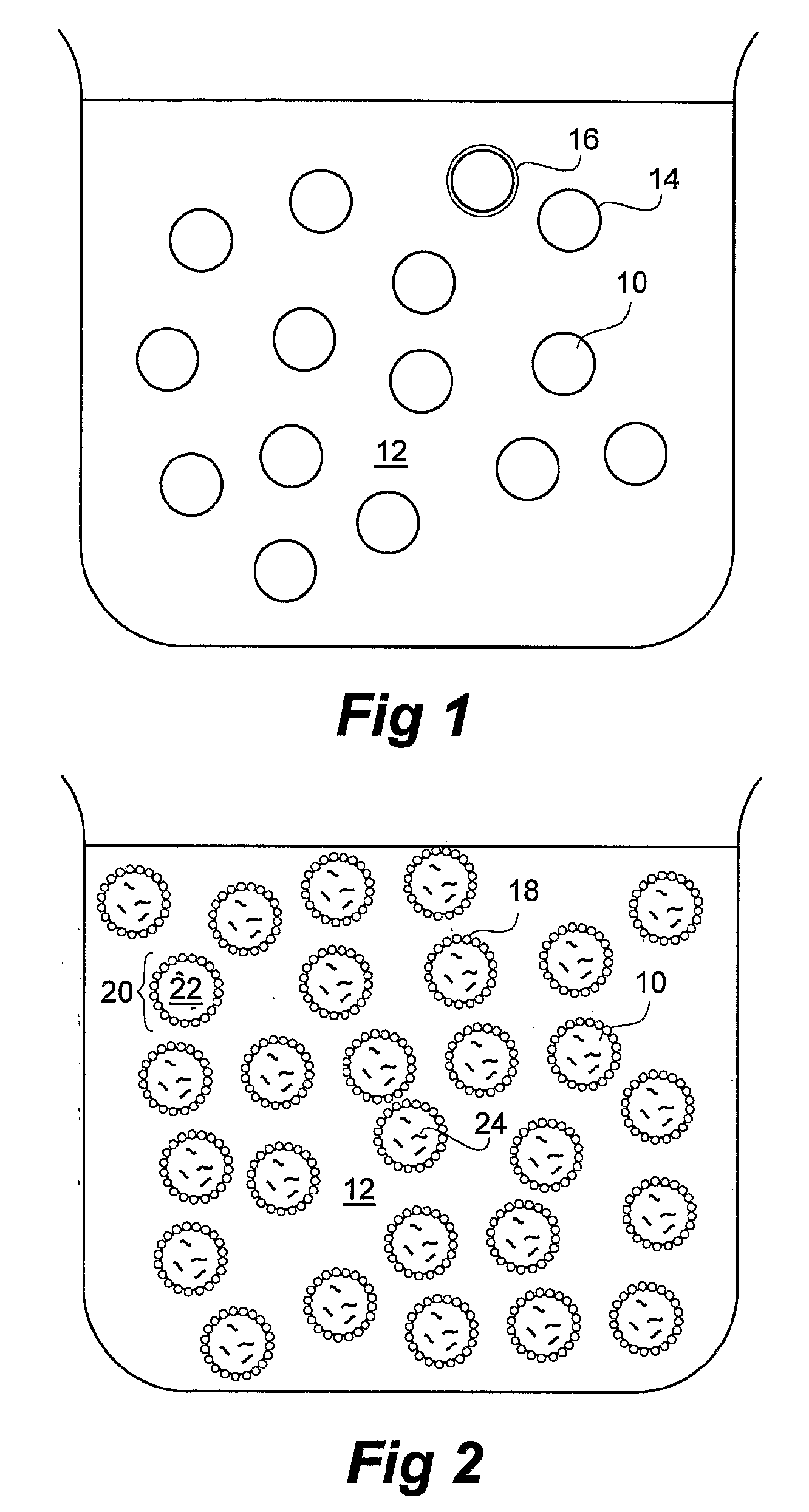
Dried Formulations of Nanoparticle-Coated Capsules
a technology of nanoparticles and capsules, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical product form changes, applications, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of inability to formulate the active substance into a deliverable form, many emulsions and liposomes, and many potentially useful active substances that have not been commercialised, etc., to achieve effective transport of active substances, facilitate adhesion to mucous membranes, and long contact time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
a) Preparation and Characterisation of Emulsion Stabilised by Lecithin
[0098]Lecithin (0.6 g) stabiliser was dissolved in triglyceride (Miglyol 812™) (10 g), and then added to water (total sample weight: 100 g) under mixing using a rotor-stator homogeniser (11,000 rpm, 10 minutes, pH=6.95±0.2). Alternatively, a high pressure homogeniser (5 cycles, 5 mBars) can be used for production of the emulsion. After 24 hours, the emulsion was characterised in terms of size (laser diffraction Malvern Mastersizer) and zeta potential (PALS).
[0099]Droplet size distribution is shown in FIG. 9a and FIG. 9b. The droplet size ranges from 0.20-0.86 μm.
b) Preparation of Nanoparticles
[0100]An aqueous dispersion of silica (Aerosil®) nanoparticles (1 wt %) was prepared by sonication over at least a one hour period. FIG. 8 shows that the average silica nanoparticle size was approximately 50 nm.
c) Capsule Formation
[0101]Emulsion formed in step (a) and nanoparticle dispersion (b) were mixed together. Subsequen...
example 2
a) Preparation of Emulsions
[0105]Simple Oil / Water lipid emulsions, containing 10% a 20% triglyceride (Miglyol® 812) as the oil phase, were prepared by high-pressure homogenizer at 500-1000 bar and ambient temperature. Negatively and positively charged emulsion oil droplets have been achieved by using lecithin and oleylamine respectively, as emulsifiers initially added to the oil phase. In the case of silica incorporated emulsions, silica nanoparticles were added to the oil phase or aqueous phase of emulsions, initially stabilised by lecithin or oleylamine, and sonicated for 60 minutes before homogenisation.
b) Size Analysis
[0106]Size measurements were carried out using laser diffraction by Malvern® Mastersizer (Malvern Instruments, UK) following appropriate dilution of samples with MilliQ water.
c) Freeze-Fracture Scanning Electron Microscopy
[0107]A freeze-fracture SEM technique (Philips XL 30 FEG scanning electron microscope with Oxford CT 1500 cryotransfer system) was used to image ...
example 3
a) Long-Term Physical Stability
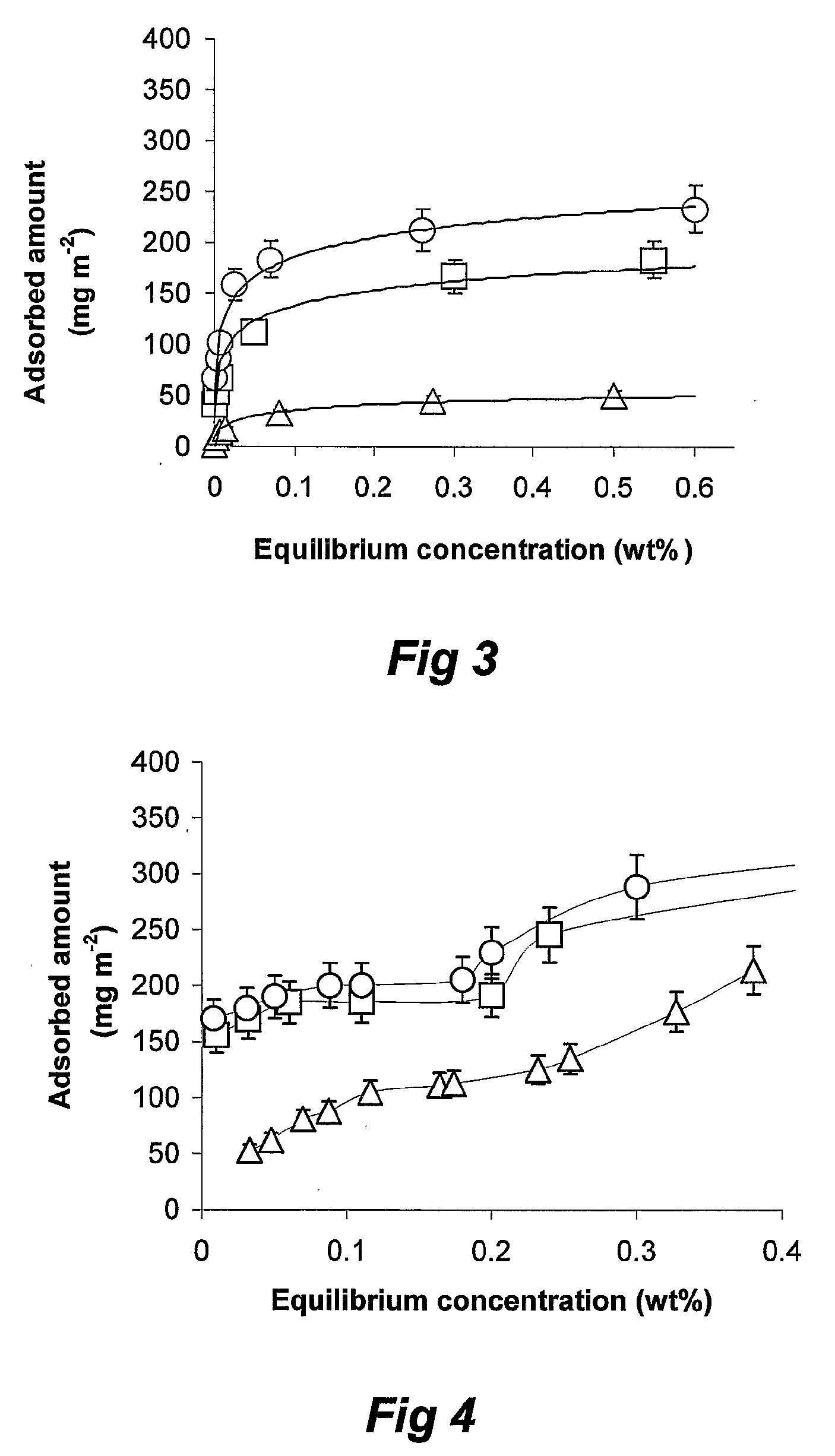
[0111]Long term physical stability of emulsions has been improved in the presence of silica nanoparticles.
[0112]D (v, 0.9) of emulsions initially stabilised by lecithin, in the absence and presence of silica nanoparticles has been shown in (FIG. 9). D (v, 0.9) of silica-added emulsions was effectively unchanged during storage at room temperature for 3 months, whereas emulsions solely stabilised by lecithin have shown a 3-fold increase in D (v, 0.9).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com