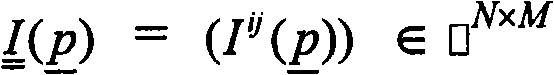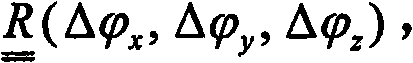Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
234 results about "Anatomic region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
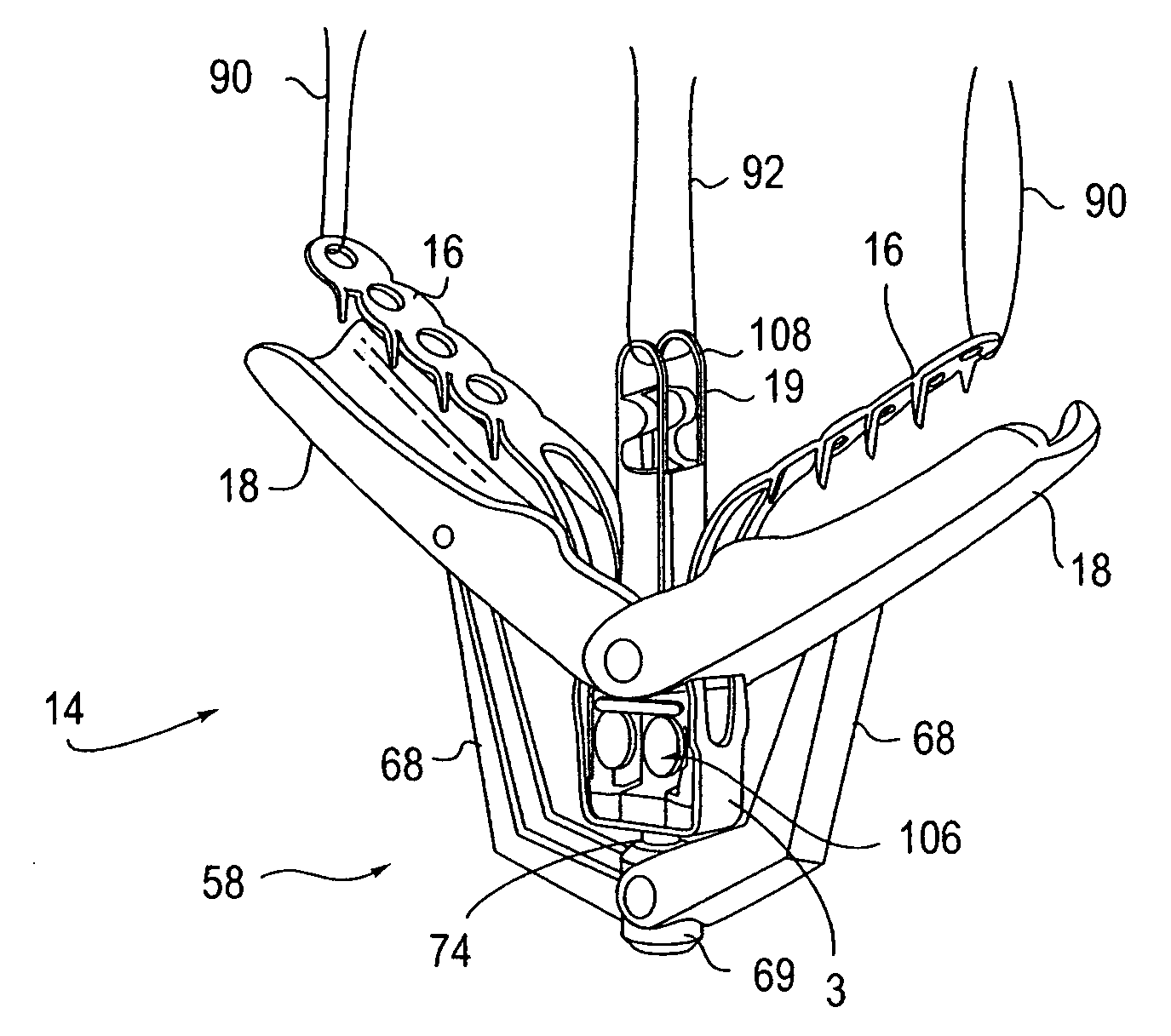
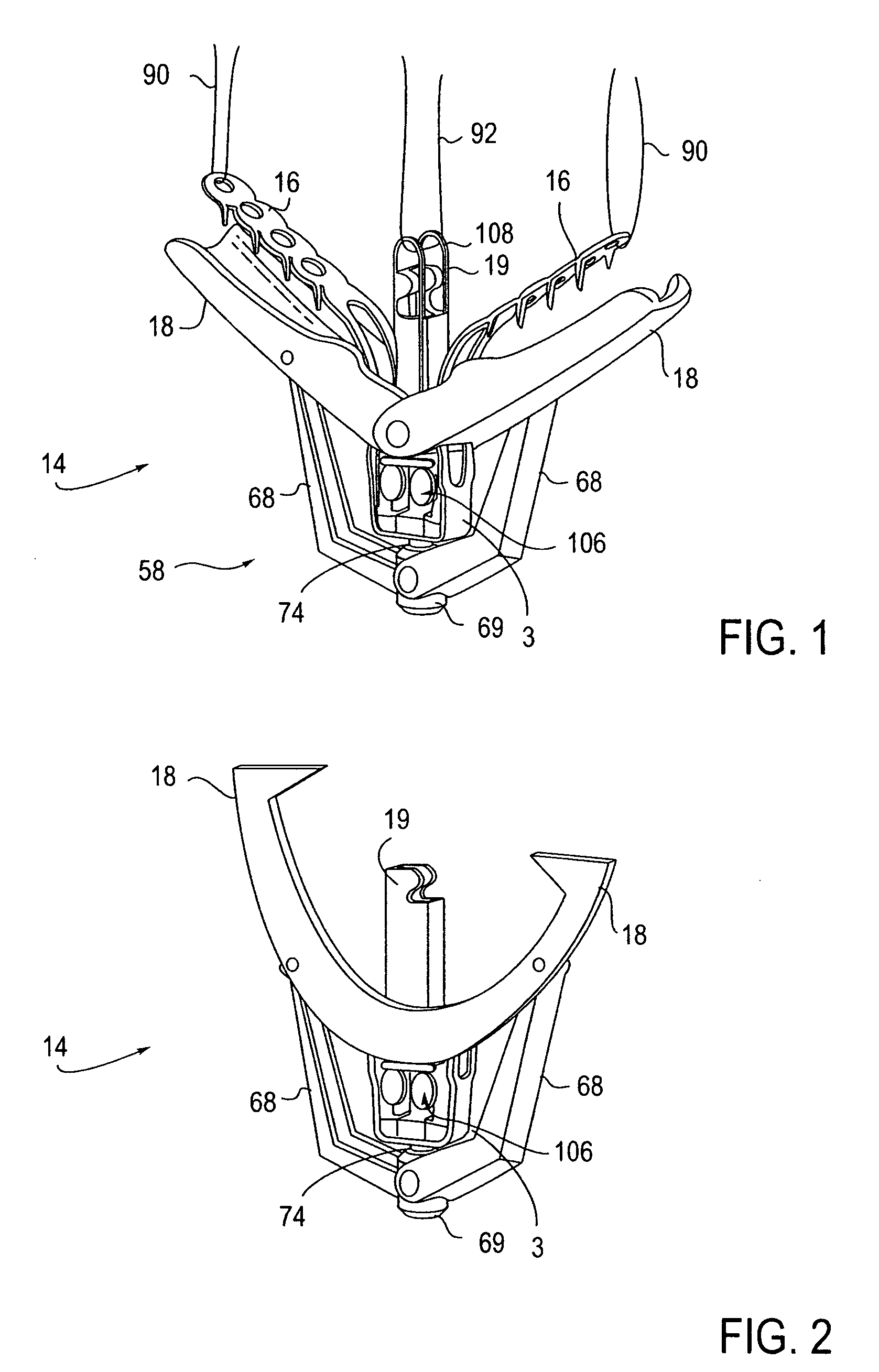
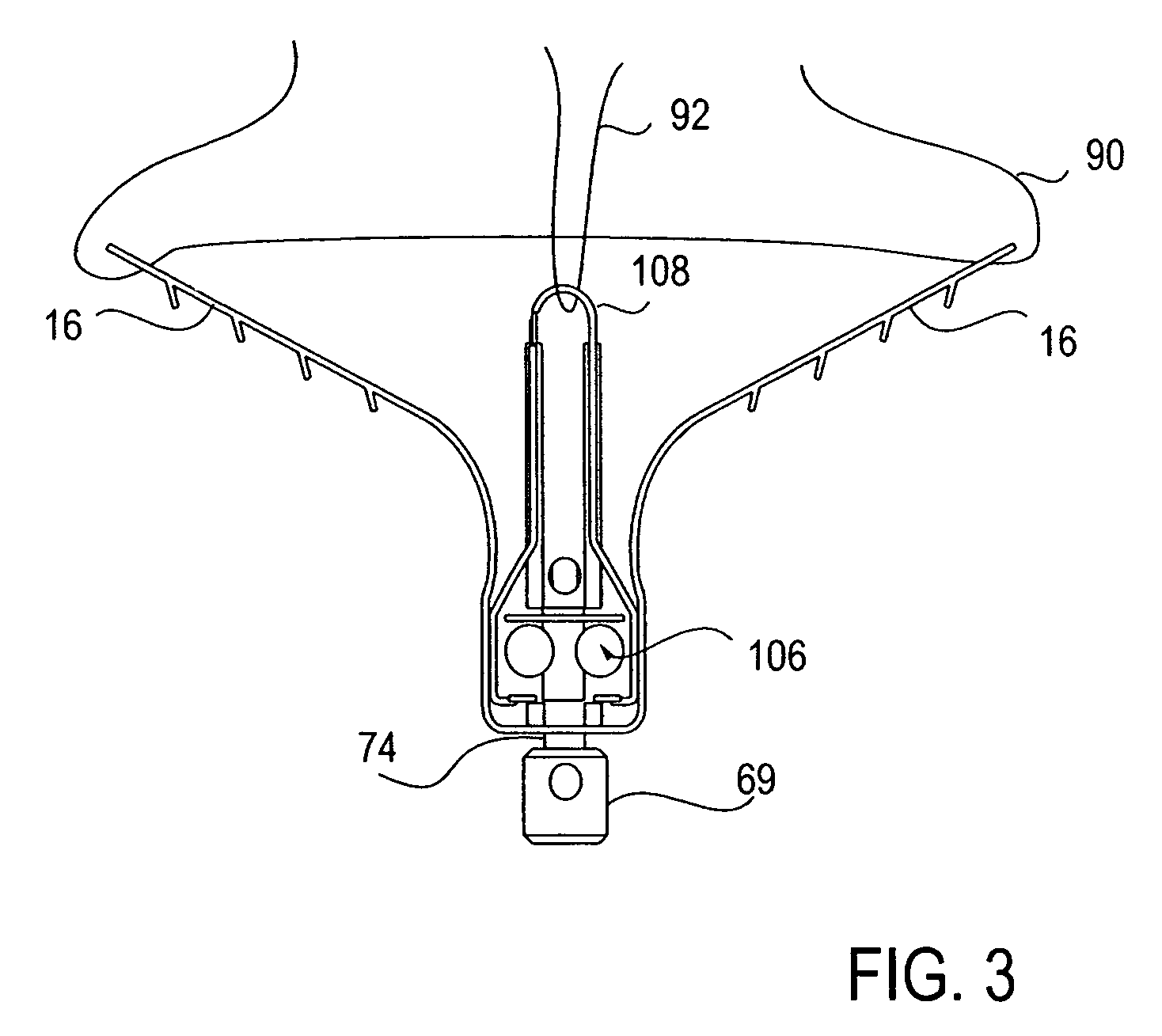
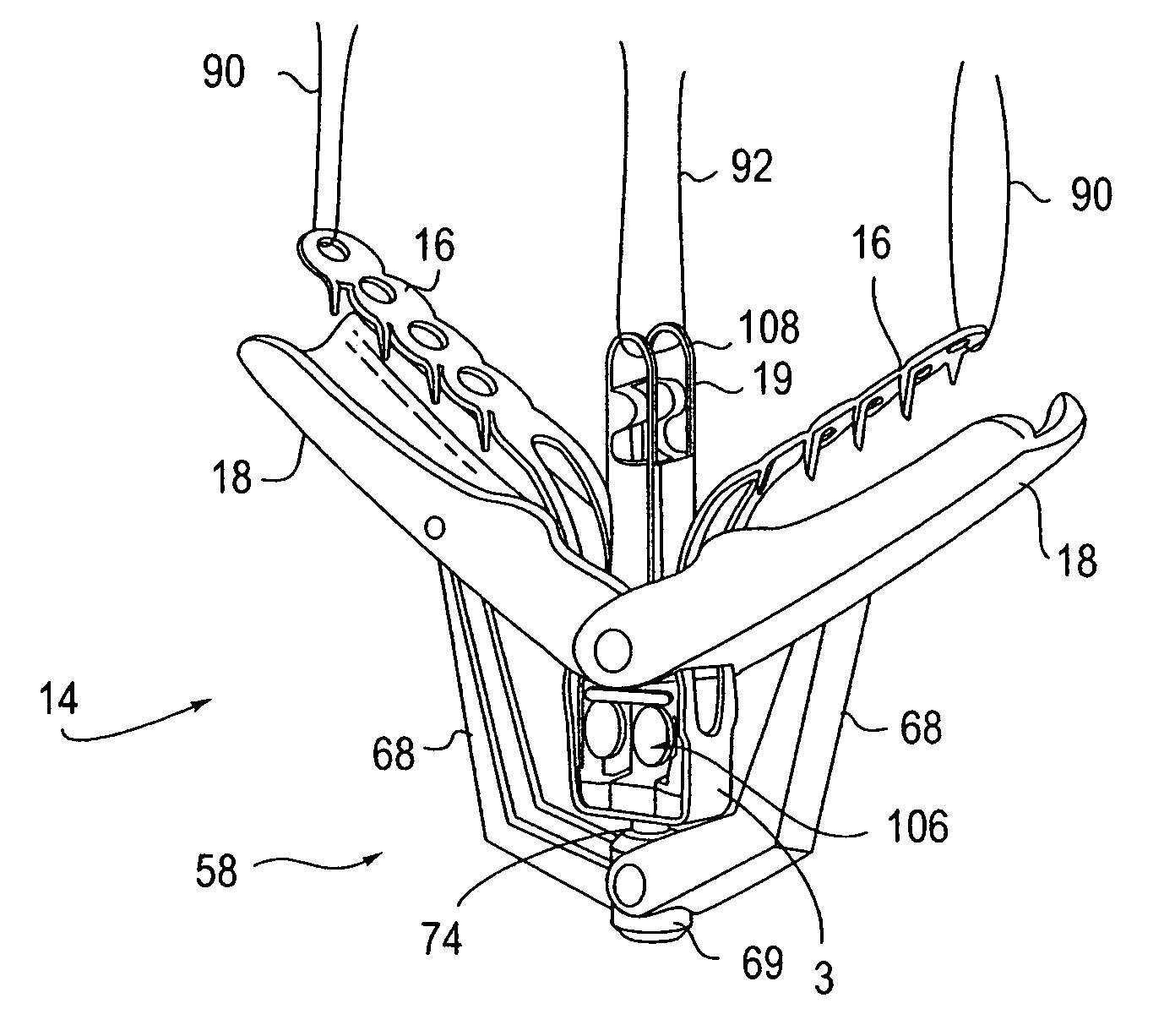
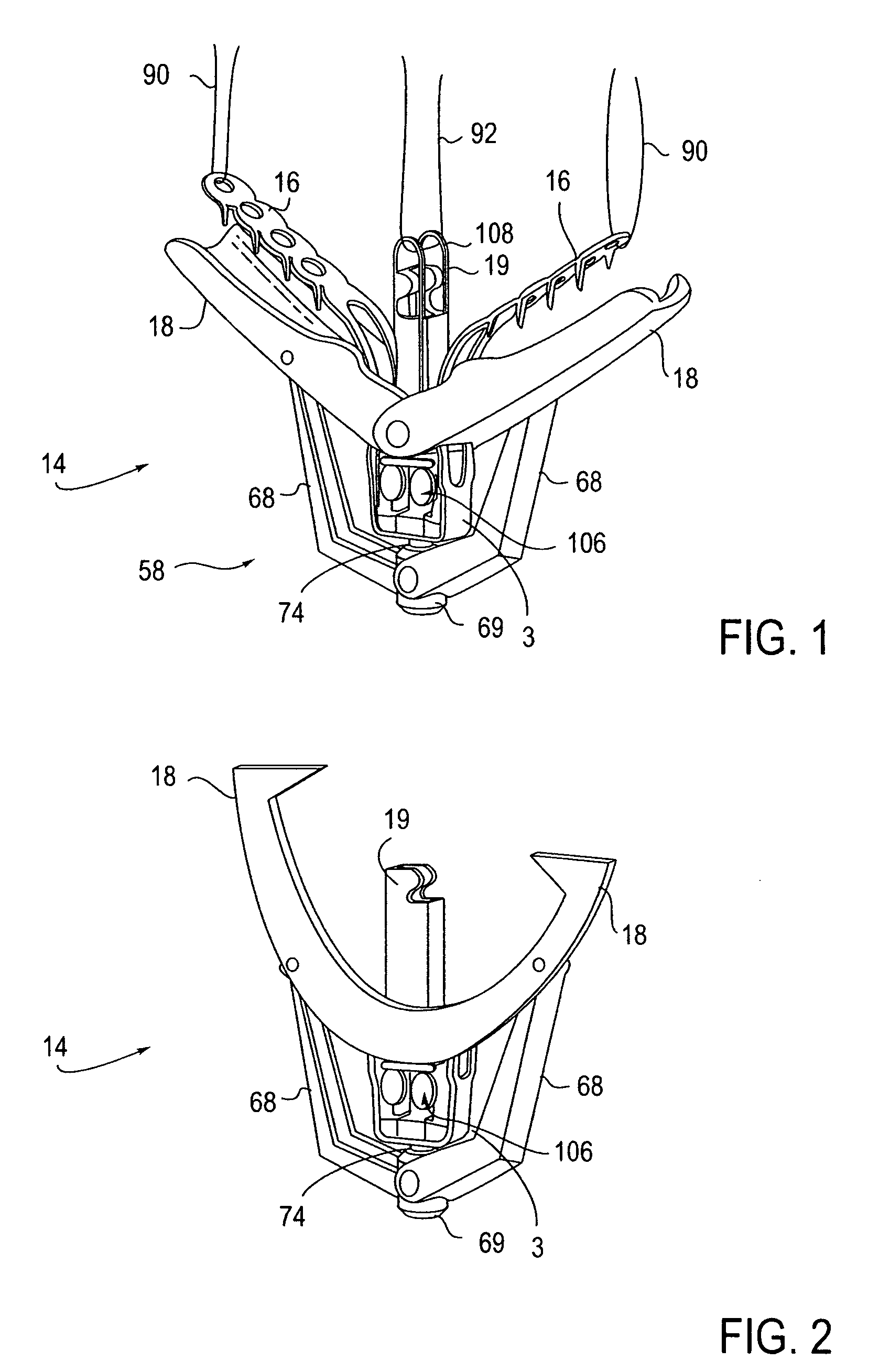
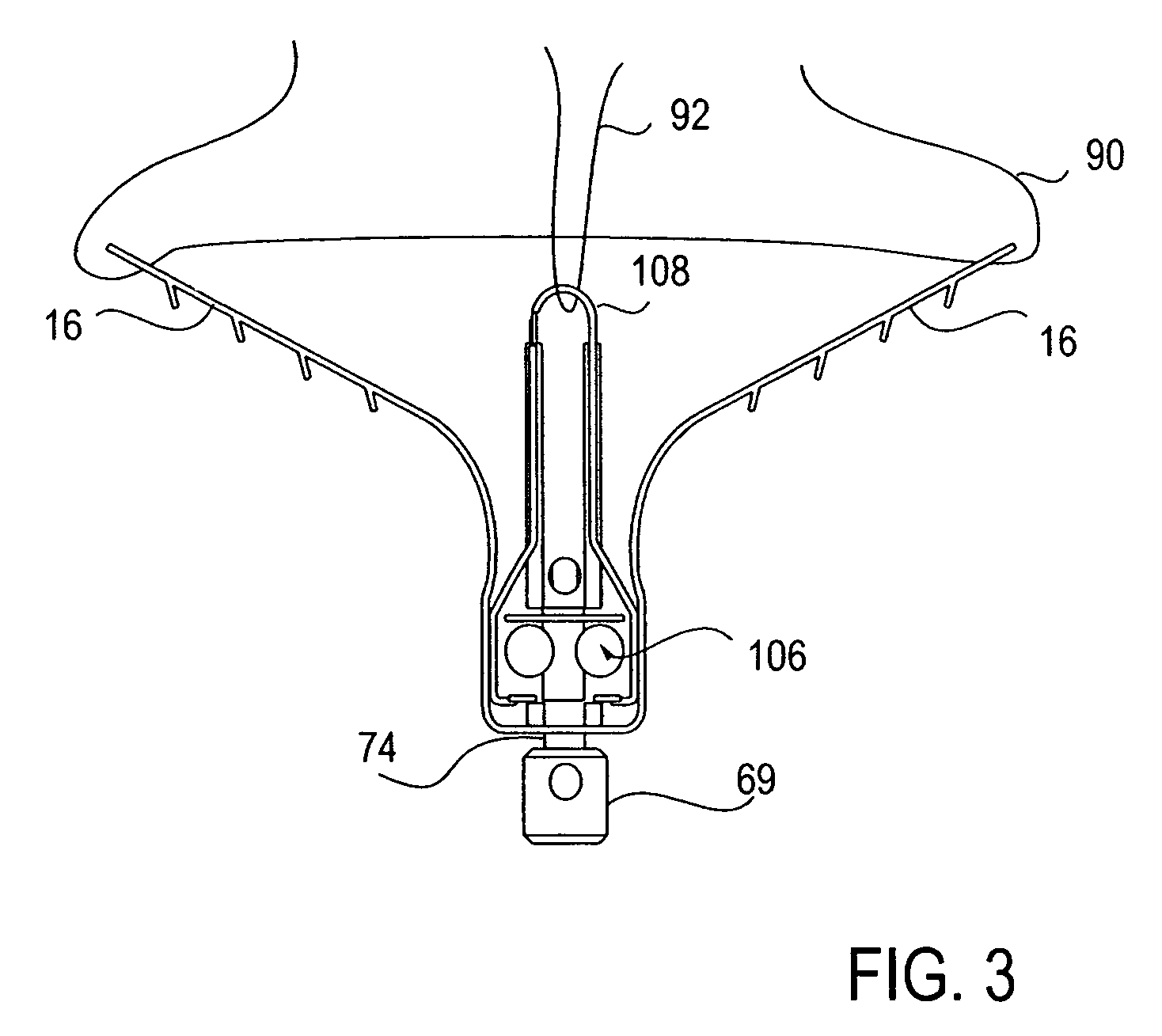
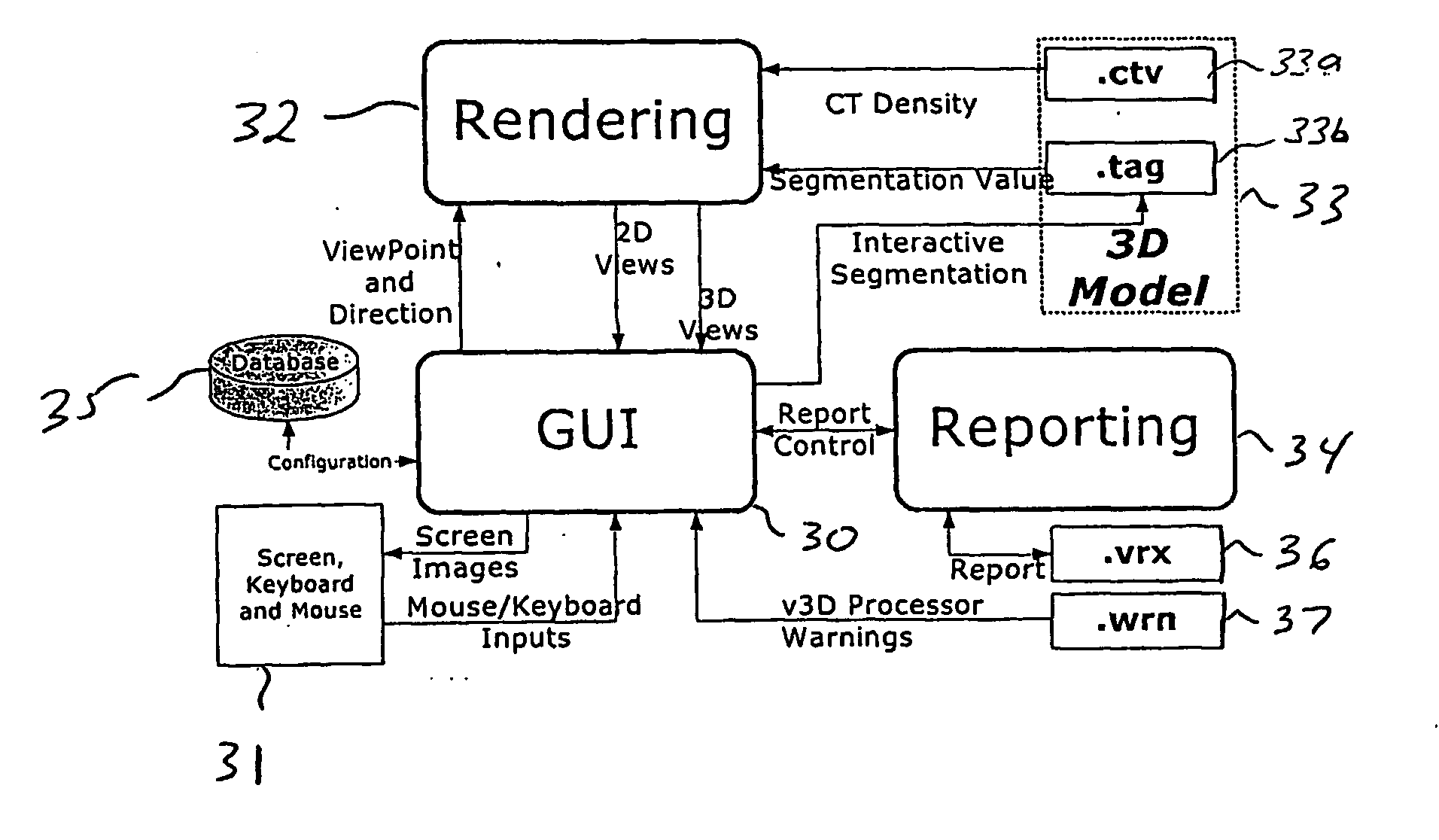
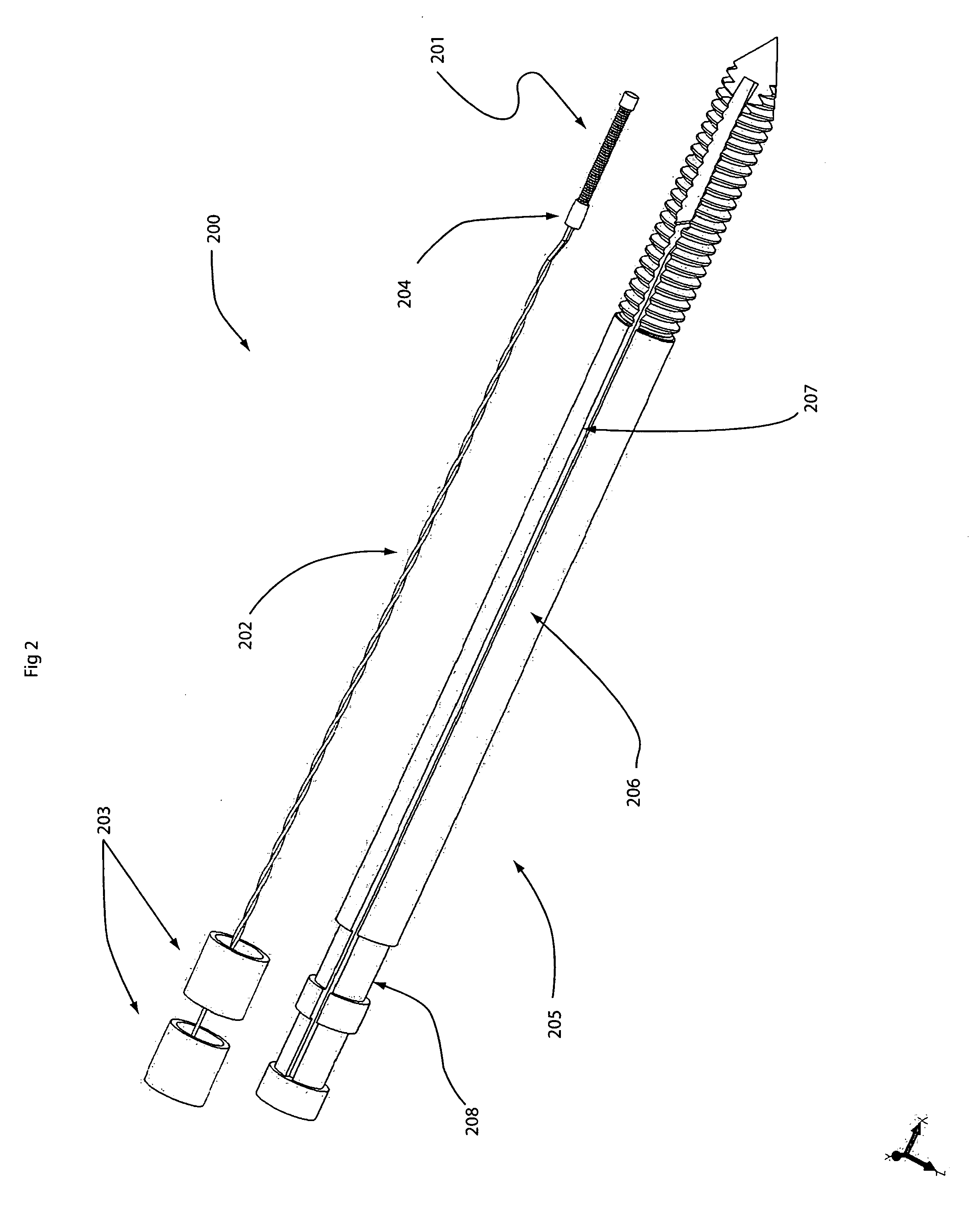
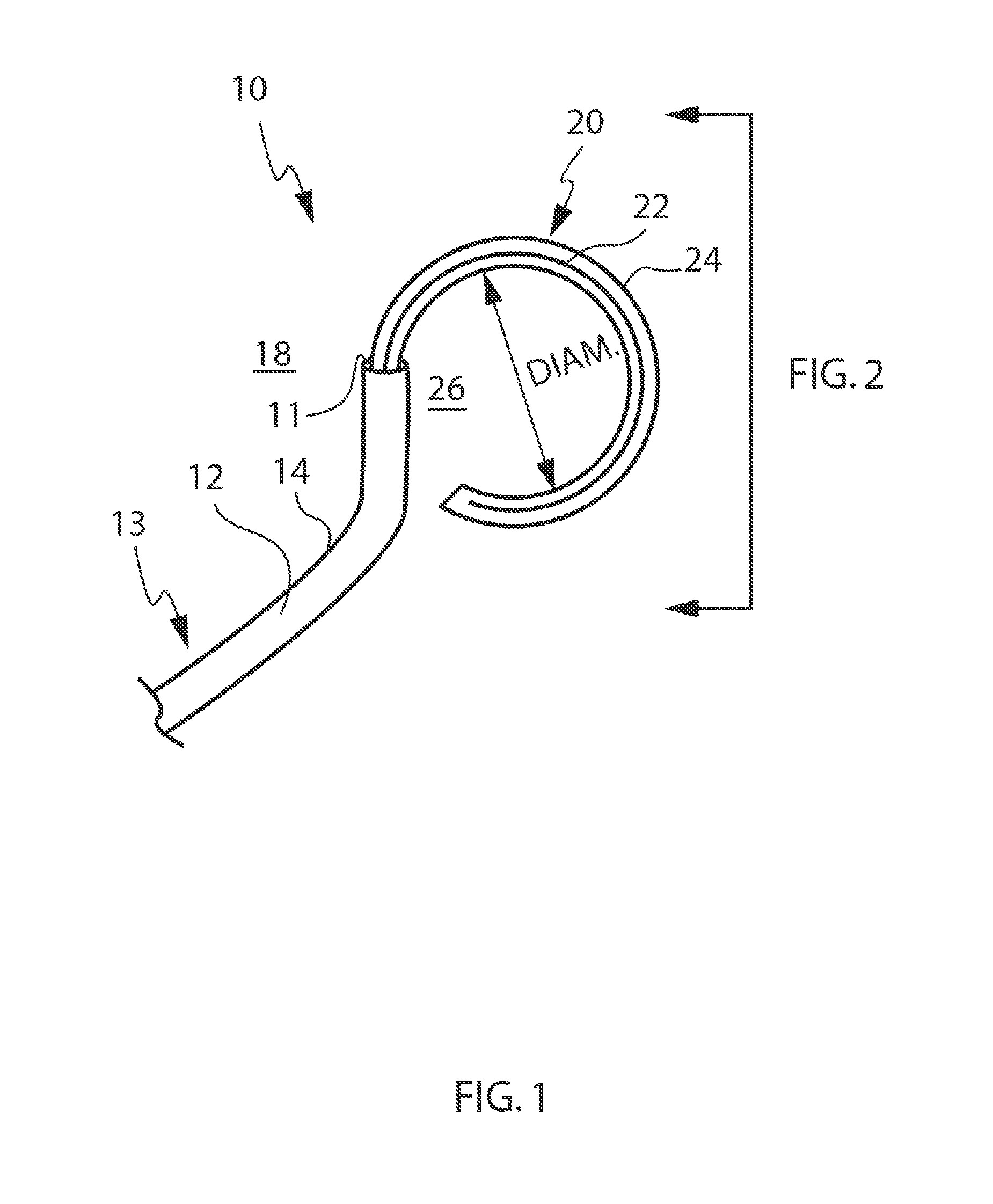
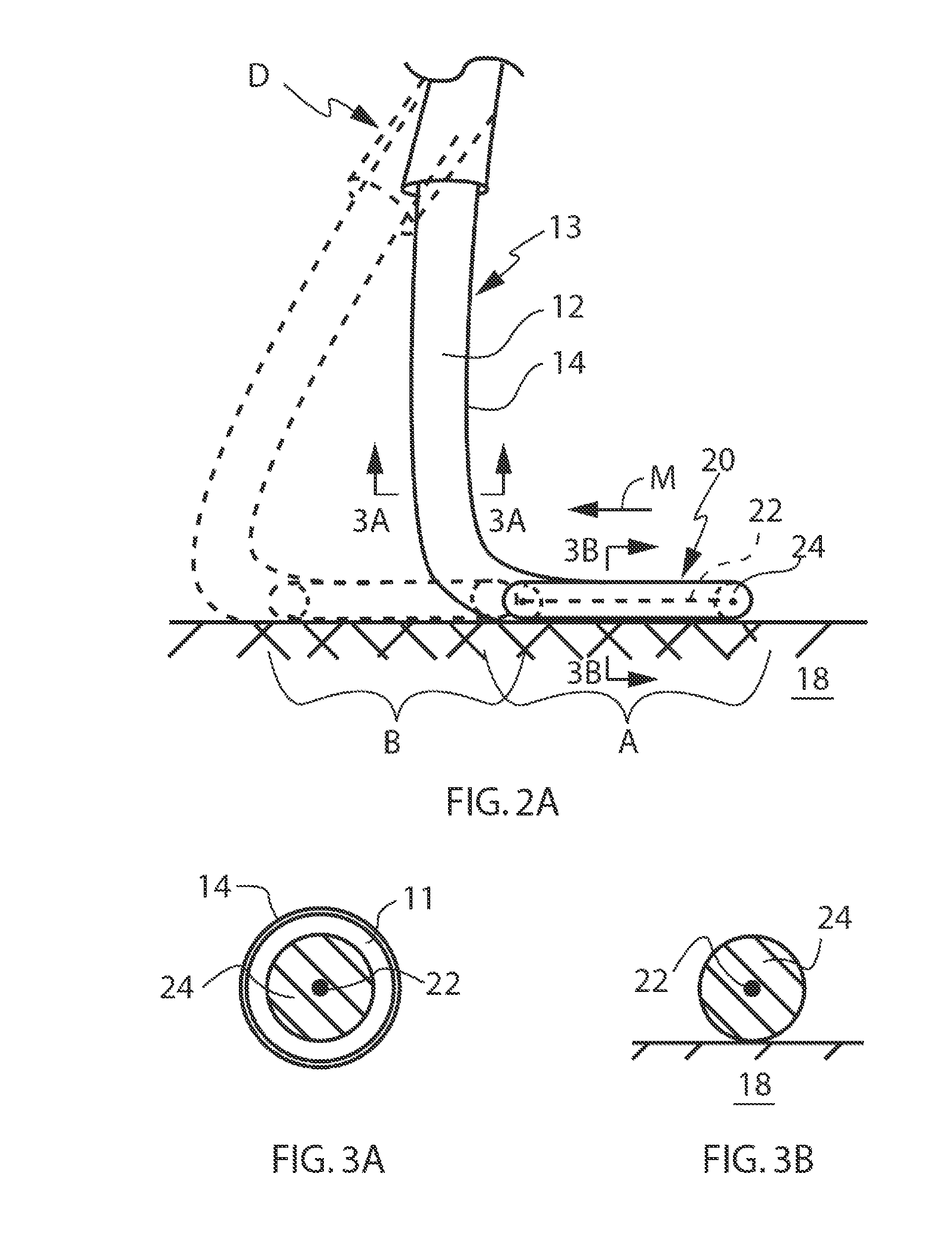
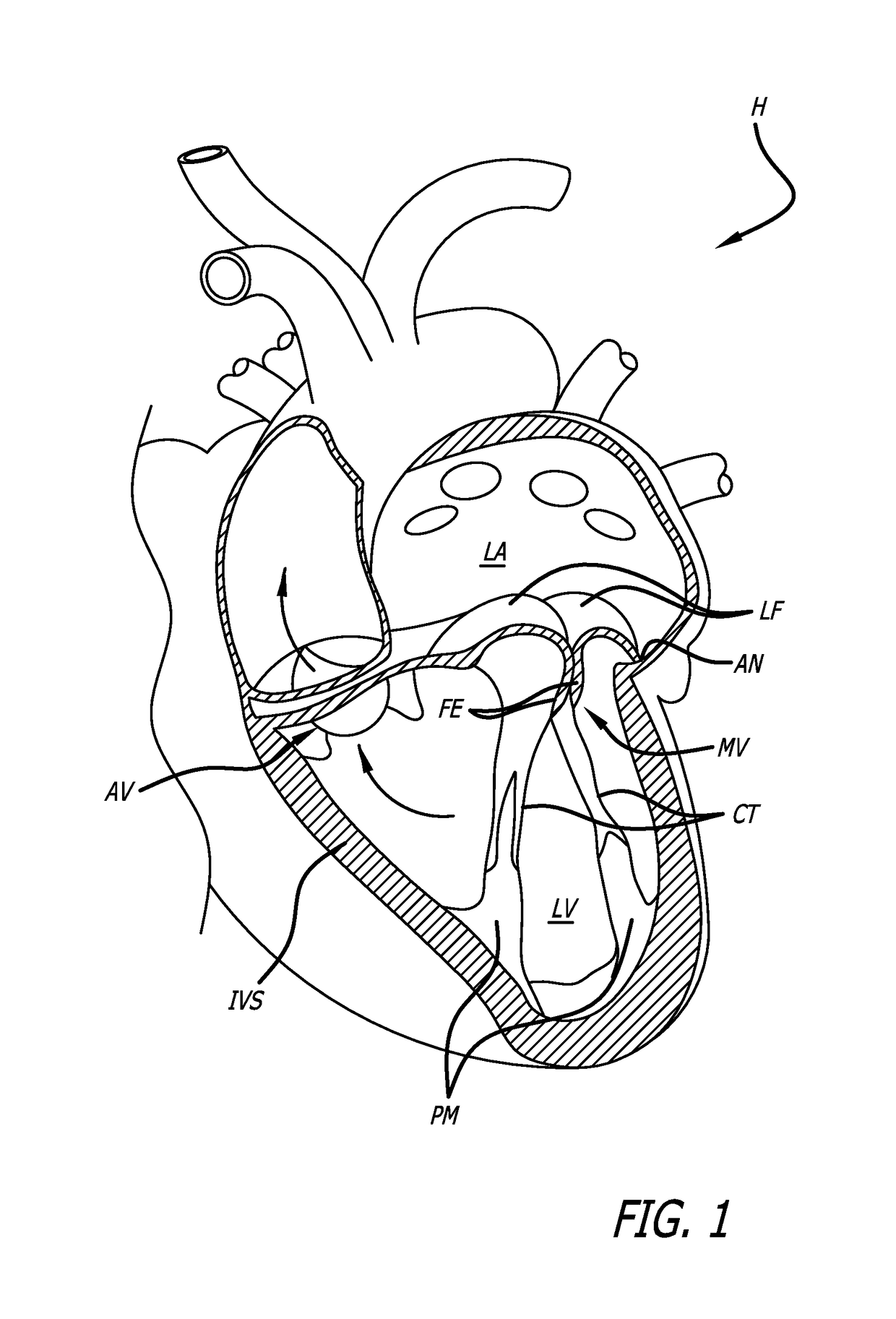
Locking mechanisms for fixation devices and methods of engaging tissue
InactiveUS20060020275A1Reduce frictional contactRestrict movementSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringThoracic cavity
Devices, systems and methods are provided for tissue approximation and repair at treatment sites. In particular, fixation devices are provided comprising a pair of elements each having a first end, a free end opposite the first end, and an engagement surface therebetween for engaging the tissue, the first ends being moveable between an open position wherein the free ends are spaced apart and a closed position wherein the free ends are closer together with the engagement surfaces generally facing each other. The fixation devices also include a locking mechanism coupled to the elements for locking the elements in place. The devices, systems and methods of the invention will find use in a variety of therapeutic procedures, including endovascular, minimally-invasive, and open surgical procedures, and can be used in various anatomical regions, including the abdomen, thorax, cardiovascular system, heart, intestinal tract, stomach, urinary tract, bladder, lung, and other organs, vessels, and tissues. The invention is particularly useful in those procedures requiring minimally-invasive or endovascular access to remote tissue locations, where the instruments utilized must negotiate long, narrow, and tortuous pathways to the treatment site.
Owner:EVALVE
Locking mechanisms for fixation devices and methods of engaging tissue
InactiveUS7604646B2Prevent movementReduce frictional contactSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsEngineeringSurgical department
Owner:EVALVE
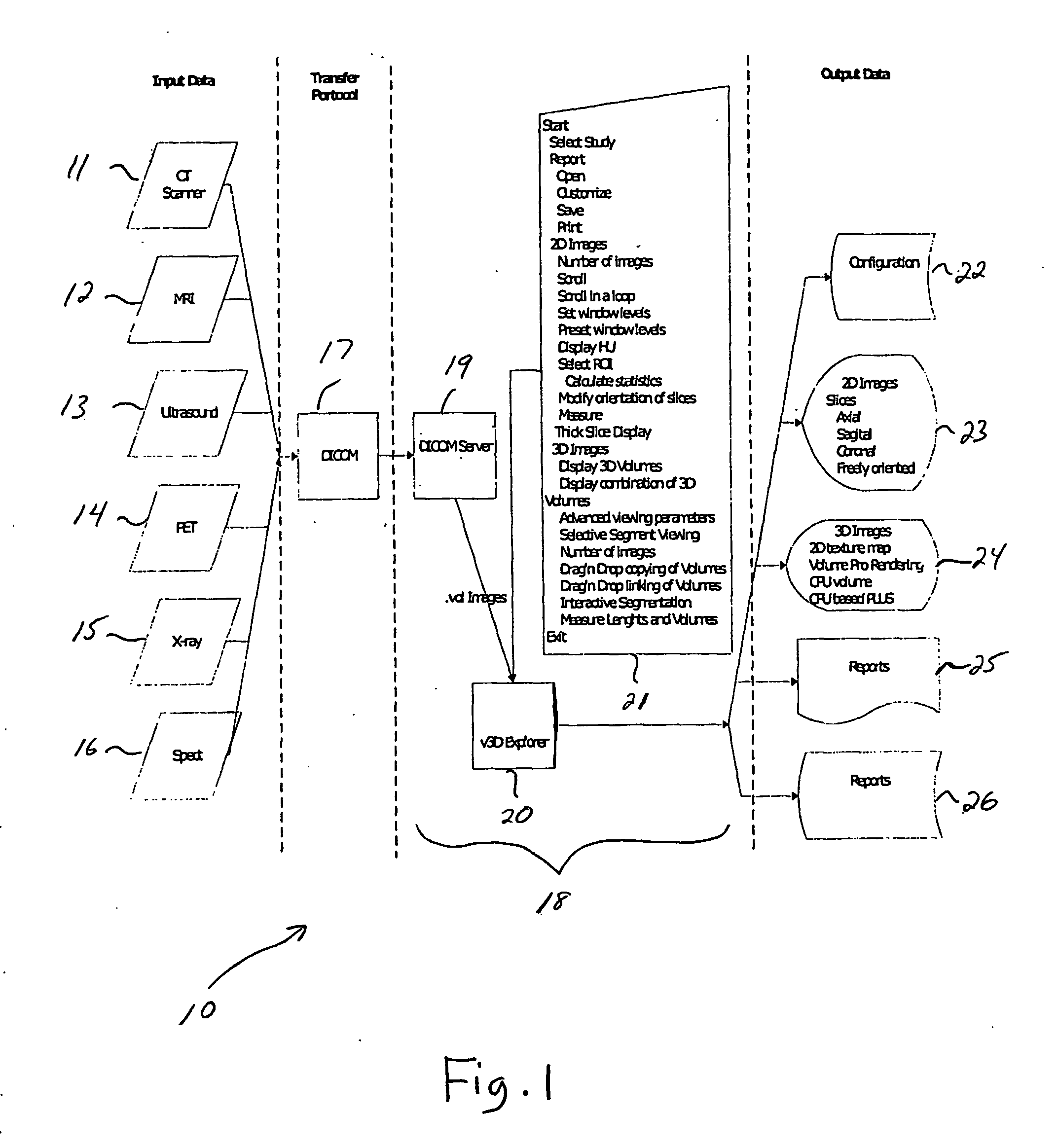
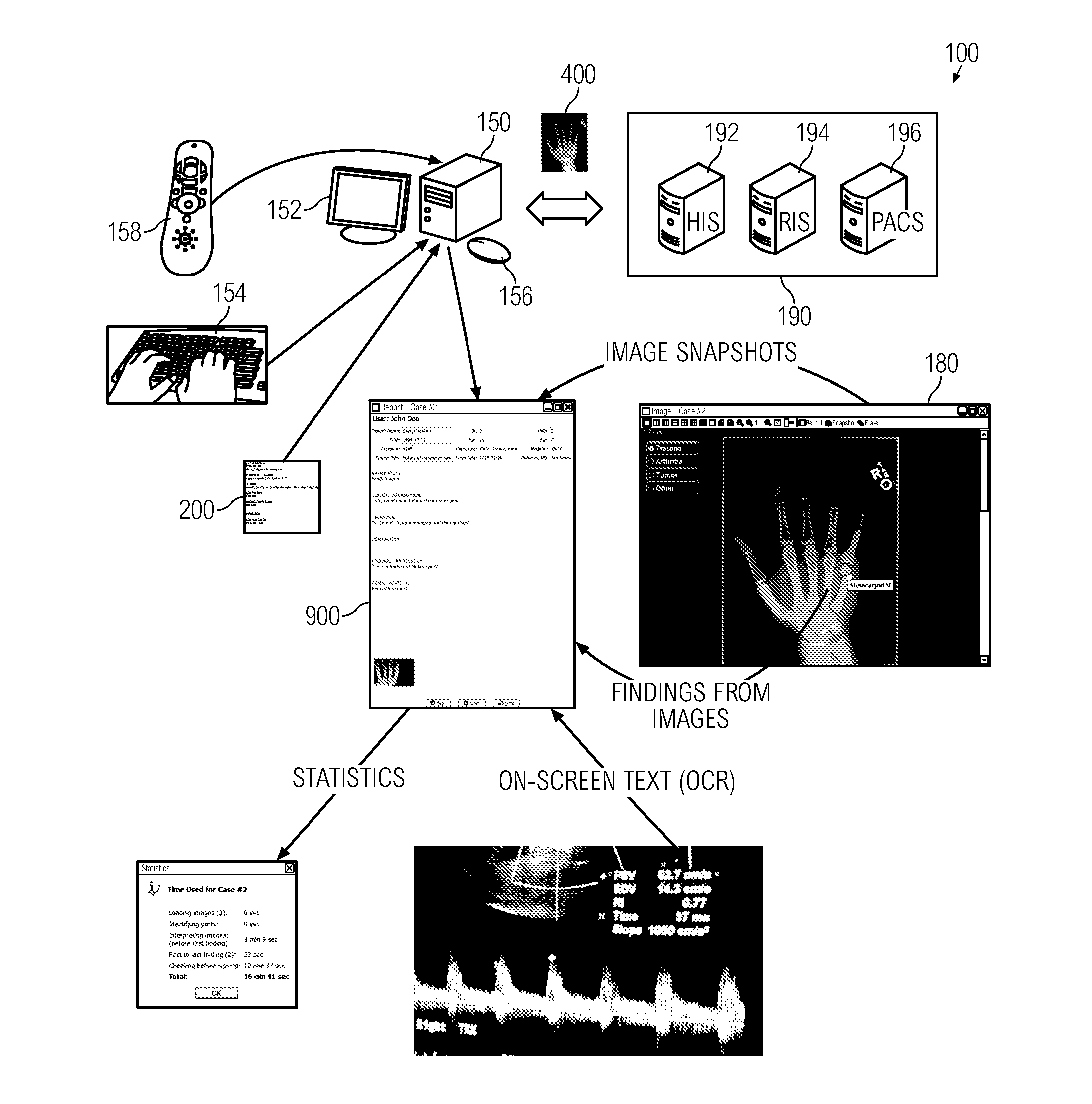
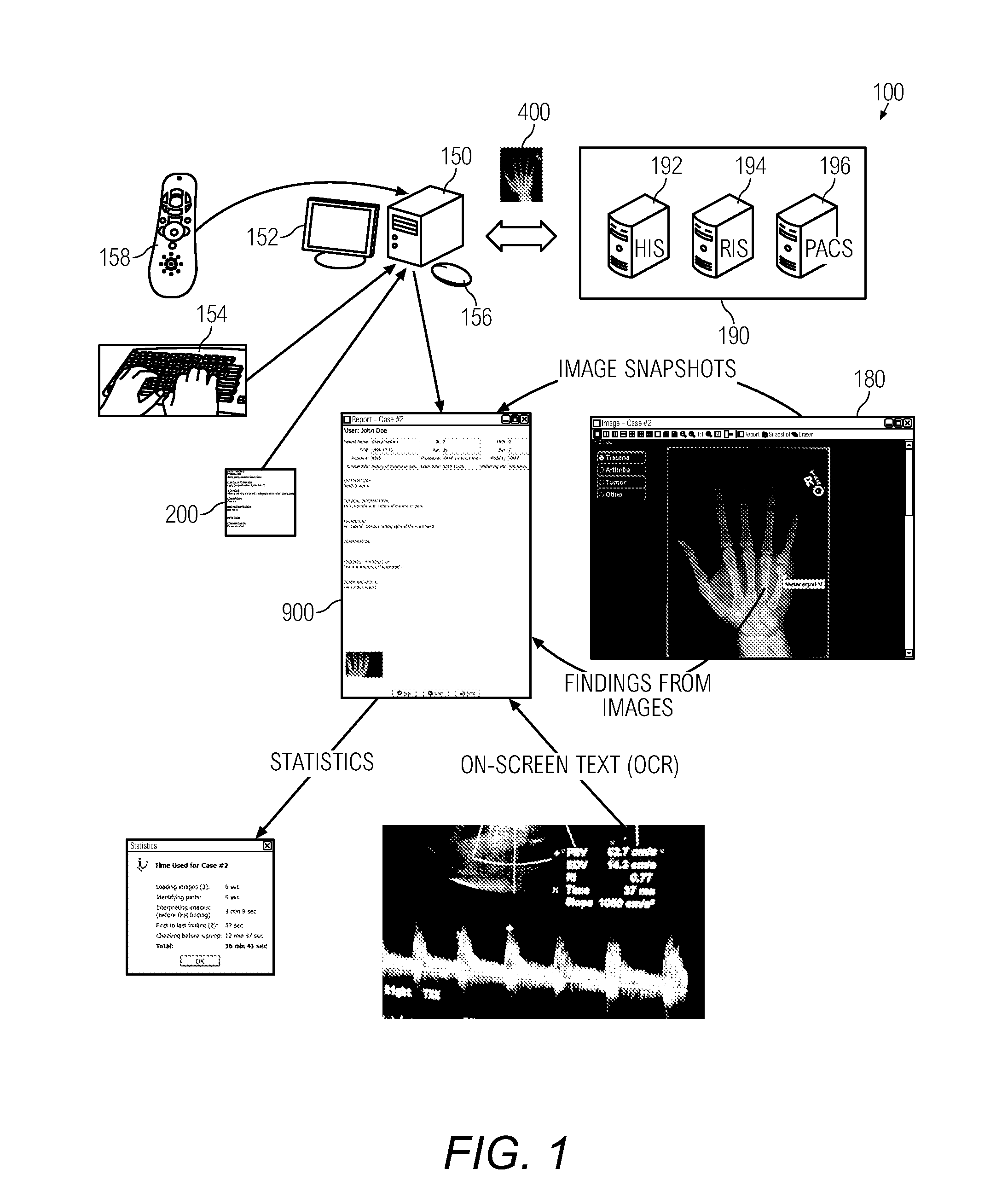
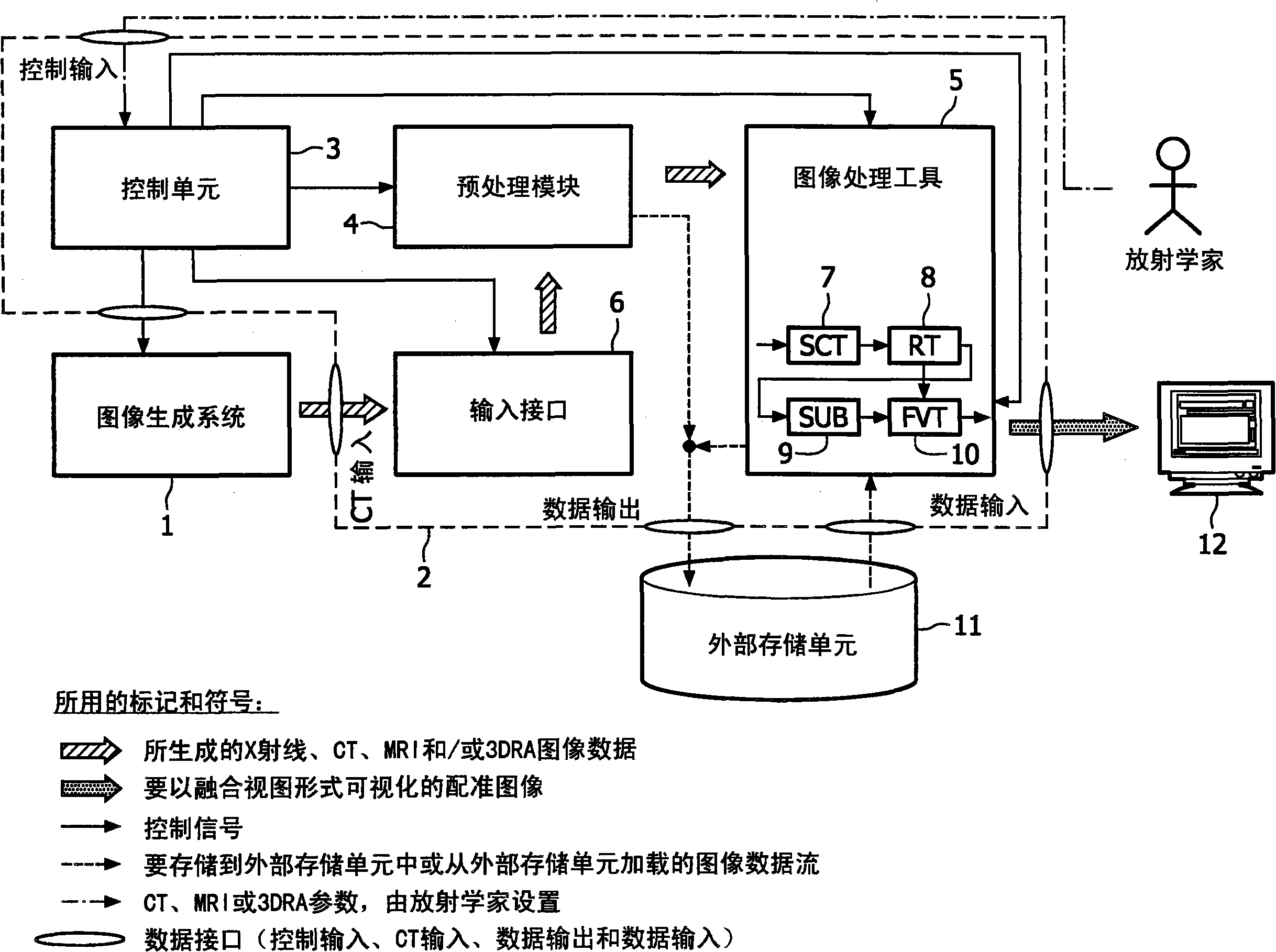
System and method for visualization and navigation of three-dimensional medical images
InactiveUS20050228250A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsAutomatic segmentationUser interface
A user interface (90) comprises an image area that is divided into a plurality of views for viewing corresponding 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional images of an anatomical region. Tool control panes (95-101) can be simultaneously opened and accessible. The segmentation pane (98) enables automatic segmentation of components of a displayed image within a user-specified intensity range or based on a predetermined intensity
Owner:VIATRONIX
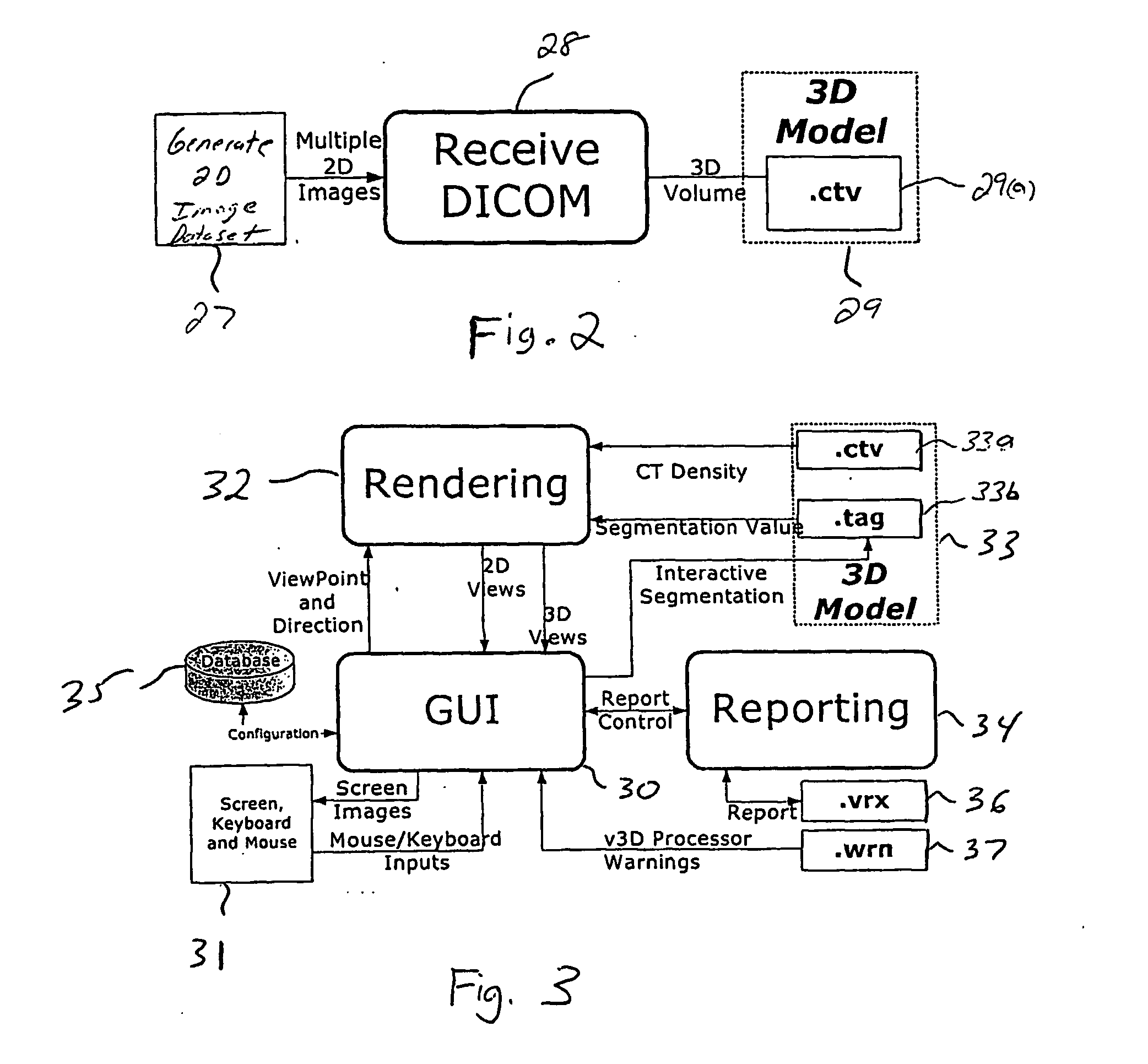
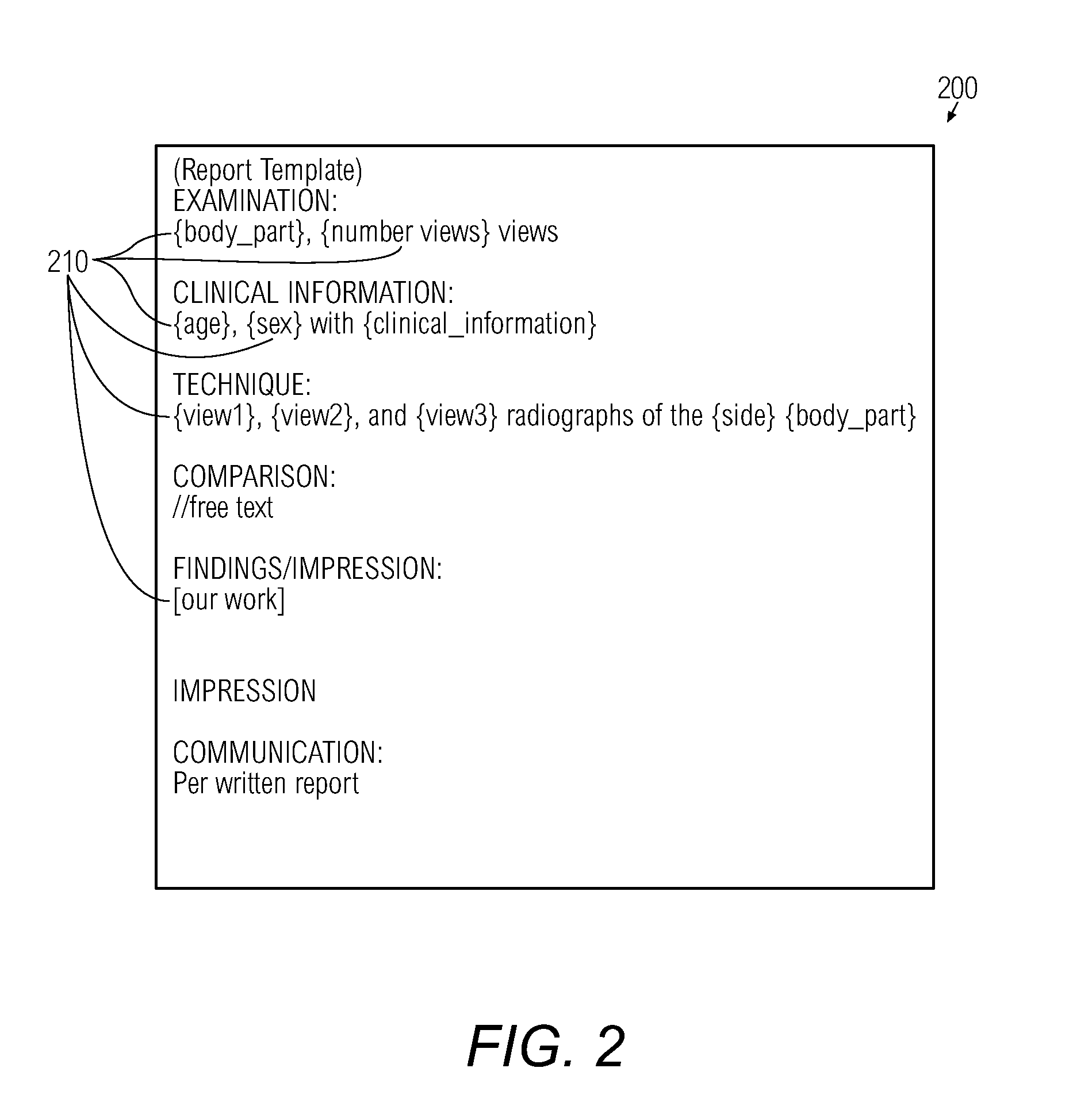
Method for creating a report from radiological images using electronic report templates
InactiveUS20130251233A1Maximize similarity scoreAccurate fitImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical landmarkReference Region
Creating a report from a radiological image using an electronic report template, the radiological image being an image of an anatomic region and the report template initially having empty fields includes displaying the radiological image on a screen of a workstation; providing a structural template, the structural template being a map of a reference region that corresponds to the anatomical region, t structural template identifying a plurality of anatomical landmarks each associated with corresponding landmark data; fitting the structural template with the radiological image such that the anatomical landmarks match corresponding anatomical landmarks of the radiological image; using the fitting to generate pathological data indicative of a pathology in one or more of the anatomical landmark and using the landmark data and pathological data to populate the empty field of the report template to thereby create the report.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Specially shaped balloon device for use in surgery and method of use
A balloon device useful for dissecting tissue or retracting tissue for the purpose of providing access for laparoscopic surgery, the device comprising a balloon which inflates to a shape specially suitable for the surgical procedure and the anatomical region of deployment. The present device, when configured with a tapered dissection balloon, is particularly useful for subfascial endoscopic perforator surgical procedures.
Owner:GEN SURGICAL INNOVATIONS
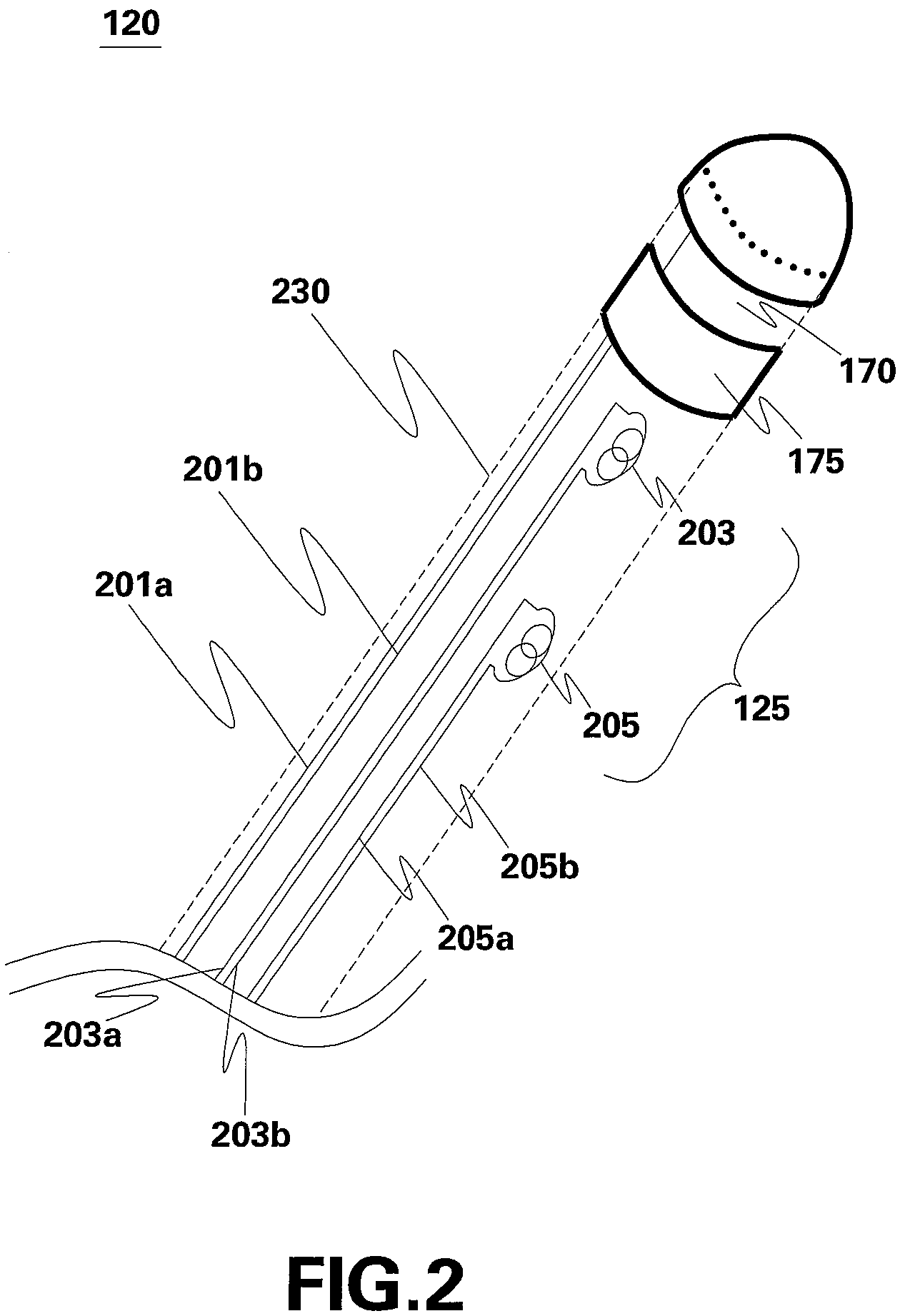
Integrated ultrasound imaging and ablation probe
InactiveUS20070073135A1Ease of evaluationConvenient treatmentUltrasound therapyElectrocardiographyUltrasound imagingTreatment demand
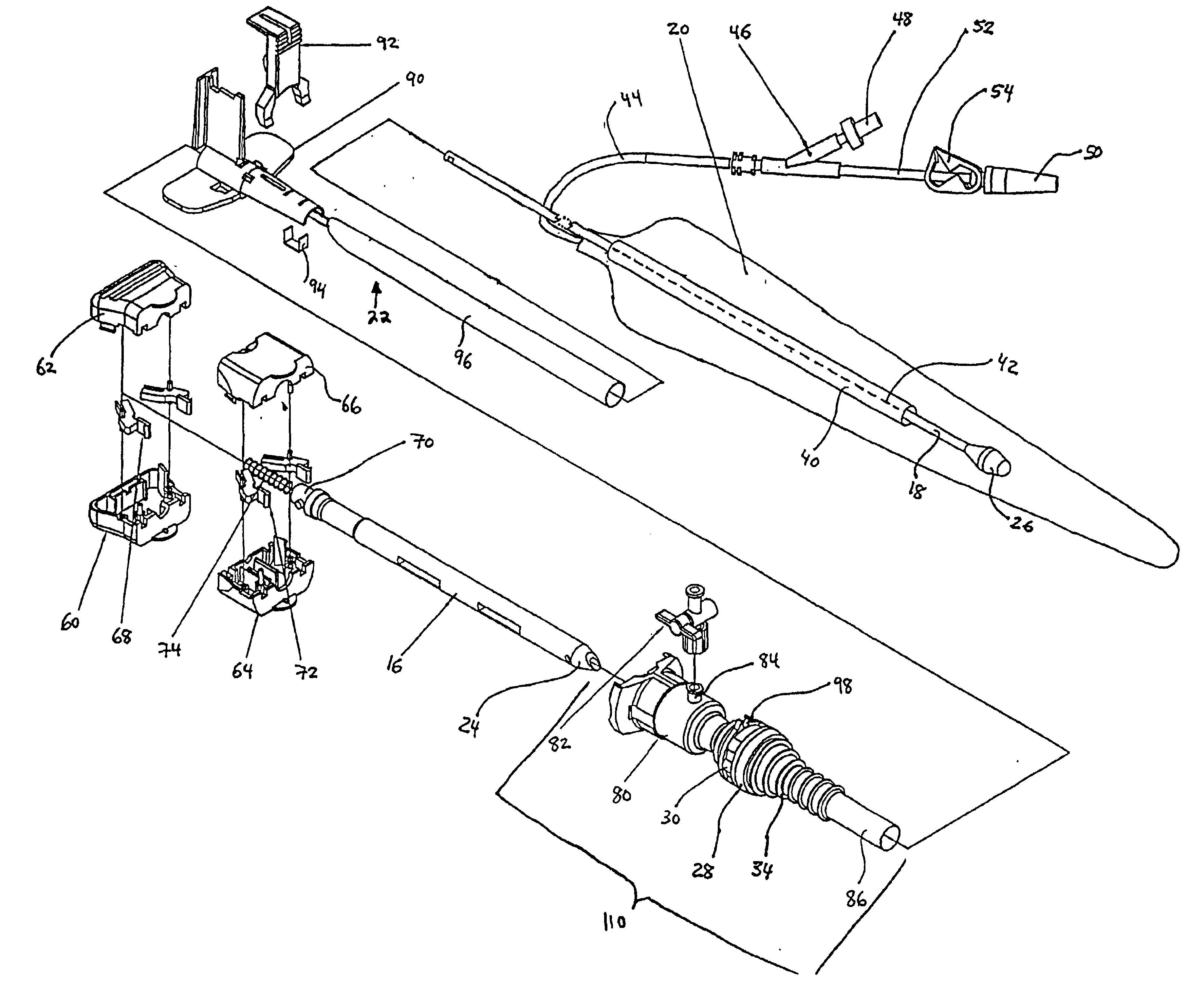
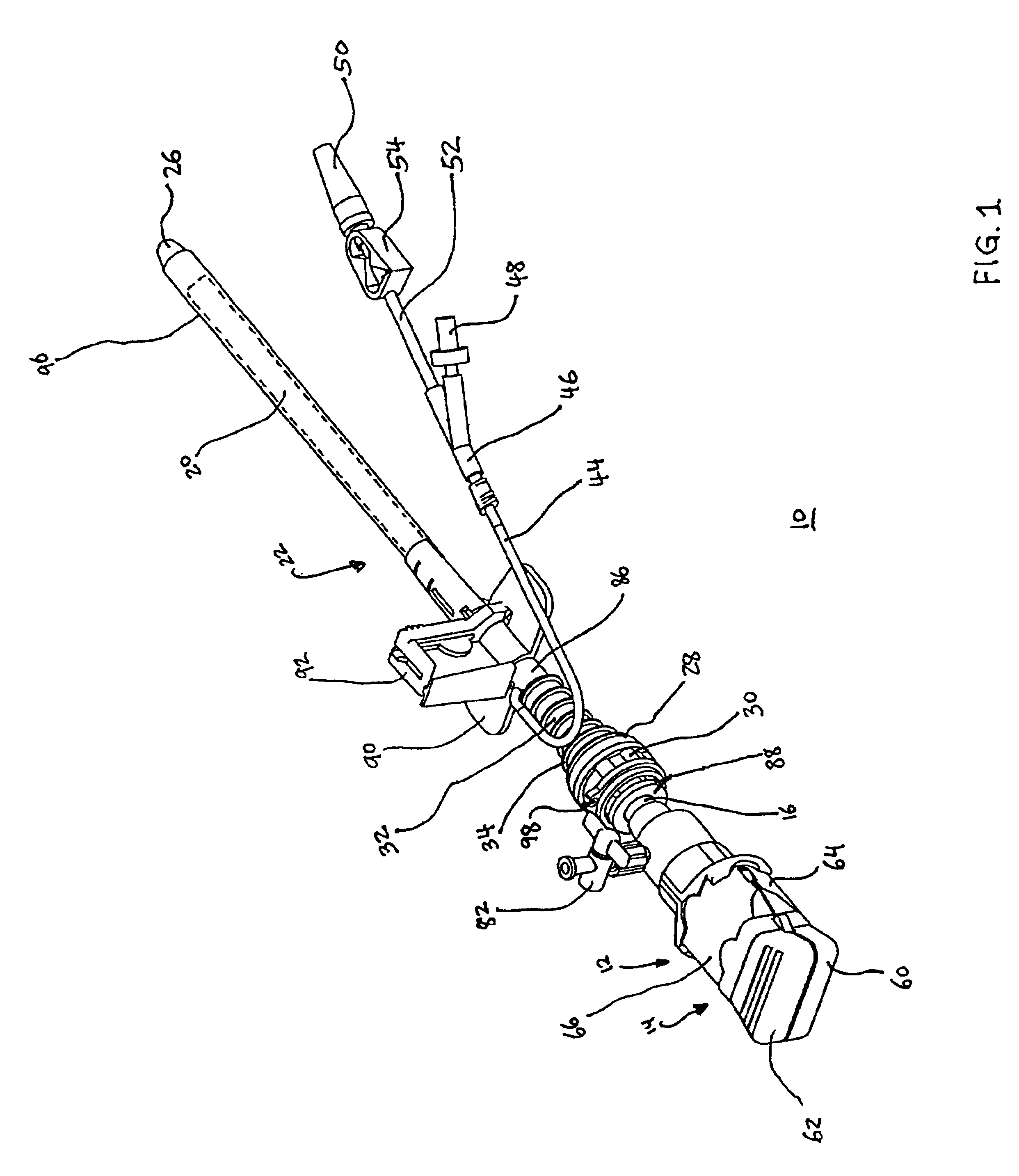
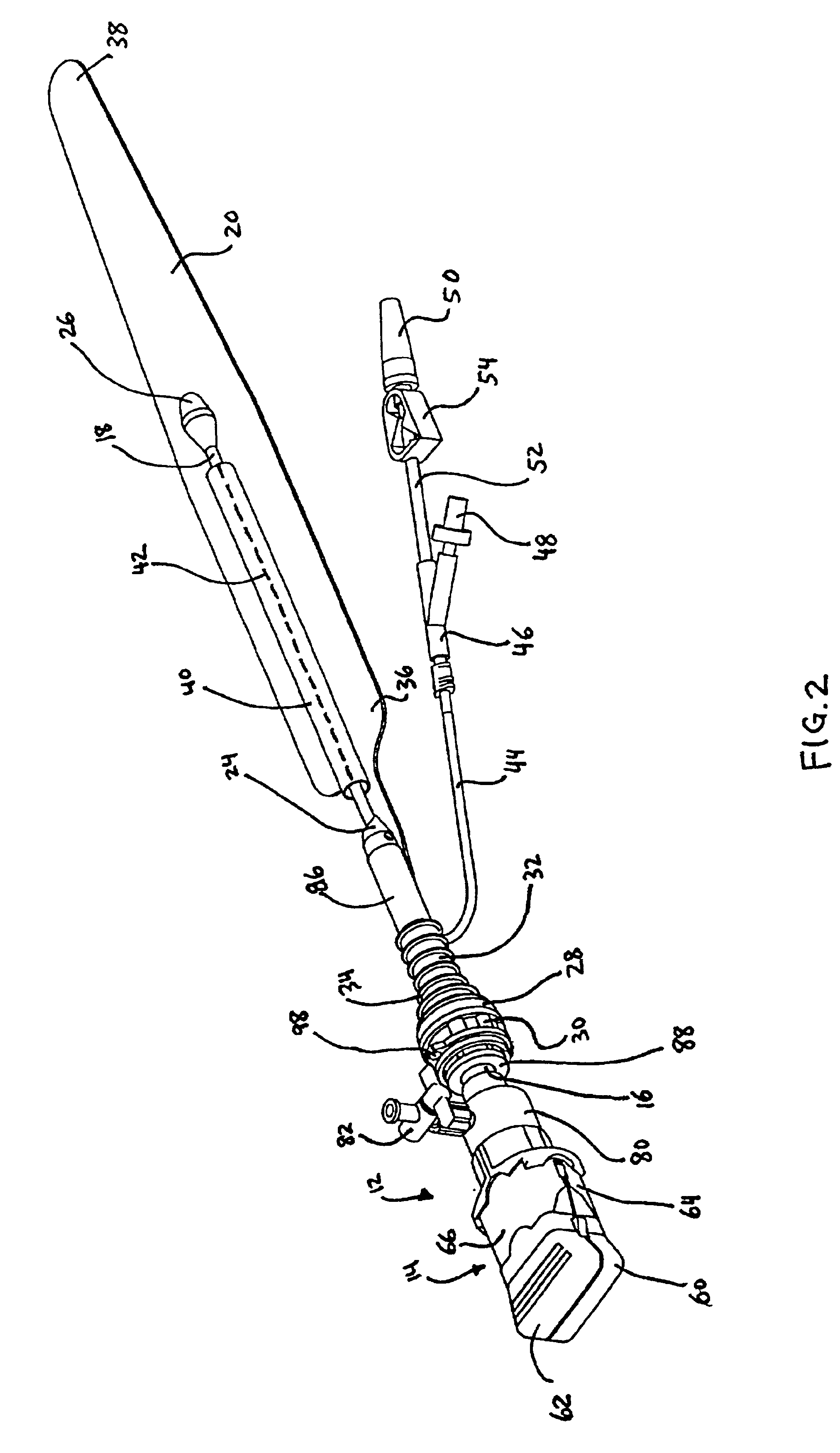
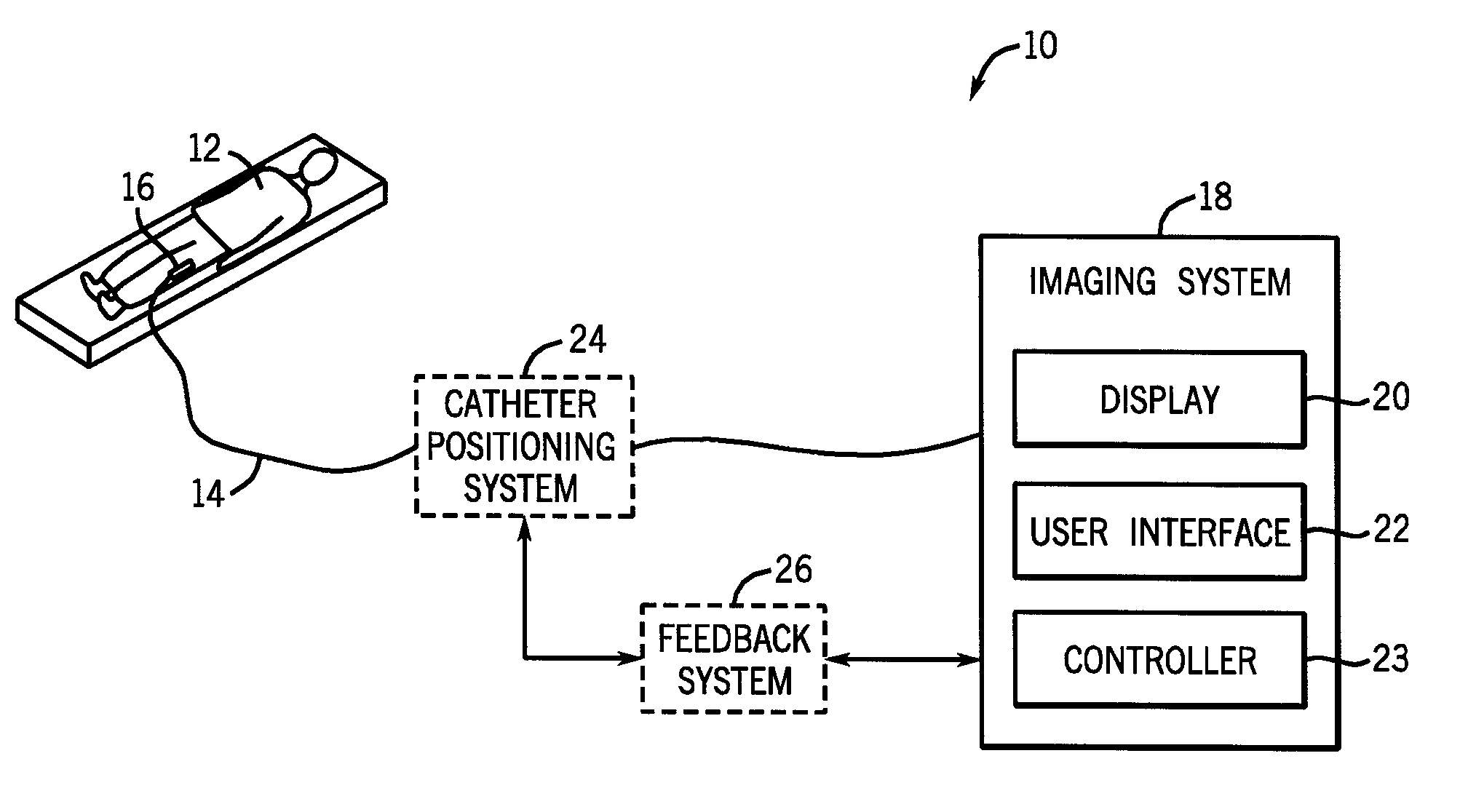
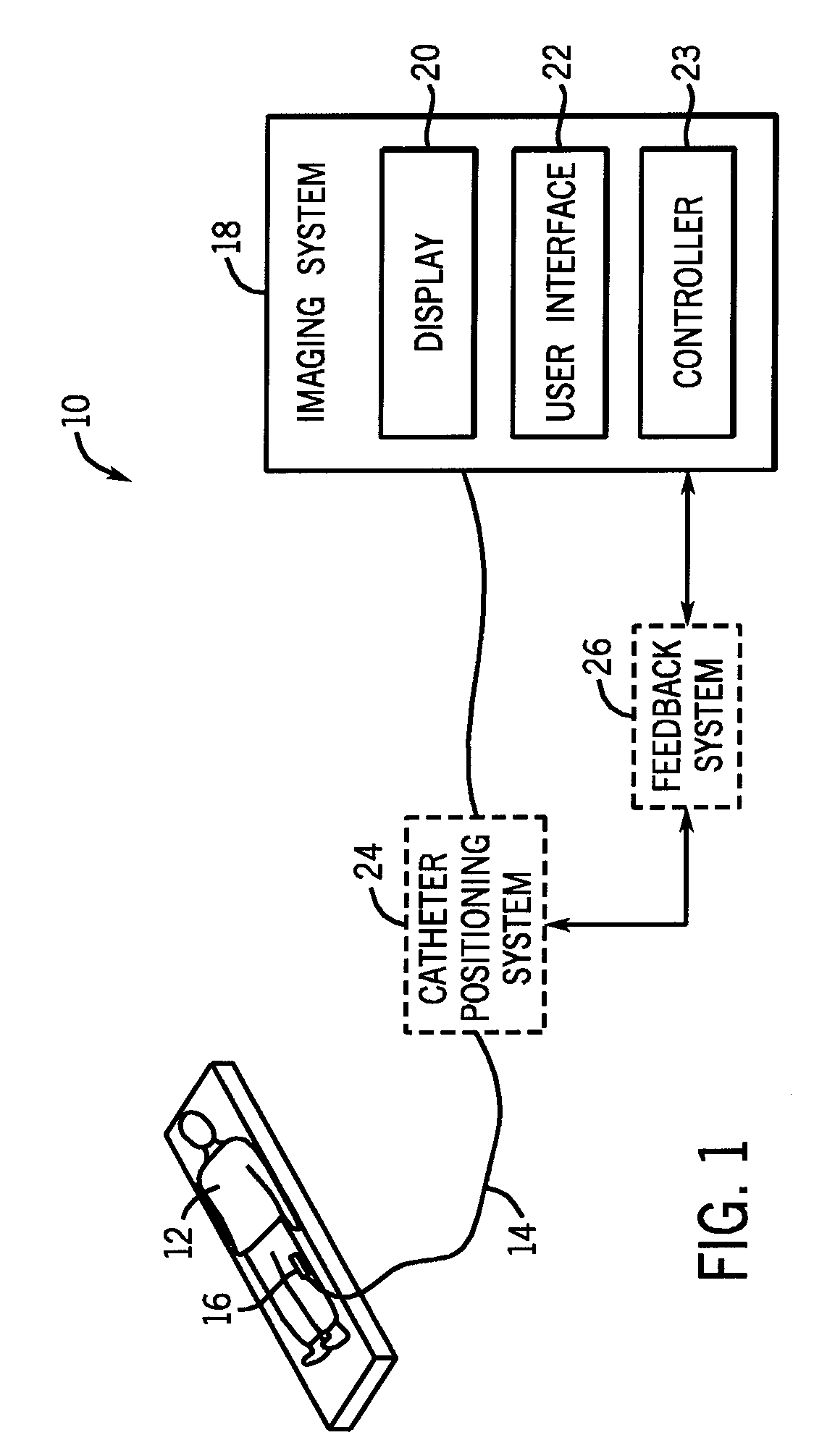
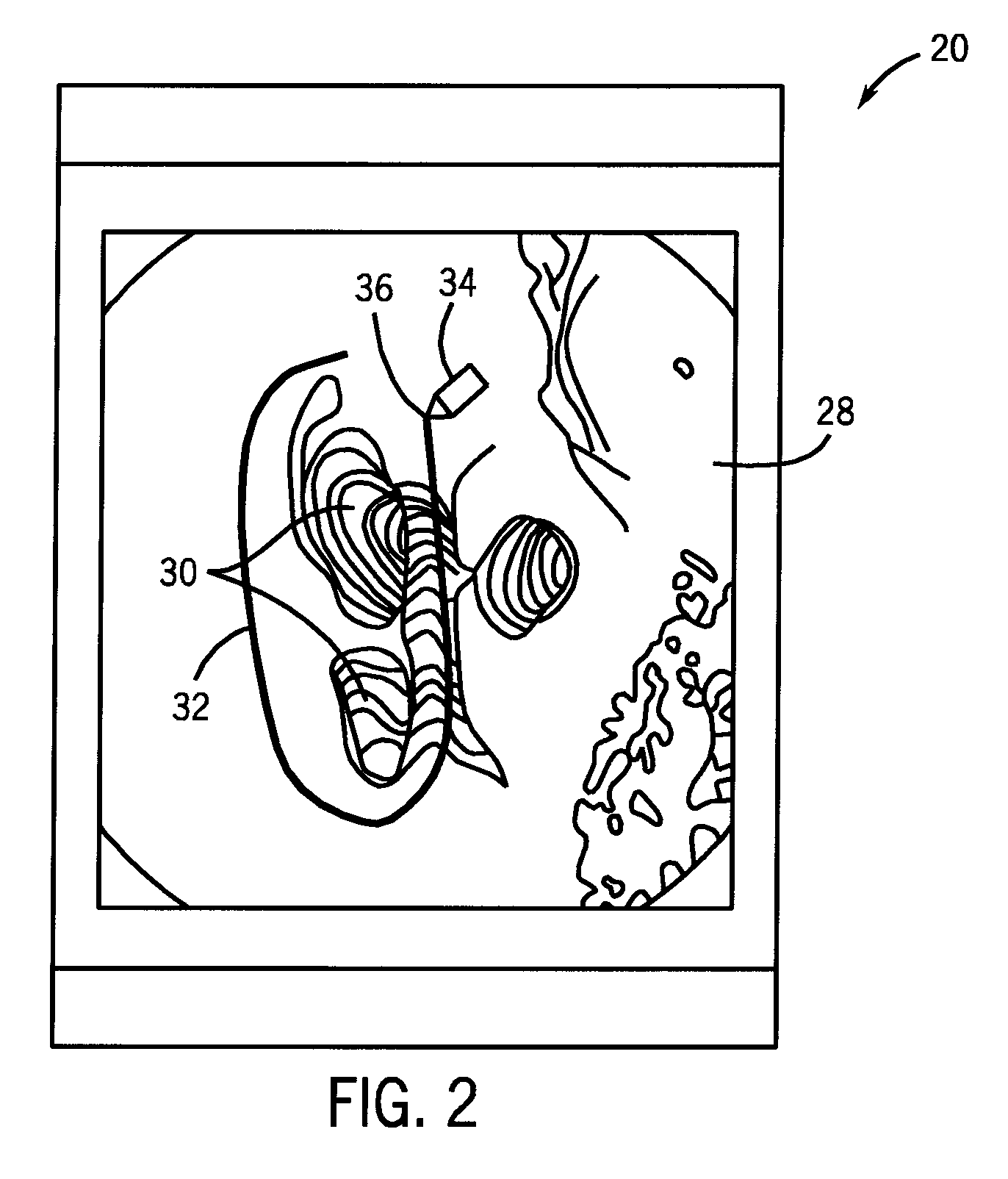
A system for imaging and providing therapy to one or more regions of interest is presented. The system includes an imaging and therapy catheter configured to image an anatomical region to facilitate assessing need for therapy in one or more regions within the anatomical region and delivering therapy to the one or more regions of interest within the anatomical region. In addition, the system includes a medical imaging system operationally coupled to the catheter and having a display area and a user interface area, wherein the medical imaging system is configured to facilitate defining a therapy pathway to facilitate delivering therapy to the one or more regions of interest.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electromagnetically tracked K-wire device
InactiveUS20060173291A1Improve accuracyReduce usageSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic markersRadiologyComputer science
Devices and methods for registering, dynamically referencing, and navigating an anatomical region of interest of a patient are provided using a tracked Kirschner wire (K-wire), where the K-wire includes a position-indicating element.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
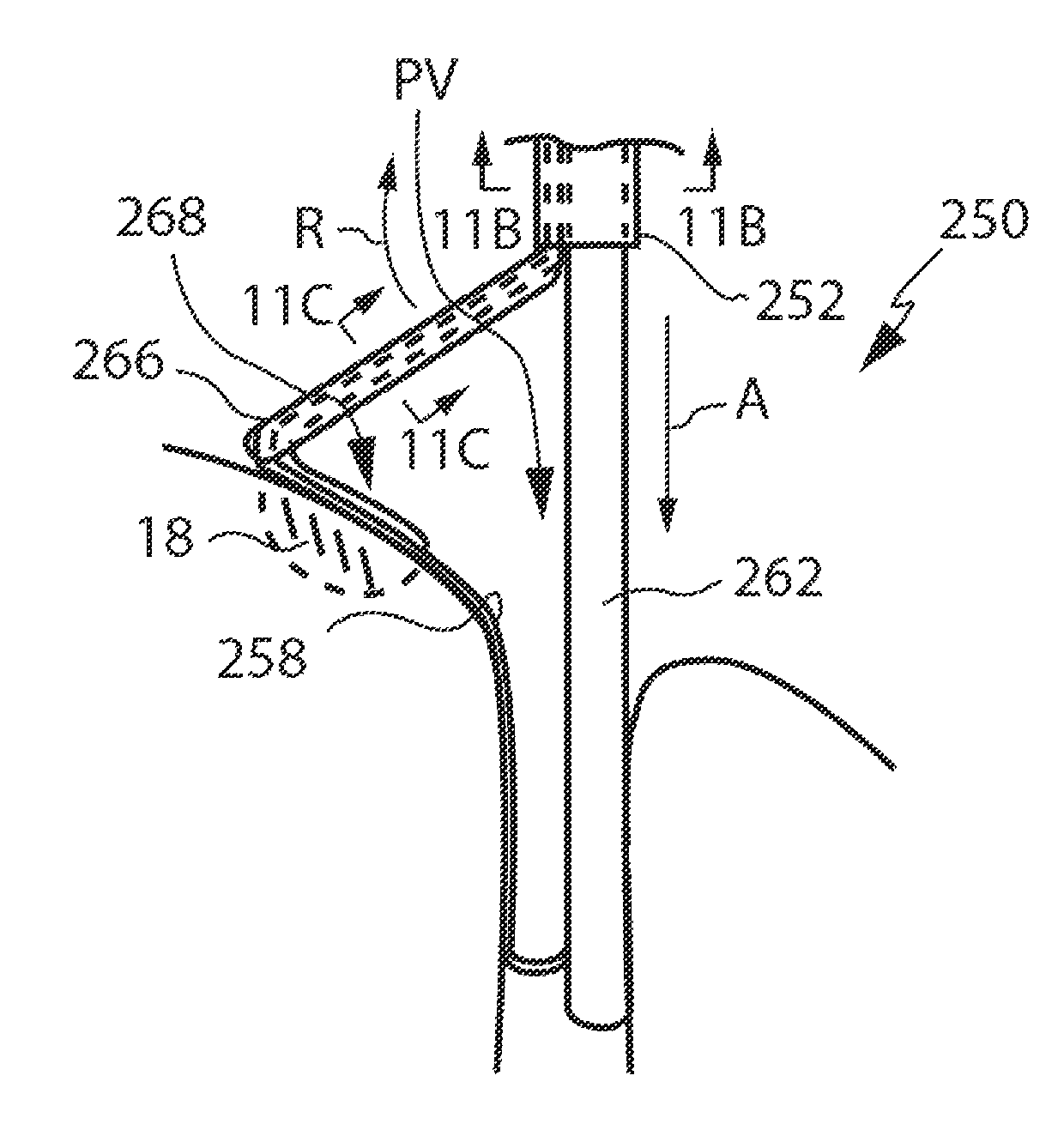
Devices and methods for creating continuous lesions
ActiveUS7736360B2Precise positioningEnhancing positioning and performanceDiagnosticsCatheterBiomedical engineeringLesion
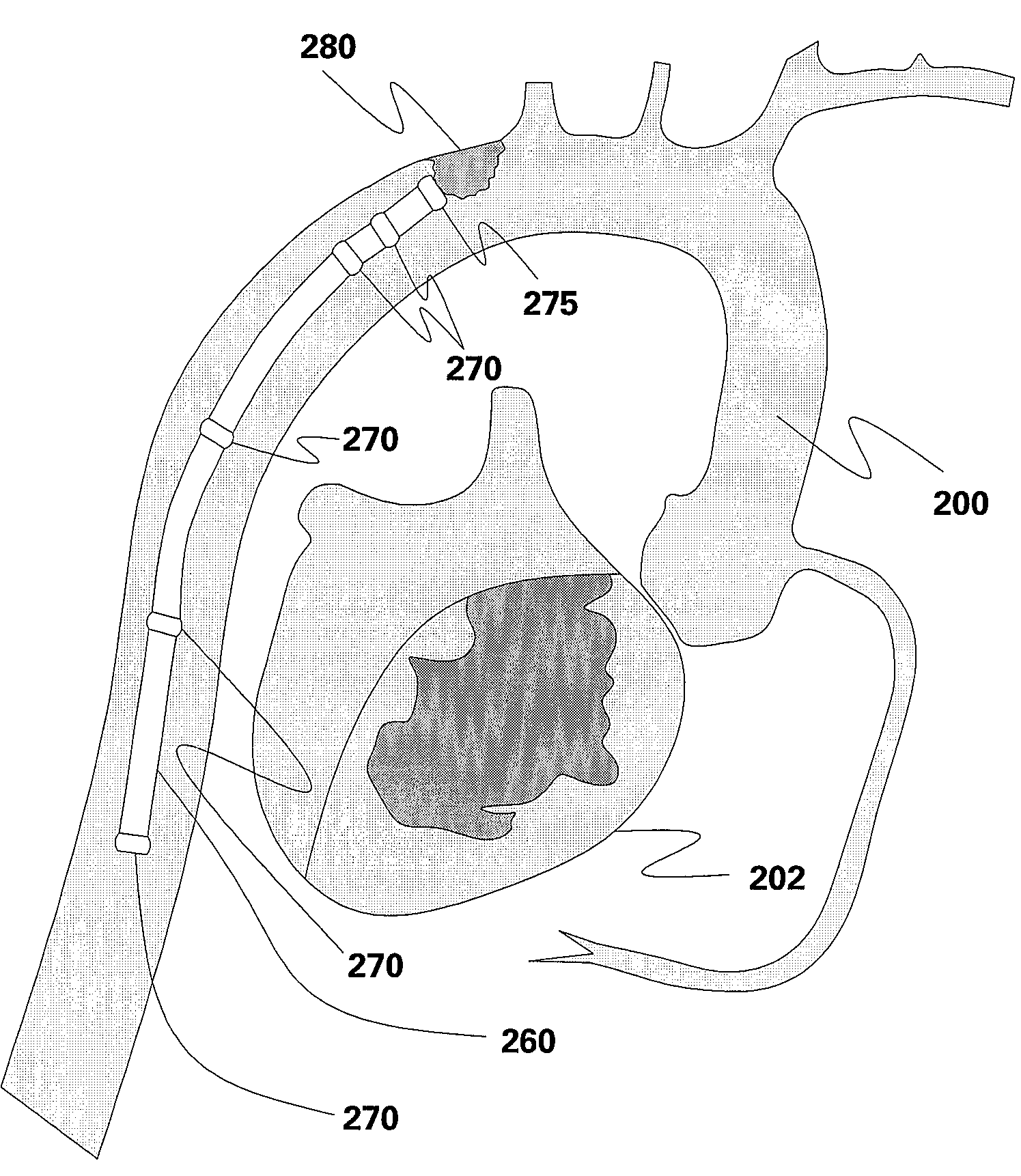
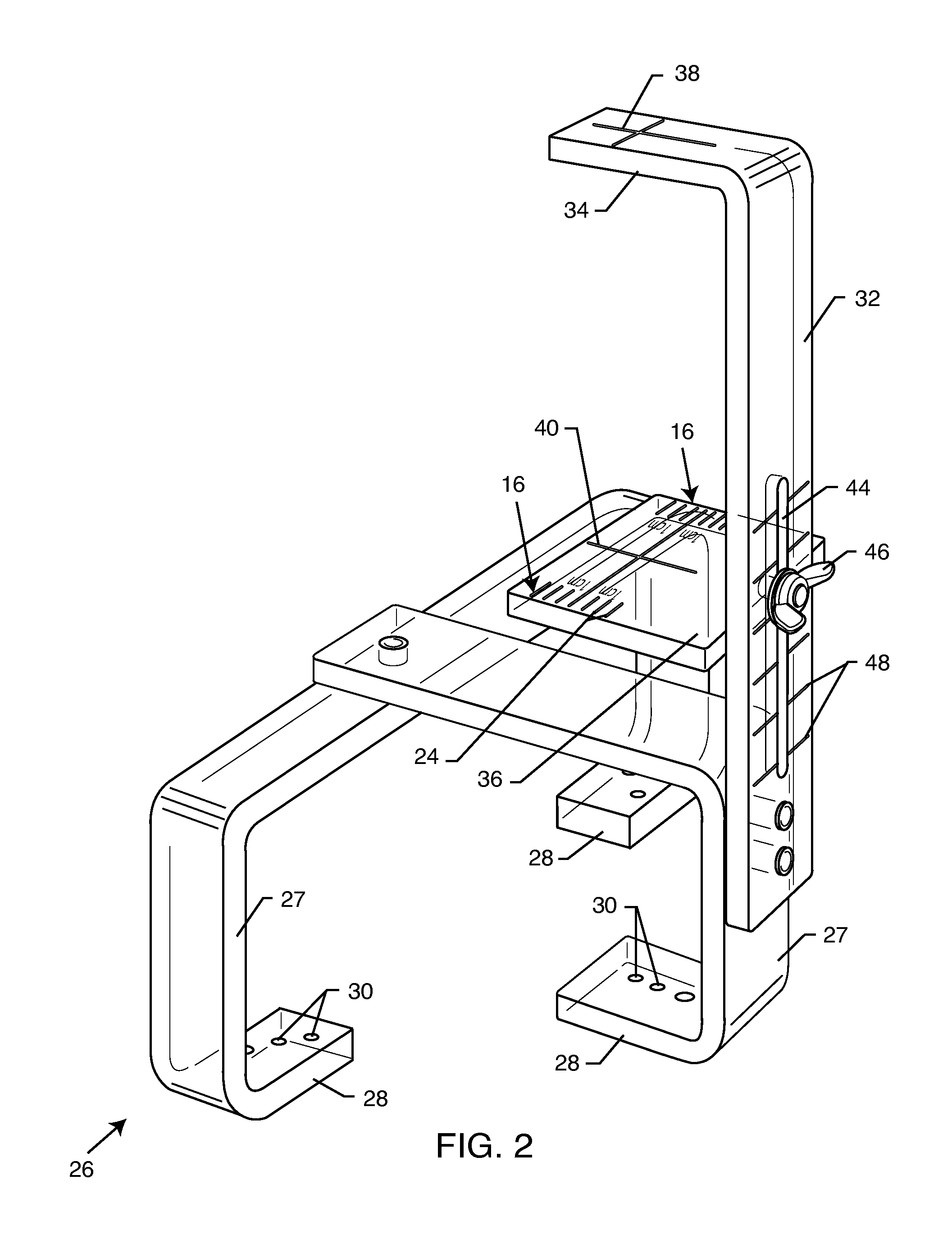
The present invention discloses devices and methods for creating multiple lesions using ablation devices in anatomical regions such as the heart, for example to treat cardiac arrhythmias. The present invention discloses methods and devices to create continuous lesions using area ablation devices. The present invention discloses various embodiments of reference assemblies for accurately positioning ablation devices having ablating portions, especially deployable ablation portions adapted for area ablation. The ablation devices are positioned using the reference assemblies in the anatomy to create one or more lesions. The present invention also discloses several method embodiments for creating continuous lesions using deployable ablating portions to produce two or more overlapping lesions.
Owner:MICROCUBE
Ablation array having independently activated ablation elements
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Devices and Methods for Perfusing an Organ
The present invention provides devices and methods for use in the perfusion of organs and anatomical regions. In one aspect the present method provides a percutaneously deliverable device for supporting a vessel in a human or animal subject including means for supporting the vessel during delivery of a fluid thereto or collection of a fluid therefrom. In another aspect the invention provides a method for delivery or collection of a fluid to or from an organ or anatomical region in a human or animal subject, the method including the step of supporting a vessel associated with the organ or anatomical region. The devices and methods may be used to deliver, remove or recirculate a therapeutic agent to an organ or anatomical region.
Owner:OSPREY MEDICAL
Automated imaging and therapy system
InactiveUS20070073151A1Ease of evaluationConvenient treatmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryTreatment demandMedical imaging
A system for imaging and providing therapy to one or more regions of interest is presented. The system includes an imaging and therapy catheter configured to image an anatomical region to facilitate assessing need for therapy in one or more regions within the anatomical region and delivering therapy to the one or more regions of interest within the anatomical region. In addition, the system includes a medical imaging system operationally coupled to the catheter and having a display area and a user interface area, wherein the medical imaging system is configured to facilitate defining a therapy pathway to facilitate delivering therapy to the one or more regions of interest.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
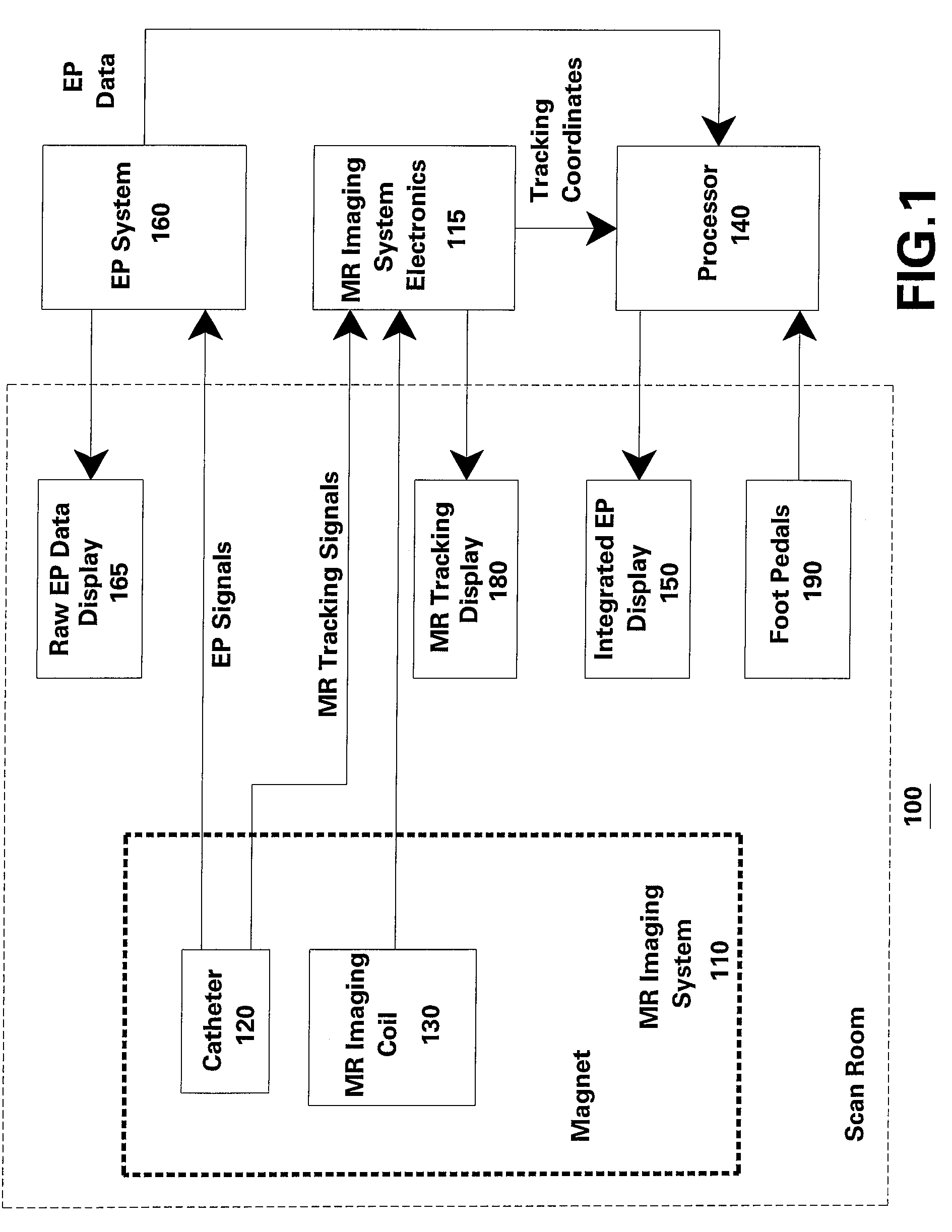
System and method for interventional procedures using MRI
InactiveUS7725157B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyImaging dataAnatomic region
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
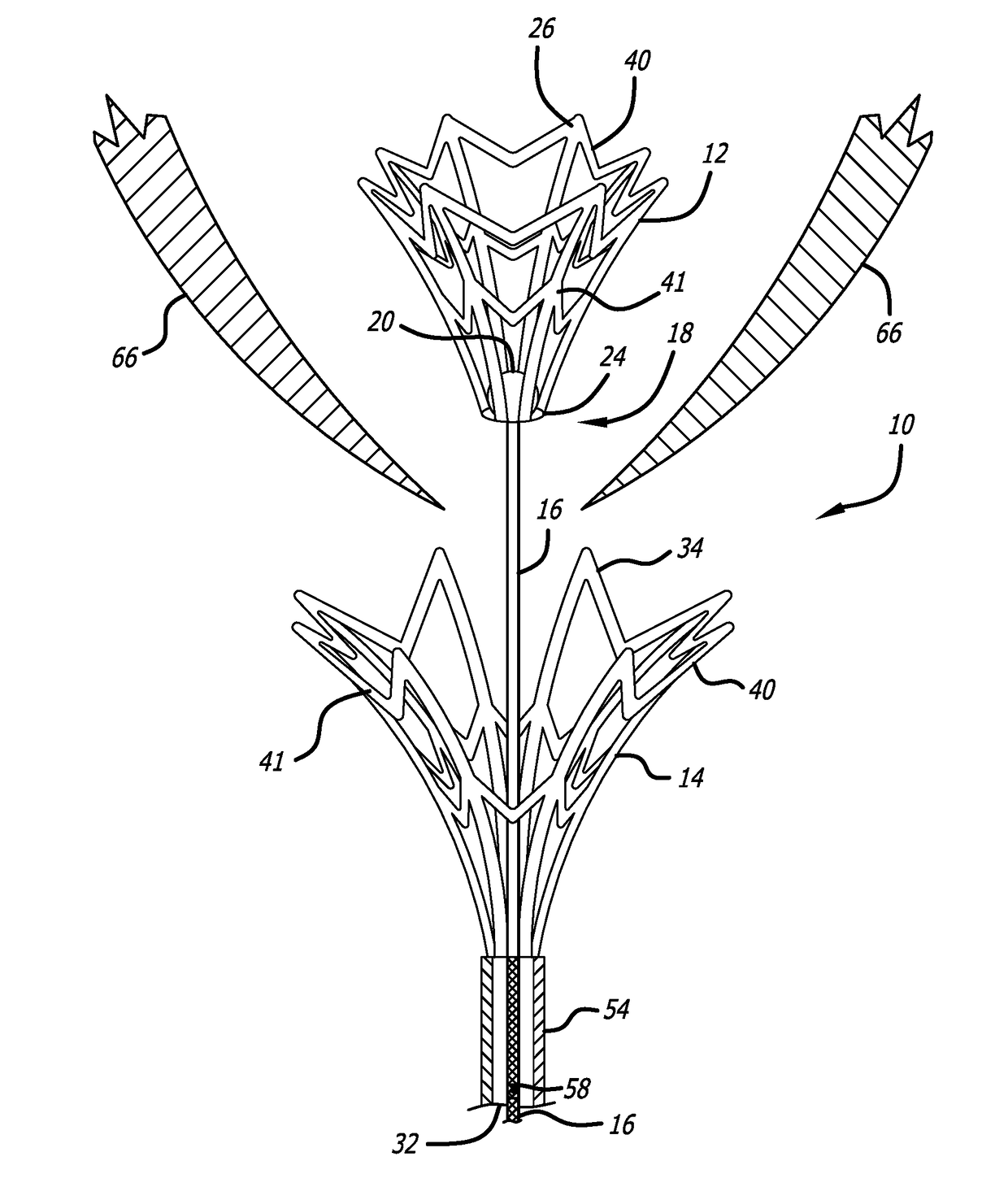
Double basket assembly for valve repair
ActiveUS20180243086A1Minimal elongationHigh compressive strengthHeart valvesDiagnosticsSurgical departmentMedical device
The invention provides medical devices, systems and methods for tissue approximation and repair and in particular to reduce mitral regurgitation by means of improved coaptation. The devices, systems and methods of the invention will find use in a variety of therapeutic procedures, including endovascular, minimally-invasive, and open surgical procedures, and can be used in various anatomical regions, including the cardiovascular system, heart, other organs, vessels, and tissues. The invention is particularly useful in those procedures requiring minimally-invasive or endovascular access to remote tissue locations, where the instruments utilized must negotiate long, narrow, and tortuous pathways to the treatment site.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
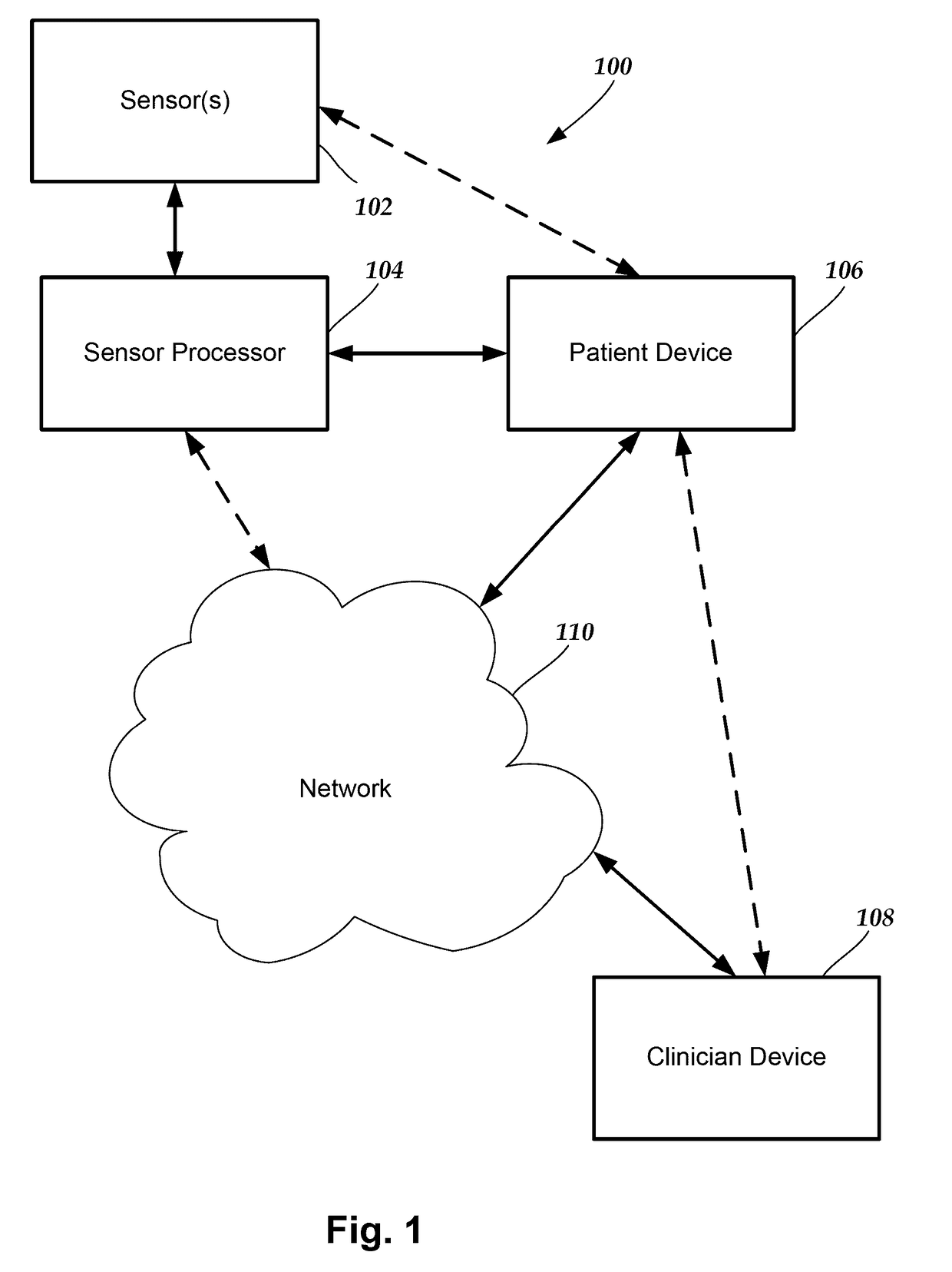
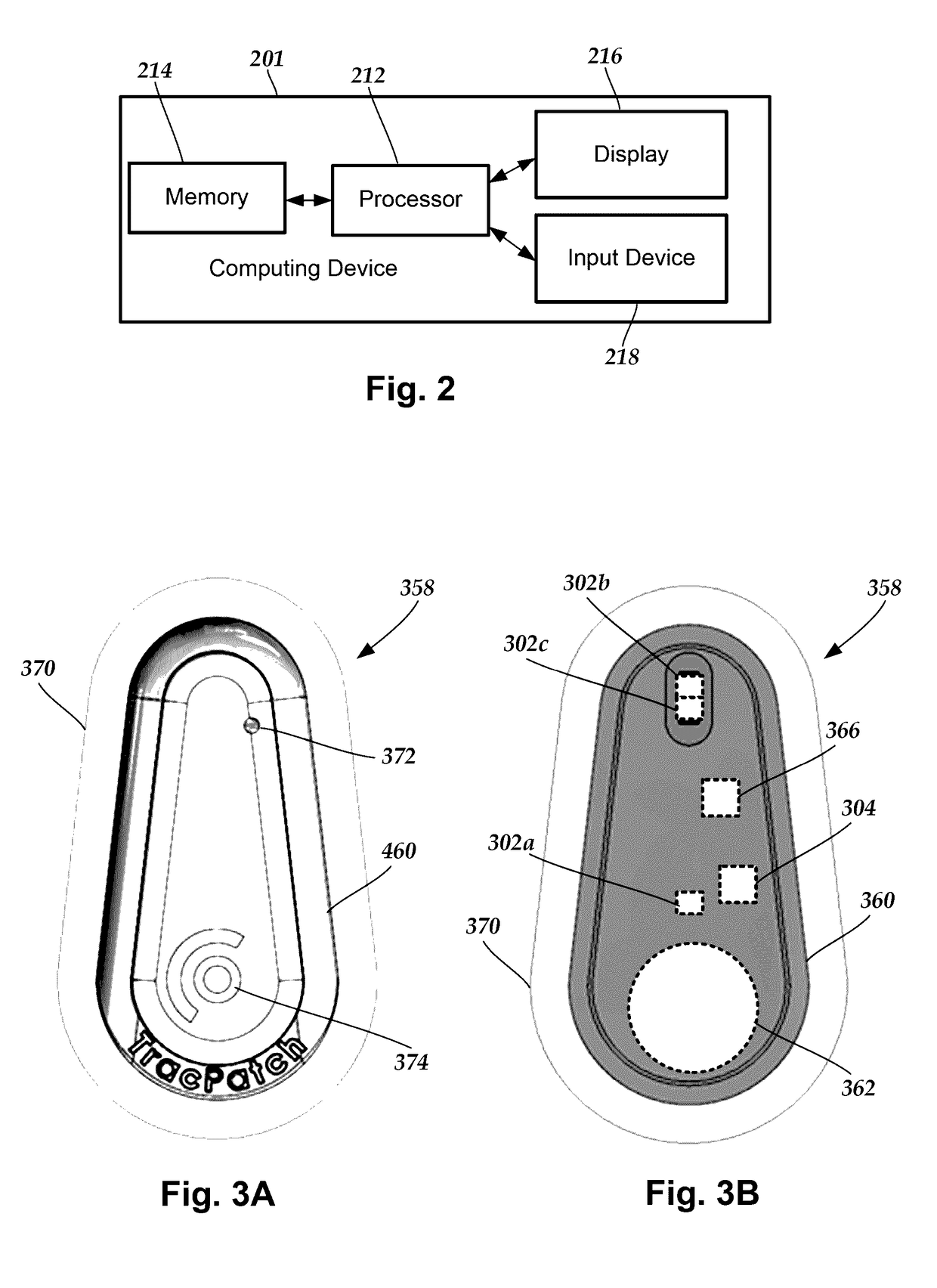
System and methods for monitoring physical therapy and rehabilitation of joints
A system for monitoring a patient includes a sensor unit having a housing and sensors disposed in or around the housing; and a base having a shell and configured and arranged to be adhesively attached to skin of the patient. The sensors can be used to monitor physical therapy and rehabilitation of the patient. The sensor unit can provide information to a patient or clinician device to facilitate the monitoring. The sensor data can be used to determine measurements such as tilt angle of the sensor unit and range of motion measurements (such as extension, flexion, or forces associated with movement) of the anatomical region to which the sensor unit is attached. The sensor data can also be used for automated identification or classification of exercises performed by the patient.
Owner:TRACPATCH HEALTH INC
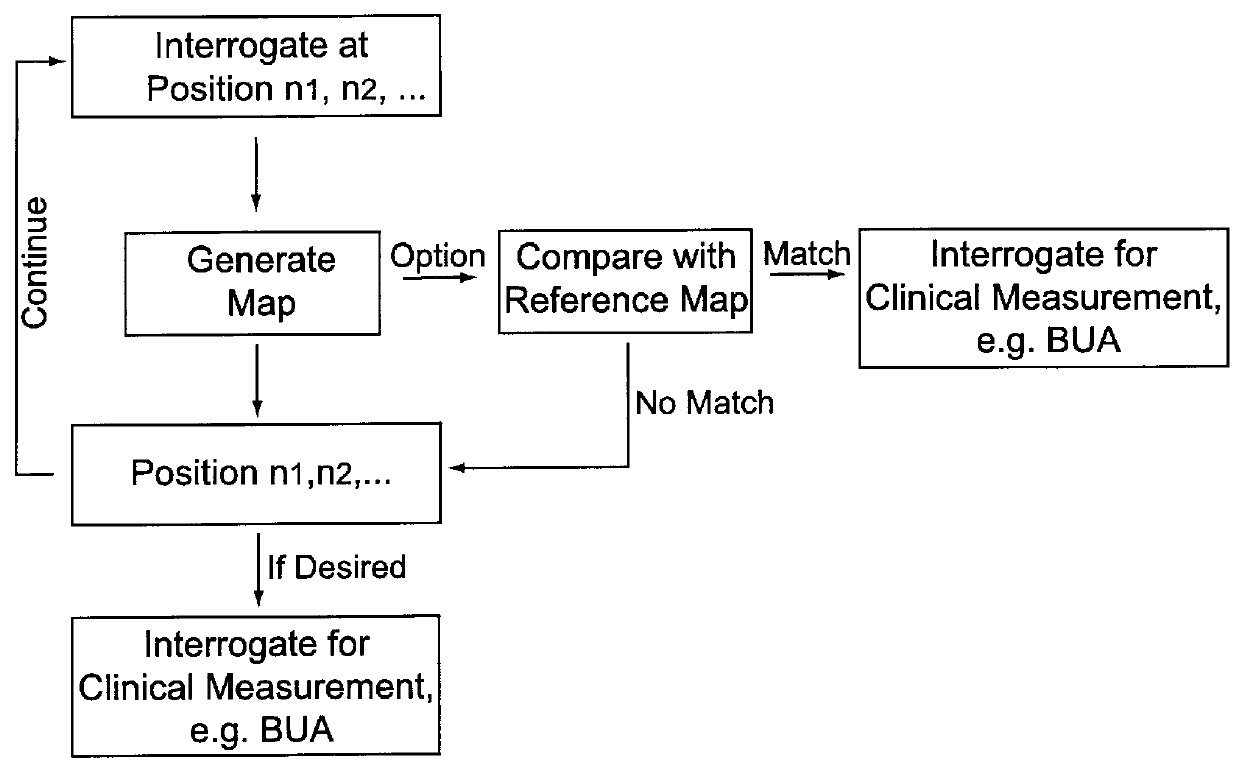
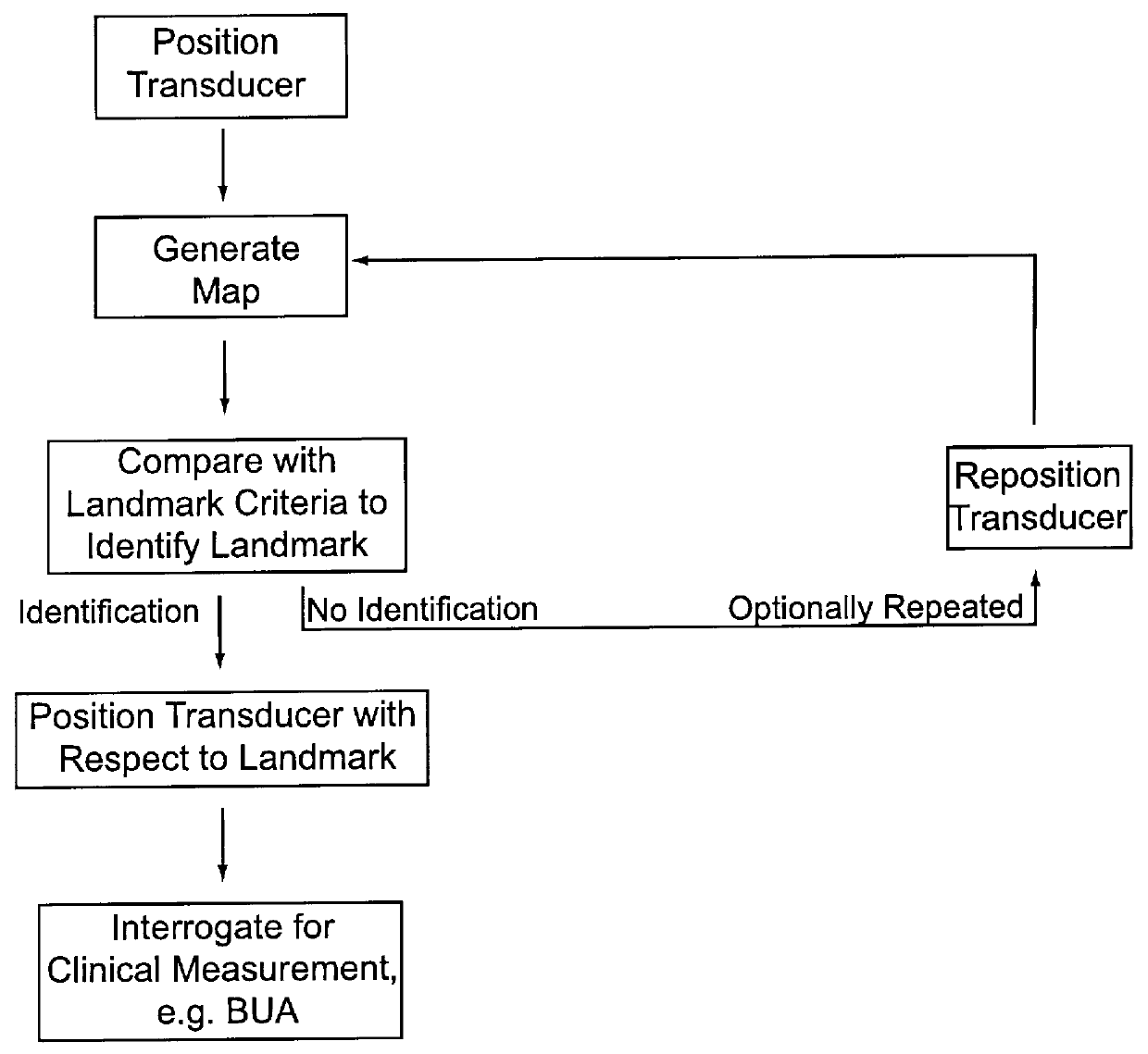
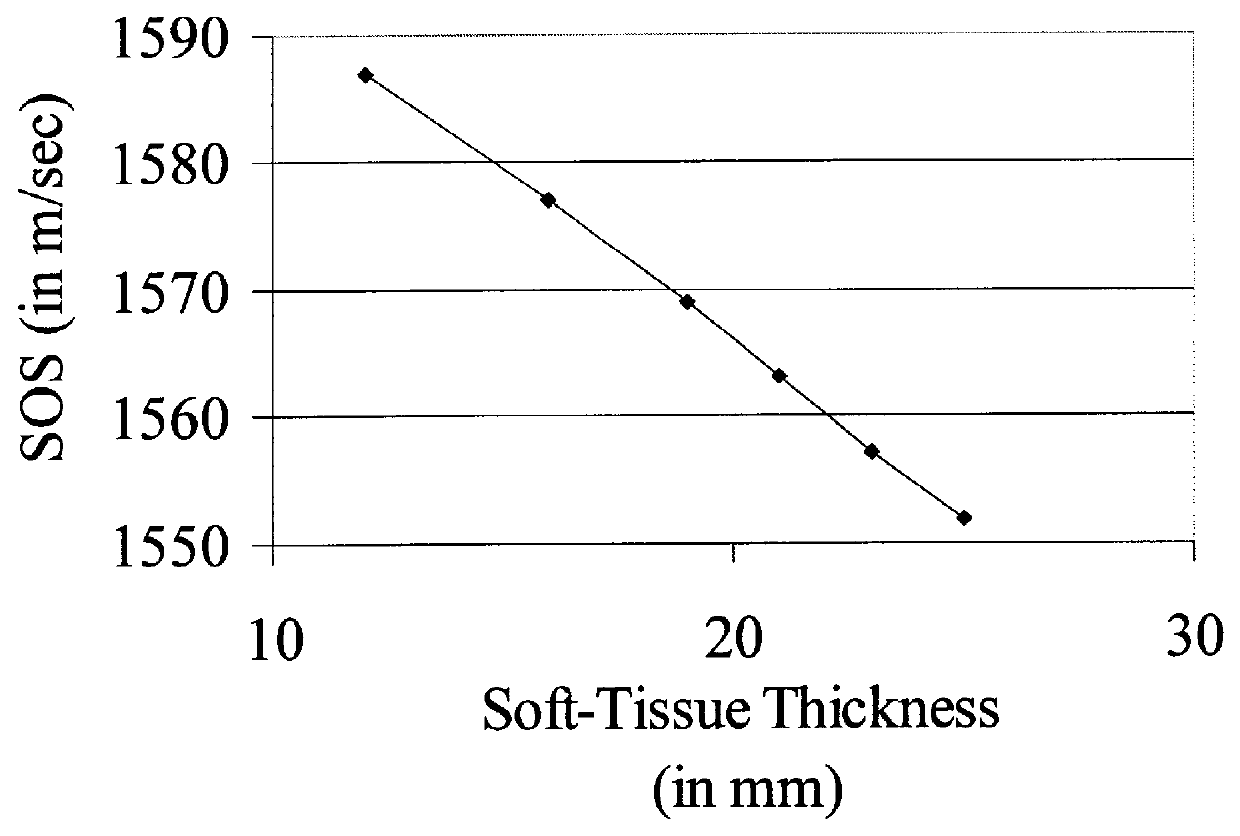
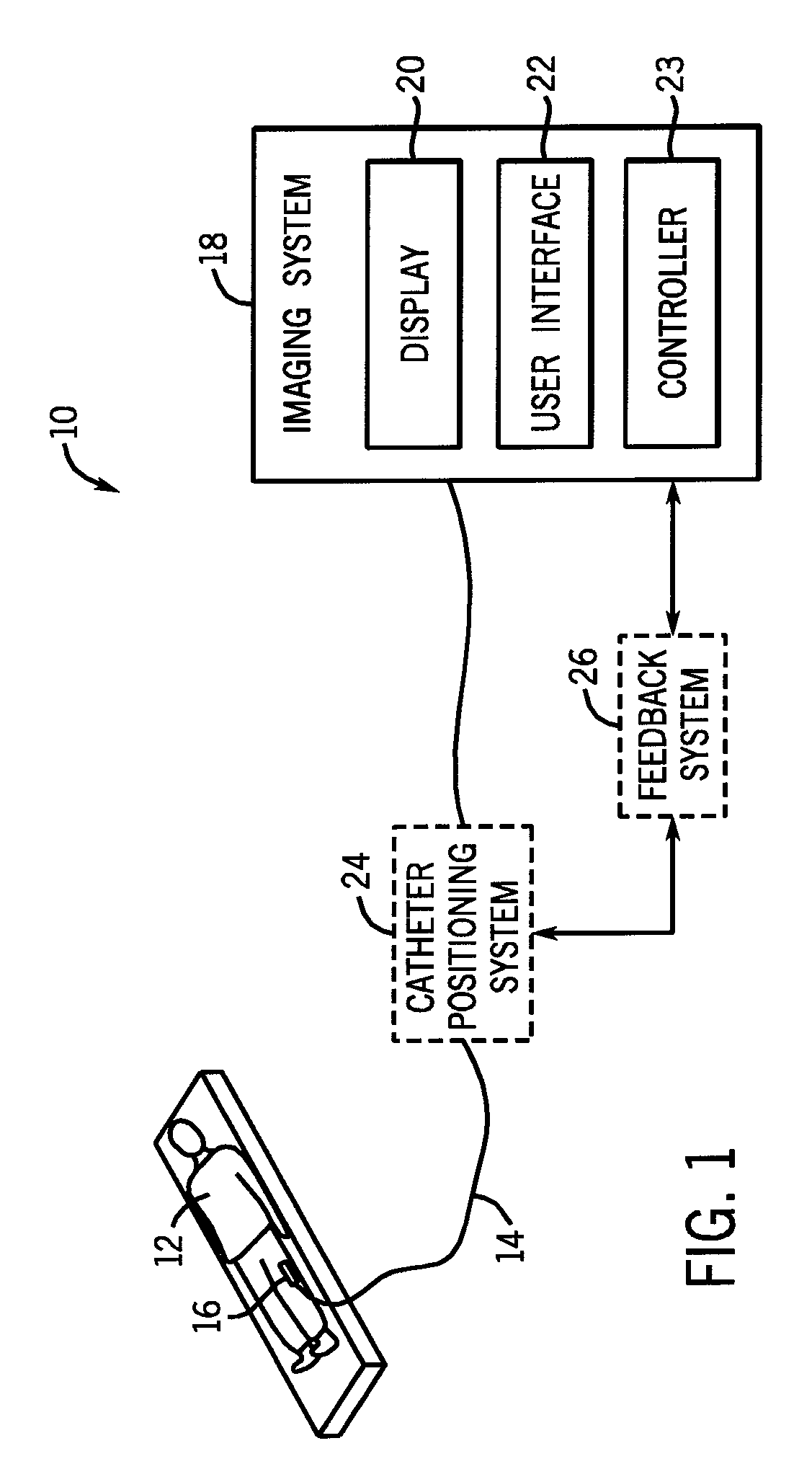
Methods and devices for improving ultrasonic measurements using anatomic landmarks and soft tissue correction
The invention provides for ultrasonic methods, compositions and devices. particularly methods, compositions and devices that provide for reproducible positioning of the ultrasonic transducer(s) over an anatomic region using anatomic landmarks. The invention provides for improved interrogation devices that reproducibly position transducer(s) over an interrogation site.
Owner:MENDLEIN JOHN D +1
Ablation array having independently activated ablation elements
ActiveUS20070129633A1Ultrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesTreatment demandAnatomic region
A system for imaging and providing therapy to one or more regions of interest is presented. The system includes an imaging and therapy catheter configured to image an anatomical region to facilitate assessing need for therapy in one or more regions within the anatomical region and delivering therapy to the one or more regions of interest within the anatomical region. The catheter includes a therapy device having a plurality of independently controllable therapy elements. The independence of the therapy elements is exploited when multiple regions are to receive therapy simultaneously or at a given catheter position within a subject.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Instrument guide and implant holder
ActiveUS7278997B1Maintain visibilityEasy to insertInternal osteosythesisProsthesisEngineeringSurgical department
An instrument guide and implant holding device is provided which releasably secures an implant to the instrument guide. The device provides a convenient guide for surgeons to perform various operative techniques on the subject bone without the need for separate devices, and allows all these operative techniques to be performed without removing the instrument guide from the dissected area until all operative techniques have been completed. The releasable mechanism allows the surgeon to easily hold the instrument to an implant using a simple press-fit approach, and easily releases from the implant with a minimal amount of force. An embodiment also allows the surgeon to releasably lock the cannula in a given orientation about the centroidal axis of the implant fastener hole.
Owner:THEKEN SURGICAL LLC
System and method for improving workflow efficiences in reading tomosynthesis medical image data
ActiveUS8983156B2Avoids sacrificing desired detailEasy to identifyImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisImaging processing
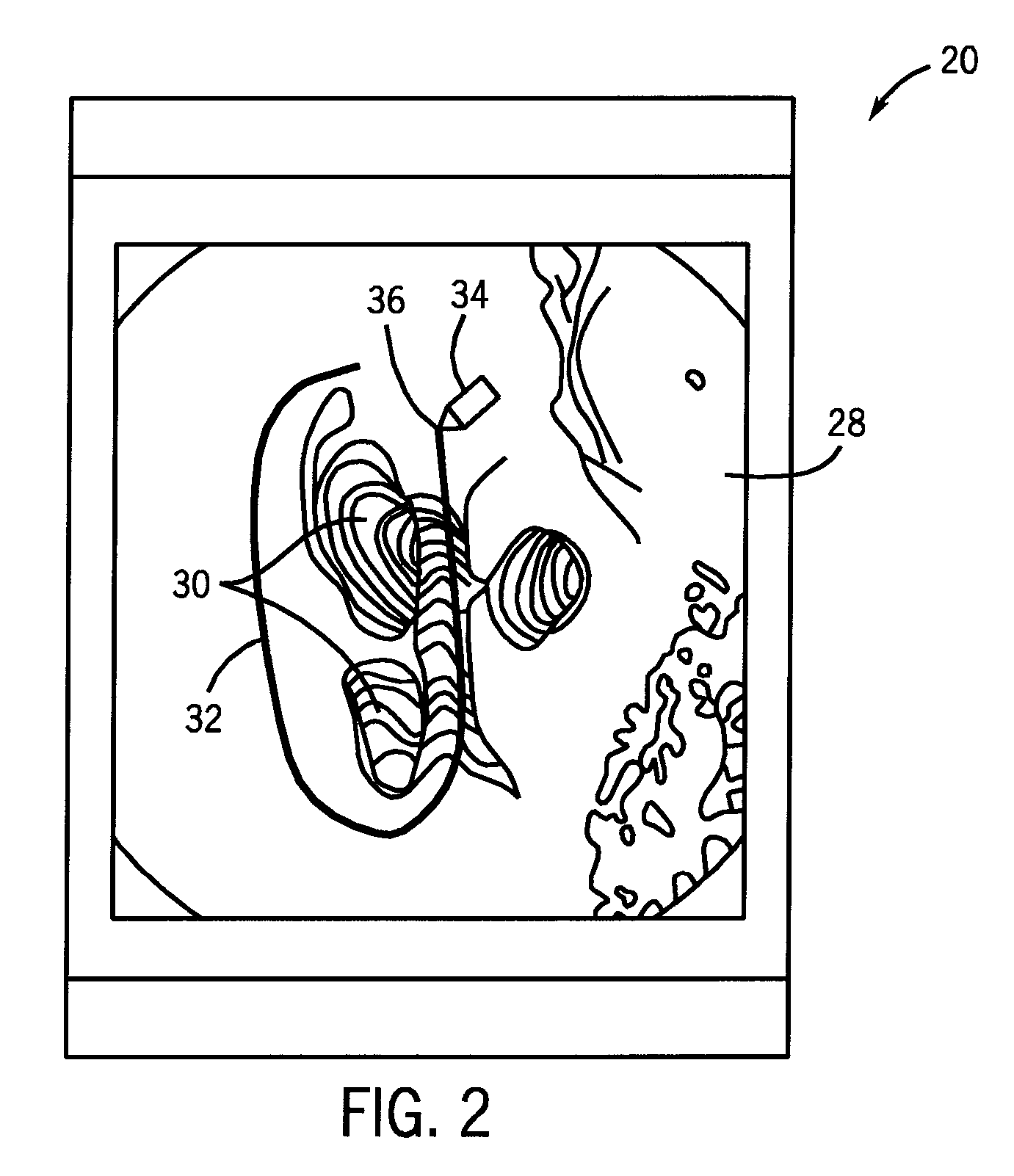
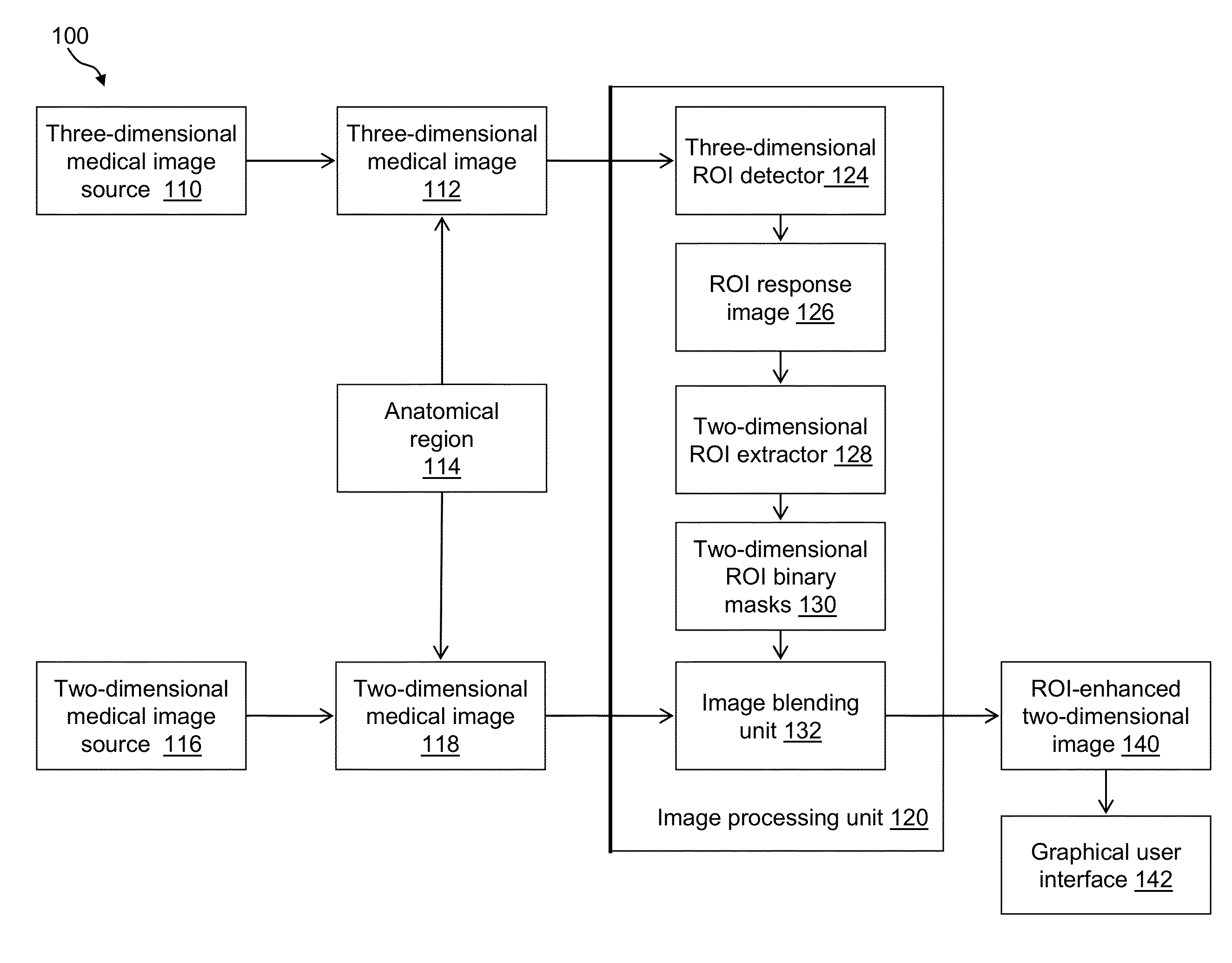
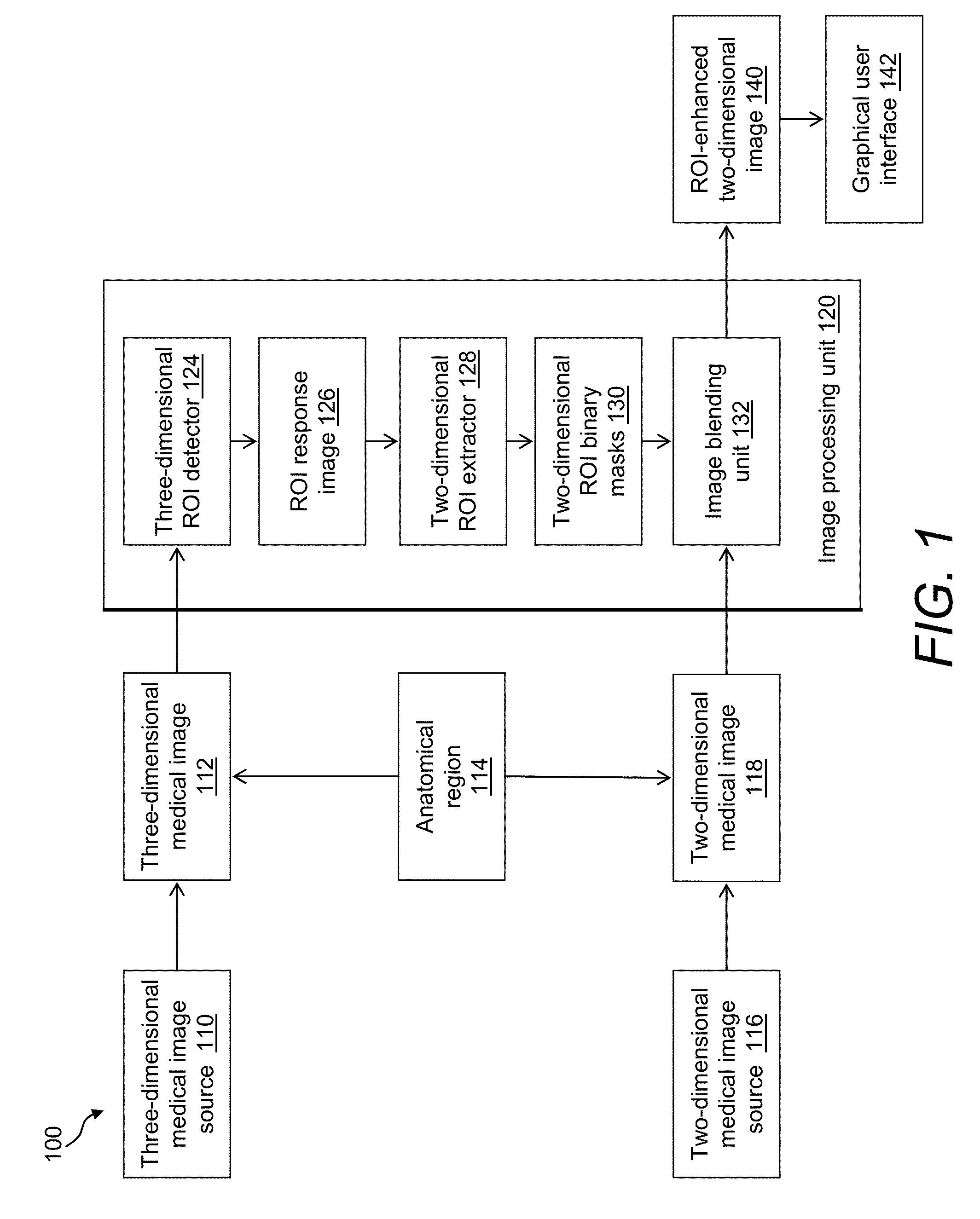
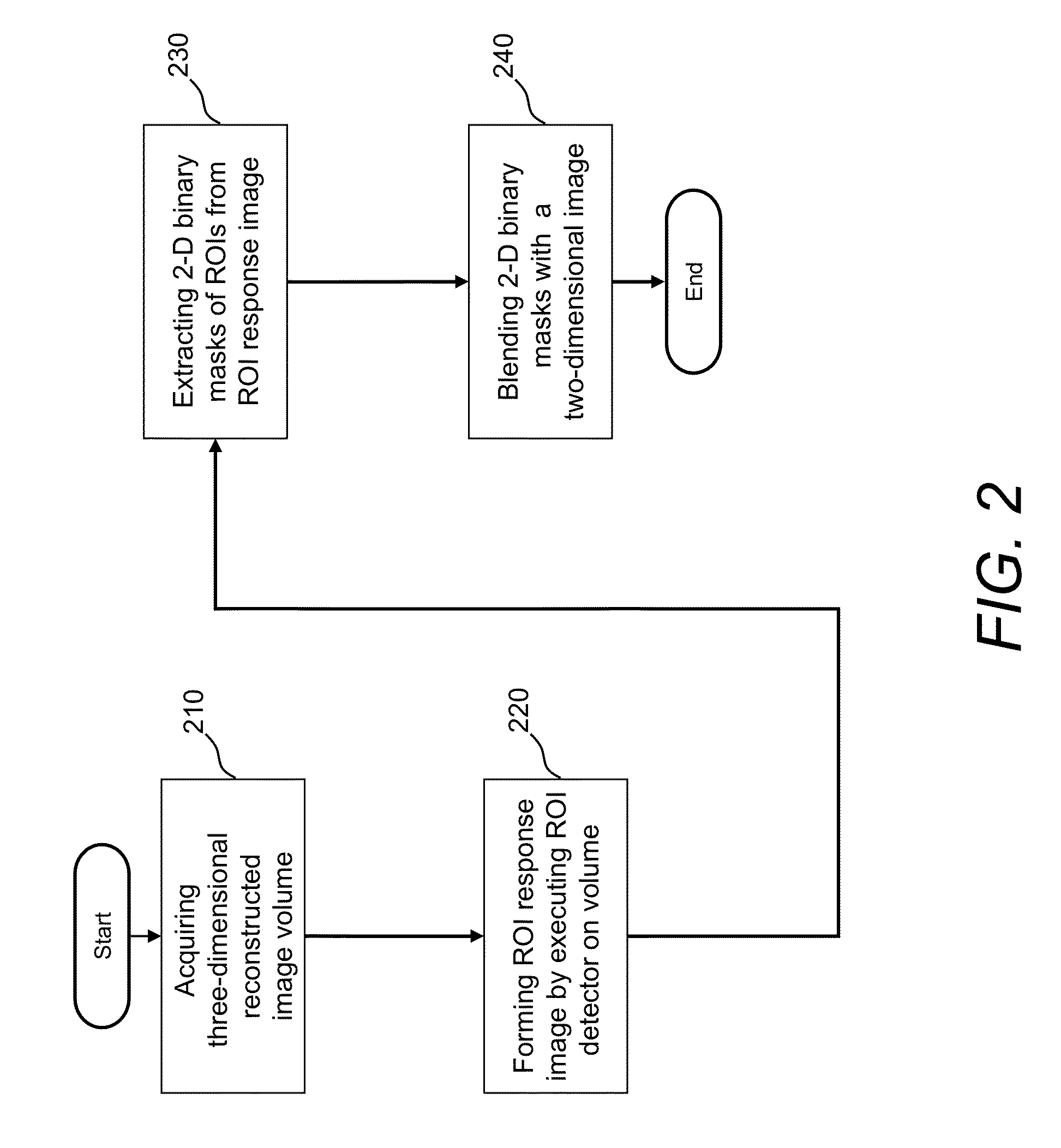
A system and a method are disclosed that forms a novel, synthetic, two-dimensional image of an anatomical region such as a breast. Two-dimensional regions of interest (ROIs) such as masses are extracted from three-dimensional medical image data, such as digital tomosynthesis reconstructed volumes. Using image processing technologies, the ROIs are then blended with two-dimensional image information of the anatomical region to form the synthetic, two-dimensional image. This arrangement and resulting image desirably improves the workflow of a physician reading medical image data, as the synthetic, two-dimensional image provides detail previously only seen by interrogating the three-dimensional medical image data.
Owner:ICAD INC
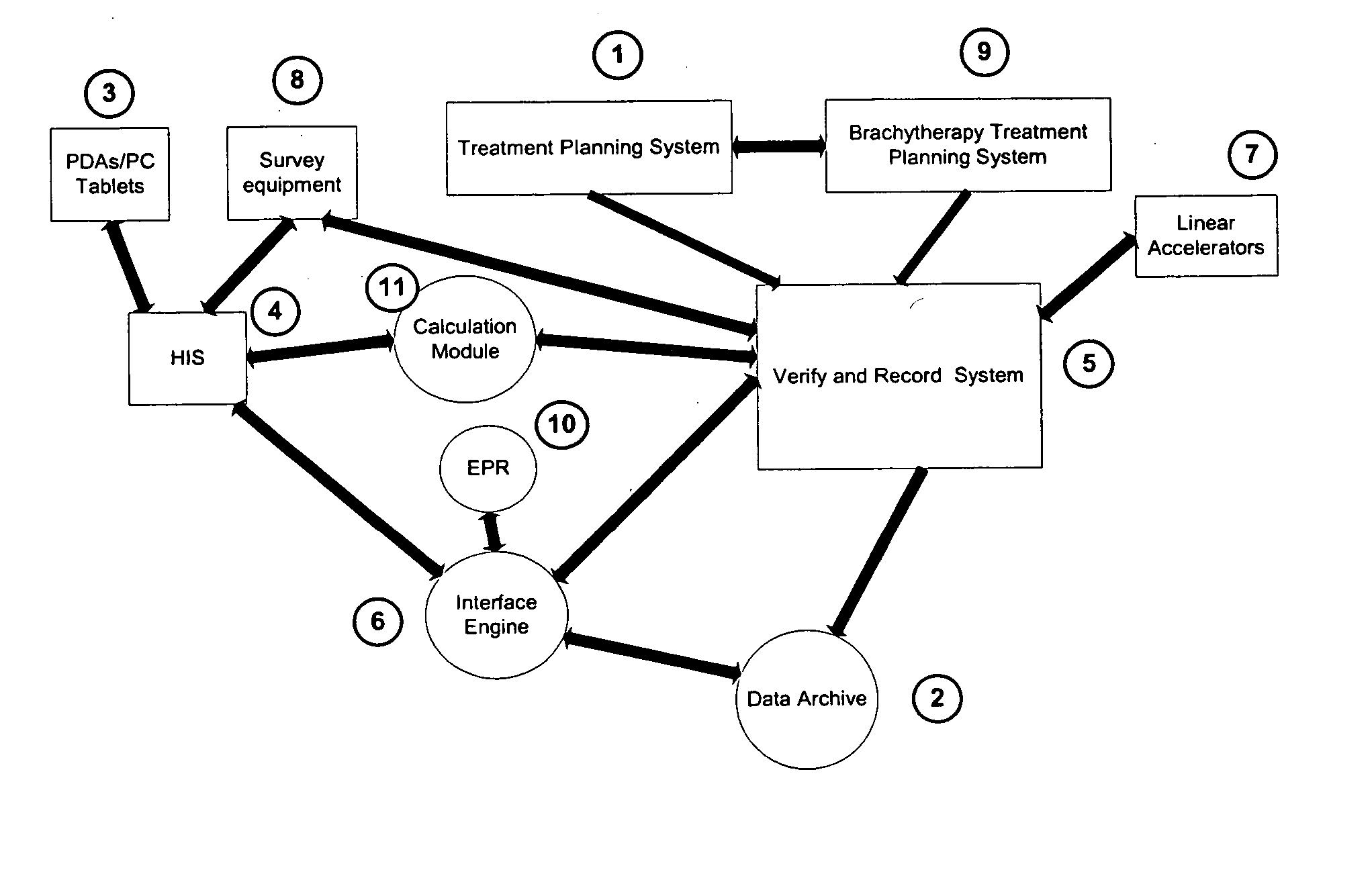
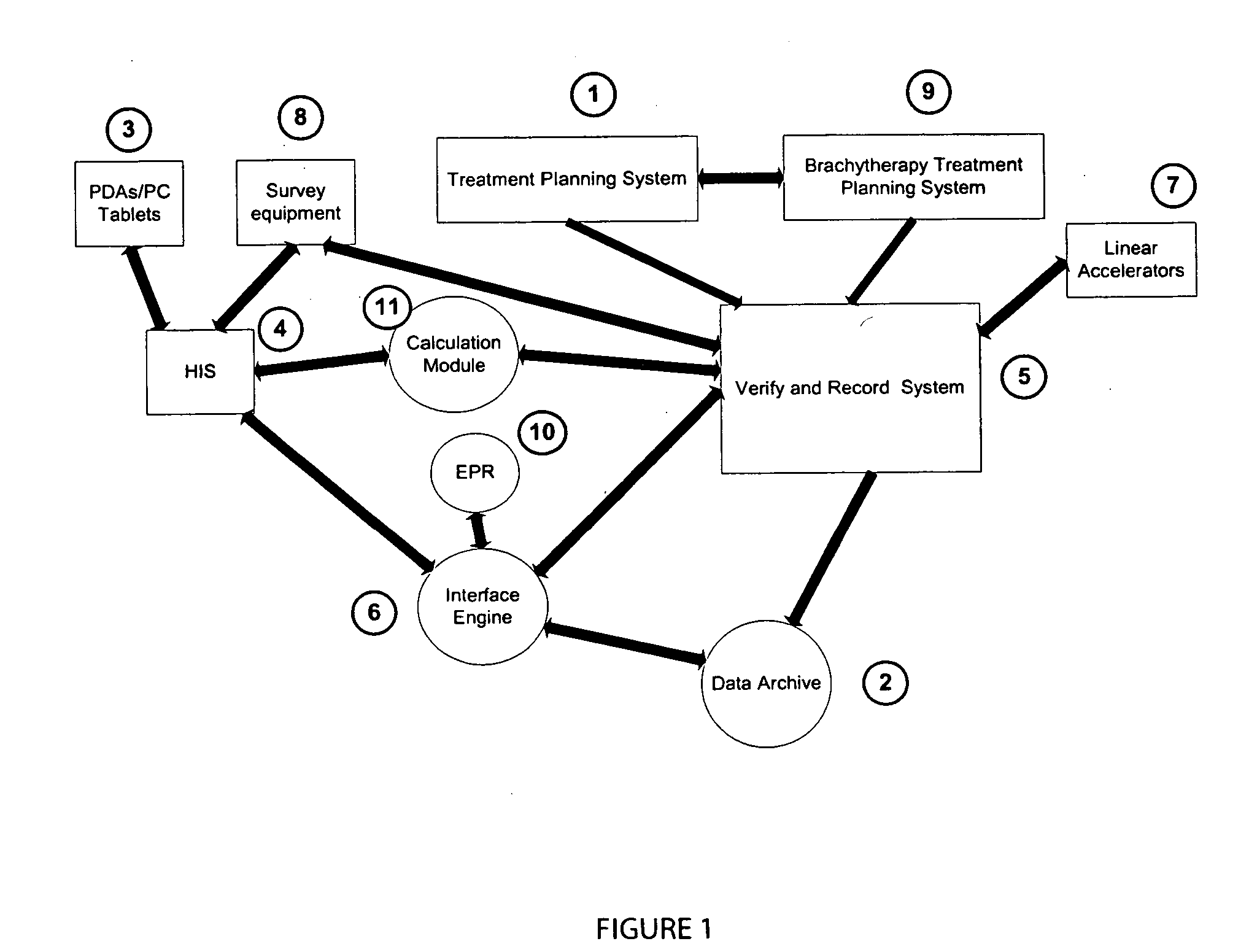
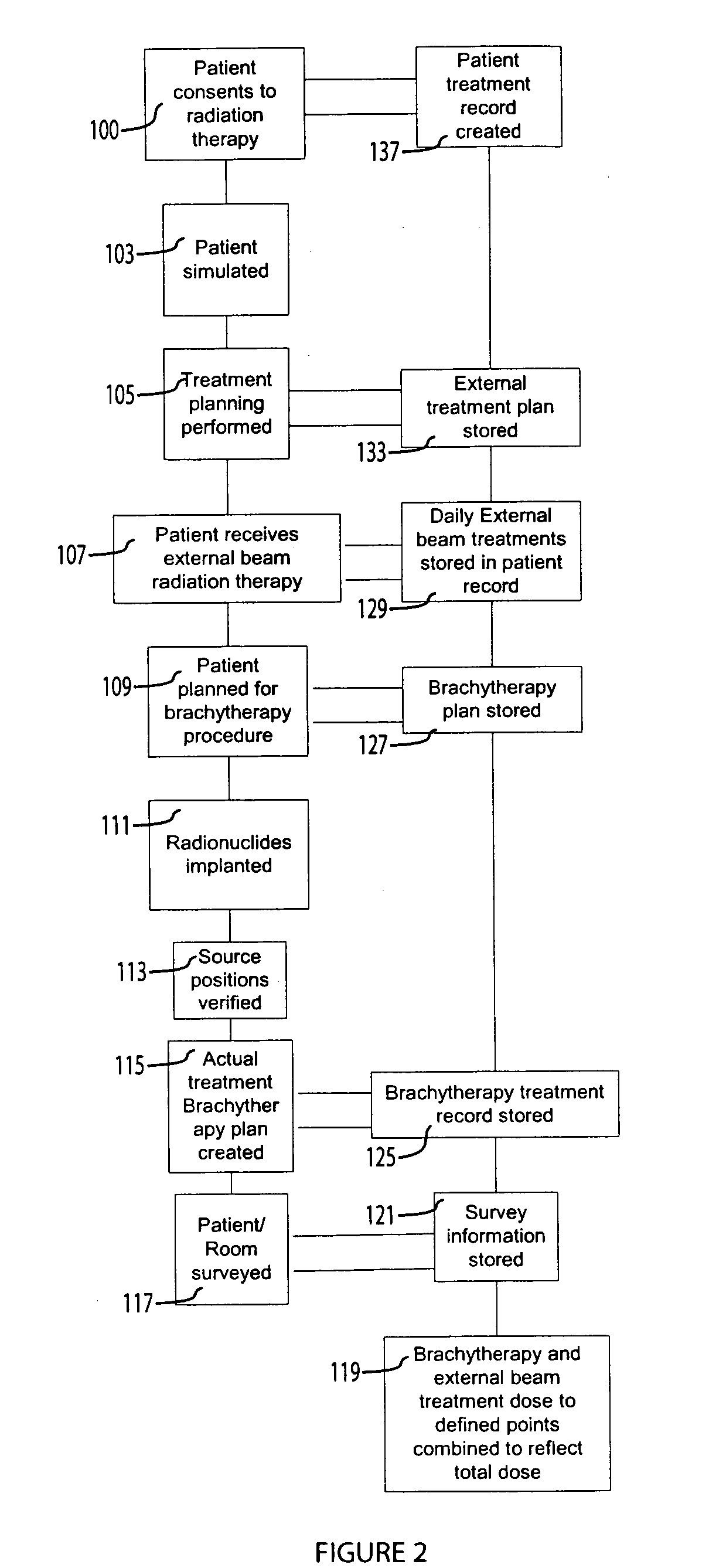
System for processing patient radiation treatment data
InactiveUS20050027196A1Convenient treatmentEasy to useRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAnatomic regionRadiation emission
A system records and documents both external beam radiation therapy and radiation from implanted sources applied to an anatomical area, in a comprehensive consolidated record of radiation treatment that also documents detected radiation emission levels from internal patient sources measured externally to the patient. A system processes data concerning patient radiation treatment. The system includes an input processor for receiving data identifying a first radiation dose received by a particular anatomical part of a patient, from a radiation source external to a patient and a second radiation dose, received by the particular anatomical part of the patient from a radiation source internal to the patient. A data processor combines data representing the first and second dose to provide a combined dose value. A storage processor stores the combined value in a record associated with the patient
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS HEALTH SERVICES CORPORAT
Integrated ultrasound imaging and ablation probe
InactiveUS20090076390A1Ultrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasound imagingTreatment demand
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rapid magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography of multiple anatomical territories
InactiveUS6493571B1Reduce osmotic pressureHigh resolutionBedsDiagnostic recording/measuringIodinated Contrast AgentSingle injection
A procedure and apparatus are provided which allow rapid positional change in the patient centering in order to facilitate the imaging of blood vessels in a series of different views. This procedure and apparatus can also facilitate the imaging of other tissues of the body at different spatial locations as well. The procedure and apparatus reduce the time required for obtaining the necessary images for a medical imaging examination using a single injection of an MRI or iodinated contrast agent.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
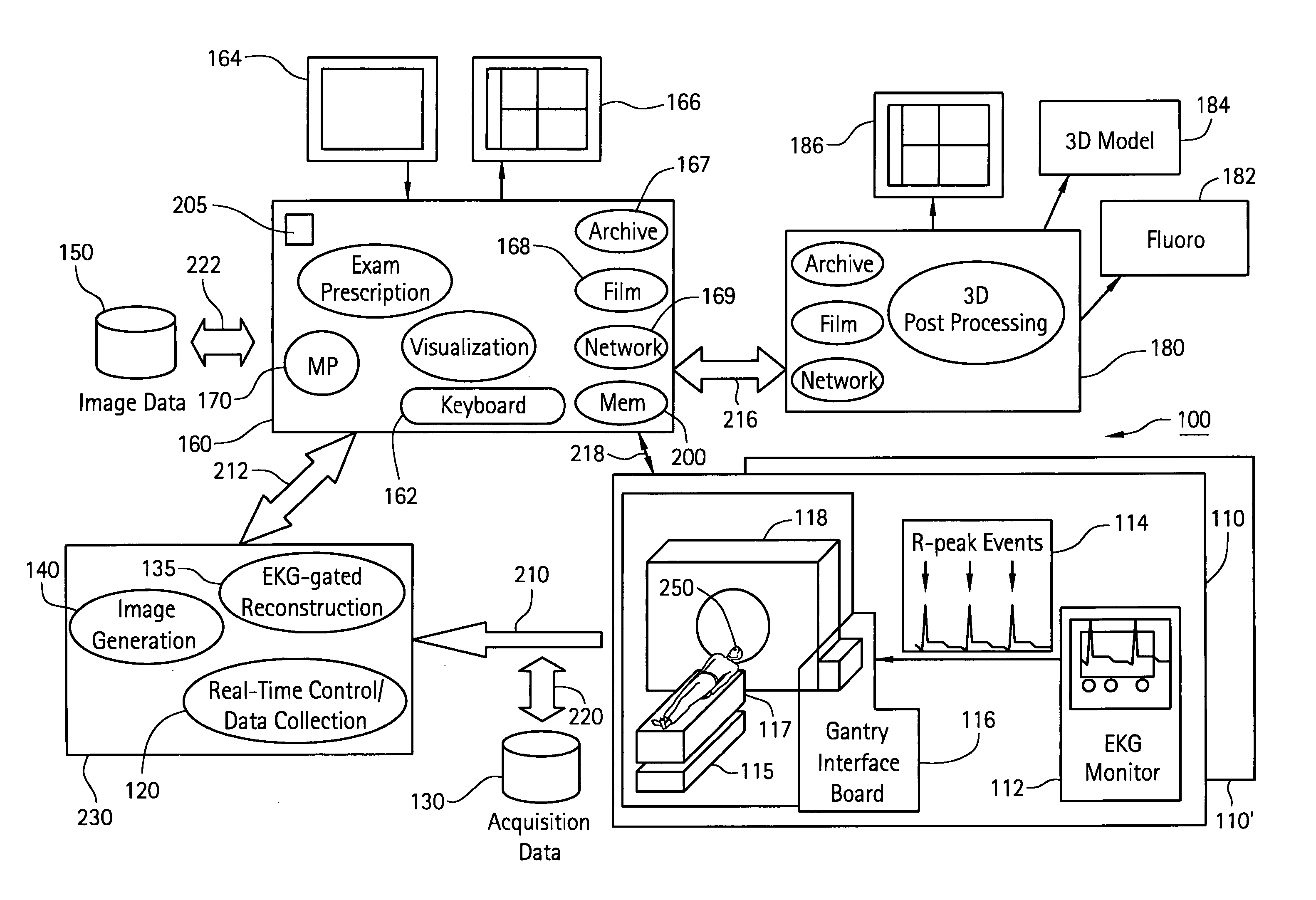
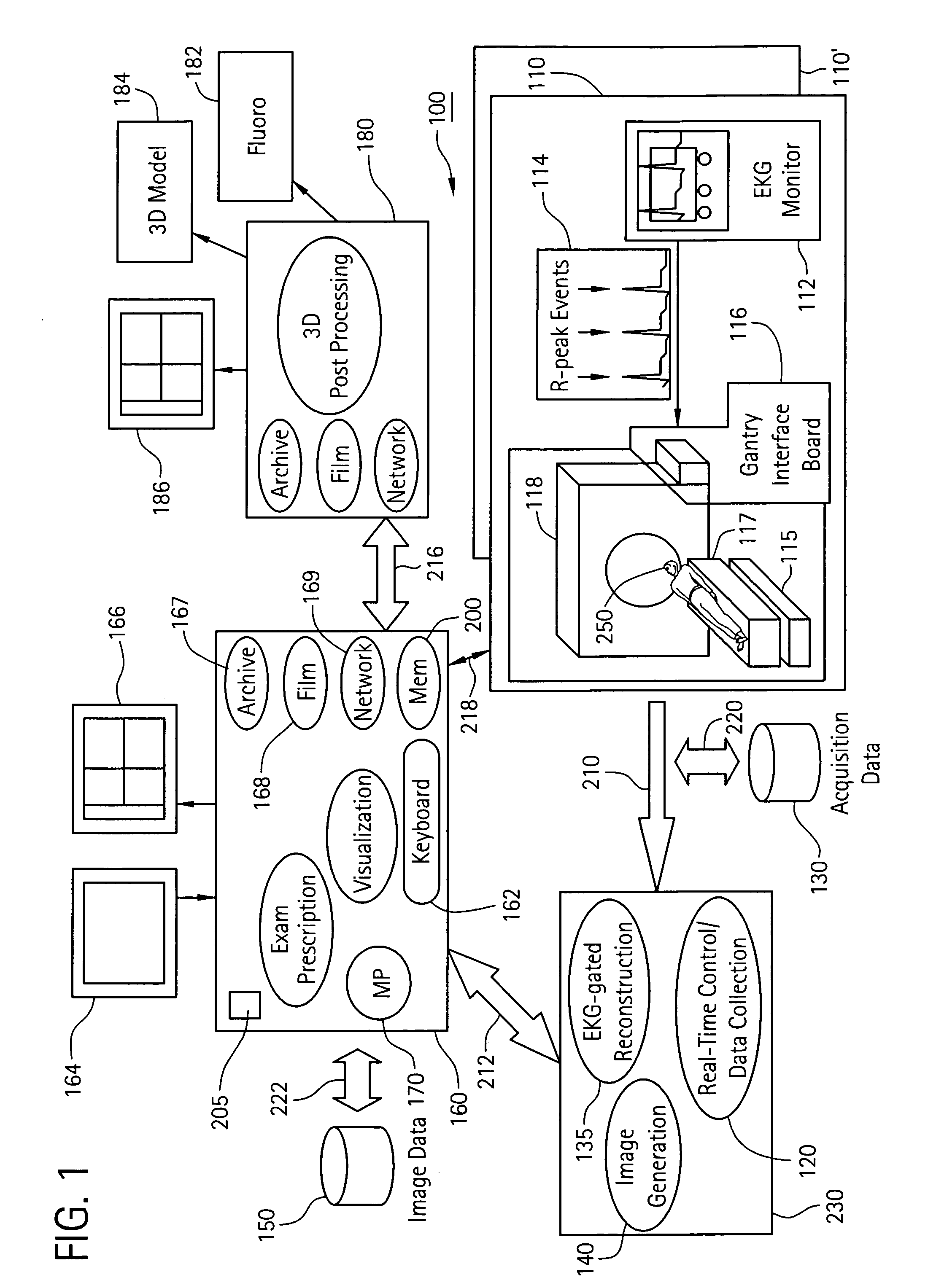
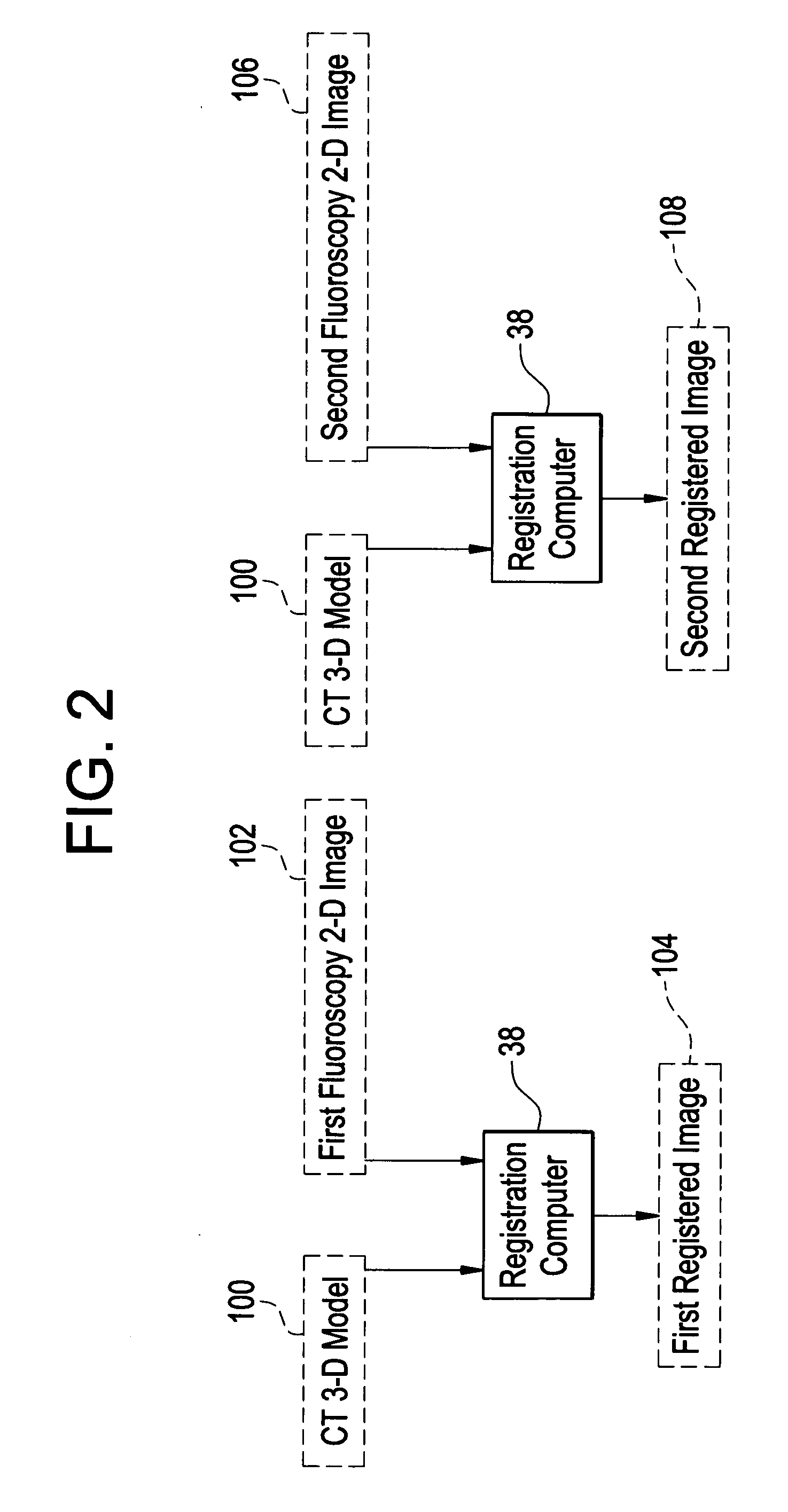
Method and system for registering 3D models of anatomical regions with projection images of the same
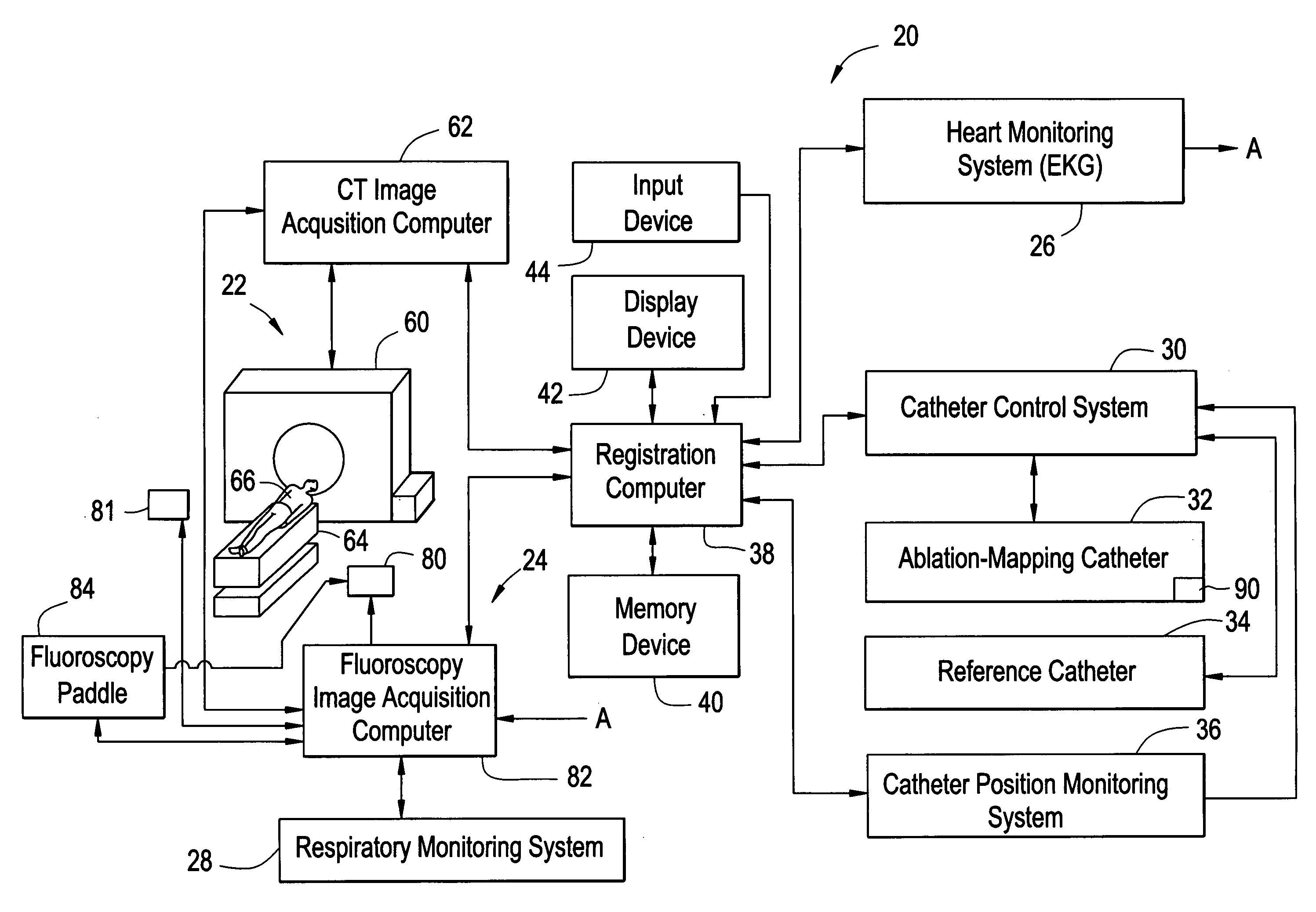
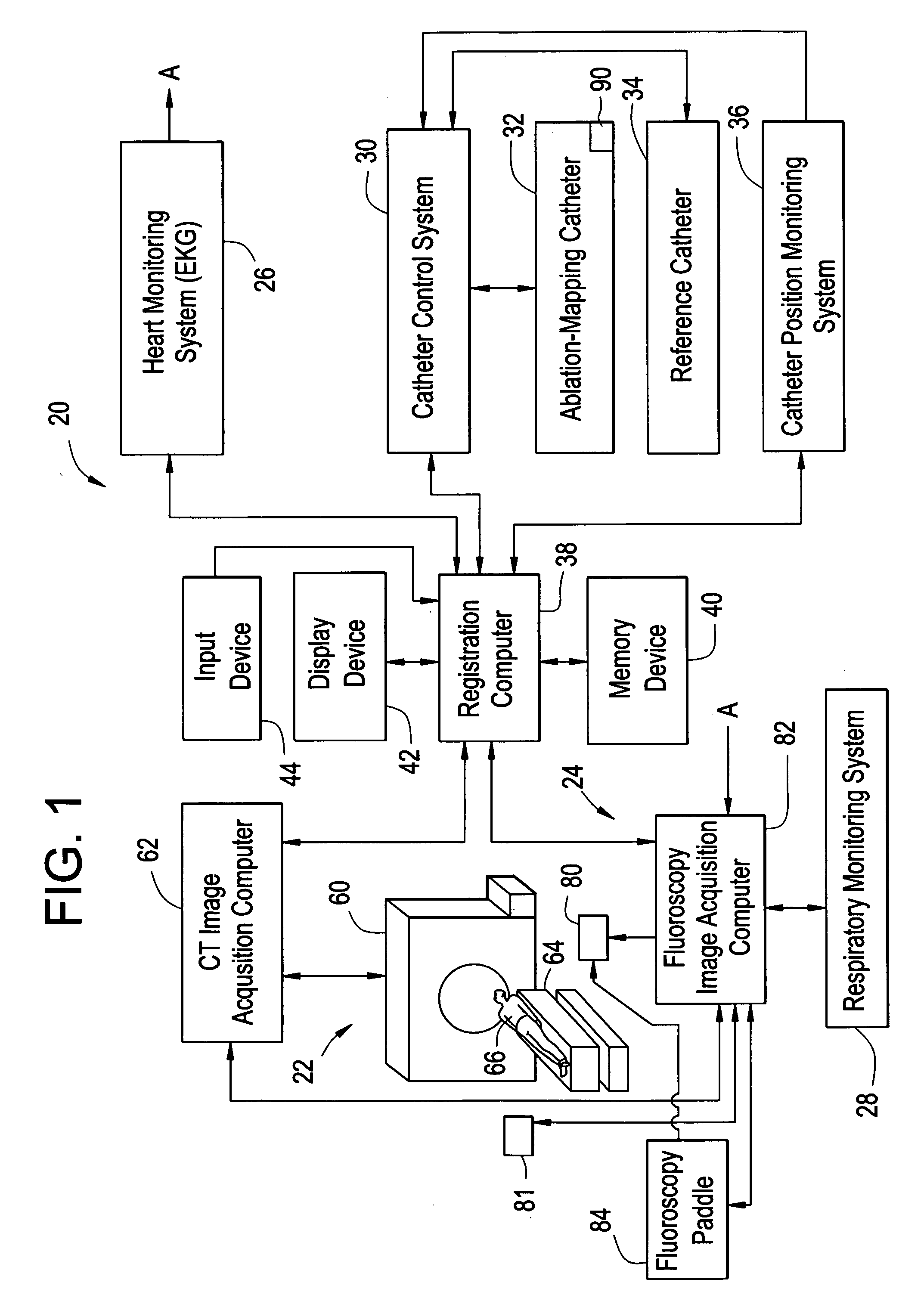
An imaging system for use in a medical intervention procedure is disclosed. A first image acquisition system of a first modality employing a catheter at an anatomical region of a patient is configured to produce a first image of the anatomical region using fluoroscopy, the first image comprising a set of fluoroscopy projection images. A second image acquisition system of a second different modality is configured to generate a 3D model of the anatomical region. An anatomical reference system is common to both the first and second image acquisition systems. A processing circuit is configured to process executable instructions for registering the 3D model with the fluoroscopy image in response to the common reference system and discernible parameters associated with the catheter in both the first and second image acquisition systems.
Owner:APN HEALTH +1
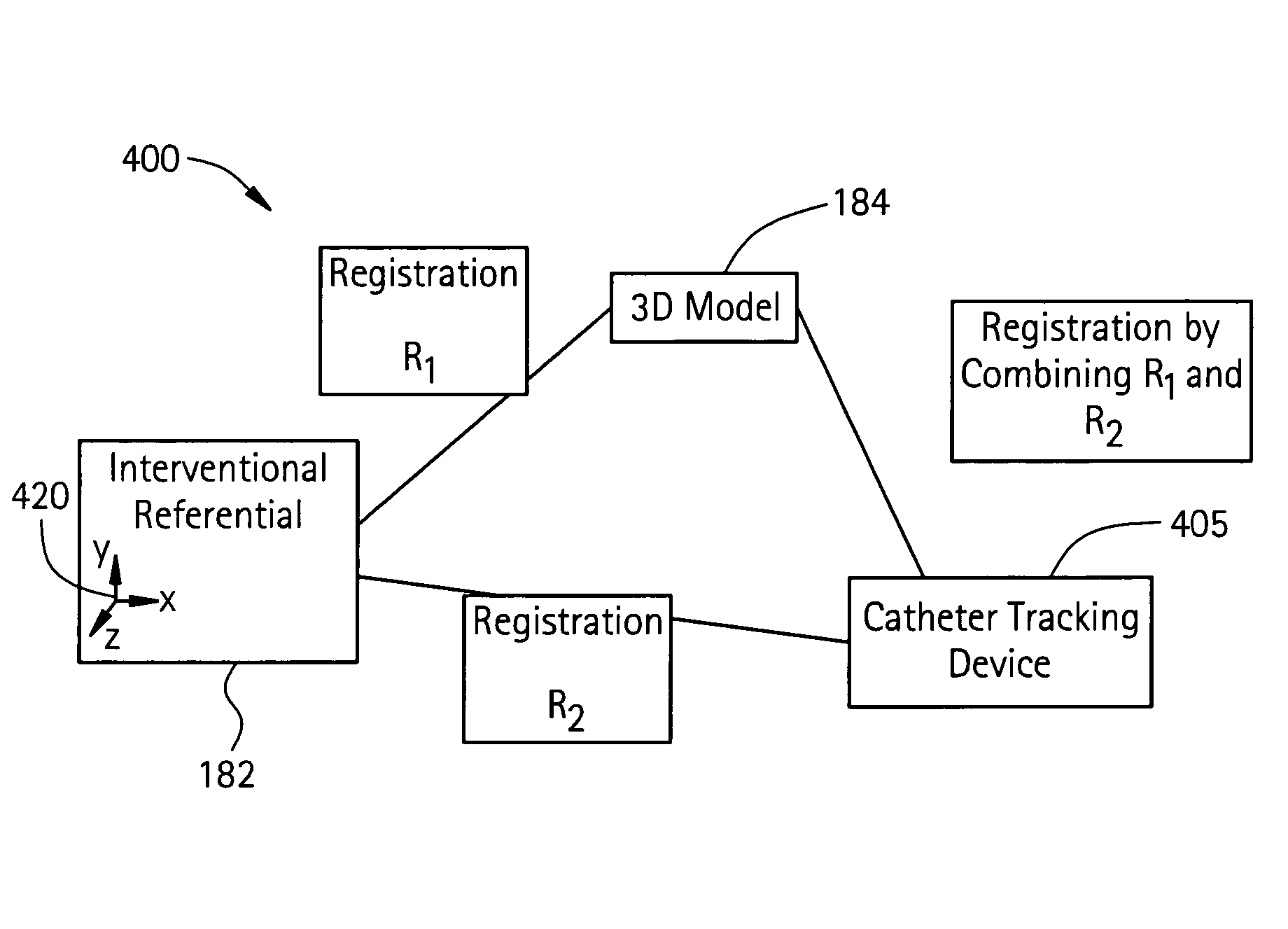
Method and apparatus for registering 3D models of anatomical regions of a heart and a tracking system with projection images of an interventional fluoroscopic system
ActiveUS8515527B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementProjection imageHeart anatomy
An imaging system for use in a medical intervention procedure is disclosed. A first image acquisition system is configured to produce a fluoroscopy image of an anatomical region. A second image acquisition system is configured to produce a 3D model of the anatomical region. An interventional tracking system, which includes a position indicator, is configured to maneuver within the anatomical region. A first anatomical reference system is common to both the first and the second image acquisition systems, and a second anatomical reference system is common to both the first image acquisition system and the interventional tracking system. A processing circuit configured to process executable instructions for registering the second image acquisition system with the first image acquisition system to define a first registration, registering the interventional tracking system with the first image acquisition system to define a second registration, and in response to the first and second registrations, registering the interventional tracking system with the second image acquisition system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
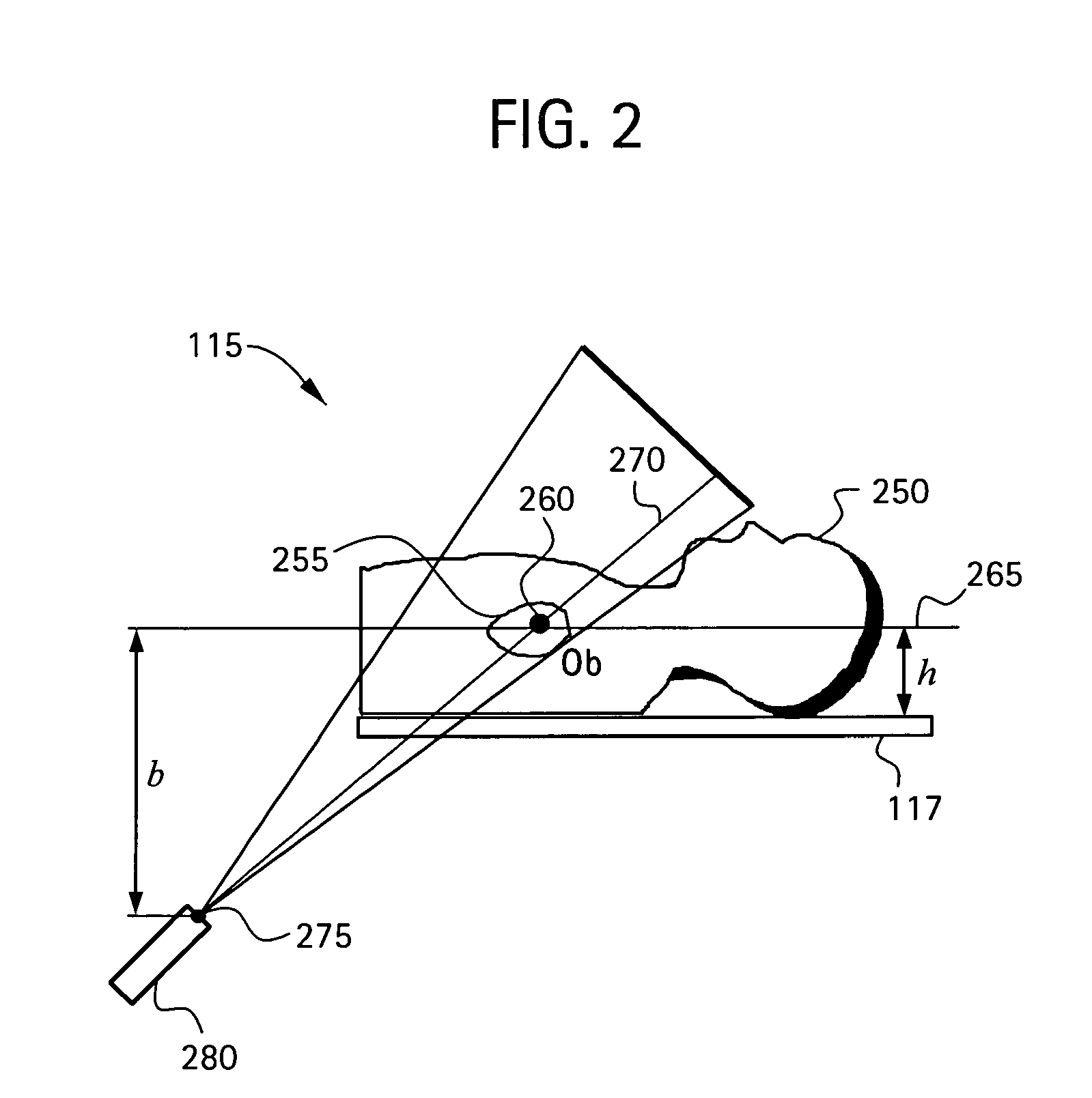
Alignment fixture for x-ray images
ActiveUS20110103556A1Quickly and easily taking X-rayForeign body detectionRadiation beam directing meansParallaxBeam source
An alignment fixture for taking X-ray images of a patient, such as an image of the patient's hip region preparatory to hip arthroplasty. The alignment fixture comprises multiple support legs for resting on the patient at known positions, such as upon known bony prominences, in combination with aiming marks used for anatomically aligning the patent's pelvis under an X-ray beam. A ruled grid plate on the fixture is adjustably positioned between an image beam source and the patient, as a function of patient thickness in the pelvic region, so that a ruled grid overlays the anatomical region of interest and exhibits an apparent parallax image magnification corresponding with the parallax image magnification of a centerline of the anatomical region, such as the hip joint. X-ray images taken by use of the alignment fixture can be viewed and / or scaled to select a properly sized prosthesis for the specific patient.
Owner:CARN RONALD M
Methods for displaying a location of a point of interest on a 3-d model of an anatomical region
ActiveUS20080152205A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTriangulationX-ray
Methods for displaying a location of a point of interest on a 3-D model of an anatomical region of a person are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, the method includes generating first and second 2-D images of the anatomical region utilizing an image acquisition system when an X-ray source of the image acquisition system is disposed at first and second positions, respectively, in a 3-D coordinate system of the image acquisition system. The method further includes selecting first and second points in the first and second 2-D images, respectively. The method further includes utilizing a triangulation technique utilizing the first and second points to determine a point of interest in a 3-D coordinate system of the 3-D model of the anatomical region.
Owner:APN HEALTH +1
Detection and tracking of interventional tools
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
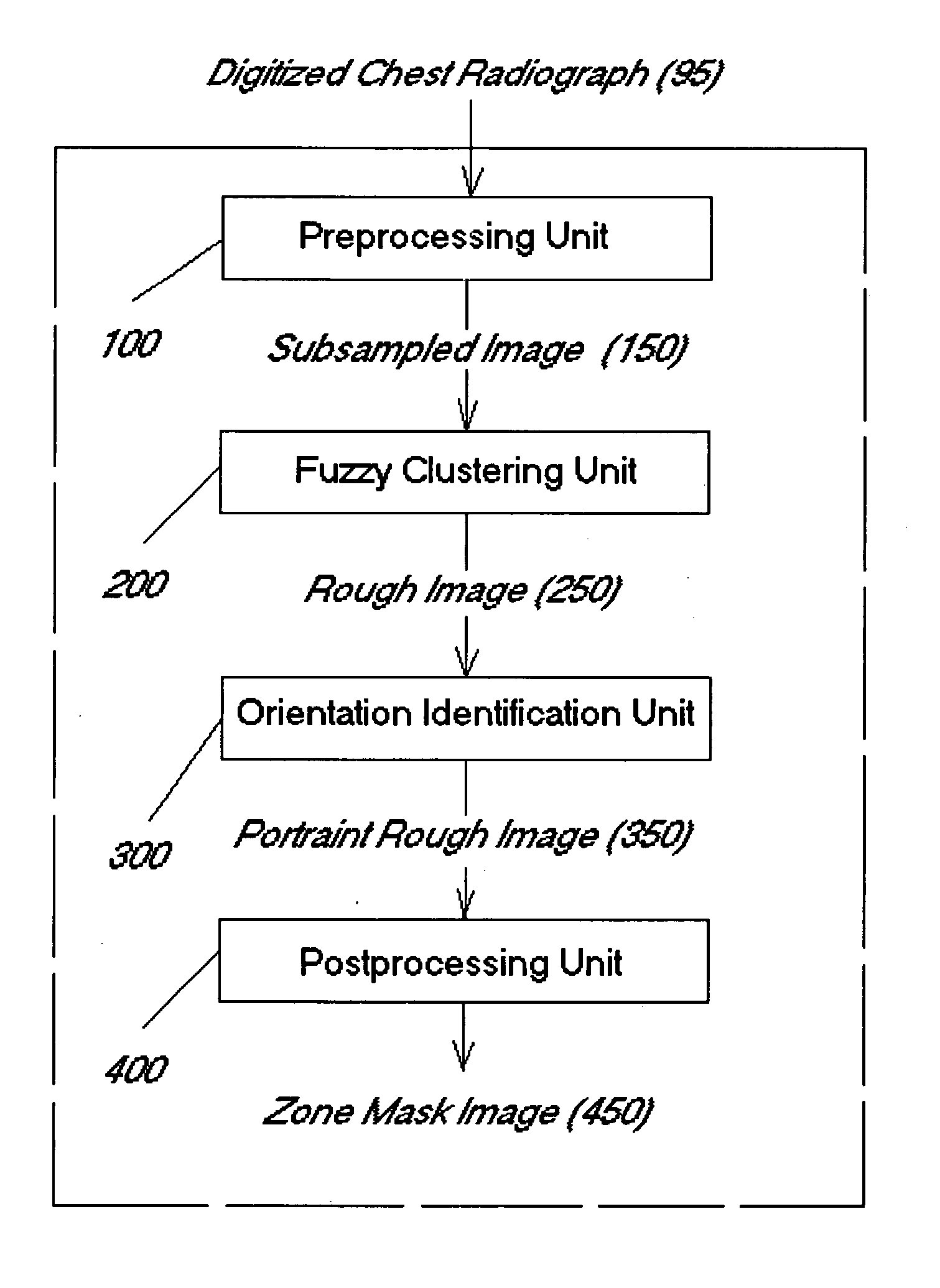
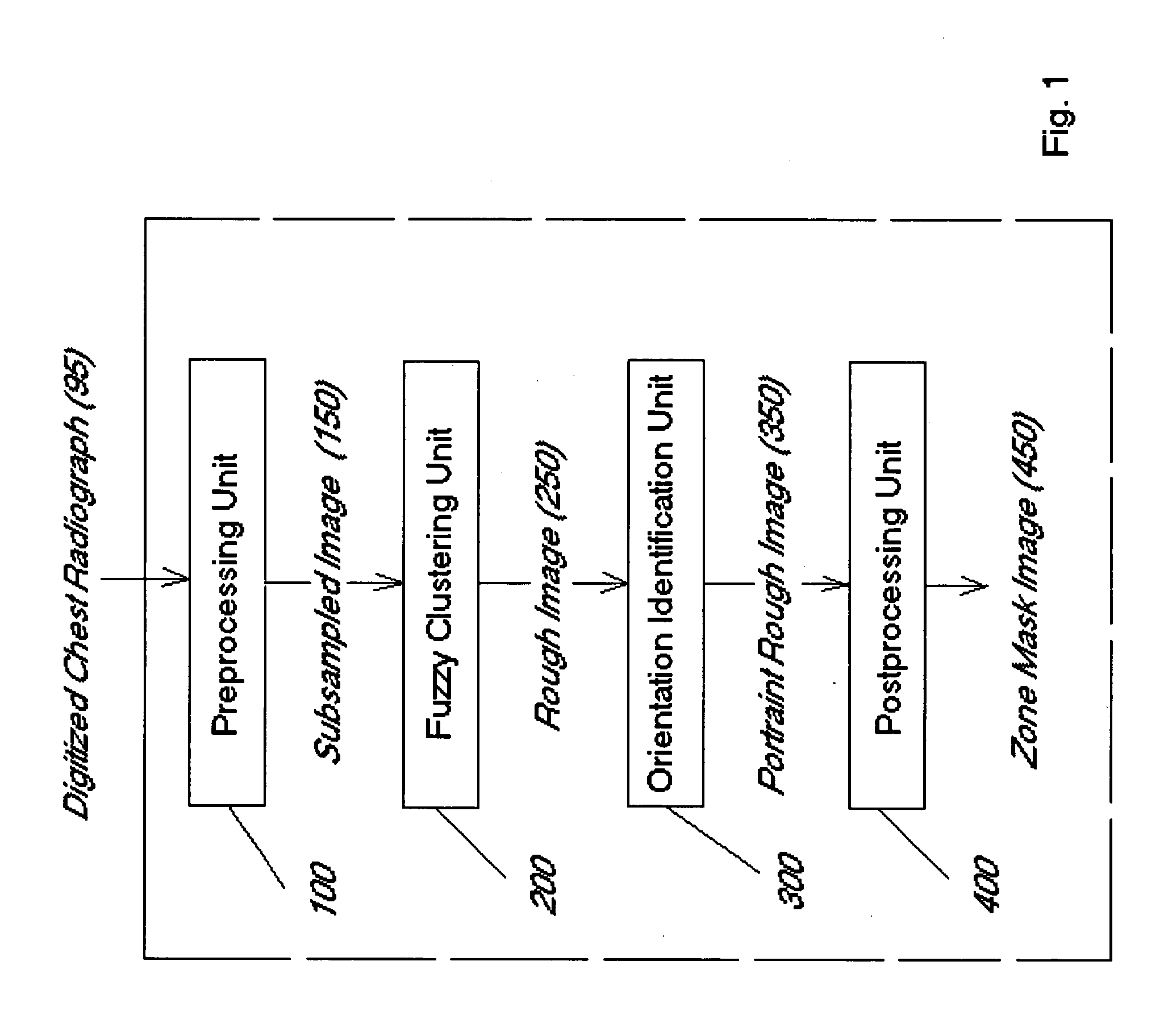
Adaptive segmentation of anatomic regions in medical images with fuzzy clustering
A method for identifying the orientation of an interesting object in a digital medical image comprises steps of creating a rectangular interesting image mask that covers the interesting object, based on the original digital medical image; generating a rough image based on the interesting image mask, the rough image coarsely describing the interesting object; and identifying the orientation of the interesting object based on the rough image. A method for segmenting interesting objects in digital medical images may also comprise steps of creating a rectangular interesting image mask that covers said interesting object, based on an original digital medical image; generating a rough image based on the interesting image mask, the rough image coarsely describing the interesting object; and performing a post-process on the rough image.
Owner:RIVERAIN MEDICAL GROUP
User interface with view finder for localizing anatomical region
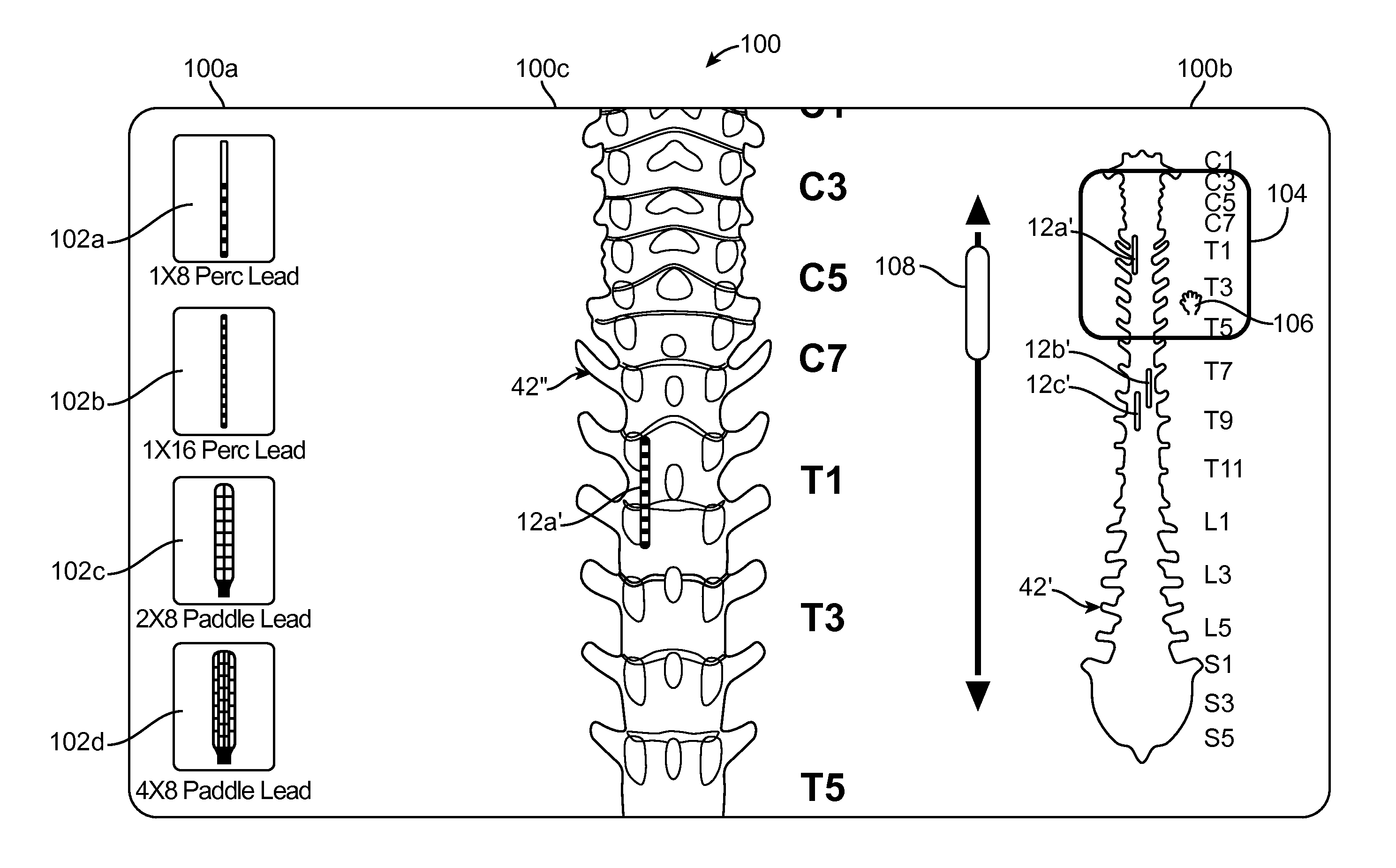
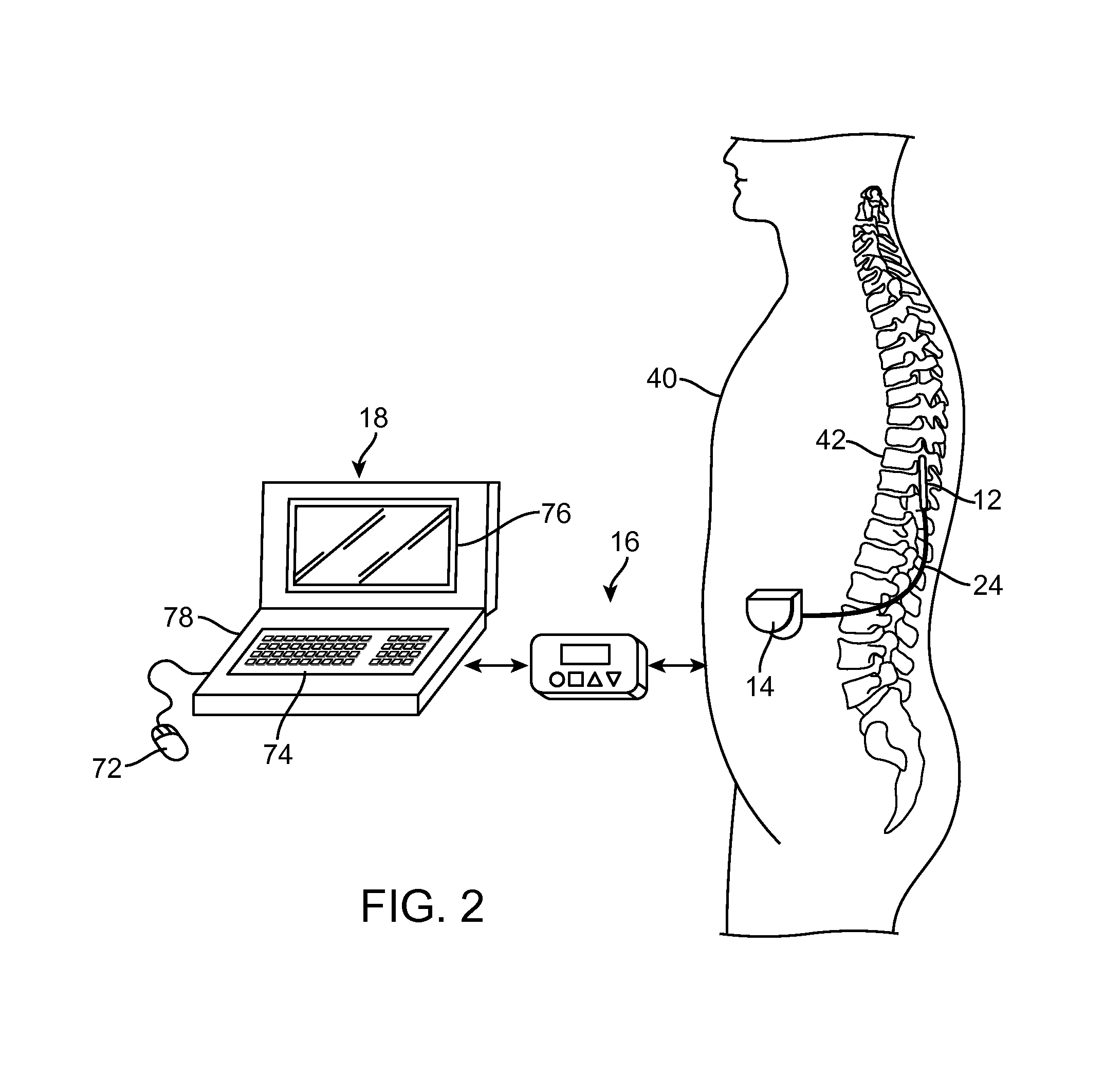
ActiveUS20120265269A1Limitation in positionSpinal electrodesInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsUser interface
An external control device for use with a medical component implanted within a patient. The device comprises a user interface configured for receiving user input, displaying a first graphical representation of the medical component in the context of a global graphical representation of an anatomical region of the patient, displaying a view finder defining a portion of the global graphical representation, and displaying a second graphical representation of the medical component in the context of a local graphical representation of the portion of the anatomical region portion. The external control device further comprises control circuitry configured for, in response to the input from the user, modifying the displayed view finder to spatially define a different portion of the global graphical representation, such that the second graphical representation of the medical component is displayed in the context of a local graphical representation of the different portion of the anatomical region.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
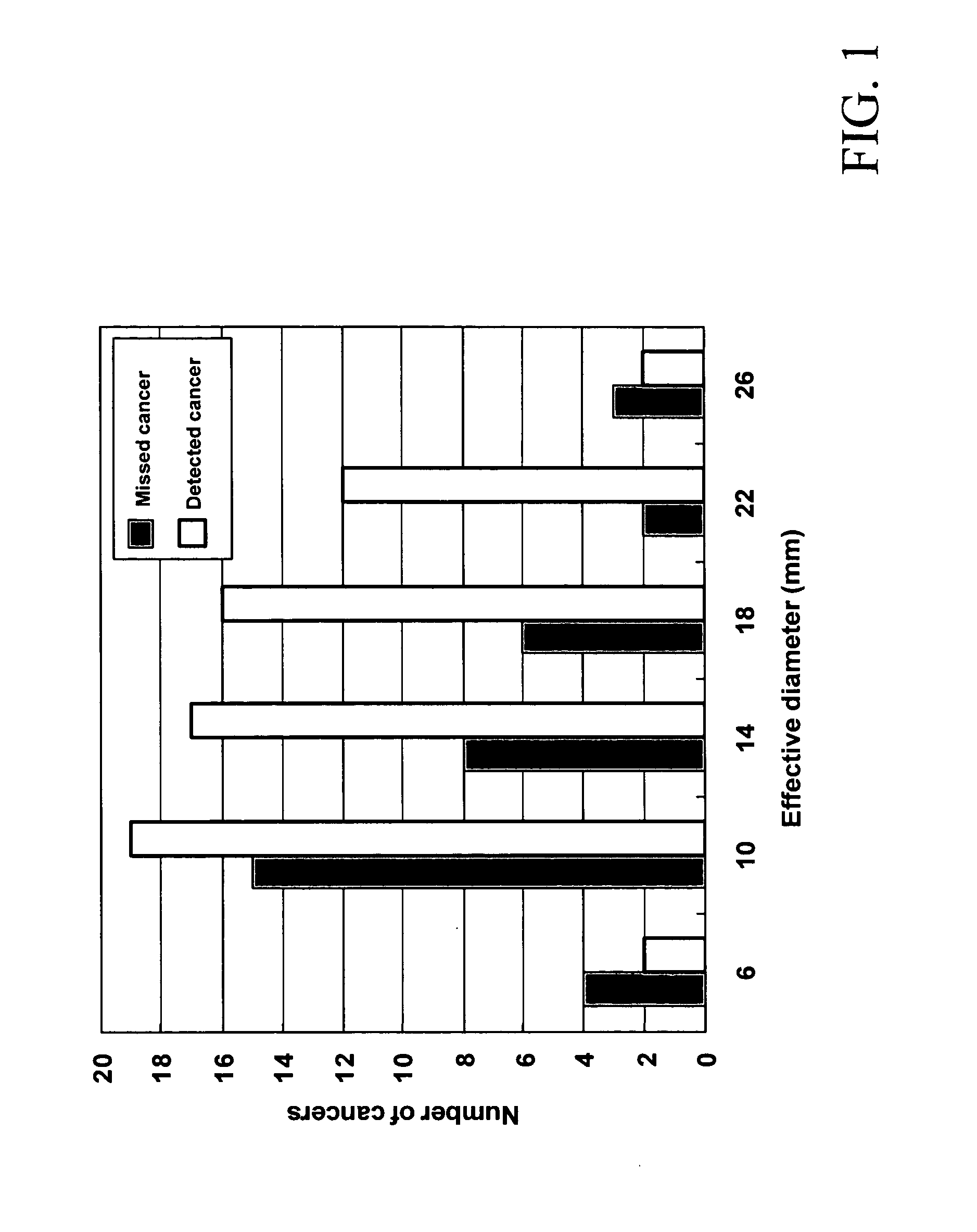
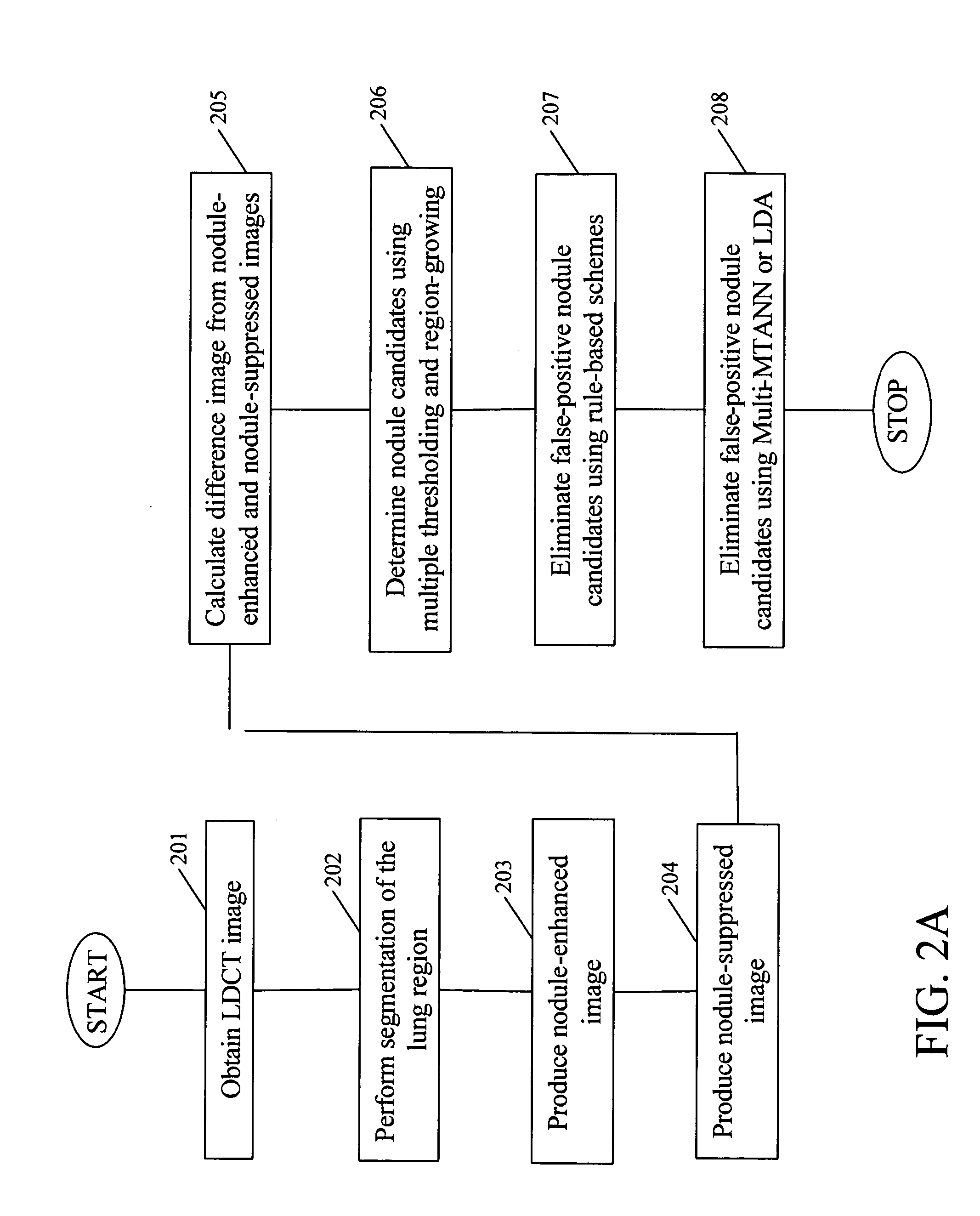
Automated method and system for the detection of lung nodules in low-dose CT image for lung-cancer screening
InactiveUS20050171409A1Image enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLinearityLinear discriminant analysis
A method, system, and computer program product for detecting at least one nodule in a medical image of a subject, including identifying, in the medical image, an anatomical region corresponding to at least a portion of an organ of interest; filtering the medical image to obtain a difference image; detecting, in the difference image, a first plurality of nodule candidates within the anatomical region; calculating respective nodule feature values of the first plurality of nodule candidates based on pixel values of at least one of the medical image and the difference image; removing false positive nodule candidates from the first plurality of nodule candidates based on the respective nodule feature values to obtain a second plurality of nodule candidates; and determining the at least one nodule by classifying each of the second plurality of nodule candidates as a nodule or a non-nodule based on at least one of the pixel values and the respective nodule feature values. True-positive nodules are identified using linear discriminant analysis and / or a Multi-MTANN.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
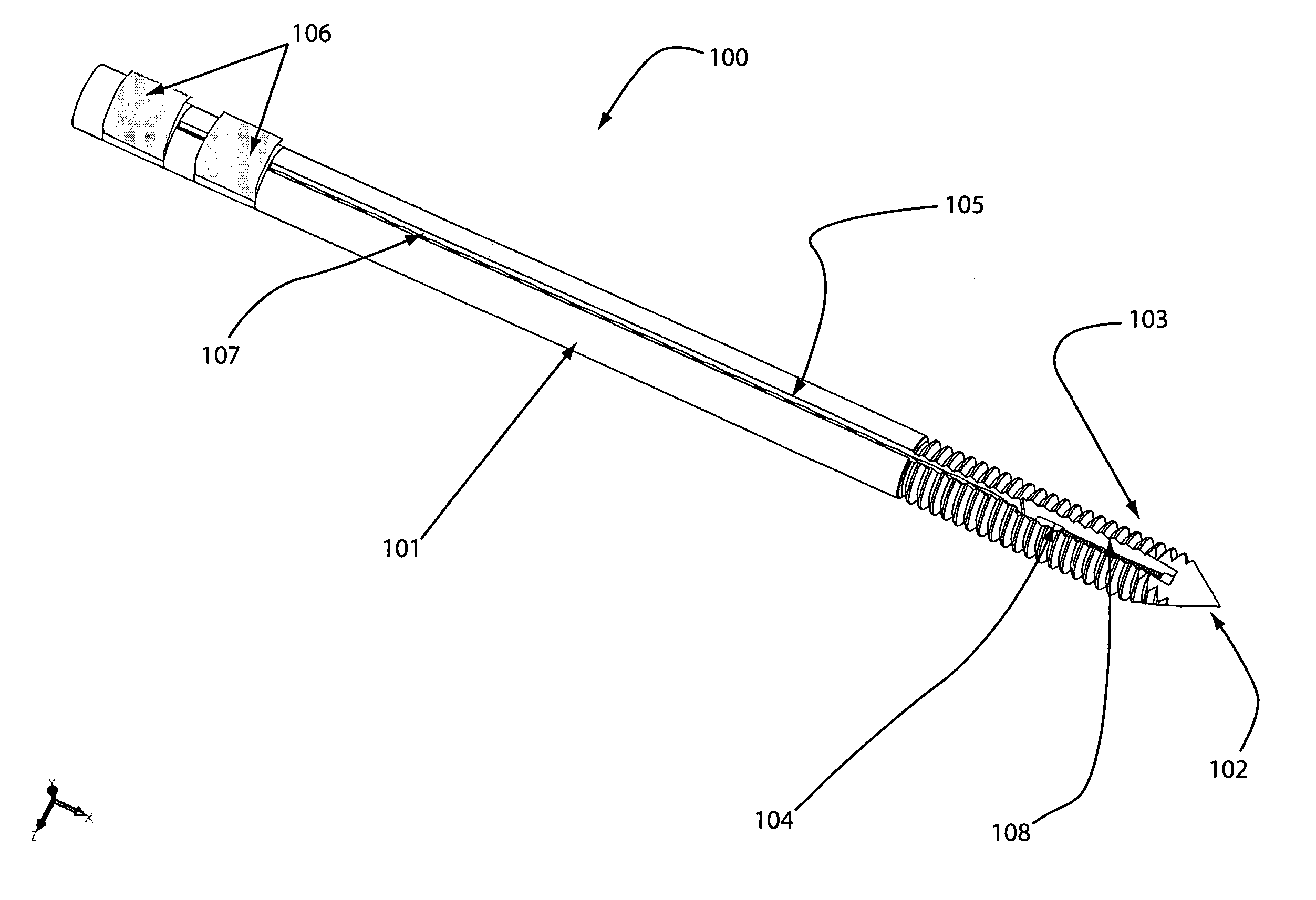
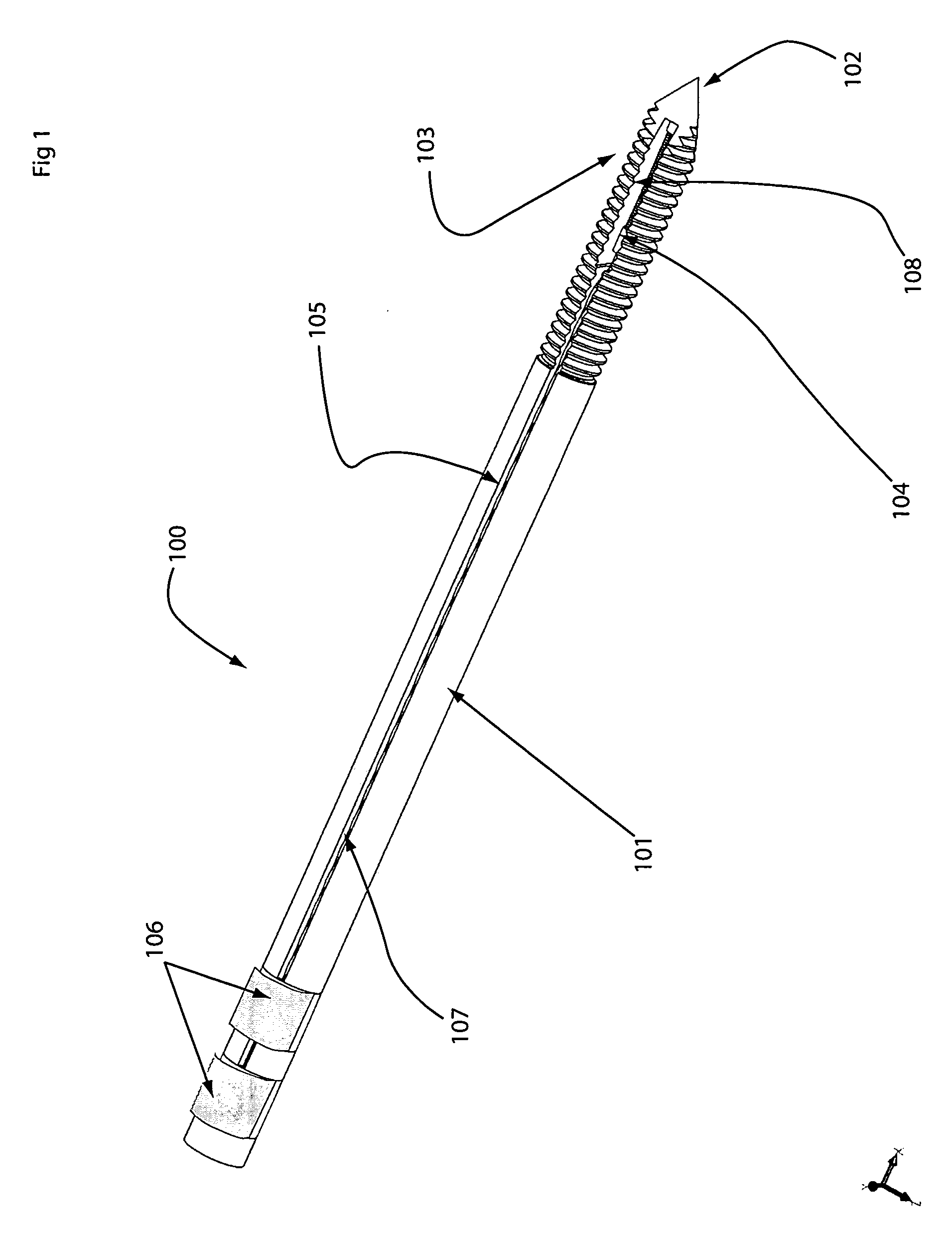
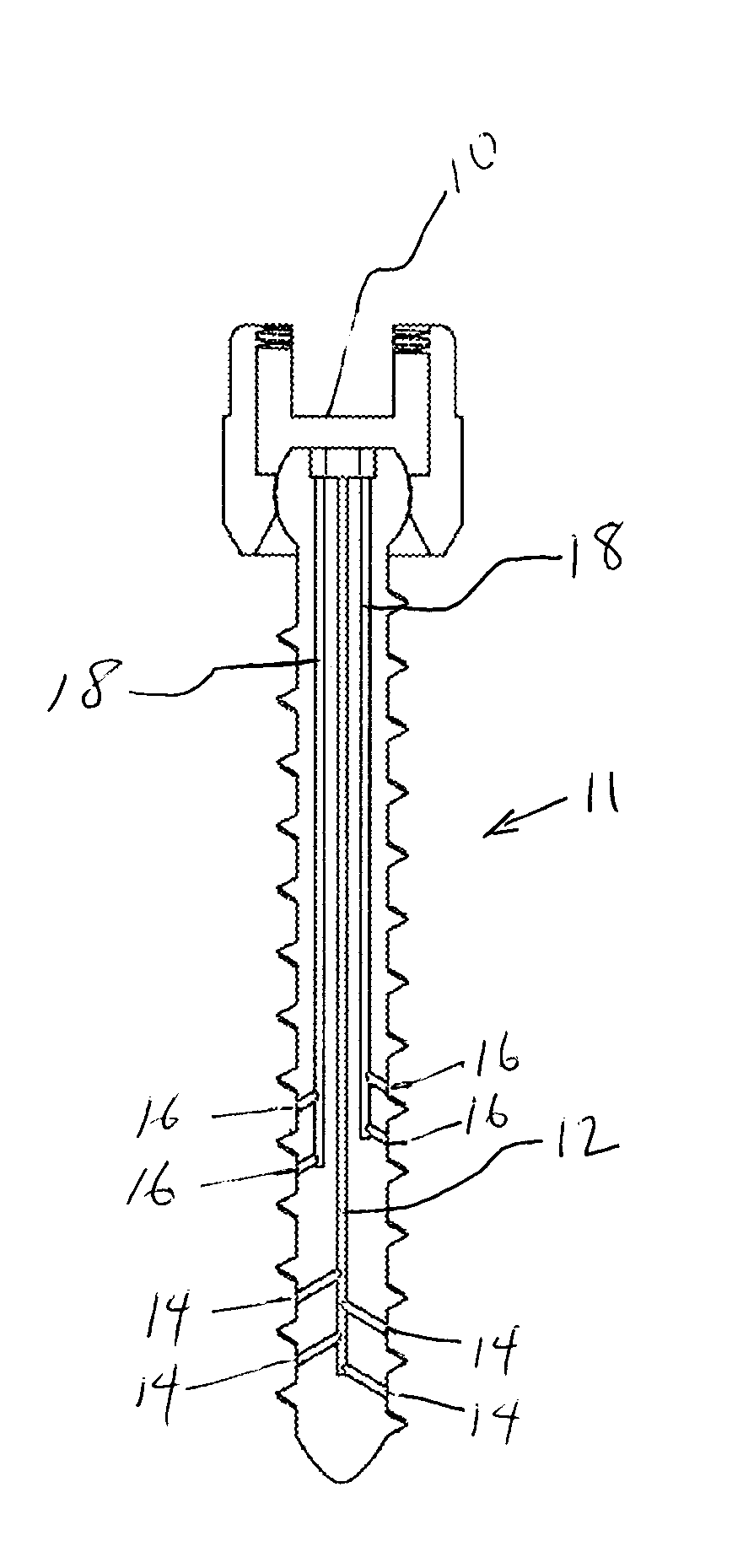
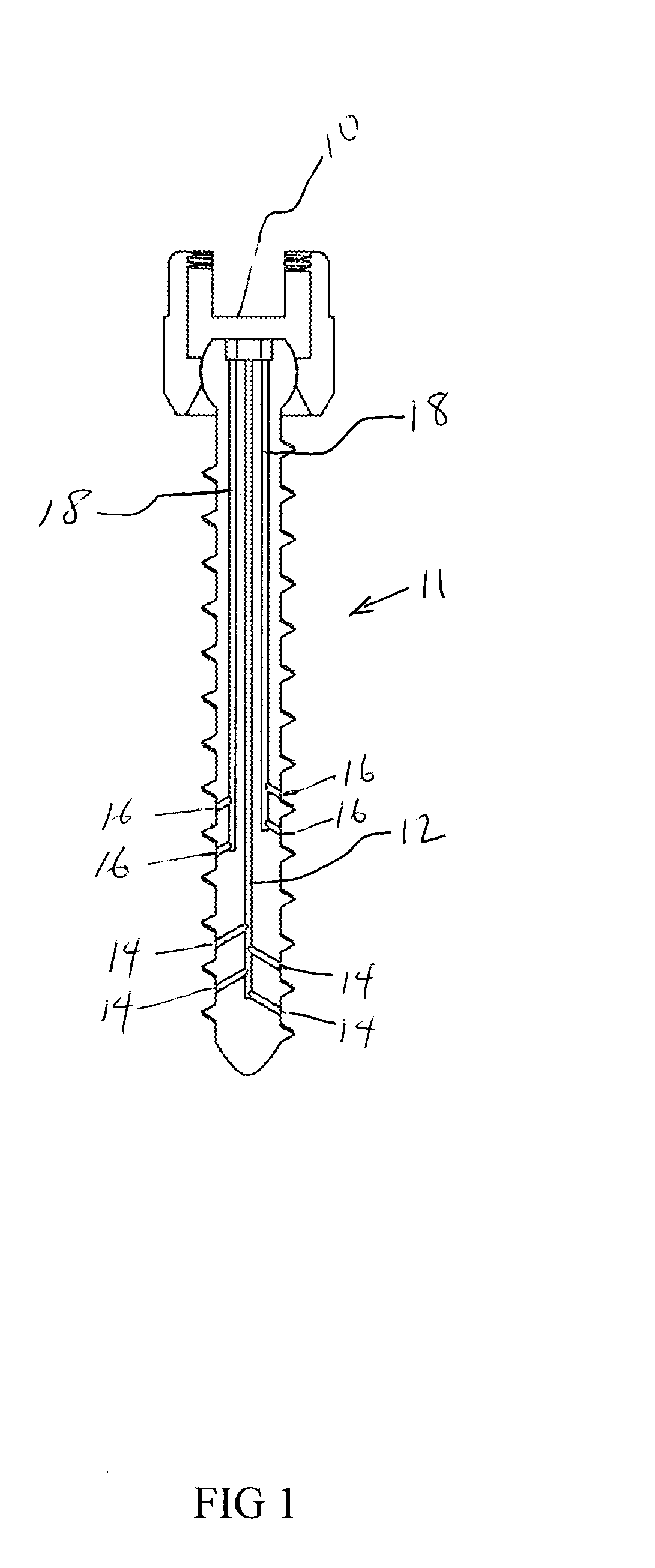
Venting/pressure adjustment to aid in delivery of material into an anatomic region via a cannula
ActiveUS20100106199A1Reduce pressureSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisIliac screwBiomedical engineering
A cannulated and possibly fenestrated device for injection of material into bone can be dangerous because large, uncontrolled pressures are introduced during injection into a somewhat closed system, and material may extrude undesirably or emboli may be introduced. Methods and devices are described for providing venting of pressure upon injection of material through cannulated and possibly fenestrated screws. The first method involves a bone screw and / or anchor device that includes multiple channels to allow material to flow in through one channel and out through another channel. The second method involves a plunger that can force material into bone if advanced or lessen pressure if withdrawn. The third method involves usage of two separate screws. Material is alternately injected or withdrawn from each screw to cause material to flow from one screw to the other in a controlled way that creates a uniform or asymmetrical distribution of material as desired.
Owner:SAWA ANNA G U +5
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com