Method for preparing thin film material of binary rare earth compounds
A technology of rare earth compounds and thin film materials, applied in metal material coating process, ion implantation plating, coating and other directions, can solve the problems of limited quantity, difficult control, small ion beam current of rare earth elements, etc., to achieve high-efficiency and high-quality growth, The effect of improving uniformity and high melting point
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
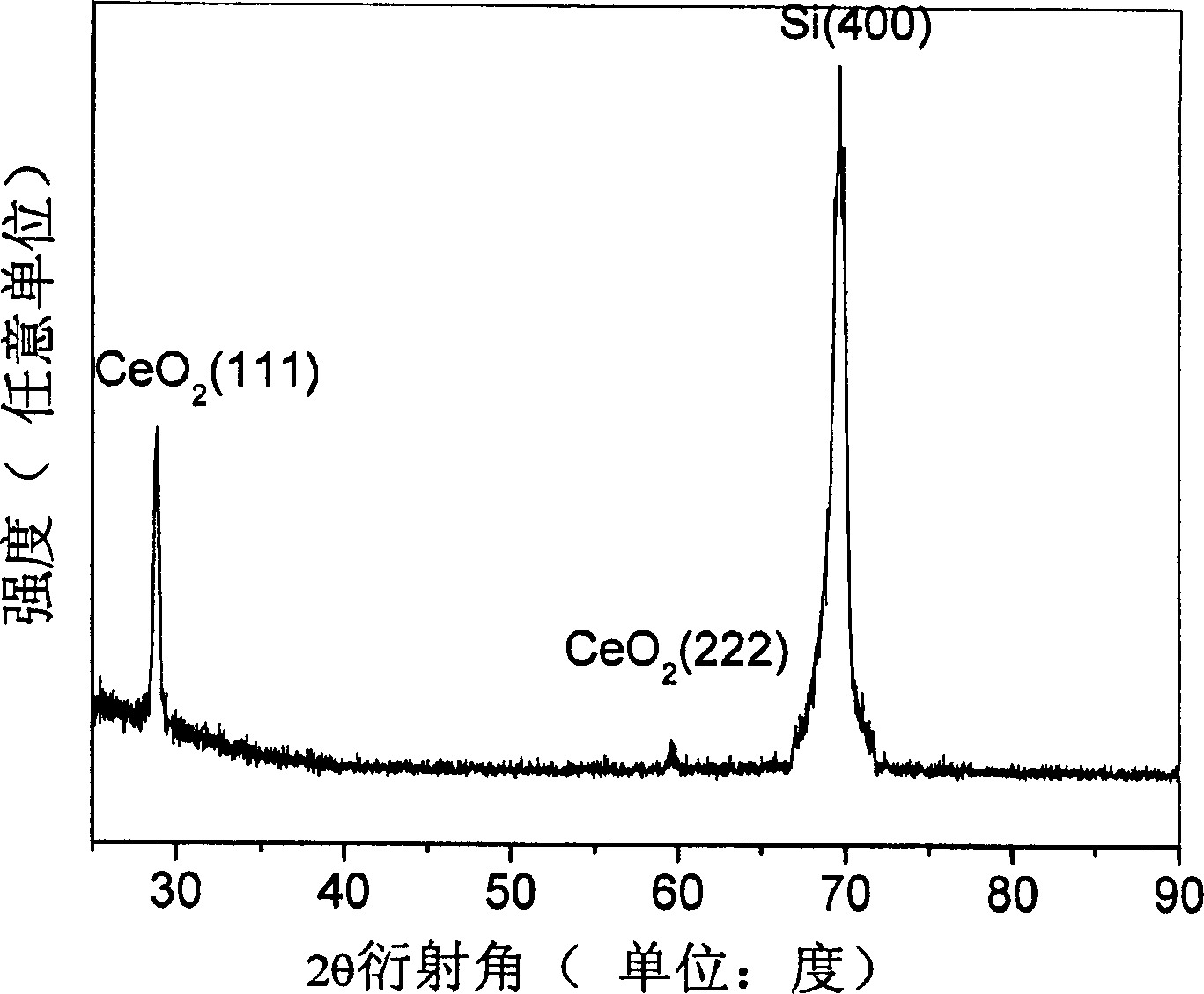
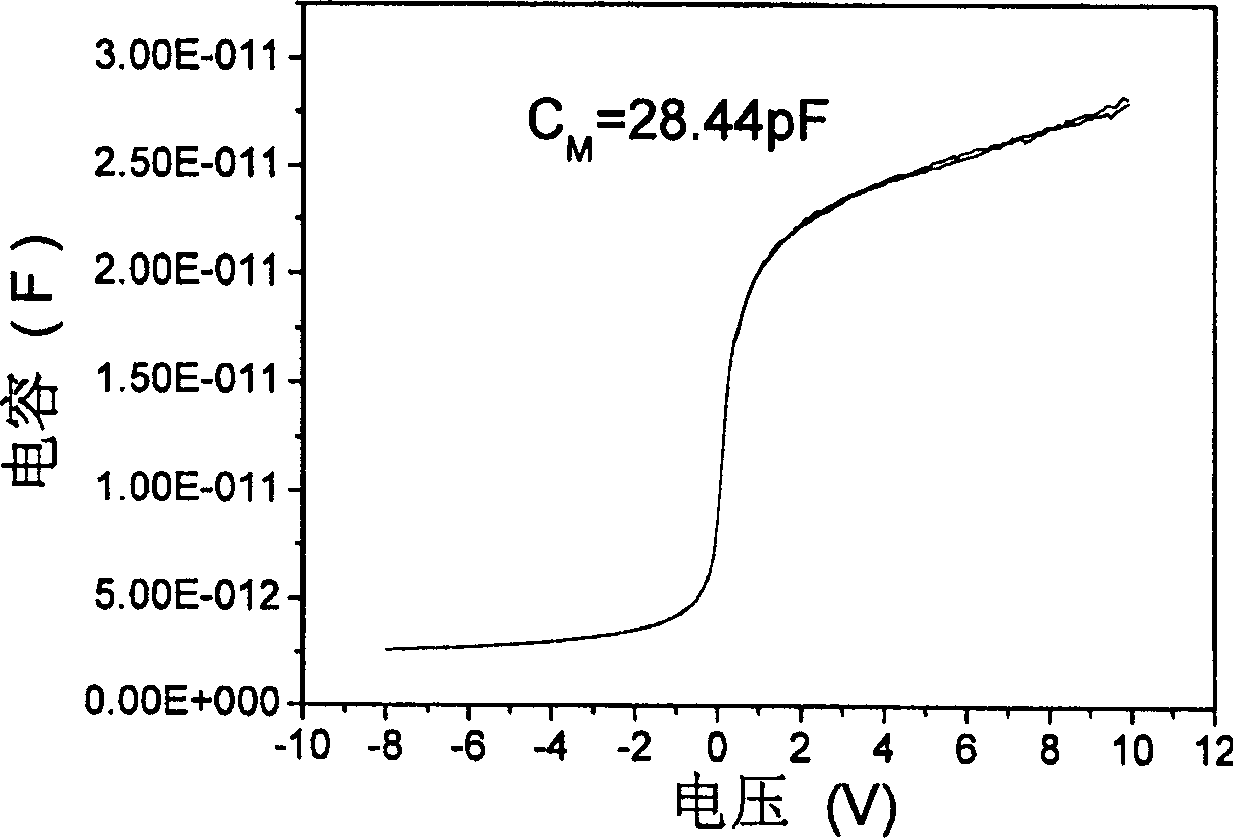
[0094] The scale of ultra-large-scale integrated circuits (ULSI) continues to increase, making the feature size of devices continue to decrease, which requires a new ideal high-dielectric material to replace the SiO commonly used in MOS devices. 2 materials, some binary rare earth oxide materials, such as cerium oxide (CeO 2 ) thin film, in addition to having a high dielectric constant and a good match with the silicon lattice, it also has good thermal stability. However, because most of these rare earth oxide materials have characteristics such as difficulty in purification and high melting point, it is difficult to prepare high-purity high-quality thin films by using the usual material growth technology. High-purity and high-quality rare earth cerium oxide (CeO 2 ) film, and the relevant experimental parameters and results are shown in Table 2. Because the present invention adopts low-cost anhydrous cerium chloride (CeCl 3 )) material is used as the raw material of the Be...
specific Embodiment 2
[0096] In recent years, the research on the luminescent properties of binary rare earth oxide materials has also attracted people's attention. Through the study of the luminescent mechanism of binary rare earth oxides, to grasp its mechanism and law, it can be used for rare earth oxides on silicon substrates. Optical applications of thin films, such as light sources, displays, imaging, optoelectronic devices, detection of radiation fields, and recording of radiation doses, lay the foundation for applications. The present invention utilizes the mass-separated low-energy dual ion beam deposition method to successfully prepare the rare earth gadolinium oxide (Gd 2 o 3 ) film material (see Figure 4 ), and for the first time in Gd 2 o 3 Four luminescence peaks were simultaneously found in the film sample (see Figure 5 ), this result is in good agreement with the "singlet-triplet exchange interaction" model, but there is no report of four luminescence peaks appearing at the sa...
specific Embodiment 3
[0098] Diluted magnetic semiconductor materials can simultaneously utilize the charge and spin properties of electrons, which is the basis for the future realization of quantum computing. However, it is difficult to obtain materials with room temperature ferromagnetism and high saturation magnetization, which restricts its wide application and promotion. In recent years, the use of magnetic rare earth elements to prepare high Tc ferromagnetic dilute magnetic semiconductor materials has gradually attracted people's attention. Process is difficult to achieve high solubility in semiconductor materials. The present invention utilizes the mass purification and energetic ion deposition functions of the low-energy ion beam deposition technology to obtain the magnetic rare earth element gadolinium (Gd + ) ions, producing Gd + The relevant experimental parameter of ion is referring to table 3, utilizes the magnetic rare earth element gadolinium (Gd) that the method of the present inv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com