Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Cardiac interventions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cardiac Interventions Today (ISSN 2572-5955 print and ISSN 2572-5963 online) is a publication dedicated to providing comprehensive coverage of the latest developments in technology, techniques, clinical studies, and regulatory and reimbursement issues in the field of coronary and cardiac interventions.
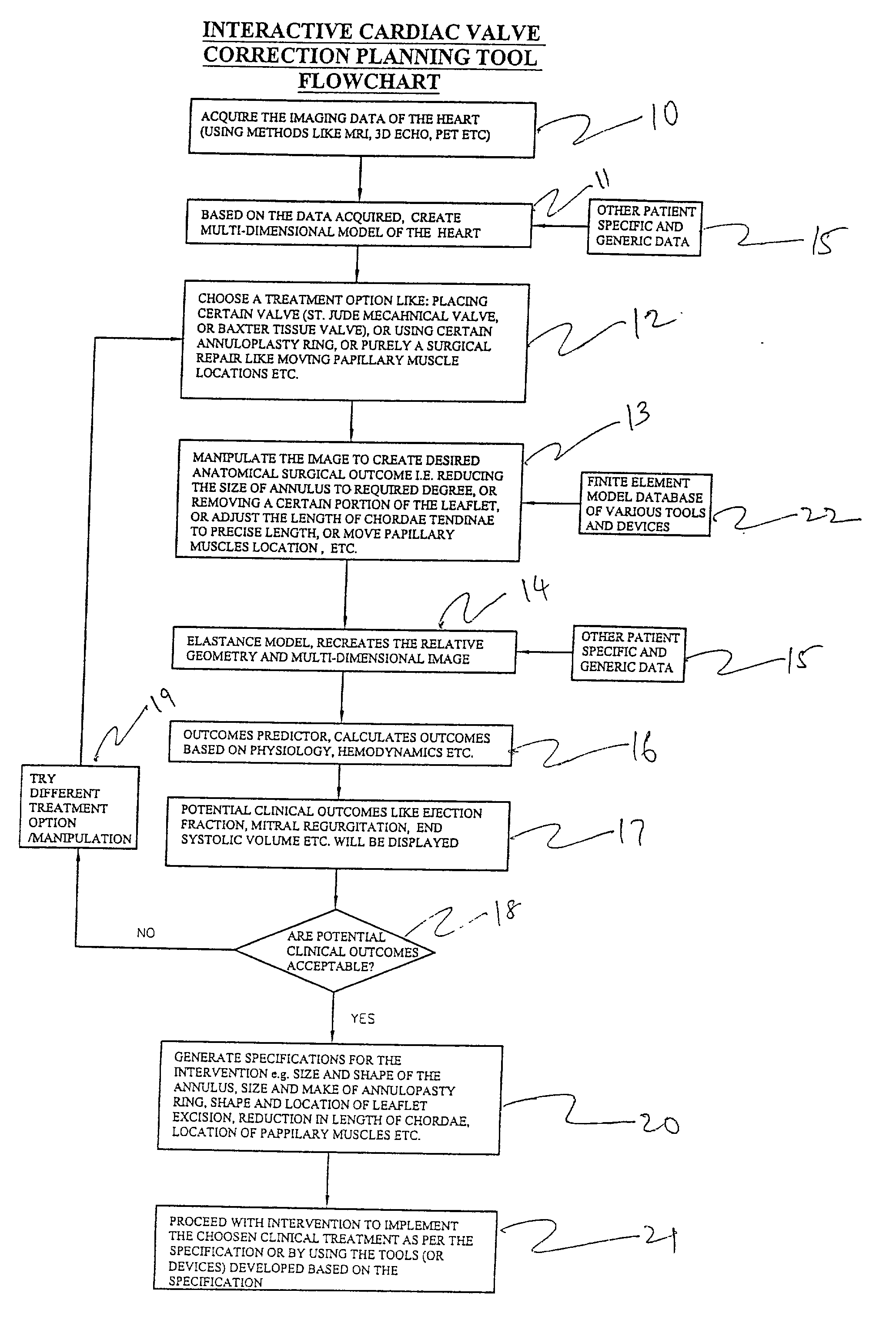
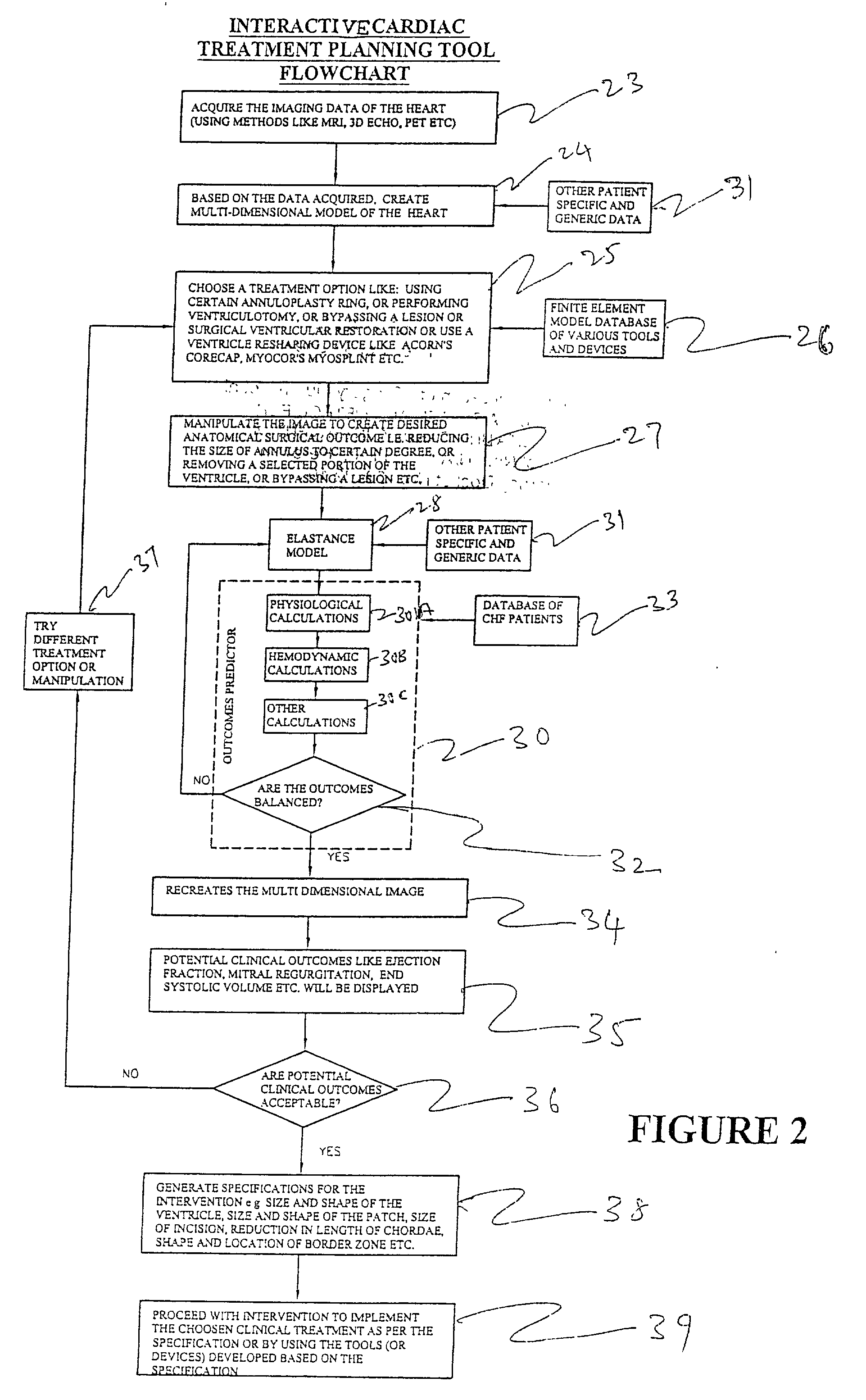
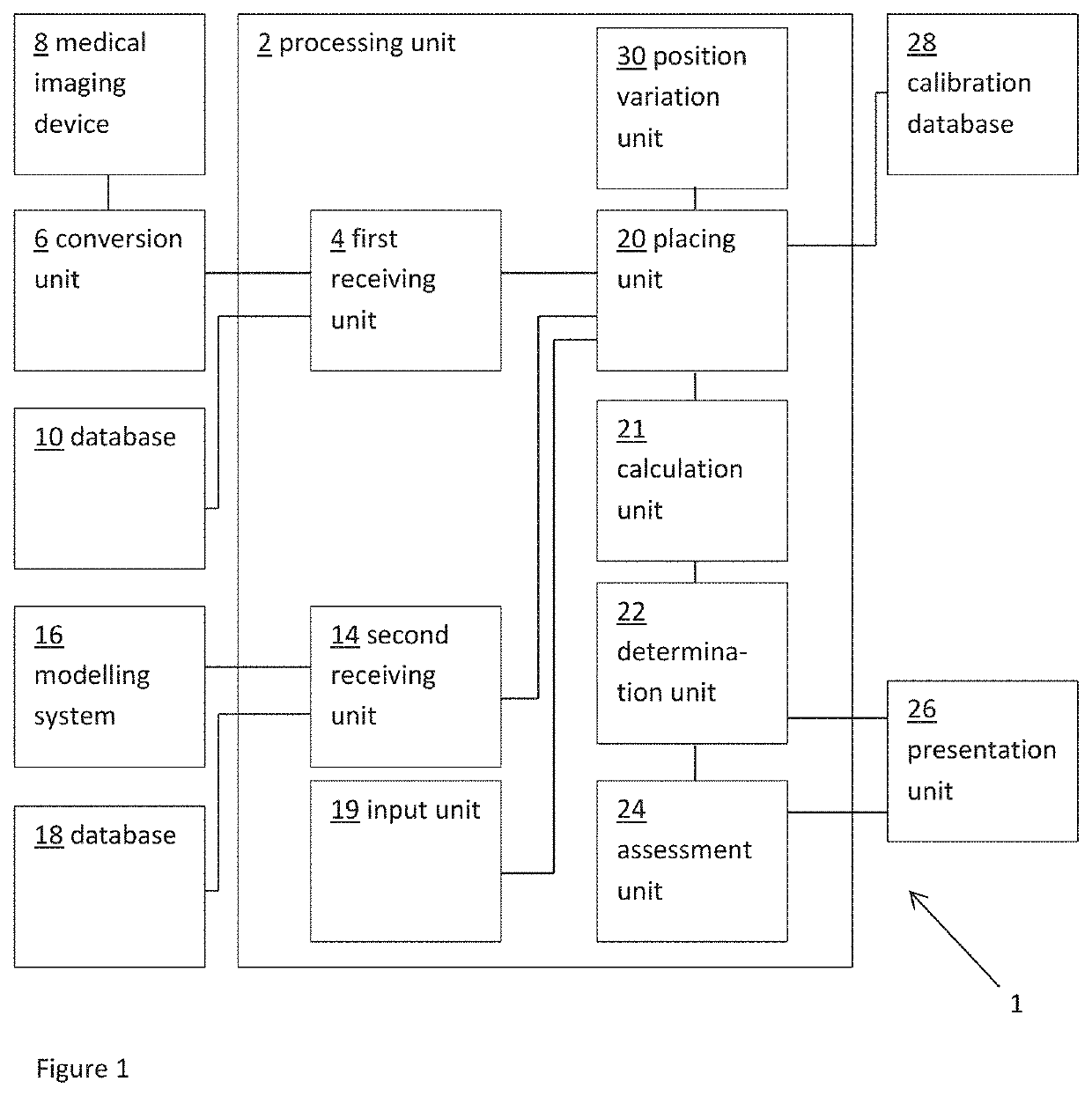
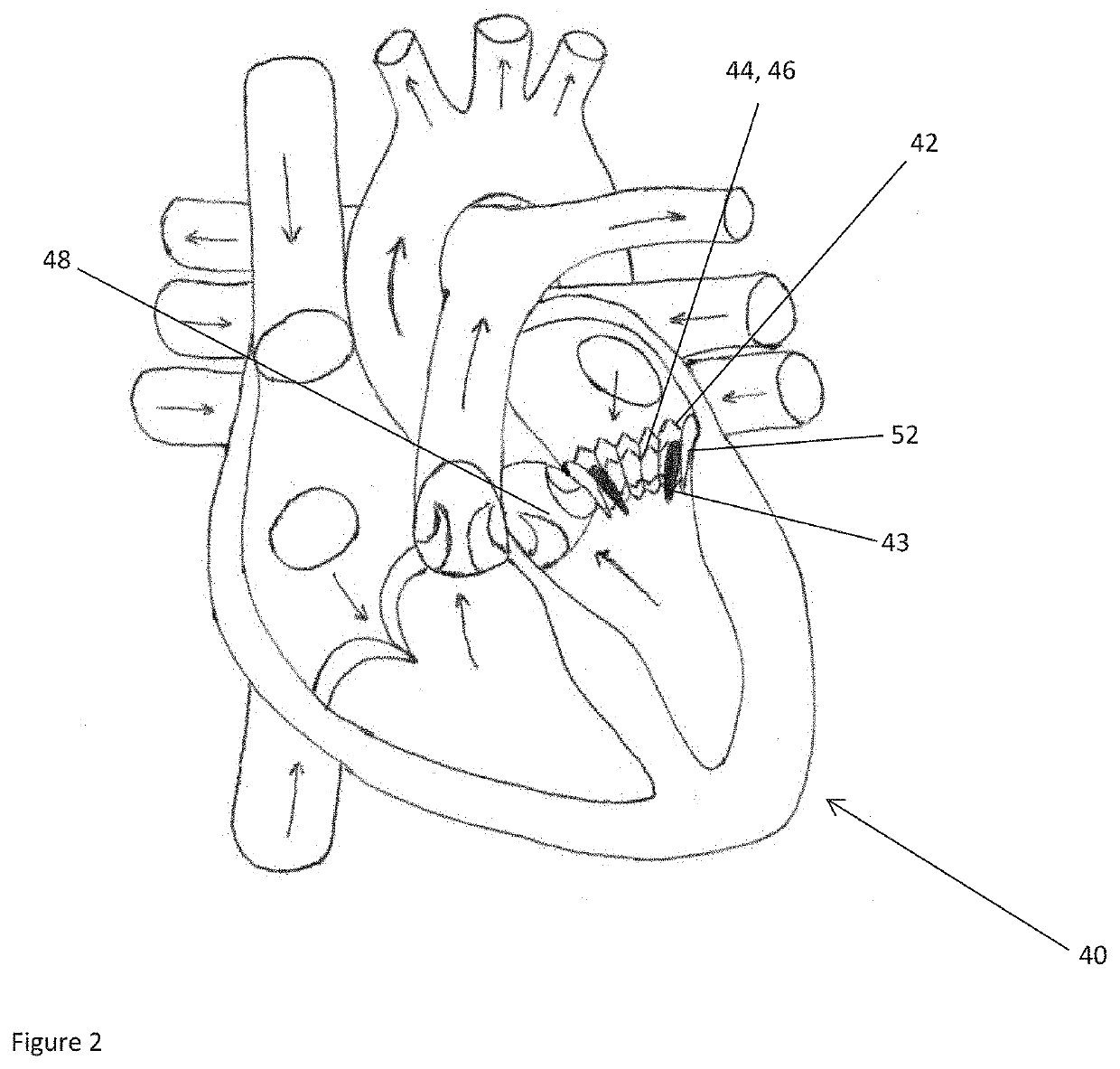
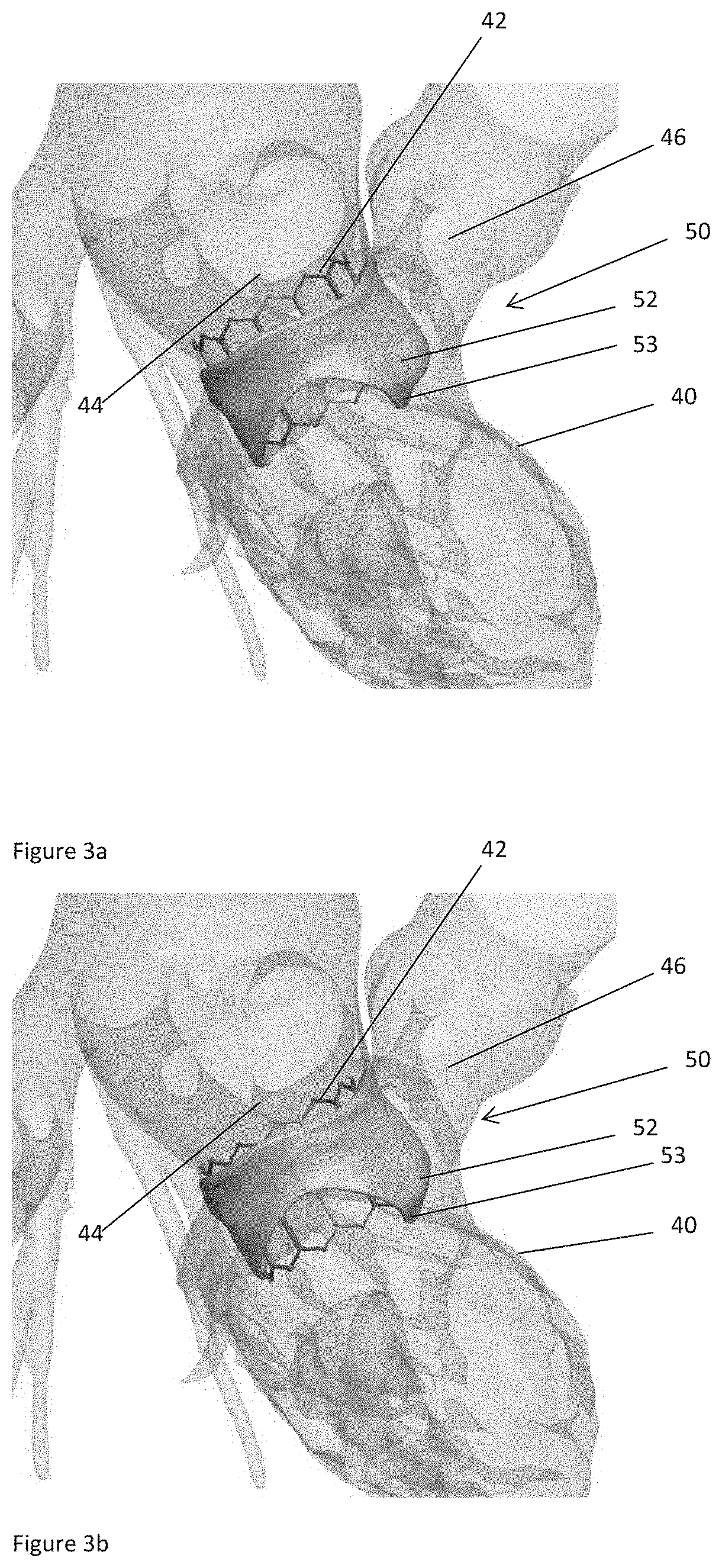
Method and system for image processing and assessment of a state of a heart
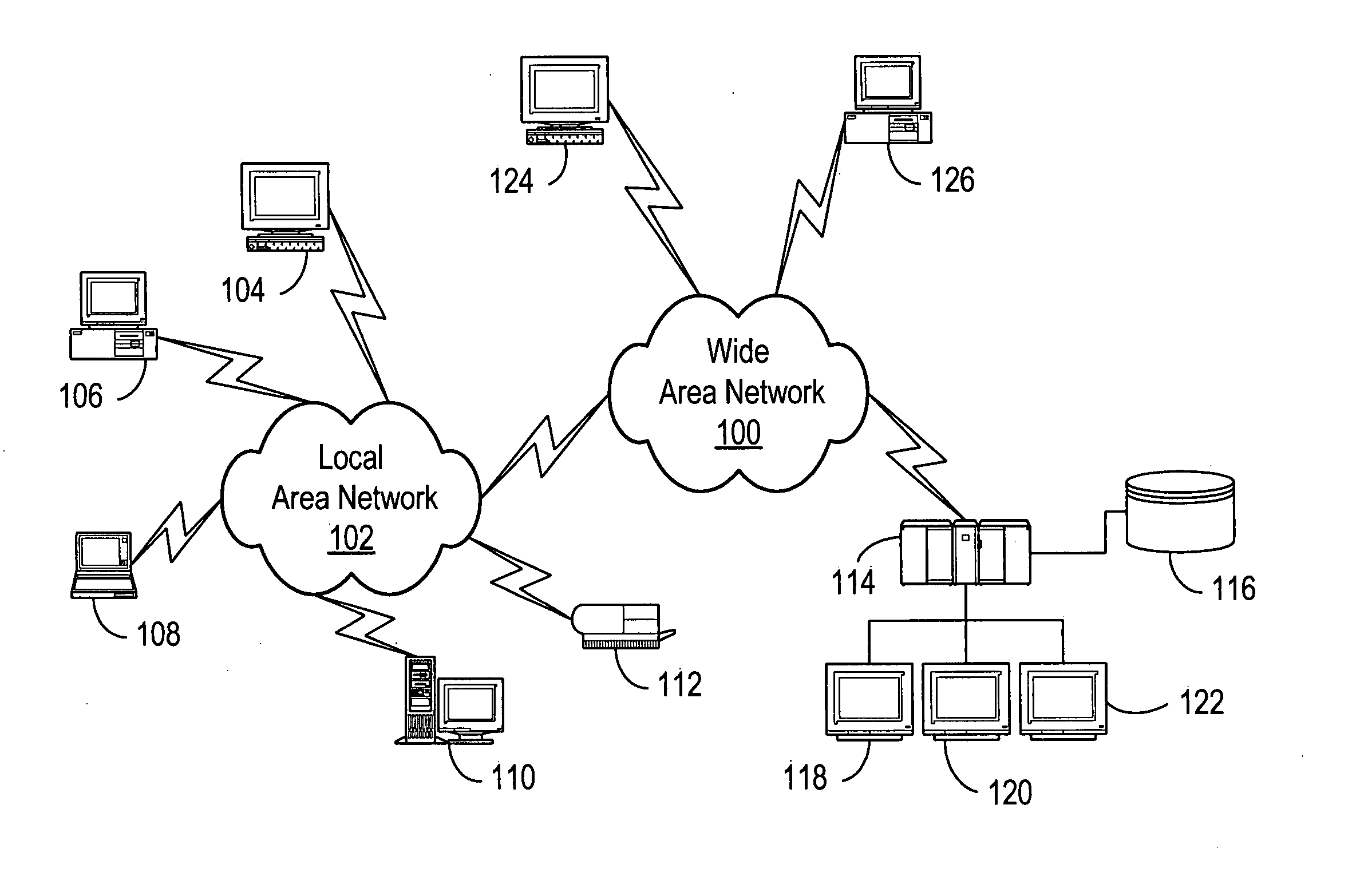
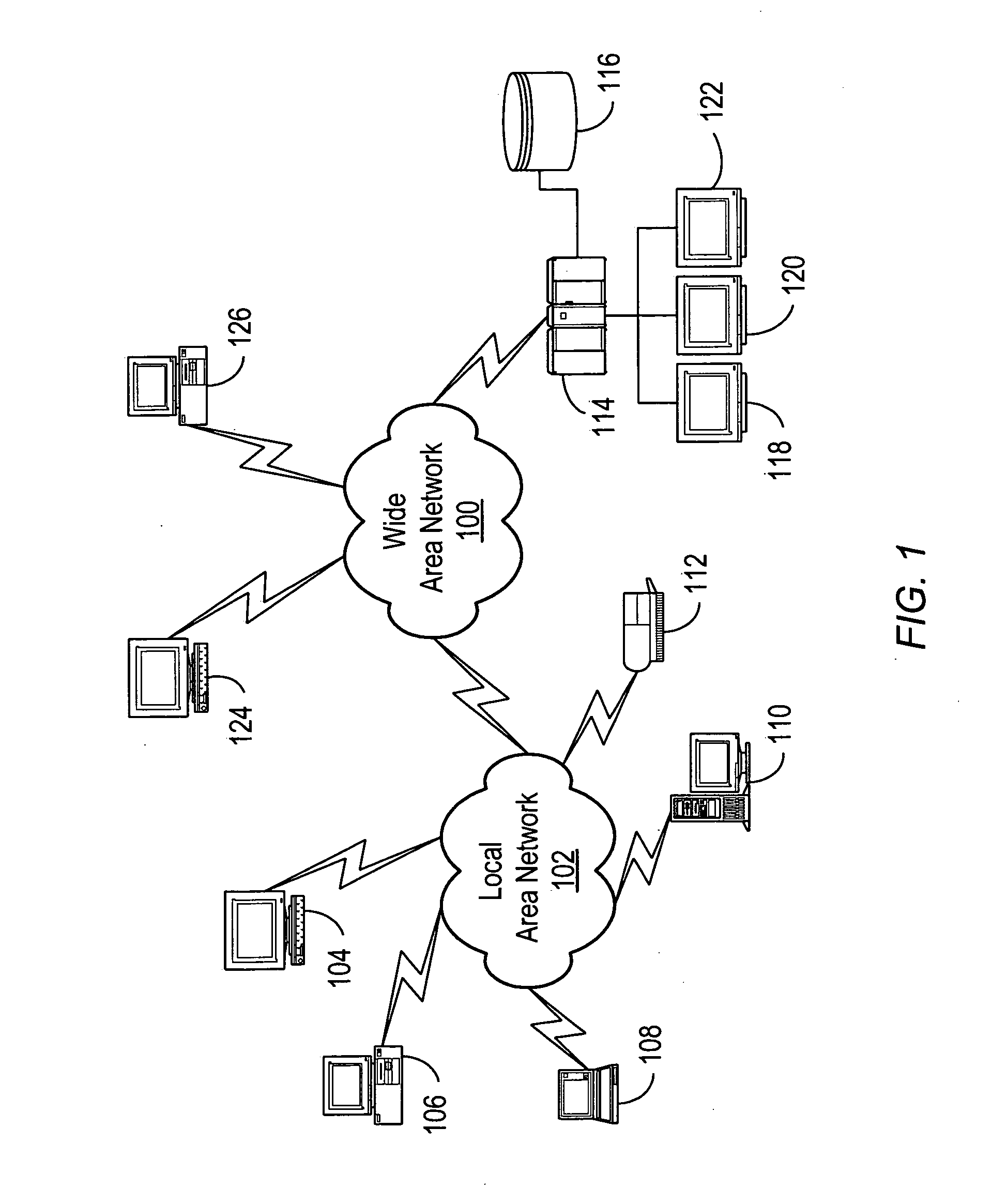
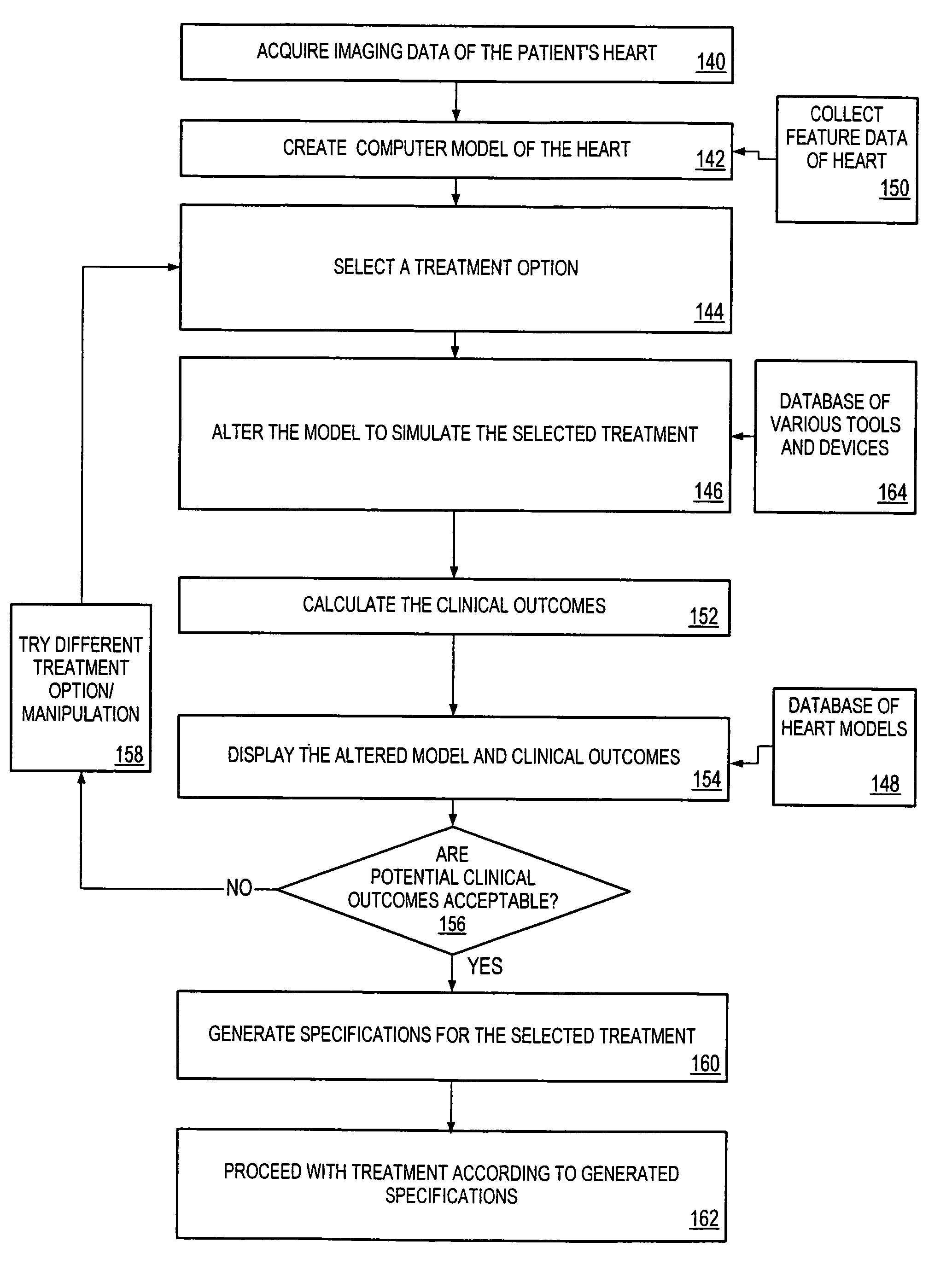
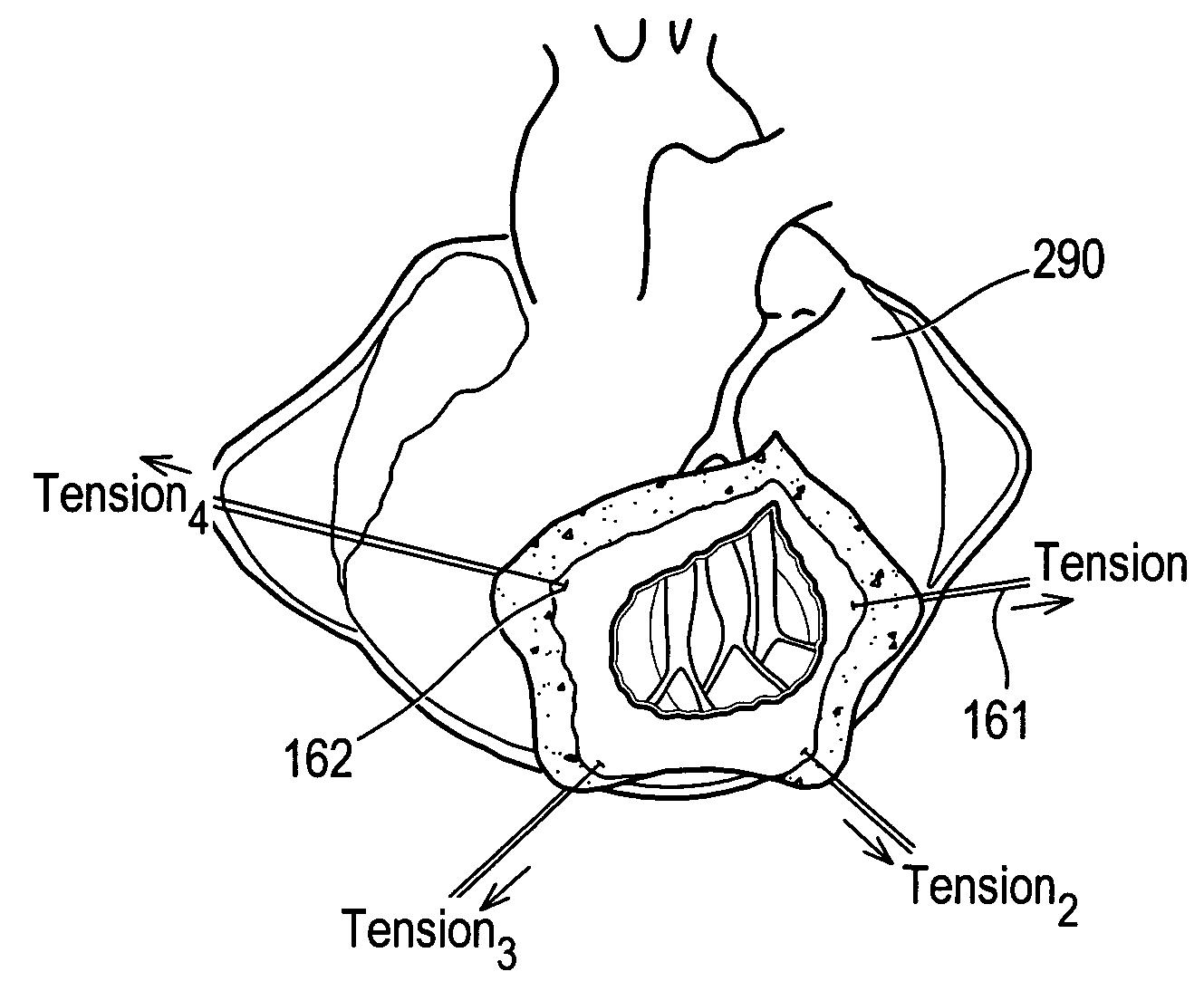
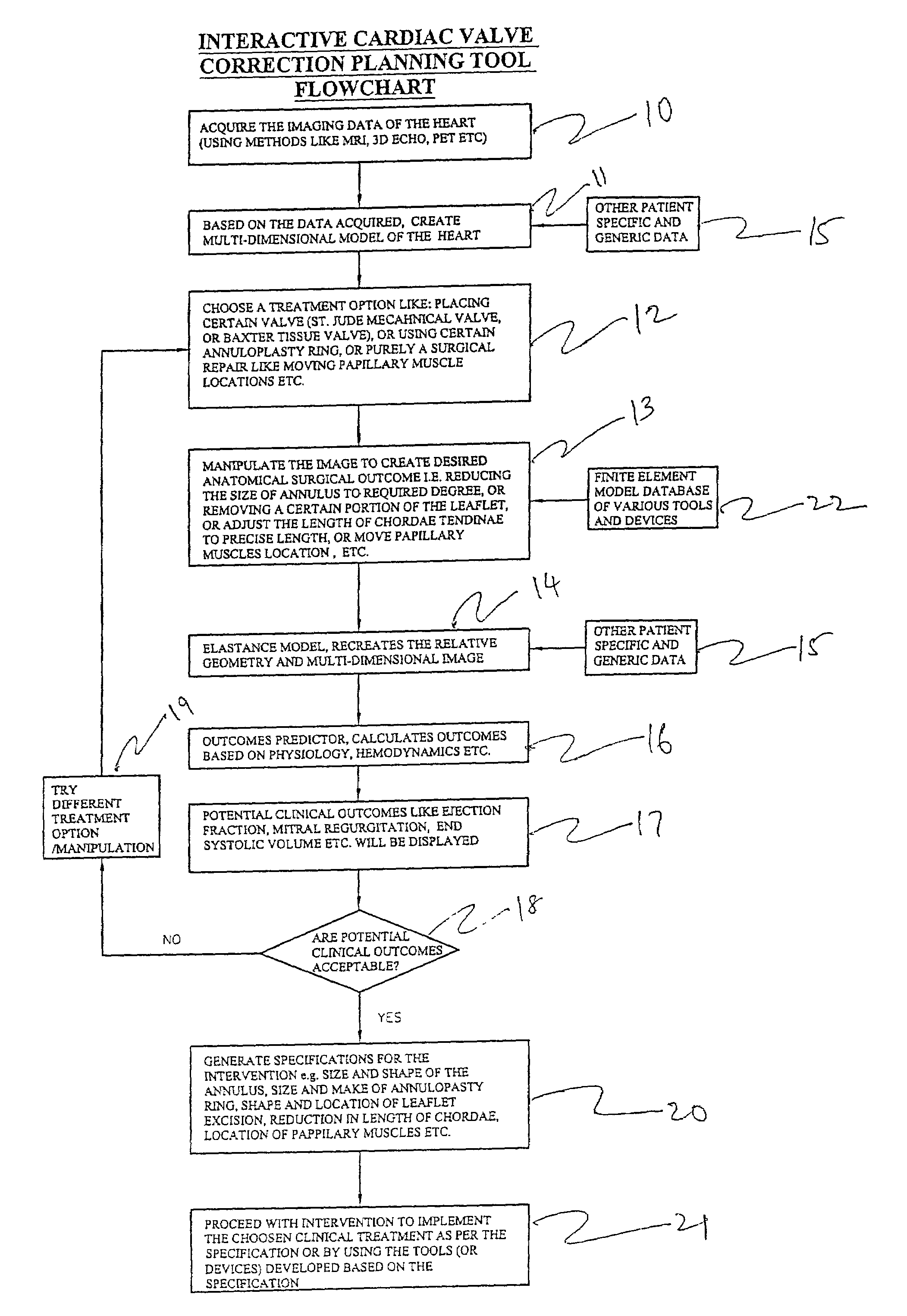
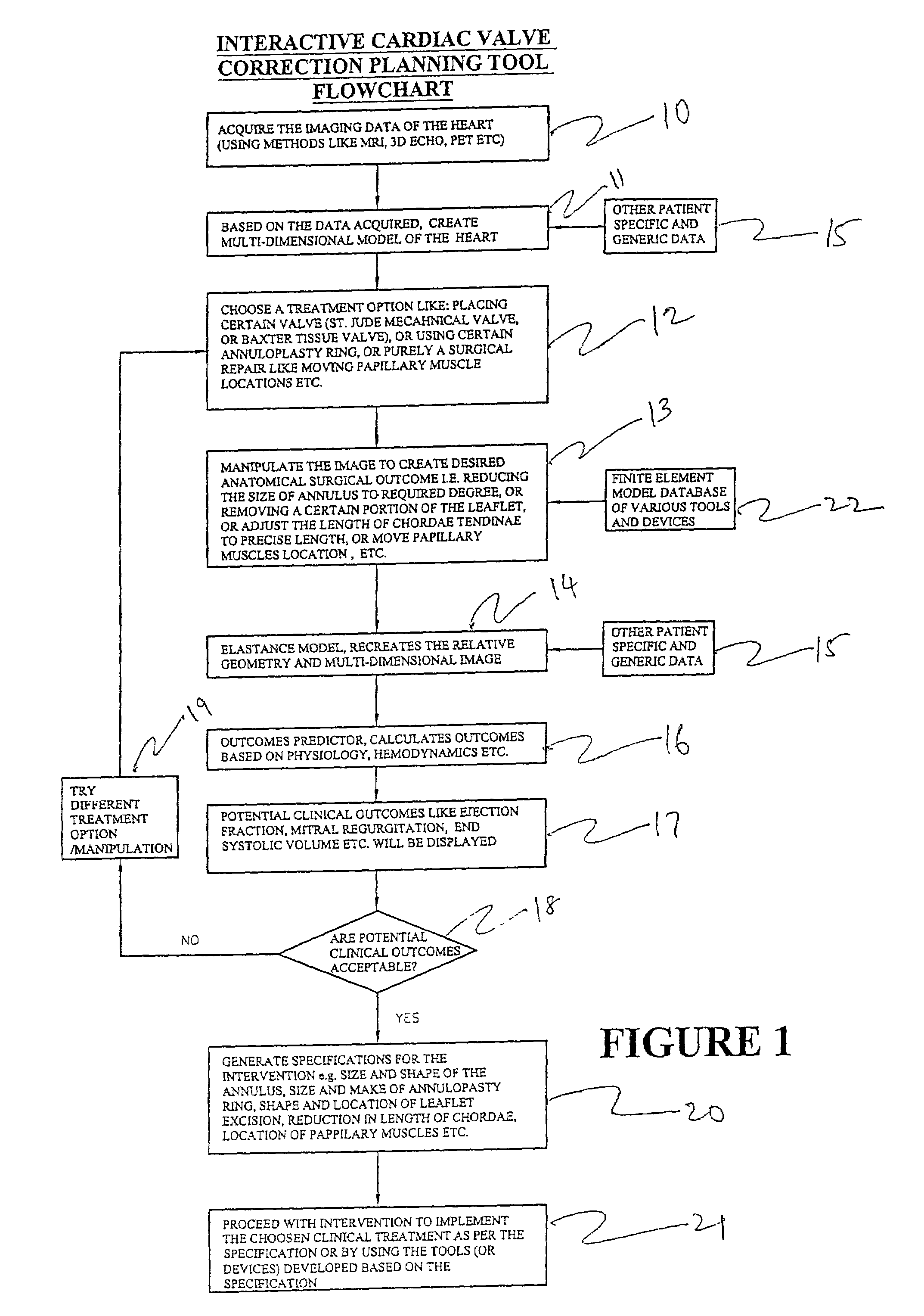
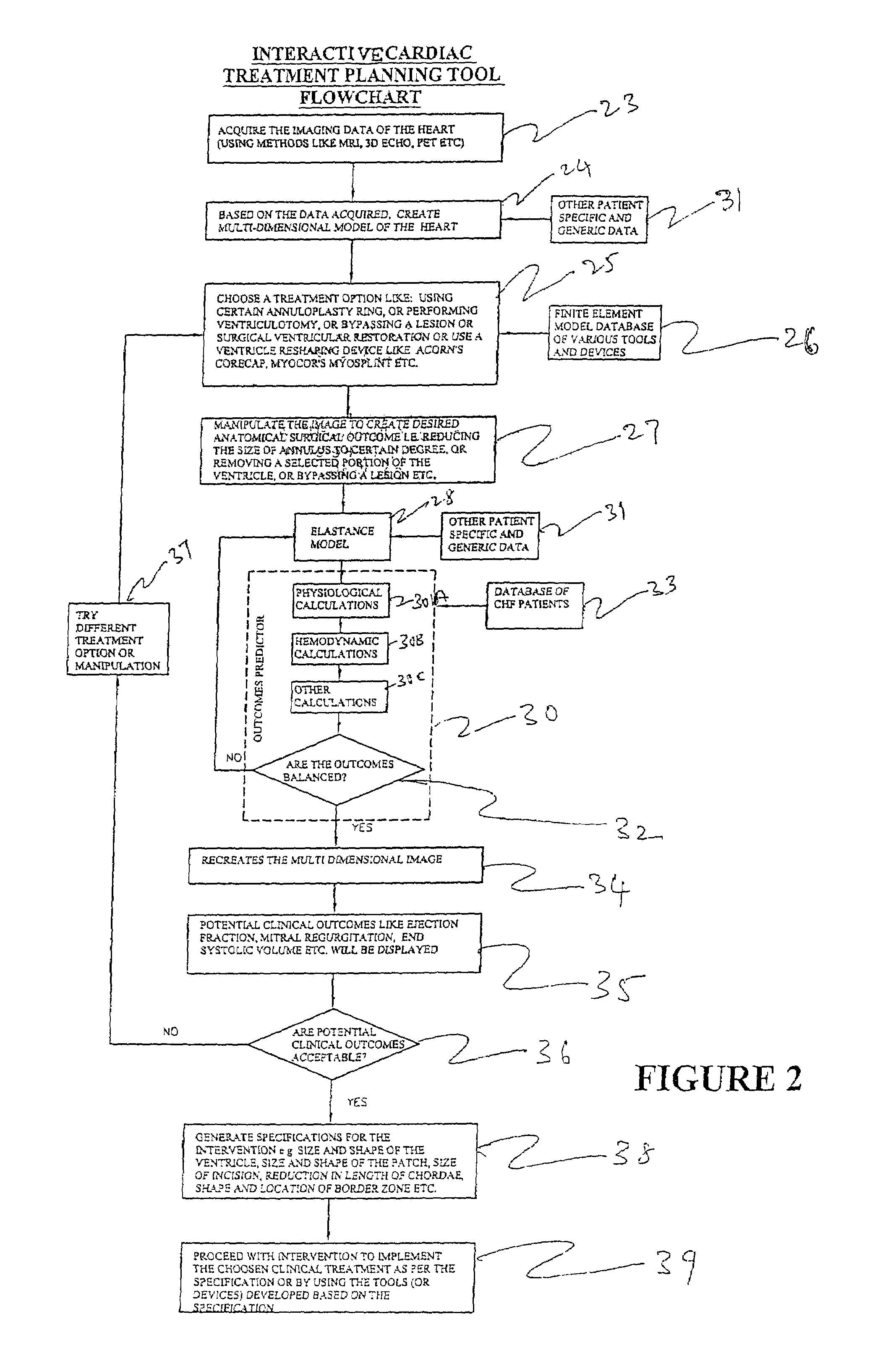
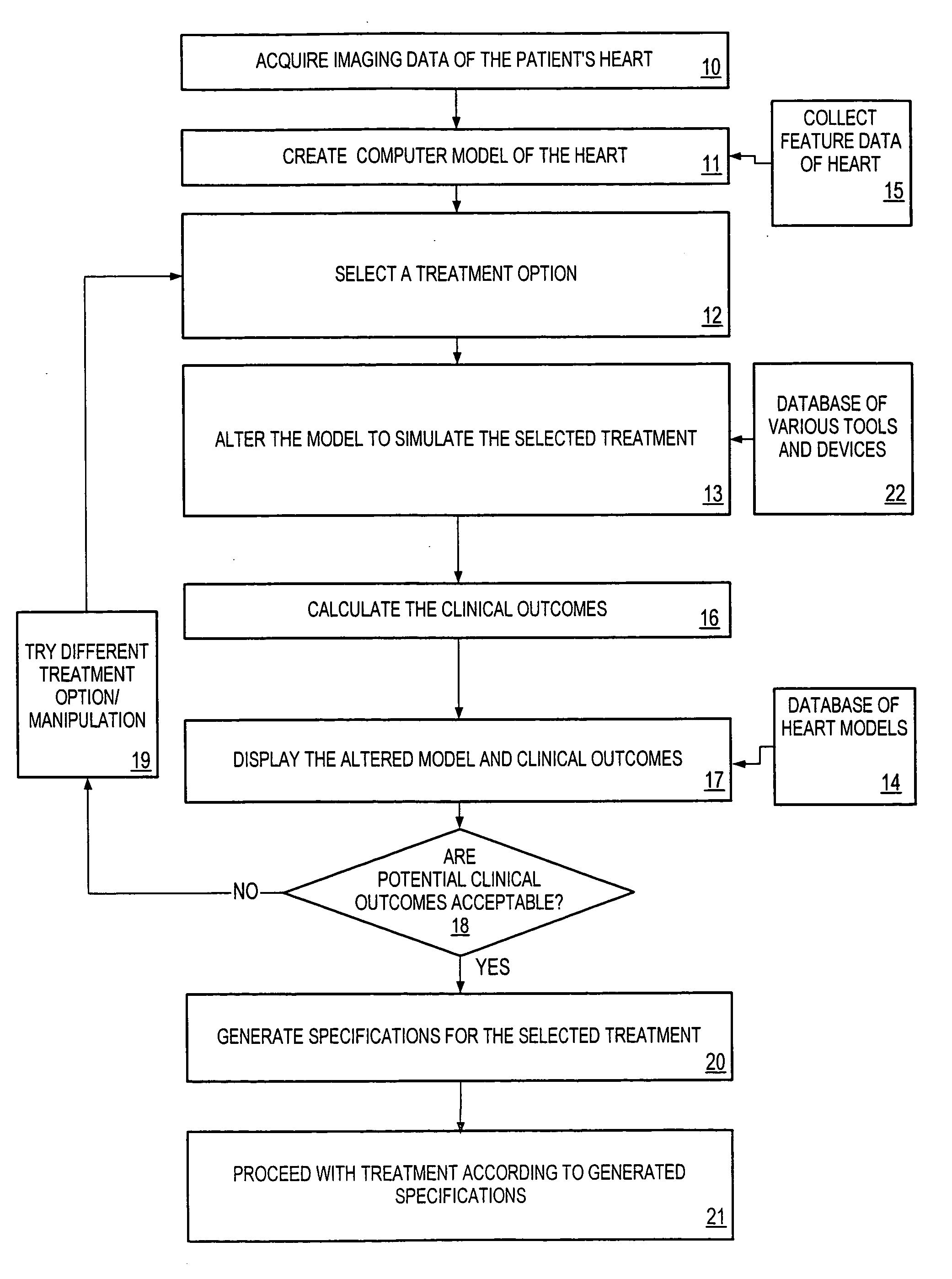
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention. The method may include inputting patient data and creating a computerized interactive model of a heart based on the patient data. The model may include features. The model may simulate at least one proposed cardiac intervention by adding or deleting features to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. A template and / or patient specific instrument may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:CAPITAL SOUTHWEST
Method for image processing and contour assessment of the heart
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention. The method may include inputting patient data and creating a computerized interactive model of a heart based on the patient data. The model may include features. The model may simulate at least one proposed cardiac intervention by adding or deleting features to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. A template and / or patient specific instrument may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:CHASE MEDICAL +1
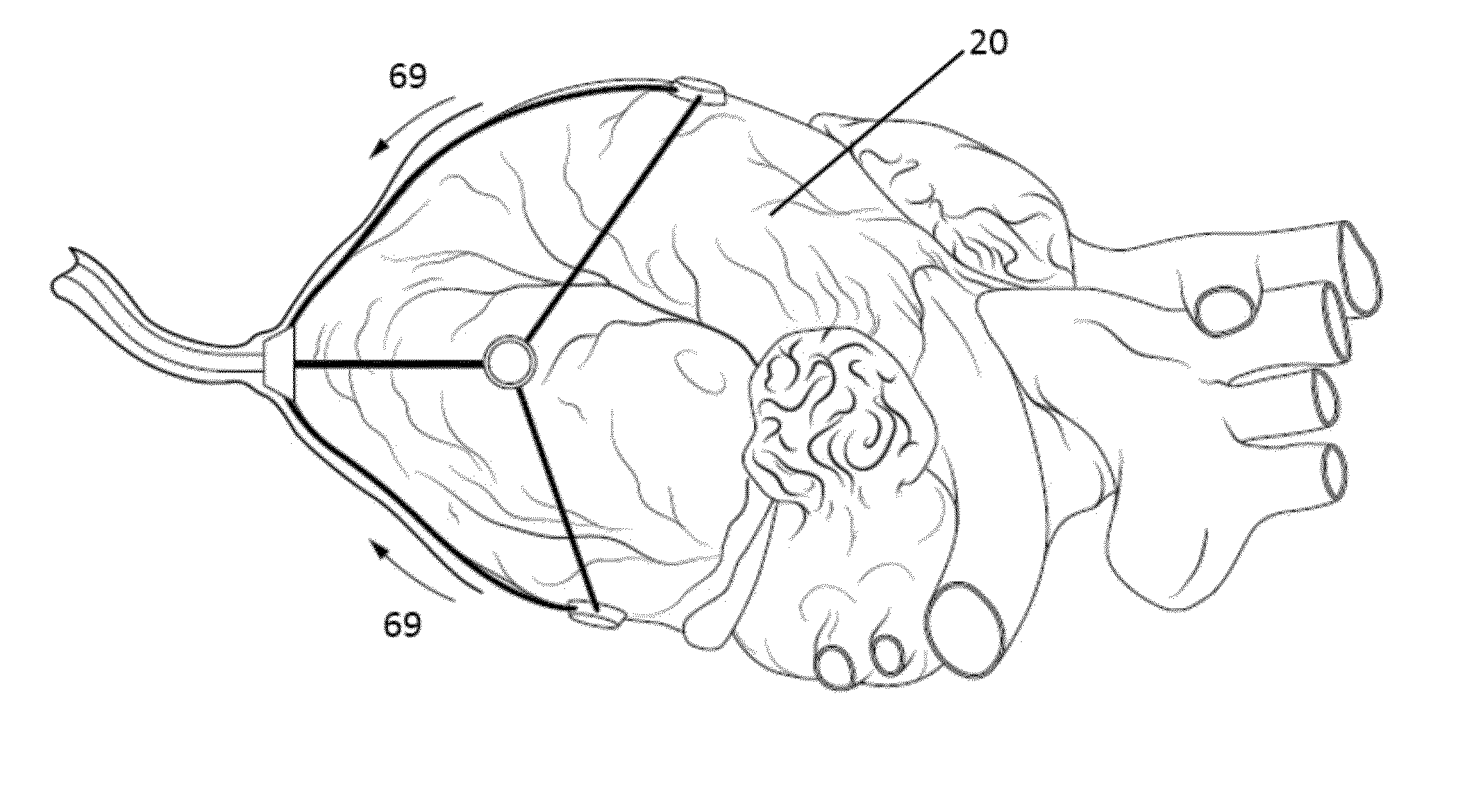
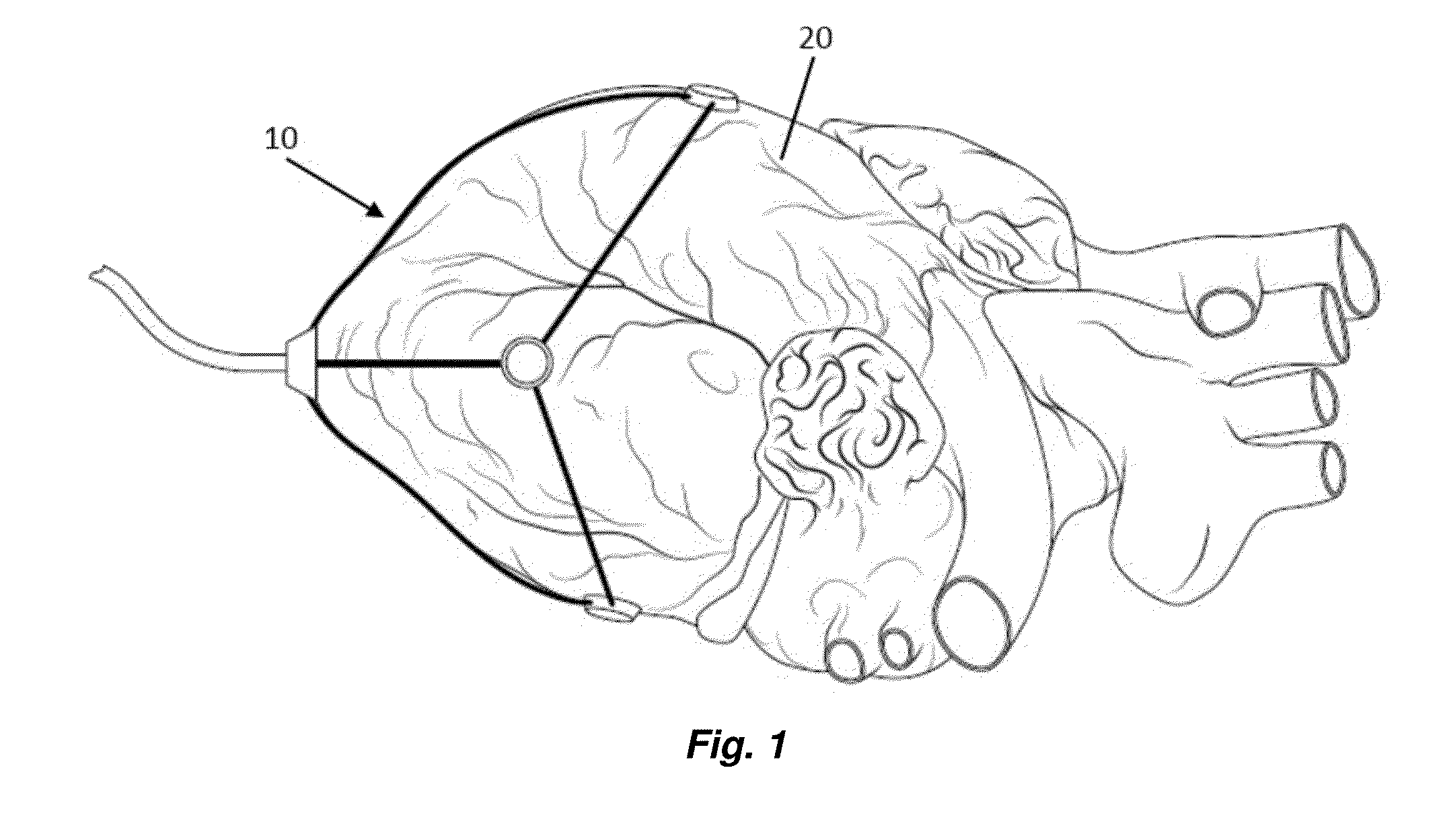
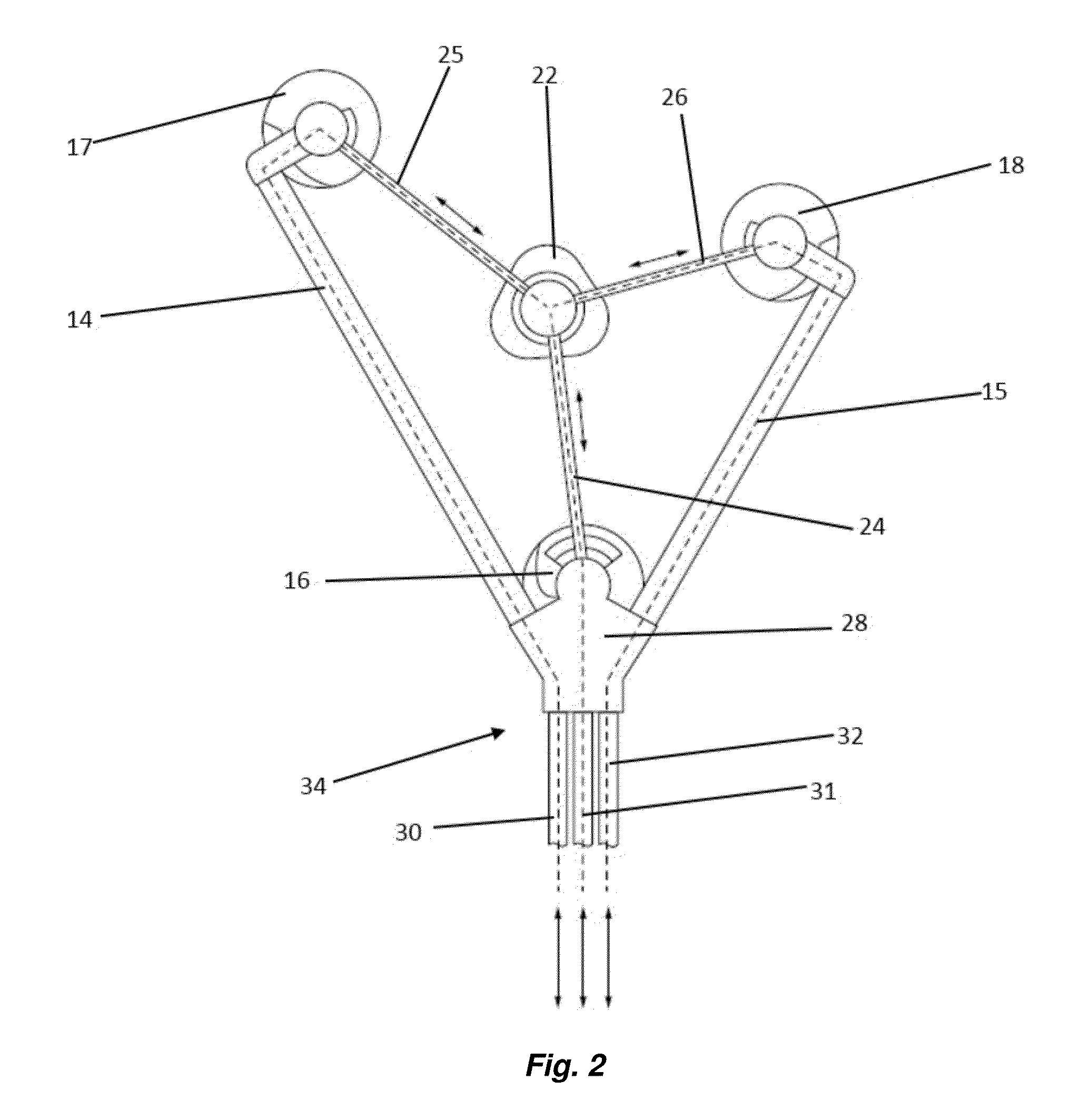
System and method for facilitating cardiac intervention
Owner:PHI HEALTH +1
System and method for facilitating cardiac intervention
InactiveUS7327862B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPatient dataStructural element
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention, comprising inputting patient data, creating a computerized interactive model of a diseased heart based on the patient data, wherein the model comprises structural elements, simulating at least one proposed cardiac intervention treatment by adding or deleting structural elements to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. Additionally, a template may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:PHI HEALTH +1
System and method for facilitating cardiac intervention
InactiveUS7333643B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPatient dataCardiac interventions
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention, comprising inputting patient data, creating a computerized interactive model of a heart based on the patient data, wherein the model comprises features, simulating at least one proposed cardiac intervention treatment by adding or deleting features to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. Additionally, a template may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:PHI HEALTH +1
System and method for facilitating cardiac intervention
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention, comprising inputting patient data, creating a computerized interactive model of a heart based on the patient data, wherein the model comprises features, simulating at least one proposed cardiac intervention treatment by adding or deleting features to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. Additionally, a template may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:CAPITAL SOUTHWEST
System and method for facilitating cardiac intervention
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention, comprising inputting patient data, creating a computerized interactive model of a heart based on the patient data, wherein the model comprises features, simulating at least one proposed cardiac intervention treatment by adding or deleting features to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. Additionally, a template may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:PHI HEALTH +1
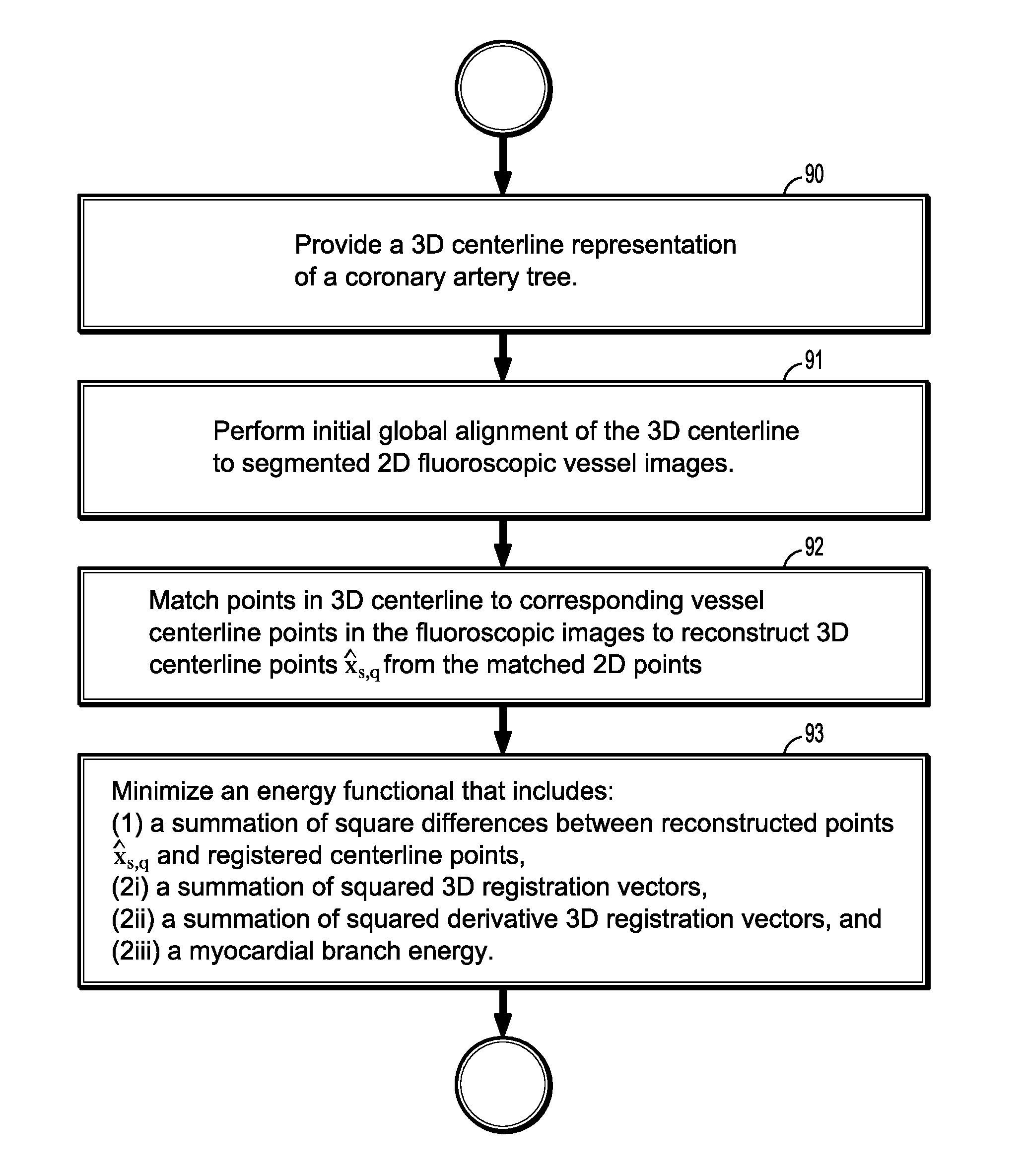
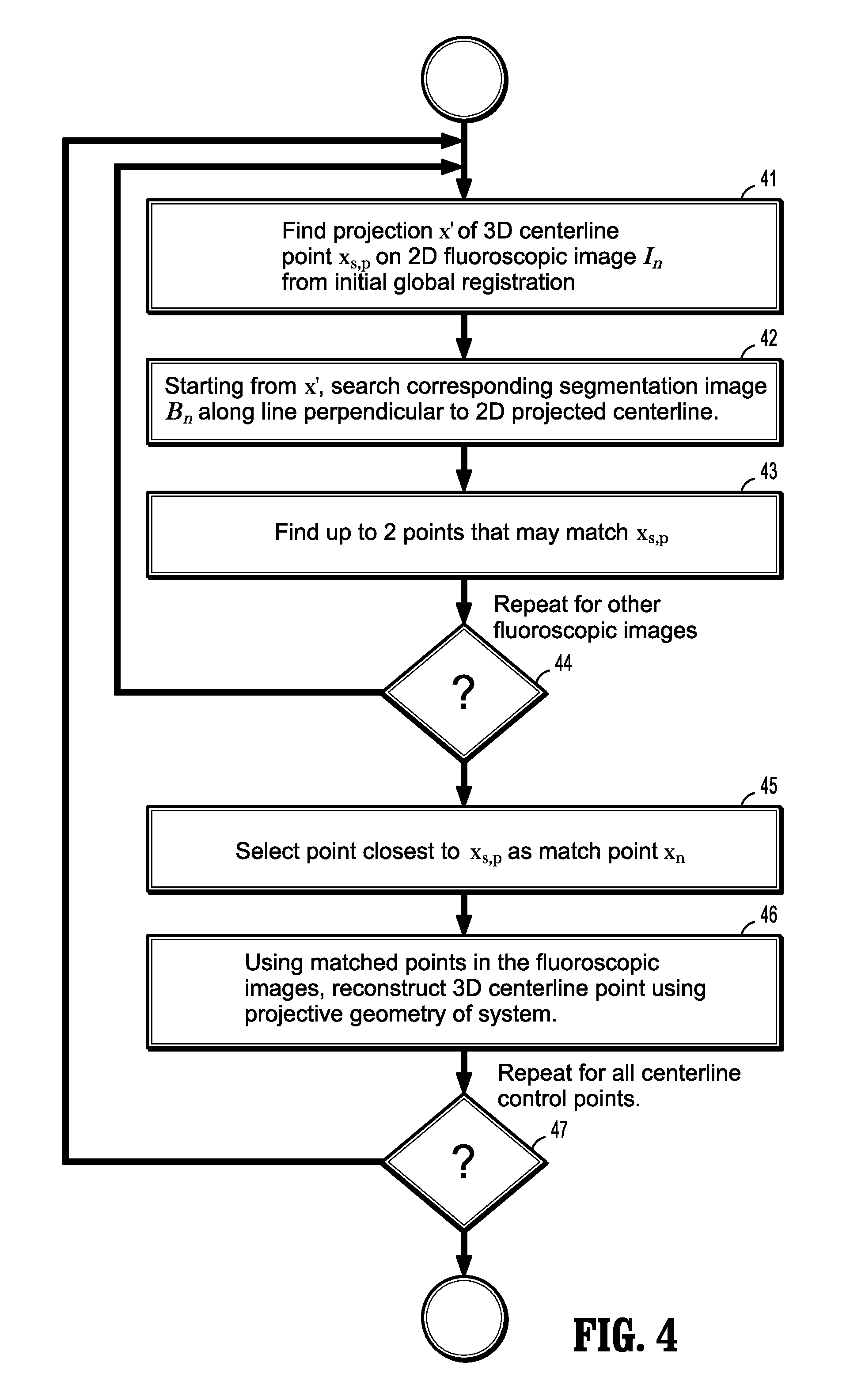
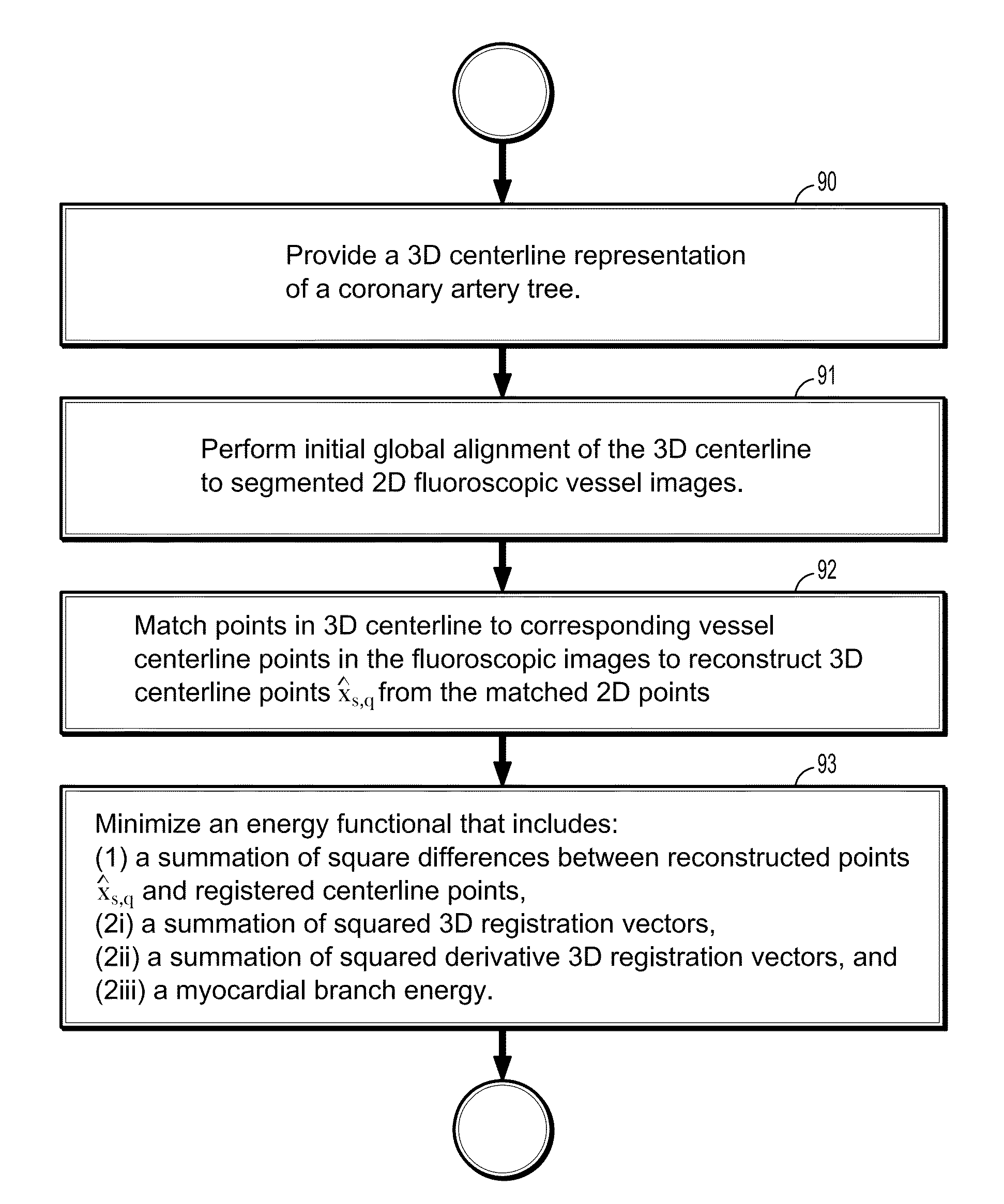
Non-rigid 2d/3d registration of coronary artery models with live fluoroscopy images
ActiveUS20130094745A1Increase heightReduce uncertaintyImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCoronary arterial tree
A method for non-rigid registration of digital 3D coronary artery models with 2D fluoroscopic images during a cardiac intervention includes providing a digitized 3D centerline representation of a coronary artery tree that comprises a set of S segments composed of QS 3D control points, globally aligning the 3D centerline to at least two 2D fluoroscopic images, and non-rigidly registering the 3D centerline to the at least two 2D fluoroscopic images by minimizing an energy functional that includes a summation of square differences between reconstructed centerline points and registered centerline points, a summation of squared 3D registration vectors, a summation of squared derivative 3D registration vectors, and a myocardial branch energy. The non-rigid registration of the 3D centerline is represented as a set of 3D translation vectors rs,q that are applied to corresponding centerline points xs,q in a coordinate system of the 3D centerline.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for facilitating cardiac intervention
InactiveUS20050187461A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPatient dataCardiac interventions
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention, comprising inputting patient data, creating a computerized interactive model of a heart based on the patient data, wherein the model comprises features, simulating at least one proposed cardiac intervention treatment by adding or deleting features to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. Additionally, a template may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:PHI HEALTH +1
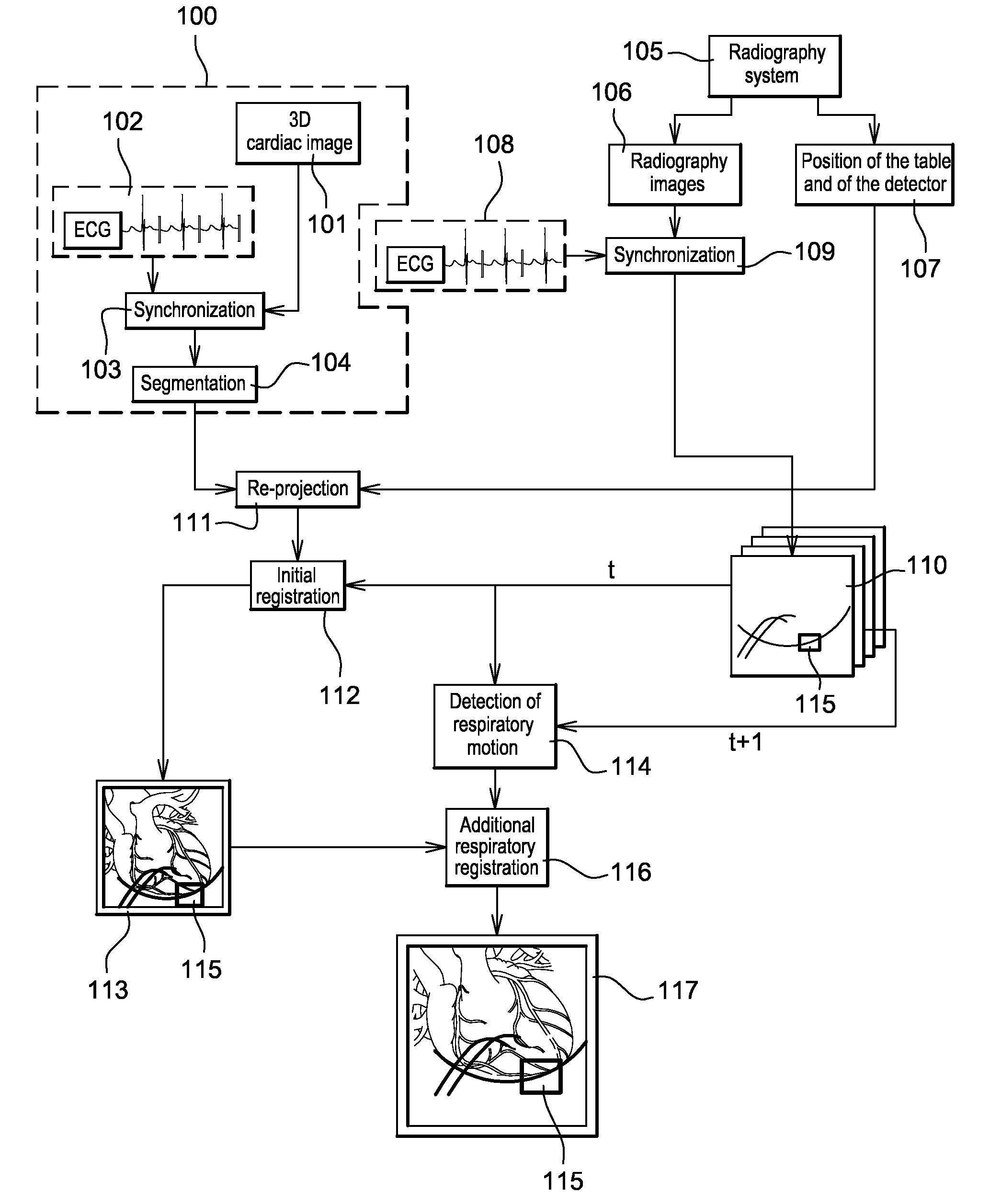
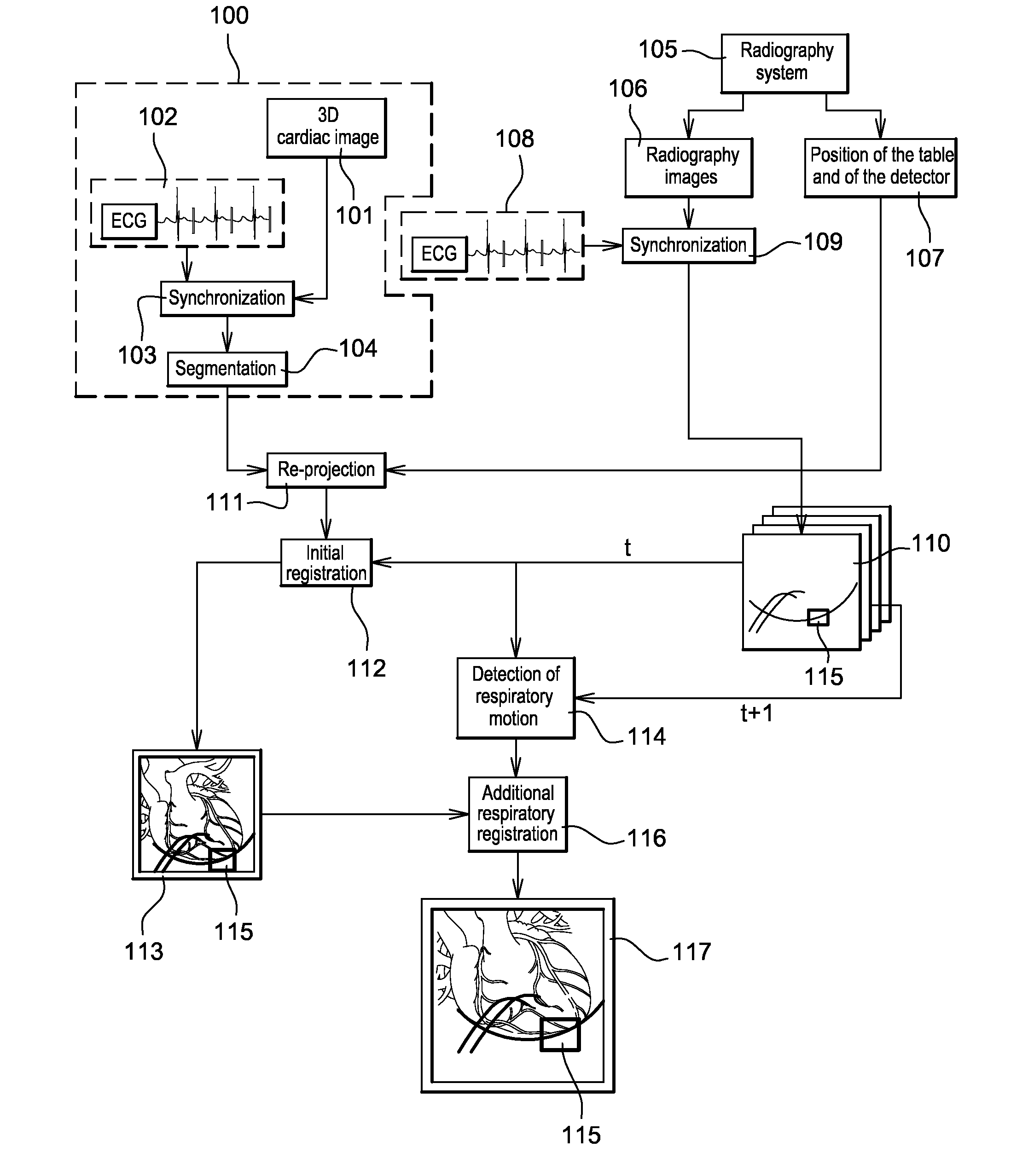
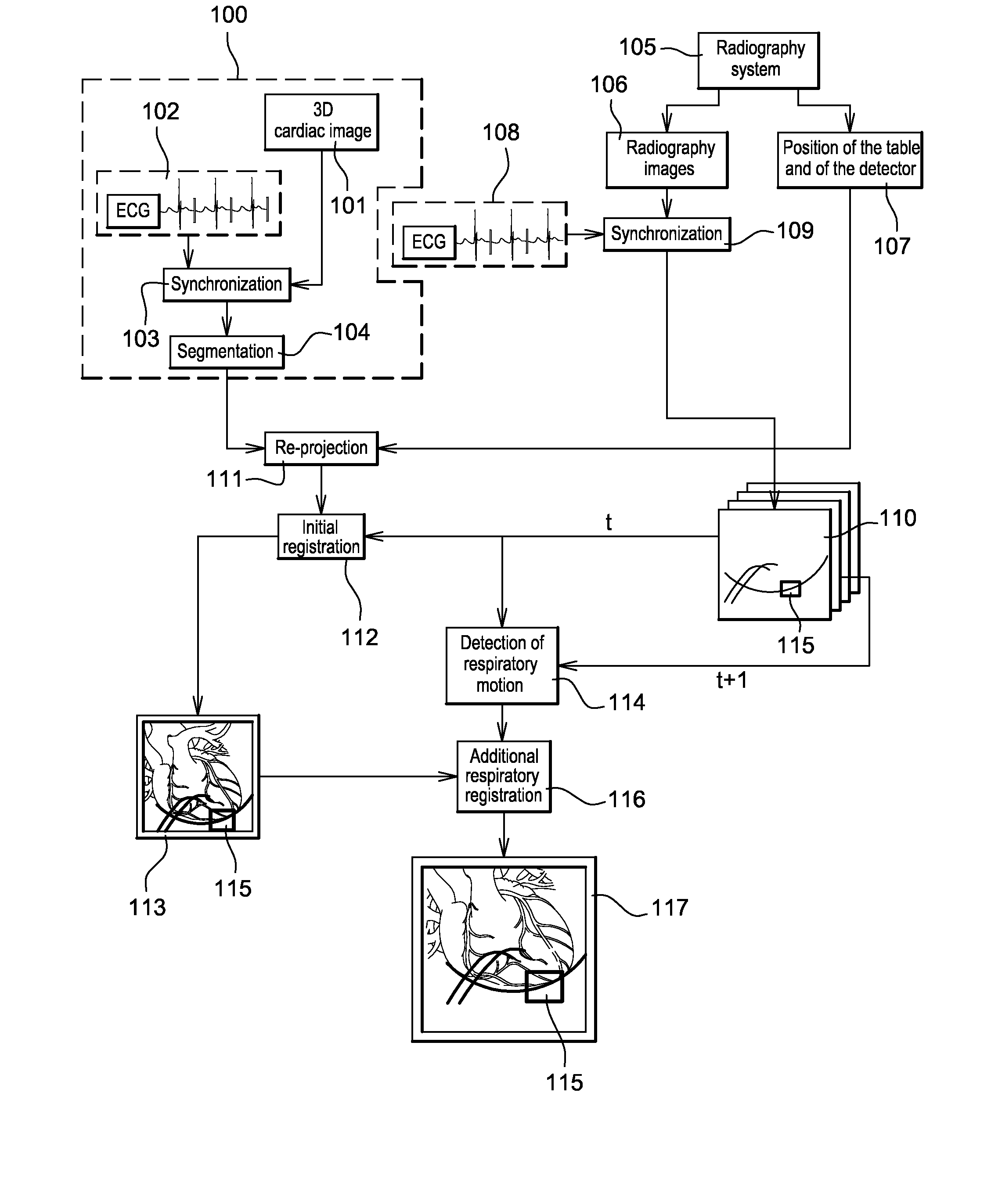
Method of detection and compensation for respiratory motion in radiography cardiac images synchronized with an electrocardiogram signal
ActiveUS20080240536A1Effective registrationGreat precision and simplicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHealth-index calculationX-rayX ray image
A method of detection and compensation for respiratory motion improves the registration between a 3D pre-operation image and X-ray images acquired during a cardiac intervention. By synchronizing the X-ray images with the electrocardiogram, the disclosed method thus eliminates the motion related to the heart cycle from these images, thus isolating the contribution of the respiratory motion. From this point, an algorithm is proposed capable of attributing the motion remaining in the radiography images to respiration. The algorithm also enables this motion to be detected and compensated for in order to obtain a registration between 3D cardiac images and radiography images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
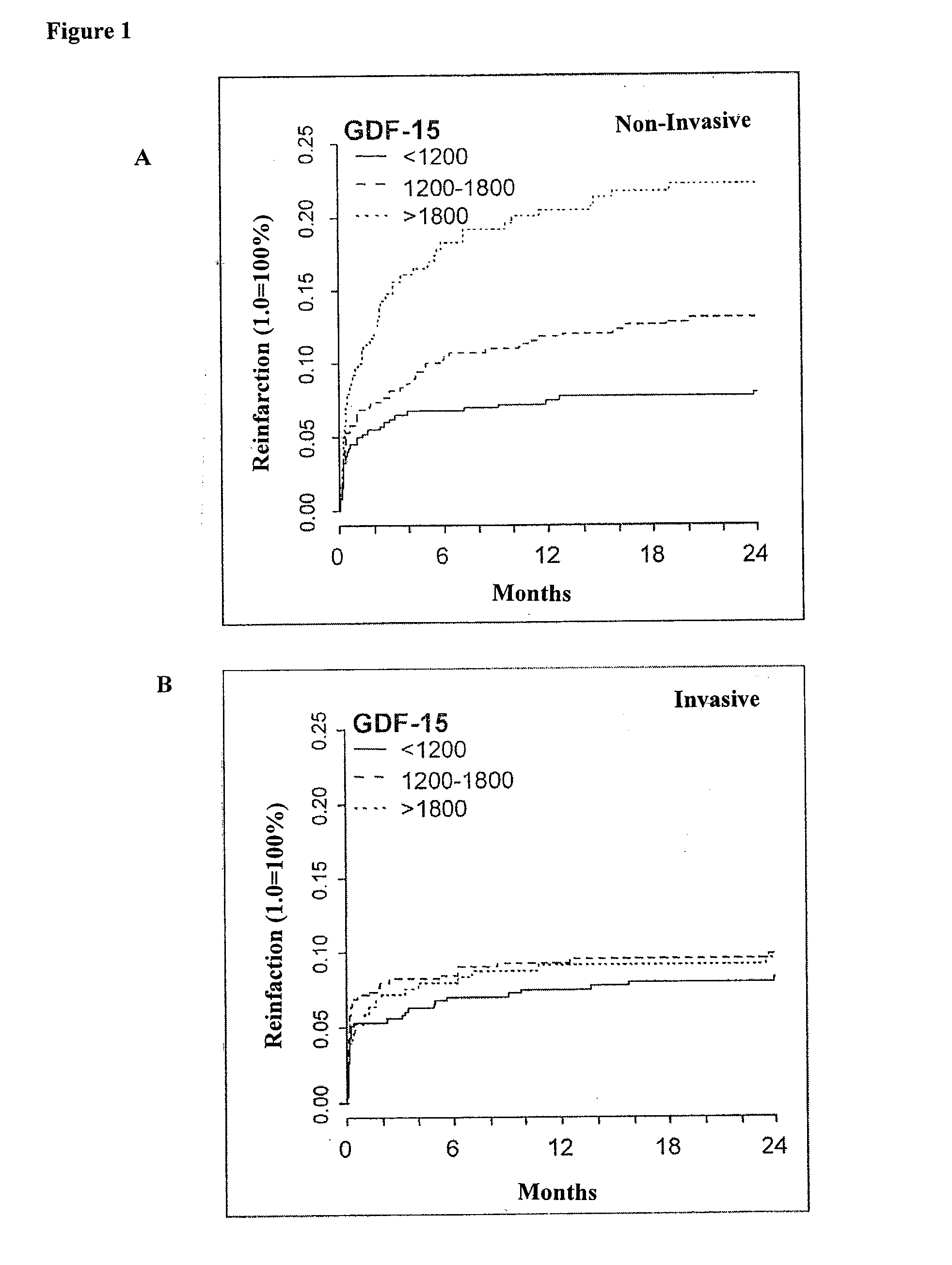
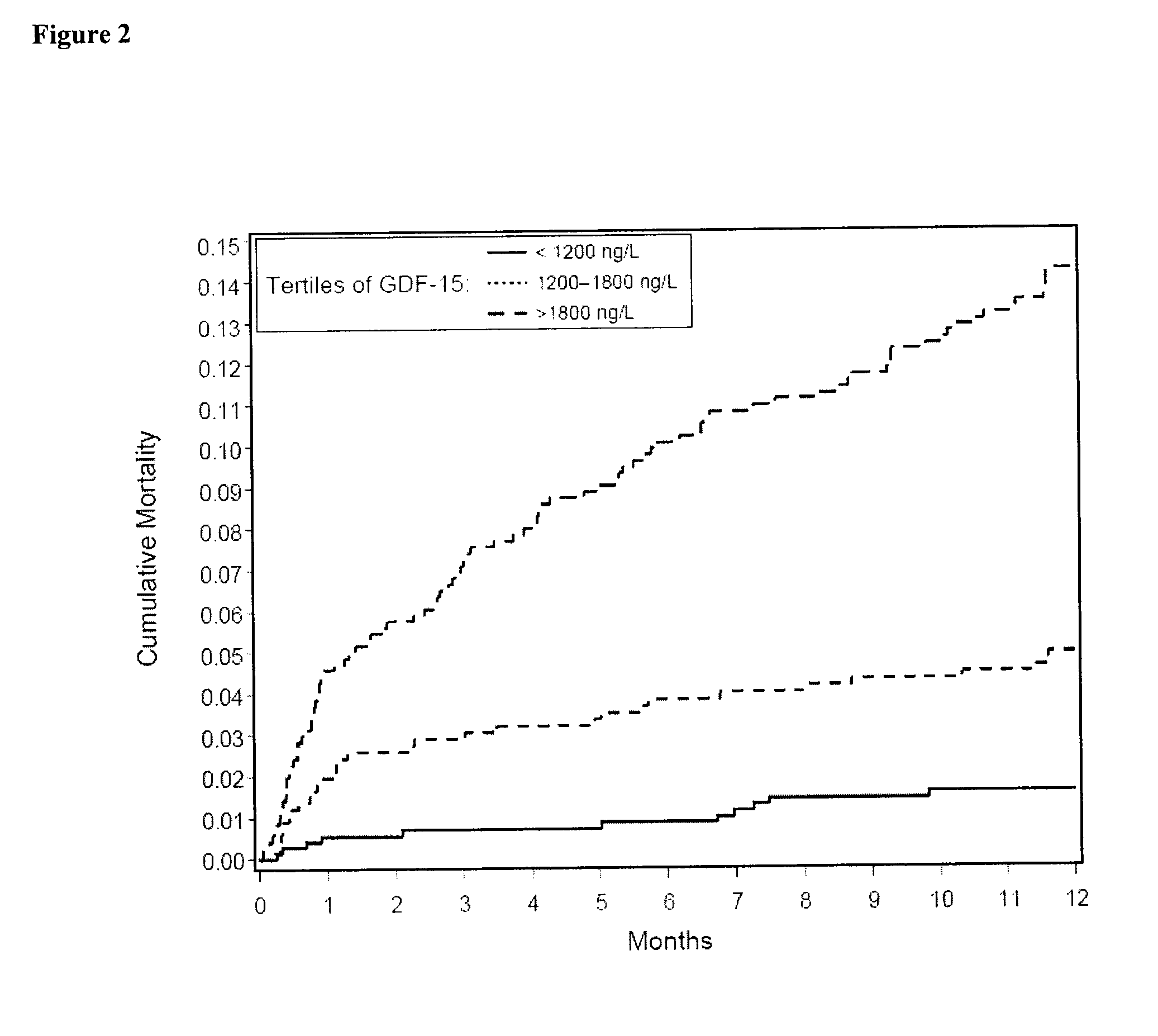
Assessing risk of cardiac intervention based on gdf-15
ActiveUS20110065204A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationRisk of mortalityNatriuretic peptide
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a subject being susceptible to a cardiac intervention based on the determination of GDF-15 in a sample of a subject in need of a cardiac intervention. Moreover, the present invention pertains to a method for predicting the risk of mortality or a further acute cardiovascular event for a subject suffering from a cardiovascular complication based on the determination of GDF-15 and a natriuretic peptide and / or a cardiac troponin in a sample the said subject. Also encompassed by the present invention are devices and kits for carrying out the aforementioned methods.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE HOCHSCHULE HANNOVER
System and method for facilitating cardiac intervention
InactiveUS20050020929A1Easy to interveneMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPatient dataStructuring element
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention, comprising inputting patient data, creating a computerized interactive model of a diseased heart based on the patient data, wherein the model comprises structural elements, simulating at least one proposed cardiac intervention treatment by adding or deleting structural elements to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. Additionally, a template may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:PHI HEALTH +1
Method and System for Pericardium Based Model Fusion of Pre-operative and Intra-operative Image Data for Cardiac Interventions
ActiveUS20130294667A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisHeart chamberComputing tomography
A method and system for model based fusion pre-operative image data, such as computed tomography (CT), and intra-operative C-arm CT is disclosed. A first pericardium model is segmented in the pre-operative image data and a second pericardium model is segmented in a C-arm CT volume. A deformation field is estimated between the first pericardium model and the second pericardium model. A model of a target cardiac structure, such as a heart chamber model or an aorta model, extracted from the pre-operative image data is fused with the C-arm CT volume based on the estimated deformation field between the first pericardium model and the second pericardium model. An intelligent weighted average may be used improve the model based fusion results using models of the target cardiac structure extracted from pre-operative image data of patients other than a current patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
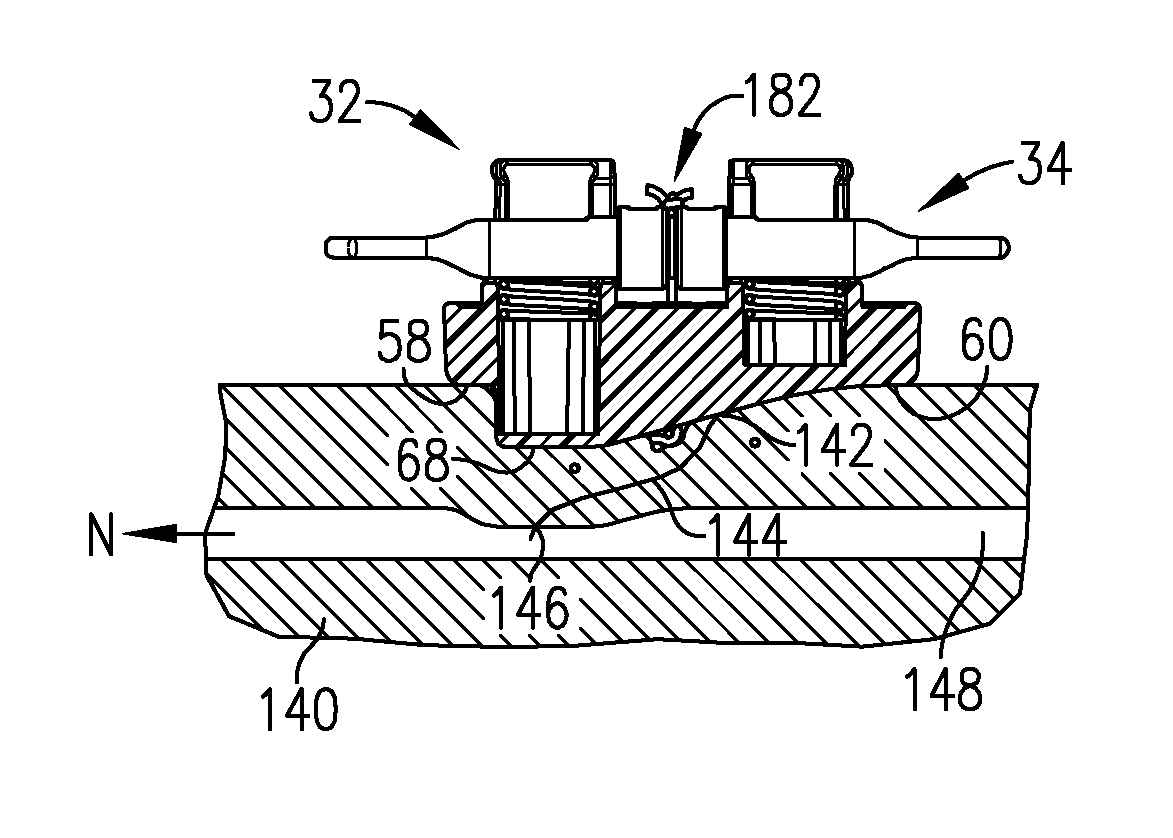
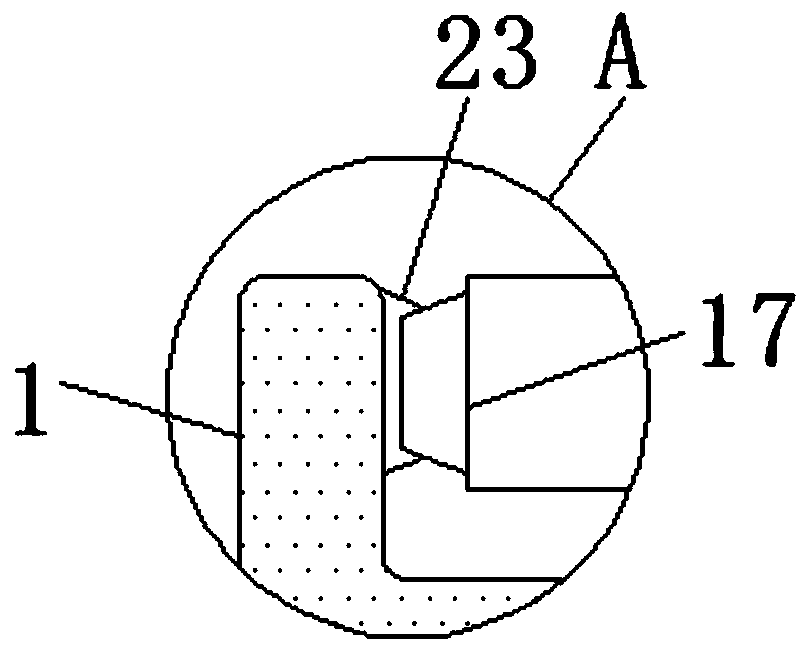
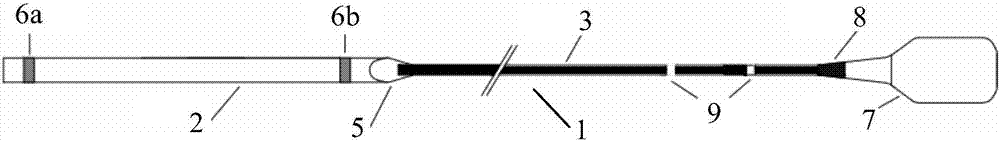
Cardiac intervention ablation catheter
ActiveCN101190146AIncrease the chance of successful treatmentAccurate temperature parameter monitoringCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineSurgical site
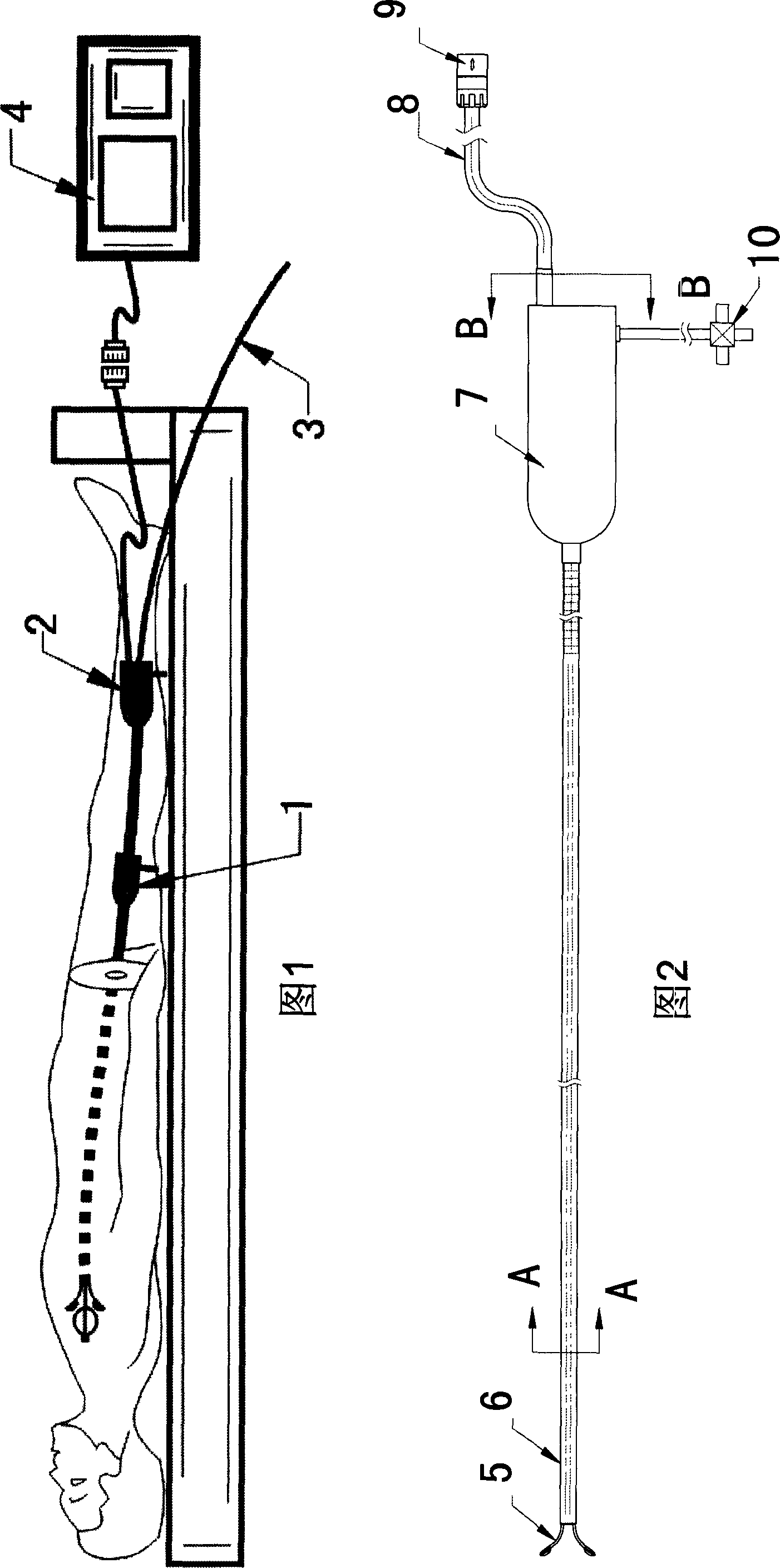
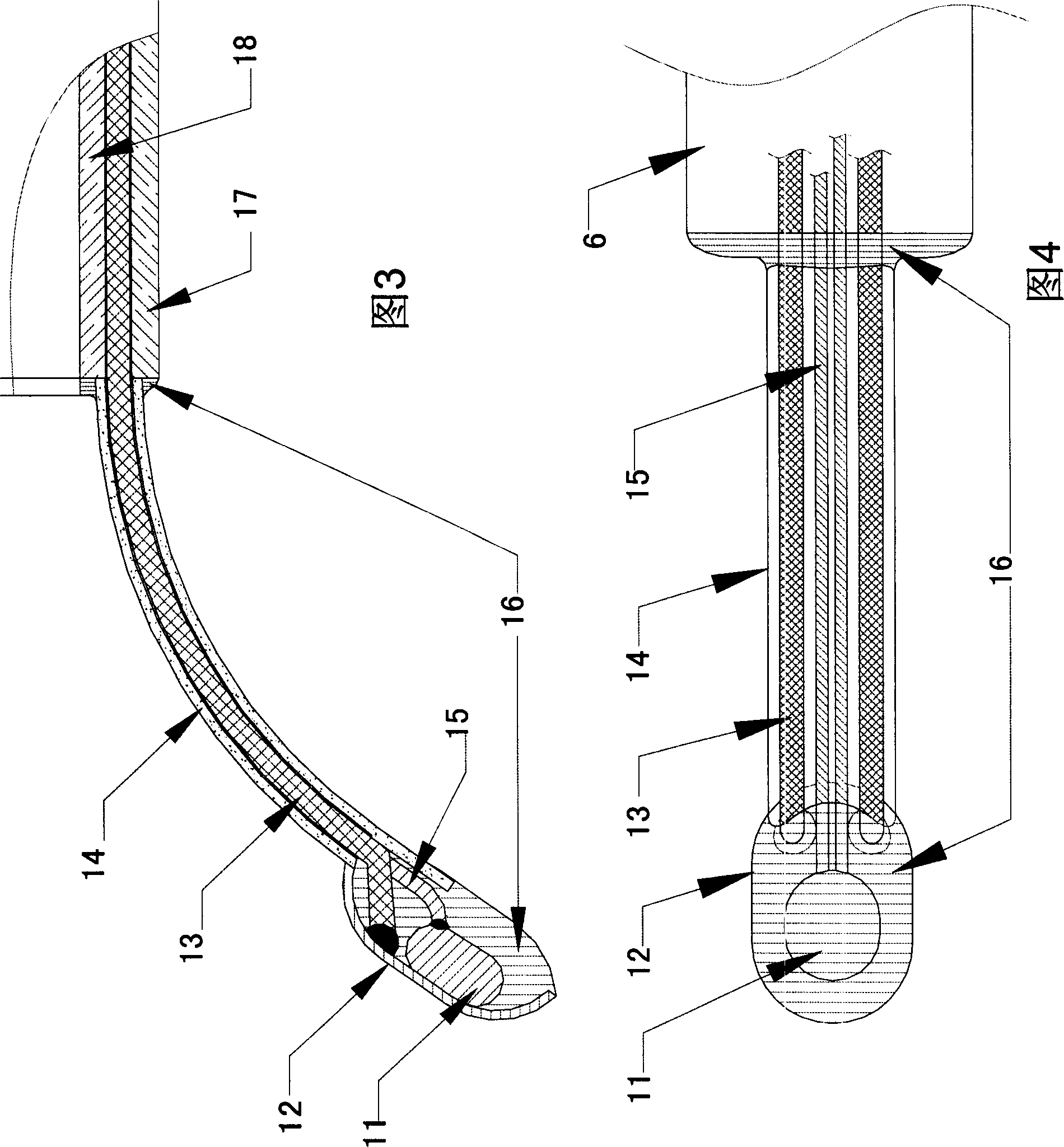
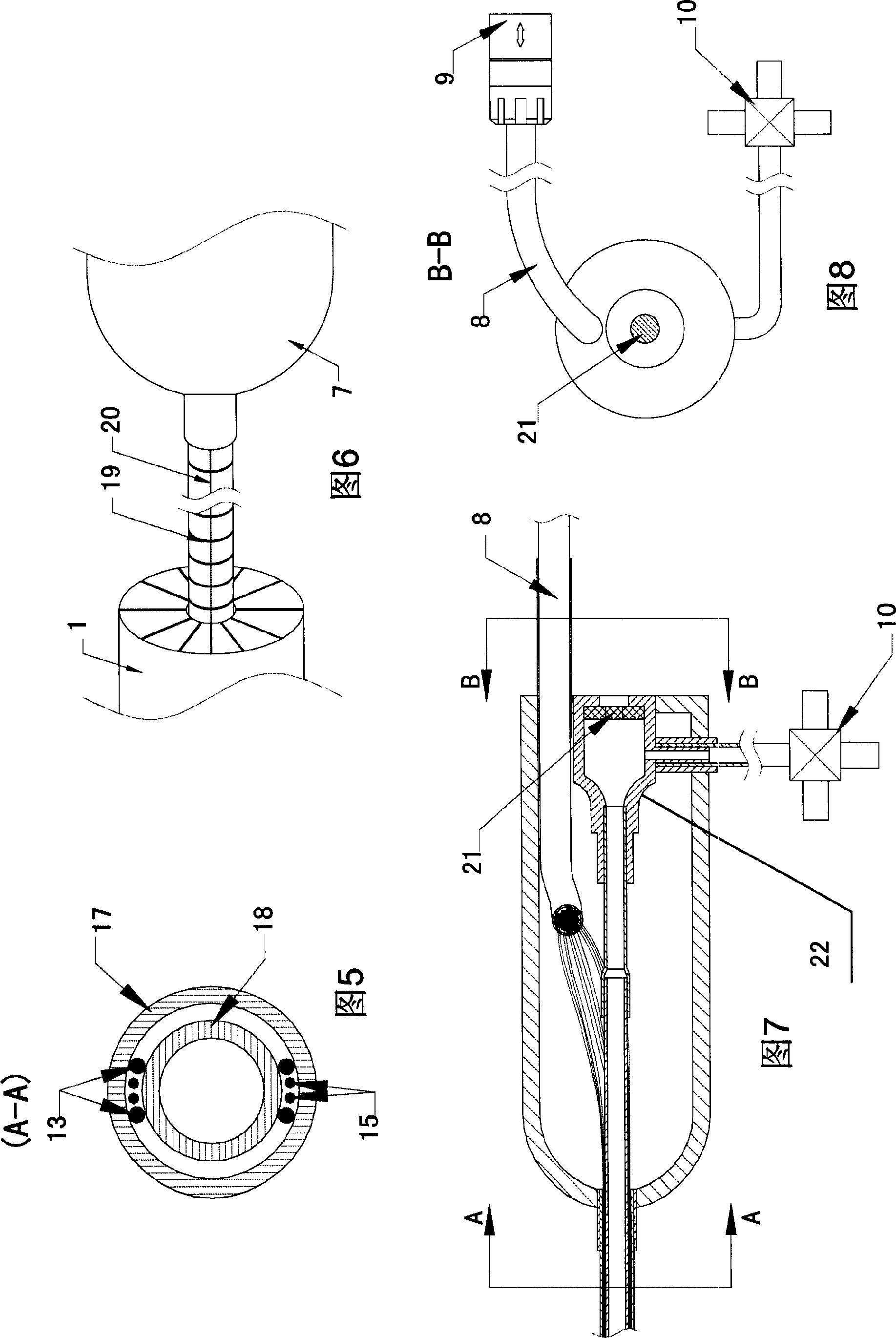
The invention discloses a cardiac intervention ablation catheter, the catheter comprises more than two branch electrodes (5), a catheter trunk (6) and an operating handle (7), wherein, all the branch electrodes (5) are distributed in a shape of petals, the top end of each petal of branch electrode (5) is a metal electrode (12), the lower ends of the metal electrodes are provided with a temperature sensor (11), the metal electrodes (12) are connected with an examination and treatment instrument (4) through a metal wire and the temperature sensor (11) which are welded at the lower ends of the metal electrodes and a connection line (15) of the sensor passes through an insulation tube (14), a catheter trunk (6) and a handle (7) sequentially. the root part of the catheter trunk (6) is provided with a depth scale (19) and an angle scale (20), the invention can realize that the invention can be tightly affixed at the surgical site of the rugged part in the heart; the invention can realize the ring-shaped ablation under the appropriate three to five times of the rotation of the catheter.
Owner:SICHUAN JINJIANG ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
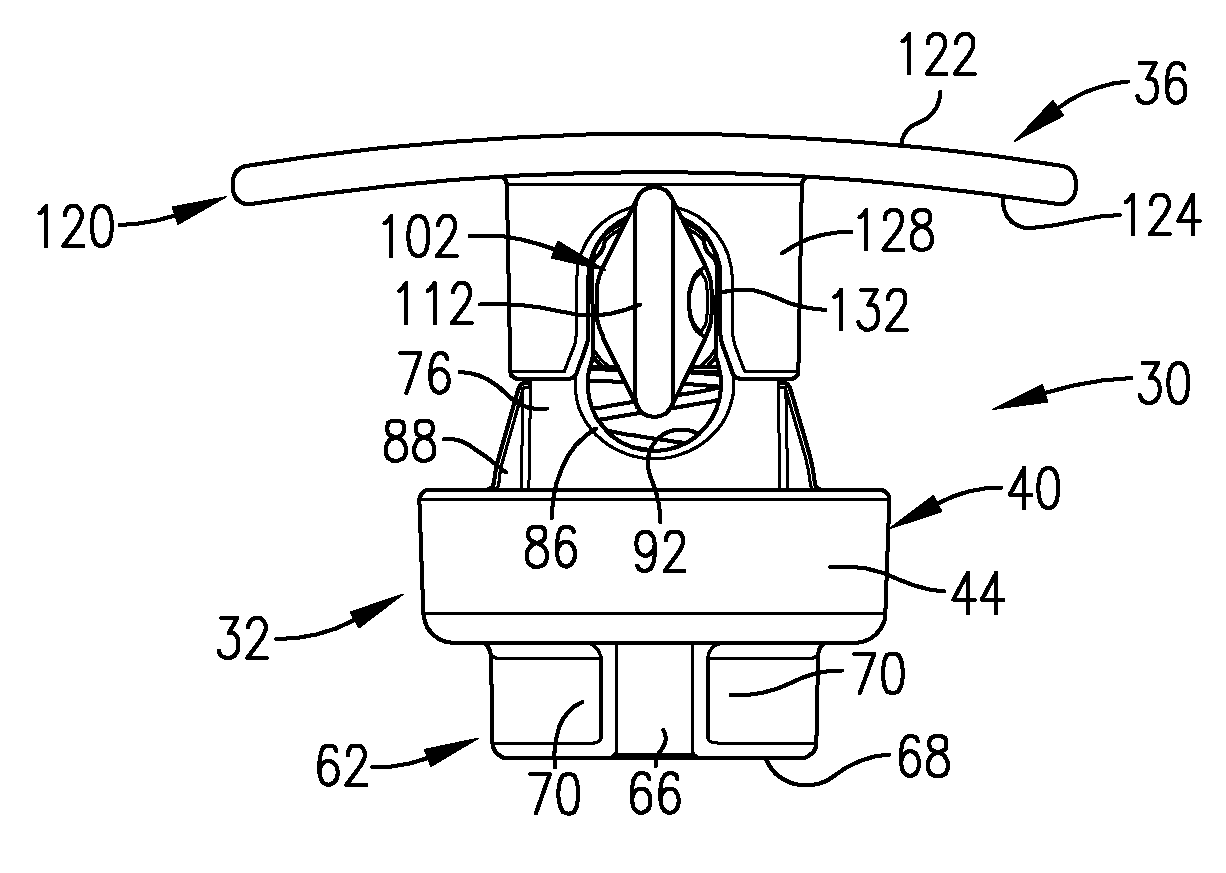
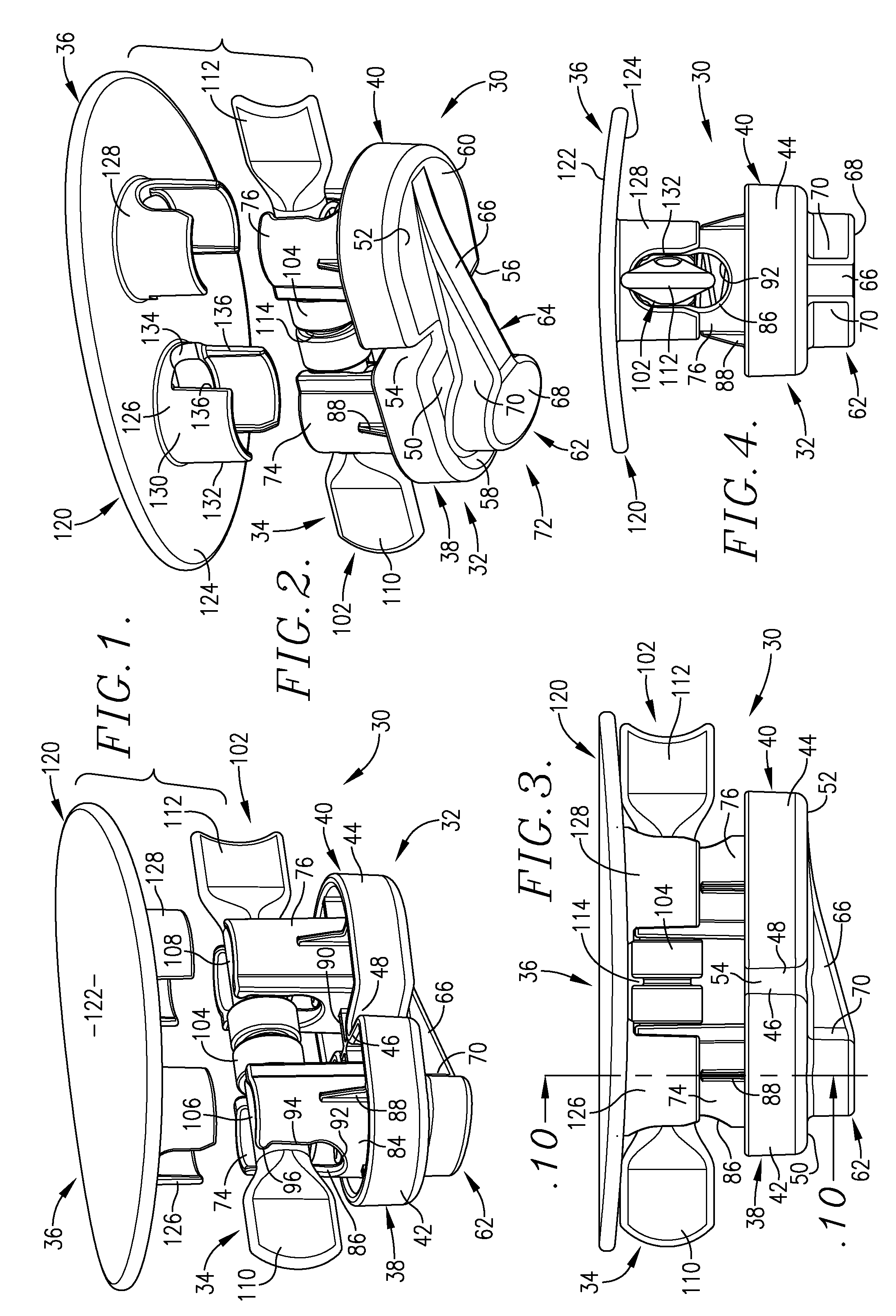
Vascular wound closing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20120191128A1Reduce patient 's blood pressureReduce flowSuture equipmentsTourniquetsPuncture WoundMedicine
Wound closure apparatus is provided including a body having an elongated, lowermost force-transmitting surface operable to be placed in a proximal, external, wound-closing position on a patient, together with a force-exerting assembly coupled with the body and operable to exert a downwardly directed force serving to generate wound-closing pressure against the patient's tissue. The force-transmitting surface is preferably three-dimensionally asymmetric so that forces of different magnitude are exerted at different locations along the length of the surface. The apparatus is especially designed for the closure of wounds attendant to endovascular interventions, e.g., a femoral artery puncture wound incident to percutaneous cardiac intervention (PCI), and is capable of quickly effecting wound closure with a time-to-ambulation (TTA) of approximately 60 minutes, and with a very low complication rate.
Owner:ENSITEVASCULAR LLC +1
Vascular wound closing apparatus and method
Wound closure apparatus is provided including a body having an elongated, lowermost force-transmitting surface operable to be placed in a proximal, external, wound-closing position on a patient, together with a force-exerting assembly coupled with the body and operable to exert a downwardly directed force serving to generate wound-closing pressure against the patient's tissue. The force-transmitting surface is preferably three-dimensionally asymmetric so that forces of different magnitude are exerted at different locations along the length of the surface. The apparatus is especially designed for the closure of wounds attendant to endovascular interventions, e.g., a femoral artery puncture wound incident to percutaneous cardiac intervention (PCI), and is capable of quickly effecting wound closure with a time-to-ambulation (TTA) of approximately 60 minutes, and with a very low complication rate.
Owner:ENSITEVASCULAR LLC
Non-rigid 2D/3D registration of coronary artery models with live fluoroscopy images
ActiveUS8948487B2Reduce uncertaintyEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imageCoronary arterial tree
A method for non-rigid registration of digital 3D coronary artery models with 2D fluoroscopic images during a cardiac intervention includes providing a digitized 3D centerline representation of a coronary artery tree that comprises a set of S segments composed of QS 3D control points, globally aligning the 3D centerline to at least two 2D fluoroscopic images, and non-rigidly registering the 3D centerline to the at least two 2D fluoroscopic images by minimizing an energy functional that includes a summation of square differences between reconstructed centerline points and registered centerline points, a summation of squared 3D registration vectors, a summation of squared derivative 3D registration vectors, and a myocardial branch energy. The non-rigid registration of the 3D centerline is represented as a set of 3D translation vectors rs,q that are applied to corresponding centerline points xs,q in a coordinate system of the 3D centerline.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
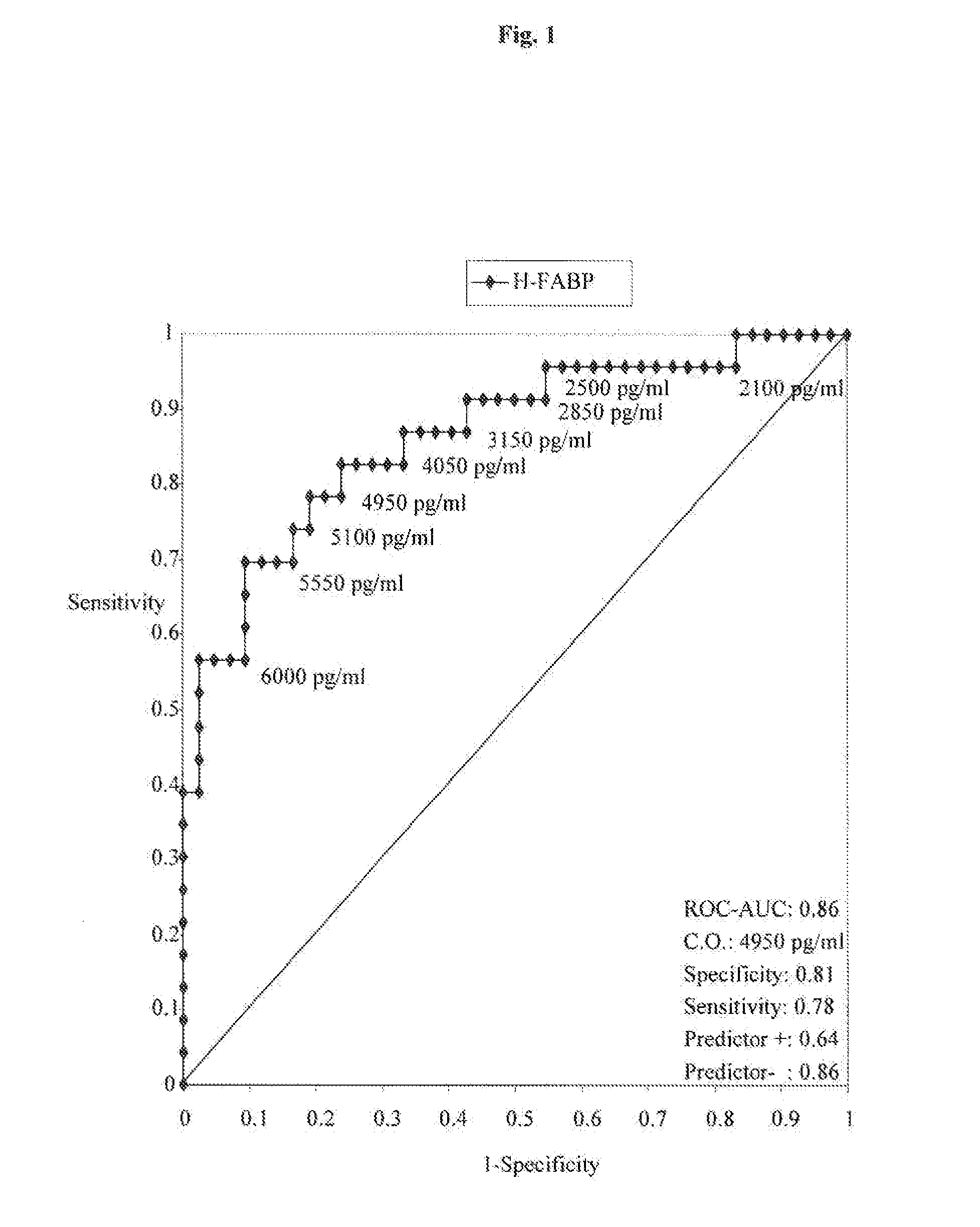
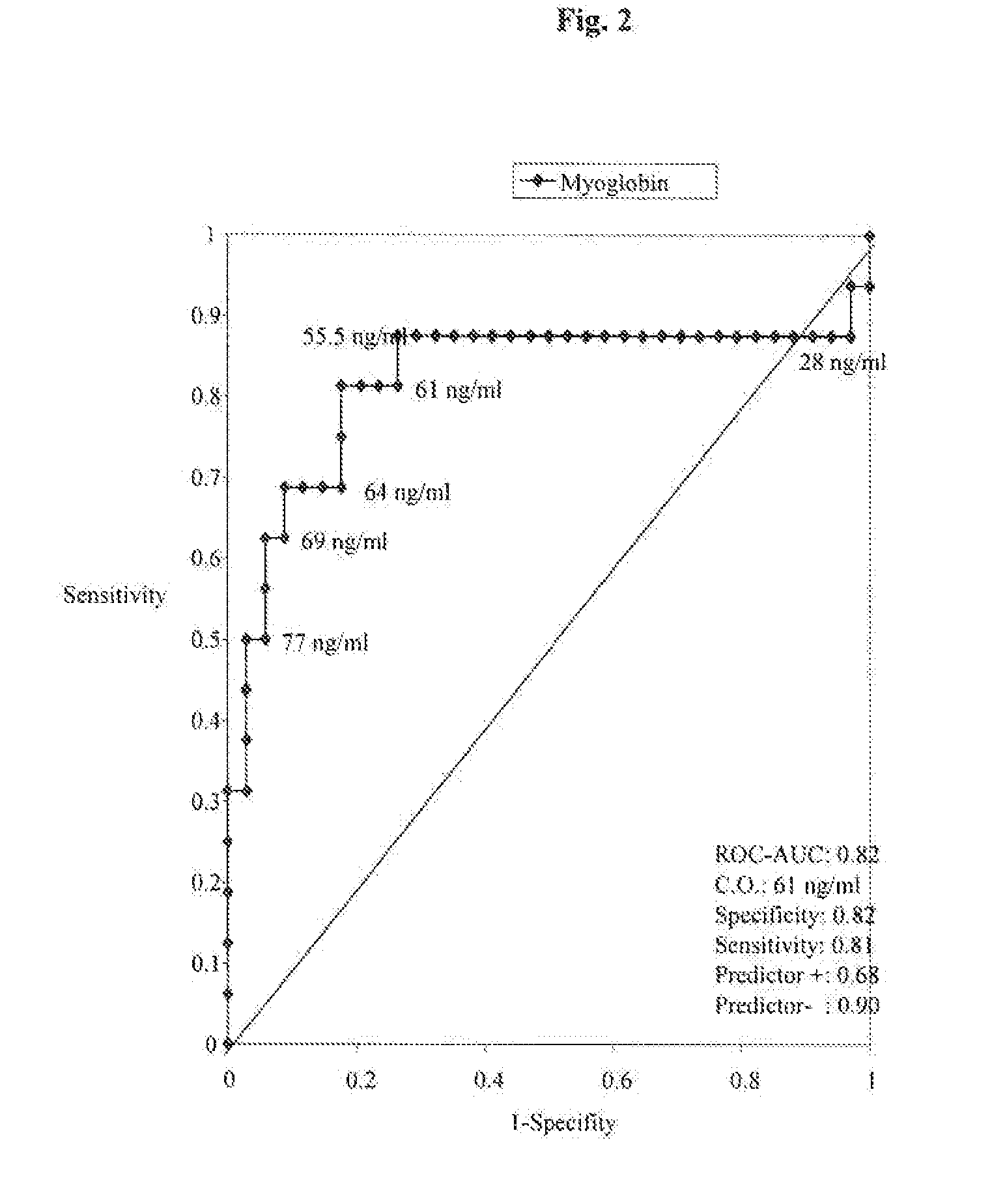
H-fabp as early predictor of myocardial infarction
InactiveUS20100159491A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCardiac muscleACS - Acute coronary syndrome
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing myocardial infarction in a subject who suffers from acute coronary syndrome and has a cardiac troponin level which is detectable but lower than the level that is considered as being indicative for a myocardial infarction. Moreover, the present invention relates to a method for identifying a subject being susceptible to cardiac intervention, wherein the subject suffers from acute coronary syndrome and has a cardiac troponin level which is detectable but lower than a level that is considered as being indicative for a myocardial infarction. The methods of the present invention are based on the determination of H-FABP and, optionally, myoglobin in a sample of the subject and comparing the amount of H-FABP and, optionally, myoglobin to reference amounts.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Method of detection and compensation for respiratory motion in radiography cardiac images synchronized with an electrocardiogram signal
ActiveUS8233688B2Effective registrationGreat precision and simplicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHealth-index calculationCardiac cycleX-ray
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for pericardium based model fusion of pre-operative and intra-operative image data for cardiac interventions
A method and system for model based fusion pre-operative image data, such as computed tomography (CT), and intra-operative C-arm CT is disclosed. A first pericardium model is segmented in the pre-operative image data and a second pericardium model is segmented in a C-arm CT volume. A deformation field is estimated between the first pericardium model and the second pericardium model. A model of a target cardiac structure, such as a heart chamber model or an aorta model, extracted from the pre-operative image data is fused with the C-arm CT volume based on the estimated deformation field between the first pericardium model and the second pericardium model. An intelligent weighted average may be used improve the model based fusion results using models of the target cardiac structure extracted from pre-operative image data of patients other than a current patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Deployable Polygonal Manipulator for Minimally Invasive Surgical Interventions
ActiveUS20150342688A1Accurate and fast positioningEfficient executionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesSurgical operationLess invasive surgery
A polygonal manipulator device for surgical interventions of the heart and other smooth organs is provided. A system implementing the device also is provided along with methods of use of the device and system. Methods of use of the device and system, such as for minimally-invasive cardiac intervention methods, are provided.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Vascular wound closing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20120277792A1Reduce flowReduce pressureSuture equipmentsTourniquetsPuncture WoundEndovascular interventions
Wound closure apparatus is provided including a body having an elongated, lowermost force-transmitting surface operable to be placed in a proximal, external, wound-closing position on a patient, together with a force-exerting assembly coupled with the body and operable to exert a downwardly directed force serving to generate wound-closing pressure against the patient's tissue. The force-transmitting surface is preferably three-dimensionally asymmetric so that forces of different magnitude are exerted at different locations along the length of the surface. The apparatus is especially designed for the closure of wounds attendant to endovascular interventions, e.g., a femoral artery puncture wound incident to percutaneous cardiac intervention (PCI), and is capable of quickly effecting wound closure with a time-to-ambulation (TTA) of approximately 60 minutes, and with a very low complication rate.
Owner:ENSITEVASCULAR LLC
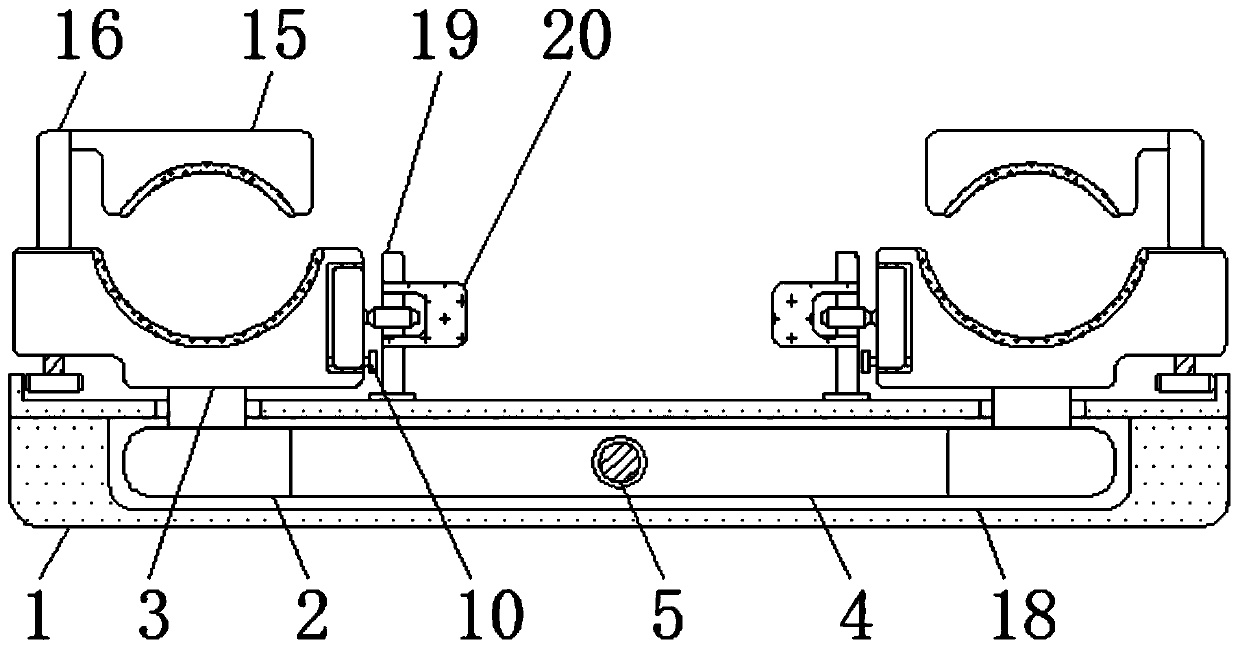
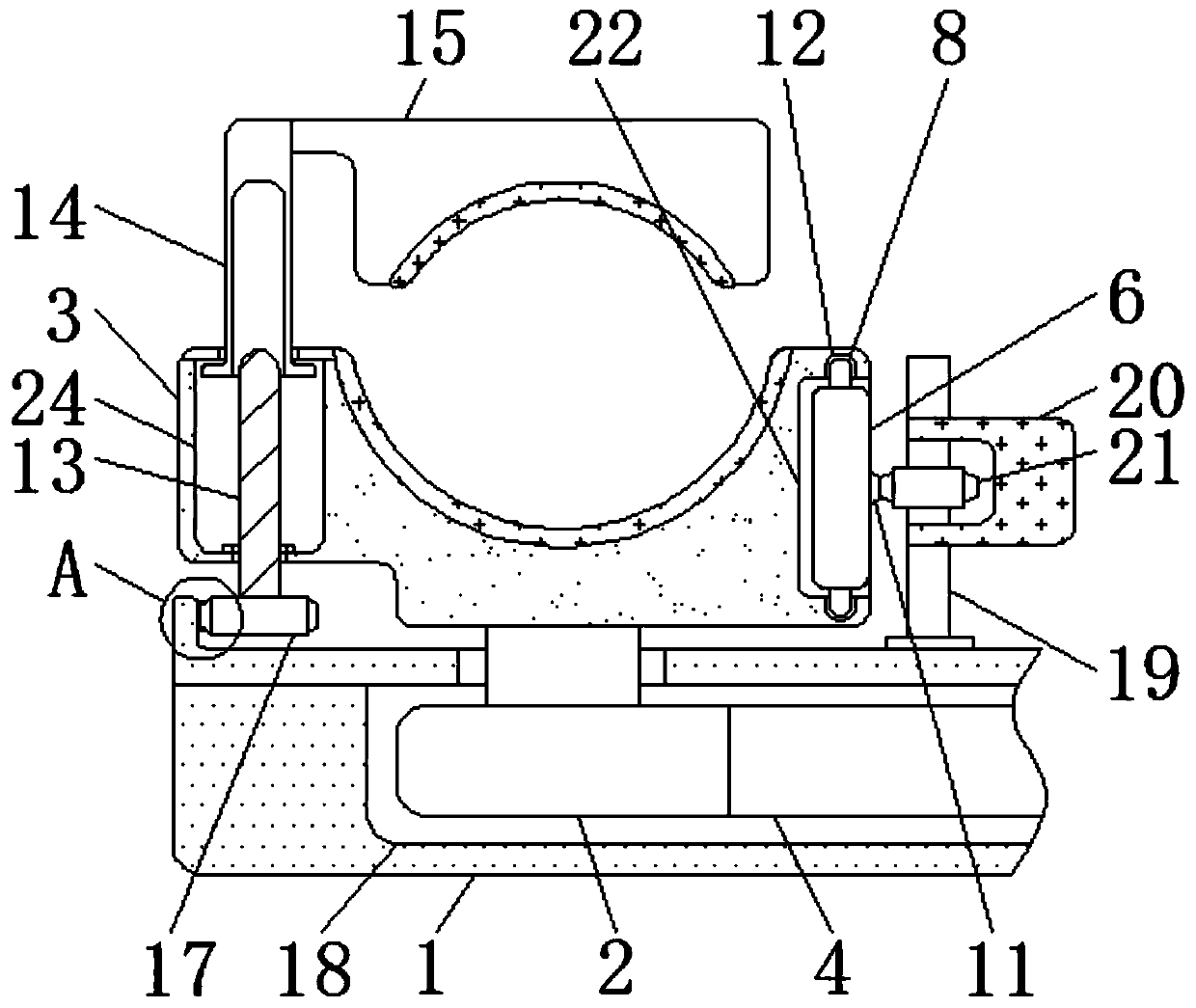
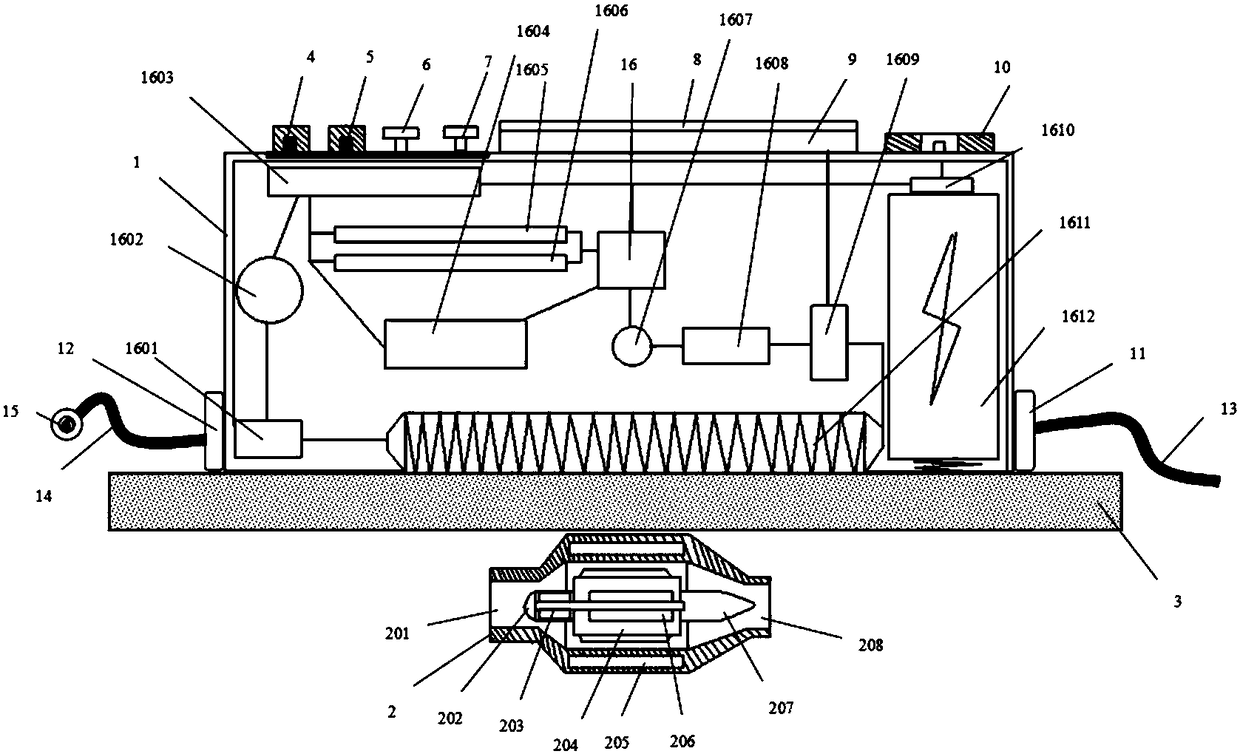
Fixing and supporting device for cardiac intervention operations
ActiveCN111568563AAvoid non-circulationEasy to fixInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryStructural engineeringRat heart
The invention discloses a fixing and supporting device for cardiac intervention operations. The device includes an installation flat plate, a connecting rod and a damping shaft; the left and right sides inside the installation flat plate are provided with adjusting blocks, and the upper parts of the adjusting blocks are connected to lower fixing seats through welding; the adjusting blocks are fixedly installed on the left and right ends of the connecting rod; a first screw rod is in threaded connection with the inside of the connecting rod; and a first screw rod bearing is connected in an adjusting groove. The device rotates to drive the first screw rod so as to drive the connecting rod and the adjusting blocks installed on the left and right ends of the connecting rod to move, so that thelower fixing seat and an upper fixing seat can be driven to move; a first gear and a second tooth block are utilized to drive a second screw rod to rotate, and the second screw rod drives a moving rod in threaded connection to move, so that the heights of the fixing seats can be adjusted; and through the utilization of the upper fixing seat and the lower fixing seat to fix the arm of a patient, good fixing effects can be achieved, local tight binding feeling can be reduced, and the poor circulation of blood can be avoided.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
Cardiac intervention type left ventricular electromagnetic assisting device
InactiveCN108525040AImprove quality of life after surgeryExtend your lifeIntravenous devicesSuction devicesLeft ventricular sizeElectromagnetic field
The invention discloses a cardiac intervention type left ventricular electromagnetic assisting device which mainly comprises an in-vitro control device and a blood pump. The in-vitro control device isisolated from the blood pump by a skin layer and is connected with the blood pump by electromagnetic fields; the in-vitro control device is a box with a rectangular cross section, a power regulationknob, a current regulation knob, a power switch, an electromagnetic auxiliary switch and a liquid crystal display are sequentially arranged on the front surface of the outer side of the box from leftto right, and a charge hole is formed in the front surface of the outer side of the box. The cardiac intervention type left ventricular electromagnetic assisting device has the advantages that electromagnetic induction type control technologies are utilized, accordingly, wire holes do not need to be drilled under the skin of patients, infection can be prevented, and the cardiac intervention type left ventricular electromagnetic assisting device is easy to operate and can be continuously controlled and regulated for a long term; the cardiac intervention type left ventricular electromagnetic assisting device with the novel magnetic suspension axial flow type blood pump is high in control precision, magnetic field gravitation on an artificial heart can be balanced, the balance of magnetic field force on the artificial heart can be kept, the service life of the artificial heart can be prolonged, and the cardiac intervention type left ventricular electromagnetic assisting device can be clinically widely applied.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF QINGDAO UNIV
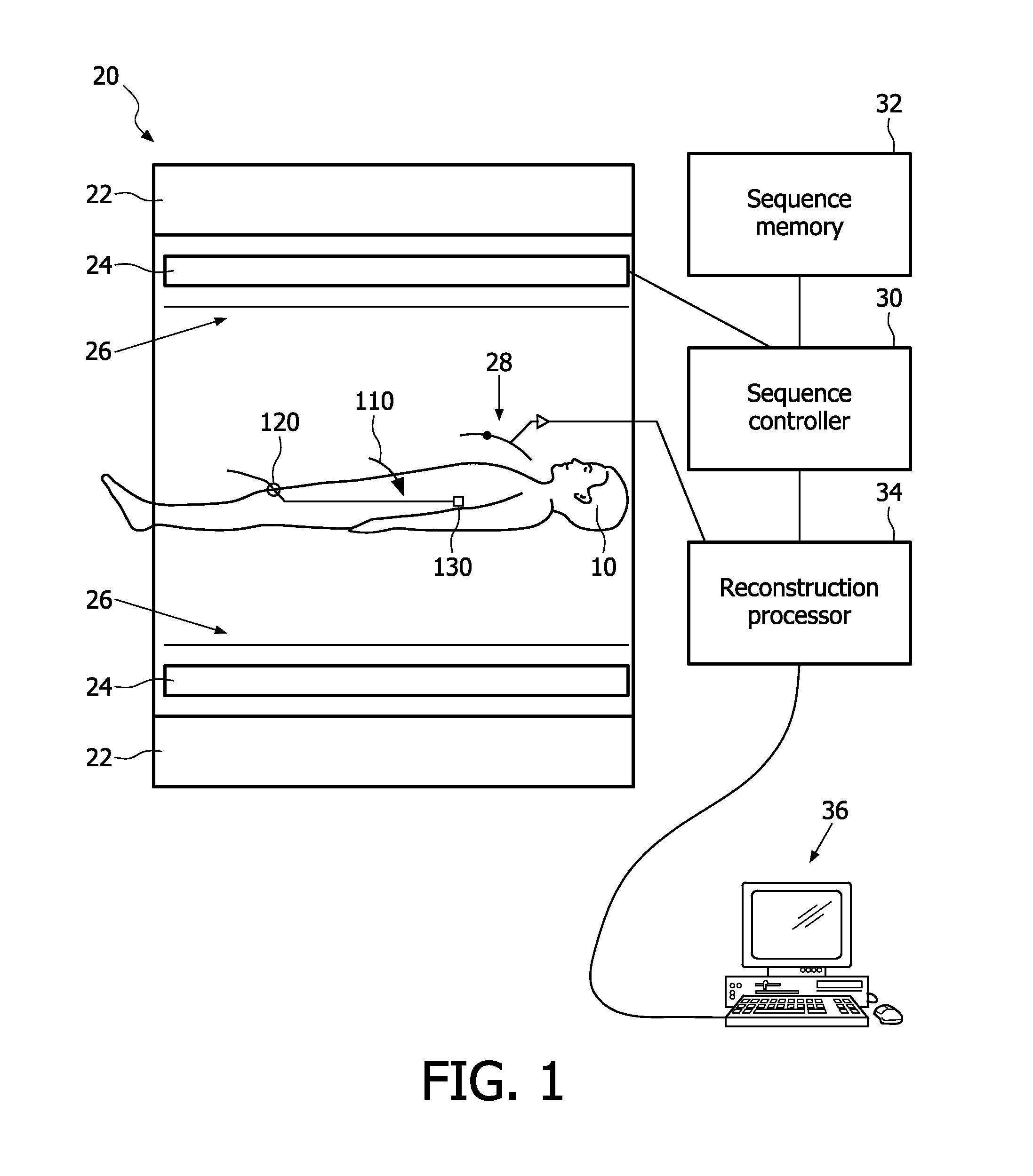
System, method and apparatus for cardiac intervention with mr stroke detection and treatment
InactiveUS20110257510A1Early treatmentPreserve more brain tissueMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSequence controlCatheter procedure
A system for the early detection and treatment of catheter-induced ischemic strokes includes a magnetic resonance system (20) and a processor (36). The magnetic resonance system includes a sequence controller for performing each of a plurality of imaging sequences and a sequence memory (32) which stores at least a magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) sequence, a diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequence, and a perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI) sequence. The processor is programmed to control the magnetic resonance system to perform the steps of: performing the MRA sequence to generate a baseline MRA image; performing a catheter-tracking procedure to track a catheter; performing the DWI sequence after the catheter procedure to generate a diffusion-weighted image; performing the PWI sequence to generate a perfusion-weighted image; and combining the diffusion-weighted image and the perfusion-weighted image to generate a combined image for evaluating the ischemic stroke.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system for determining a risk of hemodynamic compromise after cardiac intervention
ActiveUS11045256B2Avoid measuringReliable measurementMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBlood flowEngineering
A method and system for predicting a measure of hemodynamic compromise as a result of transcatheter cardiac treatment. The method includes providing a patient-specific anatomical model representing cardiac region and an implant model representing a three-dimensional representation of a cardiac implant. The method includes virtually deploying said implant model into said patient-specific anatomical model. A deformation of the patient-specific anatomical model is calculated as a result of implant model deployment A measure of hemodynamic compromise is determined from the virtually deployed implant model and the deformed patient-specific anatomical model.
Owner:FEOPS NV
Method and System for Determining a Risk of Hemodynamic Compromise After Cardiac Intervention
ActiveUS20190357981A1Reliable measurementAvoid measuringMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesCatheterCvd risk
A method and system for predicting a measure of hemodynamic compromise as a result of transcatheter cardiac treatment. The method includes providing a patient-specific anatomical model representing cardiac region and an implant model representing a three-dimensional representation of a cardiac implant. The method includes virtually deploying said implant model into said patient-specific anatomical model. A deformation of the patient-specific anatomical model is calculated as a result of implant model deployment A measure of hemodynamic compromise is determined from the virtually deployed implant model and the deformed patient-specific anatomical model.
Owner:FEOPS NV
Assessing risk of cardiac intervention in patients suffering from stable coronary heart disease based on gdf-15
InactiveUS20100167331A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCoronary heart diseaseHeart disease
Described is a method for diagnosing whether a percutaneous cardiac intervention (PCI) in a subject suffering from a stable coronary heart disease was successful, the method comprising determining the amount of GDF-15 in a first sample of the subject which has been obtained after PCI and comparing the determined amount of GDF-15 with a reference amount of GDF-15 which is determined in a second sample of the subject suffering from a stable coronary heart disease obtained prior to PCI, whereby it is diagnosed whether PCI was successful. The invention also relates to the use of means for determining the amount of GDF-15 and, preferably, a natriuretic peptide and / or a cardiac troponin for the preparation of a diagnostic composition for diagnosing whether a PCI in a subject suffering from a stable coronary heart disease was successful.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Coronary artery delivery catheter, catheter and device for cardiac intervention treatment
The invention discloses a coronary artery delivery catheter, a catheter and a device for cardiac intervention treatment. Particularly, the coronary artery delivery catheter comprises a hollow pipe and a metal rod; the hollow pipe comprises a pipe body section and an oblique opening section, and the hollow pipe is used for containing a coronary artery balloon dilatation catheter or a stent delivery system; the length of the hollow pipe section ranges from 220 mm to 380 mm, the length of the oblique opening section ranges from 2 mm to 6 mm, the outer diameter of the hollow pipe ranges from 1.60 mm to 1.80 mm, the inner diameter of the hollow pipe ranges from 1.00 mm to 1.64 mm, and the effectively length of the coronary artery delivery catheter ranges from 135 cm to 165 cm; the hardness of the pipe body section gradually reduced from the rear end to the front end; an oblique opening is formed in the rear end of the oblique opening section, and the included angle formed by the oblique opening and the hollow pipe in the axial direction is alpha, wherein the alpha is larger than or equal to 20 degrees and smaller than or equal to 90 degrees; the rear end of the oblique opening and the front end of the metal rod are fixed through welding, and the hollow pipe and the metal rod form a fixed whole body. The coronary artery delivery catheter can be used together with a guiding catheter, lengthens the guiding catheter and delivers the coronary artery balloon dilatation catheter, a stent and the like to the more distal position of the coronary artery and position closer to a diseased region.
Owner:J ROBOTICS MEDICAL LTD
Catheter vibration control method of cardiac intervention type magnetic navigation system
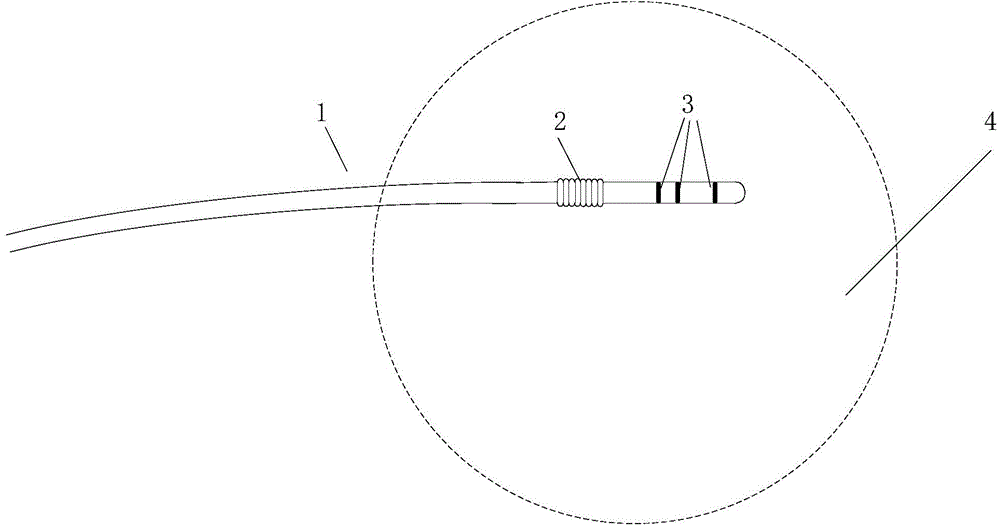
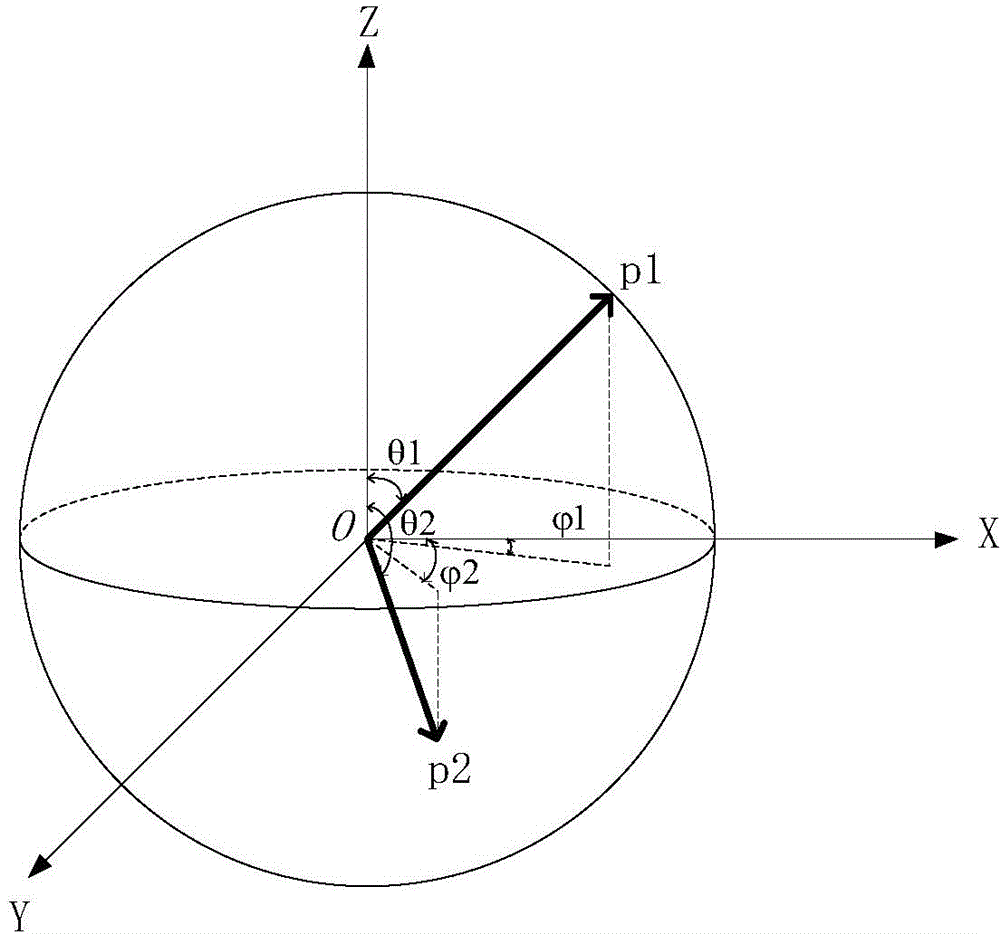
InactiveCN104127243AGood controlImprove navigation and positioning accuracyDiagnosticsSurgeryVibration controlNavigation system
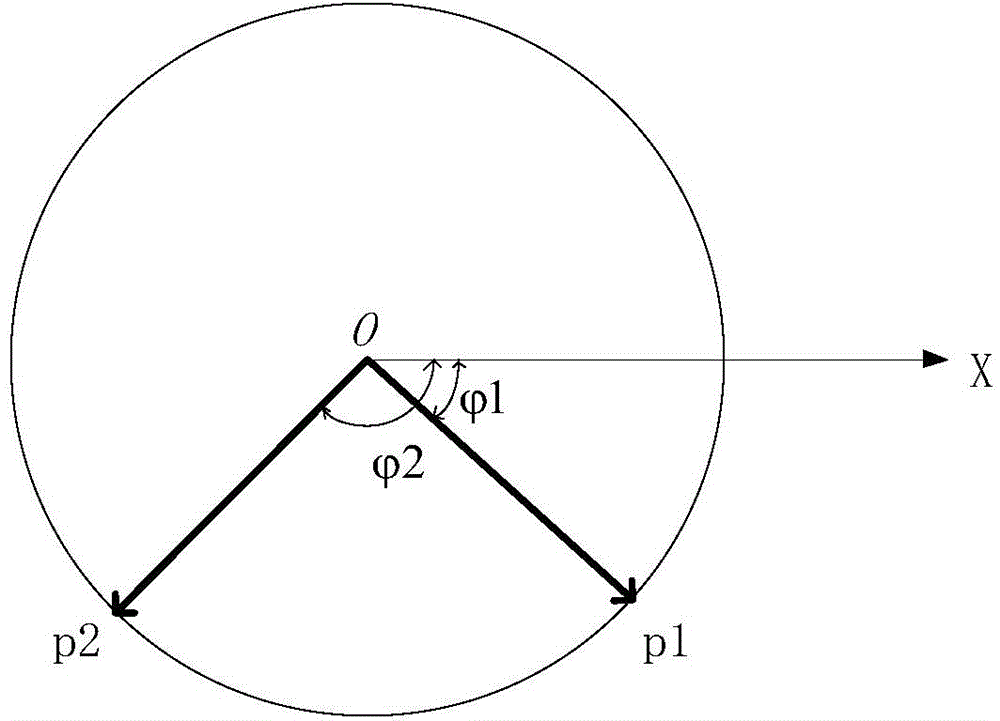
Provided is a catheter vibration control method of a cardiac intervention type magnetic navigation system. The method includes the following control strategies that a track suitable for a catheter (1) to follow after the catheter (1) changes the posture is found out according to an angular difference value between a current posture and a next target posture of the catheter (1), and the catheter (1) is made to be always in a posture controllable state in the posture changing process; in the two-dimensional plane, the current posture phi1 of the end of the catheter (1) is measured through a three-dimensional cardiac mapping system, a next position posture phi2 and a following step size delta phi of the catheter (1) are determined according to the operation requirements, and therefore an any-time posture phit(n) of the catheter (1) from the current posture phi1 to the next position posture phi2 is determined; in the three-dimensional spherical coordinate space, the current posture (phi1, theta1) of the end of the catheter (1) is measured through the three-dimensional cardiac mapping system, a next position posture (phi2, theta2) and following step sizes delta phi and delta theta of the catheter (1) are determined according the operation requirements, and therefore an any-time posture (phit(n), thetat(m)) of the catheter between the current posture (phi1, theta1) and the next position posture (phi2, theta2) can be determined.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com