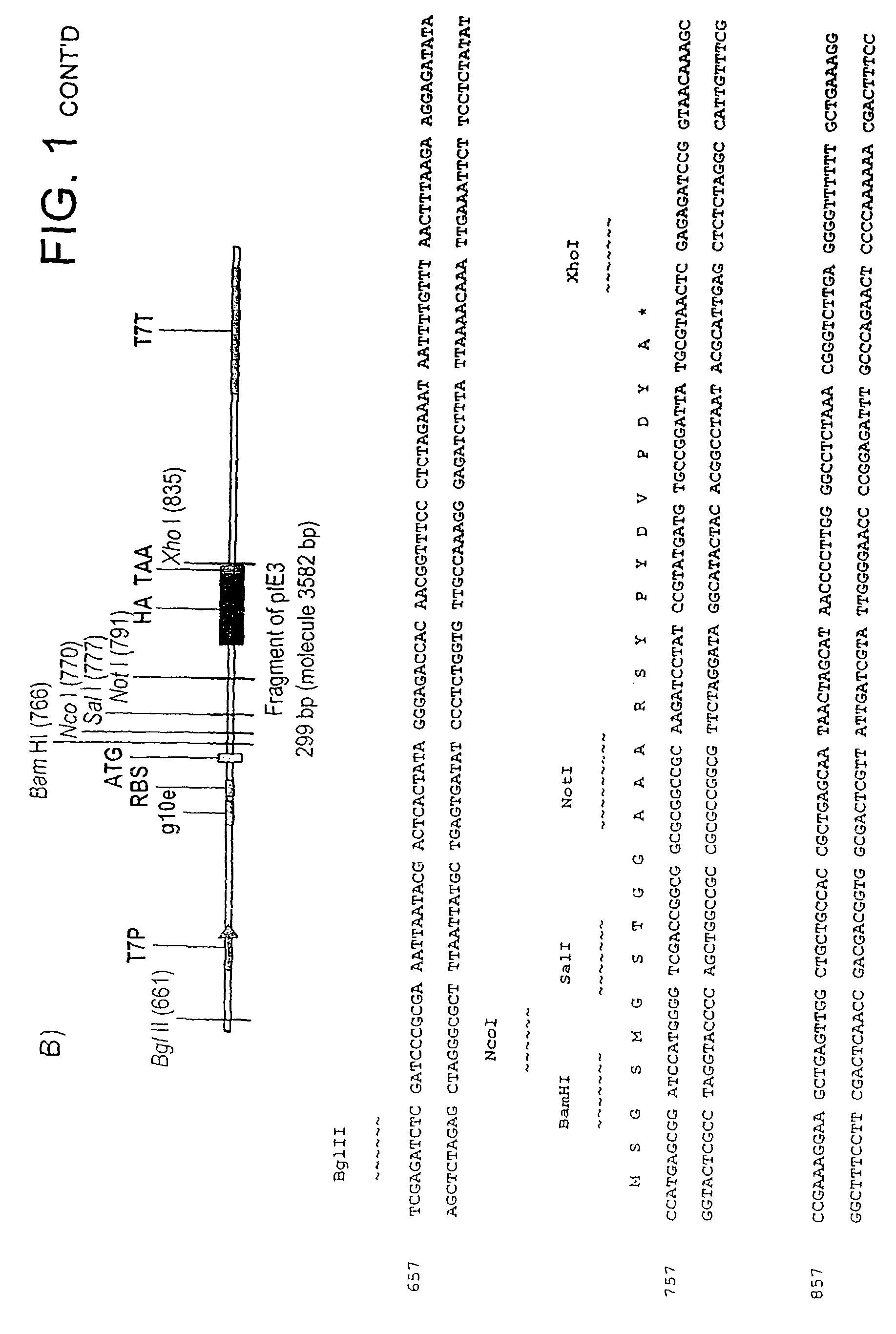
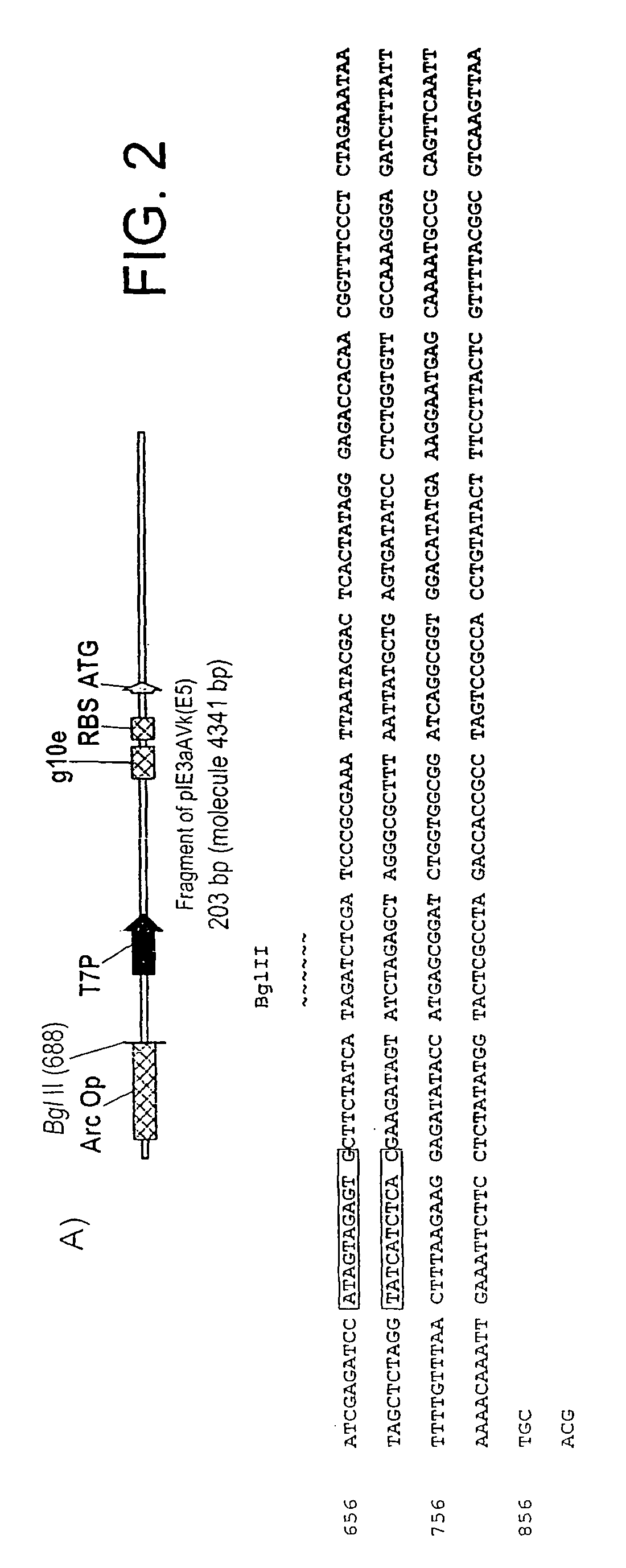
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "DNA binding site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA binding sites are a type of binding site found in DNA where other molecules may bind. DNA binding sites are distinct from other binding sites in that (1) they are part of a DNA sequence (e.g. a genome) and (2) they are bound by DNA-binding proteins. DNA binding sites are often associated with specialized proteins known as transcription factors, and are thus linked to transcriptional regulation. The sum of DNA binding sites of a specific transcription factor is referred to as its cistrome. DNA binding sites also encompasses the targets of other proteins, like restriction enzymes, site-specific recombinases (see site-specific recombination) and methyltransferases.
Method to screen phage display libraries with different ligands
InactiveUS6846634B1Overcome inherent biasGuaranteed effective sizePeptide librariesLibrary screeningBinding siteBacteriophage
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Response element
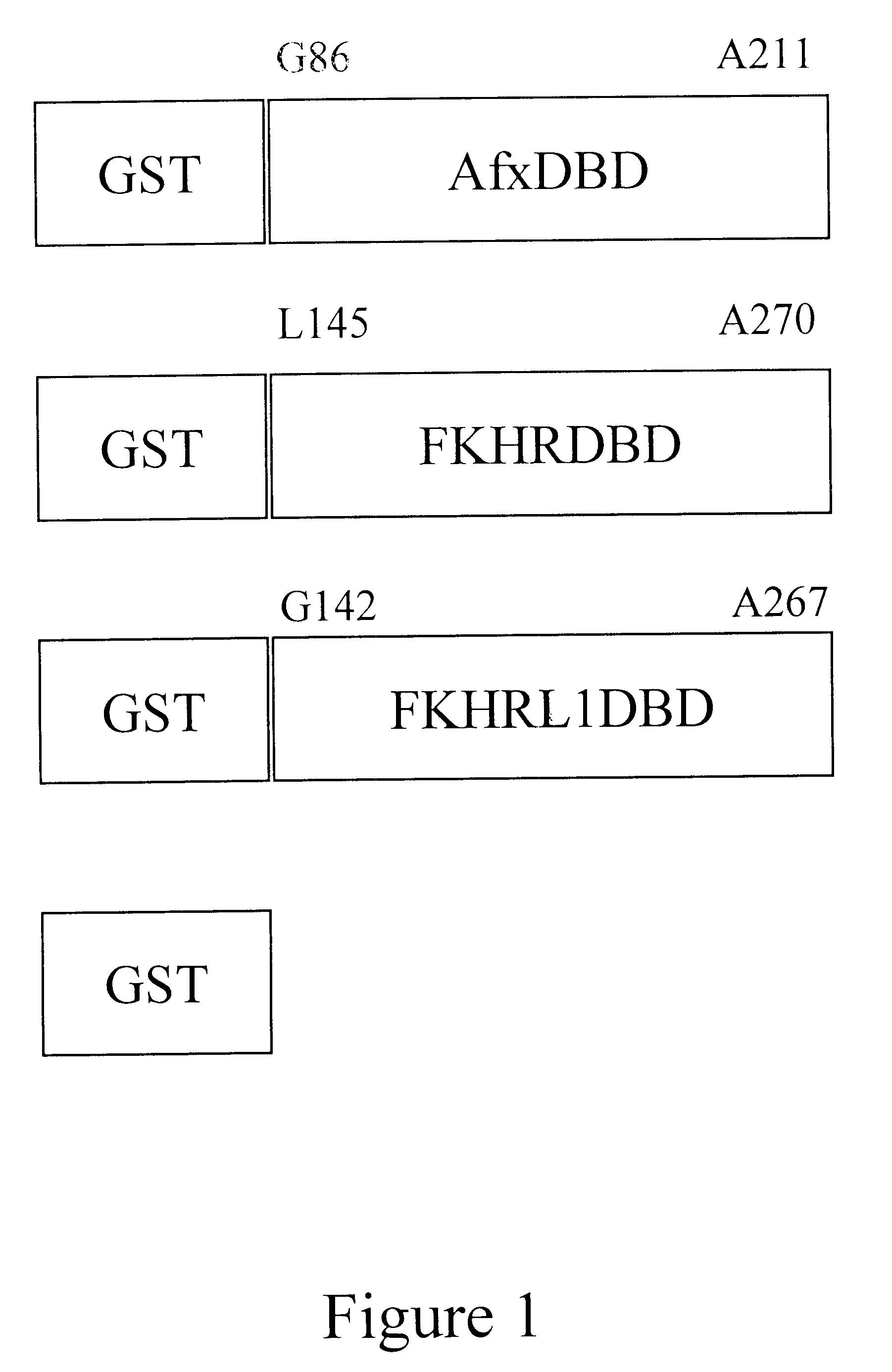
The present invention is directed to a novel Afx response element comprising the nucleotide sequence AACATGTT, said nucleotide sequence having a DNA binding site for the human fork head transkription factor Afx. The invention also relates to the use of the Afx response element in the screening for genes as diabetes drug targets and in the bioinformatic analysis of the human genome, said genes in turn being useful in other screening methods for compounds modifying the insulin receptor signaling pathway. A further aspect of the invention is a vector construct comprising the novel nucleotide sequence, a host cell transformed with said vector construct as well as the fusion protein expressed by said host cell.
Owner:BIOVITRUM AB (PUBL) +1
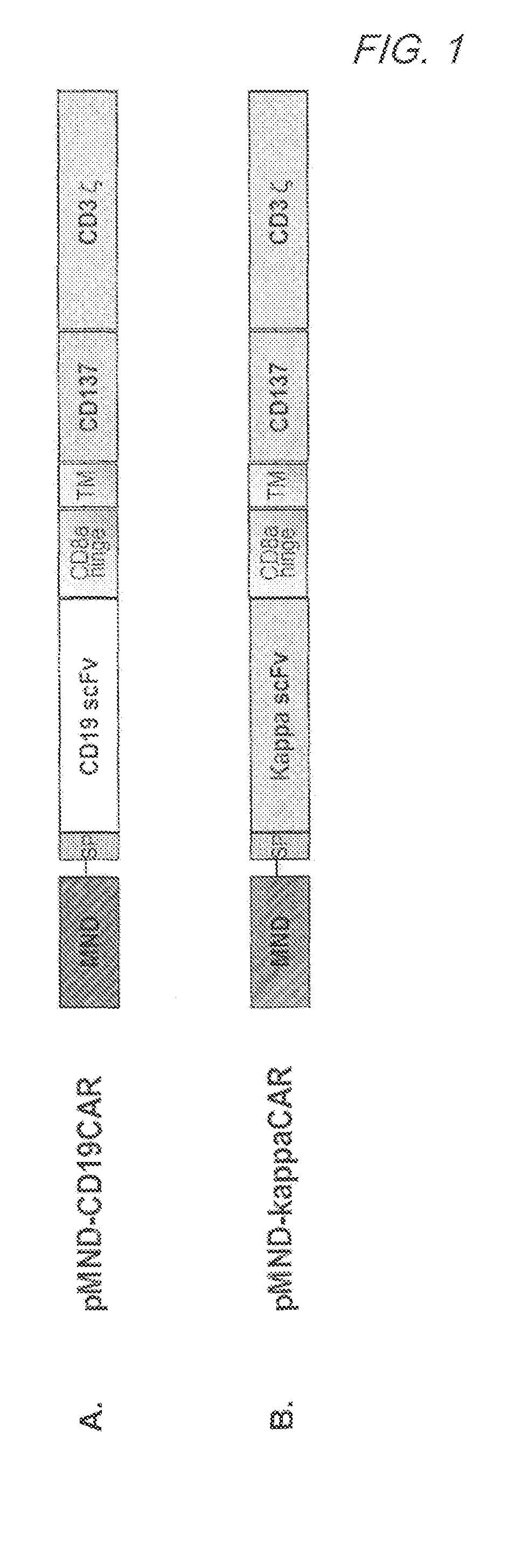
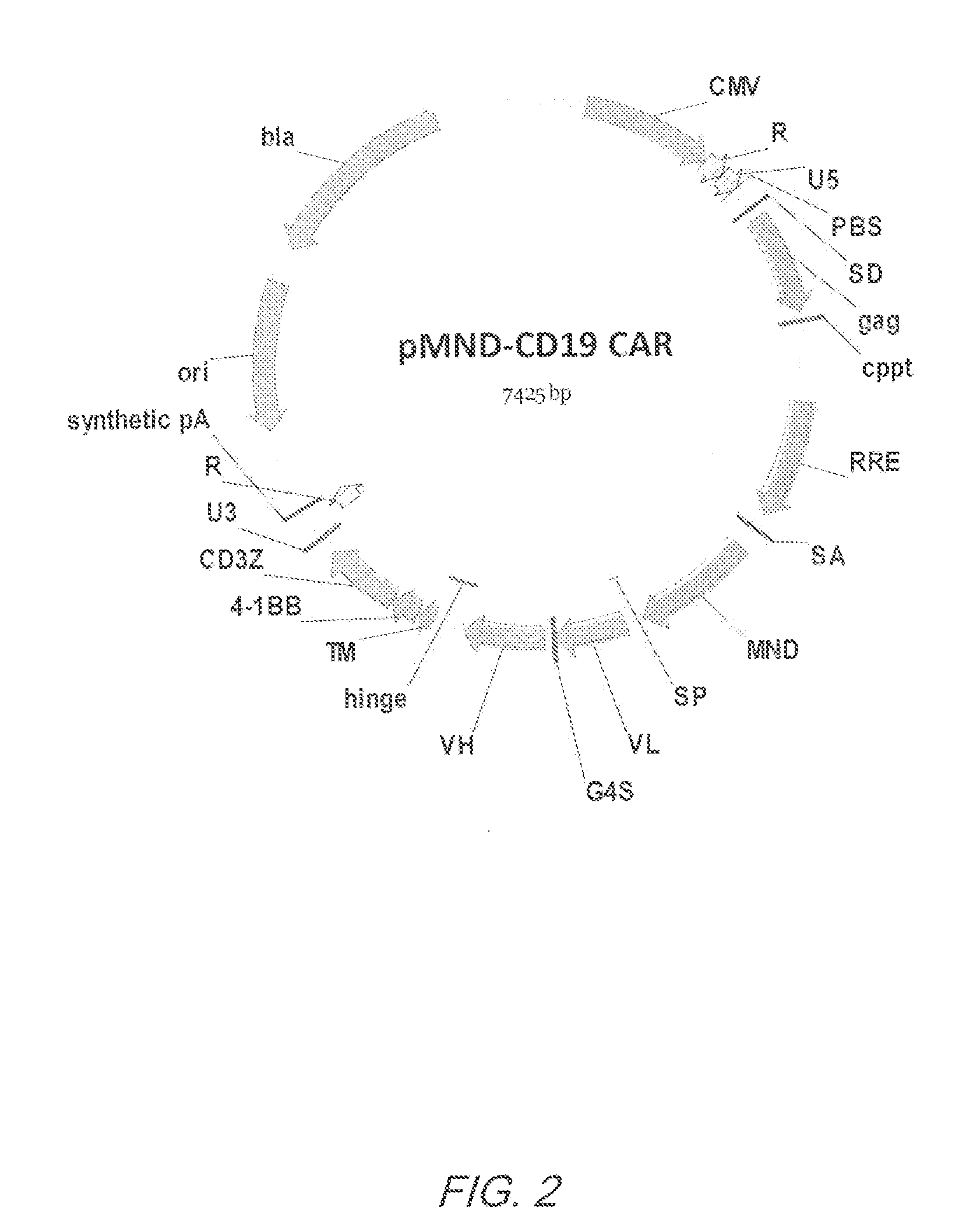
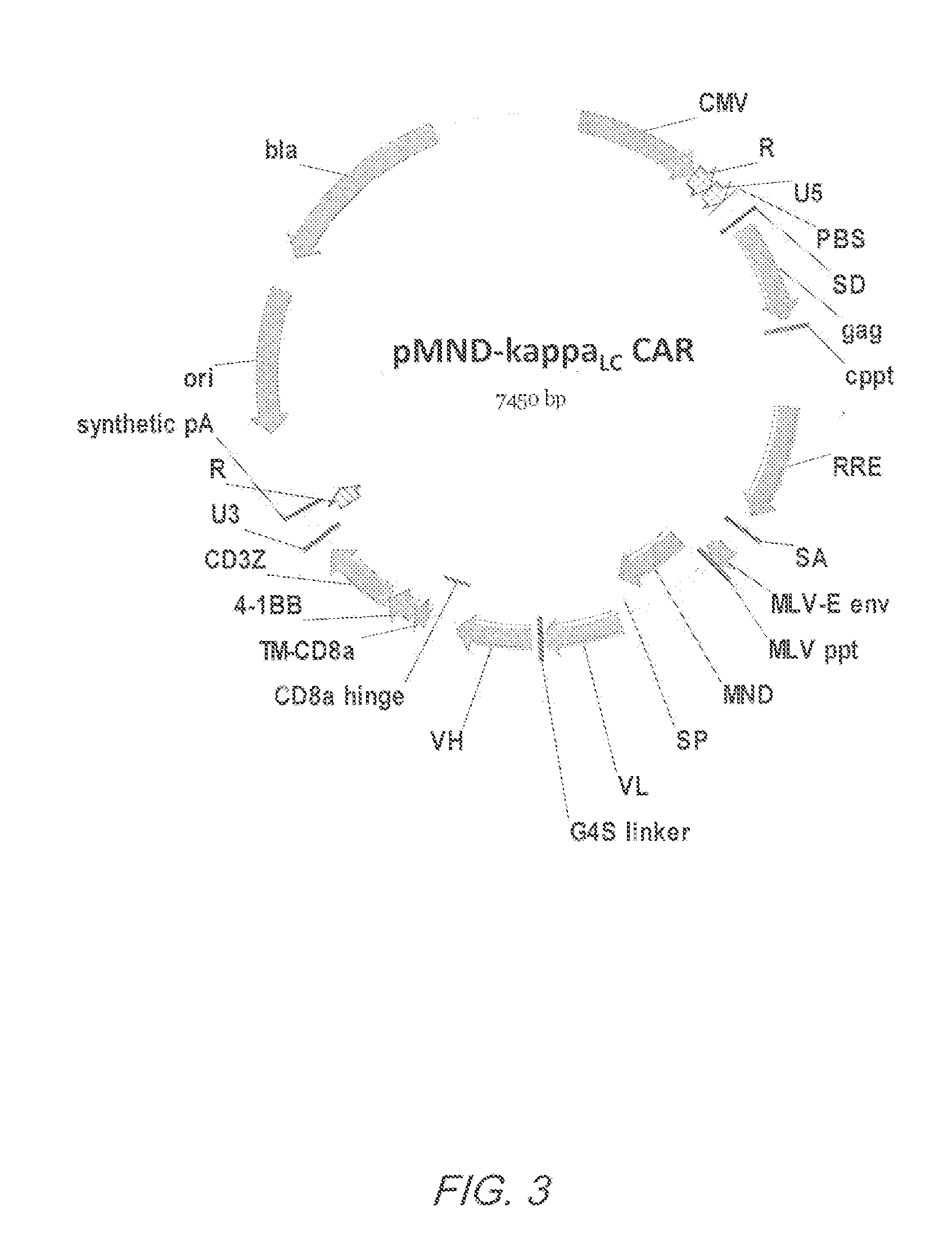
Mnd promoter chimeric antigen receptors
ActiveUS20170051308A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsBinding siteAntigen receptors
Vector compositions comprising a myeloproliferative sarcoma virus enhancer, negative control region deleted, dl587rev primer-binding site substituted (MND) promoter operably linked to a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) are provided.
Owner:2SEVENTY BIO INC
Chemically programmable immunity
InactiveUS8604184B2Solve the real problemImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBinding siteHalf-life
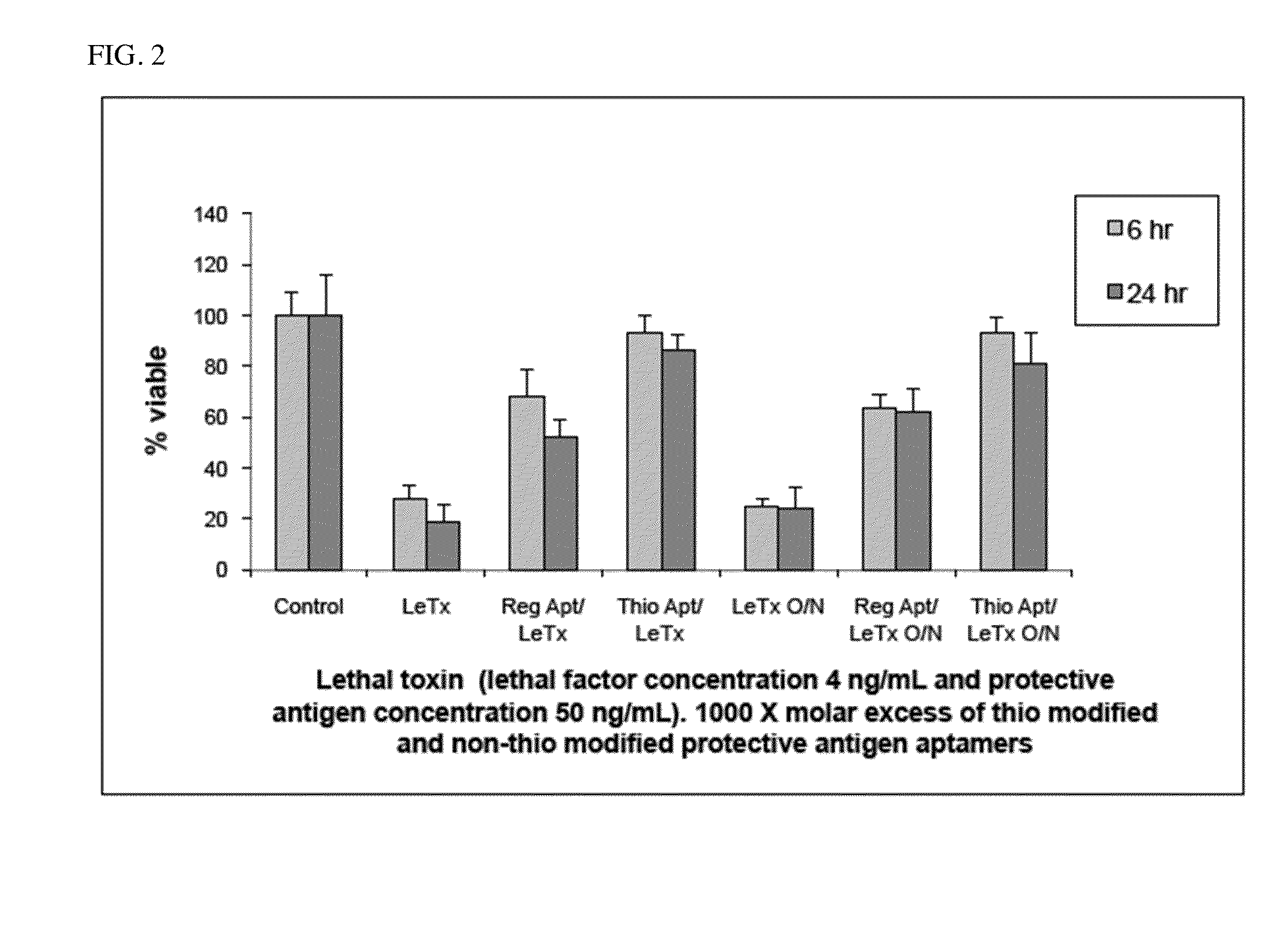
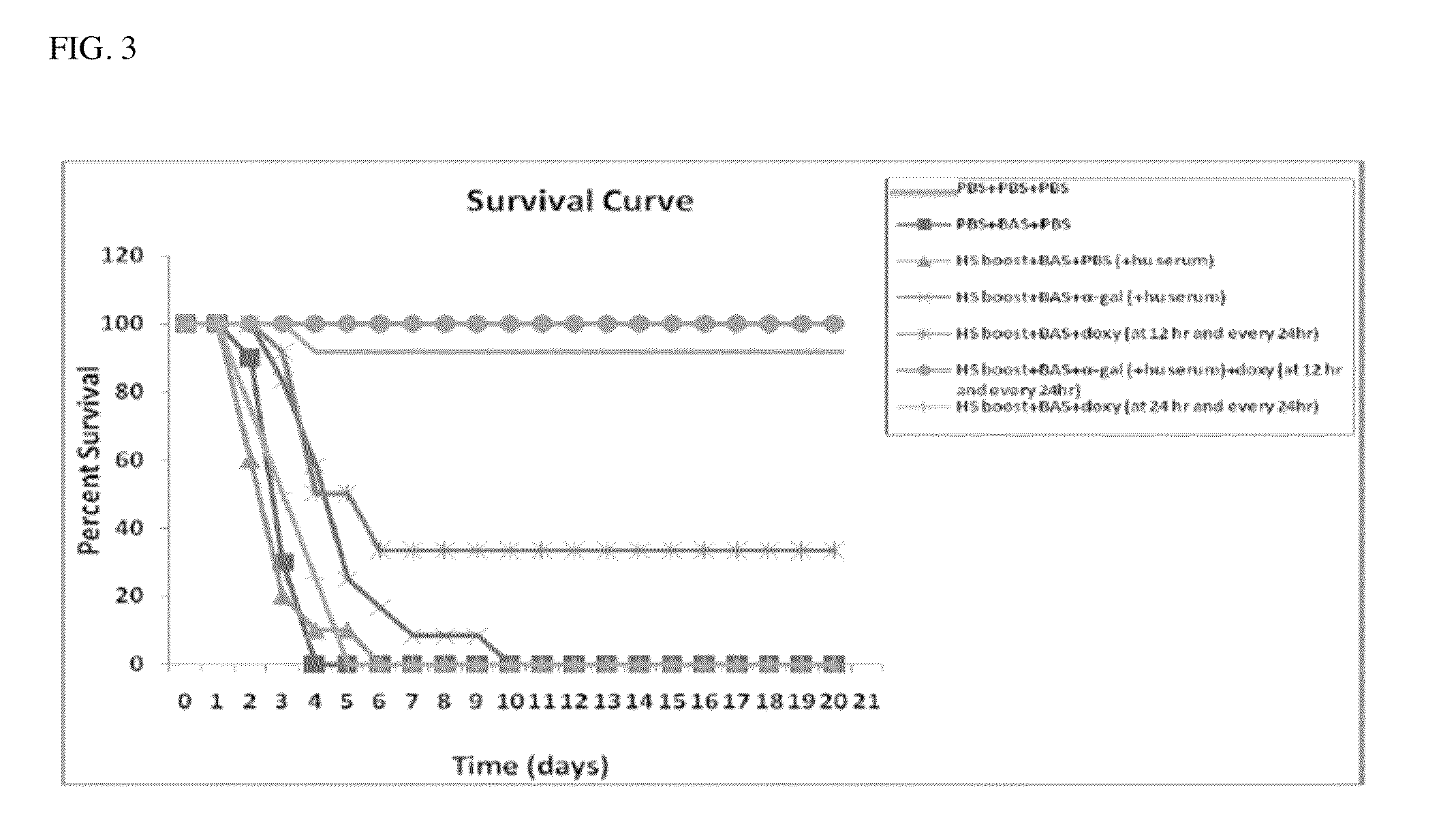
Methods and compositions for immediately immunizing an individual against any molecule or compound are provided. The present invention is directed to an immunity linker with at least two sites; (1) at least one first binding site that binds to an immune response component in an individual, and (2) at least one second binding site that binds specifically to a desired compound or molecule, the target. The second binding sites are preferably thiolated aptamers that have the benefit of increased stability, resistance to degradation and longer circulating half life. Methods of making and using pharmaceutical compositions including immunity linker molecules having a thiolated aptamer are also provided.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Universal light-switchable gene promoter system
InactiveUS6858429B2Low background activityImprove induction abilityFungiBacteriaProtein kinase domainLight activation
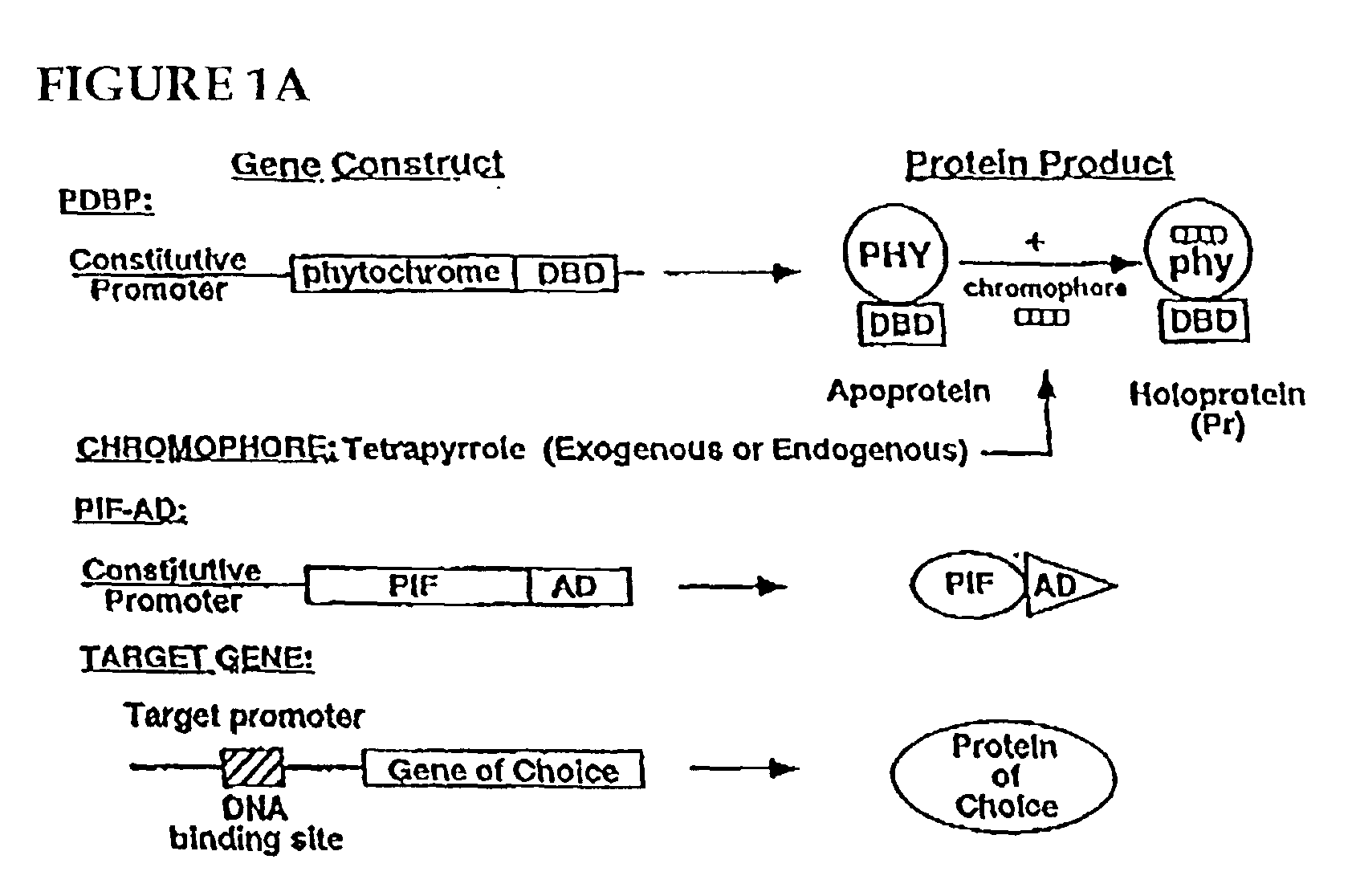
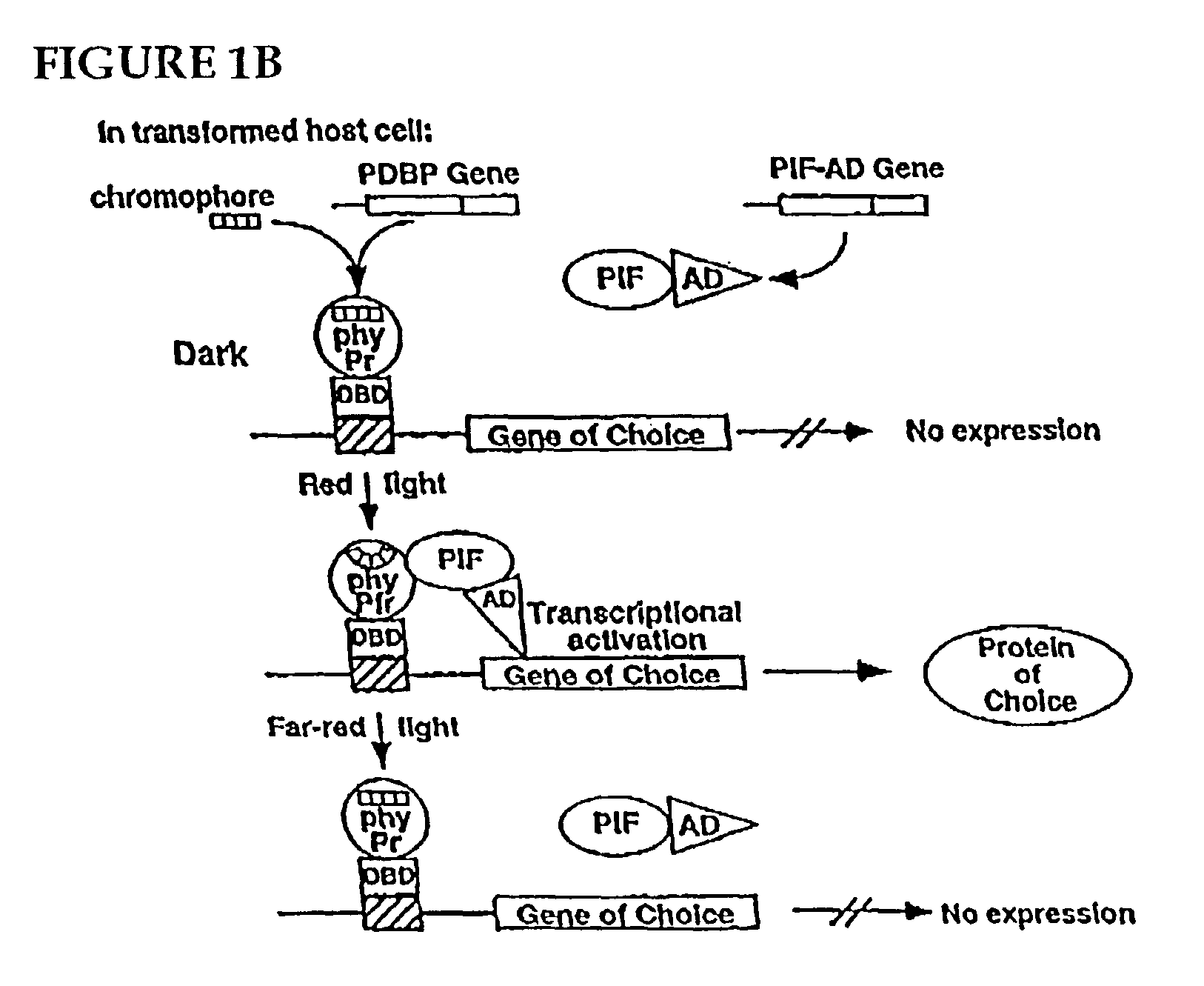
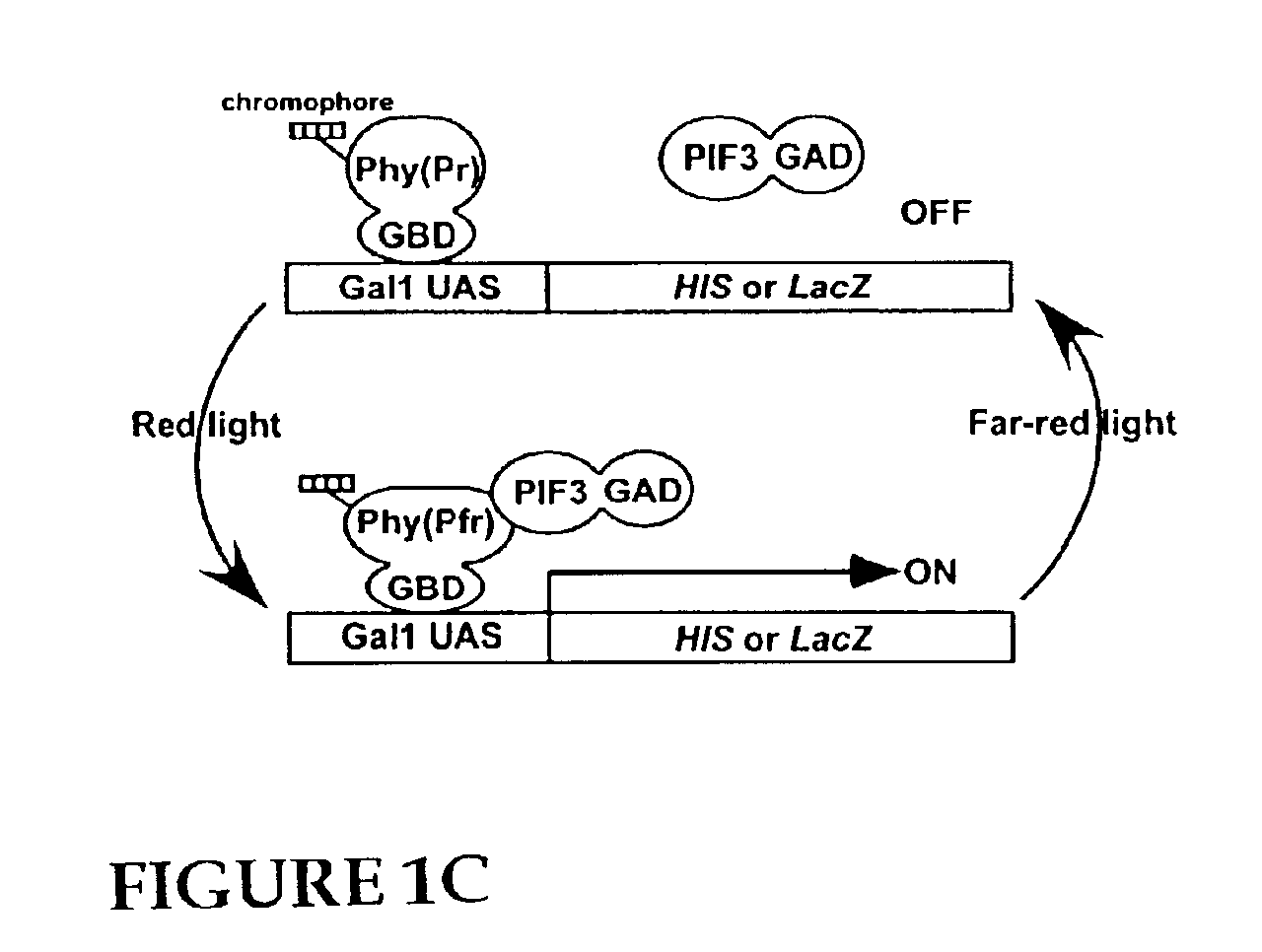
An artificial promoter system that can be fused upstream of any desired gene enabling reversible induction or repression of the expression of the gene at will in any suitable host cell or organisms by light is described. The design of the system is such that a molecule of the plant photoreceptor phytochrome is targeted to the specific DNA binding site in the promoter by a protein domain that is fused to the phytochrome and that specifically recognizes this binding site. This bound phytochrome, upon activation by light, recruits a second fusion protein consisting of a protein that binds to phytochrome only upon light activation and a transcriptional activation domain that activates expression of the gene downstream of the promoter.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
G-rich oligo aptamers and methods of modulating an immune response
InactiveUS6994959B1Modulate T cell responseInhibit transcriptionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderInsulin dependentAllograft rejection
Aptamer oligonucleotides specifically bind to the DNA binding site of proteins such as Sp1 and Sp1-related proteins which regulate the genes which encode costimulatory molecules such as CD28 and cytokines such as IL-2 and GMCSF. The oligonucleotides compete with the DNA-binding sites of regulatory proteins which specifically regulate molecules to modulate T-cell activation. This serves to modulate gene expression by preventing transcription of the gene. Aptamers are administered to provide therapies for diseases which involve aberrant T-cell activation such as psoriasis, Type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune uveitis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's and ulcerative colitis), and septic shock and to regulate normal T-cell activation such as in allograft rejection.
Owner:VALEANT RES & DEV
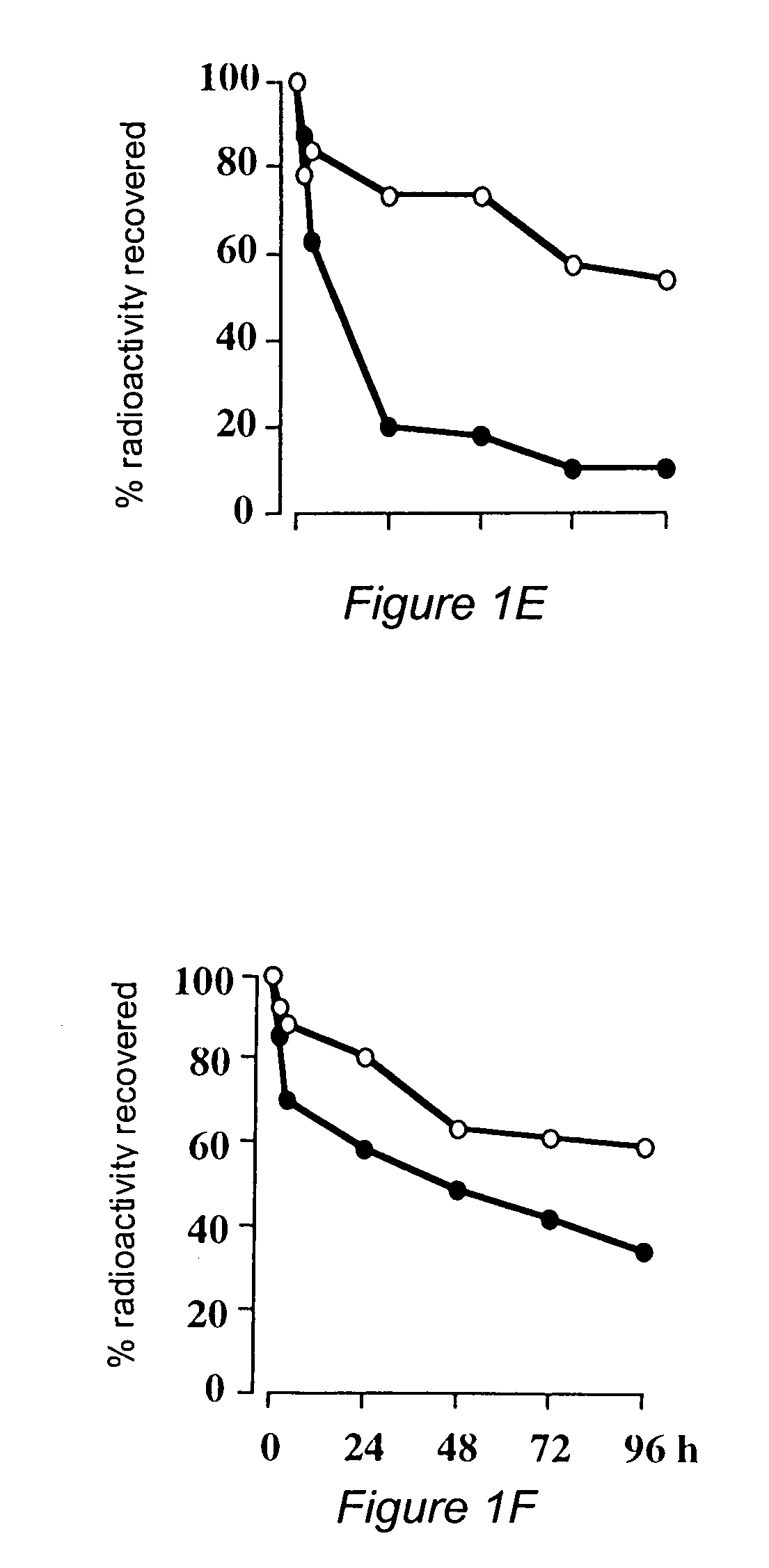
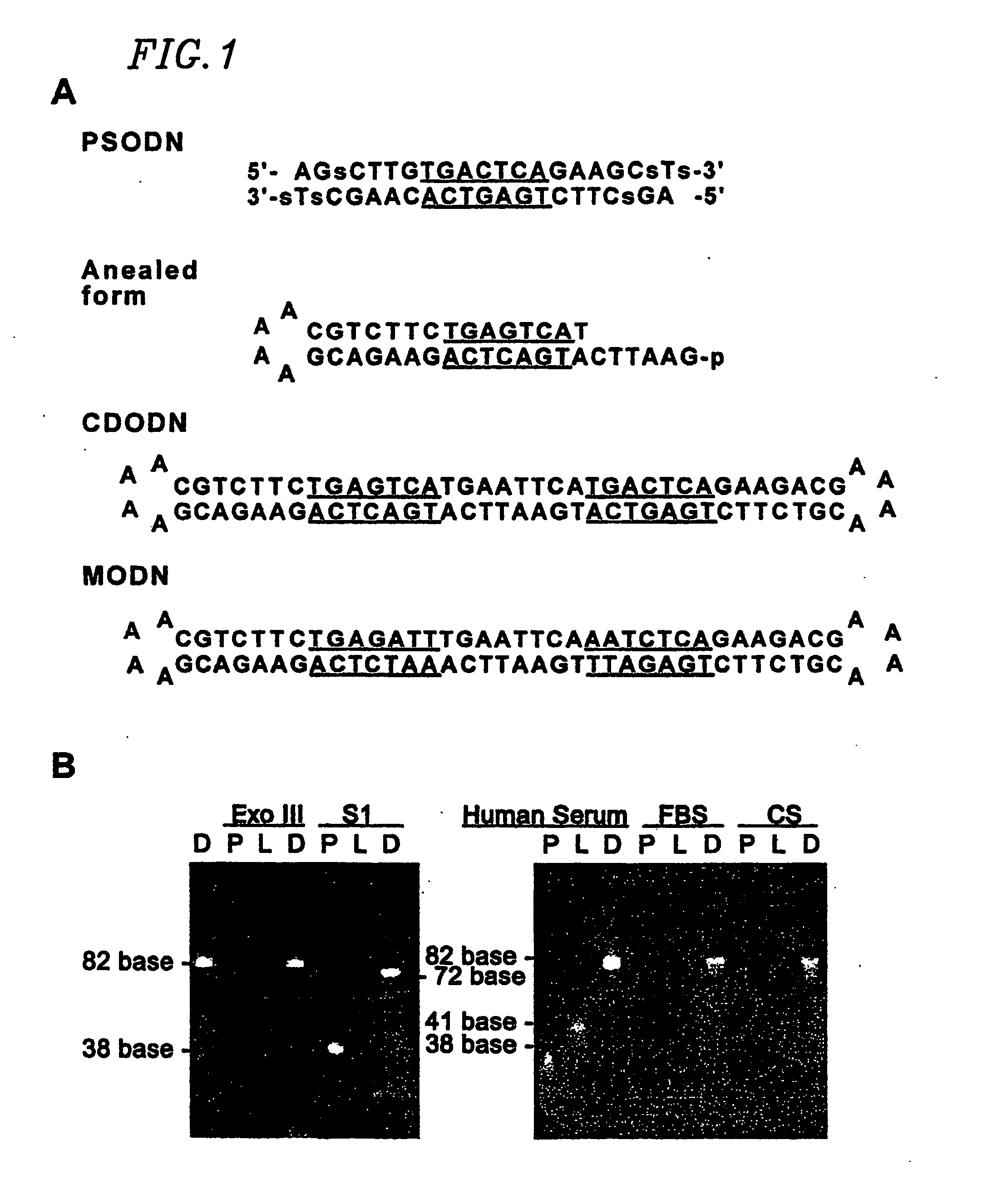
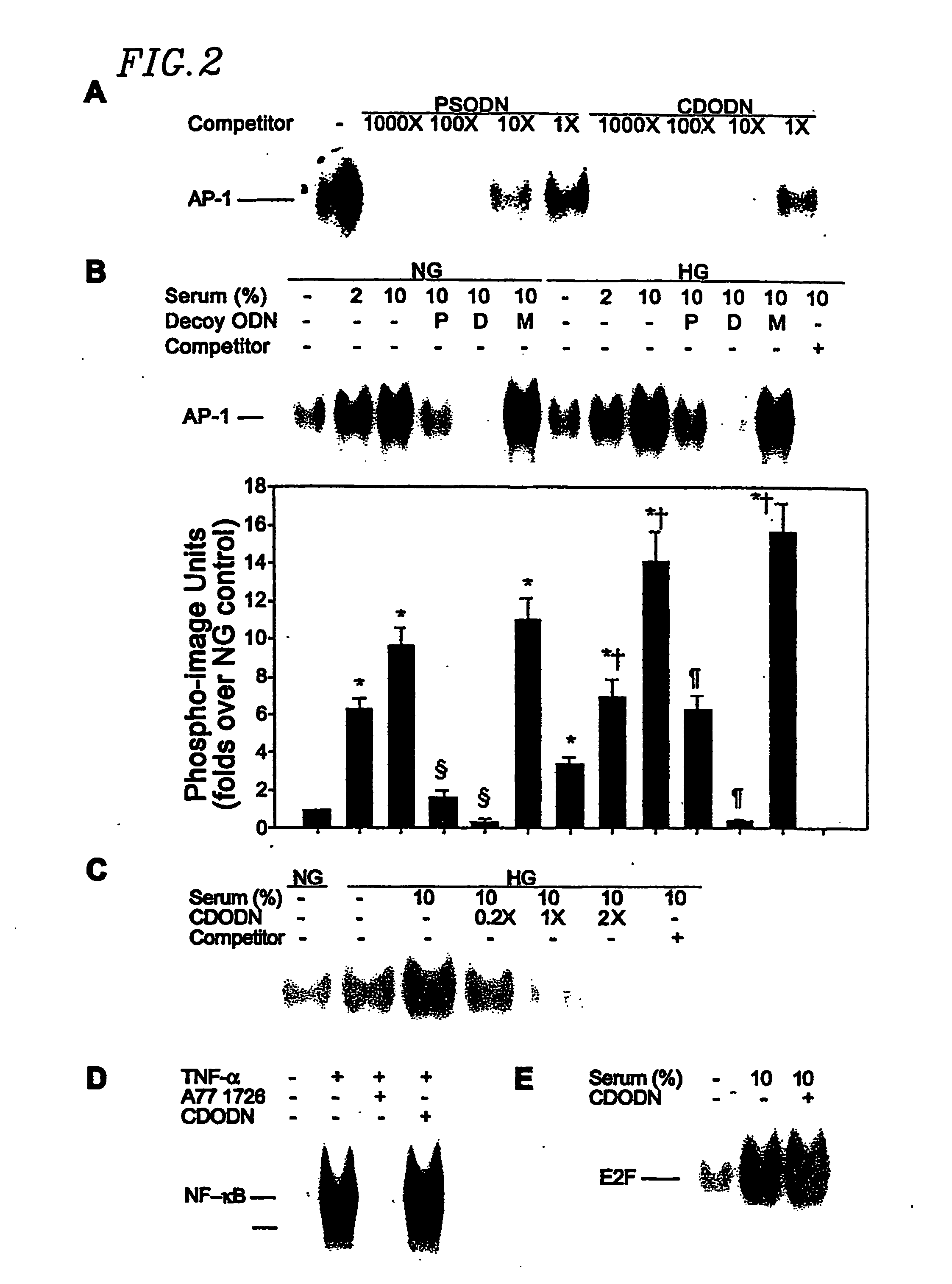
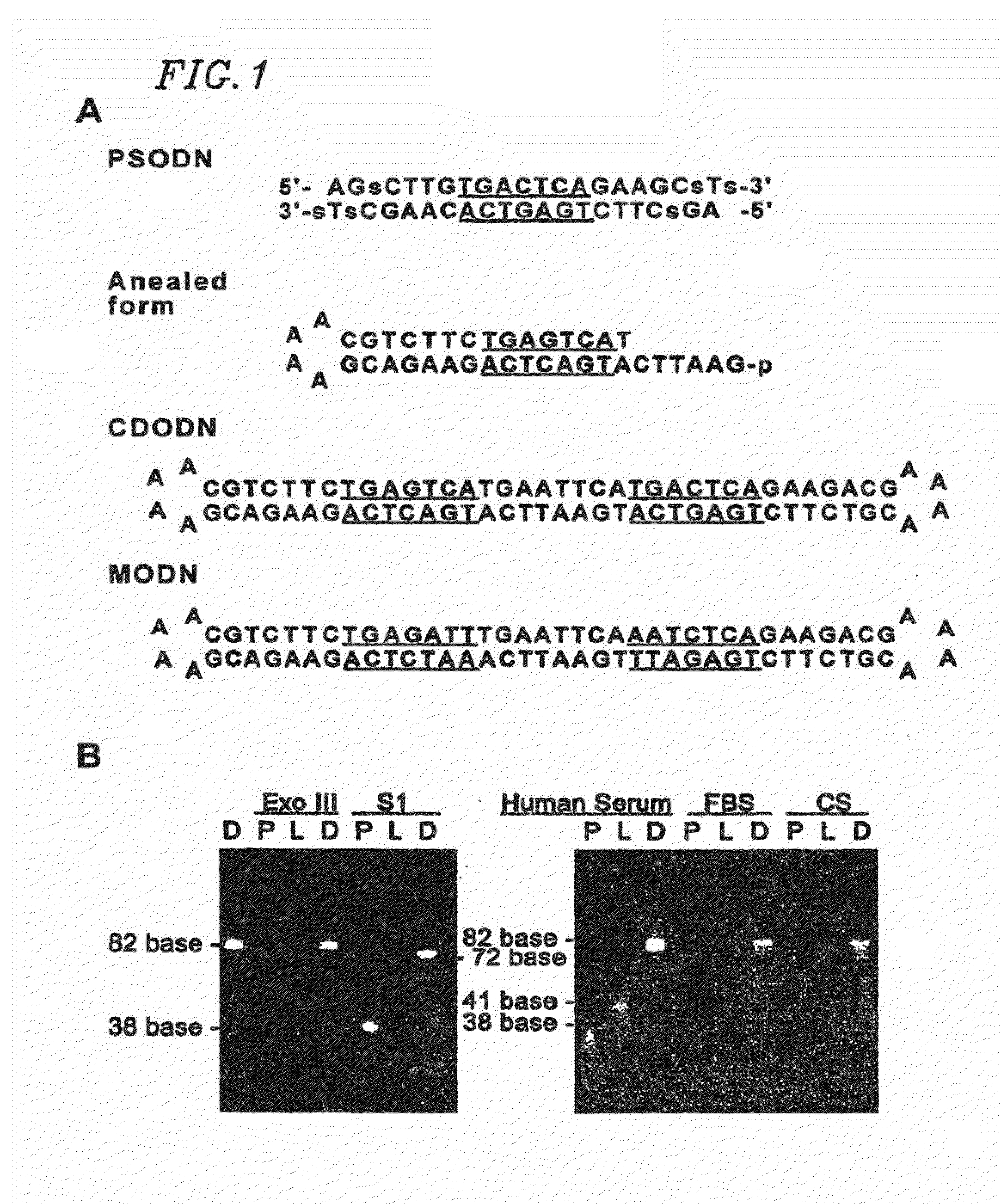
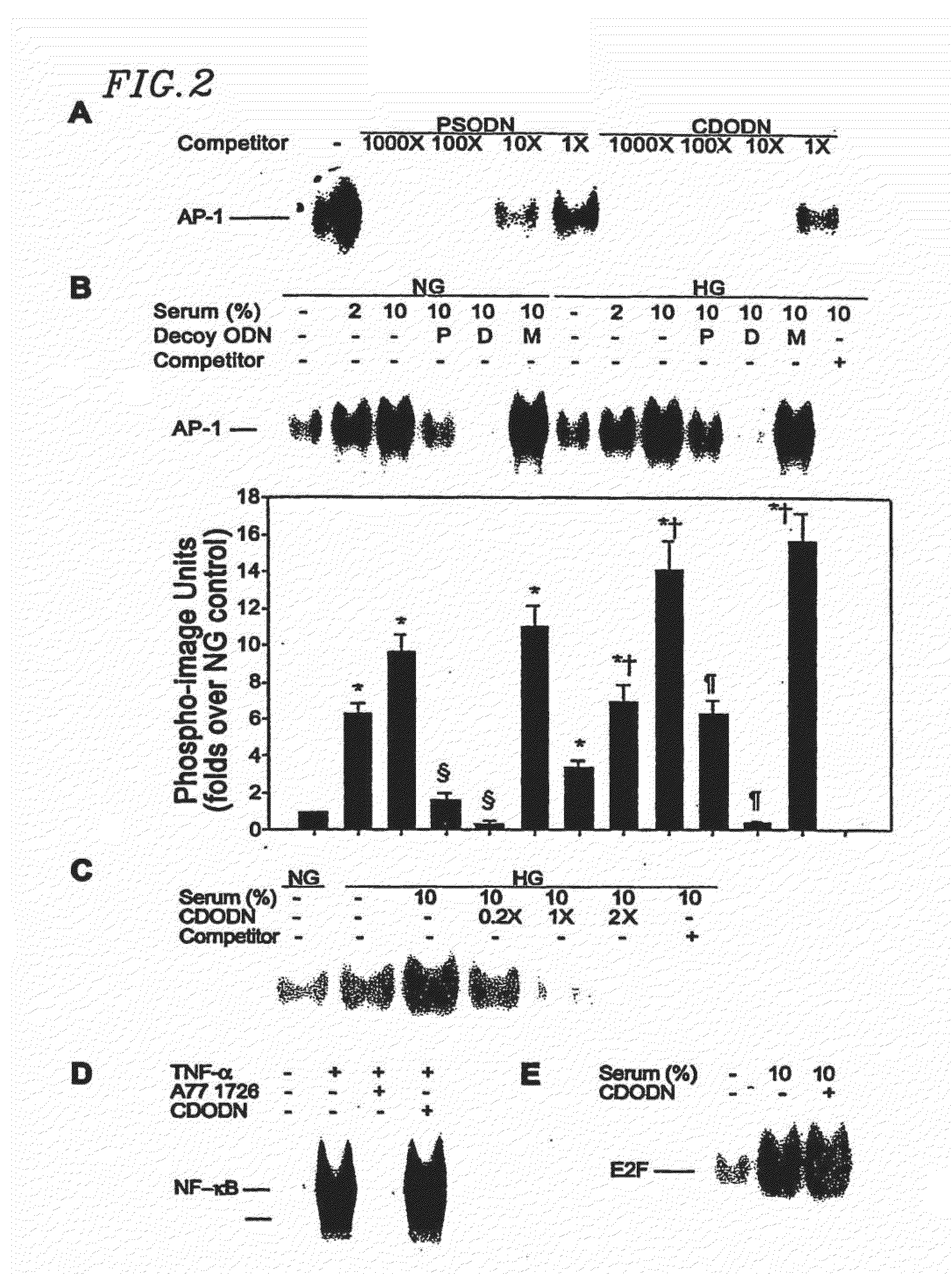
Circular dumbbell decoy oligodeoxynucleotides (cdodn) containing dna bindings sites of transcription
InactiveUS20070014840A1Effectively bind APPrevent trans-activationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA-binding domainDecoy
The present invention provides a circular dumbbell oligodeoxynucleotide (CDODN) comprising two loop structures and a stem structure, wherein the stem structure comprises a nucleotide sequence capable of binding the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional factor. The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising said CDODN. The pharmaceutical composition can be used for treating and / or preventing a disease or disorder related to such a transcriptional factor. The present invention also provides a method for treating and / or preventing a disease or disorder related to such a transcriptional factor, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a CDODN comprising two loop structures and a stem structure, wherein the stem structure comprises a nucleotide sequence capable of binding the DNA-binding domain of the transcriptional factor.
Owner:LEE IN KYU DR +1
Tumor selective E1a and E1b mutants
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Chemically programmable immunity
InactiveUS7422746B2Solve the real problemSave livesBiocideSnake antigen ingredientsBinding siteImmunogen
Methods and compositions for immediately immunizing an individual against any molecule or compound. The present invention comprises an immunity linker with at least two sites; (1) at least one first binding site that binds to an immune response component in an individual that has been pre-immunized with a universal immunogen, and (2) at least one second binding site that binds specifically to a desired compound or molecule, the target.
Owner:CENTAURI THERAPEUTICS LTD
Chemically Programmable Immunity
InactiveUS20100285052A1Solve the real problemImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBinding siteHalf-life
Methods and compositions for immediately immunizing an individual against any molecule or compound are provided. The present invention is directed to an immunity linker with at least two sites; (1) at least one first binding site that binds to an immune response component in an individual, and (2) at least one second binding site that binds specifically to a desired compound or molecule, the target. The second binding sites are preferably thiolated aptamers that have the benefit of increased stability, resistance to degradation and longer circulating half life. Methods of making and using pharmaceutical compositions including immunity linker molecules having a thiolated aptamer are also provided.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Protein-ligand binding site predicting method based on inquiry drive
InactiveCN103617203ATargetedEfficient use ofBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsData setBinding site
The invention provides a protein-ligand binding site predicting method based on inquiry drive. The method includes the steps of firstly, for an given inquiry input, searching protein sequences with high homology to form a training data set based on inquiry drive; secondly, extracting all the binding residues in the training data set as the positive sample set and extracting all the non-binding residues in the training data set as the negative sample set; thirdly, extracting the feature vector of each sample from evolution information and secondary structure perspective to obtain the feature vector sets of the positive and negative samples; fourthly, using a standard support vector machine algorithm for training to obtain an SVM prediction model based on the inquiry input q; fifthly, for the inquiry input, using the same feature extracting method to extract the feature vector of each residue, inputting the feature vector of each residue into the SVM prediction model, and predicting by using a threshold segmentation method. By the method, prediction precision can be increased, and the possible problems of over-optimization and over-fitting on the fixed training data set can be prevented.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multispecific reagent for selectively stimulating cell surface receptors
ActiveUS8058399B2Not to damageHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBinding siteReceptor degradation
A multispecific reagent has at least one first binding site for a cell surface receptor which requires multimeric ligand binding to be stimulated. The reagent possesses a second binding site for a target antigen which is expressed on the same cell as the cell surface receptor.
Owner:JUNG GUNDRAM
Chemically programmable immunity
InactiveUS7645743B2Solve the real problemSave livesOrganic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsBinding siteImmunogen
Methods and compositions for immediately immunizing an individual against any molecule or compound. The present invention comprises an immunity linker with at least two sites; (1) at least one first binding site that binds to an immune response component in an individual that has been pre-immunized with a universal immunogen, and (2) at least one second binding site that binds specifically to a desired compound or molecule, the target.
Owner:CENTAURI THERAPEUTICS LTD
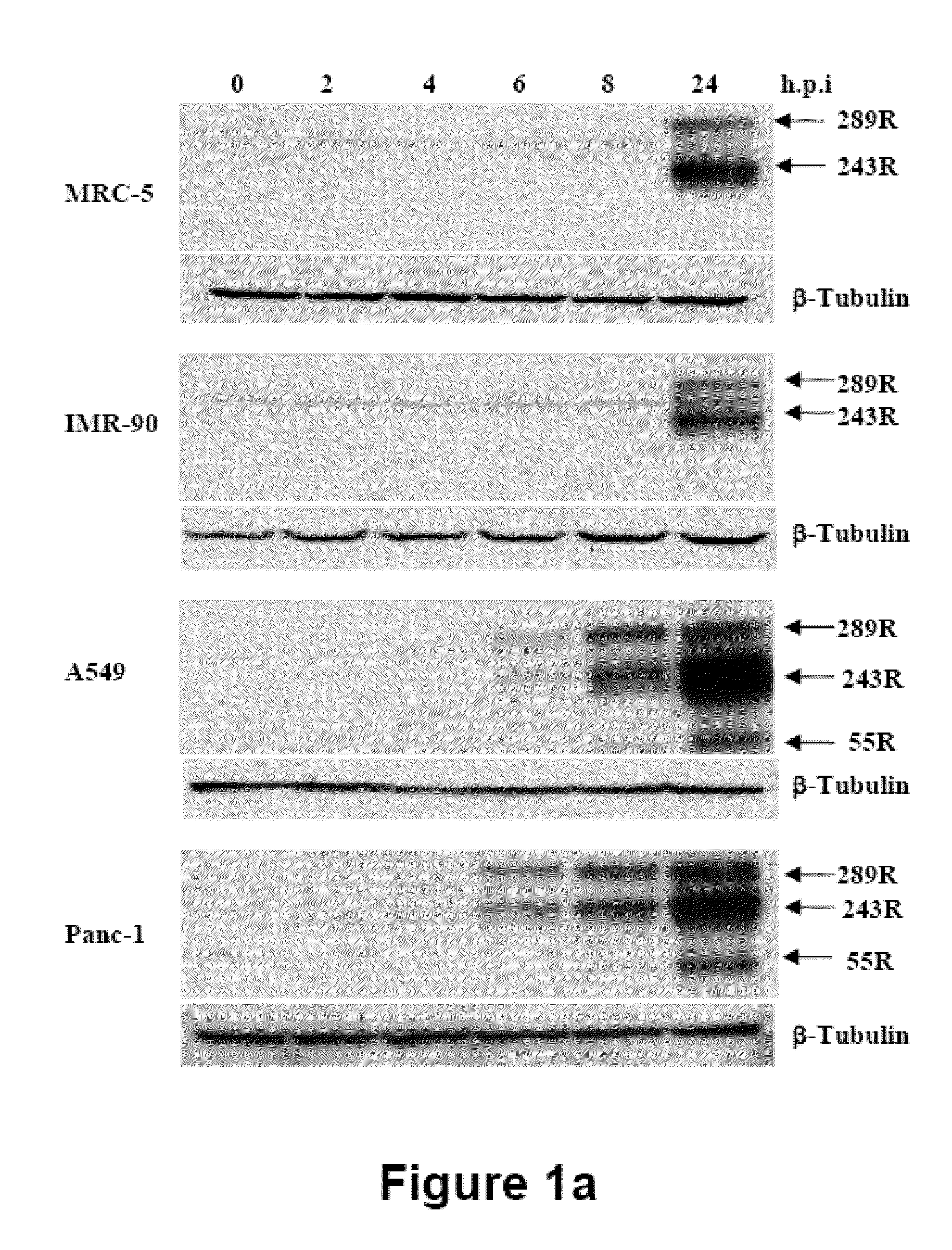
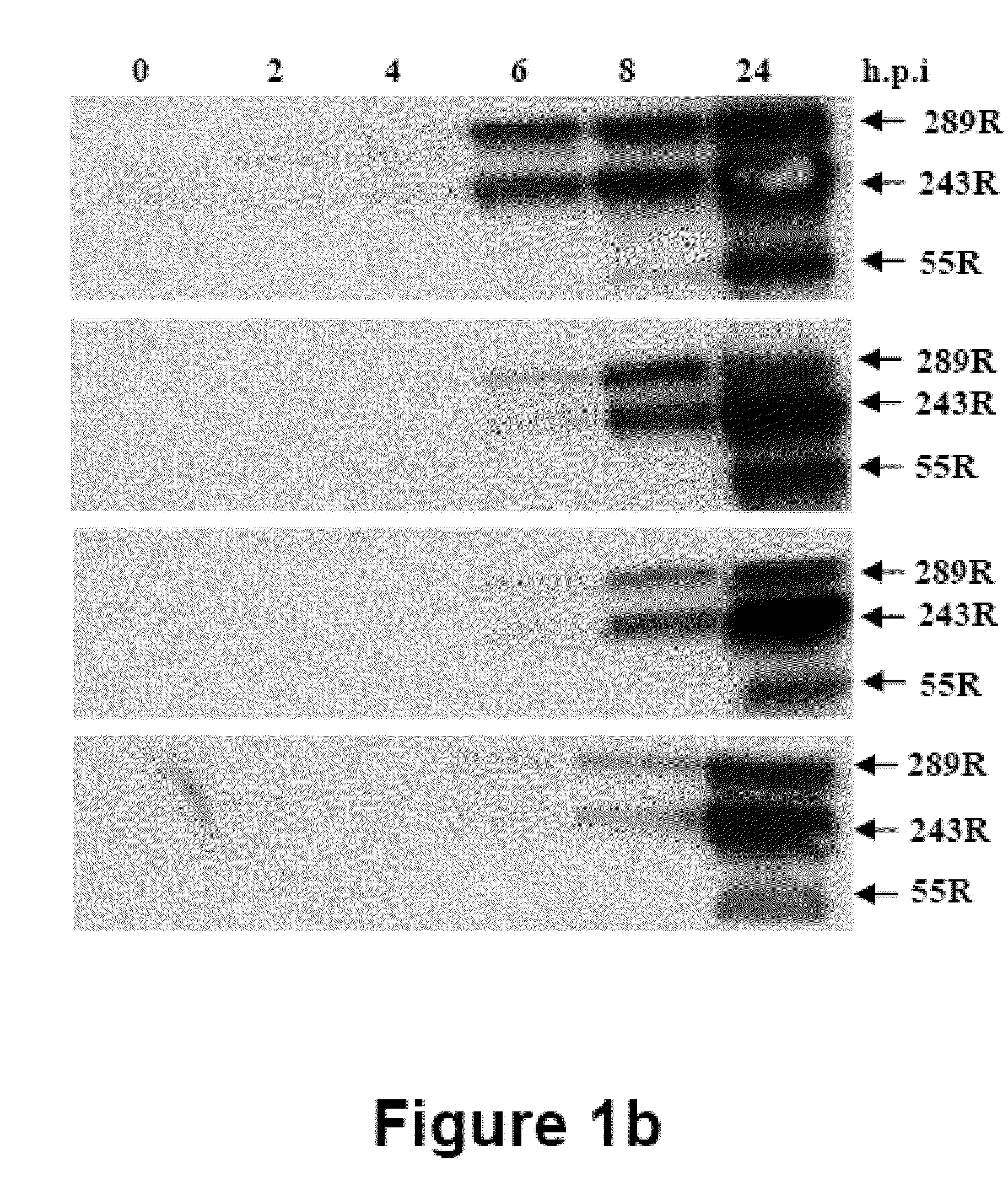
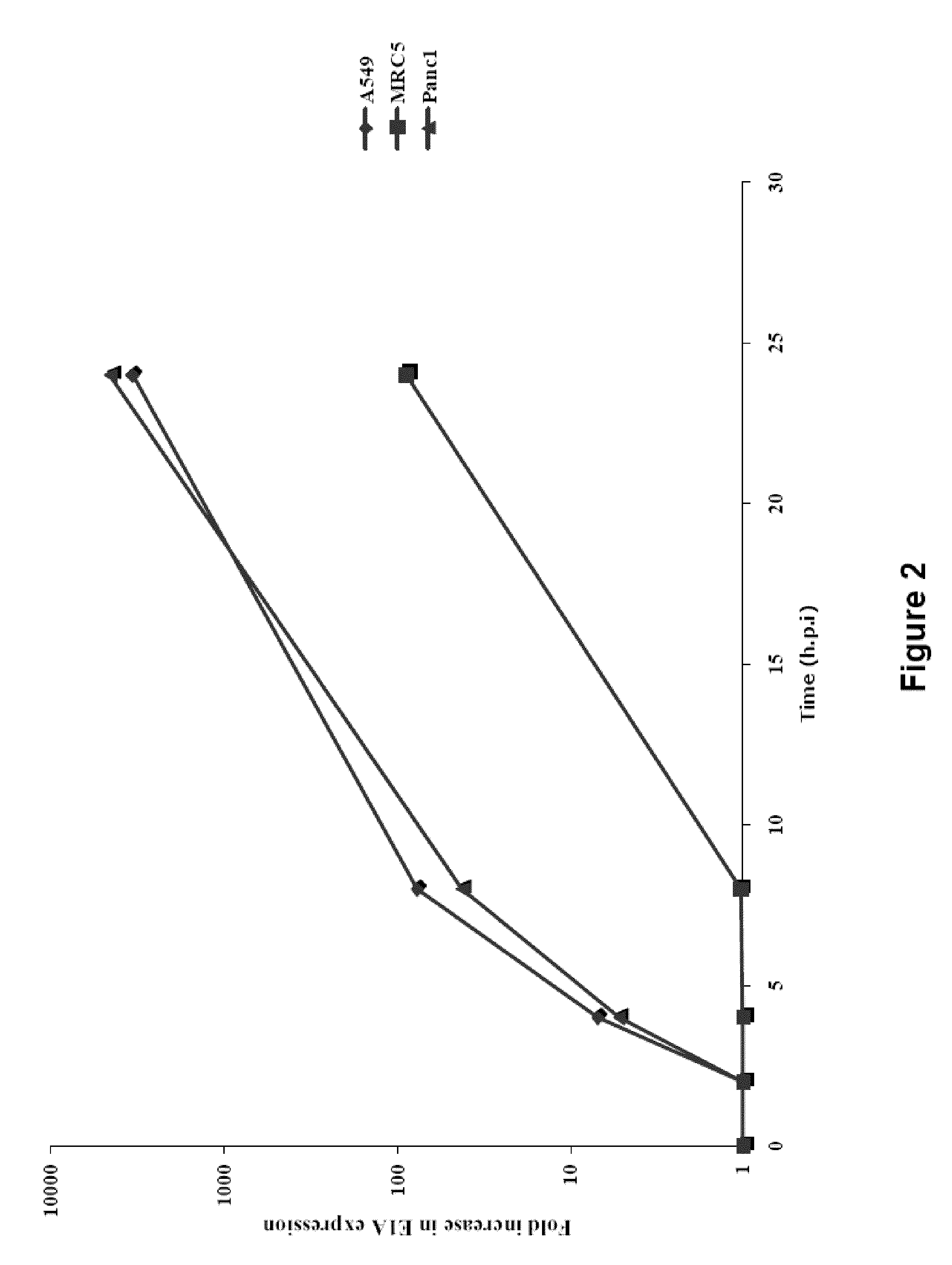
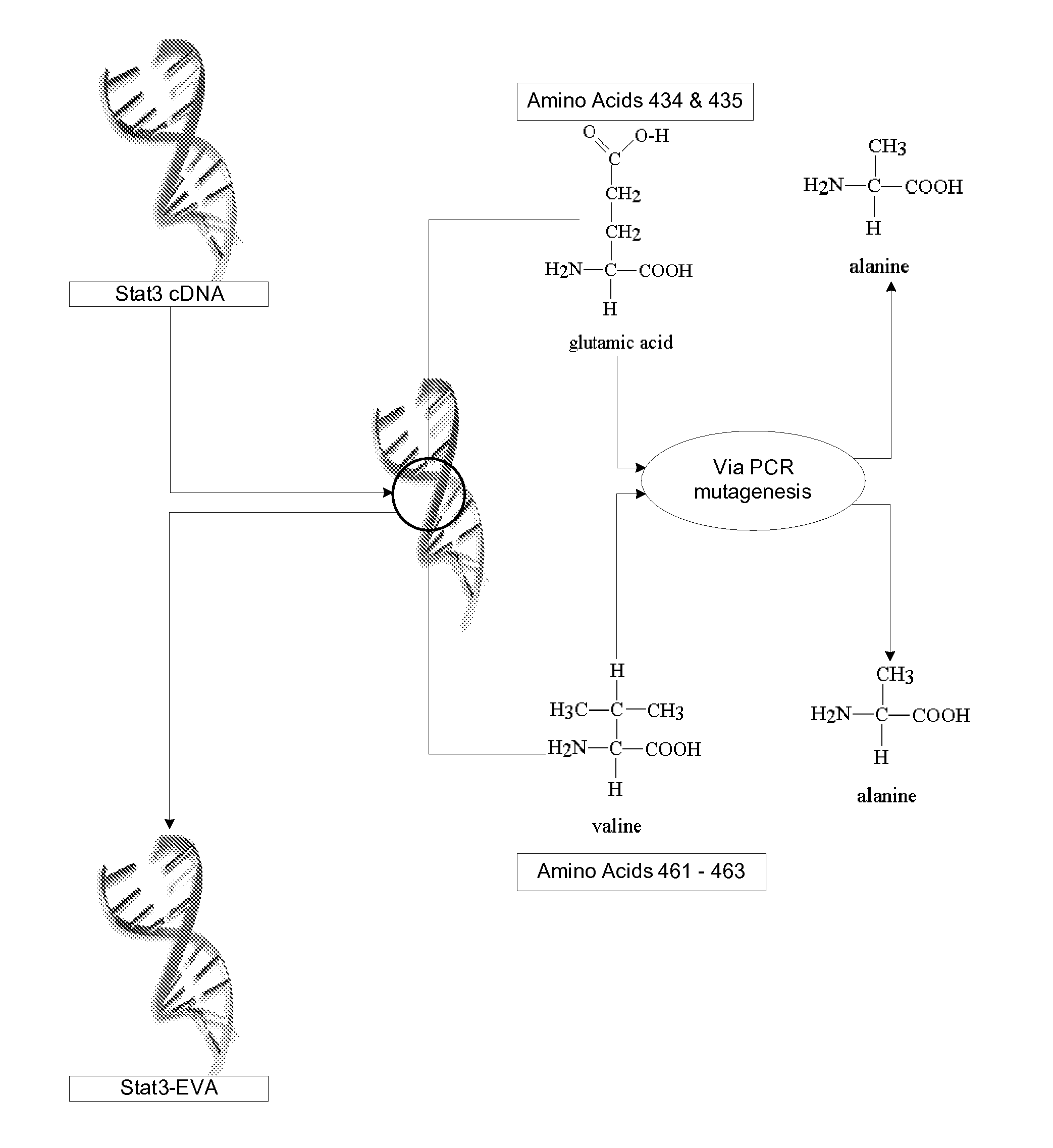
Adenoviral Vector Capable of Infecting Tumor Cells and Eliminating the Function of STAT3
An adenoviral vector which expresses a dominant negative form of Stat3 called Stat3-EVA for the treatment of non-small cell lung carcinoma. This construct has two mutations in the DNA binding site of Stat3 which prevents binding to DNA but has no effect on tyrosine phosphorylation or dimerization.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
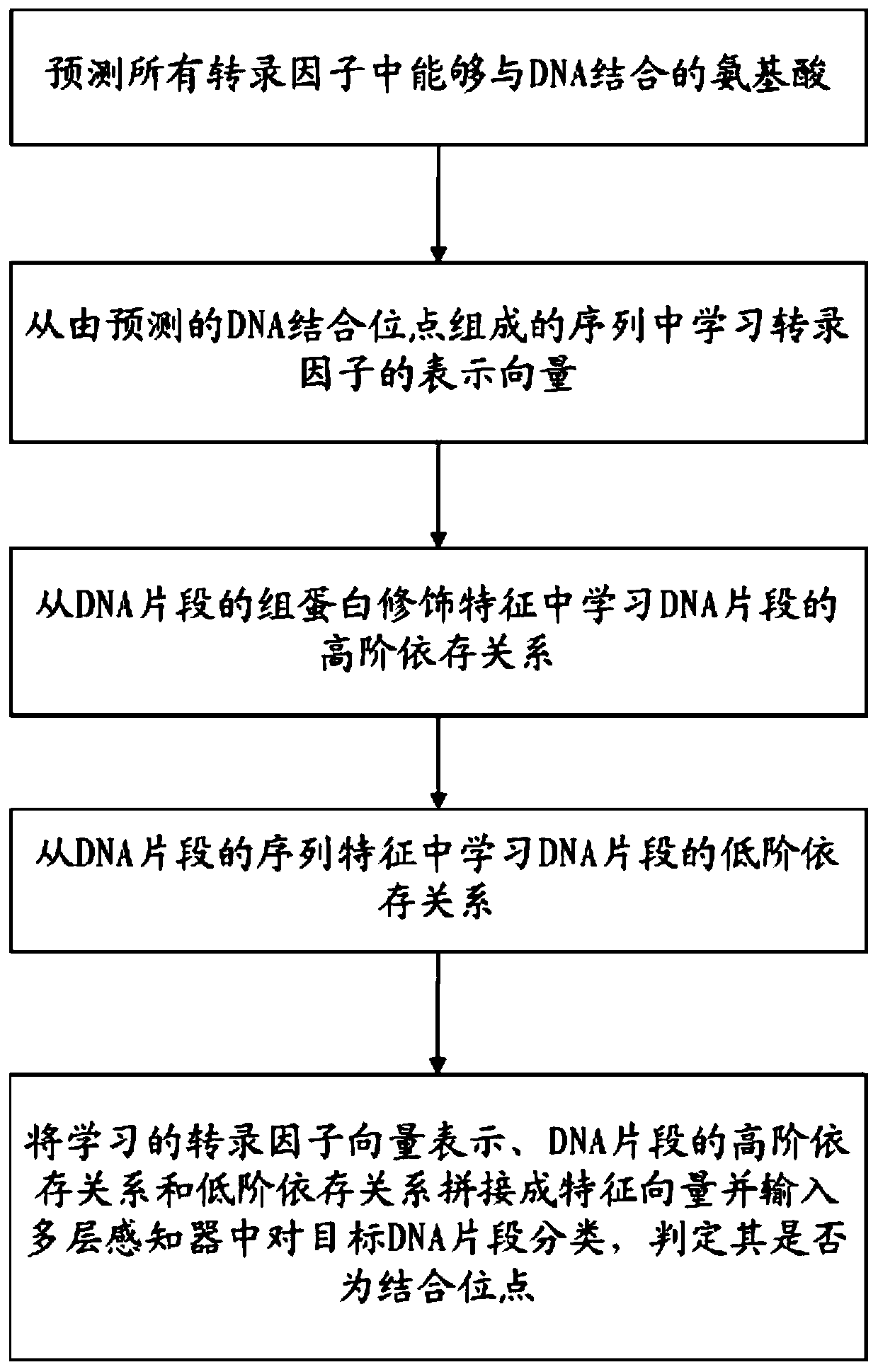
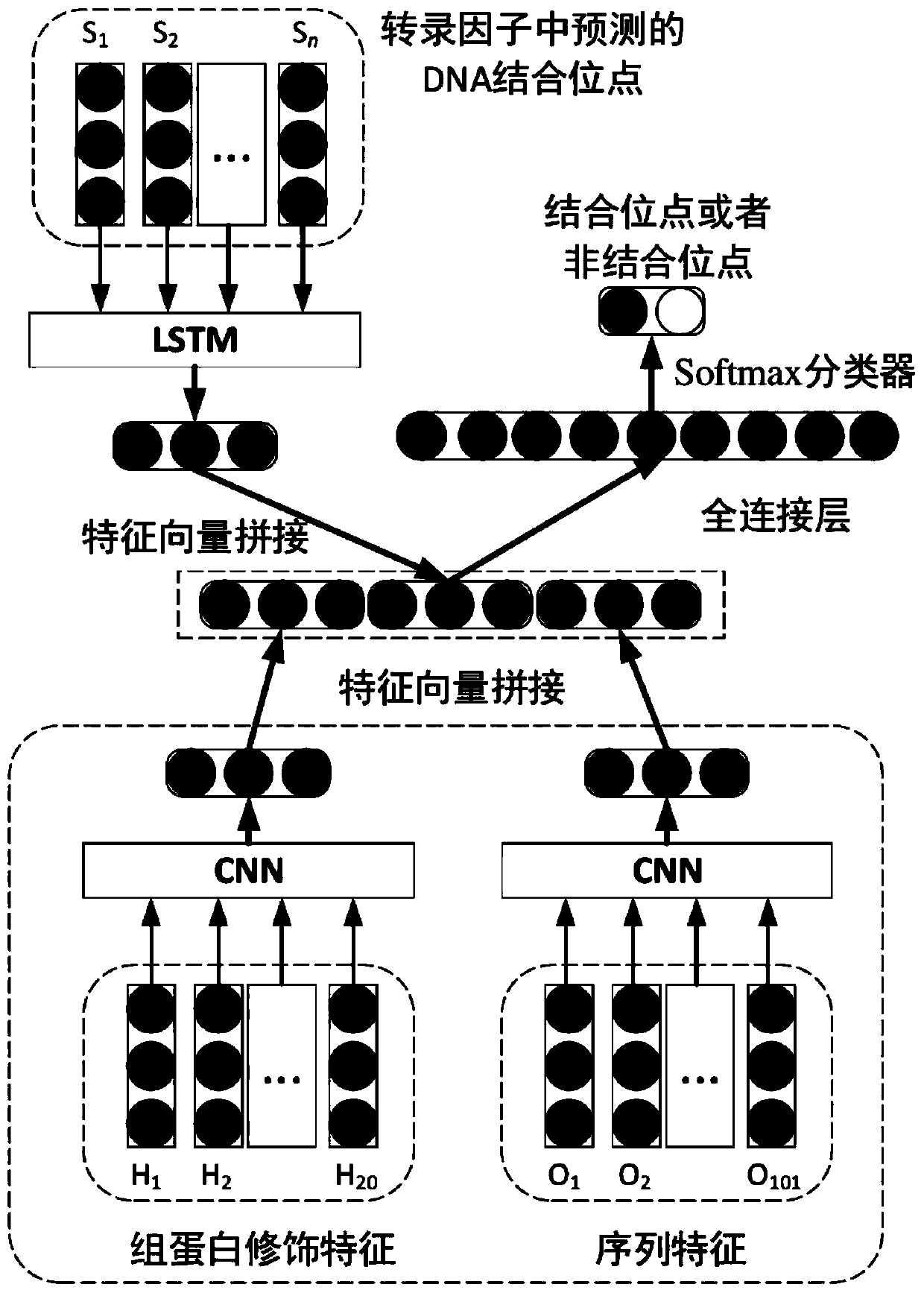
Transcription factor binding site prediction algorithm and device across transcription factors
The invention provides a transcription factor binding site prediction algorithm and device across transcription factors. The method comprises the following steps: 1, predicting amino acids capable ofbinding to DNA in all transcription factors, namely DNA binding sites, wherein the predicted DNA binding sites are mainly used for measuring contributions of labeled data of different transcription factors in a target transcription factor model training process; 2, learning a representation vector of transcription factors from a sequence composed of the predicted DNA binding sites; 3, learning thehigh-order dependency relationship of the DNA fragments from the histone modification characteristics of the DNA fragments; 4, learning the low-order dependency relationship of the DNA fragments fromthe sequence characteristics of the DNA fragments; 5, splicing the learned vector representation of the transcription factors, the high-order dependency relationship and the low-order dependency relationship of the DNA fragments into a feature vector, inputting the feature vector into a multilayer perceptron to classify the target DNA fragments, and judging whether the target DNA fragments are binding sites of the target transcription factor or not.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
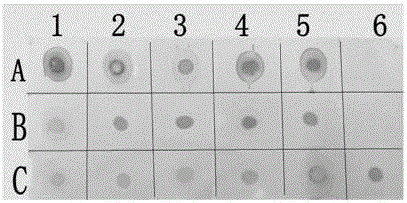
Method for detecting dsRNA virus of edible fungus
ActiveCN106226524AHigh sensitivityImprove reliabilityMaterial analysisBinding siteMonoclonal antibody
The present invention discloses a method for detecting dsRNA virus of edible fungus, the dsRNA virus of edible fungus can be detected by use of dsRNA monoclonal antibody J2 by dot hybridization, and the method is as follows: an edible fungus detection sample is prepared, the edible fungus detection sample is applied to a hybridization membrane, a closing liquid is used to fast close redundant nonspecific DNA binding sites on the hybridization membrane, the hybridization membrane is respectively incubated with the dsRNA monoclonal antibody J2 and goat anti-mouse IgG for color development, color changes are viewed by naked eyes, and toxic situations of the edible fungus can be determined. A plurality of samples can be detected by the method simultaneously, and the method has the advantages of convenient operation, fast and convenient operation, no need of special instruments and equipment, clear positive signals, easy judgment and the like.
Owner:INST OF EDIBLE FUNGI FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Chemically Programmable Immunity
InactiveUS20100247535A1Solve the real problemSave livesBiocideImmunoglobulins against bacteriaChemical compoundBinding site
Methods and compositions for immediately immunizing an individual against any molecule or compound. The present invention comprises an immunity linker with at least two sites; (1) at least one first binding site that binds to an immune response component in an individual that has been pre-immunized with a universal immunogen, and (2) at least one second binding site that binds specifically to a desired compound or molecule, the target.
Owner:ALTERMUNE TECH
Method for separating DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein and accurately positioning DNA binding site
InactiveCN104725465AAccurately locate the site of actionEasy to introduceMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsMagnetic beadBinding site
The invention provides a method for separating DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein and accurately positioning DNA binding site, which comprises the following steps: DNA binding protein separation: carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on a DNA segment to be researched by using biotin-labeled primers, sequentially adding nucleoprotein or cytoplast protein and avidin-coated magnetic beads, co-incubating, washing off nonspecific binding protein, and adding SDS (sodium dodecylsulfate) to denature and release the protein; and protein DNA binding site positioning: by using the DNA segment to be researched as a template, carrying out PCR reaction by using different primers to obtain overlapping DNA segments, and positioning the DNA binding site of the isolated protein according to the affinity difference of the overlapping DNA segments for the isolated protein.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Biologically-active DNA-binding sites and related methods
The invention relates to the identification of biologically-active DNA-binding sites to which a protein of interest binds in a cell. The invention also relates to the identification of agents and conditions which alter the biologically-active DNA-binding sites to which a protein binds. One aspect of the invention also provides methods for identifying pathways that are regulated by transcriptional regulators and for modulating the activity of the pathways.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Antiviral methods using human rhinovirus receptor (ICAM-1)
Method of inhibiting human rhinovirus (HRV) Infection by contacting said HRV with a polypeptide comprising a fragment of human rhinovirus major receptor (HRR), said fragment comprising the HRV binding site and being selected from a specific group consisting of HRR domains.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
A method for analyzing the geometric structure characteristics of DNA bin protein interface
InactiveCN109101784AIn-depth understanding of the binding mechanismSpecial data processing applicationsBinding siteSingle strand dna
The invention relates to an analysis method for the geometrical structure characteristics of DNA binding protein interface, belonging to the technical field of biological computing. The present invention first derives proteins-DNA binding site information from proteins-DNA complex dataset; and then based on the protein-DNA Binding Site Information, residue Morphological Index and Spatial Environment of proteins-DNA Binding Sites are determined; finally, the morphological index and spatial environment of the identified protein-DNA binding sites are used as feature vectors to classify the obtained feature vectors by using classification model. As the binding specificity of double-stranded DNA binding protein (DSBs) and single-stranded DNA binding proteins (SSBs) is analyzed from the angles of the morphological structure of the residues and the characteristics of the space environment, the invention is conducive to the in-depth understanding of the proteins, and the binding specificity ofthe double-stranded DNA binding proteins and the single-stranded DNA binding proteins is analyzed. Based on the DNA binding mechanism, the present invention can also be applied to proteins-RNA, protein-Protein and other fields.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Selection
InactiveUS8084213B2Stabilise the protein-DNA complexLow dissociation ratePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainNucleotide
The present invention to a nucleotide sequence encoding one or more Arc DNA binding domains, one or more Arc DNA binding sites and at least one polypeptide domain.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
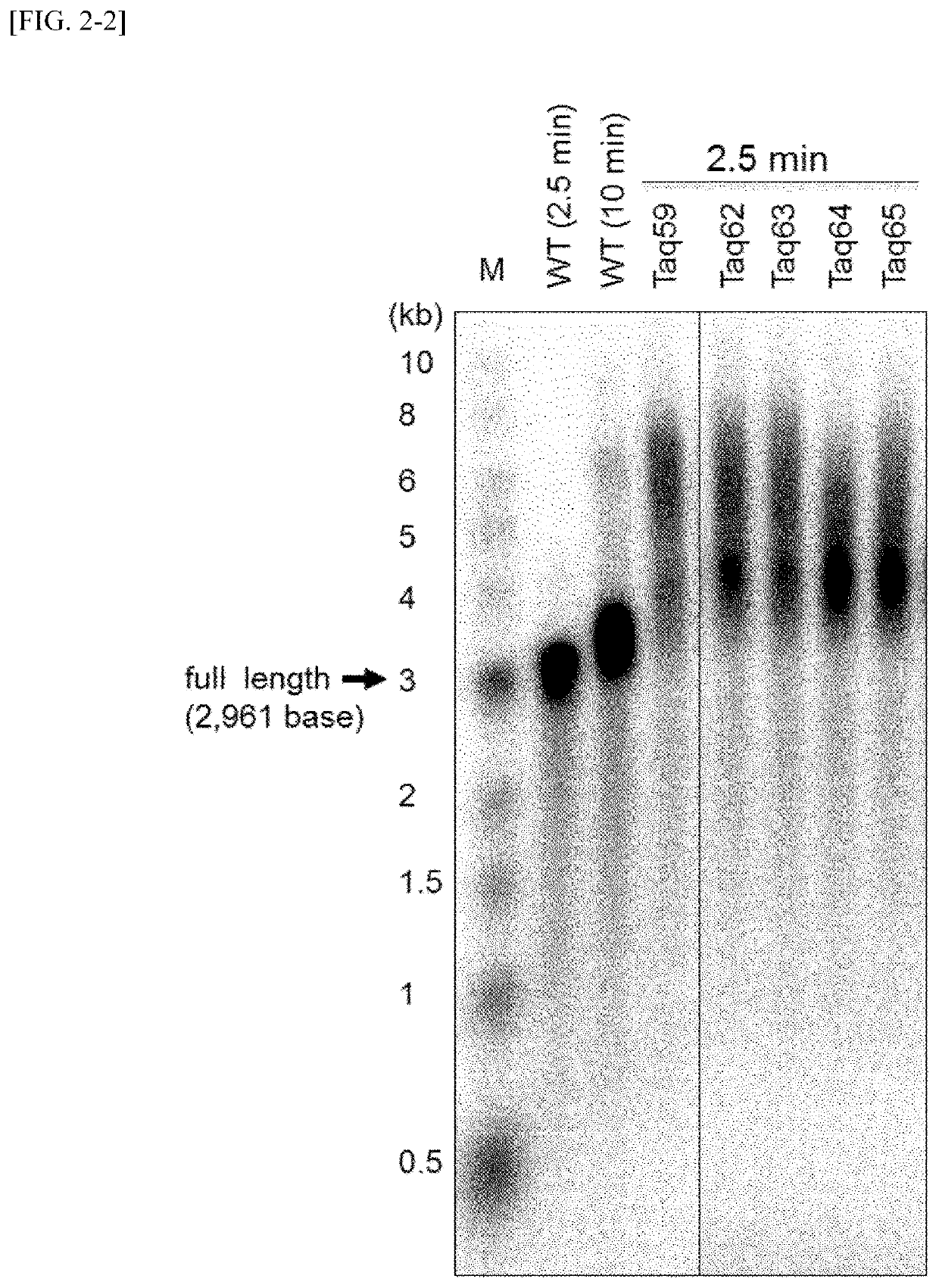
DNA polymerase variant
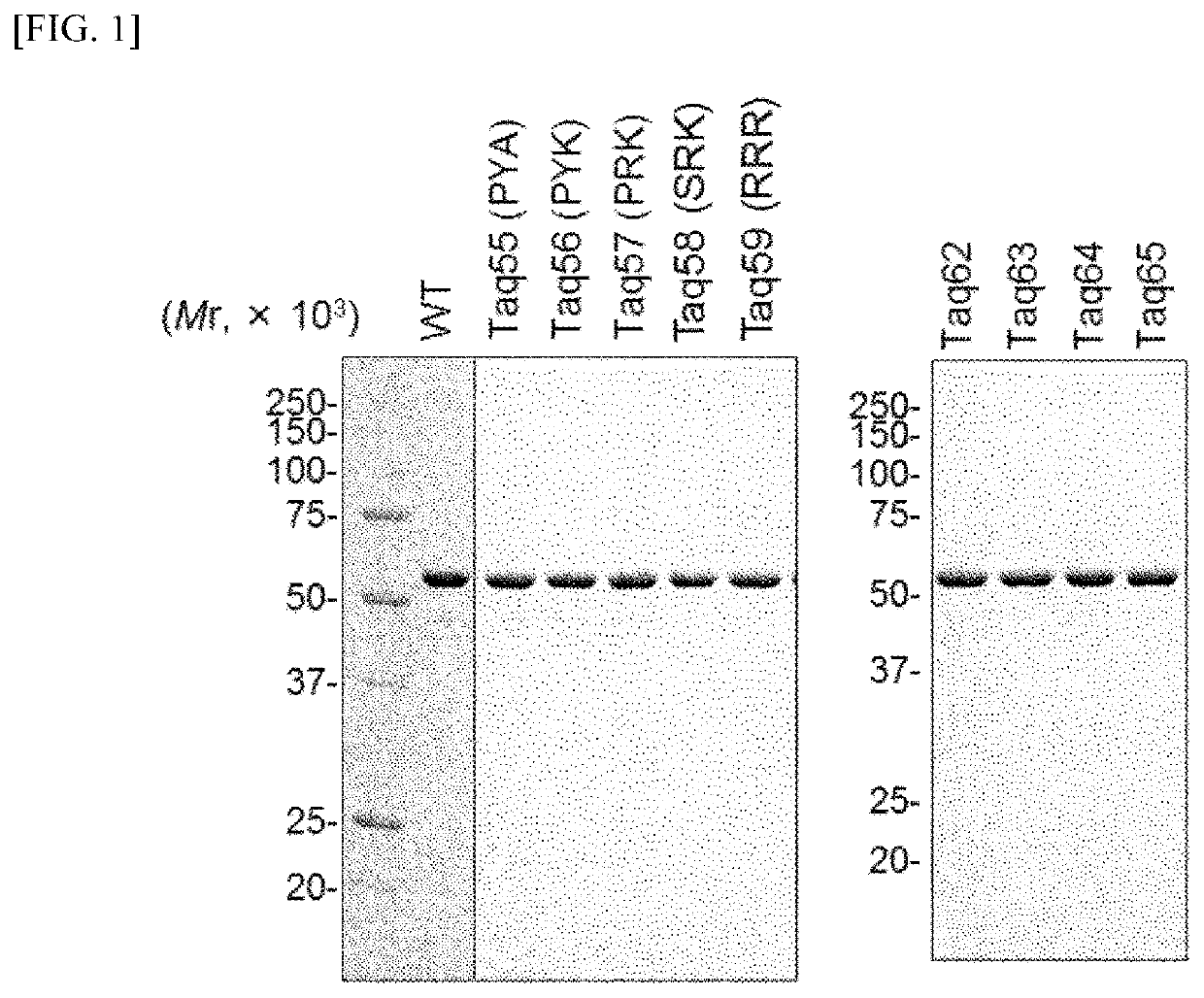
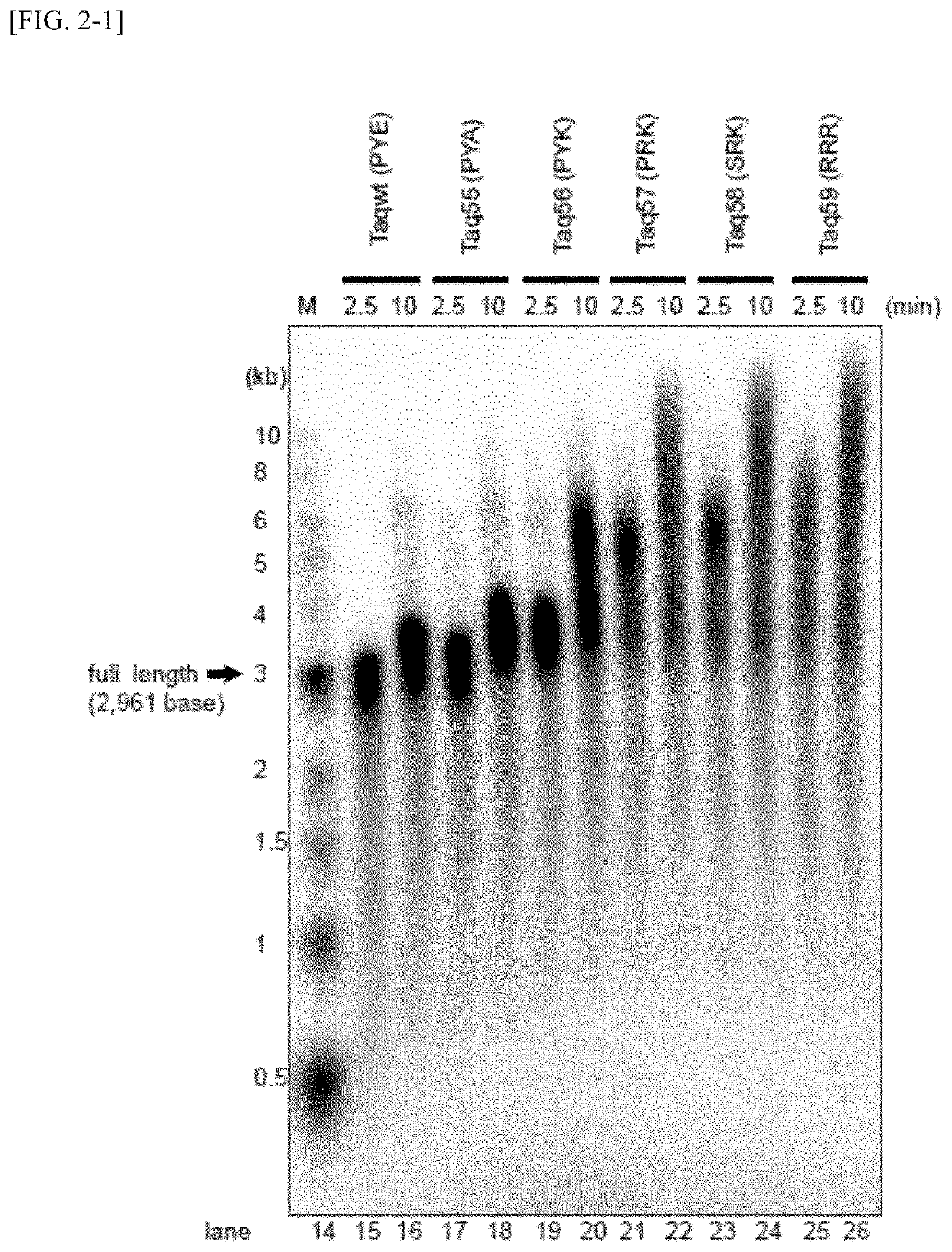
ActiveUS11046939B2Improve heat resistanceEfficient replicationBacteriaTransferasesBinding siteAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to a Thermus aquaticus (Taq) polymerase having a strand displacement activity in which an amino acid residue in a template DNA binding site of the DNA polymerase is substituted with an amino acid to increase a total charge in the site, a nucleic acid encoding the polymerase, a vector containing the nucleic acid, a transformant containing the vector containing the nucleic acid or the nucleic acid, a method for producing the polymerase, a method for amplifying nucleic acids utilizing the polymerase, and a kit containing the polymerase. According to the present invention, a DNA polymerase having a high thermostability, capable of efficiently replicating a long-strand of a template DNA, and having a strong strand displacement activity is provided.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV +1
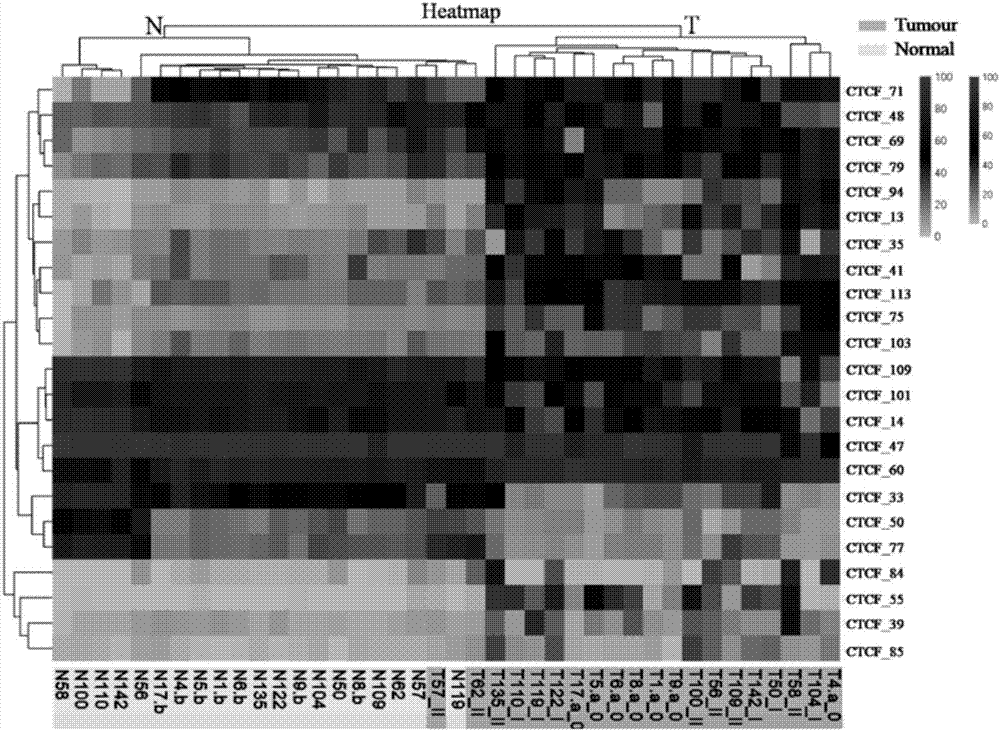
Application of DNA binding site CTCF_113 of multifunctional transcriptional regulatory factor CTCF
ActiveCN107227366AImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationParanasal Sinus Carcinoma
The invention discloses a novel purpose of a DNA binding site CTCF_113 of a multifunctional transcriptional regulatory factor CTCF, i.e., the application thereof to prevention of a kit for early diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma. The binding site has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The accuracy of the CTCT binding site provided by the invention for detecting rectal adenoma and colorectal cancer is obviously higher than that of the reported DNA methylation molecular markers; the DNA binding site of the CTCF can be likely to become a biomarker for tumor treatment effect monitoring, prognosis effect evaluation and tumor molecular subtyping (such as CIMP subtyping). Generally, the invention provides a novel idea for finding the more effective tumor early stage diagnosis, treatment effect monitoring, prognosis effect evaluation and molecular subtyping molecular markers, and has the important significance on tumor prevention and treatment.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV
Circular dumbbell decoy oligodeoxynucleotides (CDODN) containing DNA bindings sites of transcription
InactiveUS20110250261A1Prevent proliferationInhibit migrationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseDecoy
The present invention provides a circular dumbbell oligodeoxynucleotide (CDODN) comprising two loop structures and a stem structure, wherein the stem structure comprises a nucleotide sequence capable of binding the DNA-binding domain of a transcriptional factor. The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising said CDODN. The pharmaceutical composition can be used for treating and / or preventing a disease or disorder related to such a transcriptional factor. The present invention also provides a method for treating and / or preventing a disease or disorder related to such a transcriptional factor, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a CDODN comprising two loop structures and a stem structure, wherein the stem structure comprises a nucleotide sequence capable of binding the DNA-binding domain of the transcriptional factor.
Owner:DR IN KYU LEE +1
Application of DNA binding site CTCF_55 of multifunctional transcriptional regulation factor CTCF
The invention discloses novel application of a DNA binding site CTCF_55 of a multifunctional transcriptional regulation factor CTCF, and particularly relates to application of the DNA binding site CTCF_55 in preparation of a kit for early diagnosis of a colorectal tumor. The nucleotide of the binding site is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The accuracy of the CTCF binding site provided by the invention for detecting colorectal adenomas or a colorectal cancer is obviously higher than that of a reported DNA methylated molecular marker; furthermore, the DNA binding site of the CTCF may be a biological marker for monitoring the tumor treatment effect, estimating the prognosis effect and tumor molecular parting (such as CIMP parting). In conclusion, the invention provides a new idea for searching a more effective molecular marker for early diagnosis of the tumor, monitoring of the treatment effect, estimation of the prognosis effect and the molecular parting, and the application has important significance for prevention and treatment of the tumor.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV
Nucleic acids encoding receptor recognition factors, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7339039B2Promote reproductionEasy to managePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological activationFhit gene
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Blue-light inducible system for gene expression
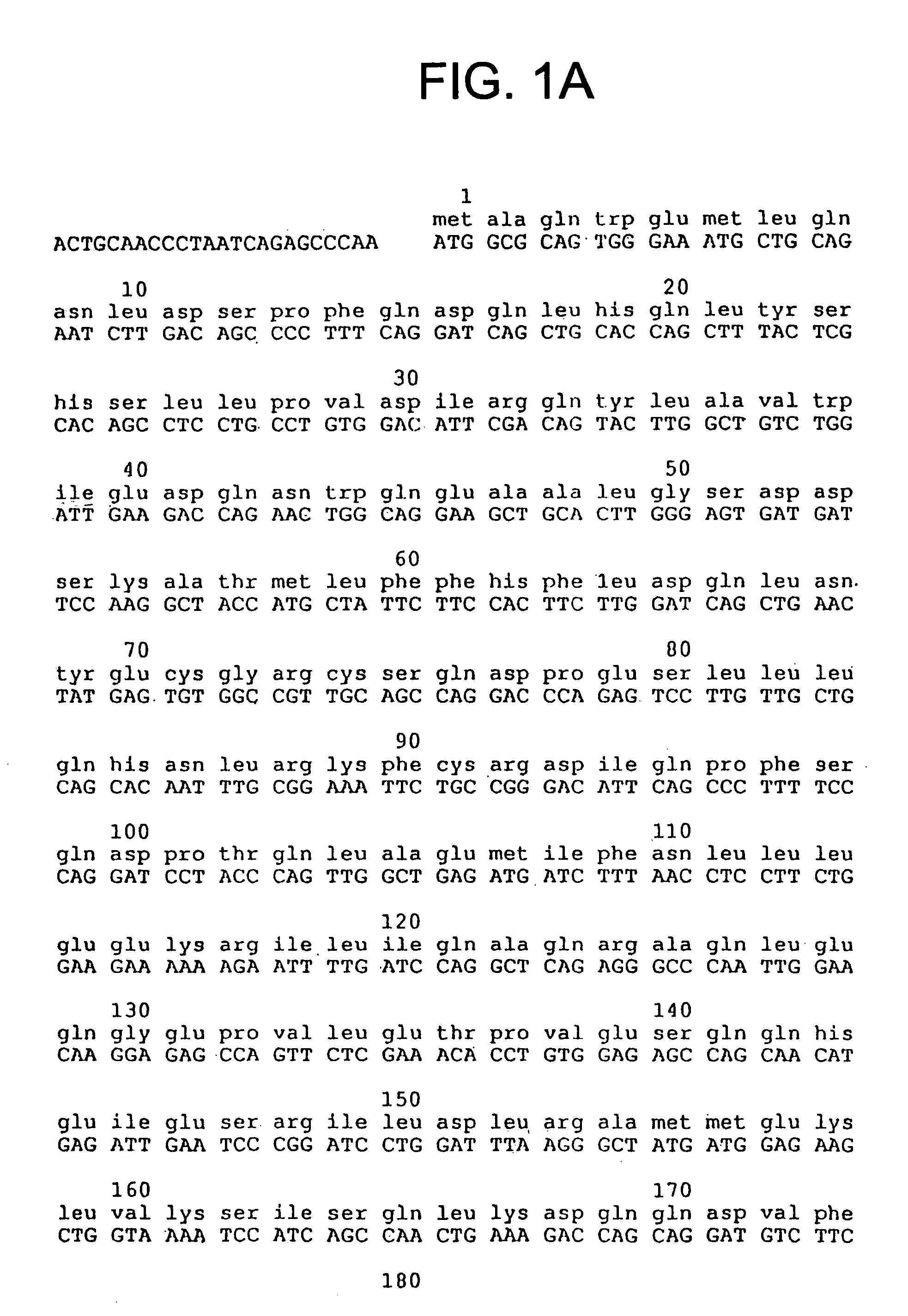
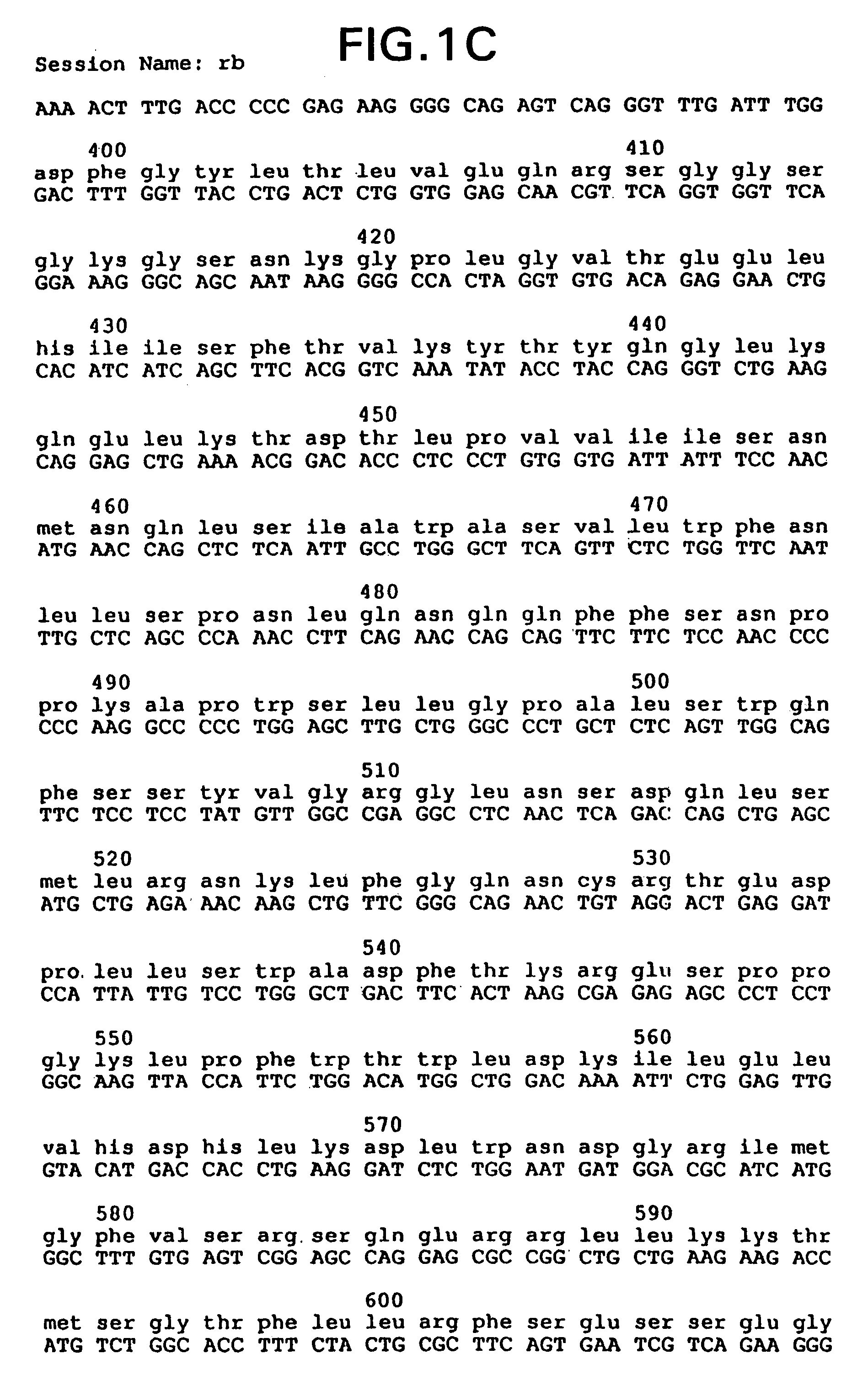
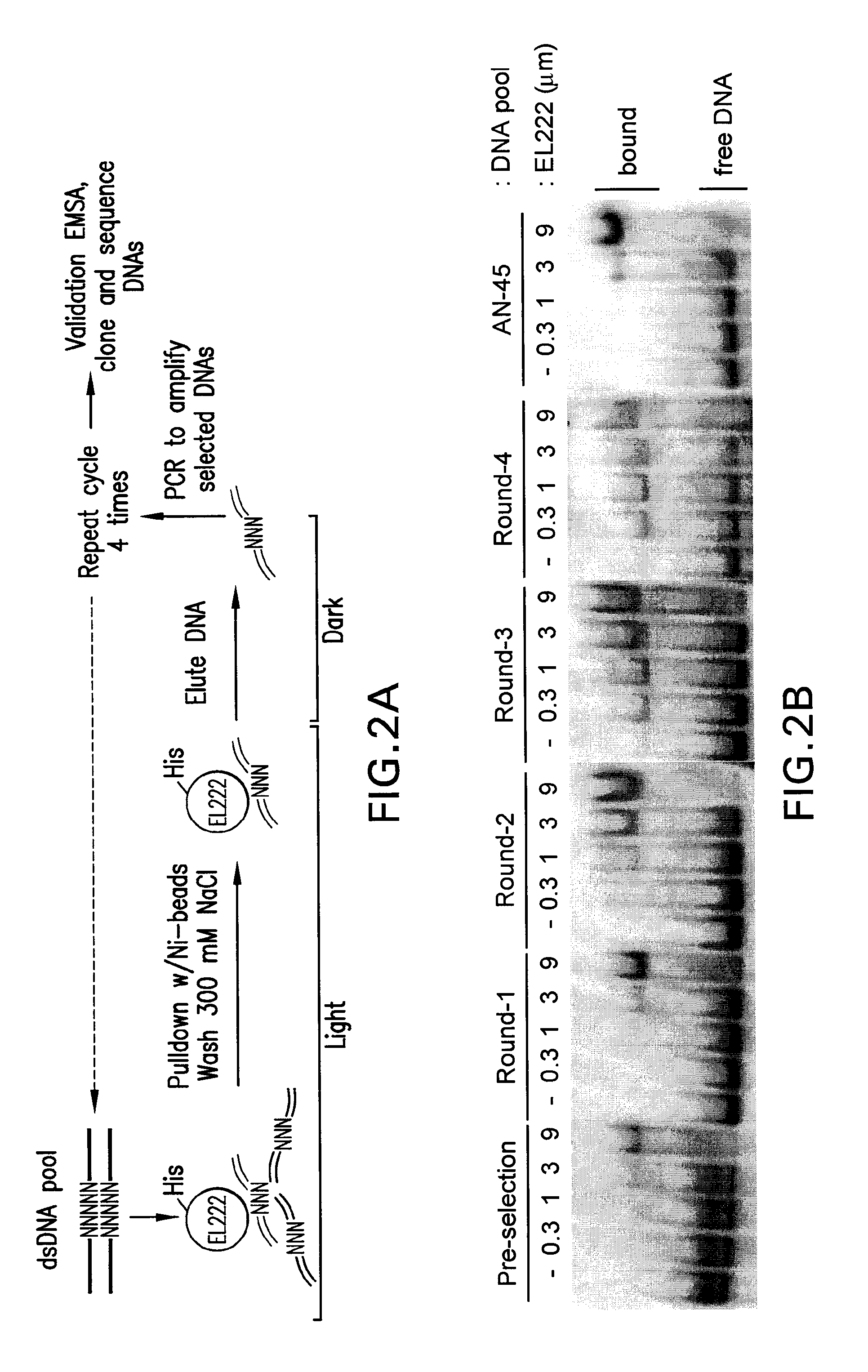
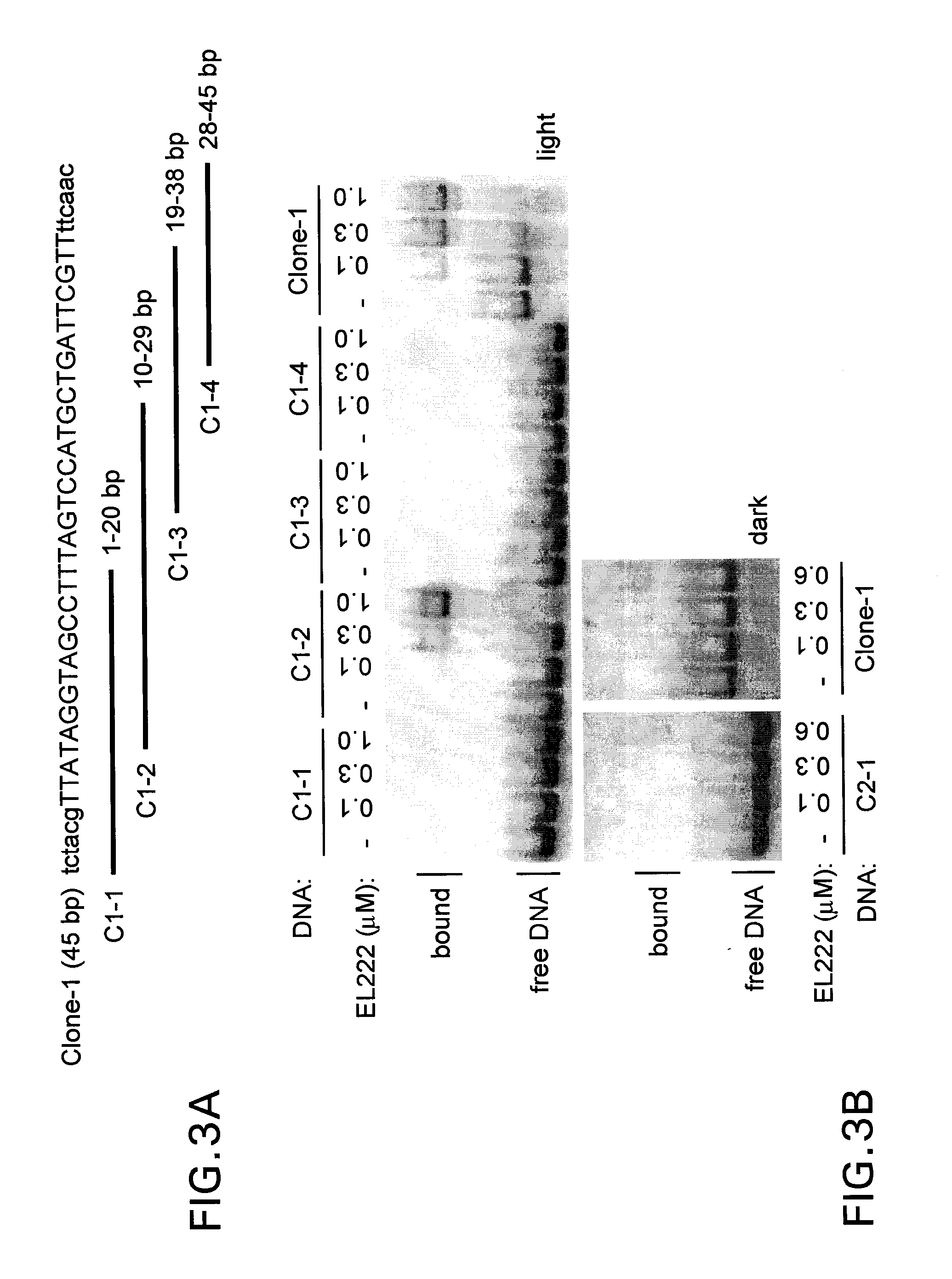
ActiveUS9506073B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainProtein moleculesBinding site
The present invention provides methods for light-dependent gene regulation using a light-responsive DNA-binding protein. Also provided are related nucleic acid molecules, and protein molecules, such as those encoding or comprising the light-responsive DNA-binding protein or DNA-binding sites recognizing the light-responsive DNA-binding protein. Kits using the present light-dependent gene regulation system are further provided by the present invention.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Selection
InactiveUS20090176209A1Strong specificityStabilise the protein-DNA complexPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainNucleotide
The present invention to a nucleotide sequence encoding one or more Arc DNA binding domains, one or more Arc DNA binding sites and at least one polypeptide domain.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Engineered open reading frame for p53
The transcription factor and tumor suppressor protein p53 is inactivated in many human cancers. Approximately forty percent of cancers carry large amounts of mutated full-length p53 protein with one of over 900 reported single amino acid changes in the p53 core domain that recognizes p53 DNA binding sites. The ability to restore function to these inactive p53 proteins would dramatically improve cancer therapy. Alternative open reading frames that are more easily engineered encode a wild-type p53. The alternative open reading frames are optimized for codon usage and expression of p53 proteins in E. coli, yeast and mammalian cells. The alternative open reading frames may additionally contain mutations that are naturally found in human cancers, substitutions that correspond to polymorphic p53 alleles, or mutations in residues that can be post-translationally modified.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com