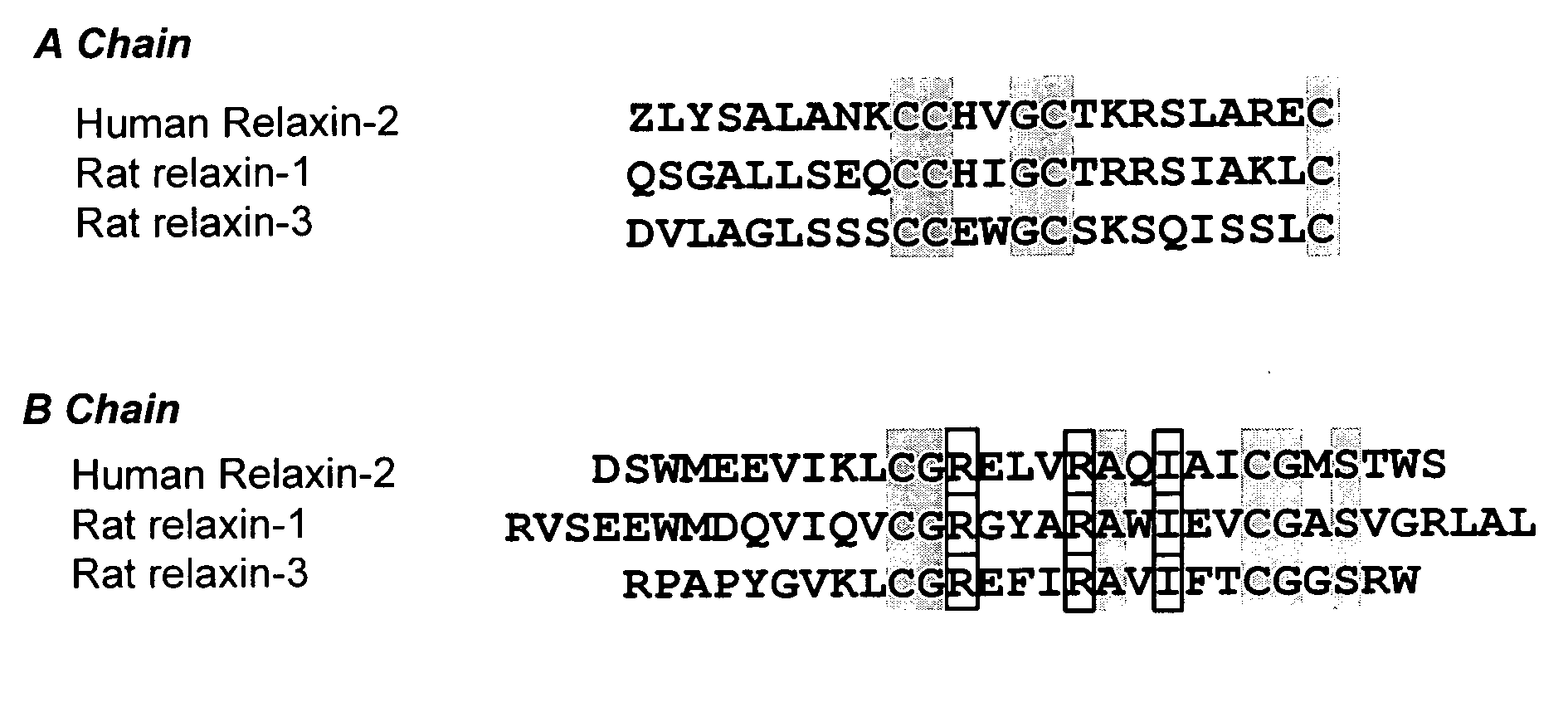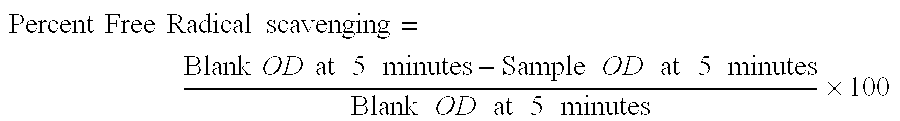Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Mammalian heart" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
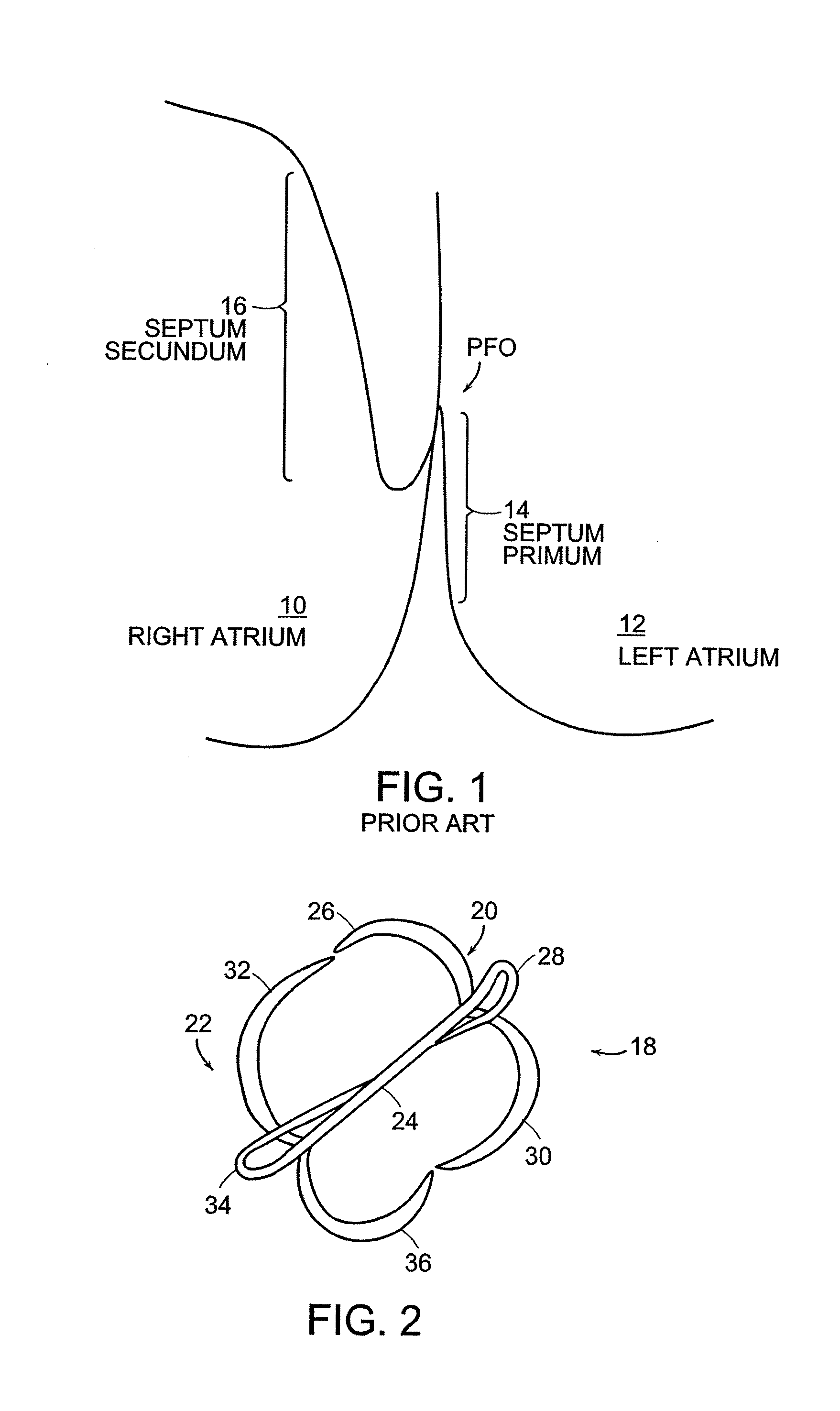
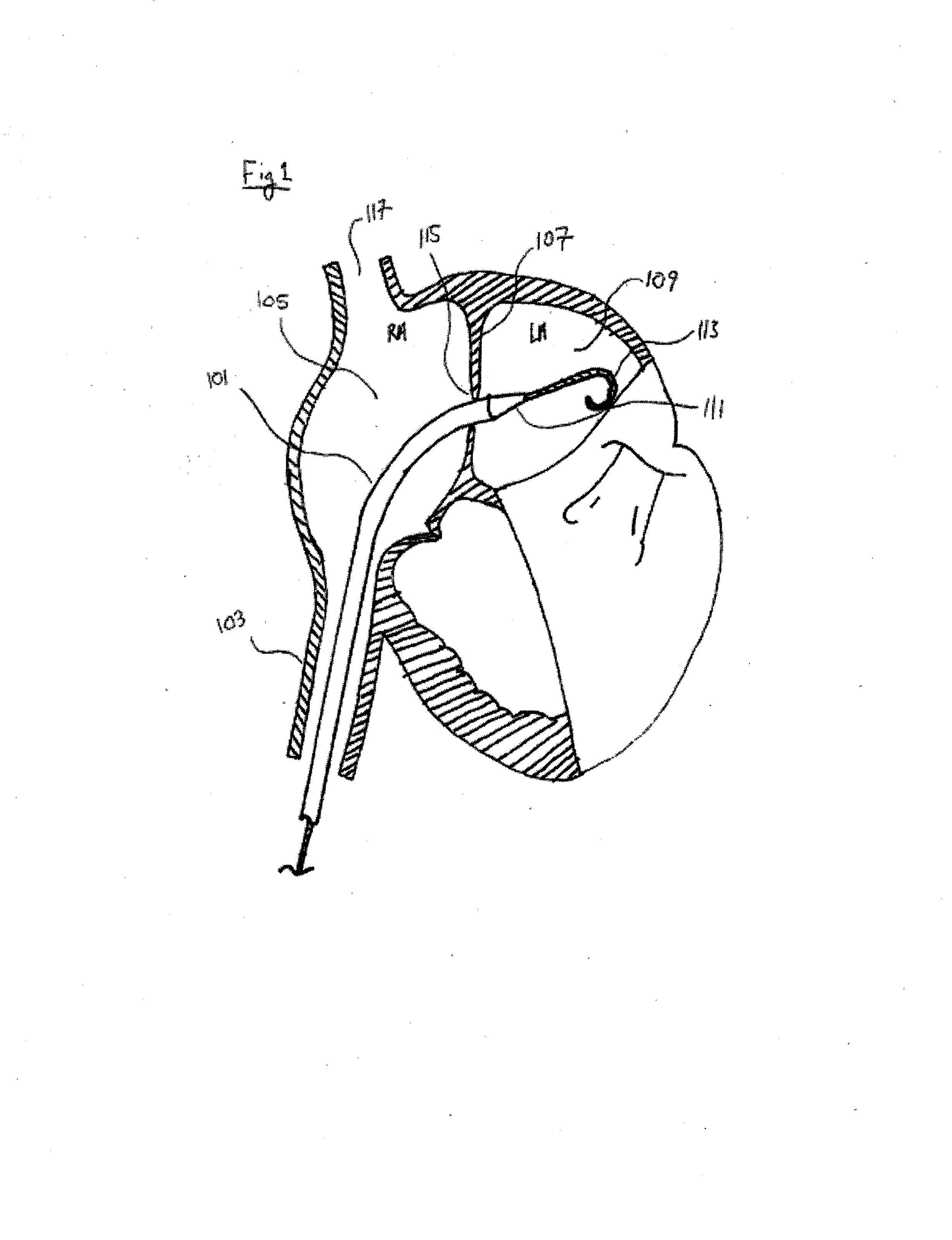
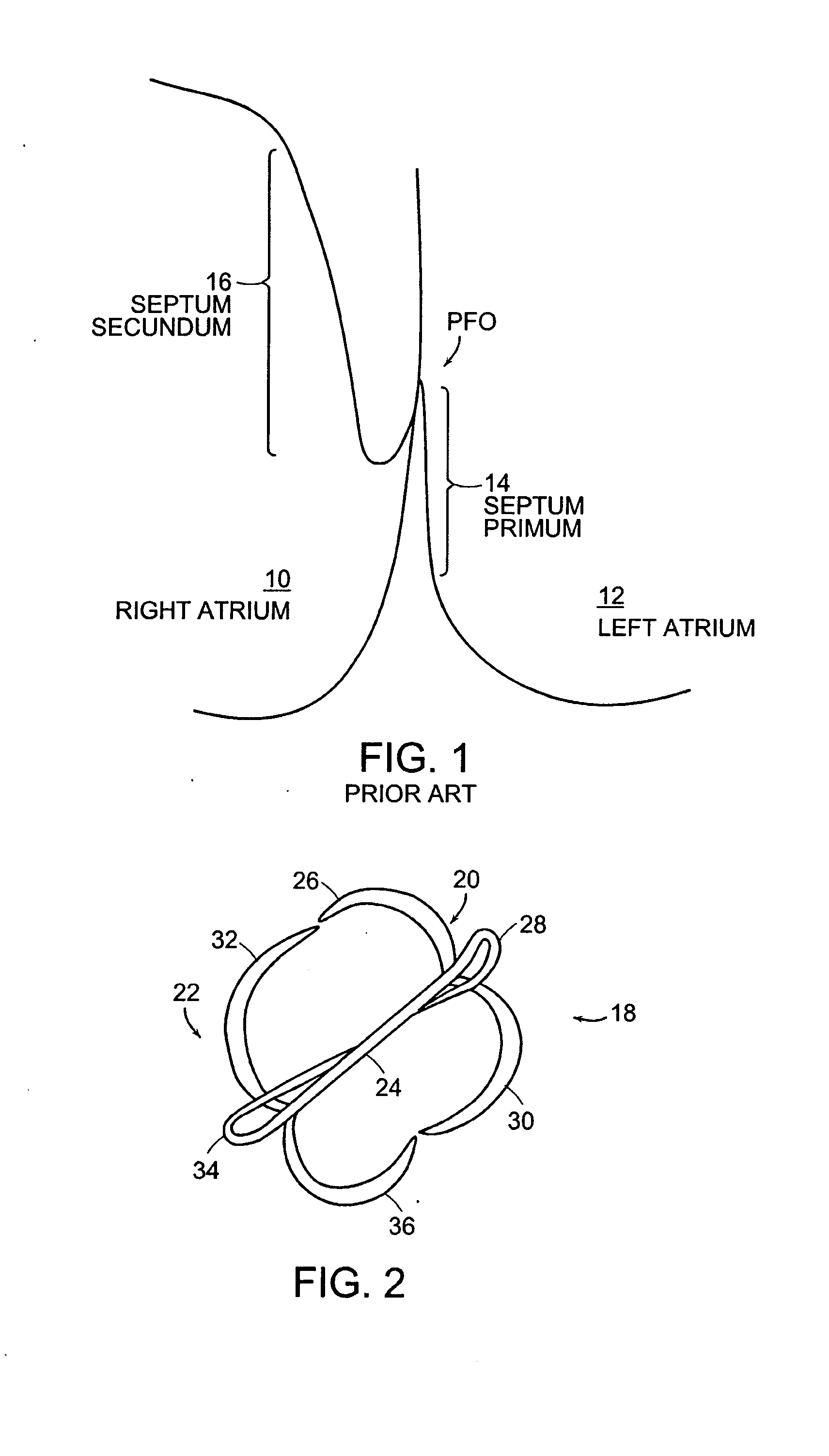
The mammalian heart has four chambers, two upper atria, the receiving chambers, and two lower ventricles, the discharging chambers. The heart has four valves, which separate its chambers and ensures blood flows in the correct direction through the heart (preventing backflow).
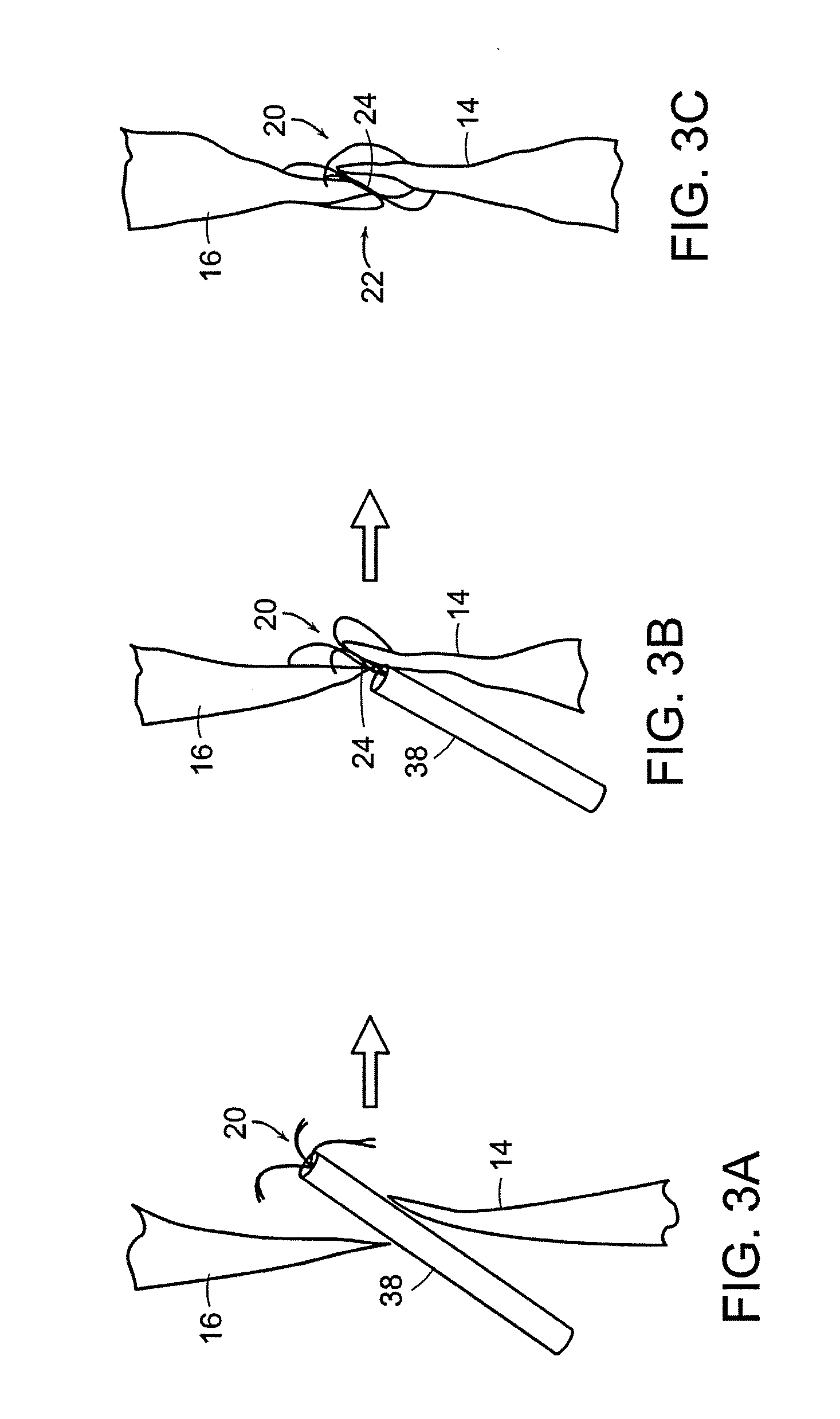
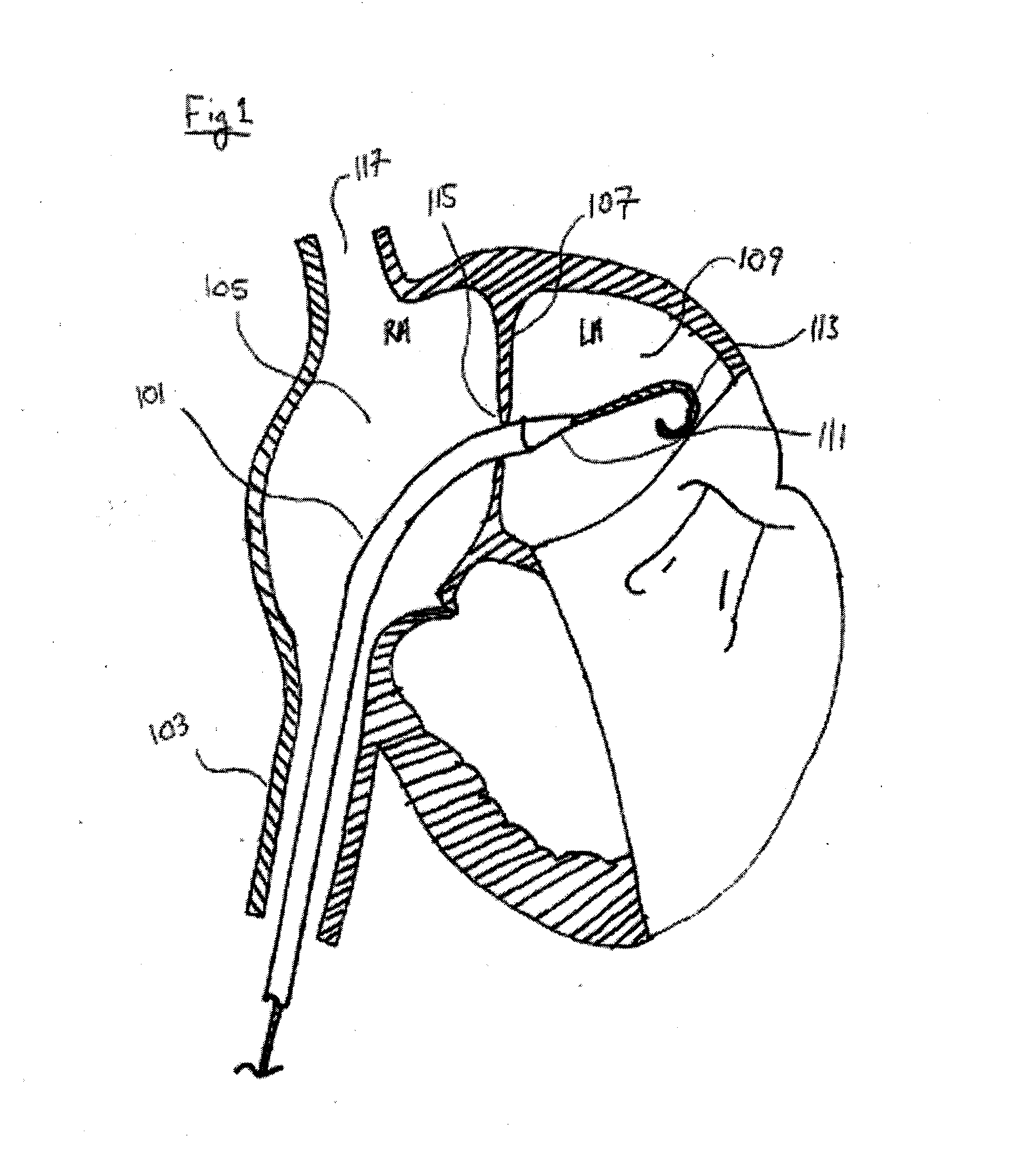
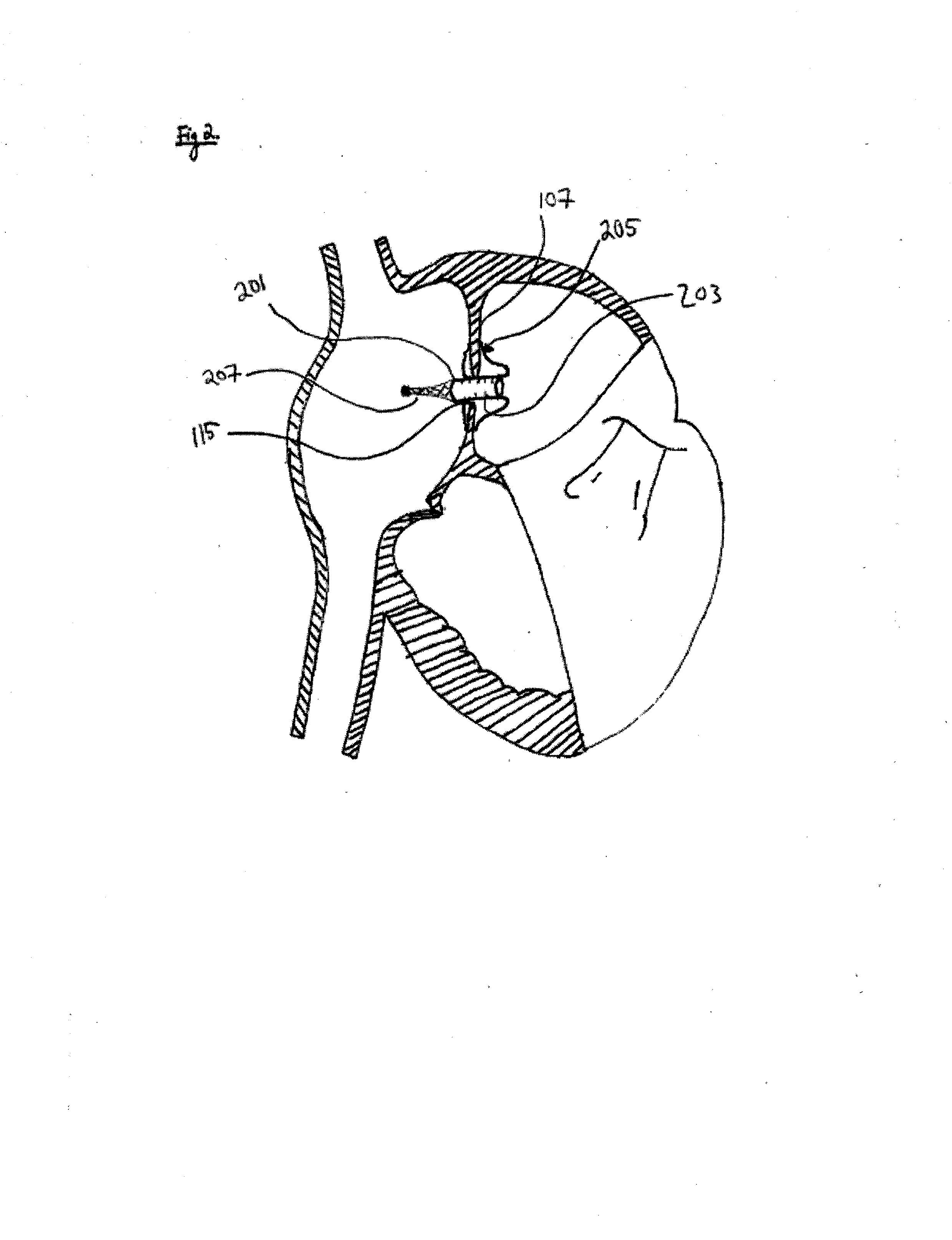
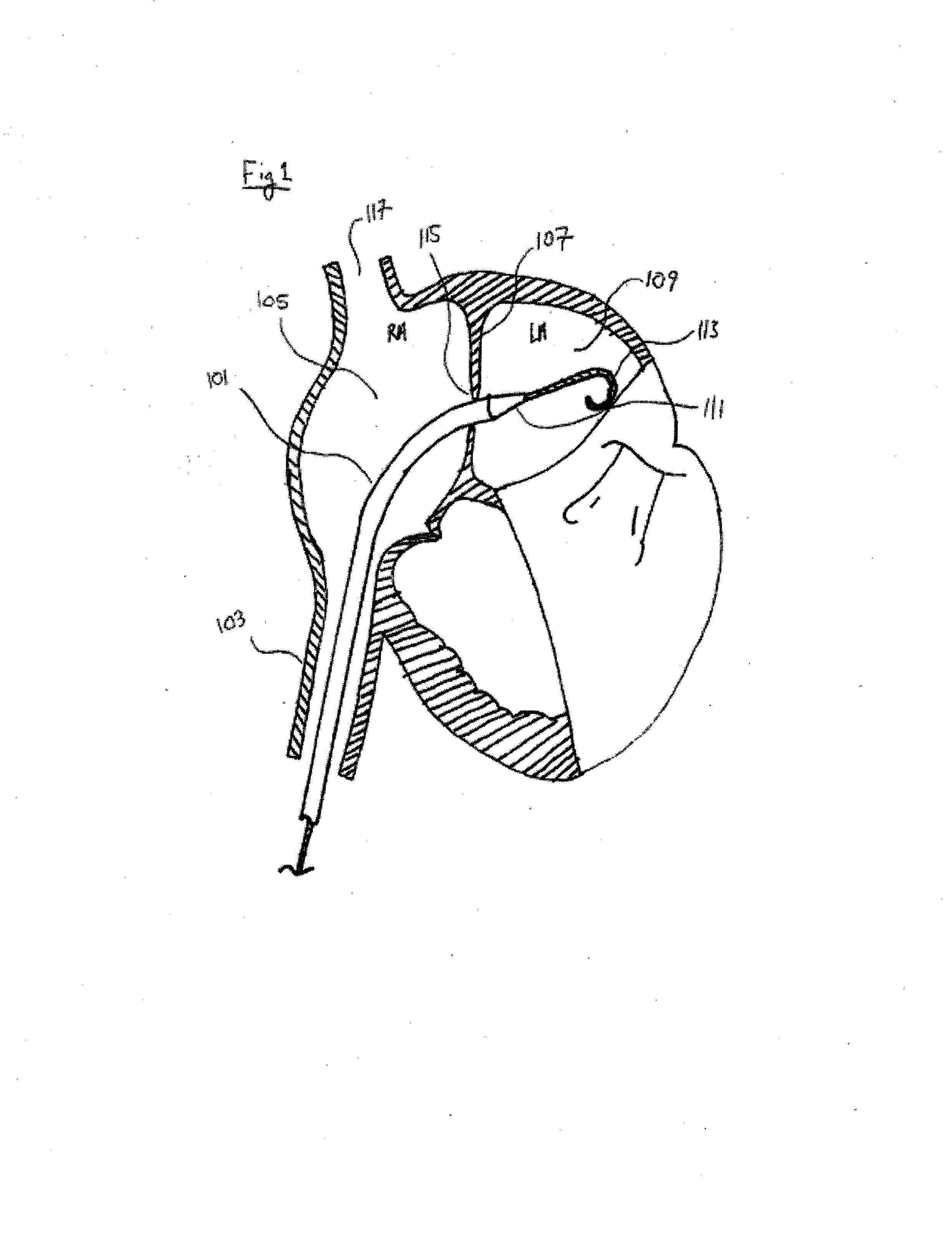
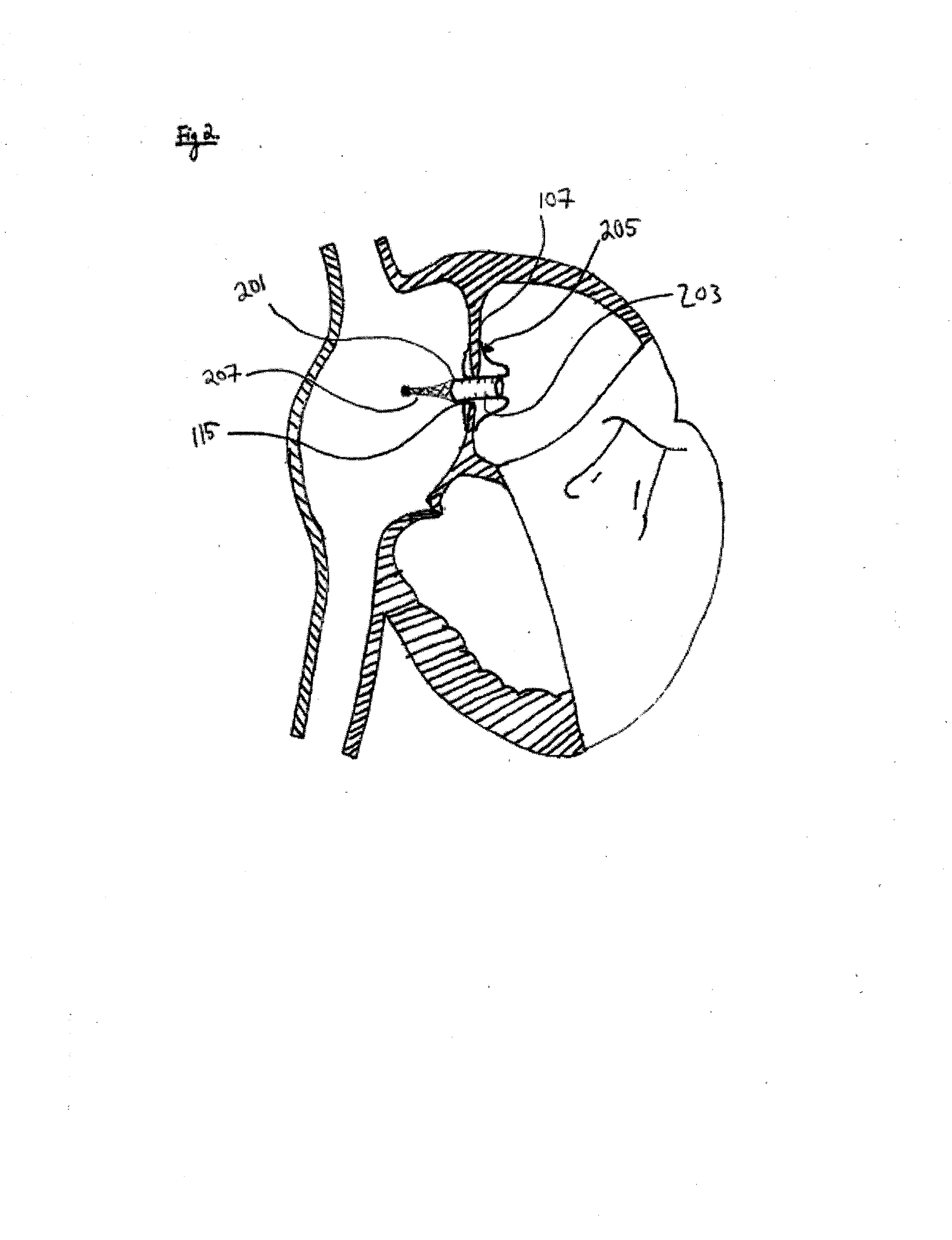
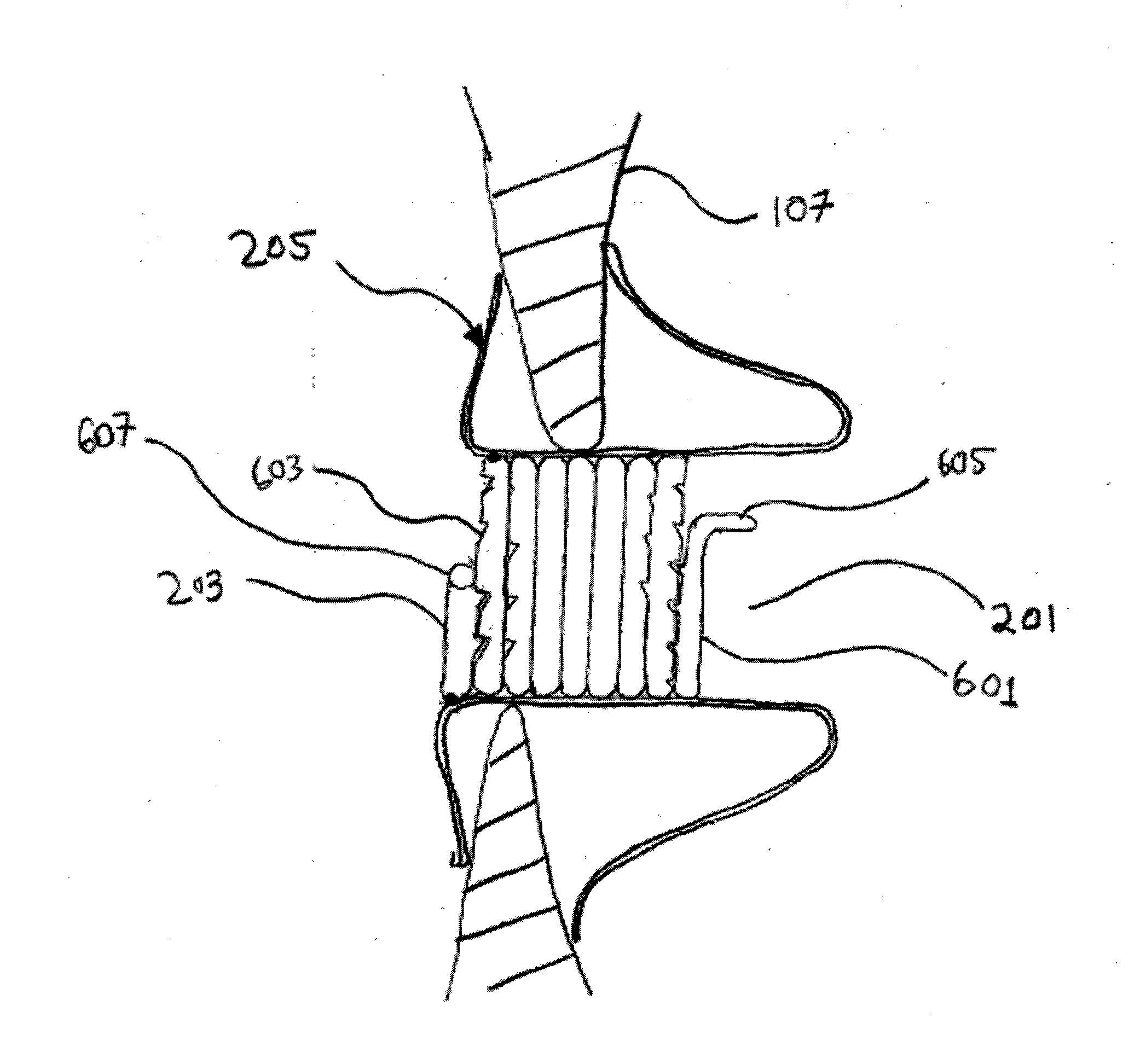
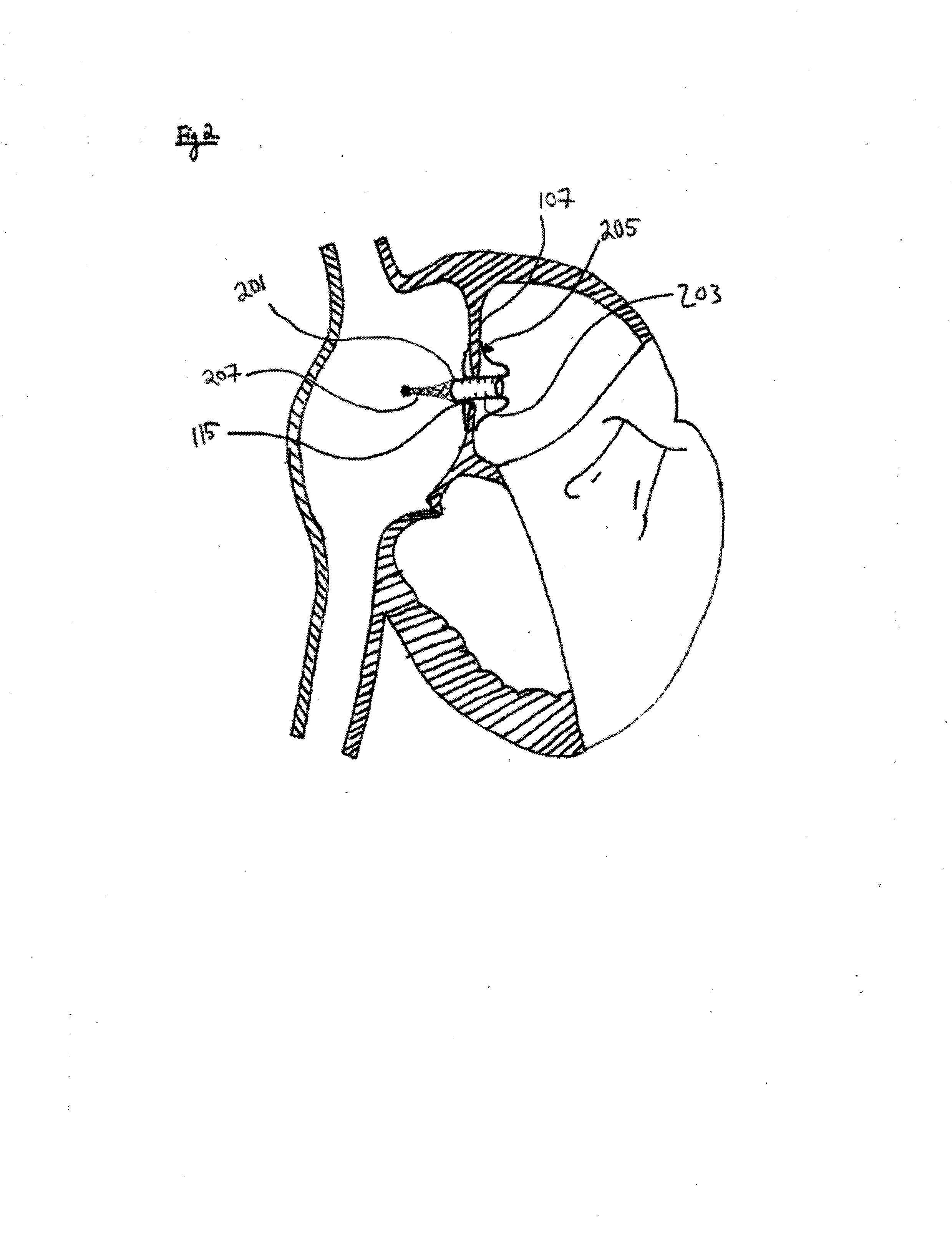
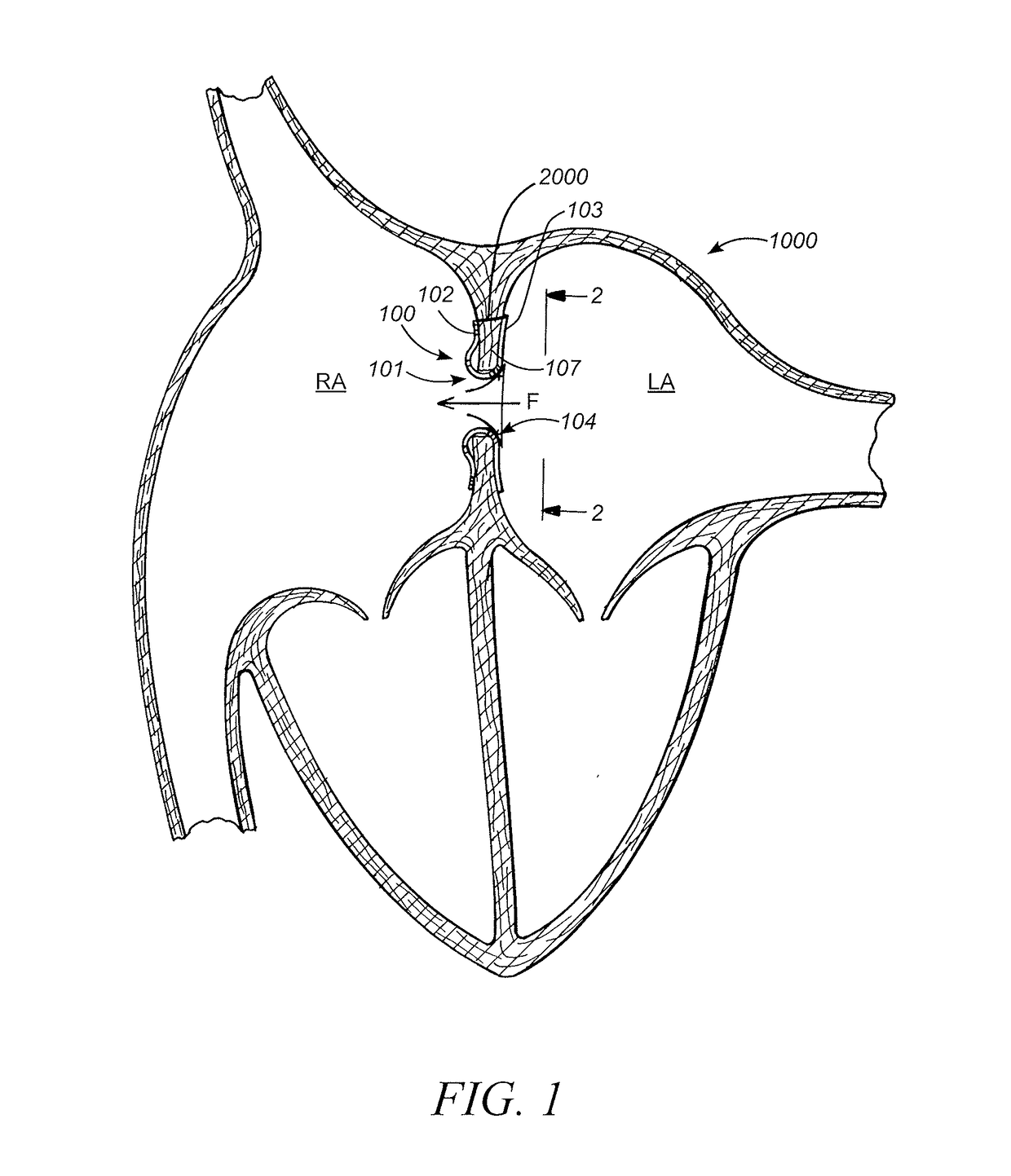
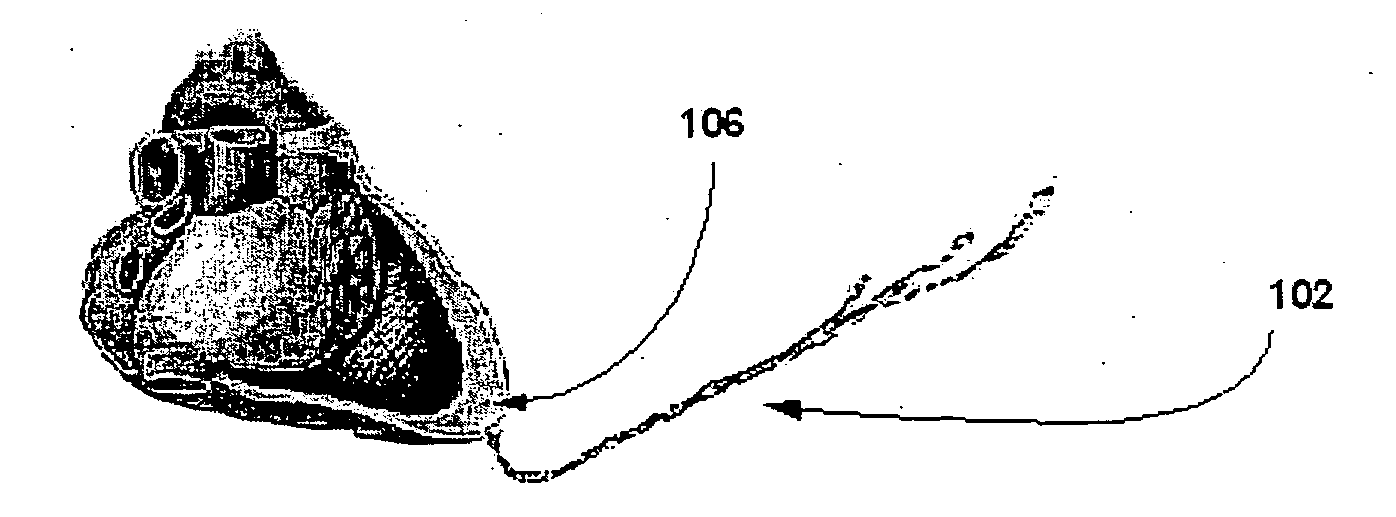
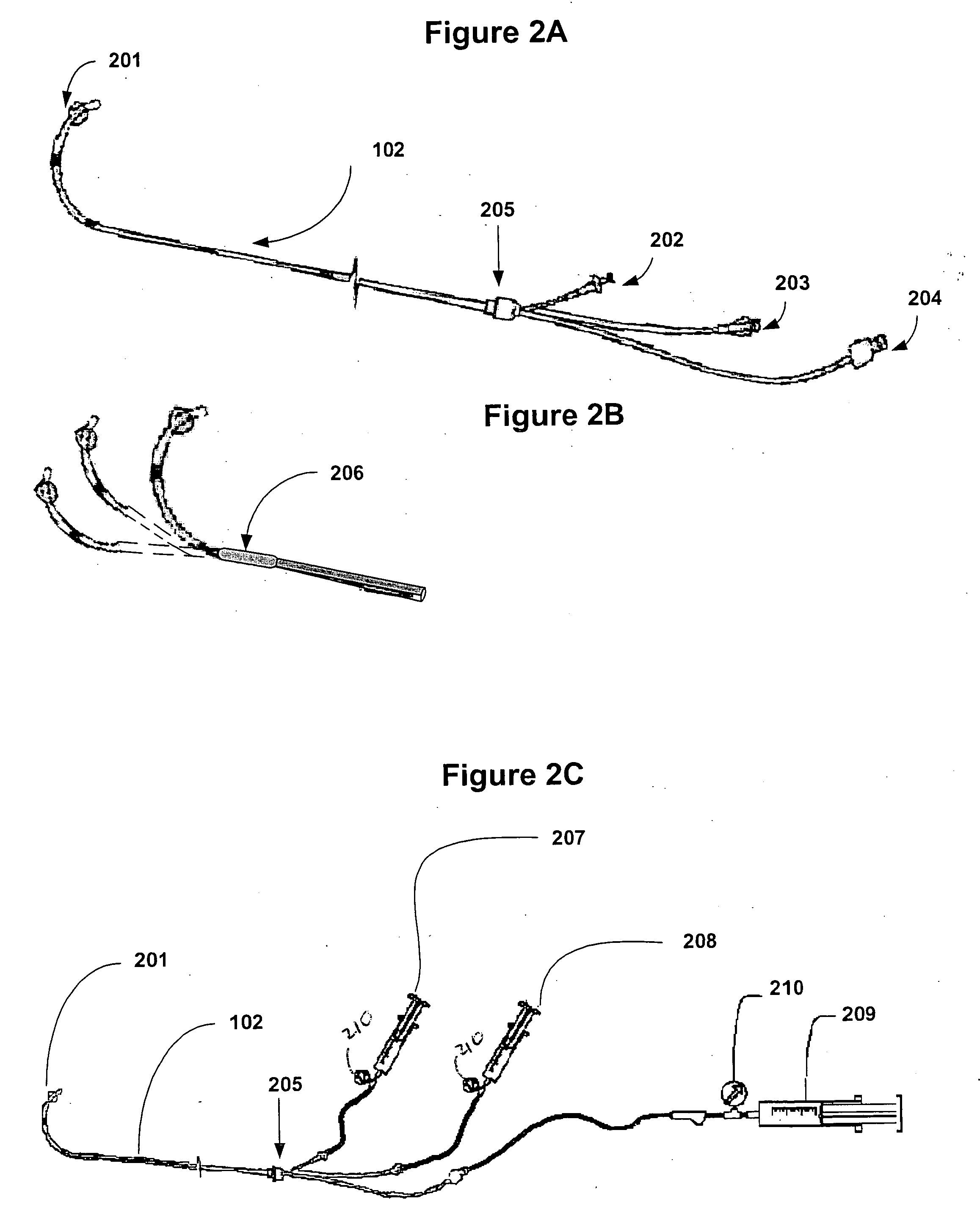
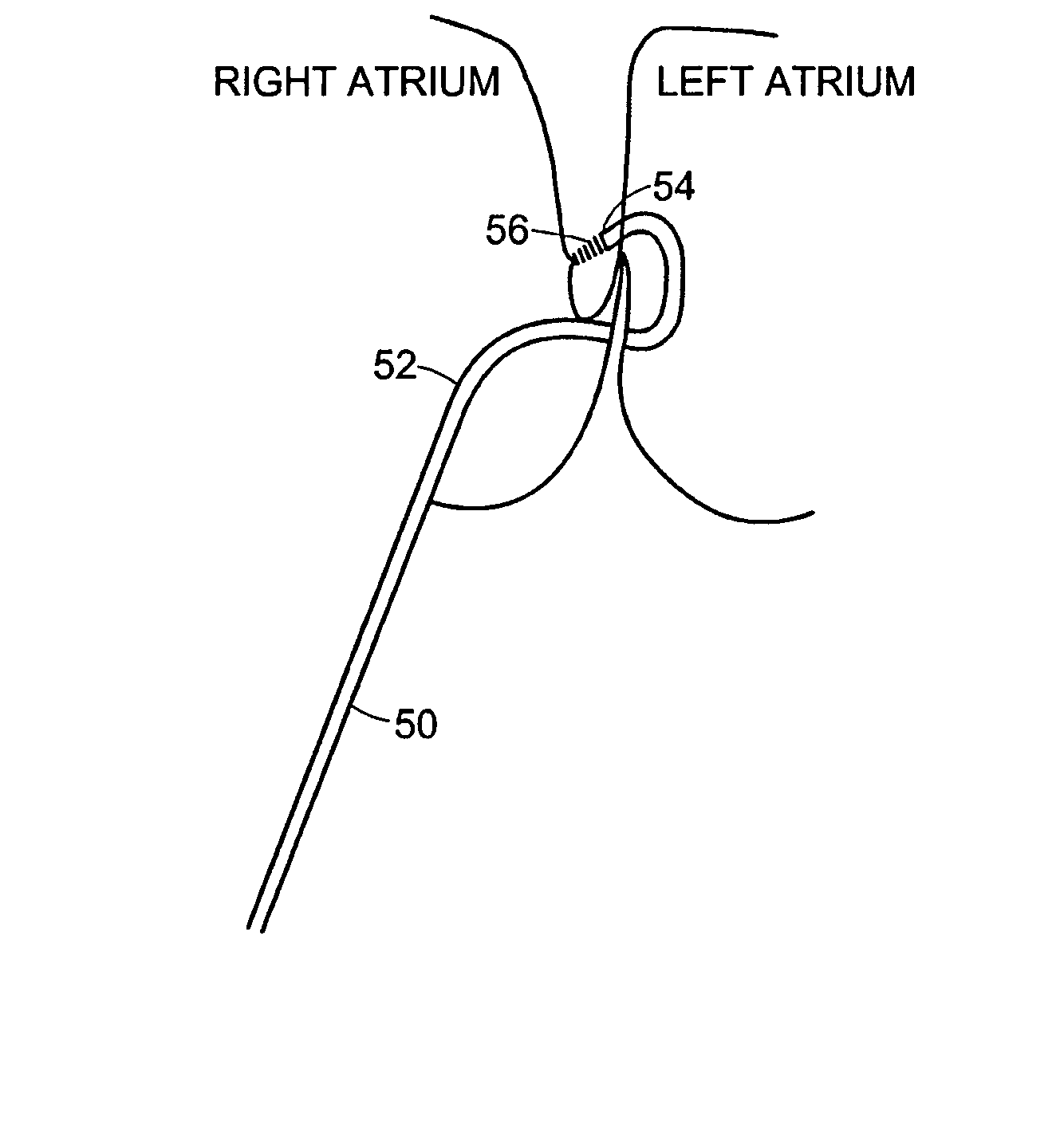
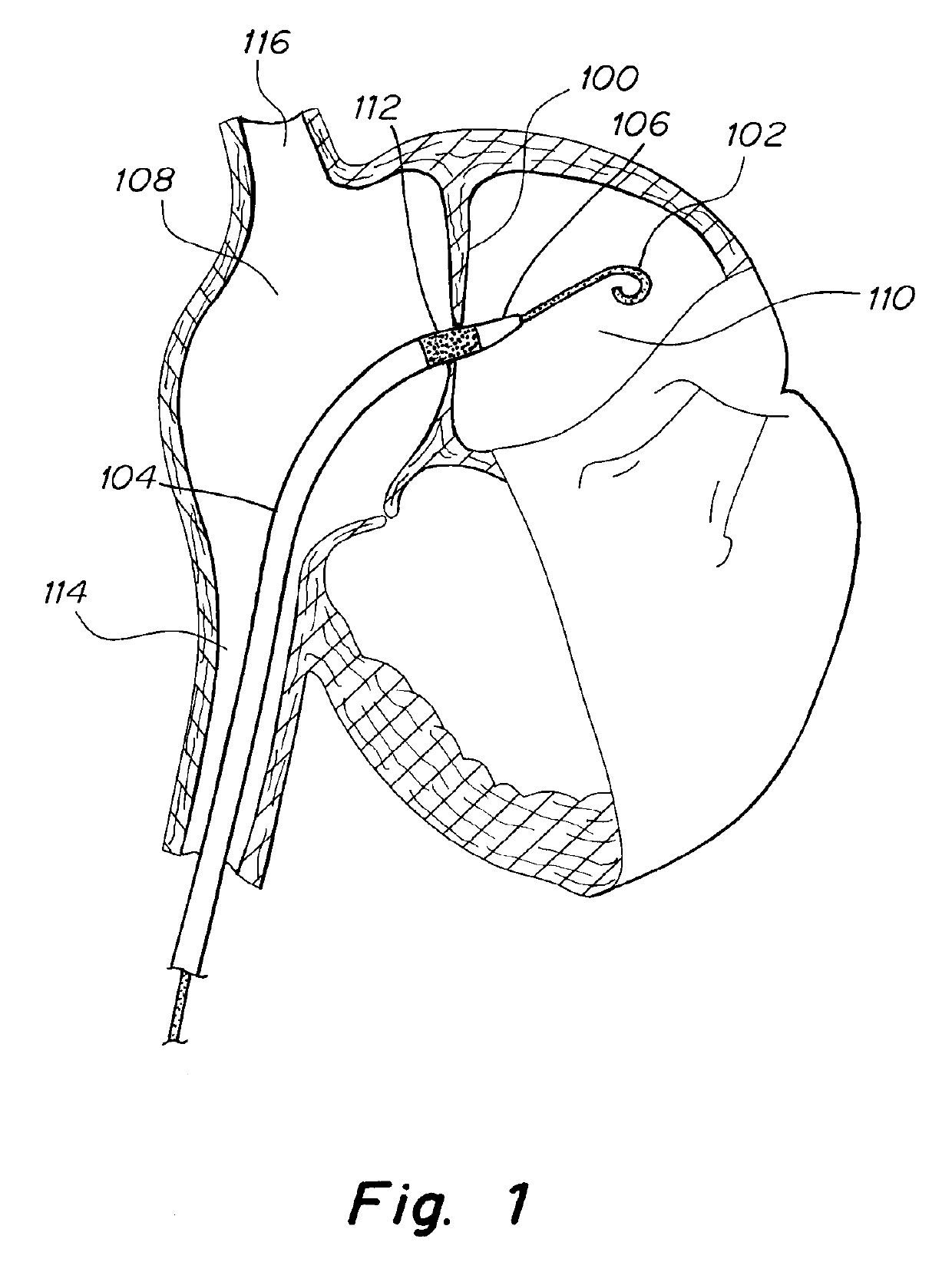
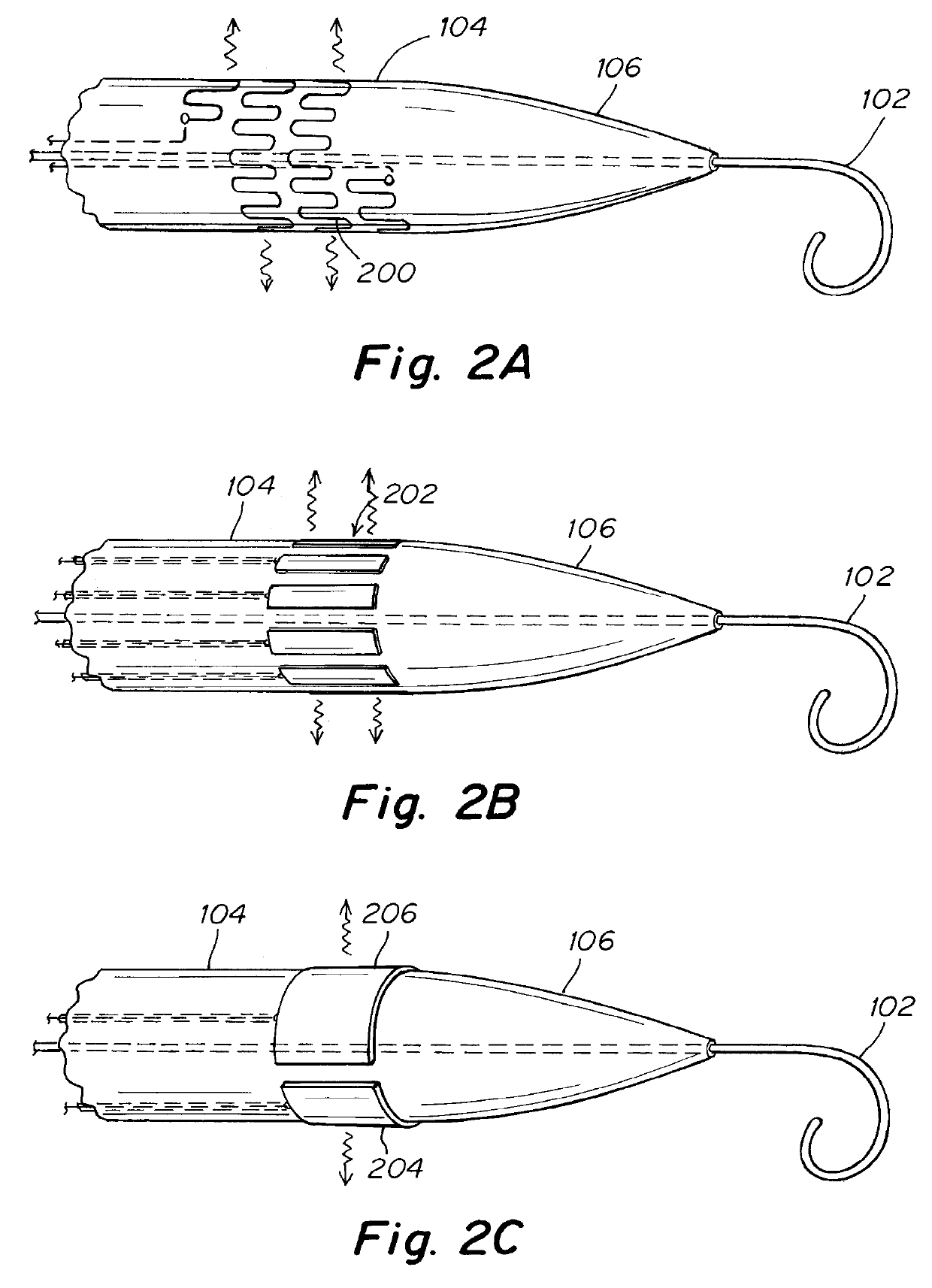
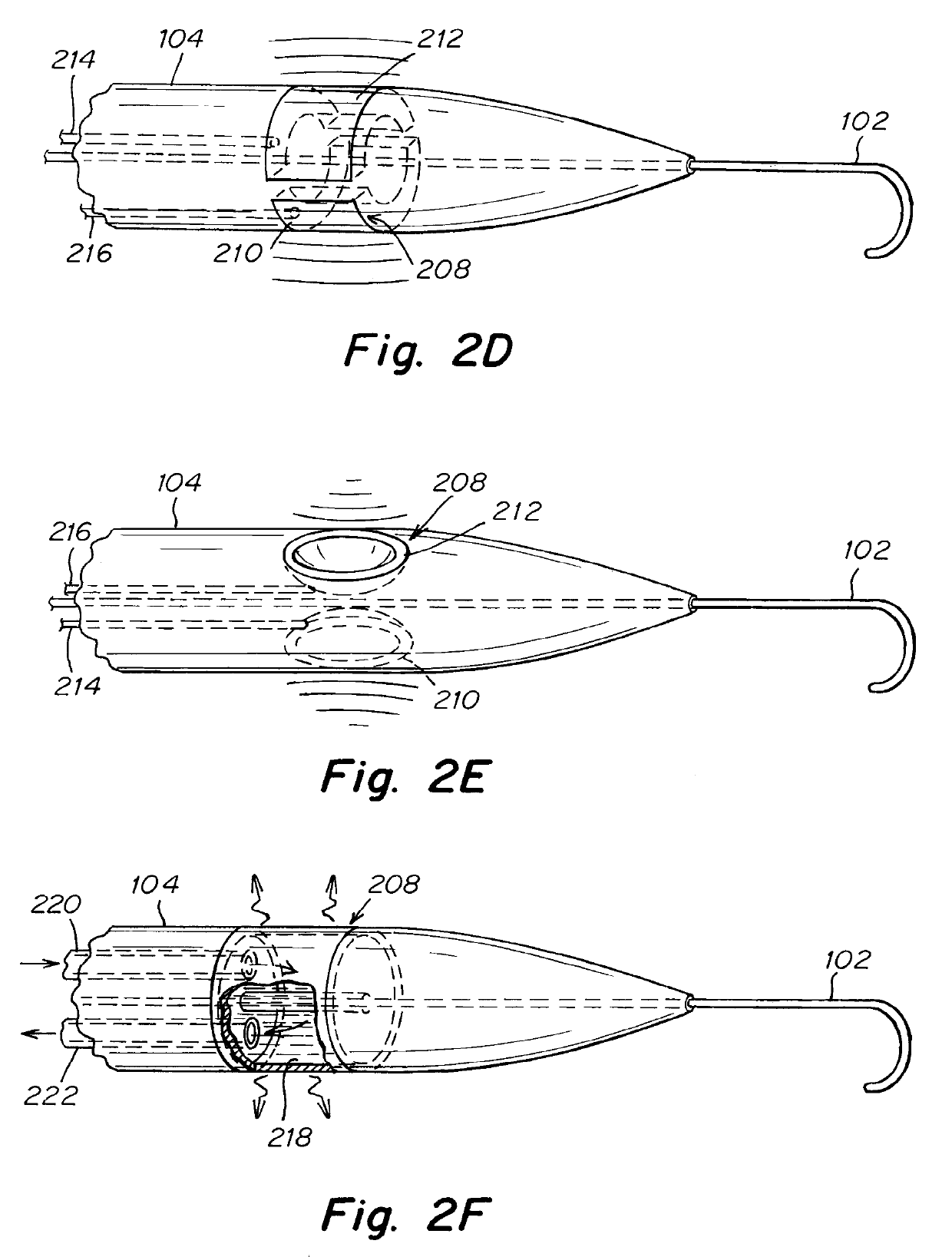
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure method and device
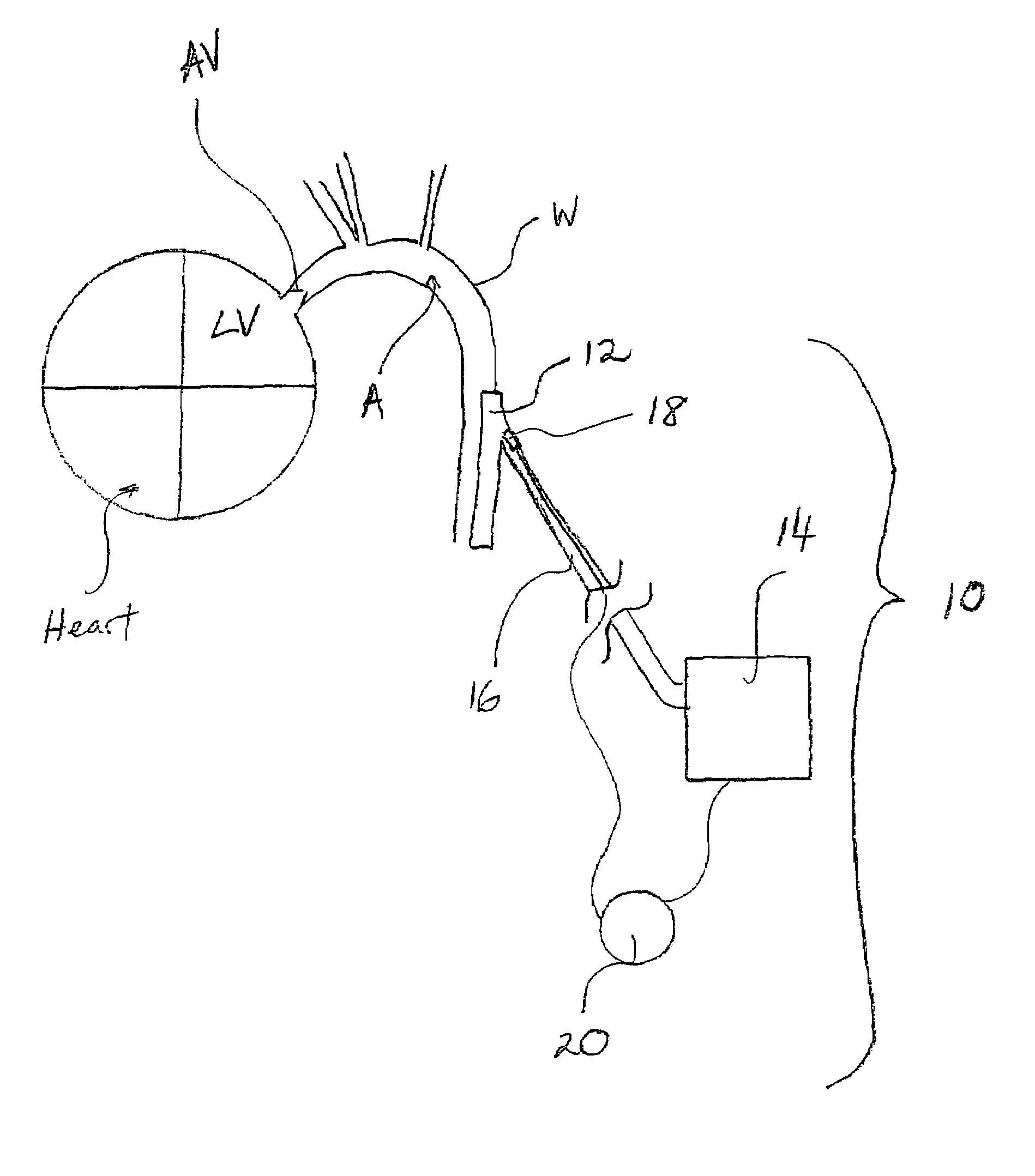
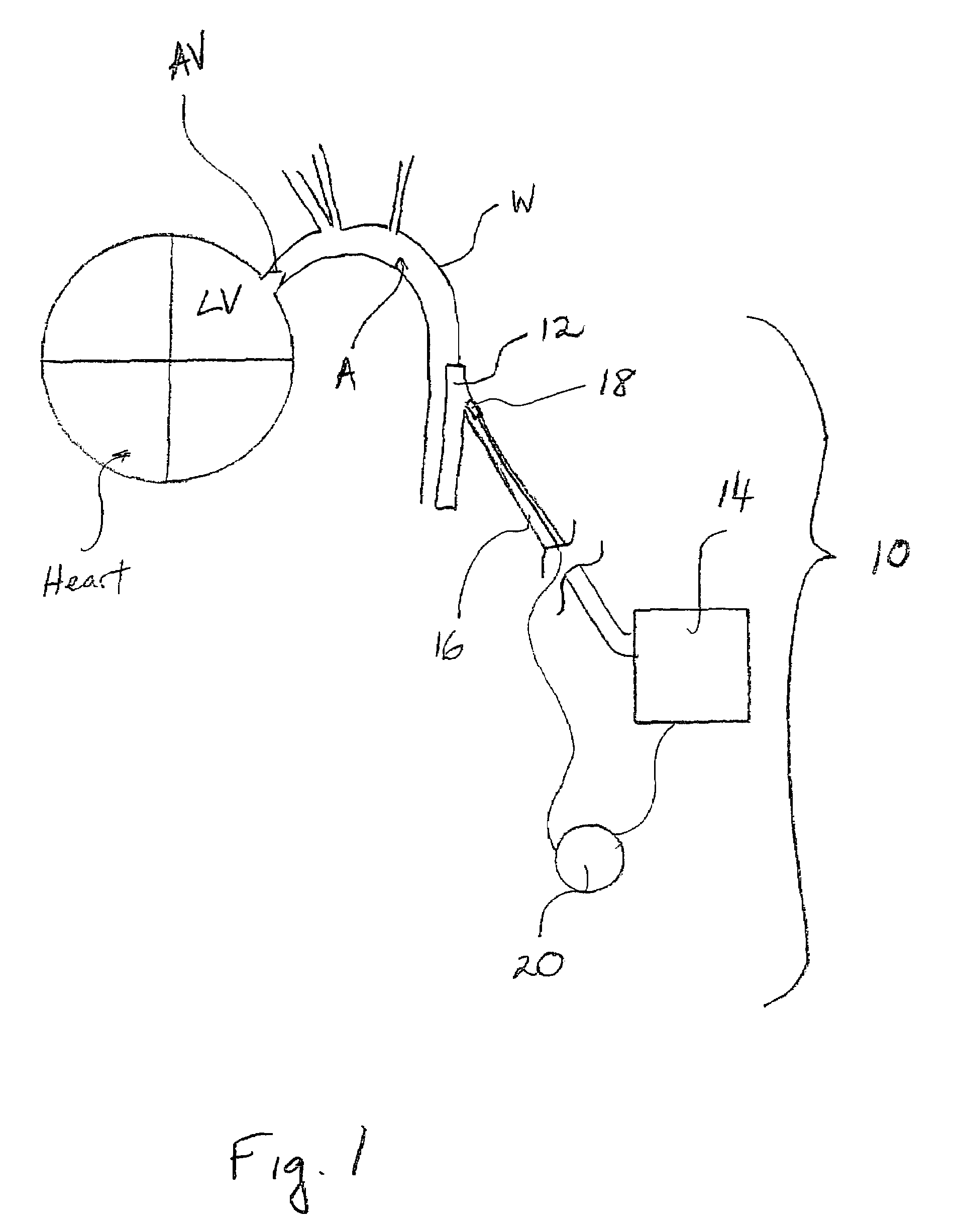
The present invention provides methods and devices for closing two overlapping layers of tissue in a mammalian heart, for example a patent foramen ovale (PFO). The closure devices may take a number of different forms and may be retrievable. In some embodiments, the closure devices may be delivered with a catheter capable of puncturing mammalian tissue.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC +1
Synchronization system between aortic valve and cardiac assist device
ActiveUS20060030747A1Achieve synchronizationControl devicesMedical devicesAccelerometerThoracic cavity
A cardiac assist device synchronization system includes a cardiac assist device and an acoustic or accelerometer sensor that provides a signal input to the cardiac assist device indicative of aortic valve closure. The cardiac assist device is coupled to a mammalian aorta and includes an inflatable chamber and a fluid pump. A fluid conduit is in communication between the chamber and the pump to provide for selective inflation of the chamber. A pump controller triggers the pump in counter-pulsation to a mammalian heart upstream from the aorta. A process for synchronizing a cardiac assist device in counter-pulsation with a left ventricle includes locating an acoustic or accelerometer sensor within a thoracic cavity of a mammal having the assist device coupled to the aorta of the mammal. Through the measurement of an acoustic or acceleration property of an aortic valve of the mammal, and the transmission of aortic valve closure measurement through a controller for the cardiac assist device, counter-pulsatile synchronization for the cardiac assist device is achieved.
Owner:KANTROWITZ ALLEN B +1
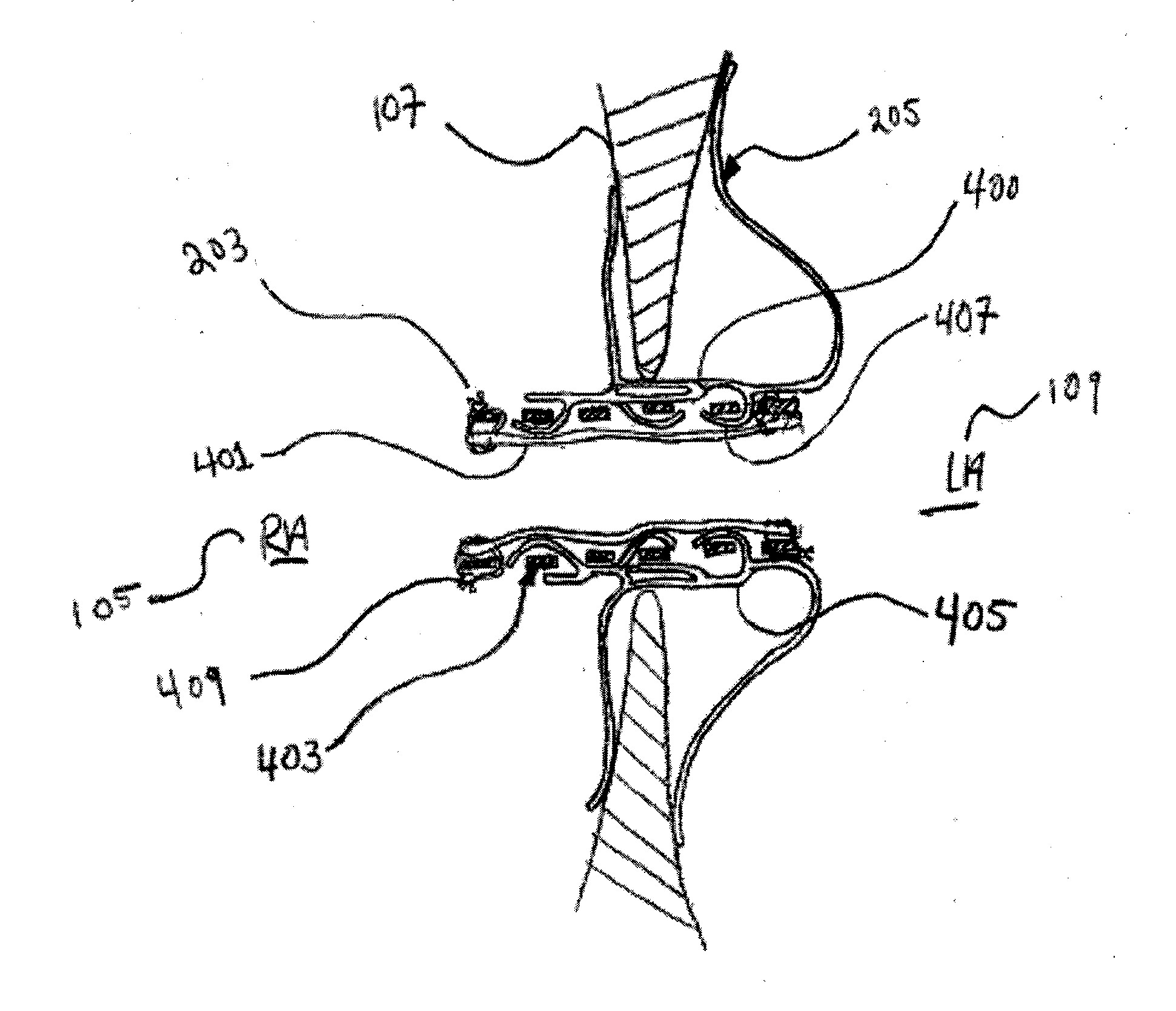
Methods and devices for intra-atrial shunts having adjustable sizes
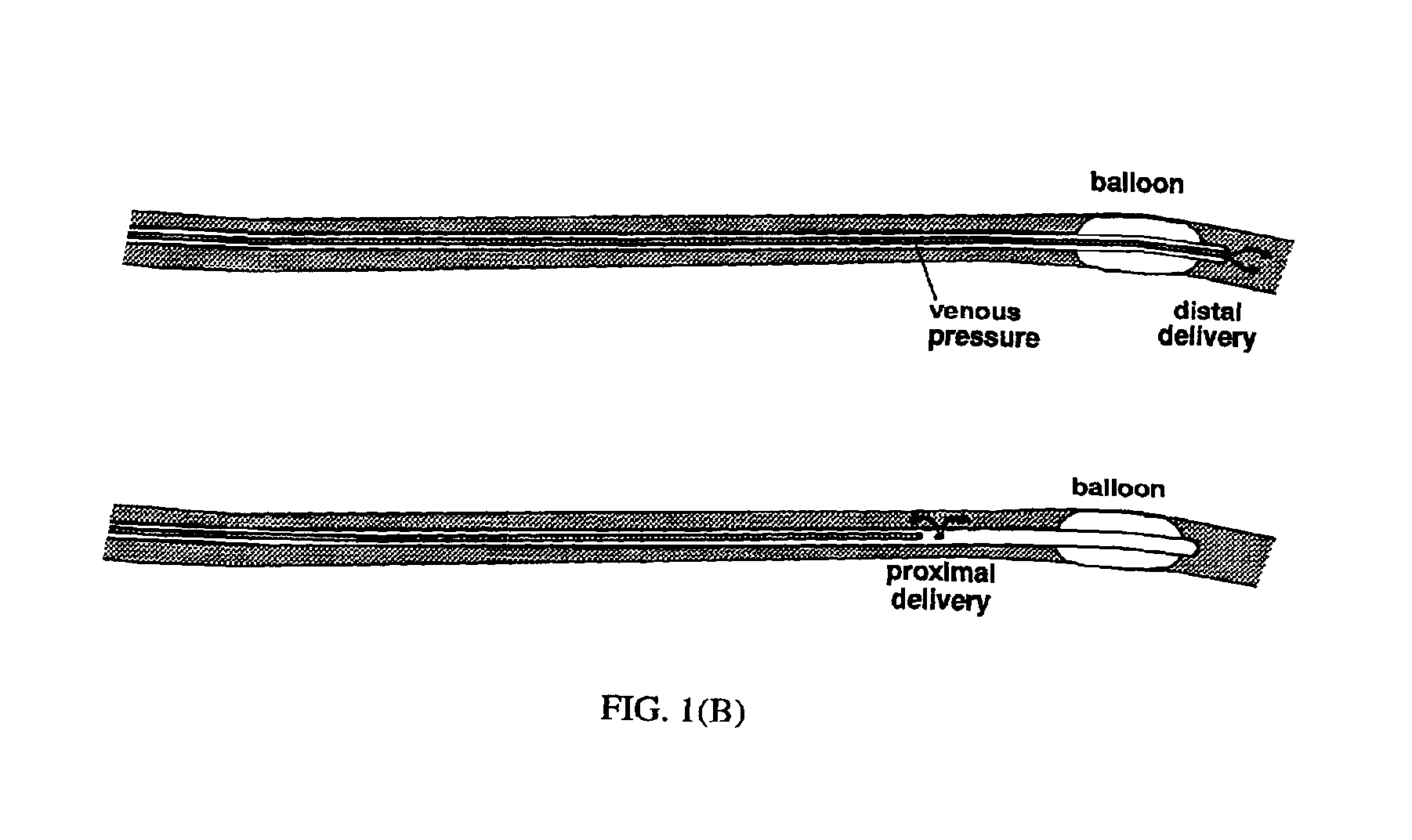
InactiveUS20130178784A1Reduce venous pressureReduce riskHeart valvesSurgeryFlow diverterHeart disease
Devices and methods for treating heart disease by normalizing elevated blood pressure in the left and right atria of a heart of a mammal are disclosed. Devices may include an adjustable hydraulic diameter shunt portion which can be manually adjusted in vivo. Methods are provided for adjusting the flow rate of the devices in vivo.
Owner:DC DEVICES
Methods and devices for intra-atrial shunts having adjustable sizes
Devices and methods for treating heart disease by normalizing elevated blood pressure in the left and right atria of a heart of a mammal are disclosed. Devices may include an adjustable hydraulic diameter shunt portion which can be manually adjusted in vivo. Methods are provided for adjusting the flow rate of the devices in vivo.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Methods and devices for intra-atrial shunts having selectable flow rates
Devices and methods for treating heart disease by normalizing elevated blood pressure in the left and right atria of a heart of a mammal are disclosed. The devices are adapted to permit fluid flow across the membrane in which the device is implanted at first rate, and at a second rate, wherein a difference between the first rate and the second rate is not solely dependent upon variations in blood pressure differential across the membrane due to the heart's pumping cycle.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Methods, systems, and devices for resizable intra-atrial shunts
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Simulation apparatus
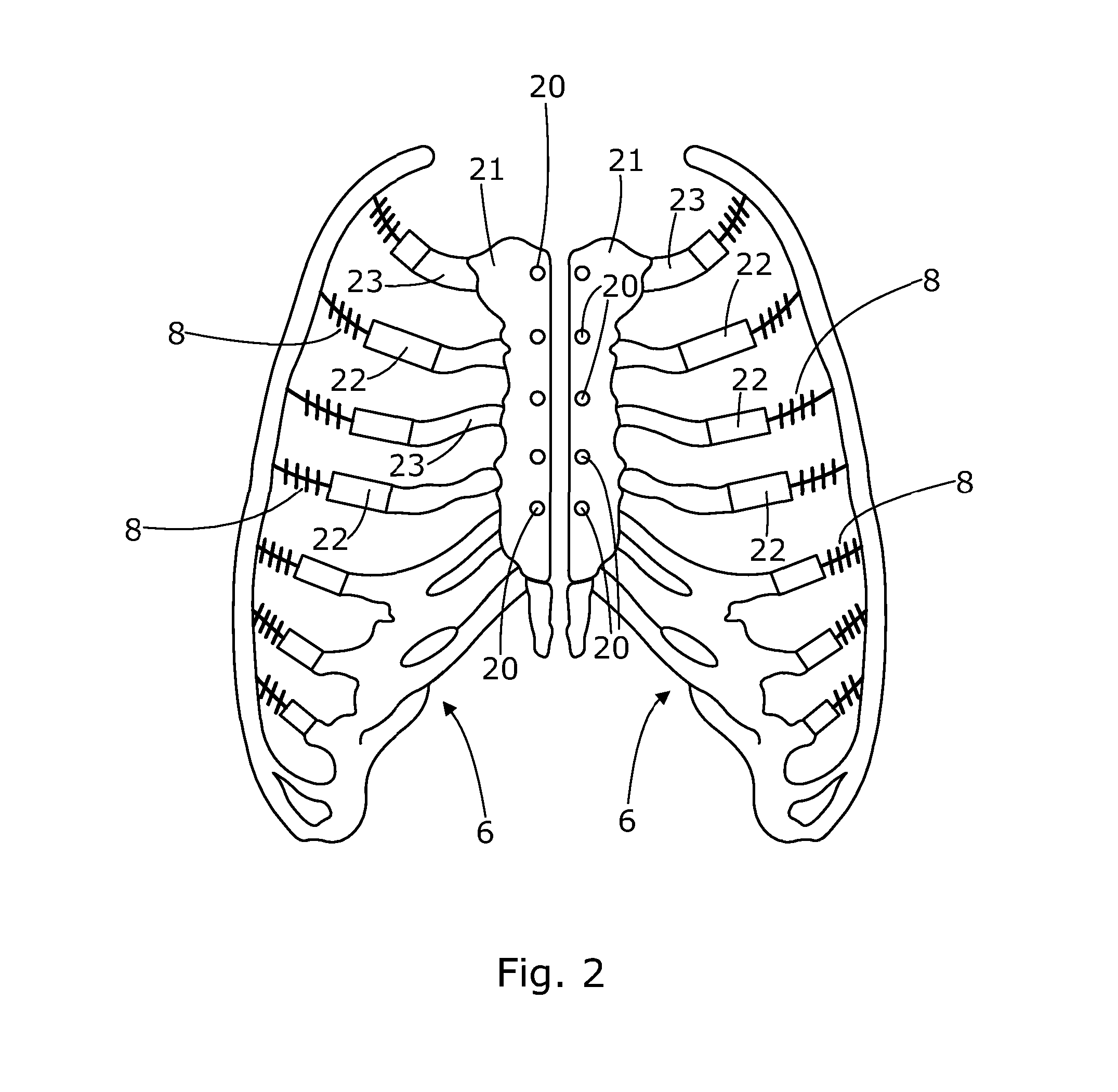
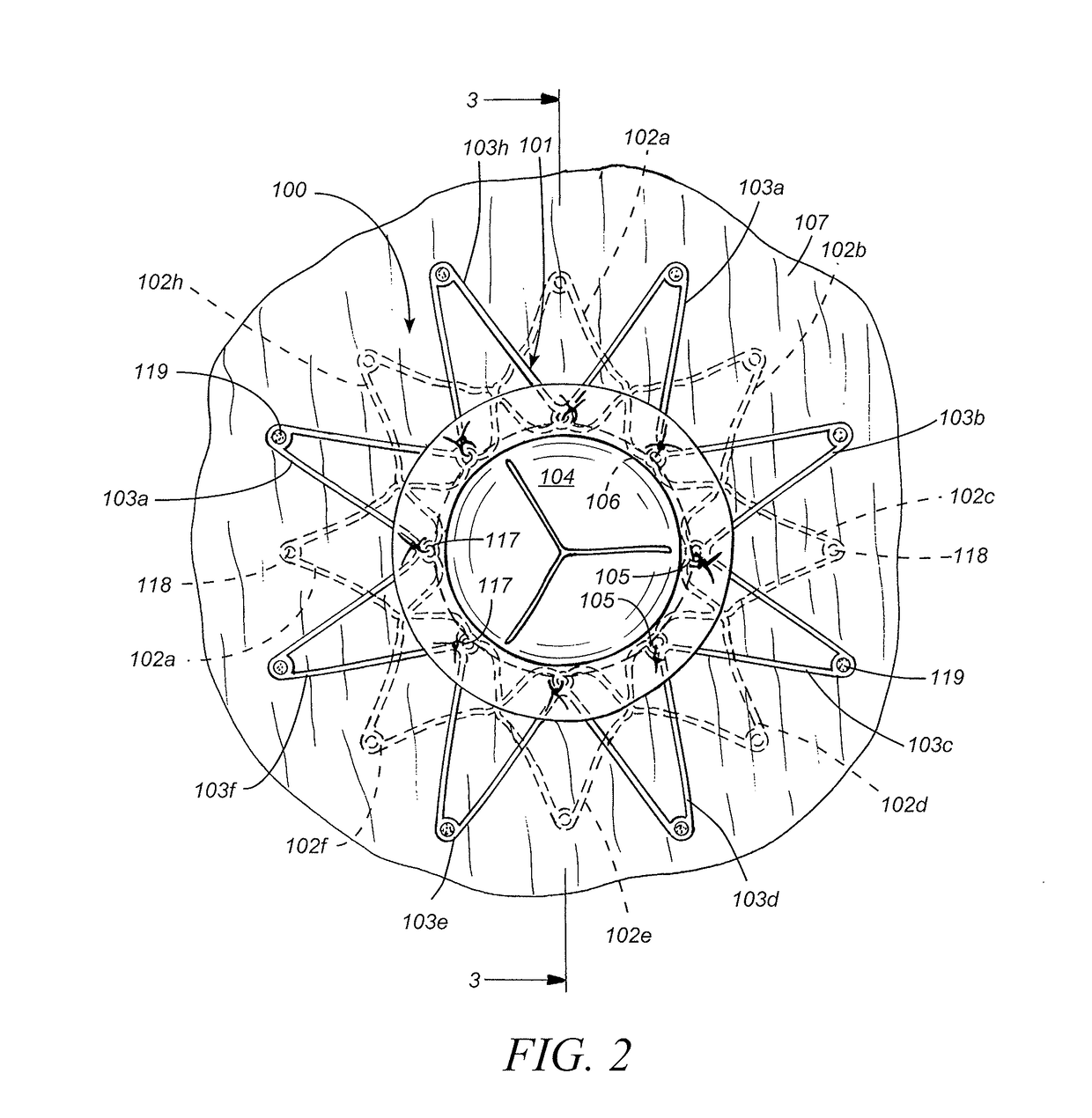
A medical simulation model is provided for use in medical training, and having a wall defining a chamber, and having a slit in the wall providing access to the interior of the chamber. A pair of rib-cage members is located within the chamber such that adjacent edges of each member are spaced apart from each other. Resilient biasing elements are connected to each rib-cage member and configured such that adjacent edges of the rib-cage members may be brought into contact with each other, or further spaced-apart, against the action of the resilient biasing elements. A conduit is provided to enable fluid to be introduced into the chamber, and a facsimile of a mammalian heart is located within the chamber.
Owner:GUYS & ST THOMAS NHS FOUND TRUST
Synchronization system between aortic valve and cardiac assist device
ActiveUS7513864B2Achieve synchronizationControl devicesMedical devicesThoracic structureAccelerometer
A cardiac assist device synchronization system includes a cardiac assist device and an acoustic or accelerometer sensor that provides a signal input to the cardiac assist device indicative of aortic valve closure. The cardiac assist device is coupled to a mammalian aorta and includes an inflatable chamber and a fluid pump. A fluid conduit is in communication between the chamber and the pump to provide for selective inflation of the chamber. A pump controller triggers the pump in counter-pulsation to a mammalian heart upstream from the aorta. A process for synchronizing a cardiac assist device in counter-pulsation with a left ventricle includes locating an acoustic or accelerometer sensor within a thoracic cavity of a mammal having the assist device coupled to the aorta of the mammal. Through the measurement of an acoustic or acceleration property of an aortic valve of the mammal, and the transmission of aortic valve closure measurement through a controller for the cardiac assist device, counter-pulsatile synchronization for the cardiac assist device is achieved.
Owner:KANTROWITZ ALLEN B +1
Process for delivering nucleic acids to cardiac tissue
InactiveUS6867196B1High level of expressionHigh pressureBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsRNATissue cell
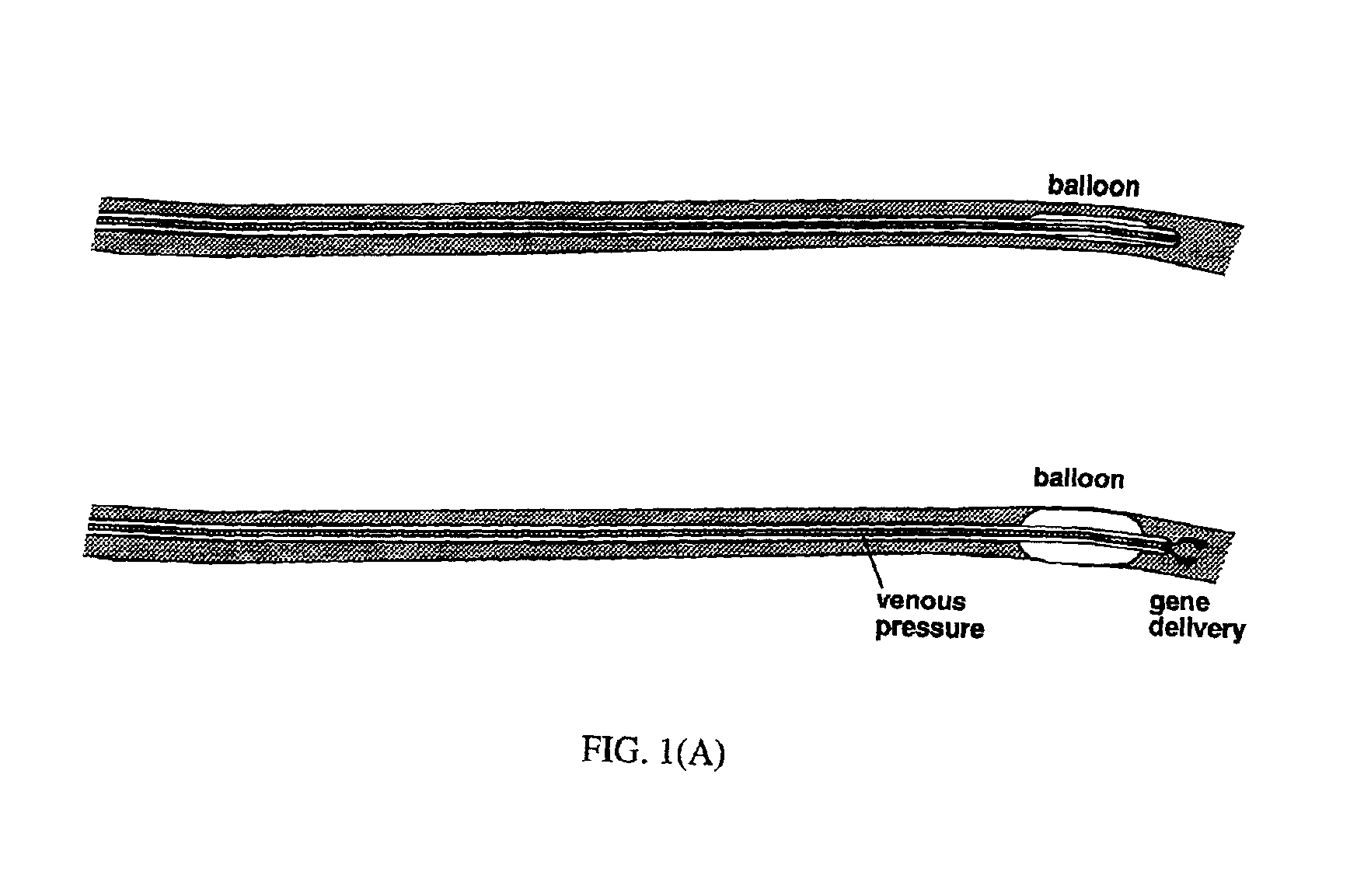
A process for delivering a nucleic acid to a cardiac tissue cell in a mammal is described, comprising introducing a composition consisting of a nucleic acid to a blood vessel, which subsequently delivers the nucleic acid to the cardiac tissue cell. The nucleic acid can be DNA or RNA or plasmid DNA or viral. This process is for purposes of gene therapy, and research.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Methods and devices for intra-atrial shunts having adjustable sizes
Devices and methods for treating heart disease by normalizing elevated blood pressure in the left and right atria of a heart of a mammal are disclosed. Devices may include an adjustable hydraulic diameter shunt portion which can be manually adjusted in vivo. Methods are provided for adjusting the flow rate of the devices in vivo.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Use of human stem cells and/or factors they produce to promote adult mammalian cardiac repair through cardiomyocyte cell division
A method for treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac disorder, in vivo, comprising (i) producing a solution comprising media conditioned from the culture of cells, in vitro, and (ii) administering the solution of step (i) to the subject, thereby treating the cardiac disorder in the subject. Methods for determining whether an agent stimulates or inhibits myocyte proliferation.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
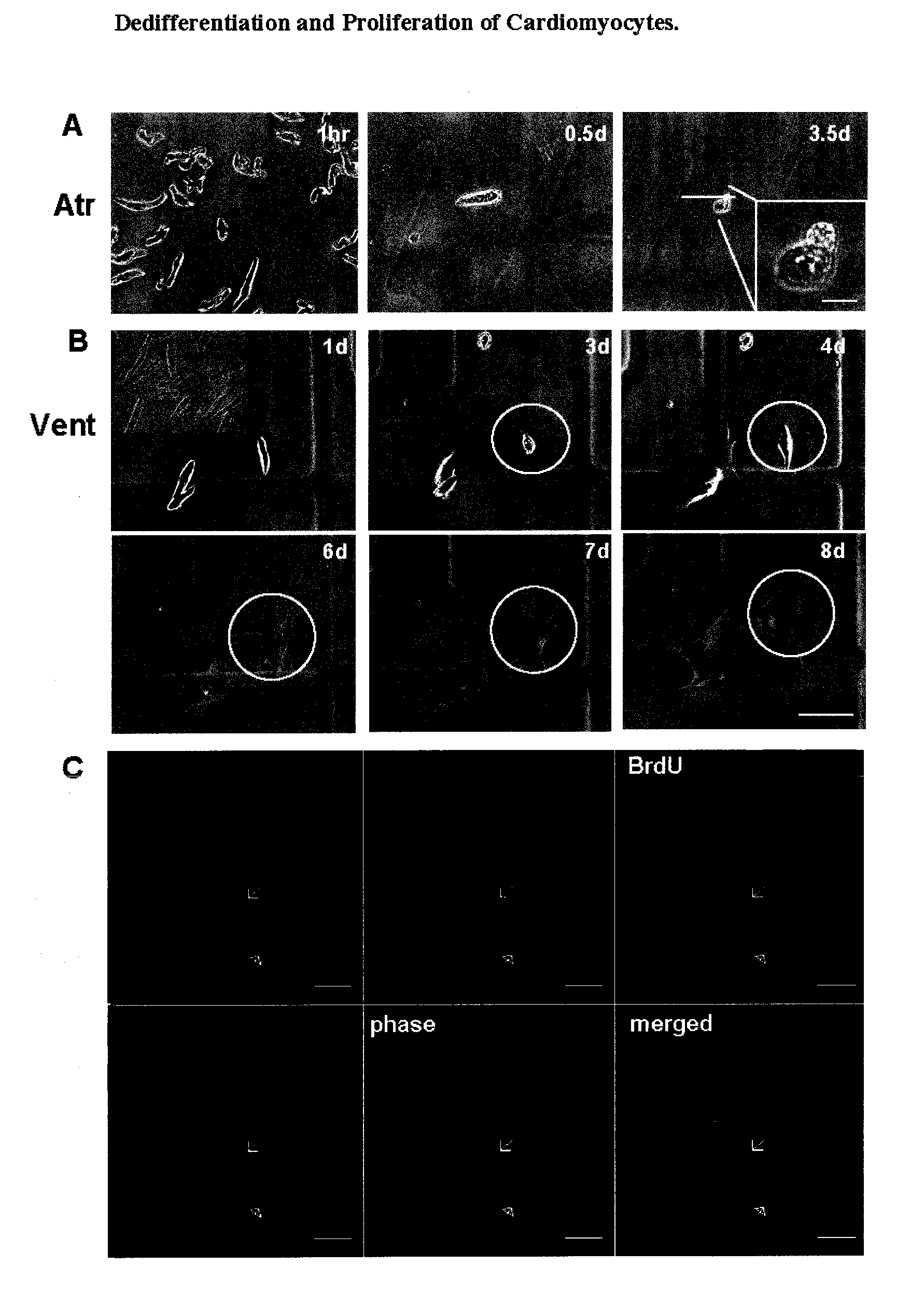
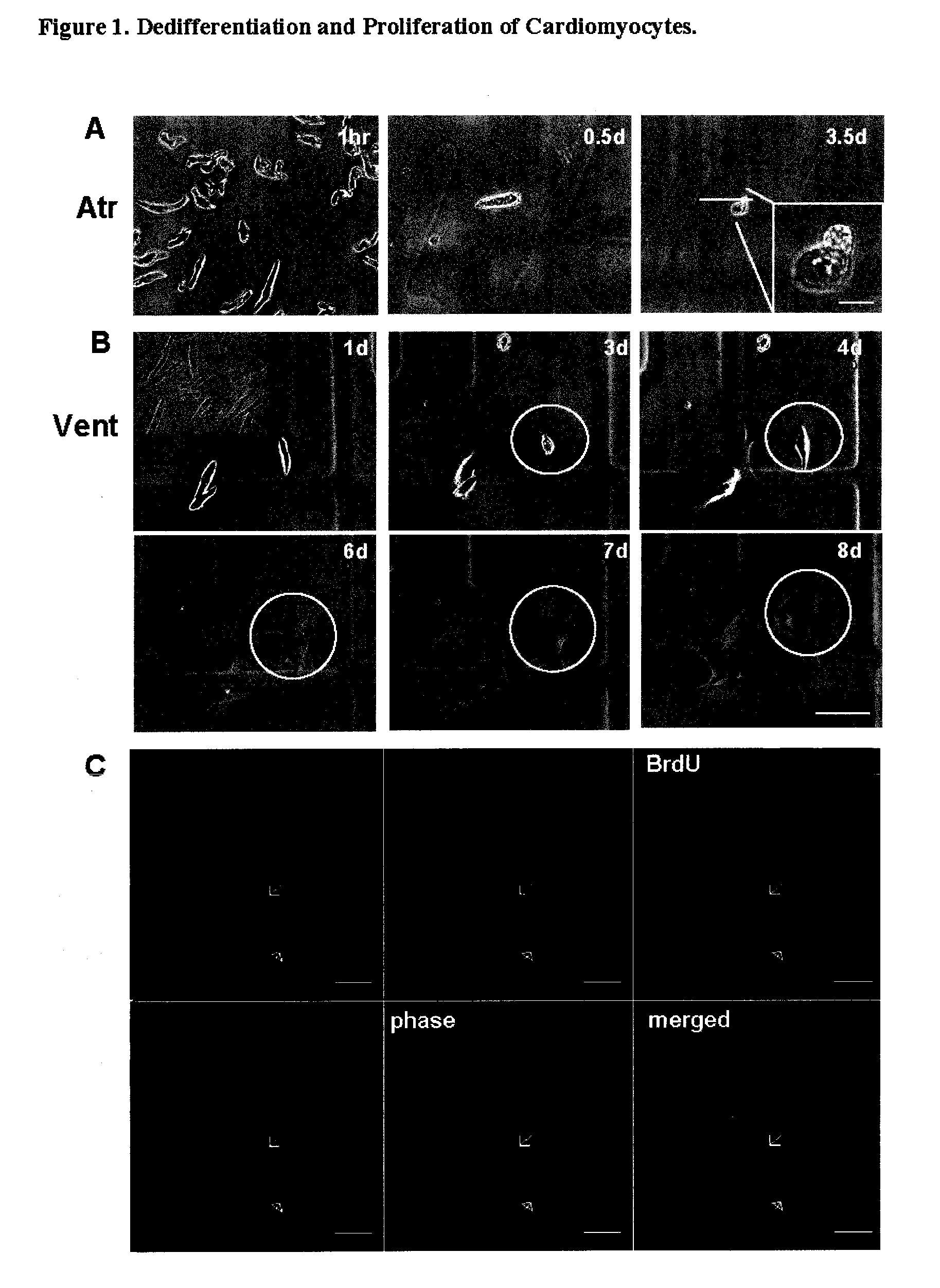
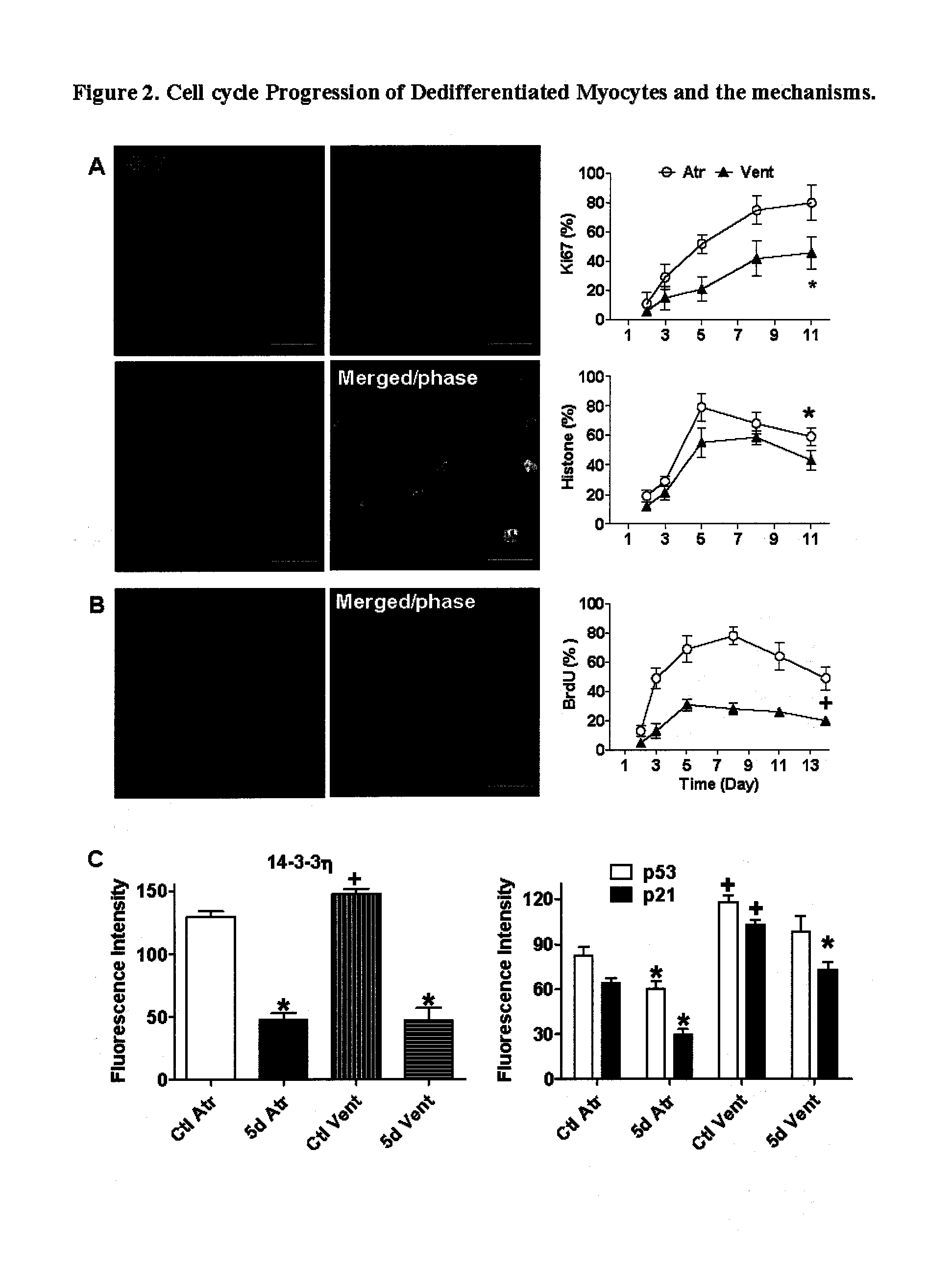
Dedifferentiation of adult mammalian cardiomyocytes into cardiac stem cells
InactiveUS20100093089A1Raise the ratioUnknown materialsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSurface markerMammal
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
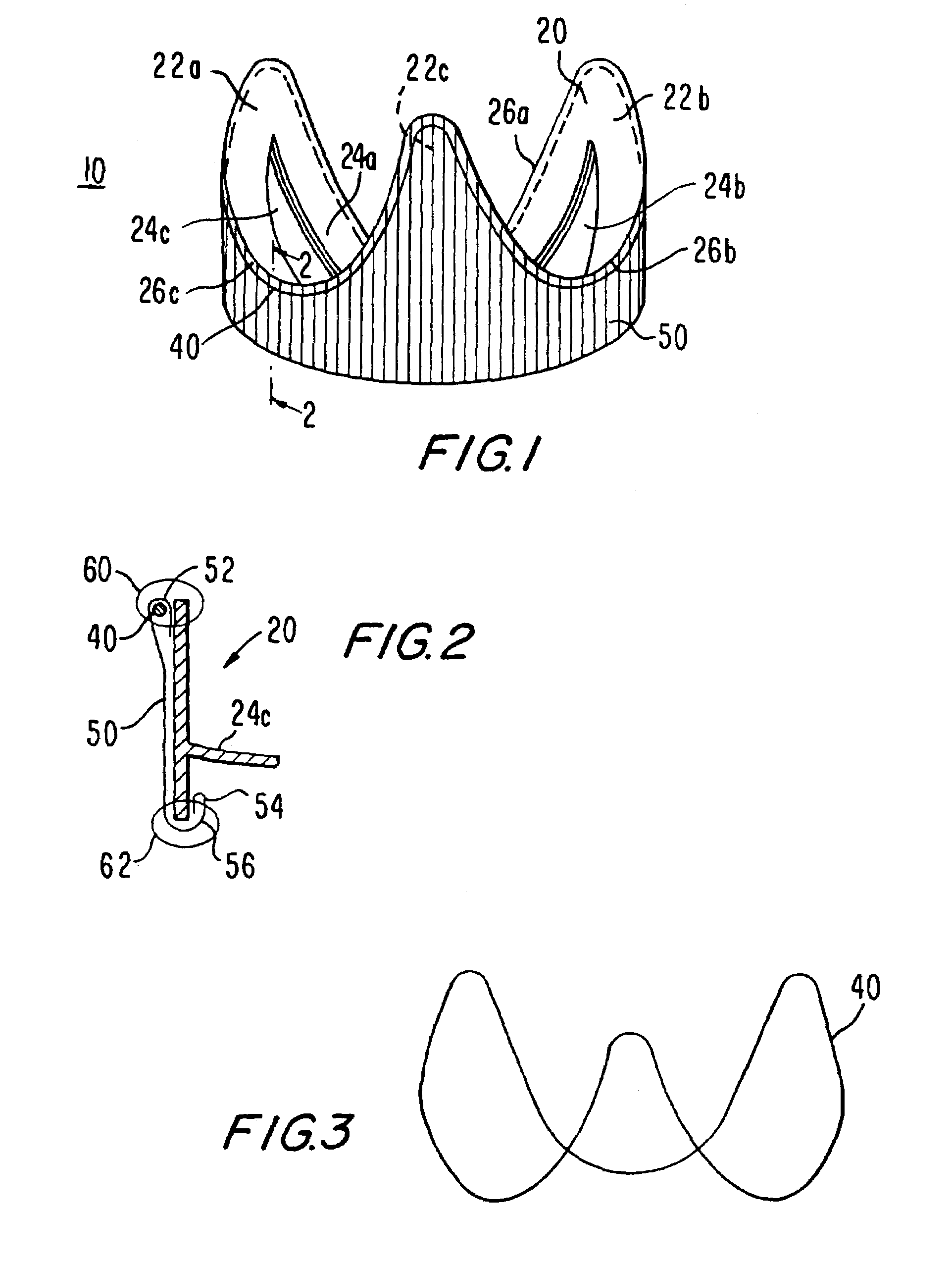
Heart valve structures
A replacement heart valve structure including a structure of tissue which is an intact, mammalian heart valve that has been harvested and treated to preserve it. A conventional fabric sleeve is typically disposed concentrically around the outside of the tissue structure. A support structure is included to facilitate implanting the heart valve by somewhat increasing the stability of the heart valve structure, but without unduly rigidifying it. An annular sewing cuff may be added adjacent the blood inflow end of the valve structure to facilitate making the annular suture line that is required at that end.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LLC
Prevention of fibrosis following cardiac injury
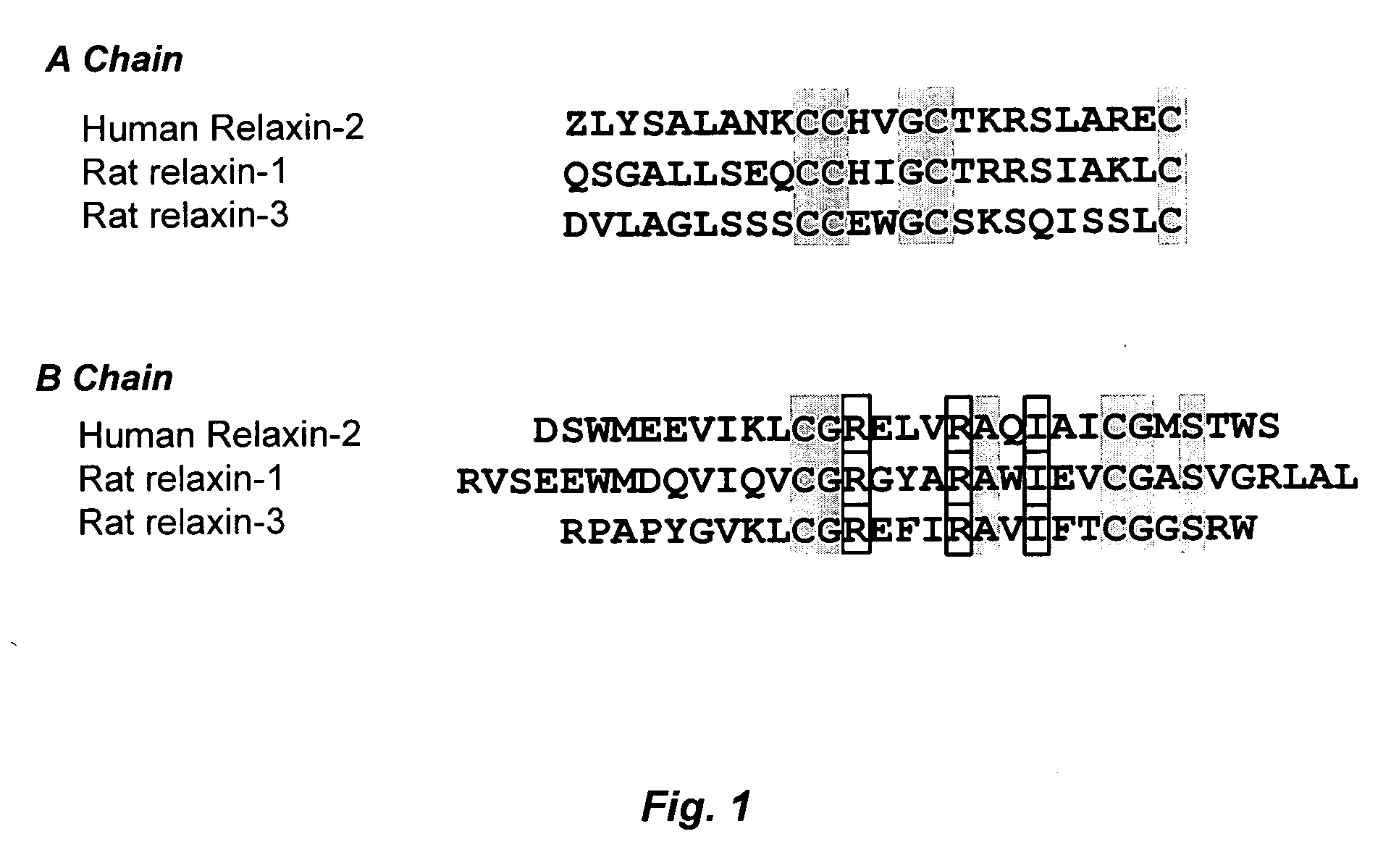
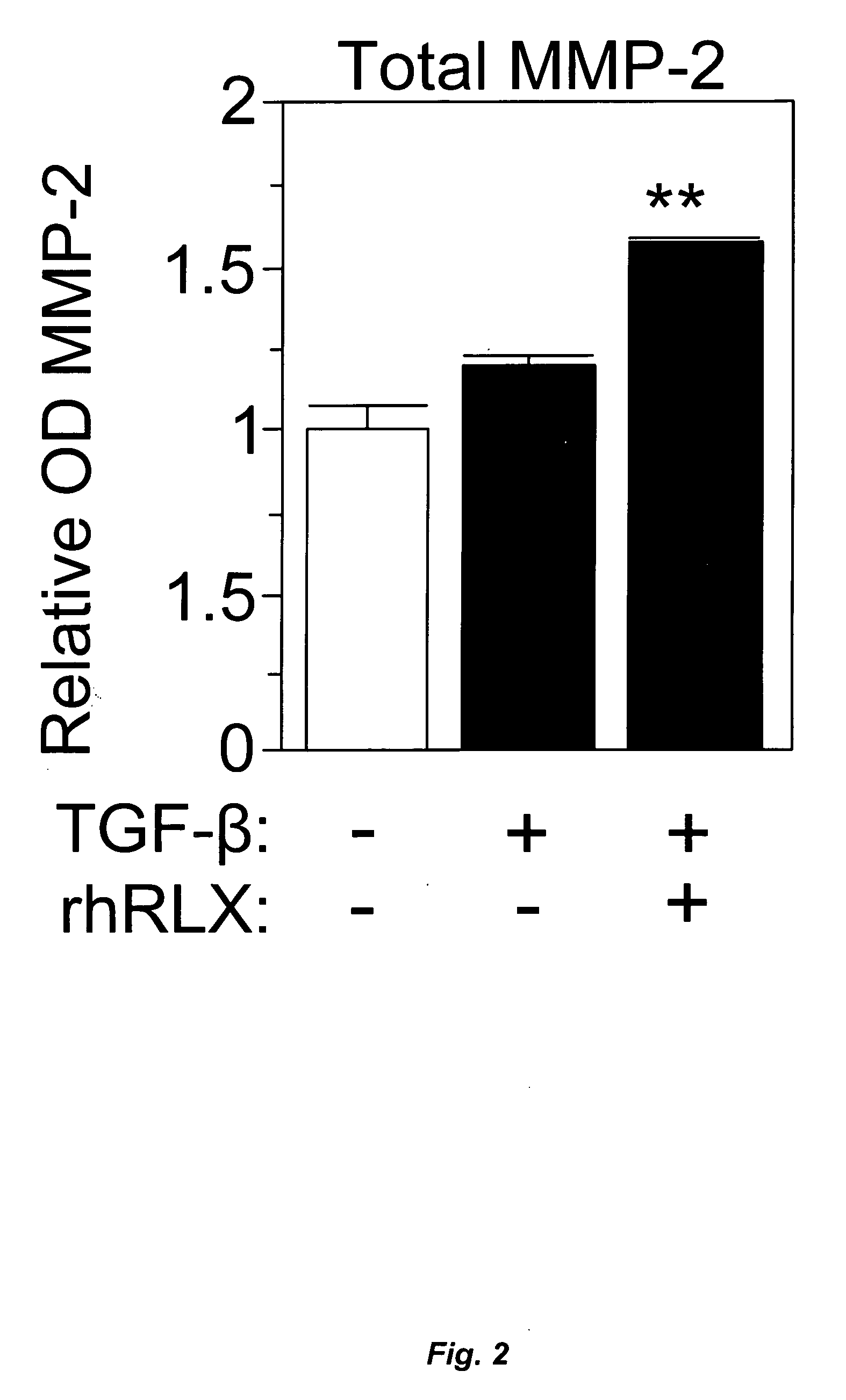
InactiveUS20060264367A1Reduce fibrosisReduce activationHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac fibrosisRelaxin
A method for treating cardiac fibrosis resulting from injury of a mammalian heart is described comprising the step of contacting a therapeutically effective amount of relaxin and / or an LGR7 activating agent with cardiac cells following the injury in an amount sufficient to reduce the fibrosis. Also described are methods for protecting the heart following an ischemic event, inhibiting the proliferation of activated fibroblasts and antagonising collagen secretion or deposition in a mammalian heart.
Owner:BAKER MEDICAL RES INST +1
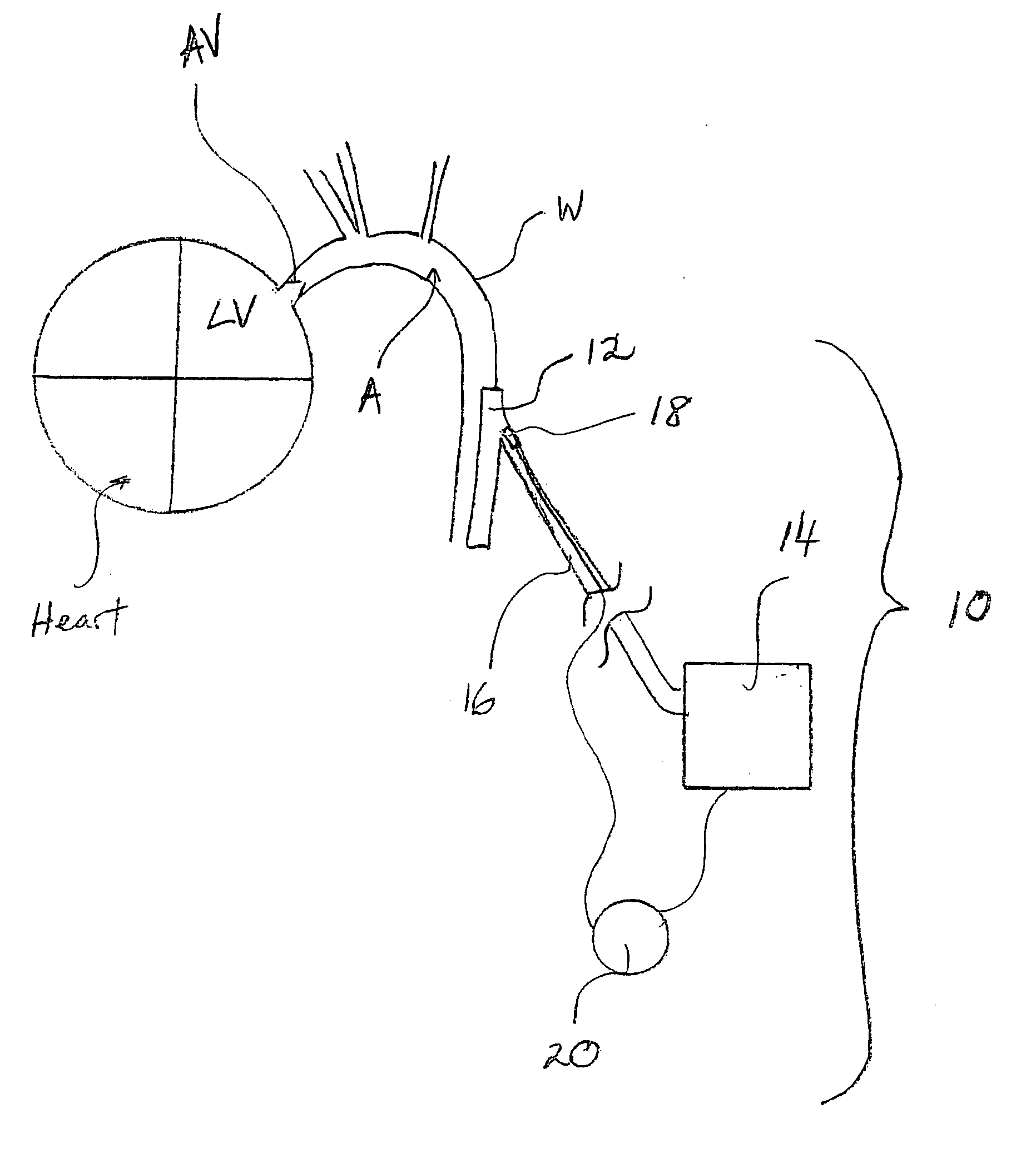
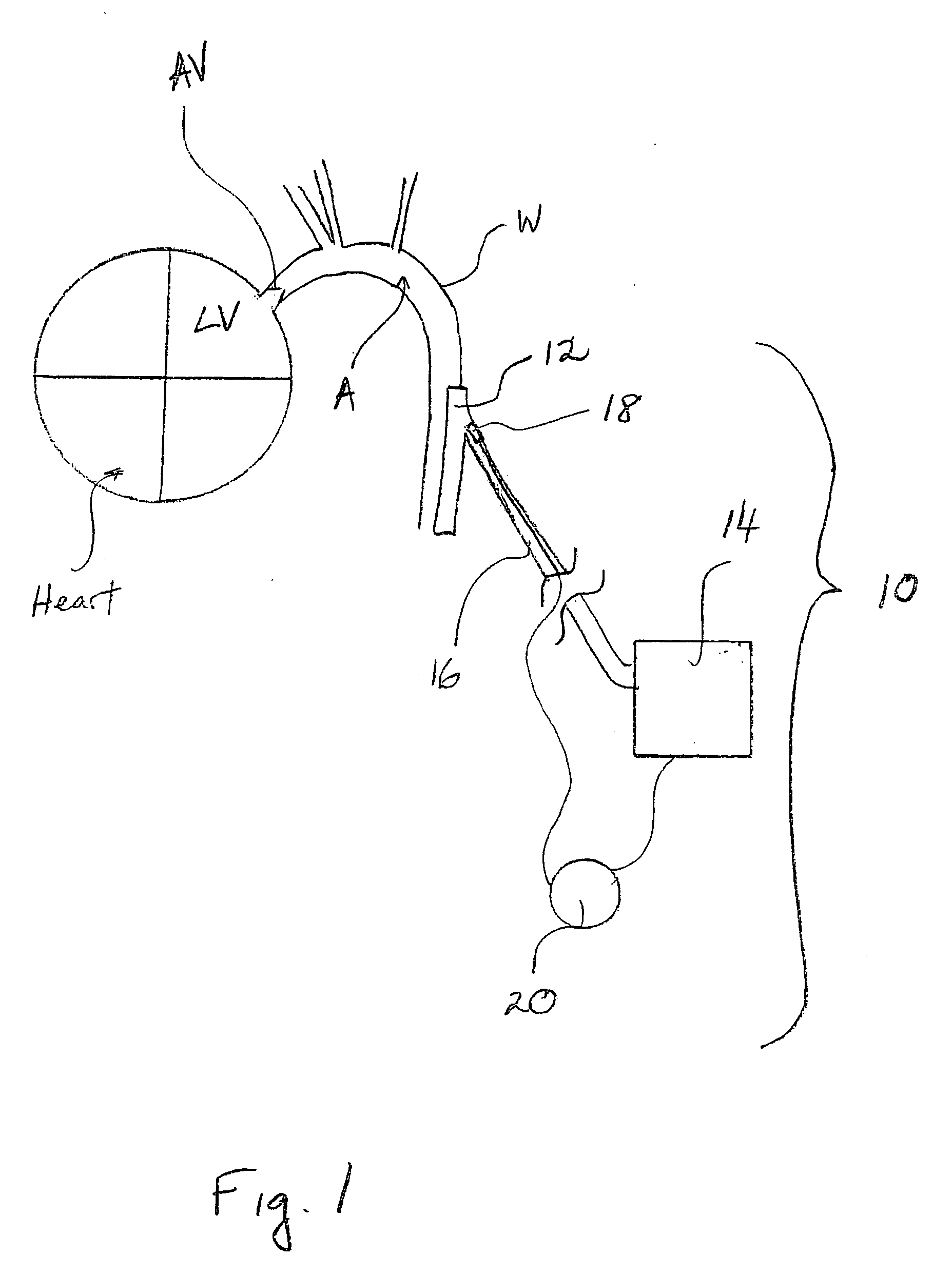
Guidewire system and method of pump installation using same
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method of positioning in a mammalian heart of a patient a blood pump including an inflow cannula, a pump housing and an outflow cannula, the method including forming an incision in a low-pressure location on the heart wall; passing the outflow cannula of the blood pump through the incision and into a left ventricle of a heart; positioning a tip of a guidewire into an aorta, distal to an aortic valve; advancing the tip through the aortic valve and into the left ventricle; connecting the tip to the outflow cannula; pulling the blood pump with the guidewire to advance at least a portion of the outflow cannula through the aortic valve and into the aorta; securing the blood pump to the heart, the aorta, or both; disconnecting the tip from the blood pump; and removing the guidewire from the patient.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Pouch-Like Construct for Preventing Heart Distension
The invention is directed to a pouch-like construct comprising mammalian tissue which can be used for preventing distension and / or resisting dilation of the heart in a mammal. Preferably, the pouch-like tissue construct has contractile properties. The invention further relates to a method for the preparation of a pouch-like construct comprising mammalian tissue which can be used for the above purposes.
Owner:TISSUE SYST HLDG
Biodegradable pericardia constraint system and method
A system has been developed for injecting a biodegradable pericardial constraint including: a biodegradable viscoelastic substance (BES); an external injection container for the BES; a cannula having a distal section adapted to be inserted into a pericardial sac of a mammalian heart and a proximal section connectable to the external injection container; wherein BES from the injection container is injected into the pericardial sac through the cannula.
Owner:G&L CONSULTING
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure method and device
The present invention provides methods and devices for closing two overlapping layers of tissue in a mammalian heart, for example a patent foramen ovale (PFO). The closure devices may take a number of different forms and may be retrievable. In some embodiments, a device is sized and shaped to extend from septum secundum, into the left atrium, through septum primum, and into the right atrium, such that the first and second ends cooperate to provide a compressive force to the overlapping layers of tissue. In some embodiments, the closure devices may be delivered with a catheter capable of puncturing mammalian tissue.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Apparatus and methods to create and maintain an intra-atrial pressure relief opening
ActiveUS20190269392A1Reduce pressureReduces atrial pressure pressureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesAtrial cavityAtrial Pressure
The present disclosure relates to a method and a device for treating heart failure by normalizing elevated blood pressure in the left and right atria of a heart of a mammal. The present disclosure includes methods for creating and maintaining an opening in the atrial septum. Tools for making an opening and enlarging the opening are also disclosed. Use of the techniques and tools described herein prolongs the patency of an intra-atrial pressure relief opening.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Nucleic acids, polypeptides, and methods for modulating apoptosis
The present invention provides methods of identifying an incidence of ischemia in mammalian tissue, particularly mammalian heart tissue. Further, a method of reducing apoptosis in mammalian tissue, preferably heat tissue, is provided. These methods involve measuring and comparing the gene expression levels of both apoptosis-specific eIF-5A and proliferating eIF-5A and correlating an incidence of ischemia when the expression level of apoptosis-specific eIF-5a is higher than proliferating eIF-5A. In the method of reducing apoptosis in mammalian tissue, there is provided an agent that inhibits expression of apoptosis-specific eIF-5A. Preferred agents are antisense oligonucleotides to human apoptosis-specific eIF-5A.
Owner:SENESCO TECHNOLOGIES INC
Portable compression device
A portable compression device for compressing at least a portion of a mammal's limb is provided. The portable compression device can use mechanical compression to apply an external pressure to the portion of the limb to thereby propagate blood flow return in the direction of the mammal's heart. In at least one embodiment, the portable compression device can accomplish this mechanical compression through the use of at least one frame, actuator, drum, and flexible elongate member. The actuator can move the drum between a first position and a second position. The flexible elongate member can be engaged with at least a portion of the drum and can at least partially circumscribe a portion of the limb of the mammal, such that the movement of the drum between the first and second positions can apply tension to the flexible elongate member to thereby apply a compressive force to the limb.
Owner:MOOMIAIE QAJAR REMO +1
Means for improving cardiovascular health
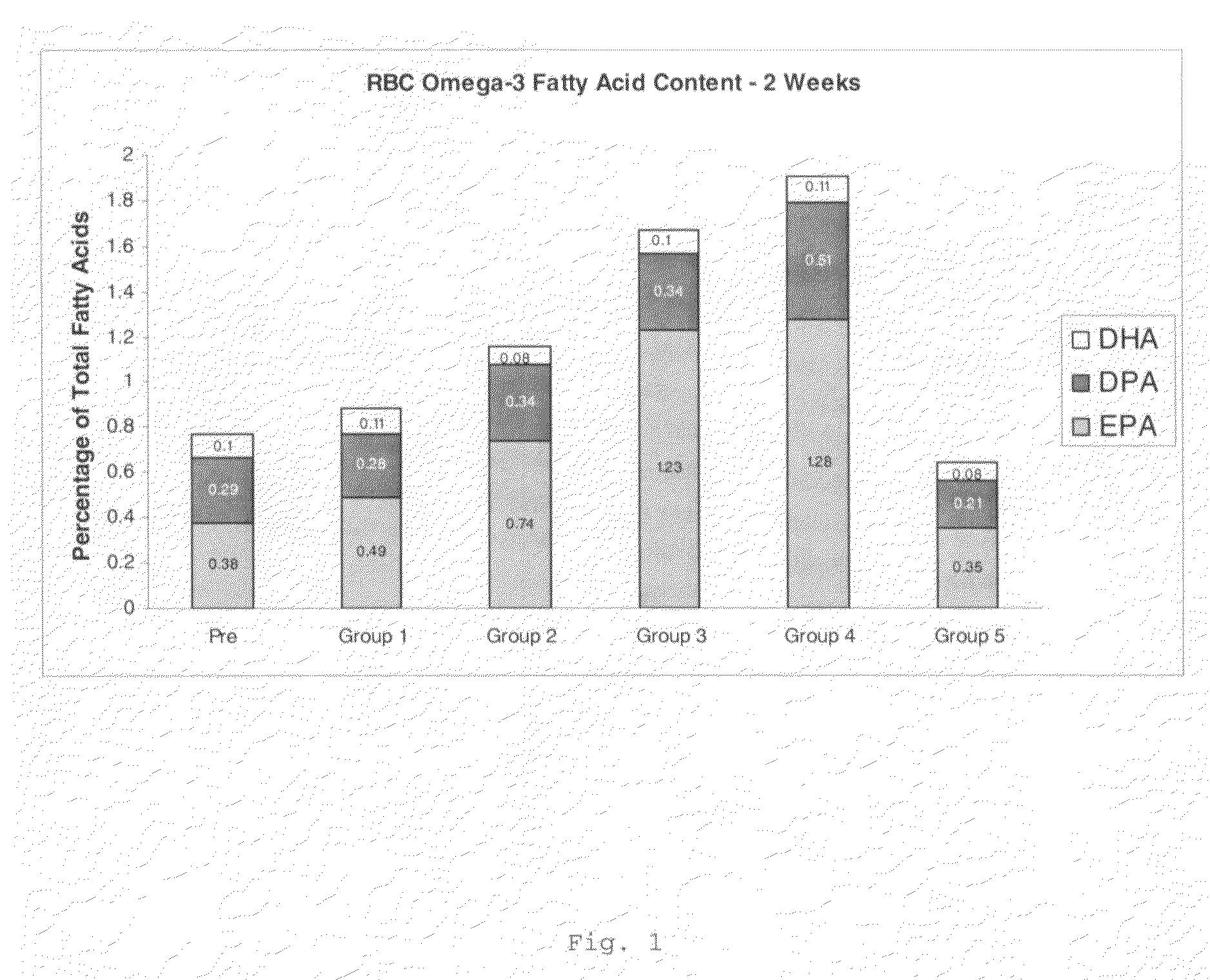
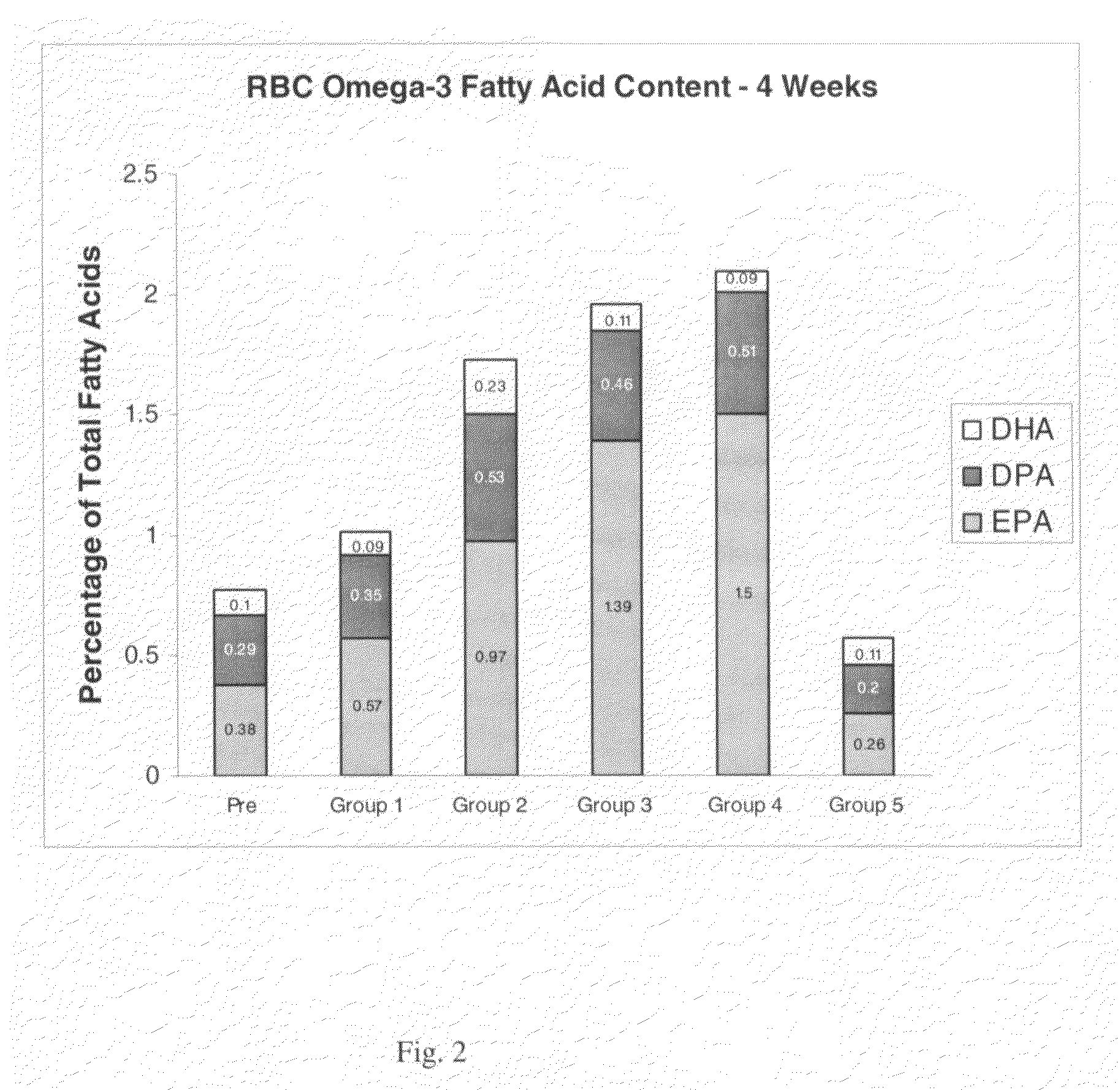
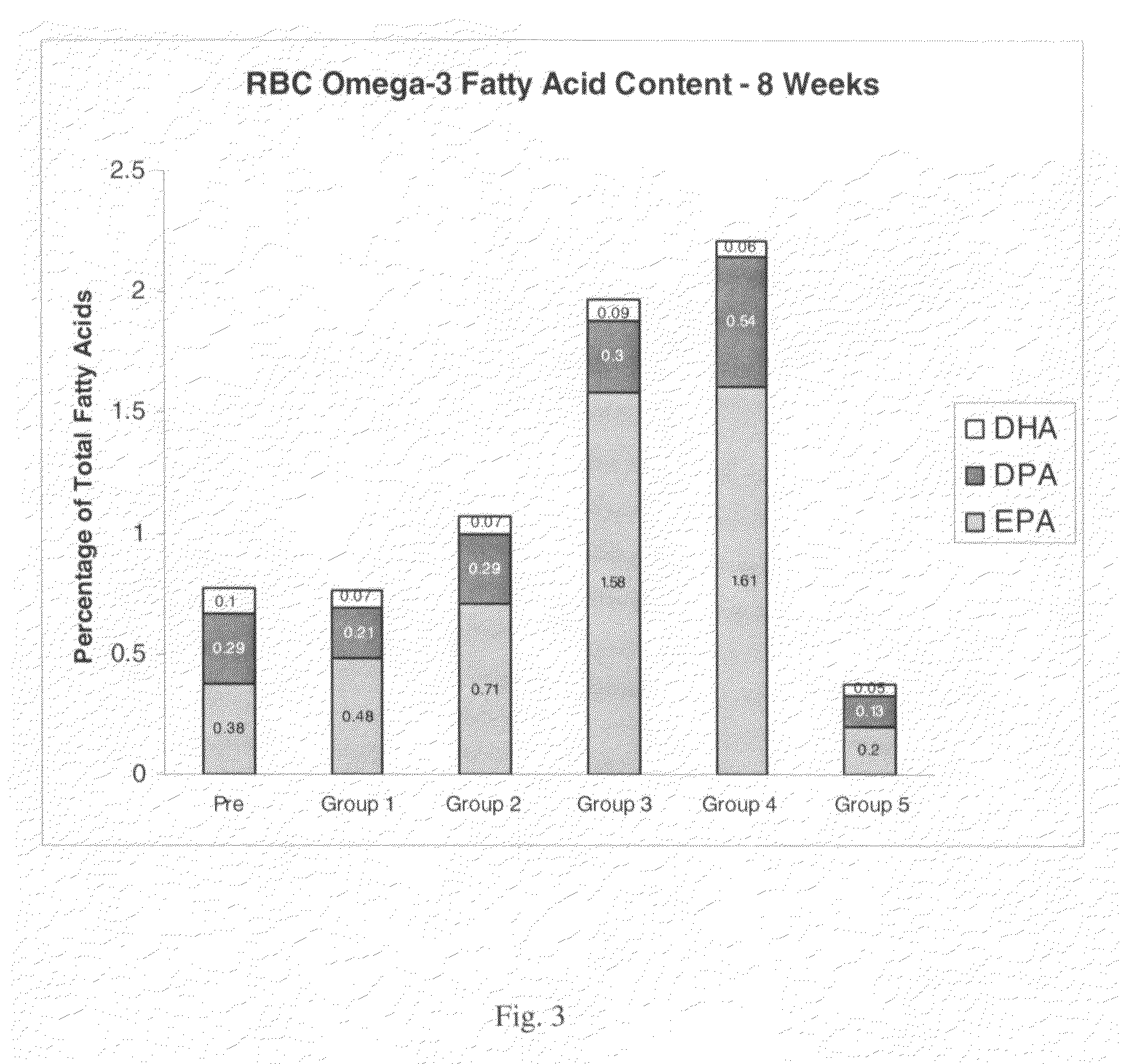
The present invention is in the fields of lipid metabolism and dietary supplementation and provides methods and compositions to improve heart health of a mammal by orally administering stearidonic acid and related compounds to the mammal. The improved heart health is evidenced by the enrichment of cardiac tissue with eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5, ω3) and docosapentaenoic acid (22:5, ω3) following the administration. Also provided are methods for promoting a stearidonic acid containing product by advertising its heart health benefits.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
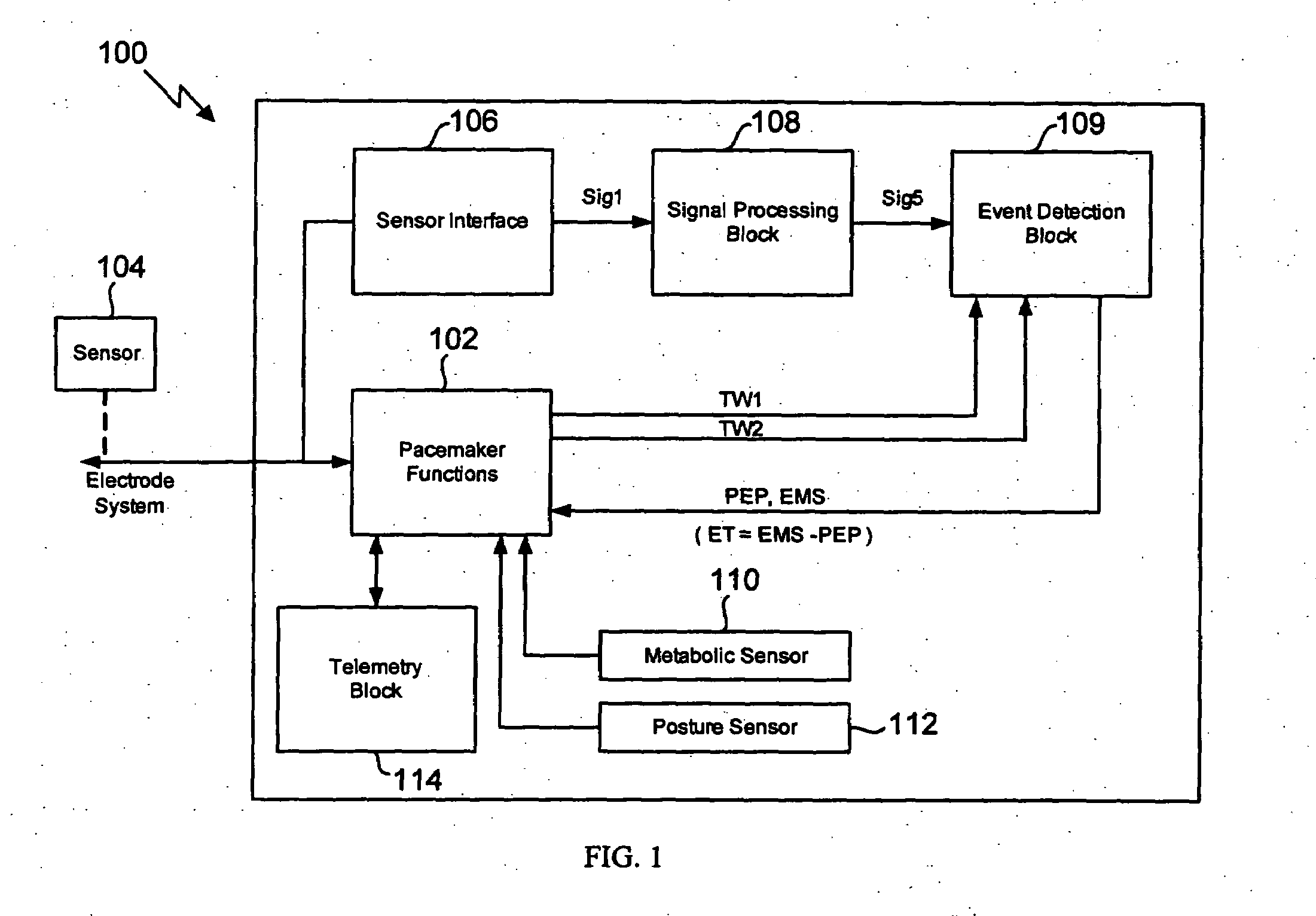
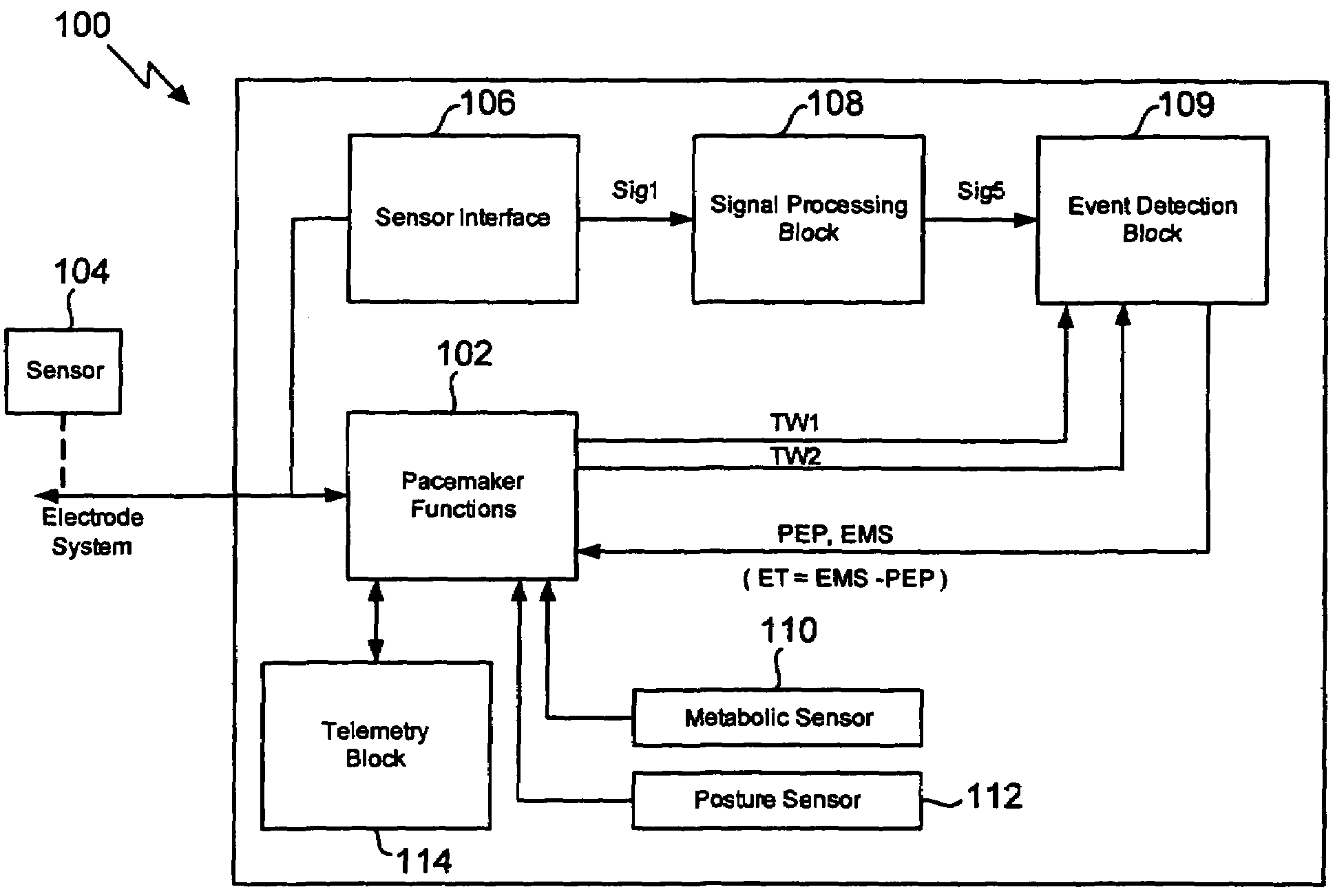
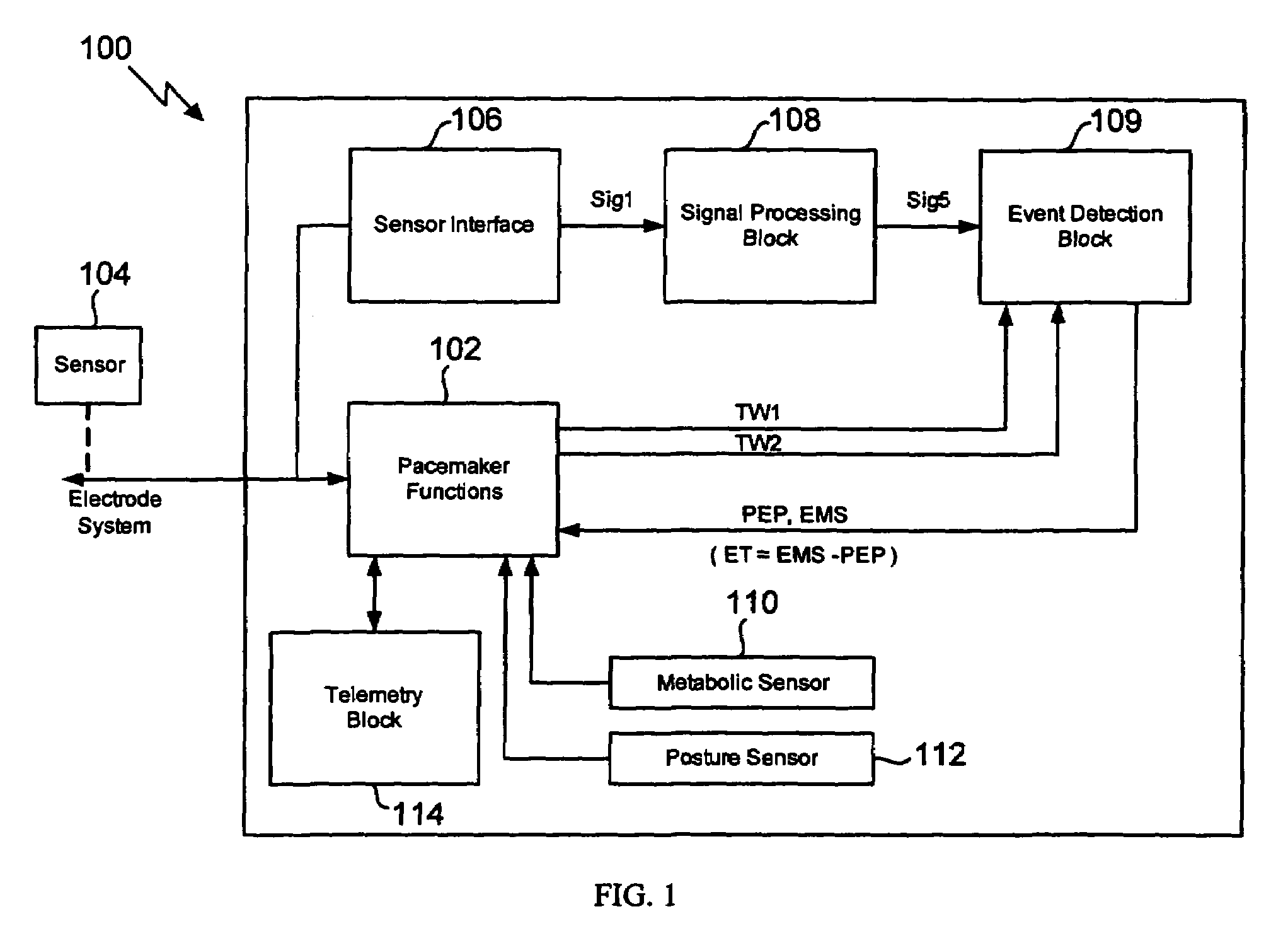
Method for extracting timing parameters using a cardio-mechanical sensor
In a method and apparatus for measuring the ejection fraction in a mammalian heart, the opening and closing of a heart valve is sensed with an implanted sensor, and a pre-ejection period is measured as a function of the sensed opening and closing of the heart valve. The ventricular ejection time also is measured, and the ejection fraction is determined as a function of the measured pre-ejection period and the ejection time.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
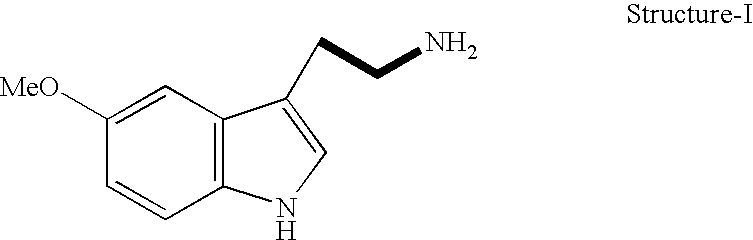
Cardioprotective agents
InactiveUS20050020666A1Prevention and treatmentAvoid damageBiocideAntinoxious agents5-MethoxytryptamineFree radicals scavenger
The invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising 5-Methoxytryptamine or a salt thereof for the prevention and / or treatment of mammalian cardiac tissue damage. 5-Methoxytryptamine and the salts thereof act as free radical scavengers in the prevention and / or treatment of mammalian cardiac tissue damage mediated by free oxygen radicals.
Owner:DABUR RESEARCH FOUNDATION
Compositions and treatments of heart failure in non-human mammal animals
InactiveUS20090270356A1Reduce morbidityReducing risk of mortalityCardiovascular disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsMammalian heartHeart failure
The invention relates to new compositions comprising an aldosterone antagonist according to a particular posology for the treatment of heart failure in non-human mammal animals.
Owner:CEVA SANTE ANIMALE
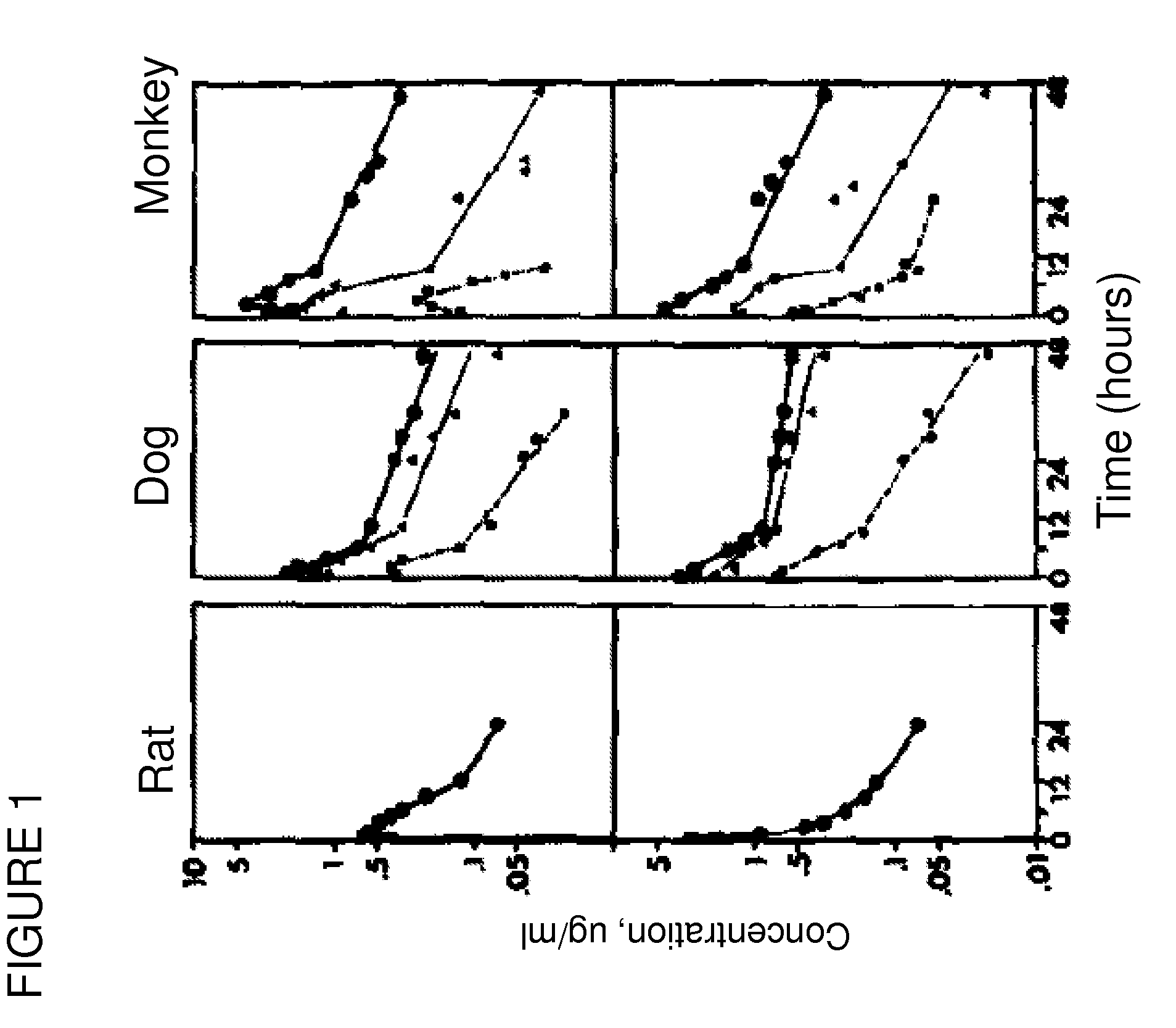
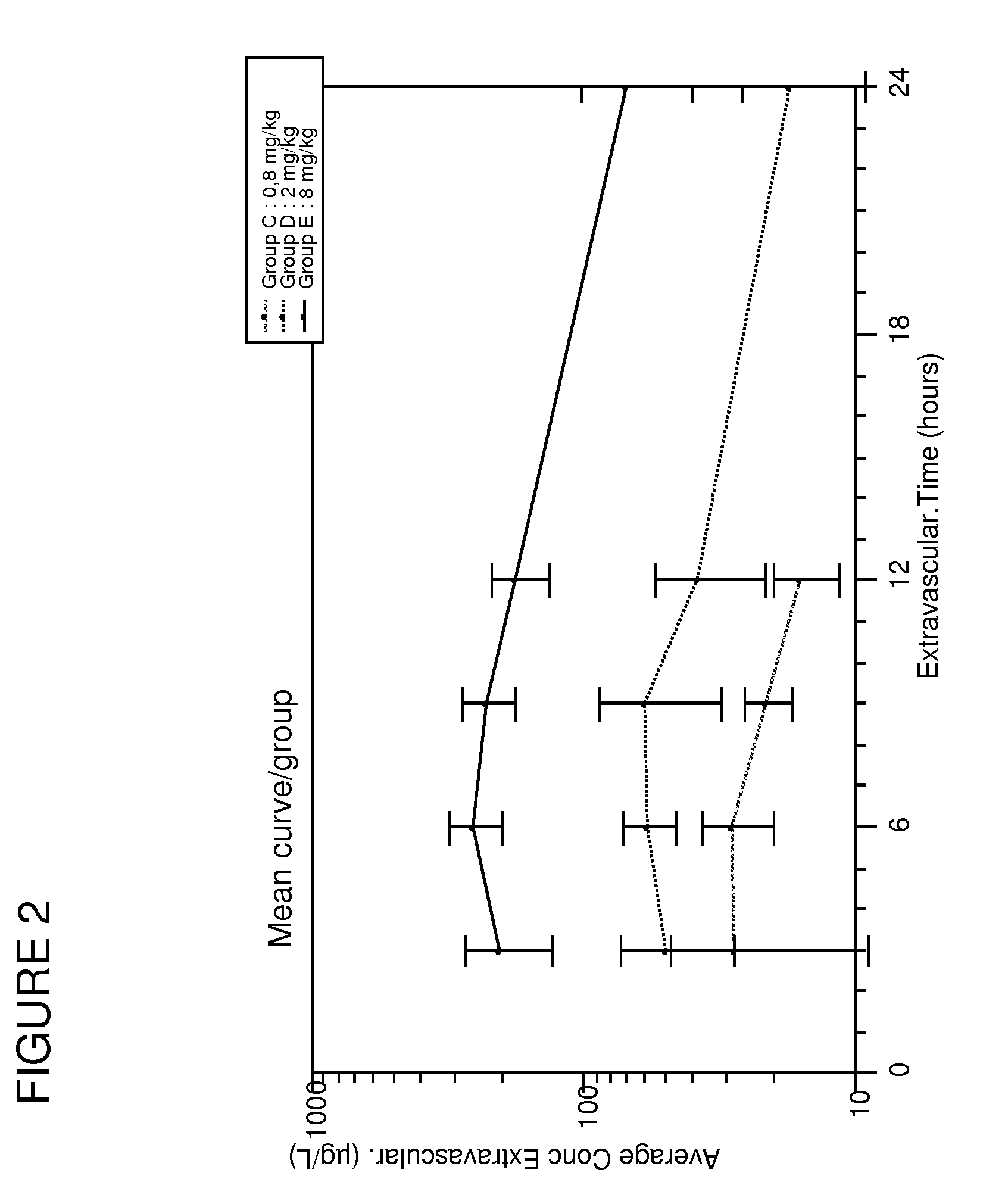
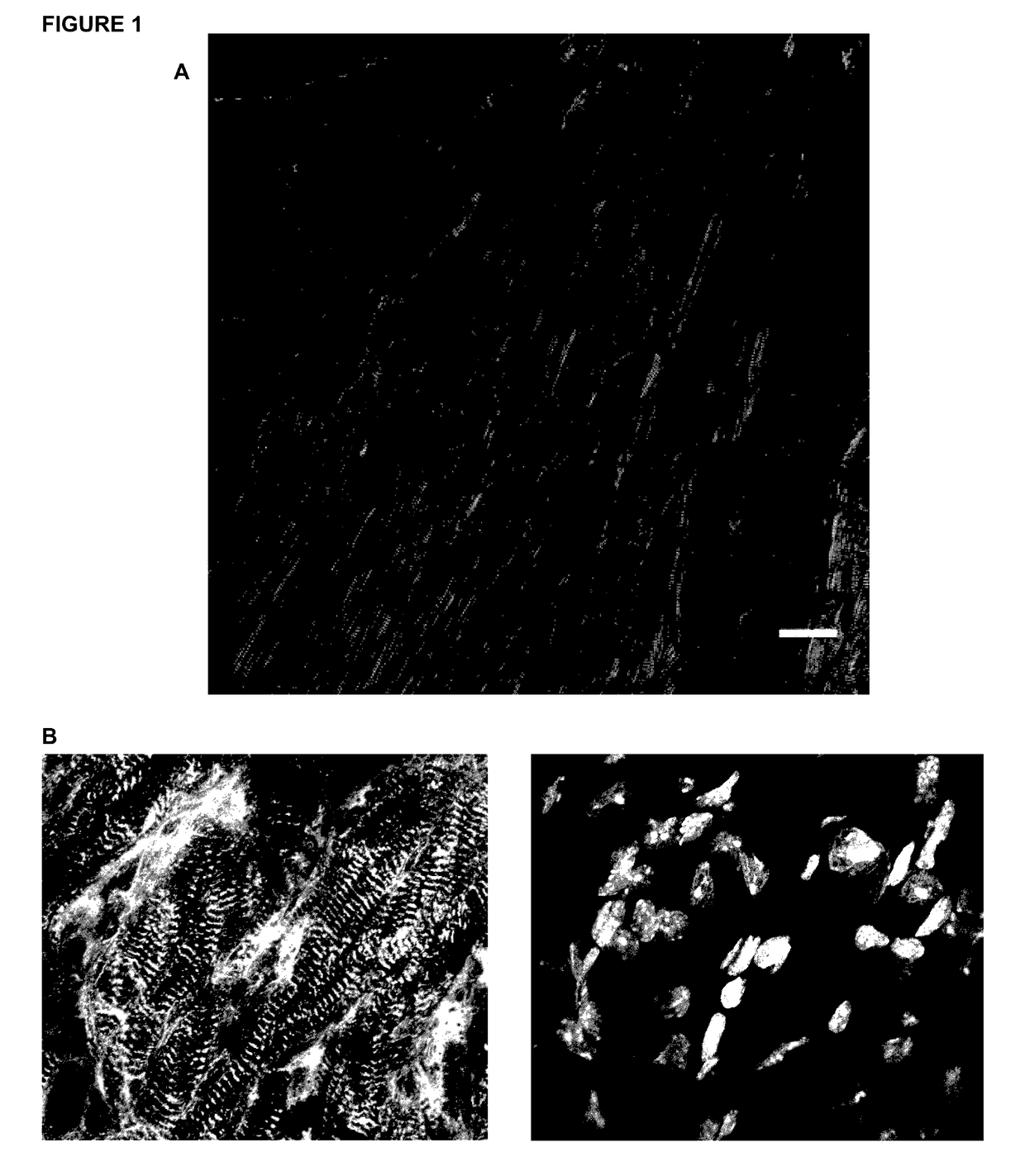
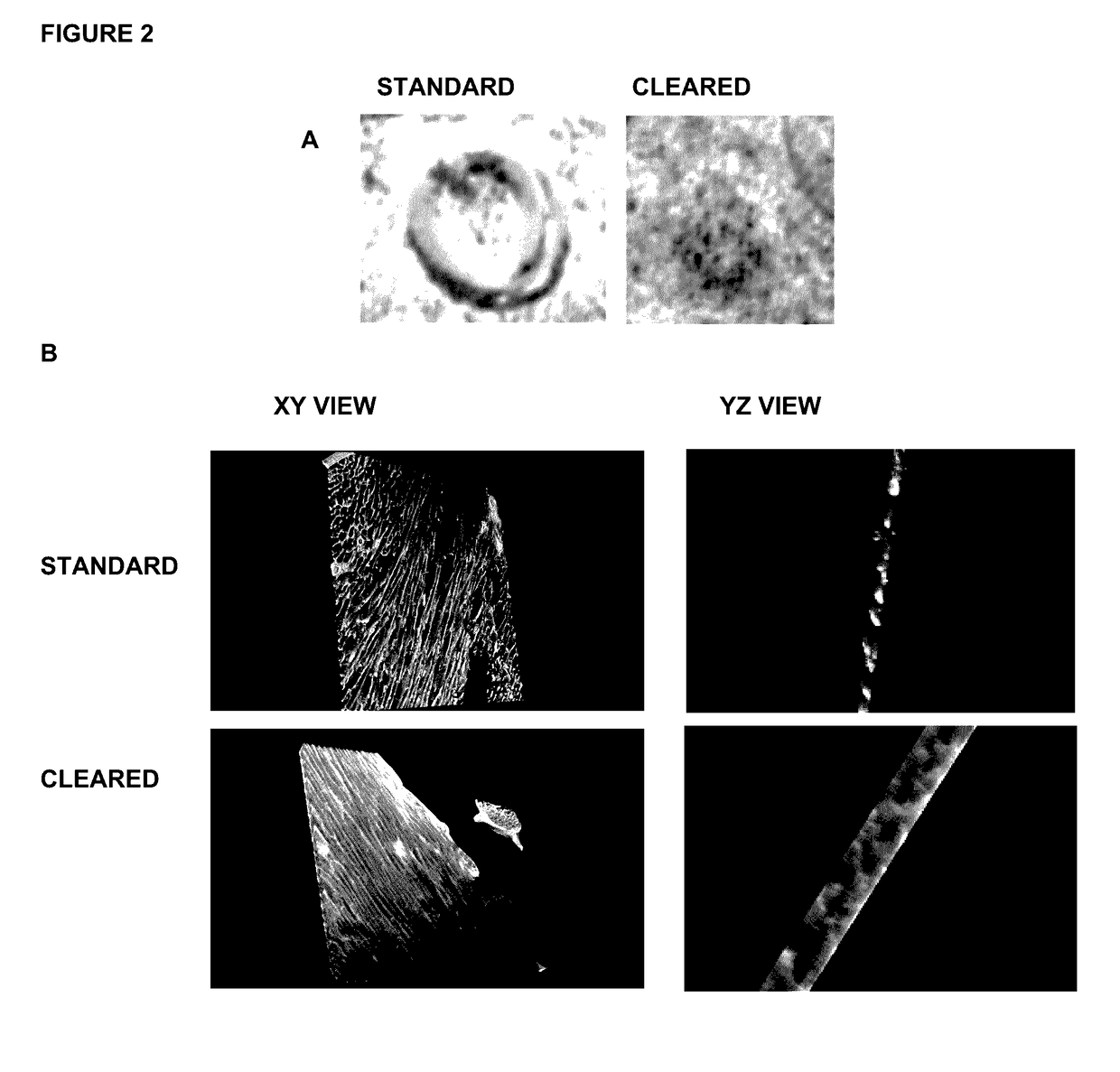
High-resolution three-dimensional imaging of mammalian hearts
InactiveUS20170108414A1High-resolution imageImage enhancementImage analysisMammalian tissueDimensional modeling
Methods and materials for high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of mammalian tissues, such as heart and intestine, are described. Both methods of tissue preparation for imaging and methods of imaging are described, as well as kits comprising materials and media for use in the methods.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
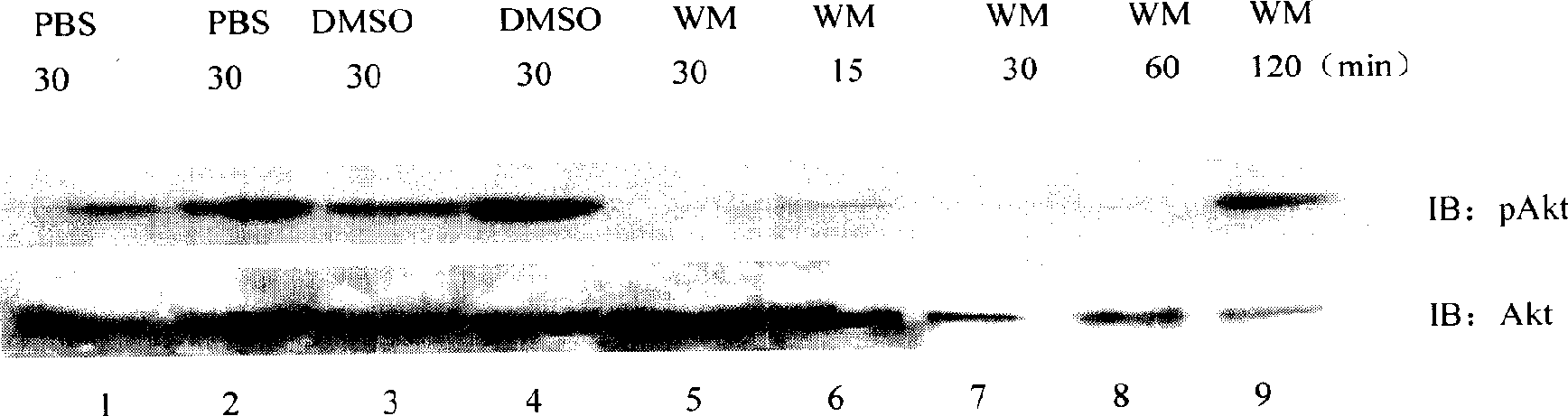
New use of MAPK inhibitor and its composition thereof
InactiveCN1743006AImprove cardiac function in heart failureIncrease EF valuePharmaceutical active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderHeart diseaseMammalian heart
The present invention finds that PI3-K inhibitor and MAPK inhibitor can obviously improve heart failure cardiac function of mammal, also finds that the combined application of PI3-K inhibitor, MAPK inhibitor and medicine rh NRG for curing heart failure of mammal can obviously improve heart failure cardiac function of mammal, they have synergistic action. Said invention also provides a method for preventing, curing and delaying heart disease of mammal by using PI3-k inhibitor and MAPK inhibitor and it's composite.
Owner:ZENSUN (SHANGHAI) SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for extracting timing parameters using a cardio-mechanical sensor
In a method and apparatus for measuring the ejection fraction in a mammalian heart, the opening and closing of a heart valve is sensed with an implanted sensor, and a pre-ejection period is measured as a function of the sensed opening and closing of the heart valve. The ventricular ejection time also is measured, and the ejection fraction is determined as a function of the measured pre-ejection period and the ejection time.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
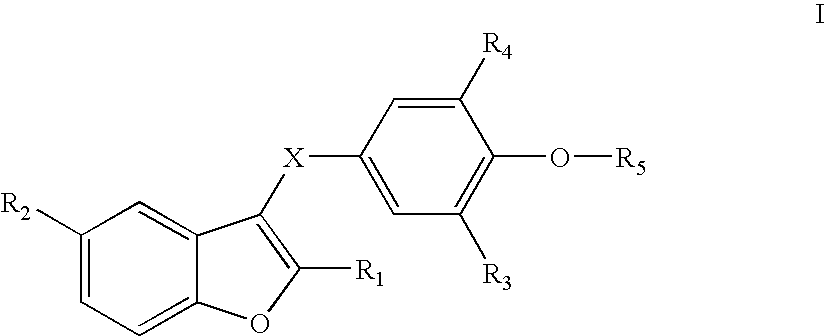
Benzofuranes and their use in the treatment of atrial fibrillation
This intention relates to new compounds and their pharmaceutical use, and to the pharmaceutical use of known compounds, which compounds inhibit certain transmembrane potassium currents in the atrium of the heart of a mammal without significantly affecting other ion channels, for the treatment of heart disease particularly atrial fibrillation. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds.
Owner:KARO BIO AB +1
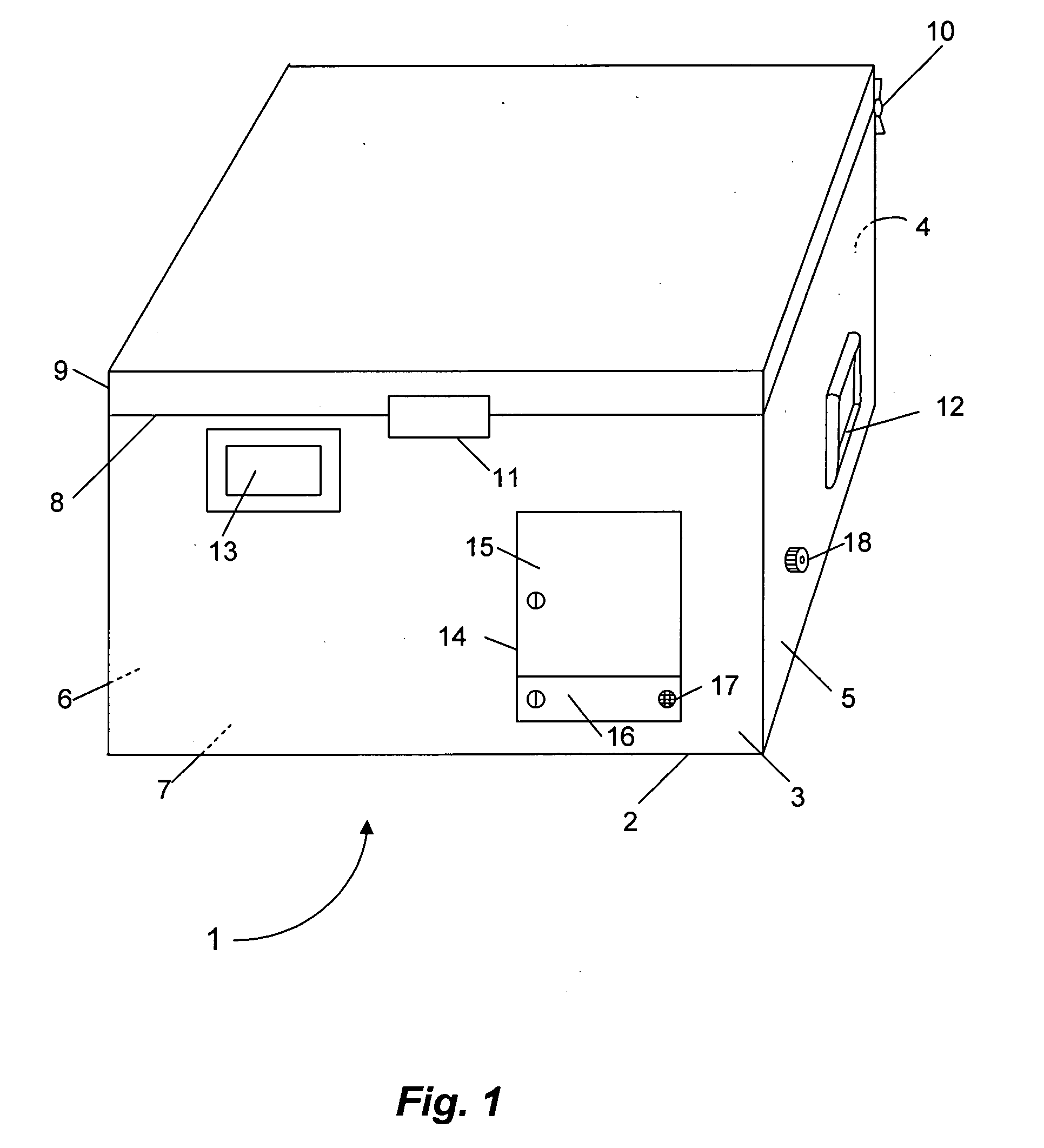
Warm intermittent perfusion
InactiveUS20050026132A1Prolong lifeImprove survivabilityDead animal preservationMammalian heartPerfusion method
The present invention provides an intermittent perfusion method and system which is capable of extending the viable life of an explanted mammalian heart for up to at least approximately 49 hours by utilizing a new and unique intermittent perfusion method or procedure. The system that implements the method includes a perfusion chest of approximately the same size as the standard ice chests that are currently being used to store and transport human organs. The perfusion chest of the present invention, however, contains all of the mechanical and electrical components needed to automatically perfuse the heart in accordance with the perfusion procedure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com