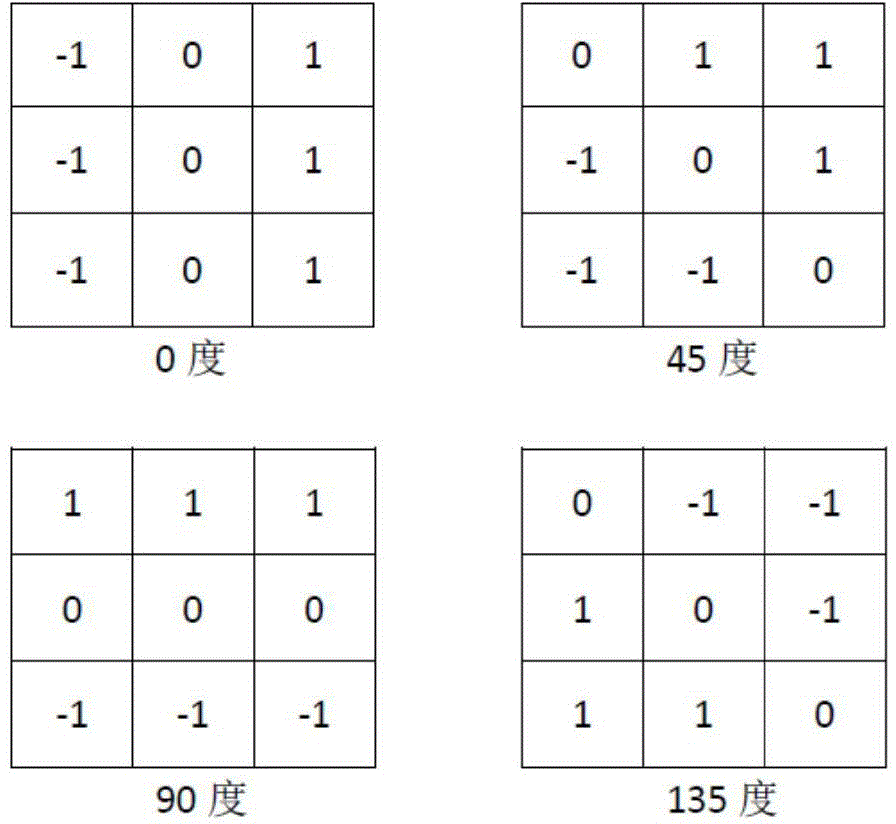
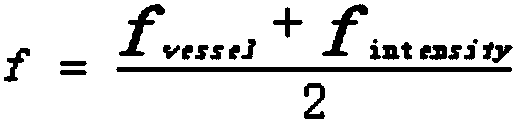Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
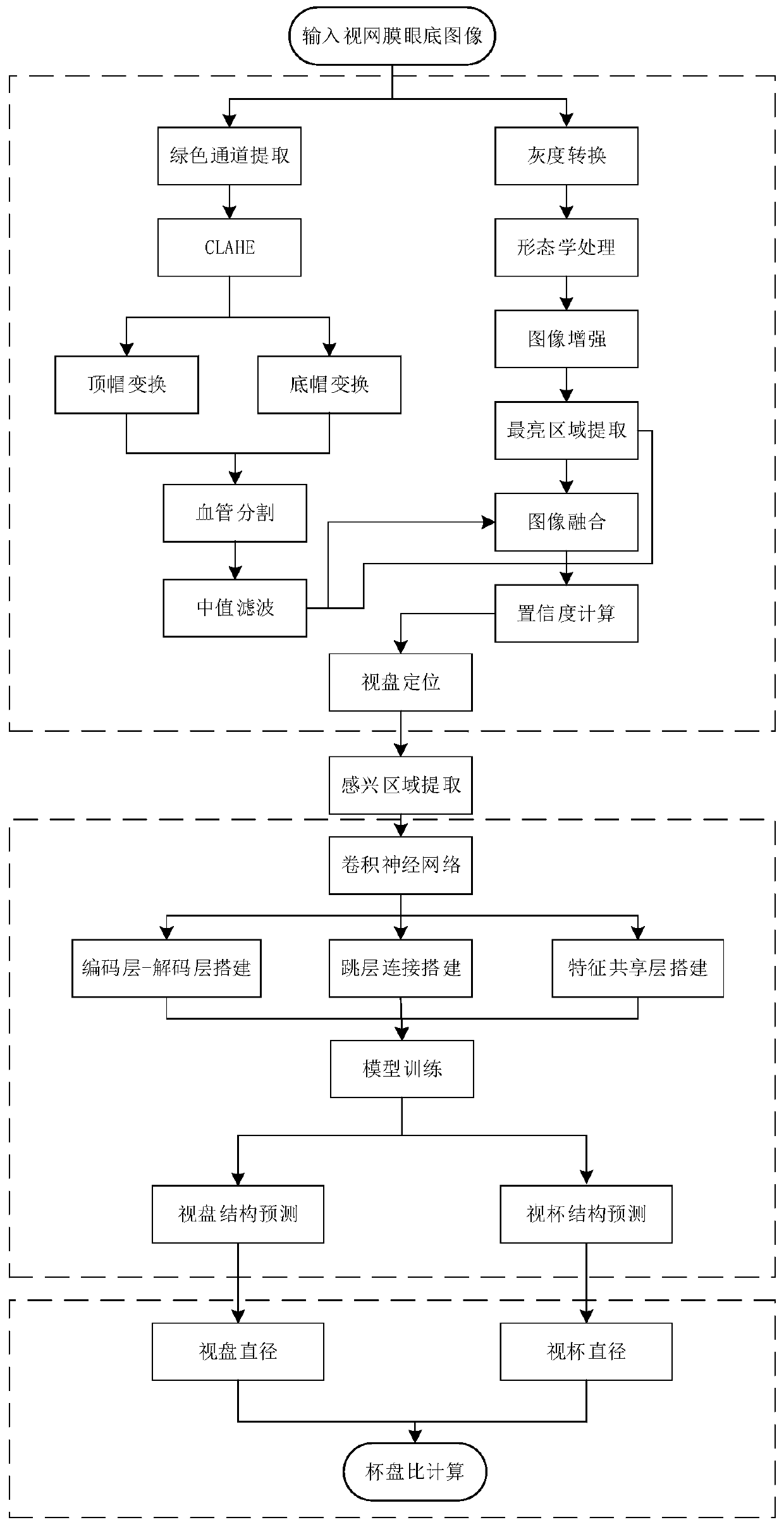
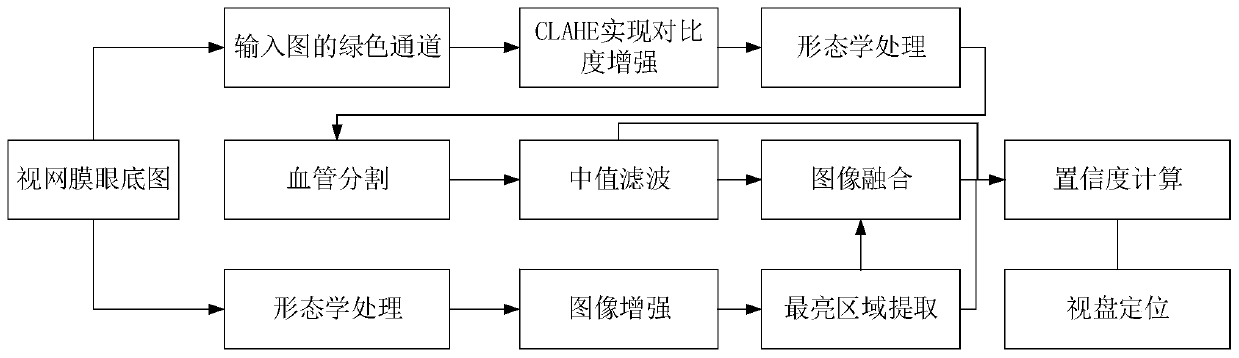
241 results about "Optic disc size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
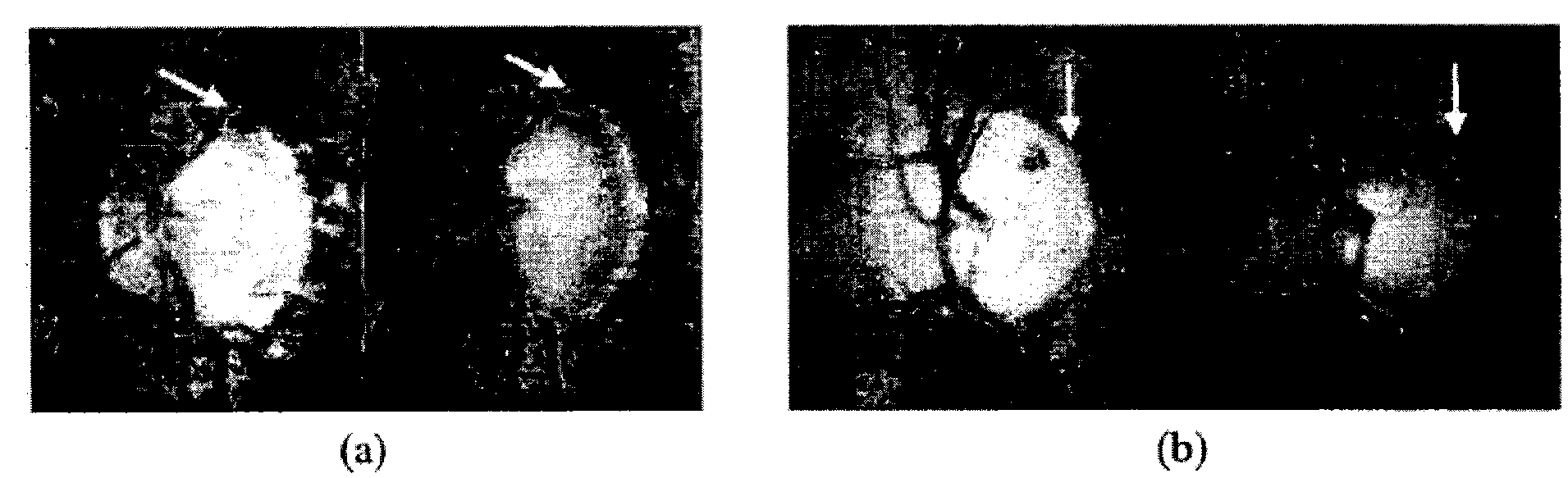
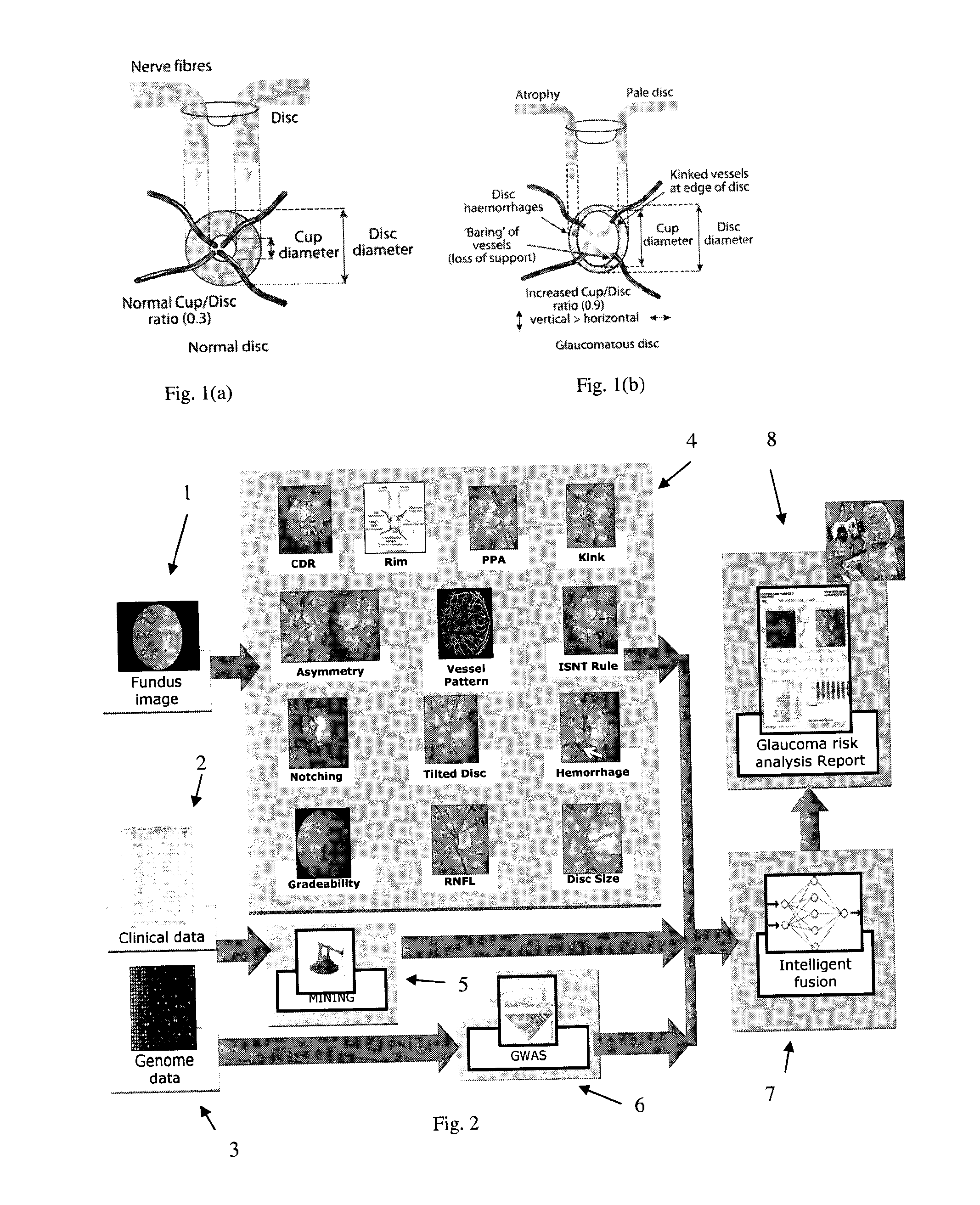
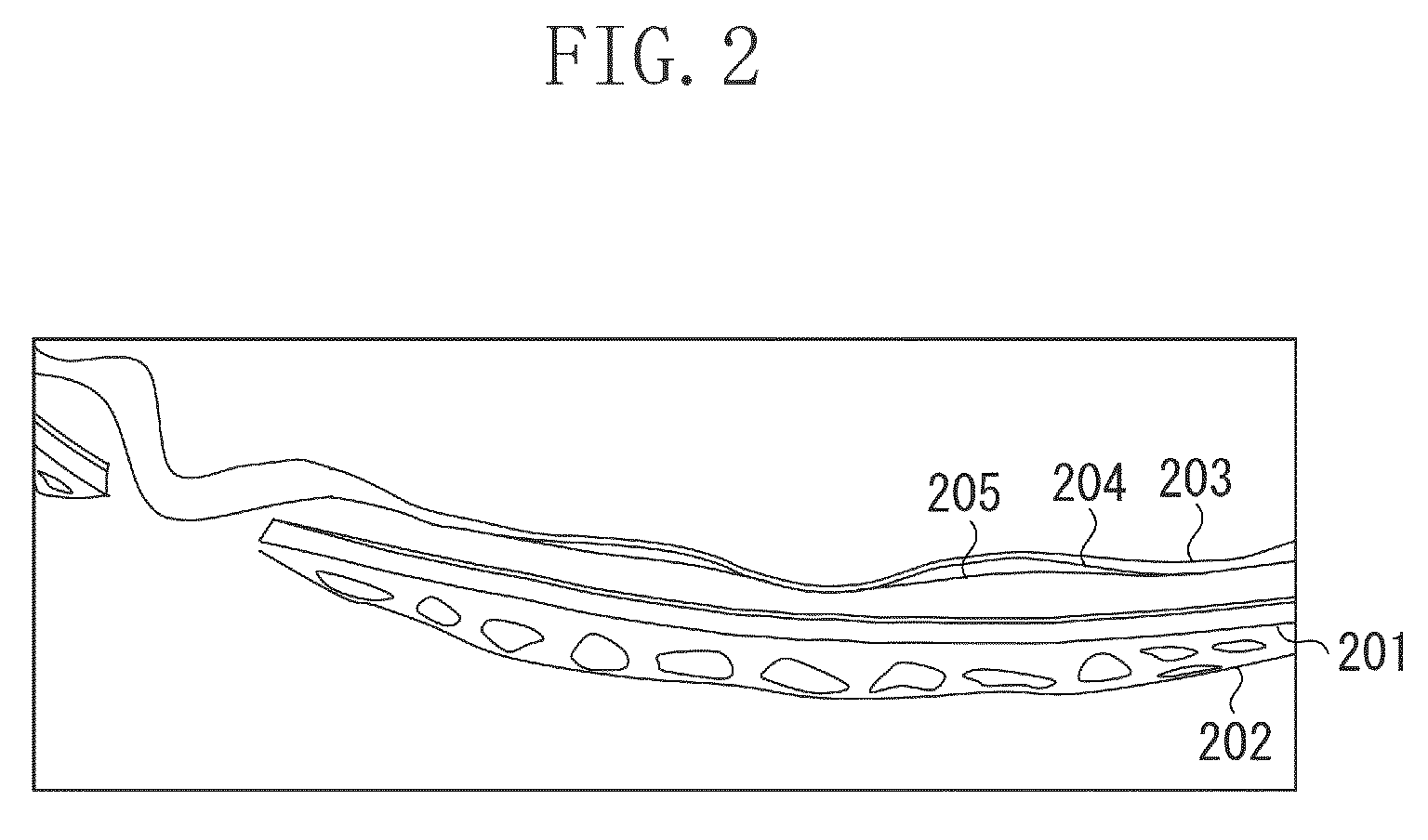
The optic disc is placed 3 to 4 mm to the nasal side of the fovea. It is a vertical oval, with average dimensions of 1.76mm horizontally by 1.92mm vertically. There is a central depression, of variable size, called the optic cup.
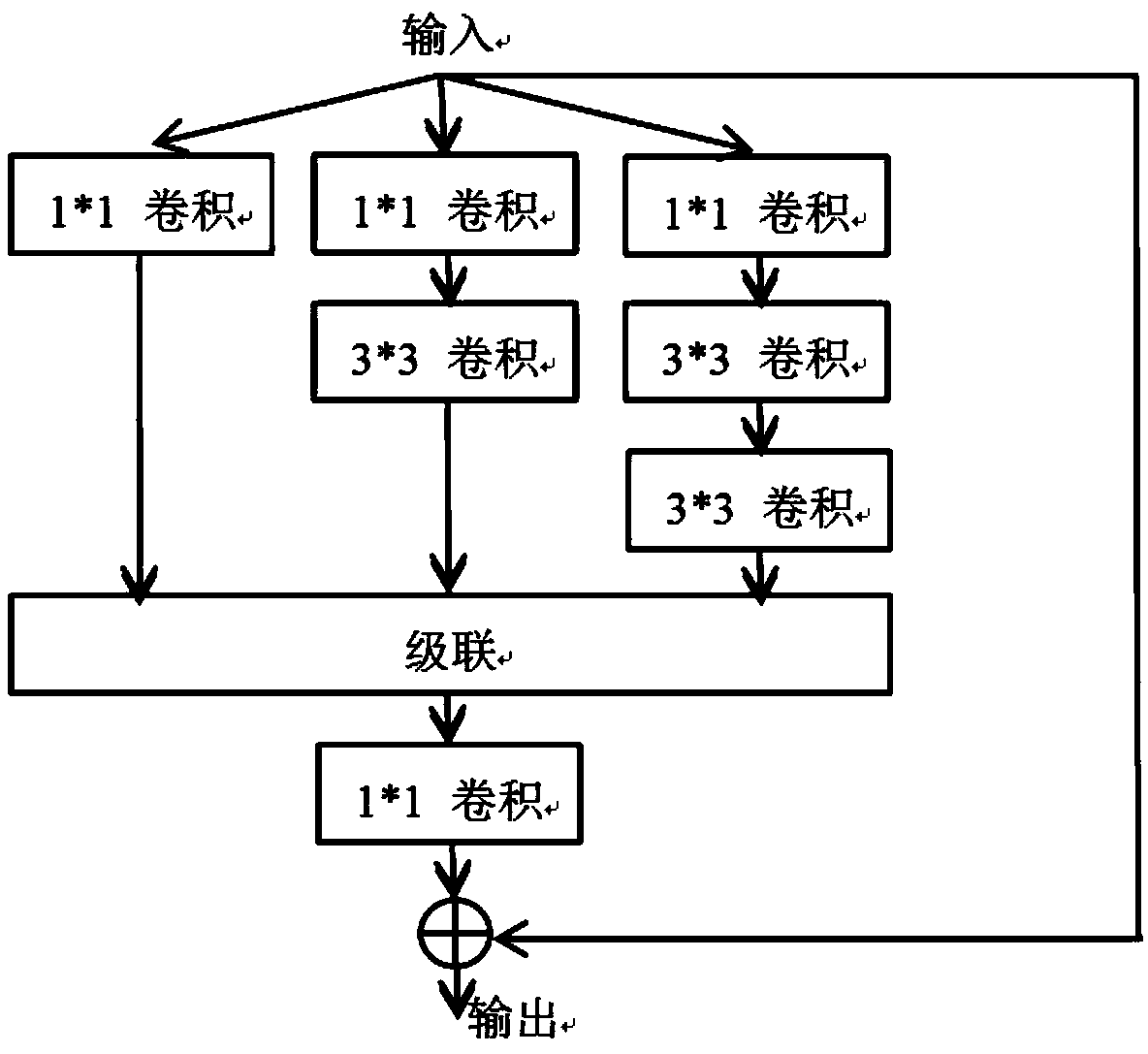
An attention mechanism U-shaped densely connected retinal blood vessel segmentation method
ActiveCN109448006AImprove performanceExtract accurate and moreImage enhancementImage analysisData setNetwork model
The invention relates to an attention mechanism U-shaped densely connected retinal (a novel retinal blood vessel segmentation method fusing DenseNet and Attention U-net network) blood vessel segmentation method, comprising the steps of retinal blood vessel image preprocessing and constructing a retinal blood vessel segmentation model. The method of the invention can effectively solve the problemsthat adjacent blood vessels are easy to connect, the micro blood vessels are too wide, the small blood vessels are easy to break, the blood vessel intersection is insufficient in segmentation, the image noise is too sensitive, the gray value of the object and the background is crossed, the optic disc and the lesion focus are missegmented, and the like. The method of the invention integrates a plurality of network models under the condition of low complexity, the excellent segmentation results are obtained on DRIVE dataset, the accuracy and sensitivity are 96.95% and 85.94%, respectively, whichare about 0.59% and 7.92% higher than those published in the latest literature.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optic disc projection location method synthesizing vascular distribution with video disc appearance characteristics
InactiveCN102842136AImprove accuracySuppress non-vascular pixelsImage enhancementImage analysisVertical projectionHysteresis
The invention discloses an optic disc projection location method synthesizing vascular distribution with video disc appearance characteristics, which comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting an interest retina fundus image region by use of a mask operation; (2) carrying out normalization enhancement on a fundus image based on an image observation model; (3) achieving extraction and segmentation of the fundus image by using a non-vascular structure inhibition operator and combining with a hysteresis multi-threshold processing technology; (4) setting a vertical window of double main blood vessel width to slide on a blood vessel segmentation image along the horizontal direction and calculating a vascular distribution degree D(x) at each horizontal position x to obtain a distribution degree curve of a horizontal projection, wherein the minimum value point of the curve is determined to be optic disc horizontal coordinate xod; (5) setting a rectangular window side length of which is equal to the optic disc diameter to slide up and down at the horizontal coordinate xod, estimating local region brightness IN(xod, y) and edge gradient information gN(xod, y) respectively, drawing a vertical projection curve reflecting a change of a characteristic value f(y)=IN(xod, y)*gN(xod, y), wherein a maximum value point of the curve is optic disc vertical coordinate yod. The method has a simple algorithm, a high success rate and excellent robustness.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Intraocular lens assembly and method
An intraocular lens assembly and method. The assembly comprises an optic disc and an annulus surrounding the optic disc. Hinges connect the optic disc to the annulus to permit anterior and posterior movement of the optic disc relative to the annulus in response to contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscle so that the eye accommodates to focus on a near object. The method comprises the steps of placing in the posterior chamber an optic disc and an annulus. The annulus surrounds the optic disc and is connected to it by hinges that permit anterior and posterior movement of the optic disc relative to annulus in response to contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscle whereby said eye accommodates to focus on a near object.
Owner:KAMERLING WILLIAM +1
Feature Detection And Measurement In Retinal Images
The invention is directed to methods of detecting and / or measuring a feature in a retinal mage. The feature detected and / or measured may be one or more of the optic disc, optic disc centre, optic disc radius, vessel edge, vessel calibre / width and vessel central reflex. One method for detecting the optic disc includes analyzing an image histogram to determine intensity levels; analyzing the intensity levels to determine a threshold intensity for potential optic disc regions; determining the number of pixels for each potential optic disc region; and calculating the centre of each potential optic disc region from the number of pixels in each potential optic disc region to thereby detect the optic disc.
Owner:CENT FOR EYE RES AUSTRALIA
A retinal fundus image cup/disc ratio automatic evaluation method
InactiveCN109829877AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisNerve networkOptic disc segmentation
The invention discloses a retinal fundus image cup / disc ratio automatic evaluation method. The method comprises the following steps: A, extracting an optic disk area image from a retinal fundus image;B, establishing and training a optic disc optic cup segmentation network based on the deep convolutional neural network; C, acquiring a to-be-detected optic disc area image from the to-be-detected retina fundus image according to the step A, and inputting the to-be-detected optic disc area image into an optic disc optic cup segmentation network to output a to-be-detected optic disc segmentation mask image and a to-be-detected optic cup segmentation mask image; And step D, calculating the cup-disc ratio of the retinal fundus image according to the to-be-detected optic disc segmentation mask image and the to-be-detected optic cup segmentation mask image. The method is high in operation speed, good in effect, free of manual participation, low in cost and high in universality, and can be widely applied to auxiliary screening of glaucoma.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
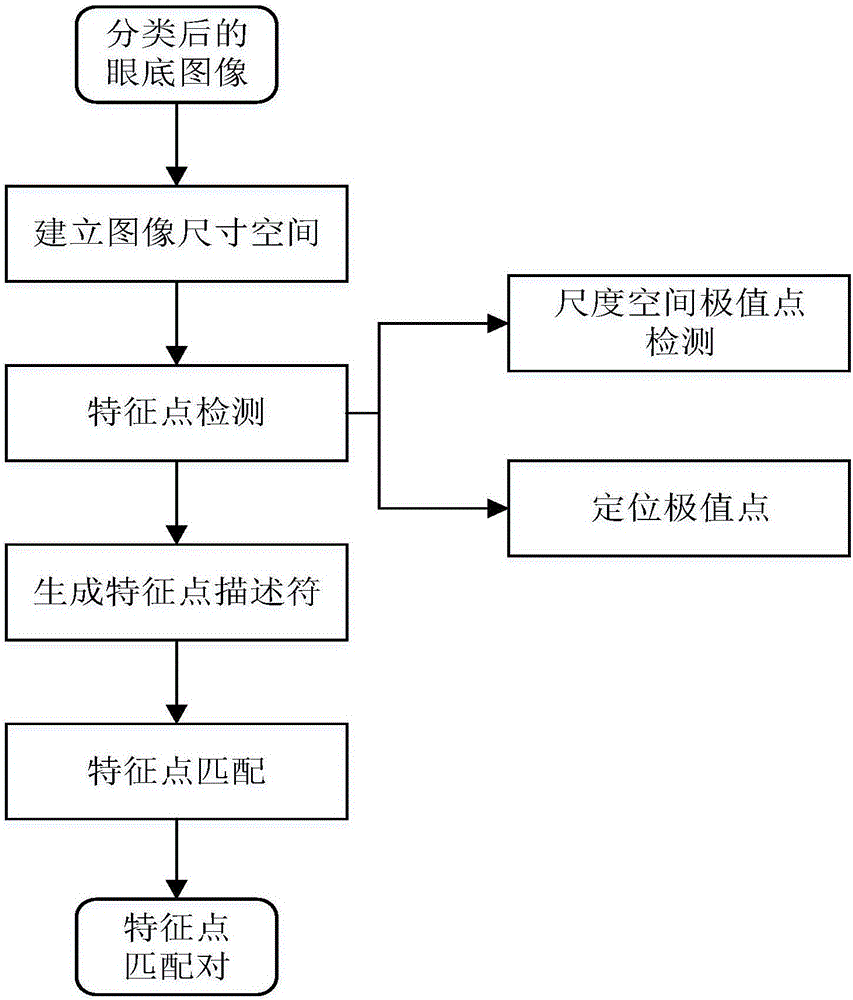
Fundus image registering method based on SIFT characteristics
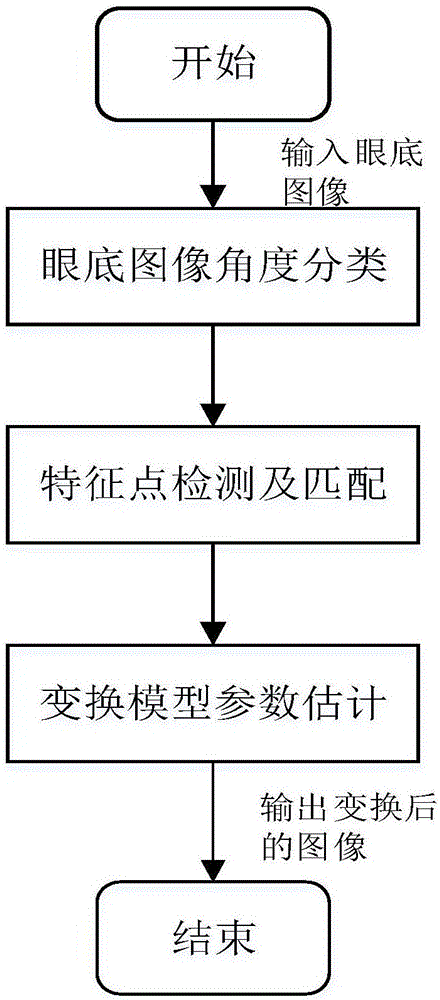
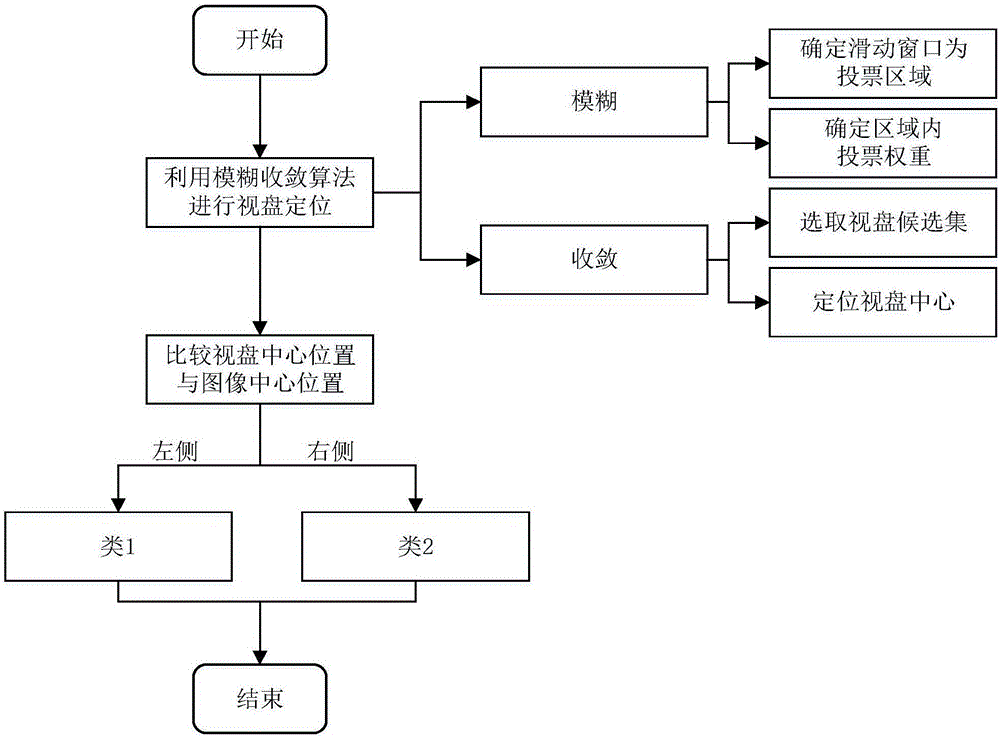
ActiveCN106651827AImprove robustnessEliminate errorsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionFuzzy convergence
The invention discloses a fundus image registering method based on SIFT characteristics. The method comprises: conducting angle classification to a batch of inputted fundus images; calculating the transformative relationship among the images; converting the images onto the same background; and through the rapid switching of the images, finding out which parts of the fundus change. The invention mainly uses a fuzzy convergence optic disc positioning algorithm and conducts angle classification to the batch of inputted fundus images according to the position of the optic disc wherein the angle classification is referred as two types: the left side and the right side; and then in each image classification, a selected and uploaded first image is used as a reference for other images to register with; the SIFT characteristic points of all the images are extracted and the matching relation between every two points is calculated. Finally, the RANSAC algorithm is used to calculate the transformation model parameters between every two images. The images are converted onto the same background according to the transformation model; and an image switching interval is configured so that through the switching of the images, it is possible to find out the change among the images rapidly and accurately.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
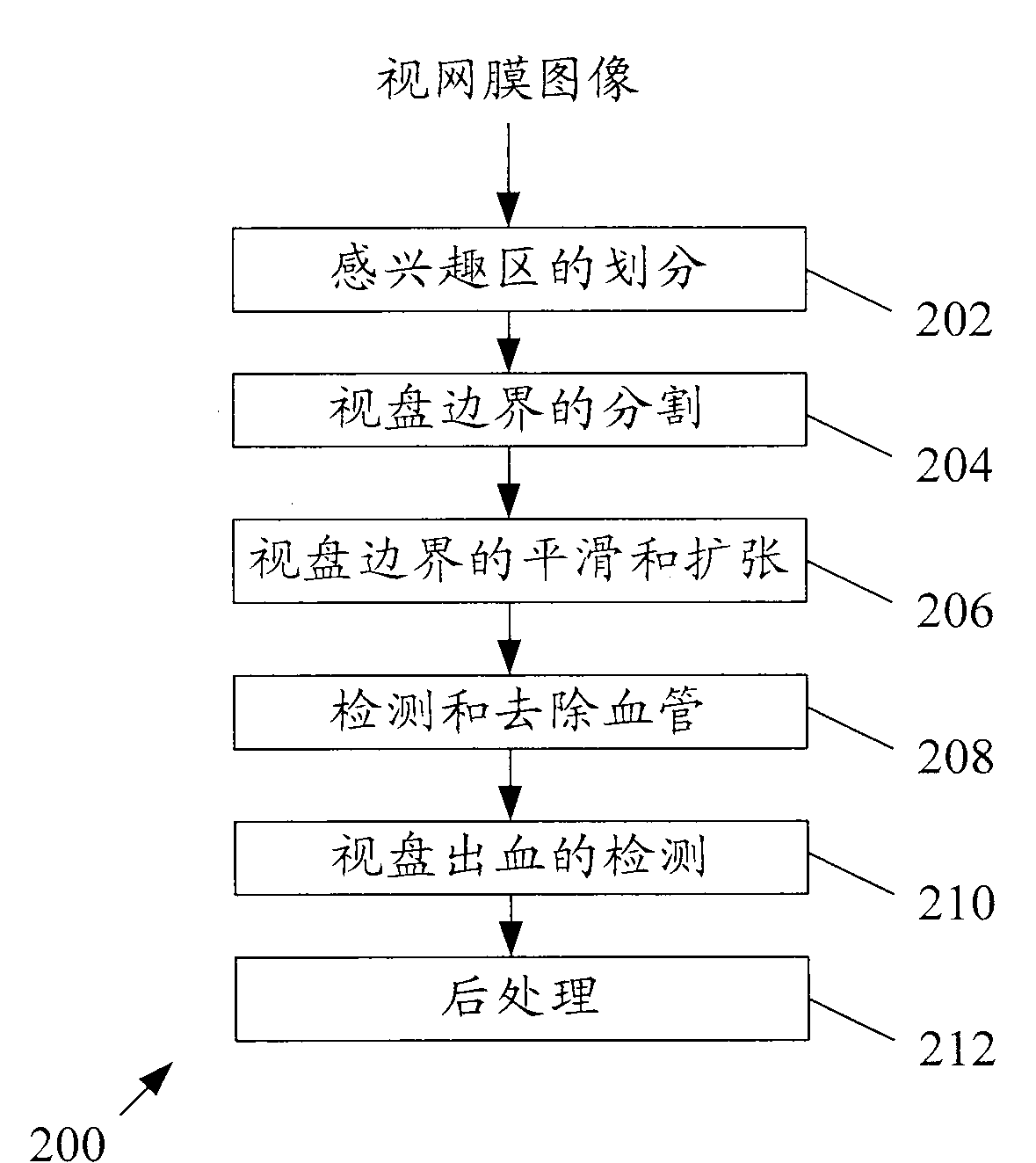
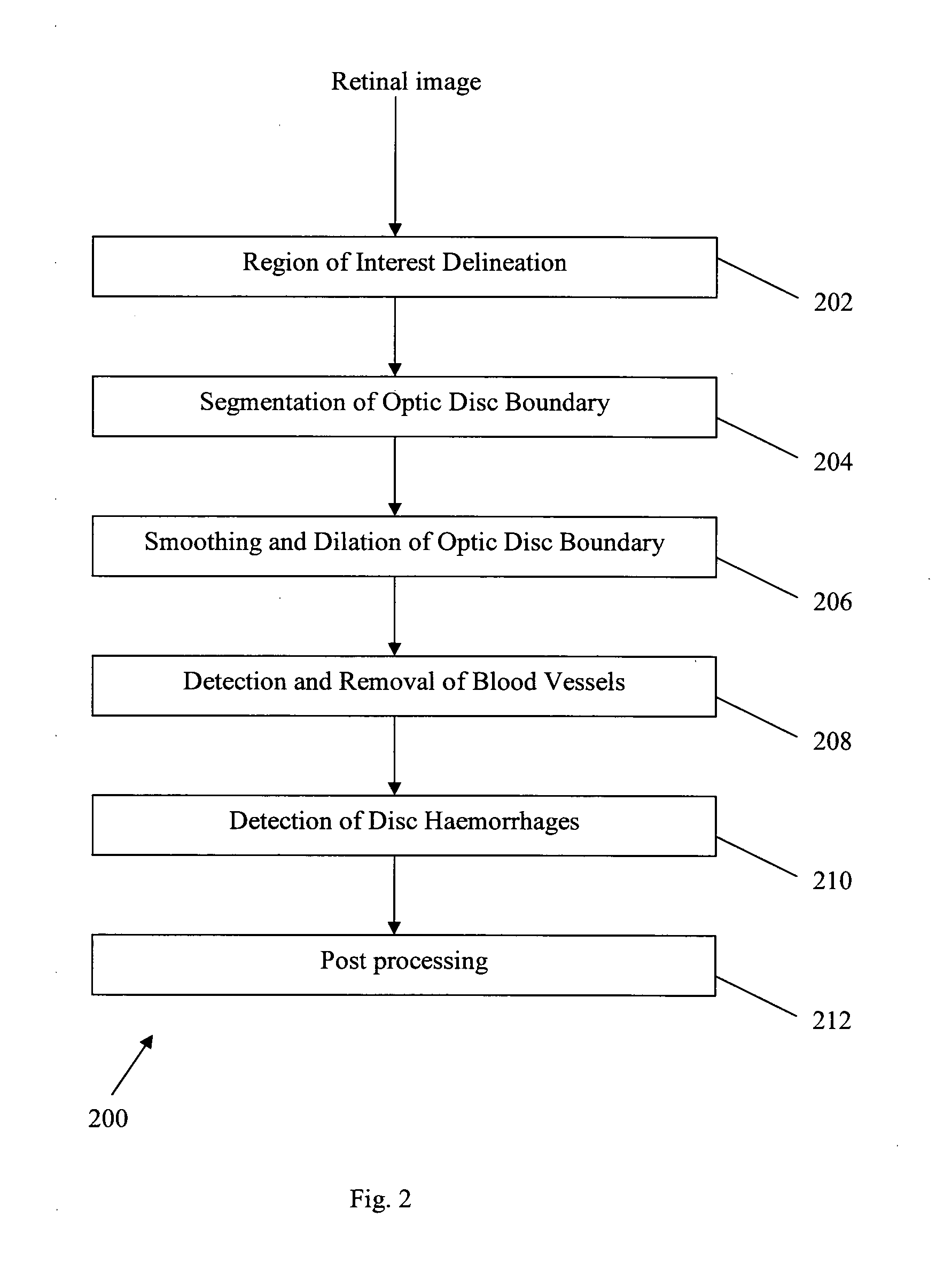
Method and system for detecting disc haemorrhages
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE +2
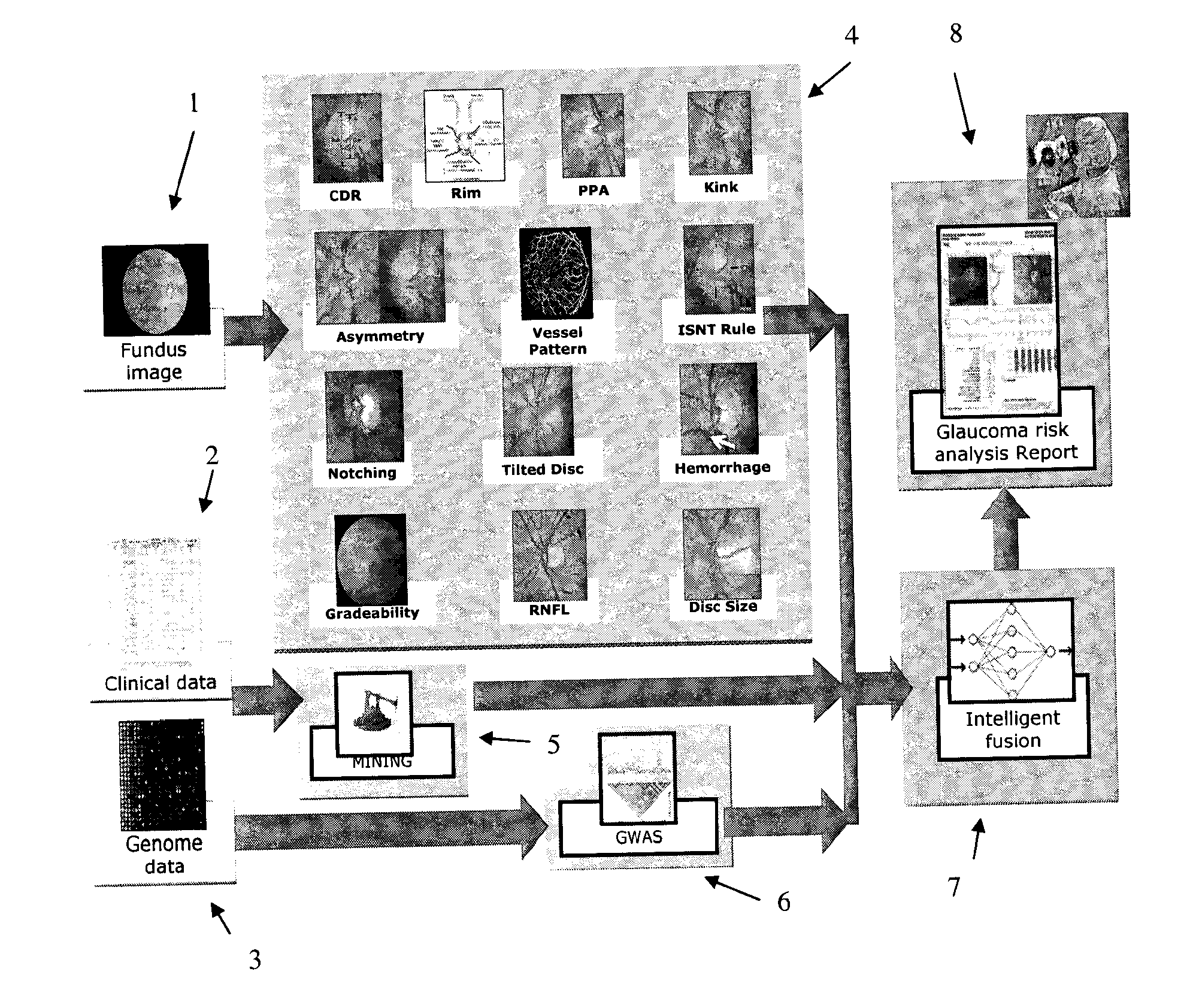
Obtaining data for automatic glaucoma screening, and screening and diagnostic techniques and systems using the data
A non-stereo fundus image is used to obtain a plurality of glaucoma indicators. Additionally, genome data for the subject is used to obtain genetic marker data relating to one or more genes and / or SNPs associated with glaucoma. The glaucoma indicators indicators and genetic marker data are input into an adaptive model operative to generate an output indicative of a risk of glaucoma in the subject. In combination, the genetic indicators and genome data are more informative about the risk of glaucoma than either of the two in isolation. The adaptive model may be a two-stage model, having a first stage in which individual genetic indicators are combined with respective portions of the genome data by first adaptive model modules to form respective first outputs, and a second stage in which the first outputs are combined by a second adaptive mode. Texture analysis is performed on the fundus images to classify them based on their quality, and only images which are determined to meet a quality criterion are subjected to an analysis to determine if they exhibit glaucoma indicators. Also, the images are put into a standard format. The system may include estimating the position of the optic cup by combining results from multiple optic cup segmentation techniques. The system may include estimating the position of the optic disc by applying edge detection to the funds image, excluding edge points that are unlikely to be optic disc boundary points, and estimating the position of an optic disc by fitting an ellipse to the remaining edge points.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE +1
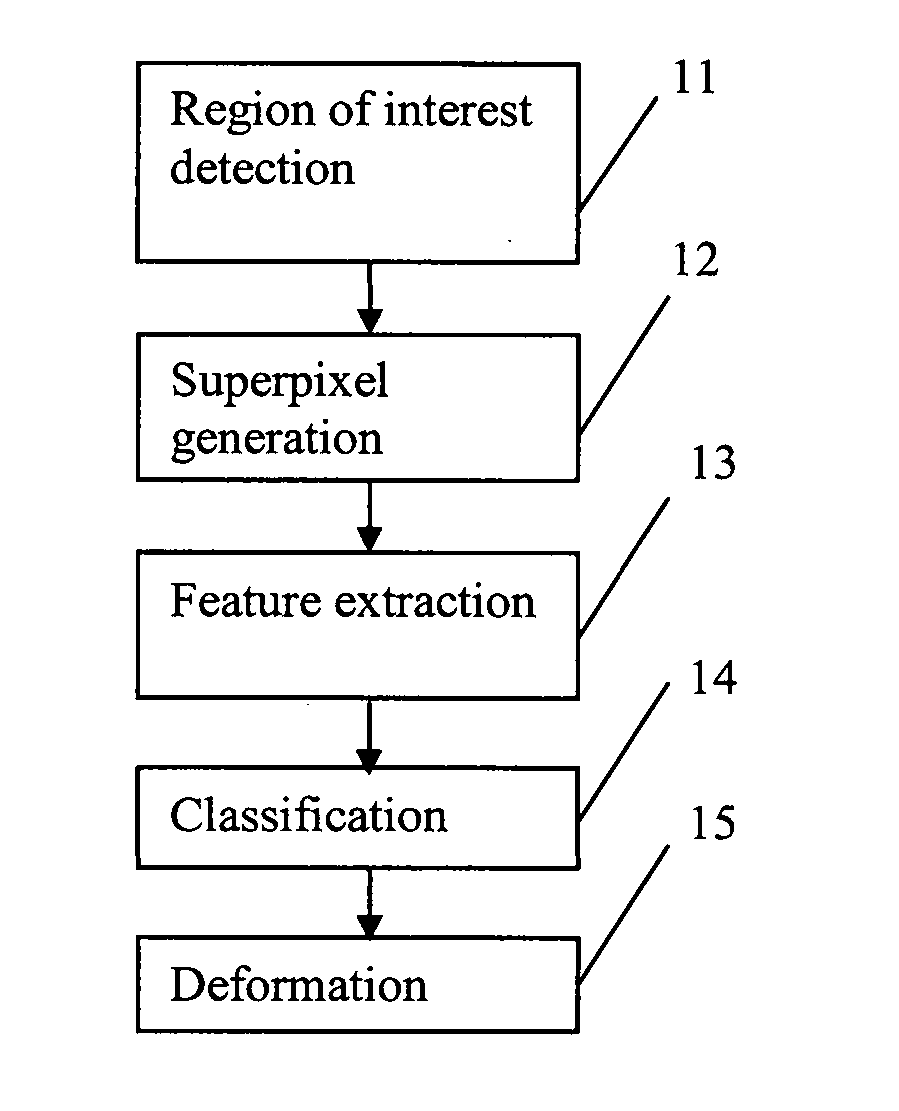
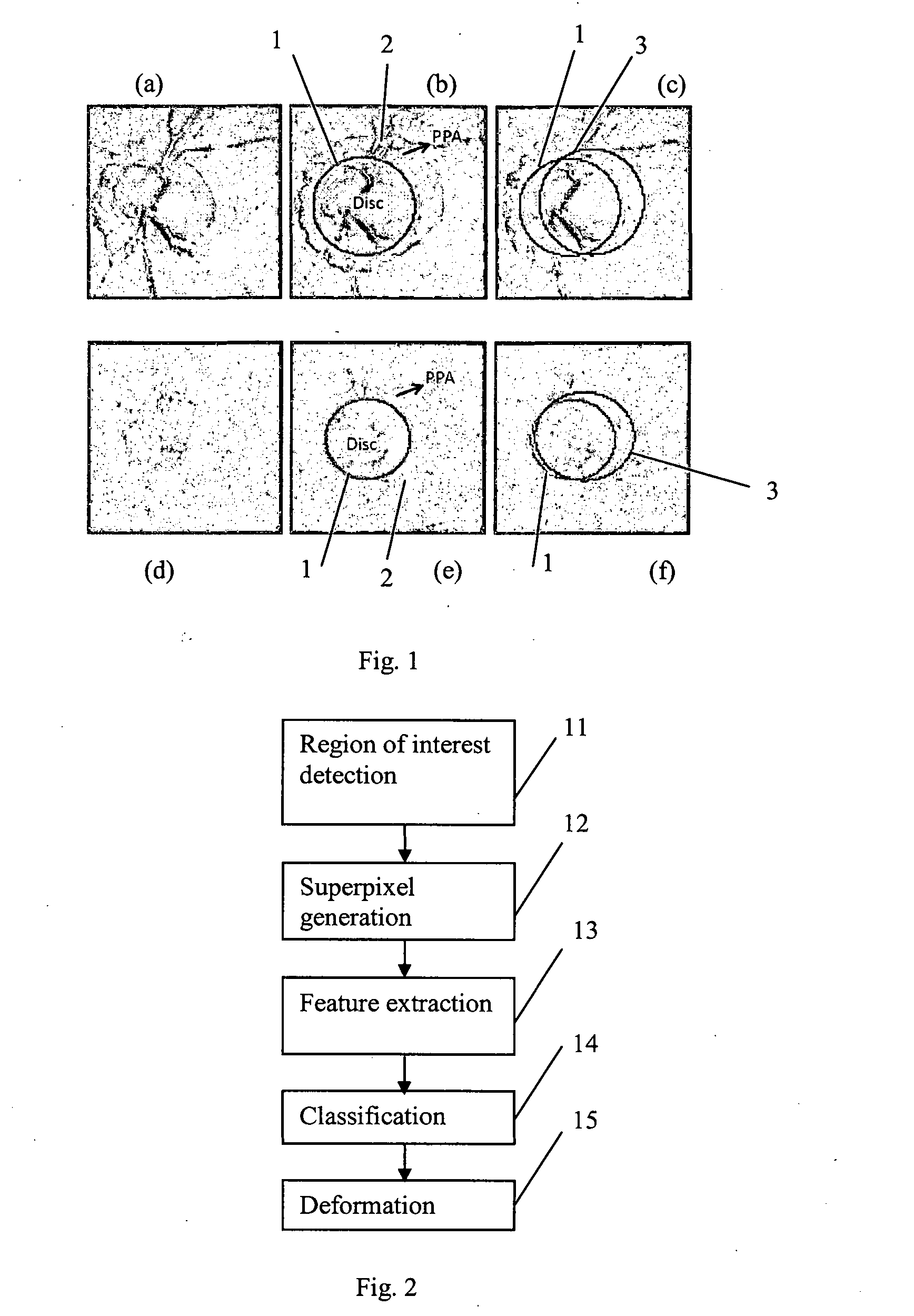
Methods and systems for automatic location of optic structures in an image of an eye, and for automatic retina cup-to-disc ratio computation
InactiveUS20150187070A1Reduce workloadReduce the possibilityImage enhancementImage analysisCup-to-disc ratioRetina
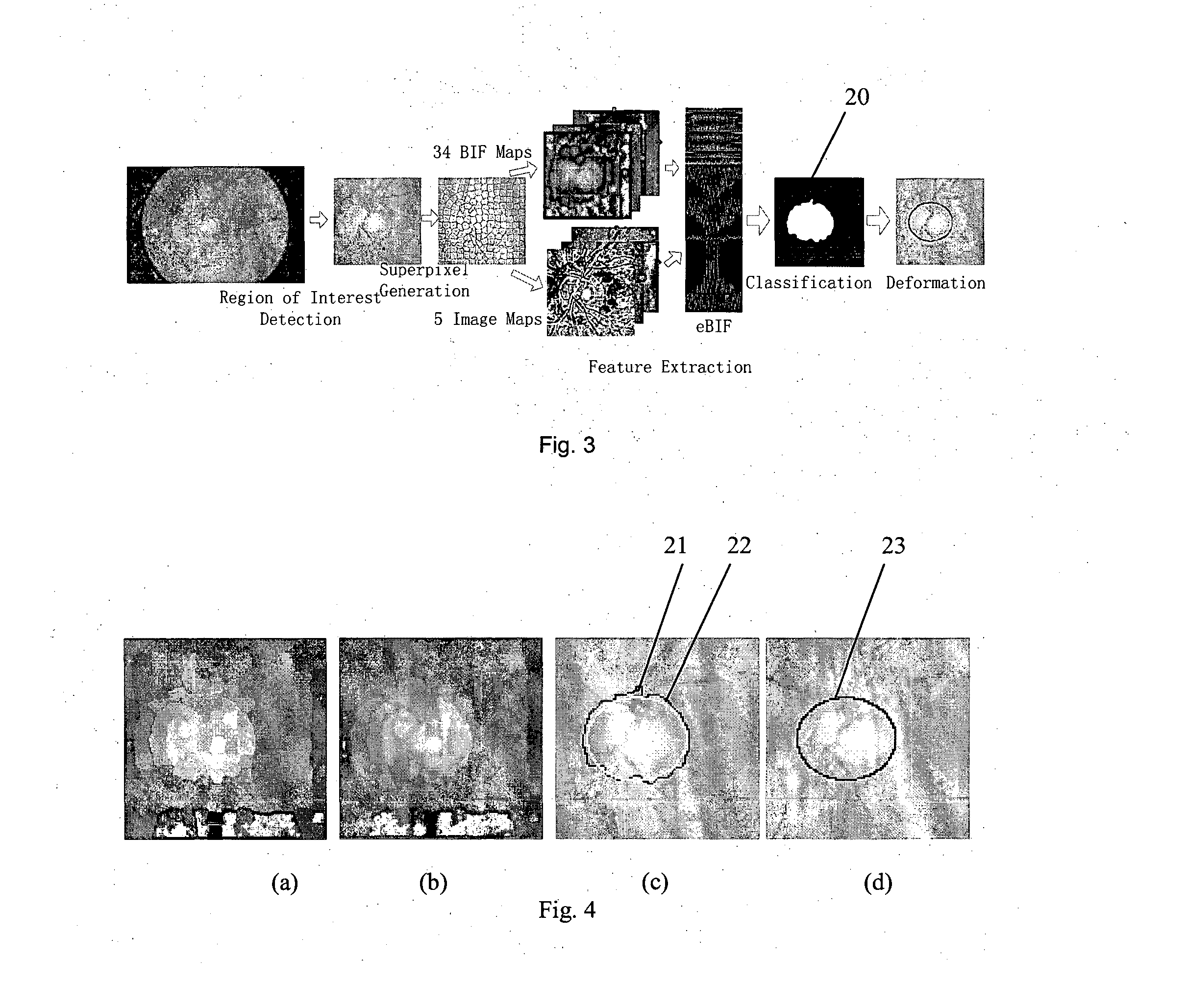
A method is proposed for automatically locating the optic disc or the optic cup in an image of the rear of an eye. A portion of the image containing the optic disc or optic cup is divided into sub-regions using a clustering algorithm. Biologically inspired features, and optionally other features, are obtained for each of the sub-regions. An adaptive model uses the features to generate data indicative of whether each sub-region is within or outside the optic disc or optic cup. The result is then smoothed, to form an estimate of the position of the optic disc or optic cup.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Vision prosthesis device based on optical-disc micro-electrode array
InactiveCN101396583AAvoid damageRepair visual functionEye treatmentArtificial respirationProsthesisMicroelectrode
A visual prosthetic device is based on videodisc microelectrode array, belonging to the technical field of medical appliance. The device comprises a microelectrode array substrate, a microelectrode array and an electrode cable, and is characterized by further comprising a cover board and a retina nail; wherein, the two ends of the microelectrode array substrate are respectively provided with a through hole of the retina nail, the middle of microelectrode array substrate is provided with 18 electrode through holes, and the retina nail passes through the through hole of the retina nail to fix the microelectrode array substrate on a videodisc of the retina; the microelectrode array consists of 18 wire electrodes which are fixed in the electrode through holes that are arranged in the center of the microelectrode array substrate, one ends of the wire electrodes are connected in vitro by the electrode cables, and the cover board covers above the electrode through holes of the microelectrode array substrate to fix the microelectrode array. The visual prosthetic device is applied for generating artificial vision and is the medical device for helping the retina blindness patients to gain brightness and vision again.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
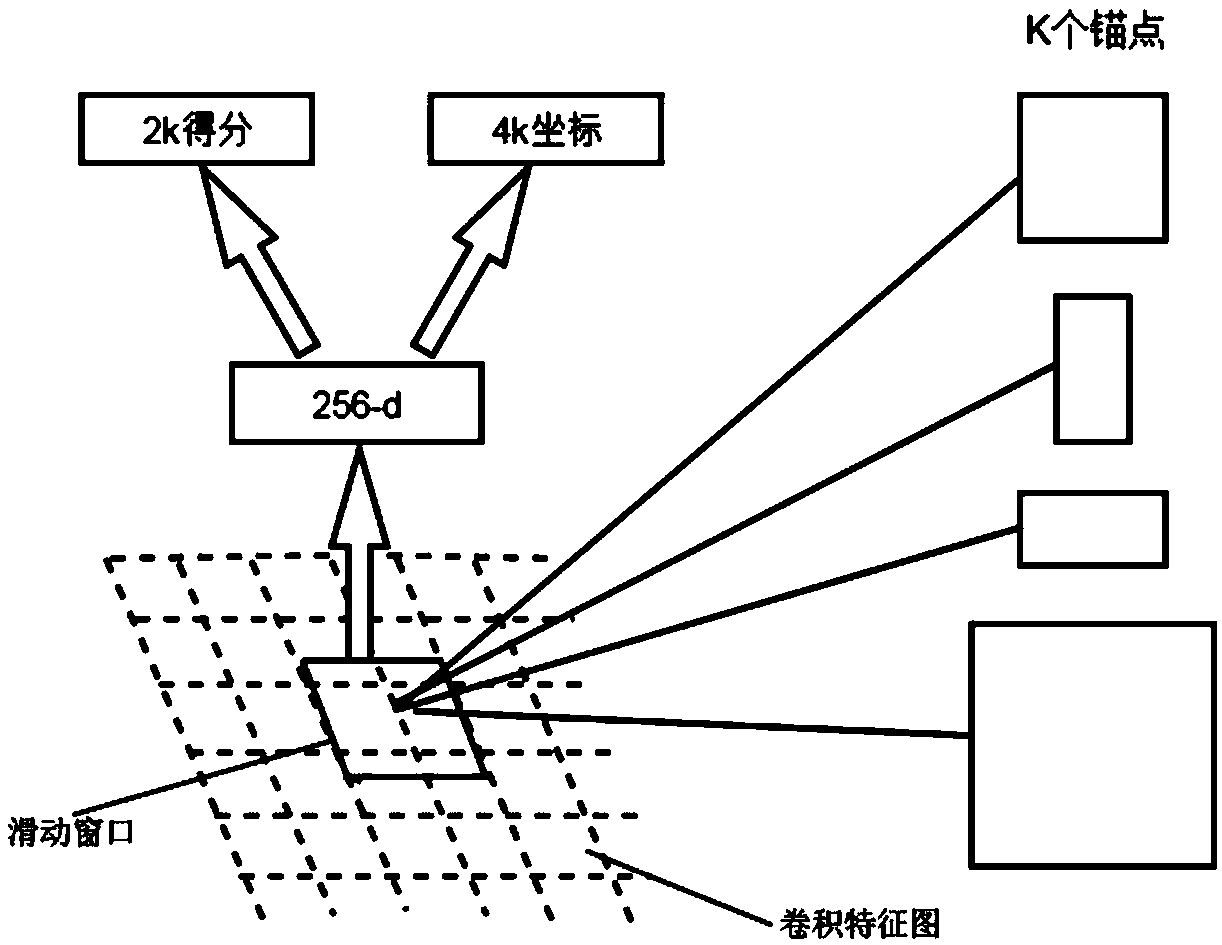
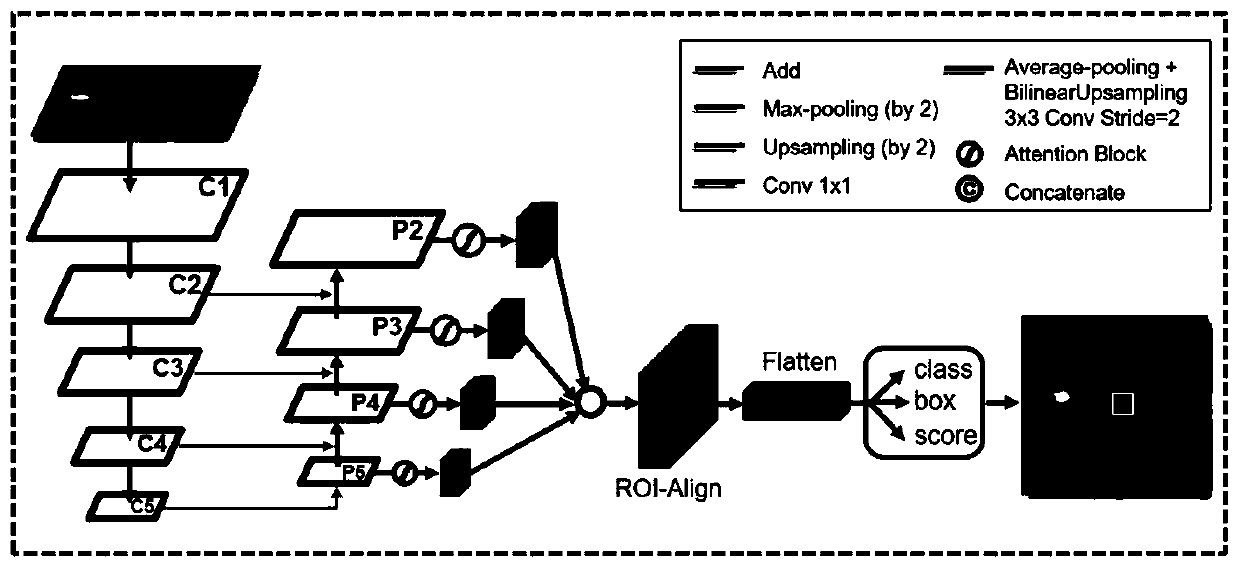
A macular location method based on improved Faster R-CNN
ActiveCN109377474AReduce the impactPrecise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisNetwork modelThree vessels
The invention discloses a macular location method based on improved Faster R-CNN, which includes collecting training samples, constructing a network model, training the network model, constructing a detection model and performing macular detection and location. The invention utilizes the improved Faster R-CNNto achieve effective localization of macular region, reduces the influence of optic disc and blood vessel on macular region and has strong anti-noise ability, which greatly improves the accurate localization of macular region and lays a foundation for the subsequent analysis and processingof fundus images.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
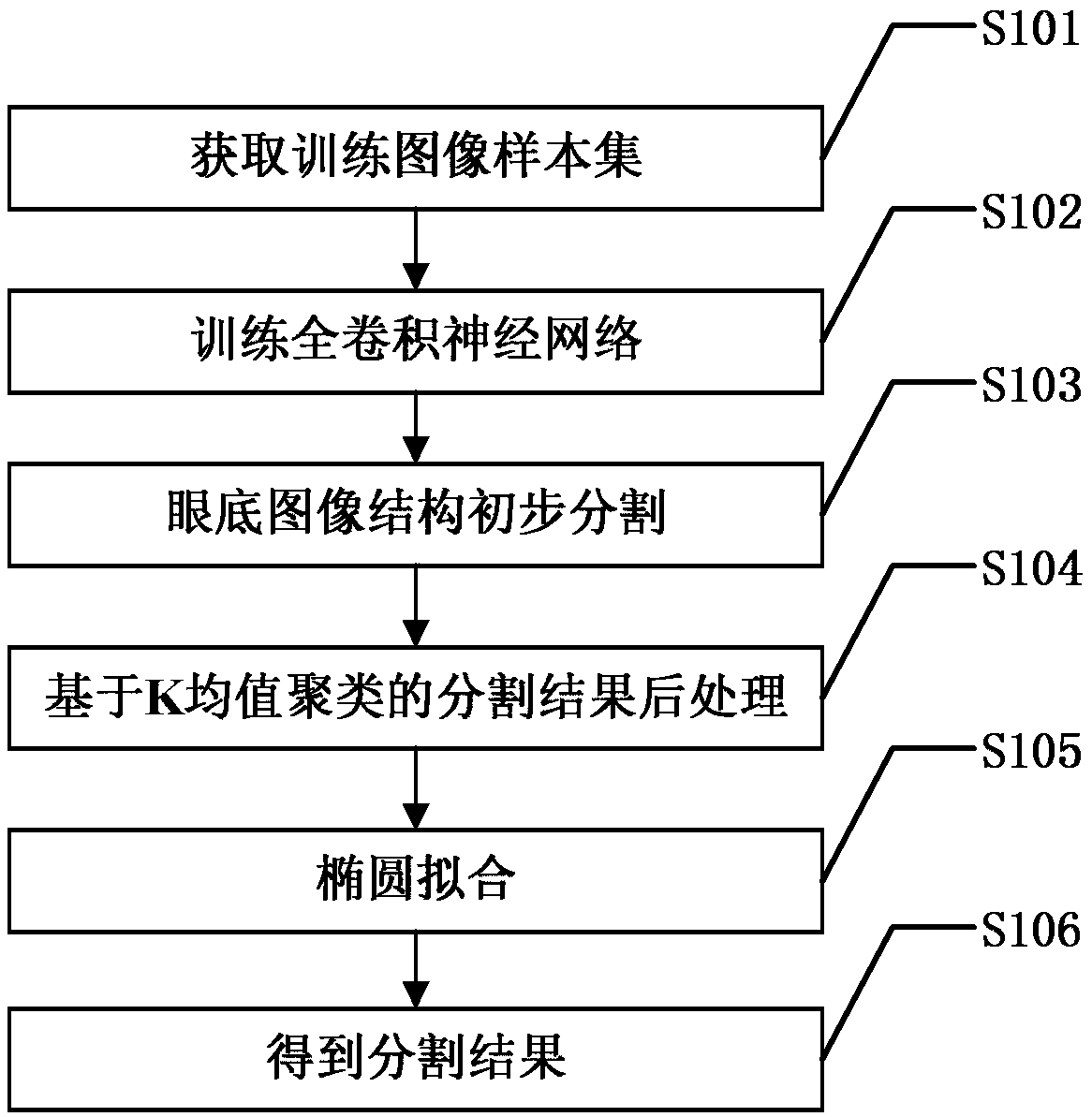
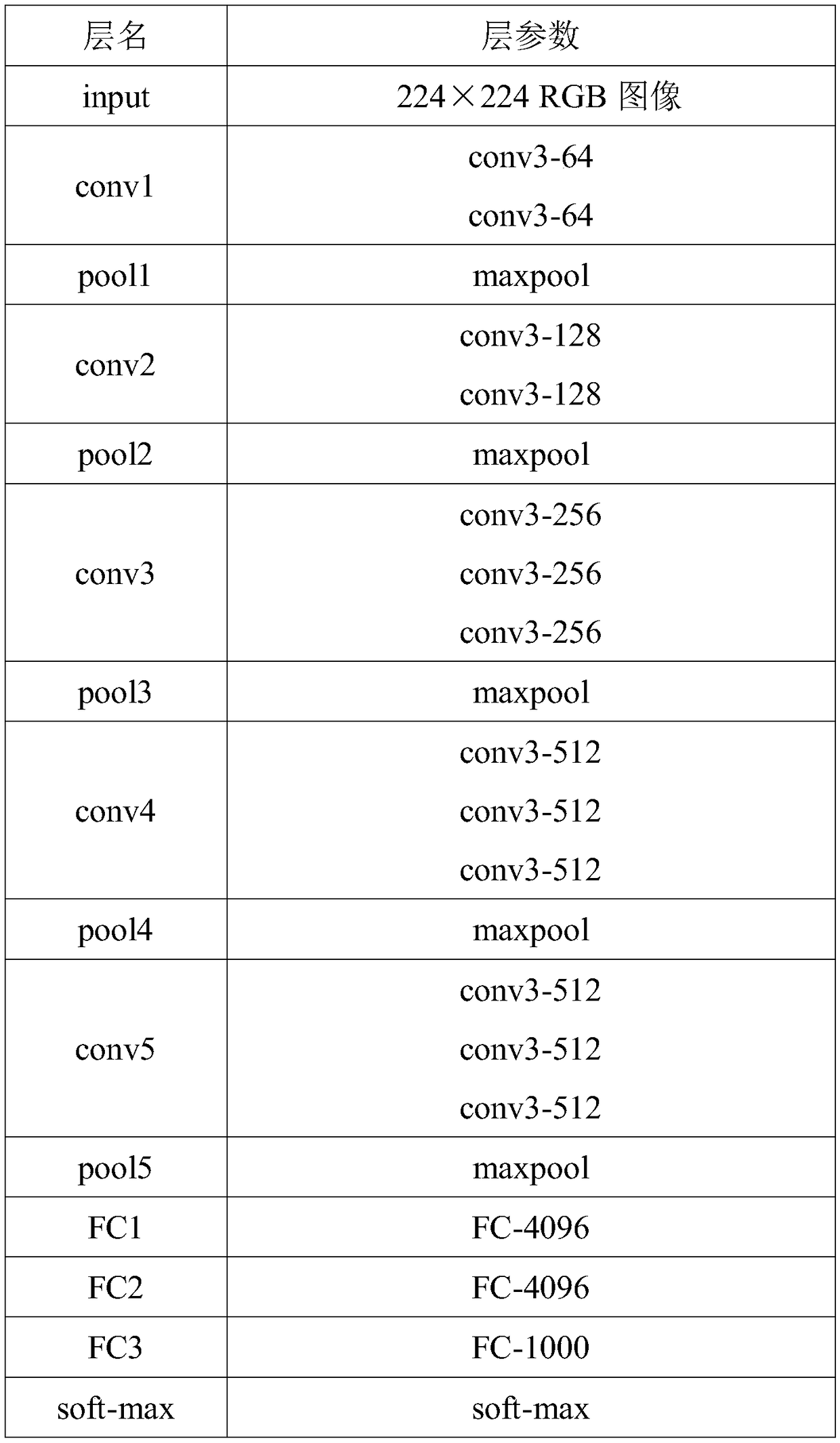
Eye fundus image structure segmentation method based on full convolution neural network
ActiveCN109325942AAccurate observationQuick observationImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationOptic disc size
The invention discloses an eye fundus image structure segmentation method based on full convolution neural network. The method comprises the steps of firstly marking the macula, optic disc and optic cup of each fundus image sample, and generating the corresponding target result map of each fundus image sample; then using each fundus image sample and corresponding target result map as a pair of training image samples to obtain the training image sample set; using the training image sample set to train the full convolution neural network, and inputting the fundus image to be segmented to the full convolution neural network to get the corresponding target result map; then using the K-means clustering and ellipse fitting to get the segmentation result. The method of the invention can improve the precision of the fundus image segmentation and better distinguish the normal physiological structure of the fundus.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method of producing glass substrate for information recording medium
InactiveCN1241169AExcellent Young's modulusHigh strengthBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageProduction ratePoise
The invention discloses a process for producing a glass substrate for an information recording medium by press-shaping a molten glass which gives a glass containing 0.1 to 30 mol% of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol% of CaO, 5 to 40 mol% of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol% of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol% of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol% of SiO2 and having properties of a liquidus temperature of 1360 DEG C or lower and a viscosity of at least 10 poise in a shaping-allowable temperature range, or by preparing a preform formed of a glass which contains 0.1 to 30 mol% of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol% of CaO, 5 to 40 mol% of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol% of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol% of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol% of SiO2 and has properties of a liquidus temperature of 1360 DEG C or lower and shaping the preform in the form of a disc by a re-heat pressing method. According to the above process, there can be mass-produced, with high productivity, high-quality glass substrates to be used for information recording media such as a magnetic disc, an optical disc, a magneto-optic disc, and the like.
Owner:HOYA CORP
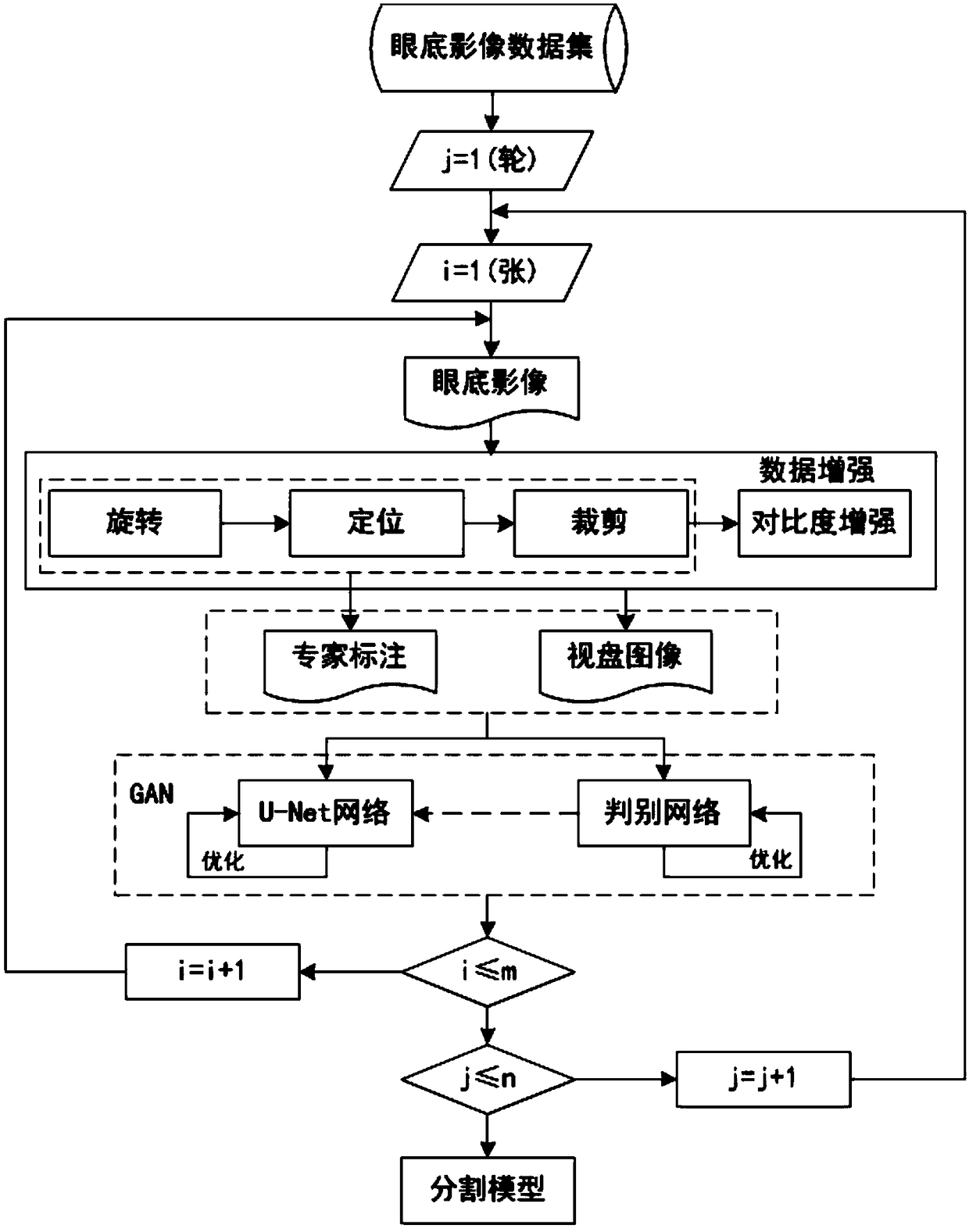
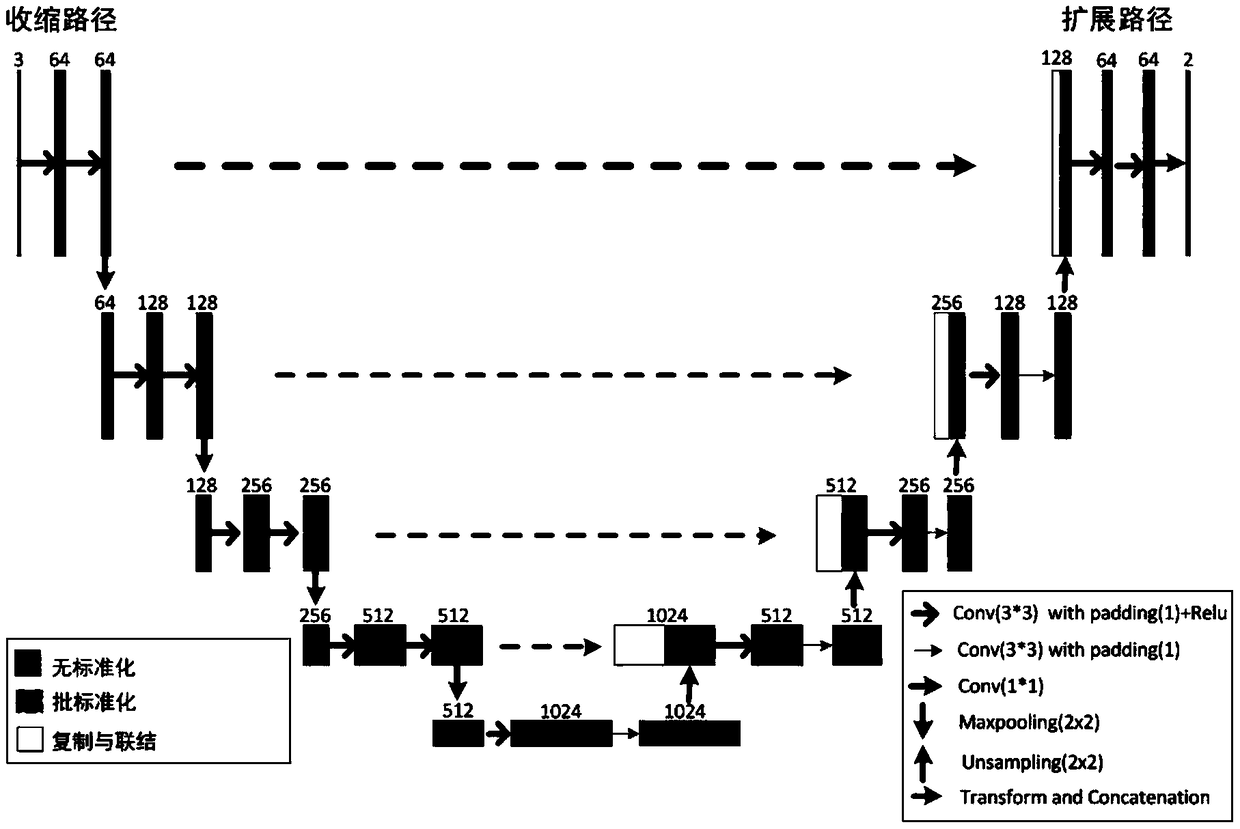
An eye fundus image cup-disc segmentation method based on generative adversarial mechanism
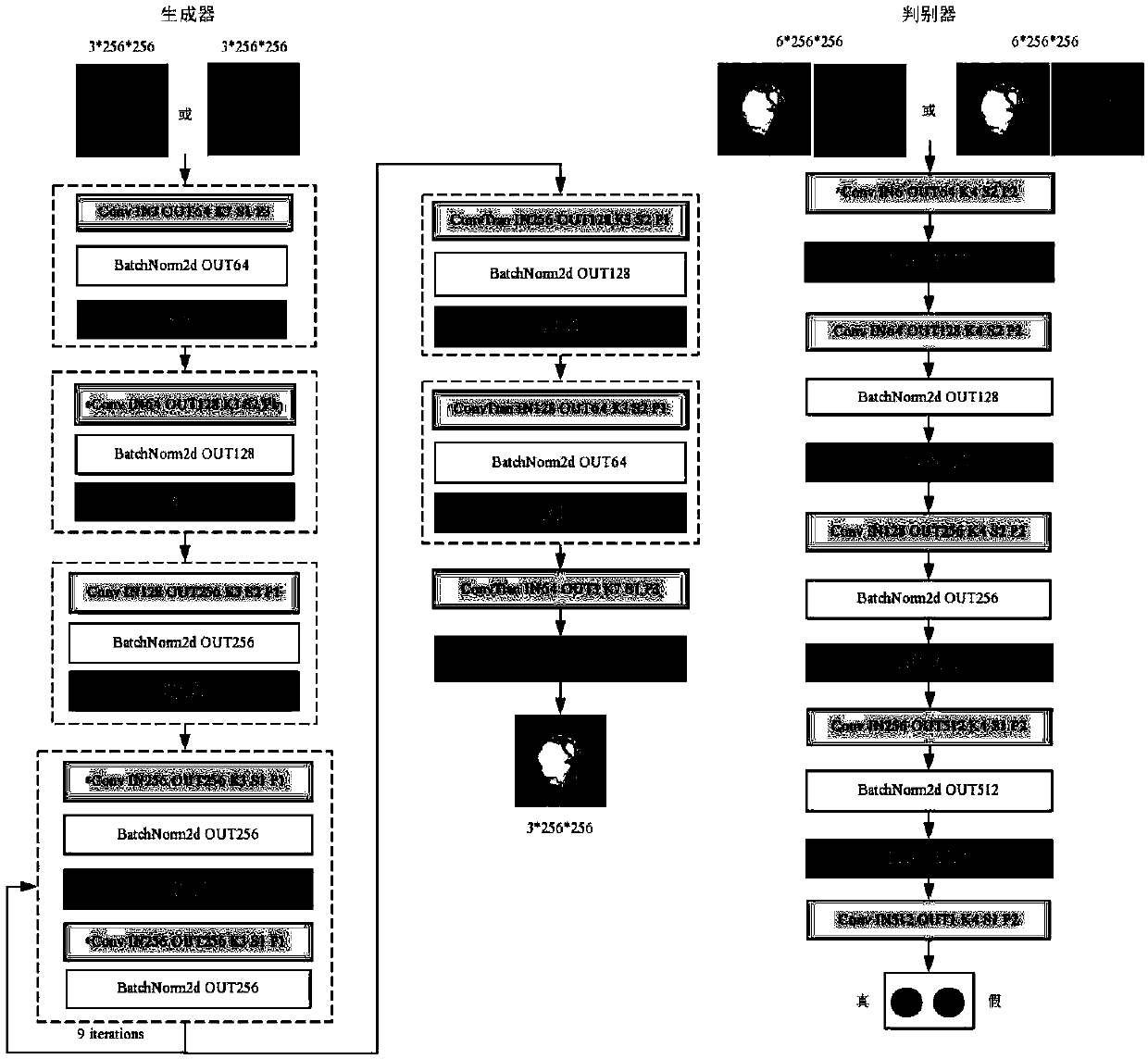
ActiveCN109166095AIncrease contrastQuick checkImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDiscriminator
The invention discloses an eye fundus image cup-disc segmentation method based on a generative adversarial mechanism. The method includes the steps that data enhancement is carried out on a single-channel or multi-channel color eye fundus image, the fundus image is segmented through a U-Net network, the predictive segmentation image will be sent to the discriminator network to identify the true and false, the true and false judgment loss returns back to adjust a model generated by the U-Net network, after many times of running of a generative adversarial network, and finally the optimal opticdisc segmentation model and optic cup segmentation model are obtained. The method achieves the optic disc and optic cup segmentation detection.
Owner:GUANGDONG POLYTECHNIC NORMAL UNIV
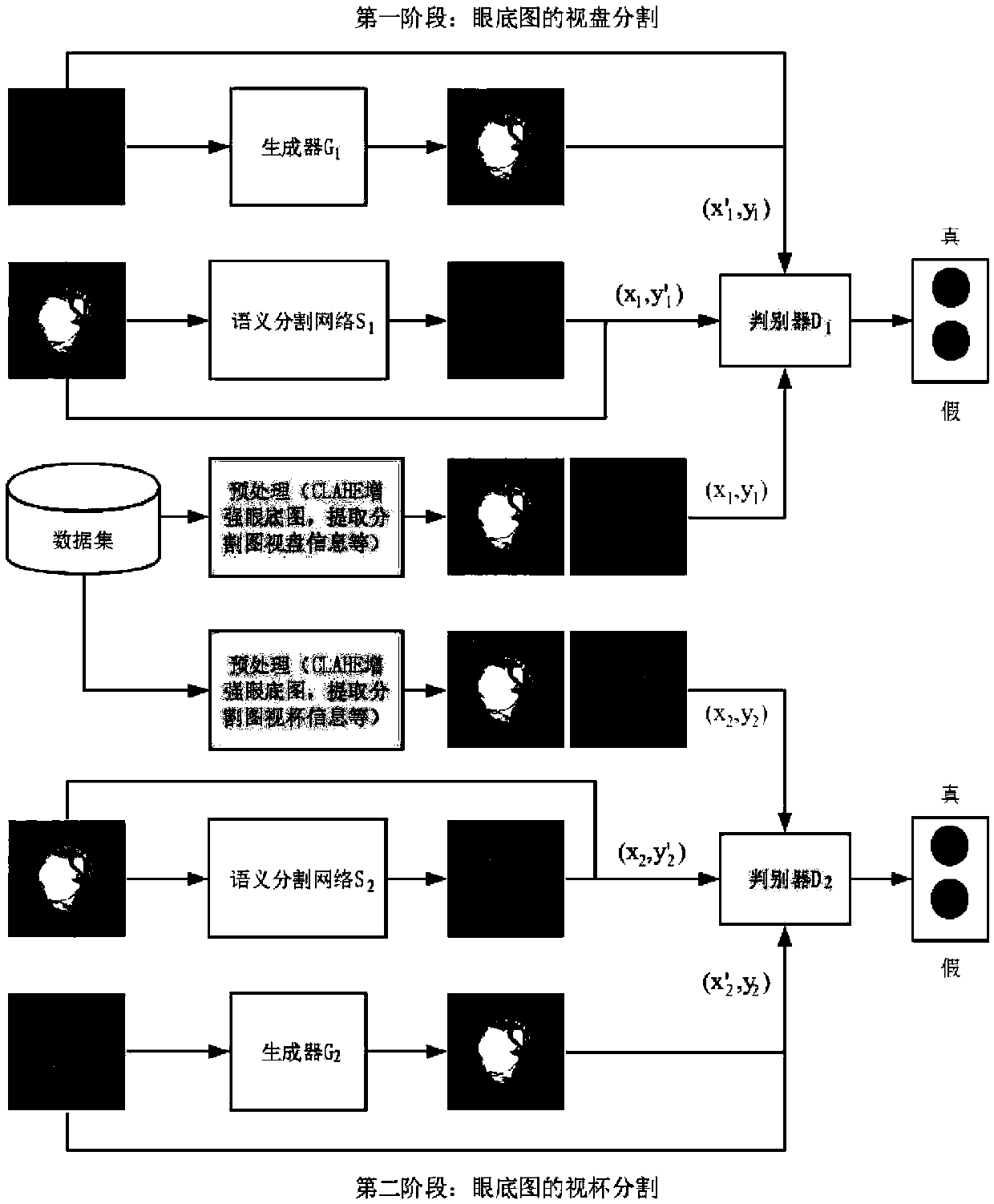
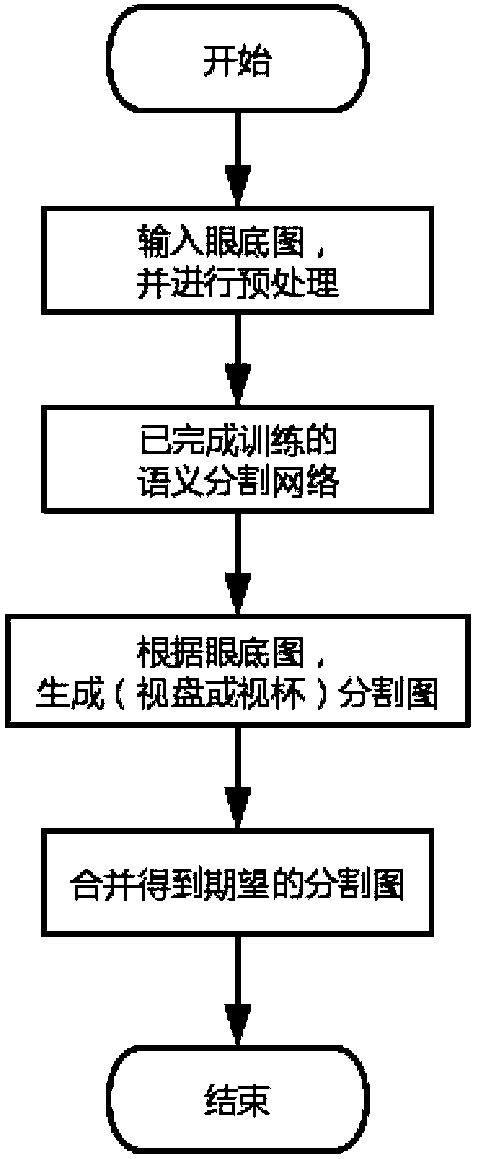
Fundus image optic disc and optic cup segmentation method based on a semi-supervised conditional generative adversarial network
ActiveCN109615632AImprove performanceSolve the problem of insufficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionGenerative adversarial network
The invention discloses a fundus image optic disc and optic cup segmentation method based on a semi-supervised conditional generative adversarial network, and the method comprises the following steps:building a network framework which comprises two stages: optic disc semantic segmentation and optic cup semantic segmentation; wherein each of the two stages comprises a semantic segmentation network, a generator and a discriminator; the semantic segmentation network generates a (optic disc or optic cup) segmentation image by utilizing the labeled and unlabeled fundus images; the generator generates an eye fundus image with a real (optic disc or optic cup) segmentation image as an input; and the discriminator identifies whether the data pairing of the fundus image and the (optic disc or opticcup) segmented image thereof is real or forged, the guide generator and the semantic segmentation network learn the joint distribution of the fundus image and the segmented image thereof, and finally, the results of the two semantic segmentation stages are combined to obtain the optic disc and optic cup segmented image of the fundus image.
Owner:GUANGDONG POLYTECHNIC NORMAL UNIV
Peripheral circulation improvers for ophthalmic tissues containing dihydropyridines
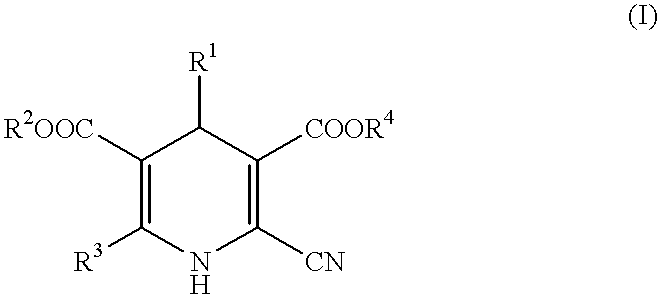
The present invention provides a peripheral ocular circulation ameliorant which contains dihydropyridines represented by the general formula (I) or their medicinally acceptable salts as active ingredients(where R1 is a nitrophenyl group and R2, R3, and R4 are lower alkyl groups), and particularly provides an optic disc blood flow ameliorant, choroidal blood flow ameliorant, retinal blood flow ameliorant, and accordingly, therapeutics for visual field defects associated with normal intraocular pressure glaucoma as well as for optic neuropathy, retinopathy, retinal-degeneration diseases, etc.
Owner:FUJISAWA PHARMA CO LTD
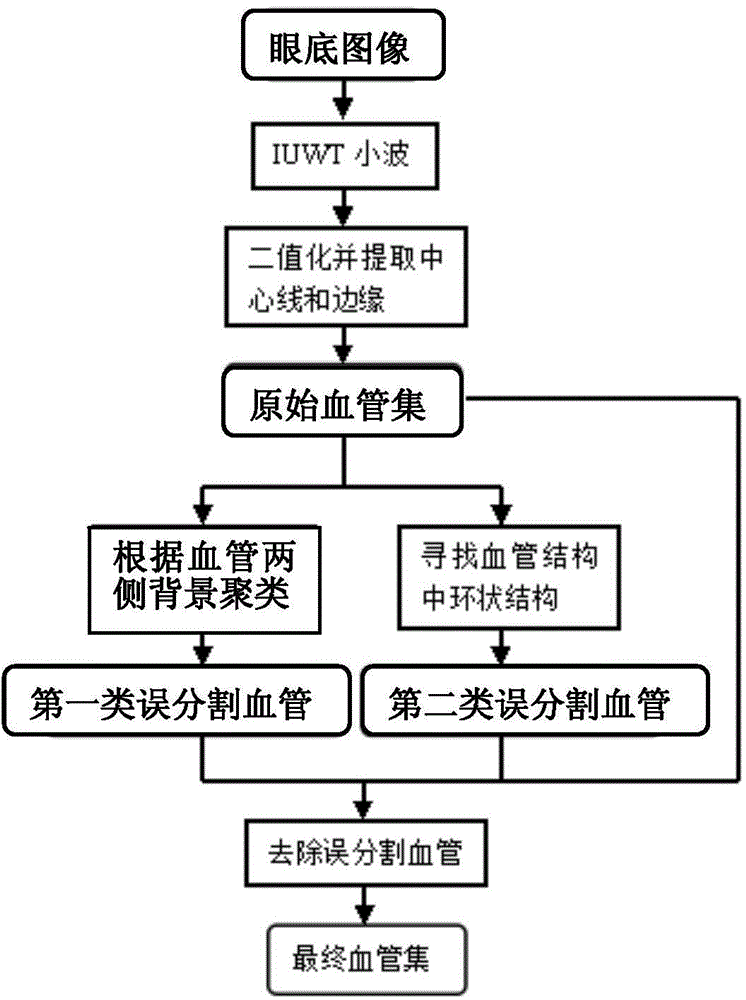
Arteriovenous retinal vessel segmentation method for eye fundus image
The invention discloses an arteriovenous retinal vessel segmentation method for an eye fundus image. The method comprises the following steps that binarization processing is carried out on a pre-processed eye fundus image according to a preset image-binary threshold value, the central line and the edge in the eye fundus image after the binarization processing are extracted, and a blood vessel tree is obtained; disconnection process is carried out on the branching portions of the blood vessel tree to obtain blood vessel segments, line segmentation is carried out on all the blood vessel segments to obtain blood vessels, and an original blood vessel set is obtained; mis-segmented blood vessels are determined and removed from the original blood vessel set to obtain a global blood vessel set. According to the method, after the original blood vessel set is obtained, the mis-segmented blood vessels are further determined through the background and the shapes of the blood vessels, mis-segmented blood vessels which are caused by annular light reflection of photograph, non-blood-vessel step edges around an optic disc, porphyritic lesions, bleeding lesions and other reasons can be removed effectively, and the segmentation precision of the blood vessels is improved.
Owner:杭州求是创新健康科技有限公司
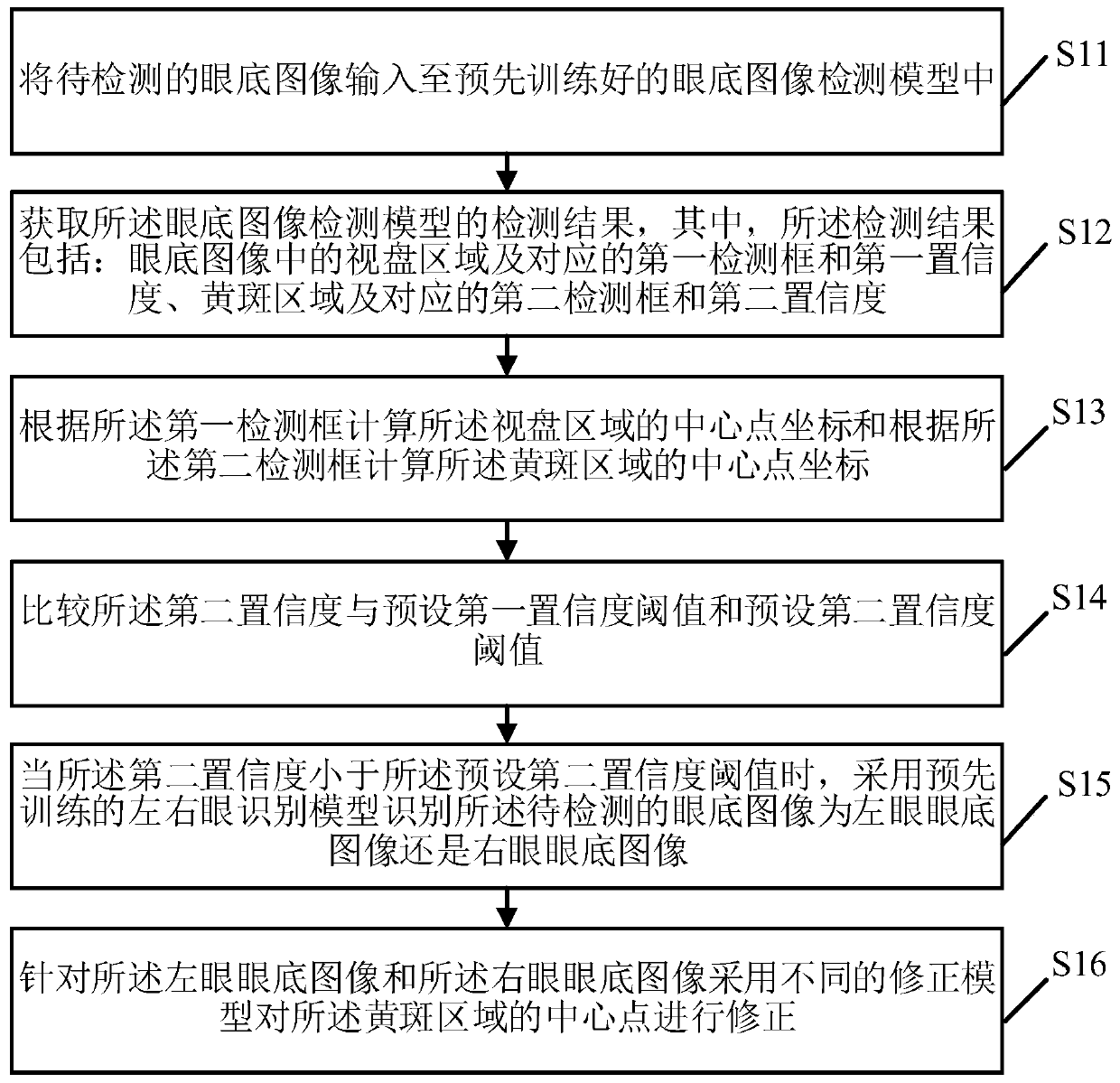
Fundus image macular center positioning method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN111046717ATroubleshoot detection failuresEliminate dependenciesImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityImage quality
The invention provides a fundus image macular center positioning method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The fundus image macular center positioning method comprises the steps that a fundus image to be detected is input into a fundus image detection model; obtaining a detection result of the fundus image detection model, wherein the detection result comprises an optic disc region and a corresponding first detection frame, a macular region and a corresponding second detection frame and confidence; calculating central point coordinates of the optic disk area according to the first detection frame and calculating central point coordinates of the macular area according to the second detection frame; and when the confidence coefficient is smaller than a preset confidence coefficient threshold, identifying whether the fundus image to be detected is a left eye fundus image or a right eye fundus image, and correcting the central point of the macular area by adopting different correction models. The problem of macular area detection failure caused by image quality, lesion shielding and the like in a macular positioning method based on deep learning is solved, and the dependence of macular center positioning and optic disc center positioning in a traditional method is eliminated.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
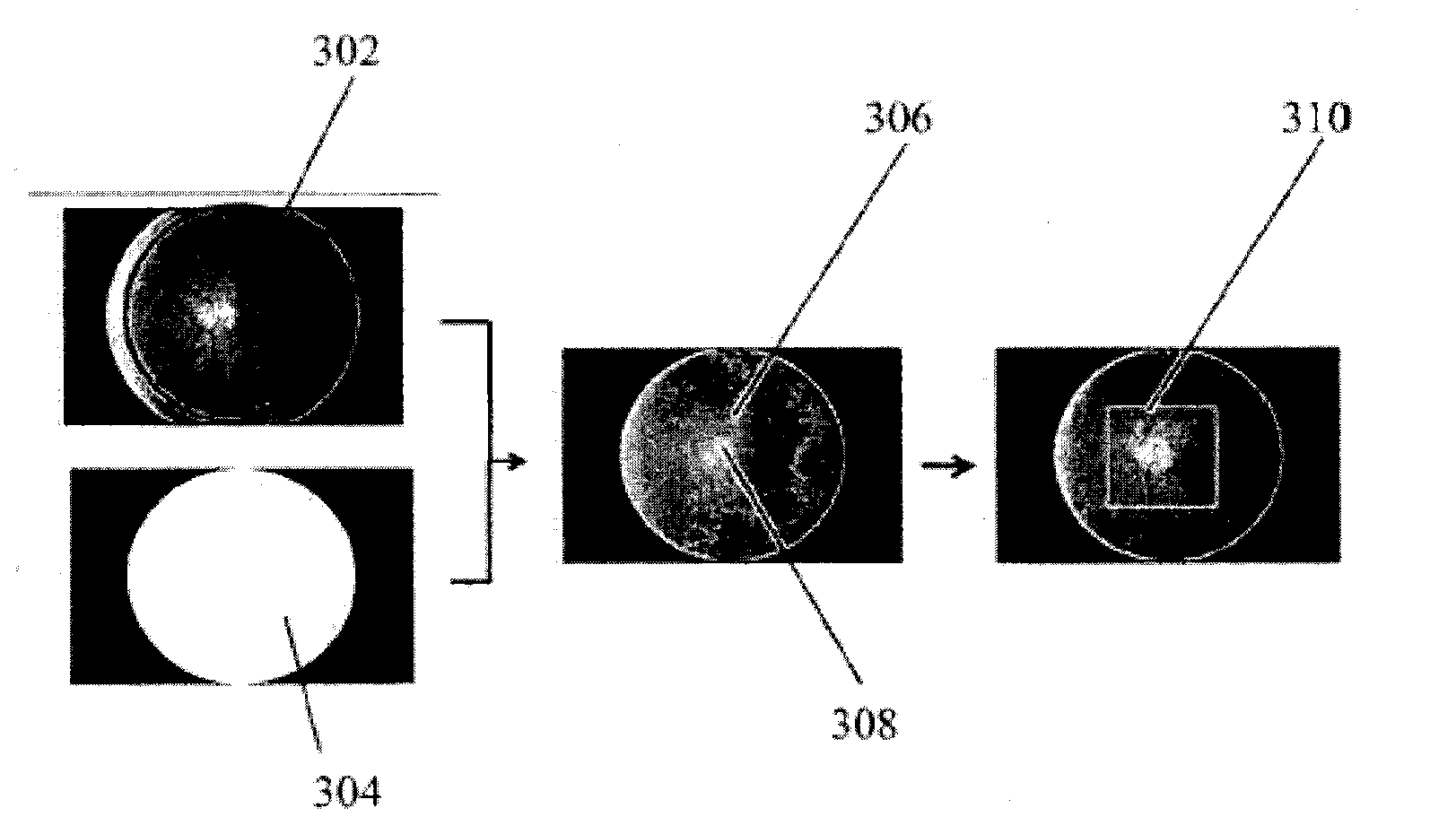
Method and device for location and segmentation of optic disc in eyeground image, and storage medium
ActiveCN107480644AImprove Segmentation AccuracyAutomatic estimateImage enhancementImage analysisEllipseGrabCut
The present invention provides a method and device for location and segmentation of an optic disc in an eyeground image, and a storage medium. The method comprises in the initial location phase of an optic disc: performing improved weighting graying of a colorful eyeground image; employing the least square method to perform ellipse fitting to estimate the radius of the optic disc; employing multiple morphological operations to eliminate the interference of artery and vein vasculars, employing histogram statistics to determine an adaptive threshold to segment an area of front 0.01% brightness in the eyeground, and taking the geometric center of the area as an estimated optic disc center; and finally determining an optic disc location rectangle frame. In the optic disc accurate location and segmentation phase, the GrabCut method is employed to segment the optic disc, and the segmented area contour employs the ellipse fitting to determine the optic disc position and size parameters so as to complete the location of the optic disc. The condition of too big radius of the optic disc in the GrabCut segmentation result is subjected to secondary segmentation to determine a new threshold and perform contour fitting to obtain a final segmentation result.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
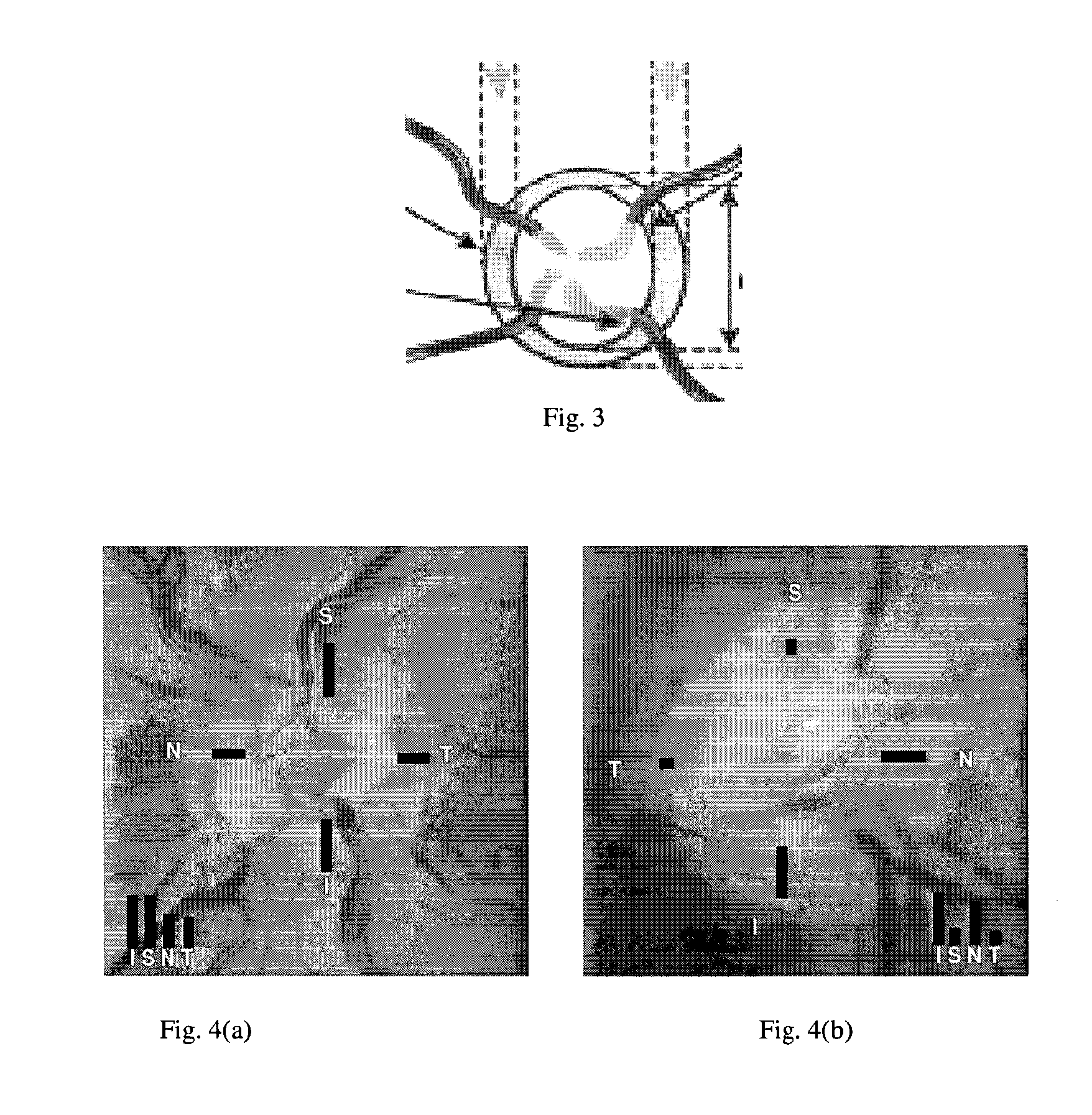
Methods and systems for detecting peripapillary atrophy
InactiveUS20130222767A1Reduce workloadReduce the possibilityImage enhancementImage analysisSupervised learningComputer science
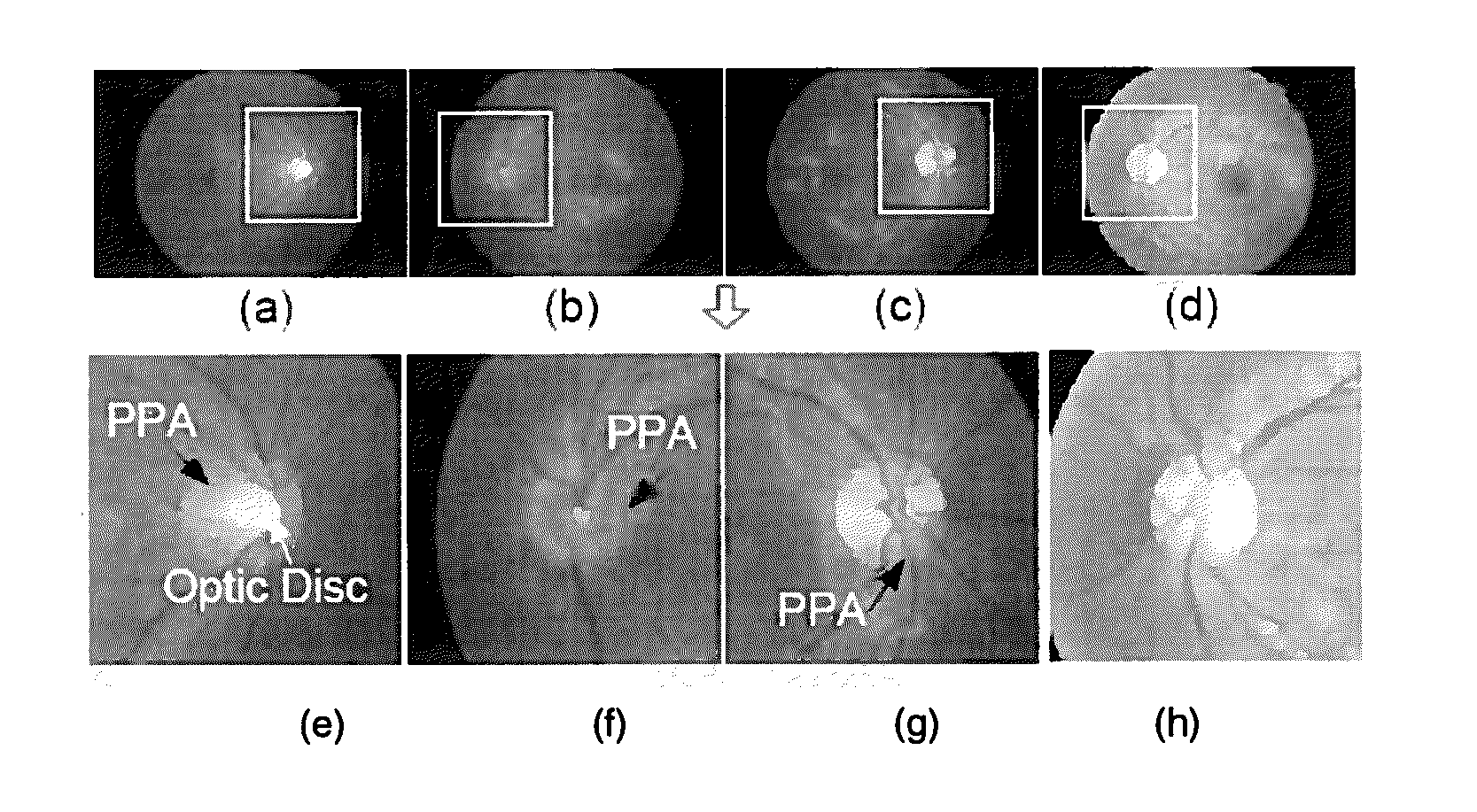
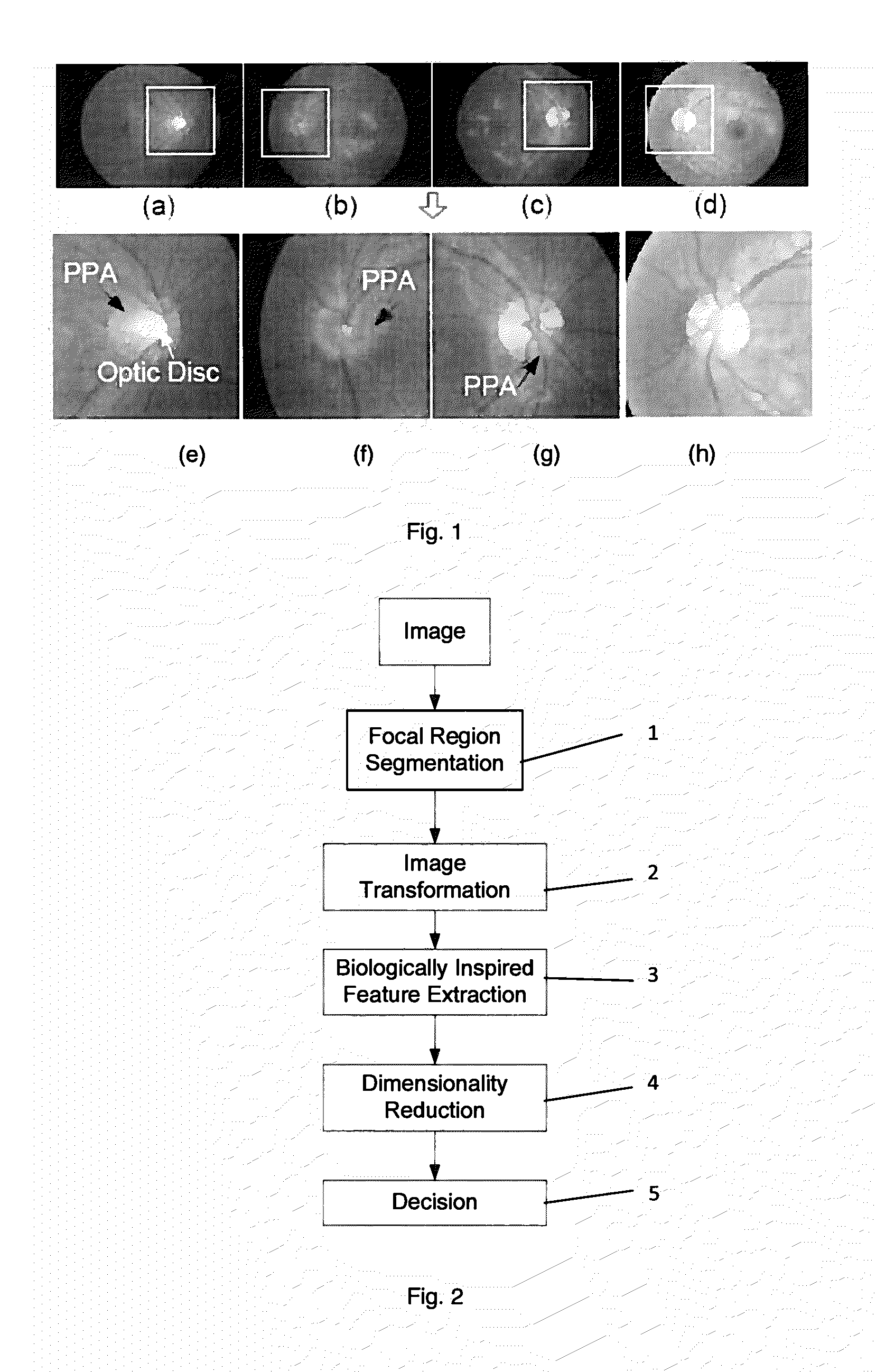
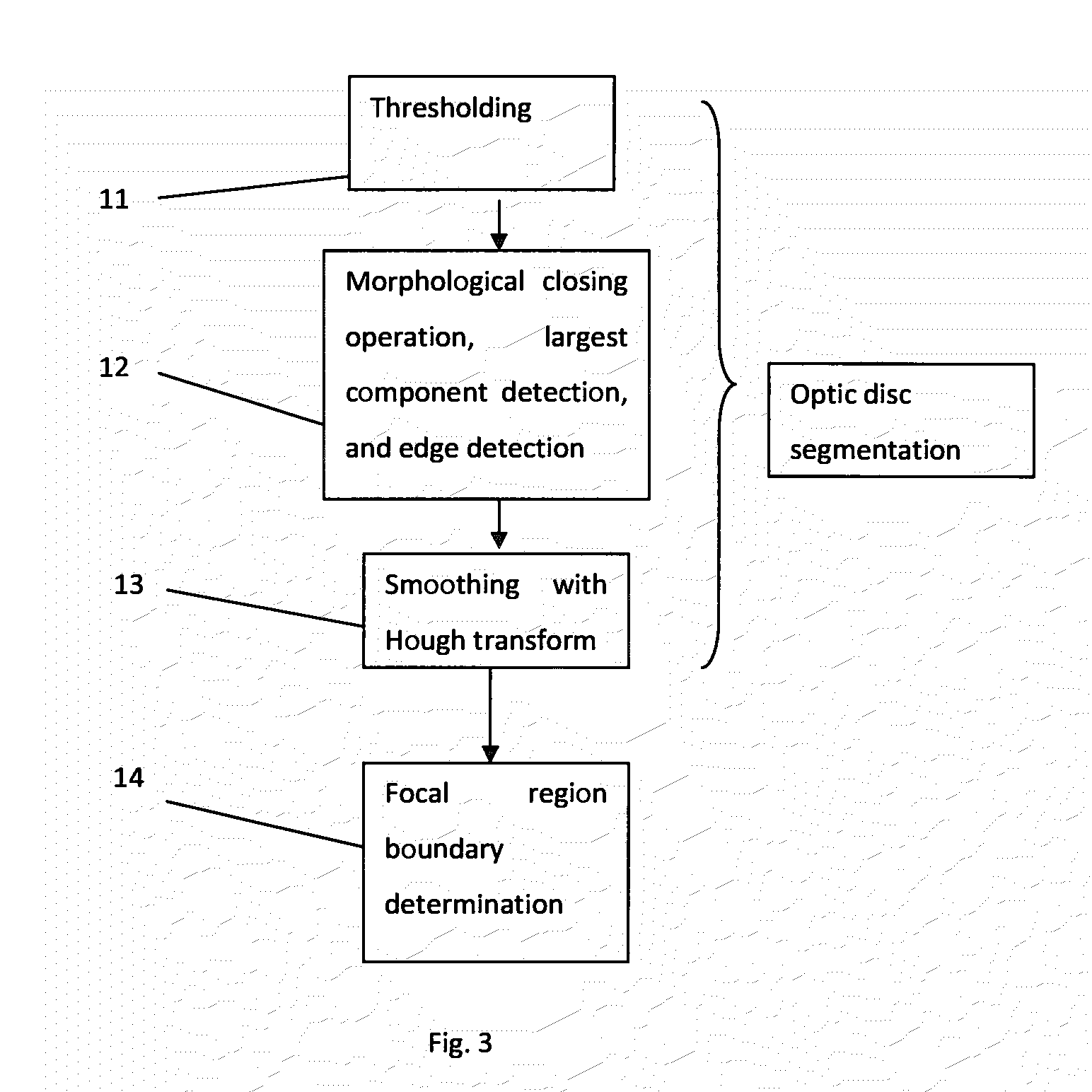
A method is presented for deciding whether an eye exhibits peripapillary atrophy (PPA). It includes a preliminary step of extracting from an image of the eye a region-of-interest which would be affected if the eye exhibits peripapillary atrophy, which is a region which surrounds the optic disc, and then processing the region in a way which mimics the processing of the cortex, to derive a plurality of numerical measures (biologically-inspired features, BIF). A decision step is then performed using the BIF, for example using an adaptive system which has been subject to a supervised learning process. Preferably, the region-of-interest is partitioned into a plurality of sub-regions, and the BIF are derived as a corresponding plurality of numerical measures for each of the sub-regions. The BIF preferably include intensity units which take values indicative of centre-surround intensity difference; and colour units which take values indicative of centre-surround difference in a parameter characterizing colour in the image. Further, the BIF preferably include direction-specific units.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
A macula lutea detection method and a storage device
ActiveCN109199322AImprove detection efficiencyGuaranteed accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisOphthalmologyImaging analysis
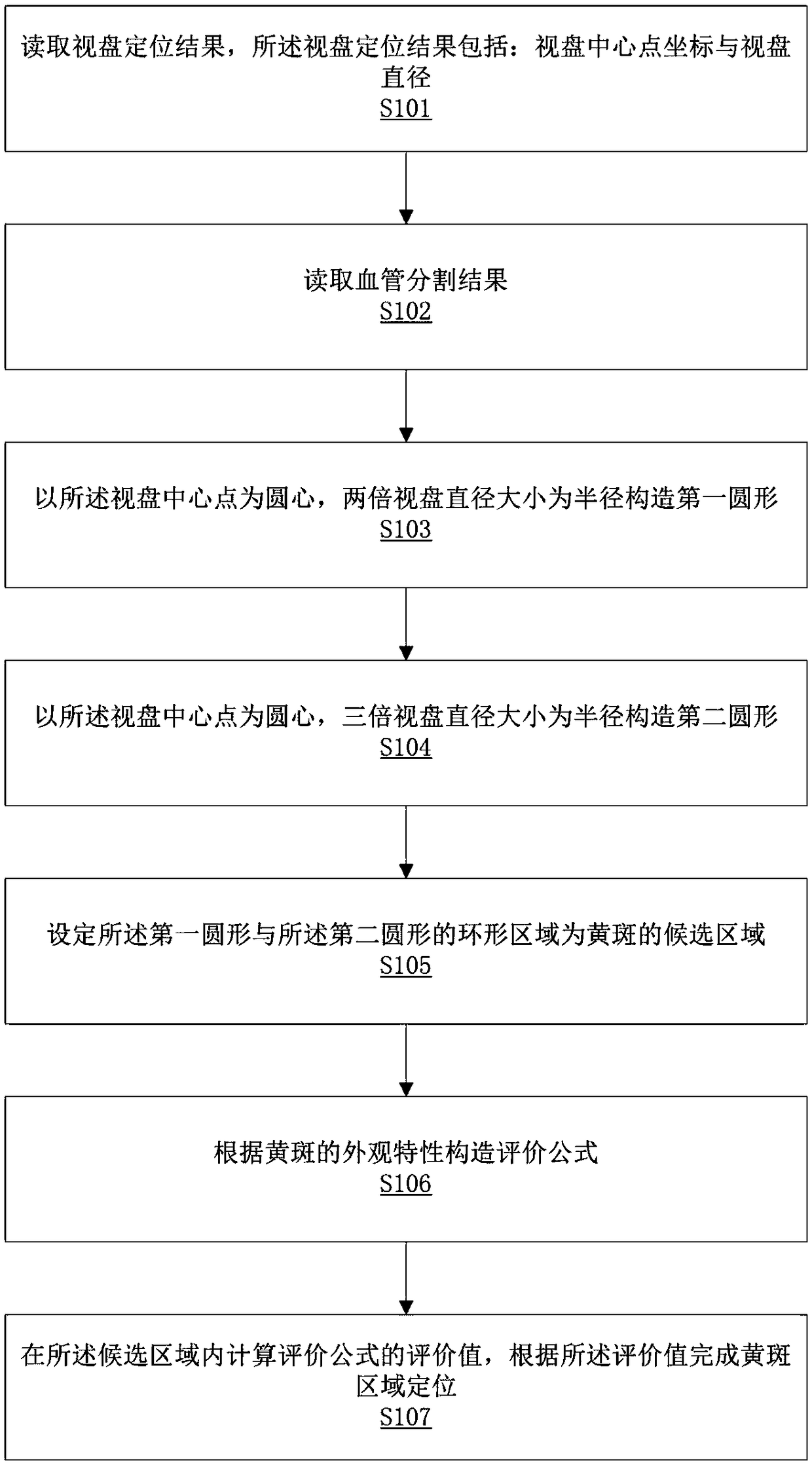
The invention relates to the field of image analysis, in particular to a macula lutea detection method and a storage device. The method comprises that steps of: reading a positioning result of an optic disc; reading the blood vessel segmentation result; constructing a first circle with the center point of the optic disc as the center and twice the diameter of the optic disc as the radius; constructing a second circle with the center point of the optic disc as the center and three times the diameter of the optic disc as the radius; setting an annular region of the first circle and the annular region of the second circle as a candidate region of macula; according to the appearance characteristics of macula, constructing an evaluation formula . The evaluation value of the evaluation formula is calculated in the candidate region, and the macular region positioning is completed according to the evaluation value. The whole process of the method is not only dependent on the appearance of macula lutea, does not need scanning a whole image, so that the detection speed is increased. The method is based on the combination of optic disc location and blood vessel segmentation and not only depends on optic disc positioning accuracy, thus ensuring optic disc detection accuracy and reliability.
Owner:FUZHOU YIYING HEALTH TECH CO LTD
Retinal vessel segmentation method fusing W-net and conditional generative adversarial network
ActiveCN110930418AIncrease contrastEasy extractionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionData set
The invention relates to application of a deep learning algorithm in the field of medical image analysis, in particular to a retinal vessel segmentation algorithm fusing W-net and a conditional generative adversarial network. According to the method, the problems of low segmentation sensitivity and insufficient micro blood vessel segmentation are well solved, great progress is made in the aspectsof the parameter utilization rate, the information circulation and the feature analysis ability of the network, complete segmentation of the main blood vessel and fine segmentation of the micro bloodvessel are facilitated, the blood vessel intersection is not prone to breakage, and a focus and an optic disc are not prone to being segmented into the blood vessel by mistake. According to the invention, a plurality of network models are fused under the condition of low complexity; the whole segmentation performance on a DRIVE data set is excellent, the sensitivity and accuracy of the method are87.18% and 96.95% respectively, the ROC curve value reaches 98.42%, the method can be used for computer-aided diagnosis in the medical field, and rapid and automatic retinal vessel segmentation is achieved.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A deep learning-based early age-related macular lesion weakly supervised classification method
ActiveCN109886946ALow costAchieve correct classificationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMedicineClassification methods
The invention discloses a deep learning-based early age-related macular lesion weakly supervised classification method, which comprises the following steps of 1, positioning a central concave positionof an eye fundus image by adopting a convolutional neural network, and intercepting a square area as a candidate area by taking the central concave position as an original point and taking a double-optic disc diameter as a side length; 2, judging whether glass membrane warts appear in the macular area or not by adopting a convolutional neural network, detecting the glass membrane warts in a weaksupervision manner, and judging whether the glass membrane warts appear in the fundus image or not; 3, performing linear interpolation by using the intermediate result of the step 2 to obtain a finalpixel-level focus marking result. According to the algorithm, a weak supervision method is adopted for classifier training and detection, only whether the fundus image has vitreous condyloma information or not needs to be provided, the classifier can be trained without specific position information, correct classification of the early-stage age-related macular lesion fundus image is achieved, andthe algorithm can effectively save the cost of marking training data while the precision is guaranteed.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
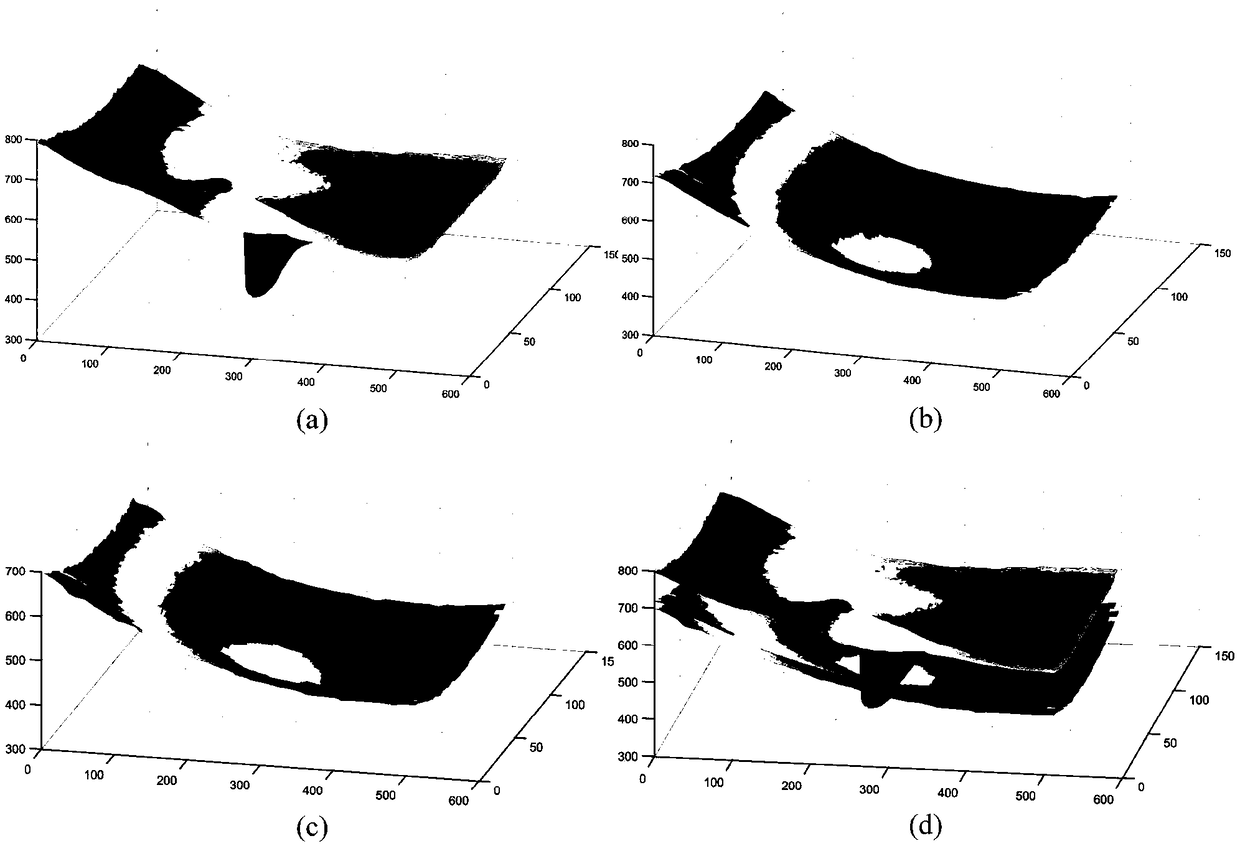
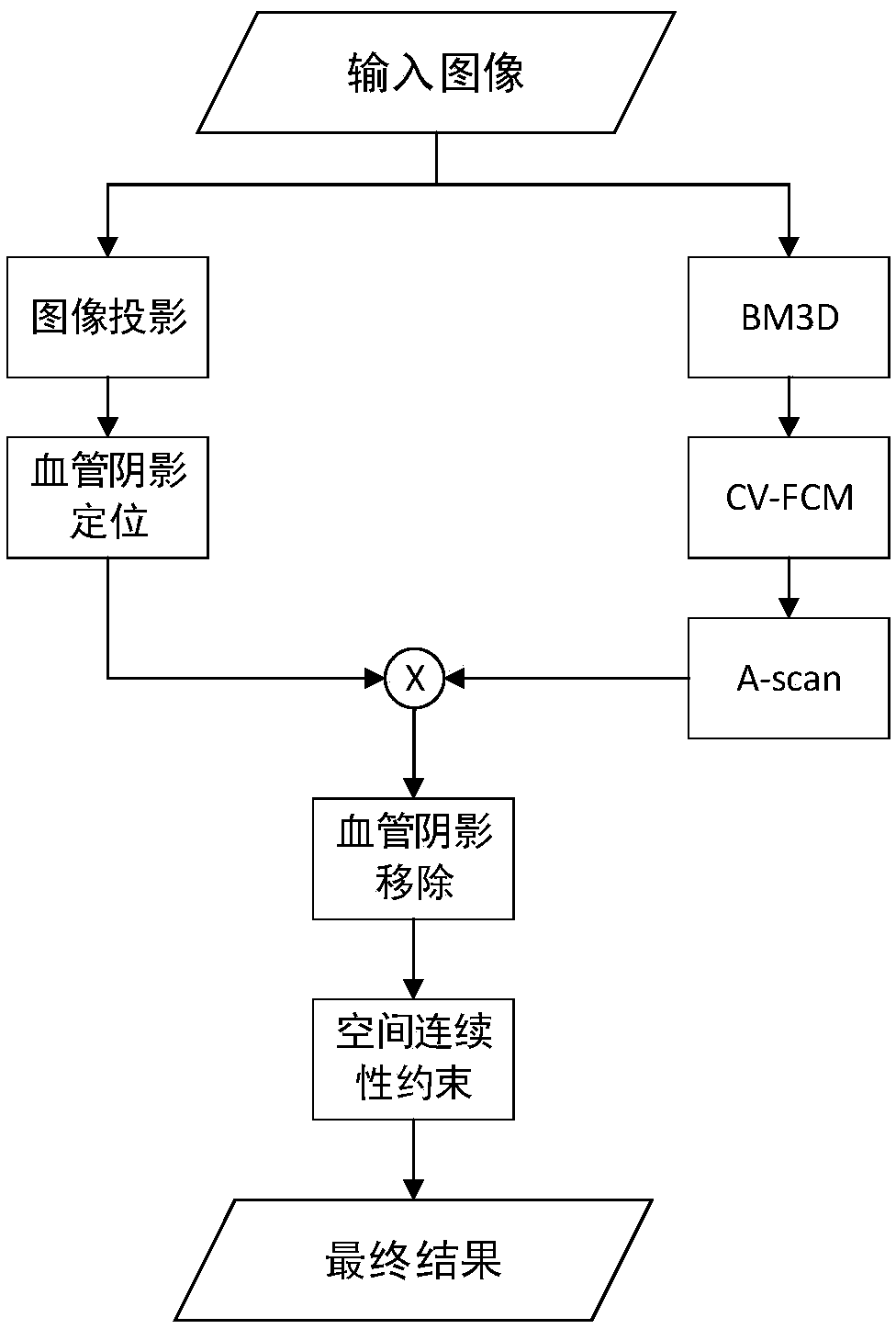
Hierarchical segmentation method for OCT (Optical Coherent Tomography) image of optic disc region based on spatial continuity constraints
ActiveCN108961261AImprove Segmentation AccuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionTomography
The invention discloses a hierarchical segmentation method for an OCT (Optical Coherent Tomography) image of an optic disc region based on spatial continuity constraints. The method comprises the steps of firstly removing speckle noise in the OCT image by using a BM3D algorithm; then mutually separating multiple high-reflection regions in the image by using an ROI (Region of Interest) segmentationmethod based on the fuzzy C-means and active contour; then positioning the vascular shadow by using an ROI region image; sequentially segmenting the ROI by using an A-scan segmentation algorithm, correcting an initial segmentation result of each image by using a vascular shadow region; and finally optimizing the corrected segmentation results by using the spatial continuity constraints to obtainsegmentation boundaries of an ILM (Internal Limiting Membrane), an IS-OS (Inner segment-Outer segment) and a BM (Bruch membrane). Disclosed by the invention is an effective hierarchical segmentation method for the OCT image of the optic disc region, is high in segmentation accuracy and has certain robustness for the speckle noise and vascular shadow.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method and system for detecting disc haemorrhages
A method for detecting disc haemorrhages in a retinal fundus image. The method includes (a) identifying a ring-shaped region of interest in the retinal fundus image encompassing the optic disc boundary; (b) removing blood vessel regions in the identified region of interest; (c) detecting candidate disc haemorrhages from the removed blood vessels regions in the identified region of interest; and (d) screening the candidate disc haemorrhages. The detected disc haemorrhages may be used to aid in the detection of glaucoma.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERIVICES PTE LTD A COMPANY ORGANIZED & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF SINGAPORE +2
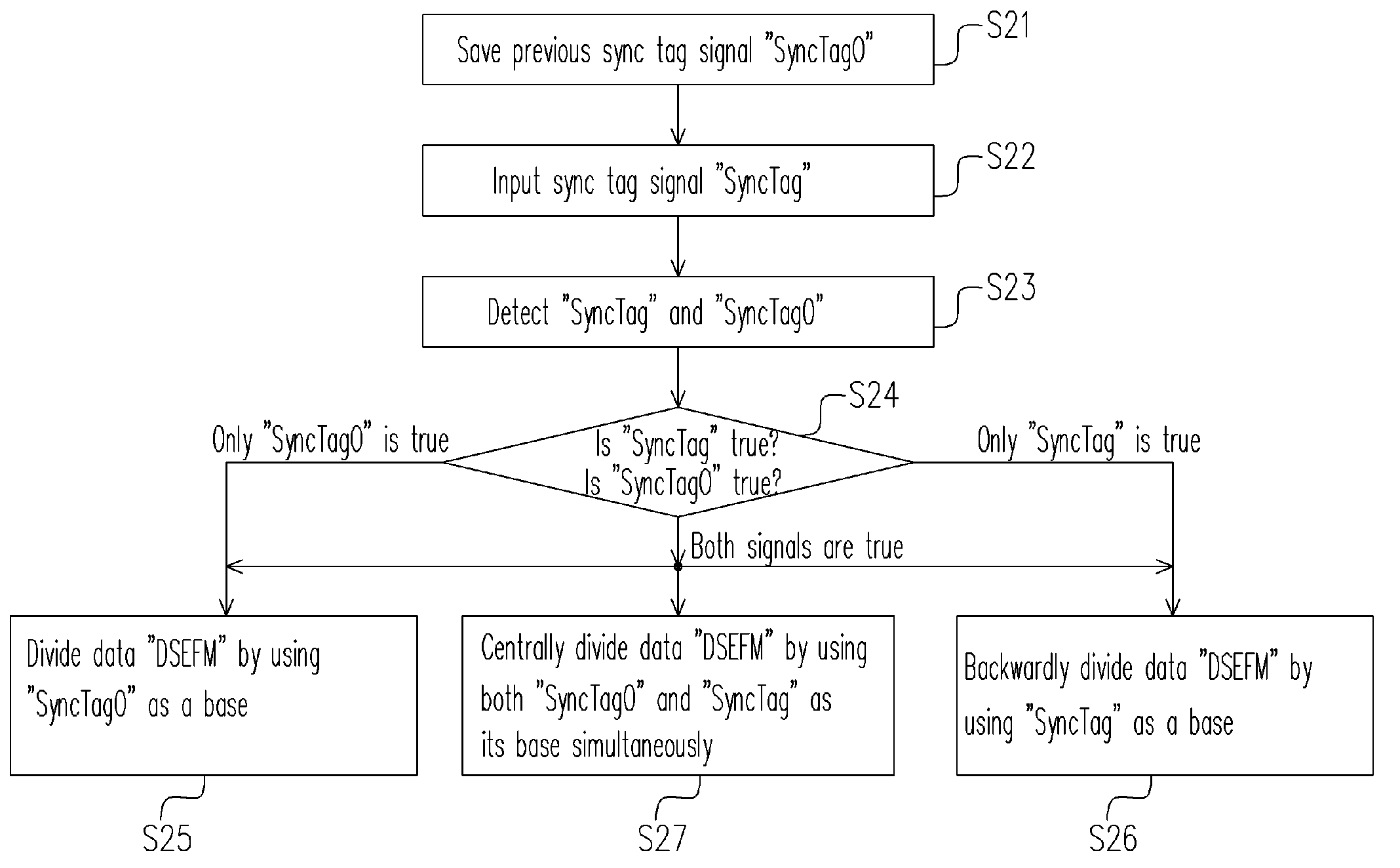
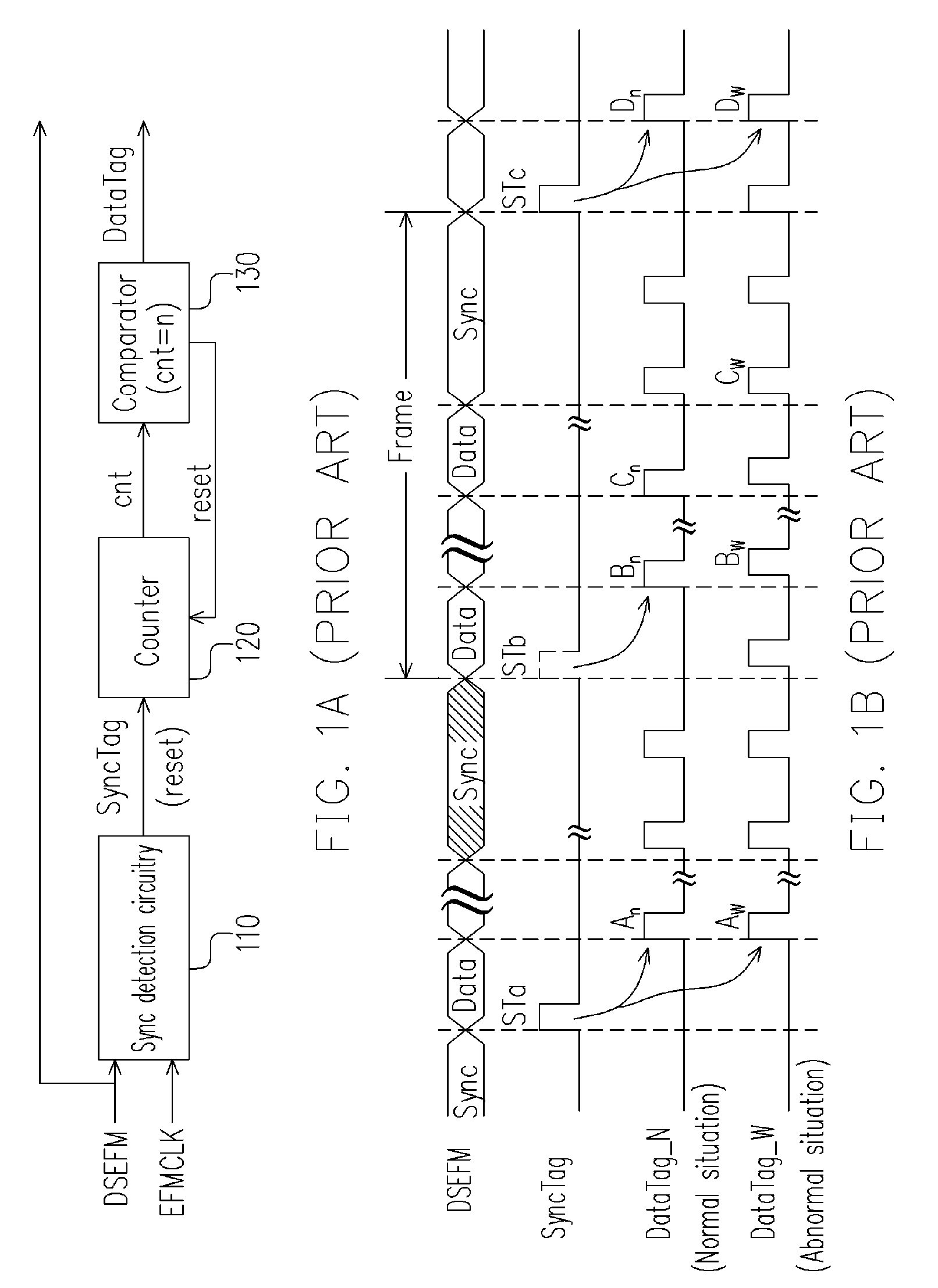
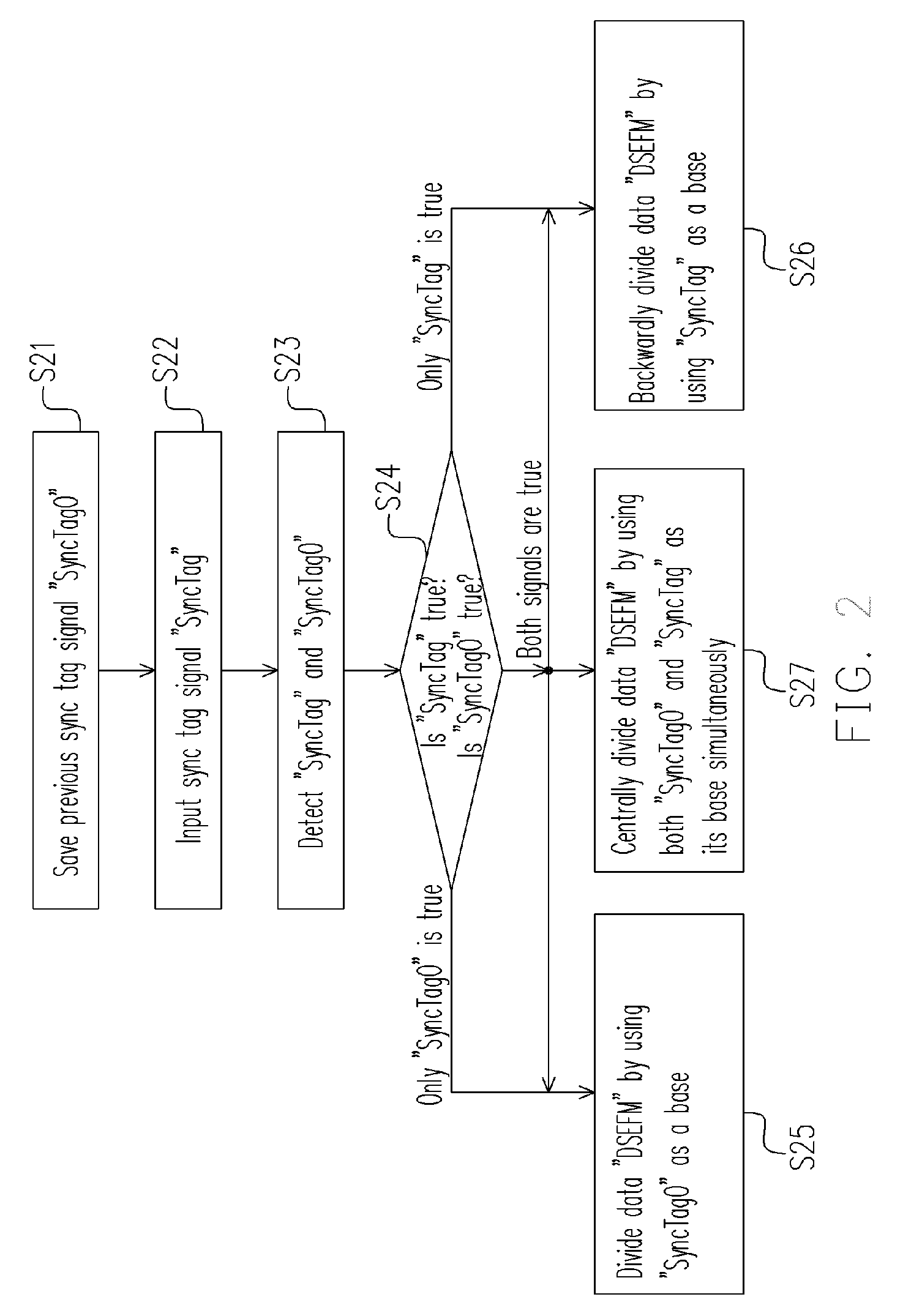
Method for sampling optic disc data and apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20050251671A1Accurate samplingImprove accuracyRecord information storageDigital recordingData signalComputer science
The present invention discloses a method for sampling optic disc data. The method includes the following steps. First, a first sync tag signal and a data signal are provided, and the previous first sync tag signal is saved as a second sync tag signal. Then, it is checked and determined whether the value of the first sync tag signal and the second sync tag signal is true or false so as to divide the data signal. Since the neighboring sync tag signals are detected simultaneously, and the timing for sampling the data in the frame is determined according to whether the two contiguous sync tag signals are true or false, the present invention can improve the disadvantages of the prior art.
Owner:TIAN HLDG
Morphological segmentation-based eye fundus image lesion detection method
InactiveCN106157279AAvoid interferenceHigh real-time operationImage analysisSpecial data processing applicationsMedicineMorphological segmentation
A fundus image lesion detection method based on morphological segmentation. First, the fundus image is smoothed and filtered, and the region growing method is used to locate the region where the optic disc is located; then the fundus background image with the exudate area removed is obtained through morphological processing, and is segmented by thresholding A mixed area image including blood vessels and hemorrhage is obtained; finally, the edge detection is performed by Kirsch operator and the blood vessel image is obtained by region growing. The invention avoids the possible interference caused by blood vessels with similar gray levels in other bleeding detection algorithms, and also speeds up the detection speed.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
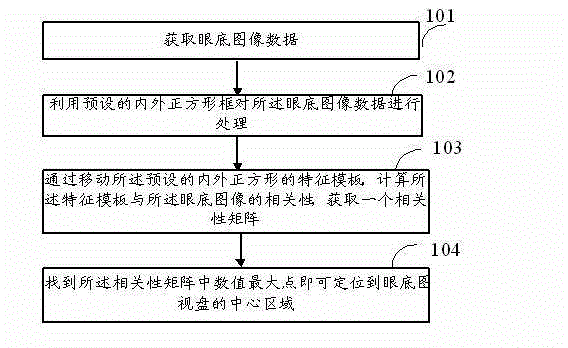
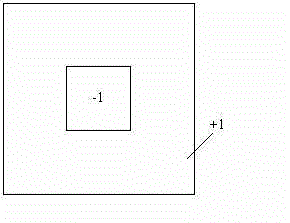
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) synthetic fundus image optic disc center positioning method and equipment
The invention discloses an OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) synthetic fundus image optic disc center positioning method and equipment. The OCT synthetic fundus image optic disc center positioning method comprises the following steps of: acquiring fundus image data; processing the fundus image data by utilizing a preset inner and outer square frames; calculating the correlation between a characteristic template and the fundus image by moving the characteristic template of the preset inner and outer square frames to acquire a correlation matrix; and finding the maximum numerical value point in the correlation matrix, so that a central area of the fundus image optic disc can be positioned. Data loss or high noise is not required in the fundus image acquisition, an optic disc area acquired by standard operation of an OCT instrument generally meets the characteristics that the central area of the optic disc is dark and the periphery is bright, and the optic disc area can be rapidly and accurately positioned; and therefore, the algorithm is higher in stability and higher in calculation speed and can be used for rapidly positioning and analyzing a lots of fundus images.
Owner:SHENZHEN CERTAINN TECH CO LTD
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
ActiveUS20130258285A1Efficiently presentedImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingTomographic image
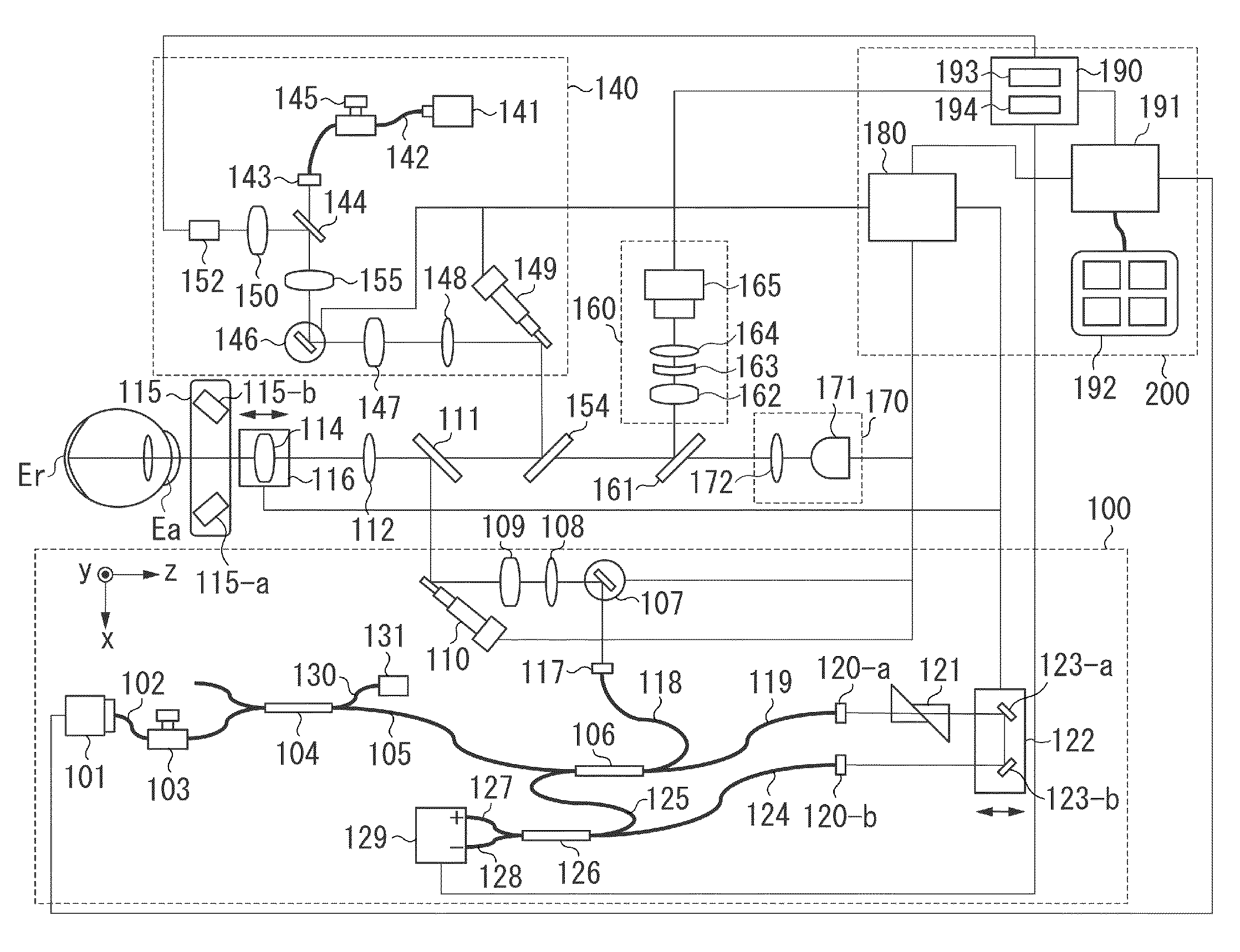
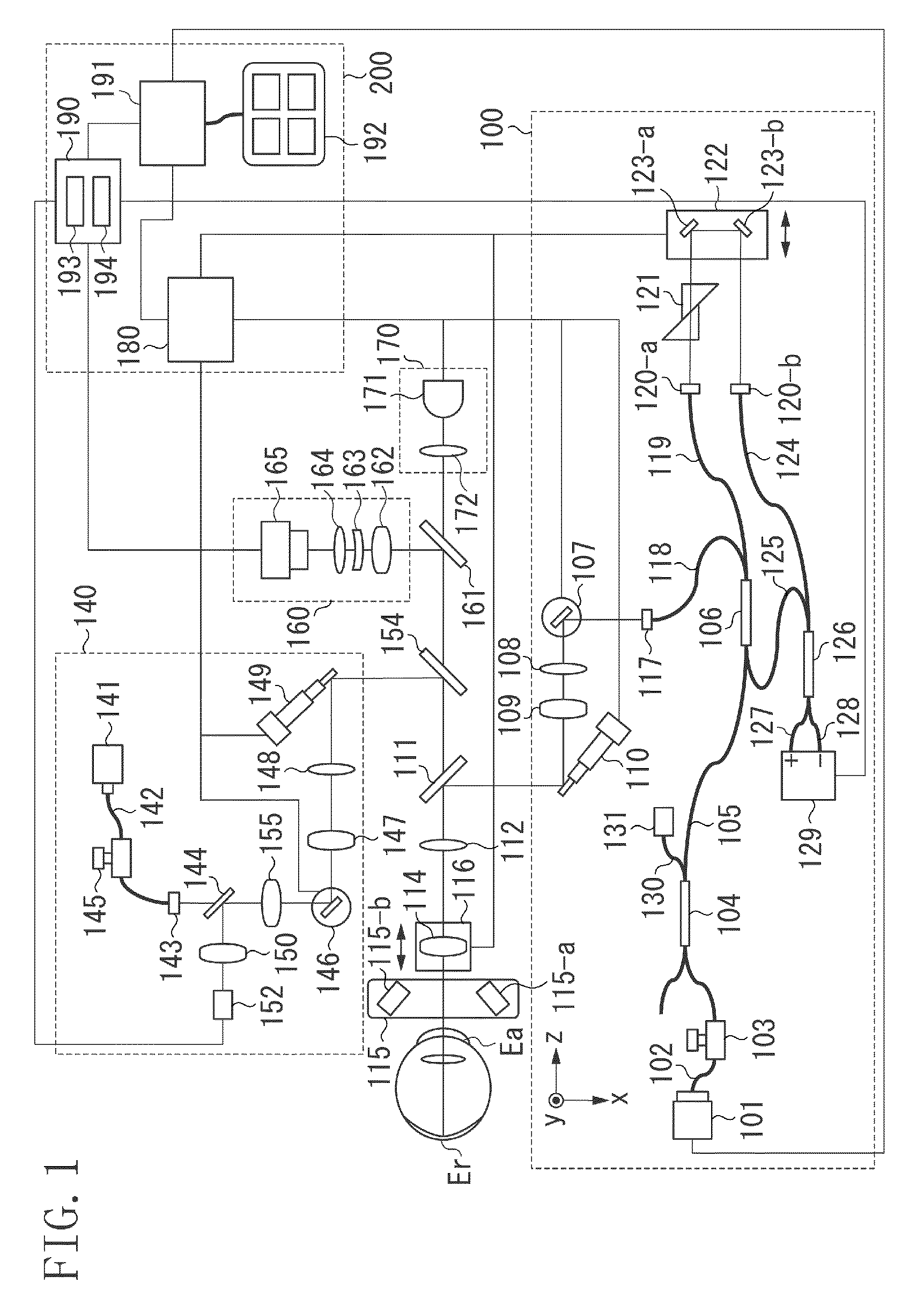
An image processing apparatus includes an obtaining unit configured to obtain a tomographic image including an optic disc portion and a macula portion of a fundus of a subject's eye, an analysis unit configured to analyze the optic disc portion and the macula portion of the fundus in the tomographic image, and a display control unit configured to display side-by-side, on a display unit, a display pattern indicating a result of analyzing the optic disc portion, and a display pattern indicating a result of analyzing the macula portion.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods and systems for assessing retinal images, and obtaining information from retinal images
ActiveUS20180181833A1Easy to useImprove reliabilityImage enhancementMedical imagingPathology diagnosisRetinal image
A method of assessing the quality of an retinal image (such as a fundus image) includes selecting at least one region of interest within a retinal image corresponding to a particular structure of the eye (e.g. the optic disc or the macula), and a quality score is calculated in respect of the, or each, region-of-interest. Each region of interest is typically one associated with pathology, as the optic disc and the macula are. Optionally, a quality score may be calculated also in respect of the eye as a whole (i.e. over the entire image, if the entire image corresponds to the retina).
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com