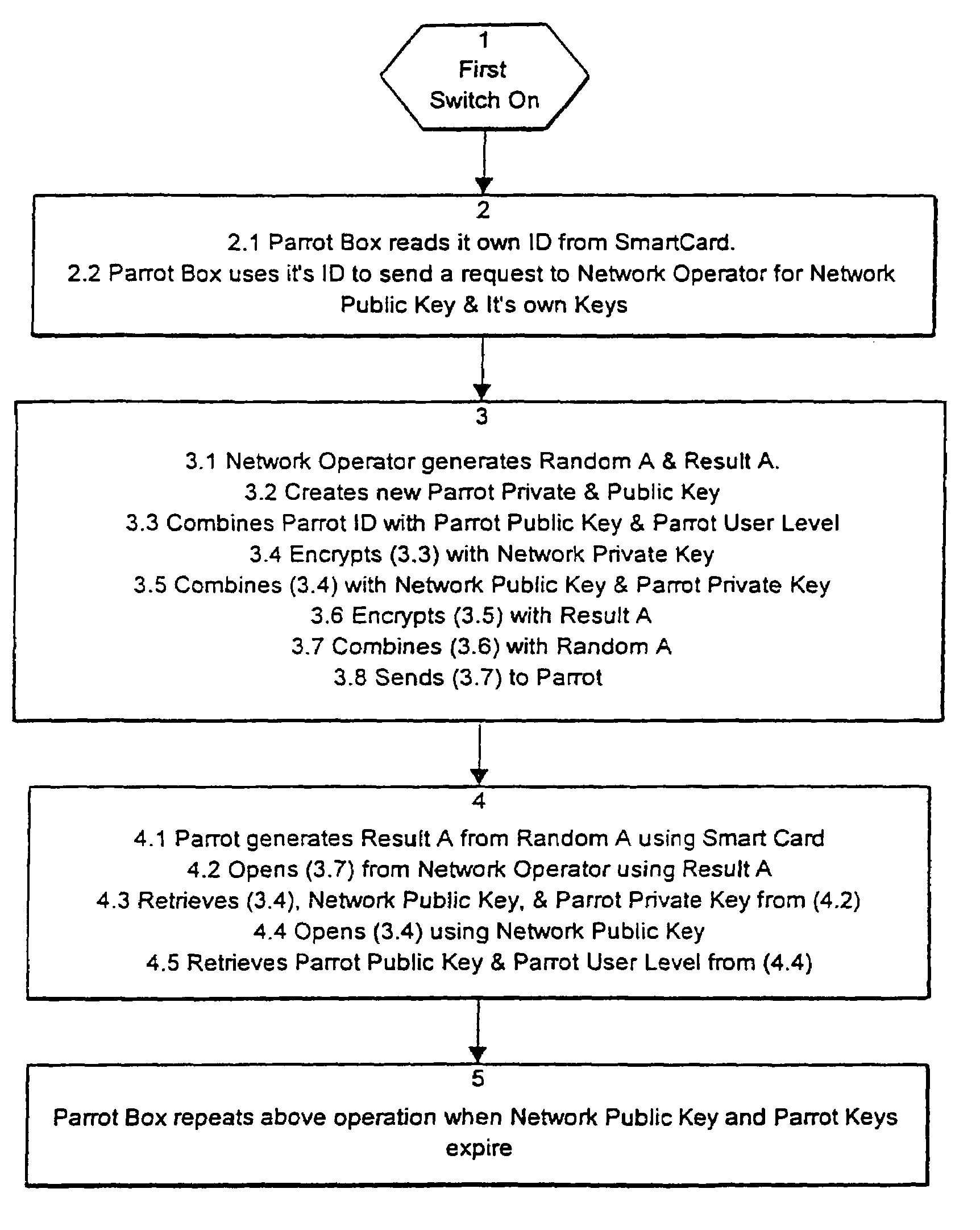
A packet radio network comprises at least one network operator station and a number of user stations. The user stations transmit message data to one another, either directly or via intermediate stations. When stations are first activated, they transmit key request messages to the network operator station. Other, authenticated stations in the network will not communicate with the new station, but will pass the key request message to the network operator station. The network operator station transmits the necessary keys back to the new station via the other stations to permit the new station to operate. Each user station transmits key probe signals from time to time which advise other stations of its public key.
Owner:IWICS INC
Mobile multipoint service
ActiveUS7680109B2Easy to useMinimum of bandwidthSpecial service provision for substationConnection managementRadio networksService provision
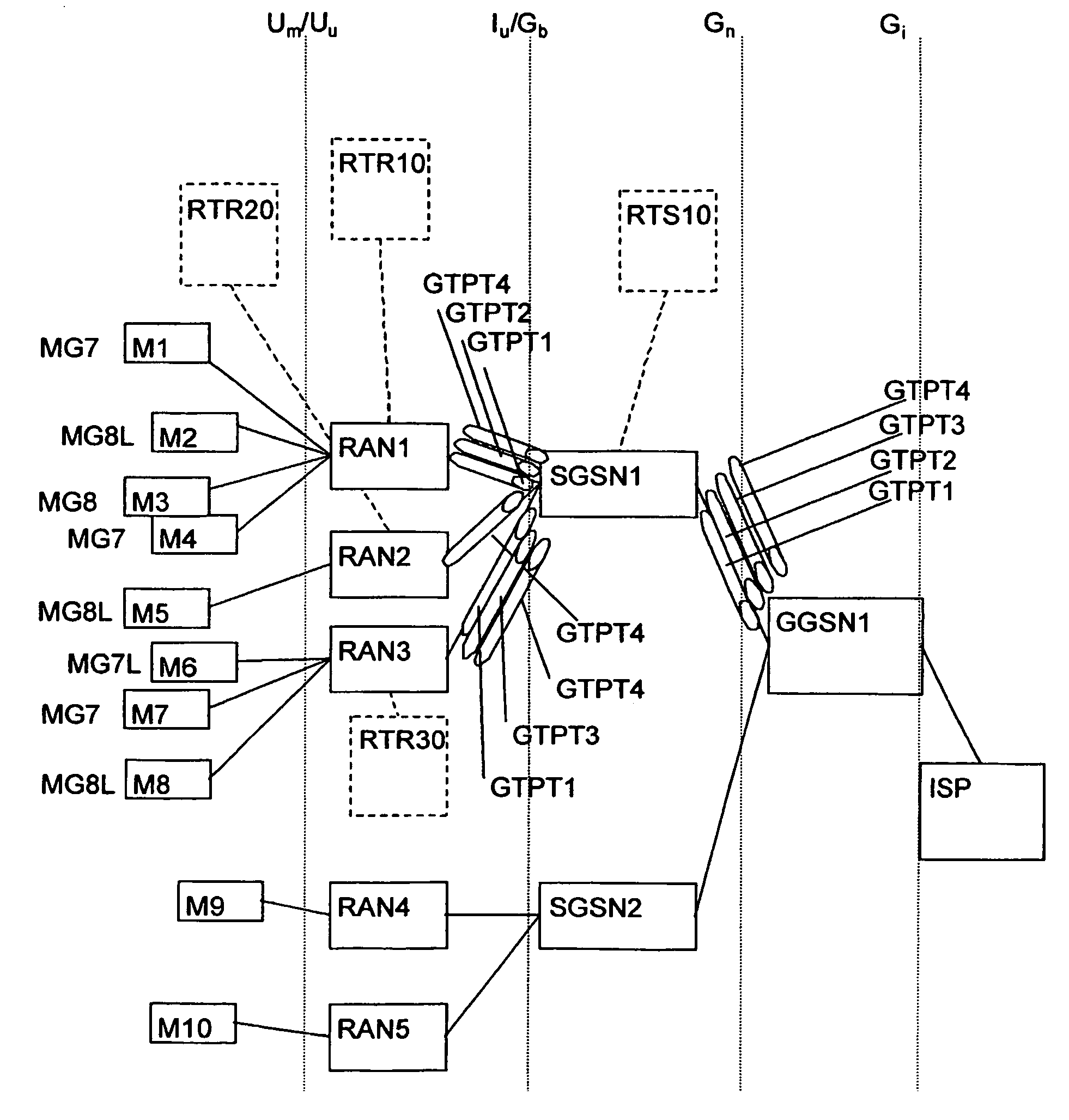
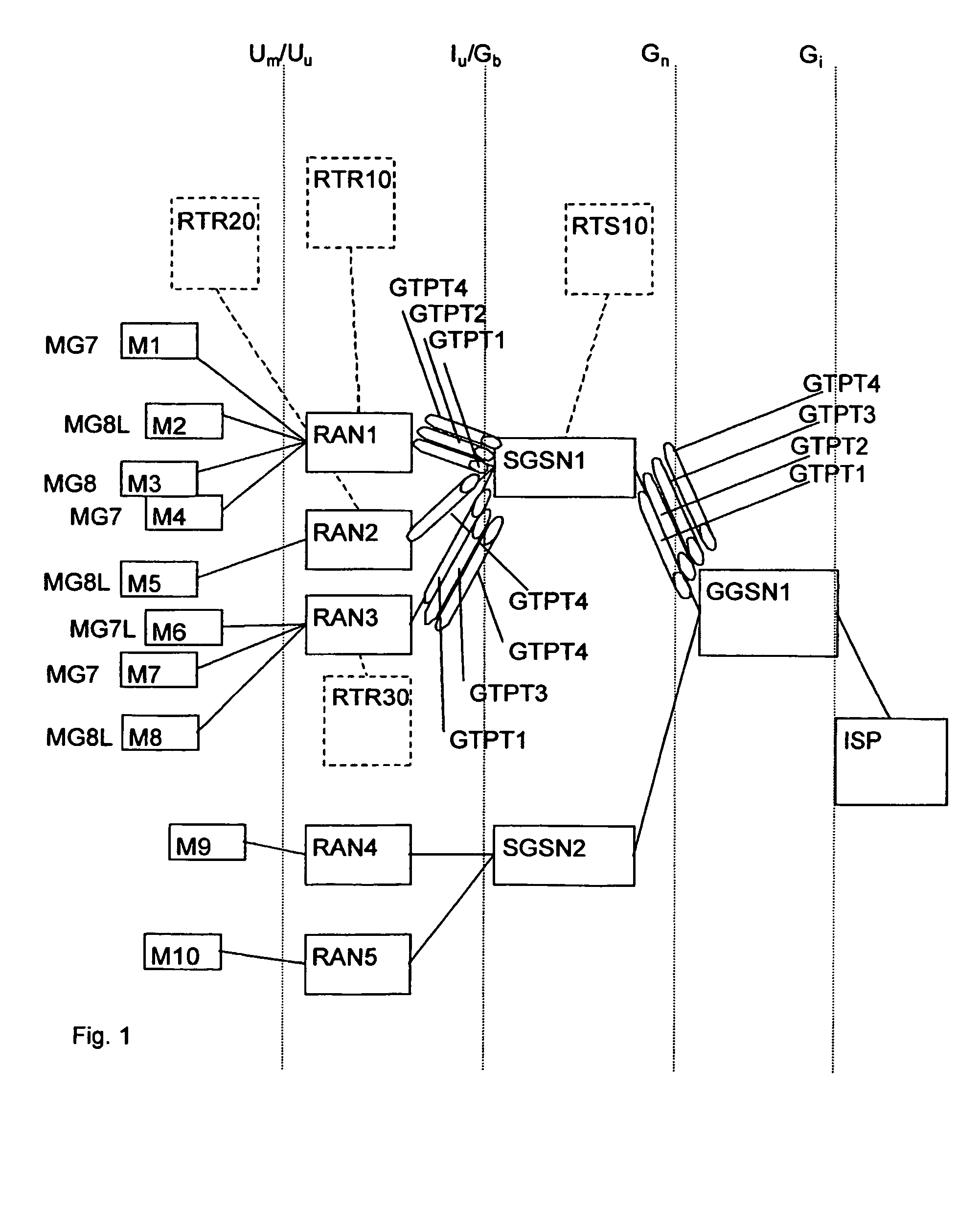
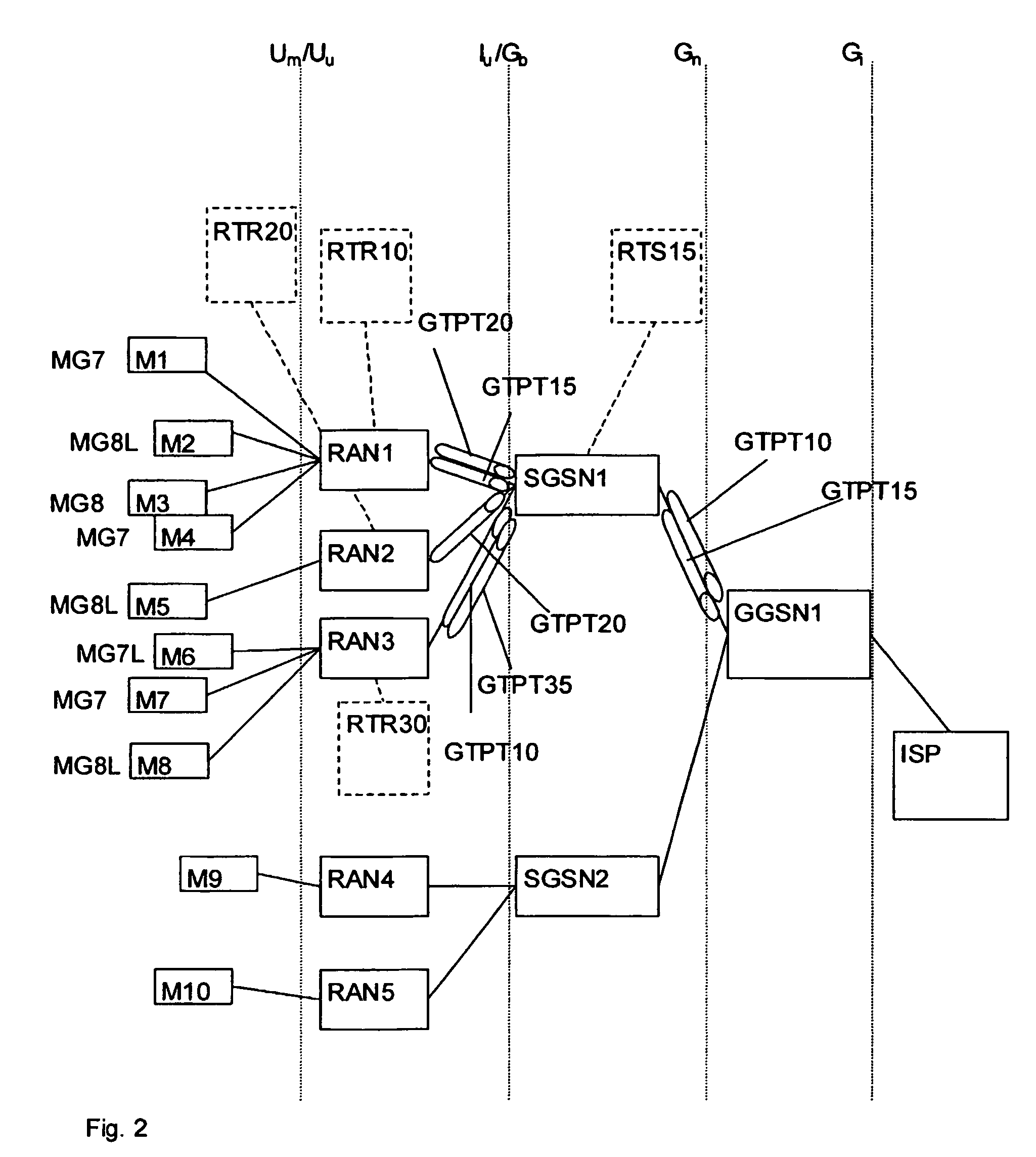
A packet radio data network and methods have been disclosed, the network comprising at least a gateway node (GGSN), at least one serving node (SGSN) connected to the gateway node, a plurality of radio access nodes (RAN) connected to the serving node (SGSN), the packet radio network transporting packet data from an external packet data network, comprising an Internet Service Provider (ISP), to mobile stations (MS) wirelessly attached to radio access nodes (RAN). The gateway node, subsequent to a PDP multipoint context activation procedure, establishes at least a first multicast tunnel (GTPT1 GTPT4, GTPT10 GTP35) between the gateway node and at least one serving node, the multicast tunnel carrying IP streams pertaining to at least two mobile stations belonging to a common multicast group.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Packet radio network and method
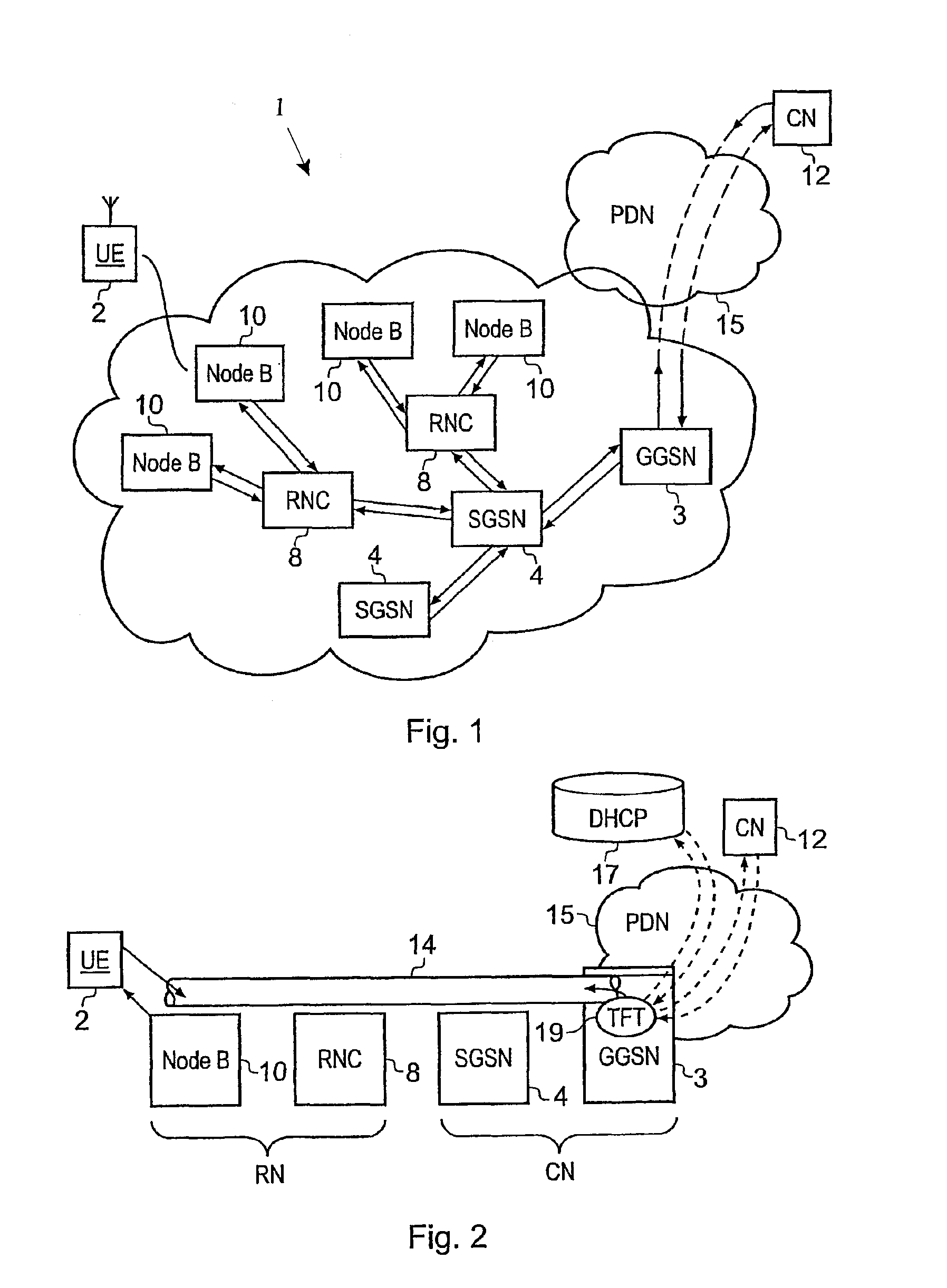
ActiveUS8064384B2Improve efficiencyEffective resourcesConnection managementData switching by path configurationTTEthernetComputer network
A packet radio network comprising a gateway support node, a serving support node and a radio network part provides a facility for communicating internet packets with mobile user equipment. The gateway support node provides a packet data protocol context for controlling communication of internet packets between the packet radio network and mobile user equipment via a packet communications bearer. The serving support node is connected to the gateway support node controls communications between the gateway support node and mobile user equipment forming the packet communications bearer. The radio network part provides a radio access bearer for communicating internet packets via a radio access interface with mobile user equipment. In response to a request message, the serving support node with the gateway support node establishes a common packet data protocol context with a packet communications bearer to communicate packets according to an internet protocol version specified by the mobile user equipment.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
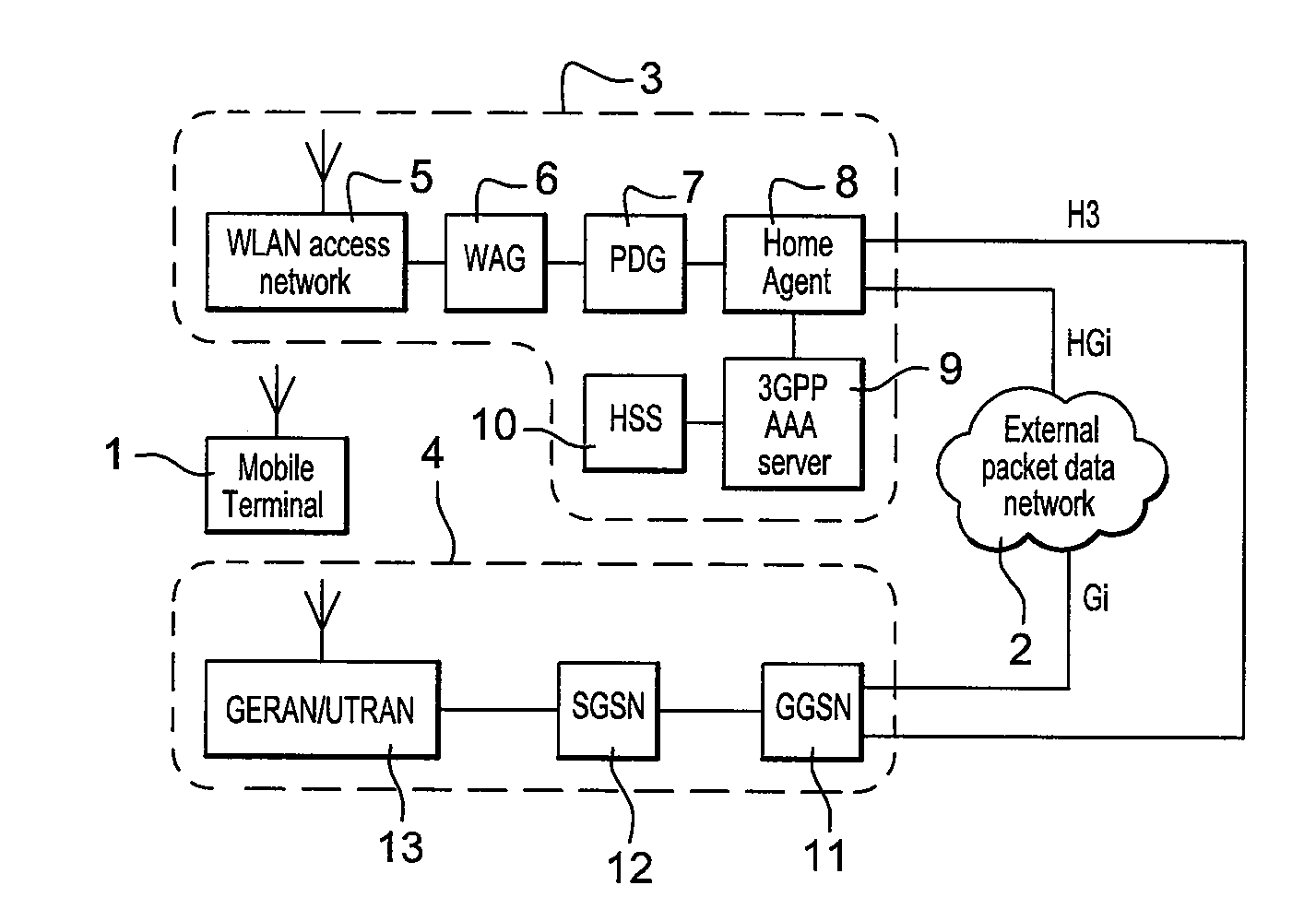
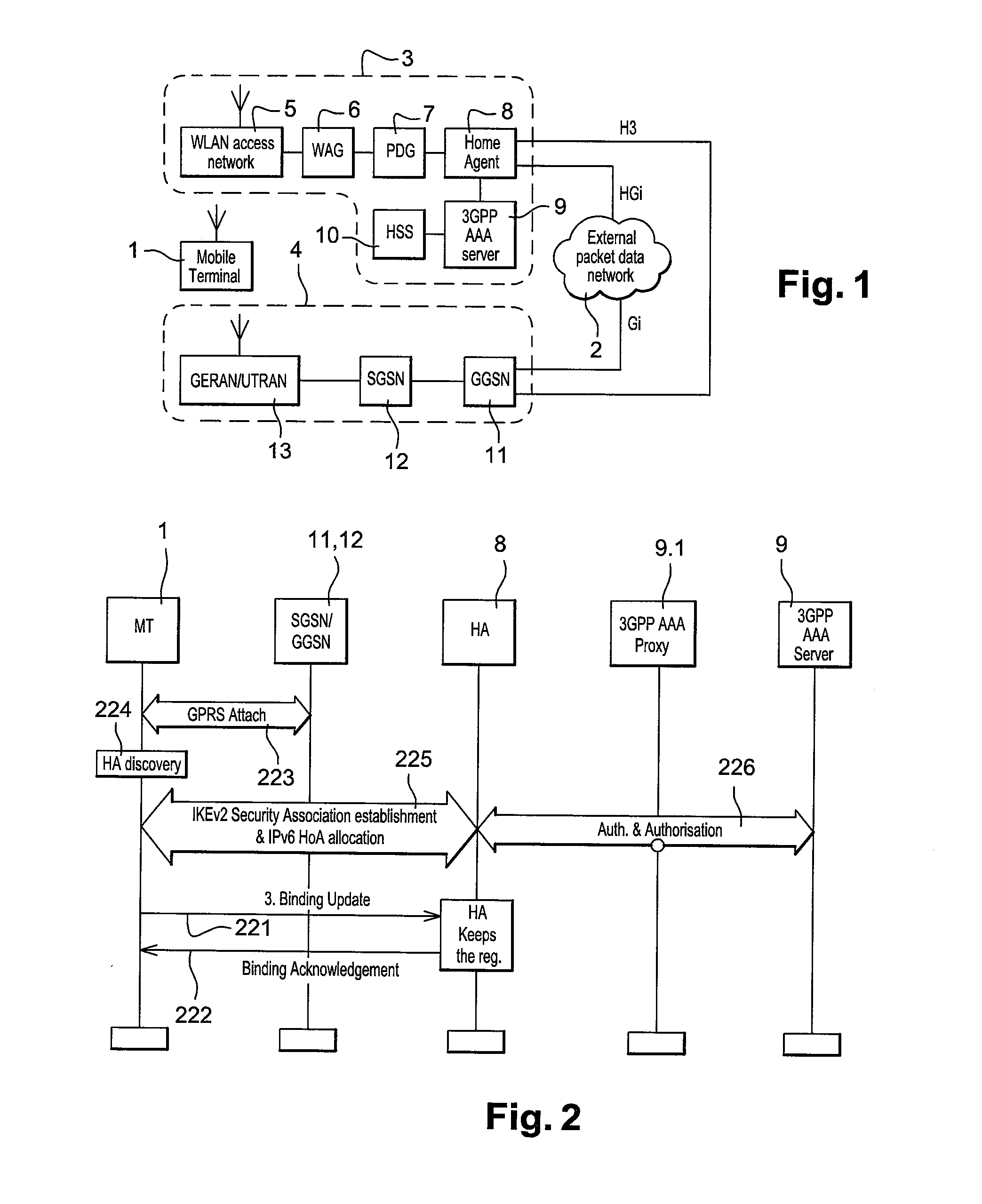
Telecommunications system and method
ActiveUS20110013614A1Good for forwardingReduce the possibilityConnection managementWireless network protocolsAccess networkRadio networks
A telecommunications system communicates data packets to and from a mobile terminal in accordance with a mobile internet protocol. The system comprises a packet radio network including a first radio access interface and a gateway support node. The packet radio network is operable to communicate data packets to and from the mobile terminal, through the gateway support node and via the first radio access interface. The gateway support node is operable to provide a home address via which a correspondent node may transmit data packets via the gateway support node to the mobile terminal when the mobile terminal is attached to the packet radio network. The system further comprises a wireless access network including a second radio access interface and a home agent, the wireless access network being operable to communicate data packets to and from the mobile terminal through the home agent via the second radio access interface, the wireless access network being operable to provide a care of address for the mobile terminal via which the correspondent node may transmit data packets via the home agent to the mobile terminal when the mobile terminal is attached to the wireless access network. The mobile terminal is arranged to connect to one of the packet radio network or the wireless access network and, when connected, to detect which of the packet radio network and the wireless access network the mobile terminal has connected. Upon detection that the mobile terminal is attached to the packet radio network, the mobile terminal and the home agent are arranged so that data packets are transmitted to and from the mobile terminal via the gateway support node in preference to the home agent.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
Packet radio network and method
ActiveUS8072923B2Improve efficiencyEffective resourcesConnection managementWireless network protocolsPacket communicationComputer network
A packet radio network comprising a gateway support node, a serving support node and a radio network controller provides a facility for communicating internet packets with mobile user equipment. The gateway support node provides a packet data protocol context for controlling communication of internet packets between the packet radio network and mobile user equipment via a packet communications bearer. The serving support node connected to the gateway support node controls communications between the gateway support node and mobile user equipment forming the packet communications bearer. The radio network part provides a radio access bearer for communicating internet packets via a radio access interface with mobile user equipment. In response to a request message, the serving support node with the gateway support node establishes a common packet data protocol context with a packet communications bearer to communicate packets. The common packet communications bearer is shared with another communications session and formed by gateway support node and serving support node using a common tunnelling protocol bearer.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
Power control of packet data transmission in cellular network
ActiveUS20060236190A1Reduce transmit powerAdequate system performancePower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio networksTransmitted power
A transmitter for a packet radio network, including means for transmitting a signal including data packets to a receiver, means for receiving acknowledgement messages from the receiver, each acknowledgement message indicating whether or not a data packet was received successfully, and means for adjusting transmit power of the signal in the transmitter on the basis of one or more acknowledgement messages.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Telecommunications System and Method
ActiveUS20100067449A1Easy to useReduce degradationConnection managementData switching by path configurationData connectionRadio networks
A telecommunications system is operable to provide a facility for mobile communications to a mobile node. The telecommunications system includes a packet radio network comprising a core network and a radio network. The core network and the radio network are arranged to communicate the internet packets in accordance with a current configuration of routing and communications resources of at least one of the core network and the radio network, established in accordance with the location of the mobile node. The mobile node is operable in accordance with a packet connection procedure for establishing a communications bearer for communicating the internet packets across the mobile radio network, to generate a packet data connection activation request. The packet data connection activation request is adapted to include a service level identifier representing a priority to be afforded to communicating internet packets to or from the mobile node with respect to the internet packets received from other mobile nodes, and to communicate the packet data connection request to the core network of the packet radio network. The core network is operable to establish a communications bearer to and from the mobile node via the core network and the radio network in accordance with the packet data connection request and to adapt the current configuration of routing and communications resources of at least one of the core network and the radio network following a change of location of the mobile node with a relative priority determined in accordance with the service level identifier. Through the inclusion of the service level identifier in the packet data connection request, the telecommunications system can give a relative priority to mobile nodes requiring a higher priority data transmission thereby reducing delays or interruptions in the transmission of data.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
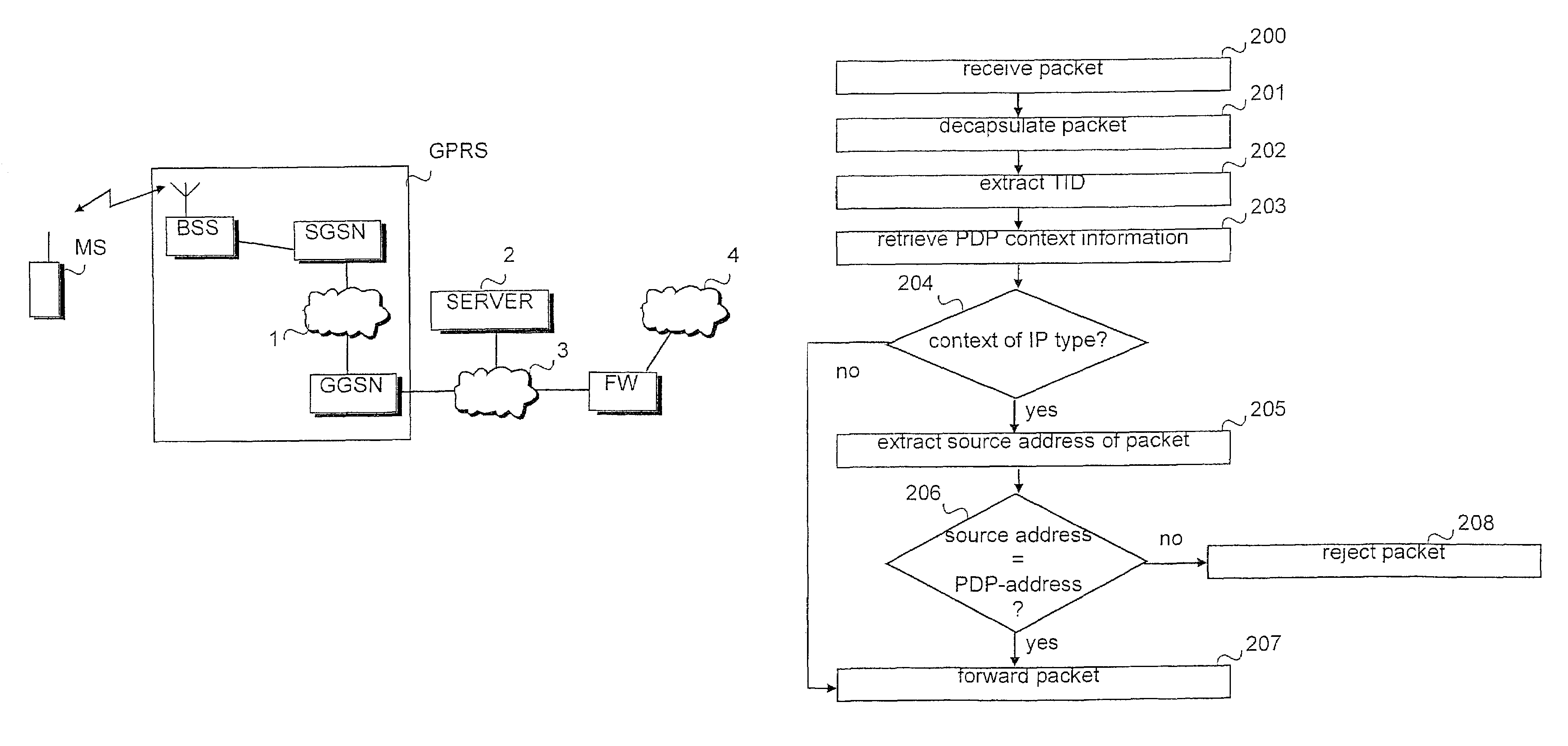
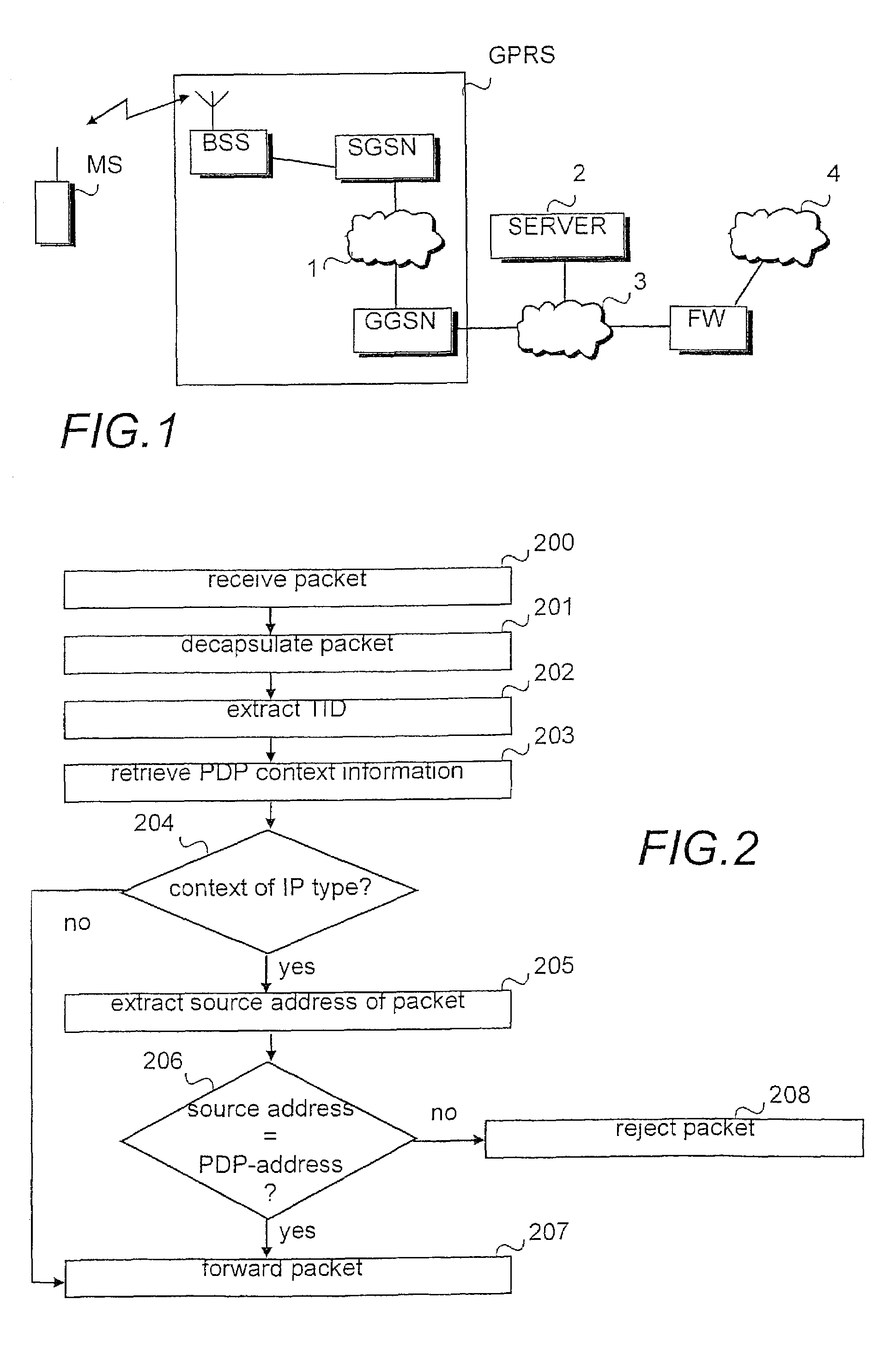
Prevention of spoofing in telecommunications systems
InactiveUS7342926B2Easy to implementDelay minimizationData switching by path configurationSecurity arrangementRadio networksEdge node
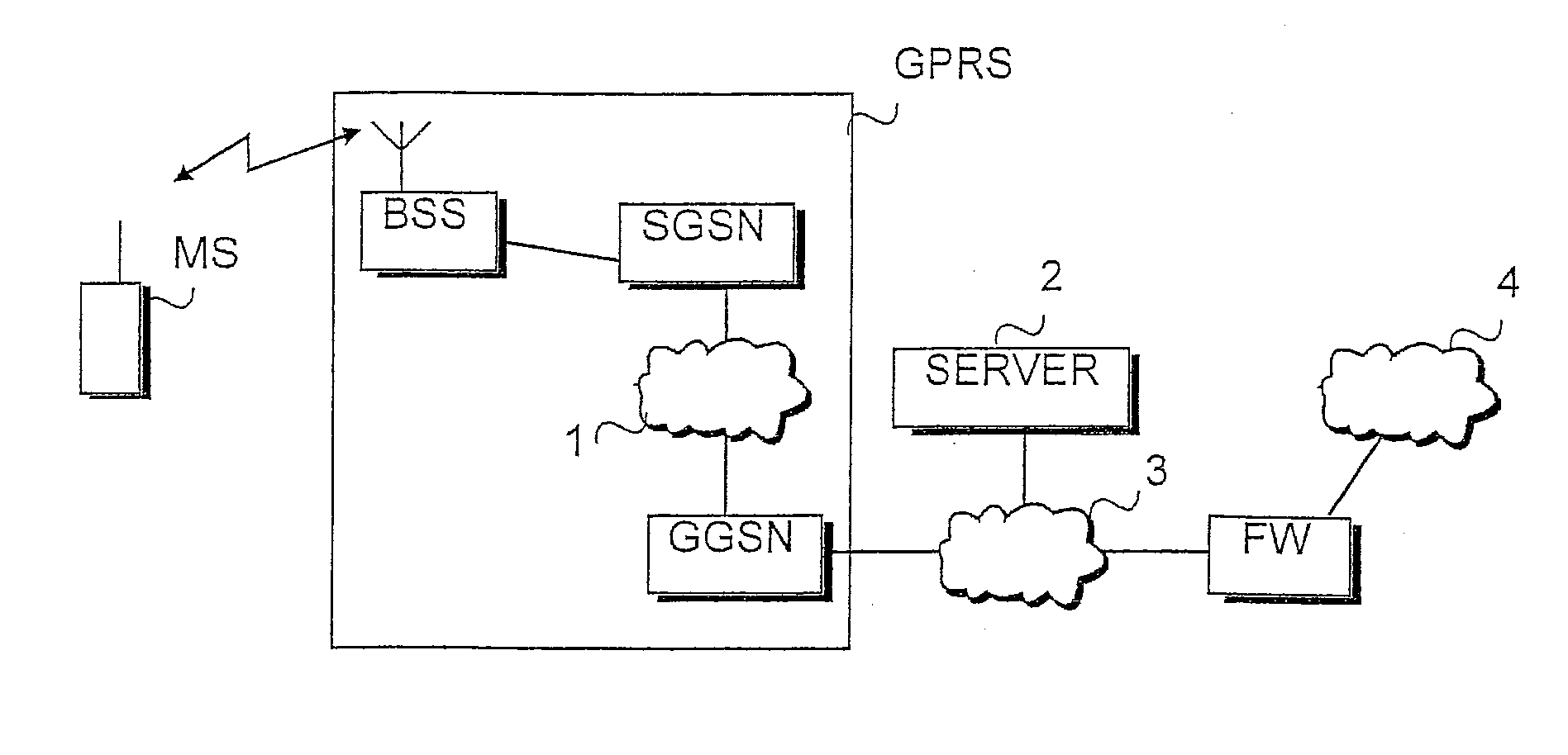
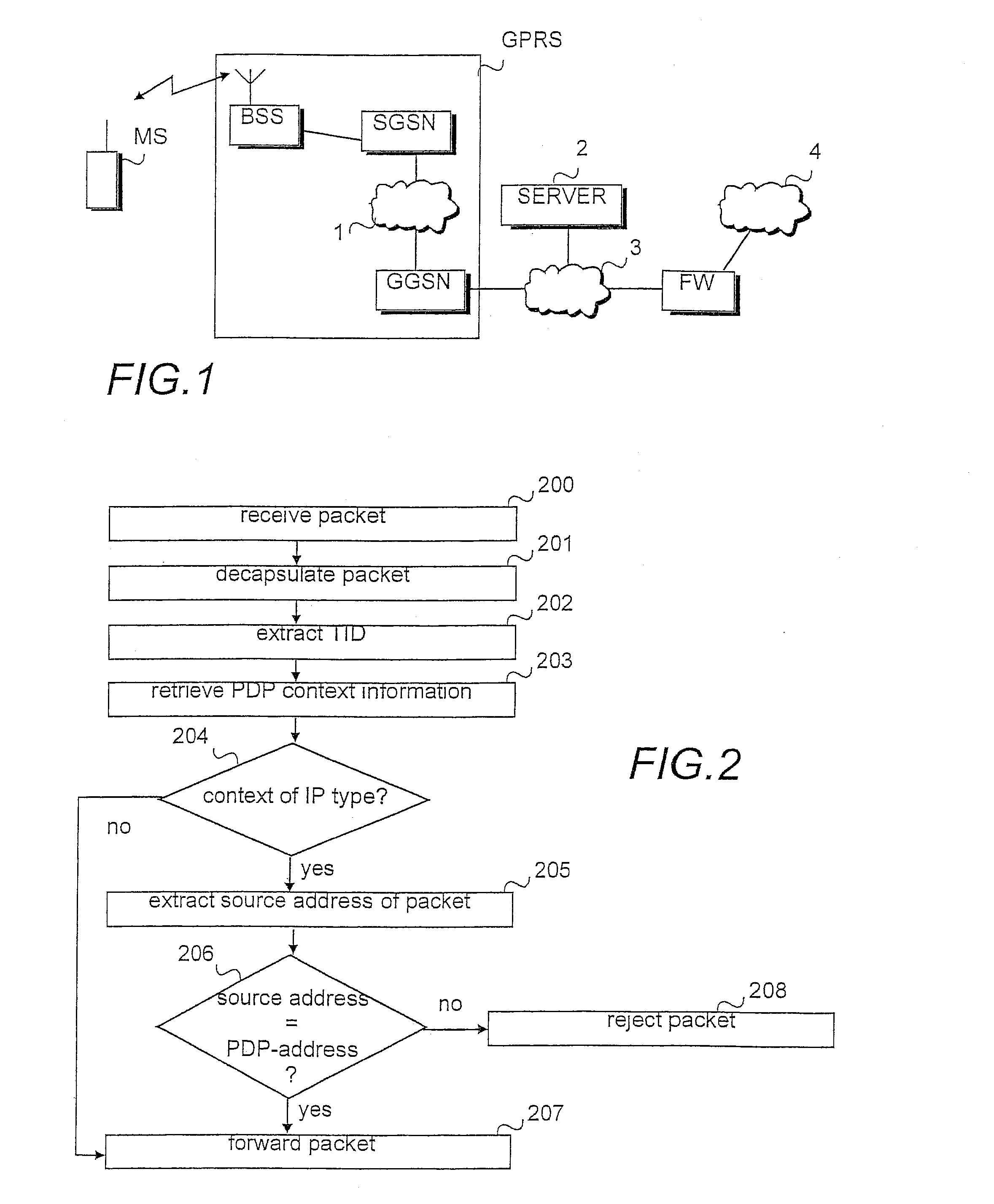
In a packet radio network a packet data address is activated for a terminal for transmitting data packets between the terminal and an external network. Information on the activated packet data address is stored at least in the edge nodes of the network. To prevent spoofing, i.e. misrepresentation of sender data, the method and network node of the invention comprise checking (206) in the node whether the source address of the packet transmitted from the terminal is the same as the packet data address used in the transmission of the packet or does the source address belong to a set of allowed packet data addresses. The packet is transmitted (207) from the node towards the destination address only if the addresses are identical or the source address belongs to the set of allowed packet data addresses.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Telecommunications system and method
ActiveUS8184646B2Easy to useReduce degradationConnection managementData switching by path configurationData connectionRadio networks
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
Prevention of spoofing in telecommunications system
InactiveUS20070297413A1Easy to implementDelay minimizationTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationRadio networksEdge node
In a packet radio network a packet data address is activated for a terminal for transmitting data packets between the terminal and an external network. Information on the activated packet data address is stored at least in the edge nodes of the network. To prevent spoofing, i.e., misrepresentation of sender data, the method and network node of the invention comprise checking in the node whether the source address of the packet transmitted from the terminal is the same as the packet data address used in the transmission of the packet or does the source address belong to a set of allowed packet data addresses. The packet is transmitted from the node towards the destination address only if the addresses are identical or the source address belongs to the set of allowed packet data addresses.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
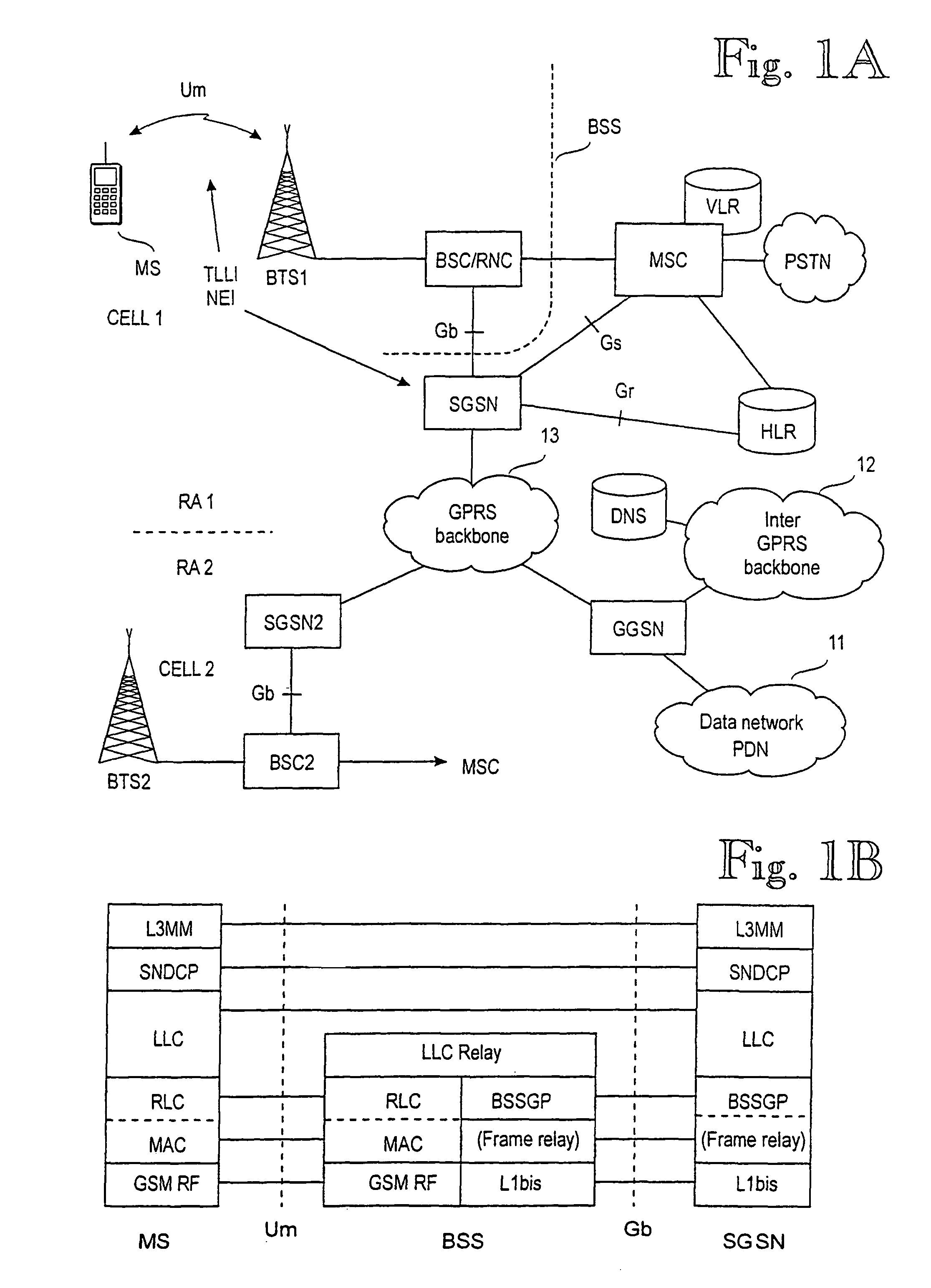
Identifying a mobile station in a packet radio network
InactiveUS7957736B1The process is simple and effectiveMinimise disadvantageTelephonic communicationWireless commuication servicesRadio networksUser identifier
In conventional cellular systems, the identifier of network elements (SGSN) allocating a temporary identity (TLLI) to a mobile station (MS) can be derived from the identities of the cells they serve. In the future, this assumption may no longer be valid. One paging area could be handled by several network elements, such as SGSN nodes, or one network element could serve many paging areas. When the mobile station changes its paging area, the new supporting network element may have trouble in determining the old supporting network element on the basis of the paging area identifier. It is also possible for two supporting network elements to allocate the same TLLI to two different mobile stations. Therefore the network element (SGSN, BSC, RNC) allocating a temporary identity (TLLI) to a mobile station (MS) should incorporate at least part of its own identifier (NEI) into the temporary identity (TLLI).
Owner:SISVEL INT
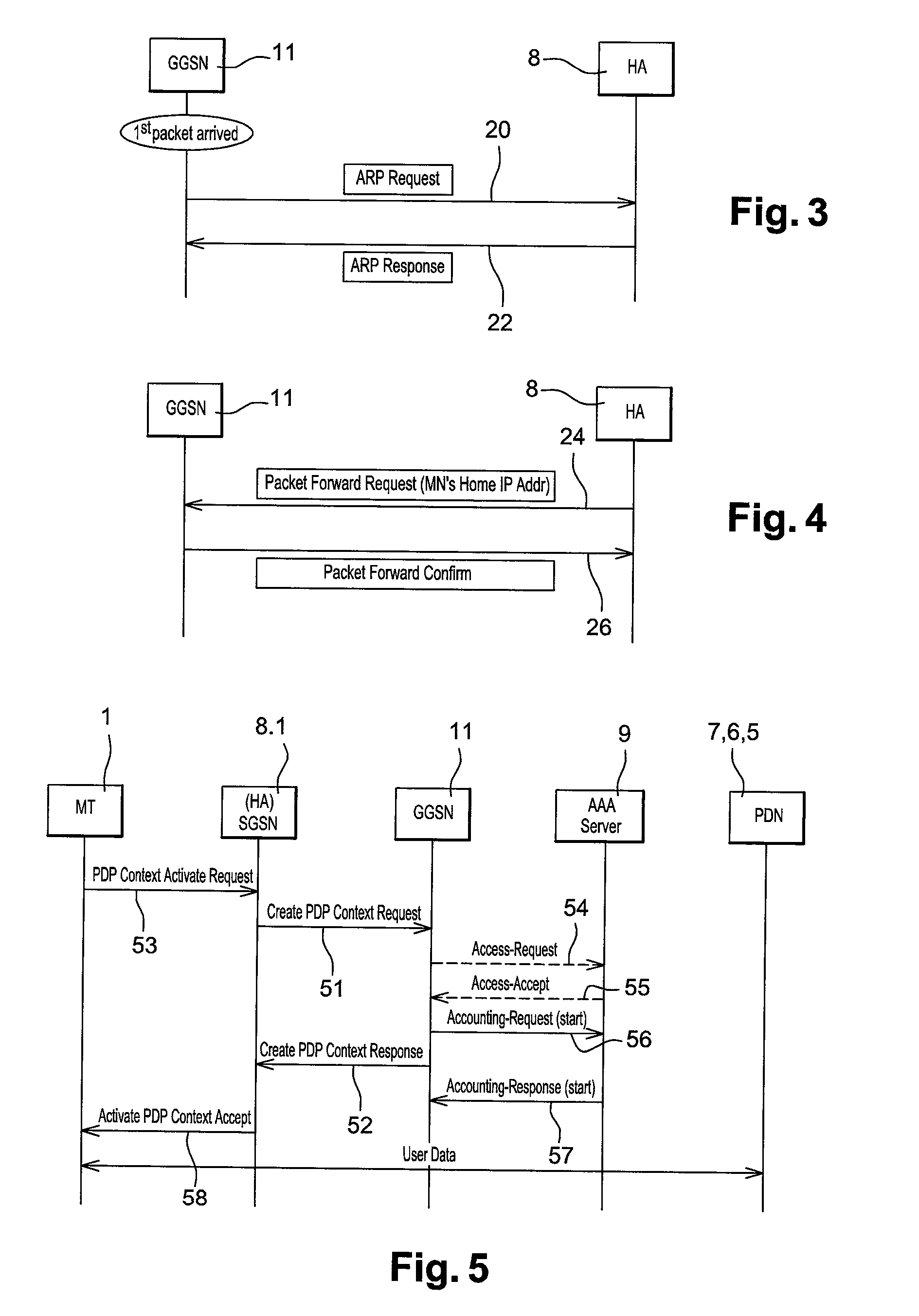
Transmitting messages in telecommunications system comprising a packet radio network
ActiveUS20090135813A1Easy to useAutomatic transmissionMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsNetwork connectionsRadio networksMobile station
A method of transmitting messages in a telecommunication system includes a first network offering circuit-switched services, a second network offering packet-switched services, and at least one mobile station supporting the first and the second network. When the need arises to transmit at least one message, a check is made to see if the mobile station is attached to the second network. The message is transmitted to the second network if the mobile station is attached to the second network. The message is transmitted to the first network in case of a failure to transmit the message via the second network.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Telecommunications system and method for communicating internet packets between an external packet data communications network and a packet radio network
ActiveUS7860037B2Reduce the possibilityFrequency-division multiplex detailsData switching by path configurationTTEthernetComputer network
A telecommunications system for communicating internet packets between a correspondent node and a mobile node. The system comprises a packet radio network providing packet data bearers for communicating internet packets with nodes. Each of the bearers is defined with respect to a source address of the internet packets, the packet radio network including a gateway support node (GGSN) to provide an interface between the external network and the packet radio network. The GGSN detects whether an internet packet is for providing a binding update to the correspondent node of a first source address of the mobile node to a care-of-address of the mobile node. If the internet packet is a binding update, the GGSN allows egress of internet packets sent from the correspondent node. By allowing egress of packets from the correspondent node having this care-of-address as the destination address, a measure of security is provided.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
Location services in a packet radio network
InactiveUS20060258373A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesConnection typeCommunications system
A method for providing location service information related to a mobile station in a mobile communications system supporting connections of a first type, for example circuit-switched, and a second type, for example packet-switched. The method comprises receiving a request from a requesting entity; retrieving the location service information related to the mobile station; and providing a response to the request. The method further comprises determining a preferred type of connection for the retrieving based on a first set of predetermined criteria; and performing, in the retrieving, at least a first attempt via a preferred type of connection.
Owner:CELLULAR COMM EQUIP LLC
Scheduling method for quality of service differentiation for non-real time services in packet radio networks
ActiveUS7502352B2Differentiated qualityTotal revenue maximizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceNon real time
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Method and apparatus for controlling a packet terminating call in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7561513B2Reduce loadImprove efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunicationsRadio networks
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Packet delivery method for packet radio networks
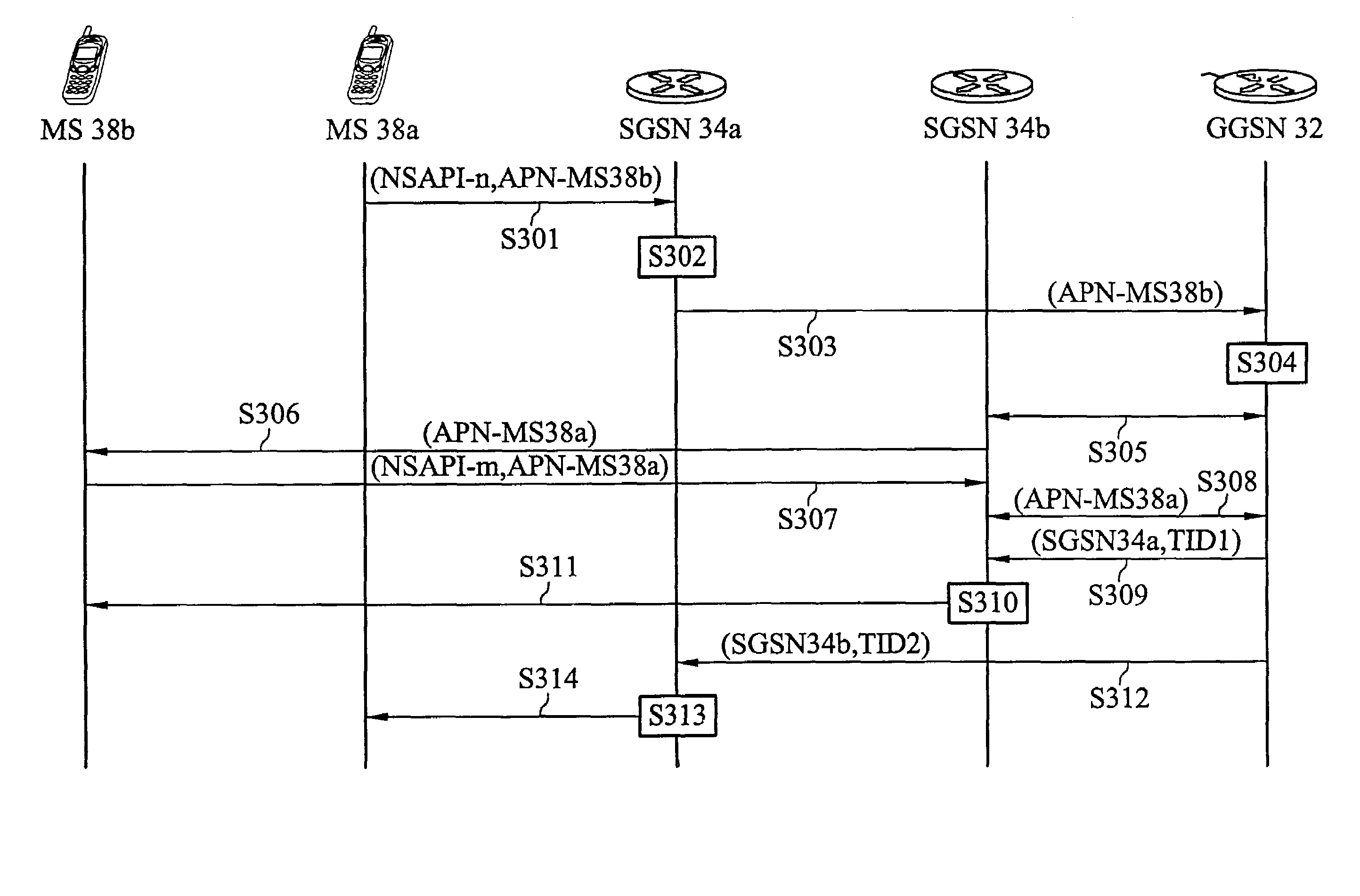
InactiveUS7342933B2Improve performanceLower end-to-end latencyTime-division multiplexConnection managementRadio networksMobile station
A packet delivery method for packet radio networks. The method used to deliver packets between a first mobile station and a second mobile station in a packet radio network is characterized by, when the first mobile station has a plurality of data packets to the second mobile station, establishing a delivery path from the first mobile station (MS) to the second mobile station (MS) through a first base station system (BSS), a first Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN), a second Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) and a second base station system (BSS); and when the second mobile station has a plurality of data packets to the first mobile station, the delivery path is established from the second mobile station (MS) to the first mobile station (MS) through the second base station system (BSS), the second Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN), the first Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) and the first base station system (BSS).
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
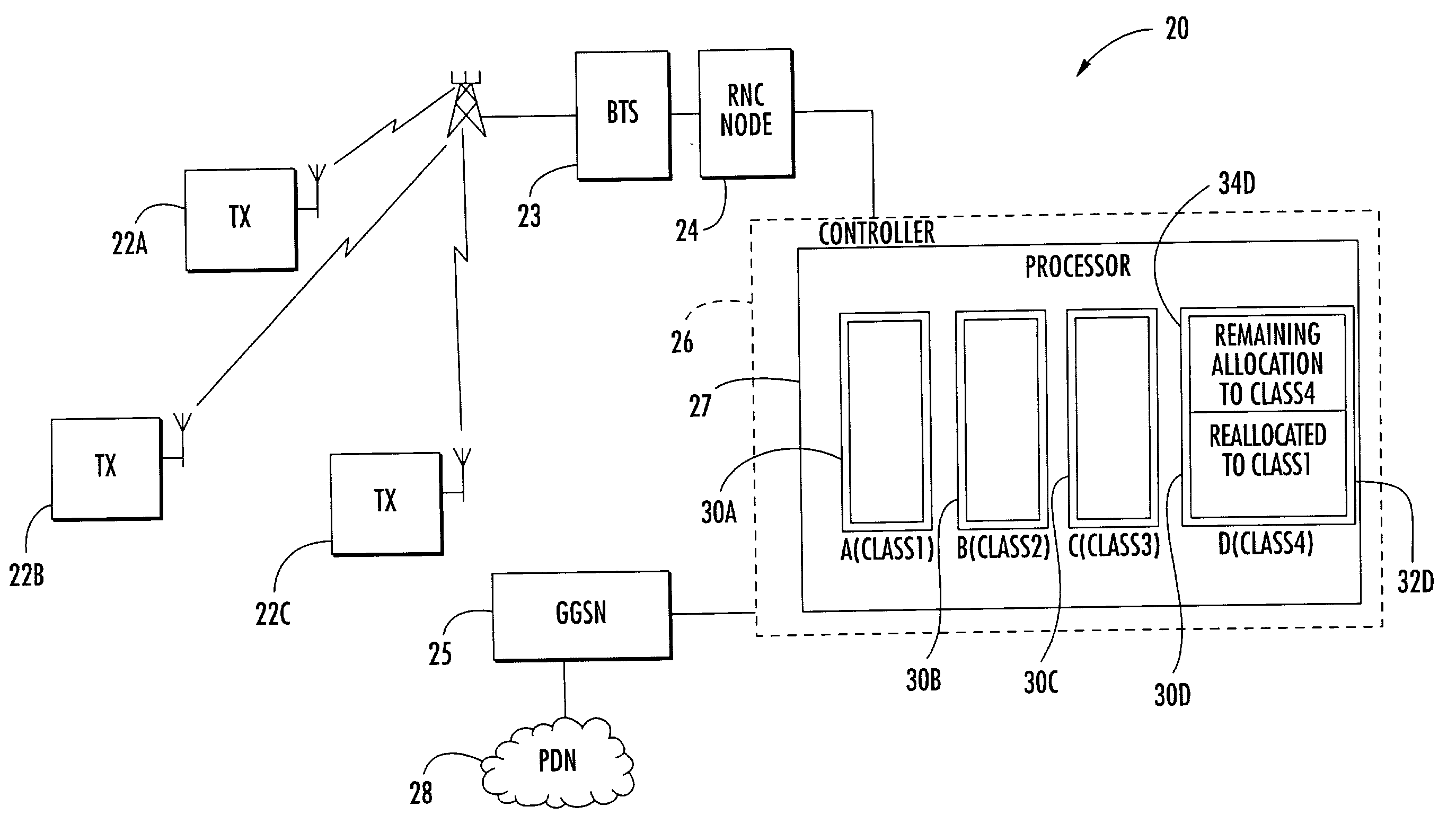
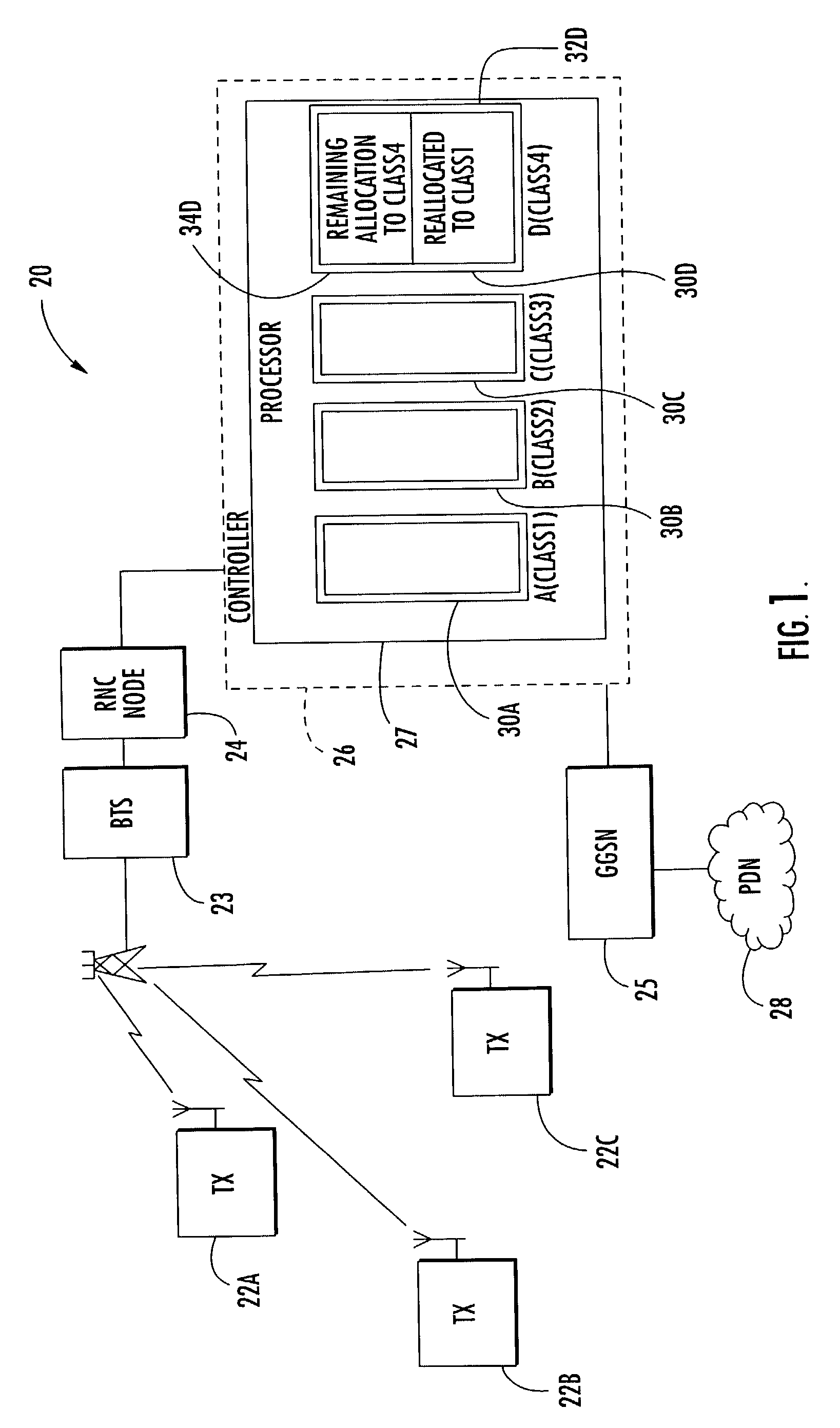
Controller for allocation of processor resources and related methods
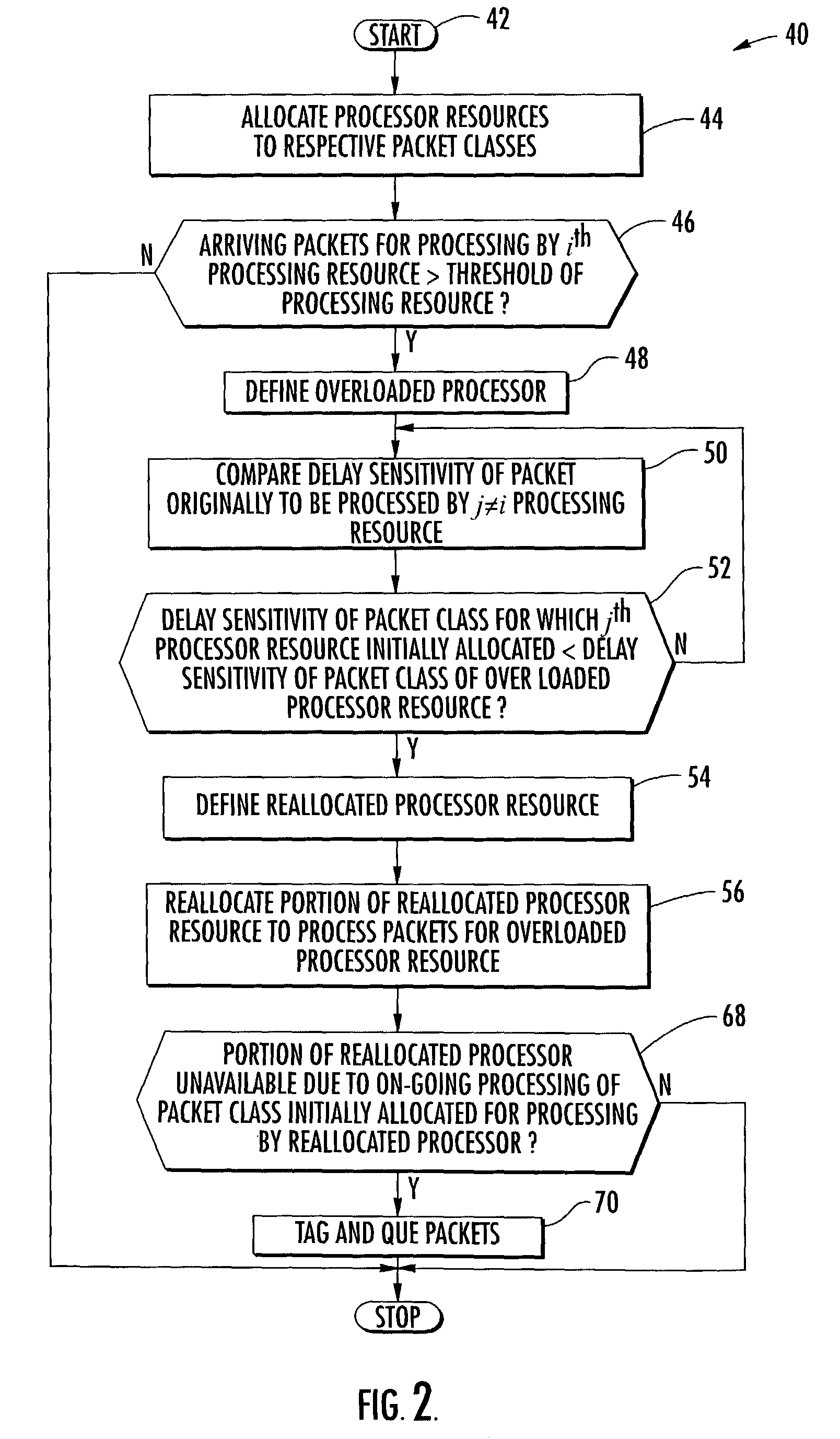
InactiveUS7221682B2Efficient processingDelay sensitivityNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexComputer sciencePacket radio networks
A controller 26 for a packet radio network 20 includes a processor 27 that, in turn, includes a plurality of processor resources 30A–30D for processing a plurality of packet classes. Each packet class has a different delay sensitivity associated therewith. The processor 27 allocates to each packet class at least a portion of at least one processor resource 30A–30D, the allocation being based on the delay sensitivities associated with each packet class. Each processor resource 30A–30D may have a processing threshold, and the processor 27 may determine, based upon arriving packets, whether at least one processor resource will exceed its processing threshold, thus defining at least one overloaded processor resource 30A. The processor 27 may reallocate at least a portion of at least one processor resource to process packets for the at least one overloaded processor resource 30A thereby defining at least one reallocated processor resource 30D.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Routing area update in packet radio network
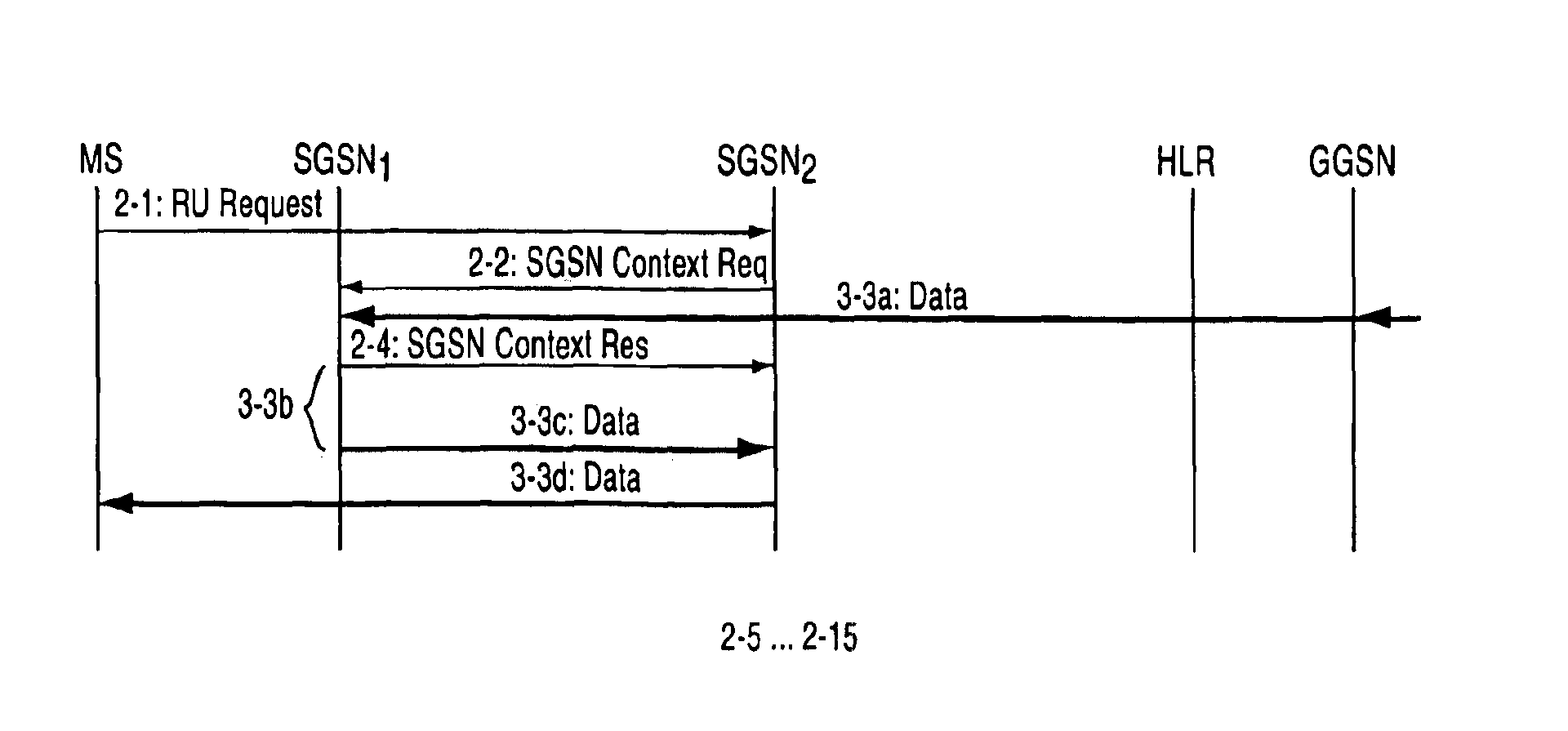
InactiveCN101052008AError prevention/detection by using return channelConnection managementQuality of serviceContext data
A method of transmitting data in a packet radio network to a mobile station (MS) performing a routing area update. The packet radio network transmits data (2-1, 2-3) to the mobile station (MS) via a first support node (SGSN1). The mobile station (MS) sends a routing area update message (2-1) to a second support node (SGSN2), which sends to the first support node (SGSN1) a request (2-3) for context data (2-5) of the mobile station from the first support node. The first support node (SGSN1) sends (2-3c, 3-3c) from its memory, data addressed to the mobile station to the second support node. It then waits for a predetermined period of time (3-3b) before sending the data to the second support node (SGSN2). The predetermined time (3-3b) may be fixed, depending preferably on the quality of service of the connection used by the mobile station. Alternatively the predetermined period of time expires when the second support note (SGSN2) sends to the first support node (SGSN1) a separate acknowledgement message indicating that the second support node has received the context data of the mobile station.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com