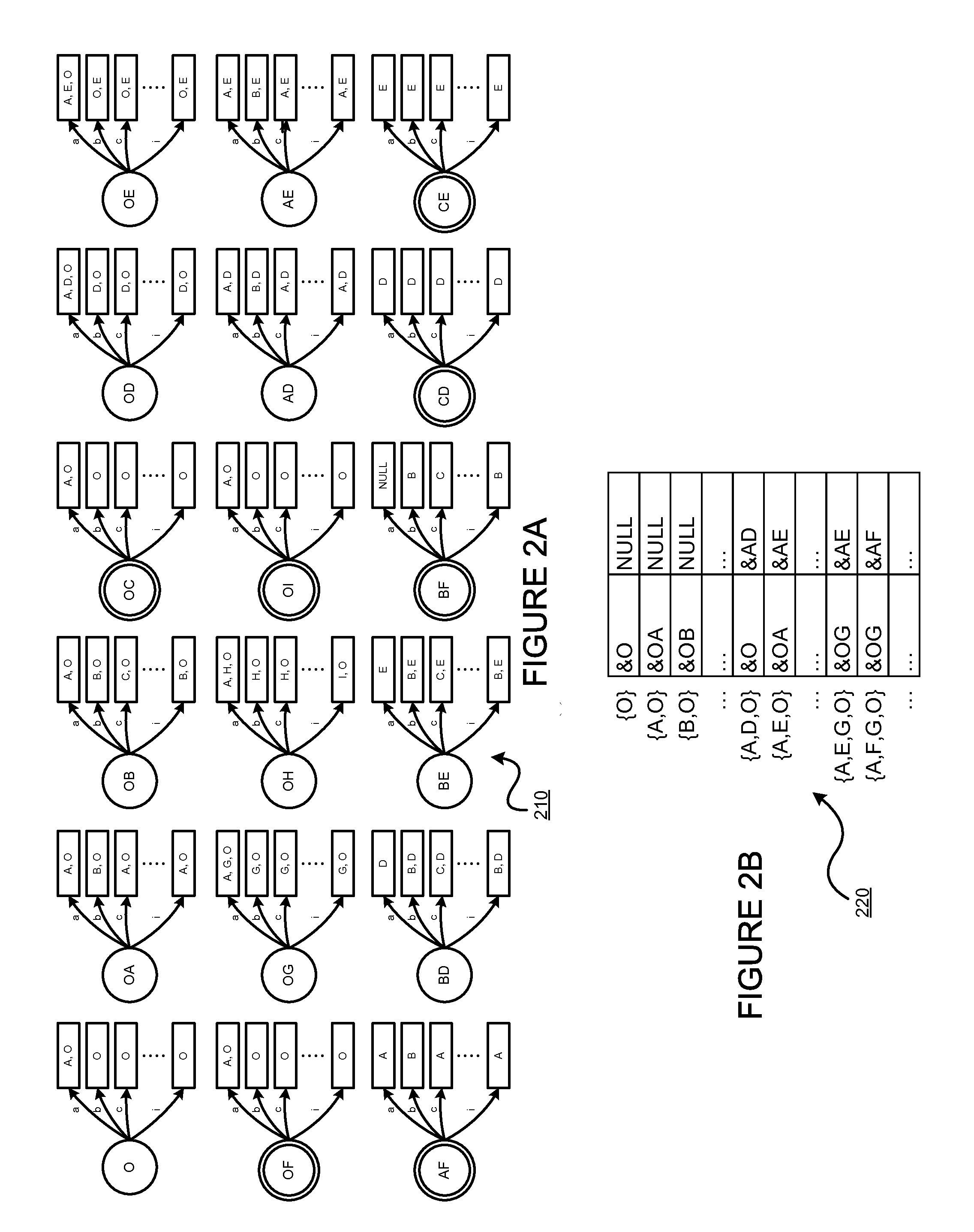
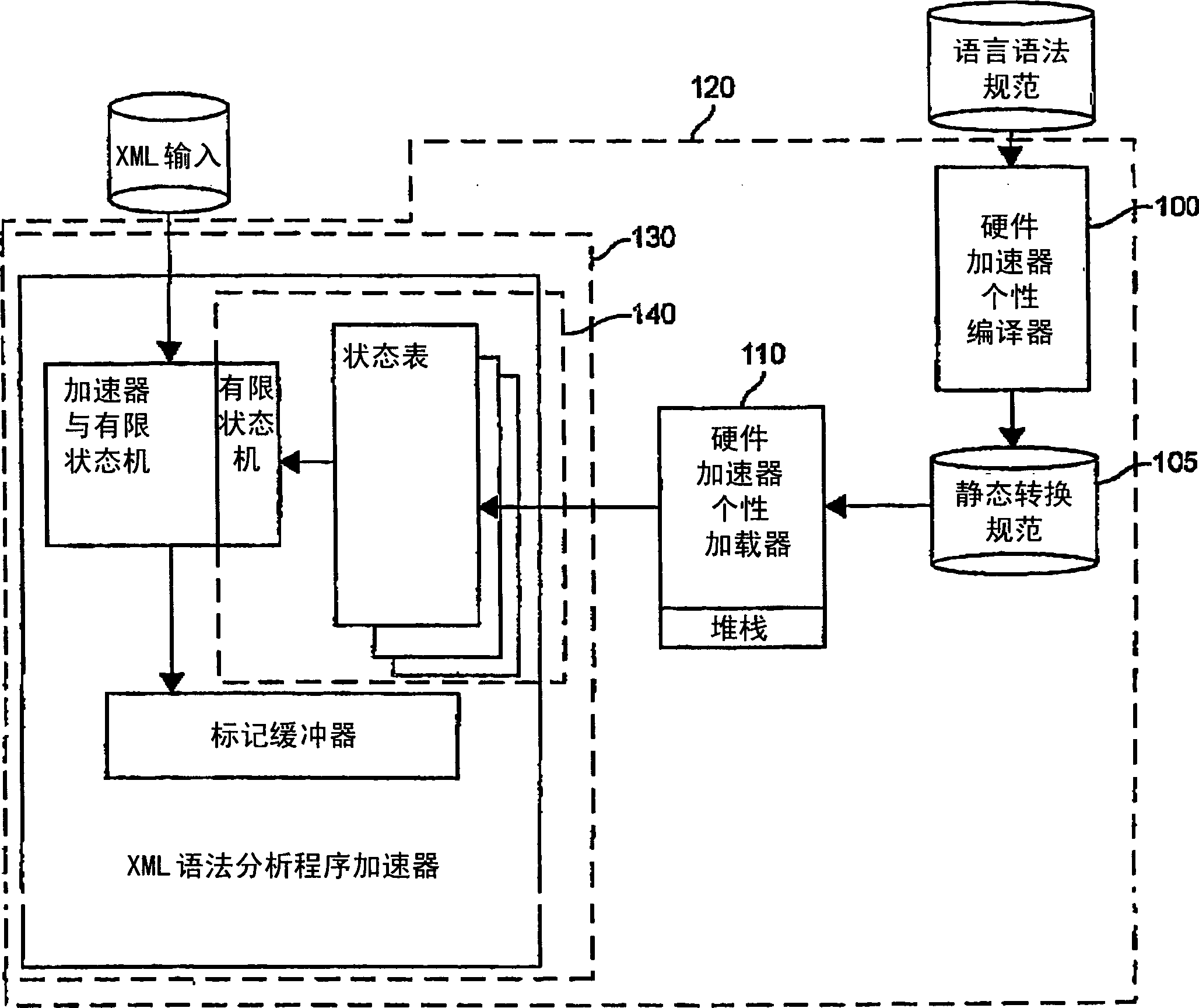
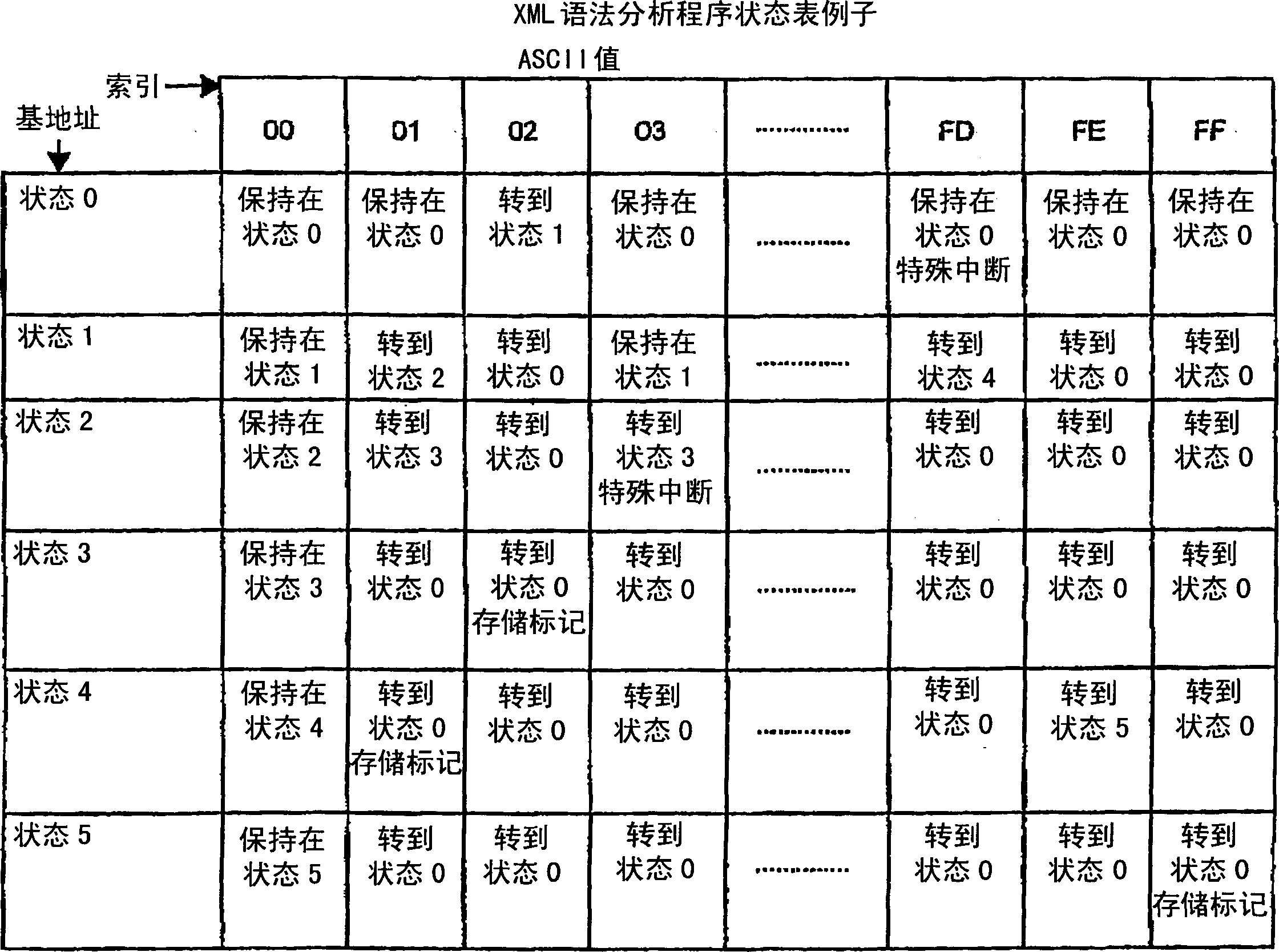
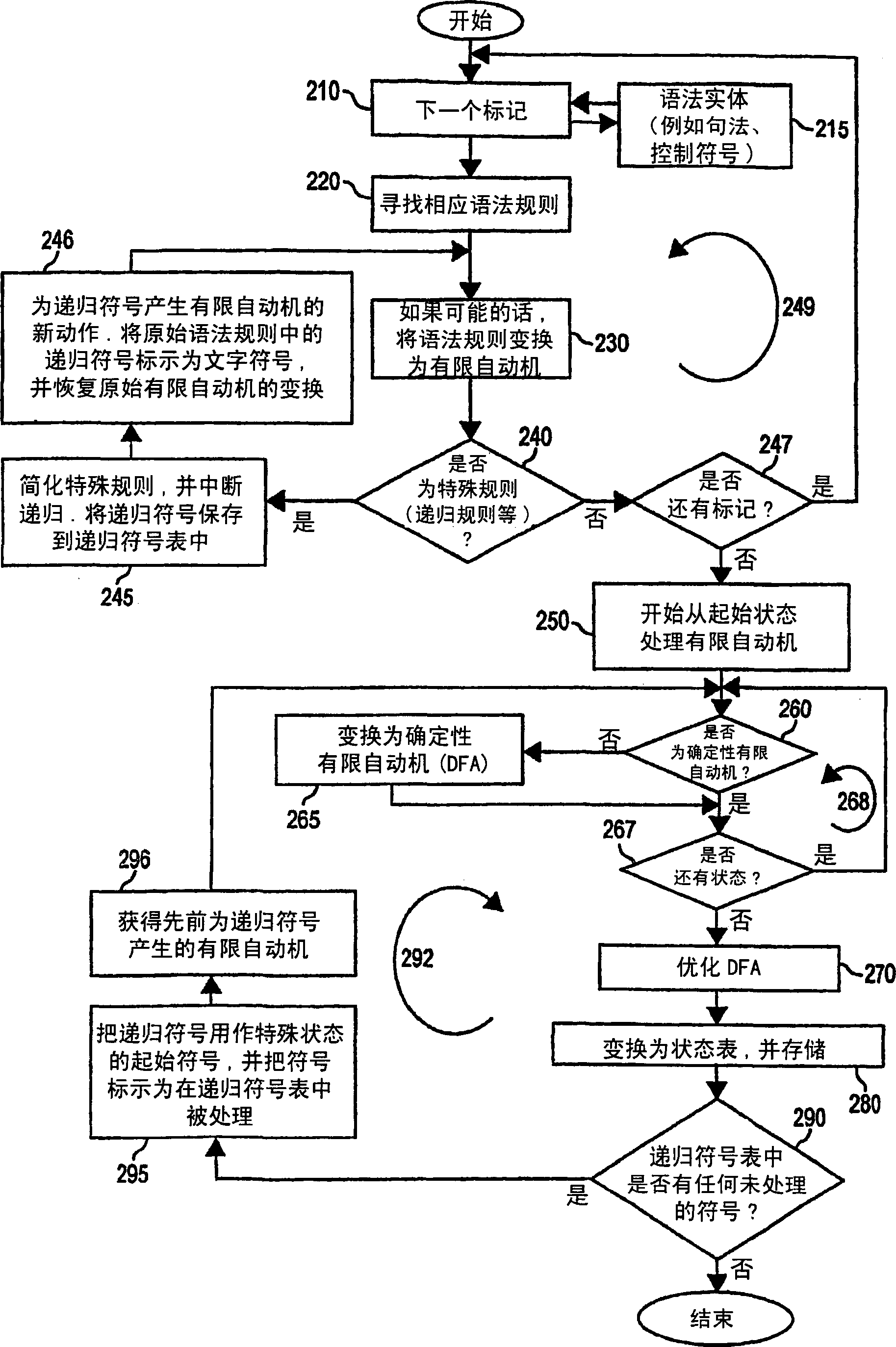
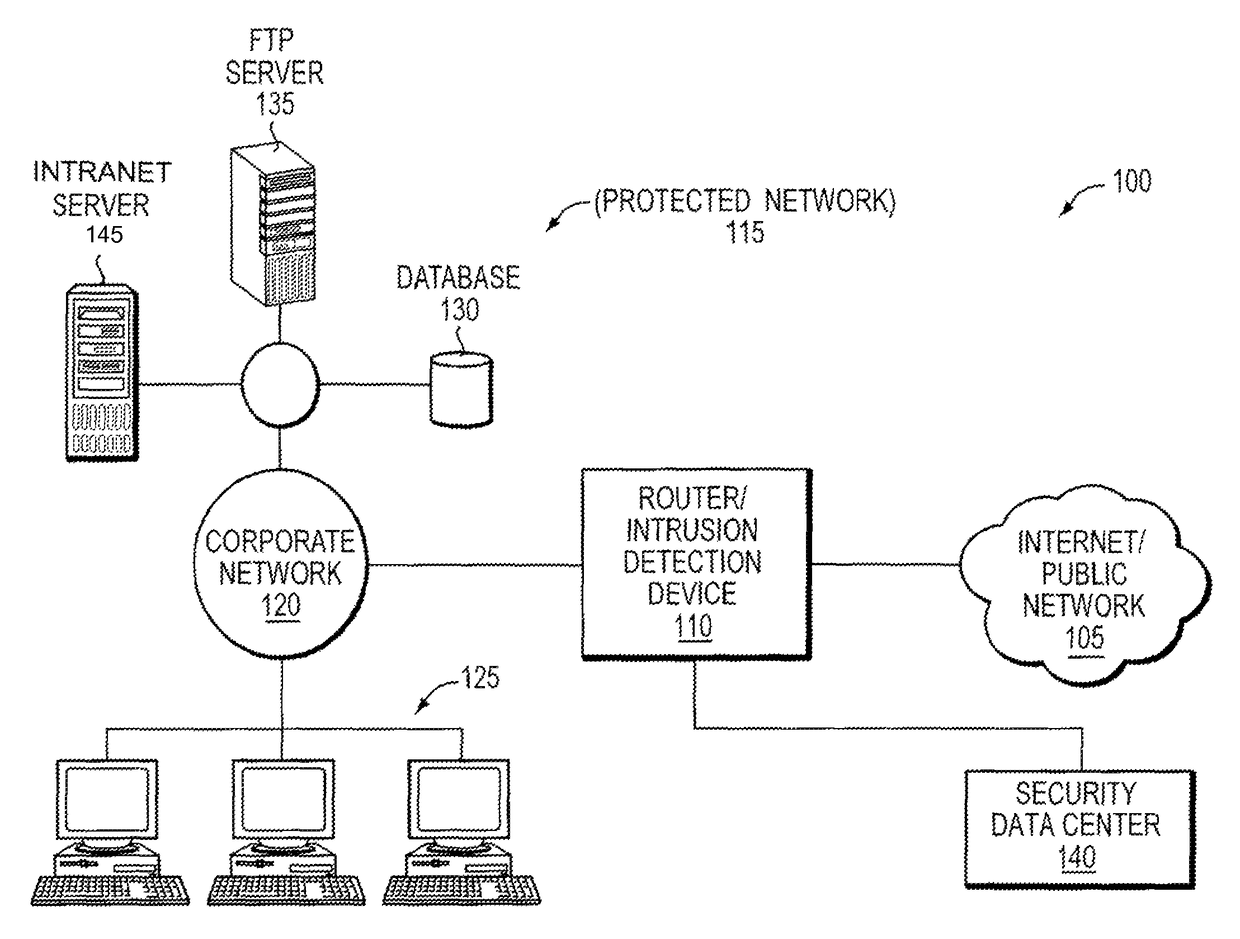
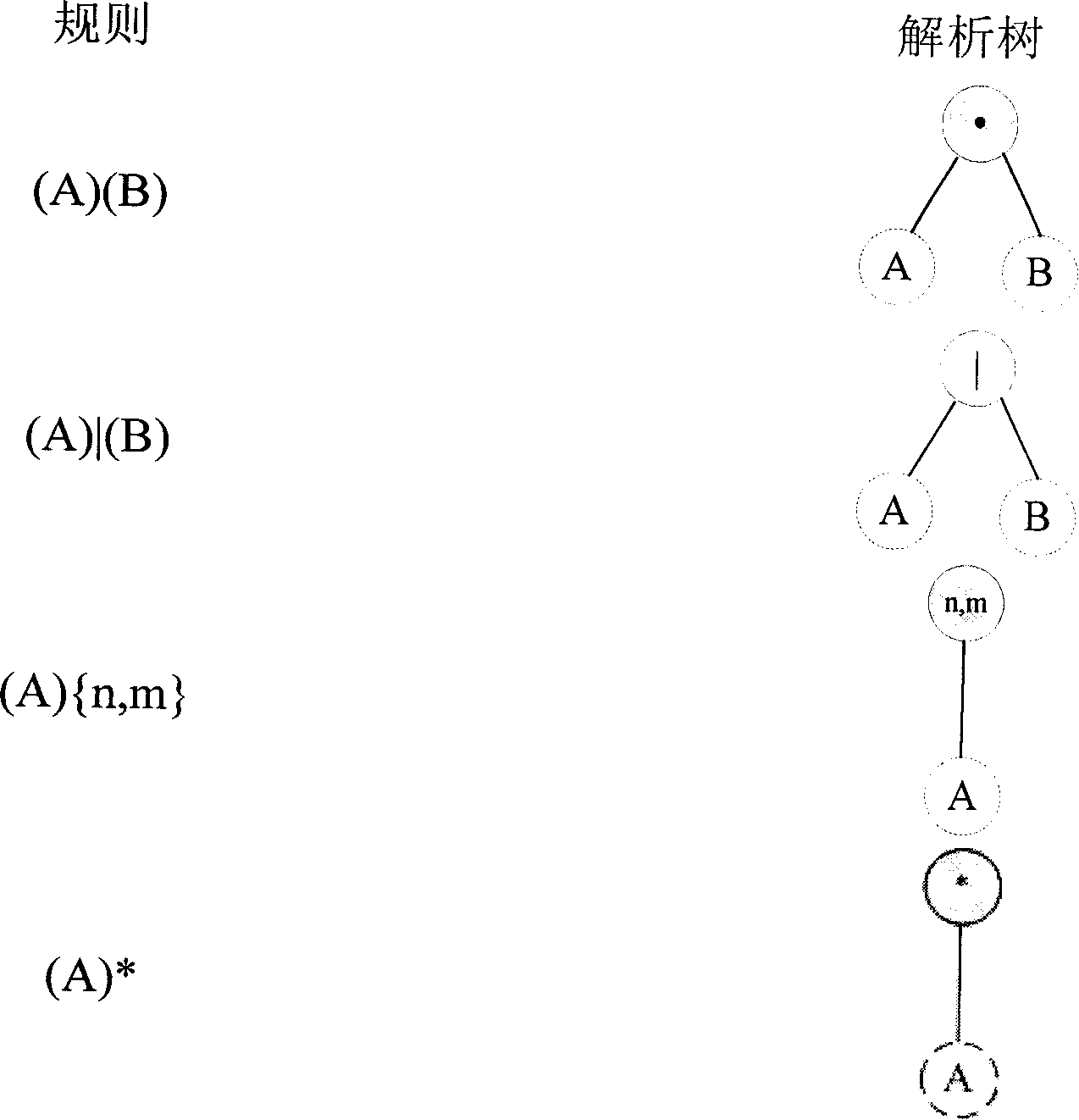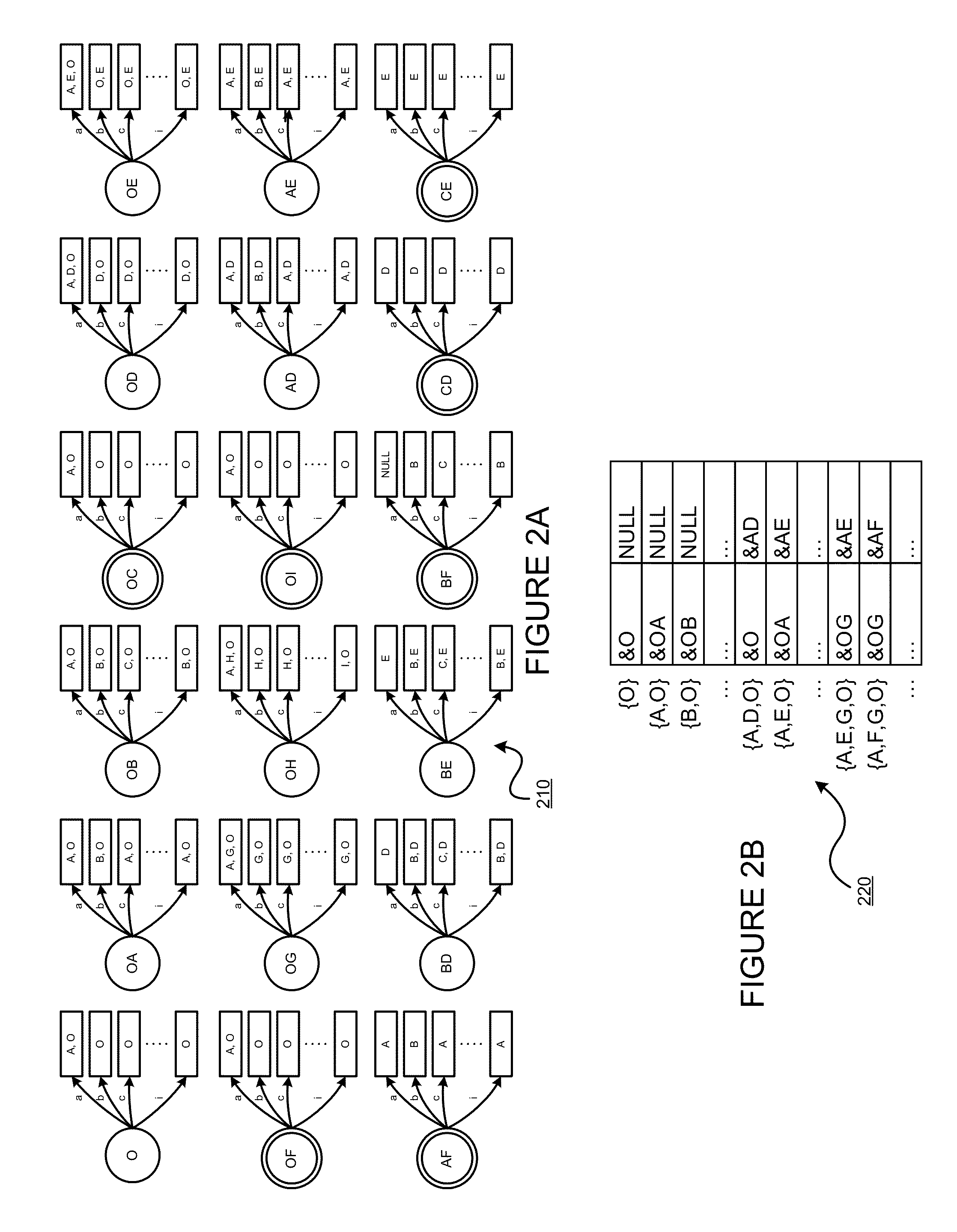Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Nondeterministic finite automaton" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
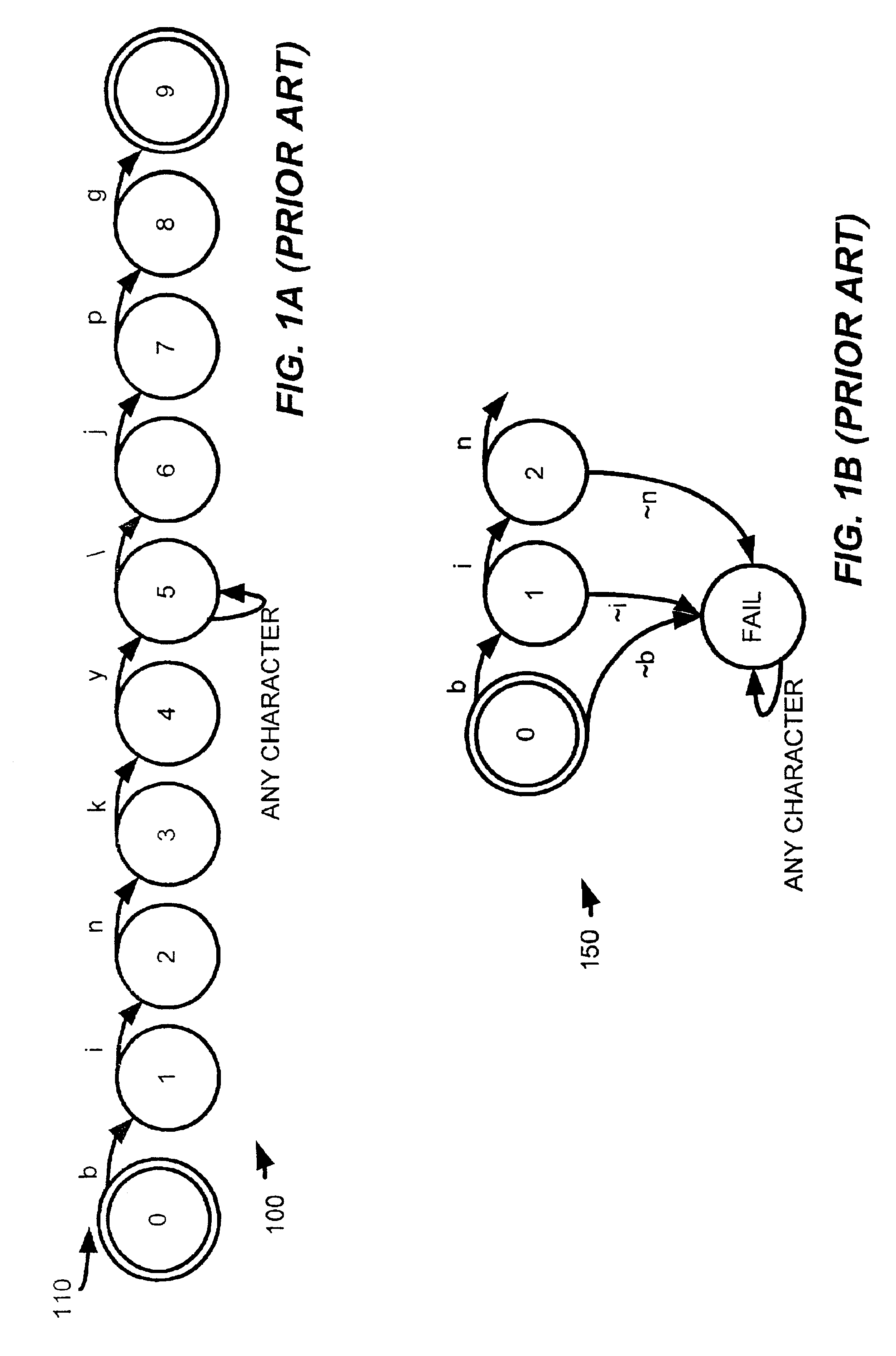
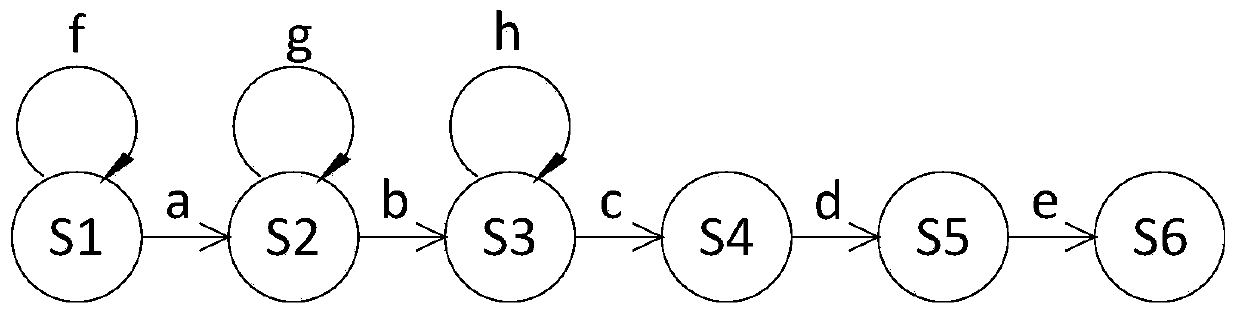
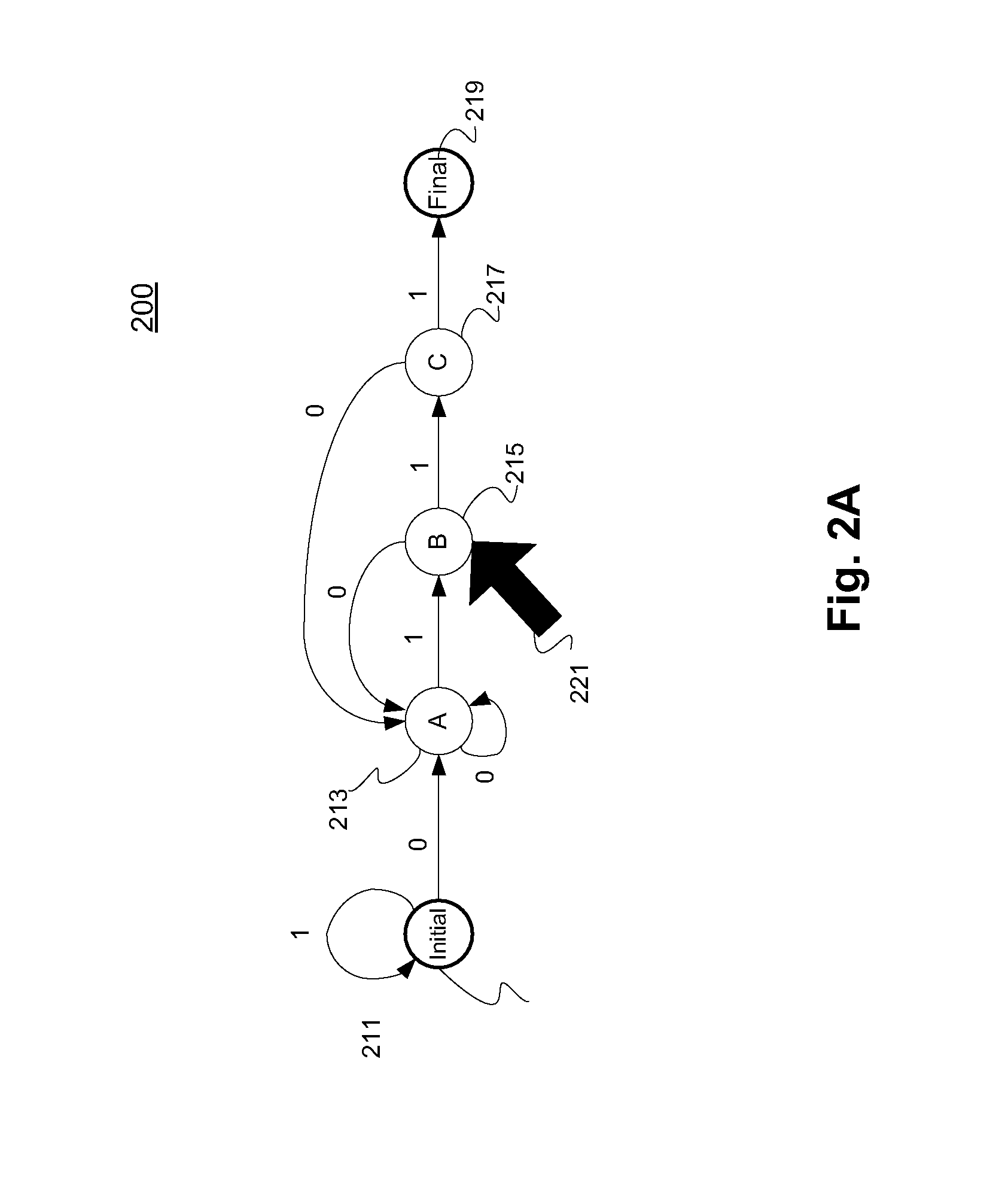
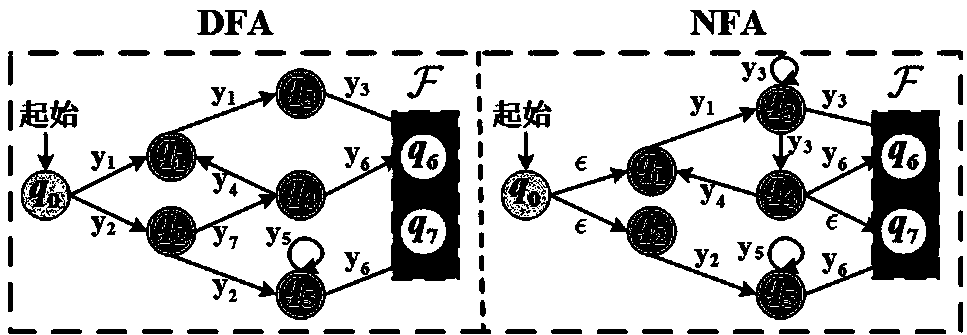
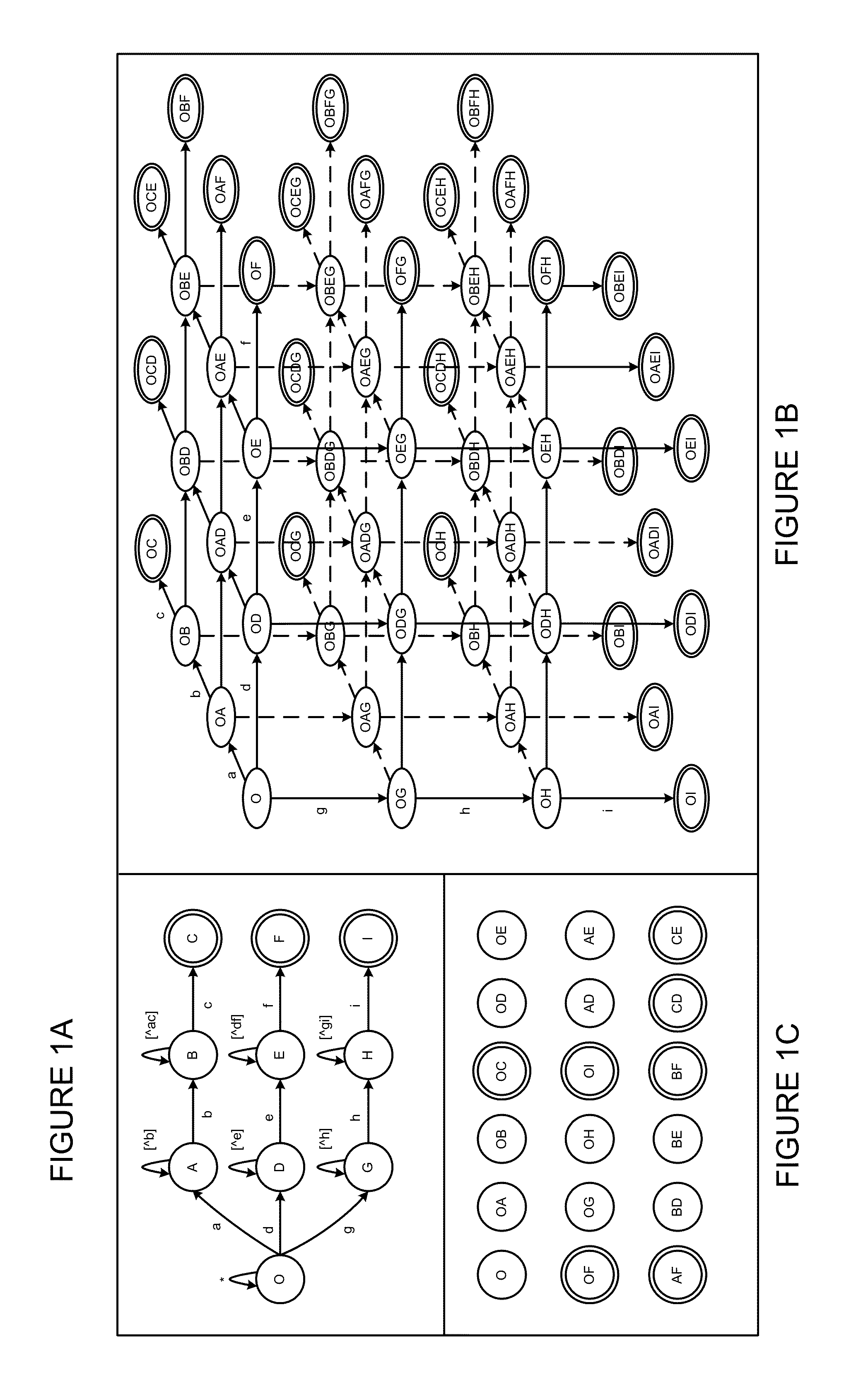
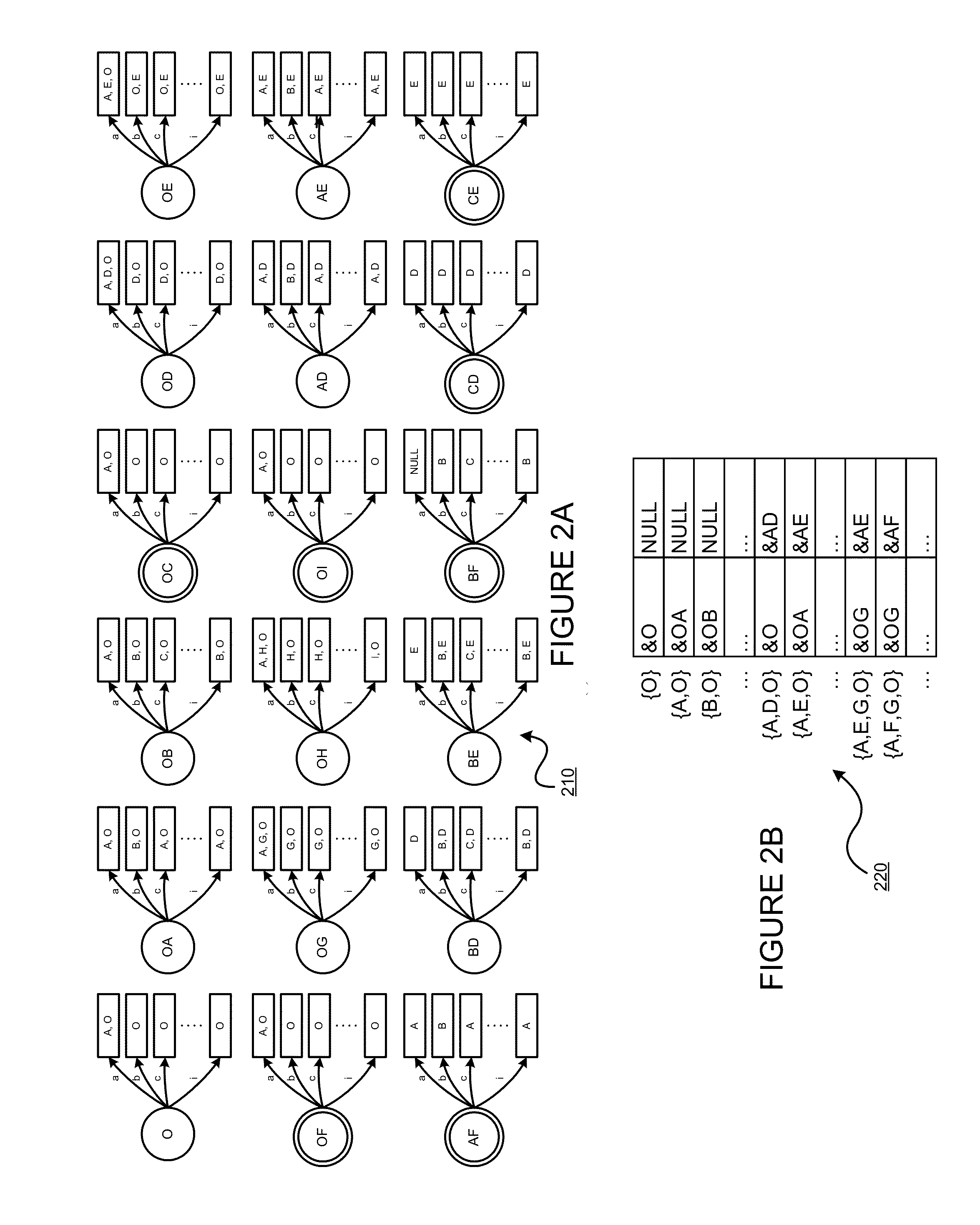
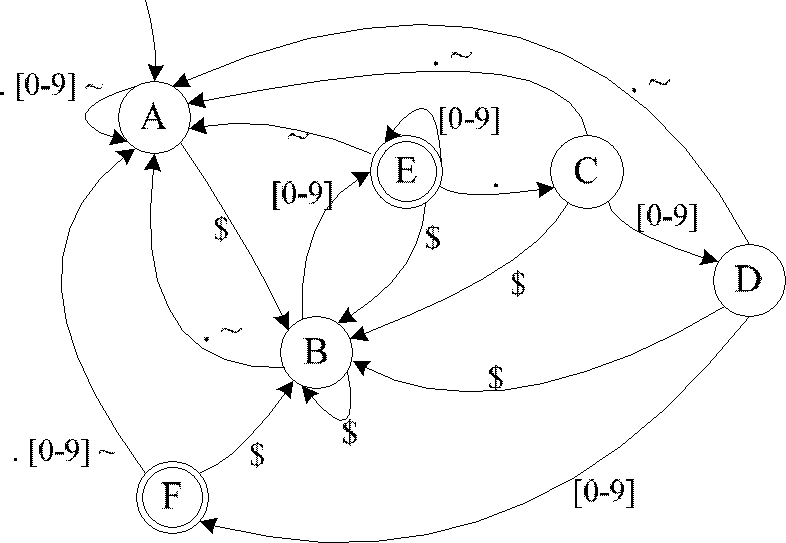
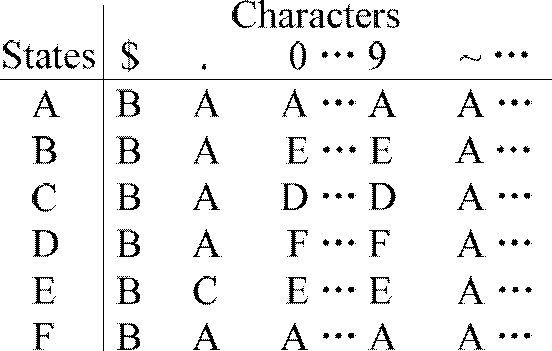
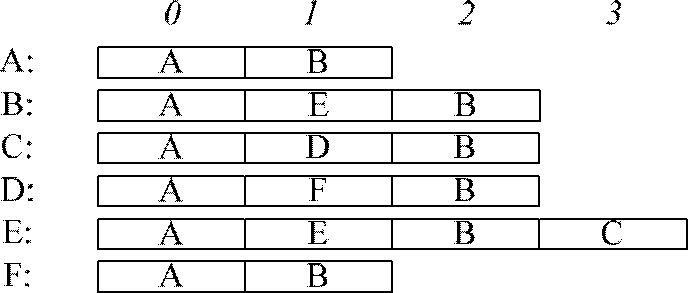
In automata theory, a finite state machine is called a deterministic finite automaton (DFA), if...
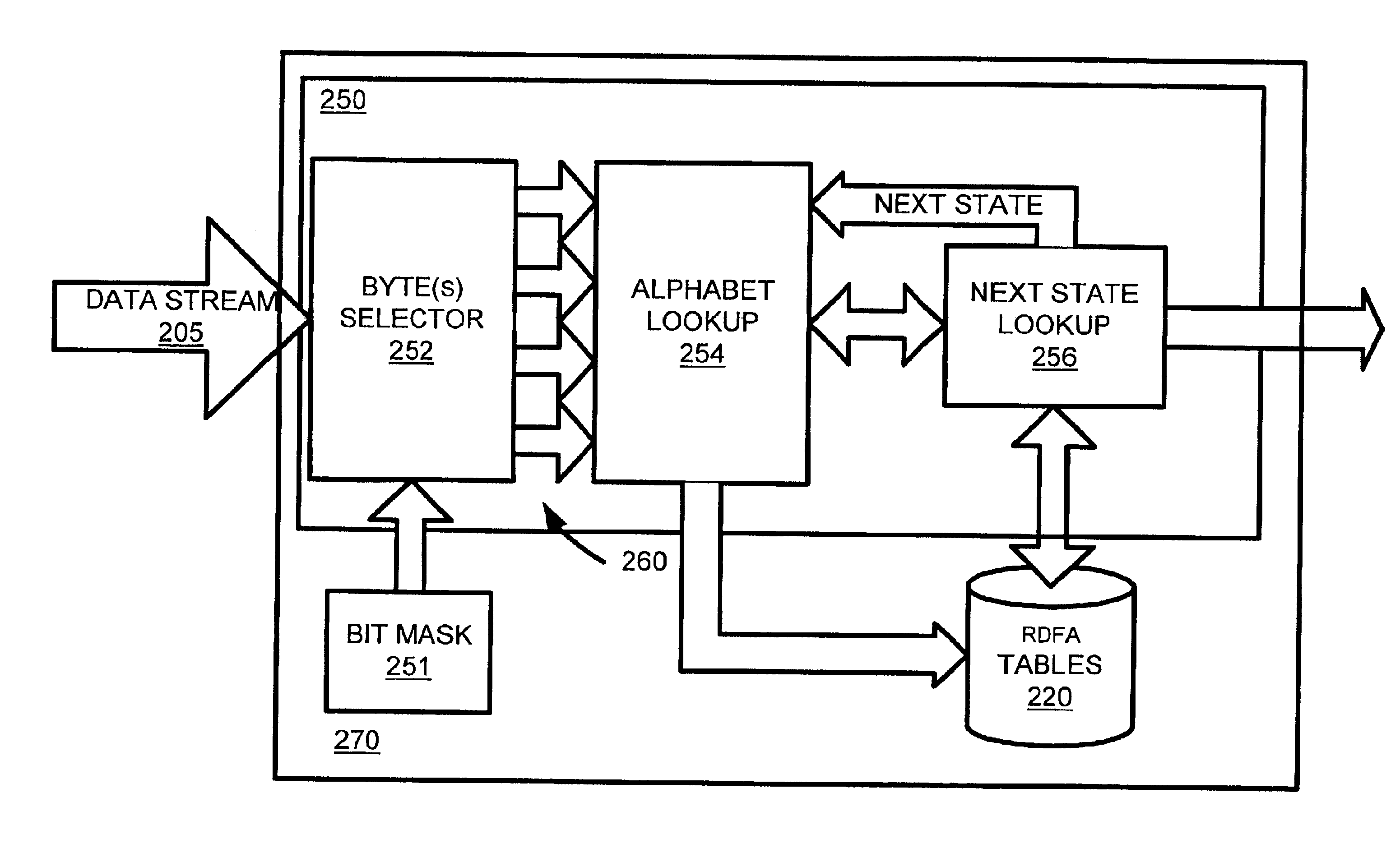
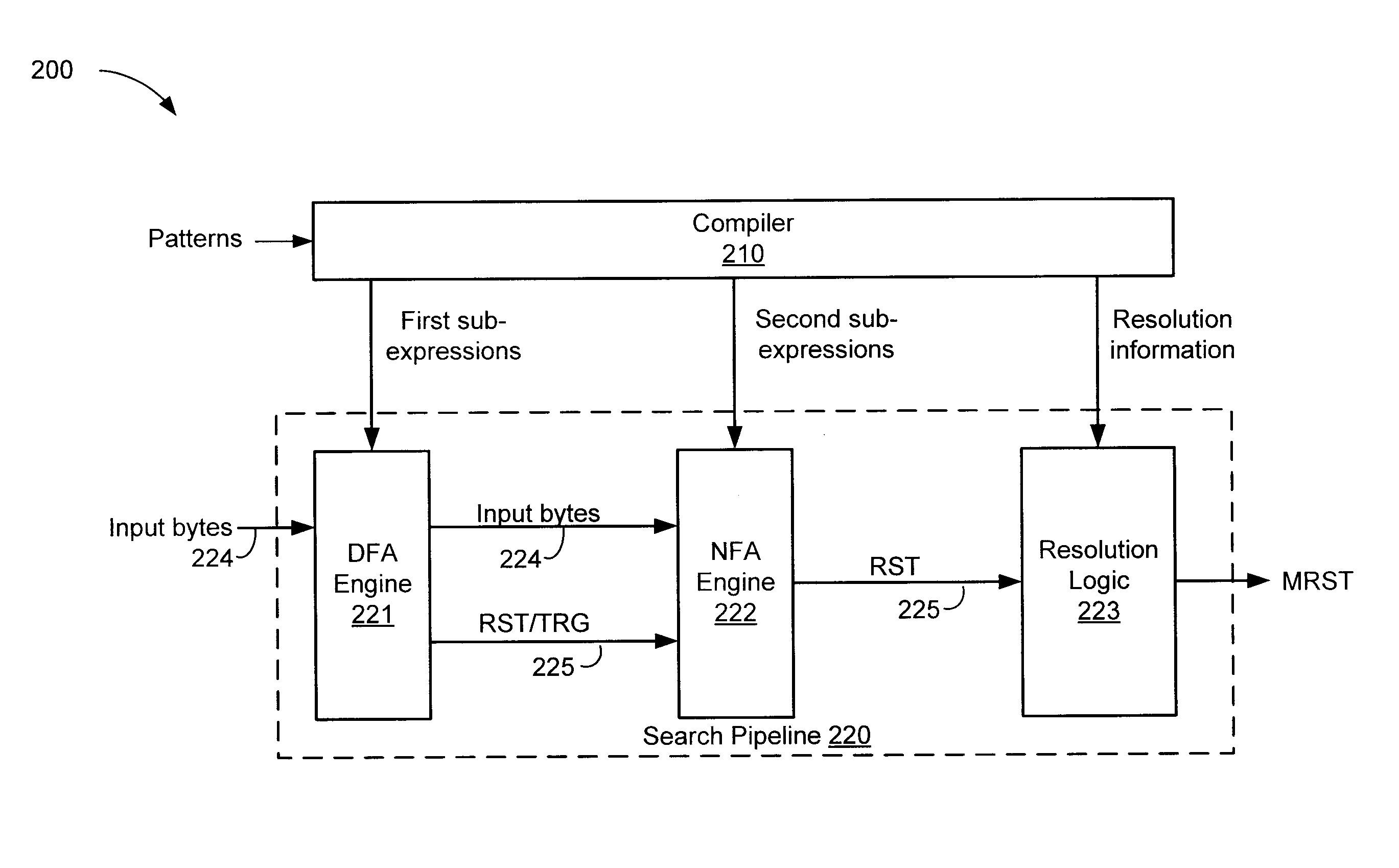
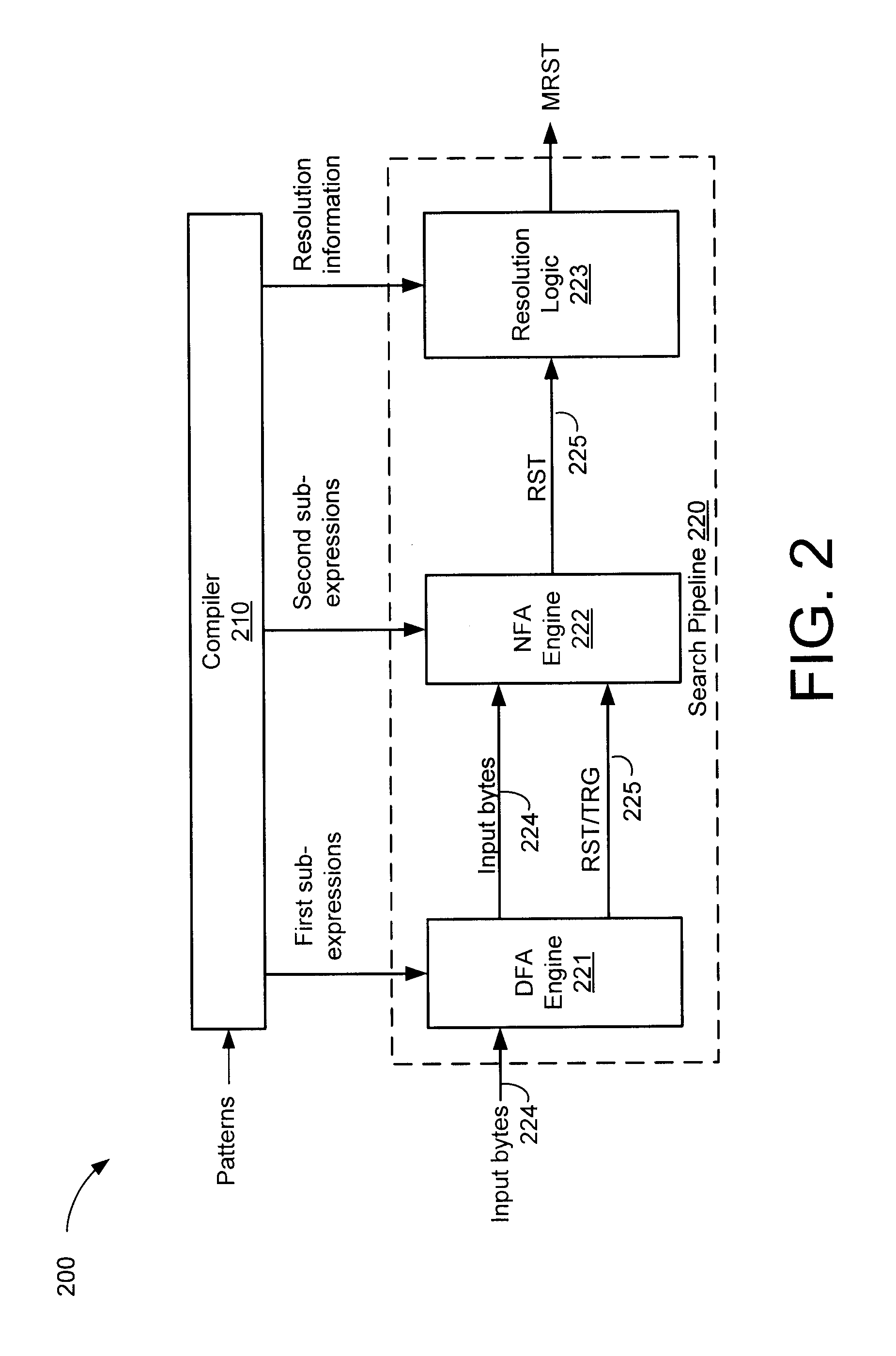
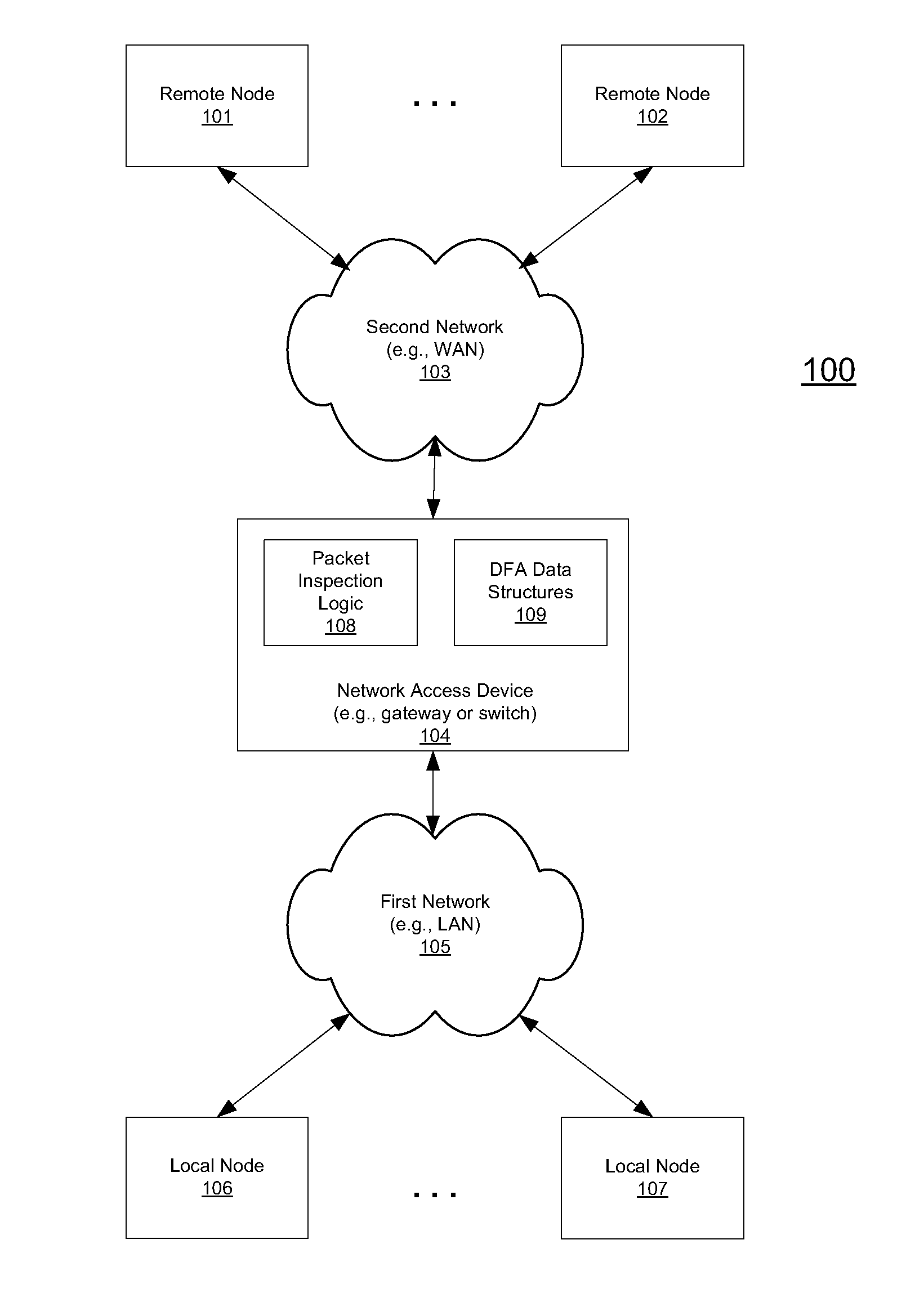
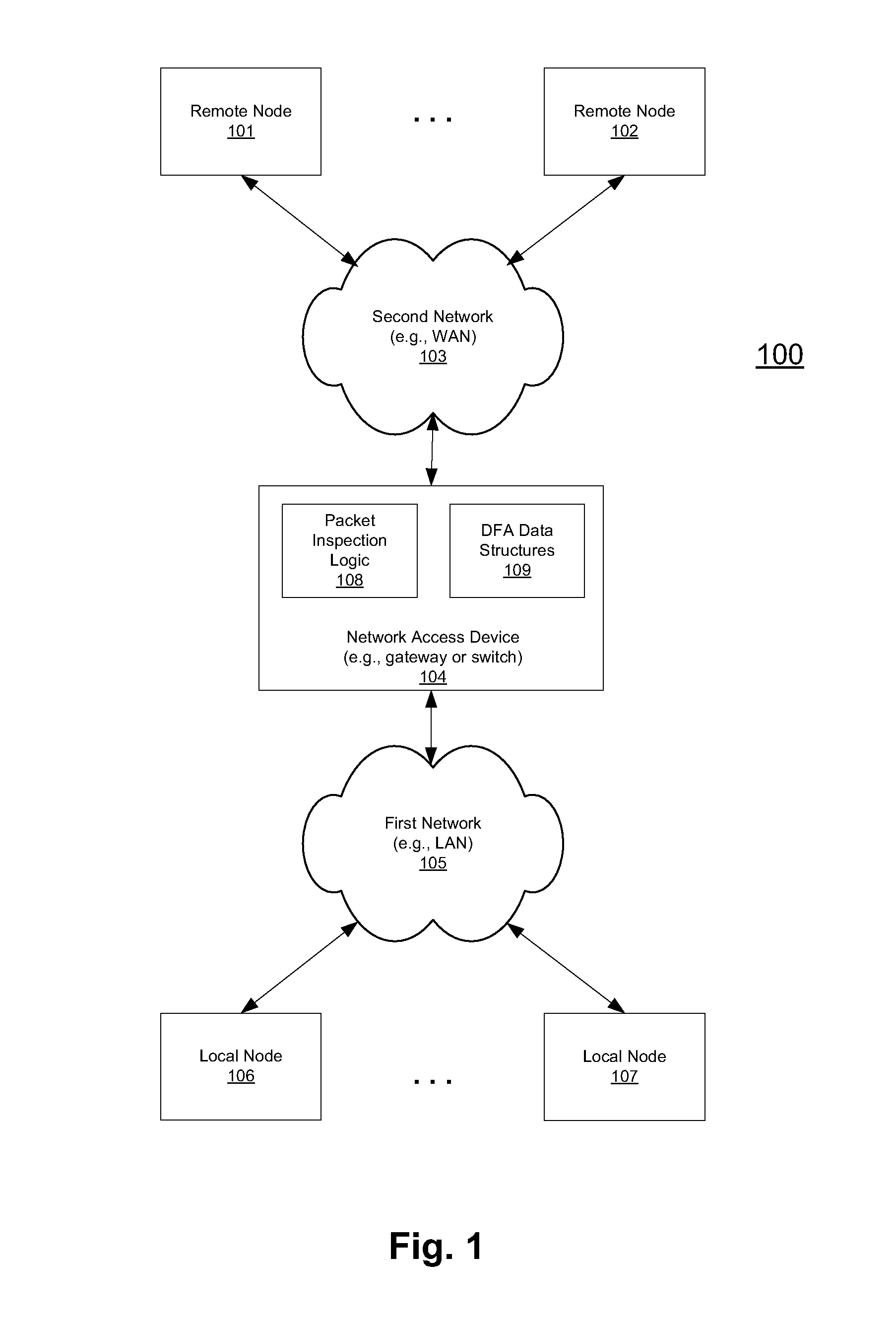
High speed data stream pattern recognition
InactiveUS6856981B2Increase speedLow memory storage requirementDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsData streamState dependent
A system and method in accordance with the present invention determines in real-time the portions of a set of characters from a data or character stream which satisfies one or more predetermined regular expressions. A Real-time Deterministic Finite state Automaton (RDFA) ensures that the set of characters is processed at high speeds with relatively small memory requirements. An optimized state machine models the regular expression(s) and state related alphabet lookup and next state tables are generated. Characters from the data stream are processed in parallel using the alphabet lookup and next state tables, to determine whether to transition to a next state or a terminal state, until the regular expression is satisfied or processing is terminated. Additional means may be implemented to determine a next action from satisfaction of the regular expression.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
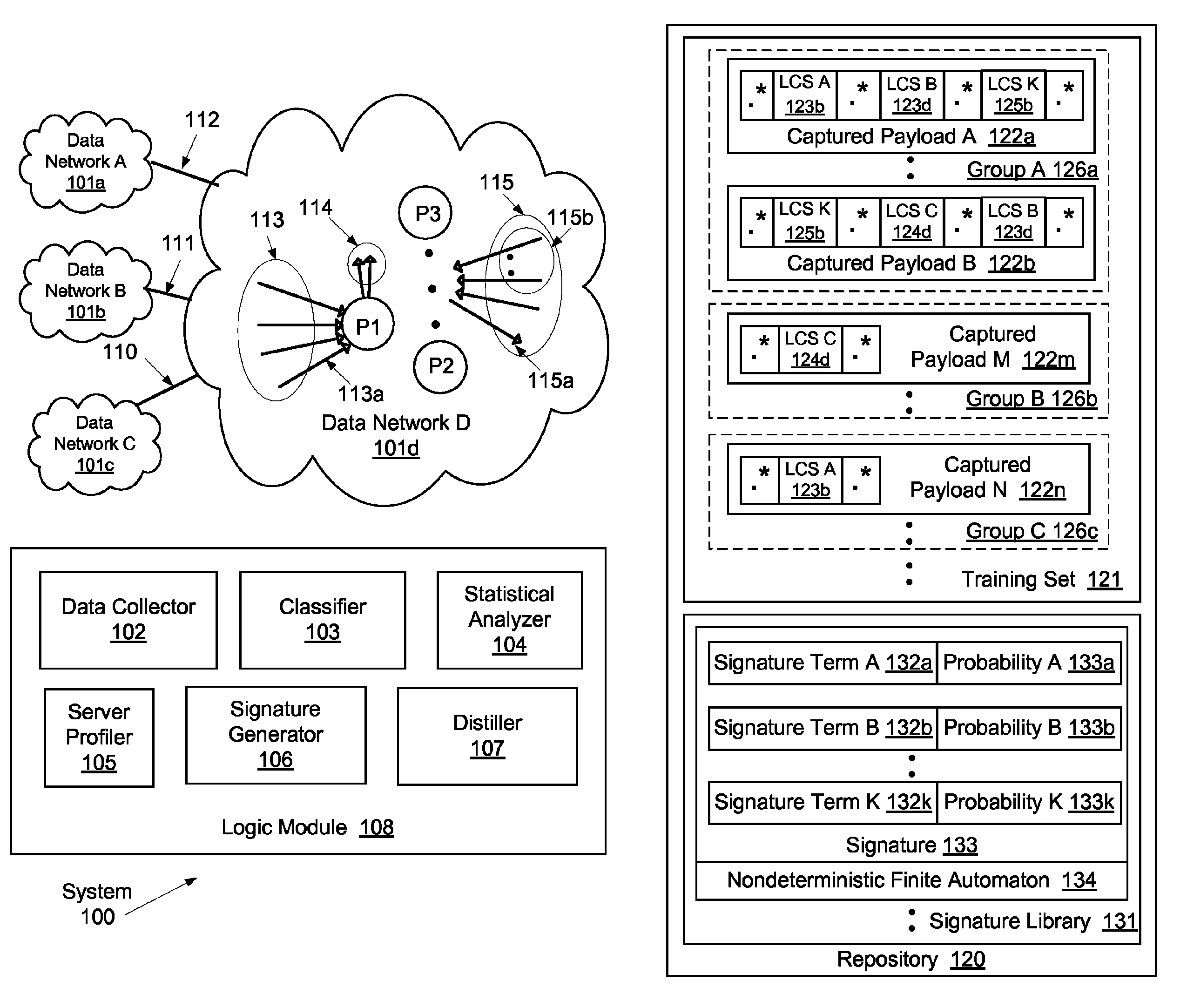
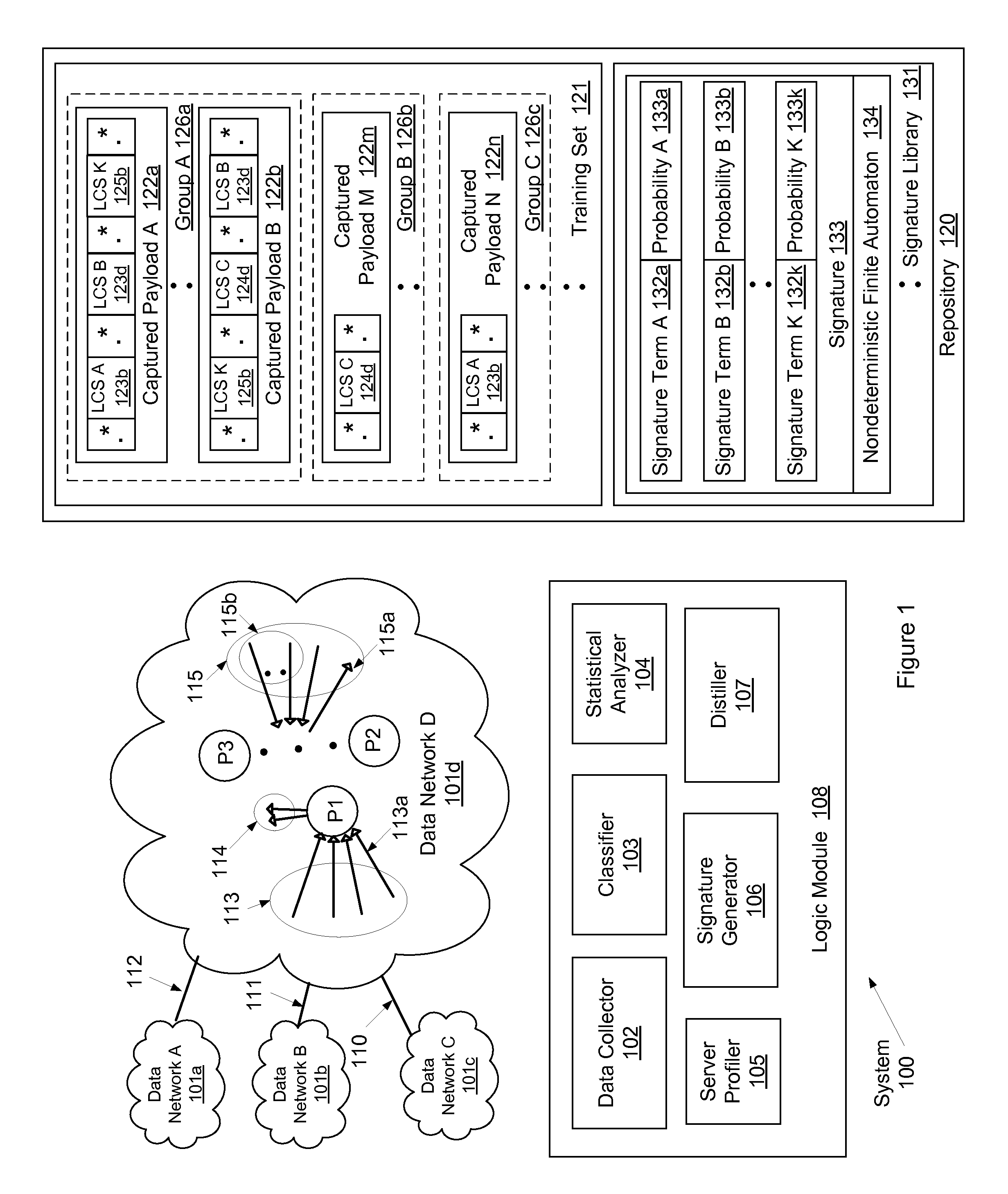
System and method for determining network application signatures using flow payloads
ActiveUS8964548B1Error preventionTransmission systemsNondeterministic finite automatonComputer science
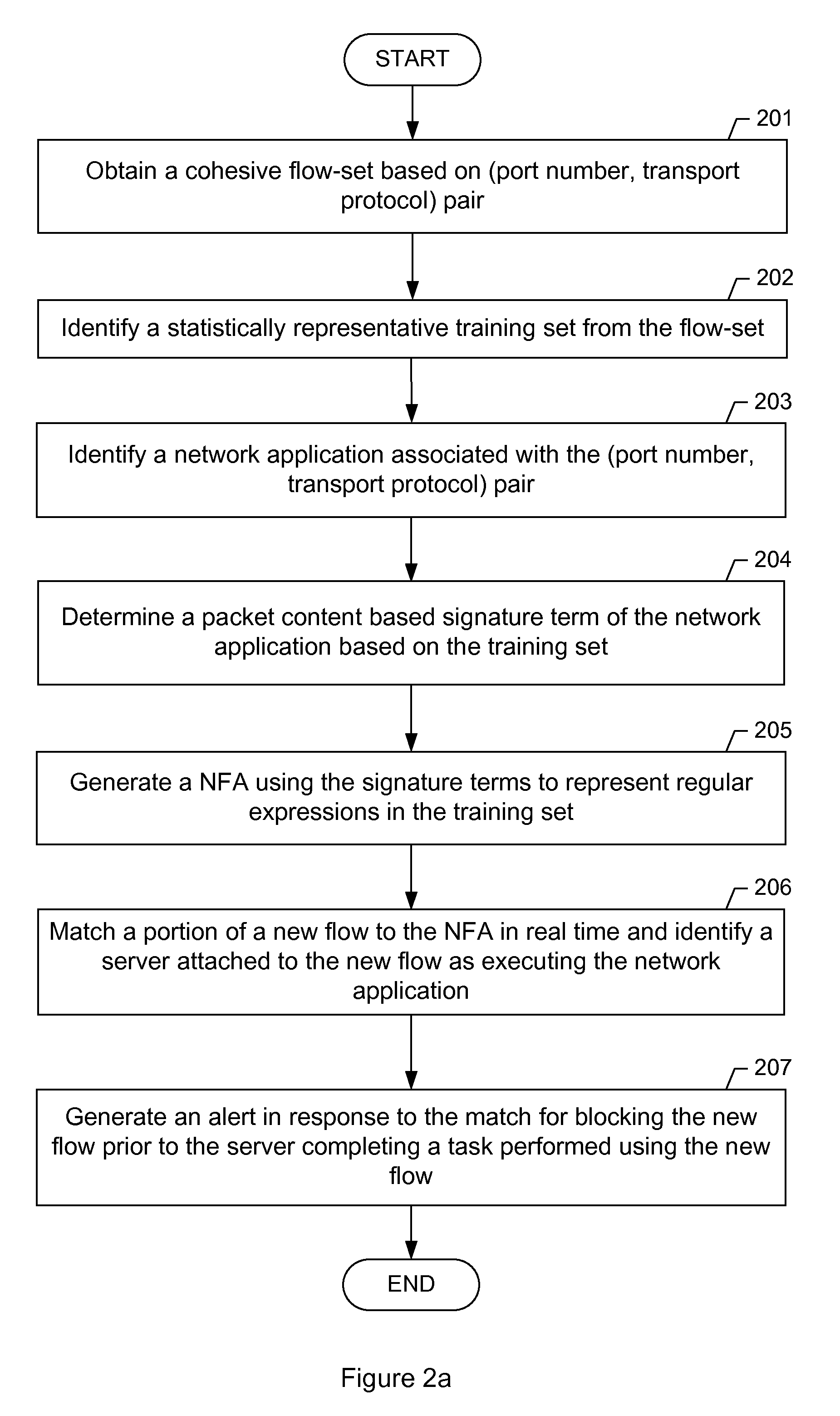
A method for profiling network traffic of a network is presented. The method includes obtaining a cohesive flow-set based on a (port number, transport protocol) pair, identifying a statistically representative training set from the flow-set, identifying a network application associated with the (port number, transport protocol) pair, determining a packet content based signature term of the network application based on the training set, generate a nondeterministic finite automaton (NFA) using the signature terms to represent regular expressions in the training set, matching a portion of a new flow to the NFA in real time and identify a server attached to the new flow as executing the network application, and generate an alert in response to the match for blocking the new flow prior to the server completing a task performed using the new flow.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for matching in speedup regular expression based on finite automaton containing memorization determination
InactiveCN101201836AReduce development difficultyReduce time spentSpecial data processing applicationsMemory footprintPattern matching
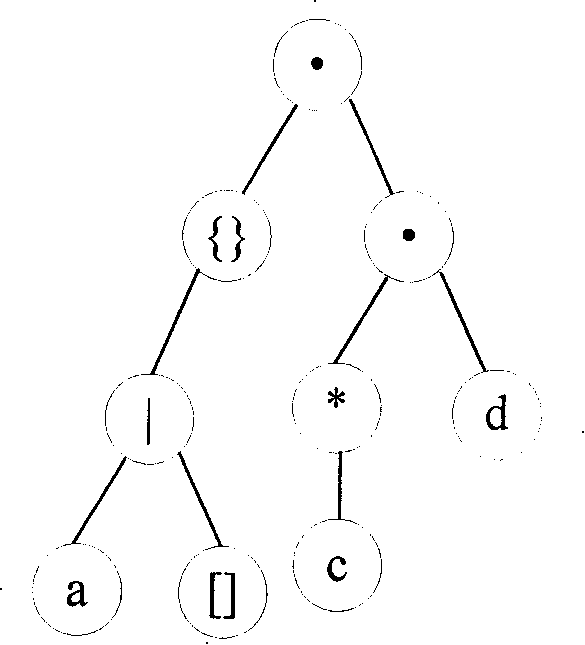
The invention discloses a matching and accelerating method of a regular expression based on a deterministic finite automaton with memory, including a rule compiler of the regular expression and a pattern matching engine; the rule compiler of the regular expression firstly transforms the regular expression into an analytic tree, and then transforms the analytic tree into a nondeterministic finite automaton with memory and the deterministic finite automaton with memory respectively; the pattern matching engine can accelerate pattern matching by using the deterministic finite automaton with memory generated by the rule compiler. The invention has the advantages that: 1) by directly supporting repeat operators, the compiler does not need to unfold the repeat expression, thus the difficulty of the development of the compiler is greatly reduced and the memory occupation and the compile time of the compiler are decreased as well; 2) for the same reason, the volume of a rules database generated by the compiler can be reduced, so the cost and complexity of the pattern matching engine can be lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Minimizing state lists for non-deterministic finite state automatons
A method and apparatus are disclosed for determining whether an input string of characters matches a pattern. The pattern has the form of an activator expression, a counter expression, and a tail. The method involves monitoring one or more active states associated with the pattern, and comparing each character to the activator expression and the counter expression for each of the one or more active states. An input character match to the activator expression comprises an activator match, and a character match to the counter expression without matching the activator expression comprises a non-activator match. The number of one or more active states corresponds to the number of non-activator to activator character transitions between adjacent received matching characters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
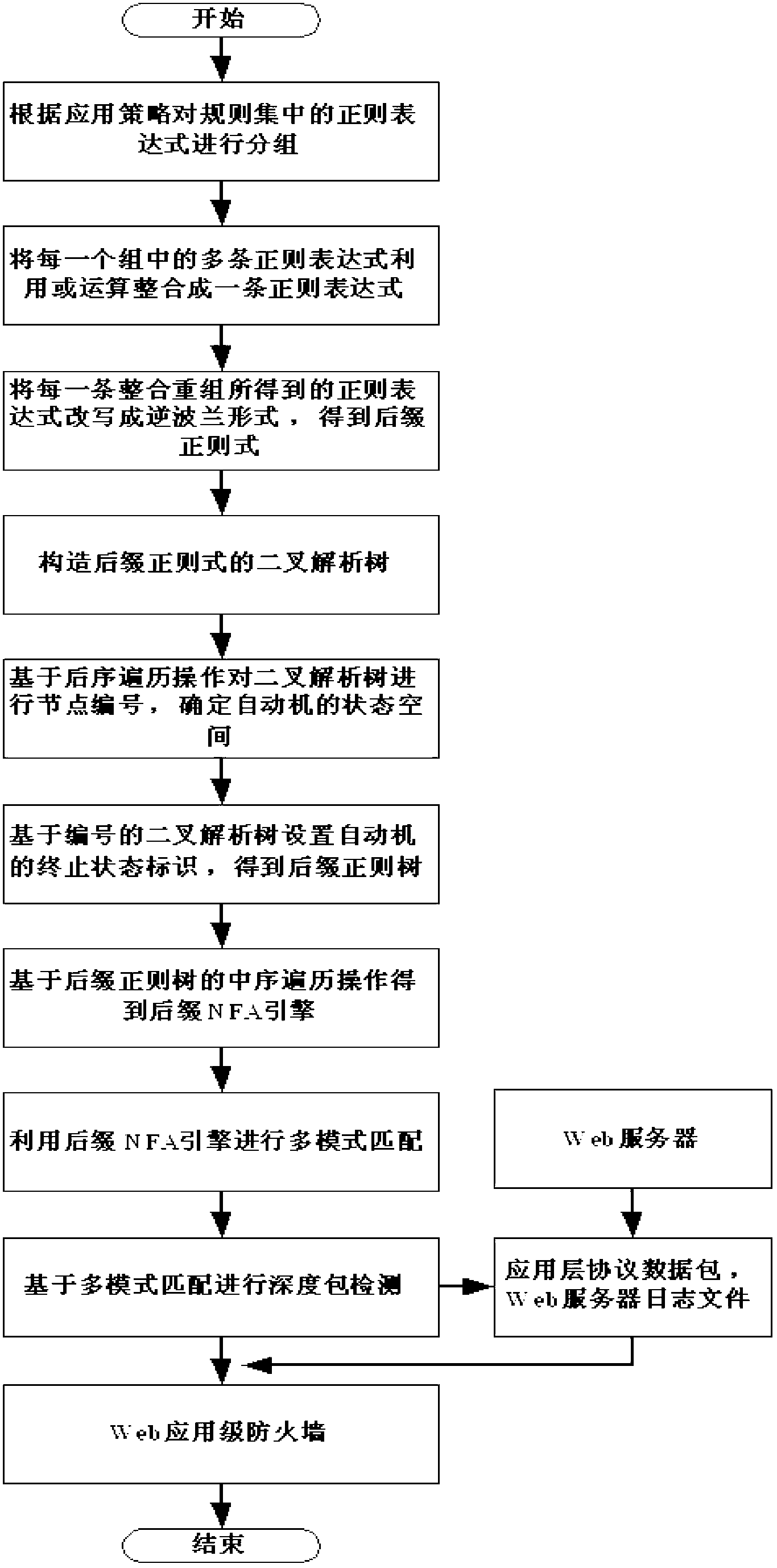
Method for inspecting deep packets based on suffix automaton regular engine structure
InactiveCN103259793ARapid Intrusion DetectionEfficient Intrusion DetectionData switching networksWeb serviceSuffix automaton
The invention discloses a method for inspecting deep packets based on a suffix automaton regular engine structure. The method comprises the following steps: S1, intruding an inspection system, extracting attack features and constructing regular expression, S2, constructing suffix nondeterministic finite automaton (NFA) engine and utilizing the suffix NFA engine to conduct multiple-pattern matching, S3, obtaining application layer protocol data packets and Web server log files from a Web server, S4, conducting deep packet inspecting on the protocol data packets and the log files and sending inspecting results to a firewall. According to the method for inspecting the deep packets based on the suffix automaton regular engine structure, matching of the multiple regular expression of a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) can be achieved by using a single automaton in a NFA mode, the problems that the NFA can not achieve the matching of the multiple regular expression and space explosion occurs when the DFA achieves the matching of the multiple regular expression are solved, the space size of the NFA is effectively reduced, the problems that a traditional NFA engine constructing method is waste in space and invalid traversal exists in the process of executing mode matching are solved, response time of deep packet inspecting is effectively shortened, and whole performance and efficiency of a system are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
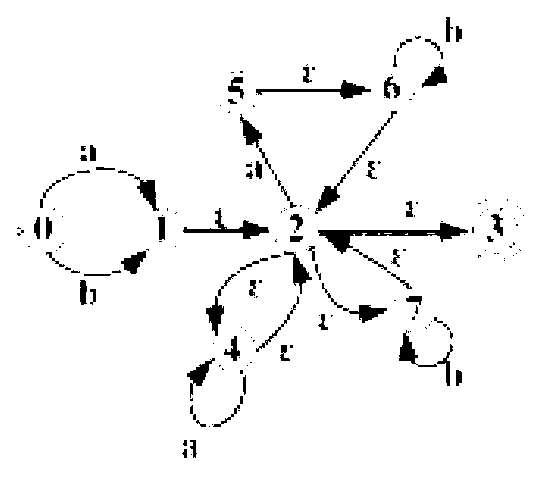
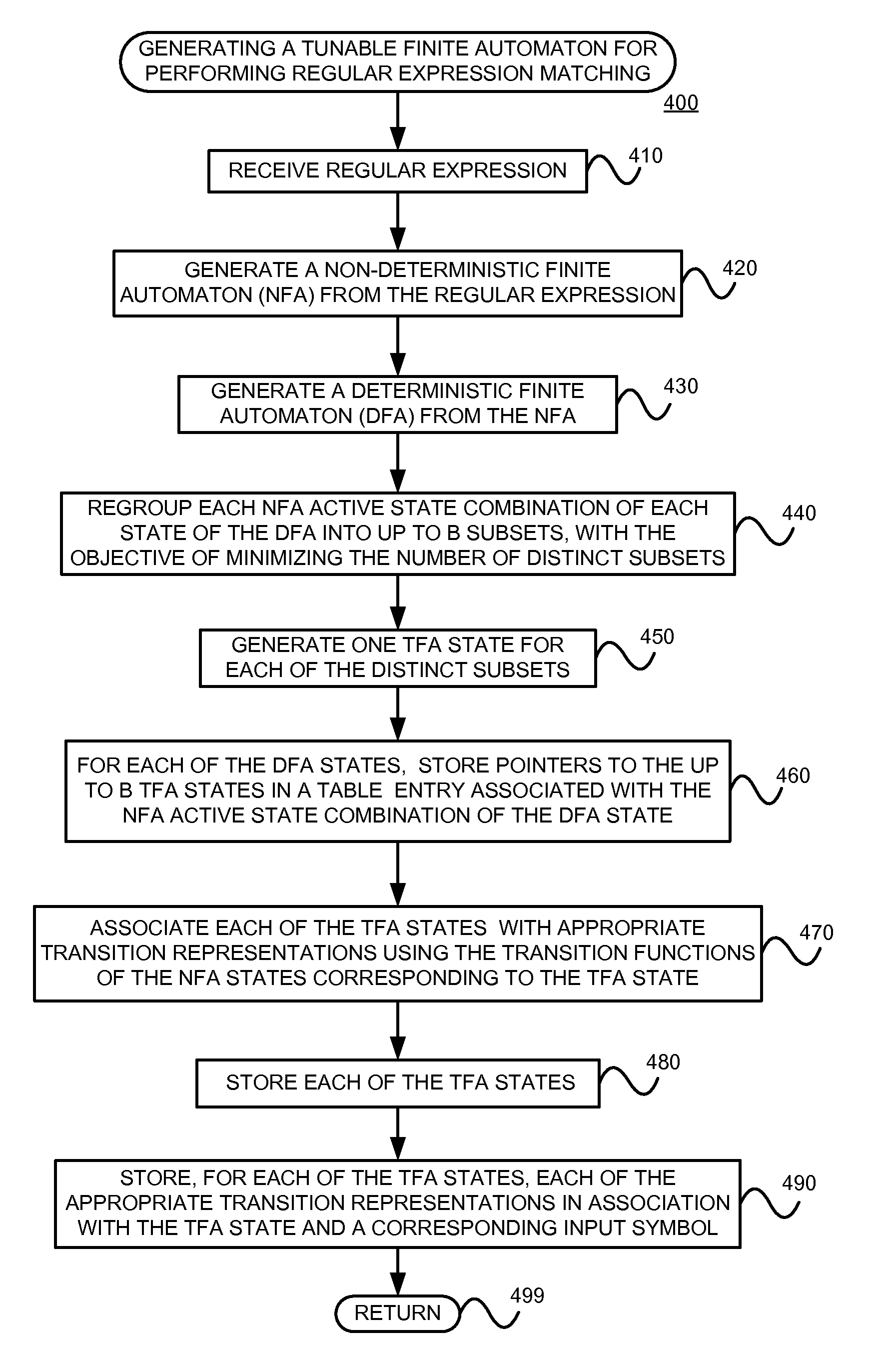
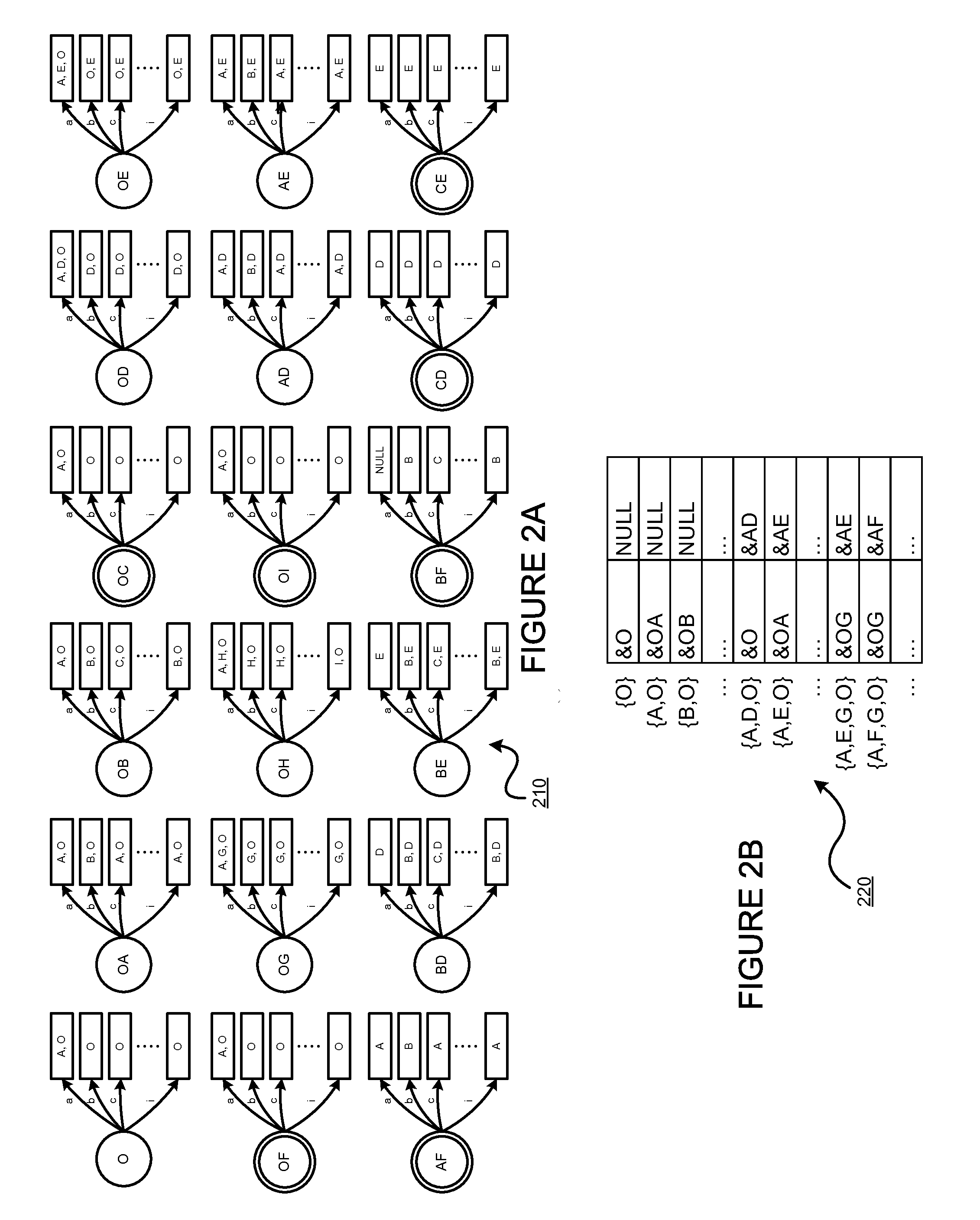
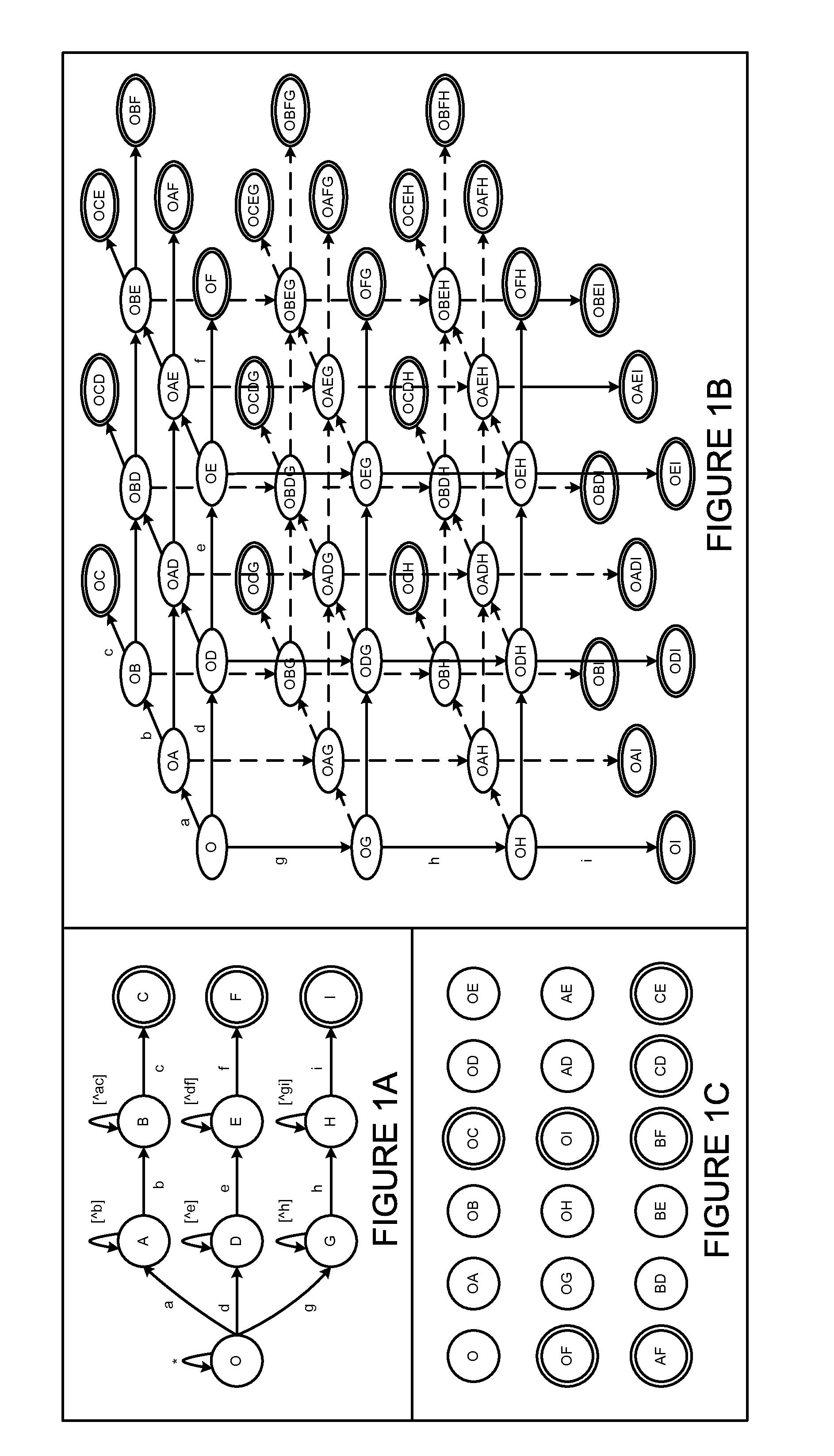
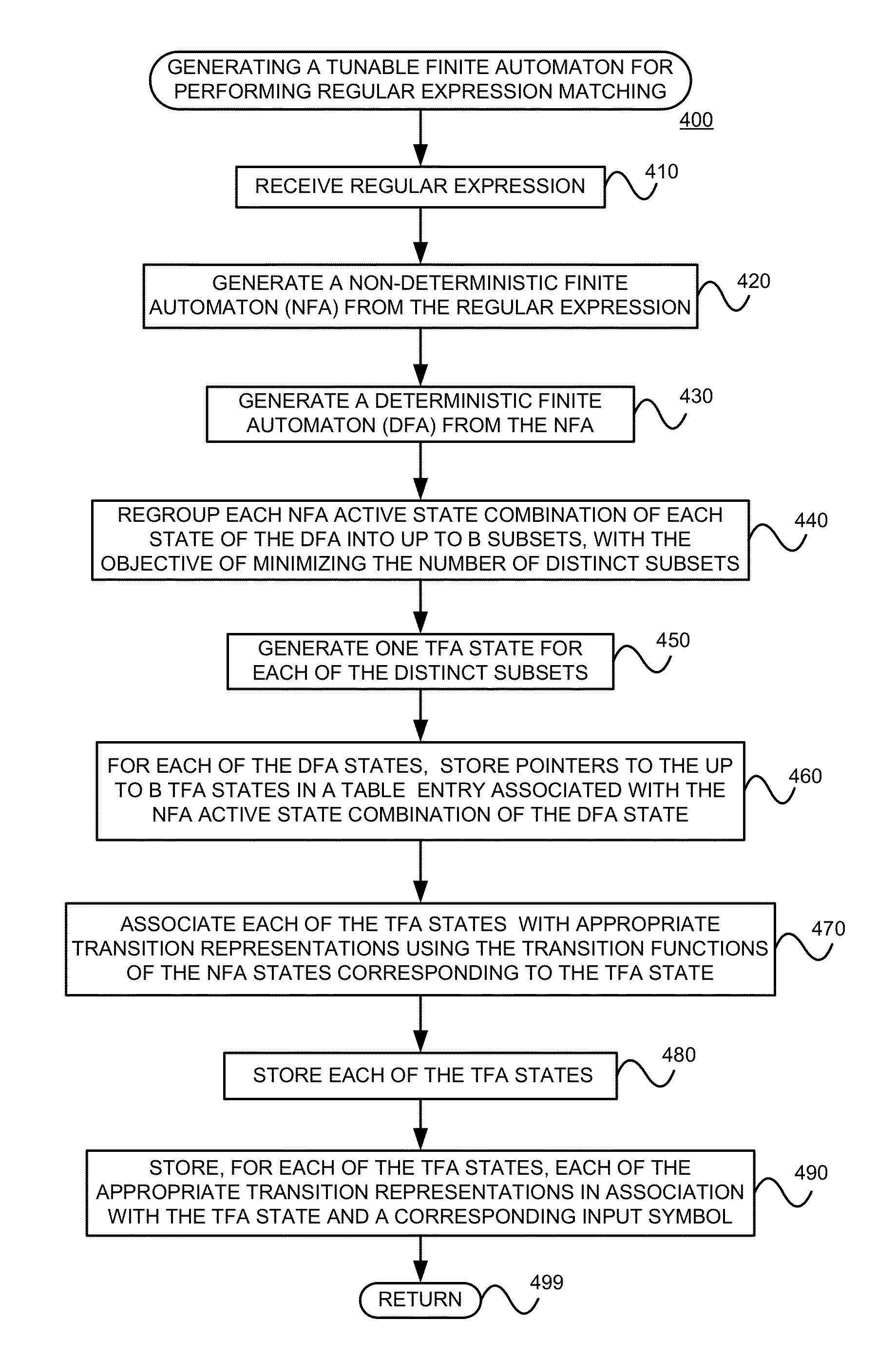
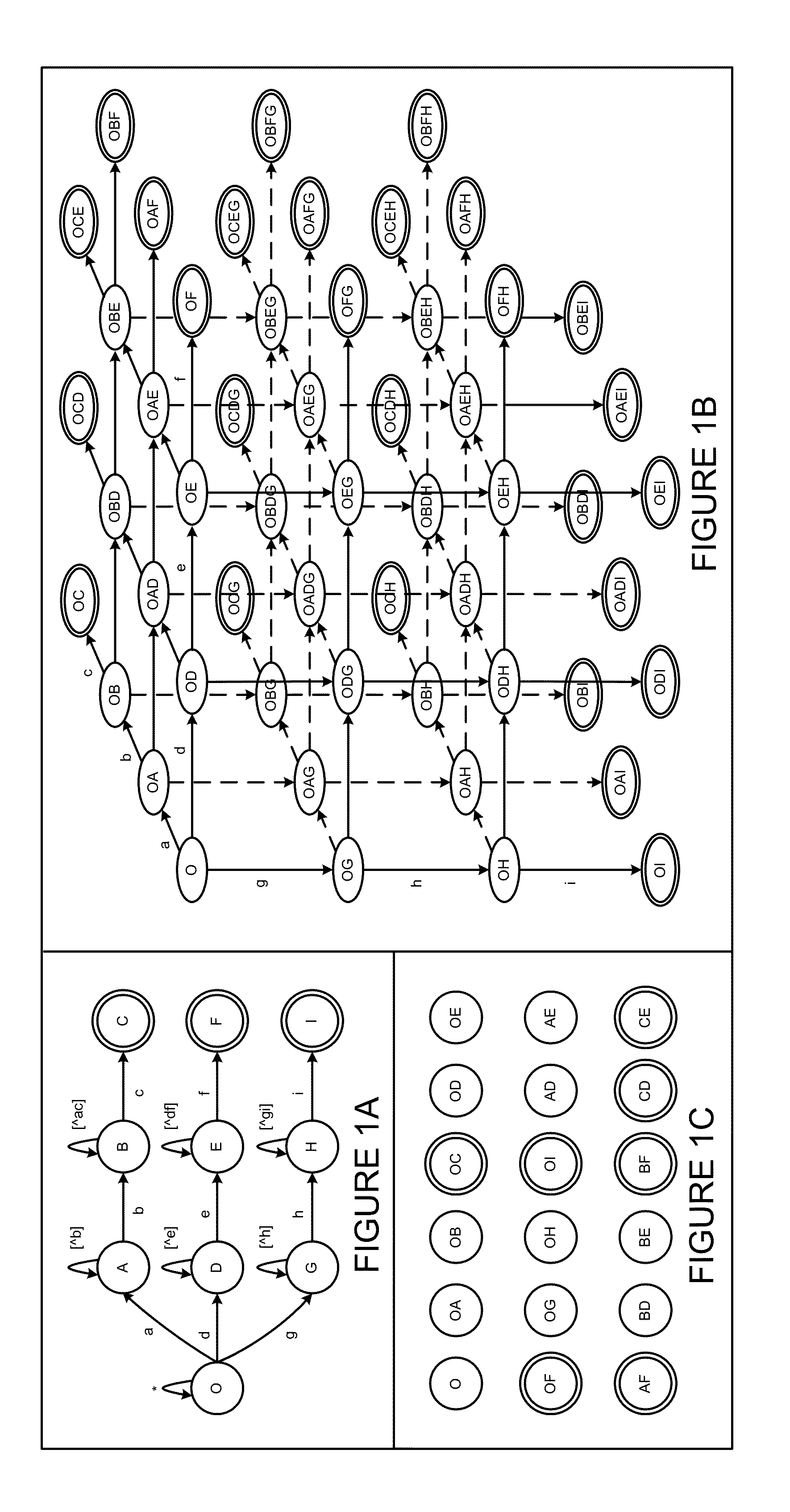
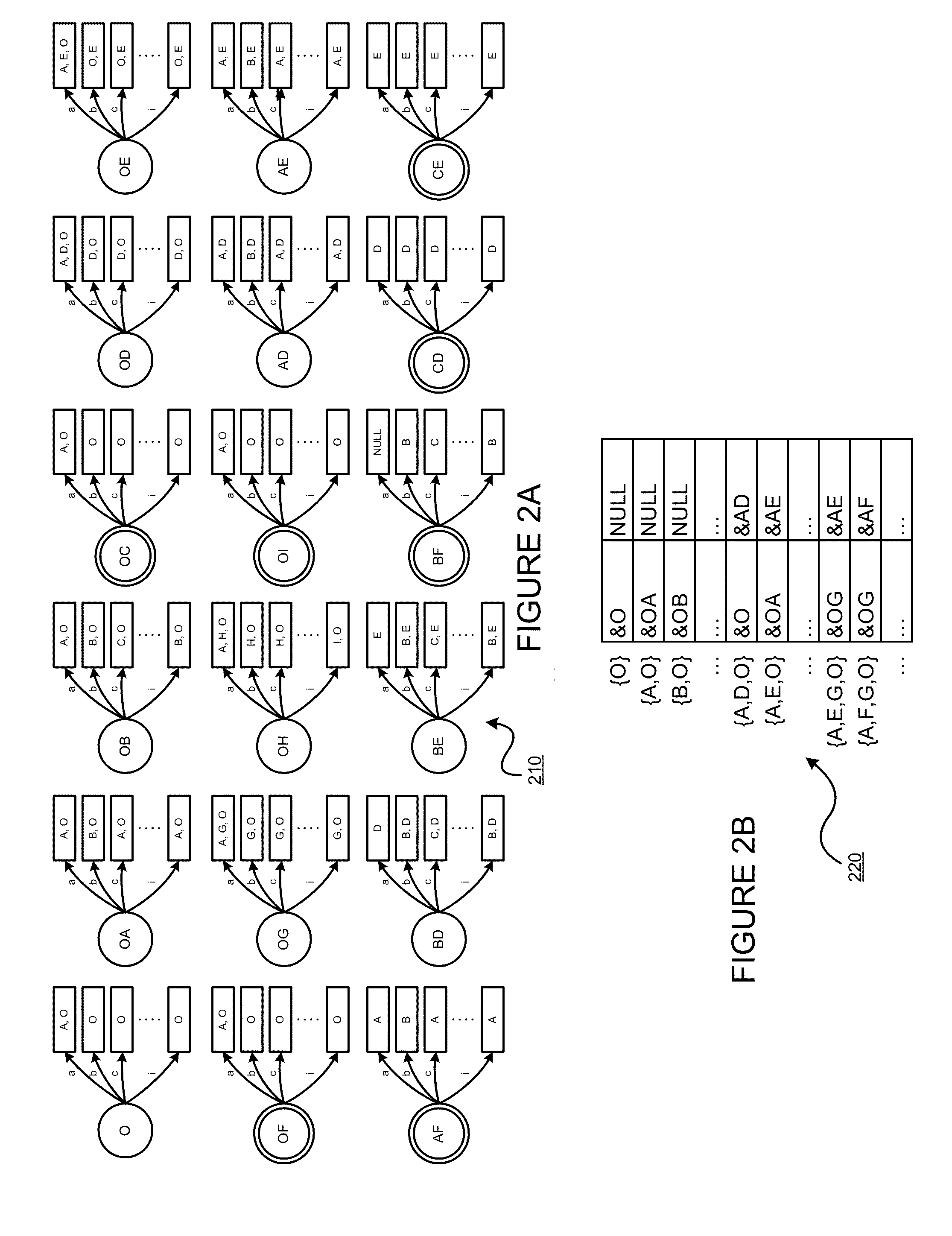
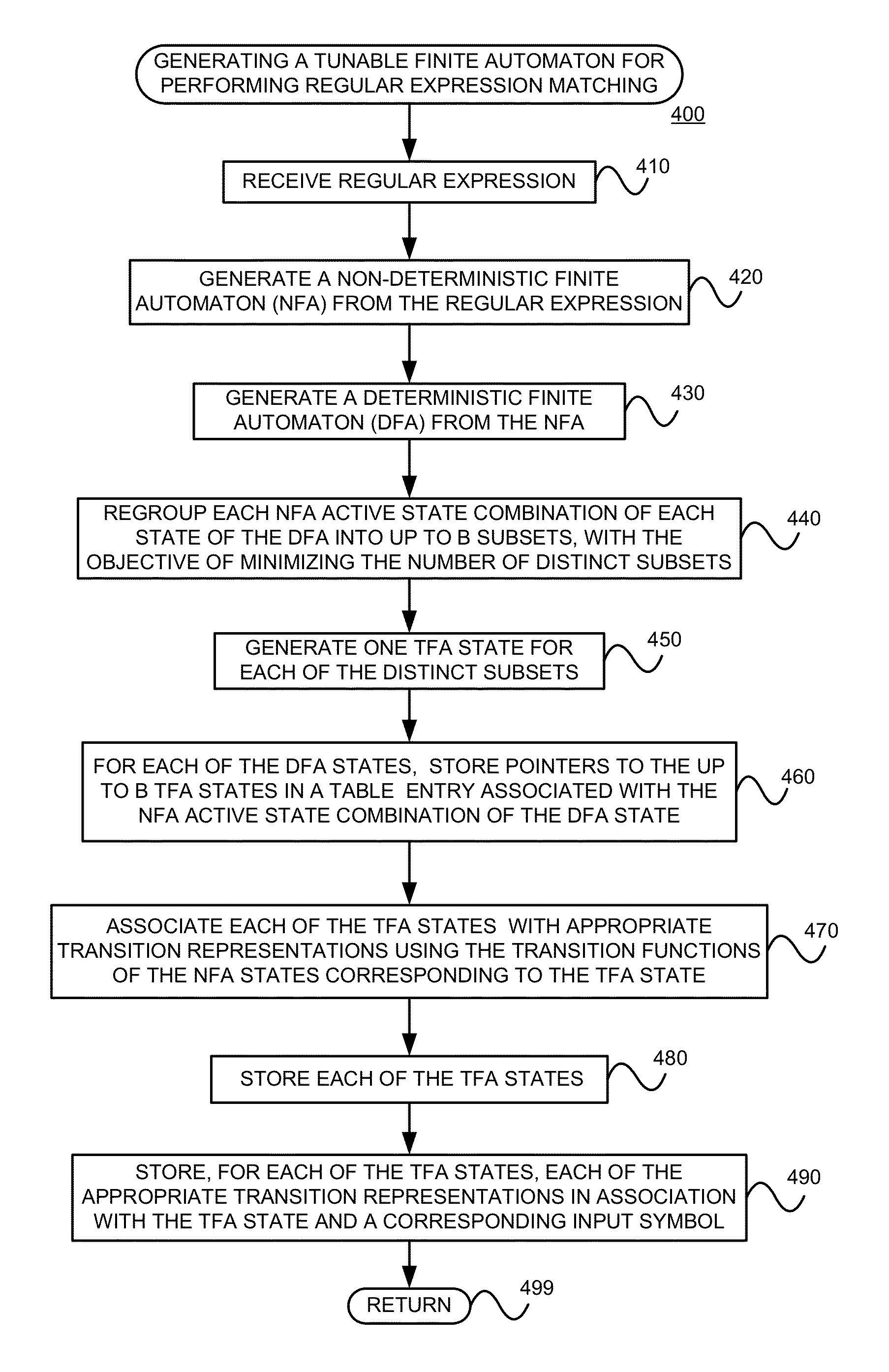
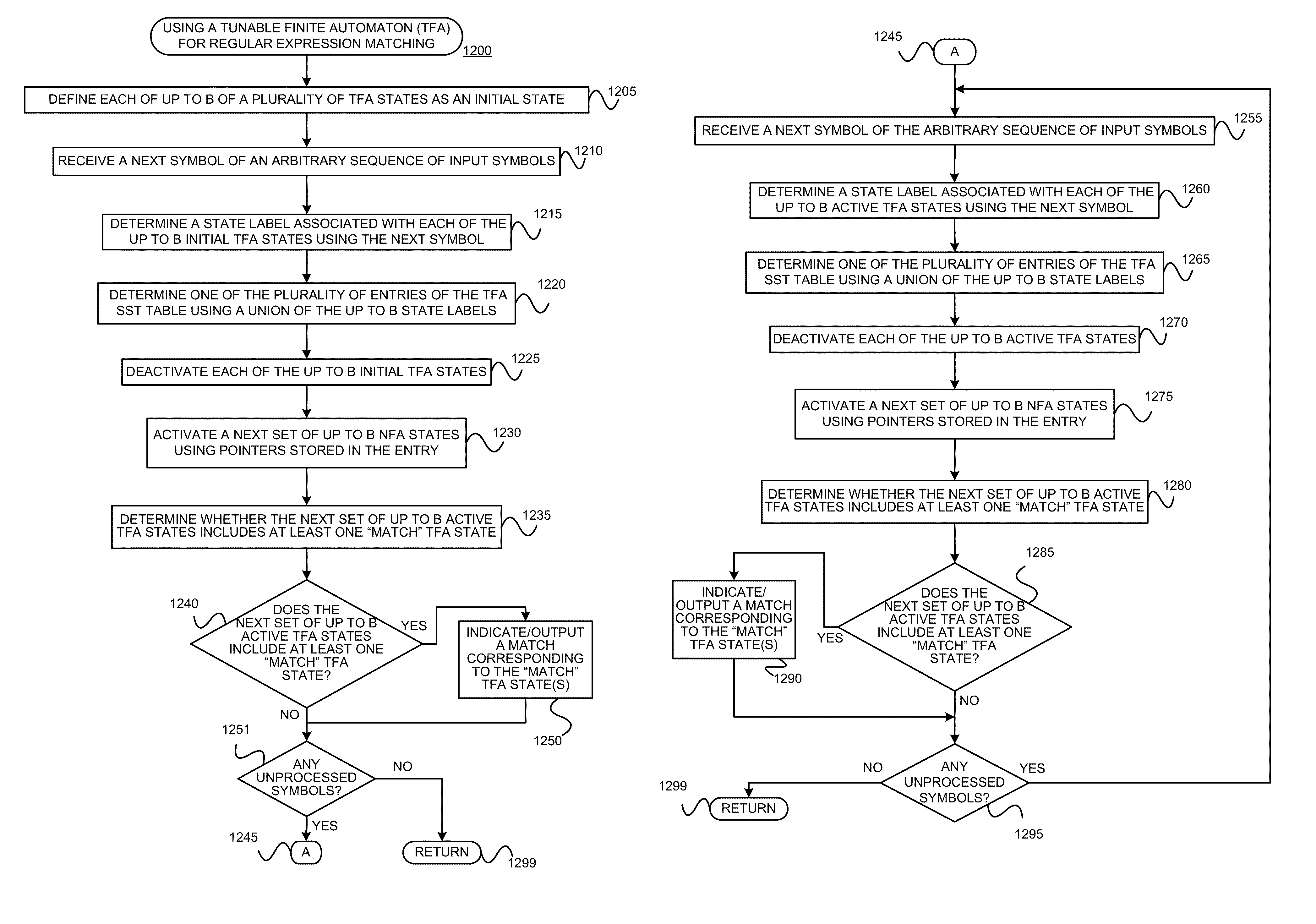
Using a tunable finite automaton for regular expression matching
InactiveUS20140101187A1Minimize the numberDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsNondeterministic finite automatonDeterministic finite automaton
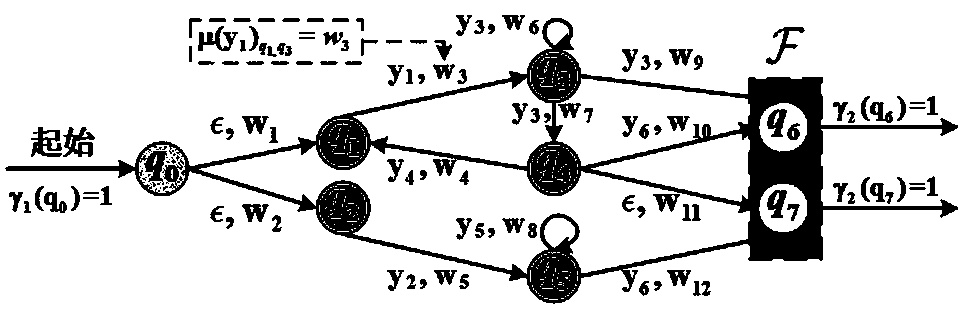
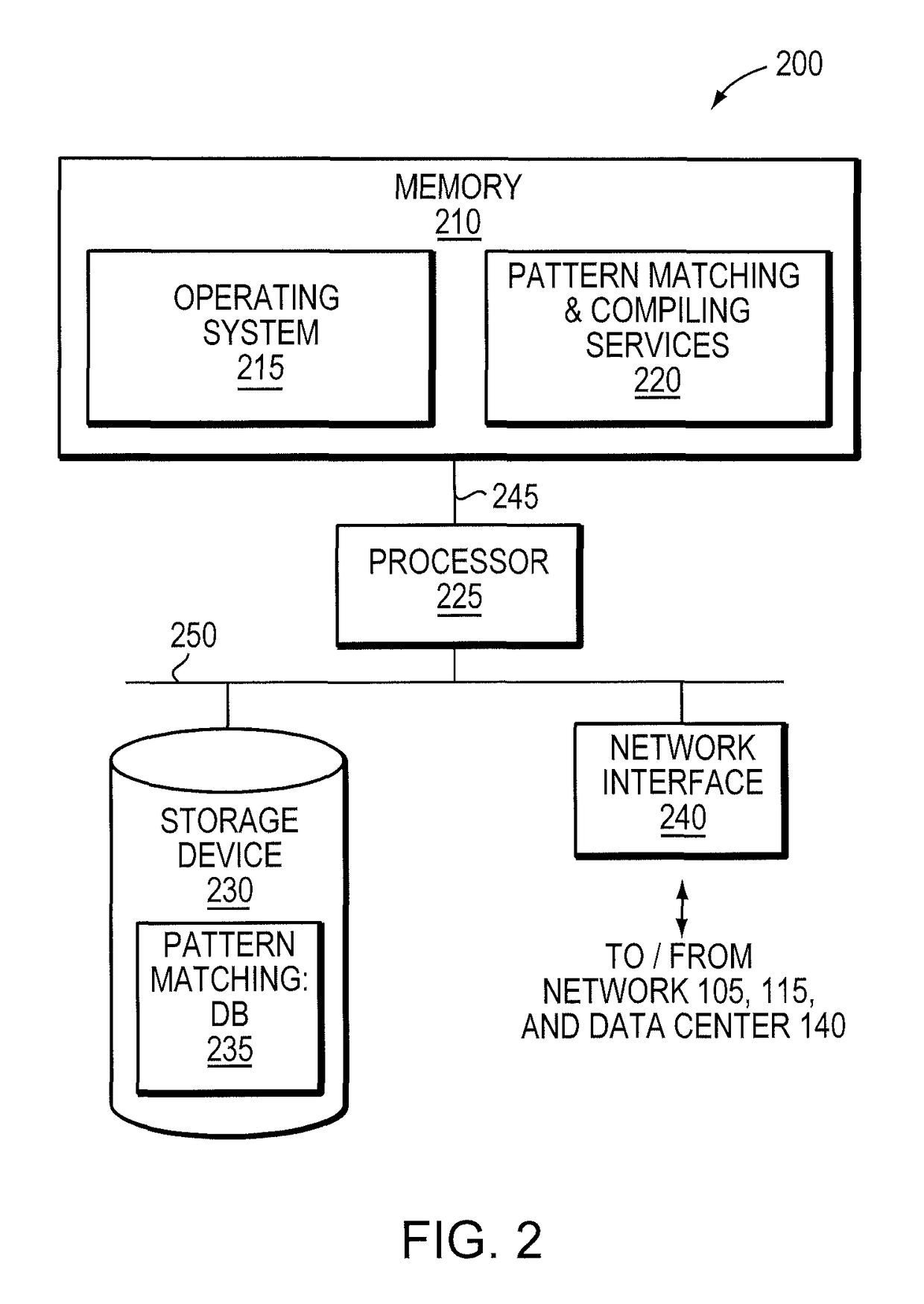
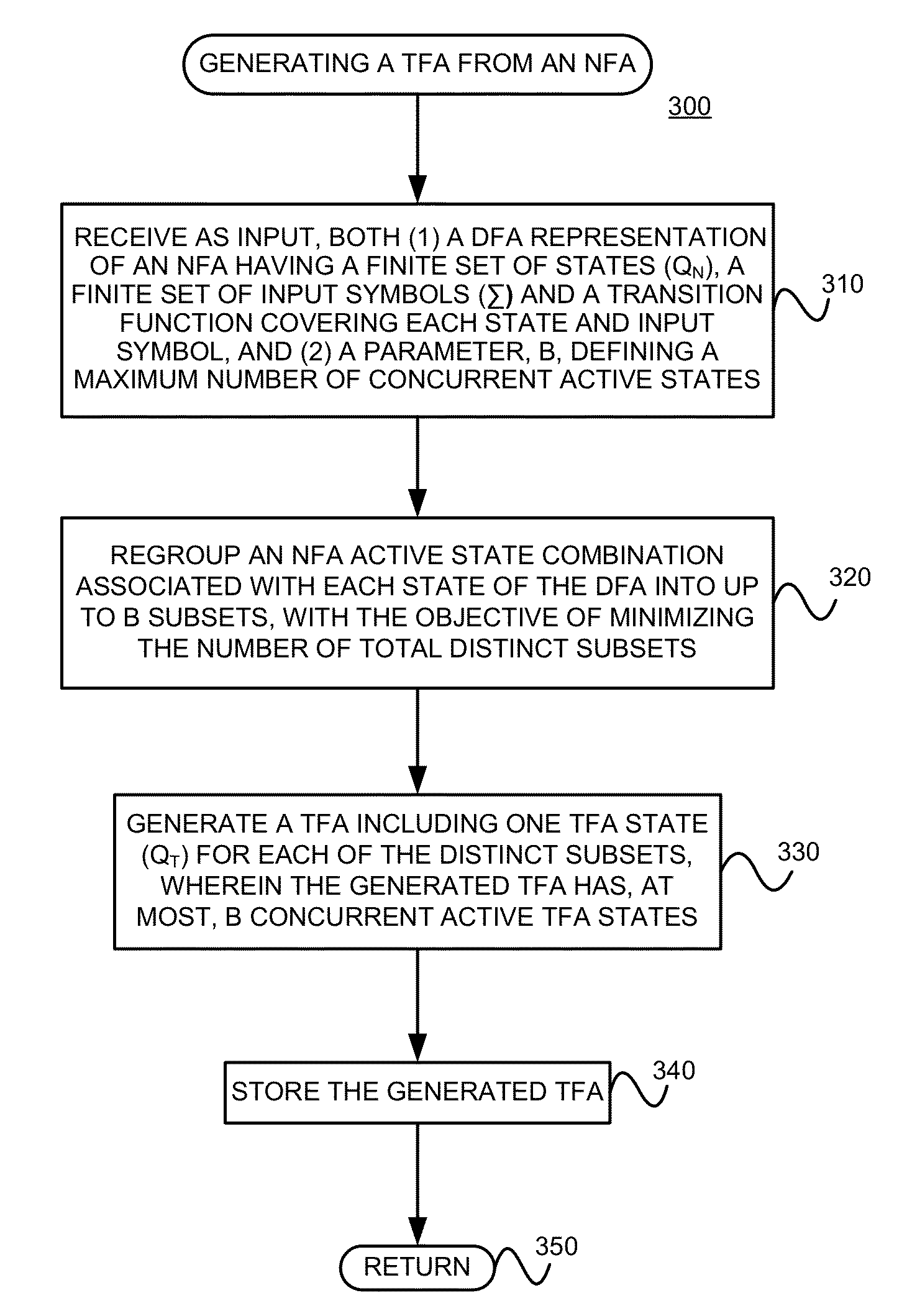
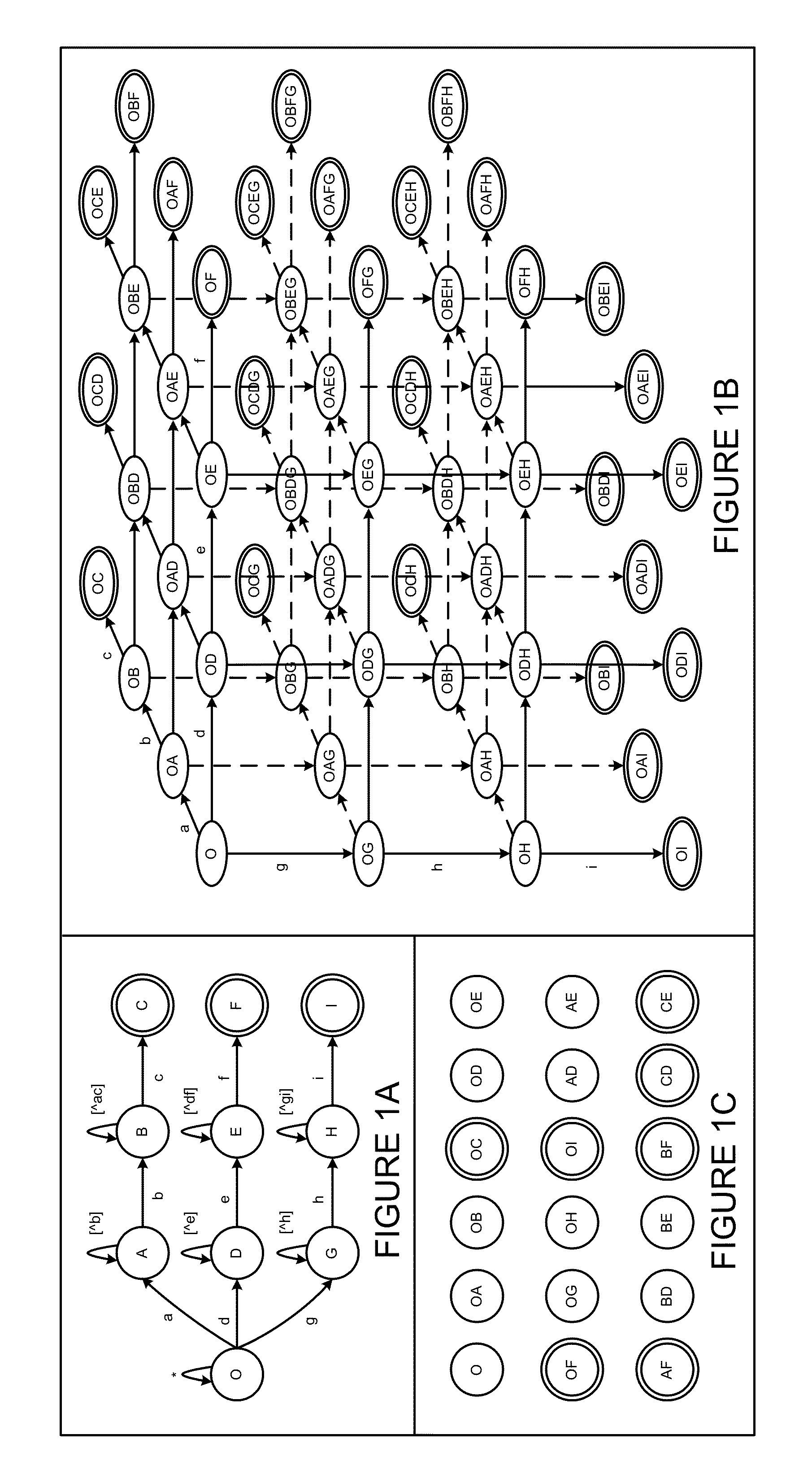
Deterministic Finite Automatons (DFAs) and Nondeterministic Finite Automatons (NFAs) are two typical automatons used in the Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS). Although they both perform regular expression matching, they have quite different performance and memory usage properties. DFAs provide fast and deterministic matching performance but suffer from the well-known state explosion problem. NFAs are compact, but their matching performance is unpredictable and with no worst case guarantee. A new automaton representation of regular expressions, called Tunable Finite Automaton (TFA), is described. TFAs resolve the DFAs' state explosion problem and the NFAs' unpredictable performance problem. Different from a DFA, which has only one active state, a TFA allows multiple concurrent active states. Thus, the total number of states required by the TFA to track the matching status is much smaller than that required by the DFA. Different from an NFA, a TFA guarantees that the number of concurrent active states is bounded by a bound factor b that can be tuned during the construction of the TFA according to the needs of the application for speed and storage. A TFA can achieve significant reductions in the number of states and memory space.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Hardware accelerator personality compiler
InactiveCN1781078APersonalitySoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsNondeterministic finite automatonDeterministic finite automaton
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Regular expression matching equipment and method on basis of deterministic finite automaton
ActiveCN102521356ASave storage spaceFast matchingSpecial data processing applicationsNondeterministic finite automatonDeterministic finite automaton
The invention provides regular expression matching equipment and a method on the basis of a deterministic finite automaton. The regular expression matching equipment comprises a packet dispatcher and a result collecting module. A regular expression matching system comprises a matching unit and a storage unit connected with the matching unit, the matching unit is respectively connected with the packet dispatcher and the result collecting module. In the method, each status transfer table is disintegrated into a character substitution table and a simplified status table, many statuses have identical character substitution tables and can be shared after disintegration, and furthermore, many statuses have identical character substitution tables, and can share the identical character substitution tables after minority skips are extracted. By the regular expression matching equipment and the method on the basis of the deterministic finite automaton, storage space for the DFA (deterministic finite automaton) is greatly reduced, and more regular expressions can be stored in a limited space.
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING +1
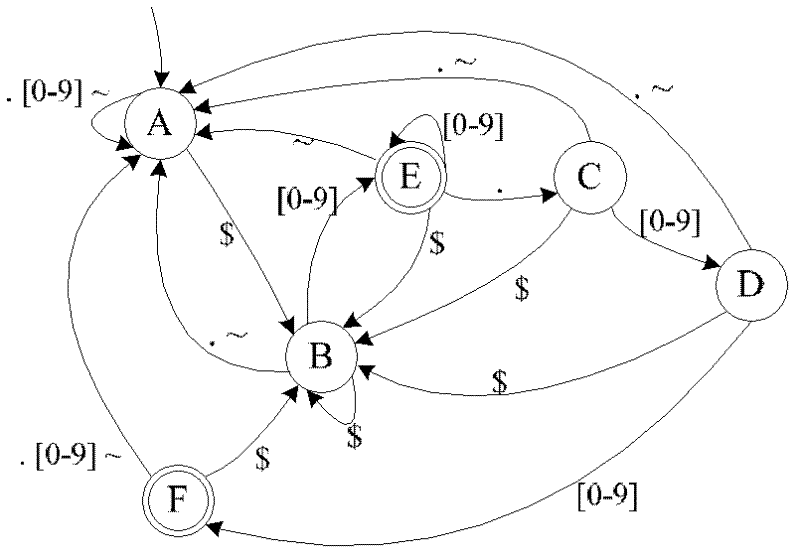
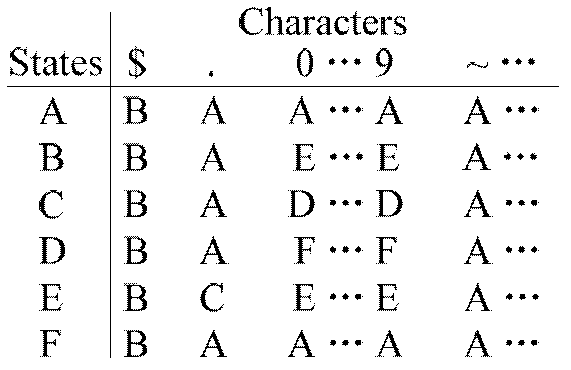
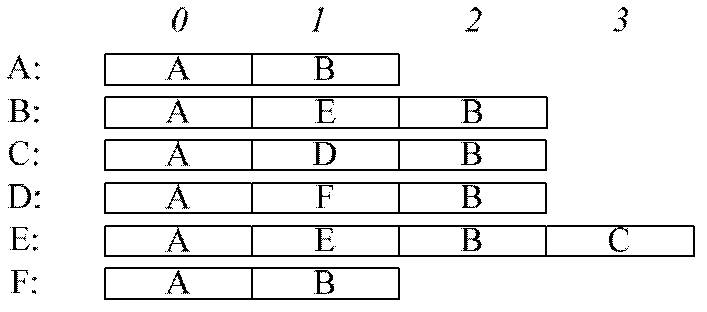
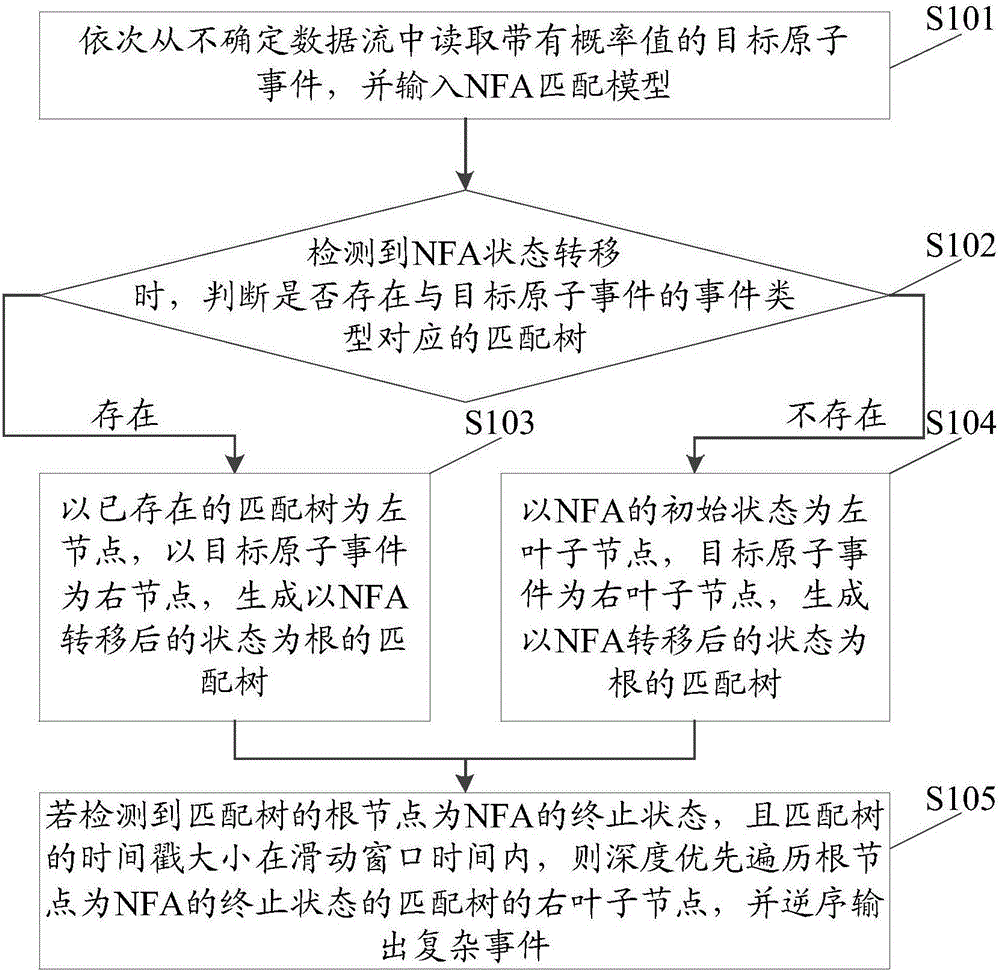
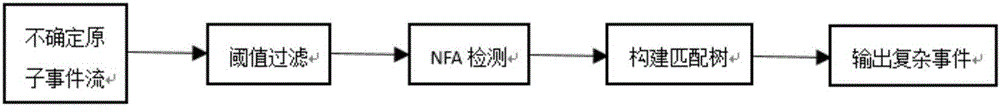
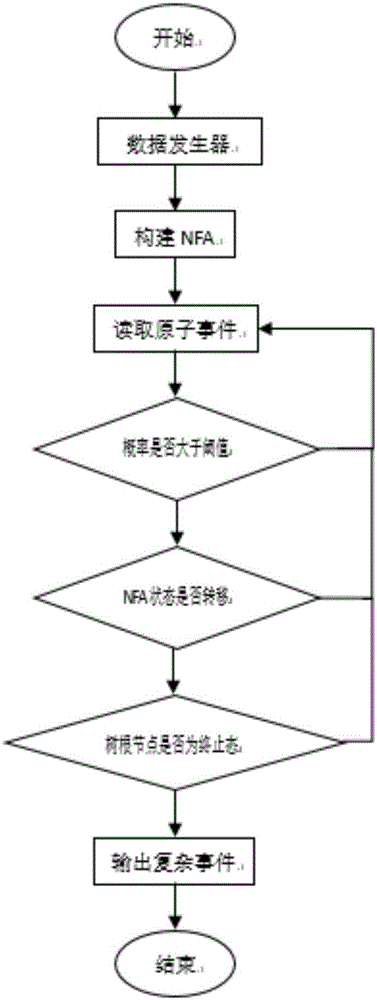
Method and system for detecting uncertain data stream-oriented complex events in manufacture internet of things
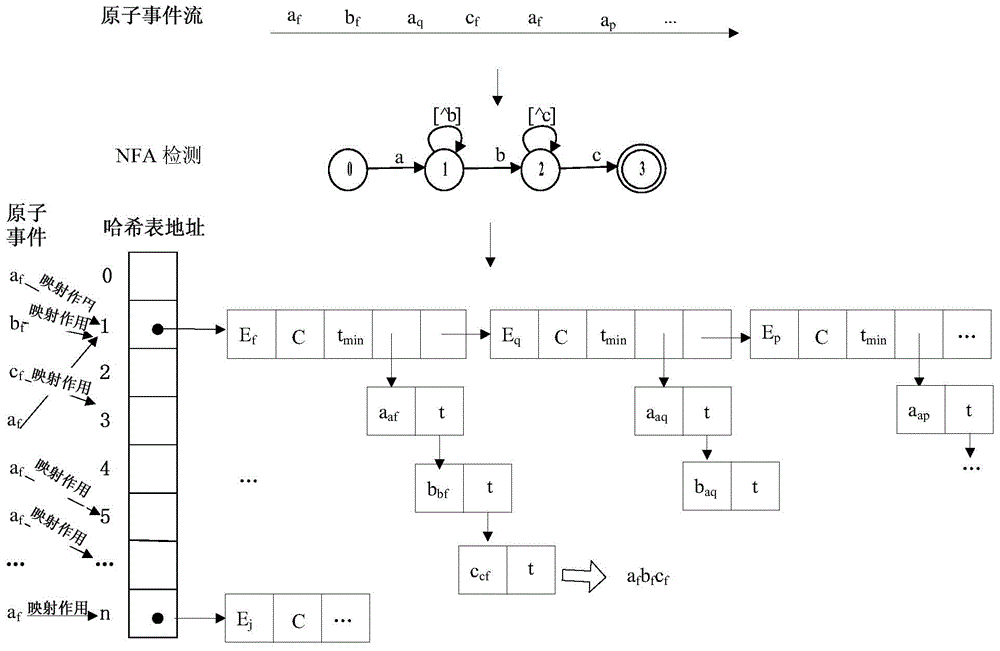
ActiveCN106294824AImprove detection efficiencySave spaceData processing applicationsTransmissionData streamTimestamp
The invention discloses a method and system for detecting uncertain data stream-oriented complex events in manufacture internet of things; the method comprises: reading a target atomic event with probability value; during NFA (nondeterministic finite automaton) state transition, if a corresponding matching tree is present, using a present matching tree as a left node and the target atomic event as a right node to generate a matching tree using post-transition NFA state as a root; if a corresponding matching tree is not present, using NFA initial state as a left leaf node and the target atomic event as a right leaf node to generate a matching tree with post-transition NFA state as a root; if it is detected that a root node of the matching tree is NFA termination state and timestamp size of the matching tree is in sliding window time, giving priority to deep traversal of the right leaf node of the matching tree with the NFA termination state as a root node, and outputting complex events in a reverse sequence; uncertain data stream complex events are detected by using NFA in conjunction with the matching tree, and event detection efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
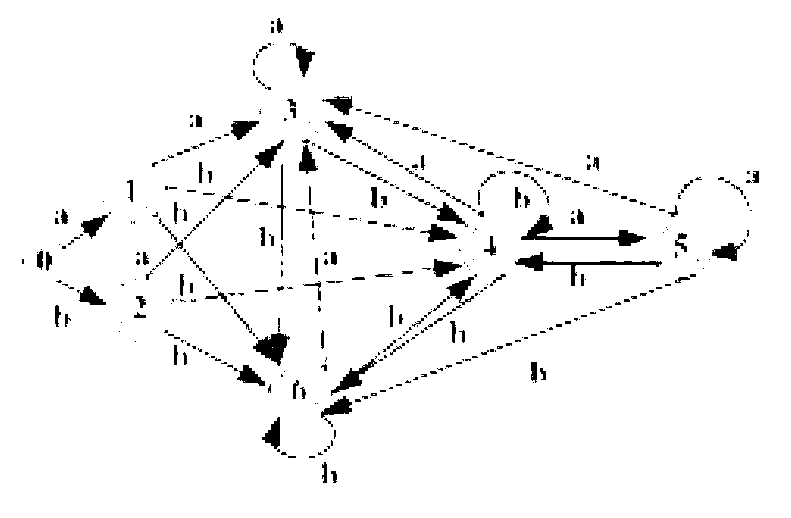
Encoding non-derministic finite automation states efficiently in a manner that permits simple and fast union operations
ActiveUS8862585B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsNondeterministic finite automatonDeterministic finite automaton
Deterministic Finite Automatons (DFAs) and Nondeterministic Finite Automatons (NFAs) are two typical automatons used in the Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS). Although they both perform regular expression matching, they have quite different performance and memory usage properties. DFAs provide fast and deterministic matching performance but suffer from the well-known state explosion problem. NFAs are compact, but their matching performance is unpredictable and with no worst case guarantee. A new automaton representation of regular expressions, called Tunable Finite Automaton (TFA), is described. TFAs resolve the DFAs' state explosion problem and the NFAs' unpredictable performance problem. Different from a DFA, which has only one active state, a TFA allows multiple concurrent active states. Thus, the total number of states required by the TFA to track the matching status is much smaller than that required by the DFA. Different from an NFA, a TFA guarantees that the number of concurrent active states is bounded by a bound factor b that can be tuned during the construction of the TFA according to the needs of the application for speed and storage. A TFA can achieve significant reductions in the number of states and memory space.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Encoding non-derministic finite automaton states efficiently in a manner that permits simple and fast union operations
ActiveUS20140101157A1Digital data processing detailsTransmissionNondeterministic finite automatonDeterministic finite automaton
Deterministic Finite Automatons (DFAs) and Nondeterministic Finite Automatons (NFAs) are two typical automatons used in the Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS). Although they both perform regular expression matching, they have quite different performance and memory usage properties. DFAs provide fast and deterministic matching performance but suffer from the well-known state explosion problem. NFAs are compact, but their matching performance is unpredictable and with no worst case guarantee. A new automaton representation of regular expressions, called Tunable Finite Automaton (TFA), is described. TFAs resolve the DFAs' state explosion problem and the NFAs' unpredictable performance problem. Different from a DFA, which has only one active state, a TFA allows multiple concurrent active states. Thus, the total number of states required by the TFA to track the matching status is much smaller than that required by the DFA. Different from an NFA, a TFA guarantees that the number of concurrent active states is bounded by a bound factor b that can be tuned during the construction of the TFA according to the needs of the application for speed and storage. A TFA can achieve significant reductions in the number of states and memory space.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Character string searching method and device based on non-determined finite automaton
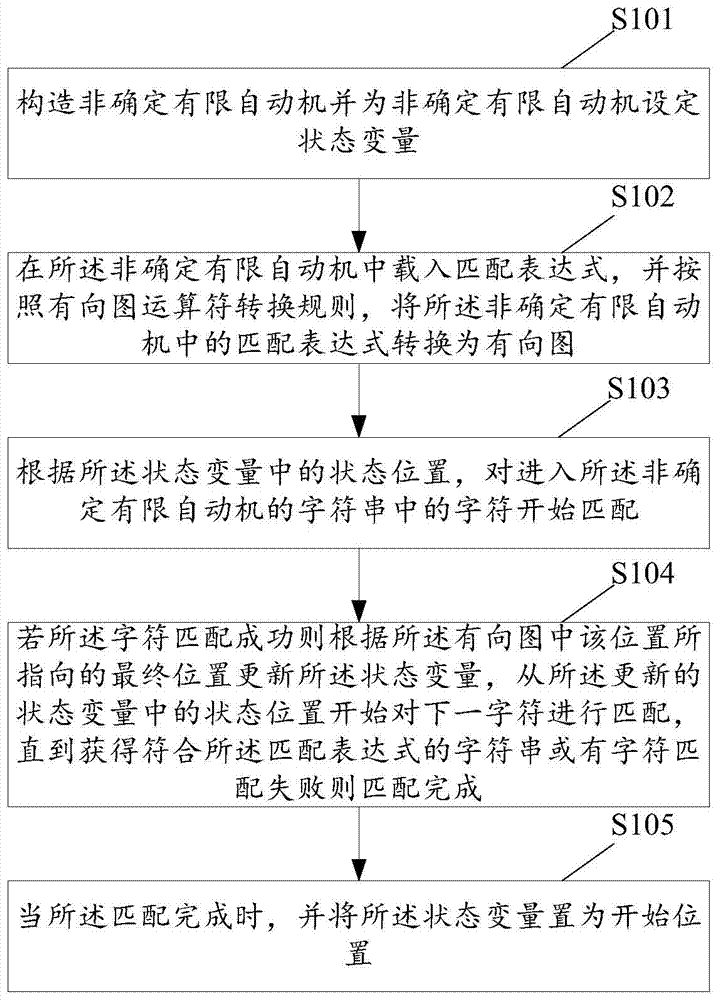
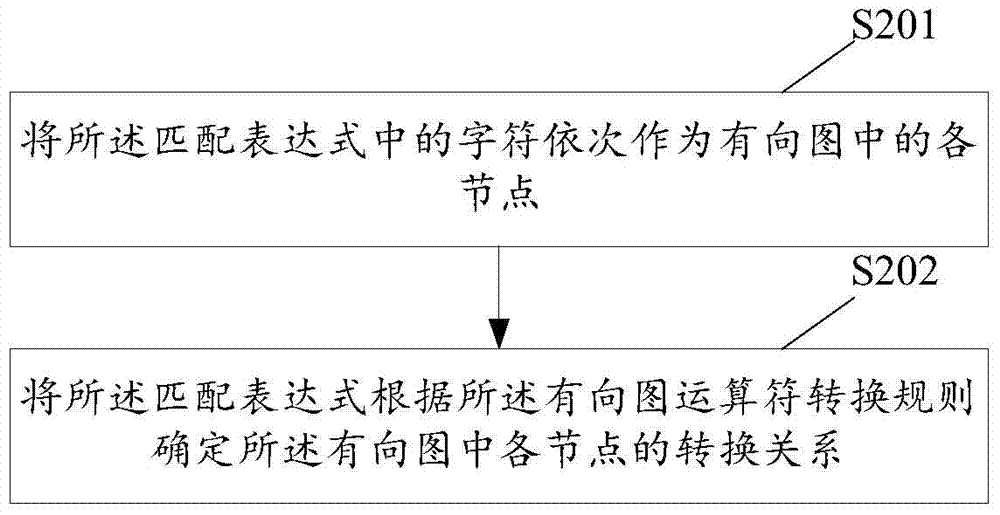
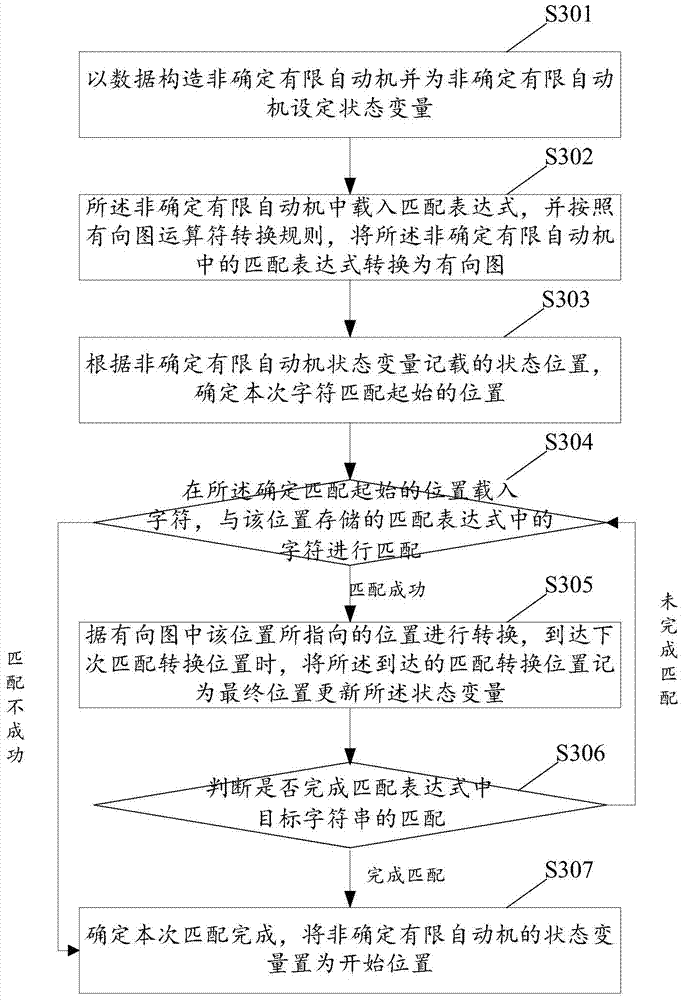
ActiveCN104750725ASearch is simple, efficient and accurateSolve matching problemsSpecial data processing applicationsDirected graphState variable
The invention discloses a character string searching method based on a non-determined finite automaton. The character string searching method based on the non-determined finite automaton includes: building the non-determined finite automaton and setting a state variable for the non-determined finite automaton; loading a matching expression in the non-determined finite automaton and transforming the matching expression in the non-determined finite automaton into a directed graph according to the operator transformational rule of the directed graph; conducting matching on the characters in the character string of the non-determined finite automaton according to the state position of the state variable; updating the state variable according to the final position directed by the position in the directed graph if the characters are matched successfully, conducting the matching on the next character from the position in the updated state variable and completing the matching till the character string which conforms to the matching expression is obtained or the character matching fails, and placing the state variable as the starting position when the matching is completed. The character string searching method based on the non-determined finite automation can realize more accuracy of the character string searching. The invention further provides a character string searching device based on the non-determined finite automaton.
Owner:天津亿阳信通科技有限公司
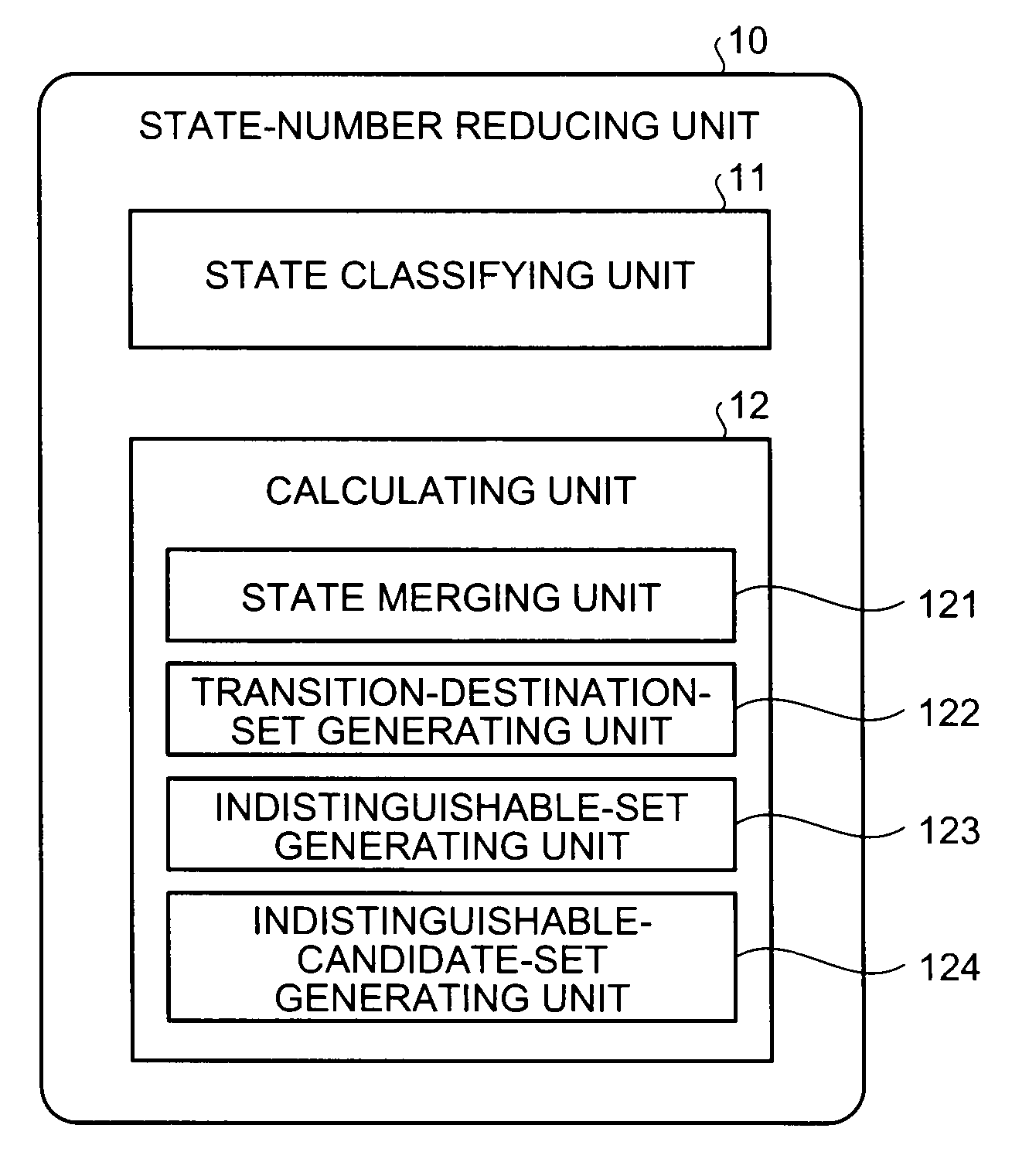
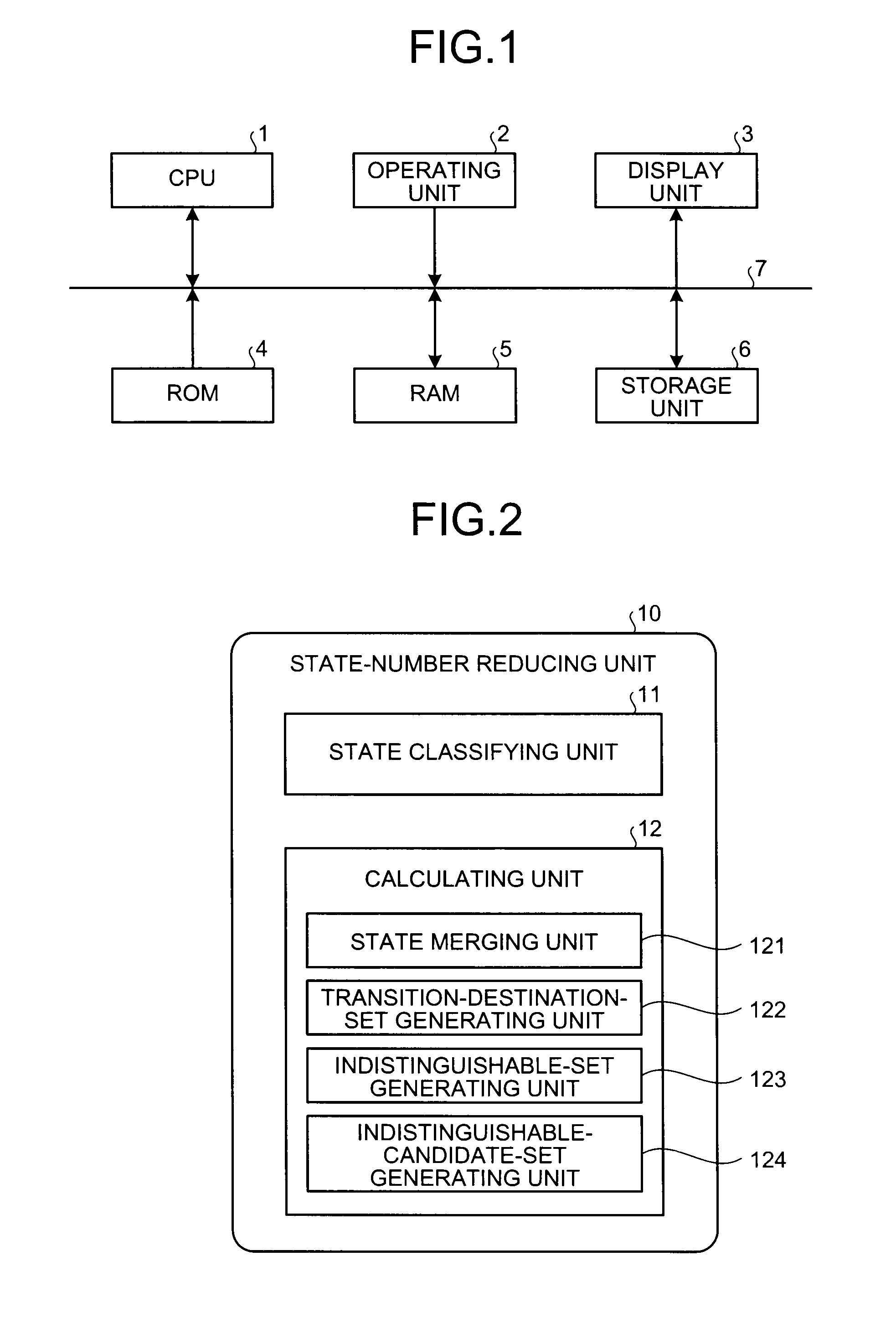
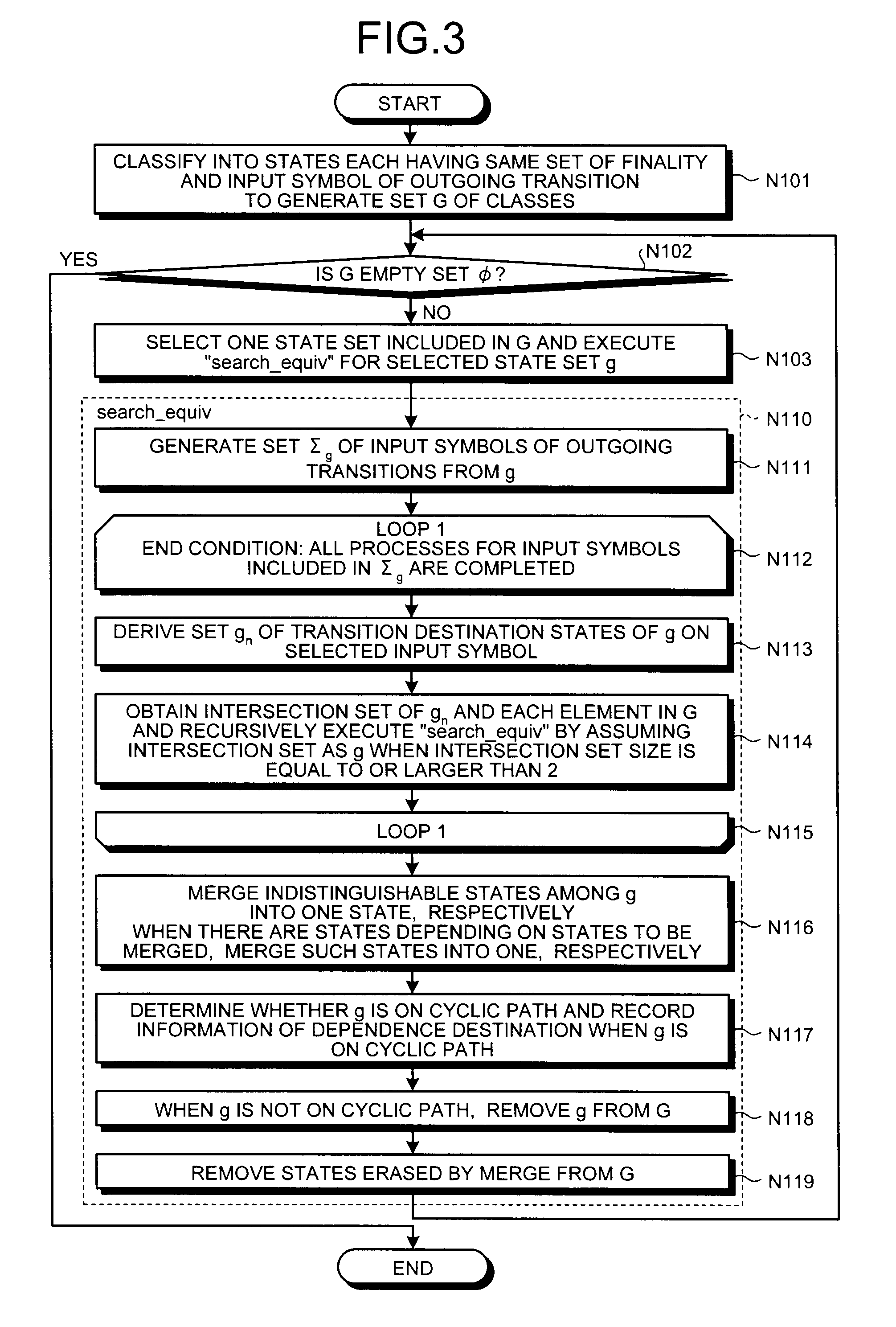
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and computer program product for reducing states in a deterministic finite state automaton
ActiveUS8275730B2Computation using non-denominational number representationFuzzy logic based systemsInformation processingNondeterministic finite automaton
States included in a deterministic finite automaton are classified into states having the same input symbols associated with outgoing transitions and the same finality, and a calculates an intersection set between each of the state sets and a set of transition destination states which is obtained by translating each of states included in the state sets, until the number of states included in the intersection set becomes equal to one, while regarding the set of the transition destination states for each of the input symbol included in the intersection set as new state sets, and plural indistinguishable states are merged into one state by tracing a route in a reverse direction to a transition direction, when the number of states has become equal to one.
Owner:TOSHIBA DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
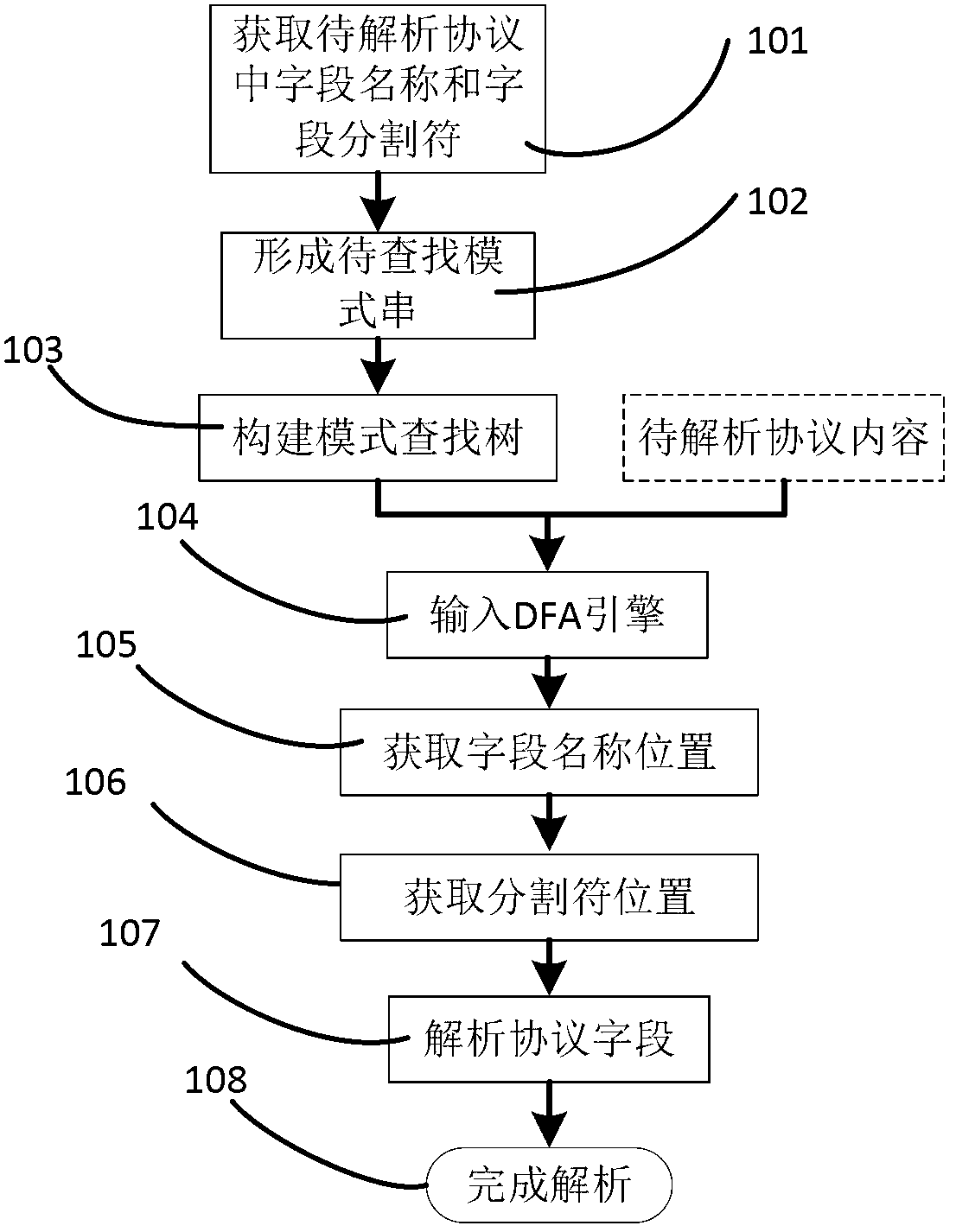
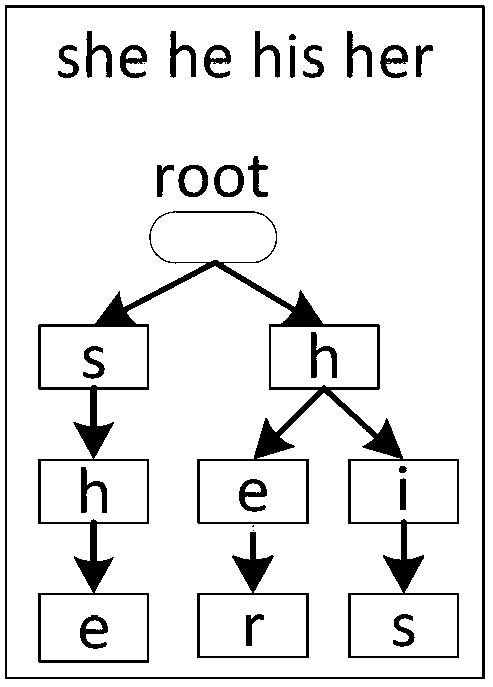
Protocol analyzing method based on DFA (Deterministic Finite Automaton)
The invention relates to a protocol analyzing method based on DFA (Deterministic Finite Automaton). The protocol analyzing method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a field name and a field decollator in to-be-analyzed protocol content; by using the field name and the filed decollator as a mode string, establishing a mode search tree according to the mode string; based on the mode search tree and the to-be-analyzed protocol content as the input of a finite state automat DFA, matching the mode string in the to-be-analyzed protocol by utilizing the DFA; and extracting the protocol field value in the to-be-analyzed protocol content according to the matching result. According to the protocol analyzing method based on the DFA, on one hand, the mode search tree is constructed by using a character string multi-mode matching; and on the other hand, each node in the mode search tree is constructed as each status in the DFA by using a DFA engine, so that the quick matching of the character string is realized by the DFA engine, and therefore, the protocol analyzing speed is greatly improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU SEANET TECH CO LTD
Multi-character-string mode matching method, device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112784127AAvoid restrictionsSave storage spaceOther databases queryingSpecial data processing applicationsNondeterministic finite automatonComputational model
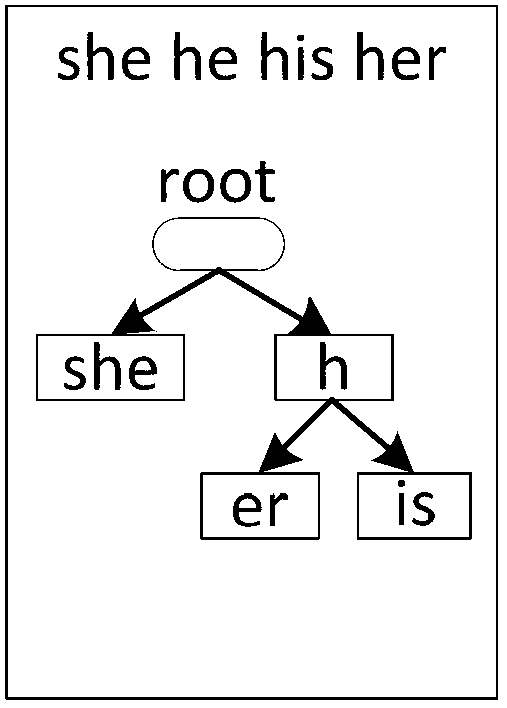
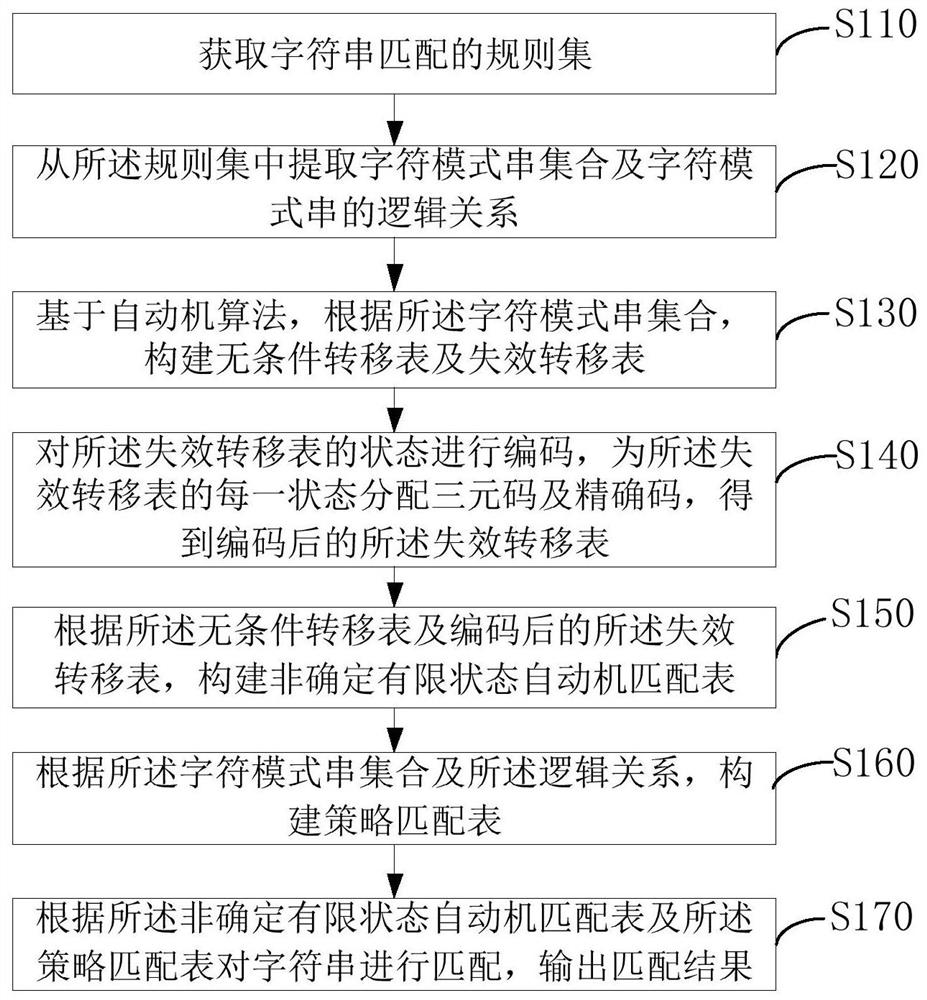
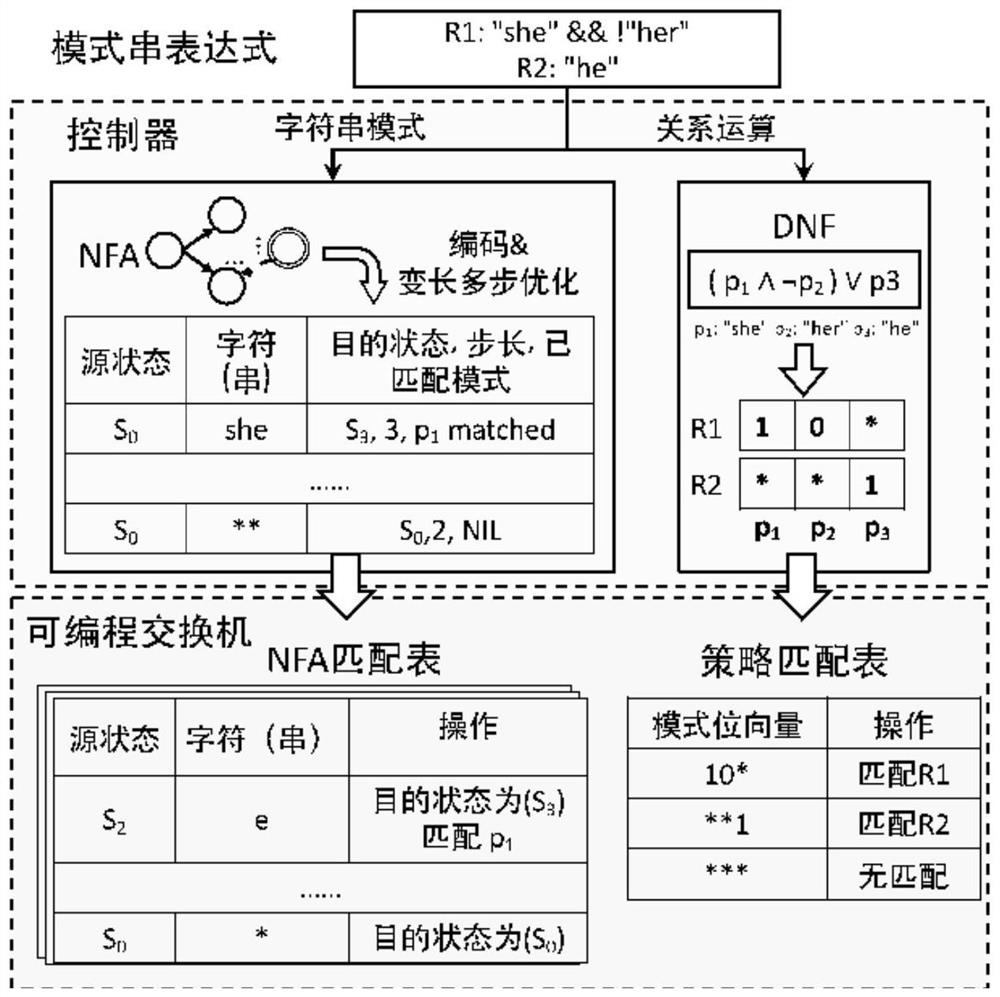
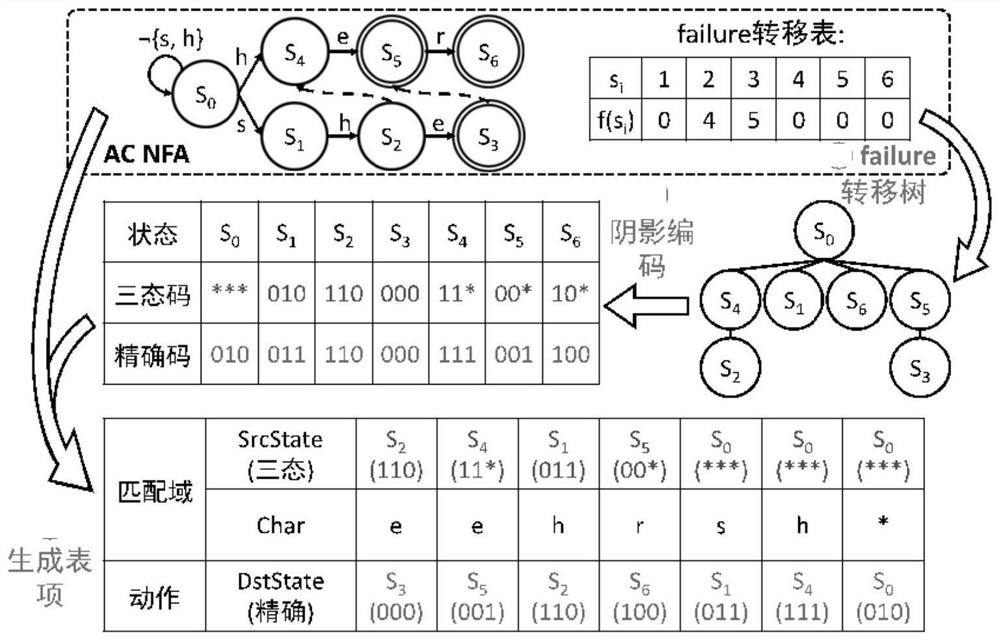
The invention provides a multi-character-string mode matching method, a device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a character string matching rule set; extracting a character pattern string set and a logic relation thereof; constructing an unconditional transfer table and a failure transfer table according to the character pattern string set based on an automaton algorithm; encoding the state of the transfer table, and distributing a ternary code and a precise code for each state of the transfer table; constructing a non-deterministic finite state automaton matching table according to the transfer table; constructing a strategy matching table according to the character pattern string set and the logic relationship; matching the character string according to the matching table, and outputting a matching result; the complete semantic meaning of the non-deterministic finite state automaton in an automaton algorithm is realized, the number of table items is ensured to be equal to the number of state transition table items of the unconditional transition table, the storage space is greatly saved, the limitation of a programmable switch calculation model and storage resources is overcome, and the number of characters processed by matching each time is increased to increase throughput.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Deterministic finite automaton (DFA) matching method and device based on TCAM (ternary content addressable memory)
InactiveCN103294735ASave storage spaceSpecial data processing applicationsChain structureNondeterministic finite automaton
The invention relates to a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) matching method and device based on TCAM (ternary content addressable memory). The method comprises the following steps: expressing all states of a DFA with a plurality of TCAM items, and identifying a chain structure in the DFA based on a chain structure in a nondeterministic finite automata (NFA) for generating the DFA and the features of an internal chain structure between the NFA and the DFA, wherein each TCAM item comprises a source state field, an input character field and a targeted state field; renumbering and recoding the DFA state based on the chain structure in the DFA, and recoding the state transitional edge of the DFA in the TCAM; and taking the matching of the specific source state field and the input character field as a search keyword, searching in all TCAM items of the DFA based on the search keyword, and taking the searched targeted state field as an output result. Through coding and compressing the state transitional edge of the DFA in the TCAM, the deterministic finite automaton matching method and device, provided by the embodiment of the invention, enable the transcript chain structure of the DFA to be combined in the TCAM so as to fulfill the purpose of reducing the storage space.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
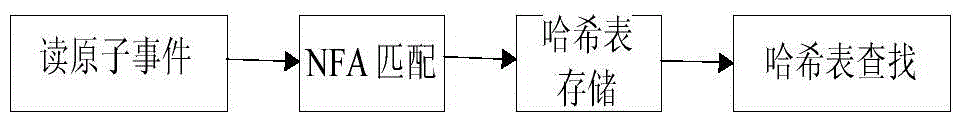
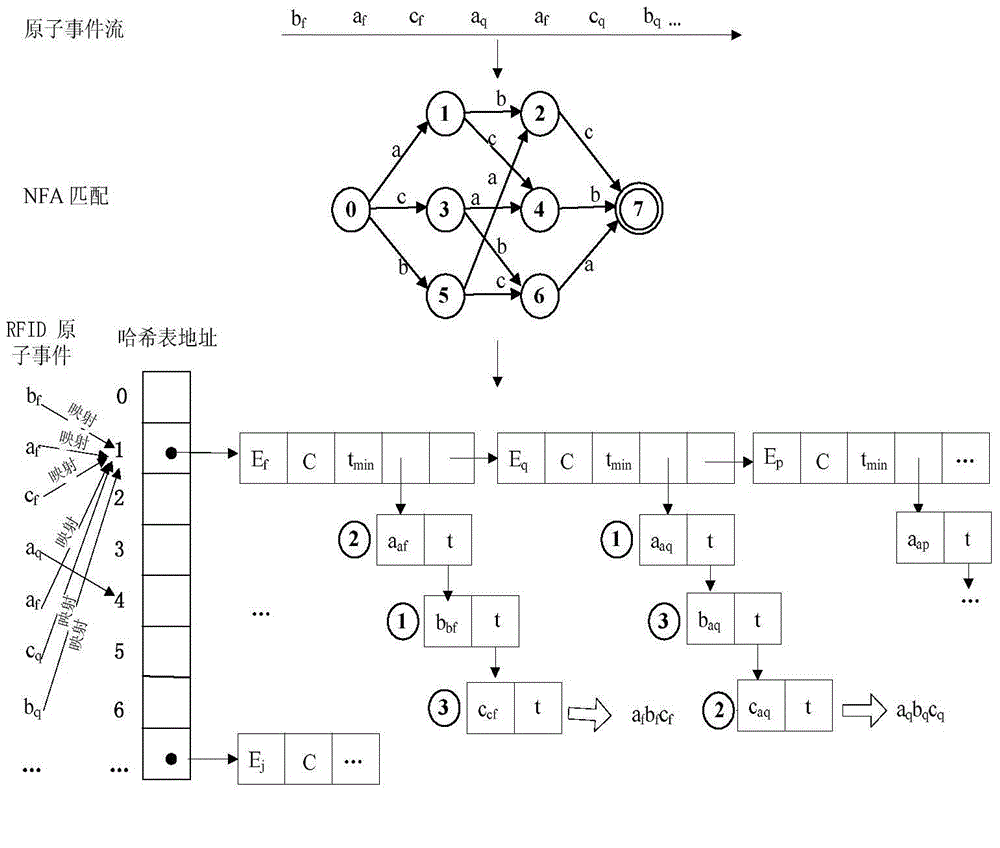
Hash structure complex event detection method for mass data flow
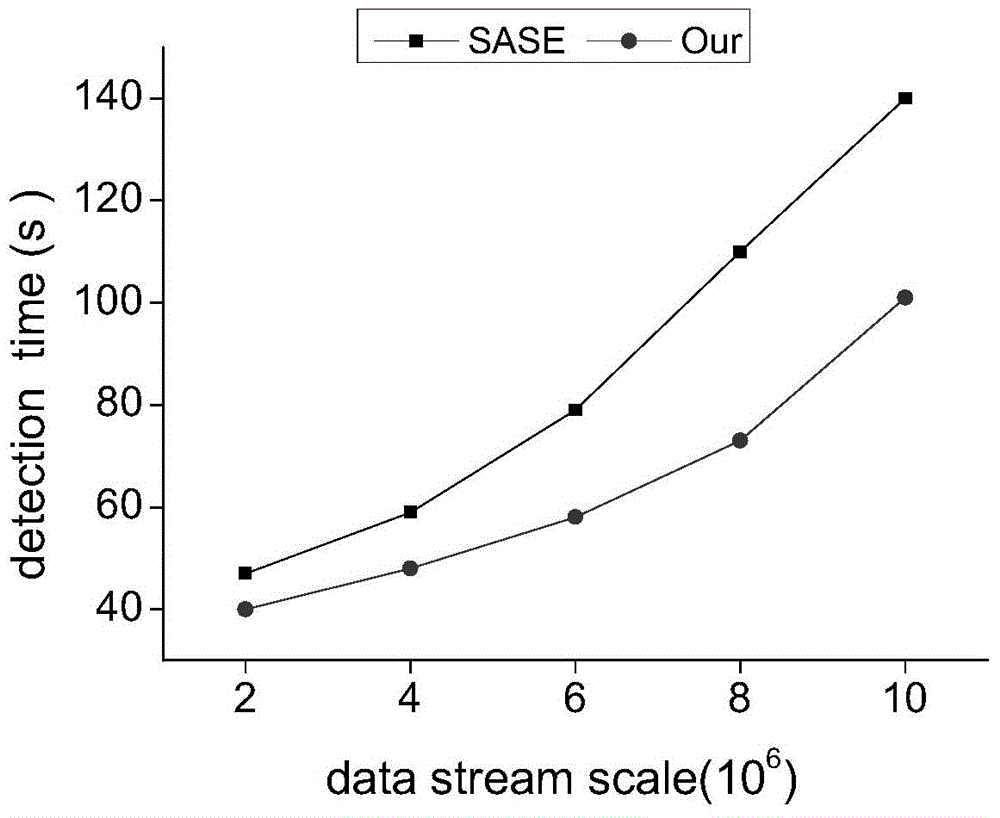
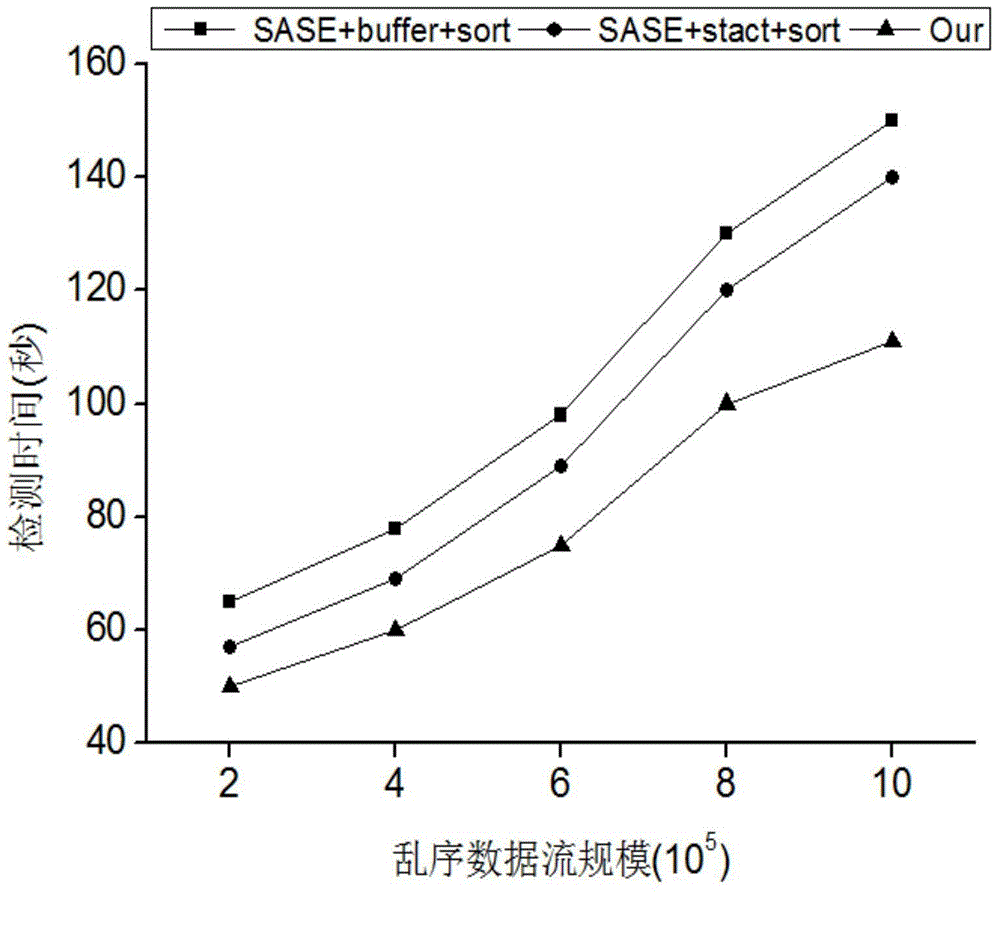
InactiveCN104361058AEasy to detectOvercome the shortcomings of long detection time, slow response speed, and low detection efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsData streamPattern detection
The invention discloses a hash structure complex event detection method for mass data flow, which mainly solves the problems of long detection time, low response speed, low detection efficiency and the like in the existing SASE method when the complex events of a mass event stream are detected. The complex event detection method for the mass event stream by an NFA (nondeterministic finite automaton) and a hash table technology has the advantages that the complex event detection capability for the mass event stream is greatly improved; the existing complex event mode detection method based on the NFA is improved, and the existing complex event detection technology is extended, so the complex event detection for the mass event stream is completed at high efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Deterministic finite-state machine construction method based on classification counter
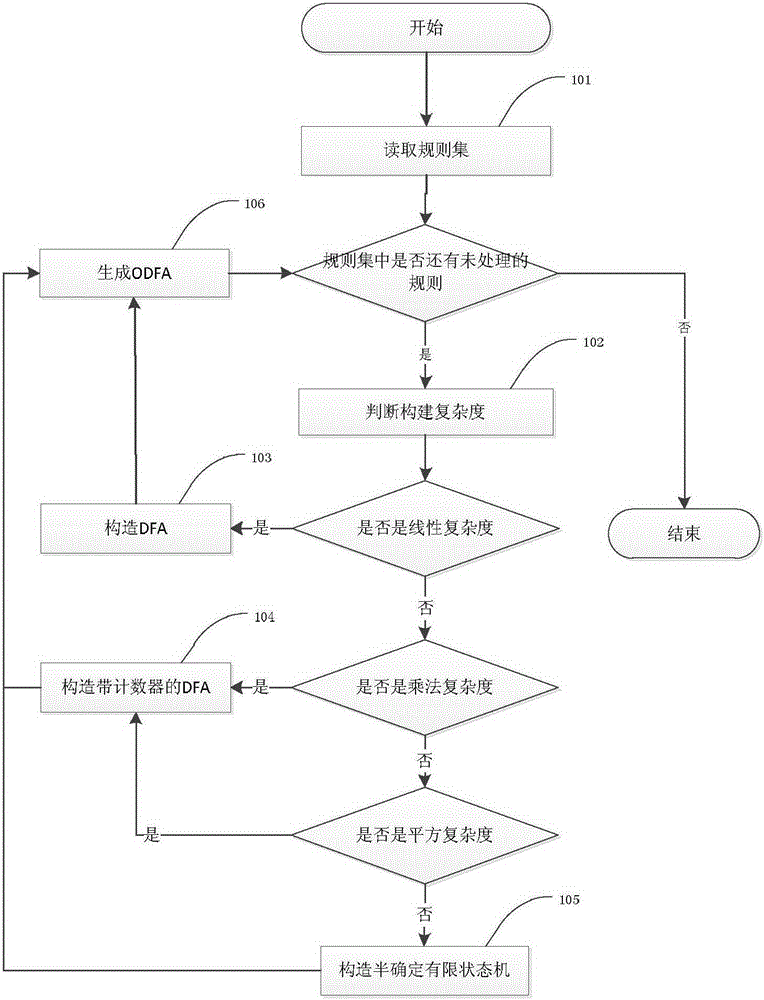
ActiveCN105184157AReduce the numberReduce consumptionPlatform integrity maintainanceTransmissionDeterministic noiseNondeterministic finite automaton
The invention disclosesa deterministic finite-state machine construction method based on a classification counter, and belongs to the field of Internet intrusion inspection. The deterministic finite-state machine construction method comprises the following steps: firstly, classifying all regular expressions in a regular expression set (rule set) into a linear-level complexity class, a multiplication-level complexity class, a square-level complexity class and an exponential-level complexity class according to DFA (Deterministic Finite Automaton) construction complexity; then, generating a specific DFA with the counter for the regular expressions of each class of complexity; and finally, combining states which contain the same output excitation, and are not internal start states and internal end states in the DFA to generate a final ODFA (Overlaid Deterministic Finite Automaton). The reception message inspection speed of an intrusion inspection system can be quickened, accuracy is improved, a false alarm rate is lowered, and the consumption of memory resources by the system can be reduced. The construction method has a great practical application value.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
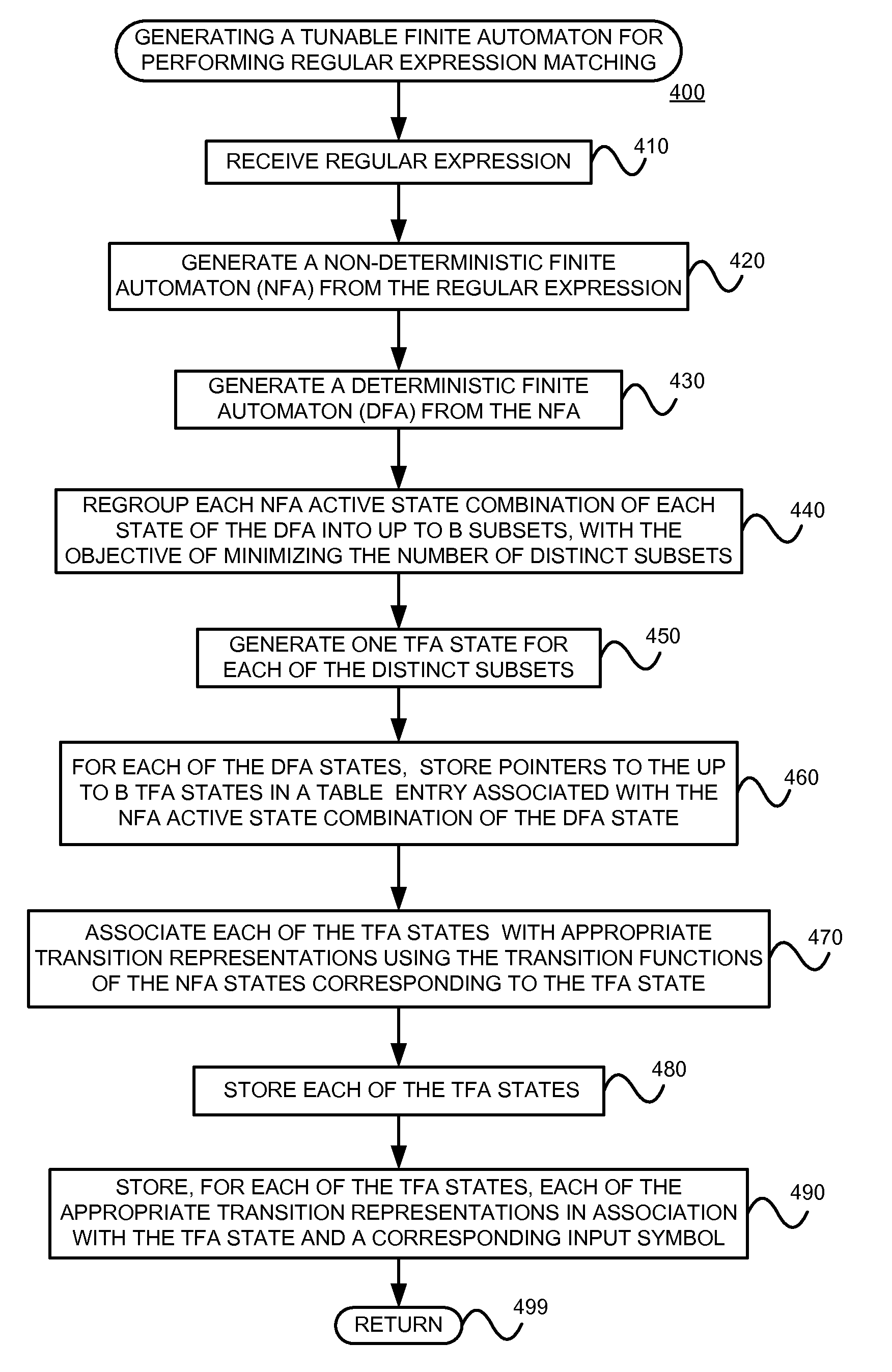
Generating a tunable finite automaton for regular expression matching
InactiveUS20140101155A1Minimize the numberDigital data processing detailsTransmissionNondeterministic finite automatonTerm memory
Deterministic Finite Automatons (DFAs) and Nondeterministic Finite Automatons (NFAs) are two typical automatons used in the Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS). Although they both perform regular expression matching, they have quite different performance and memory usage properties. DFAs provide fast and deterministic matching performance but suffer from the well-known state explosion problem. NFAs are compact, but their matching performance is unpredictable and with no worst case guarantee. A new automaton representation of regular expressions, called Tunable Finite Automaton (TFA), is described. TFAs resolve the DFAs' state explosion problem and the NFAs' unpredictable performance problem. Different from a DFA, which has only one active state, a TFA allows multiple concurrent active states. Thus, the total number of states required by the TFA to track the matching status is much smaller than that required by the DFA. Different from an NFA, a TFA guarantees that the number of concurrent active states is bounded by a bound factor b that can be tuned during the construction of the TFA according to the needs of the application for speed and storage. A TFA can achieve significant reductions in the number of states and memory space.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
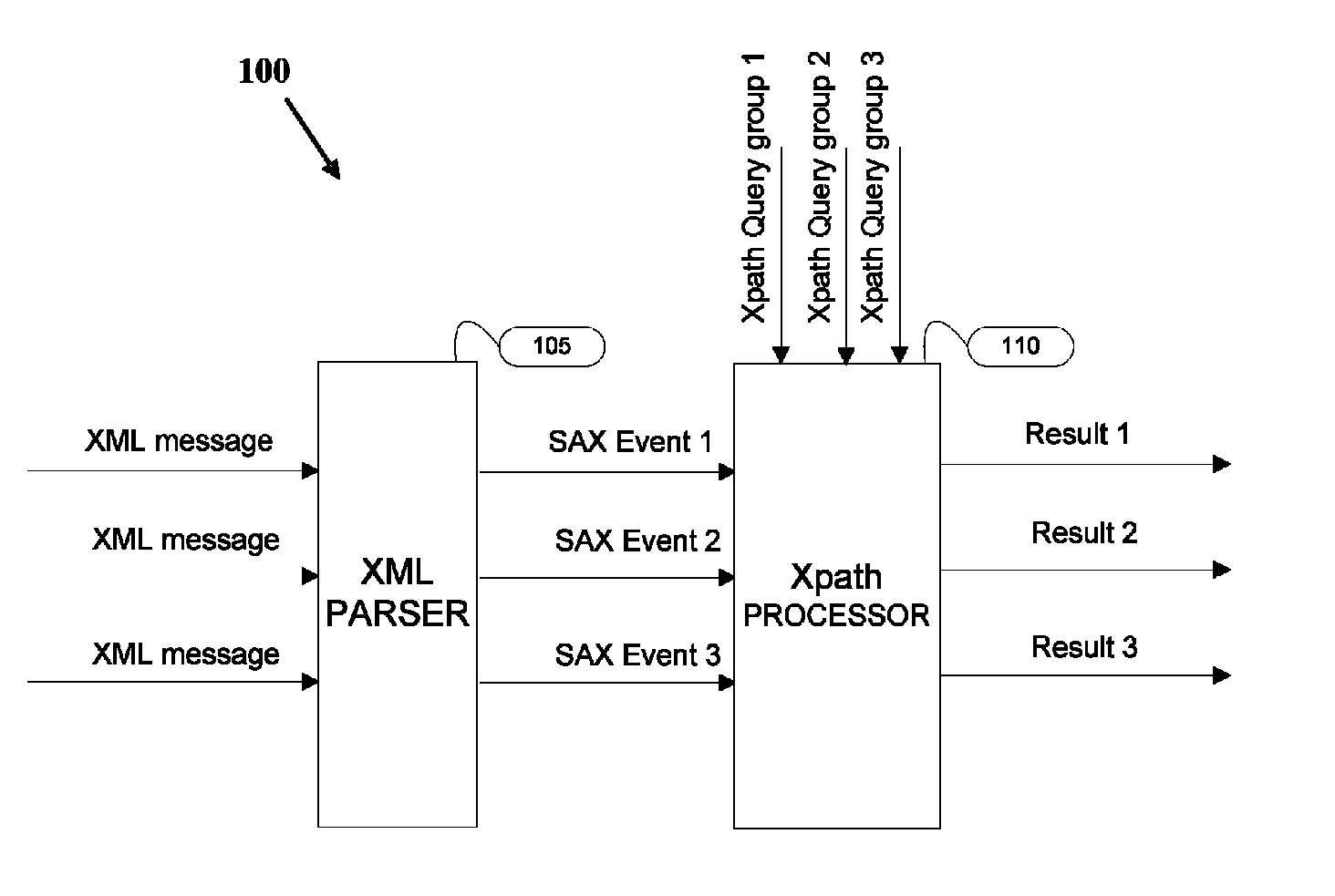
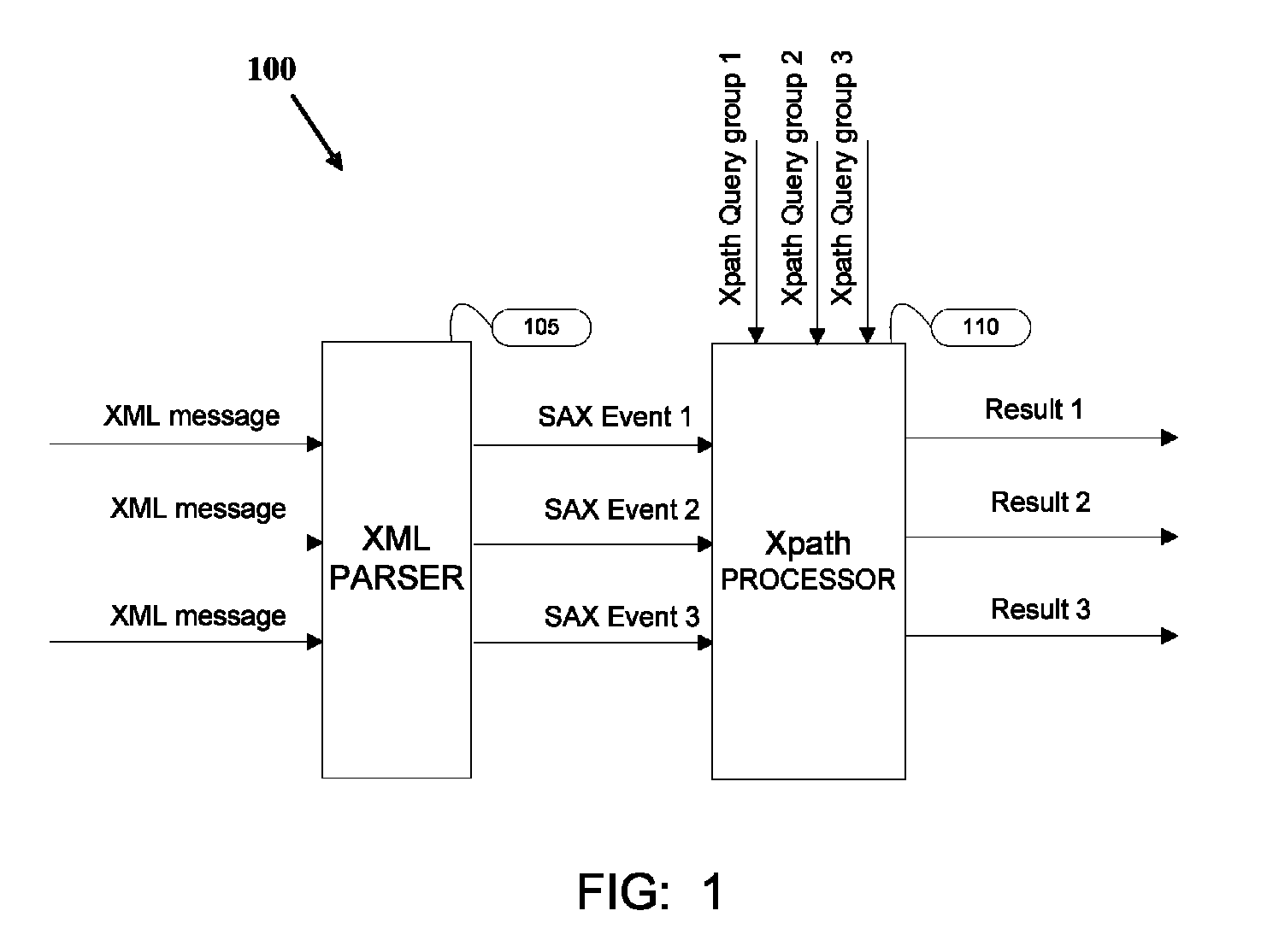
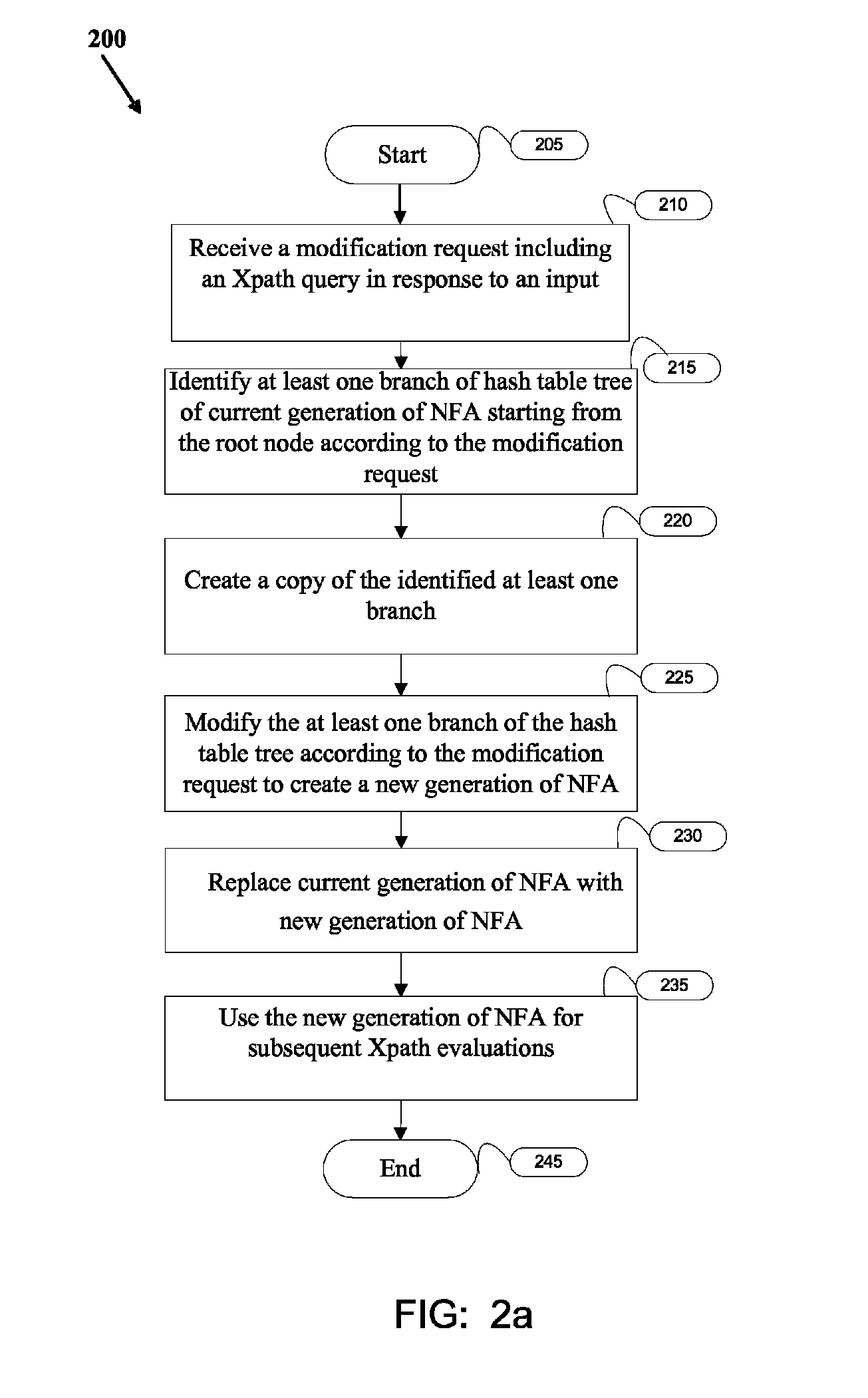
Dynamic modification of Xpath queries
ActiveUS8055652B1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceNondeterministic finite automaton
Modifying Xpath queries dynamically during an ongoing Xpath evaluation. A modification request comprising at least one Xpath query in response to an input is received in an ongoing Xpath evaluation on an online stream of XML messages. A current generation of Nondeterministic Finite Automaton (NFA) is generated and the branches starting from the root node are identified according to the modification request. The identified branches are copied and modified to create a new generation of NFA. New generation of NFA is used for subsequent Xpath evaluations.
Owner:SONOA NETWORKS INDIA PVT
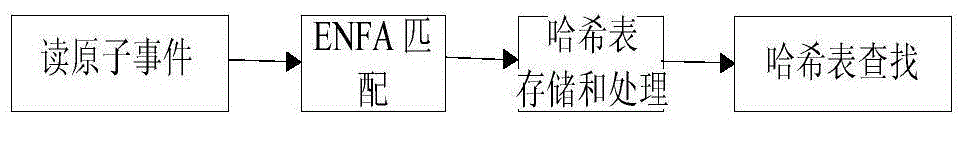
Detection method for complex events in mass disordered data streams of Internet of Things Manufacturing
InactiveCN104408142ADetection Technology ImprovementImprove incident detection capabilitiesSpecial data processing applicationsData streamPattern detection
The invention discloses a detection method for complex events in mass disordered data streams of Internet of Things Manufacturing, and aims at solving the problem of low efficiency on detecting the events in mass disordered data streams in the Internet of Things Manufacturing. The method is characterized in that ENFA (Extended Nondeterministic Finite Automaton) is utilized for selecting events in mass disordered data streams, and the storage relationship of a hash table structure is utilized to handle events in the mass disordered data streams, so as to realize the detection of the complex events in mass disordered data streams. The method has the advantages that the existing automaton-based complex event mode detection method is improved, the existing complex event detection technology is expanded to be able to efficiently detect the complex events in the mass disordered data streams, and therefore, the detection efficiency is raised.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Generating a tunable finite automaton for regular expression matching
InactiveUS8943063B2Digital data processing detailsTransmissionNondeterministic finite automatonDeterministic finite automaton
Deterministic Finite Automatons (DFAs) and Nondeterministic Finite Automatons (NFAs) are two typical automatons used in the Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS). Although they both perform regular expression matching, they have quite different performance and memory usage properties. DFAs provide fast and deterministic matching performance but suffer from the well-known state explosion problem. NFAs are compact, but their matching performance is unpredictable and with no worst case guarantee. A new automaton representation of regular expressions, called Tunable Finite Automaton (TFA), is described. TFAs resolve the DFAs' state explosion problem and the NFAs' unpredictable performance problem. Different from a DFA, which has only one active state, a TFA allows multiple concurrent active states. Thus, the total number of states required by the TFA to track the matching status is much smaller than that required by the DFA. Different from an NFA, a TFA guarantees that the number of concurrent active states is bounded by a bound factor b that can be tuned during the construction of the TFA according to the needs of the application for speed and storage. A TFA can achieve significant reductions in the number of states and memory space.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
A printing and dyeing quotation structured demand data extraction method based on a finite state automaton
ActiveCN109947835AReduce duplication of workImprove efficiencyDatabase management systemsVisual data miningData ingestionReusability
The invention relates to a printing and dyeing quotation structured demand data extraction method based on a finite state automaton. The method is characterized in that a formalized definition of theuncertain finite-state automaton is given according to an actual quotation process and requirements, a real quotation process is simulated through the uncertain finite-state automaton, a user is gradually guided to give an accurate requirement, and structured data is arranged and provided for a customer service. Compared with the prior art, the printing and dyeing quotation structured demand dataextraction method based on the finite state automaton provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the method does not depend on manual collection and arrangement demands, and the efficiency is remarkably improved. The method is short in processing period and has reusability; the method is low in processing cost and high in accuracy.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Data pattern analysis using optimized deterministic finite automation
ActiveUS8626689B1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsNODALArray data structure
Techniques for data pattern analysis using deterministic finite automaton are described herein. In one embodiment, a number of transitions from a current node to one or more subsequent nodes representing one or more sequences of data patterns is determined, where each of the current node and subsequent nodes is associated with a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) state. A data structure is dynamically allocated for each of the subsequent nodes for storing information associated with each of the subsequent nodes, where data structures for the subsequent nodes are allocated in an array maintained by a data structure corresponding to the current node if the number of transitions is greater than a predetermined threshold. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Privacy protection medical diagnosis and treatment system based on non-deterministic finite automaton
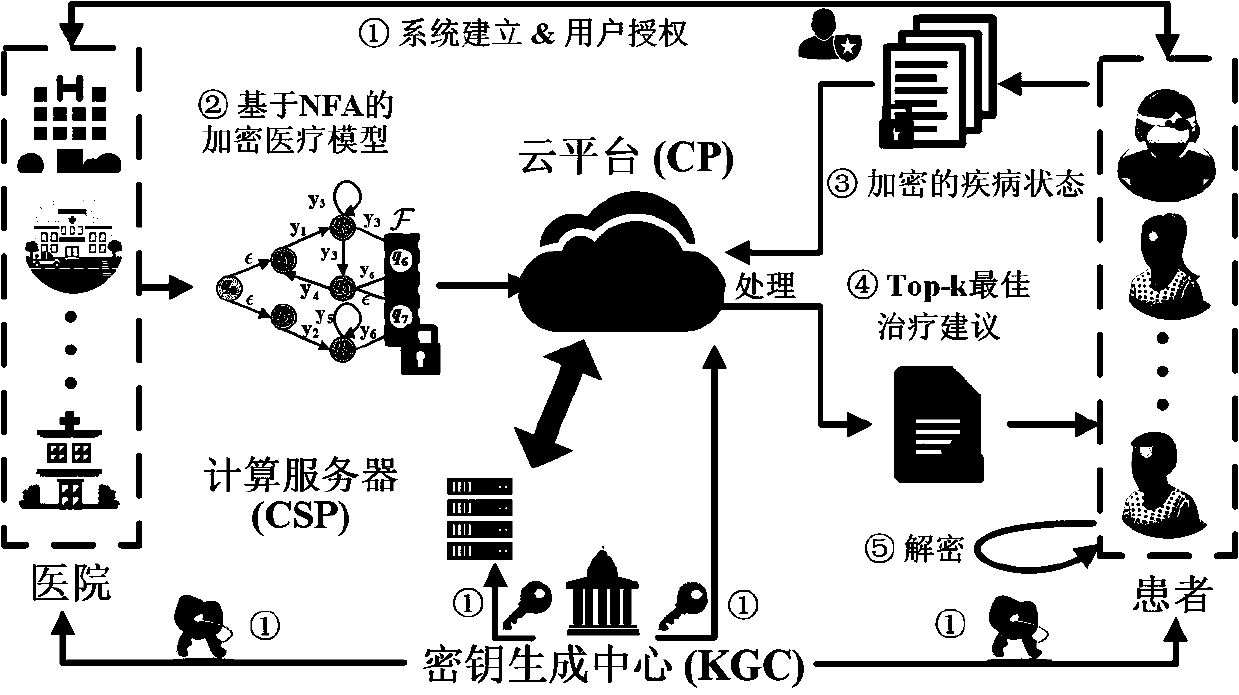
ActiveCN110611567APrivacy protectionBest Encryption Healing Process SuggestionsMedical communicationKey distribution for secure communicationDiseaseNondeterministic finite automaton
The invention relates to a privacy protection medical diagnosis and treatment system based on a non-deterministic finite automaton. The system comprises a key generation center which is responsible for generating system public parameters, distributing a private key of a server and a public / private key of a user and executing remote medical authorization operation; a hospital which is used for designing different medical models for different diseases and outsourcing the encrypted medical models to the cloud platform so as to provide remote diagnosis and treatment service; a patient who sends the encrypted medical data to the cloud platform to request to obtain the diagnosis and treatment service, and decrypts the diagnosis and treatment result returned by the cloud server by using the own key; a cloud platform which is used for providing storage service of the encrypted medical model for the hospital; and a computing server which is used for interactively executing a security outsourcing computing protocol by the computing server and the cloud platform after receiving a remote diagnosis and treatment request of the patient, and calculating an optimal encryption treatment process. The optimal encryption treatment suggestion can be recommended to the patient, and the privacy of the patient cannot be leaked.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Using a tunable finite automaton for regular expression matching
InactiveUS8938454B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsNondeterministic finite automatonTerm memory
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Regex compiler
ActiveUS9858051B2Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionNondeterministic finite automatonAutomaton
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
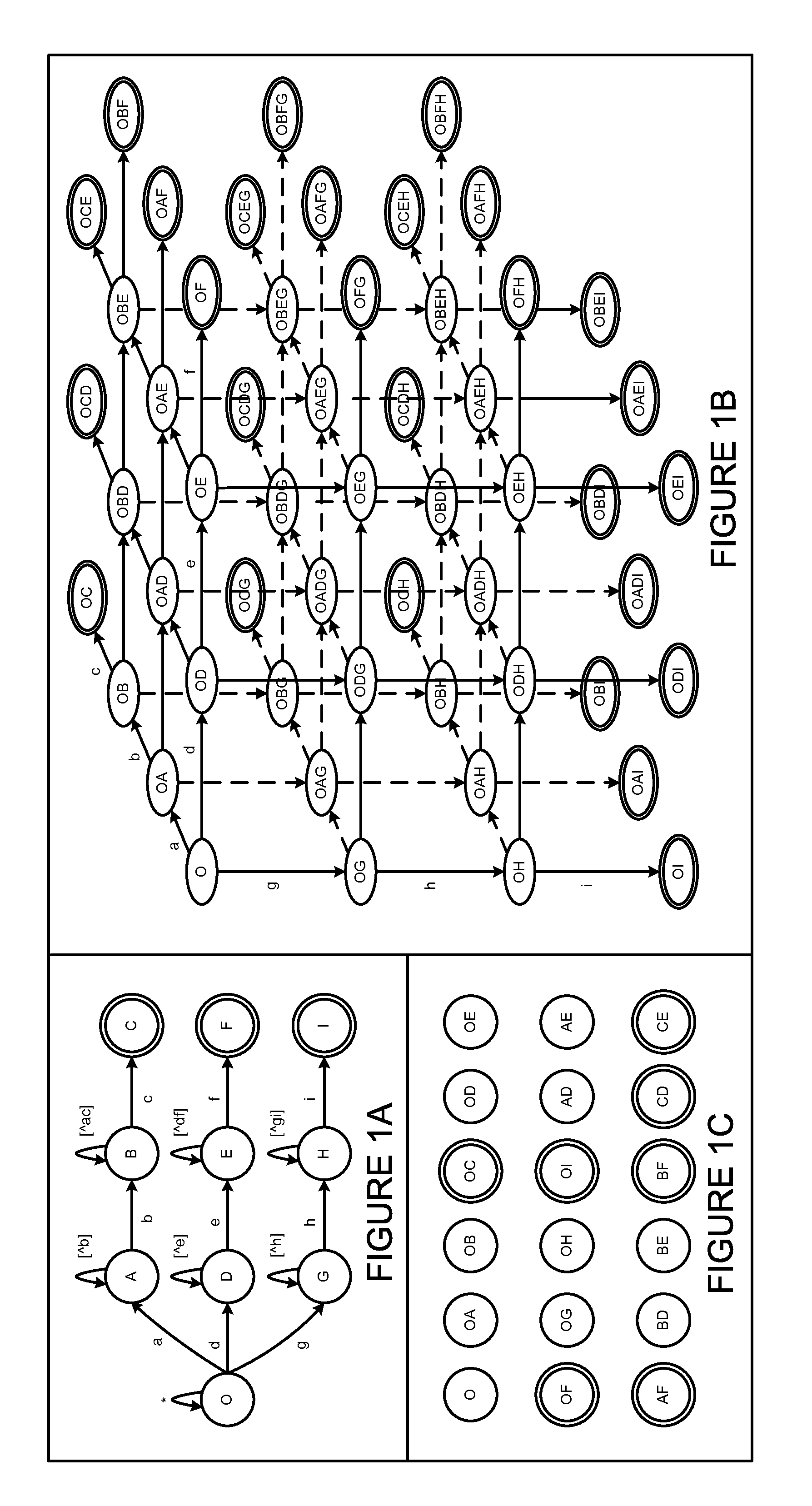
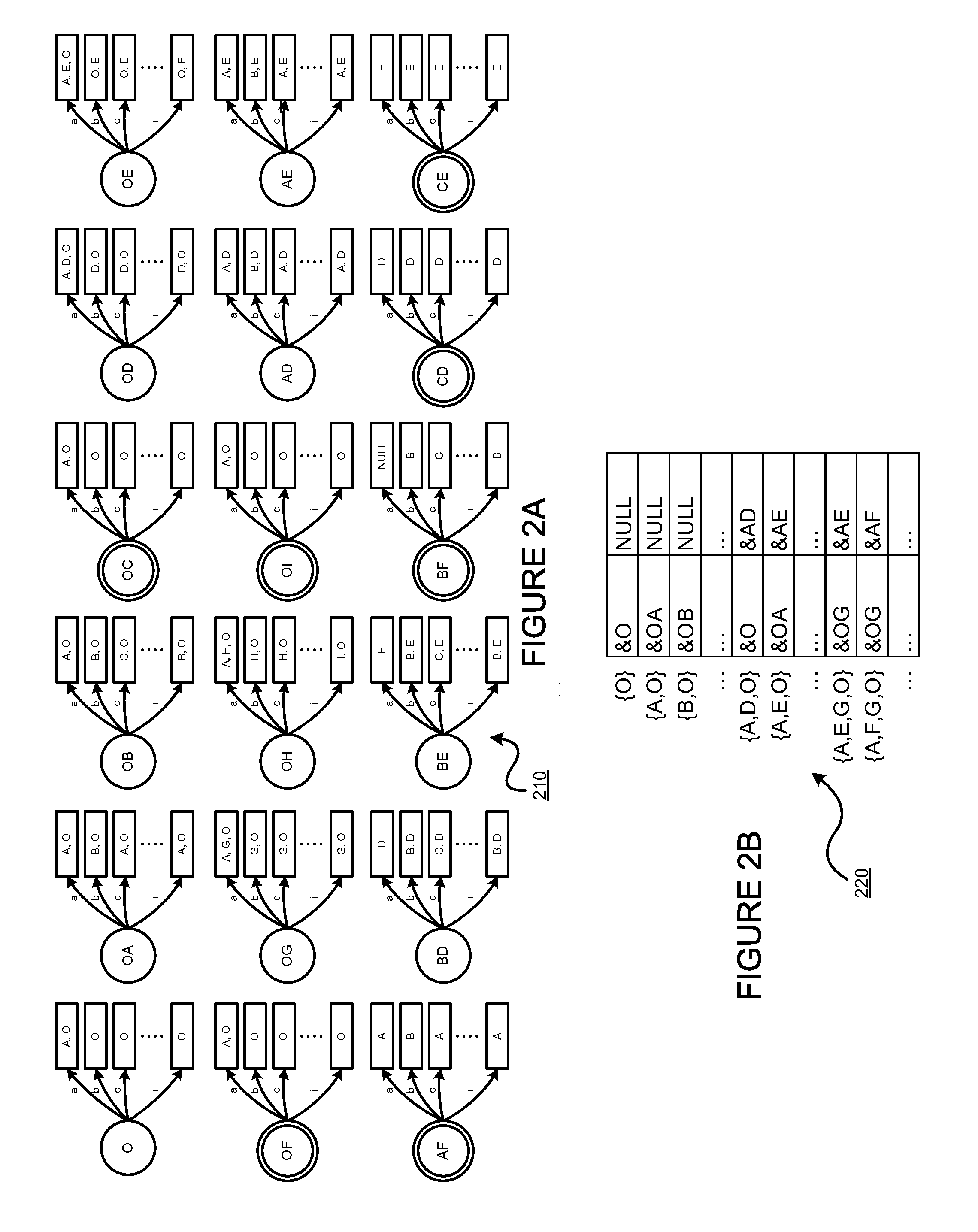
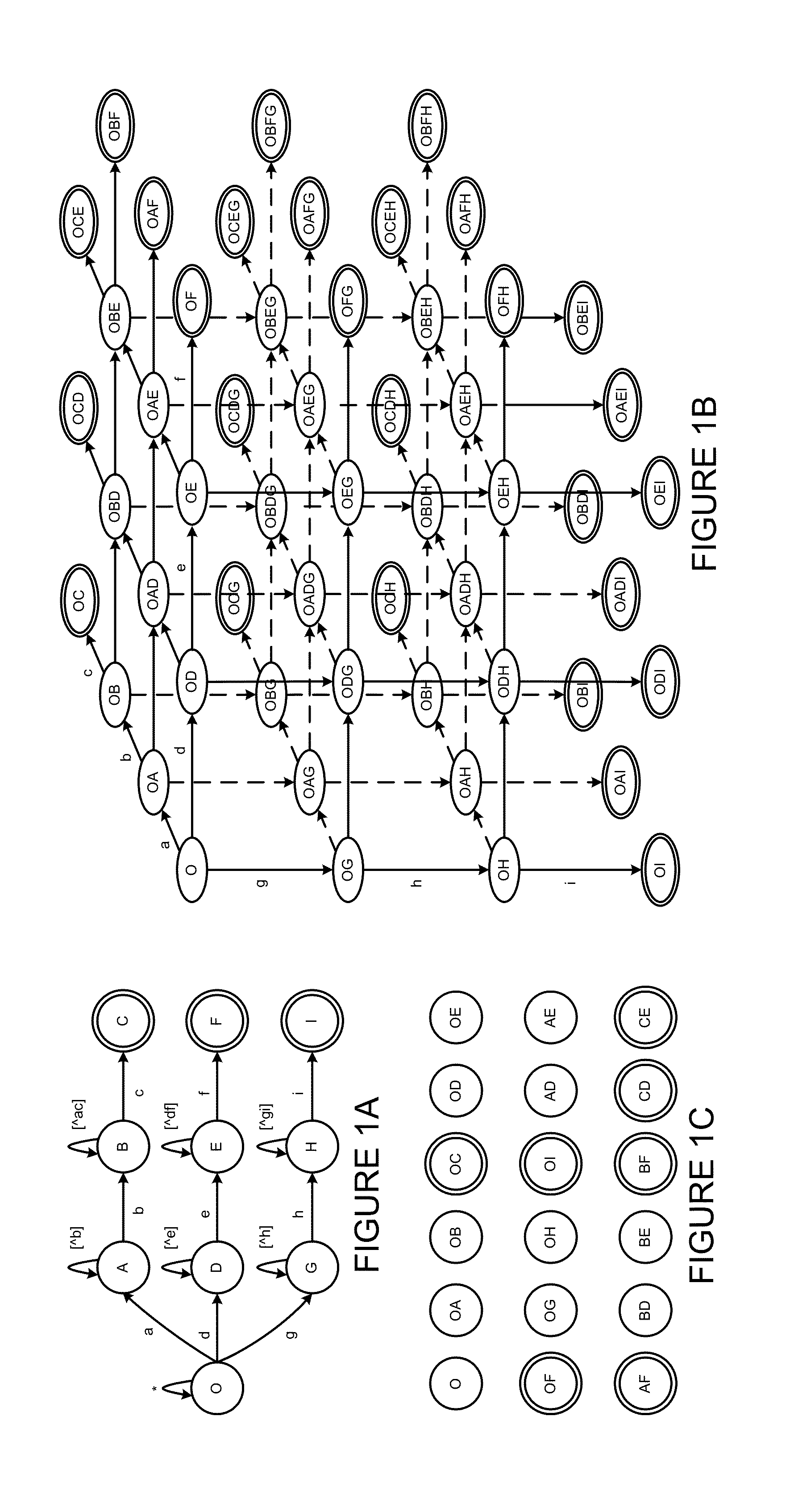
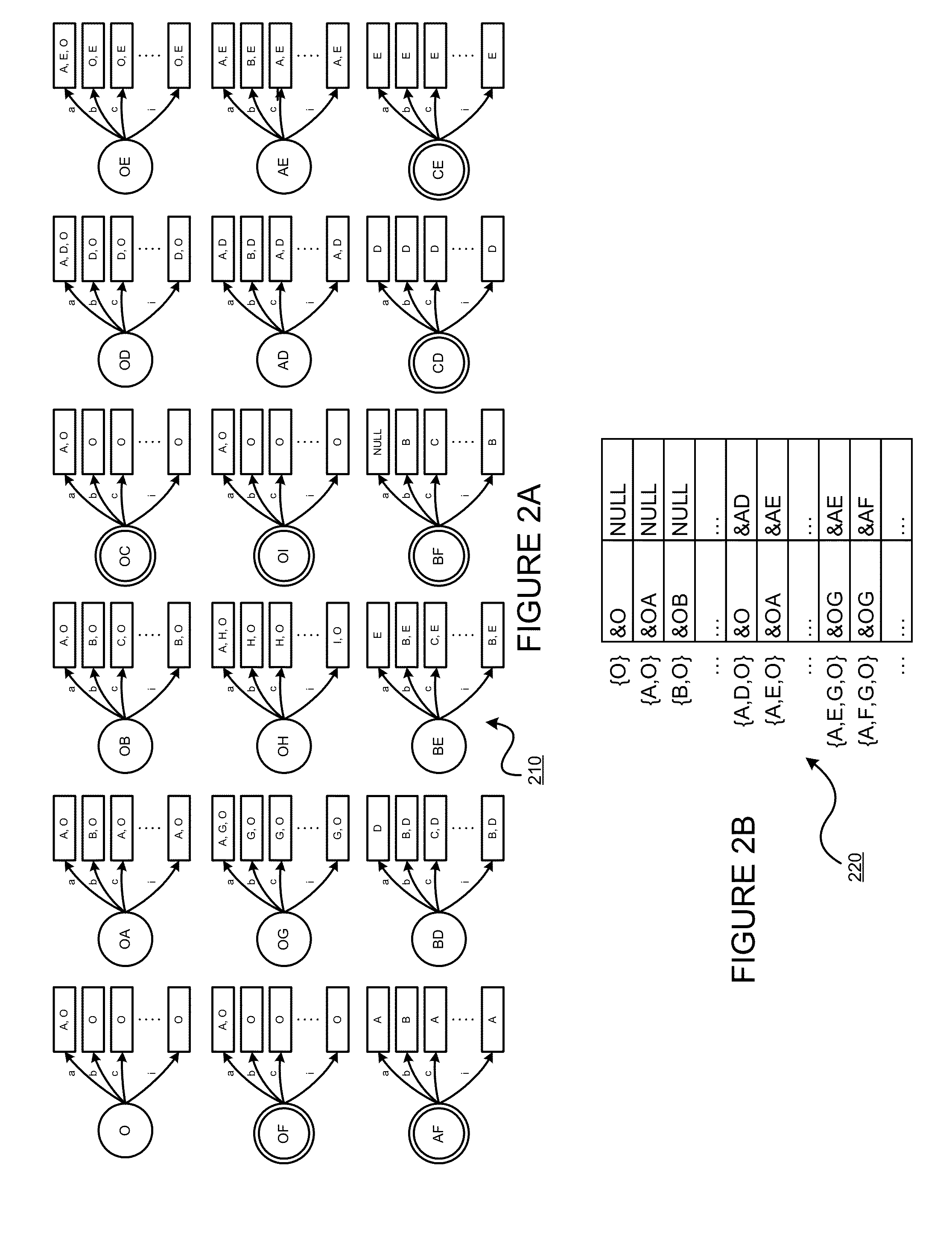
Regrouping non-derministic finite automaton active states to minimize distinct subsets
InactiveUS8935250B2Digital data processing detailsTransmissionAlgorithmNondeterministic finite automaton
Deterministic Finite Automatons (DFAs) and Nondeterministic Finite Automatons (NFAs) are two typical automatons used in the Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS). Although they both perform regular expression matching, they have quite different performance and memory usage properties. DFAs provide fast and deterministic matching performance but suffer from the well-known state explosion problem. NFAs are compact, but their matching performance is unpredictable and with no worst case guarantee. A new automaton representation of regular expressions, called Tunable Finite Automaton (TFA), is described. TFAs resolve the DFAs' state explosion problem and the NFAs' unpredictable performance problem. Different from a DFA, which has only one active state, a TFA allows multiple concurrent active states. Thus, the total number of states required by the TFA to track the matching status is much smaller than that required by the DFA. Different from an NFA, a TFA guarantees that the number of concurrent active states is bounded by a bound factor b that can be tuned during the construction of the TFA according to the needs of the application for speed and storage. A TFA can achieve significant reductions in the number of states and memory space.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Regular expression matching equipment and method on basis of deterministic finite automaton
ActiveCN102521356BSave storage spaceFast matchingSpecial data processing applicationsNondeterministic finite automatonDeterministic finite automaton
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING +1
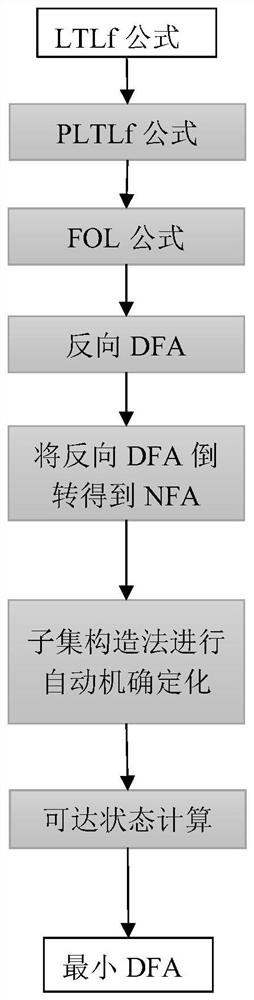
Method and device for obtaining LTLf minimum automaton, and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN114371849ASimple structureTransformation of program codeAlgorithmNondeterministic finite automaton
The invention provides a method for obtaining an LTLf minimum automaton. According to the method, LTLf to minimum DFA construction is completed on the basis of a Brzozowski minimum automaton construction theory. Comprising the steps that for a given LTLf formula, firstly, a reverse deterministic automaton corresponding to LTLf is constructed through a tool MONA, and the automaton can receive a reverse sequence of an original LTLf receiving language; the method comprises the steps that a reverse deterministic automaton is obtained, the reverse deterministic automaton is inverted, and therefore a non-deterministic finite state automaton (NFA) is obtained; subset construction method calculation is performed on the NFA, and reachable state calculation is performed after the calculation, thereby deleting all unreachable states. According to the Brzozowski theory, the DFA is the minimum DFA corresponding to the LTLf formula.
Owner:上海工业控制安全创新科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com