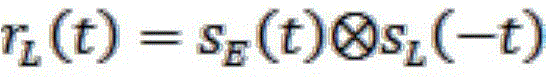Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Auditory cueing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
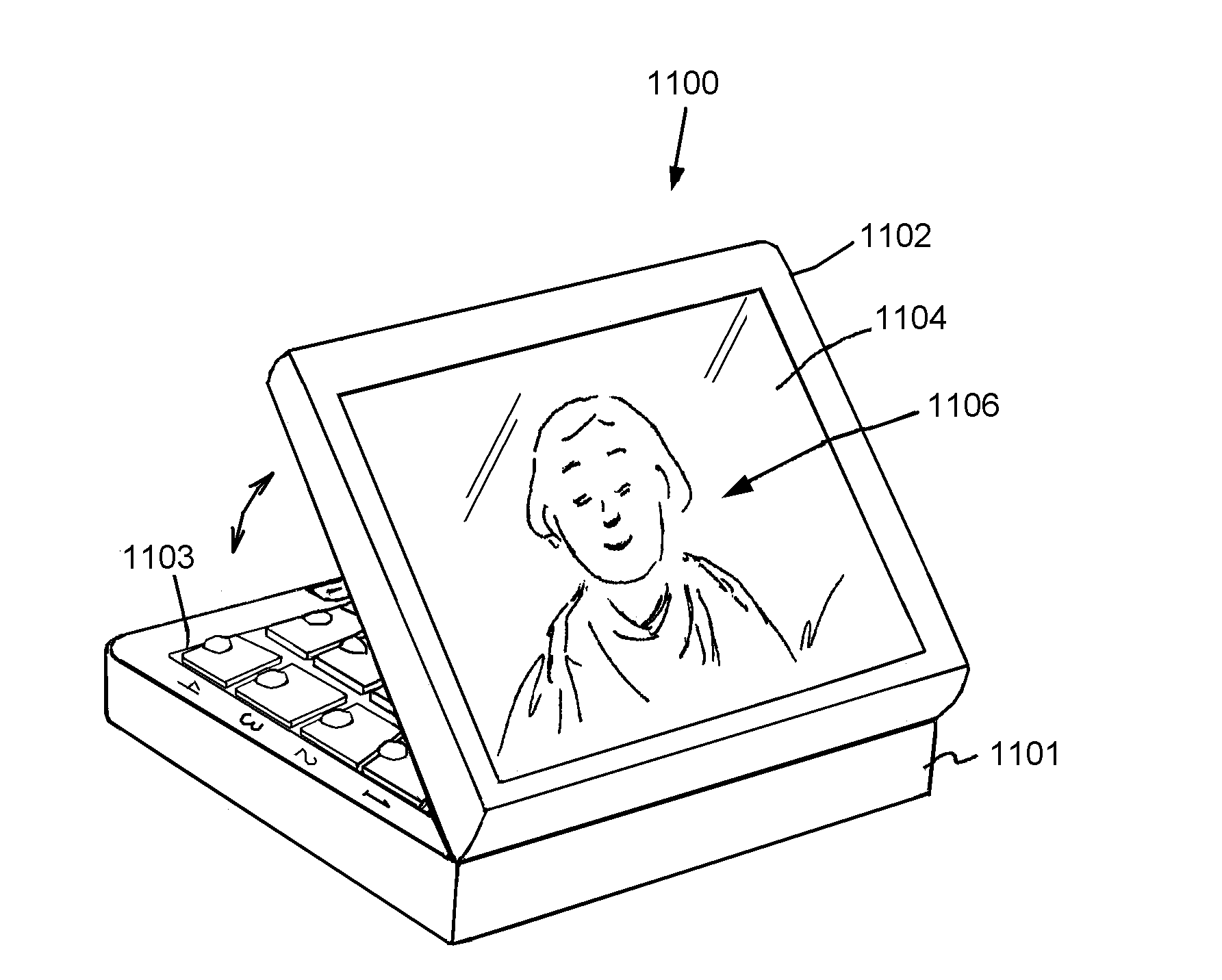
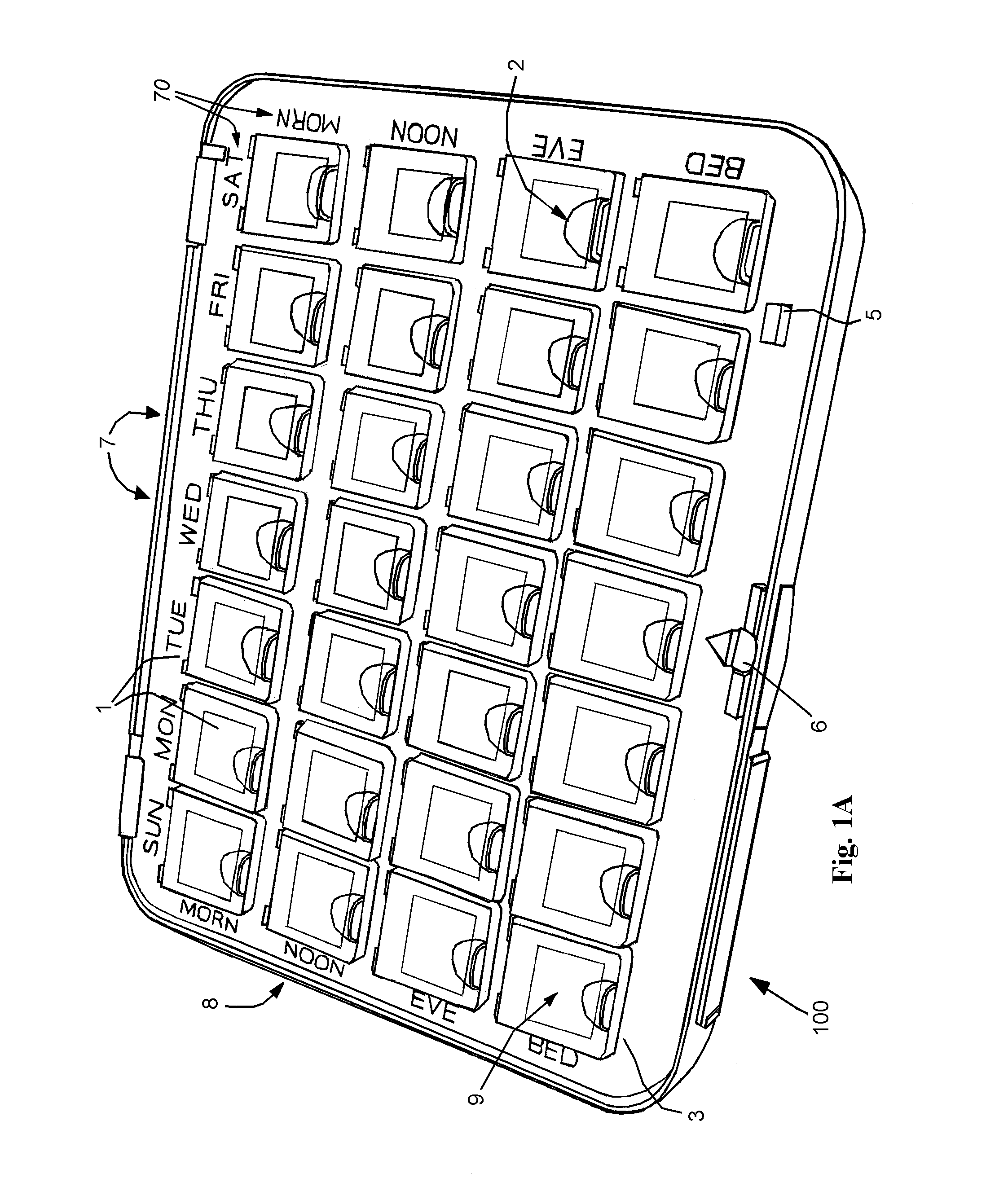
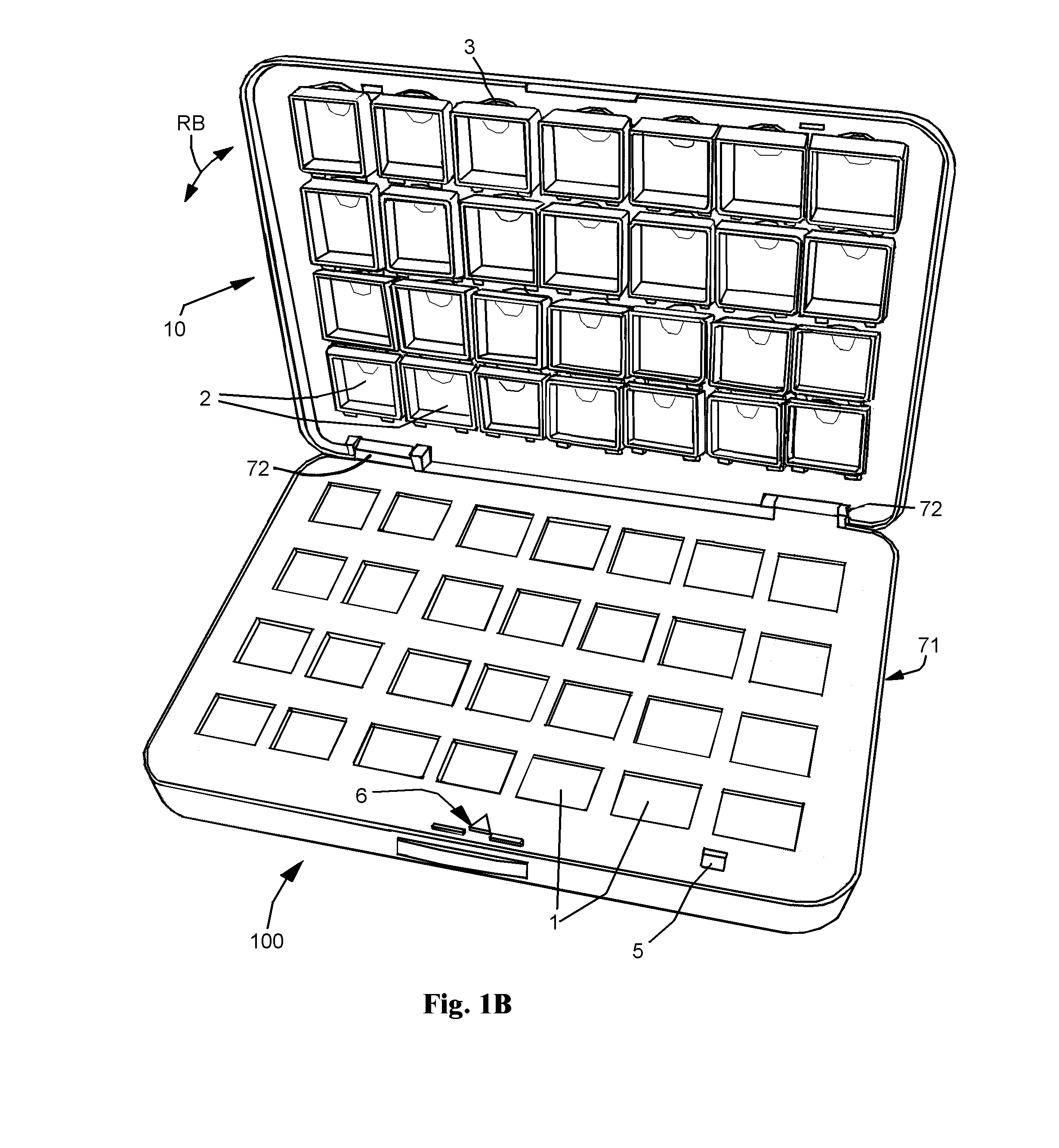
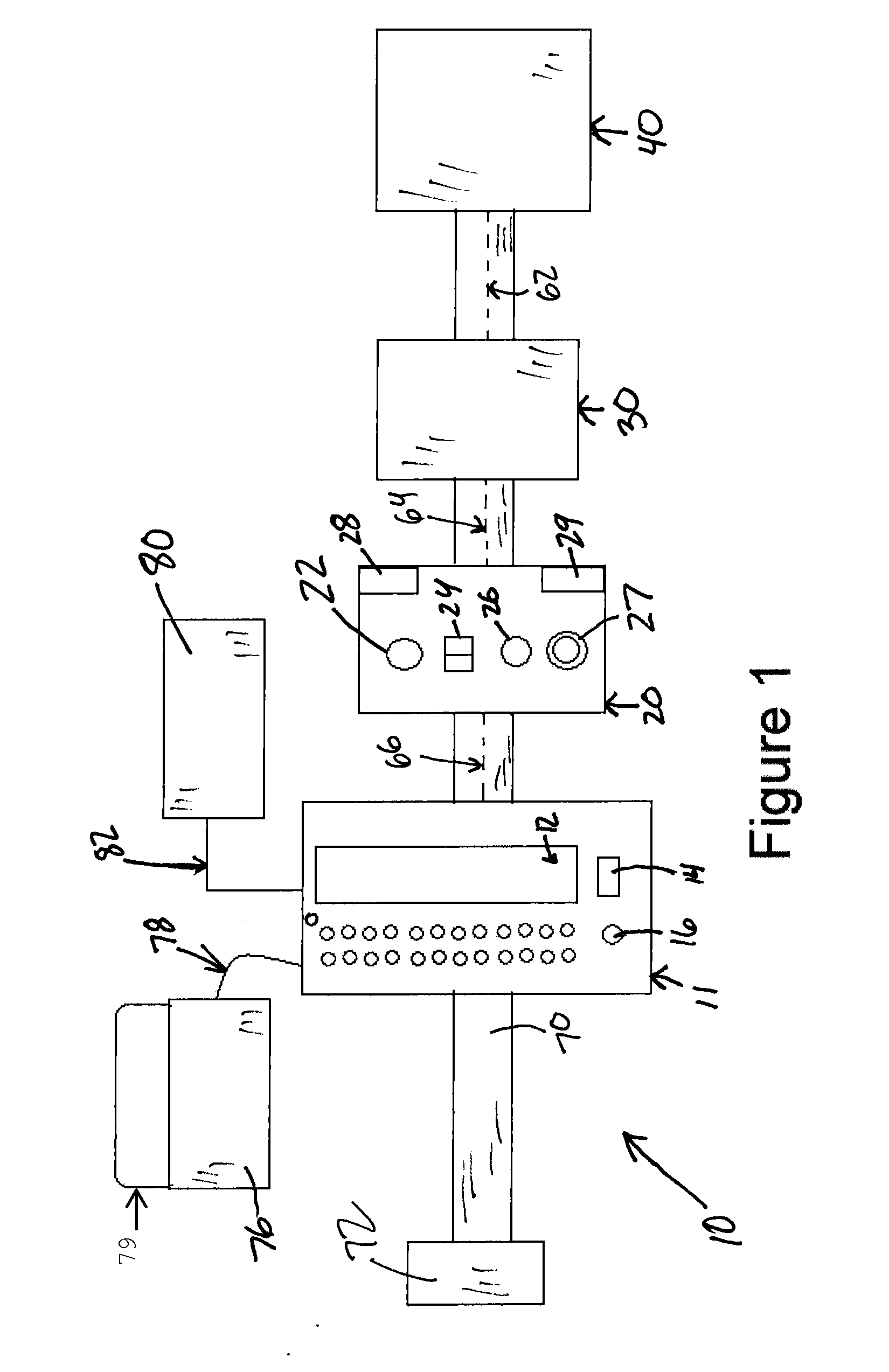
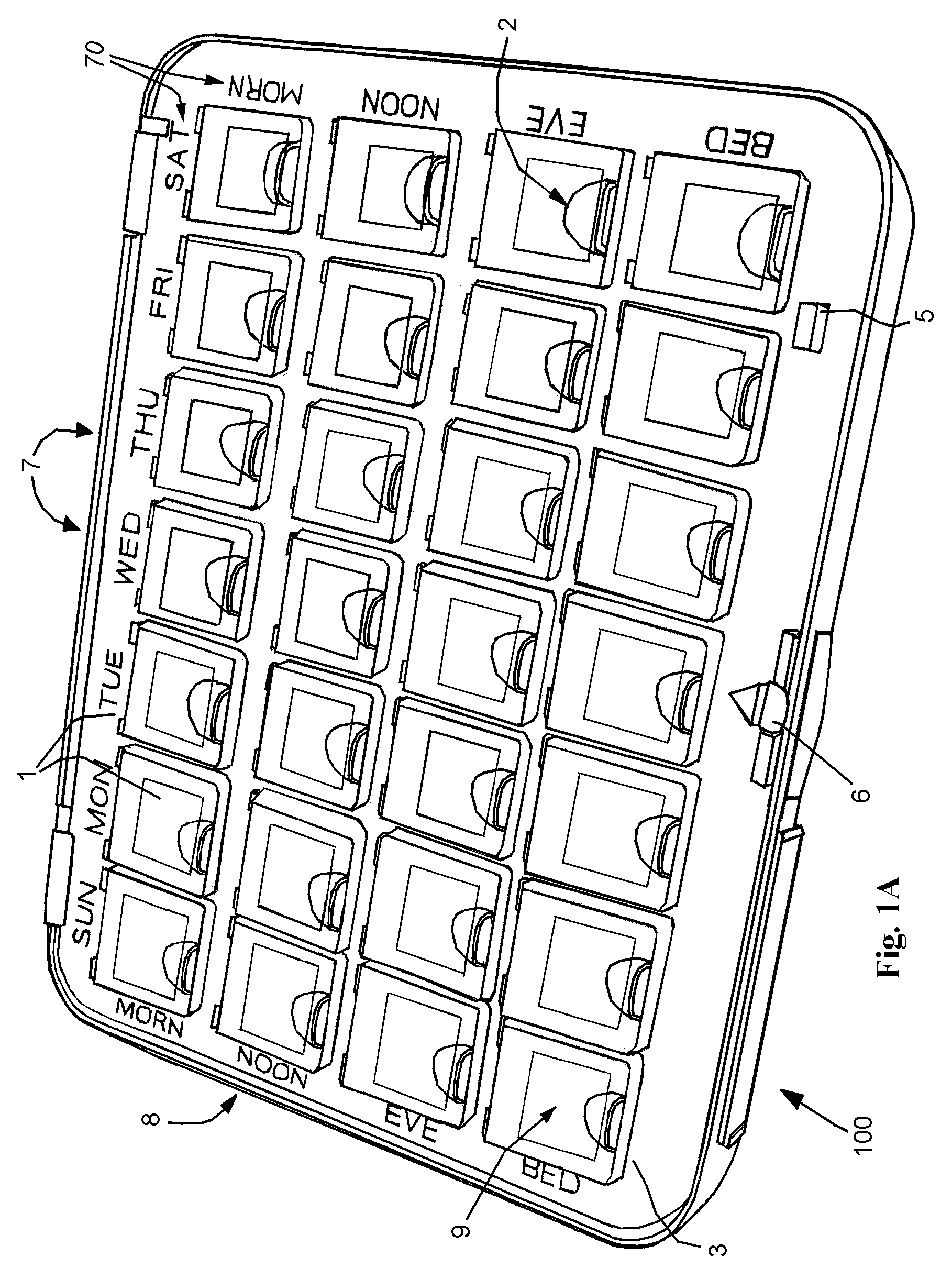
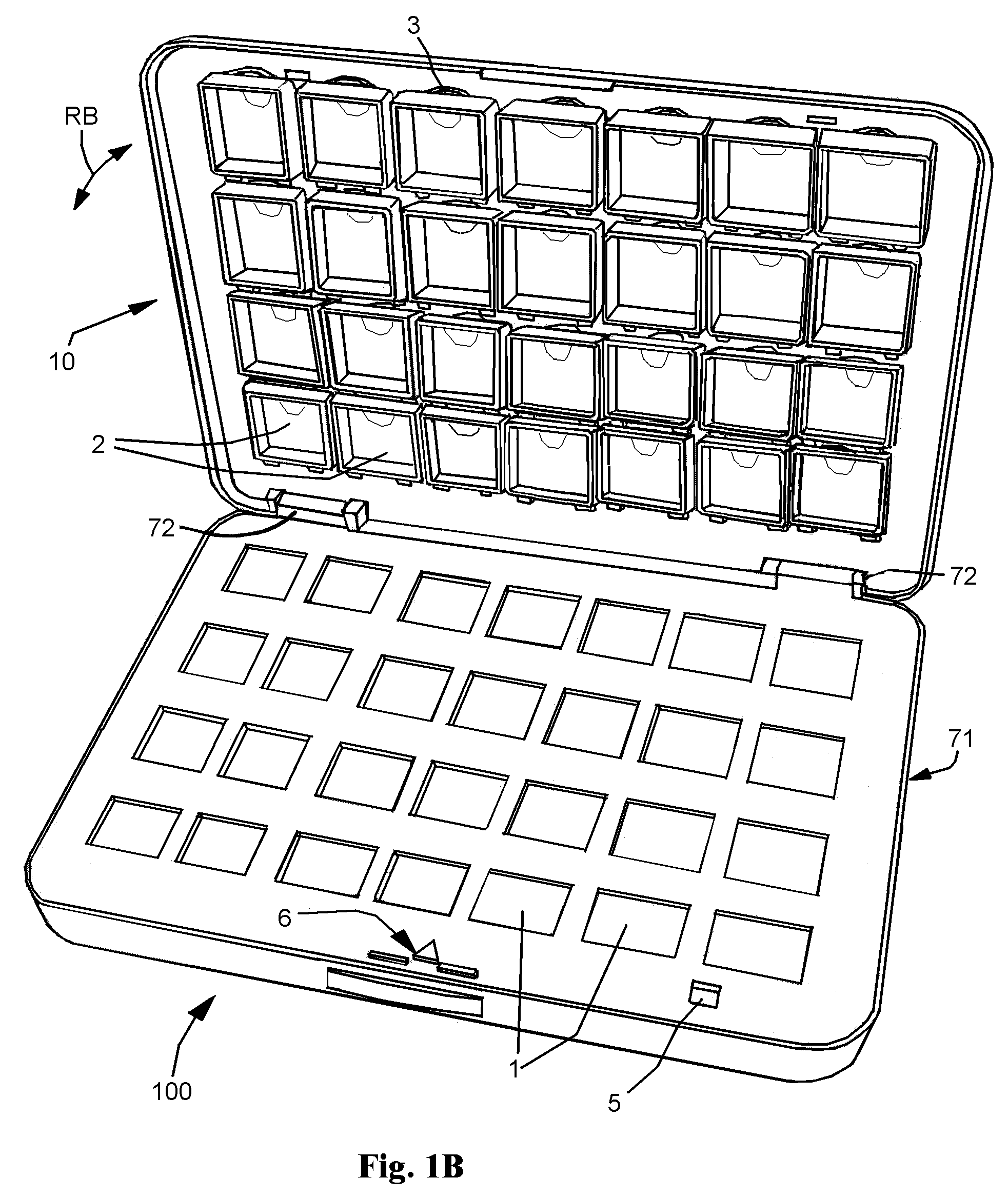
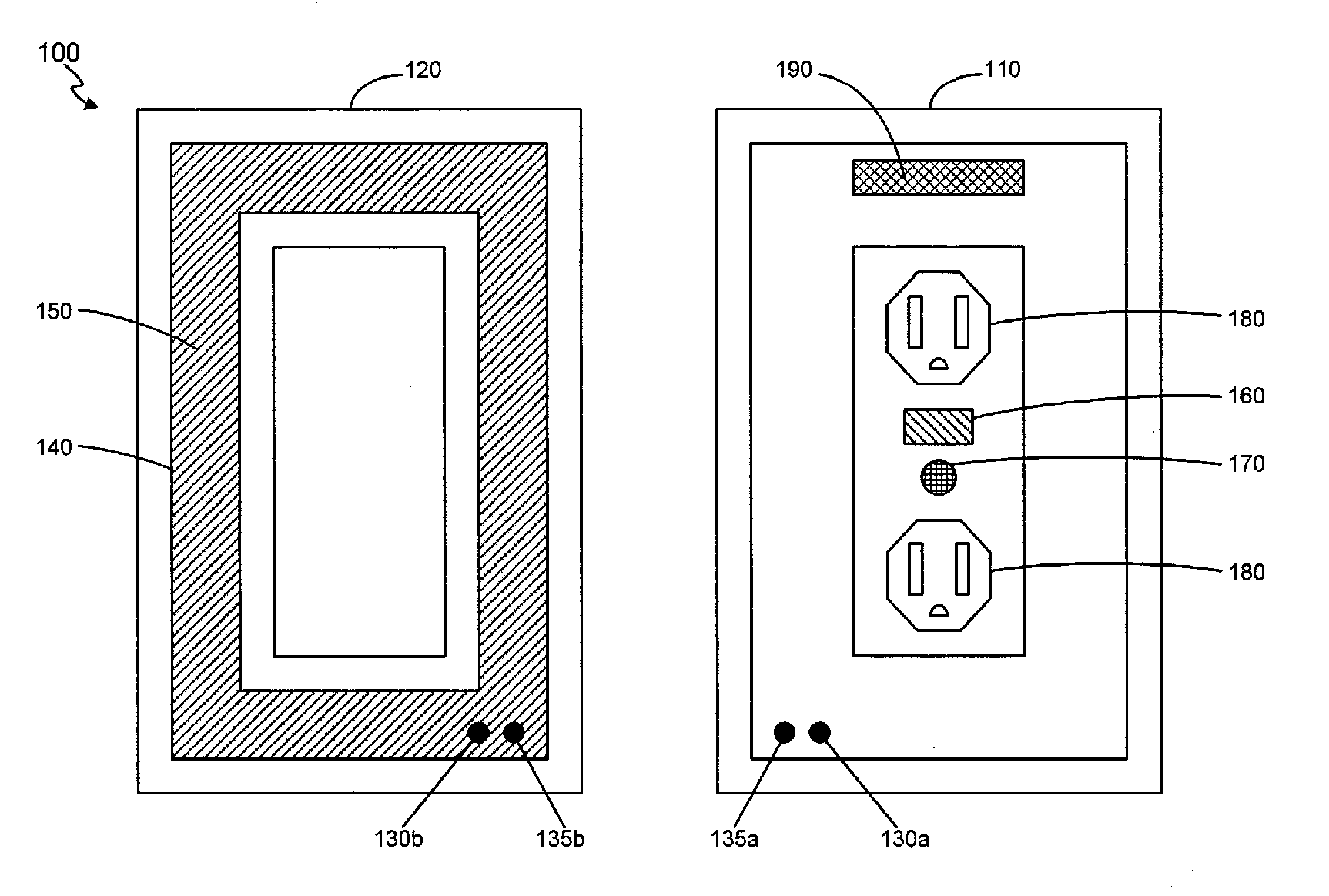
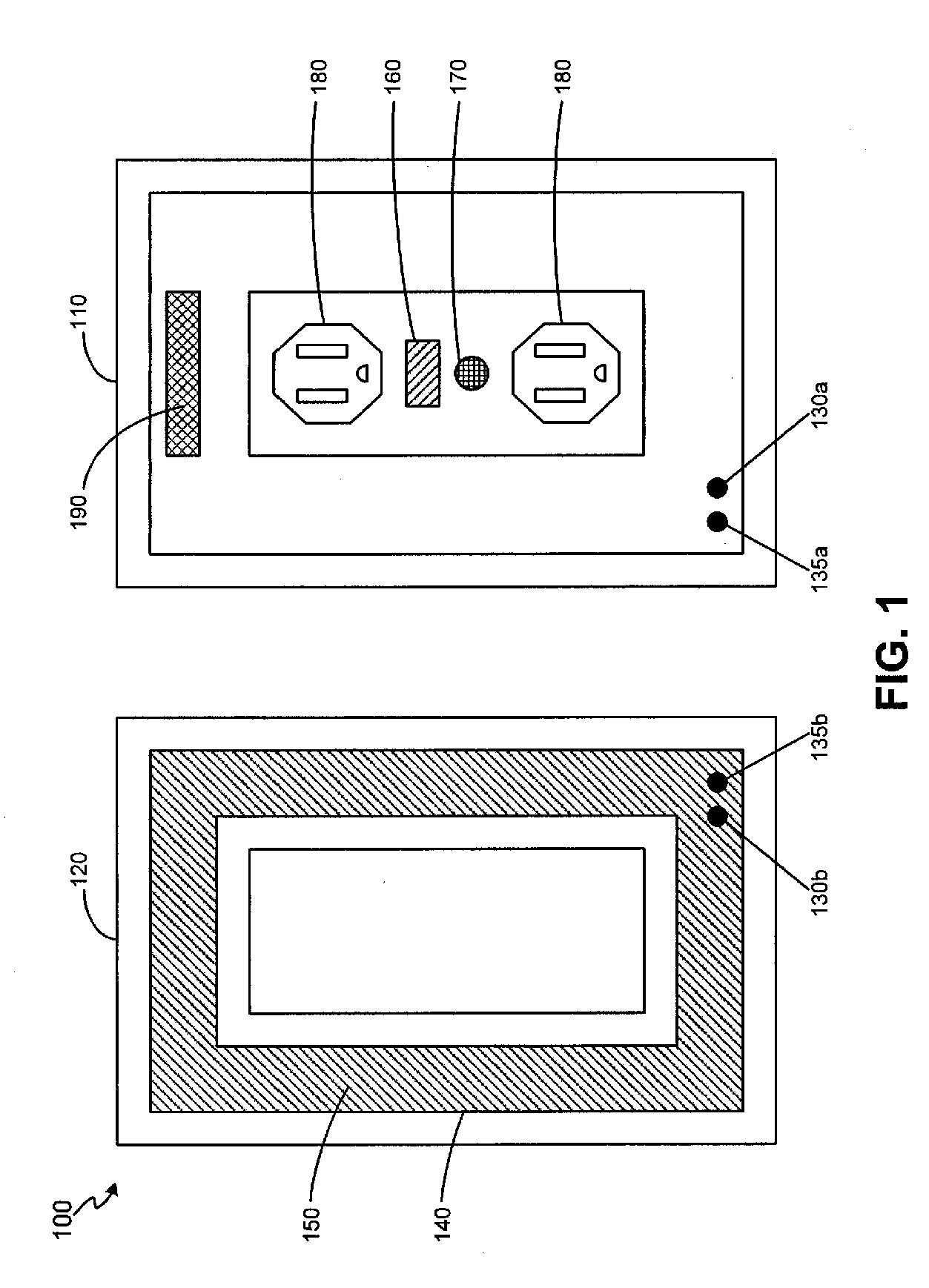
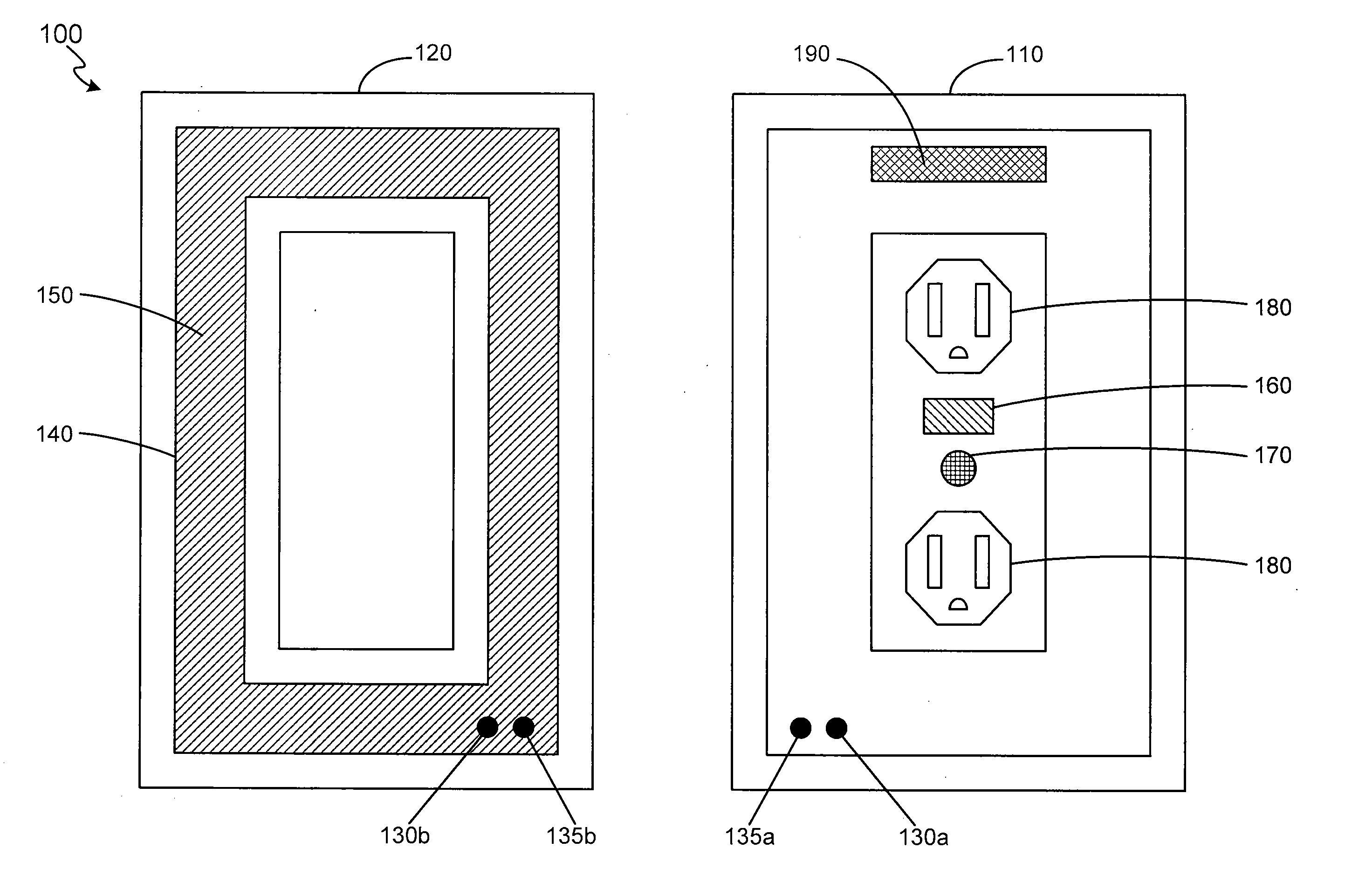
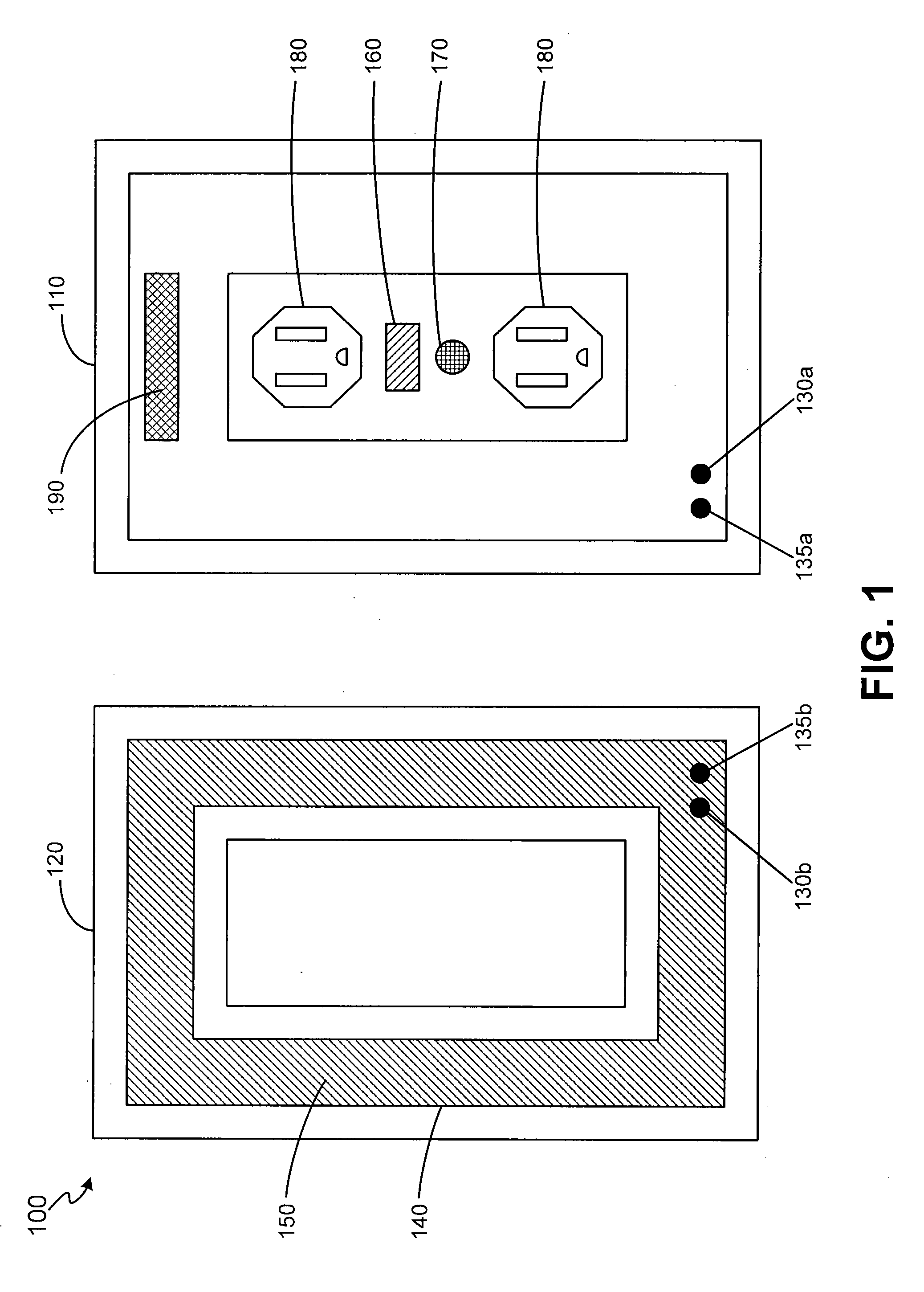
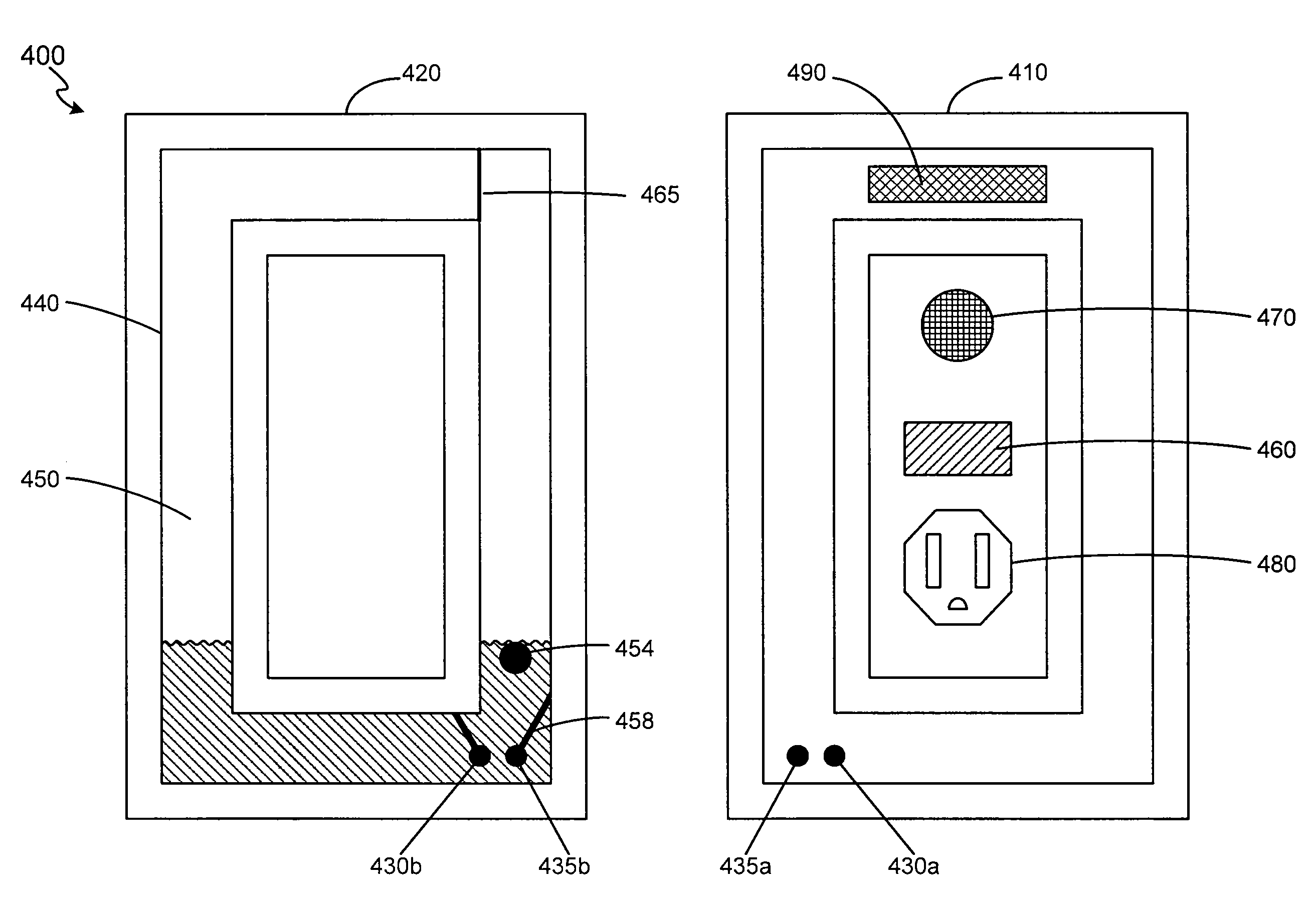
Interactive medication dispensing system
ActiveUS20130002795A1Simplifies refill processMonitor complianceOral administration deviceTwo-way working systemsGraphicsTreatment Schedule
This invention provides a medication dispensing system that instructs the user through visual and audio cues, such as the illumination of individual medication cups that are arrayed in accordance with a daily and weekly schedule in separate orifices within the dispenser body. It monitors compliance by determining when an indicated cup is accessed, based upon at least one of manipulating a lid and / or placing into, removing from, or replacing into the correct orifice based upon the indication. The cups can be refilled based upon an indication, and / or can be provided in removable prefilled refill tray. The dispenser can include an on-board processor that stores a current configuration including the treatment schedule. The configuration can be programmed / re-programmed, and compliance can be monitored, via a wired or wireless server connection that communicates with interested parties, and that supports a graphical user interface. Communication, messaging and / or display systems can also be integrated.
Owner:MEDMINDER SYST
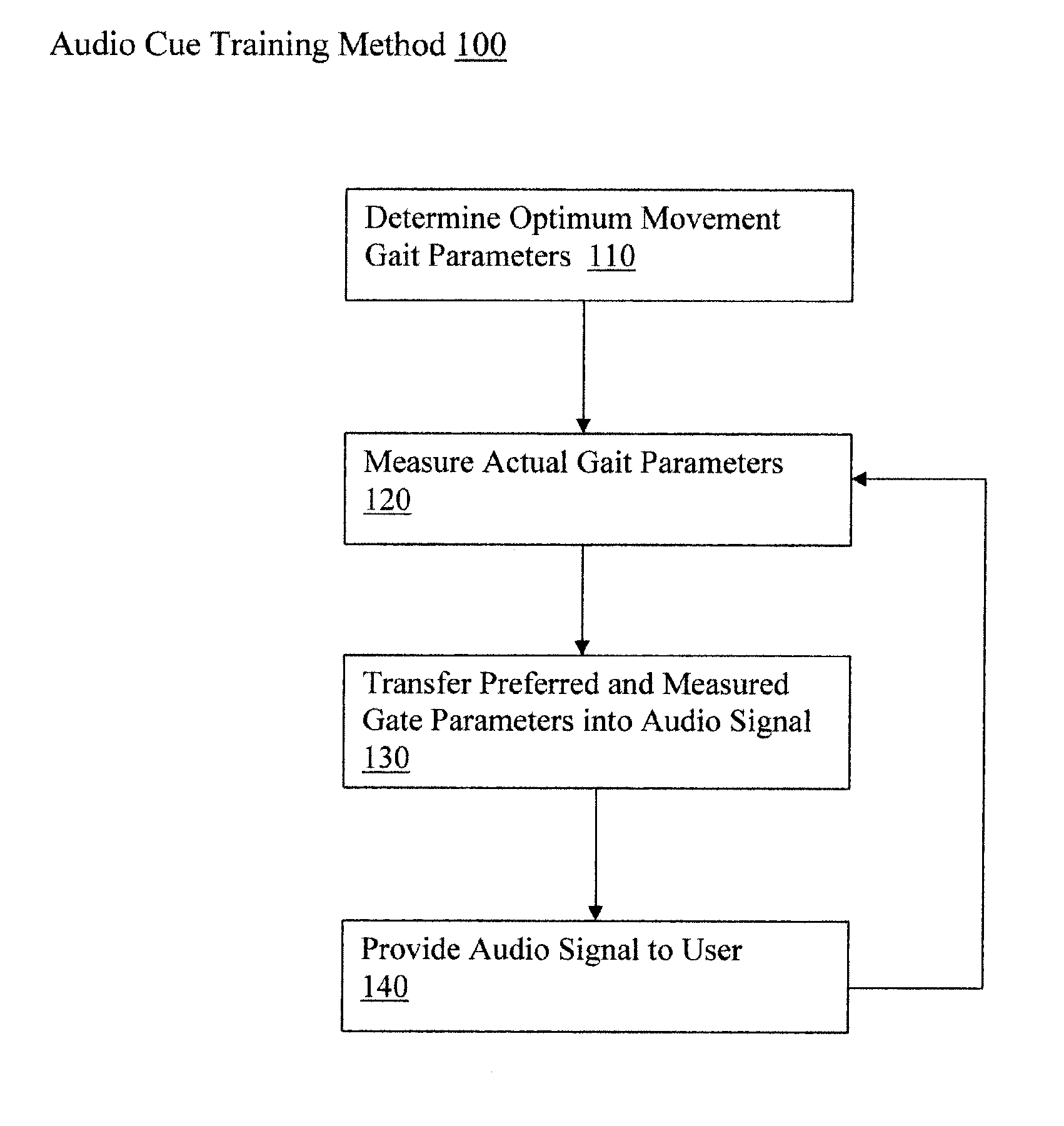
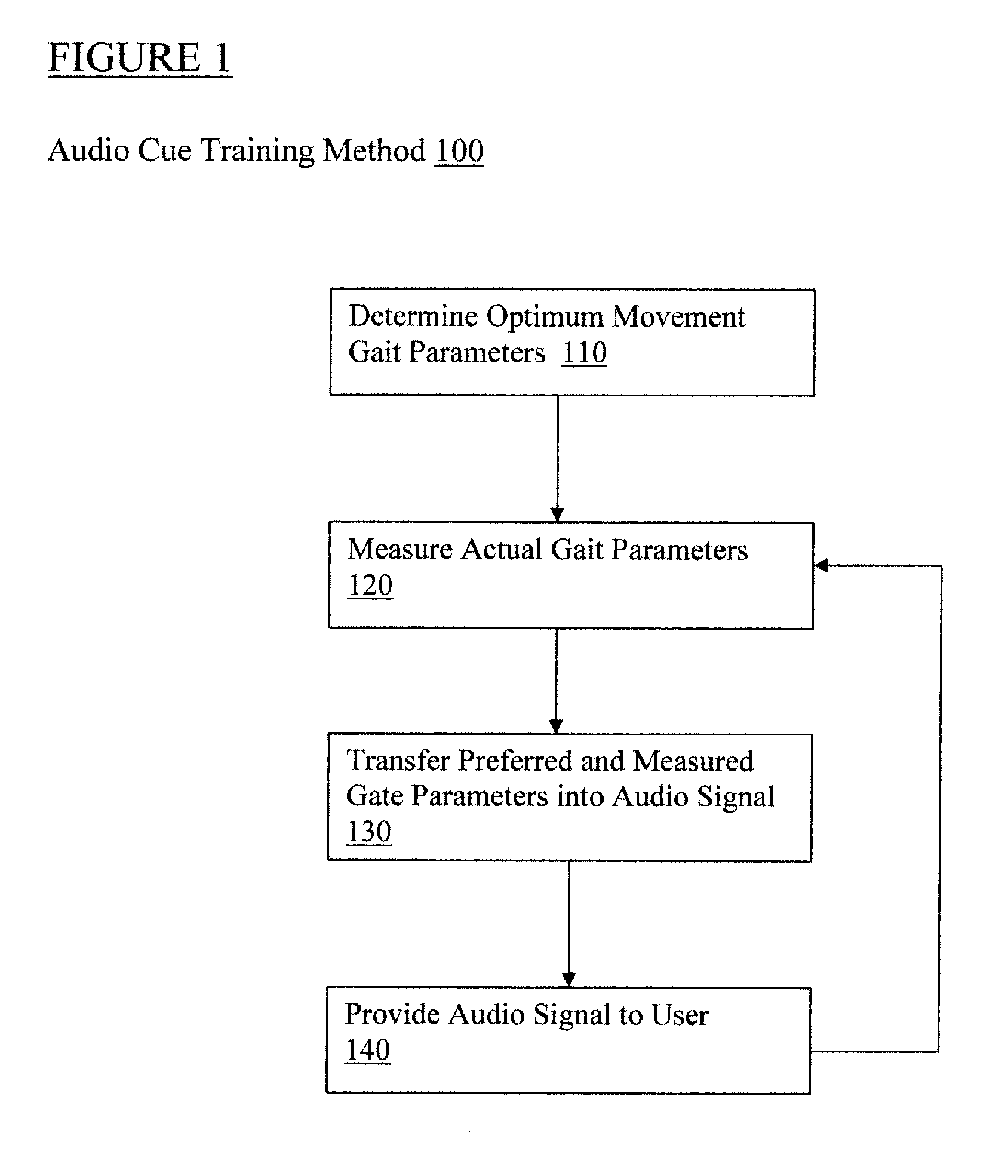
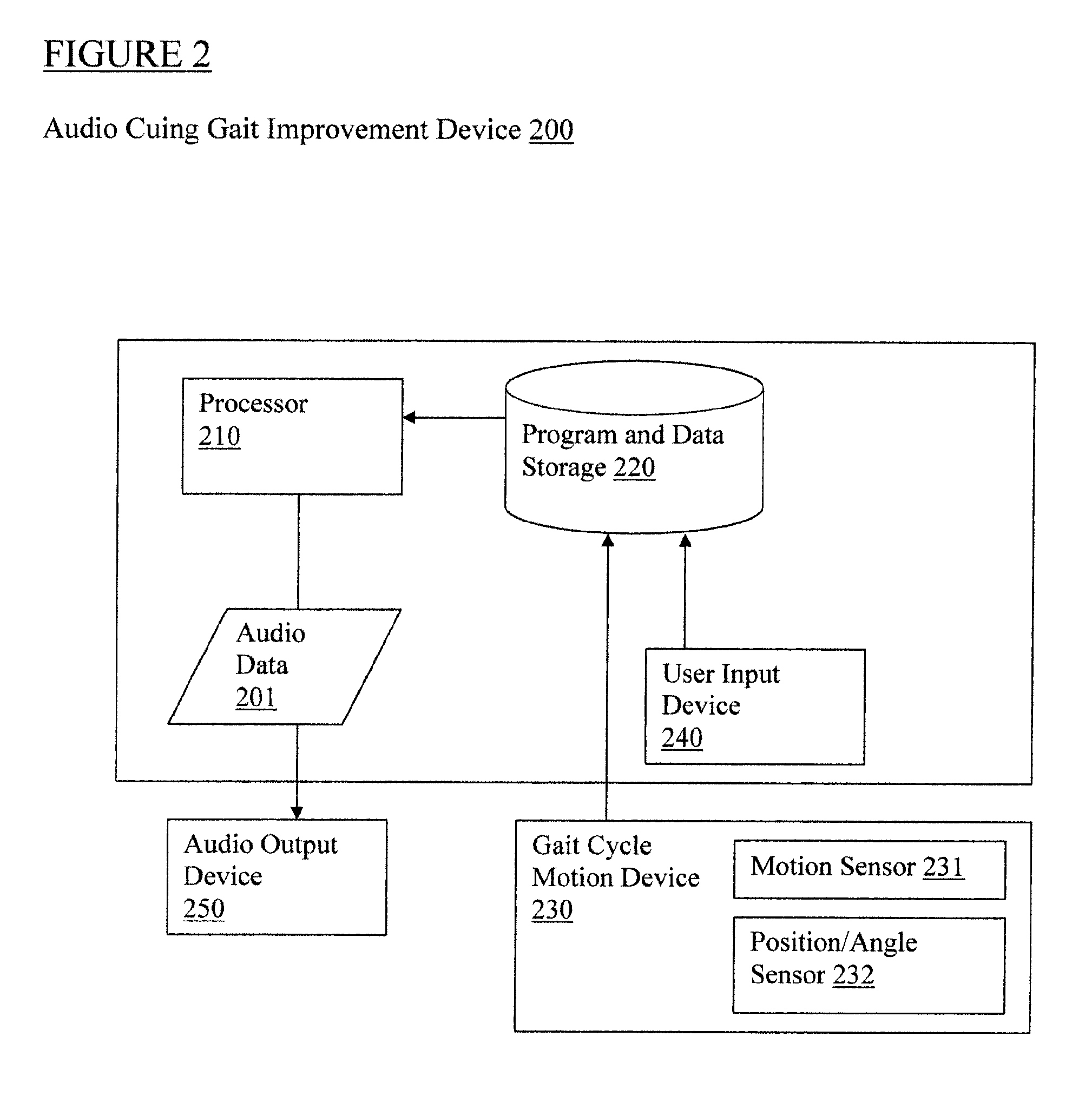
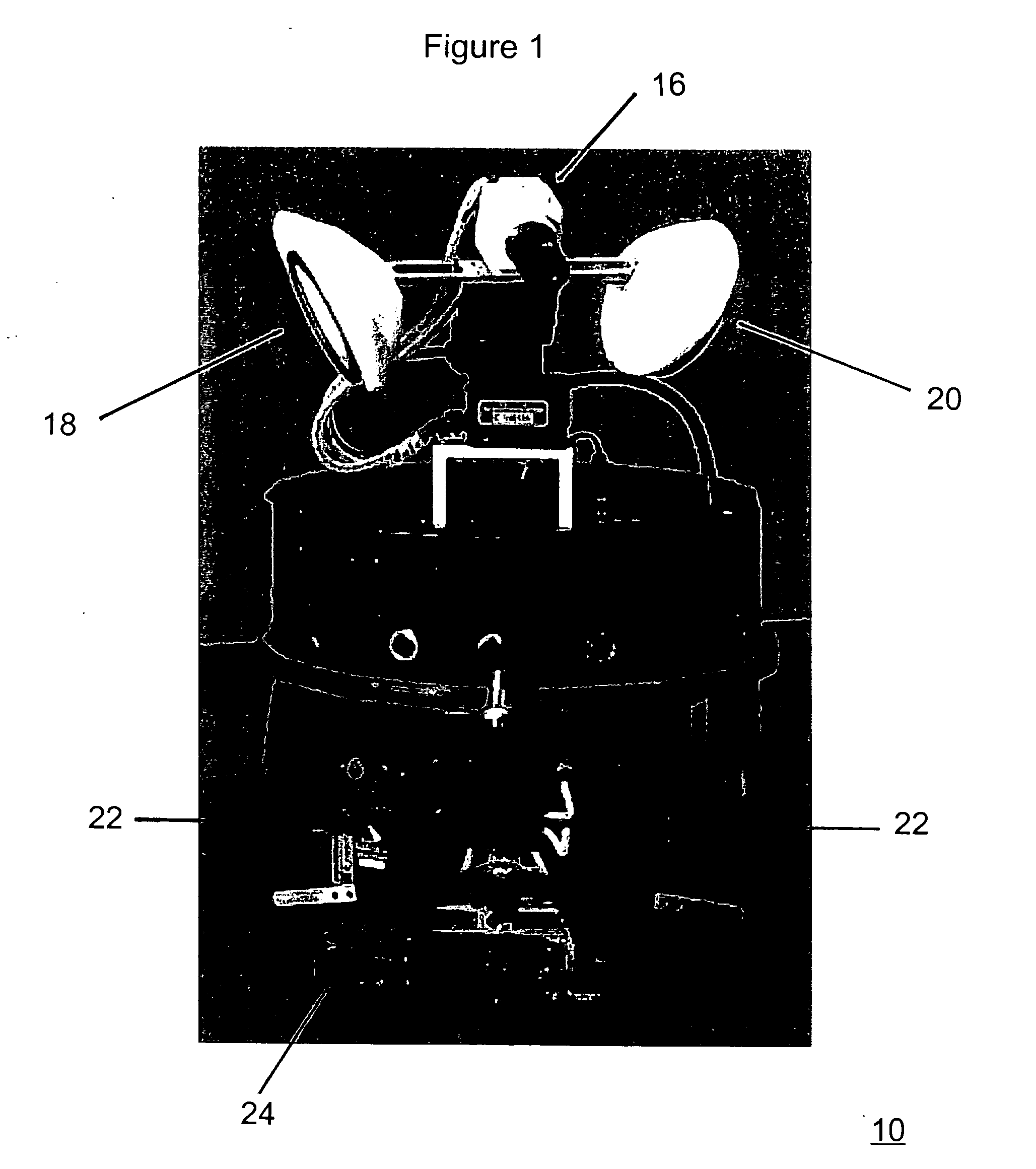
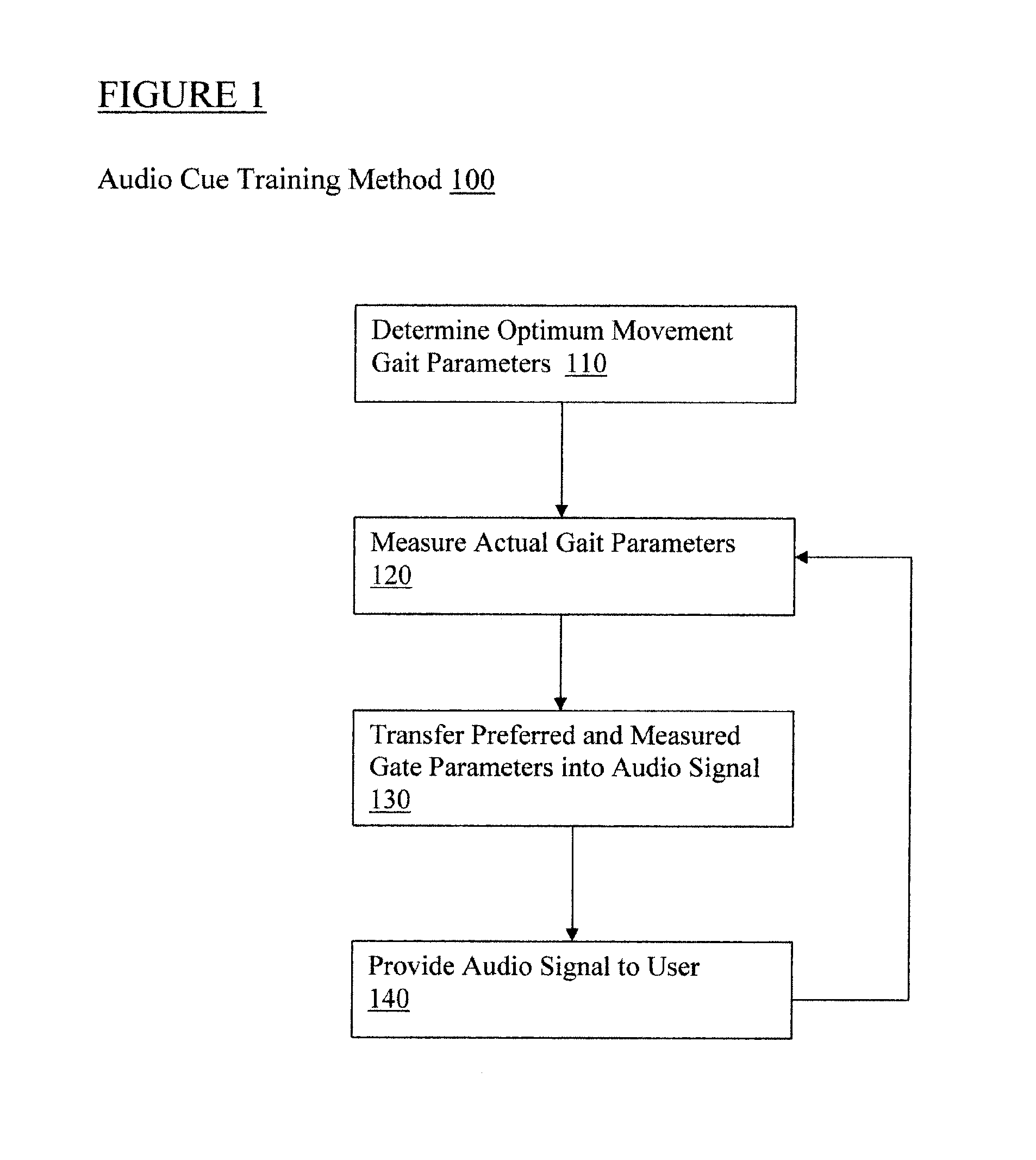
Step trainer for enhanced performance using rhythmic cues
InactiveUS20110184225A1Easy to changeImprove the person's gaitGymnastic exercisingWalking aidsHeadphonesGait
A person's step length and rate may be measured, for example, through sensors that collect spatial and temporal gait parameter data. The measurements are then used to determine the rate of a rhythmic auditory cue to improve the person's gait. For example, a system links sensors to detect step rate and length to an audio cue provided to headphones, while providing the appropriate algorithms to accomplish real time adjustments to the audio cues as needed to better help change the person's step length vs. step rate ratio in a desired direction depending on therapeutic or performance goals.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
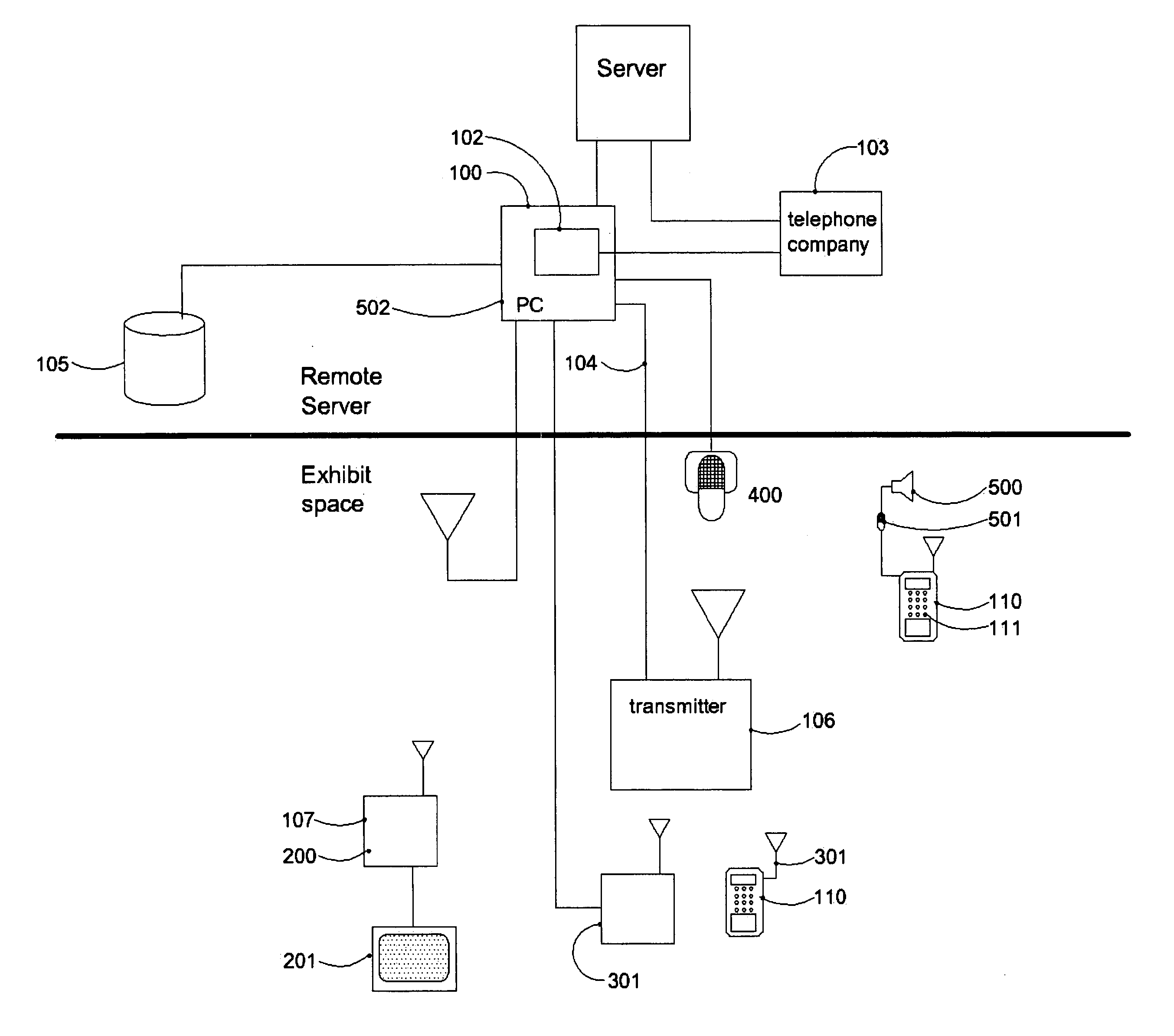
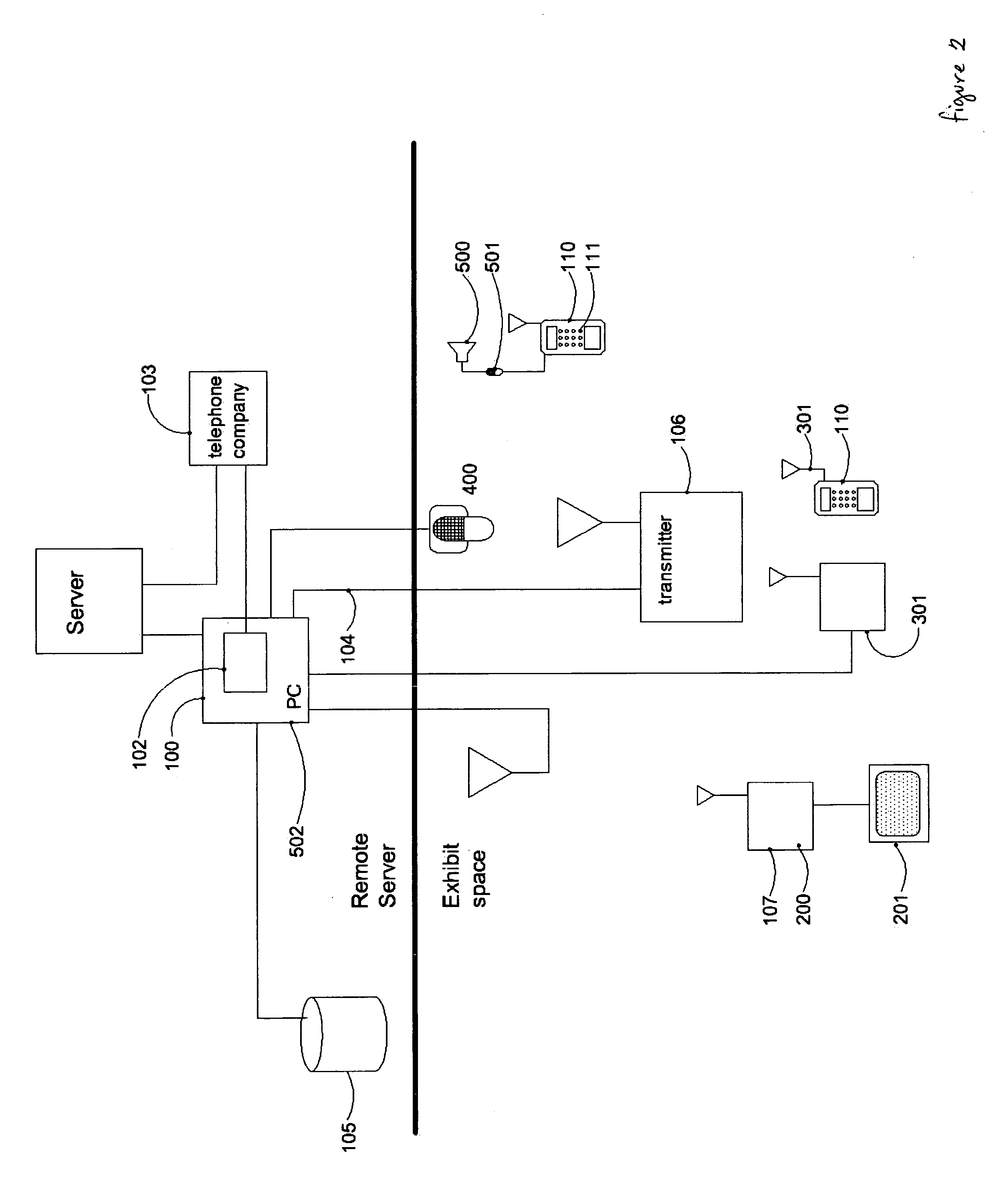
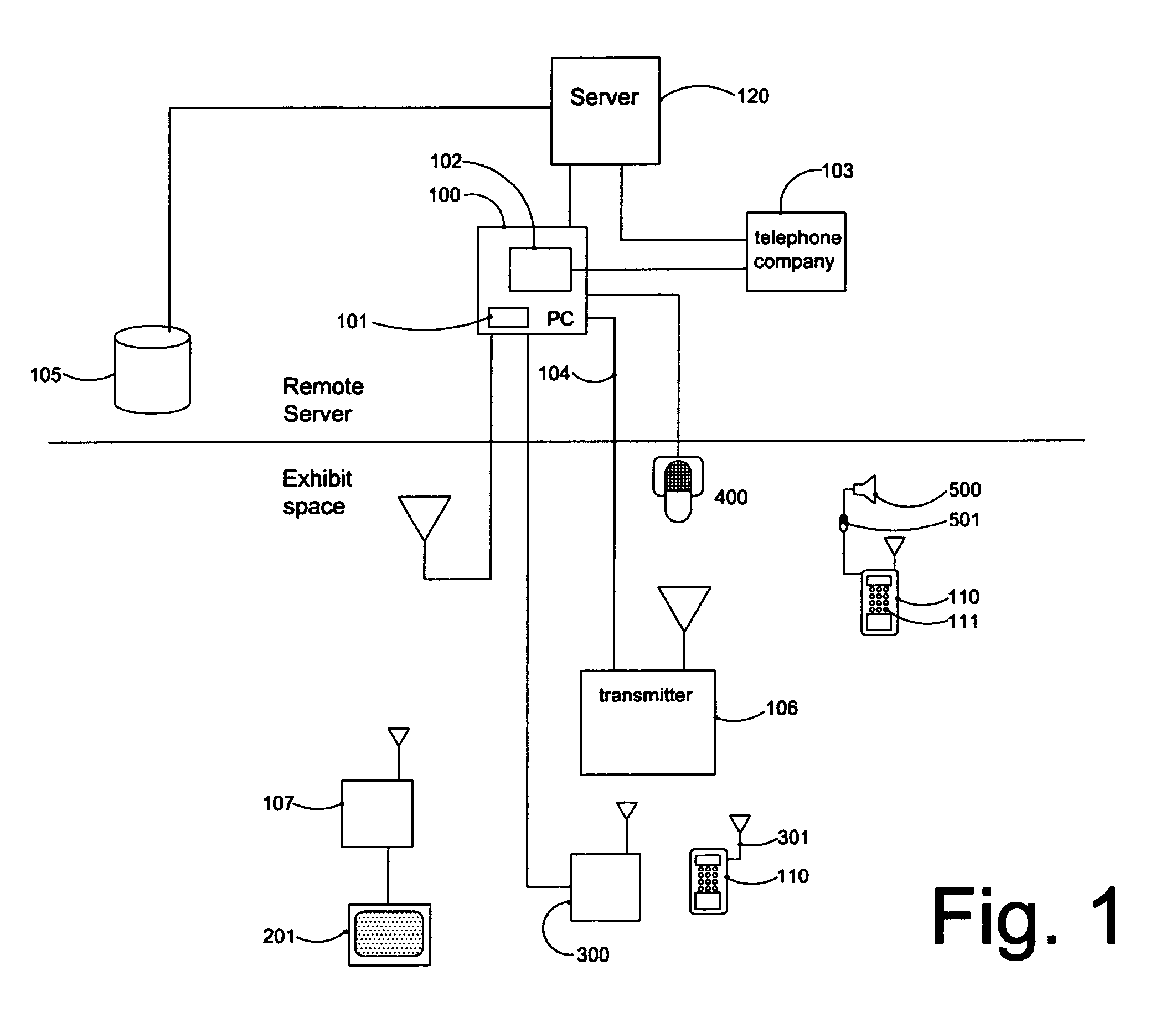
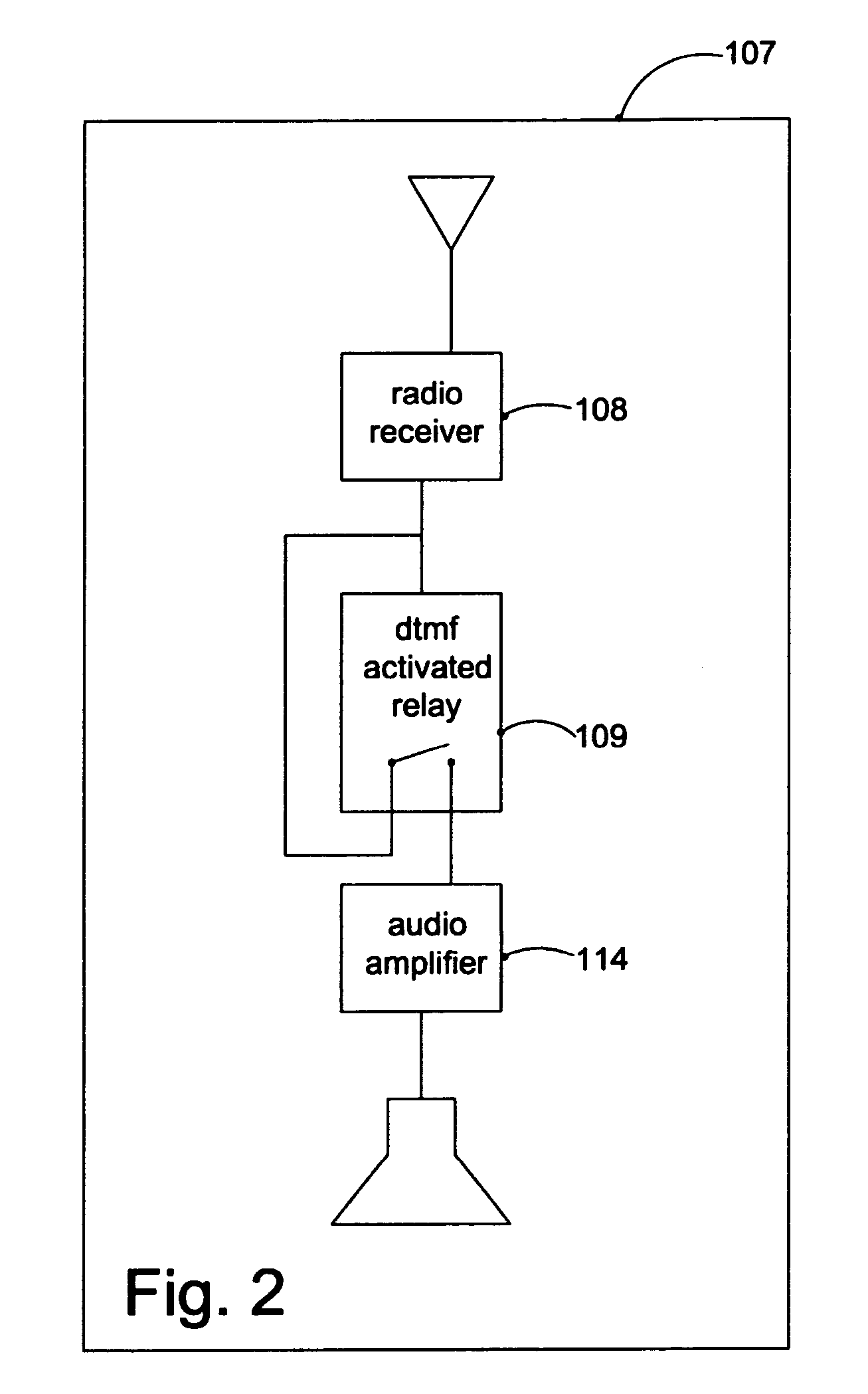
System for guiding visually impaired pedestrian using auditory cues
InactiveUS20050099291A1Beacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesInstruments for road network navigationTransceiverHuman–computer interaction
A system that provides a means for blind or visually impaired people to navigate through a complex environment using auditory cues. Two-way transceiver devices, held by the person, connect through a communications network to a computer system. The computer system activates appropriate auditory signals that are output from audio beacons located throughout the environment based on input provided through the transceiver. Additional interactivity can be incorporated into the system by means of the computer system.
Owner:LANDAU STEVEN
Light-Weight Analyzer For Odor Recognition
The invention provides a light weight analyzer, e.g., detector, capable of locating clandestine graves. The detector utilizes the very specific and unique chemicals identified in the database of human decompositional odor. This detector, based on specific chemical compounds found relevant to human decomposition, is the next step forward in clandestine grave detection and will take the guess-work out of current methods using canines and ground-penetrating radar, which have historically been unreliable. The detector is self contained, portable and built for field use. Both visual and auditory cues are provided to the operator.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
System for guiding visually impaired pedestrian using auditory cues
InactiveUS7039522B2Beacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesInstruments for road network navigationTransceiverComputerized system
A system that provides a means for blind or visually impaired people to navigate through a complex environment using auditory cues. Two-way transceiver devices, held by the person, connect through a communications network to a computer system. The computer system activates appropriate auditory signals that are output from audio beacons located throughout the environment based on input provided through the transceiver. Additional interactivity can be incorporated into the system by means of the computer system.
Owner:LANDAU STEVEN
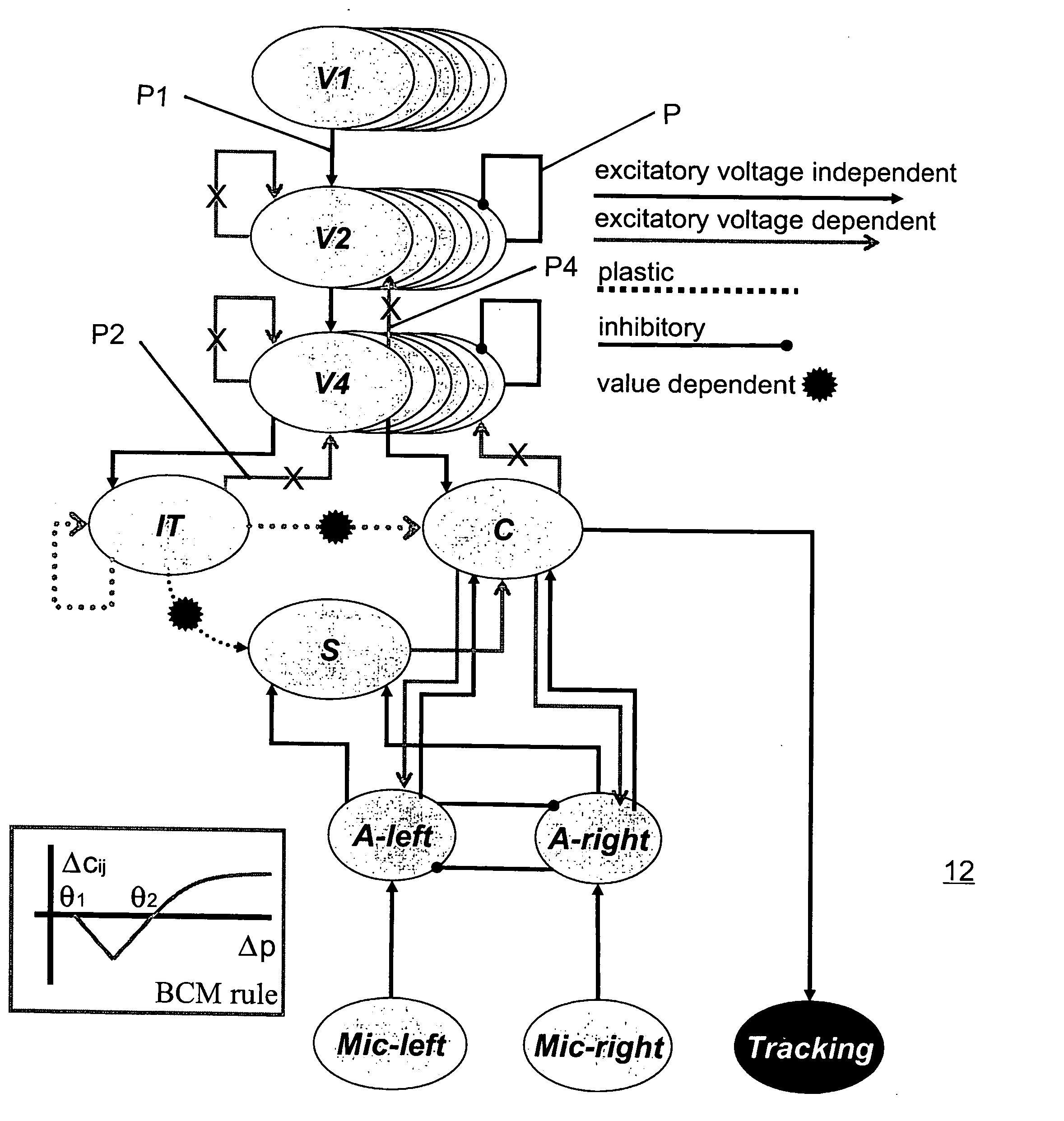
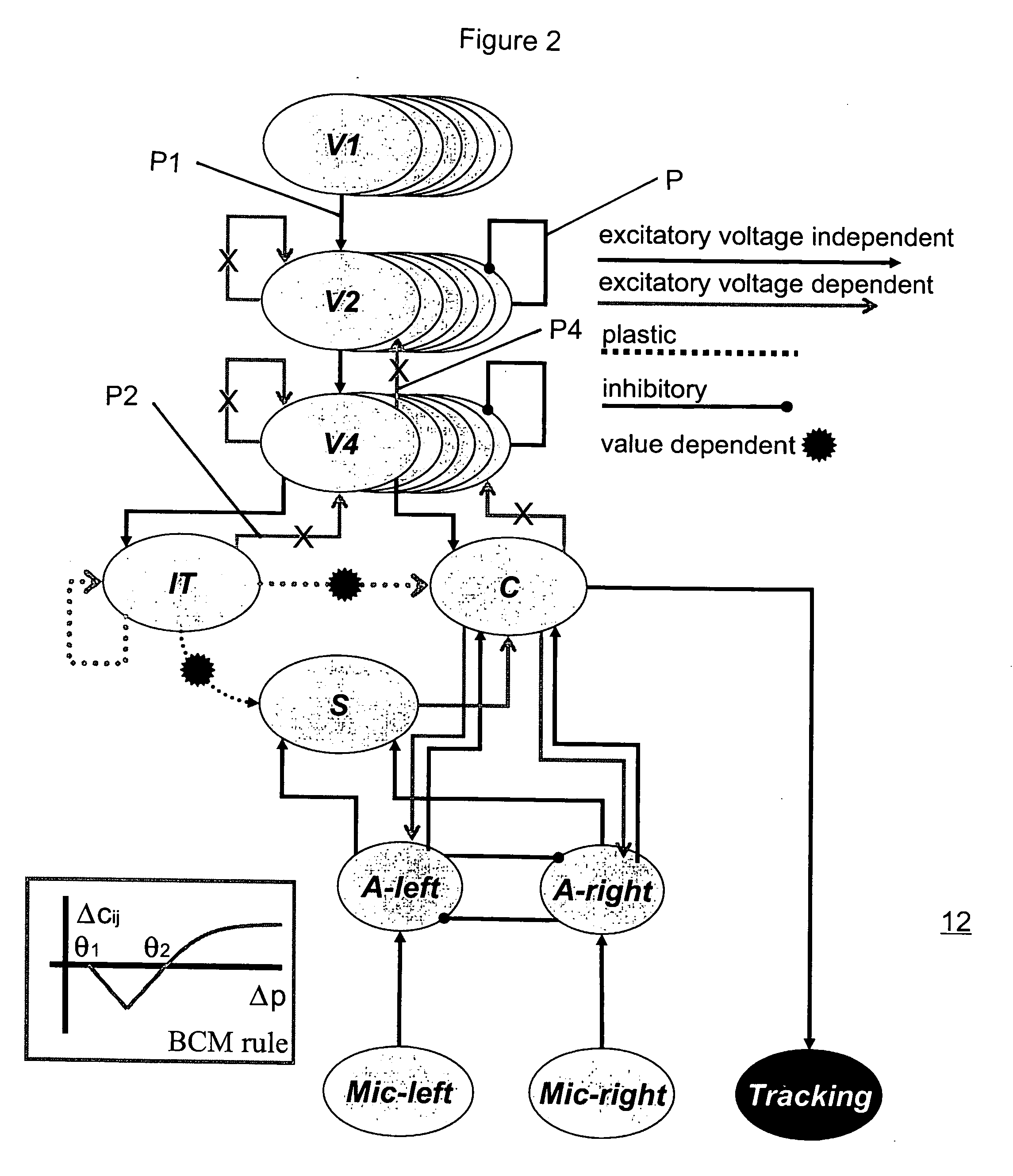
Mobile brain-based device for use in a real world environment
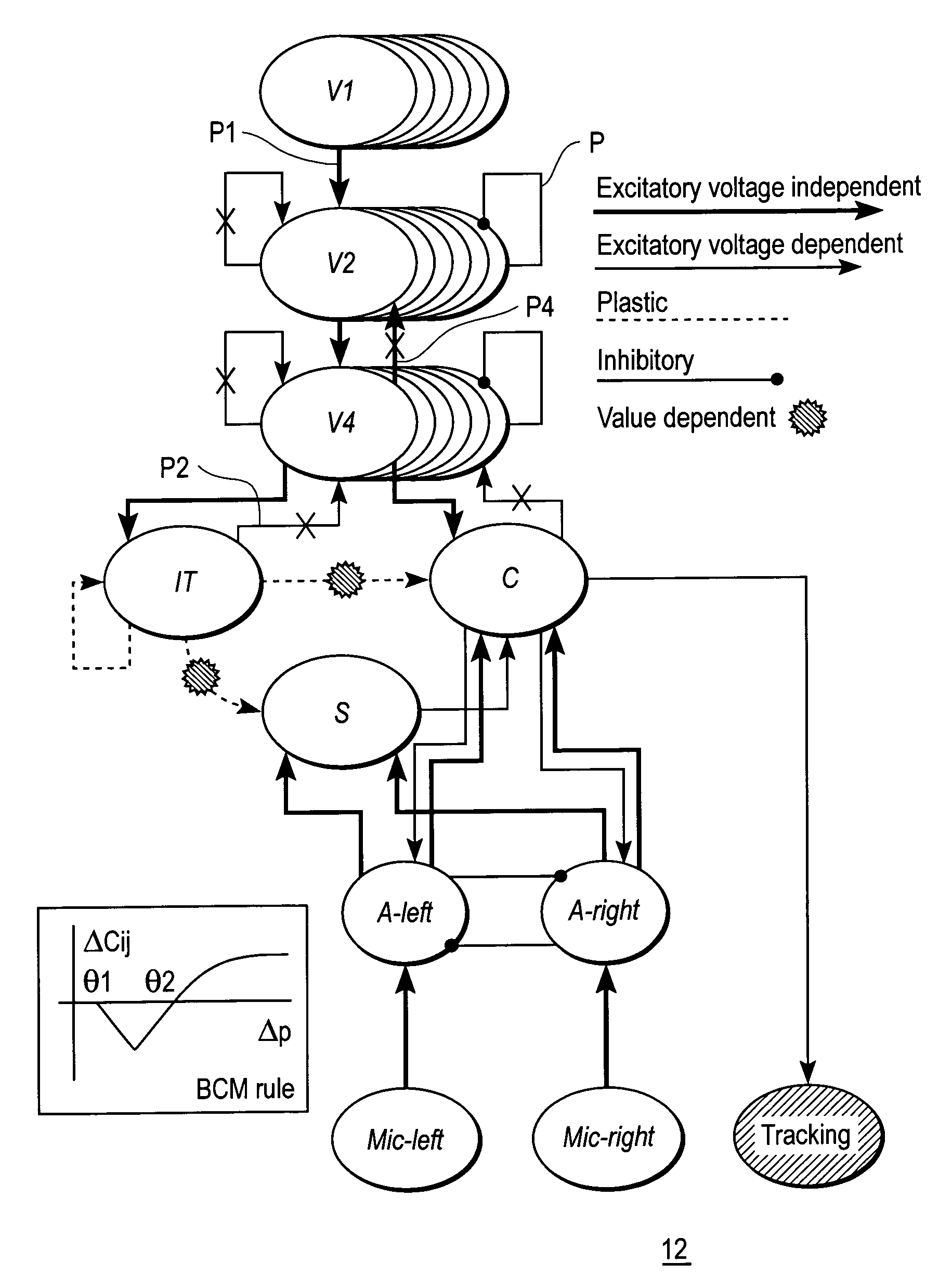
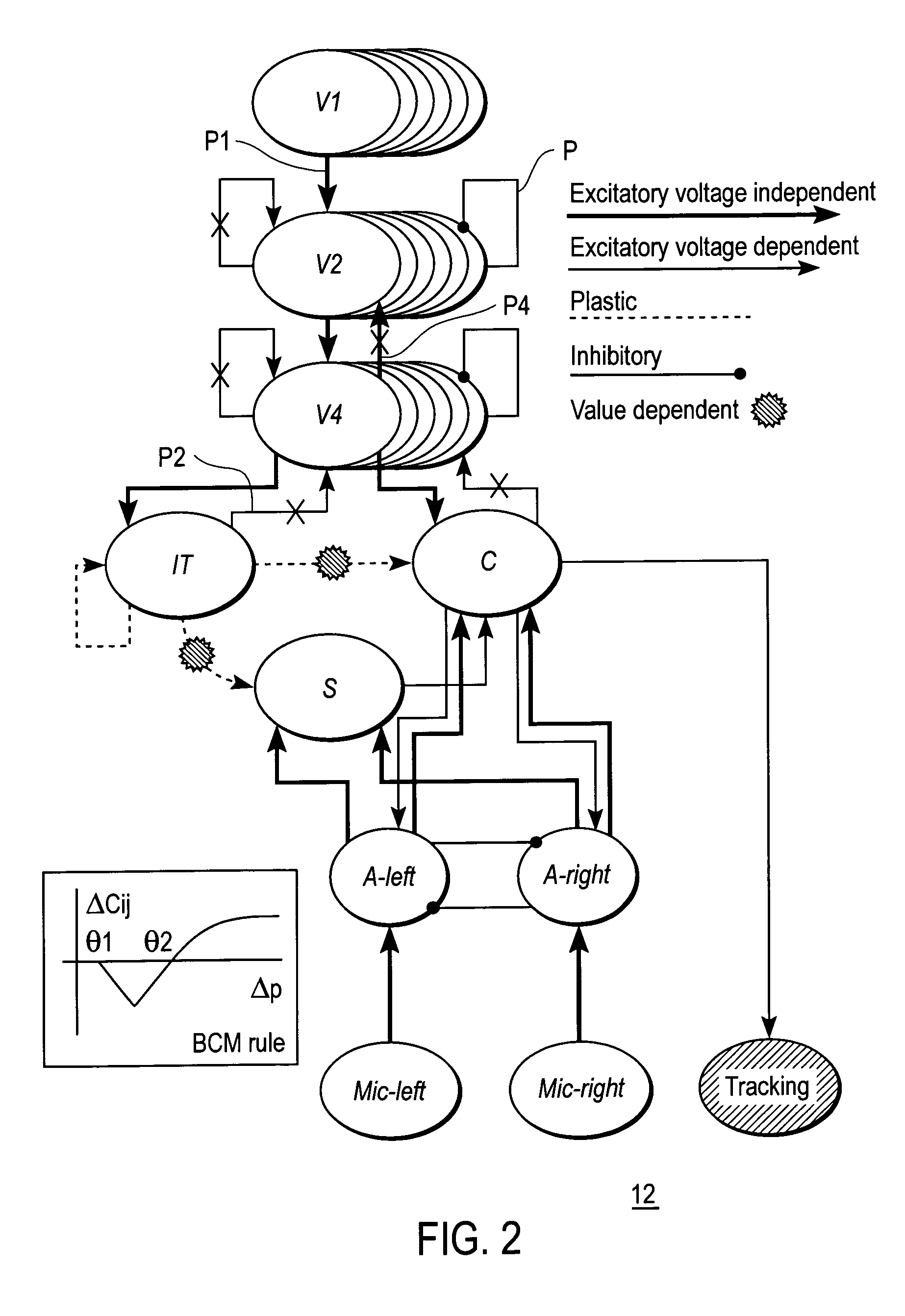
InactiveUS20050261803A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionNervous systemVisual Objects
A mobile brain-based device BBD includes a mobile base equipped with sensors and effectors (Neurally Organized Mobile Adaptive Device or NOMAD), which is guided by a simulated nervous system that is an analogue of cortical and sub-cortical areas of the brain required for visual processing, decision-making, reward, and motor responses. These simulated cortical and sub-cortical areas are reentrantly connected and each area contains neuronal units representing both the mean activity level and the relative timing of the activity of groups of neurons. The brain-based device BBD learns to discriminate among multiple objects with shared visual features, and associated “target” objects with innately preferred auditory cues. Globally distributed neuronal circuits that correspond to distinct objects in the visual field of NOMAD 10 are activated. These circuits, which are constrained by a reentrant neuroanatomy and modulated by behavior and synaptic plasticity, result in successful discrimination of objects. The brain-based device BBD is moveable, in a rich real-world environment involving continual changes in the size and location of visual stimuli due to self-generated or autonomous, movement, and shows that reentrant connectivity and dynamic synchronization provide an effective mechanism for binding the features of visual objects so as to reorganize object features such as color, shape and motion while distinguishing distinct objects in the environment.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
Step trainer for enhanced performance using rhythmic cues
InactiveUS8845494B2Improve the person's gaitEasy to changePerson identificationWalking aidsHeadphonesGait
A person's step length and rate may be measured, for example, through sensors that collect spatial and temporal gait parameter data. The measurements are then used to determine the rate of a rhythmic auditory cue to improve the person's gait. For example, a system links sensors to detect step rate and length to an audio cue provided to headphones, while providing the appropriate algorithms to accomplish real time adjustments to the audio cues as needed to better help change the person's step length vs. step rate ratio in a desired direction depending on therapeutic or performance goals.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
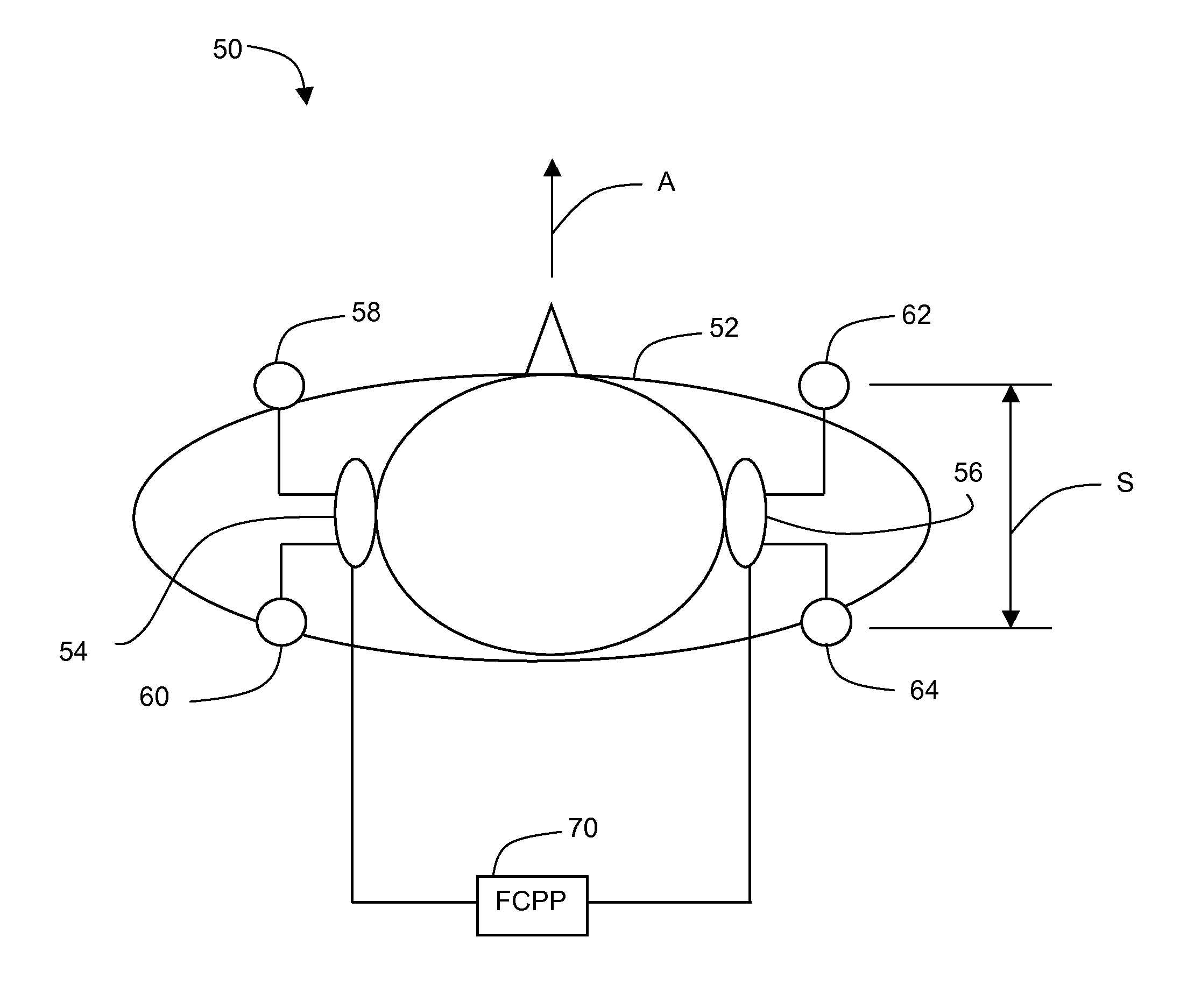
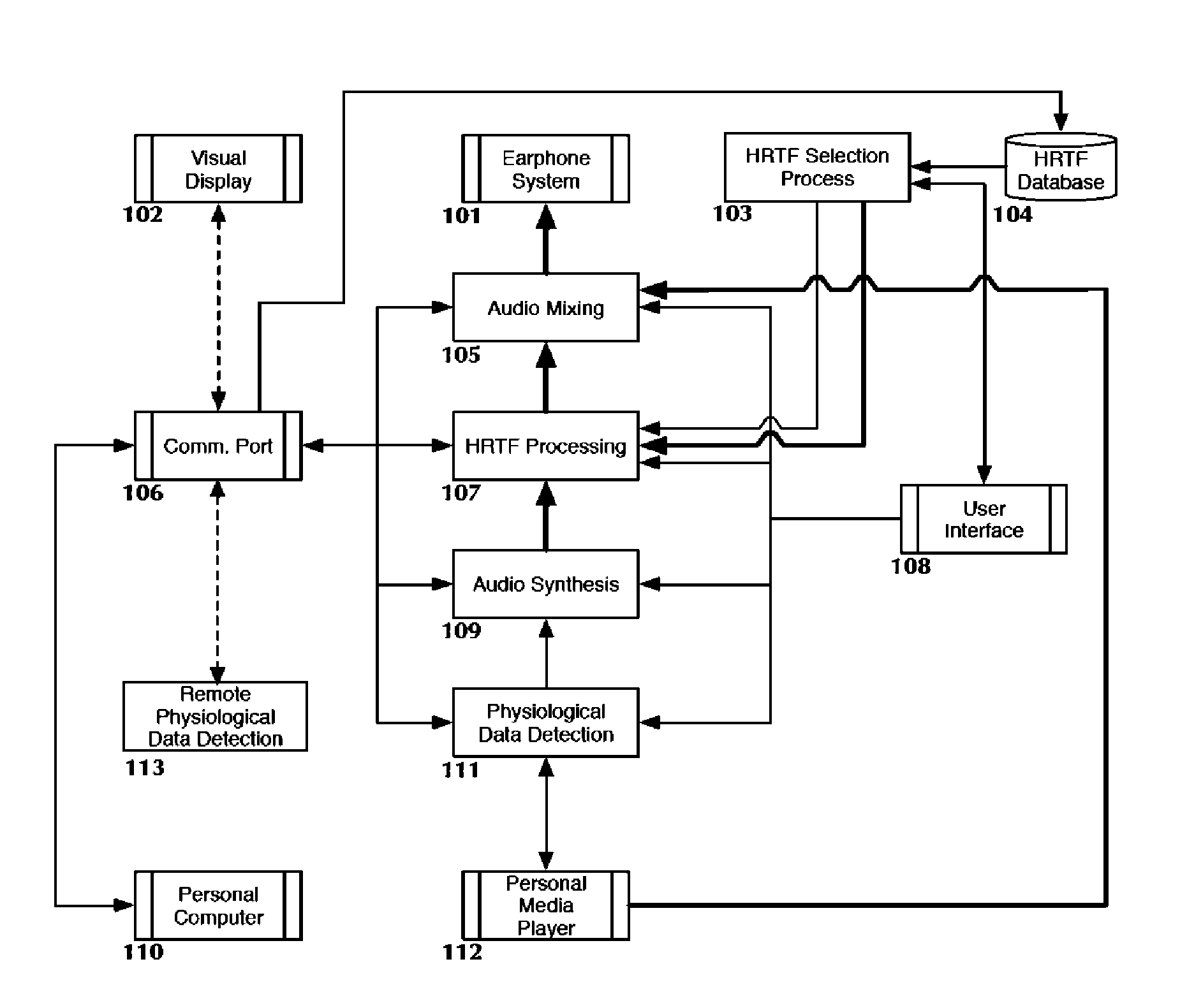
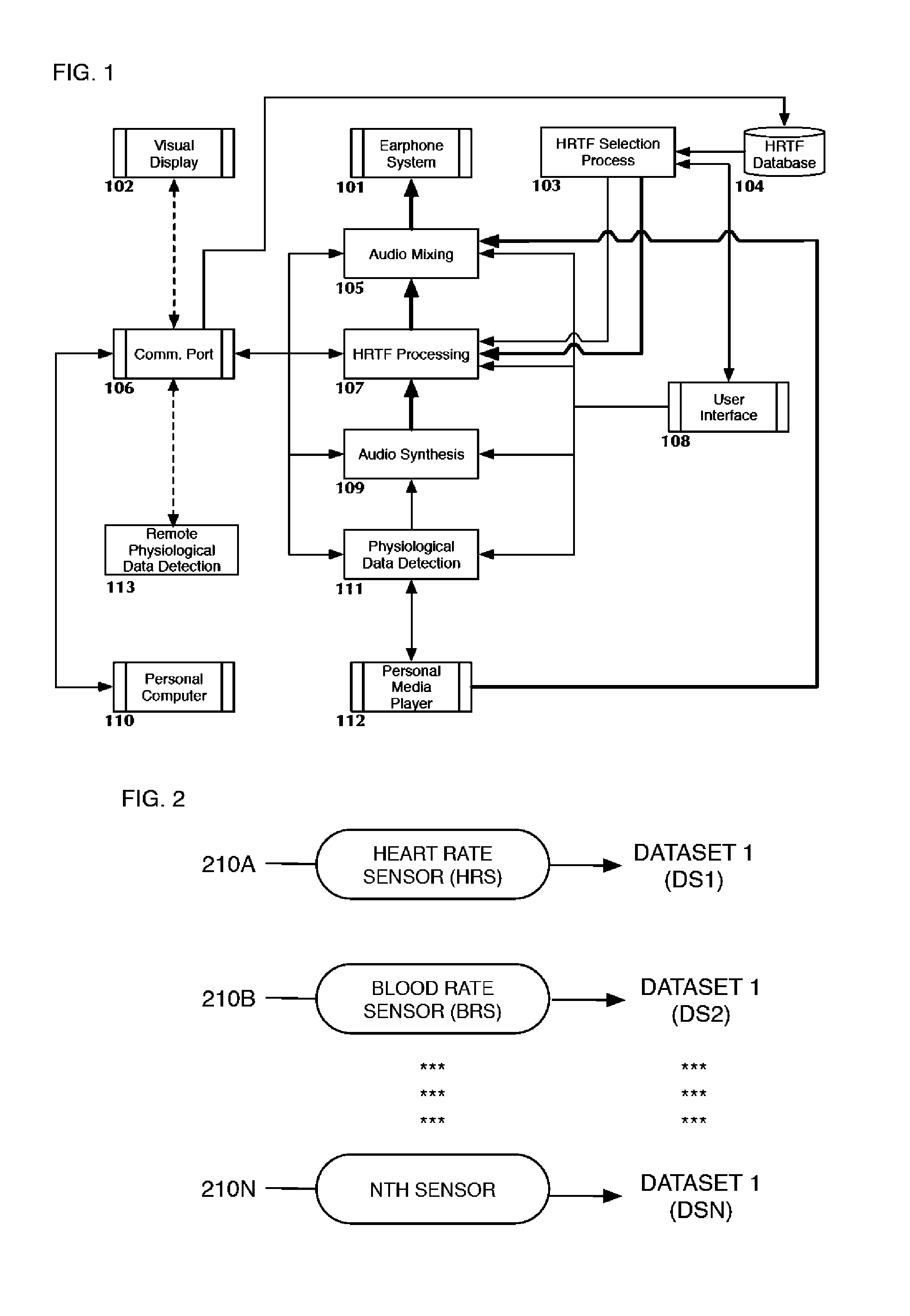
Apparatus, systems and methods for binaural hearing enhancement in auditory processing systems
InactiveUS20100183158A1Reduce rearward directional interferenceEliminate distractionsDeaf-aid setsStereophonic arrangmentsTarget signalComputer science
According to one aspect, a system for binaural hearing enhancement, including at least one auditory receiver and at least one processor coupled to the at least one auditory receiver. The at least one auditory receiver is configured to receive an auditory signal that includes a target signal. The at least one processor configured to extract a plurality of auditory cues from the auditory signal, prioritize at least one of the plurality of auditory cues based on the robustness of the auditory cues, and based on the prioritized auditory cues, extract the target signal from the auditory signal.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
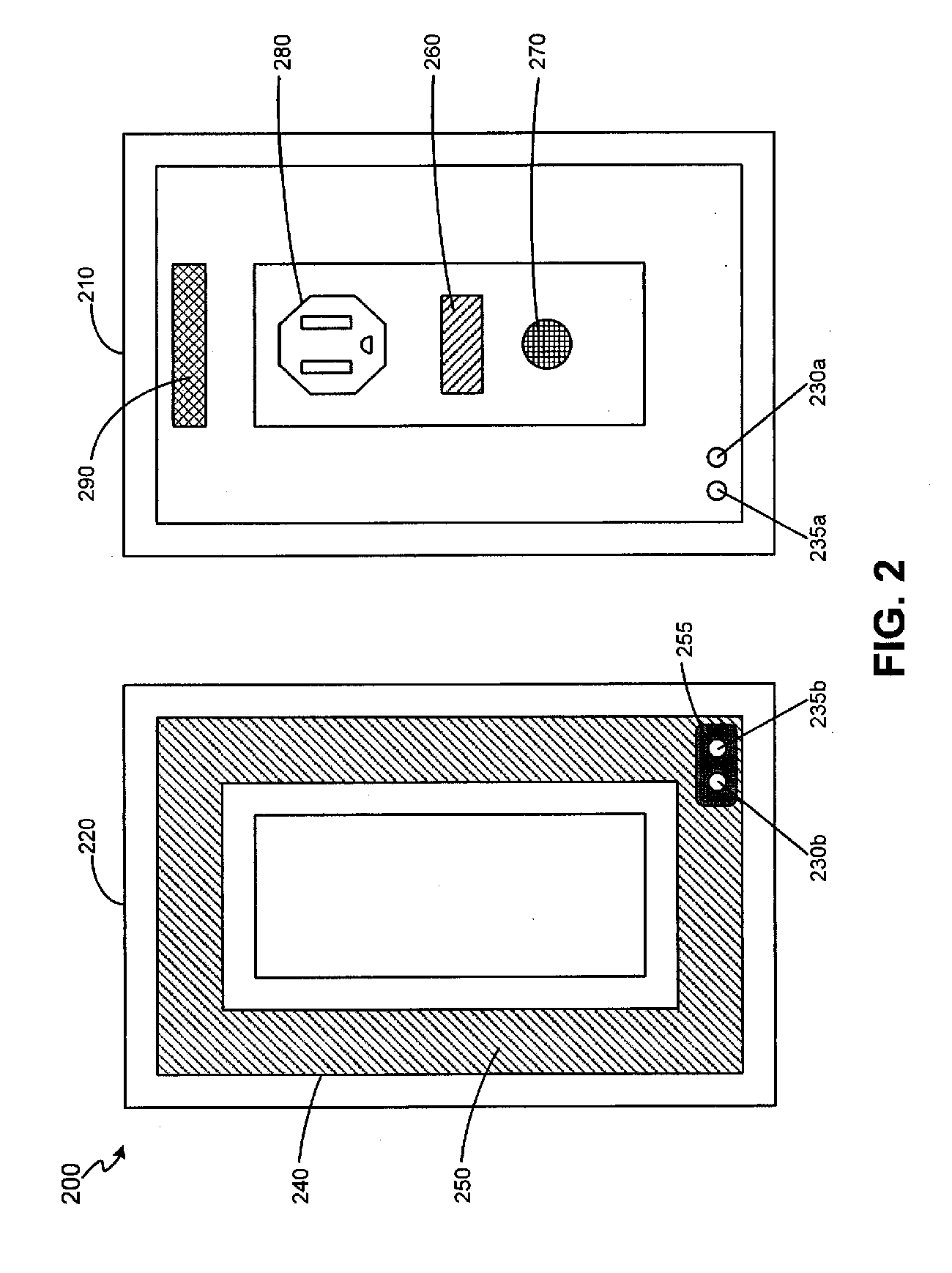
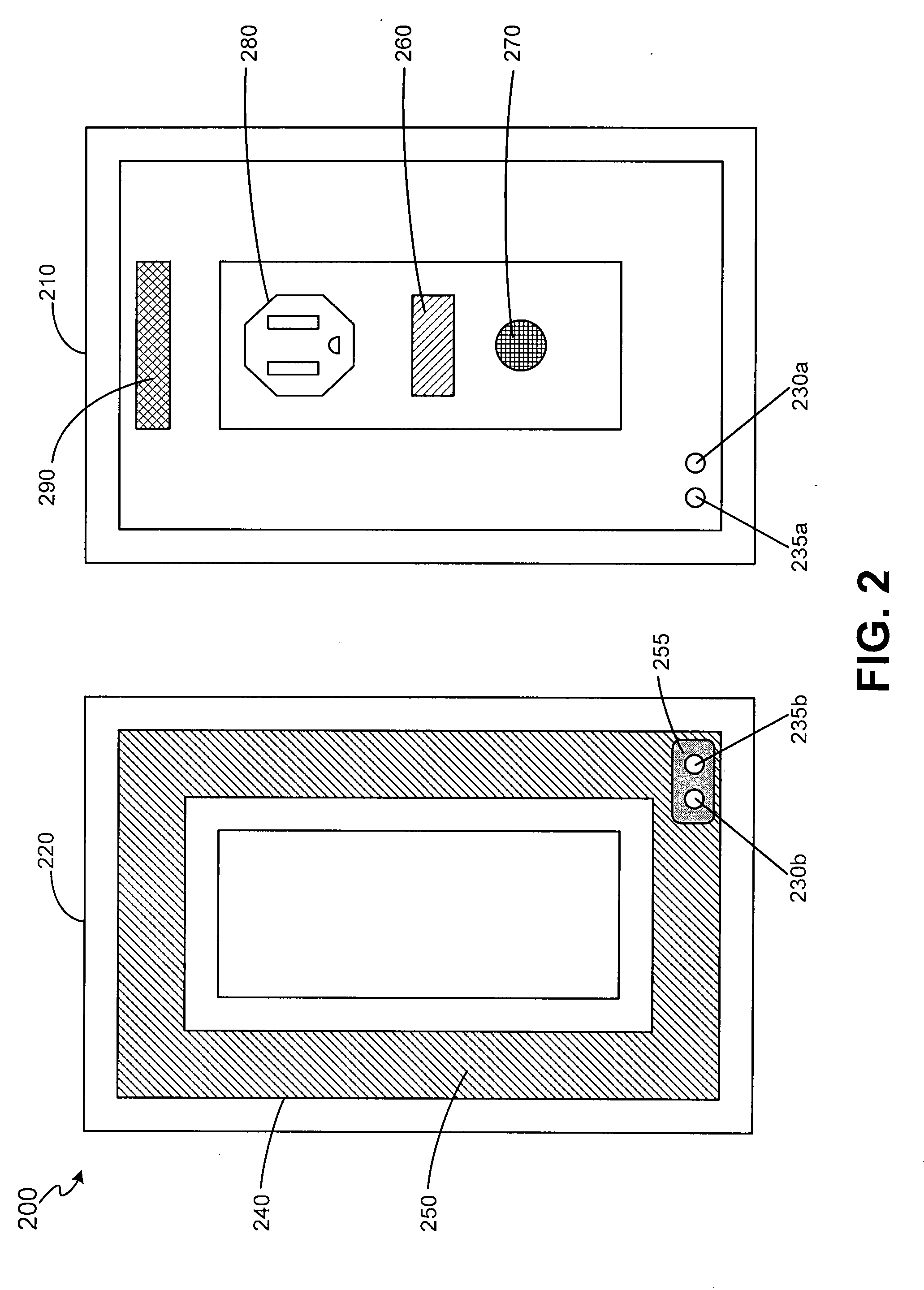
Interactive medication dispensing system
ActiveUS9211233B2Monitor complianceSimple processSignalling system detailsOral administration deviceTreatment ScheduleGraphical user interface
This invention provides a medication dispensing system that instructs the user through visual and audio cues, such as the illumination of individual medication cups that are arrayed in accordance with a daily and weekly schedule in separate orifices within the dispenser body. It monitors compliance by determining when an indicated cup is accessed, based upon at least one of manipulating a lid and / or placing into, removing from, or replacing into the correct orifice based upon the indication. The cups can be refilled based upon an indication, and / or can be provided in removable prefilled refill tray. The dispenser can include an on-board processor that stores a current configuration including the treatment schedule. The configuration can be programmed / re-programmed, and compliance can be monitored, via a wired or wireless server connection that communicates with interested parties, and that supports a graphical user interface. Communication, messaging and / or display systems can also be integrated.
Owner:MEDMINDER SYST
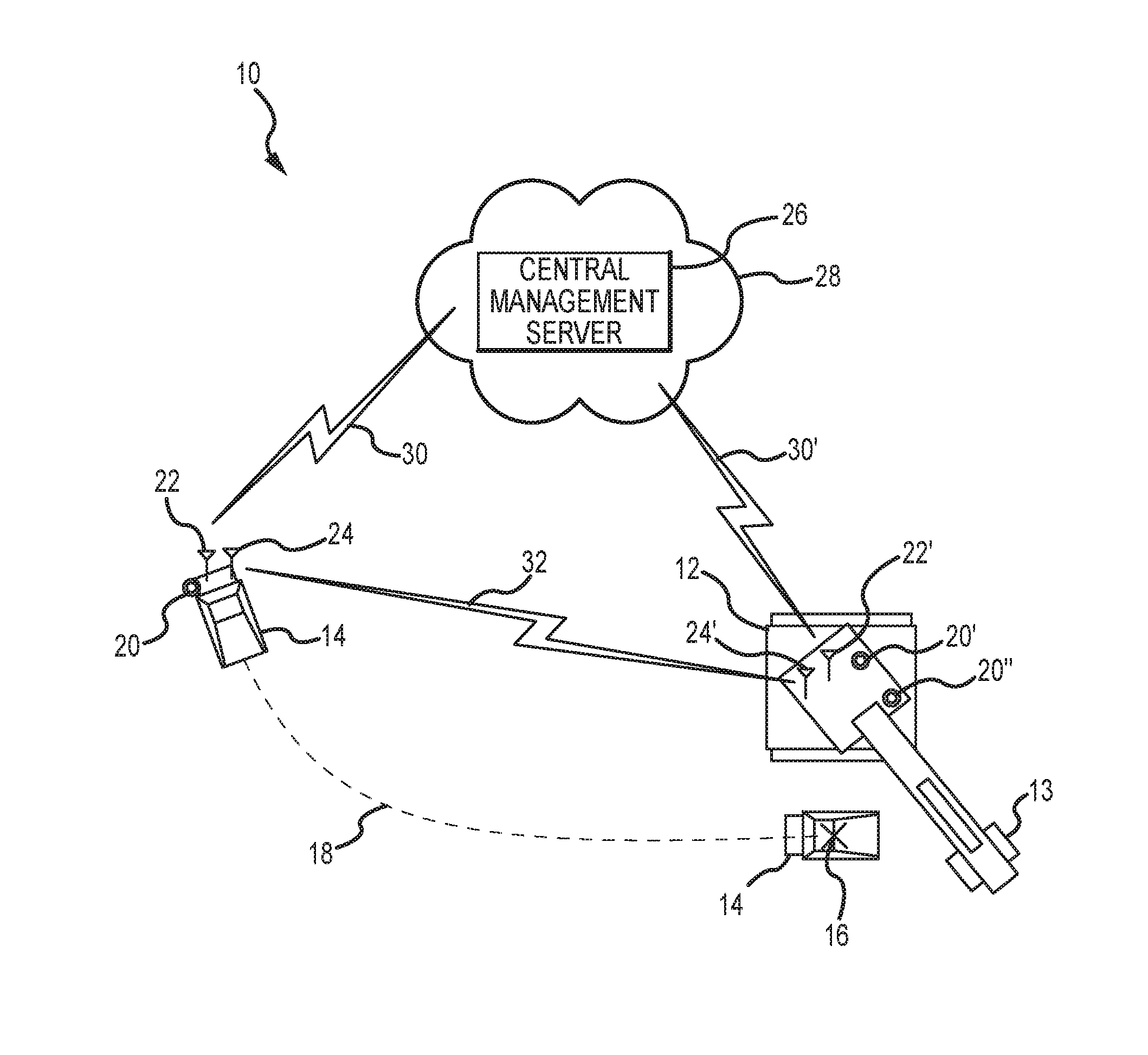
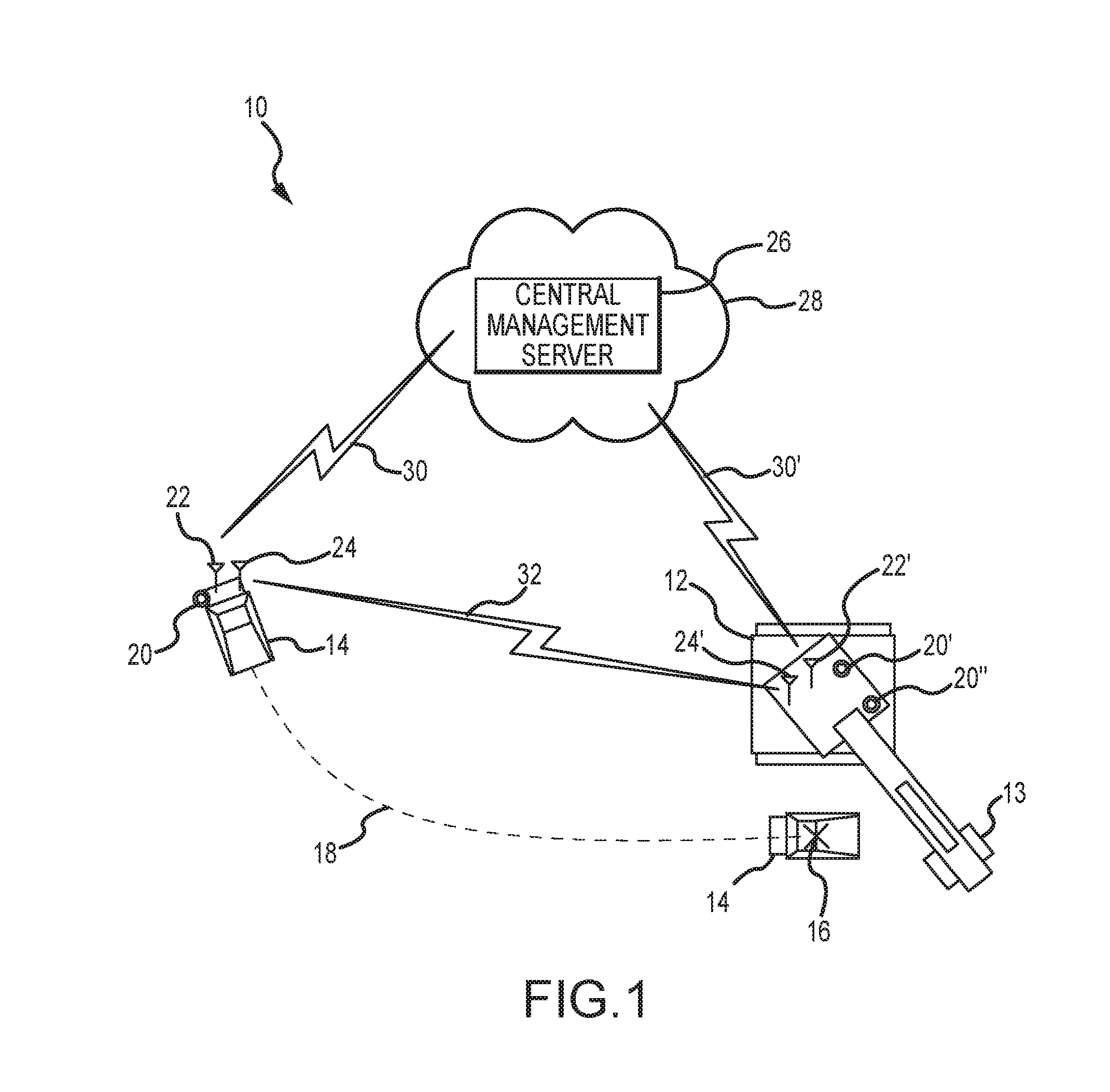
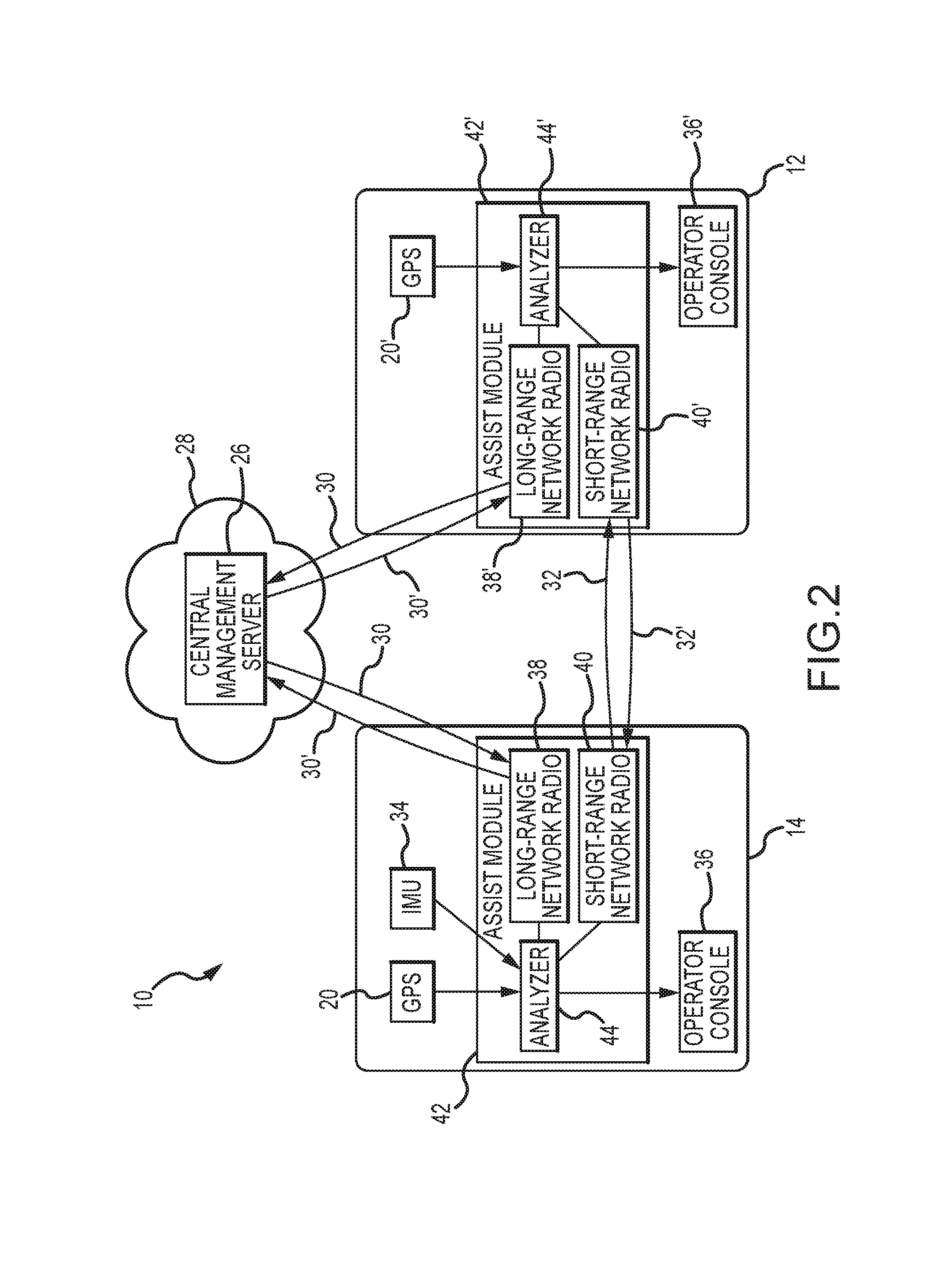
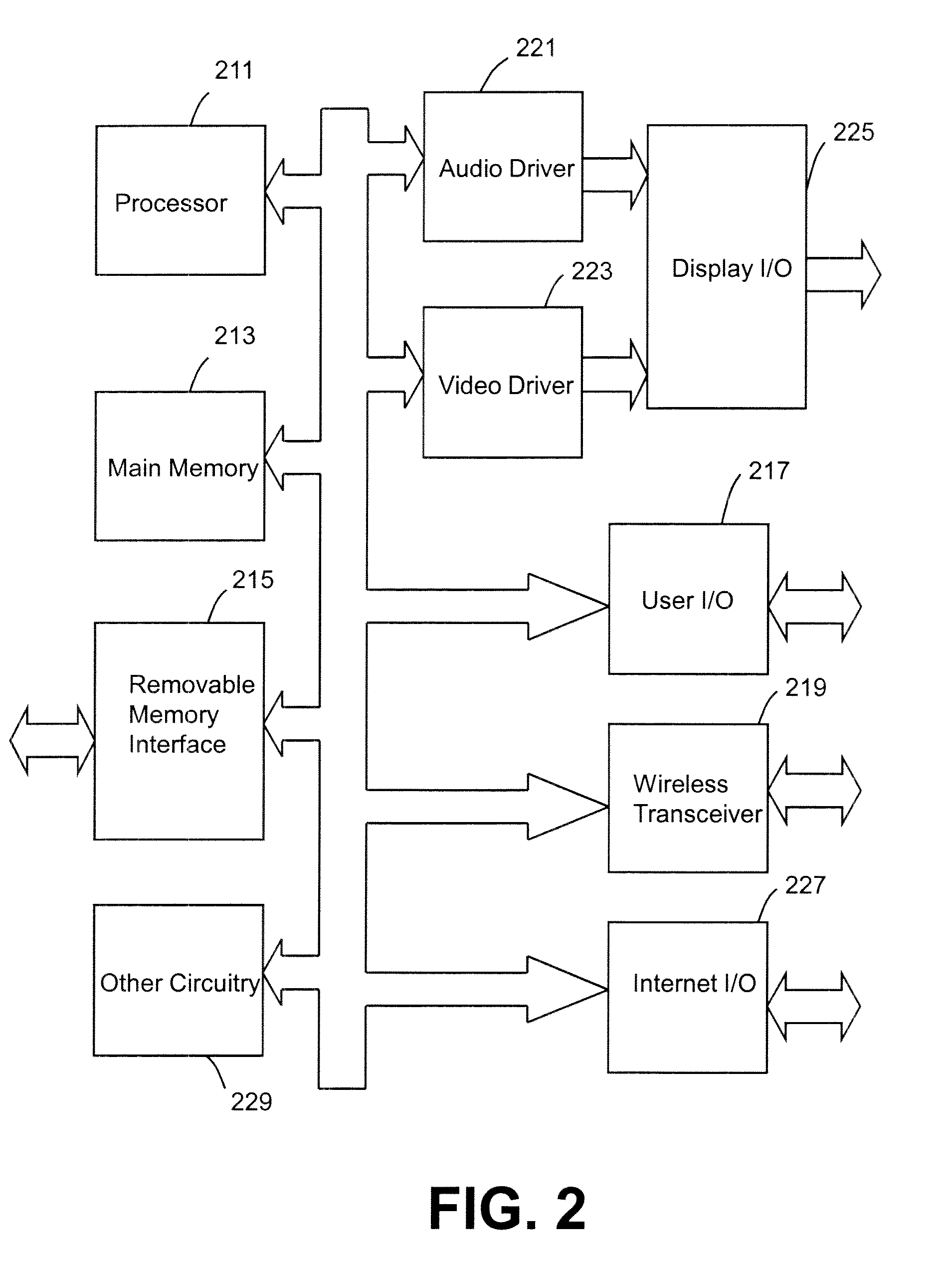
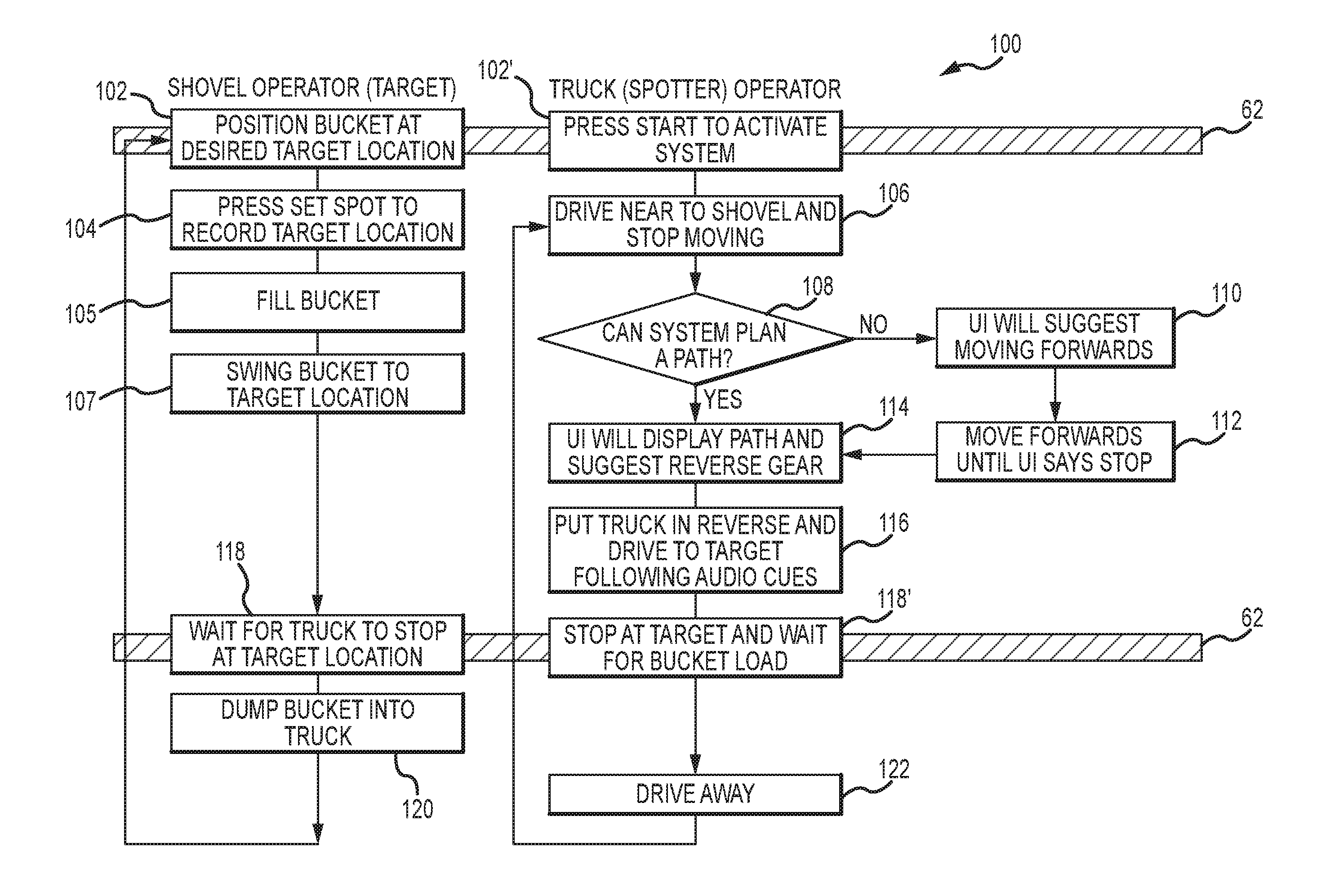
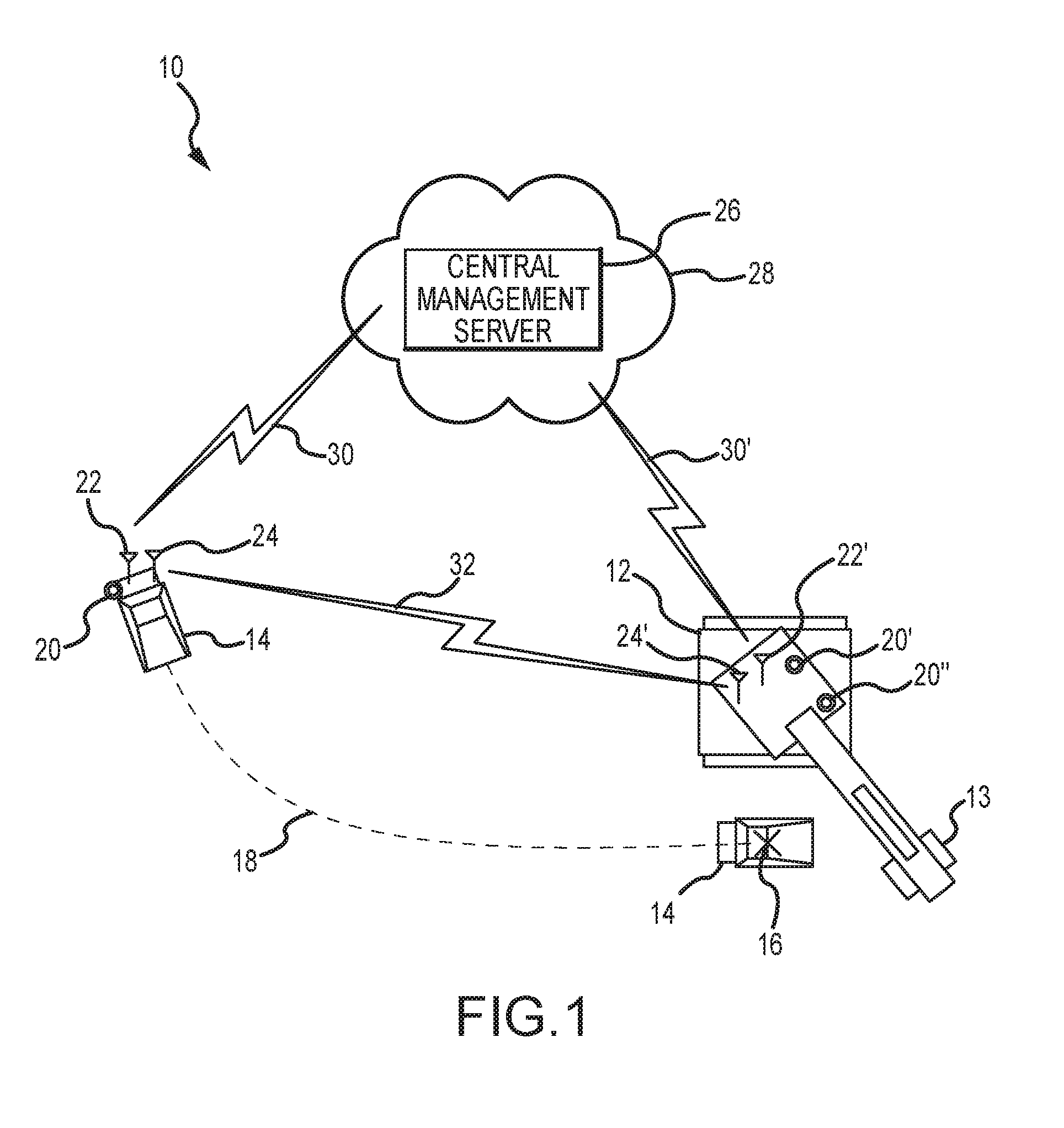
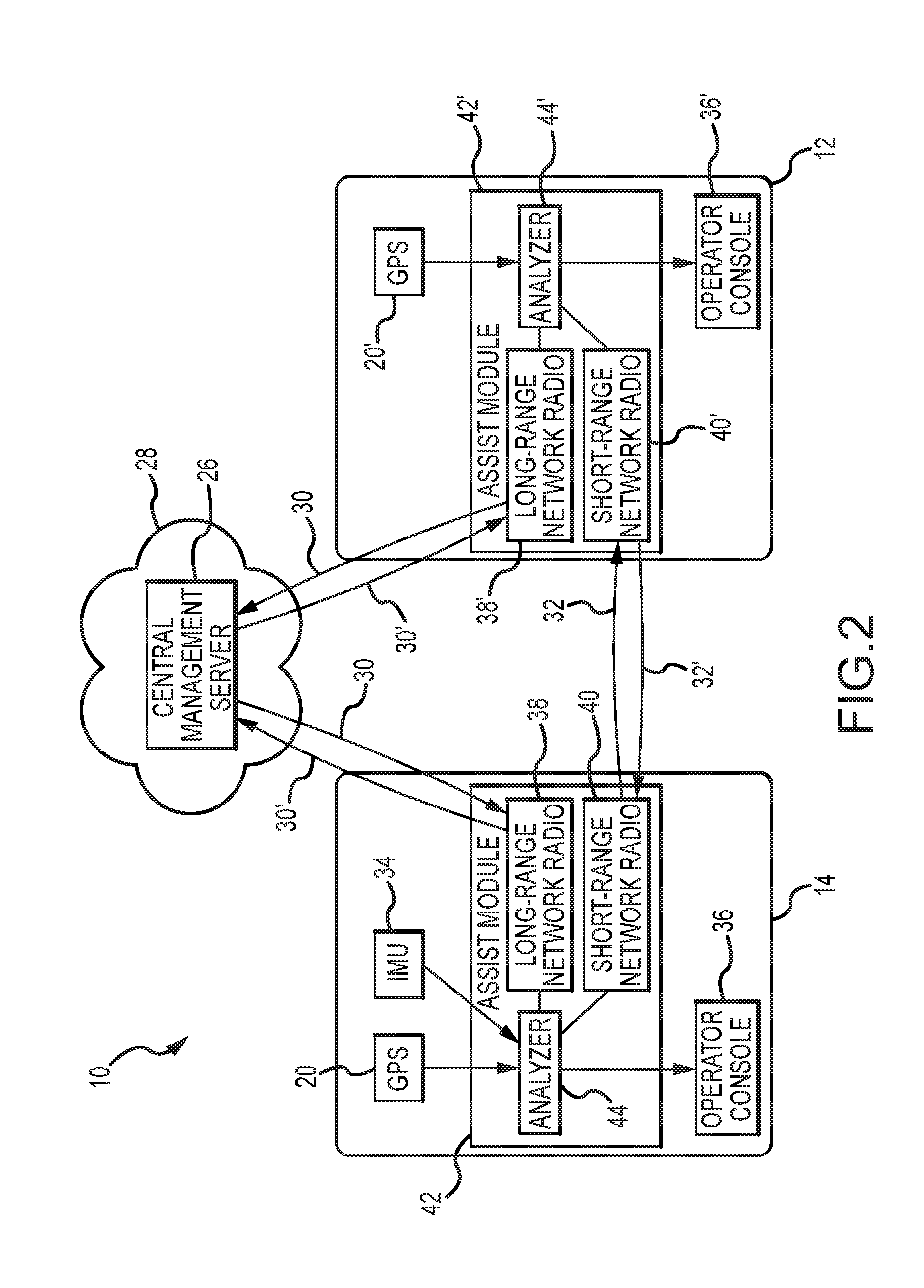
Assistive vehicular guidance system and method
ActiveUS9464913B2Instruments for road network navigationSteering partsGuidance systemCommunications system
An assistive vehicular guidance system for locating a spotter vehicle in a target location near a target machine. The guidance system has a positioning system including global positioning sensors on the spotter vehicle and target machine, and user interfaces providing visual and / or auditory cues. An assist module includes long-range and short-range network radios and an analyzer. The analyzer interfaces with the global positioning sensors, the long-range and short-range network radios, and the user interfaces, planning a path for the spotter vehicle and providing cues in guiding the spotter vehicle along the path to the target location. A communications system includes short-range and long-range networks, the short-range network connecting the short-range network radios of the spotter vehicle and the target machine. The long-range network includes a VPN and server, connecting the long-range radios of the spotter vehicle and target machine with the server via the VPN.
Owner:RAVEN INDUSTRIES INC
Vapor-emitting device with an active end of use indicator
ActiveUS7164849B1Lower levelSpace heating and ventilationMachines/enginesEngineeringVisual perception
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
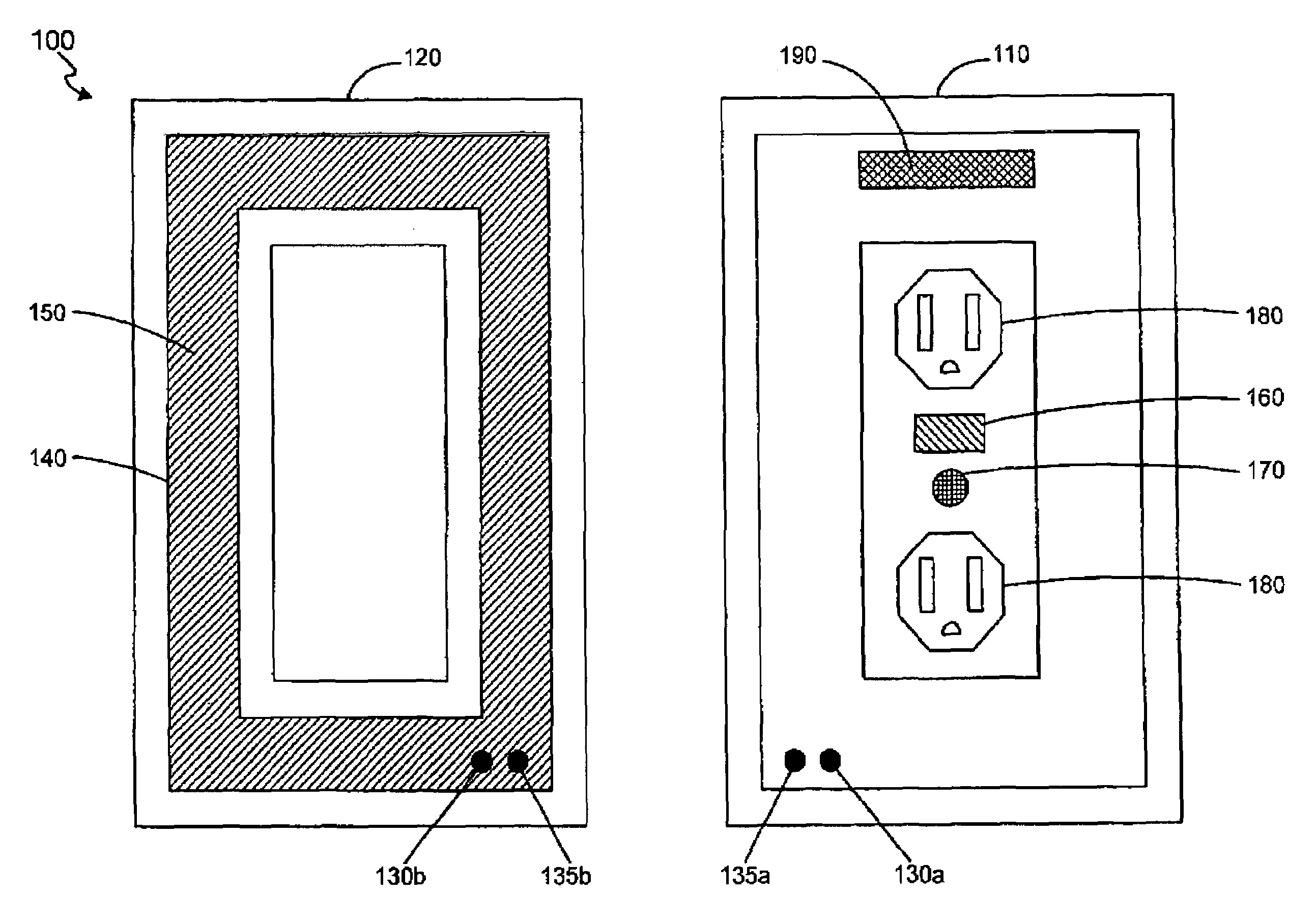
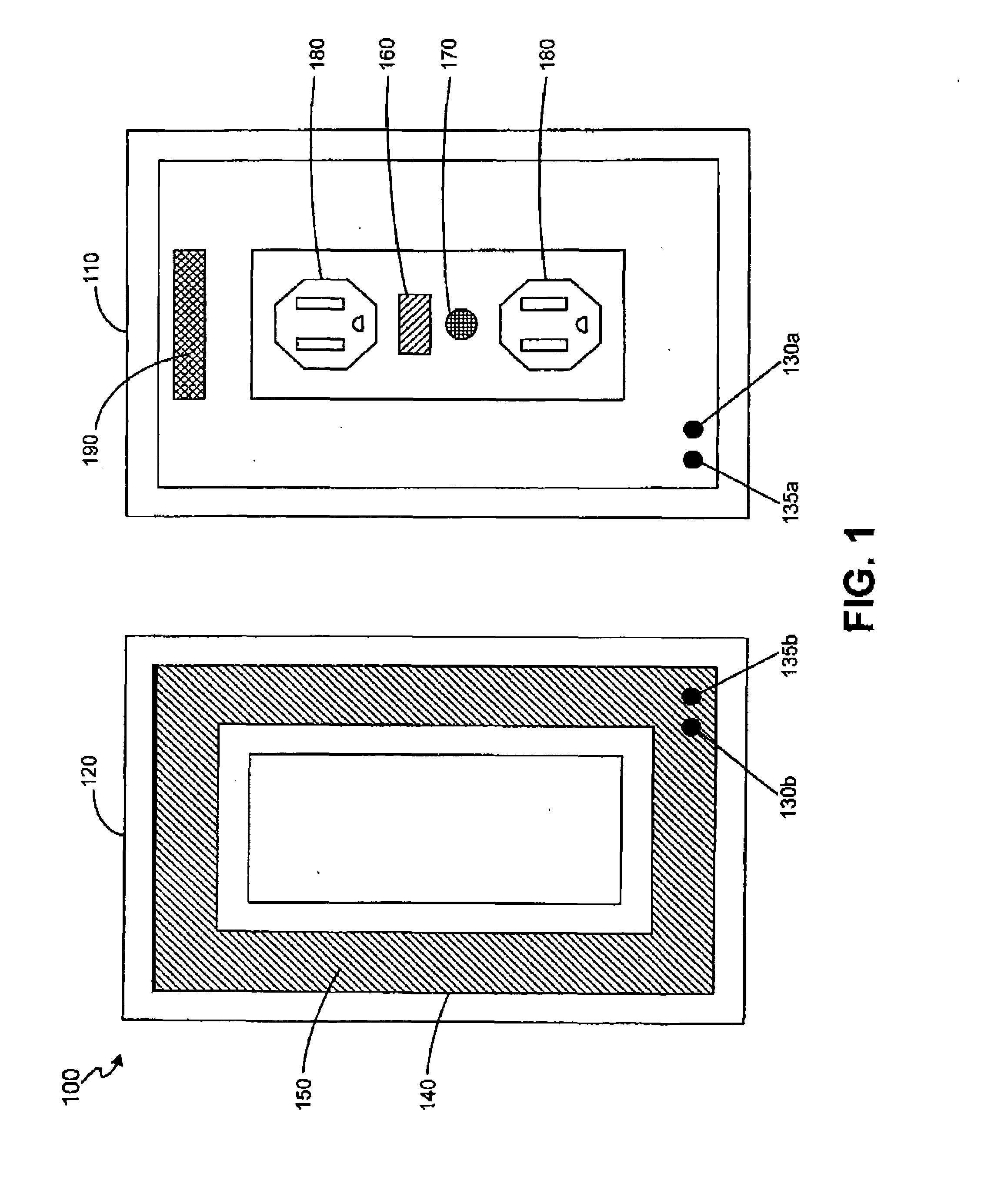
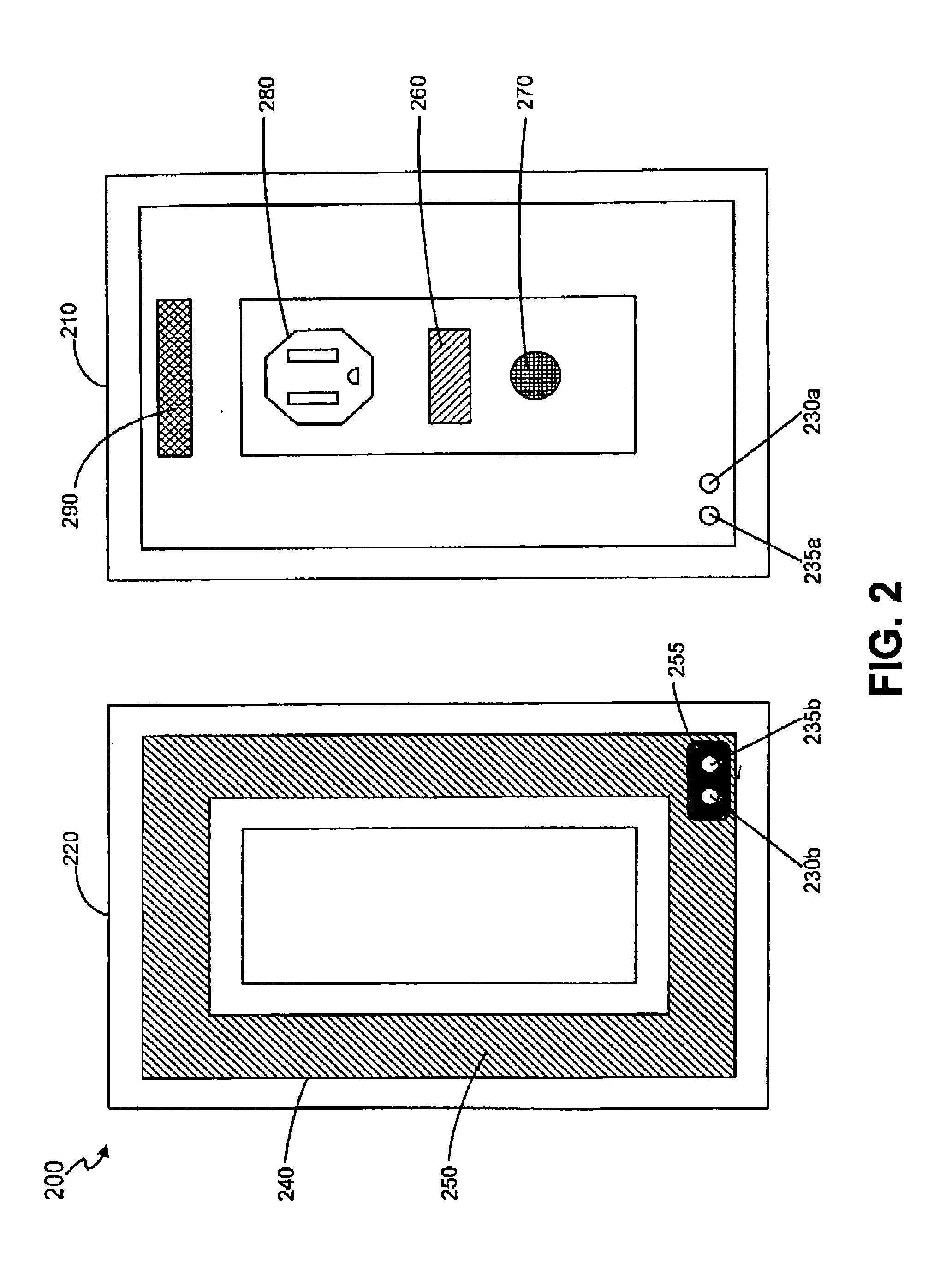
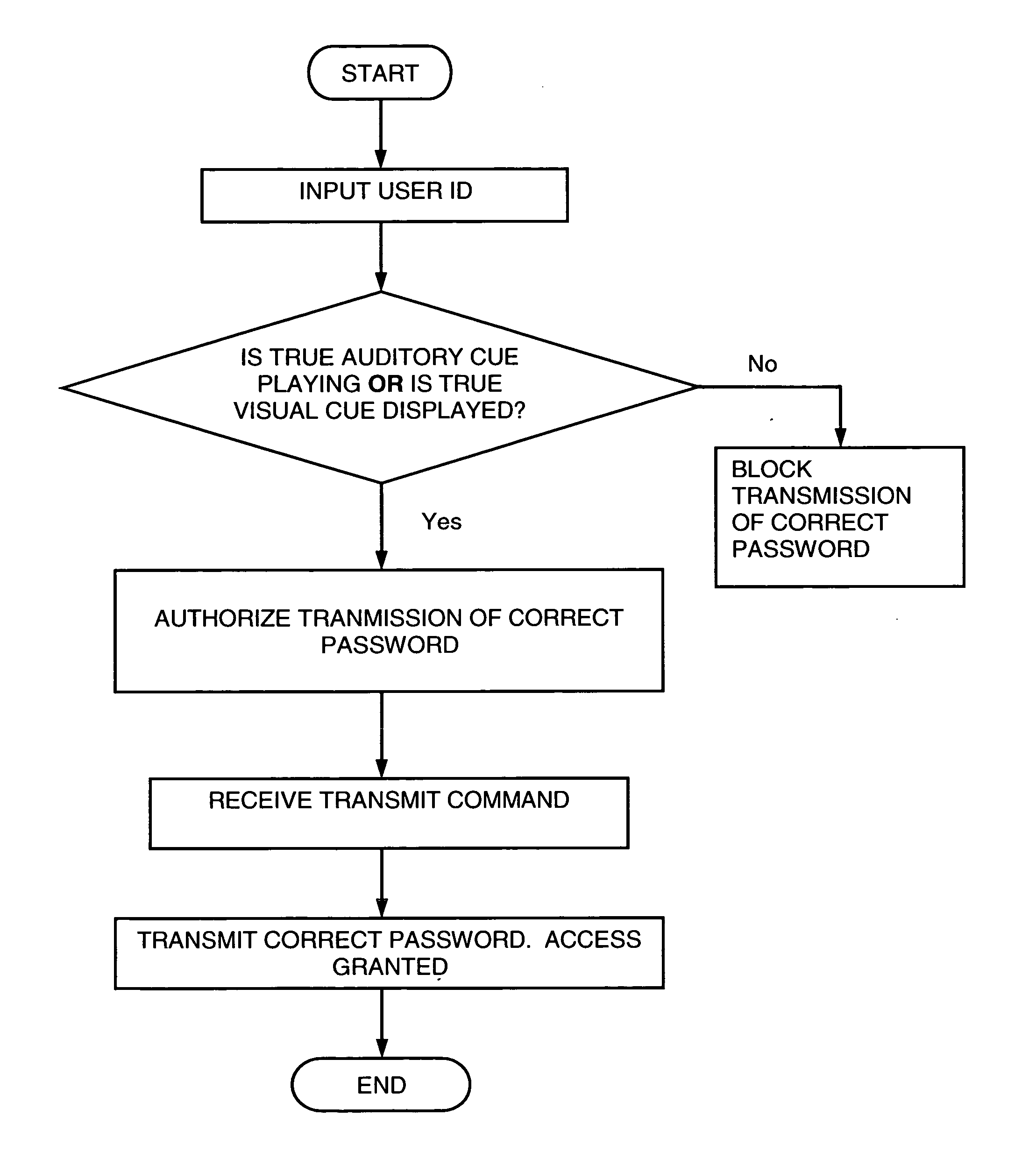
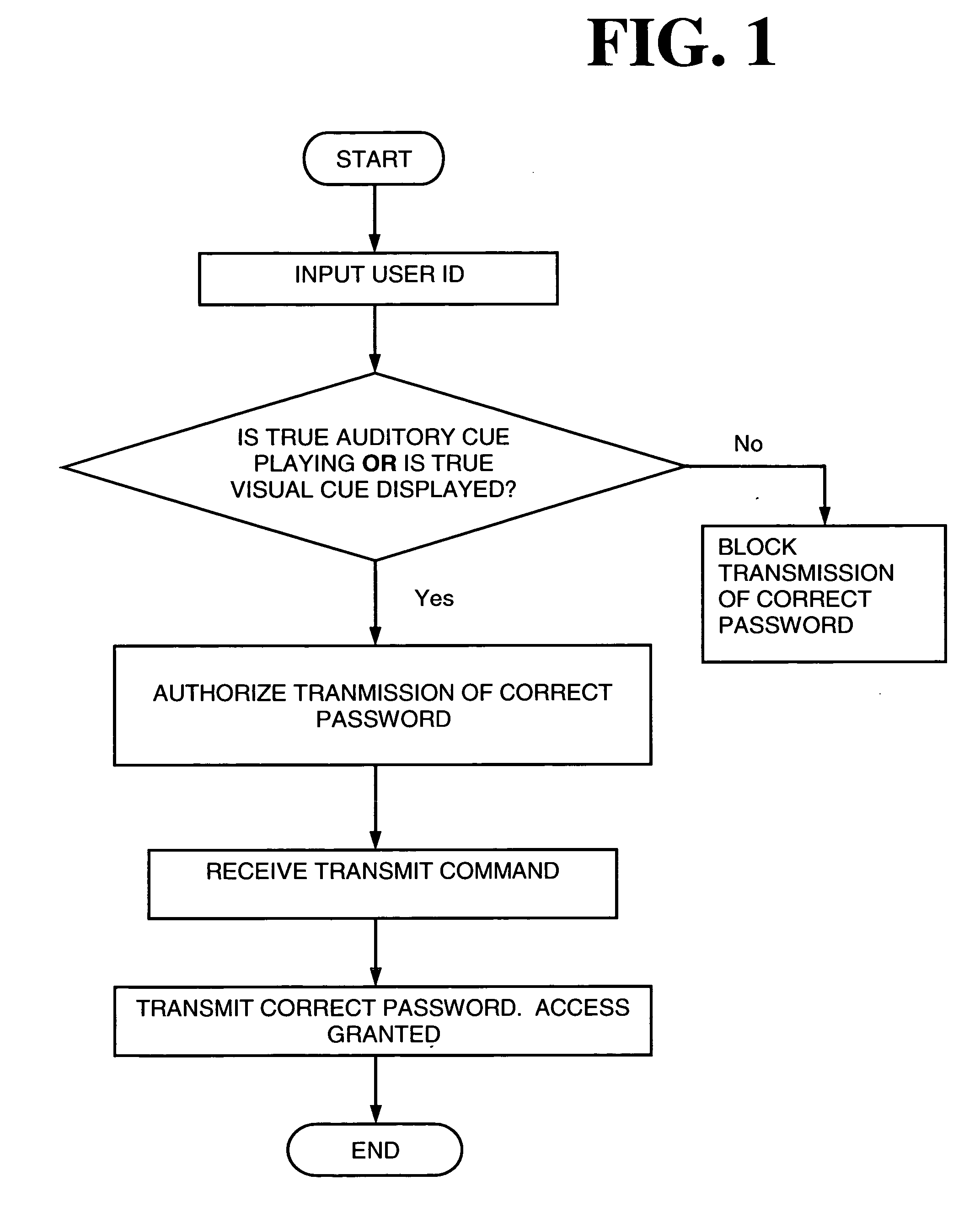
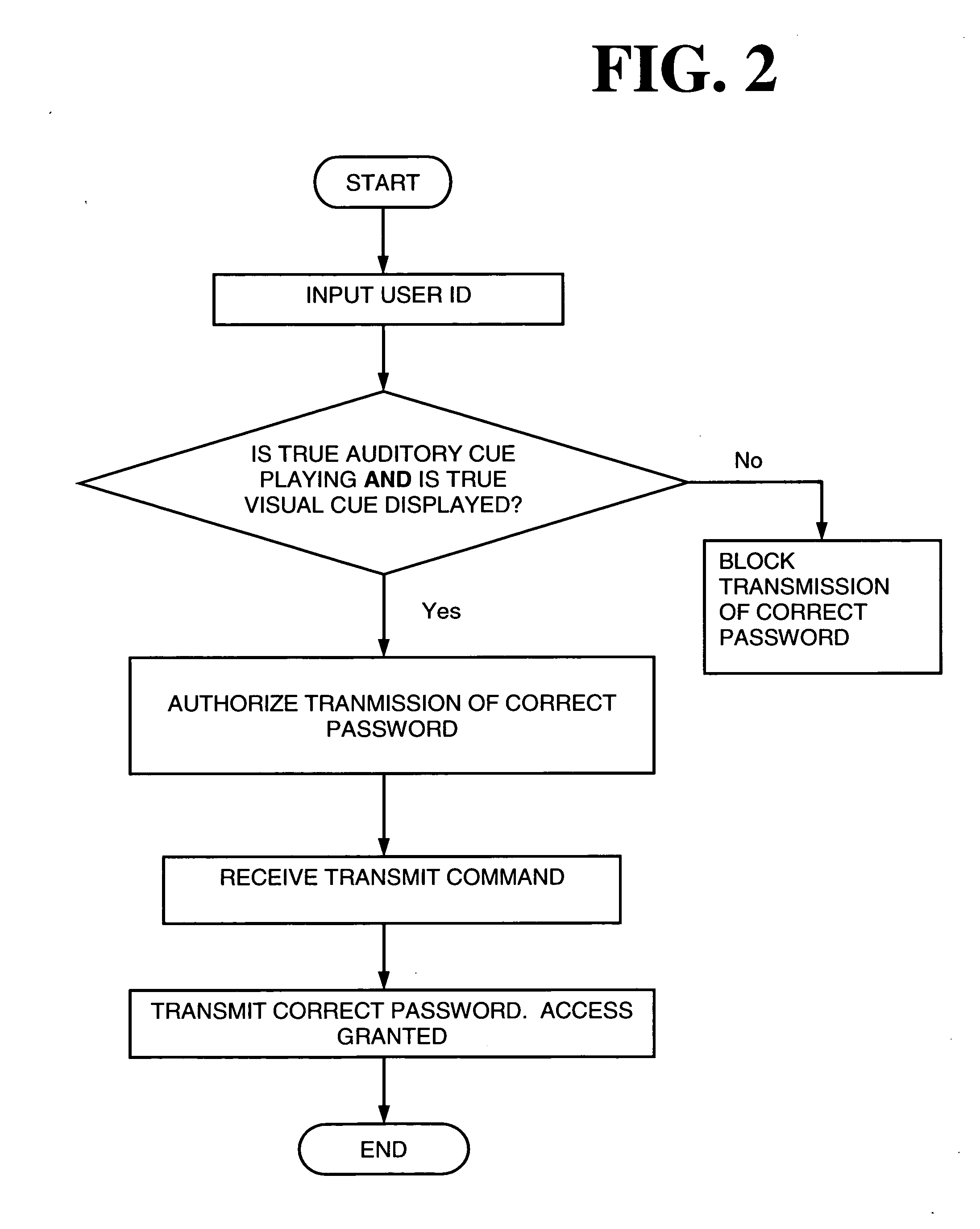
System and method for user authentication employing portable handheld electronic devices
InactiveUS20060218408A1Easy to useImprove purposeRandom number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwarePassword
A system and method for user authentication employing a portable handheld electronic device to store, in digital form, a user's password, access code, or PIN. The portable handheld electronic device can be any such device capable of visual output and / or auditory output, such as a mobile telephone, a personal music player, or a PDA. When the user receives a true visual cue and / or a true auditory cue from the portable handheld electronic device, an input command can be entered that will cause the password, access code, or PIN to be transmitted to gain access. In an alternative embodiment, the password, access code, or PIN is changed during each access granted session and stored in the portable handheld electronic device. A new security code is therefore used each time the user seeks access.
Owner:SERPA MICHAEL LAWRENCE
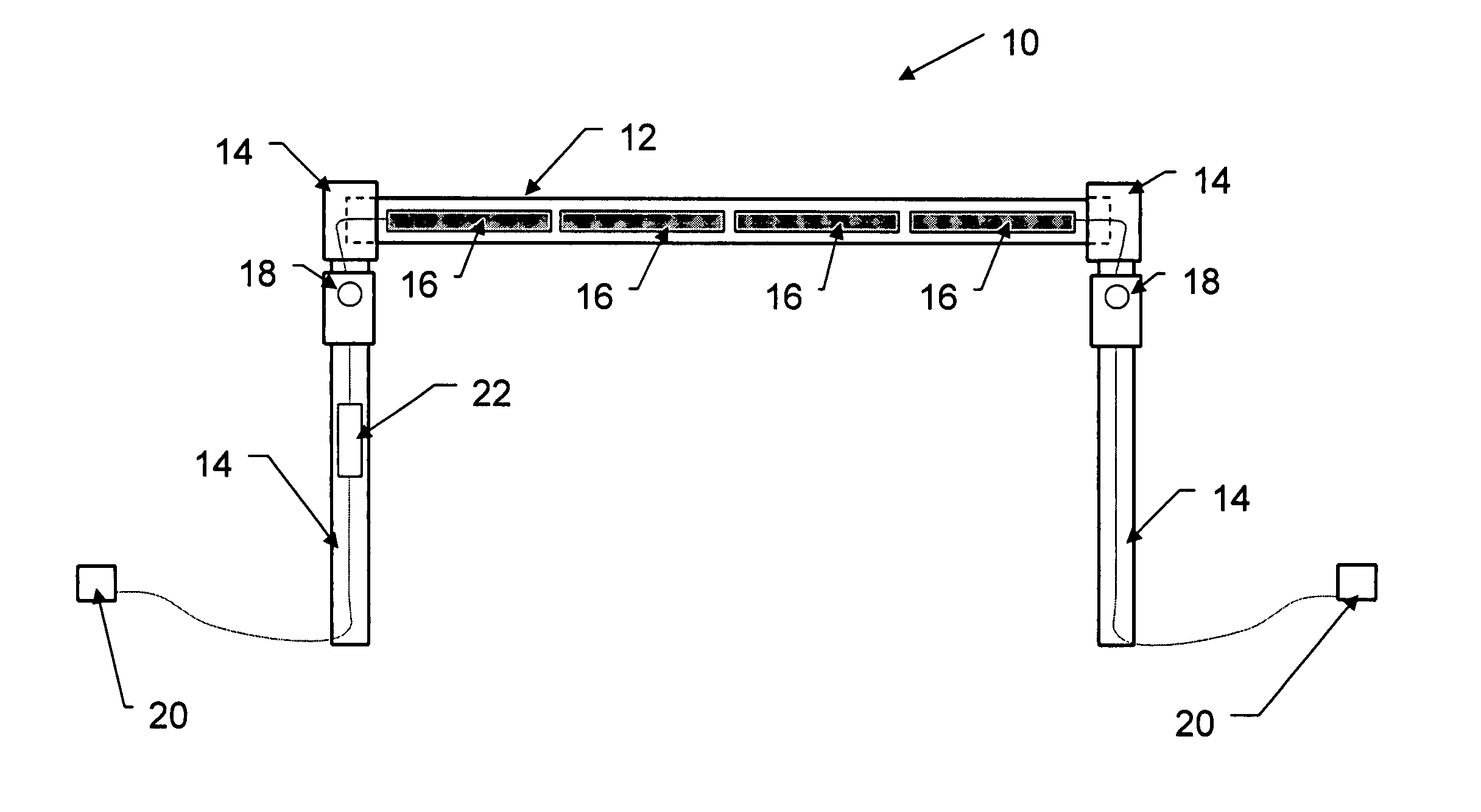
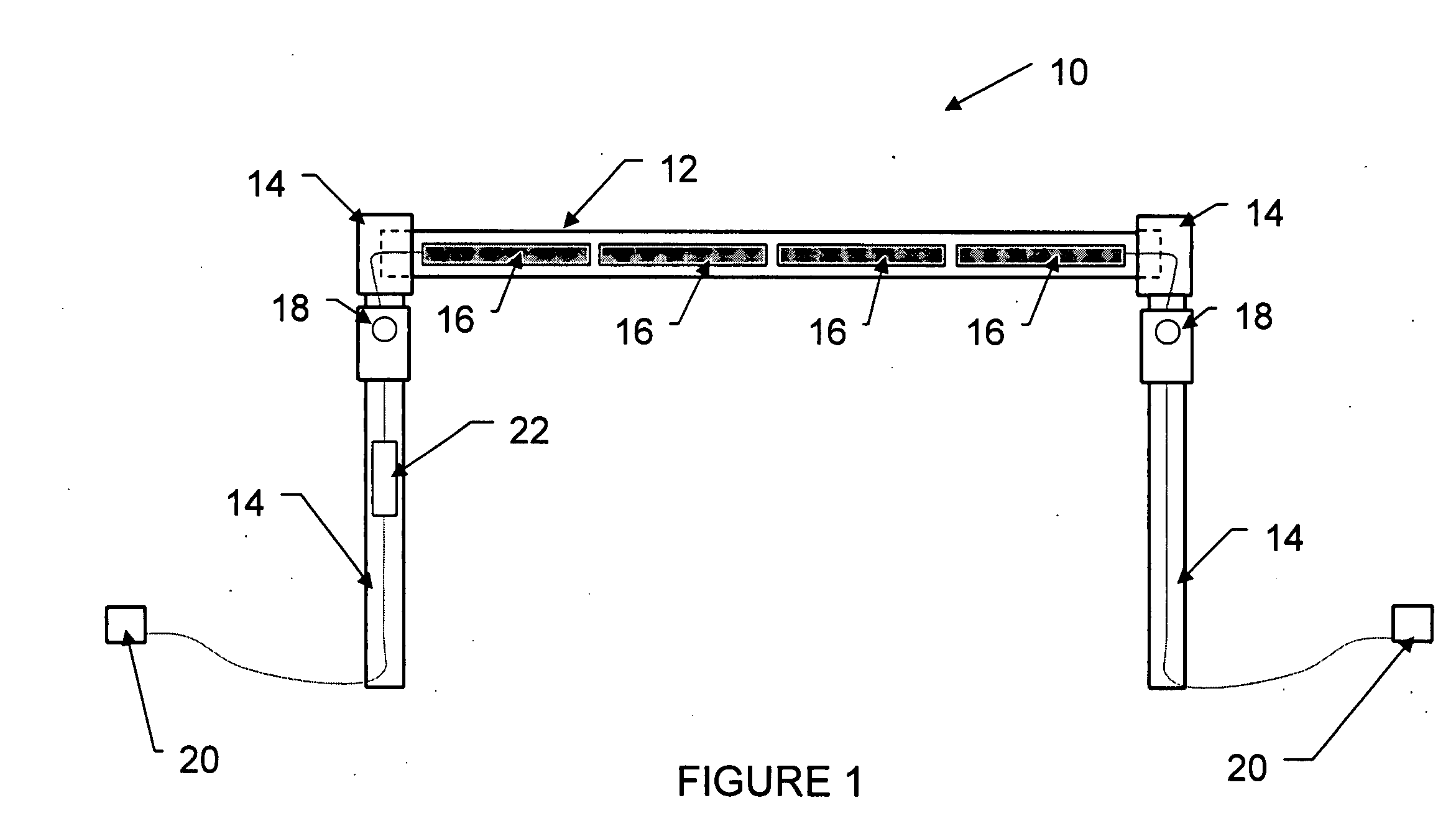
Proximity-triggered handrail cueing system with automatic attention capture
InactiveUS20080007418A1Improve abilitiesStable supportAdvertisingVisible signalling systemsEngineeringReach and grasp
The present invention provides a proximity-triggered handrail cueing system with automatic attention capture for providing visual and auditory cues that automatically and involuntarily (subconsciously) attract attention to the handrail. The system includes a hand railing (i.e. handrail or grab bar) constructed from translucent or transparent plastic tubing, a series of lights mounted inside the railing, along the longitudinal axis, one or more auditory speakers built into the railing or railing brackets, and a proximity detector (e.g. photoelectric sensor) and controller that activates the lights and speakers whenever a person approaches the railing. The speakers can be used to issue a verbal prompt to hold the handrail. The lights inside the railing are triggered to suddenly start flashing in such a way as to automatically and subconsciously attract attention to the handrail, thereby facilitating ability to rapidly and effectively reach and grasp the handrail for support in the event that the person does not hold the railing voluntarily and subsequently experiences a sudden unexpected loss of balance. Sounds emitted by the speakers can also be used to improve the ability to rapidly grab the railing in response to loss of balance. Embodiments of the system may include: 1) a proximity-triggered handrail cueing system with automatic attention capture elicited by visual cueing, 2) a proximity-triggered handrail cueing system with automatic attention capture elicited by auditory cueing; and 3) a proximity-triggered handrail cueing system with automatic attention capture elicited by a combination of visual and auditory cueing.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
Vapor-emitting device with a solar-powered, active end of use indicator
Owner:DIAL CORPORATION
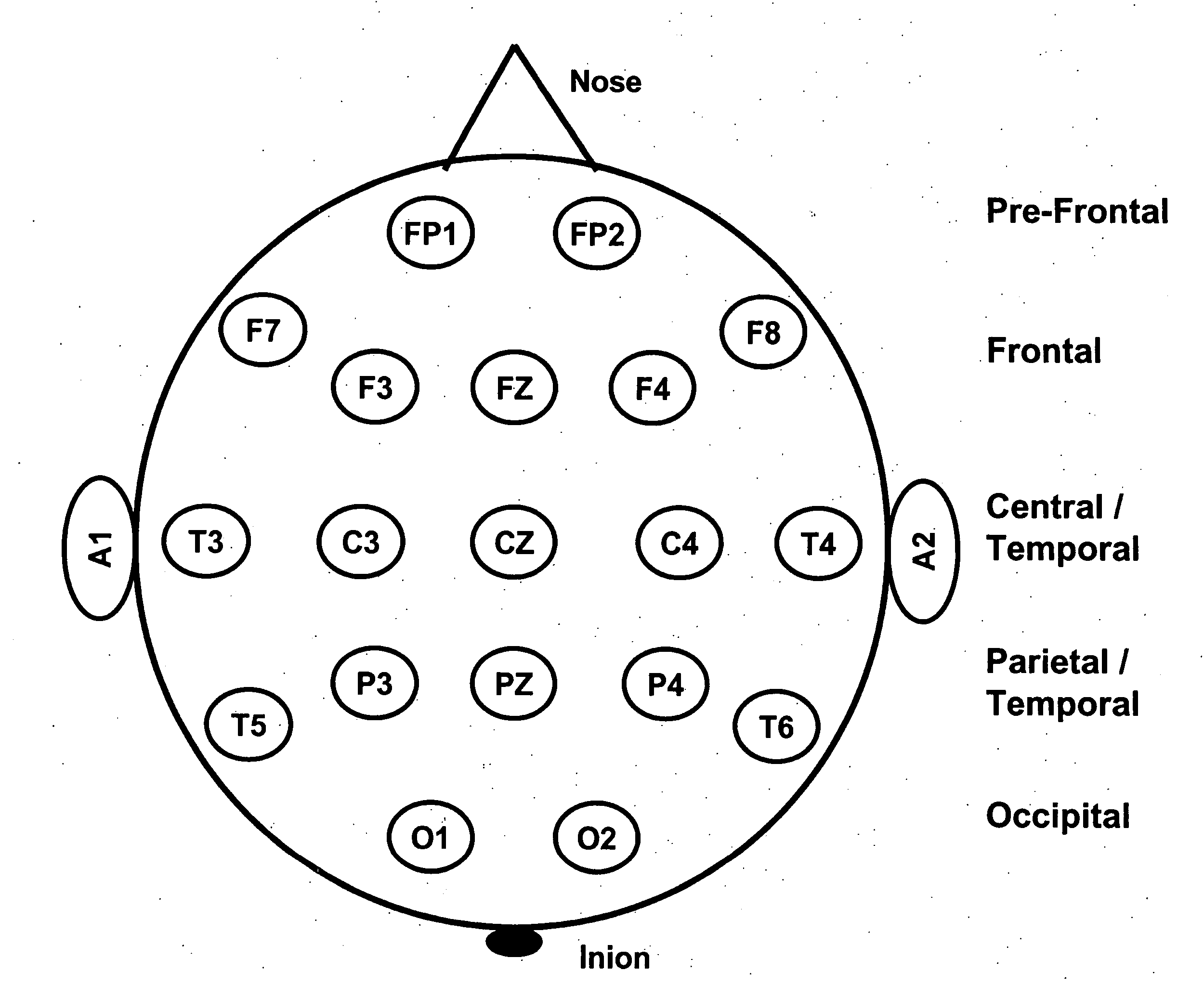
Stimulation of central nervous system
InactiveUS20050149144A1Suppression problemElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyNervous systemMedicine
The present invention provides a method of stimulating the central nervous system and brain waves of a human subject by stimulating a beta frequency in the left brain hemisphere while simultaneously stimulating a low beta frequency in the right brain hemisphere and subsequently stimulating the left and the right brain hemispheres at an alpha frequency. The present invention also provides a process for suppressing aberrant brain wave frequencies, by stimulating the brain at approximately twice the aberrant brain wave frequency. The present invention further provides a process for dissociating a subject by stimulating a left brain hemisphere at a frequency that differs by 0.1 to 3 Hz from a frequency at which right brain hemisphere is stimulated. The present invention also provides a method of pacing breathing in a subject to a predetermined rate comprising exposing the subject to an auditory cue and simultaneously exposing the subject to various frequencies and combinations of stimulation.
Owner:MIND ALIVE
Disc jockey video game and controller
A disc jockey music-based video game with a controller for the same. The disc jockey music-based video game presents instructive cues for manipulation of the controller and evaluates game player's performance based on the player's compliance with the instructive cues. A display with visual indicators of instructive cues and visual indicators representing player performance may be provided. Additionally, other forms of game player feedback may be provided, for example music, simulated crowd response other forms of generally auditory cues.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
Assistive vehicular guidance system and method
ActiveUS20160238403A1Instruments for road network navigationSteering partsGuidance systemCommunications system
An assistive vehicular guidance system for locating a spotter vehicle in a target location near a target machine. The guidance system has a positioning system including global positioning sensors on the spotter vehicle and target machine, and user interfaces providing visual and / or auditory cues. An assist module includes long-range and short-range network radios and an analyzer. The analyzer interfaces with the global positioning sensors, the long-range and short-range network radios, and the user interfaces, planning a path for the spotter vehicle and providing cues in guiding the spotter vehicle along the path to the target location. A communications system includes short-range and long-range networks, the short-range network connecting the short-range network radios of the spotter vehicle and the target machine. The long-range network includes a VPN and server, connecting the long-range radios of the spotter vehicle and target machine with the server via the VPN.
Owner:RAVEN INDUSTRIES INC
Vapor-emitting device with an active end of use indicator
Owner:ARMALY SPONGE CO
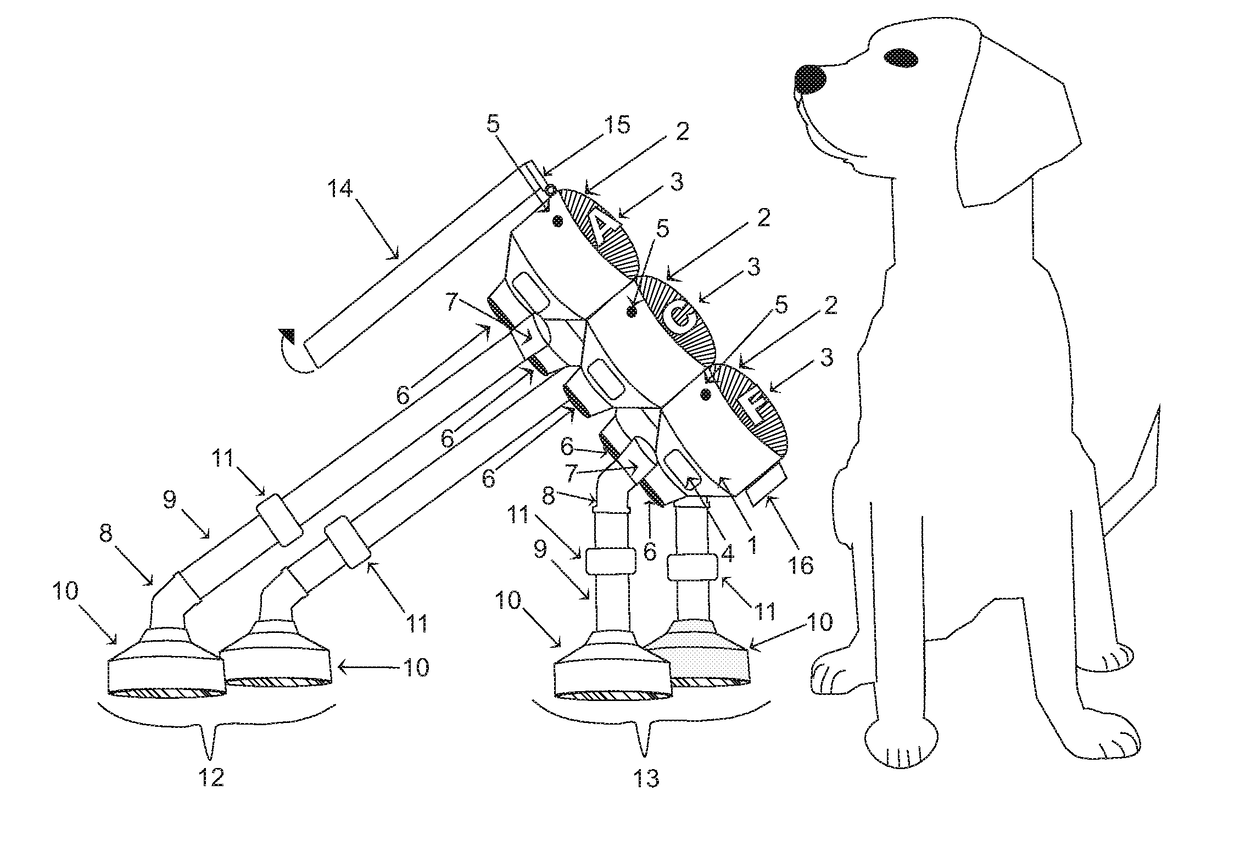
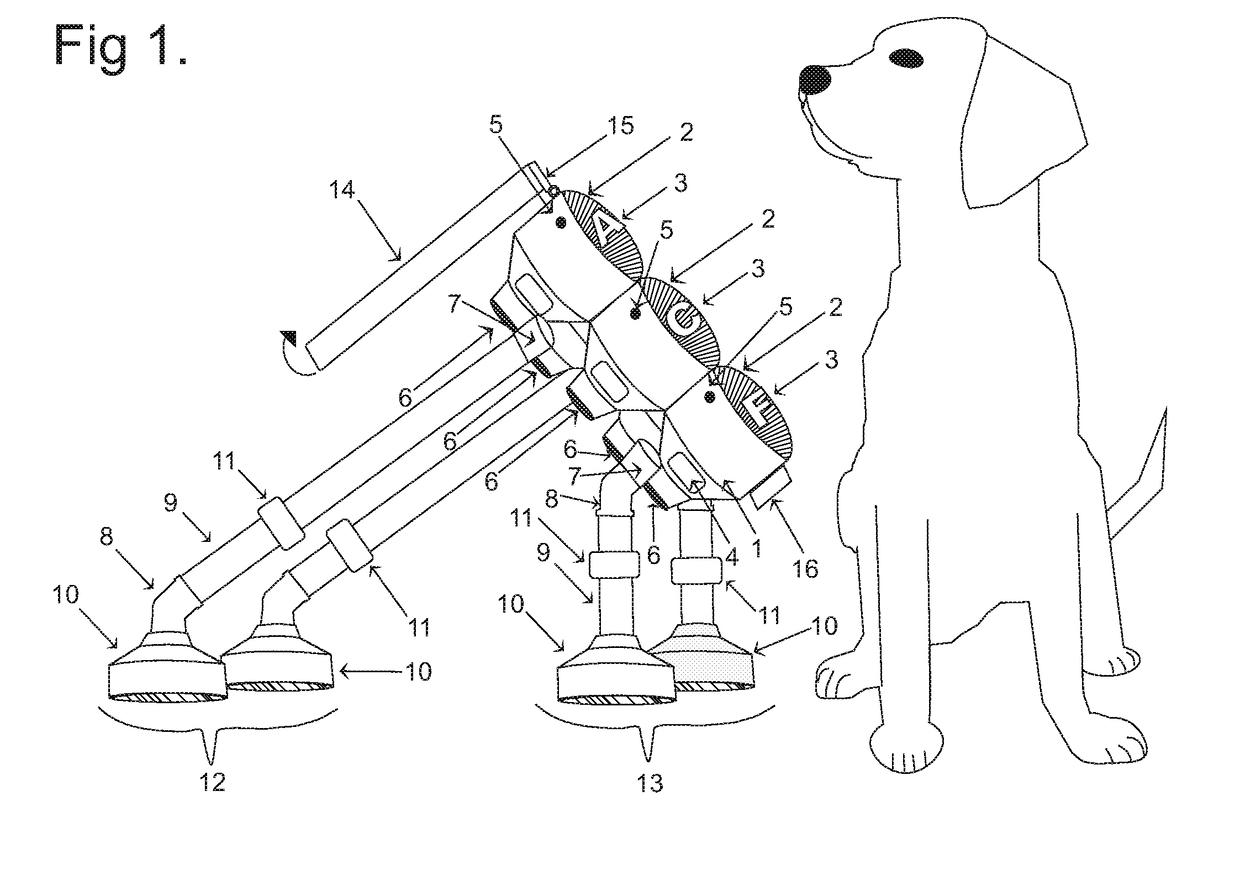
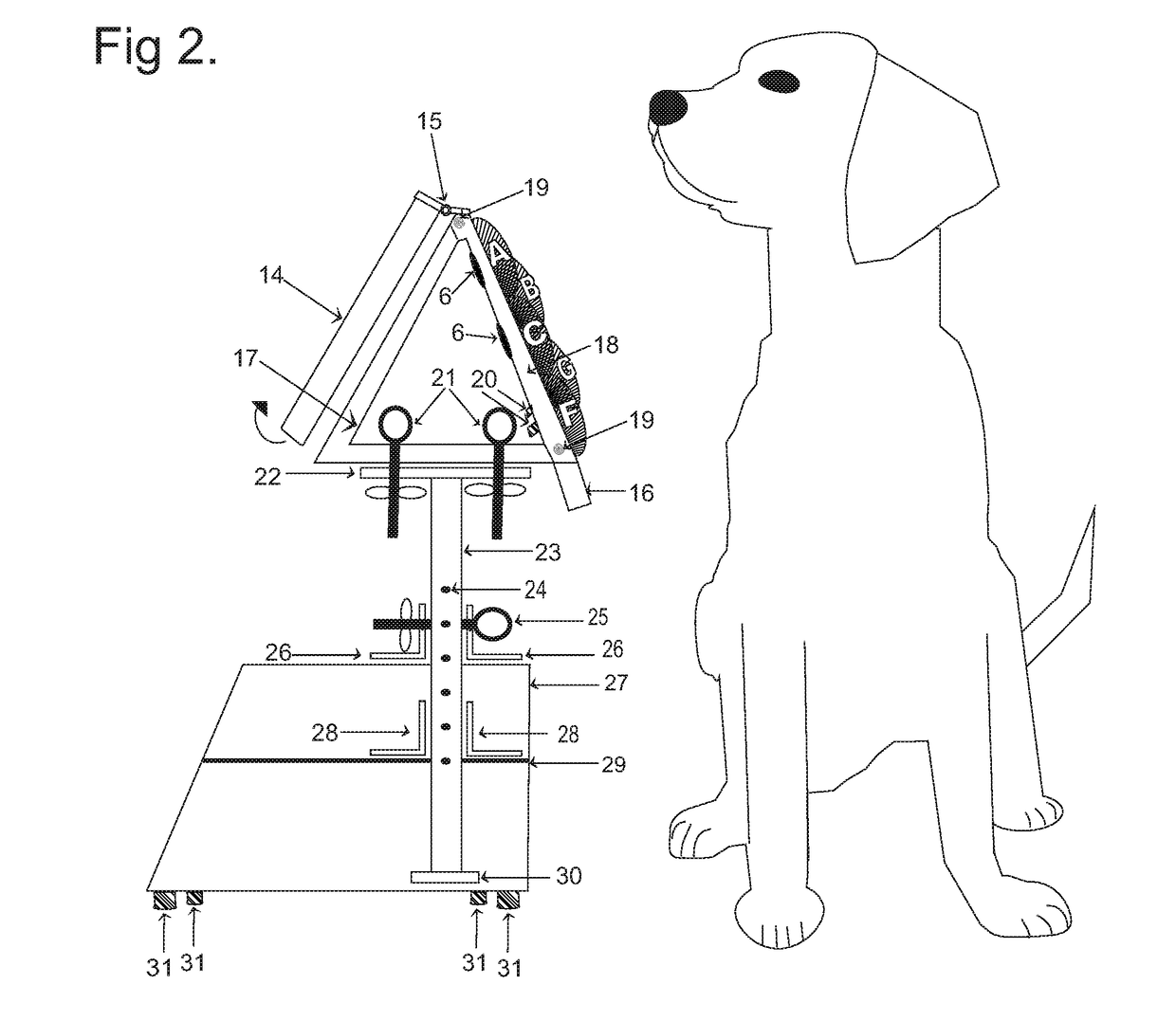
Functional Communication Lexigram Device and Training Method for Animal and Human
ActiveUS20180132453A1Improve accuracyEasy to controlTaming and training devicesSpoken languageTouch Perception
The present invention is a functional communication lexigram device and training method for operation thereof that animals autonomously operate to initiate communication to “voice” their choices to (a) the people around them using recorded spoken words or sounds (or other detectable cue) and / or to (b) wired, wireless or internet connected accessory devices receiving an output signal from the device. The invention includes the method for training the human and the animal how to operate the device using operant conditioning techniques. Using the training method, the animal is taught to press or touch button-like modalities that are identified by visual-tactile-auditory cues and by position in a fixed array and to associate pressing each of the particular button-like modalities with particular positive consequences. The device is used by animals to initiate a communicative interaction with humans; it provides humans with an easily understood cue to meet an animal's needs to improve caregiving, and it provides the animal with more autonomy, choices, and control over environmental features important to it.
Owner:FOSTER MARGARET JEANNETTE
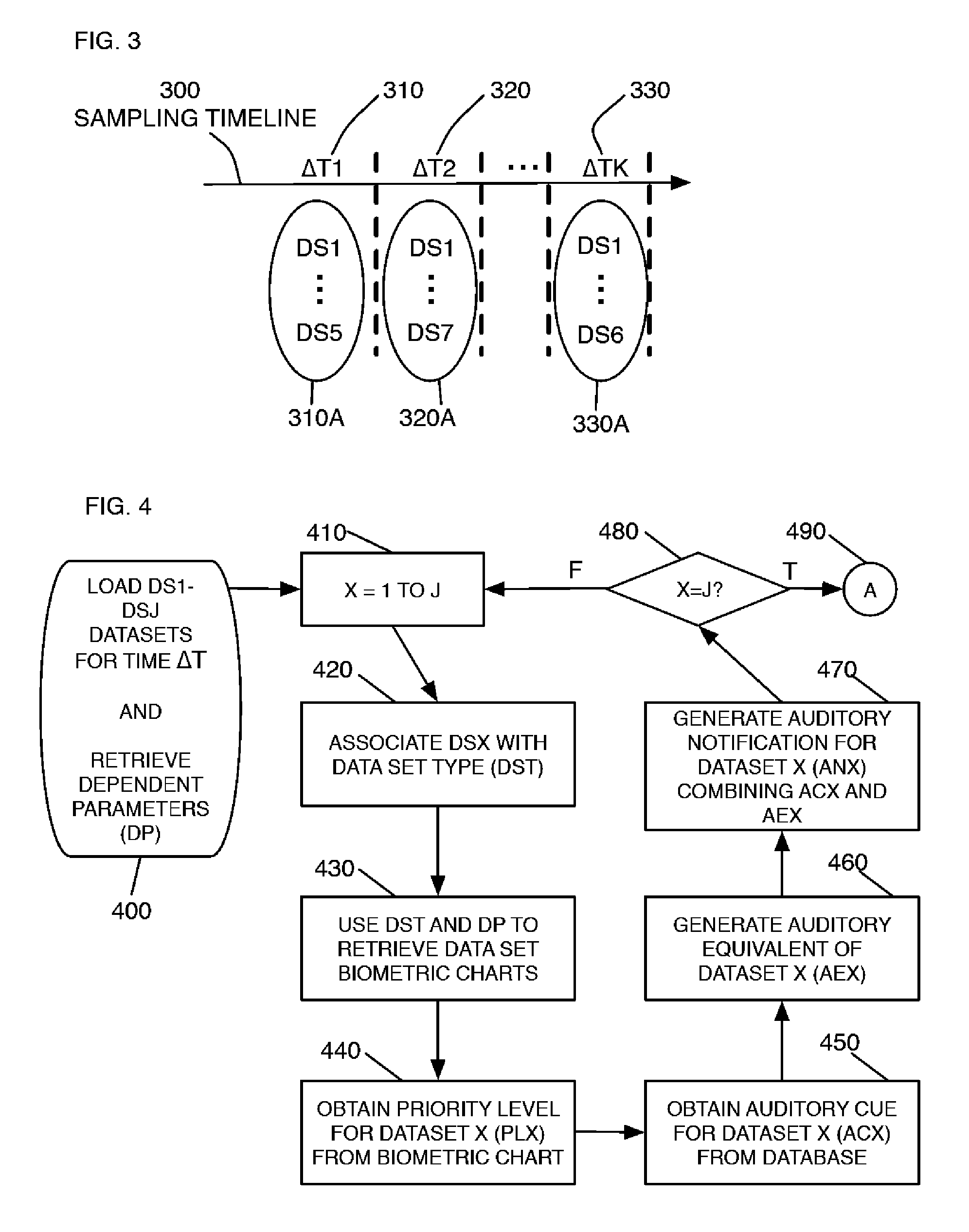
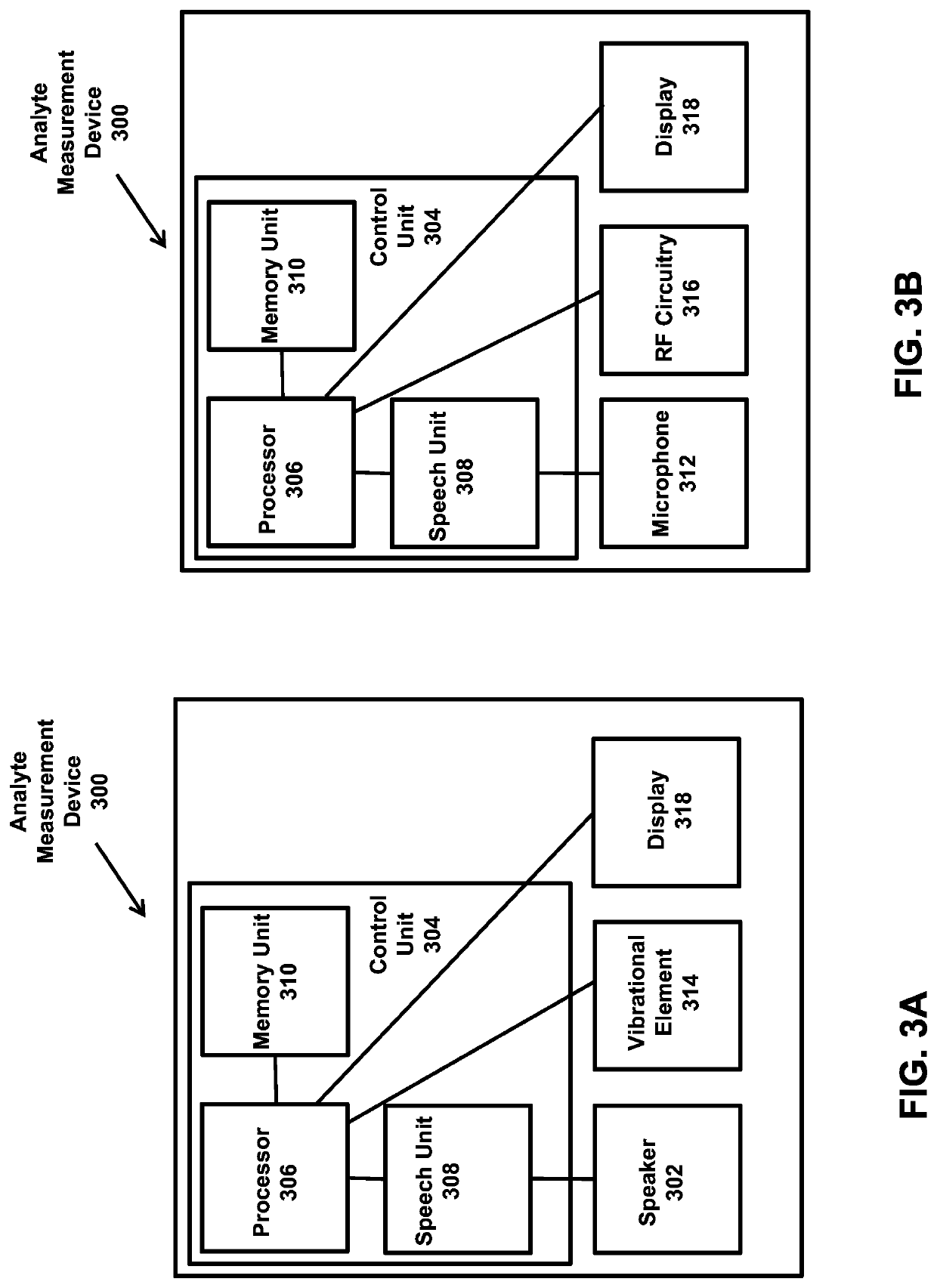
Analyte monitoring system with audible feedback
Owner:INTUITY MEDICAL INC
Mobile brain-based device for use in a real world environment
InactiveUS7519452B2Input/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionVision processingNervous system
A mobile brain-based device BBD includes a mobile base equipped with sensors and effectors (Neurally Organized Mobile Adaptive Device or NOMAD), which is guided by a simulated nervous system that is an analogue of cortical and sub-cortical areas of the brain required for visual processing, decision-making, reward, and motor responses. These simulated cortical and sub-cortical areas are reentrantly connected and each area contains neuronal units representing both the mean activity level and the relative timing of the activity of groups of neurons. The brain-based device BBD learns to discriminate among multiple objects with shared visual features, and associated “target” objects with innately preferred auditory cues. Globally distributed neuronal circuits that correspond to distinct objects in the visual field of NOMAD 10 are activated. These circuits, which are constrained by a reentrant neuroanatomy and modulated by behavior and synaptic plasticity, result in successful discrimination of objects. The brain-based device BBD is moveable, in a rich real-world environment involving continual changes in the size and location of visual stimuli due to self-generated or autonomous, movement, and shows that reentrant connectivity and dynamic synchronization provide an effective mechanism for binding the features of visual objects so as to reorganize object features such as color, shape and motion while distinguishing distinct objects in the environment.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
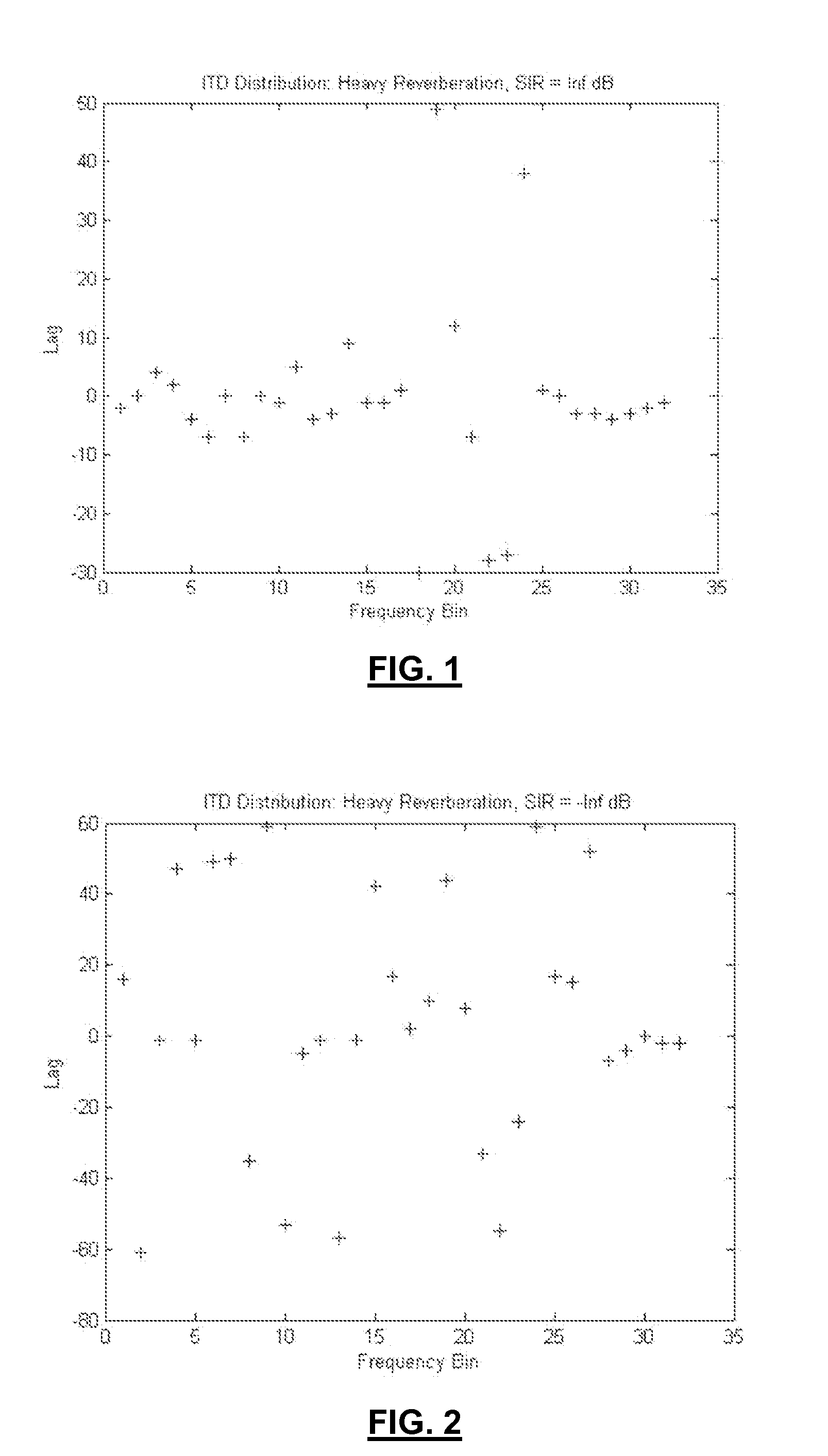
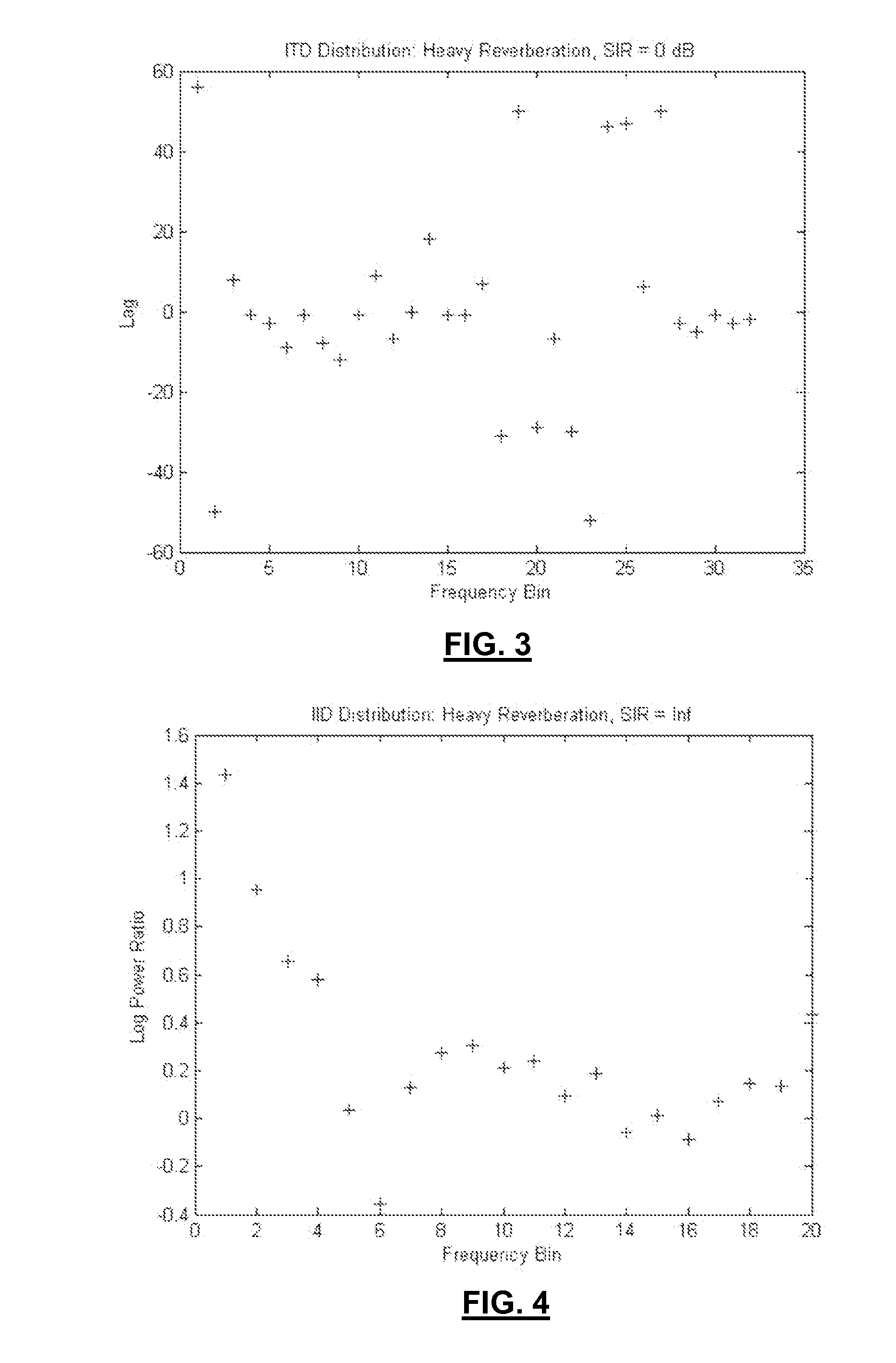
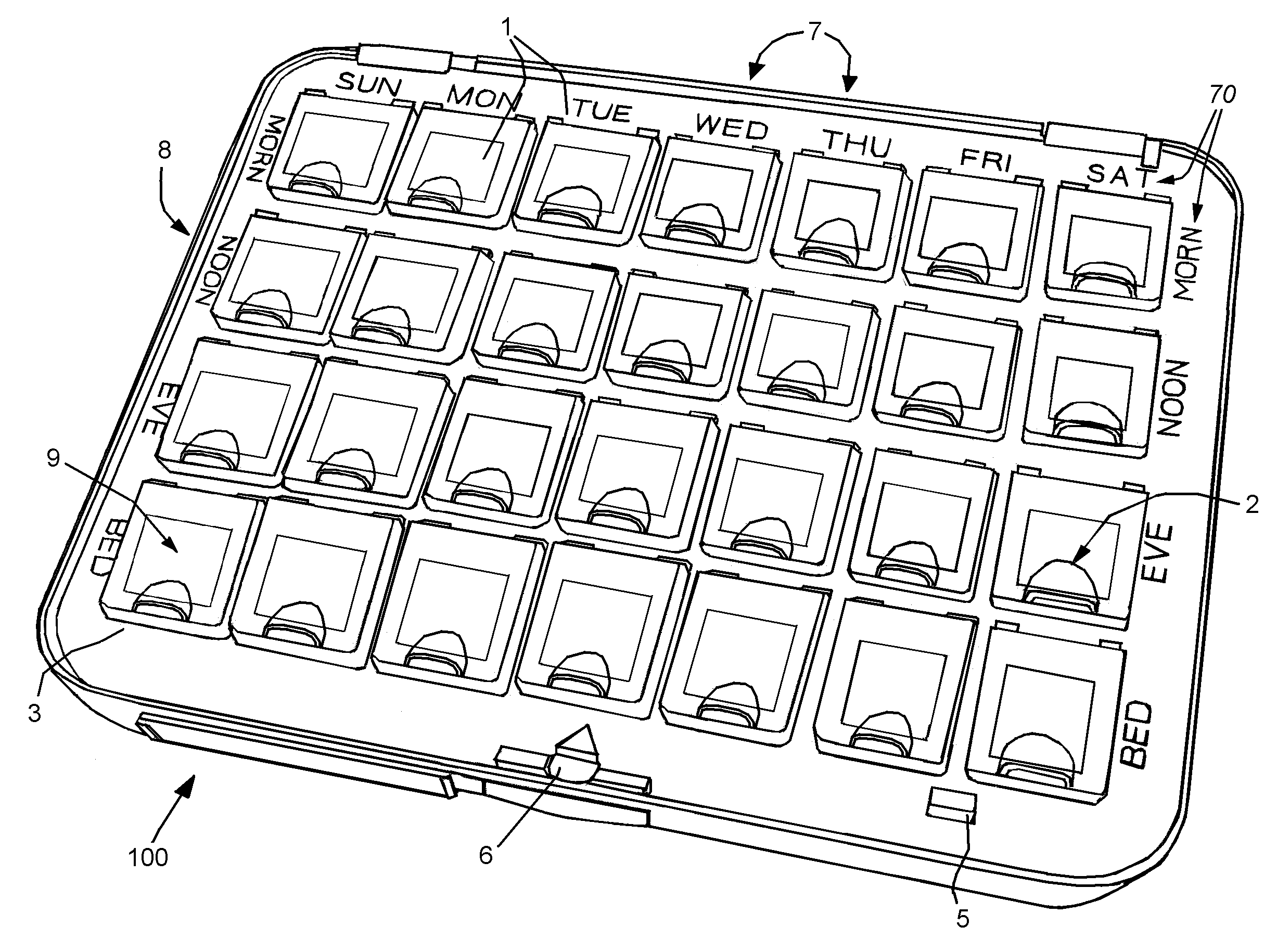
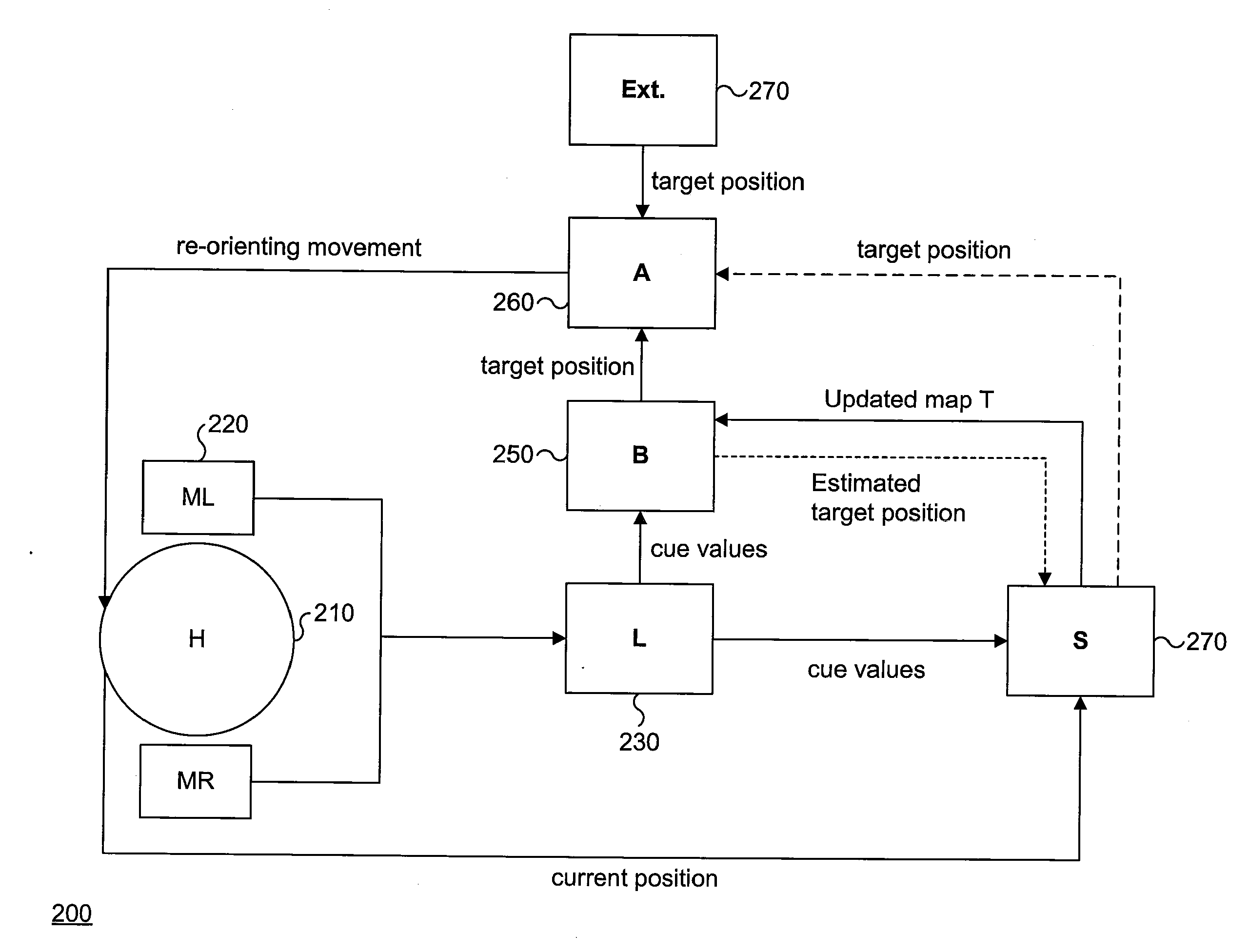
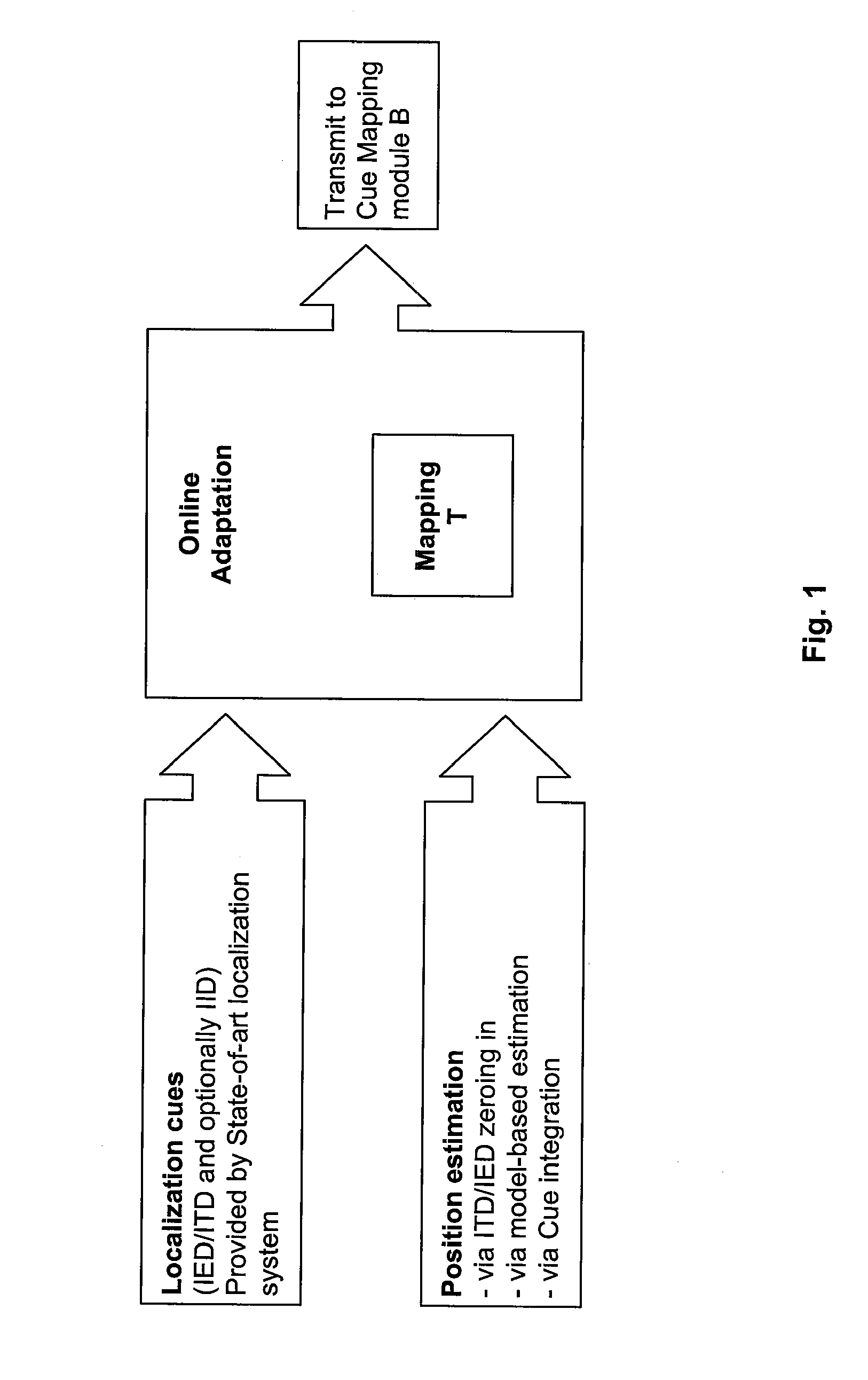
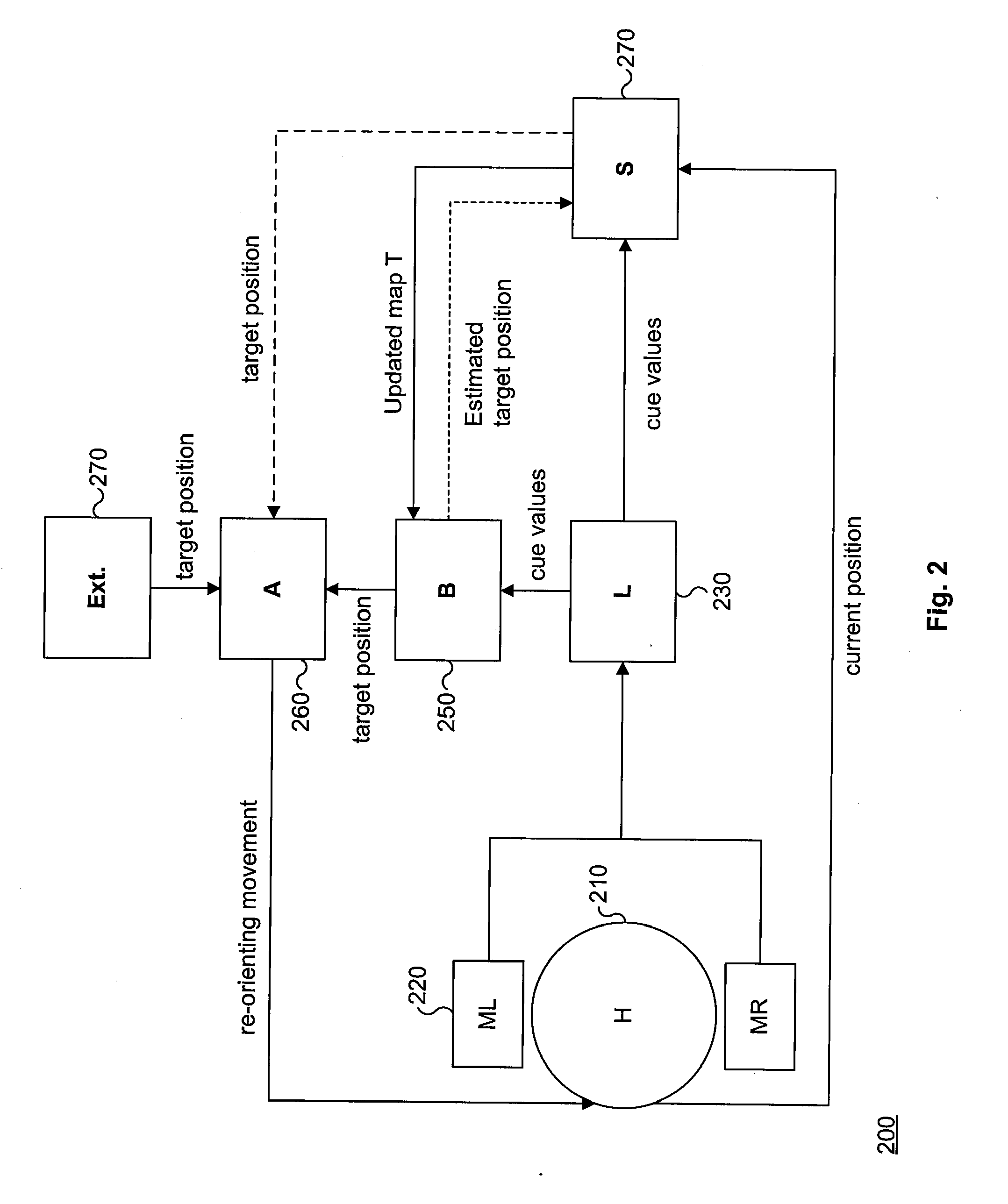
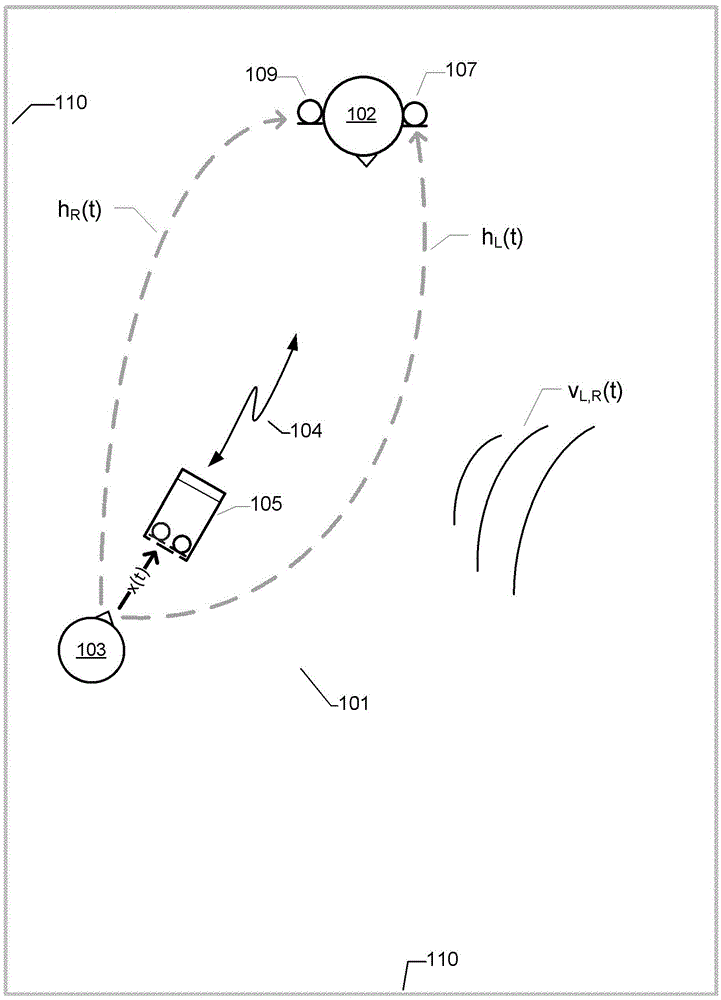
Method for Estimating the Position of a Sound Source for Online Calibration of Auditory Cue to Location Transformations
ActiveUS20070291968A1Reduce hardware costsReducing the constraints on the method and systemDirection findersLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsSound source locationSound sources
A method for estimating the location of a sound source. First, a first microphone and a second microphone are moved relative to the sound source. Then the Intra-aural Time Difference (ITD) between the two microphones is measured. The moving and the measuring are repeated until the Intra-aural Time Difference (ITD) is smaller than a predefined threshold.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
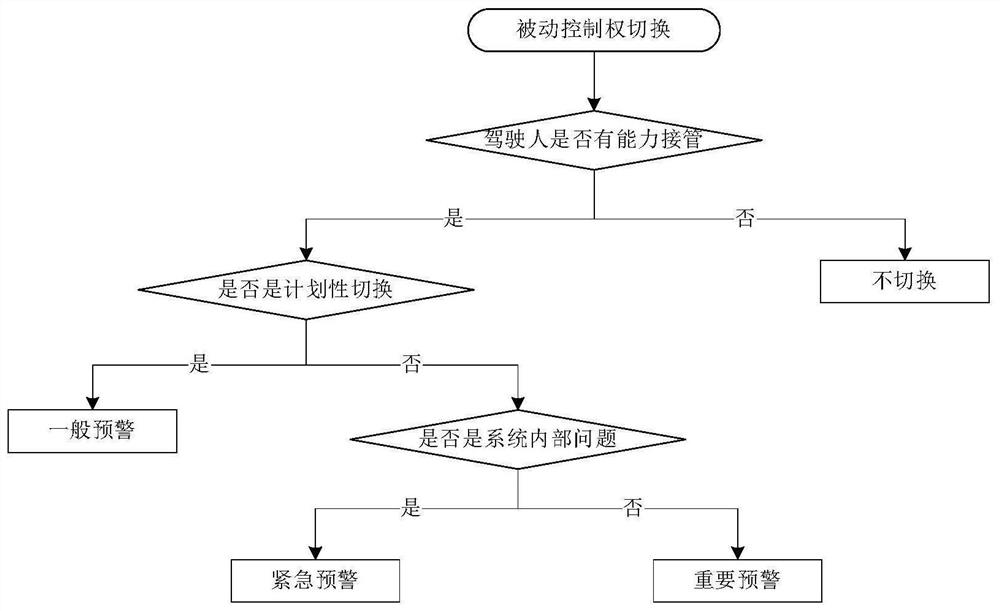
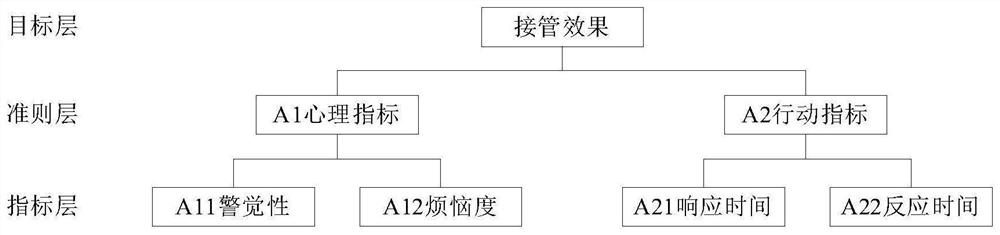
Passive control right switching auditory prompt design method under automatic driving
InactiveCN111703434AImprove accuracyGuide in timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDriver/operatorDriving simulator
The invention discloses a passive control right switching auditory prompt design method under automatic driving, and relates to an auditory prompt design method in the field of automatic driving. Theinvention aims to solve the problems that the requirement of an existing prompting method for the attention of a driver is high and the driver cannot be guided to distract the attention to a driving monitoring task. Firstly, passive control right scenes are classified, auditory prompt tones are designed according to scene types and human ear auditory characteristics, then an auditory prompt tone experiment is carried out through a driving simulator to obtain psychological indexes and action indexes of a driver, and finally a unified scoring standard is established to determine the auditory prompt tones suitable for various scenes. According to the passive control right switching auditory prompt design, prompt tones with different sound frequencies are designed for planned control right switching and non-planned switching initiated by the system according to human ear auditory characteristics. The method is used for passive control right switching auditory prompt design under automaticdriving.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
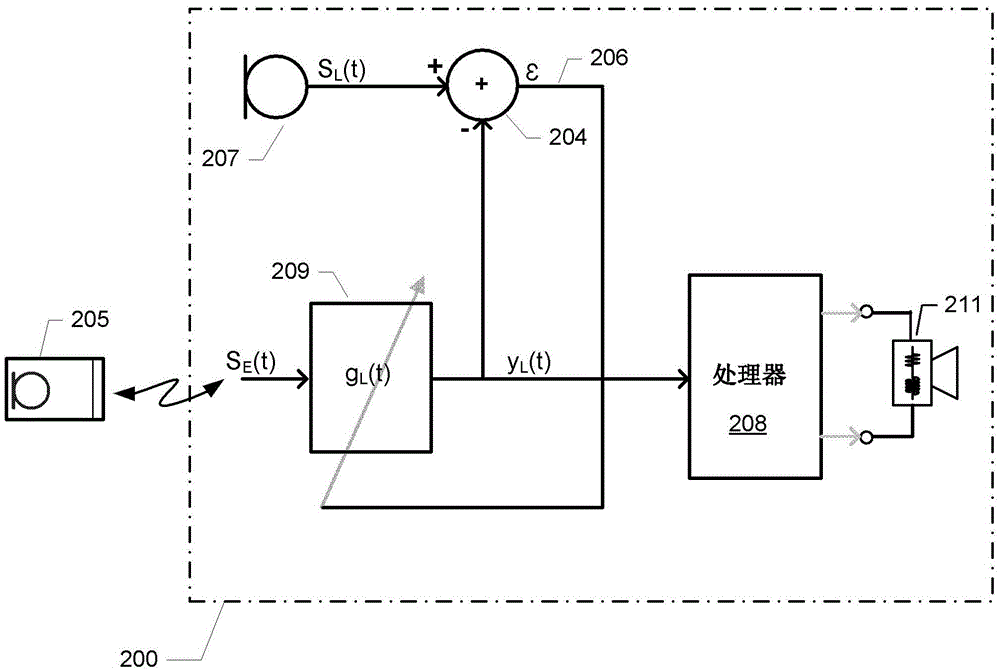
Method of superimposing spatial auditory cues on externally picked-up microphone signals
ActiveCN105744455ASignal processingElectronic input selection/mixingTelecommunications linkMicrophone signal
The invention on one hand relates to a method of superimposing spatial auditory cues on externally picked-up microphone signals in a hearing instrument. The method comprises the following steps: an external microphone apparatus generating an external microphone signal and transmitting the external microphone signal to a wireless receiver of a first hearing instrument through a first wireless communication link. The method further includes the following steps: associating the external microphone signal and a first hearing auxiliary microphone signal of the first hearing instrument so as to determine a responding characteristic of a first spatial synthesis filter; and filtering the external microphone signal by the first spatial synthesis filter so as to generate a first synthesis microphone signal including a first spatial hearing cue.
Owner:GN HEARING AS
Vapor-emitting device with an active end of use indicator
Owner:ARMALY SPONGE CO
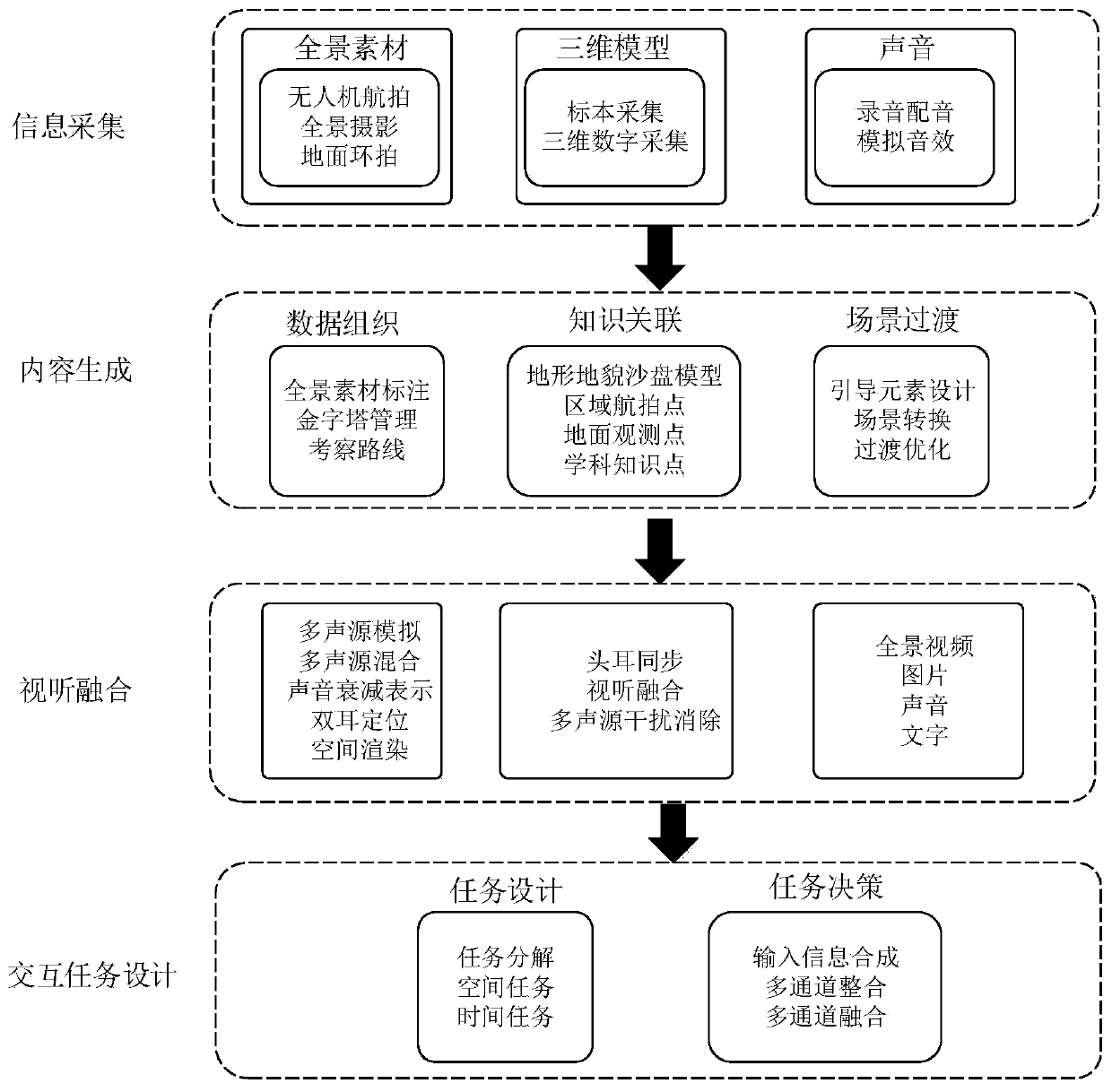
Virtual learning environment multi-channel fusion display method for field practice teaching
ActiveCN111009158AImprove realismAdd interactive discrimination modeElectrical appliancesInteraction designData acquisition
The invention belongs to the field of teaching application of a virtual reality technology, and provides a virtual learning environment multi-channel fusion display method for field practice teaching,which comprises three steps of content generation, audio-visual channel fusion and multichannel interaction design. According to the characteristics of teaching contents in a VR learning environment,a set of generation method from data acquisition, knowledge organization and scene switching is established; synchronous updating of audio-visual channels is realized through a space rendering mode;the input and output priorities of each interaction channel are evaluated, and the multi-sensory collaborative interaction of learners in the VR learning environment is completed. Through adding of auditory cues and multi-channel user interaction discrimination modes, the VR learning environment fusion display is realized, the sense of reality of a learning environment can be improved, and the immersion experience of participants is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
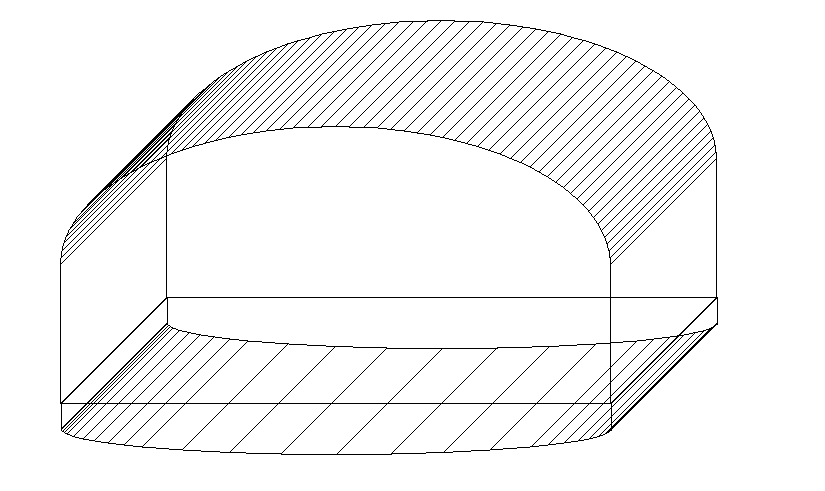
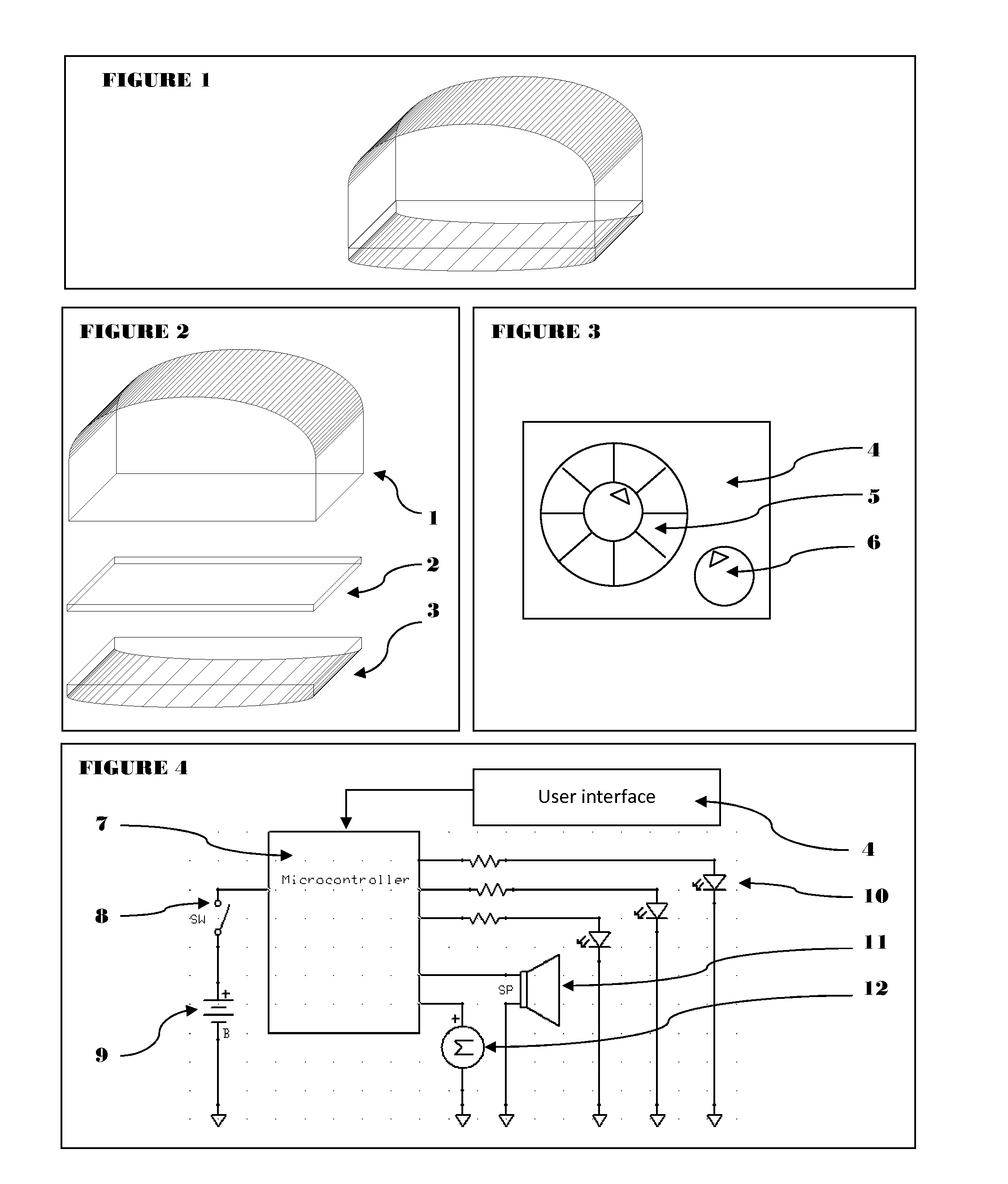
Meditation Device
InactiveUS20140357939A1Facilitate meditationMedical devicesSleep inducing/ending devicesVisual perceptionComputer science
A meditation device including a body portion, electronics, and integrated user interface. The device includes a user interface that allows the user to set the meditation session duration, color of light, and choice of sound. The electronics enables the device to emit visual and auditory cues for when the meditation session begins and ends. The device is portable and easy to manufacture.
Owner:THEEUWES MARC FRANS
Light-weight analyzer for odor recognition
InactiveUS8726719B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansConfocalChemical compound
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method, Apparatus and Computer Program for Processing Multi-Channel Signals
ActiveUS20120195435A1Reduce bitrateQuality improvementSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsNeuronComputer science
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus in which samples of at least a part of an audio signal of a first channel and a part of an audio signal of a second channel are used to produce a sparse representation of the audio signals to increase the encoding efficiency. In an example embodiment one or more audio signals are input and relevant auditory cues are determined in a time-frequency plane. The relevant auditory cues are combined to form an auditory neurons map. Said one or more audio signals are transformed into a transform domain and the auditory neurons map is used to form a sparse representation of said one or more audio signal.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com