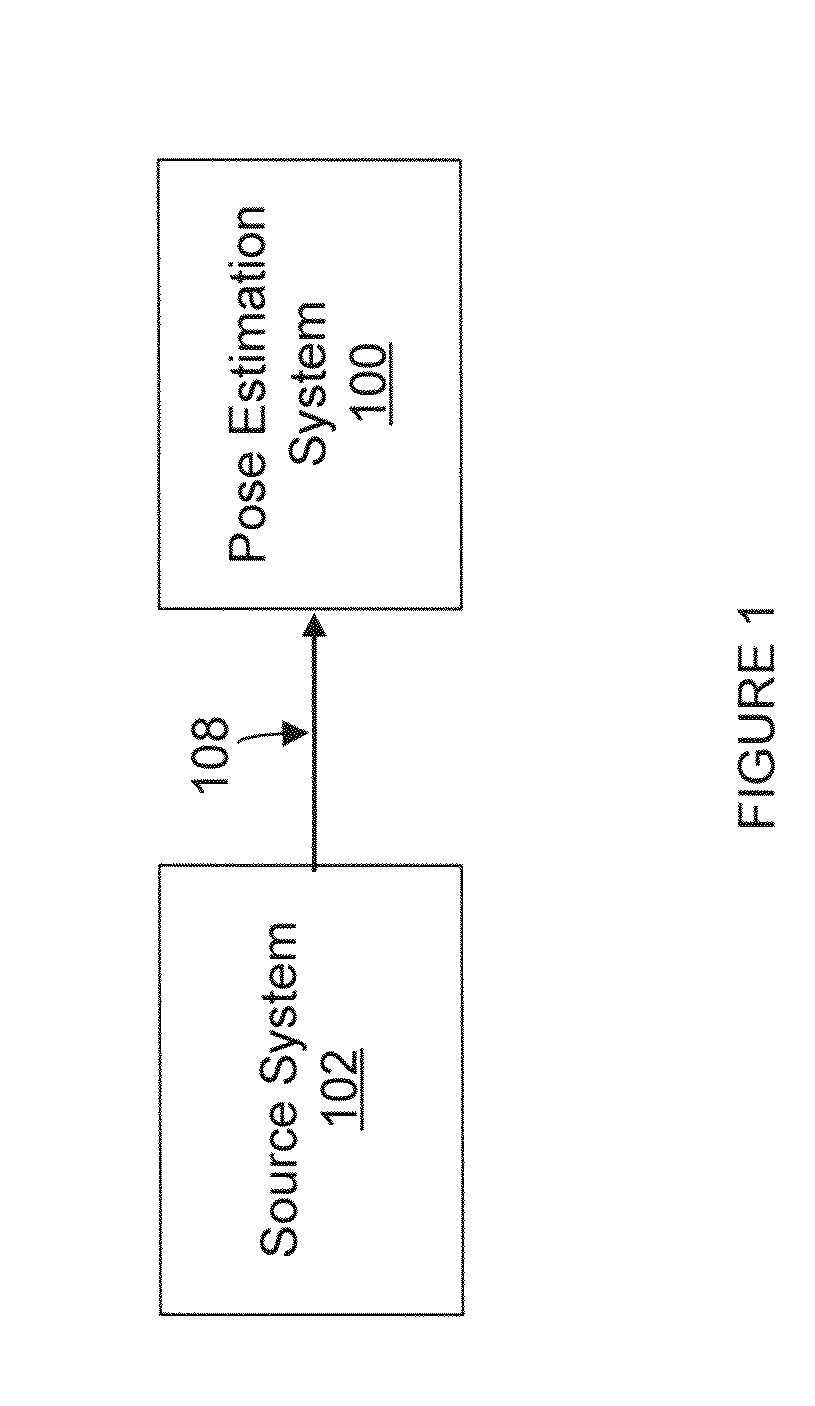
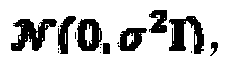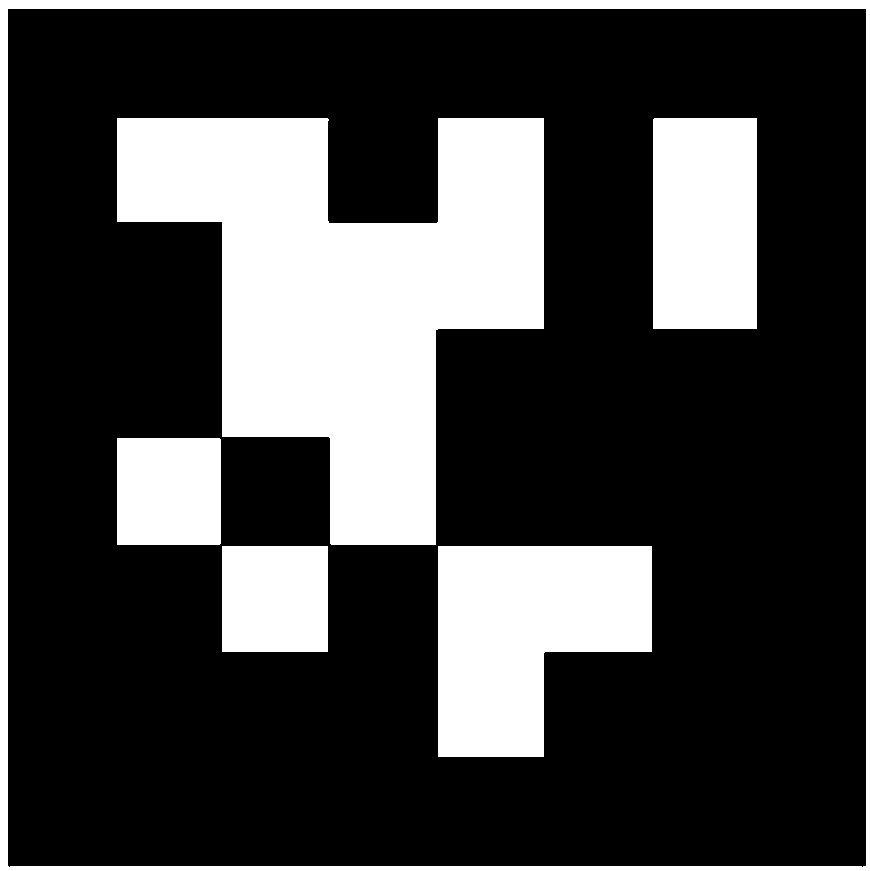Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
128 results about "3D pose estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
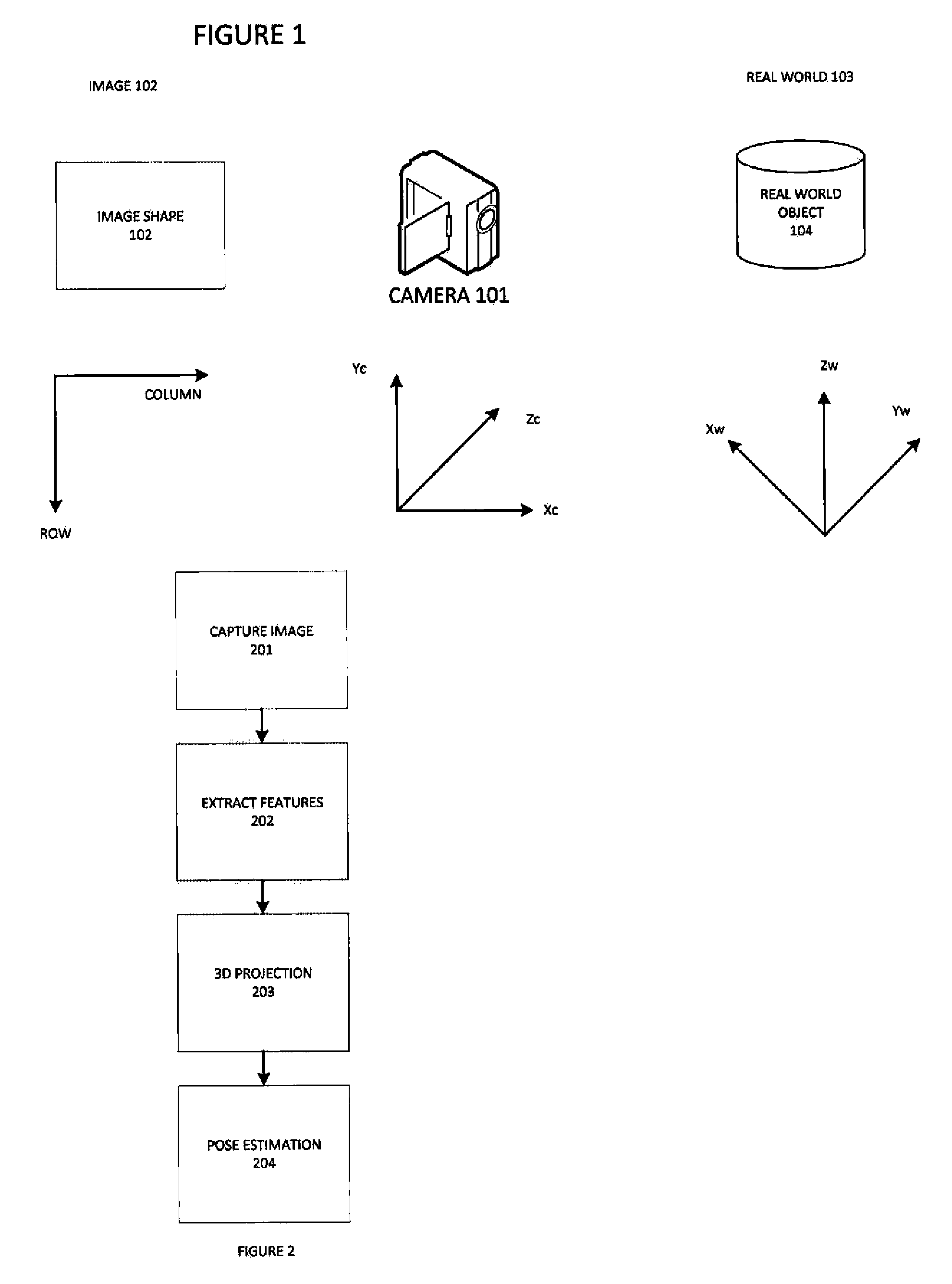
3D pose estimation is the problem of determining the transformation of an object in a 2D image which gives the 3D object. One of the requirements of 3D pose estimation arises from the limitations of feature-based pose estimation. There exist environments where it is difficult to extract corners or edges from an image. To circumvent these issues, the object is dealt with as a whole in noted techniques through the use of free-form contours.
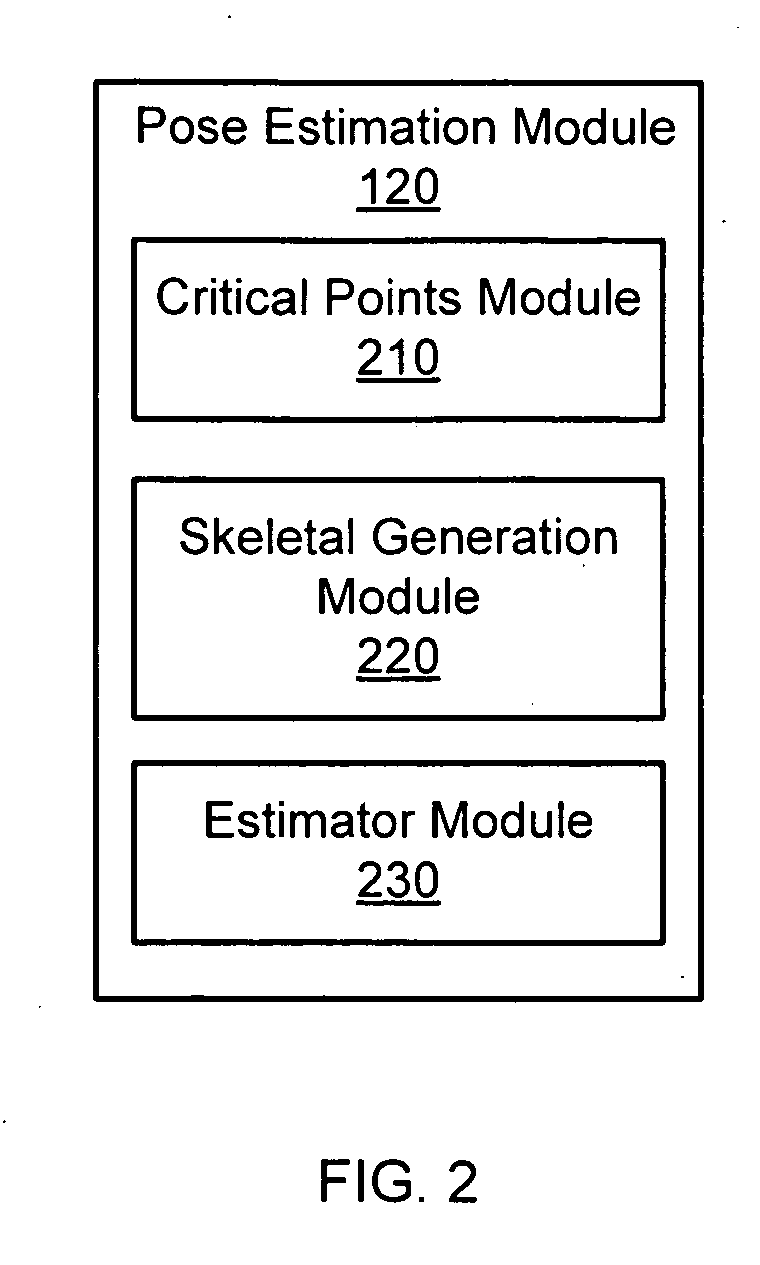
Pose estimation based on critical point analysis
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
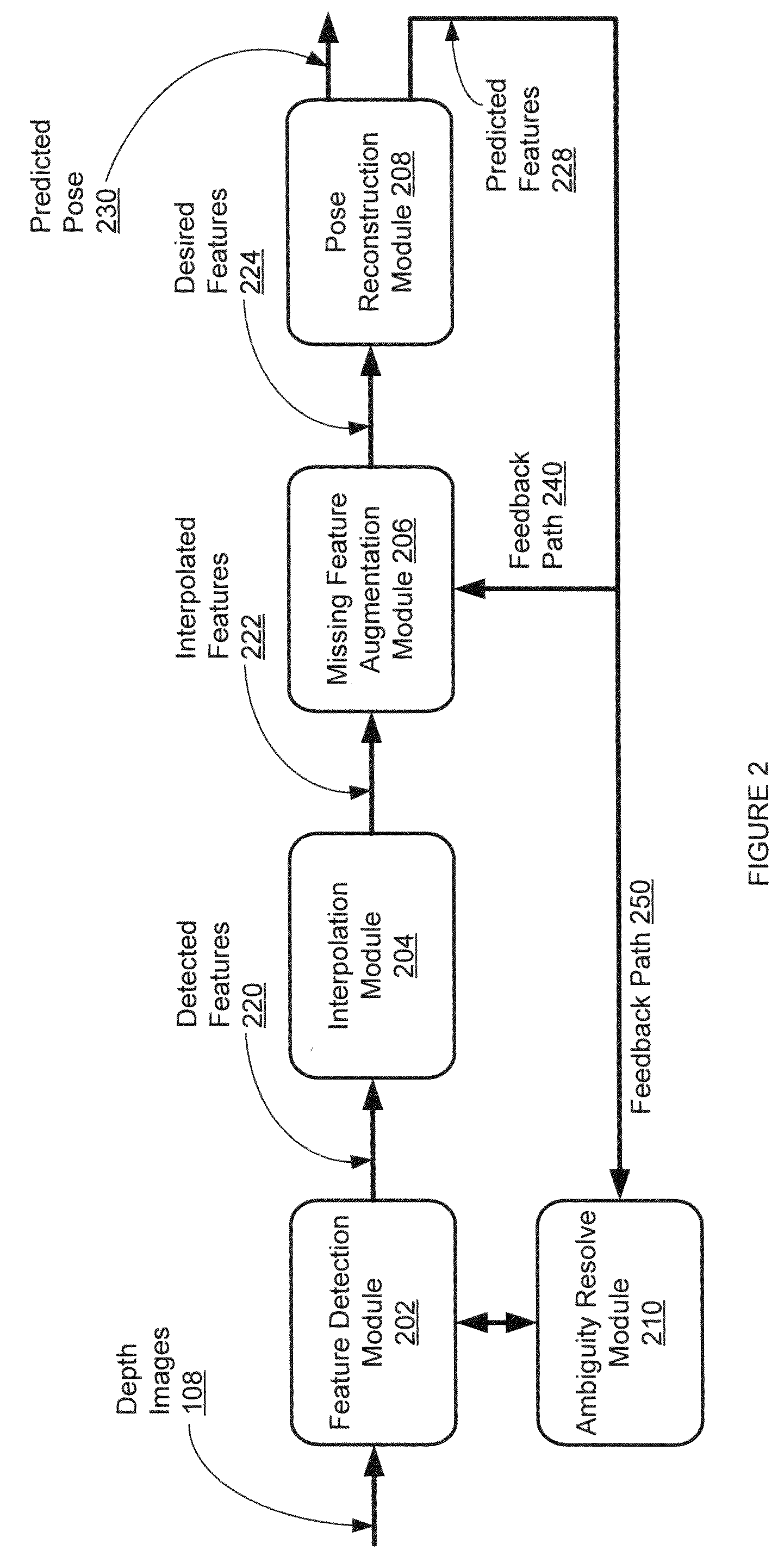
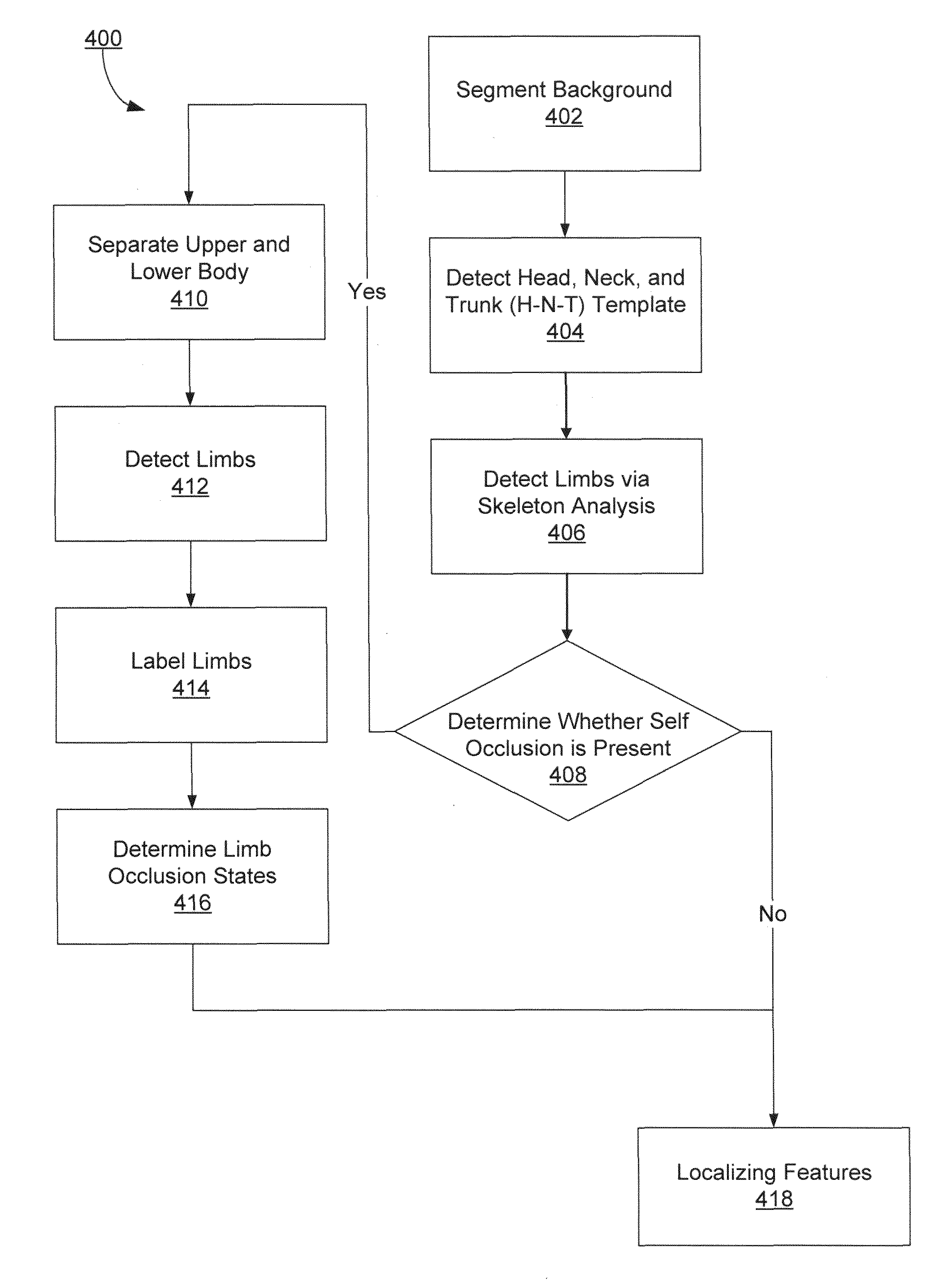
Controlled human pose estimation from depth image streams
A system, method, and computer program product for estimating human body pose are described. According to one aspect, anatomical features are detected in a depth image of a human actor. The method detects a head, neck, and trunk (H-N-T) template in the depth image, and detects limbs in the depth image based on the H-N-T template. The anatomical features are detected based on the H-N-T template and the limbs. An estimated pose of a human model is estimated based on the detected features and kinematic constraints of the human model.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
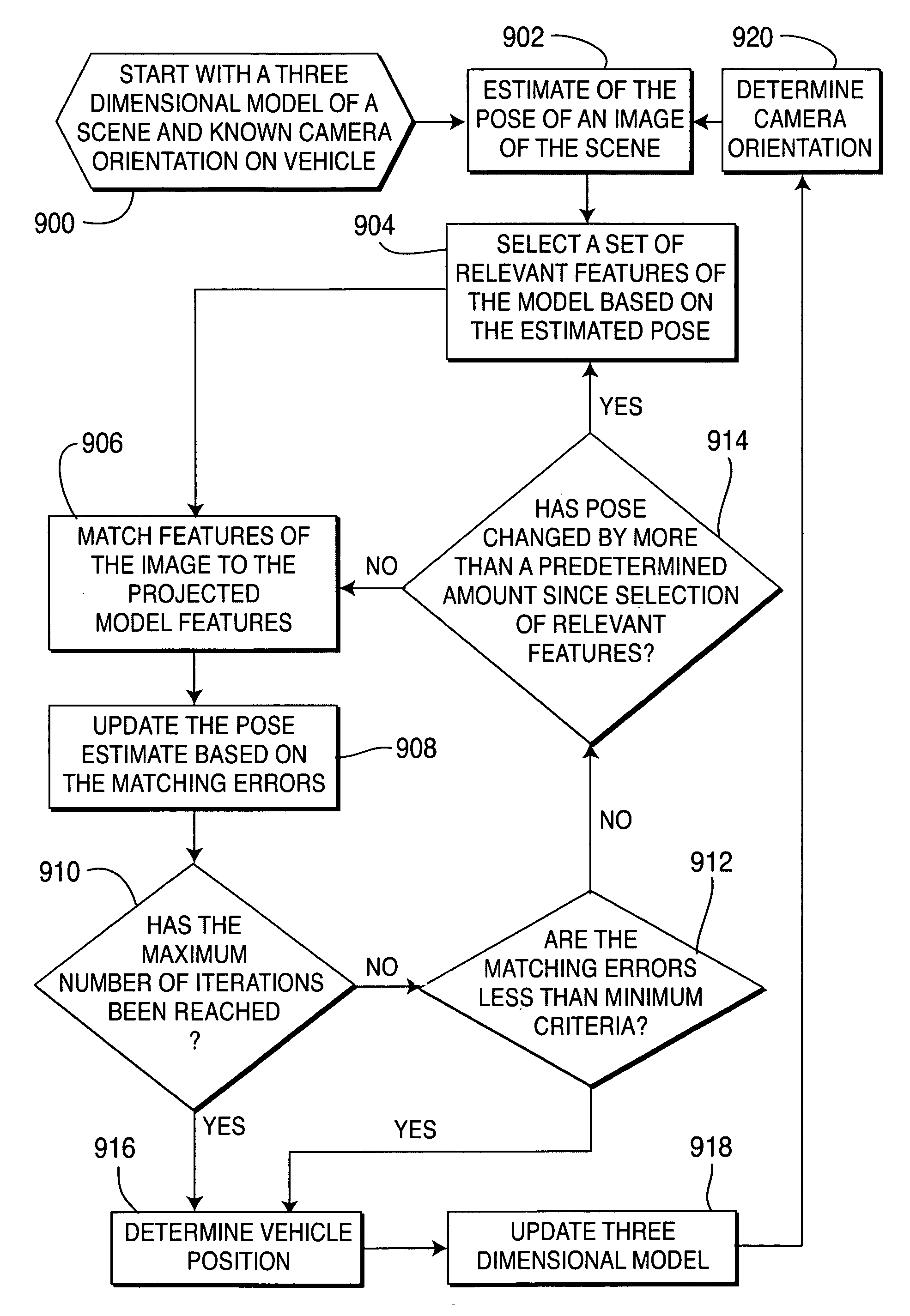
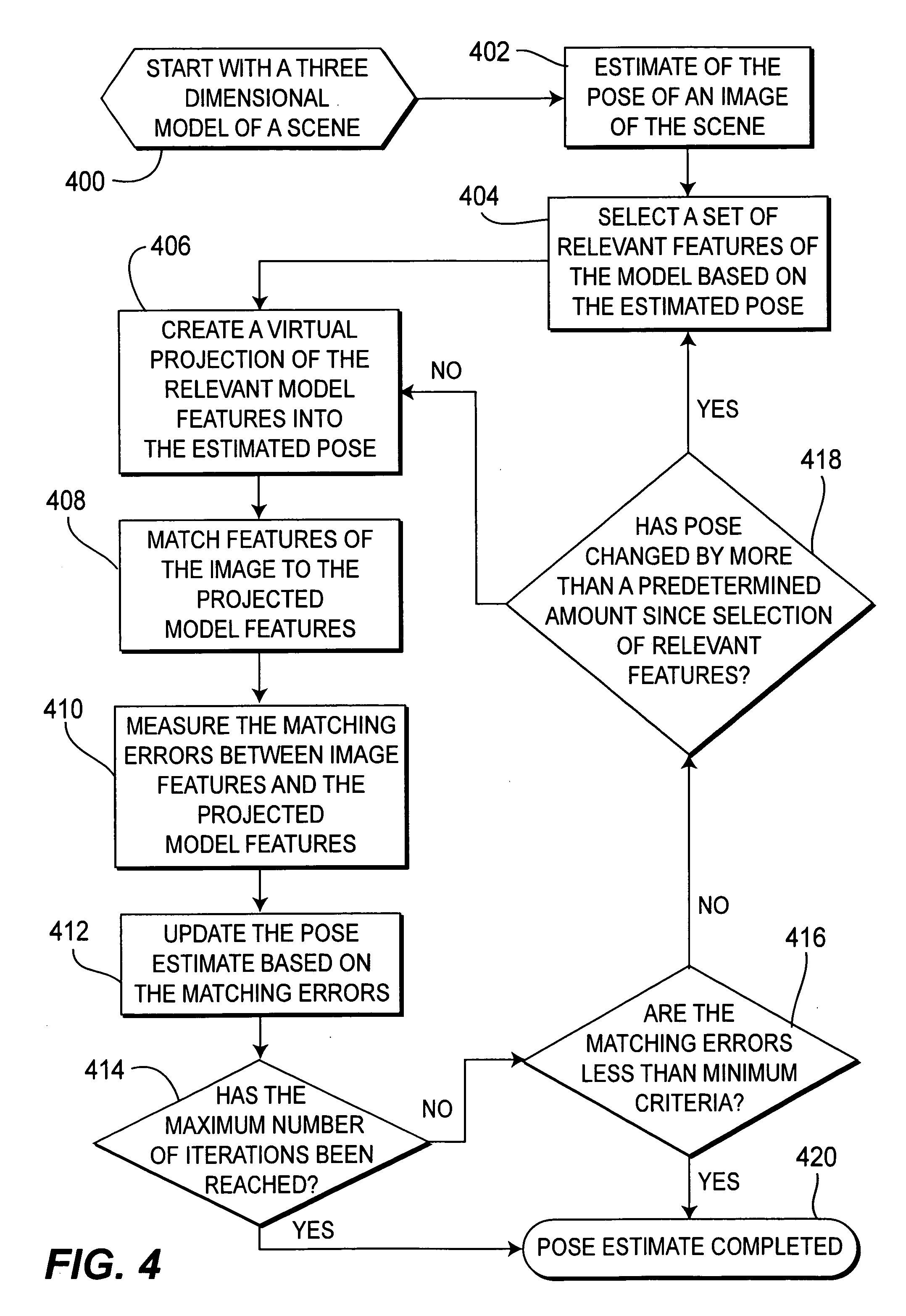
Method of pose estimation and model refinement for video representation of a three dimensional scene
InactiveUS6985620B2Accurate estimatePrecise positioningImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsViewpointsModel refinement
The present invention is embodied in a video flashlight method. This method creates virtual images of a scene using a dynamically updated three-dimensional model of the scene and at least one video sequence of images. An estimate of the camera pose is generated by comparing a present image to the three-dimensional model. Next, relevant features of the model are selected based on the estimated pose. The relevant features are then virtually projected onto the estimated pose and matched to features of the image. Matching errors are measured between the relevant features of the virtual projection and the features of the image. The estimated pose is then updated to reduce these matching errors. The model is also refined with updated information from the image. Meanwhile, a viewpoint for a virtual image is selected. The virtual image is then created by projecting the dynamically updated three-dimensional model onto the selected virtual viewpoint.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Controlled human pose estimation from depth image streams
A system, method, and computer program product for estimating upper body human pose are described. According to one aspect, a plurality of anatomical features are detected in a depth image of the human actor. The method detects a head, neck, and torso (H-N-T) template in the depth image, and detects the features in the depth image based on the H-N-T template. An estimated pose of a human model is estimated based on the detected features and kinematic constraints of the human model.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
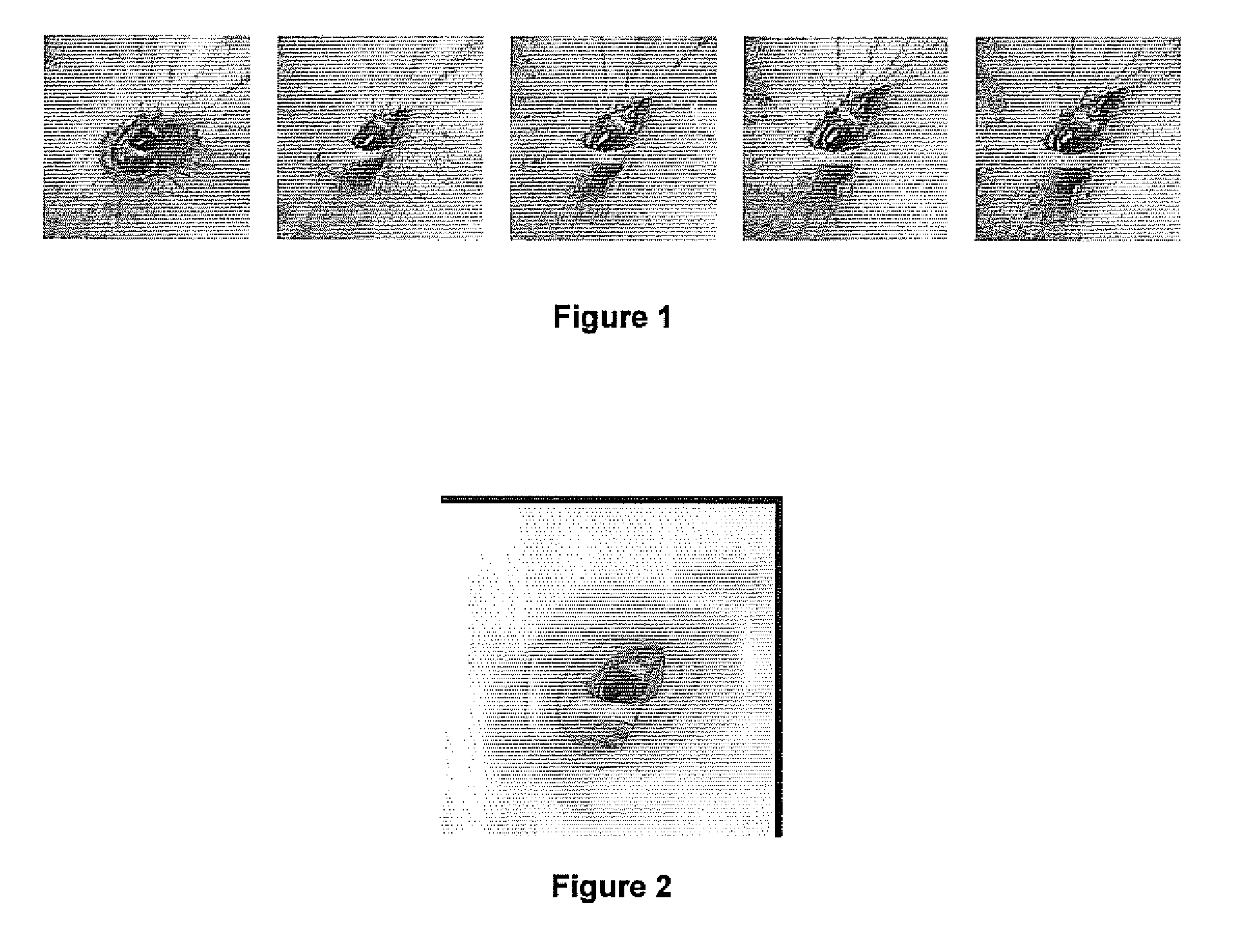
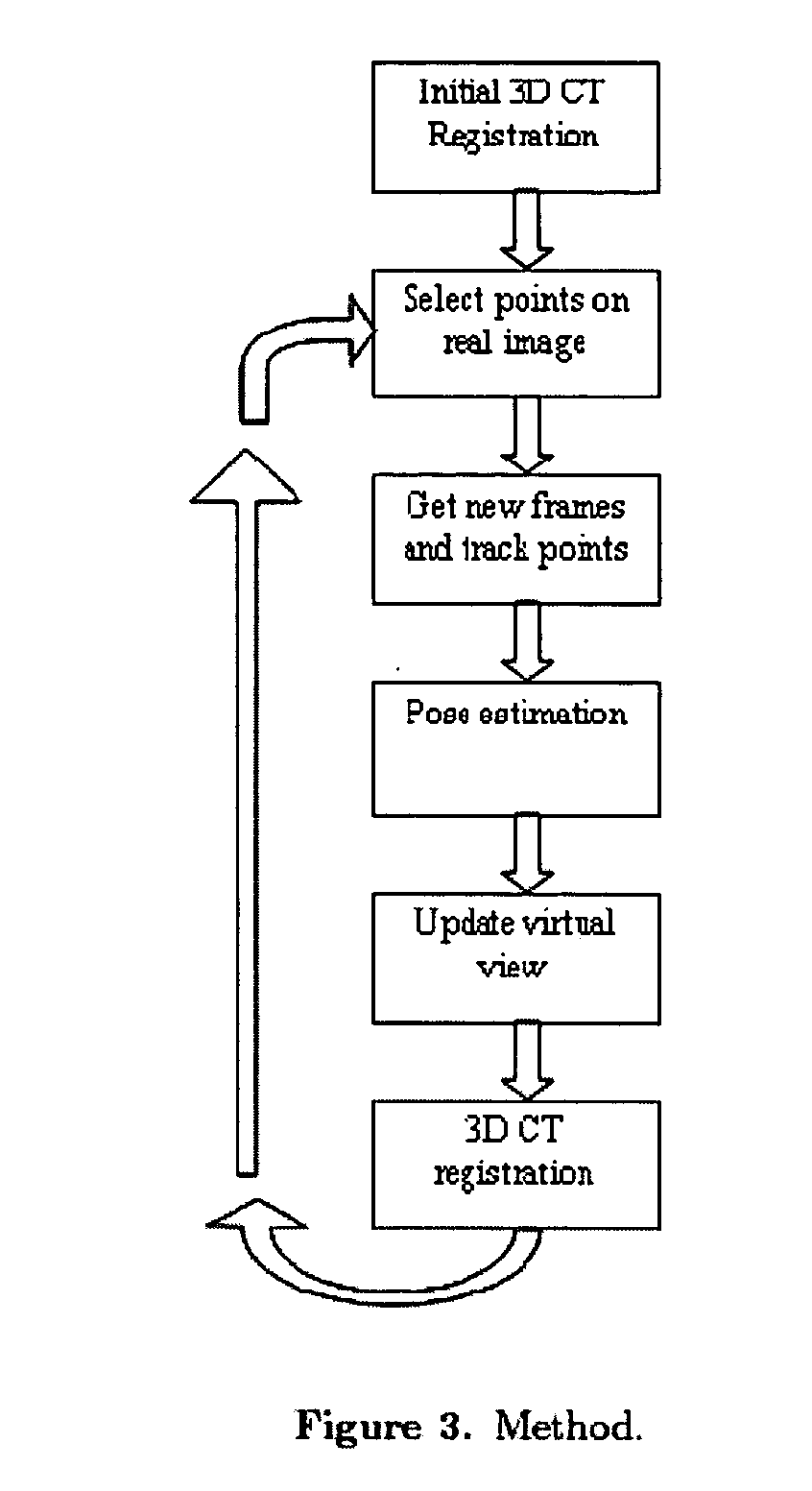
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS7756563B2Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
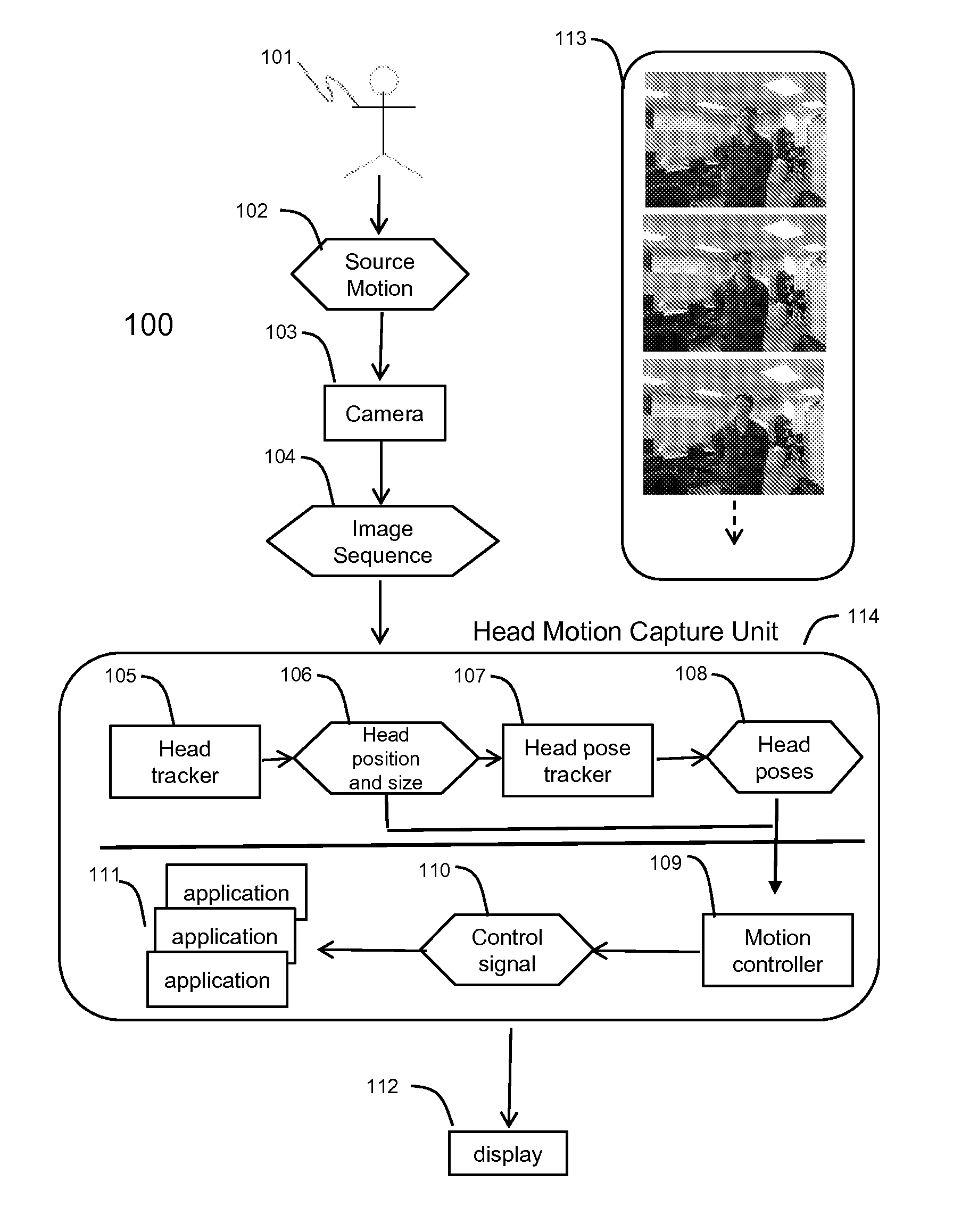
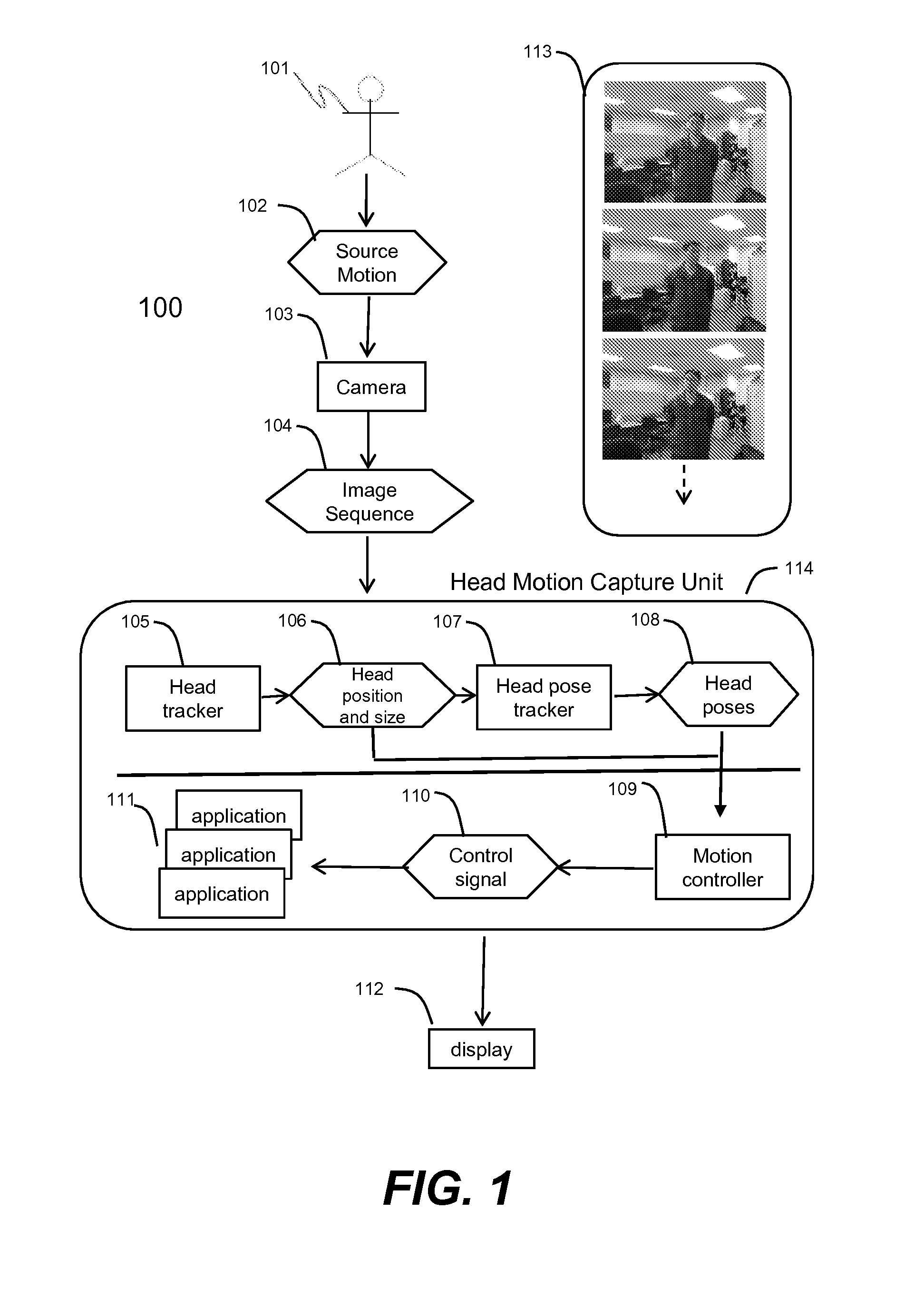
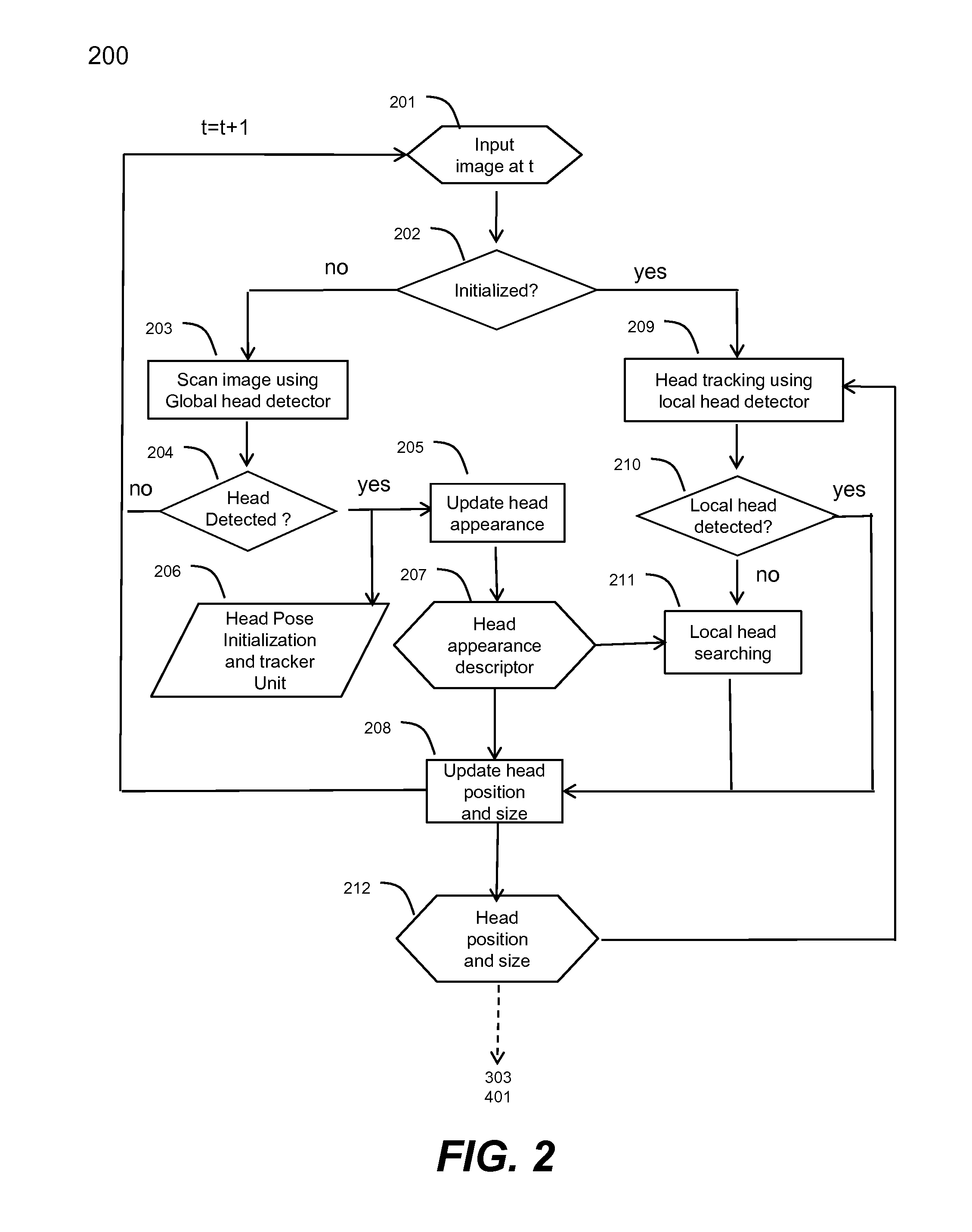
Method and system for head tracking and pose estimation
Techniques for performing accurate and automatic head pose estimation are disclosed. According to one aspect of the techniques, head pose estimation is integrated with a scale-invariant head tracking method along with facial features detected from a located head in images. Thus the head pose estimation works efficiently even when there are large translational movements resulting from the head motion. Various computation techniques are used to optimize the process of estimation so that the head pose estimation can be applied to control one or more objects in a virtual environment and virtual character gaze control.
Owner:YEN WEI
Method and apparatus for machine-vision
A system and method facilitate machine-vision, for example three-dimensional pose estimation for target objects, using one or more images sensors to acquire images of the target object at one or more positions, and to identify features of the target object in the resulting images. A set of equations is set up exploiting invariant physical relationships between features such as constancy of distances, angles, and areas or volumes enclosed by or between features. The set of equations may be solved to estimate a 3D pose. The number of positions may be determined based on the number of image sensors, number of features identified, and / or number of known physical relationships between less than all features. Knowledge of physical relationships between image sensors and / or between features and image sensors may be employed. A robot path may be transformed based on the pose, to align the path with the target object.
Owner:ROBOTICVISIONTECH INC
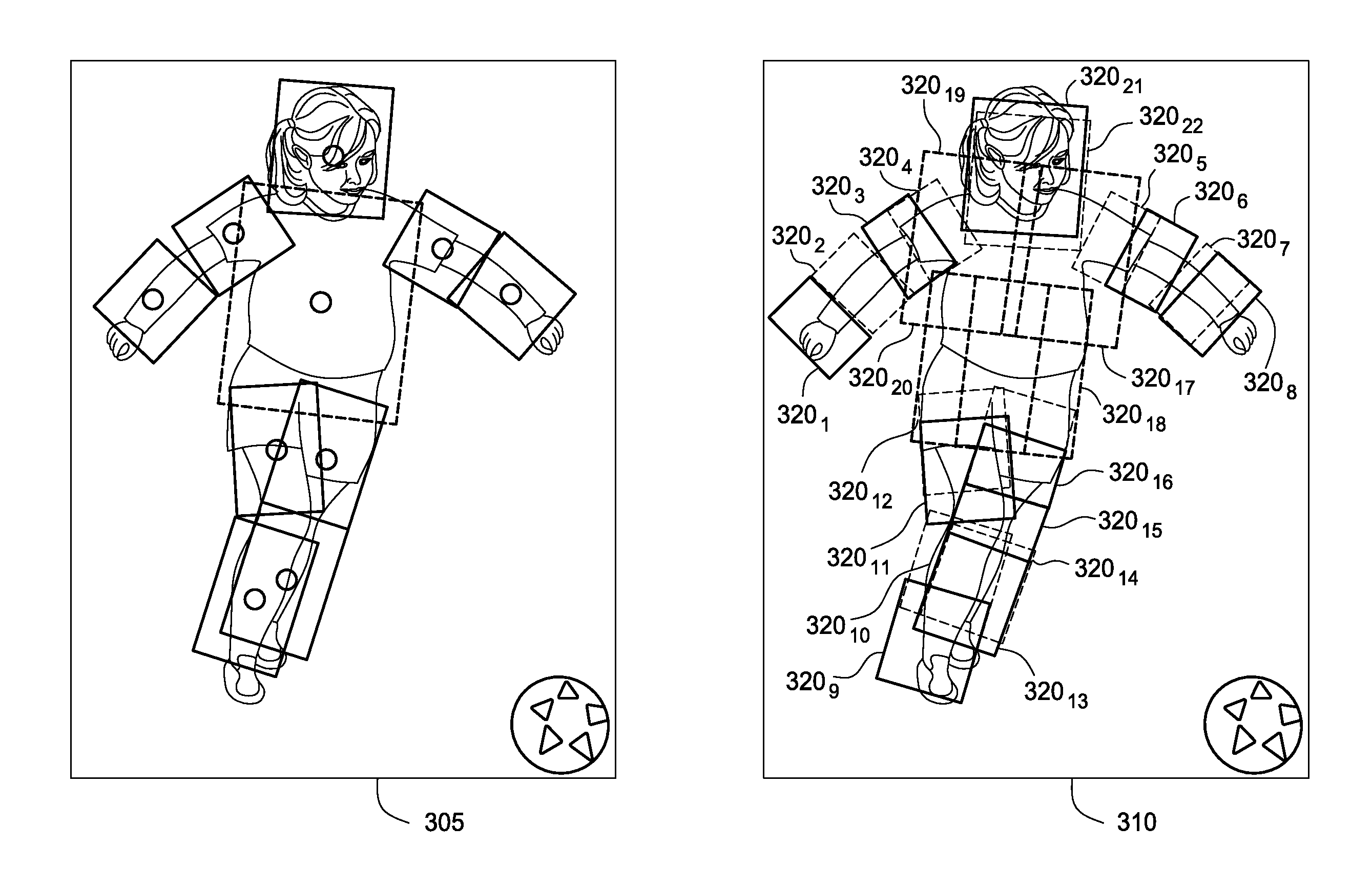
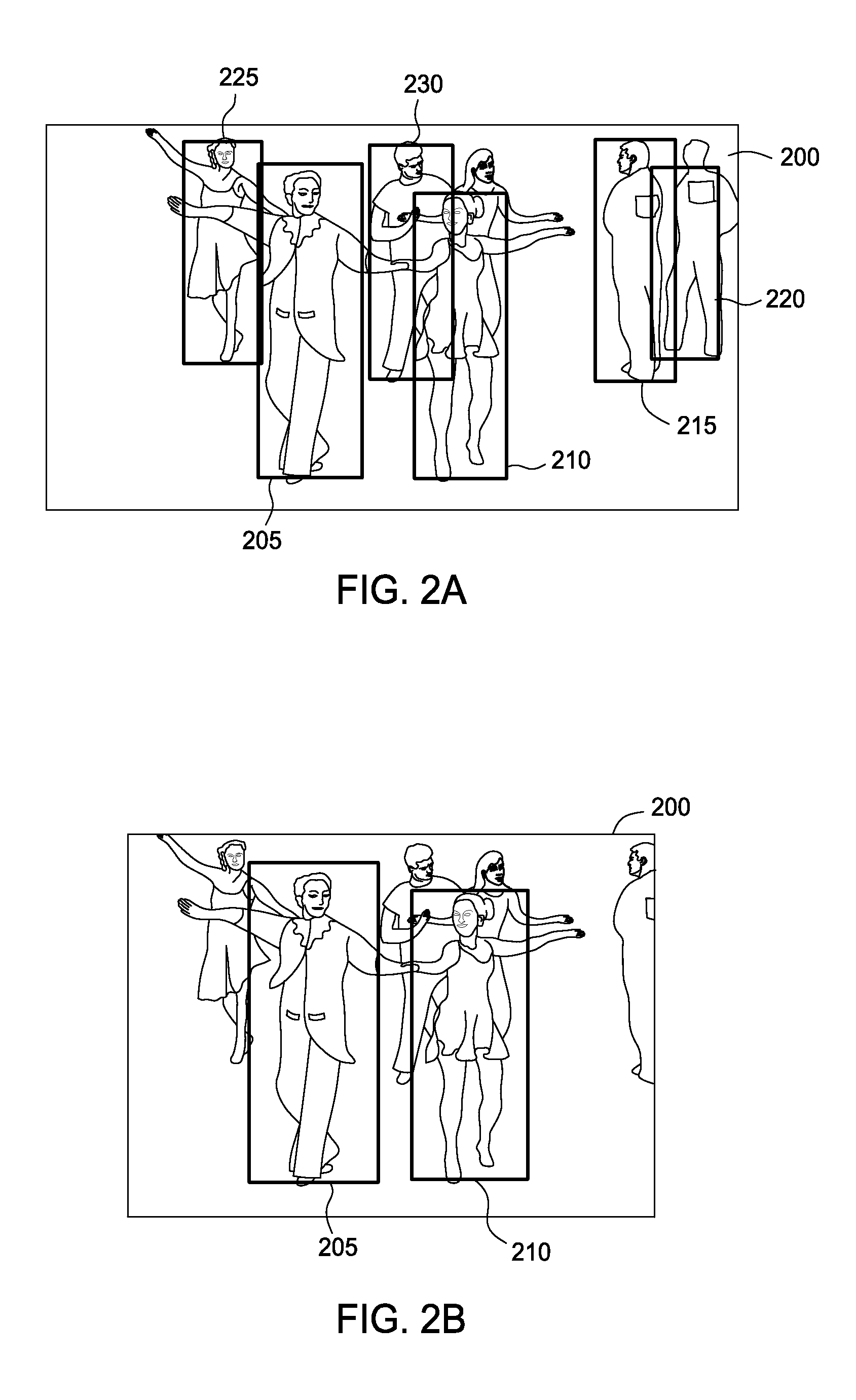
Modeling human-human interactions for monocular 3D pose estimation
Techniques are disclosed for the automatic recovery of two dimensional (2D) and three dimensional (3D) poses of multiple subjects interacting with one another, as depicted in a sequence of 2D images. As part of recovering 2D and 3D pose estimates, a pose recovery tool may account for constraints on positions of body parts of the first and second person resulting from the correlated activity. That is, individual subjects in the video are treated as mutual context for one another.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Pose estimation using long range features
ActiveUS9062979B1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsCamera imageGeographic site
Aspects of the present disclosure relate to using an object detected at long range to increase the accuracy of a location and heading estimate based on near range information. For example, an autonomous vehicle may use data points collected from a sensor such as a laser to generate an environmental map of environmental features. The environmental map is then compared to pre-stored map data to determine the vehicle's geographic location and heading. A second sensor, such as a laser or camera, having a longer range than the first sensor may detect an object outside of the range and field of view of the first sensor. For example, the object may have retroreflective properties which make it identifiable in a camera image or from laser data points. The location of the object is then compared to the pre-stored map data and used to refine the vehicle's estimated location and heading.
Owner:WAYMO LLC
Body feature detection and human pose estimation using inner distance shape contexts
A system, method, and computer program product for estimating human body pose are described. According to one aspect, a human figure silhouette is segmented from a depth image of a human actor. Contour points are sampled along the human figure silhouette. Inner Distance Shape Context (IDSC) descriptors of the sample contour points are determined and compared to IDSC descriptors of the feature points in an IDSC gallery for similarity. For each of the feature points, the sample contour point with the IDSC descriptor that is most similar to an IDSC of the feature point is identified as that feature point in the depth image. An estimated pose of a human model is estimated based on the detected feature points and kinematic constraints of the human model.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
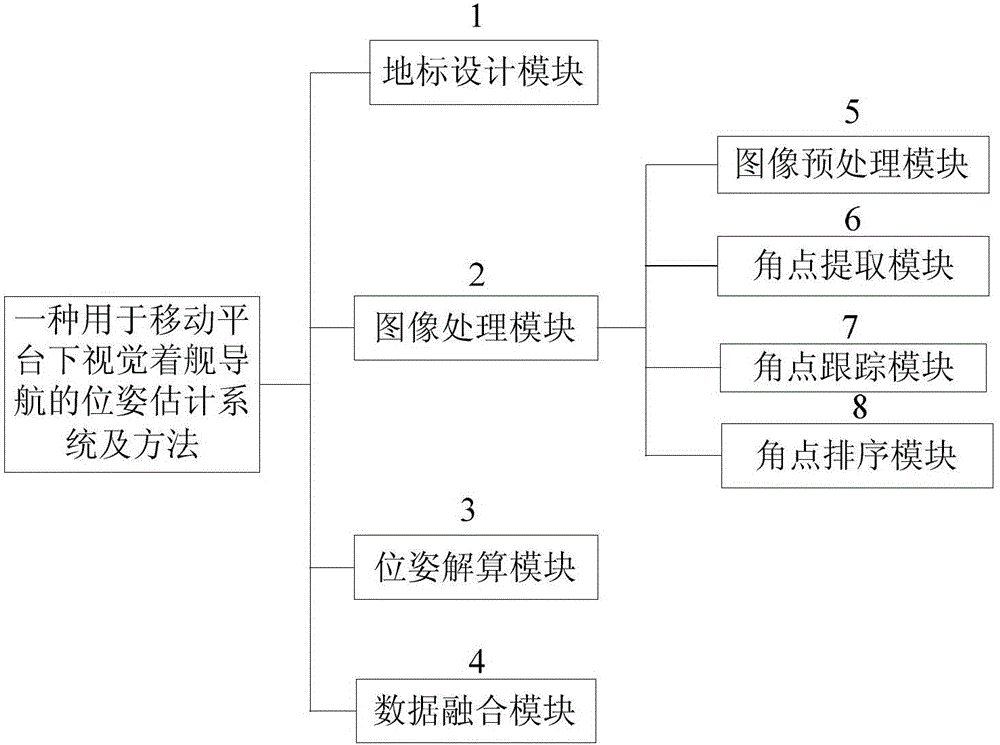
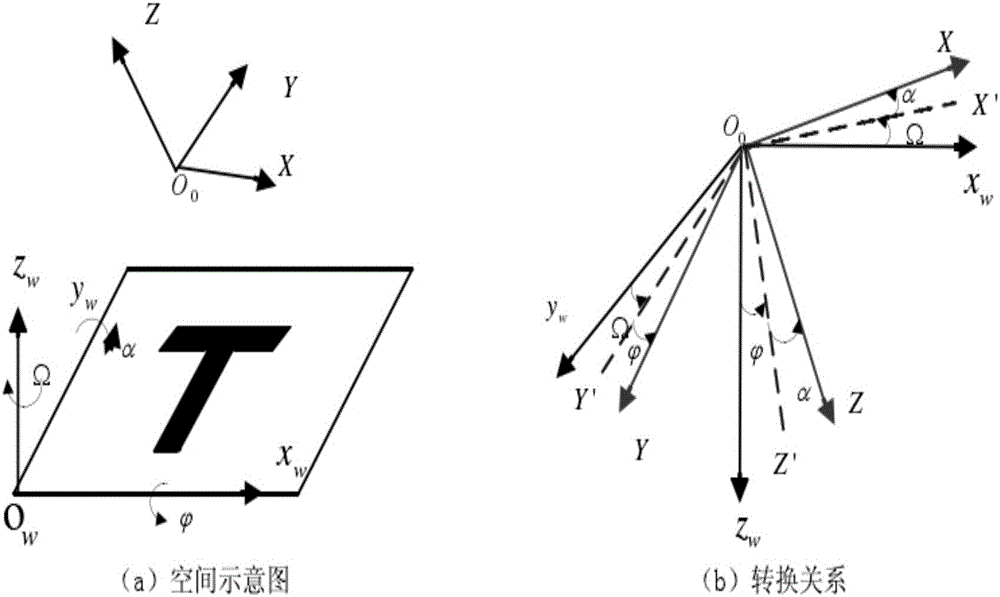
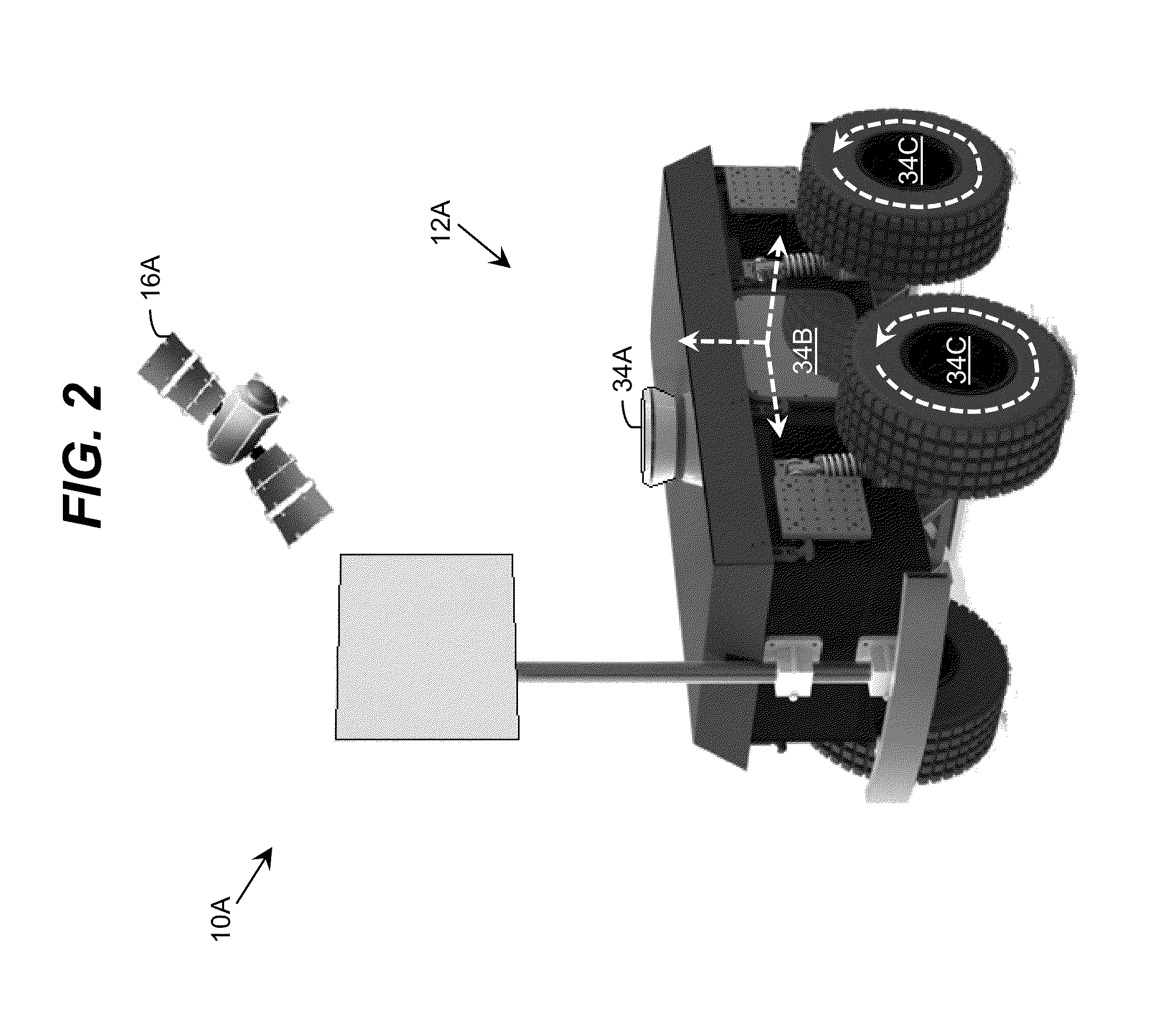
Pose estimation system and method for visual carrier landing navigation on mobile platform
ActiveCN105021184ASmall amount of calculationImprove real-time performanceNavigation instrumentsUncrewed vehicleComputer science
The invention belongs to unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous carrier landing field, and in particular relates to a pose estimation system and method for visual carrier landing navigation on mobile platform. The system and method can resolve the pose information of a moving ship relative to a UAV on a real-time basis through treatment of a collaborative landmark, have the advantages of small amount of calculation in the algorithm, good real-time property, and simple implementation, and provides a premise for safe landing of the UAV. The method uses a camera as a main sensor to reduce development costs and shorten the development cycle.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Computer vision-based express parcel violent sorting identification method
ActiveCN106897670ALow priceFacilitate large-scale deploymentCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyFeature extraction
The present invention discloses a computer vision-based express parcel violent sorting identification method. The method comprises the following steps of: a depth camera-based pose estimation: a human pose estimation problem is converted into a problem of classifying depth image pixels captured by a depth camera, and human body pose estimation is realized by using a random forest method; human body three-dimensional pose relative spatial-temporal feature extraction: relative spatial-temporal positions of geometric elements of points, lines and surfaces formed by joints in three-dimensional poses and the measures of the change of the relative spatial-temporal positions are extracted and are adopted as the feature representations of the poses; and recurrent neural network-based violent sorting identification: modeling training is performed on the pose spatial-temporal relative features which are continuous in time and are extracted from the human body three-dimensional poses through a long and short memory model (LSTM), so that the identification of express parcel violent sorting behaviors can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
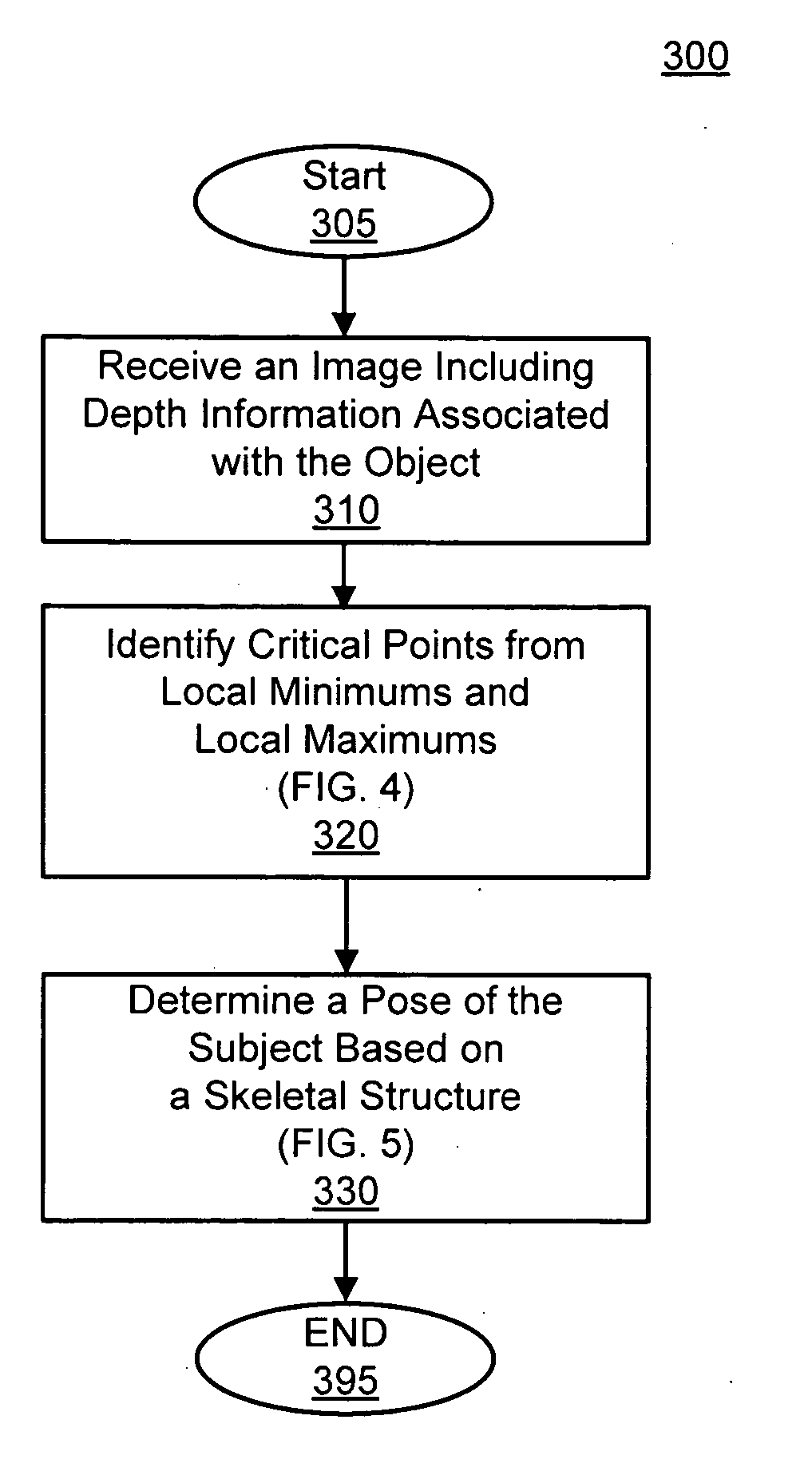
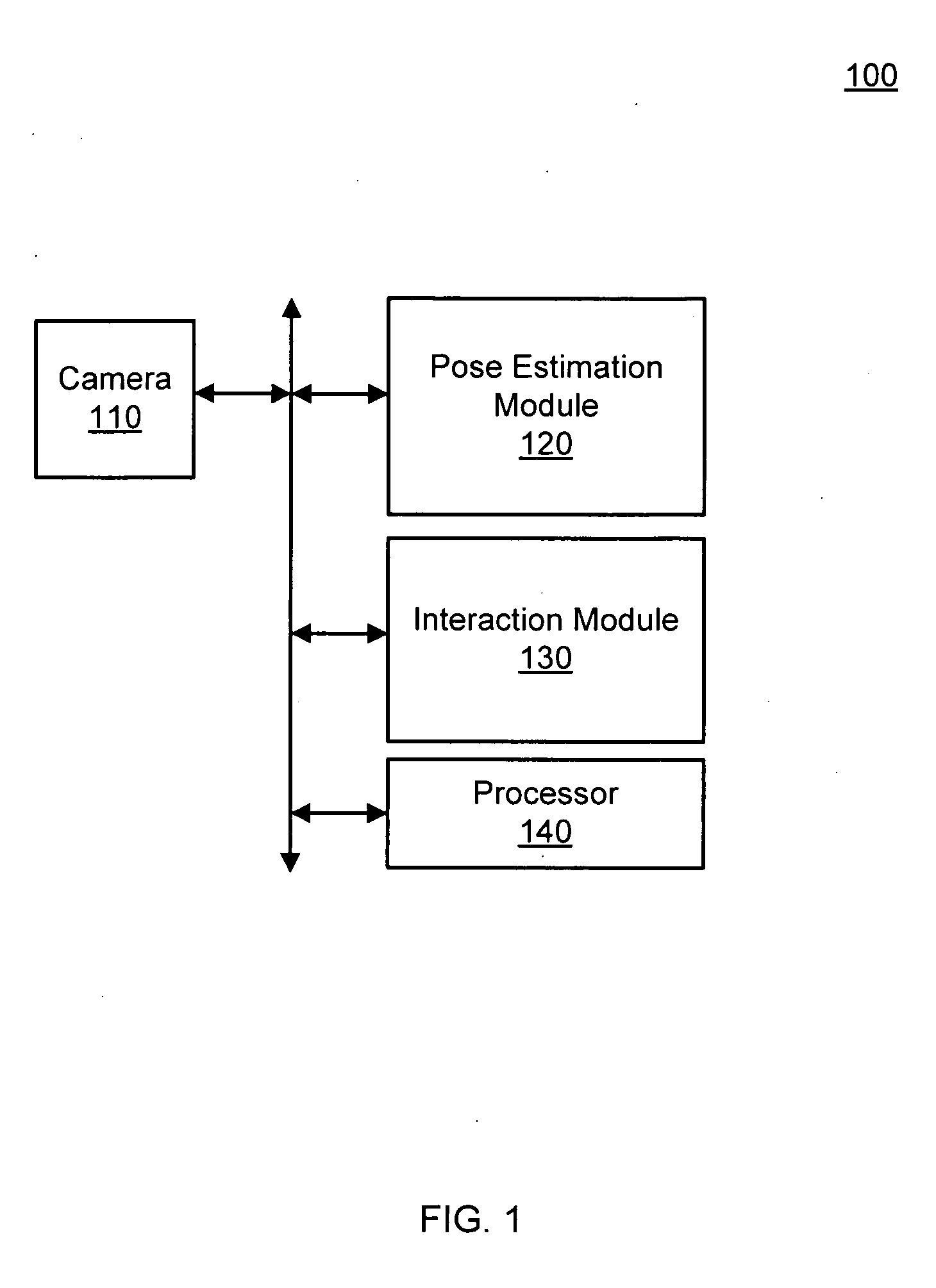
Pose estimation based on critical point analysis
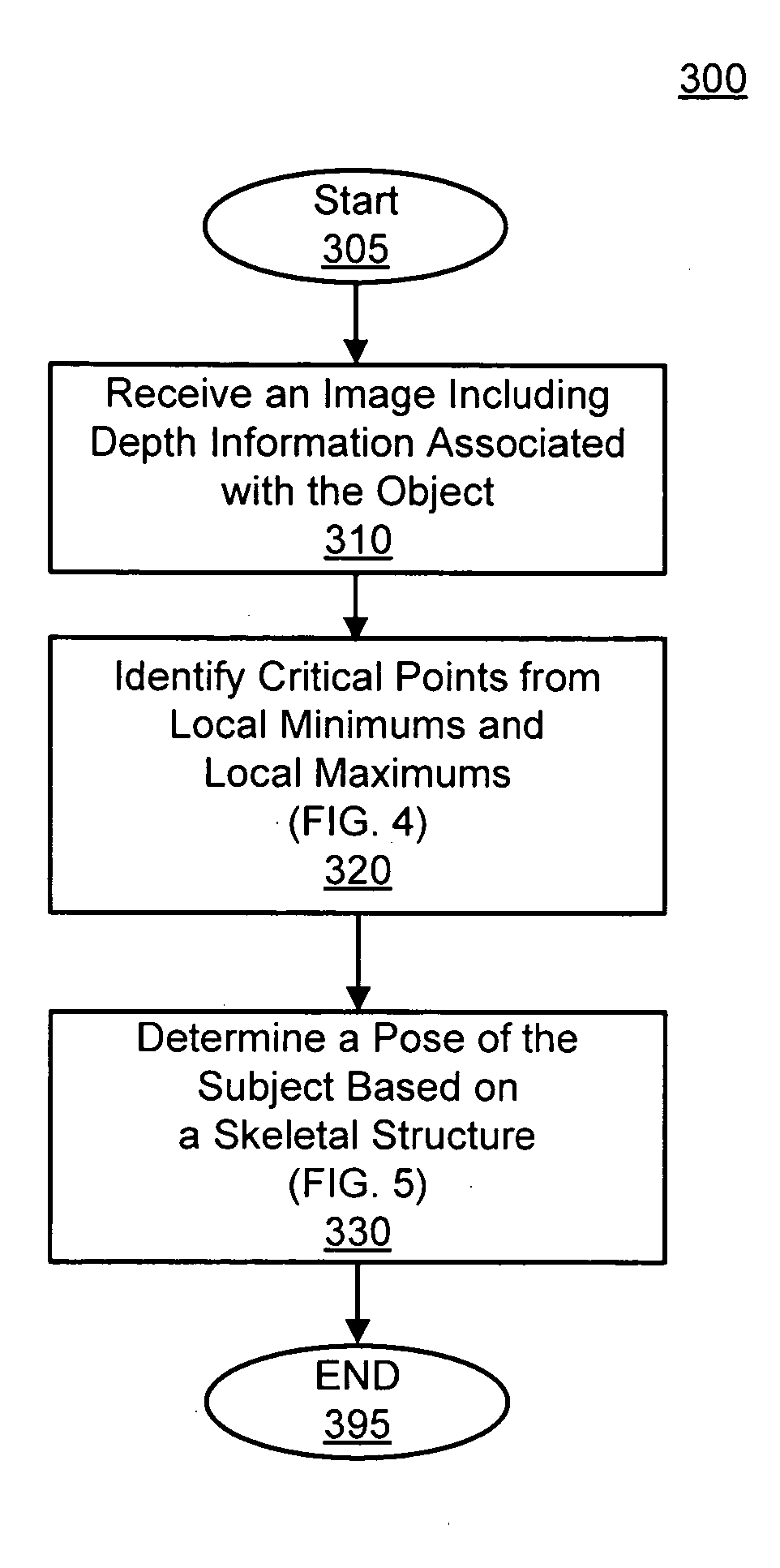
Methods and systems for estimating a pose of a subject. The subject can be a human, an animal, a robot, or the like. A camera receives depth information associated with a subject, a pose estimation module to determine a pose or action of the subject from images, and an interaction module to output a response to the perceived pose or action. The pose estimation module separates portions of the image containing the subject into classified and unclassified portions. The portions can be segmented using k-means clustering. The classified portions can be known objects, such as a head and a torso, that are tracked across the images. The unclassified portions are swept across an x and y axis to identify local minimums and local maximums. The critical points are derived from the local minimums and local maximums. Potential joint sections are identified by connecting various critical points, and the joint sections having sufficient probability of corresponding to an object on the subject are selected.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS20070015997A1Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Human pose estimation with data driven belief propagation
A statistical formulation estimates two-dimensional human pose from single images. This is based on a Markov network and on inferring pose parameters from cues such as appearance, shape, edge, and color. A data-driven belief propagation Monte Carlo algorithm performs efficient Bayesian inferencing within a rigorous statistical framework. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in estimating human pose from single images.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
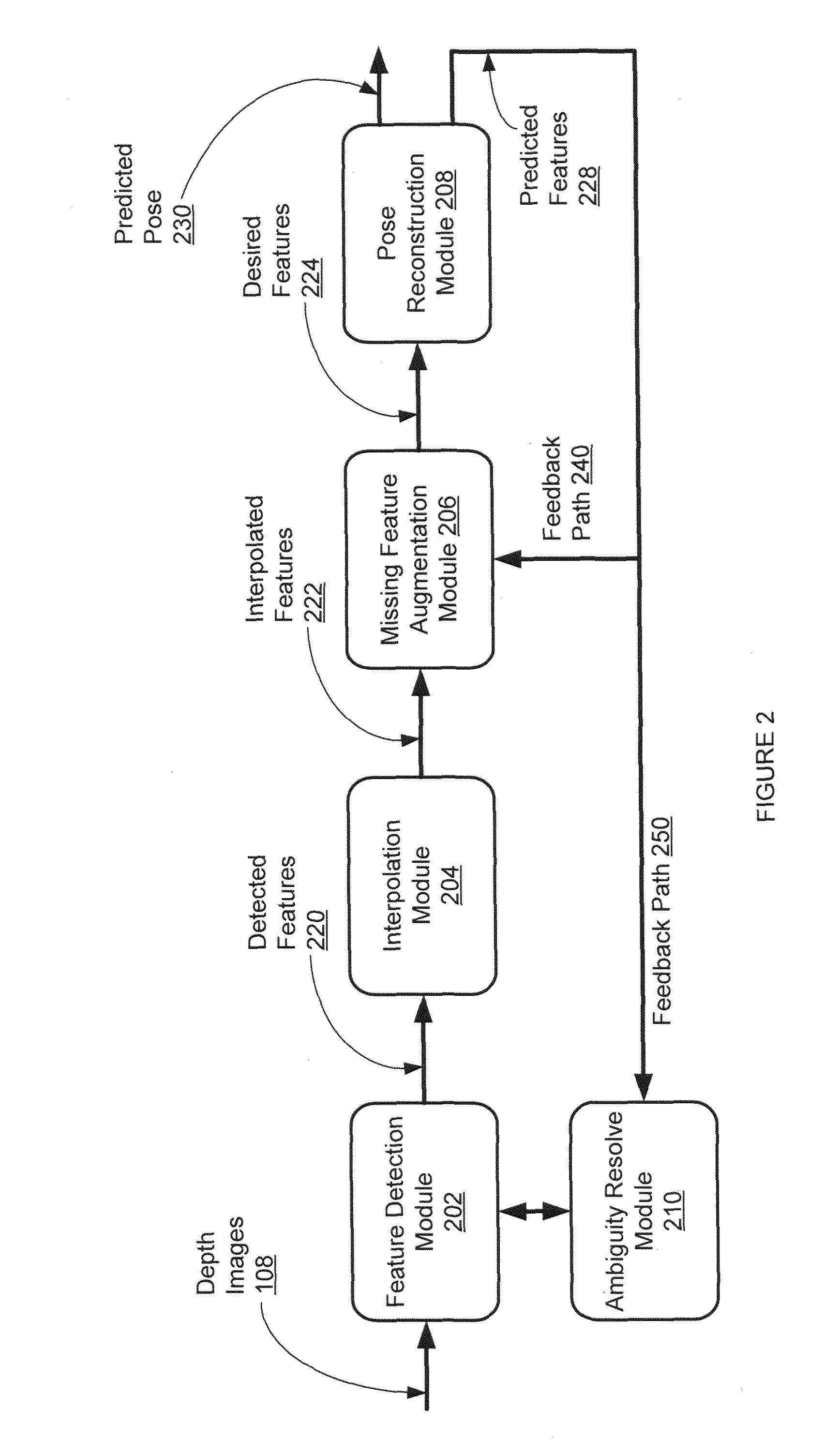
Monocular 3D pose estimation and tracking by detection
InactiveUS20130142390A1Low applicabilityReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisThree stageBayesian formulation
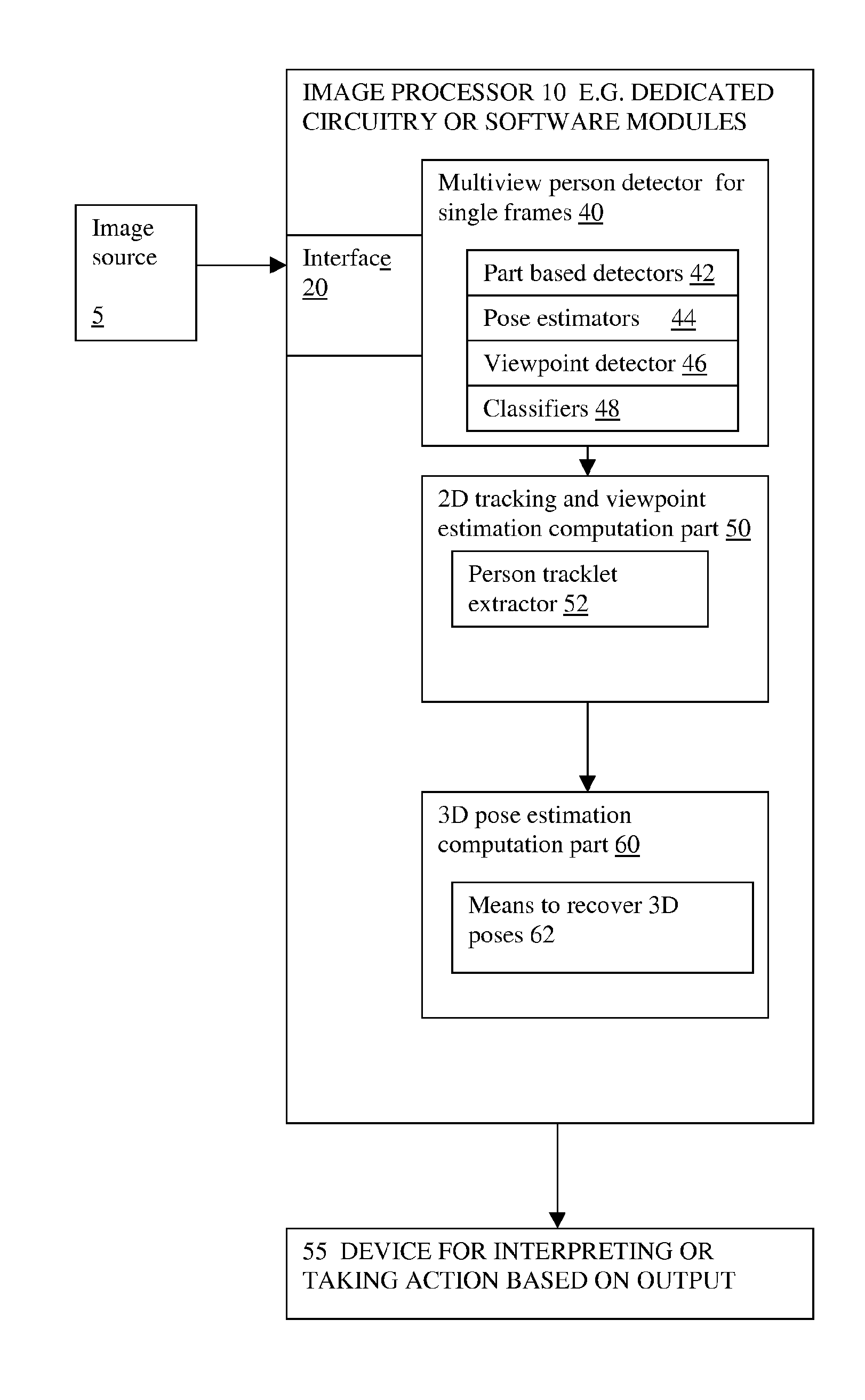
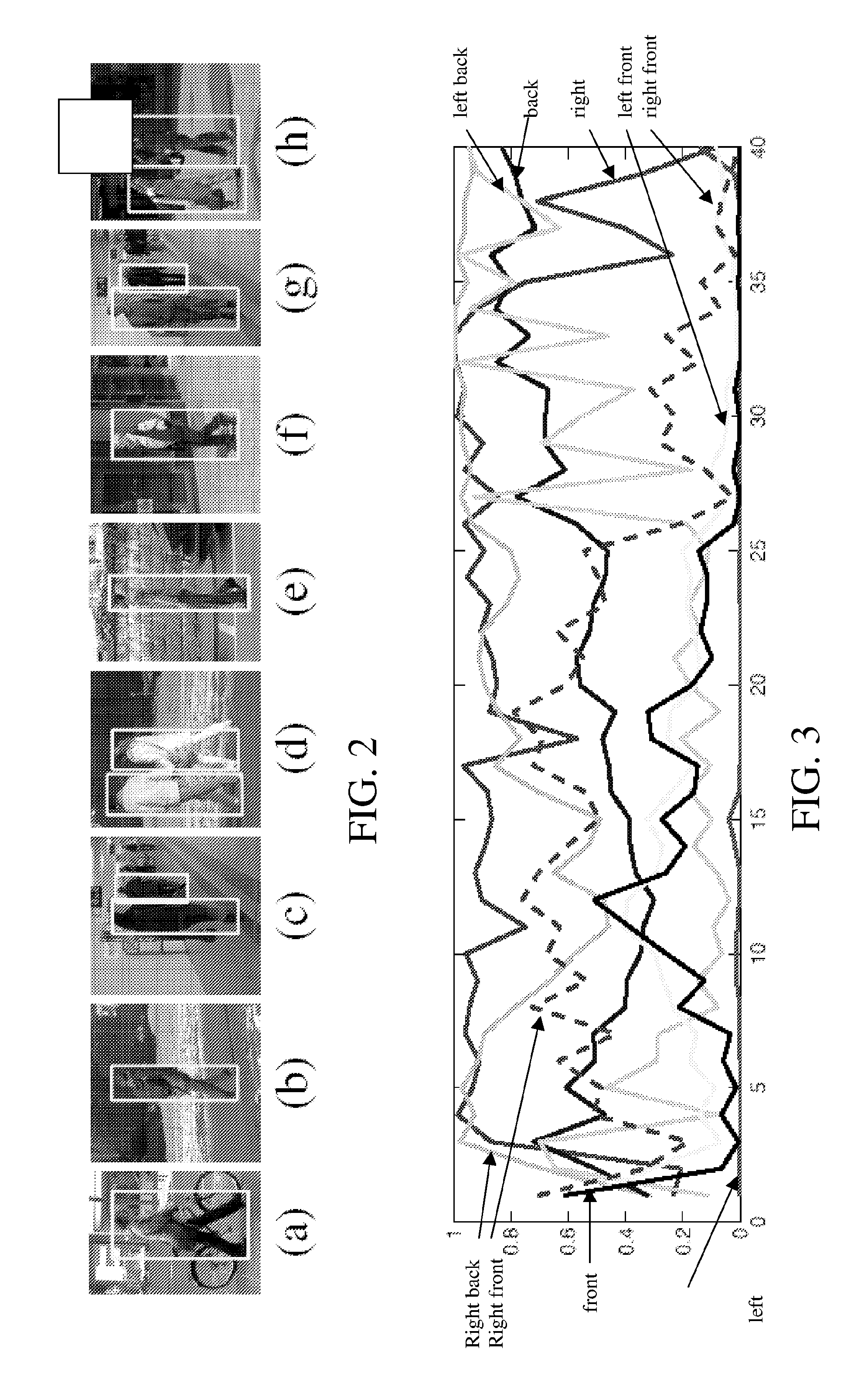
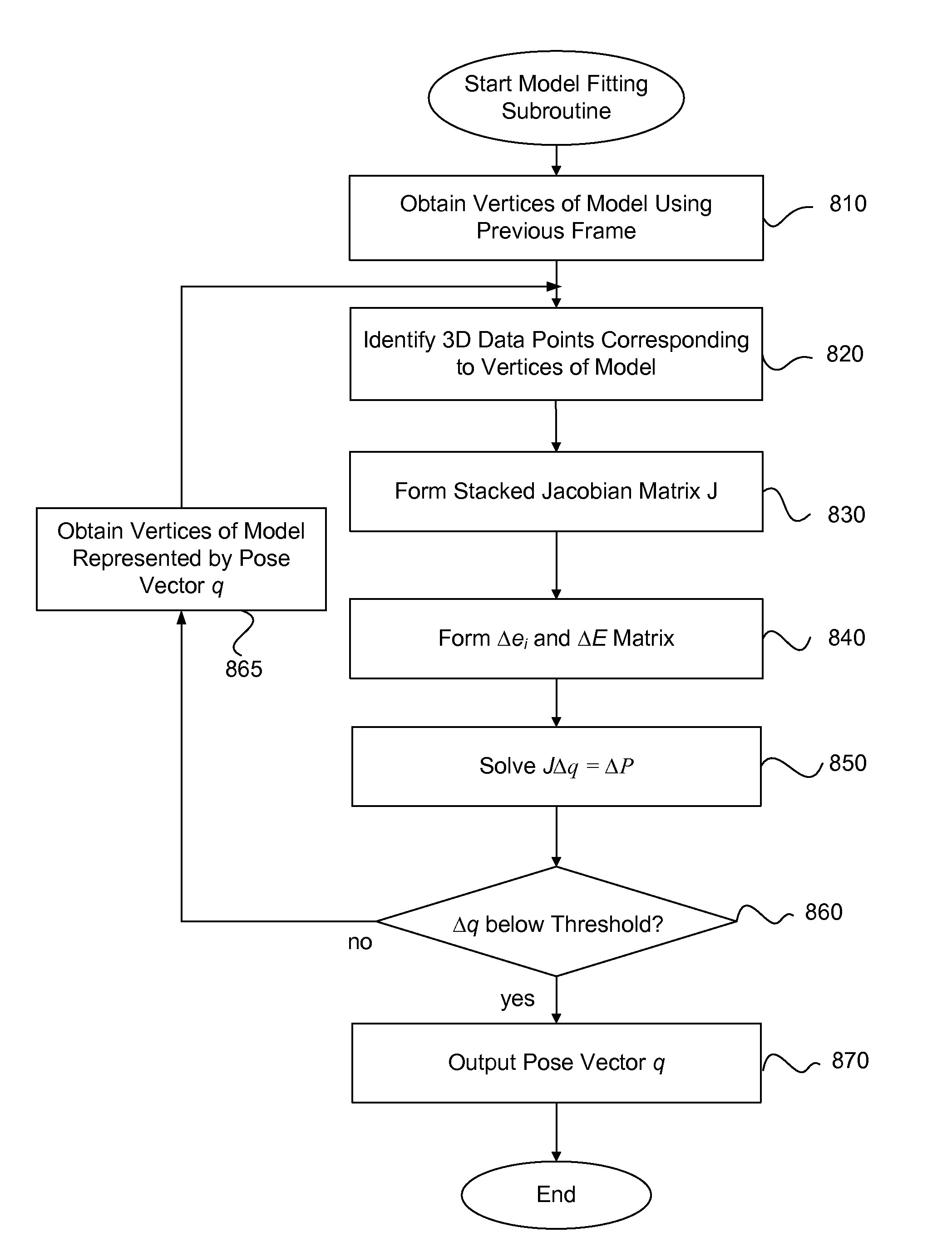
Methods and apparatus are described for monocular 3D human pose estimation and tracking, which are able to recover poses of people in realistic street conditions captured using a monocular, potentially moving camera. Embodiments of the present invention provide a three-stage process involving estimating (10, 60, 110) a 3D pose of each of the multiple objects using an output of 2D tracking-by detection (50) and 2D viewpoint estimation (46). The present invention provides a sound Bayesian formulation to address the above problems. The present invention can provide articulated 3D tracking in realistic street conditions.The present invention provides methods and apparatus for people detection and 2D pose estimation combined with a dynamic motion prior. The present invention provides not only 2D pose estimation for people in side views, it goes beyond this by estimating poses in 3D from multiple viewpoints. The estimation of poses is done in monocular images, and does not require stereo images. Also the present invention does not require detection of characteristic poses of people.
Owner:TECH UNIV DARMSTADT +1
Human pose estimation and tracking using label assignment
ActiveUS8351646B2Minimize cost functionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPostural orientation
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method of pose estimation
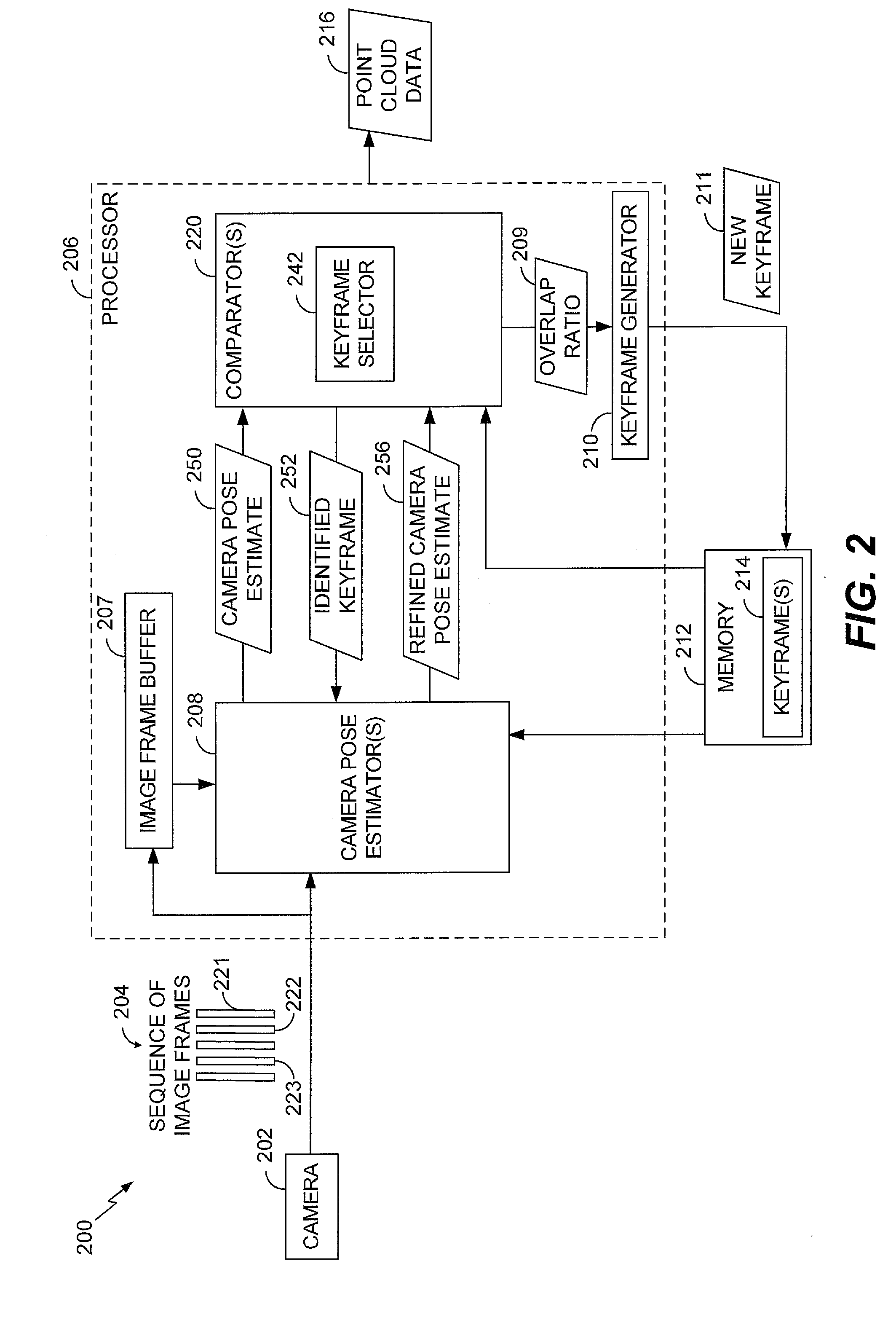
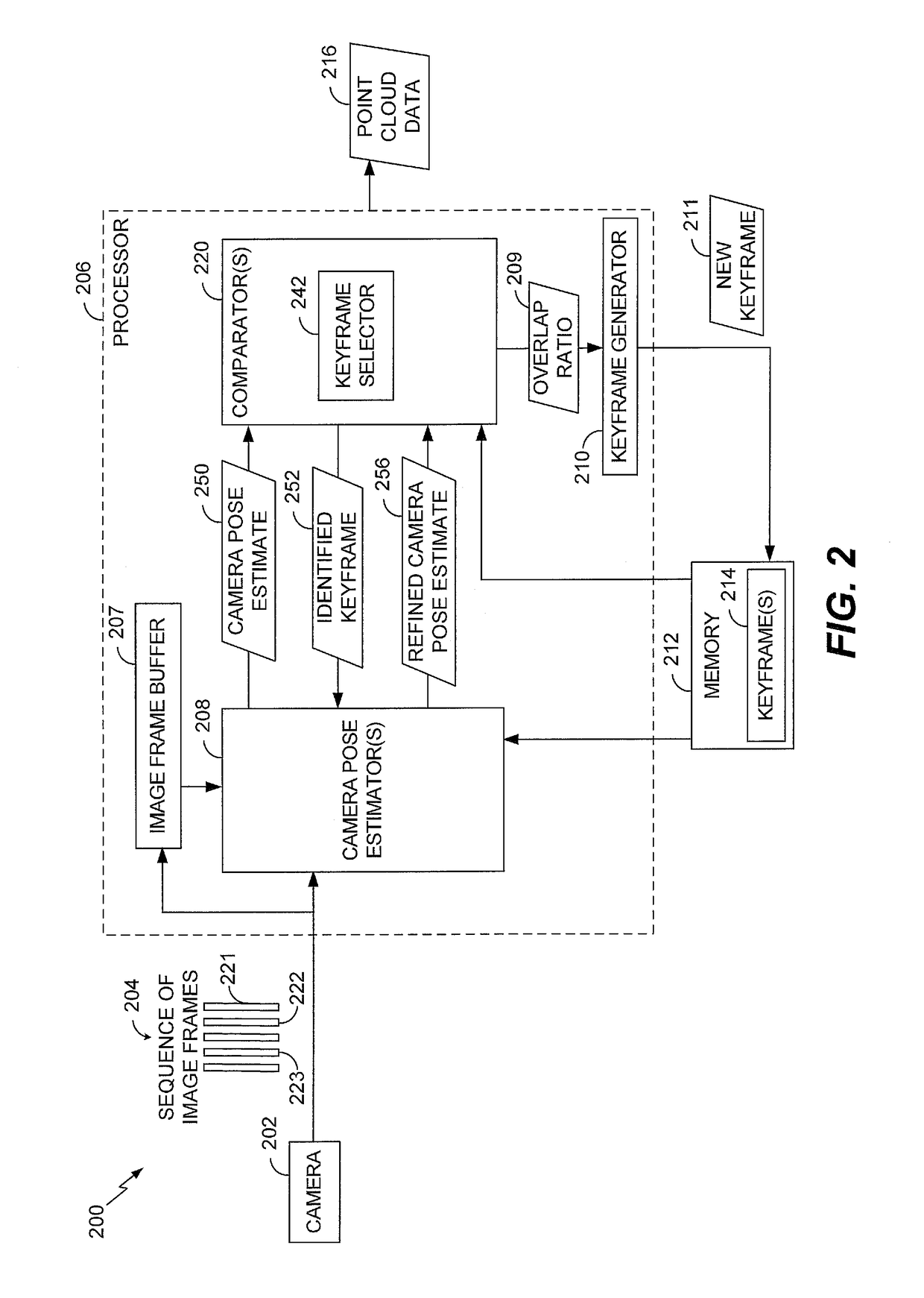
A method includes receiving, from an image capture device, a first image frame of a sequence of image frames. The method also includes estimating, at a processor, a camera pose corresponding to the first image frame by comparing the first image frame to a second image frame. The second image frame precedes the first image frame in the sequence of image frames. The method further includes estimating, at the processor, a refined camera pose corresponding to the first image frame by comparing the first image frame to a keyframe. The keyframe corresponds to a particular image frame that precedes the second image frame in the sequence of image frames.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Collaborative visual SLAM method based on multiple cameras
InactiveCN105869136AQuick updateReconstruct 3D trajectoryImage analysisSimultaneous localization and mappingTemporal change
The present invention provides a multi-camera-based collaborative visual SLAM method, in particular to a collaborative visual SLAM method using multiple cameras in a dynamic environment. The method of the invention allows the relative position and direction of the cameras to change with time, so that multiple cameras can move independently and be installed on different platforms, and solve problems related to camera pose estimation, map point classification and camera group management, etc. problem, so that the method works robustly in dynamic scenes and can reconstruct the 3D trajectories of moving objects. Compared with the existing SLAM method based on single camera, the method of the present invention is more accurate and robust, and can be applied to micro-robots and wearable augmented reality.
Owner:BEIJING ROBOTLEO INTELLIGENT TECH
Multiview Estimation of 6D Pose
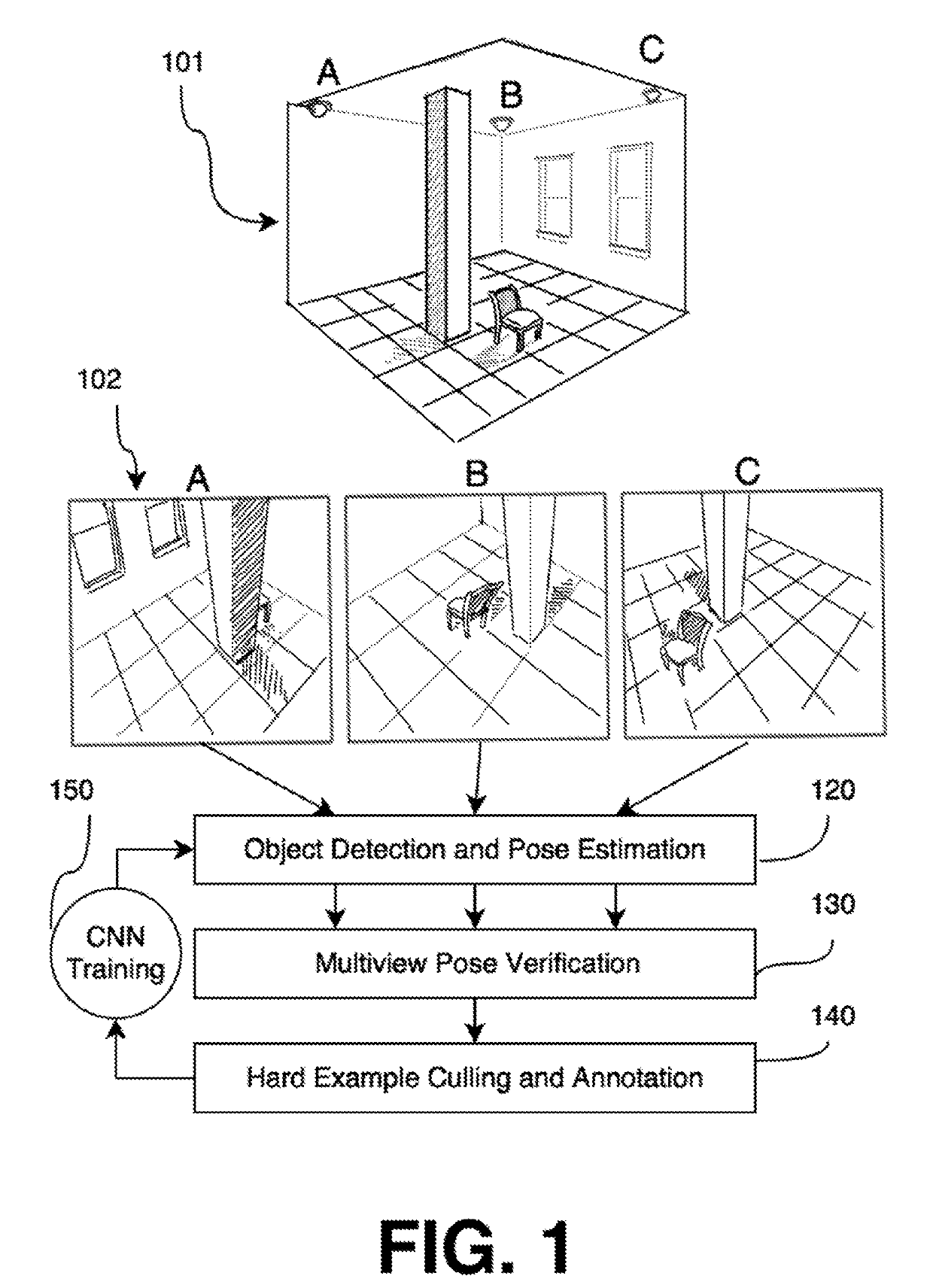
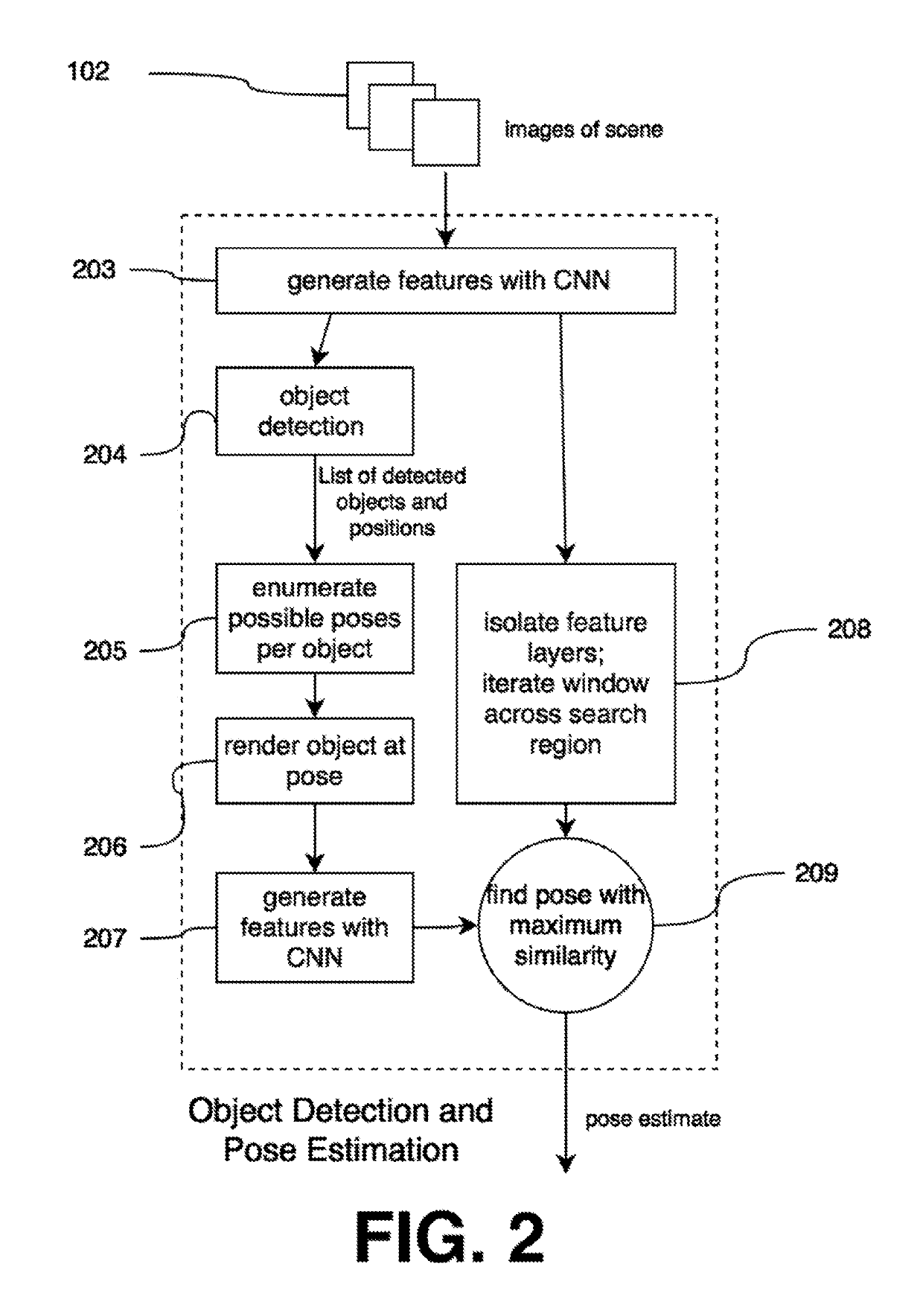
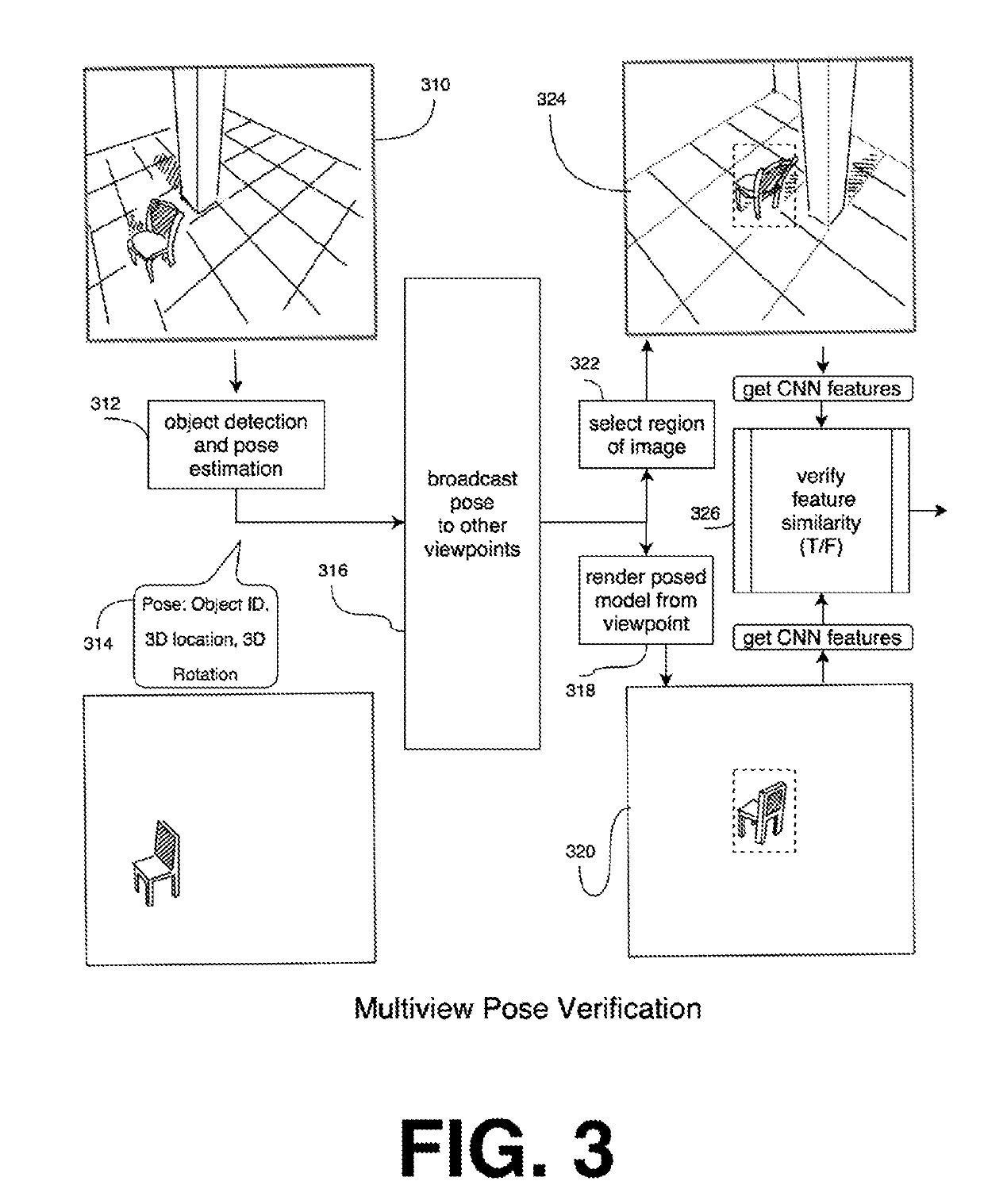
ActiveUS20190304134A1CNN-based detector can be iteratively improvedQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisGround truthObject detector
This disclosure describes a method and system to perform object detection and 6D pose estimation. The system comprises a database of 3D models, a CNN-based object detector, multiview pose verification, and a hard example generator for CNN training.The accuracy of that detection and estimation can be iteratively improved by retraining the CNN with increasingly hard ground truth examples. The additional images are detected and annotated by an automatic process of pose estimation and verification.
Owner:MAUCHLY J WILLIAM +1
A six-degree-of-freedom attitude estimation method based on Tag
ActiveCN109345588AImprove robustnessImprove pose estimation accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisEstimation methodsImaging quality
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom attitude estimation method based on Tag, By adding a tag to the object to aid detection, the Tag on the object is identified by the camera, Help SLAM complete initialization, After initialization, A feature point is continuously extracted from each frame of the image, and according to whether the speed matrix corresponding to the previous frame is empty, Camera pose estimation is carried out, and the initial value of camera pose estimation is taken as the initial value, and the re-projection error function of map points corresponding to feature points is adopted as the objective function to optimize camera pose, so as to obtain the optimized camera pose and map points corresponding to feature points, and then the camera pose is converted intothe pose of the object. The method of the invention has good robustness when the imaging quality is poor and the object moves at high speed, and has very high attitude estimation accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for tracking natural planar shapes for augmented reality applications
ActiveUS20110129118A1High computational complexityLow accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging FeatureSix degrees of freedom
The present system discloses systems and methods for tracking planar shapes for augmented-reality (AR) applications. Systems for real-time recognition and camera six degrees of freedom pose-estimation from planar shapes are disclosed. Recognizable shapes can be augmented with 3D content. Recognizable shapes can be in form of a predefined library being updated online using a network. Shapes can be added to the library when the user points to a shape and asks the system to start recognizing it. The systems perform shape recognition by analyzing contour structures and generating projective invariant signatures. Image features are further extracted for pose estimation and tracking. Sample points are matched by evolving an active contour in real time.
Owner:APPLE INC
Pose Estimation
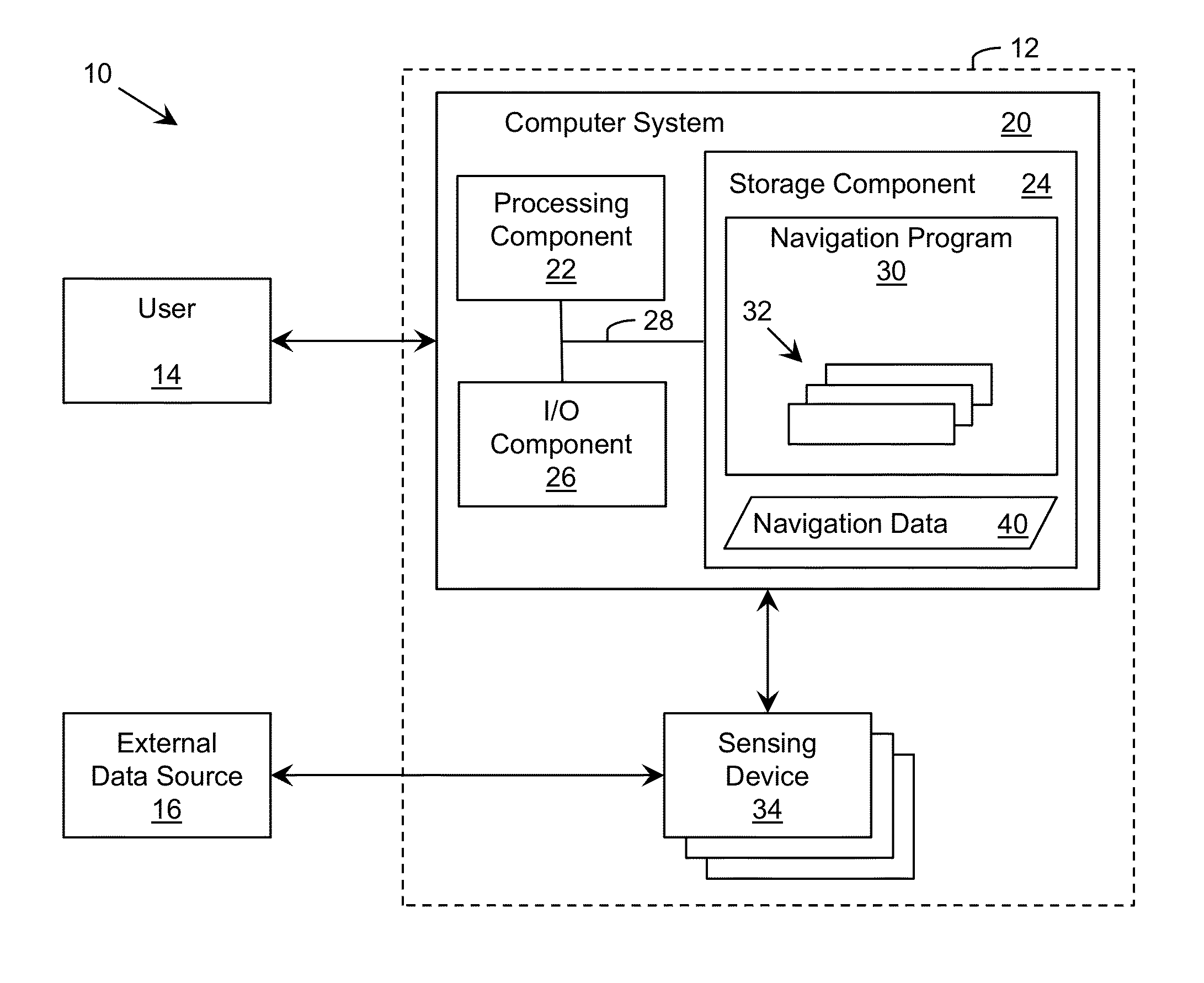
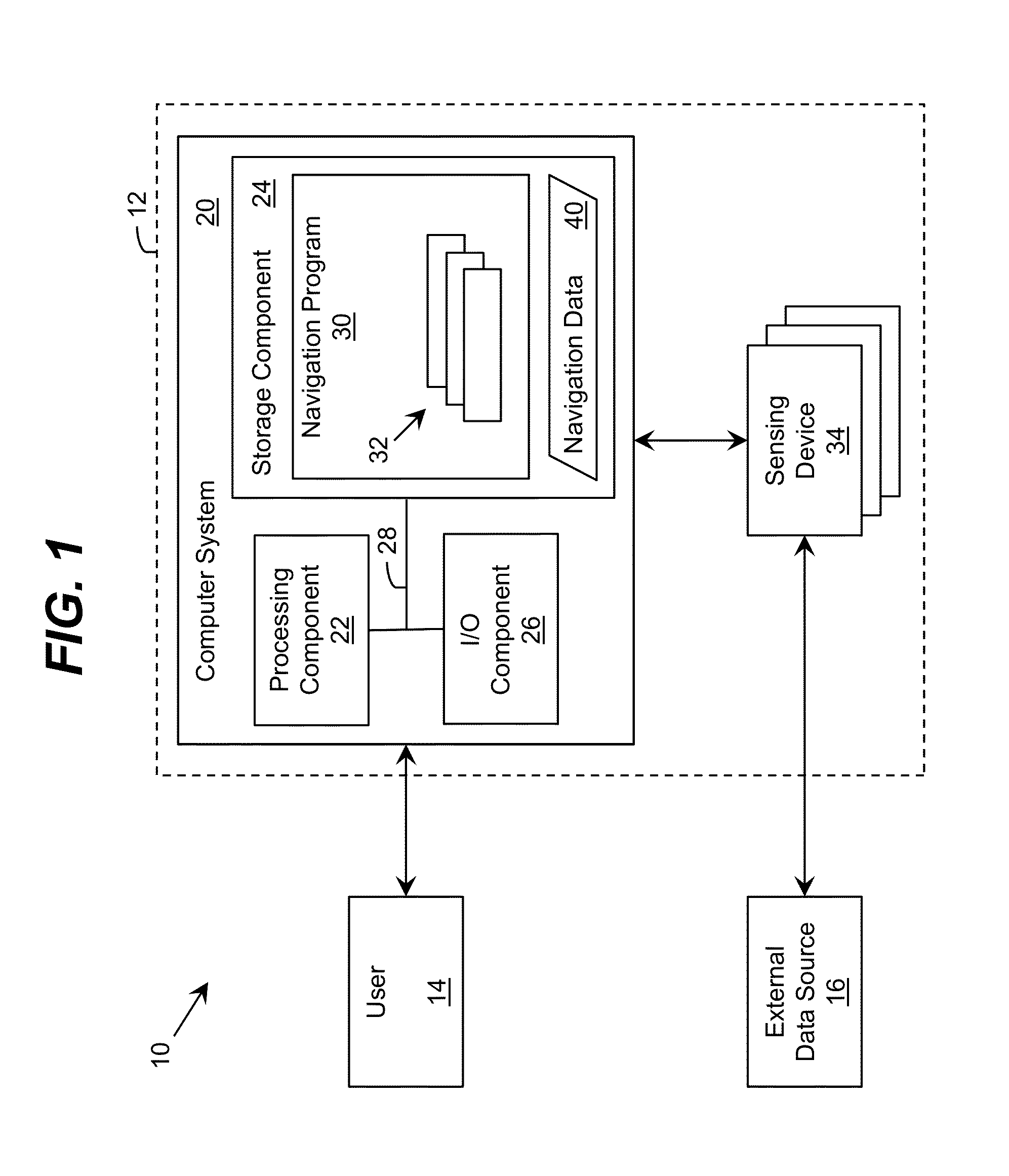
ActiveUS20130325334A1Navigation instrumentsVehicle position/course/altitude controlComputer scienceCovariance matrix
A solution for estimating the pose of a platform, such as a vehicle, is provided. Data from a plurality of types of sensing devices located on the platform can be used to independently calculate a plurality of preliminary estimates corresponding to the pose. A plurality of estimates corresponding to the pose can be generated using the preliminary estimates and at least one covariance matrix. One or more entries in the covariance matrix are adjusted based on an uncertainty for the corresponding preliminary estimate. The uncertainty can vary based on time, distance, and / or velocity of the platform.
Owner:CSX TRANSPORTATION +1
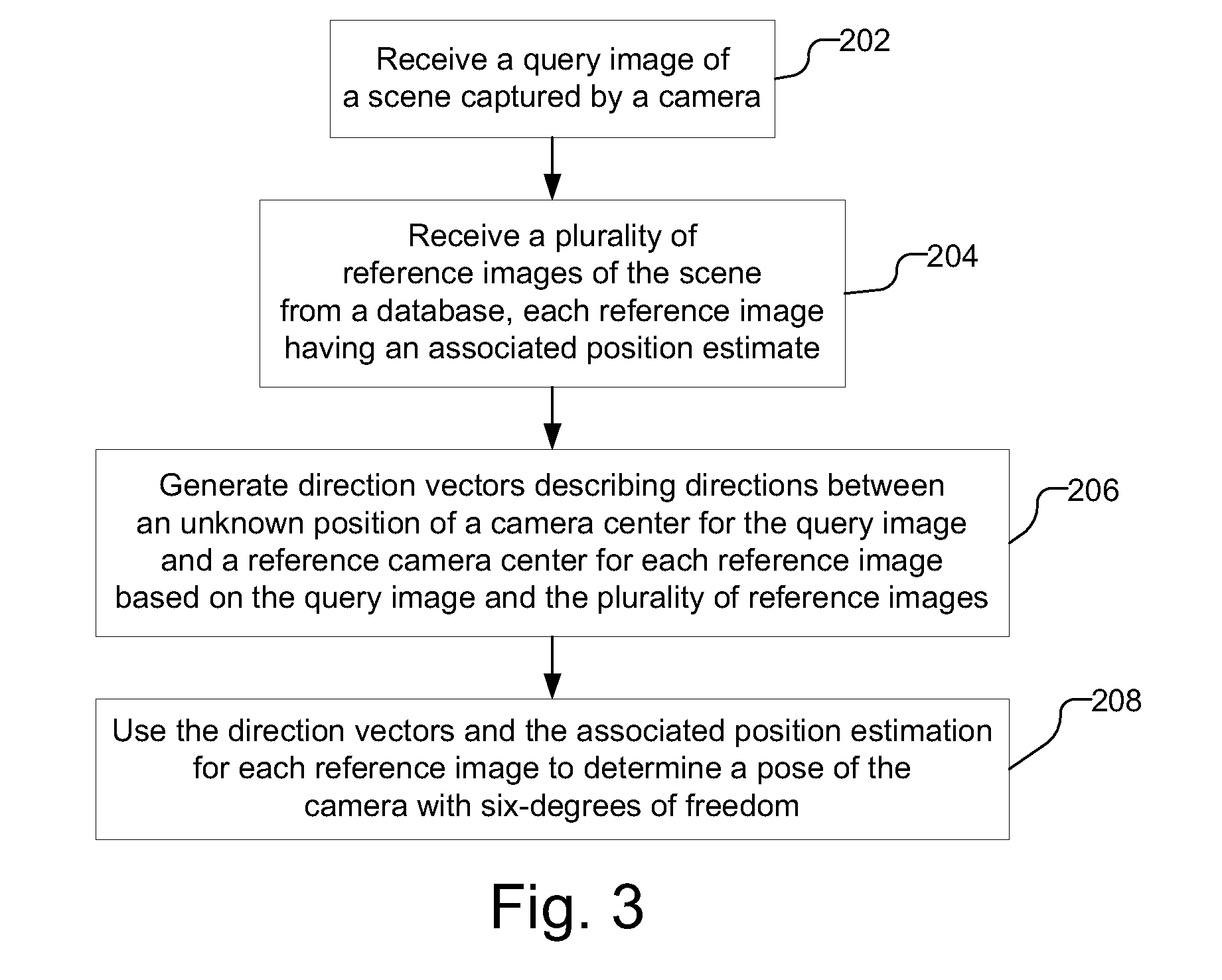
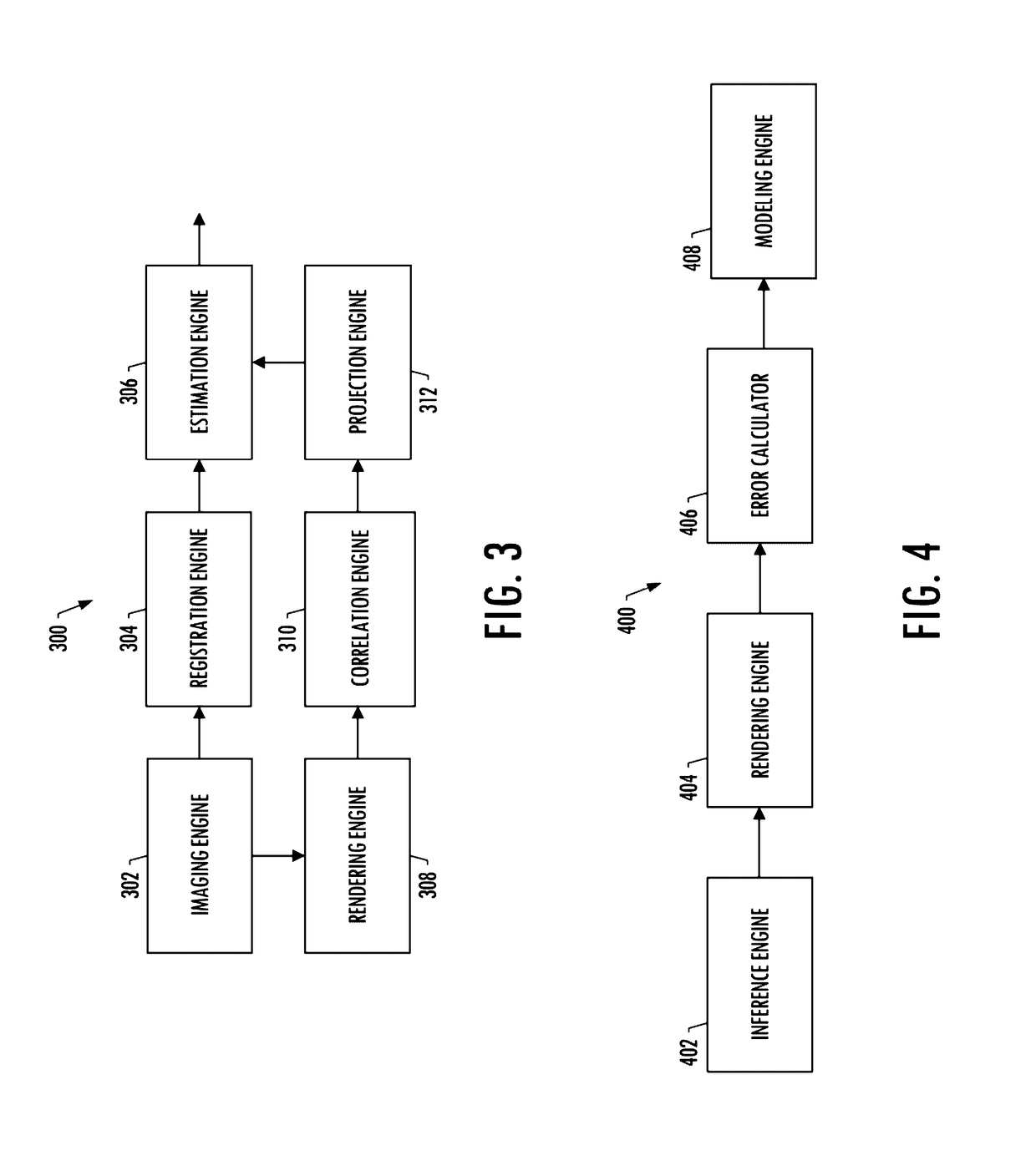
Scene structure-based self-pose estimation
Pose estimation is performed using a scene structure captured in a query image and reference images from a database. Each of the reference images has an associated position estimate. Direction vectors are generated that describe directions between an unknown position of a camera center for the query image and a reference camera center for each reference image based on the query image and the plurality of reference images. The direction vectors may be generated using, e.g., homographies, essential matrices, or fundamental matrices. A pose estimation with six degrees of freedom is determined using the direction vectors and the associated position estimate for each reference image. The pose estimation, for example, may be determined by solving a three-point pose problem using the direction vectors and the associated position estimate for each reference image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
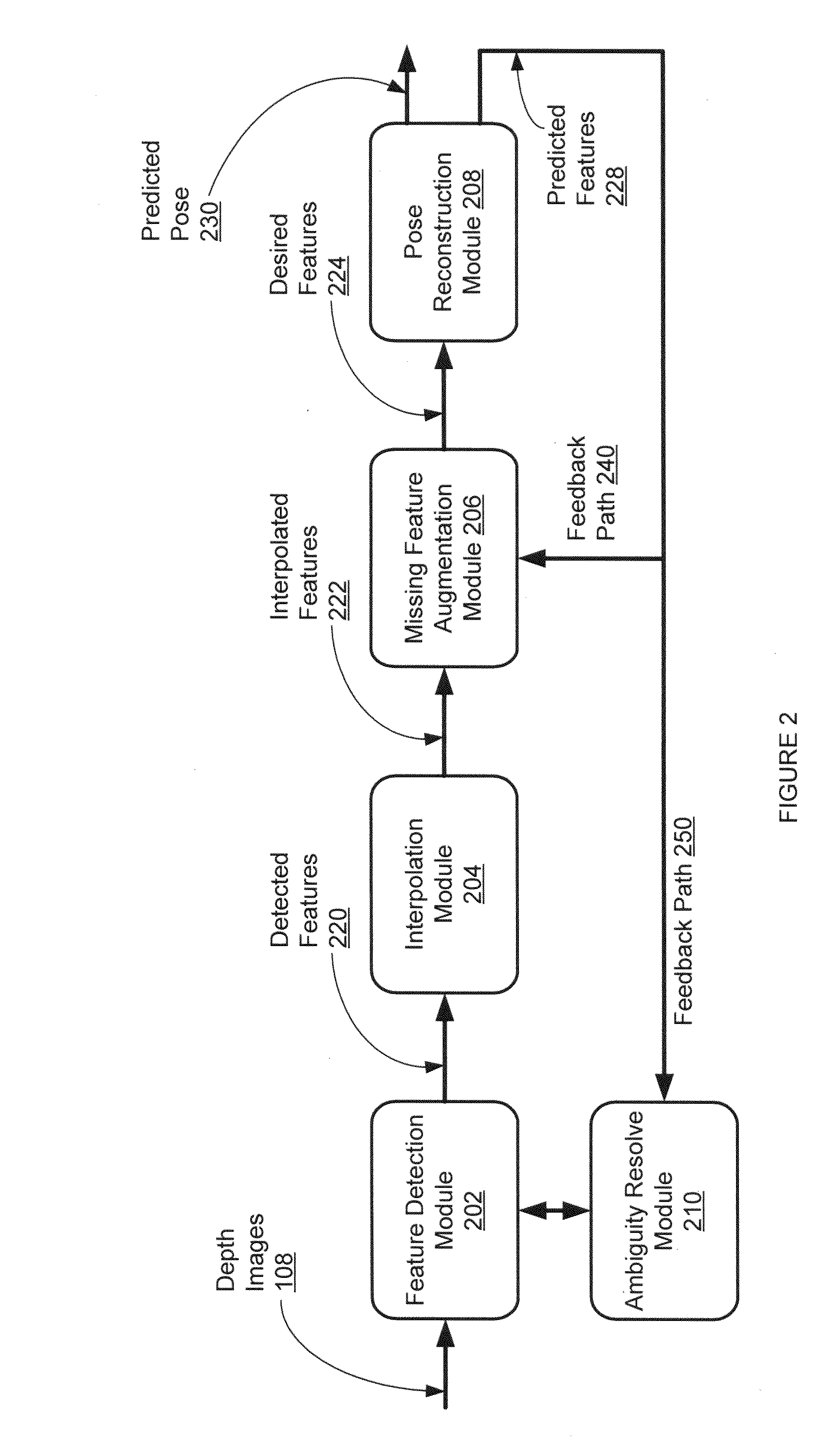
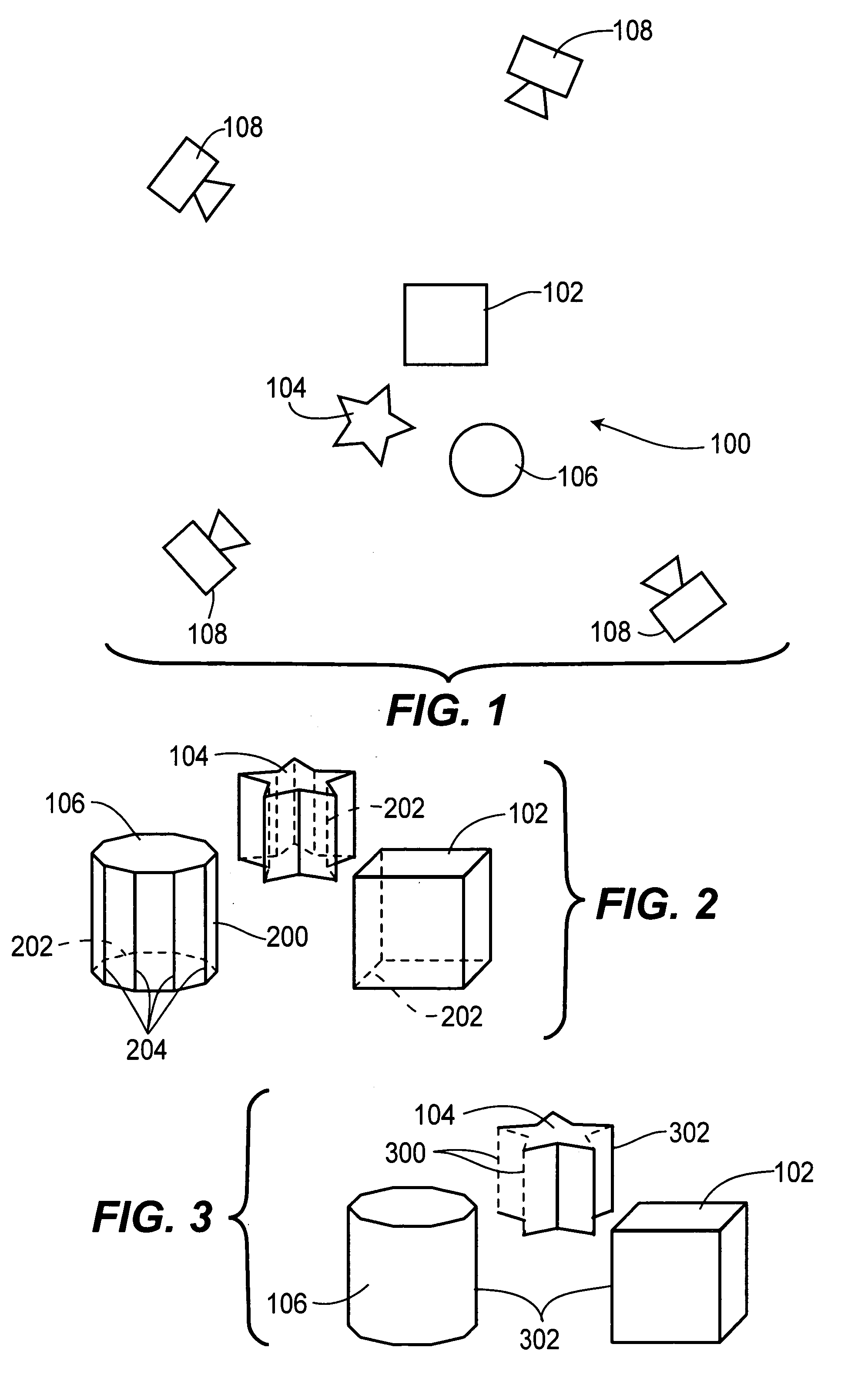
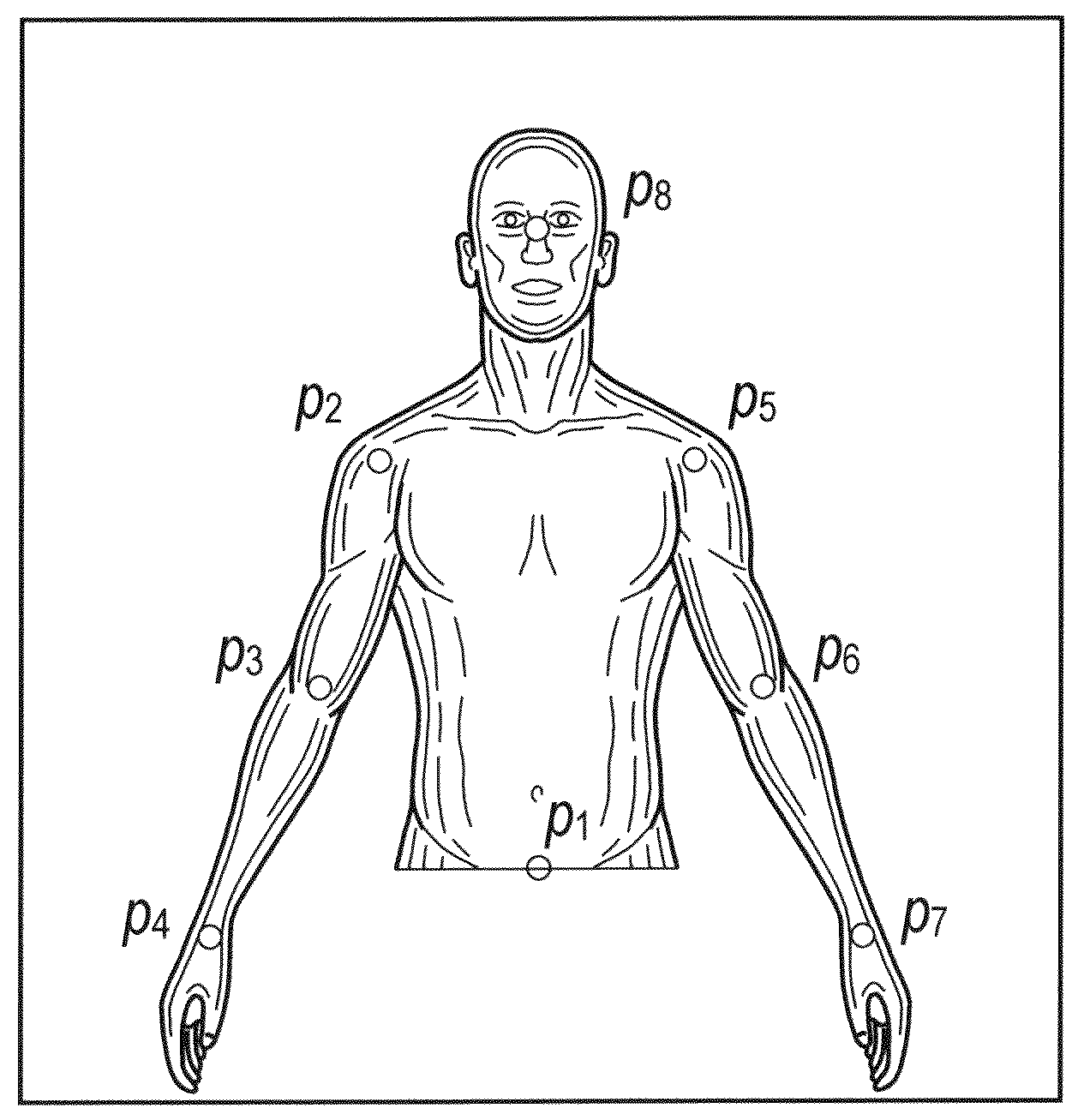
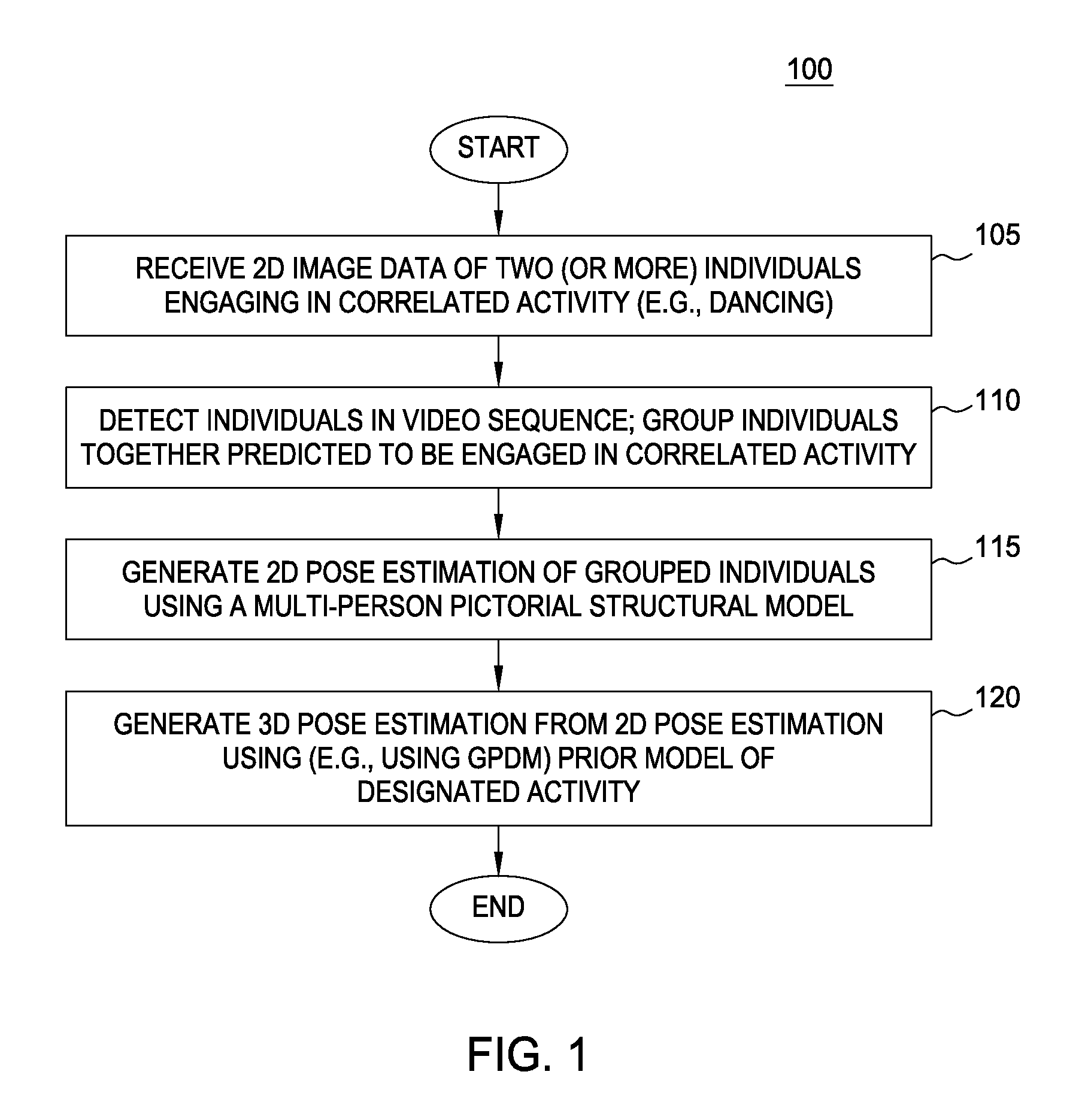
Systems and methods for 3D pose estimation
ActiveUS20140092132A1Inhibition of informationImage enhancementImage analysisRelevant featureVisual perception
The present system provides a tool to estimate the relative pose of a generic object with respect to a camera view-point by processing 2D images from a monocular camera in real-time. The capability of solving the pose estimation problem relies on the robust detection and matching in consecutive image frames of significant visual features belonging to an object of interest. To accomplish this, the system incorporates 3D modeling of the object of interest. In one embodiment, the shape of interest may be approximated by a parametric surface such as a cylinder, sphere, ellipsoid, or even complex non-parametric models. The system can restrain information retrieved at a 2D image level to estimate parameters about the pose. In operation, the accuracy of the 3D pose estimation of the object is a function of the degree of approximation of the selected model and the ability to select and track relevant features across consecutive image frames.
Owner:AUGMENTED REALITY LAB
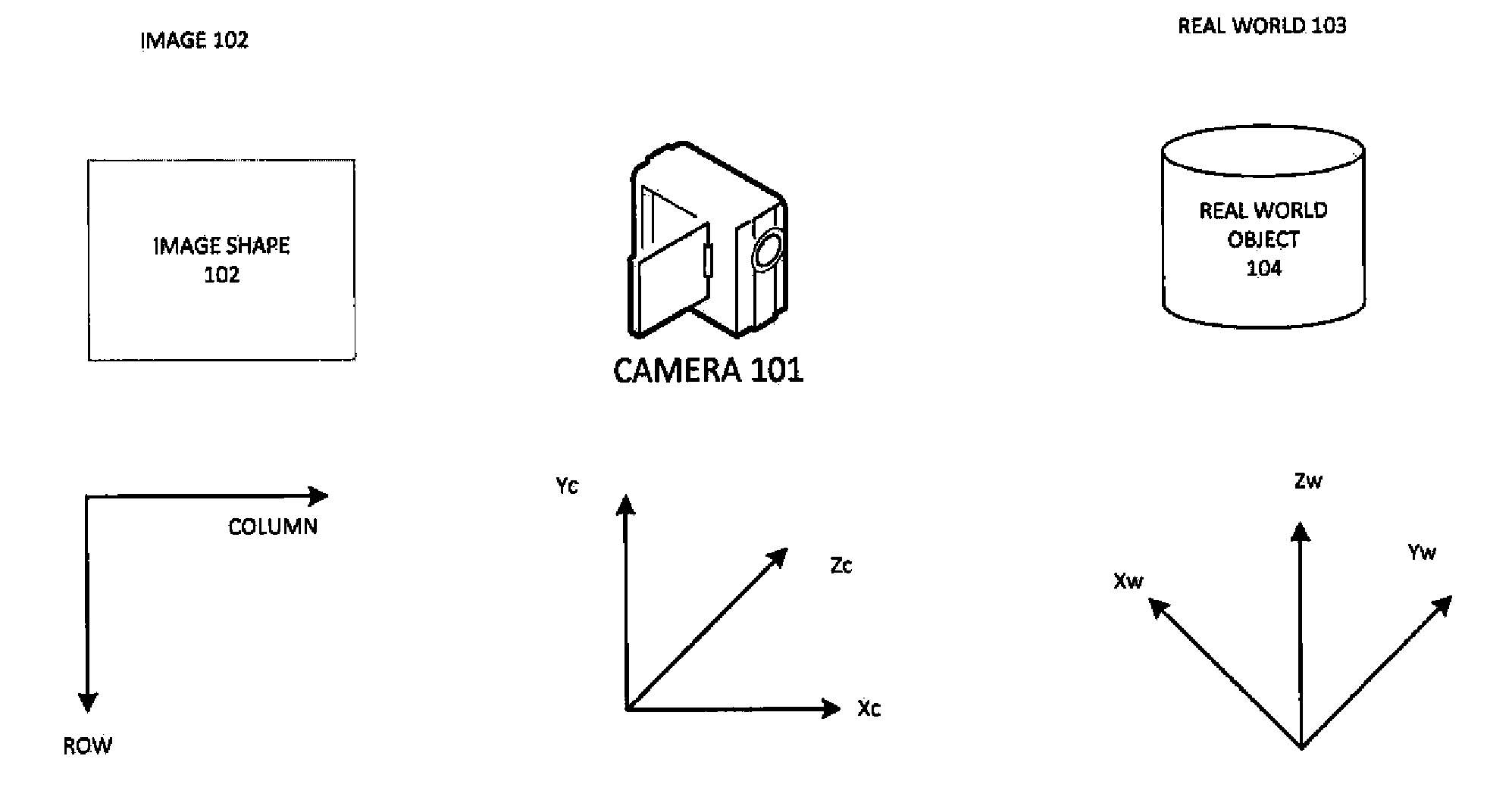
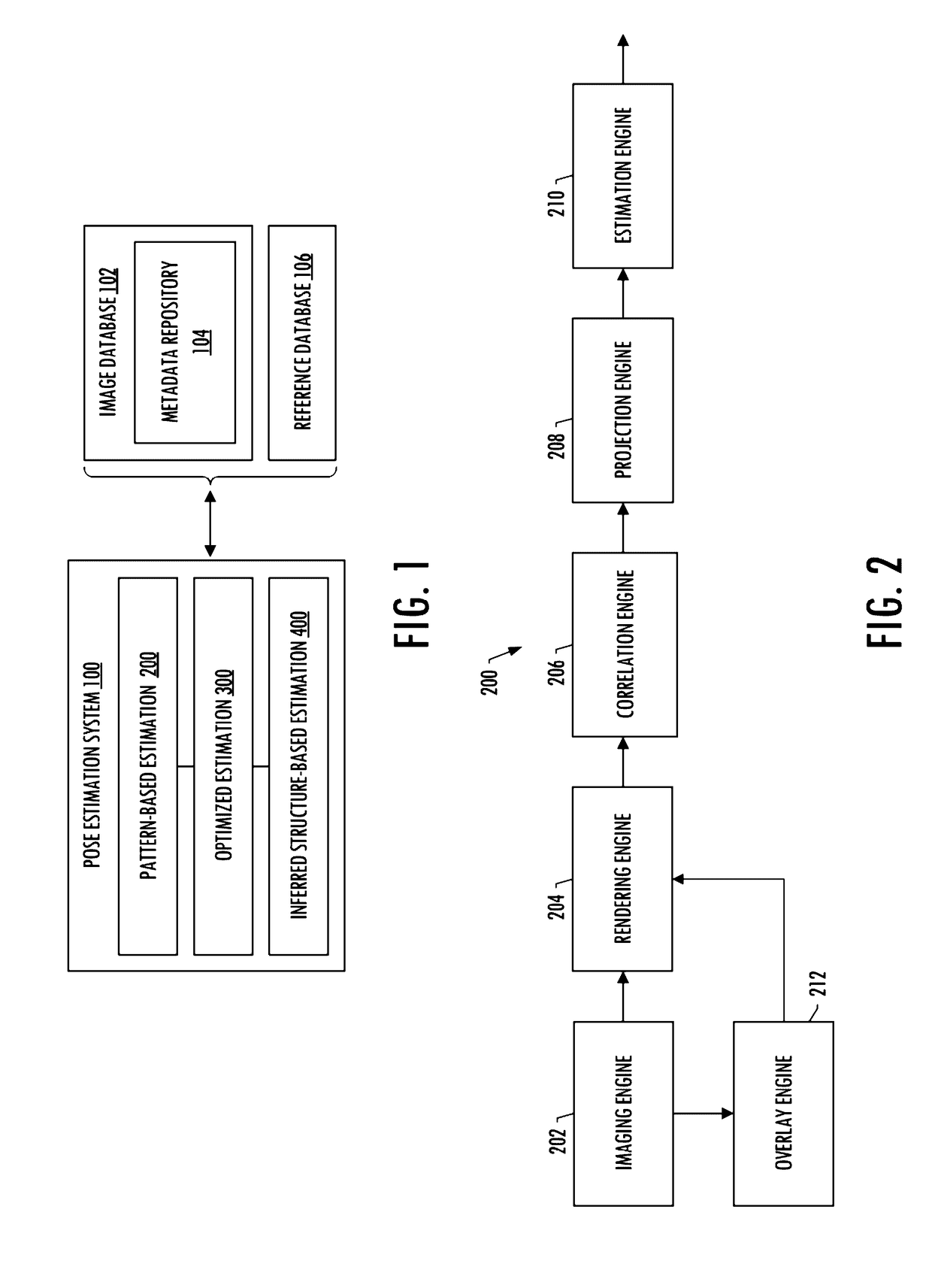
Pattern-based camera pose estimation system
A camera pose estimation system is provided for estimating the position of a camera within an environment. The system may be configured to receive a 2D image captured by a camera within the environment, and interpret metadata of the 2D image to identify an estimated position of the camera. A synthetic 2D image from a 3D model of the environment may be rendered by a synthetic camera within the model at the estimated position. A correlation between the 2D image and synthetic 2D image may identify a 2D point of correlation, and the system may project a line from the synthetic camera through the 2D point on the synthetic 2D image rendered in an image plane of the synthetic camera such that the line intersects the 3D model at a corresponding 3D point therein. A refined position may be determined based on the 2D point and corresponding 3D point.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
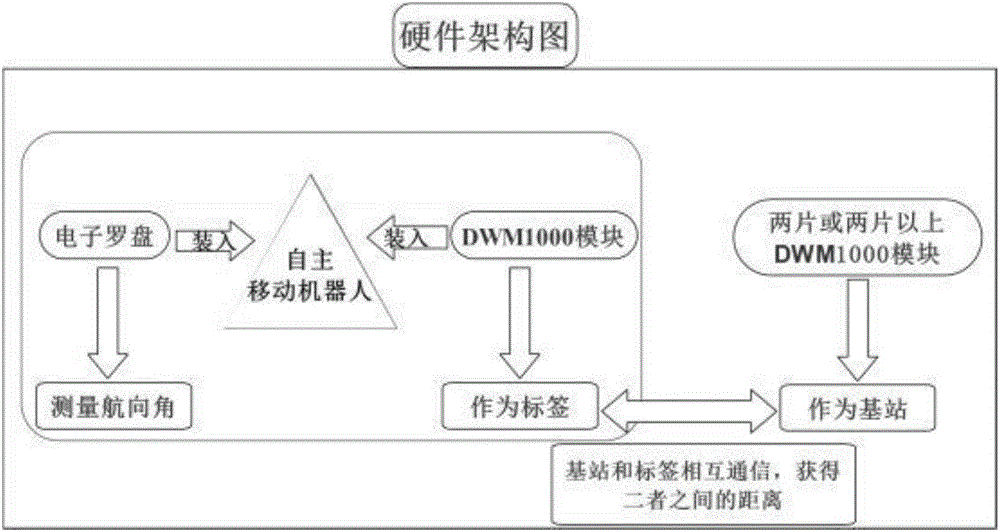
Indoor localization system for mobile robot and calculation method thereof
ActiveCN106352869APositioning results are reliableImprove environmental applicabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsLocalization systemElectromagnetic pulse
The invention discloses an indoor localization system for a mobile robot. The indoor localization system for the mobile robot, which improves localization accuracy, is designed on the basis of UWB (ultra wide band) technology combined with information of a motor encoder. A localization calculation method provided in the invention is a localization calculation method for the indoor mobile robot, and includes five steps: 1, confirming an origin of coordinates, starting a base station and the indoor mobile robot, and using a pose 2 of the indoor mobile robot, measured when starting the indoor mobile robot, as an initial pose; 2, obtaining an instant pose 1 of the mobile robot at moment t through the motor encoder; 3, receiving a high frequency electromagnetic pulse transmitted by the base station through a label, and confirming the self position of the mobile robot through a calculation method; 4, using a course angle measured by an electronic compass for augmenting the position of the mobile robot, obtained in the step 3, and obtaining an initial pose 2 at the moment t; 5, using the calculation method to fuse the initial pose 1 and the initial pose 2, obtaining pose estimation of the moment t, and saving the pose estimation and returning to the step 2.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method of pose estimation
A method includes receiving, from an image capture device, a first image frame of a sequence of image frames. The method also includes estimating, at a processor, a camera pose corresponding to the first image frame by comparing the first image frame to a second image frame. The second image frame precedes the first image frame in the sequence of image frames. The method further includes estimating, at the processor, a refined camera pose corresponding to the first image frame by comparing the first image frame to a keyframe. The keyframe corresponds to a particular image frame that precedes the second image frame in the sequence of image frames.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Controlled human pose estimation from depth image streams
A system, method, and computer program product for estimating human body pose are described. According to one aspect, anatomical features are detected in a depth image of a human actor. The method detects a head, neck, and trunk (H-N-T) template in the depth image, and detects limbs in the depth image based on the H-N-T template. The anatomical features are detected based on the H-N-T template and the limbs. An estimated pose of a human model is estimated based on the detected features and kinematic constraints of the human model.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
A method for estimating that posture of a three-dimensional human body based on a video stream
ActiveCN109271933AImprove accuracyImprove real-time performanceBiometric pattern recognition3D modellingHuman bodyDeep level
A method for estimating that posture of a three-dimensional human body based on a video stream. The method based on depth learning is used to estimate 3D pose of human body in video stream, which avoids many defects caused by two-dimensional vision analysis errors, and makes full use of the temporal relationship between video frames to improve the accuracy and real-time of 3D pose inference results of video stream. The method includes, for n(n >= 2) th frame of video, (1) inputting two-dimensional image of current frame and using shallow neural network module to generate image shallow map; 2)inputting a two-dimensional joint thermodynamic map of the human body generated by the (n-1)th frame and an image shallow map generated by the current frame to an LSTM module to generate a deep-levelcharacteristic map; 3) outputting the deep image characteristic map generated by the current frame to the residual module to generate a two-dimensional human body joint thermodynamic map of the current frame; 4) outputting the human body two-dimensional joint thermodynamic map of the current frame to a three-dimensional joint inference module for carrying out two-dimensional to three-dimensionalspatial mapping; and superimposing the three-dimensional human body joint thermodynamic map generated in each frame to generate a video stream of three-dimensional human body posture estimation.
Owner:QINGDAO RES INST OF BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com