Floatable pharmaceutical microcapsule composition
A technology of microcapsules and drugs, applied in the direction of drug combination, microcapsules, and capsule delivery, which can solve problems such as drug-resistant TB
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
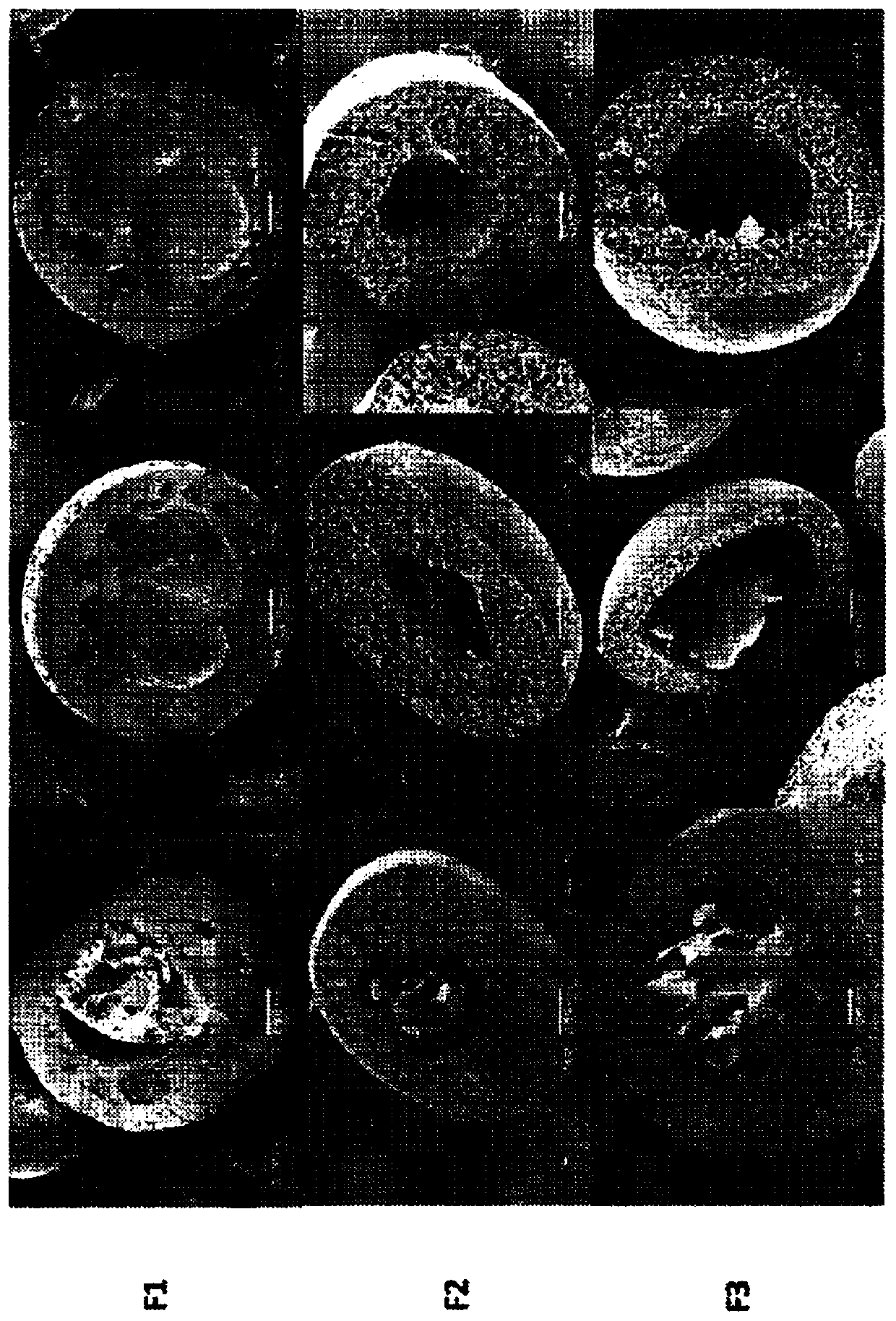
[0207] Embodiment 1: the preparation procedure of microcapsule
[0208] Using water-oil-water (W 1 / O / W 2) double emulsification method to encapsulate the drug in casein-PLLA / PCL microcapsules. The amphiphile casein is capable of encapsulating both hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs. Casein is the major protein in milk and has unique hydrophobic and hydrophilic domains (ie, amphipathic).
[0209] Aqueous casein solutions were prepared by dissolving 10, 30 or 50 mg of casein in distilled water, using 2 mg of sodium chloride (1 mL) as osmotic agent. Separately, a polymer solution was prepared by dissolving 0.3 g of PLLA and 0.1 g of PCL in 5 mL of DCM. Depending on the target disease (see table below), specific hydrophilic drugs were dissolved in the casein solution, while hydrophobic drugs were dissolved in the PLLA / PCL solution.
[0210]
[0211]
[0212] The resulting casein solution was then added dropwise to the polymer solution under magnetic stirring, and 10 μ...
Embodiment 2
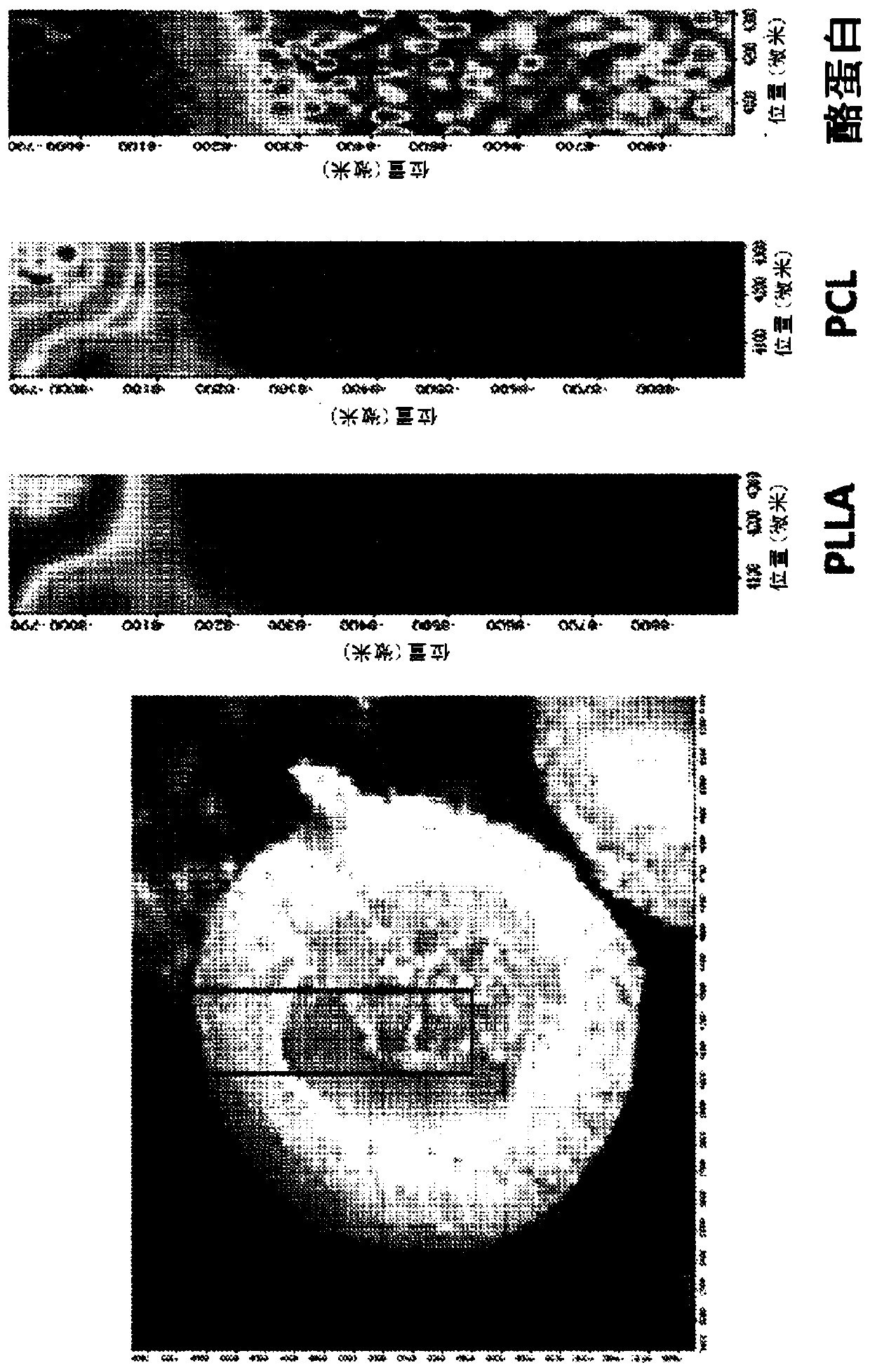
[0235] Embodiment 2: the in vitro drug release profile of microcapsules
[0236] To test the hypothesis that microcapsules can provide better sustained and controlled release of multiple drugs, the release profiles of individual drugs from samples in simulated gastric fluid (SGF) and simulated intestinal fluid (SIF) were studied.
[0237] method
[0238] In vitro release studies were performed in SGF for 48h. In some experiments, studies were conducted in SGF and then in SIF, where the total duration in SGF and SIF was 48h. Each microcapsule sample (20 mg) was added to a bottle containing SGF or SIF medium (20 mL). Both SGF and SIF bottles were placed in a 37°C rotary incubator. At various time points, half of the medium (10 mL) in each bottle was withdrawn and replaced with 10 mL of new medium. Time points include hourly intervals within 48 hours. By the procedure mentioned in Example 1, the drug content in the extracted medium was analyzed using RP-HPLC to determine t...
Embodiment 3
[0247] Embodiment 3: the in vivo drug release profile of microcapsules
[0248] Pharmacokinetic release of three different PD drugs (i.e., levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone) from optimized casein (3% (w / v))-microparticles fed to healthy mice Kinetics were compared to a commercial formulation (ie control) with the same drug ratio as the microcapsules.
[0249] method
[0250] Experimental mice were divided into two groups (control group and F2), each consisting of five animals. Control preparations were freshly prepared (as solutions) in 0.6% methylcellulose diluted with saline solution on each experimental day. Then use a feeding syringe to administer 200ul (control) or 300μl (bolus) to mice by oral gavage at LD:CD:ENT=10:2.5:20mg.kg -1 (group 1, conventional preparation) and LD:CD:ENT=10:2.5:20mg.kg -1 (group 2, F2) a single dose of the drug solution. At defined time points of 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24 hr, mice were euthanized and blood was collected by cardiac p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com