Method for improving low-temperature impact toughness of low-nickel ferrite-austenitic stainless steel
A low-temperature impact toughness, stainless steel technology, applied in the field of steel alloy materials, can solve the problems of low strength and elongation, low corrosion resistance element content, poor corrosion resistance and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
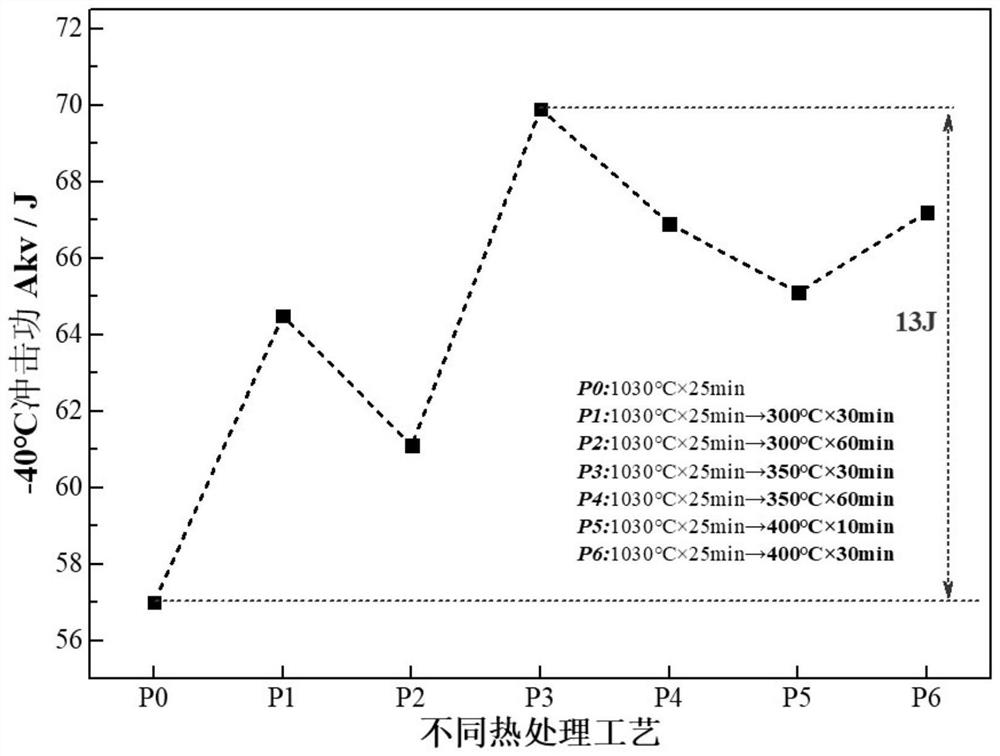
[0022] Such as figure 1 Shown is the first preferred embodiment of the present invention.
[0023] The low-nickel ferritic-austenitic stainless steel involved in this embodiment includes the following components in terms of mass percentage: C: 0.03%, Cr: 21.5%, Mo: 0.25%, Ni: 1.5%, Mn: 4.9%, Si: 0.2%, N: 0.24%, and the balance is iron and other unavoidable impurities.
[0024] The above stainless steel is placed in a vacuum induction melting furnace and melted under a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain an ingot, which is then forged with an initial temperature of 1150°C and a final forging temperature of 1000°C, followed by air cooling to obtain a forged billet.
[0025] The method for improving the low-temperature impact toughness of the above-mentioned low-nickel ferritic-austenitic stainless steel comprises the following steps in sequence:
[0026] 1) Hot rolling: the above-mentioned forged billet is subjected to multi-pass hot rolling, the starting rolling temperature is con...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The main difference between this example and Example 1 is that the process parameters are different, specifically, in step 1), the starting rolling temperature is 1200°C, the finishing rolling temperature is 950°C, and the total reduction rate is 95%; step 2) In step 3), the solution temperature is 1000°C, the holding time is 40min, and the ferrite ratio is 45%, and the austenite ratio is 55%; in step 3), the low temperature tempering temperature is 350°C, and the tempering time is 30min.
[0034] After the ferritic-austenitic stainless steel of this embodiment is tempered at 350° C. for 30 minutes, its low-temperature impact energy at -40° C. reaches 80 J. The tensile strength is 950MPa, the yield strength is 600MPa, the elongation is 45%, and the pitting potential in 3.5% NaCl aqueous solution is 460mV.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The main difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: 1. The low-nickel ferrite-austenitic stainless steel is different, specifically, the low-nickel ferrite-austenitic stainless steel involved in this embodiment, according to In terms of mass percentage, it includes the following components: C: 0.02%, Cr: 22.8%, Mo: 0.30%, Ni: 0.9%, Mn: 6.7%, Si: 0.3%, N: 0.28%, and the balance is iron and other unavoidable impurities.
[0039] 2. The process parameters are different. Specifically, in step 1), the starting rolling temperature is 1230°C, the finishing rolling temperature is 1000°C, and the total reduction rate is 95%; in step 2), the solution temperature is 1100°C, and the holding time is 20 minutes, the proportion of ferrite is 46%, and the proportion of austenite is 54%. In step 3), the low-temperature tempering temperature is 350° C., and the tempering time is 30 minutes.
[0040] After the ferritic-austenitic stainless steel of this embodiment is tempere...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com