Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Insulin delivery device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
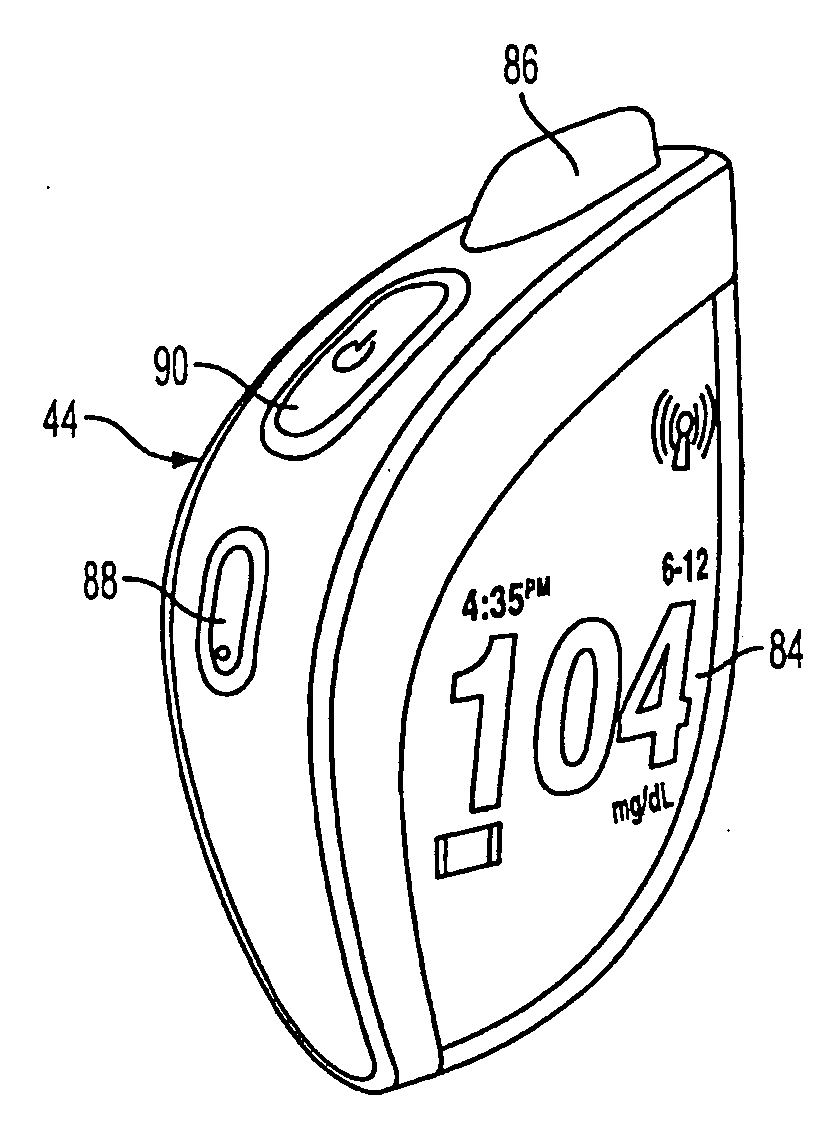
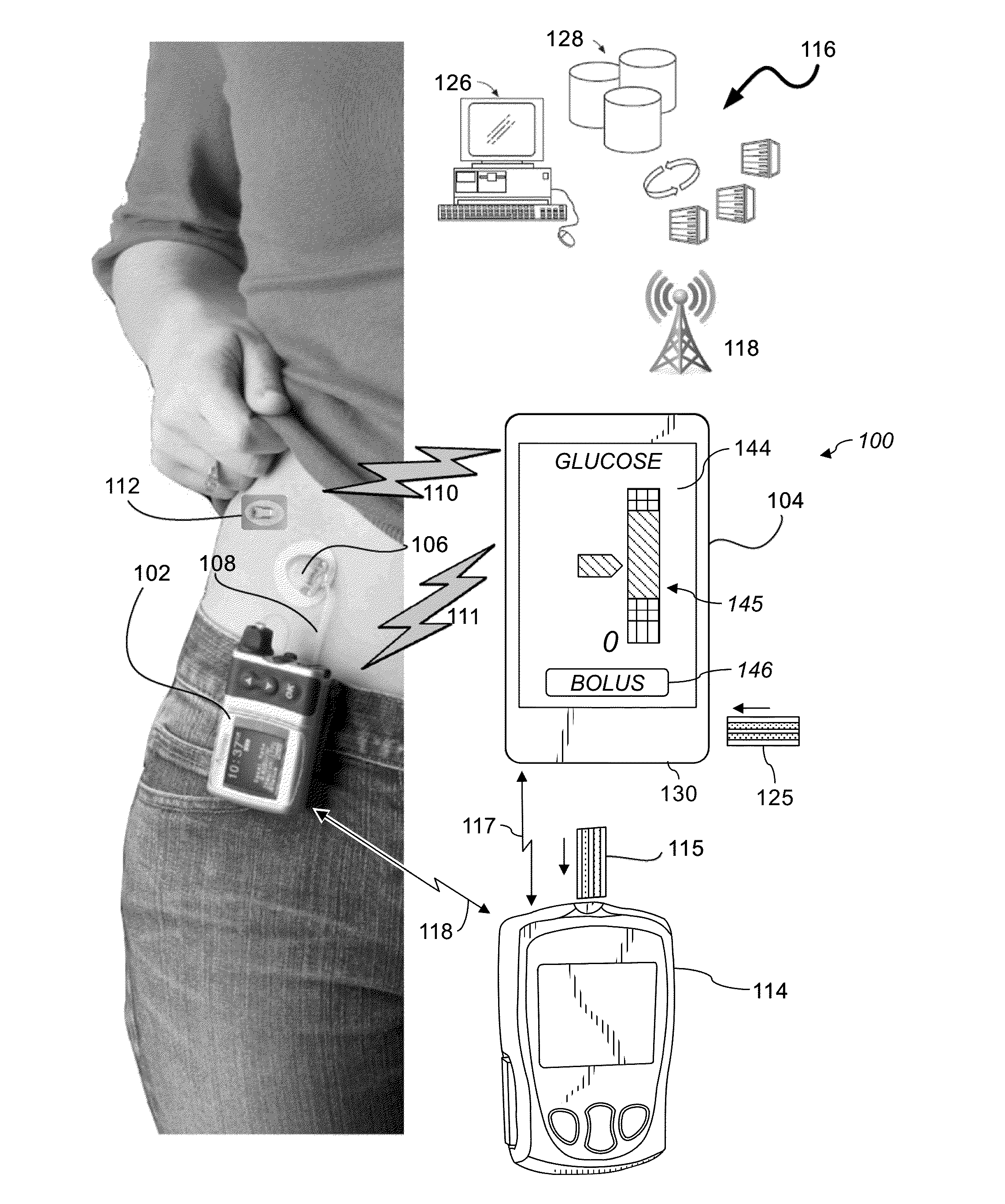
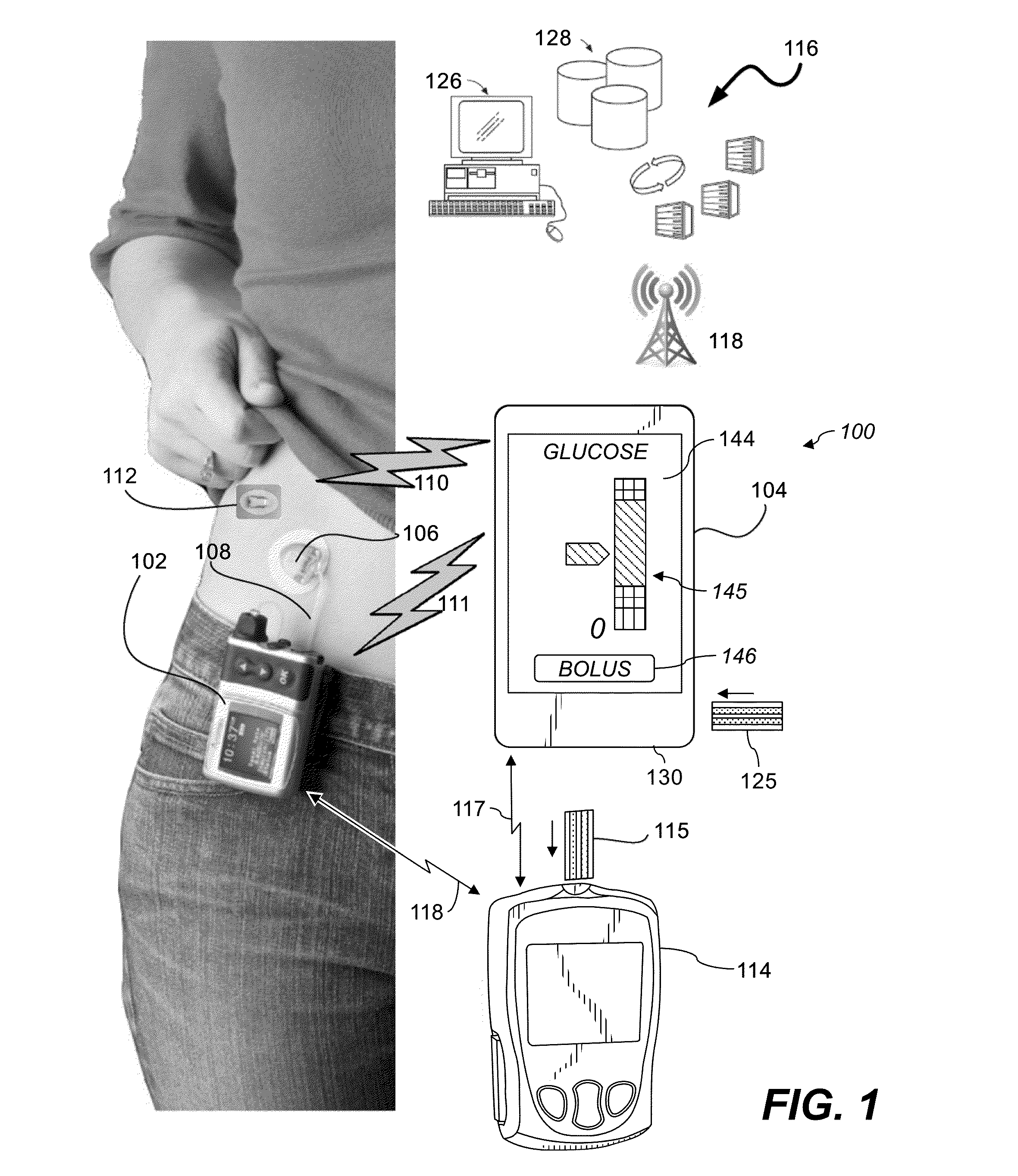
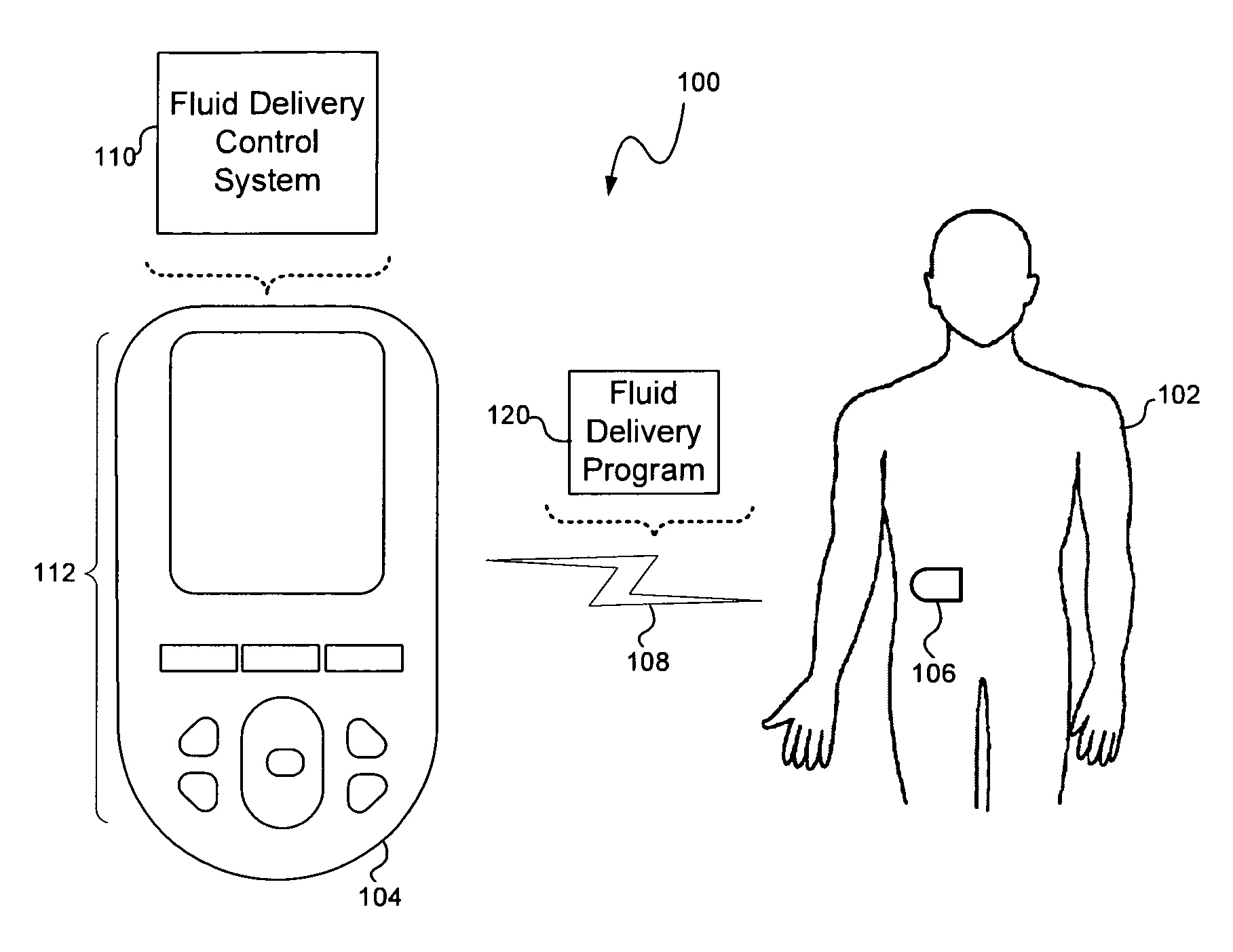
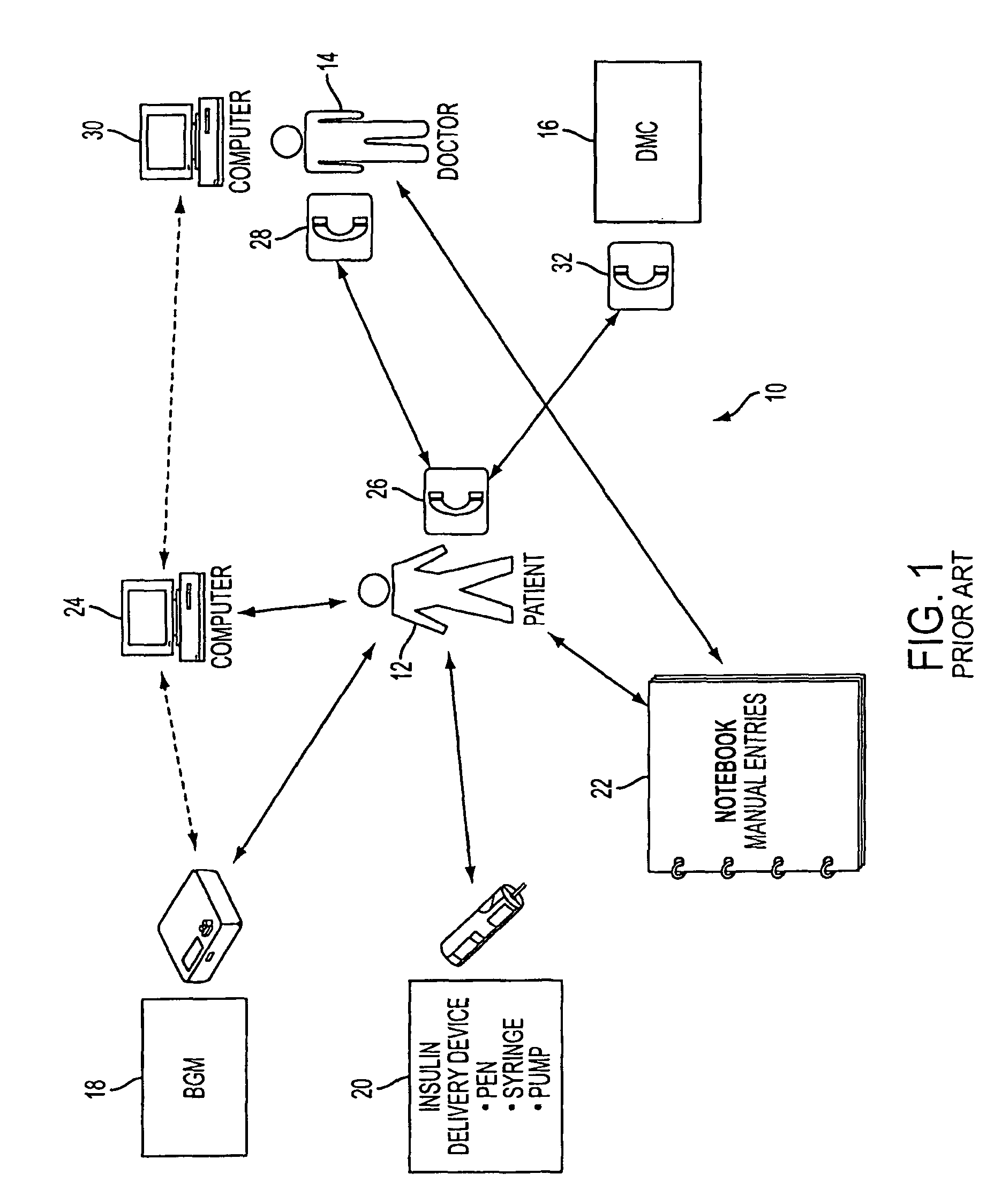
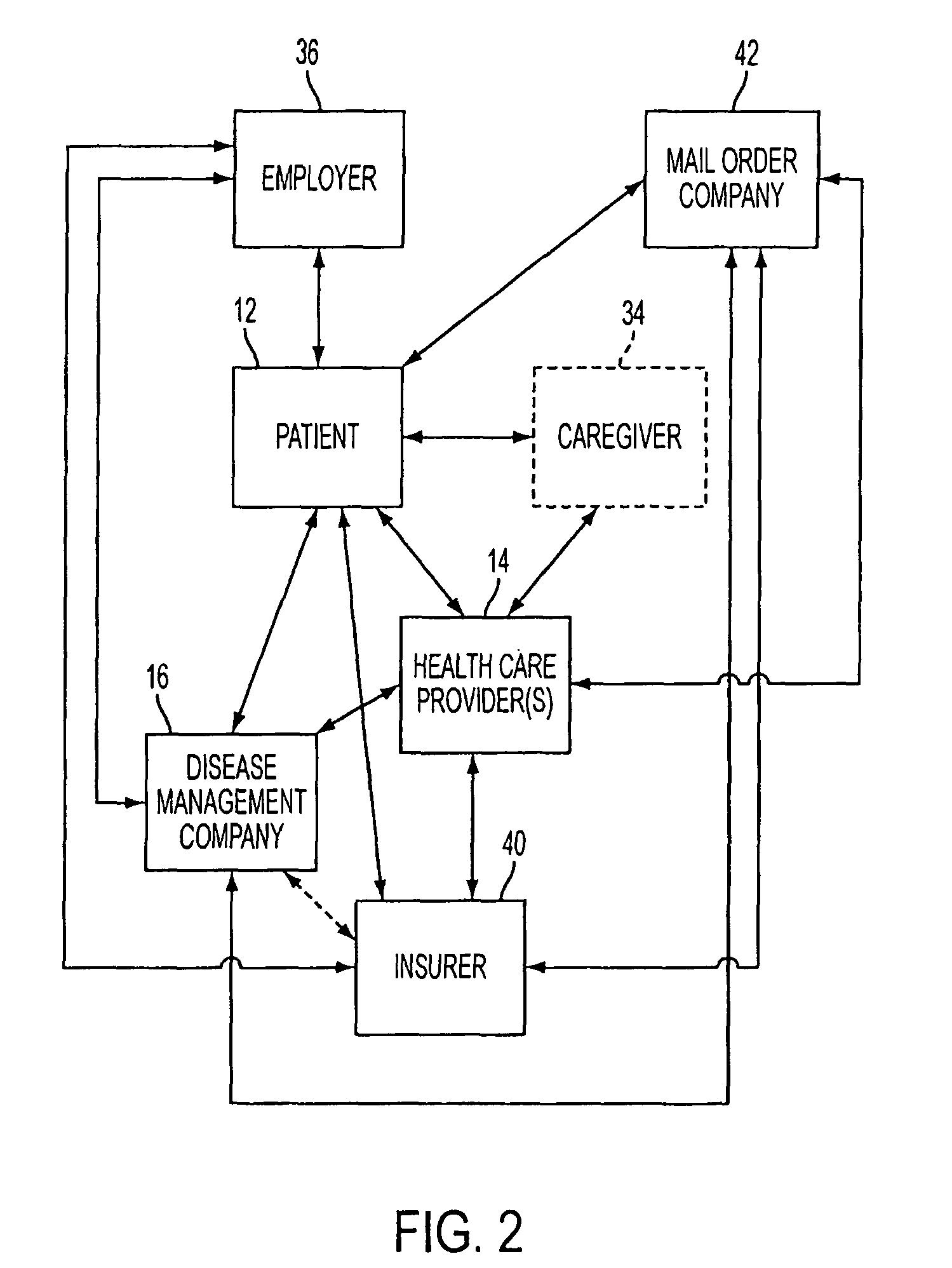
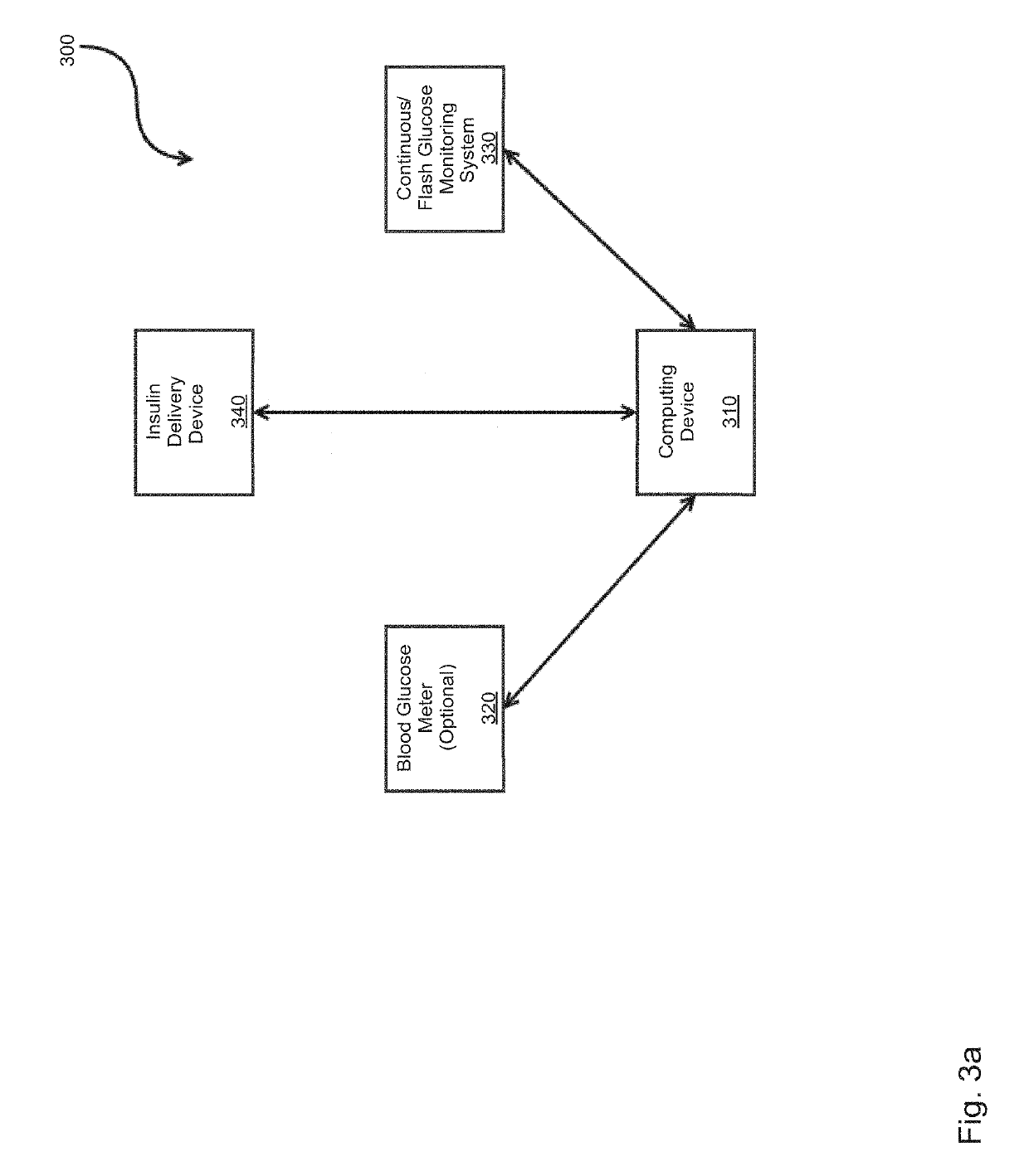
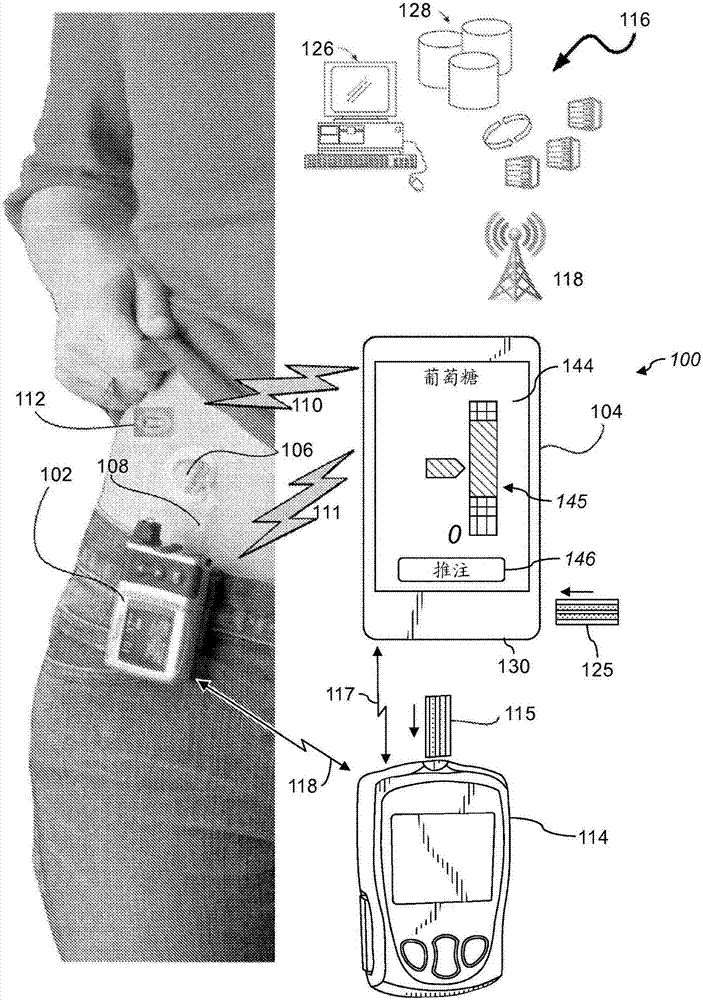
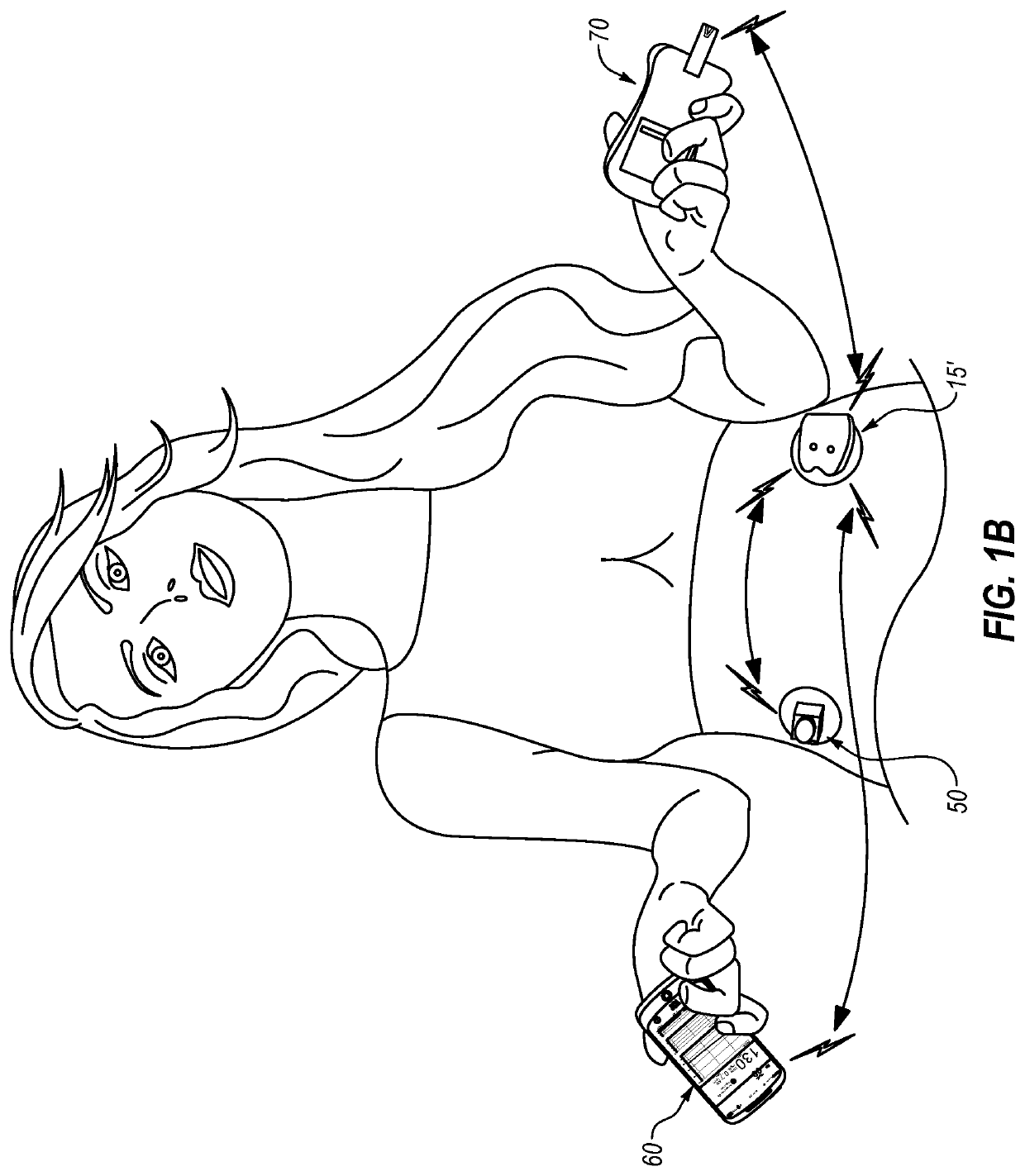
System and Methods for Improved Diabetes Data Management and Use Employing Wireless Connectivity Between Patients and Healthcare Providers and Repository of Diabetes Management Information
ActiveUS20100069730A1Shorten development timeExtended service lifePhysical therapies and activitiesDrug and medicationsDiseaseInformation repository
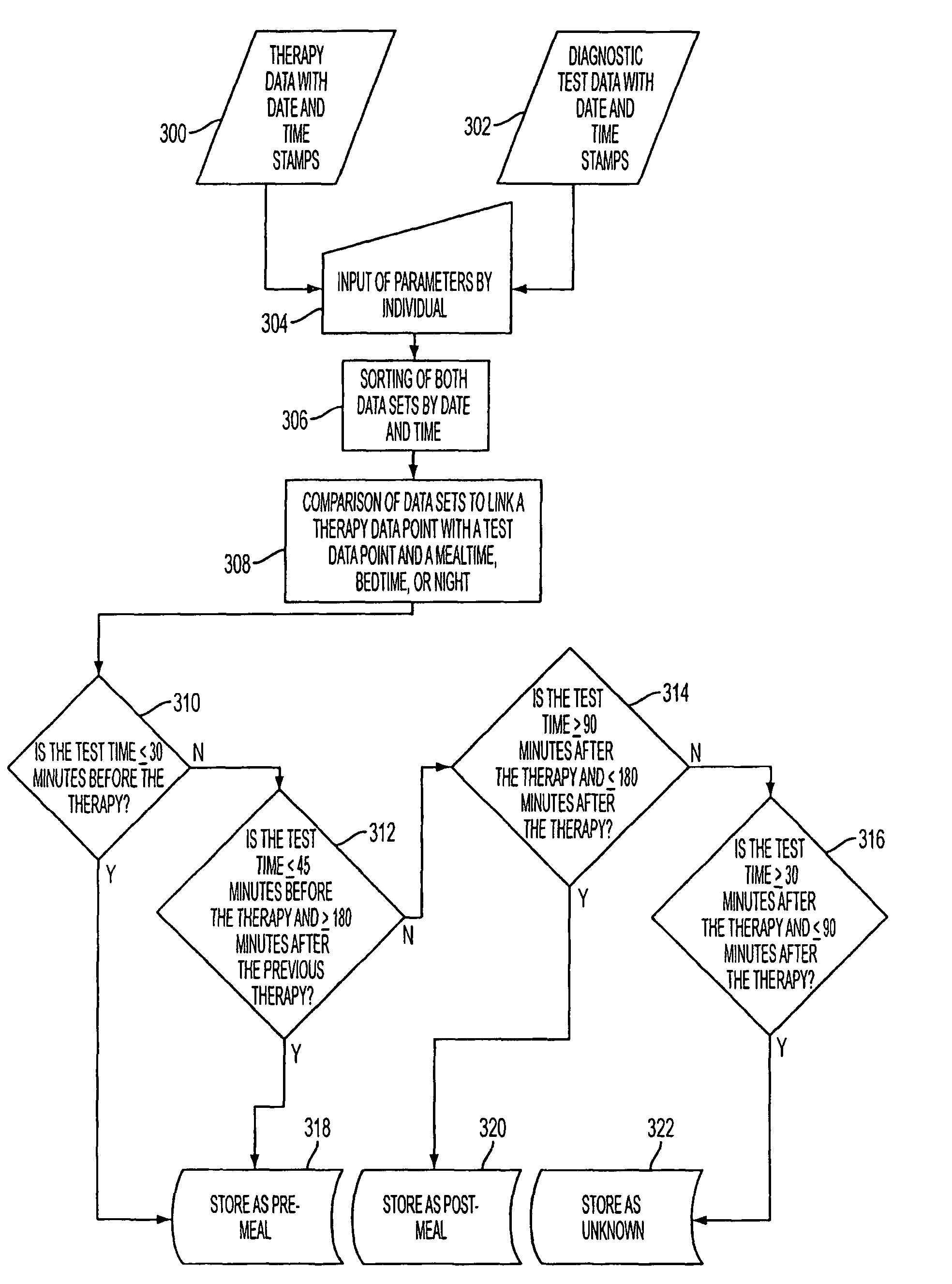
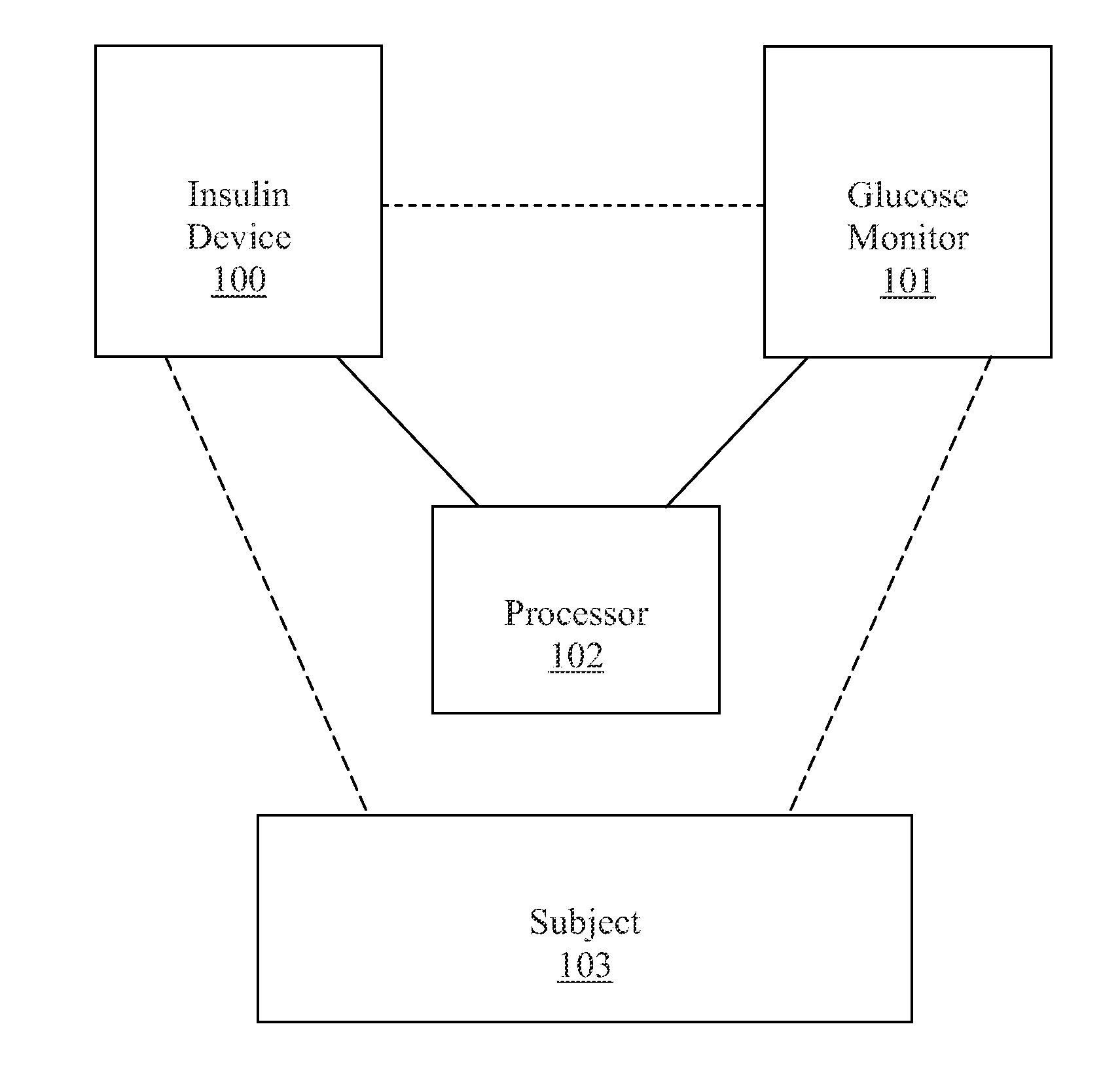
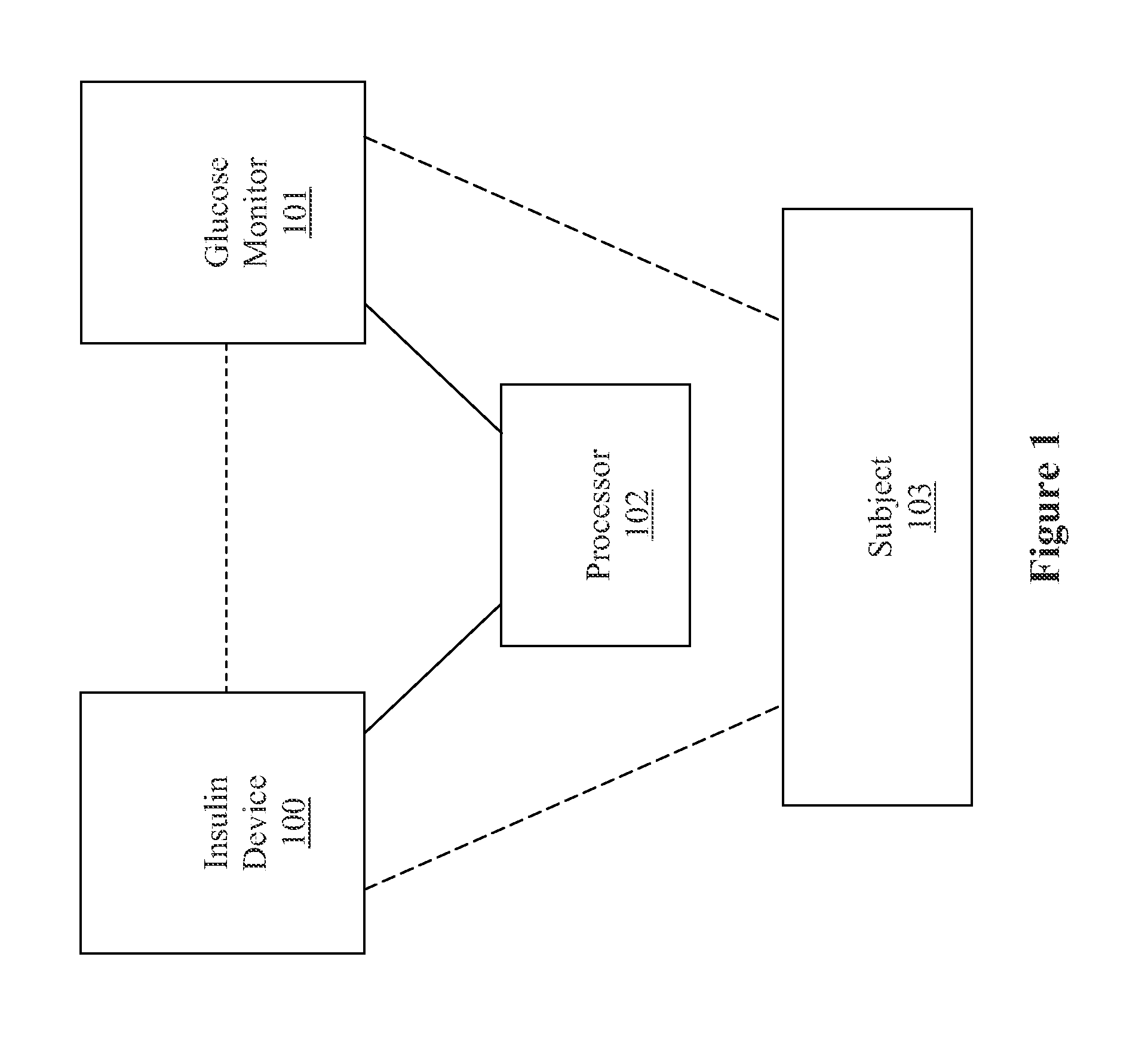
Methods, devices and a system for disease management are provided that employ diagnostic testing devices (e.g., blood glucose meters) and medication delivery devices (e.g., insulin delivery devices) for providing data to a repository in real-time and automatically. Repository data can be analyzed to determine such information as actual test strip use, patient health parameters to outside prescribed ranges, testing and medication delivery compliance, patient profiles or stakeholders to receive promotional items or incentives, and so on. Connected meters and medication delivery devices and repository data analysis are also employed to associate a diagnostic test to a mealtime based on timing of a therapeutic intervention performed by an individual.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
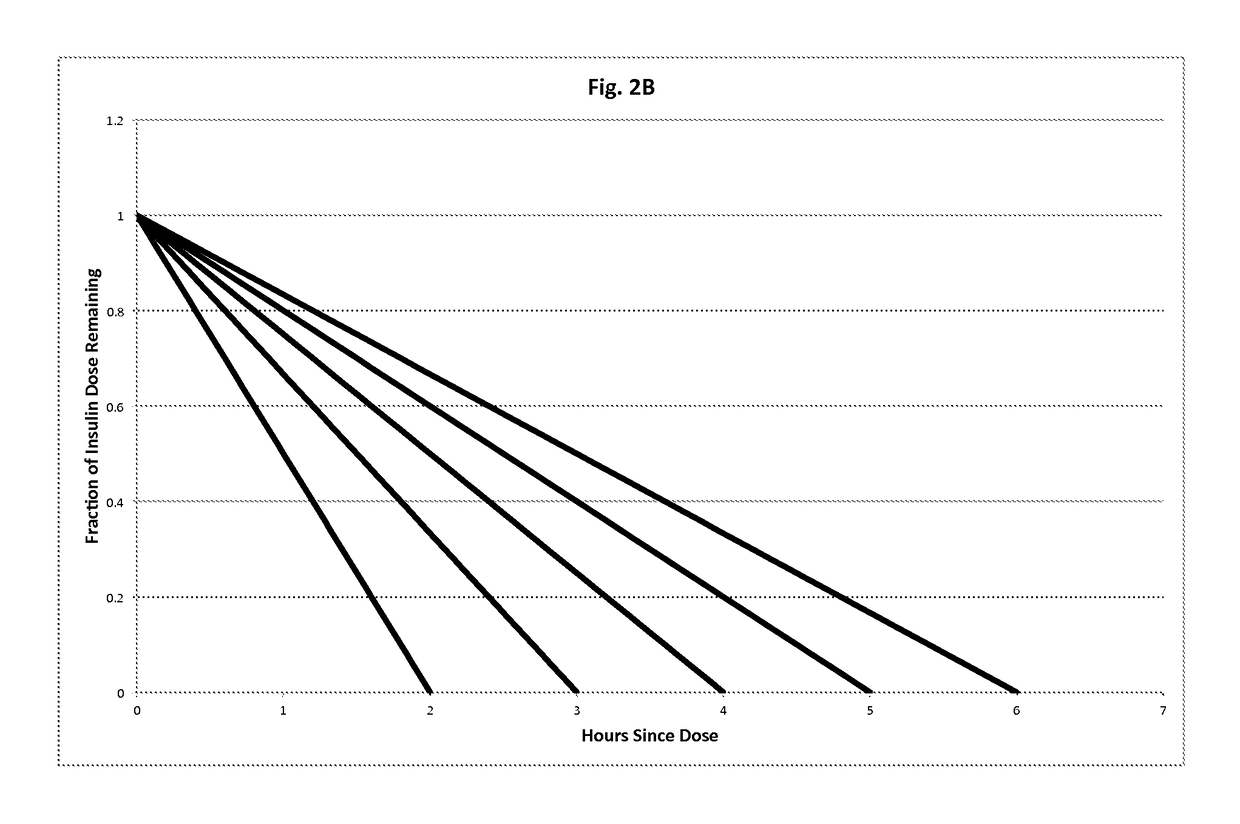
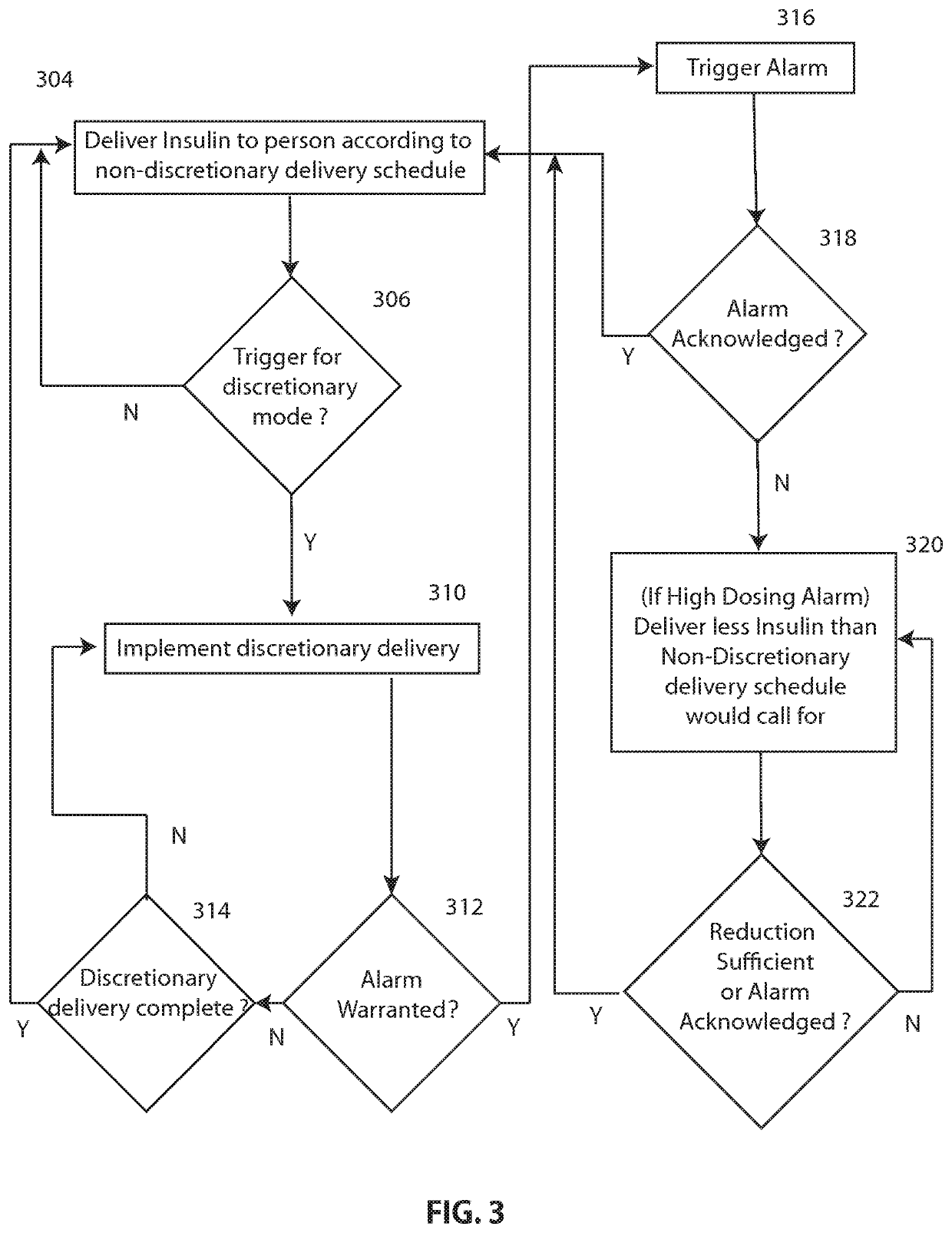
Discretionary insulin delivery systems and methods
InactiveUS20140309615A1Improved glycemic controlImproved insulin deliveryDrug and medicationsMedical devicesUser interfaceEndocrinology
A method of facilitating delivery of a discretionary dose of insulin to a user includes: enabling the user or a caregiver to specify, via a computer-based user interface, parameters associated with a discretionary delivery of insulin that may be delivered to the user; subsequently receiving data that represents the user's glucose level during a period of time associated with the discretionary delivery; automatically determining, with a computer-based processor, based on the received data, if, when and how much discretionary insulin should be delivered to the user during the period of time associated with the discretionary delivery; delivering insulin to the user during the period of time associated with the discretionary delivery according to the automatic determination; and delivering insulin to the user with the insulin delivery device according to a non-discretionary insulin delivery schedule unless a discretionary insulin delivery mode has been triggered.
Owner:INSULET CORP
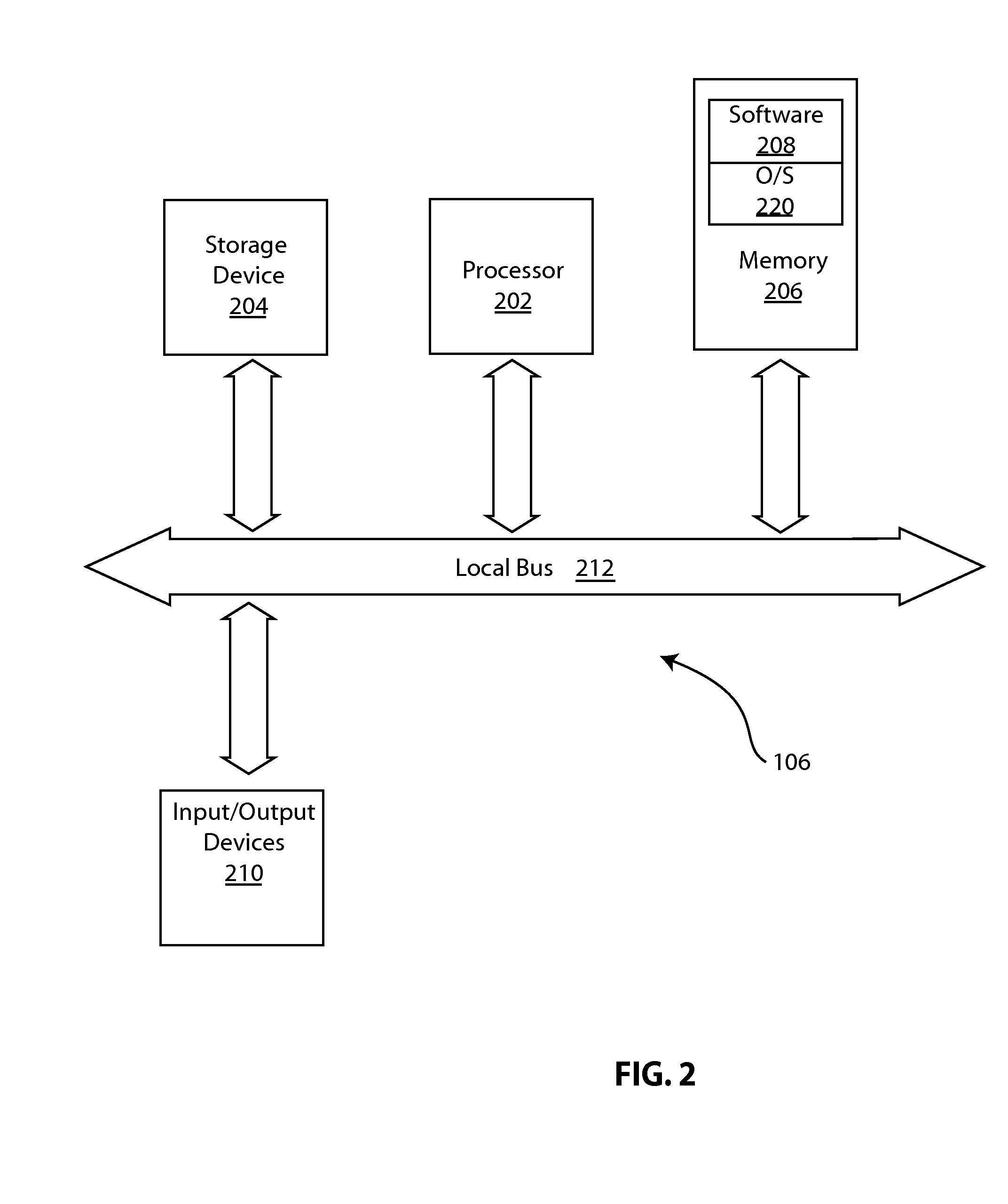
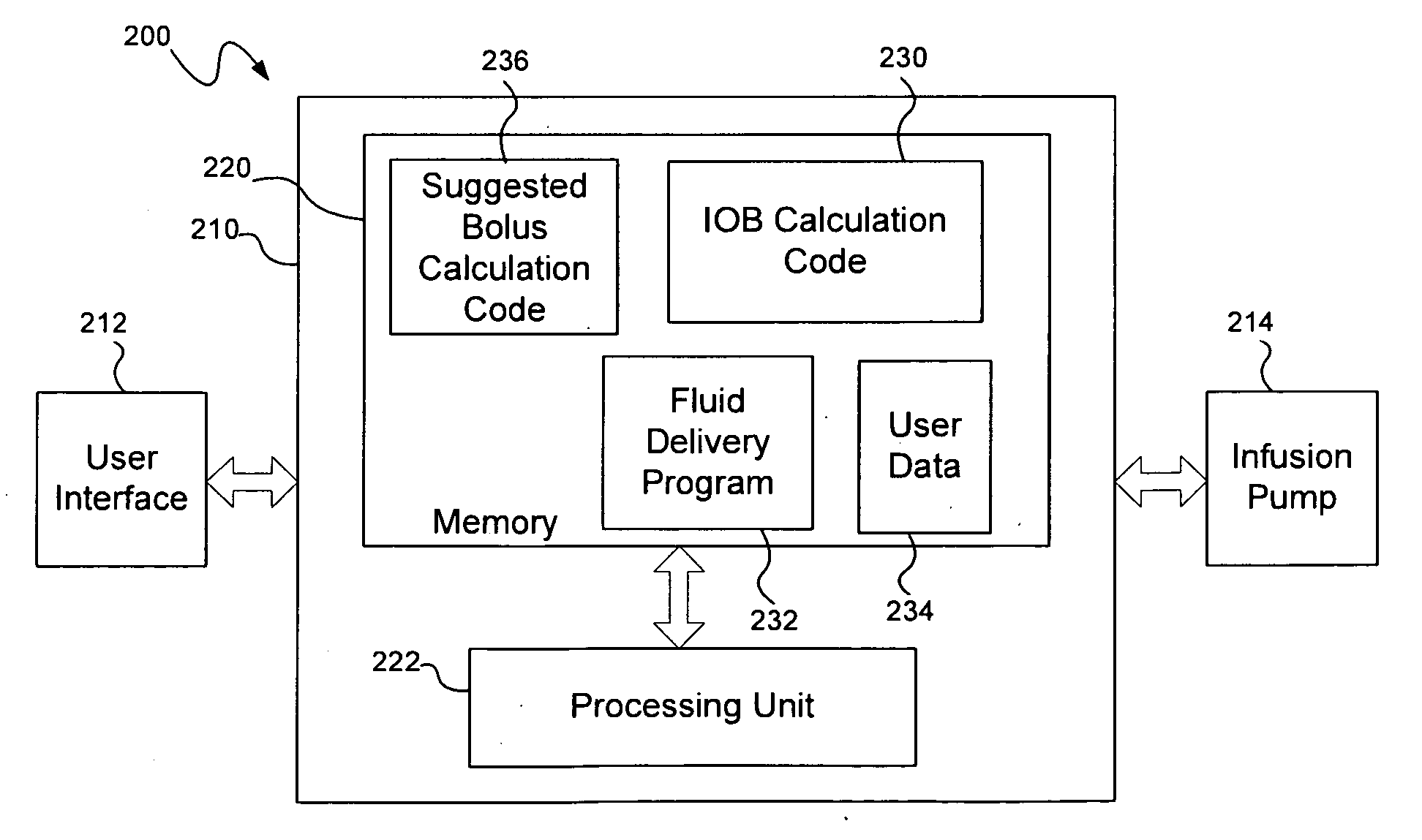
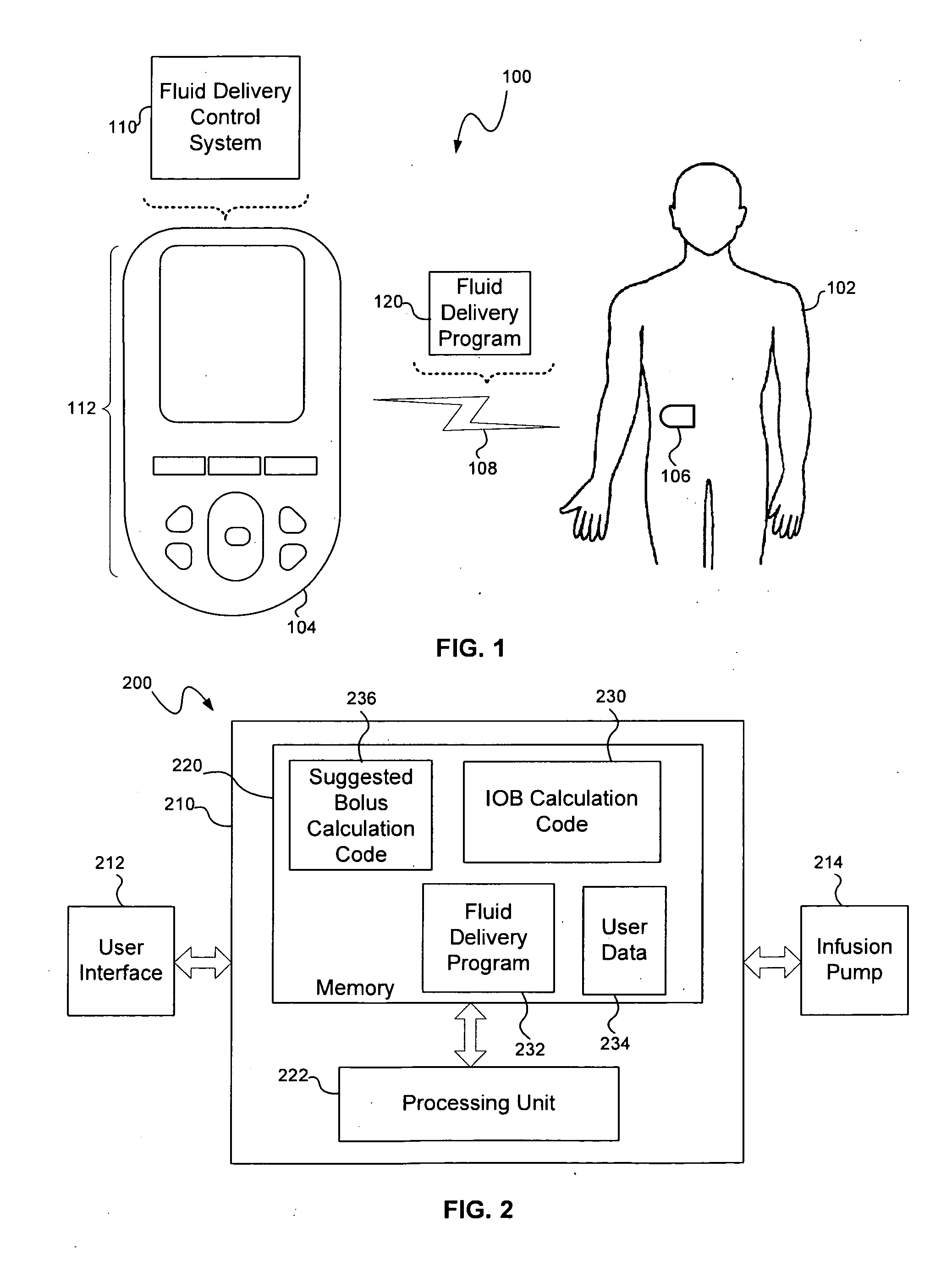
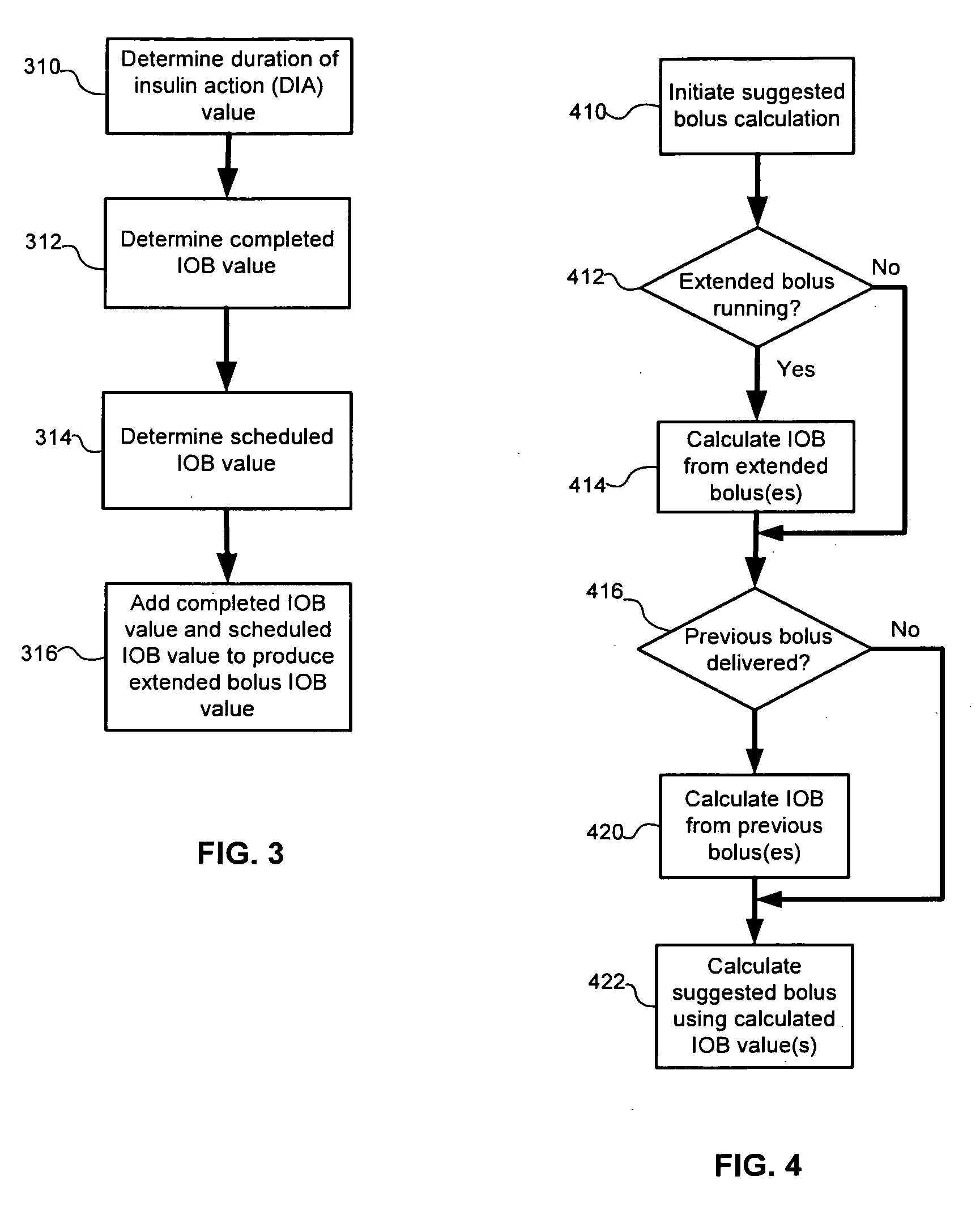
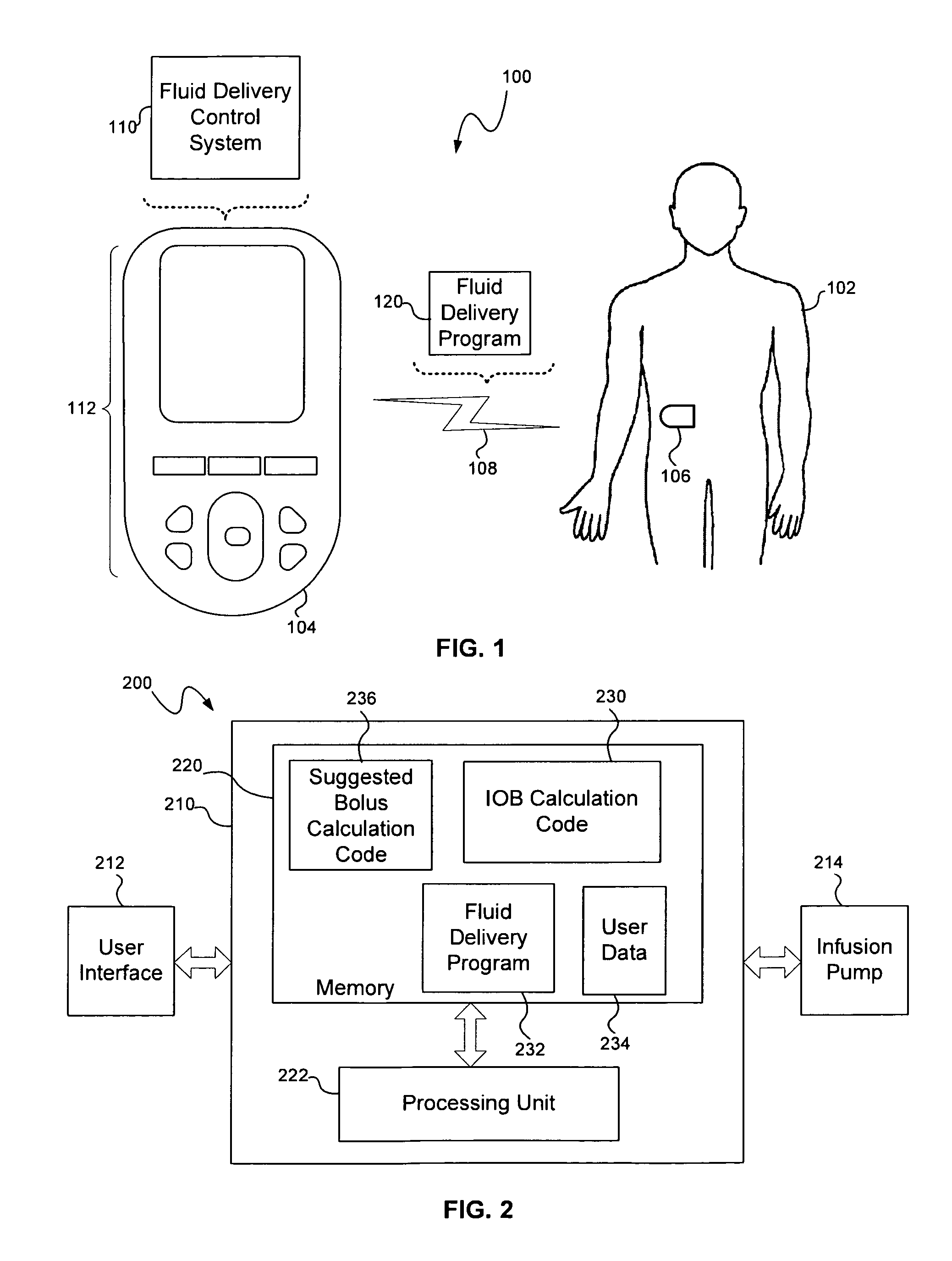
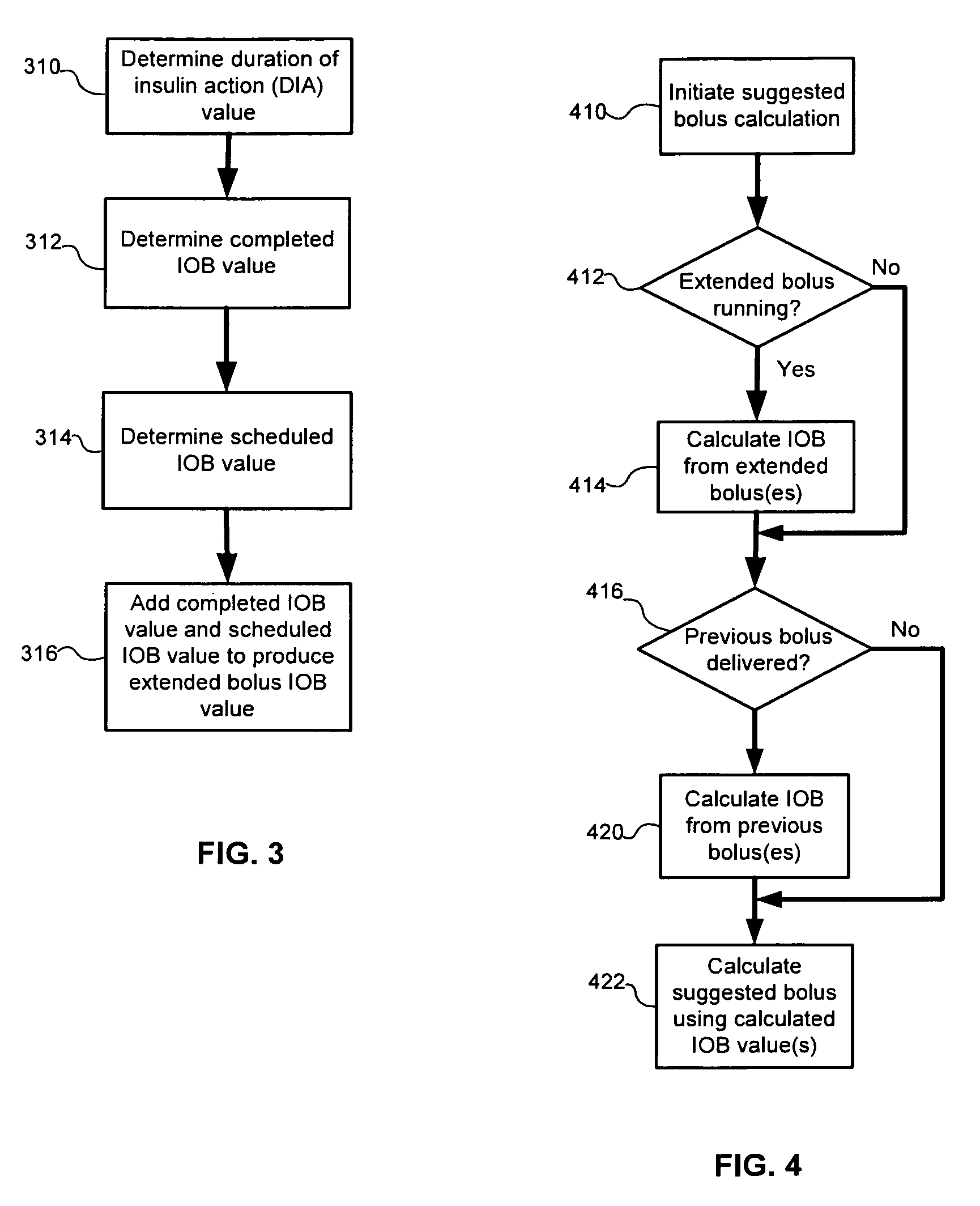
Calculating insulin on board for extended bolus being delivered by an insulin delivery device
A system and method may be used to calculate insulin on board (IOB) for an extended bolus being delivered by an insulin infusion pump. In general, the system and method calculates an extended bolus IOB value for the extended bolus, which takes into account the insulin currently on board from the extended bolus and the insulin scheduled to be delivered by the extended bolus over a subsequent time period equivalent to a duration of insulin action. The extended bolus IOB value may be used to calculate a suggested bolus.
Owner:INSULET CORP
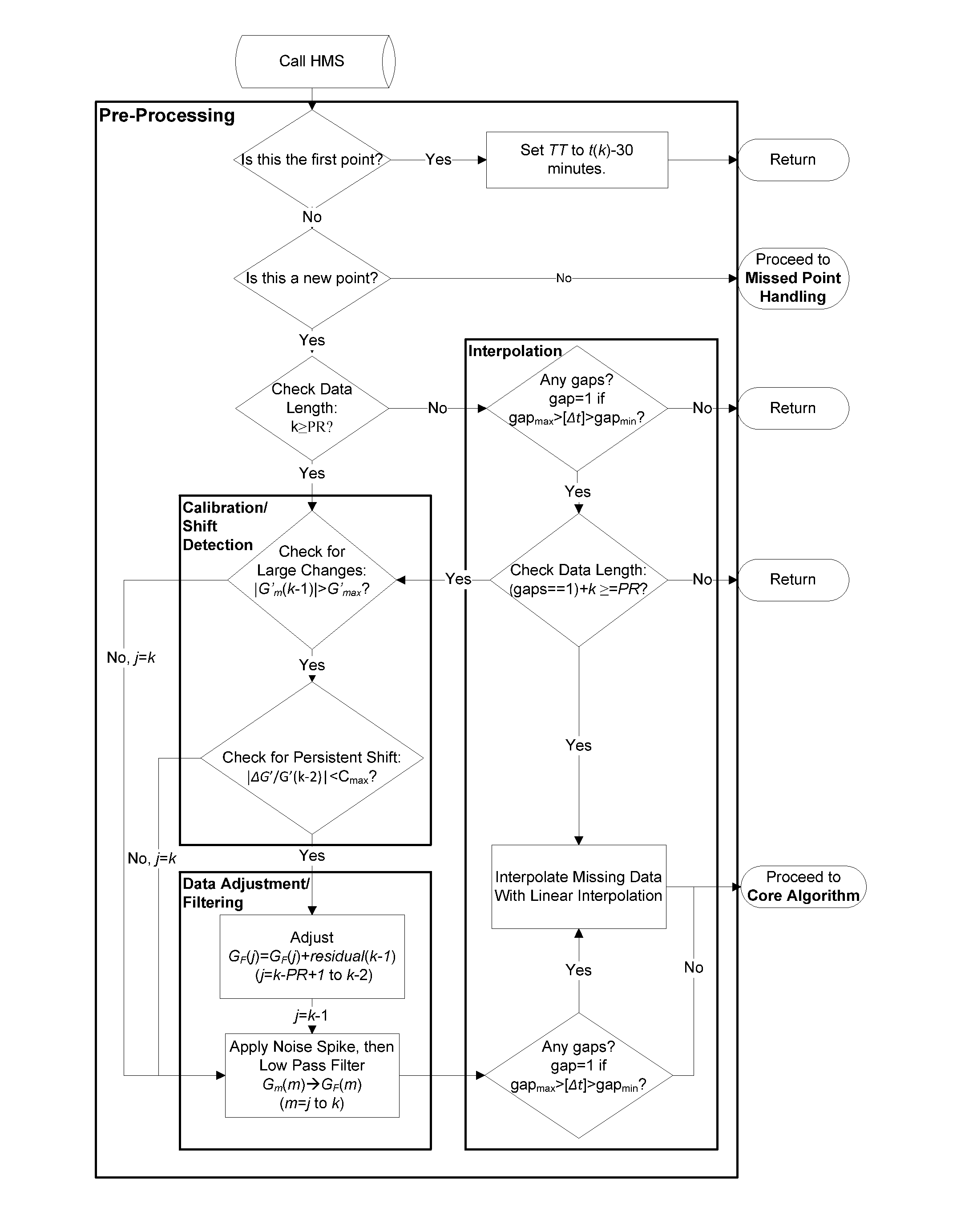
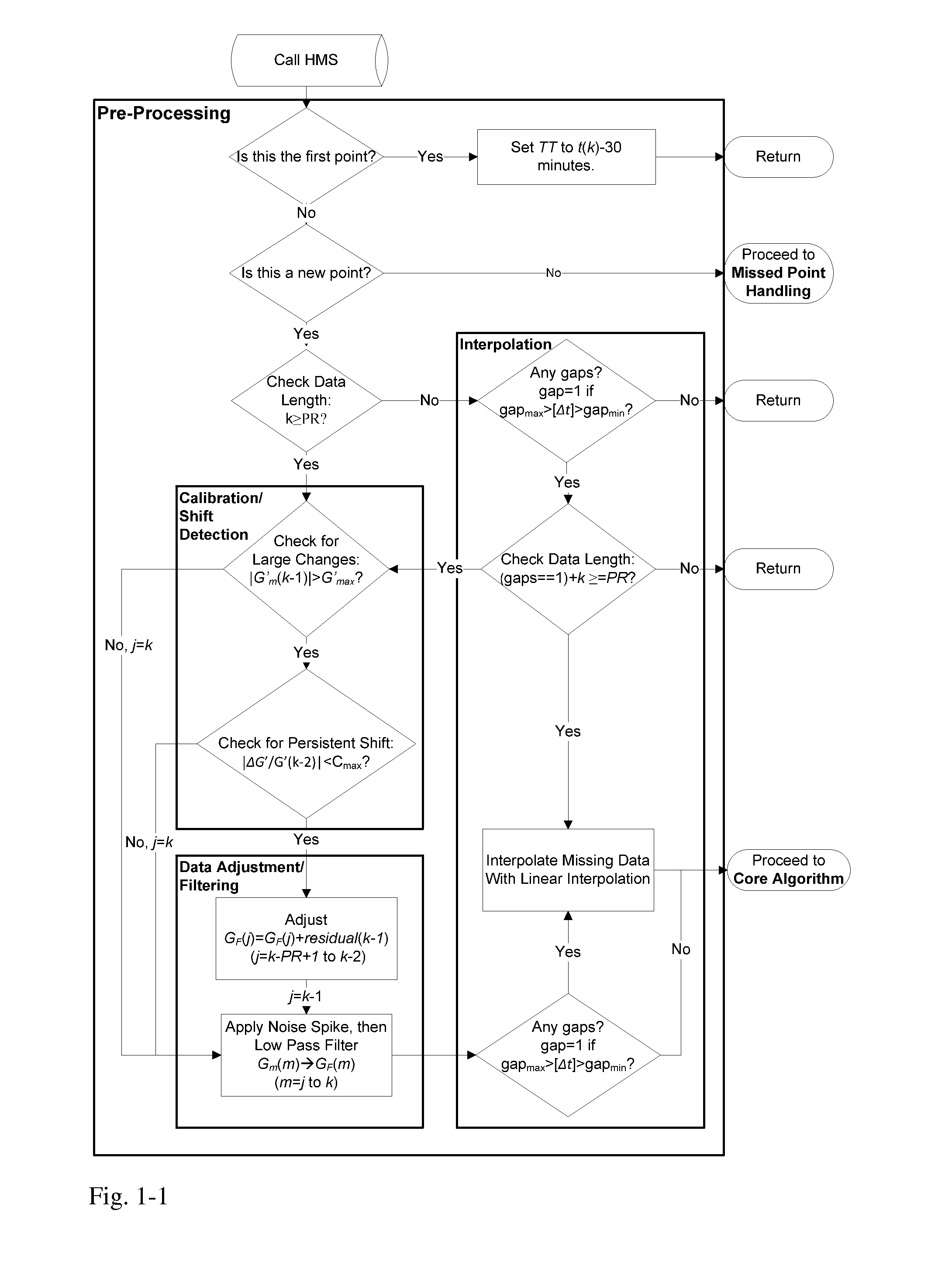
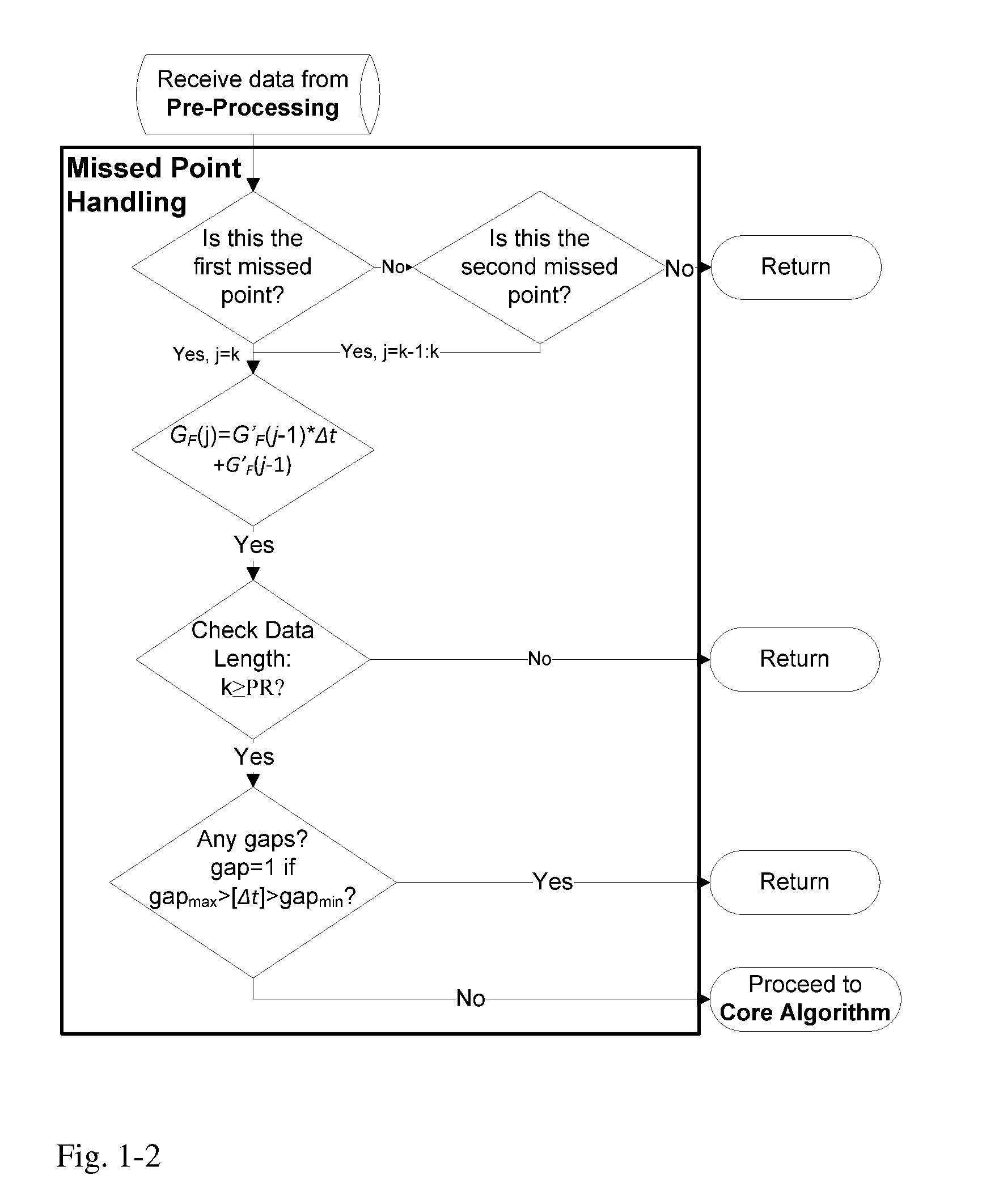
Health Monitoring System
InactiveUS20110313680A1Reduce noisePoint was missedTelemedicineNutrition controlNegative feedbackMissing data
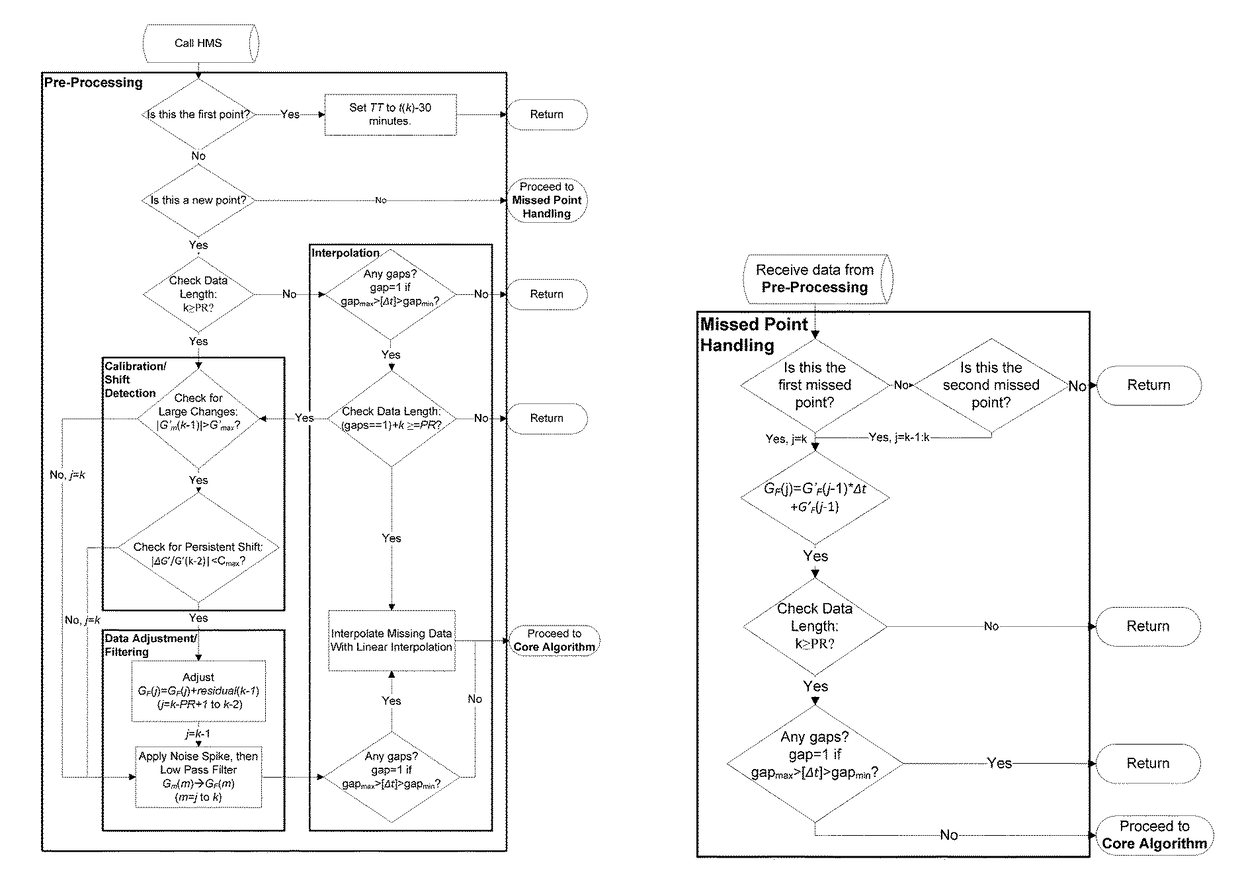
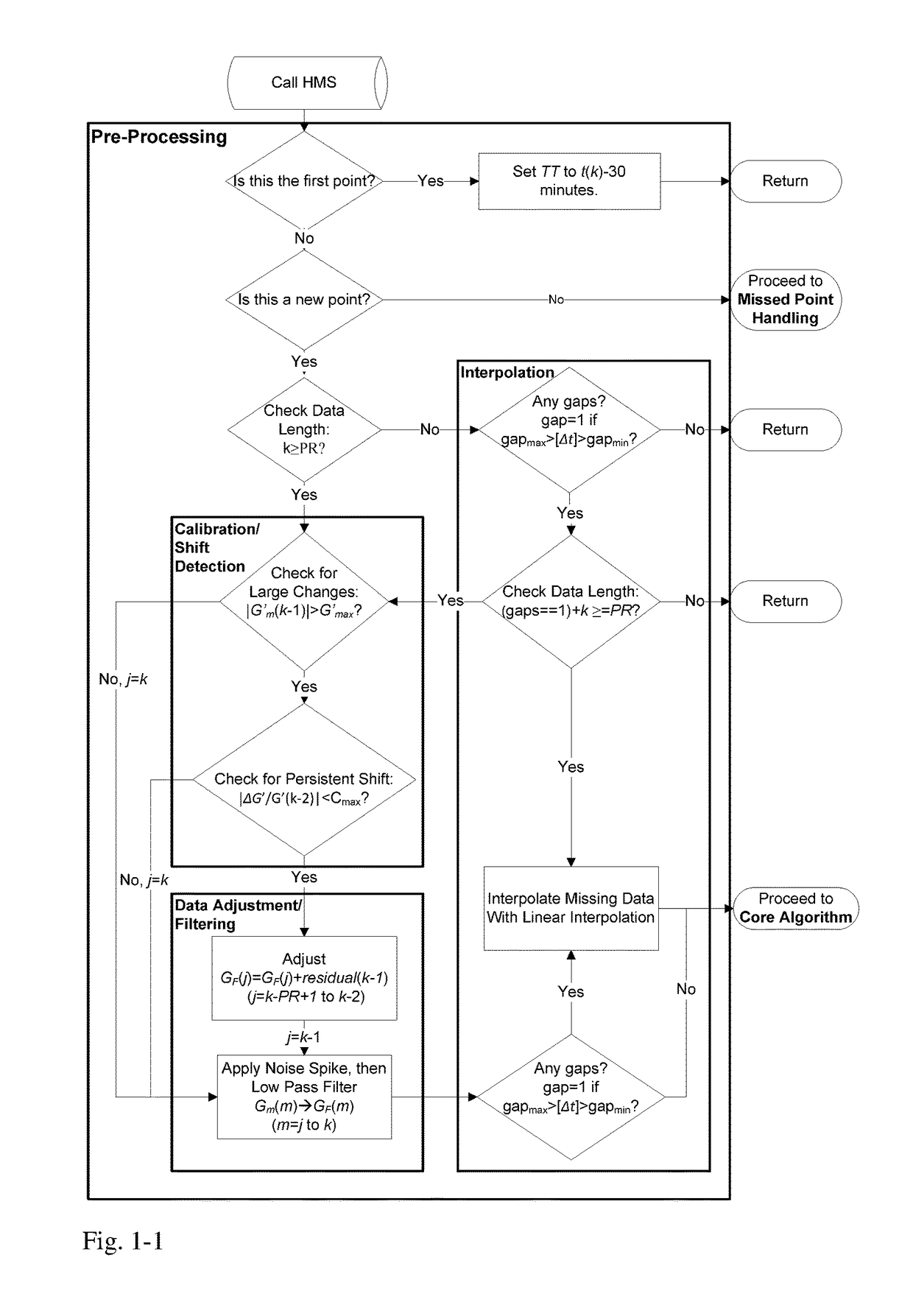
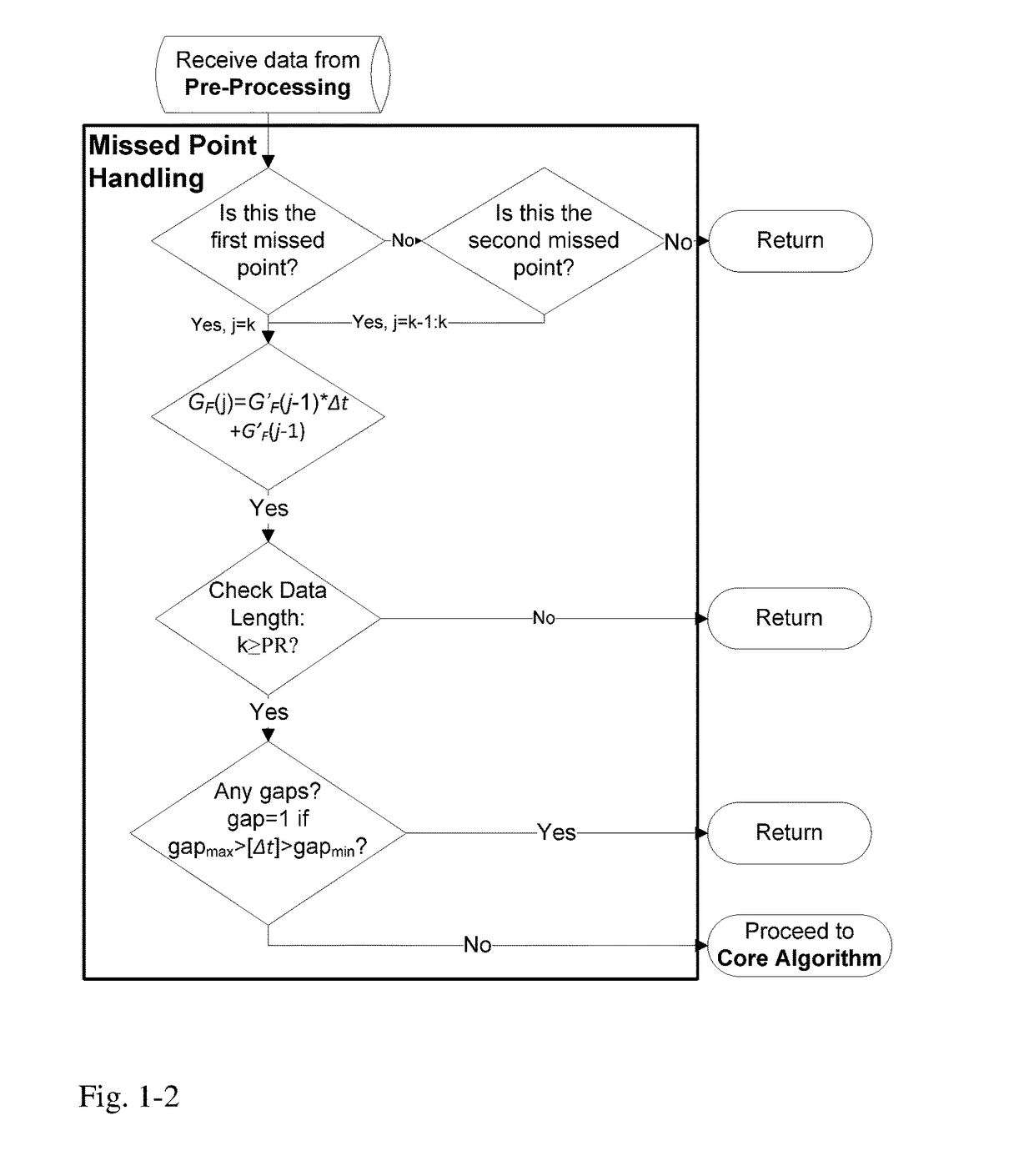
A machine for processing continuous glucose monitoring data and issuing an alert if hypoglycemia is imminent has three modules: (a) a pre-processing module that receives and modulates continuous glucose monitoring data by reducing noise and adjusting for missed data points and shifts due to calibration; (b) a core algorithm module that receives data from the pre-processing module and calculates a rate of change to make a hypoglycemia prediction, and determine if hypoglycemia is imminent; and (c) an alarm mode module that receives data from the core algorithm and issues an audio or visual alert or warning message or a negative feedback signal to an insulin delivery device if hypoglycemia is imminent.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
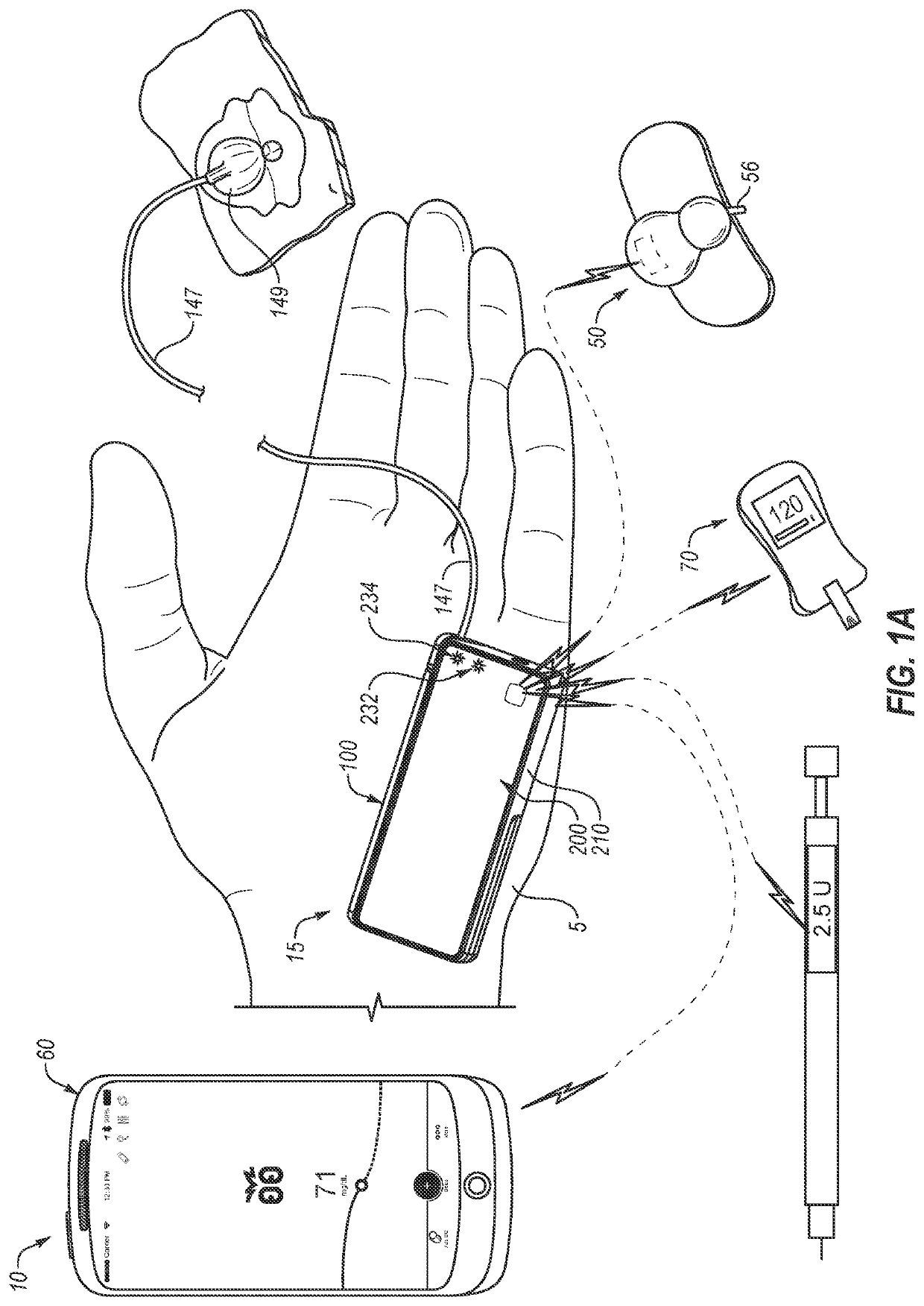
Continuous glucose monitoring injection device
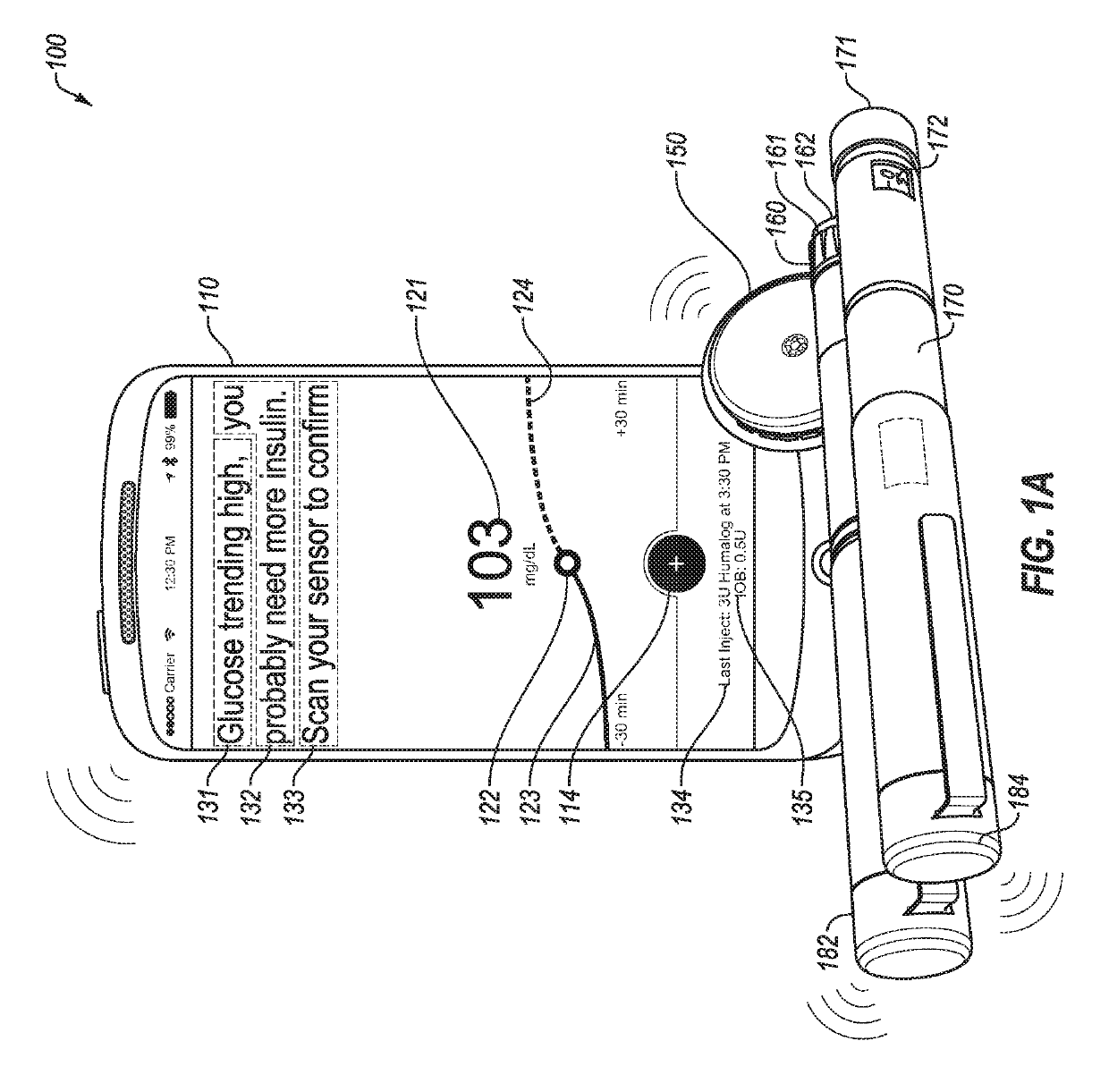
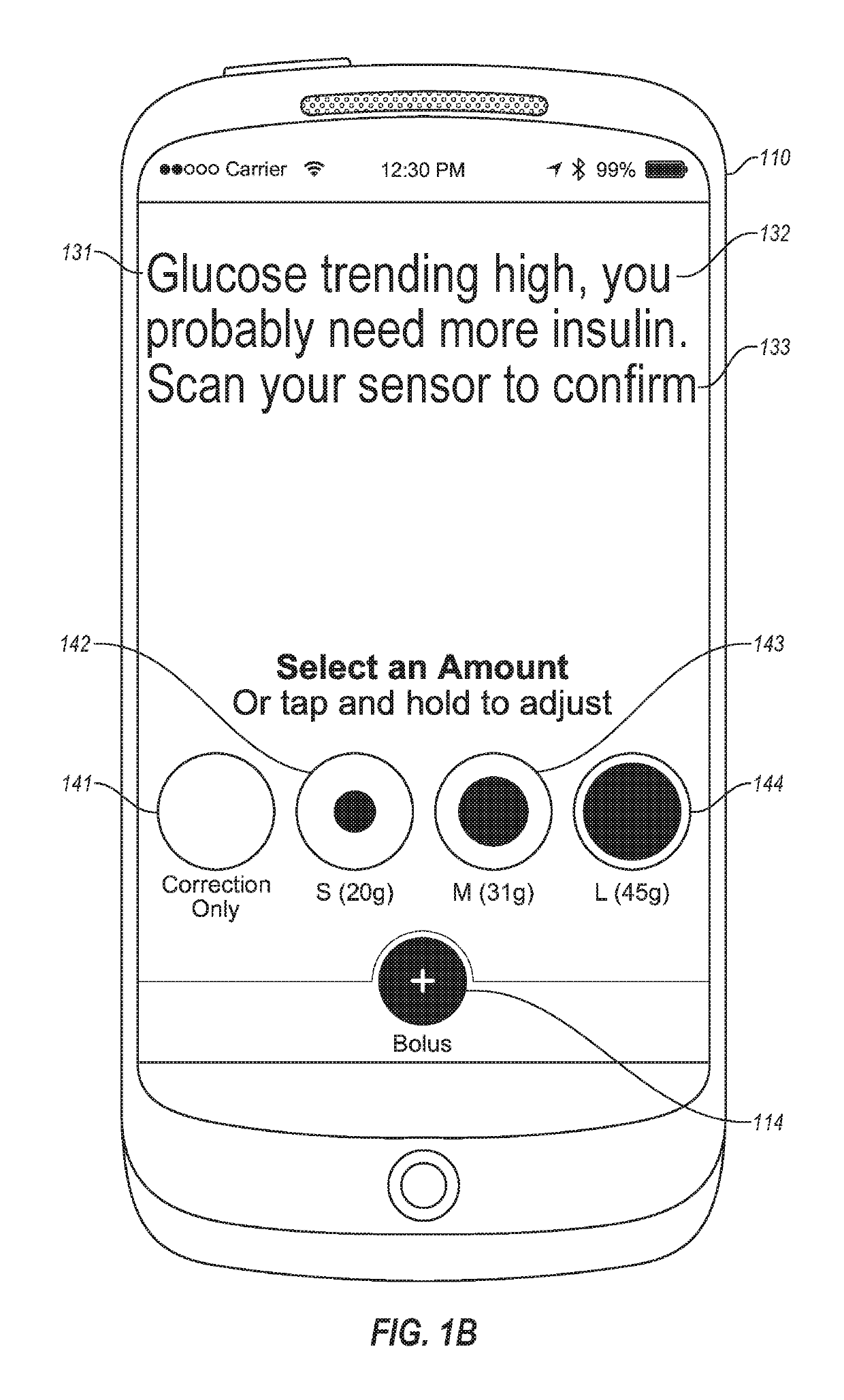
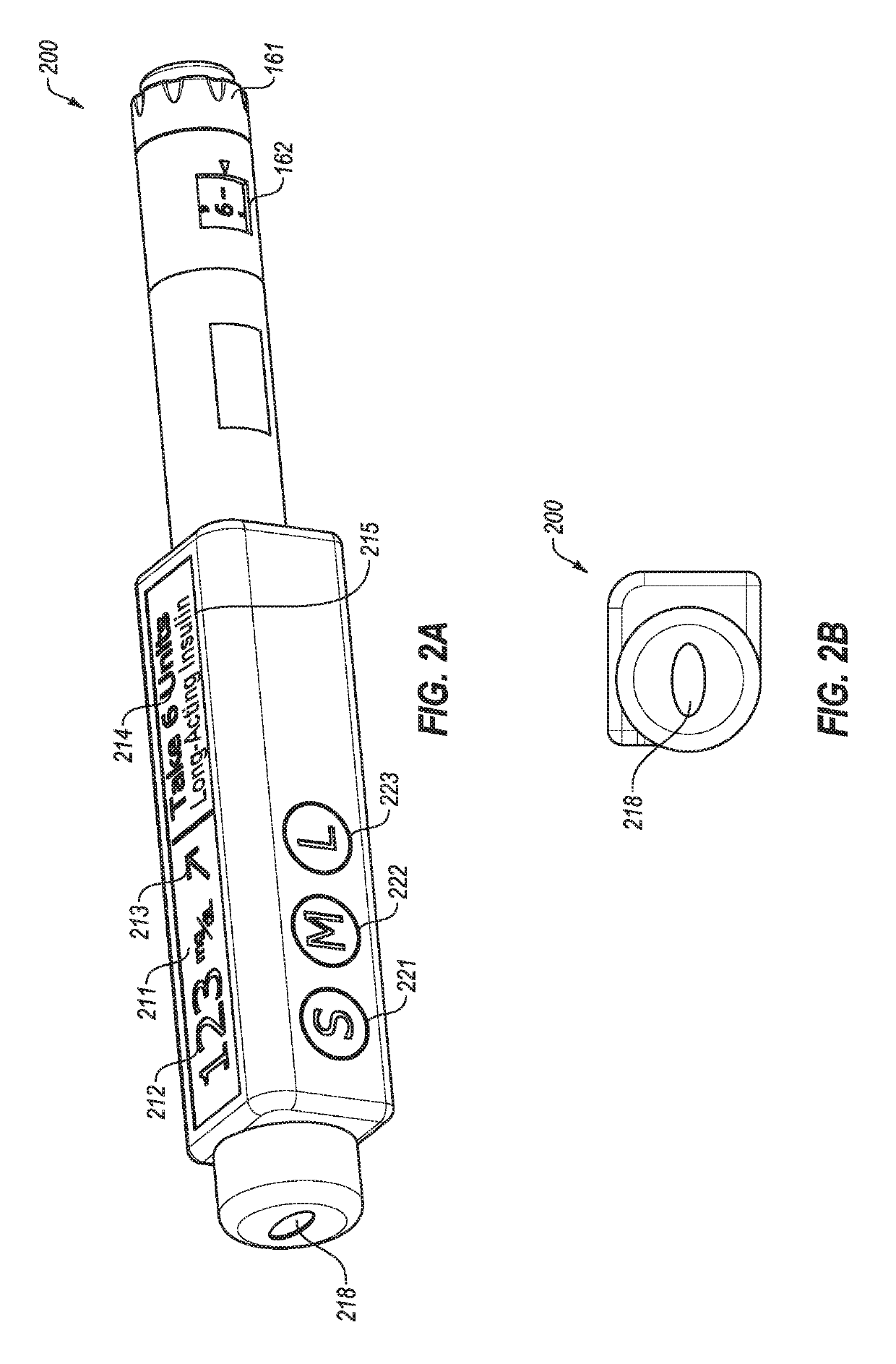
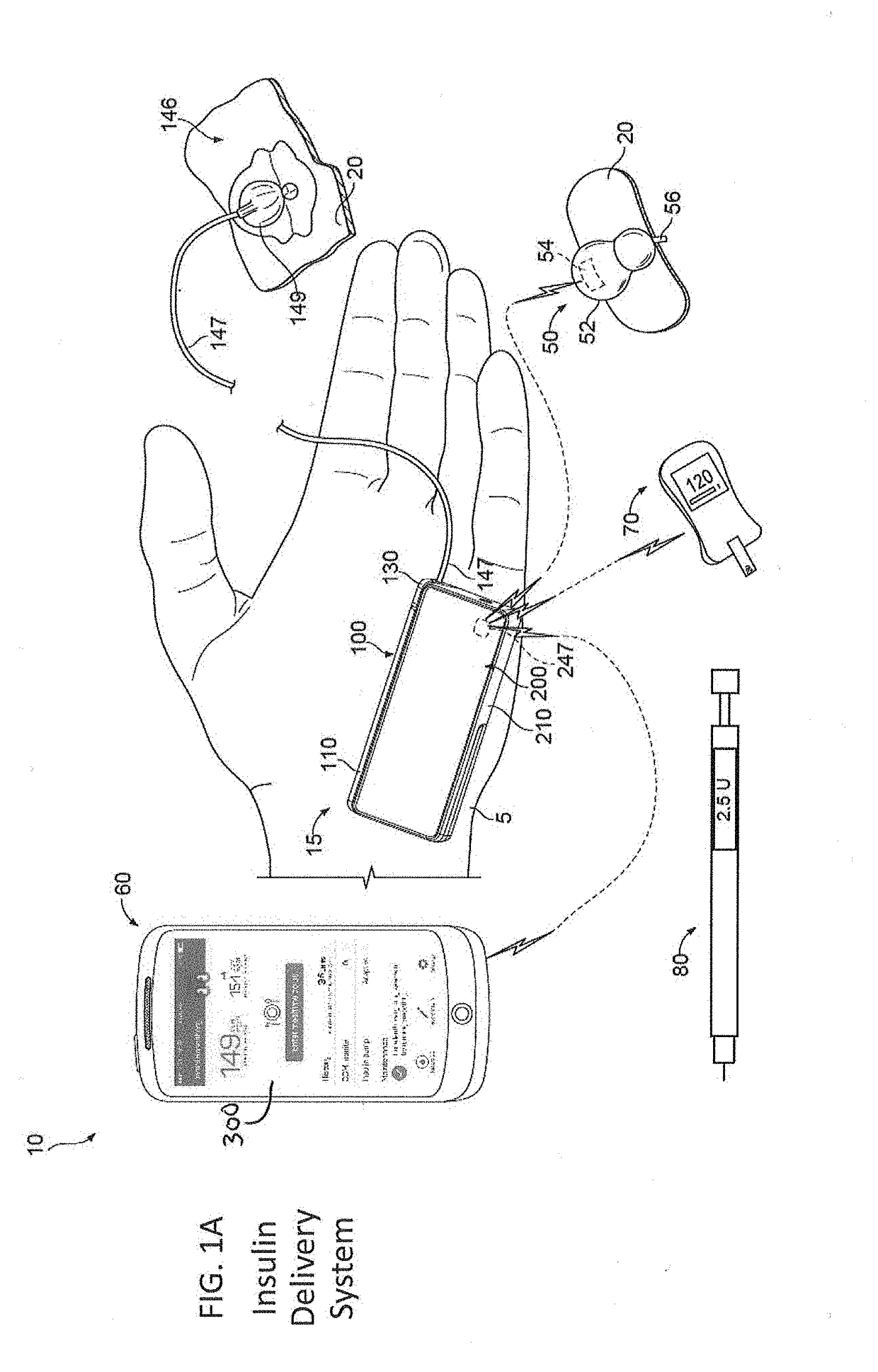
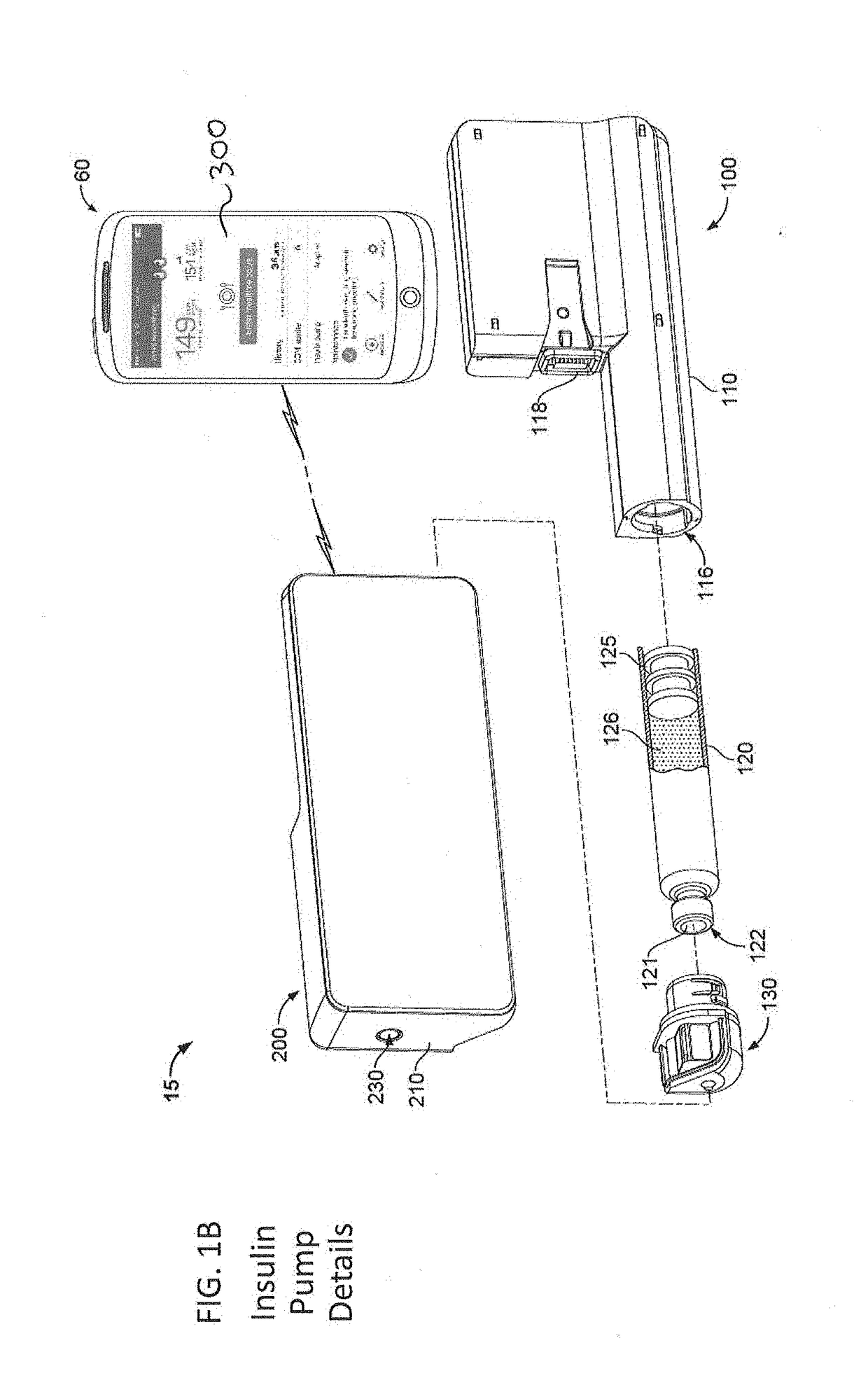
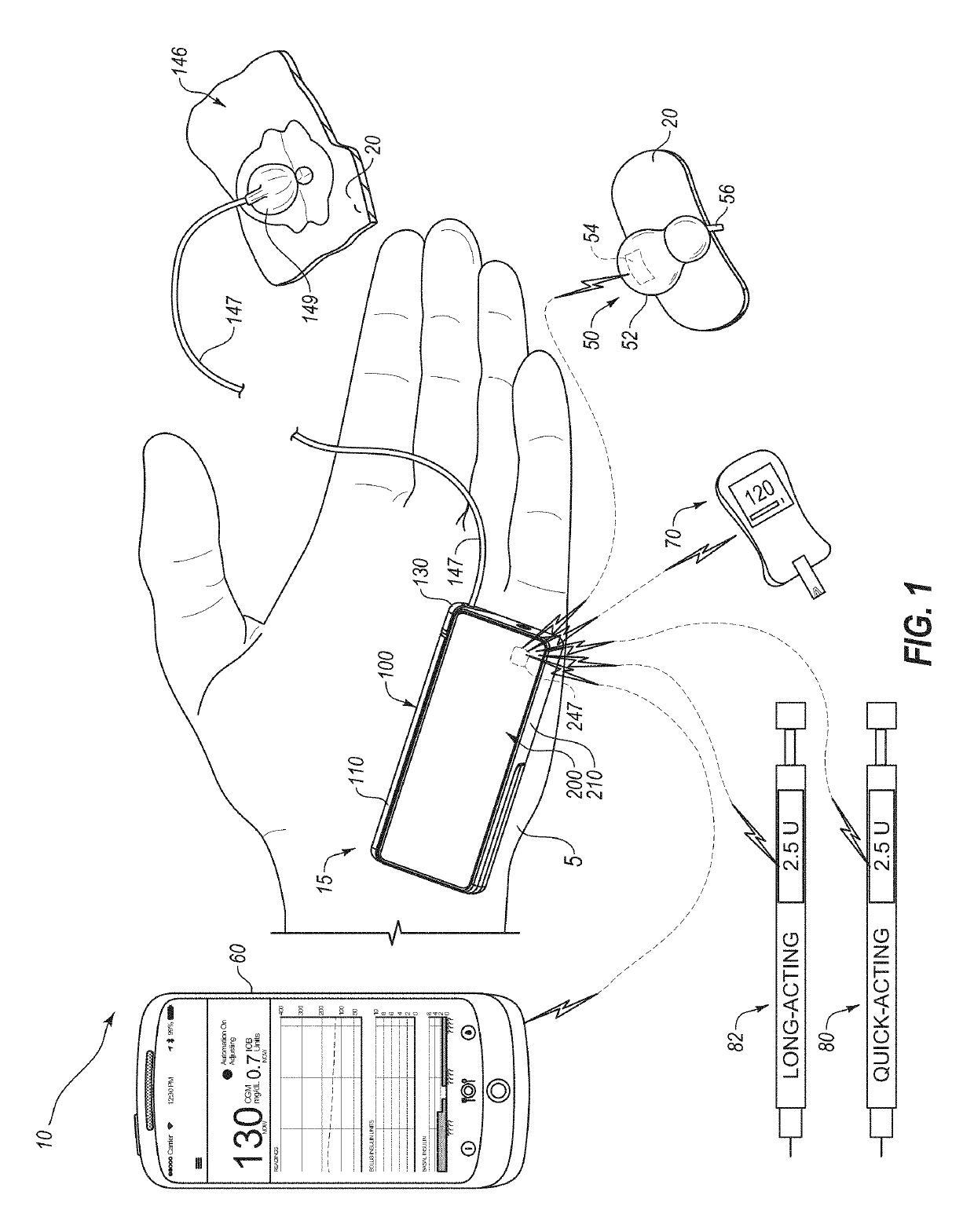
An electronic insulin delivery device receives glucose data from a glucose monitor and sets a bolus dose amount. The device may take the form of an insulin pen with automatic priming and accurate dosing provided by a motor in connection with an encoder. The device may communicate with and be controlled by a smart phone device. The smart phone device provides a user interface to receive user data including patient weight, insulin to carbohydrate ratio and exercise factor, and to send instructions to the device, including dose amount. The dose amount is determined taking into account glucose level and trend, and other factors. The delivery device may be in continuous communication with the glucose monitor and smart phone to provide for near real-time adjustments in glucose treatment. Glucose data, insulin injection data, and other relevant data may be stored and accessible to interested parties.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Insulin pump
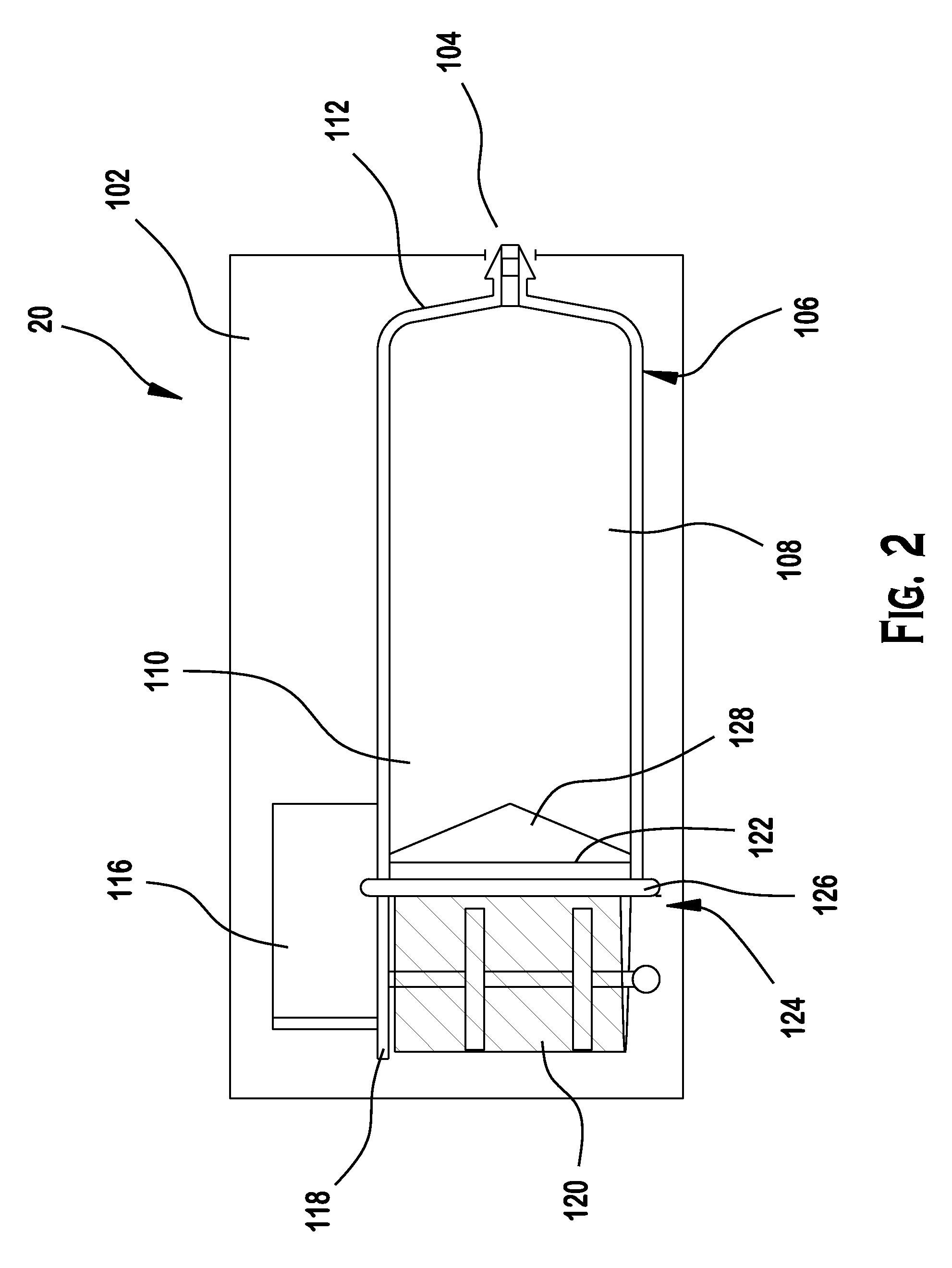
A portable insulin delivery device that supplies insulin in a pre-pressurized chamber, passes the insulin through a pressure-dropping labyrinth to a flow control valve. The valve is activated by a piezoelectric actuator. This allows for precise insulin delivery. An electronic package provides for programming of basal rates and bolus. A pressure sensor relays data concerning normal operation and pressure changes that indicate problems. The processor, keypad, displays power source, fluid pressure sensor and fluid flow control actuator are housed in a base unit. A removable cartridge unit houses the pre-pressurized fluid reservoir, flow path labyrinth, and flow control valve.
Owner:NILI MED LTD
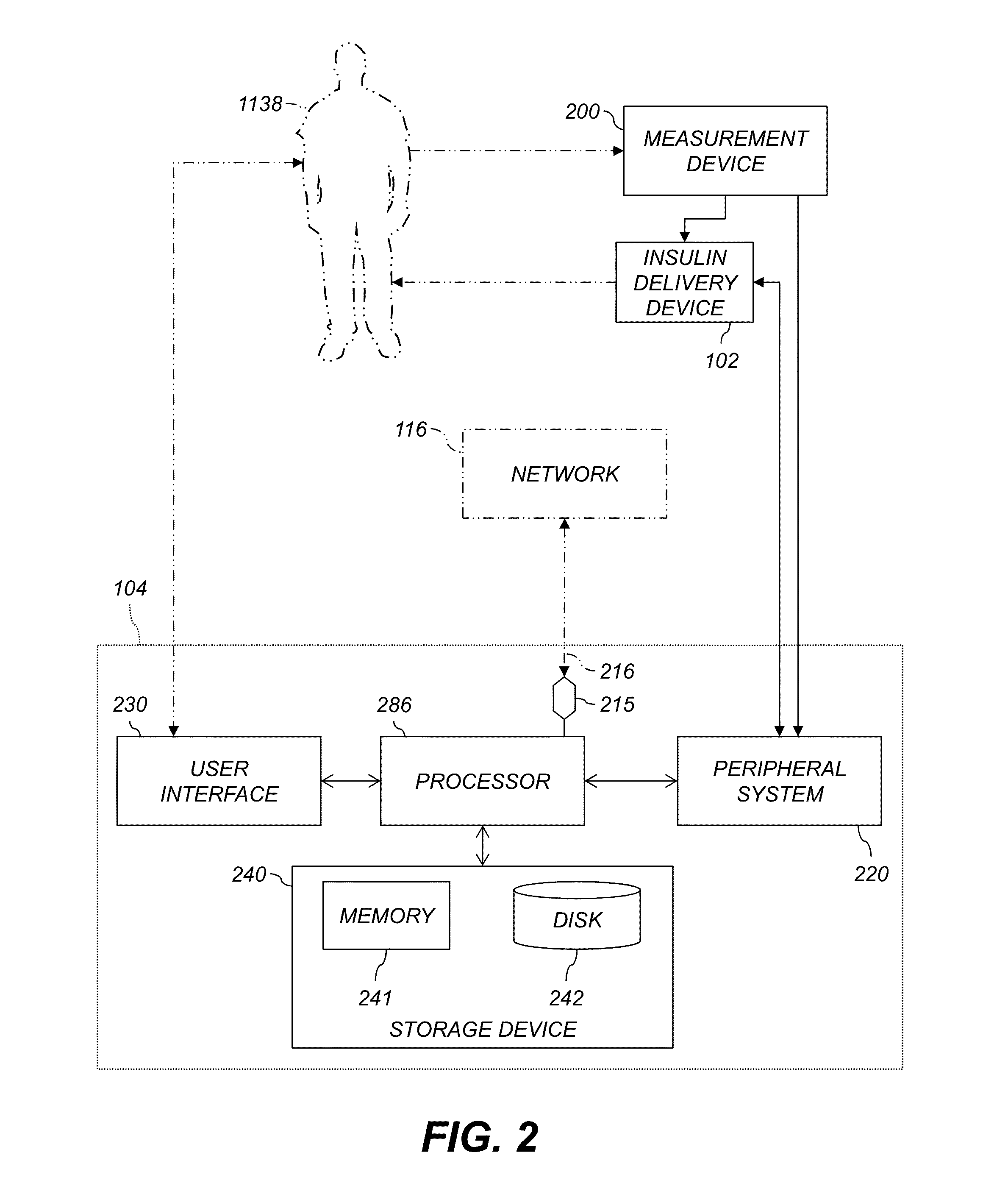
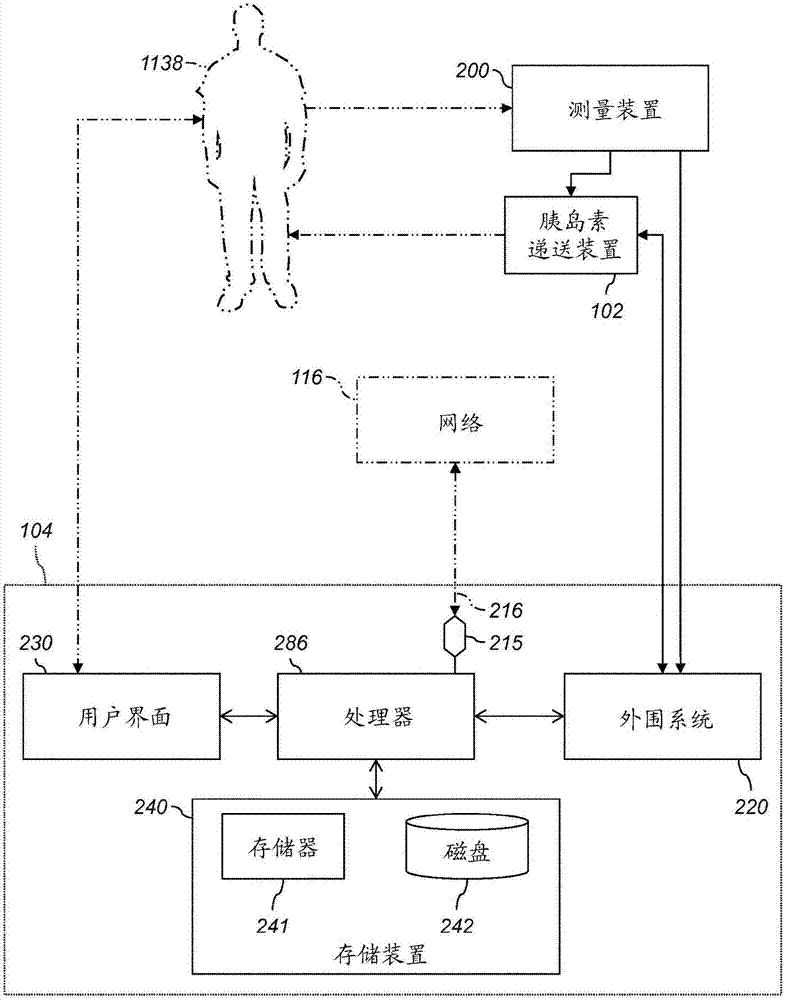
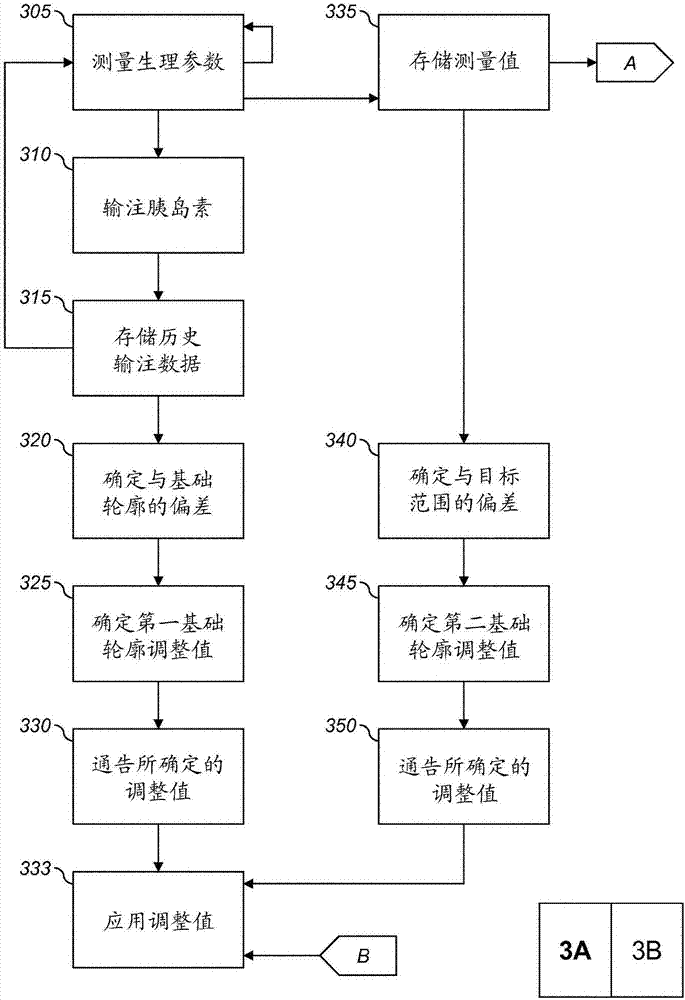
Decisions support for patients with diabetes
InactiveUS20160082187A1Improve determinationImprove quality of careMedical devicesPressure infusionMeasurement deviceBasal rate
A decision support system includes a measurement device configured to continuously measure a physiological parameter of a patient. An insulin delivery device provides insulin to the patient per an initial basal profile and the parameter measurements. A storage device holds historical data of insulin delivery to the patient. A processor determines deviations of the delivery of insulin from the basal profile for one or more time period(s) using the historical data, computes a respective first basal-profile adjustment for each of the one or more time period(s) using the determined deviations, and annunciates the computed first basal-profile adjustment(s). A method of recommending a basal-rate adjustment includes measuring the parameter, infusing the patient with insulin and storing the historical data, determining the deviations from the basal profile, computing the first basal-profile adjustments, and annunciating the computed first basal-profile adjustment(s).
Owner:ANIMAS CORP
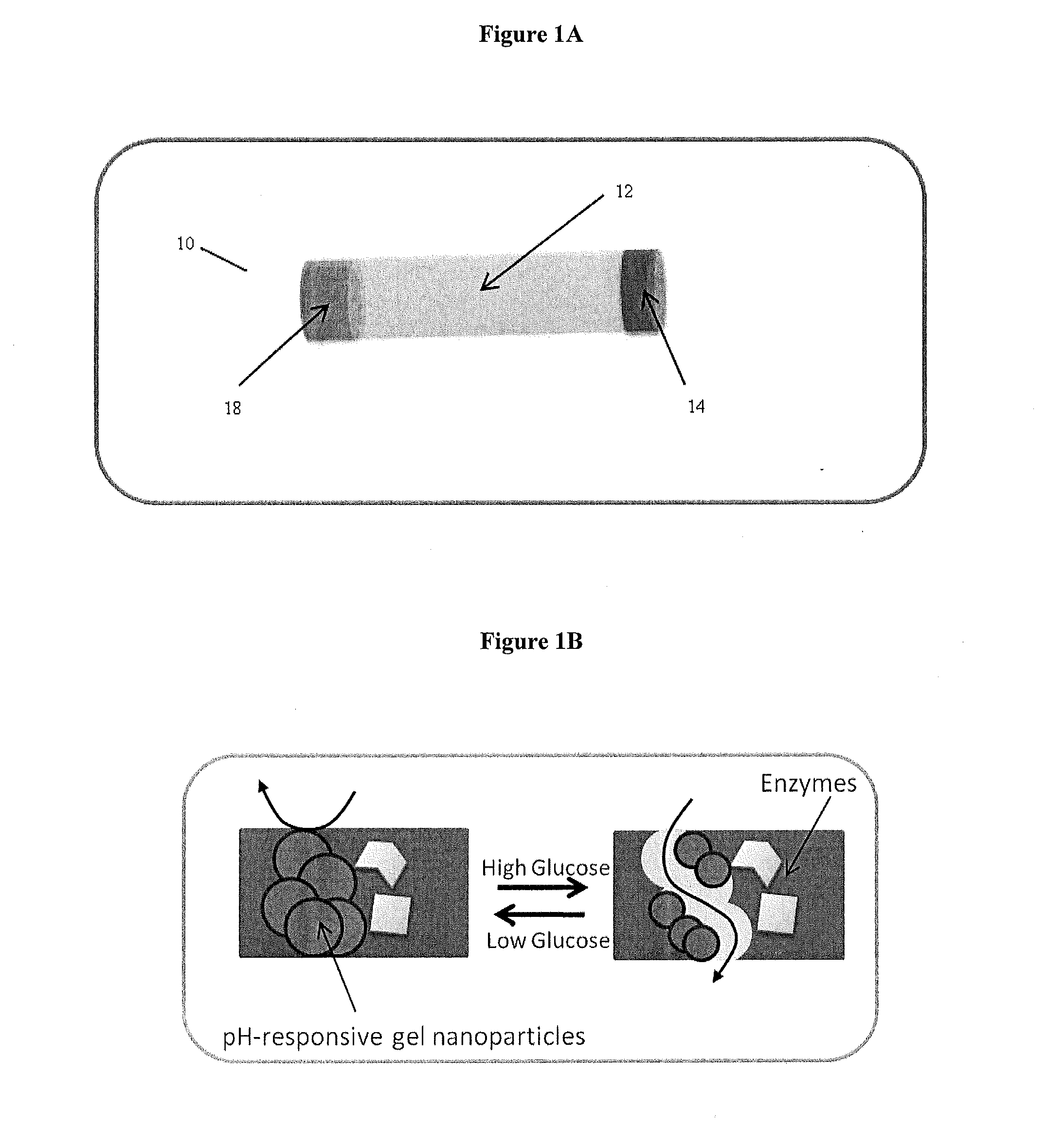
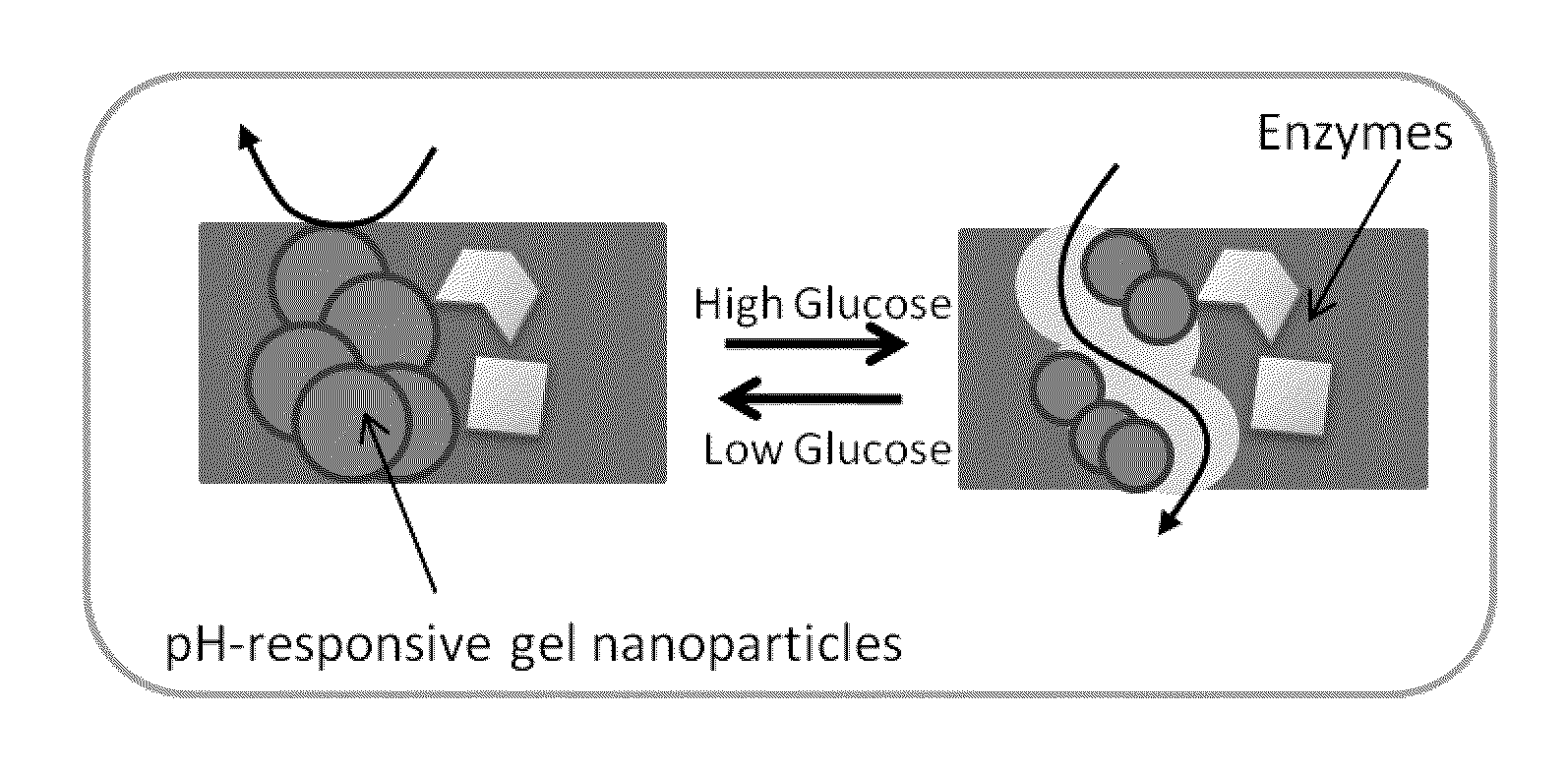
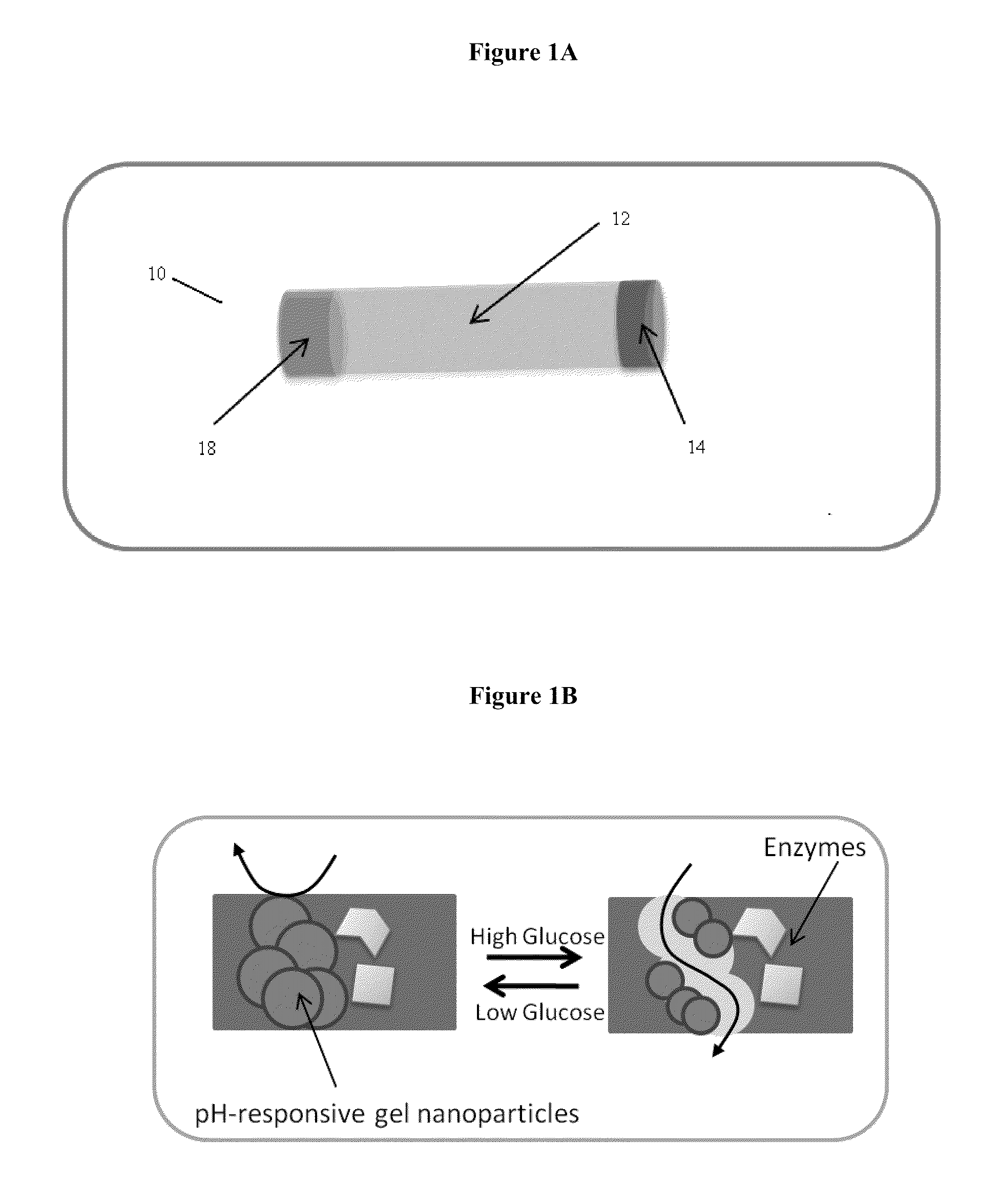
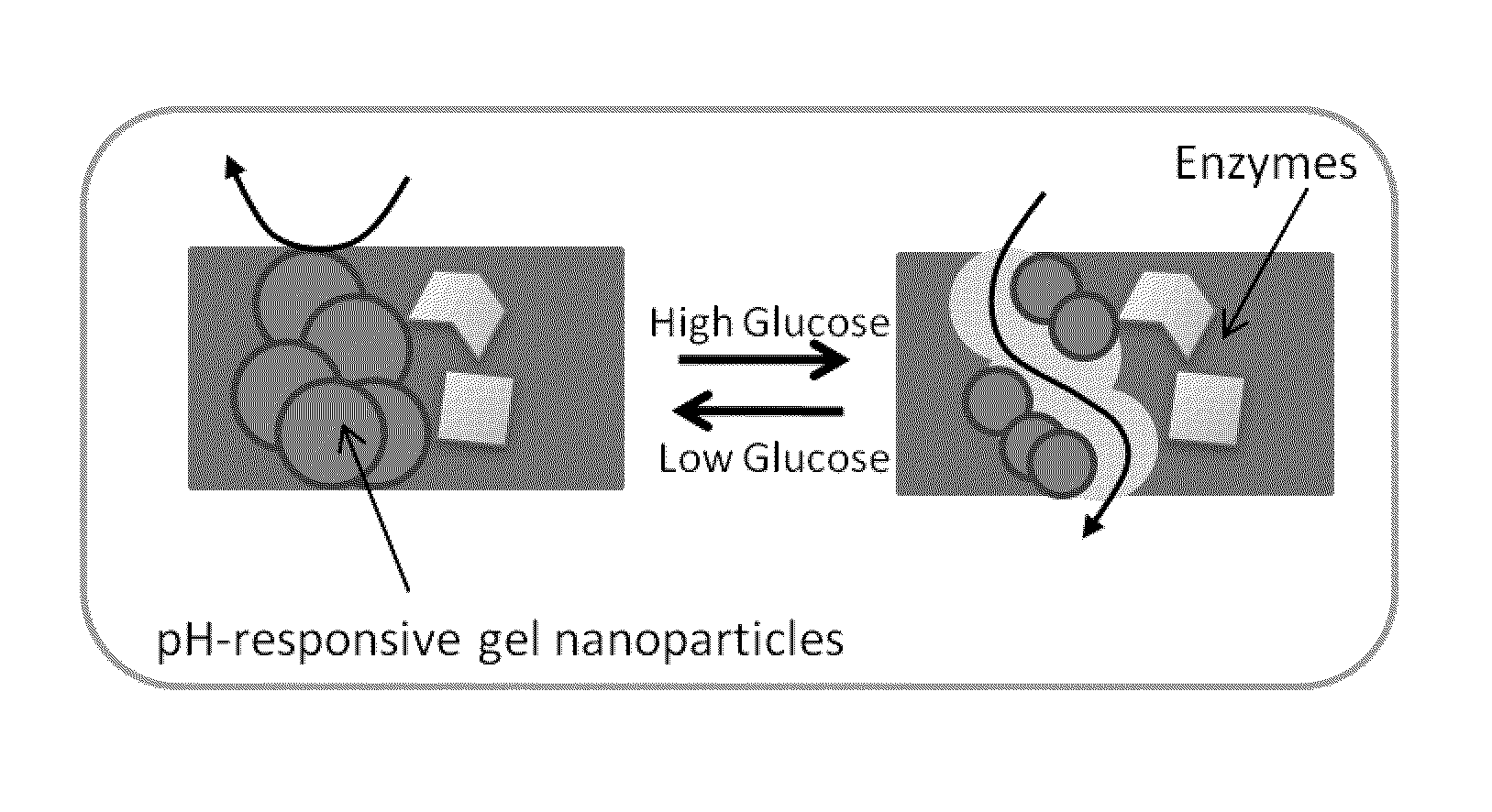
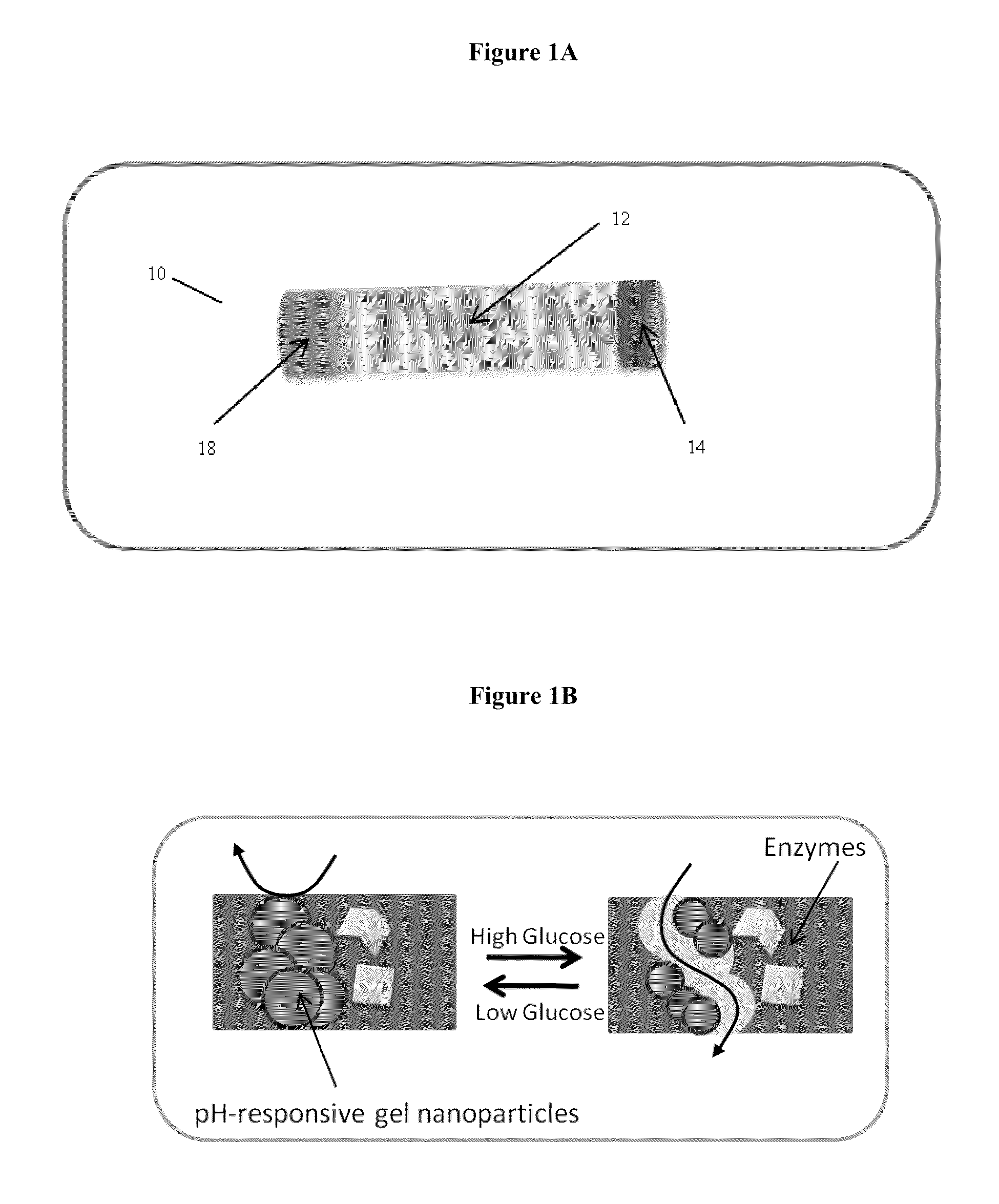
Implantable-glucose responsive insulin delivery device
A biocompatible insulin delivery device is provided comprising an insulin reservoir sealed with a glucose-responsive plug or membrane. The plug functions to release insulin from the reservoir in response to a hyperglycemic glucose concentration and to prevent insulin release from the reservoir in response to hypoglycemic glucose concentration. In one embodiment, the plug is made of a biocompatible polymeric matrix comprising an inorganic component, a stimulus-responsive component and a catalytic component.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
Medicine injection and disease management systems, devices, and methods
ActiveUS10426896B2Simple calculationSimplifying the collection of an estimated glucose valueDrug and medicationsInfusion syringesDiseaseGlucose polymers
One or more embodiments of the present disclosure may include an insulin delivery system that includes an insulin delivery device, a user interface that includes multiple user-selectable icons or buttons each representing different meal characteristics, memory to store one or more user-specific dosage parameter, and a processor in communication with the memory and adapted to receive blood glucose data. The processor may also be adapted to determine initial meal characteristics associated with each of the user-selectable icons or buttons based on at least one of the user-specific dosage parameters. The processor may also be adapted to update the meal characteristics associated with each of the user-selectable icons or buttons based upon the blood glucose data.
Owner:BIGFOOT BIOMEDICAL INC
Calculating insulin on board for extended bolus being delivered by an insulin delivery device
A system and method may be used to calculate insulin on board (IOB) for an extended bolus being delivered by an insulin infusion pump. In general, the system and method calculates an extended bolus IOB value for the extended bolus, which takes into account the insulin currently on board from the extended bolus and the insulin scheduled to be delivered by the extended bolus over a subsequent time period equivalent to a duration of insulin action. The extended bolus IOB value may be used to calculate a suggested bolus.
Owner:INSULET CORP
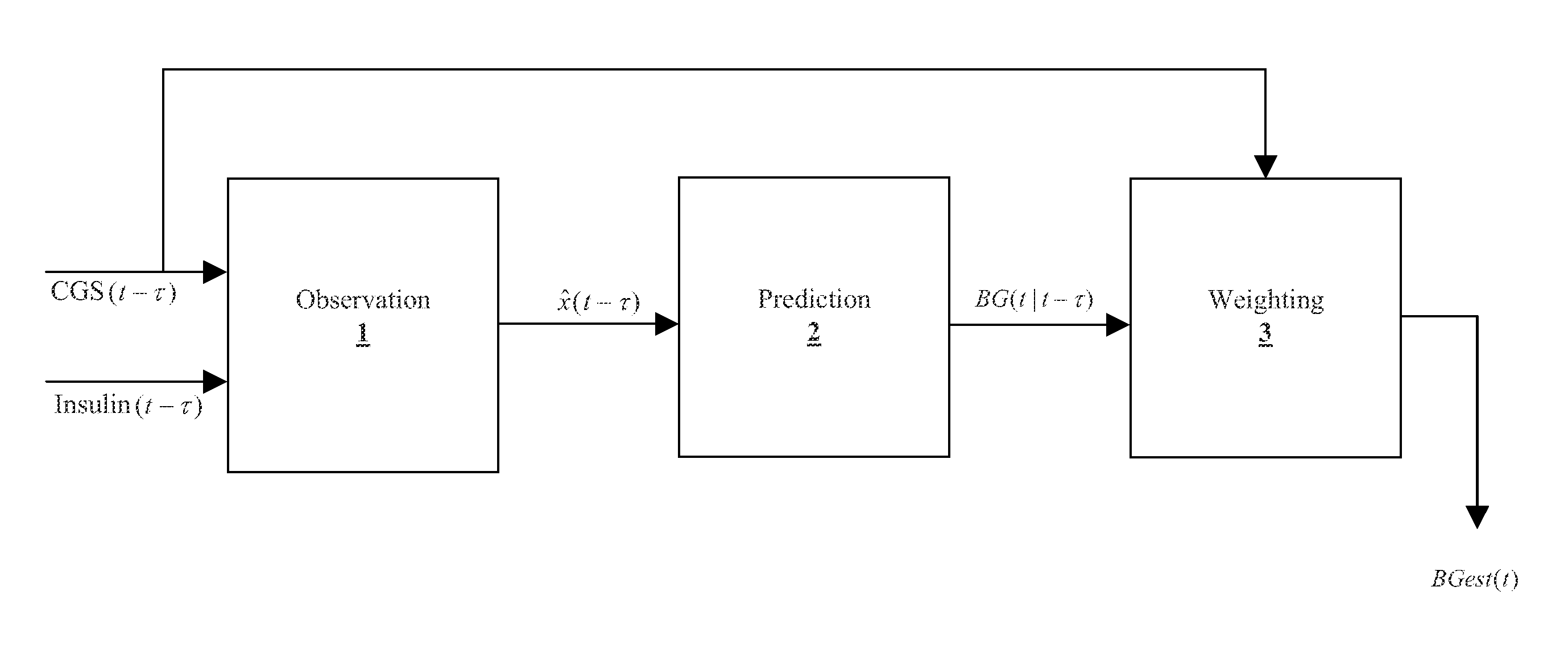
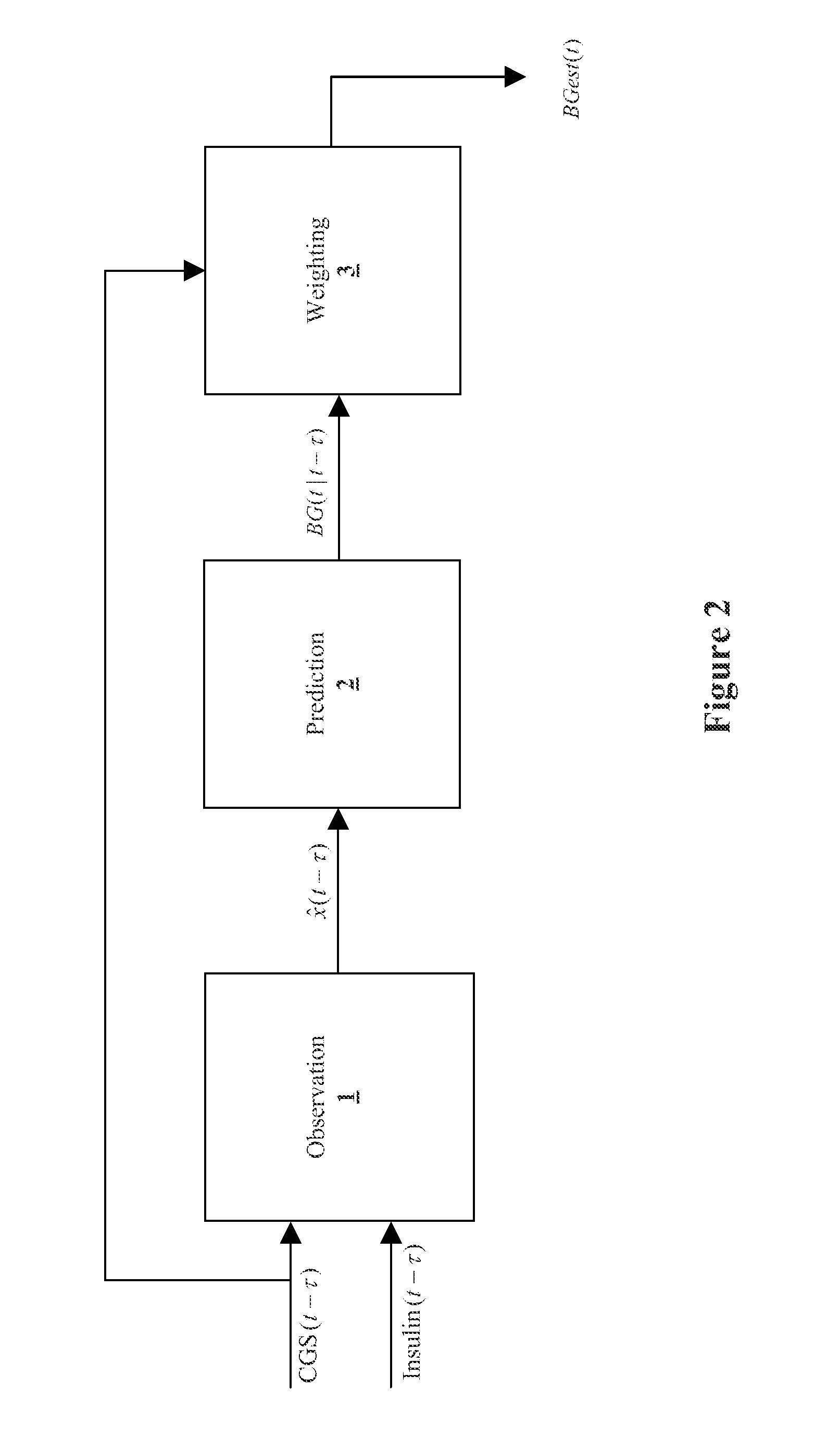
Method, system, and computer program product for improving the accuracy of glucose sensors using insulin delivery observation in diabetes
ActiveUS9398869B2Improve accuracyImprove sensor accuracyOther blood circulation devicesPressure infusionGlucose sensorsInsulin pump
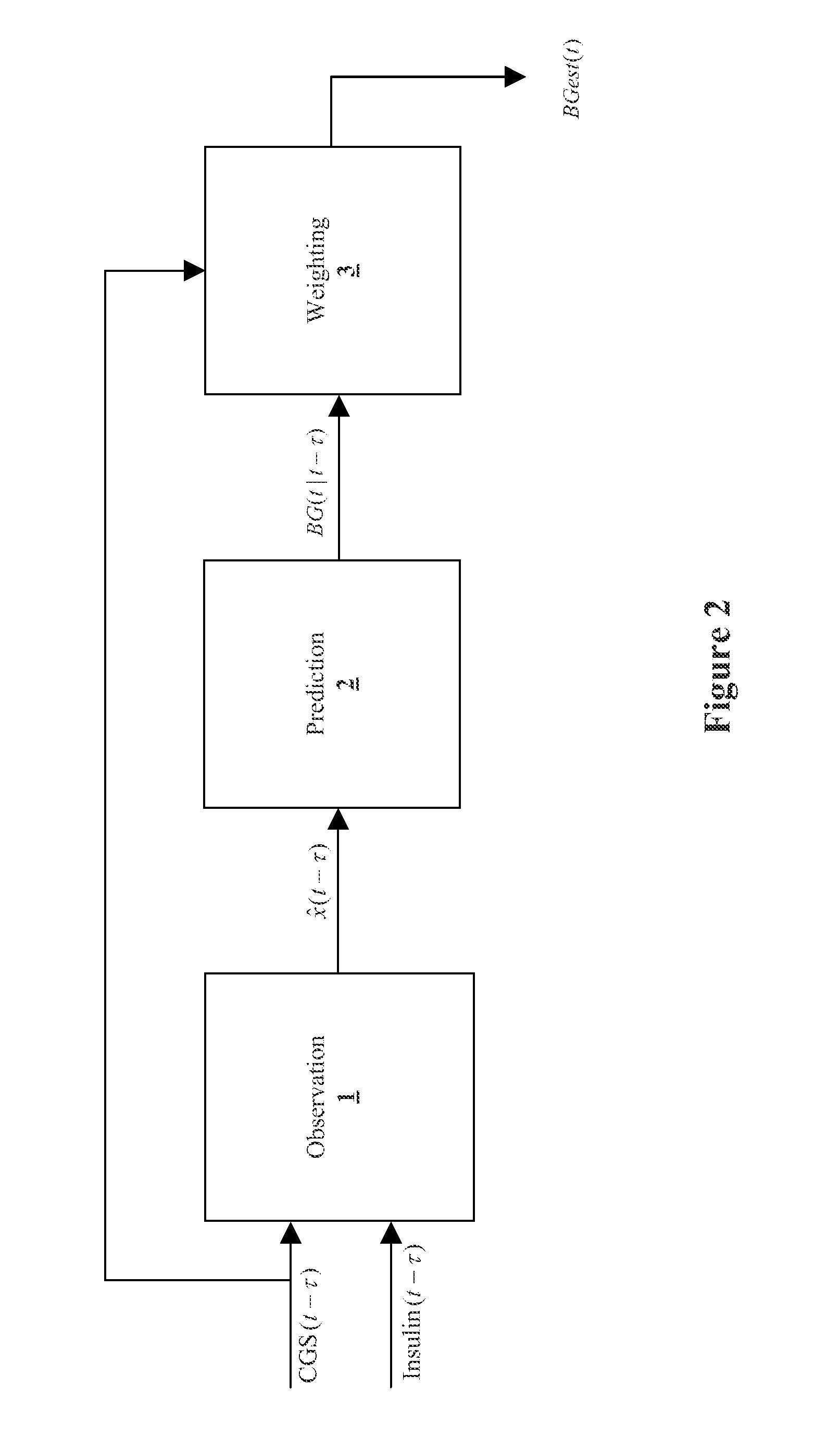
Method and System for providing a signal from an insulin pump, artificial pancreas, or another insulin delivery device as a source of information for improving the accuracy of a continuous glucose sensor (CGS). The effect of using insulin information to enhance sensor accuracy is most prominent at low blood glucose levels, i.e. in the hypoglycemic range, which is critical for any treatment. A system for providing a filtering / state estimation methodology that may be used to determine a glucose state estimate at time t-τ. The estimation may be extrapolated to some future time t and then the extrapolated value is used to extract the blood glucose component. The blood glucose component of the extrapolation and the output of the CGS are weighted and used to estimate the blood glucose level of a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Health Monitoring System
ActiveUS20170156682A1Reduce noiseNutrition controlMedical automated diagnosisNegative feedbackMissing data
A machine for processing continuous glucose monitoring data and issuing an alert if hypoglycemia is imminent has three modules: (a) a pre-processing module that receives and modulates continuous glucose monitoring data by reducing noise and adjusting for missed data points and shifts due to calibration; (b) a core algorithm module that receives data from the pre-processing module and calculates a rate of change to make a hypoglycemia prediction, and determine if hypoglycemia is imminent; and (c) an alarm mode module that receives data from the core algorithm and issues an audio or visual alert or warning message or a negative feedback signal to an insulin delivery device if hypoglycemia is imminent.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and methods for improved diabetes data management and use employing wireless connectivity between patients and healthcare providers and repository of diabetes management information
ActiveUS8285487B2Simplifies involvementPatient compliance is goodPhysical therapies and activitiesDrug and medicationsDiseasePatient profile
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
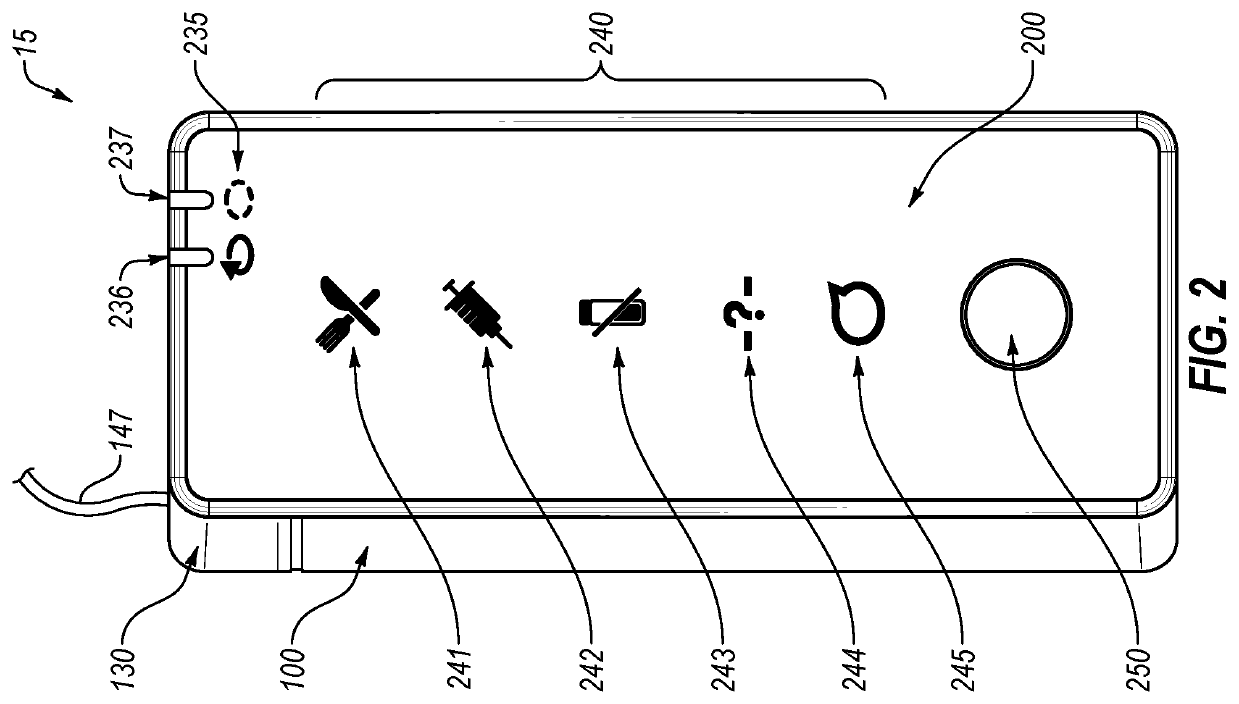
User interface for diabetes management system
ActiveUS20170199985A1Simplify the management processReduce cognitive loadLocal control/monitoringDrug and medicationsDiseaseSystem maintenance
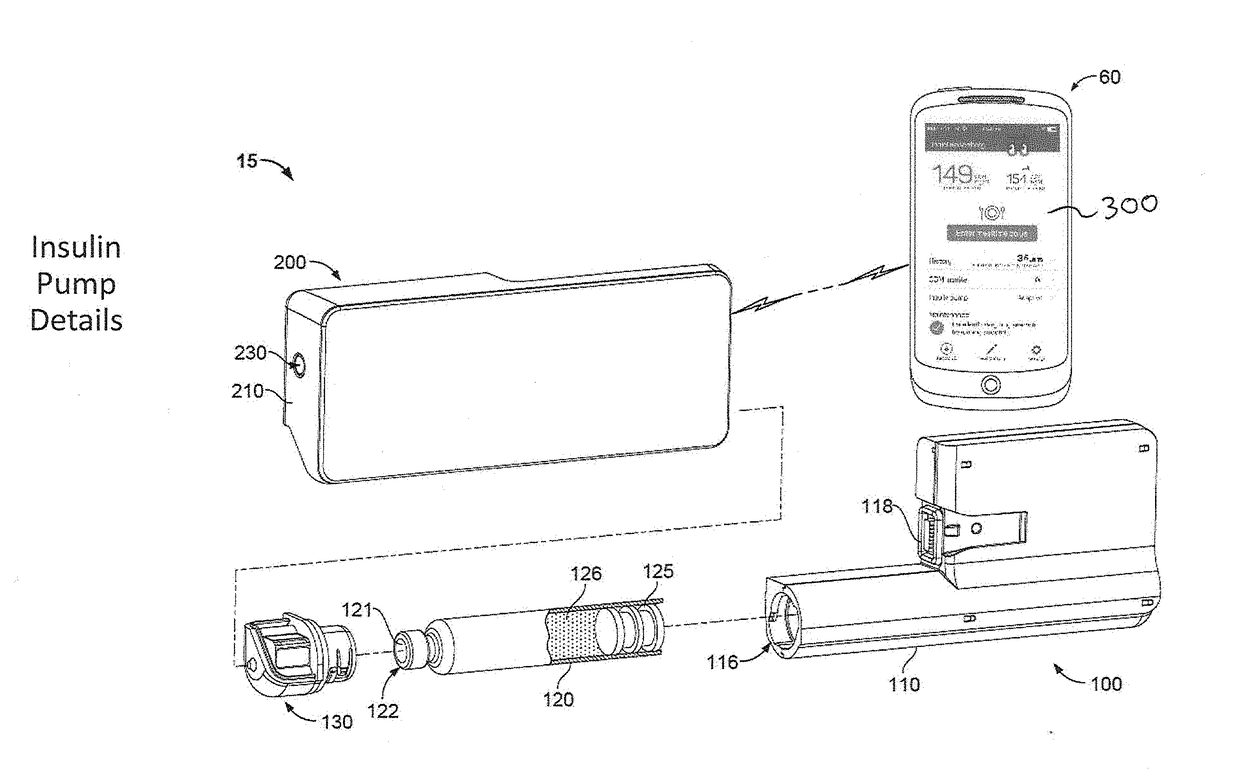
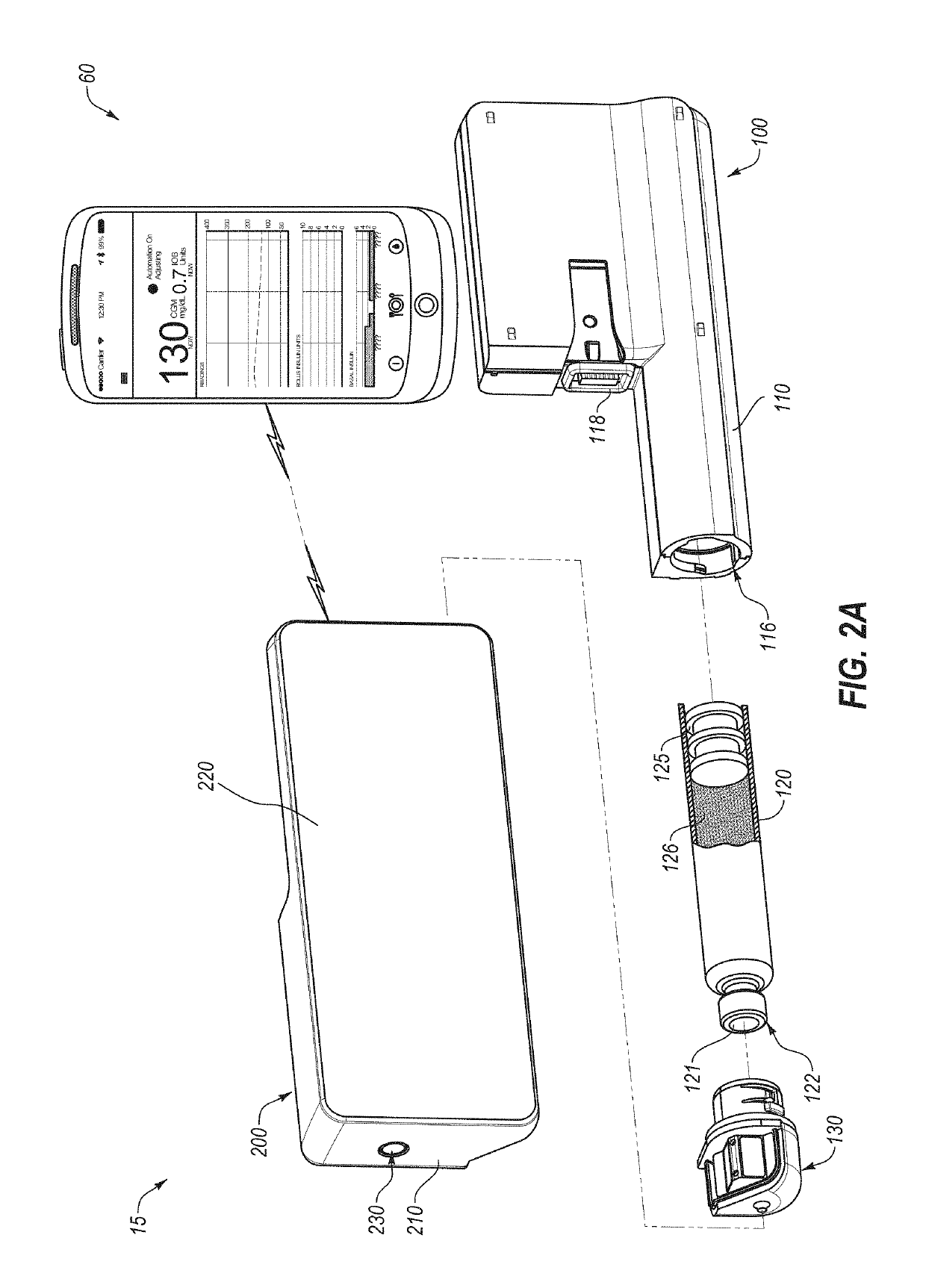
A diabetes management system including a pump for dispensing a medicant and a control device for controlling the pump includes a user interface for controlling functions of the pump and providing information related to operation of the pump and other information. The user interface can display blood glucose information and insulin dosing data such that a user can appropriately act on the information and / or gain confidence that the diabetes management system is operating appropriately to manage the disease. User interfaces provided herein can include displays of current and projected glucose values, bolus calculators, charts displaying glucose levels and / or insulin delivery data, system maintenance reminders, system status information, patient configuration input screens, and log-in screens. Diabetes management systems can include insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitors, blood glucose monitors, mobile computing devices, servers, and / or other insulin delivery devices (e.g., insulin pens).
Owner:INSULET CORP
Method, system, and computer program product for improving the accuracy of glucose sensors using insulin delivery observation in diabetes
ActiveUS20130079613A1Improve accuracyImprove sensor accuracyOther blood circulation devicesPressure infusionGlucose sensorsInsulin pump
Method and System for providing a signal from an insulin pump, artificial pancreas, or another insulin delivery device as a source of information for improving the accuracy of a continuous glucose sensor (CGS). The effect of using insulin information to enhance sensor accuracy is most prominent at low blood glucose levels, i.e. in the hypoglycemic range, which is critical for any treatment. A system for providing a filtering / state estimation methodology that may be used to determine a glucose state estimate at time t-τ. The estimation may be extrapolated to some future time t and then the extrapolated value is used to extract the blood glucose component. The blood glucose component of the extrapolation and the output of the CGS are weighted and used to estimate the blood glucose level of a subject.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method and System for Personalized Injection and Infusion Site Optimization
Provided herein are methods and systems for generating dynamic, personalized injection site recommendations. Further provided herein are methods and systems for identifying inconsistencies in medicament absorption and performance at an injection site. Further provided herein are methods and systems for generating a personalized insulin delivery device recommendation.
Owner:ILLUME HEALTH LLC
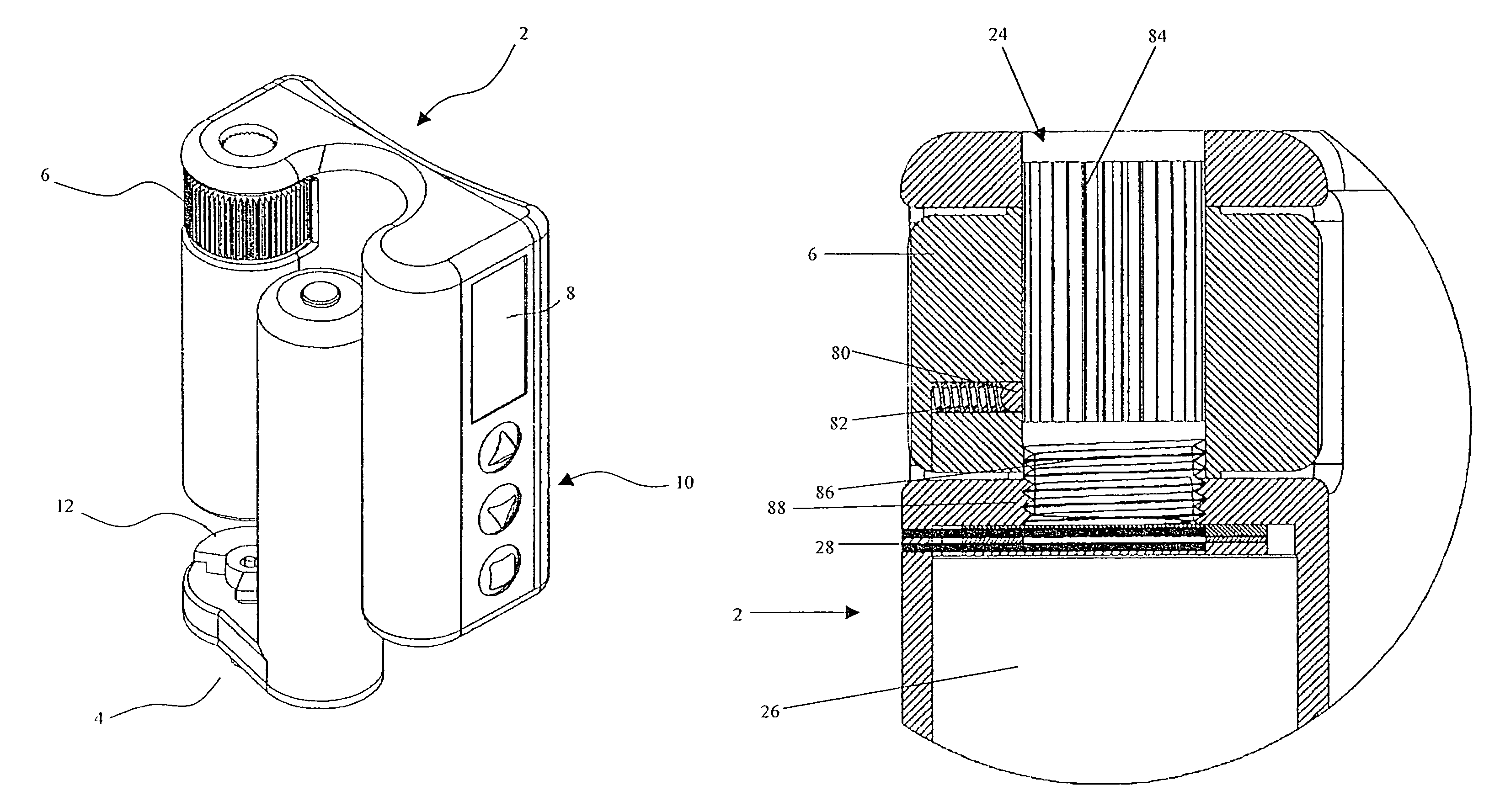
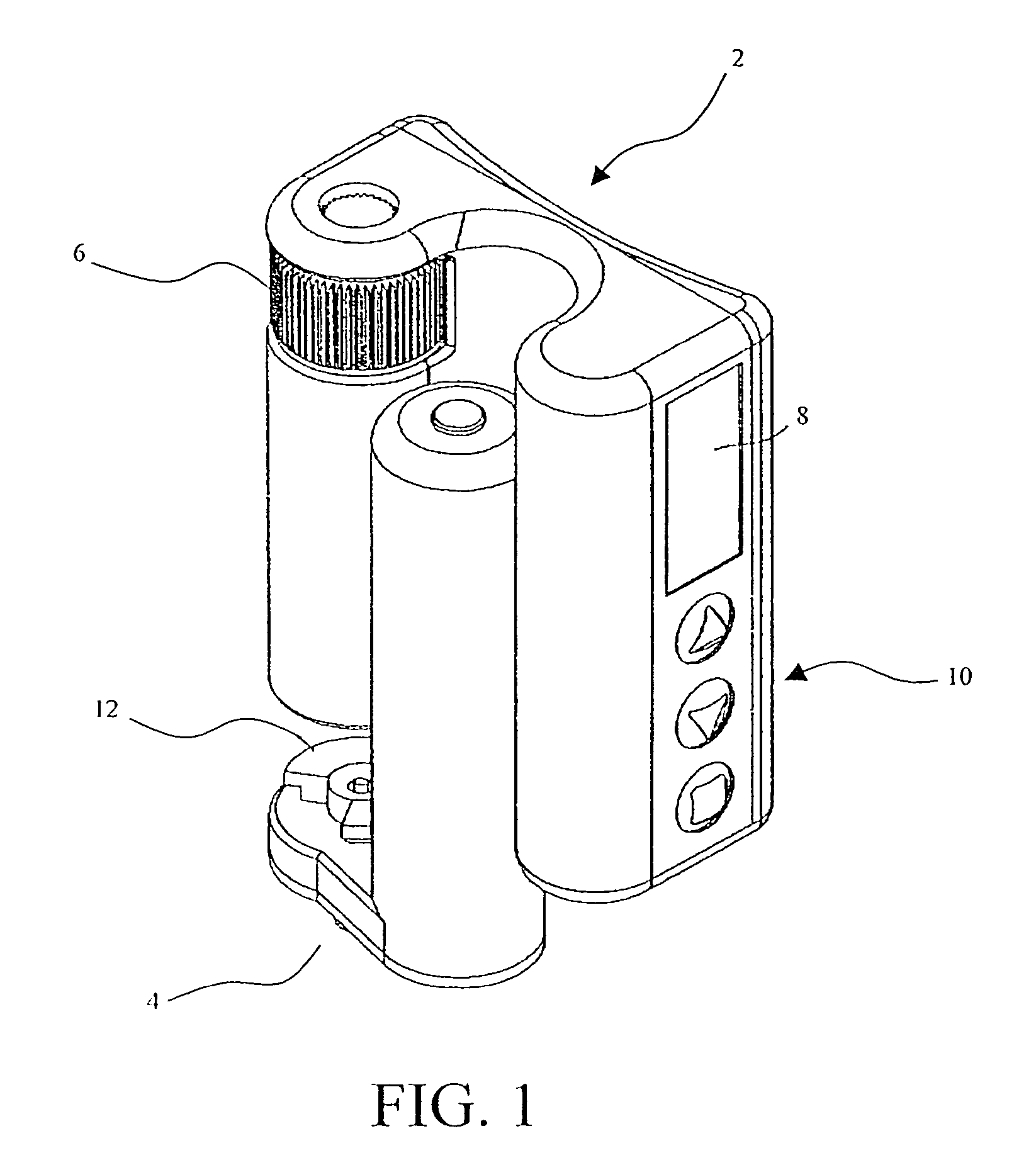
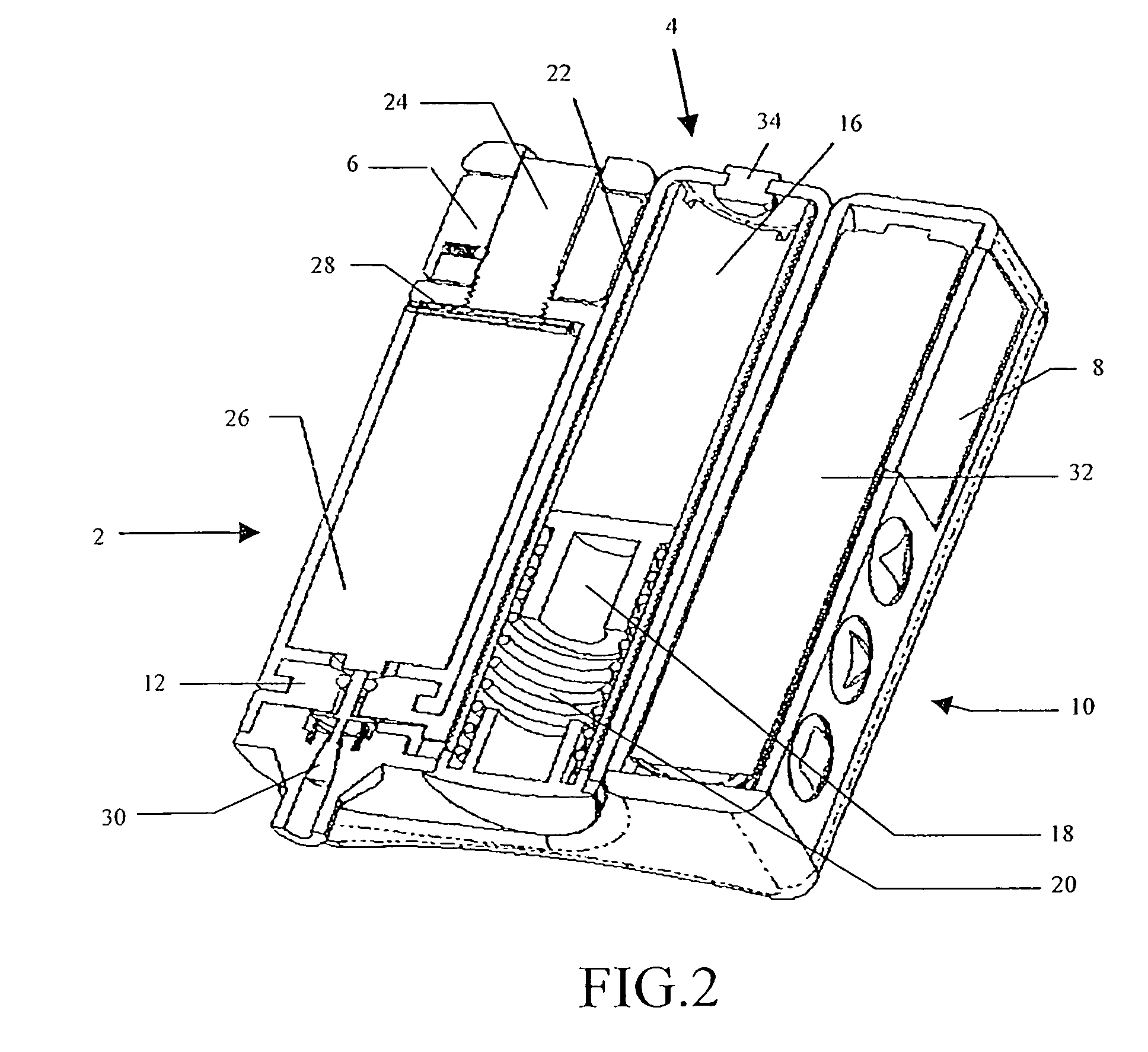
Drive system for use with an insulin delivery device
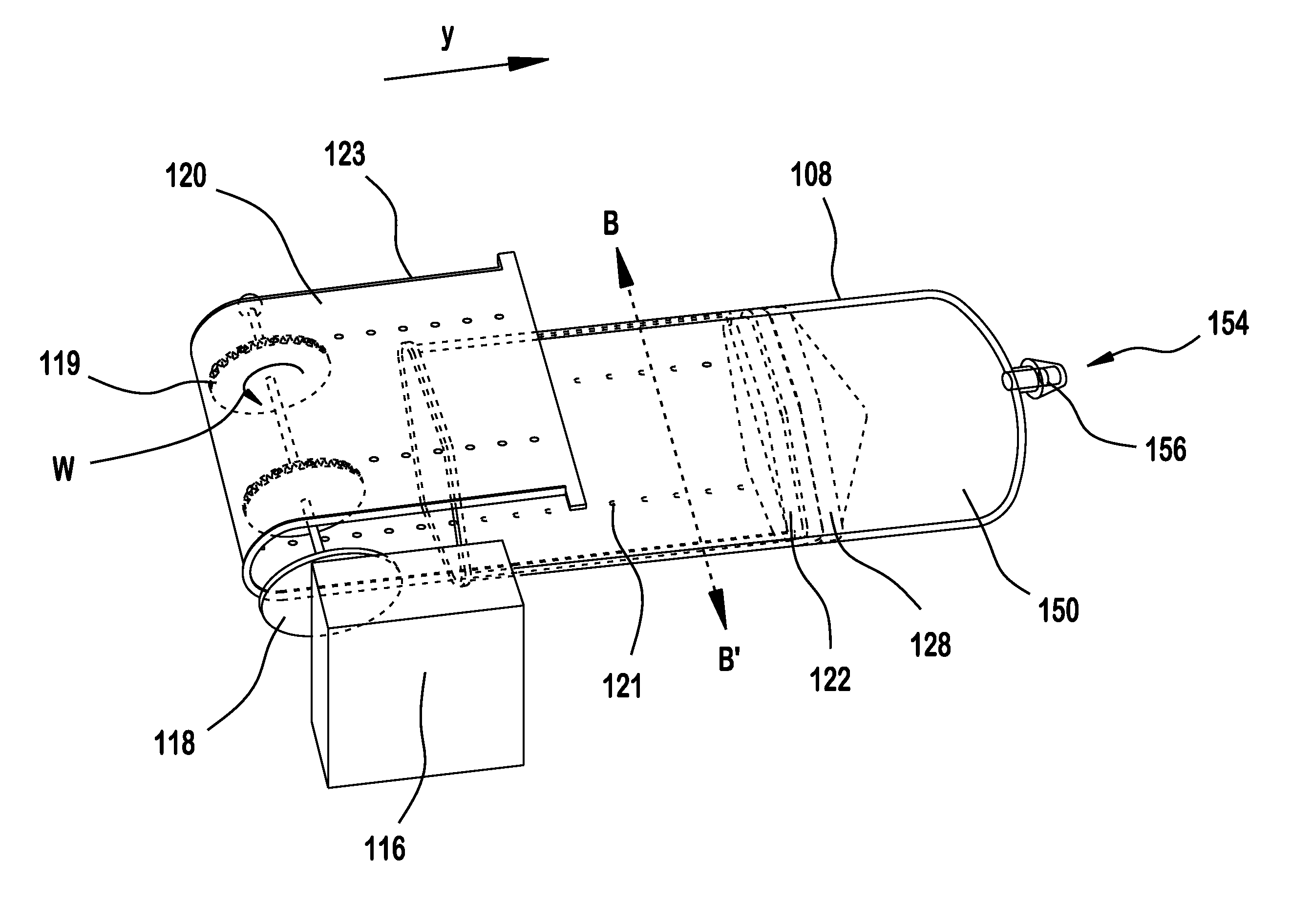
InactiveUS8517991B2Easy to useSave spaceLiquid surface applicatorsAutomatic syringesGear wheelEngineering
The invention relates to a mechanical drive system for a medical infusion device. The disclosed drive system employs a flexible tape with recesses or holes that are configured to mate with tabs or protrusions on a gear to advance the rotation of the gear at a rate determined by the pattern of recesses or holes on the flexible tape.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
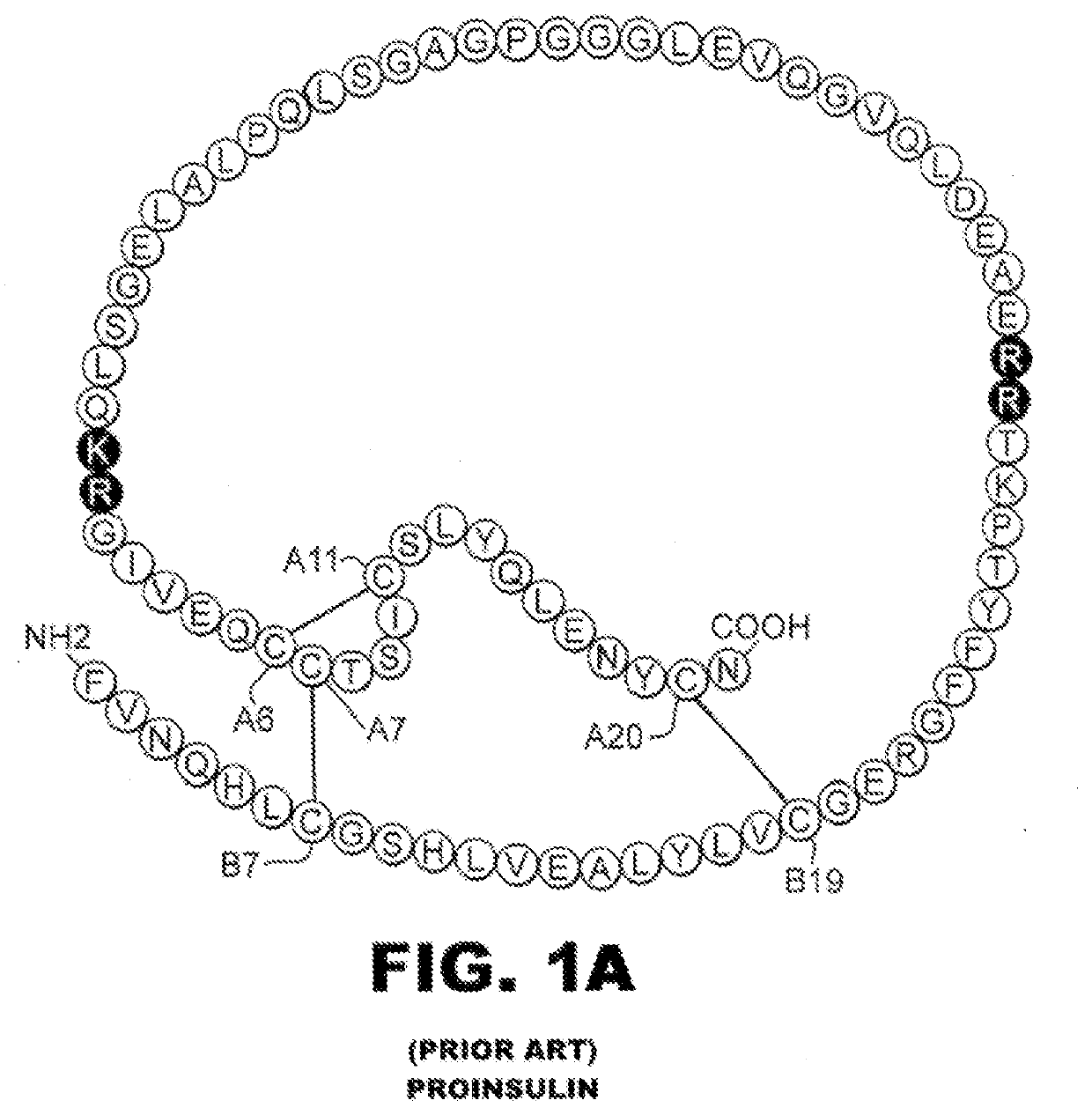
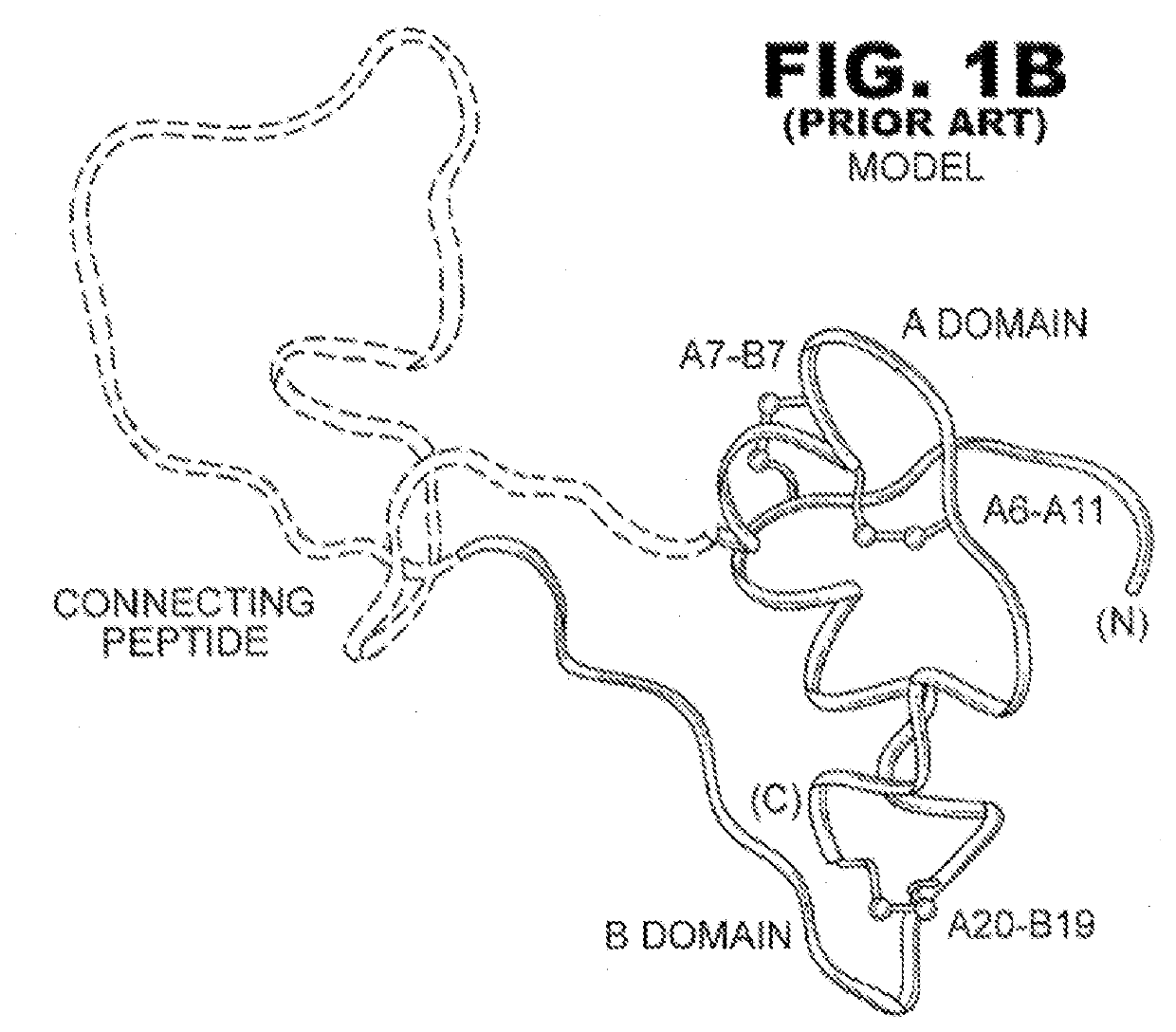
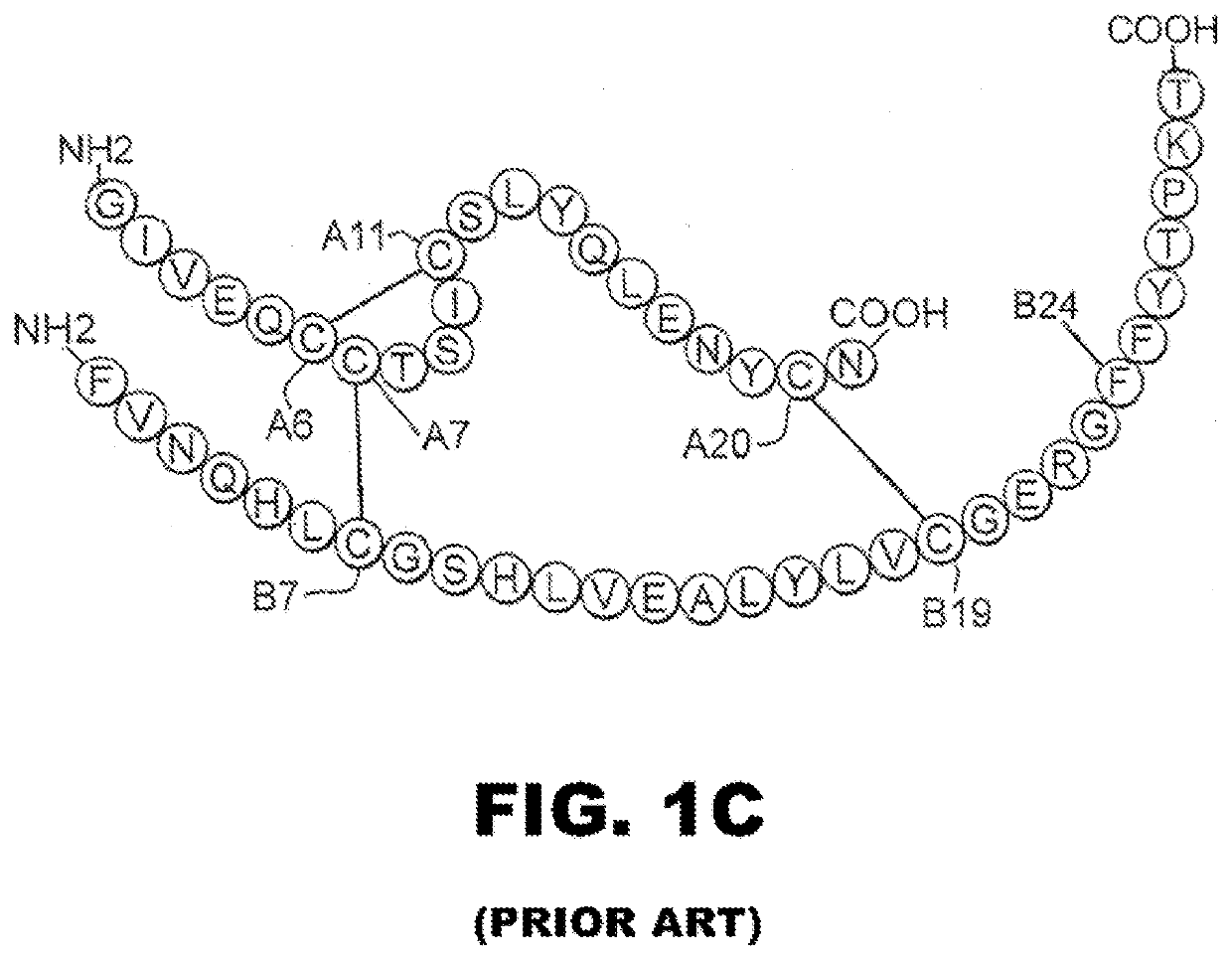
Single-chain insulin analogues stabilized by a fourth disulfide bridge
ActiveUS20200140517A1Unfavorable effectReduces conformational fluctuationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDisulfide bondingDiabetes mellitus
A single-chain insulin analogue comprises a B-chain insulin polypeptide connected to an A-chain insulin polypeptide by a C-domain polypeptide. The B-chain insulin polypeptide contains a Cysteine substitution at position B4. The A-chain insulin polypeptide contains a Cysteine substitution at position A10. The C-domain polypeptide is 4 to 11 amino acids long. The analogue mitigates the unfavorable activity of this 4th disulfide bridge in conventional two-chain insulin analogues resulting in a duration of insulin signaling similar to that of wild-type insulin. A method of treating a patient with diabetes mellitus comprises the administration of a physiologically effective amount of the protein or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof to a patient. Use of a single-chain insulin analogue of the present invention in an insulin delivery device (such as a pump or pen) or as part of a high-temperature polymer-melt manufacturing process.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
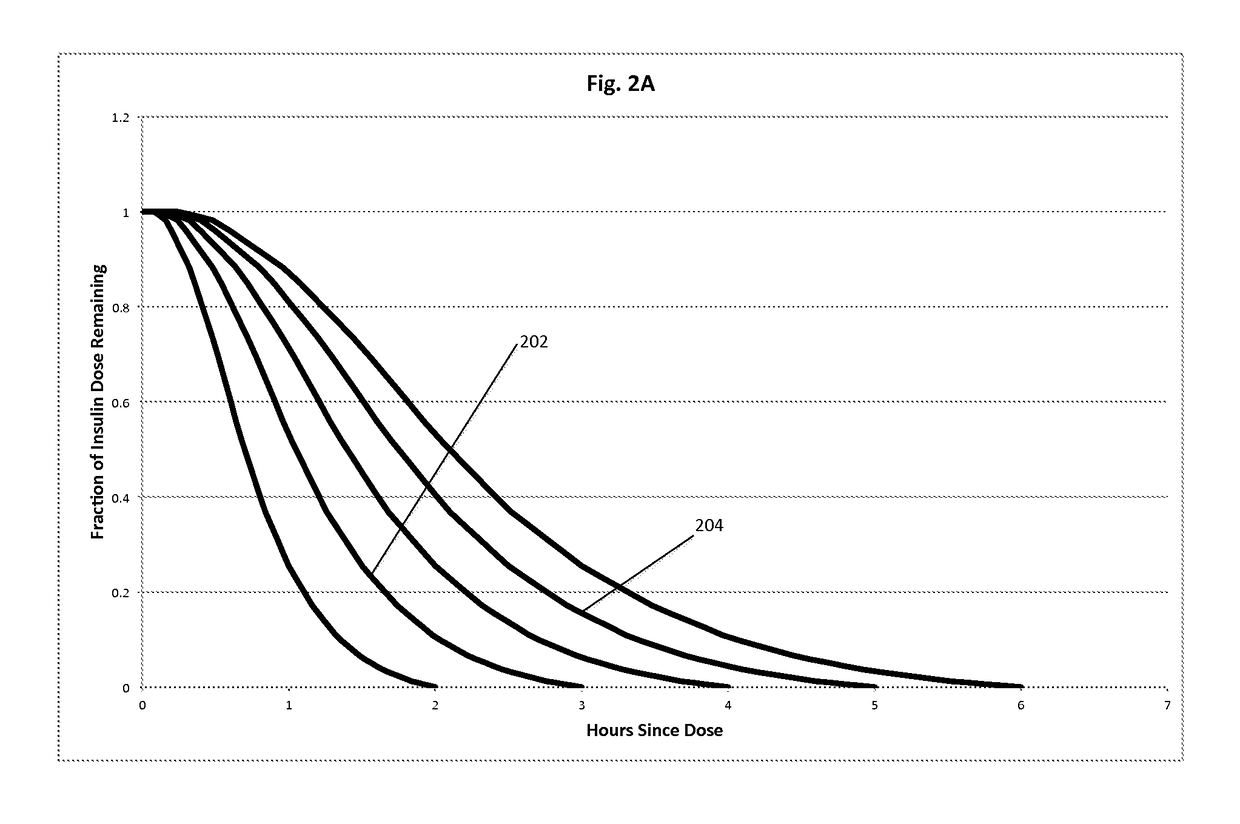
Insulin on board calculation, schedule and delivery
ActiveUS10188793B2Increase and reduction in insulin deliveryReduce deliveryDrug and medicationsMedical devicesInsulin on boardSpecific time
A system is provided with an insulin delivery device configured to deliver insulin to a user of the system and a computer-based control unit associated with the insulin delivery device. The computer-based control unit includes a user interface and a computer-based processor. The computer-based processor is configured to calculate a relative insulin on board value for a specific time by calculating a first value that represents a reference insulin on board value at the specific time, calculating a second value that represents an automated insulin on board value at the specific time, and subtracting one of the first and second values from the other. The automated insulin on board value represents at least one insulin delivery automatically specified by the computer-based control unit. Methods of use are also disclosed.
Owner:INSULET CORP
Novel drive system for use with an insulin delivery device
This invention provides a novel device system for use with an insulin delivery device. A liquid infusion device is a separate type and is easy for the patient to use. Specifically, the liquid infusion device, comprising a flexible drive tape having a plurality of holes aligned essentially linearly along the length of the drive tape, the plurality of holes spaced apart at a fixed increment; a drive shaft comprising at least one gear, the gears comprising a plurality of teeth that align and engage the holes in the flexible drive tape, a piezoelectric motor for advancing the flexible drive tape; a plunger attached to or in communication with at least one end of the flexible drive tape, and a cartridge for containing a liquid medication for receiving the plunger and expelling the liquid medication upon movement of the plunger in the cartridge, wherein the piezoelectric motor turns the drive shaft, thereby advancing the flexible drive tape and driving the plunger into the cartridge in an increment correlating to the fixed increment between holes.
Owner:ANIMAS CORP
Discretionary insulin delivery systems and methods
PendingUS20200179602A1Reduce deliveryReduce the burden onDrug and medicationsMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringInsulin
Owner:INSULET CORP
System and method for adjusting insulin delivery
The embodiments described herein may relate to methods and systems for adjusting insulin delivery. Some methods and systems may be configured to adjust insulin delivery to personalize automated insulin delivery for a person with diabetes. Some methods and systems may be configured to adjust insulin delivery to a person with diabetes according to one or more conditions of an insulin delivery device. Some methods and systems may be configured to enable a lock-out mode where adjustment to insulin delivery to personalize automated insulin delivery is restricted.
Owner:INSULET CORP
Implantable-glucose responsive insulin delivery device
A biocompatible insulin delivery device is provided comprising an insulin reservoir sealed with a glucose-responsive plug or membrane. The plug functions to release insulin from the reservoir in response to a hyperglycemic glucose concentration and to prevent insulin release from the reservoir in response to hypoglycemic glucose concentration. In one embodiment, the plug is made of a biocompatible polymeric matrix comprising an inorganic component, a stimulus-responsive component and a catalytic component.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
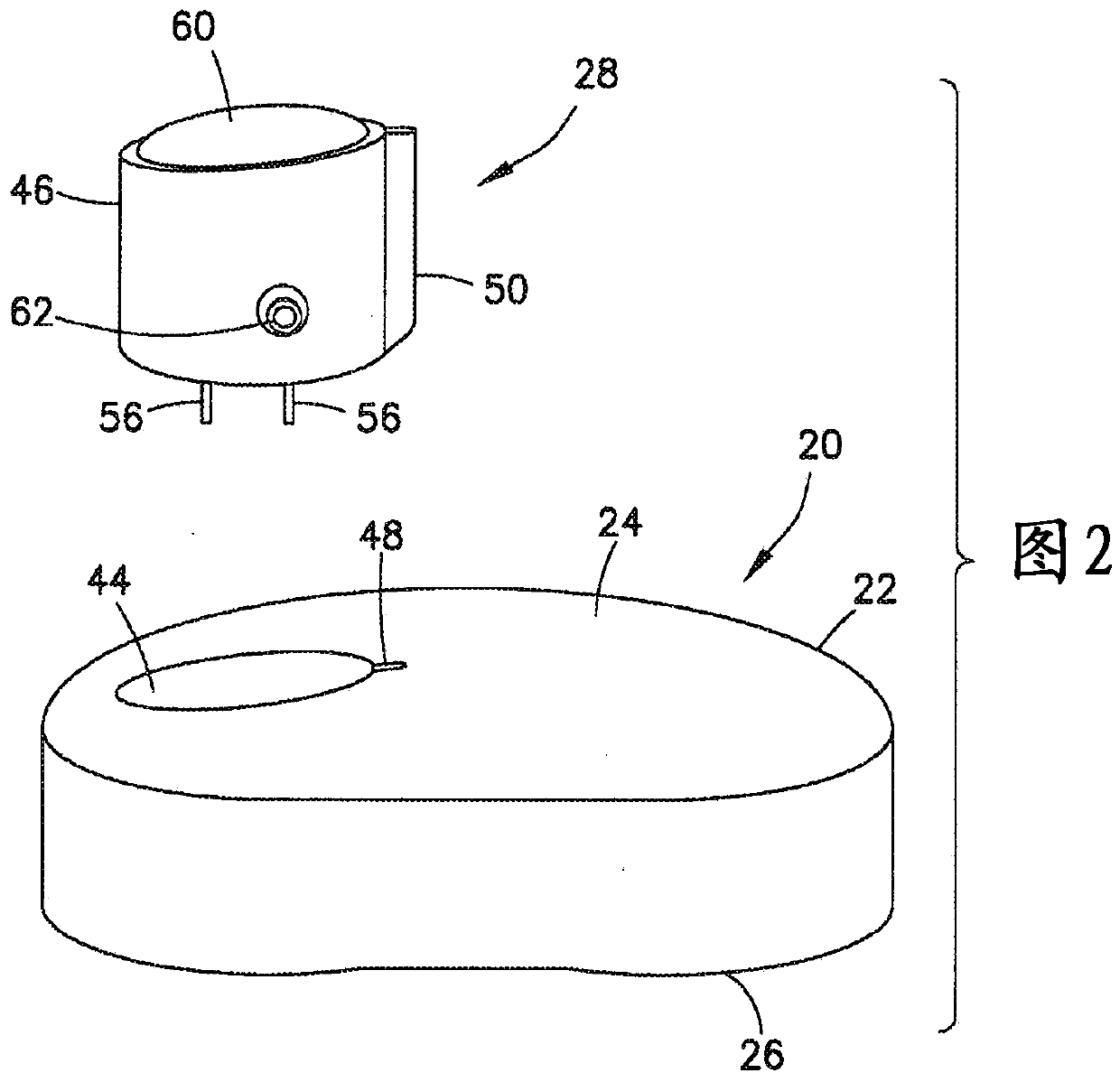
Insulin leakage sensor with electric control to stop insulin flow
An insulin delivery device (10) includes a cannula (40) for delivering insulin to a patient at an infusion site, a pump assembly (30), and a valve (36) for controlling the flow of insulin. A removableleak detector unit (28) is coupled to the delivery device for sensing and detecting leakage of insulin at the infusion site. The leak detector unit (28) has electrodes (56) positioned for contactingthe insulin leaking from the infusion site, a sensing electrical circuit (54) and a power source (58) for operating the leak detector unit. The removable leak detector unit (28) has an electrical contact (62) for mating with an electrical contact (64) of the delivery device for electrically and operatively connecting the leak detector unit (28) to the delivery device. The leak detector unit (28) sends a signal to the pump assembly (30) and / or valve (36) to stop the flow of insulin when leakage is detected at the infusion site.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Adjusting insulin delivery rates
ActiveUS10806859B2Simple deliveryReduce cognitive loadHealth-index calculationDrug and medicationsPhysiologyHypoglycemia
A method may include displaying to a user an interface at which the user inputs a fear of hypoglycemia index (FHI), the FHI corresponding to an acceptable probability of a blood glucose level being below a threshold blood glucose level. The method may also include receiving blood glucose data for a person with diabetes (PWD). The method may additionally include calculating a probability of the PWD having a blood glucose level below the threshold blood glucose level based on the variability of the received blood glucose data. The method may also include setting one or more target blood glucose levels to align the probability of the PWD having a blood glucose level below the threshold blood glucose level with the acceptable probability associated with the user input FHI. The method may additionally include delivering insulin, using the insulin delivery device, based on the target blood glucose level.
Owner:INSULET CORP
Decisions support for patients with diabetes
A decision support system includes a measurement device configured to continuously measure a physiological parameter of a patient. An insulin delivery device provides insulin to the patient per an initial basal profile and the parameter measurements. A storage device holds historical data of insulin delivery to the patient. A processor determines deviations of the delivery of insulin from the basal profile for one or more time period(s) using the historical data, computes a respective first basal-profile adjustment for each of the one or more time period(s) using the determined deviations, and annunciates the computed first basal-profile adjustment(s). A method of recommending a basal-rate adjustment includes measuring the parameter, infusing the patient with insulin and storing the historical data, determining the deviations from the basal profile, computing the first basal-profile adjustments, and annunciating the computed first basal-profile adjustment(s).
Owner:ANIMAS CORP
Alarms and alerts for medication delivery devices and systems
ActiveUS11096624B2Save powerReduce needSensorsBlood characterising devicesDiabetes mellitusGlucose sensors
Owner:BIGFOOT BIOMEDICAL INC
Implantable-glucose responsive insulin delivery device
A biocompatible insulin delivery device is provided comprising an insulin reservoir sealed with a glucose-responsive plug or membrane. The plug functions to release insulin from the reservoir in response to a hyperglycemic glucose concentration and to prevent insulin release from the reservoir in response to hypoglycemic glucose concentration. In one embodiment, the plug is made of a biocompatible polymeric matrix comprising an inorganic component, a stimulus-responsive component and a catalytic component.
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO
Alarms and alerts for medication delivery devices and systems
ActiveUS20190274624A1Save powerReduce needSensorsBlood characterising devicesGlucose sensorsDiabetes management
Systems, methods, and devices provide alarms and alerts in an on-body networked diabetes management system. Methods may include receiving glucose sensor data from a continuous glucose monitor and determining a dosage of insulin delivery based at least in part on the glucose sensor data. The method may include detecting an alarm or alert condition, and sending a wireless communication regarding the alarm or alert condition to a remote user-interface device. The method may include triggering an audible, visual, or haptic alarm or alert on the insulin delivery device unless an acknowledgement of the alarm or alert condition is received within a predetermined period of time.
Owner:BIGFOOT BIOMEDICAL INC
Continuous glucose monitoring injection device
An electronic insulin delivery device receives glucose data from a glucose monitor and sets a bolus dose amount. The device may take the form of an insulin pen with automatic priming and accurate dosing provided by a motor in connection with an encoder. The device may communicate with and be controlled by a smart phone device. The smart phone device provides a user interface to receive user data including patient weight, insulin to carbohydrate ratio and exercise factor, and to send instructions to the device, including dose amount. The dose amount is determined taking into account glucose level and trend, and other factors. The delivery device may be in continuous communication with the glucose monitor and smart phone to provide for near real-time adjustments in glucose treatment. Glucose data, insulin injection data, and other relevant data may be stored and accessible to interested parties.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com