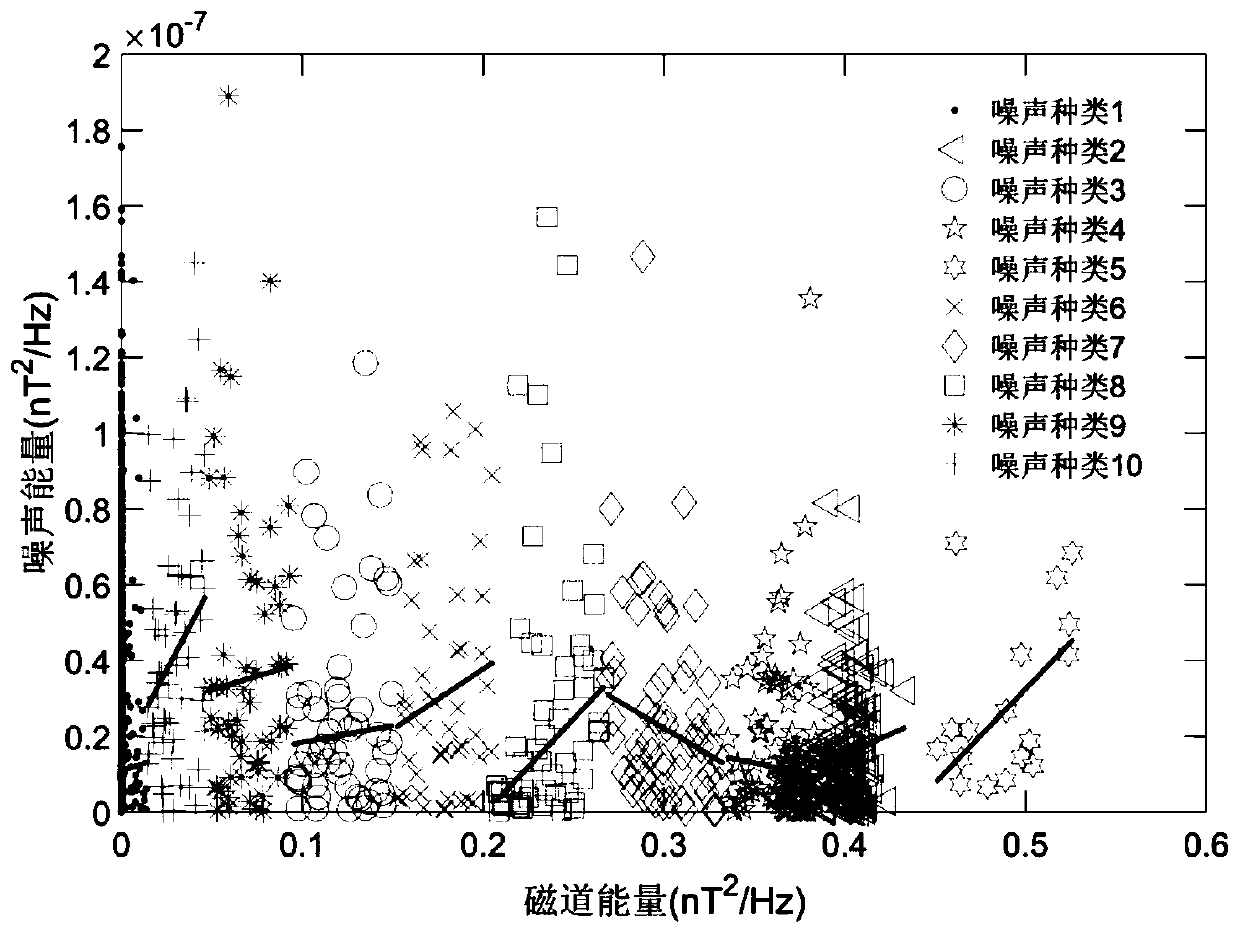
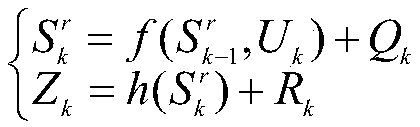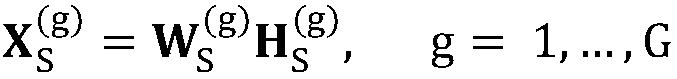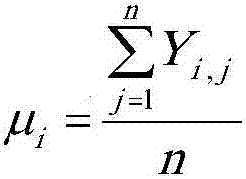Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Noise weighting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A noise weighting is a specific amplitude-vs.-frequency characteristic that is designed to allow subjectively valid measurement of noise. It emphasises the parts of the spectrum that are most important.
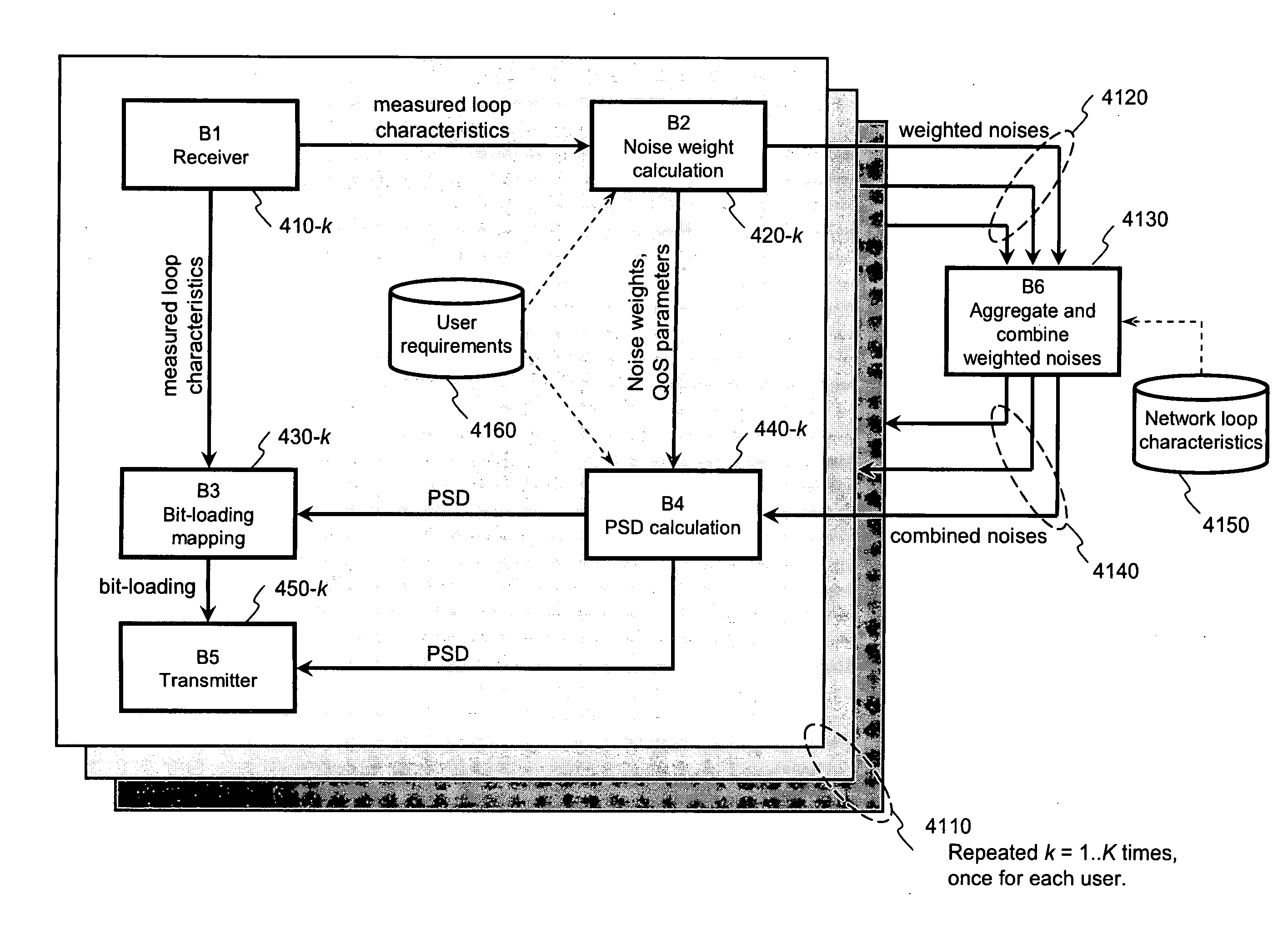
Method for distributed spectrum management of digital communications systems
ActiveUS20070274404A1Lower Level RequirementsManagement overheadFrequency-division multiplex detailsAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A method for distributed spectrum management of digital communication systems having a plurality of communication lines on which signals are transmitted and received by respective users, the method comprising the steps of: collecting information about line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines from a plurality of sources; determining the line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines; varying power allocation of particular plurality of the communication lines between respective transmitter and receiver taking into consideration the determined line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines and consideration of a noise weight of a plurality of the communication lines to enable a minimum power on a plurality of the communication lines and to allow required effective data-rates for each of said respective users to be satisfied.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
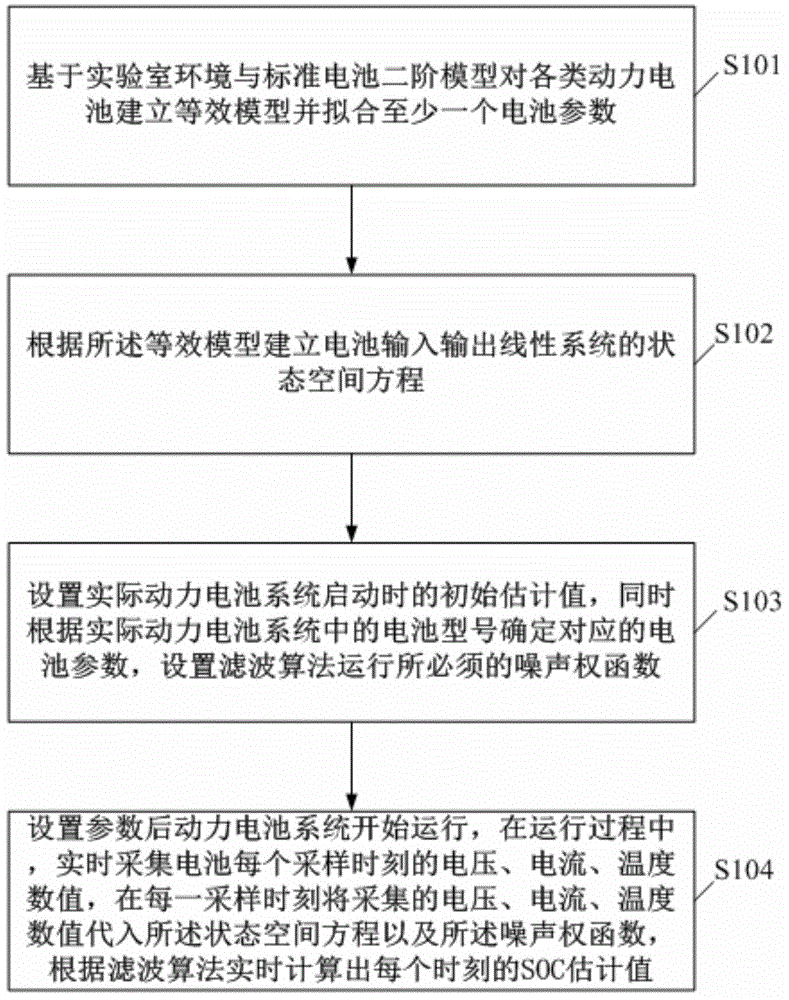
Power battery charge state estimation method and system
InactiveCN104977545AGuaranteed stabilityImprove estimation calculation accuracyElectrical testingSpecial data processing applicationsPower batteryElectrical battery
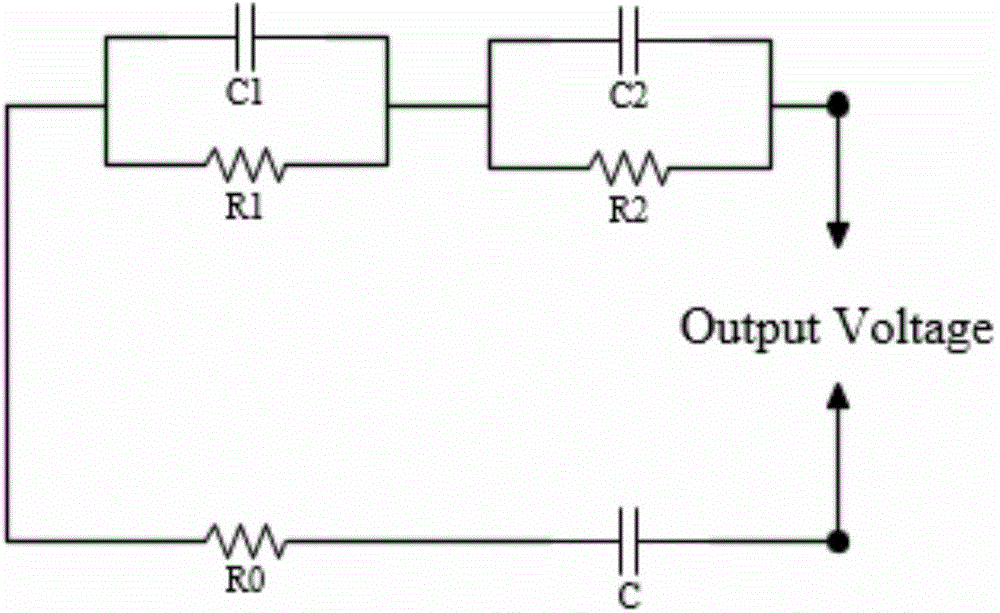
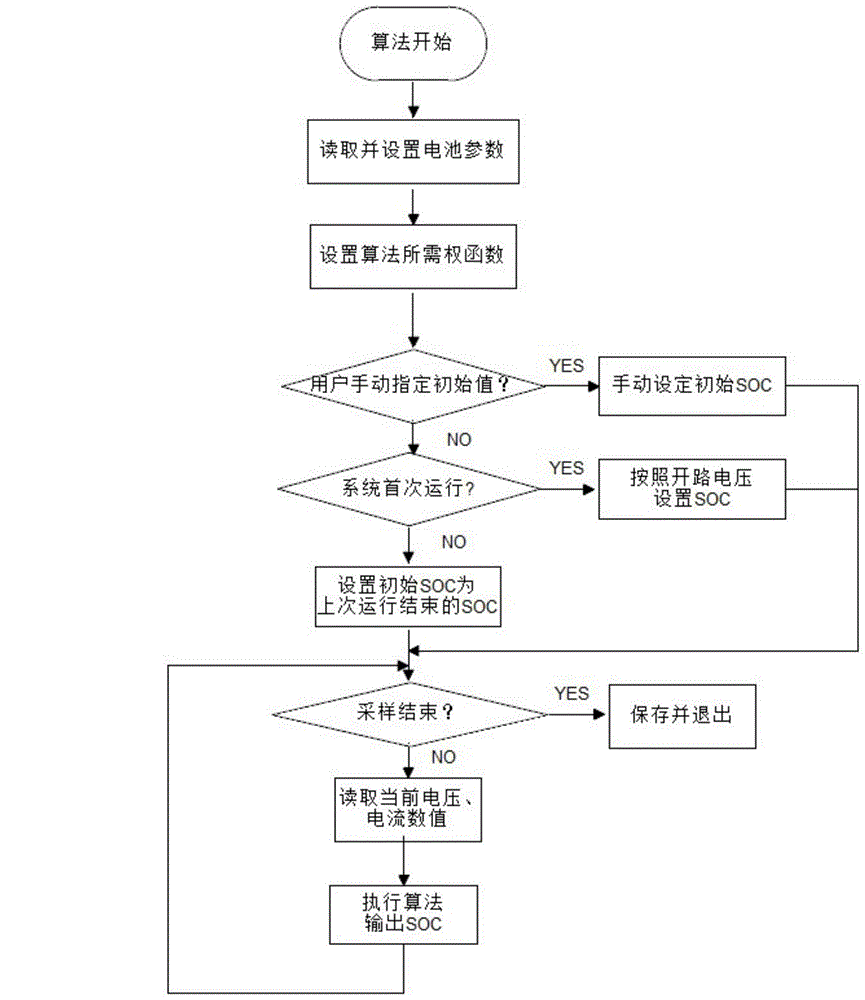
The invention discloses a power battery charge state estimation method and system. The method comprises the steps: building equivalent models for all kinds of power batteries based on laboratory environments and a standard battery second-order model, and fitting battery parameters; building a state-space equation of a battery output-input linear system according to the equivalent models; setting the initial SOC estimated value when a practical power battery system is started, determining the corresponding battery parameters according to the types of batteries in the practical power battery system, and setting a noise weight function needed by running of an H(infinity) filtering algorithm; and starting the running of the power battery system after the parameters are set, in the running process, collecting values of voltage, current and temperature of each battery at each sampling moment in real time, substituting the collected values of voltage, current and temperature of each battery at each sampling moment into the state-space equation and the noise weight function, and calculating to obtain the SOC estimated value at each moment in real time by adopting the H(infinity) filtering algorithm. According to the method, any assumption on outside noise is not required, so that the estimated accuracy is obviously improved, and the antijamming capability is greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
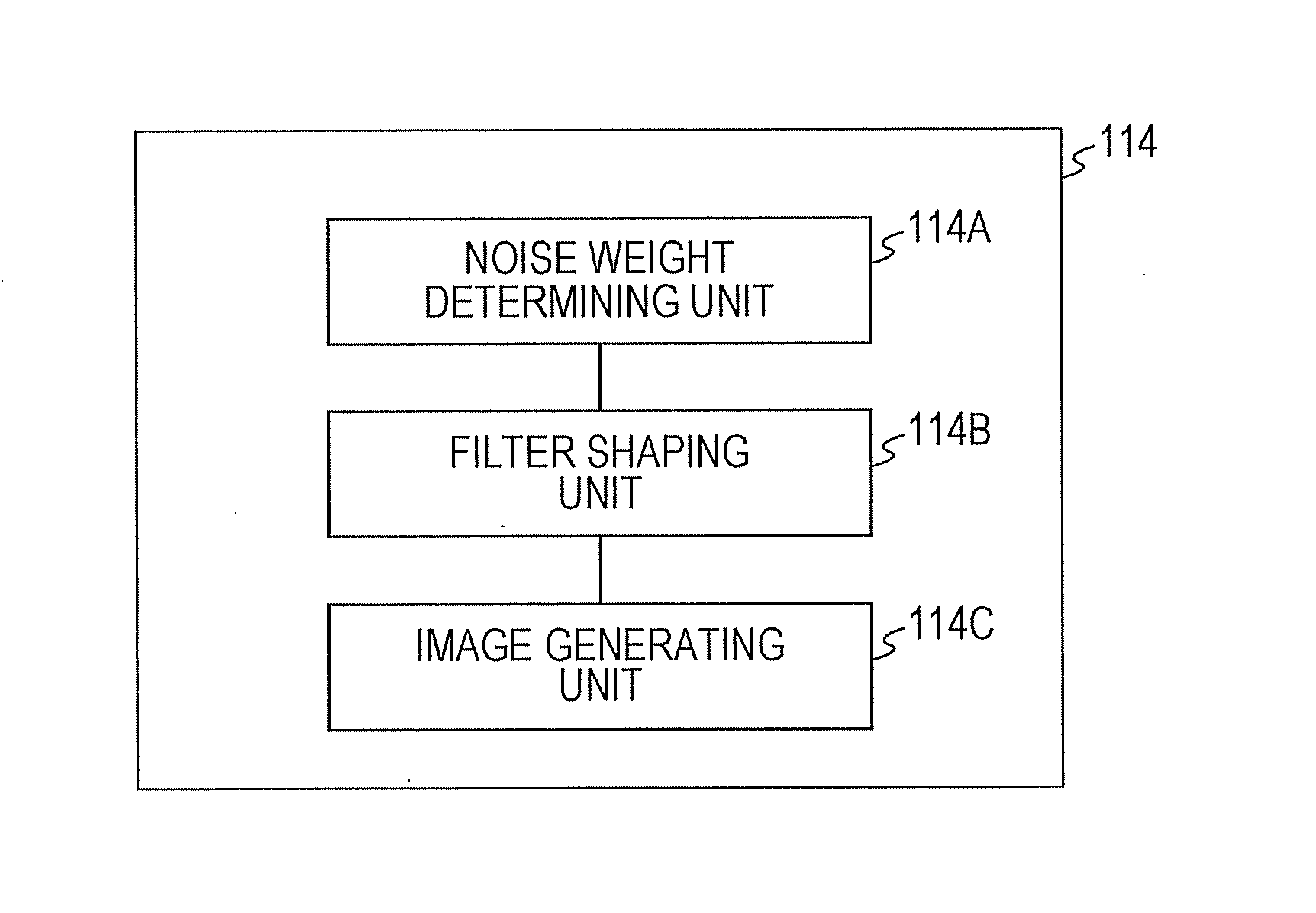
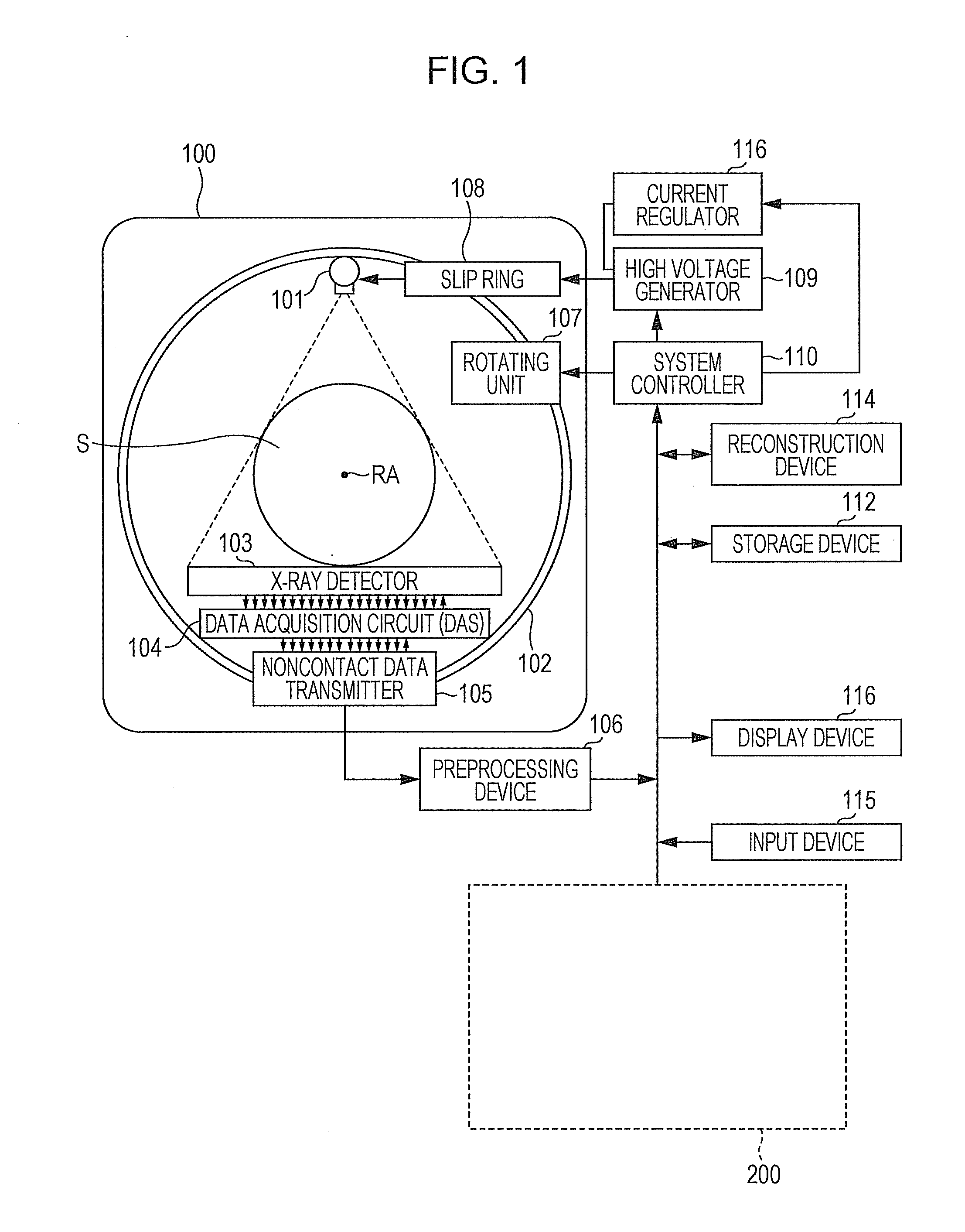
Method and system for generating image using filtered backprojection with noise weighting and or prior in
ActiveUS20140029819A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionReconstruction filterComputer vision
An image is reconstructed based upon a filtered backprojection (FBP) technique using a reconstruction filter which is customized or shaped by parameters including a weight value that is determined for weighing projection data according to a predetermined noise model. The weight value is determined based upon rays or views in the projection data. A regularization term is also combined with the noise-weighted FBP.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
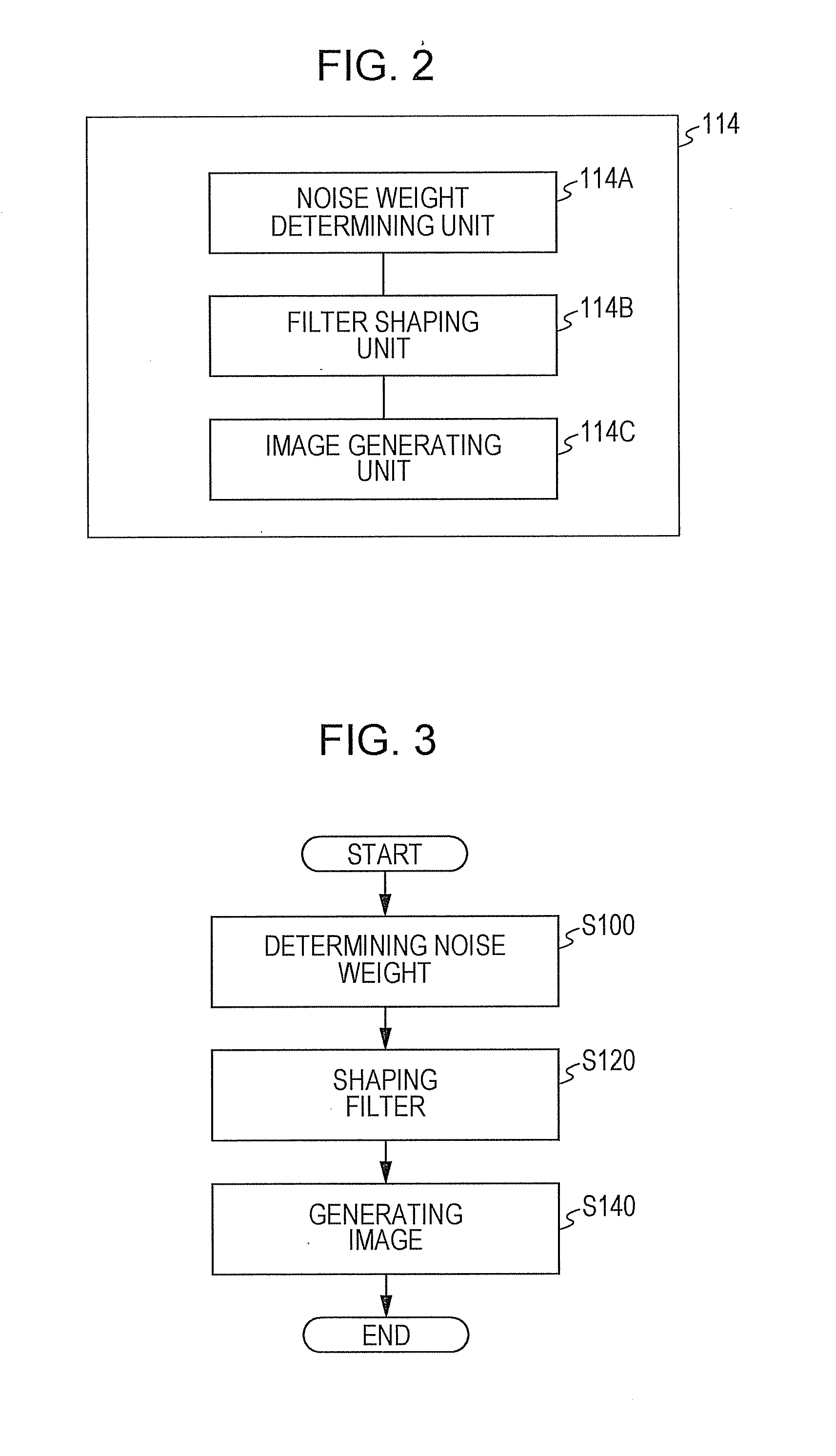
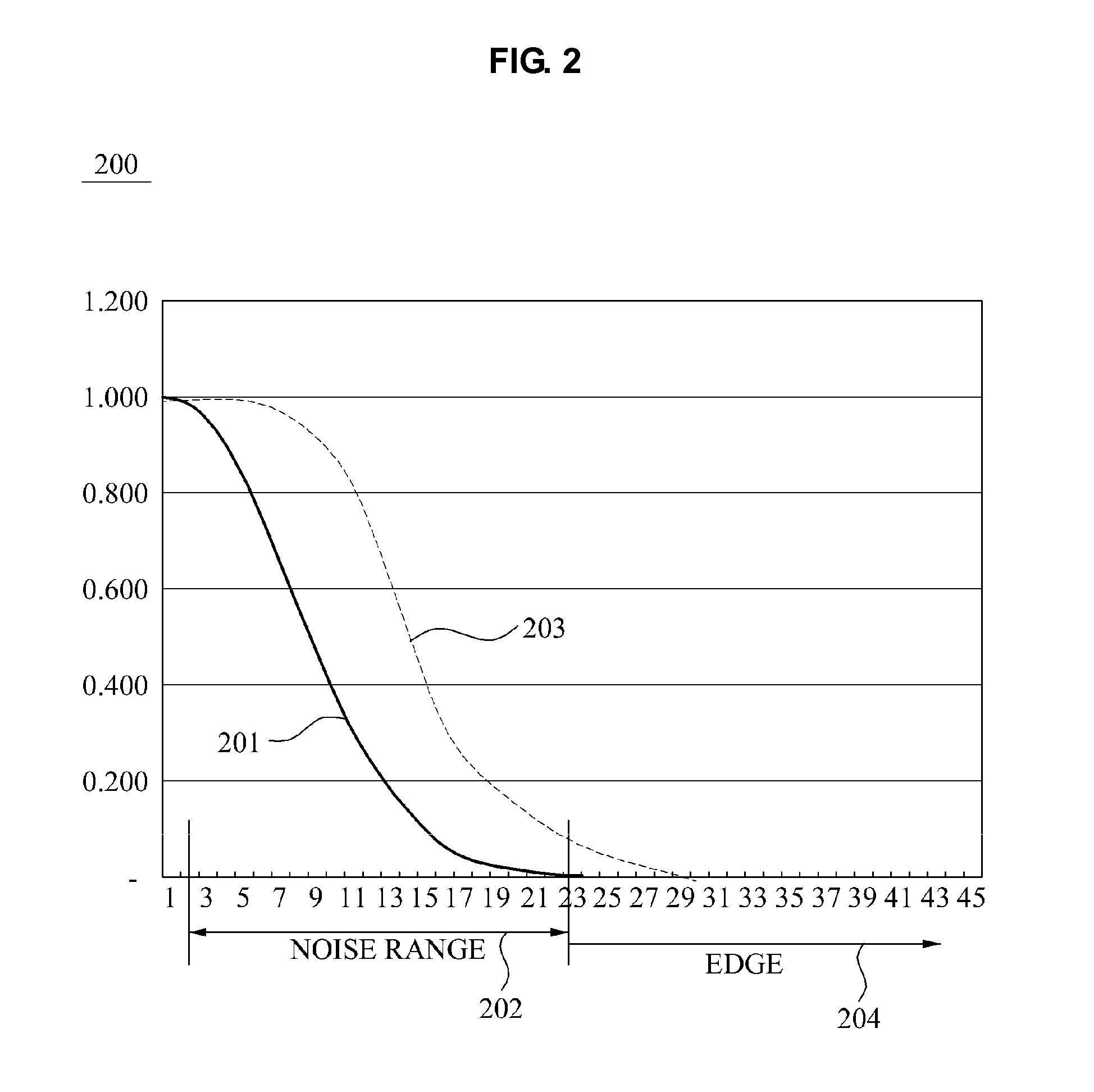
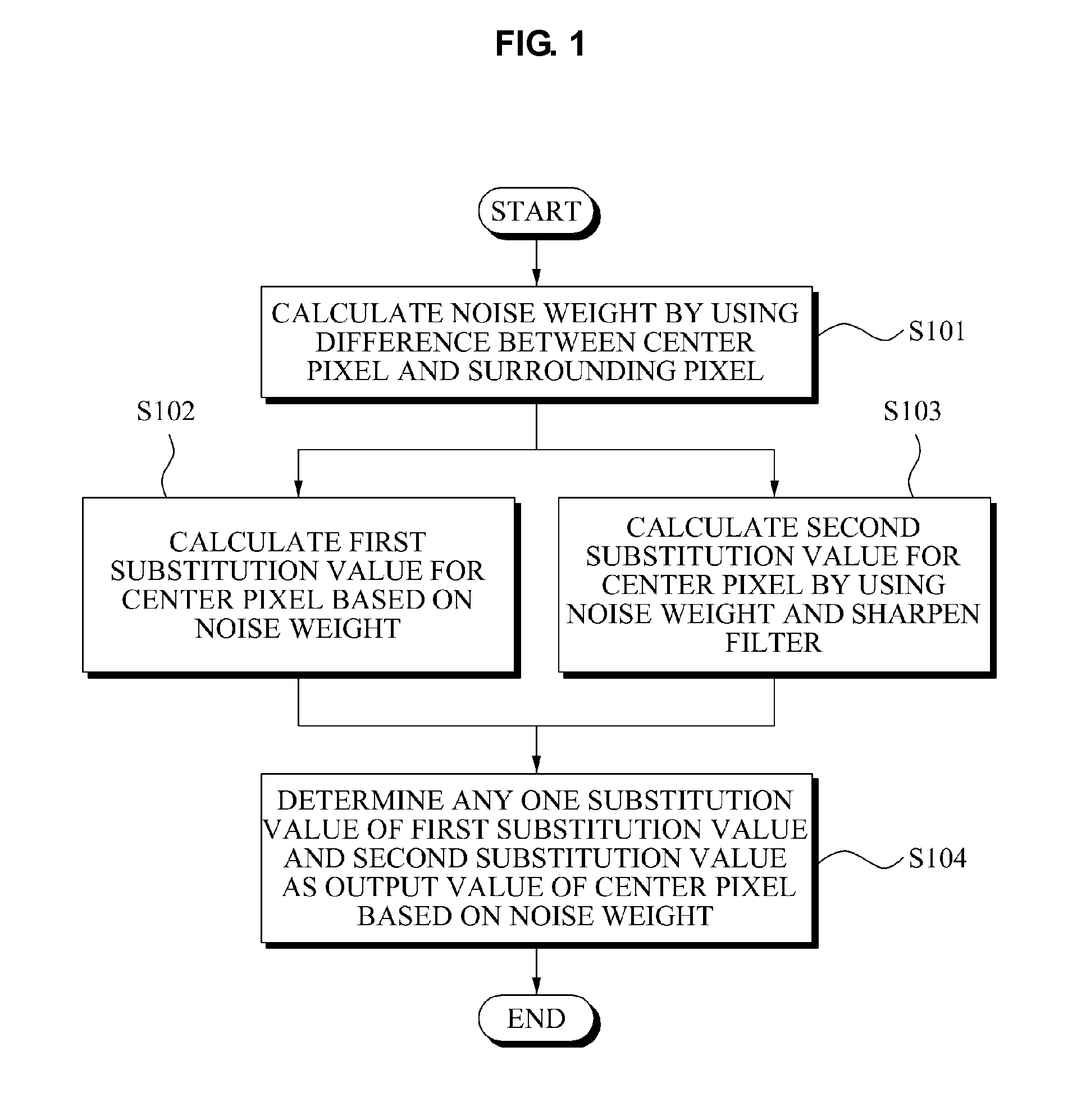
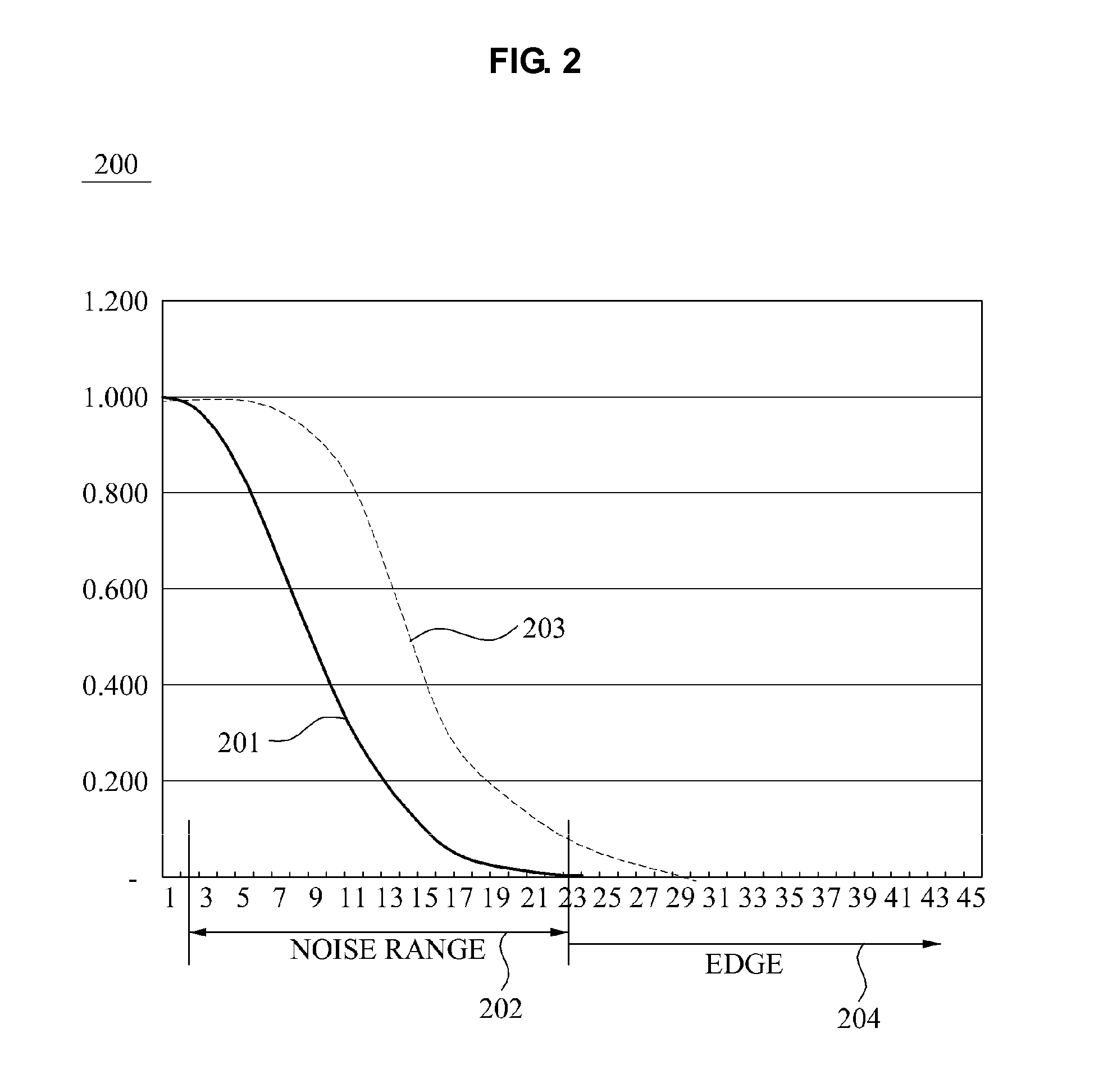
Method and apparatus for enhancing detail based on noise elimination, and method and apparatus for calculating noise weight
ActiveUS20090087121A1Enhance detailsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionPixel based
A method to enhance detail of an image based on noise elimination includes calculating a noise weight corresponding to a probability that a center pixel, located in a block of pixels of a region of the image, is noise by using a difference between the center pixel and a surrounding pixel located in the block of pixels, calculating a first substitution value for the center pixel based on the noise weight; and calculating a second substitution value for the center pixel by using the noise weight and a sharpen filter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adapted method for spectrum management of digital communication systems
ActiveUS20090034554A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
Provided is a method of determining a spectrum management of digital communication systems having a plurality of communication lines by determination of the power levels within each band, for each user, assuming a predetermined maximum interference from other users. The spectral management center has a power allocation determinator for receiving a modelled power level and a noise weight from each user communication line and is able to determine allocated power of its respective communication line based on the optimised determined power needs of the plurality of communication lines of the digital communication systems. In one form the calculations are undertaken in the SMC. In another form the master is undertaken in the SMC while the slave is undertaken at the user's modem and the power level of an individual communication line and its interference by adjacent lines is determined at the user's modem and communicated to the spectral management center.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
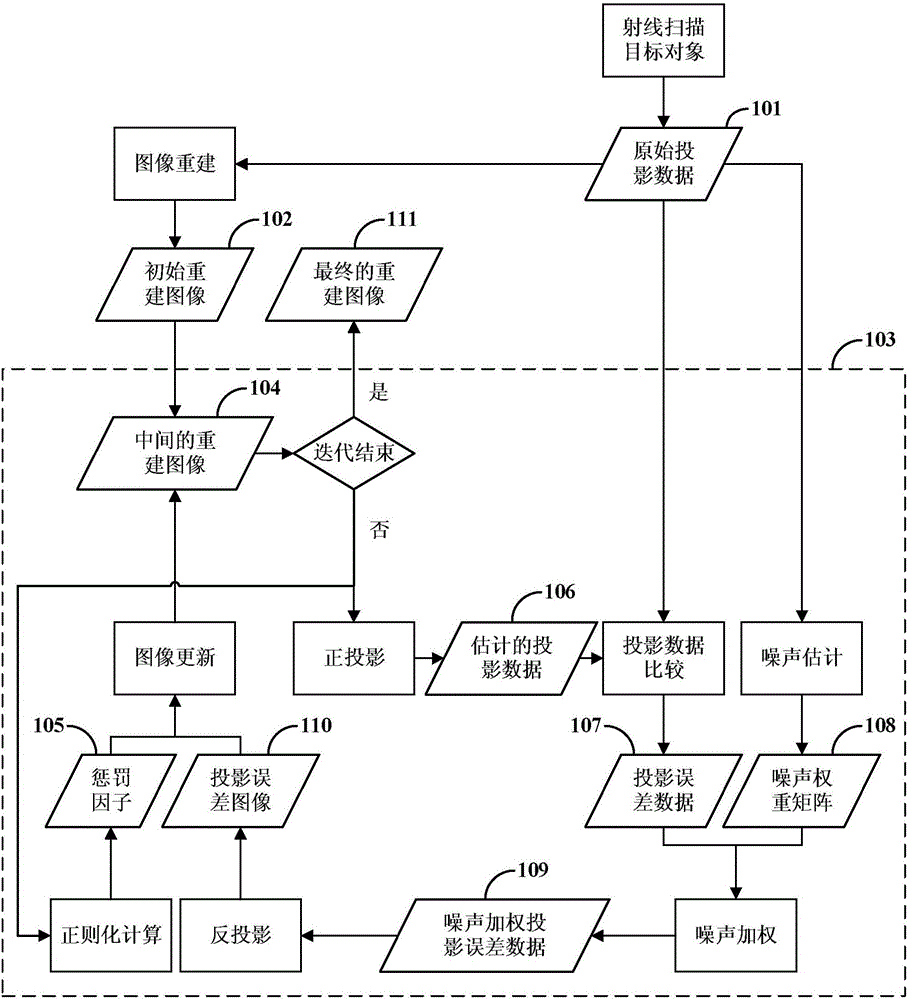
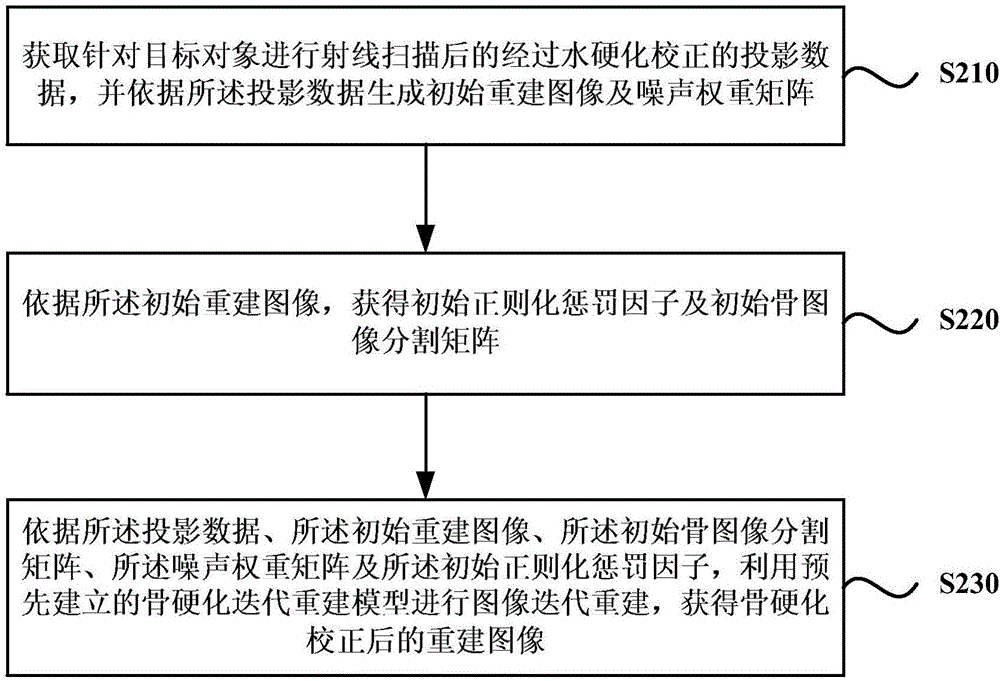
Image iteration reconstruction method and device
ActiveCN106683144AQuality assuranceReconstruction from projectionImage analysisReconstruction methodImage segmentation
The embodiment of the invention discloses an image iteration reconstruction method and a device. The method comprises steps of acquiring projection data subjected to water hardening correction after a target object is subjected to ray scanning, and according to the projection data, generating an initial reconstruction image and a noise weight matrix; according to the initial reconstruction image, acquiring an initial regularization penalty factor and an initial bone image segmentation matrix; according to the projection data, the initial reconstruction image, the initial bone image segmentation matrix, the noise weight matrix and the initial regularization penalty factor, using a pre-established bone hardening iteration reconstruction model to carry out image iteration reconstruction and acquiring a reconstruction image subjected to the bone hardening correction. In this way, it is achieved that bone hardening artifacts are gradually eliminated in an image iteration reconstruction process; bone hardening artifacts in the iteration reconstruction image can be effectively reduced; and quality of the iteration reconstruction image is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
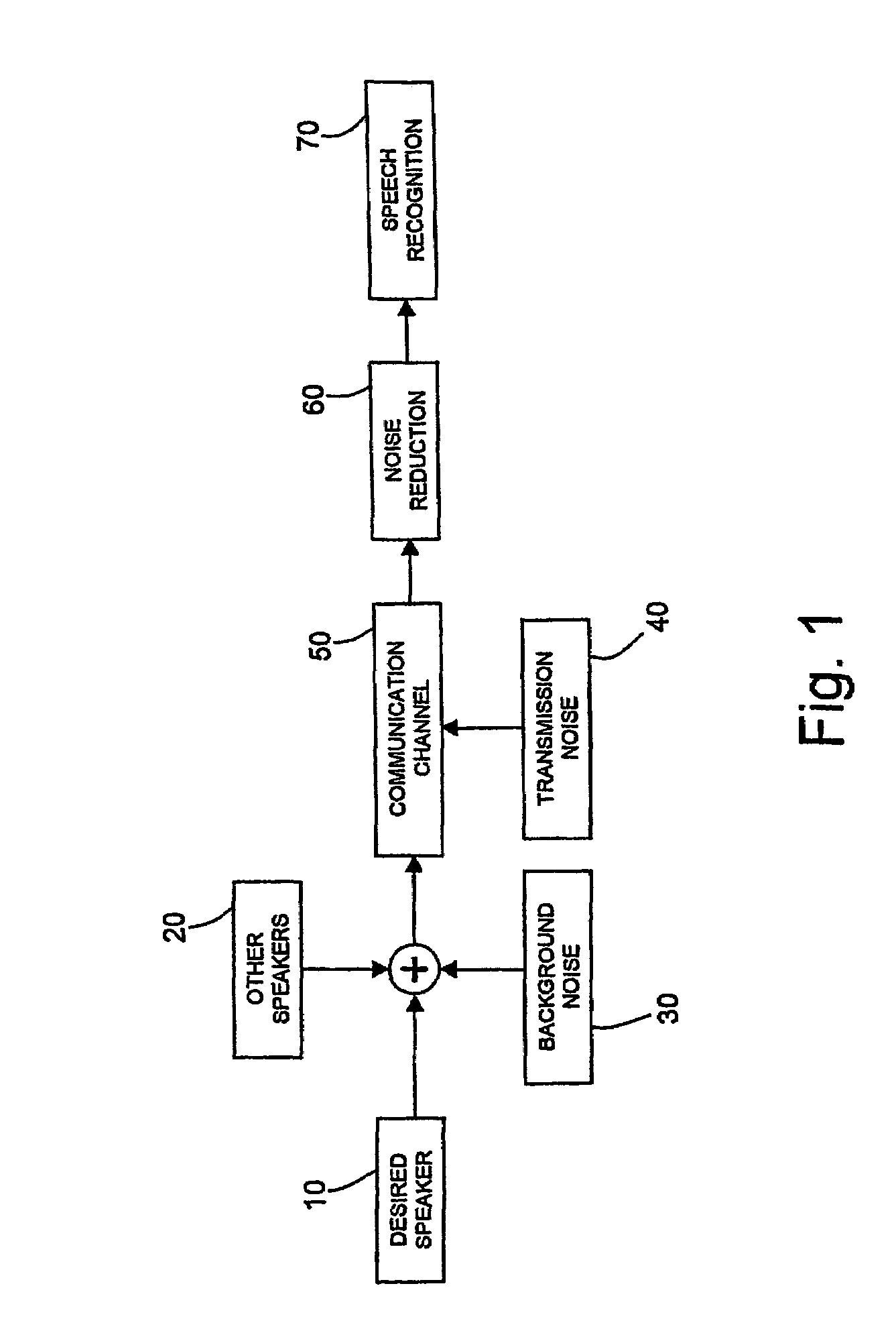
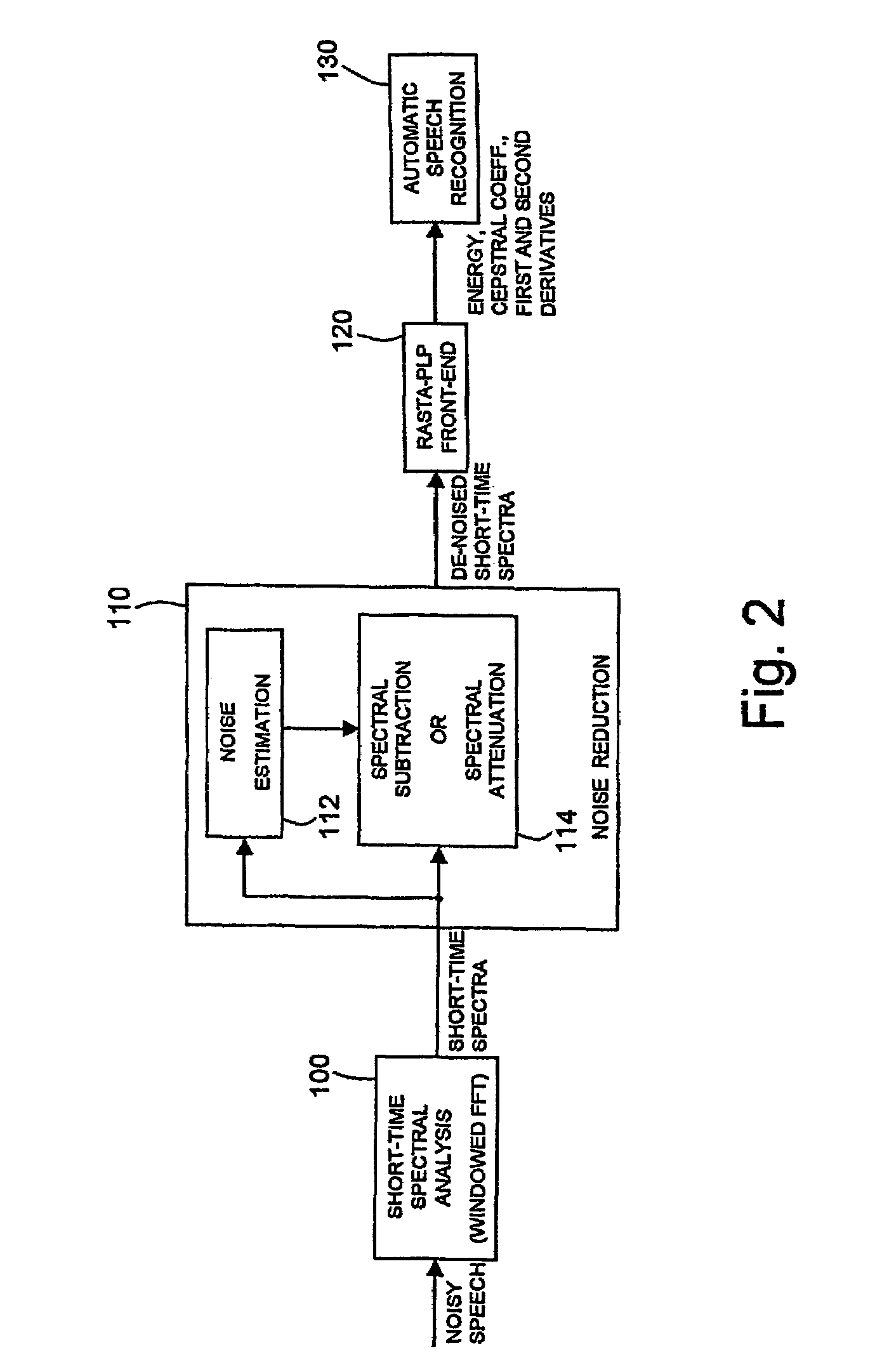
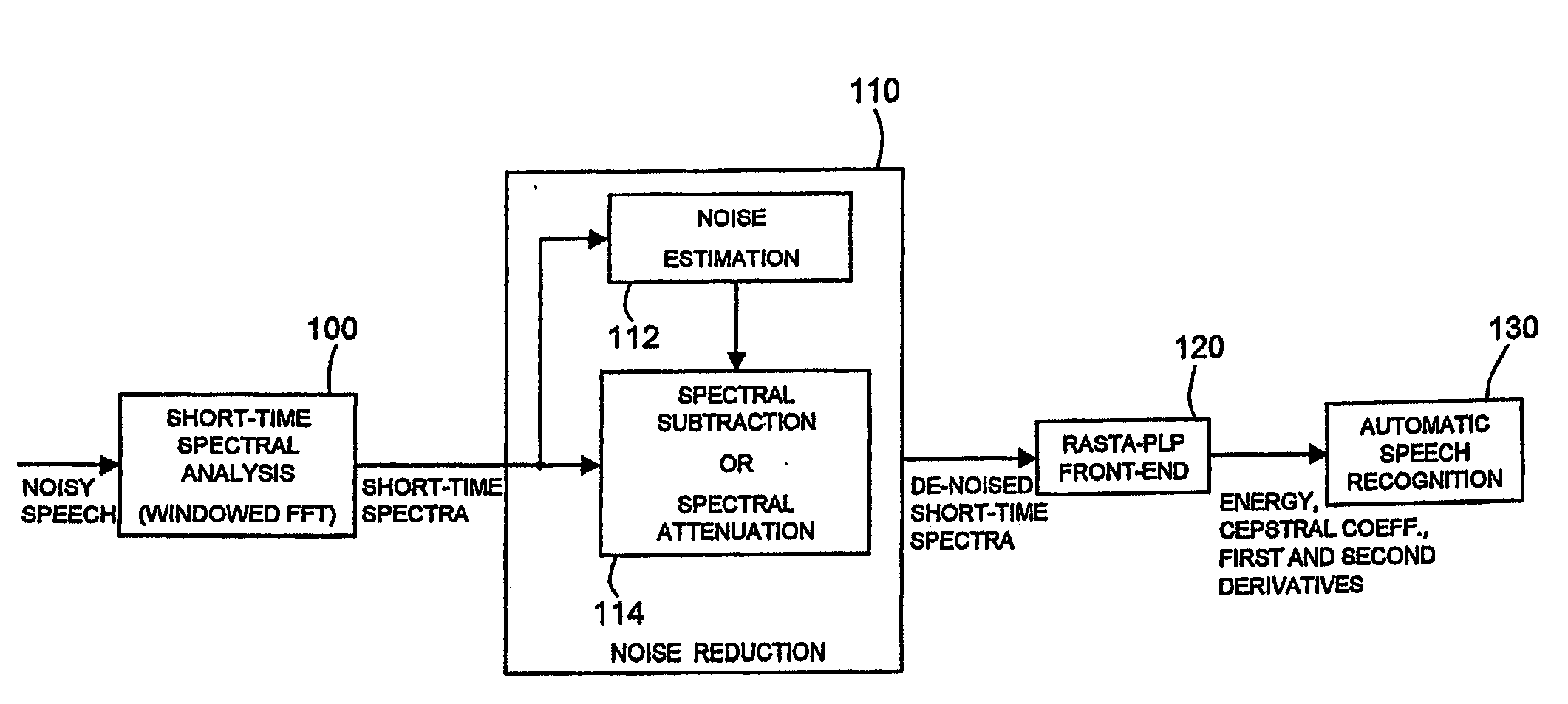
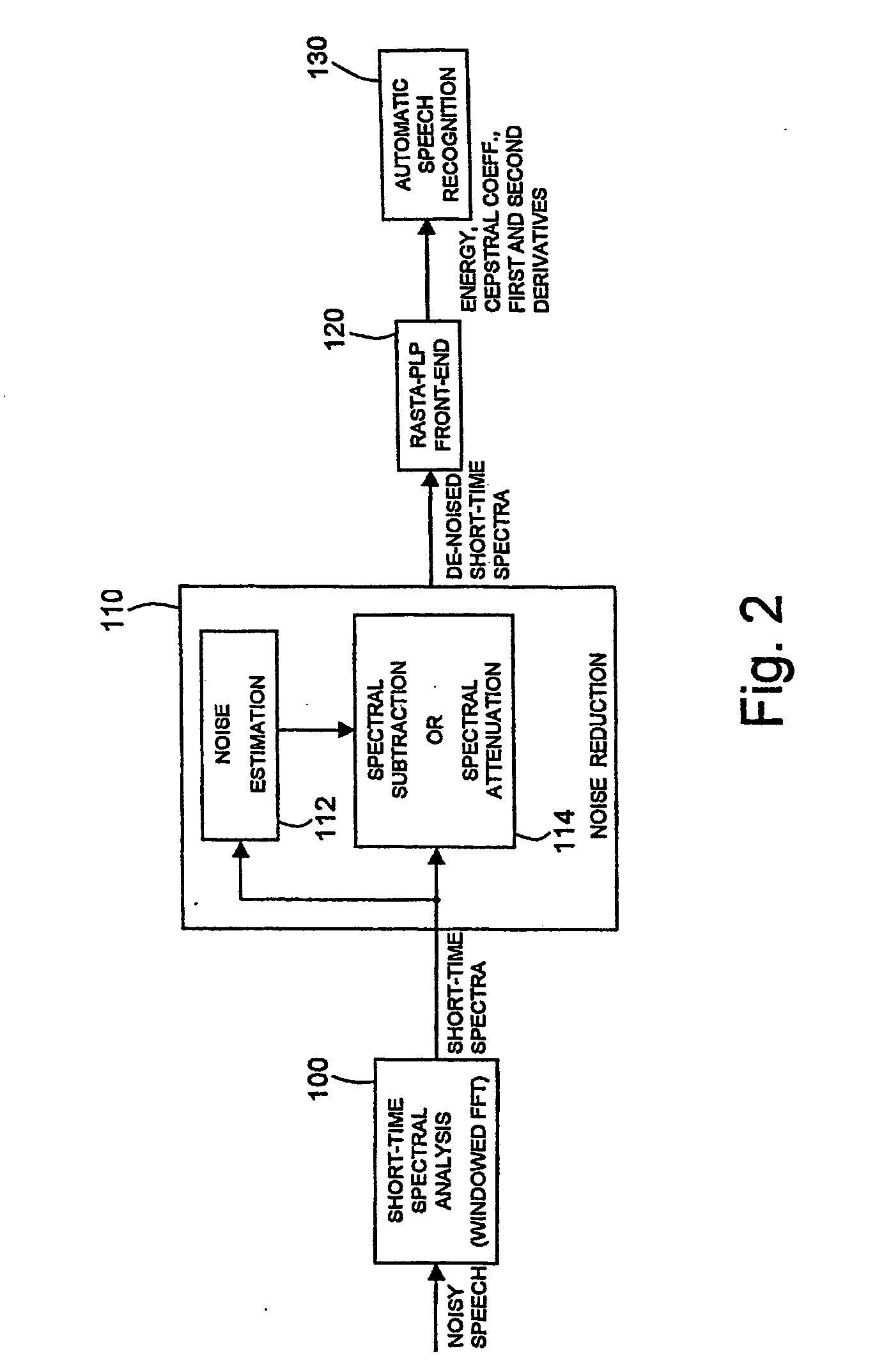
Noise reduction for automatic speech recognition
InactiveUS7376558B2Reduce noiseReduce spectral distortionSpeech recognitionUltrasound attenuationNoise power spectrum
Disclosed herein is a noise reduction method for automatic speech recognitionl. A noise reduction method for automatic speech recognition, including: computing a magnitude spectrum of a noisy speech containing a clean speech to be recognized and noise affecting the clean speech; computing a power spectrum of the noisy speech; computing an estimate of a power spectrum of the clean speech; computing an estimate of a power spectrum of the noise; computing an estimate of an a priori signal-to-noise ratio as a function of the estimate of the power spectrum of the clean speech and the estimate of the power spectrum of the noise; computing an estimate of an a posteriori signal-to-noise ratio as a function of the power spectrum of the noisy speech and the estimate of the power spectrum of the noise; computing an attenuation gain as a function of the estimate of the a priori signal-to-noise ratio and the estimate of the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratio; and computing an estimate of a magnitude spectrum of the clean speech as a function of the magnitude spectrum of the noisy speech and the attenuation gain. Computing the estimates of the a priori and the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratios includes computing a noise weighting factor for weighting the estimate of the power spectrum of the noise in the computation of the estimates of the a priori and the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratios; computing a spectral flooring factor for flooring the estimates of the a priori and the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratios; and computing the estimates of the a priori and the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratios also as a function of the noise weighting factor and the spectral flooring factor.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Noise reduction for automatic speech recognition
InactiveUS20070260454A1Reduce spectral distortionImprove performanceSpeech recognitionUltrasound attenuationNoise power spectrum
Disclosed herein is a noise reduction method for automatic speech recognitionl. A noise reduction method for automatic speech recognition, including: computing a magnitude spectrum of a noisy speech containing a clean speech to be recognized and noise affecting the clean speech; computing a power spectrum of the noisy speech; computing an estimate of a power spectrum of the clean speech; computing an estimate of a power spectrum of the noise; computing an estimate of an a priori signal-to-noise ratio as a function of the estimate of the power spectrum of the clean speech and the estimate of the power spectrum of the noise; computing an estimate of an a posteriori signal-to-noise ratio as a function of the power spectrum of the noisy speech and the estimate of the power spectrum of the noise; computing an attenuation gain as a function of the estimate of the a priori signal-to-noise ratio and the estimate of the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratio; and computing an estimate of a magnitude spectrum of the clean speech as a function of the magnitude spectrum of the noisy speech and the attenuation gain. Computing the estimates of the a priori and the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratios includes computing a noise weighting factor for weighting the estimate of the power spectrum of the noise in the computation of the estimates of the a priori and the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratios; computing a spectral flooring factor for flooring the estimates of the a priori and the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratios; and computing the estimates of the a priori and the a posteriori signal-to-noise ratios also as a function of the noise weighting factor and the spectral flooring factor
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
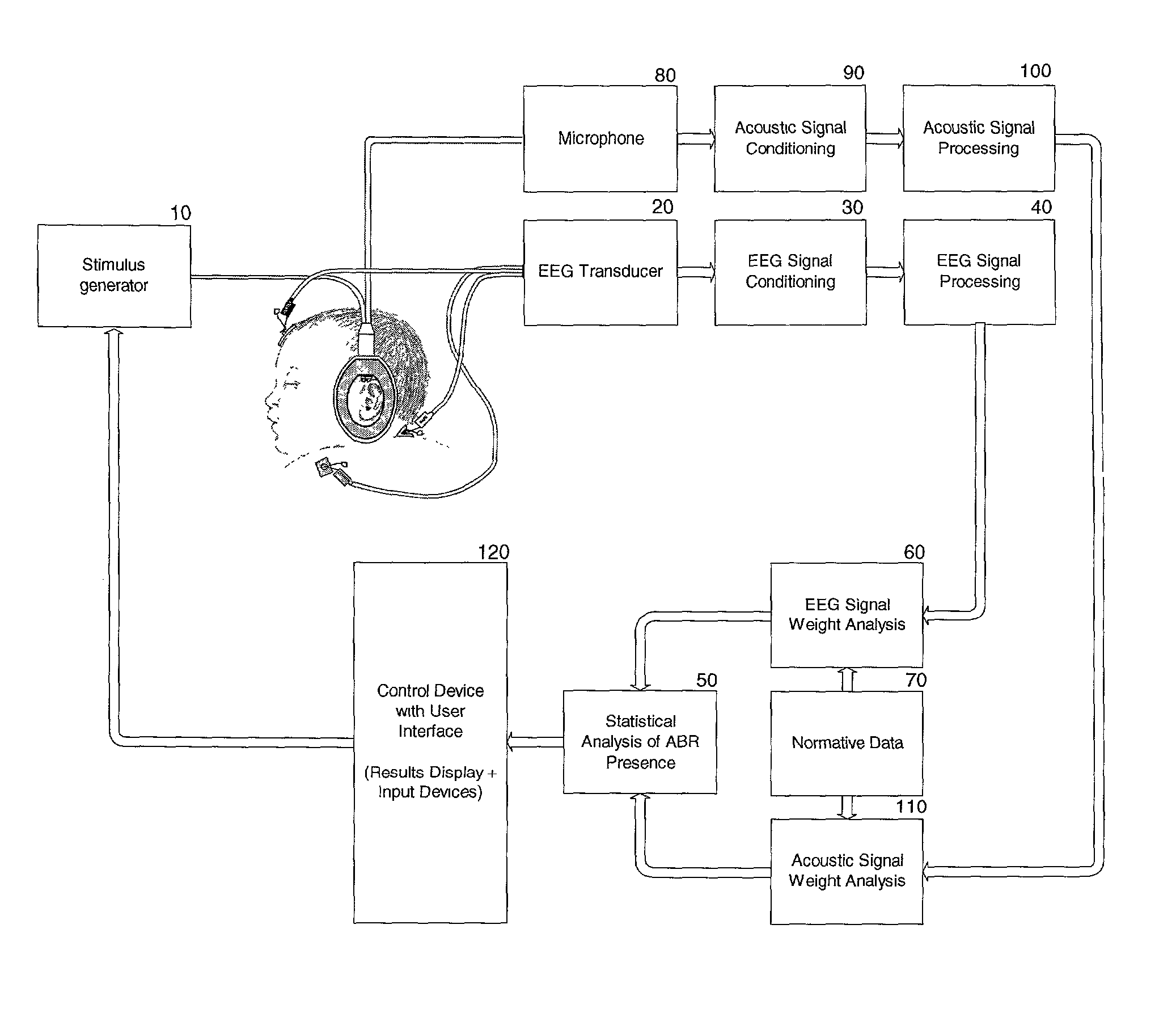
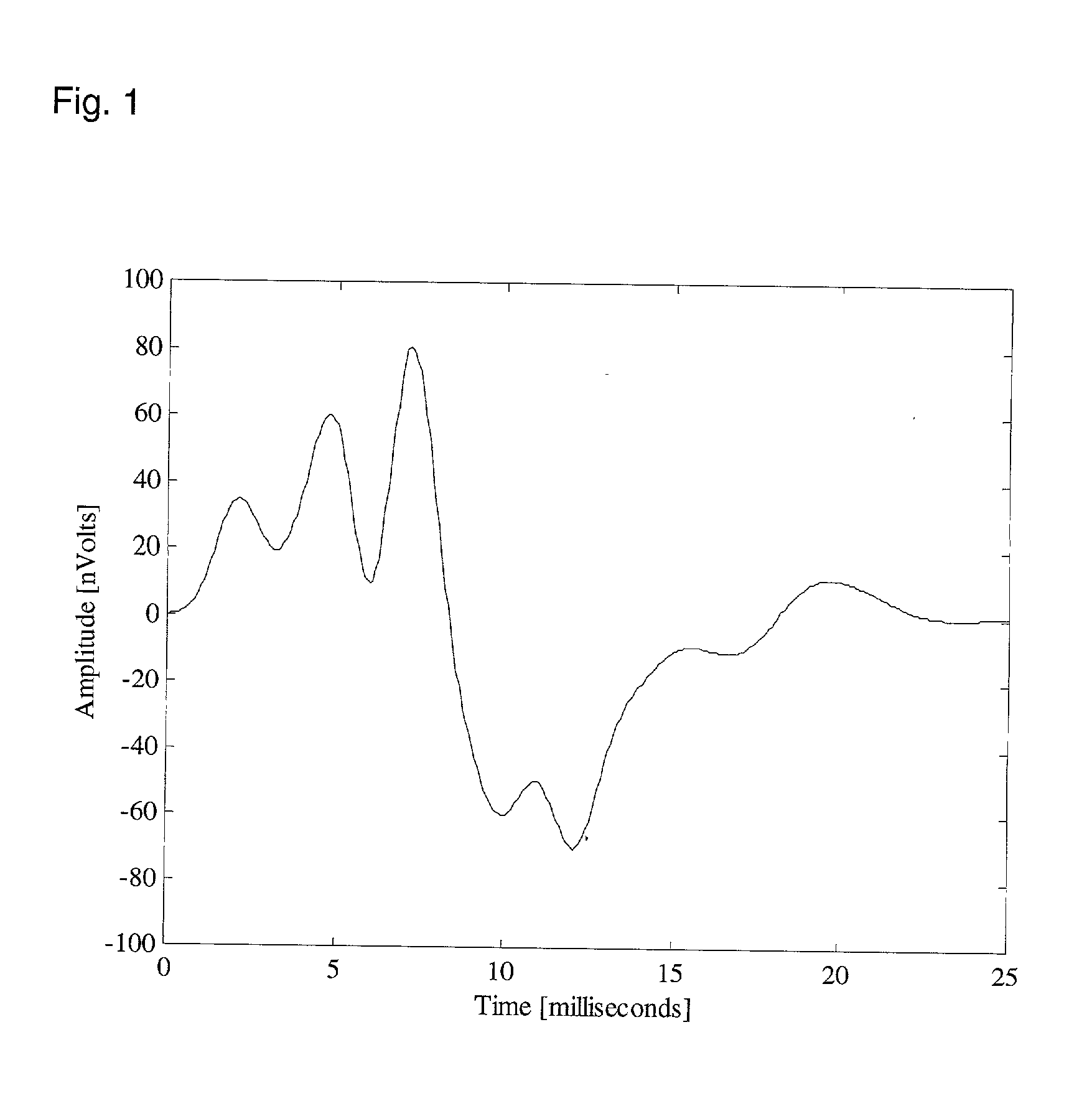
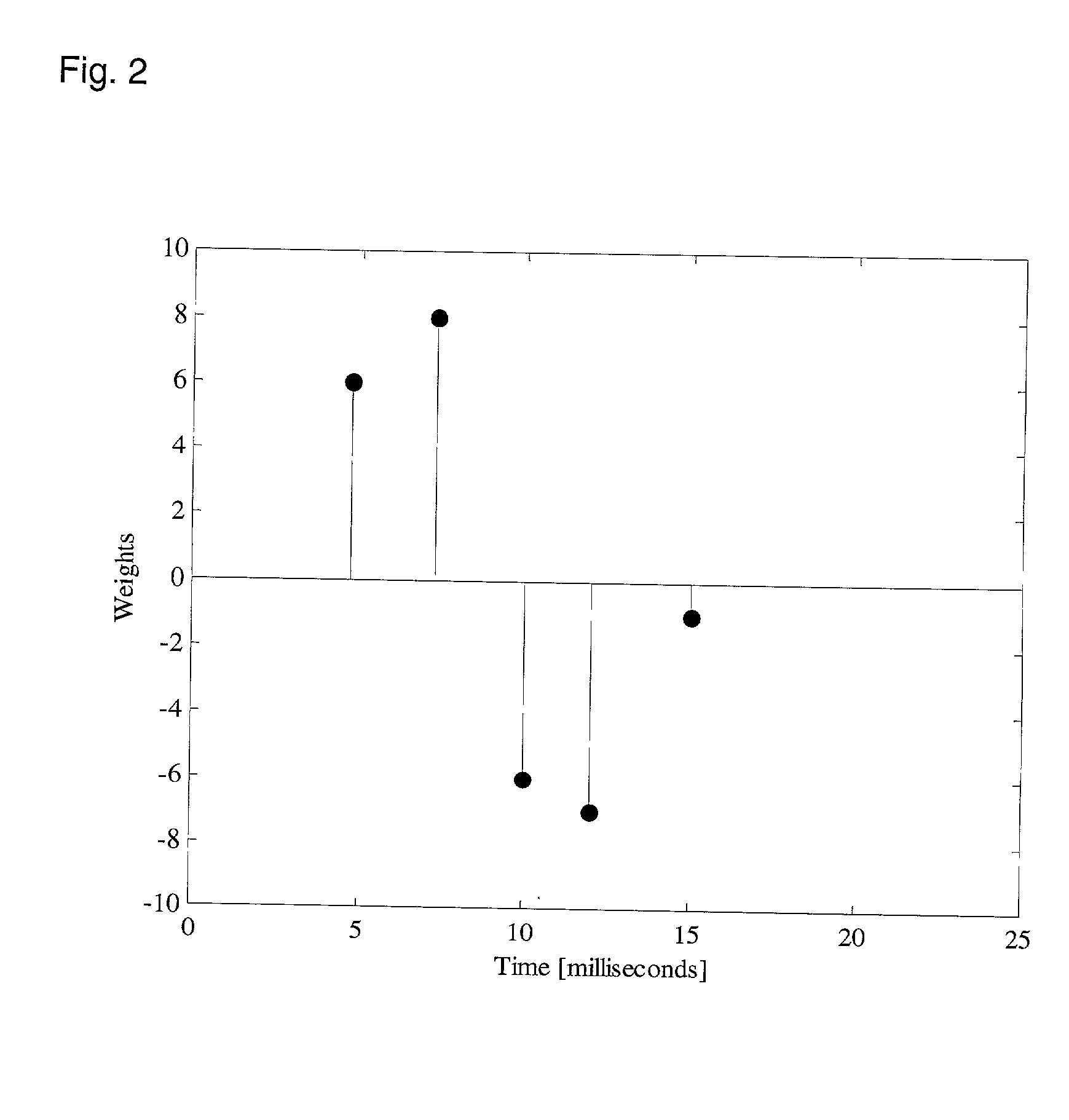
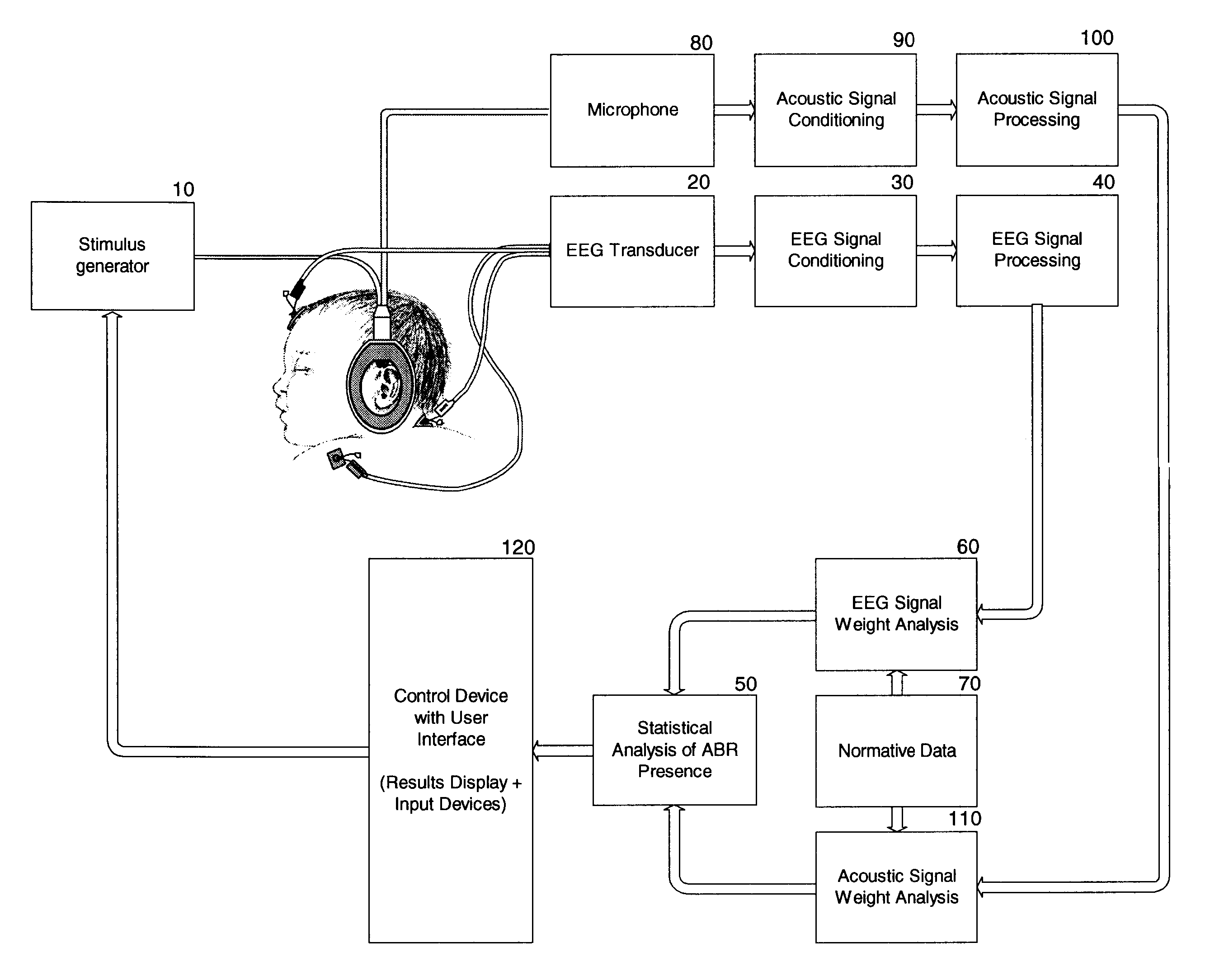
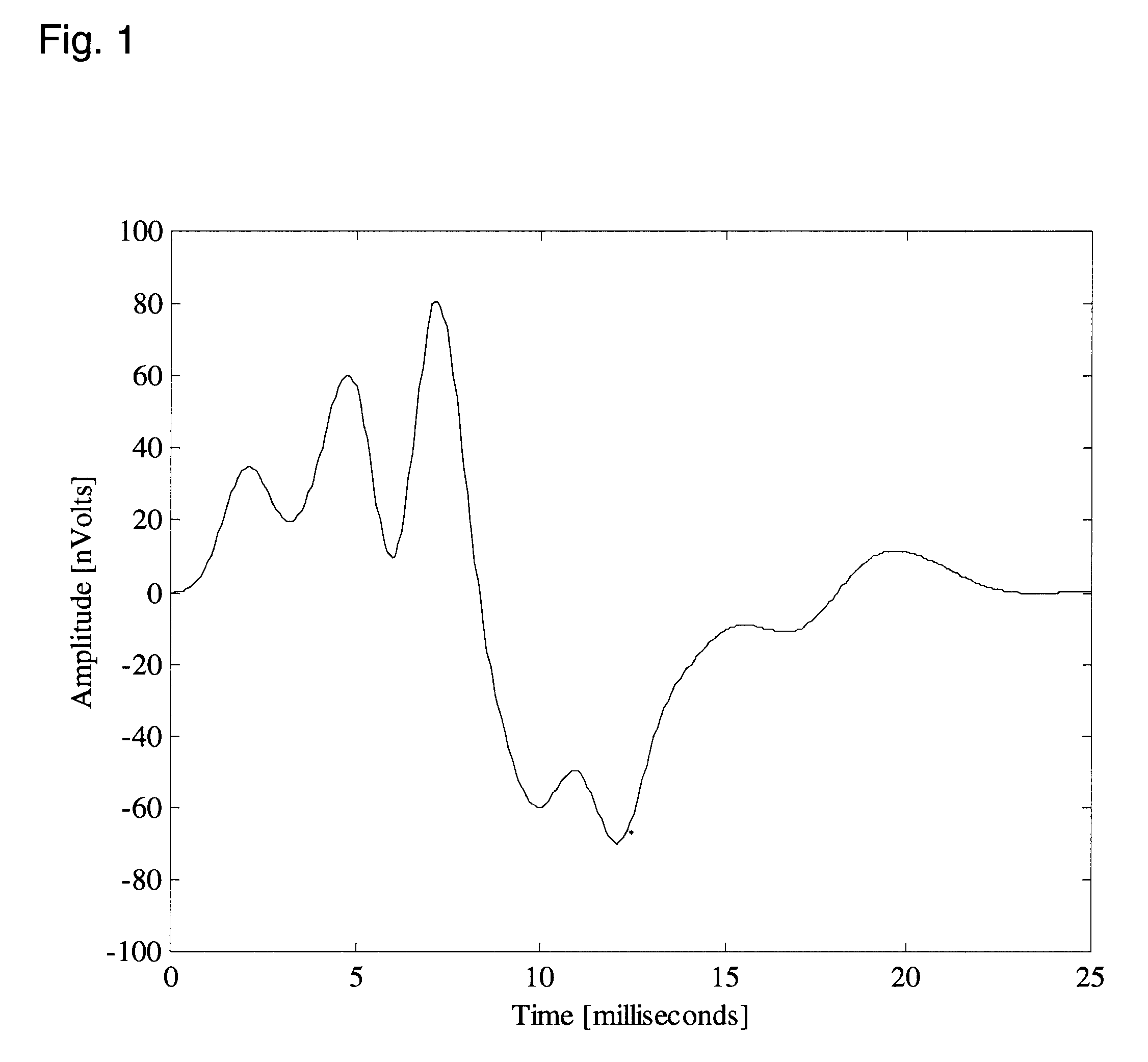
Hearing evaluation device with noise-weighting capabilities
InactiveUS20030073920A1Conserving evaluation timeSave resourcesElectroencephalographyAudiometeringElectrophonic hearingEngineering
An apparatus and method for evaluation of hearing loss is disclosed. The apparatus and method use evoked Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABR) to determine if the subject is able to hear repeatedly administered click stimuli. In order to optimize evaluation, the present invention uses normative data to accurately weight the auditory responses, so that evaluation will be possible in different or changing noise conditions.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
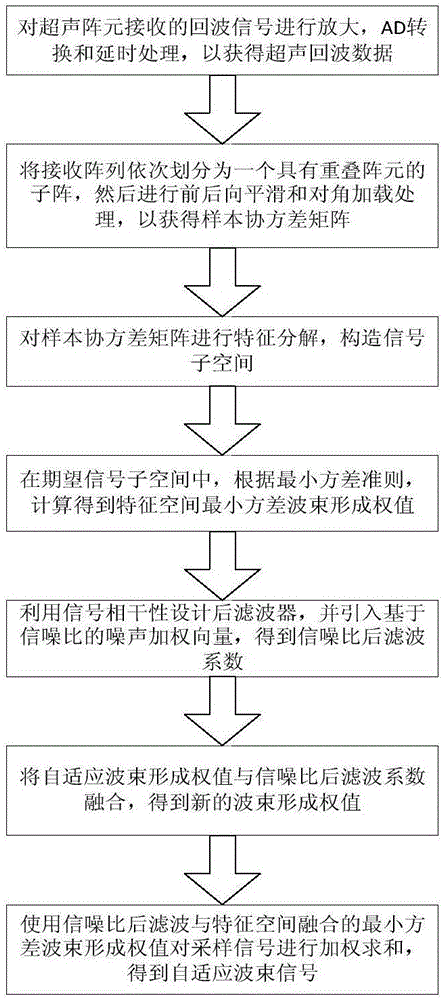
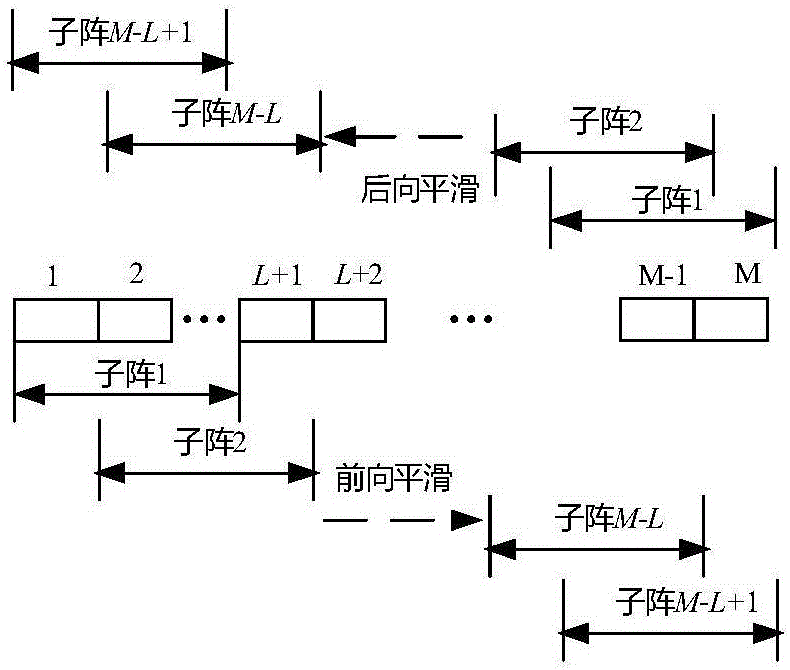
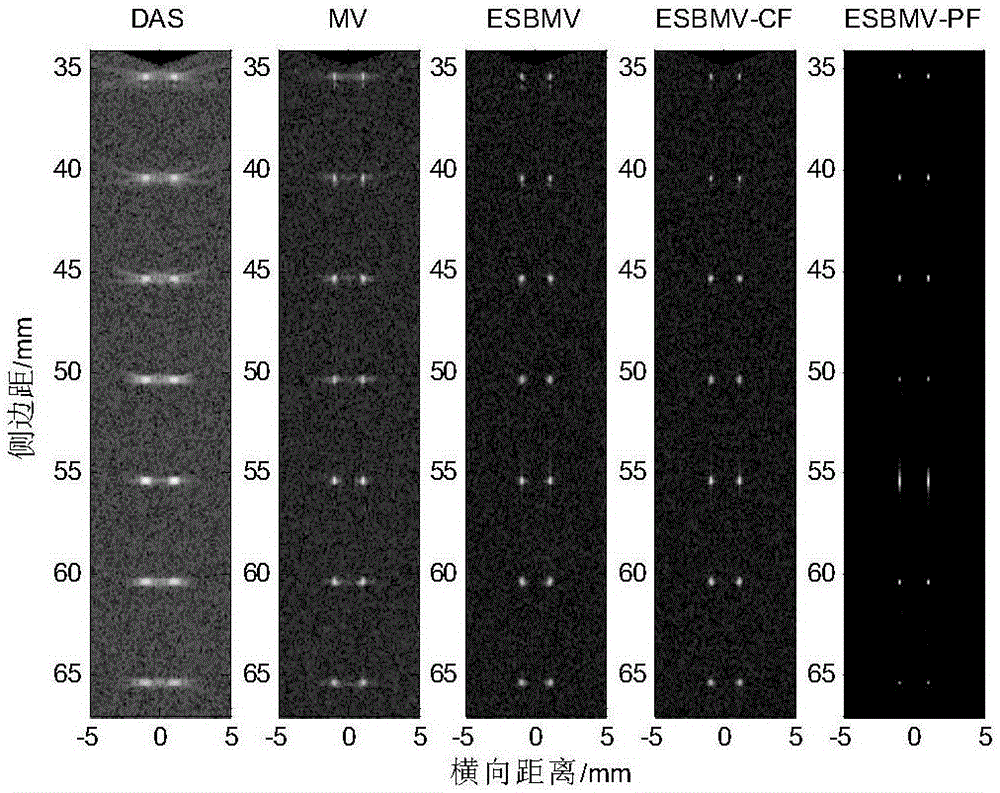
Signal-noise-ratio-post-filtering-and-characteristic-space-fusion minimum-variance ultrasonic imaging method
ActiveCN106510761AImprove robustnessIncrease contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementRobustificationSonification
The invention relates to a signal-noise-ratio-post-filtering-and-characteristic-space-fusion minimum-variance ultrasonic imaging method. The signal-noise-ratio-post-filtering-and-characteristic-space-fusion minimum-variance ultrasonic imaging method includes the steps that sampling signals received by array elements are delayed, subjected to forward-backward smoothing and subjected to diagonal loading treatment, and an estimated sample covariance matrix is obtained; the estimated covariance matrix is subjected to characteristic decomposition, and signal subspace is constructed; in the desired signal subspace, according to the minimum-variance criterion, an adaptive beam-forming weight value is calculated; then a post-filtering coefficient is designed according to the signal coherence, a noise weighting coefficient is introduced according to the input signal noise ratio, and a signal-noise-ratio-filtering coefficient is calculated; the adaptive beam-forming weight value and the signal-noise-ratio-filtering coefficient are fused to obtain the novel weight vector; finally, multiple pieces of data subjected to forward-backward smoothing treatment are weighted and summed through the obtained minimum-variance weight value fusing the signal-noise-ratio post filtering and the characteristic space, and an adaptive beam signal is obtained. By means of the signal-noise-ratio-post-filtering-and-characteristic-space-fusion minimum-variance ultrasonic imaging method, the properties of ultrasonic images in the resolution ratio aspect, the contrast ratio aspect, the noise robustness aspect and the like can be improved, and therefore the quality of ultrasonic imaging is improved as a whole.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
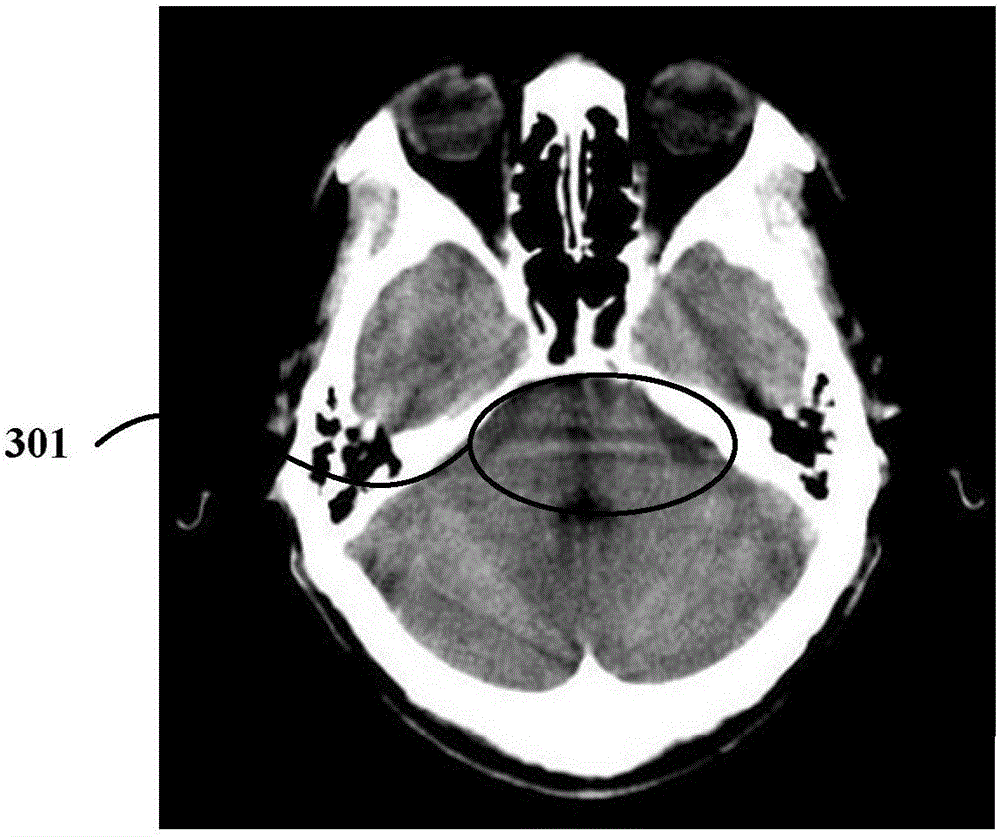
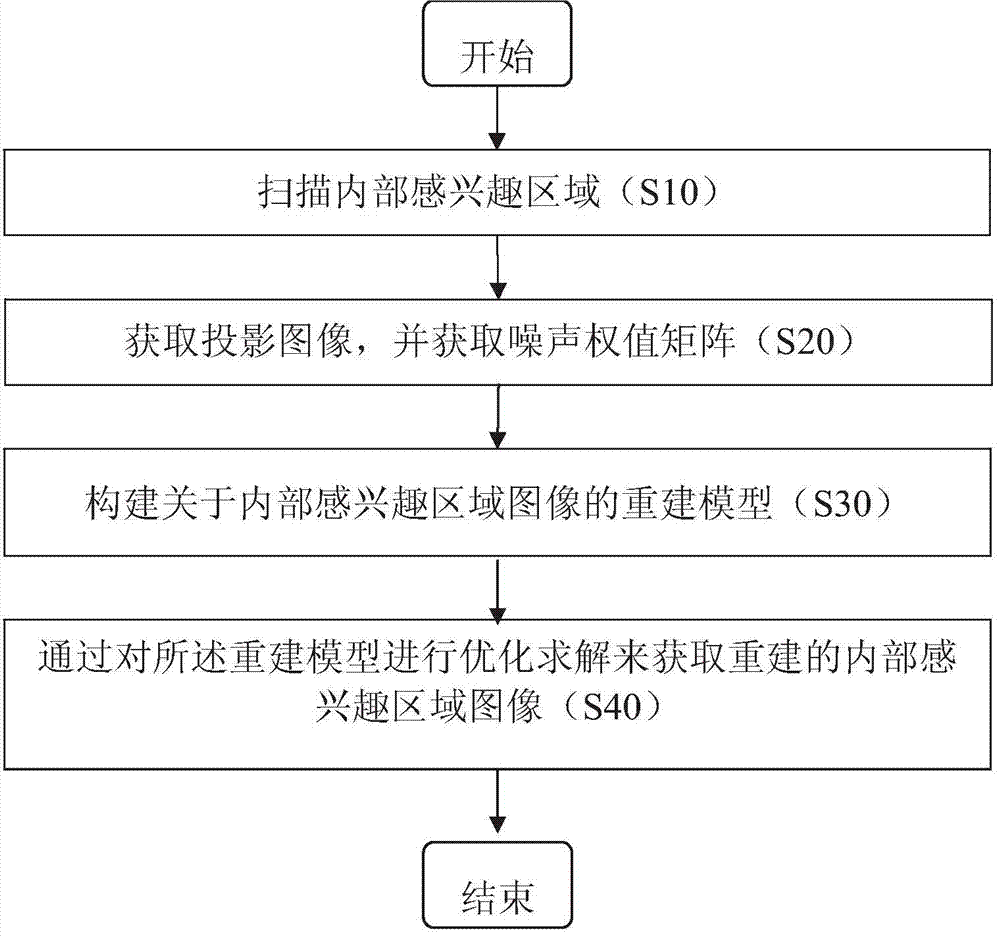
Method and system for reconstructing internal region-of-interest image
ActiveCN104504743AAchieve accurate reconstructionSuppress noiseImage enhancement2D-image generationPattern recognitionComputed tomography
The invention provides a method and a system for reconstructing an internal region-of-interest image. The method includes: (a), scanning an internal region-of-interest of an object by CT (computed tomography) equipment; (b), acquiring a projection image formed by projection of all rays of the internal region-of-interest, and acquiring a noise weight matrix of the projection image; (c), constructing a reconstruction model related to the internal region-of-interest image according to the projection image, the noise weight matrix and a system matrix expressing CT equipment system parameters; (d), performing optimization solution on the reconstruction model to acquire the reconstructed internal region-of-interest image. According to the method for reconstructing the internal region-of-interest image, existence of a known region in the internal ROI (region-of-interest) is not needed, robustness of data with noise is high, and application range is wider.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
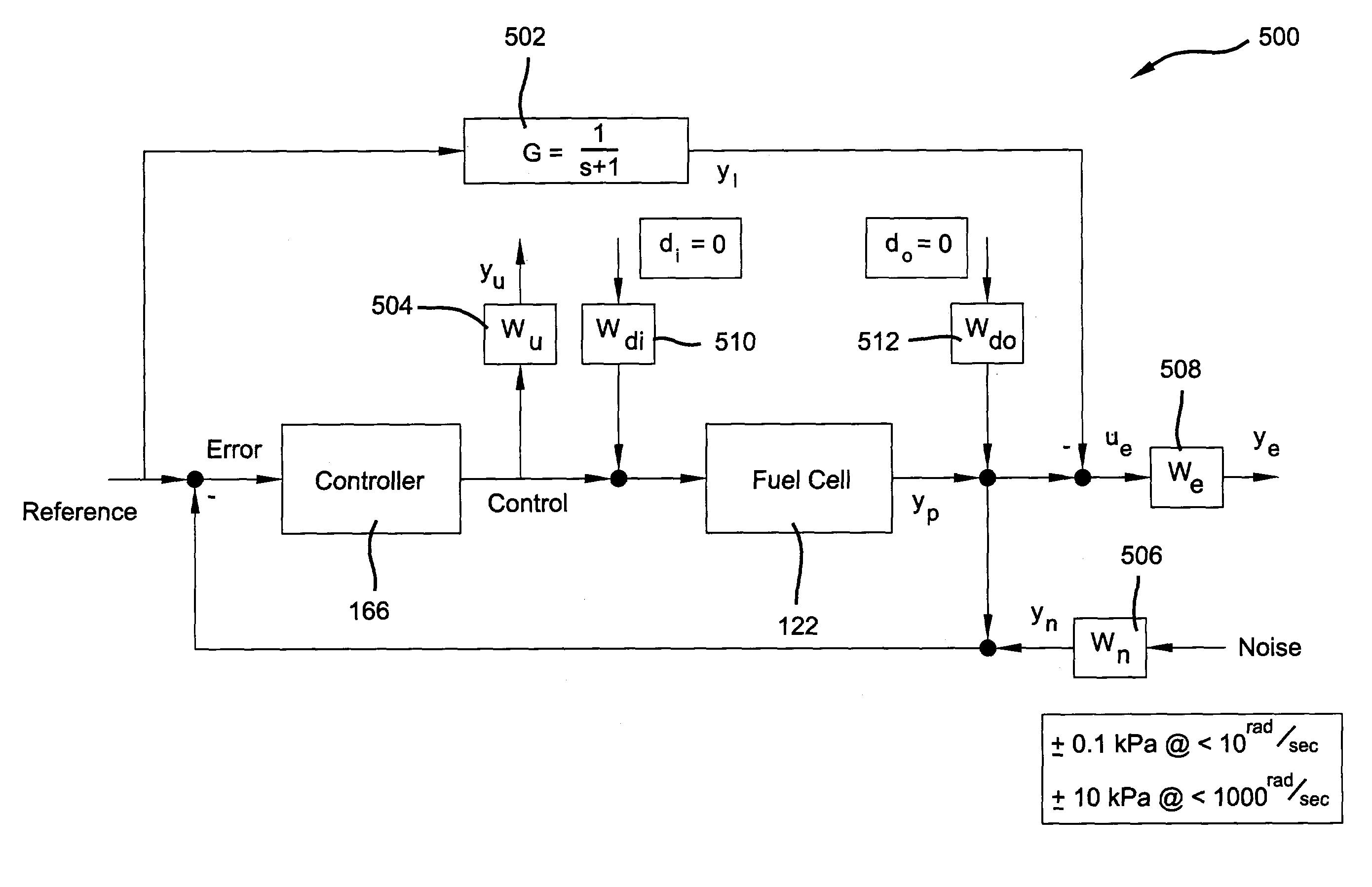
H-infinity control with integrator compensation for anode pressure control in a fuel cell stack
ActiveUS7087335B2Improve performanceEasy to operateFuel cell auxillariesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsIntegratorCost Controls
Pressure control in a fuel cell is achieved by using an H-infinity controller coupled in a feedback loop between a reactant feed gas valve and a pressure sensor on gas flows to the membrane electrode assembly of the fuel cell. To maintain pressure balance across the membrane, the pressure of the oxidant reactant is used to regulate fuel reactant flow. An integrator windup compensator manages integral windup in the H-infinity control scheme. Control weight, sensor noise weight, and performance weight matrices are incorporated into the H-infinity control model. Respective to PID control, the H-infinity model provides superior performance in the presence of high frequency feedback noise enabling use of low cost control components in the fuel cell and a minimum of EMI shielding.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for distributed spectrum management of digital communications systems
ActiveUS7813293B2Maximization of data-ratesMinimal powerFrequency-division multiplex detailsAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A method for distributed spectrum management of digital communication systems having a plurality of communication lines on which signals are transmitted and received by respective users, the method comprising the steps of: collecting information about line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines from a plurality of sources; determining the line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines; varying power allocation of particular plurality of the communication lines between respective transmitter and receiver taking into consideration the determined line, signal and interference characteristics of a plurality of the communication lines and consideration of a noise weight of a plurality of the communication lines to enable a minimum power on a plurality of the communication lines and to allow required effective data-rates for each of said respective users to be satisfied.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Hearing evaluation device with noise-weighting capabilities
InactiveUS6620100B2Improve accuracySave resourcesElectroencephalographyAudiometeringEngineeringElectrophonic hearing
An apparatus and method for evaluation of hearing loss is disclosed. The apparatus and method use evoked Auditory Brainstem Responses (ABR) to determine if the subject is able to hear repeatedly administered click stimuli. In order to optimize evaluation, the present invention uses normative data to accurately weight the auditory responses, so that evaluation will be possible in different or changing noise conditions.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
Square root volume fuzzy adaptive Kalman filtering SLAM method
InactiveCN109520503AReduce complexityResolve distortionNavigational calculation instrumentsSimultaneous localization and mappingDynamic models
The invention discloses a square root volume fuzzy adaptive Kalman filtering SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) method. The method comprises the steps of: modeling a mobile robot, to establishing a dynamic model and an observation model; by means of a fuzzy adaptive noise dynamic adjustment algorithm, setting control weights for motion noise and observation noise in the dynamic model andthe observation model and fuzzily adjusting the noise weights by dynamically adjusting innovation mean and variance; predicting pose information of the robot at the moment k through the pose information of the robot at the moment k-1; and updating the post information in a calculator after carrying out iteration preset times. The method has the beneficial effects that an iterative method is combined with strong tracking and aiming at the problems of the motion noise and the observation noise of the robot, different noises are adaptively dynamically adjusted by adopting an improved fuzzy adaptive method; and the complexity of the algorithm is reduced, the distortion problem of a sampling point in the nonlinear case is solved, the trajectory deviation phenomenon caused by the increase of feature points is corrected and the pose accuracy is increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
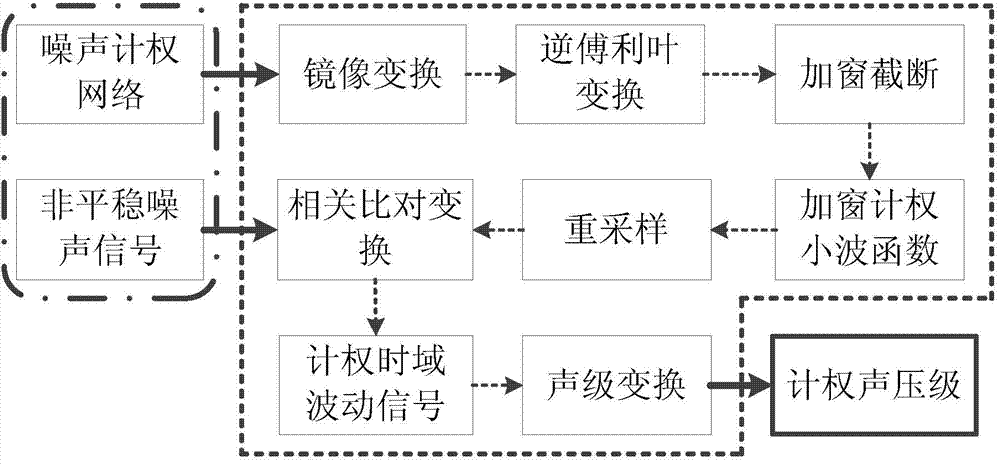
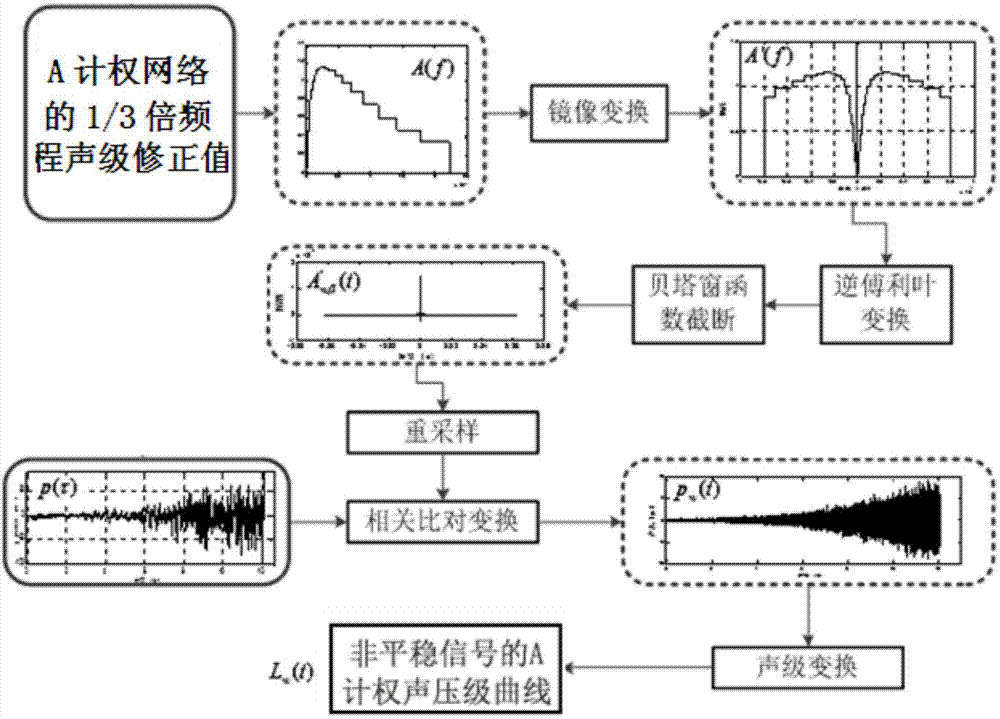
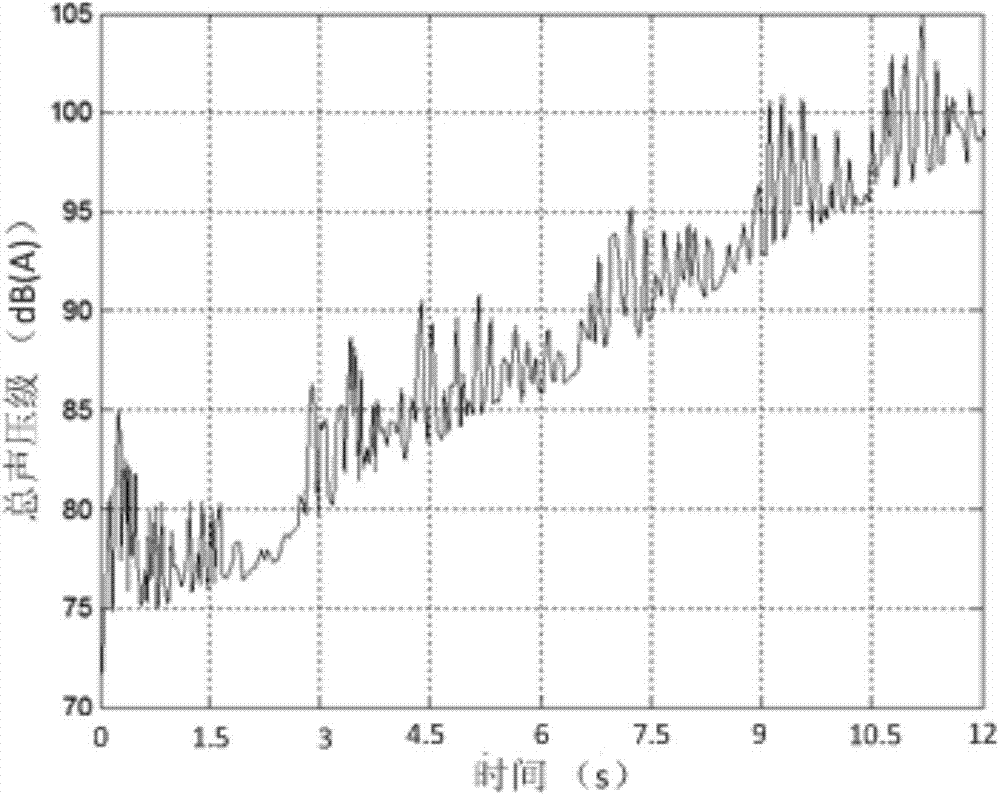
Time domain digit weighting method for non-stable noise signals
ActiveCN104729677AUnaffected by agingLow costSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementOctaveData acquisition
The invention relates to a time domain digit weighting method for non-stable noise signals. The method includes the following steps that (1) data acquisition is conducted on the non-stable noise signals to acquire noise digital signals p(Tau); (2) a weighting amplitude curve A(f) is established according to the octave sound level modification value of a noise weighting network; (3) mirror transformation processing is conducted on the weighting amplitude curve A(f), and a non-periodic real even function A'(f) of a frequency domain weighting network is acquired; (4) inverse Fourier transform is carried out to acquire an impulse response function A'(t) of the weighting network; (5) a window function Wbeta(t) is selected to conduct windowing truncation processing on the A'(t); (6) a windowing weighting wavelet function A'wbeta(t) is acquired; (7) interpolation resampling is conducted on the windowing weighting wavelet function, and the time interval of the windowing weighting wavelet function is made to be consistent with the time interval of collected original noise digital signals; (8) the acquired non-stable noise digital signals p(Tau) and the windowing weighting wavelet function are subjected to related comparison transform, so that time domain weighting fluctuation signals pw(t) are acquired; (9) a weighting overall sound pressure level curve Lw(t) of the non-stable signals is obtained through sound level transform calculation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
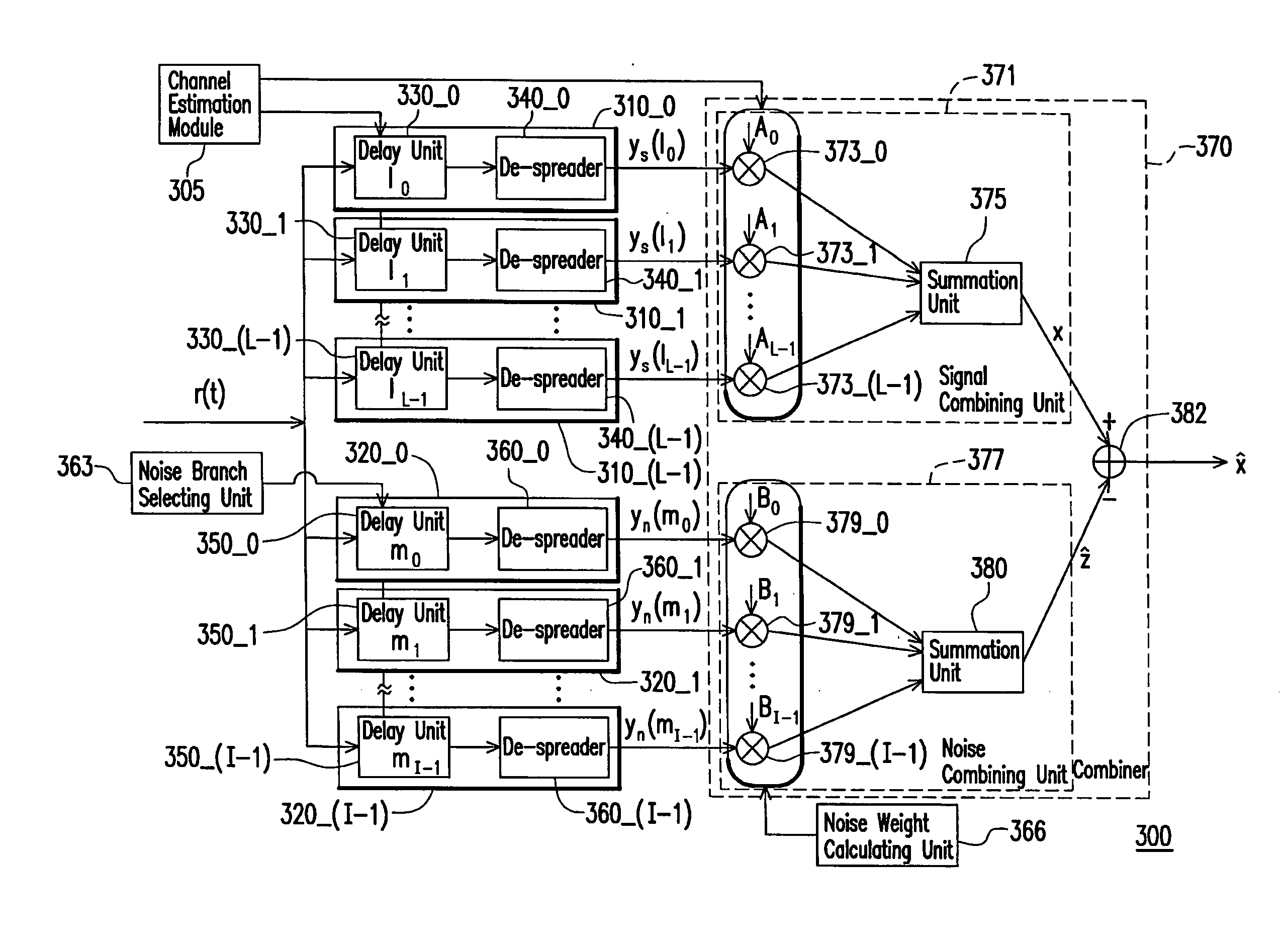
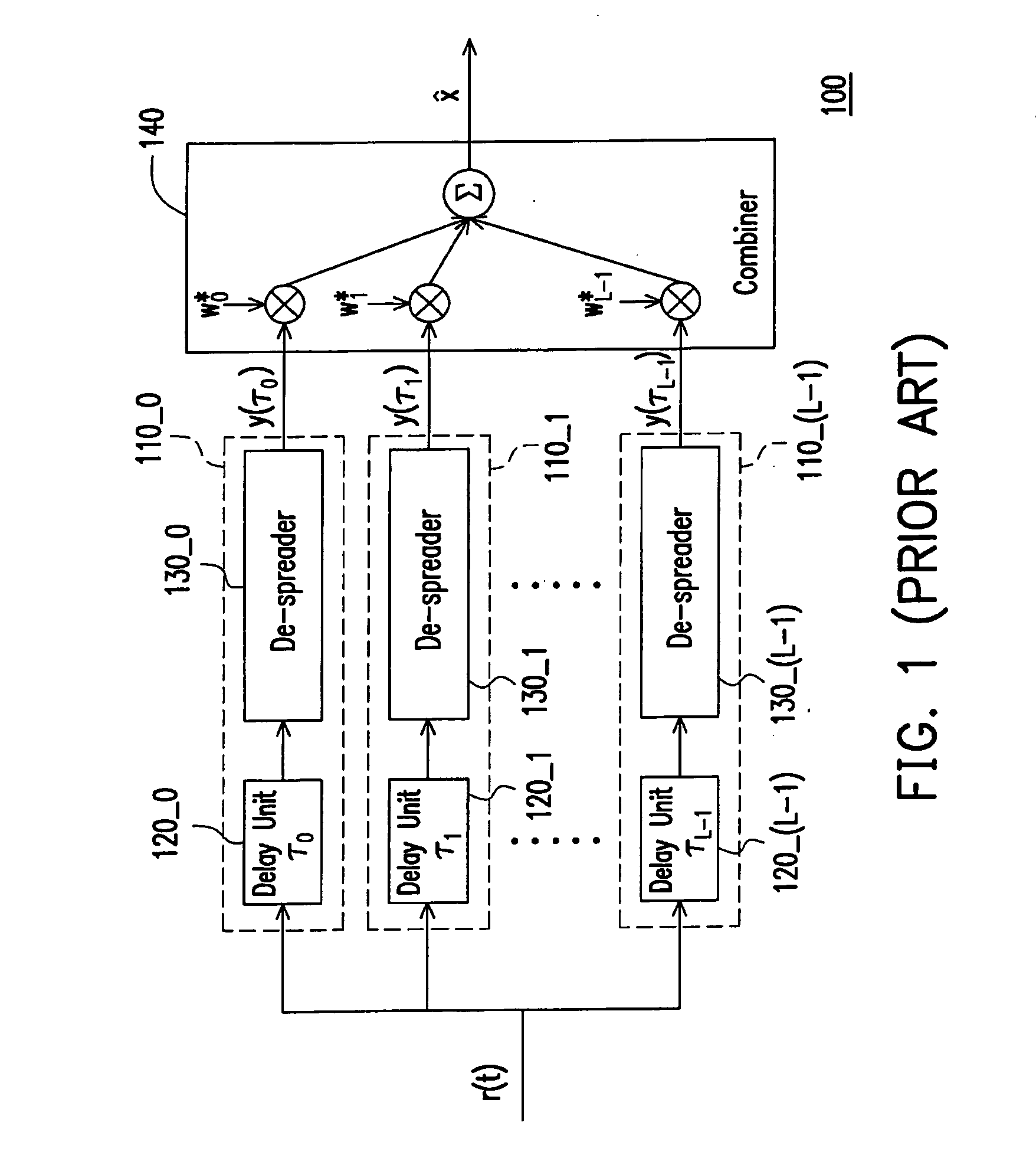
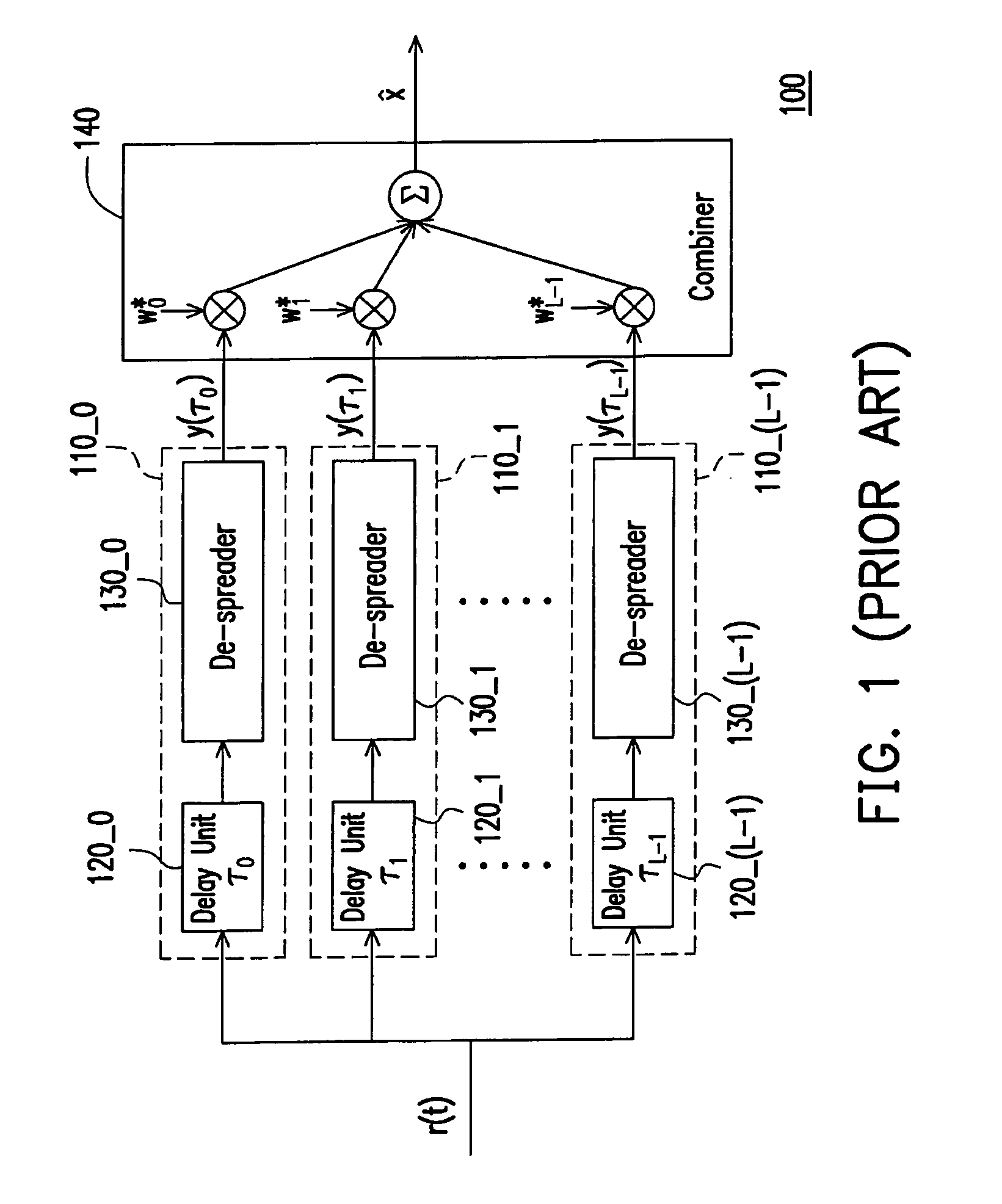
Rake receiver and de-spreading method thereof
ActiveUS20090003415A1Reducing the bit error rate of a signalReduce complexityBaseband systemsRake receiverNoise estimation
The invention relates to a rake receiver and a method for de-spreading thereof. A plurality of noise branches is adopted for producing a plurality of noise components in the rake receiver. Next, a noise combining unit adjusts each noise component according to a plurality of noise weights, so as to combine the noise components to obtain an interference-plus-noise estimation value. The rake receiver eliminates the noises in the main signal generated by the signal branches through using the interference-plus-noise estimation value. Therefore, the performance of a receiving terminal can be enhanced.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
COLD array arrival direction and polarization parameter joint estimation method based on resampling
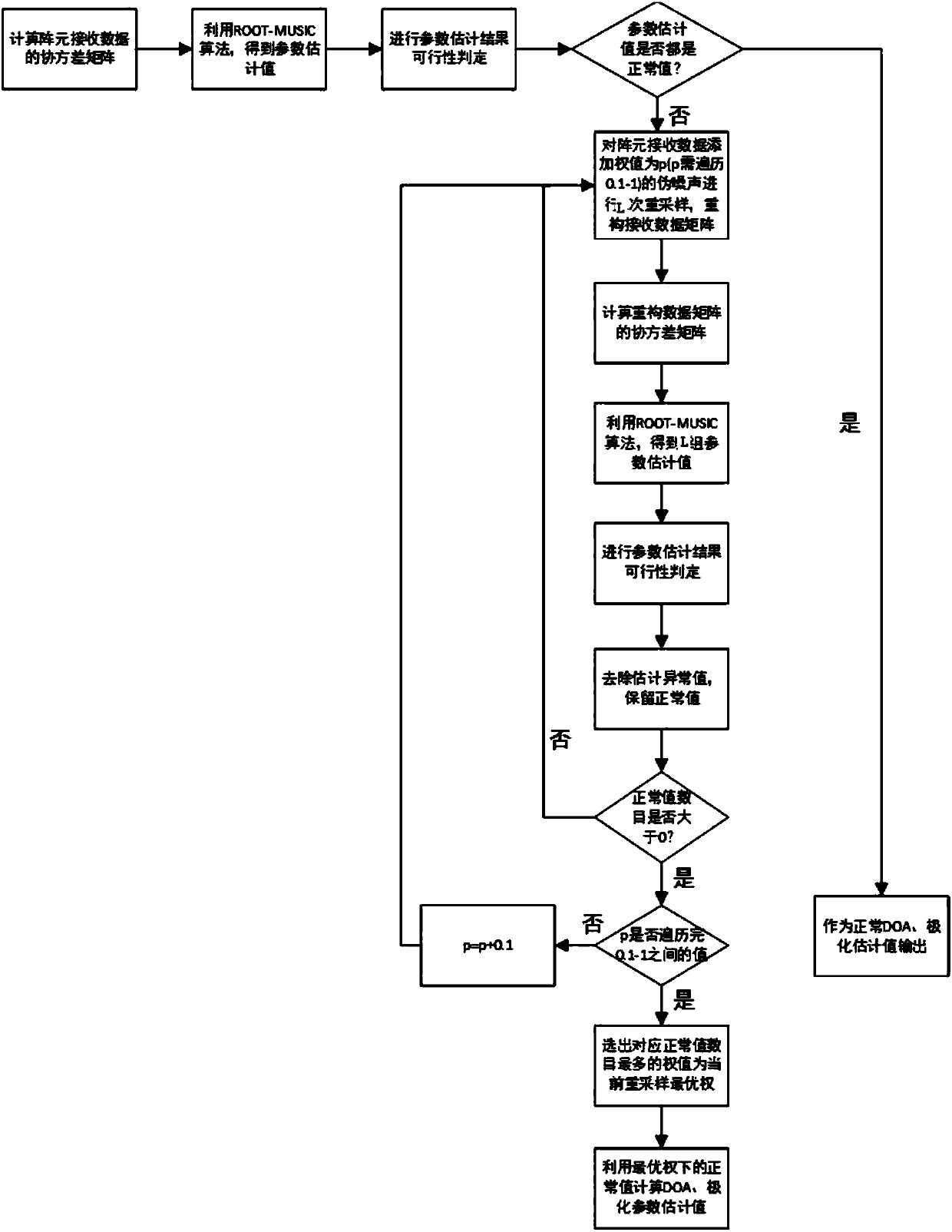
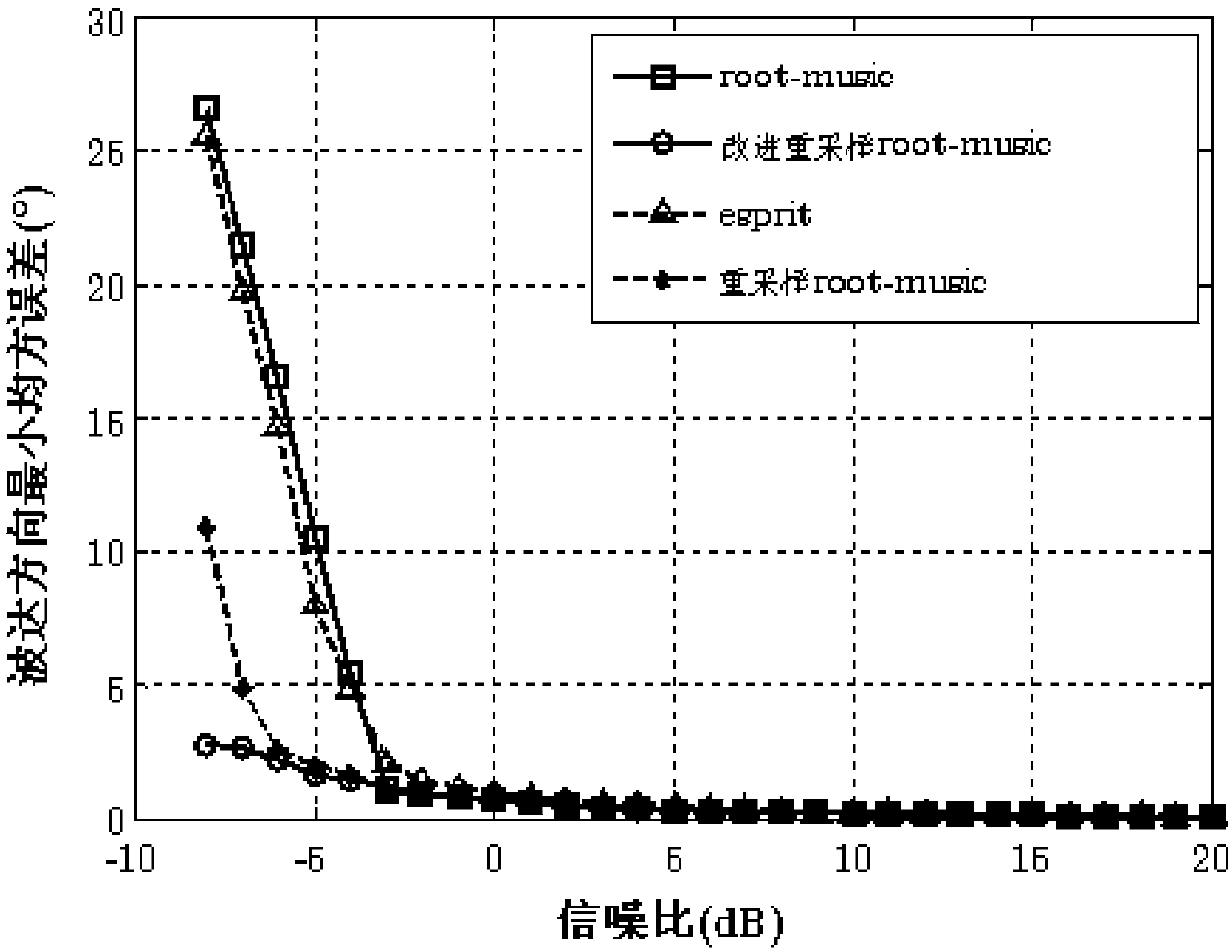
ActiveCN108414993AImprove estimation accuracyAvoid searchingWave based measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radar
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar array signal processing, and discloses a COLD array arrival direction and polarization parameter joint estimation method based on resampling. Theproblems of large computation load and greatly reduced parameter estimation precision under low signal to noise ratio in the prior art are solved. According to the main idea, the range of the incomingwave direction and polarization parameters is pre-estimated and combined with resampling, so that resampled parameter estimation values are normal values rather than abnormal values; a pseudo noise adding method is changed; and the optimal pseudo noise weight is selected for each group of resampling. According to the invention, spectrum peak search can be avoided; the root polynomial order is reduced; the computation load and the hardware complexity are reduced; the arrival direction and polarization parameter estimation performance under low signal to noise ratio is greatly improved; and thedisadvantages of large computation load and severely reduced parameter estimation performance under low signal to noise ratio, which are caused by spectrum peak search in the prior art, are overcome.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Adapted method for spectrum management of digital communication systems
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
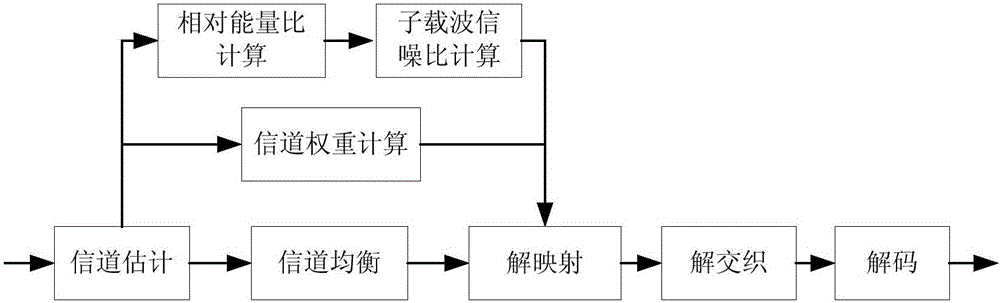
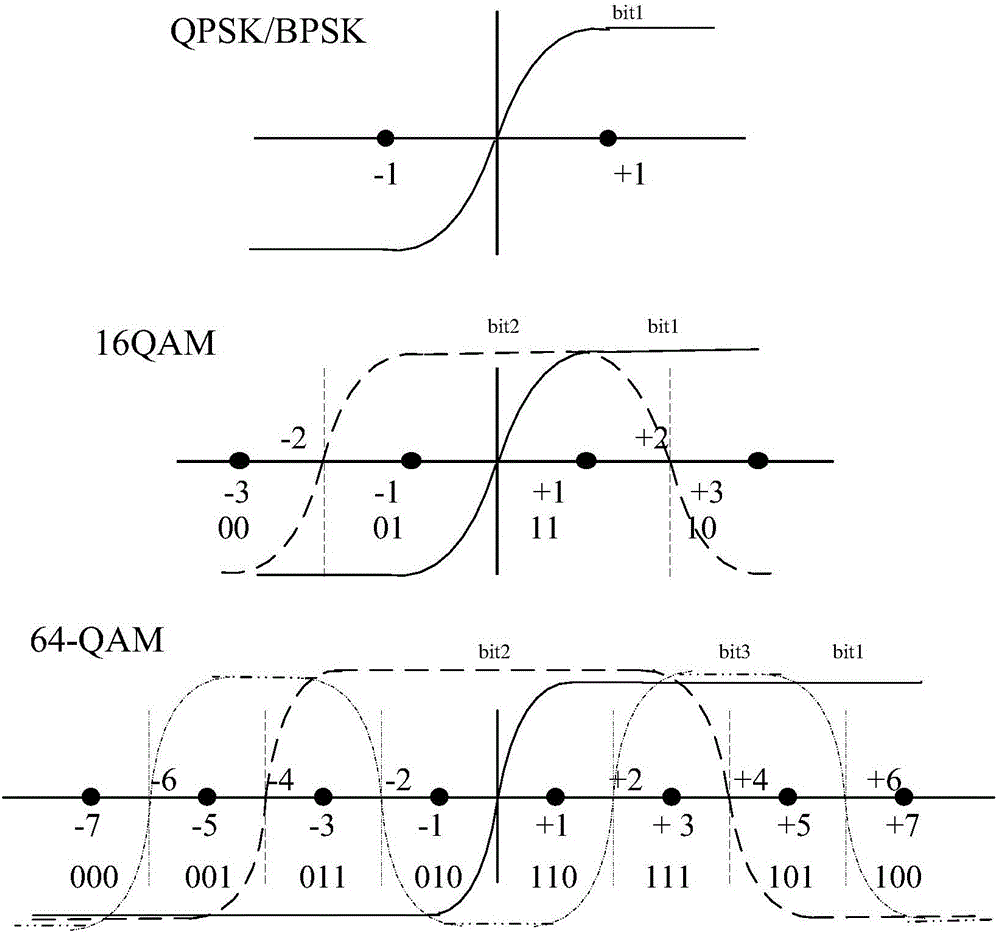
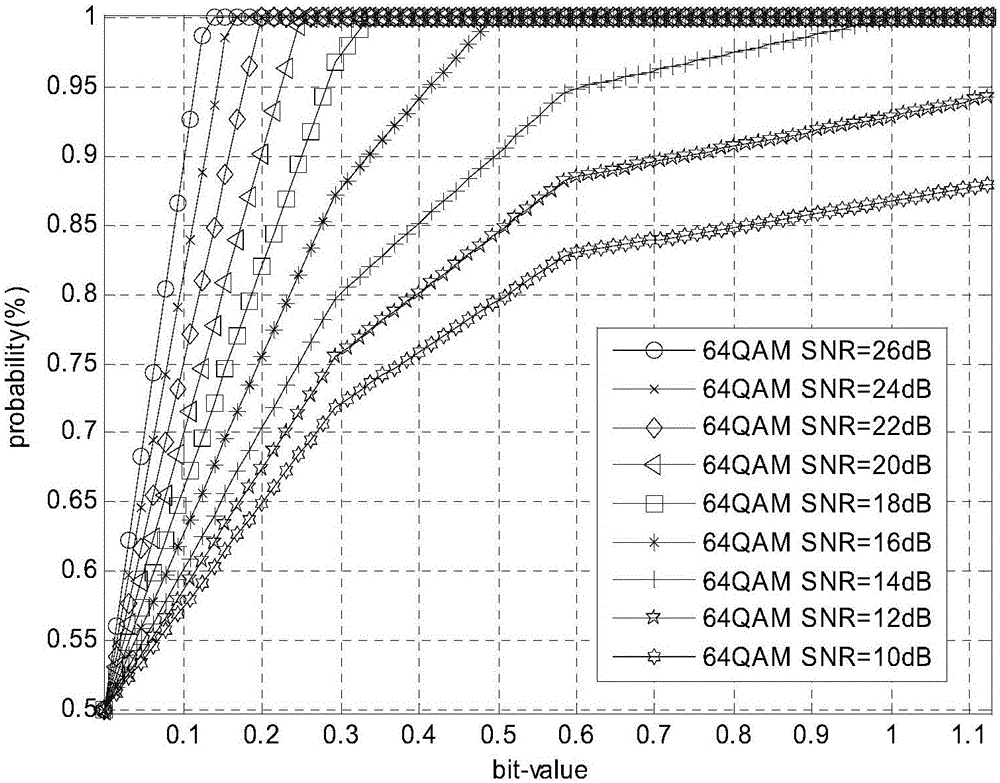
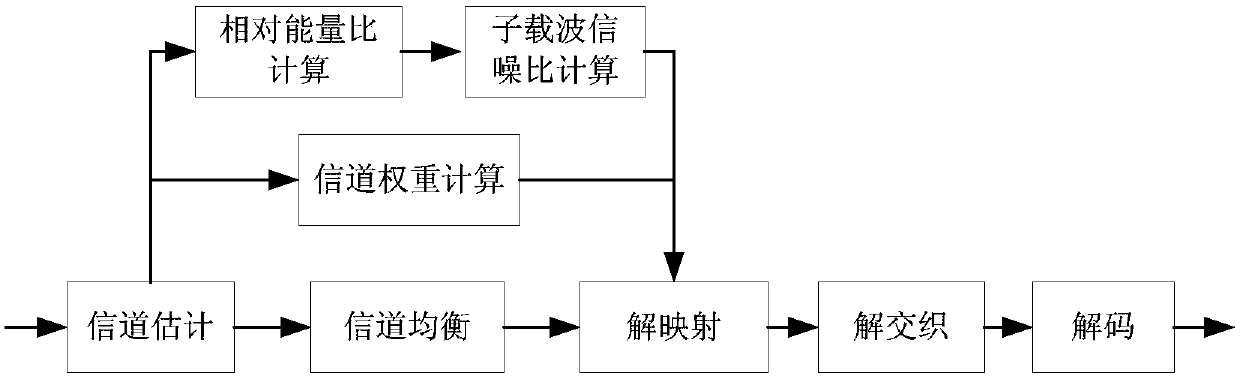
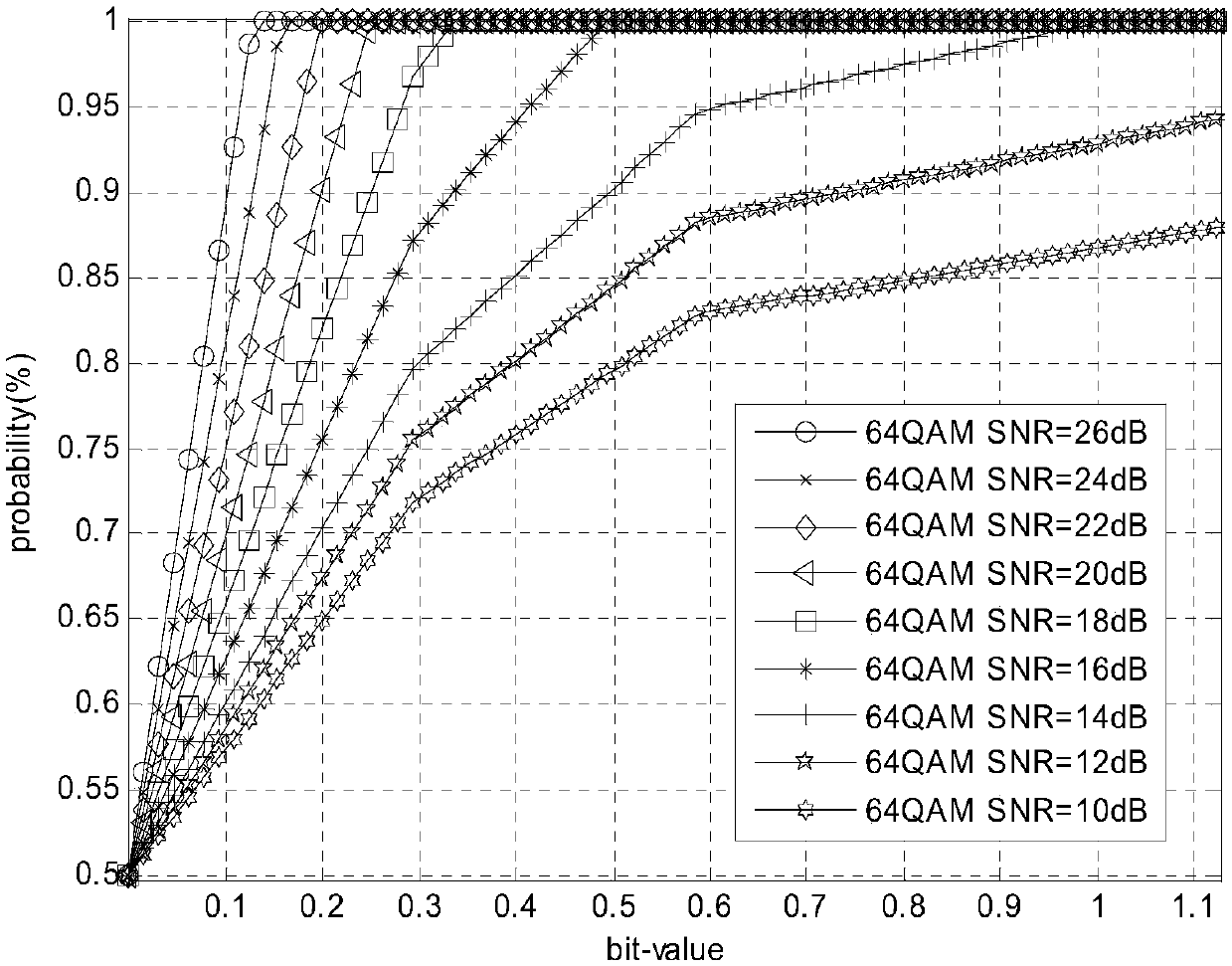
Signal-to-noise ratio weighting based OFDM system non-linear demapping method
InactiveCN105721110AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityError preventionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Carrier signal
The present invention relates to a signal-to-noise ration weighting based OFDM system non-linear demapping method, which is used for obtaining soft decision information required for decoding a receiving data signal of an OFDM system. The method comprises: according to a channel coefficient of each sub-carrier in the receiving data signal and an overall signal-to-noise ratio of the signal, calculating an absolute signal-to-noise ratio of each sub-carrier; based on the absolute signal-to-noise ratio and a reference signal-to-noise ratio of the signal, calculating a non-linear demapping curve of each sub-carrier; and mapping channel equalizing data of each sub-carrier in each symbol of the receiving data signal via the non-linear demapping curve subjected to signal-to-noise ratio weighting so as to obtain a signal-to-noise ratio weighting quantified value, and obtaining soft decision information by mapping the signal-to-noise weighting quantified value. With adoption of the signal-to-noise ratio weighting based OFDM system non-linear demapping method provided by the present invention, more precise and more reliable soft decision information can be obtained, and the information is used for improving decoding performance of receivers, especially receiver performance under deep fading channels.
Owner:中科威发半导体(苏州)有限公司
Magnetotelluric impedance estimation method
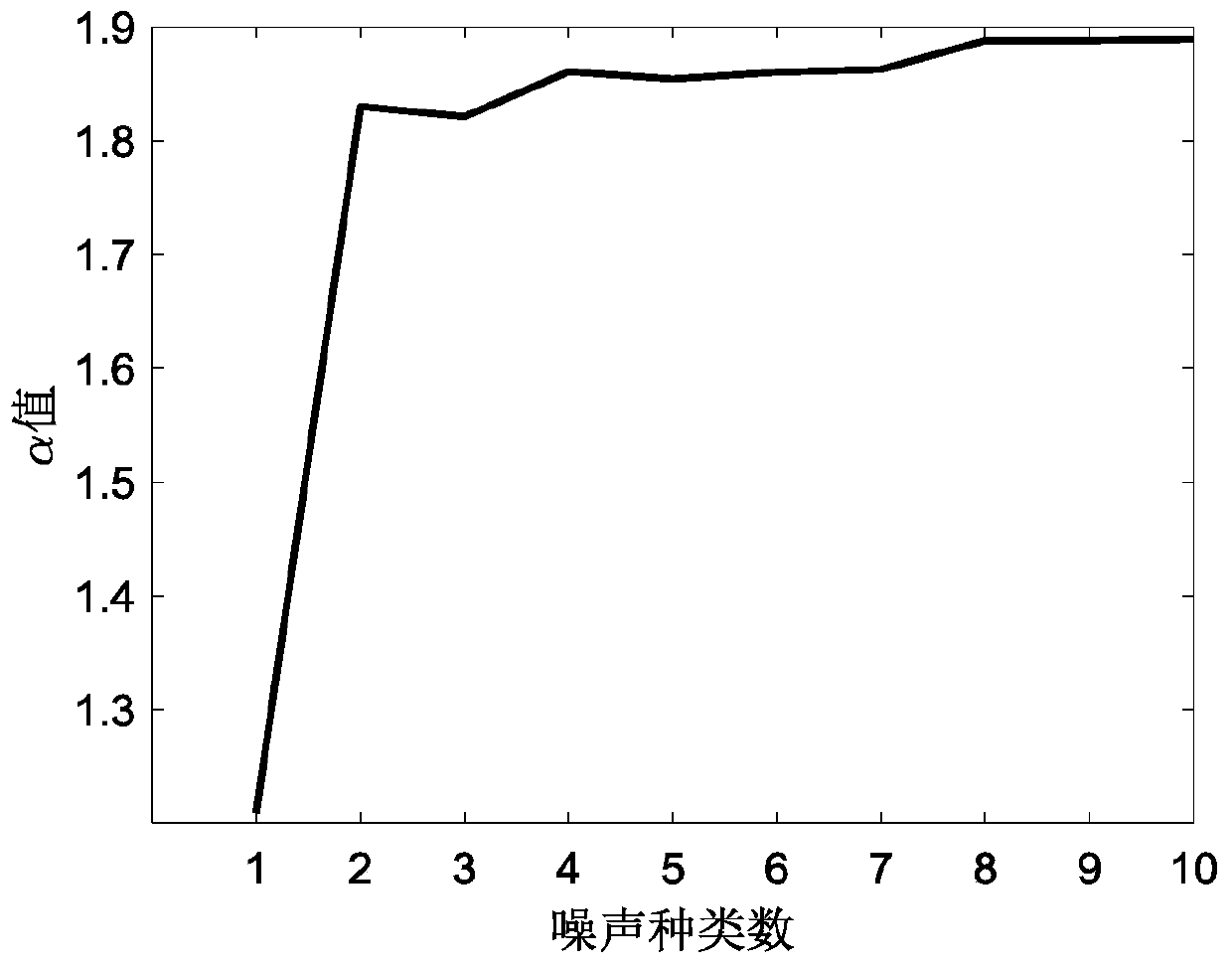
ActiveCN111273367ASolve the problem of Gaussian noiseElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationTime domainNoise
The invention provides a magnetotelluric impedance estimation method. The method comprises the following steps: performing Fourier transform on a time domain magnetotelluric signal measured from an observation station to a frequency domain; estimating initial impedance by using a least square method, obtaining an initial residual error, distinguishing various noises, obtaining a weight value corresponding to magnetic field normalization, obtaining estimated magnetotelluric impedance, judging a numerical value of a parameter for measuring whether the noise is close to Gaussian noise, outputtingthe impedance and the like. According to the method, impedance estimation is carried out on the basis of a noise weighting mode, the relation between noise and signals can be well utilized, weightingnormalization is carried out by utilizing the correlation, and Gaussian noise increased along with increase of signal strength is restored into Gaussian noise after weighting normalization; comparedwith a traditional least square method and a traditional steady method, the method based on noise weighting truly solves the problem that Gaussian noise is increased along with increase of signal strength.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Rake receiver and de-spreading method thereof
ActiveUS7848392B2Reducing the bit error rate of a signalReduce complexityBaseband systemsRake receiverNoise estimation
The invention relates to a rake receiver and a method for de-spreading thereof. A plurality of noise branches is adopted for producing a plurality of noise components in the rake receiver. Next, a noise combining unit adjusts each noise component according to a plurality of noise weights, so as to combine the noise components to obtain an interference-plus-noise estimation value. The rake receiver eliminates the noises in the main signal generated by the signal branches through using the interference-plus-noise estimation value. Therefore, the performance of a receiving terminal can be enhanced.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Nonlinear demapping method of ofdm system based on SNR weighting
InactiveCN105721110BHigh precisionImprove reliabilityError preventionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Data signal
The present invention relates to a signal-to-noise ration weighting based OFDM system non-linear demapping method, which is used for obtaining soft decision information required for decoding a receiving data signal of an OFDM system. The method comprises: according to a channel coefficient of each sub-carrier in the receiving data signal and an overall signal-to-noise ratio of the signal, calculating an absolute signal-to-noise ratio of each sub-carrier; based on the absolute signal-to-noise ratio and a reference signal-to-noise ratio of the signal, calculating a non-linear demapping curve of each sub-carrier; and mapping channel equalizing data of each sub-carrier in each symbol of the receiving data signal via the non-linear demapping curve subjected to signal-to-noise ratio weighting so as to obtain a signal-to-noise ratio weighting quantified value, and obtaining soft decision information by mapping the signal-to-noise weighting quantified value. With adoption of the signal-to-noise ratio weighting based OFDM system non-linear demapping method provided by the present invention, more precise and more reliable soft decision information can be obtained, and the information is used for improving decoding performance of receivers, especially receiver performance under deep fading channels.
Owner:中科威发半导体(苏州)有限公司
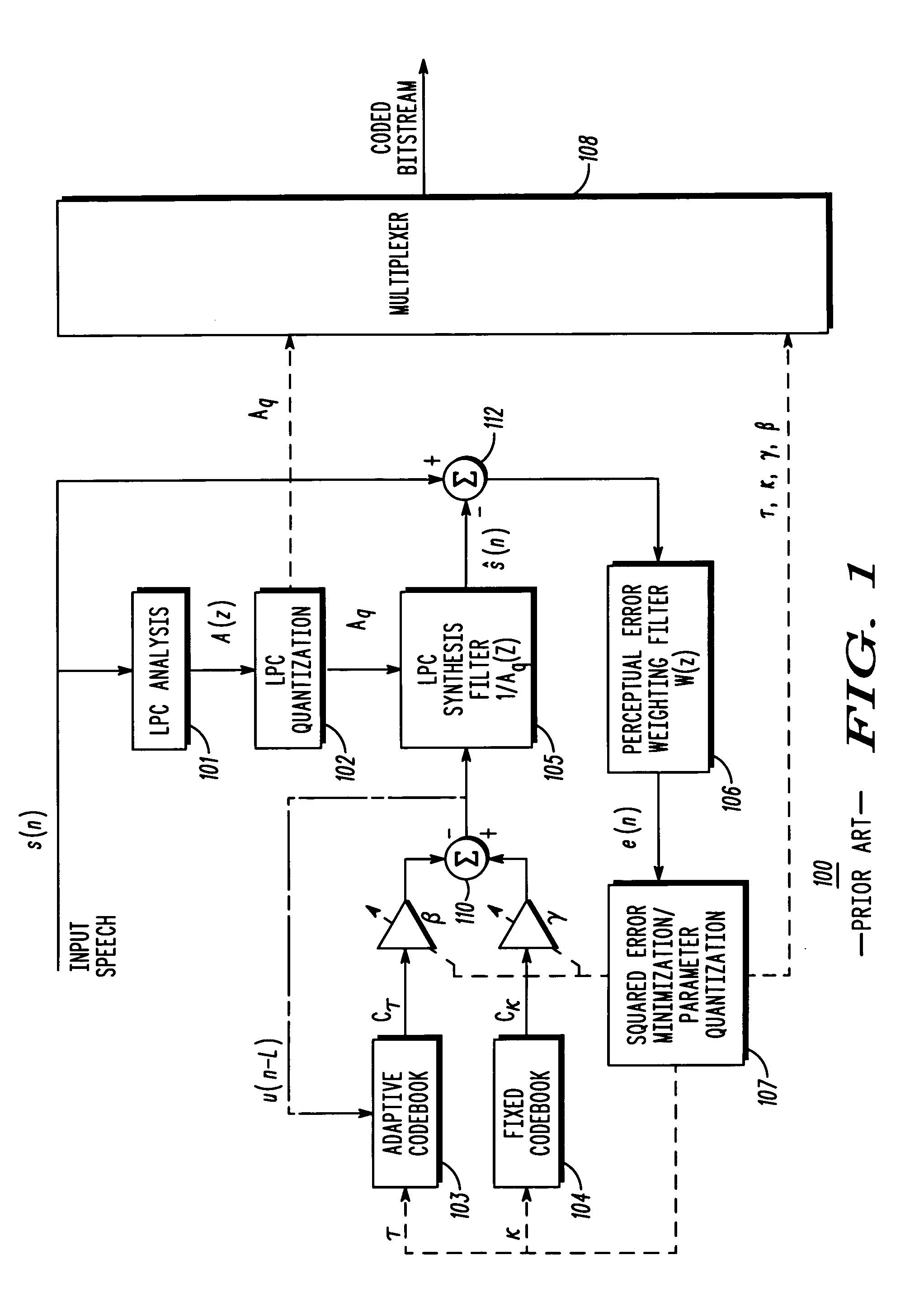
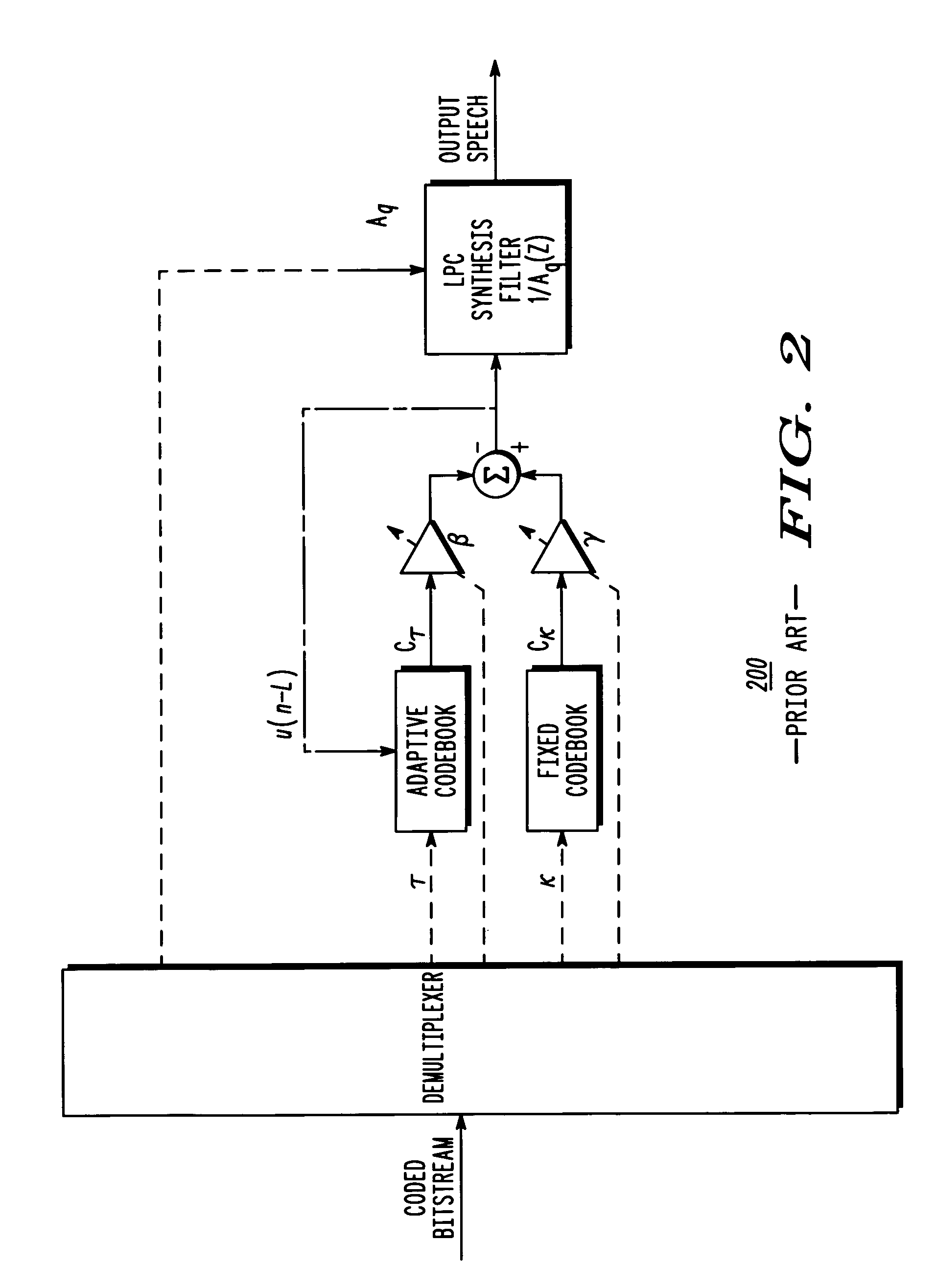
Method and apparatus for performing harmonic noise weighting in digital speech coders
To address the need for choosing values of harmonic noise weighting (HNW) coefficient (εp) so that the amount of harmonic noise weighting cam be optimized, a method and apparatus for performing harmonic noise weighting in digital speech coders is provided herein. During operation, received speech is analyzed to determine a pitch period. HNW coefficients are then chosen based on the pitch period, and a perceptual noise weighting filter (C(z)) is determined based on the harmonic-noise weighting (HNW) coefficients (εp).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Train noise weighting current testing and processing method
ActiveCN105572466ASolving Noise Current Test ProblemsGet test resultsMeasurement using digital techniquesComplete dataComputer module
The invention relates to a train noise weighting current testing and processing method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) mounting current probes on each current feeding module; 2) transmitting multi-path current signals received from the current feeding modules to a multi-channel summator by the current probes; 3) processing the received multi-path current signals by the multi-channel summator, and outputting a total current signal; 4) transmitting the total current signal output from the multi-channel summator to a data recorder; 5) acquiring and recording the received total current signal by the data recorder, and outputting the acquired data; and 6) according to the standard demand, editing software, completing data processing on the acquired data output from the data recorder, and finishing the test. The train noise weighting current testing and processing method effectively solves the noise current testing problem for asymmetric marshalling and asymmetric power unit vehicles, and can more visually and effectively obtain the test result.
Owner:CRRC NANJING PUZHEN CO LTD
Unsupervised single microphone voice noise reduction method and system
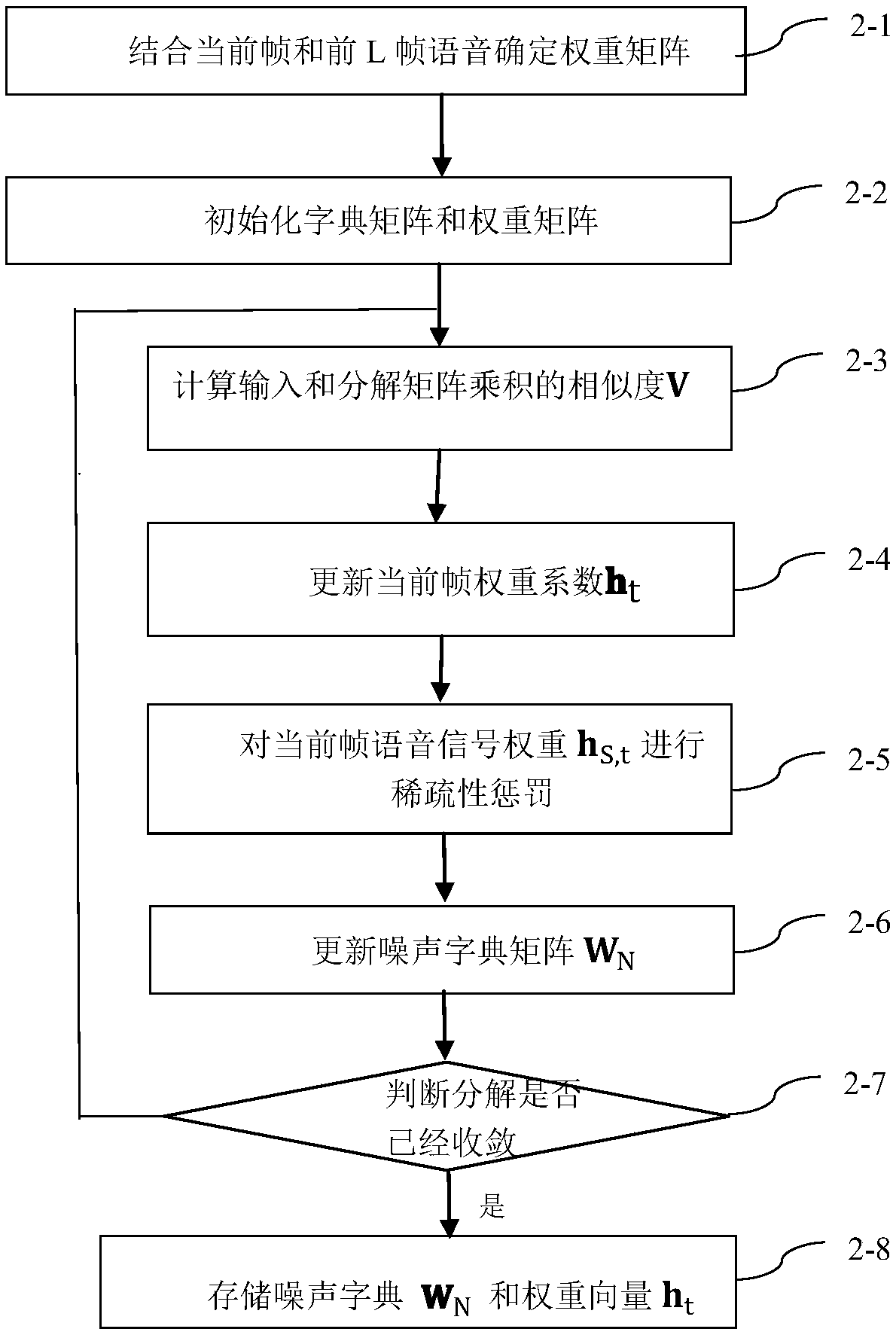
The invention discloses an unsupervised single microphone voice noise reduction method. The method comprises the steps that 1, frequency spectrum extraction is conducted on acquired voice training data covering all phonemes, k-means clustering is conducted on amplitude spectra to obtain voice dictionaries corresponding to all classes, and all the different classes of voice dictionaries are combined into a complete voice dictionary WS; 2, short-time Fourier transform is conducted on a noisy voice reaching at the current moment to obtain an amplitude spectrum xt of a current frame, the amplitudespectrum is combined with the processed amplitude spectra of previous L frames to serve as an output voice spectrum X=[x<t-L>,..., x<t-1>, xt], a noise matrix WN estimated by the last frame and the voice dictionary WS are combined into a total dictionary matrix W=[WS WN], and non-negative matrix factorization is conducted on the output voice spectrum X by adopting an iterative algorithm to obtaina noise matrix and a voice noise weight vector corresponding to the current frame; and 3, a current-frame voice signal after noise reduction is reconstructed by means of the estimated noise matrix and noise weight vector.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for reconstructing a target signal from a noisy input signal
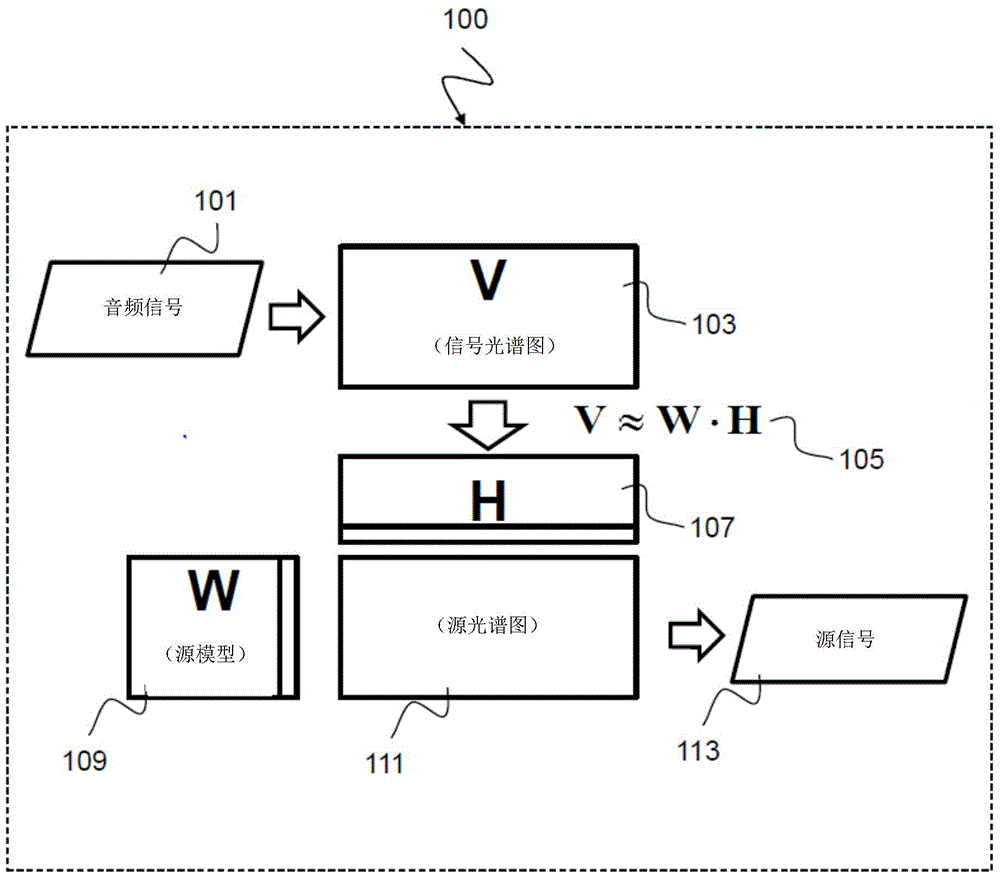
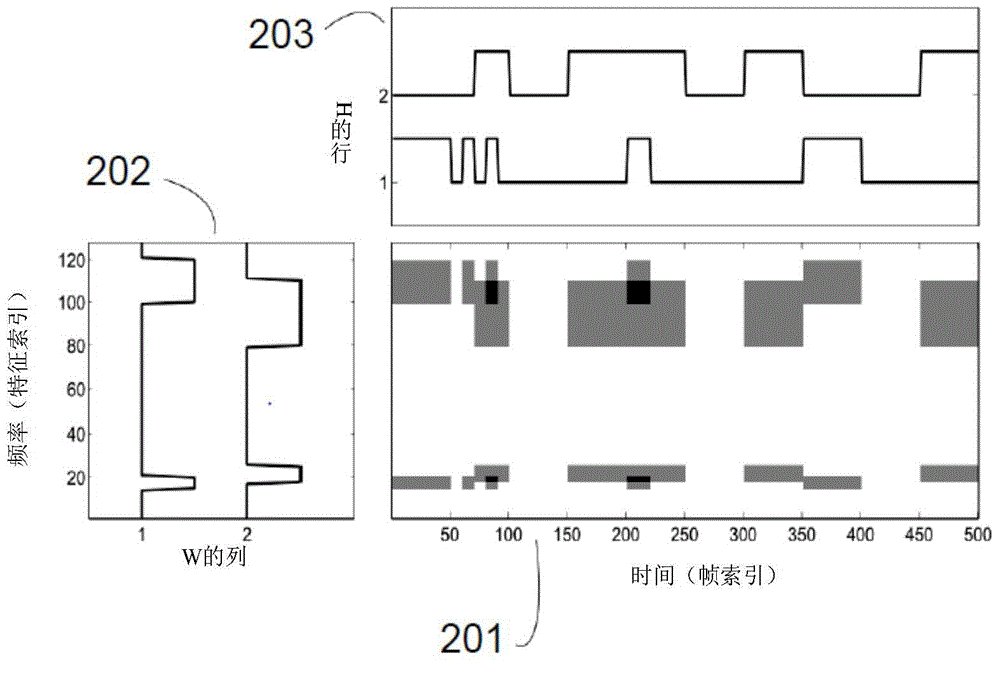
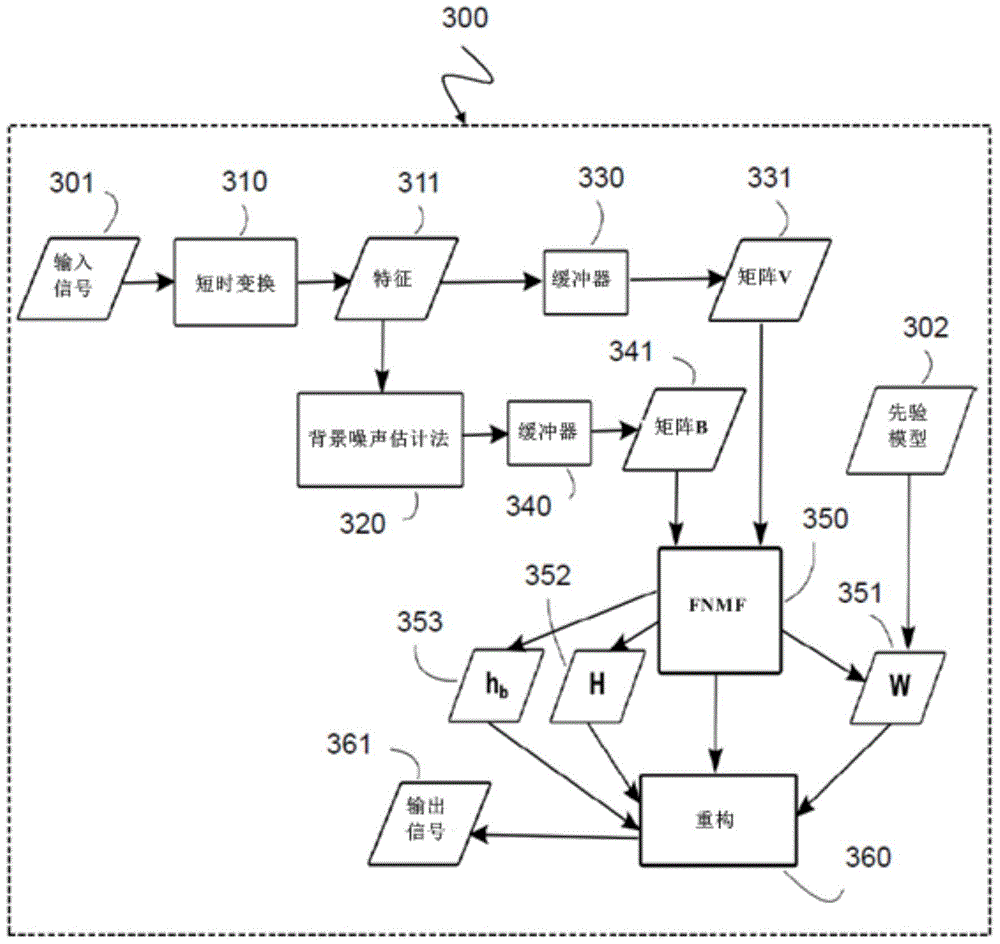
Method and device for reconstructing a target signal from a noisy input signal The invention relates to a method (300) for reconstructing at least one target signal (361) from an input signal (301) corrupted by noise, the method (300) comprising: determining (310) a first set of feature vectors (311) from the input signal (301), the first set of feature vectors (311) forming anon-negative input matrix (V, 331) representing signal characteristics of the input signal (301); determining (320) a second set of feature vectors from the first set of feature vectors (311), the second set of feature vectors forming a non-negative noise matrix (B, 341) representing noise characteristics of the input signal (301); decomposing (350) the input matrix (V, 331) into a sum of a first matrix and a second matrix, the first matrix representing a product of a non-negative bases matrix (W, 351) and a non-negative weight matrix (H, 352), and the second matrix representing a combination of the noise matrix (B, 341) and a noise weight vector (hb, 353); and reconstructing (360) the at least one target signal (361) based on the non-negative bases matrix (W, 351) and the non-negative weight matrix (H, 352).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Parameter design method of electronic system comprehensively considering manufacturing and temperature noise
ActiveCN107357955ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Electronic systems
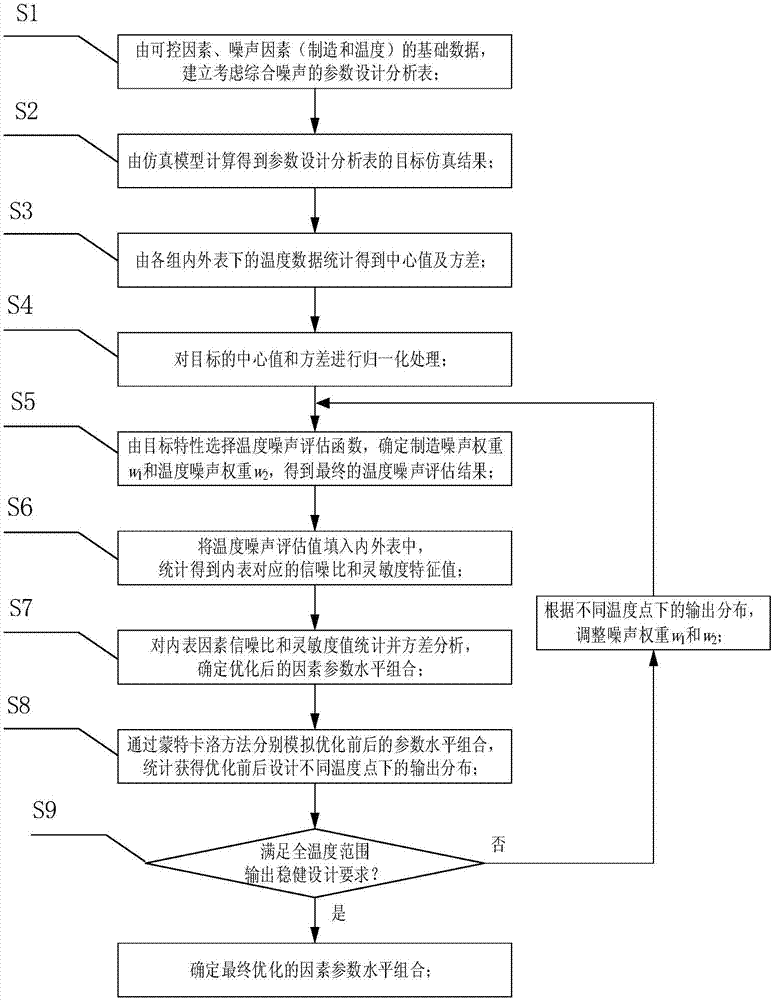
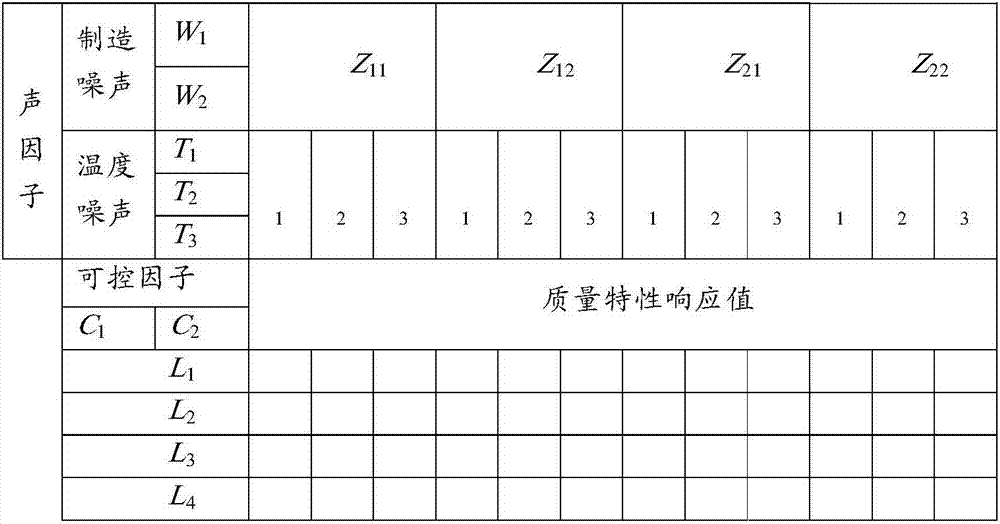
The invention discloses a parameter design method of an electronic system comprehensively considering manufacturing and temperature noise. The method comprises following steps: establishing a robustness parameter design analysis table from controllable factors and basic data of first parameter noise factors and second parameter noise factors; calculating a target simulation result of the analysis table; performing second parameter statistics of inner and external table to obtain center value and variance; performing normalization; determining first parameter noise weight and second parameter noise weight to obtain second parameter noise assessment value; filling the second parameter noise assessment value in the inner and external table and performing statistics on the signal to noise ratio and sensitivity characteristic value corresponding to the inner table; performing variance analysis on the signal to noise ratio and sensitivity characteristic value to determine optimized parameter level combination; obtaining output distribution under second parameter of different designs before and after optimization through simulation; if the optimization scheme satisfies requirements, then optimization is stopped; otherwise, adjusting the first parameter noise weight and the second parameter noise weight and optimizing the parameter level combination again.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for enhancing detail based on noise elimination, and method and apparatus for calculating noise weight
ActiveUS8699816B2Enhance detailsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionPixel based
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Video image enhancement method and device
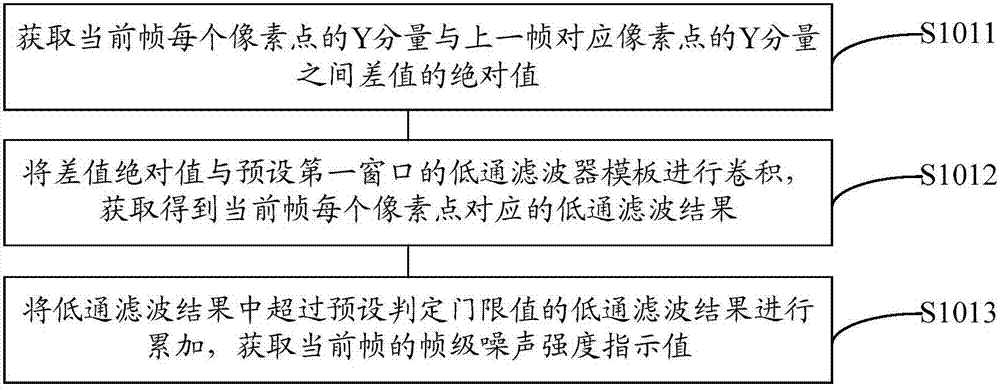
ActiveCN107333027AAvoid enhancementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVideo imageNoise weighting
The embodiment of the invention discloses a video image enhancement method and device. The method can comprise the following steps: acquiring the frame level noise intensity indicator value of a current frame according to corresponding pixel points of the current frame and a previous frame of a video image; acquiring noise weights and direct current components corresponding to the pixel points according to the pixel points of the current frame and a preset first window; acquiring a high-frequency coefficient group corresponding to the current frame from the pixel points of the current frame according to a preset sequencing strategy; acquiring an image enhancement gain value according to the frame level noise intensity indicator value of the current frame and the high-frequency coefficient group; acquiring high-frequency values corresponding to the pixel points according to the image enhancement gain value, the pixel points of the current frame and the direct current components corresponding to the pixel points; and performing image enhancement on the pixel points of the current frame according to the high-frequency values corresponding to the pixel points of the current frame and the noise weights corresponding to the pixel points based on a preset image enhancement strategy to obtain a corresponding frame of the current frame after image enhancement.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com